id
int64 2.05k
16.6k
| title
stringlengths 5
75
| fromurl
stringlengths 19
185
| date
timestamp[s] | tags
sequencelengths 0
11
| permalink
stringlengths 20
37
| content
stringlengths 342
82.2k
| fromurl_status
int64 200
526
⌀ | status_msg
stringclasses 339
values | from_content
stringlengths 0
229k
⌀ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
15,117 | DevOps 将去向何方? | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/where-is-devops-headed/ | 2022-10-08T15:09:43 | [
"DevOps",
"DevSecOps",
"AIOps"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15117-1.html | 
>
> 微软、谷歌、亚马逊、IBM 和甲骨文如今都在关注云上的 DevOps。这些大公司正在给企业提供 IT 自动化的服务。然而,DevOps 仍然在持续的演进中。DevSecOps、AIOps 和 NoOps 正在成为下一个流行词。
>
>
>
随着开发和管理人员看到及时交付高质量软件的商业价值,<ruby> 敏捷 <rt> Agile </rt></ruby>方法论和 DevOps 也变得流行起来。拥有灵活的发布周期,并且交付具有<ruby> 可扩展 <rt> scalable </rt></ruby>和<ruby> 可定制 <rt> customizable </rt></ruby>的软件,是世界上每个企业的目标。通过将 CI/CD 工具和<ruby> 管道 <rt> pipeline </rt></ruby>部署到云端,DevOps 使发布过程变得更加流畅。融合了 DevOps 的 Polyglot 微服务架构正在帮助企业降低总拥有成本(TCO)。他们现在有能力用渐进式网络应用程序和最新的 UI 框架升级他们的技术栈。总的来说,团队正在以更好的效率执行任务,并且正在开发高质量的软件模块。
### 自治 DevOps
容器和 DevOps 与云原生应用走到了一起。Kubernetes 和 Docker 正在被用作容器,一个新的名词 NoOps 现在正在流行。对于不同的容器,<ruby> 编排 <rt> Orchestration </rt></ruby>都是一个重要的功能。为了扩展应用,开发环境中要创建容器集群。有一些新的容器正在进入云原生应用这个领域,比如 Mesos、Swarm、Openshift Rancher 和 Nomad。NoOps 有助于缩短编码周期,从而监控和管理应用程序。缺陷修复和热修复是不同的活动,它们都是 NoOps 的一部分。NoOps 有助于提高技术团队和业务运营人员之间的协同作用。它也有助于更好的监控、管理和流程自动化。NoOps 基础设施能够控制应用程序在云上的部署。企业从中获得的好处包括更好的交付、弹性的服务、更快的发布、良好的质量和 CI/CD 自动化。
### DevSecOps
DevSecOps 算是另一个流行趋势,它与在开发操作中的安全问题有关。最近与<ruby> 漏洞 <rt> vulnerabilities </rt></ruby>(log4j),<ruby> 安全泄露 <rt> security breach </rt></ruby>(谷歌、脸书、微软),和安全攻击相关的问题增加了 DevSecOps 在企业中的重要性。<ruby> 左移 <rt> shift left </rt></ruby>方法强调了在软件生命周期的早期处理安全性和质量的重要性。在架构阶段就需要考虑隐私和<ruby> 遵从性 <rt> compliances </rt></ruby>(如 GDPR)。这有助于降低成本,并且提升软件交付的速度。审计工具和安全检查列表是 DevOps 工具和系统的一部分,现在我们称为 DevSecOps。
### AIOps
AI DevOps 现在被称为 AIOps。据预测,将来 AI 应用会由 AIOps 来管理。与 AIOps 相关的工具和软件正在开发中,并且将很快发布首个版本。AI/ML 应用部署和模型更新可以由 AIOps 来处理。这将在<ruby> 工业 4.0 <rt> Industry 4.0 </rt></ruby> 以及数据科学中扮演重要角色。有一种观点认为,NoOps 将会是 AIOps 的最终形态。AIOps 包括数据集管理、模型训练、模型服务、元数据管理、模型更新和服务更新。分布式训练将由 AIOps 来完成,这会提供<ruby> 超参数 <rt> hyper parameter </rt></ruby>优化,工作流程管理和“<ruby> 假设 <rt> what if </rt></ruby>”的分析能力。
### 微服务配置管理
当前,DevOps 和微服务正在成为标准部署和<ruby> 架构蓝图 <rt> architectural blueprints </rt></ruby>来实施。应用可以在模块级别上就进行扩展。微服务可以在简化缺陷修复和问题区域隔离上提供帮助。经过设计,微服务可以通过添加更多<ruby> 计算能力 <rt> computing power </rt></ruby>的<ruby> 实例 <rt> instances </rt></ruby>来进行扩展。但是当它们没有被正确实现的时候,数据安全和管理的问题就会突然出现。
### 平台即产品
云上的<ruby> 软件即服务 <rt> Software as a Service </rt></ruby>和<ruby> 平台即产品 <rt> Platform as a Product </rt></ruby>最近非常流行。通过加速向平台部署和功能交付,DevOps 使这些变成现实。从编码到上线阶段,CI/CD 管道有助于可视化应用的部署。持续交付、集成和部署都是 DevOps 的一部分。DevOps 生产线模拟工业生产线是未来要关注的。
DevOps 正在慢慢地向 DevSecOps 和 AIOps 转变。对于企业,NoOps 才是未来。现在需要的是减少与安全相关的攻击、事故和破坏发生。对于企业来说,数据安全和隐私的优先级更高,并且这些新技术都将在这方面有所帮助。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/where-is-devops-headed/>
作者:[Bhagvan Kommadi](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/bhagvan-kommadi/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Yufei-Yan](https://github.com/Yufei-Yan) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Microsoft, Google, Amazon, IBM, and Oracle are today focusing on DevOps on the cloud. IT automation is what these big companies are offering enterprises. However, DevOps is evolving continuously. DevSecOps, AIOps and NoOps are set to be the next buzzwords.*
Agile methodology and DevOps have become popular as developers and managers see the business value in delivering good quality software in time. To have flexible release cycles and deliver software with scalable and customisable features is the goal of every enterprise in the world. DevOps has smoothened the release process with CI/CD tools and pipelines being deployed on to the cloud. Polyglot microservices architecture blended with DevOps is helping enterprises to cut down the total cost of ownership. They now have capabilities to upgrade their technology stack with progressive Web apps and the latest UI frameworks. Overall, teams are performing with better efficiency and quality software modules are being developed.
## Autonomous DevOps
Containers and DevOps go together with cloud native applications. Kubernetes and Docker are being used as containers and a new term called NoOps is trending now. Orchestration is an important feature of different containers. Container clusters are being created in developer environments to scale the application. There are new containers like Mesos, Swarm, Openshift Rancher and Nomad getting into the cloud native application space. NoOps helps in cutting down the coding cycles in order to monitor and manage the application. Defect fixing and hotfixes are different activities, which are part of NoOps. NoOps helps to improve the synergy between technical teams and business operations personnel. It helps in better monitoring, management, and process automation. NoOps infrastructure enables control of app deployment on the cloud. Enterprises derive benefits like better delivery, service resilience, faster time to market, good quality, and CI/CD automation.
## DevSecOps
DevSecOps is another popular trend related to the security concerns addressed during development operations. Recent issues related to vulnerabilities (log4j), security breaches (Google, Facebook, Microsoft), and security attacks have increased the importance of DevSecOps in enterprises. A shift left approach emphasises the importance of security and quality to be addressed earlier in the software life cycle. Privacy and compliances like GDPR need to be considered at the architectural phase itself. This helps in cutting down costs and improving the speed of the software delivery. Auditing tools and security checklists are part of the DevOps tools and systems, which we call DevSecOps now.
## AIOps
AI DevOps is now called AIOps. It is being predicted that AI applications will be managed by AIOps in future. Tools and software related to AIOps are being developed and available as first releases. AI/ML applications deployment and model updates can be handled by AIOps. This will play an important role in Industry 4.0 and data science. There is a school of thought that NoOps will be the end point for AIOps. AIOps consists of data set management, model training, model serving, metadata management, model updates, and service updates. Distributed training is enabled by AIOps, which gives the capabilities for hyper parameter optimisation, workflow management, and ‘what if’ analysis.
## Microservices configuration management
DevOps and microservices are being implemented as standard deployment and architectural blueprints these days. Apps can be scaled at the module level. Microservices help in simplifying the fixing of defects and isolating problem areas. Microservices by design can be scaled by adding more instances of computing power. But when they are not implemented correctly, issues related to data security and management crop up.
## Platform as a Product
Software as a Service and Platform as a Product are popular these days on the cloud. DevOps makes these a reality by accelerating the deployment and delivery of features to the platform. CI/CD pipelines help in visualising the app deployment, right from coding to live phases. Continuous delivery, integration and deployment are all part of DevOps. The future is about DevOps assembly lines simulating industry assembly lines.
DevOps is slowly graduating to DevSecOps and AIOps. NoOps for enterprises is the future. The need of the hour is to cut down the occurrence of security related attacks, incidents, and breaches. Data security and privacy is a high priority for enterprises, and these new technologies will all help with that. |
15,119 | 准备好在 Debian Linux 上获得 Ubuntu MATE 的体验吧! | https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-mate-debian/ | 2022-10-09T12:04:00 | [
"MATE",
"Ubuntu MATE",
"Debian"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15119-1.html |
>
> Ubuntu MATE 的体验将在 2023 年进入 Debian 的 MATE 版中?从这里了解更多。
>
>
>

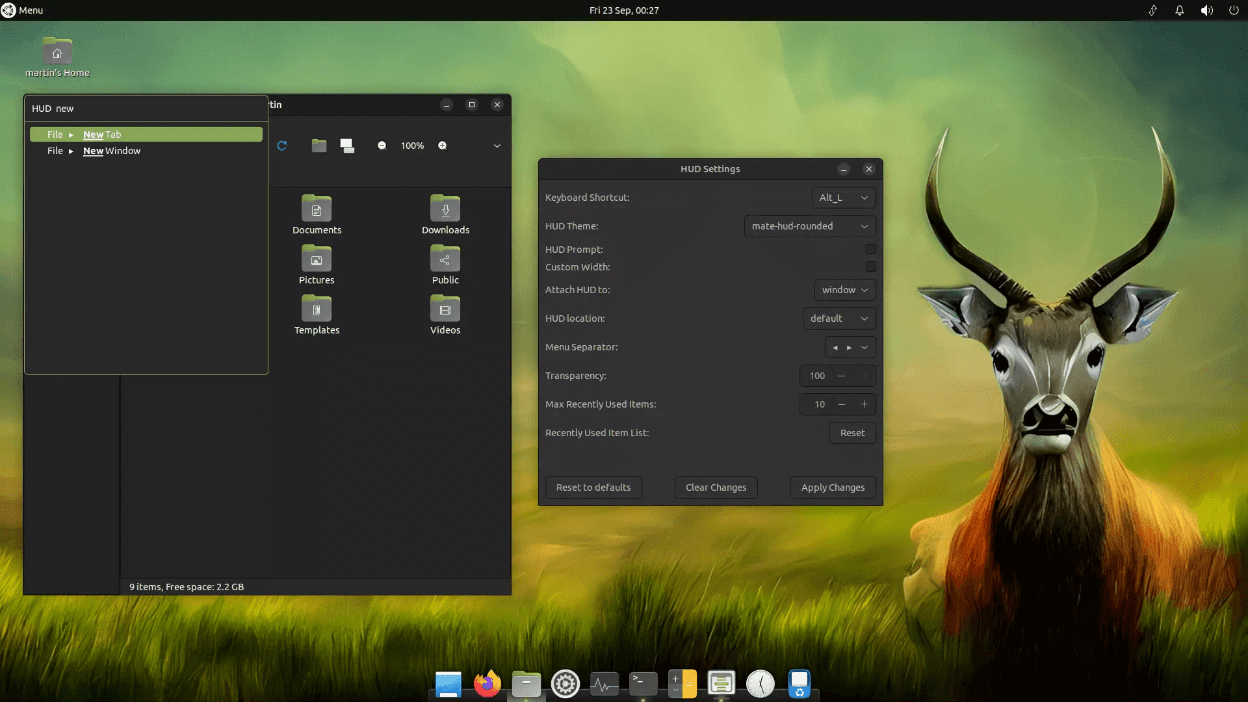
Ubuntu MATE 的创始人与维护者之一 **Martin Wimpress**,在 Ubuntu MATE 22.10 的测试版发布说明中提到了一些相当有趣的事情。
他的目标是将 Ubuntu MATE 的体验带到 Debian ?。
等等,你不是已经可以在 Debian 上安装 MATE 了吗?
是的,但是怎样使用 Debian 上的所有现代工具获得与 Ubuntu MATE 类似的用户体验呢?
### 将 Ubuntu MATE 的体验带入 Debian 的版本中

以下是 Martin 提到的内容:
>
> 用最近的标准来说,Ubuntu MATE 22.10 是一个适度更新,专注与“提高生活质量”。而这个版本的 Ubuntu MATE 没有采用你通常期望的桶状 ? 变化清单是有原因的,这是因为我一直在帮助将 Ubuntu MATE 的完整体验带到 Debian MATE ?。
>
>
>
这是很吸引人的东西。
**这是否意味着 Ubuntu MATE 未来不会有任何重大更新?**
不,Ubuntu MATE 仍然会收到更新。
另外,Martin 还澄清说,他并没有退出 Ubuntu MATE 的开发,并且将和往常一样进行。
然而,如果你想看看 Ubuntu MATE 的主要功能更新的长列表,你必须要等待一段时间。
他打算在 Debian MATE 和 Ubuntu MATE 之间提供一致的体验。
Debian MATE 在用户中不那么受欢迎并**不足为奇**。主要是因为它不提供 Ubuntu MATE 那样的现代改进。
因此,他们的目标是为 Debian MATE 带来类似的体验,这将使现有用户既可以使用 Debian 也可以使用 Ubuntu。
\*\*此外,\*\*这将使开发变得更容易:
>
> 使 Debian 和 Ubuntu 中的 MATE 体验保持一致,使所有相关人员的维护变得更加容易。
>
>
>
**那么,我们是否可以期待与 Debian 上是否能和 Ubuntu MATE 22.10(Kinetic Kudu)非常相似?**

大概是。但这需要时间。
>
> ? 他们希望在 Debian 12 的 Debian MATE 上提供类似的体验。我们已经知道 Debian 12 计划于 2023 年发布。因此,有足够的时间等待它。
>
>
>
你可以期待将 MATE Tweak 和 [Ayatana Indicators](https://ayatanaindicators.github.io/about/) 等应用程序集成到 Debian MATE 中。
这让我认为 Debian MATE 可以成为 Ubuntu MATE 用户寻求改变或想要尝试 Debian 的MATE 风格的绝佳选择。
当然,这并不会让即将到来的 Ubuntu MATE 22.10 变得不那么令人兴奋。它仍将包括许多有价值的好东西;你可能想查看它的 [beta 版本说明](https://ubuntu-mate.org/blog/ubuntu-mate-kinetic-kudu-release-notes/) 以了解更多信息。
? *在了解了这一发展之后,你如何看待 Debian 未来的 MATE 版本?你会为此放弃 Ubuntu MATE 吗?让我知道你的想法!*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-mate-debian/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[KevinZonda](https://github.com/KevinZonda) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

**Martin Wimpress**, one of the founders and maintainers of Ubuntu MATE, has mentioned something rather interesting in the beta release notes for Ubuntu MATE 22.10.
He aims to bring the Ubuntu MATE experience to Debian 🧐
Wait, can't you already install MATE on Debian?
Yes, but what about an akin user experience to Ubuntu MATE with all the modern tools on Debian?
## Bringing Ubuntu MATE Experience to Debian's Spin

Here's what Martin mentions:
Ubuntu MATE 22.10 is a modest update by recent standards and focused on “quality of life improvements”. And there is good reason why this release of Ubuntu MATE doesn’t feature the usual bucket 🪣 list of changes you’d typically expect, and that’s because I’ve been helping bring the full Ubuntu MATE experience to Debian MATE 🧉
That's something fascinating.
**Does this mean there won't be any significant future updates to Ubuntu MATE?**
No, Ubuntu MATE will still receive updates.
Also, Martin has clarified that he is not stepping away from the development of Ubuntu MATE and will continue as usual.
However, if you are looking for a long list of major feature updates to Ubuntu MATE, you must wait a while.
### Suggested Read 📖
[13 Interesting Distributions Based on Debian Linux - It’s FOSSDebian is the mother of so many Linux distributions. It is not easy to select the best among them. Here, I share some of the interesting Debian-based distros.](https://itsfoss.com/debian-based-distros/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

He intends to provide a consistent experience across Debian's MATE spin and Ubuntu MATE.
**It is no surprise** that Debian MATE is not as popular among users. Mainly because it does not offer the modern refinements, you get with Ubuntu MATE.
Hence, they aim to bring in a similar experience to Debian MATE, which will enable existing users to use either Debian or Ubuntu as the base.
**Furthermore, **this development will make things easier for the development:
Making the MATE experience in Debian and Ubuntu consistent makes maintenance easier for all involved.
**So, can we expect something very similar to Ubuntu MATE 22.10 (Kinetic Kudu) on Debian?**
Probably yes. But, it will take time.
**Debian 12**. We already know that Debian 12 has been slated for release in
**2023**. So, there is plenty of time to wait for it.
You can expect apps such as MATE Tweak and [Ayatana Indicators](https://ayatanaindicators.github.io/about/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) integrated into Debian's MATE spin.
This makes me think that Debian MATE can be an excellent alternative for Ubuntu MATE users looking for a change or wanting to try the Debian flavor of MATE.
Of course, this does not make the upcoming Ubuntu MATE 22.10 less exciting. It will still include numerous valuable goodies; you might want to check out its [beta release notes](https://ubuntu-mate.org/blog/ubuntu-mate-kinetic-kudu-release-notes/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to learn more.
💬 *What do you think about Debian's future MATE spin after learning about this development? Would you ditch Ubuntu MATE for it? Let me know your thoughts!*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,120 | Ubuntu Pro 现在免费为你提供 10 年的安全更新 | https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-pro-free/ | 2022-10-09T16:36:22 | [
"Ubuntu Pro",
"Ubuntu",
"LTS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15120-1.html |
>
> 好消息:一个免费的 Ubuntu Pro 计划,每个人都可以获得 10 年的安全更新。
>
>
>

Canonical 为 Ubuntu Pro 引入了一个免费计价层,该层针对个人使用和小规模部署。
**Ubuntu Pro** 订阅(以前称为 “Ubuntu Advantage”)最初是为企业提供的,用于为他们额外提供 5 年的 Ubuntu LTS 版本的扩展安全维护更新。
该免费计价层已在公共测试版中提供。
### 对于个人与数据中心的 Ubuntu Pro
目前作为测试版提供,Ubuntu Pro 的免费计价层可供个人用户或小型数据中心使用,最多可容纳五台机器。
随着此次发布,Canonical 首席执行官 Mark Shuttleworth 表示:
>
> 自从我们首次推出 Ubuntu LTS 以来,并为这个主要的操作系统免费提供五年的安全保障,我们的企业客户要求我们在私人商业协议下覆盖越来越广泛的开源领域。今天,我们很高兴通过免费的个人 Ubuntu Pro 订阅免费向世界上的任何人提供!
>
>
>
与标准发行版相比,Ubuntu Pro 的主要优势在于不断提供安全补丁。

**对于希望系统稳定而又不会丢失安全更新的用户来说,这是一个难以置信的好消息。**
安全维护更新会定期推出,尤其是在发现新的 CVE(常见漏洞和暴露)时。
用户可以利用 [Livepatch](https://ubuntu.com/security/livepatch) 来应用安全补丁,而无需关闭他们的系统。这包含在 Ubuntu Pro 订阅中。
小型企业和个人还可以使用合规管理所需的各种工具,支持 PCI-DSS、HIPAA、FedRAMP 等合规标准,并作为 Ubuntu Pro 订阅的一部分。
**那么,个人和企业使用 Ubuntu 的更多激励措施?**
>
> ? 如果你最多有五台机器要用,Ubuntu Pro 的免费个人层应该是一个不折不扣正确的选择,而不是其他平台。
>
>
>
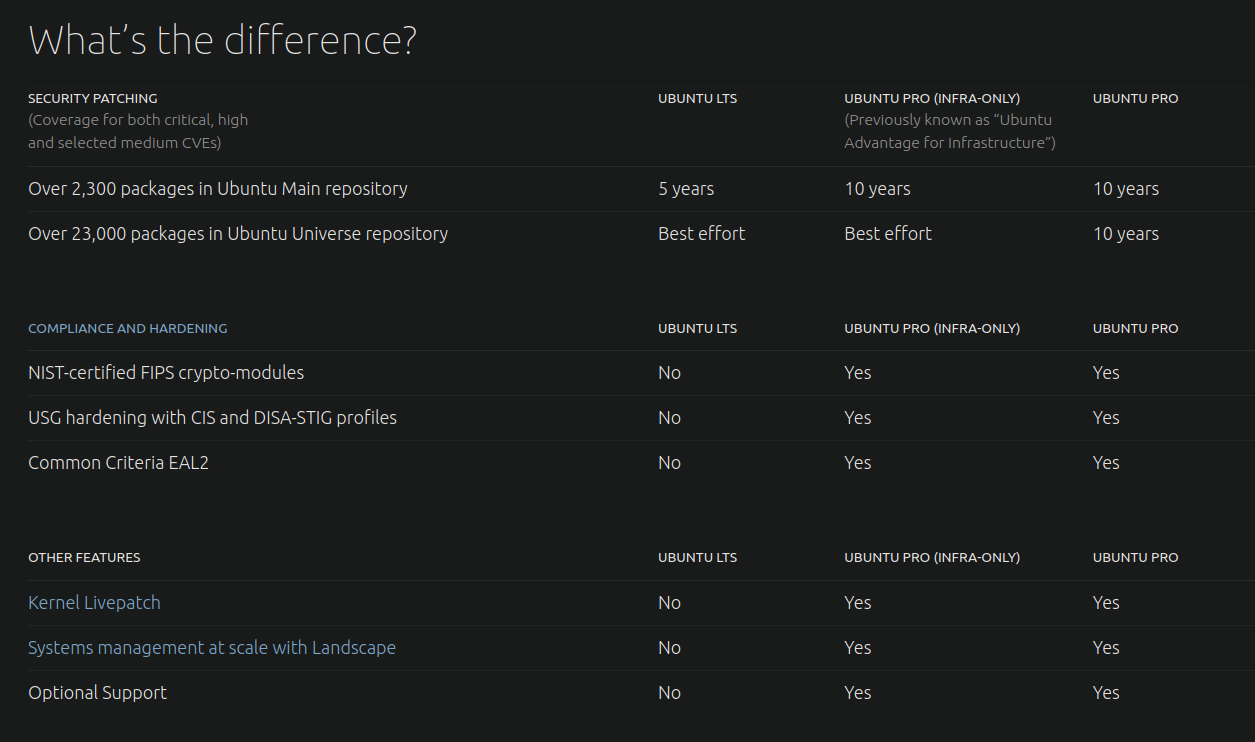
借助个人 Ubuntu Pro 计划,小规模用户现在可以享受 10 年安全保障(*5 年 LTS 更新 + 5 年扩展安全维护更新*),**其中包括对额外 23,000 个软件包的支持。**
这个免费的 Ubuntu Pro 订阅层的推出可以帮助 [Canonical](https://canonical.com/) 吸引更多用户使用 Ubuntu,这对于计算机用户采用 Linux 来说是一件好事。
你只需在他们的 [官方网站](https://ubuntu.com/pro) 上注册个人 Ubuntu Pro 订阅。
更多详情,请查看[官方公告](https://ubuntu.com//blog/ubuntu-pro-beta-release)。
>
> **[注册 Ubuntu Pro](https://ubuntu.com/pro)**
>
>
>
? *你会考虑选择免费的个人 Ubuntu Pro 订阅吗? 或者,你认为你会每 5 年升级到新的 LTS 版本吗?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-pro-free/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[KevinZonda](https://github.com/KevinZonda) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Canonical has introduced a free tier to Ubuntu Pro which is aimed at personal use and small-scale deployments.
**Ubuntu Pro** subscription (formerly known as Ubuntu Advantage) was originally offered to enterprises for providing them with extended security maintenance updates to Ubuntu LTS releases for an extra 5 years of updates.
The free tier has been made available in public beta.
## Ubuntu Pro for Personal and Data Centers
Currently available as a beta release, the free tier of Ubuntu Pro can be used by individual users or small-scale data centers for a maximum number of five machines.
With this launch, CEO of Canonical, Mark Shuttleworth said:
Since we first launched Ubuntu LTS, with five years free security coverage for the main OS, our enterprise customers have asked us to cover more and more of the wider open-source landscape under private commercial agreements. Today, we are excited to offer the benefits of all of that work, free of charge, to anyone in the world, with a free personal Ubuntu Pro subscription
The main advantage of Ubuntu Pro over the standard distribution, are the constant security patches.
**This is an incredibly good news for users who want stability on their systems without losing out on security updates.**
The security maintenance updates are pushed out on a regular basis, especially when a new CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) is found.
Users can take advantage of [Livepatch](https://ubuntu.com/security/livepatch?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to apply security patches without shutting down their systems. This is included with the Ubuntu Pro subscription.
Small businesses and individuals can also make use of various tools required for compliance management, support for compliance standards such as PCI-DSS, HIPAA, FedRAMP and as part of Ubuntu Pro subscription.
**So, more incentives to use Ubuntu for individuals and businesses?**
With the personal Ubuntu Pro plan small-scale users can now take advantage of the 10-year security coverage (*5 Year LTS updates + 5 Year Extended Security Maintenance updates*), **which includes support for an additional 23,000 packages.**
The launch of this free tier of the Ubuntu Pro subscription can help [Canonical](https://canonical.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) attract more users to use Ubuntu, which is a good thing for Linux adoption among computer users.
You just have to sign up for a personal Ubuntu Pro subscription on their [official website](https://ubuntu.com/pro?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
For more details, check out the [official announcement](https://ubuntu.com//blog/ubuntu-pro-beta-release?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
💬 *Do you think you will be opting for the free personal Ubuntu Pro subscription? Or, do you think you will be upgrading to a new LTS release every 5 years?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,121 | 负载均衡的初学者指南 | https://opensource.com/article/21/4/load-balancing | 2022-10-09T17:10:41 | [
"负载均衡"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15121-1.html |
>
> 负载均衡就是将资源分配到某一时刻最需要它的地方。
>
>
>

当个人电脑刚开始发展的时候,一个家庭可能只有一台(或更少)的电脑。孩子们白天玩电脑游戏,家长们晚上在业务支撑系统上做会计、编程,或者漫游。然而,想象一下今天一个只有一台电脑的家庭,你可以预想到这样会产生什么样的冲突。每个人都想使用电脑,而只有一副键盘和鼠标。
随着计算机变得越来越普遍,IT 行业或多或少也出现了同样的情况。对服务和服务器的需求已经增长到了会因为用量过大而停机的程度。幸运的是,我们现在有了负载均衡的概念来帮助我们处理需求。
### 负载均衡是什么?
负载均衡是一个通用术语,指的是为了确保高效分配所管理的资源而做的事情。对于 Web 服务器的系统管理员来说,负载均衡通常意味着确保 Web 服务器软件(例如 [Nginx](https://opensource.com/business/15/4/nginx-open-source-platform))配置了足够的工作节点来处理激增的访客。换言之,如果一个网站突然变得非常受欢迎,其访问者在几分钟内增加了四倍,那么运行服务器的软件必须能够响应每个访问者,并不能让任何访问者发现服务质量下降。对于简单的网站,这就像修改一行配置选项一样简单,但对于具有动态内容的复杂站点,每个用户都有多个数据库查询,这可能是一个严重的问题。
这个问题本应随着云计算的发展而解决,但当 Web 应用程序遇到意外激增时,无法扩展也不是不可能。
在进行负载均衡时,需要记住的重要一点是,*高效地*分配资源并不一定意味着*平均地*分配资源。并非所有任务都在任何时候都需要所有的可用资源。一个智能的负载均衡策略仅在需要资源时才为用户和任务提供资源。这通常是应用程序开发人员的领域,而不是 IT 基础架构的责任。异步应用程序对于确保离开计算机休息的用户不占用服务器上的宝贵资源至关重要。
### 负载均衡是怎么工作的?
负载均衡通过在多个计算节点上分配工作负载来避免瓶颈。这些节点可能是数据中心中的物理服务器、云环境中的容器、用于边缘计算而战略性放置的服务器、复杂应用程序框架中的独立 Java 虚拟机(JVM),或在单个 Linux 服务器上运行的守护进程。
这个想法是把一个大问题分成几个小任务,并把每个任务分配给一台专用计算机。例如,对于一个要求用户登录的网站,该网站可能托管在服务器 A 上,而登录页面和所有随附的身份验证查询都托管在服务器 B 上。这样,新用户登录帐户时就不会占用其它使用该站点的用户的资源。
#### 云计算负载均衡
云计算使用 [容器](https://opensource.com/resources/what-are-linux-containers),因此通常没有单独的物理服务器来处理不同的任务(实际上,有许多单独的服务器,但它们被聚集在一起作为一个计算“大脑”)。相反,“<ruby> 容器荚 <rt> pod </rt></ruby>” 是由几个容器创建的。当一个容器荚由于其用户或任务负载而开始耗尽资源时,会生成一个相同的容器荚。容器荚共享存储和网络资源,每个容器荚在创建时被分配给一个计算节点。可以根据负载需要创建或销毁容器荚,这样无论有多少用户,用户都可以体验到一致的服务质量。
#### 边缘计算
[边缘计算](https://opensource.com/article/18/5/edge-computing) 在负载均衡时考虑到了现实世界。云计算自然是一个分布式系统,但实际上,云计算的节点通常集中在几个数据中心。用户离运行云计算的数据中心越远,他们为获得最佳服务所必须克服的物理障碍就越多。即使有光纤连接和适当的负载均衡,位于 3000 英里外的服务器的响应时间也可能比仅仅 300 英里外的响应时间长。
边缘计算将计算节点带到云计算的“边缘”,试图弥合地理鸿沟,为云计算形成一种卫星网络,因此它也在良好的负载均衡工作中发挥了作用。
### 什么是负载均衡算法?
有许多负载均衡策略,它们的复杂性取决于所涉及的技术和需求。负载均衡不必复杂,而且从一开始就负载均衡很重要,即使在使用 [Kubernetes](https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-kubernetes) 和 [Keepalived](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/keepalived-basics) 这样的专用软件时也是如此。
当你可以设计应用程序,自己为它采取简单的预防措施时,不要依赖容器来均衡负载。如果你从一开始就将应用程序设计为模块化和临时性的,那么你将受益于通过巧妙的网络设计、容器编排和其他未来技术带来的负载均衡机会。
可以指导应用程序开发人员或网络工程师工作的一些流行算法包括:
* 按顺序将任务分配给服务器(这通常被称为轮询调度)。
* 将任务分配给当前最不繁忙的服务器。
* 将任务分配给具有响应最快的服务器。
* 随机分配任务。
举个例子,在分配特别复杂的任务时,可以组合或加权这些原则以分配到组中最强大的服务器。通常使用 [编排](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/orchestration-vs-automation),这样管理员就不必为负载均衡寻找完美的算法或策略,尽管有时需要由管理员选择使用哪种负载均衡方案组合。
### 预料意料之外
负载均衡实际上并不是要确保在整个网络中均匀使用所有资源。负载均衡实际上是确保即使发生意外情况也能提供可靠的用户体验。良好的基础设施可以承受计算机崩溃、应用程序过载、网络流量冲击和用户错误。思考你的服务如何才能具有弹性,并从头开始相应地设计负载均衡策略。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/4/load-balancing>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[FYJNEVERFOLLOWS](https://github.com/FYJNEVERFOLLOWS) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When the personal computer was young, a household was likely to have one (or fewer) computers in it. Children played games on it during the day, and parents did accounting or programming or roamed through a BBS in the evening. Imagine a one-computer household today, though, and you can predict the conflict it would create. Everyone would want to use the computer at the same time, and there wouldn't be enough keyboard and mouse to go around.
This is, more or less, the same scenario that's been happening to the IT industry as computers have become more and more ubiquitous. Demand for services and servers has increased to the point that they could grind to a halt from overuse. Fortunately, we now have the concept of load balancing to help us handle the demand.
## What is load balancing?
Load balancing is a generic term referring to anything you do to ensure the resources you manage are distributed efficiently. For a web server's systems administrator, load balancing usually means ensuring that the web server software (such as [Nginx](https://opensource.com/business/15/4/nginx-open-source-platform)) is configured with enough worker nodes to handle a spike in incoming visitors. In other words, should a site suddenly become very popular and its visitor count quadruple in a matter of minutes, the software running the server must be able to respond to each visitor without any of them noticing service degradation. For simple sites, this is as simple as a one-line configuration option, but for complex sites with dynamic content and several database queries for each user, it can be a serious problem.
This problem is supposed to have been solved with cloud computing, but it's not impossible for a web app to fail to scale out when it experiences an unexpected surge.
The important thing to keep in mind when it comes to load balancing is that distributing resources *efficiently* doesn't necessarily mean distributing them *evenly*. Not all tasks require all available resources at all times. A smart load-balancing strategy provides resources to users and tasks only when those resources are needed. This is often the application developer's domain rather than the IT infrastructure's responsibility. Asynchronous applications are vital to ensuring that a user who walks away from the computer for a coffee break isn't occupying valuable resources on the server.
## How does load balancing work?
Load balancing avoids bottlenecks by distributing a workload across multiple computational nodes. Those nodes may be physical servers in a data center, containers in a cloud, strategically placed servers enlisted for edge computing, separate Java Virtual Machines (JVMs) in a complex application framework, or daemons running on a single Linux server.
The idea is to divide a large problem into small tasks and assign each task to a dedicated computer. For a website that requires its users to log in, for instance, the website might be hosted on Server A, while the login page and all the authentication lookups that go along with it are hosted on Server B. This way, the process of a new user logging into an account doesn't steal resources from other users actively using the site.
### Load balancing the cloud
Cloud computing uses [containers](https://opensource.com/resources/what-are-linux-containers), so there aren't usually separate physical servers to handle distinct tasks (actually, there are many separate servers, but they're clustered together to act as one computational "brain"). Instead, a "pod" is created from several containers. When one pod starts to run out of resources due to its user or task load, an identical pod is generated. Pods share storage and network resources, and each pod is assigned to a compute node as it's created. Pods can be created or destroyed on demand as the load requires so that users experience consistent quality of service regardless of how many users there are.
### Edge computing
[Edge computing](https://opensource.com/article/18/5/edge-computing) takes the physical world into account when load balancing. The cloud is naturally a distributed system, but in practice, a cloud's nodes are usually concentrated in a few data centers. The further a user is from the data center running the cloud, the more physical barriers they must overcome for optimal service. Even with fiber connections and proper load balancing, the response time of a server located 3,000 miles away is likely greater than the response time of something just 300 miles away.
Edge computing brings compute nodes to the "edge" of the cloud in an attempt to bridge the geographic divide, forming a sort of satellite network for the cloud, so it also plays a part in a good load-balancing effort.
## What is a load-balancing algorithm?
There are many strategies for load balancing, and they range in complexity depending on what technology is involved and what the requirements demand. Load balancing doesn't have to be complicated, and it's important, even when using specialized software like [Kubernetes](https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-kubernetes) or [Keepalived](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/keepalived-basics), to start load balancing from inception.
Don't rely on containers to balance the load when you could design your application to take simple precautions on its own. If you design your application to be modular and ephemeral from the start, then you'll benefit from the load balancing opportunities made available by clever network design, container orchestration, and whatever tomorrow's technology brings.
Some popular algorithms that can guide your efforts as an application developer or network engineer include:
- Assign tasks to servers sequentially (this is often called
*round-robin*). - Assign tasks to the server that's currently the least busy.
- Assign tasks to the server with the best response time.
- Assign tasks randomly.
These principles can be combined or weighted to favor, for instance, the most powerful server in a group when assigning particularly complex tasks. [Orchestration](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/orchestration-vs-automation) is commonly used so that an administrator doesn't have to drum up the perfect algorithm or strategy for load balancing, although sometimes it's up to the admin to choose which combination of load balancing schemes to use.
## Expect the unexpected
Load balancing isn't really about ensuring that all your resources are used evenly across your network. Load balancing is all about guaranteeing a reliable user experience even when the unexpected happens. Good infrastructure can withstand a computer crash, application overload, onslaught of network traffic, and user errors. Think about how your service can be resilient and design load balancing accordingly from the ground up.
## 3 Comments |
15,124 | 一个全新的用于英伟达显卡的开源 Vulkan 驱动已经准备好测试了! | https://news.itsfoss.com/nvidia-nvk/ | 2022-10-10T15:21:56 | [
"英伟达"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15124-1.html |
>
> 为英伟达显卡开发的一个全新的开源驱动正在开发中!这里有一些好的进展……
>
>
>

**NVK** 是一个全新的用于英伟达显卡的开源 Vulkan 驱动,它的目标是成为新的主流显卡驱动。
这成为可能的部分原因是因为英伟达开源了数据中心 GPU 和消费级 GPU(GTX/RTX)的 GPU 内核模块。
>
> **[英伟达在改善其 GPU 在 Linux 上的体验方面迈出了重要的一步](https://news.itsfoss.com/nvidia-open-source-linux/)**
>
>
>
它使开发人员能够改进开源驱动程序并启用比以前更多的功能。
让我们来看看 NVK 可以提供什么。
### 新的适用于英伟达 GPU 的 NVK 开源驱动程序
**Jason Ekstrand**(Collabora 的工程师)和 Red Hat 的其他人已经在过去几个月里编写了 NVK 的代码。
他们可以利用 Turing 系列显卡提供的统一固件 BLOB,然后在其上构建 Vulkan 支持。
**但是,不是已经有了 nouveau 开源驱动程序了吗?**
NVK 与其他的 nouveau 驱动非常不同,因为它是从头开始编写的。
nouveau 是一个主要的英伟达显卡的开源驱动程序,已经年久失修了,试图在它的基础上构建是一个很多人都无法承担的任务。
当然,它是由有很多才华的工程师开发的,但是缺乏公司的支持和贡献者的影响了它的发展。
**NVK 旨在克服这些问题,同时专注于对 Turing 系列及更高版本 GPU 的支持。**
由于内核的开发方式,对于 Kepler、Maxwell 和 Pascal 等较旧的 GPU 的支持可能不会很容易地加入 NVK。它也许极大地依赖于新内核,从而只支持较新的 GPU。
同时,nouveau 内核接口与 Vulkan 不兼容,阻碍了对较旧 GPU 的支持。
但是,仍然有进一步测试的空间,这可能会让 NVK 可以支持较旧的 GPU。
当然,随着更多的社区贡献,NVK 可以通过增加额外的功能和 GPU 支持来改进。
### 如何尝试它?
NVK 目前处于非常初级的状态,有很多功能缺失,并且正在持续开发中。
**所以,它还不适合让所有类型的用户尝试。**
你还是可以通过拉取 [freedesktop.org](http://freedesktop.org) 上的 [nouveau/mesa 项目](https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/nouveau/mesa) 的 nvk/main 分支并构建它来尝试它。
如果你想的话,你也可以通过贡献到该项目下的 [nvk/main 分支](https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/nouveau/mesa/-/tree/nvk/main/) 来帮助 NVK 的开发。
对于更多的技术信息,你可以参考 [官方公告](https://www.collabora.com/news-and-blog/news-and-events/introducing-nvk.html)。
### 未来潜力
NVK 有很多潜力,尤其是与老化的 [nouveau](https://nouveau.freedesktop.org/) 图形驱动套件相比。
这可以为 nouveau 带来一个合适的继承者,同时为 Linux 提供一个带有很多功能的、主流的开源英伟达图形驱动套件。
? *你对此有什么看法?你认为这最终能够实现 nouveau 驱动程序所未能实现的吗?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/nvidia-nvk/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Cubik65536](https://github.com/Cubik65536) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

**NVK** is a new open-source Vulkan driver for NVIDIA Graphics hardware and aims to be the new go-to graphics driver.
This was made possible in part due to Nvidia releasing open-source GPU kernel modules for its data center GPUs and consumer cards (GTX/RTX).
[NVIDIA Takes a Big Step to Improve its GPU Experience on LinuxLinus Torvalds will be happy to hear this… NVIDIA finally announced an open-source initiative to improve the GPU experience on Linux. Unfortunately, it isn’t exactly what you think, you will still find proprietary drivers around. But, it’s as significant as ditching the proprietary dr…](https://news.itsfoss.com/nvidia-open-source-linux/)

It has enabled developers to improve open-source drivers and enable more features than what was possible before.
Let's take a look at what NVK has to offer.
## New NVK Open-Source Driver for NVIDIA GPU
**Jason Ekstrand** (engineer at Collabora) and a few others from Red Hat have been writing the code for NVK for the past few months.
They could take advantage of the unified firmware BLOBs that Turing GPUs offer, and built on top of it with Vulkan support.
**But, open-source nouveau drivers exist, right?**
NVK is very different from the nouveau drivers, as it has been written from scratch.
Nouveau, a major open-source driver suite for Nvidia GPUs has fallen into disrepair, and trying to build on it is a task not many can take up.
Of course, skillful engineers worked on it, but lack of corporate backing and contributors affected its evolution.
**NVK aims to get over those while focusing on support for GPUs of the Turing series and later to start with.**
Support for older GPUs such as Kepler, Maxwell, and Pascal might not come to NVK that easily, because of how the kernel is being developed. It might have a hard dependency on the new kernel, resulting in support for newer GPUs only.
Also, the nouveau kernel interface not playing nice with Vulkan and hindering support for older GPUs.
But, there is still scope for further testing, which can result in support for older GPUs with NVK.
Of course, with more community contributions, NVK can be improved with additional features and GPU support.
## How To Try It Out?
NVK is currently available in a very alpha-build state, with many features missing and under constant development.
**So, it is not yet ready for all kinds of users to get a hands on it.**
You can still try it out by pulling and building it from the nvk/main branch from the [nouveau/mesa project](https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/nouveau/mesa?ref=news.itsfoss.com) on freedesktop.org.
If you want, you can also contribute to the development of NVK by heading over to the [nvk/main branch](https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/nouveau/mesa/-/tree/nvk/main/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) of the same.
For more technical info, you can refer to the [official announcement](https://www.collabora.com/news-and-blog/news-and-events/introducing-nvk.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Future Potential
NVK has a lot of potential, especially compared to the aging [nouveau](https://nouveau.freedesktop.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) graphics driver suite.
This can lead to a proper successor of nouveau and a mainstream open-source Nvidia graphics driver suite for Linux with a lot of functionality on offer.
💬 *What are your thoughts on this? Do you think this will finally achieve what nouveau drivers failed to?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,125 | 当今世界的开源安全问题 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/10/security-issues-with-open-source-in-todays-world/ | 2022-10-10T16:09:20 | [
"开源",
"安全"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15125-1.html | 
>
> 开源代码可能是当今大多数公司最可行的选择,但它也伴随着自己的问题。
>
>
>
许多人支持使用 <ruby> 开源软件 <rt> open source software </rt></ruby>(OSS)。毕竟,我们为什么要不断地尝试构建代码来解决别人已经解决过的问题?为什么不分享信息并逐步和迭代地增强当前的开源解决方案呢?这些<ruby> 平等主义价值观 <rt> egalitarian values </rt></ruby>,可能是整个文明的根本,更不用说软件了,但还是包含了几千年来一直存在的冲突。
开源软件安全的问题在于,尽管任何人都可以查看源代码,但这并不意味着他们会这么做。有一些广泛使用的开源项目仅由数量有限的工程师维护。这些工程师无法完全自愿地提供时间和精力,因为他们也需要支付他们的账单。
即使对于更复杂的开源项目,这也是一个问题。举个例子,Linux 内核项目由 3000 多万行代码组成,包含数百个需要解决的缺陷,并有近 2000 名活跃的开发者。每个活跃的开发者都写了超过 15000 行的代码。
根据 Linux 基金会最近的一项研究,一个应用程序平均有 5.1 个重大漏洞仍未解决,41% 的企业对其开源软件的安全性缺乏信心。而更糟糕的是,只有 49% 的企业拥有开源安全策略。
即使开源软件有安全漏洞,这也不能保证它能被修复。调查显示,目前修复一个漏洞平均需要 97.8 天,使使用该软件的企业在几个月内容易受到攻击。这就是开源软件安全有时被忽视的地方:就像好人可以寻找代码中的错误和漏洞来修复它们一样,坏人也可以寻找同样的漏洞来利用它们。
仅仅依靠志愿者社区来发现漏洞、报告漏洞和修复漏洞是一个漫长的过程。在你继续受益于开源的广泛优势的同时,花钱请人检查你的开源解决方案的安全性可以帮助弥补这个问题。
由于必须部署开源软件的更新和补丁以保证系统的安全,这一要求会带来独特的困难。如果你的解决方案依赖于某个软件版本,更新你的关键任务软件可能会导致功能损失和/或计划外的停机。当情况对业务至关重要时,聘请专家来回传补丁并维护一个时间更长的版本可能比让大型社区愿意去做更加优雅。
开源社区经常使用的一句话是:“这是开源的,去改变它吧!”它强调了一个关键点:当别人在项目中投入时间、精力或金钱的时候,期望白白得到良好的安全水平是不合理的,也是不可持续的。
要么按原定计划为开源做出贡献,改进代码并为他人发布,要么聘请专业人士管理开源代码并在必要时进行调试,这些都是选择。然而,这个行业无法承担完全不做贡献。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/10/security-issues-with-open-source-in-todays-world/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[KevinZonda](https://github.com/KevinZonda) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Open source may be the most viable option for most companies today but it comes with its own set of problems too.*
Many people support the use of open source software (OSS). After all, why would we keep trying to build code that addresses issues that have already been resolved by others? Why not share the information and progressively and iteratively enhance the current open source solutions? These egalitarian values, however perhaps fundamental to civilization in general, not to mention software, nonetheless include conflicts that have been a problem for millennia.
The problem with open source software security is that just because anyone can view the source code doesn’t imply they will. There are extensively used open-source projects that are only being maintained by a limited number of engineers. These engineers are unable to provide their time and effort completely voluntarily since they also need to pay their bills.
Even for more complex open source projects, this can be a problem. As an illustration, the Linux kernel project consists of more than 30 million lines of code, contains hundreds of flaws that need to be resolved, and has close to 2000 active developers. Each active developer has written more than 15,000 lines of code.
According to a recent research from the Linux Foundation, an application has an average of 5.1 significant vulnerabilities that are still open, and 41% of enterprises lack confidence in the security of their open source software. And to make matters worse, only 49% of businesses have an open source security policy.
Even if open source software has a security flaw, that does not guarantee that it will be fixed. The survey revealed that it presently takes 97.8 days on average to repair a vulnerability, leaving businesses using that software vulnerable to assaults for several months. This is the sometimes overlooked aspect of open source software security: just as the good men can look for faults and vulnerabilities in the code to repair them, the bad guys can look for the same bugs to exploit them.
It is a long shot to rely solely on a volunteer community to find vulnerabilities, report them, and fix them. While you continue to benefit from open source’s broader advantages, paying someone to examine the security of your open source solutions can help close this gap.
Since OSS updates and patches must be implemented to secure systems, this requirement can bring unique difficulties. Updating your mission-critical software could result in functionality loss and/or unplanned downtime if your solution depends on a certain software version. When a situation is business-critical, it may be more elegant to hire a specialist to backport the patch and maintain a version for longer than the larger community is willing to.
The open source community frequently uses the phrase “It’s open source, go change it!” and it emphasises a crucial point: It is unreasonable and unsustainable to expect good security levels for nothing while others invest their time, effort, or money in the project.
Either contribute to open source as it was intended, improve the code and publish it for others, or hire professionals to manage the OSS code and debug it as necessary are options. However, the industry cannot afford to contribute nothing at all. |
15,126 | 如何在最小安装的 CentOS、RHEL、Rocky Linux 中设置互联网 | https://www.debugpoint.com/setup-internet-minimal-install-server/ | 2022-10-10T16:24:00 | [
"网络",
"最小安装"
] | /article-15126-1.html | 
>
> 在最小安装的服务器中设置互联网或网络非常容易。本指南将解释如何在最小安装的 CentOS、RHEL 和 Rocky Linux 中设置互联网或网络。
>
>
>
当你安装了任何服务器发行版的最小安装环境,你将没有任何 GUI 或桌面环境来设置你的网络或互联网。因此,当你只能访问终端时,了解如何设置互联网非常重要。NetworkManager 工具提供了必要的工具,辅以 systemd 服务来完成这项工作。以下是方法。
### 在最小安装的 CentOS、RHEL、Rocky Linux 中设置互联网
在你完成了服务器的安装后,启动进入服务器终端。理想情况下,你会看到一个终端提示符。使用 root 或管理员账户登录。
首先,尝试使用 [nmcli](https://linux.die.net/man/1/nmcli) 检查网络接口的状态和详细信息。`nmcli` 是用于控制 NetworkManager 服务的命令行工具。使用以下命令进行检查。
```
nmcli device status
```
这将显示设备名称、状态等。

运行工具 `nmtui` 来配置网络接口。
`nmtui` 是 NetworkManager 工具的一部分,它为你提供了一个友好的用户界面来配置网络。
这是 `NetworkManager-tui` 包的一部分,在你完成最小服务器安装后默认安装。
```
nmtui
```
单击 nmtui 窗口中的“<ruby> 编辑连接 <rt> Edit a connection </rt></ruby>”。

选择接口名称

在“<ruby> 编辑连接 <rt> Edit Connection </rt></ruby>”窗口中,为 IPv4 和 IPv6 选择“<ruby> 自动 <rt> Automatic </rt></ruby>”选项。并选择“<ruby> 自动连接 <rt> Automatically Connect </rt></ruby>”。完成后按 “OK”。

使用以下命令通过 [systemd systemctl](https://www.debugpoint.com/2020/12/systemd-systemctl-service/) 重启 NetworkManager 服务。
```
systemctl restart NetworkManager
```
如果一切顺利,你可以在最小安装的 CentOS、RHEL 和 Rocky Linux 服务器中连接到网络和互联网。前提是你的网络有互联网连接。你可以使用 `ping` 来验证它是否正常工作。

### 附加技巧:在最小化服务器中设置静态 IP
当你将网络配置设置为自动时,接口会在你连接到互联网时动态分配 IP。在你设置局域网的某些情况下,你可能希望将静态 IP 分配给你的网络接口。这非常容易。
打开你的网络配置脚本。将 `ens3` 改为为你自己的设备名。
```
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens3
```
在上面的文件中,使用 `IPADDR` 属性添加所需的 IP 地址。保存文件。
```
IPADDR=192.168.0.55
```
在 `/etc/sysconfig/network` 中为你的网络添加网关。
```
NETWORKING=yes
HOSTNAME=debugpoint
GATEWAY=10.1.1.1
```
在 `/etc/resolv.conf` 中添加任意公共 DNS 服务器。
```
nameserver 8.8.8.8
nameserver 8.8.4.4
```
然后重启网络服务。
```
systemctl restart NetworkManager
```
这就完成了静态 IP 的设置。你还可以使用 `ip addr` 命令检查 IP 详细信息。
### 总结
我希望本指南可以帮助你在最小化安装的服务器中设置网络、互联网和静态 IP。如果你有任何问题,请在评论区告诉我。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/setup-internet-minimal-install-server/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,128 | 谷歌 AI 推出新的数组存储开源库 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/10/google-ai-unveils-a-new-open-source-library-for-array-storage/ | 2022-10-11T10:19:15 | [
"AI",
"谷歌"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15128-1.html | 
>
> 谷歌 AI 引入了一个用于数组存储的高性能开源库 TensorStore。
>
>
>
谷歌开发的开源 C++ 和 Python 框架 TensorStore 旨在加速大型多维数组的读写设计。覆盖单一大型坐标系的多维数据集通常用于当代计算机科学和机器学习应用程序中。使用这些数据集具有挑战性,因为客户经常希望进行涉及多个工作站并行操作的调查,并且可能会以不可预测的间隔和不同的规模接收和输出数据。
谷歌研究院开发了 TensorStore,该库为用户提供了一个可以管理巨大数据集的 API,而无需复杂的硬件,以解决数据存储和操作问题。该库支持许多存储系统,包括本地和网络文件系统、谷歌云存储等。
为了加载和处理大量数据,TensorStore 提供了一个简单的 Python API。任何任意大小的基础数据集都可以加载和更新,而无需将数据集完整存储在内存中,因为在需要精确切片之前不需要在内存中读取或保存实际数据。
这是通过索引和操作语法实现的,它与 NumPy 操作的语法非常相似。除了虚拟视图、广播、对齐和其他复杂的索引功能,TensorStore 还支持如数据类型转换、降低取样和随意创建的数组这些功能。
此外,TensorStore 包含一个异步 API,可以并发进行读取或写入操作。在执行其他工作时,软件可以进行内存缓存处理(可配置),从而减少在访问常用数据时处理较慢存储系统的需要。
大型数值数据集需要大量的处理能力来检查和分析。实现这一点的常用方法是在分散在许多设备上的大量 CPU 或加速器内核之间并行化任务。在保持出色速度的同时并行分析单个数据集的能力一直是 TensorStore 的关键目标。 PaLM、脑图和其他复杂的大规模机器学习模型是 TensorStore 应用案例的一些例子。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/10/google-ai-unveils-a-new-open-source-library-for-array-storage/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[KevinZonda](https://github.com/KevinZonda) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *TensorStore, a High-Performance Open Source Library for Array Storage, has been introduced by Google AI.*
The open source C++ and Python framework TensorStore, developed by Google, aims to accelerate the design for reading and writing huge multidimensional arrays. Multidimensional datasets that cover a single large coordinate system are commonly used in contemporary computer science and machine learning applications. These datasets are challenging to work with because customers frequently wish to conduct investigations involving numerous workstations operating in parallel and may receive and output data at unpredictable intervals and varied scales.
Google Research developed TensorStore, a library that provides users with access to an API that can manage huge datasets without the requirement for sophisticated hardware, to address issues with data storage and manipulation. Numerous storage systems, including local and network filesystems, Google Cloud Storage, and others are supported by this library.
To load and work with enormous arrays of data, TensorStore provides a simple Python API. Any arbitrary big underlying datasets can be loaded and updated without having to store the complete dataset in memory because no actual data is read or kept in memory until the precise slice is required.
This is made possible by the indexing and manipulation grammar, which is quite similar to the syntax used for NumPy operations. Along with virtual views, broadcasting, alignment, and other sophisticated indexing features like data type conversion, downsampling, and haphazardly created arrays, TensorStore also supports these.
Additionally, TensorStore includes an asynchronous API that enables read or write operations to go concurrently. While performing other duties, a software can perform configurable in-memory caching, which reduces the need to deal with a slower storage system when accessing frequently used data.
Large numerical datasets demand a lot of processing power to examine and analyse. The usual method for accomplishing this is via parallelizing tasks among a sizable number of CPU or accelerator cores scattered across many devices. The ability to analyse individual datasets in parallel while retaining excellent speed has been a key goal of TensorStore. PaLM, brain mapping, and other complex large-scale machine learning models are some examples of TensorStore application cases. |
15,129 | 用这个开源工具从任何网站获取变化提醒 | https://opensource.com/article/22/9/changedetection-io-open-source-website-changes | 2022-10-11T15:36:00 | [
"变更监测"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15129-1.html |
>
> 使用 changedetection.io 在网站发生变化或更新时获得提醒。
>
>
>

那一年是 2020 年,关于大流行病的消息迅速涌来,每个人都感到完全被类似的新闻文章所淹没,提供了不同程度的更新。
但我需要知道的是,我们的官方准则何时改变。最后,这就是对我来说最重要的事情。
无论关注的是大流行病还是最新的科技新闻,提前了解网站内容的变化都至关重要。
changedetection.io 项目为网站变更检测和通知提供了一个简单但强大的开源解决方案。它很容易设置,而且可以通知 70 多个(还在不断增加)不同的通知系统,如 Matrix、Mattermost、[Nextcloud](https://opensource.com/tags/nextcloud)、[Signal](https://opensource.com/article/19/10/secure-private-messaging)、[Zulip](https://opensource.com/article/22/3/open-source-chat-zulip)、[Home Assistant](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/home-assistant)、电子邮件等等。它还能通知专有应用,如 Discord、Office365、Reddit、Telegram 和许多其他应用。
但 changedetection.io 并不只是局限于观察网页内容。你也可以监视 XML 和 JSON 源,它将建立一个 RSS 馈送,记录变化的网站。
由于其内置的 JSON 简单存储系统,不需要设置复杂的数据库来接收和存储信息。你可以 [使用 Docker 镜像运行](https://github.com/dgtlmoon/changedetection.io#docker) 或用 `pip` 安装它。该项目有一个 [全面的维基帮助页](https://github.com/dgtlmoon/changedetection.io/wiki),大多数常见的问题都有涵盖。
对于使用复杂 JavaScript 的网站,你可以用内置的 [Playwright 内容获取器](https://github.com/dgtlmoon/changedetection.io/wiki/Playwright-content-fetcher) 将你的 changedetection.io 连接到 Chromium 或 Chrome 浏览器。
运行后,在你的浏览器(默认情况下是 `http://localhost:5000`)中访问该应用。如果你的电脑可以从外部网络访问,你可以在 <ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby>中设置一个密码。

提交你想监控的页面的 URL。有几个与如何过滤该网页有关的设置。例如,你很可能不想知道一家公司在其网站页脚列出的股票价格何时发生变化,但你可能想知道他们在其博客上发布的新闻文章。
### 监控一个网站
想象一下,你想添加你最喜欢的网站 [Opensource.com](http://Opensource.com) 进行监控。你只想知道主要标注文章何时包含 “python” 一词,并且通过 Matrix 收到通知。
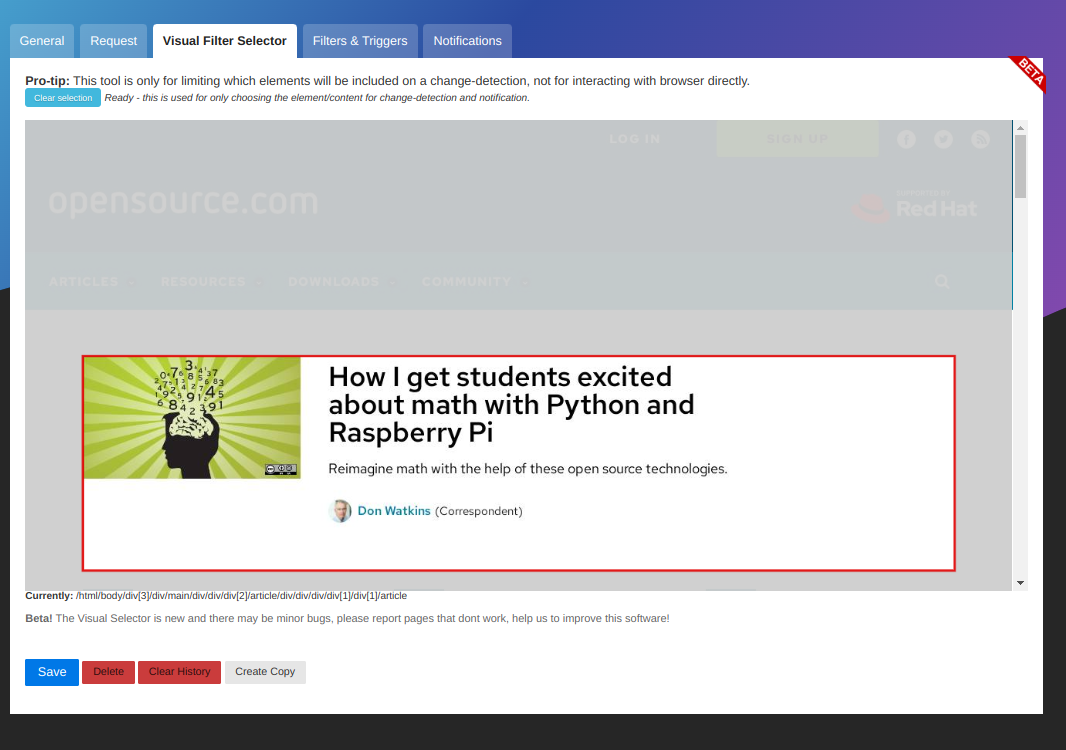
要做到这点,首先要使用“<ruby> 视觉选择器 <rt> Visual Filter Selector </rt></ruby>”工具。(这需要连接 **playwright** 浏览器界面)。

该工具会自动计算出针对内容的最佳 Xpath 或 CSS 过滤器。否则,你会从每天的页面更新中得到大量的噪音。
接下来,访问“<ruby> 过滤器和触发器 <rt> Filters & Triggers </rt></ruby>”标签。

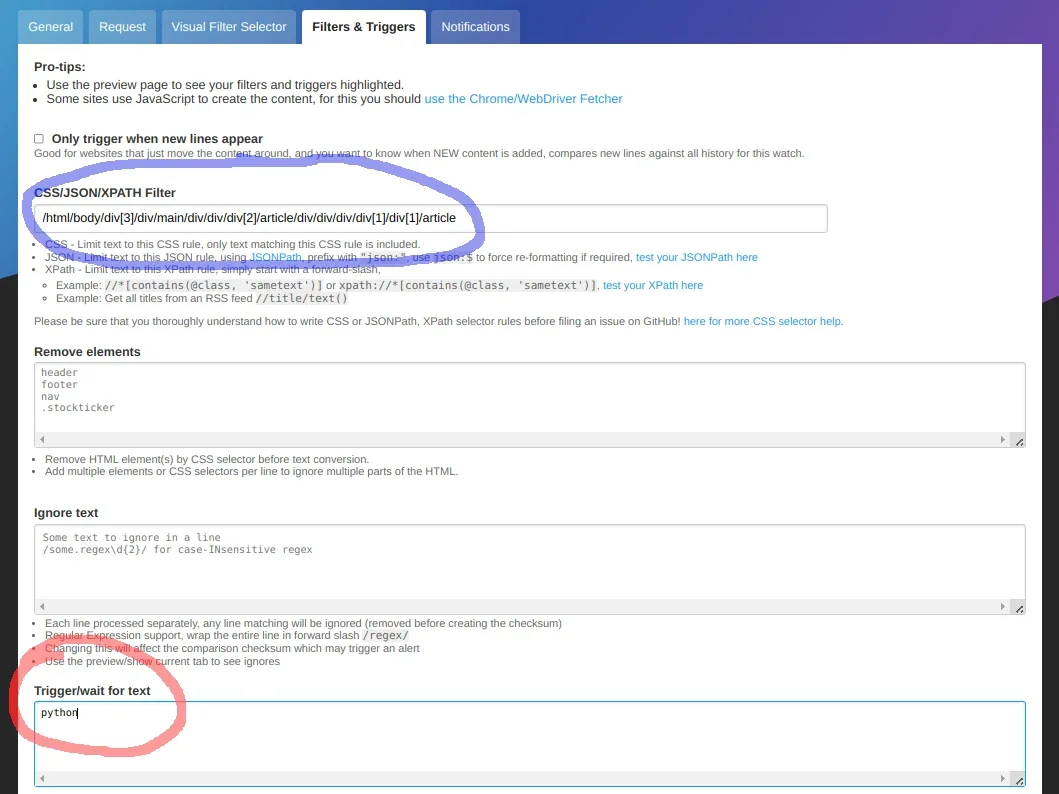
在 “<ruby> CSS/JSON/XPATH 过滤器 <rt> CSS/JSON/XPATH Filter </rt></ruby>”区域(蓝色圆圈),你可以看到上一步自动生成的 CSS 过滤器。
有几个有用的过滤器,比如“<ruby> 移除元素 <rt> Remove elements </rt></ruby>”(适合移除嘈杂的元素)、“<ruby> 忽略文本 <rt> Ignore text </rt></ruby>”、“<ruby> 触发/等待文本 <rt> Trigger/wait for text </rt></ruby>”,和“<ruby> 如果文本匹配则阻止变化检测 <rt> Block change-detection if text matches </rt></ruby>”(用于等待一些文本消失,如“售罄”)。
在“<ruby> 触发/等待文本 <rt> Trigger/wait for text </rt></ruby>”(红色圆圈)中,输入你想监测的关键词。(在这个例子中是 “python”)。
最后一步是在“<ruby> 通知 <rt> Notifications </rt></ruby>”选项卡中,你要在那里配置你想收到的通知。下面我使用 Matrix API 添加了一个 Matrix 房间作为通知目标。

通知的 URL 的格式是 `matrixs://username:[email protected]/#/room/#room-name:matrix.org`。
然而,[t2Bot](https://t2bot.io/) 格式也支持。这里有更多的 [Matrix 通知选项](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_matrix)。
就是这些了! 现在只要内容有变化,你就会通过 Matrix 收到信息。
### 还有更多
changedetection.io 还有很多东西。如果你喜欢调用一个自定义的 JSON API,你不需要使用通知的 API(使用 `jsons://` )。你还可以创建一个自定义的 HTTP 请求(POST 和 GET),在检查前执行 JavaScript(也许是为了预先填充一个用户名和密码的登录字段),以及更多有趣的功能,更多的功能将陆续推出。
不要再浏览网站,而是开始监测网络吧!
*图片提供:(Leigh Morresi, CC BY-SA 4.0)*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/9/changedetection-io-open-source-website-changes>
作者:[Leigh Morresi](https://opensource.com/users/dgtlmoon) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The year was 2020, and news about COVID-19 came flooding in so quickly that everyone felt completely overwhelmed with similar news articles providing updates with varying degrees of accuracy.
But all I needed to know was when my official government guidelines changed. In the end, that's all that mattered to me.
Whether the concern is a pandemic or just the latest tech news, keeping ahead of changes in website content can be critical.
The [changedetection.io](https://github.com/dgtlmoon/changedetection.io) project provides a simple yet highly capable, open source solution for website change detection and notification. It's easy to set up, and it can notify over 70 (and counting) different notification systems, such as Matrix, Mattermost, [Nextcloud](https://opensource.com/tags/nextcloud), [Signal](https://opensource.com/article/19/10/secure-private-messaging), [Zulip](https://opensource.com/article/22/3/open-source-chat-zulip), [Home Assistant](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/home-assistant), email, and more. It also notifies proprietary applications like Discord, Office365, Reddit, Telegram, and many others.
But [changedetection.io](https://github.com/dgtlmoon/changedetection.io) isn't just limited to watching web page content. You can also monitor XML and JSON feeds, and it will build an RSS feed of the websites that changed.
Thanks to its built-in JSON simple storage system, there's no need to set up complicated databases to receive and store information. You can [run it as a Docker image](https://github.com/dgtlmoon/changedetection.io#docker) or install it with `pip`
. The project has an [extensive wiki help section](https://github.com/dgtlmoon/changedetection.io/wiki), and most common questions are covered there.
For sites using complex JavaScript, you can connect your changedetection.io installation to a Chromium or Chrome browser with the built-in [Playwright content fetcher](https://github.com/dgtlmoon/changedetection.io/wiki/Playwright-content-fetcher).
Once running, access the application in your browser (`http://localhost:5000`
, by default). You can set a password in the **Settings** section if your computer can be reached from an outside network.
(Leigh Morresi, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Submit the URL of a page you want to monitor. There are several settings related to how the page is filtered. For example, you more than likely do not want to know when a company's stock price listed in their site footer has changed, but you may want to know when they post a news article to their blog.
## Monitor a site
Imagine you want to add your favorite website, Opensource.com, to be monitored. You only want to know when the main call-out article contains the word "python" and you want to be notified over Matrix.
To do this, begin with the **visual-selector** tool. (This requires the **playwright** browser interface to be connected.)
(Leigh Morresi, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The **visual-selector** tool automatically calculates the best Xpath or CSS filter to target the content. Otherwise, you would get a lot of noise from the daily page updates.
Next, visit the **Filters & Triggers** tab.
(Leigh Morresi, CC BY-SA 4.0)
In **CSS/JSON/XPATH Filter** field (the blue circle), you can see the automatically generated CSS filter from the previous step.
There are several useful filters available, such as **Remove elements** (good for removing noisy elements), **Ignore text, Trigger/wait for text,** and **Block change-detection if text matches** (used for waiting for some text to disappear, like "sold out").
In **Trigger/wait for text** (the red circle), type in the keyword you want to monitor for. (That's "python" in this example.)
The final step is in the **Notifications** tab, where you configure where you want to receive your notification. Below I added a Matrix room as the notification target, using the Matrix API.
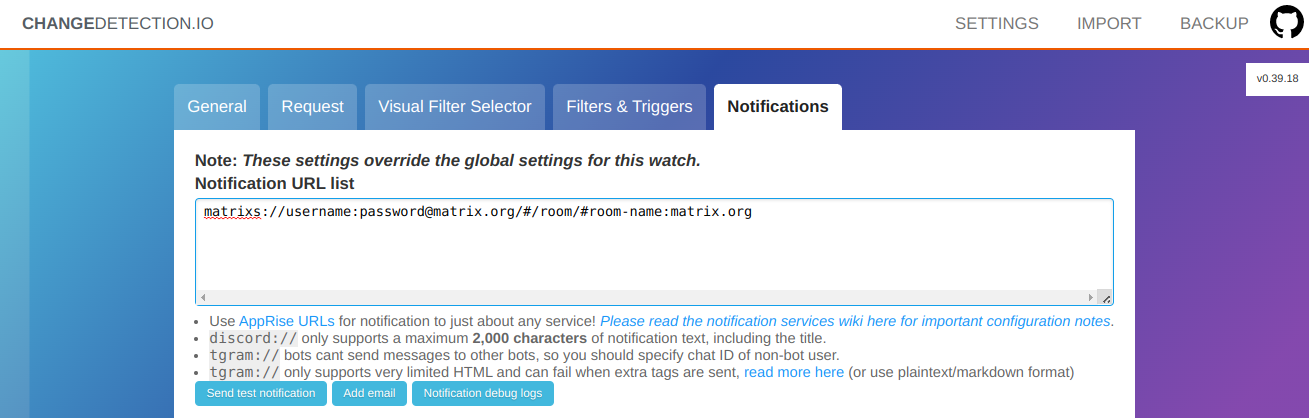
(Leigh Morresi, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The notification URL is in the format of `matrixs://username:[email protected]/#/room/#room-name:matrix.org`
However, [t2Bot](https://t2bot.io/) format is also supported. Here are more [Matrix notification options](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_matrix).
And that's it! Now you'll receive a message over Matrix whenever the content changes.
## There's more
There's so much more to changedetection.io. If you prefer calling a custom JSON API, you don't have to use an API for notifications (use `jsons://`
). You can also create a custom HTTP request (POST and GET), execute JavaScript before checking (perhaps to pre-fill a username and password login field), and many more interesting features, with more to come.
Stop browsing the web and start watching the web instead!
## Comments are closed. |
15,130 | 我在 Linux 中使用的 5 个 Git 配置 | https://opensource.com/article/22/9/git-configuration-linux | 2022-10-11T16:23:40 | [
"Git"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15130-1.html |
>
> 这份简要指南能够帮助你快速开始使用 Git,以及配置一些选项。
>
>
>

在 Linux 中设置 Git 十分简单,但为了获得完美的配置,我做了以下五件事:
1. 创建全局配置
2. 设置默认名称
3. 设置默认邮箱地址
4. 设置默认分支名称
5. 设置默认编辑器
我使用 Git 管理我的代码、命令行脚本以及文档版本。这意味着每次我开始一项新的任务,首先我需要创建一个文件目录并将其添加到 Git 库中:
```
$ mkdir newproject
$ cd newproject
$ git init
```
有一些我一直想要的常规设置。不多,但可以避免我每次都进行配置。我喜欢利用 Git 的 *全局* 配置功能。
Git 提供了进行手动配置的 `git config` 命令,但这有一些注意事项。例如,通常你会设置邮箱地址。你可以通过运行 `git config user.email 你的邮件地址` 命令进行设置。然而,这只会在你当前所在的 Git 目录下起作用。
```
$ git config user.email [email protected]
fatal: not in a git directory
```
此外,当这个命令在 Git 仓库中运行时,它只会配置特定的一个仓库。在新的仓库中,你不得不重复这个步骤。我可以通过全局配置来避免重复。选项 `--global` 会指示 Git 将邮箱地址写入全局配置 `~/.gitconfig` 文件中,甚至在必要时会创建它:
>
> 请记住,波浪线(`~`)代表你的主文件夹。在我的电脑中它是 `/home/alan`。
>
>
>
```
$ git config --global user.email [email protected]
$ cat ~/.gitconfig
[user]
email = [email protected]
```
这里的缺点是,如果你有大量偏好设置,需要输入很多命令,这将花费大量时间并且很容易出错。Git 提供了更加快捷有效的方式,可以直接编辑你的全局配置文件——这是我列表中的第一项!
### 1、创建全局配置
如果你刚开始使用 Git,或许你还没有该文件。不用担心,让我们直接开始。只需要用 `--edit` 选项:
```
$ git config --global --edit
```
如果没有该文件,Git 将会创建一个包含以下内容的新文件,并使用你终端的默认编辑器打开它:
```
# This is Git's per-user configuration file.
[user]
# Please adapt and uncomment the following lines:
# name = Alan
# email = alan@hopper
~
~
~
"~/.gitconfig" 5L, 155B 1,1 All
```
现在我们已经打开了编辑器,并且 Git 已经在后台创建了全局配置文件,我们可以继续接下来的设置。
### 2、设置默认名称
名字是该文件中的首要条目,让我们先从它开始。用命令行设置我的名称是 `git config --global user.name "Alan Formy-Duval"`。不用在命令行中运行该命令,只需要在配置文件中编辑 `name` 条目就行:
```
name = Alan Formy-Duval
```
### 3、设置默认邮箱地址
邮箱地址是第二个条目,让我们添加它。默认情况下,Git 使用你的系统提供的名称和邮箱地址。如果不正确或者你想要更改,你可以在配置文件中具体说明。事实上,如果你没有配置这些,Git 在你第一次提交时会友好的提示你:
```
Committer: Alan <alan@hopper>
Your name and email address were configured automatically based
on your username and hostname. Please check that they are accurate....
```
在命令行中运行 `git config --global user.email "[email protected]"` 会设置好我的邮箱。同样,我们在配置文件中编辑 `email` 条目,提供你的邮箱地址:
```
email = [email protected]
```
我喜欢设置的最后两个设置是默认分支名称和默认编辑器。当你仍在编辑器中时,需要添加这些指令。
### 4、设置默认分支名称
目前有一种趋势,即不再使用 `master` 作为默认分支名称。事实上,在新存储库初始化时,Git 将通过友好的消息提示更改默认分支名称:
```
$ git init
hint: Using 'master' as the name for the initial branch. This default branch name
hint: is subject to change. To configure the initial branch name to use in all
hint: of your new repositories, which will suppress this warning, call:
hint:
hint: git config --global init.defaultBranch <name>
```
这个名为 `defaultBranch` 的指令需要位于一个名为 `init` 的新部分中。现在普遍接受的是,许多程序员使用 `main` 这个词作为他们的默认分支。这是我喜欢使用的。将此部分后跟指令添加到配置中:
```
[init]
defaultBranch = main
```
### 5、设置默认编辑器
第五个设置是设置默认的编辑器。这是指 Git 将使用的编辑器,用于在你每次将更改提交到存储库时输入你的提交消息。不论是 [nano](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/gnu-nano)、[emacs](https://opensource.com/resources/what-emacs)、[vi](https://opensource.com/article/19/3/getting-started-vim) 还是其他编辑器,每个人都有他喜欢的。我喜欢用 vi。添加 `core` 部分,并设置 `editor` 指令为你喜欢的编辑器。
```
[core]
editor = vi
```
这是最后一项。退出编辑器。Git 在主目录下保存全局配置文件。如果你再次运行编辑命令,将会看到所有内容。注意配置文件是明文存储的文本文件,因此它可以很容易使用文本工具查看,如 [cat](https://opensource.com/article/19/2/getting-started-cat-command) 命令。这是我的配置文件内容:
```
$ cat ~/.gitconfig
[user]
email = [email protected]
name = Alan Formy-Duval
[core]
editor = vi
[init]
defaultBranch = main
```
这是一个简单的指南,可以让你快速开始使用 Git 和它的一些配置选项。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/9/git-configuration-linux>
作者:[Alan Formy-Duval](https://opensource.com/users/alanfdoss) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Setting up Git on Linux is simple, but here are the five things I do to get the perfect configuration:
[Create global configuration](https://opensource.com/article/22/9/git-configuration-linux#create-global-configuration)[Set default name](https://opensource.com/article/22/9/git-configuration-linux#set-default-name)[Set default email address](https://opensource.com/article/22/9/git-configuration-linux#set-default-email-address)[Set default branch name](https://opensource.com/article/22/9/git-configuration-linux#set-default-branch-name)[Set default editor](https://opensource.com/article/22/9/git-configuration-linux#set-default-editor)
I manage my code, shell scripts, and documentation versioning using Git. This means that for each new project I start, the first step is to create a directory for its content and make it into a Git repository:
```
``````
$ mkdir newproject
$ cd newproject
$ git init
```
There are certain general settings that I always want. Not many, but enough that I don't want to have to repeat the configuration each time. I like to take advantage of the *global* configuration capability of Git.
Git offers the `git config`
command for manual configuration but this is a lot of work with certain caveats. For example, a common item to set is your email address. You can set it by running `git config user.email`
followed by your email address. However, this will only take effect if you are in an existing Git directory:
```
``````
$ git config user.email [email protected]
fatal: not in a git directory
```
Plus, when this command is run within a Git repository, it only configures that specific one. The process must be repeated for new repositories. I can avoid this repetition by setting it globally. The *--global* option will instruct Git to write the email address to the global configuration file; `~/.gitconfig`
, even creating it if necessary:
Remember, the` tilde (~)` character represents your home directory. In my case that is /home/alan. |
```
``````
$ git config --global user.email [email protected]
$ cat ~/.gitconfig
[user]
email = [email protected]
```
The downside here is if you have a large list of preferred settings, you will have a lot of commands to enter. This is time-consuming and prone to human error. Git provides an even more efficient and convenient way to directly edit your global configuration file—that is the first item on my list!
[1. Create global configuration]
If you have just started using Git, you may not have this file at all. Not to worry, let's skip the searching and get started. Just use the `--edit `
option:
```
````$ git config --global --edit`
If no file is found, Git will generate one with the following content and open it in your shell environment's default editor:
```
``````
# This is Git's per-user configuration file.
[user]
# Please adapt and uncomment the following lines:
# name = Alan
# email = alan@hopper
~
~
~
"~/.gitconfig" 5L, 155B 1,1 All
```
Now that we have opened the editor and Git has created the global configuration file behind the scenes, we can continue with the rest of the settings.
[2. Set default name]
Name is the first directive in the file, so let's start with that. The command line to set mine is `git config --global user.name "Alan Formy-Duval"`
. Instead of running this command, just edit the *name* directive in the configuration file:
```
````name = Alan Formy-Duval`
[3. Set default email address]
The email address is the second directive, so let's update it. By default, Git uses your system-provided name and email address. If this is incorrect or you prefer something different, you can specify it in the configuration file. In fact, if you have not configured them, Git will let you know with a friendly message the first time you commit:
```
``````
Committer: Alan <alan@hopper>
Your name and email address were configured automatically based
on your username and hostname. Please check that they are accurate....
```
The command line to set mine is` `
`git config --global user.email`
** " [email protected]"**. Instead, edit the
```
````email = [email protected]`
The last two settings that I like to set are the default branch name and the default editor. These directives will need to be added while you are still in the editor.
[4. Set default branch name]
There is currently a trend to move away from the usage of the word *master* as the default branch name. As a matter of fact, Git will highlight this trend with a friendly message upon initialization of a new repository:
```
``````
$ git init
hint: Using 'master' as the name for the initial branch. This default branch name
hint: is subject to change. To configure the initial branch name to use in all
hint: of your new repositories, which will suppress this warning, call:
hint:
hint: git config --global init.defaultBranch <name>
```
This directive, named *defaultBranch*, needs to be located in a new section named *init*. It is now generally accepted that many coders use the word *main* for their default branch. This is what I like to use. Add this section followed by the directive to the configuration:
```
``````
[init]
defaultBranch = main
```
[5. Set default editor]
The fifth setting that I like to set is the default editor. This refers to the editor that Git will present for typing your commit message each time you commit changes to your repository. Everyone has a preference whether it is [nano](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/gnu-nano), [emacs](https://opensource.com/resources/what-emacs), [vi](https://opensource.com/article/19/3/getting-started-vim), or something else. I'm happy with vi. So, to set your editor, add a *core* section that includes the *editor* directive:
```
``````
[core]
editor = vi
```
That's the last one. Exit the editor. Git saves the global configuration file in your home directory. If you run the editing command again, you will see all of the content. Notice that the configuration file is a plain text file, so it can also be viewed using text tools such as the [ cat command](https://opensource.com/article/19/2/getting-started-cat-command). This is how mine appears:
```
``````
$ cat ~/.gitconfig
[user]
email = [email protected]
name = Alan Formy-Duval
[core]
editor = vi
[init]
defaultBranch = main
```
This is a simple guide to quickly get started working with Git and a few of its many configuration options. There are many other articles on Git here at Opensource.com, as well as our downloadable [Git cheat sheet](https://opensource.com/downloads/cheat-sheet-git).
## Comments are closed. |
15,132 | 使用 PostgreSQL 建立你的数据库 | https://opensource.com/article/22/9/drop-your-database-for-postgresql | 2022-10-12T10:03:18 | [
"PostgreSQL",
"数据库"
] | /article-15132-1.html | 
>
> PostgreSQL 是最灵活的数据库之一,并且它是开源的。
>
>
>
数据库是以一种有组织且灵活的方式存储信息的工具。电子表格在本质上就是一个数据库,但是图形化应用程序这一限制使得大多数的电子表格应用程序对程序员毫无用处。随着 [边缘计算](https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/edge-computing/what-is-edge-computing?intcmp=7013a000002qLH8AAM) 和物联网设备成为重要的平台,开发者们需要更有效且轻量级的方法,来存储、处理、查询大量的数据。我最爱的一种组合是使用 [Lua 连接](https://github.com/arcapos/luapgsql) PostgreSQL 数据库。无论你使用什么编程语言,PostgreSQL 一定是数据库的绝佳选择,但是在使用 PostgreSQL 之前,首先你需要知道一些基本的东西。
### 安装 PostgreSQL
在 Linux 上安装 PostgreSQL,要使用你的软件库。在 Fedora,CentOS,Megeia 等类似的 Linux 版本上使用命令:
```
$ sudo dnf install postgresql postgresql-server
```
在 Debian, Linux Mint, Elementary 等类似的 Linux 版本上使用命令:
```
$ sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib
```
在 macOs 和 Windows 上,可以从官网 [postgresql.org](https://www.postgresql.org/download/) 下载安装包。
### 配置 PostgreSQL
大多数发行版安装 PostgreSQL 数据库时没有启动它,但是为你提供了一个脚本或 [systemd 服务](https://opensource.com/article/21/4/sysadmins-love-systemd),能够可靠地启动 PostgreSQL。但是,在启动 PostgreSQL 之前,必须创建一个数据库集群。
#### Fedora
在 Fedora,CentOS 等类似的版本上,PostgreSQL 安装包中提供了一个 PostgreSQL 配置脚本。运行这个脚本,可以进行简单地配置:
```
$ sudo /usr/bin/postgresql-setup --initdb
[sudo] password:
* Initializing database in '/var/lib/pgsql/data'
* Initialized, logs are in /var/lib/pgsql/initdb_postgresql.log
```
#### Debian
在基于 Debian 的发行版上,在安装 Postgres 的过程中,配置会通过 `apt` 自动完成。
#### 其他版本
最后,如果你是在其他版本上运行的,那么你可以直接使用 PostgreSQL 提供的一些工具。`initdb` 命令会创建一个数据库集群,但是这个命令必须在 `postgres` 用户下运行,你可以使用 `sudo` 来暂时地成为 `postgres` 用户:
```
$ sudo -u postgres \
"initdb -D /var/lib/pgsql/data \
--locale en_US.UTF-8 --auth md5 --pwprompt"
```
### 运行 PostgreSQL
现在,数据库集群已经存在了,使用 `initdb` 的输出中提供给你的命令或者使用 systemd 启动 PostgreSQL 服务器:
```
$ sudo systemctl start postgresql
```
### 创建一个数据库用户
使用 `createuser` 命令来创建一个数据库用户。`postgres` 用户是 Postgres 安装的超级用户。
```
$ sudo -u postgres createuser --interactive --password bogus
Shall the new role be a superuser? (y/n) n
Shall the new role be allowed to create databases? (y/n) y
Shall the new role be allowed to create more new roles? (y/n) n
Password:
```
### 创建一个数据库
使用 `createdb` 命令来创建一个新的数据库。在这个例子中,我创建了数据库 `exampledb`,并把该数据库的拥有者分配给用户 `bogus`。
```
$ createdb exampledb --owner bogus
```
### 与 PostgreSQL 交互
你可以使用 `psql` 命令来与 PostgreSQL 中的数据库进行交互。这个命令提供了一个交互界面,所以你可以用它来查看和更新你的数据库。你需要指定要使用的用户和数据库,来连接到一个数据库。
```
$ psql --user bogus exampledb
psql (XX.Y)
Type "help" for help.
exampledb=>
```
#### 创建一个表
数据库包含很多表。这些表可以可视化为表格,有很多行(在数据库中称为 *记录*)和很多列。行和列的交集称为 *字段*。
结构化查询语言(SQL)是以它提供的内容而命名的,它能提供可预测且一致的语法,来查询数据库内容,从而收到有用的结果。
目前,你的数据库是空的,没有任何的表。你可以用 `CREATE` 语句来创建一个表。结合使用 `IF NOT EXISTS` 是很有用的,它可以避免破坏现有的表。
在你创建一个表之前,想想看你希望这个表包含哪一种数据(在 SQL 术语中称为“数据类型”)。在这个例子中,我创建了一个表,包含两列,有唯一标识符的一列和最多九个字符的可变长的一列。
```
exampledb=> CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_sample_table(
exampledb(> id SERIAL,
exampledb(> wordlist VARCHAR(9) NOT NULL
);
```
关键字 `SERIAL` 并不是一个数据类型。`SERIAL` 是 [PostgreSQL 中的一个特殊的标记](https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/datatype-numeric.html#DATATYPE-SERIAL),它可以创建一个自动递增的整数字段。关键字 `VARCHAR` 是一个数据类型,表示限制内字符数的可变字符。在此例中,我指定了最多 9 个字符。PostgreSQL 中有很多数据类型,因此请参阅项目文档以获取选项列表。
#### 插入数据
你可以使用 `INSERT` 语句来给你的新表插入一些样本数据:
```
exampledb=> INSERT INTO my_sample_table (wordlist) VALUES ('Alice');
INSERT 0 1
```
如果你尝试在 `wordlist` 域中输入超过 9 个字符,则数据输入将会失败:
```
exampledb=> INSERT INTO my_sample_table (WORDLIST) VALUES ('Alexandria');
ERROR: VALUE too long FOR TYPE CHARACTER VARYING(9)
```
#### 改变表或者列
当你需要改变一个域的定义时,你可以使用 `ALTER` 这一 SQL 关键字。例如,如果你想改变 `wordlist` 域中最多只能有 9 个字符的限制,你可以重新设置这个数据类型。
```
exampledb=> ALTER TABLE my_sample_table
ALTER COLUMN wordlist SET DATA TYPE VARCHAR(10);
ALTER TABLE
exampledb=> INSERT INTO my_sample_table (WORDLIST) VALUES ('Alexandria');
INSERT 0 1
```
#### 查询表中的内容
SQL 是一种查询语言,因此你可以通过查询来查看数据库的内容。查询可以是很简单的,也可以涉及连接多个不同表之间的复杂关系。要查看表中的所有内容,请使用 `SELECT` 关键字和 `*`(`*` 是通配符):
```
exampledb=> SELECT * FROM my_sample_table;
id | wordlist
----+------------
1 | Alice
2 | Bob
3 | Alexandria
(3 ROWS)
```
### 更多数据
PostgreSQL 可以处理很多数据,但是对于任何数据库来说,关键之处在于你是如何设计你的数据库的,以及数据存储下来之后你是怎么查询数据的。在 [OECD.org](https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=LAND_COVER) 上可以找到一个相对较大的公共数据集,你可以使用它来尝试一些先进的数据库技术。
首先,将数据下载为逗号分隔值格式(CSV)的文件,并将文件另存为 `Downloads` 文件夹中的 `land-cover.csv`。
在文本编辑器或电子表格应用程序中浏览数据,来了解有哪些列,以及每列包含哪些类型的数据。仔细查看数据,并留意错误情况。例如,`COU` 列指的是国家代码,例如 `AUS` 表示澳大利亚和 `GRC` 表示希腊,在奇怪的 `BRIICS` 之前,这一列的值通常是 3 个字符。
在你理解了这些数据项后,你就可以准备一个 PostgreSQL 数据库了。
```
$ createdb landcoverdb --owner bogus
$ psql --user bogus landcoverdb
landcoverdb=> create table land_cover(
country_code varchar(6),
country_name varchar(76),
small_subnational_region_code varchar(5),
small_subnational_region_name varchar(14),
large_subnational_region_code varchar(17),
large_subnational_region_name varchar(44),
measure_code varchar(13),
measure_name varchar(29),
land_cover_class_code varchar(17),
land_cover_class_name varchar(19),
year_code integer,
year_value integer,
unit_code varchar(3),
unit_name varchar(17),
power_code integer,
power_name varchar(9),
reference_period_code varchar(1),
reference_period_name varchar(1),
value float(8),
flag_codes varchar(1),
flag_names varchar(1));
```
#### 引入数据
Postgres 可以使用特殊的元命令 `\copy` 来直接引入 CSV 数据:
```
landcoverdb=> \copy land_cover from '~/land-cover.csv' with csv header delimiter ','
COPY 22113
```
插入了 22113 条记录。这是一个很好的开始!
#### 查询数据
用 `SELECT` 语句可以查询这 22113 条记录的所有列,此外 PostgreSQL 将输出通过管道传输到屏幕上,因此你可以轻松地滚动鼠标来查看输出的结果。更进一步,你可以使用高级 SQL 语句,来获得一些有用的视图。
```
landcoverdb=> SELECT
lcm.country_name,
lcm.year_value,
SUM(lcm.value) sum_value
FROM land_cover lcm
JOIN (
SELECT
country_name,
large_subnational_region_name,
small_subnational_region_name,
MAX(year_value) max_year_value
FROM land_cover
GROUP BY country_name,
large_subnational_region_name,
small_subnational_region_name
) AS lcmyv
ON
lcm.country_name = lcmyv.country_name AND
lcm.large_subnational_region_name = lcmyv.large_subnational_region_name AND
lcm.small_subnational_region_name = lcmyv.small_subnational_region_name AND
lcm.year_value = lcmyv.max_year_value
GROUP BY lcm.country_name,
lcm.large_subnational_region_name,
lcm.small_subnational_region_name,
lcm.year_value
ORDER BY country_name,
year_value;
```
下面是样例的一些输出:
```
---------------+------------+------------
Afghanistan | 2019 | 743.48425
Albania | 2019 | 128.82532
Algeria | 2019 | 2417.3281
American Samoa | 2019 | 100.2007
Andorra | 2019 | 100.45613
Angola | 2019 | 1354.2192
Anguilla | 2019 | 100.078514
Antarctica | 2019 | 12561.907
[...]
```
SQL 是一种很丰富的语言,超出了本文的讨论范围。通读 SQL 的内容,看看你是否可以对上面的查询语句进行修改,以提供不同的数据集。
### 拓展数据库
PostgreSQL 是伟大的开源数据库之一。有了它,你可以为结构化数据设计存储库,然后使用 SQL 以不同的方式查询它,以便能够获得有关该数据的新视角。PostgreSQL 也能与许多语言集成,包括 Python、Lua、Groovy、Java 等,因此无论你使用什么工具集,你都可以充分利用好这个出色的数据库。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/9/drop-your-database-for-postgresql>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
15,133 | 了解开放组织的新途径 | https://opensource.com/open-organization/21/6/celebrate-sixth-anniversary | 2022-10-12T14:34:21 | [
"开放组织",
"开放领导力定义"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15133-1.html |
>
> 通过参与两个令人兴奋的新项目来庆祝开放组织社区的六周年。
>
>
>

2021 年 6 月 2 日,<ruby> 开放组织 <rt> Open Organization </rt></ruby>社区庆祝其成立六周年。这是六年来([上百篇的](https://opensource.com/open-organization))文章、([一系列的](https://theopenorganization.org/books))书籍、([具有启发性的](https://www.theopenorganization.community/))对话、(我们所 [喜欢的](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Snf6vICDbzw&list=PLLIYDJHuxOkaPEH76mIJe-HHplsiSAVej))教学和学习。我们非常自豪地成为一个充满活力的开放专家和领导者的社区,致力于将 [开放原则](https://theopenorganization.org/definition) 带到大大小小的组织。事实上,许多 <ruby> <a href="https://theopenorganization.org/about"> 开放组织大使 </a> <rt> Open Organization Ambassadors </rt></ruby> 以帮助他人变得更加开放为职业,我们的社区仍然致力于帮助各行业的领导者以开放的心态和行为融入他们的社区和环境中。
[去年](https://opensource.com/open-organization/20/6/scaling-energetic-community) 是开放组织项目的一个 [成长](https://opensource.com/open-organization/20/7/evolving-project-governance) 和 [发展](https://opensource.com/open-organization/20/8/open-community-rebrands) 时期。今年,我们将在这一势头的基础上继续努力。今天,我们很自豪地介绍两项新的倡议——当然,也邀请你的参加。
### 开启,调整,开放
首先,我们很高兴地宣布:我们社区的工作有了一个全新的场所。[OpenOrgTV](http://theopenorganization.tv)。这不仅仅是一个新的平台。它也是另一种媒介的实验:视频。
在我们的频道上,我们将举办各种对话 —— 从深层次的书评到社区圆桌会议。首先,请查看“<ruby> <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=07YBs0ss9rU&list=PLLIYDJHuxOkYDTLbKRjcd9THTFtpnK8lh"> 开放领导力对话 </a> <rt> Open Leadership Conversations </rt></ruby>”系列,其中包括对某些富有洞察力的领导者的采访,提供他们对根据开放原则进行领导的意义的观点。或者观看我们的 Q&A 式写作节目 “<ruby> <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ukkZMYqRuUQ&list=PLLIYDJHuxOkY1gDbOFLDxGxwwmxeOATrI"> 问大使 </a> <rt> Ask the Ambassadors </rt></ruby>”,由社区专家回答你关于组织文化和设计的问题。也想参与这个节目吗?在我们的 [新的专门的论坛](https://www.theopenorganization.community/c/ask-community/19) 中向社区成员提交你的问题。
整个月,我们都会介绍 <ruby> <a href="http://theopenorganization.org/roster/"> 开放组织大使 </a> <rt> Open Organization Ambassadors </rt></ruby>,让你终于可以看到他们的面孔,并听到你多年来阅读的故事、案例研究和采访背后的声音。
### 定义开放领导力
自从我们几年前发布它以来,<ruby> <a href="https://theopenorganization.org/definition/"> 开放组织定义 </a> <rt> Open Organization Definition </rt></ruby> 已成为更好地理解开放组织文化和设计本质的组织指导框架(并且我们已经做了很多工作来 [教导其他人](https://youtu.be/NYngFYGgxro))。随着时间的推移,我们甚至开发了 [一个成熟度模型](https://github.com/open-organization/open-org-maturity-model) 来操作该定义,因此组织可以评估自己的开放程度并制定具体计划以变得 *更加* 开放。
现在,我们认为是时候将这项工作更进一步了。
但是,开放组织社区不仅仅是平台、工具或项目的任何组合。它是所有人都热情地一起工作,以帮助传播开放原则和实践。
受我们自己经验、[红帽](https://github.com/red-hat-people-team/red-hat-multiplier) 和 [Mozilla](https://mozilla.github.io/open-leadership-framework/framework/#the-open-leadership-framework) 等开放组织已有的框架、多年研究和采访该领域的开放领袖的启发,以及我们对更好地理解开放领导力如何 *真正* 发挥作用的渴望,我们很高兴公布一份全新文件的早期草案:<ruby> 开放领导力定义 <rt> Open Leadership Definition </rt></ruby>。
本文档概述了建立开放型组织,并使其成为思想开放的人能够成长和茁壮成长的地方的各类领导者所特有的心态和行为。它建立在<ruby> 开放领导力定义 <rt> Open Leadership Definition </rt></ruby>的基础上,解释了开放型领导者如何体现和倡导开放型组织的特征,如透明度、包容性、适应性、协作性和社区性。
而且我们渴望与世界分享。
从今天开始(在接下来的两周内),我们将收集你对我们文件草案的见解和意见。我们渴望听到你的想法,并将接受你的意见的 *整体* 或片段。你可以对文件的个别部分或整个文件提出意见。请查看下面的链接。我们期待着听到你的意见。

*Laura Hiliger 提供的开放领导力定义词云 (CC BY-SA)*
#### 开放领导力定义
* [开放领导力定义:简介](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1blmf94ED_p4BHGv0luU_XrU26aF7tCzV6WTmh_v-PDY/edit?usp=sharing)
* [开放领导力定义:透明度](https://docs.google.com/document/d/14ssBBL0h2vxU0WZoMnWs6eo_8oRfJhnAr5yr-fAiLGU/edit?usp=sharing)
* [开放领导力定义:包容性](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1lRutADes5E0mcwtc6GR_Qw06PuJLc9-wUK5W1Gcf_BA/edit?usp=sharing)
* [开放领导力定义:适应性](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1RcwWTpkT42bgkf6EPiECt8LyAJ1XZjNGhzk0cQuBB7c/edit?usp=sharing)
* [开放领导力定义:协作](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1hTvnpqQkOc76-0UJbV6tAvRxOE--bdt96mqGmAKGqiI/edit?usp=sharing)
* [开放领导力定义:社区](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1Zl1smi-4jDZNNWd0oNY8qRH-GDi9q5VfvgyZ7YLkvm4/edit?usp=sharing)
在我们的共享文件夹中 [阅读全文](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1e1N_0p5lJEwAo_s6hQ3OK0KaJIfc7fgF?usp=sharing)。
### 联系我们
当然,你仍然可以在所有常见的地方找到我们的社区,如:
* [我们的项目网站](http://theopenorganization.org/),你通往整个开放组织项目和社区的门户。
* [我们的对话中心](https://www.theopenorganization.community/),在这里你可以与社区成员互动,提出问题,了解新项目,寻找资源,并帮助他人。
* [我们的 GitHub 组织](https://github.com/open-organization),我们一直在公开研究新项目,并邀请你加入我们
* [我们在 Opensource.com 的发表频道](https://opensource.com/open-organization),我们在这里为各地区和各行业的从业人员发布最新的分析、案例研究、访谈和资源。
* 我们的 [Twitter](https://twitter.com/openorgproject) 和 [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/company/the-open-organization/) 平台,我们将在这里分享我们的最新进展,并促进新的对话。
但开放组织社区不仅仅是平台、工具或项目的任何组合。 是 *人*,所有人都热情地一起工作以帮助传播开放的原则和实践。正是这些人使我们的社区如此伟大。
六年来一直如此,并将永远保持下去。
### 从数字上看

*Jen Kelchner 提供的信息图*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/open-organization/21/6/celebrate-sixth-anniversary>
作者:[Laura Hilliger](https://opensource.com/users/laurahilliger) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[MareDevi](https://github.com/MareDevi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The Open Organization community celebrates its sixth anniversary on June 02. That's six years of articles ([hundreds](https://opensource.com/open-organization)), books (an [evolving series](https://theopenorganization.org/books)), conversations ([always inspiring](https://www.theopenorganization.community/)), teaching (we [love it](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Snf6vICDbzw&list=PLLIYDJHuxOkaPEH76mIJe-HHplsiSAVej)), and learning. We're so proud to be a vibrant community of open experts and leaders working to bring [open principles](https://theopenorganization.org/definition) to organizations large and small. In fact, many of the [Open Organization Ambassadors](https://theopenorganization.org/about) have made careers out of helping others become more open, and our community remains dedicated to helping leaders across various industries integrate open mindsets and behaviors into their communities and contexts.
[Last year](https://opensource.com/open-organization/20/6/scaling-energetic-community) was a period of [growth](https://opensource.com/open-organization/20/7/evolving-project-governance) and [renewal](https://opensource.com/open-organization/20/8/open-community-rebrands) for the Open Organization project. And this year, we're building on that momentum. Today, we're proud to introduce two new initiatives—and, of course, invite you to participate.
## Turn on, tune in, open up
First, we're excited to announce a brand new venue for our community's work: [OpenOrgTV](http://theopenorganization.tv). It's more than a new platform. It's an experiment in another medium: video.
On our channel, we'll be hosting all kinds of conversations—from in-depth book reviews to community roundtables. To get started, check out the "[Open Leadership Conversations](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=07YBs0ss9rU&list=PLLIYDJHuxOkYDTLbKRjcd9THTFtpnK8lh)" series, which features interviews with insightful leaders offering their perspectives on what it means to lead according to open principles. Or watch "[Ask the Ambassadors](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ukkZMYqRuUQ&list=PLLIYDJHuxOkY1gDbOFLDxGxwwmxeOATrI)," our Q&A-style write-in show starring community experts answering *your* questions about organizational culture and design. Want to be part of the show? Submit your questions to community members in our [new dedicated forum](https://www.theopenorganization.community/c/ask-community/19).
All month long, we'll be featuring introductions to the [Open Organization Ambassadors](http://theopenorganization.org/roster/), so you can finally see the faces and hear the voices behind the stories, case studies, and interviews you've been reading for years.
## Defining open leadership
Since we released it several years ago, the [Open Organization Definition](https://theopenorganization.org/definition/) has become a guiding framework for organizations looking to better understand the nature of open organizational culture and design (and we've done lots to [teach others about it](https://youtu.be/NYngFYGgxro)). Over time, we even developed [a maturity model](https://github.com/open-organization/open-org-maturity-model) that operationalizes the definition, so organizations can assess their own levels of openness and make concrete plans to become even *more* open.
Now we think it's time to take that work a step further.
Inspired by our own experience, pre-existing frameworks from open organizations like [Red Hat](https://github.com/red-hat-people-team/red-hat-multiplier) and [Mozilla](https://mozilla.github.io/open-leadership-framework/framework/#the-open-leadership-framework), years of studying and interviewing open leaders in the field, and a desire to better understand how open leadership *really* works, we're pleased to unveil an early draft of a brand new document: the Open Leadership Definition.
This document outlines the mindsets and behaviors unique to the kinds of leaders who build open organizations and make them places where open-minded people can grow and thrive. It builds on the Open Organization Definition, explaining how open leaders embody and champion open organization characteristics—like transparency, inclusivity, adaptability, collaboration, and community.
And we're keen to share it with the world.
Beginning today (and continuing for the next two weeks), we're collecting *your* insights and comments on our draft document. We're eager to hear your ideas, and will take them *en masse* or in snippets. You can comment on individual parts of the document, or the entire thing. Just see the links below. We look forward to hearing from you.

Open Leadership Definition word cloud by Laura Hiliger (CC BY-SA)
### The Open Leadership Definition
[Open Leadership: Collaboration](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1hTvnpqQkOc76-0UJbV6tAvRxOE--bdt96mqGmAKGqiI/edit?usp=sharing)
[Read the entire thing](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1e1N_0p5lJEwAo_s6hQ3OK0KaJIfc7fgF?usp=sharing) in our shared folder.
## Let's connect
And of course, you can still find our community in all the usual places like:
[Our project website](http://theopenorganization.org/), your portal to the entire Open Organization project and community[Our conversation hub](https://www.theopenorganization.community/), where you can interact with community members, ask questions, learn about new projects, find resources, and help others[Our GitHub organization](https://github.com/open-organization), where we're always working on new materials in the open and invite you to join us[Our publication channel at Opensource.com](https://opensource.com/open-organization), where we're publishing the latest analyses, case studies, interviews, and resources for practitioners in various regions and industries- Our
[Twitter](https://twitter.com/openorgproject)and[LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/company/the-open-organization/)platforms, where we're sharing our latest updates and fostering new conversations
But the Open Organization community is more than any combination of platforms, tools, or projects. It's *people*, all working enthusiastically together to help spread open principles and practices. Those people are what makes our community so great.
That's been the case for six years now. And it always will be.
## By the numbers
*Infographic via Jen Kelchner*
## Comments are closed. |
15,134 | 使用 Topgrade 一次升级 Linux 中的各种软件包 | https://itsfoss.com/topgrade/ | 2022-10-12T15:21:00 | [
"更新",
"软件包"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15134-1.html | 
更新 Linux 系统并没有那么复杂,不是吗?毕竟,要更新 Ubuntu 之类的发行版,你只需要使用 `apt update` 和 `apt upgrade` 就行。
如果所有的包都是通过一个包管理器安装的,就会是这样。
但现在情况不再如此。你有经典的 apt/dnf/pacman,还有 Snap、Flatpak、Appimages。不止于此,你还可以使用 PIP(用于 Python)和 Cargo(用于 Rust)安装应用。
使用 Node? NPM 包需要单独更新。Oh My Zsh?需要单独更新。[Vim 中的插件](https://linuxhandbook.com/install-vim-plugins/)、Atom 等也可能不被 apt/dnf/pacman 覆盖。
你现在看到问题了吗?这就是名为 Topgrade 的新工具旨在解决的问题。
### Topgrade:处理各种更新的单一程序
[Topgrade](https://github.com/r-darwish/topgrade) 是一个 CLI 程序,它会检测你使用的工具,然后运行适当的命令来更新它们。

除了通常的 Linux 包管理器,它还可以检测和更新 Brew、Cargo、PIP、Pihole、Vim 和 Emacs 插件、R 软件包等。你可以在 [维基页面](https://github.com/r-darwish/topgrade/wiki/Step-list) 上查看支持的包列表。
##### Topgrade 的主要特点:
* 能够更新来自不同的包管理器的软件包,**包括固件**!
* 你可以如何控制更新包。
* 高度可定制。
* 甚至能够在更新包之前进行概览。
所以不要浪费任何时间,让我们跳到安装。
### 使用 Cargo 在 Linux 中安装 Topgrade
安装过程非常简单,因为我将使用 Cargo 包管理器。
我们已经有了 [详细指南,其中包含设置 Cargo 包管理器的多种方法](https://itsfoss.com/install-rust-cargo-ubuntu-linux/)。所以我将在我的示例中使用 Ubuntu 来快速完成。
因此,让我们以最少方式安装依赖项以及 Cargo:
```
sudo apt install cargo libssl-dev pkg-config
```
安装 Cargo 后,使用给定的命令安装 Topgrade:
```
cargo install topgrade
```
它会抛出一个警告:

你只需添加 `cargo` 路径即可运行二进制文件。这可以通过给定的命令来完成,你需要使用你的用户名替换 `sagar`:
```
echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/home/sagar/.cargo/bin' >> /home/sagar/.bashrc
```
现在,重启系统,Topgrade 就可以使用了。但是等等,我们需要安装另一个包来更新 Cargo 以获取最新的包。
```
cargo install cargo-update
```
这样我们完成了安装。
### 使用 Topgrade
使用 Topgrade 非常简单。使用一个命令,就是这样:
```
topgrade
```
但这不会给你除了系统包之外的任何控制,但正如我所提到的,你可以将不想更新的仓库列入黑名单。
#### 从 Topgrade 中排除包管理器和仓库
假设我想排除 Snap 和从默认包管理器下载的包,所以我的命令是:
```
topgrade --disable snap system
```

要进行永久更改,你必须在其配置文件中进行一些更改,这些更改可以通过给定的命令访问:
```
topgrade --edit-config
```
对于此示例,我排除了 Snap 和默认系统仓库:

#### 试运行 Topgrade
评估将要更新的过时软件包总是一个好主意,我从 Topgrade 的整个目录中找到了这个最有用的选项。
你只需使用带有 `-n` 选项的 `topgrade` 命令,它就会生成过期软件包的摘要。
```
topgrade -n
```

检查需要更新的软件包的一种简洁方法。
### 总结
在使用 Topgrade 几周后,它成为了我的 Linux 武器库中不可或缺的一部分。 像大多数其他 Linux 用户一样,我只是通过我的默认包管理器更新包。 Python 和 Rust 包被完全忽略了。 感谢 Topgrade,我的系统现在完全更新了。
我知道这不是每个人都想使用的工具。那你呢?愿意试一试吗?
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/topgrade/>
作者:[Sagar Sharma](https://itsfoss.com/author/sagar/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Updating a Linux system is not that complicated, is it? After all, to update Ubuntu-like distros, you just have to use apt update && apt upgrade.
That would have been the case if all the packages had been installed through a single package manager.
But that’s not the case anymore. You have the classic apt/dnf/pacman and then come Snap, Flatpak, and AppImage files. It doesn’t end here...
You may also install applications using PIP (for Python) and Cargo (for Rust) as well.
Use Node.js? The npm packages need to be updated separately. And, **Oh My Zsh?** It needs to be updated separately too.
[Plugins in Vim](https://linuxhandbook.com/install-vim-plugins/), Atom, etc, may also not be covered by apt/dnf/pacman.
Do you see the problem now? It may not be convenient to update all packages in your system. This is the problem a new tool called **topgrade** aims to solve.
## Topgrade: A single utility to take care of all kinds of updates
This [topgrade](https://github.com/topgrade-rs/topgrade) is a CLI utility that detects which tools you use and then runs the appropriate commands to update them.
Apart from the usual Linux package managers, it can detect and update brew, cargo, PIP, pihole, Vim and Emacs plugins, R packages etc.
You can explore its [GitHub page](https://github.com/topgrade-rs/topgrade) to know more.
#### Key Features of Topgrade:
- Ability to update packages from different package managers,
**including firmware!** - You do have control over how you want to update packages.
- Extremely customizable.
- Ability to have an overview even before updating packages.
So without wasting any time, let’s jump to the installation.
## Install Topgrade in Linux using Cargo
The installation process is quite straightforward as I’m going to use the cargo package manager.
We already have a [detailed guide with multiple methods for setting up a cargo package manager](https://itsfoss.com/install-rust-cargo-ubuntu-linux/) So I’m going to make it quick by using Ubuntu in my example.
So let’s start with some dependencies and installation of cargo in the least extensive way:
`sudo apt install cargo libssl-dev pkg-config`
Once the cargo has been installed, utilize the given command to install topgrade:
`cargo install topgrade`
And it will throw a warning as given:
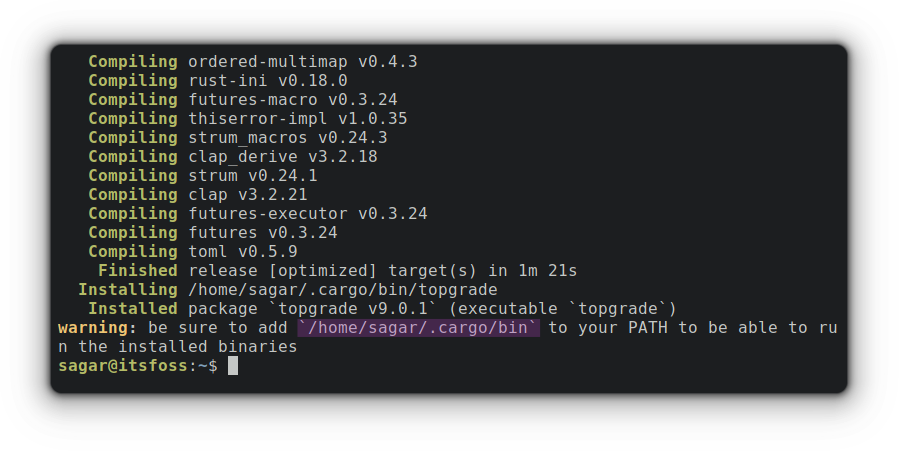
Where you just have to add the path of cargo to run binaries. This can be done through given command where you’ve to change `sagar`
with your username:
`echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/home/sagar/.cargo/bin' >> /home/sagar/.bashrc`
Now, reboot your system and topgrade is ready to use. But wait, we need to install another package that will update cargo to get the most recent packages.
`cargo install cargo-update`
And we’re done with installation.
## Using Topgrade
Using topgrade is extremely easy. Use a single command and that’s it:
`topgrade`
But this won’t give you any control apart from system packages, but as I mentioned, you can blacklist the repo you don’t want to get updated.
### Exclude package managers and repositories from Topgrade
Let’s suppose I want to exclude snaps and packages downloaded from the default package manager, so my command would be:
`topgrade --disable snap system`
For making a permanent change, you’d have to make a few changes in its config file which can be accessed through the given command:
`topgrade --edit-config`
For this example, I discluded snaps and default system repo:

### Dry run topgrade
Having an estimation of outdated packages that will be updated is always a good idea and I find this most useful option from the entire catalog of topgrade.
You just have to use topgrade with `-n`
option and it will generate a summary of outdated packages.
`topgrade -n`
A neat way of checking packages that need to be updated.
## Final Words
After using Topgrade for a few weeks, it became an integral part of my Linux arsenal. Like most other Linux users, I only updated packages through my default package manager. Python and Rust packages were ignored completely. Thanks to topgrade, my system is updated entirely now.
I understand that this is not a tool everyone would want to use. What about you? Willing to give it a try? |
15,136 | 使用 Linux 的优势和劣势 | https://itsfoss.com/advantages-linux/ | 2022-10-13T00:05:00 | [
"Linux"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15136-1.html | 
*开源朗读者:淮晋阳*
Linux 是一个流行词,你到处都能听到与 Linux 相关的内容。人们在技术论坛上讨论它、Linux 是课程中的一部分;你最喜欢的 YouTube 技术主播在兴奋地展示构建他们的 Linux 内核;你在 Twitter 上关注的 <ruby> 10 倍效率开发者 <rt> 10x developers </rt></ruby>都是 Linux 粉丝。
基本上,Linux 无处不在,每个人都在谈论它,因此你可能会不自主地陷入到对错失了 “学习 Linux” 的不安中。
所以,你想知道 Linux 的优势是什么,以及它是否值得去学习。
在这篇文章中,我总结了很多 Linux 的优势和劣势。
如果你在选择 Linux 还是你喜欢的操作系统上犹豫不决,我们愿意为你提供一些帮助。
>
> 在开始之前,我们要指出的是,“Linux” 本身并不是一个操作系统,它的操作系统被称为 [Linux 发行版](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-linux/),而且 Linux 的发行版有数百种。为简单起见,我将其称为 Linux 操作系统,而不是某个特定的 Linux 发行版。可以参考 [这篇文章](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-linux/),来更好地理解这些东西。
>
>
>
### 使用 Linux 的优势
如果你想使用 Linux 替代现在的操作系统,那么只有当你了解 Linux 的优势,才会有意义。
如果 Linux 在你想要它做的事情上表现出色,你将永远都不会后悔你的决定。
#### 不用购买许可证

你需要拥有苹果公司的设备,才能使用 macOS 作为日常使用;你需要拥有 Windows 许可证,才能使用微软的 Windows。
因此,你需要对这些东西进行一定的投资。但是,对于 Linux 呢?它是完全免费的!
与 Windows 和 macOS 相比,不仅仅是操作系统上的不同,Linux 上还有许多免费的软件包。
你无需支付许可证费用,就可以使用所有主流的 Linux 发行版。当然,你可以选择捐赠来支持该项目,但这完全取决于你自己的意愿。
**此外**,Linux 是完全开源的,这意味着所有人都能检查源代码的透明度。
#### 能以最小的系统资源运行

通常,用户考虑尝试另一个操作系统,是因为他们对现有系统的性能感到沮丧。
这也是我的个人经历。我受朋友的委托,使用 Linux 来更新他们的旧笔记本电脑或经常滞后的系统。
而且,Linux 发行版能够在普通的硬件配置上运行,你不需要拥有最新最好的硬件。此外,还有专门的 [轻量级 Linux 发行版](https://itsfoss.com/lightweight-linux-beginners/) 可以在较旧的硬件上运行而不会出现问题。
因此,如果你立即使用 Linux,你有更多的机会恢复你的旧系统,或在短时间内获得一个快速的计算机。
#### 更少地受到恶意软件的威胁

没有操作系统可以免受恶意文件或脚本的侵害。如果你从未知来源下载并运行某些内容,则无法保证其安全性。
然而,对于 Linux,情况会更好一些。诚然,研究人员已经发现了针对 Linux 物联网设备的攻击者。但是,对于桌面 Linux,还无须担心。
恶意攻击者攻击的目标是更受家庭欢迎的平台,而 Linux 在桌面领域并没有很大的市场份额来吸引到这种关注。在某种程度上,这可能是一件好事。
你要做的就是坚持使用官方软件包,并在执行任何操作之前阅读指导说明。
另外,在 Linux 上,你也不用安装防病毒程序,来保护本机免受恶意软件的威胁。
#### 可个性化定制

有了开源的代码,你就可以根据需要自由定制你的 Linux 体验。
当然,你需要具备一些专业知识,才能充分地定制你的 Linux。但是与 macOS 和 Windows 相比,即使你没有任何经验,也可以在 Linux 操作系统中获得更多自定义功能。

如果你想要个性化你的体验,并愿意付出额外的努力,那么 Linux 就非常适合你。例如,你可以参考 [KDE 定制指南](https://itsfoss.com/kde-customization/) 和 [停靠区选项](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-docks/) 以获得基本的自定义方法。
#### 适用于所有人
使用 macOS 或 Windows,你只能在微软或苹果最终确定的设计/偏好选择中,做出你的选择。
但是,对于 Linux,你能发现专注于各种事情的不同的 Linux 发行版。
例如,你可以选择能始终获取最新功能的 Linux 发行版,或者你也可以选择只为你提供安全/维护更新的 Linux 发行版。
你可以使用有开箱即用、外观好看的 Linux 发行版,或提供最大程度的自定义选项的 Linux 发行版。Linux 发行版的选择是多种多样的。
我建议你从 [能提供最佳用户体验的选项](https://itsfoss.com/beautiful-linux-distributions/) 开始。
#### 完整的开发环境
如果你是软件开发人员或学习编程的学生,Linux 绝对是有优势的。许多构建工具都能在 Linux 上使用,并能够集成到 Linux 中。使用容器(Docker),你可以轻松创建专门的测试环境。
微软知道这个价值,因此它创建了 WSL,让开发人员可以在 Windows 内访问 Linux 环境。尽管如此,WSL 并没有接近真正的 Linux 体验,在 Windows 上使用 Docker 也同样如此。
但是这并不适用于网页设计,因为极为好用的 Adobe 工具并不能在 Linux 上使用。但是,如果你的工作不需要 Adobe,Linux 会是一个不错的选择。
#### Linux 是一项必须学习的技能!
使用 Linux 有一个学习曲线,刚开始时掌握的速度最快,之后则逐渐变得平缓,但是它给你提供了对各种事物的洞察力。
你可以通过探索和自由定制 Linux,或者仅仅是通过使用它,来了解操作系统中的事物是如何工作的。
不是每个人都知道如何使用 Linux。
因此,通过学习 Linux 来获得和扩展你对软件和计算机的知识会是一项很棒的技能。
#### Linux 是一个必要的工作技能

正如我之前提及的,学习 Linux 是一个很好的技能,这不仅仅能增长你的知识,它在职业方面也很有用。
通过学习 Linux 的基础知识,你可以成为 Linux 系统管理员或安全专家,并且能胜任很多其他的工作。
因此,学习 Linux 开辟了一系列机会!
#### 保护隐私
如果你没有微软账号,那么你就不能使用 Windows。当你启动 Windows 时,你会发现它会在很多的服务和应用中记录你的数据。

虽然你可以找到此类设置并禁用它们,但很明显,Windows 的默认配置不会考虑你的隐私。
而在 Linux 中,并非如此。虽然某些应用程序/发行版会有一个可选功能,让你可以与他们分享有用的东西,但这并不是什么大问题。Linux 上的大多数东西都是经过定制的,默认情况下可以为你提供最大的隐私,从而无需配置任何东西。
但是,苹果和微软会采用巧妙的策略从你的计算机收集匿名的使用数据。偶尔,他们会记录你在他们的应用商店的活动,以及当你通过你的账户登录时的信息。
#### 自定义项目和自托管
你是一个喜欢捣鼓小发明的人吗?如果你喜欢制作电子或软件项目,Linux 会是你的发明天堂。
你可以在 [诸如树莓派这样的单板机](https://itsfoss.com/raspberry-pi-alternatives/) 上使用 Linux,开发出一些很酷的东西,例如复古游戏机、家庭自动化系统等等。
你也能在你自己的服务器上部署开源的软件,并维护他们。这称为自托管,它有以下的优点:
* 减少托管费用
* 掌控你的数据
* 对于你的每个需求,定制应用/服务
你能直接使用 Linux 或者使用基于 Linux 的工具,来做这所有的事情。
### 使用 Linux 的劣势
Linux 并不是一个没有缺点的选择。任何事都具有两面性,Linux 也有一些不好的地方,包括:
#### 不容易快速上手

学习的目的通常不在于掌握一项新技能,更重要的是尽可能快地适应。
如果用户使用某一个东西,却无法完成任务,那么它并不适合他们。对于每个操作系统也是如此。例如,使用 Windows/macOS 的用户可能不会很快适应 Linux。
你可以阅读我们的比较文章以了解 [macOS 和 Linux 之间的区别](https://itsfoss.com/mac-linux-difference/)。
我同意一些人会比其他人学习速度更快。但是,总体而言,当你踏入 Linux 世界时,你需要付出一点努力,去学习那些不明显的东西。
#### 多样性
虽然我们建议使用 [为初学者量身定制的最佳 Linux 发行版](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-beginners/),但一开始就选择你喜欢的版本,可能会让人不知所措。
你可能会想尝试其中多个版本,以查看最适合你的 Linux 发行版,但是这既耗时又令人十分困惑。
最好选择其中一种 Linux 发行版。但是,如果你仍然感到困惑,你可以仍旧使用 Windows/macOS。
#### 在桌面领域的市场份额相对较低

Linux 不是流行的桌面操作系统。
这不应该是用户关心的问题。但是,如果没有大的市场占有率,就不能指望应用程序开发人员为 Linux 开发/维护工具。
当然,现在 Linux 有很多重要且流行的工具,比以往任何时候都多。但是,这仍然是一个因素,意味着并非所有好的工具/服务都可以在 Linux 上运行。
请参阅我们定期更新的关于 [Linux 的市场份额](https://itsfoss.com/linux-market-share/) 的文章,了解相关内容。
#### 缺少专有软件
正如我上面提到的,并不是开发者都对将他们的工具/应用程序引入 Linux 感兴趣。
因此,你可能在 Linux 上找不到适用于 Windows/macOS 的所有优质专有产品。诚然,你可以使用兼容层在 Linux 上运行 Windows/macOS 程序。
但这并不总是有效。例如,你没有支持 Linux 的官方微软 365 和像 Wallpaper Engine 这样的工具。
#### 不是游戏优先的操作系统

如果你想在电脑上玩游戏,Windows 仍然是支持最新硬件和技术的最佳选择。
谈到 Linux,有很多 “如果和但是” 需要一个明确的答案。
请注意,你可以在 Linux 上玩很多现代游戏,但在各种不同的硬件上可能不会有一致的体验。正如我们的一位读者在评论中建议的那样,你可以使用 Steam Play 在 Linux 上尝试许多 Windows 独占的游戏,而不会出现潜在的障碍。
Steam Deck 正在鼓励更多的游戏开发者使他们的游戏在 Linux 上运行得更好。而且,这在不久的将来只会得到改善。因此,如果你能花点功夫在 Linux 上尝试你最喜欢的游戏,可能不会让人失望。
话虽如此,在 Linux 上玩游戏并不方便。如果你有兴趣,可以参考我们的 [Linux 游戏指南](https://itsfoss.com/linux-gaming-guide/) 以了解更多信息。
#### 缺少专业的技术支持
我知道不是每个人都需要技术支持。但是,一些技术支持选项能够在他们的笔记本电脑或计算机上远程指导用户/修复问题。
使用 Linux,你可以向社区寻求帮助,但它可能不像某些专业技术支持服务那样好用。
你仍然需要自己完成大部分努力,并自己尝试一些东西,并不是每个人都喜欢这样做的。
### 总结
我主要是 Linux 用户,但我在玩游戏时使用 Windows。虽然我偏好 Linux,但我尽力在这篇文章中对 Linux 保持中立态度,并给你足够的指导,以便你可以决定 Linux 是否适合你。
如果你打算使用 Linux,并且从未使用过它,请迈出你的第一步吧,可以参考 [在虚拟机中使用 Linux 的第一步](https://itsfoss.com/why-linux-virtual-machine/)。如果你有 Windows 11,你也可以使用 WSL2。
我非常乐意收到你的评价和建议。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/advantages-linux/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Linux is a buzzword and you keep hearing about Linux here and there. People discuss it in the tech forum, it is part of the course curriculum and your favorite tech YouTubers get excited while showing their Linux build. The 10x developers you follow on Twitter are all Linux fans.
Basically, Linux is everywhere and everyone keeps talking about it. And that gives you FOMO.
So, you wonder about the advantages of Linux and whether is it really worth trying.
I have compiled various possible advantages and disadvantages of Linux in this article.
If you are on the fence about choosing Linux over your preferred operating system, we would like to help you out.
Before you start, you should know that Linux is not an operating system on its own. The operating systems are called [Linux distributions and there are hundreds of them](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-linux/). For simplicity, I’ll address it as Linux OS instead of a specific Linux distribution. This [article](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-linux/) explains things better.
## Advantages of Using Linux
Considering you are curious about Linux as an alternative operating system choice, it only makes sense that you know its advantages.
You might never regret your decision if it excels at what you want it to do.
### No Need to Purchase a License

You need to own an Apple device to use macOS as your daily driver and a Windows license to use Microsoft’s Windows.
Therefore, you need a bit of investment with these options. But, with Linux? It’s entirely free.
Not just the OS, there are many software packages available for free on Linux when compared to Windows and macOS.
You can try every mainstream Linux distribution without paying for a license. Of course, you get the option to donate to support the project, but that is up to you if you really like it.
**Additionally**, Linux is totally open-source, meaning anyone can inspect the source code for transparency.
### Can Run With Minimal System Resources
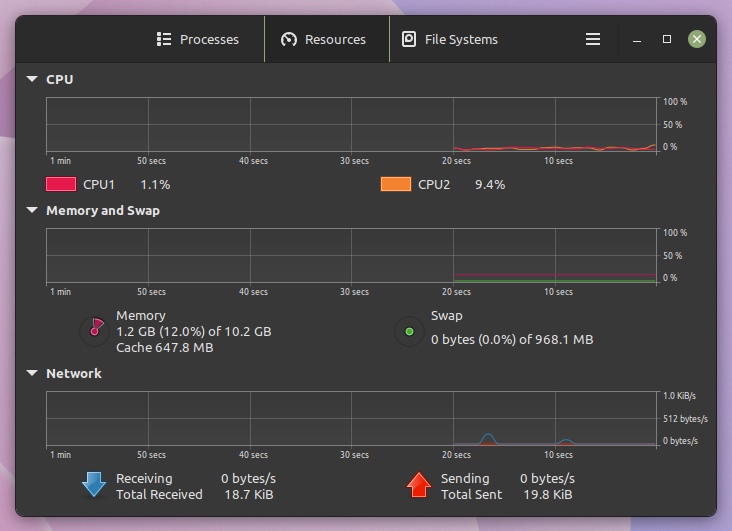
Typically, when users think of trying another operating system, it is because they are frustrated with the performance of their system.
This is from my personal experience. I have had friends willing to try Linux to revive their old laptop or a system that constantly lags.
And, when it comes to Linux distributions, they are capable of running on decent hardware configurations. You do not need to have the latest and greatest. Moreover, there are specialized [lightweight Linux distributions](https://itsfoss.com/lightweight-linux-beginners/) that are tailored to run on older hardware with no hiccups.
So, you have more chances to revive your old system or get a fast-performing computer in no time with Linux.
### Less Exposed to Malware

No operating system is safe from malicious files or scripts. If you download and run something from an unknown source, you cannot guarantee its safety.
However, things are better for Linux. Yes, researchers have found attackers targeting Linux IoT devices. But, for desktop Linux, it is not “yet” something to worry about.
Malicious actors target platforms that are more popular among households, and Linux does not have a big market share in the desktop space to attract that kind of attention. In a way, it can be a good thing.
All you have to do is just stick to the official software packages, and read instructions before you do anything.
As an extra plus, you do not necessarily need an antivirus program to get protection from malware.
### Customization
With an open-source code, you get the freedom to customize your Linux experience as much as you want.
Of course, you require a bit of technical expertise to go utilize the best of it. Even without any experience, you get more customization features in your operating system when compared to macOS and Windows.
[u/ZB652](https://www.reddit.com/r/unixporn/comments/wzu5nl/plasma_cscx2n/?ref=itsfoss.com)
If you are into personalizing your experience and willing to put in extra effort, Linux is for you. As an example, refer to the [KDE customization guide](https://itsfoss.com/kde-customization/) and [dock options](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-docks/) to get basic ideas.
### Something for Everyone
With macOS or Windows, you get limited to the design/preference choices finalized by Microsoft or Apple.
But, with Linux, you will find several Linux distributions that try to focus on various things.
For instance, you can opt for a Linux distribution that focuses on getting the latest features all the time, or you can opt for something that only gives you security/maintenance updates.
You can get something that looks beautiful out of the box or something that you provide crazy customization options. You will not run out of options with Linux.
I recommend starting with [options that give you the best user experience](https://itsfoss.com/beautiful-linux-distributions/).
### Complete Development Environment
If you are a software developer or student learning to code, Linux definitely has an edge. A lot of your build tools are available and integrated into Linux. With Docker, you can create specialized test environment easily.
Microsoft knows about this part and this is why it created WSL to give developers access to Linux environments inside Windows. Still, WSL doesn’t come close to the real Linux experience. The same goes for using Docker on Windows.
I know the same cannot be said about web designing because the coveted Adobe tools are not available on Linux yet. But if you don’t need Adobe for your work, Linux is a pretty good choice.
### Learning Linux is a Skill One Must Have!
There is a learning curve to using Linux, but it provides you with insights on various things.
You get to learn how things work in an operating system by exploring and customizing it, or even just by using it.
Not everyone knows how to use Linux.
So, it can be a great skill to gain and expand your knowledge of software and computers.
### Linux is an in-demand Job Skill

As I mentioned above, it is a great skill to have. But, not just limited to expanding your knowledge, it is also useful professionally.
You can work your way to become a Linux system administrator or a security expert and fill several other job roles by learning the fundamentals of Linux.
So, learning Linux opens up a whole range of opportunities!
### Privacy-Friendly
These days you cannot use Windows without a Microsoft account. And when you set up Windows, you’ll find that it tries to track your data from a number of services and applications.
While you can find such settings and disable them, it is clear that Windows is configured to disregard your privacy by default.
That’s not the case in Linux. While some applications/distributions may have an optional feature to let you share useful insights with them, it has never been a big deal. Most of the things on Linux are tailored to give you maximum privacy by default without needing to configure anything.
Apple and Microsoft on the other hand have clever tactics to collect anonymous usage data from your computer. Occasionally, they log your activity on their app store and while you are signed in through your account.
### DIY projects and Self-hosting
Got a tinkerer in you? If you like to make electronics or software projects, Linux is your paradise.
You can use Linux on [single-board computers like Raspberry Pi](https://itsfoss.com/raspberry-pi-alternatives/) and create cool things like retro gaming consoles, home automation systems, etc.
You can also deploy open source software on your own server and maintain them. This is called self-hosting and it has the following advantages:
- Reduce hosting costs
- Take control of your data
- Customize the app/service as per your requirements
Clearly, you’ll be doing all this either directly with Linux or tools built on top of it.
## Disadvantages of Linux
Linux is not a flawless choice. Just like everything, there are some downsides to Linux as well. Those include:
### Learning Curve

Every so often it is not just about learning a new skill, it is more about getting comfortable as quickly as possible.
If a user cannot get their way around the task they intend to do, it is not for them. It is true for every operating system. For instance, a user who uses Windows/macOS, may not get comfortable with Linux as quickly.
You can read our comparison article to know the [difference between macOS and Linux](https://itsfoss.com/mac-linux-difference/).
I agree that some users catch on quicker than others. But, in general, when you step into the Linux world, you need to be willing to put a bit of effort into learning the things that are not obvious.
### Variety
While we recommend using the [best Linux distributions tailored for beginners](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-beginners/), choosing what you like at first can be overwhelming.
You might want to try multiple of them to see what works with you best, which can be time-consuming and confusing.
It’s best to settle with one of the Linux distributions. But, if you remain confused, you can stick to Windows/macOS.
### Market Share in Desktop Space

Linux is not a popular desktop operating system.
This should not be of concern to a user. However, without having a significant market presence, you cannot expect app developers to make/maintain tools for Linux.
Sure, there are lots of essential and popular tools available for Linux, more than ever. But, it remains a factor that may mean that not all good tools/services work on Linux.
Refer to our regularly updated article on [Linux’s market share](https://itsfoss.com/linux-market-share/), to get an idea.
### Lack of Proprietary Software
As I mentioned above, not everyone is interested in bringing their tools/apps to Linux.
Hence, you may not find all the good proprietary offerings for Windows/macOS. Sure, you can use a compatibility layer to run Windows/macOS programs on Linux.
But that doesn’t work all the time. For instance, you do not have official Microsoft 365 support for Linux and tools like Wallpaper Engine.
### Not a Gaming-first OS

If you want to game on your computer, Windows remains the best option for its support for the newest hardware and technologies.
When it comes to Linux, there are a lot of “ifs and buts” for a clear answer.
Note that you can play a lot of modern games on Linux, but it may not be a consistent experience across a range of hardware. As one of our readers suggested in the comments, you can use [Steam Play](https://itsfoss.com/steam-play/) to try many of the Windows-exclusive games on Linux without potential hiccups.
Steam Deck is encouraging more game developers to make their games run better on Linux. And, this will only improve in the near future. So, if you can take a little effort to try your favorite games on Linux, it may not be disappointing.
That being said, it may not be a seamless experience for everyone. You can refer to our [gaming guide for Linux](https://itsfoss.com/linux-gaming-guide/) to explore more if interested.
### Lack of Professional Tech Support
I know not everyone needs it. But, there are tech support options that can guide users/fix issues remotely on their laptop or computer.
With Linux, you can seek help from the community, but it may not be as seamless as some professional tech support services.
You’ll still have to do most of the hit and try stuff on your own and not everyone would like it.
## Wrapping Up
I am primarily a Linux user but I use Windows when I have to play games. Though my preference is Linux, I have tried to be unbiased and give you enough pointers so that you can make up your mind if Linux is for you or not.
If you are going for Linux and have never used it, take the baby step and [use Linux in a virtual machine first](https://itsfoss.com/why-linux-virtual-machine/). You can also use WSL2 if you have Windows 11.
I welcome your comments and suggestions. |
15,137 | 如何在 Brave 浏览器中使用画中画模式 | https://itsfoss.com/picture-in-picture-brave/ | 2022-10-13T00:30:00 | [
"Brave",
"画中画"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15137-1.html | 
>
> Brave 是一款出色的类似于 Chrome,但可 [替代 Chrome 的网络浏览器](https://itsfoss.com/open-source-browsers-linux/)。
>
>
>
[Firefox 和 Brave](https://itsfoss.com/brave-vs-firefox/) 是我喜欢在 Linux 系统上使用的两种浏览器。两者都有不同的优势。
Firefox 比 Brave 做得更好的一件事就是画中画(PIP)模式,它适用于 YouTube、Netflix 和大多数流媒体网站。
Brave 也有画中画模式,但它是如此隐藏,以至于你觉得它根本没有 PIP 支持。
内置画中画适用于某些网站(如 YouTube),但可能不适用于其他网站(如 Prime Video)。不用担心!你可以为此使用专用扩展。
让我在本教程中展示这两种方法。
### 方法 1:在视频上双击右键
**技巧是依次单击两次右键,你应该会看到画中画模式选项。**
让我通过一个例子来说明这一点。在 Brave 中播放 YouTube 视频。现在右键单击视频。

再次右键单击。它应该在视频上,但不在上一个上下文菜单上,而在视频的其他地方。
现在你应该看到另一个带有画中画选项的上下文菜单。

选择画中画,视频将从窗口中弹出。你可以将其移动到浏览器中的任何位置。

当你使用其他应用时,你还可以让它在屏幕上的任何位置播放。

在最近的 Brave 版本中,你可以根据自己的喜好调整弹出窗口的大小。
我不明白为什么 Brave 把它隐藏成这样。为什么不突出它?
无论如何,这适用于 YouTube 等网站,但可能不适用于 Prime 视频。如果你愿意,你可以安装一个扩展。
### 方法 2:使用画中画扩展
谷歌提供了一个官方插件,可让你在谷歌 Chrome 中获得画中画功能。由于 Brave 基于 Chromium,你可以在 Brave 中使用相同的扩展。
>
> **[画中画扩展](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/picture-in-picture-extens/hkgfoiooedgoejojocmhlaklaeopbecg/related?hl=en-US)**
>
>
>
进入扩展页面并点击 “<ruby> 添加到 Brave <rt> Add to Brave </rt></ruby>” 按钮。

当你单击它时,它会提示添加扩展的选项。

添加扩展后,你应该会在浏览器的右上角看到它。

播放视频时,单击该扩展图标,视频应该会弹出。
### 你能在 Brave 中启用 PIP 模式吗?
画中画模式已成为休闲流媒体消费的必备功能。我觉得奇怪的是,Brave 和其他浏览器没有足够重视它。 Firefox 处理得很好。
我希望这个快速的小技巧可以帮助你在 Brave 浏览器中获得 PIP 体验。你更喜欢这两种方法中的哪一种?右键单击还是扩展?
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/picture-in-picture-brave/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Brave is an excellent Chrome-like and yet [Chrome alternative web browser](https://itsfoss.com/open-source-browsers-linux/).
[Firefox and Brave](https://itsfoss.com/brave-vs-firefox/) are two browsers I like using on my Linux system. Both have different advantages.
There is one thing that Firefox does better than Brave: the picture-in-picture (PIP) mode that works on YouTube, Netflix and most streaming sites.
Brave, too, has picture-in-picture mode but it’s so hidden that you feel like there is no PIP support at all.
The built-in picture-in-picture works on some websites (like YouTube) but may not work on others (like Prime Video). Worry not! You can use a dedicated extension for that.
Let me show both methods in this tutorial.
## Method 1: Use two right clicks on the video
*The trick is to do two right clicks one after another and you should see the option Picture in Picture mode.*
Let me show this by an example. Play a YouTube video in Brave. Now right-click on the video. You

Do another right click. It should be on the video but not on the previous context menu. Just someplace else on the video.
Now you should see another context menu with the Picture in picture option.
Select the Picture in picture and the video will pop out in its own window. You can move it anywhere in the browser.
You can also keep it playing anywhere on the screen while you use some other application.
You can resize the pop-up window as per your liking in the recent Brave versions.
I don’t understand why Brave has it hidden like this. Why not give it prominence?
Anyway, this works on websites like YouTube but may not work on Prime videos. If you want that, you can install an extension.
## Method 2: Use Picture-in-Picture extension
There is an official plugin from Google that allows you to get the Picture-in-Picture feature in Google Chrome. Since Brave is based on Chromium, you can use the same extension in Brave.
Go to the extension page and **hit the Add to Brave button**.
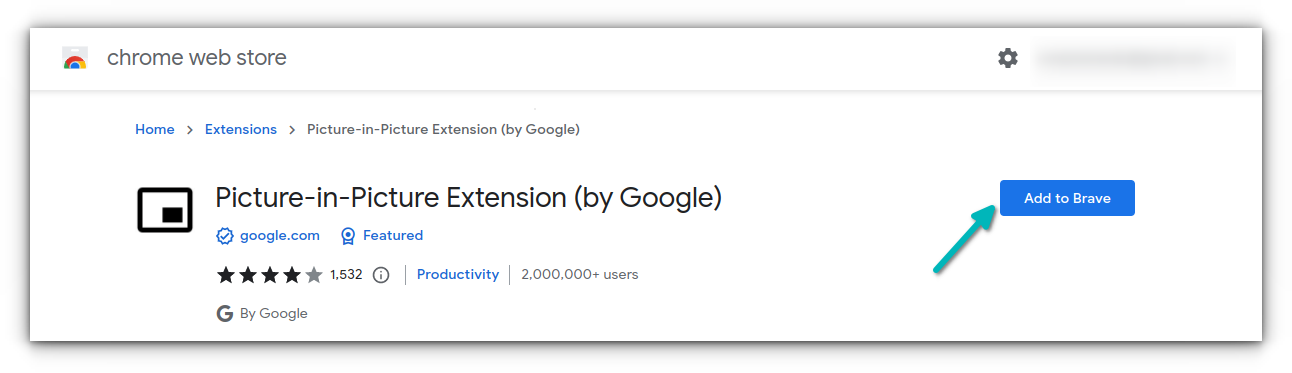
When you click on that, it gives you the option to add the extension.
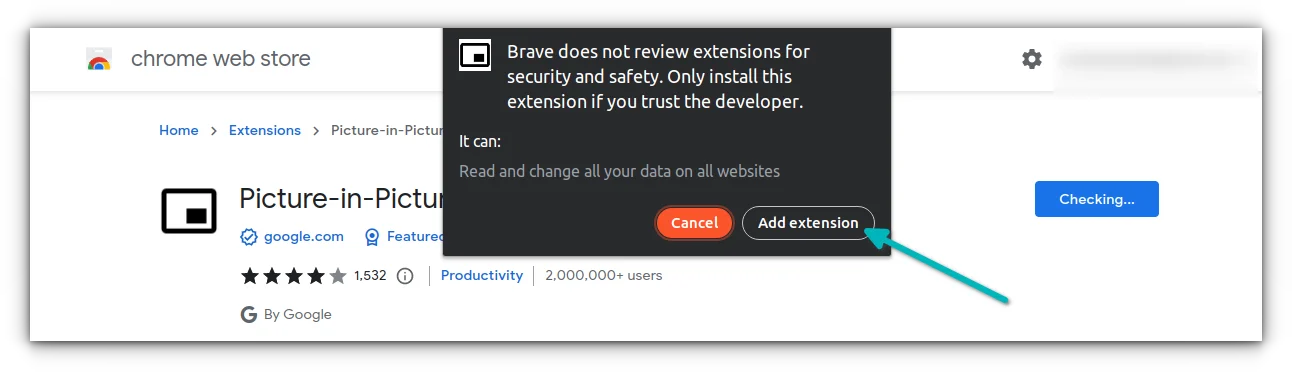
Once you have added the extension, you should see it in the top right corner of the browser.
When you are playing a video, click on the extension and the video should pop out.
[How to Save Downloaded Files Automatically in Brave BrowserI always use two browsers on my system. Firefox is the primary browser and these days Brave is what I rely for my second browser. Brave browser is an excellent choice for someone who wants a Chrome/Chromium feel without the Google touch. It blocks ads and trackers by default](https://itsfoss.com/save-files-automatically-brave-browser/)

## Were you able to enable PIP mode in Brave?
Picture in Picture mode has become an essential feature for casual streaming consumption. I find it strange that Brave and other browsers haven’t paid enough attention to it. Firefox handles it excellently.
I hope this quick little tip helped you to get the PIP experience in the Brave browser. Which of the two methods do you prefer? Right-click or the extension? |
15,139 | ARPANET 的真正创新之处 | https://twobithistory.org/2021/02/07/arpanet.html | 2022-10-14T18:01:59 | [
"ARPANET"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15139-1.html | 
如果你在搜索引擎中输入“ARPANET”,搜索相关图片,你会看到许多地图的图片,上面是这个上世纪六十年代末七十年代初 [美国政府创建的研究网络](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARPANET),该网络不断延伸扩展,横跨了整个美国。我猜很多人第一次了解到 ARPANET 的时候都看过这种地图。
可以说,这些地图很有意思,毕竟我们很难想象过去连接网络的计算机是那么少,就连如此低保真的图片都可以表示出美国全部机器的所在位置(这里的<ruby> 低保真 <rt> lo-fi </rt></ruby>指的是高射投影仪成像技术,而不是大家熟知的 lo-fi 氛围音乐)。不过,这些地图是有问题的。地图上用加粗的线条连接着大陆各地,强化了人们的一种观念:ARPANET 最大的贡献就是首次将横跨美国东西两地的电脑连接了起来。
今天,即便是在病毒肆虐、人们困居家中的情况下,网络也能把我们联系起来,可谓是我们的生命线。所以,如果认为 ARPANET 是最早的互联网,那么在那之前世界必然相互隔绝,毕竟那时还没有今天的互联网,对吧?ARPANET 首次通过计算机将人们连接起来,一定是一件惊天动地的大事。
但是,这一观点却与历史事实不符,而且它也没有进一步解释 ARPANET 的重要性。
### 初露锋芒
华盛顿希尔顿酒店坐落于<ruby> 国家广场 <rt> National Mall </rt></ruby>东北方向约 2.4 千米处的一座小山丘山顶附近。酒店左右两侧白色的现代化立面分别向外延展出半个圆形,活像一只飞鸟的双翼。1965 年,酒店竣工之后,《纽约时报》报道称这座建筑物就像“一只栖息在山顶巢穴上的海鸥” <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn1" id="fnref1"> [1] </a></sup>。
不过,这家酒店最有名的特点却深藏在地下。在车道交汇处下方,有着一个巨大的蛋形活动场地,这就是人们熟知的<ruby> 国际宴会厅 <rt> International Ballroom </rt></ruby>,多年来一直是华盛顿特区最大的无柱宴会厅。1967 年,大门乐队在此举办了一场音乐会。1968 年,“吉他之神”吉米·亨德里克斯也在此举办了一场音乐会。到了 1972 年,国际宴会厅隐去了以往的喧嚣,举办了首届<ruby> 国际计算机通信会议 <rt> International Conference on Computing Communication </rt></ruby>(ICCC)。在这场大会上,研究项目 ARPANET 首次公开亮相。
这场会议举办时间为 10 月 24-26 日,与会人数约八百人 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn2" id="fnref2"> [2] </a></sup>。在这场大会上,计算机网络这一新兴领域的领袖人物齐聚一堂。<ruby> 因特网 <rt> internet </rt></ruby>的先驱<ruby> 鲍勃·卡恩 <rt> Bob Kahn </rt></ruby>称,“如果有人在华盛顿希尔顿酒店上方丢了一颗炸弹,那么美国的整个网络研究领域将会毁于一旦” <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn3" id="fnref3"> [3] </a></sup>。
当然,不是所有的与会人员都是计算机科学家。根据当时的宣传广告,这场大会将“以用户为中心”,面向“律师、医务人员、经济学家、政府工作者、工程师以及通信员等从业人员”<sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn4" id="fnref4"> [4] </a></sup>。虽然大会的部分议题非常专业,比如《数据网络设计问题(一)》与《数据网络设计问题(二)》,但是正如宣传广告所承诺的,大部分会议的主要关注点还是计算机网络给经济社会带来的潜在影响。其中甚至有一场会议以惊人的先见之明探讨了如何积极利用法律制度“保护计算机数据库中的隐私权益” <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn5" id="fnref5"> [5] </a></sup>。
展示 ARPANET 的目的是作为与会者的一个附带景点。在国际宴会厅或酒店更下一层的其他地方举行的会议间歇,与会者可以自由进入<ruby> 乔治敦宴会厅 <rt> Georgetown Ballroom </rt></ruby>(在国际宴会厅走廊尽头的一个较小的宴会厅,也可以说是会议室)<sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn6" id="fnref6"> [6] </a></sup>,那里放置着用以访问 ARPANET 的 40 台由不同制造商生产的终端 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn7" id="fnref7"> [7] </a></sup>。这些终端属于<ruby> 哑终端 <rt> dumb terminal </rt></ruby>,也就是说,只能用来输入命令、输出结果,本身无法进行计算。事实上,在 1972 年,所以这些终端可能都是<ruby> 硬拷贝终端 <rt> hardcopy terminal </rt></ruby>,即<ruby> 电传打字机 <rt> teletype machine </rt></ruby>。哑终端与一台被称为“<ruby> 终端接口信息处理机 <rt> Terminal Interface Message Processor </rt></ruby>”(TIP)的计算机相连接,后者放置在宴会厅中间的一个高台上。TIP 是早期的一种路由器,哑终端可通过 TIP 连接到 ARPANET。有了终端和 TIP,ICCC 与会者可以尝试登录和访问组成 ARPANET 的 29 个主机站的计算机 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn8" id="fnref8"> [8] </a></sup>。
为了展示网络的性能,美国全国各主机站的研究员们通力合作,准备了 19 个简易的“情景”,供用户测试使用。他们还出了 [一份小册子](https://archive.computerhistory.org/resources/access/text/2019/07/102784024-05-001-acc.pdf),将这些情景收录其中。如果与会人员打算进入这个满是电线与哑终端的房间,就会得到这样一本小册子 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn9" id="fnref9"> [9] </a></sup>。通过这些情景,研究员不仅要证明网络这项新技术的可行性,还要证明其实用性,因为 ARPANET 那时还只是“一条没有汽车驶过的公路”。此外,来自国防部的投资者们也希望,公开展示 ARPANET 可以进一步激发人们对网络的兴趣 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn10" id="fnref10"> [10] </a></sup>。
因此,这些情景充分展示了在 ARPANET 网络上可以使用的软件的丰富性:有程序语言解释器,其中一个用于麻省理工学院(MIT)的 Lisp 语言,另一个用于加州大学洛杉矶分校的数值计算环境 Speakeasy;还有一些游戏,包括国际象棋和 <ruby> 康威生命游戏 <rt> Conway's Game of Life </rt></ruby>;以及几个也许最受与会者欢迎的人工智能聊天程序,包括由 MIT 的计算机科学家<ruby> 约瑟夫·魏泽堡 <rt> Joseph Weizenbaum </rt></ruby>开发的著名聊天程序<ruby> 伊莉莎 <rt> ELIZA </rt></ruby>。
设置这些情景的研究人员小心翼翼地列出了他们想让用户在终端机上输入的每一条命令。这点很重要,因为用于连接 ARPANET 主机的命令序列可能会因为主机的不同而发生变化。比如,为了能在 MIT 人工智能实验室的 PDP-10 微型电脑上测试人工智能国际象棋程序,与会者需要按照指示输入以下命令:
>
> 在下方代码块中,`[LF]`、`[SP]` 以及 `[CR]` 分别代表换行、空格以及回车键。我在每行的 `//` 符号后面都解释了当前一行命令的含义,不过当时的小册子本来是没有使用这一符号的。
>
>
>
```
@r [LF] // 重置 TIP
@e [SP] r [LF] // “远程回显”设置, 主机回显字符,TIP 不回显
@L [SP] 134 [LF] // 连接 134 号主机
:login [SP] iccXXX [CR] // 登录 MIT 人工智能实验室的系统,“XXX”代表用户名首字母缩写
:chess [CR] // 启动国际象棋程序
```
如果与会者输入了上述命令,那么他就可以体验当时最先进的国际象棋程序,其棋盘布局如下:
```
BR BN BB BQ BK BB BN BR
BP BP BP BP ** BP BP BP
-- ** -- ** -- ** -- **
** -- ** -- BP -- ** --
-- ** -- ** WP ** -- **
** -- ** -- ** -- ** --
WP WP WP WP -- WP WP WP
WR WN WB WQ WK WB WN WR
```
与之不同的是,如果要连接加州大学洛杉矶分校的 IBM System/360 机器,运行 Speakeasy 数值计算环境,与会者需要输入以下命令:
```
@r [LF] // 重置 TIP
@t [SP] o [SP] L [LF] // “传递换行”设置
@i [SP] L [LF] // “插入换行”设置,即回车时发送换行符。
@L [SP] 65 [LF] // 连接 65 号主机
tso // 连接 IBM 分时可选软件系统
logon [SP] icX [CR] // 输入用户名,进行登录,“X”可为任意数字
iccc [CR] // 输入密码(够安全!)
speakez [CR] // 启动 Speakeasy
```
输入上述命令后,与会者可以在终端中对矩阵进行乘法、转置以及其他运算,如下所示:
```
:+! a=m*transpose(m);a [CR]
:+! eigenvals(a) [CR]
```
当时,这场演示给许多人都留下了深刻的印象,但原因并不是我们所想的那样,毕竟我们有的只是后见之明。今天的人们总是记不住,在 1972 年,即便身处两个不同的城市,远程登录使用计算机也已经不是一件新鲜事儿了。在那之前的数十年,电传打字机就已经用于与相隔很远的计算机传递信息了。在 ICCC 第一届大会之前,差不多整整五年前,在西雅图的一所高中,<ruby> 比尔·盖茨 <rt> Bill Gates </rt></ruby>使用电传打字机,在该市其他地方的<ruby> 通用电气 <rt> General Electric </rt></ruby>(GE)计算机上运行了他的第一个 BASIC 程序。在当时,登录远程计算机,运行几行命令或者玩一些文字游戏,只不过是家常便饭。因此,虽说上文提到的软件的确很不错,但是即便没有 ARPANET,我刚刚介绍的两个情景勉强也是可以实现的。
当然,ARPANET 一定带来了新的东西。参加本次大会的律师、政治家与经济学家可能被国际象棋游戏与聊天机器人所吸引,但是网络专家们可能对另外两个情景更感兴趣,因为它们将 ARPANET 的作用更好地展示了出来。
在其中一个情景下,MIT <ruby> 非兼容分时系统 <rt> Incompatible Timesharing System </rt></ruby>(ITS)上运行了一个名为 `NETWRK` 的程序。`NETWRK` 命令下有若干个子命令,输入这些子命令就能得到 ARPANET 各方面的运行状态。`SURVEY` 子命令可以列出 ARPANET 上哪些主机正在运行和可用(它们都在一个列表中);`SUMMARY.OF.SURVEY` 子命令汇总了过去 `SURVEY` 子命令过去的运行结果,得出每台主机的“正常运行比率”,以及每台主机响应消息的平均时间。`SUMMARY.OF.SURVEY` 子命令以表格的形式输出结果,如下所示:
```
--HOST-- -#- -%-UP- -RESP-
UCLA-NMC 001 097% 00.80
SRI-ARC 002 068% 01.23
UCSB-75 003 059% 00.63
...
```
可以看到,主机编号的占位不超过三个数字(哈!)。其他 `NETWRK` 子命令能够查看较长时间内查询结果的概要,或者检查单个主机查询结果的日志。
第二个情景用到了斯坦福大学开发的一款软件 —— SRI-ARC 联机系统。这款软件功能齐全,非常优秀。美国发明家<ruby> 道格拉斯·恩格尔巴特 <rt> Douglas Engelbart </rt></ruby>在 “<ruby> 所有演示之母 <rt> Mother of All Demos </rt></ruby>” 上演示的正是 SRI-ARC 联机系统。这款软件可以在加州大学圣芭芭拉分校的主机上运行本质上属于文件托管的服务。使用华盛顿希尔顿酒店的终端,用户可以将斯坦福大学主机上创建的文件复制到加州大学圣芭芭拉分校的主机上。操作也很简单,只需执行 `copy` 命令,然后回答计算机的下列问题:
>
> 在下方的代码块中,`[ESC]`、`[SP]` 与 `[CR]` 分别代表退出、空格与回车键;圆括号中的文字是计算机打印出的提示信息;第三行中的退出键用于自动补全文件名。此处复制的文件是 `<system>sample.txt;1`,其中文件名末尾的数字 1 代表文件的版本号,`<system>` 表示文件路径。这种文件名是 TENEX 操作系统上面的惯用写法。<sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn11" id="fnref11"> [11] </a></sup>
>
>
>
```
@copy
(TO/FROM UCSB) to
(FILE) <system>sample [ESC] .TXT;1 [CR]
(CREATE/REPLACE) create
```
这两个情景看起来好像和最初提及的两个情景没有太大区别,但是此二者却意义非凡。因为它们证明了,在 ARPANET 上面,不仅人们可以与计算机进行交流,计算机与计算机也可以 *相互* 交流。MIT 主机上的 `SURVEY` 命令的结果并非由人类定期登录并检查每台机器的运行状态收集而来,而是由一款能在网络上与其他机器进行交流的软件收集得到的。同样的道理,在斯坦福大学与加州大学圣芭芭拉分校之间传输文件的情景下,也没有人守在两所大学的终端旁边,华盛顿特区的终端用户仅仅使用了一款软件,就能让其他两地的计算机相互对话。更重要的是,这一点无关乎你使用的是宴会厅里的哪一台电脑,因为只要输入同样的命令序列,就能在任意一台电脑上浏览 MIT 的网络监视数据,或者在加州大学圣芭芭拉分校的计算机上储存文件。
这才是 ARPANET 的全新之处。本次国际计算机通信会议演示的不仅仅是人与远程电脑之间的交互,也不仅仅是远程输入输出的操作,更是一个软件与其他软件之间的远程通讯,这一点才是史无前例的。
为什么这一点才是最重要的,而不是地图上画着的那些贯穿整个美国、实际连接起来的电线呢(这些线是租赁的电话线,而且它们以前就在那了!)?要知道,早在 1966 年 ARPANET 项目启动之前,美国国防部的高级研究计划署(ARPA)打造了一间终端室,里面有三台终端。三台终端分别连接着位于 MIT、加州大学伯克利分校以及圣塔莫尼卡三地的计算机 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn12" id="fnref12"> [12] </a></sup>。对于 ARPA 的工作人员来说,即便他们身处华盛顿特区,使用这三台计算机也非常方便。不过,这其中也有不便之处:工作人员必须购买和维护来自三家不同制造商的终端,牢记三种不同的登录步骤,熟悉三种不同的计算环境。虽然这三台终端机可能就放在一起,但是它们只是电线另一端主机系统的延申,而且操作也和那些计算机一样各不相同。所以说,在 ARPANET 项目诞生之前,远程连接计算机进行通讯就已经实现了,但问题是不同的计算系统阻碍了通讯朝着更加先进复杂的方向发展。
### 集合起来,就在此刻
因此,我想说的是,说法一(ARPANET 首次通过计算机将不同地方的人们连接了起来)与说法二(ARPANET 首次将多个计算机系统彼此连接了起来)之间有着云泥之别。听起来似乎有些吹毛求疵,咬文嚼字,但是相较于说法二,说法一忽略了一些重要的历史发展阶段。
首先,历史学家<ruby> 乔伊·利西·兰金 <rt> Joy Lisi Rankin </rt></ruby>指出,早在 ARPANET 诞生之前,人们就已经在网络空间中进行交流了。在《<ruby> 美国计算机的人民历史 <rt> A People’s History of Computing in the United States </rt></ruby>》一书中,兰金介绍了几个覆盖全美的数字社区,这些社区运行在早于 ARPANET 的<ruby> 分时网络 <rt> time-sharing network </rt></ruby>上面。从技术层面讲,分时网络并不是计算机网络,因为它仅仅由一台大型主机构成。这种计算机放置在地下室中,为多台哑终端提供计算,颇像一只又黑又胖的奇怪生物,触手向外伸展着,遍及整个美国。不过,在分时网络时代,被后社交媒体时代称为“网络”的大部分社会行为应有尽有。例如,Kiewit 网络是<ruby> 达特茅斯分时系统 <rt> Dartmouth Time-Sharing System </rt></ruby>的延伸应用,服务于美国东北部的各个大学和高中。在 Kiewit 网络上,高中生们共同维护着一个“<ruby> 八卦档案 <rt> gossip file </rt></ruby>”,用来记录其他学校发生的趣闻趣事,“在康涅狄格州和缅因州之间建立起了社交联系” <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn13" id="fnref13"> [13] </a></sup>。同时,曼荷莲女子学院的女生通过网络与达特茅斯学院的男生进行交流,或者是安排约会,或者是与男朋友保持联系 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn14" id="fnref14"> [14] </a></sup>。这些事实都发生在上世纪六十年代。兰金认为,如果忽视了早期的分时网络,我们对美国过去 50 年数字文化发展的认识必然是贫瘠的:我们眼里可能只有所谓的“<ruby> 硅谷神话 <rt> Silicon Valley mythology </rt></ruby>”,认为计算机领域的所有发展都要归功于少数的几位天才,或者说互联网科技巨头的创始人。
回到 ARPANET,如果我们能意识到真正的困难是计算机 *系统* 的联通,而非机器本身的物理连接,那么在探讨 ARPANET 的创新点时,我们就会更加倾向于第二种说法。ARPANET 是有史以来第一个<ruby> 分组交换网络 <rt> packet-switched network </rt></ruby>,涉及到许多重要的技术应用。但是如果仅仅因为这项优势,就说它是一项突破,我觉得这种说法本身就是错的。ARPANET 旨在促进全美计算机科学家之间的合作,目的是要弄明白不同的操作系统、不同语言编写的软件如何配合使用,而非如何在麻省和加州之间实现高效的数据传输。因此,ARPANET 不仅是第一个分组交换网络,它还是一项非常成功且优秀的标准。在我看来,后者更有意思,毕竟我在博客上曾经写过许多颇有失败的标准:[语义网](https://twobithistory.org/2018/05/27/semantic-web.html)、[RSS](https://twobithistory.org/2018/12/18/rss.html) 与 [FOAF](https://twobithistory.org/2020/01/05/foaf.html)。
ARPANET 项目初期没有考虑到网络协议,协议的制定是后来的事情了。因此,这项工作自然落到了主要由研究生组成的组织 —— <ruby> 网络工作组 <rt> Network Working Group </rt></ruby>(NWG)身上。该组织的首次会议于 1968 年在加州大学圣芭芭拉分校举办 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn15" id="fnref15"> [15] </a></sup>。当时只有 12 人参会,大部分都是来自上述四所大学的代表 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn16" id="fnref16"> [16] </a></sup>。来自加州大学洛杉矶分校的研究生<ruby> 史蒂夫·克罗克 <rt> Steve Crocker </rt></ruby>参加了这场会议。他告诉我,工作组首次会议的参会者清一色都是年轻人,最年长的可能要数会议主席<ruby> 埃尔默·夏皮罗 <rt> Elmer Shapiro </rt></ruby>了,他当年 38 岁左右。ARPA 没有派人负责研究计算机连接之后如何进行通信,但是很明显它需要提供一定的协助。随着工作组会议的陆续开展,克罗克一直期望着更有经验与威望的“法定成年人”从东海岸飞过来接手这项工作,但是期望终究还是落空了。在 ARPA 的默许之下,工作组举办了多场会议,其中包括很多长途旅行,差旅费由 ARPA 报销,这些就是它给与工作组的全部协助了 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn17" id="fnref17"> [17] </a></sup>。
当时,网络工作组面临着巨大的挑战。从没有人有过使用通用方式连接计算机系统的经验,而且这本来就与上世纪六十年代末计算机领域盛行的全部观点相悖:
>
> 那个时候典型的主机表现得就像是它是全宇宙唯一的计算机。即便是最简短的交流会话,两台主机也无法轻易做到。并不是说机器没办法相互连接,只是连接之后,两台计算机又能做些什么呢?当时,计算机和与其相连的其他设备之间的通讯,就像帝王与群臣之间的对话一般。连接到主机的设备各自执行着自己的任务,每台外围设备都保持着常备不懈的状态,等待着上司的命令。当时的计算机就是严格按照这类互动需求设计出来的;它们向读卡器、终端与磁带机等下属设备发号施令,发起所有会话。但是,如果一台计算机拍了拍另一台计算机的肩膀,说道,“你好,我也是一台计算机”,那么另一台计算机可就傻眼了,什么也回答不上来 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn18" id="fnref18"> [18] </a></sup>。
>
>
>
于是,工作组的最初进展很缓慢 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn19" id="fnref19"> [19] </a></sup>。直到 1970 年 6 月,也就是首次会议将近两年之后,工作组才为网络协议选定了一套“正式”规范 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn20" id="fnref20"> [20] </a></sup>。
不过,到了 1972 年,在国际计算机通信会议上展示 ARPANET 的时候,所有的协议已经准备就绪了。会议期间,这些协议运用到了国际象棋等情景之中。用户运行 `@e r` 命令(`@echo remote` 命令的缩写形式),可以指示 TIP 使用新 TELNET 虚拟终端协议提供的服务,通知远程主机它应该回显用户输入的内容。接着,用户运行 `@L 134` 命令(`@login 134` 命令的缩写形式),让 TIP 在 134 号主机上调用<ruby> 初始连接协议 <rt> Initial Connection Protocol </rt></ruby>,该协议指示远程主机分配出连接所需的全部必要资源,并将用户带入 TELNET 会话中。上述文件传输的情景也许用到了 <ruby> 文件传输协议 <rt> File Transfer Protocol </rt></ruby>(FTP),而该协议恰好是在大会举办前夕才刚刚完成的 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn21" id="fnref21"> [21] </a></sup>。所有这些协议都是“三层”协议,其下的第二层是主机到主机的协议,定义了主机之间可以相互发送和接收的信息的基本格式;第一层是主机到接口通信处理机(IMP)的协议,定义了主机如何与连接的远程设备进行通信。令人感到不可思议的是,这些协议都能正常运行。
在我看来,网络工作组之所以能够在大会举办之前做好万全的准备,顺利且出色地完成任务,在于他们采用了开放且非正式的标准化方法,其中一个典型的例子就是著名的 <ruby> 征求意见 <rt> Request for Comments </rt></ruby>(RFC)系列文档。RFC 文档最初通过<ruby> 传统信件 <rt> snail mail </rt></ruby>在工作组成员之间进行传阅,让成员们在没有举办会议的时候也能保持联系,同时收集成员反馈,汇集各方智慧。RFC 框架是克罗克提出的,他写出了第一篇 RFC 文档,并在早期负责管理 RFC 的邮寄列表。他这样做是为了强调工作组开放协作的活动本质。有了这套框架以及触手可及的文档,ARPANET 的协议设计过程成了一个大熔炉,每个人都可以贡献出自己的力量,步步推进,精益求精,让最棒的想法脱颖而出,而没有人失去面子。总而言之,RFC 获得了巨大成功,并且直至今天,长达半个世纪之后,它依旧是网络标准的“说明书”。
因此,说起 ARPANET 的影响力,我认为不得不强调的一点正是工作组留下的这一成果。今天,互联网可以把世界各地的人们连接起来,这也是它最神奇的属性之一。不过如果说这项技术到了上世纪才开始使用,那可就有些滑稽可笑了。要知道,在 ARPANET 出现之前,人们就已经通过电报打破了现实距离的限制。而 ARPANET 打破的应该是各个主机站因使用不同的操作系统、字符编码、程序语言以及组织策略而在逻辑层面产生的差异限制。当然,将第一个分组交换网络投入使用在技术方面绝对是一大壮举,这肯定值得一提,不过,制定统一的标准并用以连接原本无法相互协作的计算机,是建立 ARPANET 网络过程中遇到的这两大难题中更为复杂的一个。而这一难题的解决方案,也成了 ARPANET 整个建立与发展历史中最为神奇的一个章节。
1981 年,高级研究计划署发表了一份“完工报告”,回顾了 ARPANET 项目的第一个十年。在《付出收获了回报的技术方面以及付出未能实现最初设想的技术方面》这一冗长的小标题下,作者们写道:
>
> 或许,在 ARPANET 的开发过程中,最艰难的一项任务就是,尽管主机制造商各不相同,或者同一制造商下操作系统各不相同,我们仍需在众多的独立主机系统之间实现通讯交流。好在这项任务后来取得了成功 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn22" id="fnref22"> [22] </a></sup>。
>
>
>
你可以从美国联邦政府获得相关信息。
*如果你喜欢这篇文章,欢迎关注推特 [@TwoBitHistory](https://twitter.com/TwoBitHistory),也可通过 [RSS 馈送](https://twobithistory.org/feed.xml) 订阅,获取最新文章。*
---
1. “Hilton Hotel Opens in Capital Today.” *The New York Times*, 20 March 1965, <https://www.nytimes.com/1965/03/20/archives/hilton-hotel-opens-in-capital-today.html?searchResultPosition=1>. Accessed 7 Feb. 2021. [↩︎](#fnref1)
2. James Pelkey. *Entrepreneurial Capitalism and Innovation: A History of Computer Communications 1968-1988,* Chapter 4, Section 12, 2007, [http://www.historyofcomputercommunications.info/Book/4/4.12-ICCC Demonstration71-72.html](http://www.historyofcomputercommunications.info/Book/4/4.12-ICCC%20Demonstration71-72.html). Accessed 7 Feb. 2021. [↩︎](#fnref2)
3. Katie Hafner and Matthew Lyon. *Where Wizards Stay Up Late: The Origins of the Internet*. New York, Simon & Schuster, 1996, p. 178. [↩︎](#fnref3)
4. “International Conference on Computer Communication.” *Computer*, vol. 5, no. 4, 1972, p. c2, <https://www.computer.org/csdl/magazine/co/1972/04/01641562/13rRUxNmPIA>. Accessed 7 Feb. 2021. [↩︎](#fnref4)
5. “Program for the International Conference on Computer Communication.” *The Papers of Clay T. Whitehead*, Box 42, <https://d3so5znv45ku4h.cloudfront.net/Box+042/013_Speech-International+Conference+on+Computer+Communications,+Washington,+DC,+October+24,+1972.pdf>. Accessed 7 Feb. 2021. [↩︎](#fnref5)
6. 我其实并不清楚 ARPANET 是在哪个房间展示的。很多地方都提到了“宴会厅”,但是华盛顿希尔顿酒店更习惯于叫它“乔治敦”,而不是把它当成一间会议室。因此,或许这场展示是在国际宴会厅举办的。但是 RFC 372 号文件又提到了预定“乔治敦”作为展示场地一事。华盛顿希尔顿酒店的楼层平面图可以点击 [此处](https://www3.hilton.com/resources/media/hi/DCAWHHH/en_US/pdf/DCAWH.Floorplans.Apr25.pdf) 查看。 [↩︎](#fnref6)
7. Hafner, p. 179. [↩︎](#fnref7)
8. ibid., p. 178. [↩︎](#fnref8)
9. Bob Metcalfe. “Scenarios for Using the ARPANET.” *Collections-Computer History Museum*, <https://www.computerhistory.org/collections/catalog/102784024>. Accessed 7 Feb. 2021. [↩︎](#fnref9)
10. Hafner, p. 176. [↩︎](#fnref10)
11. Robert H. Thomas. “Planning for ACCAT Remote Site Operations.” BBN Report No. 3677, October 1977, <https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA046366.pdf>. Accessed 7 Feb. 2021. [↩︎](#fnref11)
12. Hafner, p. 12. [↩︎](#fnref12)
13. Joy Lisi Rankin. *A People’s History of Computing in the United States*. Cambridge, MA, Harvard University Press, 2018, p. 84. [↩︎](#fnref13)
14. Rankin, p. 93. [↩︎](#fnref14)
15. Steve Crocker. Personal interview. 17 Dec. 2020. [↩︎](#fnref15)
16. 克罗克将会议记录文件发给了我,文件列出了所有的参会者。 [↩︎](#fnref16)
17. Steve Crocker. Personal interview. [↩︎](#fnref17)
18. Hafner, p. 146. [↩︎](#fnref18)
19. “Completion Report / A History of the ARPANET: The First Decade.” BBN Report No. 4799, April 1981, <https://walden-family.com/bbn/arpanet-completion-report.pdf>, p. II-13. [↩︎](#fnref19)
20. 这里我指的是 RFC 54 号文件中的“正式协议”。 [↩︎](#fnref20)
21. Hafner, p. 175. [↩︎](#fnref21)
22. “Completion Report / A History of the ARPANET: The First Decade,” p. II-29. [↩︎](#fnref22)
---
via: <https://twobithistory.org/2021/02/07/arpanet.html>
作者:[Two-Bit History](https://twobithistory.org) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[aREversez](https://github.com/aREversez) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | If you run an image search for the word “ARPANET,” you will find lots of maps
showing how the [government research
network](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARPANET) expanded steadily across the
country throughout the late ’60s and early ’70s. I’m guessing that most people
reading or hearing about the ARPANET for the first time encounter one of these
maps.
Obviously, the maps are interesting—it’s hard to believe that there were once so few networked computers that their locations could all be conveyed with what is really pretty lo-fi cartography. (We’re talking 1960s overhead projector diagrams here. You know the vibe.) But the problem with the maps, drawn as they are with bold lines stretching across the continent, is that they reinforce the idea that the ARPANET’s paramount achievement was connecting computers across the vast distances of the United States for the first time.
Today, the internet is a lifeline that keeps us tethered to each other even as an airborne virus has us all locked up indoors. So it’s easy to imagine that, if the ARPANET was the first draft of the internet, then surely the world that existed before it was entirely disconnected, since that’s where we’d be without the internet today, right? The ARPANET must have been a big deal because it connected people via computers when that hadn’t before been possible.
That view doesn’t get the history quite right. It also undersells what made the ARPANET such a breakthrough.
## The Debut
The Washington Hilton stands near the top of a small rise about a mile and a
half northeast of the National Mall. Its two white-painted modern facades sweep
out in broad semicircles like the wings of a bird. The New York Times,
reporting on the hotel’s completion in 1965, remarked that the building looks
“like a sea gull perched on a hilltop nest.”[1](#fn:1)
The hotel hides its most famous feature below ground. Underneath the driveway roundabout is an enormous ovoid event space known as the International Ballroom, which was for many years the largest pillar-less ballroom in DC. In 1967, the Doors played a concert there. In 1968, Jimi Hendrix also played a concert there. In 1972, a somewhat more sedate act took over the ballroom to put on the inaugural International Conference on Computing Communication, where a promising research project known as the ARPANET was demonstrated publicly for the first time.
The 1972 ICCC, which took place from October 24th to 26th, was attended by
about 800 people. 2 It brought together all of the leading researchers in the
nascent field of computer networking. According to internet pioneer Bob Kahn,
“if somebody had dropped a bomb on the Washington Hilton, it would have
destroyed almost all of the networking community in the US at that point.”
[3](#fn:3)Not all of the attendees were computer scientists, however. An advertisement
for the conference claimed it would be “user-focused” and geared toward
“lawyers, medical men, economists, and government men as well as engineers and
communicators.” 4 Some of the conference’s sessions were highly technical,
such as the session titled “Data Network Design Problems I” and its sequel
session, “Data Network Design Problems II.” But most of the sessions were, as
promised, focused on the potential social and economic impacts of computer
networking. One session, eerily prescient today, sought to foster a discussion
about how the legal system could act proactively “to safeguard the right of
privacy in the computer data bank.”
[5](#fn:5)The ARPANET demonstration was intended as a side attraction of sorts for the
attendees. Between sessions, which were held either in the International
Ballroom or elsewhere on the lower level of the hotel, attendees were free to
wander into the Georgetown Ballroom (a smaller ballroom/conference room down
the hall from the big one), 6 where there were 40 terminals from a variety of
manufacturers set up to access the ARPANET.
These terminals were dumb terminals—they only handled input and output and could do no computation on their own. (In fact, in 1972, it’s likely that all of these terminals were hardcopy terminals, i.e. teletype machines.) The terminals were all hooked up to a computer known as a Terminal Interface Message Processor or TIP, which sat on a raised platform in the middle of the room. The TIP was a kind of archaic router specially designed to connect dumb terminals to the ARPANET. Using the terminals and the TIP, the ICCC attendees could experiment with logging on and accessing some of the computers at the 29 host sites then comprising the ARPANET.
[7](#fn:7)
[8](#fn:8)To exhibit the network’s capabilities, researchers at the host sites across
the country had collaborated to prepare 19 simple “scenarios” for users to
experiment with. These scenarios were compiled into [a
booklet](https://archive.computerhistory.org/resources/access/text/2019/07/102784024-05-001-acc.pdf)
that was handed to conference attendees as they tentatively approached the maze
of wiring and terminals. 9 The scenarios were meant to prove that the
new technology worked but also that it was useful, because so far the ARPANET
was “a highway system without cars,” and its Pentagon funders hoped that a
public demonstration would excite more interest in the network.
[10](#fn:10)The scenarios thus showed off a diverse selection of the software that could be accessed over the ARPANET: There were programming language interpreters, one for a Lisp-based language at MIT and another for a numerical computing environment called Speakeasy hosted at UCLA; there were games, including a chess program and an implementation of Conway’s Game of Life; and—perhaps most popular among the conference attendees—there were several AI chat programs, including the famous ELIZA chat program developed at MIT by Joseph Weizenbaum.
The researchers who had prepared the scenarios were careful to list each command that users were expected to enter at their terminals. This was especially important because the sequence of commands used to connect to any given ARPANET host could vary depending on the host in question. To experiment with the AI chess program hosted on the MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory’s PDP-10 minicomputer, for instance, conference attendees were instructed to enter the following:
`[LF]`
, `[SP]`
, and `[CR]`
below stand for the line feed, space,
and carriage return keys respectively. I’ve explained each command after `//`
,
but this syntax was not used for the annotations in the original.
```
@r [LF] // Reset the TIP
@e [SP] r [LF] // "Echo remote" setting, host echoes characters rather than TIP
@L [SP] 134 [LF] // Connect to host number 134
:login [SP] iccXXX [CR] // Login to the MIT AI Lab's system, where "XXX" should be user's initials
:chess [CR] // Start chess program
```
If conference attendees were successfully able to enter those commands, their reward was the opportunity to play around with some of the most cutting-edge chess software available at the time, where the layout of the board was represented like this:
```
BR BN BB BQ BK BB BN BR
BP BP BP BP ** BP BP BP
-- ** -- ** -- ** -- **
** -- ** -- BP -- ** --
-- ** -- ** WP ** -- **
** -- ** -- ** -- ** --
WP WP WP WP -- WP WP WP
WR WN WB WQ WK WB WN WR
```
In contrast, to connect to UCLA’s IBM System/360 and run the Speakeasy numerical computing environment, conference attendees had to enter the following:
```
@r [LF] // Reset the TIP
@t [SP] o [SP] L [LF] // "Transmit on line feed" setting
@i [SP] L [LF] // "Insert line feed" setting, i.e. send line feed with each carriage return
@L [SP] 65 [LF] // Connect to host number 65
tso // Connect to IBM Time-Sharing Option system
logon [SP] icX [CR] // Log in with username, where "X" should be a freely chosen digit
iccc [CR] // This is the password (so secure!)
speakez [CR] // Start Speakeasy
```
Successfully running that gauntlet gave attendees the power to multiply and transpose and do other operations on matrices as quickly as they could input them at their terminal:
```
:+! a=m*transpose(m);a [CR]
:+! eigenvals(a) [CR]
```
Many of the attendees were impressed by the demonstration, but not for the reasons that we, from our present-day vantage point, might assume. The key piece of context hard to keep in mind today is that, in 1972, being able to use a computer remotely, even from a different city, was not new. Teletype devices had been used to talk to distant computers for decades already. Almost a full five years before the ICCC, Bill Gates was in a Seattle high school using a teletype to run his first BASIC programs on a General Electric computer housed elsewhere in the city. Merely logging in to a host computer and running a few commands or playing a text-based game was routine. The software on display here was pretty neat, but the two scenarios I’ve told you about so far could ostensibly have been experienced without going over the ARPANET.
Of course, something new was happening under the hood. The lawyers, policy-makers, and economists at the ICCC might have been enamored with the clever chess program and the chat bots, but the networking experts would have been more interested in two other scenarios that did a better job of demonstrating what the ARPANET project had achieved.
The first of these scenarios involved a program called `NETWRK`
running on
MIT’s ITS operating system. The `NETWRK`
command was the entrypoint for several
subcommands that could report various aspects of the ARPANET’s operating
status. The `SURVEY`
subcommand reported which hosts on the network were
functioning and available (they all fit on a single list), while the
`SUMMARY.OF.SURVEY`
subcommand aggregated the results of past `SURVEY`
runs to
report an “up percentage” for each host as well as how long, on average, it
took for each host to respond to messages. The output of the
`SUMMARY.OF.SURVEY`
subcommand was a table that looked like this:
```
--HOST-- -#- -%-UP- -RESP-
UCLA-NMC 001 097% 00.80
SRI-ARC 002 068% 01.23
UCSB-75 003 059% 00.63
...
```
The host number field, as you can see, has room for no more than three digits
(ha!). Other `NETWRK`
subcommands allowed users to look at summary of survey
results over a longer historical period or to examine the log of survey results
for a single host.
The second of these scenarios featured a piece of software called the SRI-ARC
Online System being developed at Stanford. This was a fancy piece of software
with lots of functionality (it was the software system that Douglas Engelbart
demoed in the “Mother of All Demos”), but one of the many things it could do
was make use of what was essentially a file hosting service run on the host at
UC Santa Barbara. From a terminal at the Washington Hilton, conference
attendees could copy a file created at Stanford onto the host at UCSB simply by
running a `copy`
command and answering a few of the computer’s questions:
`[ESC]`
, `[SP]`
, and `[CR]`
below stand for the escape, space, and carriage
return keys respectively. The words in parentheses are prompts printed by the
computer. The escape key is used to autocomplete the filename on the third
line. The file being copied here is called `<system>sample.txt;1`
, where the
trailing one indicates the file’s version number and `<system>`
indicates the
directory. This was a convention for filenames used by the TENEX operating
system.[11](#fn:11)
```
@copy
(TO/FROM UCSB) to
(FILE) <system>sample [ESC] .TXT;1 [CR]
(CREATE/REPLACE) create
```
These two scenarios might not look all that different from the first two, but
they were remarkable. They were remarkable because they made it clear that, on
the ARPANET, humans could talk to computers but computers could also talk to
*each other.* The `SURVEY`
results collected at MIT weren’t collected by a
human regularly logging in to each machine to check if it was up—they were
collected by a program that knew how to talk to the other machines on the
network. Likewise, the file transfer from Stanford to UCSB didn’t involve any
humans sitting at terminals at either Stanford or UCSB—the user at a terminal
in Washington DC was able to get the two computers to talk each other merely by
invoking a piece of software. Even more, it didn’t matter which of the 40
terminals in the Ballroom you were sitting at, because you could view the MIT
network monitoring statistics or store files at UCSB using any of the terminals
with almost the same sequence of commands.
This is what was totally new about the ARPANET. The ICCC demonstration didn’t just involve a human communicating with a distant computer. It wasn’t just a demonstration of remote I/O. It was a demonstration of software remotely communicating with other software, something nobody had seen before.
To really appreciate why it was this aspect of the ARPANET project that was
important and not the wires-across-the-country, physical connection thing that
the host maps suggest (the wires were leased phone lines anyhow and were
already there!), consider that, before the ARPANET project began in 1966, the
ARPA offices in the Pentagon had a terminal room. Inside it were three
terminals. Each connected to a different computer; one computer was at MIT, one
was at UC Berkeley, and another was in Santa Monica. 12 It was convenient for
the ARPA staff that they could use these three computers even from Washington
DC. But what was inconvenient for them was that they had to buy and maintain
terminals from three different manufacturers, remember three different login
procedures, and familiarize themselves with three different computing
environments in order to use the computers. The terminals might have been right
next to each other, but they were merely extensions of the host computing
systems on the other end of the wire and operated as differently as the
computers did. Communicating with a distant computer was possible before the
ARPANET; the problem was that the heterogeneity of computing systems limited
how sophisticated the communication could be.
## Come Together, Right Now
So what I’m trying to drive home here is that there is an important distinction between statement A, “the ARPANET connected people in different locations via computers for the first time,” and statement B, “the ARPANET connected computer systems to each other for the first time.” That might seem like splitting hairs, but statement A elides some illuminating history in a way that statement B does not.
To begin with, the historian Joy Lisi Rankin has shown that people were
socializing in cyberspace well before the ARPANET came along. In *A People’s
History of Computing in the United States*, she describes several different
digital communities that existed across the country on time-sharing networks
prior to or apart from the ARPANET. These time-sharing networks were not,
technically speaking, computer networks, since they consisted of a single
mainframe computer running computations in a basement somewhere for many dumb
terminals, like some portly chthonic creature with tentacles sprawling across
the country. But they nevertheless enabled most of the social behavior now
connoted by the word “network” in a post-Facebook world. For example, on the
Kiewit Network, which was an extension of the Dartmouth Time-Sharing System to
colleges and high schools across the Northeast, high school students
collaboratively maintained a “gossip file” that allowed them to keep track of
the exciting goings-on at other schools, “creating social connections from
Connecticut to Maine.” 13 Meanwhile, women at Mount Holyoke College
corresponded with men at Dartmouth over the network, perhaps to arrange dates
or keep in touch with boyfriends.
This was all happening in the 1960s. Rankin argues that by ignoring these early time-sharing networks we impoverish our understanding of how American digital culture developed over the last 50 years, leaving room for a “Silicon Valley mythology” that credits everything to the individual genius of a select few founding fathers.
[14](#fn:14)As for the ARPANET itself, if we recognize that the key challenge was
connecting the computer *systems* and not just the physical computers, then
that might change what we choose to emphasize when we tell the story of the
innovations that made the ARPANET possible. The ARPANET was the first ever
packet-switched network, and lots of impressive engineering went into making
that happen. I think it’s a mistake, though, to say that the ARPANET was a
breakthrough because it was the first packet-switched network and then leave it
at that. The ARPANET was meant to make it easier for computer scientists across
the country to collaborate; that project was as much about figuring out how
different operating systems and programs written in different languages would
interface with each other than it was about figuring out how to efficiently
ferry data back and forth between Massachusetts and California. So the ARPANET
was the first packet-switched network, but it was also an amazing standards
success story—something I find especially interesting given [how](/2018/05/27/semantic-web.html) [many](/2018/12/18/rss.html) [times](/2020/01/05/foaf.html) I’ve written about failed standards on this blog.
Inventing the protocols for the ARPANET was an afterthought even at the time,
so naturally the job fell to a group made up largely of graduate students.
This group, later known as the Network Working Group, met for the first time at
UC Santa Barbara in August of 1968. 15 There were 12 people present at that
first meeting, most of whom were representatives from the four universities
that were to be the first host sites on the ARPANET when the equipment was
ready.
Steve Crocker, then a graduate student at UCLA, attended; he told me over a Zoom call that it was all young guys at that first meeting, and that Elmer Shapiro, who chaired the meeting, was probably the oldest one there at around 38. ARPA had not put anyone in charge of figuring out how the computers would communicate once they were connected, but it was obvious that some coordination was necessary. As the group continued to meet, Crocker kept expecting some “legitimate adult” with more experience and authority to fly out from the East Coast to take over, but that never happened. The Network Working Group had ARPA’s tacit approval—all those meetings involved lots of long road trips, and ARPA money covered the travel expenses—so they were it.
[16](#fn:16)
[17](#fn:17)The Network Working Group faced a huge challenge. Nobody had ever sat down to connect computer systems together in a general-purpose way; that flew against all of the assumptions that prevailed in computing in the late 1960s:
The typical mainframe of the period behaved as if it were the only computer in the universe. There was no obvious or easy way to engage two diverse machines in even the minimal communication needed to move bits back and forth. You could connect machines, but once connected, what would they say to each other? In those days a computer interacted with devices that were attached to it, like a monarch communicating with his subjects. Everything connected to the main computer performed a specific task, and each peripheral device was presumed to be ready at all times for a fetch-my-slippers type command…. Computers were strictly designed for this kind of interaction; they send instructions to subordinate card readers, terminals, and tape units, and they initiate all dialogues. But if another device in effect tapped the computer on the shoulder with a signal and said, “Hi, I’m a computer too,” the receiving machine would be stumped.
[18]
As a result, the Network Working Group’s progress was initially slow. 19 The
group did not settle on an “official” specification for any protocol until
June, 1970, nearly two years after the group’s first meeting.
[20](#fn:20)But by the time the ARPANET was to be shown off at the 1972 ICCC, all the key
protocols were in place. A scenario like the chess scenario exercised many of
them. When a user ran the command `@e r`
, short for `@echo remote`
, that
instructed the TIP to make use of a facility in the new TELNET virtual teletype
protocol to inform the remote host that it should echo the user’s input. When a
user then ran the command `@L 134`
, short for `@login 134`
, that caused the TIP
to invoke the Initial Connection Protocol with host 134, which in turn would
cause the remote host to allocate all the necessary resources for the
connection and drop the user into a TELNET session. (The file transfer scenario
I described may well have made use of the File Transfer Protocol, though that
protocol was only ready shortly before the conference. 21) All of these
protocols were known as “level three” protocols, and below them were the
host-to-host protocol at level two (which defined the basic format for the
messages the hosts should expect from each other), and the host-to-IMP protocol
at level one (which defined how hosts communicated with the routing equipment
they were linked to). Incredibly, the protocols all worked.
In my view, the Network Working Group was able to get everything together in time and just generally excel at its task because it adopted an open and informal approach to standardization, as exemplified by the famous Request for Comments (RFC) series of documents. These documents, originally circulated among the members of the Network Working Group by snail mail, were a way of keeping in touch between meetings and soliciting feedback to ideas. The “Request for Comments” framing was suggested by Steve Crocker, who authored the first RFC and supervised the RFC mailing list in the early years, in an attempt to emphasize the open-ended and collaborative nature of what the group was trying to do. That framing, and the availability of the documents themselves, made the protocol design process into a melting pot of contributions and riffs on other people’s contributions where the best ideas could emerge without anyone losing face. The RFC process was a smashing success and is still used to specify internet standards today, half a century later.
It’s this legacy of the Network Working Group that I think we should highlight when we talk about ARPANET’s impact. Though today one of the most magical things about the internet is that it can connect us with people on the other side of the planet, it’s only slightly facetious to say that that technology has been with us since the 19th century. Physical distance was conquered well before the ARPANET by the telegraph. The kind of distance conquered by the ARPANET was instead the logical distance between the operating systems, character codes, programming languages, and organizational policies employed at each host site. Implementing the first packet-switched network was of course a major feat of engineering that should also be mentioned, but the problem of agreeing on standards to connect computers that had never been designed to play nice with each other was the harder of the two big problems involved in building the ARPANET—and its solution was the most miraculous part of the ARPANET story.
In 1981, ARPA issued a “Completion Report” reviewing the first decade of the ARPANET’s history. In a section with the belabored title, “Technical Aspects of the Effort Which Were Successful and Aspects of the Effort Which Did Not Materialize as Originally Envisaged,” the authors wrote:
Possibly the most difficult task undertaken in the development of the ARPANET was the attempt—which proved successful—to make a number of independent host computer systems of varying manufacture, and varying operating systems within a single manufactured type, communicate with each other despite their diverse characteristics.
[22]
There you have it from no less a source than the federal government of the United States.
*
If you enjoyed this post, more like it come out every four weeks! Follow
@TwoBitHistory
on Twitter or subscribe to the
RSS feed
to make sure you know when a new post is out.
*
*Previously on TwoBitHistory…*
It's been too long, I know, but I finally got around to writing a new post. This one is about how REST APIs should really be known as FIOH APIs instead (Fuck It, Overload HTTP):
— TwoBitHistory (@TwoBitHistory)[https://t.co/xjMZVZgsEz][June 28, 2020]
-
“Hilton Hotel Opens in Capital Today.”
*The New York Times*, 20 March 1965,[https://www.nytimes.com/1965/03/20/archives/hilton-hotel-opens-in-capital-today.html?searchResultPosition=1](https://www.nytimes.com/1965/03/20/archives/hilton-hotel-opens-in-capital-today.html?searchResultPosition=1). Accessed 7 Feb. 2021.[↩](#fnref:1) -
James Pelkey.
*Entrepreneurial Capitalism and Innovation: A History of Computer Communications 1968-1988,*Chapter 4, Section 12, 2007,[http://www.historyofcomputercommunications.info/Book/4/4.12-ICCC%20Demonstration71-72.html](http://www.historyofcomputercommunications.info/Book/4/4.12-ICCC%20Demonstration71-72.html). Accessed 7 Feb. 2021.[↩](#fnref:2) -
Katie Hafner and Matthew Lyon.
*Where Wizards Stay Up Late: The Origins of the Internet*. New York, Simon & Schuster, 1996, p. 178.[↩](#fnref:3) -
“International Conference on Computer Communication.”
*Computer*, vol. 5, no. 4, 1972, p. c2,[https://www.computer.org/csdl/magazine/co/1972/04/01641562/13rRUxNmPIA](https://www.computer.org/csdl/magazine/co/1972/04/01641562/13rRUxNmPIA). Accessed 7 Feb. 2021.[↩](#fnref:4) -
“Program for the International Conference on Computer Communication.”
*The Papers of Clay T. Whitehead*, Box 42,[https://d3so5znv45ku4h.cloudfront.net/Box+042/013_Speech-International+Conference+on+Computer+Communications,+Washington,+DC,+October+24,+1972.pdf](https://d3so5znv45ku4h.cloudfront.net/Box+042/013_Speech-International+Conference+on+Computer+Communications,+Washington,+DC,+October+24,+1972.pdf). Accessed 7 Feb. 2021.[↩](#fnref:5) -
It’s actually not clear to me which room was used for the ARPANET demonstration. Lots of sources talk about a “ballroom,” but the Washington Hilton seems to consider the room with the name “Georgetown” more of a meeting room. So perhaps the demonstration was in the International Ballroom instead. But RFC 372 alludes to a booking of the “Georgetown Ballroom” for the demonstration. A floorplan of the Washington Hilton can be found
[here](https://www3.hilton.com/resources/media/hi/DCAWHHH/en_US/pdf/DCAWH.Floorplans.Apr25.pdf).[↩](#fnref:6) -
Hafner, p. 179.
[↩](#fnref:7) -
ibid., p. 178.
[↩](#fnref:8) -
Bob Metcalfe. “Scenarios for Using the ARPANET.”
*Collections-Computer History Museum*,[https://www.computerhistory.org/collections/catalog/102784024](https://www.computerhistory.org/collections/catalog/102784024). Accessed 7 Feb. 2021.[↩](#fnref:9) -
Hafner, p. 176.
[↩](#fnref:10) -
Robert H. Thomas. “Planning for ACCAT Remote Site Operations.” BBN Report No. 3677, October 1977,
[https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA046366.pdf](https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA046366.pdf). Accessed 7 Feb. 2021.[↩](#fnref:11) -
Hafner, p. 12.
[↩](#fnref:12) -
Joy Lisi Rankin.
*A People’s History of Computing in the United States*. Cambridge, MA, Harvard University Press, 2018, p. 84.[↩](#fnref:13) -
Rankin, p. 93.
[↩](#fnref:14) -
Steve Crocker. Personal interview. 17 Dec. 2020.
[↩](#fnref:15) -
Crocker sent me the minutes for this meeting. The document lists everyone who attended.
[↩](#fnref:16) -
Steve Crocker. Personal interview.
[↩](#fnref:17) -
Hafner, p. 146.
[↩](#fnref:18) -
“Completion Report / A History of the ARPANET: The First Decade.” BBN Report No. 4799, April 1981,
[https://walden-family.com/bbn/arpanet-completion-report.pdf](https://walden-family.com/bbn/arpanet-completion-report.pdf), p. II-13.[↩](#fnref:19) -
I’m referring here to RFC 54, “Official Protocol Proffering.”
[↩](#fnref:20) -
Hafner, p. 175.
[↩](#fnref:21) -
“Completion Report / A History of the ARPANET: The First Decade,” p. II-29.
[↩](#fnref:22) |
15,141 | VirtualBox 7.0 发布,支持安全启动和全加密虚拟机 | https://news.itsfoss.com/virtualbox-7-0-release/ | 2022-10-15T10:10:45 | [
"VirtualBox"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15141-1.html |
>
> VirtualBox 7.0 是自其上次大版本更新以来的一次重大升级。有一些不错的进步!
>
>
>

对 VirtualBox 来说,这是一次大的升级。这个版本值得关注,因为我们在最近几年没有看到过它的大版本更新。
对于那些不熟悉 VirtualBox 的人来说,它是一个由 [甲骨文公司](https://www.oracle.com/in/) 开发的虚拟化软件。
随着 VirtualBox 7.0 的推出,增加了许多新功能。
让我们来看看其中最关键的一些。
### VirtualBox 7.0 的新内容

VirtualBox 7.0 是一次有益的升级。有图标更新、主题改进,以及一些关键的亮点,包括:
* 一个显示运行中的<ruby> 客体 <rt> Guest </rt></ruby>的性能统计的新工具。
* 支持安全启动。
* 支持<ruby> 全加密虚拟机 <rt> Full VM Encryption </rt></ruby>(通过 CLI)。
* 重新设计的新建虚拟机向导。
#### 通过命令行管理的全加密虚拟机
虚拟机(VM)现在可以完全加密了,但只能通过命令行界面。
这也包括加密的配置日志和暂存状态。
截至目前,用户只能通过命令行界面对机器进行加密,未来将增加不同的方式。
#### 新的资源监控工具

新的实用程序可以让你监控性能统计,如 CPU、内存使用、磁盘 I/O 等。它将列出所有正在运行的客体的性能统计。
这不是最吸引人的补充,但很有用。
#### 改进的主题支持
对主题的支持在所有平台上都得到了改进。在 Linux 和 macOS 上使用原生引擎,而在 Windows 上,有一个单独的实现。
#### 对安全启动的支持
VirtualBox 现在支持安全启动,增强了对恶意软件、病毒和间谍软件的安全性。
它还将防止虚拟机使用损坏的驱动程序启动,这对企业应用非常重要。
使用那些需要安全启动才能运行的操作系统的用户现在应该能够轻松创建虚拟机了。
#### 其他变化
VirtualBox 7.0 是一次重大的升级。因此,有几个功能的增加和全面的完善。
例如,新件虚拟机向导现在已经重新设计,以整合无人值守的客体操作系统安装。

其他改进包括:
* 云端虚拟机现在可以被添加到 VirtualBox,并作为本地虚拟机进行控制。
* VirtualBox 的图标在此版本中得到了更新。
* 引入了一个新的 3D 栈,支持 DirectX 11。它使用 [DXVK](https://github.com/doitsujin/dxvk) 来为非 Windows 主机提供同样的支持。
* 支持虚拟 TPM 1.2/2.0。
* 改进了多显示器设置中的鼠标处理。
* Vorbis 是音频录制的默认音频编解码器。
你可以查看 [发行说明](https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Changelog-7.0) 以了解更多信息。
如果你正在寻找增强的功能,如更好的主题支持、加密功能、安全启动支持和类似的功能添加,VirtualBox 7.0 是一个不错的升级。
? *你对这次升级有什么看法?你会使用较新的版本还是暂时坚持使用旧版本的虚拟机?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/virtualbox-7-0-release/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

A big upgrade for VirtualBox. This release is pretty interesting because we haven't seen a major update in recent years.
For those unfamiliar with VirtualBox, it is a virtualization software developed by [Oracle](https://www.oracle.com/in/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
With the launch of VirtualBox 7.0, many new features have been added.
Let's take a look at some of the most crucial ones.
## VirtualBox 7.0: What's New?
VirtualBox 7.0 is a helpful upgrade. There are icon updates, theme improvements, and some key highlights, including:
**A new utility to show performance statistics for running guests.****Secure boot support.****Full VM encryption support (via CLI).****Reworked new virtual machine wizard.**
### Full VM Encryption via CLI
Virtual Machines (VM) can now be fully encrypted, but only through the command-line interface.
This also includes the config logs and saved states.
As of now, users can encrypt their machines only through the command-line interface, and different methods are to be added in the future.
### New Resource Monitor Utility
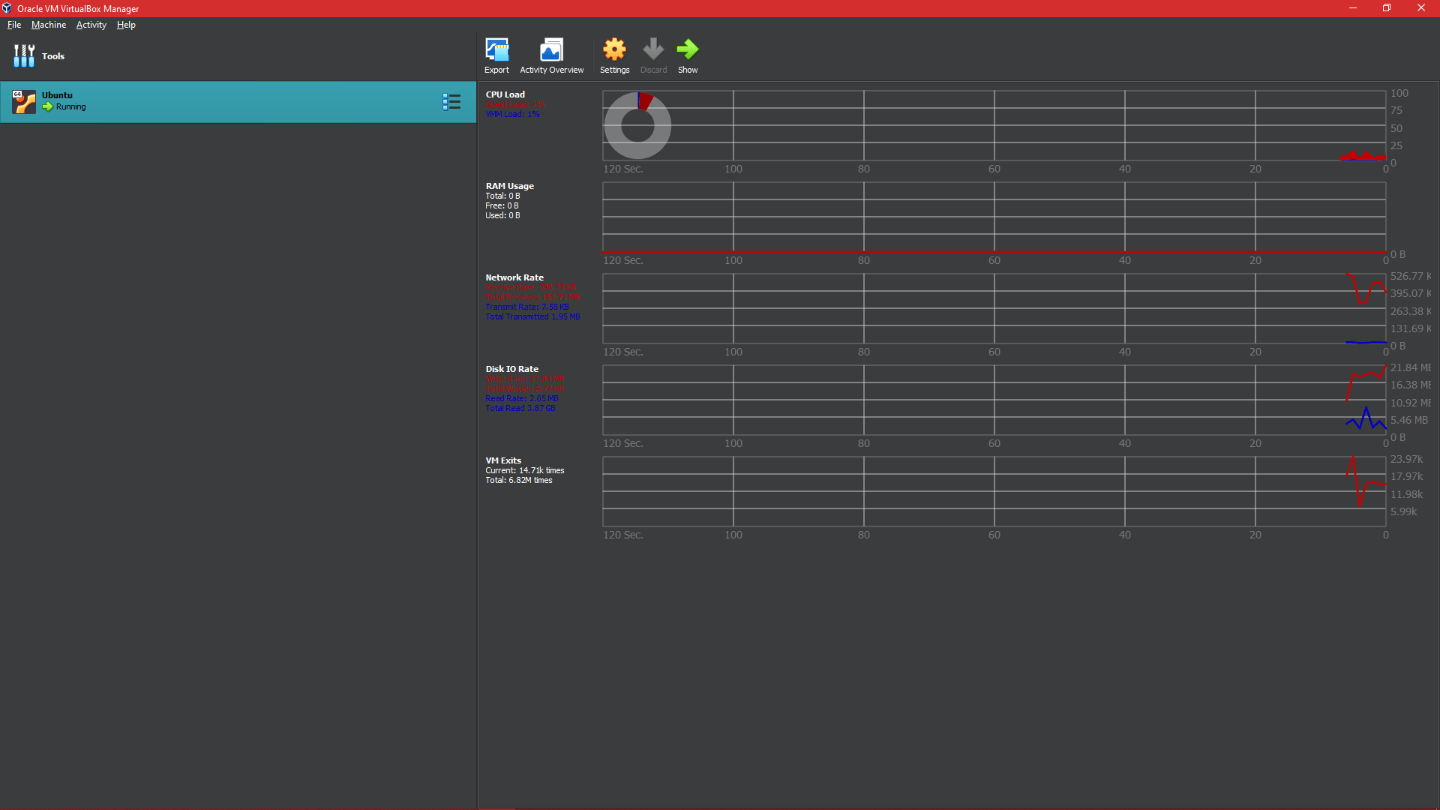
The new utility lets you monitor performance statistics like CPU, RAM usage, disk I/O, and more. It would list the performance stats for all the running guests.
Not the most attractive addition, but useful.
### Improved Theme Support
The support for themes has been improved on all platforms. The native engine is used on Linux and macOS, and on Windows, a separate implementation is in place.
### Support for Secure Boot
VirtualBox now supports Secure Boot, enhancing security against malware, viruses, and spyware.
It will also prevent a VM from booting up with broken drivers, which is very important for enterprise applications.
Users who use operating systems that require a secure boot to run should be able to create VMs easily.
### Other Changes
VirtualBox 7.0 is a significant upgrade. So, there are several feature additions and refinements across the board.
For instance, the new VM wizard has now been reworked to integrate unattended guest OS installations.
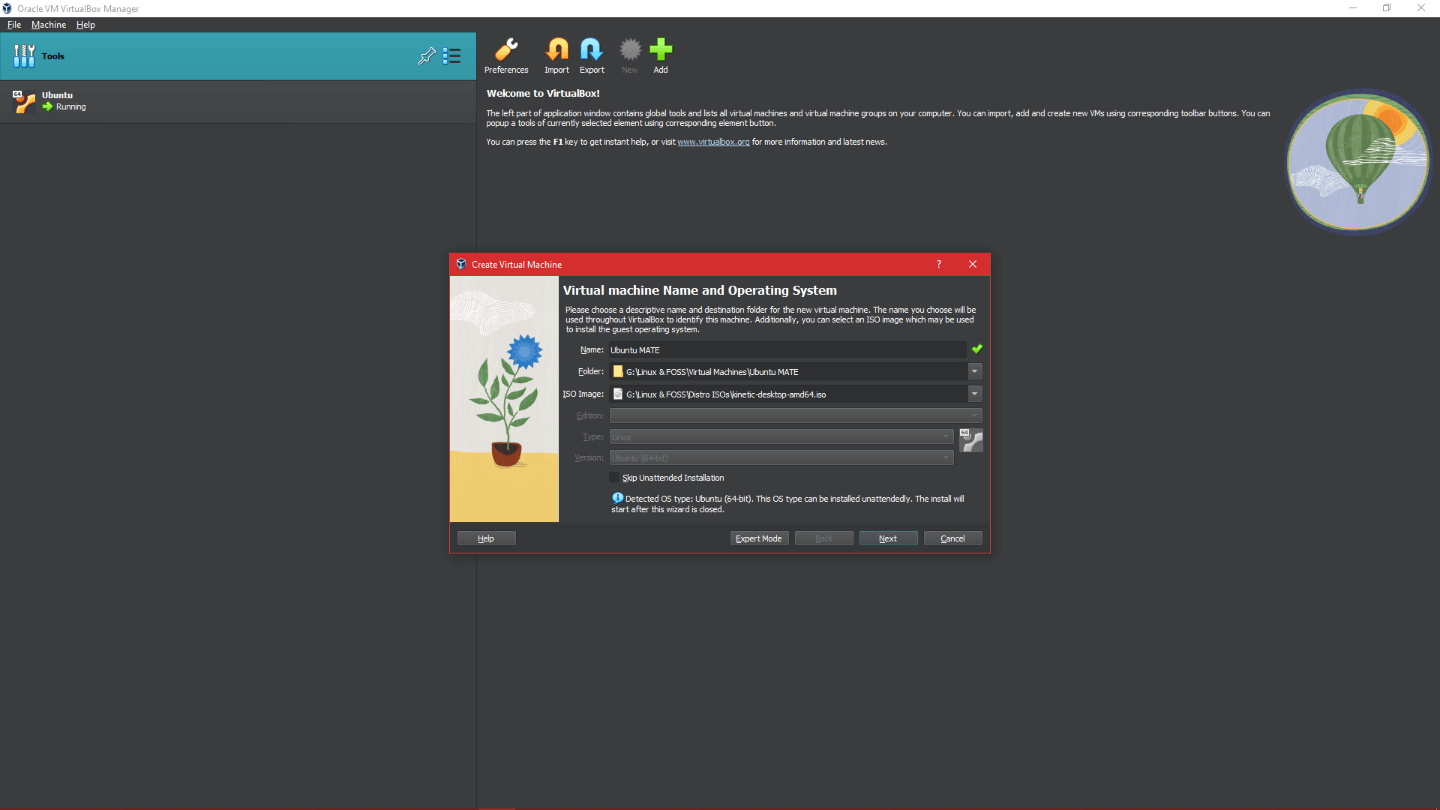
Other improvements include:
**Cloud virtual machines can now be added to VirtualBox and controlled as local VMs.****The VirtualBox icon has been updated with this release.****A new 3D stack has been introduced that supports DirectX 11. It uses**[DXVK](https://github.com/doitsujin/dxvk?ref=news.itsfoss.com)to provide the same support for non-Windows hosts.**Support for virtual TPM 1.2/2.0.****Improved mouse handling in multi-monitor setups.****Vorbis is the default audio codec for audio recording.**
You can review the [release notes](https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Changelog-7.0?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for additional information.
If you were looking for enhanced features, such as better theme support, encryption features, secure boot support, and similar feature additions, VirtualBox 7.0 is a nice upgrade.
💬 *What do you think about the upgrade? Would you use the newer version or stick to the older version for your VMs for now?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,142 | 服务器支持 IPv6 的原因 | https://jvns.ca/blog/2022/01/29/reasons-for-servers-to-support-ipv6/ | 2022-10-15T15:51:14 | [
"IPv6"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15142-1.html | 
我一直在努力学习关于 IPv6 的相关知识。一方面,IPv6 的基础概念是很简单的(没有足够的 IPv4 地址可以满足互联网上的所有设备,所以人们发明了 IPv6!每个人都能有足够的 IPv6 地址!)
但是当我试图进一步理解它时,我遇到了很多问题。其中一个问题是:为什么 [twitter.com](http://twitter.com) 不支持 IPv6。假设,网站不支持 IPv6 并不会造成很多困难,那么为什么网站需要支持 IPv6 呢?
我在 Twitter 上询问了很多人 [为什么他们的服务器支持 IPv6](https://twitter.com/b0rk/status/1487156306884636672),我得到了很多很好的答案,我将在这里总结一下。事先说明一下,因为我对 IPv6 基本上毫无经验,所以下面所总结的理由中可能会有写得不准确的地方,请大家多多包涵。
首先,我想解释一下为什么 [twitter.com](http://twitter.com) 可以不支持 IPv6,因为这是最先让我困惑的地方。
### 怎么知道 [twitter.com](http://twitter.com) 不支持 IPv6 呢?
你可以使用 `dig` 命令以 `AAAA` 的选项查询某一个域名的 IPv6 地址记录,如果没有记录,则表明该域名不支持 IPv6。除了 [twitter.com](http://twitter.com),还有一些大型网站,如 [github.com](http://github.com) 和 [stripe.com](http://stripe.com) 也不支持 IPv6。
```
$ dig AAAA twitter.com
(empty response)
$ dig AAAA github.com
(empty response)
$ dig AAAA stripe.com
(empty response)
```
### 为什么 [twitter.com](http://twitter.com) 仍然适用于 IPv6 用户?
我发现这真的很令人困惑。我一直听说因为 IPv4 地址已经用完了,从而很多互联网用户被迫要使用 IPv6 地址。但如果这是真的,[twitter.com](http://twitter.com) 怎么能继续为那些没有 IPv6 支持的人提供服务呢?以下内容是我昨天从 Twitter 会话中学习到的。
互联网服务提供商(ISP)有两种:
1. 能为所有用户拥有足够 IPv4 地址的 ISP
2. 不能为所有用户拥有足够 IPv4 地址的 ISP
我的互联网服务提供商属于第 1 类,因此我的计算机有自己的 IPv4 地址,实际上我的互联网服务提供商甚至根本不支持 IPv6。
但是很多互联网服务提供商(尤其是北美以外的)都属于第 2 类:他们没有足够的 IPv4 地址供所有用户使用。这些互联网服务提供商通过以下方式处理问题:
* 为所有用户提供唯一的 IPv6 地址,以便他们可以直接访问 IPv6 网站
* 让用户 *共享* IPv4 地址,这可以使用 CGNAT(“<ruby> <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carrier-grade_NAT"> 运营商级 NAT </a> <rt> carrier-grade NAT </rt></ruby>”)或者“464XLAT”或其他方式。
所有互联网服务提供商都需要 *一些* IPv4 地址,否则他们的用户将无法访问 [twitter.com](http://twitter.com) 等只能使用 IPv4 的网站。
### 为什么网站要支持 IPv6?
现在,我们已经解释了为什么可以 *不支持* IPv6。那为什么要支持 IPv6 呢?有下面这些原因。
#### 原因一:CGNAT 是一个性能瓶颈
对我而言,支持 IPv6 最有说服力的论点是:CGNAT 是一个瓶颈,它会导致性能问题,并且随着对 IPv4 地址的访问变得越来越受限,它的性能会变得更糟。
有人也提到:因为 CGNAT 是一个性能瓶颈,因此它成为了一个有吸引力的拒绝服务攻击(DDoS)的目标,因为你可以通过攻击一台服务器,影响其他用户对该服务器的网站的可用性。
支持 IPv6 的服务器减少了对 CGNAT 的需求(IPv6 用户可以直接连接!),这使得互联网对每个人的响应速度都更快了。
我认为这个论点很有趣,因为它需要各方的努力——仅仅你的网站支持 IPv6,并不会让你的网站更好地运行,而更重要的是如果 *几乎每个网站* 都支持 IPv6,那么它将使每个人的互联网体验更好,尤其对于那些无法轻松访问 IPv4 地址的国家/地区。
实际上,我不知道这在实践中会有多大的关系。
不过,使用 IPv6 还有很多更自私的论点,所以让我们继续探讨吧。
#### 原因二:只能使用 IPv6 的服务器也能够访问你的网站
我之前说过,大多数 IPv6 用户仍然可以通过 NAT 方式访问 IPv4 的网站。但是有些 IPv6 用户是不能访问 IPv4 网站的,因为他们发现他们运行的服务器只有 IPv6 地址,并且不能使用 NAT。因此,这些服务器完全无法访问只能使用 IPv4 的网站。
我想这些服务器并没有连接很多主机,也许它们只需要连接到一些支持 IPv6 的主机。
但对我来说,即使没有 IPv4 地址,一台主机也应该能够访问我的站点。
#### 原因三:更好的性能
对于同时使用 IPv4 和 IPv6(即具有专用 IPv6 地址和共享 IPv4 地址)的用户,IPv6 通常更快,因为它不需要经过额外的 NAT 地址转换。
因此,有时支持 IPv6 的网站可以为用户提供更快的响应。
在实际应用中,客户端使用一种称为“Happy Eyeballs”的算法,该算法能够从 IPv4 和 IPv6 中为用户选择一个最快的链接。
以下是网站支持 IPv6 的一些其他性能优势:
* 使用 IPv6 可以提高搜索引擎优化(SEO),因为 IPv6 具有更好的性能。
* 使用 IPv6 可能会使你的数据包通过更好(更快)的网络硬件,因为相较于 IPv4,IPv6 是一个更新的协议。
#### 原因四:能够恢复 IPv4 互联网中断
有人说他碰到过由于意外的 BGP 中毒,而导致仅影响 IPv4 流量的互联网中断问题。
因此,支持 IPv6 的网站意味着在中断期间,网站仍然可以保持部分在线。
#### 原因五:避免家庭服务器的 NAT 问题
将 IPv6 与家庭服务器一起使用,会变得简单很多,因为数据包不必通过路由器进行端口转发,因此只需为每台服务器分配一个唯一的 IPv6 地址,然后直接访问服务器的 IPv6 地址即可。
当然,要实现这一点,客户端需要支持 IPv6,但如今越来越多的客户端也能支持 IPv6 了。
#### 原因六:为了拥有自己的 IP 地址
你也可以自己购买 IPv6 地址,并将它们用于家庭网络的服务器上。如果你更换了互联网服务提供商,可以继续使用相同的 IP 地址。
我不太明白这是如何工作的,是如何让互联网上的计算机将这些 IP 地址路由转发给你的?我猜测你需要运行自己的自治系统(AS)或其他东西。
#### 原因七:为了学习 IPv6
有人说他们在安全领域中工作,为保证信息安全,了解互联网协议的工作原理非常重要(攻击者正在使用互联网协议进行攻击!)。因此,运行 IPv6 服务器有助于他们了解其工作原理。
#### 原因八:为了推进 IPv6
有人说因为 IPv6 是当前的标准,因此他们希望通过支持 IPv6 来为 IPv6 的成功做出贡献。
很多人还说他们的服务器支持 IPv6,是因为他们认为只能使用 IPv4 的网站已经太“落后”了。
#### 原因九:IPv6 很简单
我还得到了一堆“使用 IPv6 很容易,为什么不用呢”的答案。在所有情况下添加 IPv6 支持并不容易,但在某些情况下添加 IPv6 支持会是很容易的,有以下的几个原因:
* 你可以从托管公司自动地获得 IPv6 地址,因此你只需要做的就是添加指向该地址的 `AAAA` 记录
* 你的网站是基于支持 IPv6 的内容分发网络(CDN),因此你无需做任何额外的事情
#### 原因十:为了实施更安全的网络实验
因为 IPv6 的地址空间很大,所以如果你想在网络中尝试某些东西的时候,你可以使用 IPv6 子网进行实验,基本上你之后不会再用到这个子网了。
#### 原因十一:为了运行自己的自治系统(AS)
也有人说他们为了运行自己的自治系统(我在这篇 [BGP 帖子](https://jvns.ca/blog/2021/10/05/tools-to-look-at-bgp-routes/) 中谈到了什么是 AS),因此在服务器中提供 IPv6。IPv4 地址太贵了,所以他们为运行自治系统而购买了 IPv6 地址。
#### 原因十二:IPv6 更加安全
如果你的服务器 *只* 有公共的 IPv6 地址,那么攻击者扫描整个网络,也不能轻易地找出你的服务器地址,这是因为 IPv6 地址空间太大了以至于不能扫描出来!
这显然不能是你仅有的安全策略,但是这是安全上的一个大大的福利。每次我运行 IPv4 服务器时,我都会惊讶于 IPv4 地址一直能够被扫描出来的脆弱性,就像是老版本的 WordPress 博客系统那样。
#### 一个很傻的理由:你可以在你的 IPv6 地址中放个小彩蛋
IPv6 地址中有很多额外的位,你可以用它们做一些不重要的事情。例如,Facebook 的 IPv6 地址之一是“2a03:2880:f10e:83:face:b00c:0:25de”(其中包含 `face:b00c`)。
### 理由还有很多
这就是到目前为止我所了解的“为什么支持 IPv6?”的理由。
在我理解这些原因后,相较于以前,我在我的(非常小的)服务器上支持 IPv6 更有动力了。但那是因为我觉得支持 IPv6,对我来说只需要很少的努力。(现在我使用的是支持 IPv6 的 CDN,所以我基本上不用做什么额外的事情)
我仍然对 IPv6 知之甚少,但是在我的印象中,支持 IPv6 并不是不需要花费精力的,实际上可能需要大量工作。例如,我不知道 Twitter 在其边缘服务器上添加 IPv6 支持需要做多少繁杂的工作。
### 其它关于 IPv6 的问题
这里还有一些关于 IPv6 的问题,也许我之后再会探讨:
* 支持 IPv6 的缺点是什么?什么会出错呢?
* 对于拥有了足够 IPv4 地址的 ISP 来说,有什么让他们提供 IPv6 的激励措施?(另一种问法是:我的 ISP 是否有可能在未来几年内转为支持 IPv6?或者他们可能不会支持 IPv6?)
* [Digital Ocean](https://docs.digitalocean.com/products/networking/floating-ips/) (LCTT 译注:一家建立于美国的云基础架构提供商,面向软件开发人员提供虚拟专用服务器(VPS))只提供 IPv4 的浮动地址,不提供 IPv6 的浮动地址。为什么不提供呢?有更多 IPv6 地址,那提供 IPv6 的浮动地址不是变得更 *便捷* 吗?
* 当我尝试 ping IPv6 地址时(例如 [example.com](http://example.com) 的 IP 地址`2606:2800:220:1:248:1893:25c8:1946`),我得到一个报错信息 `ping: connect: Network is unreachable`。这是为什么呢?(回答:因为我的 ISP 不支持 IPv6,所以我的电脑没有公共 IPv6 地址)
这篇 [来自 Tailscale 的 IPv4 与 IPv6 文章](https://tailscale.com/kb/1134/ipv6-faq/) 非常有意思,并回答了上述的一些问题。
---
via: <https://jvns.ca/blog/2022/01/29/reasons-for-servers-to-support-ipv6/>
作者:[Julia Evans](https://jvns.ca/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | null |
15,144 | PyLint 的优点、缺点和危险 | https://opensource.com/article/22/9/pylint-good-bad-ugly | 2022-10-16T09:38:00 | [
"Python",
"PyLint"
] | /article-15144-1.html | 
>
> 充分利用 PyLint。
>
>
>
敲黑板:PyLint 实际上很好!
“PyLint 可以拯救你的生命”,这是一句夸张的描述,但没有你想象的那么夸张。PyLint 可以让你远离非常难找到的和复杂的缺陷。最差的情况下,它只可以节省测试运行的时间。最好的情况下,它可以帮你避免生产环境中复杂的错误。
### 优点
我不好意思说这种情况是多么普遍。测试的命名总是*那么奇怪*:没有人关心这个名称,而且通常也找不到一个自然的名称。例如以下代码:
```
def test_add_small():
# Math, am I right?
assert 1 + 1 == 3
def test_add_large():
assert 5 + 6 == 11
def test_add_small():
assert 1 + 10 == 11
```
测试生效:
```
collected 2 items
test.py ..
2 passed
```
但问题是:如果你覆盖了一个测试的名称,测试框架将愉快地跳过这个测试!
实际上,这些文件可能有数百行,而添加新测试的人可能并不知道所有的名称。除非有人仔细查看测试输出,否则一切看起来都很好。
最糟糕的是,*被覆盖测试的添加*、*被覆盖测试造成的破坏*,以及*连锁反应的问题*可能要几天、几月甚至几年才能发现。
### PyLint 会找到它
就像一个好朋友一样,PyLint 可以帮助你。
```
test.py:8:0: E0102: function already defined line 1
(function-redefined)
```
### 缺点
就像 90 年代的情景喜剧一样,你对 PyLint 了解的越多,问题就越多。以下是一个库存建模程序的常规代码:
```
"""Inventory abstractions"""
import attrs
@attrs.define
class Laptop:
"""A laptop"""
ident: str
cpu: str
```
但 PyLint 似乎有自己的观点(可能形成于 90 年代),并且不怕把它们作为事实陈述出来:
```
$ pylint laptop.py | sed -n '/^laptop/s/[^ ]*: //p'
R0903: Too few public methods (0/2) (too-few-public-methods)
```
### 危险
有没有想过在一个数百万人使用的工具中加入自己未证实的观点?PyLint 每月有 1200 万次下载。
>
> “如果太挑剔,人们会取消检查” — 这是 PyLint GitHub 的 6987 号议题,于 2022 年 7 月 3 号提出
>
>
>
对于添加一个可能有许多误报的测试,它的态度是 ... “*嗯*”。
### 让它为你工作
PyLint 很好,但你需要小心地与它配合。为了让 PyLint 为你工作,以下是我推荐的三件事:
#### 1、固定版本
固定你使用的 PyLint 版本,避免任何惊喜!
在你的 `.toml` 文件中定义:
```
[project.optional-dependencies]
pylint = ["pylint"]
```
在代码中定义:
```
from unittest import mock
```
这与以下代码对应:
```
# noxfile.py
...
@nox.session(python=VERSIONS[-1])
def refresh_deps(session):
"""Refresh the requirements-*.txt files"""
session.install("pip-tools")
for deps in [..., "pylint"]:
session.run(
"pip-compile",
"--extra",
deps,
"pyproject.toml",
"--output-file",
f"requirements-{deps}.txt",
)
```
#### 2、默认禁止
禁用所有检查,然后启用那些你认为误报比率高的。(不仅仅是漏报/误报的比率!)
```
# noxfile.py
...
@nox.session(python="3.10")
def lint(session):
files = ["src/", "noxfile.py"]
session.install("-r", "requirements-pylint.txt")
session.install("-e", ".")
session.run(
"pylint",
"--disable=all",
*(f"--enable={checker}" for checker in checkers)
"src",
)
```
#### 3、检查器
以下是我喜欢的检查器。加强项目的一致性,避免一些明显的错误。
```
checkers = [
"missing-class-docstring",
"missing-function-docstring",
"missing-module-docstring",
"function-redefined",
]
```
### 使用 PyLint
你可以只使用 PyLint 好的部分。在 CI 中运行它以保持一致性,并使用常用检查器。
放弃不好的部分:默认禁止检查器。
避免危险的部分:固定版本以避免意外。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/9/pylint-good-bad-ugly>
作者:[Moshe Zadka](https://opensource.com/users/moshez) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
15,145 | 如何在 Fedora、CentOS、RHEL 中启用 RPM Fusion 仓库 | https://www.debugpoint.com/enable-rpm-fusion-fedora-rhel-centos/ | 2022-10-16T11:09:00 | [
"Fusion",
"RPM"
] | /article-15145-1.html |
>
> 本指南解释了在 Fedora Linux 发行版中启用第三方软件仓库 RPM Fusion 的步骤。
>
>
>
[RPM Fusion](https://rpmfusion.org/) 软件仓库是一个社区维护的软件仓库,它为 Fedora Linux 提供额外的软件包,这些软件包不是由 Fedora 官方团队分发,例如 DVD 播放、媒体播放、来自 GNOME 和 KDE 的软件等。这是因为许可证、其他法律原因和特定国家/地区的软件规范而导致的。
RPM Fusion 为 Red Hat Enterprise Linux(RHEL)以及 Fedora 提供了 .rpm 包。
本指南介绍了在 Fedora Linux 中启用 RPM Fusion 仓库所需的步骤。本指南适用于所有 Fedora 发行版本。
这在所有当前支持的 Fedora 版本(35、36 和 37)中进行了测试。

### 如何在 Fedora Linux、RHEL、CentOS 中启用 RPM Fusion 仓库
RPM Fusion 有两种版本的仓库:自由和非自由。
顾名思义,自由版包含软件包的自由版本,非自由版包含封闭源代码的编译软件包和“非商业”开源软件。
在继续之前,首先检查你是否安装了 RPM fusion。打开终端并运行以下命令。
```
dnf repolist | grep rpmfusion
```
如果安装了 RPM,你应该会看到如下所示的消息。就不用下面的步骤。如果未安装,你可以继续执行以下步骤。

打开终端并根据你的操作系统版本运行以下命令。请注意,这些命令包含自由和非自由版本。如果你愿意,你可以在运行时省略下面的任何一个。
#### Fedora
自由版:
```
sudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm
```
非自由版:
```
sudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm
```
#### 在 Silverblue 上使用 rpm-ostree
自由版:
```
sudo rpm-ostree install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm
```
非自由版:
```
sudo rpm-ostree install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm
```
#### RHEL 8
先安装 EPEL:
```
sudo dnf install --nogpgcheck https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
```
自由版:
```
sudo dnf install --nogpgcheck https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/el/rpmfusion-free-release-8.noarch.rpm
```
非自由版:
```
sudo dnf install --nogpgcheckhttps://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/el/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-8.noarch.rpm
```
开发相关软件包:
```
sudo subscription-manager repos --enable "codeready-builder-for-rhel-8-$(uname -m)-rpms"
```
#### CentOS 8
先安装 EPEL:
```
sudo dnf install --nogpgcheck https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
```
自由版:
```
sudo dnf install --nogpgcheck https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/el/rpmfusion-free-release-8.noarch.rpm
```
非自由版:
```
sudo dnf install --nogpgcheckhttps://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/el/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-8.noarch.rpm
```
启用 PowerTools:
```
sudo dnf config-manager --enable PowerTools
```
### 附加说明
RPM Fusion 还可以帮助用户安装来自 GNOME 软件或 KDE Discover 的软件包。要在 Fedora 中启用它,请运行以下命令:
```
sudo dnf groupupdate core
```
你还可以通过以下命令启用 RPM Fusion 来使用 gstreamer 和其他多媒体播放包来播放媒体文件。
```
sudo dnf groupupdate multimedia --setop="install_weak_deps=False" --exclude=PackageKit-gstreamer-plugin
```
```
sudo dnf groupupdate sound-and-video
```
启用 RPM Fusion 以使用 libdvdcss 播放 DVD。
```
sudo dnf install rpmfusion-free-release-taintedsudo dnf install libdvdcss
```
通过以下命令启用 RPM Fusion 以启用非 FLOSS 硬件包。
```
sudo dnf install rpmfusion-nonfree-release-taintedsudo dnf install *-firmware
```
运行命令后,如果你使用的是 Fedora 或 CentOS/RHEL,请在重启前运行以下命令。
```
sudo dnf check-updatesudo dnf update
```
### 如何使用 dnf 删除仓库
如果要删除仓库,请按照以下步骤操作。
首先,使用以下命令查看添加到 Fedora 系统的仓库列表。
```
dnf repolist
```

如你所见,添加了 rpmfusion 自由和非自由仓库。要通过 dnf 删除它,你需要使用以下命令准确知道仓库文件名。
```
rpm -qa 'rpmfusion*'
```
这将列出仓库的确切名称。在示例中,它们是 “rpmfusion-free-release”。

现在你可以简单地运行以下命令来删除它。
```
sudo dnf remove rpmfusion-free-release
```
你可以重复上面的例子从 Fedora 中删除 rpmfusion,也可以使用它从系统中删除任何其他仓库。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/enable-rpm-fusion-fedora-rhel-centos/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,147 | 类似 Notion 的 Markdown 笔记应用黑曜石推出测试版 | https://news.itsfoss.com/obsidian-1-release/ | 2022-10-16T23:58:37 | [
"Markdown"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15147-1.html |
>
> 黑曜石 1.0 做了重新设计,带来了有价值的新功能。
>
>
>

<ruby> 黑曜石 <rt> Obsidian </rt></ruby> 是一款强大的笔记应用,可以用来制作知识图谱,同时还提供 [Notion](https://notion.grsm.io/itsfoss) 类似的功能。
在 1.0 更新之前,我们已经有一篇关于它的 [详细文章](/article-14230-1.html)。
黑曜石 1.0 的发布标志着该应用在桌面和移动体验方面的发展迈出了关键一步。
>
> ? 黑曜石不是一个开源的应用程序,但可以在 Linux 上使用。
>
>
>
让我们来看看它的桌面版提供的新功能。
### ? 黑曜石 1.0 的新功能

1.0 版本增加了大量的新功能、主要的视觉变化和错误修复,其中一些亮点包括:
* 改良的用户界面
* 新的外观设置
* 带有标签堆叠的标签功能
* 大修的主题画廊
* 各种错误的修复
#### ? 用户界面的改造

用户界面已经得到了全面改造,这使得用户体验更加直观和强大。

除此之外,黑曜石现在还有一个专门的外观设置部分。它包含了切换显示内联标题、标签标题栏、改变重点颜色等选项的设置。

#### 带有标签堆叠的标签功能

现在你可以在黑曜石中打开多个标签,并使用热键来帮助你在忙碌的一天中完成多个任务。
一个额外的好处是,即使你退出黑曜石,它也会记住你曾经打开的标签和你在这些标签中的活动状态。

标签也可以分组形成堆叠,并在它们之间进行切换,从而使工作空间变得更加整齐。
#### ?️ 其他变化
其他值得一提的变化包括:
* 改变缩放级别的能力
* 改进了黑曜石的同步
* 内存泄漏修复
* 用于折叠行的折叠命令
你可以通过 [发布说明](https://forum.obsidian.md/t/obsidian-release-v1-0-0/44873),以及 [发布公告](https://obsidian.md/1.0) 来了解更多的细节。
### ? 下载黑曜石 1.0
你可以到 [官方网站](https://obsidian.md/download) 下载黑曜石 1.0。在手机上,也可以在谷歌应用商店和苹果的应用商店上找到它。
为 Linux 用户提供了三个软件包:**AppImage、Flatpak 和 Snap**。
开发者还澄清说,他们不会向个人用户收取黑曜石的使用费。
*? 你对黑曜石 1.0 有什么看法?一个值得替代其他记事本的应用程序吗?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/obsidian-1-release/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Obsidian is a powerful note-taking app that can be used to make knowledge graphs while still offering [Notion](https://notion.grsm.io/itsfoss?ref=news.itsfoss.com)-like features.
We already had a detailed article on it before the 1.0 update:
[Obsidian is a Notion Alternative for Hardcore Markdown Users for Creating Knowledge Graph of Notes - It’s FOSSIt’s like Visual Studio Code for Markdown and it has potential to become a true alternative to the likes of Notion.](https://itsfoss.com/obsidian-markdown-editor/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

The release of Obsidian 1.0 marks a crucial step in the development of the app for its desktop and mobile experience.
Let's take a look at the new features on offer for desktops.
## 🆕 Obsidian 1.0: What's New?
The 1.0 release has added a bunch of new features, major visual changes, and bug fixes, some of the highlights include:
**Revamped UI****New Appearance Settings****Tabs With Tab Stacking****Overhauled Theme Gallery****Various Bug Fixes**
[Notion – One workspace. Every team.We’re more than a doc. Or a table. Customize Notion to work the way you do.](https://notion.grsm.io/itsfoss?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

### 🎨 User Interface Makeover
The user interface has received an extensive makeover, which has resulted in a more intuitive and robust user experience.
In addition to that, Obsidian now has a dedicated section for appearance settings. It contains settings to toggle options for showing the inline title, tab title bar, changing accent color, and more.
### Tabs With Tab Stacking
You can now open multiple tabs in Obsidian and use hotkeys to help you multitask throughout a busy day.
An added bonus, even if you quit Obsidian, it will remember which tabs you had opened and your active state in those tabs.
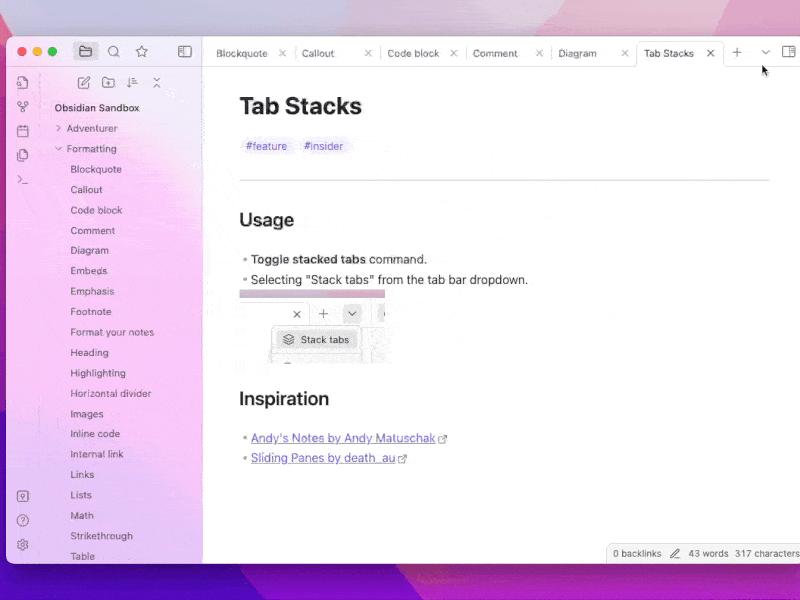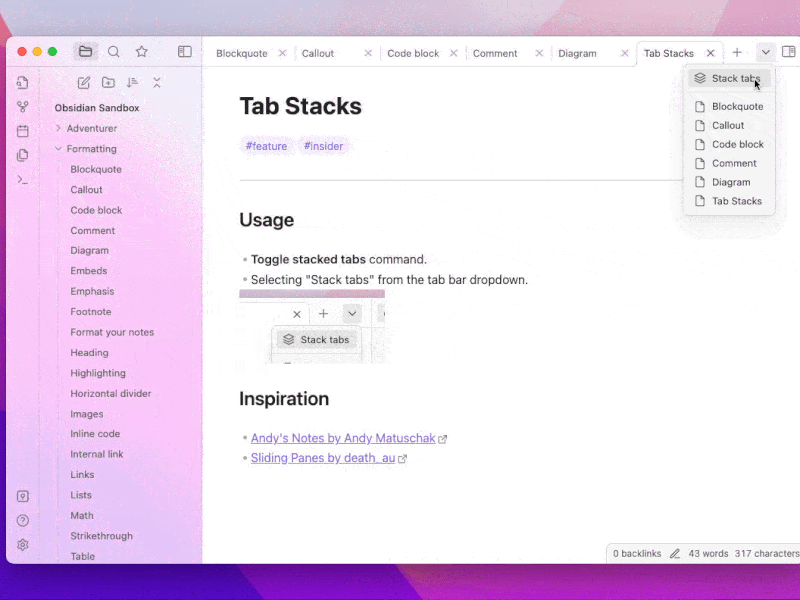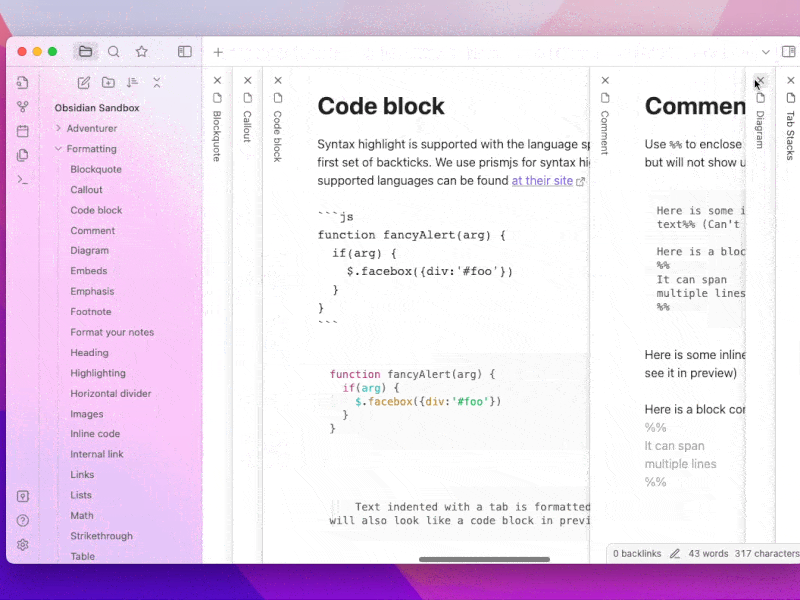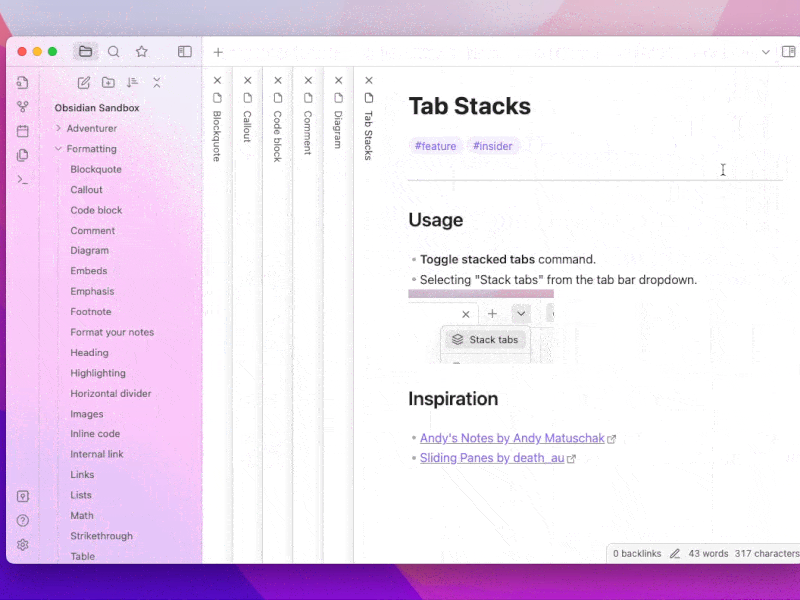
Tabs can also be grouped to form a stack and switched between, resulting in a decluttered workspace.
### 🛠️ Other Changes
Other changes worth mentioning include:
- Ability to change the zoom level.
- Improved Obsidian sync.
- Memory leak fix.
- Fold Commands for folding lines.
You can go through the [release notes](https://forum.obsidian.md/t/obsidian-release-v1-0-0/44873?ref=news.itsfoss.com), and its [release announcement](https://obsidian.md/1.0?ref=news.itsfoss.com) too get into the finer details.
### Suggested Read [📖](https://emojipedia.org/open-book/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)
[Here Are The Best Note Apps For Linux We Found For YouNotes taking is a good habit. A good note taking application makes the habit even better. Here are some of the best notes apps that you can use on Linux.](https://itsfoss.com/note-taking-apps-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## 📥 Download Obsidian 1.0
You can download Obsidian 1.0 by heading over to the [official website](https://obsidian.md/download?ref=news.itsfoss.com). For mobiles, it is available on Google Play Store and Apple's App Store.
Three packages have been made available for Linux users: **AppImage, Flatpak, and Snap**.
The developers have also clarified that they won't be charging personal users for access to Obsidian.
*💬 What do you think of Obsidian 1.0? A worthy alternative to other note-taking apps? *
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,148 | 开发你的第一个 Web 组件 | https://opensource.com/article/21/7/web-components | 2022-10-17T10:11:36 | [
"Web 组件"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15148-1.html |
>
> 不要做重复的工作;基于浏览器开发 Web App 时,需要制作一些可重用的模块。
>
>
>

Web 组件是一系列开源技术(例如 JavaScript 和 HTML)的集合,你可以用它们创建一些 Web App 中可重用的自定义元素。你创建的组件是独立于其他代码的,所以这些组件可以方便地在多个项目中重用。
首先,它是一个平台标准,所有主流的浏览器都支持它。
### Web 组件中包含什么?
* **定制元素**:JavaScript API 支持定义 HTML 元素的新类别。
* **影子 DOM**:JavaScript API 提供了一种将一个隐藏的、独立的 [文档对象模型](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Document_Object_Model)(DOM)附加到一个元素的方法。它通过保留从页面的其他代码分离出来的样式、标记结构和行为特征对 Web 组件进行了封装。它会确保 Web 组件内样式不会被外部样式覆盖,反之亦然,Web 组件内样式也不会“泄露”到页面的其他部分。
* **HTML 模板**:该元素支持定义可重用的 DOM 元素。可重用 DOM 元素和它的内容不会呈现在 DOM 内,但仍然可以通过 JavaScript 被引用。
### 开发你的第一个 Web 组件
你可以借助你最喜欢的文本编辑器和 JavaScript 写一个简单的 Web 组件。本指南使用 Bootstrap 生成简单的样式,并创建一个简易的卡片式的 Web 组件,给定了位置信息,该组件就能显示该位置的温度。该组件使用了 [Open Weather API](https://openweathermap.org/api),你需要先注册,然后创建 APPID/APIKey,才能正常使用。
调用该组件,需要给出位置的经度和纬度:
```
<weather-card longitude='85.8245' latitude='20.296' />
```
创建一个名为 `weather-card.js` 的文件,这个文件包含 Web 组件的所有代码。首先,需要定义你的组件,创建一个模板元素,并在其中加入一些简单的 HTML 标签:
```
const template = document.createElement('template');
template.innerHTML = `
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body"></div>
</div>
`
```
定义 Web 组件的类及其构造函数:
```
class WeatherCard extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
this._shadowRoot = this.attachShadow({ 'mode': 'open' });
this._shadowRoot.appendChild(template.content.cloneNode(true));
}
......
}
```
构造函数中,附加了 `shadowRoot` 属性,并将它设置为开启模式。然后这个模板就包含了 shadowRoot 属性。
接着,编写获取属性的函数。对于经度和纬度,你需要向 Open Weather API 发送 GET 请求。这些功能需要在 `connectedCallback` 函数中完成。你可以使用 `getAttribute` 方法访问相应的属性,或定义读取属性的方法,把它们绑定到本对象中。
```
get longitude() {
return this.getAttribute('longitude');
}
get latitude() {
return this.getAttribute('latitude');
}
```
现在定义 `connectedCallBack` 方法,它的功能是在需要时获取天气数据:
```
connectedCallback() {
var xmlHttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
const url = `http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?lat=${this.latitude}&lon=${this.longitude}&appid=API_KEY`
xmlHttp.open("GET", url, false);
xmlHttp.send(null);
this.$card = this._shadowRoot.querySelector('.card-body');
let responseObj = JSON.parse(xmlHttp.responseText);
let $townName = document.createElement('p');
$townName.innerHTML = `Town: ${responseObj.name}`;
this._shadowRoot.appendChild($townName);
let $temperature = document.createElement('p');
$temperature.innerHTML = `${parseInt(responseObj.main.temp - 273)} °C`
this._shadowRoot.appendChild($temperature);
}
```
一旦获取到天气数据,附加的 HTML 元素就添加进了模板。至此,完成了类的定义。
最后,使用 `window.customElements.define` 方法定义并注册一个新的自定义元素:
```
window.customElements.define('weather-card', WeatherCard);
```
其中,第一个参数是自定义元素的名称,第二个参数是所定义的类。这里是 [整个组件代码的链接](https://gist.github.com/rkpattnaik780/acc683d3796102c26c1abb03369e31f8)。
你的第一个 Web 组件的代码已完成!现在应该把它放入 DOM。为了把它放入 DOM,你需要在 HTML 文件(`index.html`)中载入指向 Web 组件的 JavaScript 脚本。
```
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<weather-card longitude='85.8245' latitude='20.296'/>
<script src='./weather-card.js'></script>
</body>
</html>
```
这就是显示在浏览器中的 Web 组件:

由于 Web 组件中只包含 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript,它们本来就是浏览器所支持的,并且可以无瑕疵地跟前端框架(例如 React 和 Vue)一同使用。下面这段简单的代码展现的是它跟一个由 [Create React App](https://create-react-app.dev/docs/getting-started/) 引导的一个简单的 React App 的整合方法。如果你需要,可以引入前面定义的 `weather-card.js`,把它作为一个组件使用:
```
import './App.css';
import './weather-card';
function App() {
return (
<weather-card longitude='85.8245' latitude='20.296'></weather-card>
);
}
export default App;
```
### Web 组件的生命周期
一切组件都遵循从初始化到移除的生命周期法则。每个生命周期事件都有相应的方法,你可以借助这些方法令组件更好地工作。Web 组件的生命周期事件包括:
* `Constructor`:Web 组件的构造函数在它被挂载前调用,意味着在元素附加到文档对象前被创建。它用于初始化本地状态、绑定事件处理器以及创建影子 DOM。在构造函数中,必须调用 `super()`,执行父类的构造函数。
* `ConnectedCallBack`:当一个元素被挂载(即,插入 DOM 树)时调用。该函数处理创建 DOM 节点的初始化过程中的相关事宜,大多数情况下用于类似于网络请求的操作。React 开发者可以将它与 `componentDidMount` 相关联。
* `attributeChangedCallback`:这个方法接收三个参数:`name`, `oldValue` 和 `newValue`。组件的任一属性发生变化,就会执行这个方法。属性由静态 `observedAttributes` 方法声明:
```
static get observedAttributes() {
return ['name', '_id'];
}
```
一旦属性名或 `_id` 改变,就会调用 `attributeChangedCallback` 方法。
* `DisconnectedCallBack`:当一个元素从 DOM 树移除,会执行这个方法。它相当于 React 中的 `componentWillUnmount`。它可以用于释放不能由垃圾回收机制自动清除的资源,比如 DOM 事件的取消订阅、停用计时器或取消所有已注册的回调方法。
* `AdoptedCallback`:每次自定义元素移动到一个新文档时调用。只有在处理 IFrame 时会发生这种情况。
### 模块化开源
Web 组件对于开发 Web App 很有用。无论你是熟练使用 JavaScript 的老手,还是初学者,无论你的目标客户使用哪种浏览器,借助这种开源标准创建可重用的代码都是一件可以轻松完成的事。
*插图:Ramakrishna Pattnaik, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/7/web-components>
作者:[Ramakrishna Pattnaik](https://opensource.com/users/rkpattnaik780) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[cool-summer-021](https://github.com/cool-summer-021) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Web components are a collection of open source technologies such as JavaScript and HTML that allow you to create custom elements that you can use and reuse in web apps. The components you create are independent of the rest of your code, so they're easy to reuse across many projects.
Best of all, it's a platform standard supported by all major modern browsers.
## What's in a web component?
**Custom elements:**This JavaScript API allows you to define new types of HTML elements.**Shadow DOM:**This JavaScript API provides a way to attach a hidden separate[Document Object Model](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Document_Object_Model)(DOM) to an element. This encapsulates your web component by keeping the styling, markup structure, and behavior isolated from other code on the page. It ensures that styles are not overridden by external styles or, conversely, that a style from your web component doesn't "leak" into the rest of the page**.****HTML templates:**The element allows you to define reusable DOM elements. The element and its contents are not rendered in the DOM but can still be referenced using JavaScript.
## Write your first web component
You can write a simple web component with your favorite text editor and JavaScript. This how-to uses bootstrap to generate simple stylings then creates a simple card web component to display the temperature of a location passed to it as an attribute. The component uses the [Open Weather API](https://openweathermap.org/api), which requires you to generate an APPID/APIKey by signing in.
The syntax of calling this web component requires the location's longitude and latitude:
`<weather-card longitude='85.8245' latitude='20.296' />`
Create a file named **weather-card.js** that will contain all the code for your web component. Start by defining your component. This can be done by creating a template element and adding some simple HTML elements into it:
```
const template = document.createElement('template');
template.innerHTML = `
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body"></div>
</div>
`
```
Start defining the WebComponent class and its constructor:
```
class WeatherCard extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
this._shadowRoot = this.attachShadow({ 'mode': 'open' });
this._shadowRoot.appendChild(template.content.cloneNode(true));
}
….
}
```
The constructor attaches the shadowRoot and sets it to open mode. Then the template is cloned to shadowRoot.
Next, access the attributes. These are the longitude and latitude, and you need them to make a GET request to the Open Weather API. This needs to be done in the `connectedCallback`
function. You can use the `getAttribute`
method to access the attributes or define getters to bind them to this object:
```
get longitude() {
return this.getAttribute('longitude');
}
get latitude() {
return this.getAttribute('latitude');
}
```
Now define the `connectedCallBack`
method that fetches weather data whenever it is mounted:
```
connectedCallback() {
var xmlHttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
const url = `http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?lat=${this.latitude}&lon=${this.longitude}&appid=API_KEY`
xmlHttp.open("GET", url, false);
xmlHttp.send(null);
this.$card = this._shadowRoot.querySelector('.card-body');
let responseObj = JSON.parse(xmlHttp.responseText);
let $townName = document.createElement('p');
$townName.innerHTML = `Town: ${responseObj.name}`;
this._shadowRoot.appendChild($townName);
let $temperature = document.createElement('p');
$temperature.innerHTML = `${parseInt(responseObj.main.temp - 273)} °C`
this._shadowRoot.appendChild($temperature);
}
```
Once the weather data is retrieved, additional HTML elements are added to the template. Now, your class is defined.
Finally, define and register a new custom element by using the method `window.customElements.define`
:
`window.customElements.define('weather-card', WeatherCard);`
The first argument is the name of the custom element, and the second argument is the defined class. Here's a [link to the entire component](https://gist.github.com/rkpattnaik780/acc683d3796102c26c1abb03369e31f8).
You've written your first web component! Now it's time to bring it to the DOM. To do that, you must load the JavaScript file with your web component definition in your HTML file (name it **index.html**):
```
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<weather-card longitude='85.8245' latitude='20.296'></weather-card>
<script src='./weather-card.js'></script>
</body>
</html>
```
Here's your web component in a browser:
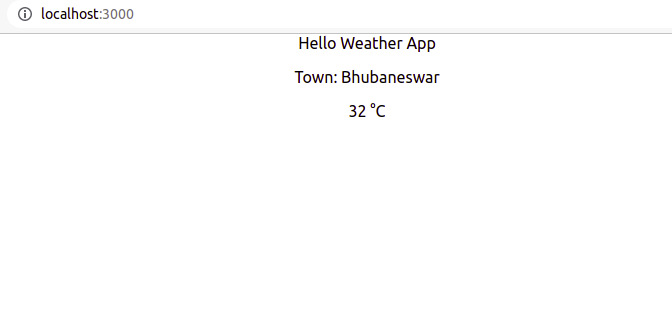
(Ramakrishna Pattnaik, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Because web components need only HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, they are natively supported by browsers and can be used seamlessly with frontend frameworks, including React and Vue. The following simple code snippet shows how to use web components with a simple React App bootstrapped with [Create React App](https://create-react-app.dev/docs/getting-started/). For this, you need to import the **weather-card.js** file you defined earlier and use it as a component:
```
import './App.css';
import './weather-card';
function App() {
return (
<weather-card longitude='85.8245' latitude='20.296'></weather-card>
);
}
export default App;
```
## Lifecycle of a web component
All components follow a lifecycle from initialization to removal from the DOM (i.e., unmount). Methods are associated with each lifecycle event so that you can control the components better. The various lifecycle events of a web component include:
**Constructor:**The constructor for a web component is called before it is mounted, meaning it's created before the element is attached to the document. It's used for initializing local state, binding event handlers, and creating the shadow DOM. The constructor must make a call to`super()`
to call the class the Web Component class extends.**ConnectedCallBack:**This is called when an element is mounted (that is, inserted into the DOM tree). It deals with initializations creating DOM nodes and is used mostly for operations like instantiating network requests. React developers can relate it to`componentDidMount`
.**attributeChangedCallback:**This method accepts three arguments:`name`
,`oldValue`
, and`newValue`
. It is called whenever one of the component's observed attributes gets changed. Attributes are declared observed attributes using a static`observedAttributes`
getter:
`static get observedAttributes() { return ['name', '_id']; }`
`attributeChangedCallback`
will be called whenever the attribute name or`_id`
is changed.**DisconnectedCallBack:**This is called when an element is removed from the DOM tree (i.e., unmounted). It is equivalent to React's`componentWillUnmount`
. It is used to free resources that won't be garbage-collected automatically, like unsubscribing from DOM events, stopping interval timers, or unregistering all registered callbacks.**AdoptedCallback:**It is called each time the custom element is moved to a new document. It only occurs when dealing with IFrames.
## Modular open source
Web components can be a powerful way to develop web apps. Whether you're comfortable with JavaScript or just getting started with it, it's easy to create reusable code with this great open standard, no matter what browser your target audience uses.
## Comments are closed. |
15,149 | Arch Linux 中用于包管理的图形化应用 | https://itsfoss.com/arch-linux-gui-package-managers/ | 2022-10-17T11:04:00 | [
"Arch Linux",
"包管理器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15149-1.html | 
[安装 Arch Linux](https://itsfoss.com/install-arch-linux/) 有一些挑战性。这就是为什么 [有几个基于 Arch 的发行版](https://itsfoss.com/arch-based-linux-distros/) 通过提供图形化的安装程序使事情变得简单。
即使你设法安装了 Arch Linux,你也会注意到它严重依赖命令行。如果你需要安装应用或更新系统,那么必须打开终端。
是的!Arch Linux 没有软件中心。我知道,这让很多人感到震惊。
如果你对使用命令行管理应用感到不舒服,你可以安装一个 GUI 工具。这有助于在舒适的图形化界面中搜索包以及安装和删除它们。
想知道你应该使用 [pacman 命令](https://itsfoss.com/pacman-command/) 的哪个图形前端?我有一些建议可以帮助你。
**请注意,某些软件管理器是特定于桌面环境的。**
### 1、Apper

Apper 是一个精简的 Qt5 应用,它使用 PackageKit 进行包管理,它还支持 AppStream 和自动更新。但是,**没有 AUR 支持**。
要从官方仓库安装它,请使用以下命令:
```
sudo pacman -Syu apper
```
>
> **[GitLab 上的 Apper](https://invent.kde.org/system/apper)**
>
>
>
### 2、深度应用商店

深度应用商店是使用 DTK(QT5)构建的深度桌面环境的应用商店,它使用 PackageKit 进行包管理,支持 AppStream,同时提供系统更新通知。 **没有 AUR 支持**。
要安装它,请使用以下命令:
```
sudo pacman -Syu deepin-store
```
>
> **[Github 上的深度商店](https://github.com/dekzi/dde-store)**
>
>
>
### 3、KDE 发现应用

<ruby> 发现 <rt> Discover </rt></ruby> 应用不需要为 KDE Plasma 用户介绍。它是一个使用 PackageKit 的基于 Qt 的应用管理器,支持 AppStream、Flatpak 和固件更新。
要在发现应用中安装 Flatpak 和固件更新,需要分别安装 `flatpak` 和 `fwupd` 包。**它没有 AUR 支持。**
```
sudo pacman -Syu discover packagekit-qt5
```
>
> **[GitLab 上的 Discover](https://invent.kde.org/plasma/discover)**
>
>
>
### 4、GNOME PackageKit

GNOME PackageKit 是一个使用 PackageKit 技术的 GTK3 包管理器,支持 AppStream。不幸的是,**没有 AUR 支持**。
要从官方仓库安装它,请使用以下命令:
```
sudo pacman -Syu gnome-packagekit
```
>
> **[freedesktop 上的 PackageKit](https://freedesktop.org/software/PackageKit/index.html)**
>
>
>
### 5、GNOME 软件应用

GNOME <ruby> 软件 <rt> Software </rt></ruby> 应用不需要向 GNOME 桌面用户介绍。它是使用 PackageKit 技术的 GTK4 应用管理器,支持 AppStream、Flatpak 和固件更新。
**它没有 AUR 支持。**要安装来自 GNOME 软件应用的 Flatpak 和固件更新,需要分别安装 `flatpak` 和 `fwupd` 包。
安装它使用:
```
sudo pacman -Syu gnome-software-packagekit-plugin gnome-software
```
>
> **[GitLab 上的 GNOME 软件](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/gnome-software)**
>
>
>
### 6、tkPacman

它是用 Tcl 编写的 Tk pacman 封装。界面类似于 [Synaptic 包管理器](https://itsfoss.com/synaptic-package-manager/)。
由于没有 GTK/Qt 依赖,它非常轻量级,因为它使用 Tcl/Tk GUI 工具包。
**它不支持 AUR**,这很讽刺,因为你需要从 [AUR](https://itsfoss.com/aur-arch-linux/) 安装它。你需要事先安装一个 [AUR 助手](https://itsfoss.com/best-aur-helpers/),如 yay。
```
yay -Syu tkpacman
```
>
> **[Sourceforge 上的 tkPacman](https://sourceforge.net/projects/tkpacman)**
>
>
>
### 7、Octopi

可以认为它是 tkPacman 的更好看的表亲。它使用 Qt5 和 Alpm,还支持 Appstream 和 **AUR(通过 yay)**。
你还可以获得桌面通知、仓库编辑器和缓存清理器。它的界面类似于 Synaptic 包管理器。
要从 AUR 安装它,请使用以下命令。
```
yay -Syu octopi
```
>
> **[GitHub 上的 Octopi](https://github.com/aarnt/octopi)**
>
>
>
### 8、Pamac

Pamac 是 Manjaro Linux 的图形包管理器。它基于 GTK3 和 Alpm,**支持 AUR、Appstream、Flatpak 和 Snap**。
Pamac 还支持自动下载更新和降级软件包。
它是 Arch Linux 衍生版中使用最广泛的应用。但因为 [DDoS AUR 网页](https://gitlab.manjaro.org/applications/pamac/-/issues/1017) 而臭名昭著。
[在 Arch Linux 上安装 Pamac](https://itsfoss.com/install-pamac-arch-linux/) 有几种方法。最简单的方法是使用 AUR 助手。
```
yay -Syu pamac-aur
```
>
> **[GitLab 上的 Pamac](https://gitlab.manjaro.org/applications/pamac)**
>
>
>
### 总结
要删除任何上面图形化包管理器以及依赖项和配置文件,请使用以下命令将 `packagename` 替换为要删除的包的名称。
```
sudo pacman -Rns packagename
```
这样看来,Arch Linux 也可以在不接触终端的情况下使用合适的工具。
还有一些其他应用程序也使用终端用户界面(TUI)。一些例子是 [pcurses](https://github.com/schuay/pcurses)、[cylon](https://github.com/gavinlyonsrepo/cylon)、[pacseek](https://github.com/moson-mo/pacseek) 和 [yup](https://github.com/ericm/yup)。但是,这篇文章只讨论那些有适当的 GUI 的软件。
**注意:** PackageKit 默认打开系统权限,因而 [不推荐](https://bugs.archlinux.org/task/50459) 用于一般用途。因为如果用户属于 `wheel` 组,更新或安装任何软件都不需要密码。
**你看到了在 Arch Linux 上使用图形化软件中心的几种选择。现在是时候决定使用其中一个了。你会选择哪一个?Pamac 或 OctoPi 还是其他?现在就在下面留言吧**。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/arch-linux-gui-package-managers/>
作者:[Anuj Sharma](https://itsfoss.com/author/anuj/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux 中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | [Installing Arch Linux](https://itsfoss.com/install-arch-linux/) is considered challenging. This is why [several Arch-based distributions exist](https://itsfoss.com/arch-based-linux-distros/) to make things easier by providing a graphical installer.
Even if you manage to install Arch Linux, you’ll notice that it relies heavily on the command line. You’ll have to open the terminal if you have to install applications or update the system.
Yes! Arch Linux does not have a software center. Shocking for many, I know.
If you feel uncomfortable using the command line for managing applications, you can install a GUI tool. This helps in searching for packages and installing and removing them from the comfort of the GUI.
Wondering which graphical frontend for [pacman commands](https://itsfoss.com/pacman-command/) you should use? I have some suggestions to help you get started.
*Please note that some software managers are desktop environment specific.*
## 1. Apper
Apper is a minimal Qt5 application and package manager using PackageKit which also supports AppStream and automatic updates. But, **there is no AUR support**.
To install it from the official repos use the command below.
`sudo pacman -Syu apper`
## 2. Deepin App Store
Deepin App Store is an app store for Deepin Desktop Environment built with DTK(Qt5), using PackageKit with AppStream support and also provides system update notifications. There is **no AUR support**.
To install it, use the command below.
`sudo pacman -Syu deepin-store`
## 3. Discover
Discover needs no introduction for KDE Plasma users. It is a Qt-based application manager using PackageKit which supports AppStream, Flatpak and Firmware updates.
For installing Flatpak and Firmware updates from Discover `flatpak`
and `fwupd`
packages need to be installed respectively.
There is no AUR support.
`sudo pacman -Syu discover packagekit-qt5`
## 4. **GNOME PackageKit**
GNOME** **PackageKit is a GTK3 package manager using PackageKit which supports AppStream. Unfortunately, there is **no AUR support**.
To install it from the official repos use the command below.
`sudo pacman -Syu gnome-packagekit`
## 5. **GNOME Software**
GNOME Software needs no introduction for GNOME desktop users. It is the GTK4 application manager using PackageKit which supports AppStream, Flatpak and Firmware updates.
There is no AUR support. To install Flatpak and Firmware updates from GNOME Software `flatpak`
and `fwupd`
packages need to be installed respectively.
Install it using:
`sudo pacman -Syu gnome-software-packagekit-plugin gnome-software`
## 6. **tkPacman**
**tkPacman**It is a Tk pacman wrapper written in Tcl. The interface is similar to [Synaptic Package Manager](https://itsfoss.com/synaptic-package-manager/).
It is quite lightweight due to no GTK/Qt dependencies as it is uses Tcl/Tk GUI toolkit.
It does not support AUR which is ironic because you need to install it from [AUR](https://itsfoss.com/aur-arch-linux/). You need to install an [AUR helper](https://itsfoss.com/best-aur-helpers/) like yay beforehand.
`yay -Syu tkpacman`
## 7. **Octopi**
Consider it a better looking cousin of tkPacman. It uses Qt5 and Alpm and also supports Appstream and **AUR (via yay)**.
You also get desktop notifications, repository editor and cache cleaner. The interface is similar to Synaptic Package Manager.
To install it from the AUR, use the following command.
`yay -Syu octopi`
## 8. Pamac
Pamac is the graphical package manager from Manjaro Linux. It based on GTK3 and Alpm and **supports AUR, Appstream, Flatpak and Snap**.
Pamac also supports automatic download of updates and downgrade of packages.
It is the most widely used Application in Arch Linux derivatives. But, has been notorious for [DDoSing the AUR webpage](https://gitlab.manjaro.org/applications/pamac/-/issues/1017).
There are several ways to [install Pamac on Arch Linux](https://itsfoss.com/install-pamac-arch-linux/). The simplest would be to use an AUR helper.
`yay -Syu pamac-aur`
## Conclusion
To remove any of the above-mentioned GUI package managers along with the dependencies and configuration files, use the following command replacing *packagename* with the name of package to be removed.
`sudo pacman -Rns `*packagename*
So it seems Arch Linux can also be used without touching the terminal with the right tools.
There are also some other applications also which use Terminal User Interface (TUI). A few examples are [pcurses](https://github.com/schuay/pcurses), [cylon](https://github.com/gavinlyonsrepo/cylon), [pacseek](https://github.com/moson-mo/pacseek), and [yup](https://github.com/ericm/yup). But, this article is about only the ones with proper GUI.
**Note:** PackageKit opens up system permissions by default, and is otherwise [not recommended](https://bugs.archlinux.org/task/50459) for general usage. Because if the user is part of the wheel group no password is required to update or install any software.
*You saw several options for using GUI software center on Arch Linux. It’s time to make a decision on using one of them. Which one would you choose? Pamac or OctoPi or something else? Leave a quick comment below right now.* |
15,151 | LURE 初窥!将 AUR 带入所有 Linux 发行版 | https://news.itsfoss.com/lure-aur/ | 2022-10-18T10:46:05 | [
"AUR",
"LURE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15151-1.html |
>
> LURE 是一个新的开源项目,它希望成为所有发行版的 AUR。
>
>
>

AUR(<ruby> Arch 用户仓库 <rt> Arch User Repository </rt></ruby>)是一个由社区驱动的基于 Arch 的 Linux 的发行版仓库。
**简而言之:** 它可以帮助你安装官方仓库中没有的软件包,并让你获得最新的版本。
我发现它对我在 [Manjaro Linux](https://news.itsfoss.com/manjaro-linux-experience/) 上的体验很有帮助。
从技术上讲,AUR 从源头构建一个软件包,然后利用软件包管理器(`pacman`)来安装它。
你也可以在我们的详细指南中探索更多关于它的信息。
>
> **[什么是 AUR? 如何在 Arch 和 Manjaro Linux 中使用 AUR?](https://itsfoss.com/aur-arch-linux/)**
>
>
>
? 现在你对 AUR 有了一个基本的了解,有一个 **新的开源项目** 旨在将 AUR 的功能带到所有的发行版中。
这个项目被称为 “<ruby> Linux 用户仓库 <rt> Linux User REpository </rt></ruby>”(LURE)。
>
> ? LURE 项目正处于 alpha 阶段,由创建者在几周前宣布。所以,它完全是一个正在进行的工作。
>
>
>
### 已经有这样的项目了?

**没有。**
开发者们已经尝试做一个 AUR 的替代品,但是是针对特定的发行版。就像 [makedeb 软件包仓库](https://mpr.makedeb.org) 是针对 Debian 的。
LURE 是一个雄心勃勃的想法,可以在你选择的任何发行版上工作。
它试图成为一个帮助你使用类似于 `PKGBUILD` 的脚本为你的发行版创建原生软件包的工具。
>
> **[创建 PKGBUILD 为 Arch Linux 制作软件包](https://itsfoss.com/create-pkgbuild/)**
>
>
>
开发者在 [Reddit 公告帖子](https://www.reddit.com/r/linux/comments/xq09nf/lure_aur_on_nonarch_distros/) 中提到了一些技术细节:
>
> 我的项目叫 LURE,是 “Linux 用户仓库”的简称。它构建原生软件包,然后使用系统软件包管理器安装它们,就像 AUR 一样。它使用一个类似于 AUR 的 `PKGBUILD` 的构建脚本来构建软件包。
>
>
> 它是用纯 Go 语言编写的,这意味着它在构建后没有任何依赖性,除了一些特权提升命令(`sudo`,`doas` 等等)和任何一个支持的软件包管理器,目前支持 `pacman`、`apt`、`apk`(Alpine Linux 上,不是安卓)、`dnf`、`yum` 和 `zypper`。
>
>
>
**听起来很棒!**
>
> **[LURE 项目Repo](https://gitea.arsenm.dev/Arsen6331/lure)**
>
>
>
你也可以在它的 [GitHub 镜像](https://github.com/Arsen6331/lure) 上探索更多信息。
### 使用 LURE
你不必安装一个额外的软件包管理器来使它工作,它可以自动与你系统的软件包管理器一起工作。
因此,如果它在其仓库(或任何其添加的仓库)中没有找到一个包,它就会转到系统的默认仓库,并从那里安装它。就像我用 `lure` 命令在我的系统上安装/移除 `neofetch` 一样。

虽然该项目处于早期开发阶段,但它为各种发行版提供了 [二进制包](https://gitea.arsenm.dev/Arsen6331/lure/releases/tag/v0.0.2),以让你安装和测试它们。

目前,它的仓库包括一个来自创建者自己的项目。但你可以尝试添加一个仓库并构建/安装东西。
为了方便起见,我试着在它的仓库中安装软件包。

命令看起来像这样:
```
lure in itd-bin
```
在它的 [官方文档页面](https://github.com/Arsen6331/lure/blob/master/docs/usage.md),你可以读到更多关于它在构建/安装/添加存储库方面的用法。
未来版本的一些计划中的功能包括:
* 自动安装脚本
* 基于 Docker 的自动测试工具
* 仓库的网页接口
### 让它变得更好
嗯,首先,这是一个优秀的项目。如果你是过去使用过 Arch 的人,或者想离开 Arch Linux,这将是一个很好的工具。
然而,对于大多数终端用户和非 Arch Linux 新手来说,像 [Pamac GUI 软件包管理器](https://itsfoss.com/install-pamac-arch-linux/) 这样的软件包管理器支持 LURE 应该是锦上添花的。
当然,在目前的阶段,它需要开源贡献者的支持。所以,如果你喜欢这个想法,请随时为该项目贡献改进意见
\*? 你对 LURE 有什么看法?请在下面的评论中分享你的想法! \*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/lure-aur/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

**AUR** (Arch User Repository) is a community-driven repository for Arch-based Linux distributions.
**Long story short:** it helps install packages not available in the official repositories and lets you get the latest releases.
I found it helpful with my experience on [Manjaro Linux](https://news.itsfoss.com/manjaro-linux-experience/).
Technically, AUR builds a package from the source and then utilizes the package manager (pacman) to install it.
You can also explore more about it in our detailed guide:
[What is AUR? How to use AUR in Arch and Manjaro Linux?What is AUR? What are the pros and cons of using AUR? How to use AUR in Arch-based Linux distributions? This beginner’s guide answers all such questions.](https://itsfoss.com/aur-arch-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

📢 Now that you have a good idea about AUR, a **new open-source project **aims to bring the utility of AUR to all the distributions.
The project is called **Linux User REpository (or LURE).**
## A Project Like This Already Exists?
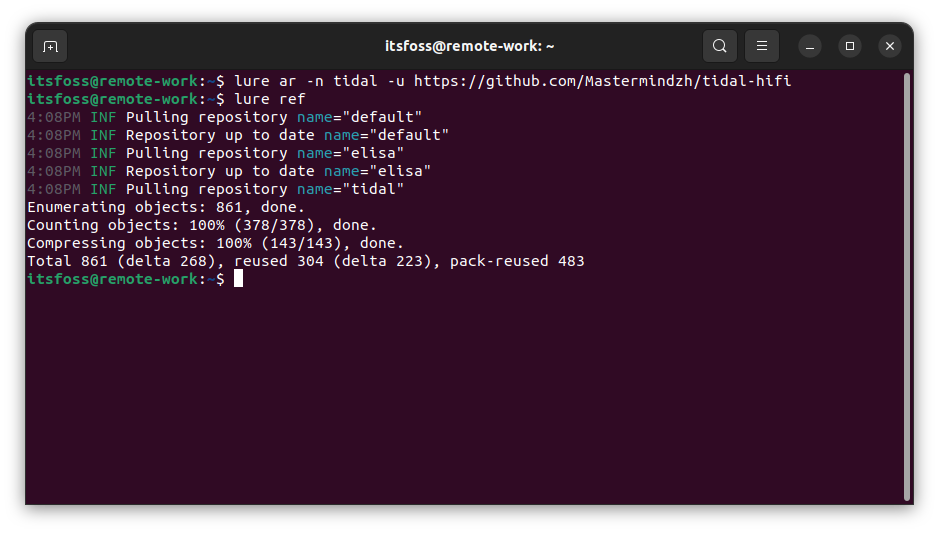
**No.**
Developers have tried making an AUR alternative, but for a specific distribution. Like [makedeb Package Repository](https://mpr.makedeb.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for Debian.
LURE is an ambitious idea that could work on any distribution of your choice.
It seeks to be a tool that helps you create native packages for your distribution using a script similar to **PKGBUILD**.
[Creating a PKGBUILD to Make Packages for Arch Linux - It’s FOSSHow do you go from a PKGBUILD to an installable package in Arch Linux? What exactly is going on between the two and how can you make them for your own packages?](https://itsfoss.com/create-pkgbuild/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

The developer mentions some of the technical details in a [Reddit announcement post](https://www.reddit.com/r/linux/comments/xq09nf/lure_aur_on_nonarch_distros/?ref=news.itsfoss.com):
My project is called LURE, short for Linux User REpository. It builds native packages and then installs them using the system package manager, just like the AUR. It uses a build script similar to the AUR's PKGBUILD to build the packages.
It is written in pure Go, which means that it has zero dependencies after it's built, other than any privilege escalation command (`sudo`
,`doas`
, etc.) and any one of the supported package managers, which currently are:`pacman`
,`apt`
,`apk`
(Alpine Linux, not Android),`dnf`
,`yum`
, and`zypper`
.
**Sounds exciting!**
You can also explore more about it on its [GitHub mirror](https://github.com/Arsen6331/lure?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Using LURE
You do not have to install an additional package manager to make it work; it works automatically with your system's package manager.
So, if it does not find a package in its repo (or any of its added repo), it moves to the system's default repo and installs it from there. Just like I installed/removed **neofetch** on my system using the lure command:
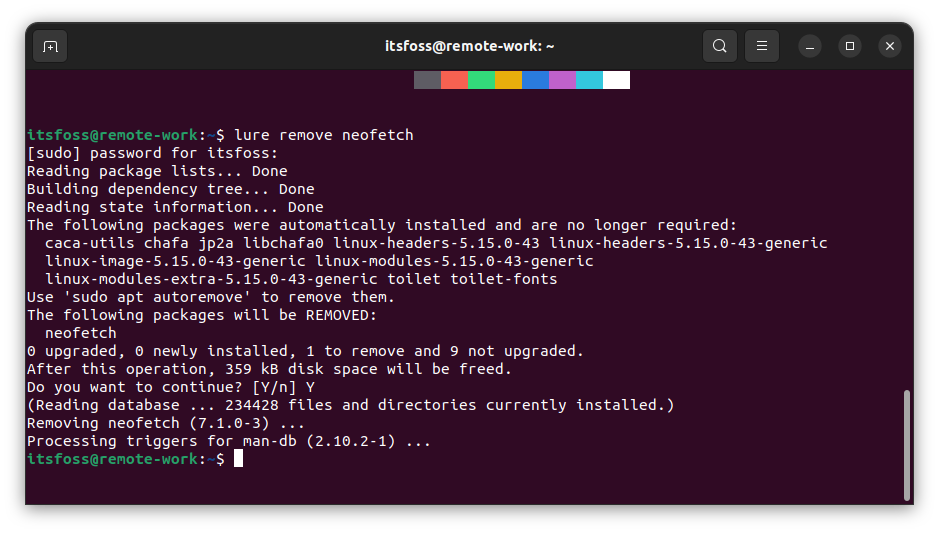
While the project is in early development, it offers [binary packages](https://gitea.arsenm.dev/Arsen6331/lure/releases/tag/v0.0.2?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for various distributions allowing you to install and test them.
Currently, its repository includes one project from the creator itself. But you can try to add a repo and build/install things.
For the sake of convenience, I tried installing the package in its repo:
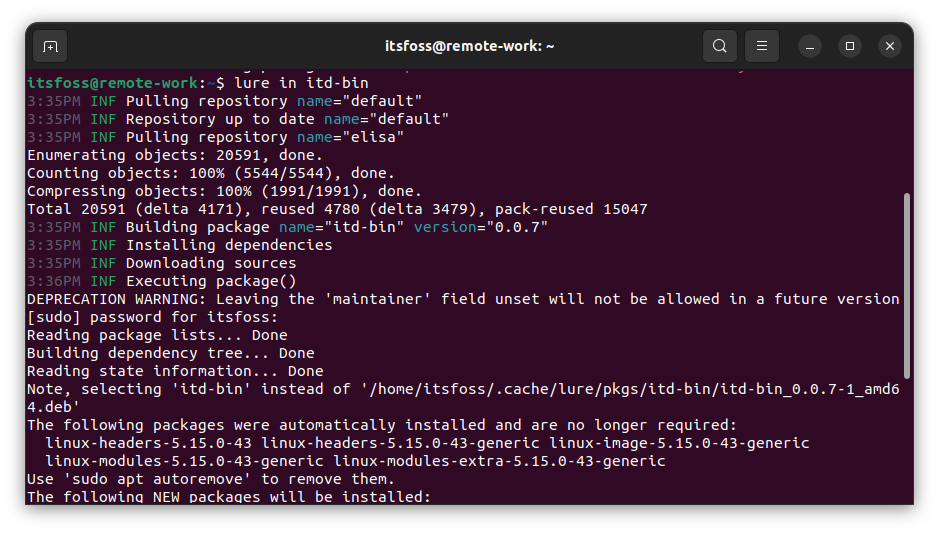
The command looks like this:
` lure in itd-bin `
On its [official documentation page](https://github.com/Arsen6331/lure/blob/master/docs/usage.md?ref=news.itsfoss.com), you can read more about its usage to build/install/add repositories.
Some of the planned features for future releases include:
**Automated install script****Automated docker-based testing tool****Web interface for repos**
## What Would Make It Better?
Well, for starters, this is an excellent project. If you are someone who used Arch in the past or want to move away from Arch Linux, this will be a good tool for you.
However, for most end-users and non-Arch Linux newbies, something like the [Pamac GUI package manager](https://itsfoss.com/install-pamac-arch-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) with LURE support should be the icing on the cake.
Of course, at its current stage, it needs support from open-source contributors. So, if you like the idea, feel free to contribute improvements to the project!
*💭 What do you think about LURE? Share your thoughts in the comments below!*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,152 | 在 Linux 中创建 LVM 分区的分步指南 | https://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-create-lvm-partition-in-linux/ | 2022-10-18T11:36:17 | [
"LVM"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15152-1.html | 
>
> 在本指南中,我们将逐步介绍如何在 Linux 中创建 LVM 分区。
>
>
>
LVM 代表 “<ruby> 逻辑卷管理 <rt> Logical Volume Management </rt></ruby>”,它是专门为服务器管理 Linux 系统上的磁盘或存储的推荐方式。 LVM 分区的主要优点之一是我们可以实时扩展其大小而无需停机。 LVM 分区也可以缩小,但不推荐。
为了演示,我在我的 Ubuntu 22.04 系统上连接了 15GB 磁盘,我们将从命令行在该磁盘上创建 LVM 分区。
##### 准备
* 连接到 Linux 系统的原始磁盘
* 具有 sudo 权限的本地用户
* 预装 lvm2 包
事不宜迟,让我们深入了解这些步骤。
### 步骤 1、识别新连接的原始磁盘
登录到你的系统,打开终端并运行以下 `dmesg` 命令:
```
$ sudo dmesg | grep -i sd
```
在输出中,查找大小为 15GB 的新磁盘。

识别新连接的原始磁盘的另一种方法是通过 `fdisk` 命令:
```
$ sudo fdisk -l | grep -i /dev/sd
```
输出:

从上面的输出,可以确认新连接的磁盘是 `/dev/sdb`。
### 步骤 2、创建 PV(物理卷)
在开始在磁盘 `/dev/sdb` 上创建<ruby> 物理卷 <rt> Physical Volume </rt></ruby>(PV)之前,请确保已安装 `lvm2` 包。如果未安装,请运行以下命令:
```
$ sudo apt install lvm2 // On Ubuntu / Debian
$ sudo dnf install lvm2 // on RHEL / CentOS
```
运行以下 `pvcreate` 命令在磁盘 `/dev/sdb` 上创建 PV:
```
$ sudo pvcreate /dev/sdb
Physical volume "/dev/sdb" successfully created.
$
```
要验证 PV 状态,运行:
```
$ sudo pvs /dev/sdb
或者
$ sudo pvdisplay /dev/sdb
```

### 步骤 3、创建 VG(卷组)
要创建<ruby> 卷组 <rt> Volume Group </rt></ruby>(VG),我们将使用 `vgcreate` 命令。创建 VG 意味着将 PV 添加到其中。
语法:
```
$ sudo vgcreare <vg_name> <pv>
```
在我们的例子中,命令是:
```
$ sudo vgcreate volgrp01 /dev/sdb
Volume group "volgrp01" successfully created
$
```
运行以下命令以验证 VG(`volgrp01`)的状态:
```
$ sudo vgs volgrp01
或者
$ sudo vgdisplay volgrp01
```
上述命令的输出:

以上输出确认大小为 15 GiB 的卷组 `volgrp01` 已成功创建,一个<ruby> 物理扩展Physical Extend</ruby>(PE)的大小为 4 MB。创建 VG 时可以更改 PE 大小。
### 步骤 4、创建 LV(逻辑卷)
`lvcreate` 命令用于从 VG 中创建<ruby> 逻辑卷 <rt> Logical Volume </rt></ruby> LV。 `lvcreate` 命令的语法如下所示:
```
$ sudo lvcreate -L <Size-of-LV> -n <LV-Name> <VG-Name>
```
在我们的例子中,以下命令将用于创建大小为 14 GB 的 LV:
```
$ sudo lvcreate -L 14G -n lv01 volgrp01
Logical volume "lv01" created.
$
```
验证 LV 的状态,运行:
```
$ sudo lvs /dev/volgrp01/lv01
或者
$ sudo lvdisplay /dev/volgrp01/lv01
```
输出:

上面的输出显示 LV(`lv01`)已成功创建,大小为 14 GiB。
### 步骤 5、格式化 LVM 分区
使用 `mkfs` 命令格式化 LVM 分区。在我们的例子中,LVM 分区是 `/dev/volgrp01/lv01`。
注意:我们可以将分区格式化为 ext4 或 xfs,因此请根据你的设置和要求选择文件系统类型。
运行以下命令将 LVM 分区格式化为 ext4 文件系统。
```
$ sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/volgrp01/lv01
```

执行下面的命令,用 xfs 文件系统格式化 LVM 分区:
```
$ sudo mkfs.xfs /dev/volgrp01/lv01
```
要使用上述格式化分区,我们必须将其挂载到某个文件夹中。所以,让我们创建一个文件夹 `/mnt/data`:
```
$ sudo mkdir /mnt/data
```
现在运行 `mount` 命令将其挂载到 `/mnt/data` 文件夹:
```
$ sudo mount /dev/volgrp01/lv01 /mnt/data/
$ df -Th /mnt/data/
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/volgrp01-lv01 ext4 14G 24K 13G 1% /mnt/data
$
```
尝试创建一些没用的文件,运行以下命令:
```
$ cd /mnt/data/
$ echo "testing lvm partition" | sudo tee dummy.txt
$ cat dummy.txt
testing lvm partition
$
$ sudo rm -f dummy.txt
```
完美,以上命令输出确认我们可以访问 LVM 分区。
要永久挂载上述 LVM 分区,请使用以下 `echo` 命令将其条目添加到 `fstab` 文件中:
```
$ echo '/dev/volgrp01/lv01 /mnt/data ext4 defaults 0 0' | sudo tee -a /etc/fstab
$ sudo mount -a
```
以上就是本指南的全部内容,感谢阅读。请在下面的评论区发表你的问题和反馈。
---
via: <https://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-create-lvm-partition-in-linux/>
作者:[James Kiarie](https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/james/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux 中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In this guide, we will show you how to create lvm partition step-by-step in Linux.
LVM stands for Logical Volume Management, it is the highly recommended way to manage disk or storage on Linux systems specially for servers. One of the main benefit of LVM partition is that we can extend its size online without any downtime. LVM partition can also be reduced but it is not recommended.
For the demo purpose, I have used Ubuntu 22.04 system and attached 15GB disk to it. We will create LVM partition on this disk from the command line.
#### Prerequisites
- Raw disk attached to Linux system
- Local User with sudo rights
- Pre-Install lvm2 package
Without further ado, let’s deep dive into the steps.
## Step 1) Identify New Attached Raw Disk
Login to your system, open the terminal and run following [dmesg command](https://www.linuxtechi.com/10-tips-dmesg-command-linux-geeks/),
$ sudo dmesg | grep -i sd
In the output, look for new disk attached of size 15GB,
Alternate way to identify new attached raw disk is via fdisk command,
$ sudo fdisk -l | grep -i /dev/sd
Output,
From output above, it is confirmed that new attached disk is ‘/dev/sdb’
## Step 2) Create PV (Physical Volume)
Before start creating pv on disk /dev/sdb, make sure lvm2 package is installed. In case it is not installed, then run following command,
$ sudo apt install lvm2 // On Ubuntu / Debian $ sudo dnf install lvm2 // on RHEL / CentOS
Run following pvcreate command to create pv on disk /dev/sdb,
$ sudo pvcreate /dev/sdb Physical volume "/dev/sdb" successfully created. $
To verify pv status run,
$ sudo pvs /dev/sdb Or $ sudo pvdisplay /dev/sdb
## Step 3) Create VG (Volume Group)
To create a volume group, we will use vgcreate command. Creating VG means adding pv to the volume group.
Syntax :
$ sudo vgcreate <vg_name> <pv>
In our case, command would be,
$ sudo vgcreate volgrp01 /dev/sdb Volume group "volgrp01" successfully created $
Run following commands to verify the status of vg (volgrp01)
$ sudo vgs volgrp01 Or $ sudo vgdisplay volgrp01
Output of above commands,
Above output confirms that volume group (volgrp01) of size 15 GiB is created successful and size of one physical extend (PE) is 4 MB. PE size can be changed while creating vg.
## Step 4) Create LV (Logical Volume)
Lvcreate command is used to create LV from the VG. Syntax of lvcreate command would look like below,
$ sudo lvcreate -L <Size-of-LV> -n <LV-Name> <VG-Name>
In our case, following command will be used to create lv of size 14 GB
$ sudo lvcreate -L 14G -n lv01 volgrp01 Logical volume "lv01" created. $
Validate the status of lv, run
$ sudo lvs /dev/volgrp01/lv01 or $ sudo lvdisplay /dev/volgrp01/lv01
Output,
Output above shows that LV (lv01) has been created successfully of size 14 GiB.
## Step 5) Format LVM Partition
Use mkfs command to format the lvm partition. In our case lvm partition is /dev/volgrp01/lv01
Note: We can format the partition either ext4 or xfs, so choose the file system type according to your setup and requirement.
Run following command to format LVM partition as ext4 file system.
$ sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/volgrp01/lv01
Execute beneath command to format the lvm partition with xfs file system,
$ sudo mkfs.xfs /dev/volgrp01/lv01
To use above formatted partition, we must mount it on some folder. So, let’s create a folder /mnt/data
$ sudo mkdir /mnt/data
Now run mount command to mount it on /mnt/data folder,
$ sudo mount /dev/volgrp01/lv01 /mnt/data/ $ df -Th /mnt/data/ Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/volgrp01-lv01 ext4 14G 24K 13G 1% /mnt/data $
Try to create some dummy file, run following commands,
$ cd /mnt/data/ $ echo "testing lvm partition" | sudo tee dummy.txt $ cat dummy.txt testing lvm partition $ $ sudo rm -f dummy.txt
Perfect, above commands output confirm that we can access lvm partition.
To mount above lvm partition permanently, add its entries in fstab file using following [echo command](https://www.linuxtechi.com/echo-command-examples-in-linux/),
$ echo '/dev/volgrp01/lv01 /mnt/data ext4 defaults 0 0' | sudo tee -a /etc/fstab $ sudo mount -a
That’s all from this guide, thanks for the reading. Kindly do post your queries and feedback in below comments section.
Read Also: [How to Extend XFS Root Partition without LVM in Linux](https://www.linuxtechi.com/extend-xfs-root-partition-without-lvm-linux/)
ArashThank you. Very helpful
MikeExcellent – exactly what I was looking for – merci
hamimWhat does the 0 0 mean? or 1 0?
and how casn you use the UUID instead of the filesystem path
Pradeep Kumarwhen you see “0 0” or “1 0” at the end of an /etc/fstab entry, it indicates the dump and pass fields respectively. The values “0 0” mean that the file system will not be dumped (backed up) and will not be checked during the boot process. The values “1 0” would mean that the file system will be dumped and checked first during the boot process. However, as mentioned earlier, the dump field is rarely used nowadays, and the pass field is typically set to 0 for most non-root file systems.
RahulPerfect
Lucianthis article and procedure is perfect
Lounisefficient and very useful, thank you
PloedI already have a VG which I did when installing Debian, with the name vg0 (Which is a Raid 0 NVMe)
Now I have another HDD, want to use it for saving big files. I created the PV, but I’m unsure if about the VG naming, should I use vg0 or name it vg1.
Is it even possible to increase the LV size on vg0 with vg1?
Pradeep KumarHi ,
Yes, you can add the new PV to the existing VG vg0 and then you can extend the size of LV.
# vgextend volume-group new-disk
# vgextend vg0 /dev/sdb
GanesanThank you for the excellent step-by-step procedure.
Joseph SpennerWhen doing:
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/volgrp01/lv01
I recommend using the -m0 option:
# mkfs.ext4 -m0 /dev/volgrp01/lv01
Otherwise, 5% of the disk will be reserved for super-user. This isn’t usually necessary on filesystems other than the / root. The m0 says to reserve no space for the super-user on that partition.
Pravin TechePerfect Document !! Thanks |
15,154 | 在 Kubernetes 上使用 Flask 搭建 Python 微服务 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/python-microservices-using-flask-on-kubernetes/ | 2022-10-19T12:44:58 | [
"微服务",
"Python",
"Flask"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15154-1.html | 
*微服务遵循领域驱动设计(DDD),与开发平台无关。Python 微服务也不例外。Python3 的面向对象特性使得按照 DDD 对服务进行建模变得更加容易。本系列的第 10 部分演示了如何将用户管理系统的查找服务作为 Python 微服务部署在 Kubernetes 上。*
微服务架构的强大之处在于它的多语言性。企业将其功能分解为一组微服务,每个团队自由选择一个平台。
我们的用户管理系统已经分解为四个微服务,分别是添加、查找、搜索和日志服务。添加服务在 Java 平台上开发并部署在 Kubernetes 集群上,以实现弹性和可扩展性。这并不意味着其余的服务也要使用 Java 开发,我们可以自由选择适合个人服务的平台。
让我们选择 Python 作为开发查找服务的平台。查找服务的模型已经设计好了(参考 2022 年 3 月份的文章),我们只需要将这个模型转换为代码和配置。
### Pythonic 方法
Python 是一种通用编程语言,已经存在了大约 30 年。早期,它是自动化脚本的首选。然而,随着 Django 和 Flask 等框架的出现,它的受欢迎程度越来越高,现在各种领域中都在应用它,如企业应用程序开发。数据科学和机器学习进一步推动了它的发展,Python 现在是三大编程语言之一。
许多人将 Python 的成功归功于它容易编码。这只是一部分原因。只要你的目标是开发小型脚本,Python 就像一个玩具,你会非常喜欢它。然而,当你进入严肃的大规模应用程序开发领域时,你将不得不处理大量的 `if` 和 `else`,Python 变得与任何其他平台一样好或一样坏。例如,采用一种面向对象的方法!许多 Python 开发人员甚至可能没意识到 Python 支持类、继承等功能。Python 确实支持成熟的面向对象开发,但是有它自己的方式 -- Pythonic!让我们探索一下!
### 领域模型
`AddService` 通过将数据保存到一个 MySQL 数据库中来将用户添加到系统中。`FindService` 的目标是提供一个 REST API 按用户名查找用户。域模型如图 1 所示。它主要由一些值对象组成,如 `User` 实体的`Name`、`PhoneNumber` 以及 `UserRepository`。

让我们从 `Name` 开始。由于它是一个值对象,因此必须在创建时进行验证,并且必须保持不可变。基本结构如所示:
```
class Name:
value: str
def __post_init__(self):
if self.value is None or len(self.value.strip()) < 8 or len(self.value.strip()) > 32:
raise ValueError("Invalid Name")
```
如你所见,`Name` 包含一个字符串类型的值。作为后期初始化的一部分,我们会验证它。
Python 3.7 提供了 `@dataclass` 装饰器,它提供了许多开箱即用的数据承载类的功能,如构造函数、比较运算符等。如下是装饰后的 `Name` 类:
```
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class Name:
value: str
def __post_init__(self):
if self.value is None or len(self.value.strip()) < 8 or len(self.value.strip()) > 32:
raise ValueError("Invalid Name")
```
以下代码可以创建一个 `Name` 对象:
```
name = Name("Krishna")
```
`value` 属性可以按照如下方式读取或写入:
```
name.value = "Mohan"
print(name.value)
```
可以很容易地与另一个 `Name` 对象比较,如下所示:
```
other = Name("Mohan")
if name == other:
print("same")
```
如你所见,对象比较的是值而不是引用。这一切都是开箱即用的。我们还可以通过冻结对象使对象不可变。这是 `Name` 值对象的最终版本:
```
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Name:
value: str
def __post_init__(self):
if self.value is None or len(self.value.strip()) < 8 or len(self.value.strip()) > 32:
raise ValueError("Invalid Name")
```
`PhoneNumber` 也遵循类似的方法,因为它也是一个值对象:
```
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class PhoneNumber:
value: int
def __post_init__(self):
if self.value < 9000000000:
raise ValueError("Invalid Phone Number")
```
`User` 类是一个实体,不是一个值对象。换句话说,`User` 是可变的。以下是结构:
```
from dataclasses import dataclass
import datetime
@dataclass
class User:
_name: Name
_phone: PhoneNumber
_since: datetime.datetime
def __post_init__(self):
if self._name is None or self._phone is None:
raise ValueError("Invalid user")
if self._since is None:
self.since = datetime.datetime.now()
```
你能观察到 `User` 并没有冻结,因为我们希望它是可变的。但是,我们不希望所有属性都是可变的。标识字段如 `_name` 和 `_since` 是希望不会修改的。那么,这如何做到呢?
Python3 提供了所谓的描述符协议,它会帮助我们正确定义 getter 和 setter。让我们使用 `@property` 装饰器将 getter 添加到 `User` 的所有三个字段中。
```
@property
def name(self) -> Name:
return self._name
@property
def phone(self) -> PhoneNumber:
return self._phone
@property
def since(self) -> datetime.datetime:
return self._since
```
`phone` 字段的 setter 可以使用 `@<字段>.setter` 来装饰:
```
@phone.setter
def phone(self, phone: PhoneNumber) -> None:
if phone is None:
raise ValueError("Invalid phone")
self._phone = phone
```
通过重写 `__str__()` 函数,也可以为 `User` 提供一个简单的打印方法:
```
def __str__(self):
return self.name.value + " [" + str(self.phone.value) + "] since " + str(self.since)
```
这样,域模型的实体和值对象就准备好了。创建异常类如下所示:
```
class UserNotFoundException(Exception):
pass
```
域模型现在只剩下 `UserRepository` 了。Python 提供了一个名为 `abc` 的有用模块来创建抽象方法和抽象类。因为 `UserRepository` 只是一个接口,所以我们可以使用 `abc` 模块。
任何继承自 `abc.ABC` 的类都将变为抽象类,任何带有 `@abc.abstractmethod` 装饰器的函数都会变为一个抽象函数。下面是 `UserRepository` 的结构:
```
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class UserRepository(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def fetch(self, name:Name) -> User:
pass
```
`UserRepository` 遵循仓储模式。换句话说,它在 `User` 实体上提供适当的 CRUD 操作,而不会暴露底层数据存储语义。在本例中,我们只需要 `fetch()` 操作,因为 `FindService` 只查找用户。
因为 `UserRepository` 是一个抽象类,我们不能从抽象类创建实例对象。创建对象必须依赖于一个具体类实现这个抽象类。数据层 `UserRepositoryImpl` 提供了 `UserRepository` 的具体实现:
```
class UserRepositoryImpl(UserRepository):
def fetch(self, name:Name) -> User:
pass
```
由于 `AddService` 将用户数据存储在一个 MySQL 数据库中,因此 `UserRepositoryImpl` 也必须连接到相同的数据库去检索数据。下面是连接到数据库的代码。注意,我们正在使用 MySQL 的连接库。
```
from mysql.connector import connect, Error
class UserRepositoryImpl(UserRepository):
def fetch(self, name:Name) -> User:
try:
with connect(
host="mysqldb",
user="root",
password="admin",
database="glarimy",
) as connection:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM ums_users where name=%s", (name.value,))
row = cursor.fetchone()
if cursor.rowcount == -1:
raise UserNotFoundException()
else:
return User(Name(row[0]), PhoneNumber(row[1]), row[2])
except Error as e:
raise e
```
在上面的片段中,我们使用用户 `root` / 密码 `admin` 连接到一个名为 `mysqldb` 的数据库服务器,使用名为 `glarimy` 的数据库(模式)。在演示代码中是可以包含这些信息的,但在生产中不建议这么做,因为这会暴露敏感信息。
`fetch()` 操作的逻辑非常直观,它对 `ums_users` 表执行 SELECT 查询。回想一下,`AddService` 正在将用户数据写入同一个表中。如果 SELECT 查询没有返回记录,`fetch()` 函数将抛出 `UserNotFoundException` 异常。否则,它会从记录中构造 `User` 实体并将其返回给调用者。这没有什么特殊的。
### 应用层
最终,我们需要创建应用层。此模型如图 2 所示。它只包含两个类:控制器和一个 DTO。

众所周知,一个 DTO 只是一个没有任何业务逻辑的数据容器。它主要用于在 `FindService` 和外部之间传输数据。我们只是提供了在 REST 层中将 `UserRecord` 转换为字典以便用于 JSON 传输:
```
class UserRecord:
def toJSON(self):
return {
"name": self.name,
"phone": self.phone,
"since": self.since
}
```
控制器的工作是将 DTO 转换为用于域服务的域对象,反之亦然。可以从 `find()` 操作中观察到这一点。
```
class UserController:
def __init__(self):
self._repo = UserRepositoryImpl()
def find(self, name: str):
try:
user: User = self._repo.fetch(Name(name))
record: UserRecord = UserRecord()
record.name = user.name.value
record.phone = user.phone.value
record.since = user.since
return record
except UserNotFoundException as e:
return None
```
`find()` 操作接收一个字符串作为用户名,然后将其转换为 `Name` 对象,并调用 `UserRepository` 获取相应的 `User` 对象。如果找到了,则使用检索到的 `User`` 对象创建`UserRecord`。回想一下,将域对象转换为 DTO 是很有必要的,这样可以对外部服务隐藏域模型。
`UserController` 不需要有多个实例,它也可以是单例的。通过重写 `__new__`,可以将其建模为一个单例。
```
class UserController:
def __new__(self):
if not hasattr(self, ‘instance’):
self.instance = super().__new__(self)
return self.instance
def __init__(self):
self._repo = UserRepositoryImpl()
def find(self, name: str):
try:
user: User = self._repo.fetch(Name(name))
record: UserRecord = UserRecord()
record.name = user.name.getValue()
record.phone = user.phone.getValue()
record.since = user.since
return record
except UserNotFoundException as e:
return None
```
我们已经完全实现了 `FindService` 的模型,剩下的唯一任务是将其作为 REST 服务公开。
### REST API
`FindService` 只提供一个 API,那就是通过用户名查找用户。显然 URI 如下所示:
```
GET /user/{name}
```
此 API 希望根据提供的用户名查找用户,并以 JSON 格式返回用户的电话号码等详细信息。如果没有找到用户,API 将返回一个 404 状态码。
我们可以使用 Flask 框架来构建 REST API,它最初的目的是使用 Python 开发 Web 应用程序。除了 HTML 视图,它还进一步扩展到支持 REST 视图。我们选择这个框架是因为它足够简单。 创建一个 Flask 应用程序:
```
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
```
然后为 Flask 应用程序定义路由,就像函数一样简单:
```
@app.route('/user/<name>')
def get(name):
pass
```
注意 `@app.route` 映射到 API `/user/<name>`,与之对应的函数的 `get()`。
如你所见,每次用户访问 API 如 `http://server:port/user/Krishna` 时,都将调用这个 `get()` 函数。Flask 足够智能,可以从 URL 中提取 `Krishna` 作为用户名,并将其传递给 `get()` 函数。
`get()` 函数很简单。它要求控制器找到该用户,并将其与通常的 HTTP 头一起打包为 JSON 格式后返回。如果控制器返回 `None`,则 `get()` 函数返回合适的 HTTP 状态码。
```
from flask import jsonify, abort
controller = UserController()
record = controller.find(name)
if record is None:
abort(404)
else:
resp = jsonify(record.toJSON())
resp.status_code = 200
return resp
```
最后,我们需要 Flask 应用程序提供服务,可以使用 `waitress` 服务:
```
from waitress import serve
serve(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8080)
```
在上面的片段中,应用程序在本地主机的 8080 端口上提供服务。最终代码如下所示:
```
from flask import Flask, jsonify, abort
from waitress import serve
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/user/<name>')
def get(name):
controller = UserController()
record = controller.find(name)
if record is None:
abort(404)
else:
resp = jsonify(record.toJSON())
resp.status_code = 200
return resp
serve(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8080)
```
### 部署
`FindService` 的代码已经准备完毕。除了 REST API 之外,它还有域模型、数据层和应用程序层。下一步是构建此服务,将其容器化,然后部署到 Kubernetes 上。此过程与部署其他服务妹有任何区别,但有一些 Python 特有的步骤。
在继续前进之前,让我们来看下文件夹和文件结构:
```
+ ums-find-service
+ ums
- domain.py
- data.py
- app.py
- Dockerfile
- requirements.txt
- kube-find-deployment.yml
```
如你所见,整个工作文件夹都位于 `ums-find-service` 下,它包含了 `ums` 文件夹中的代码和一些配置文件,例如 `Dockerfile`、`requirements.txt` 和 `kube-find-deployment.yml`。
`domain.py` 包含域模型,`data.py` 包含 `UserRepositoryImpl`,`app.py` 包含剩余代码。我们已经阅读过代码了,现在我们来看看配置文件。
第一个是 `requirements.txt`,它声明了 Python 系统需要下载和安装的外部依赖项。我们需要用查找服务中用到的每个外部 Python 模块来填充它。如你所见,我们使用了 MySQL 连接器、Flask 和 Waitress 模块。因此,下面是 `requirements.txt` 的内容。
```
Flask==2.1.1
Flask_RESTful
mysql-connector-python
waitress
```
第二步是在 `Dockerfile` 中声明 Docker 相关的清单,如下:
```
FROM python:3.8-slim-buster
WORKDIR /ums
ADD ums /ums
ADD requirements.txt requirements.txt
RUN pip3 install -r requirements.txt
EXPOSE 8080
ENTRYPOINT ["python"]
CMD ["/ums/app.py"]
```
总的来说,我们使用 Python 3.8 作为基线,除了移动 `requirements.txt` 之外,我们还将代码从 `ums` 文件夹移动到 Docker 容器中对应的文件夹中。然后,我们指示容器运行 `pip3 install` 命令安装对应模块。最后,我们向外暴露 8080 端口(因为 waitress 运行在此端口上)。
为了运行此服务,我们指示容器使用使用以下命令:
```
python /ums/app.py
```
一旦 `Dockerfile` 准备完成,在 `ums-find-service` 文件夹中运行以下命令,创建 Docker 镜像:
```
docker build -t glarimy/ums-find-service
```
它会创建 Docker 镜像,可以使用以下命令查找镜像:
```
docker images
```
尝试将镜像推送到 Docker Hub,你也可以登录到 Docker。
```
docker login
docker push glarimy/ums-find-service
```
最后一步是为 Kubernetes 部署构建清单。
在之前的文章中,我们已经介绍了如何建立 Kubernetes 集群、部署和使用服务的方法。我假设仍然使用之前文章中的清单文件来部署添加服务、MySQL、Kafka 和 Zookeeper。我们只需要将以下内容添加到 `kube-find-deployment.yml` 文件中:
```
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ums-find-service
labels:
app: ums-find-service
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ums-find-service
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: ums-find-service
spec:
containers:
- name: ums-find-service
image: glarimy/ums-find-service
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ums-find-service
labels:
name: ums-find-service
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- port: 8080
selector:
app: ums-find-service
```
上面清单文件的第一部分声明了 `glarimy/ums-find-service` 镜像的 `FindService`,它包含三个副本。它还暴露 8080 端口。清单的后半部分声明了一个 Kubernetes 服务作为 `FindService` 部署的前端。请记住,在之前文章中,mysqldb 服务已经是上述清单的一部分了。
运行以下命令在 Kubernetes 集群上部署清单文件:
```
kubectl create -f kube-find-deployment.yml
```
部署完成后,可以使用以下命令验证容器组和服务:
```
kubectl get services
```
输出如图 3 所示:

它会列出集群上运行的所有服务。注意查找服务的外部 IP,使用 `curl` 调用此服务:
```
curl http://10.98.45.187:8080/user/KrishnaMohan
```
注意:10.98.45.187 对应查找服务,如图 3 所示。
如果我们使用 `AddService` 创建一个名为 `KrishnaMohan` 的用户,那么上面的 `curl` 命令看起来如图 4 所示:

用户管理系统(UMS)的体系结构包含 `AddService` 和 `FindService`,以及存储和消息传递所需的后端服务,如图 5 所示。可以看到终端用户使用 `ums-add-service` 的 IP 地址添加新用户,使用 `ums-find-service` 的 IP 地址查找已有用户。每个 Kubernetes 服务都由三个对应容器的节点支持。还要注意:同样的 mysqldb 服务用于存储和检索用户数据。

### 其他服务
UMS 系统还包含两个服务:`SearchService` 和 `JournalService`。在本系列的下一部分中,我们将在 Node 平台上设计这些服务,并将它们部署到同一个 Kubernetes 集群,以演示多语言微服务架构的真正魅力。最后,我们将观察一些与微服务相关的设计模式。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/python-microservices-using-flask-on-kubernetes/>
作者:[Krishna Mohan Koyya](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/krishna-mohan-koyya/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Microservices follow domain driven design (DDD), irrespective of the platform on which they are developed. Python microservices are not an exception. The object-oriented features of Python 3 make it even easier to model services on the lines of DDD. Part 10 of this series demonstrates how to deploy FindService of user management system as a Python microservice on Kubernetes.*
The power of microservices architecture lies partly in its polyglot nature. The enterprises decompose their functionality into a set of microservices and each team chooses a platform of its choice.
Our user management system was already decomposed into four microservices, namely, AddService, FindService, SearchService and JournalService. The AddService was developed on the Java platform and deployed on the Kubernetes cluster for resilience and scalability. This doesn’t mean that the remaining services are also developed on Java. We are free to choose a suitable platform for individual services.
Let us pick Python as the platform for developing the FindService. The model for FindService has already been designed (refer to the March 2022 issue of Open Source For You). We only need to convert this model into code and configuration.
## The Pythonic approach
Python is a general-purpose programming language that has been around for about three decades. In the early days, it was the first choice for automation scripting. However, with frameworks like Django and Flask, its popularity has been growing and it is now adopted in various other domains like enterprise application development. Data science and machine learning pushed the envelope further and Python is now one of the top three programming languages.
Many people attribute the success of Python to its ease of coding. This is only partially true. As long as your objective is to develop small scripts, Python is just like a toy. You love it. However, the moment you enter the domain of serious large-scale application development, you will have to handle lots of ifs and buts, and Python becomes as good as or as bad as any other platform. For example, take an object-oriented approach! Many Python developers may not even be aware of the fact that Python supports classes, inheritance, etc. Python does support full-blown object-oriented development, but in its own way — the Pythonic way! Let us explore it!
## The domain model
AddService adds the users to the system by saving the data into a MySQL database. The objective of the FindService is to offer a REST API to find the users by their name. The domain model is reproduced in Figure 1. It primarily consists of value objects like Name, PhoneNumber along with User entity and UserRepository.
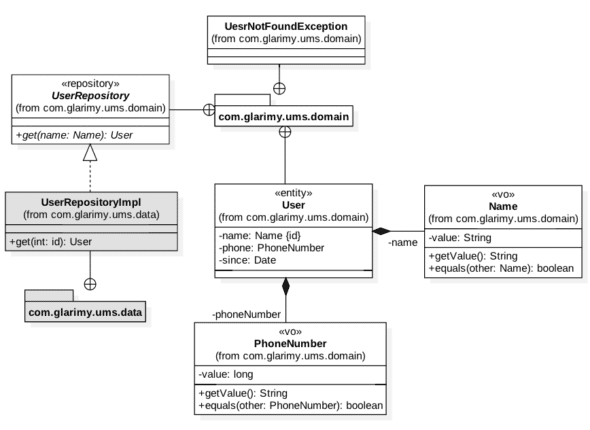

Let us begin with the Name. Since it is a value object, it must be validated by the time it is created and must remain immutable. The basic structure looks like this:
class Name: value: str def __post_init__(self): if self.value is None or len(self.value.strip()) < 8 or len(self.value.strip()) > 32: raise ValueError(“Invalid Name”)
As you can see, the Name consists of a value attribute of type str. As part of the post initialization, the value is validated.
Python 3.7 offers @dataclass decorator, which offers many features of a data-carrying class out-of-the-box like constructors, comparison operators, etc.
Following is the decorated Name:
from dataclasses import dataclass @dataclass class Name: value: str def __post_init__(self): if self.value is None or len(self.value.strip()) < 8 or len(self.value.strip()) > 32: raise ValueError(“Invalid Name”)
The following code can create an object Name:
name = Name(“Krishna”)
The value attribute can be read or written as follows:
name.value = “Mohan” print(name.value)
Another Name object can be compared as easily as follows:
other = Name(“Mohan) if name == other: print(“same”)
As you can see, the objects are compared by their values, not by their references. This is all out-of-the-box. We can also make the object immutable, by freezing. Here is the final version of Name as a value object:
from dataclasses import dataclass @dataclass(frozen=True) class Name: value: str def __post_init__(self): if self.value is None or len(self.value.strip()) < 8 or len(self.value.strip()) > 32: raise ValueError(“Invalid Name”)
The PhoneNumber also follows a similar approach, as it is also a value object:
@dataclass(frozen=True) class PhoneNumber: value: int def __post_init__(self): if self.value < 9000000000: raise ValueError(“Invalid Phone Number”)
The User class is an entity, not a value object. In other words, the User is not immutable. Here is the structure:
from dataclasses import dataclass import datetime @dataclass class User: _name: Name _phone: PhoneNumber _since: datetime.datetime def __post_init__(self): if self._name is None or self._phone is None: raise ValueError(“Invalid user”) if self._since is None: self.since = datetime.datetime.now()
You can observe that the User is not frozen as we want it to be mutable. However, we do not want all the properties mutable. The identity field like _name and fields like _since are not expected to be modified. Then, how can this be controlled?
Python 3 offers the so-called Descriptor protocol. It helps us in defining the getters and setters appropriately. Let us add the getters to all the three fields of User using the @property decorator:
@property def name(self) -> Name: return self._name @property def phone(self) -> PhoneNumber: return self._phone @property def since(self) -> datetime.datetime: return self._since
And the setter for the phone field can be added using @<field>.setter decoration:
@phone.setter def phone(self, phone: PhoneNumber) -> None: if phone is None: raise ValueError(“Invalid phone”) self._phone = phone
The User can also be given a method for easy print representation by overriding the __str__() function:
def __str__(self): return self.name.value + “ [“ + str(self.phone.value) + “] since “ + str(self.since)
With this the entities and the value objects of the domain model are ready. Creating an exception class is as easy as follows:
class UserNotFoundException(Exception): pass
The only other one remaining in the domain model is the UserRepository. Python offers a useful module called abc for building abstract methods and abstract classes. Since UserRepository is only an interface, we can use the abc package.
Any Python class that extends abc.ABC becomes abstract. Any function with the @abc.abstractmethod decorator becomes an abstract function. Here is the resultant structure of UserRepository:
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod class UserRepository(ABC): @abstractmethod def fetch(self, name:Name) -> User: pass
The UserRepository follows the repository pattern. In other words, it offers appropriate CRUD operations on the User entity without exposing the underlying data storage semantics. In our case, we need only fetch() operation since FindService only finds the users.
Since the UserRepository is an abstract class, we cannot create instance objects from this class. A concrete class must implement this abstract class for object creation.The data layer
The UserRepositoryImpl offers the concrete implementation of UserRepository:
class UserRepositoryImpl(UserRepository): def fetch(self, name:Name) -> User: pass
Since the AddService stores the data of the users in a MySQL database server, the UserRepositoryImpl also must connect to the same database server to retrieve the data. The code for connecting to the database is given below. Observe that we are using the connector library of MySQL.
from mysql.connector import connect, Error
class UserRepositoryImpl(UserRepository): def fetch(self, name:Name) -> User: try: with connect( host=”mysqldb”, user=”root”, password=”admin”, database=”glarimy”, ) as connection: with connection.cursor() as cursor: cursor.execute(“SELECT * FROM ums_users where name=%s”, (name.value,)) row = cursor.fetchone() if cursor.rowcount == -1: raise UserNotFoundException() else: return User(Name(row[0]), PhoneNumber(row[1]), row[2]) except Error as e: raise e
In the above snippet, we are connecting to a database server named mysqldb using root as the user and admin as the password, in order to use the database schema named glarimy. It is fine to have such information in the code for an illustration, but surely not a suggested approach in production as it exposes sensitive information.
The logic of the fetch() operation is quite intuitive. It executes a SELECT query against the ums_users table. Recollect that the AddService was writing the user data into the same table. In case the SELECT query returns no records, the fetch() function throws UserNotFoundException. Otherwise, it constructs the User entity from the record and returns it to the caller. Nothing unusual.
## The application layer
And finally, we need to build the application layer. The model is reproduced in Figure 2. It consists of just two classes: a controller and a DTO.
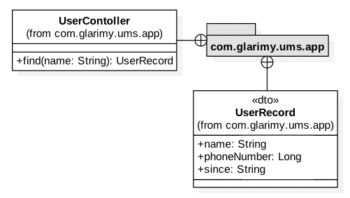

As we already know, a DTO is just a data container without any business logic. It is primarily used for carrying data between the FindService and the outside world. We just offer a way to convert the UserRecord into a dictionary for JSON marshalling in the REST layer:
class UserRecord: def toJSON(self): return { “name”: self.name, “phone”: self.phone, “since”: self.since }
The job of a controller is to convert DTOs to domain objects for invoking the domain services and vice versa, as can be observed in the find() operation.
class UserController: def __init__(self): self._repo = UserRepositoryImpl() def find(self, name: str): try: user: User = self._repo.fetch(Name(name)) record: UserRecord = UserRecord() record.name = user.name.value record.phone = user.phone.value record.since = user.since return record except UserNotFoundException as e: return None
The find() operation receives a string as a name, converts it as a Name object and invokes the UserRepository to fetch the corresponding User object. If it is found, a UserRecord is created by using the retrieved User object. Recollect that it is necessary to convert the domain objects as DTO to hide the domain model from the external world.
The UserController need not have multiple instances. It can be a singleton as well. By overriding the __new__ operation, it can be modelled as a singleton:
class UserController: def __new__(self): if not hasattr(self, ‘instance’): self.instance = super().__new__(self) return self.instance def __init__(self): self._repo = UserRepositoryImpl() def find(self, name: str): try: user: User = self._repo.fetch(Name(name)) record: UserRecord = UserRecord() record.name = user.name.getValue() record.phone = user.phone.getValue() record.since = user.since return record except UserNotFoundException as e: return None
We are done with implementing the model of the FindService fully. The only task remaining is to expose it as a REST service.
## The REST API
Our FindService offers only one API and that is to find a user by name. The obvious URI is as follows:
GET /user/{name}
This API is expected to find the user with the supplied name and returns the details of phone number, etc, of the user in JSON format. In case no such user is found, the API is expected to return a 404 status.
We can use the Flask framework to build the REST API. This framework was originally built for developing Web applications using Python. It is further extended to support the REST views besides the HTML views. We pick this framework for its simplicity.
Start by creating a Flask application:
from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__)
Then define the routes for the Flask application as simple functions:
@app.route(‘/user/<name>’) def get(name): pass
Observe that the @app.route is mapped to the API /user/<name> on one side and to the function get() on the other side.
As you may already have figured out, this get() function will be invoked every time the user accesses the API with a URI like http://server:port/user/Krishna. Flask is intelligent enough to extract ‘Krishna’ as the name from the URI and pass it to the get() function.
The get() function is straightforward. It asks the controller to find the user and returns the same after marshalling it to the JSON format along with the usual HTTP headers. In case the controller returns None, the get() function returns the response with an appropriate HTTP status.
from flask import jsonify, abort controller = UserController() record = controller.find(name) if record is None: abort(404) else: resp = jsonify(record.toJSON()) resp.status_code = 200 return resp
And, finally, the Flask app needs to be served. We can use the waitress server for this purpose.
from waitress import serve serve(app, host=”0.0.0.0”, port=8080)
In the above snippet, the app is served on port 8080 on the local host.
The final code looks like this:
from flask import Flask, jsonify, abort from waitress import serve app = Flask(__name__) @app.route(‘/user/<name>’) def get(name): controller = UserController() record = controller.find(name) if record is None: abort(404) else: resp = jsonify(record.toJSON()) resp.status_code = 200 return resp serve(app, host=”0.0.0.0”, port=8080)
## Deployment
The FindService is now ready with code. It has its domain model, data layer, and application layer besides the REST API. The next step is to build the service, containerise it, and then deploy it on Kubernetes. The process is in no way different from any other service, though there are some Python-specific steps.
Before proceeding further, let us have a look at the folder/file structure:
+ ums-find-service + ums - domain.py - data.py - app.py - Dockerfile - requirements.txt - kube-find-deployment.yml
As you can observe, the whole work is under the ums-find-service folder. It contains the code in the ums folder and configurations in Dockerfile, requirements.txt and kube-find-deployment.yml files.
The domain.py consists of the domain model classes, data.py consists of UserRepositoryImpl and app.py consists of the rest of the code. Since we have seen the code already, let us move on to the configuration files.
The first one is the file named requirements.txt. It declares the external dependencies for the Python system to download and install. We need to populate it with every external Python module that we use in the FindService. As you know, we used MySQL connector, Flask and Waitress modules. Hence the following is the content of the requirements.txt.
Flask==2.1.1 Flask_RESTful mysql-connector-python waitress
The second step is to declare the manifestation for dockerisation in Dockerfile. Here it is:
FROM python:3.8-slim-buster WORKDIR /ums ADD ums /ums ADD requirements.txt requirements.txt RUN pip3 install -r requirements.txt EXPOSE 8080 ENTRYPOINT [“python”] CMD [“/ums/app.py”]
In summary, we used Python 3.8 as the baseline and moved our code from the ums folder to a corresponding folder in the Docker container, besides moving the requirements.txt. Then we instructed the container to run the pip3 install command. And, finally, we exposed port 8080 (since the waitress was running on that port).
In order to run the service, we instructed the container to use the following command:
python /ums/app.py
Once the Dockerfile is ready, run the following command from within the ums-find-service folder to create the Dockerised image:
docker build -t glarimy/ums-find-service
It creates the Docker image, which can be found using the following command:
docker images
Try pushing the image to the Docker Hub as appropriate. You may log in to Docker as well.
docker login docker push glarimy/ums-find-service
And the last step is to build the manifest for the Kubernetes deployment.
We have already covered the way to set up the Kubernetes cluster, and deploy and use services, in the previous part. I am assuming that we still have the manifest file we used in the previous part for deploying the AddService, MySQL, Kafka and Zookeeper. We only need to add the following entries into the kube-find-deployment.yml file:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: ums-find-service labels: app: ums-find-service spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: app: ums-find-service template: metadata: labels: app: ums-find-service spec: containers: - name: ums-find-service image: glarimy/ums-find-service ports: - containerPort: 8080 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: ums-find-service labels: name: ums-find-service spec: type: LoadBalancer ports: - port: 8080 selector: app: ums-find-service
The first part of the above manifest declares a deployment of FindService from the image glarimy/ums-find-service with three replicas. It also exposes port 8080. And the latter part of the manifest declares a Kubernetes service as the front-end for the FindService deployment. Recollect that the MySQL service in the name of mysqldb was already part of the above manifest from the previous part.
Run the following command to deploy the manifest on a Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl create -f kube-find-deployment.yml
Once the deployment is finished, you can verify the pods and services using the following command:
kubectl get services
It gives an output as shown in Figure 3.
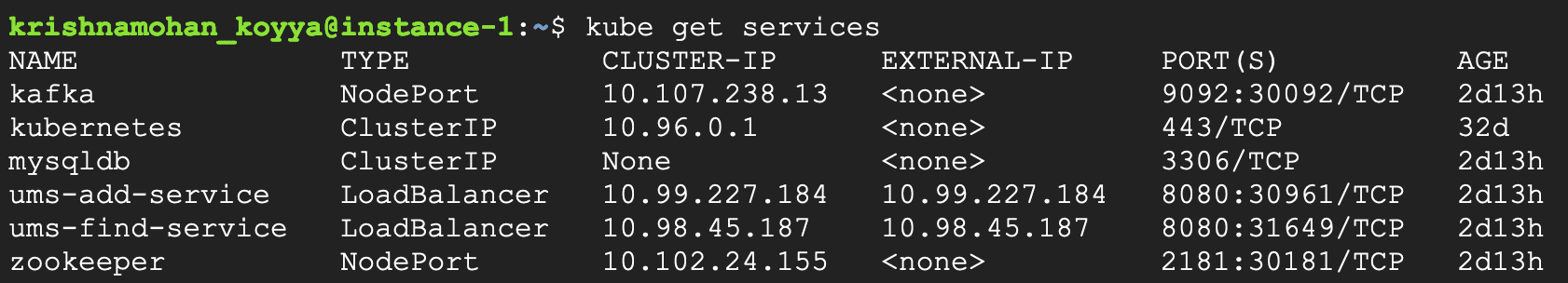

It lists all the services running on the cluster. Make a note of the external-ip of the FindService and use the curl command to invoke the service:
curl http://10.98.45.187:8080/user/KrishnaMohan
Note that the IP address 10.98.45.187 corresponds to the FindService, as found in Figure 3.
If we have used the AddService to create a user by the name KrishnaMohan, the above curl command looks like what is shown in Figure 4.


With the AddService and FindService, along with the required back-end services for storage and messaging, the architecture of the user management system (UMS) stands as shown in Figure 5, at this point. You can observe that the end-user uses the IP address of the ums-add-service for adding a new user, whereas it uses the IP address of the ums-find-service for finding existing users. Each of these Kubernetes services are backed by three pods with the corresponding containers. Also note that the same mysqldb service is used for storing and retrieving the user data.
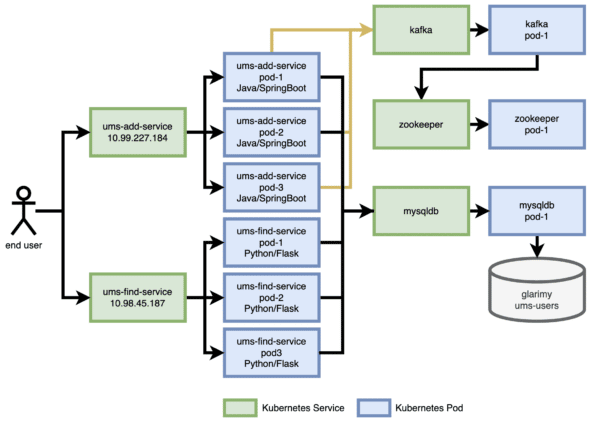

## What about the other services?
The UMS consists of two more services, namely, SearchService and JournalService. We will design these services in the next part of this series on the Node platform, and deploy them on the same Kubernetes cluster to demonstrate the real power of polyglot microservices architecture. We will conclude by observing some design patterns pertaining to microservices. |
15,155 | Xubuntu 22.10:热门新功能 | https://www.debugpoint.com/xubuntu-22-10-features/ | 2022-10-19T16:55:55 | [
"Xubuntu",
"Xfce"
] | /article-15155-1.html |
>
> 这是 Xubuntu 22.10 Kinetic Kudu 及其新功能的快速总结。
>
>
>

质量需要时间来建立。它适用于生活的各个方面,包括软件。
自 Xfce 4.16 发布以来,Xfce 4.17(开发版)已经被添加了许多新功能。这包括核心 Xfce、原生应用,GNOME 43、MATE 1.26 和 libadwaita。由于 Xfce 也是 GNOME 和 MATE 的组合,正确地合并和测试这些更改需要时间。
在 Xubuntu 22.10 Kinetic Kudu 版本中,你将体验到自 2020 年 12 月以来所做的所有改进:将近两年的错误修复和增强。
让我们快速查看一下时间表。目前,Xubuntu 22.10 beta 已经发布,并正在测试中(本问末尾提供了 ISO 链接)。最终版本预计于 2022 年 10 月 20 日发布。
### Xubuntu 22.10 新功能
#### 核心更新和 GNOME 框架
在其核心,Xubuntu 22.10 同其基于的 Ubuntu 22.10 一样,采用 Linux 内核 5.19。另外,Xfce 桌面版本是 Xfce 4.17。
4.17 版本是一个开发版,因为它是下一个大版本 Xfce 4.18 的基础,该版本 [计划在今年圣诞节发布](https://debugpointnews.com/xfce-4-18-announcement/)。
让我们谈谈 GNOME 和相关应用。 Xubuntu 22.10 中的 Xfce 4.17 首次获得了带有 GNOME 43 更新的 libadwaita。这意味着默认的 GNOME 应用程序可以在 Xfce 桌面下正确呈现。
这就是说,GNOME <ruby> 软件应用 <rt> Software </rt></ruby> 43 在 Xubuntu 22.10 的 Xfce 桌面下看起来很棒。如果你将其与 Xfce 原生外观和带有 CSD/SSD(例如 “<ruby> 磁盘应用 <rt> Disk </rt></ruby>”)的 GNOME 应用进行比较,它们看起来都很顺眼。
我对 GNOME 软件应用 43 在 Xfce 桌面下的 libadwaita/GTK4 渲染效果如此之好感到惊讶。

#### Xfce 应用
Xfce 桌面带来了自己的原生应用集。在此版本中,所有应用都从 4.16 升级到 4.17 版本。
值得注意的变化包括:Xfce 面板获得了对任务列表插件的中键单击支持,和托盘时钟中的二进制时间模式。PulseAudio 插件引入了一个新的录音指示器,可以过滤掉多个按钮按下事件。
Thunar 文件管理器获得了大量的底层功能和错误修复。如果你将 Thunar 4.16 与 Thunar 4.17 进行比较,它是变化巨大的。更改包括更新的上下文菜单、路径栏、搜索、导航等。你可以在 [此处](https://gitlab.xfce.org/xfce/thunar/-/blob/master/NEWS) 阅读 Thunar 的所有更改日志。
此外,截屏应用 ScreenShooter 默认支持 WebP。蓝牙管理器 Blueman 在系统托盘新增配置文件切换器,并更新了 Catfish 文件搜索工具。
这是 Xfce 应用版本的更新列表和指向其更改日志的链接(如果你想进一步挖掘)。
* Appfinder [4.17.0](https://gitlab.xfce.org/xfce/xfce4-appfinder/-/blob/master/NEWS)
* Catfish [4.16.4](https://gitlab.xfce.org/apps/catfish/-/blob/master/NEWS)
* Mousepad [0.5.10](https://gitlab.xfce.org/apps/mousepad/-/blob/master/NEWS)
* Panel [4.17.3](https://gitlab.xfce.org/xfce/xfce4-panel/-/blob/master/NEWS)
* PulseAudio 插件 [0.4.4](https://gitlab.xfce.org/panel-plugins/xfce4-pulseaudio-plugin/-/blob/master/NEWS)
* Ristretto [0.12.3](https://gitlab.xfce.org/apps/ristretto/-/blob/master/NEWS)
* Screenshooter [1.9.11](https://gitlab.xfce.org/apps/xfce4-screenshooter/-/blob/master/NEWS)
* Task Manager [1.5.4](https://gitlab.xfce.org/apps/xfce4-taskmanager/-/blob/master/NEWS)
* Terminal [1.0.4](https://gitlab.xfce.org/apps/xfce4-terminal/-/blob/master/NEWS)
* Thunar [4.17.9](https://gitlab.xfce.org/xfce/thunar/-/blob/master/NEWS)
#### 外观和感觉
默认的 elementary-xfce 图标集(浅色和深色)得到了更新,带有额外的精美图标,让你的 Xfce 桌面焕然一新。默认的 Greybird GTK 主题对窗口装饰进行了必要的改进,并添加了 Openbox 支持。
你可能会注意到的重要且可见的变化之一是 `ALT+TAB` 外观。图标更大一些,眼睛更舒适,可以在深色背景下更快地切换窗口。


上述更改使默认应用与其所基于的 [Ubuntu 22.10 版本](https://www.debugpoint.com/ubuntu-22-10/) 保持一致。以下是 Xubuntu 22.10 中的更改概括。
### 概括
* Linux 内核 5.19,基于 Ubuntu 22.10
* Xfce 桌面版 4.17
* 原生应用全部更新到 4.17
* 核心与 GNOME 43、libadwaita、GTK4 保持一致
* MATE 应用程序升级到 1.26
* Mozilla Firefox 网页浏览器 105.0
* Thunderbird 邮件客户端 102.3
* LibreOffice 7.4.4.2
### 总结
Xfce 桌面最关键的整体变化将在 4.18 版本中到来。例如,最初的 Wayland 支持、更新的 glib 和 GTK 包。如果一切顺利,你可以在明年 4 月发布的 Xubuntu 中期待这些最好的变化。
最后,如果你想试用,可以从 [这个页面](https://cdimage.ubuntu.com/xubuntu/releases/kinetic/beta/) 下载 Beta 镜像。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/xubuntu-22-10-features/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,157 | 来自开源爱好者的 7 本读物推荐 | https://opensource.com/article/22/6/2022-opensourcecom-summer-reading-list | 2022-10-20T11:55:00 | [
"书籍"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15157-1.html |
>
> 社区的成员们推荐这些书籍,涵盖了从有趣的悬疑小说到发人深省的非小说作品的各种类型,你一定能从中找到一本你想看的书!
>
>
>

很高兴能为大家介绍 [Opensource.com](http://Opensource.com) 的 2022 年暑期阅读清单。今年的榜单包含来自 [Opensource.com](http://Opensource.com) 社区成员的 7 本精彩的读物推荐。你可以发现各种各样的书籍,涵盖从有趣舒适的谜团到探索发人深省主题的非小说类作品。我希望你能在这个榜单中找到感兴趣的书本。
希望你喜欢!
### 《每个 Java 程序员都应该知道的 97 件事:专家的集体智慧》

>
> **《<ruby> <a href="https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/97-things-every/9781491952689/"> 每个 Java 程序员都应该知道的 97 件事:专家的集体智慧 </a> <rt> 97 Things Every Java Programmer Should Know: Collective Wisdom from the Experts </rt></ruby>》**
>
>
>
编辑:Kevlin Henney 和 Trisha Gee
*[由 Seth Kenlon 推荐](https://opensource.com/users/seth)*
这本书是由 73 位在软件行业工作的不同作者共同撰写。它的优秀之处在于它不仅仅适用于 Java 编程。当然,有些章节会涉及 Java,但是也还有一些其他话题,例如了解你的容器环境、如何更快更好地交付软件、以及不要隐藏你的开发工具,这些适用于任何语言的开发。
更好的是,有些章节同样适用于生活中的问题。将问题和任务分成小的部分是解决任何问题的好建议;建立多样化的团队对所有合作者都很重要;由从散乱的一块块拼图到拼好的完成品,看起来像是拼图玩家的思路,也适用于不同的工作角色。
每章只有几页,总共有 97 个章节,你可以轻松跳过不适用于你自己的章节。无论你是一直在写 Java 代码、或者只是学过一点 Java,亦或是尚未开始学习 Java,对于对代码和软件开发过程感兴趣的极客来说,这都会是一本好书。
### 《城市不是计算机:其他的城市智能》

>
> **《<ruby> <a href="https://press.princeton.edu/books/paperback/9780691208053/a-city-is-not-a-computer"> 城市不是计算机:其他的城市智能 </a> <rt> A City is Not a Computer: Other Urban Intelligences </rt></ruby>》**
>
>
>
作者:Shannon Mattern
*[由 Scott Nesbitt 推荐](https://opensource.com/users/scottnesbitt)*
如今,让一切变得智能已经成为一种 *时尚*:我们的手机、家用电器、手表、汽车,甚至是城市都变得智能化了。
对于城市的智能化,这意味着传感器变得无处不在,在我们开展业务时收集数据,并根据这些数据向我们推送信息(无论数据有用与否)。
这就引出了一个问题,将所有高科技技术嵌入到城市中是否会使得城市智能化呢?在《城市不是计算机》这本书中,作者 Shannon Mattern 认为并不是这样的。
城市智能化的目标之一是为市民提供服务和更好的城市参与感。Mattern 指出,但是实际上,智慧城市“希望将技术专家的管理想法与公共服务相融合,从而将公民重新设置为‘消费者’和‘用户’”,然而,这并不是在鼓励公民积极参与城市的生活和治理。
第二个问题是关于智慧城市收集的数据。我们不知道收集了什么数据,以及收集了多少数据。我们也不知道这些数据使用在什么地方,以及是谁使用的。收集的数据太多了,以至于处理数据的市政工作人员会不堪重负。他们无法处理所有数据,因此他们专注于短期容易实现的任务,而忽略了更深层次和更紧迫的问题。这绝对达不到在推广智慧城市时所承诺的目标:智慧城市将成为解决城市困境的良药。
《城市不是计算机》是一本短小精悍、经过深入研究的、反对拥抱智慧城市的论证。这本书让我们思考智慧城市的真正目的:要让百姓真正受益于城市智能化,并引发我们的思考:发展智慧城市是否必要呢。
### 《git sync 谋杀案》

>
> **《<ruby> <a href="https://mwl.io/fiction/crime#gsm"> git sync 谋杀案 </a> <rt> git sync murder </rt></ruby>》**
>
>
>
作者:Michael Warren Lucas
*[由 Joshua Allen Holm 推荐](https://opensource.com/users/holmja)*
Dale Whitehead 宁愿呆在家里,通过他的电脑终端与世界连接,尤其是在他参加的最后一次会议上发生的事情之后。在那次会议上,Dale 扮演了一个业余侦探的角色,解决了一桩谋杀案。你可以在该系列的第一本书《<ruby> git commit 谋杀案 <rt> git commit murder </rt></ruby>》中读到那个案件。
现在,Dale 回到家,参加另一个会议,他再次发现自己成为了侦探。在《<ruby> git sync 谋杀案 <rt> git sync murder </rt></ruby>》中,Dale 参加了一个当地科技会议/科幻大会,会议上发现一具尸体。这是谋杀,还是只是一场意外?现在,Dale 是这些问题的“专家”,他发现自己被卷入了这件事,并要亲自去弄清楚到底发生了什么。再多说的话就剧透了,所以我能说《git sync 谋杀案》这本书十分引人入胜,而且读起来很有趣。不必先阅读《git commit 谋杀案》,才能阅读《git sync 谋杀案》,但我强烈推荐一起阅读该系列中的这两本书。
作者 Michael Warren Lucas 的《git 谋杀案》系列非常适合喜欢悬疑小说的科技迷。Lucas 写过很多复杂的技术题材的书,这本书也延续了他的技术题材,《git sync 谋杀案》这本书中的人物在会议活动上谈论技术话题。如果你因为新冠疫情,最近没有参加过会议,怀念参会体验的话,Lucas 将带你参加一个技术会议,其中还有一个谋杀之谜以待解决。Dale Whitehead 是一个有趣的业余侦探,我相信大多数读者会喜欢和 Dale 一起参加技术会议,并充当侦探破解谜案的。
### 《像女孩一样踢球》

>
> **《<ruby> <a href="https://innerwings.org/books/kick-like-a-girl"> 像女孩一样踢球 </a> <rt> Kick Like a Girl </rt></ruby>》**
>
>
>
作者:Melissa Di Donato Roos
*[由 Joshua Allen Holm 推荐](https://opensource.com/users/holmja)*
没有人喜欢被孤立,当女孩 Francesca 想在公园里踢足球时,她也是这样。男孩们不会和她一起玩,因为她是女孩,所以她不高兴地回家了。她的母亲安慰她,讲述了有重要影响力的著名女性的故事。《像女孩一样踢球》中详述的历史人物包括历史中来自许多不同领域的女性。读者将了解 Frida Kahlo、Madeleine Albright、<ruby> 阿达·洛芙莱斯 <rt> Ada Lovelace </rt></ruby>、Rosa Parks、Amelia Earhart、<ruby> 玛丽·居里 <rt> Marie Curie </rt></ruby>(居里夫人)、Valentina Tereshkova、<ruby> 弗洛伦斯·南丁格尔 <rt> Florence Nightingale </rt></ruby> 和 Malala Yousafzai 的故事。听完这些鼓舞人心的人物故事后,Francesca 回到公园,向男孩们发起了一场足球挑战。
《像女孩一样踢球》这本书的特色是作者 Melissa Di Donato Roos(SUSE 的 CEO,LCTT 译注:SUSE 是一家总部位于德国的软件公司,创立于 1992 年,以提供企业级 Linux 为主要业务)引人入胜的写作和 Ange Allen 的出色插图。这本书非常适合年轻读者,他们会喜欢押韵的文字和书中的彩色插图。Melissa Di Donato Roos 还写了另外两本童书,《<ruby> 美人鱼如何便便 <rt> How Do Mermaids Poo? </rt></ruby>》和《<ruby> 魔盒 <rt> The Magic Box </rt></ruby>》,这两本书也都值得一读。
### 《这是我的!:所有权的潜规则如何控制着我们的生活》

>
> **《<ruby> <a href="https://www.minethebook.com/"> 这是我的!:所有权的潜规则如何控制着我们的生活 </a> <rt> Mine!: How the Hidden Rules of Ownership Control Our Lives </rt></ruby>》**
>
>
>
作者:Michael Heller 和 James Salzman
*[由 Bryan Behrenshausen 推荐](https://opensource.com/users/bbehrens)*
作者 Michael Heller 和 James Salzman 在文章《这是我的!》中写道:“你对所有权的很多了解都是错误的”。这是一种被吸引到开源领域的人不得不接受所有权规则的对抗性邀请。这本书肯定是为开源爱好者而写的,他们对代码、思想、各种知识产权的所有权的看法往往与主流观点和普遍接受的认知不同。在本书中,Heller 和 Salzman 列出了“所有权的隐藏规则”,这些规则管理着谁能控制对什么事物的访问。这些所有权规则是微妙的、强大的、有着深刻的历史惯例。这些所有权规则已经变得如此普遍,以至于看起来无可争议,这是因为“先到先得”或“种瓜得瓜,种豆得豆”的规则已经成为陈词滥调。然而,我们看到它们无处不在:在飞机上,为宝贵的腿部空间而战;在街道上,邻居们为铲好雪的停车位发生争执;在法庭上,陪审团决定谁能控制你的遗产和你的 DNA。在当下的数字时代,所有权的替代理论能否为重新思考基本权利创造空间?作者们认为这是可以的。如果这是正确的,我们可能会回应:在未来,开源软件能否成为所有权运作的模型呢?
### 《并非所有童话故事都有幸福的结局:雪乐山公司的兴衰》

>
> **《<ruby> <a href="https://kensbook.com/"> 并非所有童话故事都有幸福的结局:雪乐山公司的兴衰 </a> <rt> Not All Fairy Tales Have Happy Endings: The Rise and Fall of Sierra On-Line </rt></ruby>》**
>
>
>
作者:Ken Williams
*[由 Joshua Allen Holm 推荐](https://opensource.com/users/holmja)*
在 1980 年代和 1990 年代,<ruby> 雪乐山公司 <rt> Sierra On-Line </rt></ruby>是计算机软件行业的巨头。这家由 Ken 和 Roberta Williams 夫妻创立的公司,出身并不起眼,但却发布了许多标志性的电脑游戏。《<ruby> 国王密使 <rt> King's Quest </rt></ruby>》、《<ruby> 宇宙传奇 <rt> Space Quest </rt></ruby>》、《<ruby> 荣耀任务 <rt> Quest for Glory </rt></ruby>》、《Leisure Suit Larry》 和 《<ruby> 狩魔猎人 <rt> Gabriel Knight </rt></ruby>》 只是该公司几个最大的专属系列中的很小一部分。
《并非所有童话故事都有幸福的结局》这本书,涵盖了从雪乐山公司发布第一款游戏 《<ruby> <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mystery_House"> 神秘屋 </a> <rt> Mystery House </rt></ruby>》,到该公司不幸地被 CUC 国际公司收购以及后续的所有内容。雪乐山品牌在被收购后仍存活了一段时间,但 Williams 创立的雪乐山已不复存在。Ken Williams 以一种只有他才能做到的方式,讲述了雪乐山公司的整个历史。雪乐山的历史叙述穿插了一些 Williams 提出的管理和计算机编程建议的章节。虽然 Ken Williams 在写这本书时,已经离开这个行业很多年了,但他的建议仍然非常重要。
虽然雪乐山公司已不复存在,但该公司对计算机游戏行业产生了持久的影响。对于任何对计算机软件历史感兴趣的人来说,《并非所有童话故事都有美好的结局》都是值得一读的。雪乐山公司在其鼎盛时期处于游戏开发的最前沿,从带领公司走过那个激动人心的岁月的 Ken Williams 身上,我们可以学到许多宝贵的经验。
### 《新机器的灵魂》

>
> **《<ruby> <a href="https://www.hachettebookgroup.com/titles/tracy-kidder/the-soul-of-a-new-machine/9780316204552/"> 新机器的灵魂 </a> <rt> The Soul of a New Machine </rt></ruby>》**
>
>
>
作者:Tracy Kidder
*[由 Guarav Kamathe 推荐](https://opensource.com/users/gkamathe)*
我是计算机历史的狂热读者。知道这些人们如此依赖(并且经常被认为是理所当然)的计算机是如何形成的,真是令人着迷!我是在 [Bryan Cantrill](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bryan_Cantrill) 的博客文章中,第一次听说 《[新机器的灵魂](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Soul_of_a_New_Machine)》这本书的。这是一本由 [Tracy Kidder](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tracy_Kidder) 编著的非虚构书籍,于 1981 年出版,作者 Tracy Kidder也因此获得了 [普利策奖](https://www.pulitzer.org/winners/tracy-kidder)。故事发生在 1970 年代,想象一下你是负责设计 [下一代计算机](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_General_Eclipse_MV/8000) 工程团队中的一员。故事的背景是在<ruby> 通用数据公司 <rt> Data General Corporation </rt></ruby>,该公司当时是一家小型计算机供应商,正在与美国<ruby> 数字设备公司 <rt> Digital Equipment Corporation </rt></ruby>(DEC)的 32 位 VAX 计算机相竞争。该书概述了通用数据公司内部两个相互竞争的团队,都想在设计新机器上一展身手,结果导致了一场争斗。接下来,细致地描绘了随之展开的事件。这本书深入地讲述了相关工程师的思想、他们的工作环境、他们在此过程中面临的技术挑战、他们是如何克服这些困难的、以及压力如何影响到了他们的个人生活等等。任何想知道计算机是怎么制造出来的人都应该阅读这本书。
以上就是 2022 年的推荐阅读书目。它提供了很多非常棒的选择,我相信读者们能得到数小时发人深省的阅读时光。想获取更多书籍推荐,请查看我们历年的阅读书目。
* [2021 年 Opensource.com 推荐阅读书目](https://opensource.com/article/21/6/2021-opensourcecom-summer-reading-list)
* [2020 年 Opensource.com 推荐阅读书目](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/summer-reading-list)
* [2019 年 Opensource.com 推荐阅读书目](https://opensource.com/article/19/6/summer-reading-list)
* [2018 年 Open Organization 推荐阅读书目](https://opensource.com/open-organization/18/6/summer-reading-2018)
* [2016 年 Opensource.com 推荐阅读书目](https://opensource.com/life/16/6/2016-summer-reading-list)
* [2015 年 Opensource.com 推荐阅读书目](https://opensource.com/life/15/6/2015-summer-reading-list)
* [2014 年 Opensource.com 推荐阅读书目](https://opensource.com/life/14/6/annual-reading-list-2014)
* [2013 年 Opensource.com 推荐阅读书目](https://opensource.com/life/13/6/summer-reading-list-2013)
* [2012 年 Opensource.com 推荐阅读书目](https://opensource.com/life/12/7/your-2012-open-source-summer-reading)
* [2011 年 Opensource.com 推荐阅读书目](https://opensource.com/life/11/7/summer-reading-list)
* [2010 年 Opensource.com 推荐阅读书目](https://opensource.com/life/10/8/open-books-opensourcecom-summer-reading-list)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/6/2022-opensourcecom-summer-reading-list>
作者:[Joshua Allen Holm](https://opensource.com/users/holmja) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | It is my great pleasure to introduce Opensource.com's 2022 summer reading list. This year's list contains seven wonderful reading recommendations from members of the Opensource.com community. You will find a nice mix of books covering everything from a fun cozy mystery to non-fiction works that explore thought-provoking topics. I hope you find something on this list that interests you.
Enjoy!

O'Reilly Press
[97 Things Every Java Programmer Should Know: Collective Wisdom from the Experts](https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/97-things-every/9781491952689/), edited by Kevlin Henney and Trisha Gee
*Recommendation written by Seth Kenlon*
Written by 73 different authors working in all aspects of the software industry, the secret to this book's greatness is that it actually applies to much more than just Java programming. Of course, some chapters lean into Java, but there are topics like Be aware of your container surroundings, Deliver better software, faster, and Don't hIDE your tools that apply to development regardless of language.
Better still, some chapters apply to life in general. Break problems and tasks into small chunks is good advice on how to tackle any problem, Build diverse teams is important for every group of collaborators, and From puzzles to products is a fascinating look at how the mind of a puzzle-solver can apply to many different job roles.
Each chapter is just a few pages, and with 97 to choose from, it's easy to skip over the ones that don't apply to you. Whether you write Java code all day, just dabble, or if you haven't yet started, this is a great book for geeks interested in code and the process of software development.
Princeton University Press
[A City is Not a Computer: Other Urban Intelligences](https://press.princeton.edu/books/paperback/9780691208053/a-city-is-not-a-computer), by Shannon Mattern
*Recommendation written by Scott Nesbitt*
These days, it's become fashionable (if not inevitable) to make everything *smart*: Our phones, our household appliances, our watches, our cars, and, especially, our cities.
With the latter, that means putting sensors everywhere, collecting data as we go about our business, and pushing information (whether useful or not) to us based on that data.
This begs the question, does embedding all that technology in a city make it smart? In *A City Is Not a Computer*, Shannon Mattern argues that it doesn't.
A goal of making cities smart is to provide better engagement with and services to citizens. Mattern points out that smart cities often "aim to merge the ideologies of technocratic managerialism and public service, to reprogram citizens as 'consumers' and 'users'." That, instead of encouraging citizens to be active participants in their cities' wider life and governance.
Then there's the data that smart systems collect. We don't know what and how much is being gathered. We don't know how it's being used and by whom. There's *so much* data being collected that it overwhelms the municipal workers who deal with it. They can't process it all, so they focus on low-hanging fruit while ignoring deeper and more pressing problems. That definitely wasn't what cities were promised when they were sold smart systems as a balm for their urban woes.
*A City Is Not a Computer* is a short, dense, well-researched polemic against embracing smart cities because technologists believe we should. The book makes us think about the purpose of a smart city, who really benefits from making a city smart, and makes us question whether we need to or even should do that.

Tilted Windmill Press
[git sync murder](https://mwl.io/fiction/crime#gsm), by Michael Warren Lucas
*Recommendation written by Joshua Allen Holm*
Dale Whitehead would rather stay at home and connect to the world through his computer's terminal, especially after what happened at the last conference he attended. During that conference, Dale found himself in the role of an amateur detective solving a murder. You can read about that case in the first book in this series, *git commit murder*.
Now, back home and attending another conference, Dale again finds himself in the role of detective. *git sync murder* finds Dale attending a local tech conference/sci-fi convention where a dead body is found. Was it murder or just an accident? Dale, now the "expert" on these matters, finds himself dragged into the situation and takes it upon himself to figure out what happened. To say much more than that would spoil things, so I will just say *git sync murder* is engaging and enjoyable to read. Reading *git commit murder* first is not necessary to enjoy *git sync murder*, but I highly recommend both books in the series.
Michael Warren Lucas's *git murder* series is perfect for techies who also love cozy mysteries. Lucas has literally written the book on many complex technical topics, and it carries over to his fiction writing. The characters in *git sync murder* talk tech at conference booths and conference social events. If you have not been to a conference recently because of COVID and miss the experience, Lucas will transport you to a tech conference with the added twist of a murder mystery to solve. Dale Whitehead is an interesting, if somewhat unorthodox, cozy mystery protagonist, and I think most Opensource.com readers would enjoy attending a tech conference with him as he finds himself thrust into the role of amateur sleuth.

Inner Wings Foundation
[Kick Like a Girl](https://innerwings.org/books/kick-like-a-girl), by Melissa Di Donato Roos
*Recommendation written by Joshua Allen Holm*
Nobody likes to be excluded, but that is what happens to Francesca when she wants to play football at the local park. The boys won't play with her because she's a girl, so she goes home upset. Her mother consoles her by relating stories about various famous women who have made an impact in some significant way. The historical figures detailed in *Kick Like a Girl* include women from throughout history and from many different fields. Readers will learn about Frida Kahlo, Madeleine Albright, Ada Lovelace, Rosa Parks, Amelia Earhart, Marie Curie, Valentina Tereshkova, Florence Nightingale, and Malala Yousafzai. After hearing the stories of these inspiring figures, Francesca goes back to the park and challenges the boys to a football match.
*Kick Like a Girl* features engaging writing by Melissa Di Donato Roos (SUSE's CEO) and excellent illustrations by Ange Allen. This book is perfect for young readers, who will enjoy the rhyming text and colorful illustrations. Di Donato Roos has also written two other books for children, *How Do Mermaids Poo?* and *The Magic Box*, both of which are also worth checking out.

Doubleday
[Mine!: How the Hidden Rules of Ownership Control Our Lives](https://www.minethebook.com/), by Michael Heller and James Salzman
*Recommendation written by Bryan Behrenshausen*
"A lot of what you know about ownership is wrong," authors Michael Heller and James Salzman write in *Mine!* It's the kind of confrontational invitation people drawn to open source can't help but accept. And this book is certainly one for open source aficionados, whose views on ownership—of code, of ideas, of intellectual property of all kinds—tend to differ from mainstream opinions and received wisdom. In this book, Heller and Salzman lay out the "hidden rules of ownership" that govern who controls access to what. These rules are subtle, powerful, deeply historical conventions that have become so commonplace they just seem incontrovertible. We know this because they've become platitudes: "First come, first served" or "You reap what you sow." Yet we see them play out everywhere: On airplanes in fights over precious legroom, in the streets as neighbors scuffle over freshly shoveled parking spaces, and in courts as juries decide who controls your inheritance and your DNA. Could alternate theories of ownership create space for rethinking some essential rights in the digital age? The authors certainly think so. And if they're correct, we might respond: Can open source software serve as a model for how ownership works—or doesn't—in the future?

Lulu.com
[Not All Fairy Tales Have Happy Endings: The Rise and Fall of Sierra On-Line](https://kensbook.com/), by Ken Williams
*Recommendation written by Joshua Allen Holm*
During the 1980s and 1990s, Sierra On-Line was a juggernaut in the computer software industry. From humble beginnings, this company, founded by Ken and Roberta Williams, published many iconic computer games. King's Quest, Space Quest, Quest for Glory, Leisure Suit Larry, and Gabriel Knight are just a few of the company's biggest franchises.
*Not All Fairy Tales Have Happy Endings* covers everything from the creation of Sierra's first game, [Mystery House](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mystery_House), to the company's unfortunate and disastrous acquisition by CUC International and the aftermath. The Sierra brand would live on for a while after the acquisition, but the Sierra founded by the Williams was no more. Ken Williams recounts the entire history of Sierra in a way that only he could. His chronological narrative is interspersed with chapters providing advice about management and computer programming. Ken Williams had been out of the industry for many years by the time he wrote this book, but his advice is still extremely relevant.
Sierra On-Line is no more, but the company made a lasting impact on the computer gaming industry. *Not All Fairy Tales Have Happy Endings* is a worthwhile read for anyone interested in the history of computer software. Sierra On-Line was at the forefront of game development during its heyday, and there are many valuable lessons to learn from the man who led the company during those exciting times.

Back Bay Books
[The Soul of a New Machine](https://www.hachettebookgroup.com/titles/tracy-kidder/the-soul-of-a-new-machine/9780316204552/), by Tracy Kidder
*Recommendation written by Gaurav Kamathe*
I am an avid reader of the history of computing. It's fascinating to know how these intelligent machines that we have become so dependent on (and often take for granted) came into being. I first heard of [The Soul of a New Machine](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Soul_of_a_New_Machine) via [Bryan Cantrill](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bryan_Cantrill)'s [blog post](http://dtrace.org/blogs/bmc/2019/02/10/reflecting-on-the-soul-of-a-new-machine/). This is a non-fiction book written by [Tracy Kidder](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tracy_Kidder) and published in 1981 for which he [won a Pulitzer prize](https://www.pulitzer.org/winners/tracy-kidder). Imagine it's the 1970s, and you are part of the engineering team tasked with designing the [next generation computer](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_General_Eclipse_MV/8000). The backdrop of the story begins at Data General Corporation, a then mini-computer vendor who was racing against time to compete with the 32-bit VAX computers from Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). The book outlines how two competing teams within Data General, both wanting to take a shot at designing the new machine, results in a feud. What follows is a fascinating look at the events that unfold. The book provides insights into the minds of the engineers involved, the management, their work environment, the technical challenges they faced along the way and how they overcame them, how stress affected their personal lives, and much more. Anybody who wants to know what goes into making a computer should read this book.
There is the 2022 suggested reading list. It provides a variety of great options that I believe will provide Opensource.com readers with many hours of thought-provoking entertainment. Be sure to check out our previous reading lists for even more book recommendations.
[2021 Opensource.com summer reading list](https://opensource.com/article/21/6/2021-opensourcecom-summer-reading-list)[2020 Opensource.com summer reading list](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/summer-reading-list)[2019 Opensource.com summer reading list](https://opensource.com/article/19/6/summer-reading-list)[2018 Open Organization summer reading list](https://opensource.com/open-organization/18/6/summer-reading-2018)[2016 Opensource.com summer reading list](https://opensource.com/life/16/6/2016-summer-reading-list)[2015 Opensource.com summer reading list](https://opensource.com/life/15/6/2015-summer-reading-list)[2014 Opensource.com summer reading list](https://opensource.com/life/14/6/annual-reading-list-2014)[2013 Opensource.com summer reading list](https://opensource.com/life/13/6/summer-reading-list-2013)[2012 Opensource.com summer reading list](https://opensource.com/life/12/7/your-2012-open-source-summer-reading)[2011 Opensource.com summer reading list](https://opensource.com/life/11/7/summer-reading-list)[2010 Opensource.com summer reading list](https://opensource.com/life/10/8/open-books-opensourcecom-summer-reading-list)
## 1 Comment |
15,158 | 在 Linux 中如何从命令行查找默认网关的 IP 地址 | https://ostechnix.com/find-default-gateway-linux/ | 2022-10-20T16:16:10 | [
"网关"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15158-1.html | 
>
> Linux 下查找网关或路由器 IP 地址的 5 种方法。
>
>
>
**网关** 是一个节点或一个路由器,当连接到同一路由器时,它允许两个或多个 IP 地址不同的主机相互通信。如果没有网关,它们将无法相互通信。换句话说,网关充当接入点,将网络数据从本地网络传输到远程网络。在本指南中,我们将看到在 Linux 和 Unix 中从命令行找到默认网关的所有可能方法。
### 在 Linux 中查找默认网关
Linux 中有各种各样的命令行工具可用于查看网关 IP 地址。最常用的工具是:`ip`、`ss` 和 `netcat`。我们将通过示例了解如何使用每种工具查看默认网关。
#### 1、使用 ip 命令查找默认网关
`ip` 命令用于显示和操作 Linux 中的路由、网络设备、接口和隧道。
要查找默认网关或路由器 IP 地址,只需运行:
```
$ ip route
```
或者:
```
$ ip r
```
或者:
```
$ ip route show
```
示例输出:
```
default via 192.168.1.101 dev eth0 proto static metric 100
172.17.0.0/16 dev docker0 proto kernel scope link src 172.17.0.1 linkdown
192.168.1.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.20 metric 100
```
你从输出中看到了 `default via 192.168.1.101` 这一行吗?它就是默认网关。我的默认网关是 `192.168.1.101`。
你可以使用 `-4` 参数只`显示 IPv4 网关`:
```
$ ip -4 route
```
或者,使用 `-6` 参数只**显示 IPv6 网关**:
```
$ ip -6 route
```
如你所见,IP 地址和子网详细信息也一并显示了。如果你想只显示默认网关,排除所有其他细节,可以使用 `ip route` 搭配 `awk` 命令,如下所示。
使用 `ip route` 和 `awk` 命令打印网关地址,执行命令:
```
$ ip route | awk '/^default/{print $3}'
```
(LCTT 译注:wsl1 上无输出结果,正常 Linux 发行版无问题)
或者:
```
$ ip route show default | awk '{print $3}'
```
这将只列出网关 IP:
示例输出:
```
192.168.1.101
```

你也可以使用 [grep](https://ostechnix.com/the-grep-command-tutorial-with-examples-for-beginners/) 命令配合 `ip route` 对默认网关进行过滤。
使用 `ip route` 和 `grep` 查找默认网关 IP 地址,执行命令:
```
$ ip route | grep default
default via 192.168.1.101 dev eth0 proto static metric 100
```
在最新的 Linux 发行版中,`ip route` 是查找默认网关 IP 地址的推荐命令。然而,你们中的一些人可能仍然在使用传统的工具,如 `route` 和 `netstat`。旧习难改,对吧?下面的部分将介绍如何在 Linux 中使用 `route` 和 `netstat` 命令确定网关。
#### 2、使用 route 命令显示默认网关 IP 地址
`route` 命令用于在较老的 Linux 发行版中显示和操作路由表,如 RHEL 6、CentOS 6 等。
如果你正在使用较老的 Linux 发行版,你可以使用 `route` 命令来显示默认网关。
请注意,在最新的 Linux 发行版中,`route` 工具已被弃用,`ip route` 命令取而代之。如果你因为某些原因仍然想使用 `route`,你需要安装它。
首先,我们需要检查哪个包提供了 `route` 命令。为此,在基于 RHEL 的系统上运行以下命令:
```
$ dnf provides route
```
示例输出:
```
net-tools-2.0-0.52.20160912git.el8.x86_64 : Basic networking tools
Repo : @System
Matched from:
Filename : /usr/sbin/route
net-tools-2.0-0.52.20160912git.el8.x86_64 : Basic networking tools
Repo : baseos
Matched from:
Filename : /usr/sbin/route
```
如你所见,`net-tools` 包提供了 `route` 命令。所以,让我们使用以下命令来安装它:
```
$ sudo dnf install net-tools
```
现在,运行带有 `-n` 参数的 `route` 命令来显示 Linux 系统中的网关或路由器 IP 地址:
```
$ route -n
```
示例输出:
```
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 192.168.1.101 0.0.0.0 UG 100 0 0 eth0
172.17.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 docker0
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 100 0 0 eth0
```

如你所见,网关 IP 地址是 192.168.1.101。你还将在 Flags 下面看到两个字母 `UG`。字母 `U` 代表接口是 “Up”(在运行),`G` 表示 “Gateway”(网关)。
#### 3、使用 netstat 命令查看网关 IP 地址
`netstat` 会输出 Linux 网络子系统的信息。使用 `netstat` 工具,我们可以在 Linux 和 Unix 系统中打印网络连接、路由表、接口统计信息、伪装连接和组播成员关系。
`netstat` 是 `net-tools` 包的一部分,所以确保你已经在 Linux 系统中安装了它。使用以下命令在基于 RHEL 的系统中安装它:
```
$ sudo dnf install net-tools
```
使用 netstat 命令打印默认网关 IP 地址:
```
$ netstat -rn
```
示例输出:
```
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface
0.0.0.0 192.168.1.101 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
172.17.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 docker0
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
```

`netstat` 命令与 `route` 命令的输出信息相同。如上输出可知,网关的 IP 地址为 `192.168.1.191`,`UG` 表示网关连接的网卡是有效的,`G` 表示网关。
请注意 `netstat` 也已弃用,建议使用 `ss` 命令代替 `netstat`。
#### 4、使用 routel 命令打印默认网关或路由器 IP 地址
`routel` 是一个脚本,它以一种漂亮格式的输出路由。`routel` 脚本的输出让一些人认为比 `ip route` 列表更直观。
`routel` 脚本也是 `net-tools` 包的一部分。
打印默认网关或路由器 IP 地址,不带任何参数运行 `routel` 脚本,如下所示:
```
$ routel
```
示例输出:
```
target gateway source proto scope dev tbl
default 192.168.1.101 static eth0
172.17.0.0/ 16 172.17.0.1 kernel linkdocker0
192.168.1.0/ 24 192.168.1.20 kernel link eth0
127.0.0.0/ 8 local 127.0.0.1 kernel host lo local
127.0.0.1 local 127.0.0.1 kernel host lo local
127.255.255.255 broadcast 127.0.0.1 kernel link lo local
172.17.0.1 local 172.17.0.1 kernel hostdocker0 local
172.17.255.255 broadcast 172.17.0.1 kernel linkdocker0 local
192.168.1.20 local 192.168.1.20 kernel host eth0 local
192.168.1.255 broadcast 192.168.1.20 kernel link eth0 local
::1 kernel lo
::/ 96 unreachable lo
::ffff:0.0.0.0/ 96 unreachable lo
2002:a00::/ 24 unreachable lo
2002:7f00::/ 24 unreachable lo
2002:a9fe::/ 32 unreachable lo
2002:ac10::/ 28 unreachable lo
2002:c0a8::/ 32 unreachable lo
2002:e000::/ 19 unreachable lo
3ffe:ffff::/ 32 unreachable lo
fe80::/ 64 kernel eth0
::1 local kernel lo local
fe80::d085:cff:fec7:c1c3 local kernel eth0 local
```

只打印默认网关,和 `grep` 命令配合,如下所示:
```
$ routel | grep default
default 192.168.1.101 static eth0
```
#### 5、从以太网配置文件中查找网关
如果你在 [Linux 或 Unix 中配置了静态 IP 地址](https://ostechnix.com/configure-static-ip-address-linux-unix/),你可以通过查看网络配置文件查看默认网关或路由器 IP 地址。
在基于 RPM 的系统上,如 Fedora、RHEL、CentOS、AlmaLinux 和 Rocky Linux 等,网络接口卡配置存储在 `/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/` 目录下。
查找网卡的名称:
```
# ip link show
```
示例输出:
```
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: eth0@if5: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether d2:85:0c:c7:c1:c3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
```
网卡名为 `eth0`。所以让我们打开这个网卡文件的网卡配置:
```
# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
```
示例输出:
```
DEVICE=eth0
ONBOOT=yes
UUID=eb6b6a7c-37f5-11ed-a59a-a0e70bdf3dfb
BOOTPROTO=none
IPADDR=192.168.1.20
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.1.101
DNS1=8.8.8.8
```
如你所见,网关 IP 为 `192.168.1.101`。
在 Debian、Ubuntu 及其衍生版中,所有的网络配置文件都存储在 `/etc/network` 目录下。
```
$ cat /etc/network/interfaces
```
示例输出:
```
auto ens18
iface ens18 inet static
address 192.168.1.150
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.101
dns-nameservers 8.8.8.8
```
请注意,此方法仅在手动配置 IP 地址时有效。对于启用 DHCP 的网络,需要按照前面的 4 种方法操作。
### 总结
在本指南中,我们列出了在 Linux 和 Unix 系统中找到默认网关的 5 种不同方法,我们还在每种方法中包含了显示网关/路由器 IP 地址的示例命令。希望它对你有所帮助。
---
via: <https://ostechnix.com/find-default-gateway-linux/>
作者:[sk](https://ostechnix.com/author/sk/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
15,160 | 如何在 Arch Linux 中启用 Snap 支持 | https://itsfoss.com/install-snap-arch-linux/ | 2022-10-21T10:01:29 | [
"Snap"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15160-1.html | 
Snap 是由 Ubuntu 的母公司 Canonical 设计的通用包格式。有些人不喜欢 Snap,但它有一些优势。
通常,某些应用仅以 Snap 格式提供。这为你提供了在 Arch Linux 中启用 Snap 的充分理由。
我知道 AUR 拥有大量应用,但 Snap 应用通常直接来自开发人员。
如果你希望能够在 Arch Linux 中安装 Snap 应用,你需要先启用 Snap 支持。
有两种方法可以做到:
* 使用 AUR 助手启用 Snap 支持(更简单)
* 通过从 AUR 获取包,手动启用 Snap 支持
让我们看看怎么做。
### 方法 1、使用 AUR 助手启用 Snap
Snap 支持在 Arch 用户仓库中以 `snapd` 包的形式提供。你可以使用 AUR 助手轻松安装它。
有 [许多 AUR 助手](https://itsfoss.com/best-aur-helpers/),但 `yay` 是我更喜欢的,因为它的语法类似于 [pacman 命令](https://itsfoss.com/pacman-command/)。
如果你还没有安装 AUR,请使用以下命令安装 Yay(需要事先安装 `git`):
```
git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/yay
cd yay
makepkg -si
```

现在 `yay` 已安装,你可以通过以下方式安装 `snapd`:
```
yay -Sy snapd
```

每当你 [更新 Arch Linux](https://itsfoss.com/update-arch-linux/) 系统时,`yay` 都会启用 `snapd` 的自动更新。
#### 验证 Snap 支持是否有效
要测试 Snap 支持是否正常工作,请安装并运行 `hello-world` Snap 包。
```
sudo snap install hello-world
hello-world
(或者)
sudo snap run hello-world
```

如果它运行良好,那么你可以轻松安装其他 Snap 包。
### 方法 2、从 AUR 手动构建 snapd 包
如果你不想使用 AUR 助手,你仍然可以从 AUR 获取 `snapd`。让我展示详细的过程。
你需要先安装一些构建工具。
```
sudo pacman -Sy git go go-tools python-docutils
```

完成依赖项安装后,现在可以克隆 `snapd` 的 AUR 目录,如下所示:
```
git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/snapd
cd snapd
```

然后构建 `snapd` 包:
```
makepkg -si
```
当它要求安装其他依赖包时输入 `yes`。

你已安装 `snapd` 守护程序。但是,需要启用它以在启动时自动启动。
```
sudo systemctl enable snapd --now
sudo systemctl enable snapd.apparmor --now #start snap applications
sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snap #optional: classic snap support
```

手动构建包的主要缺点是每次新更新启动时你都必须手动构建。使用 AUR 助手为我们解决了这个问题。
### 总结
我更喜欢 Arch Linux 中的 pacman 和 AUR。很少能看到不在 AUR 中但以其他格式提供的应用。尽管如此,在某些你希望直接从源获取它的情况下,使用 Snap 可能是有利的,例如 [在 Arch 上安装 Spotify](https://itsfoss.com/install-spotify-arch/)。
希望本教程对你有所帮助。如果你有任何问题,请告诉我。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/install-snap-arch-linux/>
作者:[Pranav Krishna](https://itsfoss.com/author/pranav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Snap is a universal package format designed by Canonical, the parent company of Ubuntu. Some people do not like Snap, but it has some advantages.
Often, some applications are only available in the Snap format. This gives you a good enough reason to enable snap in Arch Linux.
I know that AUR has a vast collection of applications but the snap apps often come directly from the developers.
If you want to be able to install Snap applications in Arch Linux, you need to enable snap support first.
There are two ways to do it:
- Enable Snap support using an AUR helper (easier)
- Enable Snap support manually by getting the packages from AUR
Let’s see how to do it.
## Method 1. Use an AUR helper to enable Snap
Snap is available in the Arch User Repository as the *snapd* package. You can install it easily using an AUR helper.
There are [many AUR helpers](https://itsfoss.com/best-aur-helpers/) out there, but *yay* is what I prefer because it has syntax similar to the [pacman command](https://itsfoss.com/pacman-command/).
If you don’t have an AUR installed already, install Yay using the command below (needs git beforehand):
```
git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/yay
cd yay
makepkg -si
```
Now that *yay* is installed, you can install snapd by:
`yay -Sy snapd`
Yay enables automatic updating of snapd whenever you [update your Arch Linux](https://itsfoss.com/update-arch-linux/) system.
## Verify that snap works
To test if snap works fine, install and run the *hello-world* snap package.
```
sudo snap install hello-world
hello-world
(or)
sudo snap run hello-world
```
If it runs fine, then you can install other snap packages easily.
## Method 2. Manually build the snap package from AUR
If you do not want to use an AUR helper, you can still get the snapd from the AUR. Let me show the detailed procedure.
You will need to install some build tools first.
`sudo pacman -Sy git go go-tools python-docutils`
Once you’re done with installing the dependencies, now you can clone the AUR directory, which goes as:
```
git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/snapd
cd snapd
```
Then make the snapd package:
`makepkg -si`
Enter yes when it asks to install other dependency packages.
You have installed the snapd daemon. However, it needs to be enabled to auto start at boot time.
```
sudo systemctl enable snapd --now
sudo systemctl enable snapd.apparmor --now #start snap applications
sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snap #optional: classic snap support
```
The major disadvantage of manually building a package is that you have to manually build every time a new update kicks in. Using an AUR helper solves that problem for us.
## Conclusion
I prefer pacman and AUR in Arch Linux. It’s rare to see an application that is not in AUR but available in some other formats. Still, using snap could be advantageous in some conditions where you want it directly from the source, like [installing Spotify on Arch](https://itsfoss.com/install-spotify-arch/) for example.
I hope you find this tutorial helpful. Let me know if you have any questions. |
15,161 | 开源笔记软件 Joplin 背后的故事 | https://opensource.com/article/22/9/joplin-interview | 2022-10-21T11:29:38 | [
"Joplin",
"笔记"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15161-1.html | 
>
> Laurent Cozic 与我坐下来,讨论了 Joplin 是如何开始的,以及这个开源笔记软件的下一步计划。
>
>
>
在这次采访中,我见到了笔记软件 Joplin 的创建者 Laurent Cozic。[Joplin](https://joplinapp.org/) 是 [20i](https://www.20i.com/foss-awards/winners) 奖励的赢家,所以我想了解是什么让它如此成功,以及他如何实现的。
### 你能概述一下什么是 Joplin 吗?
[Joplin](https://opensource.com/article/19/1/productivity-tool-joplin) 是一个开源的笔记软件。它可以让你捕获你的想法并从任何设备安全地访问它们。
### 显然,还有很多其他的笔记应用,那么除了免费使用之外,它还有什么不同呢?
对我们的许多用户来说,它是开源的这一事实是一个非常重要的方面,因为这意味着没有供应商对数据的封锁,而且数据可以很容易地被导出并以各种方式访问。
我们还关注用户的安全和数据隐私,特别是端到端加密同步功能,以及通过对应用的任何连接保持透明。我们还与安全研究人员合作,以保证软件更加安全。
最后,Joplin 可以通过几种不同的方式进行定制 —— 通过插件(可以添加新的功能)和主题来定制应用程序的外观。我们还公开了一个数据 API,它允许第三方应用程序访问 Joplin 的数据。
>
> **[相关阅读:5 款 Linux 上的笔记应用](https://opensource.com/article/22/8/note-taking-apps-linux)**
>
>
>
### 这是一个竞争非常激烈的市场,那么是什么激发了你创建它的想法?
这是有原因的的。我从 2016 年开始研究它,因为我不喜欢现有的商业记事应用程序:笔记、附件或标签不能轻易被其他工具导出或操作。
这主要是由于供应商的封锁,另外还有供应商缺乏动力,因为他们没有动力帮助用户将他们的数据转移到其他应用程序。还有一个问题是,这些公司通常会以纯文本形式保存笔记,而这有可能造成数据隐私和安全方面的问题。
因此,我决定开始创建一个简单且具有同步功能的移动和终端应用程序,使我的笔记能够轻松地在我的设备上访问。之后又创建了桌面应用程序,项目从此开始发展。

### 编写 Joplin 花了多长时间呢?
自 2016 年以来,我一直在断断续续地开发,但并不是专门去维护。不过在过去的两年里,我更加专注于它。
### 对于准备创建自己的开源应用的人,你有什么建议?
挑选一个你自己使用的项目和你喜欢的技术来工作。
管理一个开源项目有时是很困难的,所以必须要有足够的兴趣去让它变得更有价值。那么我想 “早发布,多发布” 原则在这里也适用,这样你就可以衡量用户的兴趣,以及是否有必要花时间进一步开发这个项目。
### 有多少人参与了 Joplin 的开发?
有 3、4 人参与开发。目前,我们还有 6 名学生在 <ruby> 谷歌编程之夏 <rt> Google Summer of Code </rt></ruby> 中为这个项目工作。
### 许多人都在创建开源项目,但 Joplin 对你来说是一个巨大的成功。关于如何获得关注,你能否给开发者提供一些建议?
没有简单的公式,说实话,我不认为我可以在另一个项目中复制这种成功!你必须对你所做的事情充满热情,但同时也要严谨、有组织、稳步前进,确保代码质量保持高水平,并拥有大量的测试单元以防止回归。
同时,对于你收到的用户反馈保持开放的态度,并在此基础上改进项目。
一旦你掌握了这些,剩下的可能就全靠运气了 —— 如果你做的项目让很多人都感兴趣,事情可能会顺利进行!
### 一旦你得到关注,但如果你没有传统的营销预算,你如何保持这种势头?
我认为这在于倾听项目周围的社区。举个例子来说,我从未计划过建立一个论坛,但有人在 GitHub 上提出了这个建议,所以我创建了一个论坛,它成为了一个分享想法、讨论功能、提供支持等很好的方式。社区也普遍欢迎新人,这形成了一种良性循环。
除此以外,定期就项目进行沟通也很重要。
我们没有一个公开的路线图,因为大多数功能的 ETA 通常是 “我不知道”,但我会试图就即将到来的功能、新版本等进行沟通。我们也会就重要的事件进行沟通,特别是谷歌编程之夏,或者当我们有机会赢得像 20i FOSS 奖的时候。
最后,我们很快将在伦敦举行一次面对面的聚会,这是与社区和合作者保持联系的另一种方式。
### 用户的反馈是如何影响路线图的?
很明显,贡献者们经常仅仅因为他们需要某个特性而从事某些工作。但除此之外,我们还根据论坛和 GitHub 问题追踪器上的信息,追踪对用户来说似乎最重要的功能。
例如,移动应用程序现在具有很高的优先级,因为我们经常从用户那里听到,它的限制和缺陷是有效使用 Joplin 的一个问题。

### 你是如何跟上最新的开发和编码的发展的?
主要是通过阅读 Hacker News!
### 你有个人最喜欢的自由/开源软件可以推荐吗?
在不太知名的项目中,[SpeedCrunch](https://heldercorreia.bitbucket.io/speedcrunch/) 作为一个计算器非常好。它有很多功能,而且很好的是它能保留以前所有计算的历史。
我还使用 [KeepassXC](https://opensource.com/article/18/12/keepassx-security-best-practices) 作为密码管理器。在过去的几年里,它一直在稳步改进。
最后,[Visual Studio Code](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/open-source-alternatives-vs-code) 作为一个跨平台的文本编辑器非常棒。
### 我原以为 Joplin 是以 Janis 的名字命名的,但维基百科告诉我来自是 Scoot Joplin。你为什么选择这个名字?
我起初想把它命名为 “jot-it”,但我想这个名字已经被人占了。
由于我那时经常听 Scoot Joplin 的 <ruby> 拉格泰姆 <rt> ragtime </rt></ruby>音乐(我相当痴迷于此),我决定使用他的名字。
我认为产品名称的含义并不太重要,只要名称本身易于书写、发音、记忆,并与一些积极的东西(或至少没有消极的东西)有关。
我觉得 “Joplin” 符合所有条件。
### 关于 Joplin 的计划,你还有什么可以说的吗?也许是对一个新功能的独家预告?
如前所述,我们非常希望在用户体验设计和新功能方面对移动应用进行改进。
我们也在考虑创建一个 “插件商店”,以便更容易地浏览和安装插件。
感谢 Laurent — 祝 Joplin 的未来好运。
*图片来自: ([Opensource.com](http://Opensource.com), CC BY-SA 4.0)*
*[这篇访谈最初发表在 20i 博客上,已获得许可进行转载。](https://www.20i.com/blog/joplin-creator-laurent-cozic/)*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/9/joplin-interview>
作者:[Richard Chambers](https://opensource.com/users/20i) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[MareDevi](https://github.com/MareDevi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In this interview, I met up with Laurent Cozic, creator of the note-taking app, Joplin. [Joplin](https://joplinapp.org/) was a winner of the [20i](https://www.20i.com/foss-awards/winners) rewards, so I wanted to find out what makes it such a success, and how he achieved it.
**Could you summarize what Joplin does?**
[Joplin](https://opensource.com/article/19/1/productivity-tool-joplin) is an open source note-taking app. It allows you to capture your thoughts and securely access them from any device.
**Obviously, there are other note-taking apps out there—but apart from it being free to use, what makes it different?**
The fact that it is open source is an important aspect for many of our users, because it means there is no vendor locking on the data, and that data can be easily exported and accessed in various ways.
We also focus on security and data privacy, in particular with the synchronization end-to-end encryption feature, and by being transparent about any connection that the application makes. We also work with security researchers to keep the app more secure.
Finally, Joplin can be customized in several different ways—through plugins, which can add new functionalities, and themes to customize the app appearance. We also expose a data API, which allows third-party applications to access Joplin data.
**[ Related read 5 note-taking apps for Linux ]**
**It's a competitive market, so what inspired you to build it?**
It happened organically. I started looking into it in 2016, as I was looking at existing commercial note-taking applications, and I didn't like that the notes, attachments, or tags could not easily be exported or manipulated by other tools.
This is probably due to vendor locking and partly a lack of motivation from the vendor since they have no incentive to help users move their data to other apps. There is also an issue with the fact that these companies usually will keep the notes in plain text, and that can potentially cause issues in terms of data privacy and security.
So I decided to start creating a simple mobile and terminal application with sync capabilities to have my notes easily accessible on my devices. Later the desktop app was created and the project grew from there.
(Opensource.com, CC BY-SA 4.0)
**How long did Joplin take to make?**
I've been working on it on and off since 2016 but it wasn't full time. The past two years I've been focusing more on it.
**What advice might you have for someone setting to create their own open source app?**
Pick a project you use yourself and technologies you enjoy working with.
Managing an open source project can be difficult sometimes so there has to be this element of fun to make it worthwhile. Then I guess "release early, release often" applies here, so that you can gauge user's interest and whether it makes sense to spend time developing the project further.
**How many people are involved in Joplin's development?**
There are 3-4 people involved in the development. At the moment we also have six students working on the project as part of Google Summer of Code.
**[ Also read Our journey to open source during Google Summer of Code ]**
**Lots of people create open source projects, yet Joplin has been a resounding success for you. Could you offer creators any tips on how to get noticed?**
There's no simple formula and to be honest I don't think I could replicate the success in a different project! You've got to be passionate about what you're doing but also be rigorous, be organized, make steady progress, ensure the code quality remains high, and have a lot of test units to prevent regressions.
Also be open to the user feedback you receive, and try to improve the project based on it.
Once you've got all that, the rest is probably down to luck—if it turns out you're working on a project that interests a lot of people, things might work out well!
**Once you get noticed, how do you keep that momentum going, if you don't have a traditional marketing budget?**
I think it's about listening to the community around the project. For example I never planned to have a forum but someone suggested it on GitHub, so I made one and it became a great way to share ideas, discuss features, provide support, and so on. The community is generally welcoming of newcomers too, which creates a kind of virtuous circle.
Next to this, it's important to communicate regularly about the project.
We don't have a public roadmap, because the ETA for most features is generally "I don't know", but I try to communicate about coming features, new releases, and so on. We also communicate about important events, the Google Summer of Code in particular, or when we have the chance to win something like the 20i FOSS Awards.
Finally, very soon we'll have an in-person meetup in London, which is another way to keep in touch with the community and collaborators.
**How does user feedback influence the roadmap?**
Significantly. Contributors will often work on something simply because they need the feature. But next to this, we also keep track of the features that seem most important to users, based on what we read about on the forum and on the GitHub issue tracker.
For example, the mobile app is now high priority because we frequently hear from users that its limitations and issues are a problem to effectively use Joplin.
(Opensource.com, CC BY-SA 4.0)
**How do you keep up to date with the latest in dev and coding?**
Mostly by reading Hacker News!
**Do you have a personal favorite FOSS that you'd recommend?**
Among the less well-known projects, [SpeedCrunch](https://heldercorreia.bitbucket.io/speedcrunch/) is very good as a calculator. It has a lot of features and it's great how it keeps a history of all previous calculations.
I also use [KeepassXC](https://opensource.com/article/18/12/keepassx-security-best-practices) as a password manager. It has been improving steadily over the past few years.
Finally, [Visual Studio Code](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/open-source-alternatives-vs-code) is great as a cross-platform text editor.
**I'd assumed that Joplin was named after Janis, but Wikipedia tells me it's Scott Joplin. What made you choose the name?**
I wanted to name it "jot-it" at first but I think the name was already taken.
Since I was listening to Scott Joplin ragtime music a lot back then (I was pretty much obsessed with it), I decided to use his name.
I think the meaning of a product name is not too important, as long as the name itself is easy to write, pronounce, remember, and perhaps is associated with something positive (or at least nothing negative).
And I think "Joplin" ticks all these boxes.
**Is there anything you can say about plans for Joplin? An exclusive tease of a new feature, perhaps?**
As mentioned earlier, we are very keen to make improvements to the mobile app, both in terms of UX design and new features.
We're also looking at creating a "Plugin Store" to make it easier to browse and install plugins.
**Thanks for your time Laurent— best of luck with the future of Joplin.**
*This interview was originally published on the 20i blog and has been republished with permission.*
## Comments are closed. |
15,163 | 如何在 Ubuntu Linux 上更新谷歌 Chrome | https://itsfoss.com/update-google-chrome-ubuntu/ | 2022-10-22T08:49:00 | [
"Chrome"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15163-1.html | 
>
> 你设法在你的 Ubuntu 系统上安装了谷歌 Chrome 浏览器。现在你想知道如何让浏览器保持更新。
>
>
>
在 Windows 和 macOS 上,当 Chrome 上有可用更新时,你会在浏览器中收到通知,你可以从浏览器中点击更新选项。
Linux 中的情况有所不同。你不会从浏览器更新 Chrome。你要使用系统更新对其进行更新。
是的。当 Chrome 上有可用的新更新时,Ubuntu 会通过系统更新工具通知你。

你只需单击“<ruby> 立即安装 <rt> Install Now </rt></ruby>”按钮,在被提示时输入你的帐户密码并将 Chrome 更新到新版本。
让我告诉你为什么会在系统级别看到更新,以及如何在命令行中更新谷歌 Chrome。
### 方法 1:使用系统更新更新谷歌浏览器
你最初是如何安装 Chrome 的?你从 [Chrome 网站](https://www.google.com/chrome/) 获得了 deb 安装程序文件,并使用它来 [在 Ubuntu 上安装 Chrome](https://itsfoss.com/install-chrome-ubuntu/)。
当你这样做时,谷歌会在你系统的源列表中添加一个仓库条目。这样,你的系统就会信任来自谷歌仓库的包。

对于添加到系统中的所有此类条目,包更新通过 Ubuntu 更新程序集中进行。
这就是为什么当 Google Chrome(和其他已安装的应用)有可用更新时,你的 Ubuntu 系统会向你发送通知。

**单击“<ruby> 立即安装 <rt> Install Now </rt></ruby>”按钮并在要求时输入你的密码**。很快,系统将安装所有可升级的软件包。
根据更新偏好,通知可能不是立即的。如果需要,你可以手动运行更新程序工具并查看适用于你的 Ubuntu 系统的更新。

### 方法 2:在 Ubuntu 命令行中更新 Chrome
如果你更喜欢终端而不是图形界面,你也可以使用命令更新 Chrome。
打开终端,并依次运行以下命令:
```
sudo apt update
sudo apt --only-upgrade install google-chrome-stable
```
第一条命令更新包缓存,以便你的系统知道可以升级哪些包。
第二条命令 [仅更新单个包](https://itsfoss.com/apt-upgrade-single-package/),即谷歌 Chrome(安装为 `google-chrome-stable`)。
### 总结
如你所见,Ubuntu 比 Windows 更精简。你会随其他系统更新一起更新 Chrome。
顺便一提,如果你对它不满意,你可以了解 [从 Ubuntu 中删除 Google Chrome](https://itsfoss.com/uninstall-chrome-from-ubuntu/)。
Chrome 是一款不错的浏览器。你可以通过 [使用 Chrome 中的快捷方式](https://itsfoss.com/google-chrome-shortcuts/) 来试验它,因为它使浏览体验更加流畅。
在 Ubuntu 上享受 Chrome!
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/update-google-chrome-ubuntu/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

So, you managed to [install Google Chrome browser on your Ubuntu system](https://itsfoss.com/install-chrome-ubuntu/). And now you wonder how to keep the browser updated.
On Windows and macOS, when there is an update available on Chrome, you are notified in the browser itself and you can hit the update option from the browser.
Things are different in Linux. You don’t update Chrome from the browser. You update it with the system updates.
Yes. When a new update is available on Chrome, Ubuntu notifies you via the system updater tool.
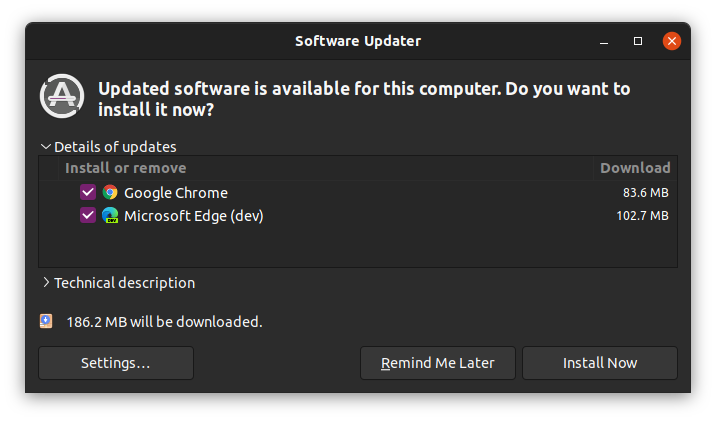
You just have to click on the **Install Now** button, enter your account’s password when asked for it and have Chrome updated to a new version.
Let me tell you why you see the updates on the system level and how you can update Google Chrome in the command line.
## Method 1: Updating Google Chrome with system updates
How did you install Chrome in the first place? You got the deb installer file from the [Chrome website](https://www.google.com/chrome/?ref=itsfoss.com) and used it to [install Chrome on Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/install-chrome-ubuntu/).
The thing is that when you do that, Google adds a repository entry into your system’s sources list. This way, your system trusts the packages coming from the Google repository.
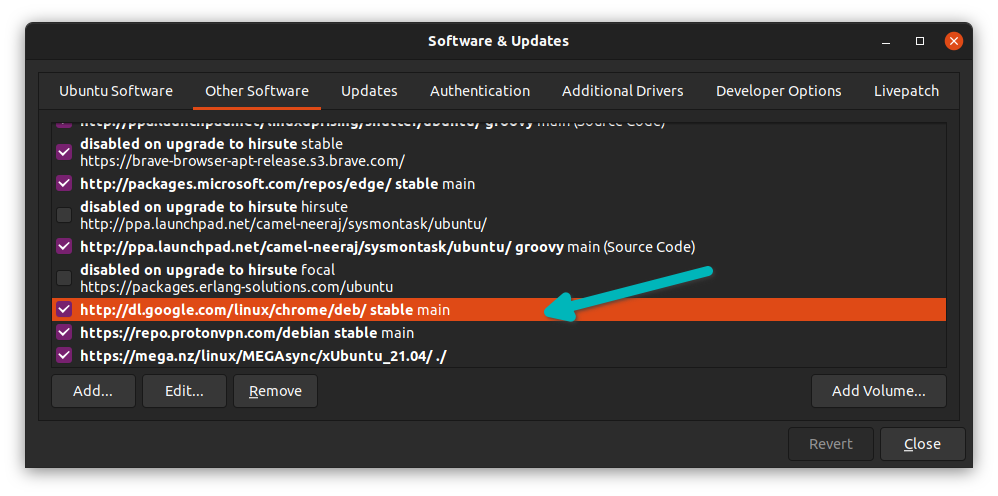
The package updates are centralized through the Ubuntu Updater for all such entries added to your system.
And this is why when an update is available to Google Chrome (and other installed applications), your Ubuntu system sends you a notification.

**Click the “Install Now” button and enter your password when asked for it**. Soon, the system will install all the upgradeable packages.
Depending on the update preference, the notification may not be immediate. You can manually run the updater tool and see what updates are available for your Ubuntu system.
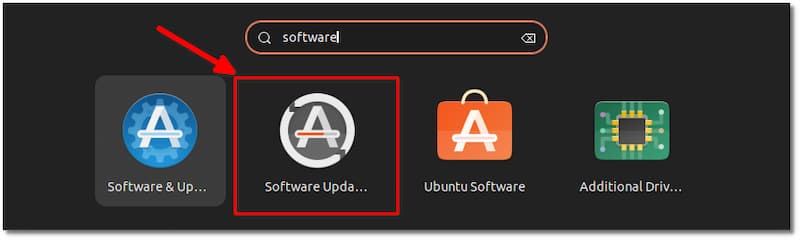
## Method 2: Updating Chrome in the Ubuntu command line
If you prefer the terminal over the graphical interface, you can also update Chrome with commands.
Open a terminal and run the following commands one by one:
```
sudo apt update
sudo apt --only-upgrade install google-chrome-stable
```
The first command updates the package cache so that your system is aware of what packages can be upgraded.
The second command [only updates the single package](https://itsfoss.com/apt-upgrade-single-package/) which is Google Chrome (installed as google-chrome-stable).
## Conclusion
As you can see, things are more streamlined in Ubuntu than in Windows. You get Chrome updated along with other system updates.
On a related note, you may learn about [removing google Chrome from Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/uninstall-chrome-from-ubuntu/) if you are unhappy with it.
[How to Completely Uninstall Google Chrome From UbuntuSo, you managed to install Google Chrome on Ubuntu. It is the most popular web browser in the world, after all. But perhaps you dislike Google products for the heavy tracking and data mining they employ on its users. You decided to opt for other web browsers on Ubuntu, perhaps](https://itsfoss.com/uninstall-chrome-from-ubuntu/)

Chrome is a fine browser. You can experiment with it by [using shortcuts in Chrome](https://itsfoss.com/google-chrome-shortcuts/) as it makes the browsing experience even smoother.
[11 Essential Keyboard Shortcuts for Google ChromeMaster these Google Chrome keyboard shortcuts for a better, smoother and more productive web browsing experience. A downloadable cheatsheet is also included.](https://itsfoss.com/google-chrome-shortcuts/)

Enjoy Chrome on Ubuntu! |
15,164 | 解决 Linux 中的 “Bash: Command Not Found” 报错 | https://itsfoss.com/bash-command-not-found/ | 2022-10-22T11:59:00 | [
"命令"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15164-1.html | 
>
> 本新手教程展示了在 Debian、Ubuntu 和其他的 Linux 发行版上如何解决 “Bash: command not found” 这一报错。
>
>
>
当你在 Linux 中使用命令时,你希望得到终端输出的结果。但有时候,你会遇到终端显示“<ruby> 命令未找到 <rt> command not found </rt></ruby>”这一报错。

对于这个问题,并没有直截了当且单一的解决方案。你必须自己做一些故障排除来解决这个报错。
老实说,要解决它并不难。该报错信息已经给出了一些提示:“命令未找到”,这说明你的 shell(或者 Linux 系统)找不到你输入的那条命令。
shell(或 Linux 系统)找不到命令,有三个可能的原因:
* 你将命令的名称拼错了
* 该命令还没有安装
* 该命令是一个可执行脚本,但其位置未知
接下来,我们会详细介绍“命令未找到”这一报错的每一个原因。
### 解决“命令未找到”报错
#### 方法 1:再次检查命令名称有没有写错
每个人都会犯错误,尤其是在打字的时候。你输入的命令可能存在错别字(也就是你写错啦)。
你应该特别注意:
* 是否拼对了正确的命令名称
* 是否在命令与其选项之间加上了空格
* 是否在拼写中混淆了 1(数字 1)、I(大写的 i)和 l(小写的 L)
* 是否正确使用了大写字母或者小写字母
看看下面的示例,因为我写错了 `ls` 命令,所以会导致“command not found”报错。

所以,请再次仔细确认你输入得对不对。
#### 方法 2:确保命令已安装在你的系统上
这是“命令未找到”错误的另一个常见原因。如果命令尚未安装,则无法运行该命令。
虽然在默认情况下,你的 Linux 发行版自带安装了大量命令,但是不会在系统中预装 *所有的* 命令行工具。如果你尝试运行的命令不是一个流行的常用命令,那么你需要先安装它。
你可以使用发行版的软件包管理器来安装命令。

有时候,某一常用命令可能也不再能使用了,甚至你也不能够安装这个命令了。这种情况下,你需要找到一个替代的命令,来得到结果。
以现已弃用的 `ifconfig` 命令为例。网络上的旧教程依旧会让你使用 `ifconfig` 命令,来 [获取本机的 IP 地址](https://itsfoss.com/check-ip-address-ubuntu/) 和网络接口信息,但是,在较新的 Linux 版本中,你已经无法使用 `ifconfig` 了。`ifconfig` 命令已被 `ip` 命令所取代。

有时候,你的系统可能甚至找不到一些非常常见的命令。当你在 Docker 容器中运行 Linux 发行版时,就通常如此。Docker 容器为了缩小操作系统镜像的大小,容器中通常不包含那些常见的 Linux 命令。
这就是为什么使用 Docker 的用户会碰到 [ping 命令未找到](https://linuxhandbook.com/ping-command-ubuntu/) 等报错的原因。

因此,这种情况下的解决方案是安装缺失的命令,或者是找到一个与缺失命令有同等功能的工具。
#### 方法 3:确保命令是真实的,而不是一个别名
我希望你知道 Linux 中的别名概念。你可以配置你自己的较短的命令来代替一个较长命令的输入。
一些发行版,如 Ubuntu,会自动提供 `ll`(`ls -l` 的别名)、`la`(`ls -a` 的别名)等命令。

想象一下,你习惯于在你的个人系统上输入 `ll` 和 `la`,而你登录到另一个 Linux 系统,发现 `ll` 命令并不存在。你甚至不能安装 `ll` 命令,因为它不是一个真正的命令。
所以,如果你找不到一个命令,甚至不能安装,你应该尝试在互联网上搜索该命令是否存在。如果不存在,可能是其他系统上的一个别名。
#### 方法 4:检查命令是否是一个路径正确的可执行脚本
这是 Linux 新手在 [运行 shell 脚本](https://itsfoss.com/run-shell-script-linux/) 时常犯的错误。
即使你在同一目录下,仅用可执行脚本的名称,来运行可执行脚本,也会显示错误。
```
[email protected]:~/scripts# sample
-bash: sample: command not found
```
因为你需要显式指定 shell 解释器或可执行脚本的路径!

如果你在其他目录下,在未提供文件正确路径的情况下,运行 shell 脚本,则会有“<ruby> 找不到文件 <rt> no such file or directory </rt></ruby>”的报错。

>
> **把可执行文件的路径加到 PATH 变量中**
>
>
> 有时候,你下载了一个软件的压缩文件(tar 格式),解压这个 tar 文件,然后找到一个可执行文件和其他程序文件。你需要运行可执行文件,来运行那个软件。
>
>
> 但是,你需要在可执行文件的同一目录下或指定可执行文件的整个路径,才能运行那个可执行文件。这很令人烦扰。
>
>
> 你可以使用 `PATH` 变量来解决这个问题。`PATH` 变量包含了有各种 Linux 命令的二进制(可执行)文件的目录集合。当你运行一个命令时,你的 Linux 系统会检查 `PATH` 变量中的上述目录,以查找该命令的可执行文件。
>
>
> 你可以使用 `which` 命令,来检查某一命令的二进制文件的位置:
>
>
> 
>
>
> 如果你想从系统上的任何地方都能运行可执行文件或脚本,你需要将可执行文件的位置添加到 `PATH` 变量中。
>
>
> 
>
>
> 然后,`PATH` 变量需要添加到 shell 的 rc 文件中,如此对 `PATH` 变量的更改就是永久性的。
>
>
> 这里的要点是:你的 Linux 系统必须了解可执行脚本的位置。要么在运行时给出可执行文件的整个路径,要么将其位置添加到 `PATH` 变量中。
>
>
>
### 以上的内容有帮到你吗?
我懂得,当你是 Linux 新手时,很多事情可能会让你不知所措。但是,当你了解问题的根本原因时,你的知识会逐渐增加。
对于“未找到命令”报错来说,没有简单的解决方案。我提供给你了一些提示和要点,我希望这对你的故障排除有帮助。
如果你仍然有疑问或需要帮助,请在评论区告诉我吧。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/bash-command-not-found/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

When you use commands in Linux, you expect to see an output. But sometimes, you’ll encounter issues where the terminal shows ‘command not found’ error.
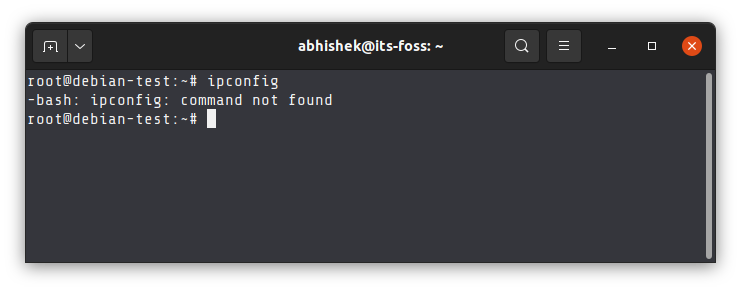
There is no straightforward, single solution to this error. You have to do a little bit of troubleshooting on your own.
It’s not too difficult, honestly. The error gives some hint already when it says “bash: command not found”. Your shell (or Linux system) cannot find the command you entered.
There could be three possible reasons why it cannot find the command:
- It’s a typo and the command name is misspelled
- The command is not even installed
- The command is basically an executable script and its location is not known
Let’s go in detail on each possible root cause.
## Fixing “bash: command not found” error

### Method 1: Double check the command name (no, seriously)
It is human to make mistakes, specially while typing. It is possible that the command you entered has a typo (spelling mistake).
You should specially pay attention to:
- The correct command name
- The spaces between the command and its options
- The use of 1 (numeral one), I (capital i) and l (lowercase L)
- Use of uppercase and lowercase characters
Take a look at the example below, where I have misspelled the common ls command.
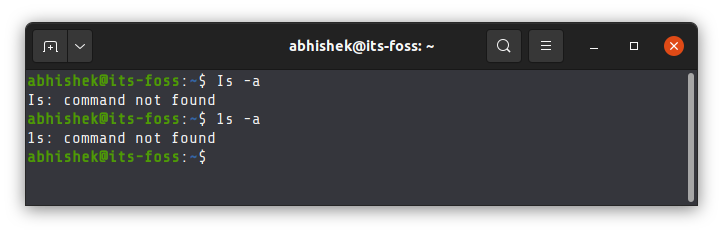
So, make double sure what you are typing.
### Method 2: Ensure that the command is installed on your system
This is another common reason behind the command not found error. You cannot run a command if it is not installed already.
While your Linux distribution comes with a huge number of commands installed by default, it is not possible to pre-install all the command line tools in a system. If the command you are trying to run is not a popular, common command, you’ll have to install it first.
You can use your distribution’s package manager to install it.
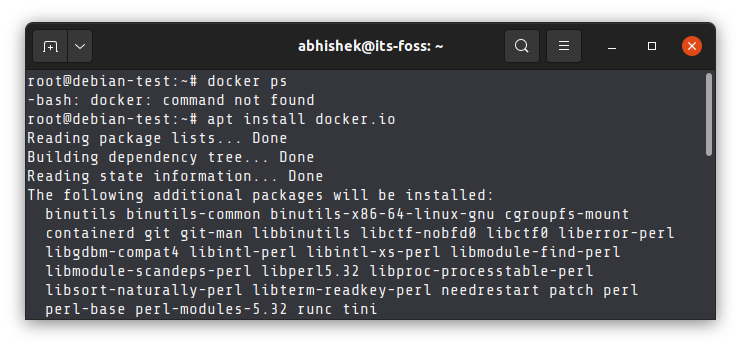
In some cases, popular commands may get discontinued and you may not even install it anymore. You’ll have to find an alternative command to achieve the result.
Take the example of ifconfig command. This deprecated command was used for [getting Ip address](https://itsfoss.com/check-ip-address-ubuntu/) and other network interface information. Older tutorials on the web still mention using this command but you cannot use it anymore in newer Linux versions. It has been replaced by the ip tool.
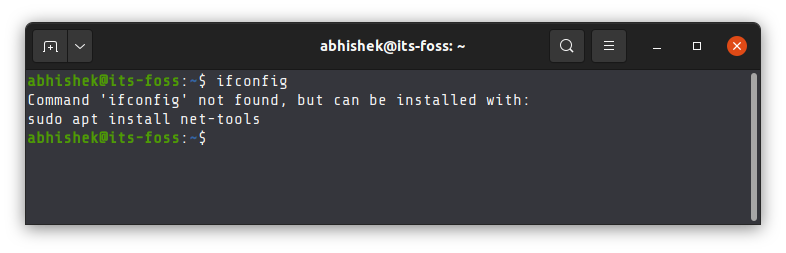
Occasionally, your system won’t find even the extremely common commands. This is often the case when you are running a Linux distribution in Docker containers. To cut down on the size of the operating system image, the containers often do not include even the most common Linux commands.
This is why Docker user stumble across things like [ping command not found error ](https://linuxhandbook.com/ping-command-ubuntu/?ref=itsfoss.com)etc.
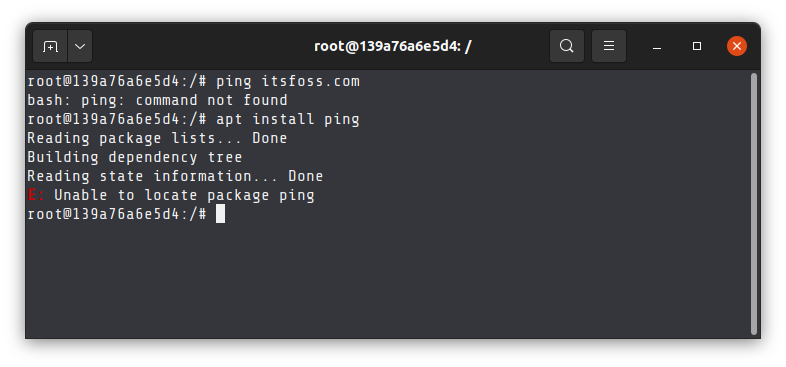
So, the solution is to either install the missing command or find a tool that could do the same thing you were trying to do with the missing command.
### Method 3: Make sure that the command is real, not an alias
I hope you are aware of the [alias concept in Linux](https://linuxhandbook.com/linux-alias-command/?ref=itsfoss.com). You can configure your own shorter commands to replace the typing of a longer command.
Some distributions like Ubuntu automatically provide commands like ll (which is aliased to ls -l), la (aliased to ls -a) and so on.
Imagine that you are used to of typing ll and la on your personal system and you log on to another Linux system and find that ll command does not exist. You cannot even install the ll command because it is not a real command.
So, if you cannot find a command and it cannot even be installed, you should try searching on the internet if that command even exists. If it does not, probably it was an alias on some other system.
### Method 4: Check if it is an executable script with correct path
This is a common mistake Linux rookies make while [running a shell script](https://itsfoss.com/run-shell-script-linux/).
Even if you are in the same directory and try to run an executable script just by its name, it will show an error.
```
root@debian-test:~/scripts# sample
-bash: sample: command not found
```
You need to either specify the shell interpreter explicitly or its absolute path.
If you are in some other directory and try to execute the shell script without giving the correct path to the file, it will complain about not finding the file.
#### Adding it to the PATH
In some cases, you download the entire software in a tar file, extract it and find an executable file along with other program files. To run the program, you need to run the executable file.
But for that, you need to be in the same directory or specify the entire path to the executable file. This is tiresome.
Here, you can [use the PATH variable](https://itsfoss.com/add-directory-to-path-linux/). This variable has a collection of directories and these directories have the binary (executable) files of various Linux commands. When you run a command, your Linux system checks the mentioned directories in the PATH variable to look for the executable file of that command.
You can check the location of the binary of a command by using the `which`
command:
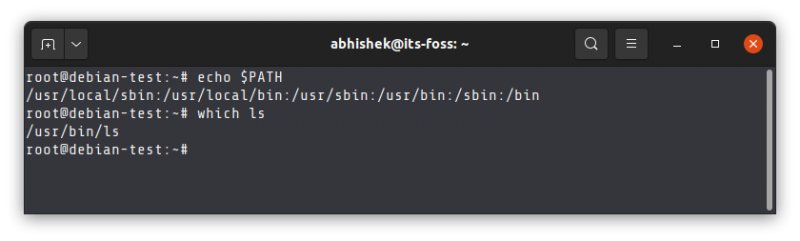
If you want to run an executable file or script from anywhere on the system, you need to add the location of the file to this PATH variable.
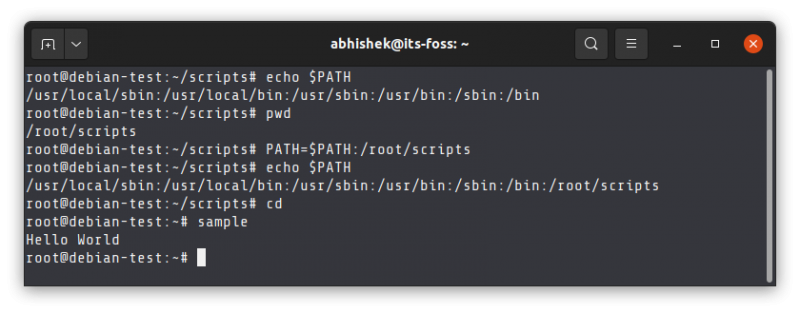
The PATH variable then needs to be added to the rc file of the shell so that the changes made to PATH variable are permanent.
You get the gist here. It is important that your Linux system has knowledge about the location of the executable script. Either you give the path while running it or you add its location to the PATH variable.
## Did it help you?
I understand that when you are new to Linux, things could be overwhelming. But when you understand the root cause of the problem, it gradually improved your knowledge.
Here, there is no straightforward solution possible for the ‘command not found error’. I gave you some hints and pointers and that should help you in troubleshooting.
Similarly, you may encounter '[unable to locate package](https://itsfoss.com/unable-to-locate-package-error-ubuntu/)' error in Ubuntu. Here's what you need to know about it.
[[Solved] “E: Unable to locate package” Error on UbuntuThis beginner tutorial shows how to go about fixing the E: Unable to locate package error on Ubuntu Linux.](https://itsfoss.com/unable-to-locate-package-error-ubuntu/)

If you still have doubts or need help, please let me know in the comment section. |
15,167 | GitHub Copilot 似乎违反了开源许可证的规定 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/10/github-copilot-appears-to-be-in-violation-of-the-open-source-licence/ | 2022-10-23T10:01:33 | [
"Copilot"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15167-1.html | 
>
> 自 Copilot 首次亮相以来,Butterick 就对该计划提出了批评。
>
>
>
微软在 2018 年支付 75 亿美元收购了 GitHub,此后将这个代码仓库整合到其开发者工具中,同时在很大程度上采取了放手的态度。Matthew Butterick 是一名作家、律师,也是一名程序员,他认为微软基于机器学习的代码助手 GitHub Copilot 存在一些问题,它似乎不正确地对待开源代码许可证。
GitHub Copilot 是 Visual Studio 和其他 IDE 的一个插件,通过在你输入时提供代码完成的 “建议” 来运作。Codex 是该系统的动力源。然而,Butterick 等开发者认为 AI 在如何学习方面存在问题,或者更具体地说,AI 是从哪里训练的。
这里的问题是,GitHub 所训练的公开代码仓库是有许可证的,当他们的工作被利用时,需要按照许可证进行。虽然微软对其使用代码的问题一直避而不谈,称其为合理使用,但 Copilot 除了提供建议外,还能生成逐字逐句的代码部分。
根据 Codex(由微软授权)的开发者 OpenAI的说法,“Codex 是在数以千万计的公开代码仓库中训练出来的,包括 GitHub 上的代码。”微软自己也含糊地将训练材料描述为数十亿行的公共代码。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/10/github-copilot-appears-to-be-in-violation-of-the-open-source-licence/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Since Copilot’s debut, Butterick has voiced criticism of the program.*
Microsoft paid $7.5 billion buying GitHub in 2018 and has since integrated the code repository into its developer tools while taking a largely hands-off stance. Matthew Butterick, a writer, attorney, and programmer, has some problems with GitHub Copilot, Microsoft’s machine-learning based code helper, and how it appears to be treating open source licences incorrectly.
GitHub Copilot, a plugin for Visual Studio and other IDEs, operates by providing “suggestions” for code completion as you type. Codex serves as the system’s power source. However, developers like Butterick are having trouble with how the AI is learned, or more specifically, from where it is trained.
The issue here is that the public repositories on which GitHub is trained are licenced and demand credit when their work is utilised. Although Microsoft has been evasive about its usage of the code, referring to it as fair use, Copilot is able to generate verbatim portions of code in addition to suggestions.
As per OpenAI, the developers of Codex (which is licensed by Microsoft), “Codex was trained on tens of millions of public repositories including code on GitHub. Microsoft itself has vaguely described the training material as billions of lines of public code”. |
15,168 | 在 GNOME 文件应用中以 Root 身份打开文件的最简单方法 | https://www.debugpoint.com/gnome-files-root-access/ | 2022-10-23T15:32:00 | [
"root",
"文件管理器"
] | /article-15168-1.html |
>
> 这是在 GNOME 文件应用中以 root 身份访问文件或目录的最简单方法。
>
>
>

在 Windows 中,你通常可以在右键单击上下文菜单中以“以管理员身份打开”的方式打开文件或文件夹。
该功能是文件管理器的一部分,对于 Windows,它是 Windows 资源管理器的一部分。但是,它是由操作系统及其权限控制模块执行的。
在 Linux 发行版及其文件管理器中,情况略有不同。不同的桌面有自己的处理方式。
由于以管理员(root)身份修改文件和文件夹是有风险的,并且可能导致系统损坏,因此用户无法通过文件管理器的 GUI 轻松使用该功能。
例如,KDE Plasma 的默认文件管理器(Dolphin)最近 [添加了此功能](https://www.debugpoint.com/dolphin-root-access/),因此当需要 root 权限时,它会通过 PolicyKit KDE Agent(polkit)窗口询问你,如下所示。

而不是相反的方式。比如,你想在文件管理器中通过 root 打开/执行一些东西时,你不能使用 `sudo dolphin` 以 root 权限运行文件管理器本身。
在某种程度上,它挽救了许多不可预见的情况。但是高级用户总是可以通过终端使用 `sudo` 来完成他们的工作。
### GNOME 文件应用(Nautilus)和对文件、目录的 root 访问权限
话虽如此,[GNOME 文件应用](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Files)(又名 Nautilus)有一种方法可以通过 root 打开文件和文件夹。
以下是方法:
* 打开 GNOME 文件应用(Nautilus)。
* 然后单击左侧窗格中的“<ruby> 其他位置 <rt> Other Locations </rt></ruby>”。
* 按 `CTRL+L` 调出地址栏。
* 在地址栏中,输入下面的内容并回车。
```
admin:///
```
* 它会要求输入管理员密码。当你成功验证,你就会以管理员身份打开系统。
* 现在,从这里开始,无论你做什么,它都是管理员或 root。



但是,与往常一样,请小心你作为管理员所做的事情。在你以 root 身份验证自己之后,通常很容易忘记。
这些选项不容易看到总是有原因的,以防止你和许多新的 Linux 用户破坏他们的系统。
祝好。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/gnome-files-root-access/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,170 | 开源 DevOps 工具的平台化未来 | https://opensource.com/article/22/10/open-source-devops-tools | 2022-10-24T09:27:50 | [
"DevOps"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15170-1.html | 
>
> 当商业 DevOps 工具市场着眼于平台时,是时候让开源 DevOps 工具重新定义它们的未来了。
>
>
>
DevOps 的开源根基是无法动摇的,即便有预言称全球的 DevOps 市场将在 2026 年之前达到 178 亿美元。不断变化的工作环境、安全和合规性问题,以及风险投资公司等等因素正在将市场推向 DevOps 平台,开发团队可以在云中获得完整的端到端 DevOps 工具链。
### 开源 DevOps 工具现状
我们要搞清楚一件事:开源工具不可能从 DevOps 世界中消失。现在,在开源和供应商提供的 DevOps 工具之间存在着一种平衡,开发人员会在两者间选择适合他们的工具。事实上,很多情况下,一个开发团队起初会为他们的 DevOps 流水线选择一个开源工具,后来又升级到商业版本。
### 三种开源 DevOps 工具实例
下面我们介绍一些开源 DevOps 工具的例子,每种工具都已经有了围绕其建立的商业化生态。
#### Git
源代码管理工具 [Git](https://opensource.com/article/22/4/our-favorite-git-commands) 作为源代码库,可能是 DevOps 工具链的主要基础之一。
Git 的两个最佳商业案例是 GitLab 和 GitHub。GitLab [接受开发者对其贡献开源项目](https://opensource.com/article/19/9/how-contribute-gitlab)。GitHub 也在着手努力成为一个 DevOps 平台,推出了人工智能版的结对编程 GitHub Copilot,在推出后受到了一些开源团体的褒贬不一的评价。
#### Jenkins
作为一个开源的自动化服务,Jenkins 因其易于安装、配置和可扩展性而受到推崇。
CloudBees 提供了 JenkinsX,JenkinsX 是一套开源的解决方案,可以为 Kubernetes 上的云原生应用提供自动化持续集成和持续交付(CI/CD)以及自动化测试工具。他们还为JenkinsX 提供商业支持,包括:
* 访问 CloudBees 的专业技术技能
* 24x7 技术支持
* 访问 CloudBees 的文档和在线知识库
#### Kubernetes
随着越来越多的组织寻求企业级的容器编排解决方案,[Kubernetes](https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-kubernetes) 的发展成为必然。尽管有人批评其复杂性。
自然而然的,Kubernetes 周边有完整的、蓬勃发展的产业。根据 Allied 市场调研的数据,全球容器和 [Kubernetes 安全](https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2019/1/kubernetes-security-4-tips-manage-risks?intcmp=7013a000002qLH8AAM) 市场在 2020 年的估值为 7.14 亿美元,预计到 2030 年将达到 8.42 亿美元。
### 目前的 DevOps 工具链
各个行业仍有很多<ruby> 自建 <rt> build-your-own </rt></ruby>(BYO)的 CI/CD 工具链在发挥作用。支持 DevOps 功能的开源项目仍在蓬勃发展。
BYO 工具链可以集成其他工具,而且非常具有扩展性,这对于持续迭代其 DevOps 实践的组织来说一直是一个优势。在出于业务、IT 和安全原因寻求标准化的企业中,缺乏标准的材料清单可能是个麻烦。
虽然 DevOps 平台的出现并没有被忽视,但许多组织早在大流行之前就将他们的 CI/CD 工具链迁移到了公有云。长期以来,工具链本身的安全性一直是一个不断上升的问题,而公有云基础设施提供了身份访问管理(IAM)和其他安全功能来控制访问。
### DevOps 平台是敌是友?
DevOps 平台是一个端到端的解决方案,它将 CI/CD 工具链的所有功能放入云中。DevOps 平台的例子包括 GitLab 和 Harness。GitHub 也在采取行动,使自己成为一个 DevOps 平台。
#### 优势(即便只从企业买家角度考虑)
DevOps 平台对那些已经适应了 SaaS 和云计算行业的基于消费和订阅的定价的企业买家很有吸引力。在这个远程和混合工作的世界里,对可维护性、安全、合规性和开发人员的生产力的担忧肯定是技术领导者的首要考虑。对这些人来说,在 DevOps 平台上实现标准化是很有吸引力的。
#### 劣势
在依赖供应商提供的 DevOps 工具链时,人们会想到对供应商锁定功能的古老担忧。开发团队构建和维护其工具链的可扩展性不会像他们从头开始制作工具链时那样,更不用说引入新的工具来改善他们的工作流程了。
DevOps 平台供应商也有潜在的经济方面的劣势。想一想,一个被高估的 DevOps 工具初创公司如果没有达到其投资者的高额财务目标,可能会发生什么。同样,也可能有一些较小的初创供应商得不到下一轮的资金,而慢慢消失。
虽然 DevOps 平台的出现在很多方面都是有意义的,但它确实违背了促成我们今天使用的 DevOps 工具的开源精神。
### DevOps 工具:一个拐点
随着工作模式的改变,人们对 DevOps 工具链的安全和合规性的关注必然会增加。
#### 正在变化的工作环境
我们的工作方式与企业其他部门一样影响着 DevOps 团队。远程和混合 DevOps 团队需要安全的工具链。整个流水线中不断变化的协作和报告要求,如异步工作和经理要求返回办公室等,也是日益增长的必要条件。
#### 软件供应链安全市场
在高调的攻击和美国联邦政府的回应之后,软件供应链安全市场引起了很多关注。目前还没有组织将软件供应链的攻击归咎于开源,但我们将看到 DevOps/DevSecOps 实践和工具的延伸,以对抗这种威胁。不过,当一切都结束时,DevOps/DevSecOps 的工具和实践将超过一些转向这一趋势的初创公司。
### 结语
对于 DevOps 领域的开源软件(OSS)项目来说,这还远远没有结束,但 DevOps 利益相关者有权开始询问未来的工具链。然而,OSS DevOps 项目确实需要考虑它们的未来,特别是考虑到日益增长的直接影响流水线的安全和合规性问题。
DevOps 平台供应商与开源工具的未来趋势是合作性竞争,即 DevOps 平台供应商向作为其平台基础的开源工具贡献时间、金钱和资源。一个有趣的例子就是 [OpsVerse](https://www.opsverse.io/),它用他们为客户管理的开源工具提供了一个 DevOps 平台。
然后,还有一个未来,随着更多的企业构建的工具链迁移到云端,开源 DevOps 工具项目将继续繁荣和创新。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/10/open-source-devops-tools>
作者:[Will Kelly](https://opensource.com/users/willkelly) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lxbwolf](https://github.com/lxbwolf) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The open source roots of DevOps tools are undeniable, even with a prediction that the global DevOps market will reach $17.8 billion by 2026. The changing world of work, security, and compliance concerns, along with venture capital firms, are pushing the market to DevOps platforms where development teams can access a complete end-to-end DevOps toolchain in the cloud.
## The current state of open source DevOps tools
Let's get one thing straight: There's no way open source tools will disappear from the DevOps world. Right now, there's a balance between open source and vendor DevOps tools, with developers using what works for them. Indeed, there are plenty of cases when a development team chooses an open source tool for their DevOps pipeline only to upgrade later to a commercial version.
## 3 examples of open source DevOps tools
Here are some examples of open source DevOps tools with a commercial business built around them.
### Git
[Git](https://opensource.com/article/22/4/our-favorite-git-commands)–the source code management tool–is probably one of the main foundations for DevOps toolchains serving as a source code repository.
The two best commercial examples of Git are GitLab and GitHub. GitLab [accepts contributions](https://opensource.com/article/19/9/how-contribute-gitlab) to its open source project. GitHub is embarking on an effort to become a DevOps platform as well with the launch of GitHub Copilot–an AI pair programmer–launching to mixed reviews and criticism from some open source groups.
### Jenkins
An open source automation server, Jenkins is prized for its easy installation, configuration, and extensibility.
CloudBees offers JenkinsX, an open-source solution that provides automated continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) and automated testing tools for cloud-native applications on Kubernetes. They also provide commercial support for JenkinsX, including:
- Access to CloudBees technical expertise
- 24x7 technical support
- Access to CloudBees documentation and online knowledge base
### Kubernetes
The growth of [Kubernetes](https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-kubernetes) is undeniable as more organizations seek an enterprise-grade container orchestration solution. Despite criticisms about its complexity, Kubernetes
There's an entire burgeoning industry around Kubernetes, and with good reason. According to Allied Market Research, the global container and [Kubernetes security](https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2019/1/kubernetes-security-4-tips-manage-risks?intcmp=7013a000002qLH8AAM) market was valued at $714 million in 2020 and is projected to reach $8242 million by 2030.
## DevOps toolchains today
There are still plenty of build-your-own (BYO) CI/CD toolchains in play across industries. The open source projects powering DevOps functions are still prospering,
BYO toolchains are integration-ready and very extensible, which has always been a strength for organizations continuing to iterate on their DevOps practices. The lack of a standard bill of materials might prove troublesome in enterprises seeking standardization for business, IT, and security reasons.
While the advent of DevOps platforms isn't going unnoticed, many organizations migrated their CI/CD toolchains to the public cloud well before the pandemic. The security of the toolchain itself has long been a rising concern, and public cloud infrastructure provides Identity Access Management (IAM) and other security features to control access.
## DevOps platforms: Friend or foe?
A DevOps platform is an end-to-end solution that places all functions of the CI/CD toolchain into the cloud. Examples of DevOps platforms include GitLab and Harness. GitHub is also making moves to become a DevOps platform in its own right.
### Advantages (even if only in the eyes of enterprise buyers)
DevOps platforms are attractive to enterprise buyers who are already comfortable with the consumption-based and subscription-based pricing of the SaaS and cloud industries. Concerns about maintenance, security, compliance, and developer productivity are certainly at the top of mind for technology leaders in this remote and hybrid work world. Standardizing on a DevOps platform becomes an appealing story to these people.
### Disadvantages
Age-old concerns about vendor lock-in come to mind when depending on a vendor for a DevOps toolchain. The extensibility of development teams building and maintaining their toolchains isn't going to be quite the experience as it was when they made their toolchains from scratch, much less bringing in new tools to improve their workflows.
There are also potential economic disadvantages with DevOps platform providers. Think what might happen to an overvalued DevOps tools startup that doesn't meet its investors' lofty financial goals. Likewise, there could be smaller startup vendors that may not receive their next round of funding and fade away into irrelevance.
While the advent of a DevOps platform makes sense in many ways, it does work against the open source ethos that has helped build the DevOps tools we use today.
## DevOps tools: An inflection point
Security and compliance concerns for DevOps toolchains continue to mount as working models change. It's only natural.
### The changing world of work
How we work affects DevOps teams just like the rest of the enterprise. Remote and hybrid DevOps teams require secure toolchains. Changing collaboration and reporting requirements across the pipelines are also growing necessities, such as asynchronous work and executives demanding a return to the office.
### Software supply chain security market
The software supply chain security market draws much attention after high-profile attacks and the federal government response. No organization has yet to blame open source for a software supply chain attack, but we're going to see an extension of DevOps/DevSecOps practices and tools to combat this threat. When it's all said and done, though, DevOps/DevSecOps tools and practices will outlast some startups that pivoted to the trend.
## Final thoughts
It's far from game over for OSS projects in the DevOps space, but DevOps stakeholders have a right to start asking questions about the toolchains of the future. However, OSS DevOps projects do need to consider their future, especially in light of growing security and compliance concerns that directly impact pipelines.
There's a future of coopetition where the DevOps platform providers donate time, money, and resources to the open source tools that serve as a foundation for their platforms. An interesting example of a potential future is [OpsVerse](https://www.opsverse.io/), which offers a DevOps platform with open source tools they manage for their customers.
Then again, there's also a future where the open source DevOps tools projects continue to prosper and innovate as more enterprise-built toolchains migrate to the cloud in more significant numbers.
**[ Kickstart an organizational culture change. Read the first article in a series, DevSecOps: 5 tips for seeding a culture transformation ]**
## Comments are closed. |
15,171 | Ubuntu 22.10 的新变化 | https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-22-10-release/ | 2022-10-24T10:15:00 | [
"Ubuntu"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15171-1.html |
>
> Ubuntu 22.10 是一个令人印象深刻的版本,它拥有新的快速切换功能、应用程序散布,以及更多。
>
>
>

Ubuntu 22.10 “<ruby> 充满活力的捻角羚 <rt> Kinetic Kudu </rt></ruby>”来了。它带来了许多重大的改进,特别是 Linux 内核 5.19 和 GNOME 43 的体验。
当然,这是一个经过定制的 GNOME 体验,现有的 Ubuntu 用户会很熟悉。
那么,Ubuntu 22.10 都有哪些新变化呢?让我们一起来看看。
### Ubuntu 22.10 的新变化

除了 GNOME 43 之外,Ubuntu 22.10 还包括:
* 一个改进的 <ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby> 应用程序。
* 经典的 Unity 应用程序<ruby> 散布模式 <rt> Spread Mode </rt></ruby>的复活。
* 一些著名的应用程序被移植到 GTK4 和 Libadwaita。
* 全系统支持 WebP。
* PipeWire 采样管默认的音频服务器。
* Linux 内核 5.19。
>
> ? Ubuntu 22.10 将被支持九个月,直到 **2023 年 7 月**。如果你想要稳定而不是功能,你应该更愿意使用 [LTS 版本](https://itsfoss.com/long-term-support-lts/)。
>
>
>
#### ? 视觉改进
当第一次测试一个新版本时,视觉上的变化总是最先被注意到的。在 Ubuntu 22.10 中尤其如此,这要归功于 [GNOME 43](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-43-release/) 所带来的重大改进。

首先,我们有全新的快速设置菜单,它取代了旧的、相当笨拙的系统菜单。与安卓、iOS 和 Windows 11 中的菜单类似,这个新增的菜单允许你打开和关闭 Wi-Fi 和蓝牙,所有这些都无需进入<ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby>应用程序。
当然,在这个版本中我们还得到了全新的壁纸。

对于这个变化,我除了喜欢并希望从社区中看到更多这样的设计之外,没有什么别的可说的。
此外,更多的应用程序被移植到了 GTK4,包括对 Nautilus 文件管理器的改进。
一些有价值的新增功能包括:
* 拖动并选择文件的能力(橡皮筋选择)。
* 自适应视图与一个紧凑的窗口。
* 新的文件上下文菜单。
你可以通过我们的详细报道来探索 Nautilus 的改进。
#### ? 应用程序散布回来了!
我不太喜欢的 GNOME 的一个部分是多窗口应用程序的切换,我相信很多其他用户都有这样的不满。

幸运的是,Ubuntu 22.10 现在提供了一个很好的解决方案,对于长期用户来说应该是很熟悉的。终于,在 2017 年放弃对 Unity 的支持五年后,Ubuntu 的开发者们又把应用程序<ruby> 散布 <rt> Spread </rt></ruby>带了回来。

这是一个重大的改进,我很惊讶 GNOME 自己没有这样做。
#### ?️ 设置的改进
虽然不是大多数人日常使用的应用程序,但<ruby> 系统设置 <rt> System Settings </rt></ruby>是 GNOME 体验的一个核心部分。考虑到这一点,看到它接受了一次重大的视觉改造,以及移植到了 GTK 4 和 Libadwaita,真是太棒了。

因此,它现在变得更好看了,而且是自适应的,这意味着它在任何尺寸下都能很好地工作,甚至在像 PinePhone 这样的 Linux 手机上也能很好地工作!
另一个与设置有关的变化是增加了一个新的 “<ruby> Ubuntu 桌面设置 <rt> Ubuntu Desktop Settings </rt></ruby>”菜单项。这提供了一个单一的、统一的地方来定制和改变你所有的 Ubuntu 特定设置。
#### Linux 内核 5.19
Ubuntu 22.10 还带来了一个更新的内核,即 [Linux 内核 5.19](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-19-release/)。这个版本的改进相当少,尽管它确实带来了对一些下一代硬件的改进支持。
你应该注意到这是 Linux 5.x 系列的最后一个版本,因为 Linux 内核下一个版本跳到了 6.0。
#### 其他变化

总的来说有几个细微的调整。但其中一些基本的调整包括:
* 图像应用程序默认支持 .WebP 图像格式。
* GNOME 文本编辑器是默认编辑器。你可以安装 gedit 并使其成为默认的。
* GNOME 图书应用程序已经不再可用。Ubuntu 推荐 [Foliate](https://itsfoss.com/foliate-ebook-viewer/) 作为替代。
* 不再默认安装 To Do 应用程序,并且它有了一个新的名字,“Endeavour”。
* GNOME 终端仍然是默认的终端应用。如果需要,可以安装 [GNOME 控制台](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-console/)。
* 更新了 Firefox 104、[Thunderbird 102](https://news.itsfoss.com/thunderbird-102-release/) 和 [Libreoffice 7.4](https://news.itsfoss.com/libreoffice-7-4-release/) 等应用程序。
* 更多的应用程序已经被移植到 GTK4,特别是 [Nautilus](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-files-43/)。
>
> ℹ️ 注意,我们的列表集中在对桌面终端用户重要的变化上。如果你想知道更多关于服务器和其他使用情况的变化/更新,请参考 [官方发布说明](https://discourse.ubuntu.com/t/kinetic-kudu-release-notes/27976)。
>
>
>
### 下载 Ubuntu 22.10
你可以从 [Ubuntu 的中央镜像库](https://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/releases/22.10/release/) 或其 [官方网站](https://ubuntu.com/download/desktop) 下载最新的 ISO。
\*\*官方网站/仓库可能需要一段时间来提供 ISO 的下载。
>
> **[下载Ubuntu 22.10](https://ubuntu.com/download/desktop)**
>
>
>
? 有兴趣尝试 Ubuntu 22.10 吗?请在评论中告诉我你的想法。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-22-10-release/>
作者:[Jacob Crume](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Ubuntu 22.10 "**Kinetic Kudu**" is here. It brings many significant improvements, notably Linux Kernel 5.19 and the GNOME 43 experience.
Of course, this is a customized GNOME experience that will be familiar to existing Ubuntu users.
So, what are all the goodies with Ubuntu 22.10? Let us find out:
## Ubuntu 22.10 Release: What's New?
Along with GNOME 43, Ubuntu 22.10 also includes:
**An improved Settings app.****The resurrection of the classic Unity application spread.****A few notable apps ported to GTK4 and Libadwaita.****System-wide WebP support.****PipeWire is the default audio server.****Linux Kernel 5.19.**
**July 2023**. If you want stability over features, you should prefer using an
[LTS version](https://itsfoss.com/long-term-support-lts/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
[Cloud IDE · Online Code Editor · CodeanywhereSave time by deploying a development environment in seconds. Collaborate, code, learn, build, and run your projects directly from your browser.](https://codeanywhere.com/?ref=itsfoss)

### 🎨 Visual Improvements
When first testing a new release, visual changes are always the first to be noticed. This is especially true with Ubuntu 22.10, thanks to the significant improvements introduced with [GNOME 43](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-43-release/).
First, we have the brand-new quick settings menu, which replaced the old and rather clunky system menu. Similar to the menus found in Android, iOS, and Windows 11, this addition allows you to switch on and off Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, all without going into the settings app.
Of course, we also get brand-new wallpaper with this release.

There's not much else to say about it other than that I love this switch and hope to see more designs like this from the community.
Additionally, more apps have been ported to GTK4, including the refinements wit the **Nautilus** file manager.
Some valuable feature additions include:
**Ability to drag and select files (rubber band selection).****Adaptive view with a compact window.****New document context menu.**
You can go through our detailed coverage to explore the improvements with Nautilus.
[6 New Changes Coming to Nautilus File Manager in GNOME 43We have a few months to go before the GNOME 43 release, but the development activity for GNOME applications is in full swing. For instance, the support for extensions in GNOME Web 43 alpha version. Similarly, there are a few exciting changes coming to GNOME Files (Nautilus), especially for…](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-files-43/)

### 👴 The Application Spread Is Back!
One of my minor favorite parts of GNOME is the multi-windows app switching, a gripe that I'm sure many other users share.
Fortunately, **Ubuntu 22.10** is now offering a great solution that should be familiar to long-time users. Finally, five years after dropping support for Unity back in 2017, the Ubuntu developers have brought back the application spread.
This is a significant improvement and something I'm surprised GNOME hasn't done itself.
### 🛠️ Settings Improvements
Although not an app that most people use daily, System Settings is a core part of the GNOME experience. With that in mind, it is fantastic to see it receiving a major visual overhaul, as well as a port to GTK 4 and Libadwaita.
As a result, it is now better-looking and adaptive, meaning it will work well at any size and even on Linux phones like the PinePhone!
Another Settings-related change is adding a new "**Ubuntu Desktop Settings**" menu item. This offers a single, unified place to customize and change all your Ubuntu-specific settings.
### Linux Kernel 5.19
Ubuntu 22.10 also brings a newer kernel i.e., [Linux kernel 5.19](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-19-release/). This release was pretty light on improvements, although it did bring improved support for some next-gen hardware.
You should note that this is the last release in the Linux 5.x series, as Linux Kernel 6.0 is the next version bump.
[Wow! Linux Kernel 6.0 Lands With Intel 13th Gen Raptor Lake CPU SupportLinux Kernel 6.0 is here with Intel Raptor lake support and more!](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-6-0-release/)

### Other Changes
There are several subtle refinements overall. But some of those essential tweaks include:
- Default image apps support
**.WebP**image format. **GNOME Text Editor**is the default editor. You can install gedit and make it the default.**GNOME Books app**is no longer available. Ubuntu recommends[Foliate](https://itsfoss.com/foliate-ebook-viewer/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)as a replacement.**To Do app**is no longer installed by default and has a new name, "*Endeavour*".**GNOME Terminal**is still the default terminal app.[GNOME Console](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-console/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)can be installed if required.- Updated apps like Firefox 104,
[Thunderbird 102](https://news.itsfoss.com/thunderbird-102-release/), and[Libreoffice 7.4](https://news.itsfoss.com/libreoffice-7-4-release/). - More apps have been ported to GTK4, notably
[Nautilus](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-files-43/).
[official release notes](https://discourse.ubuntu.com/t/kinetic-kudu-release-notes/27976?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
### Suggested Read 📖
[Install Gedit on Ubuntu 22.10 and Make it Default Text Editor - It’s FOSSgedit is not the default text editor in Ubuntu 22.10. Here’s how to install Gedit on Ubuntu and make it the default text editor again.](https://itsfoss.com/install-gedit-ubuntu/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## Download Ubuntu 22.10
You can download the latest ISO from [Ubuntu's central image repository](https://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/releases/22.10/release/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) or its [official website](https://ubuntu.com/download/desktop?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
**It might take a while for the official website/repo to make the ISO available to download.**
💬 *Interested in trying Ubuntu 22.10? Let me know your thoughts in the comments.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,173 | Kubuntu 22.10 的新变化 | https://news.itsfoss.com/kubuntu-22-10-release/ | 2022-10-24T23:23:44 | [
"Kubuntu"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15173-1.html |
>
> Kubuntu 22.10 可能不是最令人兴奋的升级。但是,它包括了一些有用的变化。
>
>
>

Kubuntu 是 Ubuntu 的一个官方版本,它在一个精致的 KDE 驱动的软件包中提供了很多功能。
Kubuntu 22.10 的发布带来了各种改进和一个 [KDE Plasma](https://kde.org/plasma-desktop/) 的更新版本。
让我们来看看这个版本的亮点。
### Kubuntu 22.10 有什么新变化?

Kubuntu 22.10 带来了很多更新,其中一些重要的更新包括:
* KDE Plasma 5.25
* Linux 内核 5.19
* PipeWire
* Firefox 104
* Qt 5.15.6
>
> ? Kubuntu 22.10 将被支持九个月,直到 **2023 年 7 月**。如果你想要稳定而不是功能,你应该更喜欢使用 [LTS 版本](https://itsfoss.com/long-term-support-lts/)。
>
>
>
#### KDE Plasma 5.25

尽管最近 [KDE Plasma 5.26](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-26-release/) 已经发布了,但 Kubuntu 22.10 还是搭载了 KDE Plasma 5.25。
然而,KDE Plasma 5.25 与 5.24 相比仍然是一个重大的更新,它包含了很多改进,例如,加强了对触摸板/触摸屏的支持,升级了用户界面等等。
你可以阅读我们对 KDE Plasma 5.25 的报道来了解更多。
>
> **[KDE Plasma 5.25:颜色、主题和其他改进](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-25-release/)**
>
>
>
另外,你可以期待 KDE Plasma 5.26 作为一个小版本发布,而不是作为 Kubuntu 22.10 发布的一部分。
#### 默认采用 PipeWire
像大多数基于 Ubuntu 22.10 的发行版一样,[PipeWire](https://pipewire.org/) 是这个版本的 Kubuntu 的默认音频/视频处理器。
它取代了 [PulseAudio](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/PulseAudio/),众所周知,它与 Ubuntu 22.10 不兼容。
#### Linux 内核 5.19

Kubuntu 22.10 采用了最新的 Linux 内核 5.19,这应该会带来对 ARM SoC 和 Arc Alchemist GPU 的支持、Btrfs 的各种改进、对 AMD RDNA3 图形的初步支持等等。
#### 测试用的 Wayland 会话

Kubuntu 22.10 具有对 Plasma Wayland 会话的初步支持,但它仅用于测试目的,并不是一个完整的集成。

#### 其他升级
其他一些更新包括:
* 自定义桌面重点颜色
* 默认浏览器是 Firefox 104 Snap
* Qt 5.15.6
* LibreOffice 7.4
* 改进的应用程序商店
要探索更多关于该版本的信息,请参考 [官方发布说明](https://wiki.ubuntu.com/KineticKudu/ReleaseNotes/Kubuntu)。
### 下载 Kubuntu 22.10
你可以从 [Ubuntu 的中央镜像库](https://cdimage.ubuntu.com/kubuntu/releases/22.10/release/) 或其 [官方网站](https://kubuntu.org/getkubuntu/) 下载最新的 ISO。
>
> **[Kubuntu 22.10](https://kubuntu.org/getkubuntu/)**
>
>
>
*它的官方网站可能需要一段时间来提供 ISO。*
? 你对这个版本感到兴奋吗?
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/kubuntu-22-10-release/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Kubuntu is an official Ubuntu flavor that offers a lot of functionality in a refined KDE-powered package.
The release of Kubuntu 22.10 promises various improvements and a newer version of [KDE Plasma](https://kde.org/plasma-desktop/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
Let us go through the highlights of this release.
## Kubuntu 22.10: What's New?

Kubuntu 22.10 is bringing in a lot of updates, some of the important ones that you can expect are:
**KDE Plasma 5.25****Linux Kernel 5.19****PipeWire****Firefox 104****Qt 5.15.6**
**July 2023**. If you want stability over features, you should prefer using an
[LTS version](https://itsfoss.com/long-term-support-lts/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
### KDE Plasma 5.25
Even though[ KDE Plasma 5.26](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-26-release/) was released recently, Kubuntu 22.10 ships with KDE Plasma 5.25.
However, KDE Plasma 5.25 is still a major update over 5.24, which contained a lot of improvements such as, enhanced support for touchpads/touchscreens, upgrades to the user interface, and more.
You can read our coverage of KDE Plasma 5.25 to learn more:
[KDE Plasma 5.25 Release is All About Color, Theme, and Other ImprovementsKDE Plasma 5.25 has been one of the most anticipated releases, considering its recent focus on visual refinements and workflow improvements. For instance, you got an updated Breeze theme and a new overview effect to improve the workflow with KDE Plasma 5.24 LTS. Finally, KDE Plasma 5.25](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-25-release/)

Also, you can expect KDE Plasma 5.26 to come as a point release instead of being part of the launch of Kubuntu 22.10.
### PipeWire Default
Like most Ubuntu 22.10-based distros, [PipeWire](https://pipewire.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is the default audio/video handler in this version of Kubuntu.
It replaces [PulseAudio](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/PulseAudio/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), known to not play nice with Ubuntu 22.10.
### Linux Kernel 5.19
Kubuntu 22.10 features the latest Linux Kernel 5.19, this should lead to improved support for ARM SoCs, Arc Alchemist GPUs, various BTRFS improvements, initial support for AMD RDNA3 graphics, and more.
[Linus Torvalds Uses Apple MacBook Hardware to Release Linux Kernel 5.19Three months after the last kernel release, Linux Kernel 5.19 is finally here. This exciting release brings plenty of improvements to every aspect of the kernel and opens up opportunities with new hardware. The most interesting part is that the Linux creator Linus Torvalds used an Apple MacBook…](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-19-release/)

### Wayland Session for Testing
Kubuntu 22.10 features initial support for a Plasma Wayland session, but it is intended for testing purposes only and is not a complete integration.
### Other Upgrades
Some of the other updates include the following:
- Ability to customize desktop accent color.
- Firefox 104 snap as the default browser.
- Qt 5.15.6
- LibreOffice 7.4
- Improved App Store.
To explore more about the release, refer to the [official release notes](https://wiki.ubuntu.com/KineticKudu/ReleaseNotes/Kubuntu?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Download Kubuntu 22.10
You can download the latest ISO from [Ubuntu's central image repository](https://cdimage.ubuntu.com/kubuntu/releases/22.10/release/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) or its [official website](https://kubuntu.org/getkubuntu/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
It might take a while for its official website to make the ISO available.
💬 Are you excited about this release?
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,174 | Ubuntu MATE 22.10 的新变化 | https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-mate-22-10-release/ | 2022-10-25T00:09:00 | [
"Ubuntu",
"Ubuntu MATE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15174-1.html |
>
> Ubuntu MATE 22.10 已经发布,其中有一些细微而有用的变化。来看看吧!
>
>
>

Ubuntu MATE 是 [Ubuntu 官方版本](https://itsfoss.com/which-ubuntu-install/) 之一,每次升级都会增加有趣的改进。
它的目标用户是那些既珍惜传统桌面的外观和感觉,又渴望现代操作系统的功能的用户。
Ubuntu MATE 22.10 版本增加了许多改进和功能,让我们来看看这些。
### Ubuntu MATE 22.10 的新变化

基于非 LTS 版本的 [Ubuntu 22.10](https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-22-10-features/) ,Ubuntu MATE 22.10 带来了多项更新,一些关键的亮点包括:
* 对 MATE 桌面的改进。
* 新的 AI 墙纸。
* PipeWire 是默认的音频服务器。
* 新的 MATE 用户管理器。
* Firefox 105 更新。
* LibreOffice 7.4。
>
> ? 注意,Ubuntu MATE 的升级通常包括更多的功能补充。但这一次,Martin Wimpress 一直致力于为 Debian MATE 版带来类似的体验。你可以在我们之前的报道中阅读更多细节。
>
>
>
>
> [准备好在 Debian Linux 上获得 Ubuntu MATE 体验吧!](https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-mate-debian/)
>
>
>
#### MATE 桌面升级

MATE 桌面收到了各种错误修复和对 Ayatana 指示器、MATE 面板的更新。
现在,你可以将小程序居中对齐,与通常的左右对齐选项一起。
这项功能将在 MATE 桌面 1.28 版中正式出现,但 Ubuntu MATE 团队在 MATE 桌面 1.27 版的基础上将其与这个版本一起推出。
#### MATE 用户管理器

MATE 用户管理器是该发行版的一个新的补充,允许你添加、修改、删除用户账户。
有了它,你可以选择哪些用户可以成为管理员、设置自动登录、设置个人资料图片,以及管理组成员资格。对于有多个用户的计算机来说,这是一个相当方便和急需的功能。
#### 新的 AI 壁纸

这个版本的另一大亮点是增加了新的 AI 生成的壁纸。
这些看起来很美 ?
鉴于人工智能生成的壁纸现在正大行其道,Ubuntu MATE 团队在 Ubuntu MATE 22.10 中加入了一批新的壁纸。
它是由 [Simon Butcher](https://twitter.com/simonjbutcher) 使用扩散模型创建的,用来描画 “捻角羚”。
#### Linux 内核 5.19
Ubuntu MATE 22.10 得益于 Linux 内核 5.19 带来的改进,对各种 ARM SoC、Arc Alchemist GPU 等提供了增强支持。
你可以阅读我们的相关报道以了解更多。
#### ?️ 其他变化和改进
与其他新版本一样,Ubuntu MATE 22.10 用 [PipeWire](https://pipewire.org/) 取代了 [PulseAudio](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/PulseAudio/),以获得更好的音频处理,并加入了额外的蓝牙编解码器,如 AAC、LDAC、aptX 和 aptX HD。
其他值得注意的变化包括:
* 更新的应用程序包括:Firefox 105、LibreOffice 7.4、Celluloid 0.20 和 Evolution 3.46。
* Ubuntu MATE HUD 支持 MATE、XFCE 和 Budgie,具有更多的配置能力。
如果你感到好奇,你可以查看 Ubuntu MATE 22.10 [官方发布说明](https://ubuntu-mate.org/blog/ubuntu-mate-kinetic-kudu-release-notes/)。
### 下载 Ubuntu MATE 22.10
你可以从 [Ubuntu 的中央镜像库](https://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-mate/releases/22.10/release/) 或其 [官方网站](https://ubuntu-mate.org/download/) 下载最新的 ISO。
*它的官方网站/仓库可能需要一段时间来提供 ISO。*
>
> ? Ubuntu MATE 22.10 将被支持九个月,直到 **2023 年 7 月** 。如果你想要稳定而不是功能,你应该更喜欢使用 [LTS 版本](https://itsfoss.com/long-term-support-lts/)。
>
>
>
>
> **[下载 Ubuntu MATE 22.10](https://ubuntu-mate.org/download/)**
>
>
>
? *有兴趣尝试 Ubuntu MATE 22.10 吗?请在评论中告诉我你的想法。*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-mate-22-10-release/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Ubuntu MATE is one of the [official Ubuntu flavours](https://itsfoss.com/which-ubuntu-install/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) that add interesting improvements with every upgrade.
It is aimed at users who cherish the look and feel of a traditional desktop but also desire the functionality of a modern operating system.
Ubuntu MATE 22.10 release adds a number of betterments and features, let us take a look at those.
## Ubuntu MATE 22.10: What's New?
Based on the non-LTS release of [Ubuntu 22.10](https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-22-10-features/) '*Kinetic Kudu*', Ubuntu MATE 22.10 brings in multiple updates, some key highlights include:
**Improvements to MATE Desktop.****New AI Wallpapers.****PipeWire is the default audio server.****New MATE User Manager.****Firefox 105 update.****LibreOffice 7.4.**
**Martin Wimpress**has been working to bring a similar experience to the Debian MATE edition. You can read more details in our previous coverage.
[Get Ready for Ubuntu MATE Experience on Debian Linux!Ubuntu MATE experience is coming to Debian’s MATE spin in 2023? Find out more here.](https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-mate-debian/)

### MATE Desktop Upgrades
MATE desktop receives various bug fixes and updates to the **Ayatana indicators** and the **MATE Panel**.
Now, you can align the applets to the **center** alongside the usual left and right alignment options.
This feature officially arrives with **MATE Desktop 1.28 **release, but the Ubuntu MATE team has made it available with this release on top of **MATE Desktop 1.27**.
### MATE User Manager
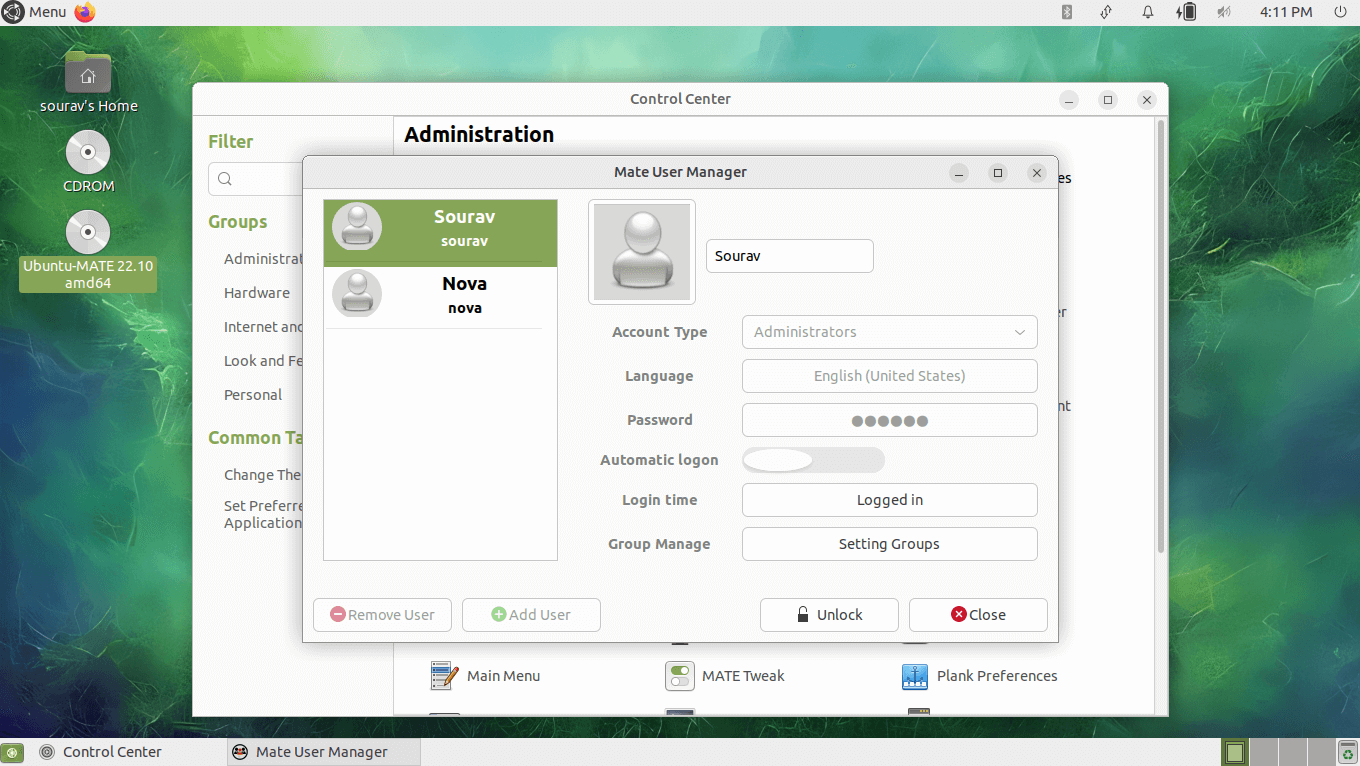
The MATE user manager is a new addition to the distro, allowing you to add/modify/remove user accounts.
With this, you can choose which users can be administrators, set up auto-login, set profile pictures, and manage group memberships. Pretty handy and a much-needed feature for computers with multiple users.
### New AI Wallpapers

Another big highlight of this release is the addition of new AI-generated wallpapers.
These look beautiful! 😍
Seeing that AI-generated wallpapers are all the rage right now, the Ubuntu MATE team has included a new bunch of them with Ubuntu MATE 22.10.
It was created by [Simon Butcher](https://twitter.com/simonjbutcher?ref=news.itsfoss.com) using diffusion models to illustrate 'kudu' (Antelope).
### Linux Kernel 5.19
Ubuntu MATE 22.10 leverages the improvements brought forward by Linux Kernel 5.19, including enhanced support for various ARM SoCs, Arc Alchemist GPUs, and more.
You can read our coverage of the same to learn more.
[Linus Torvalds Uses Apple MacBook Hardware to Release Linux Kernel 5.19Three months after the last kernel release, Linux Kernel 5.19 is finally here. This exciting release brings plenty of improvements to every aspect of the kernel and opens up opportunities with new hardware. The most interesting part is that the Linux creator Linus Torvalds used an Apple MacBook…](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-19-release/)

### 🛠️ Other Changes and Improvements
As with every other new release, Ubuntu MATE 22.10 replaces [PulseAudio](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/PulseAudio/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) with [PipeWire](https://pipewire.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for better audio handling and the inclusion of additional Bluetooth codecs such as AAC, LDAC, aptX, and aptX HD.
Other notable changes include:
**Updated apps include Firefox 105, LibreOffice 7.4, Celluloid 0.20 and Evolution 3.46.****Ubuntu MATE HUD supports MATE, XFCE, and Budgie with more configuration ability.**
You can check out Ubuntu MATE 22.10 [official release notes](https://ubuntu-mate.org/blog/ubuntu-mate-kinetic-kudu-release-notes/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) if you are curious.
## Download Ubuntu MATE 22.10
You can download the latest ISO from [Ubuntu's central image repository](https://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-mate/releases/22.10/release/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) or its [official website](https://ubuntu-mate.org/download/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
It might take a while for its official website/repo to make the ISO available.
**July 2023**. If you want stability over features, you should prefer using an
[LTS version](https://itsfoss.com/long-term-support-lts/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
💬 *Interested in trying Ubuntu MATE 22.10? Let me know your thoughts in the comments.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,175 | 在 Ubuntu 中配置 SSH 的完整指南 | https://itsfoss.com/set-up-ssh-ubuntu/ | 2022-10-25T10:21:20 | [
"SSH"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15175-1.html | 
>
> 如今 SSH 已成为了登录远程服务器的默认方式。
>
>
>
SSH 的全称是 “<ruby> 安全的 Shell <rt> Secure Shell </rt></ruby>”,它功能强大、效率高,这个主流的网络协议用于在两个远程终端之间建立连接。让我们不要忘记它名称的“安全”部分,SSH 会加密所有的通信流量,以防止如劫持、窃听等攻击,同时提供不同的身份认证方式和无数个配置选项。
在这份新手指南中,你会学到:
* SSH 的基本概念
* 设置 SSH 服务器(在你想要远程登录的系统上)
* 从客户端(你的电脑)通过 SSH 连接远程服务器
### SSH 的基本概念
在学习配置过程前,让我们先了解一下 SSH 的全部基础概念。
SSH 协议基于<ruby> 客户端-服务器 <rt> server-client </rt></ruby>(CS)架构。“<ruby> 服务器 <rt> Server </rt></ruby>”允许“<ruby> 客户端 <rt> Client </rt></ruby>”通过通信通道进行连接。该信道是经过加密的,信息交换通过 SSH 公私钥进行管理。

[OpenSSH](https://www.openssh.com/) 是在 Linux、BSD 和 Windows 系统上提供 SSH 功能的最流行的开源工具之一。
想要成功配置 SSH,你需要:
* 在作为服务器的机器上部署 SSH 服务器组件,它由 `openssh-server` 包提供。
* 在你远程访问服务器的客户端机器上部署 SSH 客户端组件,它由 `openssh-client` 包提供,大多数 Linux 和 BSD 发行版都已经预装好了。
区分服务器和客户端是十分重要的事情。或许你不想要你的 PC 作为 SSH 服务器,除非你有充分理由希望其他人通过 SSH 连接你的系统。
通常来说,你有一个专用的服务器系统。例如,一个 [运行 Ubuntu 的树莓派](https://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu-server-raspberry-pi/)。你可以 [启用树莓派的 SSH 服务](https://itsfoss.com/ssh-into-raspberry/),这样你可以在你 PC 中的终端中,通过 SSH 控制并管理该设备。
有了这些信息,让我们看看如何在 Ubuntu 上设置 SSH 服务器。
### 在 Ubuntu 服务器中配置 SSH
设置 SSH 并不复杂,只需要以下几步。
#### 前提
* 一个在服务器端拥有 `sudo` 权限的用户
* 可以下载所需包的互联网连接
* 在你的网络中至少有另一个系统。可以是局域网中的另一台电脑,远程服务器或者计算机中托管的虚拟机。
**再次强调,在你想要通过 SSH 远程登录的系统上安装 SSH 服务。**
#### 第一步:安装所需包
让我们从打开终端输入一些必要命令开始。
注意,在安装新的包或者软件前,要 [更新你的 Ubuntu 系统](https://itsfoss.com/update-ubuntu/),以确保运行的是最新版本的程序。
```
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
```
你要运行 SSH 服务器的包由 OpensSSH 的 `openssh-server` 组件提供:
```
sudo apt install openssh-server
```

#### 第二步:检查服务器状态
当你下载并安装完包后,SSH 服务器应该已经运行了,但是为了确保万无一失我们需要检查一下:
```
service ssh status
```
你还可以使用 `systemctl` 命令:
```
sudo systemctl status ssh
```
你应该会看到这样的结果,其中 `active` 是高亮的。输入 `q` 退出该页面。

如果你的结果中 SSH 服务没有运行,使用这个命令运行它:
```
sudo systemctl enable --now ssh
```
#### 第三步:允许 SSH 通过防火墙
Ubuntu 带有名为 [UFW](https://itsfoss.com/set-up-firewall-gufw/)(<ruby> 简单的防火墙 <rt> Uncomplicated Firewall </rt></ruby>)的防火墙,这是管理网络规则的 `iptables` 的一个接口。如果启动了防火墙,它可能会阻止你连接服务器。
想要配置 UFW 允许你的接入,你需要运行如下命令:
```
sudo ufw allow ssh
```
UFW 的运行状态可以通过运行 `sudo ufw status` 来检查。
现在,我们的 SSH 服务器已经开始运行了,在等待来自客户端的连接。
### 连接远程服务器
你本地的 Linux 系统已经安装了 SSH 客户端。如果没有,你可以在 Ubuntu 中使用如下命令安装:
```
sudo apt install openssh-client
```
要连接你的 Ubuntu 系统,你需要知道它的 IP 地址,然后使用 `ssh` 命令,就像这样:
```
ssh username@address
```
将 **用户名**(`username`)改为你的系统上的实际用户名,并将 **地址**(`address`)改为你服务器的 IP 地址。
如果你 [不知道 IP 地址](https://itsfoss.com/check-ip-address-ubuntu/),可以在服务器的终端输入 `ip a` 查看结果。应该会看到这样的结果:

可以看到我的 IP 地址是 `192.168.1.111`。让我们使用 `username@address` 格式进行连接。
```
ssh [email protected]
```
这是你第一次连接到该 SSH 服务器,它会请求添加主机。输入 `yes` 并回车即可。

SSH 会立即告诉你该主机已经被永久添加了,并要求你输入指定用户的密码,输入密码并再次按回车即可。

瞧,你远程登录了你的 Ubuntu 系统!

现在,你可以在远程服务器的终端里和寻常一样工作了。
#### 关闭 SSH 连接
你只需要输入 `exit` 即可关闭连接,它会立马关闭不需要确认。

### 在 Ubuntu 中关闭并禁止 SSH
如果你想要停止 SSH 服务,需要运行该命令:
```
sudo systemctl stop ssh
```
该命令会关闭 SSH 服务,直到重启它或者系统重启。想要重启它,输入:
```
sudo systemctl start ssh
```
现在,如果你想要禁止 SSH 跟随系统启动,使用该命令:
```
sudo systemctl disable ssh
```
该命令不会停止当前的 SSH 会话,只会在启动的时候生效。如果你想要它跟随系统启动,输入:
```
sudo systemctl enable ssh
```
#### 其他 SSH 客户端
从 Linux 到 macOS,大多数 \*nix 系统中都有 `ssh` 工具,但这并不是唯一的选项,这里有几个可以在其他操作系统中使用的客户端:
* [PuTTY](https://www.putty.org/) 是一个自由开源的 Windows 系统上的 SSH 客户端。它功能强大并且简单易用。如果你从 Windows 系统上连接你的 Ubuntu 服务器,PuTTY 是最好的选择。(LCTT 译注:切记从官方网站下载。)
* 对安卓用户来说,[JuiceSSH](https://juicessh.com/) 是十分优秀的工具。如果你在旅途中需要一个移动客户端来连接你的 Ubuntu 系统,我强烈建议你试试 JuiceSSH。它已经出现了将近 10 年,并且可以免费使用。
* 最后是 [Termius](https://termius.com/),它可用于 Linux、Windows、macOS、iOS 和安卓。它有一个免费版本和几个付费选项。如果你运行大量服务器并进行共享连接的团队合作,那么 Termius 对你来说是一个不错的选择。
#### 总结
在这份指导中,你可以在 Ubuntu 系统中设置 SSH 作为服务器,允许来自你电脑的远程安全的连接,便于你通过命令行开展工作。
此,我推荐以下文章:
* [Linux SSH 入门教程](https://linuxhandbook.com/ssh-basics/)
* [利用 SSH 配置文件管理多个 SSH 连接](https://linuxhandbook.com/ssh-config-file/)
* [向 SSH 服务器添加公钥以进行无密码身份验证](https://linuxhandbook.com/add-ssh-public-key-to-server/)
* [保护你的 SSH 服务器的 SSH 加固技巧](https://linuxhandbook.com/ssh-hardening-tips/)
远程工作快乐!
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/set-up-ssh-ubuntu/>
作者:[Chris Patrick Carias Stas](https://itsfoss.com/author/chris/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

SSH has become the default method of accessing a remote Linux server these days.
SSH stands for Secure Shell and it’s a powerful, efficient, and popular network protocol used to establish communication between two computers in a remote fashion. And let’s not forget the secure part of its name; SSH encrypts all traffic to prevent attacks like hijacking and eavesdropping while offering different authentication methods and a myriad of configuration options.
In this beginner’s guide, you’ll learn:
- The basic concept of SSH
- Setting up SSH server (on the system you want to access remotely)
- Connecting to remote server via SSH from the client machine (your personal computer)
## The absolute basics of SSH
Before you see any configuration process, it will be better to go through the absolute basic concept of SSH.
The SSH protocol is based on server-client architecture. The “server” allows the “client” to be connected over a communication channel. This channel is encrypted and the exchange is governed by the use of public and private SSH keys.
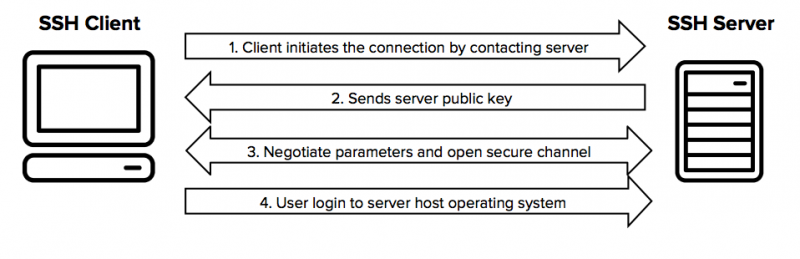
[SSH](https://www.ssh.com/academy/ssh?ref=itsfoss.com)
[OpenSSH](https://www.openssh.com/?ref=itsfoss.com) is one of the most popular open source tools that provides the SSH functionality on Linux, BSD and Windows.
For a successful SSH set up, you need to:
- Have SSH server components on the machine that acts as the server. This is provided by
**openssh-server**package. - Have SSH client component on the machine from where you want to connect to the remote server machine. This is provided by
**openssh-client**package and most Linux and BSD distributions come preinstalled with it.
It is important to keep a distinction between the server and client. You might not want your personal computer to act as SSH server unless you have good reasons where you want others to connect to your system via SSH.
Generally, you have a dedicated system working as the server. For example, a [Raspberry Pi running Ubuntu server](https://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu-server-raspberry-pi/). You [enable SSH on the Raspberry Pi](https://itsfoss.com/ssh-into-raspberry/) so that you could control and manage the device from your main personal computer using SSH in a terminal.
With that information, let’s see how you can set up a SSH server on Ubuntu.
## Configuring SSH Server on Ubuntu
Setting up SSH is not complicated and just needs a few steps to do it.
### Prerequisites
- A user with
**sudo**privileges on the server machine - Internet connection to download the required packages
- At least another system in your network. It can be another computer on your LAN, a remote server via Internet, or a virtual machine hosted in your computer.
*Again, the SSH server installation should be done on the system that you want to act as a server and to which you want to connect remotely via SSH.*### Step 1: Install required packages
Let’s start by opening a terminal window to enter the necessary commands.
Remember to [update your Ubuntu system](https://itsfoss.com/update-ubuntu/) before installing new packages or software with to make sure that you are running the latest versions.
` sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade `
The package you need to run SSH Server is provided by openssh-server component from OpenSSH:
`sudo apt install openssh-server`
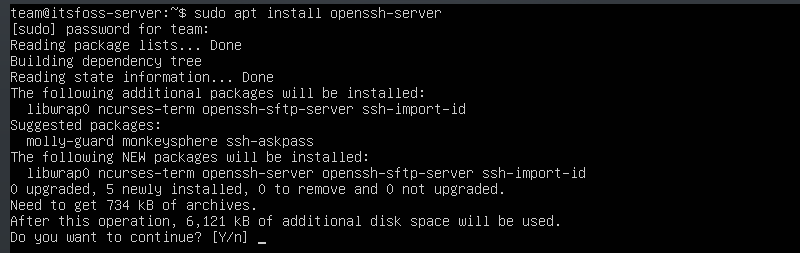
### Step 2: Checking the status of the server
Once the downloading and installation of the package is done the SSH service should be already running, but to be sure we will check it with:
`service ssh status`
You may also use the systemd commands:
`sudo systemctl status ssh`
You should see something like this, with the word Active highlighted. Hit `q`
to return to the command prompt.
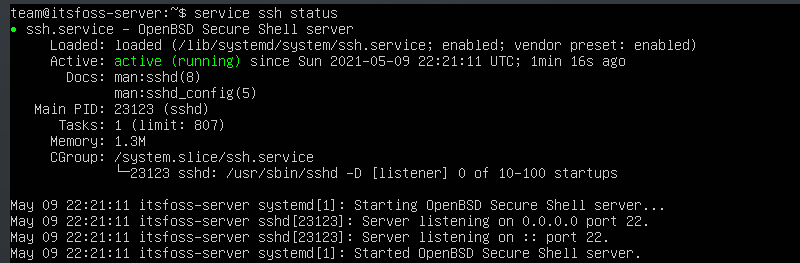
If in your case the service is not running you will have to activate like this:
`sudo systemctl enable --now ssh`
### Step 3: Allowing SSH through the firewall
Ubuntu comes with a firewall utility called [UFW](https://itsfoss.com/set-up-firewall-gufw/) (UncomplicatedFirewall) which is an interface for **iptables** that in turn manages the network’s rules. If the firewall is active, it may prevent the connection to your SSH Server.
To [configure UFW](https://itsfoss.com/ufw-ubuntu/) so that it allows the wanted access, you need to run the following command:
`sudo ufw allow ssh`
The status of UFW can be checked running `sudo ufw status`
.
At this time our SSH Server is up and running, just waiting for a connection from a client.
## Connecting to the remote system from your local machine
Your local Linux system should already have an SSH client installed. If not, you may always install it using the following command on Ubuntu:
`sudo apt install openssh-client`
To connect to your Ubuntu system you need to know the IP address of the computer and use the `ssh`
command, like this:
`ssh username@address `
Change **username** to your actual user in the system and **address** to the IP address of your Ubuntu machine.
If you don’t [know the IP address of your computer](https://itsfoss.com/check-ip-address-ubuntu/) you can type `ip a`
in the terminal of the server and check the output. You should have something like this:
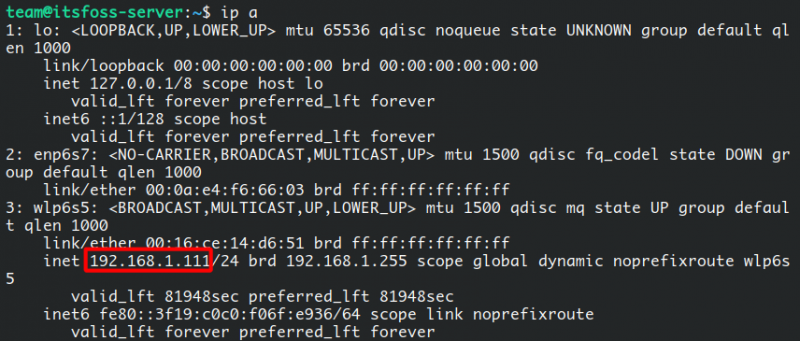
As can be seen here my IP address is **192.168.1.111**. Let’s try connecting using the **username@address** format.
`ssh `[[email protected]](/cdn-cgi/l/email-protection)
The first time you connect to a SSH server, it will ask for permission to add the host. Type `yes`
and hit Enter to continue.
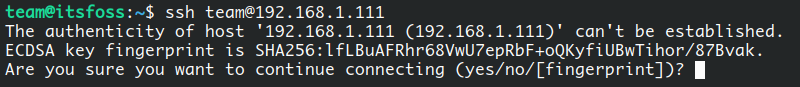
Immediately SSH tells you that the host was permanently added and then asks for the password assigned to the username. Type in the password and hit Enter one more time.

And voila! You will be logged into your Ubuntu system remotely!
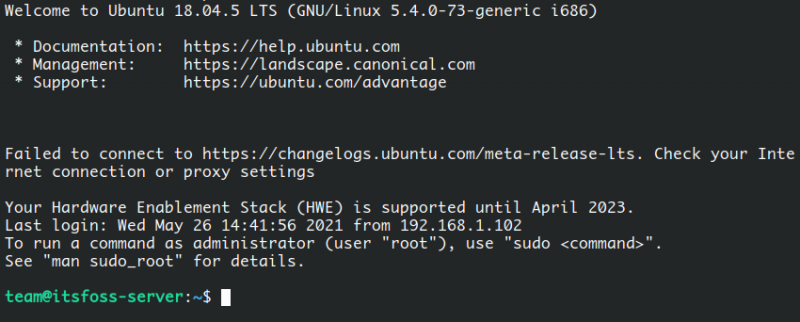
Now you can work in your remote system’s terminal as normal.
## Closing the SSH connection
To close the connection you just need to type `exit`
and it will close it at once, without asking for confirmation.

## Stopping and Disabling SSH in Ubuntu
If you want to stop SSH service you will need this command:
`sudo systemctl stop ssh`
This will stop the service until you restart it or until the system is rebooted. To restart it, type:
`sudo systemctl start ssh`
Now, if you want to disable it from starting during system boot, use this:
`sudo systemctl disable ssh`
This won’t stop the service from running during the current session, just from loading during startup. If you want to let it start again during system boot, type:
`sudo systemctl enable ssh`
## Other SSH clients
The tool ssh is included in most *nix systems, from Linux to macOS, but those are not the only options in existence, here are a couple of clients that can be used from other operating systems:
[PuTTY](https://www.putty.org/?ref=itsfoss.com)is a free and open source SSH client which is hugely popular among Windows users. You can also[install PuTTY on Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/putty-linux/). It’s full of features and very easy to use. If you are connecting to your Ubuntu machine from a Windows station, PuTTY is a great option.[JuiceSSH](https://juicessh.com/?ref=itsfoss.com)is an amazing tool for Android users. If you are on the go and need a mobile client to connect to your Ubuntu system, I amply recommend giving JuiceSSH a go. It’s been around for almost 10 years and it’s free to use.- And finally,
[Termius](https://termius.com/?ref=itsfoss.com)is available for Linux, Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android. It has a free tier version and also several premium options. If you are running a lot of servers and working with teams sharing connections then Termius is a good option for you.
## Wrapping Up
With these instructions, you can set up SSH as a server service in our Ubuntu systems to be able to connect remotely and securely to your computer in order to work with the command line and perform any required task.
Our other website, Linux Handbook, has various informational articles on SSH. From here, I recommend reading the following:
[Getting started with SSH on Linux](https://linuxhandbook.com/ssh-basics/?ref=itsfoss.com)[Using SSH Config file to manage multiple SSH connections](https://linuxhandbook.com/ssh-config-file/?ref=itsfoss.com)[Adding public key to SSH server for password less authentication](https://linuxhandbook.com/add-ssh-public-key-to-server/?ref=itsfoss.com)[SSH hardening tips](https://linuxhandbook.com/ssh-hardening-tips/?ref=itsfoss.com)to secure your SSH server
If you find it overwhelming, [Linux Handbook has a premium video course that explains SSH for beginners](https://linuxhandbook.com/sshcourse/?ref=itsfoss.com) along with hands-on labs to follow. This will give you a more streamlined knowledge of the topic.
Happy remote working! |
15,178 | 优化 Kubernetes 中的 Java 无服务器函数 | https://opensource.com/article/21/6/java-serverless-functions-kubernetes | 2022-10-26T15:16:34 | [
"Kubernetes",
"无服务器",
"Quarkus"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15178-1.html |
>
> 在 Kubernetes 中运行无服务器函数时,实现更快的启动速度和更小的内存占用。
>
>
>

由于运行上千个应用程序<ruby> 容器荚 <rt> Pod </rt></ruby>所耗费的资源多,令它实现较少工作节点和资源占用所需成本也较高,所以在使用 [Kubernetes](https://opensource.com/article/19/6/reasons-kubernetes) 时,快速启动和较少的内存占用是至关重要的。在 Kubernetes 平台运行容器化微服务时,内存占用是比吞吐量更重要的考量因素,这是因为:
* 由于需要持续运行,所以耗费资源更多(不同于 CPU 占用)
* 微服务令开销成本成倍增加
* 一个单体应用程序变为若干个微服务的情况(例如 20 个微服务占用的存储空间约有 20GB)
这些情况极大影响了无服务器函数的发展和 Java 部署模型。到目前为止,许多企业开发人员选择 Go、Python 或 Node.js 这些替代方案来解决性能瓶颈,直到出现了 [Quarkus](https://quarkus.io/) 这种基于 kubernetes 的原生 Java 堆栈,才有所改观。本文介绍如何在使用了 Quarkus 的 kubernetes 平台上进行性能优化,以便运行无服务器函数。
### 容器优先的设计理念
由于 Java 生态系统中传统的框架都要进行框架的初始化,包括配置文件的处理、`classpath` 的扫描、类加载、注解的处理以及构建元模型,这些过程都是必不可少的,所以它们都比较耗费资源。如果使用了几种不同的框架,所耗费的资源也是成倍增加。
Quarkus 通过“<ruby> 左移 <rt> shifting left </rt></ruby>”,把所有的资源开销大的操作都转移到构建阶段,解决了这些 Java 性能问题。在构建阶段进行代码和框架分析、字节码转换和动态元模型生成,而且只有一次,结果是:运行时可执行文件经过高度优化,启动非常快,不需要经过那些传统的启动过程,全过程只在构建阶段执行一次。

更重要的是:Quarkus 支持构建原生可执行文件,它具有良好性能,包括快速启动和极小的<ruby> 驻留集大小 <rt> resident set size </rt></ruby>(RSS)内存占用,跟传统的云原生 Java 栈相比,具备即时扩展的能力和高密度的内存利用。

这里有个例子,展示如何使用 Quarkus 将一个 [Java 无服务器](https://opensource.com/article/21/5/what-serverless-java) 项目构建为本地可执行文件。
### 1、使用 Quarkus 创建无服务器 Maven 项目
以下命令生成一个 Quarkus 项目,(例如 `quarkus-serverless-native`)以此创建一个简单的函数:
```
$ mvn io.quarkus:quarkus-maven-plugin:1.13.4.Final:create \
-DprojectGroupId=org.acme \
-DprojectArtifactId=quarkus-serverless-native \
-DclassName="org.acme.getting.started.GreetingResource"
```
### 2、构建一个本地可执行文件
你需要使用 GraalVM 为 Java 程序构建一个本地可执行文件。你可以选择 GraalVM 的任何发行版,例如 [Oracle GraalVM Community Edition (CE)](https://www.graalvm.org/community/) 或 [Mandrel](https://github.com/graalvm/mandrel)(Oracle GraalVM CE 的下游发行版)。Mandrel 是为支持 OpenJDK 11 上的 Quarkus-native 可执行文件的构建而设计的。
打开 `pom.xml`,你将发现其中的 `native` 设置。你将使用它来构建本地可执行文件。
```
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>native</id>
<properties>
<quarkus.package.type>native</quarkus.package.type>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
```
>
> **注意:** 你可以在本地安装 GraalVM 或 Mandrel 发行版。你也可以下载 Mandrel 容器映像来构建它(像我那样),因此你还需要在本地运行一个容器引擎(例如 Docker)。
>
>
>
假设你已经打开了容器运行时,此时需要运行一下 Maven 命令:
使用 [Docker](https://www.docker.com/) 作为容器引擎:
```
$ ./mvnw package -Pnative \
-Dquarkus.native.container-build=true \
-Dquarkus.native.container-runtime=docker
```
使用 [Podman](https://podman.io/) 作为容器引擎:
```
$ ./mvnw package -Pnative \
-Dquarkus.native.container-build=true \
-Dquarkus.native.container-runtime=podman
```
输出信息结尾应当是 `BUILD SUCCESS`。

不借助 JVM 直接运行本地可执行文件:
```
$ target/quarkus-serverless-native-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-runner
```
输出信息类似于:
```
__ ____ __ _____ ___ __ ____ ______
--/ __ \/ / / / _ | / _ \/ //_/ / / / __/
-/ /_/ / /_/ / __ |/ , _/ ,< / /_/ /\ \
--\___\_\____/_/ |_/_/|_/_/|_|\____/___/
INFO [io.quarkus] (main) quarkus-serverless-native 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT native
(powered by Quarkus xx.xx.xx.) Started in 0.019s. Listening on: http://0.0.0.0:8080
INFO [io.quarkus] (main) Profile prod activated.
INFO [io.quarkus] (main) Installed features: [cdi, kubernetes, resteasy]
```
简直是超音速!启动只花了 19 毫秒。你的运行时间可能稍有不同。
使用 Linux 的 `ps` 工具检测一下,结果内存占用还是很低。检测的方法是:在应用程序运行期间,另外打开一个终端,运行如下命令:
```
$ ps -o pid,rss,command -p $(pgrep -f runner)
```
输出结果类似于:
```
PID RSS COMMAND
10246 11360 target/quarkus-serverless-native-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-runner
```
该进程只占 11MB 内存。非常小!
>
> **注意:** 各种应用程序(包括 Quarkus)的驻留集大小和内存占用,都因运行环境而异,并随着应用程序载入而上升。
>
>
>
你也可以使用 REST API 访问这个函数。输出结果应该是 `Hello RESTEasy`:
```
$ curl localhost:8080/hello
Hello RESTEasy
```
### 3、把函数部署到 Knative 服务
如果你还没有创建命名空间,现在就在 [OKD](https://docs.okd.io/latest/welcome/index.html)(OpenShift Kubernetes 发行版)[创建一个命名空间](https://docs.okd.io/latest/applications/projects/configuring-project-creation.html)(例如 `quarkus-serverless-native`),进而把这个本地可执行文件部署为无服务器函数。然后添加 `quarkus-openshift` 扩展:
```
$ ./mvnw -q quarkus:add-extension -Dextensions="openshift"
```
向 `src/main/resources/application.properties` 文件中添加以下内容,配置 Knative 和 Kubernetes 的相关资源:
```
quarkus.container-image.group=quarkus-serverless-native
quarkus.container-image.registry=image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000
quarkus.native.container-build=true
quarkus.kubernetes-client.trust-certs=true
quarkus.kubernetes.deployment-target=knative
quarkus.kubernetes.deploy=true
quarkus.openshift.build-strategy=docker
```
构建本地可执行文件,并把它直接部署到 OKD 集群:
```
$ ./mvnw clean package -Pnative
```
>
> **注意:** 提前使用 `oc login` 命令,确保登录的是正确的项目(例如 `quarkus-serverless-native`)。
>
>
>
输出信息结尾应当是 `BUILD SUCCESS`。完成一个本地二进制文件的构建并部署为 Knative 服务需要花费几分钟。成功创建服务后,使用 `kubectl` 或 `oc` 命令工具,可以查看 Knative 服务和版本信息:
```
$ kubectl get ksvc
NAME URL [...]
quarkus-serverless-native http://quarkus-serverless-native-[...].SUBDOMAIN True
$ kubectl get rev
NAME CONFIG NAME K8S SERVICE NAME GENERATION READY REASON
quarkus-serverless-native-00001 quarkus-serverless-native quarkus-serverless-native-00001 1 True
```
### 4、访问本地可执行函数
运行 `kubectl` 命令,搜索无服务器函数的节点:
```
$ kubectl get rt/quarkus-serverless-native
```
输出信息类似于:
```
NAME URL READY REASON
quarkus-serverless-native http://quarkus-serverless-restapi-quarkus-serverless-native.SUBDOMAIN True
```
用 `curl` 命令访问上述信息中的 `URL` 字段:
```
$ curl http://quarkus-serverless-restapi-quarkus-serverless-native.SUBDOMAIN/hello
```
过了不超过一秒钟,你也会得到跟本地操作一样的结果:
```
Hello RESTEasy
```
当你在 OKD 群集中访问 Quarkus 运行中的节点的日志,你会发现本地可执行文件正在以 Knative 服务的形式运行。

### 下一步呢?
你可以借助 GraalVM 发行版优化 Java 无服务器函数,从而在 Knative 中使用 Kubernetes 将它们部署为无服务器函数。Quarkus 支持在普通的微服务中使用简易配置进行性能优化。
本系列的下一篇文章将指导你在不更改代码的情况下跨多个无服务器平台实现可移植函数。
*(Daniel Oh, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/6/java-serverless-functions-kubernetes>
作者:[Daniel Oh](https://opensource.com/users/daniel-oh) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[cool-summer-021](https://github.com/cool-summer-021) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | A faster startup and smaller memory footprint always matter in [Kubernetes](https://opensource.com/article/19/6/reasons-kubernetes) due to the expense of running thousands of application pods and the cost savings of doing it with fewer worker nodes and other resources. Memory is more important than throughput on containerized microservices on Kubernetes because:
- It's more expensive due to permanence (unlike CPU cycles)
- Microservices multiply the overhead cost
- One monolith application becomes
*N*microservices (e.g., 20 microservices ≈ 20GB)
This significantly impacts serverless function development and the Java deployment model. This is because many enterprise developers chose alternatives such as Go, Python, and Nodejs to overcome the performance bottleneck—until now, thanks to [Quarkus](https://quarkus.io/), a new Kubernetes-native Java stack. This article explains how to optimize Java performance to run serverless functions on Kubernetes using Quarkus.
## Container-first design
Traditional frameworks in the Java ecosystem come at a cost in terms of the memory and startup time required to initialize those frameworks, including configuration processing, classpath scanning, class loading, annotation processing, and building a metamodel of the world, which the framework requires to operate. This is multiplied over and over for different frameworks.
Quarkus helps fix these Java performance issues by "shifting left" almost all of the overhead to the build phase. By doing code and framework analysis, bytecode transformation, and dynamic metamodel generation only once, at build time, you end up with a highly optimized runtime executable that starts up super fast and doesn't require all the memory of a traditional startup because the work is done once, in the build phase.
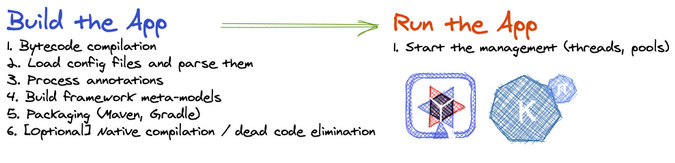
(Daniel Oh, CC BY-SA 4.0)
More importantly, Quarkus allows you to build a native executable file that provides [performance advantages](https://quarkus.io/blog/runtime-performance/), including amazingly fast boot time and incredibly small resident set size (RSS) memory, for instant scale-up and high-density memory utilization compared to the traditional cloud-native Java stack.

(Daniel Oh, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Here is a quick example of how you can build the native executable with a [Java serverless](https://opensource.com/article/21/5/what-serverless-java) function project using Quarkus.
## 1. Create the Quarkus serverless Maven project
This command generates a Quarkus project (e.g., `quarkus-serverless-native`
) to create a simple function:
```
$ mvn io.quarkus:quarkus-maven-plugin:1.13.4.Final:create \
-DprojectGroupId=org.acme \
-DprojectArtifactId=quarkus-serverless-native \
-DclassName="org.acme.getting.started.GreetingResource"
```
## 2. Build a native executable
You need a GraalVM to build a native executable for the Java application. You can choose any GraalVM distribution, such as [Oracle GraalVM Community Edition (CE)](https://www.graalvm.org/community/) and [Mandrel](https://github.com/graalvm/mandrel) (the downstream distribution of Oracle GraalVM CE). Mandrel is designed to support building Quarkus-native executables on OpenJDK 11.
Open `pom.xml`
, and you will find this `native`
profile. You'll use it to build a native executable:
```
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>native</id>
<properties>
<quarkus.package.type>native</quarkus.package.type>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
```
Note:You can install the GraalVM or Mandrel distribution locally. You can also download the Mandrel container image to build it (as I did), so you need to run a container engine (e.g., Docker) locally.
Assuming you have started your container runtime already, run one of the following Maven commands.
For [Docker](https://www.docker.com/):
```
$ ./mvnw package -Pnative \
-Dquarkus.native.container-build=true \
-Dquarkus.native.container-runtime=docker
```
For [Podman](https://podman.io/):
```
$ ./mvnw package -Pnative \
-Dquarkus.native.container-build=true \
-Dquarkus.native.container-runtime=podman
```
The output should end with `BUILD SUCCESS`
.
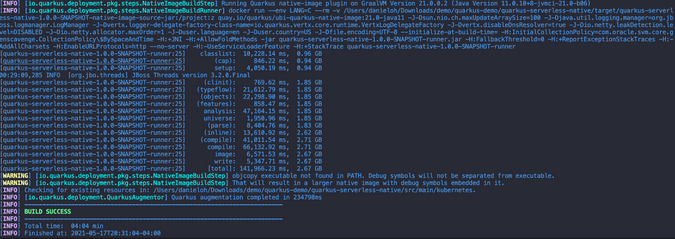
(Daniel Oh, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Run the native executable directly without Java Virtual Machine (JVM):
`$ target/quarkus-serverless-native-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-runner`
The output will look like:
```
__ ____ __ _____ ___ __ ____ ______
--/ __ \/ / / / _ | / _ \/ //_/ / / / __/
-/ /_/ / /_/ / __ |/ , _/ ,< / /_/ /\ \
--\___\_\____/_/ |_/_/|_/_/|_|\____/___/
INFO [io.quarkus] (main) quarkus-serverless-native 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT native
(powered by Quarkus xx.xx.xx.) Started in 0.019s. Listening on: http://0.0.0.0:8080
INFO [io.quarkus] (main) Profile prod activated.
INFO [io.quarkus] (main) Installed features: [cdi, kubernetes, resteasy]
```
Supersonic! That's *19* *milliseconds* to startup. The time might be different in your environment.
It also has extremely low memory usage, as the Linux `ps`
utility reports. While the app is running, run this command in another terminal:
`$ ps -o pid,rss,command -p $(pgrep -f runner)`
You should see something like:
```
PID RSS COMMAND
10246 11360 target/quarkus-serverless-native-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-runner
```
This process is using around *11MB* of memory (RSS). Pretty compact!
Note:The RSS and memory usage of any app, including Quarkus, will vary depending on your specific environment and will rise as application experiences load.
You can also access the function with a REST API. Then the output should be `Hello RESTEasy`
:
```
$ curl localhost:8080/hello
Hello RESTEasy
```
## 3. Deploy the functions to Knative service
If you haven't already, [create a namespace](https://docs.okd.io/latest/applications/projects/configuring-project-creation.html) (e.g., `quarkus-serverless-native`
) on [OKD](https://docs.okd.io/latest/welcome/index.html) (OpenShift Kubernetes Distribution) to deploy this native executable as a serverless function. Then add a `quarkus-openshift`
extension for Knative service deployment:
`$ ./mvnw -q quarkus:add-extension -Dextensions="openshift"`
Append the following variables in `src/main/resources/application.properties`
to configure Knative and Kubernetes resources:
```
quarkus.container-image.group=quarkus-serverless-native
quarkus.container-image.registry=image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000
quarkus.native.container-build=true
quarkus.kubernetes-client.trust-certs=true
quarkus.kubernetes.deployment-target=knative
quarkus.kubernetes.deploy=true
quarkus.openshift.build-strategy=docker
```
Build the native executable, then deploy it to the OKD cluster directly:
`$ ./mvnw clean package -Pnative`
Note:Make sure to log in to the right project (e.g.,`quarkus-serverless-native`
) using the`oc login`
command ahead of time.
The output should end with `BUILD SUCCESS`
. It will take a few minutes to complete a native binary build and deploy a new Knative service. After successfully creating the service, you should see a Knative service (KSVC) and revision (REV) using either the `kubectl`
or `oc`
command tool:
```
$ kubectl get ksvc
NAME URL [...]
quarkus-serverless-native http://quarkus-serverless-native-[...].SUBDOMAIN True
$ kubectl get rev
NAME CONFIG NAME K8S SERVICE NAME GENERATION READY REASON
quarkus-serverless-native-00001 quarkus-serverless-native quarkus-serverless-native-00001 1 True
```
## 4. Access the native executable function
Retrieve the serverless function's endpoint by running this `kubectl`
command:
`$ kubectl get rt/quarkus-serverless-native`
The output should look like:
```
NAME URL READY REASON
quarkus-serverless-native http://quarkus-serverless-restapi-quarkus-serverless-native.SUBDOMAIN True
```
Access the route `URL`
with a `curl`
command:
`$ curl http://quarkus-serverless-restapi-quarkus-serverless-native.SUBDOMAIN/hello`
In less than one second, you will get the same result as you got locally:
`Hello RESTEasy`
When you access the Quarkus running pod's logs in the OKD cluster, you will see the native executable is running as the Knative service.
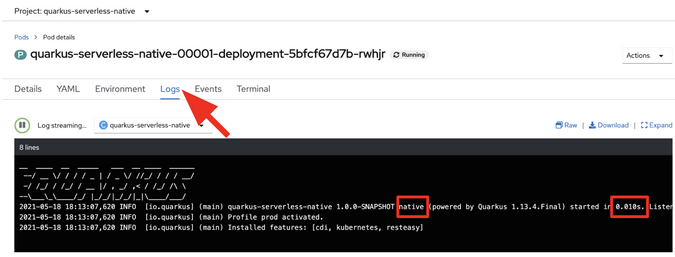
(Daniel Oh, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## What's next?
You can optimize Java serverless functions with GraalVM distributions to deploy them as serverless functions on Knative with Kubernetes. Quarkus enables this performance optimization using simple configurations in normal microservices.
The next article in this series will guide you on making portable functions across multiple serverless platforms with no code changes.
## Comments are closed. |
15,179 | Ubuntu Budgie 22.10 的新变化 | https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-budgie-22-10-release/ | 2022-10-26T17:13:49 | [
"Ubuntu Budgie",
"Ubuntu"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15179-1.html |
>
> Ubuntu Budgie 22.10 是一个有趣的版本,它删除了几个 GNOME 应用程序,以及一些其他改进。
>
>
>

[Ubuntu Budgie](https://ubuntubudgie.org/) 是 Ubuntu 的官方版本,因其传统的桌面界面和最小的软件膨胀而广受欢迎。
Ubuntu Budgie 22.10 的发布带来了一些关键的调整和补充。
### ? Ubuntu Budgie 22.10 有什么新变化

基于 Ubuntu 22.10 “<ruby> 充满活力的捻角羚 <rt> Kinetic Kudu </rt></ruby>”,Ubuntu Budgie 22.10 带来了 Budgie 桌面 10.6.4 和许多其他改进。
一些值得注意的亮点包括:
* 增强型 Budgie <ruby> 控制中心 <rt> Control Center </rt></ruby>
* 更新了 Budgie 的“<ruby> 欢迎 <rt> Welcome </rt></ruby>”应用
* 替换各种基于 GNOME 的应用程序
* 对翻译进行了更新
#### Budgie 桌面和控制中心

Budgie 桌面以及更新到 V10.6.4, 它添加了一个新的全局选项来控制小程序之间的间距,并对工作区和时钟小程序进行了各种改进。

Budgie <ruby> 控制中心 <rt> Control Center </rt></ruby>也得到了一堆调整,例如重新设计的显示颜色配置文件支持,修改了对屏幕分享的支持,如 [RDP](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Remote_Desktop_Protocol) 和 [VNC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_Network_Computing),用于显示缩放的选项,等等。
#### 升级了欢迎应用

Ubuntu Budgie 22.10 特别升级了 [Budgie 的欢迎应用](https://ubuntubudgie.org/2022/02/quick-overview-of-budgie-welcome-application/),改善了翻译以及一些其他改进。
#### 默认的应用的变化
Ubuntu Budgie 的开发人员已经开始替换和删除基于 GNOME 的应用程序,转而使用基于 MATE 的应用程序和其他替代品。
他们决定这样做是因为基于 GNOME 的应用程序在 Budgie 中的外观与其他具有圆角边缘的应用程序的外观不一致。
这些不一致是由于 GNOME 根据其样式和主题需求而转到 Libadwaita 库造成的。
Libadwaita 库是 GNOME 的一个有争议的补充,没有多少用户喜欢,你可以通过我们的报道来了解更多信息。
>
> **[你对在 Linux 世界中 GNOME 的 Libadwaita 库怎么看?](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-libadwaita-library/)**
>
>
>
以下是一些已删除或替换的应用程序:
* GNOME 计算器被 MATE 计算器取代。
* 删除了 GNOME 日历。
* GNOME 系统监视器已由 MATE 系统监视器取代。
* 删除了 GNOME 截图。
* [字体管理器](https://itsfoss.com/font-manager/) 替代了 GNOME 字体查看器。
#### ?️ 其他改变
其他改变包括以下:
* 重新开发的内置主题
* 移除 PulseAudio,并支持 PipeWire
* 原生的截图功能
* 支持 WebP 图像
* 能够查看显示器的刷新率
你可以通过 [发行说明](https://ubuntubudgie.org/2022/09/ubuntu-budgie-22-10-release-notes/) 了解更多。
### ? 下载 Ubuntu Budgie 22.10
你可以在 [Ubuntu 中央镜像仓库](https://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-budgie/releases/22.10/) 或者它的 [官方网站](https://ubuntubudgie.org/downloads/) 下载最新的 ISO。
*其官方网站可能需要一段时间才能提供 ISO。*
>
> **[下载 Ubuntu Budgie 22.10](https://ubuntubudgie.org/downloads/)**
>
>
>
>
> ? Ubuntu Budgie 22.10 将支持 9 个月直到 **2023 年 6 月**。如果你想使用稳定的功能,更应该选择 [LTS 版本](https://itsfoss.com/long-term-support-lts/)。
>
>
>
? 你如何看待这个非 LTS 版本?愿意尝试一下吗?
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-budgie-22-10-release/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

[Ubuntu Budgie](https://ubuntubudgie.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is an official flavor of Ubuntu, which is popular for its traditional desktop interface and minimal software bloat.
The release of Ubuntu Budgie 22.10 brings in a few crucial tweaks and additions.
## 🆕 Ubuntu Budgie 22.10: What's New?
Based on Ubuntu 22.10 'Kinetic Kudu', Ubuntu Budgie 22.10 features Budgie Desktop 10.6.4 and a host of other improvements.
Some of the notable highlights include:
**Enhanced Budgie Control Center****Updated Budgie Welcome app****Replacing various GNOME-based apps****Updated Translations**
### Budgie Desktop and Control Center
Budgie Desktop has been updated to V10.6.4, which adds a new global option to control the spacing between applets and features various improvements to the workspace and clock applets.
The Budgie Control Center has also received a bunch of tweaks, such as reworked display color profile support, revamped screen-sharing with support for [RDP](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Remote_Desktop_Protocol?ref=news.itsfoss.com) and [VNC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_Network_Computing?ref=news.itsfoss.com), an option for fractional scaling of display, and more.
### Welcome App Updates
Ubuntu Budgie 22.10 features the updated [Budgie Welcome app](https://ubuntubudgie.org/2022/02/quick-overview-of-budgie-welcome-application/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) with improved translations and a few changes.
### Change in Default Apps
The developers of Ubuntu Budgie have started replacing and removing GNOME-based apps in favor of MATE-based apps and other alternatives.
They decided to do so, because of the inconsistent way GNOME-based apps look in Budgie alongside other apps with their rounded-off edges.
The inconsistencies have been caused due to GNOME moving on to the Libadwaita library for its styling and theming needs.
The Libadwaita library was a controversial addition to GNOME, that not many users liked, you can go through our coverage to learn more.
[What’s the Fuss About GNOME’s Libadwaita Library in Linux World?Back in March 2020, the GNOME project announced a new library called Libadwaita. This promised to fix numerous fundamental issues with GTK, the library GNOME uses to build its desktop environment. Unfortunately, this announcement also resulted in some significant community backlash. While this…](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-libadwaita-library/)

Here are some of the apps that have been removed or replaced:
- GNOME-Calculator replaced by MATE Calculator.
- GNOME-Calendar removed.
- GNOME System Monitor replaced by MATE System Monitor.
- GNOME Screenshot removed.
- GNOME Font Viewer replaced by
[Font-Manager](https://itsfoss.com/font-manager/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
### 🛠️ Other Changes
Some of the other changes include:
**Rework of In-Built Theme****Removal of PulseAudio in favor of PipeWire****Native Screenshot Capability****Support for WebP Images****Ability to View Monitor's Refresh Rate**
You can go through the [release notes](https://ubuntubudgie.org/2022/09/ubuntu-budgie-22-10-release-notes/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to know more.
## 📥 Download Ubuntu Budgie 22.10
You can download the latest ISO from [Ubuntu's central image repository](https://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-budgie/releases/22.10/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) or its [official website](https://ubuntubudgie.org/downloads/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
It might take a while for its official website to make the ISO available.
**July 2023**. If you want stability over features, you should prefer using an
[LTS version](https://itsfoss.com/long-term-support-lts/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
💬 What do you think of this non-LTS release? Willing to give it a try?
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,181 | 如何在 Ubuntu 服务器 22.04 上设置静态 IP 地址 | https://www.linuxtechi.com/static-ip-address-on-ubuntu-server/ | 2022-10-27T09:13:00 | [
"IP"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15181-1.html | 
>
> 在这篇文章中,我们将介绍如何在 Ubuntu 服务器 22.04 上设置静态 IP 地址。
>
>
>
强烈建议在 Linux 服务器上使用静态 IP,因为它会在重启后保持不变。静态 IP 对邮件服务器、Web 服务器和文件服务器等服务器起着重要作用。
**准备条件**
* 最小安装的 Ubuntu 服务器 22.04
* 具有 `sudo` 管理员权限的普通用户
在 Ubuntu 服务器 22.04 中,网络由 netplan 程序控制,因此我们将使用 netplan 在 Ubuntu 服务器上配置静态 IP 地址。
注意:我们不能使用 [nmcli 程序](https://www.linuxtechi.com/configure-ip-with-nmcli-command-linux/),因为它不是 Ubuntu 服务器上默认安装的一部分。
### 在 Ubuntu 服务器 22.04 上设置静态 IP 地址
登录到你的 Ubuntu 服务器 22.04,查找 netplan 配置文件。它位于 `/etc/netplan` 目录下。
```
$ cd /etc/netplan/
$ ls -l
total 4
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 116 Oct 12 04:03 00-installer-config.yaml
$
```
运行以下 `cat` 命令以查看 `00-installer-config.yaml` 的内容。
注意:配置文件的名称可能因你的设置而异。由于它是一个 yaml 文件,因此请确保在编辑时保持缩进和语法。
```
$ cat 00-installer-config.yaml
```
输出:

根据上面的输出,它说我们有 `ens33` 接口,它正在从 DHCP 服务器获取 IP。查看接口名称的另一种方法是通过 `ip` 命令。
现在,要配置静态 IP 代替 DHCP,使用 `vi` 或 `nano` 编辑器编辑 netplan 配置文件并添加以下内容。
```
$ sudo vi 00-installer-config.yaml
# This is the network config written by 'subiquity'
network:
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
ens33:
addresses:
- 192.168.1.247/24
nameservers:
addresses: [4.2.2.2, 8.8.8.8]
routes:
- to: default
via: 192.168.1.1
version: 2
```
保存并关闭文件。

在上面的文件中,我们使用了以下内容,
* `ens33` 为接口名称
* 用于设置静态 IP 的地址
* `nameservers` 用于指定 DNS 服务器的 IP
* 用于指定默认网关的路由
注意:根据你的环境更改 IP 详细信息和接口名称。
要是上述修改生效,请使用以下 `netplan` 命令应用这些更改:
```
$ sudo netplan apply
```
运行以下 IP 命令查看接口上的 IP 地址:
```
$ ip addr show ens33
```
要查看默认路由,请运行:
```
$ ip route show
```
上述命令的输出。

完美,以上命令的输出确认静态 IP 和路由配置成功。
这就是这篇文章的全部内容。请在下面的评论部分发表你的问题和反馈。
---
via: <https://www.linuxtechi.com/static-ip-address-on-ubuntu-server/>
作者:[Pradeep Kumar](https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In this post, we will cover how to set static ip address on Ubuntu server 22.04.
It is highly recommended to have a static ip on linux server because it would be persistent across the reboot. Static IP plays an important role for servers like Mail Server, Web Server and File server etc.
#### Prerequisites
- Minimal Installed Ubuntu Server 22.04
- Regular User with sudo admin rights
In Ubuntu server 22.04, networking is controlled by netplan utility, so we will use netplan to configure static ip address on Ubuntu server.
Note: we cannot use [nmcli utiltity](https://www.linuxtechi.com/configure-ip-with-nmcli-command-linux/) as it is not the part of default installation on Ubuntu server.
## Setting up Static IP address on Ubuntu Server 22.04
Login to your Ubuntu server 22.04, look for the netplan configuration file. It is located under /etc/netplan directory.
$ cd /etc/netplan/ $ ls -l total 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 116 Oct 12 04:03 00-installer-config.yaml $
Run below [cat command](https://www.linuxtechi.com/cat-command-examples-for-beginners-in-linux/) to view the contents of ‘00-installer-config.yaml’
Note: Name of configuration file may differ as your per setup. As it is an yaml file, so make sure to maintain the indentation and syntax while editing.
$ cat 00-installer-config.yaml
Output,
As per above output, it says that we have ens33 interface and it is getting ip from dhcp server. Alternate way to view interface name is via ip command.
Now, to configure static ip in place of dhcp, edit netplan configuration file using vi or nano editor and add the following content.
$ sudo vi 00-installer-config.yaml # This is the network config written by 'subiquity' network: renderer: networkd ethernets: ens33: addresses: - 192.168.1.247/24 nameservers: addresses: [4.2.2.2, 8.8.8.8] routes: - to: default via: 192.168.1.1 version: 2
save and close the file.
In the above file we have used following,
- ens33 is the interface name
- addresses are used to set the static ip
- nameservers used to specify the DNS server ips
- routes used to specify the default gateway
Note: Change the IP details and interface name as per your environment.
To make above changes into the effect the apply these changes using following netplan command,
$ sudo netplan apply
Run following [ip command](https://www.linuxtechi.com/ip-command-examples-for-linux-users/) to view the ip address on interface,
$ ip addr show ens33
To view the default route, run
$ ip route show
Output of above commands,
Perfect, above commands’ output confirms that static ip and route has been configured successfully.
That’s all from this post. Kindly do post your queries and feedback in below comments section.
Gerald BrownHow do I use Netplan to set up a static IP address on WIFI?
Aaronchange the network device “ens33” to something else, it will be listed when you run “ip a”; it;s probably wlan0 but that’s not guaranteed.
ronssmthere will be a config file for the wifi interface. look for something like 00-installer-config-wifi.yaml
David PinosHey! thanks I had problems before setting up the DNS and none config would work!
This one did and you made this post really simple to follow!
Surf40Your text for configuring a static IP address does not work in my Ubuntu 20.04.5 server’s NIC. No matter how I space or tab the indentations, I get “Ivalid YAML: inconsistent indentation: addresses:
I’ve been at the problem for a couple of weeks, with no fix in site; no spacing or tabbing change I make fixes it. Can anyone please advise me? Thanks.
choctry paste the YAML into here ‘https://www.yamllint.com/’
VietCopy paste not work here, you should try typing instead or if you paste, try to delete all the space before each line and tab key until the same format
MikaelThe spacing must be done with the space key. If you try to make spaces in a yaml file with the tab key it will not work.
Also you should let yamllint.com correct the file for you
sylvaYour article is quite nice and clear! but after followed, following error occurred when ping google.com:
“temporary failure in name resolution”, meanwhile localhost can be visited. Is anyone facing this issue as well? I’ll quite appreciate it if can get some advise.
ganeshcan we use default DHCP ip configuration along with another static ip in ubuntu 22.04 ?
i already have ens33 then i added eth0 as static ip , netplan apply did not thrown any errors but unable to see my static ip , when i do ifconfig 🙁
even after reboot its not applying, any suggestions..
Wiilliami successfully set up my static ip but I cant ping to 192.168.1.1 why |
15,182 | 利用习惯练习开放式组织原则 | https://opensource.com/open-organization/22/6/using-habits-practice-open-organization-principles | 2022-10-27T09:49:25 | [
"开放式组织",
"习惯"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15182-1.html |
>
> 你可以按照以下步骤,来养成符合开放文化的习惯,并改掉那些不符合开放文化的习惯。
>
>
>

很久以来,我就对习惯很感兴趣。几年前,我做了一次关于习惯利弊的演讲,并且介绍了如何改变坏习惯、养成好习惯。不久前,我阅读了 Art Markman 教授的 《Smart Thinking》一书,这本书主要讨论的也是习惯。或许你会问习惯与 [开放式组织的原则](https://theopenorganization.org/definition/open-organization-definition/) 有什么关系?这其中有一定的联系!我将会分成两篇文章,来解释你可以如何管理你的习惯。
在本文中,我们将讨论习惯如何工作的,以及更重要的是你如何去开始改变你的习惯。在下一篇文章中,我们将回顾 Markman 教授在他书中所表达的思想。
### 开放式组织原则和习惯的交集
设想你学习过开放式组织的原则,尽管你认为它们很有趣并且很有价值,但是你还没有对这些原则形成自己的习惯。以下就是你现实中会表现出来的样子。
社区:如果你面对一项重要挑战,但是你不知道如何独自解决它,你很有可能会由于习惯而放弃这项挑战。养成与由志同道合的人组成的社区,共同解决问题的习惯,不是更好吗?
协作:假设你认为你不善于合作,你喜欢独立完成任务。你知道有一些需要合作才能完成的事情,但是你并没有参与合作的习惯。为了弥补这种情况,你必须养成与他人更多合作的习惯。
信息共享:假如说你喜欢将你所做的事以及所知道的东西当作秘密。但是,你知道如果你不共享信息,你也无法从他人那里获取有用的信息。因此,你必须拥有共享信息的习惯。
包容性:想象一下,你与你不熟悉的人,或者是在个性、文化还是语言上都与你不同的人一起工作,你会感到不自在。但是,你知道如果你想要成功的话,你必须要和各种各样的人一同工作。那你该如何培养包容的习惯呢?
适应能力:假设当你所做的事情不再能达到你所希望的结果之后,你往往会拒绝改变。但是,你知道你必须适应这种情况,并重新调整你的努力,那你如何才能养成适应的习惯呢?
### 习惯是什么?
在我给出关于上述开放式组织原则的示例之前,我想先解释一下习惯的一些相关特征。
* 习惯是重复很多次的行为,最终习惯会成为你下意识的行为。
* 习惯是自动的并且当时会感觉良好。当一个人在养成习惯后,做习惯行为会使他感觉很好,但是当他跳出习惯做事时,会感到不舒服。或许之后他会再次考虑尝试。
* 一些习惯是有益的,并且能够节省你很多的能量。大脑只占身体质量的 2%,但是却会消耗 20% 的能量。因为大脑在思考和集中精力上需要消耗很多能量,你可以通过培养下意识的习惯来节省能量。
* 一些习惯对你有害,因此你渴望改变这些坏习惯。
* 所有的习惯都会给你回报,即使回报是短暂的。
* 习惯是基于你熟悉的事情和你知道的东西而形成的,即使你可能并不一定需要这个习惯。
### 养成习惯的 3 个步骤
1. 提示(触发器):首先,提示或者触发器会告诉大脑,进入之前学习的习惯性行为的自动模式之中。这里的提示可以是某件事,比如每天在确定的时间点、在确定的地点,看到一包糖果或者看到电视购物节目,亦或者看到某个特定的人。时间压力会触发你去做例行事项(routine)。在令人崩溃的环境下也会触发例行事项。简而言之,某件事提醒你开始做一些固定的事情。
2. <ruby> 例行事项 <rt> routine </rt></ruby>:例行事项会被触发。一个例行事项是一系列的身体、心理或者情绪上的表现,可以是非常复杂的,也可以十分简单。诸如与心情相关的一些习惯可以在很短时间内被触发。
3. 奖励:最后一步是奖励,奖励会帮助你的大脑计算一个特定的行为是否值得记住。奖励的范围很广泛,可以是食物或者其他令你感到快乐的东西。
### 商业环境中的坏习惯
习惯不仅仅是个人行为。所有的组织或多或少都有一些好的坏的制度习惯。然而,一些组织会有先见之明地设计好他们的习惯,而其他组织却不会设计习惯,只是随着竞争或者担心落伍而演变。以下是一些组织的坏习惯示例:
* 总是晚提交报告
* 单独工作或者分组合作,然而采用相反的方法才合适
* 上级对下级施压很大
* 不关心销售额的下降
* 由于内卷,销售团队之间不协同合作
* 让一个健谈的人主导会议
### 逐步改变习惯
习惯不是一成不变的,你可以改变你的行为习惯。首先,要知道不能一下子改变所有坏习惯。相反,先找到一个关键的习惯进行改变,这会产生小而快速的奖励。请记住,改变了一个关键的习惯后,会产生连锁反应。
以下是你可以用来改变任何习惯的四步框架,其中还包括与开放式组织原则相关的习惯。
#### 第一步:调整例行事项
确定你的习惯循环和例行事项,例如,当面临一件你无法独自解决的重大挑战之时。例行事项(你表现出的行为)最容易确定,所以先从它下手:例如,“在我的组织中,没人愿意和别人讨论问题。大家都会早早地放弃”。决定好你想要调整、改变或者学习的事情:例如:“每次重大挑战到来的时候,我应该和他人讨论一下,并且尝试建立一个志同道合、有能力解决问题的社区。”
#### 第二步:有奖励的实验
奖励是很重要的,因为它会满足你强烈的渴望。但是,我们通常没有意识到强烈的渴望会驱动我们的行为。只有在事后,才会被我们察觉。比方说,开会时很多次你都想尽快离开会议室,避免讨论话题,即使内心清楚你应该弄明白如何解决问题。
要了解强烈的渴望是什么,你必须要实验。这可能会花费你几天、几周甚至更久的时间。你必须要感受到触发压力,才能完全识别它。例如,问问你自己当你试图推卸责任时的感受。
把你自己当作科学家,进行实验并收集数据。这是你调查研究的步骤:
1. 第一个行为结束后,开始调整后面的行为,看看有没有奖励变化。例如,如果你每次碰到自己无法解决的挑战时都放弃,那么奖励就是不承担责任的解脱。更好的解决方法是与至少一个同样关心该问题的人讨论该问题。关键是要测试不同的假设,以确定哪种渴望驱使你的日常生活。你真的想逃避责任吗?
2. 在经历四至五个不同的例行事项和奖励之后,写下在收到每个奖励后立即想到的前三、四件事。例如,你不会在面对挑战时放弃,而是与其他人讨论这个问题。然后,你决定可以做什么。
3. 写下你的感受或渴望后,设置一个 15 分钟的计时器。当计时器结束时,问问自己是否依旧渴望。在屈服于渴望之前,请休息一会儿并再考虑一两次这个问题。这会迫使你意识到这一刻,并帮助你稍后回忆起你当时的想法。
4. 试着记住你在那一刻的想法和感受,然后在例行事项后 15 分钟。如果渴望消失了,你就已经确定了回报是什么。
#### 第三步:分析出坏习惯的提示或触发器
坏习惯的提示信息很难鉴定,因为通常有太多信息干扰你未定型的行为。要在干扰中鉴别提示,你可以在你的坏习惯出现的时候,观察以下四个因素:
地点:它在哪里发生?例如:“我最大的挑战在会议中出现。”
时间:它什么时候出现?例如:“如果我累了,下午的会议就是在浪费时间,因为我没兴趣付出努力。”
感受:你当时的情绪状态是怎样的?例如:“当我听到这个问题时,我感到压力山大并且很沮丧。”
人们:当时有谁或者哪一类人在你周围,还是你是独自一人?例如:“在会议上,大多数人似乎对这个问题也不感兴趣。剩下的人主导会议讨论。”
#### 第四步:制定养成好习惯的计划
一旦你确定奖励可以驱动你的行为,某些提示会触发你的坏习惯,那你就可以开始改变你的行动。请跟随以下三个简单的步骤:
1. 首先,规划好习惯的提示。例如:“在会议上,我将发现并将我的注意力集中在重要的问题上。”
2. 其次,选择一种能带来相同回报的好行为,但不会遭受你现在坏习惯的惩罚。例如:“我将找到解决这个问题的方法,并考虑我需要哪些资源和技能才能成功。当我创建一个能够成功解决问题的社区时,我会感觉很棒。”
3. 最后,让你选择的行为成为深思熟虑的选择,直到你不再需要考虑它,就能下意识地做它了。例如:“我将有意识地关注重要问题,直到我可以不假思索地做到这一点。我会查看近期会议的安排表,这样我就可以提前知道会发生什么。在每次会议开始前和会议期间,我会问自己‘为什么我会来开会’,来确保我集中注意于重要的事情。”
#### 制定计划来避免忘记必做事项
为了成功地开始做你经常忘记的事情,请按照以下步骤:
1. 计划你想要做什么
2. 决定何时完成
3. 将计划分为必要的小任务
4. 用计时器或者日常计划进行提示,并开始每项任务
5. 按计划完成每个任务
6. 按时完成后就奖励自己
### 习惯的改变
习惯的改变需要很长时间。有时候互助小组会帮助你改变习惯。有时候,在低压力环境中,进行大量的练习和角色预演能够更好地帮助你改变。想要找到有效的奖励,你需要不断的尝试。
有时,习惯是更重要、更深层次问题的反映。在这些情况下,你可能需要专业帮助。但是,如果你有改变的愿望,并接受在此过程中会有一些小失败,你就可以控制任何习惯。
在本文中,我使用了使用 *提示-例行事项-奖励* 三个过程的社区开发示例。它同样可以应用于其他开放式组织的原则。我希望这篇文章能让你思考如何通过了解习惯如何运作、采取措施改变习惯,以及制定计划避免忘记你想做的事情,来管理习惯。无论是开放式组织原则,还是其他任何东西,你现在都可以判断出提示、常规和奖励。当提示出现时,这将引导你制定改变习惯的计划。
在我的下一篇文章中,我将通过 Art Markman 教授在《Smart Thinking》中观点来继续讨论习惯。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/open-organization/22/6/using-habits-practice-open-organization-principles>
作者:[Ron McFarland](https://opensource.com/users/ron-mcfarland) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Habits are a long-term interest of mine. Several years ago, I gave a presentation on habits, both good and bad, and how to expand on good habits and change bad ones. Just recently, I read the habits-focused book * Smart Thinking* by Art Markman. You might ask what this has to do with
[open organization principles.](https://theopenorganization.org/definition/open-organization-definition/)There is a connection, and I'll explain it in this two-part article on managing habits.
In this first article, I talk about habits, how they work, and—most important—how you can start to change them. In the second article, I review Markman's thoughts as presented in his book.
## The intersection of principles and habits
Suppose you learned about open organization principles and although you found them interesting and valuable, you just weren't in the habit of using them. Here's how that might look in practice.
**Community: **If you're faced with a significant challenge but think you can't address it alone, you're likely in the habit of just giving up. Wouldn't it be better to have the habit of building a community of like-minded people that collectively can solve the problem?
**Collaboration:** Suppose you don't think you're a good collaborator. You like to do things alone. You know that there are cases when collaboration is required, but you don't have a habit of engaging in it. To counteract that, you must build a habit of collaborating more.
**Transparency:** Say you like to keep most of what you do and know a secret. However, you know that if you don't share information, you're not likely to get good information from others. Therefore, you must create the habit of being more transparent.
**Inclusivity:** Imagine you are uncomfortable working with people you don't know and who are different from you, whether in personality, culture, or language. You know that if you want to be successful, you must work with a wide variety of people. How do you create a habit of being more inclusive?
**Adaptability:** Suppose you tend to resist change long after what you're doing is no longer achieving what you had hoped it would. You know you must adapt and redirect your efforts, but how can you create a habit of being adaptive?
## What is a habit?
Before I give examples regarding the above principles, I'll explain some of the relevant characteristics of a habit.
- A habit is a behavior performed repeatedly—so much so that it's now performed without thinking.
- A habit is automatic and feels right at the time. People are so used to it, that it feels good when doing it, and to do something else would require effort and make them feel uncomfortable. They might have second thoughts afterward though.
- Some habits are good and extremely helpful by saving you a lot of energy. The brain is 2% of the body's weight but consumes 20% of your daily energy. Because thinking and concentration require a lot of energy, your mind is built to save it through developing unconscious habits.
- Some habits are bad for you, so you desire to change them.
- All habits offer some reward, even if it is only temporary.
- Habits are formed around what you are familiar with and what you know, even habits you don’t necessarily like.
## The three steps of a habit
**Cue (trigger):**First, a cue or trigger tells the brain to go into automatic mode, using previously learned habitual behavior. Cues can be things like seeing a candy bar or a television commercial, being in a certain place at a certain time of day, or just seeing a particular person. Time pressure can trigger a routine. An overwhelming atmosphere can trigger a routine. Simply put, something reminds you to behave a certain way.**Routine:**The routine follows the trigger. A routine is a set of physical, mental, and/or emotional behaviors that can be incredibly complex or extremely simple. Some habits, such as those related to emotions, are measured in milliseconds.**Reward:**The final step is the reward, which helps your brain figure out whether a particular activity is worth remembering for the future. Rewards can range from food or drugs that cause physical sensations to joy, pride, praise, or personal self-esteem.
## Bad habits in a business environment
Habits aren't just for individuals. All organizations have good and bad institutional habits. However, some organizations deliberately design their habits, while others just let them evolve without forethought, possibly through rivalries or fear. These are some organizational habit examples:
- Always being late with reports
- Working alone or working in groups when the opposite is appropriate
- Being triggered by excess pressure from the boss
- Not caring about declining sales
- Not cooperating among a sales team because of excess competition
- Allowing one talkative person to dominate a meeting
## A step-by-step plan to change a habit
Habits don't have to last forever. You can change your own behavior. First, remember that many habits can not be changed concurrently. Instead, find a keystone habit and work on it first. This produces small, quick rewards. Remember that one keystone habit can create a chain reaction.
Here is a four-step framework you can apply to changing any habit, including habits related to open organization principles.
#### Step one: identify the routine
Identify the habit loop and the routine in it (for example, when an important challenge comes up that you can't address alone). The routine (the behaviors you do) is the easiest to identify, so start there. For example: "In my organization, no one discusses problems with anyone. They just give up before starting." Determine the routine that you want to modify, change, or just study. For example: "Every time an important challenge comes up, I should discuss it with people and try to develop a community of like-minded people who have the skills to address it."
#### Step two: experiment with the rewards
Rewards are powerful because they satisfy cravings. But, we're often not conscious of the cravings that drive our behavior. They are only evident afterward. For example, there may be times in meetings when you want nothing more than to get out of the room and avoid a subject of conversation, even though down deep you know you should figure out how to address the problem.
To learn what a craving is, you must experiment. That might take a few days, weeks, or longer. You must feel the triggering pressure when it occurs to identify it fully. For example, ask yourself how you feel when you try to escape responsibility.
Consider yourself a scientist, just doing experiments and gathering data. The steps in your investigation are:
- After the first routine, start adjusting the routines that follow to see whether there's a reward change. For example, if you give up every time you see a challenge you can't address by yourself, the reward is the relief of not taking responsibility. A better response might be to discuss the issue with at least one other person who is equally concerned about the issue. The point is to test different hypotheses to determine which craving drives your routine. Are you craving the avoidance of responsibility?
- After four or five different routines and rewards, write down the first three or four things that come to mind right after each reward is received. Instead of just giving up in the face of a challenge, for instance, you discuss the issue with one person. Then, you decide what can be done.
- After writing about your feeling or craving, set a timer for 15 minutes. When it rings, ask yourself whether you still have the craving. Before giving in to a craving, rest and think about the issue one or two more times. This forces you to be aware of the moment and helps you later recall what you were thinking about at that moment.
- Try to remember what you were thinking and feeling at that precise instant, and then 15 minutes after the routine. If the craving is gone, you have identified the reward.
#### Step three: isolate the cue or trigger
The cue is often hard to identify because there's usually too much information bombarding you as your behaviors unfold. To identify a cue amid other distractions, you can observe four factors the moment the urge hits you:
**Location:** Where did it occur? ("My biggest challenges come out in meetings.")
**Time:** When did it occur? ("Meetings in the afternoon, when I'm tired, are the worst time, because I'm not interested in putting forth any effort.")
**Feelings:** What was your emotional state? ("I feel overwhelmed and depressed when I hear the problem.")
**People:** Who or what type of people were around you at the time, or were you alone? ("In the meetings, most other people don't seem interested in the problem either. Others dominate the discussion.")
#### Step four: have a plan
Once you have confirmed the reward driving your behavior, the cues that trigger it, and the behavior itself, you can begin to shift your actions. Follow these three easy steps:
- First, plan for the cue. ("In meetings, I'm going to look for and focus my attention on important problems that come up.")
- Second, choose a behavior that delivers the same reward but without the penalties you suffer now. ("I'm going to explore a plan to address that problem and consider what resources and skills I need to succeed. I'm going to feel great when I create a community that's able to address the problem successfully.")
- Third, make the behavior a deliberate choice each and every time, until you no longer need to think about it. ("I'm going to consciously pay attention to major issues until I can do it without thinking. I might look at agendas of future meetings, so I know what to expect in advance. Before and during every meeting, I will ask why should I be here, to make sure I'm focused on what is important."
#### Plan to avoid forgetting something that must be done
To successfully start doing something you often forget, follow this process:
- Plan what you want to do.
- Determine when you want to complete it.
- Break the project into small tasks as needed.
- With a timer or daily planner, set up cues to start each task.
- Complete each task on schedule.
- Reward yourself for staying on schedule.
## Habit change
Change takes a long time. Sometimes a support group is required to help change a habit. Sometimes, a lot of practice and role play of a new and better routine in a low-stress environment is required. To find an effective reward, you need repeated experimentation.
Sometimes habits are only symptoms of a more significant, deeper problem. In these cases, professional help may be required. But if you have the desire to change and accept that there will be minor failures along the way, you can gain power over any habit.
In this article, I've used examples of community development using the *cue-routine-reward* process. It can equally be applied to the other open organization principles. I hope this article got you thinking about how to manage habits through knowing how habits work, taking steps to change habits, and making plans to avoid forgetting things you want done. Whether it's an open organization principle or anything else, you can now diagnose the cue, the routine, and the reward. That will lead you to a plan to change a habit when the cue presents itself.
In my next article, I'll look at habits through the lens of Art Markman's thoughts on Smart Thinking.
## 1 Comment |
15,183 | 使用 VirtualBox 安装 Linux 虚拟机 | https://opensource.com/article/21/6/try-linux-virtualbox | 2022-10-27T10:43:00 | [
"虚拟机",
"VirtualBox"
] | /article-15183-1.html |
>
> VirtualBox 能帮助任何人(即使是命令行新手)安装一个新的虚拟机。
>
>
>

VirtualBox 能让任何人都可以轻松安装 Linux 虚拟机。你不需要有使用命令行的经验,就可以自己安装一个简单的 Linux 虚拟机。在虚拟机方面,我精通很多东西,但这篇文章将向新手展示如何安装一个 Linux 虚拟机。此外,这篇文章还概述了如何使用开源虚拟机管理程序 [VirtualBox](https://www.virtualbox.org/) ,来运行以及安装一个测试目的的 Linux 系统。
### 一些术语
在开始之前,你需要了解在本安装教程中的两个操作系统(OS)之间的区别:
* <ruby> 主机系统 <rt> host system </rt></ruby>:这指的是你安装 VirtualBox 的操作系统(即本机的操作系统)。
* <ruby> 客体系统 <rt> guest system </rt></ruby>:这指的是你想要在主机系统之上运行的虚拟化系统。
在输入/输出、网络、文件访问、剪贴板、音频和视频方面,主机系统和客体系统都必须能够交互。
在本教程中,我将使用 Windows 10 作为 *主机系统*,[Fedora 33](https://getfedora.org/) 作为 *客体系统*。
### 安装前的准备
当我们谈论虚拟化时,实际上,我们指的是 [硬件辅助虚拟化](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hardware-assisted_virtualization)。硬件辅助虚拟化需要兼容的 CPU。过去十年来,几乎每个普通的 x86 CPU 都有这一功能。AMD 公司称这样的 x86 CPU 是具有 **AMD 虚拟化技术(AMD-V)** 的处理器,英特尔公司则称其是具有 **Intel 虚拟化技术(VT-x)** 的处理器。虚拟化功能增加了一些额外的 CPU 指令,你可以在 BIOS 中启用或禁用这些指令。
在安装虚拟机之前:
* 确保在 BIOS 中启用了虚拟化技术(AMD-V 或 VT-x)。
* 下载并安装好 [VirtualBox](https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads)。
### 准备虚拟机
下载你要用的 Linux 发行版的镜像文件。下载 32 位还是 64 位的操作系统镜像都没有关系,因为在 32 位的主机系统上也可以启动 64 位的操作系统镜像(当然内存的使用会受限),反之亦然。
>
> **注意事项:** 如果可以的话,请下载附带有 [逻辑卷管理器](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logical_Volume_Manager_(Linux))(LVM)的 Linux 发行版。LVM 会将文件系统与物理硬盘驱动器解耦。如果你的空间不足时,这能够让你增加客体系统的硬盘驱动器的大小。
>
>
>
现在,打开 VirtualBox,然后单击黄色的“<ruby> 新建 <rt> New </rt></ruby>”按钮:

接下来,配置客体操作系统允许使用多少内存:

我的建议是:**不要吝啬分配给客体操作系统使用的内存!**当客体操作系统的内存不足时,客体系统将开始从随机存取存储器(RAM)向硬盘驱动器进行内存分页,这样会极大地恶化系统的性能和响应能力。如果底层的主机系统开始分页,你很可能不会注意到。对于具有图形化桌面环境的 Linux 工作站系统,我建议至少分配 4GB 内存。
接下来,创建虚拟磁盘:

虚拟磁盘的格式选择默认的选项 “VDI(VirtualBox 磁盘镜像)” 就可以了:

在以下的窗口中,我建议选择“<ruby> 动态分配 <rt> dynamically allocated </rt></ruby>”,因为这允许你在之后增加虚拟磁盘的大小。如果你选择了“<ruby> 固定大小 <rt> fixed size </rt></ruby>”,磁盘的速度可能会更快,但你将无法修改虚拟磁盘的大小了:

建议你使用附带有逻辑卷管理器(LVM)的 Linux 发行版,这样你就可以先创建一个较小的硬盘。如果之后你的客体系统的空间快用完了,你可以按需增加磁盘的大小。
>
> **注意**:我选择的客体系统为 Fedora,在 Fedora 的官网说明:[Fedora 至少需要分配 20GB 的空闲磁盘空间](https://getfedora.org/en/workstation/download/)。我强烈建议你遵守该规范。在这里,我选择了 8GB,以便稍后演示如何用命令行增加磁盘空间。如果你是 Linux 新手,或者对命令行没有经验,请依旧选择 20GB。
>
>
>

创建好硬盘驱动器后,从 VirtualBox 主窗口的列表中选择新创建的虚拟机,然后单击“<ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby>”。在设置菜单中,点击“<ruby> 系统 <rt> System </rt></ruby>”,然后选择“<ruby> 处理器 <rt> Processor </rt></ruby>”标签。默认情况下,VirtualBox 只向客体系统分配一个 CPU 内核。在现代多核 CPU 计算机上,分配至少两个内核是没有任何问题的,这能显著地加快客体系统的速度:

#### 设置网络适配器
接下来,要处理的是网络设置。默认情况下, VirtualBox 会创建一个 NAT 连接,这对于大多数情况来说,是没有问题、不用做其他更改的:

你也可以创建多个网络适配器。以下是网络适配器最常见的类型:
* NAT:NAT 适配器能自动执行 [网络地址转换](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_address_translation)。从外部看,主机和客体系统使用着相同的 IP 地址。你无法通过网络从主机系统内访问客体系统。(尽管,你也可以通过定义 [端口转发](https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch06.html#natforward),来访问某些服务。)当你的主机系统可以访问互联网时,则你的客体系统也可以访问互联网。NAT 不再需要进一步的配置。
+ *如果你只需要让客体系统接入互联网就可以的话,请选择 “NAT”。*
* <ruby> 桥接适配器 <rt> Bridged adapter </rt></ruby>:在此配置中,客体系统和主机系统可以共享相同的物理以太网设备。这两个系统都将拥有独立的 IP 地址。从外部看,网络中会有两个独立的系统,它们共享相同的物理以太网适配器。这种设置更灵活,但需要更多的配置。
+ *如果你想要共享客体系统的网络服务的话,请选择 “桥接适配器”。*
* <ruby> 仅限主机的适配器 <rt> Host-only adapter </rt></ruby>:在此配置中,客体系统只能与主机,或在同一主机上运行的其他客体系统相互通信。主机系统也可以连接到客体系统。但客体系统不能接入互联网或物理网络。
+ *如果你想要获得高安全性,请选择 “仅限主机的适配器”。*
#### 分配操作系统镜像
在设置菜单中,点击“<ruby> 存储 <rt> Storage </rt></ruby>”,然后选择虚拟光盘驱动器。单击右侧的 “光盘”图标,然后点击“<ruby> 选择一个磁盘文件…… <rt> Choose a disk file… </rt></ruby>”,然后分配你想要安装的、已下载的 Linux 发行版镜像:

### 安装 Linux
现在,就已经配置好了虚拟机。右上角关闭“<ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby>”菜单,返回主窗口。点击“绿色箭头”(即“开始”按钮)。虚拟机将从虚拟光盘驱动器启动,你将发现你已经进入到 Linux 发行版的安装程序中:

#### 设置分区
安装程序将在安装过程中要求你提供分区信息。选择“<ruby> 自定义 <rt> Custom </rt></ruby>”:

>
> **注意:** 我假设,你创建这一虚拟机的目的是为了测试。此外,你也无需关心客体系统的休眠,因为此功能会由 VirtualBox 来隐式地提供。因此,你可以省略交换分区,以节省主机系统的磁盘空间。请记住,如果你需要的话,你可以稍后自己添加交换分区。在 《[Linux 系统交换空间的介绍](https://opensource.com/article/18/9/swap-space-linux-systems)》 这篇文章中,作者 David Both 进一步解释了如何添加交换分区,并选择交换分区正确的大小。
>
>
>
Fedora 33 及之后更高的版本提供了一个 [zram 分区](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Changes/SwapOnZRAM),zram 分区可以用于存放分页和交换、并经过压缩过后的硬盘数据。zram 分区可以按需地调整大小,并且它比硬盘交换分区快得多。
为了简单,我们只添加以下两个<ruby> 挂载点 <rt> Mount Point </rt></ruby>:

保存更改,接下来我们继续安装。
### 安装 VirtualBox 增强功能
完成安装后,从硬盘驱动器启动,并登录到虚拟机。现在,你可以安装 <ruby> VirtualBox 增强功能 <rt> VirtualBox Guest Additions </rt></ruby>,其中包括特殊的设备驱动程序和系统应用程序,它们能提供以下功能:
* 共享剪贴板
* 共享文件夹
* 更好的性能
* 可自由扩展的窗口大小
点击顶部菜单栏的“<ruby> 设备 <rt> Devices </rt></ruby>”,然后选择“<ruby> 插入增强功能的 CD 镜像…… <rt> Insert Guest Additions CD image... </rt></ruby>”,来安装 VirtualBox 增强功能:

在大多数 Linux 发行版上,带有增强功能的 CD 镜像会自动挂载,并且能够在文件管理器中找到。Fedora 会问你是否要运行安装脚本。单击“<ruby> 运行 <rt> Run </rt></ruby>”,并授予该安装进程 root 权限:

安装完成后,需要重新启动系统。
### LVM:扩大磁盘空间
我在之前给 Fedora 虚拟机分配了 8GB 硬盘空间,是一个愚蠢的决定,因为 Fedora 很快就会告警空间不足:

正如我提到的,Fedora 官网建议安装时分配 20GB 的磁盘空间。因为 8GB 是 Fedora 33 安装启动就需要的最少空间。没有安装其他软件(除了 VirtualBox 增强功能)的一个新安装的系统就几乎占用了整个 8GB 的可用空间。这时候,不要打开 GNOME 软件中心或任何其他可能从互联网下载文件的东西。
幸运的是,我选择了附带有 LVM 的 Fedora,这样我就可以用命令行轻松地修复这个问题。
要增加虚拟机中文件系统的空间,你必须先增加主机系统上分配的虚拟硬盘驱动器。
关闭虚拟机。如果你的主机系统运行的是 Windows,请打开终端,并进入到 `C:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox` 目录下。使用以下命令,将磁盘大小扩大到 12,000MB:
```
VBoxManage.exe modifyhd "C:\Users\StephanA\VirtualBox VMs\Fedora_33\Fedora_33.vdi" --resize 12000
```
然后启动虚拟机,并打开“<ruby> 磁盘 <rt> Disks </rt></ruby>”工具。你可以看到你刚刚新创建且未分配的可用空间。选择“<ruby> 可用空间 <rt> Free Space </rt></ruby>”,然后单击 “+” 按钮:

现在,创建一个新的分区。选择你要使用的可用空间的大小:

如果你不想在新分区上创建文件系统或任何其他内容,请选择“<ruby> 其他 <rt> Other </rt></ruby>”:

选择“<ruby> 无文件系统 <rt> No Filesystem </rt></ruby>”:

现在,磁盘空间应该如下图所示:

虚拟机有了一个新的分区设备:`/dev/sda3`。通过输入 `vgscan` ,来检查你的 LVM 卷组,找到 `fedora_localhost_live` 这一 LVM 卷组 :

现在,已经万事俱备了。在新分区 `/dev/sda3` 中扩展卷组 `fedora_localhost_live`:
```
vgextend fedora_localhost-live /dev/sda3
```

由于卷组比逻辑卷大,你可以增加逻辑卷的大小。命令 `vgdisplay` 显示了共有 951 个可用的物理扩展(PE):

将逻辑卷增加 951 个物理扩展:
```
lvextend -l+951 /dev/mapper/fedora_localhost--live-root
```

在增加了逻辑卷后,最后一件事就是调整文件系统的大小:
```
resize2fs /dev/mapper/fedora_localhost--live-root
```

这样磁盘空间就增加完成了!检查“<ruby> 磁盘使用分析器 <rt> Disk Usage Analyzer </rt></ruby>”,你就可以看到扩展空间已经可用于文件系统了。
### 总结
使用虚拟机,你可以检查在一个特定的操作系统或一个特定版本的操作系统、软件是如何操作的。除此之外,你还可以尝试任何想测试的 Linux 发行版,而不必担心系统损坏。对于资深用户来说,VirtualBox 在测试、网络和模拟方面提供了广泛的可能性。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/6/try-linux-virtualbox>
作者:[Stephan Avenwedde](https://opensource.com/users/hansic99) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
15,185 | 安装 Ubuntu 22.10 后要做的 10 件事 | https://www.debugpoint.com/things-to-do-ubuntu-22-10/ | 2022-10-28T08:28:00 | [
"Ubuntu"
] | /article-15185-1.html |
>
> 以下是我们安装 Ubuntu 22.10 “Kinetic Kudu”(GNOME 版)后,推荐做的 10 件事列表。
>
>
>

Ubuntu 22.10 带来了很多令人兴奋的新功能,例如 GNOME 43、最新的内核、重新设计的托盘菜单、文件应用的功能和 Pipewire 等 [新功能](https://www.debugpoint.com/ubuntu-22-10/)。
我相信你已经迫不及待地想尝试 Ubuntu 22.10 上的这些新功能了。
但是请先等一等。
在你前往享受你新安装的 Ubuntu 22.10 之前,我要向你推荐一个不容错过的 Ubuntu 定制技巧列表。
### 安装 Ubuntu 22.10 后要做的 10 件事
#### 1、更新你的系统
安装好 Ubuntu 22.10 后,第一件要做的事就是更新你的系统。因为时差的原因,最新的 ISO 镜像通常不会包括所有的系统更新。所以,你要打开一个终端窗口,并运行以下命令,来更新你的系统。
```
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
```
上述命令执行完成后,你就可以进行下一步啦。
#### 2、删除 Firefox Snap,并安装 Flatpak 或者 deb 版本的 Firefox
自去年发布的 Ubuntu 21.10 版本以来,默认的网页浏览器 Firefox 开始以 Snap 软件包的形式出现。如果你是普通用户,这可能不是一个问题或者需要担心的事情。但是出于几个原因,例如 Snap 软件包的 Firefox 启动时间较长、且当 Firefox 有后台更新时,会有不必要的 Snap 更新通知等等原因,导致许多用户不太喜欢 Firefox 的 Snap 软件包。
因此,你可以按照 [我写的另一篇操作指南](https://www.debugpoint.com/remove-firefox-snap-ubuntu/),来完全删除 Firefox 的 Snap 软件包。这一过程有点复杂,需要花费一点时间。删除完成后,再从个人软件包存档(PPA)安装 deb 版本的 Firefox,或者使用 [Flatpak 版本](https://flathub.org/apps/details/org.mozilla.firefox) 的 Firefox。
这是一个可选的动作,你也可以跳过这一步骤。
#### 3、安装并启用 Flatpak
虽然,几乎所有最新的 Linux 发行版都会默认安装 Flatpak,但是 Ubuntu 并没有默认安装 Flatpak,这是因为 Ubuntu 使用了它自己的沙箱技术 Snap。
但 Flatpak 这一应用程序还是最适合于每个人。Flatpak 能够帮助你快速安装多个应用程序,并在使用过程中无需担心依赖性和其他事情。
大多数 Flatpak 应用程序都在集中的仓库 Flathub 中。
要在 Ubuntu 22.10 中启用 Flatpak 应用程序,请按照以下命令进行操作。
```
sudo apt install flatpakflatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakreporeboot
```
如果你想进一步了解关于此安装过程的更多信息,请阅读我们不久前发布的 [指南](https://www.debugpoint.com/how-to-install-flatpak-apps-ubuntu-linux/)。
#### 4、查看隐私设置
我建议你在安装 Ubuntu 后,手动退出任何数据收集项。大家都知道,无论怎么努力尝试,在互联网上保护自己的隐私都很困难。因此,这些小步骤很重要。
要配置隐私项,请打开“<ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby>”并选择“<ruby> 隐私 <rt> Privacy </rt></ruby>”。然后查看隐私菜单下列出的项目。
此外,请确保禁用对 Ubuntu 服务器的后台报告。需要运行以下命令来手动禁用,因为在设置中没有禁用它的选项。
```
sudo ubuntu-report -f send no
```

#### 5、探索 GNOME 43 的功能
在 Ubuntu 22.10 版本中,最具视觉和功能性的变化是 GNOME 43。因为 GNOME 43 有一些根本性和核心变化,所以它会影响每个人和他们的工作。GNOME 43 带来了一个新的药丸形状的托盘菜单,并更新了文件应用和 GNOME Web 等原生应用程序的功能。
请查看更为详细的 [GNOME 43 功能](https://www.debugpoint.com/gnome-43/) 一文,以了解更多信息,或者你也可以自己探索 GNOME 43。

#### 6、确保音频可以与 Pipewire 配合使用
如果你经常使用音频,或者你的工作范围涉及到声音捕获、播放等内容,请确保在 Ubuntu 22.10 中,你的音频在有线或蓝牙情况下都能正常工作。
因为 Ubuntu 22.10 这个版本中的音频服务器是多年来第一次发生了变化,传统的 PulseAudio 被现代的 Pipewire 所取代。因此,请务必进行验证音频是否能正常使用。
#### 7、安装其他软件包
确保你可以在 Ubuntu 桌面上播放所有视频和音频格式是很重要的。如果你在设置期间跳过了额外的软件包安装,可以通过以下命令进行安装。
```
sudo apt install ubuntu-restricted-extras
```
这可以解决 Ubuntu 中的任何视频或音频的播放问题,特别是 GNOME 视频无法播放的情况(因为GNOME 视频在默认情况下将无法播放任何内容)。
#### 8、安装基本的应用程序
带有 GNOME 的 Ubuntu 基础版本只有非常基本的应用程序。因此,在你使用 Ubuntu 之前,你需要安装一些其他必要的应用程序。
由于每个人的工作范围不同,每个人所需的应用程序也都不同。因此,在这里我仅提供一个通用的应用程序的列表,我认为你可以把这些应用程序都安装上,因为这些应用程序对所有人来说都很常用。
* GIMP – 进阶的照片编辑器
* VLC – 无需额外编解码器即可播放任何内容的媒体播放器
* Leafpad – 轻量级文本编辑器(甚至比默认的文本编辑器 gedit 还要更轻量级)
* Synaptic – 更好的软件包管理器
安装这些应用程序的命令:
```
sudo apt install -y gimp vlc leafpad synaptic
```
#### 9、获取一些 GNOME 扩展
你可以使用几个很酷的扩展程序,来扩展 GNOME 43 的功能,包括自定义顶部栏、托盘、更改 adwaita 外观等等。首先,使用下面的命令通过 Flatpak 来安装 GNOME 扩展管理器。
```
flatpak install flathub com.mattjakeman.ExtensionManager
```
安装完成后,你就可以在 GNOME 扩展管理器中搜索你想要的任何扩展了。以下是一些必要扩展,你可以用它们来快速扩展 GNOME 43 的功能,我认为它们非常适合你全新的 Ubuntu 桌面。你只需在扩展管理器应用程序中,搜索这些名称即可。
* Caffeine
* Custom Hot Corners
* Dash to Dock
* Blur my shell
* Gradients
* Hide Activities Button
* Net speed simplified
#### 10、准备备份
我们总是在我们遇到困难时,才觉得有必要备份。所以,请确保从一开始你就为备份做好了准备。理想的备份应用程序是 Timeshift,它很容易安装和使用。
以下是你可以从终端安装 Timeshift 的一组命令。安装完成后,你可以打开 Timeshift,并按照屏幕上的说明,设置备份了。
```
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:teejee2008/ppasudo apt-get updatesudo apt-get install timeshift
```
### 额外小技巧
如果你想进一步定制你新安装的 Ubuntu 系统,以下是一些额外的小技巧。
#### 安装漂亮的字体
字体是一个很小却影响很大的设置项。虽然,Ubuntu 自带有好用的“Ubuntu regular”字体。
但是,你也可以从 Ubuntu 的官方仓库中安装一些其他漂亮的字体。以下是安装字体的一些命令。
```
sudo apt install fonts-roboto fonts-cascadia-code fonts-firacode
```
安装完成后,你可以使用 [GNOME Tweak 工具](https://www.debugpoint.com/customize-your-ubuntu-desktop-using-gnome-tweak/),来更改字体。
#### 安装 TLP
如果你经常使用笔记本电脑,那么你要好好爱惜电脑的电池。虽然电池用久了总是会损坏的,但你可以采取一些步骤,来减缓电池的老化。TLP 是 Linux 中自动优化电池使用、减缓电池老化的最好的程序之一。你可以使用以下命令来安装 TLP。
```
sudo apt install tlp
```
我建议你将电池的电量始终保持在 50% 至 80% 之间。不要过度充电或让电池电量消耗到 50% 以下,也不要给电脑连续插电。
### 总结
以上就是安装桌面 Ubuntu 22.10 后要做的 10 件事啦。
我希望这篇文章会对你有帮助,你能够通过本文的方法来定制和调整你的 Ubuntu 桌面。那么你认为在安装好 Ubuntu 后,什么事是最推荐做的呢?请在评论区中告诉我吧。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/things-to-do-ubuntu-22-10/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/%E6%A0%A1%E5%AF%B9%E8%80%85ID)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,186 | 在你的 Linux 终端中玩经典的贪吃蛇游戏 | https://www.debugpoint.com/snake-game-linux-terminal/ | 2022-10-28T09:15:00 | [
"贪吃蛇"
] | /article-15186-1.html | 
>
> 这是你在 Linux 终端中安装和玩经典贪吃蛇的方法。
>
>
>
还记得老式手机经典简单的贪吃蛇吗?我记得玩了几个小时。嘿,当时没有其他选择,对吧?智能手机仍未上市。而你所拥有的只有这个。

但随着时间的推移,贪吃蛇被具有各种选项的更高级的图形游戏所取代。但没有什么能比得上经典贪吃蛇游戏。
如果我告诉你,你可以在 Linux 终端中玩这个游戏呢?无论你运行的是 Ubuntu Linux、Fedora Linux 还是 Arch Linux,都无关紧要。该游戏适用于大多数 [发行版](https://www.debugpoint.com/category/distributions)。

### 安装 nSnake – Linux 终端的贪吃蛇
你可以使用以下方法通过终端安装 [此游戏](https://github.com/alexdantas/nsnake)。
对于 Ubuntu、Linux Mint 或其他相关发行版:
```
sudo apt install nsnake
```
对于 Fedora Linux 和其他:
```
sudo dnf install nsnake
```
对于 Arch Linux,此游戏可在 [Arch 用户仓库(AUR)](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/nsnake/) 中获得。你可以使用以下步骤安装它。
* [设置 Yay AUR 助手](https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/01/install-yay-arch/)
* 然后打开终端并运行以下命令
```
yay -S nsnake
```
上面的命令会安装游戏的软件仓库版本,它可能不是最新的。但是,如果你想要最新版本,你可能需要通过 GitHub 编译源代码。我在本页末尾添加了编译说明供你参考。
### 玩游戏
玩游戏非常简单。在终端中输入 `nsnake`,这将启动游戏。
要立即退出,请按 `q`。
以下是默认键绑定。
* `箭头键` - 移动蛇
* `q` – 退出游戏
* `p` – 暂停游戏
你还可以通过主菜单以各种方式配置游戏。

完成了,玩吧!
### 编译
要编译最新版本,请在所有 Linux 发行版中使用以下命令。
哦,确保你已经安装了 `git` 和 `ncurses-devel`,它们是编译所需的包。
```
git clone https://github.com/alexdantas/nSnake.git
cd nsnake
make
make install
```
那么,你喜欢贪吃蛇游戏吗?与其他基于终端的游戏相比,你更喜欢它吗?在下面的评论框中与其他读者分享你的观点。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/snake-game-linux-terminal/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,188 | Xubuntu 22.10 的新变化 | https://news.itsfoss.com/xubuntu-22-10-release/ | 2022-10-29T16:08:27 | [
"Xubuntu",
"Ubuntu"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15188-1.html |
>
> Xubuntu 22.10 提供了精致的 Xfce 体验。请读此文了解详情。
>
>
>

Xubuntu 是基于 Xfce 的 Ubuntu 官方版本。
它也是最好的轻量级 Linux 发行版之一。
随着最新的 Xubuntu 22.10 “Kinetic Kudu” 版本,你可以看到改进的桌面环境、添加的功能,以及全面的细化。
### Xubuntu 22.10 的新变化

Xubuntu 22.10 带来了一些令人兴奋的升级。一些亮点包括:
* Xfce 4.16(或 Xfce 4.17 开发版)
* Catfish 的外观进行了更新。
* 更新了新图标,弃用了 elementary-xfce-darker 主题。
* Mousepad 搜索历史。
* Thundar 文件管理器的改进。
* Xfce 任务管理器。
>
> ? Xubuntu 22.10 将支持九个月,直到 **2023 年 7 月**。如果你想要稳定性而不是功能,你应该首选使用 [LTS 版本](https://itsfoss.com/long-term-support-lts/)。
>
>
>
#### Xfce 4.17 开发版还是 Xfce 4.16?
Xubuntu 22.10 的发行说明说它专门提供了 Xfce 4.17 开发版本。
但是,当我安装 Xubuntu 22.10 的 beta 版本(并将其更新到最新版本)时,只具有 Xfce 4.16。

不确定他们是否退出了 Xfce 4.17 开发版本,或者 Xfce 4.16 现在是否存在。
#### Catfish 外观

Catfish 是 Xubuntu 上的一个文件搜索工具。通过新的升级,它具有焕然一新的外观,并做了底层的改进。
与你搜索的文件交互时,你还会获得一个“打开方式”上下文菜单。

Catfish 还添加了一些细微而有用的功能。
#### GNOME 43 软件应用
在值得注意的应用程序更新中,GNOME 的最新软件中心是一个不错的选择。这是 Xubuntu 22.10 的外观:

当然,它可能无法与 Xfce 上的其他应用程序保持一致,但我认为你应该不会介意。
#### 图标更新
随着 elementary-xfce 0.17 图标更新,有许多新图标和更简洁的选项,可提供一致的 Xubuntu 桌面体验。

此外,elementary-xfce-darkest 主题图标包已被弃用。

#### 任务管理器右键选项

你现在可以将完整的进程路径复制到剪贴板。这对于需要从命令行进行故障排除或停止操作很有用。
### 其他增强功能

还有其他几个值得注意的变化,包括:
* Linux 内核 5.19。
* Firefox 浏览器 105。
* `Alt-Tab` 视图通过更突出的图标进行了改进。
* 马赛克拼图添加到 SGT 拼图系列。
* Mousepad 文本编辑器现在包括搜索历史记录,以及更多调整。
要了解有关更改的更多信息,请查看 [官方发行说明](https://wiki.xubuntu.org/releases/22.10/release-notes)。
### 下载 Xubuntu 22.10
你可以从 [Ubuntu 的中央镜像库](https://cdimage.ubuntu.com/xubuntu/releases/22.10/release/) 或它的 [官方网站](https://xubuntu.org/download/) 下载最新的 ISO 文件。
官方网站可能需要一段时间才能提供 ISO。
>
> **[下载Xubuntu 22.10](https://xubuntu.org/download/)**
>
>
>
? 你觉得 Xubuntu 22.10 如何?请在评论中告诉我。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/xubuntu-22-10-release/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Xubuntu is an XFCE-powered official Ubuntu flavour.
It is also one of the best lightweight Linux distributions available.
[16 Best Lightweight Linux Distributions for Older Computers in 2020 [With System Requirements]Get your older hardware new life with these lightweight beginner-friendly Linux distributions. System requirements for the Linux distributions have also listed.](https://itsfoss.com/lightweight-linux-beginners/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

With the latest Xubuntu 22.10 "**Kinetic Kudu**" release, you can expect desktop environment improvements, feature additions, and several refinements across the board.
## Xubuntu 22.10: What's New?

Xubuntu 22.10 brings in some exciting upgrades. Some of the highlights include:
**Xfce 4.16 (or Xfce 4.17 dev)****Catfish appearance update.****New icon refresh and deprecated elementary-xfce-darker-theme.****Mousepad search history.****Thundar file manager improvements.****Xfce task manager.**
**July 2023**. If you want stability over features, you should prefer using an
[LTS version](https://itsfoss.com/long-term-support-lts/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
### XFCE 4.17 Development Version or XFCE 4.16?
The release notes for Xubuntu 22.10 say it features the Xfce 4.17 development version.
However, when I installed the beta version for Xubuntu 22.10 (and updated it to the latest), it said it features Xfce 4.16.
Not sure if they pulled out Xfce 4.17 development version or if Xfce 4.16 is here for now.
### Catfish Appearance
Catfish is a file search utility on Xubuntu. With the new upgrade, it has a refreshed appearance with tweaks under the hood.
You also get an "**Open With**" context menu when interacting with the files you searched for.
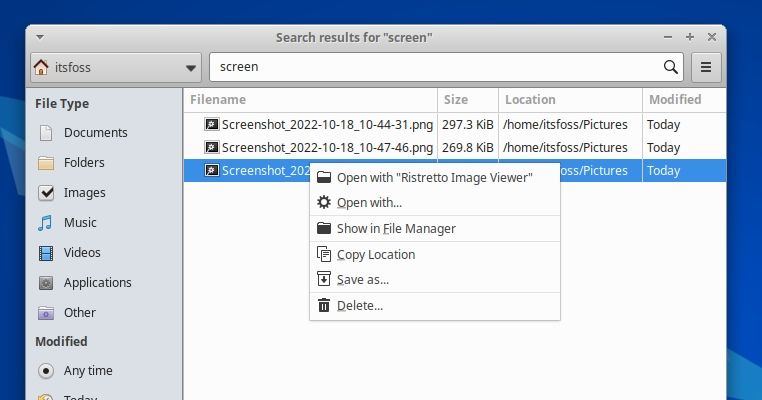
A pretty subtle but valuable feature addition for catfish.
### GNOME 43 Software
Among notable app updates, GNOME's latest Software Center is a nice thing to have. This is how it looks with Xubuntu 22.10:
Of course, it may not give you a consistent look with other applications on Xfce, but I think you can give it an excuse.
### Icon Updates
With elementary-xfce 0.17 icon update, there are many new icons and cleaner options that provide a consistent Xubuntu desktop experience.
Additionally, the **elementary-xfce-darkest theme** icon pack has been deprecated.
### Task Manager Right-Click Option
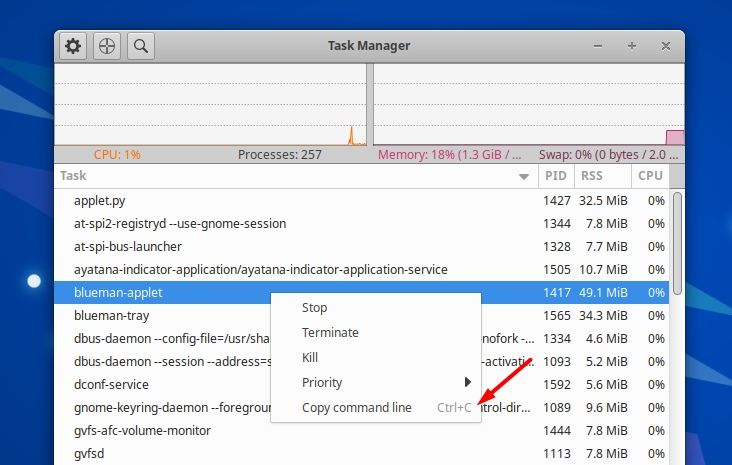
You can now copy the full process path to the clipboard. This could be useful to troubleshoot or stop things from the command line when required.
## Other Enhancements
There are several other notable changes that include:
**Linux Kernel 5.19****Mozilla Firefox 105.****Alt-Tab view improved with more prominent icons.****Mosaic puzzle added to SGT Puzzles collection.****Thunar archive plugin now supports compressing zip files.****Mousepad text editor now includes a search history and a few more tweaks.**
To learn more about the changes, check out the [official release notes](https://wiki.xubuntu.org/releases/22.10/release-notes?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Download Xubuntu 22.10
You can download the latest ISO from [Ubuntu's central image repository](https://cdimage.ubuntu.com/xubuntu/releases/22.10/release/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) or its [official website](https://xubuntu.org/download/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
It might take a while for its official website to make the ISO available.
💬 *What do you think about Xubuntu 22.10? Let me know your thoughts in the comments.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,189 | 通过示例来学习 Bash base64 的编码和解码 | https://www.debugpoint.com/bash-base64-encode-decode/ | 2022-10-29T16:33:52 | [
"base64"
] | /article-15189-1.html |
>
> 你想了解 Base64 编码和解码的方法吗?在本教程中,我们使用 Bash shell 脚本和各种示例解释了 Base64 编码和解码步骤。
>
>
>

Base64 编码方法可以将二进制数据转换为文本,如此编码数据可以在任何通信媒介进行传输。这种编码方法主要用于电子邮件加密的过程。
总体而言,Base64 编码方法是一种二进制到文本的编码方案,以 ASCII 字符串格式表示 8 字节的二进制数据。使用这种编码方法在各种媒介之间传输数据时有几个优势,尤其是对于那些能可靠地支持文本内容的媒介。因此,Base64 编码方法在万维网上被广泛使用。这种编码方案最常用于电子邮件附件的编码上。
根据 Base64 编码表,二进制数据可以经 Base64 编码后可以转换为 64 个不同的 ASCII 字符,包含大写字母 `A` 到 `Z`,小写字母 `a` 到 `z`,数字 `0` 到 `9`,以及符号 `+` 和 `/`,这些字符在传输和打印上十分便捷。
这 64 个 ASCII 字符代表着从 `000000` 到 `111111` 的二进制值。每个非末尾的 Base64 编码字符恰好代表 6 位二进制值。

### Bash base64 的编码和解码
#### 句法
在我们提供示例之前,首先介绍 Base64 的基本语法。
```
base64 [OPTIONs] [INFILE] [OUTFILE]
```
* 选项(`Option`):参照下面的表格,你可以提供任何的选项或组合多个选项。
* 输入(`INFILE`):你可以从标准输入(如命令行)或文件中输入。
* 输出(`OUTFILE`):你可以将输出重定向到标准输出,如终端或文件中。
| 选项 | 描述 |
| --- | --- |
| `-e` 或者 `--encode` | 此选项用于对标准输入的数据或从文件中读入的数据进行编码。这是默认选项。 |
| `-d` 或者 `--decode` | 此选项用于对标准输入的数据或从文件中读入的已 Base64 编码数据进行解码。 |
| `-n` 或者 `--noerrcheck` | 默认情况下,Base64 在解码数据时,会自动检查是否有错误。你可以使用该选项在解码时忽略检查。 |
| `-i` 或 `--ignore-garbage` | 此选项用于在解码时忽略非字母字符。 |
| `-u` 或者 `--help` | 此选项用于获取有关使用此命令的信息。 |
#### 示例 1:基本编码
在 Linux 中,默认已安装好 Base64 软件包。因此,你可以轻松地从命令行使用 Base64。要对一个字符串或文本进行编码,你可以通过管道将其传递到 `base64` 命令,并获取待编码的文本。在下面的示例中,对字符串 `debugpoint.com` 进行了 Base64 编码。
```
echo "debugpoint.com" | base64
```

结果是经过 Base64 编码后的字符串。
#### 解释
Base64 编码方法使用下面的几个步骤来转换输入的数据。首先,每个输入字符转换为 8 位二进制值,接着,二进制字符串拆分为一组组 6 位的二进制值,然后,每个 6 位的二进制值被转换为十进制值。
最后,每个十进制值都通过 Base64 编码索引表转换为 Base64 字符。
在上面的示例中,第一个字符 `d` 被转换为二进制 `01100100`。前 6 位是 `011001`,转换为十进制是 `25`。`25` 在 Base64 编码索引表中对应着 `Z`。整个输入的文本流都像如此编码。请参阅以下编码过程的示例。

#### 示例 2:基本解码
要解码字符串,需要将编码值传递给 `base64` 命令,选项为 `--decode`,它将输出你之前输入的字符串。

#### 示例 3:对文本文件进行编码
示例 1 中的同一命令也可用于编码文本文件,并将输出重定向到另一个文本文件。方法如下。
```
base64 example3.txt > example3-encoded.txt
```

#### 示例 4:对文本文件进行解码
要解码使用 Base64 编码的文本文件,只需使用 `--decode` 或 `-d` 选项,并传递文本文件名。
```
base64 -d example3-encoded.txt
```
#### 示例 5:对用户输入的数据进行编码
使用 Bash shell 编程,你可以通过终端接收用户的输入,并对其进行 Base64 编码。你需要先编写一个简单的 shell 脚本,并在授予可执行权限后执行。
以下就是一个简单的示例,它从用户那里获得输入,然后进行 Base64 编码,最终显示编码的字符串。
```
#!/bin/bash
#Sample program to take input, encode to base64 and display on terminal
#Example by www.debugpoint.com
echo "Enter text for encoding to base64:"
read input_text
output_text=`echo -n $input_text | base64`
echo "The Base64 Encoded text is: $output_text"
```

#### 示例 6:用 Base64 进行简单的身份认证
你可以运用上述的编码和解码方法,实现一个简单的身份验证系统。你可以让用户输入密码或密码,然后将密码存储在文件中。或者进行实时比较。
如果存储的编码字符串与用户输入的文本再编码的字符串相匹配,则用户可以通过验证。虽然这是一种检查身份验证的很简单的方法,但有时这对一些简单的业务案例很有用。
```
#!/bin/bash
#Sample program to take input, encode to base64 and display on terminal
#Example by www.debugpoint.com
echo "Type your password"
read pwd1
decoded_text=`echo 'U2lsZW5jZSBpcyBnb2xkZW4h' | base64 --decode`
if [[ $pwd1 == $decoded_text ]]
then
echo "You are a valid user."
else
echo "You are NOT a valid user."
fi
```

### 总结
我希望你能通过这些示例,学会 [Base64](https://linux.die.net/man/1/base64) 编码和解码的基础知识。此外,你也了解到 Base64 的内部编码方式。如果这对你很有帮助,或你还需要有关此主题的其他教程,请在下面的评论区中告诉我吧。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/bash-base64-encode-decode/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,190 | 打造万圣节 Linux 桌面 | https://itsfoss.com/linux-halloween-makeover/ | 2022-10-29T17:14:00 | [
"桌面",
"万圣节"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15190-1.html | 马上就到万圣节了,太棒啦!
我相信你已经有了一些庆祝万圣节的想法。给你的 Linux 桌面做一个像幽灵般的黑暗改造,就类似于下面的屏幕截图,你觉得怎么样?

可定制是 Linux 的一大优势,对 Linux 可进行的定制是多种多样且没有尽头的。之前,我们向你展示过 [如何让你的 Linux 看起来像 macOS](https://itsfoss.com/make-ubuntu-look-like-macos/) 的方法。今天,我将继续分享一些定制“万圣节”Linux 桌面的技巧。
可以通过主题、图标、扩展、字体、Conky 等一系列配置组合起来,来实现 Linux 桌面的定制。*虽然,你可以在任何的 Linux 发行版和桌面环境中配置这些东西,但是仅在一个教程中展示所有 Linux 发行版和桌面环境的桌面定制方法,是不太可行的。*
因此,在本文中,我将介绍 Ubuntu 与 GNOME 桌面环境的桌面定制方法。
### 安装所需工具
你需要一些软件包和工具。在开始定制桌面前,请确保你安装了全部(或大多数)的软件包和工具。
*你不必做**所有**这些桌面改变。但你做的越多,你的桌面也会美化得更好看。*
#### 安装 GNOME 优化工具和 GMOME 扩展管理器
使用以下命令,来安装 GNOME <ruby> 优化 <rt> Tweaks </rt></ruby> 工具和 GMOME <ruby> 扩展管理器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Extensions manager </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>:
```
sudo apt install gnome-tweaks gnome-extension-manager
```
在基于 KDE 的 Linux 系统中,没有可以更改 Linux 桌面外观的优化工具。但是,你可以使用 Kvantum-Manager 这一应用程序来更改外观,请参考我在 [KDE 主题指南](https://itsfoss.com/properly-theme-kde-plasma/) 中的讨论。
#### 安装 Conky(可选)
你可以选择是否要安装 Conky ,因为现在 conky-manager 项目已经不再维护了,因此继续使用 Conky 可能会有点棘手。但无论如何,我们用它来增加万圣节外观的感觉。
```
sudo apt install conky-all
```
#### 安装 Neofetch 或者 Shell-color 脚本
这个步骤也可以由你自主选择。你可以选择使用 [neofetch](https://itsfoss.com/using-neofetch/),因为 `neofetch` 工具已经在 Ubuntu 仓库中了,你可以直接通过 `apt install` 安装,并且 `neofetch` 使用起来也很简单。
```
sudo apt install neofetch
```
[Shell-color 脚本](https://gitlab.com/dwt1/shell-color-scripts) 是另一个不错的选择。在 Arch 用户仓库(AUR)中有该软件包,Arch Linux 用户可以从 AUR 安装 Shell-color 脚本。而在 Ubuntu 中,你则需要手动安装它。
```
git clone https://gitlab.com/dwt1/shell-color-scripts.git
cd shell-color-scripts
sudo make install
```
#### 安装主题、图标、字体和壁纸工具
我正在使用的是 [Sweet](https://www.gnome-look.org/p/1253385) 主题工具、[Beautiline](https://www.gnome-look.org/p/1425426) 图标软件包、[simple1e](https://www.gnome-look.org/p/1405210) 光标工具和 [Grey-Minimalistic](https://www.deviantart.com/bryantlloyd/art/Grey-Minimalistic-634726564) Conky 主题,下载好这些工具后,再解压包。你还要下载 [Creepster](https://fonts.google.com/specimen/Creepster?query=creepster) 字体。
最后,从互联网上下载一张 [万圣节幽灵氛围的壁纸](https://www.wallpaperflare.com/search?wallpaper=spooky)。
>
> 请注意!你即将要进行大量的定制和更改。要恢复到原来普通的外观,你可以通过撤销你所做的所有更改。一个更简单的方法是:创建一个管理员权限的新用户,并使用该新用户进行所有这些更改。这样,你的原始用户帐户和外观就不会受到影响。在万圣节结束后,你可以删除这个新增的用户。
>
>
>
现在,你有了所有定制桌面的工具和资源,是时候使用它们了!
### 安装并使用扩展
打开 GMOME <ruby> 扩展管理器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Extensions manager </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。在 Ubuntu 22.04 中,你可以在<ruby> 浏览 <rt> Browse </rt></ruby>菜单下安装扩展。

在其他版本的 Ubuntu 和其他带有 GNOME 的发行版上,你可以通过浏览器 [安装 shell 扩展](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-shell-extensions/),来安装扩展。为了实现打造万圣节桌面的目的,请安装以下扩展程序:
* [User Themes](https://extensions.gnome.org/extension/19/user-themes/)
* [Dash to Dock](https://extensions.gnome.org/extension/307/dash-to-dock/)
* [Blur my Shell](https://extensions.gnome.org/extension/3193/blur-my-shell/)
此外,请确保所有的扩展都已启用。
### 配置主题、图标和字体
你需要将解压的主题文件夹复制,并粘贴到 `~/.themes` 目录下,将解压的图标和光标文件夹复制,并粘贴到 `~/.icons` 目录下。
接下来,打开 GNOME <ruby> 优化 <rt> Tweaks </rt></ruby> 工具,并应用主题、图标和字体等设置,如下的截图所示。

要 [在 Ubuntu 中使用自定义字体](https://itsfoss.com/install-fonts-ubuntu/),请右键单击你下载和解压的字体文件,然后选择使用<ruby> 字体管理器 <rt> Font manager </rt></ruby>打开。我打算使用的是 [Creepster](https://fonts.google.com/specimen/Creepster?query=creepster) 字体。

然后,点击右上角的<ruby> 安装 <rt> Install </rt></ruby>按钮。

请注意:在某些系统中,点击安装按钮不会显示“<ruby> 已安装 <rt> installed </rt></ruby>”的提示。在这种情况下,你只需关闭界面就行了,因为一旦你点击了安装按钮,该字体就已经安装上了。
再重新打开 GNOME <ruby> 优化 <rt> Tweaks </rt></ruby> 工具,然后前往<ruby> 字体 <rt> Fonts </rt></ruby>边栏,在这里,你可以更改各个文件类型的字体,如下图所示。

请注意,对于终端,需要等宽字体。在这里,我使用了普通字体,这里可能会让你稍稍有点迷失。
### 应用 Dash to Dock 扩展设置
首先,你要使用 GNOME 扩展应用程序,来**关闭 Ubuntu Dock 扩展**。

如果 Dash to Dock 扩展还尚未运行的话,请先运行它。
然后,右键单击在底部显示的 “Dash to Dock” 按钮,然后选择 “Dash to Dock Settings”。

在设置中,你需要调整一些小东西。
首先,使用滑块,来缩小图标的大小。

之后,你需要减少程序坞的不透明度,我更喜欢完全透明的程序坞。
所以,我将不透明度设置为 <ruby> 固定 <rt> fixed </rt></ruby>,并使用滑块将其降至零,如下图所示。

### GNOME 终端的设置
你想得到的 Linux 桌面的主要变化是自定义**模糊且有一定透明度**的 `neofetch` 外观(或 shell-color 脚本外观)。
我们之前在 GNOME <ruby> 优化 <rt> Tweaks </rt></ruby> 工具中应用了等宽字体,因此 GNOME 终端中的字体也会被更改。
首先,从 <ruby> 偏好设置 <rt> preferences </rt></ruby> 中创建一个新的配置文件。

单击 `+` ,来创建一个新配置文件。输入文件的名称,并点击 <ruby> 创建 <rt> create </rt></ruby>,如下所示:

在这个新配置文件中,更改透明度设置,将透明度的滑块放在中间,如下图所示:

完成后,要将此配置文件设置为默认的配置文件,单击与新配置文件关联的三角形按钮,然后选择 “<ruby> 设置为默认 <rt> Set as Default </rt></ruby>”。

#### 设置模糊效果
上述的步骤只会将终端变成一个透明的 shell。但是,如果你还需要有利于提高可见性的模糊效果,你需要进入到 “Blur my Shell” 扩展进行设置。

首先,进入到 <ruby> 应用程序 <rt> Application </rt></ruby> 菜单。现在,确保终端已打开,并置于屏幕明显的位置。单击 <ruby> 添加 <rt> Add </rt></ruby> 窗口,然后选择 GNOME 终端窗口,以设置模糊效果。请注意:此功能还处于测试阶段,因此可能会出现一些小故障。

也可以对其他应用程序(例如 Nautilus 文件管理器)重复此过程,来设置模糊效果。
#### 定制 Neofetch
Neofetch 的最佳功能之一是其可定制性。你可以使用多种方法来调整 Neofetch 的外观。为了更有万圣节氛围,我选择了一个南瓜图像,来代替发行版的徽标。
Neofetch 提供以各种格式添加自定义图像的功能。为此,也有各种供支持的后端。在这里,我使用 jp2a 后端,它将使用 [转换成 ASCII 的图片](https://itsfoss.com/ascii-image-converter/)。
```
neofetch --jp2a /path/to/your/image/file.png
```

上述命令将创建一个带有自定义图片的 Neofetch 实例。你可以将此命令写入你的 `.bashrc` 文件,以便永久放置该图片。
*不幸的是,这在我的 Wayland 实例上并不起作用。*
#### 自定义 Shell-Color 脚本
如果你安装的是 Shell Color 脚本工具,则会有多种 shell 脚本。要列出可用的脚本,请使用命令:
```
colorscript -l
```

你可以通过将 `colorscript random` 写入你的 `.bashrc` 文件,以每次都获得一个随机的颜色脚本,或者通过将`colorscript -e <name>`写入你的 `.bashrc` 文件,来得到一个特定的颜色脚本。
### 设置 Conky
我使用的是 Deviantart 的 [Grey-Minimalistic](https://www.deviantart.com/bryantlloyd/art/Grey-Minimalistic-634726564) conky 主题。Conky 主题的每种类型都有不同的安装方法。因此,如果你想要使用另一个 Conky 文件的话,请遵循它的 `README` 文件中描述的设置方法,进行设置。
解压 Conky 主题文件,里面有几个文件夹。首先,你需要安装关联的图标和字体,也就是说,使用 <ruby> 字体管理器 <rt> font-manager </rt></ruby> 安装给定的字体。接着,将图标文件夹拷贝,并粘贴到 `~/.icons` 文件夹。

然后,进入 Conky 文件夹。确保你已 [启用查看隐藏文件](https://itsfoss.com/hide-folders-and-show-hidden-files-in-ubuntu-beginner-trick/),将 `.conkyrc` 文件和 `.conky-vision-icons` 文件复制到你的主目录,如上图所示。
现在,启动 Conky,看起来就变成下图这样了。

将 Conky 添加到 [自启动应用程序列表](https://itsfoss.com/manage-startup-applications-ubuntu/) 中,以便在每次开机时都能自启动。

### 更改壁纸
快要完成啦。你现在唯一需要做的就是 [更改背景壁纸](https://itsfoss.com/change-wallpaper-ubuntu/)。我相信你之前已经下载好了有万圣节幽灵气氛的壁纸,右键 “<ruby> 设置为壁纸 <rt> Set as Wallpaper </rt></ruby>” 就好啦。

### 看看最终成果吧!
如果你遵循上面的大多数步骤的话,你就会得到一个与以下截图相似的桌面。

这个桌面对于万圣节来说够吓人了吗?你觉得怎么样?在评论区中告诉我吧。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/linux-halloween-makeover/>
作者:[Sreenath](https://itsfoss.com/author/sreenath/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Halloween is around the corner. Boo!
Of course, there are ways to celebrate Halloween, and I believe you might have a few ideas of your own. How about giving your Linux desktop a spooky, dark makeover? Something like the screenshot below?
Customization is a high point of Linux, and there is no end to it. Earlier, we showed you[ how to make your Linux look like macOS](https://itsfoss.com/make-ubuntu-look-like-macos/). Today, I’ll share a few tips to keep up with the Halloween ‘spirit’.
This is possible with a combination of themes, icons, extensions, fonts, conky, etc. *While you can do these things on any distribution and desktop environment, it’s not feasible for me to show them all in a single tutorial.*
Here, I have used Ubuntu with the GNOME desktop environment.
## Getting all the tools
You need several packages and tools. Make sure you have them all (or most of them) before you start the customization.
*It’s not mandatory to make all of the changes. But the more you do, the better look and feel you get.*
**GNOME Tweaks and GMOME Extensions manager**
Get the Tweaks tool and the extension manager with this command:
`sudo apt install gnome-tweaks gnome-extension-manager `
In KDE-based systems, you don’t any tweak tool to change the look. But surely, you will need the **Kvantum-Manager** app that I discussed in the [KDE theming](https://itsfoss.com/properly-theme-kde-plasma/) guide.
**Conky**
This is actually optional. Since the conky-manager project is not receiving any maintenance, it will be a bit tricky to use conky. But anyway, let’s use it for the additional look-and-feel.
`sudo apt install conky-all`
**Neofetch or shell color scripts**
This step is also a personal choice. You can choose [neofetch](https://itsfoss.com/using-neofetch/) because it’s already available in the repository and can be used easily.
`sudo apt install neofetch`
[Shell-color scripts](https://gitlab.com/dwt1/shell-color-scripts?ref=itsfoss.com) are another excellent choice. The package is available in AUR and Arch Linux users can install it from there. In Ubuntu, you need to install it manually.
```
git clone https://gitlab.com/dwt1/shell-color-scripts.git
cd shell-color-scripts
sudo make install
```
**Themes, icons, fonts, and wallpaper**
I am using [Sweet](https://www.gnome-look.org/p/1253385?ref=itsfoss.com) theme, [Beautiline](https://www.gnome-look.org/p/1425426?ref=itsfoss.com) icon pack, [simple1e](https://www.gnome-look.org/p/1405210?ref=itsfoss.com) cursors, and [Grey-Minimalistic](https://www.deviantart.com/bryantlloyd/art/Grey-Minimalistic-634726564?ref=itsfoss.com) conky theme. Once downloaded, extract them. You should also get [Creepster](https://fonts.google.com/specimen/Creepster?query=creepster&ref=itsfoss.com) font.
Download a [spooky wallpaper](https://www.wallpaperflare.com/search?wallpaper=spooky&ref=itsfoss.com) from the internet.
Alert! You’ll be doing a lot of customization and change. You can go back to the usual look by reverting all the changes you made. An easier way out would be to create a new user with admin access and make all these changes with this new user. This way, your original user account and appearance doesn’t get impacted. When Halloween is over, you can delete this additional user.
With all resources in hand, it’s time to utilize them.
## Install and use the extensions
Open the gnome-extensions app. In Ubuntu 22.04, you can install extensions from within the app, by using the browse section.
In other versions of Ubuntu and other GNOME distributions, you can [install shell extensions](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-shell-extensions/) through the browser. For our purpose, install the following extensions :
Also, make sure that all the extensions are enabled.
## Apply theme, icon, and font
You need to copy and paste the extracted theme folder to `~/.themes`
directory and icon and cursor folder to the `~/.icons`
directory.
Now open GNOME tweaks and apply the settings as shown in the screenshot below.
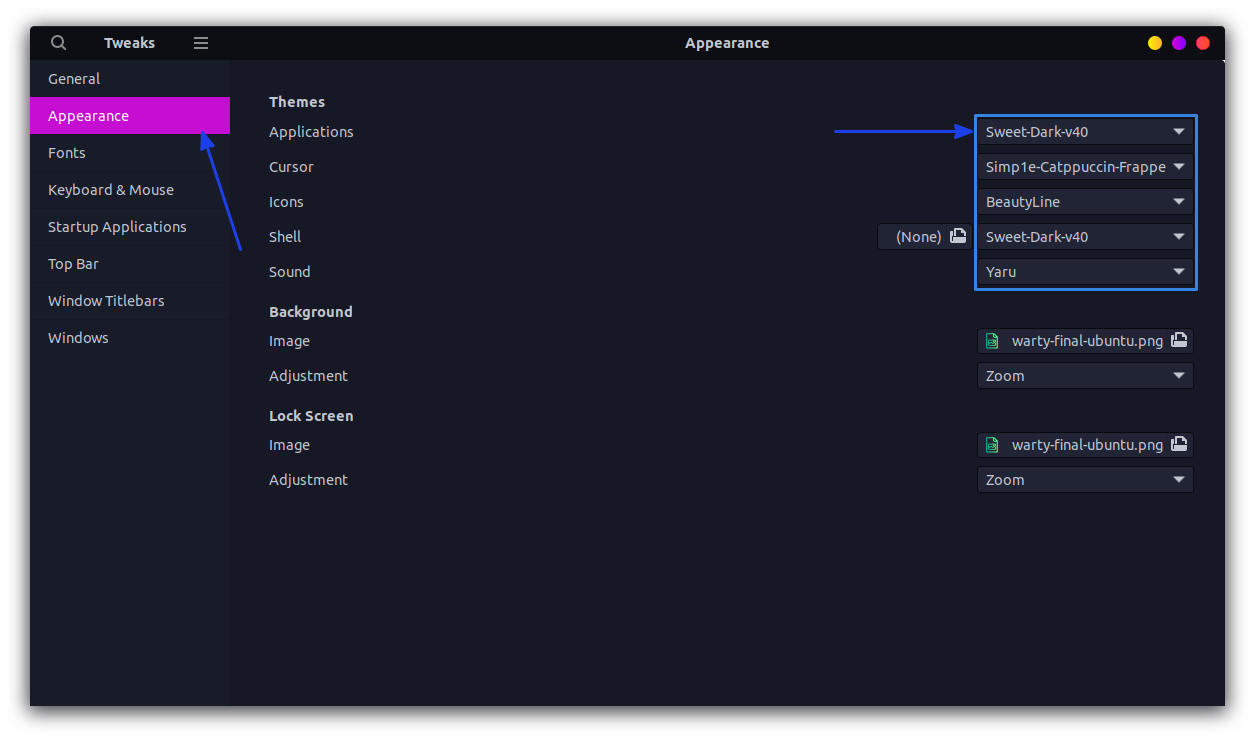
To use a [custom font in Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/install-fonts-ubuntu/), right-click on the font file that you have downloaded and extracted and select open with Font manager. I am using [Creepster](https://fonts.google.com/specimen/Creepster?query=creepster&ref=itsfoss.com) font.
Here, press the install button.
Note: In some systems, pressing the install button won’t show the “installed” prompt. In that case, you can just close the app because once you press the install button, it has been installed.
Now open the Tweaks app and move to the fonts section. Here, you can change the fonts of various sections as shown in the screenshot below.
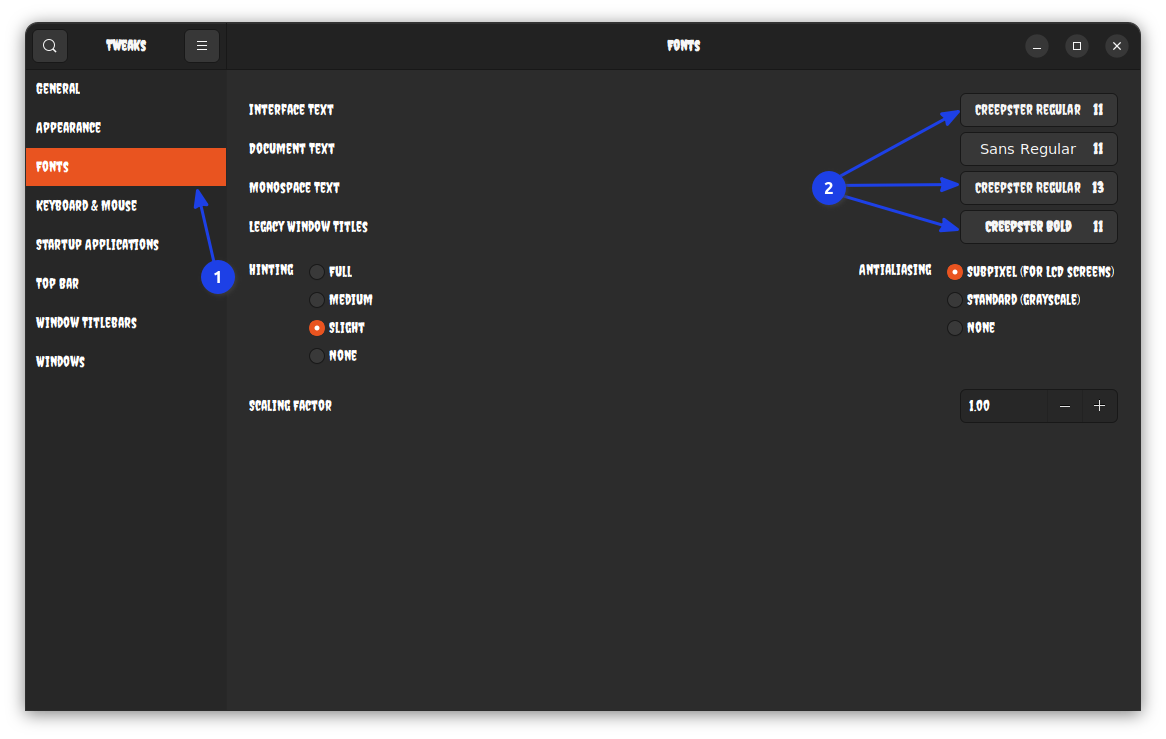
Note that, for terminals, a monospace font is required. Here, I am using a regular font and thus it may give you a slightly disoriented look sometimes.
## Apply Dash to Dock Extension settings
First, you need to **turn off the Ubuntu Dock extension** using the GNOME Extensions application.
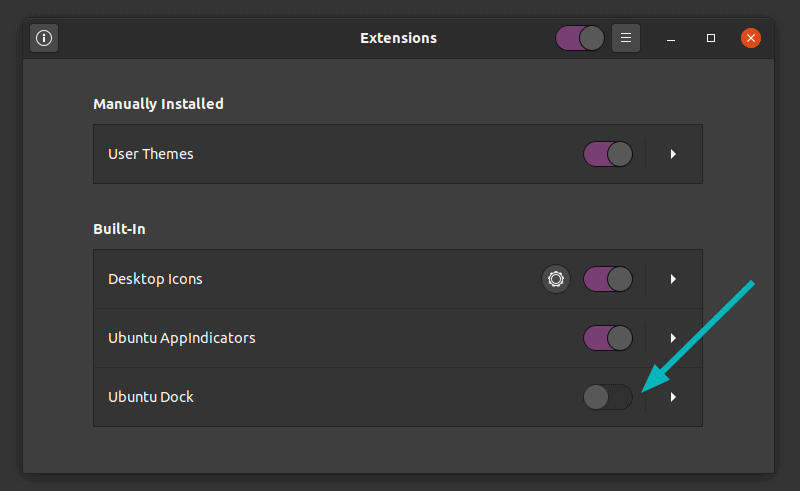
Run the Dash to Dock extension if it’s not running already.
Now, right-click on the dash to dock application button appearing on the bottom and select dash to dock settings.
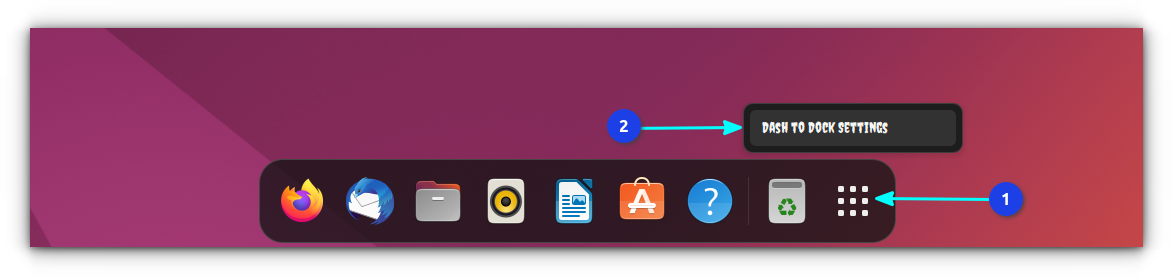
Here, you need to tweak some small things.
First, reduce the icon size using the respective slider.
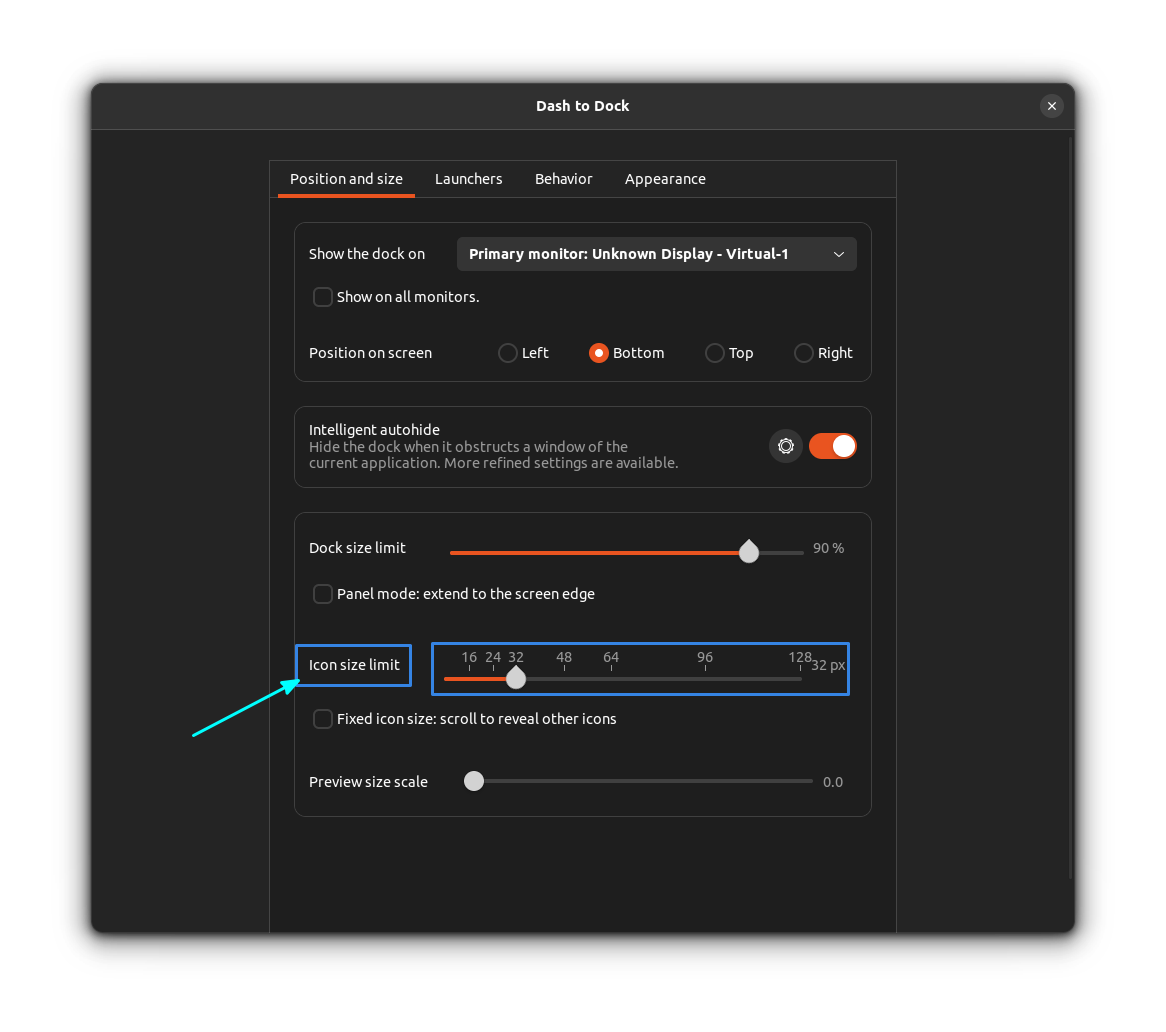
After that, you need to reduce the opacity of the dock. I prefer a fully transparent dock.
For this, set the opacity to **fixed** and reduce it to zero with the slider, as shown in the screenshot below.
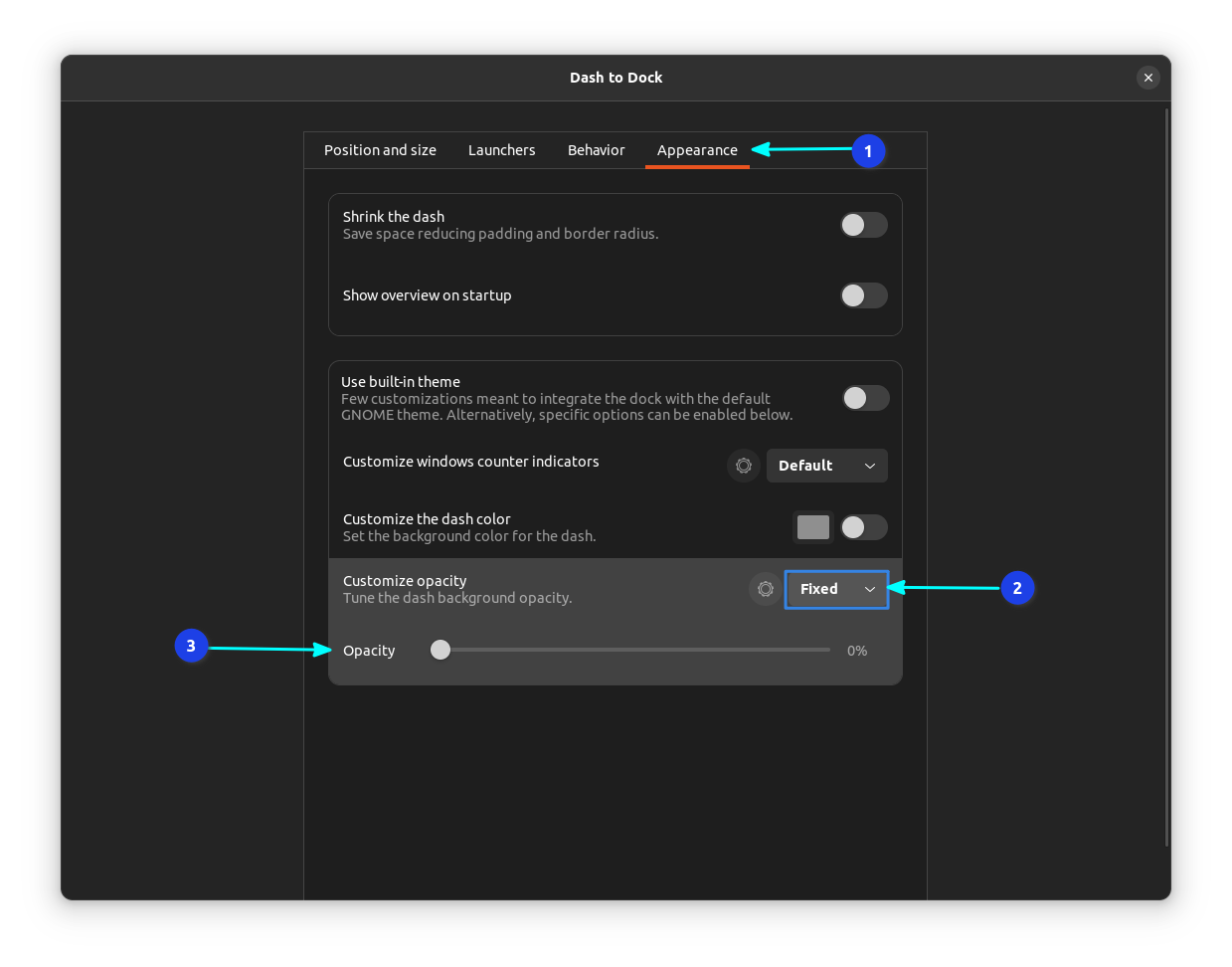
## GNOME terminal setting
The main tweak you want to get is a custom neofetch look (or a shell color script) with some blurred transparency.
On applying monospace font in GNOME-tweaks earlier, the font in the GNOME terminal is also changed.
First, create a new profile from **preferences**.
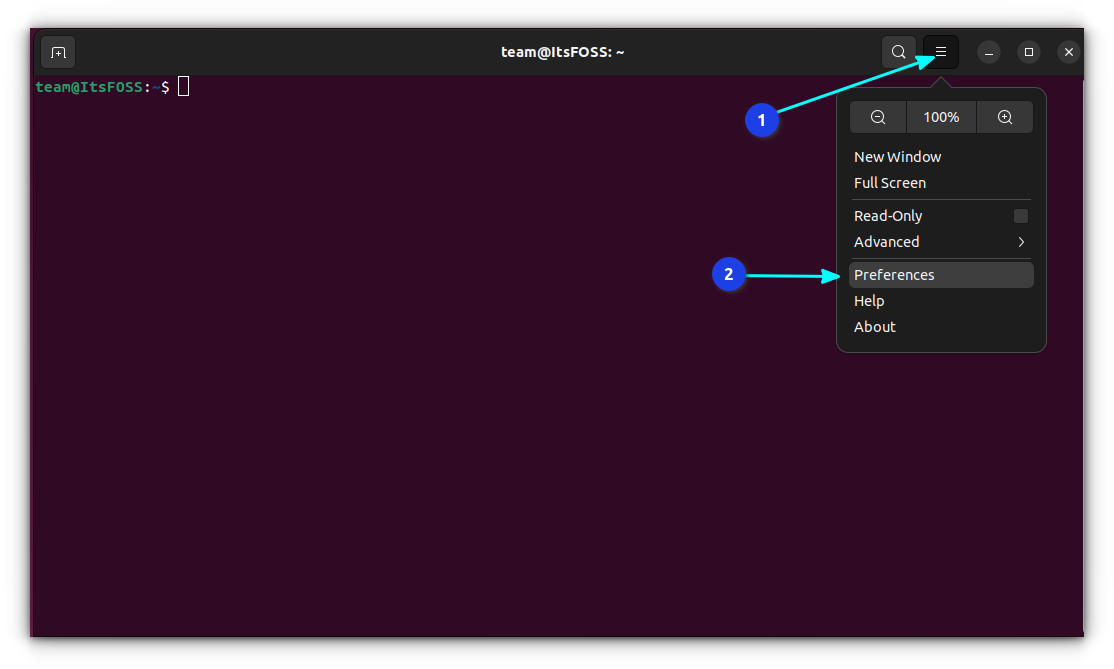
Here, Click + sign to create a new profile. Type in a name and press **create** as shown below:
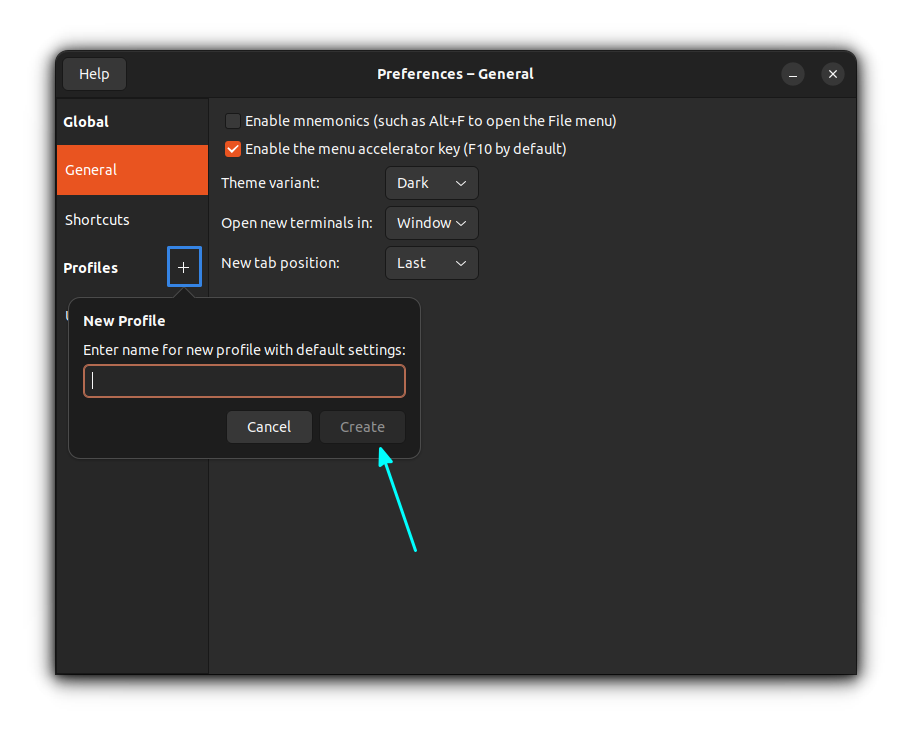
Inside the new profile, change the transparency setting and set it around the middle, as shown in the screenshot:
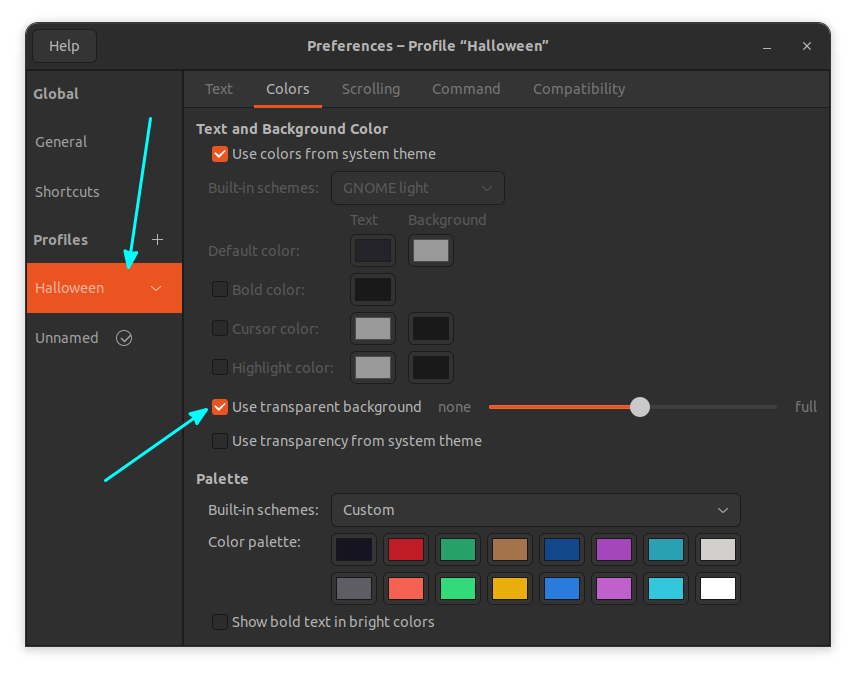
Once finished, set this profile as the default. To do this, click on the triangle button associated with the new profile and select **Set as Default**.
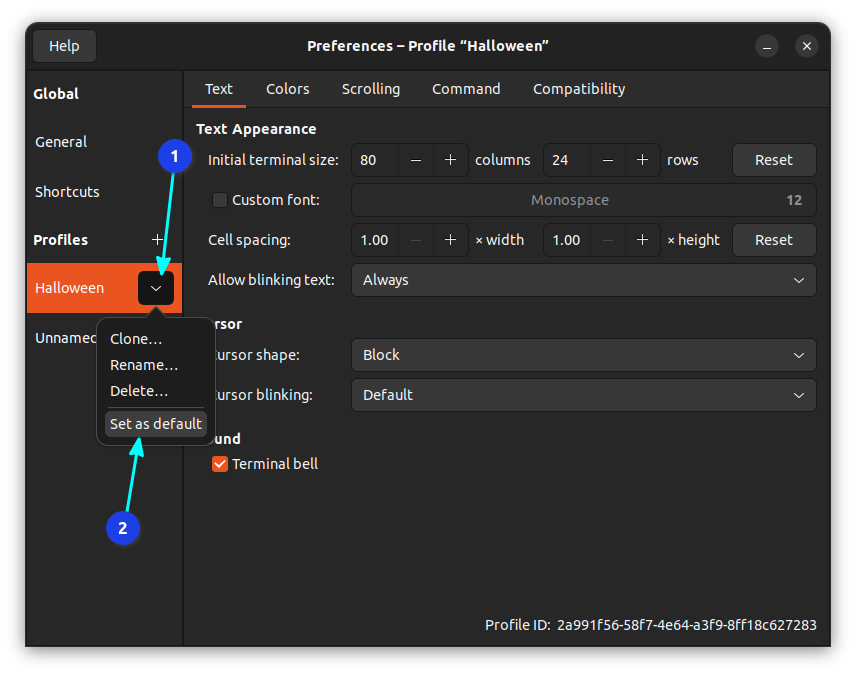
### Setting blur effect
The above step will only create a transparent shell. But if you need a blur effect, which is good for better visibility, you need to go to the Blur my Shell extension settings.

Here, go to the **Application** tab. Now, ensure that the terminal is opened and placed conveniently on the desktop. Click on **Add Window** button and select gnome-terminal window, to set the blur effect. Note: This feature is in beta so expect minor glitches.
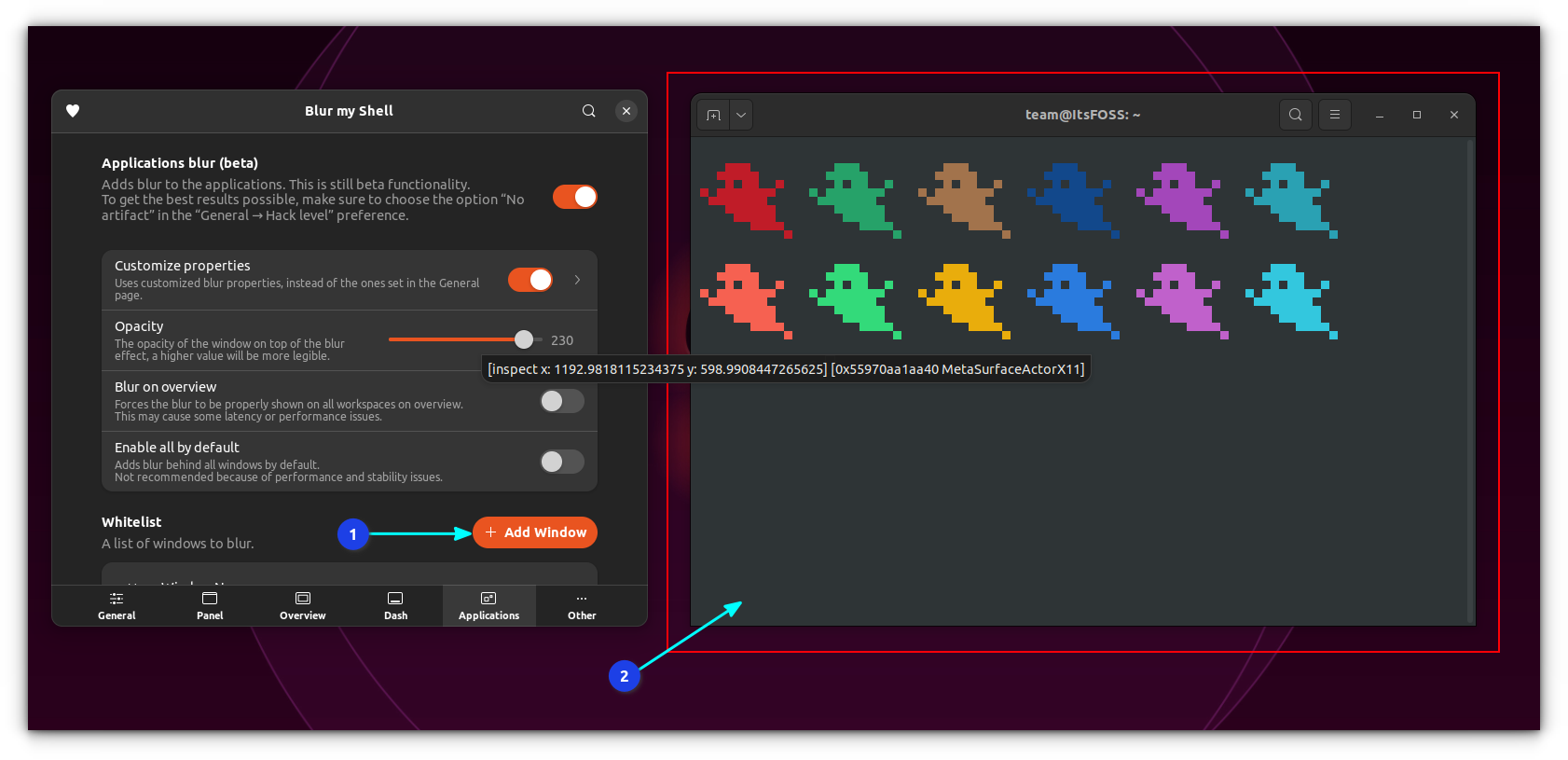
This same procedure can be repeated for other apps also, like the Nautilus file manager.
### Customizing Neofetch
One of the best features of neofetch is its customizability. You can tweak the look with a wide range of methods. For Halloween, I choose a pumpkin image to appear in place of the distro logo.
Neofetch supports adding custom images in a variety of formats. For that purpose, there are a variety of backends supported. Here, I use the jp2a backend, which will use an [ASCII converted image](https://itsfoss.com/ascii-image-converter/).
`neofetch --jp2a /path/to/your/image/file.png`
The above code will create a neofetch instance with the custom image. You can write this code to your .bashrc file, for permanent placement.
*Unfortunately, this didn’t work on my Wayland instance.*
### Customizing Shell Color Scripts
If you installed shell color scripts, you have a variety of shell scripts. To list the available scripts, use:
`colorscript -l`
You can either get a random script each time by placing `colorscript random`
in your .bashrc file. Or you can get any particular script by placing `colorscript -e <name>`
## Setting up Conky
I am using the [Grey-Minimalistic conky theme](https://www.deviantart.com/bryantlloyd/art/Grey-Minimalistic-634726564?ref=itsfoss.com) from Deviantart. Each type of conky theme has a different installation method. So if you are using another conky file, follow its setup method, described in its README files.
Extract the conky theme file. Inside, we have several folders. First, you need to install the associated icons and fonts. That is, install the given font using font-manager. Copy and paste the icon folder to your ~/.icons folder.
Now, go to the conky folder. Make sure that, you have [enabled viewing hidden files](https://itsfoss.com/hide-folders-and-show-hidden-files-in-ubuntu-beginner-trick/). Now copy the `.conkyrc`
file and `.conky-vision-icons`
file to your Home directory, as shown above.
Now start conky to get a look like this.
Add the conky to the [list of startup applications](https://itsfoss.com/manage-startup-applications-ubuntu/) so that it starts automatically at each boot.
## Change wallpaper
You are almost there. The only thing you need to do now is to [change the background wallpaper](https://itsfoss.com/change-wallpaper-ubuntu/). You have already downloaded the spooky wallpapers I believe.
## Behold the final look!
If you followed most of the steps above, you should get a desktop that looks like the one in the below screenshots.

Is it scary enough for Halloween? What do you think? Let me know in the comments. |
15,192 | Rhino Linux:滚动发布但也很稳定的 Ubuntu | https://news.itsfoss.com/rhino-linux/ | 2022-10-30T10:12:25 | [
"Ubuntu",
"滚动发布"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15192-1.html |
>
> 滚动发布的 Ubuntu 发行版?等等,什么? Rhino Linux 听起来不错……
>
>
>

Rhino Linux 将成为 [Rolling Rhino Remix](https://github.com/rollingrhinoremix) 的继任者。这个由 http.llamaz 构建的 Linux 发行版,提供了滚动发布的**非官方的** Ubuntu 变体版本。
需要澄清的是,该项目从未旨在取代其他稳定的发行版,而纯粹是一个充满乐趣的激情项目。
而随着人们开始将其用作日常使用并对其期望更多,开发人员决定将其变成一个严肃的项目。
Rhino Linux 作为它的继任者。那么,你对它的期待是什么?
### 有请继任者 Rhino Linux
其主要目标是提供稳定的 Ubuntu 体验,同时仍提供滚动发布模式。
目标仍保持不变,但 Rhino Linux 的基础将得到彻底改变。他们有可能使它成为一个令人印象深刻的滚动发布的 Ubuntu 发行版。
**听起来很令人兴奋!?**
在其核心,Rhino Linux 将使用稍微修改过的 [Xfce](https://www.xfce.org/) 版本作为其桌面环境;之所以选择它是因为它众所周知的稳定性和速度。
Rhino Linux 的创始人提到了以下几点:
>
> 滚动版 Ubuntu 仍然是我们的核心理念。Rhino Linux 并不是从 Rolling Rhino Remix 中分离出来的,而是将它重新设想为更稳定、更成熟的发行版,它原本就应该以这种方式出厂。
>
>
>

除此之外,[Pacstall](https://github.com/pacstall/pacstall) 将用作 Rhino Linux 上的默认包管理器及其存储库之一。
>
> ? Pacstall 是一个受 [AUR](https://itsfoss.com/aur-arch-linux/) 启发的 Ubuntu 包管理器。
>
>
>
Pacstall 的开发由其创始人 [Plasma](https://github.com/Henryws) 领导。他还作为新开发人员之一(副项目负责人)加入,而 [Sourajyoti Basak](https://github.com/wizard-28) 作为另一位核心成员加入。
### 前进:可用性和发布
在撰写本文时,Rhino Linux 尚未确定任何具体的发布日期,但你可以预计它会在 **2023** 年的某个时间发布。
Rolling Rhino Remix 会发生什么?
开发者澄清说,它将在 Rhino Linux 发布后继续维护三个月。但是,在 2022 年 1 月 11 日后继发布之后,它没有新的发布镜像。
你可以通过访问其 [官方网站](https://rhinolinux.org/) 了解更多关于 Rhino Linux 的信息。
*? 你觉得 Rhino Linux 怎么样?它可以成为值得尝试的官方 Ubuntu 风格的竞争者吗?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/rhino-linux/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Rhino Linux will be the successor of [Rolling Rhino Remix](https://github.com/rollingrhinoremix?ref=news.itsfoss.com). A Linux distro built by [http.llamaz](https://github.com/httpllamaz?ref=news.itsfoss.com) that offered a rolling-release **unofficial** variant of Ubuntu.
To clarify, the project was never aimed to replace other stable distributions and was purely a passion project made for fun.
Considering people started using it as a daily driver and expected more from it, the developer has decided to turn this into a serious project.
Rhino Linux is its next step for it. So, what can you expect?
[Notion – One workspace. Every team.We’re more than a doc. Or a table. Customize Notion to work the way you do.](https://notion.grsm.io/itsfoss?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## Meet Rhino Linux: The Successor
The main goal is to provide a stable Ubuntu experience while still providing a rolling-release model.
The aim remains the same, but the fundamentals for Rhino Linux will receive a complete overhaul. They are potentially making it an impressive rolling-release Ubuntu distribution.
**Sounds exciting! 🤯**
At its core, Rhino Linux will be using a slightly modified version of [XFCE](https://www.xfce.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) as its desktop environment; it was chosen due to its well-known stability and speed.
The founder of Rhino Linux mentioned the following:
Ubuntu as a rolling release is still at the very core of our concept. Rhino Linux is not a depature from Rolling Rhino Remix, but rather re-imagines it as the more stable, mature distribution it should have shipped as originally.
Alongside that, [Pacstall](https://github.com/pacstall/pacstall?ref=news.itsfoss.com) will be used as the default package manager on Rhino Linux with one of their repositories.
[AUR](https://itsfoss.com/aur-arch-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)-inspired package manager for Ubuntu.
The development of which is headed by the founder of Pacstall, [ Plasma](https://github.com/Henryws?ref=news.itsfoss.com). He has also joined as one of the new developers (Deputy Project Lead), and
[Sourajyoti Basak](https://github.com/wizard-28?ref=news.itsfoss.com)as another core member.
**Suggested Read 📖**
[Linux Jargon Buster: What is a Rolling Release Distribution?After understanding what Linux is, what a Linux distribution is, when you start using Linux, you might come across the term “rolling release” in Linux forum discussions. In this Linux jargon buster, you’ll learn about the rolling release model of Linux distributions. What is a rolling rel…](https://itsfoss.com/rolling-release/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## Moving Forward: Availability and Release
As of writing, Rhino Linux has not received any specific release date, but you can expect it to release sometime in **2023**.
What happens to Rolling Rhino Remix?
The developer clarified that it would continue to be maintained for three months after the release of Rhino Linux. However, it won't have a new release image after its subsequent release on **11.01.2022**.
You can find out more about Rhino Linux by visiting its [official website](https://rhinolinux.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
*💬 What do you think of Rhino Linux? Can it be a contender for official Ubuntu flavors worth trying?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,193 | Kubernetes 能否帮助解决自动化挑战? | https://opensource.com/article/22/10/kubernetes-solve-automation-challenges | 2022-10-30T10:56:27 | [
"Kubernetes",
"自动化"
] | /article-15193-1.html | 
>
> 组织层面的自动化一直是一个难以实现的目标,但 Kubernetes 或许能够改变这一切。
>
>
>
当我在 2002 年采用 Gentoo Linux 作为我的主要操作系统时,我开始了我的自动化之旅。二十年后,自动化还没有完成。当我与客户和合作伙伴会面时,他们分享了团队内部的自动化成果,但他们也描述了在组织层面实现类似成功所面临的挑战。
大多数 IT 组织都能够端到端地提供虚拟机,从而将过去 4 周的交付周期缩短到仅 5 分钟。这种级别的自动化本身就是一个复杂的工作流程,需要网络(IP 地址管理、DNS、代理、网络区域等)、身份访问管理、[虚拟机管理程序](https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/virtualization/what-is-a-hypervisor?intcmp=7013a000002qLH8AAM)、存储、备份、更新操作系统、应用最新的配置文件、监控、安全和强化以及合规性基准测试,等等。哇,这么多!
满足高速、可扩展和按需自动化的业务需求并不容易。例如,来看看经典的网上商店或提交纳税申报表的在线政府服务,其工作负载有明确的峰值需要面对。
处理此类负载的一种常见方法是拥有一个超大的服务器集群,以供 IT 专业人员的特定团队使用,监控客户或公民的季节性涌入。每个人都希望及时部署整个栈。他们希望基础架构在混合云场景的上下文中运行工作负载,使用“<ruby> 构建-消耗-回收 <rt> build-consume-trash </rt></ruby>”模型来优化成本,同时从无限弹性中受益。
换句话说,每个人都想要乌托邦式的“云体验”。
### 云真的能交付吗?
尚有一线机会,这主要归功于 [Kubernetes](https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/containers/what-is-kubernetes?intcmp=7013a000002qLH8AAM) 的设计方式。Kubernetes 的指数级普及推动了创新,取代了管理平台和应用的标准传统做法。 Kubernetes 需要使用 “<ruby> 万物皆代码 <rt> Everything-as-Code </rt></ruby>”(EaC)来定义从简单的计算节点到 TLS 证书的所有资源的期望状态。Kubernetes 强制使用三种主要的设计结构:
* 一个标准接口,以减少内部和外部组件之间的整合问题
* API 优先及仅 API 的方法来标准化其所有组件的 CRUD(创建、读取、更新、删除)操作
* 使用 [YAML](https://opensource.com/article/21/9/yaml-cheat-sheet) 作为通用语言,以简单易读的方式定义这些组件的所有所需状态
这三个关键组成部分基本上是选择自动化平台的相同要求,至少如果你想让跨职能团队轻松采用是这样的。这也模糊了团队之间的职责分工,有助于提高跨越孤岛的协作,这是一件好事!
事实上,采用 Kubernetes 的客户和合作伙伴正在加速进入超自动化状态。Kubernetes 有机地推动团队采用多种 [DevOps 基础和实践](https://opensource.com/resources/devops),如:EaC、[使用 Git 进行版本控制](https://opensource.com/life/16/7/stumbling-git)、同行评审、<ruby> <a href="https://opensource.com/article/21/3/devops-documentation"> 文档即代码 </a> <rt> Documentation as Code </rt></ruby>,并鼓励跨职能协作。这些实践有助于提高团队的自动化技能,并帮助团队在处理应用生命周期和基础架构的 GitOps 和 CI/CD 管道方面取得良好的开端。
### 让自动化成为现实
你没看错!网络商店或政府报告等复杂系统的整个栈可以用清晰、可理解、通用的术语定义,可以在任何本地或云提供商上执行。可以定义具有自定义指标的自动伸缩器以触发所需栈的即时部署,以解决季节性高峰期间客户或市民的涌入问题。当指标恢复正常,且云计算资源不再有存在的理由时,你将它们回收并恢复常规运营,而由一组核心资产在本地接管业务,直到下一次激增。
### 鸡和蛋的悖论
考虑到 Kubernetes 和云原生模式,自动化是必须的。但它提出了一个重要的问题:一个组织可以在解决自动化战略之前采用 Kubernetes 吗?
似乎从 Kubernetes 开始可以激发更好的自动化,但这并不是一个一成不变的结论。工具不是对技能、实践和文化问题的解决方案。但是,设计良好的平台可以成为 IT 组织内学习、变革和跨职能协作的催化剂。
### 开始使用 Kubernetes
即使你觉得自己错过了自动化列车,也不要害怕从简单、不复杂的栈上开始使用 Kubernetes。当你 [掌握了初始步骤](https://opensource.com/article/17/11/getting-started-kubernetes),就可以拥抱这个出色的编排系统的简单性,并根据更复杂的需求进行迭代。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/10/kubernetes-solve-automation-challenges>
作者:[Rom Adams](https://opensource.com/users/romdalf) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
15,194 | 在 Ubuntu 22.10 上安装 Gedit 并将其设为默认文本编辑器 | https://itsfoss.com/install-gedit-ubuntu/ | 2022-10-30T12:41:12 | [
"Gedit",
"GNOME"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15194-1.html | 
[GNOME 有了一个全新的文本编辑器](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-text-editor/),以取代旧的 Gedit 编辑器。
虽然 GNOME 42 已经可以使用了它,但 Ubuntu 22.04 还依赖于 Gedit。
这在 Ubuntu 22.10 中发生了变化。 GNOME <ruby> 文本编辑器 <rt> Text Editor </rt></ruby> 现在是默认程序,甚至没有安装 Gedit。

虽然新编辑器足够好,但并不是每个人都喜欢它。如果你将 Gedit 与其他插件一起频繁使用,则尤其如此。
如果你属于这类人,让我向你展示如何在 Ubuntu 上安装 Gedit。我还将分享如何将其设为默认文本编辑器。
### 在 Ubuntu 上安装 Gedit
这实际上是不费吹灰之力的。虽然默认未安装 Gedit,但它仍然可以在 Ubuntu 仓库中找到。
所以,你所要做的就是使用 `apt` 命令来安装它:
```
sudo apt install gedit
```
Gedit 也可以在软件中心中找到,但它是 Snap 包。如果你愿意,你可以安装它。

#### 安装 Gedit 插件(可选)
默认情况下,Gedit 为你提供访问一些插件的选项。你可以从 “汉堡菜单-><ruby> 偏好 <rt> Preference </rt></ruby>-><ruby> 插件 <rt> Plugins </rt></ruby>” 启用或禁用插件。

你可以在这里看到可用的插件。检查已安装或正在使用的插件。

但是,你可以通过安装 gedit-plugins 元数据包将插件选择提升到一个新的水平。
```
sudo apt install gedit-plugins
```
这将使你可以访问其他插件,如书签、括号补全、Python 控制台等。

**提示**:如果你发现 Gedit 因缺少底角而显得有些格格不入,你可以安装一个名为 [Round Bottom Corner](https://extensions.gnome.org/extension/5237/rounded-window-corners/) 的 GNOME 扩展。这将为包括 Gedit 在内的所有应用强制添加圆底角。
### 使 Gedit 成为默认文本编辑器
好了!你已经安装了 Gedit,但文本文件仍然在双击操作后使用 GNOME 文本编辑器打开。要使用 Gedit 打开文件,你需要右键单击,然后选择“<ruby> 打开方式 <rt> open with </rt></ruby>”选项。
如果你希望一直使用 Gedit 打开文本文件,你可以将其设置为默认程序。
右键单击文本文件并选择“<ruby> 打开方式 <rt> open with </rt></ruby>”选项。在此处选择 Gedit 并从底部启用“<ruby> 始终用于此文件类型 <rt> Always use for this file type </rt></ruby>”选项。

### 删除 Gedit
觉得 Gedit 没达到预期么?这很少见,但我不会评判你。要从 Ubuntu 中删除 Gedit,请使用以下命令:
```
sudo apt remove gedit
```
你也可以尝试从软件中心卸载它。
### 总结
GNOME 文本编辑器是下一代从头开始创建的编辑器,它与新的 GNOME 完美融合。
对于简单的文本编辑来说已经足够了。然而,Gedit 有一个插件生态系统,赋予它更多功能。
对于那些将它广泛用于编码和其他事情的人来说,安装 Gedit 仍然是 Ubuntu 中的一个选项。
那你呢?你会坚持使用默认的新文本编辑器还是回到旧的 Gedit?
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/install-gedit-ubuntu/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux 中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

[GNOME has a brand new text editor](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-text-editor/) to replace the good old Gedit editor.
While it was already available with GNOME 42, Ubuntu 22.04 relied on Gedit.
This is changing in Ubuntu 22.10. GNOME Text Editor is the default here and Gedit is not even installed.
While the new editor is good enough, not everyone would like it. This is especially if you use Gedit extensively with additional plugins.
If you are among those people, let me show you how to install Gedit on Ubuntu. I’ll also share how you can make it the default text editor.
## Install Gedit on Ubuntu
This is actually a no-brainer. While Gedit is not installed by default, it is still available in Ubuntu repositories.
So, all you have to do is to use the apt command to install it:
`sudo apt install gedit`
Gedit is also available in the software center but it is the snap package. You could install that if you want.
### Install Gedit Plugins (optional)
By default, Gedit gives you the option to access a few plugins. You can enable or disable the plugins from the menu->preference->plugins.
You should see the available plugins here. The installed or in-use plugins are checked.
However, you can take the plugin selection to the next level by installing the gedit-plugins meta package.
`sudo apt install gedit-plugins`
This will give you access to additional plugins like bookmarks, bracket completion, Python console and more.
[Round Bottom Corner](https://extensions.gnome.org/extension/5237/rounded-window-corners/). This will force round bottom corners for all applications, including Gedit.
## Make Gedit the default text editor
Alright! So you have installed Gedit but the text files still open in GNOME Text Editor with double click action. To open a file with Gedit, you need to right click and then select the ‘open with’ option.
If you want Gedit to open text files all the time, you can set it as default.
Right click on a text file and go with “open with” option. Select Gedit here and enable the “Always use for this file type” option from the bottom.
## Remove Gedit
Don’t feel Gedit is up to the mark? That’s rare, but I am not judging you. To remove Gedit from Ubuntu, use the following command:
`sudo apt remove gedit`
You may also try uninstalling it from the software center.
## Conclusion
GNOME Text Editor is the next-gen, created-from-scratch editor that blends well with the new GNOME.
It’s good enough for simple text editing. However, Gedit has a plugin ecosystem that gives it more features.
For those who use it extensively for coding and other stuff, installing Gedit is still an option in Ubuntu.
What about you? Will you stick with the default new text editor or will you return to the good old Gedit? |
15,195 | 如何在 Ubuntu 和其他相关 Linux 中安装 Python 3.10 | https://www.debugpoint.com/install-python-3-10-ubuntu/ | 2022-10-30T15:26:00 | [
"Python"
] | /article-15195-1.html | 
>
> 计划为工作安装 Python 3.10?以下是在 Ubuntu 和相关发行版中安装 Python 3.10 的方法。
>
>
>
Python 3.10 于 2021 年 10 月 25 日发布,具有附加功能和更新。此版本带来了更好的错误消息处理、新的模式匹配功能、<ruby> 类型别名 <rt> TypeAlias </rt></ruby>、用户定义的类型保护等。你可以在 [此处](https://docs.python.org/3.10/whatsnew/3.10.html) 阅读发布重点。
在编写本指南时,大多数当前发行版都采用 Python 3.10。例如,Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 和 Fedora 36 默认都有 Python 3.10。
也就是说,如果你现在在任何不支持的版本中需要 Python 3.10,你可以使用 [下面的可靠 PPA](https://github.com/deadsnakes) 在 Ubuntu 中安装最新的 Python 3.10。下面是方法。
### 如何在 Ubuntu 上安装 Python 3.10
此 PPA 可用于 Ubuntu 21.10、Ubuntu 21.04、Ubuntu 20.04 LTS、Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 和 Linux Mint 20.x、Elementary OS 6 和其他相关的基于 Ubuntu 的发行版。这些发行版大多数默认情况下不支持 3.10。
打开终端并添加以下 PPA:
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
```
使用以下命令刷新缓存:
```
sudo apt update
```
并使用以下命令安装 Python 3.10:
```
sudo apt install python3.10
```
### 设置 Python 版本
将 Python 3.10 设置为默认值需要一些额外的步骤。如下。
>
> **警告**:你的 Ubuntu 系统中的许多应用程序依赖于 Python 3.9 的库存版本。因此,请确保你的工作应用(例如 GIMP、GNOME 终端等)与 Python 3.10 兼容。所以,要小心。
>
>
>
**快速提示:** 如果要检查已安装的系统包中的哪些依赖于特定版本,请使用 `apt-cache` 命令的 `rdepends` 开关。在下面的示例中,我检查哪些已安装的包依赖于 Python 3.8。
```
apt-cache rdepends python3.8
```
```
[~]$ apt-cache rdepends python3.8
python3.8
Reverse Depends:
python3.8-dbg
virtualbox
python3.8-venv
python3.8-full
libpython3.8-testsuite
libglib2.0-tests
idle-python3.8
idle-python3.8
python3.8-minimal
python3.8-doc
python3.8-dev
python3.8-dbg
python3-uno
gedit
virtualbox
stimfit
python3.8-venv
python3-stfio
python3-escript-mpi
python3-escript
python3-csound
pitivi
obs-studio
liferea
libpython3.8-testsuite
libglib2.0-tests
kitty
kdevelop-python
idle-python3.8
idle-python3.8
rhythmbox-plugins
python3.8-minimal
python3.8-doc
python3.8-dev
python3
python3-uno
python3-all
cluster-glue
gedit
[~]$
```
#### 使用 Python 3.10 作为默认 Python3
首先,使用终端中的以下命令检查当前默认版本。
```
python3 --version
```
使用 `update-alternatives` 创建指向 `python3` 的符号链接。
```
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python3 python3 /usr/bin/python3.9 1
```
```
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python3 python3 /usr/bin/python3.10 2
```
并通过以下命令选择使用哪一个作为 `python3`:
```
sudo update-alternatives --config python3
```

这就是所有步骤。现在,你可以开始在当前的 Ubuntu 版本中使用最新的 Python 进行工作/学习。你可以使用上述命令切换到库存版本并在任何时间更改版本号。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/install-python-3-10-ubuntu/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,198 | 为什么我爱 Chromebook:当然是因为它是一个 Linux 桌面系统 | https://www.theregister.com/2022/10/28/column/ | 2022-10-31T18:27:00 | [
"Chromebook"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15198-1.html |
>
> 我们喜欢强力的机器,但有时是为了更快地启动和运行。
>
>
>

我喜欢 Linux 桌面这件事对任何读过我作品的人来说都不会感到惊讶。我的意思是,我曾经是一个早已消失的出版物《Linux 桌面》的主要作者和编辑。那么,为什么我在底特律召开的 Kubecon 北美峰会上,在我的惠普 Chromebook x360 上写这篇文章呢?
很简单,因为 Chrome OS 是一个 Linux 发行版。以前是,以后也是。
而这让一些 Linux 粉丝很恼火。他们对 Linux 桌面未来的设想是让每个人都“运行 Ubuntu,不是 Fedora 或 Arch Linux!”,“拜托,Linux Mint 才是赢家”,“MX Linux”,“现实点吧!使用 openSUSE Tumbleweed!” 等等,不一而足。有 [上千种 Linux 发行版](https://distrowatch.com/),这就是我们永远不会看到他们的 “[Linux 桌面消灭 Windows](https://www.theregister.com/2022/10/14/year_of_linux_desktop/)” 的梦想实现的一个重要原因。
但 Chromebook 不同。当然,Chromebook 的销售已经 [崩溃](https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/14/chromebook_sales/) 了,但部分原因是 Chromebook 太皮实耐用了。与 Windows 机器不同的是,Windows 机器的寿命大概是三年,而我有的 Chromebook 已经运行了七年了。
的确,它们的 [自动更新到期(AUE)日期](https://support.google.com/chrome/a/answer/6220366?hl=en) 已经成为过去了,所以我不能再获得自动更新。但是,那又怎样?甚至谷歌也 [承认](https://support.google.com/chromebook/answer/7052113?hl=en) 你可以在它们的平均五年到期日期之后继续使用它们。
而如果是 Windows,那就不一样了。任何仍在运行 Windows 7 的人都是邀请黑客来黑他,除非他们购买了 [扩展安全更新(ESU)合同](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/faq/extended-security-updates)。而且,即使是这样,ESU 也将在 2023 年 1 月结束。
然而,Chrome OS 呢?与每个月都有重大安全补丁的 Windows 不同,Chrome OS 的严重安全问题很少,也很难出现。例如,上一次 Chrome OS 的 [重大安全漏洞](https://www.cvedetails.com/vulnerability-list.php?vendor_id=1224&product_id=20320&version_id=&page=1&hasexp=0&opdos=0&opec=0&opov=0&opcsrf=0&opgpriv=0&opsqli=0&opxss=0&opdirt=0&opmemc=0&ophttprs=0&opbyp=0&opfileinc=0&opginf=0&cvssscoremin=0&cvssscoremax=0&year=0&month=0&cweid=0&order=1&trc=45&sha=b4fed875175c2d9b0370914ce0ba1d4fc2289f40) 突然出现并被修复的时间是 2019 年。
当然,Chrome 浏览器又是另一件事。这个浏览器也是 Chrome OS 的桌面界面,经常有重要的安全更新。但是,谷歌有望将 Chrome OS 和 Chrome 浏览器分开,所以即使你不能得到 Chrome OS 的升级,你也会得到 [浏览器的更新](https://chromeunboxed.com/googles-ceo-may-have-just-confirmed-the-split-of-chrome-and-chrome-os/)。
此外,谷歌和它的合作伙伴现在也在延长 AUE。例如,2022 年 3 月的三星 Galaxy Chromebook 2 的 AUE 支持到 2028 年 6 月。
当然,在这一切之下,是 Linux。而且,如果你愿意,你还可以安装一个全面的 Linux 发行版来搭配它。默认选择是 Debian Bullseye。这很容易。只要多做一点,你也可以安装其他发行版。
我这样做是因为虽然我可以用谷歌文档完成大部分工作,但我喜欢使用 Linux 的 Shell 命令、GIMP 图形编辑器和 LibreOffice 办公套件。
那么,为什么我不在笔记本电脑上运行 Linux 呢?嗯,我也这么做了。我有一台装有 Ubuntu Linux 的戴尔 XPS 13 开发者版,还有一台装有 Mint Linux 的旧 XPS 13,以及我的联想 ThinkPad X1 上的 Fedora 工作站。但是,当我在路上的时候,我喜欢有一台轻便、便宜的笔记本电脑,如果我把它弄坏了,我就可以随时换一台。
作为一个笨手笨脚的人,我经常弄坏我的笔记本电脑。最近,当我在德克萨斯州奥斯汀举行的北美开源峰会上,一个电涌把我的联想 IdeaPad Duet 5,一个顶级的二合一 Chromebook/tablet 炸掉了。衰!
现在,如果我运行的是一台普通的 Windows、MacBook 或 Linux 笔记本电脑,我就会啥也干不了了。我必须买一个新的机器,更新它 —— 如果我是一个 Windows 用户,这绝不是小事 —— 然后安装和更新我的软件。至少,我会损失一天的工作时间,我不知道你怎么想,但我不能占用那么多的工作时间。
相反,我跑到最近的百思买,买了前面提到的惠普 Chromebook X360。从我的旧 Chromebook 爆炸到回到我之前工作的那条线,我的总停机时间只有一个多小时。其中大部分时间是在往返商店的路上度过的。
另一个 Chromebook 的优点是,更换系统的费用不到 500 美元。当然,也有昂贵的 Chromebook。我有很多台 Chromebook,而且我很喜欢它们。但是,你不必在 Chromebook 上花太多的钱,就能获得良好的用户体验。
有许多很棒的、便宜的 Chromebook,价格低于 500 美元。今天,即使是最低端的 Chromebook 也拥有 Chrome OS 和Linux 工作所需的所有能力。如处理器、内存和存储这些技术规格对大多数用户来说并不重要。你只想找一个有体面的屏幕和键盘的产品。
对于 Linux、Mac 和 Windows 则是不同的情况。我不会去碰那些标价低于 800 美元的产品。你可以在任何东西上运行 Linux —— 我是说任何东西 —— 但购买预装了 Linux 的笔记本电脑往往和 Windows 一样贵。此外,当我需要立即恢复工作时,我没有时间去找一台旧的笔记本电脑来安装 Linux。当然,即使是最便宜的 Mac 也要 1000 美元。
因此,至少对我来说,我首选的公路战士 Linux 笔记本电脑是 Chromebook。想想吧,试一试 —— 上帝都知道 Chromebook 足够便宜 —— 你可能会发现你同意我的观点。
---
via: <https://www.theregister.com/2022/10/28/column/>
作者:[Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols](https://www.theregister.com/Author/Steven-J-Vaughan-Nichols) 选题:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](/article-15195-1.html) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | This article is more than **1 year old**
# Why I love my Chromebook: Reason 1, it's a Linux desktop
## We appreciate power but sometimes it's about getting up and running sooner
Column The fact that I like the Linux desktop will come as no surprise to anyone who reads my work. I mean, I was once the lead writer and editor for a long-gone publication called *Linux Desktop*. So why is it as I sit at Kubecon North America in Detroit that I'm writing this on an HP Chromebook x360?
Simple, because Chrome OS is a Linux distro. Always has been; always will be.
Now this annoys the heck out of some Linux fans. Their vision of the Linux desktop future has everyone running [Ubuntu](https://ubuntu.com/) - no [Fedora](https://docs.google.com/document/u/0/d/1jHyDbOkD-vUZVTq3k98ncPgLlOYbz53Htk91CHSDjgc/edit)! - or [Arch Linux](https://archlinux.org/) - please, [Linux Mint](https://linuxmint.com/) for the win! - or MX Linux - get real! Use [openSUSE Tumbleweed](https://get.opensuse.org/tumbleweed/)! - and on and on. There are over a [thousand Linux distros](https://distrowatch.com/), which is a big reason we'll never see their [dream of the Linux desktop wiping out Windows](https://www.theregister.com/2022/10/14/year_of_linux_desktop/) come true.
But Chromebooks are a different story. Sure, [Chromebook sales have crashed](https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/14/chromebook_sales/), but part of the reason is that Chromebooks last pretty much forever. Unlike Windows machines, which have a lifespan of about three years, I still have Chromebooks running that are seven years old.
True, their [Auto Update Expiration (AUE) dates](https://support.google.com/chrome/a/answer/6220366?hl=en) are now history, so I can't get automatic updates anymore. But, so what? Even [Google admits you can keep using them](https://support.google.com/chromebook/answer/7052113?hl=en) after their average five-year expiration date.
Now, if this were Windows, it would be a different story. Anyone still running Windows 7 is just asking to be hacked unless they got an [Extended Security Update (ESU) contract](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/faq/extended-security-updates). And, even that is finally ending in January 2023.
[Is it time to retire C and C++ for Rust in new programs?](https://www.theregister.com/2022/09/28/is_it_time_to_retire_c/)[Securing open-source code isn't going to be cheap](https://www.theregister.com/2022/02/09/secure_open_source_software/)[The next deep magic Linux program to change the world? Io_uring](https://www.theregister.com/2022/09/16/column/)[But why](https://www.theregister.com/2021/12/08/wireguard_linux/)*that*VPN? How WireGuard made it into Linux
Chrome OS, though? Unlike Windows, with its monthly major security patches, serious security problems are few and far between. For example, the [last major Chrome OS security holes popped up and were fixed in 2019](https://www.cvedetails.com/vulnerability-list.php?vendor_id=1224&product_id=20320&version_id=&page=1&hasexp=0&opdos=0&opec=0&opov=0&opcsrf=0&opgpriv=0&opsqli=0&opxss=0&opdirt=0&opmemc=0&ophttprs=0&opbyp=0&opfileinc=0&opginf=0&cvssscoremin=0&cvssscoremax=0&year=0&month=0&cweid=0&order=1&trc=45&sha=b4fed875175c2d9b0370914ce0ba1d4fc2289f40).
Of course, the Chrome browser is another story. The browser, which is also Chrome OS's desktop interface, often has important security updates. But, Google is expected to separate Chrome OS and the Chrome browser, so even if you [can't get Chrome OS upgrades, you'll still get browser updates](https://chromeunboxed.com/googles-ceo-may-have-just-confirmed-the-split-of-chrome-and-chrome-os/).
Besides, Google and its partners are also now extending AUEs. For example, March 2022's [Samsung Galaxy Chromebook 2](https://www.cnet.com/tech/computing/samsung-galaxy-chromebook-2-review-still-premium-but-with-a-better-price-and-battery-life/) has an AUE of June 2028.
Underneath it all, of course, is Linux. And, if you want, [you can also install a full scale Linux distro](https://support.google.com/chromebook/answer/9145439?hl=en) to go with it. The default choice is [Debian Bullseye](https://www.debian.org/releases/bullseye/). It's easy as pie. With a bit more work, you can install other distros.
I do this because while I can do most of my work with Google Docs, I like having access to Linux's shell commands, the [GIMP](https://www.gimp.org/) graphics editor, and the [LibreOffice](https://www.libreoffice.org/) office suite.
So, why don't I just run Linux on a laptop? Well, I do that too. I have a [Dell XPS 13 Developer Edition](https://www.dell.com/en-us/shop/dell-laptops/new-xps-13-developer-edition/spd/xps-13-linux) with Ubuntu Linux, an older XPS 13 with Mint Linux on it, and Fedora Workstation on my [Lenovo ThinkPad X1](https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/d/thinkpad-x1-carbon/). But, when I'm on the road, I like having a lightweight, cheap laptop that I can replace if I break it.
And, alas, as a klutz, I break my laptops a lot. Recently, when I was at Open Source Summit North America in Austin, Texas, when an electrical surge blew out my [Lenovo IdeaPad Duet 5](https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/p/laptops/lenovo/lenovo-edu-chromebooks/duet-5-chromebook-gen-6-(13-inch-qcom)/len101i0023), a top two-in-one Chromebook/tablet. Yarg!
Now, I'd be stuck if I were running an ordinary Windows, MacBook, or Linux laptop. I'd have to buy one, update it - which is never trivial if I were a Windows user- and then install and update my software. At a minimum, I'd lose a day's work, and I don't know about you, but I can't afford to use that much work time.
Instead, I ran out to the closest Best Buy and picked up the aforementioned HP Chromebook X360. My total downtime from when my old Chromebook went bang to returning to the exact same line I'd been working on earlier was just over an hour. Most of that time was spent riding to and from the store.
Another Chromebook plus is that replacing the system costs me less than $500. Sure, there are expensive Chromebooks. I've owned many, and I like them a lot. But, you don't have to spend serious coin on a Chromebook to get a great user experience.
There are many [great, cheap Chromebooks for under $500](https://www.cnet.com/tech/computing/best-chromebook/). Today, even a bottom-line Chromebook has all the power you need for Chrome OS and Linux work. The technical specifications, such as the processor, memory, and storage, don't matter much for most users. You just want to look for one with a decent screen and keyboard.
It's a different story for Linux, Macs, and Windows. I wouldn't touch any of those with price tags under $800. You can run Linux on anything - and I mean anything - but buying a laptop with Linux preinstalled tends to be as pricey as Windows. Besides, I don't have time to hunt down an old laptop to install Linux on when I need to get back to work immediately. And, of course, even the cheapest Macs cost a grand.
So, for me, at least, my preferred road warrior Linux laptop is a Chromebook. Give it a thought, give it a try - Lord knows Chromebooks are cheap enough - and you just might find that you agree with me. ®
152 |
15,199 | 如何从 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 升级到 22.10 | https://www.debugpoint.com/upgrade-ubuntu-22-04-22-10/ | 2022-11-01T11:04:00 | [
"Ubuntu"
] | /article-15199-1.html | 
>
> 这里是如何将你当前的 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish 升级到 Ubuntu 22.10 Kinetic Kudu 的步骤。
>
>
>
始终停留在长期支持的发布版本,这是金科玉律。因为,先前的 [Ubuntu 22.04 LTS](https://www.debugpoint.com/ubuntu-22-04-review/) Jammy Jellyfish 将被支持到 2027 年 4 月。这是一段很长的时间。
此外,LTS 版本超级稳定。它们很少损坏并变得不稳定。因此,如果你在笔记本电脑/台式机电脑或服务器上安装使用 LTS 版本,保持使用它。
然而,如果你想要最新的内核、GNOME 43 和 Pipewire 之类的最新技术 – 你可能会想完成版本跳级,并升级到 [Ubuntu 22.10 Kinetic Kudu](https://www.debugpoint.com/ubuntu-22-10/)。
这里是如何做的方法。
### 升级 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 到 Ubuntu 22.10
**注意**:我希望你没有运行去年 10 月份发布的 Ubuntu 21.10 Impish Indri 。因为它已经不被支持。但是鉴于某些原因,你正在运行它,我建议你直接重新安装 22.10 。或者,先升级到 22.04 ,再升级到 22.10 。
#### 在你升级前
在你升级前,做一些内务整理。这是非常重要的。
* 备份你的 `/home`、/`downloads` 和其它的文件到 USB 驱动器或任意独立的分区,以防升级失败。
* 如果你随着时间的流逝而添加了一些额外的 PPA ,确保将它们记录下来。虽然,在升级过程开始前,升级过程将禁用 PPA 。而在升级完成后,确保手动启用 PPA 。
* 记录并禁用所有的 GNOME 扩展。如果开发人员没有按照 GNOME 版本进行更新,那么扩展在升级后将会损坏。
* 家中常备一个现场 USB 磁盘。
#### 升级步骤
打开 “<ruby> 软件包和更新 <rt> Software & Update </rt></ruby>” 。
转到 “<ruby> 更新 <rt> Updates </rt></ruby>” 标签页。
转到 “<ruby> 通知我新的 Ubuntu 版本 <rt> Notify me of a new Ubuntu version </rt></ruby>”,选择并将其更改为 “<ruby> 任意新的版本 <rt> For any new version </rt></ruby>”。
这将告诉软件包管理器来查找 Ubuntu 22.10 发布版本的详细信息。

打开一个终端,并运行下面的命令:
```
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
```
或者,你也可以打开软件包更新程序。安装所有的准备就绪的软件包。
在两个命令完成后,打开软件包更新。你将会看到一个升级到 Ubuntu 22.10 的提示(如下图所示)。

现在,单击 “<ruby> 升级 <rt> Upgrade </rt></ruby>” 按钮,并按照屏幕上的说明进行操作。升级过程需要一些时间,因此,要耐心等待,直至升级完成。确保在整个升级过程中有稳定的互联网链接。
如果你尚未获得更新,请等待一、两天后再次尝试。
如果你没有看到上述提示,手动重新启动一次系统。并再次添加尝试。
#### 通过终端
在终端中通过 nano 文件编辑器打开下面的文件。
```
nano /etc/update-manager/release-upgrades
```
将 `Prompt=LTS` 更改为 `Prompt=normal` 。注意:如果你已经如上所述将更新标签页更改为 “<ruby> 任意新的版本 <rt> For any new version </rt></ruby>” ,那么这个文件应该已经更新了。但是,要验证它一次。

分别按下组合键 `CTRL+O` 和组合键 `CTRL+X` 来保存和退出。
最后,你也可以运行下面的命令来从终端中强制升级过程。
```
sudo do-release-upgrade -c
```

升级过程需要花费一些时间(最少半个小时,上不封顶),这主要取决于你的互联网连接和硬件。直至等到其完成。在完成后,重新启动并享受 Ubuntu 22.10 Kinetic Kudu.

在升级过程进行时,看看我们 [不久前发布的关于 Ubuntu 22.10](https://www.debugpoint.com/tag/ubuntu-22-10) 的精彩文章。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/upgrade-ubuntu-22-04-22-10/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,200 | 设置路径在 Powershell 中使用开源命令 | https://opensource.com/article/22/10/set-path-powershell | 2022-11-01T16:01:00 | [
"路径"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15200-1.html | 
>
> 在 Windows 上设置你的路径,这样你就可以使用开源的命令。
>
>
>
当你在操作系统上启动应用程序时,操作系统需要使用某些代码库和实用程序来运行该应用程序。你的操作系统知道如何找到这些库和实用程序,因为它有一个 *系统路径*,这是一个通往许多应用程序需要的共同共享数据的地图。所有操作系统都有这一点,但用户通常不会意识到这一点,因为他们通常不需要在意它。然而,当你需要编程或使用特殊的网络实用程序或命令时,你可能需要关心你自己的 `PATH` 变量配置。
`PATH` 变量使你可以将命令保存到一致的位置,并使用命令提示符或更强大(而开源的)[Powershell](https://opensource.com/article/18/2/powershell-people) 从系统上的任何位置调用它们。
例如,假设你想安装开源应用程序 `pscp.exe`,它是 Windows 上著名的 PuTTY OpenSSH 客户端的命令行界面。你可以将它下载到你的硬盘,但是你的命令行如何知道它的存在呢?其实一开始,它并不知道:
```
PS> pscp
pscp: 命令 “pscp” 不能被识别为 cmdlet、脚本文件或可操作程序的名称。
检查名称的拼写,或者如果包含了路径,则检查路径是否正确,然后再试一次。
```
如果你正在使用一个开源命令行,例如 Powershell 或 [Cmder](http://cmder.app/),那么你将得到一个有用的错误提示,提示这可能是你的路径有问题(或缺少路径)。下面是解决这个问题的方法。
### 设置 PATH
首先,在桌面上创建一个名为 `App` 的文件夹。
接下来,右键单击屏幕左下角的 Windows 菜单,然后选择 “<ruby> 系统 <rt> System </rt></ruby>”。

在弹出的 “<ruby> 系统 <rt> System </rt></ruby>” 窗口中,单击窗口左侧的 “<ruby> 高级系统设置 <rt> Advanced system settings </rt></ruby>” 链接。
在出现的 “<ruby> 系统属性 <rt> System properties </rt></ruby>” 窗口中,单击窗口底部的 “<ruby> 环境变量 <rt> Environment variables </rt></ruby>” 按钮。

在 “<ruby> 环境变量 <rt> Environment variables </rt></ruby>” 窗口中,单击 “<ruby> 用户变量 <rt> User variables </rt></ruby>” 面板下的 “<ruby> 新建 <rt> New </rt></ruby>” 按钮。

在弹出的对话框中,为 “<ruby> 变量名 <rt> Variable name </rt></ruby>” 字段输入 `PATH`,为 “<ruby> 变量值 <rt> Variable value </rt></ruby>” 字段输入 `%USERPROFILE\Desktop\App` 。单击 “<ruby> 确定 <rt> OK </rt></ruby>” 按钮保存更改。

在 `Desktop/Apps` 中放置你想从命令提示符中访问的命令和应用程序,Powershell、Cmder 甚至 Cmd 都能找到它们。
```
PS> pscp –version
pscp: Release 0.XY
Build platform: 64-bit x86 Windows
PS>
```
### 自动设置路径
许多应用程序会在安装过程中自动添加到系统路径中。然而,并不是所有的程序都如此,要么是因为你在安装过程中遗漏了一个复选框,要么是因为应用程序开发人员希望你自己添加它。当自动路径失败时,你现在知道如何自己设置路径。
*(图像来自:Alan Smithee, CC BY-SA 4.0)*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/10/set-path-powershell>
作者:[Alan Smithee](https://opensource.com/users/alansmithee) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[qfzy1222](https://github.com/qfzy1233) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When you launch an application on an operating system, there are certain code libraries and utility applications that your OS needs to use for that app to run. Your OS knows how to find these libraries and utilities because it has a *system path,* a map to common shared data that lots of apps need. Every OS has this, but users aren’t usually aware of it because they don’t usually need to care about it. However, when you start coding or using special network utilities or commands, you might care about your own PATH variable.
The PATH variable makes it so that you can save commands to a consistent location, and use them from anywhere on your system using the command prompt or the more powerful (and open source) [Powershell](https://opensource.com/article/18/2/powershell-people).
For instance, say you want to install the open source application `pscp.exe`
, a command-line interface to the famous PuTTY OpenSSH client on Windows. You can download it to your hard drive, but how does your command-line know that it exists? Well at first, it doesn’t:
```
``````
PS> pscp
pscp: The term 'pscp' is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, script file, or operable program.
Check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the path is correct and try again.
```
If you’re using an open source command line, such as Powershell or [Cmder](http://cmder.app/), you get a useful error hinting that this might be a problem with your path (or the lack thereof). Here’s how to solve that problem.
## Setting a PATH
-
First, create a folder called
`App`
on your Desktop. -
Next, right-click on the Windows menu in the bottom left corner of your screen, and select
**System**.
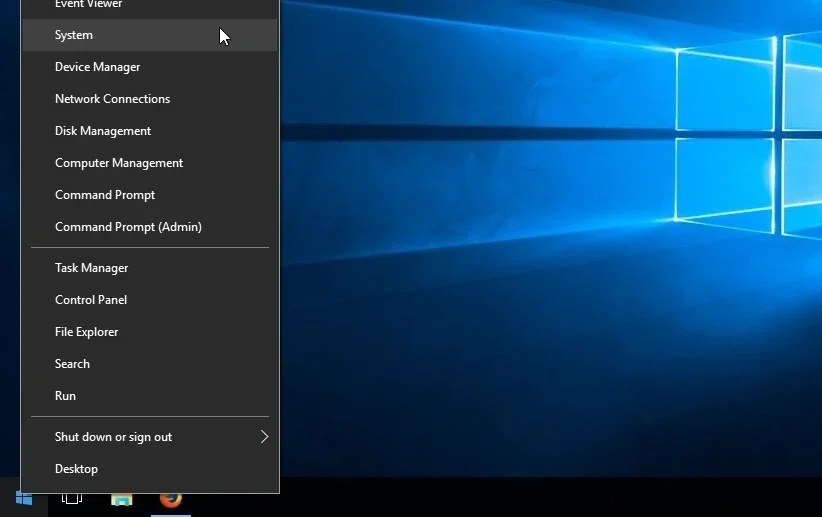
(Alan Smithee, CC BY-SA 4.0)
-
In the
**System**window that appears, click the link to**Advanced system settings**on the left of the window. -
In the
**System properties**window that appears, click the**Environment variables**button at the bottom of the window.
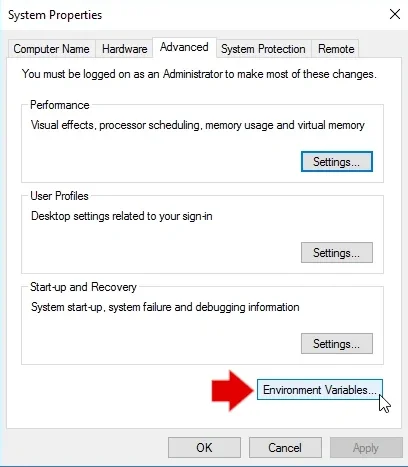
(Alan Smithee, CC BY-SA 4.0)
- In the
**Environment variables**window, click the**New**button under the**User variables**panel.
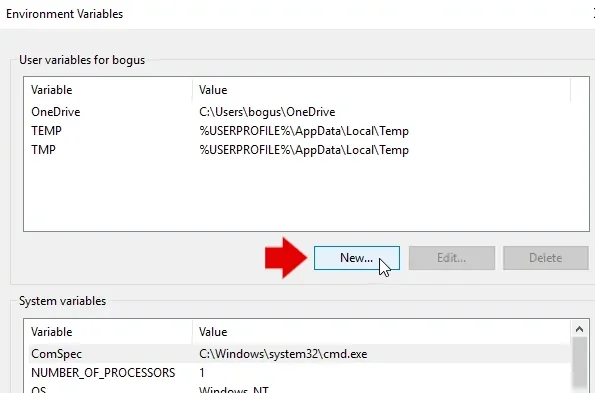
(Alan Smithee, CC BY-SA 4.0)
- In the dialog box that appears, enter
`PATH`
for the**Variable name**field, and`%USERPROFILE\Desktop\App`
for the**Variable value**field. Click the**OK**button to save your changes.
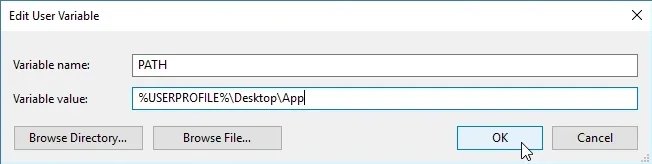
(Alan Smithee, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Place commands and applications you want to have access to from a command prompt in `Desktop\Apps`
and Powershell, Cmder, and even Cmd will find them:
```
``````
PS> pscp –version
pscp: Release 0.XY
Build platform: 64-bit x86 Windows
PS>
```
## Automatic PATH settings
Many applications get automatically added to the system path during installation. However, not all of them do, either because you missed a check box during the install process, or because the application developer expects you to add it yourself. When automatic paths fail, you now know how to forge your own path.
## 3 Comments |
15,202 | 如何通过 chroot 恢复 Arch Linux 安装 | https://www.debugpoint.com/recover-arch-linux/ | 2022-11-01T21:30:00 | [
"Chroot",
"Arch Linux"
] | /article-15202-1.html | 
>
> 这篇速成指南诠释了一些步骤,它对于恢复一个 Arch Linux 安装很有帮助。
>
>
>
作为一个滚动发布版本,Arch Linux 有时会崩溃。那不是你自身的问题,而是因为数百个其它的原因,例如一个新内核与你的硬件或软件的兼容性。但是,即使如此,Arch Linux 仍然是比较优秀的,并且提供最新的软件包和应用程序。
但是,有些时候,它会给你带来麻烦,最后你只会看到一个闪烁的光标。
因此,在这种情况下,在你放弃希望前,你可能希望尝试恢复系统的安装以及数据,而不是重新格式化或重新安装。这篇指南在这些方面概述了一些步骤。
### 恢复 Arch Linux 安装
第一步是创建一个可启动的 Arch Linux 的<ruby> 现场 <rt> Live </rt></ruby> USB 。从下面的链接中下载 ISO 镜像文件,并创建一个可启动的 ISO 的启动盘。你可以查看 [这篇](/article-15020-1.html) 关于如何使用 Etcher 创建可启动的 ISO 的启动盘的指南。记住,这一步骤需要在另一个工作稳定的系统上完成,很明显,这是因为你当前系统是不可用的。
>
> **[下载 arch linux](https://archlinux.org/download/)**
>
>
>
你需要知道在 **你的 Arch Linux 安装在哪个分区上**。这是关键的一步。如果你不知道,你可以使用 GParted 来找出来。或者在你的 Grub 菜单中查看,或者也可以运行下面的命令来找出来。这将列出你所有的磁盘分区、大小和标签。
```
sudo lsblk -o name,mountpoint,label,size,uuid
```
在完成后,插入 USB 设备,并从中启动。你应该会在现场 USB 启动后看到 Arch Linux 提示符。
现在,使用下面的命令挂载 Arch Linux 分区。将 `/dev/sda3` 更改为你实际对应的分区。
```
mount /dev/sda3 /mnt
arch-chroot /mnt
```
`arch-chroot` 命令将在终端中挂载你的 Arch Linux 分区,然后,使用你的 Arch 用户名和密码来登录系统。现在,取决于你在这个阶段的需要,你可能有下面的一些选项。
* 你可以前往 `/home` 文件夹来备份你的数据。为防止排错手段不能解决问题。你可以复制这些文件到一块外部的 USB 磁盘或其它的分区。
* 检查日志文件,尤其是 pacman 日志,因为升级一些软件包可能会导致系统不稳定工作,例如,图形驱动程序或其它一些驱动程序。依据日志的记载,如果你有需要的话,你可以降级一些具体指定的软件包。
你可以使用下面的命令来查看 pacman 日志文件的最新的 200 行日志,来找出一些引起失败的项或依赖项的缺失。
```
tail -n 200 /var/log/pacman.log | less
```
上面的命令给出 `pacman.log` 文件的末尾处的 200 行来用于查对。现在,仔细检查自你上次成功启动以来更新了哪些软件包。
在某个地方记录下软件包的名称和版本。你可以尝试逐个降级软件包,或者,如果你认为是某个特定的软件包造成的问题的话,你可以使用 `pacman` 命令的 `-U` 开关选项来降级它。
```
pacman -U <package name>
```
在降级后(如果有一些软件包进行降级的话),你可以运行下面的命令来启动你的 Arch 系统。
```
exec /sbin/init
```
检查你的显示管理器的状态,并检查其是否有一些错误。有时,显示管理器会产生不能与 <ruby> X 服务器 <rt> X Server </rt></ruby> 通信的问题。例如,如果你正在使用 Lightdm ,那么你可以通过下面的命令来检查它的状态。
```
systemctl status lightdm
```
或者,你可能希望通过下面的命令来启动它并检查错误。
```
lightdm --test-mode --debug
```
这里是一个 Lightdm 故障的示例,它导致了 Arch 系统不稳定工作。

或者,使用 `startx` 来启动 X 服务器进行检查。
根据我的经验,如果你在上面的命令中看到这些错误,尝试安装另外一个显示管理器(例如 sddm)并启动它可以消除错误。
* 根据你的系统的实际状态来尝试上面的步骤并解决问题。针对特定的显示管理器 Lightdm 的错误,我们有一份 [指南](https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/03/failed-to-start-lightdm/),你可能会想查看它。
* 如果你正在使用 sddm ,那么,试试 [这些排错步骤](https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/SDDM#Troubleshooting) 看看是否工作。
### 结语
每个系统环境都是不同的。上面的步骤不一定适合你。但是,它值得一试,根据我的经验,它是可行的。如果它可行,那么恭喜你。否则,在下面的评论区让我知晓你是如何进行的。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/recover-arch-linux/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,203 | Vanilla OS:不只是原味 GNOME 的 Ubuntu | https://news.itsfoss.com/vanilla-os-beta/ | 2022-11-02T11:28:03 | [
"Vanilla OS",
"GNOME",
"Ubuntu"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15203-1.html |
>
> Vanilla OS 是建立在 GNOME 上的、具有按需不变性和软件包选择自由的 Ubuntu。听起来很有趣?在这里阅读更多信息。
>
>
>

这正是我第一次接触 Vanilla OS 时的想法。
当 [Bottles](https://usebottles.com) 的创建者 **Mirko Brombin** 在 Twitter 上宣布它时,让我对它产生了兴趣 ?。
我加入了他们的 Discord 频道并成为了一名测试者。虽然我没有做出什么贡献,但关注项目发展是很有趣的。
回到至关重要的问题上:**什么是 Vanilla OS?**
**Vanilla OS 的目标是提供一个干净、原味的 GNOME 体验,并具有按需不变性的能力。**
听起来很有趣?让我告诉你我试了试它的第一个开放测试版本后的一些细节。
>
> ? Vanilla OS 计划在 11 月有一个稳定的版本。
>
>
> 它将跟随 Ubuntu 的小版本发布。
>
>
> 因此,你可以期待每年发布**两个版本**。例如,你可以从 Ubuntu 22.04 升级到 Ubuntu 22.10 甚至更之后的版本。
>
>
> 除非你知道自己在做什么,否则你不应该把它作为日常系统来使用。
>
>
>
### Vanilla OS:又一个基于 Ubuntu 的发行版?

**是,也不是**。
对于初学者来说,我认为有以下独特的理由可以尝试一下:
* 在 Ubuntu 之上获得 **原装 GNOME 体验**。(Fedora 也是一个很好的选择,但并不适合所有人!)
* 在其安装后的首次设置时,**允许你选择并启用 Flatpak/Snap/AppImage**。
* **按需不变性**,意味着你可以使系统变成只读,以防止来自第三方应用程序和更新的关键变化。
* **一个新的软件包管理器**(apx)允许你默认在管理的容器内安装软件包。
首次设置过程的体验很轻松。
>
> ℹ️ 目前,它使用 Calamares 安装程序。他们打算用 Crystal Linux 中使用的 Jade 取代它。
>
>
>

越来越多的发行版投身于此;我相信更多的用户会乐意加入到 Linux 中来。

*Vanilla OS 对软件包管理器的选择*
当然,像 Ubuntu MATE 和 Pop!\_OS 这样的发行版已经付出了巨大的努力,而 Vanilla OS 也为此增加了一些改进。

这看起来是一种漂亮的体验!?
一旦你完成了首次设置,你就没有什么可担心的了。你会得到通常的 GNOME 桌面,以及由 **Patrik Kramolis** 制作的漂亮的壁纸。

接下来,我试着检查了按需不变性,你可以用以下命令查看和调整:

你可以在 [GitHub](https://github.com/Vanilla-OS/almost) 上了解更多这个(基本上)使之成为可能的工具。
接下来,看看新的软件包管理器,我喜欢 Distrobox 的底层概念,使其与 apx 成为可能。
Distrobox 的创建者 **Luca di Maio** 也参与了 Vanilla OS 的开发。
不过,当用 apx 安装一个软件包时,你需要用命令来初始化容器:
```
apx init
```
如果它能自动完成,那就更直观了。

当然,我不知道技术上的限制。但是,对于用户端来说会感觉更顺滑!
总的来说,一个利用容器安装应用程序的软件包管理器、获得选择你的软件包管理器的能力、按需不变性,以及原味的 GNOME 使它看起来是一个值得关注的好东西。
### 前面的路:第一印象
我觉得,一旦它进入稳定版,它就会成为我的日常使用系统。
**原因是**:我总是喜欢原装的 GNOME 体验,而且不需要处理 Fedora 的定期升级。
当然,等我使用了稳定版之后,我可以给你写一篇整体的用户体验评判。
在那之前,我想说这是一个我相信很多用户都会喜欢的项目 ?。
目前,你可以通过加入其 Discord 频道来下载 ISO。该 ISO 还没有公开向所有人提供。如果你感兴趣,可以看看它的 [文档](https://documentation.vanillaos.org)。
>
> **[Vanilla OS](https://vanillaos.org/roadmap)**
>
>
>
然而,按照路线图,他们计划很快就会有一个候选版本。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/vanilla-os-beta/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

That was precisely my thought when I first came across Vanilla OS.
When** Mirko Brombin**, the creator of [Bottles](https://usebottles.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), announced it on Twitter, that had me interested in it 😎
I joined their Discord channel and hopped in to become a tester. While I did not point out anything new that other testers already did, keeping an eye on the project development is fun.
Back to the vital question: **What is Vanilla OS?**
**Vanilla OS aims to offer a clean vanilla GNOME experience with on-demand immutability.**
Sounds interesting? Let me tell you a few details about it while I give its first open beta build a try.
It will follow Ubuntu point releases. So, you can expect
**two releases per year**. For example, you can upgrade from Ubuntu 22.04 to Ubuntu 22.10.
You should not replace it as a daily driver unless you know what you are doing.
## Vanilla OS: Yet Another Ubuntu-based Distro?
**Yes and no.**
For starters, I see the following unique reasons to give it a try:
- To get a
**stock GNOME experience**on top of Ubuntu. (*Fedora is an excellent option too, but not for everyone!*) **Allows you to choose and enable Flatpak/Snap/AppImage**with its first-time setup after installation.**On-demand immutability**, meaning you can make the system read-only to prevent critical changes from third-party applications and updates.**A new package manager**(apx) allows you to install packages inside a managed container by default.
The first-time setup process is a breeze to experience.
[Vanilla Installer](https://vanillaos.org/2022/11/01/vanilla-installer.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
[Crystal Linux: An Avant-garde Mix of Arch Linux and GNOMECrystal Linux is an upcoming Arch-based distro with a focus to make the setup easy while using latest technologies. Sounds interesting?](https://news.itsfoss.com/crystal-linux-dev/)

The more distributions do things like this; I believe more users would be happy to get on board with Linux.
Of course, distributions like Ubuntu MATE and Pop!_OS have already put in great efforts, and Vanilla OS also adds some improvement to the table.
It looks like a pretty experience! 😊
Once you finish the first-time setup, you have nothing else to worry about. You get the usual GNOME desktop with nice wallpapers out of the box by **Patrik Kramolis.**
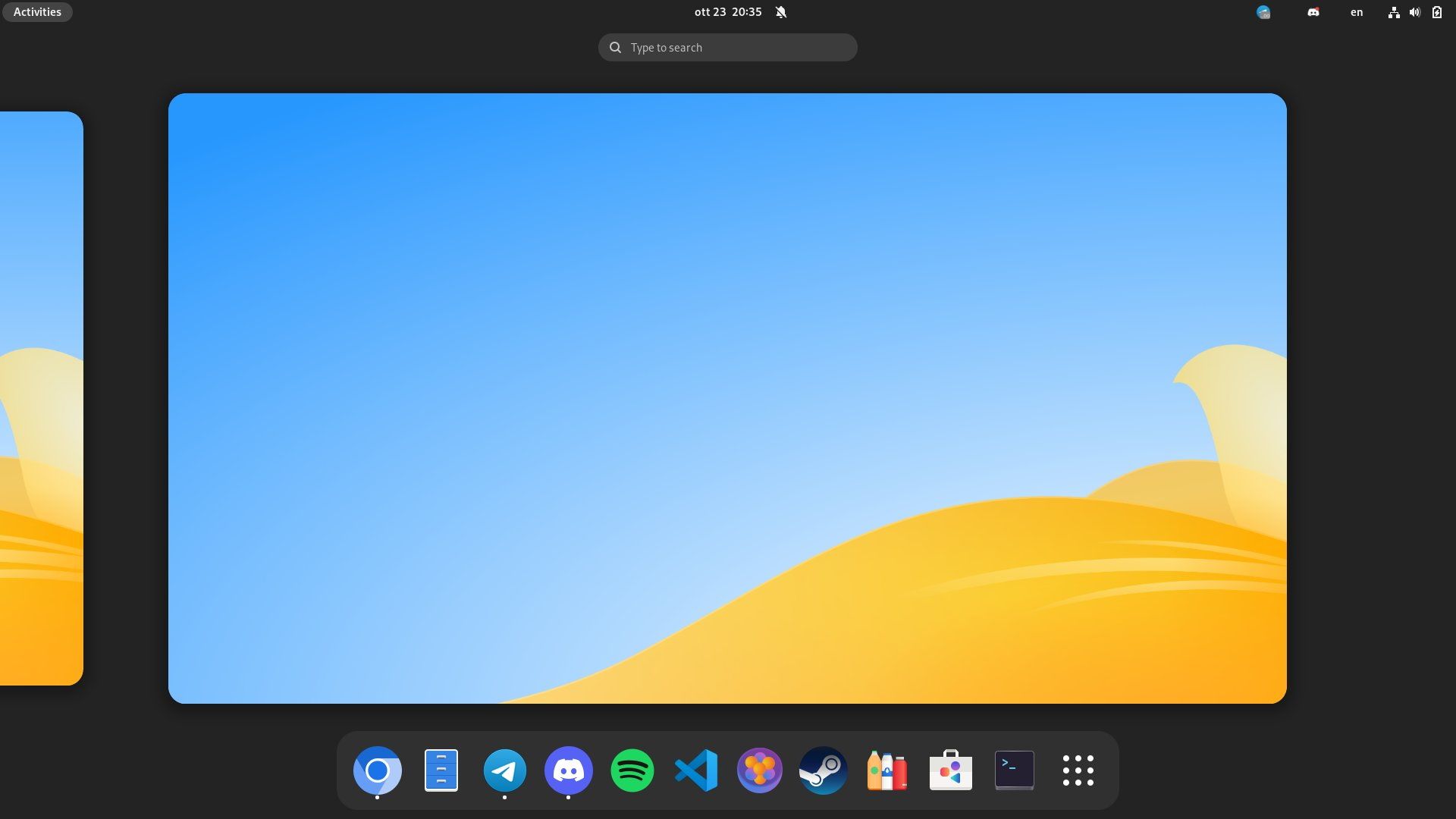
Next, I tried checking the on-demand immutability, which you can see and tweak using the following commands:
You can explore more about the utility (almost) that makes this possible on [GitHub](https://github.com/Vanilla-OS/almost?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
Next, coming to the new package manager, I like the concept of distrobox under the hood, making this possible with apx.
The Distrobox creator **Luca di Maio** is also involved in developing Vanilla OS.
[Distrobox: Try Multiple Linux Distributions via the TerminalDistrobox is an interesting terminal tool that lets you run multiple Linux distributions without any hassle. Learn more about it here.](https://itsfoss.com/distrobox/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

However, when installing a package with apx, you need to initialize the container using the command:
`apx init`
If it had done it automatically, I would call it intuitive.
Of course, I'm not aware of the technical limitations. But, for the user end, that would feel seamless!
Overall, a package manager that installs applications utilizing a container, getting the ability to choose your package managers, on-demand immutability, and vanilla GNOME make it seem like a good deal to keep an eye on.
[Notion – One workspace. Every team.We’re more than a doc. Or a table. Customize Notion to work the way you do.](https://notion.grsm.io/itsfoss?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## The Road Ahead: First Impressions
I can see it as my daily driver once it hits the stable release.
**The reason is**: I always like the stock GNOME experience, and I do not have to deal with Fedora's regular upgrades.
Of course, once I get to use the stable release, I can give you a verdict on the entire user experience.
Until then, I'd say it is a project that I believe a lot of users will appreciate 👏
You can download the ISO by joining its Discord channel for now. The ISO is not yet publicly available to all. Take a look at its [documentation](https://documentation.vanillaos.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) if you are curious.
However, as per the [roadmap](https://vanillaos.org/roadmap?ref=news.itsfoss.com), they plan to have a release candidate soon enough.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,205 | 如何在 Ubuntu 中安装 Viber | https://www.debugpoint.com/install-viber-linux/ | 2022-11-02T16:19:56 | [
"Viber"
] | /article-15205-1.html | 
>
> 这是在 Ubuntu 和其他 Linux 系统中安装 Viber 的快速指南。
>
>
>
[Viber](https://www.viber.com/) 是一个免费、安全的通话和聊天程序,适用于所有流行的移动平台和操作系统。
它具有丰富的功能,例如语音/视频通话、支持 GIF 的文本消息、贴纸、照片和视频。此外,Viber 还具有群聊、群呼和消失消息功能。
Viber 是一个闭源程序,但有免费的 Linux 原生可执行客户端。
下面是安装它的方法。
### 在 Linux 上安装 Viber
它以 AppImage 可执行文件、deb 和 rpm 包的形式提供。按照下面的相应按钮直接下载。平均可执行文件大小约为 180MB。
>
> **[下载适用于所有 Linux 发行版的 Appimage](https://download.cdn.viber.com/desktop/Linux/viber.AppImage)**
>
>
>
>
> **[适用于 Ubuntu 的 Deb 可执行文件](https://download.cdn.viber.com/cdn/desktop/Linux/viber.deb)**
>
>
>
>
> **[Fedora 的 RPM 包](https://download.cdn.viber.com/desktop/Linux/viber.rpm)**
>
>
>
如果你已下载 AppImage,只需从任意文件管理器将权限更改为可执行文件即可。然后运行。
对于 Ubuntu、Linux Mint、Debian 和相关发行版,你可以通过[多种方法](https://www.debugpoint.com/install-deb-files/)安装 deb 包。
你可以通过已安装的软件管理器双击打开。或者通过 `dpkg` 命令安装,如下所示。
```
sudo dpkg -i viber.deb
```
对于 Fedora 和基于 RPM 的软件包,你可以通过以下命令安装。
```
sudo dnf localinstall viber.rpm
```
对于 Arch Linux 和其他发行版,你可以使用我上面提到的 Appimage。
### 使用
完成安装 Viber 后,通过应用菜单打开它。以下是你需要记住的几件事。
在从笔记本电脑/台式机开始使用 Viber 之前,你需要在手机上进行设置。从以下链接为你的移动平台下载并安装 Viber。
* [谷歌应用商店](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.viber.voip&hl=en_IN&gl=US)
* [苹果应用商店](https://apps.apple.com/us/app/viber-messenger-chats-calls/id382617920)
安装后,设置 Viber。请记住,它需要你的手机号码才能注册。
设置完成后,在 Linux 桌面上打开应用。你应该会看到如下页面。

从你的手机应用扫描二维码,你应该可以在 Linux 桌面上使用 Viber。
**注意:** 由于它是一个闭源应用,请确保你在使用 Viber 时了解此应用的条款和与隐私相关的情况。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/install-viber-linux/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,206 | 关于配置 Terraform 的五条建议 | https://opensource.com/article/21/8/terraform-tips | 2022-11-02T22:07:00 | [
"Terraform"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15206-1.html |
>
> 本文介绍我使用 Terraform 五年之后吸取到的经验。
>
>
>

使用 Terraform 五年的经历让我吸取到一些重要经验。无论团队大小、项目性质,有五条要点对于配置合乎逻辑且可用的 Terraform 平台至关重要。
### 1、了解你的目标受众
这一点似乎显而易见,但我也见过一些在这方面犯错的案例。当组织和规划 Terraform 的相关代码时,无论是将目录结构标准化还是确定命名规范,考虑目标受众是非常重要的。例如:你的团队是否会使用这些 Terraform 脚本和模块?你是否会向其他团队交接工作?你的团队是否会有新成员加入?你是否正在独自进行项目开发?你是否会半年或一年后仍然使用这些配置,还是会将它安排给别人?
这类问题会影响某些决策。理想情况下,无论如何都应该有 <ruby> <a href="https://www.terraform.io/docs/language/state/index.html"> 远程状态 </a> <rt> Remote State </rt></ruby> 和 <ruby> <a href="https://www.terraform.io/docs/language/state/locking.html"> 状态锁定 </a> <rt> State Locking </rt></ruby> 两种状态。远程状态确保你的笔记本电脑不是你的 Terraform 唯一运行的机器,状态锁定确保同一时刻只有一个人对基础设施进行修改操作。
命名规范应该对项目的最终拥有者有意义,而不是只对开发团队有意义。如果项目会转交给其他团队,应该确保他们对命名规范有发言权。如果代码由非技术的利益相关者或内部安全/ GCR 团队负责审查,应该确保他们会检查命名规范。另外,对于资源名称,为了让代码审查人员更仔细地进行检查,你应该使用资源标签,把有关的数据分类/隐私需求(高、中、低)标示出来。
### 2、重用,重用,重用
[Terraform 注册表](https://registry.terraform.io/) 为大多数普通用例提供了现成模块类库。我已经使用过 VPC 模块和安全模块中的大量功能,这些功能只需要提供相关的参数就能使用。使用不同的参数,简单调用这些模块对于处理大部分用例已经足够了。尽可能多地重用这些公共模块,可以避免大量且重复的编码、测试、检查、修复、重构等操作。
我也发现,基于使用或变更的频率划分模块和资源大有好处。例如,只使用一次的基础设施手脚架,例如 VPC 相关设置、安全模块、路由表、VPC 端点等,可以放在一起。但是像私有托管域条目、自动伸缩模块、目标模块、负载均衡器等,每次部署时都会变化,所以把这些与一次性的基础设施手脚架分离开来,会令代码检查更方便,调试更快速。
### 3、要明确,而非隐含
Terraform 代码中有一些常见的模式,它会导致设计中出现错误的假设。团队可以假设用来写代码的 Terraform 版本永远保持不变,外部模块不会变化,或它们使用的提供者不会变更。当这些外部依赖不可避免地发生变化时,就会导致一些难以发现的问题。
无论何处(包括主要的 Terraform 组、提供者组、功能模块组)都要确保定义是明确的。事先定义版本,可以确保依赖库是固定的,因此你可以在讨论、审查、测试后,明明白白地更新依赖关系。
### 4、自动化每一处,包括笔记本电脑、共享虚拟机、CI/CD。
在部署的各个阶段使用自动化方法,可以避免可能发生的问题。
在你提交代码前,使用 [Git 预提交钩子](https://opensource.com/life/16/8/how-construct-your-own-git-server-part-6) 运行 `terraform fmt` 和 `terraform validate`。预提交钩子的作用是确保你的代码满足最低程度的格式和语法正确。把这个预提交文件检入到仓库,对你的团队成员都有好处。项目的第一步就进行质量控制相关的操作,它虽然表面上是小事一桩,但也很重要,能为项目节省大量时间。
一切现代化部署工具都有 CI 流程。当你向原始仓库推送代码时,可以使用它来运行 SAST 和单元测试工具。我写过一篇 [博客](https://notes.ayushsharma.in/2021/07/cloud-infrastructure-sast-terraform-checkov),是关于使用 Checkov 测试 Terraform 代码的安全性和合规性,并为组织特定的惯例创建自定义检查。把这些单元测试工具加入到你的 CI 管道,可以改进代码质量和健壮性。
### 5、写个好的 README.md 文件
我们都认为 Terraform 代码是自文档化的。的确如此,但是只有当未来的团队已经了解你的公司的命名规范、开发指南、机密通信、圈内笑话,以及你的仓库内除有效的 Terraform 代码之外其他所有东西,才会如此。维护 `README.md` 文件是个好习惯,它能节省大量时间,而且团队成员要为自己向 README 文件提交的任何内容负责,这样也就确保团队成员的忠诚度。
你的 README 文件至少应该包含在你的工作环境下(Linux、 Windows、Mac 等等)初始化 Terraform 环境的步骤,包括 Terraform 的版本信息。它应当确定需要的依赖库(Checkov、 TerraGrunt 及其他依赖)和其版本,以及团队使用的方便的 Linux 别名(例如有人喜欢将 `terraform fmt` 简写为 `tff`)。最重要的是,需要确定分支和 PR 审核策略和流程、命名规范和资源标签的相关标准。
README 文件需要通过这样的检验:如果团队有新成员加入,能否告诉他们做什么以及如何正确地完成工作?如果不能,在后续的几个月内,你将面对的是无休止的标准和流程讨论会议。
### 结束语
这些就是我使用 Terraform 多年后,认为需要传授给大家的五条有用的建议。也欢迎你分享自己的最佳实践。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/8/terraform-tips>
作者:[Ayush Sharma](https://opensource.com/users/ayushsharma) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[cool-summer-021](https://github.com/cool-summer-021) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Working with Terraform for over five years has taught me some key lessons. Five practices have been critical to having a logical and usable Terraform setup regardless of the size of the team or the nature of the project.
## 1. Know your target audience.
This one might seem obvious, but I've seen it go wrong several times. When organizing Terraform code, either standardizing the directory structure or defining naming conventions, it's vital to consider the intended audience. Will your team be using these Terraform scripts and modules? Are you handing the work over to another team? Will new people be joining your team sooner or later? Are you working on this project solo? Will you be using this setup in six months or a year, or will it be assigned to someone else?
Questions like these affect several decisions. Ideally, you should have [Remote State](https://www.terraform.io/docs/language/state/index.html) and [State Locking](https://www.terraform.io/docs/language/state/locking.html) in place regardless of the team size now or in the future. Remote State will ensure your laptop is not the only place your Terraform works, and State Locking will ensure that only one person at a time is changing the infrastructure.
The naming convention should make sense to the eventual owners of the project, not just the team that is writing the code. If the project is for another team, make sure they have a say in the naming convention. If non-technical stakeholders or internal security/GCR teams review the code, make sure they check the naming convention. In addition to resource names, you should leverage resource tags to highlight any data classification/privacy requirements (high, medium, low) for more careful examination by reviewers.
## 2. Reuse. Reuse. Reuse.
The [Terraform Registry](https://registry.terraform.io/) provides a library of ready-to-use modules for the most common use-cases. I've written about the extensive parameterization available in the VPC module and security groups. Simply calling modules with different parameters is enough to handle most, if not all, potential use cases. Reuse these shared modules as much as possible to avoid endless typing, testing, checking, fixing, and refactoring.
I've also found that separating modules and resources based on the frequency of use or change is beneficial. For example, infrastructure scaffolding used only once belongs together, such as setting up the VPC, security groups, routing tables, VPC endpoints, and so on. But things like private hosted zone entries, autoscaling groups, target groups, load balancers, etc., might change with every deployment, so separating these from the one-time scaffolding will make code reviews easier and debugging faster.
## 3. Be explicit rather than implicit.
There are common patterns to Terraform code that I have seen lead to incorrect assumptions baked into the design. Teams can assume that the Terraform version used to write the code today will never change, or the external modules won't change, or the providers they are using won't change. These lead to invisible issues a few weeks down the road when these external dependencies inevitably get updated.
Ensure you explicitly define versions everywhere possible: In the main Terraform block, in the provider block, in the module block, etc. Defining versions ensures that your dependent libraries stay frozen so that you can explicitly update dependencies when required after thorough discussions, reviews, and testing.
## 4. Automate everywhere. Your laptop. Your shared VM. Your CI/CD.
Leveraging automation at every stage of the deployment process can avoid future problems before they even arise.
Use [Git pre-commit hooks](https://opensource.com/life/16/8/how-construct-your-own-git-server-part-6) to run `terraform fmt `
and `terraform validate`
before you commit your code. Pre-commit hooks ensure that code is, at a bare minimum, adequately formatted and syntactically correct. Check-in this pre-commit file to the repo, and everyone on your team can benefit from the same automation. This small but vital quality control at the first step of the process can achieve substantial time savings as your project progresses.
All modern deployment tools have CI processes. You can use these to run SAST and unit testing tools when pushing your code to origin. I've written on my blog about how [Checkov can test Terraform code for security and compliance and create custom checks](https://notes.ayushsharma.in/2021/07/cloud-infrastructure-sast-terraform-checkov) for organization-specific conventions. Add these unit testing tools to your CI pipeline to improve code quality and robustness.
## 5. Have an awesome README.md.
We all like to think that Terraform code is self-documenting. Sure it is, but only if your future team already knows your company's naming conventions and guidelines and secret handshakes and inside jokes and whatever else your repo contains besides valid Terraform code. Getting into the habit of having a good `README.md`
can be a huge time saver, and it keeps your team honest by holding them accountable for everything explicitly committed to in the README.
At a minimum, your README should contain the steps to initialize the right Terraform environment on your workstations (Linux, Windows, Mac, and so on), including the Terraform version to install. It should specify the required dependencies (Checkov, TerraGrunt, and others) with versions and any handy Linux aliases your team uses (some people like to define `tff`
as a short-hand for` terraform fmt`
). Most importantly, the branching and PR review strategy and process, naming conventions, and resource tagging standards should be specified.
The README should pass a simple test: if a new member joins your team tomorrow, is the README enough to teach them what to do and how to do it correctly? If not, you may find yourself hosting never-ending standards and process meetings repeatedly for the next few months.
## Wrap up
After many years of working with Terraform, these are my five best bits of wisdom to pass along. Feel free to share your own best practices below.
## Comments are closed. |
15,212 | Linux Lite 6.2 发布 | https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-lite-6-2-release/ | 2022-11-04T05:01:00 | [
"Linux Lite"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15212-1.html |
>
> Linux Lite 6.2 是一个理想的升级,带来一些有用的变化,没什么太花哨的东西。
>
>
>

Linux Lite 是一种流行的轻量级的类 Windows 发行版,为用户提供了一个熟悉的操作系统感受。
最新版本 Linux Lite 6.2 基于 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS,对 UI 进行了各种更改以及各种错误的修复。
### Linux Lite 6.2:有什么新功能?

此版本的 Linux Lite 侧重于用户界面调整和错误修复,并对一些应用程序进行了更改。
一些主要亮点包括:
* 更新的图标
* 新壁纸
* Shotcut 视频编辑器
* 删除微软 Teams
* LibreOffice 7.3.6.2
* Linux 内核 5.15
#### Shotcut 取代 OpenShot

是的,[Shotcut](https://shotcut.org/) 现在取代了 [OpenShot](https://www.openshot.org/),成为 Linux Lite 6.2 上的默认视频编辑器。
OpenShot 之所以被删除,是因为它不能很好地与 Ubuntu 22.04 配合使用,而如果没有一个好用的视频编辑器,用户将不得不自己寻找一个。
Shotcut 无疑是一款出色的视频编辑器。所以,应该是一个不错的选择。
#### 微软 Teams 已删除
另一个重大变化是微软 Teams 不再包含在发行版中。
其原因是微软停止了 Linux 应用程序,转而支持一个渐进式 Web 应用程序版本。
我们之前的报道可以让你更深入地了解:
>
> **[微软决定放弃 Teams 的 Linux 应用,代之以渐进式Web应用](https://news.itsfoss.com/microsoft-linux-app-retire/)**
>
>
>
#### 更新的图标和新壁纸

Linux Lite 6.2 具有最新的 [Papirus](https://github.com/PapirusDevelopmentTeam/papirus-icon-theme) 图标集以及一系列新的 Linux Lite 主题壁纸。
这应该会给发行版带来用户可能喜欢的焕然一新的外观。
#### ?️ 其他更改和改进

其他值得注意的变化包括:
* 任务管理器的更新
* 改进了 Lite 升级应用程序中的结束对话。
* 各种应用程序的最新更新、错误修复等。
你可以阅读完整的发行说明以 [了解更多信息](https://www.linuxliteos.com/forums/release-announcements/linux-lite-6-2-final-released/)。
Linux Lite 6.2 看起来是对以前版本的令人满意的升级,有许多重大的变化和补充。
### ? 下载 Linux Lite 6.2
你可以从其官方网站下载最新的 ISO 或使用 Lite 升级工具升级到它。
>
> **[Linux Lite 6.2](https://www.linuxliteos.com/download.php)**
>
>
>
? 你如何看待 Linux Lite 6.2?愿意试一试吗?
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-lite-6-2-release/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Linux Lite is a popular lightweight Windows-like distro that gives users a familiar operating system.
The latest release, Linux Lite 6.2, is based on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS and has brought forward a variety of changes to the UI along with various bug fixes.
## Linux Lite 6.2: What's New?

This release of Linux Lite focuses on user interface tweaks and bug fixes, with changes to a few applications.
Some key highlights include:
**Updated Icons****New Wallpapers****Shotcut Video Editor****Removal Of Microsoft Teams****LibreOffice 7.3.6.2****Linux Kernel 5.15**
[Unlocator Smart DNSRemove geographic blocks from streaming services using Unlocator Smart DNS. Simple to use and with a full free trial included.](https://unlocator.com/account/aff/go/KeijkZZVhNSBsJmLTeQr?cr=aHR0cHM6Ly91bmxvY2F0b3IuY29tL3NtYXJ0LWRucy8%3D&ref=news.itsfoss.com)

### Shotcut Replaces OpenShot
Yes, [Shotcut](https://shotcut.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) now replaces [OpenShot](https://www.openshot.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) as the default video editor on Linux Lite 6.2.
OpenShot gets the place because it didn't work well with Ubuntu 22.04, and without a utility like this, users would have to look for one on their own.
Shotcut is undoubtedly a good video editor. So, it should be a good option.
[9 Best Free Video Editing Software for Linux in 2020Looking for a free video editor for Linux? Here are the best options for various kind of video editing needs on Linux.](https://itsfoss.com/best-video-editing-software-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

### Microsoft Teams Removed
Another significant change is that Microsoft Teams is no longer included in the distro.
The reason for that is the discontinuation of the Linux application by Microsoft in favor of a progressive web app version.
Our previous coverage can give you more insight into that:
[Microsoft Decides to Drop the Linux App for Teams to Replace it as a Progressive Web App InsteadMicrosoft will no longer offer a Linux app for Teams. Here’s how you can access Microsoft Teams on Linux moving forward.](https://news.itsfoss.com/microsoft-linux-app-retire/)

### Updated Icons and New Wallpapers
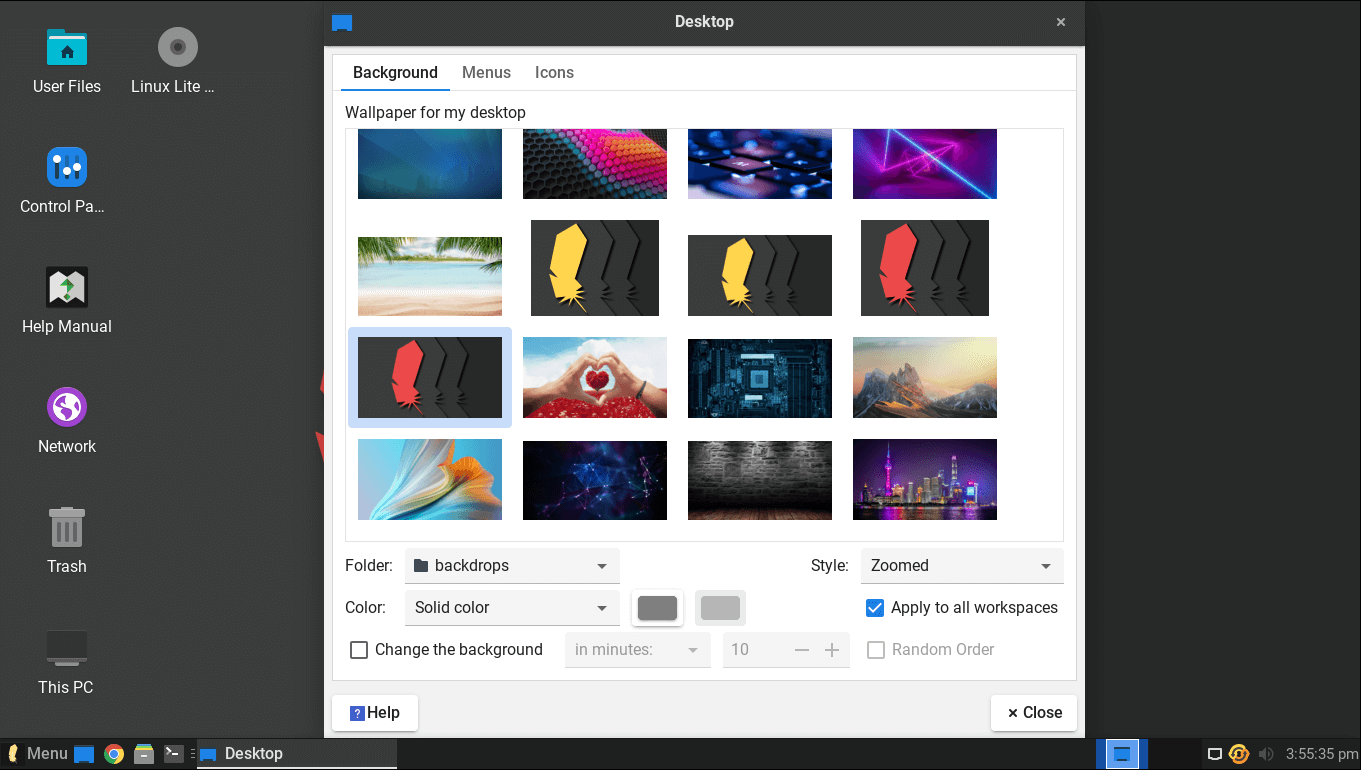
Linux Lite 6.2 features the latest [Papirus](https://github.com/PapirusDevelopmentTeam/papirus-icon-theme?ref=news.itsfoss.com) icon set alongside a bunch of new Linux Lite-themed wallpapers.
This should give the distro a refreshed look that users might like.
### 🛠️ Other Changes and Improvements
Other notable changes include:
- Updates to the task manager
- Improved end dialogue in the Lite Upgrade application.
- The latest updates for various applications, bug fixes, and more.
You can go through the [full release notes](https://www.linuxliteos.com/forums/release-announcements/linux-lite-6-2-final-released/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to learn more.
Linux Lite 6.2 seems to be a satisfactory upgrade over the previous version, with many significant changes and additions.
## 📥 Download Linux Lite 6.2
You can download the latest ISO from its official website or upgrade to it using the Lite Upgrade tool.
*💬 What do you think of Linux Lite 6.2? Willing to give it a try?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,213 | 关于编译代码你应该知道的 | https://opensource.com/article/22/10/compiling-code | 2022-11-04T05:42:22 | [
"编译"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15213-1.html | 
>
> 用这个方便的捕鼠器比喻来理解编译代码。
>
>
>
源代码必须要经过编译才能够运行程序,而对于开源软件,每个人都可以获取源代码。无论你是自己编写了代码,想要编译和运行它,还是下载了某人的项目来尝试它,了解如何通过 [编译器](https://opensource.com/article/19/5/primer-assemblers-compilers-interpreters) 处理源代码,以及编译器如何处理这些代码,这都很有用。
### 创建一个更好的捕鼠器
一般情况我们不会将一个捕鼠器比作电脑,但不管你信不信,它确实与你正在使用的设备(手机或电脑)的 CPU 有一些相似之处。经典的捕鼠器(我说的不是 ?)有两种状态:打开或者释放。你可以认为 *打开* 是将捕鼠器设置好准备捕获老鼠,以及 *释放* 是捕鼠器被老鼠触发。某种意义上来说,捕鼠器就像是一台有鼠标的电脑。你可以想象一下这个代码,用一种虚构的语言来描述这个过程:
```
if mousetrap == 0 then
There's a mouse!
else
There's no mouse yet.
end
```
换句话说,你可以基于捕鼠器的状态发现是否有老鼠(数据)。当然,捕鼠器不是万无一失的,有可能有一只老鼠在捕鼠器旁边,由于老鼠还没有触发捕鼠器,所以它的状态还是 *打开* 的。因此该程序可以进行改进,这都是非常典型的。
### 开关
总的来说,捕鼠器就是一个开关。你会在家里使用开关打开灯。可以从开关中获得许多信息。比如,人们会从你家灯的状态了解到你是否在家。
你可以根据邻居家灯的状态来改变行为。如果邻居家所有的灯都熄灭了,那么请关掉你大声的音乐,因为人们可能已经上床睡觉了。
CPU 也使用这样的逻辑,只不过乘以几个数量级,缩小到了微观级别。当 CPU 在特定寄存器上接收到电信号时,可以触发其他一些寄存器,然后触发另一个,以此类推。如果这些寄存器有特定的意义,那么就可以通信。也许激活同一主板上某处的芯片,或者使 LED 亮起,或者改变屏幕上的像素颜色。
种瓜得瓜,种豆得豆。如果你真的想在多个位置而不是仅限于一处发现老鼠,但是你只有一个捕鼠器,那你应该开发一个应用才行。使用网络摄像头和一些基本的图像识别软件,你可以建立空厨房的模型,然后扫描变化。当老鼠进入厨房,在原先没有老鼠的图像上会有像素的变化。记录下这些数据,如果有无人机可以追踪老鼠并捕获会更好,这样就可以将老鼠赶出厨房了。这时,你通过打开和关闭信号的魔法,创造了一个更好的捕鼠器。
### 编译器
代码编译器将人们可阅读的代码转换成 CPU 可以理解的机器语言。这是非常复杂的过程,因为 CPU 非常复杂(甚至比捕鼠器更加复杂),同时因为该过程比严格“需要”的更加灵活。并不是所有的编译器都很灵活。有一些编译器只有一个目标,它们只会处理特定格式的代码文件,处理过程也因此而简单明了。
幸运的是,现代的通用编译器并不简单。它们允许你编写不同语言的代码,也允许你用不同的方式链接库文件,并且可以生成运行在不同架构上的文件。[GNU 编译器集合](https://opensource.com/article/22/5/gnu-c-compiler)(GCC)的 `gcc` 编译器 `--help` 会输出超过 50 行的选项,LLVM 的 `clang` 编译器的 `--help` 输出超过 1000 行。GCC 指导手册的字数超过 10 万。
当你在编译代码时会有很多选项。
当然,大多数人并不需要知道所有的选项。我从未读过 GCC 的手册页,因为它们是针对 Objective-C、Fortran 以及我从未听说过的芯片架构的。不过我重视它将代码编译为不同的架构 —— 64 位或者 32 位 —— 的能力,以及在其他行业已经落后的计算机上运行开源软件的能力。
### 编译生命周期
同样重要的是,理解编译代码的不同阶段。这是一个简单的 C 语言程序的生命周期:
1. 带有宏定义的 C 源代码 `.c` 文件,用 `cpp` 预处理为 `.i` 文件。
2. 扩展了宏定义的 C 源代码 `.i` 文件,会被 `gcc` 转译成 `.s` 文件。
3. 以汇编语言写的文本文件 `.s` 文件被汇编为目标 `.o` 文件。
4. 带有 CPU 指令的二进制目标代码,以及其他目标文件和库 `*.o` 文件,以内存区域无关的偏移量,使用 `ld` 链接以生成可执行文件。
5. 最终的二进制文件要么包含所有需要的目标,要么设置以动态链接库 `*.so` 文件加载。
你可以试试这个简单示例(可能需要对库路径做一些调整):
```
$ cat << EOF >> hello.c
#include
int main(void)
{ printf("hello world\n");
return 0; }
EOF
$ cpp hello.c > hello.i
$ gcc -S hello.i
$ as -o hello.o hello.s
$ ld -static -o hello \
-L/usr/lib64/gcc/x86_64-slackware-linux/5.5.0/ \
/usr/lib64/crt1.o /usr/lib64/crti.o hello.o \
/usr/lib64/crtn.o --start-group -lc -lgcc \
-lgcc_eh --end-group
$ ./hello
hello world
```
### 可获得的知识
计算机已经变得非常强大,并且用户友好。请不要走向这两种可能的极端中的任何一种:计算机不像捕鼠器和电灯开关那么简单,但它们也不是无法理解的。你可以了解编译代码、如何链接以及针对不同架构进行编译。一旦你知道了,你就可以更好地调试代码。你可以理解你下载的代码,甚至可以修复其中的一两个错误。同时从理论上来讲,你可以建造一个更好的捕鼠器,或者用捕鼠器造一个 CPU。由你决定。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/10/compiling-code>
作者:[Alan Smithee](https://opensource.com/users/alansmithee) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Source code must be compiled in order to run, and in open source software everyone has access to source code. Whether you've written code yourself and you want to compile and run it, or whether you've downloaded somebody's project to try it out, it's useful to know how to process source code through a [compiler](https://opensource.com/article/19/5/primer-assemblers-compilers-interpreters), and also what exactly a compiler does with all that code.
## Build a better mousetrap
We don't usually think of a mousetrap as a computer, but believe it or not, it does share some similarities with the CPU running the device you're reading this article on. The classic (non-cat) mousetrap has two states: it's either set or released. You might consider that *on* (the kill bar is set and stores potential energy) and *off* (the kill bar has been triggered.) In a sense, a mousetrap is a computer that calculates the presence of a mouse. You might imagine this code, in an imaginary language, describing the process:
```
``````
if mousetrap == 0 then
There's a mouse!
else
There's no mouse yet.
end
```
In other words, you can derive mouse data based on the state of a mousetrap. The mousetrap isn't foolproof, of course. There could be a mouse next to the mousetrap, and the mousetrap would still be registered as *on* because the mouse has not yet triggered the trap. So the program could use a few enhancements, but that's pretty typical.
## Switches
A mousetrap is ultimately a switch. You probably use a switch to turn on the lights in your house. A lot of information is stored in these mechanisms. For instance, people often assume that you're at home when the lights are on.
You could program actions based on the activity of lights on in your neighborhood. If all lights are out, then turn down your loud music because people have probably gone to bed.
A CPU uses the same logic, multiplied by several orders of measure, and shrunken to a microscopic level. When a CPU receives an electrical signal at a specific register, then some other register can be tripped, and then another, and so on. If those registers are made to be meaningful, then there's communication happening. Maybe a chip somewhere on the same motherboard becomes active, or an LED lights up, or a pixel on a screen changes color.
**[ Related read 6 Python interpreters to try in 2022 ]**
What comes around goes around. If you really want to detect a rodent in more places than the one spot you happen to have a mousetrap set, you could program an application to do just that. With a webcam and some rudimentary image recognition software, you could establish a baseline of what an empty kitchen looks like and then scan for changes. When a mouse enters the kitchen, there's a shift in the pixel values where there was previously no mouse. Log the data, or better yet trigger a drone that focuses in on the mouse, captures it, and moves it outside. You've built a better mousetrap through the magic of on and off signals.
## Compilers
A code compiler translates human-readable code into a machine language that speaks directly to the CPU. It's a complex process because CPUs are legitimately complex (even more complex than a mousetrap), but also because the process is more flexible than it strictly "needs" to be. Not all compilers are flexible. There are some compilers that have exactly one target, and they only accept code files in a specific layout, and so the process is relatively straight-forward.
Luckily, modern general-purpose compilers aren't simple. They allow you to write code in a variety of languages, and they let you link libraries in different ways, and they can target several different architectures. The [GNU C Compiler (GCC)](https://opensource.com/article/22/5/gnu-c-compiler) has over 50 lines of options in its `--help`
output, and the LLVM `clang`
compiler has over 1000 lines in its `--help`
output. The GCC manual contains over 100,000 words.
You have lots of options when you compile code.
Of course, most people don't need to know all the possible options. There are sections in the GCC man page I've never read, because they're for Objective-C or Fortran or chip architectures I've never even heard of. But I value the ability to compile code for several different architectures, for 64-bit and 32-bit, and to run open source software on computers the rest of the industry has left behind.
## The compilation lifecycle
Just as importantly, there's real power to understanding the different stages of compiling code. Here's the lifecycle of a simple C program:
-
C source with macros (
**.c****) is preprocessed with**`cpp`
to render an`.i`
file. -
C source code with expanded macros (
**.i****) is translated with**`gcc`
to render an`.s`
file. -
A text file in Assembly language (
**.s****) is assembled with**`as`
into an`.o`
file. -
Binary object code with instructions for the CPU, and with offsets not tied to memory areas relative to other object files and libraries (
`*.o`
) is linked with`ld`
to produce an executable. -
The final binary file either has all required objects within it, or it's set to load linked dynamic libraries (
`*.so`
files).
And here's a simple demonstration you can try (with some adjustment for library paths):
```
``````
$ cat << EOF >> hello.c
#include
int main(void)
{ printf("hello world\n");
return 0; }
EOF
$ cpp hello.c > hello.i
$ gcc -S hello.i
$ as -o hello.o hello.s
$ ld -static -o hello \
-L/usr/lib64/gcc/x86_64-slackware-linux/5.5.0/ \
/usr/lib64/crt1.o /usr/lib64/crti.o hello.o \
/usr/lib64/crtn.o --start-group -lc -lgcc \
-lgcc_eh --end-group
$ ./hello
hello world
```
## Attainable knowledge
Computers have become amazingly powerful, and pleasantly user-friendly. Don't let that fool you into believing either of the two possible extremes: computers aren't as simple as mousetraps and light switches, but they also aren't beyond comprehension. You can learn about compiling code, about how to link, and compile for a different architecture. Once you know that, you can debug your code better. You can understand the code you download. You may even fix a bug or two. Or, in theory, you could build a better mousetrap. Or a CPU out of mousetraps. It's up to you.
**Download our new eBook: An open source developer's guide to building applications**
## 1 Comment |
15,215 | 12 个对新手最重要的 Linux 命令 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/essential-linux-commands | 2022-11-05T09:23:10 | [
"命令"
] | /article-15215-1.html |
>
> 我向所有的 Linux 初学者推荐以下这些命令。
>
>
>

在使用 Linux 命令行时,很容易就会迷失方向,这可能会导致灾难性的后果:我有一次使用删除命令 `rm` 删除文件,然而删除之后我才意识到我刚刚是删除了计算机的引导目录。后来,我学会了使用 `pwd` 命令,来知道当前在文件系统的哪个目录下;并且我使用了 [trashy 和 trash-cli](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/recover-file-deletion-linux) 这一命令行回收站工具(LCTT 译注:在删除文件时 `trash-cli` 会充当中间人,将文件先“删除”到桌面上的垃圾箱中,能够通过垃圾箱或通过终端的 `trash` 命令,来恢复垃圾箱中已删除的文件。)
当我刚开始使用 Linux 时,我有一个放在桌子上的“速查表”,它就是《101 条你应该知道的 Linux 命令》,我在管理 Linux 服务器时能参考速查表上面的这些命令。随着我越来越熟悉这些命令,我越来越精通服务器管理了。
以下是我认为最有用的 12 个 Linux 命令。
### 1、打印工作目录(pwd)
`pwd` 命令会打印出你的工作目录。换句话来说,它输出你当前所在目录的路径。`pwd` 命令有两种选项:`-L` 或 `--logical`(即逻辑路径)用来打印当前的目录路径(不解析符号链接),`-P` 或 `--physial`(即物理路径)会打印出解析符号链接后的物理目录。(LCTT 译注:你可以进一步阅读我们翻译的 [另一篇文章](/article-4356-1.html)。)
### 2、创建目录(mkdir)
使用 `mkdir` 命令来创建一个新目录,是非常容易的。以下命令,创建了一个名为 `example` 目录(若 `example` 已存在,则无法创建):
```
$ mkdir example
```
你也可以在嵌套地创建目录及其子目录:
```
$ mkdir -p example/one/two
```
如果目录 `example` 和目录 `one` 都已存在,则仅会创建目录 `two`。如果上述目录都不存在,则会创建这三个嵌套的目录。
### 3、列出文件(ls)
我最早使用的是 MS-DOS(微软磁盘操作系统),因此我习惯于使用 `dir` 命令,来列出文件。我不记得当时是否能在 Linux 上使用 `dir` 命令,但是如今 `dir` 命令已经包含在 <ruby> GNU 核心实用程序包 <rt> GNU Core Utilities package </rt></ruby> 中了。大多数人会使用 `ls` 命令,来显示目录中的文件及其所有的属性。`ls` 命令有许多选项,包括 `-l` 查看文件的长列表,显示文件所有者和权限等信息。
### 4、更改当前工作目录(cd)
在 Linux 中经常要更改当前工作目录,这就是 `cd` 命令的功能。例如,以下的示例将让你从 <ruby> 主目录 <rt> home </rt></ruby> 进入 `Documents` 目录:
```
$ cd Documents
```
你可以使用 `cd ~` 或者 `cd`,来快速转换到你的主目录。你可以使用 `cd ..` 来返回到上一级目录。
### 5、删除文件(rm)
删除文件是很危险的,因为在 Linux 终端上用 `rm` 命令会**彻底地**删除文件,并没有像桌面的垃圾桶那样依旧保存着删除的文件。许多终端用户有一个坏习惯,他们会永久地删除他们认为不再需要的文件。然而,因为没有“取消删除”命令,这个坏习惯可能会导致严重的问题:你会不小心删除了包含重要数据的目录。
Linux 系统为文件删除提供了 `rm` 和 `shred` 命令。要删除文件 `example.txt`,请输入以下内容:
```
$ rm example.txt
```
然而,使用 `trash` 命令要安全得多,例如 [trashy](https://gitlab.com/trashy/trashy) 或者 [trash-cli](https://github.com/andreafrancia/trash-cli),它会将文件先“删除”到桌面上的垃圾箱中:
```
$ trash example.txt
```
(LCTT 译注:关于 Trash-Cli 的更多信息可以参考我们翻译的 [另一篇文章](/article-10029-1.html)。)
### 6、复制文件(cp)
使用 `cp` 命令,来复制文件。`cp` 的语法是从*旧文件*复制到*新文件*。这里有一个例子:
```
$ cp file1.txt newfile1.txt
```
你也可以复制整个目录:
```
$ cp -r dir1 newdirectory
```
### 7、移动并重命名文件(mv)
重命名和移动文件在功能上是相同的过程。当你移动文件时,从一个目录中取出一个文件,并将其放入一个新目录中;当你重命名文件时,将一个目录中的文件更改为新名称,并放回到同一目录或另一个目录下。无论是重命名还是移动文件,你都可以使用 `mv` 命令:
```
$ mv file1.txt file_001.txt
```
### 8、创建一个空文件(touch)
使用 `touch` 命令可以简单地创建一个空文件:
```
$ touch one.txt
$ touch two.txt
$ touch three.md
```
### 9、更改权限(chmod)
使用 `chmod` 命令,来更改文件的权限。`chmod` 最常见的用途是让文件能够执行:
```
$ chmod +x myfile
```
以下的示例展示了如何用 `chmod` 命令给文件赋予权限,这对于脚本来说特别方便。尝试一下这个简单的练习吧:
```
$ echo 'echo Hello $USER' > hello.sh
$ chmod +x hello.sh
$ ./hello.sh
Hello, Don
```
### 10、提升为 root 权限(sudo)
在管理自己的 Linux 系统时,可能需要提升为超级用户(也称为 root),这就是 `sudo`(即 <ruby> 以超级用户做 <rt> super user do </rt></ruby>)命令的来源。假设你想要做一些只有管理员(或 root 用户)才能做的事情,只需在命令前加一个 `sudo` 即可:
```
$ touch /etc/os-release && echo "Success"
touch: cannot touch '/etc/os-release': Permission denied
$ sudo touch /etc/os-release && echo "Success"
Success
```
### 11、关机(poweroff)
`poweroff` 命令的功能和它的字面意思一样:把你的计算机关机。需要在 `poweroff` 前面加一个 `sudo` 才能成功关机。
实际上,还有很多方法可以关闭你的计算机,这些方法有略微的不同。例如,`shutdown` 命令会在指定的时间(例如 60 秒)后关闭计算机:
```
$ sudo shutdown -h 60
```
或者立即关闭计算机:
```
$ sudo shutdown -h now
```
你也可以用 `sudo shutdown -r now` 或者 `reboot` 来重启计算机。
### 12、阅读手册(man)
`man` 命令可能是 Linux 中最重要的命令了,你可以通过 `man` 命令查看 Linux 系统上每个命令的官方文档。例如,要阅读更多有关 `mkdir` 的信息,可以输入:
```
$ man mkdir
```
一个与 `man` 相关的命令是 `info` 命令,它提供了一组不同的手册,它通常会提供比简洁的 `man` 页面更详细一点的内容。
### 你最喜欢的 Linux 命令是什么?
Linux 系统上还有数百个其他命令!你最喜欢使用的 Linux 命令是什么呢?什么命令是你一直反复使用的呢?
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/essential-linux-commands>
作者:[Don Watkins](https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
15,216 | 如何检查: 是 Xorg 还是 Wayland 显示服务器? | https://www.debugpoint.com/check-wayland-or-xorg/ | 2022-11-05T10:29:32 | [
"Xorg",
"Wayland"
] | /article-15216-1.html | 
>
> 以下是快速检查在运行 Xorg 还是 Wayland 显示服务器的方法。
>
>
>
随着时间的推移,现代 Wayland 显示服务器正在进入所有 Linux 发行版。尽管老旧的 Xorg 仍然能用并且会继续存在,但 Wayland 无疑在安全性和其他性能方面更好。
但是,Xorg 不会很快完全淘汰。可能永远不会。
如果你在运行任何 Linux 发行版,如何检查运行的是 Xorg 还是 Wayland?下面是方法。
### Wayland 或 Xorg:你在运行哪一个?
在你的 Linux 发行版(例如 Ubuntu、Fedora、Arch 等)中打开一个终端窗口(`CTRL+ALT+T`)。
然后输入以下命令并回车:
```
echo $XDG_SESSION_TYPE
```
命令输出会告诉你当前会话是 Wayland 还是 Xorg(X11)。
```
[debugpoint@fedora ~]$ echo $XDG_SESSION_TYPEwayland
```

这很简单。但是,还有其他方法。
### 其他方法
#### 使用设置
如果你需要图形方法,请打开你的 Linux 发行版的设置应用。在关于部分,你应该看到某个标签下中的 Wayland/X11。
例如,在 GNOME 设置中,你可以在 “<ruby> 窗口子系统 <rt> Windowing system </rt></ruby>” 下找到它,如下图所示:

#### 使用会话值
你还可以使用 [systemd](https://www.debugpoint.com/tag/systemd/) 登录管理器 `loginctl` 找到它。请记住,它仅适用于基于 systemd 的系统。
打开终端并运行以下命令。你可以看到会话 id 值。在此示例中为 `c2`:
```
loginctl
```
现在,将会话 ID 传递给以下命令以获取显示服务器类型。确保将 c2 更改为你的系统规格。
```
loginctl show-session c2 -p Type
```

### 总结
这些是你可以确定在 Linux 系统中运行的是 Systemd 还是 Xorg 的一些方法。你还可以在 shell 脚本中使用上述命令来实现进一步的流程自动化。
祝好。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/check-wayland-or-xorg/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,217 | 在 Ubuntu 上安装 WoeUSB 来创建一个可启动 Windows USB | https://itsfoss.com/install-woeusb-ubuntu/ | 2022-11-05T15:10:38 | [
"USB",
"Windows"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15217-1.html |
>
> 想在 Linux 上创建一个可启动 Windows USB ?Ventoy 是一个很好的选择。
>
>
>
但是,在 Ventoy 出道之前,WoeUSB 是用于创建可启动 Windows USB 的首选工具。原版 WoeUSB 工程在 2014 年左右香消玉损。
鉴于其流行程度,一位新的开发者接过了将其起死回生的任务。因此,WoeUSB-ng 诞生了。在这里,“ng” 是 <ruby> 新生代 <rt> new generation </rt></ruby> 的缩写。换句话说,[WoeUSB-ng](https://github.com/WoeUSB/WoeUSB-ng) 是新生代的 WoeUSB 。但是,因为原版的工具已经不存在了,我将 WoeUSB-ng 描述为 WoeUSB 。
在这篇教程中,我将向你展示如何在 Ubuntu Linux 上安装 WoeUSB 。我也将分享使用 WoeUSB 来创建可启动 Windows USB 的步骤。
但是,在此之前,让我们快速查看这个令人惊叹的工具的特色。
### WoeUSB

WoeUSB 是一个简单的工具,其唯一的目的是 [在 Linux 上创建可启动 Windows USB](https://itsfoss.com/bootable-windows-usb-linux/) 。
原版 WoeUSB 是一个 shell 脚本。这个原版 WoeUSB 被使用 Python 重写为 WoeUSB-ng ,它可以安装在你的系统上,并且通过命令行或 GUI 界面。
特色:
* 支持老式 PC 启动或 UEFI 启动
* 支持 FAT32 和 NTFS 文件系统
* 支持使用物理安装盘或磁盘镜像作为源
* 它可以用于 Windows Vista 及其更高版本的任意语言或变体版本
* 老式的 MBR/IBM PC 兼容启动模式
* 本机 UEFI 启动支持 Windows 7 及其更高版本的镜像(仅限于将 FAT 文件系统作为目标的情况)
### 在 Ubuntu 和其它的 Linux 发行版上安装 WoeUSB
Arch Linux 用户可以从 AUR 安装 WoeUSB-ng 。
对于其它的发行版,可以使用 PIP 来安装 WoeUSB 。毕竟,它是一个 Python 应用程序。在这里,我将为 Ubuntu/Debian 提供一些命令。
为安装 WoeUSB-ng ,你首先需要 [安装 PIP](https://itsfoss.com/install-pip-ubuntu/) 和其它必要的依赖项。
```
sudo apt install git p7zip-full python3-pip python3-wxgtk4.0 grub2-common grub-pc-bin
```
在这之后,你可以安装 WoeUSB-ng ,通过运行:
```
sudo pip3 install WoeUSB-ng
```
对于所有的其它安装,你可以参考其 [操作指南](https://github.com/WoeUSB/WoeUSB-ng#installation) 。
>
> **[WoeUSB-ng](https://github.com/WoeUSB/WoeUSB-ng)**
>
>
>
### 前提条件: 获取 Windows 的 ISO 文件和一个兼容的 USB 磁盘
这一点没有什么需要说的。你需要有一个你将要安装的 Windows 版本的 ISO 文件。
从微软的网站,你应该能够获取 Windows 10 和 11 的ISO 文件。
>
> **[下载 Windows](https://www.microsoft.com/en-in/software-download/)**
>
>
>
如果你有较旧的 Windows 版本的 ISO 文件,也可以使用它们。
除此之外,你需要有一个至少 8 GB 大小的 USB 驱动器磁盘。你应该使用 NTFS 的文件系统来格式化它filesystem.
### 方法 1: 使用图形用户界面化的 WoeUSB 来创建一个可启动的 Windows USB(推荐)
从 <ruby> 活动概述 <rt> activity overview </rt></ruby> 或菜单中打开 woeusb-gui 。

在应用程序窗口中,选择下载的 Windows ISO 和所希望的 USB 驱动器,如截屏所示,然后按下 <ruby> 安装 <rt> Install </rt></ruby> 按钮。

在应用程序中也其它可用的调整,可以通过顶部的菜单栏来访问使用。
在按下“安装”按钮后,woeUSB 将开始格式化和复制文件。你需要等待一些时间,因为这里有大约 6 GB 的文件需要复制。

在复制完成后,WoeUSB 将会提示一个成功的对话框。你现在可以安全地弹出 USB 驱动器,并将其作为一个可启动 USB 驱动器来使用。

### 方法 2: 从终端中使用 WoeUSB(针对专家)
WoeUSB-ng 软件包也提供一个名称为 `woeusb` 的命令行实用程序。
为使用 WoeUSb 来创建一个可启动的 Windows USB ,你需要运行下面的命令:
```
sudo woeusb --device <path/to/Windows/ISO> <name/of/the/USB/device> --target-filesystem ntfs
```
在这里,`--device` 标识用于擦除 USB 和从零开始创建一个可启动 USB 驱动器。同样,`--target-filesystem` 标识用于设置为 NTFS ,来避免将要复制的文件大小超过 FAT 文件系统的限制。

该过程将花费一些时间来完成复制。在完成复制后,它将显示一条成功的信息。

此时,你可以安全地弹出 USB 驱动器,并在其它的个人电脑上将其作为一个 Windows 可启动 USB 来使用。
### 超值: 使用 WoeUSB 的 Bash Shell 脚本(针对专家)
WoeUSB 也提供一个 Bash Shell 脚本,在你的系统上,它不需要安装任何东西就可以使用。
首先,你需要从 [该工程的发布版本页面](https://github.com/WoeUSB/WoeUSB/releases/tag/v5.2.4) 下载 Shell 脚本。
在 [执行 Shell 文件](https://itsfoss.com/run-shell-script-linux/) 之前,你需要获取所需要的依赖项。为安装它,运行:
```
sudo apt install wimtools
```
现在,通过文件管理器或通过命令行来使它可执行。

或者,你可以运行 `chmod +x <path/to/script>` 来使它可执行。现在,运行已下载目录中的 `./woeusb-5.2.4.bash -h` 来获取帮助。
为创建一个现场 USB ,该进程类似于 woeusb-ng 的命令行部分,但是你没有安装任何东西。
因此,在一个终端中,运行:
```
sudo <path/to/downloaded/script/file> --device <path/to/windows/ISO> <name-of-USB-device> --target-filesystem ntfs
```
这将开始将 ISO 写入 USB 驱动器,如下面的截屏所示:

在完成后,你可以安全地弹出 USB 驱动器,并将其作为可启动 USB 使用。
### 移除 WoeUSB
如果你使用 PIP 安装 WoeUSB ,你也可以类似地移除它:
```
pip3 uninstall WoeUSB-ng
```
你可以在你的系统上保留或移除已安装的依赖项。这完全取决于你。我建议保留它们。
### 总结
大约 10 年前,WoeUSB 是一个非常流行的工具。其他人以另外一种形式将其复活是很好的,这就是开源的艺术。
我希望这篇教程会帮助你。如果通过 WoeUSB 创建的 Windows USB 不能按部就班地工作,你可以 [尝试使用 Ventoy](https://itsfoss.com/bootable-windows-usb-linux/) 。享受它。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/install-woeusb-ubuntu/>
作者:[Sreenath](https://itsfoss.com/author/sreenath/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Want to create a bootable Windows USB on Linux? Ventoy is a pretty good option.
But before Ventoy, WoeUSB used to be the go-to tool for this purpose. The original WoeUSB project got discontinued around 2014.
Owing to its popularity, a new developer took the task of bringing the project back from the dead. And hence WoeUSB-ng was born. “ng” here stands for “new generation”. In other words, [WoeUSB-ng](https://github.com/WoeUSB/WoeUSB-ng) is the new generation WoeUSB. But since the original tool doesn’t exist anymore, I’ll be referring WoeUSB-ng as WoeUSB.
In this tutorial, I’ll show you how to install WoeUSB on Ubuntu Linux. I’ll also share the steps for creating bootable Windows USBs with WoeUSB.
But before that, let’s quickly look at the features of this awesome tool.
## WoeUSB

WoeUSB is a simple tool that has the sole purpose of [creating bootable Windows USB on Linux](https://itsfoss.com/bootable-windows-usb-linux/).
The original WoeUSB is a shell script. This same WoeUSB is rewritten as WoeUSB-ng in python, which can be installed on your system and provides both a command-line and GUI interface.
**Features:**
- Support Legacy PC/UEFI booting
- Support FAT32 and NTFS filesystems
- Support using physical installation disc or disk image as source
- It can be used for Windows Vista and later with any language or edition variants
- Legacy/MBR-style/IBM PC compatible boot mode
- Native UEFI booting is supported for Windows 7 and later images (limited to the FAT filesystem as the target)
## Installing WoeUSB on Ubuntu and other Linux distros
Arch Linux users can install WoeUSB-ng from AUR.
For other distros, WoeUSB can be installed using PIP. It’s a Python application, after all. I am going to provide commands for Ubuntu/Debian here.
To install WoeUSB-ng, you need to [install PIP](https://itsfoss.com/install-pip-ubuntu/) and other necessary dependencies first.
`sudo apt install git p7zip-full python3-pip python3-wxgtk4.0 grub2-common grub-pc-bin`
After this, you can install WoeUSB-ng by running:
`sudo pip3 install WoeUSB-ng`
For all other installations, you can refer to their [instructions](https://github.com/WoeUSB/WoeUSB-ng#installation).
## Prerequisite: Get Windows ISO and a compatible USB
This one goes without saying. You need to have the ISO file of the Windows version you want to install.
From the Microsoft website, you should be able to get the ISO for Windows 10 and 11.
If you have ISOs for older Windows versions, they can also be used.
Apart from that, you need to have a USB key/pen drive of at least 8 GB in size. You should format it in NTFS filesystem.
## Method 1: Using WoeUSB to create a bootable Windows USB graphically (recommended)
Open woeusb-gui from the activity overview or menu.
In the application window, select the downloaded Windows ISO and the desired USB drive as shown in the screenshot and press **Install**.
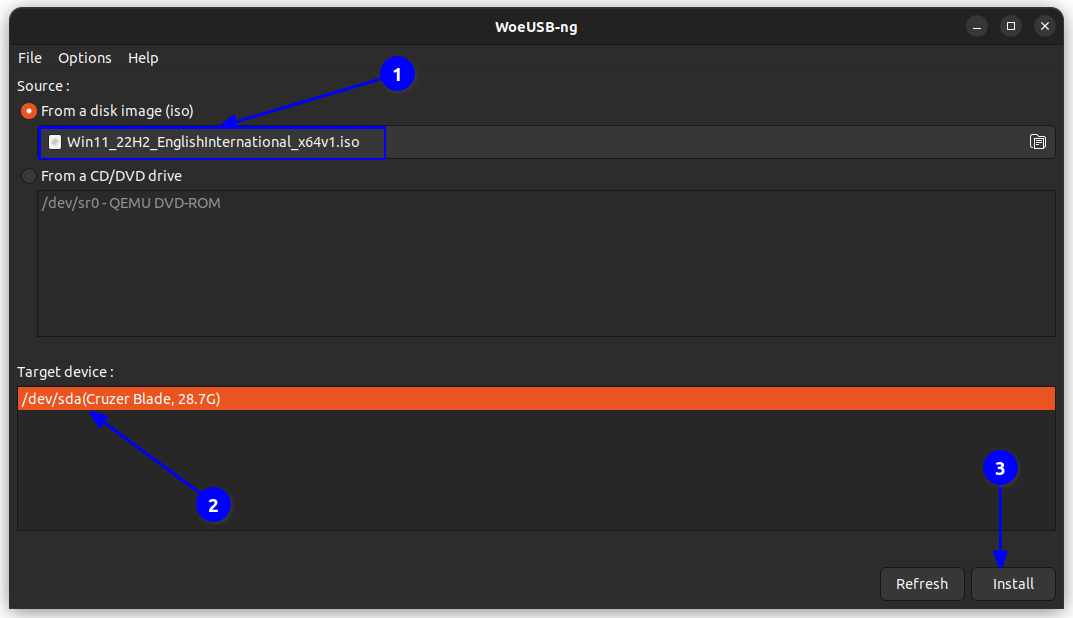
There are also other tweaks available within the app, which can be accessed by the top menu bar.
After pressing install, the woeUSB will start formatting and copying files. You need to wait for some time because there are approximately 6 GB of files to be copied.
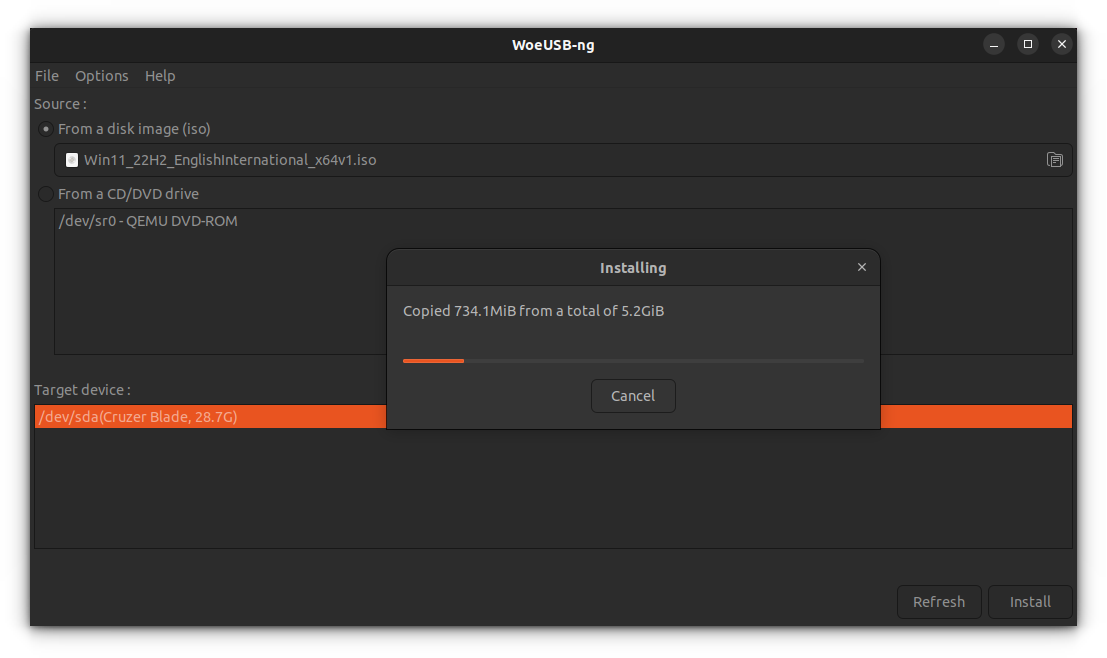
Once copying completes, WoeUSB will prompt a success dialog. You can now safely eject the USB and use it as a bootable USB.
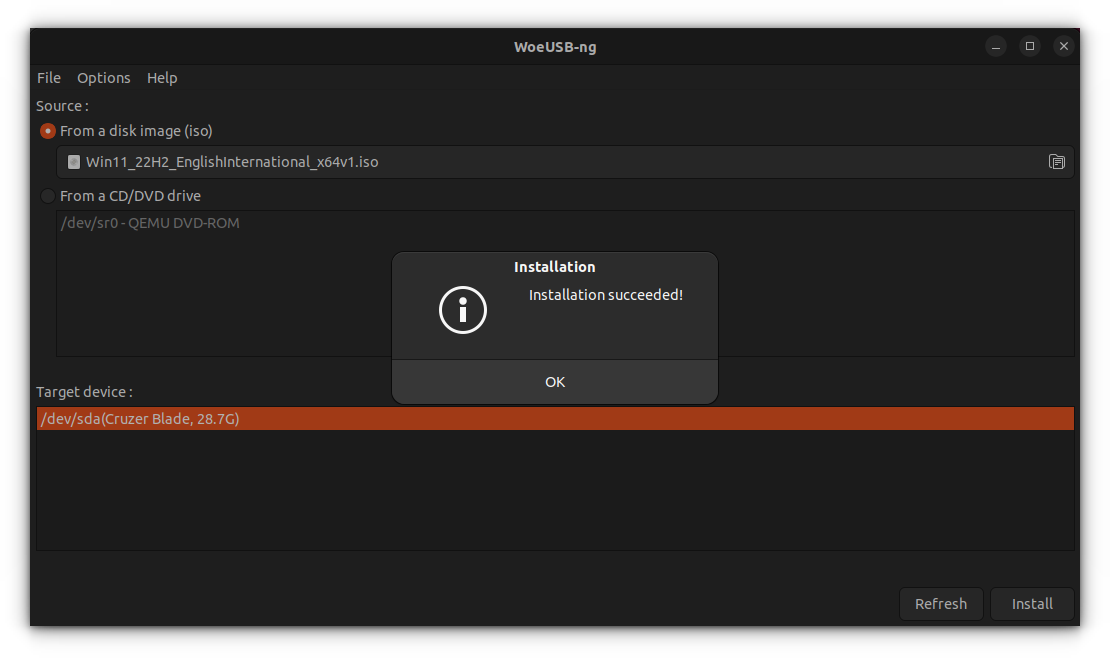
## Method 2: Using WoeUSB from the terminal (for experts)
WoeUSB-ng package also provides a command-line utility called woeusb.
To create the bootable Windows USB using WoeUSb, you need to run the following command:
`sudo woeusb --device <path/to/Windows/ISO> <name/of/the/USB/device> --target-filesystem ntfs`
Here, the `--device`
flag is used to wipe the USB and create a bootable from scratch completely. Also, the –target-filesystem flag is set to NTFS, to avoid problems of copying files more than the size limits of the FAT system.
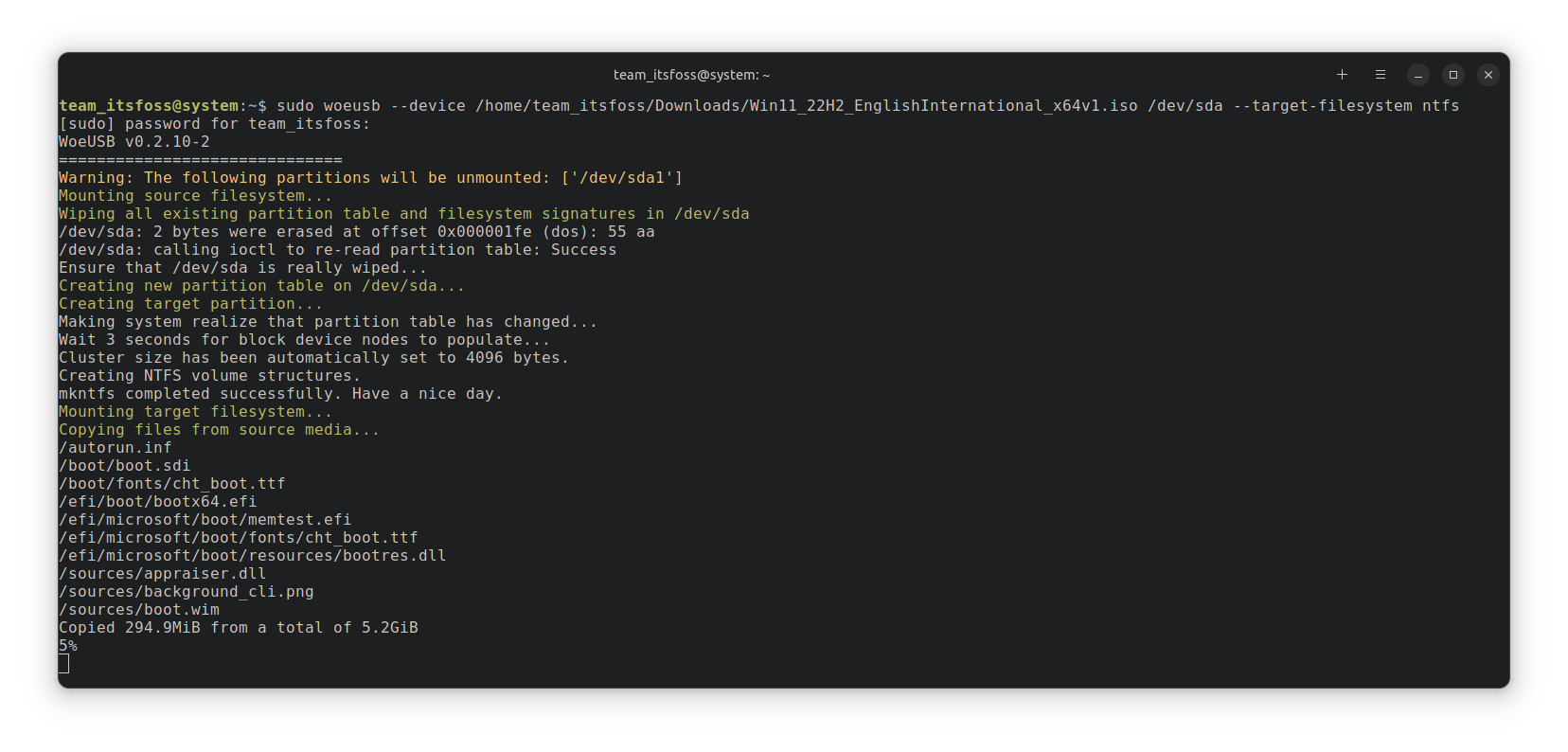
The process will take some time to complete copying. Once completed, it will display a success message.
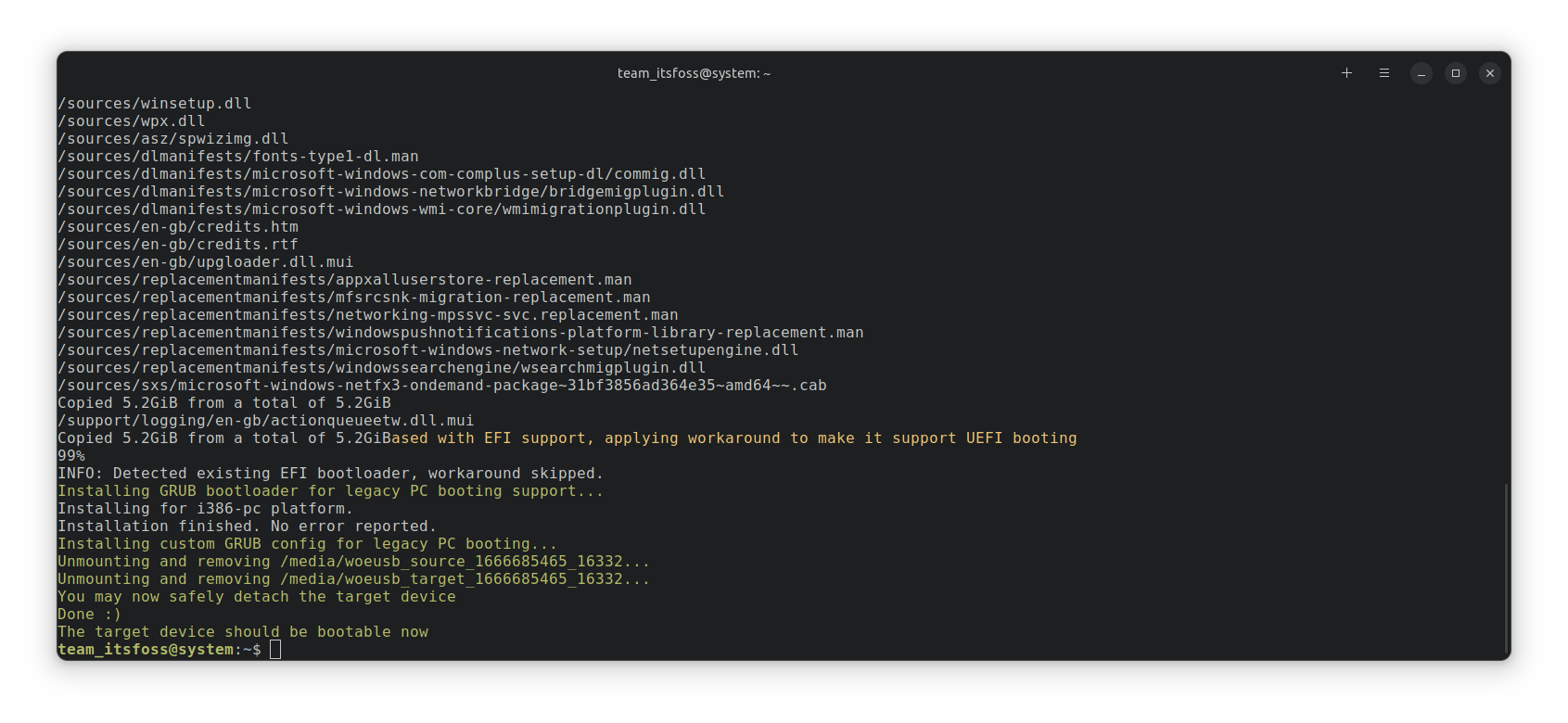
At this point, you can eject the USB safely and use it as a Windows bootable USB on other PCs.
## Bonus: Using WoeUSB Bash shell script (for experts)
WoeUSB is also available as a bash shell script, which can be used without installing anything on your system.
First, you want to download the shell script from the [releases page of the project](https://github.com/WoeUSB/WoeUSB/releases/tag/v5.2.4).
Before [executing the shell file](https://itsfoss.com/run-shell-script-linux/), you need to get the required dependencies. To install, run:
`sudo apt install wimtools`
Now make it executable either through file manager or through command-line.
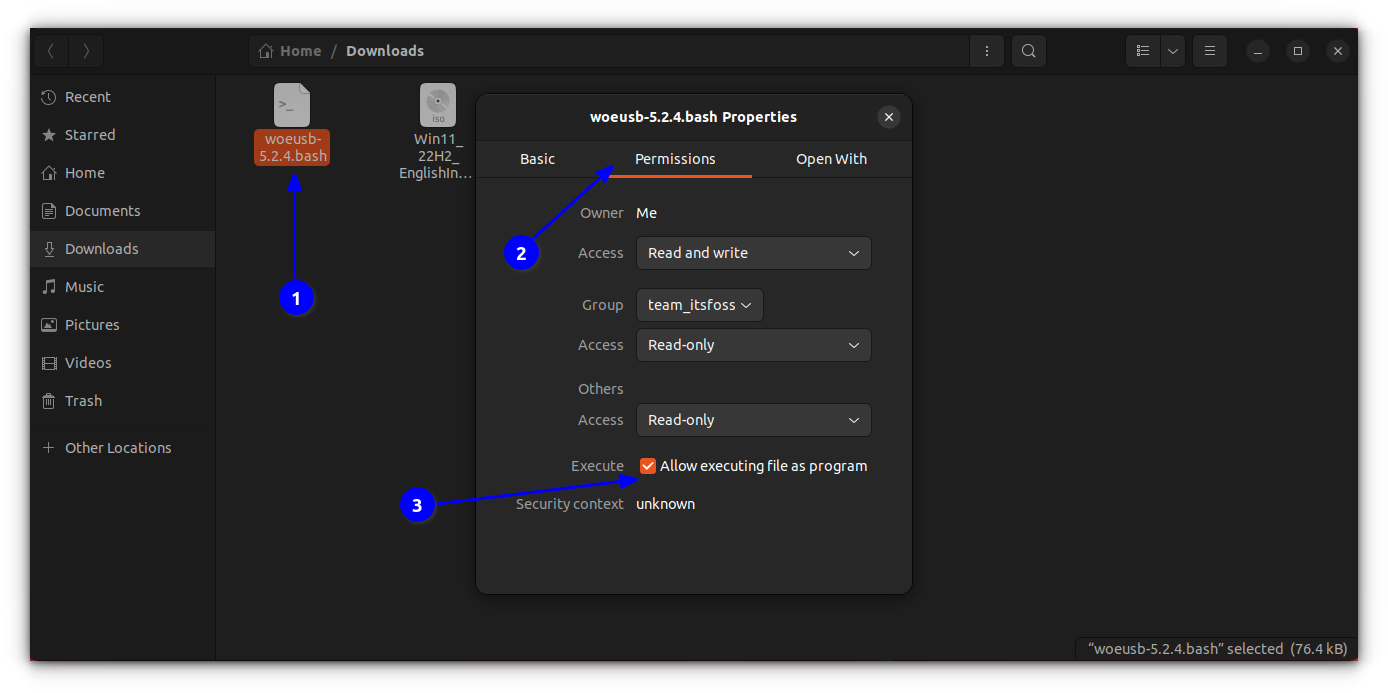
Or you can run `chmod +x <path/to/script>`
to make it executable. Now, run` ./woeusb-5.2.4.bash -h`
inside the downloaded directory to get help.
In order to create a live USB, the process is same as the command-line part of woeusb-ng, except, you are not installing anything.
So, in a terminal, run:
`sudo <path/to/downloaded/script/file> --device <path/to/windows/ISO> <name-of-USB-device> --target-filesystem ntfs`
This will start writing the ISO to USB drive, as shown in the screenshot below:
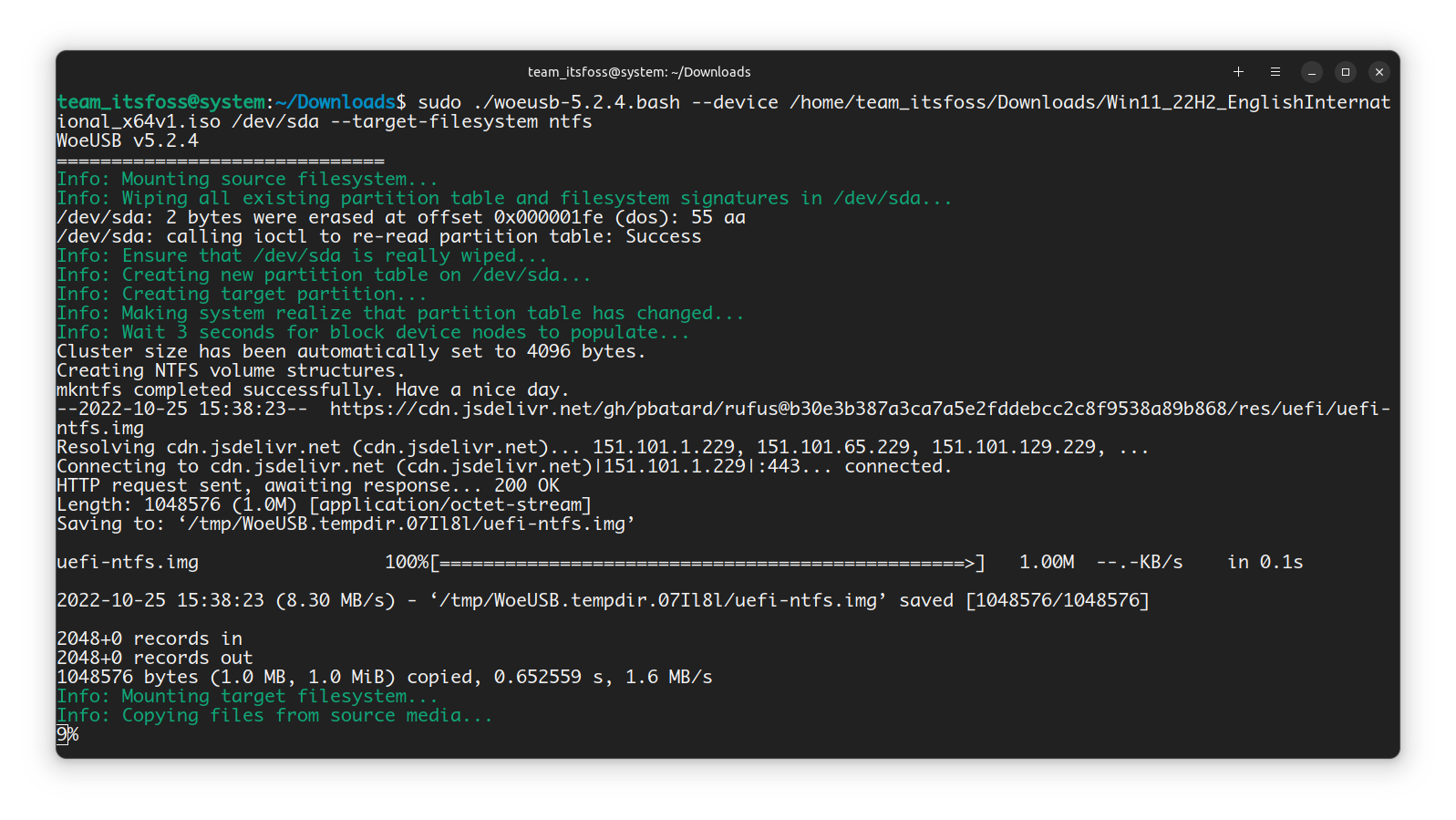
Once completed, you can safely eject the USB and use it as bootable USB.
## Removing WoeUSB
If you installed WoeUSB using PIP, you can also remove it similarly:
`pip3 uninstall WoeUSB-ng`
You can keep the installed dependencies on your system or remove them. That’s entirely up to you. I would suggest keeping them.
## Wrapping Up
WoeUSB was an immensely popular tool around ten years ago. It’s good that someone else has continued in another form. That’s the beauty of open source.
There are other ways of creating bootable Windows USB. If interested, check them out 👇
[How to Create a Bootable Windows 10 USB in LinuxBrief: This tutorial shows you how to create a bootable Windows 10 USB in Linux with and without a GUI tool called Ventoy. I have talked a lot about creating bootable USB of Linux in Windows. How about the other way round? How about creating a bootable Windows 10 USB](https://itsfoss.com/bootable-windows-usb-linux/)

I hope this tutorial helped you. If somehow the Windows USB created by WoeUSB doesn’t work as expected, you may [try using Ventoy](https://itsfoss.com/use-ventoy/). Enjoy it. |
15,219 | 如何清理 Snap 版本以释放磁盘空间 | https://www.debugpoint.com/clean-up-snap/ | 2022-11-06T08:29:00 | [
"磁盘空间",
"Snap"
] | /article-15219-1.html | 
>
> 这个带有脚本的快速指南有助于清理旧的 Snap 版本并释放 Ubuntu 系统中的一些磁盘空间。
>
>
>
我正在使用的 Ubuntu 测试系统中的磁盘空间不足。因此,我通过 GNOME 的磁盘使用分析器进行调查,以找出哪个包正在消耗宝贵的 SSD 空间。除了通常的缓存和主目录,令我惊讶的是,我发现 Snap 和 Flatpak 消耗了大量的存储空间。

尽管如此,我始终坚持一个规则:除非必要,否则不要使用 Snap 或 Flatpak。这主要是因为它们的安装尺寸和其他问题。我更喜欢原生 deb 和 rpm 包。多年来,我在这个测试系统中安装和移除了一定数量的 Snap 包。
但卸载后还有问题。Snap 在系统中保留了一些残留文件,一般用户不知道。
所以我打开了 Snap 文件夹 `/var/lib/snapd/snaps`,发现 Snap 保留了以前安装/卸载的软件包的旧版本。
例如,在下图中,你可以看到 GNOME 3.28、3.34 和 Wine 都被删除了。但它们还在那里。发生这种情况是因为 Snap 的设计,它在正确卸载后保留已卸载软件包的版本。

或者,你可以在终端中使用:
```
snap list --all
```

对于保留的版本,默认值为 3。这意味着 Snap 会保留每个软件包的三个旧版本,包括活动版本。如果你对磁盘空间没有限制,这是可以的。
但是对于服务器和其他情况,这很容易遇到成本问题,它会消耗你的磁盘空间。
但是,你可以使用以下命令轻松修改计数。该值可以在 2 到 20 之间。
```
sudo snap set system refresh.retain=2
```
### 清理 Snap 版本
在 SuperUser 的一篇文章中,Canonical 的前工程经理 Popey [提供了一个简单的脚本](https://superuser.com/a/1330590),它可以清理旧版本的 Snaps 并保留最新版本。
这是我们将用来清理 Snap 的脚本。
```
#!/bin/bash
#Removes old revisions of snaps
#CLOSE ALL SNAPS BEFORE RUNNING THIS
set -eu
LANG=en_US.UTF-8 snap list --all | awk '/disabled/{print $1, $3}' |
while read snapname revision; do
snap remove "$snapname" --revision="$revision"
done
```
将上面的脚本以 `.sh` 扩展名保存在一个目录中(例如 `clean_snap.sh`),赋予它可执行权限并运行。
```
chmod +x clean_snap.sh
```
当我运行脚本后,它减少了很多磁盘空间。该脚本还将显示要删除的包的名称。


### 结束语
对于 Snap 的设计效率如何,人们总是争论不休。许多人说,它的设计是坏的,是臃肿的,是消耗系统资源的。这种说法的某些部分是真实的,我不会否认它。如果实施和加强得当,整个沙盒应用的概念是很好的。但我相信,与 Snap 相比,Flatpak 工作做得更好。
也就是说,我希望这可以帮助你清理一些磁盘空间。尽管它只在 Ubuntu 中进行了测试,但它应该适用于所有支持 Snap 的 Linux 发行版。
此外,请查看我们关于 [如何清理 Ubuntu](https://www.debugpoint.com/2018/07/4-simple-steps-clean-ubuntu-system-linux/) 的指南以及其他步骤。
最后,如果你要清理 **Flatpak** 应用,请参阅 [这篇指南](https://www.debugpoint.com/clean-up-flatpak/)。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/clean-up-snap/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,220 | 用 git log 命令显示在特定日期的提交记录 | https://opensource.com/article/22/10/git-log-command | 2022-11-06T08:54:56 | [
"git"
] | /article-15220-1.html | 
>
> `git log` 命令是 Git 中一个很重要的查看提交记录的工具,它也是人们喜欢使用 Git 的原因之一。
>
>
>
`git log` 命令能够让你了解到更多关于贡献者 <ruby> 提交 <rt> commit </rt></ruby> 的记录。使用 `git log` 的一种方式是按日期查看提交记录 。要查看**在指定日期或日期范围内**创建的 Git 存储库中的提交记录,请使用带有选项 `--since` 或 `--until` 或者同时使用以上两个选项的 `git log` 命令。
首先,进入你要查看的分支(例如,`main` 分支):
```
$ git checkout main
```
接下来,你可以使用以下命令,来显示当前日期(即今天)的提交记录:
```
$ git log --oneline --since="yesterday"
```
仅显示某一特定用户(例如,用户 `Agil`)在今天的提交记录:
```
$ git log --oneline --since="yesterday" --author="Agil"
```
还可以显示在某一日期范围内的提交记录。使用以下命令,显示在任意两个日期之间(例如,2022 年 4 月 22 日至 2022 年 4 月 24 日)的提交记录:
```
$ git log --oneline --since="2022-04-22" --until="2022-04-24"
```
在上面这个例子中,会输出 2022 年 4 月 22 日至 2022 年 4 月 24 日期间,不包括 2022 年 4 月 22 日的所有提交记录。如果你想要包括 2022 年 4 月 22 日的提交记录,请将命令中的 `2022-04-22` 替换为 `2022-04-21`。
运行以下命令,能够显示某一特定用户(例如,用户 `Agil`)在两个指定的日期之间的提交记录:
```
$ git log --oneline --since="2022-04-22" --until="2022-04-24" --author="Agil"
```
### 总结
Git 有很多优点,其中一个优点就是 Git 让你能够收集你项目的相关数据。`git log` 命令是一个重要的查看提交记录的工具,也是人们喜欢使用 Git 的原因之一!
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/10/git-log-command>
作者:[Agil Antony](https://opensource.com/users/agantony) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
15,221 | 安卓开源项目(AOSP)现在兼容 RISC-V 了 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/11/the-android-open-source-project-is-now-risc-v-compatible/ | 2022-11-06T09:11:44 | [
"安卓",
"RISC-V"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15221-1.html |
>
> 安卓的一个重要进展是将<ruby> 安卓开源项目 <rt> Android Open Source Project </rt></ruby>(AOSP)移植到 RISC-V 处理器架构。
>
>
>

AOSP 已经开始在上游启用 RISC-V,这将促进 RISC-V CPU 在可穿戴设备、物联网,以及最终在智能手机和笔记本电脑中的使用。
为了开放生态系统,中国科学院 PLCT 实验室的工程师和软件开发人员在 2020 年开始将 Android 10 移植到 RISC-V 架构上。阿里巴巴的云计算部门和平头哥芯片子公司一起努力保持开发与最新的安卓版本同步。
“我们很高兴看到谷歌对构建针对 RISC-V 的 AOSP 的更多支持!阿里云一直致力于通过一系列的创新来支持 RISC-V 社区的发展,比如将安卓的基本功能移植到 RISC-V 上,这证明了在从多媒体到信号处理、设备互联和人工智能等场景中使用基于 RISC-V 的设备的可行性。”阿里云生态系统总监、RISC-V 国际组织的应用与工具水平委员会副主席 David Chen 博士说:“我们期待着与安卓团队合作,为繁荣的 RISC-V 社区做出贡献。”
通过增强 RISC-V 上的安卓系统的基本功能,在 2021 年,阿里云的专家们付出了巨大的努力,积极推动了软件生态系统的发展。 RISC-V on Android 的工作集中在 RISC-V Android 工作组和软件库中进行。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/11/the-android-open-source-project-is-now-risc-v-compatible/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *A crucial advancement for the technology is the porting of the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) to the RISC-V processor architecture.*
The AOSP has begun enabling RISC-V upstream, which will promote the use of RISC-V CPUs in wearables, the Internet of Things, and eventually smartphones and laptops.
In an effort to open up the ecosystem, engineers and software developers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ PLCT Lab started porting Android 10 to the RISC-V architecture in 2020. Together, Alibaba’s Cloud division and T-Head chip subsidiary have worked hard to maintain the development up to date with the latest Android releases.
“We are glad to see more support from Google for building AOSP targeting RISC-V! Alibaba Cloud has been committed to supporting the RISC-V community through a series of innovations, such as progressing the porting of basic Android functions onto RISC-V, which proves the feasibility of using RISC-V based devices in scenarios ranging from multimedia to signal processing, device interconnection, and artificial intelligence. We look forward to engaging with the Android team to contribute to the thriving RISC-V community down the road,” said Dr. David Chen, Director of Ecosystem from Alibaba Cloud and Vice Chair of the Applications & Tools Horizontal Committee at RISC-V International.
By enhancing the fundamental capabilities of Android on RISC-V, experts at Alibaba Cloud made a significant effort to actively assist the software ecosystem throughout 2021. The RISC-V Android Working Group and the software repository are where the RISC-V on Android efforts are concentrated. |
15,223 | 如何在 Ubuntu 和其他 Linux 中检查 CPU 和硬盘温度 | https://www.debugpoint.com/cpu-hdd-temperature-ubuntu/ | 2022-11-07T15:16:00 | [
"温度"
] | /article-15223-1.html | 
>
> 想知道如何在台式机或笔记本电脑上检查 Ubuntu 和其他 Linux 中的 CPU 和硬盘温度?这是一个快速指南。
>
>
>
如果你是普通用户,那么实际上不需要检查 CPU 或 HDD 温度。但是,如果你使用的是非常旧的硬件或轻薄型的硬件,你可能会遇到过热问题。因为这些薄的硬件内部紧密耦合在一起,无论做了多少传热机制,它都会升温。因此,必须监控硬件的温度。然而,现代 Linux 发行版能够通过软件传感器很好地处理过热情况。
### 在 Ubuntu 上监控 CPU 和硬盘温度的步骤
#### 使用终端
我们将使用几个包来实现相同的目的。在基于 Ubuntu 的系统中打开一个终端并安装以下内容。
```
sudo apt install hddtemp
sudo apt install lm-sensors
```
[hddtemp](https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/Hddtemp) 程序为你提供硬盘和 SSD (根据我的测试)的温度。 [lm-sensors](https://github.com/lm-sensors/lm-sensors) 包为你提供来自 CPU 和其他通过 PCI 端口访问的传感器的温度详细信息。
安装后,从终端运行以下命令。你需要知道你的磁盘标识符,例如 `/dev/sda` 或 `/dev/sdb` 等。
要找出磁盘标识符,你可以使用 `fdisk`。
```
sudo fdisk -l
```
然后运行以下命令检查 HDD 或 SSD 温度。
```
sudo hddtemp
```

*来自终端的 HDD 或 SSD 温度*
检查 CPU 温度和其他信息需要额外的步骤。
首先,运行以下命令,以便传感器程序可以检测到系统中的传感器。
```
sudo sensors-detect
```
上面的命令可能会问你一些是/否的问题。继续按回车选择默认选项。
完成后,运行以下命令查看 CPU 和其他接口温度。
```
sensors
```

*使用传感器*
#### 使用 GUI 工具
如果你更喜欢能完成上述所有操作的漂亮 GUI,你可以安装 [psensor](https://wpitchoune.net/psensor/)。该程序适用于 Linux 系统,例如 Ubuntu、Fedora、[Arch](https://www.debugpoint.com/tag/arch-linux) 和其他变体。它为你提供了漂亮的图形和表格视图:
Ubuntu 及其衍生版:
```
sudo apt install psensor
```
Fedora 和基于 RPM 的衍生版:
```
sudo dnf install psensor
```
Arch、Manjaro 和类似的衍生版:
```
pacman -S psensor
```
安装后,从终端运行 `psensor` 或从应用菜单启动它。
正如你在下面的截图中所见,它通过漂亮的图表让你可以很好地了解 CPU、GPU 和 HDD 的所有重要温度。使用它的首选项,你可以根据需要对其进行调整。这个轻量级的程序在很多情况下都会很有帮助。

*psensor 运行*
因此,这些是你可以在 Ubuntu 和其他 Linux 系统中监控 CPU、GPU 或 HDD 温度的一些方法。如果你知道其他方法,请通过下面的评论栏告诉我。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/cpu-hdd-temperature-ubuntu/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,224 | 使用 Pip 升级 Python 软件包 | https://itsfoss.com/upgrade-pip-packages/ | 2022-11-07T15:34:10 | [
"Python",
"Pip"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15224-1.html | 
你上次更新通过 Pip 安装的 Python 软件包是什么时候?大多数用户往往会忘记这些 Python 软件包也需要手动更新,因为仅仅更新系统存储库对于软件包来说是不起作用的。
因此,让我们花点时间看看如何使用 Pip,来更新旧的 Python 软件包吧。
### 如何使用 Pip 升级 Python 软件包
[Pip(Pip Installs Packages)](https://itsfoss.com/install-pip-ubuntu/) 是一个用于管理 Python 软件包的 <ruby> 命令行实用程序 <rt> command line utility </rt></ruby> 。你可以将 Pip 安装 Python 软件包,类比为在 Ubuntu 和 Debian 中使用 `apt` 管理软件包那样。
因此,接下来就让我们深入了解如何使用这个极好的工具 Pip,来管理与 Python 软件包相关的内容吧。
#### 1、列出过时的 Python 软件包
在计划更新什么软件包之前,我们先要列出有哪些过时的软件包,你可以在其中选择想要更新的软件包,因为大多数人不会想一下子更新整个软件包库。
要列出过时的 Python 软件包,你只需将 `pip` 命令与 `list` 选项、`--outdated` 标志一同使用即可,如下图所示:
```
pip list --outdated
```

#### 2、升级特定的软件包
获得可更新的软件包列表后,你可以像我之前提到的那样,选择你要更新的那个特定的软件包,pip 升级软件包命令的语法如下:
```
pip install package_name -U
```
例如,我想将名为 `anime-api` 的软件包升级到最新版本,所以我将使用下面的命令来升级:
```
pip install anime-api -U
```

#### 3、将软件包升级到特定的版本
没有必要总是使用软件的最新版本,如果你想将软件包升级到不是最新的某个特定版本,参考如下的命令语法:
```
pip install --upgrade <package>==<version>
```
例如,我想将名为 `xdg` 的软件包更新到 5.1 版本,5.1 版本是最新版本的前一个版本,所以可以使用以下命令:
```
pip install --upgrade xdg==5.1
```

#### 4、使用 Pip 一次性升级所有软件包
**请注意:我不建议你一次性升级所以软件包,因为 Python 软件包的依赖项太复杂了,一次性的升级无法处理相互依赖项。**
要一次性升级所有 python 软件包,你可以使用以下命令:
```
pip3 list --outdated --format=freeze | grep -v '^\-e' | cut -d = -f 1 | xargs -n1 pip3 install -U
```

上面的命令使用了 [xargs](https://linuxhandbook.com/xargs-command/)。首先,会得到所有需要更新的软件包,然后对每个软件包执行 `pip3 install -U` 命令。
我在这里使用的是 `pip3`,而不是 `pip`。在 Ubuntu 22.04 及更高的版本中,`pip` 和 `pip3` 命令都可以使用。
### 总结
使用 Pip 一次性更新所有 Python 软件包并不是一个好主意。我发现一次性更新后,软件包之间的依赖关系被破坏了,所以请确保只更新你想要更新的软件包。
如果你还有其他的疑问,就请在评论区中留言吧。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/upgrade-pip-packages/>
作者:[Sagar Sharma](https://itsfoss.com/author/sagar/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

When was the last that you updated Python packages installed via Pip? Most of the users tend to forget that those packages also need to be updated, as just updating the system repository is not going to work here.
So let’s take a moment and see how to update old Python packages with Pip.
## How to use pip to upgrade Python packages
[Pip (Pip Installs Packages)](https://itsfoss.com/install-pip-ubuntu/) is a command line utility to manage python packages. You can think of this as how we use apt to manage packages in Ubuntu and Debian.
So let’s dive deep into how you can use this fab utility to manage everything related to Python packages.
### 1. List outdated packages
Listing the outdated packages is the best idea to plan how you want to update packages as not many want to update their entire library of packages at once and wants to be selective.
To list outdated packages of Python, you just have to pair `pip`
command with `list`
option and `--outdated`
flag as shown:
`pip list --outdated`
### 2. Upgrade a specific package
Once you get the list of the packages that need to be updated, you can be selective as I mentioned earlier, and to update a specific package, you’ll need to follow the given command syntax:
`pip install package_name -U`
For example, I want to upgrade the package named `anime-api`
to the most recent version, so I’ll be using the given command:
`pip install anime-api -U`
### 3. Upgrade package to specific version
It is not necessary to use only the most recent version of the software (cough [Debian](https://www.debian.org/?ref=itsfoss.com) cough) and if you are in need of using packages to a specific version that may or may not be the most recent software, can be done using the given command syntax:
`pip install --upgrade <package>==<version>`
So I want to update the package named `xdg`
to version 5.1 which is one point release behind the most recent build so my command would be:
`pip install --upgrade xdg==5.1`
### 4. Upgrade every package using Pip
*While this is doable in theory,**I do not recommend upgrading every package at once as most of the time, the dependencies are too complex to be handled.*To upgrade every python package, you’d need to follow the given command:
`pip3 list --outdated --format=freeze | grep -v '^\-e' | cut -d = -f 1 | xargs -n1 pip3 install -U `
The above command utilizes [xargs](https://linuxhandbook.com/xargs-command/?ref=itsfoss.com). First, it will grab the packages that are needed to be updated and then perform `pip3 install -U`
command over each package.
And I used pip3 here instead of pip. In Ubuntu 22.04 and later, both pip and pip3 commands are available.
## Wrapping Up
Upgrading everything at once has never been a good idea in the case of pip. And I found myself in a state of broken dependencies so make sure you know what you will have.
Considering that [Ubuntu is deprecating the use of pip](https://itsfoss.com/externally-managed-environment/), it's better to start moving to Pipx instead.
[Install and Use pipx in Ubuntu & Other LinuxPipx addresses the shortcomings of the popular pip tool. Learn to install and use Pipx in Linux.](https://itsfoss.com/install-pipx-ubuntu/)

And if you have any queries, feel free to ask in the comments. |
15,226 | 如何在 Web 浏览器中启用深色模式 | https://www.debugpoint.com/dark-mode-browser/ | 2022-11-08T11:06:00 | [
"浏览器",
"深色模式"
] | /article-15226-1.html | 
>
> 本指南旨在帮助你在 Firefox、Chrome、Chromium 和 Edge 等流行的网页浏览器中启用深色模式。
>
>
>
我们都喜欢深色模式。与标准浅色模式相比,许多人更喜欢它。许多桌面应用原生提供深色模式,而一些应用则是通过桌面环境的底层模式适应深色模式。
不可否认,我们都在网页浏览器上花费了很多时间。我们很少使用桌面应用(除非你从事专门的工作,例如视频编辑等)。因此,当你花费大量时间在浏览器中阅读和学习时,你始终可以选择深色模式。不过,对于网页浏览器,启用深色模式的方法略有不同。
本指南为你提供了在 Firefox、Chromium、Chrome 和 Edge 浏览器中启用深色模式的简单步骤。
### 在网页浏览器中启用深色模式
#### 在 Firefox 中启用深色模式
打开 Firefox 并点击右上角的菜单。
单击 “<ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby> > <ruby> 扩展和主题 <rt> Extension and Themes </rt></ruby>”。
选择 “<ruby> 深色主题 <rt> Dark Theme </rt></ruby>” 并点击 “<ruby> 启用 <rt> enable </rt></ruby>”。你应该会看到深色模式已应用于 Firefox。

*在 Firefox 浏览器中启用深色模式*

*深色模式下的 Firefox*
要将其还原,请按照相同的步骤并选择浅色主题。
#### Chromium 和 Chrome 中的深色模式
默认情况下,Chromium 或 Chrome 不会预安装任何深色主题。因此,你需要前往 Chrome 应用商店并下载你想要的深色主题。对于本指南,我会推荐超过一百万用户使用的 “Morpheon Dark” 主题。
从 Chromium 浏览器打开 Morpheon Dark 主题页面(以下链接)。
>
> **[Chrome 应用商店中的 Morpheon Dark 主题](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/morpheon-dark/mafbdhjdkjnoafhfelkjpchpaepjknad?hl=en-GB)**
>
>
>
点击 “<ruby> 添加到 Chrome <rt> Add To Chrome </rt></ruby>” 按钮。它应该会在 Chrome 中启用。
你可能想探索 Chrome 应用店中提供的其他深色或浅色主题。 [访问此页面获取所有深色主题的集合](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/category/collection/dark_themes)。
但是,你应该要记住的一件事是:此主题不会更改设置或上下文菜单,这是显而易见的。因为它只是改变了浏览器窗口,而这些菜单(有时)是操作系统本身的一部分。

*Chromium 深色主题*
对 Chrome 浏览器也遵循相同的步骤。
#### Edge 浏览器 – 深色模式
但是,[Edge 浏览器](https://www.debugpoint.com/2020/10/how-to-install-edge-ubuntu-linux/) 默认带有更好的深色主题。它允许你从设置中使用 GTK+、浅色和深色模式。
打开 Edge 浏览器,点击右上角的三个小点。
转到 “<ruby> 外观 <rt> Appearance </rt></ruby>” 并选择 “<ruby> 深色 <rt> Dark </rt></ruby>”。这样应该就好了。
Edge 的这种深色主题实现更好,因为它改变了上下文菜单和地址栏。

*深色主题的 Edge*
### 总结
如果你是高级用户,你可能不需要本指南。你可以自己弄清楚。
但我们为所有读者涵盖了所有基础到高级教程。许多新的 Linux 用户可能不知道如何在浏览器中启用深色模式。
所以,就是说,我希望这对你和其他人有帮助。如果你遇到任何问题,请在下面的评论框中告诉我。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/dark-mode-browser/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux 中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,227 | 我们如何建立一个开源的设计系统来创造新的社区徽标 | https://opensource.com/article/21/4/ansible-community-logos | 2022-11-08T12:32:00 | [] | https://linux.cn/article-15227-1.html |
>
> 了解 Ansible 的新徽标是如何根据相关人员的意见开发的,以确保整个项目的品牌一致性。
>
>
>

作为红帽的用户体验(UX)设计和 Ansible 产品团队的交互设计师,我们花了大约 6 个月的时间为 Ansible 社区设计了一系列徽标。这件事其实在更早的时候就开始了,当时一位项目经理要求我们为一个幻灯片提供一个 “快速而简单” 的徽标。在收集了一些需求后,我们在几天内就向相关人员展示了一个徽标,而且没有经过太多调整。几个月后,另一个相关人员说他们也需要类似的徽标,所以我们重复了这个过程。
于是,我们注意到一个模式:像这样的徽标资源不仅仅代表个人的要求,而是整个 Ansible 项目的共同需要。在完成了几个徽标要求后,我们有了一系列临时的设计,但在没有意识到品牌和设计惯例的情况下,这可能给整个 Ansible 的品牌视觉造成了不一致。随着这个徽标系列的增加,我们认识到了这个迫在眉睫的问题,并需要解决它。
我们的解决方案是创建一个 Ansible 设计系统,这是一个针对品牌的资源,可以指导未来一致的徽标设计。
### 什么是设计系统?
设计系统是一个可重复使用的资源和指导方法的集合,有助于告知任何数字产品套件的视觉语言。设计系统创造了一些模式,将独立的产品整合在一起,并通过可扩展性和一致性提升品牌。
特别是在一个有多种产品的大公司里,如果没有标准化,扩展起来就不容易,因为不同的团队对每个产品都有贡献。设计系统可以作为每个团队建立新资产的基线。有了标准化的外观和感觉,产品在整个组合中被统一为一个家族。
### 从头构建一个设计系统
在收到相关人员提出的为 Ansible 开源社区(如 Ansible Builder、Ansible Runner 和Project Receptor)创建徽标的一系列要求后,我们决定为我们的工作流程设计一个结构,并创建一个单一的事实来源,为之努力。
首先,我们对现有的徽标进行了视觉审计,以确定我们要做的是什么。Ansible 的原始徽标系列由四个主要图像组成:代表 AWX 的 Angry Spud,代表 Ansible 核心/引擎的 Ansibull,以及代表 AWX 的带翅膀的显示器。大部分的徽标都是用一致的红色阴影和公牛的形象联系在一起的,但是笔画的宽度、笔画的颜色、线条的质量和排版复杂而多样。

Angry Spud 使用棕褐色的轮廓和手绘风格,而 Ansibull 则是一个对称的几何矢量图。AWX 显示器是一个异类,它有细线画的翅膀,蓝色的矢量矩形,以及古英语字体(这里没有包括在内,但与家族中其他使用现代无衬线的字体相比,它是一个例外)。
### 确立新的设计标准
考虑到调色板、排版和图像,我们产生了一个一致的构图,以 Ansibull 代表所有核心的 Ansible 产品,以及大胆的线条和充满活力的颜色。

新的 Ansible 社区徽标设计风格指南详细说明了 Ansible 产品徽标的调色、排版、尺寸、间距和徽标变化。
新的风格指南展示了一种全新的、现代的定制字体,该字体基于瑞士独立字体厂商 [Grilli Type](https://www.grillitype.com/) 的 GT America 字体。我们为该字体创造了一个柔和的外观,通过圆润每个字母某些角落来配合图像的圆润度。
我们决定通过在光谱中加入更多的颜色并以原色为基础,设计一个更生动、更饱和、更普遍的调色板。新的调色板以浅蓝色、黄色和粉红色为主色调,每种颜色都有较浅的高光和较深的阴影。这种更广泛的颜色范围使系统内有更多的灵活性,并引入了 3D 的外观和感觉。

我们还引入了新的图像,如 Receptor 和 AWX 徽标中的六边形,以保持视觉上的连续性。最后,我们确保每个徽标在浅色和深色背景上都能使用,以获得最大的灵活性。
### 拓展设计组合
一旦我们建立了核心徽标系列,我们就开始为 Ansible 服务创建徽章,如 Ansible Demo 和 Ansible Workshop。为了将服务与产品区分开来,我们决定将服务图形包围在一个圆圈中,圆圈中包含了相同的定制排版的服务名称。新的服务徽章显示了幼儿版的 Ansibull(来自 Ansible Builder 的徽标)正在完成与每个服务相关的任务,例如 Ansible Demo 指向白板,Ansible Workshop 则使用构建工具。

### 利用开放源码进行设计决策
最初的 AWX 徽标受到了摇滚乐图像的影响,如翅膀和重金属字体(此处省略)。

(Fiona Lin and Taufique Rahman, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
Ansible 社区的一些成员,包括红帽多样性和包容性小组,提请我们注意,这些元素类似于仇恨团体使用的图像。
考虑到原徽标的社会影响,我们必须迅速与 Ansible 社区合作,设计一个替代徽标。我们没有像最初的徽标那样闭门造车,而是扩大了项目的范围,仔细考虑了更多的相关人员,包括 Ansible 社区、红帽多样性和包容性小组,以及红帽法律团队。
我们开始了头脑风暴,向 Ansible 开源社区征求意见。Ansible 的一位工程师 Rebeccah Hunter 在草图绘制阶段做出了贡献,后来成为我们设计团队中的一员。让一大群相关人员参与进来的挑战之一是,我们对新的徽标概念有了各种各样的想法,比如一条辅助电缆、一碗拉面等等。
我们勾画了五个社区贡献的徽标创意,每个徽标都有不同的品牌视觉:一个芽、一个火箭、一个显示器、一碗拉面和一个辅助电缆。

在完成这些初步的概念草图后,我们建立了一个虚拟的投票机制,并在整个迭代过程中使用。这个投票系统使我们能够利用社区的反馈,从五个初始概念缩小到三个:火箭、一碗拉面和显示器。我们在这三个方向上进一步迭代,并通过专门的 Slack 频道进行反馈,直到我们找到一个符合社区愿景的方向,即 AWX 显示器。

以社区的意见为指导,我们围绕显示器为 AWX 打造了徽标概念。我们保留了原徽标中的显示器元素,同时使其外观和感觉现代化,以配合我们更新的设计系统。我们使用了更鲜艳的色调,更简洁的无衬线字体,以及来自 Project Receptor 徽标的元素,包括六角形图案。
通过从一开始就与我们的社区接触,我们能够在公开场合进行设计和迭代,所有相关人员都有一种包容感。最后,我们认为这是取代一个有争议的徽标的最好方法。最终的版本被移交给了红帽法律团队,在获得批准后,我们用这个新的徽标替换了所有的现有资产。
### 主要收获
为设计系统创建一套规则和资源,使你的数字产品全面保持一致,消除品牌混乱,并实现可扩展性。
当你探索在自己的社区建立一个设计系统时,你可能会从我们在这条路上学到的这些关键经验中受益:
* 用设计系统来扩展新的徽标,比没有设计系统要容易得多。
* 当你使用投票系统来验证结果时,杂乱无章的设计方案就会变得不那么令人生畏。
* 将大量受众的注意力引向三套方案,可以消除决策疲劳,集中社区反馈。
我们希望这篇文章能够提供用于开源社区的设计系统的启示,并帮助你认识到在早期开发一个系统的好处。如果你正在创建一个新的设计系统,你有什么问题?如果你已经创建了一个,你学到了什么教训?请在评论中分享你的想法。
*(图像来自:Fiona Lin and Taufique Rahman, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/4/ansible-community-logos>
作者:[Fiona Lin](https://opensource.com/users/fionalin) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[MareDevi](https://github.com/MareDEvi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | As interaction designers on Red Hat's User Experience (UX) Design and Ansible product teams, we worked for about six months to build a logo family with the Ansible community. This journey started even earlier when a project manager asked us for a "quick and easy" logo for a slide deck. After gathering a few requirements, we presented a logo to the stakeholders within a few days and without much need for iteration. A few months later, another stakeholder decided they would also benefit from having imagery for their materials, so we repeated the process.
At this point, we noticed a pattern: logo resources like these no longer represented individual requests but rather a common need across the Ansible project. After completing several logo requests, we had built a makeshift series that—without conscious branding and design conventions—created the potential for visual inconsistencies across the Ansible brand. As the logo collection grew, we recognized this looming problem and the need to combat it.
Our solution was to create an Ansible design system, a brand-specific resource to guide consistent logo design well into the future.
## What is a design system?
A design system is a collection of reusable assets and guidelines that help inform the visual language of any digital product suite. Design systems create patterns to bring separate products together and elevate brands through scalability and consistency.
Especially in a large corporation with multiple products in the portfolio, scaling does not come easily without standardization as different teams contribute to each product. Design systems work as a baseline for each team to build new assets on. With a standardized look and feel, products are unified as one family across the portfolio.
## Getting started building a design system
After receiving a series of requests from stakeholders to create logos for the open source Ansible community, such as Ansible Builder, Ansible Runner, and Project Receptor, we decided to design a structure for our workflow and create a single source of truth to work for moving forward.
First, we conducted a visual audit of the existing logos to determine what we had to work with. Ansible's original logo family consists of four main images: the Angry Spud for AWX, the Ansibull for Ansible Core/Engine, and the monitor with wings for AWX. Most of the logos were tied together with a consistent shade of red and bull imagery, but the stroke width, stroke color, line quality, and typography were vast and varied.

(Fiona Lin and Taufique Rahman, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The Angry Spud uses a tan outline and a hand-drawn style, while the bull is a symmetrical, geometric vector. The AWX monitor was the outlier with its thin line-art wings, blue vector rectangle, and Old English typeface (not included here, but an exception from the rest of the family, which uses a modern sans serif).
## Establishing new design criteria
Taking color palette, typography, and imagery into consideration, we generated a consistent composition that features the Ansibull for all core Ansible products, along with bold lines and vibrant colors.

(Fiona Lin and Taufique Rahman, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The new Ansible community logo design style guide details the color palette, typography, sizing, spacing, and logo variations for Ansible product logos.
The new style guide presents a brand new, modern custom typeface based on GT America by [Grilli Type](https://www.grillitype.com/), an independent Swiss type foundry. We created a softer look for the typeface to match the imagery's roundedness by rounding out certain corners of each letter.
We decided to curate a more lively, saturated, and universal color palette by incorporating more colors in the spectrum and basing them on primary colors. The new palette features light blue, yellow, and pink, each with a lighter highlight and darker shadow. This broader color scope allows more flexibility within the system and introduces a 3D look and feel.

(Fiona Lin and Taufique Rahman, CC BY-SA 4.0)
We also introduced new imagery, such as the hexagons in the Receptor and AWX logos for visual continuity. Finally, we made sure each logo works on both light and dark backgrounds for maximum flexibility.
## Expanding the design portfolio
Once we established the core logo family, we moved onto creating badges for Ansible services, such as Ansible Demo and Ansible Workshop. To differentiate services from products, we decided to enclose service graphics in a circle that contains the name of the service in the same custom typography. The new service badges show the baby Ansibull (from the Ansible Builder logo) completing tasks related to each service, such as pointing to a whiteboard for Ansible Demo or using building tools for Ansible Workshop.

(Fiona Lin and Taufique Rahman, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Using open source for design decisions
The original AWX logo was influenced by rock-and-roll imagery, such as the wings and the heavy metal typeface (omitted from the image here).

(Fiona Lin and Taufique Rahman, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Several members of the Ansible community, including the Red Hat Diversity and Inclusion group, brought to our attention that these elements resemble imagery used by hate groups.
Given the social implications of the original logo's imagery, we had to work quickly with the Ansible community to design a replacement. Instead of working in a silo, as we did for the initial logos, we broadened the project's scope to carefully consider a wider range of stakeholders, including the Ansible community, Red Hat Diversity and Inclusion group, and Red Hat Legal team.
We started brainstorming by reaching out to the Ansible open source community for ideas. One of the Ansible engineers, Rebeccah Hunter, contributed in the sketching phase and later became an embedded part of our design team. Part of the challenge of involving a large group of stakeholders was that we had a variety of ideas for new logo concepts, ranging from an auxiliary cable to a bowl of ramen.
We sketched five community-surfaced logos, each featuring a different branded visual: a sprout, a rocket, a monitor, a bowl of ramen, and an auxiliary cable.
(Fiona Lin and Taufique Rahman, CC BY-SA 4.0)
After completing these initial concept sketches, we set up a virtual voting mechanism that we used throughout the iteration process. This voting system allowed us to use community feedback to narrow from five initial concepts down to three: the rocket, the bowl of ramen, and the monitor. We further iterated on these three directions and presented back, via a Slack channel dedicated to this effort, until we landed on one direction, the AWX monitor, that aligned with the community's vision.

(Fiona Lin and Taufique Rahman, CC BY-SA 4.0)
With community voices as our guide, we pursued the monitor logo concept for AWX. We preserved the monitor element from the original logo while modernizing the look and feel to match our updated design system. We used a more vibrant color palette, a cleaner sans-serif typeface, and elements, including the hexagon motif, from the Project Receptor logo.
By engaging with our community from the beginning of the process, we were able to design and iterate in the open with a sense of inclusiveness from all stakeholders. In the end, we felt this was the best approach for replacing a controversial logo. The final version was handed off to the Red Hat Legal team, and after approval, we replaced all current assets with this new logo.
## Key takeaways
Creating a set of rules and assets for a design system keeps your digital products consistent across the board, eliminates brand confusion, and enables scalability.
As you explore building a design system with your own community, you may benefit from these key takeaways we learned along our path:
- Scaling new logos with a design system is a much easier process than without one.
- Juggling design options becomes less daunting when you use a polling system to validate results.
- Directing a large audience's attention on sets of three eliminates decision fatigue and focuses community feedback.
We hope this article provides insight into designing a system with an open source community and helps you recognize the benefit of developing a system early in your process. If you are creating a new design system, what questions do you have? And if you have created one, what lessons have you learned? Please share your ideas in the comments.
## Comments are closed. |
15,228 | 前瞻:Xfce 4.18 主要新功能 | https://www.debugpoint.com/xfce-4-18-features/ | 2022-11-08T15:32:00 | [
"Xfce"
] | /article-15228-1.html |
>
> 有关 Xfce 4.18 的核心和原生应用程序的功能的全面介绍。
>
>
>
经过近两年的开发,Xfce 4.18 将在 2022 年圣诞节期间发布。作为 [Xfce 4.16](https://www.debugpoint.com/xfce-4-16-review/) 以来的重要的版本,其一直在开发标签 4.17 下进行开发,以增强这个轻量级桌面。
考虑到 GTK4 的更新、初步的 Wayland 支持,以及核心和本地应用程序的改进,Xfce 4.18 是一个重要的里程碑版本,其带来了大量更新。
从发布时间来看,第一个 Xfce 4.18 预发布版(pre1)已经发布。2022 年 12 月的第一周会有另一个预发布版。而 Xfce 4.18 的最终版本预计将在 2022 年 12 月 15 日至 12 月 29 日之间发布。
由于目前还没有官方的详细介绍,我在这篇文章中总结了 Xfce 4.18 的基本和主要功能。
请继续阅读。

### Xfce 4.18 的新功能
#### 1、核心库更新
Xfce 4.18 的依赖关系有所改变,并使用以下版本进行编译:
* glib-2.0 >= 2.66
* gtk >= 3.24
* libcairo >= 1.16
* gdk-pixbuf-2.0 >= 2.40
* gobject-introspection >= 1.66
#### 2、桌面和面板
顶部的主面板带来了新的设置和调整。但整体外观仍与以前的 4.16 版本中的一样。一些默认的面板小程序在这个版本中也有变化。桌面图标、右键上下文菜单和项目保持不变。
面板的首选项设置有两个新的选项。首先,面板的长度现在以**像素**设置,而不是百分比。其次,一个新的选项,“<ruby> 保持面板在窗口上方 <rt> Keep panel above windows </rt></ruby>” ,可以让你将窗口对话放到面板后面。之前,应用程序的窗口只能达到面板的边缘。

彻底修改了时钟小程序的设置。是的,你终于可以改变 Xfce 时钟小程序的字体风格。与此同时,它提供了四种时钟布局:
* 只有日期
* 只有时间
* 日期和时间
* 时间和日期
此外,你还可以向日历中添加命令。

#### 3、Thunar 文件管理器
也许这个版本中最令人兴奋的变化是 Thunar 文件管理器的功能。首先,一个新的“搜索”图标取代了工具栏上的“重新加载”按钮。当点击时,它会在地址栏上出现搜索,可以使用你的搜索关键词进行递归搜索。重新加载按钮被放到了 “<ruby> 查看 <rt> View </rt></ruby>” 菜单中。
其次,在左边的导航栏上增加了一个的新项目,“<ruby> 最近 <rt> Recent </rt></ruby>”。在底部,元数据更有条理(从逗号分隔改为竖线分隔),还有一个新的上下文菜单项可以选择你想要显示的元数据。

Thunar 的主菜单有很多变化。下面列出了主要的变化。在下面的图片中还标注了自 4.16 以来的变化。
* 引入了一个**新的书签菜单**,可以将当前文件夹作为快捷方式添加到侧边栏。
* “<ruby> 编辑 <rt> Edit </rt></ruby>”菜单有了 “<ruby> 撤销 <rt> undo </rt></ruby>” 和 “<ruby> 重做 <rt> redo </rt></ruby>” 选项。
* “<ruby> 前往 <rt> Go </rt></ruby>” 菜单有了 “<ruby> 最近 <rt> Recent </rt></ruby>” 和 “<ruby> 搜索 <rt> Search </rt></ruby>” 的选项。
Thunar 首次通过 “<ruby> 视图 <rt> View </rt></ruby>”菜单项有了“<ruby> 分割视图 <rt> Split view </rt></ruby>”! 是的,你现在可以在视图面板中拖放项目。
前不久,我 [报道](https://debugpointnews.com/thunar-image-preview/) 说图像预览即将在 Thunar 中出现。而它终于来了。作为谷歌代码之夏 2022 的部分开发成果,你现在可以嵌入在侧边栏中看到图片预览。或者在右边的一个独立的新面板上查看。它可以通过偏好设置来改变。
下面是它的外观。


#### 4、Thunar 的首选项
Thunar 设置中出现了大量调整。首先,一个新的选项卡可以为 Thunar 定制你的键盘快捷键。你可以直接指定新的快捷键组合,并从这个选项卡中改变现有的快捷键组合。

“<ruby> 显示 <rt> Display </rt></ruby>” 设置中新增了一个缩略图部分,你现在可以指定缩略图的文件大小。缩略图的具体设置也被归为一组。

“<ruby> 侧面板 <rt> Side Pane </rt></ruby>” 选项卡有了一个新的图像预览选项,你在上面看到过。你可以设置为嵌入式或独立式预览。此外,“<ruby> 行为 <rt> Behaviour </rt></ruby>” 选项卡增加了 “<ruby> 启动时恢复选项卡 <rt> restore tabs on startup </rt></ruby>” 和在选项卡标题中显示 “<ruby> 完整的目录路径 <rt> full directory path </rt></ruby>” 的选项,这将有很大帮助。
“<ruby> 高级 <rt> Advanced </rt></ruby>” 选项卡为 “<ruby> 文件传输 <rt> File Transfer </rt></ruby>” 提供了一个新的设置部分,有两个新的选项:“<ruby> 中间文件复制 <rt> Intermediate file copy </rt></ruby>”和“<ruby> 验证校验和 <rt> Verify checksum </rt></ruby>”。此外,在这个选项卡中还增加了一个新的递归搜索的选项。你还可以通过以下选项将 Thunar 设置为直接 “<ruby> 执行 Shell 脚本 <rt> Execute Shell script </rt></ruby>”。

除了上述变化外,文件夹属性对话框现在可以显示文件和文件夹的数量。另外,一个新的高亮选项使你能够为你的文件夹图标背景和前景选择任何自定义颜色。如果你有一个复杂的文件夹结构,这将使你能够快速导航。
下面是它的外观。

#### 设置
“<ruby> 外观 <rt> Appearances </rt></ruby>” 设置现在允许你打开和关闭对话框的标题栏。
“<ruby> 桌面 <rt> Desktop </rt></ruby>” 设置允许文件上下文菜单中的删除选项(打开或关闭)。
“<ruby> 显示 <rt> Display </rt></ruby>” 设置现在允许你为多种显示情况设置默认值:镜像、扩展显示还是什么都不做。早些时候,这些选项在显示器被连接时才可用。
#### Wayland 和其他更新
除了上述 Xfce 4.18 的功能外,窗口管理器和桌面还有许多额外的错误修复和性能改进。这些都是在底层的,你应该能感受到一个更精良的 Xfce 桌面体验。
Xfce 桌面核心和原生应用程序的 Wayland 迁移工作开始了。离它完全准备好还有很长的路要走。在这个版本中,你可能不会看到很多 Wayland 的更新。然而,许多应用程序在 Wayland 下已经可以正常工作了。你可以在 [本页](https://wiki.xfce.org/releng/wayland_roadmap) 了解更多关于迁移状态的信息。
### 下载及什么时候出现在发行版
Xfce 4.18 应该会在 2023 年 4 月进入 Ubuntu 23.04 Lunar Lobster,并在 Fedora 38 中出现。基于滚动发布的发行版,如 Arch Linux、Manjaro 和 OpenSUSE Tumbleweed 应该会在 2022 年 12 月发布后的几天内得到它。轻量级的流行发行版 [MX Linux](https://www.debugpoint.com/tag/mx-linux) 应该在 2023 年采用这个版本,这个时候也是 Debian Bookworm 更新的时候。
Xfce 4.18 的第一个预发布版本 [现已发布](https://www.reddit.com/r/xfce/comments/yjiwwv/announce_xfce_418pre1_released/)。你可以从下面的页面下载源码压缩包,并编译它们。请参考官方的 [编译指南](https://docs.xfce.org/xfce/building)。
>
> **[下载 Xfce 4.18 源代码(pre1)](https://archive.xfce.org/xfce/4.18pre1/fat_tarballs)**
>
>
>
### 总结
总的来说,变化的数量巨大。许多核心变化和需要的变化都进入了这个版本。Thunar 文件管理器的更新是早该进行的,对于 Xfce 的爱好者来说应该是完美的。
随着 Wayland 的支持,未来的 Xfce 版本可能会带来一个可行的 Xfce 版本。Wayland 的支持仍在进行中,每个组件都有许多决定有待作出。许多发行版和关键部署仍然喜欢 Xfce 而不是 KDE Plasma 或 GNOME。考虑到这些用例和未来的路线图,Xfce 4.18 是下一个版本之前的一个重要的里程碑。
列表中你最喜欢的功能是什么?请在评论栏里告诉我。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/xfce-4-18-features/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,230 | 如何在 Ubuntu 等 Linux 中安装 Python 3.11 | https://www.debugpoint.com/install-python-3-11-ubuntu/ | 2022-11-09T08:45:00 | [
"Python"
] | /article-15230-1.html |
>
> 打算为你的项目开发工作安装 Python 3.11?下面是如何在 Ubuntu 等发行版中安装 Python 3.11 的方法。
>
>
>

Python 3.11 于 2022 年 10 月 25 日发布,并声称比之前的 [Python 3.10](https://www.debugpoint.com/install-python-3-10-ubuntu/) 版本快 10% - 60%。
一如既往,3.11 中的功能和改进列表明显较多。下面是一个简介:
* 错误回溯更明确,可以指出导致错误的确切语句。
* 引入异常组和新的 except\* 语法。
* 你可以在基础表达式中添加自定义文本,以便在你的代码中更好地处理错误。
* 引入 Variadic 泛型,允许在 Python 数值库(如 NumPy)中使用类似数组的结构。
* 字典类型 TypedDict 得到了改进,现在你可以指定个别字典项目是必须的还是可选的。
* 引入了 Self 注解,允许类返回它们自己的类型实例。
还有很多,你可以在官方的 [3.11 亮点页面](https://docs.python.org/3.11/whatsnew/3.11.html) 上详细了解。
### Linux 发行版中的当前 Python 版本
[Ubuntu 22.04 LTS](https://www.debugpoint.com/ubuntu-22-04-review/) 带有 Python 3.10,而最近发布的 [Ubuntu 22.10 Kinetic Kudu](https://www.debugpoint.com/ubuntu-22-10/) 也是同样的版本。然而, Kinetick Kudu 可能会在几周内采用 3.11。
另外,[Fedora 37](https://www.debugpoint.com/fedora-37/) 已经有了 Python 3.11 RC2,并将提供该版本。
所以,如果你正在运行 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS、[Linux Mint 21](https://www.debugpoint.com/linux-mint-21-review/) 或任何基于 Ubuntu-LTS 的发行版,这里是你如何通过 PPA 安装 Python 3.11 的方法。
**注意**:谨慎地使用这个方法。确保你知道你在做什么,因为替换 Linux 发行版的基础 Python 版本可能会导致系统不稳定。许多默认的应用程序和软件包都依赖于 3.10 版本。
### 如何在 Ubuntu 和相关发行版中安装 Python 3.11
打开终端提示,添加以下 PPA:
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
```
使用下面的命令刷新缓存:
```
sudo apt update
```
并使用下面的命令安装 Python 3.11:
```
sudo apt install python3.11
```

### 设置默认的 Python 版本
理论上,你可以在 Linux 发行版中安装多个版本的 Python,但只能默认一个版本。将 Python 3.11 设置为默认版本需要一些额外的步骤。请跟我做。
然而,在这之前,请确保你知道哪些应用程序依赖于 Python 3.10。你可以使用 `apt-cache rdepends` 命令轻松地找到它,如下所示:
```
debugpoint@debugpoint-22-04:~$ apt-cache rdepends python3.10
python3.10
Reverse Depends:
python3.10-dbg
python3.10-venv
python3.10-full
libpython3.10-testsuite
idle-python3.10
idle-python3.10
python3.10-minimal
python3.10-doc
python3.10-dev
python3
[截断]
python3
python3-uno
python3-all
gedit
```
#### 使用 Python 3.11 作为默认的 Python3
首先,从终端使用以下命令检查当前的默认版本:
```
python3 --version
```
使用 `update-alternatives` 来创建 `python3` 的符号链接:
```
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python3 python3 /usr/bin/python3.10 1
```
```
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python3 python3 /usr/bin/python3.11 2
```
并通过命令选择哪一个作为 Python3 使用:
```
sudo update-alternatives --config python3
```

现在你可以开始在你当前的 Ubuntu 版本中使用最新的 Python 来进行工作/学习了。你可以使用上述命令切换到库存版本,并随时改变版本。
如果你使用上述安装方法切换到 3.11,那么请确保你检查所有必要的应用程序,看它们是否工作正常。
最后,如果你遇到问题,请在评论区告诉我。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/install-python-3-11-ubuntu/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,231 | 为你的 awk 脚本注入 Groovy | https://opensource.com/article/22/9/awk-groovy | 2022-11-09T10:01:00 | [
"awk",
"Groovy"
] | /article-15231-1.html | 
>
> awk 和 Groovy 相辅相成,可以创建强大、有用的脚本。
>
>
>
最近我写了一个使用 Groovy 脚本来清理我的音乐文件中的标签的系列。我开发了一个 [框架](https://opensource.com/article/22/8/music-tagging-framework-groovy),可以识别我的音乐目录的结构,并使用它来遍历音乐文件。在该系列的最后一篇文章中,我从框架中分离出一个实用类,我的脚本可以用它来处理文件。
这个独立的框架让我想起了很多 awk 的工作方式。对于那些不熟悉 awk 的人来说,你学习下这本电子书:
>
> **[《awk 实用指南》](https://opensource.com/downloads/awk-ebook)**
>
>
>
我从 1984 年开始大量使用 awk,当时我们的小公司买了第一台“真正的”计算机,它运行的是 System V Unix。对我来说,awk 是非常完美的:它有<ruby> 关联内存 <rt> associative memory </rt></ruby>——将数组视为由字符串而不是数字来索引的。它内置了正则表达式,似乎专为处理数据而生,尤其是在处理数据列时,而且结构紧凑,易于学习。最后,它非常适合在 Unix 工作流使用,从标准输入或文件中读取数据并写入到输出,数据不需要经过其他的转换就出现在了输入流中。
说 awk 是我日常计算工具箱中的一个重要部分一点也不为过。然而,在我使用 awk 的过程中,有几件事让我感到不满意。
可能主要的问题是 awk 善于处理以分隔字段呈现的数据,但很奇怪它不善于处理 CSV 文件,因为 CSV 文件的字段被引号包围时可以嵌入逗号分隔符。另外,自 awk 发明以来,正则表达式已经有了很大的发展,我们需要记住两套正则表达式的语法规则,而这并不利于编写无 bug 的代码。[一套这样的规则已经很糟糕了](http://regex.info/blog/2006-09-15/247)。
由于 awk 是一门简洁的语言,因此它缺少很多我认为有用的东西,比如更丰富的基础类型、结构体、`switch` 语句等等。
相比之下,Groovy 拥有这些能力:可以使用 [OpenCSV 库](http://opencsv.sourceforge.net/),它很擅长处理 CSV 文件、Java 正则表达式和强大的匹配运算符、丰富的基础类型、类、`switch` 语句等等。
Groovy 所缺乏的是简单的面向管道的概念,即把要处理数据作为一个传入的流,以及把处理过的数据作为一个传出的流。
但我的音乐目录处理框架让我想到,也许我可以创建一个 Groovy 版本的 awk “引擎”。这就是我写这篇文章的目的。
### 安装 Java 和 Groovy
Groovy 是基于 Java 的,需要先安装 Java。最新的、合适的 Java 和 Groovy 版本可能都在你的 Linux 发行版的软件库中。Groovy 也可以按照 [Groovy 主页](https://groovy.apache.org/download.html) 上的说明进行安装。对于 Linux 用户来说,一个不错的选择是 [SDKMan](https://opensource.com/article/22/3/manage-java-versions-sdkman),它可以用来获得多个版本的 Java、Groovy 和其他许多相关工具。在这篇文章中,我使用的是 SDK 的版本:
* Java:OpenJDK 11 的 11.0.12 的开源版本
* Groovy:3.0.8
### 使用 Groovy 创建 awk
这里的基本想法是将打开一个或多个文件进行处理、将每行分割成字段、以及提供对数据流的访问等复杂情况封装在三个部分:
* 在处理数据之前
* 在处理每行数据时
* 在处理完所有数据之后
我并不打算用 Groovy 来取代 awk。相反,我只是在努力实现我的典型用例,那就是:
* 使用一个脚本文件而不是在命令行写代码
* 处理一个或多个输入文件
* 设置默认的分隔符为 `|`,并基于这个分隔符分割所有行
* 使用 OpenCSV 完成分割工作(awk 做不到)
### 框架类
下面是用 Groovy 类实现的 “awk 引擎”:
```
@Grab('com.opencsv:opencsv:5.6')
import com.opencsv.CSVReader
public class AwkEngine {
// With admiration and respect for
// Alfred Aho
// Peter Weinberger
// Brian Kernighan
// Thank you for the enormous value
// brought my job by the awk
// programming language
Closure onBegin
Closure onEachLine
Closure onEnd
private String fieldSeparator
private boolean isFirstLineHeader
private ArrayList<String> fileNameList
public AwkEngine(args) {
this.fileNameList = args
this.fieldSeparator = "|"
this.isFirstLineHeader = false
}
public AwkEngine(args, fieldSeparator) {
this.fileNameList = args
this.fieldSeparator = fieldSeparator
this.isFirstLineHeader = false
}
public AwkEngine(args, fieldSeparator, isFirstLineHeader) {
this.fileNameList = args
this.fieldSeparator = fieldSeparator
this.isFirstLineHeader = isFirstLineHeader
}
public void go() {
this.onBegin()
int recordNumber = 0
fileNameList.each { fileName ->
int fileRecordNumber = 0
new File(fileName).withReader { reader ->
def csvReader = new CSVReader(reader,
this.fieldSeparator.charAt(0))
if (isFirstLineHeader) {
def csvFieldNames = csvReader.readNext() as
ArrayList<String>
csvReader.each { fieldsByNumber ->
def fieldsByName = csvFieldNames.
withIndex().
collectEntries { name, index ->
[name, fieldsByNumber[index]]
}
this.onEachLine(fieldsByName,
recordNumber, fileName,
fileRecordNumber)
recordNumber++
fileRecordNumber++
}
} else {
csvReader.each { fieldsByNumber ->
this.onEachLine(fieldsByNumber,
recordNumber, fileName,
fileRecordNumber)
recordNumber++
fileRecordNumber++
}
}
}
}
this.onEnd()
}
}
```
虽然这看起来是相当多的代码,但许多行是因为太长换行了(例如,通常你会合并第 38 行和第 39 行,第 41 行和第 42 行,等等)。让我们逐行看一下。
第 1 行使用 `@Grab` 注解从 [Maven Central](https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.opencsv/opencsv) 获取 OpenCSV 库的 5.6 本周。不需要 XML。
第 2 行我引入了 OpenCSV 的 `CSVReader` 类
第 3 行,像 Java 一样,我声明了一个 `public` 实用类 `AwkEngine`。
第 11-13 行定义了脚本所使用的 Groovy 闭包实例,作为该类的钩子。像任何 Groovy 类一样,它们“默认是 `public`”,但 Groovy 将这些字段创建为 `private`,并对其进行外部引用(使用 Groovy 提供的 getter 和 setter 方法)。我将在下面的示例脚本中进一步解释这个问题。
第 14-16 行声明了 `private` 字段 —— 字段分隔符,一个指示文件第一行是否为标题的标志,以及一个文件名的列表。
第 17-31 行定义了三个构造函数。第一个接收命令行参数。第二个接收字段的分隔符。第三个接收指示第一行是否为标题的标志。
第 31-67 行定义了引擎本身,即 `go()` 方法。
第 33 行调用了 `onBegin()` 闭包(等同于 awk 的 `BEGIN {}` 语句)。
第 34 行初始化流的 `recordNumber`(等同于 awk 的 `NR` 变量)为 0(注意我这里是从 00 而不是 1 开始的)。
第 35-65 行使用 `each` `{}` 来循环处理列表中的文件。
第 36 行初始化文件的 `fileRecordNumber`(等同于 awk 的 `FNR` 变量)为 0(从 0 而不是 1 开始)。
第 37-64 行获取一个文件对应的 `Reader` 实例并处理它。
第 38-39 行获取一个 `CSVReader` 实例。
第 40 行检测第一行是否为标题。
如果第一行是标题,那么在 41-42 行会从第一行获取字段的标题名字列表。
第 43-54 行处理其他的行。
第 44-48 行把字段的值复制到 `name:value` 的映射中。
第 49-51 行调用 `onEachLine()` 闭包(等同于 awk 程序 `BEGIN {}` 和 `END {}` 之间的部分,不同的是,这里不能输入执行条件),传入的参数是 `name:value` 映射、处理过的总行数、文件名和该文件处理过的行数。
第 52-53 行是处理过的总行数和该文件处理过的行数的自增。
如果第一行不是标题:
第 56-62 行处理每一行。
第 57-59 调用 `onEachLine()` 闭包,传入的参数是字段值的数组、处理过的总行数、文件名和该文件处理过的行数。
第 60-61 行是处理过的总行数和该文件处理过的行数的自增。
第 66 行调用 `onEnd()` 闭包(等同于 awk 的 `END {}`)。
这就是该框架的内容。现在你可以编译它:
```
$ groovyc AwkEngine.groovy
```
一点注释:
如果传入的参数不是一个文件,编译就会失败,并出现标准的 Groovy 堆栈跟踪,看起来像这样:
```
Caught: java.io.FileNotFoundException: not-a-file (No such file or directory)
java.io.FileNotFoundException: not-a-file (No such file or directory)
at AwkEngine$_go_closure1.doCall(AwkEngine.groovy:46)
```
OpenCSV 可能会返回 `String[]` 值,不像 Groovy 中的 `List` 值那样方便(例如,数组没有 `each {}`)。第 41-42 行将标题字段值数组转换为 list,因此第 57 行的 `fieldsByNumber` 可能也应该转换为 list。
### 在脚本中使用这个框架
下面是一个使用 `AwkEngine` 来处理 `/etc/group` 之类由冒号分隔并没有标题的文件的简单脚本:
```
def ae = new AwkEngine(args, ':')
int lineCount = 0
ae.onBegin = {
println “in begin”
}
ae.onEachLine = { fields, recordNumber, fileName, fileRecordNumber ->
if (lineCount < 10)
println “fileName $fileName fields $fields”
lineCount++
}
ae.onEnd = {
println “in end”
println “$lineCount line(s) read”
}
ae.go()
```
第 1 行 调用的有两个参数的构造函数,传入了参数列表,并定义冒号为分隔符。
第 2 行定义一个脚本级的变量 `lineCount`,用来记录处理过的行数(注意,Groovy 闭包不要求定义在外部的变量为 `final`)。
第 3-5 行定义 `onBegin()` 闭包,在标准输出中打印出 “in begin” 字符串。
第 6-10 行定义 `onEachLine()` 闭包,打印文件名和前 10 行字段,无论是否为前 10 行,处理过的总行数 `lineCount` 都会自增。
第 11-14 行定义 `onEnd()` 闭包,打印 “in end” 字符串和处理过的总行数。
第 15 行运行脚本,使用 `AwkEngine`。
像下面一样运行一下脚本:
```
$ groovy Test1Awk.groovy /etc/group
in begin
fileName /etc/group fields [root, x, 0, ]
fileName /etc/group fields [daemon, x, 1, ]
fileName /etc/group fields [bin, x, 2, ]
fileName /etc/group fields [sys, x, 3, ]
fileName /etc/group fields [adm, x, 4, syslog,clh]
fileName /etc/group fields [tty, x, 5, ]
fileName /etc/group fields [disk, x, 6, ]
fileName /etc/group fields [lp, x, 7, ]
fileName /etc/group fields [mail, x, 8, ]
fileName /etc/group fields [news, x, 9, ]
in end
78 line(s) read
$
```
当然,编译框架类生成的 `.class` 文件需要在 classpath 中,这样才能正常运行。通常你可以用 `jar` 把这些 class 文件打包起来。
我非常喜欢 Groovy 对行为委托的支持,这在其他语言中需要各种诡异的手段。许多年来,Java 需要匿名类和相当多的额外代码。Lambda 已经在很大程度上解决了这个问题,但它们仍然不能引用其范围之外的非 final 变量。
下面是另一个更有趣的脚本,它很容易让人想起我对 awk 的典型使用方式:
```
def ae = new AwkEngine(args, ';', true)
ae.onBegin = {
// nothing to do here
}
def regionCount = [:]
ae.onEachLine = { fields, recordNumber, fileName, fileRecordNumber ->
regionCount[fields.REGION] =
(regionCount.containsKey(fields.REGION) ?
regionCount[fields.REGION] : 0) +
(fields.PERSONAS as Integer)
}
ae.onEnd = {
regionCount.each { region, population ->
println “Region $region population $population”
}
}
ae.go()
```
第 1 行调用了三个函数的构造方法,`true` 表示这是“真正的 CSV” 文件,第一行为标题。由于它是西班牙语的文件,因此它的逗号表示数字的`点`,标准的分隔符是分号。
第 2-4 行定义 `onBegin()` 闭包,这里什么也不做。
第 5 行定义一个(空的)`LinkedHashmap`,键是 String 类型,值是 Integer 类型。数据文件来自于智利最近的人口普查,你要在这个脚本中计算出智利每个地区的人口数量。
第 6-11 行处理文件中的行(加上标题一共有 180,500 行)—— 请注意在这个案例中,由于你定义 第 1 行为 CSV 列的标题,因此 `fields` 参数会成为 `LinkedHashMap<String,String>` 实例。
第 7-10 行是 `regionCount` 映射计数增加,键是 `REGION` 字段的值,值是 `PERSONAS` 字段的值 —— 请注意,与 awk 不同,在 Groovy 中你不能在赋值操作的右边使用一个不存在的映射而期望得到空值或零值。
第 12-16 行,打印每个地区的人口数量。
第 17 行运行脚本,调用 `AwkEngine` 。
像下面一样运行一下脚本:
```
$ groovy Test2Awk.groovy ~/Downloads/Censo2017/ManzanaEntidad_CSV/Censo*csv
Region 1 population 330558
Region 2 population 607534
Region 3 population 286168
Region 4 population 757586
Region 5 population 1815902
Region 6 population 914555
Region 7 population 1044950
Region 8 population 1556805
Region 16 population 480609
Region 9 population 957224
Region 10 population 828708
Region 11 population 103158
Region 12 population 166533
Region 13 population 7112808
Region 14 population 384837
Region 15 population 226068
$
```
以上为全部内容。对于那些喜欢 awk 但又希望得到更多的东西的人,我希望你能喜欢这种 Groovy 的方法。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/9/awk-groovy>
作者:[Chris Hermansen](https://opensource.com/users/clhermansen) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lxbwolf](https://github.com/lxbwolf) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
15,234 | 使用 PSCP 将文件和文件夹从 Windows 传输到 Linux | https://opensource.com/article/22/10/transfer-files-windows-linux-pscp | 2022-11-10T07:45:00 | [
"pscp"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15234-1.html | 
>
> 开源的 PSCP 程序可以轻松地在 Windows 和 Linux 计算机之间传输文件和文件夹。
>
>
>
你是否正在寻找一种将文件从 Windows 计算机快速传输到 Linux 计算机并再次传输回来的方法?开源的 PSCP 程序可以轻松传输文件和文件夹,当然它是开源的。
### 在 Windows 中设置 PATH
了解如何在 Windows 中设置命令路径可以更轻松地使用 PSCP 等方便的程序。如果你不熟悉该过程,请阅读 [如何在 Windows 上设置 PATH](https://opensource.com/article/22/10/set-path-powershell)。
### 使用 PSCP
PSCP(PuTTY 安全复制协议)是一个命令行工具,用于将文件和文件夹从 Windows 计算机传输到 Linux 计算机。
* 从 [网站](https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/latest.html) 下载 `pscp.exe`。
* 将 `pscp.exe` 移动到 `PATH` 中的文件夹(例如,如果你按照 [Opensource.com](http://Opensource.com) 上的 PATH 教程进行操作,则为 `Desktop\App`)。如果你没有设置 `PATH` 变量,你也可以将 `pscp.exe` 移动到保存要传输的文件的文件夹中。
* 使用 Windows 任务栏中的搜索栏在 Windows 计算机上打开 Powershell(在搜索栏中输入 `powershell`。)
* 输入 `pscp -version` 以确认你的计算机可以找到该命令。
### IP 地址
在进行传输之前,你必须知道目标计算机的 IP 地址或完全限定域名。假设它是同一网络上的计算机,并且你没有运行 DNS 服务器来解析计算机名称,你可以在 Linux 机器上使用 `ip` 命令找到目标 IP 地址:
```
[linux]$ ip addr show |grep 'inet '
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
inet 192.168.1.23/24 brd 10.0.1.255 scope global noprefixroute eth0
```
在所有情况下,127.0.0.1 都是计算机仅用于与自身通信的环回地址,因此在此示例中,正确的地址是 192.168.1.23。在你的系统上,IP 地址可能不同。如果你不确定哪个是哪个,你可以连续尝试每个,直到找到正确的(然后在某处写下来!)
或者,你可以查看路由器的设置,其中列出了通过 DHCP 分配的所有地址。
### 防火墙和服务器
`pscp` 命令使用 OpenSSH 协议,因此你的 Linux 计算机必须运行 OpenSSH 服务器软件,并且防火墙必须允许 SSH 流量。
如果你不确定你的 Linux 机器是否正在运行 SSH,请在 Linux 机器上运行以下命令:
```
[linux]$ sudo systemctl enable --now sshd
```
要确保你的防火墙允许 SSH 流量,请运行以下命令:
```
[linux]$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-servicessh --permanent
```
有关 Linux 上的防火墙的更多信息,请阅读 [使用防火墙使 Linux 更强大](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/make-linux-stronger-firewalls)。
### 传输文件
在这个例子中,我有一个名为 `pscp-test.txt` 的文件,我想将它从我的 Windows 计算机上的 `C:\Users\paul\Documents` 传输到我的目标 Linux 计算机主目录 `/home/paul`。
现在你已经有了 `pscp` 命令和目标地址,你可以传输测试文件 `pscp-test.txt`。打开 Powershell 并使用 `dir` 命令切换到示例文件所在的 `Documents` 文件夹:
```
PS> dir %USERPROFILE%\Documents\
```
现在执行传输:
```
PS> pscp pscp-test.txt [email protected]:/home/paul
| Password:
End of keyboard-interactive prompts from server
pscp-test.txt | 0 kb | 0.0 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100%
```
这是语法,逐字逐句来:
* `pscp`:用于传输文件的命令。
* `pscp-test.txt` 是你要从 Windows 传输的文件的名称。
* `[email protected]` 是我在 Linux 计算机上的用户名,以及 Linux 计算机的 IP 地址。你必须将其替换为你自己的用户和目的地信息。请注意,`pscp` 需要目标计算机上的目标路径,而 IP 地址末尾的 `:/home/paul` 指定我希望将文件复制到我的主文件夹。
对 Linux 计算机进行身份验证后,`pscp-test.txt` 文件将传输到 Linux 计算机。
### 验证已传输
在你的 Linux 计算机上,打开终端并使用 `ls` 命令验证文件 `pscp-test.txt` 是否出现在你的主目录中。
```
[linux]$ ls
Documents
Downloads
Music
Pictures
pscp-test.txt
```
### 从 Linux 系统复制文件
你不仅限于将文件复制到 Linux 系统。使用 `pscp`,你还可以将文件从 Linux 复制到 Windows。语法是一样的,只是反过来:
```
PS> pscp [email protected]:/home/paul/pscp-test.txt %USERPROFILE%\Documents\pscp-win.txt
```
这是语法:
* `pscp`:用于传输文件的命令。
* `[email protected]:/home/paul/pscp-test.txt` 是我在 Linux 计算机上的用户名、Linux 计算机的 IP 地址,以及我要复制的文件的路径。
* `%USERPROFILE%\Documents` 是我的 Windows 计算机上我要保存文件的位置。 请注意,在将文件复制回我的 Windows 计算机时,我可以给它一个新名称,例如 `pscp-win.txt`,以区别于原始文件。 当然,你不必重命名文件,但对于本演示来说,它是一个有用的快捷方式。
打开文件管理器以验证 `pscp-win.txt` 文件是否已从 Linux 计算机复制到 Windows `C:\Users\paul\Documents` 下。

### 远程复制
借助开源 `pscp` 命令的强大功能,你可以访问家中的任何计算机、拥有帐户的服务器,甚至是移动设备和 [边缘设备](https://opensource.com/tags/edge-computing)。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/10/transfer-files-windows-linux-pscp>
作者:[Paul](https://opensource.com/users/plaubscher) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Are you looking for a way to quickly transfer files from your Windows computer to your Linux computer and back again? The open source PSCP utility makes it easy to transfer files and folders, and of course it's open source.
## Setting your PATH in Windows
Knowing how to set your command path in Windows makes it easier to use a handy utility like PSCP. If you're unfamiliar with that process, read [how to set a PATH on Windows](https://opensource.com/article/22/10/set-path-powershell).
## Using PSCP
PSCP (PuTTY Secure Copy Protocol) is a command-line tool for transferring files and folders from a Windows computer to a Linux computer.
-
Download
`pscp.exe`
from its[website](https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/latest.html). -
Move
`pscp.exe`
to a folder in your PATH (for example,`Desktop\App`
if you followed the PATH tutorial here on[Opensource.com](http://Opensource.com)). If you haven't set a PATH variable for yourself, you can alternately move`pscp.exe`
to the folder holding the files you're going to transfer. -
Open Powershell on your Windows computer using the search bar in the Windows taskbar (type 'powershell` into the search bar.)
-
Type
`pscp –version`
to confirm that your computer can find the command.
## IP address
Before you can make the transfer, you must know the IP address or fully-qualified domain name of the destination computer. Assuming it's a computer on your same network, and that you're not running a DNS server to resolve computer names, you can find the destination IP address using the `ip`
command on the Linux machine:
```
``````
[linux]$ ip addr show | grep 'inet '
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
inet 192.168.1.23/24 brd 10.0.1.255 scope global noprefixroute eth0
```
In all cases, 127.0.0.1 is a loopback address that the computer uses only to talk to itself, so in this example the correct address is 192.168.1.23. On your system, the IP address is likely to be different. If you're not sure which is which, you can try each one in succession until you get the right one (and then write it down somewhere!)
Alternately, you can look in the settings of your router, which lists all addresses assigned over DHCP.
## Firewalls and servers
The `pscp`
command uses the OpenSSH protocol, so your Linux computer must be running the OpenSSH server software, and its firewall must allow SSH traffic.
If you're not sure whether your Linux machine is running SSH, then run this command on the Linux machine:
```
``````
[linux]$ sudo systemctl enable --now sshd
```
To ensure your firewall allows SSH traffic, run this command:
```
``````
[linux]$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-service ssh --permanent
```
For more information on firewalls on Linux, read [Make Linux stronger with firewalls](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/make-linux-stronger-firewalls).
## Transfer the file
In this example, I have a file called `pscp-test.txt`
that I want to transfer from `C:\Users\paul\Documents`
on my Windows computer to my destination Linux computer home directory `/_home_/paul`
.
Now that you have the `pscp`
command and the destination address, you're ready to transfer the test file `pscp-test.txt`
. Open Powershell and use the `dir`
command to change to the `Documents`
folder, where the sample file is located:
PS> dir %USERPROFILE%\Documents\
Now execute the transfer:
```
``````
PS> pscp pscp-test.txt [email protected]:/home/paul
| Password:
End of keyboard-interactive prompts from server
pscp-test.txt | 0 kb | 0.0 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100%
```
Here's the syntax, word for word:
-
`pscp`
: The command used to transfer the file. -
`pscp-test.txt`
is the name of the file you want to transfer from Windows. -
`[email protected]`
is my username on the Linux computer, and the IP address of the Linux computer. You must replace this with your own user and destination information. Notice that`pscp`
requires a destination path on the target computer, and`:/home/paul`
at the end of the IP address specifies that I want the file copied to my home folder.
After you authenticate to the Linux computer, the `pscp-test.txt`
file is transferred to the Linux computer.
**[ Related read Share files between Linux and Windows computers ]**
## Verifying the transferred
On your Linux computer, open a terminal and use the `ls`
command to verify that the file `pscp-test.txt`
appears in your home directory.
```
``````
[linux]$ ls
Documents
Downloads
Music
Pictures
pscp-test.txt
```
## Copying a file off of a Linux system
You aren't limited to just copying files to your Linux system. With `pscp`
, you can also copy a file from Linux onto Windows. The syntax is the same, only in reverse:
```
````PS> pscp [email protected]:/home/paul/pscp-test.txt %USERPROFILE%\Documents\pscp-win.txt`
Here's the syntax:
-
`pscp`
: The command used to transfer the file. -
`[email protected]:/home/paul/pscp-test.txt`
is my username on the Linux computer, the IP address of the Linux computer, and the path to the file I want to copy. -
`%USERPROFILE%\Documents`
is the location on my Windows computer where I want to save the file. Notice that in copying the file back to my Windows computer, I can give it a new name, such as`pscp-win.txt`
, to differentiate it from the original. You don't have to rename the file, of course, but for this demonstration it's a useful shortcut.
Open your file manager to verify that the `pscp-win.txt`
file was copied to the Windows `C:\Users\paul\Documents`
path from the Linux computer.
(Paul Laubscher, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Remote copying
With the power of the open source `pscp`
command, you have access to any computer in your house, and servers you have accounts on, and even mobile and [edge devices](https://opensource.com/tags/edge-computing).
## Comments are closed. |
15,235 | 使用 Lua 解析配置文件 | https://opensource.com/article/21/6/parsing-config-files-lua | 2022-11-10T08:46:20 | [
"Lua",
"配置文件"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15235-1.html | 
>
> 使用 Lua 配置持久化应用设置。
>
>
>
不是所有的应用都需要配置文件;对很多应用来说,在启动时变得焕然一新对它们更有利。例如,简单的工具就极少需要偏好项和设置在使用过程中保持稳定不变。然而,当你编写一个复杂的应用程序时,如果能让用户设置与应用的交互方式,以及应用与系统交互的方式会很不错。这就是配置文件用来做的事情。本文将讨论一些利用 Lua 进行持久化配置的方法。
### 选择一种格式
关于配置文件很重要的两点是一致性和可预见性。你不会希望为了保存用户偏好项,将信息转储到文件中,然后再花几天去编码实现“逆向工程”,处理最后出现在文件里的随机信息。
这里用一些常用的 [配置文件格式](https://opensource.com/article/21/6/config-files-and-their-formats)。Lua 有一些库可以处理大多数常用的配置格式;在本文中,我会采用 INI 格式。
### 安装库
Lua 库的核心仓库是 [Luarocks.org](https://opensource.com/article/19/11/getting-started-luarocks)。你可以在这个网站搜索库,或者你可以安装并使用 `luarocks` 终端命令。
Linux 环境中,你可以从发行版的软件仓库中下载它,例如:
```
$ sudo dnf install luarocks
```
在 macOS 上,请使用 [MacPorts](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/macports) 或者 [Homebrew](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/homebrew-mac)。在 Windows 上,请使用 [Chocolatey](https://opensource.com/article/20/3/chocolatey)。
`luarocks` 安装后,你可以使用 `search` 子命令来搜索一个恰当的库。如果你不知道库的名字,可以通过关键词来搜索这个库,例如 `ini`、xml`或者`json`,这取决于你想要用这个库做什么。打个比方,你可以搜索`inifile`, 这个库被我用来解析 INI 格式的文本文件。
```
$ luarocks search inifile
Search results:
inifile
1.0-2 (rockspec) - https://luarocks.org
1.0-2 (src) - https://luarocks.org
1.0-1 (rockspec) - https://luarocks.org
[...]
```
一个开发者容易犯的错误是在系统上安装了这个库却忘了把它和应用打包。这会给没有安装这个库的用户带来麻烦。为了防止这个问题发生,可以使用 `--tree` 选项将它安装在项目的本地文件夹中。如果你没有这个项目文件夹,那就先创建这个文件夹再安装库:
```
$ mkdir demo
$ cd demo
$ luarocks install --tree=local inifile
```
`--tree` 选项指示 `luarocks` 创建一个新文件夹并在其中安装你的库,例如这个例子中的 `local` 文件夹。 使用这个简单的技巧,你可以将所有你项目要使用的依赖项直接安装到项目文件夹中。
### 配置代码
首先,在一个名 `myconfig.ini` 的文件中创建一些 INI 数据。
```
[example]
name=Tux
species=penguin
enabled=false
[demo]
name=Beastie
species=demon
enabled=false
```
将这个文件保存到你的主目录下,命名为 `myconfig.ini`, *不要* 存到项目文件夹下。你通常会希望配置文件独立于你的文件存在,这样当用户卸载你的应用时,使用应用时产生的数据可以保存在系统中。有些用户会删除不重要的配置文件,但大多数不会。最终,如果他们要重装这个应用,还会保留着所有的用户偏好项。
配置文件的位置以技术来说并不重要,但每一个操作系统都有存储它们的特定或者默认的路径。在 Linux 中,这个路径由 [Freedesktop 规范](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Specifications) 指定。它规定配置文件被保存在一个名为 `~/.config` 的隐藏文件夹中。为了操作时更加清晰明确,可以在主目录下存储配置文件,以便于使用和寻找。
创建第二个文件,命名为 `main.lua`,并在你喜欢的文本编辑器中打开它。
首先,你必须告诉 Lua 你将想要使用的附加库放置在哪里。`package.path` 变量决定了 Lua 到哪里去寻找这些库。你可以从终端中查看 Lua 默认的包地址:
```
$ Lua
> print(package.path)
./?.lua;/usr/share/lua/5.3/?.lua;/usr/share/lua/5.3/?/init.lua;/usr/lib64/lua/5.3/?.lua;/usr/lib64/lua/5.3/?/init.lua
```
在你的 Lua 代码中,将你本地库的路径添加到 `package.path` 中:
```
package.path = package.path .. ';local/share/lua/5.3/?.lua
```
### 使用 Lua 解析 INI 文件
当包的位置确定以后,下一件事就是引入 `inifile` 库并处理一些操作系统逻辑。即使这是一个很简单的应用,代码也需要从操作系统获取到用户主目录的路径,并建立在必要时将文件系统路径返回给操作系统的通信方式。
```
package.path = package.path .. ';local/share/lua/5.3/?.lua
inifile = require('inifile')
-- find home directory
home = os.getenv('HOME')
-- detect path separator
-- returns '/' for Linux and Mac
-- and '\' for Windows
d = package.config:sub(1,1)
```
现在你可使用 `inifile` 来从配置文件解析数据到 Lua 表中。一旦这些数据被导入进表中,你可以像查询其他的 Lua 表一样查询它。
```
-- parse the INI file and
-- put values into a table called conf
conf = inifile.parse(home .. d .. 'myconfig.ini')
-- print the data for review
print(conf['example']['name'])
print(conf['example']['species'])
print(conf['example']['enabled'])
```
在终端中运行代码可以看见结果:
```
$ lua ./main.lua
Tux
penguin
false
```
这看起来是正确的。试试在 `demo` 块中执行同样的操作。
### 使用 INI 格式存储数据
不是所有用来解析的库都会读写数据(通常被称为 \_编码 和 *解码*),但是 `inifile` 会这样做。这意味着你可以使用它对配置文件进行修改。
为了改变配置文件中的值,你可以对被解析的表中的变量进行设置,然后把表重写回配置文件中。
```
-- set enabled to true
conf['example']['enabled'] = true
conf['demo']['enabled'] = true
-- save the change
inifile.save(home .. d .. 'myconfig.ini', conf)
```
现在再来看看配置文件:
```
$ cat ~/myconfig.ini
[example]
name=Tux
species=penguin
enabled=true
[demo]
name=Beastie
species=demon
enabled=true
```
### 配置文件
按照用户的设想来存储数据对程序来说是至关重要的。幸运的是,这对工程师来说是一个很常规的任务,大多数工作可能早已被完成了。只要找到一个好用的库完成开放格式下编码和解码,你就能为用户提供一致且持续的体验。
以下是完整的演示代码,可供参考。
```
package.path = package.path .. ';local/share/lua/5.3/?.lua'
inifile = require('inifile')
-- find home directory
home = os.getenv('HOME')
-- detect path separator
-- returns '/' for Linux and Mac
-- and '\' for Windows
d = package.config:sub(1,1)
-- parse the INI file and
-- put values into a table called conf
conf = inifile.parse(home .. d .. 'myconfig.ini')
-- print the data for review
print(conf['example']['name'])
print(conf['example']['species'])
print(conf['example']['enabled'])
-- enable Tux
conf['example']['enabled'] = true
-- save the change
inifile.save(home .. d .. 'myconfig.ini', conf)
```
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/6/parsing-config-files-lua>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hadisi1993](https://github.com/hadisi1993) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Not all applications need configuration files; many applications benefit from starting fresh each time they are launched. Simple utilities, for instance, rarely require preferences or settings that persist across uses. However, when you write a complex application, it's nice for users to be able to configure how they interact with it and how it interacts with their system. That's what configuration files are for, and this article discusses some of the ways you can implement persistent settings with the Lua programming language.
## Choose a format
The important thing about configuration files is that they are consistent and predictable. You do not want to dump information into a file under the auspices of saving user preferences and then spend days writing code to reverse-engineer the random bits of information that have ended up in the file.
There are several popular [formats for configuration files](https://opensource.com/article/21/6/config-files-and-their-formats). Lua has libraries for most of the common configuration formats; in this article, I'll use the INI format.
## Installing the library
The central hub for Lua libraries is [Luarocks.org](https://opensource.com/article/19/11/getting-started-luarocks). You can search for libraries on the website, or you can install and use the `luarocks`
terminal command.
On Linux, you can install it from your distribution's software repository. For example:
`$ sudo dnf install luarocks`
On macOS, use [MacPorts](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/macports) or [Homebrew](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/homebrew-mac). On Windows, use [Chocolatey](https://opensource.com/article/20/3/chocolatey).
Once `luarocks`
is installed, you can use the `search`
subcommand to search for an appropriate library. If you don't know the name of a library, you can search for a keyword, like `ini`
or `xml`
or `json`
, depending on what's relevant to what you're trying to do. In this case, you can just search for `inifile`
, which is the library I use to parse text files in the INI format:
```
$ luarocks search inifile
Search results:
inifile
1.0-2 (rockspec) - https://luarocks.org
1.0-2 (src) - https://luarocks.org
1.0-1 (rockspec) - https://luarocks.org
[...]
```
A common trap programmers fall into is installing a library on their system and forgetting to bundle it with their application. This can create problems for users who don't have the library installed. To avoid this, use the `--tree`
option to install the library to a local folder within your project directory. If you don't have a project directory, create one first, and then install:
```
$ mkdir demo
$ cd demo
$ luarocks install --tree=local inifile
```
The `--tree`
option tells `luarocks`
to create a new directory, called `local`
in this case, and install your library into it. With this simple trick, you can install all the dependency code your project uses directly into the project directory.
## Code setup
First, create some INI data in a file called `myconfig.ini`
:
```
[example]
name=Tux
species=penguin
enabled=false
[demo]
name=Beastie
species=demon
enabled=false
```
Save the file as `myconfig.ini`
into your home directory, *not* into your project directory. You usually want configuration files to exist outside your application so that even when a user uninstalls your application, the data they generate while using the application remains on their system. Users might remove unnecessary config files manually, but many don't. As a result, if they reinstall an application, it will retain all of their preferences.
Config file locations are technically unimportant, but each operating system (OS) has a specification or a tradition of where they ought to be placed. On Linux, this is defined by the [Freedesktop specification](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Specifications). It dictates that configuration files are to be saved in a hidden folder named `~/.config`
. For clarity during this exercise, just save the file in your home directory so that it's easy to find and use.
Create a second file named `main.lua`
and open it in your favorite text editor.
First, you must tell Lua where you've placed the additional library you want it to use. The `package.path`
variable determines where Lua looks for libraries. You can view Lua's default package path in a terminal:
```
$ Lua
> print(package.path)
./?.lua;/usr/share/lua/5.3/?.lua;/usr/share/lua/5.3/?/init.lua;/usr/lib64/lua/5.3/?.lua;/usr/lib64/lua/5.3/?/init.lua
```
In your Lua code, append your local library location to `package.path`
:
`package.path = package.path .. ';local/share/lua/5.3/?.lua`
## Parsing INI files with Lua
With the package location established, the next thing to do is to require the `inifile`
library and then handle some OS logistics. Even though this is a simple example application, the code needs to get the user's home directory location from the OS and establish how to communicate filesystem paths back to the OS when necessary:
```
package.path = package.path .. ';local/share/lua/5.3/?.lua
inifile = require('inifile')
-- find home directory
home = os.getenv('HOME')
-- detect path separator
-- returns '/' for Linux and Mac
-- and '\' for Windows
d = package.config:sub(1,1)
```
Now you can use `inifile`
to parse data from the config file into a Lua table. Once the data has been placed into a table, you can query the table as you would any other Lua table:
```
-- parse the INI file and
-- put values into a table called conf
conf = inifile.parse(home .. d .. 'myconfig.ini')
-- print the data for review
print(conf['example']['name'])
print(conf['example']['species'])
print(conf['example']['enabled'])
```
Run the code in a terminal to see the results:
```
$ lua ./main.lua
Tux
penguin
false
```
That looks correct. Try doing the same for the `demo`
block.
## Saving data in the INI format
Not all parser libraries read and write data (often called *encoding* and *decoding*), but the `inifile`
library does. That means you can use it to make changes to a configuration file.
To change a value in a configuration file, you set the variable representing the value in the parsed table, and then you write the table back to the configuration file:
```
-- set enabled to true
conf['example']['enabled'] = true
conf['demo']['enabled'] = true
-- save the change
inifile.save(home .. d .. 'myconfig.ini', conf)
```
Take a look at the configuration file now:
```
$ cat ~/myconfig.ini
[example]
name=Tux
species=penguin
enabled=true
[demo]
name=Beastie
species=demon
enabled=true
```
## Config files
The ability to save data about how a user wants to use an application is an important part of programming. Fortunately, it's a common task for programmers, so much of the work has probably already been done. Find a good library for encoding and decoding into an open format, and you can provide a persistent and consistent user experience.
Here's the entire demo code for reference:
```
package.path = package.path .. ';local/share/lua/5.3/?.lua'
inifile = require('inifile')
-- find home directory
home = os.getenv('HOME')
-- detect path separator
-- returns '/' for Linux and Mac
-- and '\' for Windows
d = package.config:sub(1,1)
-- parse the INI file and
-- put values into a table called conf
conf = inifile.parse(home .. d .. 'myconfig.ini')
-- print the data for review
print(conf['example']['name'])
print(conf['example']['species'])
print(conf['example']['enabled'])
-- enable Tux
conf['example']['enabled'] = true
-- save the change
inifile.save(home .. d .. 'myconfig.ini', conf)
```
## Comments are closed. |
15,239 | Kate 文本编辑器增加了四个非常棒的新功能 | https://news.itsfoss.com/kate-editor-22-12-features/ | 2022-11-10T23:47:53 | [
"KDE",
"Kate"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15239-1.html |
>
> 这个由 KDE 开发的功能丰富的文本编辑器正在变得更好和更有用!
>
>
>

[Kate 文本编辑器](https://kate-editor.org/) 是一个不断发展和强大的开源文本编辑器,它可以作为微软的 Visual Studio Code 应用程序的替代品。
它可以在 Linux、Windows 和 macOS 上使用。
这个代码编辑器在 2021 年进行了重大升级,这可能使它成为了 KDE 对微软产品的回应。
在即将到来的 Kate 和 KWrite 22.12 版本上,他们的目标是添加许多非常有用的功能。
来简单看看我们可以从 Kate 中期待什么。
### ? Kate Editor 的新增功能
如果你读了 [Nate 的博客](https://pointieststick.com) 了解 KDE 的改进,你可能已经知道了 KDE Plasma 和应用程序即将获得的升级。
但是,我想强调一些 Kate 22.12 将会带来的令人激动的新功能:
* 对 Qt 部件的支持
* 更新的欢迎页面
* Git 差异查看器
* 配置标签页
* 剪切板历史
#### 欢迎页面

和许多其他 [KDE 应用程序](https://news.itsfoss.com/content/images/2022/11/Kate_22.12_GitDiff-1.png) 一样,Kate 现在将显示一个欢迎页面,该页面将欢迎用户并显示创建或打开文件、启动新会话、查看最近的文档等选项。
对于不喜欢这个页面的用户,欢迎页面上将提供一个选项,以在新窗口上禁用欢迎页面。
#### Git 差异查看器

Kate 终于增加了对显示 git-diff 的支持;用户将能够比较他们的代码以检查差异,并找到那些令人讨厌的、会导致他们的应用程序无法正常运行错误。
用户也可以从多种视图中进行选择,例如统一视图、并排视图和原始视图。
#### 新的剪贴板历史粘贴对话框

Kate 现在添加了一个新的对话框,在粘贴的时候显示用户剪贴板内容的列表。
当你在多行代码之间切换,而又不想丢失重要的内容时,这可能会很有用。
#### 配置标签页

Kate 也将添加一个配置标签页,让用户可以更改重要的设置,并添加了一个搜索栏,使用户可以快速查找特定的设置。
#### ?️ 其他变更和改进
Kate 22.12 将带来的其他值得注意的改进包括:
* 优化的状态栏
* 对构建插件的改进
* 可移动的侧边栏按钮
* 对窗口处理的改进
Kate 正在成为微软的 [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) 的合适替代品,并且自 2021 年大规模重构以来已经取得了很大的进步。
在 Kate 的 [官方博客文章](https://kate-editor.org/post/2022/2022-10-31-treats-for-kate/) 中,你可以了解更多关于这些变化的信息,并看看它们实际是怎么工作的。
? 你期待 Kate 22.12 的发布吗?还是更喜欢 VS Code?
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/kate-editor-22-12-features/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Cubik65536](https://github.com/Cubik65536) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

[Kate Editor](https://kate-editor.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is a constantly evolving and powerful open-source text editor that acts as a viable alternative to Microsoft's Visual Studio Code application.
It is available for Linux, Windows, and macOS.
The code editor received a significant upgrade in 2021 potentially making it KDE's answer to Microsoft's offering.
[Kate Editor Set to Become KDE’s Answer to Microsoft’s Visual Studio CodeKDE has revealed some details on the upcoming 21.04 release of their Kate text editor, or KDE Advanced Text Editor. With this release comes a huge range of new features, such as a new HUD style command palette and improved search in files. To the Visual Studio Code users](https://news.itsfoss.com/kate/)

With the upcoming Kate and KWrite 22.12 release, they aim to add a number of much-needed features.
Let's take a brief look at what we can expect from Kate.
## 🆕 Kate Editor: New Feature Additions
If you have been reading [Nate's blog](https://pointieststick.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for KDE improvements, you probably know all about the upgrades coming to KDE Plasma and the applications.
However, some exciting additions are coming to Kate 22.12 that I wanted to highlight:
**Support for Qt Widgets****Updated Welcome Page****Git Diff Viewer****Configuration Tab****Clipboard History**
[Unlocator Smart DNSRemove geographic blocks from streaming services using Unlocator Smart DNS. Simple to use and with a full free trial included.](https://unlocator.com/account/aff/go/KeijkZZVhNSBsJmLTeQr?cr=aHR0cHM6Ly91bmxvY2F0b3IuY29tL3NtYXJ0LWRucy8%3D&ref=news.itsfoss.com)

### Welcome Page
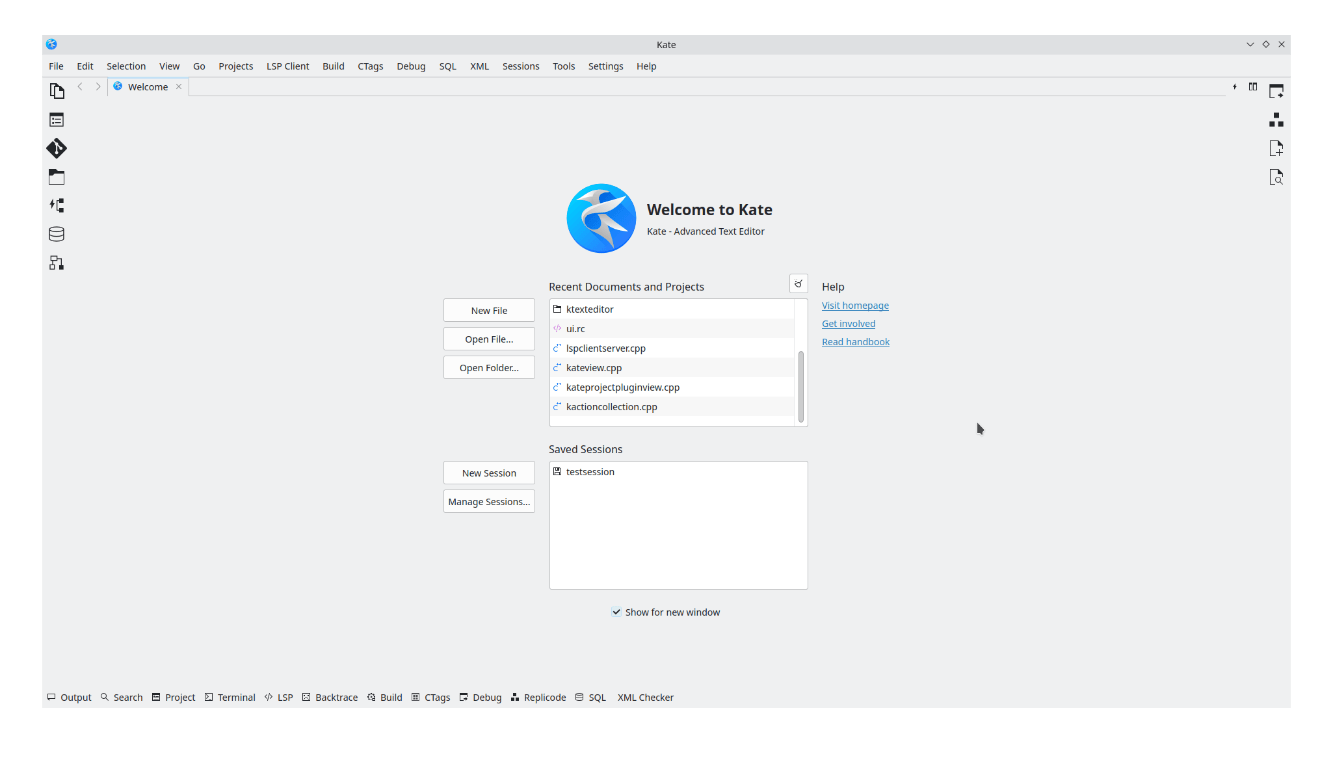
Like many other [KDE apps](https://apps.kde.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), Kate will now show a welcome page that will greet users with a welcome screen and include options like creating or opening a file, starting a new session, viewing recent documents, and more.
For users who might not like this, an option will be provided on the welcome page to disable this behavior for a new window.
### Git Diff Viewer
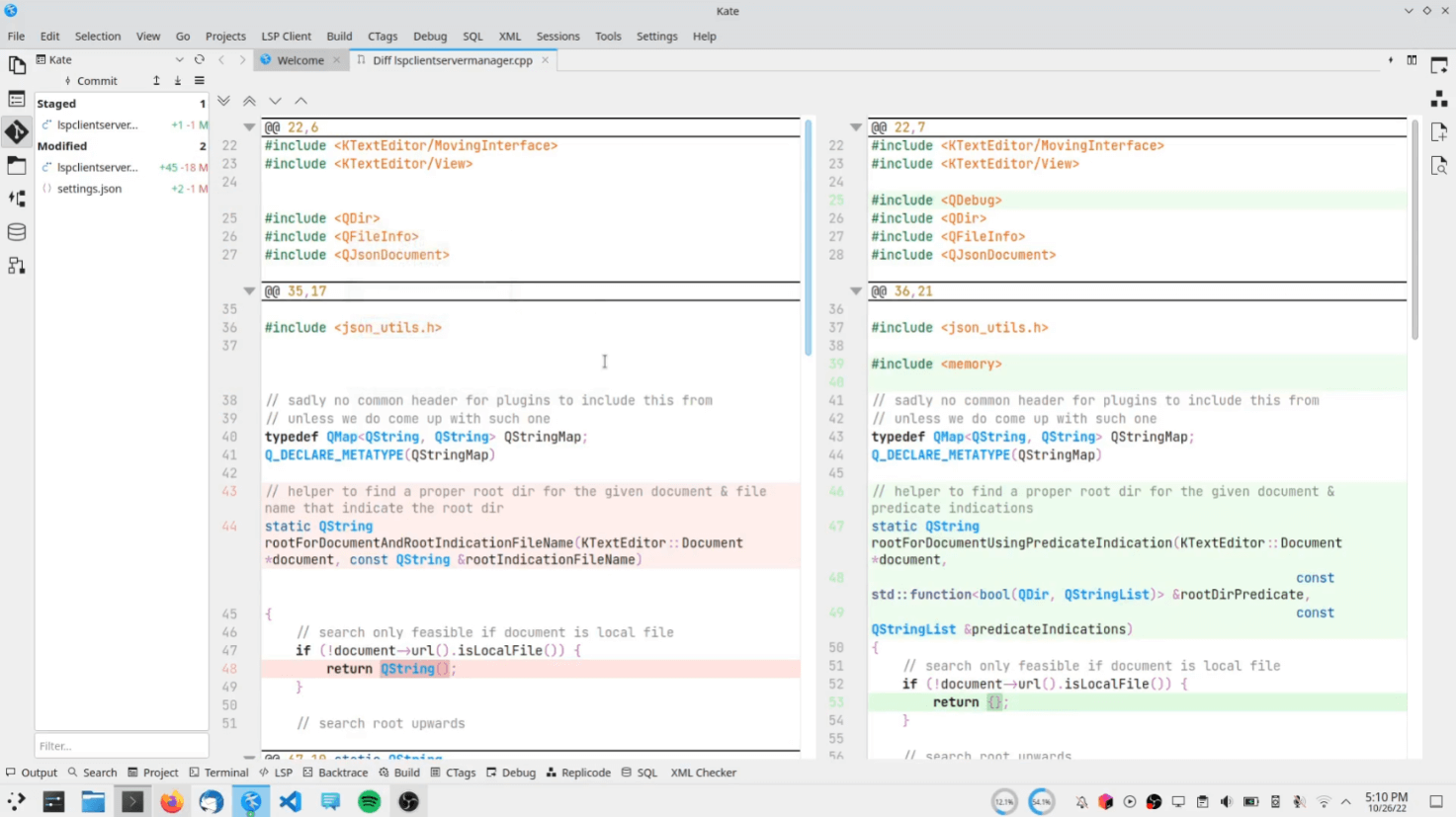
Kate will finally get support for viewing git-diff; users will be able to compare their code to check for differences and find those pesky bugs that are causing their application not to run correctly.
Users will also be able to choose from a variety of views, such as unified, side-by-side, and raw.
### New Clipboard History Paste Dialog
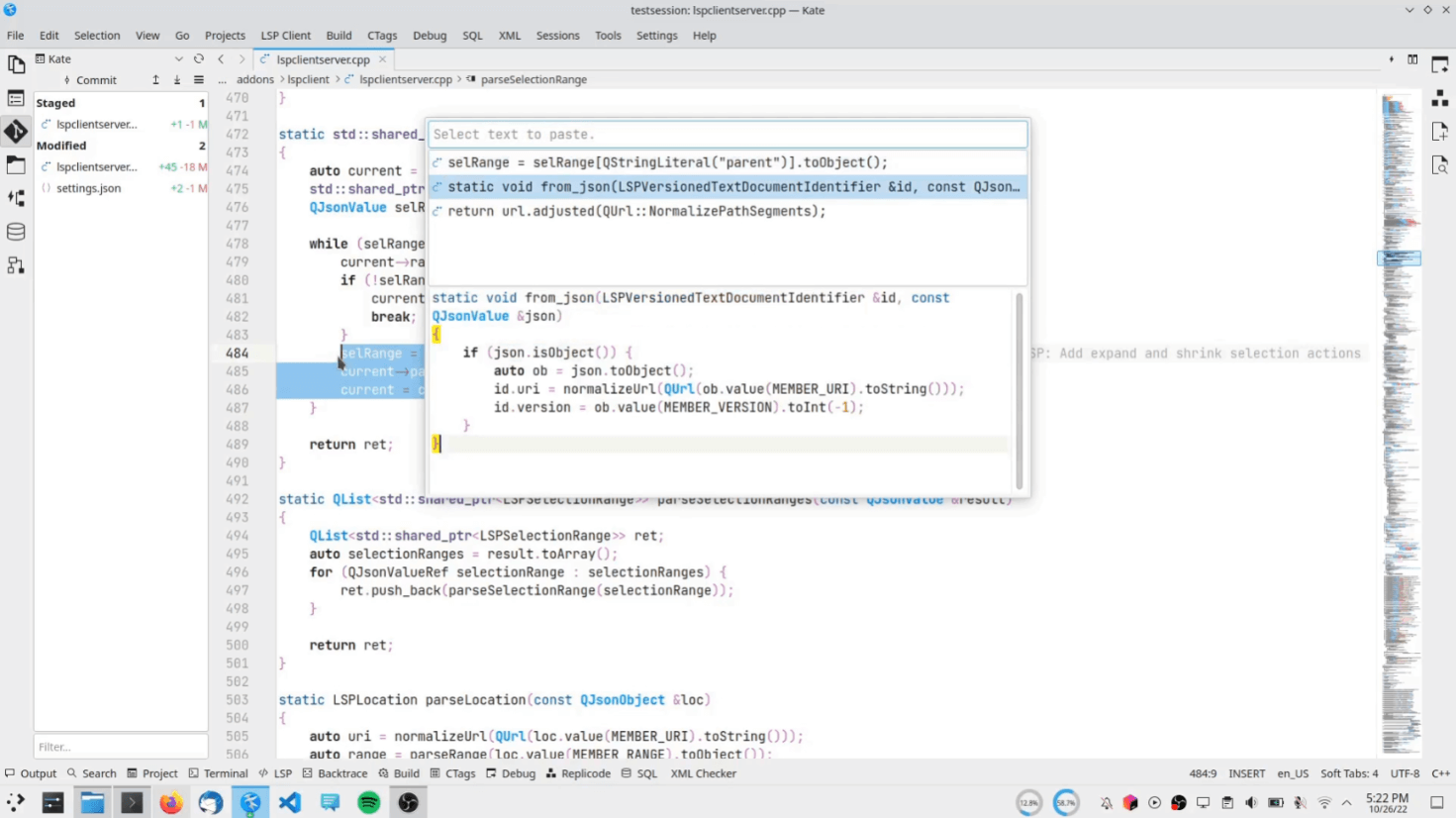
A new dialog has been added to Kate, showing users a list of previous clipboard content while pasting.
This can be helpful if you are juggling between multiple lines of code and don't want to lose track of the essential bits.
### Configuration Tab
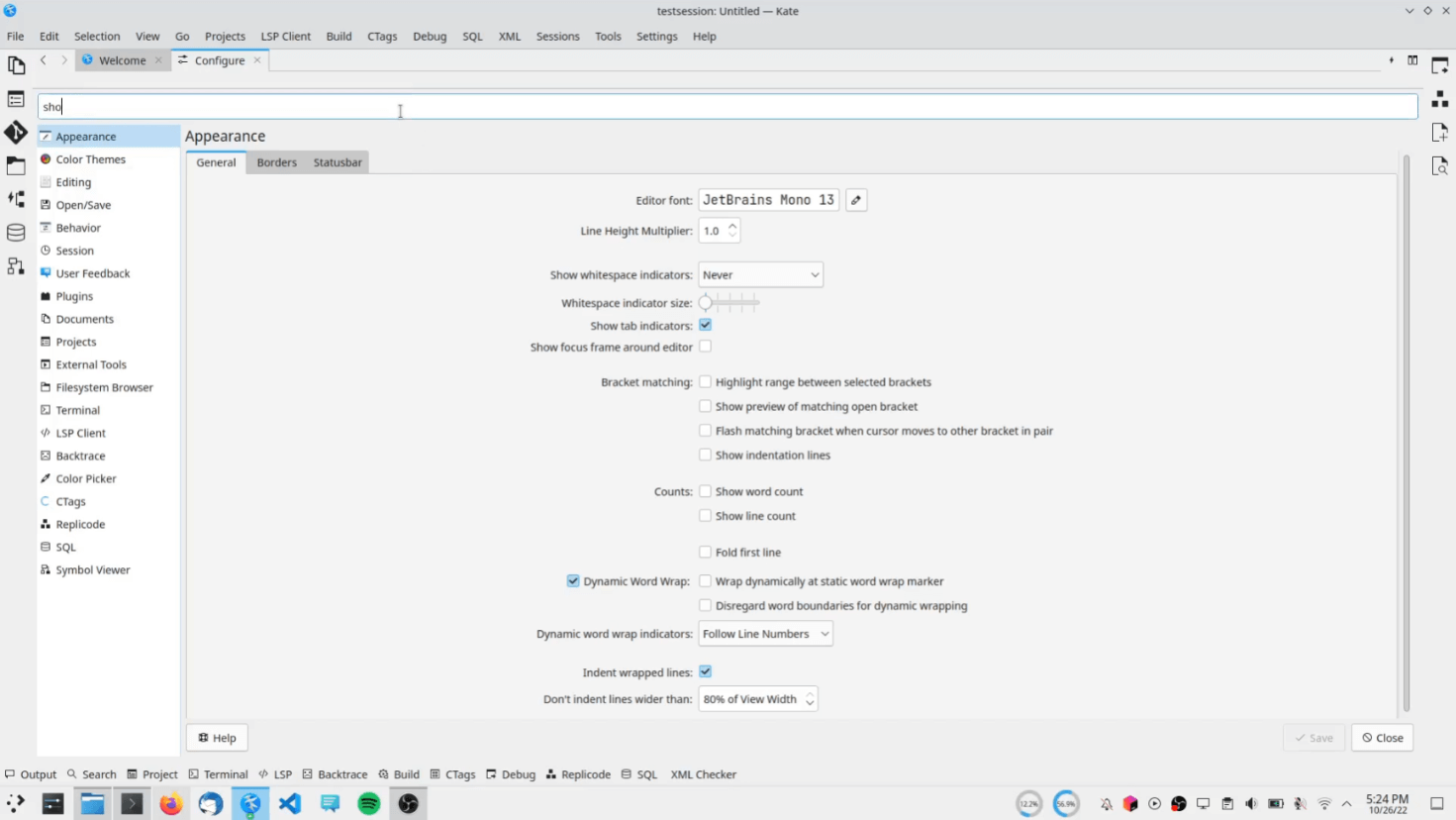
Kate will also feature a configuration tab that lets users change significant settings and a search bar to quickly find specific settings.
### 🛠️ Other Changes and Improvements
Some other notable improvements to be featured on Kate 22.12 are:
**Optimized Status Bar****Improvements to the Build Plugin****Moveable Sidebar Buttons****Improvements to Window Handling**
Kate is shaping to be a suitable alternative to Microsoft's [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) and has come a long way since its major revamp in 2021.
In Kate's [official blog post](https://kate-editor.org/post/2022/2022-10-31-treats-for-kate/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), you can learn more about these changes and watch them in action.
*💬 Are you looking forward to the release of Kate 22.12? Or do you prefer VS Code?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,240 | Ubuntu 所有版本的吉祥物 | https://itsfoss.com/all-Ubuntu-mascots/ | 2022-11-11T13:05:00 | [
"Ubuntu",
"代号",
"吉祥物"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15240-1.html | 
>
> 在这篇文章中,我们会介绍迄今为止所有 Ubuntu 发行版本的吉祥物。
>
>
>
你可能已经注意到了:每个 Ubuntu 版本都会有一个版本名称和代号。代号由两个单词组成,这两个单词有相同的首字母,第一个单词是形容词,另一个单词通常是一个濒危的物种名称。
对应于其代号,这些 Ubuntu 版本也有一个吉祥物。例如,Ubuntu 22.04 的代号为 “Jammy Jellyfish”,因此 Ubuntu 22.04 的桌面壁纸上有 **吉祥物:水母** 的图像。
但是实际上,这些“吉祥物”并不总是 Ubuntu 版本的一部分,因为吉祥物在早期的 Ubuntu 版本中是没有的。
有史以来第一个 Ubuntu 版本是在 2004 年 10 月发布的 4.10 版(LCTT 译注:Ubuntu 的版本号是由年份和月份的组合来表示的。)但是,直到 Ubuntu 8.04 LTS “Hardy Heron” 版本,你才会看到相关的吉祥物。
在我之前写的 [另一篇文章](https://itsfoss.com/Ubuntu-default-wallpapers-download/) 中,我整理了所有 Ubuntu 版本的默认壁纸。在本文中,你将了解到所有 Ubuntu 版本的吉祥物。
现在,就让我们按时间倒序,一起进入 Ubuntu 的吉祥物之旅吧。
(LCTT 校注:本文原文发表时,Ubuntu 22.10 尚未发布,它的代号是 “Kinetic Kudu”,吉祥物是“捻角羚”。)
(LCTT 校注:由于 Ubuntu 系列的代号和吉祥物选择的都是比较少见的动物和晦涩的描述,因此尽管译者和校对虽然尽力了,但是应该还有谬误。我觉得原文作者为了找出这些说明也尽力,恐怕真正权威的诠释只有 Canonical 才能给出吧。)
### Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish(幸运水母)

于 2021 年 4 月 21 日发布。
Jammy 的意思是被果酱覆盖着的、充满果酱的。不太正式地,Jammy 还有**幸运**的意思。
<ruby> 水母 <rt> Jellyfish </rt></ruby> 是一种自由游动的水生动物,它的身体就像是一把透明伞,还具有拖曳的触须。少数水母是通过茎干固定在海床上,而不能移动。全世界的海洋中有超过两百种的水母,它们分布于全球各地的水域里。
### Ubuntu 21.10 Impish Indri(顽皮大狐猴)

于 2021 年 10 月 14 日发布。
Impish 的意思是以**顽皮**而不是严肃的方式,对某人/某事不太尊重。
<ruby> 大狐猴 <rt> Indri </rt></ruby>,也称为 babakoto,是现存的最大的狐猴之一。它的头身长约 64 至 72 厘米,体重在 6 至 9.5 公斤之间。它的毛发是黑白相间的。在攀爬或攀爬时,它会保持竖直的姿势。
>
> 据维基:2014 年的世界自然保护联盟(IUCN) <ruby> 红色名录 <rt> Red List </rt></ruby> 中,仅出现在马达加斯加的大狐猴首次被提升至极危级别。
>
>
>
### Ubuntu 21.04 Hirsute Hippo(多毛河马)

于 2021 年 4 月 22 日发布。
Hirsute 的意思是**多毛的**。
<ruby> 河马 <rt> Hippo </rt></ruby>,是一种生活在非洲大陆撒哈拉以南的大型半水生哺乳动物。河马是河马科中仅有的两个现存物种之一,另一个物种是 <ruby> 侏儒河马 <rt> pygmy hippopotamus </rt></ruby>。河马的名字来源于古希腊语“river horse”。
>
> 据维基:在 2006 年 5 月已被 IUCN 红色名录中分为易危物种,世界仅存约 12.5 万-15 万头
>
>
>
但是其实,我并没有见过很多多毛的河马 ?。
### Ubuntu 20.10 Groovy Gorilla(时髦大猩猩)

于 2020 年 10 月 22 日发布。
Groovy 的意思是**时尚的**和令人兴奋的。
<ruby> 大猩猩 <rt> Gorilla </rt></ruby>,是一种草食性的地栖巨猿。它主要栖息在赤道非洲的热带森林中。大猩猩属分为两个物种:东部大猩猩和西部大猩猩,以及进一步可分为四个或五个亚种。
### Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa(瞩目狸猫)

于 2020 年 4 月 23 日发布。
Focal 的意思是令人注目的、**瞩目**。
<ruby> 马岛长尾狸猫 <rt> Fossa </rt></ruby>,是**马达加斯加岛上最大的食肉性哺乳动物**。它身体的长度可以达到近六英尺,其中它们的长尾巴占了一半。它们看起来就像是猫、狗和獴的杂交体。它们有细长的身体、肌肉发达的四肢和短的红棕色毛发。
### Ubuntu 19.10 Eoan Ermine(东方白鼬)

于 2019 年 10 月 17 日发布。
Eoan 的意思是**与黎明或东方有关的**。
<ruby> 白鼬 <rt> Stoat </rt></ruby>,也被称为欧亚貂、白令貂,简称 <ruby> 貂 <rt> Ermine </rt></ruby>,是一种原产于欧亚大陆和北美北部的鼬科动物。由于鼬在极地广泛分布,因此它被 IUCN 列为最不担忧灭绝的物种。
>
> 据维基:IUCN 将其列为世界百大外来入侵种。
>
>
>
### Ubuntu 19.04 Disco Dingo(迪斯科野犬)

于 2019 年 4 月 18 日发布。
Disco 与**迪斯科**音乐和夜总会有关。
<ruby> 澳洲野犬 <rt> Dingo </rt></ruby>,是在澳大利亚发现的一种古老的犬种。澳洲野犬的科属分类在不同出版物中不太一样,因此它的科属分类存在争议。
### Ubuntu 18.10 Cosmic Cuttlefish(外星墨鱼)

于 2018 年 10 月 18 日发布。
Cosmic 意味着与地球**不同的**、宇宙的。
<ruby> 墨鱼 <rt> Cuttlefish </rt></ruby>,是乌贼目的一种海洋软体动物。它属于头足类,这一类还包含了鱿鱼、章鱼和鹦鹉螺。墨鱼有一个独特的内壳,即墨鱼骨,它可以用于控制浮力。
### Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Bionic Beaver(仿生河狸)

于 2018 年 4 月 26 日发布。
Bionic 意味着**仿生的**,或者是机电的。
<ruby> 河狸 <rt> Beaver </rt></ruby>,是北半球温带的一种大型半水生啮齿动物。有两种现存的海狸:北美河狸和欧亚河狸。河狸是仅次于水豚的现存第二大啮齿动物。
>
> 据维基:它们处于 IUCN 哺乳动物红色名录中的无危物种,在中国河狸被列为一级保护动物。
>
>
>
英国用户认为这个版本的名称特别有趣。
### Ubuntu 17.10 Artful Aardvark(机灵土豚)

于 2017 年 10 月 19 日发布。
Ubuntu 在此版本中默认切换回了 GNOME。
Artful 的意思是聪明的或**机灵的**。
<ruby> 土豚 <rt> Aardvark </rt></ruby>,是一种原产于非洲的穴居、夜间活动的中型哺乳动物。它是管齿目中唯一的现存物种。与大多数其他食虫动物不同,它有一个长长的像猪一样的鼻子,可以闻出食物在哪里。
### Ubuntu 17.04 Zesty Zapus(开心跳鼠)

于 2017 年 4 月 13 日发布。
这个版本是最后一个以 Unity 桌面为特色的版本。
Zesty 意味着有一种强烈的、**令人开心的**、有点辛辣的味道。
<ruby> 跳鼠 <rt> Zapus </rt></ruby> 是北美跳鼠中唯一一个有牙齿的一个属。跳鼠是除 <ruby> 指猴 <rt> Aye-aye </rt></ruby>之外,唯一现存的有 18 颗牙齿的哺乳动物。
### Ubuntu 16.10 Yakkety Yak(唠叨牦牛)

于 2016 年 10 月 13 日发布。
Yakkety 有很多意思。OMG Ubuntu 说,“yakking” 有唠唠叨叨这一非正式意思,yakkety 还可能是一种知名的流行爵士乐器 “Yakety Sax” 的另一种拼写。
<ruby> 牦牛 <rt> Yak </rt></ruby>,是一种大型驯养的野牛。它的毛发蓬松,肩部隆起,有很大的角。在一些地方它是一种驮畜,人们也可以食用它的奶和肉、以及加工它的皮制作东西。
### Ubuntu 16.04 LTS Xenial Xerus(好客地松鼠)

于 2016 年 4 月 21 日发布。
Xenial 的意思是**热情好客的**。
<ruby> 非洲地松鼠 <rt> Xerus </rt></ruby>,有四个亚种,分别是**开普地松鼠,条纹地松鼠,山地松鼠和无条纹地松鼠**。这些动物是昼行性的,是食草动物,通常吃坚果、根和种子。然而,有时它们也会吃蛋类和其他小动物。
### Ubuntu 15.10 Wily Werewolf(狡猾狼人)

于 2015 年 10 月 22 日发布。
这个版本可能是少有的发布代号中带有虚构动物的 Ubuntu 版本之一。
Wily 的意思是善于获得优势,尤其在欺骗上十分**狡猾的**。
<ruby> 狼人 <rt> Werewolf </rt></ruby>,是可以隐藏住耳朵和尾巴的一种神话生物。它是人,也是狼,大多数人因为它们的长相而害怕它们。
### Ubuntu 15.04 Vivid Vervet(活泼绿猴)

于 2015 年 4 月 23 日发布。
Vivid 的意思是**活泼**的、明亮的。
<ruby> 黑长尾猴 <rt> Vervet monkey </rt></ruby>,是一种原产于非洲的角猿科的旧大陆猴。“vervet”一词也用于表示<ruby> 绿猴属 <rt> Chlorocebus </rt></ruby>的所有动物,其中包含五个不同的亚种,这五个不同的亚种主要分布在南部非洲以及一些东部国家。
### Ubuntu 14.10 Utopic Unicorn(乌托邦独角兽)

于 2014 年 10 月 23 日发布。
这个版本是另一个其发布代号中带有虚构动物的 Ubuntu 版本。
Utopic 与**乌托邦**有关,乌托邦是一个虚构的、不存在但是一个理想的地方。
<ruby> 独角兽 <rt> Unicorn </rt></ruby>,是一种传说中的生物。自古以来,它就被描述为前额有一个巨大的、尖的、螺旋状的角的一种野兽。
### Ubuntu 14.04 LTS Trusty Tahr(可靠塔尔羊)

于 2014 年 4 月 17 日发布。
Trusty 意味着**可靠的**或忠实的。
<ruby> 塔尔羊 <rt> Tahr </rt></ruby>,是一种很像山羊的哺乳动物。它们会栖息在阿曼、印度南部和喜马拉雅山脉的悬崖和山坡上。
### Ubuntu 13.10 Saucy Salamander(活泼蝾螈)

于 2013 年 10 月 17 日发布。
Saucy 意味着大胆的、**活泼的**或精神饱满的。
<ruby> 蝾螈 <rt> Salamander </rt></ruby>是一类两栖动物。其典型特征是有着蜥蜴般的外观,它们有细长的身体,钝的鼻子,以及与身体成直角突出的短肢,并且幼体和成体都有尾巴。现存的所有十个蝾螈科都属于有尾目。
### Ubuntu 13.04 Raring Ringtail(热情猫熊)

于 2013 年 4 月 25 日发布。
Raring 的意思是热情的和**非常渴望做某事**。
<ruby> 猫熊 <rt> Ringtail </rt></ruby>,是**一种像猫一样大的食肉动物,类似于一只长着浣熊尾巴的小狐狸**。它浓密的尾巴是扁平的,几乎和头部和身体一样长,有黑白交替的环。它们是夜行动物,一天中的大部分时间都在它们的巢穴里睡觉。
### Ubuntu 12.10 Quantal Quetzal(量子大咬鹃)

于 2012 年 10 月 18 日发布。
Quantal 意味着与**量子**或量子理论有关的。
<ruby> 大咬鹃 <rt> Quetzal </rt></ruby>,是咬鹃家族中的一种色彩鲜艳的鸟类。它们生活在森林中,主要是在潮湿的高地。来自*凤尾绿咬鹃属*的五种物种生活在新热带的,而另外一个物种,即角咬鹃,生活在墨西哥和美国最南端的局部地区。大咬鹃相当地大,它们的身体长度超过 32 厘米或者有 13 英寸长,比其他咬鹃科的物种都大。绚丽的大咬鹃因其鲜艳的色彩,而成为危地马拉的国鸟。
### Ubuntu 12.04 LTS Precise Pangolin(精准穿山甲)

于 2012 年 4 月 26 日发布。
Precise 意味着能**精确**或准确地表达细节。
<ruby> 穿山甲 <rt> Pangolin </rt></ruby>,有时被称为有鳞食蚁兽,是鳞甲目的一种哺乳动物。它现存的一个科是穿山甲科,有三个属:穿山甲亚属、长尾穿山甲亚属和地穿山甲亚属。穿山甲亚属包括在亚洲发现的四种物种,而长尾穿山甲亚属和地穿山甲亚属各包括两种物种,均在撒哈拉以南非洲发现。
>
> 据维基百科:2014 年,IUCN 红色名录物种存续委员会穿山甲专门小组,指出穿山甲是目前全世界最常被走私买卖的哺乳动物。所有穿山甲都面临巨大的生存威胁,其中中华穿山甲和马来穿山甲被 IUCN 评估为“极危”物种,非法走私的活动极为猖獗。随着亚洲的 4 种穿山甲数量锐减,走私贸易商家已转移目标至非洲,以满足市场上的庞大需求。
>
>
>
### Ubuntu 11.10 Oneiric Ocelot(梦幻豹猫)

于 2011 年 10 月 13 日发布。
Oneiric 的意思是与**梦**有关的。
<ruby> 豹猫 <rt> Ocelot </rt></ruby>,是一种中等大小的斑点野猫。它的肩长可达 40 至 50 厘米,体重在 8 至 15.5 公斤之间。<ruby> 卡尔·林奈 <rt> Carl Linnaeus </rt></ruby> 于 1758 年首次在书中描述了它。
>
> 据维基:华盛顿公约将孟加拉国、印度以及泰国的豹猫族群列入附录一禁止进行国际贸易,而其他族群亦列入华盛顿公约附录二。
>
>
>
### Ubuntu 11.04 Natty Narwhal(聪明独角鲸)

于 2011 年 4 月 28 日发布。
这个版本是第一个采用 Unity 桌面的版本。
Natty 意味着**聪明**和时尚的。
<ruby> 独角鲸 <rt> Narwhal </rt></ruby>,是一种中等大小的齿鲸。拥有一颗突出的犬齿的大“獠牙”。它常年生活在格陵兰、加拿大和俄罗斯周围的北极水域。它是一角鲸科中现存的两种鲸鱼物种之一,另一个物种是 <ruby> 白鲸 <rt> Beluga whale </rt></ruby>。
### Ubuntu 10.10 Maverick Meerkat(独行猫鼬)

于 2010 年 10 月 10 日发布。
Maverick 的意思是**特立独行的**或有独立思想的。
<ruby> 猫鼬 <rt> Meerkat </rt></ruby>,是一种在南部非洲发现的小型猫鼬。它的特点是头宽、眼睛大、鼻子尖、腿长、尾巴很细,毛色有斑纹。
### Ubuntu 10.04 LTS Lucid Lynx(清醒猞狸)

于 2010 年 4 月 29 日发布。
Lucid 意味着**易于理解的**或明亮的。
<ruby> 猞猁 <rt> Lynx </rt></ruby>,是中型野猫属猞猁中的一种。猞猁这个名字起源于中古英语,源自希腊语 λύγξ,λύγξ 又源自于印欧语词根 leuk-,指的是它眼睛能反射发光的样子。
### Ubuntu 9.10 Karmic Koala(幸运考拉)

于 2009 年 10 月 29 日发布。
Karmic 意味着与**命运**、业力有关。
<ruby> 考拉 <rt> Koala </rt></ruby>,是一种原产于澳大利亚的树栖草食性的有袋动物。它是袋鼠科唯一现存的物种,它的近亲是<ruby> 袋熊 <rt> Wombat </rt></ruby>。
>
> 据维基:在 19 世纪初树袋熊遭到捕杀出口,数量由百万只锐减至一千多只,于是澳大利亚政府立法保护。
>
>
>
### Ubuntu 9.04 Jaunty Jackalope(自信鹿角兔)

于 2009 年 4 月 23 日发布。
这个版本是我用的第一个 Ubuntu 版本。
Jaunty 是指拥有活泼、开朗和**自信**的态度。
<ruby> 鹿角兔 <rt> Jackalope </rt></ruby>,是**北美民间传说中的一种神话动物**,被描述为长着羚羊角的可怕的长角兔。Jackalope 这个词是由 jackrabbit 和 antelope 组合而成的。许多鹿角兔的标本都是由用鹿角制成的。
### Ubuntu 8.10 Intrepid Ibex(无畏野山羊)

于 2008 年 10 月 30 日发布。
Intrepid 意味着**无所畏惧**、冒险的。
<ruby> 野山羊 <rt> Ibex </rt></ruby>,以雄性的大弯角为特征,在前面形成像横向的脊那样。它主要分布于欧亚大陆、北非和东非。
### Ubuntu 8.04 LTS Hardy Heron(坚韧苍鹭)

于 2008 年 4 月 24 日发布。
这个版本是第一个吉祥物出现在其默认壁纸上的 Ubuntu 版本。
Hardy 意味着能够**忍受**困难条件的、强大的。
<ruby> 苍鹭 <rt> Heron </rt></ruby>,是一种长腿、长颈、生活在淡水和沿海的鸟类。
### Ubuntu 7.10 Gutsy Gibbon(阵风长臂猿)

于 2007 年 10 月 18 日发布。
Gusty 表示以**阵风**的方式吹动。
<ruby> 长臂猿 <rt> Gibbon </rt></ruby>,是一种猿类,它们生活在孟加拉国东部、印度东北部、中国南部和印度尼西亚的亚热带和热带雨林地区。
### Ubuntu 7.04 Feisty Fawn(活泼小鹿)

于 2007 年 4 月 19 日发布。
Feisty 意味着**小而坚定**的。
<ruby> 小鹿 <rt> Fawn </rt></ruby>,指的是第一年刚出生的小鹿。
### Ubuntu 6.10 Edgy Eft(紧张水蜥)

于 2006 年 10 月 26 日发布。
Edgy 的意思是**紧张的**。
<ruby> 水蜥 <rt> Eft </rt></ruby>,是蝾螈的陆生幼年期。蝾螈是一种蜥蜴,它具有三个不同的发育生命阶段:水生幼虫、陆生幼体和成体。
所以水蜥指的是一个青年的蝾螈。
### Ubuntu 6.06 Dapper Drake(整洁公鸭)

于 2006 年 6 月 1 日发布。
Dapper 的意思是衣着整洁,**外表整洁的**。
<ruby> 公鸭 <rt> Drake </rt></ruby>,是完全性成熟的成年雄性鸭子。
### Ubuntu 5.10 Breezy Badger(微风之獾)

于 2005 年 10 月 12 日发布。
Breezy 的意思是有**微风**的。
<ruby> 獾 <rt> Badger </rt></ruby>,一种是短腿的杂食动物,经常蹲下身挤在一起。
### Ubuntu 5.04 Hoary Hedgehog(灰白刺猬)

于 2005 年 4 月 8 日发布。
Hoary 是**灰白色的**意思。
<ruby> 刺猬 <rt> Hedgehogis </rt></ruby>,是一种多刺的哺乳动物,遍布于欧洲、亚洲和非洲的部分地区,并引入到了新西兰。
### Ubuntu 4.10 : Warty Warthog(有疣疣猪)

于 2004 年 10 月 20 日发布。
Ubuntu 就是从这个版本开始的。
Wart 是由病毒引起的一种小的、坚硬的、良性的皮肤生长物。Warty 的意思是**长满疣的**。
<ruby> 疣猪 <rt> Warthog </rt></ruby>,是猪科的一种野生动物,它是在撒哈拉以南非洲的草原、稀树草原和林地中被发现的。
### 总结
本文有没有让 Ubuntu 用户了解了更多知识呢?从技术上讲,并没有,但回顾历史是件好事。如果你多年来一直是 Ubuntu 用户,那么这篇文章可能会引发你的怀旧之情。
Ubuntu 9.04 是我第一次尝试 Linux 桌面。如果我没记错的话,那是在 2009 年 9 月下旬。仅仅几周后,我的系统就升级到了 Ubuntu 9.10。那些天我经常在 Ubuntu 论坛上浏览,探索这个新的操作系统,并学习新的东西。
那么,这篇文章有没有勾起你的一些美好的回忆呢?你的第一个 Ubuntu 版本又是哪个呢?在评论区中分享你的 Ubuntu 使用经历吧。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/all-Ubuntu-mascots/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
15,241 | 如何在 VLC 播放器中裁剪视频 | https://itsfoss.com/vlc-trim-video/ | 2022-11-11T15:32:21 | [
"VLC",
"视频"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15241-1.html | 
VLC 媒体播放器是 [最好的媒体播放器](https://itsfoss.com/video-players-linux/) 之一。这款跨平台播放器功能丰富,可以播放任何可用的媒体格式。
你会惊讶地发现 VLC 不仅仅是一个视频播放器。它可以对你的媒体文件做很多事情。
我们分享过 [使用 VLC 下载 YouTube 视频](https://itsfoss.com/download-youtube-videos-vlc/) 的 [VLC 技巧](https://itsfoss.com/simple-vlc-tips/)。
让我再和你分享一个。用 VLC 裁剪视频怎么样?这不是 [裁剪视频](https://itsfoss.com/video-trimmer/) 的最佳方式,但它可以作为一个选择使用。
### 使用 VLC 裁剪视频
在 VLC 中裁剪视频本质上意味着从所需部分的开头到结尾录制视频。默认情况下,录制控制工具通常在 VLC 面板中不可见。
让我详细介绍一下步骤。
#### 步骤 1:启用高级控件
要获取控件,你需要使其在主控制面板上可见。
首先选择“<ruby> 视图 <rt> View </rt></ruby>”选项,然后选中“<ruby> 高级控件 <rt> Advanced Controls </rt></ruby>”复选框。现在,如截图所示,出现了带有几个按钮的新控件行。

#### 步骤 2:打开视频
为了裁剪视频,你需要在 VLC 中打开它。你可以通过“<ruby> 媒体 <rt> Media </rt></ruby> > <ruby> 打开文件 <rt> Open File </rt></ruby>”在 VLC 播放器中打开视频:

或者你可以使用 Nautilus 文件管理器中的 VLC 打开视频文件:

#### 步骤 3:使用 VLC 的录制功能裁剪视频
打开视频文件后,将时间线设置为所需输出的起点并暂停视频。之后,按“录制”按钮并播放视频。

当达到所需输出的终点时,暂停视频并再次按下“录制”按钮停止录制。

这应该将裁剪后的输出保存到你的 `~/Videos` 目录中。

### 故障排除:无法识别的输出文件
VLC 以 .ts 文件格式录制视频。这在 VLC 中受支持,你可以根据需要使用它。但是 Ubuntu 中的许多其他播放器,包括本地视频播放器,都无法识别该格式。因此,在这种情况下,有两种解决方案。
#### Gnome-Video 提示安装 GStreamer 包
当你尝试打开文件时,GNOME-Videos 会提示错误并建议安装 Gstreamer 多媒体编解码器。

你可以点击上图所示的 “<ruby> 在 Ubuntu 软件应用中查找 <rt> Find in Ubuntu Software </rt></ruby>” 按钮,这将打开 Ubuntu 软件中心。你可以在那里安装所需的编解码器包。

同样安装 Gnome-videos 并使用它打开视频将解决问题。
#### 使用 VLC 转换视频文件
如果你不想为此安装任何额外的软件包,你可以使用 VLC 本身将 .ts 文件转换为 mp4 格式以在任何其他播放器中播放。
为此,打开 VLC 并在“<ruby> 媒体 <rt> Media </rt></ruby>”菜单下选择“<ruby> 转换/保存 <rt> Conver/Save </rt></ruby>”选项。

现在,使用“<ruby> 添加 <rt> Add </rt></ruby>”按钮提供需要转换的文件的位置,然后选择“<ruby> 转换/保存 <rt> Conver/Save </rt></ruby>”,如截图所示。

选择所需的输出配置(MP4)并为输出设置文件名,然后按“<ruby> 开始 <rt> Start </rt></ruby>”。

这将开始转换,并根据源的时长决定转换时间。完成后,你可以从 `~/Videos` 目录访问转换后的输出。

### 总结
虽然确实可以使用 VLC 播放器来裁剪视频,但整个过程与专门的 [视频编辑器](https://itsfoss.com/open-source-video-editors/) 完全不同。
最大的问题是你需要观看所有裁剪部分才能完成裁剪,如果你要裁剪跨越数分钟的视频的一大部分,这就不方便了。
无论如何,这个很酷的功能在某些情况下可能是一个方便的工具,比如你想要的只是裁剪一个特定的小剪辑或从电影场景中制作一个 Gif。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/vlc-trim-video/>
作者:[Sreenath](https://itsfoss.com/author/sreenath/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

VLC media player is one of the [best media players](https://itsfoss.com/video-players-linux/) out there. This cross-platform player is feature rich and it can literally play any media format that’s available.
You’ll be surprised to know that VLC is much more than just a video player. It can do a lot of things with your media files.
[Downloading YouTube video with VLC](https://itsfoss.com/download-youtube-videos-vlc/) is one of the [VLC tips](https://itsfoss.com/simple-vlc-tips/) we have shared on It’s FOSS.
Let me share another one with you. How about trimming a video with VLC? It’s not the best way to [trim videos](https://itsfoss.com/video-trimmer/) but it is available as an option.
## Trim videos using VLC
Trimming a video in VLC essentially means recording the video from the beginning to end of the required portion. The recording control tools are usually not visible in the VLC panel by default.
Let me show the steps in detail.
**Step 1: Enable advanced controls**
To get the controls, you need to make it visible on the main control panel.
First select the view option and then check the Advanced controls check box. Now, a new row of controls with a couple of buttons appears as shown in the screenshot.
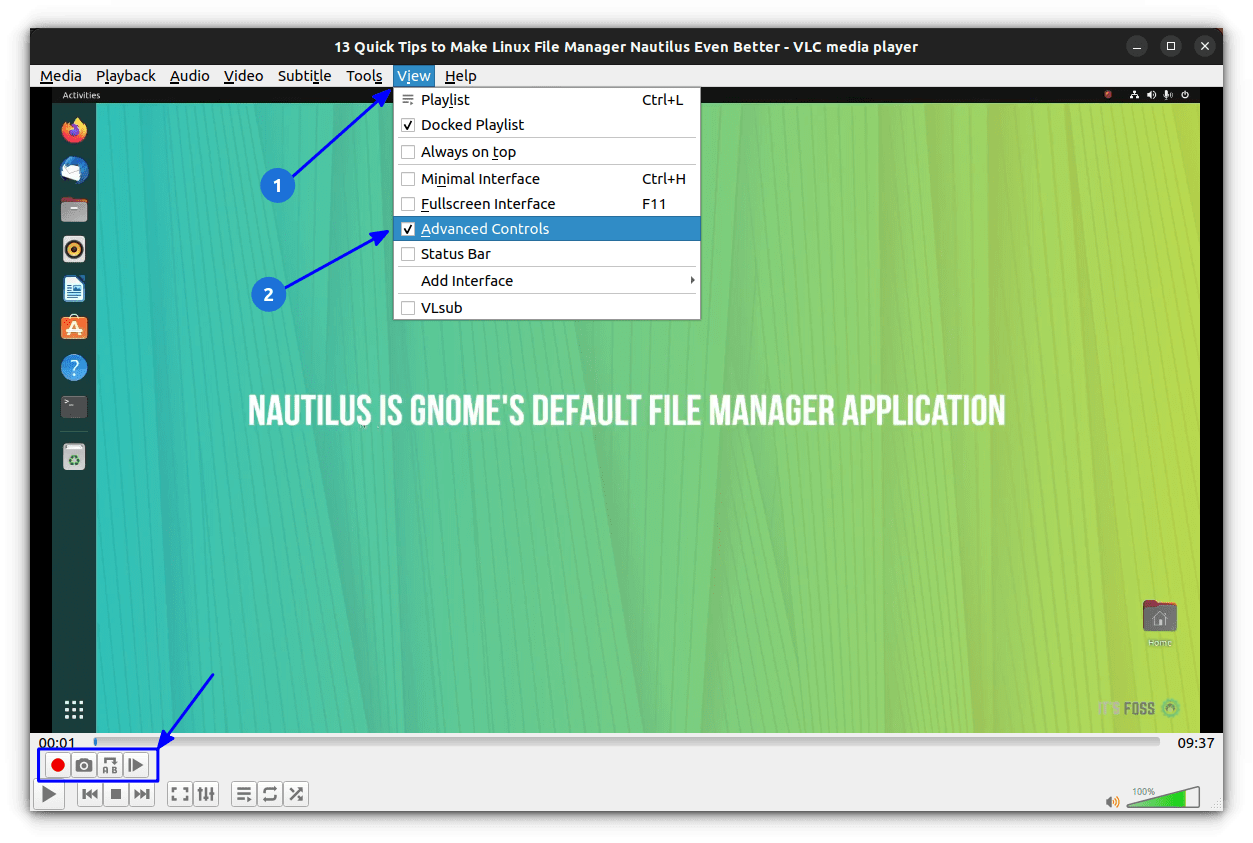
### Step 2: Open the video
In order to trim a video, you need to open it in VLC. You can either open the video in VLC player by Media > Open File:
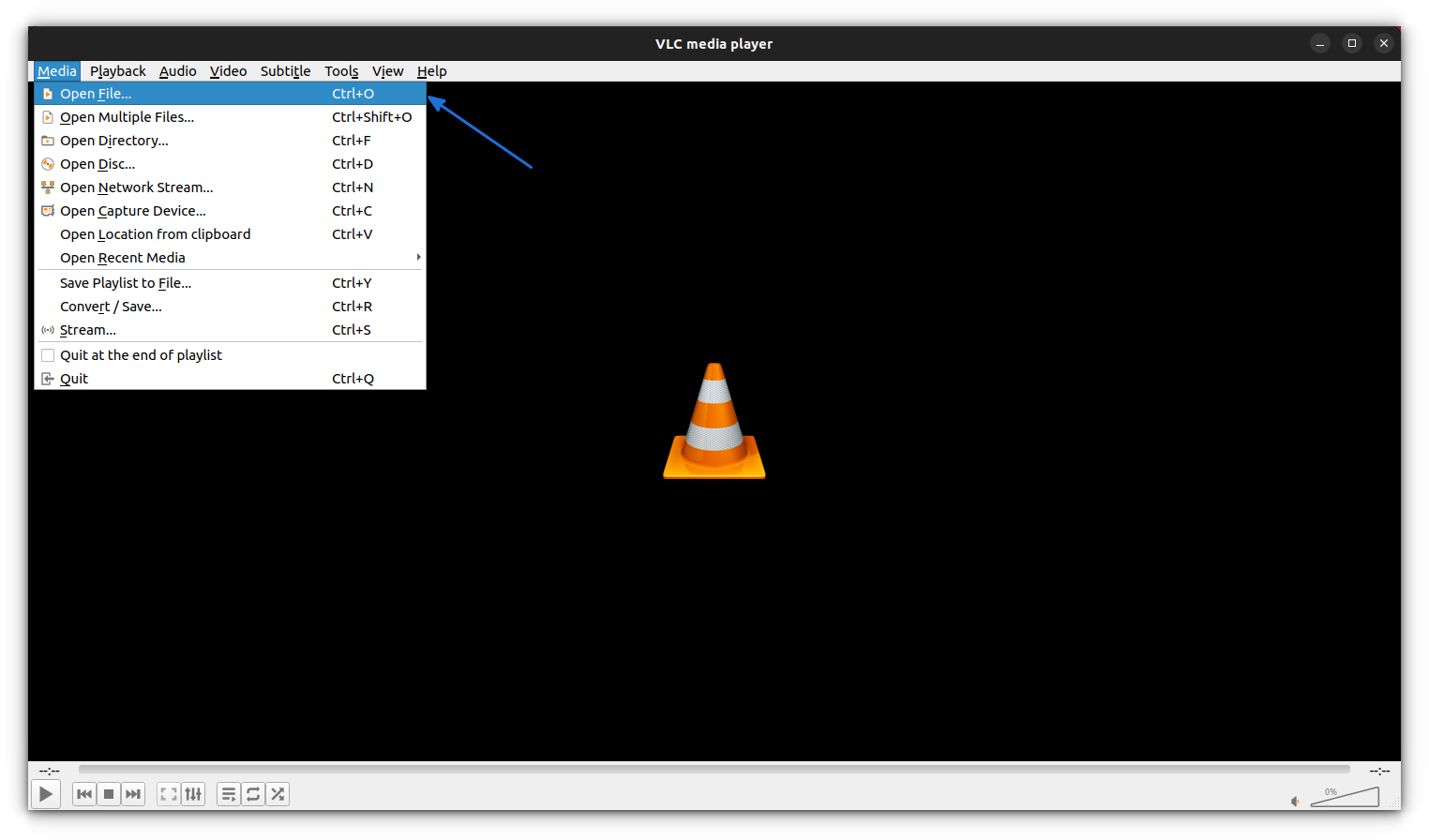
Or you can open the video file with VLC from Nautilus file manager:
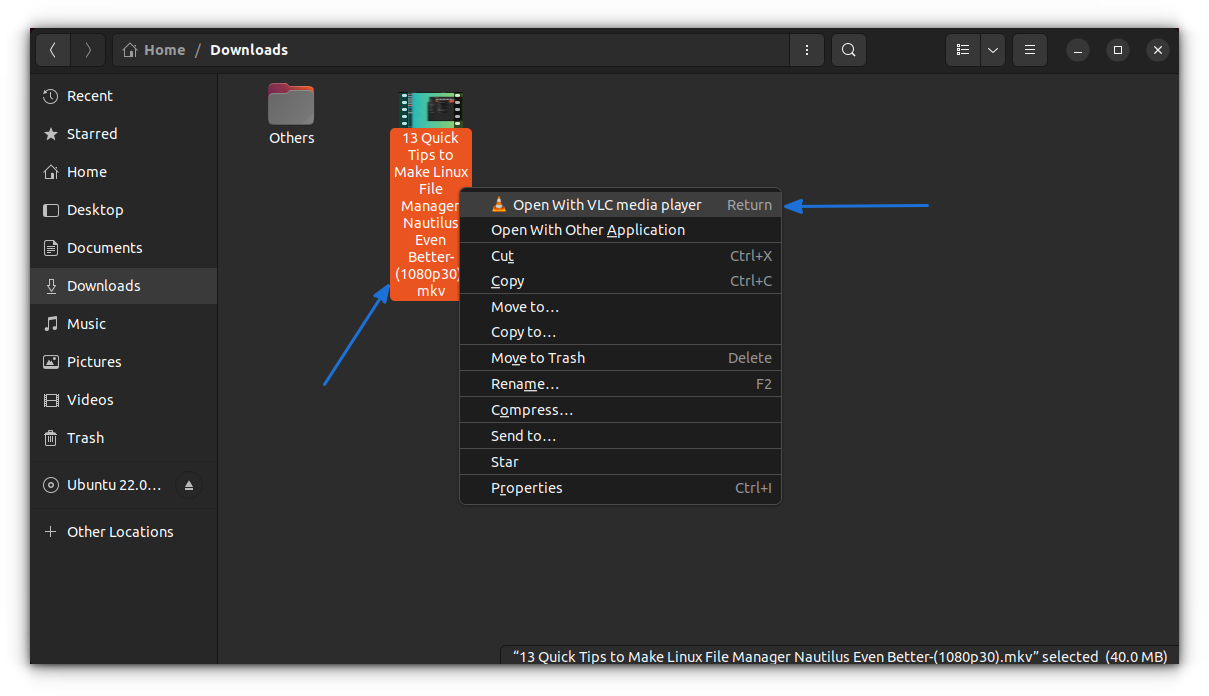
### Step 3: Trim video using VLC’s recording feature
Once video file is opened, set the timeline to the starting point of the required output and pause the video. After that, press the record button and play the video.
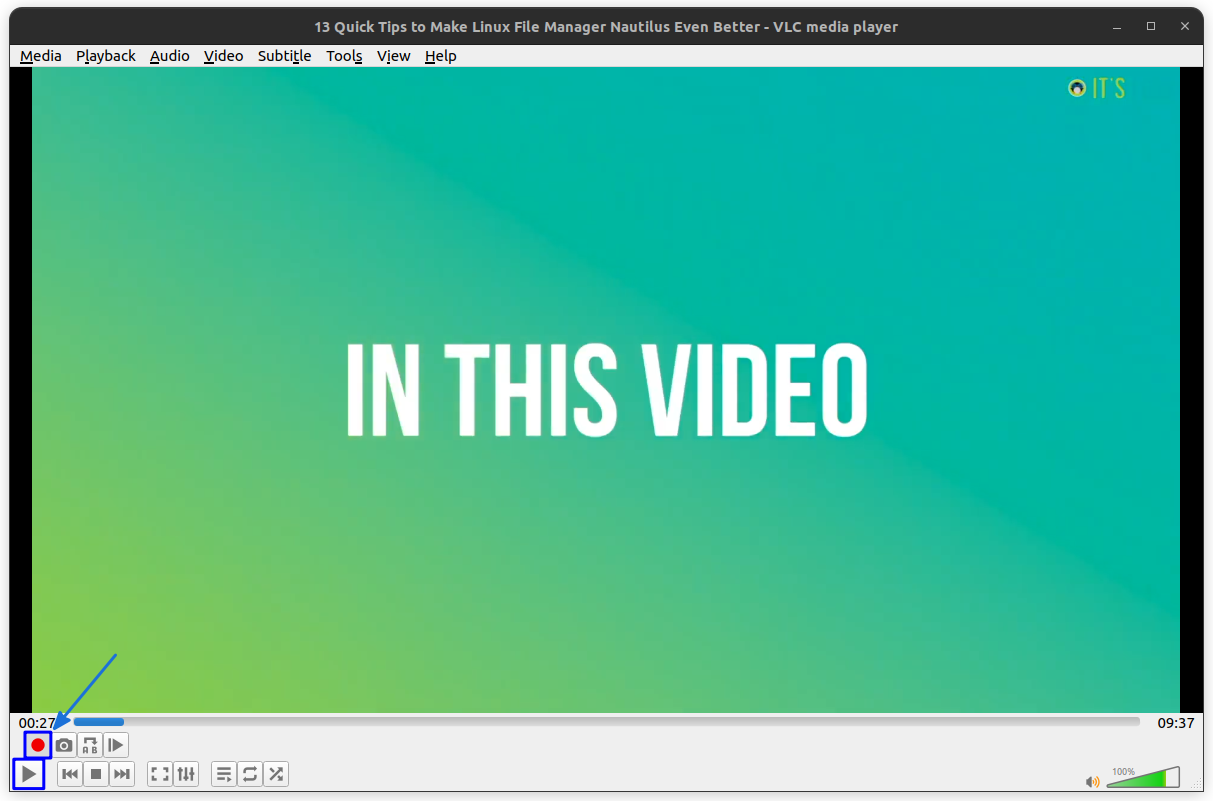
When the end point of the required output is reached, pause the video and press the record button again to stop recording.
This should save the trimmed output to your ~/Videos directory.
## Troubleshooting: Unrecognized Output File
VLC records the videos in .ts file format. This is supported in VLC, and you can use that as you want. But many other players in Ubuntu, including the native video player doesn’t recognize the format. So, in this case, there are two solutions.
**Gnome-Video prompts Installation of GStreamer package**
When you try to open the file, GNOME-Videos will prompt an error and suggestion to install Gstreamer multimedia codecs.
You can click on the “Find in Ubuntu Software” button as shown above, which will open ubuntu software center. There you can install the required codec package.
Install the same and open the video with Gnome-videos again will solve the problem.
**Convert the Video file using VLC**
If you don’t want to install any additional packages for the purpose, you can use VLC itself to convert the .ts file to mp4 format to play in any other player.
For this, open VLC and select Convert option under File menu.
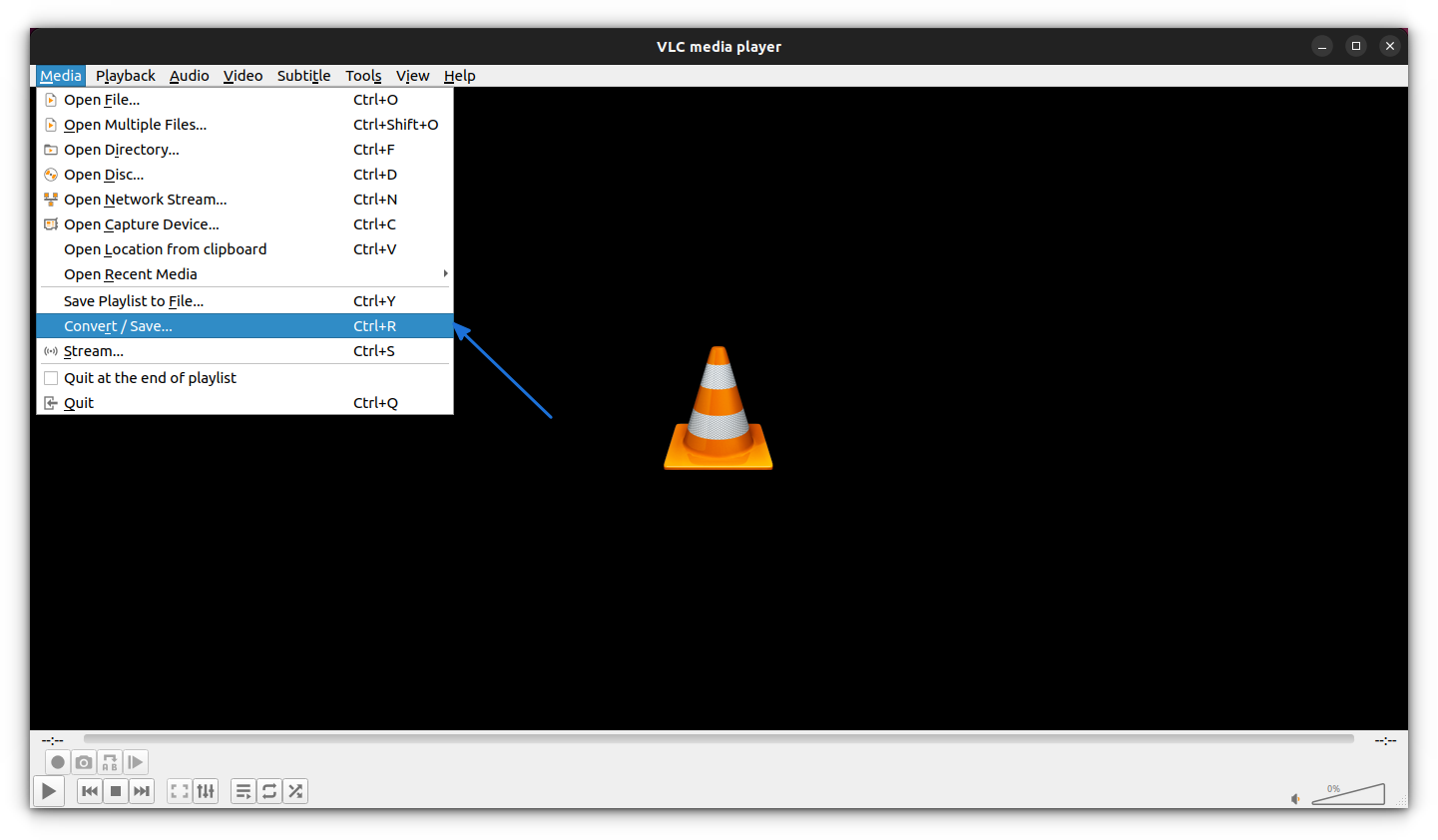
Now, provide the location of the file that needs to be converted using the “Add” button and select Convert/Save as shown in the screenshot.
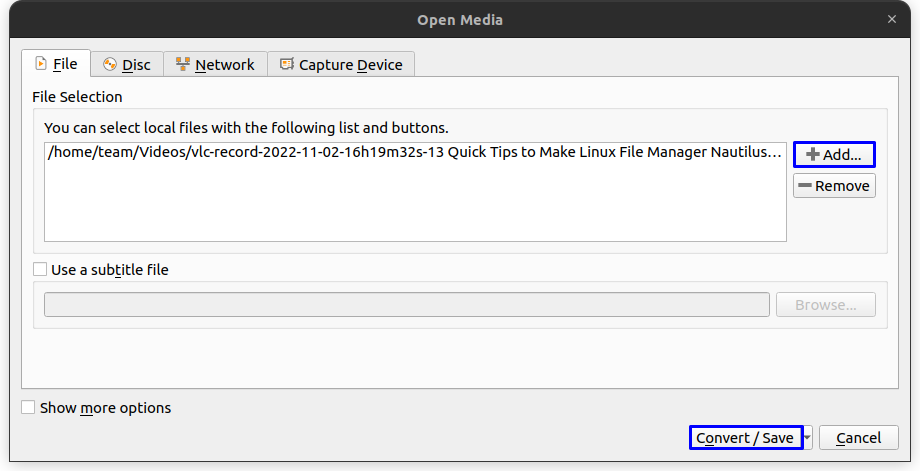
Select the required output profile (MP4) and set a file name for the output and press Start.
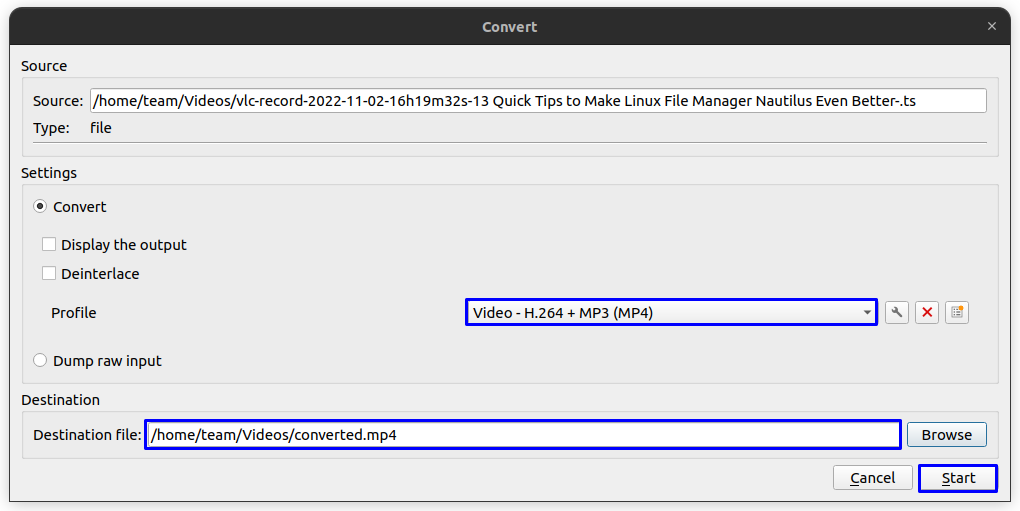
This will start the conversion and will be completed as per the duration of the source. Once done, you can access the converted output from your ~/Videos directory.
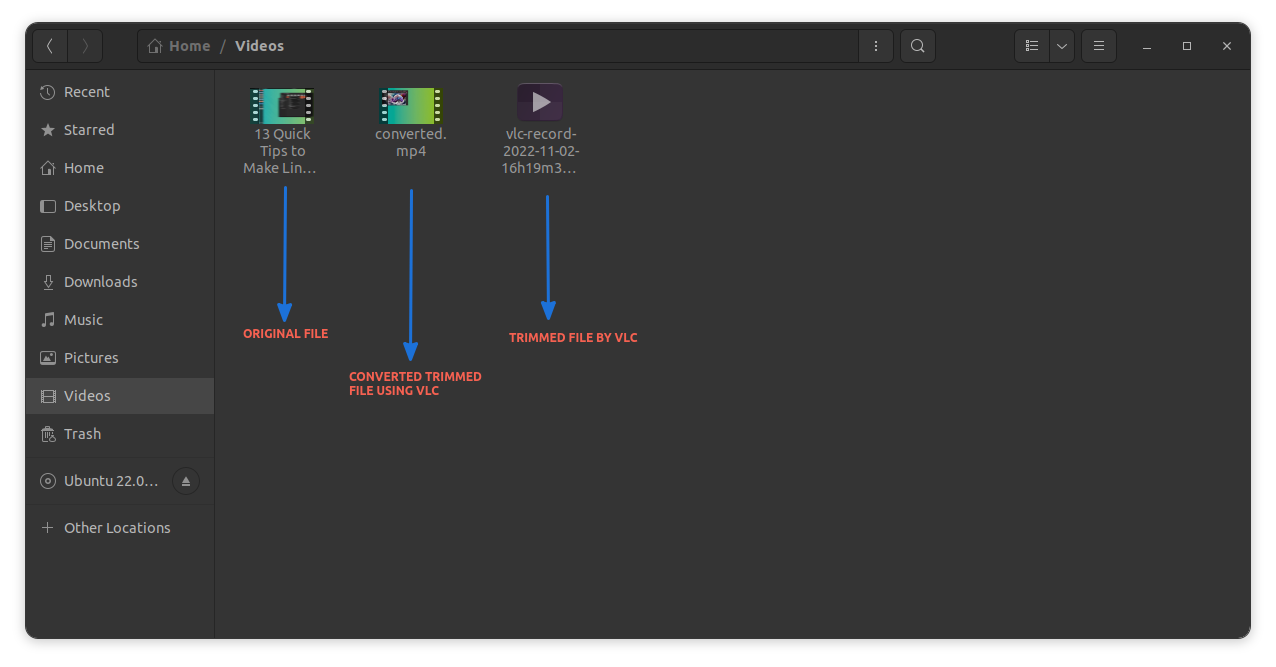
## Wrapping Up
While it is true that VLC player can be used to trim videos, the entire process is in no way similar to a dedicated [video editor](https://itsfoss.com/open-source-video-editors/).
The biggest issue is that you need to watch the entire trim portion to complete the trimming, which is not convenient if you are trimming a large portion of a video spanning several minutes.
Anyway, this cool feature can be a handy tool on some occasions, where you only want to trim a small clip or make a gif from a movie scene. |
15,243 | Lua 值得学习吗? | https://opensource.com/article/22/11/lua-worth-learning | 2022-11-12T11:19:46 | [
"Lua"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15243-1.html | 
>
> Lua 是一个有趣而强大的语言,随着各个版本的推进,功能愈发的强大,开发者群体也在不断的增长。这篇文章我们将探索一下它的各种前景。
>
>
>
Lua 是一个脚本语言,它面向过程、函数式编程,甚至可以是 [面向对象的](https://opensource.com/article/22/10/object-oriented-lua%20)。它使用类 C 语言的语法,但却是动态类型,具有自动内存管理和垃圾回收功能,使用基于寄存器的虚拟机来解释字节码。这些特点使得它对于初学者来说是个很好的语言,同时也是经验丰富的程序员的强大工具。
虽然与 [Python](https://opensource.com/resources/python) 和 [JavaScript](https://opensource.com/article/22/9/javascript-glossary) 相比,Lua 现在已经有点儿黯然失色了,但是 Lua 拥有的一些优点使得它在许多的重大软件项目中很受欢迎。Lua 很容易嵌入到其他语言当中, 这意味着你可以在(例如)Java 编写的代码中包含 Lua 文件,就像原生的 Java 代码一样运行。这听起来就像魔法一般,现在有许多项目如 [luaj](https://github.com/luaj/luaj) 使得其成为可能,之所以可以实现,正是因为 Lua 就是为此而设计的。部分出于这种灵活性,你可以在许多游戏、图形应用的程序中发现 Lua 脚本的身影。
就像其他任何事情一样,做到完美是需要时间的,但 Lua 是很易于学习(并且有趣)的语言。它是一种一致的语言、一种带有有用的错误消息的友好的语言,并且可以在网上轻松找到许多有用的资料。那么就让我们开始吧!
### 安装 Lua
在 Linux 下,你可以使用发行版自带的包管理来安装 Lua。例如,在 Fedora、CentOS、 Mageia、OpenMandriva 以及类似发行版中:
```
$ sudo dnf install lua
```
在 Debian 以及基于 Debian 的系统中:
```
$ sudo apt install lua
```
对于 Mac,你可以使用 [MacPorts](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/macports) 或者 [Homebrew](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/homebrew-linux):
```
$ sudo port install lua
```
对于 Windows,可以使用 [Chocolatey](https://opensource.com/article/20/3/chocolatey) 安装 Lua。
完成安装后,可以在终端中输入 `lua` 来在交互式解释器中使用 Lua。
### 函数
如许多编程语言一样,Lua 的语法通常是一个内建的函数或关键字,后面跟着参数。例如,`print` 函数显示你传给它的所有参数。
```
$ lua
Lua 5.4.2 Copyright (C) 1994-2020 Lua.org,PUC-Rio
> print('hello')
hello
```
Lua 的 `string` 库可以操作单词(在编程中称为“字符串”)。例如,要统计字符串中的字母数量,你可以使用 `string` 库中 `len` 函数:
```
> string.len('hello')
5
```
### 变量
变量允许你在计算机内存中为临时的数据创建一个指定的空间。Lua 中创建变量的方法是赋予变量一个名字,接着将数据放入其中。
```
> foo = "hello world"
> print(foo)
hello world
> bar = 1+2
> print(bar)
3
```
### 表
在编程中,数组的使用频率仅次于变量。“数组”这个词的字面意思就是一种排列,而这就是程序中数组的意义了。它是数据的一种排列,因为有排列,所有数组具有结构化的优势。本质上,数组通常用于和变量相同的目的,只不过数组会给对其中的数据进行排序。在 Lua 中,数组被称为“表”。(LCTT 译注:使用过其它编程语言的同学可以发现,Lua 的表相当于其它语言中的关联数组、哈希。)
创建表和创建变量类似,区别仅在于它的初始化内容被设置为 `{}`:
```
> mytable = {}
```
当往表中增加数据时,它就如同创建变量一样,区别在于这里的变量之前总是以表名开头,中间使用 `.` 来连接:
```
> mytable.foo = "hello world"
> mytable.bar = 1+2
> print(mytable.foo)
hello world
> print(mytable.bar)
3
```
### 使用 Lua 编写脚本
在终端交互环境中运行 Lua 可以得到良好的反馈,但是将 Lua 作为脚本运行会更为有用。Lua 脚本就是包含 Lua 代码的文本文件,Lua 命令可以解析并执行此文件。
在刚刚开始学习一门编程语言时,一个永恒的问题是你怎么知道该写什么。这篇文章将提供一个不错的开端,截至目前,你仅知道了两三个 Lua 函数。懂得查阅文档是很关键的。Lua 并不是一个复杂的语言,可以通过 [Lua 文档网站](http://www.lua.org/docs.html) 很方便的获取关键字以及函数的用法。
下面是一个练习题。
假设你想编写一个 Lua 脚本来统计句子中的单词数量。与众多的编程挑战一样,有许多方法可以解决这个问题,假设你在 Lua 文档中找到的第一个相关的函数是 `string.gmatch`,此函数可以搜索字符串中的特定字符。单词通常通过空格分隔开来,所以你决定计算空格数并加 1 来作为单词的数量。
下面是实现的代码:
```
function wc(words,delimiter)
count=1
for w in string.gmatch(words,delimiter) do
count = count + 1
end
return count
end
```
下面是这个样例代码的解释:
* `function`:这是声明函数开始的关键字。自定义函数的工作方式与内置函数(如 `print` 和 `string.len`)基本相同。
* `words` 和 `delimiter`:这是函数运行所需的参数。正如 `print('hello')` 当中,`hello` 是一个参数。
* `counter`:一个变量,且被初始化为 `1`。
* `for`:在循环中使用 `string.gmatch` 作为迭代器遍历 `words`,并且在其中搜索`delimiter`。
* `count = count + 1`:当搜索到了 `delimiter`,则对 `count` 进行自增 1 的操作。
* `end`:`for` 循环的结束关键字。
* `return count`:这个函数输出(或返回)`count` 变量的内容。
* `end`:函数结束的关键字。
现在你已经创建了一个函数,你可以使用它。需要记住,函数不会自动运行,而是等待你在代码中调用它。
将下面的代码写入文件并保存为 `words.lua`:
```
function wc(words,delimiter)
count=1
for w in string.gmatch(words,delimiter) do
count = count + 1
end
return count
end
result = wc('zombie apocalypse',' ')
print(result)
result = wc('ice cream sandwich',' ')
print(result)
result = wc('can you find the bug? ',' ')
print(result)
```
你现在创建了一个 Lua 脚本。你可以使用 Lua 运行它。随后你会发现统计单词的结果有些问题:
```
$ lua ./words.lua
2
3
6
```
你也许已经注意到了最后一个句子的单词统计不正确,因为在句子的最后带有一个额外的空格。Lua正确的检测到了空格,并将其计入 `count` 中,但是单子的统计是错误的,因为有个空格并没有作为单词的分隔出现。我把这个问题留给你来解决,或者去发现其他方法,即使方法不太理想。编程中有很多需要思考的地方。有时是纯粹学术性的思考,有时也许是应用是否运训正常的思考。
### 学习 Lua
Lua 是一个有趣且强大的语言,随着版本的推进,功能愈发的强大,开发者群体也在不断的增长。你可以将 Lua 作为实用性的个人脚本使用,或者在工作中使用,或者仅仅是体验一下一个新的语言。尝试一下,看看 Lua 能给你带来什么吧。
(LCTT 译注:顺便问一句,你知道 “Lua” 怎么发音吗? ?)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/11/lua-worth-learning>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[MuggleWei](https://github.com/MuggleWei) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Lua is a scripting language used for procedural programming, functional programming, and even [object-oriented programming](https://opensource.com/article/22/10/object-oriented-lua ). It uses a C-like syntax, but is dynamically typed, features automatic memory management and garbage collection, and runs by interpreting bytecode with a register-based virtual machine. This makes it a great language for beginners, but also a powerful tool for experienced programmers.
Lua has been somewhat eclipsed from the public view by languages like [Python](https://opensource.com/resources/python) and [JavaScript](https://opensource.com/article/22/9/javascript-glossary), but Lua has several advantages that make it popular in some major software projects. Lua is easily embedded within other languages, meaning that you can include Lua files in the code base of something written in (for instance) Java and it runs as if it were native Java code. It sounds like magic, but of course there are projects like [luaj](https://github.com/luaj/luaj) working to make it possible, and it's only possible because Lua is designed for it. It's partly because of this flexibility that you're likely to find Lua as the scripting language for video games, graphic applications, and more.
As with anything, it takes time to *perfect*, but Lua is easy (and fun) to learn. It's a consistent language, a friendly language with useful error messages, and there's lots of great support online. Ready to get started?
## Installing Lua
On Linux, you can install Lua using your distribution's package manager. For instance, on Fedora, CentOS, Mageia, OpenMandriva, and similar distributions:
```
````$ sudo dnf install lua`
On Debian and Debian-based systems:
```
````$ sudo apt install lua`
For Mac, you can use [MacPorts](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/macports) or [Homebrew](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/homebrew-linux).
```
````$ sudo port install lua`
For Windows, install Lua using [Chocolatey](https://opensource.com/article/20/3/chocolatey).
To test Lua in an interactive interpreter, type `lua`
in a terminal.
## Functions
As with many programming languages, Lua syntax generally involves a built-in function or keyword, followed by an argument. For instance, the `print`
function displays any argument you provide to it.
```
``````
$ lua
Lua 5.4.2 Copyright (C) 1994-2020 Lua.org, PUC-Rio
> print('hello')
hello
```
Lua's `string`
library can manipulate words (called "strings" in programming.) For instance, to count the letters in a string, you use the `len`
function of the `string`
library:
```
``````
> string.len('hello')
5
```
## Variables
A variable allows you to create a special place in your computer's memory for temporary data. You can create variables in Lua by inventing a name for your variable, and then putting some data into it.
```
``````
> foo = "hello world"
> print(foo)
hello world
> bar = 1+2
> print(bar)
3
```
## Tables
Second only to the popularity of variables in programming is the popularity of *arrays*. The word "array" literally means an *arrangement*, and that's all a programming array is. It's a specific arrangement of data, and because there is an arrangement, an array has the advantage of being structured. An array is often used to perform essentially the same purpose as a variable, except that an array can enforce an order to its data. In Lua, an array is called a `table`
.
Creating a table is like creating a variable, except that you set its initial content to two braces (`{}`
):
```
````> mytable = {}`
When you add data to a table, it's also a lot like creating a variable, except that your variable name always begins with the name of the table, and is separated with a dot:
```
``````
> mytable.foo = "hello world"
> mytable.bar = 1+2
> print(mytable.foo)
hello world
> print(mytable.bar)
3
```
## Scripting with Lua
Running Lua in the terminal is great for getting instant feedback, but it's more useful to run Lua as a script. A Lua script is just a text file containing Lua code, which the Lua command can interpret and execute.
The eternal question, when just starting to learn a programming language, is how you're supposed to know what to write. This article has provided a good start, but so far you only know two or three Lua functions. The key, of course, is in documentation. The Lua language isn't that complex, and it's very reasonable to refer to the [Lua documentation site](http://www.lua.org/docs.html) for a list of keywords and functions.
Here's a practice problem.
Suppose you want to write a Lua script that counts words in a sentence. As with many programming challenges, there are many ways to go about this, but say the first relevant function you find in the Lua docs is `string.gmatch`
, which can search for a specific character in a string. Words are usually separated by an empty space, so you decide that counting spaces + 1 ought to render a reasonably accurate count of the words they're separating.
Here's the code for that function:
```
``````
function wc(words,delimiter)
count=1
for w in string.gmatch(words, delimiter) do
count = count + 1
end
return count
end
```
These are the components of that sample code:
-
`function`
: A keyword declaring the start of a function. A custom function works basically the same way as built-in functions (like`print`
and`string.len`
.) -
`words`
and`delimiter`
:*Arguments*required for the function to run. In the statement`print('hello')`
, the word`hello`
is an argument. -
`counter`
: A variable set to 1. -
`for`
: A loop using the`string.gmatch`
function as it iterates over the`words`
you've input into the function, and searches for the`delimiter`
you've input. -
`count = count +1`
: For each`delimiter`
found, the value of`count`
is re-set to its*current value*plus 1. -
`end`
: A keyword ending the`for`
loop. -
`return count`
: This function outputs (or*returns*) the contents of the`count`
variable. -
`end`
: A keyword ending the function.
Now that you've created a function all your own, you can use it. That's an important thing to remember about a function. It doesn't run on its own. It waits for you to call it in your code.
Type this sample code into a text file and save it as `words.lua`
:
```
``````
function wc(words,delimiter)
count=1
for w in string.gmatch(words, delimiter) do
count = count + 1
end
return count
end
result = wc('zombie apocalypse', ' ')
print(result)
result = wc('ice cream sandwich', ' ')
print(result)
result = wc('can you find the bug? ', ' ')
print(result)
```
You've just created a Lua script. You can run it with Lua. Can you find the problem with this method of counting words?
```
``````
$ lua ./words.lua
2
3
6
```
You might notice that the count is incorrect for the final phrase because there's a trailing space in the argument. Lua correctly detected the space and tallied it into `count`
, but the word count is incorrect because that particular space happens not to delimit a word. I leave it to you to solve that problem, or to find other ways in which this method isn't ideal. There's a lot of rumination in programming. Sometimes it's purely academic, and other times it's a question of whether an application works at all.
## Learning Lua
Lua is a fun and robust language, with progressive improvements made with each release, and an ever-growing developer base. You can use Lua as a utilitarian language for personal scripts, or to advance your career, or just as an experiment in learning a new language. Give it a try, and see what Lua brings to the table.
## 1 Comment |
15,244 | 使用 GNOME Boxes 将虚拟机镜像移动到另一台主机 | https://www.debugpoint.com/move-virtual-machine-image-another-host/ | 2022-11-12T11:37:00 | [
"虚拟机",
"GNOME Boxes"
] | /article-15244-1.html | 
>
> 本指南介绍了使用 GNOME Boxes 将虚拟机镜像移动到另一台主机所需的步骤。
>
>
>
GNOME Boxes 是由 GNOME 项目创建的虚拟化程序。此程序用作 libvirt 的前端。libvirt 是用于管理平台虚拟化的开源 API、守护进程和管理工具。它支持不同的虚拟化技术,如 KVM、Xen、VMware ESXi、QEMU 等。
如果你想使用 GNOME Boxes 创建虚拟机,[请参阅本指南](https://www.debugpoint.com/2020/05/install-use-gnome-boxes/)。
在本教程中,我将解释如何将任何虚拟机镜像文件(已使用 GNOME Boxes 创建并运行)移动到不同的主机并运行它。
这样,你不再需要从操作系统重新安装虚拟机。此外,它是便携式的,你可以将虚拟机镜像放在 U 盘中。
### 如何使用 GNOME Boxes 将虚拟机镜像移动到另一台主机
我希望你已经在 GNOME Boxes 中创建了一个虚拟机。如果没有,请查看 [本指南](https://www.debugpoint.com/2020/05/install-use-gnome-boxes/)。
GNOME Boxes 和 [libvert](https://libvirt.org/) 使用以下目录存储虚拟机镜像和配置。如下所述,你需要仔细备份每个文件。
GNOME Boxes 将虚拟机的物理镜像(通常为数 GB 大小)保存在以下路径中。对于你的每个虚拟机,你都会在其中找到一个镜像。
```
~/.local/share/gnome-boxes/images/
```

将图像文件复制到新主机的路径:`~/.local/share/gnome-boxes/images/`。
将 libvirt 的 XML 配置从以下路径复制到新主机的相同位置。
```
~/.config/libvirt/qemu/
```

在上述路径中,你应该会看到每个虚拟机的单独 xml 文件。复制你需要的那个。
在你当前的系统中打开以下文件。
```
~/.config/gnome-boxes/sources/'QEMU Session'
```
复制属于你的虚拟机的部分(从 `[display` ... 到本部分的末尾)。你可以使用名称轻松找到它(看下面的 `last-seen-name`)。

在另一台主机上打开相同的上述文件并将复制的内容附加到末尾。保存文件。
关闭新主机中的所有应用,包括 GNOME Boxes。
现在打开 GNOME Boxes,你应该会看到你的虚拟机和它的内容一起被移动到新主机中。
你现在可以拥有一个可以轻松携带和移动的便携式虚拟机。请记住,目标机器应该安装了 GNOME Boxes 才能完成这项工作。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/move-virtual-machine-image-another-host/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,246 | 使用这个多功能的 Linux 命令转换音频文件 | https://opensource.com/article/20/2/linux-sox | 2022-11-13T10:43:18 | [
"音频",
"SoX"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15246-1.html |
>
> SoX Sound Exchange 甚至可以为你的音频文件添加特效。
>
>
>

我工作需要使用音视频媒体,不管你处理哪种媒体,你肯定知道标准化是一种有价值的工具。就像你不会试图把一个分数加到一个小数上而不转换其中一个一样,我已经知道,把不同格式的媒体组合起来并不理想。为了方便用户,大多数爱好者级应用程序使转换过程不可见。然而,对于那些需要控制媒体细节的用户的灵活软件,会通常让你自己提前将媒体转换为所需的格式。我有一些最喜欢的音频转换工具,其中之一就是号称“音频的瑞士军刀” —— [SoX](http://sox.sourceforge.net/sox.html)。
### 安装
在 Linux 或 BSD 上,可以从软件存储库或 Ports 树中安装 `sox` 命令(,以及一些有用的符号链接)。
你也可以从 [Sourceforge.net](http://sox.sourceforge.net) 上安装 SoX。它不经常发布,但它的代码库往往是稳定的,所以如果你想要最新的功能(如 Opus 支持),构建它是容易和安全的。
SoX 主要提供了 `sox` 命令,但是创建了一些有用的符号链接:`play`、`rec` 和 `soxi`。
### 使用 SoX 获取文件信息
SoX 可以读取和重写音频数据。它是否存储重写的音频数据取决于你。在有些情况下,你不需要存储转换后的数据,例如,当你将输出直接发送到扬声器进行回放时。然而,在进行任何转换之前,最好首先确定要处理的是什么。
使用 `soxi` 命令也可以收集音频文件信息。`soxi` 会符号链接到 `soxi --info`。
```
$ soxi countdown.mp3
Input File(输入文件) : '/home/tux/countdown.mp3'
Channels(通道数) : 1
Sample Rate(采样率) : 44100
Precision(数据精度) : 16-bit(16 比特)
Duration(时长) : 00:00:11.21 = 494185 samples...(11.21 秒 = 494185 采样点)
File Size(文件大小) : 179k
Bit Rate(比特率) : 128k
Sample Encoding(编码格式): MPEG audio (layer I, II or III)
```
这个输出可以让你很好地了解音频文件的编码方式、文件长度、文件大小、采样率和通道数。其中一些你可能*认为*你已经知道了,但当客户把媒体带到我面前时,我从不相信这些假设。使用 `soxi` 验证媒体属性。
### 转换文件
在本例中,,一个游戏节目倒计时的音频是以MP3文件的形式提供的。虽然几乎所有的编辑应用程序都接受压缩音频,但它们并不是在压缩的数据上进行编辑。转换是在某个地方发生的,可能是一个秘密的后台任务,也可能提示让你保存一份副本。我通常喜欢自己提前完成转换。这样,我可以控制使用的格式。我可以在夜间批量处理大量的媒体,而不是浪费宝贵的制作时间,等待编辑应用程序按需处理它们。
`sox` 命令用于转换音频文件。在 `sox` 流程中有几个阶段:
* 输入
* 合并
* 特效
* 输出
但在命令语法中,特效步骤令人困惑地放到了*最后一步*。这意味着 `sox` 流程是这样组成的:
```
输入 → 合并 → 输出 → 特效
```
### 编码
最简单的转换命令只涉及一个输入文件和一个输出文件。下面是转换 MP3 文件为无损 FLAC 文件的命令:
```
$ sox countdown.mp3 output.flac
$ soxi output.flac
Input File(输入文件) : 'output.flac'
Channels(通道数) : 1
Sample Rate(采样率) : 44100
Precision(数据精度) : 16-bit(16 比特)
Duration(时长) : 00:00:11.18 = 493056 samples...(11.18 秒 = 493056 采样点)
File Size(文件大小) : 545k
Bit Rate(比特率) : 390k
Sample Encoding(编码格式): 16-bit FLAC
Comment(注释) : 'Comment=Processed by SoX'
```
#### 特效
特效可以在命令末尾指定。它可以在将数据发送到最终目的地之前更改音频。例如,有时声音太大会在转换过程中造成问题:
```
$ sox bad.wav bad.ogg
sox WARN sox: `bad.ogg' output clipped 126 samples; decrease volume?
```
应用**增益**(`gain`)效果通常可以解决此问题:
```
$ sox bad.wav bad.ogg gain -1
```
#### 淡入淡出
另一个常用的效果是**淡入淡出**(`fade`)。此效果允许你定义淡入或淡出的类型,以及你希望淡入淡出效果持续的时间。
下面是一个使用倒抛物线的 6 秒淡入示例:
```
$ sox intro.ogg intro.flac fade p 6
```
这将对音频的头部应用 3 秒的淡入,并从 8 秒标记开始淡出(这段音乐只有 11 秒,因此在这种情况下淡出也是 3 秒):
```
$ sox intro.ogg intro.flac fade p 3 8
```
`sox` 手册页中列出了不同类型的淡入淡出(正弦、线性、倒抛物线等)以及淡入淡出提供的选项。
#### 特效语法
每个特效插件都有自己的语法,因此请参阅手册页了解如何调用每个特效插件的详细信息。
效果可以在一个命令中以菊花链的方式进行,至少在你想组合它们的范围内是如此。换句话说,没有语法可以只在六秒钟的淡出期间应用一个镶边效果。对于如此精确的东西,你需要一个图形声波编辑器或数字音频工作站,例如 [LMMS](https://opensource.com/life/16/2/linux-multimedia-studio) 或 [Rosegarden](https://opensource.com/article/18/3/make-sweet-music-digital-audio-workstation-rosegarden)。但是,如果你只想应用一次特效,可以在同一命令中将它们一起列出。
此命令应用了一个 -1 的**增益**效果、1.35 的节奏**拉伸**和**淡出**:
```
$ sox intro.ogg output.flac gain -1 stretch 1.35 fade p 0 6
$ soxi output.flac
Input File(输入文件) : 'output.flac'
Channels(通道数) : 1
Sample Rate(采样率) : 44100
Precision(数据精度) : 16-bit(16 比特)
Duration(时长) : 00:00:15.10 = 665808 samples...(15.10 秒 = 665808 采样点)
File Size(文件大小) : 712k
Bit Rate(比特率) : 377k
Sample Encoding(编码格式): 16-bit FLAC
Comment(注释) : 'Comment=Processed by SoX'
```
### 组合音频
SoX 还可以通过连接或混合音频文件来组合音频文件。
要连接(或者说*拼接*)文件合并为一个文件,请在命令中提供多个输入文件:
```
$ sox countdown.mp3 intro.ogg output.flac
```
在本例中,`output.flac` 现在包含 `countdown.mp3` 音频,紧接着是 `intro.ogg` 音乐。
但是,如果你希望两首曲目同时播放,可以使用 `--combine mix` 选项:
```
$ sox --combine mix countdown.mp3 intro.ogg output.flac
```
然而,想象一下,这两个输入文件的不同之处不仅仅在于它们的编解码器。人声音轨用单声道(一个声道)录制并不少见,但音乐至少要用立体声(至少两个声道)来录制。SoX 不会给出默认的解决方案,因此你必须首先自己标准化这两个文件的格式。
#### 更改音频文件
选项与后面列出文件名有关。例如,此命令中的 `--channels` 选项将*仅仅*应用于 `input.wav`,而*不被*应用于 `example.ogg` 和 **output.flac**:
```
$ sox --channels 2 input.wav example.ogg output.flac
```
这意味着在 SoX 中,选项的位置非常重要。如果你在命令开始时指定一个选项,那么实际上只会覆盖 SoX 自己从输入文件中收集的内容。然而,在*输出文件*名前的选项决定了 SoX 如何写入音频数据。
要解决前面的通道不兼容问题,你可以首先标准化输入,然后混合:
```
$ sox countdown.mp3 --channels 2 countdown-stereo.flac gain -1
$ soxi countdown-stereo.flac
Input File(输入文件) : 'countdown-stereo.flac'
Channels(通道数) : 2
Sample Rate(采样率) : 44100
Precision(数据精度) : 16-bit(16 比特)
Duration(时长) : 00:00:11.18 = 493056 samples...(11.18 秒 = 493056 采样点)
File Size(文件大小) : 545k
Bit Rate(比特率) : 390k
Sample Encoding(编码格式): 16-bit FLAC
Comment(注释) : 'Comment=Processed by SoX'
$ sox --combine mix \
countdown-stereo.flac \
intro.ogg \
output.flac
```
SoX 绝对需要多个命令来执行复杂的操作,因此根据需要创建几个临时和中间文件是正常的。
### 多通道音频
当然,并非所有音频都被限制在一个或两个声道。如果你想将多个音频通道组合成一个文件,可以使用 SoX 的 `--combine merge` 选项:
```
$ sox --combine merge countdown.mp3 intro.ogg output.flac
$ soxi output.flac
Input File : 'output.flac'
Channels : 3
[...]
```
### 简单的音频操作
在没有视觉界面的情况下操作音频似乎很奇怪,而且对于某些任务来说,SoX 绝对不是最好的工具。然而,对于许多任务,SoX 提供了一个简单而轻量级的工具包。SoX 是一个具有强大潜力的简单命令。有了它,你可以转换音频,操纵通道和波形,甚至生成自己的声音。本文仅简要概述了其功能,因此请阅读其手册页或 [在线文档](http://sox.sourceforge.net/sox.html),然后看看你能创造什么。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/20/2/linux-sox>
作者:[Klaatu](https://opensource.com/users/klaatu) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[FYJNEVERFOLLOWS](https://github.com/FYJNEVERFOLLOWS) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | I work with media, and when you work with any kind of media, you learn pretty quickly that standardization is a valuable tool. Just as you wouldn't try to add a fraction to a decimal without converting one or the other, I've learned that it's not ideal to combine media of differing formats. Most hobbyist-level applications make the conversion process invisible to the user as a convenience. Flexible software aimed at users needing control over the fine details of their assets, however, often leave it up to you to convert your media to your desired format in advance. I have a few favorite tools for conversion, and one of those is the so-called *Swiss army knife of sound*, [SoX](http://sox.sourceforge.net/sox.html).
## Installing
On Linux or BSD, you can install the **sox** command (and some helpful symlinks) from your software repository or ports tree.
You can also install SoX from its home on [Sourceforge.net](http://sox.sourceforge.net). It doesn't release often, but its codebase tends to be stable, so if you want the latest features (such as Opus support), it's easy and safe to build.
SoX provides primarily the **sox** command, but installation also creates a few useful symlinks: **play**, **rec**, and **soxi**.
## Getting information about files with SoX
SoX reads and rewrites audio data. Whether it stores the rewritten audio data is up to you. There are use cases in which you don't need to store the converted data, for instance, when you're sending the output directly to your speakers for playback. Before doing any conversion, however, it's usually a good idea to determine exactly what you're dealing with in the first place.
To gather information about an audio file, use the **soxi** command. This is a symlink to **sox --info**.
```
$ soxi countdown.mp3
Input File : '/home/tux/countdown.mp3'
Channels : 1
Sample Rate : 44100
Precision : 16-bit
Duration : 00:00:11.21 = 494185 samples...
File Size : 179k
Bit Rate : 128k
Sample Encoding: MPEG audio (layer I, II or III)
```
This output gives you a good idea of what codec the audio file is encoded in, the file length, file size, sample rate, and the number of channels. Some of these you might *think* you already know, but I never trust assumptions when media is brought to me by a client. Verify media attributes with **soxi**.
## Converting files
In this example, the audio of a game show countdown has been delivered as an MP3 file. While nearly all editing applications accept compressed audio, none of them actually edit the compressed data. Conversion is happening somewhere, whether it's a secret background task or a prompt for you to save a copy. I generally prefer to do the conversion myself, in advance. This way, I can control what format I'm using. I can do lots of media in batches overnight instead of wasting valuable production time waiting for an editing application to churn through them on demand.
The **sox** command is meant for converting audio files. There are a few stages in the **sox** pipeline:
- input
- combine
- effects
- output
In command syntax, the effects step is, confusingly, written *last*. That means the pipeline is composed this way:
`input → combine → output → effects`
## Encoding
The simplest conversion command involves only an input file and an output file. Here's the command to convert an MP3 file to a lossless FLAC file:
```
$ sox countdown.mp3 output.flac
$ soxi output.flac
Input File : 'output.flac'
Channels : 1
Sample Rate : 44100
Precision : 16-bit
Duration : 00:00:11.18 = 493056 samples...
File Size : 545k
Bit Rate : 390k
Sample Encoding: 16-bit FLAC
Comment : 'Comment=Processed by SoX'
```
### Effects
The effects chain is specified at the end of a command. It can alter audio prior to sending the data to its final destination. For instance, sometimes audio that's too loud can cause problems during conversion:
```
$ sox bad.wav bad.ogg
sox WARN sox: `bad.ogg' output clipped 126 samples; decrease volume?
```
Applying a **gain** effect can often solve this problem:
`$ sox bad.wav bad.ogg gain -1`
### Fade
Another useful effect is **fade**. This effect lets you define the shape of a fade-in or fade-out, along with how many seconds you want the fade to span.
Here's an example of a six-second fade-in using an inverted parabola:
`$ sox intro.ogg intro.flac fade p 6`
This applies a three-second fade-in to the head of the audio and a fade-out starting at the eight-second mark (the intro music is only 11 seconds, so the fade-out is also three-seconds in this case):
`$ sox intro.ogg intro.flac fade p 3 8`
The different kinds of fades (sine, linear, inverted parabola, and so on), as well as the options **fade** offers (fade-in, fade-out), are listed in the **sox** man page.
### Effect syntax
Each effect plugin has its own syntax, so refer to the man page for details on how to invoke each one.
Effects can be daisy-chained in one command, at least to the extent that you want to combine them. In other words, there's no syntax to apply a **flanger** effect only during a six-second fade-out. For something that precise, you need a graphical sound wave editor or a digital audio workstation such as [LMMS](https://opensource.com/life/16/2/linux-multimedia-studio) or [Rosegarden](https://opensource.com/article/18/3/make-sweet-music-digital-audio-workstation-rosegarden). However, if you just have effects that you want to apply once, you can list them together in the same command.
This command applies a -1 **gain** effect, a tempo **stretch** of 1.35, and a **fade-out**:
```
$ sox intro.ogg output.flac gain -1 stretch 1.35 fade p 0 6
$ soxi output.flac
Input File : 'output.flac'
Channels : 1
Sample Rate : 44100
Precision : 16-bit
Duration : 00:00:15.10 = 665808 samples...
File Size : 712k
Bit Rate : 377k
Sample Encoding: 16-bit FLAC
Comment : 'Comment=Processed by SoX'
```
## Combining audio
SoX can also combine audio files, either by concatenating them or by mixing them.
To join (or *concatenate*) files into one, provide more than one input file in your command:
`$ sox countdown.mp3 intro.ogg output.flac`
In this example, **output.flac** now contains **countdown **audio, followed immediately by **intro** music.
If you want the two tracks to play over one another at the same time, though, you can use the **--combine mix** option:
`$ sox --combine mix countdown.mp3 intro.ogg output.flac`
Imagine, however, that the two input files differed in more than just their codecs. It's not uncommon for vocal tracks to be recorded in mono (one channel), but for music to be recorded in at least stereo (two channels). SoX won't default to a solution, so you have to standardize the format of the two files yourself first.
### Altering audio files
Options related to the file name listed *after* it. For instance, the **--channels** option in this command applies *only* to **input.wav** and NOT to **example.ogg** or **output.flac**:
`$ sox --channels 2 input.wav example.ogg output.flac`
This means that the position of an option is very significant in SoX. Should you specify an option at the start of your command, you're essentially only overriding what SoX gleans from the input files on its own. Options placed immediately before the *output* file, however, determine how SoX writes the audio data.
To solve the previous problem of incompatible channels, you can first standardize your inputs, and then mix:
```
$ sox countdown.mp3 --channels 2 countdown-stereo.flac gain -1
$ soxi countdown-stereo.flac
Input File : 'countdown-stereo.flac'
Channels : 2
Sample Rate : 44100
Precision : 16-bit
Duration : 00:00:11.18 = 493056 samples...
File Size : 545k
Bit Rate : 390k
Sample Encoding: 16-bit FLAC
Comment : 'Comment=Processed by SoX'
$ sox --combine mix \
countdown-stereo.flac \
intro.ogg \
output.flac
```
SoX absolutely requires multiple commands for complex actions, so it's normal to create several temporary and intermediate files as needed.
## Multichannel audio
Not all audio is constrained to one or two channels, of course. If you want to combine several audio channels into one file, you can do that with SoX and the **--combine merge** option:
```
$ sox --combine merge countdown.mp3 intro.ogg output.flac
$ soxi output.flac
Input File : 'output.flac'
Channels : 3
[...]
```
## Easy audio manipulation
It might seem strange to work with audio using no visual interface, and for some tasks, SoX definitely isn't the best tool. However, for many tasks, SoX provides an easy and lightweight toolkit. SoX is a simple command with powerful potential. With it, you can convert audio, manipulate channels and waveforms, and even generate your own sounds. This article has only provided a brief overview of its capabilities, so go read its man page or [online documentation](http://sox.sourceforge.net/sox.html) and then see what you can create.
## Comments are closed. |
15,247 | 如何从 Ubuntu 21.10 及以后版本中删除 Firefox Snap | https://www.debugpoint.com/remove-firefox-snap-ubuntu/ | 2022-11-13T11:25:40 | [
"Firefox",
"Snap"
] | /article-15247-1.html | 
>
> Ubuntu 21.10 “Impish Indri” 及之后的版本将 Firefox Snap 设为默认浏览器。如果你不喜欢 Snap,可以通过以下方式将其删除并使用库存版本。
>
>
>
关于 Snap 是否是 APT 的更好替代品,一直存在争议。而许多用户更喜欢 Snap 系统,也有一些人非常讨厌它。Ubuntu 和 Canonical 认为它是 Linux 的最佳安装仓库和包管理工具之一。 Snap 被讨厌的主要原因是它的启动很慢。然而,这个论点是另一篇文章的内容。
### 从 Ubuntu 中删除 Firefox Snap 版本
所以,如果你还没有 [听说过这件事](https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/ubuntu-release-upgrader/+bug/1943840),Ubuntu 21.10(和所有后续版本)默认提供 Firefox Snap 包。因此,当你从 Ubuntu 21.10 开始安装时,默认的左侧停靠区的快捷方式是 Firefox 的 Snap 版本。你可以使用以下各种方法对其进行验证。


如果你因为 [性能](https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/03/clean-up-snap/) 和存储问题而不喜欢 Snap,可以通过以下命令将其删除。
如果已经打开,那么关闭所有 Firefox 实例。
打开一个终端。然后运行以下命令:
```
sudo snap remove firefox
```
等待命令完成。这将从你的系统中删除它的 Snap 可执行文件,并断开 Firefox 与各种系统服务的连接。但是主目录下的 Snap 目录仍然存在。你可以使用以下命令手动删除它:
```
cd ~/snap
rm -r firefox
```
### 安装 Firefox 替代方法
现在,当你删除了 Firefox,你可以通过以下方式来使用此浏览器。
#### 方法 1 – 使用 PPA(推荐)
在使用此方法之前,请确保如上删除了 Firefox 的 Snap 版本。
有一个 [官方 Firefox PPA](https://launchpad.net/~mozillateam/+archive/ubuntu/ppa),由其开发团队维护。你可以将此 PPA 添加到你的软件源中,并使用它来安装最新的 Firefox。
确保使用文本编辑器创建一个首选项文件,以阻止 Ubuntu 在运行 `apt update` 命令时获取 Firefox 的 Snap 版本:
```
sudo gedit /etc/apt/preferences.d/firefox-no-snap
```
将以下行添加到上面的文件并保存:
```
Package: firefox*
Pin: release o=Ubuntu*
Pin-Priority: -1
```
依次使用以下命令。第一个命令将其从你的系统中完全清除它:
```
sudo apt purge firefox
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:mozillateam/firefox
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt install firefox
```
安装完成后,请确保使用以下命令启用自动升级:
```
echo 'Unattended-Upgrade::Allowed-Origins:: "LP-PPA-mozillateam:${distro_codename}";' | sudo tee /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/51unattended-upgrades-firefox
```
重启系统(可选)并使用 deb 版本的 Firefox。
#### 方法 2 – 使用 Firefox 的压缩可执行文件
你可以从官方网站(链接如下)下载适用于 Ubuntu 和其他 Linux 的 Firefox 可执行文件压缩包。然后解压并双击运行 Firefox 可执行文件。这是最安全的方法。如果你使用此方法,你仍然可以获得更新。
>
> **[下载 Firefox](https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/new/)**
>
>
>


#### 方法 3 – 使用 Flatpak 版本的 Firefox
你也可以使用 [Flatpak 版本的 Firefox](https://flathub.org/apps/details/org.mozilla.firefox),这在 [Ubuntu 中设置 Flatpak](https://www.debugpoint.com/2018/07/how-to-install-flatpak-apps-ubuntu-linux/) 后可用。然后你可以运行以下命令进行安装:
```
flatpak install flathub org.mozilla.firefox
```
#### 方法 4 – 使用与系统耦合更少的 Snap 版本 Firefox
如果你认为你仍然可以继续使用 Snap 版本,但希望在系统中减少沙盒化,那么你可能需要使用以下命令和 [classic 开关](https://snapcraft.io/docs/snap-confinement) 重新安装 Firefox:
```
sudo snap install firefox --classic
```
### 结束语
因此,这是从 Ubuntu 21.10 开始删除 firefox Snap 版本的步骤,以及一些替代方案。我很想知道 Linux Mint 采取了什么措施,因为他们不支持 Snap。此外,这些发行版依赖于 Firefox 的 Ubuntu 上游仓库,看看它们会做什么很有趣。Debian 维护自己的仓库,但主要是 ESR 版本。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/remove-firefox-snap-ubuntu/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,248 | 我使用的 4 款开源编辑器 | https://opensource.com/article/22/10/open-source-editors | 2022-11-13T15:39:24 | [
"编辑器",
"Vi"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15248-1.html | 
>
> 分享一些我最喜欢的开源写作工具。
>
>
>
在我的职业生涯中,我已经写过很多东西,主要是作为一名 IT 顾问,创建产品文档作为给的客户可交付成果。这些文档通常针对不同操作系统和软件产品提供说明。
自 2018 年,我开始在 [www.opensource.com](http://www.opensource.com) 上发表关于开源软件的文章。当然,我使用开源软件进行协作。接下来我将介绍我使用过的四款开源编辑器。
### 1、Vi
[Vi](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/vi-text-editor) 也被称为 `Vim`(LCTT 校注:此外不确,Vi 和 Vim 是两个软件,只是 Vim 取代了 Vi,并以 `vi` 的名字运行。),是我学习的第一款开源编辑器。这是我在计算机科学课程中学习的编辑器,并且我所有的 C 语言编程都是通过它完成的。自 1995 年以来,实际上我一直使用它作为命令行编辑器。这款工具有多个迭代版本,以至于我都可以为之写一系列文章了。我只想说,在我的日常使用中,我坚持使用它的基本命令行形式,并进行最小的定制。
### 2、LibreOffice Writer
Writer 是 LibreOffice 开源办公套件的一部分。它是由<ruby> 文档基金会 <rt> Document Foundation </rt></ruby>维护的全功能文字处理器。它支持行业标准格式,例如开放文档格式 (ODF)、Open XML 和 MS Office DOC、DOCX。可以在其官方网站上 [了解有关 Writer 的更多信息](https://www.libreoffice.org/discover/writer/)。
### 3、Ghostwriter
Ghostwriter 是一个用于 [Markdown 的文本编辑器](https://opensource.com/article/21/10/markdown-editors)。它有一个很好的实时查看器和语法指南或备忘单功能。[访问官方网站](https://github.com/KDE/ghostwriter) 了解更多内容。
### 4、Gedit
Gedit 是许多 Linux 发行版中的基本图形编辑器,被描述为“用于 GNOME 桌面的小型轻量级文本编辑器”。我最近开始使用它来创建 Asciidoc 格式的文章。使用 Asciidoc 的好处是语法易于管理并可导入到 Drupal 等 Web 渲染系统中。通过 [Gedit Wiki](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Gedit) 了解许多提示和技巧。
### 编辑文本
开源世界中有大量编辑软件。随着我继续写作,这个列表可能会增加。我的主要目标是格式简单。我希望我的文章易于在互联网平台上导入、转换和发布。
你的写作风格、功能需求和目标受众将指导你确定首选工具。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/10/open-source-editors>
作者:[Alan Formy-Duval](https://opensource.com/users/alanfdoss) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | I've done a lot of writing throughout my career, mostly as an IT consultant creating product documentation as client deliverables. These documents generally provide instructions on installing various operating systems and software products.
Since 2018, I've contributed to opensource.com with articles about open source software. Of course, I use open source editors to write my pieces. Here are the four open source editors that I have used.
## 1. Vi
[Vi](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/vi-text-editor), also referred to as Vim, is the first open source editor that I learned. This was the editor taught by my computer science classes and that I used for all of my C programming. I have used it as my de facto command line editor since the mid-1990s. There are so many iterations of this tool that I could write a whole series on them. Suffice it to say that I stick to its basic command line form with minimal customization for my daily use.
## 2. LibreOffice Writer
Writer is part of the open source LibreOffice office suite. It is a full-featured word processor maintained by The Document Foundation. It supports industry-standard formats such as the Open Document Format (ODF), Open XML, and MS Office DOC, DOCX. [Learn more about Writer](https://www.libreoffice.org/discover/writer/) on its official site.
## 3. Ghostwriter
Ghostwriter is a [text editor for Markdown](https://opensource.com/article/21/10/markdown-editors). It has a nice real-time viewer and syntax guide or cheat sheet feature. [Visit the official website](https://github.com/KDE/ghostwriter) to discover more.
## 4. Gedit
Gedit is the basic graphical editor found in many Linux distributions and is described as "a small and lightweight text editor for the GNOME desktop." I have begun using it lately to create articles in the Asciidoc format. The benefit of using Asciidoc is that the syntax is easily manageable and importable into web rendering systems such as Drupal. [See the Gedit Wiki](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Gedit) for many tips and tricks.
## Editing text
An extensive list of editing software is available in the open source world. This list will likely grow as I continue writing. The primary goal for me is simplicity in formatting. I want my articles to be easy to import, convert, and publish in a web-focused platform.
Your writing style, feature needs, and target audience will guide you in determining your preferred tools.
## 3 Comments |
15,250 | 如何提高 Ubuntu 和其他 Linux 系统中的扬声器音量 | https://www.debugpoint.com/boost-speaker-volume-ubuntu/ | 2022-11-14T08:24:10 | [
"音量"
] | /article-15250-1.html | 
>
> 以下是如何在 Ubuntu 和其他 Linux 发行版中提高笔记本和桌面的音量的方法。
>
>
>
你有没有觉得你的 Ubuntu 笔记本的音量太小,尽管你把音量调到了 100%?我相信你有过。主要原因是:很明显,笔记本电脑的扬声器输出强度比大型扬声器要低。
此外,Ubuntu 和其他发行版将默认的最大音量设置为 100%,也就是 0dB(分贝)。0dB 是最大音量的参考值。做个比较,如果你把音量设置为 -10dB,这意味着你的音量比最大的 0dB 安静。
VLC 和一些媒体播放器允许你将音量提高到 200%。在最新的 Ubuntu 中使用一些设置,你可以将音量进一步提高。
>
> **注意**:在你尝试和使用以下方法之前,请记住,每个扬声器都有其制造商设定的硬件限制。偶尔一次,播放超过 100% 的音频是可以的。但是,连续放大到更高的分贝可能会使输出的音频失真,并且从长远来看可能会损坏你的扬声器。因此,在使用时要小心谨慎,并有所限制。
>
>
>
### 在 Ubuntu 和其他发行版中提高扬声器音量
#### 对于最新的 Ubuntu 22.04 及以上版本(GNOME)
从应用菜单中打开“<ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby>”,进入“<ruby> 声音 <rt> Sound </rt></ruby>”标签。
启用 “<ruby> 过度放大 <rt> Over Amplification </rt></ruby>” 开关。在你启用的那一刻,你应该看到音量条被扩大了。

现在你可以享受音量提升来听音乐了。
#### Fedora、Arch Linux 和其他发行版
如果你使用带有 GNOME 的 Fedora 工作站,你将看不到上述选项,因为这是 Ubuntu 特有的设置。见下面。

因此,对于任何其他 Linux 发行版(Arch、Fedora、RedHat 等)或桌面(KDE、Xfce、LXQt 等),打开终端并安装 [PulseAudio 音量控制器](https://freedesktop.org/software/pulseaudio/pavucontrol/)。
Fedora、RedHat Linux、OpenSUSE 等基于 RPM 的发行版:
```
sudo dnf install pavucontrol
```
对于 Arch Linux、Manjaro:
```
sudo pacman -S pavucontrol
```
基于 Ubuntu 的非 GNOME 发行版:
```
sudo apt install pavucontrol
```
### 如何使用
安装后,从应用菜单中打开 `pavucontrol`,它应该有个 “PulseAudio Volume Control” 菜单项。

### 总结
记住,上述方法可以提高整个系统的扬声器音量。这意味着系统的声音和警报也会受到影响。所以,要记住这一点。正如我前面提到的,如果连续使用,提升扬声器音量超过 100% 可能会导致扬声器变形或损坏。
我希望这个教程能帮助你提高系统音量。如果你遇到问题,请在评论栏里告诉我。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/boost-speaker-volume-ubuntu/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,251 | 13 个从头开始构建的独立 Linux 发行版 | https://itsfoss.com/independent-linux-distros/ | 2022-11-14T09:55:00 | [
"Linux",
"发行版"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15251-1.html | 
时至今日,世界上已经有成百上千种不同的 Linux 发行版。
它们中的大多数都可以被划归为三个大类 : Debian、Red Hat(Fedora)以及 Arch Linux。
使用基于 Debian/Ubuntu、Red Hat/SUSE 或者 Arch 的 Linux 发行版自然有它们的优势。它们很受大众欢迎,因此它们的包管理器能够提供大量的软件包。
然而,有一些用户更倾向于使用从头开始构建、独立于 DEB/RPM 这类包管理系统之外的发行版。
在这篇文章当中,我们将列出一些优秀的独立 Linux 发行版。
>
> **注意 :** 显然,下面的列表显然不会包括一些广受欢迎,通常作为创建新发行版的基础的发行版,如 Debian、Ubuntu 和 Fedora 等。此外,列表顺序不分先后,没有特定的排名。
>
>
>
### 1、NixOS

NixOS 最初发布于 2003 年,NixOS 建立在 Nix 包管理器之上。它每年发布两个版本,通常是在 5 月和 11 月。
NixOS 可能不是一个直接面向新用户或普通用户的发行版。然而,其独特的 [包管理](https://itsfoss.com/package-manager/) 方法吸引了各种用户。
此外,它仍然支持 32 位系统。
其他特性:
* 构建隔离的包
* 可靠的升级,并且具有回滚功能
* 可重现的系统配置
>
> **[NixOS](https://nixos.org/)**
>
>
>
### 2、Gentoo Linux

Geetoo Linux 是一个主要针对操作系统专家的独立 Linux 发行版。它是为那些希望自由定制、微调和优化操作系统以满足其要求的用户而构建。
Gentoo 使用 [Portage 包管理器](https://wiki.gentoo.org/wiki/Portage) 来创建和安装软件包,通常还允许你针对你的硬件来优化它们。Chrome 的开源版本 **Chromium OS** 便是使用 Gentoo 作为其核心的。
不要忘记,Gentoo 是 [仍然支持 32 位架构的发行版](https://itsfoss.com/32-bit-linux-distributions/) 之一。
其他特性:
* 增量更新
* 基于源码的软件管理方法
* 支持 GURU(Gentoo 用户仓库)的<ruby> 层叠 <rt> Overlay </rt></ruby>仓库的概念,允许用户添加 Gentoo 尚未提供的软件包
>
> **[Gentoo Linux](https://www.gentoo.org/)**
>
>
>
### 3、Void Linux

Void Linux 是一个 [滚动发布的发行版](https://itsfoss.com/rolling-release/),使用 X 二进制软件包系统(XBPS)来安装和删除软件。它由前 NetBSD 开发者 Juan Romero Pardines 创建。
它使用 runit 而不是 systemd 作为其初始化系统。此外,它还让你可以选择使用多个 [桌面环境](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/)。
其他特性:
* 最小化的系统要求
* 官方库也提供非自由软件包
* 支持树莓派
* 集成 OpenBSD 的 LibreSSL
* 支持 musl C 库
* 支持 32 位系统
>
> **[Void Linux](https://voidlinux.org/)**
>
>
>
### 4、Solus Linux

Solus 的前身是 EvolveOS,它从头开始构建并提供了一些令人兴奋的特性。Solus 的旗舰版本使用自己打造的 Budgie 作为桌面环境。
与本篇文章介绍的其他系统相比,Solus 对于新手较为友好。它设法成为 [最好的 Linux 发行版](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-distributions/) 之一。
它使用 eopkg 作为其包管理系统,支持版滚动发布模型。按照开发人员的说法,开发 Solus 的目标是用于个人电脑。
其他特性:
* 支持 Budgie、Gnome、MATE 和 KDE Plasma
* 各种开箱即用的软件,从而减少设置工作
>
> **[Solus Linux](https://getsol.us/home/)**
>
>
>
### 5、Mageia

Mageia 始于 2010 年,它是 Mandriva Linux 的一个分支。它的目标是成为稳定且安全的桌面和服务器操作系统。
Mageia 是一个社区驱动的项目,由非营利组织和贡献者支持。每年会发布一个大版本。
其他特性:
* 支持 32 位系统
* 支持 KDE Plasma、Gnome 和 XFCE
* 最低的系统要求
>
> **[Mageia](https://www.mageia.org/en/)**
>
>
>
### 6、Clear Linux

Clear Linux 是一个由英特尔发布的发行版,主要设计考虑是性能和云服务的使用。
有趣的是,Clear Linux 升级时是作为一个整体而非去升级单个的软件包。所以,即使你不小心弄乱了系统设置,它也可以正确的启动,执行恢复出厂设置,并让用户重新设置。
它不太适合个人用户使用。但可以作为一个独特的选择而尝试一下。
其他特性:
* 针对英特尔平台的高度调优
* 用户和系统文件之间严格分离
* 持续的漏洞扫描
>
> **[Clear Linux OS](https://clearlinux.org/)**
>
>
>
### 7、PCLinuxOS

PCLinuxOS 是一个 x86\_64 的 Linux 发行版,使用 APT/RPM 包管理。你可以使用 KDE Plasma、Mate 以及 XFCE 桌面,它同时还提供了更多特性的社区版本的桌面。
得益于 [Synaptic 包管理器](https://itsfoss.com/synaptic-package-manager/),本地安装的 PCLinuxOS 采用了 APT 包管理系统。但你也可以从它的仓库中找到 RPM 包。
其他特性:
* mylivecd 脚本允许用户去生成一个当前已安装的硬件驱动的“快照”(所有的配置、应用、文档等)并且将它压缩为 ISO CD/DVD/USB 镜像
* 额外支持超过 85 种语言
>
> **[PCLinuxOS](https://www.pclinuxos.com/)**
>
>
>
### 8、4MLinux

[4MLinux](https://itsfoss.com/4mlinux-review/) 是一个通用的 Linux 发行版,重点聚焦于下面四个 **“M”**
* <ruby> 维护 <rt> Maintenance </rt></ruby>(系统救援 Live CD)
* <ruby> 多媒体 <rt> Multimedia </rt></ruby>(支持大量的图形、音频和视频格式)
* <ruby> 微服务器 <rt> Miniserver </rt></ruby>(支持 DNS、FTP、HTTP、MySQL、NFS、Proxy、SMTP、SSH 和 Telnet)
* <ruby> 神秘 <rt> Mystery </rt></ruby>(包含了经典 Linux 游戏的集合)
它具有最低的系统要求,可作为桌面和服务器版本使用.
其他特性:
* 支持大量的图形、音频和视频格式
* 是小型并且通用的 Linux 发行版
>
> **[4MLinux](http://4mlinux.com/)**
>
>
>
### 9、Tiny Core Linux

Tiny Core Linux 专注于使用 BusyBox 和 FLTK 提供一个基础的系统。它不是一个完备的桌面,所以,并不能保证它可以运行于任何系统。
它只是一个启动到非常精简的 X 桌面所需的核心,通常带有有线互联网访问权限。
用户可以很好的控制一切,但对于新 Linux 用户来说,它并不是一个轻松的开箱即用的系统。
其他特性:
* 旨在从启动时创建的内存副本中运行
* 默认情况下,其操作就像像云端 / 互联网客户端一样
* 用户可以使用 appbrowser 来游览库以及下载应用
>
> **[Tiny Core Linux](http://www.tinycorelinux.net/)**
>
>
>
### 10、Linux From Scratch(LFS)

Linux From Scratch(LFS)并不是一个系统,而是通过手动构建所有组件来安装 Linux 的一种方法。一旦完成,它提供了一个紧凑、灵活和安全的系统,并且可以很好的理解一个基于 Linux 的操作系统内部是如何工作的。
如果你希望去深入理解 Linux 是如何工作的并且探寻其具体细节,那么 Linux From Scratch(LFS) 是你一定要去尝试,不能错过的一个项目。
其他特性
* 完全从头开始,定制化的构建 Linux 系统
* 极度的灵活性
* 由于从源码开始编译,提供了额外的安全性
>
> **[Linux From Scratch](https://www.linuxfromscratch.org/)**
>
>
>
### 11、Slackware

Slackware 是现今还在维护的最古老的发行版。最初创建于 1993 年,以 Softlanding Linux 系统为基础,随后,许多的 Linux 发行版都是基于 Slackware。
Slackware 目标是称为最类似于 UNIX 的 Linux 发行版,同时保持简单和稳定。
其他特性:
* 支持 32 位和 64 位系统
* 大量的在线文档
* 从奔腾处理器到最新的机器,它都可以运行
>
> **[Slackware](http://www.slackware.com/)**
>
>
>
### 12、Alpine Linux

Alpine Linux 是一个社区开发的操作系统,专为路由器、防火墙、VPN、VoIP 盒子和服务器而设计。它是 LEAF 项目的一个分支。
Alpine Linux 使用 apk-tools 包管理器,最初由 shell 脚本编写,而后使用 c 语言重构。它是最小的 Linux 发行版之一,仍然支持 32 位系统,并且是一个可以完全从电脑内存运行的操作系统。
其他特性:
* 提供大小仅为 5MB 的最小容器镜像
* 对于主库,提供 2 年的支持;对于社区库,在下一个稳定版本发布前提供支持
* 使用 musl libc 制作,Busybox 使用资源效率高的容器
>
> **[Alpine Linux](https://www.alpinelinux.org/)**
>
>
>
### 13、KaOS

KaOS 是一个受到 Arch 启发,从头开始构建的 Linux 发行版。它使用 [pacman 包管理器](https://itsfoss.com/pacman-command/)。它是按照"*一个桌面环境(KDE Plasma),一个工具包(Qt),一个架构(X86\_64)*"的理念构建的。
它的软件库比较有限,但依然为普通用户提供了许多工具。
其他特性:
* 最新的 Plasma 桌面
* 紧密集成的滚动和透明的现代桌面发行版
>
> **[KaOS](https://kaosx.us/)**
>
>
>
### 总结
如果你需要一些独特的体验,那么这些独立 Linux 发行版应该能很好的满足你。
然而,如果你想要用其来替换如 Ubuntu 这样主流的 Linux 发行版作为你的桌面系统……你也许需要三思而后行,上面大多数的发行版(并不代表所有)都不是一个日常使用的桌面系统的理想的选项。
但是话又说回来,如果你对 Linux 发行版充满了经验,那么毫无疑问,你会享受这项冒险的任务的。
*如果你想尝试这些独立发行版的其中一种,哪一个会是你的优先选择呢 ? 请在评论中与我们分享。*
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/independent-linux-distros/>
作者:[sreenath](https://itsfoss.com/author/sreenath/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[MuggleWei](https://github.com/MuggleWei) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux 中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

There are hundreds of Linux distributions available.
But most of them fall into these three categories: Debian, Red Hat (Fedora) and Arch Linux.
Using a distribution based on Debian/Ubuntu, Red Hat/SUSE or Arch Linux has its advantages. They are popular and hence their package manager offers a huge range of software.
However, some users prefer to use Linux distributions built from scratch and be independent of DEB/RPM packaging system.
In this article, we will list some of the best Linux distributions developed independently.
**Note:** Obviously, this list excludes popular options like Debian, Ubuntu, and Fedora, which are used as bases for creating new distros. Moreover, the distributions are in no particular order of ranking.
## 1. NixOS
Initially released in 2003, Nix OS is built on top of the Nix Package Manager. It provides two releases every year, usually scheduled in May and November.
NixOS may not be a distribution directly geared to new and average users. However, its unique approach to [package management](https://itsfoss.com/package-manager/) attracts various kinds of users.
Additionally, 32-bit support systems are also supported.
#### Other Features:
- Builds packages isolated
- Reliable upgrade with rollback feature
- Reproducible system configuration
[6 Advanced Distributions for Expert Linux UsersSo, you think you are a Linux guru? Why not test your Linux expertise by using these advanced Linux distributions that are not everyone’s cup of tea?](https://itsfoss.com/advanced-linux-distros/)

## 2. Gentoo Linux
Gentoo Linux is an independently developed distribution aimed mainly at system experts. It is built for users who want the freedom to customize, fine-tune and optimize the operating system to suit their requirements.
Gentoo uses [Portage package management](https://wiki.gentoo.org/wiki/Portage?ref=itsfoss.com) that lets you create and install packages, often allowing you to optimize them for your hardware. **Chromium OS**, the open-source version of Chrome OS, uses Gentoo at its core.
Not to forget, Gentoo is one of those [distributions that still support 32-bit architectures](https://itsfoss.com/32-bit-linux-distributions/).
#### Other Features:
- Incremental Updates
- Source-based approach to software management
- Concept of overlay repositories like GURU (Gentoo’s user repository), where users can add packages not yet provided by Gentoo
## 3. Void Linux
Void Linux is a [rolling release distribution](https://itsfoss.com/rolling-release/) with its own X Binary Package System (XBPS) for installing and removing software. It was created by **Juan Romero Pardines**, a former NetBSD developer.
It avoids systemd and instead uses runit as its init system. Furthermore, it gives you the option to use several [desktop environments](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/).
#### Other Features:
- Minimal system requirements
- Offers an official repository for non-free packages
- Support for Raspberry Pi
- Integration of OpenBSD’s LibreSSL software
- Support for musl C library
- 32-bit support
[Not a Systemd Fan? Here are 14 Systemd-Free Linux Distributionssystemd is a popular init system adopted by most of the major Linux distributions backed by dozens of developers and companies. In case you’re curious, the init system is the first process after the Linux Kernel comes into action in the boot process to initialize various device management, logg…](https://itsfoss.com/systemd-free-distros/)

## 4. Solus Linux

Formerly EvolveOS, Solus Linux offers some exciting features while built from scratch. Solus features its own homegrown budgie desktop environment as its flagship version.
Compared to other options, Solus Linux is one of the few independent distributions that new Linux users can use. It manages to be one of the [best Linux distributions](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-distributions/) available.
It uses eopkg package management with a semi-rolling release model. As per the developers, Solus is exclusively developed for personal computing purposes.
#### Other Features:
- Available in Budgie, Gnome, MATE, and KDE Plasma editions
- Variety of software out of the box, which reduces setup efforts
## 5. Mageia
Mageia started as a fork of Mandriva Linux back in 2010. It aims to be a stable and secure operating system for desktop and server usage.
Mageia is a community-driven project supported by a non-profit organization and elected contributors. You will notice a major release every year.
#### Other Features
- Supports 32-bit system
- KDE Plasma, Gnome, and XFCE editions are available from the website
- Minimal system requirements
[Top 15 Linux Distros That Still Support 32 Bit SystemsIf you have vintage hardware with 32-bit processor and you would like to keep on using it, here are the best choices of Linux distros with 32-bit support.](https://itsfoss.com/32-bit-linux-distributions/)

## 6. Clear Linux
Clear Linux is a distribution by Intel, primarily designed with performance and cloud use cases in mind.
One interesting thing about Clear Linux is the operating system upgrades as a whole rather than individual packages. So, even if you mess up with the system accidentally, it should boot correctly, performing a factory reset to let you set it up again.
It is not geared toward personal use. But it can be a unique choice to try.
#### Other Features:
- Highly tuned for Intel platforms
- A strict separation between User and System files
- Constant vulnerability scanning
## 7. PCLinuxOS

PCLinuxOS is an x86_64 Linux distribution that uses APT-RPM packages. You can get KDE Plasma, Mate, and XFCE desktops, while it also offers several community editions featuring more desktops.
Locally installed versions of PCLinuxOS utilize the APT package management system thanks to [Synaptic package manager](https://itsfoss.com/synaptic-package-manager/). You can also find rpm packages from its repositories.
#### Other Features:
- mylivecd script allows the user to take a ‘snapshot’ of their current hard drive installation (all settings, applications, documents, etc.) and compress it into an ISO CD/DVD/USB image.
- Additional support for over 85 languages.
## 8. 4MLinux
[4MLinux](https://itsfoss.com/4mlinux-review/) is a general-purpose Linux distribution with a strong focus on the following four **“M”** of computing:
**M**aintenance (system rescue Live CD)**M**ultimedia (full support for a huge number of image, audio and video formats)**M**iniserver (DNS, FTP, HTTP, MySQL, NFS, Proxy, SMTP, SSH, and Telnet)**M**ystery (meaning a collection of classic Linux games)
It has a minimal system requirement and is available as a desktop and server version.
#### Other Features
- Support for large number of image, audio/video formats
- Small and general-purpose Linux distribution
## 9. Tiny Core Linux
Tiny Core Linux focuses on providing a base system using BusyBox and FLTK. It is not a complete desktop. So, you do not expect it to run on every system.
It represents only the core needed to boot into a very minimal X desktop, typically with wired internet access.
The user gets great control over everything, but it may not be an easy out-of-the-box experience for new Linux users.
#### Other Features
- Designed to run from a RAM copy created at boot time
- By default, operates like a cloud/internet client
- Users can run appbrowser to browse repositories and download applications
## 10. Linux From Scratch
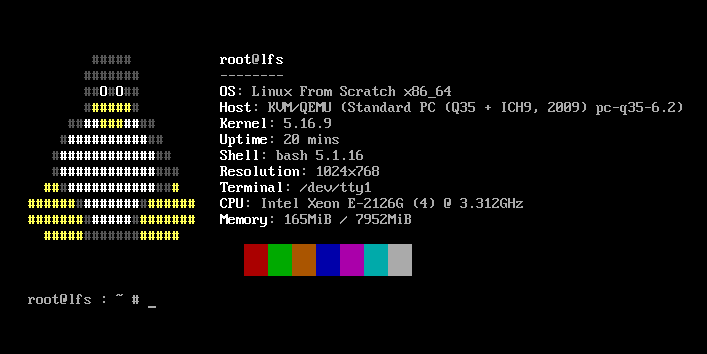

Linux From Scratch is a way to install a working Linux system by building all its components manually. Once completed, it provides a compact, flexible and secure system and a greater understanding of the internal workings of the Linux-based operating systems.
If you need to dive deep into how a Linux system works and explore its nuts and bolts, Linux From Scratch is the project you need to try.
#### Other Features
- Customised Linux system, entirely from scratch
- Extremely flexible
- Offers added security because of self compile from source
## 11. Slackware
Slackware is the oldest distribution that is still being maintained. Originally created in 1993, with Softlanding Linux System as base, Slackware later became the base for many Linux distributions.
Slackware aims at producing the most UNIX-like Linux distribution while keeping simplicity and stability.
#### Other Features
- Available for 32-bit and 64-bit systems
- Extensive online documentation
- Can run on Pentium system to latest machines
## 12. Alpine Linux
Alpine Linux is a community-developed operating system designed for routers, firewalls, VPNs, VoIP boxes, and servers. It began as a fork of the LEAF Project.
Alpine Linux uses apk-tools package management, initially written as a shell script and later written in C programming language. This is a minimal Linux distribution, which still supports 32-bit systems and can be installed as a run-from-RAM operating system.
#### Other Features:
- Provides a minimal container image of just 5 MB in size
- 2-year support for the main repository and support until the next stable release for the community repository
- Made around musl libc and Busybox with resource-efficient containers
## 13. KaOS
KaOS is a Linux distribution built from scratch and inspired by Arch Linux. It uses [pacman for package management](https://itsfoss.com/pacman-command/). It is built with the philosophy “* One Desktop Environment (KDE Plasma), One Toolkit (Qt), One Architecture (x86_64)*“.
It has limited repositories, but still, it offers plenty of tools for a regular user.
#### Other Features:
- Most up-to-date Plasma desktop
- Tightly integrated rolling and transparent distribution for the modern desktop
### Wrapping Up
If you need a unique experience, these independent Linux distributions should serve the purpose.
However, if you want to replace it with a mainstream distribution like Ubuntu for your desktop…
You might want to think twice, considering most of the options (if not all) above are not ideal options for day-to-day desktop usage.
But then again, if you have a fair share of experience with Linux distributions, you can undoubtedly take up the task for an adventure!
*If you were to try one of these indie distros, which one would it be? Share with us in the comments.* |
15,253 | 如何在没有互联网连接的情况下离线更新 Ubuntu | https://www.debugpoint.com/how-to-update-or-upgrade-ubuntu-offline-without-internet/ | 2022-11-14T23:29:53 | [
"Ubuntu",
"更新",
"离线"
] | /article-15253-1.html | 
>
> 本指南介绍了如何在没有互联网连接的情况下离线更新 Ubuntu 的步骤。
>
>
>
在很多情况下,你可能需要在没有互联网连接的情况下更新你的 Ubuntu 系统。你可能在外地不方便上网,也可能你需要更新一堆未联网的 Ubuntu,不管是哪种情况,保持你的系统更新最新的软件包总是需要的。
当然,始终建议通过联网来更新系统。
但有时,出于安全考虑,这是不行的。连接到互联网可能需要给你的系统进行额外的加固,以保护它们免受黑客和恶意软件的攻击。
以下的方法使用 [apt-offline](https://github.com/rickysarraf/apt-offline) 来解决这些问题,并概述了在没有互联网的情况下离线更新 Ubuntu 的步骤。
### 准备环节
* 一台能连接到网络的 Ubuntu(你朋友的、咖啡馆、实验室系统)
* 存储了软件包的 U 盘
* 两个系统都安装了 `apt-offline`:一个系统离线,另一个系统联网
### 安装 apt-offline
在两个系统下安装 `apt-offline`。你可以使用以下命令安装:
```
sudo apt install apt-offline
```
如果你想在离线的目标系统安装 `apt-offline`,你可以提前下载到 U 盘里,然后复制到目标系统,再使用下面的命令安装。
Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 和其他版本的下载链接如下所示。你可以选择一个镜像并下载 deb 文件。
>
> **[下载 .deb 文件 – apt-offline](https://packages.ubuntu.com/focal/all/apt-offline/download)**
>
>
>
```
sudo dpkg -i name_of_package.deb
```
### 如何更新 Ubuntu
在离线的目标系统上打开终端,使用以下命令创建一个 .sig 签名文件:
```
sudo apt-offline set ~/offline-data.sig
```

在这个刚创建的签名文件中,包含下载所需的软件包的路径和详细信息。

把签名文件复制到 U 盘中,再插到联网的 Ubuntu 系统上。
在联网的 Ubuntu 上创建一个目录(参见下面)来存放这些文件。
打开一个终端,运行以下命令来下载所需的软件包。记得根据你的系统,更改下载目录和 .sig 签名文件的路径。
```
apt-offline get -d ~/offline-data-dir offline-data.sig
```

你可以看到文件相应下载,然后复制整个下载目录到 U 盘,再插到离线的 Ubuntu 系统。
运行以下命令将下载的软件包安装到离线系统,记得根据你的系统更改目录路径。
```
sudo apt-offline install offline-data-dir/
```

如果一切顺利,你将获得一个更新完的 Ubuntu。
重复以上步骤,就可以保持你的离线 Ubuntu 为最新版本。
希望以上教程能帮到你更新离线的 Ubuntu 系统,如果你遇到任何问题,请在下面的评论框中告诉我。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/how-to-update-or-upgrade-ubuntu-offline-without-internet/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,254 | 为什么有时候域名的末尾有个点? | https://jvns.ca/blog/2022/09/12/why-do-domain-names-end-with-a-dot-/ | 2022-11-15T00:11:00 | [
"域名",
"DNS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15254-1.html | 
大家好!今年早些时候,我在写《[DNS 是如何工作的](https://wizardzines.com/zines/dns/)》 时,有人问我——为什么人们有时在域名的末尾加一个点?例如,如果你通过运行 `dig example.com` 查询 `example.com` 的 IP,你会看到一下内容:
```
$ dig example.com
example.com. 5678 IN A 93.184.216.34
```
执行完 `dig` 命令后,`example.com` 有一个 `.` ——变成了 `example.com.`!发生了什么?
有些 DNS 工具也要求传给它的域名后加一个 `.`:如果你在使用 [miekg/dns](https://github.com/miekg/dns) 时传给它 `example.com`,它会报错:
```
// trying to send this message will return an error
m := new(dns.Msg)
m.SetQuestion("example.com", dns.TypeA)
```
最初我以为我知道这个问题的答案(“呃,末尾的点意味着域名是完全限定的?”)。这是对的 —— 一个<ruby> 完全限定域名 <rt> fully qualified domain name </rt></ruby>(FQDN)是一个末尾有 `.` 的域名!
但是*为什么*末尾的点是有用且重要的呢?
### 在 DNS 的请求/响应中,域名的末尾并没有 “.”
我曾经(错误地)认为 “为什么末尾有一个点?”的答案可能是 “在 DNS 请求/响应中,域名末尾有一个 `.`,所以我们把它放进去,以匹配你的计算机实际发送/接收的内容”。但事实并不是这样!
当计算机发送 DNS 请求/响应时,域名的末尾并没有点。实际上,域名中*没有*点。
域名会被编码成一系列的长度/字符串对。例如,域名 `example.com` 被编码为这 13 个字节。
```
7example3com0
```
编码后的内容一个点也没有。一个 ASCII 域名(如 `example.com`)被转成了各种 DNS 软件的 DNS 请求/响应中使用的格式。
今天我们来讨论域名被转成 DNS 响应的一个地方:区域文件。
### 区域文件中域名末尾的 “.”
一些人管理域名的 DNS 记录的方法是创建一个被称为 “区域文件” 的文本文件,然后配置一些 DNS 服务器软件(如 `nsd` 或 `bind`)来为该区域文件中指定的 DNS 记录提供服务。
下面是一个对应 `example.com` 的示例区域文件:
```
orange 300 IN A 1.2.3.4
fruit 300 IN CNAME orange
grape 3000 IN CNAME example.com.
```
在这个文件中,任何不以 `.` 结尾的域名(比如 `orange`)后都会自动加上 `.example.com`。所以 `orange` 成了 `orange.example.com` 的简称。DNS 服务器从它的配置中得知这是一个 `example.com` 的区域文件,所以它知道在所有不以点结尾的名字后面自动添加 `example.com`。
我想这里的想法只是为了少打几个字符——如果要打出全称,区域文件会是这样:
```
orange.example.com. 300 IN A 1.2.3.4
fruit.example.com. 300 IN CNAME orange.example.com.
grape.example.com. 3000 IN CNAME example.com.
```
确实多了很多字符。
### 你也可以不通过区域文件来使用 DNS
尽管官方的 DNS RFC([RFC 1035](https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc1035#section-4.1.1))中定义了区域文件格式,但你也可以不通过区域文件来使用 DNS。例如,AWS Route 53 就不用区域文件来存储 DNS 记录!你可以通过 Web 界面或 API 来创建记录,我猜他们是用某种数据库而不是一堆文本文件来存储记录。
不过,Route 53(像许多其他 DNS 工具一样)确实支持导入和导出区域文件,这个功能或许在你更换 DNS 提供商时很有用。
### dig 命令输出中末尾的 “.”
现在我们来讨论下 `dig` 命令的输出:
```
$ dig example.com
; <<>> DiG 9.18.1-1ubuntu1.1-Ubuntu <<>> +all example.com
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 10712
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 65494
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;example.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
example.com. 81239 IN A 93.184.216.34
```
有一件奇怪的事是,几乎每一行都以 `;;` 开头,这是怎么回事?`;` 是区域文件中的注释字符!
我想 `dig` 以这种奇怪的方式输出的原因可能是为了方便你粘贴这些内容到区域文件时,不用修改就可以直接用。
这也是 `example.com` 末尾有个 `.` 的原因 —— 区域文件要求域名末尾必须有点(否则它们会被解释为是相对于该区域的)。因此 `dig` 也这么处理了。
我真的希望 dig 有一个 `+human` 选项,以更人性化的方式打印出这些信息,但现在我太懒了,懒得花工夫去实际贡献代码来做这件事(而且我并不擅长 C),所以我只能在我的博客上抱怨一下 :smiley:
### curl 命令输出中末尾的 “.”
我们来看下另一个末尾有 `.` 的例子:`curl`!
我家里有台计算机名为 `grapefruit`,其上运行着 Web 服务器。当我执行 `curl grapefruit` 时,会输出:
```
$ curl grapefruit
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd">
<html>
<head>
......
```
这样运行没问题!但是如果我在域名后加一个 `.` 会怎样呢?它报错了:
```
$ curl grapefruit.
curl: (6) Could not resolve host: grapefruit.
```
发生了什么?为了搞清楚,我们需要先来学习下搜索域:
### 初识搜索域
当我执行 `curl grapefrult` 时,它是怎么被转成一个 DNS 请求的?你可能会认为我的计算机会向域名 `grapefruit` 发送一个请求,对吗?但事实并不是这样。
让我们用 `tcpdump` 来看看到底是什么域名在被查询。
```
$ sudo tcpdump -i any port 53
[...] A? grapefruit.lan. (32)
```
实际上是向 `grapefruit.lan.` 发送的请求。为什么呢?
解释一下:
1. `curl` 调用函数 `getaddrinfo` 来查询 `grapefruit`
2. `getaddrinfo` 查询了我计算机上的文件 `/etc/resolv.conf`
3. `/etc/resolv.conf` 包含两行内容:
```
nameserver 127.0.0.53
search lan
```
4. 因为有 `search lan` 这行内容,所以 `getaddrinfo` 在 `grapefruit` 的末尾添加了一个 `lan`,去查询 `grapefruit.lan`
### 什么时候搜索域被使用?
现在我们知道了一些奇怪的事情:当我们查询一个域名时,有时会有一个额外的东西(如 `lan`)被加到最后。但是什么时候会发生这种情况呢?
1. 如果我们在域名**末尾**添加一个 `.`,那么这时不会用到搜索域
2. 如果域名**中间包含**一个 `.`(如 `example.com`),那么默认也不会用到搜索域。但是可以通过修改配置来改变处理逻辑(在 [ndots](https://pracucci.com/kubernetes-dns-resolution-ndots-options-and-why-it-may-affect-application-performances.html) 里有更详细的说明)
我们现在知道了 `curl grapefruit.` 与 `curl grapefruit` 结果不一样的原因——因为一个查询的是 `grapefruit.`,而另一个查询的是 `grapefruit.lan.`。
### 我的计算机怎么知道使用哪个搜索域呢?
当我连接路由时,它会通过 DHCP 告诉我它的搜索域是 `lan` —— 它也是通过这个方式给我的计算机分配 IP。
### 所以为什么要在域名末尾加一个点呢?
现在我们已经了解了区域文件和搜索域,下面是我认为的人们要在域名末尾加点的原因:
有两种情况下,域名会被修改,并在末尾添加其他东西。
* 在 `example.com` 的区域文件中,`grapefruit` 会被转为 `grapefruit.example.com`
* 在我的本地网络(我的计算机已经配置了使用搜索域 `lan`),`grapefruit` 被转为 `grapefruit.lan`
因此,由于域名在某些情况下实际上可能被转成其他名字,人们就在结尾处加一个 `.`,以此来表示 “**这是域名,末尾不需要添加任何东西,这就是全部内容**”。否则会引起混乱。
“这就是全部内容”的技术术语是\*\*“完全限定域名”**,简称为**“FQDN”\*\*。所以 `google.com.` 是一个完全限定域名,而 `google.com` 不是。
我总是要提醒自己这样做的原因,因为我很少使用区域文件和搜索域,所以我经常觉得——“我当然是指 `google.com` 而不是 `google.com.something.else`! 我为什么要指其他东西?那太傻了!”
但是有些人确实在使用区域文件和搜索域(例如 Kubernetes 中使用了搜索域!),所以结尾的 `.` 很有用,可以让人确切的知道,不应该再添加其他东西。
### 什么时候在末尾添加 “.”?
以下是关于何时在域名末尾加 ". " 的几个简单说明:
**需要添加:配置 DNS 时**
在配置 DNS 时,使用完全限定域名从来都不是坏事。你不一定要这样做:非完全限定域名通常也能正常工作,但我从来没有遇到过不接受完全限定域名的 DNS 软件。
有些 DNS 软件需要这样做:现在我为 `jvns.ca` 使用的 DNS 服务器让我在域名的末尾加上 `.`(例如在 CNAME 记录中),并提示如果我不添加,它将在我输入的内容末尾加上 `.jvns.ca`。我不同意这个设计决定,但这不是什么大问题,我只是在最后加一个 `.`。
**不需要加:在浏览器中**
令人困惑的是,在浏览器中,在域名结尾处加一个 `.` *不能*正常运行。例如,如果我在浏览器中输入 `https://twitter.com.`,它就会报错。它会返回 404。
我认为这里发生的事情是,它将 HTTP `Host` 标头设置为 `Host:twitter.com.`,而对端的 Web 服务器则期望 `Host:twitter.com`。
同样地,`https://jvns.ca.` 由于某种原因,返回了一个 SSL 错误。
### 我认为相对域名在过去是比较常见的
最后一件事:我认为“相对”域名(比如我用 `grapefruit` 来指代我家的另一台计算机 `grapefruit.lan`)在过去更常用,因为 DNS 是在大学或其他有大型内部网络的大机构中开发的。
在今天的互联网上,使用“绝对”域名(如 `example.com`)似乎更为普遍。
---
via: <https://jvns.ca/blog/2022/09/12/why-do-domain-names-end-with-a-dot-/>
作者:[Julia Evans](https://jvns.ca/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[lxbwolf](https://github.com/lxbwolf) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | null |
15,256 | 如何在 Linux 中确定运行的是那种初始化系统 | https://www.debugpoint.com/systemd-or-init/ | 2022-11-15T18:30:13 | [
"初始化",
"systemd",
"init"
] | /article-15256-1.html | 
>
> 你可以通过以下方式确定你的 Linux 发行版中是否正在运行 systemd 或其它初始化系统。
>
>
>
首个进程在你启动 Linux 发行版时开始运行,它称为初始化进程 init(<ruby> 初始化 <rt> initialization </rt></ruby>的缩写)。它的进程标识符为 1(即 pid=1)。基于 Unix 的系统中的所有进程和应用程序都是这个初始化进程的后代。
根据功能和特性,存在不同类型的初始化进程。例如,[systemd](https://www.debugpoint.com/tag/systemd)、Runit、OpenRC、sysVinit 等。其中,systemd 是最流行和最现代的一种,被包括 Ubuntu 和 Fedora 在内的所有现代 Linux 发行版使用和采用。
与传统的基于 Unix 的初始化系统相比,systemd 及其性能一直存在争议。但这就是另外一个话题了。
让我们看看如何确定在 Linux 发行版中运行的是 systemd 还是其它初始化系统。
### systemd 还是其它初始化系统?
不幸的是,没有直接的命令可以找到它。你可以从初始化进程追溯它,它基本上是到 `/sbin/init` 的符号链接,即 pid=1。
使用 [strings](https://linux.die.net/man/1/strings) 命令打印嵌入在二进制文件 `/sbin/init` 中的文本并使用以下命令搜索 `init`:
```
strings /sbin/init | grep init
```
#### 示例 1
在下面的输出中,它是一个运行 Debian(Peppermint OS)的 sysVinit 系统。如你所见,它清楚地显示了 `init` 进程名称。
```
strings /sbin/init | grep init
```

如果在上述同一个系统中找 `systemd`,那么不会有任何结果。因此,你可以得出结论,你正在运行 sysVinit 而不是 systemd。
#### 示例 2
如果你在 systemd 系统中运行上述命令,你可以在输出的第一行轻松看到 systemd 及其版本。
```
strings /sbin/init | grep systemd
```

#### 示例 3
你也可以尝试使用 `pstree` 命令打印进程树,它应该会显示第一个进程名称。它应该是 `systemd` 或 `init`,如下例所示。
```
pstree
```


这就好了。这样你就可以轻松找出你的发行版是使用 systemd 还是其他的。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/systemd-or-init/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,257 | Linux Mint 的更新管理器现在支持 Flatpak | https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-mint-update-manager/ | 2022-11-16T09:01:00 | [
"Linux Mint"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15257-1.html |
>
> Linux Mint 的更新管理器变得更有用了!
>
>
>

Linux Mint 的更新管理器是该发行版的一个重要组成部分,它使新用户可以获得更为方便简易的体验。
最近的一次更新 Linux Mint 21 推出了许多改进,包括更新管理器对 Flatpak 的支持。
**你只需要更新你的系统就可以获得这些改进。**
### ⭐ 更新管理器中支持 Flatpak

是的,你没看错。这终于实现了。
Flatpak 支持已被添加到更新管理器中,用户只需单击几下就能更新 Flatpak 应用程序和运行时。
这将为进一步改善用户体验的统一更新体验提供了帮助。
这对新用户来说很有好处,他们不需要熟悉终端命令就能更新 Flatpak。此外,你不需要将 Flatpak 与软件中心集成(对于 GNOME 而言)。
换句话说,Linux Mint 团队增强了你使用 Flatpak 应用程序的体验。
**除了对 Flatpak 的支持,本次更新还包括对 Linux Mint 21 的更多增强,这是一个开箱即用的更新。**
这些改进包括:
### 对角栏的改进

Linux Mint 21 中的 <ruby> 角栏 <rt> Corner Bar </rt></ruby> 添加了两项新特性:
* 能够在角栏设置左键点击和中键点击的动作;你可以配置它以显示桌面、工作区选择器或桌面。
* 一个允许你将鼠标悬停在角栏上以显示桌面的新选项。
### Nemo 的更新

Nemo 文件管理器做了一些调整;现在,当文件被选中时,只会高亮显示文件名,而不是图标和文件名。
**如果你还不知道**, 你也可以通过我们建议的一些调整来增强 Nemo 文件管理器的体验:
>
> **[调整 Linux 中的 Nemo 文件管理器,让它更好用的 15 种方法](https://itsfoss.com/nemo-tweaks/)**
>
>
>
此外,桌面图标被垂直翻转,桌面上下文菜单中添加了一个新的快捷方式,可以快速打开显示设置。
### 更少的密码提示
这是很多人可能喜欢的另一个用户体验调整。
当删除 Flatpak 或任何快捷方式或本地应用程序时,它将不再要求你输入密码。
类似地,在新立得(LCTT 译注:Linux 下的一个包管理工具)和更新管理器的情况下,将使用 pkexec 来记住密码。
这样,用户就不需要每次执行多个操作时都输入密码。
你可以浏览 [Linux Mint 月度博客](https://blog.linuxmint.com/?p=4424) 以了解其它变化。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-mint-update-manager/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[qfzy1233](https://github.com/qfzy1233) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Linux Mint's Update Manager is an essential part of the distro that makes the experience easier for new users.
A recent update has pushed many improvements to Linux Mint 21, including Flatpak support with the update manager.
**You just need to update your system to get these refinements.**
[Get a free, secure, and private email with Proton MailProton Mail is the world’s largest secure email service with over 70 million users. Available on Web, iOS, Android, and desktop. Protected by Swiss privacy law.](http://proton.go2cloud.org/aff_c?offer_id=15&aff_id=1173&ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## ⭐ Flatpak Support In Update Manager
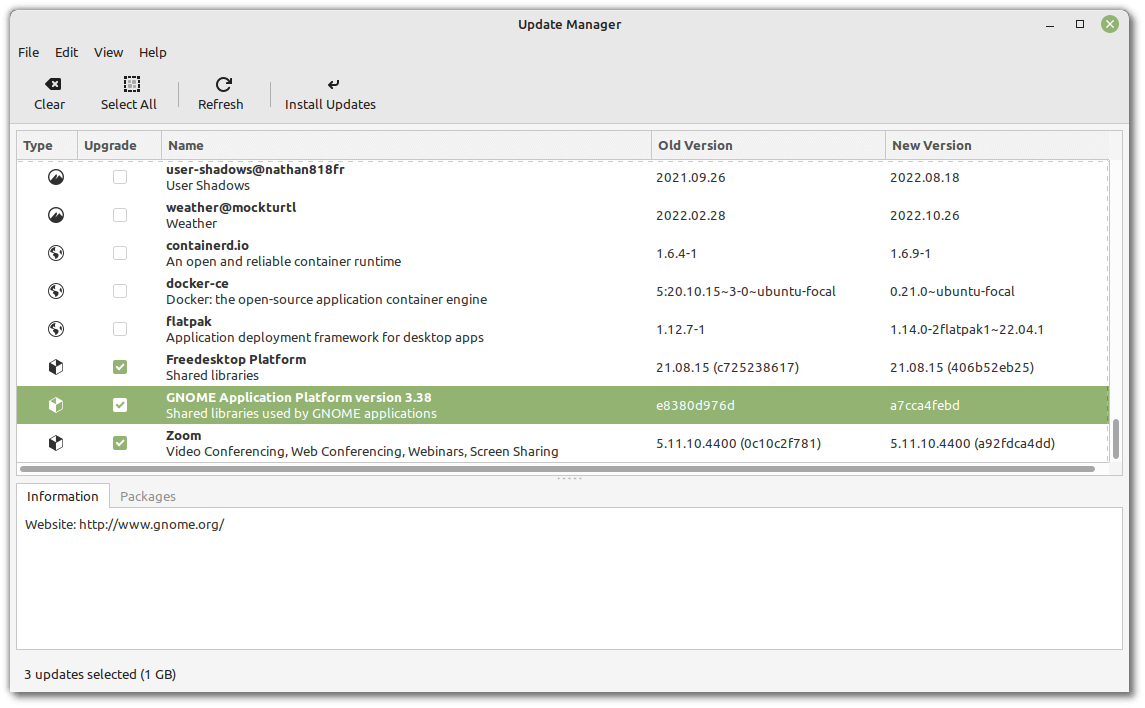
Yes, you read that right. It is finally happening.
Flatpak support has been added to the Update Manager, letting users update Flatpak applications and runtimes in a few clicks.
This should make way for a unified update experience that further improves the user experience.
It is beneficial for new users who need not be familiar with terminal commands to update Flatpak. Also, you do not require to integrate Flatpak with the software center (for GNOME).
In other words, the Linux Mint team enhanced your experience with Flatpak apps.
[6 Tips and Tools to Enhance Your Flatpak Experience in Linux - It’s FOSSIf you love using Flatpak applications, here are a few tips, tools, and tweaks to make your Flatpak experience better and smoother.](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-tips-tweaks/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

**Alongside Flatpak support, the update includes a few more enhancements to Linux Mint 21, which is immediately available as an update.**
Some of the refinements include:
## Improvements To Corner Bar
The corner bar on Linux Mint 21 has received two new additions:
**Ability to set left click and middle click actions to the corner bar; you can configure it to show the desktop, the workspace selector, or the desklets.****A new option lets you hover your mouse on the corner bar to show the desktop.**
### Suggested Read 📖
[Linux Mint 21 Review: Best Distro Just Got a Little BetterLinux Mint is undoubtedly the best distribution for the beginners. The Mint 21 release makes it a bit better in terms of features and functionalities.](https://itsfoss.com/linux-mint-21-review/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## Updates To Nemo
The Nemo file manager has received a few tweaks; now, when files are selected, only the file names will be highlighted instead of the icon and file name.
**If you did not know**, you could enhance the Nemo file manager experience with some of our suggested tweaks as well:
[15 Ways to Tweak Nemo File Manager in Linux to Get More Out of it - It’s FOSSNemo is a good file manager with plenty of features. You can further enhance your experience by using these extensions, tweaks and tips.](https://itsfoss.com/nemo-tweaks/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

Furthermore, the desktop icon has been flipped vertically, and a new shortcut has been added to the desktop's context menu to give quick access to the display settings.
## Fewer Password Prompts
This is another user experience tweak that many of you might like.
When removing a Flatpak or any shortcut or local application, it will no longer ask you for a password.
Similarly, in the case of Synaptic and the Update Manager, pkexec will be used to remember the password.
This way, users do not have to enter the password every time they perform multiple operations.
You can refer to [Linux Mint's monthly blog post](https://blog.linuxmint.com/?p=4424&ref=news.itsfoss.com) to learn about other changes.
**Via: DebugPointNews**
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,258 | Fedora Linux 37 发布 | https://fedoramagazine.org/announcing-fedora-37/ | 2022-11-16T10:03:24 | [
"Fedora"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15258-1.html | 
今天我很兴奋地与大家分享成千上万的 Fedora 项目贡献者的辛勤工作成果:Fedora Linux 37 版本来了!让我们看看这个最新版本给你带来了什么。一如既往,在从以前的版本升级之前,你应该确保你的系统是完全最新的。迫不及待地想开始了吗?在你阅读的同时 [下载](https://getfedora.org)!
>
> **[下载 Fedora Linux 37](https://getfedora.org)**
>
>
>
### 两个新的版本
Fedora 的各个“<ruby> 版本 <rt> Edition </rt></ruby>”是针对某一特定“市场”的旗舰产品。在 Fedora Linux 37 中,我们增加了两个新版本:Fedora CoreOS 是你可能还记得的 Atomic Host 的后续版本。从 Project Atomic 和 CoreOS 的初始的工作中汲取营养,它提供了一种自动更新机制,以托管基于容器的工作负载。通过原子更新和简单的回滚,它为你的基础设施增加了安全感。
Fedora Cloud 也作为一个版本回来了。云计算工作组的活动已经重新开始了。Cloud 版本提供了一个很棒的 Fedora 基础,可以在你喜欢的公共或私有云中运行。AMI 将在本周晚些时候在 AWS 市场上提供,在社区频道上现在已经可以使用。请查看 [此网站](https://getfedora.org/en/cloud/) 以了解可以在其他云供应商或你自己的云上运行的镜像!
### 桌面的改进
Fedora Workstation 专注于桌面体验。像往常一样,Fedora Workstation 采用了最新的 GNOME 版本。[GNOME 43](https://release.gnome.org/43/) 在设置中包括一个新的设备安全面板,为用户提供关于系统中硬件和固件的安全信息。在上一个版本的基础上,更多的 GNOME 核心应用程序被移植到了最新版本的 GTK 工具包,提供了更好的性能和现代的外观。
在这个版本中,我们做了一些改变,让你的安装变得更精简。我们把 Firefox 浏览器的语言包分成了子包。这意味着如果你不需要本地化,你可以删除 `firefox-langpacks` 包。gettext 的运行包(帮助其他包产生多语言文本的工具)被分割成一个单独的、可选择的子包。
当然,我们生产的不仅仅是“版本”。Fedora <ruby> <a href="https://spins.fedoraproject.org/"> 定制版 </a> <rt> Spins </rt></ruby> 和 <ruby> <a href="https://labs.fedoraproject.org/"> 实验室 </a> <rt> Labs </rt></ruby> 针对的是不同的受众和使用情况,包括 [Fedora Comp Neuro](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/en/comp-neuro/) ,它为计算神经科学提供工具,以及像 [Fedora LXQt](https://spins.fedoraproject.org/en/lxqt/) 这样的桌面环境,它提供一个轻量级桌面环境。而且,别忘了我们的备用架构。[ARM AArch64、Power 和 S390x](https://alt.fedoraproject.org/alt/)。
### 系统管理方面的改进
Fedora Server 现在可以生成一个 KVM 磁盘镜像,使在虚拟机中运行 Server 更加容易。如果你已经禁用了 SELinux(没关系 —— 我们仍然爱你!),你可以在影响较小的情况下重新开启它。自动标签现在以并行方式运行,使 “fixfiles” 操作更快。
为了跟上密码学的发展,这个版本引入了一个 `TEST-FEDORA39` 策略,预览了计划在未来版本中的变化。新策略之一是不再使用 SHA-1 签名。研究人员早就知道这种哈希值(就像之前的 MD5 一样)在许多安全方面的使用是不安全的。
在未来,我们可能会将 SHA-1 从 Fedora Linux 可接受的安全算法列表中移除。(正如 `TEST-FEDORA39` 这个名字所暗示的那样,也许最快也要到明年。)不过我们知道如今 SHA-1 哈希值仍然在使用。新的策略可以帮助你现在就测试你的关键应用程序,这样你就可以做好准备。请尝试一下,并让我们知道你在哪里遇到了问题。
说到密码学,openssl1.1 包现在已经废弃了。它还能用,但我们建议你更新你的代码,以使用 openssl 3。
### 其他更新
树莓派 4 现在在 Fedora Linux 中得到了正式支持,包括图形加速。在 ARM 的其他方面,Fedora Linux 37 放弃了对 ARMv7 架构(也被称为 arm32 或 armhfp)的支持。
在我们的“[First](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/project/#_first)”基础上,我们已经更新了关键的编程语言和系统库包,包括 Python 3.11、Golang 1.19、glibc 2.36 和 LLVM 15。
我们很高兴你能试用这个新版本!请到 <https://getfedora.org/> 下载。或者如果你已经在运行 Fedora Linux,请按照 [简易升级说明](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/upgrading/)。更多关于 Fedora Linux 37 的新功能的信息,请看 [发行说明](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/fedora/f37/release-notes/)。
### 在不太可能发生的情况下...
如果你遇到了问题,请访问我们的 [Ask Fedora](https://ask.fedoraproject.org/) 用户支持论坛。这里有一个 [常见问题](https://ask.fedoraproject.org/c/common-issues/141/none) 的分类。
### 谢谢大家
感谢在这个发布周期为 Fedora 项目做出贡献的成千上万的人。我们很高兴 Fedora 社区有你们。
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/announcing-fedora-37/>
作者:[Matthew Miller](https://fedoramagazine.org/author/mattdm/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Today I’m excited to share the results of the hard work of thousands of Fedora Project contributors: the Fedora Linux 37 release is here! Let’s see what the latest release brings you. As always, you should make sure your system is fully up-to-date before upgrading from a previous release. Can’t wait to get started? [Download](https://getfedora.org) while you read!
## New editions
Fedora Editions are flagship offerings targeted at a particular “market”. With Fedora Linux 37, we’re adding two new Editions. Fedora CoreOS is the successor to what you may remember as Atomic Host. Drawing from Project Atomic and the original CoreOS work, it provides an automatic update mechanism geared toward hosting container-based workloads. With atomic updates and easy rollback, it adds peace of mind to your infrastructure.
Fedora Cloud is also back as an Edition. The Cloud Working Group has seen a resurgence in activity. Cloud provides a great Fedora base to run in your favorite public or private cloud. AMIs will be available in the AWS Marketplace later this week and community channels are available now. Check the [website](https://getfedora.org/en/cloud/) for images in other cloud providers or for your own cloud!
## Desktop improvements
Fedora Workstation focuses on the desktop experience. As usual, Fedora Workstation features the latest GNOME release. [GNOME 43](https://release.gnome.org/43/) includes a new device security panel in Settings, providing the user with information about the security of hardware and firmware on the system. Building on the previous release, more core GNOME apps have been ported to the latest version of the GTK toolkit, providing improved performance and a modern look.
With this release, we’ve made a few changes to allow you to slim down your installation a bit. We split the language packs for the Firefox browser into subpackages. This means you can remove the “firefox-langpacks” package if you don’t need the localization. The runtime packages for gettext — the tools that help other packages produce multilingual text — are split into a separate subpackage.
Of course, we produce more than just the Editions. [Fedora Spins](https://spins.fedoraproject.org/) and [Labs](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/) target a variety of audiences and use cases, including [Fedora Comp Neuro](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/en/comp-neuro/), which provides tools for computational neuroscience, and desktop environments like [Fedora LXQt](https://spins.fedoraproject.org/en/lxqt/), which provides a lightweight desktop environment. And, don’t forget our alternate architectures: [ARM AArch64, Power, and S390x](https://alt.fedoraproject.org/alt/).
## Sysadmin improvements
Fedora Server now produces a KVM disk image to make running Server in a virtual machine easier. If you’ve disabled SELinux (it’s okay — we still love you!), you can turn it back on with less impact. The autorelabel now runs in parallel, making the “fixfiles” operation much faster.
In order to keep up with advances in cryptography, this release introduces a TEST-FEDORA39 policy that previews changes planned for future releases. The new policy includes a move away from SHA-1 signatures. Researchers have long known that this hash (like MD5 before it) is not safe to use for many security purposes.
In the future, we are likely to remove SHA-1 from the list of acceptable security algorithms in Fedora Linux. (As the name TEST-FEDORA39 implies, perhaps as soon as next year.) We know there are still SHA-1 hashes in use today, however. The new policy helps you test your critical applications now so that you’ll be ready. Please try it out, and let us know where you encounter problems.
Speaking of cryptography, the openssl1.1 package is now deprecated. It will remain available, but we recommend you update your code to work with openssl 3.
## Other updates
The Raspberry Pi 4 is now officially supported in Fedora Linux, including accelerated graphics. In other ARM news, Fedora Linux 37 drops support for the ARMv7 architecture (also known as arm32 or armhfp).
Following our “[First](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/project/#_first)” foundation, we’ve updated key programming language and system library packages, including Python 3.11, Golang 1.19, glibc 2.36, and LLVM 15.
We’re excited for you to try out the new release! Go to [https://getfedora.org/](https://getfedora.org/) and download it now. Or if you’re already running Fedora Linux, follow the [easy upgrade instructions](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/upgrading/). For more information on the new features in Fedora Linux 37, see the [release notes](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/fedora/f37/release-notes/).
## In the unlikely event of a problem…
If you run into a problem, visit our [Ask Fedora](https://ask.fedoraproject.org/) user-support forum. This includes a category for [common issues](https://ask.fedoraproject.org/c/common-issues/141/none).
## Thank you everyone
Thanks to the thousands of people who contributed to the Fedora Project in this release cycle. We love having you in the Fedora community.
## Joel
Thank you very much!
I was looking forward to this great news. Fedora Linux is undoubtedly the best distro of all. I am a fan and user of Fedora since 2013.
## Sergio Corrales
Great News! thanks for the hard work
## Ryan
Thanks Fedora team for all the hard work you do! Happy release day 🎉
## Kevin G
Awesome, as a user, thank you to everyone involved for all your hard work. It truly does get appreciated.
## Joshua H
Been using Fedora since 32 released and it’s just been brilliant! Every release just keeps getting better. Can’t wait for more btrfs improvements to be implemented. Thanks all who create Fedora!
## Gnanesh
Thanks to the incredible team at Fedora. Installed the F37 Cinnamon spin… First impression is it’s smooth and polished. Great effort by the team. Luv’in it!
## Fernando
Thanks, great job
## Steven Urkel
Was eagerly waiting for this release. Time to download the ISO and give it a go.
## Boopathi R
I’ve been waiting for Fedora 37 release so long. Thank you for everything!
<3 for fedora!
## VSHADOW
It must be said since version 1 of fedora is a big step and being at 37. In general I wait for the stable version but I ventured to use 36 to 37 in Beta and I have no complaints it made me even happy that everything worked fine without congratulations big problems.
## David Etengoff
Hi – I’m excited as well! Unfortunately, I get an error on my Fedora 36 ARM installation when trying to upgrade.
## Fernando San Martín
Already installed!, thank you for such awesome Work!
## Onyango Michael
Was eagerly waiting for the release thanks so much@mattdm
## Kamil
The specific link for F37 Common Issues is:
https://ask.fedoraproject.org/tags/c/common-issues/141/f37
## John Willemsen
Yes! Thank you
## yodatak
Don’t update if you have a nvidia driver propietary driver there is problem with existing Nvidia driver
https://bugzilla.rpmfusion.org/show_bug.cgi?id=6466
https://www.reddit.com/r/Fedora/comments/y9te2e/nvidia_drm_errors_on_nvidia_driver_5205606/
https://forums.developer.nvidia.com/t/in-fedora-37-nvidia-driver-520-56-06-is-buged-and-crash-apex-legend-drm-nv-drm-fence-context-create-ioctl-nvidia-drm-error-nvidia-drm-gpu-id/232940
## arielale
Soy Nuevo con fedora, tengo la version 36, como hago para actualizar a 37 con knome 43, alguien me puede ayudar…
## Gregory Bartholomew
https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/upgrading/
## Tim H
I only installed Fedora 36 a few days ago ! this is great news well done guys. Really loving fedora as a distro, wish I had switched sooner.
## Jim
There’s a typo in this post in the “Other updates” section:
“For more information on the new features in Fedora Linux 36, see the release notes.”
Should be Fedora 37, and the link needs correcting too 🙂
## Gregory Bartholomew
Thanks Jim! Fixed!
## Hawar Hekmat
Slow dnf as usual, and slow website downloading ISO from fedora workstation takes ever to complete
## Gregory Bartholomew
Sounds like Fedora Linux could use more mirrors (https://admin.fedoraproject.org/mirrormanager/). I guess you could run one. Or get someone in your area with good bandwidth to do so.
## Andrew Moore
Or there may be an issue with some download servers? F37 Server ISO downloaded at 11 MB/s whereas F37 Workstation ISO didn’t download at all. Upon second try a couple minutes later, F37 Workstation ISO also downloaded at 11 MB/s. Looks less like a load issue than just a bad server…
Fedora rocks! Thank you guys 🙂
## ziprasidone
Thank You all Fedora team!
## Aman Das
Fantastic! I’ll be updating my system now 🥳
## idanka
Use torrent, not slow:
https://torrent.fedoraproject.org/
## Piotr
/etc/fstab
Created by anaconda on Tue Aug 23 02:44:14 2022
I’ve been using F37 Silverblue since August 23. 😉 I’d say it was fairly reliable in late September.
Great job!!!
## Richard
I usually update my system every six months after a new release, anyway, this is an amazing update, see you in six!.
## Rodrigo
Awesome work, I was using Fedora 37 beta and is great
## Dwight
Excellent way to kick off the holidays. Thanks so much to the Fedora team for this.
## Peter
WooHoo, downloading now by torrent!
Thank you to all at Fedora.
## Derek
I have been running the beta and now the final on three of my machines and all run like a dream.Thank you for all the hard work which is so appreciated.
## WhoKnows
Thank you so much! Fedora is great!!
Any idea when Fedora Silverblue 37 iso will be available? (Would like to do a new clean install instead of rebase)
## WhoKnows
Nevermind – Saw that the iso is listed in https://torrent.fedoraproject.org/
## James
Can anyone give me a link to download the fedora silverblue 37? The official silverblue website only has links to the 36 iso.
Although the torrent url in a comment above has a link to the 37 silverblue iso torrent, I don’t have a torrent client on this machine, and so wanted to download the iso direct.
## James
I found the 37 silverblue iso download at the following link:
https://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/fedora/linux/releases/37/Silverblue/
## Darvond
Mazeltov. I’ll wait for Sway and a few other packages to update before taking it fully.
## msztr
Is there any way to disable this new menu style and go back to the old one?
https://mega.nz/file/OjZGFTYT#mVdpmao5XgQxII7ChK5yI55hsP4xdL2WIyshrzkU4_g
thanks
msztr
## Jesse
Yeah, stay on Fedora 36 – that menu isn’t from Fedora, it is the style from GNOME 43.
## Marko
Indeed it’s coming from Gnome 43. It’s a bit different and might take using to, but what I’d like is to be adoptable based on where is your taskbar. Mine is in the bottom so having power button at the top makes it very non-intuitive to use.
## Darvond
Sure. Dump Gnome for a better desktop environment/window manager. Fedora doesn’t exactly have a shortage of them. I personally suggest WIndowmaker or i3. If you want something
less esoteric, Cinnamon and Mate are based on the GTK without Gnome’s baggage.A metaphor: As Comstar became to the Inner Sphere, so has Gnome become to Linux.
## Viacheslav
Thank you for new Fedora 37, it is perfect!
## tfks
Worth the wait! Thank you Fedora Team!
## Jesse
Woohoo! Thank you Fedora Team for the great work. It was worth the wait!
## Christian
I ‘ve just installed F37 to my laptops ssd from a usb-stick created with Fedora Media Writer. My plan was to keep the existing Windows 10 and F33 OS and installed F37 beside them.
In Anaconda i did choose: custom installation > in following agent > “auto create F37 partions”. the process created serveral new Brtfs partitions/volumes, starting from p6 to p8.
###
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS
zram0 252:0 0 7,4G 0 disk [SWAP]
nvme0n1 259:0 0 238,5G 0 disk
├─nvme0n1p1 259:1 0 260M 0 part /boot/efi
├─nvme0n1p2 259:2 0 16M 0 part
├─nvme0n1p3 259:3 0 42,4G 0 part
├─nvme0n1p4 259:4 0 1000M 0 part
├─nvme0n1p5 259:5 0 1G 0 part
├─nvme0n1p6 259:6 0 117,7G 0 part
├─nvme0n1p7 259:7 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─nvme0n1p8 259:8 0 75,1G 0 part /home
/
###
After the installation process had finished i did a reboot. The Grub bootloader now shows entries for Windows 10, F37 and F37-rescue (all are working) but the previous F33 entry is gone. Please help me with instructions to restore F33 grub boot entry!
## Christian
correction: In Anaconda i did choose: custom installation > in following agent > “auto create F37 partions”. the process created serveral new Brtfs partitions/volumes: p7 and p8, and i think modified p1
## Gregory Bartholomew
@Christian This sort of problem is better discussed on Fedora’s help forum: https://ask.fedoraproject.org/
## LiuYan
Since there’s EFI partition, my guess: the /boot/efi/EFI/fedora/ directory was overridden with Fedora 37 installation, so F33 grub boot entry was lost.
From the partition list, I didn’t seen a large partition that can hold Fedora 33 installation (assuming p3 is Windows 10 installation). Maybe Fedora 33 installation was overridden too ?
## Máirín Duffy
F37 also features brand new non-default wallpapers created on Fedora using Blender 🙂
https://gitlab.com/fedora/design/community-design-team/issues/-/issues/5
Enjoy!
## Stan
What package?
## Máirín Duffy
It’s this one, you can see my commit in the log:
https://packages.fedoraproject.org/pkgs/fedora-workstation-backgrounds/fedora-workstation-backgrounds/
## Stan
Thanks. With the MATE Desktop Environment, that package has to be explicitly installed:
dnf install fedora-workstation-backgrounds.noarch
And “Add…” must be clicked in the “Appearance Preferences” window.
It’s amazing what can be done with Blender.
BTW, the tooltips show “Artist: unknown”.
## Stan
‘BTW, the tooltips show “Artist: unknown”.’
This file needs to be updated:
$ rpm -ql fedora-workstation-backgrounds | grep AUTHORS
/usr/share/doc/fedora-workstation-backgrounds/AUTHORS
## Alireza Haghshenas
Fedora is a real life saver for me. Thanks for the great product.
On my desktop computer, I’m having real trouble: The Fedora 37 live cannot boot when my monitor is connected to the Nvidia Rtx 4090. It does boot properly when monitor is connected to the integrated AMD graphics.
This is not new. In Fedora 36 any Kernel starting and after 5.19.16 have the same problem. I’ve reported this to https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=2142277
Can someone help me?
## Gregory Bartholomew
I think the Live images usually have a “Install Fedora in basic graphics mode” option that should workaround most video card problems. Beyond that, you’ll probably need to ask for help on Fedora’s help forum — https://ask.fedoraproject.org/
## Viacheslav
Hi, have you tried disabling the built-in amd graphics in the bios and reinstalling the nvidia graphics driver via the akmod script? It worked for me with intel graphics paired with a gtx 1050 ti.
## Alireza Haghshenas
Thank you Viacheslav, I’ll try that.
In general, I’m reasonably happy with the open source Nvidia drivers. There are some rough edges, but the overall experience is good.
## spital
NVDA always had problems, the best is to have their driver, so either go to text mode, install it, telinit 5 or I can create a bootable ISO with the driver installed. Just ping me
## Gineesh Madapparambath
Awesome 😎
## Mohaki
It’s beautiful, clean, minimalist and fast. I think most of the community should migrate from Ubuntu into Fedora. I need arch for my use-cases otherwise I would used Fedora as main. Although I use it as main for server side work.
## c
(retyping because this UI makes it look like I can only have 1 reply per email?)
Was excited to see that I can scale to something besides 200%. However scaling to 125, 150, or 175 makes the graphics very choppy. Most notable when having System Monitor open and list Processes. The mouse just bounces around. Everything is very smooth at 100% or 200%.
This is on a Framework laptop using the recommended resolution 2256×1504.
This is on the Cinnamon spin. But I’m about to try going to regular Gnome edition and then install Cinnamon and others ontop.
## Linus Inkinen
Like a desert without a rain i’ve been waiting this.
Only one request: could the torrent downloads be “less well hidden”? I think those should even be promoted as via torrent the integrity and the genuinety of ISO are affirmed (am i right?).
## Stan
Verification is a separate step from downloading:
https://getfedora.org/en/security/
## Stan
BTW, this will show you what is in fedora.gpg:
$ gpg –show-keys ./fedora.gpg
## Antonio Rafael Izquierdo Carrasco
In my understanding is a workstation OS. Is it recommended to use in production environments. If it does not, Is there any flavor of Fedora to compare, for example; with RHEL, CentOS (before sold it) or Current Rocky Linux?
Thanks in advance for your comments and support.
Just a comment, it was my fist Linux flavor that implemented and I started to learn Linux with this. Thank you so much!
Best regards!
## Eduard Lucena
Sure, try the Fedora Server, I used at home to my local servers: a docker apps server and a file server, both are super stable with streaming and everything. https://getfedora.org/es/server/download/
## Oleg
Rocky is great for production environments. Fedora is a test platform for RHEL. However, Fedora is suitable for use as a workstation in non-critical environments.
## Kyrylo
i love Fedora, thank you Fedora team <3
## Oleg
I do not recommend updating right now. The last few releases have been released with a bunch of problems and this release was no exception. The Firefox does not start, this is the first thing I found. GTK errors.
## Stan
Firefox starts fine with Gnome and Xfce on bare metal and with MATE in a VM.
Try starting in safe mode:
$ firefox –safe-mode
For further debugging, try posting the details here:
https://ask.fedoraproject.org/
## user
Works fine with default Fedora (Gnome).
## Verolomstvo
HP Pavilion Laptop 15-eh1083ur
alt + shift does not work when changing the layout
how to make the keyboard backlight turn on when you touch the touchpad?
## Supermelon
Using it. Enjoying it. Being grateful I am.
## Leandro Hermida
I love Fedora – I use it every day… it’s one of the first I start up every morning what an amazing OS!
## Leandro Hermida
I love Fedora – I use it every day… it’s one of the first things I start up every morning what an amazing OS!
## cv
Nice job, team. Thank you for the update. Upgraded yesterday and I’m enjoying it a lot! Very well polished experience.
## saibug
Yeah…
Fedora forever 🙂
## Odin Wis
Hi Guys, many people suggest that we should fresh install every new release. Is it really true? Should I do this? I have installed Flatpaks, snaps etc.
## Gregory Bartholomew
No it isn’t. Upgrades work fine. About the only time you should need to reinstall is if you want to change the filesystem. And even then, it is possible to copy the existing OS from one filesystem to another. So you wouldn’t strictly
haveto reinstall even in that case. I run Fedora Linux on PCs and servers that I haven’t done a fresh install on in over a decade.## Dave Yendrembam
Everytime fedora comes out with a new flavour I wait atleast 6 months, because you won’t find new yum repo for stuff that works on fedora new. I recently installed fedora 26 and I have to make install half of the stuff or I have to Google a week to make my workstation work. Honestly whenever I upgrade to new fedora I wastes at least a week figuring out how to make my previous work works
## Stan
Those issues are too complicated to debug here. Try posting the details here:
https://ask.fedoraproject.org/
## Alexis
Could the RPMfusion be already enabled right from the installation program by clicking in the next release?
Not even Twitch plays video without it enabled and libraries additionally added. A common user cannot figure out this need from the settings, and gives a very bad impression?
I don’t think even Steam and Chrome are there to instal without enabling RPMfusion…
Why not add those to check alongside proprietary codecs during install? Choice would still be there.
## Steve
For legal reasons, the Fedora project does not support patent-encumbered technology:
https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/packaging-guidelines/what-can-be-packaged/
## Alexis
But RPMfusion is not patent-encumbered tech outside Fedora thoiugh? Why can’t its enablement at least be just added there behind a one click? (with an explanation for the not knowing new user).
## user
Exactly. Furthermore, nobody cares about stupid software patents outside stupid USA.
## Stan
During the first boot after installation of F37 Workstation, users are given an option to:
“Enable Third-Party Repositories”.
## Joachim
Great Work!
Updating all my machines went smoothly by command line.
Thanks to all participants!
## Jason
Control-flow integrity?
## Dean Hunter
I love it. Finally, my very old video works without problems.
80:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation G72 [GeForce 7300 LE] (rev a1)
Subsystem: Jaton Corp Device 01d1
Kernel driver in use: nouveau
Kernel modules: nouveau
## Bob Sisk
Trying to use Stratis storage but when /etc/fstab is changed per Stratis instructions computer will not reboot. When the Stratis mount point is removed from /etc/fstab it will boot. I think 5e problem is with the UUID. Has anyone been able to install Stratis that works after reboot?
## Philip Cobbin
What bunch of phoneys. IBM morons. Claim to have a Raspberi Pi 4 release. Good luck finding it.
## Richard England
See the instructions here:
https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/raspberry-pi/#installing-fedora-on-a-raspberry-pi-using-the-fedora-arm-installer_rpi
## Gregory Bartholomew
The links for the 32-bit installers are broken because Fedora is no longer building/shipping 32-bit images. If, however, you go to the download page for all the “alternative” architectures — https://alt.fedoraproject.org/alt/ — the links for the 64-bit arm installers are there and those work. Apparently there was some lack of coordination between the people who build the images and the people who update the web pages. It should get fixed soon.
## user
Great release, terrible wallpaper. As always.
## A.A. Witherspoon
Thank you guys for the hard work that’s being put in to keep Fedora running smoothly.
## dragonauta
Thanks!! Upgrading since F33 without issues!
Why Oh Why there’s still people whining about waiting 6 months to upgrade because “it breaks things” or “doesn’t have my precious app packed yet”. Geez! Grow up!
Fedora is a Workstation distro… Work – Station
Want an edgy distro with latest version of software? Fine, install Arch.
Want build all by yourself? use Slackware or better: LFS.
If I need an application that’s not available for my current version of Fedora, I use GnomeBoxes… Just put a VM (ubuntu, debian, arch or whatever) install the app and get the job done!
Heck! I even use wine to run some Windows app for my day to day work (I’m looking at you Mikrotik Winbox… when will you release a linux version?)
Again, my laptop is running Fedora since F33, and I didn’t have a single issue. Thanks
## MR DAVID W LEGG
Fedora is stable nowadays. I think it’s probably the top distro. Well done.
## Matthew Murrian
I was on Debian then Ubuntu for the last 25 years.
I just came over to Fedora a few months ago and I don’t have any regrets.
Agreed. Solid distro.
## Matthew Murrian
Does anything need to be done if already running Fedora 37 Beta?
I would assume the repositories are the same so that “Beta” versus “Release” is just an announcement for me.
But better to ask the dumb question on the off chance.
## Matthew Miller
Behind the scenes, the repositories are different, but it’s the same content set — just apply updates as normal and it’ll be the same as if you installed the release.
This is not guaranteed to be true — there could be cases where we find something bad in the beta we need to back out and manual intervention might be required. But it’s usually fine, and that includes this time around.
## Matthew Murrian
Thank Matthew. Much appreciated.
## Brian Chadwick
it all looks perfectly wonderful, except it doesn’t work on my machine … firefox, thunderbird, or any firefox derivative like librewolf refuse to load … I reported this several times during the beta release, but seems its not considered a show stopper … my machine? … a Ryzen 5 5600, 32GB DRAM, an AMD W4300 FirePro workstation graphics card and Asus A520 based mainboard … nothing particularly “out there”
F36 works quite fine. F37? … Nope … disabling hardware acceleration in the Firefox based apps makes no difference … I have tried everything I can think of except for putting an nVidia or Intel GPU in the system, which I am not doing. I have tried the same configuration on an Intel i7-6700 using its iGPU, and all works no problems at all. So, there is something going on between Gnome 43, the AMD W4300, and maybe the Ryzen.
## Gregory Bartholomew
Did you try reporting the problem on https://ask.fedoraproject.org/? (ideally along with some sort of error message; e.g., try running the “firefox” command from the terminal to see if it provides any additional clues as to what is going wrong)
## Brian Chadwick
yes, and there is no terminal output … firefox seems to think it is running just fine and appears normally in the process list … but it wont display for some reason … and as for journalctl, zero entries … go figure … I might just add that this occurs in Gnome (Xorg) as well … so … no error messages, no display under X or Wayland …
## Gregory Bartholomew
I saw something like that once where there was a hidden session of X running in a backgrounded remote desktop instance (it was X2Go). The output of the applications was being redirected to the wrong display. I would guess something like that is happening in your case. But again, this isn’t a good place to troubleshoot that sort of problem. Please use ask.fedoraproject.org. Thanks.
## Stan
Also check the system log:
$ journalctl -b
## Dan
Upgraded to Fedora 37 from 36. But after logging in to Gnome on Wayland, I lost the keyboard and couldn’t type in anything. Gnome with xorg works fine though.
## AsciiWolf
Another amazing Fedora release! 🙂 Every new release is getting better and better. Looking forward to what Fedora brings us in the Future.
The last remaining thing that I miss on Fedora (and/or in GNOME) is better background apps and AppIndicators (tray icon) support. I am using the “AppIndicator and KStatusNotifierItem Support” Shell Extension, but an out-of-box upstream solution would be much better. Fortunately, it looks like that this is now being worked on by GNOME[1] and Fedora[2] folks.
[1] https://gitlab.gnome.org/Teams/Design/os-mockups/-/issues/191
[2] https://pagure.io/fedora-workstation/issue/264
## IsaacTso
Amazing as usual! I upgraded from Fedora 36 to 37 on a Dell Latitude laptop. Before upgrading, I uninstalled some applications, and added them back after system was upgraded to FC37. No any issue, upgrading was fast and smooth, and there was no single error or warning.
Thank you the Fedora Team for making my computing easy and robust! Life couldn’t be easier.
## Loïc
Thank you very much for your hard work, I’m new using your distribution and I love it ! You’re awesome :pray:
## hf
This upgrade worked without even a single tiny issue.
Great work.
## Lupe Victoria`
I’m a NEW Linux user trying to walk away from the Microsoft / Adobe empires, had to download and install almost every distro that exist out there, just recently came across this new release from you guys, and I have to say Fedora 37 blow my mind! I’m loving it !
## mike
This is truly a work of art. I have been using Fedora for a few years now and this version is the most refined. Awesome work!
## David Frantz
One big huge THANK YOU to the Fedora team. I’ve been using Fedora or RedHat, since RedHat 4 and frankly it just keeps getting better and better.
As a most likely future ARM user (various embedded boards) thank you again for supporting ARM and hopefully beyond the PI universe. One of those universes will hopefully be Apples laptops when support there is ready. I’m not a big fan of Apple but lets face it their ARM based laptops are game changing. I do wish for an ARM based laptop hardware option beyond Apple’s offering that doesn’t suck.
## Lee Darcy
Running it now! So far so good! Great work Fedora team!
## lexonight
sweet
## desemyr
I appreciate your work !
been using fedora since 28
the most stable system i know by now
## Hiwa
A heartfelt thank you to those who contributed to this amazing Linux distro. I have been using it for years and can’t be happier. |
15,260 | 如何在 RHEL 9 上安装 Node.js | https://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-install-nodejs-on-rhel/ | 2022-11-17T09:22:31 | [
"Node.js",
"NVM"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15260-1.html | 
>
> 在这篇文章中,我们将逐步解释如何在 RHEL 9 系统上安装 Node.js。
>
>
>
[Node.js](https://nodejs.org/en/about/) 基于谷歌的 V8 JavaScript 引擎构建,它是一个自由开源的跨平台 JavaScript 运行时环境,主要用于构建服务器端应用。它使用事件驱动和异步模型,帮助开发人员构建高度可扩展的数据密集型的实时应用(RTA)。你可以使用 NodeJS 来构建前端和后端应用。
Node.js 通常用于构建以下应用:
* 聊天应用
* 流媒体应用
* 浏览器游戏
* 命令行工具
* 嵌入式系统
在其技术栈中使用 NodeJS 的顶级公司包括 PayPal、NetFlix 和 Uber 等等。
安装 Node.js 主要有以下三种方式:
* 从 NodeSource 仓库安装 Node.js
* 从发行版的官方仓库安装 Node.js
* 使用 NVM 安装 Node.js
让我们看看如何使用这些方法在 RHEL 9 上安装 Node.js。
先决条件:
* 最小化安装的 RHEL 9 系统
* 具有管理员权限的 [sudo 用户](https://www.linuxtechi.com/create-sudo-user-on-rhel-rocky-linux-almalinux/)
* 互联网连接
* Red Hat 订阅或本地配置的仓库
### 从 NodeSource 存储库安装 Node.js
[NodeSource](https://nodesource.com/) 是一家技术公司,旨在帮助组织运行生产就绪的 Node.js 应用,关注资源使用以及增强的安全性和应用程序性能。它提供了最新版本的 Node.js 和 NPM。
要从 NodeSource 安装 Node.js,首先,按如下所示更新系统包。
```
$ sudo dnf update -y
```

接下来,安装这期间所需的构建工具。其中包括 GCC C/C++ 编译器、Perl 和 Python 调试器等等。
```
$ sudo dnf groupinstall 'Development Tools' -y
```

接下来,我们将从 NodeSource 安装 Node.js 18.x。为此,请下载并运行 NodeSource 设置脚本,如下所示。
```
$ curl -fsSL https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_18.x | sudo bash -
```
该脚本在其他任务中将 NodeSource 仓库添加到你的系统。

在输出的末尾,你将看到一些关于如何安装 Node.js 和 NPM 的附加说明。

因此,要安装 Node.js 和 NPM(Node 包管理器),请运行以下命令:
```
$ sudo dnf install nodejs -y
```

安装完成后,按如下所示验证 Node.js 和 NPM 的版本。
```
$ node -v
$ npm -v
```

输出显示我们正在运行 Node v18.12,它是最新的 LTS 版本和 NPM 8.19.2。
### 从官方 RHEL 仓库安装 Node.js
安装 NodeJS 和 NPM 的另一种方法是从发行版的官方仓库中安装它们。但是,这种方法不提供最新版本。
如果你不介意不安装最新版本的 Node 和 NPM。 那么在命令行上运行以下命令。
```
$ sudo dnf update -y
$ sudo dnf install nodejs npm -y
```

### 使用 NVM 安装 Node.js
最后,你可以使用 NVM(Node 版本管理器)安装 Node.js,这是一种用于管理系统上 Node 版本的工具。该工具可帮助开发人员在需要不同版本 Node.js 的不同项目上高效工作。
默认情况下没安装 NVM。你需要通过运行 [官方 GitHub 页面](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm) 上提供的 Shell 脚本来安装它。
```
$ curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.2/install.sh | bash
```
这会下载 NVM 并将其保存在主目录的 `.nvm` 目录中。

安装后,关闭终端会话并打开一个新终端。然后运行以下命令确认 NVM 已经安装。
```
$ command -v nvm
```

接下来,你可以使用以下命令列出所有可用的 Node.js 版本:
```
$ nvm ls-remote
```

或者,你可以列出 Node.js 版本的所有最新 LTS 版本,如图所示。
```
$ nvm ls-remote | grep -i latest
```

要安装最新版本的 Node.js(当前为 v19.0.0),请运行以下命令:
```
$ nvm install node
```

然后,你可以验证安装的 Node.js 版本,如下所示。
```
$ node -v
```

此外,你可以安装特定版本的 Node.js。例如,要安装 v18.2.0,请运行以下命令:
```
$ nvm install v18.12.0
```

要列出系统上所有已安装的 NodeJS 版本,请运行以下命令:
```
$ nvm ls
```
第一行带有 “->” 符号的条目指向当前使用的 Node.js 版本。然后是其他版本。

要切换到另一个版本的 Node.js,请使用以下语法:
```
$ nvm use <version>
```
例如,要使用 Node 版本 19.0.0,请运行以下命令:
```
$ nvm use 19.0.0
```

再次检查已安装的 Node.js 版本,这次“->” 符号将指向 v19.0.0。

### 总结
在本指南中,我们演示了如何使用三种不同的方法安装 Node.js。此外,我们还提供了几种使用 NVM 管理 Node 版本的方法。我们希望可以帮助你轻松地在 RHEL 上安装 NodeJS,并选择你想要在项目中使用的版本。
---
via: <https://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-install-nodejs-on-rhel/>
作者:[James Kiarie](https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/james/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In this post, we will explain how to install Node.js on RHEL 9 system step-by-step.
Built on Google’s V8 Javascript engine, [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/en/about/) is a free and opensource, cross-platform JavaScript runtime that is mostly used for building server-side applications. It uses an event-driven and asynchronous model that helps developers build highly scalable, data-intensive real-time applications (RTAs ). You can use NodeJS to build both front-end and back-end applications.
Node.js is commonly used in building the following applications:
- Chat applications
- Streaming applications
- Browser games
- Command-line tools
- Embedded systems
Top companies that use NodeJS in their tech stacks include PayPal, Netflix, and Uber to mention a few.
There are three main ways of installing Node.JS:
- Installing Node.JS from the NodeSource repository
- Installing Node.JS from the distribution’s Official repository
- Installing Node.JS using NVM
Let us check out how to install Node.JS on RHEL 9 using each of these methods.
#### Prerequisites
- Minimal Installed RHEL 9 System
[Sudo User](https://www.linuxtechi.com/create-sudo-user-on-rhel-rocky-linux-almalinux/)with admin rights- Internet Connectivity
- Red Hat Subscription or locally configured repository
## Installing Node.js from NodeSource Repository
[NodeSource ](https://nodesource.com/)is a technology company that seeks to help organizations run production-ready Node.Js applications with more focus on resource usage and enhanced security and application performance. It provides the latest versions of Node.JS and NPM.
To install Node.SJ from Nodesource, first, update the system packages as shown.
$ sudo dnf update -y
Next, install the required build tools which will be required during the installation of Node.JS. These include the GCC c/c++ compiler, Perl, and Python debuggers to mention a few.
$ sudo dnf groupinstall 'Development Tools' -y
Next, we are going to install Node.JS 18.x from Nodesource. To do this, download and run the NodeSource setup script as follows.
$ curl -fsSL https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_18.x | sudo bash -
The script adds the Nodesource repository to your system among other tasks
At the tail end of the output, you will see some additional instructions provided on how to install Node.JS and npm.
Therefore, to install Node.JS and npm (Node Package Manager), run the command:
$ sudo dnf install nodejs -y
Once the installation is complete, verify the version of Node.JS and NPM as shown.
$ node -v $ npm -v
The output shows that we are running Node v18.12 which is the latest LTS release and NPM 8.19.2.
## Installing Node.js from the official RHEL repositories
The other way of installing NodeJS and NPM is by installing them from your distribution’s official repository. However, this approach does not provide the latest versions.
If you don’t mind not installing the latest versions of Node and NPM. , then run the following command on the command line.
$ sudo dnf update -y $ sudo dnf install nodejs npm -y
## Installing Node.js using NVM
Lastly, you can install Node.JS using NVM ( Node Version Manager) which is a tool for managing Node versions on your system. The tool helps developers work efficiently on different projects which require different versions of Node.JS
NVM is not installed by default You need to install it by running the Shell script which is available on the [Official GitHub Page](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm).
$ curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.2/install.sh | bash
This downloads and saves nvm in the .nvm directory in your home directory.
Once installed, close your terminal sessions and open a new terminal. Then run the following command to confirm that NVM has been installed.
$ command -v nvm
Next, you can list all the available versions of Node.JS using the following command:
$ nvm ls-remote
Alternatively, you can list all the latest LTS releases for Node.JS versions as shown.
$ nvm ls-remote | grep -i latest
To install the very latest version of Node.JS (currently v19.0.0 ), run the command:
$ nvm install node
You can then verify the version of Node installed as shown.
$ node -v
In addition, you can install a specific version of Node. JS. For example, to install v18.2.0, run the command:
$ nvm install v18.12.0
To list all the installed versions of NodeJS on your system, run the command:
$ nvm ls
The first entry with the sign ( – > ) points to the version of Node.JS that is currently in use. This is then followed by other versions as indicated below
To switch to another version of Node.JS, use the syntax:
$ nvm use <version>
For example, to use Node version 19.0.0, run the command:
$ nvm use 19.0.0
Again, check the installed versions of Node.JS, and this time the ( – > ) sign will point to v19.0.0
#### Conclusion
In this guide, we have demonstrated how to install Node.js using three different methods. In addition, we have provided a few ways in which you can manage the Node versions using NVM. We hope that you can now comfortably install NodeJS on RHEL and choose the version that you want to work with on your project. |
15,261 | 在 VS Code 和 Codium 中编写 Python 程序 | https://opensource.com/article/22/11/python-vs-code-codium | 2022-11-17T10:09:00 | [
"Python",
"Codium"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15261-1.html | 
>
> 如果你正在寻找一个优秀的、通用的、开源的、带有 Python 集成的代码编辑器,那么你可以尝试一下 Codium。
>
>
>
在过去几年内,我有幸和中学生们一起,并带他们入门 [Python 开发](https://opensource.com/article/22/8/math-python-raspberry-pi) 和树莓派 400。这一切都很有趣,树莓派对于学生和我来说都是一个很好的平台。我们使用了 [Code with Mu](https://codewith.mu/),并且一切都很成功。我们的 Python 技能随着经验的增长而增长,因此最近我开始寻找给这些学生提供更多东西的方法。
我参与了一个 Python 课程并在课程中接触了微软的 Visual Studio Code。我在课程中学到了很多关于如何为 Python 设置虚拟环境,以及如何为 Python 编程配置 VS Code 的知识。在学习过程中,我也认识了 [Codium](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/open-source-alternatives-vs-code),它基本上是没有微软品牌和遥测的 VS Code。
如果你正在寻找一个优秀的、通用的、开源的、带有 Python 集成的代码编辑器,那么你可以尝试一下 Codium。下面是我在 Linux 系统上为 Python 设置 Codium 的方法。
### 在 Linux 上安装或更新 Python
首先,确保你正在运行最新版本的 Python。你可以使用你的软件包管理器来完成这项工作。在 Debian 和基于 Debian 的系统上:
```
$ sudo apt install python3-pip
```
在 Fedora、CentOS、Mageia、OpenMandriva 和类似的系统上:
```
$ sudo dnf update python3
```
在某些系统上,你可能还需要安装创建 Python 虚拟环境的软件:
```
$ sudo apt install python3.10-venv
```
### 安装 Codium
接下来,在你的电脑上 [安装 Codium](https://github.com/VSCodium/vscodium/releases)。在 Linux 上,你可以下载一个包并使用你的包管理器安装它,或者 [使用 Flatpak](https://flathub.org/apps/details/com.vscodium.codium)。
在安装好 Codium 之后,打开你的应用程序或活动菜单,输入 `code` 以启动它。
### 安装 VS Code Python 扩展
代码其实不是什么特别的东西。它只是一些其他应用程序(编译器或运行时)解释的纯文本。你可以在 Codium 中编写 Python 代码而不需要特殊的扩展。但是,有一个 Python 扩展可以为你带来一些方便的功能。
点击“<ruby> 文件 <rt> File </rt></ruby>”菜单,选择“<ruby> 首选项 <rt> Preferences </rt></ruby>”,然后选择“<ruby> 扩展 <rt> Extensions </rt></ruby>”。在“<ruby> 扩展 <rt> Extensions </rt></ruby>”面板中,搜索 Python IntelliSense 扩展。

你已经在 Codium 中设置了 Python。剩下的就是把它用起来。
### 为 VS Code 或 Codium 设置虚拟环境
我们可以创建一个项目目录,并将其添加到 Codium 中,这样在工作时,你创建和保存的文件都将默认保存到活动项目目录。这是一种快速的管理方式,可以让你不必经常点击文件保存和打开对话框。
在你创建一个虚拟 Python 环境作为工作目录时,Codium 会检测到它(因为你已经安装了 Python 扩展)。当你激活一个虚拟环境文件夹作为活动项目目录时,Codium 会自动运行使用虚拟环境所需的激活代码。
要为 Python 创建一个虚拟环境,请打开终端并输入:
```
$ python3 -m venv ~/PythonCoding
```
### 添加项目目录
在 Codium 中,点击“<ruby> 文件 <rt> File </rt></ruby>”菜单,选择“<ruby> 将文件夹添加到工作区 <rt> Add Folder to Workspace </rt></ruby>”。打开你刚刚设置的虚拟环境(对我来说,是 `/home/don/PythonCoding`)。
现在你已经准备好写一些 Python 代码了!在你的工作区中创建一个新的 Python 文件并插入一些基本代码。当你输入时,你可能会注意到,Codium 会为环境包含的 Python 模块提供自动补齐建议。
```
import sys
print("Codium running Python " + sys.version)
```
现在点击 Codium 窗口右上角的“运行”按钮。这会在窗口底部打开一个控制台面板显示你的代码的输出:
```
(PythonCode) sh-5.1$ /home/bogus/PythonCode/bin/python
/home/bogus/PythonCode/app.py
Codium running Python 3.10.6 (main…)[GCC 12.1.0]
(PythonCode) sh-5.1$
```
就像你从输出中看到的,Codium 在 `PythonCode` 环境中运行,并成功运行了你的 Python 代码。
### Codium 和 Python
使用 Codium 编写 Python 代码比以往任何时候都更容易,但 Python 并不是 Codium 支持的唯一语言。你可以轻松地从 [Open VSX Registry](https://open-vsx.org/) 中找到并安装其他扩展,这是一个中立的开源 VS Code 扩展 “市场”。
Codium 的界面比一些基本的编辑器更复杂,但它有我在学习过程中所需要的东西。如果你需要一个更专业的编辑器,或者你想从当前的编辑器切换到新的编辑器,那么试试 Codium 吧。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/11/python-vs-code-codium>
作者:[Don Watkins](https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Cubik65536](https://github.com/Cubik65536) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Over the past couple of years, I have had the privilege of working with middle school children to introduce them to [Python coding](https://opensource.com/article/22/8/math-python-raspberry-pi) and the Raspberry Pi 400. It's been a lot of fun, and the Pi has been a great platform for the students and me. We've used [Code with Mu](https://codewith.mu/) and it's been quite successful. Our aptitude with Python has grown with experience, and so recently I started looking for ways to offer these students more.
I participated in a Python learning class, and during that class I got introduced to Microsoft's Visual Studio Code. I learned a lot in that class about how to set up a virtual environment for Python, and how to configure VS Code for Python programming. During that learning journey, I also got introduced to [Codium](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/open-source-alternatives-vs-code), which is essentially VS Code without Microsoft's branding and telemetry.
If you're looking for a good, general-purpose, open source code editor with Python integration, then you might give Codium a try. Here's how I got Codium set up for Python on my Linux system.
## Install or update Python on Linux
First, make sure you are running the latest version of Python. You can do this with your package manager. On Debian and Debian-based systems:
```
````$ sudo apt install python3-pip`
On Fedora, CentOS, Mageia, OpenMandriva, and similar:
```
````$ sudo dnf update python3`
On some systems, you may also need to install the software to create Python virtual environments:
```
````$ sudo apt install python3.10-venv`
## Install Codium
Next, [install Codium](https://github.com/VSCodium/vscodium/releases) on your computer. On Linux, you can download a package and install it with your package manager, or [use the Flatpak](https://flathub.org/apps/details/com.vscodium.codium).
To launch Codium once it's installed, open your application or Activities menu and type "Code".
## Install the VS Code Python extension
There's nothing special about code. It's just plain text that gets interpreted by some other application, whether it's a compiler or a runtime. You can write Python code in Codium without special extensions. However, having a Python extension adds several conveniences.
Click on the **File** menu, select **Preferences**, and choose **Extensions**. In the **Extensions** panel, find the Python IntelliSense extension.
(Opensource.com, CC BY-SA 4.0)
You've got Python set up in Codium. All that's left to do is to put it to good use.
## Setup a virtual environment for VS Code or Codium
You can create a project directory and add it to Codium so that while you work, the files you create and save default to the active project directory. It's a fast way to stay organized, and it saves you from having to click around File Save and Open dialogues constantly.
When you create a virtual Python environment as a work folder, Codium (because you have the Python extension installed) detects it. When you activate a virtual environment folder as the active project directory, Codium automatically runs the activation code required to use the virtual environment.
To create a virtual environment for Python, open a terminal and type:
$ python3 -m venv ~/PythonCoding
## Add a project directory
In Codium, click on the **File** menu and choose **Add Folder to Workspace**. Open the virtual environment you've just set up (for me, that's `/home/don/PythonCoding`
.)
Now you're ready to write some Python code! Create a new Python file in your workspace and insert some basic code. You may notice, as you type, that Codium helpfully suggests auto-completion for the Python modules the environment contains.
```
``````
import sys
print ("Codium running Python " + sys.version)
```
Now click the **Play** button in the top right corner of the Codium window. This opens a console panel at the bottom of the window, displaying the output of your code:
```
``````
(PythonCode) sh-5.1$ /home/bogus/PythonCode/bin/python /home/bogus/PythonCode/app.py
Codium running Python 3.10.6 (main…) [GCC 12.1.0]
(PythonCode) sh-5.1$
```
As you can see from this output, Codium is running within the `PythonCode`
environment, and it's successfully run your Python code.
## Codium and Python
Using Codium for Python makes writing and running code easier than ever, but Python isn't the only language Codium supports. You can easily find and install other extensions from the [Open VSX Registry](https://open-vsx.org/), a vendor-neutral open source "marketplace" for VS Code extensions.
The Codium interface is more complicated than some basic editors, but it has what I'm looking for at this point in my learning journey. If you're looking to graduate to something professional, or you're looking to switch from your current editor to something new, then give Codium a try.
## Comments are closed. |
15,263 | 通过 SSH 在远程 Linux 系统上执行命令 | https://ostechnix.com/execute-commands-on-remote-linux-systems-via-ssh/ | 2022-11-17T16:39:12 | [
"SSH"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15263-1.html | 
>
> 通过安全的网络连接在远程计算机上调用命令或程序。
>
>
>
有一天,我正在测试如何在 [将文件或目录复制到多个位置和系统时保持完整的文件权限](https://ostechnix.com/how-to-keep-ownership-and-file-permissions-intact-when-copying-files-or-directories/)。当我想检查远程系统上的文件权限时,我必须通过 SSH 登录它并检查属性。从远程系统多次登录和注销的过程让我有点烦,我想,如果我可以**在远程 Linux 系统上通过 SSH 执行命令**就好了。
幸运的是,在浏览了 `ssh` 命令的手册页后,我找到了一个解决办法。
如果你想知道如何本地运行远程系统上运行命令或脚本,而不登录到远程系统,下面的内容会告诉你如何做。
### 1、通过 SSH 在远程 Linux 系统上执行命令
从本地系统通过 SSH 在远程系统上运行命令或脚本的典型方法是:
```
$ ssh <username@IP_Address-or-Doman_name> <Command-or-Script>
```
允许我给你们举几个例子:
#### 1.1、通过 SSH 在远程系统上运行单个命令
假设你想要 [查找远程 Linux 系统的内核详细信息](https://ostechnix.com/find-out-the-linux-distribution-name-version-and-kernel-details/)。为此,只需运行:
```
$ ssh [email protected] uname -a
```
这里,
* `sk` 是远程系统的用户名,
* `192.168.225.22` 是远程系统的 IP 地址,
* `uname -a` 是我想在远程系统上运行的命令。
示例输出:

看到没?我并没有实际登录到远程系统,但通过 SSH 在远程系统上执行了 `uname` 命令,并在本地系统的终端上显示了输出。
你还可以像下面这样用引号指定命令。
```
$ ssh [email protected] "uname -a"
```
或者,
```
$ ssh [email protected] 'uname -a'
```
如果你已经 [更改了 SSH 协议的默认端口](https://ostechnix.com/how-to-change-apache-ftp-and-ssh-default-port-to-a-custom-port-part-3/),只需使用 `-p` 参数指定它。
```
$ ssh -p 2200 [email protected] uname -a
```
#### 1.2、通过 SSH 在远程主机上执行多个命令
你还可以在远程主机上运行多个命令,方法是将它们放在引号中。
```
$ ssh [email protected] "uname -r && lsb_release -a"
```
或者:
```
$ ssh [email protected] "uname -r ; lsb_release -a"
```
上面的命令将显示我的 Ubuntu 服务器的内核版本和发行版详细信息。
示例输出:

正如一位读者在下面的评论部分提到的那样,你应该用引号指定多个命令。如果不使用引号,第一个命令将在远程系统上执行,第二个命令将仅在本地计算机上执行。整个带引号的命令将按预期在远程计算机上运行。
>
> **提示:** 了解 `&&` 和 `;` 在命令中的区别:
>
>
> `&&` 操作符只有在第一个命令成功时才执行第二个命令。
>
>
> 示例:
>
>
>
> ```
> sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
>
> ```
>
> 在上述示例中,如果第一个命令成功,才会执行 `sudo apt-get upgrade`。否则,它将不会运行。
>
>
> `;` 操作符会执行第二个命令,无论第一个命令是成功还是失败。
>
>
> 示例:
>
>
>
> ```
> sudo apt-get update ; sudo apt-get upgrade
>
> ```
>
> 在上述示例中,即使第一个命令失败,`sudo apt-get upgrade` 也会执行。
>
>
>
#### 1.3、通过 SSH 在远程机器上调用有 sudo 权限的命令
有些命令需要 `sudo` 权限才能运行。例如,以下命令将在我的远程系统上安装 `apache2`。
```
$ ssh -t [email protected] sudo apt install apache2
```
示例输出:

注意到了吗?我在上面的命令中使用了 `-t` 标志,我们需要使用它来强制进行伪终端分配。它用于在远程机器上执行任意基于屏幕的程序,这非常有用。例如,在实现菜单服务时。
另外,我输入了**两次**密码。第一次是远程用户的密码,以便从本地系统通过 SSH 访问远程系统,第二次是为了向远程用户赋予 sudo 权限,以便安装应用程序(在本例中为 apache2)。
让我们用以下命令检查 Apache 服务是否正在运行:
```
$ ssh -t [email protected] sudo systemctl status apache2
[email protected]'s password:
[sudo] password for sk:
● apache2.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/apache2.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Drop-In: /lib/systemd/system/apache2.service.d
└─apache2-systemd.conf
Active: active (running) since Thu 2019-12-19 11:08:03 UTC; 52s ago
Main PID: 5251 (apache2)
Tasks: 55 (limit: 2318)
CGroup: /system.slice/apache2.service
├─5251 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
├─5253 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
└─5254 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
Dec 19 11:08:03 ubuntuserver systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server...
Dec 19 11:08:03 ubuntuserver apachectl[5227]: AH00558: apache2: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using 2409:4072:51f:a1b6:a00:27ff:f
Dec 19 11:08:03 ubuntuserver systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server.
```
同样的,我们可以通过 SSH 在本地系统上运行远程系统上的任何命令或脚本。
#### 1.4、通过 SSH 在远程系统上运行本地脚本
让我们在本地系统上创建一个简单的脚本来显示关于远程系统的发行版名称、包管理和基本细节等。
```
$ vi system_information.sh
```
添加以下行:
```
#!/bin/bash
#Name: Display System Details
#Owner: OSTechNIx
#----------------------------
echo /etc/*_ver* /etc/*-rel*; cat /etc/*_ver* /etc/*-rel*
```
按下 `ESC` 键,输入 `:wq` 保存退出。
现在,通过 SSH 命令在远程系统上运行这个脚本:
```
$ ssh [email protected] 'bash -s' < system_information.sh
```
示例输出:
```
[email protected]'s password:
/etc/debian_version /etc/lsb-release /etc/os-release
buster/sid
DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu
DISTRIB_RELEASE=18.04
DISTRIB_CODENAME=bionic
DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS"
NAME="Ubuntu"
VERSION="18.04.2 LTS (Bionic Beaver)"
ID=ubuntu
ID_LIKE=debian
PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS"
VERSION_ID="18.04"
HOME_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/"
SUPPORT_URL="https://help.ubuntu.com/"
BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/"
PRIVACY_POLICY_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/legal/terms-and-policies/privacy-policy"
VERSION_CODENAME=bionic
UBUNTU_CODENAME=bionic
```
如果你没有在上面的命令中指定 `bash -s`,你将获得远程系统的详细信息,但伪终端不会被分配。
#### 1.5、将远程主机的命令输出保存到本地主机
如果你希望与支持团队或同事共享远程系统上运行的命令输出,那么这非常有用。
以下命令将通过 SSH 在远程系统运行 `du -ah`,并将输出保存在本地系统的 `diskusage.txt` 文件中。
```
$ ssh [email protected] du -ah > diskusage.txt
```
然后,你可以通过使用 `cat` 命令或文本编辑器查看 `diskusage.txt` 文件来分析磁盘使用细节。
```
$ cat diskusage.txt
4.0K ./.profile
4.0K ./.gnupg/private-keys-v1.d
8.0K ./.gnupg
76K ./data/image.jpg
128K ./data/file.pdf
20K ./data/text.docx
5.9M ./data/audio.mp3
6.1M ./data
0 ./.sudo_as_admin_successful
4.0K ./pacman?inline=false
4.0K ./.bash_logout
4.0K ./.wget-hsts
4.0K ./.bash_history
0 ./.cache/motd.legal-displayed
4.0K ./.cache
4.0K ./deb-pacman_1.0-0.deb
4.0K ./.bashrc
6.2M .
```
#### 1.6、配置 SSH 密钥认证,避免输入密码
如果你经常在远程系统上运行命令,你可能需要配置基于 SSH 密钥的身份验证,以便每次跳过密码输入。更多细节可以在以下链接中找到。
>
> **[Linux 系统下如何配置 SSH 密钥认证](https://ostechnix.com/configure-ssh-key-based-authentication-linux/)**
>
>
>
配置了基于 SSH 密钥的认证后,我们可以通过 SSH 在远程机器上执行命令,从而不需要输入密码:
```
$ ssh [email protected] sudo apt update
```
### 2、通过 sshpass 在远程机器上运行命令
如果你不想配置基于 SSH 密钥的身份验证,你可以使用 `sshpass` 实用程序。
#### 2.1、什么是 sshpass?
`sshpass` 是为使用键盘交互密码身份验证模式运行 ssh 而设计的,但它以非交互的方式。简单来说,`sshpass` 提供了非交互式的方式来验证 SSH 会话。
SSH 使用直接 TTY 访问来确保密码确实是由交互式键盘用户发出的。`sshpass` 在一个专用 tty 中运行 SSH,让它误以为从交互用户那里获得了密码。
#### 2.2、在 Linux 中安装 sshpass
在许多 Linux 发行版的默认仓库中都有 `sshpass` 实用程序。例如,在 Debian、Ubuntu 及其衍生版本中,你可以使用下面的命令来安装 `sshpass`:
```
$ sudo apt install sshpass
```
#### 2.3、通过 SSH 和 sshpass 在远程机器上执行命令
`sshpass` 可以通过参数接受密码,或者通过环境变量读取密码,也可以从文本文件中读取密码。
**警告:** 所有这些方法都是 **高度不安全的**。所有系统用户都可以通过 `ps` 命令看到命令中的密码。**不建议**在生产中使用这些方法。最好使用基于密钥的身份验证。
让我们看看每种方法的示例。
##### 将密码作为参数提供
将密码作为参数提供,使用 `-p` 选项,如下所示:
```
$ sshpass -p <remote-password> ssh remoteuser@ip-address <command-to-execute>
```
示例输出:
```
$ sshpass -p ubuntu ssh [email protected] uname -a
```
其中,
* `-p ubuntu` - 提供远程系统的密码。
* `[email protected]` - 远程系统用户名和地址。
* `uname -a` - 要在远程计算机上执行的命令。
示例输出:
```
Linux Ubuntu22CT 5.15.60-1-pve #1 SMP PVE 5.15.60-1 (Mon, 19 Sep 2022 17:53:17 +0200) x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
```
##### 密码作为环境变量提供
在这个方法中,我们声明一个名为 `SSHPASS` 的环境变量,用远程环境的密码作为其值。然后我们使用 `-e` 标志,如下所示:
```
$ SSHPASS=ubuntu sshpass -e ssh [email protected] uname -a
```
##### 从文本文件中读取密码
使用 `echo` 命令在文本文件中追加密码:
```
$ echo "ubuntu" > mypassword.txt
```
现在,将密码文件传递给带有 `-f` 标志的 `sshpass`,如下所示:
```
$ sshpass -f mypassword.txt ssh [email protected] uname -a
```

### 总结
在本教程中,我们学习了一些通过安全的网络连接在远程计算机上调用命令或程序的方法。在所有的方法中,`sshpass` 方法是最不安全的,建议用户避免在生产系统中使用它。
---
via: <https://ostechnix.com/execute-commands-on-remote-linux-systems-via-ssh/>
作者:[sk](https://ostechnix.com/author/sk/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
15,264 | 在 Linux 上使用 Checksec 识别二进制文件的安全属性 | https://opensource.com/article/21/6/linux-checksec | 2022-11-18T09:57:08 | [
"Checksec",
"二进制"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15264-1.html |
>
> 这篇文章能让你了解如何使用 Checksec ,来识别一个可执行文件的安全属性,了解安全属性的含义,并知道如何使用它们。
>
>
>

编译源代码会生成一个二进制文件(LCTT 译注:即 `.o` 文件)。在编译期间,你可以向 `gcc` 编译器提供 <ruby> 标志 <rt> flags </rt></ruby>,以启用或禁用二进制文件的某些属性,这些属性与安全性相关。
Checksec 是一个漂亮的小工具,同时它也是一个 shell 脚本。Checksec 可以识别编译时构建到二进制文件中的安全属性。编译器可能会默认启用一些安全属性,你也可以提供特定的标志,来启用其他的安全属性。
本文将介绍如何使用 Checksec ,来识别二进制文件的安全属性,包括:
1. Checksec 在查找有关安全属性的信息时,使用了什么**底层的命令**
2. 在将源代码编译成二进制文件时,如何使用<ruby> GNU 编译器套件 <rt> GNU Compiler Collection </rt></ruby>(即 GCC)来**启用安全属性**。
### 安装 checksec
要在 Fedora 和其他基于 RPM 的 Linux 系统上,安装 Checksec,请使用以下命令:
```
$ sudo dnf install checksec
```
对于基于 Debian 的 Linux 发行版,使用对应的 `apt` 命令,来安装 Checksec。
```
$ sudo apt install checksec
```
### shell 脚本
在安装完 Checksec 后,能够发现 Checksec 是一个**单文件**的 shell 脚本,它位于 `/usr/bin/checksec`,并且这个文件挺大的。Checksec 的一个优点是你可以通过快速通读这个 shell 脚本,从而了解 Checksec 的执行原理、明白所有能查找有关二进制文件或可执行文件的安全属性的**系统命令**:
```
$ file /usr/bin/checksec
/usr/bin/checksec: Bourne-Again shell script, ASCII text executable, with very long lines
$ wc -l /usr/bin/checksec
2111 /usr/bin/checksec
```
以下的命令展示了如何对你每天都会使用的:`ls` 命令的二进制文件运行 Checksec。Checksec 命令的格式是:`checksec --file=`,后面再跟上二进制文件的绝对路径:
```
$ checksec --file=/usr/bin/ls
RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE
Full RELRO Canary found NX enabled PIE enabled No RPATH No RUNPATH No Symbols Yes 5 17 /usr/bin/ls
```
当你在终端中对某个二进制文件运行 Checksec 时,你会看到安全属性有颜色上的区分,显示什么是好的安全属性(绿色),什么可能不是好的安全属性(红色)。我在这里说 **“可能”** 是因为即使有些安全属性是红色的,也不一定意味着这个二进制文件很糟糕,它可能只是表明发行版供应商在编译二进制文件时做了一些权衡,从而舍弃了部分安全属性。
Checksec 输出的第一行提供了二进制文件的各种安全属性,例如 `RELRO`、`STACK CANARY`、`NX` 等(我将在后文进行详细解释)。第二行打印出给定二进制文件(本例中为 `ls`)在这些安全属性的状态(例如,`NX enabled` 表示为堆栈中的数据没有执行权限)。
### 示例二进制文件
在本文中,我将使用以下的 “hello world” 程序作为示例二进制文件。
```
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
}
```
请注意,在编译源文件 `hello.c` 的时候,我没有给 `gcc` 提供任何额外的标志:
```
$ gcc hello.c -o hello
$ file hello
hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=014b8966ba43e3ae47fab5acae051e208ec9074c, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
$ ./hello
Hello World
```
使用 Checksec 运行二进制文件 `hello`,打印的某些安全属性的状态,与上面的 `ls` 二进制文件的结果不同(在你的屏幕上,某些属性可能显示为红色):
```
$ checksec --file=./hello
RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE
Partial RELRO No canary found NX enabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 85) Symbols No 0 0./hello
$
```
(LCTT 译注:在我的 Ubuntu 22.04 虚拟机,使用 11.3.0 版本的 `gcc`,结果与上述不太相同,利用默认参数进行编译,会得到 RELRO、PIE、NX 保护是全开的情况。)
### 更改 Checksec 的输出格式
Checksec 允许自定义各种输出格式,你可以使用 `--output` 来自定义输出格式。我将选择的输出格式是 JSON 格式,并将输出结果通过管道传输到 `jq` 实用程序,来得到漂亮的打印。
接下来,确保你已安装好了 [jq](https://stedolan.github.io/jq/download/),因为本教程会使用 `jq` 从 Checksec 的输出结果中,用 `grep` 来快速得到某一特定的安全属性状态,并报告该安全属性是否启动(启动为 `yes`,未启动为 `no`):
```
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq
{
"hello": {
"relro": "partial",
"canary": "no",
"nx": "yes",
"pie": "no",
"rpath": "no",
"runpath": "no",
"symbols": "yes",
"fortify_source": "no",
"fortified": "0",
"fortify-able": "0"
}
}
```
### 看一看所有的安全属性
上面的二进制文件 `hello` 包括几个安全属性。我将该二进制文件与 `ls` 的二进制文件进行比较,以检查启用的安全属性有何不同,并解释 Checksec 是如何找到此信息。
#### 1、符号(Symbol)
我先从简单的讲起。在编译期间,某些 <ruby> 符号 <rt> symbols </rt></ruby>包含在二进制文件中,这些符号主要用作于调试。开发软件时,需要用到这些符号,来调试和修复错误。
这些符号通常会从供用户普遍使用的最终二进制文件中删除。删除这些符号不会影响到二进制文件的执行。删除符号通常是为了节省空间,因为一旦符号被删除了,二进制文件就会稍微小一些。在闭源或专有软件中,符号通常都会被删除,因为把这些符号放在二进制文件中,可以很容易地推断出软件的内部工作原理。
根据 Checksec 的结果,在二进制文件 `hello` 中有符号,但在 `ls` 的二进制文件中不会有符号。同样地,你还可以用 `file` 命令,来找到符号的信息,在二进制文件 `hello` 的输出结果的最后,看到 `not stripped`,表明二进制文件 `hello` 有符号:
```
$ checksec --file=/bin/ls --output=json | jq | grep symbols
"symbols": "no",
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep symbols
"symbols": "yes",
$ file hello
hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=014b8966ba43e3ae47fab5acae051e208ec9074c, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
```
Checksec 是如何找到符号的信息呢?Checksec 提供了一个方便的 `--debug` 选项,来显示运行了哪些函数。因此,运行以下的命令,会显示在 shell 脚本中运行了哪些函数:
```
$ checksec --debug --file=./hello
```
在本教程中,我试图寻找 Checksec 查找安全属性信息时,使用了什么**底层命令**。由于 Checksec 是一个 shell 脚本,因此你始终可以使用 Bash 功能。以下的命令将输出从 shell 脚本中运行的每个命令:
```
$ bash -x /usr/bin/checksec --file=./hello
```
如果你滚动浏览上述的输出结果的话,你会看到 `echo_message` 后面有各个安全属性的类别。以下显示了 Checksec 检测二进制文件是否包含符号时,运行的底层命令:
```
+ readelf -W --symbols ./hello
+ grep -q '\\.symtab'
+ echo_message '\033[31m96) Symbols\t\033[m ' Symbols, ' symbols="yes"' '"symbols":"yes",'
```
上面的输出显示,Checksec 利用 `readelf`,来读取二进制文件,并提供一个特殊 `--symbols` 标志,来列出二进制文件中的所有符号。然后它会查找一个特殊值:`.symtab`,它提供了所能找到的条目的计数(即符号的个数)。你可以在上面编译的测试二进制文件 `hello` 上,尝试以下命令,得到与 Checksec 查看二进制文件类似的符号信息:
```
$ readelf -W --symbols ./hello
$ readelf -W --symbols ./hello | grep -i symtab
```
(LCTT 译注:也可以通过直接查看 `/usr/bin/checksec` 下的 Checksec 源文件。)
##### 如何删除符号
你可以在编译后或编译时删除符号。
* **编译后:** 在编译后,你可以使用 `strip`,手动地来删除二进制文件的符号。删除后,使用 `file` 命令,来检验是否还有符号,现在显示 `stripped`,表明二进制文件 `hello` 无符号了:
```
$ gcc hello.c -o hello
$
$ file hello
hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=322037496cf6a2029dcdcf68649a4ebc63780138, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
$
$ strip hello
$
$ file hello
hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=322037496cf6a2029dcdcf68649a4ebc63780138, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, stripped
$
```
* **编译时:** 你也可以在编译时,用 `-s` 参数让 gcc 编译器帮你自动地删除符号:
```
$ gcc -s hello.c -o hello
$
$ file hello
hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=247de82a8ad84e7d8f20751ce79ea9e0cf4bd263, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, stripped
$
```
重新运行 Checksec,你可以看到现在二进制文件 `hello` 的 `symbols` 这一属性的值是`no`:
```
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep symbols
"symbols": "no",
$
```
#### 2、Canary(堆栈溢出哨兵)
Canary 是放置在缓冲区和 <ruby> 栈 <rt> stack </rt></ruby> 上的控制数据之间的已知值,它用于监视缓冲区是否溢出。当应用程序执行时,会为其分配两种内存,其中之一就是 *栈*。栈是一个具有两个操作的数据结构:第一个操作 `push`,将数据压入堆栈;第二个操作 `pop`,以后进先出的顺序从栈中弹出数据。恶意的输入可能会导致栈溢出,或使用特制的输入破坏栈,并导致程序崩溃:
```
$ checksec --file=/bin/ls --output=json | jq | grep canary
"canary": "yes",
$
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep canary
"canary": "no",
$
```
Checksec 是如何确定二进制文件是否启用了 Canary 的呢?使用上述同样的方法,得到 Checksec 在检测二进制文件是否启用 Canary 时,运行的底层命令:
```
$ readelf -W -s ./hello | grep -E '__stack_chk_fail|__intel_security_cookie'
```
##### 启用 Canary
为了防止栈溢出等情况,编译器提供了 `-stack-protector-all` 标志,它向二进制文件添加了额外的代码,来检查缓冲区是否溢出:
```
$ gcc -fstack-protector-all hello.c -o hello
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep canary
"canary": "yes",
```
Checksec 显示 Canary 属性现已启用。你还可以通过以下方式,来验证这一点:
```
$ readelf -W -s ./hello | grep -E '__stack_chk_fail|__intel_security_cookie'
2: 0000000000000000 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UND __stack_chk_fail@GLIBC_2.4 (3)
83: 0000000000000000 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UND __stack_chk_fail@@GLIBC_2.4
$
```
#### 3、位置无关可执行文件(PIE)
<ruby> 位置无关可执行文件 <rt> Position-Independent Executable </rt></ruby>(PIE),顾名思义,它指的是放置在内存中某处执行的代码,不管其绝对地址的位置,即代码段、数据段地址随机化(ASLR):
```
$ checksec --file=/bin/ls --output=json | jq | grep pie
"pie": "yes",
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep pie
"pie": "no",
```
通常,PIE 仅对 <ruby> 库 <rt> libraries </rt></ruby>启用,并不对独立命令行程序启用 PIE。在下面的输出中,`hello` 显示为 `LSB executable`,而 `libc` 标准库(`.so`) 文件被标记为 `LSB shared object`:
```
$ file hello
hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=014b8966ba43e3ae47fab5acae051e208ec9074c, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
$ file /lib64/libc-2.32.so
/lib64/libc-2.32.so: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (GNU/Linux), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=4a7fb374097fb927fb93d35ef98ba89262d0c4a4, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
```
Checksec 查找是否启用 PIE 的底层命令如下:
```
$ readelf -W -h ./hello | grep EXEC
Type: EXEC (Executable file)
```
如果你在共享库上尝试相同的命令,你将看到 `DYN`,而不是 `EXEC`:
```
$ readelf -W -h /lib64/libc-2.32.so | grep DYN
Type: DYN (Shared object file)
```
##### 启用 PIE
要在测试程序 `hello.c` 上启用 PIE,请在编译时,使用以下命令:
```
$ gcc -pie -fpie hello.c -o hello`
```
你可以使用 Checksec,来验证 PIE 是否已启用:
```
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep pie
"pie": "yes",
$
```
现在,应该会显示为 “<ruby> PIE 可执行 <rt> pie executable </rt></ruby>”,其类型从 `EXEC` 更改为 `DYN`:
```
$ file hello
hello: ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=bb039adf2530d97e02f534a94f0f668cd540f940, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
$ readelf -W -h ./hello | grep DYN
Type: DYN (Shared object file)
```
#### 4、NX(堆栈禁止执行)
NX 代表 <ruby> 不可执行 <rt> non-executable </rt></ruby>。它通常在 CPU 层面上启用,因此启用 NX 的操作系统可以将某些内存区域标记为不可执行。通常,缓冲区溢出漏洞将恶意代码放在堆栈上,然后尝试执行它。但是,让堆栈这些可写区域变得不可执行,可以防止这种攻击。在使用 `gcc` 对源程序进行编译时,默认启用此安全属性:
```
$ checksec --file=/bin/ls --output=json | jq | grep nx
"nx": "yes",
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep nx
"nx": "yes",
```
Checksec 使用以下底层命令,来确定是否启用了 NX。在尾部的 `RW` 表示堆栈是可读可写的;因为没有 `E`,所以堆栈是不可执行的:
```
$ readelf -W -l ./hello | grep GNU_STACK
GNU_STACK 0x000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x000000 0x000000 RW 0x10
```
##### 演示如何禁用 NX
我们不建议禁用 NX,但你可以在编译程序时,使用 `-z execstack` 参数,来禁用 NX:
```
$ gcc -z execstack hello.c -o hello
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep nx
"nx": "no",
```
编译后,堆栈会变为可读可写可执行(`RWE`),允许在堆栈上的恶意代码执行:
```
$ readelf -W -l ./hello | grep GNU_STACK
GNU_STACK 0x000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x000000 0x000000 RWE 0x10
```
#### 5、RELRO(GOT 写保护)
RELRO 代表 “<ruby> 重定位只读 <rt> Relocation Read-Only </rt></ruby>”。可执行链接格式(ELF)二进制文件使用全局偏移表(GOT)来动态地解析函数。启用 RELRO 后,会设置二进制文件中的 GOT 表为只读,从而防止重定位攻击:
```
$ checksec --file=/bin/ls --output=json | jq | grep relro
"relro": "full",
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep relro
"relro": "partial",
```
Checksec 使用以下底层命令,来查找是否启用 RELRO。在二进制文件 `hello` 仅启用了 RELRO 属性中的一个属性,因此,在 Checksec 验证时,显示 `partial`:
```
$ readelf -W -l ./hello | grep GNU_RELRO
GNU_RELRO 0x002e10 0x0000000000403e10 0x0000000000403e10 0x0001f0 0x0001f0 R 0x1
$ readelf -W -d ./hello | grep BIND_NOW
```
##### 启用全 RELRO
要启用全 RELRO,请在 `gcc` 编译时,使用以下命令行参数:
```
$ gcc -Wl,-z,relro,-z,now hello.c -o hello
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep relro
"relro": "full",
```
现在, RELRO 中的第二个属性也被启用,使程序变成全 RELRO:
```
$ readelf -W -l ./hello | grep GNU_RELRO
GNU_RELRO 0x002dd0 0x0000000000403dd0 0x0000000000403dd0 0x000230 0x000230 R 0x1
$ readelf -W -d ./hello | grep BIND_NOW
0x0000000000000018 (BIND_NOW)
```
#### 6、Fortify
Fortify 是另一个安全属性,但它超出了本文的范围。Checksec 是如何在二进制文件中验证 Fortify,以及如何在 `gcc` 编译时启用 Fortify,作为你需要解决的课后练习。
```
$ checksec --file=/bin/ls --output=json | jq | grep -i forti
"fortify_source": "yes",
"fortified": "5",
"fortify-able": "17"
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep -i forti
"fortify_source": "no",
"fortified": "0",
"fortify-able": "0"
```
### 其他的 Checksec 功能
关于安全性的话题是永无止境的,不可能在本文涵盖所有关于安全性的内容,但我还想提一下 Checksec 命令的一些其他功能,这些功能也很好用。
#### 对多个二进制文件运行 Checksec
你不必对每个二进制文件都进行一次 Checksec。相反,你可以提供多个二进制文件所在的目录路径,Checksec 将一次性为你验证所有文件:
```
$ checksec --dir=/usr
```
#### 对进程运行 Checksec
Checksec 除了能检查二进制文件的安全属性,Checksec 还能对程序起作用。以下的命令用于查找你系统上所有正在运行的程序的安全属性。如果你希望 Checksec 检查所有正在运行的进程,可以使用 `--proc-all`,或者你也可以使用进程名称,选择特定的进程进行检查:
```
$ checksec --proc-all
$ checksec --proc=bash
```
#### 对内核运行 Checksec
除了本文介绍的用 Checksec 检查用户态应用程序的安全属性之外,你还可以使用它来检查系统内置的 <ruby> 内核属性 <rt> kernel properties </rt></ruby>:
```
$ checksec --kernel
```
### 快来试一试 Checksec 吧
Checksec 是一个能了解哪些用户空间和内核的安全属性被启用的好方法。现在,你就可以开始使用 Checksec,来了解每个安全属性是什么,并明白启用每个安全属性的原因,以及它能阻止的攻击类型。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/6/linux-checksec>
作者:[Gaurav Kamathe](https://opensource.com/users/gkamathe) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[chai001125](https://github.com/chai001125) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Compiling source code produces a binary. During compilation, you can provide flags to the compiler to enable or disable certain properties on the binary. Some of these properties are relevant to security.
Checksec is a nifty little tool (and shell script) that, among other functions, identifies the security properties that were built into a binary when it was compiled. A compiler might enable some of these properties by default, and you might have to provide specific flags to enable others.
This article explains how to use checksec to identify the security properties on a binary, including:
- The underlying commands checksec uses to find information on the security properties
- How to enable security properties using the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) when compiling a sample binary
## Install checksec
To install checksec on Fedora and other RPM-based systems, use:
`$ sudo dnf install checksec`
For Debian-based distros, use the equivalent `apt`
command.
## The shell script
Checksec is a single-file shell script, albeit a rather large one. An advantage is that you can read through the script quickly and understand all the system commands running to find information about binaries or executables:
```
$ file /usr/bin/checksec
/usr/bin/checksec: Bourne-Again shell script, ASCII text executable, with very long lines
$ wc -l /usr/bin/checksec
2111 /usr/bin/checksec
```
Take checksec for a drive with a binary you probably run daily: the ubiquitous `ls`
command. The command's format is `checksec --file=`
followed by the absolute path of the `ls`
binary:
```
$ checksec --file=/usr/bin/ls
RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE
Full RELRO Canary found NX enabled PIE enabled No RPATH No RUNPATH No Symbols Yes 5 17 /usr/bin/ls
```
When you run this in a terminal, you see color-coding that shows what is good and what probably isn't. I say "probably" because even if something is in red, it doesn't necessarily mean things are horrible—it might just mean the distro vendors made some tradeoffs when compiling the binaries.
The first line provides various security properties that are usually available for binaries, like `RELRO`
, `STACK CANARY`
, `NX`
, and so on (I explain in detail below). The second line shows the status of these properties for the given binary (`ls`
, in this case). For example, `NX enabled`
means some property is enabled for this binary.
## A sample binary
For this tutorial, I'll use the following "hello world" program as the sample binary.
```
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
}
```
Note that I did not provide `gcc`
with any additional flags during compilation:
```
$ gcc hello.c -o hello
$ file hello
hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=014b8966ba43e3ae47fab5acae051e208ec9074c, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
$ ./hello
Hello World
```
Run the binary through checksec. Some of the properties are different than with the `ls`
command above (on your screen, these may be displayed in red):
```
$ checksec --file=./hello
RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE
Partial RELRO No canary found NX enabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 85) Symbols No 0 0./hello
$
```
## Changing the output format
Checksec allows various output formats, which you can specify with `--output`
. I'll choose the JSON format and pipe the output to the `jq`
utility for pretty printing.
To follow along, [ensure you have jq installed](https://stedolan.github.io/jq/download/) because this tutorial uses this output format to quickly grep for specific properties from the output and report
`yes`
or `no`
on each:```
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq
{
"./hello": {
"relro": "partial",
"canary": "no",
"nx": "yes",
"pie": "no",
"rpath": "no",
"runpath": "no",
"symbols": "yes",
"fortify_source": "no",
"fortified": "0",
"fortify-able": "0"
}
}
```
## Walking through the security properties
The binary above includes several security properties. I'll compare that binary against the `ls`
binary above to examine what is enabled and explain how checksec found this information.
### 1. Symbols
I'll start with the easy one first. During compilation, certain symbols are included in the binary, mostly for debugging. These symbols are required when you are developing software and require multiple cycles for debugging and fixing things.
These symbols are usually stripped (removed) from the final binary before it's released for general use. This does not affect the binary's execution in any way; it will run just as it would with the symbols. Stripping is often done to save space, as the binary is somewhat lighter once the symbols have been stripped. In closed-source or proprietary software, symbols often are removed because having these symbols in a binary makes it somewhat easy to infer the software's inner workings.
According to checksec, symbols are present in this binary, yet they were not in the `ls`
binary. You can also find this information by running the `file`
command on the program—you see `not stripped`
in the output towards the end:
```
$ checksec --file=/bin/ls --output=json | jq | grep symbols
"symbols": "no",
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep symbols
"symbols": "yes",
$ file hello
hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=014b8966ba43e3ae47fab5acae051e208ec9074c, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
```
How did checksec find this information? Well, it provides a handy `--debug`
option to show which functions ran. Therefore, running the following command should show you which functions ran within the shell script:
`$ checksec --debug --file=./hello`
In this tutorial, I'm looking for the underlying commands used to find this information. Since it's a shell script, you can always utilize Bash features. This command will output every command that ran from within the shell script:
`$ bash -x /usr/bin/checksec --file=./hello`
If you scroll through the output, you should see an `echo_message`
followed by the security property's category. Here is what checksec reports about whether the binary contains symbols:
```
+ readelf -W --symbols ./hello
+ grep -q '\.symtab'
+ echo_message '\033[31m96) Symbols\t\033[m ' Symbols, ' symbols="yes"' '"symbols":"yes",'
```
To simplify this, checksec utilizes the `readelf`
utility to read the binary and provides a special `--symbols`
flag that lists all symbols within the binary. Then it greps for a special value, `.symtab`
, that provides a count of entries (symbols) it finds. You can try out the following commands on the test binary you compiled above:
```
$ readelf -W --symbols ./hello
$ readelf -W --symbols ./hello | grep -i symtab
```
## How to strip symbols
You can strip symbols after compilation or during compilation.
**Post compilation:**After compilation, you can use the`strip`
utility on the binary to remove the symbols. Confirm it worked using the`file`
command, which now shows the output as`stripped`
:
`$ gcc hello.c -o hello $ $ file hello hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=322037496cf6a2029dcdcf68649a4ebc63780138, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped $ $ strip hello $ $ file hello hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=322037496cf6a2029dcdcf68649a4ebc63780138, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, stripped $`
## How to strip symbols during compilation
Instead of stripping symbols manually after compilation, you can ask the compiler to do it for you by providing the `-s`
argument:
```
$ gcc -s hello.c -o hello
$
$ file hello
hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=247de82a8ad84e7d8f20751ce79ea9e0cf4bd263, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, stripped
$
```
After rerunning checksec, you can see that `symbols`
are shown as `no`
:
```
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep symbols
"symbols": "no",
$
```
### 2. Canary
Canaries are known values that are placed between a buffer and control data on the *stack* to monitor buffer overflows. When an application executes, two kinds of memory are assigned to it. One of them is a *stack*, which is simply a data structure with two operations: `push`
, which puts data onto the stack, and `pop`
, which removes data from the stack in reverse order. Malicious input could overflow or corrupt the stack with specially crafted input and cause the program to crash:
```
$ checksec --file=/bin/ls --output=json | jq | grep canary
"canary": "yes",
$
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep canary
"canary": "no",
$
```
How does checksec find out if the binary is enabled with a canary? Using the method above, you can narrow it down by running the following command within the shell script:
`$ readelf -W -s ./hello | grep -E '__stack_chk_fail|__intel_security_cookie'`
#### Enable canary
To protect against these cases, the compiler provides the `-stack-protector-all`
flag, which adds extra code to the binary to check for such buffer overflows:
```
$ gcc -fstack-protector-all hello.c -o hello
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep canary
"canary": "yes",
```
Checksec shows that the property is now enabled. You can also verify this with:
```
$ readelf -W -s ./hello | grep -E '__stack_chk_fail|__intel_security_cookie'
2: 0000000000000000 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UND __stack_chk_fail@GLIBC_2.4 (3)
83: 0000000000000000 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UND __stack_chk_fail@@GLIBC_2.4
$
```
### 3. PIE
PIE stands for position-independent executable. As the name suggests, it's code that is placed somewhere in memory for execution regardless of its absolute address:
```
$ checksec --file=/bin/ls --output=json | jq | grep pie
"pie": "yes",
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep pie
"pie": "no",
```
Often, PIE is enabled only for libraries and not for standalone command-line programs. In the output below, `hello`
is shown as `LSB executable`
, whereas, the `libc`
standard library (`.so`
) file is marked `LSB shared object`
:
```
$ file hello
hello: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=014b8966ba43e3ae47fab5acae051e208ec9074c, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
$ file /lib64/libc-2.32.so
/lib64/libc-2.32.so: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (GNU/Linux), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=4a7fb374097fb927fb93d35ef98ba89262d0c4a4, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
```
Checksec tries to find this information with:
```
$ readelf -W -h ./hello | grep EXEC
Type: EXEC (Executable file)
```
If you try the same command on a shared library instead of `EXEC`
, you will see a `DYN`
:
```
$ readelf -W -h /lib64/libc-2.32.so | grep DYN
Type: DYN (Shared object file)
```
#### Enable PIE
To enable PIE on a test program, send the following arguments to the compiler:
`$ gcc -pie -fpie hello.c -o hello`
You can verify PIE is enabled using checksec:
```
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep pie
"pie": "yes",
$
```
It should show as a PIE executable with the type changed from `EXEC`
to `DYN`
:
```
$ file hello
hello: ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=bb039adf2530d97e02f534a94f0f668cd540f940, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
$ readelf -W -h ./hello | grep DYN
Type: DYN (Shared object file)
```
### 4. NX
NX stands for "non-executable." It's often enabled at the CPU level, so an operating system with NX enabled can mark certain areas of memory as non-executable. Often, buffer-overflow exploits put code on the stack and then try to execute it. However, making this writable area non-executable can prevent such attacks. This property is enabled by default during regular compilation using `gcc`
:
```
$ checksec --file=/bin/ls --output=json | jq | grep nx
"nx": "yes",
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep nx
"nx": "yes",
```
Checksec determines this information with the command below. `RW`
towards the end means the stack is readable and writable; since there is no `E`
, it's not executable:
```
$ readelf -W -l ./hello | grep GNU_STACK
GNU_STACK 0x000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x000000 0x000000 RW 0x10
```
#### Disable NX for demo purposes
It's not recommended, but you can disable `NX`
when compiling a program by using the `-z execstack`
argument:
```
$ gcc -z execstack hello.c -o hello
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep nx
"nx": "no",
```
Upon compilation, the stack becomes executable (`RWE`
), which allows malicious code to execute:
```
$ readelf -W -l ./hello | grep GNU_STACK
GNU_STACK 0x000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x000000 0x000000 RWE 0x10
```
### 5. RELRO
RELRO stands for Relocation Read-Only. An Executable Linkable Format (ELF) binary uses a Global Offset Table (GOT) to resolve functions dynamically. When enabled, this security property makes the GOT within the binary read-only, which prevents some form of relocation attacks:
```
$ checksec --file=/bin/ls --output=json | jq | grep relro
"relro": "full",
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep relro
"relro": "partial",
```
Checksec finds this information by using the command below. Here, one of the RELRO properties is enabled; therefore, the binary shows "partial" when verifying via checksec:
```
$ readelf -W -l ./hello | grep GNU_RELRO
GNU_RELRO 0x002e10 0x0000000000403e10 0x0000000000403e10 0x0001f0 0x0001f0 R 0x1
$ readelf -W -d ./hello | grep BIND_NOW
```
#### Enable full RELRO
To enable full RELRO, use the following command-line arguments when compiling with `gcc`
:
```
$ gcc -Wl,-z,relro,-z,now hello.c -o hello
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep relro
"relro": "full",
```
Now, the second property is also enabled, making the program full RELRO:
```
$ readelf -W -l ./hello | grep GNU_RELRO
GNU_RELRO 0x002dd0 0x0000000000403dd0 0x0000000000403dd0 0x000230 0x000230 R 0x1
$ readelf -W -d ./hello | grep BIND_NOW
0x0000000000000018 (BIND_NOW)
```
### 6. Fortify
Fortify is another security property, but it's out of scope for this article. I will leave learning how checksec verifies fortify in binaries and how it's enabled with `gcc`
as an exercise for you to tackle.
```
$ checksec --file=/bin/ls --output=json | jq | grep -i forti
"fortify_source": "yes",
"fortified": "5",
"fortify-able": "17"
$ checksec --file=./hello --output=json | jq | grep -i forti
"fortify_source": "no",
"fortified": "0",
"fortify-able": "0"
```
## Other checksec features
The topic of security is never-ending, and while it's not possible to cover everything here, I do want to mention a few more features of the `checksec`
command that make it a pleasure to work with.
### Run against multiple binaries
You don't have to provide each binary to checksec individually. Instead, you can provide a directory path where multiple binaries reside, and checksec will verify all of them for you in one go:
`$ checksec --dir=/usr/bin`
### Processes
In addition to binaries, checksec also works on programs during execution. The following command finds the security properties of all running programs on your system. You can use `--proc-all`
if you want it to check all running processes, or you can select a specific process by using its name:
```
$ checksec --proc-all
$ checksec --proc=bash
```
### Kernel properties
In addition to checksec's userland applications described in this article, you can also use it to check the kernel properties built into your system:
`$ checksec --kernel`
## Give it a try
Checksec is a good way to understand what userland and kernel properties are enabled. Go through each security property in detail, and try to understand the reasons for enabling each feature and the kinds of attacks it prevents.
## Comments are closed. |
15,265 | 如何在 Linux 上安装 AWS 命令行工具 | https://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-install-aws-cli-on-linux/ | 2022-11-18T11:30:31 | [
"AWS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15265-1.html | 
>
> 本文讲述如何一步步在 Linux 上安装 AWS CLI(命令行工具)。
>
>
>
AWS CLI 是一个能够和 AWS 账户进行交互的命令行程序。开发者和系统管理员用它管理日常的活动和自动化。
### 准备环节
* 安装好的 Linux 系统
* 具有管理员权限的 sudo 账户
* 能够联网
现在让我们开始安装:
### 1、下载安装文件
打开终端使用 `curl` 命令下载 AWS CLI 的安装文件:
```
$ curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
```

以上命令会在当前工作目录下载一个 `awscliv2.zip` 的文件。
使用 [ls 命令](https://www.linuxtechi.com/linux-ls-command-examples-beginners/) 确认当前下载下来的文件:
```
$ ls -l awscliv2.zip
-rw-rw-r-- 1 linuxtechi linuxtechi 47244662 Oct 20 10:53 awscliv2.zip
$
```
### 2、解压缩下载的文件
使用 [unzip 命令](https://www.linuxtechi.com/linux-zip-unzip-command-examples/) 解压安装包:
```
$ unzip awscliv2.zip
```
它会在当前目录创建一个 `aws` 文件夹,把解压好的文件放进去:
```
$ ls -ld aws
drwxr-xr-x 3 linuxtechi linuxtechi 4096 Oct 19 17:18 aws
$
```
### 3、运行安装脚本
使用以下命令运行安装脚本:
```
$ sudo ./aws/install
```

脚本会把所有安装的文件放到 `/usr/local/aws-cli` 目录下,然后创建一个链接文件到 `/usr/local/bin` 目录。
### 4、检查 AWS CLI 的版本
运行以下脚本检查版本:
```
$ aws --version
aws-cli/2.8.4 Python/3.9.11 Linux/5.15.0-48-generic exe/x86_64.ubuntu.22 prompt/off
$
```
### 5、配置 AWS CLI
为了验证 AWS CLI 是否安装正确,开始配置 AWS CLI:
登录你的 AWS 管理控制台,取得 AWS <ruby> 访问密钥 ID <rt> Access Key ID </rt></ruby> 和 <ruby> 安全访问密钥 <rt> Secret Access Key </rt></ruby>。
如果还没完成创建,请先创建,并把它们复制到安全的地方。

然后回到命令行,运行以下命令:
```
$ aws configure
AWS Access Key ID [None]: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
AWS Secret Access Key [None]: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Default region name [None]: us-west-2
Default output format [None]: json
$
```
以上的证书会被保存到这个文件:
```
$ cat ~/.aws/credentials
```
上面的命令的输出:

运行 `aws` 命令列出你账户中的 s3 储存和 VPC:
```
$ aws s3 ls
$ aws ec2 describe-vpcs
```
输出如下:

成功输出内容,说明你的 AWS CLI 已经配置完成。
这就是这篇文章的全部内容,请在下面的评论区发表你的疑问和反馈。
---
via: <https://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-install-aws-cli-on-linux/>
作者:[Pradeep Kumar](https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | This post describes how to install AWS CLI on linux step-by-step. AWS CLI is a command line interface which allows us to interact with our AWS account. Developer and sysadmin use [aws cli](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/getting-started-install.html) to perform day to day activities and automation.
#### Prerequisites
- Pre-Installed Linux System
- Sudo User with admin rights
- Internet Connectivity
Without any further delay, let’s jump into AWS Cli installations steps.
## 1) Download Installation File
Open the terminal and run following curl command to download aws cli installation file,
$ curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
Above command will download file as ‘awscliv2.zip’ in current working directory.
Execute below [ls command](https://www.linuxtechi.com/linux-ls-command-examples-beginners/) to verify downloaded file,
$ ls -l awscliv2.zip -rw-rw-r-- 1 linuxtechi linuxtechi 47244662 Oct 20 10:53 awscliv2.zip $
## 2) Unzip Downloaded Installation File
Run beneath [unzip command](https://www.linuxtechi.com/linux-zip-unzip-command-examples/) to unzip the installer.
$ unzip awscliv2.zip
It will create aws folder in present working directory and unzip all required files into it.
$ ls -ld aws drwxr-xr-x 3 linuxtechi linuxtechi 4096 Oct 19 17:18 aws $
## 3) Install AWS Cli on Linux Using Install Script
To install aws cli, run following install script,
$ sudo ./aws/install
Script will install all files under /usr/local/aws-cli and will create symbolic link in /usr/local/bin.
## 4) Verify AWS CLI version
To verify the aws cli version, run
$ aws --version aws-cli/2.8.4 Python/3.9.11 Linux/5.15.0-48-generic exe/x86_64.ubuntu.22 prompt/off $
## 5) Configure AWS CLI
To verify the AWS Cli installation, let’s configure aws cli.
Login to your AWS management console and retrieve AWS access key id and secret access key.
In case it is not created yet then create access key ID and secret access key. Copy these keys somewhere safe.
Now head back to Linux terminal, run following aws command,
$ aws configure AWS Access Key ID [None]: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx AWS Secret Access Key [None]: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Default region name [None]: us-west-2 Default output format [None]: json $
Above credentials will be saved in following file,
$ cat ~/.aws/credentials
Output of above commands,
Run aws command to list s3 bucket and vpc of your account.
$ aws s3 ls $ aws ec2 describe-vpcs
Output,
Output above confirms that aws cli has been configured successfully.
That’s all from this post, feel free to post your queries and feedback in below comments sections. |
15,267 | 学习 Python:我最喜欢的 7 个资源 | https://opensource.com/article/22/11/learn-python | 2022-11-19T10:57:23 | [
"Python"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15267-1.html | 
>
> 这些年来,我通过这些开源资源提高了我的 Python 技能。
>
>
>
我最近决定进一步学习 Python,以便提高我的教学技能,拓宽我的学生的视野。在这个过程中,我发现了这些优秀的资源,让我学习新的代码,并提高了对 Python 的整体理解。
### 1、《教孩子学编程 Python 语言版》
我的 Python 之旅大约是 7 年前开始的,当时我发现了 Apple LOGO 和 Python 中的 [Turtle 模块](https://opensource.com/article/21/9/logo-python-turtle) 之间的联系。当时使用的 Linux 计算机的默认 Python 版本为 Python 2.7,我很快发现我想使用 Python 3。我成功地安装了它,并开始使用 Turtle 模块编写一些简单的程序。在阅读 Dr. Bryson Payne 的 《[教孩子学编程 Python 语言版](https://opensource.com/education/15/9/review-bryson-payne-teach-your-kids-code)》 之后,我意识到 Python 不仅仅是 Turtle。那时我安装了 [IDLE](https://docs.python.org/3/library/idle.html)。
### 2、IDLE
在使用 IDLE 工作的过程中,交互式界面优化了我的体验,并让我有足够的信心来考虑向学生教授 Python。我志愿帮助我社区中的一群在家学习的孩子,很快我发现自己在教授一个有十六个孩子的班级!我很高兴他们的父母同意帮助我,否则我想我会被压垮。这个经历激发了我学习更多的欲望,以便我可以教授更多。
### 3.、Mu 编辑器
2018 年春天,我参加了 PyConUS。我听了一场由中学老师 [Nicholas Tollervey](https://us.pycon.org/2018/speaker/profile/194/) 主讲的演讲,他为学龄前儿童编写了一个 Python 开发环境。[Mu 编辑器](https://opensource.com/article/20/9/teach-python-mu) 内置了一个可以帮助我找到代码中的错误的 <ruby> 质检工具 <rt> Linter </rt></ruby>。Mu 帮助我提高了我的编码技能,我也能够与学生分享这些技能,他们也从中受益。
我的自信和经验增长后,我希望与更多的学生分享 Python 之旅。我与其他人合作撰写了一个申请书,以教授一个使用树莓派 4 和 Python 的课程。疫情打断了这个计划。在此期间,树莓派基金会发布了树莓派 400。2021 年春天,我使用了前一年开发的材料和一个来自当地图书馆的慷慨的资助,来 [教授两组](https://opensource.com/article/21/6/teach-python-raspberry-pi) 学生如何编程。这个活动非常成功并在今年再次举办。
### 4、Codium
几年前,我了解到微软的 VS Code 是一个可以在 Linux 上使用的开源代码编辑器。我最近才了解到,如何在 VS Code 中配置和使用 Python 虚拟环境。我的问题在一篇 [关于虚拟环境的文章](https://opensource.com/article/20/10/venv-python) 中得到了解答,这让我可以知道如何在 Linux 计算机上设置和配置 Python 虚拟环境。大约在同一时间,我发现了 [Codium](https://opensource.com/article/22/11/python-vs-code-codium),一个围绕 VS Code 构建的社区项目。
现在我希望与我的学生分享 VS Codium 的体验,并让他们对 Python 的理解不再局限于 Turtle 模块。这种学习的热情让我寻找开源且可以在互联网上随意获得的教学资源。
### 5、《Python 编程练习,简单解释》
《[Python 编程快速上手 让繁琐工作自动化](https://automatetheboringstuff.com/#toc)》 这本书是我最喜欢的一本书。现在,作者已经发布了 《[Python 编程练习,简单解释](https://inventwithpython.com/pythongently/)》。这两本书都可以免费在线阅读,并且都采用了知识共享许可证。
### 6、《每个人都可以使用 Python》
Dr. Charles Severance 在 2017 年发布了 《[每个人都可以使用 Python](https://www.py4e.com/lessons)》,我非常推荐这本书。他为像我这样的有抱负的程序员提供了简短的课程。课程的代码可以在 [GitHub](https://github.com/csev/py4e) 上找到,所以你可以下载它并在自己的计算机或学校网络上安装它。
### 7. Python 视频
最近,我了解到 [Jay LaCroix](https://opensource.com/users/jlacroix) 在 YouTube 上有一系列精彩的视频,其中包括 28 个免费视频,从 Python 基础开始,涵盖了 [Python 编程](https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLT98CRl2KxKGIazPd2nQEPbG7sQpT8LEj) 的全面介绍。最重要的是,他使用的是 Linux 计算机,因此他的课程特别适合 Linux 编程环境。这些视频的其中一个收获是学习如何使用 [nano](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/gnu-nano) 作为编程环境,它默认情况下包含在大多数 Linux 发行版中。
### 你的学习之路
此处提到的这七个资源帮助我成长为一名程序员,它们都是开源的并可以与其他人分享。你是如何提高编程技能的?你有什么要分享的吗?在评论中告诉我们。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/11/learn-python>
作者:[Don Watkins](https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Cubik65536](https://github.com/Cubik65536) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | I made a decision recently that I wanted to learn more Python so I could improve my instructional skills and broaden the horizons of my students. In the process, I have discovered these excellent resources that have me learning new code and improving my understanding of Python in general.
## 1. Teach your kids to code
I began the Python journey about seven years ago when I discovered connections between Apple LOGO and the [Turtle module](https://opensource.com/article/21/9/logo-python-turtle) in Python. The Linux computer I was using at the time defaulted to Python 2.7, and I soon discovered that I wanted to use Python 3. I managed to get it installed and began writing some simple programs using the Turtle module. After reading Dr. Bryson Payne’s [Teach Your Kids to Code](https://opensource.com/education/15/9/review-bryson-payne-teach-your-kids-code), I realized there was a lot more to Python than just Turtle. That’s when I installed [IDLE](https://docs.python.org/3/library/idle.html).
## 2. IDLE
Working with IDLE, the interactive interface improved my experience and made me confident enough to consider teaching Python to students. I volunteered to help a group of home-schooled children in my community and soon found myself teaching a class of sixteen! I’m glad their parents stayed and agreed to be my assistants, otherwise I think I’d have been overwhelmed. The experience whetted my appetite to learn more so I could teach more.
## 3. Mu Editor
The following spring in 2018 I attended PyConUS. I listened to a talk by [Nicholas Tollervey](https://us.pycon.org/2018/speaker/profile/194/), a middle school teacher, who had written a Python development environment for school-age children. The [Mu editor](https://opensource.com/article/20/9/teach-python-mu) has a linter built into it, which helped me to see where my errors in programming were. Mu helped me improve my coding skills, and I was able to share that with students, who benefitted as well.
As my confidence and experience grew, I became eager to share the Python journey with still more students. I co-wrote a grant the following year to teach a class that used Raspberry Pi 4 computers and Python. The pandemic interrupted that experience. In the interim, the Raspberry Pi Foundation released the Pi 400. In the spring of 2021, I used the materials I had developed the previous year and a generous grant from a local library to [teach two groups](https://opensource.com/article/21/6/teach-python-raspberry-pi) of students how to program. That event was so successful that it was repeated this year.
## 4. Codium
Several years ago, I learned that Microsoft’s Visual Studio Code is an open source code editor that can be used on Linux. One of the aspects of my Python learning journey that had eluded me until recently was how to set up and use a virtual environment for Python programming, which had been suggested when using VS Code. My questions were answered here on Opensource.com in an [article about venv](https://opensource.com/article/20/10/venv-python), and that opened the door to learning how to set up and configure Python virtual environments on my Linux computer. Around the same time, I found [Codium](https://opensource.com/article/22/11/python-vs-code-codium), a community project built around VS Code.
Now I want to share the VS Codium experience with my students and open their understanding of Python beyond the Turtle module. This zest for learning has me looking for training resources that are open source and freely available on the internet.
## 5. Python gently explained
The book [Automate the Boring Stuff with Python](https://automatetheboringstuff.com/#toc) by Al Sweigart has long been a favorite of mine. Now, the author has released [Python Programming Exercises, Gently Explained](https://inventwithpython.com/pythongently/). Both books are available online for free and are openly licensed with Creative Commons license.
## 6. Python for everyone
Dr. Charles Severance released [Python for Everyone](https://www.py4e.com/lessons) in 2017, which I highly recommend. He provides "bite size" lessons for aspiring programmers like me. The code for the course is available on [GitHub](https://github.com/csev/py4e), so you can download it and install it on your own computer or school network.
## 7. Python videos
Recently I learned that Opensource.com alumnus [Jay LaCroix](https://opensource.com/users/jlacroix) has an excellent series of twenty-eight videos available for free on YouTube that begin with Python basics and span the gamut of a solid introduction to [Python programming](https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLT98CRl2KxKGIazPd2nQEPbG7sQpT8LEj). Best of all, he uses a Linux computer, so his lessons are especially appropriate for a Linux programming environment. One of the takeaways from these videos is learning to use [nano](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/gnu-nano) as a programming environment, and it’s included by default in most Linux distributions.
## Your learning path
These seven resources have helped me grow as a programmer, and it’s all open source and available to share with others. How have you been honing your programming skills? What would you like to share? Let us know in the comments.
## 1 Comment |
15,268 | 使用 ImageMagick 修复扫描图像 | https://opensource.com/article/22/11/fixing-scanned-images-imagemagick | 2022-11-19T15:58:30 | [
"ImageMagick"
] | /article-15268-1.html | 
>
> 使用这个开源工具,即使是批量校正图像也很容易。
>
>
>
多年前,在翻阅一家旧书店的书架上的内容时,我偶然发现了一本名为 《UNIX System Command Summary for Berkeley 4.2 & 4.3 BSD》 的小册子,由 Specialized Systems Consultants 出版。我买它是出于好奇,因为它已经有将近 20 年的历史了,但仍然在很大程度上适用于现代 Linux 和 BSD。
无论是当时还是现在,我都很开心。一本写于 1986 年的小册子在 2016 年仍然很重要,而同一个书架上关于专有操作系统的书籍并不值得印刷它们的纸张。(想一想:你认为什么技术可以在僵尸末日中幸存下来?)这本小册子已经放在我自己的书架上好几年了,但我突然想到可能值得对这个作品做一点数字保存,所以我决定扫描这本小册子来创建一本 [CBZ 电子书](https://opensource.com/article/19/3/comic-book-archive-djvu)。
使用 [Skanlite](https://opensource.com/article/22/2/scan-documents-skanlite-linux-kde) 进行扫描很容易,但很耗时。然而,当我完成后,我发现有些页面不是很平整。

在打印中,这称为配准问题,这意味着打印内容的位置在页面上的方向不正确。
### ImageMagick
[ImageMagick](https://opensource.com/article/17/8/imagemagick) 是基于终端的非交互式图形编辑器。尝试在无图形环境(如纯文本终端)中编辑图形似乎违反直觉,但实际上很常见。例如,当你将图像上传到 Web 应用用作个人资料图片时,应用服务器上的脚本可能会使用 ImageMagick 或其库处理你的图像。非交互式编辑器的优点是你可以制定需要对示例图像执行的操作,然后只需按一下按钮即可将这些效果应用于数百个其他图像。
ImageMagick 通常与其他图形编辑器一样强大,只要你花时间了解它的许多功能以及如何组合它们以实现所需的效果。在这种情况下,我想旋转歪斜的页面。在搜索了 ImageMagick 的文档后,我发现我需要的解决方案的 ImageMagick 术语称为纠偏。将你的术语与其他人的术语保持一致对于你不知道的任何事情都是一个挑战,因此当你使用 ImageMagick(或其他任何东西)时,请记住,你描述问题或解决方案的用词可能和别人不一样。
要使用 ImageMagick 对带有弯曲文本的图像进行校正:
```
$ convert page_0052.webp -deskew25% fix_0052.webp
```
`-deskew` 选项表示可接受偏差的阈值。通过跟踪看似字母的对象的峰谷来确定倾斜。根据扫描的弯曲程度,你可能需要多于或少于 25% 的阈值。我已经达到了 80%,到目前为止,低于 25% 没用效果。
结果如下:

修复了!将其应用于文档的剩余 55 页以修复倾斜的页面,而对已经笔直的页面不做任何事情。换句话说,由于我的阈值设置,在不需要调整的页面上运行此命令是安全的。
### 使用 ImageMagick 裁剪图像
在纠正了歪斜之后,因为我扫描每一页都比必要的范围要多,以防止意外切断单词,我认为裁剪我纠正的页面是有意义的。我很高兴在页边空白处保留一些空间,但没有以前那么多。我经常使用 ImageMagick 的“裁剪”功能来处理这个网站上的图像,所以我很熟悉这个选项。但是,我需要确定如何裁剪每一页。
首先,我需要图像的大小:
```
$ identify fixed_0052.webp
WEBP 1128x2593 1128x2593+0+08-bit sRGB 114732B 0.020u 0:00.021
```
知道尺寸后,我能够对我可以承受的丢失多少像素做出一些估计。经过几次试运行,我得到了这个:
```
convert fix_0052.webp -gravity Center -crop 950x2450+0+0 crop_0052.webp
```
这并不完全适合,但当我将它应用于册子中的其他图像时,它被证明很重要。这些页面的内容和扫描仪位置各不相同,所以我很高兴给每一页一点空余空间。
这是校正和裁剪的图像:

### 使用开源批量编辑图像
ImageMagick 的美妙之处在于,当你确定了修复图像的公式,你就可以将该修复应用于需要相同修复的所有图像。我使用 [GNU Parallel](http://LINK-TO-SETH-GNU-PARALLEL-REDHAT.COM/SYSADMIN) 执行此操作,它使用我所有的 CPU 内核来完成数百页的图像校正。这并不需要很长时间,而且结果不言而喻。更重要的是,我已经有了一个 UNIX 历史上有趣作品的数字档案。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/11/fixing-scanned-images-imagemagick>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.