Augmented SBERT
Motivation
Bi-encoders (a.k.a. sentence embeddings models) require substantial training data and fine-tuning over the target task to achieve competitive performances. However, in many scenarios, there is only little training data available.
To solve this practical issue, we release an effective data-augmentation strategy known as Augmented SBERT where we utilize a high performing and slow cross-encoder (BERT) to label a larger set of input pairs to augment the training data for the bi-encoder (SBERT).
For more details, refer to our publication - Augmented SBERT: Data Augmentation Method for Improving Bi-Encoders for Pairwise Sentence Scoring Tasks which is a joint effort by Nandan Thakur, Nils Reimers and Johannes Daxenberger of UKP Lab, TU Darmstadt.
Chien Vu also wrote a nice blog article on this technique: Advance BERT model via transferring knowledge from Cross-Encoders to Bi-Encoders
Extend to your own datasets
**Scenario 1: Limited or small annotated datasets (few labeled sentence-pairs (1k-3k))**
If you have specialized datasets in your company or research which are small-sized or contain labeled few sentence-pairs. You can extend the idea of Augmented SBERT (in-domain) strategy by training a cross-encoder over your small gold dataset and use BM25 sampling to generate combinations not seen earlier. Use the cross-encoder to label these unlabeled pairs to create the silver dataset. Finally train a bi-encoder (i.e. SBERT) over your extended dataset (gold+silver) dataset as shown in train_sts_indomain_bm25.py.
**Scenario 2: No annotated datasets (Only unlabeled sentence-pairs)**
If you have specialized datasets in your company or research which only contain unlabeled sentence-pairs. You can extend the idea of Augmented SBERT (domain-transfer) strategy by training a cross-encoder over a source dataset which is annotated (for eg. QQP). Use this cross-encoder to label your specialised unlabeled dataset i.e. target dataset. Finally train a bi-encoder i.e. SBERT over your labeled target dataset as shown in train_sts_qqp_crossdomain.py.
Methodology
There are two major scenarios for the Augmented SBERT approach for pairwise-sentence regression or classification tasks.
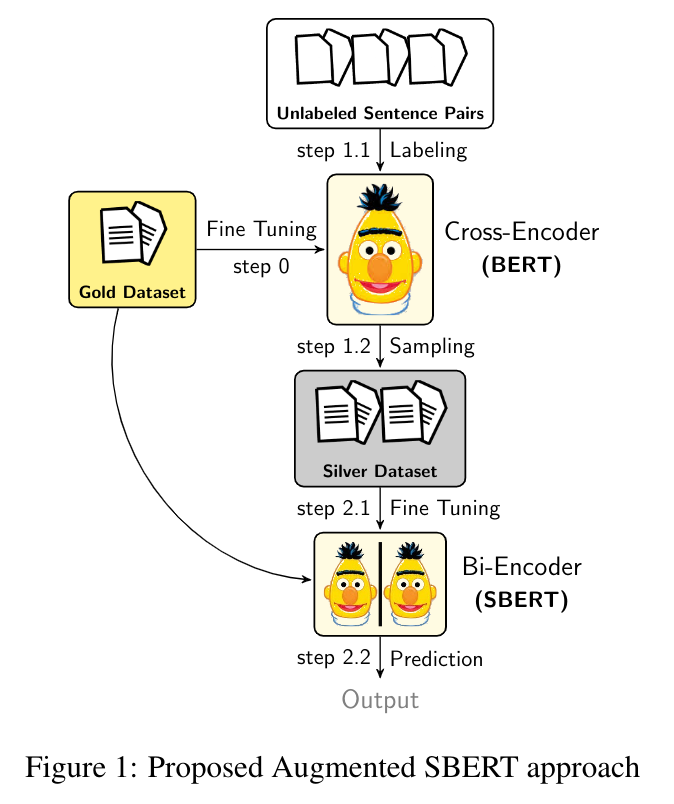
Scenario 1: Limited or small annotated datasets (few labeled sentence-pairs)
We apply the Augmented SBERT (In-domain) strategy, it involves three steps -
Step 1: Train a cross-encoder (BERT) over the small (gold or annotated) dataset
Step 2.1: Create pairs by recombination and reduce the pairs via BM25 or semantic search
Step 2.2: Weakly label new pairs with cross-encoder (BERT). These are silver pairs or (silver) dataset
Step 3: Finally, train a bi-encoder (SBERT) on the extended (gold + silver) training dataset
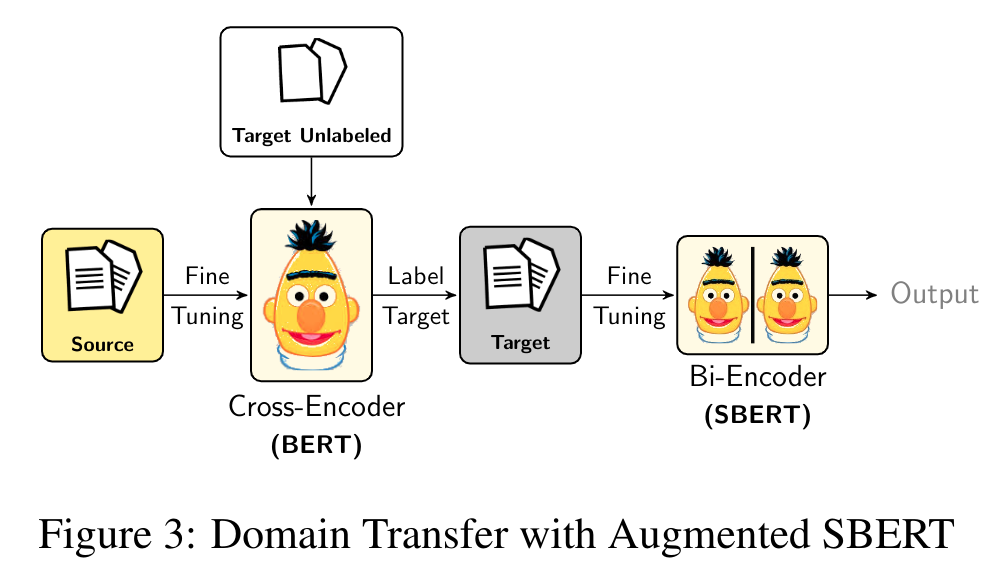
Scenario 2: No annotated datasets (Only unlabeled sentence-pairs)
We apply the Augmented SBERT (Domain-Transfer) strategy, it involves three steps -
Step 1: Train from scratch a cross-encoder (BERT) over a source dataset, for which we contain annotations
Step 2: Use this cross-encoder (BERT) to label your target dataset i.e. unlabeled sentence pairs
Step 3: Finally, train a bi-encoder (SBERT) on the labeled target dataset
Training
The examples/training/data_augmentation folder contains simple training examples for each scenario explained below:
train_sts_seed_optimization.py
- This script trains a bi-encoder (SBERT) model from scratch for STS benchmark dataset with seed-optimization.
- Seed optimization technique is inspired from (Dodge et al., 2020).
- For Seed opt., we train our bi-encoder for various seeds and evaluate using an early stopping algorithm.
- Finally, measure dev performance across the seeds to get the highest performing seeds.
-
- This script trains a bi-encoder (SBERT) model from scratch for STS benchmark dataset using easy data augmentation.
- Data augmentation strategies are used from popular nlpaug package.
- Augment single sentences with synonyms using (word2vec, BERT or WordNet). Forms our silver dataset.
- Train bi-encoder model on both original small training dataset and synonym based silver dataset.
-
- Script initially trains a cross-encoder (BERT) model from scratch for small STS benchmark dataset.
- Recombine sentences from our small training dataset and form lots of sentence-pairs.
- Limit number of combinations with BM25 sampling using ElasticSearch.
- Retrieve top-k sentences given a sentence and label these pairs using the cross-encoder (silver dataset).
- Train a bi-encoder (SBERT) model on both gold + silver STSb dataset. (Augmented SBERT (In-domain) Strategy).
train_sts_indomain_semantic.py
- This script initially trains a cross-encoder (BERT) model from scratch for small STS benchmark dataset.
- We recombine sentences from our small training dataset and form lots of sentence-pairs.
- Limit number of combinations with Semantic Search sampling using pretrained SBERT model.
- Retrieve top-k sentences given a sentence and label these pairs using the cross-encoder (silver dataset).
- Train a bi-encoder (SBERT) model on both gold + silver STSb dataset. (Augmented SBERT (In-domain) Strategy).
-
- This script initially trains a cross-encoder (BERT) model from scratch for STS benchmark dataset.
- Label the Quora Questions Pair (QQP) training dataset (Assume no labels present) using the cross-encoder.
- Train a bi-encoder (SBERT) model on the QQP dataset. (Augmented SBERT (Domain-Transfer) Strategy).
Citation
If you use the code for augmented sbert, feel free to cite our publication Augmented SBERT: Data Augmentation Method for Improving Bi-Encoders for Pairwise Sentence Scoring Tasks:
@article{thakur-2020-AugSBERT,
title = "Augmented SBERT: Data Augmentation Method for Improving Bi-Encoders for Pairwise Sentence Scoring Tasks",
author = "Thakur, Nandan and Reimers, Nils and Daxenberger, Johannes and Gurevych, Iryna",
journal= "arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.08240",
month = "10",
year = "2020",
url = "https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.08240",
}