id
int64 2.05k
16.6k
| title
stringlengths 5
75
| fromurl
stringlengths 19
185
| date
timestamp[s] | tags
sequencelengths 0
11
| permalink
stringlengths 20
37
| content
stringlengths 342
82.2k
| fromurl_status
int64 200
526
⌀ | status_msg
stringclasses 339
values | from_content
stringlengths 0
229k
⌀ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
14,669 | Linux Lite 6.0 发布:弃用 Firefox,默认浏览器使用 Chrome | https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-lite-6-0-release/ | 2022-06-03T18:12:28 | [
"Linux Lite"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14669-1.html |
>
> Linux Lite 6.0 是一个有趣的版本,有一个新的默认浏览器,改进了无障碍性、新的主题、新的系统监视器等等改进。
>
>
>

Linux Lite,是 [最好的类 Windows 发行版](https://itsfoss.com/windows-like-linux-distributions/) 之一,刚刚发布了它的最新版本 6.0。
Linux Lite 6.0 基于 [Ubuntu 22.04 LTS](https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-22-04-release/),内置了 [Linux 内核 5.15 LTS](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-15-release/)。
这次升级包含了相当多的令人兴奋的新功能,包括一个新的窗口主题和无障碍技术。
让我们深入了解一下新的内容!
### Linux Lite 6.0 概述
Linux Lite 6.0 包括许多变化,包括:
* 更新了软件
* 新的窗口主题
* 新的屏幕键盘
* 屏幕阅读器
* 屏幕放大镜
* Chrome 取代 Firefox 成为默认浏览器
* 新的 GRUB 菜单
#### 无障碍性的改进

Linux Lite 通过这一改变已经步入了大联盟。无障碍性,在历史上一直是 GNOME 特有的优势,它现在有了很大的改进。这主要体现在三个不同的工具上:一个屏幕键盘,一个屏幕阅读器(Orca),和一个屏幕放大镜。
屏幕键盘对于许多触摸屏用户和没有键盘的用户来说是相当有用的。另一方面,屏幕阅读器对于视障用户来说将是完美的。

最后一项无障碍改进屏幕放大镜,也是针对与屏幕阅读器相同的受众。然而,它与传统的桌面理念相当吻合,所以众多用户可能更青睐它,而不是屏幕阅读器。
这些无障碍性的改进有助于 Linux Lite 6.0 成为一个主流的选择。
#### 更新的软件
与几乎所有的发行版升级一样,Linux Lite 6.0 包括更新的软件。最值得注意的是最新的 LibreOffice 稳定版 7.2.6。
其他更新包括 VLC 3.0.16、Thunderbird 91.7、Chrome 100、GIMP 2.10.30 等等。
虽然本身不一定是大规模的升级,但它表明了所包含的 LibreOffice 版本的重大变化。
以前,由于提供了更多的稳定性,Linux Lite 停留在更多老版本上。然而,Linux Lite 的开发者现在觉得使用最新的稳定版本也很放心,因为测试新 LibreOffice 版本的人比以往任何时候都多。
#### 新的窗口主题

Linux Lite 6.0 引入了一个新的窗口主题,叫做 “Materia”。那些主题社区的人可能会对它相当熟悉,因为它已经被移植到几乎所有的平台。这些平台包括 GTK 2、3 和 4、GNOME Shell、Budgie、Cinnamon、MATE、Unity、Xfce、LightDM、GDM,甚至是 Chrome 浏览器。
改用 Materia 应该会让 ChromeOS 用户感觉界面很熟悉,因为它是基于谷歌开发的 Material UI 的。
#### 谷歌 Chrome 浏览器成为新的默认浏览器

随着 Ubuntu 将其 Firefox 版本转移到一个 Snap 应用中,Linux Lite 已经完全抛弃了 Firefox,转而使用谷歌 Chrome。虽然我不能说我是这个变化的粉丝,但它确实有意义,特别是对于一个针对 Windows 用户的发行版来说。
虽然你可以自由地安装任何你喜欢的东西,但无论如何,Chrome 是大多数用户的流行选择。
此外,如果你想在访问文件之前扫描文件,Linux Lite 的开发者在 Chrome 中包含了一个 Virus Total 扫描器扩展(默认是禁用的)。
注意,你可以从 Linux Lite 的软件中心安装 Firefox,但它是 Snap 版本的。
#### 系统监控中心替代了任务管理器

Linux Lite 6.0 现在打包了<ruby> <a href="https://itsfoss.com/system-monitoring-center/"> 系统监控中心 </a> <rt> System Monitoring Center </rt></ruby> 来替代任务管理器和进程查看器。
请注意,Linux Lite 的开发者复刻了这个应用程序,在系统标签中提供了关于发行版的具体信息。
它提供了所有关注你的资源的必要功能。
### 其他改进
除了基本的变化之外,Linux Lite 6.0 还包括对 GRUB 菜单的更新、推送紧急修复包的能力、新的 whisker 菜单,以及更多的调整。

正如你所注意到的,新的 GRUB 菜单还包括关闭和重启,同时删除了内存测试选项。
你可以在其 [官方公告帖子](https://www.linuxliteos.com/forums/release-announcements/linux-lite-6-0-final-released/) 中了解更多的技术细节。
### 总结
Linux Lite 6.0 看起来是一个可靠的版本,特别是对于那些等待无障碍功能和新的视觉感受的人。
如果你想自己尝试一下,ISO 文件可以从官方下载页面获得。
>
> **[下载Linux Lite](https://www.linuxliteos.com/download.php#current)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-lite-6-0-release/>
作者:[Jacob Crume](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Linux Lite, one of the [best Windows-like distros](https://itsfoss.com/windows-like-linux-distributions/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), has just released its latest version, 6.0.
Linux Lite 6.0 is based on [Ubuntu 22.04 LTS](https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-22-04-release/) and includes [Linux Kernel 5.15](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-15-release/) LTS out of the box.
This upgrade packs in a considerable number of exciting new features, including a new window theme and assistive technologies.
Let’s dive into what’s new!
## Linux Lite 6.0: Overview
Linux Lite 6.0 includes numerous changes, including:
- Updated software
- New window theme
- New on-screen keyboard
- Screen reader
- Screen magnifier
- Firefox replaced by Chrome as the default browser
- New grub menu
### Accessibility Improvements
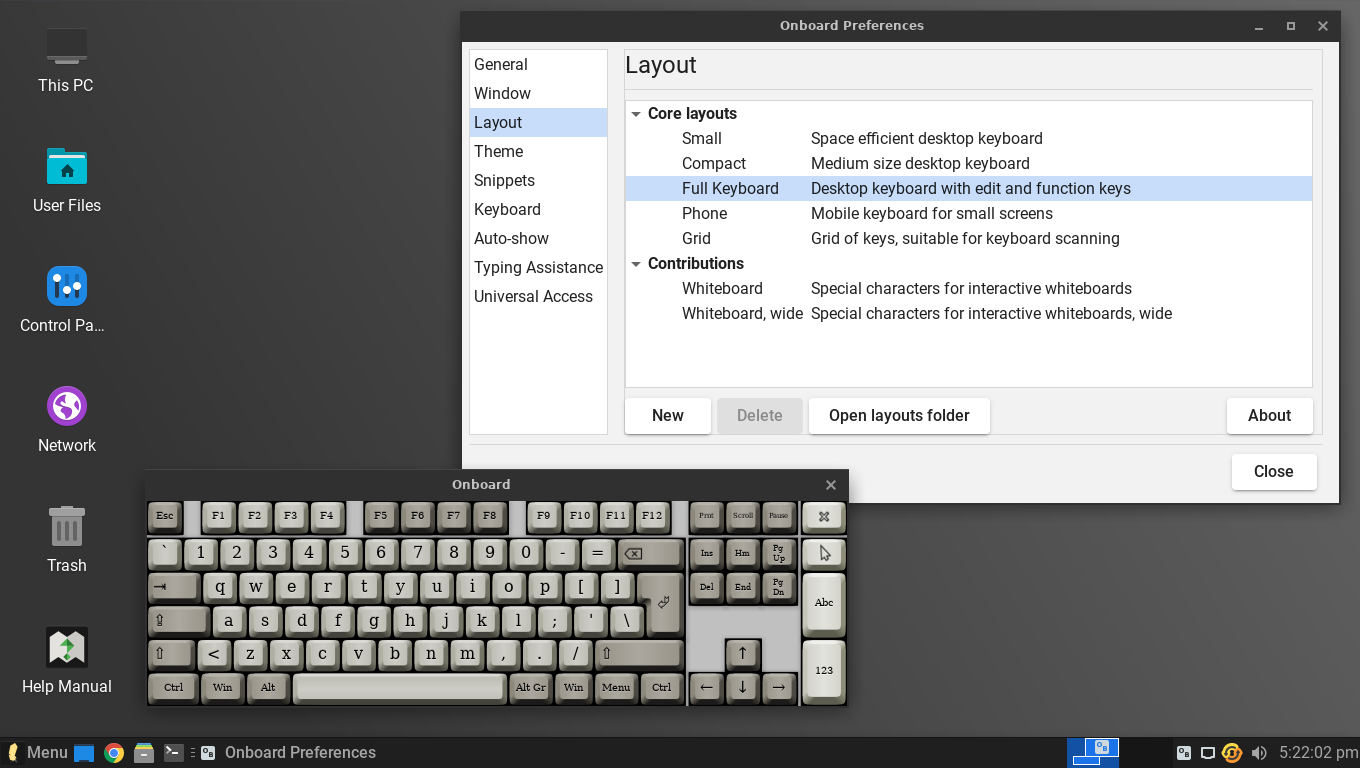
Linux Lite has stepped up into the big leagues with this change. Accessibility, which has historically been a GNOME-specific advantage, has greatly improved. This comes in three different tools: An on-screen keyboard, a screen reader (Orca), and a screen magnifier.
The on-screen keyboard will be pretty useful for many touchscreen users and those without a keyboard. On the other hand, the screen reader will be perfect for sight-impaired users.

The final accessibility improvement, the screen magnifier, also targets the same audience as the screen reader. However, it is quite a bit more aligned with the traditional desktop philosophy, so it may be preferred by numerous users over the screen reader.
These accessibility improvements help bring Linux Lite 6.0 as a mainstream alternative.
### Updated Software
As with almost all distribution upgrades, Linux Lite 6.0 includes updated software. Most notable is the latest stable LibreOffice version, 7.2.6.
Other updates include VLC 3.0.16, Thunderbird 91.7, Chrome 100, GIMP 2.10.30, and more.
Although not necessarily a massive upgrade in itself, it demonstrates a significant change in the included LibreOffice version.
Previously, Linux Lite was held back with an older release due to the increased stability offered. However, the Linux Lite developers now feel comfortable using the latest stable release, with more people testing new LibreOffice versions than ever.
### New Window Theme
Linux Lite 6.0 introduces a new window theme called ‘**Materia**.’ Those in the theming community will probably be quite familiar with it, as it has been ported to almost every platform. These include GTK 2, 3, and 4, GNOME Shell, Budgie, Cinnamon, MATE, Unity, Xfce, LightDM, GDM, and even Google Chrome.
The switch to Materia should bring a familiar interface to ChromeOS users, as it is based on the Material UI that Google develops.
### Google Chrome is the new default browser
With Ubuntu moving its Firefox version to a snap app, Linux Lite has completely ditched Firefox for Google Chrome. While I can’t say I’m a fan of this change, it does make sense, especially for a distro targeting Windows users.
While you are free to install anything you like, Chrome is a popular option for most users, no matter what.
Furthermore, Linux Lite developers include a Virus Total scanner extension (disabled by default) with Chrome if you want to scan files before accessing them.
Note that you can install Firefox from the Linux Lite’s software center, but it will install the snap package.
### System Monitor Center as a replacement for Task Manager
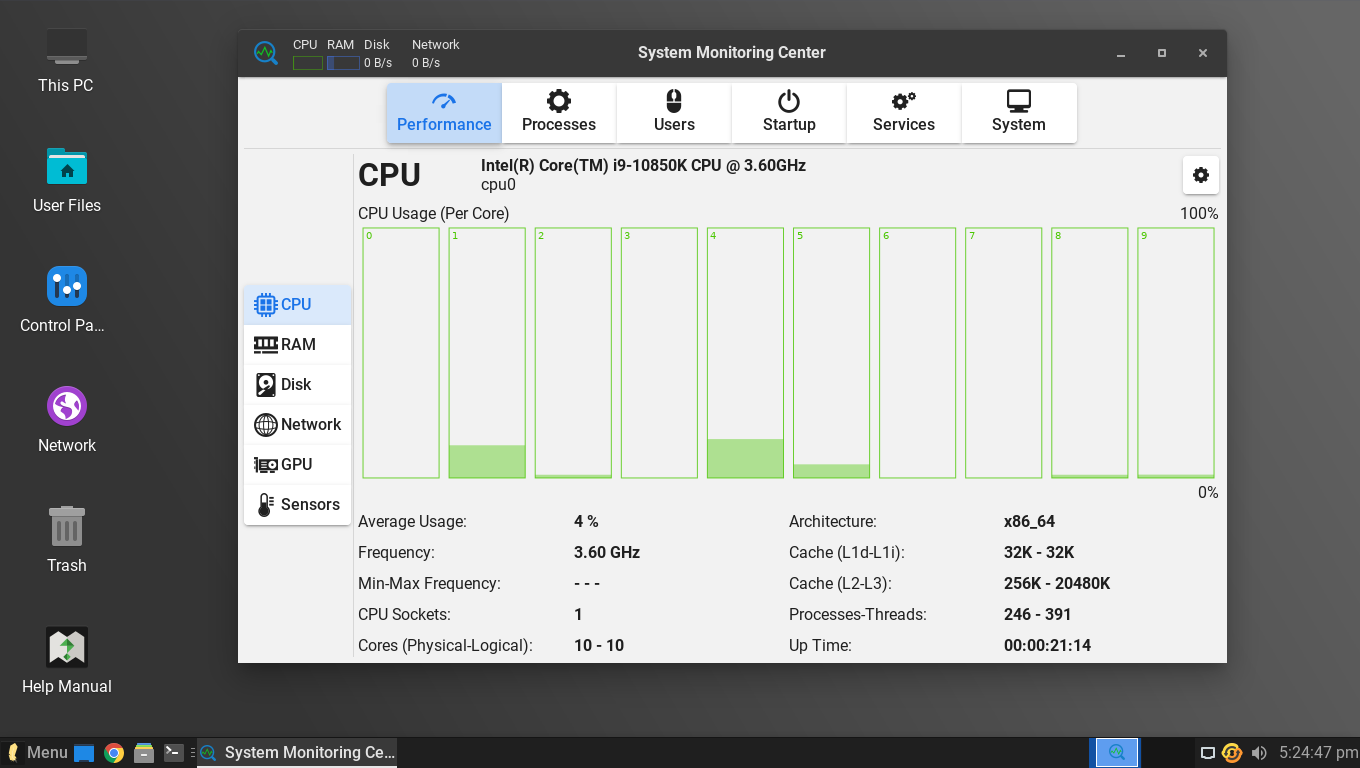
Linux Lite 6.0 now comes packed with the [System Monitoring Center](https://itsfoss.com/system-monitoring-center/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to replace the task manager and the process viewer.
Note that Linux Lite developers have forked the application to provide specific information regarding the distribution in the system tab.
It offers all the essential functionalities to help you keep an eye on your resources.
## Other Improvements
In addition to the fundamental changes, Linux Lite 6.0 involves updates to the grub menu, the ability to push emergency fixes to packages, a new whisker menu, and many more tweaks.
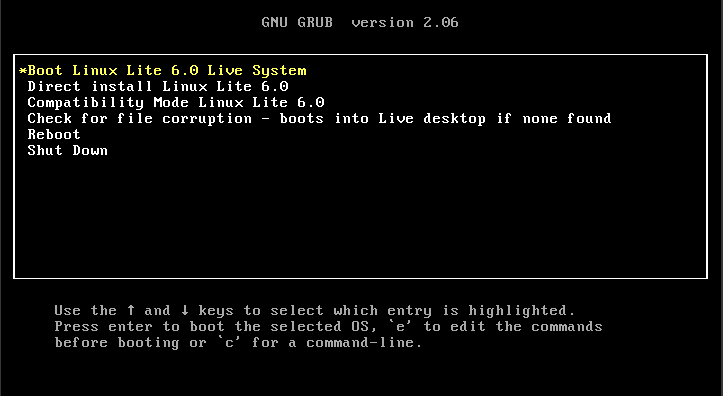
As you can notice, the new grub menu also includes shut down and reboot while removing the memtest option.
You can explore more technical details in its [official announcement post](https://www.linuxliteos.com/forums/release-announcements/linux-lite-6-0-final-released/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Wrapping Up
Linux Lite 6.0 appears to be a solid release, especially for those waiting for accessibility features and visual refreshments.
The ISO file is available from the official download page if you want to try it out for yourself.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,671 | Collision:用于验证 ISO 和其他文件的 Linux 应用 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/collision/ | 2022-06-04T11:14:31 | [
"MD5",
"SHA-1"
] | /article-14671-1.html | 
>
> 本教程概述了 Collision 的功能和使用指南。它是一个基于 GUI 且易于使用的程序,可让你使用加密哈希函数验证文件。
>
>
>
### 为什么需要验证文件?
人们每天都通过互联网下载文件。但许多用户从不费心去验证他们的完整性或真实性。这意味着不知道该文件是否合法且未被任何恶意代码篡改。
以作为标准安装镜像的 [Linux 发行版](https://www.debugpoint.com/category/distributions) 的 ISO 文件为例。所有流行的发行版制造商在 ISO 文件还提供哈希文件。使用该文件,你可以轻松比较下载文件的哈希值。让你可以放心你的文件是正确的并且没有以任何方式损坏。
此外,如果你通过不稳定的互联网连接下载大文件,该文件可能会损坏。在这些情况下,它也有需要验证。
### Collision – 功能和使用方法
[Collision](https://collision.geopjr.dev/) 使用加密哈希函数来帮助你验证文件。加密哈希函数是一种流行的算法,它通过多种加密算法将文件数据生成为固定长度的数据流。最受欢迎的是 MD5、SHA-1、SHA-256 和 SHA-512。所有这些 Collision 都支持。
除此之外,Collision 还提供了一个简洁的用户界面,它对每个 Linux 用户都简单易用。这是它的外观。

首先,它有两个主要特点。 a、上传文件以获取校验和和或哈希值;b、将校验和与上传的文件进行比较。
例如,如果你有一个简单的文件,你可以通过“<ruby> 打开文件 <rt> Open a File </rt></ruby>”按钮上传一个文件,或“<ruby> 打开 <rt> Open </rt></ruby>”按钮重新上传另一个文件。
如下图所示,该文本文件具有以下各种哈希函数的校验和。现在你可以通过互联网/与任何人共享该文件,以及用于验证的校验和值。

此外,如果有人篡改文件(即使是单个字节)或文件在分发过程中被破坏,那么哈希值就会完全改变。
其次,如果要验证已下载文件的完整性,请点击“<ruby> 验证 <rt> Verify </rt></ruby>”选项卡。然后上传文件,输入你收到的上传文件的哈希值。
如果匹配,你应该会看到一个绿色勾号,显示其真实性。

此外,这是另一个示例,我修改了测试文件并保持大小相同。这个场景清楚地表明它对该文件无效。

#### 重要说明
这里值得一提的是,哈希方法不会验证文件元属性,如修改时间、修改日期等。如果有人篡改了文件并将其还原为原始内容,这种哈希方式将其称为有效文件。
现在,让我们看一个验证 ISO 文件的典型示例。
### 使用 Collision 验证 Ubuntu Linux 的示例 ISO 文件
我相信你在使用 Linux 时通常会下载许多 ISO 文件。为了说明,我从官方 Ubuntu 下载页面下载了流行的 Ubuntu ISO 服务器镜像。

`SHA256SUMS` 文件带有上面的该安装程序的以下校验和值:

下载后,打开 Collision 应用并通过“<ruby> 验证 <rt> Verify </rt></ruby>”选项卡上传 ISO 文件。然后复制 SHA-256 值并将其粘贴到左侧的校验和框中。
如果你已正确下载并按照步骤操作,你应该会看到该文件是真实有效的。

### 如何安装 Collision
使用 Flatpak 可以轻松安装 Collision 应用。你需要为你的 Linux 发行版 [设置 Flatpak](https://flatpak.org/setup/),并单击以下链接以安装 Collision。
>
> **[通过 Flathub 安装 Collision](https://dl.flathub.org/repo/appstream/dev.geopjr.Collision.flatpakref)**
>
>
>
安装后,你应该通过发行版的应用菜单找到它。
### 有没有其他方法可以在没有任何应用的情况下验证文件?
是的,所有 Linux 发行版中都有一些内置程序,你还可以使用它们来使用终端验证文件及其完整性。
下面的终端程序可用于确定任何文件的哈希值。它们默认安装在所有发行版中,你甚至可以将它们用于你的 shell 脚本以实现自动化。
```
md5sum <文件名>
```
```
sha1sum <文件名>
```
```
sha256sum <文件名>
```
使用上述程序,你可以找出哈希值。但是你需要比较它们以手动验证。

### 结束语
我希望本指南可以帮助你使用 Collision GTK 应用验证你的文件。它使用起来很简单。此外,你可以在终端中使用命令行方法来验证您想要的任何文件。尽可能始终检查文件完整性总是应该的。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/collision/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,672 | 移动版 GNOME Shell:希望之始,期望满满 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/06/gnome-shell-mobile-announcement/ | 2022-06-04T15:25:00 | [
"GNOME"
] | /article-14672-1.html | 
>
> GNOME 开发人员在最近的一篇博文中提出了将 GNOME Shell 完全移植到手机上的想法。下面是我对这个项目的一些看法。
>
>
>
### 移动版 GNOME Shell
作为一个桌面环境,GNOME 在过去的十年中发展成为了 [GNOME 40](https://www.debugpoint.com/tag/gnome-40)。GNOME 40 是一个重要的版本,它以一种现代的方式改变了完整的用户界面设计。
看着 GNOME 40 的设计方式,你可能会觉得 Shell 和它的底层技术已经为小屏幕做好了准备。手势驱动的工作区、图标网格和停靠区 —— 在某种程度上感觉更接近于像安卓这样的移动操作系统,而不是桌面环境。
此外,系统托盘、日历、通知和原生的应用程序,可以有效地在较小尺寸的设备上工作。得益于 GTK4 和 libadwaita,其设计是响应式的,应用程序和控件的外观与移动平台很匹配。
在 GNOME 40 之后,GNOME 开发者为较小尺寸的设备(如平板电脑和手机)设计了几个 GNOME Shell 的概念验证。
#### 为什么是现在?
任何项目的开发和研究工作都要花费时间和金钱。虽然有来自主要科技公司对 GNOME 的捐赠,但这次有一个 “<ruby> 原型基金 <rt> Prototype Fund </rt></ruby>” 帮助该团队继续进行这项努力。[原型基金](http://www.prototypefund.de) 是德国教育部(BMBF)支持公共利益软件的资助项目。
#### 包括什么?
设计一个完整的移动用户界面,并将其与移动操作系统整合是一个非常复杂的项目。它需要一个精心设计的愿景来支持成千上万的移动硬件和用户支持。更不用说,用户在移动设备上的隐私和安全问题了。
因此,有了这个基金,团队可以集中精力进行概念验证,以满足 GNOME Shell 中一些基本的用户互动。
* 启动器
* 应用程序网格
* 轻扫、手势和导航
* 用手机键盘搜索
* 检测屏幕大小和支持屏幕旋转
* 工作空间和多任务
* 设置
* 屏幕键盘

始终要记住的是,移动体验远不止用户界面这么简单。另外,GNOME 本身并不是一个操作系统。它由底层的稳定的操作系统组成,它提供了非常需要的隐私和安全。另外,“应用商店”的概念也是如此。手机制造商需要与 GNOME 开发者合作,让他们的产品采用这个概念。
#### 进展如何?
在写这篇文章时,团队给我们快速演示了取得的进展。在下面的视频中可以看到:
*Phone*
复杂的任务是识别触摸屏手机中的各种手势。例如,你可能会使用长触摸、短触摸、双指轻扫和拖动,以及许多只有在小尺寸设备中才可行的可能性。这需要在各自的 GNOME Shell 组件中推倒重构。
而完全在现有的 GNOME Shell 基础上开发它们是很有挑战性的工作。
此外,该团队使用著名的 Pinephone Pro 进行开发和测试。Pinephone 已经是一个商业产品,装有 “友商” KDE Plasma 手机和其他 Linux 操作系统。
*Tablet*
### 结语
如果一切按计划进行,我们可能在一个完整的开源手机中获得原生的 GNOME 体验。而你可以重新拥有你的隐私!
另外,我不确定 Phosh(它也是基于 GNOME 的)会发生什么。虽然 Phosh 是由 Purism 开发和管理的,但看看 GNOME Shell 在移动设备上的努力和 PHosh 在未来一段日子的发展方向将是很有趣的。
那么,你对这个项目的前景怎么看?请在下面的评论栏里告诉我。
*图片和视频来源:GNOME 开发者 [博客](https://blogs.gnome.org/shell-dev/2022/05/30/towards-gnome-shell-on-mobile/)*
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/06/gnome-shell-mobile-announcement/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,673 | 龙芯 CPU 已经一只脚迈入 Linux 5.19 | https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=LoongArch-Merged-Linux-5.19 | 2022-06-04T18:45:00 | [
"龙芯"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14673-1.html | 
在本周为龙芯 CPU 架构支持进入 [Linux 5.19](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=Linux+5.19) 而进行的疯狂冲刺之后,Linus Torvalds 今天成功地将这个受 MIPS64 启发的中国架构代码合并到了 Linux 主线内核中。然而,由于一些代码尚未通过审查,虽然该 CPU 架构代码已经到位,但一些关键的驱动程序还没有到位,因此 Linux 5.19 还无法龙芯架构上启动。
如果你不太了解这件事的进展,我来补充介绍一下:<ruby> <a href="https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=LoongArch"> 龙芯架构 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> LoongArch </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 是由龙芯公司开发的 CPU 架构,长期以来以其基于 MIPS64 的系统而为人所熟知。但是随着上游 MIPS64 架构已经实际消亡,龙芯公司开始开发他们自己的 ISA。龙芯架构自称受到了 MIPS64 和 RISC-V 的启发,但一些龙芯架构的内核代码实际上是重新使用或精密复制自现有的 MIPS 代码。
今年早些时候,龙芯架构被 [添加到 GCC 12](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=LoongArch-Merged-GCC-12) 中作为主要系统编译器。与其他 Arm 或 RISC-V 设计相比,目前这一代 [龙芯 3A5000 CPU 的性能](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Loongson-3A5000-Benchmark) 在现今阶段并不太诱人。不过我们将拭目以待这个中国国产 CPU 架构在未来几年的发展情况。
正如本周早些时候所写的,有迫切的压力促使 [龙芯架构进入 Linux 5.19](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=LoongArch-Maybe-For-5.19),即使这意味着系统还无法启动。开发人员希望将 CPU 架构的代码主线化,这样他们就能腾出手来为 GNU C 库(Glibc)提交龙芯架构的支持代码。主线化他们的 Glibc 目标首先需要有一个坚实的用户空间 ABI 来解决内核支持。但由于 Glibc 2.38 预计在 8 月发布,龙芯架构需要合并到 Linux 5.19,以便有足够的时间在 7 月发布,才能使龙芯架构的代码赶得上 Glibc 的下一个版本截止线。
现在合并龙芯架构也减少了对 Linux 5.20 中可能出现的任何主线树范围变化的维护负担。
因此,大部分的龙芯架构代码已经出现在 Linux 5.19 中了,但缺少一些启动所需的 EFI 代码,IRQ 驱动与 Linux 的 MIPS 支持共享同一段代码,但由于情况复杂,还不能使用,PCI 部分的龙芯代码需要修改并通过 PCI 子系统区域进行合并。
[龙芯架构的合并](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/commit/?id=c6f2f3e2c80e975804360665d973211e4d9390cb) 对内核来说意味着增加了 21000 行的新代码,这还不包括尚未到达的所需驱动程序。据推测,到今年夏天晚些时候的 Linux 5.20 内核开发周期时,其余所需的驱动支持将会通过审查,从而产生一个可启动的龙芯架构系统。
就在四年前,著名的 Linux 内核开发者 Arnd Bergmann [预测](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=C-SKY-Approved-Last-Arch) C-SKY 将是“我们最后一个添加到内核的新 CPU 架构”。C-SKY 是另一个中国架构,当时的想法是所有未来的 CPU 工作都将走向 RISC-V,但现在发现龙芯架构也许将是最后一个添加到 Linux 内核的新 CPU 架构。
---
via: <https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=LoongArch-Merged-Linux-5.19>
作者: [Michael Larabel](https://www.michaellarabel.com/) 选题:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](/article-14671-1.html) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
14,675 | 软件包 “被标记为手动安装”?这是什么意思? | https://itsfoss.com/package-set-manually-installed/ | 2022-06-05T15:45:19 | [
"软件包"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14675-1.html | 
如果你使用 `apt` 命令在终端中安装软件包,你将看到各种输出。
如果你注意并查看输出,有时你会注意到一条消息:
```
package_name set to manually installed
```
你有没有想过这条消息是什么意思,为什么你没有在所有包上看到它?让我在本篇中分享一些细节。
### 理解 “软件包被标记为手动安装”
当你尝试安装已安装的库或开发包时,你会看到此消息。此依赖包是与另一个包一起自动安装的。如果删除了主包,则使用 `apt autoremove` 命令删除依赖包。
但是由于你试图显式安装依赖包,你的 Ubuntu 系统认为你需要这个包独立于主包。因此,该软件包被标记为手动安装,因此不会自动删除。
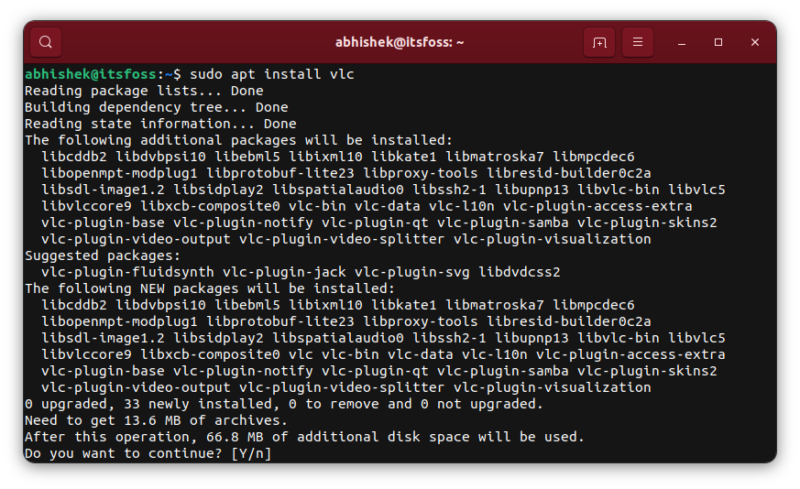
不是很清楚,对吧?以 [在 Ubuntu 上安装 VLC](https://itsfoss.com/install-latest-vlc/) 为例。
由于主 VLC 包依赖于许多其他包,因此这些包会自动安装。

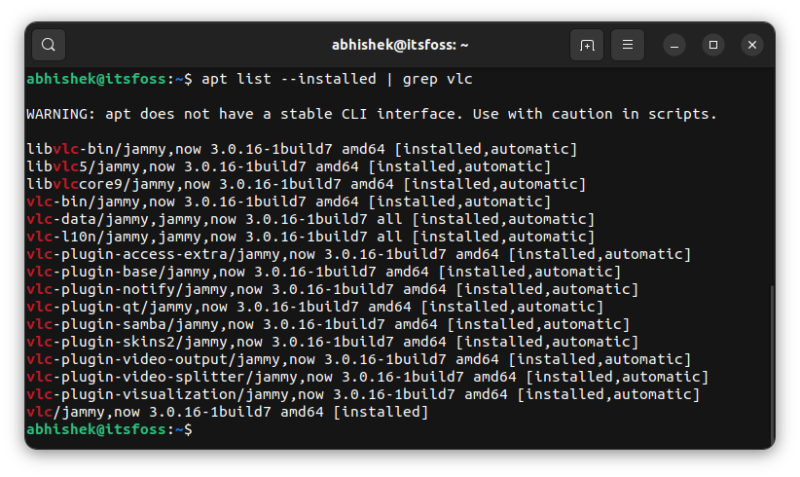
如果你检查名称中包含 `vlc` 的 [已安装软件包列表](https://itsfoss.com/list-installed-packages-ubuntu/),你会看到除了 VLC,其余都标记为“自动”。这表明这些软件包是(跟着 vlc)自动安装的,当 VLC 被卸载时,它们将使用 `apt autoremove` 命令自动删除。

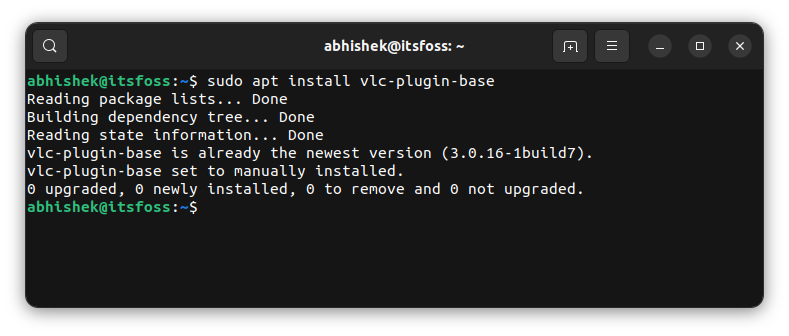
现在假设你出于某种原因考虑安装 `vlc-plugin-base`。如果你在其上运行 `apt install` 命令,系统会告诉你该软件包已安装。同时,它将标记从自动更改为手动,因为系统认为在尝试手动安装表明你明确需要此 `vlc-plugin-base`。

可以看到它的状态已经从 `[installed,automatic]` 变成了 `[installed]`。

现在,让我删除 VLC 并运行 `autoremove` 命令。你可以看到 `vlc-plugin-base` 不在要删除的软件包列表中。

再次检查已安装软件包的列表。`vlc-plugin-base` 仍然安装在系统上。

你可以在这里看到另外两个与 VLC 相关的包。这些是 `vlc-plugin-base` 包的依赖项,这就是为什么它们也存在于系统上但标记为 `automatic` 的原因。
我相信现在有了这些例子,事情就更清楚了。让我给你一个额外的技巧。
### 将包重置为自动
如果包的状态从自动更改为手动,你可以通过以下方式将其设置回自动:
```
sudo apt-mark auto package_name
```

### 结论
这不是一个重大错误,也不会阻止你在系统中进行工作。但是,了解这些小事会增加你的知识。
**好奇心可能会害死猫,但它会让企鹅变得更聪明**。这是为这篇原本枯燥的文章增添幽默感的原始引述 : )
如果你想阅读更多这样的文章,这些文章可能看起来微不足道,但可以帮助你更好地了解您的 Linux 系统,请告诉我。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/package-set-manually-installed/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

If you use the apt command to install packages in the terminal, you’ll see all kinds of output.
If you pay attention and read the output, sometimes you’ll notice a message that reads:
*package_name set to manually installed*
Have you ever wondered what this message means and why you don’t see it for all packages? Let me share some details in this explainer.
## Understanding “Package set to manually installed”
You’ll see this message when you try installing an already installed library or development package. This dependency package was installed automatically with another package. The dependency package gets removed with the apt autoremove command if the main package is removed.
But since you tried to install the dependency package explicitly, your Ubuntu system thinks that you need this package independent of the main package. And hence the package is marked as manually installed so that it is not removed automatically.
Not very clear, right? Take the example of [installing VLC on on Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/install-latest-vlc/).
Since the main vlc package depends on a number of other packages, those packages are automatically installed with it.
If you check the [list of installed packages](https://itsfoss.com/list-installed-packages-ubuntu/) that have vlc in their name, you’ll see that except vlc, the rest are marked ‘automatic’. This indicates that these packages were installed automatically (with vlc) and they will be removed automatically with apt autoremove command (when vlc is uninstalled).
Now suppose you thought to install “vlc-plugin-base” for some reason. If you run the apt install command on it, the system tells you that the package is already installed. At the same time, it changes the mark from automatic to manual because the system thinks that you need this vlc-plugin-base explicitly as you tried to manually install it.
You can see that its status has been changed to [installed] from [installed,automatic].
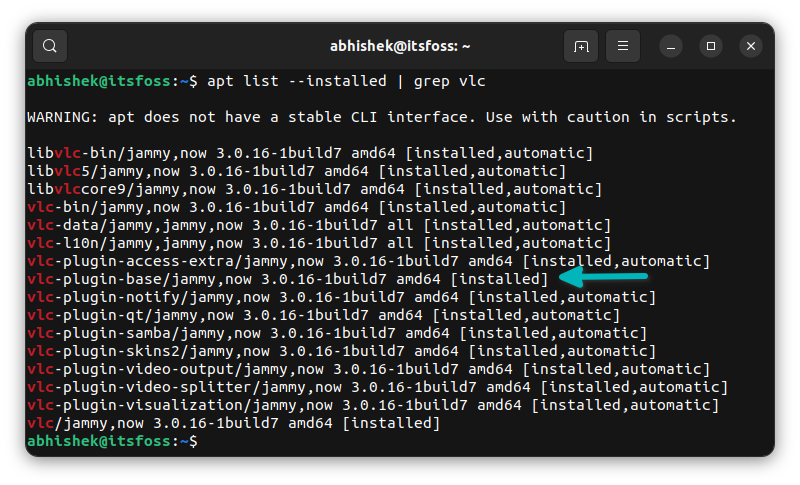
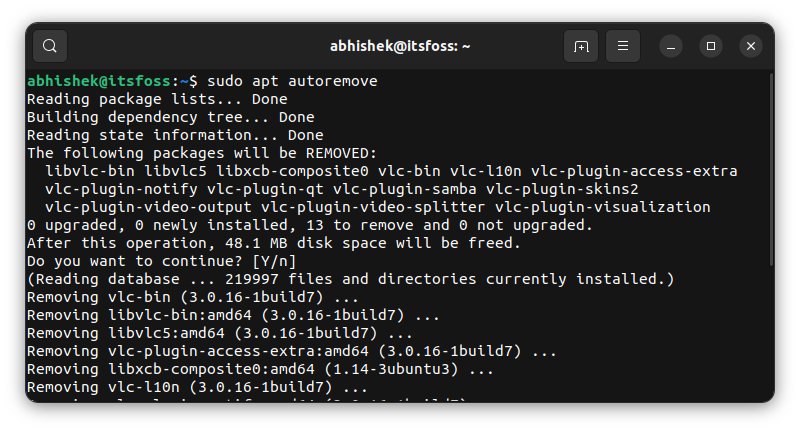
Now, let me remove VLC and run the auoremove command. You can see that “vlc-plugin-base” is not in the list of packages to be removed.
Check the list of installed packages again. vlc-plugin-base is still installed on the system.
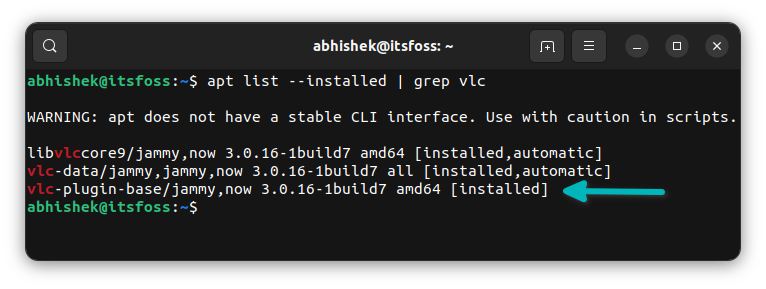
You can see two more vlc-related packages here. These are the dependencies for the vlc-plugin-base package and this is why they are also present on the system but marked ‘automatic’.
I believe things are more clear now with the examples. Let me add a bonus tip for you.
## Reset package to automatic
If the state of the package got changed to manual from automatic, you can set it back to automatic in the following manner:
`sudo apt-mark auto package_name`
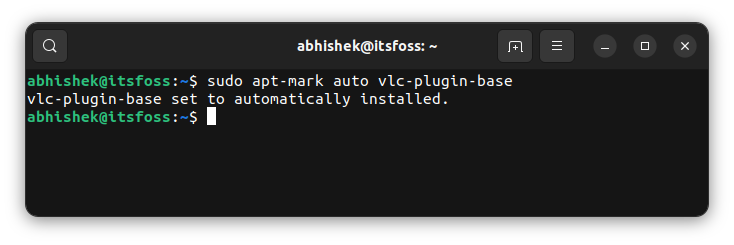
## Conclusion
This is not a major error and doesn’t stop you from doing your work in your system. However, knowing these little things increase your knowledge a little.
*Curiosity may have killed the cat, but it makes a penguin smarter*. That’s an original quote to add humor to this otherwise dull article :)
Since you are curious about the small details of the apt packages, here are a few more such articles for you.
[apt remove vs apt purge: What’s the Difference?To uninstall an application in the Ubuntu terminal, you can use: sudo apt remove package_name But in various forums, you may come across the suggestion to use the apt purge command for removing applications completely. This leaves you confused because using apt purge is quite similar…](https://itsfoss.com/apt-remove-purge/)

[Understanding sources.list](https://itsfoss.com/sources-list-ubuntu/) also helps improve your apt package manager knowledge.
[What is the Use of sources.list File in Ubuntu Linux?Understanding the concept of sources.list in Ubuntu will help you understand and fix common update errors in Ubuntu.](https://itsfoss.com/sources-list-ubuntu/)

Let me know if you would like to read more such articles that may seem insignificant but help you understand your Linux system a tiny bit better. |
14,676 | 机器学习:使用 Python 进行分类 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/machine-learning-classification-using-python/ | 2022-06-05T16:13:00 | [
"机器学习",
"分类"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14676-1.html |
>
> 机器学习(ML)就是,分析一组数据以预测结果。Python 被认为是 ML 的最佳编程语言选择之一。在本文中,我们将讨论使用 Python 进行分类的机器学习。
>
>
>

假设你想教孩子区分苹果和橙子。有多种方法可以做到这一点。你可以让孩子触摸这两种水果,让他们熟悉形状和柔软度。你还可以向她展示苹果和橙子的多个例子,以便他们可以直观地发现差异。这个过程的技术等价物被称为机器学习。
机器学习教计算机解决特定问题,并通过经验变得更好。这里讨论的示例是一个分类问题,其中机器被赋予各种标记示例,并期望使用它从标记样本中获得的知识来对未标记样本进行标记。机器学习问题也可以采用回归的形式,其中期望根据已知样本及其解决方案来预测给定问题的<ruby> 实值 <rt> real-valued </rt></ruby>解决方案。<ruby> 分类 <rt> Classification </rt></ruby>和<ruby> 回归 <rt> Regression </rt></ruby>被广泛称为<ruby> 监督学习 <rt> supervised learning </rt></ruby>。机器学习也可以是<ruby> 无监督 <rt> unsupervised </rt></ruby>的,机器识别未标记数据中的模式,并形成具有相似模式的样本集群。机器学习的另一种形式是<ruby> 强化学习 <rt> reinforcement learning </rt></ruby>,机器通过犯错从环境中学习。
### 分类
分类是根据从已知点获得的信息来预测一组给定点的标签的过程。与一个数据集相关的类别或标签可以是二元的,也可以是多元的。举例来说,如果我们必须给与一个句子相关的情绪打上标签,我们可以把它标记为正面、负面或中性。另一方面,我们必须预测一个水果是苹果还是橘子的问题将有二元标签。表 1 给出了一个分类问题的样本数据集。
在该表中,最后一列的值,即贷款批准,预计将基于其他变量进行预测。在接下来的部分中,我们将学习如何使用 Python 训练和评估分类器。
| 年龄 | 信用等级 | 工作 | 拥有房产 | 贷款批准 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| 35 | 好 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 32 | 差 | 是 | 不 | 不 |
| 22 | 一般 | 不 | 不 | 不 |
| 42 | 好 | 是 | 不 | 是 |
*表 1*
### 训练和评估分类器
为了训练<ruby> 分类器 <rt> classifier </rt></ruby>,我们需要一个包含标记示例的数据集。尽管本节不涉及清理数据的过程,但建议你在将数据集输入分类器之前阅读各种数据预处理和清理技术。为了在 Python 中处理数据集,我们将导入 `pandas` 包和<ruby> 数据帧 <rt> DataFrame </rt></ruby>结构。然后,你可以从多种分类算法中进行选择,例如<ruby> 决策树 <rt> decision tree </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 支持向量分类器 <rt> support vector classifier </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 随机森林 <rt> random forest </rt></ruby>、XG boost、ADA boost 等。我们将看看随机森林分类器,它是使用多个决策树形成的集成分类器。
```
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn import metrics
classifier = RandomForestClassifier()
#creating a train-test split with a proportion of 70:30
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.33)
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train) # 在训练集上训练分类器
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test) # 用未知数据评估分类器
print("Accuracy: ", metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)) # 用测试计划中的实际值比较准确率
```
虽然这个程序使用准确性作为性能指标,但应该使用多种指标的组合,因为当测试集不平衡时,准确性往往会产生非代表性的结果。例如,如果模型对每条记录都给出了相同的预测,而用于测试模型的数据集是不平衡的,即数据集中的大多数记录与模型预测的类别相同,我们就会得到很高的准确率。
### 调整分类器
调优是指修改模型的<ruby> 超参数 <rt> hyperparameter </rt></ruby>值以提高其性能的过程。超参数是可以改变其值以改进算法的学习过程的参数。
以下代码描述了随机搜索超参数调整。在此,我们定义了一个搜索空间,算法将从该搜索空间中选择不同的值,并选择产生最佳结果的那个:
```
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
#define the search space
min_samples_split = [2, 5, 10]
min_samples_leaf = [1, 2, 4]
grid = {‘min_samples_split’ : min_samples_split, ‘min_samples_leaf’ : min_samples_leaf}
classifier = RandomizedSearchCV(classifier, grid, n_iter = 100)
# n_iter 代表从搜索空间提取的样本数
# result.best_score 和 result.best_params_ 可以用来获得模型的最佳性能,以及参数的最佳值
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
```
### 投票分类器
你也可以使用多个分类器和它们的预测来创建一个模型,根据各个预测给出一个预测。这个过程(只考虑为每个预测投票的分类器的数量)被称为硬投票。软投票是一个过程,其中每个分类器产生一个给定记录属于特定类别的概率,而投票分类器产生的预测是获得最大概率的类别。
下面给出了一个创建软投票分类器的代码片段:
```
soft_voting_clf = VotingClassifier(
estimators=[(‘rf’, rf_clf), (‘ada’, ada_clf), (‘xgb’, xgb_clf), (‘et’, et_clf), (‘gb’, gb_clf)],
voting=’soft’)
soft_voting_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
```
这篇文章总结了分类器的使用,调整分类器和结合多个分类器的结果的过程。请将此作为一个参考点,详细探讨每个领域。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/machine-learning-classification-using-python/>
作者:[Gayatri Venugopal](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/gayatri-venugopal/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *In machine learning (ML), a set of data is analysed to predict a result. Python is considered one of the best programming language choices for ML. In this article, we will discuss machine learning with respect to classification using Python.*
Let’s say you want to teach a child to differentiate between apples and oranges. There are various ways to do this. You could ask the child to touch both kinds of fruits so that they get familiar with the shape and the softness. You could also show her multiple examples of apples and oranges, so that they can visually spot the differences. The technological equivalent of this process is known as machine learning.
Machine learning teaches computers to solve a particular problem, and to get better at it through experience. The example discussed here is a classification problem, where the machine is given various labelled examples, and is expected to label an unlabelled sample using the knowledge it acquired from the labelled samples. A machine learning problem can also take the form of regression, where it is expected to predict a real-valued solution to a given problem based on known samples and their solutions. Classification and regression are broadly termed as supervised learning. Machine learning can also be unsupervised, where the machine identifies patterns in unlabelled data, and forms clusters of samples with similar patterns. Another form of machine learning is reinforcement learning, where the machine learns from its environment by making mistakes.
**Classification**
Classification is the process of predicting the label of a given set of points based on the information obtained from known points. The class, or label, associated with a data set could be binary or multiple in nature. As an example, if we have to label the sentiment associated with a sentence, we could label it as positive, negative or neutral. On the other hand, problems where we have to predict whether a fruit is an apple or an orange will have binary labels. Table 1 gives a sample data set for a classification problem.
In this table, the value of the last column, i.e., loan approved, is expected to be predicted based on the other variables. In the subsequent sections, we will learn how to train and evaluate a classifier using Python.
Age | Credit rating | Job | Property owned | Load approval |
35 | good | yes | yes | yes |
32 | poor | yes | no | no |
22 | fair | no | no | no |
42 | good | yes | no | yes |
Table 1
**Training and evaluating a classifier**
In order to train a classifier, we need to have a data set containing labelled examples. Though the process of cleaning the data is not covered in this section, it is recommended that you read about various data preprocessing and cleaning techniques before feeding your data set to a classifier. In order to process the data set in Python, we will import the pandas package and the data frame structure. You may then choose from a variety of classification algorithms such as decision tree, support vector classifier, random forest, XG boost, ADA boost, etc. We will look at the random forest classifier, which is an ensemble classifier formed using multiple decision trees.
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier from sklearn import metrics classifier = RandomForestClassifier() #creating a train-test split with a proportion of 70:30 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.33) classifier.fit(X_train, y_train) #train the classifier on the training set y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test) #evaluate the classifier on unknown data print(“Accuracy: “, metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)) #compare the predictions with the actual values in the test set
Although this program uses accuracy as the performance metric, a combination of metrics should be used, as accuracy tends to generate non-representative results when the test set is imbalanced. For instance, we will get a high accuracy if the model gives the same prediction for every record and the data set that is used to test the model is imbalanced, i.e., most of the records in the data set have the same class that the model predicted.
**Tuning a classifier**
Tuning refers to the process of modifying the values of the hyperparameters of a model in order to improve its performance. A hyperparameter is a parameter whose value can be changed to improve the learning process of the algorithm.
The following code depicts random search hyperparameter tuning. In this, we define a search space from which the algorithm will pick different values, and choose the one that produces the best results:
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV #define the search space min_samples_split = [2, 5, 10] min_samples_leaf = [1, 2, 4] grid = {‘min_samples_split’ : min_samples_split, ‘min_samples_leaf’ : min_samples_leaf} classifier = RandomizedSearchCV(classifier, grid, n_iter = 100) #n_iter represents the number of samples to extract from the search space #result.best_score and result.best_params_ can be used to obtain the best performance of the model, and the best values of the parameters classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
**Voting classifier**
You can also use multiple classifiers and their predictions to create a model that will give a single prediction based on the individual predictions. This process (in which only the number of classifiers that voted for each prediction is considered) is called hard voting. Soft voting is a process in which each classifier generates a probability of a given record belonging to a particular class, and the voting classifier generates as its prediction, the class that obtained the maximum probability.
A code snippet for creating a soft voting classifier is given below:
soft_voting_clf = VotingClassifier( estimators=[(‘rf’, rf_clf), (‘ada’, ada_clf), (‘xgb’, xgb_clf), (‘et’, et_clf), (‘gb’, gb_clf)], voting=’soft’) soft_voting_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
This article has summarised the use of classifiers, tuning a classifier and the process of combining the results of multiple classifiers. Do use this as a reference point and explore each area in detail. |
14,678 | Linux 桌面刻薄版点评 | https://www.theregister.com/2022/05/31/the_cynics_guide_to_linux/ | 2022-06-06T10:15:00 | [
"Linux",
"发行版"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14678-1.html | 
>
> 厌倦了 Windows 却买不起 Mac?这里有一份讲道理的最不坏发行版清单供你参考。
>
>
>
众所周知,所有的操作系统都很糟糕,只是有些比其他的更差一些。
在几乎在每一篇关于 Linux 的文章下都有这样的评论:*有太多的发行版了,不知道该试试哪个*。因此,我们觉得应该帮你简化一下,列出不同的发行版到底怎么样,告诉你它们在哪些方面很 [糟糕](http://harmful.cat-v.org/software/operating-systems/os-suck)。
由于 Distrowatch 目前列出了多达 [270](https://distrowatch.com/dwres.php?resource=popularity) 个发行版,如果我们把所有的发行版都体验一遍,那简直是件不可能完成的事。因此,我们需要对这个列表做个瘦身。
如果你对这样的比较感兴趣,那么可能你还没有找到最喜欢的。
### 0. 小众而寂寂无名的发行版,我说的是全部
避免在所有的小众的发行版上费劲。原因如下:首先,它们很小众。没有多少人使用它们,所以你很难找到可以寻求帮助的人。其次,第三方硬件和软件可能无法开箱即用,如果你向供应商寻求帮助,无论是游戏、显卡还是打印机,他们都不会听说过 Ultimate SuperL33tOS 树莓派版。然后就完了。不要选它们,坚持主流。
### 1. ChromeOS Flex
年年都在喊 Linux 桌面年来了,然而根本没有人注意到它是不是来了 —— 也许是因为上面没有写 “Linux” 吧。ChromeOS 只能运行在 ChromeBook 和 ChromeBox 上,但在全球疫情大流行之前,它们的销量曾一度超过 Mac。“Flex” 是适用于普通 PC 的版本,大概因为它是 1.5 万亿美元的谷歌做的而因此得名吧。ChromeOS Flex 非常好用,因为它只做一件事:浏览网页。你不能安装应用程序,甚至不能安装安卓应用程序:只有官方套件才可以。你可以运行 Debian 容器:如果你知道这意味着什么,就去运行 Debian。如果你不知道这意味着什么,相信我们,你不会想知道的。
### 2. Ubuntu
>
> “Ubuntu 是一个古老的非洲单词,[意思](https://www.urbandictionary.com/define.php?term=ubuntu) *是我用不来 Debian*。”
>
>
>
Ubuntu 一开始是为了通过制造一个更容易安装和运行的 Linux 来取代 Windows 的头号消费操作系统的地位。它成功了。于是微软 [威胁要起诉](https://www.theregister.com/2007/05/24/microsoft_novell_patents/) 它,因为如果你不细看的话,它看起来有点像 Windows,[所以取代失败了](https://www.theregister.com/2013/06/03/thank_microsoft_for_linux_desktop_fail/)。Ubuntu 决定,如果它不能看起来像 Windows,那么就 [让它就像 Mac OS X](https://www.theregister.com/2011/04/01/ubuntu1004_beta_review/)。然后它又 [回到了 GNOME](https://www.theregister.com/2017/04/05/ubuntu_euthanizes_unity/)。
Ubuntu 曾经是显而易见的选择,但是它把目光从“<ruby> <a href="https://ubuntu.com/blog/for-human-beings"> 为人类服务 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> for human beings </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”的球上移开了(解释得很好,伙计们),转而关注服务器 —— 公平地说,这是赚钱的地方 —— 并且确实赚到了。当它放弃了所有内部的东西时,它保留了 Snap,这是它的通用应用程序打包格式,其他发行版都不用。这东西能用,但会占用磁盘空间,并使开机速度变慢。如果你只是想继续使用它,而不是摆弄和与之战斗,可以试试 Ubuntu MATE 或 Xubuntu,但这时你再想想我们对小众发行版的警告。
>
> 玩笑归玩笑,“Ubuntu” 是<ruby> 恩古尼 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Nguni </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>语(<ruby> 恩德贝莱语 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Ndebele </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 科萨语 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Xhosa </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 祖鲁语 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Zulu </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)的一个词,在南部非洲是一个更广泛的哲学概念,与社区中的尊重、仁慈和慷慨有关。其理念是,只有通过与他人进行亲社会互动,你才是一个人类。“umuntu ngumuntu ngabantu” —— “我是,因为你是”。
>
>
>
### 3. Linux Mint
Mint 是一个微调版的 Ubuntu 翻版。多年来它一直是个卢瑟,但是当 Ubuntu 变得像 Mac 一样时,它看到了机会并抓住了它 —— 同时也够到了榜单上第一的位置。它摒弃了 Ubuntu 中一些有问题的部分,比如 GNOME 和 Snap,但却用自己的不可靠的东西取代了它们,比如不是一个、不是两个、而是三个类 Windows 桌面的混乱选择,以及对更新和升级过于谨慎的态度。
### 4. Debian
Debian 是自由发行版的鼻祖,它发明了一种自动安装依赖关系的打包工具。它让安装 Linux 比以前更容易,但却陷入了 [政治](https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/25/debian_firmware_debate/) 的 [泥潭](https://www.theregister.com/2020/09/10/debian_project_address/)。它有点像 Ubuntu,但更过时,[更难安装](https://www.theregister.com/2021/01/22/debian_free_hard_to_install/),而且驱动程序更少。如果这听起来正是你所需要的,那就去安装它吧。
### 5. Fedora
红帽公司通过从免费发行版转而销售异常无聊的企业服务器版而赚取了数十亿美元。这让那些吃白食的人很不高兴。Fedora 是红帽公司扔给他们的骨头。它已经成熟到可以与 Ubuntu 相媲美,但没有稳定的版本。你将会每年升级两次,除非你推迟升级,躺平啥都不干,并希望跳过每一个其他版本。除非你的日常工作是试图阻止你的 RHEL 机器倒下,或者试图构建能在 RHEL 机器上运行而不倒下的代码,否则可能不值得使用它。
### 6. openSUSE
SUSE 比红帽公司整整大半岁,它是另一个昂贵的企业发行版供应商,把免费的东西丢到了墙外。它对 Fedora 的不稳定版本问题的创新解决方案是有两个不同的发行版。一个是 “Leap”,与付费的 SUSE Linux Enterprise(SLE)同步 —— 也就是说,它的发布周期慢得令人痛苦。另一个,“Tumbleweed”,有一个滚动的发布模式,这意味着每天都有可能出现令人刺激的破坏性变化。
作为补偿,它使用 Btrfs 和快照来使回滚更新变得容易 —— 但软件包管理器不知道快照,也不了解 Btrfs 有名的无法告诉你有多少可用的磁盘空间的 [习惯](https://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/FAQ#Help.21_Btrfs_claims_I.27m_out_of_space.2C_but_it_looks_like_I_should_have_lots_left.21),所以它偶尔会填满你的文件系统并破坏它。沮丧的无聊或畏缩的恐怖,这是你的选择:愿你玩得开心!
SUSE 和 KDE 都产自于德国,它大约永远是 KDE 的最佳发行版。为了显示对 Linux 世界的深刻理解,Novell 收[购了 SUSE](https://www.theregister.com/2003/11/04/novell_bags_suse_for_210m/),然后又 [收购](https://www.theregister.com/2003/08/04/novell_buys_ximian/) 了 GNOME 供应商 Ximian,然后强迫他们进行了一场 [包办婚姻](https://www.theregister.com/2004/01/07/novell_marries_suse_to_ximian/)。所以现在 SLE 甚至不提供 KDE 作为选项。
### 7. RHEL 一家
IBM 的子公司红帽仍然是 Linux 世界的巨人。特别像克洛诺斯,他吃了自己的孩子。所以它 [买下了 CentOS](https://www.theregister.com/2014/01/08/red_hat_to_team_up_with_communitybased_rhel_lookalike_centos/),然后把它 [干掉](https://www.theregister.com/2021/01/26/killing_centos/),就像它 [对 CoreOS 所做](https://www.theregister.com/2018/01/31/red_hat_coreos_acquisition/) 的那样。
让我们随便混用一下古典典故,这导致了一个九头蛇的局面:又有许多脑袋冒了出来。如果 Fedora 是 RHEL 的一个 alpha 版本,那么 CentOS Stream 就是一种 beta 版本。
还有 Rocky Linux 和 AlmaLinux,它们是锉掉了序列号的 RHEL。如果你以后要在 RHEL 上部署东西,或者如果你正在为在红帽商店工作而提高技能,或者如果你只是买不起真货,这都是理想的选择。如果你觉得现在 Oracle 比红帽更值得信赖,那么还有 Oracle 的版本。
对于你自己的笔记本电脑来说,这些都是长期以来有点落后于时代的东西:如果你是一个大企业,这正是你想要的,但如果你在家里运行它,就不是了。
### 8. Pop!\_OS
Pop!\_OS 可以说是最有趣的 Ubuntu 翻版之一。说到这里,请记住那句关于生活在 [有趣的时代](https://quoteinvestigator.com/2015/12/18/live/) 的名言,而开源世界的座右铭是 [快速行动和打破常规](https://www.theregister.com/2017/11/28/break_up_google_and_facebook_if_you_want_tech_innovation_ever_again/)。如果你一定要这么做,那就把它放在一台全新的电脑上,不要尝试双启动。另外,请记住我们对小众发行版说的话,这也适用于所有的 Ubuntu 翻版。
### 9. Arch Linux
最后,我们来到了名单上的第 10 个条目,因为 Unix 人要的就是不同,喜欢从零开始计算。作为最初的滚动发布的发行版之一,Arch 是快速行动和打破常规的体现。如果你是一个业余爱好者或游戏玩家,那就太好了,如果你有工作要做,那就不太好了。这也适用于它的后代,如 EndeavourOS、Manjaro 和 Garuda。
### 结论
有很多值得一试的发行版没有进入我们讽刺而(实则)深情的名单。这是列入前十名的原因:这个名单上的所有发行版都是目前领先的 Linux 发行版,这里的每一个都以自己的方式成为一个很好的、可靠的竞争者。
自由软件的世界之所以存在,是因为人们对正确的做事方式有强烈的感受,因此,它既有强烈的社区意识,也有深刻的、根本上对立的派别,如<ruby> 蝶变党 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Debianistas </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>与<ruby> 帽子客 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Hatters </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的对立。而这还没有涉及到桌面或编辑器的战争。
还有很多其他的发行版也有完全合理的存在理由,比如我们的办公桌面就主要运行一个根本不在这个名单上的 [发行版](https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/26/ubuntu_unity_and_ubuntu_cinnamon/)。
都挺好,真的。
---
via: <https://www.theregister.com/2022/05/31/the_cynics_guide_to_linux/>
作者:[Liam Proven in Prague](https://www.theregister.com/Author/Liam-Proven "Read more by this author") 选题:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](/article-14675-1.html) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | This article is more than **1 year old**
# Sick of Windows but can't afford a Mac? Consult our cynic's guide to desktop Linux
## For your consideration: A reasonable list of the least bad distros
It is a truth universally acknowledged that all operating systems suck. Some just suck less than others.
It is also a comment under pretty much every *Reg* article on Linux that there are too many to choose from and that it's impossible to know which one to try. So we thought we'd simplify things for you by listing how and in which ways the different options [suck](http://harmful.cat-v.org/software/operating-systems/os-suck).
This would be an impossibly long list if we looked at all of them since Distrowatch currently lists [270](https://distrowatch.com/dwres.php?resource=popularity). So we need to thin the herd a bit.
If you're interested in a comparison like this, you probably don't have a favorite already.
### 0. Tiny obscure distros. All of them.
Avoid all the niche efforts. Here's why. Firstly, they're small. Not many people use them, so you'll have difficulty finding people to ask for help. Secondly, third-party hardware and software probably won't work out of the box, and if you ask the vendor for help, whether it's a game or a graphics card or a printer, they won't have heard of Ultimate SuperL33tOS version Pi. Game over. Just don't. Stick to the mainstream.
###
1. [ChromeOS Flex](https://www.theregister.com/2022/02/16/google_chrome_os/)
The year of Linux on the desktop came and went, and nobody noticed – maybe because it doesn't say "Linux" on it. ChromeOS only runs on ChromeBooks and ChromeBoxes, but they outsold Macs for a while before the pandemic. "Flex" is the version for ordinary PCs, presumably named because it's what puny $1.5 trillion Google is doing. ChromeOS Flex works great, because it only does one thing: browse the web. You can't install apps, not even Android ones: only official kit does that. You *can* run Debian containers: if you know what that means, go run Debian. If you don't know what that means, trust us, you don't want to.
###
2. [Ubuntu](https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/21/ubuntu_22_04/)
"Ubuntu is an ancient African word that [means](https://www.urbandictionary.com/define.php?term=ubuntu) *I can't configure Debian.**"
Ubuntu started out as an effort to displace Windows from the number one consumer OS spot by making a Linux that was easier to install and run. It worked. So Microsoft [threatened to sue](https://www.theregister.com/2007/05/24/microsoft_novell_patents/) because it looked a bit like Windows if you squinted, and the [whole thing fell apart](https://www.theregister.com/2013/06/03/thank_microsoft_for_linux_desktop_fail/). Ubuntu decided that if it was dodgy to look Windows-like, it would look [like Mac OS X instead](https://www.theregister.com/2011/04/01/ubuntu1004_beta_review/). Then it went [back to GNOME again](https://www.theregister.com/2017/04/05/ubuntu_euthanizes_unity/).
Ubuntu *used* to be the obvious choice, but it took its eye off the "for human beings" [ball](https://ubuntu.com/blog/for-human-beings) (great explanation there, folks) to grab at servers – which, to be fair, is where the money is – and it shows. When it gave up on all its in-house stuff, it kept Snap, its universal app-packaging format that no other distro uses. They work, but they gobble disk space and make bootup slower. If you just want to get on with using it rather than fiddling and fighting, try Ubuntu MATE or Xubuntu, but then our warning about niche distros applies.
###
3. [Linux Mint](https://www.theregister.com/2022/01/12/mint_203_mozilla/)
Mint is an Ubuntu remix with knobs on. It was an also-ran for years, but when Ubuntu went all Mac-like it saw its chance and grabbed it – along with the number one spot in the charts. It dispenses with some of the questionable bits of recent Ubuntu, such as GNOME and Snaps, but replaces them with dodgy bits of its own, such as a confusing choice of not one, not two, but *three* Windows-like desktops, and overly cautious approaches to updates and upgrades.
###
4. [Debian](https://www.theregister.com/2021/06/16/debian_11/)
Debian is the daddy of free distros, and the one that invented the idea of a packaging tool that automatically installs dependencies. It's easier than it used to be, but [mired](https://www.theregister.com/2020/09/10/debian_project_address/) in [politics](https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/25/debian_firmware_debate/). It's sort of like Ubuntu, but more out of date, [harder to install](https://www.theregister.com/2021/01/22/debian_free_hard_to_install/), and with fewer drivers. If that sounds just your sort of thing, go for it.
###
5. [Fedora](https://www.theregister.com/2022/05/12/fedora_36_released/)
Red Hat made billions by switching from a free distro to selling an exceptionally boring corporate-server one. This upset the freeloaders. Fedora is the bone Red Hat threw over the fence to them. It's matured into something comparable to Ubuntu, but without the stable releases. You'll be upgrading twice a year, unless you put it off, cross your fingers, and hope that skipping every other version works. Probably not worth the effort unless your day job is trying to stop RHEL boxes falling over, or trying to build code that runs on RHEL boxes without falling over.
###
6. [openSUSE](https://www.theregister.com/2021/06/04/opensuse_leaps_to_153_now/)
A whole six months older than Red Hat, SUSE is another vendor of expensive enterprise distros which tosses freebies over the wall. Its innovative solution to Fedora's no-stable-releases issue is to have two different distros. One, "Leap", is synchronized with the paid-for SUSE Linux Enterprise – which is to say it has a painfully slow release cycle. The other, "Tumbleweed", has a rolling release model, which means the exciting potential of breaking changes *every single day*.
To compensate, it uses Btrfs and snapshots to make it easy to roll back updates – but the package manager doesn't know about snapshots, or Btrfs's famed [inability](https://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/FAQ#Help.21_Btrfs_claims_I.27m_out_of_space.2C_but_it_looks_like_I_should_have_lots_left.21) to tell you how much free disk space you have, so it occasionally fills up your file system and corrupts it. Frustrated boredom or cringing terror, it's your choice: have a lot of fun!
SUSE and KDE are both German and it's been the best distro for KDE approximately forever. Demonstrating its deep understanding of the Linux world, Novell [bought SUSE](https://www.theregister.com/2003/11/04/novell_bags_suse_for_210m/), then [bought GNOME vendor Ximian](https://www.theregister.com/2003/08/04/novell_buys_ximian/), then [forced them into an arranged marriage](https://www.theregister.com/2004/01/07/novell_marries_suse_to_ximian/). Now SLE doesn't even offer KDE as an option.
###
7. A [RHEL spin-off](https://www.theregister.com/2022/05/18/rhel_86_and_rocky_and_alma/)
IBM subsidiary Red Hat remains the titan of the Linux world. Specifically, Cronus, who ate his own children. So it [bought CentOS](https://www.theregister.com/2014/01/08/red_hat_to_team_up_with_communitybased_rhel_lookalike_centos/), then [killed it](https://www.theregister.com/2021/01/26/killing_centos/), as it [did with CoreOS](https://www.theregister.com/2018/01/31/red_hat_coreos_acquisition/).
Freely mixing classical allusions, this has resulted in a hydra situation: many more heads have sprouted. If Fedora is an alpha release of RHEL, CentOS Stream is a sort of beta.
[Unity and Trinity: New releases for forks of abandoned Linux desktops](https://www.theregister.com/2022/05/04/unity_trinity_desktops/)[Debian faces firmware furore from FOSS freedom fighters](https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/25/debian_firmware_debate/)[Why the Linux desktop is the best desktop](https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/13/linux_column/)[Zorin OS 16 beta claims largest built-in app library 'of any open source desktop ever'](https://www.theregister.com/2021/04/15/zorin_os_16_beta/)[Why make games for Linux if they don't sell? Because the nerds are just grateful to get something that works](https://www.theregister.com/2020/12/26/linux_game_development_scene/)
Or there are Rocky Linux and AlmaLinux, which are RHEL with the serial numbers filed off. Ideal for prototyping stuff you'll later deploy on RHEL, or if you're upskilling for a job in a Red Hat shop, or if you just can't afford the real thing. And there's Oracle if you feel that it looks more trustworthy than the Hat these days.
For your own laptop, these are all perennially a bit behind the times: just what you want if you're a big enterprise, but not if you're running it at home.
###
8. [Pop!_OS](https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/28/pop_os_2204_is_here/)
Pop!_OS is arguably one of the most interesting Ubuntu remixes. Saying that, bear in mind the famous line about living in [interesting times](https://quoteinvestigator.com/2015/12/18/live/), and that a motto of the open-source world is to [move fast and break things](https://www.theregister.com/2017/11/28/break_up_google_and_facebook_if_you_want_tech_innovation_ever_again/). If you must, put it on a brand-new PC and don't try to dual-boot. Also, remember what we said about niche distros, which applies to all the Ubuntu remixes.
###
9. [Arch Linux](https://www.theregister.com/2022/03/15/arch_linux_20/)
Finally we come to the 10th entry in our list, because Unix people are difficult and like to count from zero. As one of the original rolling-release distros, Arch is the embodiment of moving fast and breaking things. Great if you're a hobbyist or a gamer, not so good if you have a job to do. This also applies to its offspring such as EndeavourOS, Manjaro, and Garuda.
### Conclusion
There are loads of worthy entries that did not make our snarky and (honestly!) affectionate list. This was a top 10 for a reason: everything on this list is one of the leading Linuxes out there, and every distro here is a good solid contender in its own way.
The world of free software came into existence because people have very strong feelings about the Right Way To Do Things, and as a result, it both has a strong sense of community *and* deeply, fundamentally opposed factions, such as the Debianistas versus the Hatters. And that's without going into the desktop or editor wars.
There are lots of others with completely valid reasons for existence, too. *The Reg* FOSS desk mainly runs [a distro](https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/26/ubuntu_unity_and_ubuntu_cinnamon/) that's not in this list at all.
It's all good. Really. ®
* Jokes aside, Ubuntu is an Nguni language (Ndebele, Xhosa, Zulu) word that is broader concept philosophically in southern Africa, to do with respect, kindness and generosity in a community. The idea is that it is only through pro-social interactions with other people that you are a human being: "umuntu ngumuntu ngabantu" – "I am because you are."
303 |
14,679 | 使用 Linux 上的开源财务工具 Skrooge 管理你的预算 | https://opensource.com/article/21/2/linux-skrooge | 2022-06-06T12:03:10 | [
"开源",
"预算"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14679-1.html |
>
> 使用开源预算工具 Skrooge 让你的财务管理更加轻松。
>
>
>

2021 年,人们喜欢 Linux 的理由比以往任何时候都多。在本系列中,我将分享使用 Linux 的 21 个不同理由。本篇介绍的是个人财务管理。
个人财务可能很难管理。当你没有足够的钱在没有经济援助的情况下度日时,这可能是令人沮丧甚至不安的,而当你确实有所需的钱却又不清楚每个月的去向时,这可能会令人惊讶地难以接受。更糟糕的是,我们经常被告知要“制定预算”,好像宣布你每个月的花销就能在某种程度上体现出你需要多少钱。底线是:制定预算是困难的,没有达到你的财务目标是令人沮丧的。但这仍然很重要,Linux 有几个工具可以帮助使任务变得可管理。
### 理财
就像生活中的其他事情一样,我们都有自己的方法来跟踪我们的财务。我过去常常采取一种简单而直接的方法:我的薪水支票被存入一个账户,然后我会提取一定比例的现金。一旦我钱包里的钱没了,我就得等到下一个发薪日才能花钱。我用了一天没有午餐的时间,就明白了我必须认真对待我的目标,并相应地调整了我的消费行为。对于当时我的简单的生活方式来说,这是一种让我对自己的收入保持诚实的有效手段,但它并不能很好地转化为在线商业交易、长期公用事业合同、投资等等。
随着我不断完善我的财务跟踪方式,我了解到个人会计始终是一个不断发展的过程。我们每个人都有独特的财务状况,这告诉我们可以或应该使用什么样的解决方案来跟踪我们的收入和债务。如果你失业了,那么你的预算目标可能是尽可能少花钱。如果你在工作,但在还学生贷款,那么你的目标可能是向银行汇款。如果你在工作,但计划退休,那么你可能会尽可能多地存钱。
关于预算,要记住的一点是,它是为了将你的财务现实与你的财务 *目标* 进行比较。你无法避免一些开支,但在这些之后,你可以设定自己的优先事项。如果你没有达到你的目标,你可以调整自己的行为或改写你的目标,使其更好地反映现实。调整你的财务计划并不意味着你失败了,这只是意味着你最初的预测并不准确。在困难时期,你可能无法达到任何预算目标,但如果你坚持你的预算,你会学到很多关于维持你目前的生活方式(无论它是什么)所需要的财务手段。随着时间的推移,你可以学习调整你可能从未意识到的变化。例如,由于远程工作已成为一种被广泛接受的选择,人们正在搬到农村城镇以降低生活成本。看到这样一种生活方式的转变可以改变你的预算报告,真是令人震惊。
重点是,预算编制是一项经常被低估的活动,这在很大程度上是因为它令人生畏。重要的是要认识到,无论你的专业水平或对财务的兴趣如何,你都可以进行预算。无论你 [只使用 LibreOffice 电子表格](https://opensource.com/article/20/3/libreoffice-templates),还是尝试专用的财务应用程序,你都可以设定目标,跟踪自己的行为,并学到许多宝贵的经验教训,这些经验教训最终可能会带来回报。
### 开源会计
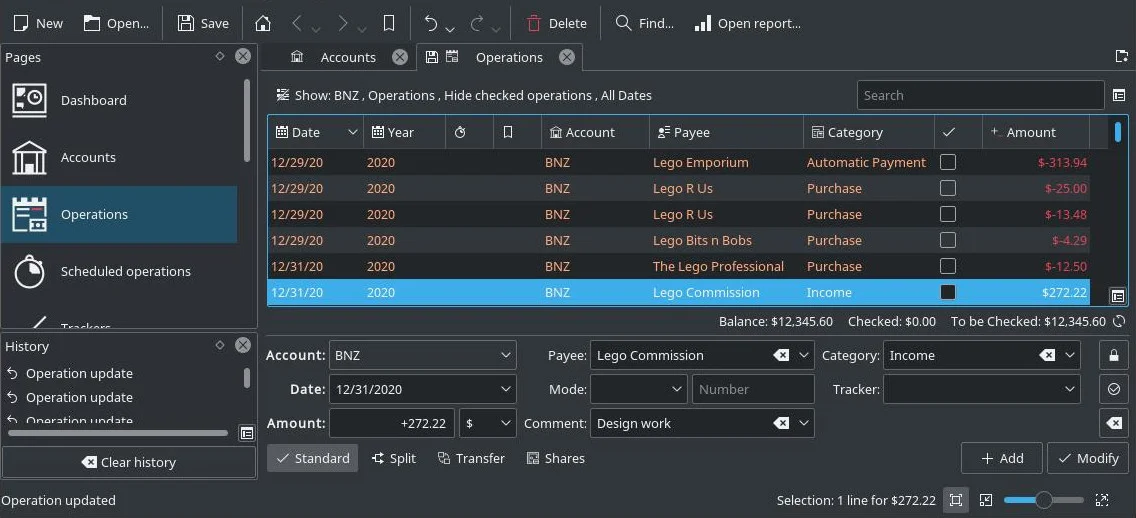
有几个专用于 [Linux 的个人理财应用程序](https://opensource.com/life/17/10/personal-finance-tools-linux),包括 [HomeBank](http://homebank.free.fr/en/index.php)、[Money Manager EX](https://www.moneymanagerex.org/download)、[GNUCash](https://opensource.com/article/20/2/gnucash)、[KMyMoney](https://kmymoney.org/download.html) 和 [Skrooge](https://apps.kde.org/en/skrooge)。所有这些应用程序本质上都是账本,你可以在每个月底(或每当你查看帐户时)退回到一个地方,从你的银行导入数据,并审查你的支出如何与你为自己设定的预算保持一致。

我使用 Skrooge 作为我的个人预算跟踪器。即便面对多个银行账户,它也能轻松自如的设置。与大多数开源金融应用程序一样,Skrooge 可以导入多种文件格式,因此我的工作流程大致如下:
1. 登录我的银行。
2. 将当月的银行对账单导出为 QIF 文件。
3. 打开 Skrooge。
4. 导入 QIF 文件。每个文件都会自动分配到相应的帐户。
5. 对照我为自己设定的预算目标审查我的支出。如果我超支了,那么我就会扣减下个月的目标(这样我就会理性地少花钱来弥补差额)。如果我尚未超出我的目标预算,那么我会把多余的部分移到 12 月的预算中(这样我在年底就会有更多的支出份额)。
我只跟踪了 Skrooge 中的家庭预算的一部分。Skrooge 通过一个动态数据库简化了这一过程,该数据库允许我使用自定义标签一次对多个交易进行分类。这使我可以轻松地从一般家庭和公用事业支出中提取我的个人支出,并且我可以在查看 Skrooge 提供的自动生成的报告时利用这些类别。

最重要的是,流行的 Linux 财务应用程序使我能够以最适合我的方式管理我的预算。例如,我的合作伙伴更喜欢使用 LibreOffice 电子表格,但我只需要付出很少的努力就可以从家庭预算中提取 CSV 文件,将其导入到 Skrooge,并使用一组更新的数据集。不存在供应商锁定和不兼容。该系统灵活敏捷,使我们能够在更多地了解有效预算和生活中的情况时调整我们的预算和跟踪支出的方法。
### 开放选择
世界各地的货币市场各不相同,我们每个人与之互动的方式也决定了我们可以使用哪些工具。归根结底,你对财务类软件的选择必须基于自己的需求。开源做得特别好的一件事是为用户提供了选择的自由。
在设定自己的财务目标时,我很欣赏我可以使用最适合我个人计算风格的任何应用程序。我可以控制我在生活中如何处理数据,即使是我不一定喜欢处理的数据。Linux 及其令人惊叹的应用程序集使它不再是一件苦差事。
在 Linux 上尝试一些财务应用程序,看看你是否可以激励自己设定一些目标并节省开支吧!
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/2/linux-skrooge>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hanszhao80](https://github.com/hanszhao80) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In 2021, there are more reasons why people love Linux than ever before. In this series, I'll share 21 different reasons to use Linux. This article is about personal financial management.
Personal finances can be difficult to manage. It can be frustrating and even scary when you don't have enough money to get by without financial assistance, and it can be surprisingly overwhelming when you do have the money you need but no clear notion of where it all goes each month. To make matters worse, we're often told to "make a budget" as if declaring the amount of money you can spend each month will somehow manifest the money you need. The bottom line is that making a budget is hard, and not meeting your financial goals is discouraging. But it's still important, and Linux has several tools that can help make the task manageable.
## Money management
As with anything else in life, we all have our own ways of keeping track of our money. I used to take a simple and direct approach: My paycheck was deposited into an account, and I'd withdraw some percentage in cash. Once the cash was gone from my wallet, I had to wait until the next payday to spend anything. It only took one day of missing out on lunch to learn that I had to take my goals seriously, and I adjusted my spending behavior accordingly. For the simple lifestyle I had at the time, it was an effective means of keeping myself honest with my income, but it didn't translate well to online business transactions, long-term utility contracts, investments, and so on.
As I continue to refine the way I track my finances, I've learned that personal accounting is always an evolving process. We each have unique financial circumstances, which inform what kind of solution we can or should use to track our income and debt. If you're out of work, then your budgeting goal is likely to spend as little as possible. If you're working but paying off a student loan, then your goal probably favors sending money to the bank. And if you're working but planning for retirement, then you're probably trying to save as much as you can.
The thing to remember about a budget is that it's meant to compare your financial reality with your financial *goals*. You can't avoid some expenses, but after those, you get to set your own priorities. If you don't hit your goals, you can adjust your own behavior or rewrite your goals so that they better reflect reality. Adapting your financial plan doesn't mean you've failed. It just means that your initial projection wasn't accurate. During hard times, you may not be able to hit any budget goals, but if you keep up with your budget, you'll learn a lot about what it takes financially to maintain your current lifestyle (whatever it may be). Over time, you can learn to adjust settings you may never have realized were available to you. For instance, people are moving to rural towns for the lower cost of living now that remote work is a widely accepted option. It's pretty stunning to see how such a lifestyle shift can alter your budget reports.
The point is that budgeting is an often undervalued activity, and in no small part because it's daunting. It's important to realize that you can budget, no matter your level of expertise or interest in finances. Whether you [just use a LibreOffice spreadsheet](https://opensource.com/article/20/3/libreoffice-templates), or try a dedicated financial application, you can set goals, track your own behavior, and learn a lot of valuable lessons that could eventually pay dividends.
## Open source accounting
There are several dedicated [personal finance applications for Linux](https://opensource.com/life/17/10/personal-finance-tools-linux), including [HomeBank](http://homebank.free.fr/en/index.php), [Money Manager EX](https://www.moneymanagerex.org/download), [GNUCash](https://opensource.com/article/20/2/gnucash), [KMyMoney](https://kmymoney.org/download.html), and [Skrooge](https://apps.kde.org/en/skrooge). All of these applications are essentially ledgers, a place you can retreat to at the end of each month (or whenever you look at your accounts), import data from your bank, and review how your expenditures align with whatever budget you've set for yourself.
Skrooge
I use Skrooge as my personal budget tracker. It's an easy application to set up, even with multiple bank accounts. Skrooge, as with most open source finance apps, can import multiple file formats, so my workflow goes something like this:
- Log in to my banks.
- Export the month's bank statement as QIF files.
- Open Skrooge.
- Import the QIF files. Each gets assigned to their appropriate accounts automatically.
- Review my expenditures compared to the budget goals I've set for myself. If I've gone over, then I dock next month's goals (so that I'll ideally spend less to make up the difference). If I've come in under my goal, then I move the excess to December's budget (so I'll have more to spend at the end of the year).
I only track a subset of the household budget in Skrooge. Skrooge makes that process easy through a dynamic database that allows me to categorize multiple transactions at once with custom tags. This makes it easy for me to extract my personal expenditures from general household and utility expenses, and I can leverage these categories when reviewing the autogenerated reports Skrooge provides.
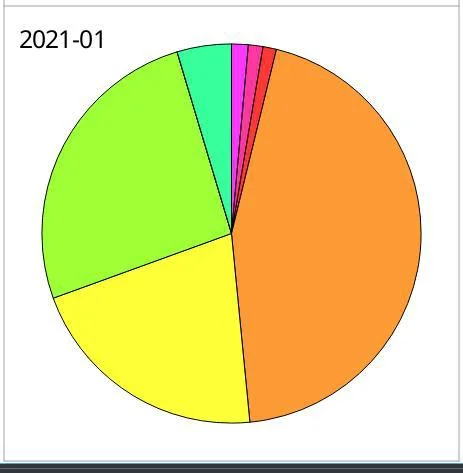
Skrooge budget pie chart
Most importantly, the popular Linux financial apps allow me to manage my budget the way that works best for me. For instance, my partner prefers to use a LibreOffice spreadsheet, but with very little effort, I can extract a CSV file from the household budget, import it into Skrooge, and use an updated set of data. There's no lock-in, no incompatibility. The system is flexible and agile, allowing us to adapt our budget and our method of tracking expenses as we learn more about effective budgeting and about what life has in store.
## Open choice
Money markets worldwide differ, and the way we each interact with them also defines what tools we can use. Ultimately, your choice of what to use for your finances is a decision you must make based on your own requirements. And one thing open source does particularly well is provide its users the freedom of choice.
When setting my own financial goals, I appreciate that I can use whatever application fits in best with my style of personal computing. I get to retain control of how I process the data in my life, even when it's data I don't necessarily enjoy having to process. Linux and its amazing set of applications make it just a little less of a chore.
Try some financial apps on Linux and see if you can inspire yourself to set some goals and save money!
## 2 Comments |
14,681 | Linux Mint 接管 Timeshift 备份工具的开发,并作为一款 XApp 来维护 | https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-mint-timeshift/ | 2022-06-07T08:18:02 | [
"Timeshift"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14681-1.html |
>
> Linux Mint 接管了 Timeshift 备份/恢复工具的开发。你可以在它新的 GitHub 仓库中找到它。
>
>
>

Timeshift 可以说是 [备份和恢复 Linux 系统的最佳工具](https://itsfoss.com/backup-restore-linux-timeshift/)。
Linux Mint 也利用它帮助用户在系统更新时更方便地创建快照,确保快捷无碍的操作。
当然,这不是 [Linux Mint 可能比 Ubuntu 更好的唯一原因](https://itsfoss.com/linux-mint-vs-ubuntu/)。
不幸的是,Timeshift 背后的开发者([Tony George](https://teejeetech.com/))计划把注意力集中在其他项目上,将不再继续维护这个项目。
Linux Mint 团队联系了这位开发者,并愿意为这个项目提供任何可能的帮助。最终,它们接管了 Timeshift 的开发。
所以,现在 Linux Mint 团队会对 Timeshift 的发布和修复,以及任何与之相关的开发工作负责。
### 将 Timeshift 调整成 XApp

Linux Mint 倾向于将某些应用作为“XApp”来维护,以确保它们能在各种不同的桌面环境下工作,不会依赖于某个特殊的桌面。
考虑到他们计划将 Timeshift 调整成一个XApp,你可以期待该工具在很长一段时间内维持当前的外观和功能,而不用顾虑你的桌面环境是什么。
不像一些 GNOME 应用程序,为了获得最好的体验,它们通常会变成 GNOME 专用的应用程序。
Timeshift 是一个必不可少的备份/恢复工具。所以,Linux Mint 接管 Timeshift 的开发并作为一个 XApp 来维护的计划听上去相当完美!
如果你想知道的话,那不妨告诉你,Timeshift 的迁移已经在 [Launchpad](https://github.com/linuxmint/timeshift) 上完成了。
新的 [GitHub仓库](https://github.com/linuxmint/timeshift)(由 Linux Mint 复刻的)可以给你提供这个应用的更多细节以及它最近的开发活动。
你也可以在 [最近每月发布的博文](https://blog.linuxmint.com/?p=4323) 中查阅官方对此的声明。
### 结语
作为 Timeshift 的维护者,Linux Mint 希望在不久的将来带来更多的新特性和改进。
你如何看待 Linux Mint 将 Timeshift 接管为一款 XApp?欢迎在下方的评论区内分享你的想法。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-mint-timeshift/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[hadisi1993](https://github.com/%E8%AF%91%E8%80%85ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/%E6%A0%A1%E5%AF%B9%E8%80%85ID)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Timeshift is arguably the [best tool to back up and restore the Linux system](https://itsfoss.com/backup-restore-linux-timeshift/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
Linux Mint also utilizes the tool to let users easily take snapshots before updates, and ensure hassle-free operation.
Of course, that’s not the only thing that makes [Linux Mint potentially better than Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/linux-mint-vs-ubuntu/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
Unfortunately, the developer ([Tony George](https://teejeetech.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)) behind Timeshift can no longer maintain the project. The developer plans to focus on other projects instead.
The Linux Mint team reached out to the developer to help the project in any capacity. And, they finalized to take over the development of Timeshift.
So, now, the Linux Mint team will be responsible for new releases/fixes, and any development activity associated with Timeshift.
## Adopting Timeshift as an XApp
Linux Mint tends to maintain certain applications as an “XApp” to make sure that they work on various desktop environments and are not dependent on a particular desktop.
Considering that they plan to adopt Timeshift as an XApp, you can expect the tool to continue offering the current look/functionality for a long time, irrespective of your desktop environment.
Unlike some GNOME apps, which are usually turning into GNOME-only applications for the best experience.
Timeshift is an essential backup/restore tool. So, Linux Mint taking over the development and maintaining it as an XApp sounds perfect!
The translations for Timeshift are now done on [Launchpad](https://github.com/linuxmint/timeshift?ref=news.itsfoss.com), if you are curious.
The [new GitHub repository](https://github.com/linuxmint/timeshift?ref=news.itsfoss.com) (forked by Linux Mint) can give you more details about the application and its latest development activity.
You can also check out the official announcement for this in the [recent monthly blog post](https://blog.linuxmint.com/?p=4323&ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Wrapping Up
With Linux Mint as the maintainer of Timeshift, we could hope for more feature additions and improvements in the near future.
What do you think about Linux Mint taking over the development of Timeshift as an XApp? You are welcome to share your thoughts on it in the comments below.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,682 | Simula 诞生之前的面向对象程序设计 | https://twobithistory.org/2019/01/31/simula.html | 2022-06-07T11:10:38 | [
"OOP",
"面向对象"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14682-1.html | 想象一下,你坐在河边,河岸上如茵绿草,不远处湍急河流;午后的阳光慵懒惬意,使人陷入冥想哲思,不觉开始思考眼前的河流是否真实存在。诚然,几米外确实有河水奔流而下。不过,我们所称为“河流”的存在究竟是什么呢?毕竟,河水奔流不息,一直处于变化之中。似乎,“河流”这个词无法指代任何固定不变的事物。
2009 年,Clojure 的创始人 <ruby> 里奇·希基 <rt> Rich Hickey </rt></ruby> 发表了 [一场精彩的演讲](https://www.infoq.com/presentations/Are-We-There-Yet-Rich-Hickey),探讨了为什么上文那样的哲学窘境会给面向对象程序的编程范式带来难题。他认为,人们看待计算机程序中的对象与看待河流的逻辑是一样的:我们想象对象是固定不变的,即使对象的许多或者说全部的属性都无时无刻不处于变化之中。所以,这种逻辑并不正确,我们无法区分在不同状态下同一对象实例的不同之处。程序中没有明确的时间的概念。人们只是单纯地用着同一个名字,以期在引用对象时,对象能够处于预期的状态中。这样,我们也就难免会遇到 <ruby> 故障 <rt> bug </rt></ruby>。
希基总结道,这一难题的应对办法就是人们应该将世界建模成作用于不可变数据的 <ruby> 进程 <rt> process </rt></ruby> 的集合,而不是可变的对象的集合。换句话说,我们应把每个对象看作一条“河流”,因果相连。总结说来,你应该使用 Clojure 等函数式语言。

*作者在远足途中思考面向对象程序设计的本体论问题。*
自从希基发表演讲之后,人们对函数式编程语言的兴趣不断提升,主流的面向对象编程语言也大多都采用了函数式编程语言。尽管如此,大多数程序员依旧沿用自己的老一套,继续将对象实例化,不断改变其状态。这些人长此以往,很难做到用不同的视角看待编程。
我曾经想写一篇关于 Simula 的文章,大概会写到我们今天所熟知的面向对象的理念是何时又是如何应用到程序语言之中的。但是,我觉得写当初的 Simula 与如今的面向对象程序设计的 *迥然不同之处*,会更有趣一些,这我敢打包票。毕竟,我们现在熟知的面向对象程序设计还未完全成型。Simula 有两个主要版本:Simula I 和 Simula 67。Simula 67 为世界带来了 <ruby> 类 <rt> class </rt></ruby>、 <ruby> 类的继承 <rt> class hierarchy </rt></ruby> 以及 <ruby> 虚拟方法 <rt> virtual method </rt></ruby>;但 Simula I 是一个初稿,它实验了如何能够将数据和进程捆绑起来的其他设想。Simula I 的模型不是希基提出的函数式模型,不过这一模型关注的是随时间展开的 *进程*,而非有着隐藏状态的对象之间的相互作用。如果 Simula 67 采用了 Simula I 的理念,那么我们如今所知的面向对象程序设计可能会大有不同——这类偶然性启示我们,不要想着现在的程序设计范式会一直占据主导地位。
### 从 Simula 0 到 Simula 67
Simula 是由两位挪威人 <ruby> 克里斯汀·尼加德 <rt> Kristen Nygaard </rt></ruby> 和 <ruby> 奥利-约翰·达尔 <rt> Ole-Johan Dahl </rt></ruby> 创建的。
20 世纪 50 年代末,尼加德受雇于 <ruby> 挪威防务科学研究中心 <rt> Norwegian Defense Research Establishment </rt></ruby>(NDRE),该研究中心隶属于挪威军方。在那里,他负责设计 <ruby> 蒙特卡洛模拟方法 <rt> Monte Carlo simulations </rt></ruby>,用于核反应堆设计与操作研究。最初,那些模拟实验是由人工完成的;后来,实验在 Ferranti Mercury 电脑 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn1" id="fnref1"> [1] </a></sup> 上编入程序运行。尼加德随后发现,将这些模拟实验输入电脑需要一种更有效的方式。
尼加德设计的这种模拟实验就是人们所知的“<ruby> 离散事件模型 <rt> discrete event model </rt></ruby>”,这种模拟记录了一系列事件随着时间改变系统状态的进程。但是问题的关键在于模拟可以从一个事件跳跃到另一个事件中,因为事件是离散的,事件之间的系统不存在任何变化。根据尼加德和达尔在 1966 年发表的一篇关于 Simula 的论文,这种模型被迅速应用于“神经网络、通信系统、交通流量、生产系统、管理系统、社会系统等” <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn2" id="fnref2"> [2] </a></sup> 领域的分析。因此,尼加德认为,其他人描述模拟实验时,可能也需要更高层级的模型。于是他开始物色人才,帮助他完成他称之为“<ruby> 模拟语言 <rt> Simulation Language </rt></ruby>”或者“<ruby> 蒙特卡洛编译器 <rt> Monte Carlo Compiler </rt></ruby>”的项目 <sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn3" id="fnref3"> [3] </a></sup>。
达尔当时也受雇于挪威防务科学研究中心,专攻语言设计,此时也加入了尼加德的项目,扮演“沃兹尼亚克”的角色(LCTT 译注:指苹果公司联合创始人斯蒂夫·盖瑞·沃兹尼亚克)。在接下来一年左右的时间,尼加德和达尔携手开发了 Simula 0 语言。<sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn4" id="fnref4"> [4] </a></sup> 这一语言的早期版本仅仅是在 ALGOL 60 基础上进行的较小拓展,当时也只是打算将其用作预处理程序而已。当时的语言要比后来的编程语言抽象得多,其基本语言结构是“<ruby> 车站 <rt> stations </rt></ruby>”与“<ruby> 乘客 <rt> customers </rt></ruby>”,这些结构可以用于针对具体某些离散事件网络建立模型。尼加德和达尔给出了一个模拟飞机离港的例子。<sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn5" id="fnref5"> [5] </a></sup> 但是尼加德和达尔最后想出了一个更加通用的语言结构,可以同时表示“车站”和“乘客”,也可以为更广泛的模拟建立模型。这是两个主要的概括,它改变了 Simula 作为 ALGOL 专属包的定位,使其转变为通用编程语言。
Simula I 没有“<ruby> 车站 <rt> stations </rt></ruby>”和“<ruby> 乘客 <rt> customers </rt></ruby>”的语言结构,但它可以通过使用“<ruby> 进程 <rt> process </rt></ruby>”再现这些结构。(LCTT 译注:此处使用的“进程”,与当前计算机中用来指代一个已执行程序的实体的概念不同,大致上,你可以将本文中所说的“进程”理解为一种“对象”。)一个进程包含大量数据属性,这些属性与作为进程的 *操作规程* 的单个行为相联系。你可能会把进程当作是只有单个方法的对象,比如 `run()` 之类的。不过,这种类比并不全面,因为每个进程的操作规程都可以随时暂停、随时恢复,因为这种操作规程属于 <ruby> 协程 <rt> coroutine </rt></ruby> 的一种。Simula I 程序会将系统建立为一套进程的模型,在概念上这些进程并行运行。实际上,一个时间点上能称为“当前进程”的只有一个进程。但是,一旦某个进程暂停运行,那么下一个进程就会自动接替它的位置。随着模拟的运行,Simula 会保持一个 “<ruby> 事件通知 <rt> event notices </rt></ruby>” 的时间线,跟踪记录每个进程恢复的时间。为了恢复暂停运行的进程,Simula 需要记录多个 <ruby> 调用栈 <rt> call stacks </rt></ruby> 的情况。这就意味着 Simula 无法再作为 ALGOL 的预处理程序了,因为 ALGOL 只有一个 <ruby> 调用栈 <rt> call stacks </rt></ruby>。于是,尼加德和达尔下定决心,开始编写自己的编译器。
尼加德和达尔在介绍该系统的论文中,借助图示,通过模拟一个可用机器数量有限的工厂,阐明了其用法。<sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn6" id="fnref6"> [6] </a></sup> 在该案例中,进程就好比订单:通过寻找可用的机器,订单得以发出;如果没有可用的机器,订单就会搁置;而一旦有机器空出来,订单就会执行下去。有一个订单进程的定义,用来实例化若干种不同的订单实例,不过这些实例并未调用任何方法。该程序的主体仅仅是创建进程,并使其运行。
历史上第一个 Simula I 编译器发布于 1965 年。尼加德和达尔在离开挪威防务科学研究中心之后,就进入了 <ruby> 挪威计算机中心 <rt> Norwegian Computer Center </rt></ruby> 工作,Simula I 也是在这里日渐流行起来的。当时,Simula I 在 UNIVAC 公司的计算机和 Burroughs 公司的 B5500 计算机上均可执行。<sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn7" id="fnref7"> [7] </a></sup> 尼加德和达尔两人与一家名为 ASEA 的瑞典公司达成了咨询协议,运用 Simula 模拟加工车间。但是,尼加德和达尔随后就意识到 Simula 也可以写一些和模拟完全不搭边的程序。
<ruby> 奥斯陆大学 <rt> University of Oslo </rt></ruby>教授 <ruby> 斯坦因·克罗达尔 <rt> Stein Krogdahl </rt></ruby> 曾写过关于 Simula 的发展史,称“真正能够促使新开发的通用语言快速发展的催化剂”就是 [一篇题为<ruby> 《记录处理》 <rt> Record Handling </rt></ruby>的论文](https://archive.computerhistory.org/resources/text/algol/ACM_Algol_bulletin/1061032/p39-hoare.pdf),作者是英国计算机科学家 <ruby> 查尔斯·安东尼·理查德·霍尔 <rt> C.A.R. Hoare </rt></ruby>。<sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn8" id="fnref8"> [8] </a></sup> 假如你现在读霍尔的这篇论文,你就不会怀疑这句话。当人们谈及面向对象语言的发展史时,一定会经常提起霍尔的大名。以下内容摘自霍尔的《记录处理》一文:
>
> 该方案设想,在程序执行期间,计算机内部存在任意数量的记录,每条记录都代表着程序员在过去、现在或未来所需的某个对象。程序对现有记录的数量保持动态控制,并可以根据当前任务的要求创建新的记录或删除现有记录。
>
>
> 计算机中的每条记录都必须属于数量有限但互不重合的记录类型中的一类;程序员可以根据需要声明尽可能多的记录类型,并借助标识符为各个类型命名。记录类型的命名可能是普通词汇,比如“牛”、“桌子”以及“房子”,同时,归属于这些类型的记录分别代表一头“牛”、一张“桌子”以及一座“房子”。
>
>
>
霍尔在这片论文中并未提到子类的概念,但是达尔由衷地感谢霍尔,是他引导了两人发现了这一概念。<sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn9" id="fnref9"> [9] </a></sup> 尼加德和达尔注意到 Simula I 的进程通常具有相同的元素,所以引入父类来执行共同元素就会非常方便。这也强化了“进程”这一概念本身可以用作父类的可能性,也就是说,并非每种类型都必须用作只有单个操作规程的进程。这就是 Simula 语言迈向通用化的第二次飞跃,此时,Simula 67 真正成为了通用编程语言。正是如此变化让尼加德和达尔短暂地萌生了给 Simula 改名的想法,想让人们意识到 Simula 不仅仅可以用作模拟。<sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn10" id="fnref10"> [10] </a></sup> 不过,考虑到 “Simula”这个名字的知名度已经很高了,另取名字恐怕会带来不小的麻烦。
1967 年,尼加德和达尔与 <ruby> 控制数据公司 <rt> Control Data </rt></ruby> 签署协议,着手开发Simula 的新版本:Simula 67。同年六月份的一场会议中,来自控制数据公司、奥斯陆大学以及挪威计算机中心的代表与尼加德和达尔两人会面,意在为这门新语言制定标准与规范。最终,会议发布了 [《Simula 67 通用基础语言》](http://web.eah-jena.de/~kleine/history/languages/Simula-CommonBaseLanguage.pdf),确定了该语言的发展方向。
Simula 67 编译器的开发由若干家供应商负责。<ruby> Simula 用户协会 <rt> The Association of Simula Users </rt></ruby>(ASU)也随后成立,并于每年举办年会。不久,Simula 67 的用户就遍及了 23 个国家。<sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn11" id="fnref11"> [11] </a></sup>
### 21 世纪的 Simula 语言
人们至今还记得 Simula,是因为后来那些取代它的编程语言都受到了它的巨大影响。到了今天,你很难找到还在使用 Simula 写程序的人,但是这并不意味着 Simula 已经从这个世界上消失了。得益于 [GNU cim](https://www.gnu.org/software/cim/),人们在今天依然能够编写和运行 Simula 程序。
cim 编译器遵循 1986 年修订后的 Simula 标准,基本上也就是 Simula 67 版本。你可以用它编写类、子类以及虚拟方法,就像是在使用 Simula 67 一样。所以,用 Python 或 Ruby 轻松写出短短几行面向对象的程序,你照样也可以用 cim 写出来:
```
! dogs.sim ;
Begin
Class Dog;
! The cim compiler requires virtual procedures to be fully specified ;
Virtual: Procedure bark Is Procedure bark;;
Begin
Procedure bark;
Begin
OutText("Woof!");
OutImage; ! Outputs a newline ;
End;
End;
Dog Class Chihuahua; ! Chihuahua is "prefixed" by Dog ;
Begin
Procedure bark;
Begin
OutText("Yap yap yap yap yap yap");
OutImage;
End;
End;
Ref (Dog) d;
d :- new Chihuahua; ! :- is the reference assignment operator ;
d.bark;
End;
```
你可以按照下面代码执行程序的编译与运行:
```
$ cim dogs.sim
Compiling dogs.sim:
gcc -g -O2 -c dogs.c
gcc -g -O2 -o dogs dogs.o -L/usr/local/lib -lcim
$ ./dogs
Yap yap yap yap yap yap
```
(你可能会注意到,cim 先将 Simula 语言编译为 C 语言,然后传递给 C 语言编译器。)
这就是 1967 年的面向对象程序设计,除了语法方面的不同,和 2019 年的面向对象程序设计并无本质区别。如果你同意我的这一观点,你也就懂得了为什么人们会认为 Simula 在历史上是那么的重要。
不过,我更想介绍一下 Simula I 的核心概念——进程模型。Simula 67 保留了进程模型,不过只有在使用 `Process` 类 和 `Simulation` 块的时候才能调用。
为了表现出进程是如何运行的,我决定模拟下述场景。想象一下,有这么一座住满了村民的村庄,村庄的旁边有条小河边,小河里有很多的鱼。但是,村里的村民却只有一条鱼竿。村民们胃口很大,每隔一个小时就饿了。他们一饿,就会拿着鱼竿去钓鱼。如果一位村民正在等鱼竿,另一位村民自然也用不了。这样一来,村民们就会为了钓鱼排起长长的队伍。假如村民要等五、六分钟才能钓到一条鱼,那么这样等下去,村民们的身体状况就会变得越来越差。再假如,一位村民已经到了骨瘦如柴的地步,最后他可能就会饿死。
这个例子多少有些奇怪,虽然我也不说不出来为什么我脑袋里最先想到的是这样的故事,但是就这样吧。我们把村民们当作 Simula 的各个进程,观察在有着四个村民的村庄里,一天的模拟时间内会发生什么。
完整程序可以通过此处 [GitHub Gist](https://gist.github.com/sinclairtarget/6364cd521010d28ee24dd41ab3d61a96) 的链接获取。
我把输出结果的最后几行放在了下面。我们来看看一天里最后几个小时发生了什么:
```
1299.45: 王五饿了,要了鱼竿。
1299.45: 王五正在钓鱼。
1311.39: 王五钓到了一条鱼。
1328.96: 赵六饿了,要了鱼竿。
1328.96: 赵六正在钓鱼。
1331.25: 李四饿了,要了鱼竿。
1340.44: 赵六钓到了一条鱼。
1340.44: 李四饿着肚子等着鱼竿。
1340.44: 李四在等鱼竿的时候饿死了。
1369.21: 王五饿了,要了鱼竿。
1369.21: 王五正在钓鱼。
1379.33: 王五钓到了一条鱼。
1409.59: 赵六饿了,要了鱼竿。
1409.59: 赵六正在钓鱼。
1419.98: 赵六钓到了一条鱼。
1427.53: 王五饿了,要了鱼竿。
1427.53: 王五正在钓鱼。
1437.52: 王五钓到了一条鱼。
```
可怜的李四最后饿死了,但是他比张三要长寿,因为张三还没到上午 7 点就饿死了。赵六和王五现在一定过得很好,因为需要鱼竿的就只剩下他们两个了。
这里,我要说明,这个程序最重要的部分只是创建了进程(四个村民),并让它们运行下去。各个进程操作对象(鱼竿)的方式与我们今天对对象的操作方式相同。但是程序的主体部分并没有调用任何方法,也没有修改进程的任何属性。进程本身具有内部状态,但是这种内部状态的改变只有进程自身才能做到。
在这个程序中,仍然有一些字段发生了变化,这类程序设计无法直接解决纯函数式编程所能解决的问题。但是正如克罗达尔所注意到的那样,“这一机制引导进行模拟的程序员为底层系统建立模型,生成一系列进程,每个进程表示了系统内的自然事件顺序。”<sup class="footnote-ref"> <a href="#fn12" id="fnref12"> [12] </a></sup> 我们不是主要从名词或行动者(对其他对象做事的对象)的角度来思考正在进行的进程。我们可以将程序的总控制权交予 Simula 的事件通知系统,克罗达尔称其为 “<ruby> 时间管理器 <rt> time manager </rt></ruby>”。因此,尽管我们仍然在适当地改变进程,但是没有任何进程可以假设其他进程的状态。每个进程只能间接地与其他进程进行交互。
这种模式如何用以编写编译器、HTTP 服务器以及其他内容,尚且无法确定。(另外,如果你在 Unity 游戏引擎上编写过游戏,就会发现两者十分相似。)我也承认,尽管我们有了“时间管理器”,但这可能并不完全是希基的意思,他说我们在程序中需要一个明确的时间概念。(我认为,希基想要的类似于 [<ruby> 阿达·洛芙莱斯 <rt> Ada Lovelace </rt></ruby> 用于区分一个变量随时间变化产生的不同数值的上标符号](https://twobithistory.org/2018/08/18/ada-lovelace-note-g.html)。)尽管如此,我们可以发现,面向对象程序设计前期的设计方式与我们今天所习惯的面向对象程序设计并非完全一致,我觉得这一点很有意思。我们可能会理所当然地认为,面向对象程序设计的方式千篇一律,即程序就是对事件的一长串记录:某个对象以特定顺序对其他对象产生作用。Simula I 的进程系统表明,面向对象程序设计的方式不止一种。仔细想一下,函数式语言或许是更好的设计方式,但是 Simula I 的发展告诉我们,现代面向对象程序设计被取代也很正常。
*如果你喜欢这篇文章,欢迎关注推特 [@TwoBitHistory](https://twitter.com/TwoBitHistory),也可通过 [RSS feed](https://twobithistory.org/feed.xml) 订阅,获取最新文章(每四周更新一篇)。*
---
1. Jan Rune Holmevik, “The History of Simula,” accessed January 31, 2019, <http://campus.hesge.ch/daehne/2004-2005/langages/simula.htm>. [↩︎](#fnref1)
2. Ole-Johan Dahl and Kristen Nygaard, “SIMULA—An ALGOL-Based Simulation Langauge,” Communications of the ACM 9, no. 9 (September 1966): 671, accessed January 31, 2019, <http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.95.384&rep=rep1&type=pdf>. [↩︎](#fnref2)
3. Stein Krogdahl, “The Birth of Simula,” 2, accessed January 31, 2019, <http://heim.ifi.uio.no/~steinkr/papers/HiNC1-webversion-simula.pdf>. [↩︎](#fnref3)
4. 出处同上。 [↩︎](#fnref4)
5. Ole-Johan Dahl and Kristen Nygaard, “The Development of the Simula Languages,” ACM SIGPLAN Notices 13, no. 8 (August 1978): 248, accessed January 31, 2019, <https://hannemyr.com/cache/knojd_acm78.pdf>. [↩︎](#fnref5)
6. Dahl and Nygaard (1966), 676. [↩︎](#fnref6)
7. Dahl and Nygaard (1978), 257. [↩︎](#fnref7)
8. Krogdahl, 3. [↩︎](#fnref8)
9. Ole-Johan Dahl, “The Birth of Object-Orientation: The Simula Languages,” 3, accessed January 31, 2019, <http://www.olejohandahl.info/old/birth-of-oo.pdf>. [↩︎](#fnref9)
10. Dahl and Nygaard (1978), 265. [↩︎](#fnref10)
11. Holmevik. [↩︎](#fnref11)
12. Krogdahl, 4. [↩︎](#fnref12)
---
via: <https://twobithistory.org/2019/01/31/simula.html>
作者:[Two-Bit History](https://twobithistory.org) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[aREversez](https://github.com/aREversez) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/%E6%A0%A1%E5%AF%B9%E8%80%85ID)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Imagine that you are sitting on the grassy bank of a river. Ahead of you, the water flows past swiftly. The afternoon sun has put you in an idle, philosophical mood, and you begin to wonder whether the river in front of you really exists at all. Sure, large volumes of water are going by only a few feet away. But what is this thing that you are calling a “river”? After all, the water you see is here and then gone, to be replaced only by more and different water. It doesn’t seem like the word “river” refers to any fixed thing in front of you at all.
In 2009, Rich Hickey, the creator of Clojure, gave [an excellent
talk](https://www.infoq.com/presentations/Are-We-There-Yet-Rich-Hickey) about
why this philosophical quandary poses a problem for the object-oriented
programming paradigm. He argues that we think of an object in a computer
program the same way we think of a river—we imagine that the object has a
fixed identity, even though many or all of the object’s properties will change
over time. Doing this is a mistake, because we have no way of distinguishing
between an object instance in one state and the same object instance in another
state. We have no explicit notion of time in our programs. We just breezily use
the same name everywhere and hope that the object is in the state we expect it
to be in when we reference it. Inevitably, we write bugs.
The solution, Hickey concludes, is that we ought to model the world not as a
collection of mutable objects but a collection of *processes* acting on
immutable data. We should think of each object as a “river” of causally related
states. In sum, you should use a functional language like Clojure.
*The author, on a hike, pondering the ontological commitments of
object-oriented programming.*
Since Hickey gave his talk in 2009, interest in functional programming languages has grown, and functional programming idioms have found their way into the most popular object-oriented languages. Even so, most programmers continue to instantiate objects and mutate them in place every day. And they have been doing it for so long that it is hard to imagine that programming could ever look different.
I wanted to write an article about Simula and imagined that it would mostly be
about when and how object-oriented constructs we are familiar with today were
added to the language. But I think the more interesting story is about how
Simula was originally so *unlike* modern object-oriented programming languages.
This shouldn’t be a surprise, because the object-oriented paradigm we know now
did not spring into existence fully formed. There were two major versions of
Simula: Simula I and Simula 67. Simula 67 brought the world classes, class
hierarchies, and virtual methods. But Simula I was a first draft that
experimented with other ideas about how data and procedures could be bundled
together. The Simula I model is not a functional model like the one Hickey
proposes, but it does focus on *processes* that unfold over time rather than
objects with hidden state that interact with each other. Had Simula 67 stuck
with more of Simula I’s ideas, the object-oriented paradigm we know today might
have looked very different indeed—and that contingency should teach us to be
wary of assuming that the current paradigm will dominate forever.
## Simula 0 Through 67
Simula was created by two Norwegians, Kristen Nygaard and Ole-Johan Dahl.
In the late 1950s, Nygaard was employed by the Norwegian Defense Research
Establishment (NDRE), a research institute affiliated with the Norwegian
military. While there, he developed Monte Carlo simulations used for nuclear
reactor design and operations research. These simulations were at first done by
hand and then eventually programmed and run on a Ferranti Mercury. 1 Nygaard
soon found that he wanted a higher-level way to describe these simulations to a
computer.
The kind of simulation that Nygaard commonly developed is known as a “discrete
event model.” The simulation captures how a sequence of events change the state
of a system over time—but the important property here is that the simulation
can jump from one event to the next, since the events are discrete and nothing
changes in the system between events. This kind of modeling, according to a
paper that Nygaard and Dahl presented about Simula in 1966, was increasingly
being used to analyze “nerve networks, communication systems, traffic flow,
production systems, administrative systems, social systems, etc.” 2 So
Nygaard thought that other people might want a higher-level way to describe
these simulations too. He began looking for someone that could help him
implement what he called his “Simulation Language” or “Monte Carlo
Compiler.”
[3](#fn:3)Dahl, who had also been employed by NDRE, where he had worked on language
design, came aboard at this point to play Wozniak to Nygaard’s Jobs. Over the
next year or so, Nygaard and Dahl worked to develop what has been called
“Simula 0.” 4 This early version of the language was going to be merely a
modest extension to ALGOL 60, and the plan was to implement it as a
preprocessor. The language was then much less abstract than what came later.
The primary language constructs were “stations” and “customers.” These could be
used to model certain discrete event networks; Nygaard and Dahl give an example
simulating airport departures.
But Nygaard and Dahl eventually came up with a more general language construct that could represent both “stations” and “customers” and also model a wider range of simulations. This was the first of two major generalizations that took Simula from being an application-specific ALGOL package to a general-purpose programming language.
[5](#fn:5)In Simula I, there were no “stations” or “customers,” but these could be
recreated using “processes.” A process was a bundle of data attributes
associated with a single action known as the process’ *operating rule*. You
might think of a process as an object with only a single method, called
something like `run()`
. This analogy is imperfect though, because each process’
operating rule could be suspended or resumed at any time—the operating rules
were a kind of coroutine. A Simula I program would model a system as a set of
processes that conceptually all ran in parallel. Only one process could
actually be “current” at any time, but once a process suspended itself the next
queued process would automatically take over. As the simulation ran, behind the
scenes, Simula would keep a timeline of “event notices” that tracked when each
process should be resumed. In order to resume a suspended process, Simula
needed to keep track of multiple call stacks. This meant that Simula could no
longer be an ALGOL preprocessor, because ALGOL had only once call stack.
Nygaard and Dahl were committed to writing their own compiler.
In their paper introducing this system, Nygaard and Dahl illustrate its use by
implementing a simulation of a factory with a limited number of machines that
can serve orders. 6 The process here is the order, which starts by looking
for an available machine, suspends itself to wait for one if none are
available, and then runs to completion once a free machine is found. There is a
definition of the order process that is then used to instantiate several
different order instances, but no methods are ever called on these instances.
The main part of the program just creates the processes and sets them running.
The first Simula I compiler was finished in 1965. The language grew popular at
the Norwegian Computer Center, where Nygaard and Dahl had gone to work after
leaving NDRE. Implementations of Simula I were made available to UNIVAC users
and to Burroughs B5500 users. 7 Nygaard and Dahl did a consulting deal with a
Swedish company called ASEA that involved using Simula to run job shop
simulations. But Nygaard and Dahl soon realized that Simula could be used to
write programs that had nothing to do with simulation at all.
Stein Krogdahl, a professor at the University of Oslo that has written about
the history of Simula, claims that “the spark that really made the development
of a new general-purpose language take off” was [a paper called “Record
Handling”](https://archive.computerhistory.org/resources/text/algol/ACM_Algol_bulletin/1061032/p39-hoare.pdf)
by the British computer scientist C.A.R. Hoare. 8 If you read Hoare’s paper
now, this is easy to believe. I’m surprised that you don’t hear Hoare’s name
more often when people talk about the history of object-oriented languages.
Consider this excerpt from his paper:
The proposal envisages the existence inside the computer during the execution of the program, of an arbitrary number of records, each of which represents some object which is of past, present or future interest to the programmer. The program keeps dynamic control of the number of records in existence, and can create new records or destroy existing ones in accordance with the requirements of the task in hand.
Each record in the computer must belong to one of a limited number of disjoint record classes; the programmer may declare as many record classes as he requires, and he associates with each class an identifier to name it. A record class name may be thought of as a common generic term like “cow,” “table,” or “house” and the records which belong to these classes represent the individual cows, tables, and houses.
Hoare does not mention subclasses in this particular paper, but Dahl credits
him with introducing Nygaard and himself to the concept. 9 Nygaard and Dahl
had noticed that processes in Simula I often had common elements. Using a
superclass to implement those common elements would be convenient. This also
raised the possibility that the “process” idea itself could be implemented as a
superclass, meaning that not every class had to be a process with a single
operating rule. This then was the second great generalization that would make
Simula 67 a truly general-purpose programming language. It was such a shift
of focus that Nygaard and Dahl briefly considered changing the name of the
language so that people would know it was not just for simulations.
But “Simula” was too much of an established name for them to risk it.
[10](#fn:10)In 1967, Nygaard and Dahl signed a contract with Control Data to implement this
new version of Simula, to be known as Simula 67. A conference was held in June,
where people from Control Data, the University of Oslo, and the Norwegian
Computing Center met with Nygaard and Dahl to establish a specification for
this new language. This conference eventually led to a document called the
[“Simula 67 Common Base
Language,”](http://web.eah-jena.de/~kleine/history/languages/Simula-CommonBaseLanguage.pdf)
which defined the language going forward.
Several different vendors would make Simula 67 compilers. The Association of
Simula Users (ASU) was founded and began holding annual conferences. Simula 67
soon had users in more than 23 different countries.[11](#fn:11)
## 21st Century Simula
Simula is remembered now because of its influence on the languages that have
supplanted it. You would be hard-pressed to find anyone still using Simula to
write application programs. But that doesn’t mean that Simula is an entirely
dead language. You can still compile and run Simula programs on your computer
today, thanks to [GNU cim](https://www.gnu.org/software/cim/).
The cim compiler implements the Simula standard as it was after a revision in 1986. But this is mostly the Simula 67 version of the language. You can write classes, subclass, and virtual methods just as you would have with Simula 67. So you could create a small object-oriented program that looks a lot like something you could easily write in Python or Ruby:
```
! dogs.sim ;
Begin
Class Dog;
! The cim compiler requires virtual procedures to be fully specified ;
Virtual: Procedure bark Is Procedure bark;;
Begin
Procedure bark;
Begin
OutText("Woof!");
OutImage; ! Outputs a newline ;
End;
End;
Dog Class Chihuahua; ! Chihuahua is "prefixed" by Dog ;
Begin
Procedure bark;
Begin
OutText("Yap yap yap yap yap yap");
OutImage;
End;
End;
Ref (Dog) d;
d :- new Chihuahua; ! :- is the reference assignment operator ;
d.bark;
End;
```
You would compile and run it as follows:
```
$ cim dogs.sim
Compiling dogs.sim:
gcc -g -O2 -c dogs.c
gcc -g -O2 -o dogs dogs.o -L/usr/local/lib -lcim
$ ./dogs
Yap yap yap yap yap yap
```
(You might notice that cim compiles Simula to C, then hands off to a C compiler.)
This was what object-oriented programming looked like in 1967, and I hope you agree that aside from syntactic differences this is also what object-oriented programming looks like in 2019. So you can see why Simula is considered a historically important language.
But I’m more interested in showing you the process model that was central to
Simula I. That process model is still available in Simula 67, but only when you
use the `Process`
class and a special `Simulation`
block.
In order to show you how processes work, I’ve decided to simulate the following scenario. Imagine that there is a village full of villagers next to a river. The river has lots of fish, but between them the villagers only have one fishing rod. The villagers, who have voracious appetites, get hungry every 60 minutes or so. When they get hungry, they have to use the fishing rod to catch a fish. If a villager cannot use the fishing rod because another villager is waiting for it, then the villager queues up to use the fishing rod. If a villager has to wait more than five minutes to catch a fish, then the villager loses health. If a villager loses too much health, then that villager has starved to death.
This is a somewhat strange example and I’m not sure why this is what first came to mind. But there you go. We will represent our villagers as Simula processes and see what happens over a day’s worth of simulated time in a village with four villagers.
The full program is [available here as a
Gist](https://gist.github.com/sinclairtarget/6364cd521010d28ee24dd41ab3d61a96).
The last lines of my output look like the following. Here we are seeing what happens in the last few hours of the day:
```
1299.45: John is hungry and requests the fishing rod.
1299.45: John is now fishing.
1311.39: John has caught a fish.
1328.96: Betty is hungry and requests the fishing rod.
1328.96: Betty is now fishing.
1331.25: Jane is hungry and requests the fishing rod.
1340.44: Betty has caught a fish.
1340.44: Jane went hungry waiting for the rod.
1340.44: Jane starved to death waiting for the rod.
1369.21: John is hungry and requests the fishing rod.
1369.21: John is now fishing.
1379.33: John has caught a fish.
1409.59: Betty is hungry and requests the fishing rod.
1409.59: Betty is now fishing.
1419.98: Betty has caught a fish.
1427.53: John is hungry and requests the fishing rod.
1427.53: John is now fishing.
1437.52: John has caught a fish.
```
Poor Jane starved to death. But she lasted longer than Sam, who didn’t even make it to 7am. Betty and John sure have it good now that only two of them need the fishing rod.
What I want you to see here is that the main, top-level part of the program does nothing but create the four villager processes and get them going. The processes manipulate the fishing rod object in the same way that we would manipulate an object today. But the main part of the program does not call any methods or modify and properties on the processes. The processes have internal state, but this internal state only gets modified by the process itself.
There are still fields that get mutated in place here, so this style of
programming does not directly address the problems that pure functional
programming would solve. But as Krogdahl observes, “this mechanism invites the
programmer of a simulation to model the underlying system as a set of
processes, each describing some natural sequence of events in that
system.” 12 Rather than thinking primarily in terms of nouns or
actors—objects that do things to other objects—here we are thinking of
ongoing processes. The benefit is that we can hand overall control of our
program off to Simula’s event notice system, which Krogdahl calls a “time
manager.” So even though we are still mutating processes in place, no process
makes any assumptions about the state of another process. Each process
interacts with other processes only indirectly.
It’s not obvious how this pattern could be used to build, say, a compiler or an
HTTP server. (On the other hand, if you’ve ever programmed games in the Unity
game engine, this should look familiar.) I also admit that even though we have
a “time manager” now, this may not have been exactly what Hickey meant when he
said that we need an explicit notion of time in our programs. (I think he’d
want something like the superscript notation [that Ada Lovelace used](/2018/08/18/ada-lovelace-note-g.html) to distinguish between the
different values a variable assumes through time.) All the same, I think it’s
really interesting that right there at the beginning of object-oriented
programming we can find a style of programming that is not all like the
object-oriented programming we are used to. We might take it for granted that
object-oriented programming simply works one way—that a program is just a
long list of the things that certain objects do to other objects in the exact
order that they do them. Simula I’s process system shows that there are other
approaches. Functional languages are probably a better thought-out
alternative, but Simula I reminds us that the very notion of alternatives
to modern object-oriented programming should come as no surprise.
*
If you enjoyed this post, more like it come out every four weeks! Follow
@TwoBitHistory
on Twitter or subscribe to the
RSS feed
to make sure you know when a new post is out.
*
*Previously on TwoBitHistory…*
Hey everyone! I sadly haven't had time to do any new writing but I've just put up an updated version of my history of RSS. This version incorporates interviews I've since done with some of the key people behind RSS like Ramanathan Guha and Dan Libby.
— TwoBitHistory (@TwoBitHistory)[https://t.co/WYPhvpTGqB][December 18, 2018]
-
Jan Rune Holmevik, “The History of Simula,” accessed January 31, 2019,
[http://campus.hesge.ch/daehne/2004-2005/langages/simula.htm](http://campus.hesge.ch/daehne/2004-2005/langages/simula.htm).[↩](#fnref:1) -
Ole-Johan Dahl and Kristen Nygaard, “SIMULA—An ALGOL-Based Simulation Langauge,” Communications of the ACM 9, no. 9 (September 1966): 671, accessed January 31, 2019,
[http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.95.384&rep=rep1&type=pdf](http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.95.384&rep=rep1&type=pdf).[↩](#fnref:2) -
Stein Krogdahl, “The Birth of Simula,” 2, accessed January 31, 2019,
[http://heim.ifi.uio.no/~steinkr/papers/HiNC1-webversion-simula.pdf](http://heim.ifi.uio.no/~steinkr/papers/HiNC1-webversion-simula.pdf).[↩](#fnref:3) -
ibid.
[↩](#fnref:4) -
Ole-Johan Dahl and Kristen Nygaard, “The Development of the Simula Languages,” ACM SIGPLAN Notices 13, no. 8 (August 1978): 248, accessed January 31, 2019,
[https://hannemyr.com/cache/knojd_acm78.pdf](https://hannemyr.com/cache/knojd_acm78.pdf).[↩](#fnref:5) -
Dahl and Nygaard (1966), 676.
[↩](#fnref:6) -
Dahl and Nygaard (1978), 257.
[↩](#fnref:7) -
Krogdahl, 3.
[↩](#fnref:8) -
Ole-Johan Dahl, “The Birth of Object-Orientation: The Simula Languages,” 3, accessed January 31, 2019,
[http://www.olejohandahl.info/old/birth-of-oo.pdf](http://www.olejohandahl.info/old/birth-of-oo.pdf).[↩](#fnref:9) -
Dahl and Nygaard (1978), 265.
[↩](#fnref:10) -
Holmevik.
[↩](#fnref:11) -
Krogdahl, 4.
[↩](#fnref:12) |
14,683 | 如何修复 “yay: error while loading shared libraries: libalpm.so.12” | https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/07/yay-error-libalpm-so-12/ | 2022-06-07T14:41:10 | [
"yay",
"错误修复"
] | /article-14683-1.html | 
>
> 这篇快速指南是为了帮助你修复 “yay error: while loading shared libraries: libalpm.so.12” 错误。
>
>
>
如果你在系统中运行 [Arch Linux](https://archlinux.org/) 的时间比较长,那么由于其滚动发布性质以及你的硬件支持,程序可能会损坏。 如果你使用 AUR 助手 Yay,那么有时,由于其他软件包的多次安装升级,Yay 可能会损坏。
Yay 助手一般是非常稳定的,但有时它会被搞乱,在修复好之前,你不能使用它安装任何程序。而其中一个令人头疼的错误是这样的:
```
yay: error while loading shared libraries: libalpm.so.12: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
```
这个错误特别是在升级到 pacman 6.0 后出现的,因为共享库不兼容。

### 如何解决 “yay: error while loading shared libraries: libalpm.so.12”
这个错误只能通过完全卸载 `yay` 来解决,包括它的依赖。然后重新安装 `yay`。
没有其他方法来解决这个错误。
我们已经有一个 [如何安装 Yay](https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/01/install-yay-arch/) 的指南,然而,以下是修复的步骤。
从 AUR 克隆 yay 仓库并构建。在终端窗口中依次运行以下命令。
```
cd /tmp
git clone 'https://aur.archlinux.org/yay.git'
cd /tmp/yay
makepkg -si
cd ~
rm -rf /tmp/yay/
```
安装完成后,你可以尝试运行给你带来这个错误的命令。然后就好了。如果你仍然有这个错误,请在下面的评论区告诉我。
很多人都遇到了这个问题,网络上有 [几个讨论](https://github.com/Jguer/yay/issues/1519)。以上是解决这个错误的唯一办法。而且我在任何地方都找不到这个问题的确切根源,除了它是在 pacman 6.0 更新后开始的。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/07/yay-error-libalpm-so-12/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,685 | Fedora Linux 37 的内核 5.18 测试周到了,一起来做贡献吧! | https://fedoramagazine.org/contribute-at-the-fedora-linux-37-test-week-for-kernel-5-18/ | 2022-06-08T09:11:46 | [
"Fedora"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14685-1.html | 
Fedora 内核团队正在为 Linux 内核 5.18 进行最终集成。这个版本刚刚发布,很快就会出现在 Fedora 中。因此,Fedora 内核和 QA 团队组织了一个测试周,截止日期为 **2022 年 6 月 12 日,星期日。** 请参阅 [维基页面](http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Test_Day:2022-06-05_Kernel_5.18_Test_Week) 来获取你将要参与的测试镜像链接。继续阅读下文,可了解更多细节~
### 测试周是如何运作的?
测试周是一个人人都可以参与的活动。在测试周,任何人都可以为 Fedora 即将发布的版本查漏补缺,确保它最终能够运行良好。Fedora 社区成员会经常参与这个活动,我们同时也欢迎公众参加这些活动。如果你以前从未做过贡献,那么这是一个绝佳的上手机会。
要想做出贡献,你只需要能够执行以下操作即可:
* 下载测试资料,包括一些大文件
* 阅读并按照说明一步一步地进行操作
内核测试日的 [维基页面](http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Test_Day:2022-06-05_Kernel_5.18_Test_Week) 提供了很多关于测试内容和测试方法的有用信息。完成一些测试后,你可以在测试日的 [Web 应用](https://testdays.fedoraproject.org/events/136) 上记录下你的测试结果。如果你在活动的当天或前后有空,请进行一些测试并报告你的结果。不知道该怎么做?没关系,我们有一份文件,其中提供了 [所有步骤](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/kernel/howto-kernel-testday/)。
希望能在测试日见到你,预祝测试愉快~
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/contribute-at-the-fedora-linux-37-test-week-for-kernel-5-18/>
作者:[Sumantro Mukherjee](https://fedoramagazine.org/author/sumantrom/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The kernel team is working on final integration for Linux kernel 5.18. This version was just recently released, and will arrive soon in Fedora. As a result, the Fedora kernel and QA teams have organized a test week now through **Sunday, June 12, 2022.** Refer to the [wiki ](http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Test_Day:2022-06-05_Kernel_5.18_Test_Week)[page](http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Test_Day:2022-06-05_Kernel_5.18_Test_Week) for links to the test images you’ll need to participate. Read below for details.
## How does a test week work?
A test week is an event where anyone can help make sure changes in Fedora work well in an upcoming release. Fedora community members often participate, and the public is welcome at these events. If you’ve never contributed before, this is a perfect way to get started.
To contribute, you only need to be able to do the following things:
- Download test materials, which include some large files
- Read and follow directions step by step
The [wiki page](http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Test_Day:2022-06-05_Kernel_5.18_Test_Week) for the kernel test day has a lot of good information on what and how to test. After you’ve done some testing, you can log your results in the test day [web](https://testdays.fedoraproject.org/events/136)[ application](https://testdays.fedoraproject.org/events/136). If you’re available on or around the day of the event, please do some testing and report your results. We have a document which provides [all the steps](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/kernel/howto-kernel-testday/) written.
Happy testing, and we hope to see you on test day.
## GEPlinux
Hello,
A little fault in the wiki just for fun : F36 instead of f37 🙂
A fully updated F36 test day image or Fedora 35 or 36 Workstation/Server installation, either on bare metal or VM (please make sure you have no important data on that installation, things might go wrong — don’t do this on your production machine!)
## skierpage
The wiki page is quite confusing. “The primary aim is to test on Fedora 35 and 34” but later “Prerequisite for Test Day: A fully updated F36 test day image or Fedora 35 or 36 Workstation/Server installation…” No mention of Fedora 34, or 37. Is the point that this will be the kernel that Fedora 37 uses, even though the kernel team want people running Fedora 35 and 36 to test it?
## wayne6001
I think that’s part of what GEPlinux was pointing out. Another one is on the wiki page the link from the first “result page” gets you to the right place to enter results for 5.18, but the second link “results page” gets you to the previous 5.17 results page instead. I think the title of this article was meant to be: “Fedora Linux 36 Test Week for Kernel 5.18” and it is meant to test on F36 or F35.
## Leslie Satenstein, Montreal,Que
Had problems to submit my test result. I am using F36KDE spin. Kwin crashed, no dump, nothing to show.
System is an ASUS laptop 8gig ram, nvme drive with lots of space, core I5 10th gen
Kernel 5.18-2-200
## skierpage
FWIW I was able to submit test result and the performance test result (which took 2 hours to run). I’m also running Fedora 36 KDE spin.
## tcg121268
What hardware did you run the tests on? 2 hours seem a bit long.
## travis mechanical man
yepo same here for like a year rando, crashes swaped pc parts out fedora kda 35 and now frezzeing on normal fedora 36 build nothing to show randon bs .This is why i stayed with winder fer so many tyears sadkly but my hatred for it has exceeded just being to lazy to reboot pc every other hour or 15 mins depends what mood the machine is in but the harder its working the faster it crashes sometimes . new to lixus by the way
new old stock build motherboard and high end power supply yep in 2022 LOL CPU :Amd .A8 8650 24 gb ddr3 ram rods ;] 500GB ssd 32 aoc 2k monitor
the stuff does not crash as much or any on ryzen 2700u laptop i barley use
## Stephen
Ran the default and performance test on a VM using Gnome Boxes and the provided ISO image. Installation went smooth, testing passed and report submission worked fine. Though my results were uploaded successfully via the test script after completion of both tests, my results do not show up on the results page noted on the test wiki.
## Luna bittin Jernberg
Did join in and helped out during the last day today
## Tomasz
Guys,
I really lost track.
For now I have on my laptop: Fedora Linux 37 (Workstation Edition Prerelease)
Kernel: vmlinuz-5.19.0-0.rc2.21.fc37.x86_64
I turned on several months ago Rawhide and I use it.
So how can I participate and give you a feedback to the developing release.
But please in points:
1) what to raport?
2) how to raport and to whom?
3) mostly ABRT is not sending errors … because “The backtrace does not contain enough meaningful function frames to be reported. It is annoying but it does not necessarily indicate a problem with your computer. ABRT will not allow you to create a report in a bug tracking system but you can contact kernel maintainers via e-mail.”
Maybe we need some kind of article where it will be pointed out exactly how tests are done, which way and how to contribute.
All the best
T.
## Gregory Bartholomew
I’m not a packager, but I think most of the Fedora Workstation development currently happens on mail lists and in IRC chat rooms. However, I think there is a goal of gradually moving from the mail lists to Discourse to make that work a little more visible. My suggestion would be to report any problems that you think might be noteworthy under the
workstationtag on Fedora’s Discourse forum: https://discussion.fedoraproject.org/tag/workstationHTH,
gb
## Glenn Johnson
I’m trying to help here but I have no network at all when running Fedora 36 Workstation and the 5.18 kernel.
## Rocky
Well done!
## Abdul Muqueem
As requested |
14,686 | 在商业之外,为学生们教授开源知识 | https://opensource.com/article/21/1/open-source-beyond-business | 2022-06-08T09:52:02 | [
"开源"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14686-1.html |
>
> Beyond 计划连接起未来科技行业的人才和开源文化。
>
>
>

那时,我还是一个大学生,我不明白人们为什么那么吹捧开源软件。我也使用 Linux 和开源软件,但是我不明白开源的运作模式,不知道如何参加一个开源项目,也不知道这对我未来的职业有什么好处。我的开发经验主要是家庭作业和学位需要的一个大型期末项目。
所以,当我开始踏足科技行业时,我发现我还有很多知识需要学习。我需要了解如何加入一个既定的、可能很大并且分散在不同地方的团队,为一个正在进行中的项目工作。我还要学会正确的沟通以保证我付出的努力不白费。
在这方面,我并不特别。我只是众多毕业生中的一员。
### 开源让毕业生的起点更高
作为一个工程师,一个管理者,从那时起我开始帮助刚入行的工程师。我发现,有开源经验的毕业生比没有开源经验的毕业生能更快的入门。
通过将开源方法纳入学术研究,学生们可以获得相关的行业经验,学会利用他们自己的知识,并建立一个陈述观点和分享知识的平台。参与开源项目可以对学生的技术知识和经验产生积极影响。这可以帮助他们更好的规划自己的职业生涯。
开源在科技行业的价值是公认的,它塑造了全球软件公司的文化。参与开源项目并采用 [开放组织文化](https://opensource.com/open-organization/resources/open-org-definition) 正在成为行业普遍现象。公司寻求知道如何在开源领域工作并培养其文化的思想新颖、才华横溢的员工。因此,科技行业必须推动学术界将开源文化作为学习科技研究的基本方法之一。
### 商业之上是开源文化
当我遇到红帽的高级软件工程师 [Liora Milbaum](https://www.linkedin.com/in/lioramilbaum) 时,我发现,我们对将开源文化和规则引入学术界有着共同的兴趣。Liora 之前创立了 [DevOps Loft](https://www.devopsloft.io/), 在其中,她与有兴趣进入这个行业的人们分享了 DevOps 实践,并希望发起一个类似的项目,教授大学生开源。我们决定启动 [Beyond](https://research.redhat.com/blog/2020/05/24/open-source-development-course-and-devops-methodology/) 计划,将科技行业拥抱开源精神的人才与红帽的实践联系起来。
我们在 [Tel Aviv-Yafo 技术学院](https://www.int.mta.ac.il/) 开始了 Beyond 计划,在那里,我们受到了信息系统学院的热烈欢迎。我们从介绍 DevOps 技术栈的 “DevOps 入门” 开始。我们开始时最大的挑战是怎么讲明白开源是什么。答案似乎很简单:实践出真理。我们不想给学生们讲授什么老套的学院课程,相反,我们想让学生接触到行业标准。
我们创建了一个包含常见的开源项目和工具的教学大纲来教授 DevOps 技术栈。该课程由工程师教授的讲座和实践组成。学生们被分成小组,每组都由一名工程师指导和支持。他们练习团队合作,分享知识(在团队内外),并有效的协作。
在我们为计算机科学学院的通讯准备的高级课程 “开源开发的基础” 中,我们遇到了另外的困难。当我们的课程开始两周以后,随着新冠疫情在全球的流行,我们完全靠远程沟通。我们通过与学生一起使用我们在红帽日常工作中使用的相同远程协作工具解决了这个问题。我们惊讶于过渡的是如此简单和顺利。

(Irit Goihman, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
### 成果展示
这两个课程取得了巨大的成功,我们甚至雇佣了我们最优秀的学生之一。我们收到了非常棒的反馈,同学们表示,我们对他们的知识、思维和软技能产生了积极影响。一些学生因为在课程期间的开源贡献而得到了他们第一份技术工作。
其他学术机构对这些课程表达出了极大的兴趣,因此我们将这个项目扩展到了另外一所大学。
很荣幸,在一群优秀工程师的参与下,与 Liora 一起领导这个成功的项目。我们一起助力开源社区的成长。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/1/open-source-beyond-business>
作者:[Irit Goihman](https://opensource.com/users/iritgoihman) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[duoluoxiaosheng](https://github.com/duoluoxiaosheng) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When I was a university student, I didn't understand the fuss about open source software. I used Linux and open source software but didn't really understand the open source model, how to contribute to projects, or how it could benefit my future career. My development experience consisted mainly of homework assignments and a large final project required for my degree.
So, when I took my first steps in the tech industry, there was a big learning curve before I felt comfortable. I needed to understand how to join established, sometimes large, and distributed teams working on an ongoing project. I also needed to know how to communicate properly so that my efforts could be recognized.
I am not special in this regard. This is a common situation among new graduates.
## Open source gives students a head start
Since then, as an engineer and later as a manager, I have helped onboard many junior engineers. One of the things I've noticed is that the new graduates who have already contributed to open source projects could onboard quickly and start contributing faster than those without this experience.
By incorporating open source methodology into academic studies, students can gain experience relevant to the industry, learn to reuse their existing knowledge, and establish a good platform for formulating ideas and sharing knowledge. Practicing open source can make a positive impact on students' technical knowledge and experience. This can help them become more successful in bootstrapping their careers.
The value of open source methodologies in the tech industry is well-established and shapes the culture of software companies worldwide. Involvement in open source projects and adoption of the [open organization culture](https://opensource.com/open-organization/resources/open-org-definition) has become an industry standard. Companies seek fresh-minded, talented employees who know how to work in open source and cultivate its culture. Therefore, the tech industry must drive the academic world to embrace open source culture as one of the fundamental methodologies to learn in tech studies.
## Moving open source culture 'Beyond' business
When I met [Liora Milbaum](https://www.linkedin.com/in/lioramilbaum), a senior principal software engineer at Red Hat, I learned we shared an interest in bringing open source culture and principles into academics. Liora had previously founded [DevOps Loft](https://www.devopsloft.io/), in which she shared DevOps practices with people interested in stepping into this world, and wished to start a similar initiative to teach open source to university students. We decided to launch the [Beyond](https://research.redhat.com/blog/2020/05/24/open-source-development-course-and-devops-methodology/) program to connect future talents in the tech industry with open source culture as Red Hat practices it.
We started the Beyond program at the [Academic College of Tel Aviv-Yafo](https://www.int.mta.ac.il/), where we were warmly welcomed by the information systems faculty. We started by teaching an "Introduction to DevOps'' course to introduce elements of the DevOps tech stack. Our biggest challenge at the start was deciding how to teach what open source is. The answer was simple: by practicing it, of course. We didn't want to deliver yet another old-school academic course; rather, we wanted to expose students to industry standards.
We created a syllabus that incorporated common open source projects and tools to teach the DevOps stack. The course consisted of lectures and hands-on participation taught by engineers. The students were divided into groups, each one mentored and supported by an engineer. They practiced working in teams, sharing knowledge (both inside and outside of their groups), and collaborating effectively.
During our second course, "Open source development pillars," for students in the computer science department, we encountered another big obstacle. Two weeks after the course started, we became fully remote as the COVID pandemic hit the globe. We solved this problem by using the same remote collaboration tools with our students that we were using for our daily work at Red Hat. We were amazed at how simple and smooth the transition was.

(Irit Goihman, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Successful early outcomes
The two courses were a huge success, and we even hired one of the top students we taught. The feedback we received was amazing; the students said we positively impacted their knowledge, thinking, and soft skills. A few students were hired for their first tech job based on their open source contributions during the course.
Other academic institutions have expressed interest in adopting these courses, so we've expanded the program to another university.
I am fortunate to co-lead this successful initiative with Liora, accompanied by a team of talented engineers. Together, we are helping increase the open source community a bit more.
## Comments are closed. |
14,687 | 不同编程语言是如何完成同一件事 | https://opensource.com/article/21/4/compare-programming-languages | 2022-06-08T11:38:54 | [
"编程",
"猜数字"
] | /article-14687-1.html |
>
> 通过一个简单的小游戏比较 13 种编程语言。
>
>
>

当我开始学习一种新的编程语言时,会把重点放在定义变量、书写声明以及计算表达式,一旦对这些概念有一个大致的了解,通常就能够自己弄清剩下的部分。大多数编程语言都具有相似性,所以如果你掌握了一种编程语言,学习下一种语言的重点就是弄清楚独有的概念以及区分不同。
我喜欢写一些测试程序来帮助练习新的编程语言。其中我经常写的是一个叫做“猜数字”的小游戏,计算机选出 1 到 100 里的任一数字,然后我来猜。程序循环进行,直到猜出正确数字。通过伪代码可以看出,这是个非常简单的程序:
* 计算机在 1 到 100 之间选出一个随机数字
* 循环进行直到猜出该随机数字
+ 计算机读取我的猜测
+ 告诉我我的猜测过高还是过低
我们发表了一些文章,用不同的语言写这个程序。这是一个比较不同语言做同样事情的有趣机会。大多数编程语言具有相似性,所以当你在学习下一种新的编程语言时,主要是学习它的独特之处。
C 语言由 Dennis Ritchie 于 1972 年在贝尔实验室创建,是一种早期的通用编程语言。C 语言非常受欢迎,并迅速成为 Unix 系统上的标准编程语言。正是因为它的流行,许多其他编程语言也采用了类似的编程语法。这就是为什么如果你已经知道如何使用 C 语言编程,学习 C++、Rust、Java、Groovy、JavaScript、awk 或 Lua 会更容易。
接下来我们看看这些不同的编程语言是如何实现 “猜数字” 游戏的主要步骤。我将把重点放在基本元素的相似或不同,跳过一些外围代码,如分配临时变量。
### 计算机在 1 到 100 之间选出一个随机数字
你可以看到这里有许多相似之处。大多数编程语言使用类似 `rand()` 的函数,你可以设定一个范围来生成随机数。而其他一些语言使用一个特殊的函数来设定范围生成随机数。
C:
```
// Using the Linux `getrandom` system call
getrandom(&randval, sizeof(int), GRND_NONBLOCK);
number = randval % maxval + 1;
// Using the standard C library
number = rand() % 100 + 1;
```
C++:
```
int number = rand() % 100+1;
```
Rust:
```
let random = rng.gen_range(1..101);
```
Java:
```
private static final int NUMBER = r.nextInt(100) + 1;
```
Groovy:
```
int randomNumber = (new Random()).nextInt(100) + 1
```
JavaScript:
```
const randomNumber = Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1
```
awk:
```
randomNumber = int(rand() * 100) + 1
```
Lua:
```
number = math.random(1,100)
```
### 循环进行直到我猜出该随机数字
循环通常是用控制流程来实现的,如 `while` 或 `do-while`。JavaScript 中的实现没有使用循环,而是 “实时 ”更新 HTML 页面,直到用户猜出正确的数字。Awk 虽然支持循环,但是通过循环读取输入信息是没有意义的,因为 Awk 是基于数据管道的,所以它从文件而不是直接从用户读取输入信息。
C:
```
do {
…
} while (guess != number);
```
C++:
```
do {
…
} while ( number != guess );
```
Rust:
```
for line in std::io::stdin().lock().lines() {
…
break;
}
```
Java:
```
while ( guess != NUMBER ) {
…
}
```
Groovy:
```
while ( … ) {
…
break;
}
```
Lua:
```
while ( player.guess ~= number ) do
…
end
```
### 计算机读取我的猜测
不同编程语言对输入的处理方式不同。例如,JavaScript 直接从 HTML 表单中读取数值,而 Awk 则从数据管道中读取数据。
C:
```
scanf("%d", &guess);
```
C++:
```
cin >> guess;
```
Rust:
```
let parsed = line.ok().as_deref().map(str::parse::<i64>);
if let Some(Ok(guess)) = parsed {
…
}
```
Java:
```
guess = player.nextInt();
```
Groovy:
```
response = reader.readLine()
int guess = response as Integer
```
JavaScript:
```
let myGuess = guess.value
```
Awk:
```
guess = int($0)
```
Lua:
```
player.answer = io.read()
player.guess = tonumber(player.answer)
```
### 告诉我猜测过高还是过低
在这些类 C 语言中,通常是通过 `if` 语句进行比较的。每种编程语言打印输出的方式有一些变化,但打印语句在每个样本中都是可识别的。
C:
```
if (guess < number) {
puts("Too low");
}
else if (guess > number) {
puts("Too high");
}
…
puts("That's right!");
```
C++:
```
if ( guess > number) { cout << "Too high.\n" << endl; }
else if ( guess < number ) { cout << "Too low.\n" << endl; }
else {
cout << "That's right!\n" << endl;
exit(0);
}
```
Rust:
```
_ if guess < random => println!("Too low"),
_ if guess > random => println!("Too high"),
_ => {
println!("That's right");
break;
}
```
Java:
```
if ( guess > NUMBER ) {
System.out.println("Too high");
} else if ( guess < NUMBER ) {
System.out.println("Too low");
} else {
System.out.println("That's right!");
System.exit(0);
}
```
Groovy:
```
if (guess < randomNumber)
print 'too low, try again: '
else if (guess > randomNumber)
print 'too high, try again: '
else {
println "that's right"
break
}
```
JavaScript:
```
if (myGuess === randomNumber) {
feedback.textContent = "You got it right!"
} else if (myGuess > randomNumber) {
feedback.textContent = "Your guess was " + myGuess + ". That's too high. Try Again!"
} else if (myGuess < randomNumber) {
feedback.textContent = "Your guess was " + myGuess + ". That's too low. Try Again!"
}
```
Awk:
```
if (guess < randomNumber) {
printf "too low, try again:"
} else if (guess > randomNumber) {
printf "too high, try again:"
} else {
printf "that's right\n"
exit
}
```
Lua:
```
if ( player.guess > number ) then
print("Too high")
elseif ( player.guess < number) then
print("Too low")
else
print("That's right!")
os.exit()
end
```
### 非类 C 编程语言会怎么样呢?
非类 C 编程语言会有很大的不同,需要学习特定的语法来完成每一步。Racket 源于 Lisp 和 Scheme,所以它使用 Lisp 的前缀符和大量括号。Python 使用空格而不是括号来表示循环之类的块。Elixir 是一种函数式编程语言,有自己的语法。Bash 是基于 Unix 系统中的 Bourne shell,它本身借鉴了 Algol68,并支持额外的速记符,如 `&&` 作为 `and` 的变体。Fortran 是在使用打孔卡片输入代码的时期创建的,所以它依赖于一些重要列的 80 列布局。
我将通过比较 `if` 语句,举例表现这些编程语言的不同。`if` 判断一个值是否小于或大于另一个值,并向用户打印适当信息。
Racket:
```
(cond [(> number guess) (displayln "Too low") (inquire-user number)]
[(< number guess) (displayln "Too high") (inquire-user number)]
[else (displayln "Correct!")]))
```
Python:
```
if guess < random:
print("Too low")
elif guess > random:
print("Too high")
else:
print("That's right!")
```
Elixir:
```
cond do
guess < num ->
IO.puts "Too low!"
guess_loop(num)
guess > num ->
IO.puts "Too high!"
guess_loop(num)
true ->
IO.puts "That's right!"
end
```
Bash:
```
[ "0$guess" -lt $number ] && echo "Too low"
[ "0$guess" -gt $number ] && echo "Too high"
```
Fortran:
```
IF (GUESS.LT.NUMBER) THEN
PRINT *, 'TOO LOW'
ELSE IF (GUESS.GT.NUMBER) THEN
PRINT *, 'TOO HIGH'
ENDIF
```
### 更多
当你在学习一种新的编程语言时 “猜数字” 游戏是一个很友好的入门程序,通过一种简单的方式练习了几个常见的编程概念。通过不同编程语言实现这个简单游戏,你可以理解一些核心概念和每种语言的细节。
学习如何用 C 和类 C 语言编写 “猜数字” 游戏:
* [C](https://opensource.com/article/21/1/learn-c), Jim Hall
* [C++](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/learn-c-game), Seth Kenlon
* [Rust](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/learn-rust), Moshe Zadka
* [Java](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/learn-java), Seth Kenlon
* [Groovy](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/groovy), Chris Hermansen
* [JavaScript](https://opensource.com/article/21/1/learn-javascript), Mandy Kendall
* [awk](https://opensource.com/article/21/1/learn-awk), Chris Hermansen
* [Lua](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/lua-guess-number-game), Seth Kenlon
其他语言:
* [Racket](https://opensource.com/article/21/1/racket-guess-number), Cristiano L. Fontana
* [Python](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/learn-python), Moshe Zadka
* [Elixir](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/elixir), Moshe Zadka
* [Bash](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/learn-bash), Jim Hall
* [Fortran](https://opensource.com/article/21/1/fortran), Jim Hall
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/4/compare-programming-languages>
作者:[Jim Hall](https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[VeryZZJ](https://github.com/VeryZZJ) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,689 | 机器学习:使用 Python 进行预测 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/using-a-machine-learning-model-to-make-predictions/ | 2022-06-09T08:52:07 | [
"机器学习"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14689-1.html |
>
> 机器学习基本上是人工智能的一个子集,它使用以前存在的数据对新数据进行预测。
>
>
>
当然,现在我们所有人都知道这个道理了!这篇文章展示了如何将 Python 中开发的机器学习模型作为 Java 代码的一部分来进行预测。

本文假设你熟悉基本的开发技巧并理解机器学习。我们将从训练我们的模型开始,然后在 Python 中制作一个机器学习模型。
我以一个洪水预测模型为例。首先,导入以下库:
```
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
```
当我们成功地导入了这些库,我们就需要输入数据集,如下面的代码所示。为了预测洪水,我使用的是河流水位数据集。
```
from google.colab import files
uploaded = files.upload()
for fn in uploaded.keys():
print('User uploaded file "{name}" with length {length} bytes'.format(name=fn, length=len(uploaded[fn])))
```
如果没有选择文件的话,选择上传的文件。
只有在当前浏览器会话中执行了该单元格时,上传部件才可用。请重新运行此单元,上传文件 `Hoppers Crossing-Hourly-River-Level.csv`,大小 2207036 字节。
完成后,我们就可以使用 `sklearn` 库来训练我们的模型。为此,我们首先需要导入该库和算法模型,如图 1 所示。

```
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
regressor = LinearRegression()
regressor.fit(X_train, y_train)
```
完成后,我们就训练好了我们的模型,现在可以进行预测了,如图 2 所示。

### 在 Java 中使用 ML 模型
我们现在需要做的是把 ML 模型转换成一个可以被 Java 程序使用的模型。有一个叫做 `sklearn2pmml` 的库可以帮助我们做到这一点:
```
# Install the library
pip install sklearn2pmml
```
库安装完毕后,我们就可以转换我们已经训练好的模型,如下图所示:
```
sklearn2pmml(pipeline, ‘model.pmml’, with_repr = True)
```
这就完成了!我们现在可以在我们的 Java 代码中使用生成的 `model.pmml` 文件来进行预测。请试一试吧!
(LCTT 译注:Java 中有第三方库 [jpmml/jpmml-evaluator](https://github.com/jpmml/jpmml-evaluator),它能帮助你使用生成的 `model.pmml` 进行预测。)
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/using-a-machine-learning-model-to-make-predictions/>
作者:[Jishnu Saurav Mittapalli](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/jishnu-saurav-mittapalli/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Machine learning is basically a subset of artificial intelligence that uses previously existing data to make a prediction on new data. Of course, all of us know this by now! This article demonstrates how a machine learning model developed in Python can be used as a part of a Java code to make predictions.*
This article assumes you are familiar with the basic development skills and understanding of machine learning. We will start with training our model, and then make a machine learning model in Python.
This article assumes you are familiar with the basic development skills and understanding of machine learning. We will start with training our model, and then make a machine learning model in Python.
I am taking the example of a flood prediction model. First, import the following libraries:
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Once we have successfully imported the libraries, we need to take in the data sets, as shown in the code below. To predict floods, I am using the river level data set.
from google.colab import files uploaded = files.upload() for fn in uploaded.keys(): print(‘User uploaded file “{name}” with length {length} bytes’.format( name=fn, length=len(uploaded[fn]))) Choose files No file chosen
The upload widget is only available when the cell has been executed in the current browser session. Please rerun this cell to enable* Saving Hoppers Crossing-Hourly-River-Level.csv to Hoppers Crossing-Hourly-River-Level.csv User uploaded file “Hoppers Crossing-Hourly-River-Level.csv”* with length 2207036 bytes.
Once this is done, we can train our model using the *sklearn library*. For this, we first need to import the library and the algorithm model, as shown in Figure 1.
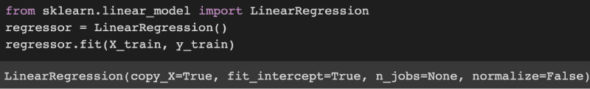

from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression regressor = LinearRegression() regressor.fit(X_train, y_train)
Once that is done we have trained our model, and it’s now ready to make predictions, as shown in Figure 2.
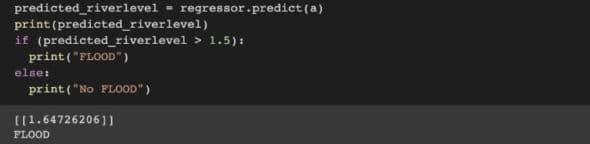

**Using ML model in Java**
What we need to do now is to convert the ML model into a model that can be used by a Java program. There is a library called sklearn2pmml that helps us do this:
Install the library, pip install sklearn2pmml
Once the library is installed we can convert our already trained model, as shown below:
sklearn2pmml(pipeline, ‘model.pmml’, with_repr = True)
This is it! We can now use the generated model.pmml file in our Java code to make predictions. Do try it out! |
14,690 | 编译代码时动态地链接库 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/compile-code-ldlibrarypath | 2022-06-09T09:46:35 | [
"动态库",
"编译"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14690-1.html | 
>
> 编译软件在你如何运行你的系统方面给你很大的灵活性。`LD_LIBRARY_PATH` 变量,以及 GCC 的 `-L` 和 `-l` 选项,是这种灵活性的组成部分。
>
>
>
编译软件是开发者经常做的事情,在开源世界中,一些用户甚至选择自己动手。Linux 播客 Dann Washko 称源码为“通用包格式”,因为它包含了使一个应用在任何平台上运行所需的所有组件。当然,并不是所有的源码都是为所有的系统编写的,所以它只是在目标系统的子集内是“通用”的,但问题是,源码是非常灵活的。有了开源,你可以决定代码的编译和运行方式。
当你在编译代码时,你通常要处理多个源文件。开发人员倾向于将不同的类或模块放在不同的文件中,这样它们可以被单独维护,甚至可能被不同的项目使用。但当你编译这些文件时,许多文件会被编译成一个可执行文件。
这通常是通过创建共享库来完成的,然后从可执行文件中动态链接回它们。这样可以通过保持模块化功能的外部性来保持可执行文件的小型化,并确保库可以独立于使用它们的应用而被更新。
### 在编译过程中定位一个共享对象
当你 [用 GCC 编译](https://opensource.com/article/22/5/what-happens-behind-scenes-during-gcc-compilation-c-programs) 时,你通常需要在你的工作站上安装一个库,以便 GCC 能够定位到它。默认情况下,GCC 假定库在系统库路径中,例如 `/lib64` 和 `/usr/lib64`。然而,如果你要链接到一个你自己的尚未安装的库,或者你需要链接到一个没有安装在标准位置的库,那么你必须帮助 GCC 找到这些文件。
有两个选项对于在 GCC 中寻找库很重要:
* `-L`(大写字母 L)在 GCC 的搜索位置上增加一个额外的库路径。
* `-l`(小写字母 L)设置你要链接的库的名字。
例如,假设你写了一个叫做 `libexample.so` 的库,并且你想在编译你的应用 `demo.c` 时使用它。首先,从 `demo.c` 创建一个对象文件:
```
$ gcc -I ./include -c src/demo.c
```
`-I` 选项在 GCC 搜索头文件的路径中增加了一个目录。在这个例子中,我假设自定义头文件在一个名为 `include` 的本地目录中。`-c` 选项防止 GCC 运行链接器,因为这个任务只是为了创建一个对象文件。结果如下:
```
$ ls
demo.o include/ lib/ src/
```
现在你可以使用 `-L` 选项为你的库设置一个路径,然后进行编译:
```
$ gcc -L`pwd`/lib -o myDemo demo.o -lexample
```
注意,`-L` 选项在 `-l` 选项*之前*。这很重要,因为如果在你告诉 GCC 查找非默认库之前没有将 `-L` 添加到 GCC 的搜索路径中,GCC 就不知道要在你的自定义位置上搜索。编译成功了,但当你试图运行它时,却出现了问题:
```
$ ./myDemo
./myDemo: error while loading shared libraries:
libexample.so: cannot open shared object file:
No such file or directory
```
### 用 ldd 排除故障
`ldd` 工具可以打印出共享对象的依赖关系,它在排除类似问题时很有用:
```
$ ldd ./myDemo
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007ffe151df000)
libexample.so => not found
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007f514b60a000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f514b839000)
```
你已经知道定位不到 `libexample`,但 `ldd` 输出至少确认了它对*工作*库的期望位置。例如,`libc.so.6`已经被定位,`ldd` 显示其完整路径。
### LD\_LIBRARY\_PATH
`LD_LIBRARY_PATH` [环境变量](https://opensource.com/article/19/8/what-are-environment-variables) 定义了库的路径。如果你正在运行一个依赖于没有安装到标准目录的库的应用程,你可以使用 `LD_LIBRARY_PATH` 添加到系统的库搜索路径。
有几种设置环境变量的方法,但最灵活的是在运行命令前放置环境变量。看看设置 `LD_LIBRARY_PATH` 对 `ldd` 命令在分析一个“损坏”的可执行文件时的作用:
```
$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=`pwd`/lib ldd ./
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007ffe515bb000)
libexample.so => /tmp/Demo/lib/libexample.so (0x0000...
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007eff037ee000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007eff03a22000)
```
这也同样适用于你的自定义命令:
```
$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=`pwd`/lib myDemo
hello world!
```
然而,如果你移动库文件或可执行文件,它又会失效:
```
$ mv lib/libexample.so ~/.local/lib64
$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=`pwd`/lib myDemo
./myDemo: error while loading shared libraries...
```
要修复它,你必须调整 `LD_LIBRARY_PATH` 以匹配库的新位置:
```
$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=~/.local/lib64 myDemo
hello world!
```
### 何时使用 LD\_LIBRARY\_PATH
在大多数情况下,`LD_LIBRARY_PATH` 不是你需要设置的变量。按照设计,库安装到 `/usr/lib64` 中,因此应用自然会在其中搜索所需的库。在两种情况下,你可能需要使用 `LD_LIBRARY_PATH`:
* 你正在编译的软件需要链接到本身刚刚编译但尚未安装的库。良好设计的构建系统,例如 [Autotools](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/introduction-gnu-autotools) 和 [CMake](https://opensource.com/article/21/5/cmake),可以帮助处理这个问题。
* 你正在使用设计为在单个目录之外运行的软件,它没有安装脚本,或安装脚本将库放置在非标准目录中。一些应用具有 Linux 用户可以下载、复制到 `/opt` 并在“不安装”的情况下运行的版本。`LD_PATH_LIBRARY` 变量是通过封装脚本设置的,因此用户通常甚至不知道它已被设置。
编译软件为你在运行系统方面提供了很大的灵活性。`LD_LIBRARY_PATH` 变量以及 `-L` 和 `-l` GCC 选项是这种灵活性的组成部分。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/compile-code-ldlibrarypath>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Compiling software is something that developers do a lot, and in open source some users even choose to do it themselves. Linux podcaster Dann Washko calls source code the "universal package format" because it contains all the components necessary to make an application run on any platform. Of course, not all source code is written for all systems, so it's only "universal" within the subset of targeted systems, but the point is that source code is extremely flexible. With open source, you can decide how code is compiled and run.
When you're compiling code, you're usually dealing with multiple source files. Developers tend to keep different classes or modules in separate files so that they can be maintained separately, and possibly even used by different projects. But when you're compiling these files, many of them get compiled into a single executable.
This is usually done by creating shared libraries, and then dynamically linking back to them from the executable. This keeps the executable small by keeping modular functions external, and ensures that libraries can be updated independently of the applications that use them.
## Locating a shared object during compilation
When you're [compiling with GCC](https://opensource.com/article/22/5/what-happens-behind-scenes-during-gcc-compilation-c-programs), you usually need a library to be installed on your workstation for GCC to be able to locate it. By default, GCC assumes that libraries are in a system library path, such as `/lib64`
and `/usr/lib64`
. However, if you're linking to a library of your own that's not yet installed, or if you need to link to a library that's not installed in a standard location, then you have to help GCC find the files.
There are two options significant for finding libraries in GCC:
`-L`
(capital L) adds an additional library path to GCC's search locations.`-l`
(lowercase L) sets the name of the library you want to link against.
For example, suppose you've written a library called `libexample.so`
, and you want to use it when compiling your application `demo.c`
. First, create an object file from `demo.c`
:
```
````$ gcc -I ./include -c src/demo.c`
The `-I`
option adds a directory to GCC's search path for header files. In this example, I assume that custom header files are in a local directory called `include`
. The `-c`
option prevents GCC from running a linker, because this task is only to create an object file. And that's exactly what happens:
```
``````
$ ls
demo.o include/ lib/ src/
```
Now you can use the `-L`
option to set a path for your library, and compile:
```
````$ gcc -L`pwd`/lib -o myDemo demo.o -lexample`
Notice that the `-L`
option comes *before* the `-l`
option. This is significant, because if `-L`
hasn't been added to GCC's search path before you tell GCC to look for a non-default library, GCC won't know to search in your custom location. The compilation succeeds as expected, but there's a problem when you attempt to run it:
```
``````
$ ./myDemo
./myDemo: error while loading shared libraries:
libexample.so: cannot open shared object file:
No such file or directory
```
## Troubleshooting with ldd
The `ldd`
utility prints shared object dependencies, and it can be useful when troubleshooting issues like this:
```
``````
$ ldd ./myDemo
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007ffe151df000)
libexample.so => not found
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007f514b60a000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f514b839000)
```
You already knew that `libexample`
couldn't be located, but the `ldd`
output at least affirms what's expected from a *working* library. For instance, `libc.so.6`
has been located, and `ldd`
displays its full path.
## LD_LIBRARY_PATH
The `LD_LIBRARY_PATH`
[environment variable](https://opensource.com/article/19/8/what-are-environment-variables) defines the path to libraries. If you're running an application that relies on a library that's not installed to a standard directory, you can add to the system's library search path using `LD_LIBRARY_PATH`
.
There are several ways to set environment variables, but the most flexible is to place them before you run a command. Look at what setting `LD_LIBRARY_PATH`
does for the `ldd`
command when it's analyzing a "broken" executable:
```
``````
$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=`pwd`/lib ldd ./
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007ffe515bb000)
libexample.so => /tmp/Demo/lib/libexample.so (0x0000...
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007eff037ee000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007eff03a22000)
```
It applies just as well to your custom command:
```
``````
$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=`pwd`/lib myDemo
hello world!
```
If you move the library file or the executable, however, it breaks again:
```
``````
$ mv lib/libexample.so ~/.local/lib64
$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=`pwd`/lib myDemo
./myDemo: error while loading shared libraries...
```
To fix it, you must adjust the `LD_LIBRARY_PATH`
to match the library's new location:
```
``````
$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=~/.local/lib64 myDemo
hello world!
```
## When to use LD_LIBRARY_PATH
In most cases, `LD_LIBRARY_PATH`
isn't a variable you need to set. By design, libraries are installed to `/usr/lib64`
and so applications naturally search it for their required libraries. You may need to use `LD_LIBRARY_PATH`
in two cases:
- You're compiling software that needs to link against a library that itself has just been compiled and has not yet been installed. Good build systems, such as
[Autotools](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/introduction-gnu-autotools)and[CMake](https://opensource.com/article/21/5/cmake), can help handle this. - You're bundling software that's designed to run out of a single directory, with no install script or an install script that places libraries in non-standard directories. Several applications have releases that a Linux user can download, copy to
`/opt`
, and run with "no install." The`LD_PATH_LIBRARY`
variable gets set through wrapper scripts so the user often isn't even aware it's been set.
Compiling software gives you a lot of flexibility in how you run your system. The `LD_LIBRARY_PATH`
variable, along with the `-L`
and `-l`
GCC options, are components of that flexibility.
## Comments are closed. |
14,692 | Linux 内核 5.19 RC1 发布,完成了 ARM 通用内核的工作 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/06/linux-kernel-5-19-rc1/ | 2022-06-10T10:04:04 | [
"内核"
] | /article-14692-1.html | 
>
> Linus Torvalds 发布了用来测试的 Linux 内核 5.19 RC1,带来了一些重大变化。
>
>
>
继上个月 [Linux 内核 5.18](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/linux-kernel-5-18/) 发布之后,Linus Torvalds 宣布了 Linux 内核 5.19 系列第一个候选版本。与此同时,Linux 内核 5.19 官方合并窗口关闭,这意味着除非是关键性的,否则不会再接受任何新功能。
简单看一下 Linux 内核 5.19 的新内容,会发现 CPU、GPU、网络、存储和核心模块都有常规的更新。此外,代码清理、淘汰过时硬件和对以后芯片组的持续支持是此版本的亮点。
在进一步介绍之前,让我们简单来看一下这些新特性。
### Linux 内核 5.19(RC1)的新特性
#### CPU
首先需要提及的是,Linux 内核 5.19 开始 [初步支持](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/commit/?id=c6f2f3e2c80e975804360665d973211e4d9390cb) 龙芯架构的 CPU 系列。龙芯由中国龙芯中科公司设计开发。龙芯架构的 CPU 是兼容 MIPS 架构的通用微处理器。不过虽然现在提供了支持,但是你仍不能在龙芯 CPU 上启动 Linux,因为一些代码还在审核中。希望在 5.20 版本中能够使用。
新的 [英特尔 IFS 驱动](https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/[email protected]/) 在该版本中落地,这有助于在部署前后发现硬件问题。它能够在早期阶段检测电路层面的 CPU 错误。
在前几个针对英特尔 CPU 的内核版本中一直在对电源管理和散热方面进行开发,[这个版本](https://lore.kernel.org/linux-acpi/CAJZ5v0hKBt3js65w18iKxzWoN5QuEc84_2xcM6paSv-ZHwe3Rw@mail.gmail.com/) 也不例外。首先,为 Raptor 和 Alder Lake 家族添加了英特尔 <ruby> 运行时平均功率限制 <rt> Run-Time Average Power Limiting </rt></ruby>(RAPL)的支持。其次,改进了 P-state 驱动以处理频率变化,并且基于 CPU 的缩放支持被添加到被动 devfreq 中。
虽然英特尔 CPU 主要是散热和电源管理方面的工作,但对 AMD CPU 系列来说有更多的性能更新。首先,计划在今年年底完成 ZMD Zen 4 CPU 的 <ruby> 基于指令的采样 <rt> Instruction-Based Sampling </rt></ruby>(IBS)模块引入了更多更新。此外,此版本引入了 PerfMonV2,提供了更多性能监视能力。
此外,该版本中移除了 a.out 支持。同样,过时的 Renesas H8/300 CPU 也被移除了。
#### 主要 ARM 更新
终于,主线 Linux 内核能够 [支持 ARM 多平台](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/commit/?id=ecf0aa5317b0ad6bb015128a5b763c954fd58708) 了。在 Linus 的 RC1 开场白中可以看到,这是该版本中的巨大改变!从 Linux 3.7 开始,跨越了十多年的工作,这是多么漫长的过程。

#### 图形和存储升级
存储子系统在各种流行的文件系统中都有性能提升。最主要的变化包括苹果 M1 NVMe 控制器支持和对 XFS 文件系统的更好支持。此外,Btrfs、F2FS 以及 exFAT 文件系统也有增强。
在代码行数方面,有一个令人兴奋的指标是仅是图形驱动程序 Linux 内核 5.19 就增加了大约[50 万行代码](https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/CAPM=9tw62EZfAm0PbiOPmMrpfR98QMFTWGEQcA34G4ap4xxNkA@mail.gmail.com/)。它包括 AMD 的 RDNA、CDNA,英特尔的 Raptor Lake、DG2/Alchemist 等图形驱动更新。
#### 重要的网络变化
鉴于数据传输大幅增长,对 Big TCP 的支持有助于支持数据中心 400 GBit 级别的流量。它还可以在高性能网络环境中降低延迟。
继续改进了 <ruby> 多路径 TCP <rt> Multi-Path TCP </rt></ruby>(MPTCP)。此外,高通 ath11k WiFi 驱动程序在此版本中添加了网络唤醒功能。同样增加了对瑞昱的 8852ce 芯片、联发科的 T700 调制解调器以及瑞萨科技的 RZ/V2M 的支持。
#### 其他值得注意的功能
首先,内核中著名的随机函数生成器(RNG)在此版本中 [继续](https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/[email protected]/T/#u) 改进。
其次,著名的新兴的 Framework 模块化笔记本电脑获得了此版本 Chrome OS EC 驱动支持。Framework 笔记本现在可以作为一个非 Chromebook 设备利用 ChromeOS 的嵌入式控制器。
此外,Wacom 绘画板以及其他相关设备也有众多更新。[包括](https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/[email protected]/) 对联想 Thinkpad TrackPoint II、谷歌 Whiskers Touchpad、联想 X12 TrackPoint 等设备支持的提升。
### Linux 内核 5.19 下载
如果你想要测试并尝试该候选版本,可以在 [这里](https://www.kernel.org/) 下载。
预计在 2022 年 7 月左右最终版本发布前,将会有多个版本更迭。
参考自:[内核邮件列表](https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/CAHk-=wgZt-YDSKfdyES2p6A_KJoG8DwQ0mb9CeS8jZYp+0Y2Rw@mail.gmail.com/T/#u)
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/06/linux-kernel-5-19-rc1/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,693 | 值得尝试的六款 Linux 文字处理程序 | https://opensource.com/article/22/6/word-processors-linux | 2022-06-10T12:00:00 | [
"文字处理"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14693-1.html |
>
> 选择一款最中意的文字处理程序把你的想法打印到纸上。
>
>
>

作家们总是在寻找更好的方法将他们的文字和想法以更好的方式呈现给他们的读者。我对文字处理程序最早的印象是在 Apple II 上使用 AppleWorks 和后来的 FrEDWriter,后者是一个创建于 1985 年的免费文字处理程序。这是我的学生们的标配,他们许多人来自没有钱购买专有软件的家庭。
### Abiword
在 20 世纪 90 年代时,我开始使用 Linux,寻找我可以使用的高质量的写作程序,并推荐给跟随我进入开源软件世界的学生们。我首先接触的文字处理程序是 [AbiWord](https://www.abisource.com/)。AbiWord 来自西班牙语 Abierto,意思是“开放”。它最早发布于 1998 年,并且之后一直在升级。它使用 GPLv2 开源协议。它支持列表、缩进,字符格式等基本功能,支持 .doc、.html、.docx、.odt 等多种格式文件的导入和导出。

### Etherpad
[Etherpad](https://etherpad.org/#) 是一个开源协作编辑项目。它可以让你像 Google Drive 那样实时编辑文档,主要的区别是它是完全开源的。据它的网站上介绍,你可以“与你的朋友、同学或同事一起写文章、新闻稿、待办事项,同时在同一个文件上工作”。其源代码可随时查看。Etherpad 采用 Apache 2.0 开源协议。你可以直接在线使用它,或者把它下载并 [安装](https://github.com/ether/etherpad-lite#installation) 到你的 Linux 电脑上。
### Cryptpad
[CryptPad](https://cryptpad.fr/what-is-cryptpad.html) 是一个端到端加密的写作套件。使用 GPLv3 开源协议,并且源代码公开在 [GitHub](https://github.com/xwiki-labs/cryptpad) 上。它由 [Xwiki](https://github.com/xwiki-labs) 实验室开发。可替代 Google Drive,并且是自主托管的。根据其网站描述,“CryptPad 旨在实现协作办公。实时同步文档的更改。由于所有数据都已加密,因此该服务及其管理员无法查看正在编辑和存储的内容。” Cryptpad 为用户提供了 [丰富的文档](https://docs.cryptpad.fr/en/user_guide/index.html)。
### Focuswriter
[FocusWriter](https://gottcode.org/focuswriter/) 是一个简单的免干扰的编辑器。它使用隐藏式界面,鼠标移动到屏幕边界时才显示界面。它使用 GPLv3 开源协议,并为 Linux 提供了 Flatpak 软件包,也为 [Ubuntu](https://packages.ubuntu.com/jammy/focuswriter) 和 [Fedora](https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/focuswriter) 提供了 DEB 和 RPM。下图是一个 FocusWriter 桌面的例子。这是一个非常简单直观的界面,菜单自动隐藏,当鼠标指向屏幕顶部或边缘时才会显示。文件默认保存为 .odt 格式,也支持纯文本、.docx 和富文本。

### LibreOffice Writer
[LibreOffice Writer](https://www.libreoffice.org/discover/writer/) 是我最喜欢的,我已经使用了十多年了。它拥有我需要的所有特性,包括富文本格式化。它还拥有我见过的最多的导入、导出方式。类似于 [APA](https://extensions.libreoffice.org/en/extensions/show/apa-style-paper-template) 这样的问卷和出版模板它拥有十多种。我最喜欢的是它可以将文件导出为 PDF 和 epub。 LibreOffice Writer 是一个自由软件,使用 Mozilla 公开许可证(MPL)2.0 开源协议。其 [源代码](https://www.libreoffice.org/about-us/source-code/) 由文档基金会提供。LibreOffice 支持大多数 Linux 发行版。同时它也提供 Flatpak、Snap 和 AppImage 软件包。另外,你也可以把它下载并安装到 MacOS 和 Windows 上。

### OpenOffice Writer
Apache [OpenOffice Writer](https://www.openoffice.org/product/writer.html) 是一个全功能的文字处理程序。它可以简单地用于备忘录,也可以复杂到足以编写你的第一本书。依据官网的描述,OpenOffice Writer 将文档自动保存为 .odt。它还支持将文档保存为 .doc、.docx、富文本和其他格式。OpenOffice Writer 使用 Apache 许可证 2.0 开源协议。源代码在 [GitHub](https://github.com/apache/openoffice) 上公开。
还有许多自由开源软件等着大家去发现。它们非常适合完成你的日常任务,你也可以为它们的发展做出贡献。你最喜欢的 Linux 文字处理器程序是什么呢?
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/6/word-processors-linux>
作者:[Don Watkins](https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[duoluoxiaosheng](https://github.com/duoluoxiaosheng) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Writers are always looking for better ways to put their words and ideas into readable formats to share with their readers. My first experiences with word processing came in my Apple II days when I used AppleWorks and later FrEDWriter, which was a free word processing application created in 1985. It was the standard for my students, many of whom came from households that lacked the money to purchase proprietary software.
## Abiword
When I made the switch to Linux in the late 1990's, I was looking for high quality writing software that I could use and recommend to students who chose to follow my lead in the world of open source software. The first word processor I became familiar with was [AbiWord](https://www.abisource.com/). The name AbiWord is derived from the Spanish word, abierto, which means open. It was Initially released in 1998 and it has been under continuous development. It is licensed as GPLv2. It supports basic word processing such as lists, indents and character formats. It supports a variety of import and export file formats including `.doc`
, `.html`
, `.docx`
, and `.odt`
.
(Don Watkins, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Etherpad
[Etherpad](https://etherpad.org/#) is an open source group editing project. It allows you to edit documents in real time much like Google Drive. The main difference is that it is entirely open source. According to their website you can, "write articles, press releases, to-do lists, together with your friends, fellow students or colleagues, all working on the same document at the same time." The source code is readily available to look at. Etherpad is licensed as Apache 2.0. You can use Etherpad in the cloud or download and [install](https://github.com/ether/etherpad-lite#installation) it on your own Linux computer.
## Cryptpad
[CryptPad](https://cryptpad.fr/what-is-cryptpad.html) is a collaboration suite that is end-to-end encrypted. It is licensed with GPLv3 and its source code is available on [GitHub](https://github.com/xwiki-labs/cryptpad). It was developed by [Xwiki](https://github.com/xwiki-labs) Labs. It is an alternative to Google Drive and is self hosted. According to their website, "CryptPad is built to enable collaboration. It synchronizes changes to documents in real time. Because all data is encrypted, the service and its administrators have no way of seeing the content being edited and stored.” Cryptpad offers extensive [documentation](https://docs.cryptpad.fr/en/user_guide/index.html) for users.
## Focuswriter
[FocusWriter](https://gottcode.org/focuswriter/) is a simple distraction free editor. It uses a hideaway interface that you access by moving your mouse to the edges of the screen. It is licensed with GPLv3 and it's available on Linux with Flatpak,via DEB on [Ubuntu](https://packages.ubuntu.com/jammy/focuswriter), and RPM on [Fedora](https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/focuswriter). This is an example of the FocusWriter desktop. A very simple and intuitive interface where the menu automatically hides until you move your mouse pointer to the top or sides of the screen. Files are saved by default as an `.odt`
, but it also supports plain text, `.docx`
, and Rich text.
(Don Watkins, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## LibreOffice Writer
[LibreOffice Writer](https://www.libreoffice.org/discover/writer/) is my favorite. I have been using it for over a dozen years. It has all the features I need including formatting for rich text. It also has the largest array of import and export options I have seen in any word processor. There are dozens of templates available for specialty formats like [APA](https://extensions.libreoffice.org/en/extensions/show/apa-style-paper-template) for research and publication. I love that I can export directly to PDF and ‘epub' from any word processor. LibreOffice Writer is free software with the Mozilla Public License 2.0. The s[ource code](https://www.libreoffice.org/about-us/source-code/) for LibreOffice is from the Document Foundation. LibreOffice comes standard with most Linux distribution. It is also available as Flatpak, Snap, and AppImage. In addition, you can download and install it on MacOS and Windows.
(Don Watkins, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## OpenOffice Writer
Apache [OpenOffice Writer](https://www.openoffice.org/product/writer.html) is a complete word processor. It's simple enough for memos yet complex enough to write your first book. According to their website, OpenOffice Writer automatically saves documents in ‘open document format'. Documents can also be saved in `.doc`
, `.docx`
, Rich Text, and other formats. OpenOffice Writer is licensed with an Apache License 2.0. Source code and is available on [GitHub](https://github.com/apache/openoffice).
There is a wealth of free open source software waiting for you to discover. They are great for getting your everyday tasks done and you can also contribute to their development. What is your favorite Linux word processor application?
## 5 Comments |
14,695 | openSUSE Leap 15.4 发布版本添加了 Leap Micro 5.2、更新桌面环境等等 | https://news.itsfoss.com/opensuse-leap-15-4-release/ | 2022-06-11T11:17:34 | [
"openSUSE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14695-1.html |
>
> 为奋起直追 SUSE Linux Enterprise 的 SP 4 ,openSUSE Leap 15.4 到来了,带来了新的升级和极其重要的改善。
>
>
>

即将到来的 openSUSE 小发布版本终于来了。如果你使用 openSUSE 作为你日常使用的桌面或服务器版本,你现在可能已经测试候选版本好几周了。
openSUSE Leap 15.4 的重点是软件包的更新,用以奋起直追 SUSE Linux Enterprise 的 SP 4 。因此,你将注意到一些弃用的软件包,以及可用于替换它们的新的升级。
当然,你应该有一些可用的软件包来确保兼容性。但是,大多数较旧的版本已经被移除。
### openSUSE Leap 15.4: 有什么新的变化?
为与最新的 SUSE Linux Enterprise(SLE)相适应,像 Python 2 和 KDE 4 一样的软件包已经被移除。你可以在这次的发布版本中找到较新的桌面环境。
此外,在容器和 AI/ML 用例方面,更新了 Podman、Containerd、Tensorflow 和 Grafana。
#### Leap Micro 5.2
Leap Micro 是针对容器和虚拟化工作负载定制的轻量级操作系统的最新版本。它也是 Leap 版的 [MicroOS](https://microos.opensuse.org/),是 Tumbleweed 的一种变体,提供了自动管理和修补。
#### 桌面环境
Xfce 4.16 继续保留,但你可以找到主要功能的一些新补充,包括新图标和调色板。
Xfce 4.16 中的设置管理器也获得了视觉上的刷新。类似地,文件管理器(Thunar)也有一些改善,新的状态托盘插件的深色模式支持等等。
KDE 4 软件包已经被弃用,Plasma 5.24 LTS 已经作为长期支持版本中包含于其中。
要深入了解这些变化,你可以查看我们之前针对 [KDE Plasma 5.24 LTS](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-24-lts-release/) 的报道。总体来说,新的 KDE Plasma 体验应该会令桌面用户赞叹。
说到 GNOME,你可以发现包含在 openSUSE Leap 15.4 中的 GNOME 41 带来了一系列的改善和新的特色功能。了解更多关于 [GNOME 41](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-41-release/) 的信息,你可以期待它的一些新的特色功能。
对于其它的可用的桌面环境来说,Leap 15.4 包括:
* MATE 桌面环境 1.26
* Enlightenment 桌面环境0.25.3
* 深度桌面环境 20.3
#### 弃用的软件包
移除了一些基础的软件包,包括 Python 2(生命终结)、Digikam、TensorFlow 1.x 和 Qt 4 等软件包。
在更新系统后,你可以使用 Qt 5 和 Plasma 5 。
#### 更新的软件包
很多重要的软件包在 Leap 15.4 中得到了更新,包含一些流行的软件包:
* TensorFlow 2.6.2
* Podman 3.4.4
* GNU Health 4.0
* sudo 1.9.9
* systemd 249.10
* AppArmor 3.04
* DNF 4.10.0
* LibreOffice 7.2.5
因此,你应该会注意到一些针对服务器用户和桌面用户的各种应用程序的有用更新。很多多媒体应用程序,像 VLC、GNOME MPV 等,都得到了升级。
#### 其它改善
随着基本软件的更新和清理,你也可以找到一个由 SUSE 维护的较新的 Linux 内核 5.14.21。
更新后的内核对硬件的支持应该会有改善。
更多信息,你可以参考针对 [openSUSE Leap 15.4](https://doc.opensuse.org/release-notes/x86_64/openSUSE/Leap/15.4/#rnotes) 的发布版本说明。
>
> **[下载 openSUSE Leap 15.4](https://get.opensuse.org/leap/15.4/)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/opensuse-leap-15-4-release/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

The upcoming openSUSE minor release is finally here. If you use OpenSUSE as your daily driver for desktop or server, you might have already tested the release candidate version available for a couple of weeks now.
The openSUSE Leap 15.4 focuses on software package updates to match the SUSE Linux Enterprise 15 Service Pack 4. So, you will notice several deprecated packages, and new upgrades available to replace them.
Of course, you should have some packages available to ensure compatibility. But, most of the older ones have been removed.
## openSUSE Leap 15.4: What’s New?
To match the latest SUSE Linux Enterprise (SLE), packages like Python 2 and KDE 4 have been removed. You can find newer desktop environments with this release.
Furthermore, for containers and AI/ML use-cases, podman, containerd, Tensorflow,and Grafana have been updated.
### Leap Micro 5.2
Leap Micro is the latest version of its lightweight operating system tailored for container and virtualized workloads. It is a new offering of [MicroOS](https://microos.opensuse.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for Leap, which is a variant of Tumbleweed, providing automated administration and patching.
### Desktop Environments
Xfce 4.16 is here to stay, but you can find additions for new major features that include new icons, and palettes.
The settings manager in Xfce 4.16 also received a visual refresh. Similarly, there were some improvements to file manager (Thunar), dark mode support for a new status tray plugin, and more.
KDE 4 packages have been dropped, Plasma 5.24 LTS has been included as an LTS release.
To explore the changes, you can check out our original coverage for [KDE Plasma 5.24 LTS](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-24-lts-release/). Overall, the new KDE Plasma experience should be impressive for desktop users.
When it comes to GNOME, you can find GNOME 41 included with Leap 15.4 with a range of improvements and new features. Learn more about [GNOME 41](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-41-release/) to know what you can expect.
For other available desktop environments, Leap 15.4 includes:
- MATE 1.26
- Enlightenment 0.25.3
- Deepin Desktop Environment 20.3
### Dropped Packages
Some essential packages removed include python 2 (end of life), digikam, tensorflow 1.x, and Qt 4 packages.
You will find Qt 5 and Plasma 5 available to update the system.
### Updated Packages
Many vital packages have been updated for Leap 15.4, some of the popular ones include:
- TensorFlow 2.6.2
- podman 3.4.4
- GNU Health 4.0
- sudo 1.9.9
- systemd 249.10
- AppArmor 3.04
- DNF 4.10.0
- LibreOffice 7.2.5
So, you should notice useful upgrades for both server users and desktop users with various application updates. Many multimedia applications like VLC, and GNOME MPV have also received upgrades.
### Other Improvements
Along with essential updates, and clean-up, you can also find a newer Linux Kernel 5.14.21 maintained by SUSE.
The hardware support should see an improvement with the updated kernel.
For more information, you can refer to the release notes for [openSUSE Leap 15.4](https://doc.opensuse.org/release-notes/x86_64/openSUSE/Leap/15.4/?ref=news.itsfoss.com#rnotes).
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,696 | 隐藏功能!在 DuckDuckGo 搜索引擎中,你可以做这 25 件有趣的事情 | https://itsfoss.com/duckduckgo-easter-eggs/ | 2022-06-11T14:29:52 | [
"DuckDuckGo"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14696-1.html | 
比起无处不在的 Google,[有些搜索引擎替代品更加尊重隐私](https://itsfoss.com/privacy-search-engines/),而 DuckDuckGo 就是其中之一。
最近,这个搜索引擎有了很大的改进,搜索一般网页十分顺畅。在搜索本地地点方面,则还远不及 Google。
不过,DuckDuckGo(简称为 DDG)有一些很酷的功能,大部分用户还没注意到。如果你是一位 DDG 狂热粉,你可能会喜欢用这些小技巧来提升你的搜索体验。
### 1、跳转到特定网页
在你最喜欢的网站名称前输入 `!` 即可直接进入这个网站。则类似于 Google 的 “运气不错” 功能,但用 DDG 的话来说,这就叫 “叹号搜索”。
有一些网站有缩写形式,开始输入时便会提示。

在网站名后面输入搜索词,就可以直接抵达那个网站的搜索结果处。
### 2、文本转 ASCII
Figlet 是一个 [有趣的 Linux 命令](https://itsfoss.com/funny-linux-commands/),可以将任意文本转换为漂亮的 ASCII 画格式。
在任意搜索词前输入 `figlet`,就会显示 ASCII 输出。无需打开终端。

### 3、检查社交媒体的状态
在某个人的 Twitter 名前加上 `@`,就会显示 TA 的状态(关注者等)。

### 4、生成强密码
输入 `password` 并加上需要的字符数,就可以生成一个独特的强密码。

### 5、生成随机密码短语
输入 `random passphrase` 可生成一段密码短语,通常长度为 4 个词。

### 6、获取一份速查表
在需要看速查表的搜索词后面,可输入 `cheatsheet`。如果要搜索的东西有速查表,就会立即显示在搜索页面。

### 7、通过色码获取颜色
输入 `color` 并加上你想查的颜色的十六进制码,便可显示这个颜色。

### 8、生成随机数
搜索 `random number` 会输出一个 0 到 1 之间的随机数。

你也可以指定需要的范围。

### 9、转换为二进制等形式
输入一个二进制数并加上 `binary`,可将其从二进制转换为十进制。

类似地,它也能用于十六进制和八进制,但我不清楚它们的处理逻辑。
### 10、寻找韵词
输入 `what rhymes with` 并带上要找同韵词的词语。作诗能力变强了,对吧?

### 11、获取拉马努金数、圆周率等常数
输入想获取数值的常数名,便可在搜索结果中看到它。

### 12、查询现在谁在太空中
输入 `people in space` 获取当前在太空中的人员名单。同时还会显示他们在太空中居住的时间。

### 13、查询网页是否无法访问
如果你想知道某个网站是你无法访问了,还是大家都无法访问了,只需在搜索词中输入 `is xyz.com down`。

### 14、获取特定话题的名言
输入一个词并带上 `quotes`,就会显示与这个词相关的名言。

### 15、获取占位文本
搜索 `lorem ipsum` 就可以获取 5 段占位文本。对 Web 开发者应该会有用。

### 16、获取任意月份的日历
在年、月、日后面输入 `calendar`,就会为你显示该月份的交互式日历。

### 17、生成二维码
在文字、链接等后面输入 `qr`,就会生成对应的二维码。

### 18、获取一些 CSS 动画
搜索 `css animations` 以获取一些 CSS 动画例子。

### 19、展开短链接
如果有一个 Bitly 链接或其他短链接,但不确定它指向哪里,不必再跳转到充满垃圾信息的网页了,只需展开短链接,看看真正的网址。
在短链接后面输入关键词 `expand`,就会显示真正的目标 URL。

### 20、获取特殊字符的 HTML 代码
搜索 `html chars`,可以获取一份很长的列表,上面有 HTML 实体及其描述,按下后会在结果中显示更多信息。

### 21、我用这东西干啥?
这功能没什么用。如果你输入 `why should I use this?` ,它就会在搜索结果顶部显示 `cause it's awesome`。显然,DuckDuckGo 在说他自己。

### 22、转换大小写
大小写都可转换。`lowercase <大写搜索词>` 就会显示小写的结果

`uppercase <小写搜索词>` 就会显示大写的结果。

### 23、编码 URL
搜索 `encode` 并加上 URL,就会给出编码后的结果

### 24、Motherboard
搜索 `Motherboard` 就会看见左侧的 DuckDuckGo 的 logo 变了。它会显示选好的几个随机 logo。

### 25、获取 HTML 色码
搜索 `color codes` 便可获得一份颜色表。一样,这个功能多为 Web 开发者和设计师所用。

### 还有很多别的···
我的伙伴 Sreenath 想到本贴的主意。他说 DuckDuckGo 中还有许多 “彩蛋”,我觉得没错。但全部列出来有诸多不便。
如果你知道更多这样有趣的 DDG 搜索功能,请在评论中分享。如果你又发现了你喜欢的搜索功能,也提出来吧。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/duckduckgo-easter-eggs/>
作者:[sreenath](https://itsfoss.com/author/sreenath/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Peaksol](https://github.com/TravinDreek) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

DuckDuckGo is one of the [alternative search engines that is less privacy intruding](https://itsfoss.com/privacy-search-engines/) than the omnipresent Google.
It has improved a lot lately and works quite satisfactorily for general web search. It is nowhere close to Google when it comes to local search.
However, DuckDuckGo (fondly nicknamed DDG) has some cool features most users are not aware of. If you are an ardent DDG fan, you may enjoy enhancing your search experience with these tricks.
## 1. Jump on a specific website
Type ! before your favorite website name and directly enter the website. This is like the ‘feeling lucky’ feature of Google but in DDG terms, it’s called ‘bangs.’
There are short forms for the websites, which will be suggested when we start typing.

Entering the search term just after the website name will land you on the required result from that website.
## 2. Convert text to ASCII
Figlet is one of the [fun Linux commands](https://itsfoss.com/funny-linux-commands/). It converts any text into a decorated ASCII format.
Type **figlet** before any search term; it will print its ASCII output. No need to open the terminal.
## 3. Check social media status
Use ‘@’ in front of the proper twitter name of someone will show their status (followers etc.).
## 4. Generate a strong password
Type ‘password’ followed by the number of characters to be included and it will generate a strong, unique password for you.
## 5. Generate Random Passphrase
Type ‘random passphrase’ to generate a passphrase, usually 4 words long.
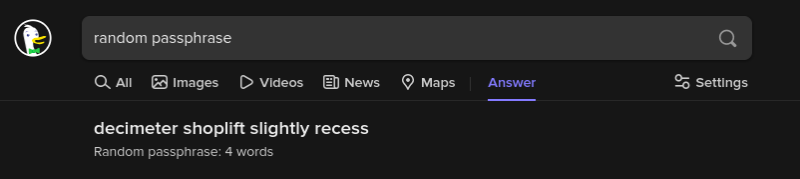
## 6. Get a cheatsheet
Type cheatsheet after the term whose cheatsheet you want. If there is a cheat sheet for the searched term, it will show it immediately on the search page.
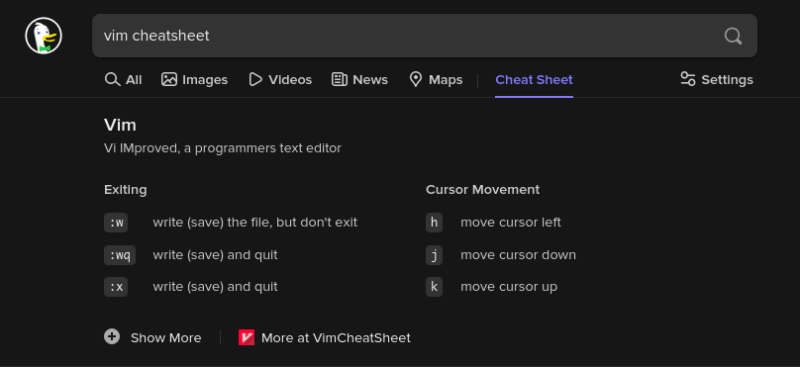
## 7. Get color from the color code
Type ‘color’ followed by the hex code of the color you want to check and it will show what that color looks like.
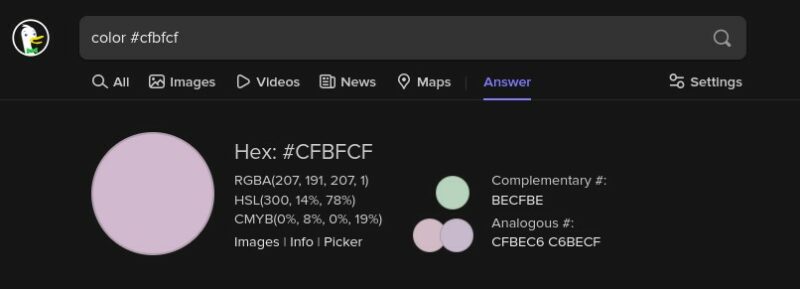
## 8. Generate a random number
Searching ‘random number’ will output a random number between 0 and 1
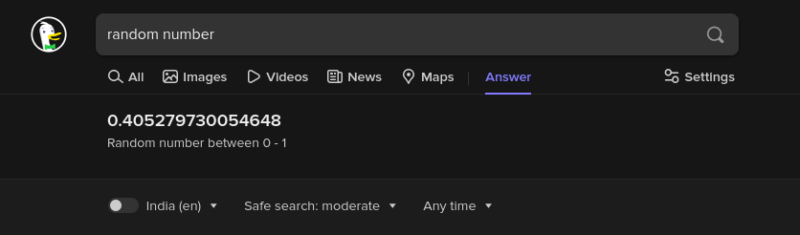
You can also specify the range to look for.
## 9. Convert to binary and other formats
Type a binary number and append it with ‘binary’ will convert it from binary to decimal
Similarly, it works for hexadecimal and oct, but I am confused about their logic.
## 10. Find rhyming words
Type ‘what rhymes with ‘ followed by the word you want to get rhymes of. Helps with your poetry skills, no?
## 11. Get Ramanujan number, Pi, and other constants
Type the name of the constant whose value you want and you get it right in the search result page.
## 12. Check who is currently in space
Type ‘people in space’ and get the list of those currently in space. It also shows how long they have been in space.
## 13. Check if a website is down
If you want to know if a particular website is down for you or for everyone, just use the “is xyz.com is down” search query.
## 14. Get quotes on certain topics
Type a word followed by quotes, and it will give quotes related to that word.
## 15. Get placeholder texts
Search for ‘lorem ipsum’ and get 5 paragraphs of placeholder texts. Useful for web developers perhaps.
## 16. Get the calendar for any month
Type calendar followed by day, month, and year and it gives you an interactive calendar of that month.
## 17. Generate QR code
Search ‘qr’ followed by any text, be it a link or anything, will generate the respective QR Code.
## 18. Get some CSS Animations
Search for ‘css animations’ to get some CSS animation examples.
## 19. Expand a shortened link
Got a bitly or some other shortened link but not sure where it takes you. Instead of landing on a spammy website, expand the shortened URL and see the actual website URL.
Use the keyword expand followed by the shortened URL and it will show the actual destination URL.
## 20. Get HTML codes for special characters
Search ‘html chars’ and get a very long list of HTML entities and their description, if pressed show more in the result
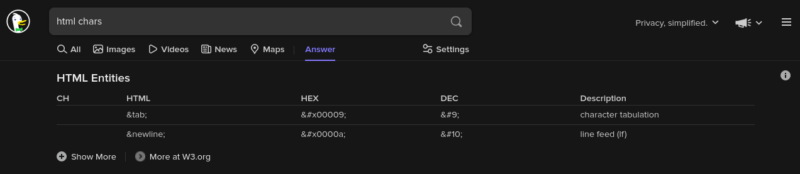
## 21. Why should I use this?
This one is pretty useless. If you enter the term “why should I use this?” it shows “cause it’s awesome” at the top of the search result page. Clearly, DuckDuckGo is referring to itself.
## 22. Convert case
This works in two cases. lowercase <searchterm in Upper-case> will show the lowered case result
uppercase <searchterm in lower case> will show an uppercase result.
## 23. Encode a URL
Search ‘encode’ followed by a URL will give an encoded result
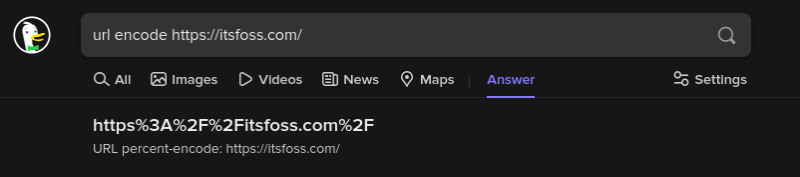
## 24. Motherboard
Search for ‘Motherboard’, and you can see that the logo of DuckDuckGo on the left side is changed. It shows a random logo from the selection of a few.
## 25. Get HTML Color Codes
Search for ‘color codes’ and you get a chart of colors. Again, this one is more for web developers and designers.
## There are many more…
My teammate Sreenath came up with this post idea. He says there are more such ‘easter eggs’ in DuckDuckGo and I believe him. But it won’t be feasible to list them all here.
If you know more such interesting DDG search features, share them in the comments. If you found your next favorite search feature, do mention that too. |
14,697 | 如何在 RHEL 9 上创建本地 Yum/DNF 仓库 | https://www.linuxtechi.com/create-local-yum-dnf-repository-rhel/ | 2022-06-11T16:41:54 | [
"软件包仓库",
"Yum",
"DNF"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14697-1.html | 
你好,技术兄弟,最近红帽发布了最新的操作系统 RHEL 9,RHEL 9 满足了混合云的所有要求。它可以安装在物理服务器、虚拟机和容器镜像中。
当我们没有订阅的时候,想安装软件包来做实验,那么设置本地的 Yum 或 DNF 仓库将是很方便的。
在本指南中,我们将介绍如何在 RHEL 9 上使用 DVD 或 ISO 文件一步一步地创建本地 Yum/DNF 资源库。
创建本地 Yum/DNF 资源库的先决条件:
* 最小化安装 RHEL 9 系统
* 具有管理权限的 sudo 用户
* RHEL 9 DVD 或 ISO 文件
### 1)挂载 RHEL 9 ISO 文件或 DVD
我们假设 RHEL 9 iso 文件已经被复制到系统中。运行下面的挂载命令,将 ISO 文件挂载到 `/opt/repo` 文件夹。
```
$ sudo mkdir /var/repo
$ sudo mount -o loop rhel-baseos-9.0-x86_64-dvd.iso /var/repo/
```

如果是 DVD 光盘,运行:
```
$ sudo mount /dev/sr0 /var/repo/
```
### 2)在 /etc/yum.repos.d/ 目录中创建仓库文件
在 `/etc/yum.repos.d/` 目录下创建一个名为 “rhel9-local.repo` 的仓库文件,内容如下:
```
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/rhel9-local.repo
[Local-BaseOS]
name=Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9 - BaseOS
metadata_expire=-1
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
baseurl=file:///var/repo//BaseOS/
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release
[Local-AppStream]
name=Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9 - AppStream
metadata_expire=-1
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
baseurl=file:///var/repo//AppStream/
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release
```
保存并关闭该文件。

### 3)刷新 Yum/DNF 和订阅管理器的缓存
执行以下命令来清理 Yum 或 DNF 和订阅管理器的缓存。
```
$ sudo dnf clean all
$ sudo subscription-manager clean
```

在上面的输出中,我们得到一个警告信息 `This system is not registered with an entitlement`(系统没有注册权限)。所以,为了抑制这个警告信息,编辑文件 `/etc/yum/pluginconf.d/subscription-manager.conf`,将参数 `enabled=1` 改为 `enabled=0`。
```
$ sudo vi /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/subscription-manager.conf
```

保存并退出该文件。
### 4)使用本地仓库安装软件包
现在我们都准备好测试我们的本地仓库了。运行下面的命令来查看配置仓库。
```
$ sudo dnf repolist
```
输出:

现在,试试用 `dnf` 命令通过上面配置的本地仓库安装软件包。
```
$ sudo dnf install nfs-utils
```
输出:


完美,上述输出证实了 `nfs-utils` 包及其依赖项已经通过本地配置的 Yum 或 DNF 仓库成功安装。
这就是本指南的全部内容。我希望你觉得它有参考价值。请在下面的评论区发表你的疑问和反馈。
---
via: <https://www.linuxtechi.com/create-local-yum-dnf-repository-rhel/>
作者:[Pradeep Kumar](https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Hello techies, recently Red Hat has released its latest operating system RHEL 9. RHEL 9 fulfill all the requirements of hybrid cloud. It can be installed on physical server, virtual machine and inside the container image.
When we don’t have subscription and want to install packages for doing the POCs then setting up local yum or dnf repository will be handy.
In this guide, we will cover how to create local yum/dnf repository on RHEL 9 using DVD or ISO file step by step.
Prerequisites for creating local Yum/DNF repository
- Minimal Install
[RHEL 9](https://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-install-rhel-9-step-by-step/)system - Sudo User with admin privileges
- RHEL 9 DVD or ISO file
## 1 ) Mount RHEL 9 ISO File or DVD
We are assuming RHEL 9 iso file is already copied into the system. Run following mount command to mount ISO file on /opt/repo folder.
$ sudo mkdir /var/repo $ sudo mount -o loop rhel-baseos-9.0-x86_64-dvd.iso /var/repo/
In case of dvd, run
$ sudo mount /dev/sr0 /var/repo/
## 2) Create Repo File in ‘/etc/yum.repos.d/’ Directory
Create a repo file with name ‘rhel9-local.repo’ under the folder /etc/yum.repos.d/ with following content
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/rhel9-local.repo [Local-BaseOS] name=Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9 - BaseOS metadata_expire=-1 gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 baseurl=file:///var/repo/BaseOS/ gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release [Local-AppStream] name=Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9 - AppStream metadata_expire=-1 gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 baseurl=file:///var/repo/AppStream/ gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release
Save and close the file.
## 3) Flush Yum/DNF & Subscription Manager Cache
Execute following commands to clean yum or dnf and subscription manager cache.
$ sudo dnf clean all $ sudo subscription-manager clean
In the above output, we are getting a warning message ‘This system is not registered with an entitlement’. So, to suppress this warning message, edit the file ‘/etc/yum/pluginconf.d/subscription-manager.conf’ , change the parameter ‘enabled=1’ to ‘enabled=0’.
$ sudo vi /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/subscription-manager.conf
Save and exit the file.
## 4) Install Packages using Local Repository
Now we are all set to test our local repository. Run beneath command to view configure repository.
$ sudo dnf repolist
Output,
Now, try Install packages using dnf command via above configure local repository.
$ sudo dnf install nfs-utils
Output,
Perfect, above output confirms that nfs-utils package along with its dependencies are installed successfully via locally configured yum or dnf repository.
That’s all from this guide. I hope you have found it informative. Kindly do post your queries and feedback in below comments section.
Also Read: [How to Install PostgreSQL 15 on RHEL 9 Step by Step](https://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-install-postgresql-on-rhel/)
Charles PhamThe instruction very clearly. Thank you very much
manaduvortesWorked perfectly, thank you very much.
easyplease how did you do this first step
“We are assuming RHEL 9 iso file is already copied into the system. Run following mount command to mount ISO file on /opt/repo folder.”
Pradeep KumarYou need to copy RHEL 9 ISO file to your system and then use mount command to mount it.
Glenn MIn step 1, mounting the iso, you state in the written step port to mount it to /opt/repo. However in your example and display snip, you have it as /var/repo. May be a bit confusing to some.
Catherine🙁 it didn’t work for me. After turned enable=0 on /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/subscription-manager.conf. Run sudo dnf repolist and install… All repos were removed.
# sudo dnf clean all
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
17 files removed
# sudo subscription-manager clean
All local data removed
# sudo vi /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/subscription-manager.conf
# sudo dnf repolist
No repositories available
# sudo dnf install nfs-utils
Error: There are no enabled repositories in “/etc/yum.repos.d”, “/etc/yum/repos.d”, “/etc/distro.repos.d”.
When I checked back to the redht.repo. It’s empty file. |
14,699 | 如何双启动 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 和 Windows 11 | https://www.linuxtechi.com/dual-boot-ubuntu-22-04-and-windows-11/ | 2022-06-12T11:06:00 | [
"Ubuntu",
"Windows",
"双启动"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14699-1.html | 
嗨,伙计们,在这篇指南中,我们将演示如何在 Windows 11 的之外配置 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS(Jammy Jellyfish)的双启动设置。
为使其能工作,你需要在你的计算机上已经安装好了 Windows 11 。接下来,你将需要在你的硬盘驱动器上创建一个单独的分区,你将在此分区上安装 Ubuntu 22.04 。我们将包含这点知识,因此不要担心。
**前置条件:**
在设置双启动前,这些是你所需要的:
* 一个 Ubuntu 22.04 的可启动 USB 驱动器,你可以转到 [Ubuntu 22.04 下载页面](https://releases.ubuntu.com/22.04/) 来下载 Ubuntu 22.04 的 ISO 镜像文件。在 ISO 镜像文件到位后,拿一个 16GB USB 驱动器,并使用 Rufus 应用程序来使其可启动。
* 快速稳定的互联网连接
### 步骤 1、在你的硬盘驱动器上创建一个可用的分区
正如介绍中所提到的,我们首先需要在硬盘驱动器上创建一个单独的分区,我们将在其中安装 Ubuntu 22.04 。
因此,通过按下 `Windows + R` 组合键来打开磁盘管理器实用程序。
在对话框中,输入 `diskmgmt.msc` ,并按下回车键。

<ruby> 磁盘管理 <rt> disk management </rt></ruby>控制台将显示当前磁盘分区,如你将在下面所看到的一样。我们将通过压缩 “卷 E” 来创建一个用于安装 Ubuntu 的分区。这在你的安装过程中可能有所不同,但是只需要跟着做,你就会理解其中的大体意思。

因此,在你想要压缩的磁盘驱动器卷上点击鼠标右键,并在弹出的菜单中选择 <ruby> 压缩卷 <rt> Shrink </rt></ruby> 选项。

将会出现一个弹出对话框,如下所示。具体指定压缩的控件大小(以 MB 为单位),并单击 <ruby> 压缩卷 <rt> Shrink </rt></ruby> 。
这是指定给 Ubuntu 22.04 安装所用的空间。

在缩小磁盘空间后,它将显示为 <ruby> 未分配 <rt> Unallocated </rt></ruby> 或 <ruby> 可用空间 <rt> Free Space </rt></ruby>,如图所示。

随着有了可用空间,现在将可启动 USB 驱动器插入到你的 PC ,并重新启动你的系统。此外,要确保访问 BIOS 设置,并修改启动优先级,来使 USB 驱动器成为第一优先级。保存 BIOS 更改并继续启动。
### 步骤 2、开始安装
在第一个屏幕中,你将得到如图所示的 GRUB 菜单。选择第一个选项 <ruby> 尝试或安装 Ubuntu <rt> Try or Install Ubuntu </rt></ruby> ,并按下 <ruby> 回车键 <rt> ENTER </rt></ruby> 按键。

Ubuntu 22.04 将开始加载,如下所示。这最多需要一分钟。

此后,安装程序向导将弹出,向你提供两个选项: <ruby> 尝试 Ubuntu <rt> Try Ubuntu </rt></ruby> 和 <ruby> 安装 Ubuntu <rt> Install Ubuntu </rt></ruby>。因为我们的使命是安装 Ubuntu ,所以选择后者。

接下来,选择你的首选键盘布局,并单击 <ruby> 继续 <rt> Continue </rt></ruby> 按钮。

在 <ruby> 更新和其它软件 <rt> Updates and Other Software </rt></ruby> 步骤中,选择 <ruby> 正常安装 <rt> Normal Installation </rt></ruby> 以便安装 Ubuntu的 GUI 版本,通过勾选其它剩余选项来允许下载更新和安装第三方的针对于图像、WIFI 硬件和其它实用程序的软件包。
接下来,单击 <ruby> 继续 <rt> Continue </rt></ruby> 按钮。

下一步提供两个安装选项。第一个选项 - <ruby> 清除整个磁盘并安装 Ubuntu <rt> Erase disk and install Ubuntu </rt></ruby> – 完全地擦除你的驱动器并安装。但是由于这是一个双启动设置,这个选项对于你现有安装的 Windows 系统来说会是灾难性的。
因此,选择 <ruby> 其它选项 <rt> Something else </rt></ruby>,单击 <ruby> 继续 <rt> Continue </rt></ruby> 按钮。

分区表将显示所有现有的磁盘分区。到目前为止,我们仅有 NTFS 分区和我们之前压缩出来的可用分区。
针对 Ubuntu 22.04 ,我们将创建下面的分区:
* `/boot` – 1 GB
* `/home` – 10 GB
* `/` – 12 GB
* 交换分区 – 2 GB
* EFI – 300 MB
为开始使用这些分区,单击 <ruby> 可用空间 <rt> Free Space </rt></ruby>分区下面的 “+” 符号。

如图显示填写 `/boot` 分区的详细信息,然后单击 <ruby> 确定 <rt> OK </rt></ruby> 按钮。

接下来,具体指定 `/home` 分区,并单击 <ruby> 确定 <rt> OK </rt></ruby> 按钮。

接下来,定义 `/`(根)分区,并单击 <ruby> 确定 <rt> OK </rt></ruby> 按钮。

为定义交换空间,设置大小,并在 <ruby> 使用为 <rt> Use as </rt></ruby>:选项中选择 <ruby> 交换区域 <rt> Swap area </rt></ruby>。

最后,如果你正在使用 UEFI 启动模式,那么创建一个 EFI 系统分区。我们将分配 300MB 到 EFI 分区。

下图是一份我们的分区表的分区摘要:

为继续安装,单击 <ruby> 现在安装 <rt> Install Now </rt></ruby>。在下图显示的弹出窗口中,单击 <ruby> 继续 <rt> Continue </rt></ruby>来保存更改到磁盘。

接下来,安装程序向导将自动侦测出你的位置,只需要单击 <ruby> 继续 <rt> Continue </rt></ruby> 按钮。

接下来,通过具体指定姓名、计算机的名称和密码来创建一个登录用户。接下来单击 <ruby> 继续 <rt> Continue </rt></ruby> 按钮。

此时,安装程序向导将复制所有的 Ubuntu 文件和软件包到手动创建的硬盘驱动器分区,并安装必要的软件包。
这个过程将需要很长一段时间,因此,要有耐心。在我们的实例中,它需要大约 30 分钟。

在安装过程完成后,单击 <ruby> 立刻重新启动 <rt> Restart Now </rt></ruby> 按钮来重新启动系统。

在这时,移除你的可启动 USB 驱动器,并按下回车键。

在系统重新启动时,你将找到包括 Ubuntu 和 Windows 11 在内的各种选项。
选择 “Ubuntu” 来启动到你的新 Ubuntu 22.04 安装。要启动到 Windows 11,请选择标有 <ruby> Windows 恢复环境 <rt> Windows Recovery Environment </rt></ruby> 的条目。

就这样。我们演示了如何双启动 Windows 11 和 Ubuntu 22.04。
---
via: <https://www.linuxtechi.com/dual-boot-ubuntu-22-04-and-windows-11/>
作者:[James Kiarie](https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/james/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Hey guys, in this guide we will demonstrate how to configure a dual-boot setup of Ubuntu 22.04 LTS (Jammy Jellyfish) alongside Windows 11.
For this to work, you need to have Windows 11 already installed on your PC. You will then need to create a separate partition on your hard drive on which Ubuntu 22.04 will be installed. We will go over all this, so don’t worry.
**Prerequisites**** **
Before setting sail with the dual-boot setup, here is what you need.
- A bootable USB drive of Ubuntu 22.04 You can download Ubuntu 22.04 ISO image by heading over to the
[Ubuntu 22.04 download page](https://releases.ubuntu.com/22.04/). With the ISO image in place, grab a 16GB USB drive and use Rufus application to make it bootable.
- A fast and stable internet connection
**Step 1) Create a Free Partition on Your Hard Drive**** **
As mentioned in the introduction, we first and foremost need to create a separate partition on the hard drive on which we are going to install Ubuntu 22.04.
So, open the disk management utility by pressing Windows Key + R
In the dialogue box, type diskmgmt.msc and hit ENTER.
The disk management console displays the current disk partitions as you can see below. We are going to create a partition for installing Ubuntu by Shrinking ‘Volume E’. This might be different in your setup, but just follow along and you will get the drift.
So, right-click on the volume that you want to shrink and select ‘Shrink’.
A pop-up dialogue box will appear as shown below. Specify the amount of space to shrink in MB and click ‘Shrink’.
This is the space that is designated for the Ubuntu 22.04 installation.
After shrinking the space, it will appear as ‘Unallocated’ or ‘Free Space’ as shown.
With the free space in place, now plug the bootable USB medium into your PC and reboot your system. Also, be sure to access the BIOS setup and modify the boot priority to have the USB drive as the first priority. Save the BIOS changes and proceed to boot.
## Step 2) Begin the installation
On the first screen, you will get the GRUB menu displayed as shown. Select the first option ‘Try or Install Ubuntu’ and press ENTER.
Ubuntu 22.04 will start loading as shown below. This takes a minute at most.
Thereafter, the installation wizard will pop open providing you with two options: ‘Try Ubuntu’ and ‘Install Ubuntu’. Since our mission is to install Ubuntu, select the latter.
Next, select your preferred Keyboard layout and click ‘Continue’.
In the ‘Updates and Other Software’ step, select ‘Normal Installation’ in order to install the GUI version of Ubuntu and check the rest of the options to allow download of updates and installation of third-party software for graphics, WiFi hardware and other utilities.
Then click ‘Continue’.
The next step provides two options for installation. The first option -’Erase disk and install Ubuntu’ – completely wipes out your drive and installs Ubuntu’. But since this is a dual boot setup, this option will be disastrous to your existing Windows installation.
Therefore, select ‘Something else’ and click ‘Continue’.
The partition table will be displayed with all the existing disk partitions. So far, we only have the NTFS partitions and the free space we shrunk earlier.
For Ubuntu 22.04, we will create the following partitions:
- /boot – 1 GB
- /home – 10 GB
- / – 12 GB
- Swap – 2 GB
- EFI – 300 MB
To get started with the partitions, click on the [ + ] sign below the ‘Free Space’ partition.
Fill in the /boot partition details as shown then click ‘OK’.
Next up, specify the /home partition and click ‘OK’.
Next, define the / ( root ) partition and click ‘OK’.
To define swap space, set the size and select ‘Swap area’ for the ‘Use as:’ option.
Finally, create an EFI system partition if you are using UEFI boot mode. We will assign 300 MB to the EFI partition.
Below is a summary of the partitions in our partition table.
To continue with the installation, click ‘Install Now’. On the pop-up shown below, click ‘Continue’ to save the changes to the disk.
Next, the installation wizard will auto-detect your location. Simply click ‘Continue’.
Next, create a login user by specifying the name, computer’s name and password. Then click ‘Continue’.
At this point, the installation wizard will copy all the Ubuntu files and packages to the manually created hard drive partitions and install the required software packages.
This process takes quite a while, so be patient. In our case, it took roughly 30 minutes.
Once the installation is completed, click on ‘Restart Now’ to reboot the system.
At this point, remove your bootable USB drive and press ‘ENTER’
When the system restarts, you will find all options for both Ubuntu and Windows 11.
Select ‘Ubuntu’ to boot into your new Ubuntu 22.04 installation. To boot into Windows 11, select the entry labeled ‘Windows Recovery Environment.
And there you have it. We have demonstrated how to dual-boot Windows 11 with Ubuntu 22.04.
Randyperfect tutorial, I can never remember all the partions and sizes needed for gpt install. thank you! |
14,700 | Amberol 是一款外观漂亮的 Linux 音乐播放器,只播放音乐,不做其他事情 | https://itsfoss.com/amberol-music-player/ | 2022-06-12T15:58:53 | [
"音乐播放器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14700-1.html | 
虽然音乐世界被流媒体服务所主导,但这并没有阻止开发者为桌面电脑创建音乐播放器。
最近,我发现了一个外观漂亮的新的 Linux 桌面音乐播放器。它名为 Amberol,我被它的美丽所震撼。

看起来不错,不是吗?让我们仔细看看它。
### Amberol,Linux 上的可爱的音乐播放器
看起来不错是它所做的两件(或几件)事情中的一件。另一件事是播放音乐。
这就是它,[Amberol](https://apps.gnome.org/app/io.bassi.Amberol/) 没有额外的花哨(和有用)的功能,如生成专辑封面、元数据编辑、歌词显示或播放列表和库管理。
这些功能也不像是会在未来的版本中加入。Amberol 只想播放音乐。就是这样。
#### 令人惊叹的用户界面
Amberol 和大多数新的 GNOME 应用一样,是用 Rust 和 GTK 编写的。
它有一个自适应的用户界面,可以根据你正在播放的专辑颜色来改变颜色。渐变效果给了它一个现代、时尚的外观,肯定会成为你的 Linux <ruby> 美化 <rt> Ricing </rt></ruby>截图的一部分。

由于其 UI 没有传统的手柄和菜单,它给应用一个统一的外观。
#### 播放列表
它会从你添加的文件夹中的文件自动生成一个播放列表,显示在左手边的侧边栏。

你可以在左上角看到整个播放列表将播放多长时间的音乐。点击“勾选”符号,你可以选择歌曲,并从播放列表中删除它们。
如果你愿意,可以隐藏播放列表的侧边栏。

#### 音乐播放选项
你可以在界面上看到歌曲的进度。该播放器与键盘上的媒体控制按钮整合得很好。你可以用专用的媒体键来播放、暂停和改变曲目(如果你的系统上有)。
Amberol 为你提供了一些播放音乐的选项。你可以打开随机播放功能,按随机顺序播放音乐。你也可以单曲循环,直到你厌倦它。

底部的汉堡菜单让你可以选择添加文件或文件夹,并显示可用的键盘快捷方式。

你也可以从这里禁用 UI 颜色变化以配合专辑封面。
### 在 Linux 上安装 Amberol
Amberol 是 [以 Flatpak 形式提供的](https://flathub.org/apps/details/io.bassi.Amberol)。请确保 [你的系统已启用 Flatpak 支持](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/)。
要安装 Amberol,请打开终端并使用以下命令:
```
flatpak install flathub io.bassi.Amberol
```
安装完毕后,在菜单中搜索该应用,并点击启动。
第一次运行时,它会要求你添加音乐文件或文件夹。你也可以拖放文件播放。

### 总结
就个人而言,我更喜欢流媒体服务,因为我没有本机音乐珍藏。但我知道有的人有大量的 CD 收藏,现在都保存在硬盘上。
Amberol 是一个外观漂亮的应用,对于播放本机音乐来说,它足够好。最吸引人的是它基于专辑封面的自适应用户界面。
请你试试它,并在评论区分享你的经验。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/amberol-music-player/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Though the world of music is dominated by streaming services, it has not discouraged developers from creating music players for desktop computers.
Recently, I came across a beautiful looking new music player for the Linux desktop. It’s called Amberol and I was awestruck by its beauty.
Looks good, no? Let’s take a closer look at it.
## Amberol, the cute looking music player for Linux
Looking good is one of the two (or few) things it does. The other thing is playing music.
And that’s about it. [Amberol](https://apps.gnome.org/app/io.bassi.Amberol/) doesn’t have additional fancy (and useful) features like album art generation, metadata editing, lyrics display or playlists and library management.
It’s not like these features will be added in future releases. Amberol just wants to play music. That’s it.
### The stunning UI
Amberol is written in Rust and GTK like most new GNOME applications.
It has an adaptive UI that changes color based on the album color you are playing. The gradient effect gives it a modern, sleek look that would surely be part of your Linux ricing screenshots.
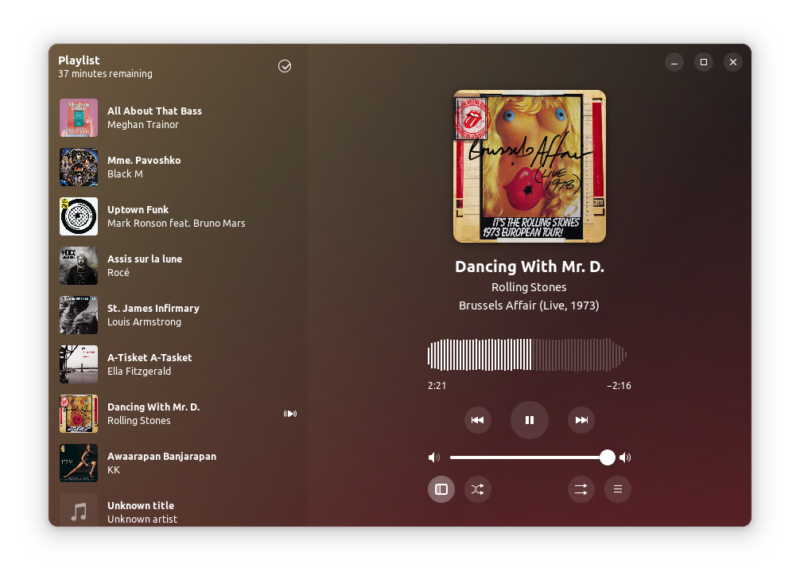
Since the UI does not have the traditional handlebar and menu, it gives the application a unified look.
### Playlists
It generates a playlist automatically from the files present in the folder you add. It is displayed in the lefthand sidebar.
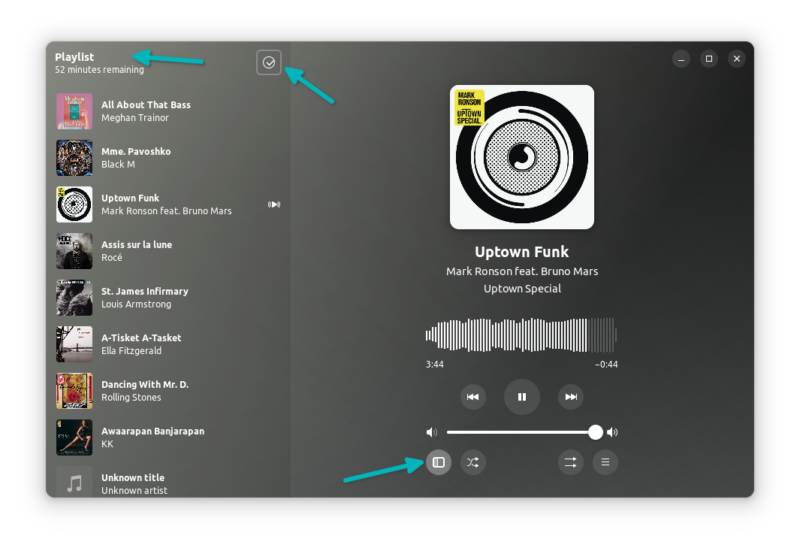
You can see how long the entire playlist will play the music in the top left corner. Clicking on the ‘correct sign’ allows you to select songs and remove them from the playlist.
If you want, you can hide the playlist sidebar.
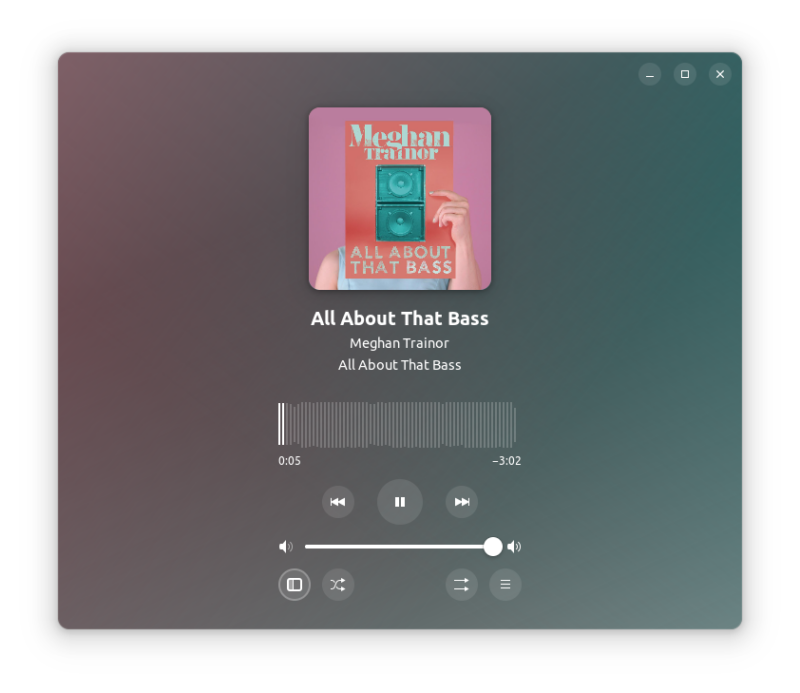
### Music playing options
You can see the progress of the songs on the interface. The player integrates well with the media control buttons on the keyboard. You can play/pause and change tracks with the dedicated media keys (if you have it on your system).
Amberol does give you a few more options for playing the music. You can turn on the shuffle to play music in random order. You may also put a song on repeat and keep on playing it till you get bored of it.
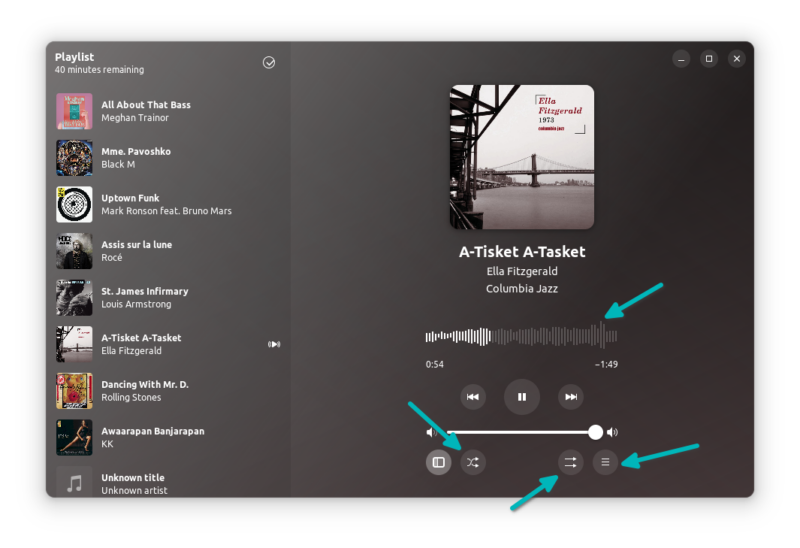
The handlebar menu at the bottom gives you the option to add a file or folder and show available keyboard shortcuts.
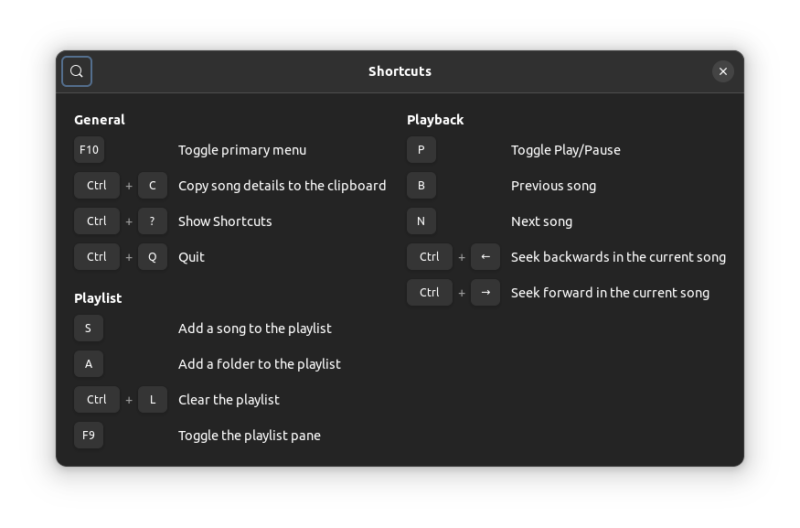
You may also disable the UI color changing to match the album art from here.
## Installing Amberol on Linux
Amberol is [available as Flatpak](https://flathub.org/apps/details/io.bassi.Amberol). Please ensure that [your system has Flatpak support enabled](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/).
To install Amberol, open a terminal and use the following command:
`flatpak install flathub io.bassi.Amberol`
Once installed search for the application in the menu and start from here.
On the first run, it asks you to add music files or folders. You can also drag and drop files.
## Conclusion
Personally, I prefer streaming services because I don’t have a good collection of local music. But I know there are people who have/had a huge collection of CDs that are now saved on the hard disk.
Amberol is a beautiful-looking application and it is good enough for playing local music. The main attraction is the adaptive UI based on the album art.
I let you play with it and share your experience in the comment section. |
14,702 | 分裂使 Linux 超越 Windows 的梦想破灭了 | https://www.theregister.com/2022/06/08/linux_desktop_blues/ | 2022-06-13T10:38:34 | [
"Linux",
"桌面"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14702-1.html | 
最近,The Register 的 Liam Proven 写了一篇关于 [最恼人的桌面 Linux 发行版](/article-14678-1.html) 的文章。他启发我写了这篇文章。
Proven 指出,Distrowatch 目前列出了多达 [270 个 Linux 发行版](https://distrowatch.com/)。当然,没有人能够都一一了解所有的这些发行版。但是,甚至在 GNOME 和 KDE 的界面大辩论之前,从 Bash 和 [Zsh](https://www.zsh.org/) 之争开始,我就一直在报道 Linux 桌面,并且曾经是一本现在已经停刊的名为《Linux 桌面》杂志的主编,我想我比任何其他用过 Windows PC 之外的计算机的人使用过更多的桌面。简而言之,[我超爱 Linux 桌面](https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/13/linux_column/)。
许多 Linux 桌面发行版都很棒。多年来,我一直是 [Linux Mint](https://linuxmint.com/) 的忠实粉丝。我也很喜欢其它桌面发行版:[Fedora](https://getfedora.org/)、[openSUSE](https://www.opensuse.org/)、[Ubuntu](https://ubuntu.com/) 和 [MX Linux](https://mxlinux.org/),排名不分先后。但是你知道吗?**这就是问题。**
我们有很多优秀的 Linux 桌面发行版,但这意味着它们中没有一个能获得足够的市场份额,从而在 **整个市场** 上产生任何真正的影响。
自从人们开始谈论何时 Linux 能在桌面上击败 Windows 以来,情况一直如此。尽管我们可能梦想着一个真正的 Linux 桌面年到来,**但它从未到来**。正如 Forrester 高级分析师 Andrew Hewitt 最近指出的那样,“总的来说,[只有 1% 的员工](https://www.windowscentral.com/can-linux-win-desktop-pc) 报告说他们用于工作的主要笔记本电脑使用了 Linux。而 60%的人仍在使用 Windows……。Linux **不太可能超越** Windows 成为主要操作系统"。
**他没有说错。**
这并不是说 Linux 不能成为一个成功的终端用户环境。事实上,它是,你可以说 **Linux 是最成功的终端用户操作系统**,而不是 Windows。这是因为现在有 [超过 30 亿部安卓手机](https://www.theregister.com/2021/08/25/linux_kernel_30_years_old/),而安卓只是一个专门针对智能手机的 Linux 发行版。
它并不是唯一隐藏在众目睽睽之下的 Linux。你会在每所学校、在我的旅行袋中发现 Chromebook,它无处不在。Chrome OS 只是 [在 Linux 基础上](https://www.zdnet.com/article/the-secret-origins-of-googles-chrome-os/) 将 Chrome 浏览器和界面进行了改造。
把这一切加起来,你可以直截了当地说,Linux 实际上早就是最受欢迎的终端用户操作系统了。
但这不是 Linux 桌面爱好者想要的。他们希望 Windows 在 Linux 重压之下被压垮,跪地求饶。
对不起。**这不可能发生**。Linus Torvalds 已经告诉我们为什么我们永远不会在每台 PC 上看到一个经典的 Linux 桌面:[碎片化](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VHFdoFKDuQA)。
想一想吧。除了 200 多个发行版之外,还有 [21 种不同的桌面界面](https://www.theregister.com/2022/05/17/linux_desktop_feature/)、六种以上的不同的主要软件安装方式,如 Debian 软件包管理系统([DPKG](https://www.debian.org/doc/manuals/debian-reference/ch02.en.html))、红帽软件包管理器([RPM](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/5/html/deployment_guide/ch-rpm))、[Pacman](https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/Pacman)、[Zypper](https://en.opensuse.org/Portal:Zypper),以及其他的方式。然后还有所有较新的容器化安装程序的方法,包括 [Flatpak](https://flatpak.org/)、[Snap](https://snapcraft.io/) 和 [AppImage](https://appimage.org/)。
我几乎不能把它们全都搞清楚,而这甚至还是我工作的一部分!你怎么能 **指望普通用户来理解这一切** 呢?不可能。
像 [Canonical](https://canonical.com/)、[红帽](https://www.redhat.com/en) 和 [SUSE](https://www.suse.com/) 这样主要的 Linux 发行商,没有一个 **真正关心 Linux 桌面**。当然,他们有 Linux 桌面发行版。他们也是 Linux 桌面的主要影响者。但他们的收入来自服务器、容器、云和物联网(IoT)。桌面?拜托。我们应该 **庆幸** 他们在桌面上花费了那么多资源。
现在,说了这么多,我 **不想** 让你得到这样的印象:我不认为传统的 Linux 桌面很重要。**事实上,我认为它很关键**。
你看,微软正在放弃传统的基于 PC 的桌面。哦,Windows 并没有消失,但它正在转移。在其对未来的预测中,微软认为基于 Azure 的 [桌面即服务(DaaS)](https://www.computerworld.com/article/3656694/we-re-one-step-closer-to-windows-in-the-cloud.html) 是其未来。当然,Windows 用户仍然会在他们的桌子上看到一个看起来像 PC 的东西,但实际上它只是一个连接到 Windows 365 Cloud PC 的智能终端。真正的计算智能将在云中。
这意味着,真正的桌面操作系统的未来将掌握在拥有 macOS 的苹果公司和拥有 Linux 的我们手中。作为一个记得从中央控制的大型机和小型机向个人拥有的 PC 过渡的人,我不想回到一个所有权力属于微软或其他公司的世界。
Linux 桌面将永远不会像 Windows 曾经那样庞大。在 DaaS 的兴起和桌面向智能手机的沦陷之间,它不可能做到。但是,它可能会 **默认成为最受欢迎的、真正的传统桌面**。
那么 2028 年将是 Linux 桌面年吗?
你怎么看?
---
via: <https://www.theregister.com/2022/06/08/linux_desktop_blues/>
作者:[Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols](https://www.theregister.com/Author/Steven-J-Vaughan-Nichols) 选题:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](/article-14678-1.html) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | This article is more than **1 year old**
# I love the Linux desktop, but that doesn't mean I don't see its problems all too well
## Fragmentation has put paid to the dream of this OS ever being bigger than Windows
Comment Recently, *The Register's* Liam Proven wrote tongue in cheek about the most annoying desktop Linux distros. He inspired me to do another take.
Proven [pointed out](https://www.theregister.com/2022/05/31/the_cynics_guide_to_linux/) that Distrowatch currently lists [270](https://distrowatch.com/) – count 'em – Linux distros. Of course, no one can look at all of those. But, having covered the Linux desktop since the big interface debate was between Bash and [zsh](https://www.zsh.org/) rather than GNOME vs KDE, and being the editor-in-chief of a now-departed publication called Linux Desktop, I think I've used more of them than anyone else who also has a life beyond the PC. In short, [I love the Linux desktop](https://www.theregister.com/2022/04/13/linux_column/).
But that's not what Linux desktop fans want. They want Windows crushed and bleeding underneath the Linux juggernaut
Many Linux desktop distros are great. I've been a big [Linux Mint](https://linuxmint.com/) fan for years now. I'm also fond, in no particular order, of [Fedora](https://getfedora.org/), [openSUSE](https://www.opensuse.org/), [Ubuntu](https://ubuntu.com/), and [MX Linux](https://mxlinux.org/). But you know what? That's a problem right there.
We have many excellent Linux desktop distros, which means none of them can gain enough market share to make any real dent in the overall market.
It's been like that since people first started talking about Linux stomping on Windows on the desktop. But dream as we might of a true year of the Linux desktop, it won't happen. As Forrester senior analyst Andrew Hewitt recently pointed out: "Overall, [just 1 percent of employees report usage of Linux](https://www.windowscentral.com/can-linux-win-desktop-pc) on their primary laptop used for work. That's compared to 60 percent that still use Windows... It is very unlikely that Linux will overtake Windows as the main operating system."
He's not wrong.
That's not to say that Linux can't be a successful end-user environment. It is. Indeed, you can argue that Linux, not Windows, is the most successful end-user operating system. That's because there are [over 3 billion Android phones out there](https://www.theregister.com/2021/08/25/linux_kernel_30_years_old/) and Android is just a smartphone-specialized Linux distro.
It's not the only Linux hiding in plain sight. Chromebooks, which you'll find in every school in the land, and in my travel bag, are everywhere. Chrome OS is simply Chrome reworked as a web browser and interface [on top of Linux](https://www.zdnet.com/article/the-secret-origins-of-googles-chrome-os/).
Add it all up and you can say with a straight face that Linux has actually long been the most popular end-user OS of all.
But that's not what Linux desktop fans want. They want Windows crushed and bleeding underneath the Linux juggernaut.
Sorry. That's not happening. Linus Torvalds already told us why we'll never see a classic Linux desktop on every PC: [fragmentation](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VHFdoFKDuQA).
[Sick of Windows but can't afford a Mac? Consult our cynic's guide to desktop Linux](https://www.theregister.com/2022/05/31/the_cynics_guide_to_linux/)[Version 251 of systemd coming soon to a Linux distro near you](https://www.theregister.com/2022/05/24/version_251_of_systemd_released/)[The sad state of Linux desktop diversity: 21 environments, just 2 designs](https://www.theregister.com/2022/05/17/linux_desktop_feature/)[Unity and Trinity: New releases for forks of abandoned Linux desktops](https://www.theregister.com/2022/05/04/unity_trinity_desktops/)
Think about it. Besides over 200 distros, there are [21 different desktop interfaces](https://www.theregister.com/2022/05/17/linux_desktop_feature/) and over half-a-dozen different major ways to install software such as the [Debian Package Management System](https://www.debian.org/doc/manuals/debian-reference/ch02.en.html) (DPKG), [Red Hat Package Manager](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/5/html/deployment_guide/ch-rpm) (RPM), [Pacman](https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/Pacman), [Zypper](https://en.opensuse.org/Portal:Zypper), and all too many others. Then there are all the newer containerized ways to install programs including [Flatpak](https://flatpak.org/), [Snap](https://snapcraft.io/), and [AppImage](https://appimage.org/).
I can barely keep them all straight and that's part of my job! How can you expect ordinary users to make sense of it all? You can't.
None of the major Linux distributors – [Canonical](https://canonical.com/), [Red Hat](https://www.redhat.com/en), and [SUSE](https://www.suse.com/) – really care about the Linux desktop. Sure, they have them. They're also major desktop influencers. But their cash comes from servers, containers, the cloud, and the Internet of Things (IoT). The desktop? Please. We should just be glad they spend as many resources as they do on them.
Now, all this said, I don't want you to get the impression that I don't think the conventional Linux desktop is important. I do. In fact, I think it's critical.
Microsoft, you see, is abandoning the traditional PC-based desktop. Oh, Windows isn't going away, but it is moving. In its crystal ball, [Microsoft sees Azure-based Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS) as its future](https://www.computerworld.com/article/3656694/we-re-one-step-closer-to-windows-in-the-cloud.html). Sure, Windows users will still see what looks like a PC on their desk, but really it will just be a smart terminal hooked into a Windows 365 Cloud PC. The real computing smarts will be in the cloud.
That means that the future of a true desktop operating system will lie in the hands of Apple with macOS and us with Linux. As someone who remembers the transition from centrally controlled mainframes and minicomputers to individually empowered PCs, I do not want to return to a world where all power belongs to Microsoft or any other company.
The Linux desktop will never be as big as Windows once was. Between DaaS's rise and the fall of the desktop to smartphones, it can't be. But it may yet, by default, become the most popular true conventional desktop.
So will 2028 be the year of the Linux desktop? What do you think? ®
270 |
14,707 | OpenInfra 基金会启动“定向资助”以支持开源项目 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/openinfra-foundation-launches-directed-funding-to-support-open-source-projects/ | 2022-06-14T08:57:50 | [
"开源基金会"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14707-1.html | 
OpenInfra 基金会的前身为 OpenStack 基金会,几年前它将范围扩展到其旗舰项目之外,于是改了名字。2022 年 6 月 7 日,它宣布了一种有趣的新方式,让企业资助基金会内的开源项目。一般来说,开源基金会的企业成员通过支付会员费来支持该组织,然后基金会按照他们认为合适的方式分发这些费用。OpenInfra 基金会现在推出了一种新的“定向资助”模式,允许成员将他们的资金直接用于项目。
此前,基金会并不允许这样做,因为正如 Bryce 指出的那样,它可能会产生混合激励和付费游戏动态,而该组织一直试图避免这种情况。然而,社区对支持特定项目有很大的兴趣,这是有道理的,因为该基金会现在拥有更多种类的项目,但并不是每个成员都对每个项目进行了大量投入。
Bryce 表示,基金会的领导层和董事会,花费了大量时间来考虑,如何使基金会的核心原则与这种新模式相协调。因此,该模型试图将过去十年运行良好的 OpenStack/OpenInfra 技术治理模型的优点,与这些新的财务考虑相结合。
在这种“定向资助”模式下,每个新项目都将拥有自己的法人实体来持有项目资金。为确保新项目的合法性,OpenInfra 白金会员(目前为 9 家,包括蚂蚁集团、华为、Meta、微软和红帽)必须担任项目的发起人,之后其他组织才能加入项目基金。如果赞助公司还不是 OpenInfra 成员,则必须成为成员。然后,所有这些资助成员组成一个项目基金管理委员会,决定创建预算的费用。与此同时,OpenInfra 基金会将为这些项目提供社区建设服务。
这种新模式暂时只适用于加入基金会的新项目。Bryce 和 Collier 指出,组织可能会在一些现有项目中追溯应用这种新模式,但这个考虑目前不在路线图上。
自从将范围扩展到 OpenStack 之外后,OpenInfra 基金会增加了一些新项目,例如用于提高容器安全性的 Kata Containers、用于基础设施生命周期管理的 Airship、Startling X 边缘计算堆栈以及 Zuul CI/CD 平台。
“我们从每个成功的项目中学到的最重要的一点是,协作是关键,支持生态系统的范围越广越好,” OpenInfra 基金会总经理 Thierry Carrez 说,“事实上,我们发现最成功的开源项目是由多家公司资助的,因为他们能够整合资源以实现更高的回报率。”
这种新模式显然是 OpenInfra 基金会引入新项目和新成员的一种方式。正如领导团队欣然承认的那样,其在多方生态系统中管理开源项目的模型 —— 无论是通过新的定向资金还是更传统的方法 —— 可能并不适合每个项目。即使 OpenInfra 基金会只收到一小部分项目,随着对这些复杂云基础设施项目需求的增长,开源项目的数量也在增加,同时它们也变得更加复杂。
基金会还宣布了其各个项目的几个里程碑版本的发布,包括 Kata Containers 2.0 版、Zuul 5.0 版和 StarlingX 6.0 。
Collier 说:“基金会今年庆祝成立 10 周年,在展望下一个十年的开放基础设施之际,我们正在推动我们的模型如此成功的关键,那就是:将希望合作的公司和个人联合起来,为他们提供一个框架和有效协作的工具,并帮助他们投资资金以最好地帮助他们关心的项目。”
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/openinfra-foundation-launches-directed-funding-to-support-open-source-projects/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The OpenInfra Foundation, formerly known as the OpenStack Foundation until it expanded its scope beyond its flagship project a few years ago, announced today an intriguing new way for companies to fund open source projects within the foundation. Corporate members of open source foundations have traditionally supported the organisation by paying a membership fee, which the foundations then distribute as they see fit. The OpenInfra foundation is now launching a new ‘Directed Funding’ model that allows members to direct their funds directly to a project.
The foundation previously did not allow this because, as Bryce pointed out, it can create mixed incentives and a pay-for-play dynamic, which the organisation has always tried to avoid. However, there was a lot of interest in the community to support specific projects, which makes sense given that the foundation is now home to a wider variety of projects, but not every member is heavily invested in every project.
Bryce stated that the foundation’s leadership and board spent a significant amount of time considering how to reconcile the foundation’s core principles with this new model. As a result, the model tries to combine the best of the OpenStack/OpenInfra technical governance model, which has worked well over the last decade, with these new financial considerations.
Under this ‘directed funding’ model, each new project will have its own legal entity that will hold the project funding. To ensure that the new projects are legitimate, an OpenInfra Platinum member (currently nine, including Ant Group, Huawei, Meta, Microsoft, and Red Hat) must serve as the project’s sponsor, after which other organisations can join the project fund. If a sponsoring company is not already an OpenInfra member, it must become one. All of these funding members then form a project fund governing board, which decides on the fees for creating a budget. Meanwhile, the OpenInfra Foundation will provide these projects with community-building services.
This new model will, for the time being, only apply to new projects that join the foundation. Bryce and Collier noted that there may be some existing projects where the organisation could retroactively apply this new model, but that is not currently on the roadmap.
The OpenInfra foundation has added projects such as Kata Containers for increased container security, Airship for infrastructure lifecycle management, the Startling X edge compute stack, and the Zuul CI/CD platform since it expanded beyond OpenStack.
“The most important thing we’ve learned from each of these successful projects is that collaboration is key and the more breadth in the ecosystem of support the better,” said Thierry Carrez, general manager of the OpenInfra Foundation. “In fact, we’ve found that the most successful open source projects are funded by multiple companies, because they are able to combine their resources to achieve a much stronger rate of return.”
This new model is clearly a way for the OpenInfra Foundation to bring new projects — and new members — into the fold. Its models for managing open source projects in a multi-party ecosystem — both through the new directed funds and its more traditional approach — may not be suitable for every project, as the leadership team readily admits. Even if the OpenInfra Foundation only receives a small percentage of projects, the number of open-source projects is increasing as the demand for these sophisticated cloud infrastructure projects grows, all while they become more complex.
The Foundation also announced a couple of milestone releases for its various projects, including version 2.0 of Kata Containers, version 5.0 of Zuul, and the release of StarlingX 6.0.
“The Foundation celebrates its 10 anniversary this year, and as we look to our next decade of open infrastructure, we’re building momentum on what makes our model so successful: aligning companies and individuals who wish to work together, providing them with a framework and tools to effectively collaborate, and helping them invest their funds to best help the project they care about,” said Collier. |
14,708 | 如何通过 chroot 恢复 Arch Linux 系统 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/07/recover-arch-linux/ | 2022-06-14T11:12:06 | [
"Arch Linux",
"恢复"
] | /article-14708-1.html | 
>
> 这个快速指南解释了恢复 Arch Linux 安装的一些方便步骤。
>
>
>
作为一个滚动发布的版本,[Arch Linux](https://www.debugpoint.com/tag/arch-linux) 中有时会出现一些问题。不是因为你自己的行为,而是数以百计的其他原因,如新内核与你的硬件或软件的兼容性。但是,Arch Linux 仍然很棒,它提供了最新的软件包和应用。
但有时,它也会给你带来麻烦,你最终只能看到一个闪烁的光标,其他什么都没有。
所以,在这种情况下,与其重新格式化或重新安装,不如在放弃希望之前尝试恢复安装和数据。本指南概述了这个方向的一些步骤。
### 恢复 Arch Linux 安装
第一步是用 Arch Linux 创建一个可启动的<ruby> 现场 <rt> Live </rt></ruby> USB。从 [这个链接](https://archlinux.org/download/) 下载 .ISO 并创建一个可启动的 USB。你可以查看这个 [如何使用 Etcher 创建可启动的 USB](https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/01/etcher-bootable-usb-linux/) 的指南。记住这一步需要另一个稳定的工作系统,因为你目前的系统不能使用。
你需要知道你的 Arch Linux 安装在哪个分区上。这是一个非常重要的步骤。如果你不知道,你可以用 GParted 来查找。或者在你的 GRUB 菜单中查看,或者你可以运行下面的命令来了解。这将列出你所有的磁盘分区及其大小、标签:
```
sudo lsblk -o name,mountpoint,label,size,uuid
```
完成后,插入 USB 盘并从它启动。你应该在现场介质中看到 Arch Linux 的提示符。
现在,用下面的方法挂载 Arch Linux 分区。记得把 `/dev/sda3` 改成你对应的分区。
```
mount /dev/sda3 /mnt
arch-chroot /mnt
```
`arch-chroot` 命令将在终端挂载你的 Arch Linux 分区,所以用你的 Arch 凭证登录。现在,在这个阶段,根据你的需要,你有以下选择。
* 你可以通过 `/home` 文件夹来备份你的数据。如果,故障排除方式无效的话。你可以把文件复制到外部 USB 或其他分区。
* 核查日志文件,特别是 pacman 日志。因为,不稳定的系统可能是由升级某些软件包引起的,如图形驱动或任何其他驱动。根据日志,如果你需要的话,可以降级任何特定的软件包。
你可以使用下面的命令来查看 pacman 日志文件的最后 200 行,以找出任何失败的项目或依赖性删除。
```
tail -n 200 /var/log/pacman.log | less
```
上面的命令给出了你的 `pacman.log` 文件末尾的 200 行来验证。现在,仔细检查哪些软件包在你成功启动后被更新了。
并记下软件包的名称和版本。你可以尝试逐一降级软件包,或者如果你认为某个特定的软件包产生了问题。使用 `pacman -U` 开关来降级。
```
pacman -U <package name>
```
如果有的话,你可以在降级后运行以下命令来启动你的 Arch 系统。
```
exec /sbin/init
```
检查你的显示管理器的状态,是否有任何错误。有时,显示管理器会产生一个问题,无法与 X 服务器通信。例如,如果你正在使用 Lightdm,那么你可以通过以下方式检查它的状态。
```
systemctl status lightdm
```
或者,可以通过下面的命令启动它,并检查出现了错误。
```
lightdm --test-mode --debug
```
下面是一个 Lightdm 失败的例子,它导致了一个不稳定的 Arch 系统。

或者通过使用 `startx` 启动 X 服务器来检查。
```
startx
```
根据我的经验,如果你在上述命令中看到错误,尝试安装另一个显示管理器并启用它,如 sddm。它可能会消除这个错误。
根据你的系统状态,尝试上述步骤,并进行故障排除。对于特定于显示管理器 lightdm 的错误,我们有一个 [指南](https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/03/failed-to-start-lightdm/),你可以看看。
如果你使用的是 sddm,那么请查看 [这些故障排除步骤](https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/SDDM#Troubleshooting)。
### 总结
每个安装环境都是不同的。上述步骤可能对你不起作用。但它值得一试,根据经验,它是有效的。如果它起作用,那么,对你来说是好事。无论哪种方式,请在下面的评论区中告诉我结果如何。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/07/recover-arch-linux/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,709 | 详解在 Ubuntu 中引导到救援模式或紧急模式 | https://ostechnix.com/how-to-boot-into-rescue-mode-or-emergency-mode-in-ubuntu-18-04/ | 2022-06-14T15:36:45 | [
"救援模式",
"引导模式",
"GRUB"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14709-1.html | 
这篇教程将介绍如何在 Ubuntu 22.04、20.04 和 18.04 LTS 版本中引导到 <ruby> 救援 <rt> Rescue </rt></ruby> 模式或 <ruby> 紧急 <rt> Emergency </rt></ruby> 模式。
>
> 你可能已经知道,在 RHEL 7 、RHEL 8 、Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 及其更新的版本的 Linux 发行版中 <ruby> 运行等级 <rt> Runlevels </rt></ruby> 已经被 <ruby> 系统目标 <rt> Systemd target </rt></ruby> 所替代。更多关于 <ruby> 运行等级 <rt> Runlevel </rt></ruby> 和 <ruby> 系统目标 <rt> Systemd targets </rt></ruby> 的信息,参考 [这篇指南](https://ostechnix.com/check-runlevel-linux/) 。
>
>
>
这篇指南是针对 Ubuntu 编写的,但是,下面所给的步骤应该也适用于大多数使用 systemd 作为默认服务管理器的 Linux 发行版。
在进入主题前,让我们简单的理解:什么是 <ruby> 救援 <rt> rescue </rt></ruby> 模式 和 <ruby> 紧急 <rt> Emergency </rt></ruby> 模式,以及这两种模式的目的是什么。
### 什么是救援模式?
在 Linux 发行版中,救援模式等效于使用 SysV 作为默认的服务器管理器的 <ruby> 单用户 <rt> single user </rt></ruby> 模式。在救援模式中,将挂载所有的本地文件系统,将仅启动一些重要的服务。但是,不会启动一般的服务(例如,网络服务)。
救援模式在不能正常引导系统的情况下是很有用的。此外,我们可以在救援模式下执行一些重要的救援操作,例如,[重新设置 root 密码](https://ostechnix.com/how-to-reset-or-recover-root-user-password-in-linux/) 。
### 什么是紧急模式?
与救援模式相比,在紧急模式中,不会启动任何的东西。不会启动服务、不会挂载挂载点、不会建立套接字、什么都不会启动。你将所拥有的只是一个 **原始的 shell** 。紧急模式适用于调试目的。
首先,我们将看到如何在 Ubuntu 22.04 和 20.04 LTS 发行版中引导到救援模式或紧急模式。在 Ubuntu 22.04 和 20.04 LTS 中的过程是完全相同的!
### 在 Ubuntu 22.04 / 20.04 LTS 中引导到救援模式
我们可以使用两种方法来引导到救援模式。
#### 方法 1
打开你的 Ubuntu 系统。在 BIOS 徽标出现后,按下 `ESC` 按键来显示 GRUB 菜单。
在 GRUB 菜单中,选择第一项,并按下 `e` 按键来编辑它。

按下 `↓` 按键,并找到以单词 `linux` 开头的一行代码,并在其结尾处添加下面的一行代码。为到达其结尾处,只需要按下 `Ctrl + e` 组合键,或使用你键盘上的 `END` 按键或 `←`/`→` 按键。
```
systemd.unit=rescue.target
```

在添加上面的代码行后,按下 `Ctrl + x` 组合键或按下 `F10` 按键来引导到救援模式。
数秒后,你将作为 root 用户来登录到救援模式(即单用户模式)。将会提示你按下回车键来进入维护。
下图是 Ubuntu 22.04 / 20.04 LTS 系统的救援模式的样子:

现在,在救援模式中做你想做的任何事。在救援模式中,在你执行任何操作前,你可能需要以 读/写模式来挂载根(`/`)文件系统。
```
mount -n -o remount,rw /
```

在完成后,按下 `Ctrl + d` 组合键来引导到正常模式。或者,你可以输入下面的任意一个命令来引导到正常模式。
```
systemctl default
```
或者,
```
exit
```
如果你想重新启动系统,而不是引导到正常的模式,输入:
```
systemctl reboot
```
#### 方法 2
在这种方法中,你不需要编辑 GRUB 启动菜单项目。
打开系统电源,并从 GRUB 启动菜单中选择 <ruby> Ubuntu 高级选项 <rt> Advanced options for Ubuntu </rt></ruby>。

接下来,你将看到一个带有内核版本的可用的 Ubuntu 版本的列表。在 Ubuntu 中的 GRUB 启动菜单中选择 <ruby> 恢复模式 <rt> Recovery mode </rt></ruby> 。

数秒后,你将看到 Ubuntu 的 <ruby> 恢复 <rt> Recovery </rt></ruby> 菜单。从恢复菜单中,选择 <ruby> 进入 root 的 shell 提示符 <rt> Drop to root shell prompt </rt></ruby> 选项 ,并按下回车键。

现在,你将进入维护。

通过输入下面的命令来 以读/写模式的方式 来挂载根(`/`)文件系统:
```
mount -n -o remount,rw /
```

在救援模式中做你想做的任何事。
在完成后,输入 `exit` 来返回到恢复菜单。
```
exit
```
最后,选择 <ruby> 救援正常启动 <rt> Resume normal boot </rt></ruby> 选项,并按下回车键。

再次按下回车键来退出恢复模式,并继续引导到正常模式。

如果你不想引导到正常模式,从救援模式中输入 `reboot` 并按下回车键来重新启动你的系统。
### 在 Ubuntu 22.04 / 20.04 LTS 中引导到紧急模式
当 GRUB 菜单出现时,按下 `e` 按键来编辑它。

找到以单词 `linux` 开头的一行代码,并在其结尾处添加下面的一行代码:
```
systemd.unit=emergency.target
```

在添加上面的代码行后,按下 `Ctrl + x` 组合键,或按下 `F10` 按键来引导到紧急模式。
数秒后,你将作为 `root` 用户来进入维护。将会提示你按下回车键来进入紧急模式。
下图是 Ubuntu 22.04 / 20.04 LTS 系统的紧急模式的样子:

现在,在紧急模式中做你想做的任何事。在紧急模式中,在你执行任何操作前,你可能需要以读/写模式来挂载根(`/`)文件系统。
```
mount -n -o remount,rw /
```
在完成后,按下 `Ctrl + d` 组合键来引导到正常模式。或者,你可以输入下面的任意一个命令来引导到正常模式。
```
systemctl default
```
或者,
```
exit
```
如果你想重新启动系统,而不是引导到正常模式,输入:
```
systemctl reboot
```
### 在 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 中引导到救援模式
启动你的 Ubuntu 系统。当 GRUB 菜单出现时,选择第一项并按下按键 `e` 来编辑。(为到达其行尾处,只需要按下 `Ctrl + e` 组合键,或使用你键盘上的 `END` 按键或 `←`/`→` 按键):

如果你没有看到 GRUB 菜单,只需要在 BIOS 徽标出现后,按下 `ESC` 按键来显示 GRUB 菜单。
找到以单词 `linux` 开头的一行代码,并在其结尾处添加下面的一行代码(为到达其行尾处,只需要按下 `Ctrl + e` 组合键,或使用你键盘上的 END`按键或`←`/`→` 按键):
```
systemd.unit=rescue.target
```

在添加上面的代码行后,只需要按下 `Ctrl + x` 组合键,或按下 `F10` 按键来引导到救援模式。数秒后,你将作为 `root` 用户进入维护(即单用户模式)。
下图是 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 服务器系统的救援模式的样子:

接下来,输入下面的命令来挂载根(`/`)文件系统为读/写模式。
```
mount -n -o remount,rw /
```
### 在 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 中引导到紧急模式
引导你的 Ubuntu 到紧急模式基本与上述方法相同。你所需要做的全部工作是,在编辑 GRUB 菜单时,将 `systemd.unit=rescue.target` 替换为 `systemd.unit=emergency.target` 。

在你添加 `systemd.unit=emergency.target` 后,按下 `Ctrl + x` 组合键,或按下 `F10` 按键来引导到紧急模式。

最后,你可以使用下面的命令来以读/写模式的方式来挂载根(`/`)文件系统:
```
mount -n -o remount,rw /
```
### 在救援模式和紧急模式之间切换
如果你正在救援模式中,你不必像我上述提到的那样来编辑 GRUB 的菜单启动项。相反,你只想要输入下面的命令来立刻切换到紧急模式:
```
systemctl emergency
```
同样,为从紧急模式切换到救援模式,输入:
```
systemctl rescue
```
### 总结
现在,你知道了什么是救援模式和紧急模式,以及如何在 Ubuntu 22.04 、20.04 和 18.04 LTS 系统中启动到这些模式。正如我已经提到的,在这里提供的这些步骤应该也适用于大多数当前使用 systemd 作为默认服务管理器的 Linux 发行版。
---
via: <https://ostechnix.com/how-to-boot-into-rescue-mode-or-emergency-mode-in-ubuntu-18-04/>
作者:[sk](https://ostechnix.com/author/sk/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
14,711 | Cloudflare 有了一个新东西,它可以替代互联网上烦人的验证码 | https://news.itsfoss.com/cloudflare-pat/ | 2022-06-15T10:49:39 | [
"验证码"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14711-1.html |
>
> 不想通过正确输入 <ruby> 验证码 <rt> CAPTCHA </rt></ruby> 来证明自己是个人类吗?Cloudflare 可能有了一个解决方案。
>
>
>

互联网服务巨头 Cloudflare 前两天 [宣布了](https://blog.cloudflare.com/eliminating-captchas-on-iphones-and-macs-using-new-standard/) <ruby> 私有访问令牌 <rt> Private Access Tokens </rt></ruby> 功能。这项功能旨在减少你在网络上看到的验证码数量,同时改善你的隐私。
你可能已经发现,验证码在移动设备上是一种可怕的体验。通常,它们会最终会占据整个屏幕,有时甚至无法完成。
作为替代方案,网站可以选择收集唯一识别数据,以证明你是人类。当然,从隐私的角度来看,这种做法是很糟糕的。如果这么做,许多重视隐私的公司都几乎无法避免他们受到 <ruby> 僵尸攻击 <rt> bot attacks </rt></ruby>。
幸运的是,私有访问令牌(PAT)的发布将改变这一点。
### 私有访问令牌会产生什么影响?
简而言之,私有访问令牌能够做到下面这些事:
* 在支持的设备上减少验证码数量
* 增强用户隐私
* 允许网站所有者确保访问者来自真实设备
然而,深入观察,我们可以看到私有访问令牌的影响力远不止于此。若使用传统的验证码,就有多个实体可以访问你的数据。
首先,你正在访问的网站知道你的 IP 地址和你正在访问的 URL。当然,这些数据是建立连接所需的最低要求。此外,对于更高级的功能,网站还会发送一些用户代理(UA)数据,还好这些数据并不是唯一可识别的。
然而,另一方,也就是验证码提供者,却可以收集更多的数据。与你要访问的网站一样,它也知道你的 IP 地址、用户代理数据和你访问的 URL。不幸的是,除此之外,他们还会收集其他数据,例如你的设备信息和交互数据。如果把这些信息,与你之前完成验证码的时间联系起来,你就会惊讶的发现,他们可以建立一个非常详细的属于你的个人资料。
幸运的是,有了 Cloudflare 的私有访问令牌,你就可以完全绕过验证码,从而阻止验证码提供者收集此类数据。
### 私有访问令牌是如何工作的?

验证码的理念是集中尽可能多的数据,私人访问令牌则恰恰相反,它将数据去中心化,因此任何一方都无法唯一识别你。在你提到数据共享之前,Cloudflare 就已经特别指出了,数据不会在各方之间共享。
当你访问使用 Cloudflare 和私人访问令牌的网站的时候,共有三方将处理你的数据的不同部分。
1. 网站。它只会知道你的 IP、URL 和用户代理,这也是建立连接所必需的。
2. 你的设备制造商。他们只会知道那些用于验证设备是否真实所需的设备数据,而不会知道你正在访问哪个网站,或你的 IP 地址是什么。验证了你的设备后,他们将生成一个令牌,该令牌将发送到 Cloudflare。
3. Cloudflare。他们将收到这个令牌,令牌中不包含你的任何设备数据,只有制造商对它是正品的“保证”。他们知道的唯一其他数据,就是你正在访问的网站,同样,这是为你提供内容所必需的。
通过这种方式,Cloudflare 无需接触你的数据,就可以对“你是一个人”充满信心。
### 支持的操作系统:没有 Linux?
你可能已经意识到,私人访问令牌需要特定的操作系统功能才能工作。目前,它们仅存在于苹果最新的操作系统上,即 iOS 和 iPadOS 16,以及 macOS Ventura。这是因为苹果的操作系统只在有限的硬件上运行,设备验证会更加容易。
另一方面,Linux 是一种通用操作系统,旨在在各种硬件上运行。因此,我认为,在可预见的未来,它都不会支持私人访问令牌。
回到苹果,我想到私人访问令牌也可能导致消费者维修设备的权利出现一些问题。例如,如果我用第三方的非正品电池更换了老旧的 iPhone 原装电池,私人访问令牌系统会特殊对待这种情况吗?
如果是 Linux 手机呢?这些制造商,如 Pine64 和 Purism,可能没有支持这样一个系统的基础设施。是否可以在这些上使用私人访问令牌呢?
Cloudflare 在 [公告](https://blog.cloudflare.com/eliminating-captchas-on-iphones-and-macs-using-new-standard/) 中提到:
>
> 我们正在积极努力让其他客户和设备制造商也使用私人访问令牌框架。每当新客户开始使用它时,从该客户进入你网站的流量将自动开始要求令牌,你的访问者将自动看到更少的验证码。
>
>
>
因此,我们希望看到它被更多的设备和操作系统采用。你如何看待 Cloudflare 的私人访问令牌呢?在下面的评论中发表你的看法吧!
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/cloudflare-pat/>
作者:[Jacob Crume](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Cloudflare, the internet services giant, has [just announced](https://blog.cloudflare.com/eliminating-captchas-on-iphones-and-macs-using-new-standard/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) Private Access Tokens. These aim to reduce the number of CAPTCHAs you see on the web while improving your privacy.
As you may have found out, CAPTCHAs are a horrible experience on mobile. They often end up occupying the entire screen and can be impossible to complete at times.
As an alternative, websites can elect to collect uniquely identifying data to prove that you are a human. Of course, from a privacy standpoint, this practice is terrible, leaving many privacy-valuing companies with little to prevent them from bot attacks.
Fortunately, the release of Private Access Tokens, or PATs, is set to change this.
## What Impact Will Private Access Tokens Have?
In short, PATs will:
- Reduce the number of CAPTCHAs on supported devices
- Increase user privacy
- Allow website owners to ensure that visitors are coming from actual devices
However, diving in a little deeper, we can see that PATs are much more impactful than at first glance. With traditional CAPTCHAs, there are multiple entities that can access your data.
Firstly, the website you are visiting knows your IP address and the URL you are visiting. Of course, this data is the minimum required to establish a connection. Additionally, for more advanced functionality, websites are also sent some user agent data, which is not uniquely identifiable.
However, the second party, the CAPTCHA provider, can collect a lot more data. Like with the website you want to visit, it knows your IP address, user agent data, and the URL you visit. Unfortunately, they also collect additional data, like your device information and interaction data. When tied back with previous times you have completed a CAPTCHA, they can build up an astonishingly detailed profile of you.
Fortunately, PATs by Cloudflare prevent such data from being collected, by ultimately bypassing the CAPTCHA altogether.
## How Do PATs Work?
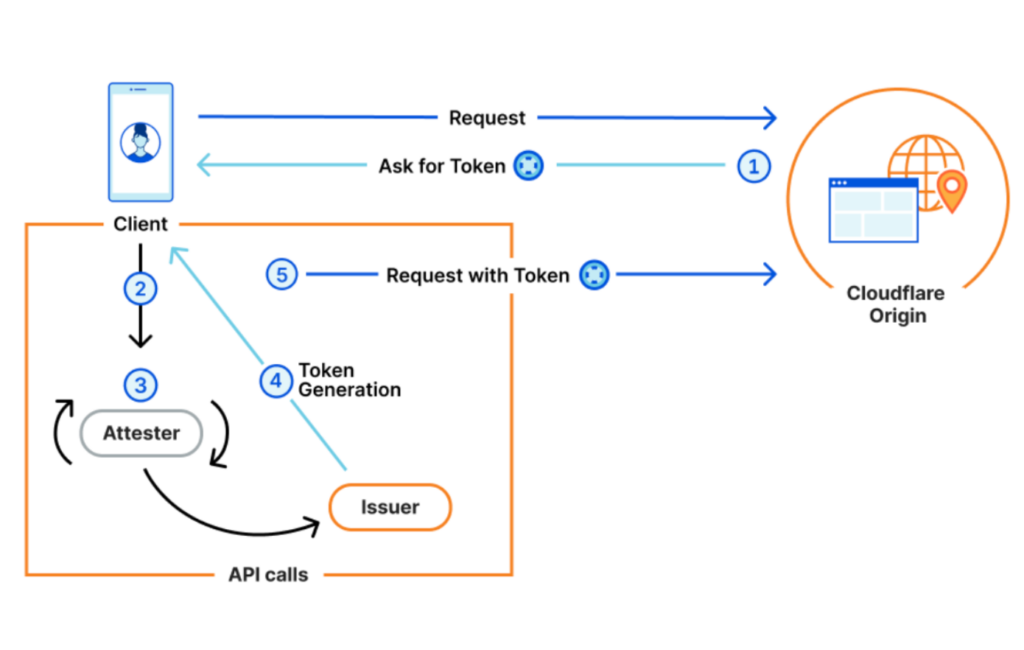
Unlike the CAPTCHA method of aggregating as much data as possible, PATs decentralize the data so that no single party can uniquely identify you. Before you mention data sharing, Cloudflare has specifically mentioned that data is not shared between parties.
When you go on to a website utilizing Cloudflare and PATs, a total of three parties will handle different portions of your data.
- The website. This will only know your IP, URL, and user agent, which again, is required for establishing a connection.
- Your device manufacturer. This will only know the device data required to verify that your device is genuine. They will NOT know what website you are visiting, or your IP address. After verifying your device, they will generate a token, which will be sent to Cloudflare.
- Cloudflare. Cloudflare will receive the token, which does not contain any of your device data, only a ‘guarantee’ of sorts from the manufacturer that it is genuine. The only other data they know is the website you are visiting, which is required to serve you the content.
The result of this is a system that gives Cloudflare confidence in you being a human, without ever having to touch your data.
## Supported Operating Systems: No Linux?
As you may have realized, PATs need specific operating system features to work. Currently, they are only present on the latest operating systems by Apple, namely iOS and iPadOS 16, as well as macOS Ventura. This is because Apple’s operating systems run on a limited set of hardware, making device verification significantly easier.
Linux, on the other hand, is a general-purpose operating system designed to run on a wide range of hardware. As a result, I don’t expect to see it support PATs in the near future.
Going back to Apple, it occurs to me that PATs could also cause some issues with consumers’ right to repair their devices. If, for example, I replaced a worn-out iPhone battery with a non-genuine one, would this be flagged by the PAT system?
What about Linux Phones? Manufacturers of these, like Pine64 and Purism, may not have the infrastructure to support such a system. Will it be possible to use PATs on these?
In the [announcement post](https://blog.cloudflare.com/eliminating-captchas-on-iphones-and-macs-using-new-standard/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), Cloudflare mentions:
We are actively working to get other clients and device makers utilizing the PAT framework as well. Any time a new client begins utilizing the PAT framework, traffic coming to your site from that client will automatically start asking for tokens, and your visitors will automatically see fewer CAPTCHAs.
So, we hope to see it being adopted by more devices, and operating systems. What do you think about PATs by Cloudflare? Let me know your thoughts in the comments down below.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,712 | 给 Linux 初学者的 7 条建议 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/linux-advice-beginners | 2022-06-15T14:39:44 | [
"初学者"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14712-1.html |
>
> 我们咨询了我们社区作者们,分享了他们的初学经验。
>
>
>

对 Linux 的新用户有什么建议?我们请社区的作者们分享了他们初学时的最佳经验。
### 1、用好 Linux 资源
我哥们儿告诉我,Linux 就像一个“软件积木搭建套装”(这是一个过时的词汇,指的是上世纪五六十年代流行的建筑积木玩具),这个比喻比较恰当。在 2001、2002 年那时,我曾经利用 Windows 3.1 和 Windows NT,尝试搭建一个安全、有用的 K12 学区网站,当时网上可用的资料不多。其中被推荐的《ROOT 用户指南》是一本“大部头”专业教程,信息丰富,但是有一定上手难度。
于我而言,Mandrake Linux 的线上课程是最有用的资源。该课程对使用和管理 Linux 桌面或服务器进行了详细的解读。我学习了该课程,并同时利用红帽公司维护的一个邮件列表服务,有问题时就在社区提问寻求帮助。
—— [Don Watkins](https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins)
### 2、在 Linux 社区寻求帮助
我的建议是要多问,你可以从网上搜索信息开始,看看其他人类似的问题(甚至是更好的提问)。问什么和如何问,需要花一定时间熟悉。
一旦你对 Linux 更加熟悉了,查看你感兴趣的各种相关论坛,在提问前,先看看是否有人已经提过相同问题,并获得了答案。
加入邮件列表也很有用,最后你会发现自己也能专业地答复提问。正如他们说的,通过回答他人的问题也会学到更多知识。
同时,你会越来越熟悉这个操作系统内部运行机制,再也不是初学时的一无所知。
—— [Greg Pittman](https://opensource.com/users/greg-p)
我的建议是利用 `man`、`info` 等帮助命令获取信息。另外,尽可能花时间熟悉命令行界面,且真正理解 UNIX 的设计理念。事实上,我最喜欢的书之一就是一本 80 年代的 UNIX 书籍,对理解文件、目录、设备、基础命令等非常有帮助。
—— [Alan Formy-Duval](https://opensource.com/users/alanfdoss)
我最好的建议是充分相信社区的答复、手册页的详细信息、介绍不同选项的 HOW-TO 文档。不管怎么说,我是在 2009 年左右开始学习的,当时有很多可用的工具和资源。有一个叫 “Linux from Scratch(LFS)”的项目 —— 从源码开始创建 Linux 系统,在这个项目我学会了很多内部原理知识,以及如何创建一个 LFS 镜像。
—— [Sumantro Mukherjee](https://opensource.com/users/sumantro)
我的建议是泛读。利用像 “Ask Fedora”、“Fedora Matrix chat” 等论坛,阅读他人的经验观点,并且尝试实践。我通过阅读他人的网上争论学习到很多东西,然后我会尝试找出问题的原因。
—— [Steve Morris](https://opensource.com/users/smorris12)
### 3、安装双操作系统
我在 90 年代末就开始安装双操作系统(Windows 和 Linux),虽然我真正想使用的是 Linux 操作系统,但我最终还是启动了 Windows 系统,以便在熟悉的桌面环境中工作。最好的建议之一是改变计算机系统启动顺序,所以每次我都反应不够快,自动进入了 Linux 系统。: )
—— [Heike Jurzik](https://opensource.com/users/hej)
我的团队里的一个人挑战我,要做一个知识交换。
他是我们的 Linux 系统管理员,利用 Joomla 搭建了一个网站(我们的 Web 团队擅长这个,他想学习更多知识),而我则安装了 Linux(以前一直是用 Windows)。我们一开始就用了双启动,因为我还有一堆依赖于操作系统的软件需要用于业务,但这让我对 Linux 的使用有了一个飞跃。
在我们各自学习新系统时,对方作为专家来互相帮助有助于共同成长,“一个都不能少!”,坚持不懈是一个很大的挑战。
我经历一个相当尴尬的低级错误后,在显示器上贴了一个大便签,上面写着“在使用任何 `rm` 操作前,首先要思考一下”。管理员给我写了一个命令行大全(网上有很多类似的),对于熟悉基础操作非常有用。我开始使用 Ubuntu 的 KDE 桌面环境时,发现对习惯于使用图形界面的初学者很有帮助。
从那以后我就开始长期使用 Linux(除了我的工作计算机),而那位管理员仍然在用 Joomla,看起来我俩都得到了成长。
—— [Ruth Cheesley](https://opensource.com/users/rcheesley)
### 4、为了安全请先备份
我的建议是使用一个带有简单且强大的备份软件的发行版。Linux 新用户会创建、编辑、破坏和恢复系统配置。当操作系统无法启动、丢失数据时,会让他们非常沮丧。
有了备份软件,他们的数据就有了保障。
我们都喜爱 Linux,因为它能让我们自由飞翔,但这是“双刃剑”,使用不当也有可能发生非常严重的错误。
—— [Giuseppe Cassibba](https://opensource.com/users/peppe8o)
### 5、分享你的 Linux 经验
我的建议是分享你的 Linux 使用经验。我曾经认为有一些发行版更适合新用户,所以当他们咨询使用 Linux 时,我总是推荐这些为“新用户准备的”发行版。但是当我坐在他们的计算机前,看起来却像是我从未用过 Linux 一样,因为一些新功能我也不熟悉。现在当有人咨询时,我会推荐自己使用的发行版,虽说这不一定是初学者的“最佳”版本,但毕竟我熟悉,他们遇到的问题我能够快速解决(当然我自己也会在分享中学到新东西)。
—— [Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth)
以前有句俗话叫“不要随便使用杂志封面上宣传的发行版,使用你朋友都在用的,当你遇到问题时才能更好地需求帮助”。将关键词“杂志封面”替换为“互联网”,这句话依然有效 : -) 。我从未听从过这个建议,因为我是方圆五十公里内唯一使用 Linux 的人,周围的人都在用 FreeBSD、IRIX、Solaris 和 Windows 3.11 等操作系统,最后,我就是那个被人们寻求 Linux 帮助的人。
—— [Peter Czanik](https://opensource.com/users/czanik)
### 6、坚持学习 Linux
在到 Red Hat 工作前,我是一名分销商合作伙伴,我有几个提供旅行护士的家庭健康代理机构客户,他们使用了一个叫“Carefacts”的软件包,最初用于 DOS,在旅行笔记本电脑和中心数据库同步中总是出错。
早期我听到的最好建议是认真研究一下开源运动。开源在 2022 年是主流思想,但在一代人以前,从 Red Hat 的零售商购买 Linux 安装光盘是带有革命性的创新行为。开源打破了常规,我认为要客观看待开源,但确实惊叹到了相当一部分人。
我的公司在 20 世纪 90 年代中期搭建了第一个客户防火墙,那是基于 Windows NT 和 Altavista 的一个产品,但是经常发生错误崩溃。我们自己又搭建了一个基于 Linux 的防火墙,再也没有出问题了。因此,我们用 Linux 替换了客户的那套 Altavista 系统,稳定地运行了多年。我们在 1999 年底搭建了另一个客户防火墙,当时我花三周读完了一本关书,介绍了数据包过滤和 ipchains 的正确使用,当我完成时感觉超赞,它解决了所有问题。在接下来的 15 年,我搭建安装了数百个防火墙系统,主要采用 iptables 技术,有些利用桥接或 ARP 代理以及 QOS 保障视频会议传输,有些利用 IPSEC 和 OpenVPN 隧道。我靠管理个人防火墙和一些双机热备系统赚取生活费,非常不错,而以前都是用的 Windows 系统。我甚至还建了一些虚拟防火墙。
但是技术在高速发展,2022 年,iptables 已过时,我以前的防火墙技术也成了美好的回忆。
目前的经验之谈?永远不要停止探索。
—— [Greg Scott](https://opensource.com/users/greg-scott)
### 7、享受过程
耐心点,Linux 和之前你熟悉的操作系统不太相同,准备拥抱一个充满无限可能的新世界,尽情享受吧。
—— [Alex Callejas](https://opensource.com/users/darkaxl)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/linux-advice-beginners>
作者:[Opensource.com](https://opensource.com/users/admin) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lightchaserhy](https://github.com/lightchaserhy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | What advice would you give a new Linux user? We asked our community of writers to share their favorite Linux advice.
## 1. Use Linux resources
My brother told me that Linux was like a "software erector set" (that's a dated reference to the old Erector sets that could be purchased in the 1950s and 1960s) which was a helpful metaphor. I was using Windows 3.1 and Windows NT at the time and was trying to build a useful and safe K-12 school district website. This was in 2001 and 2002 and there were very few texts or resources on the web that were helpful. One of the resources recommended was the "Root Users Guide," a very large book that had lots of printed information in it but was tough to decipher and know just how to proceed.
One of the most useful resources for me was an online course that Mandrake Linux maintained. It was a step-by-step explanation of the nuances of using and administering a Linux computer or server. I used that along with a listserv that Red Hat maintained in those days, where you could pose questions and get answers.
## 2. Ask the Linux community for help
My advice is to ask questions, in all of their settings. You can start out with an Internet search, looking for others who have had the same or similar questions (maybe even better questions.) It takes a while to know what to ask and how to ask it.
Once you become more familiar with Linux, check through the various forums out there, to find one or more that you like, and again, before you ask something yourself, look to see if someone else has already had the question and had it answered.
Getting involved in a mail list is also helpful, and eventually, you may find yourself knowledgeable enough to answer some questions yourself. As they say, you learn the most about something by becoming able to answer someone else's questions about it.
Meanwhile, you also become more familiar with using a system that's not a black box that you never understand how something is done except by paying for it.
My advice is to get familiar with help utilities such as man and info. Also, spend as much time as possible at the command line interface and really get used to the fundamental UNIX design. As a matter of fact, one of my favorite books is a UNIX book from the 80s because it really helps in understanding files, directories, devices, basic commands, and more.
The best advice I got was to trust the community with answers and manual pages for detailed information and "how-to" use different options. However, I started off around 2009-ish, there were a lot of tools and resources available, including a project called [Linux from Scratch (LFS)](https://linuxfromscratch.org/). This project really taught me a lot about the internals and how to actually build an LFS image.
My advice is to read. Using places like [Ask Fedora](https://ask.fedoraproject.org) or the Fedora Matrix chat or other forum type areas. Just read what others are saying, and trying to fix. I learned a lot from just reading what others were struggling with, and then I would try to figure out how the issue was caused.
## 3. Try dual booting
I started with a dual-boot system in the late 90s (Windows and Linux), and while I wanted to really use Linux, I ended up booting Windows to work in my familiar desktop environment. One of the best pieces of advice was to change the boot order, so every time I wasn't quick enough, I ended up using Linux. ;)
I was challenged by one of my team to do a knowledge swap.
He (our Linux sysadmin) built his website in **Joomla!** (which our web team specialized in, and he wanted to know more about) and I adopted Linux (having been Windows only to that point.) We dual booted to start with, as I still had a bunch of OS-dependent software I needed to use for the business, but it jump-started my adoption of Linux.
It was really helpful to have each other as an expert to call on while we were each learning our way into the new systems, and quite a challenge to keep going and not give up because he hadn't!
I did have a big sticky note on my monitor saying "anything with `rm`
in the command, ask first" after a rather embarrassing blunder early on. He wrote a command-line cheat sheet (there are dozens [online now](https://opensource.com/downloads/linux-common-commands-cheat-sheet)) for me, which really helped me get familiar with the basics. I also started with the [KDE version](https://opensource.com/article/22/2/why-i-love-linux-kde) of Ubuntu, which I found really helpful as a novice used to working with a GUI.
I've used Linux ever since (aside from my work computer) and he's still on Joomla, so it seemed to work for both of us!
## 4. Back it up for safety
My advice is to use a distro with an easy and powerful backup app. A new Linux user will touch, edit, destroy and restore configurations. They probably will reach a time when their OS will not boot and losing data is frustrating.
With a backup app, they're always sure that their data is safe.
We all love Linux because it allows us to edit everything, but the dark side of this is that making fatal errors is always an option.
## 5. Share the Linux you know and use
My advice is to share the Linux you use. I used to believe the hype that there were distributions that were "better" for new users, so when someone asked me to help them with Linux, I'd show them the distro "for new users." Invariably, this resulted in me sitting in front of their computer looking like I had never seen Linux before myself, because something would be just unfamiliar enough to confuse me. Now when someone asks about Linux, I show them how to use what I use. It may not be branded as the "best" Linux for beginners, but it's the distro I know best, so when their problems become mine, I'm able to help solve them (and sometimes I learn something new, myself.)
There was a saying back in the old days, "Do not just use a random Linux distro from a magazine cover. Use the distro your friend is using, so you can ask for help when you need it." Just replace "from a magazine cover" with "off the Internet" and it's still valid :-) I never followed this advice, as I was the only Linux user in a 50km radius. Everyone else was using FreeBSD, IRIX, Solaris, and Windows 3.11 around me. Later I was the one people were asking for Linux help.
## 6. Keep learning Linux
I was a reseller partner prior to working at Red Hat, and I had a few home health agencies with traveling nurses. They used a quirky package named Carefacts, originally built for DOS, that always got itself out of sync between the traveling laptops and the central database.
The best early advice I heard was to take a hard look at the open source movement. Open source is mainstream in 2022, but it was revolutionary a generation ago when nonconformists bought Red Hat Linux CDs from retailers. Open source turned conventional wisdom on its ear. I learned it was not communism and not cancer, but it scared powerful people.
My company built its first customer firewall in the mid-1990s, based on Windows NT and a product from Altavista. That thing regularly crashed and often corrupted itself. We built a Linux-based firewall for ourselves and it never gave us a problem. And so, we replaced that customer Altavista system with a Linux-based system, and it ran trouble-free for years. I built another customer firewall in late 1999. It took me three weeks to go through a book on packet filtering and get the `ipchains`
commands right. But it was beautiful when I finally finished, and it did everything it was supposed to do. Over the next 15+ years, I built and installed hundreds more, now with `iptables`
; some with bridges or proxy ARP and QOS to support video conferencing, some with [IPSEC](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/run-your-own-vpn-libreswan) and [OpenVPN tunnels](https://opensource.com/article/21/8/openvpn-server-linux). I got pretty good at it and earned a living managing individual firewalls and a few active/standby pairs, all with Windows systems behind them. I even built a few virtual firewalls.
But progress never stops. By 2022, [iptables is obsolete](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/make-linux-stronger-firewalls) and my firewall days are a fond memory.
The ongoing lesson? Never stop exploring.
## 7. Enjoy the process
Be patient. Linux is a different system than what you are used to, be prepared for a new world of endless possibilities. Enjoy it.
## 4 Comments |
14,715 | 开源电子邮件客户端 Thunderbird 即将登陆 Android | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/thunderbird-the-open-source-email-client-is-coming-to-android/ | 2022-06-16T08:41:20 | [
"Thunderbird"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14715-1.html | 
开源电子邮件客户端 Thunderbird 将通过 K-9 Mail Android 电子邮件应用项目登陆 Android,该项目与 Thunderbird 合并后的产品就是 Thunderbird Android 电子邮件应用。两年前,Thunderbird 被转移到了 Mozilla 基金会的子公司 MZLA Technologies Corporation 下,该公司的所有权结构与基金会子公司 Mozilla 公司旗下的 Firefox 类似。有了 OpenPGP 端到端加密和期待已久的移动应用等新功能,Thunderbird 项目能够开辟出一条自己的道路。
根据 Thunderbird 团队的说法,Thunderbird 产品经理 Ryan Lee Sipes 和 K-9 的主要维护者 Christian Ketterer,两人早在 2018 年就开始讨论可能的 Thunderbird 电子邮件应用合作了。到了 2022 年,两人决定不再让 Thunderbird 从头开始开发自己的应用程序,而是直接让 K-9 加入 Thunderbird。
Thunderbird 团队表示:“许多 Thunderbird 用户都要求在移动设备上获得 Thunderbird 体验,我们打算通过把 K-9 打造成令人惊叹的产品(并将其变成 Android 上的 Thunderbird)来提供这种体验。K-9 将补充提供 Thunderbird 体验,并增强它的使用场景和方式,让用户获得出色的电子邮件体验。我们对桌面 Thunderbird 的承诺没有改变,我们团队中的大多数人都致力于将其打造为一流的电子邮件客户端,并将保持这种状态。”
虽然 K-9 在 Google Play 上并不是特别受欢迎的电子邮件应用,但它已经获得了 500 万次下载。K-9 Mail 的路线图目前包括:使用 Thunderbird 帐户自动配置的帐户设置、改进的文件夹管理、消息过滤器支持,以及桌面和移动 Thunderbird 之间的同步。虽然 Thunderbird 知道人们对 iOS 版 Thunderbird 应用程序也很感兴趣,但在常见问题解答(FAQ)中,该项目仅声明它正在“评估”这种可能性。
Thunderbird 团队还打算将 Firefox Sync 作为一种在 Thunderbird 和 K-9 Mail 之间同步帐户的方法。它应该会在 2023 年夏天正式投入使用。该项目还在研究将哪些 Thunderbird 功能引入 Android 应用程序,例如日历、任务、提要和聊天支持等。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/thunderbird-the-open-source-email-client-is-coming-to-android/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Thunderbird, the open source email client, is coming to Android via the K-9 Mail Android email app project, which is merging with Thunderbird to form the Thunderbird Android email app. Thunderbird was moved to the Mozilla Foundation’s subsidiary MZLA Technologies Corporation two years ago, in a similar ownership structure to Firefox under the foundation’s subsidiary, Mozilla Corporation. With new features such as OpenPGP end-to-end encryption and a long-awaited mobile app, the Thunderbird project was able to forge its own path.
According to the Thunderbird team, discussions began in 2018 between Thunderbird product manager Ryan Lee Sipes and K-9’s lead maintainer Christian Ketterer about a possible collaboration for a Thunderbird email app. In 2022, the two have decided that rather than Thunderbird developing its own app from scratch, K-9 should simply join Thunderbird.
“Many Thunderbird users have asked for a Thunderbird experience on mobile, which we intend to provide by helping make K-9 amazing (and turning it into Thunderbird on Android). K-9 will supplement the Thunderbird experience and enhance where and how users are able to have a great email experience. Our commitment to desktop Thunderbird is unchanged, most of our team is committed to making that a best-in-class email client and it will remain that way,” Thunderbird said.
K-9 isn’t a particularly popular email app on Google Play, but it has received 5 million downloads. K-9 Mail’s roadmap currently includes: account setup using Thunderbird account auto-configuration; improved folder management; message filter support; and syncing between desktop and mobile Thunderbird. While Thunderbird acknowledges that there has been interest in a Thunderbird app for iOS, the project only states in a FAQ that it is “evaluating” the possibility.
The Thunderbird team also intends to include Firefox Sync as a method for syncing accounts between Thunderbird and K-9 Mail. This should go into effect in the summer of 2023. The project is also investigating which Thunderbird features to bring to the Android app, such as calendar, task, feed, and chat support. |
14,716 | 在 Linux 上安装 FFmpeg | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/06/install-ffmpeg-ubuntu/ | 2022-06-16T10:33:00 | [
"FFmpeg"
] | /article-14716-1.html | 
>
> 本教程介绍了在 Ubuntu 及其他 Linux 发行版上安装 FFmpeg 的步骤。
>
>
>
FFmpeg 是一套处理多媒体文件的软件库。凭借这些强大的库,FFmpeg 能够转换格式、推流以及处理音频和视频文件。许多 Linux 的前端应用都使用 FFmpeg 作为后端支持,所以这些应用对 FFmpeg 的依赖度非常高。举个例子,录屏软件可能会用到 FFmpeg 将录屏转换为 gif 动图。
VLC 多媒体播放器、YouTube、Blender、Kodi、Shotcut 和 Handbrake 等流行的应用与服务都在使用 FFmpeg,这仅仅一小部分。
趣事:NASA 火星 2020 计划的探测器“毅力”号在将图像和视频发送到地球之前,会先使用 FFmpeg 对其进行处理。
### 关于 FFmpeg
[FFmpeg](https://ffmpeg.org/) 本身是一款非常强大的命令行实用程序,在 Linux 发行版、Windows 以及 macOS 等系统上均可运行,支持多种架构。FFmpeg 是用 C 语言和汇编语言编写的,性能强大,提供跨平台支持。
#### 核心
FFmpeg 的核心是命令行实用程序,既可在命令行上使用,也可以经由任何程序语言调用。比如,你可以在 Shell 程序或 python 脚本中使用 FFmpeg。
* `ffmpeg`:用于转换音视频格式,包括来自视频直播的信号源。
* `ffplay`:FFmpeg 配套使用的媒体播放器
* `ffprobe`:显示媒体文件信息的命令行工具,可将信息输出为 csv、xml、json 等格式。
### FFmpeg 安装
在 Ubuntu 等 Linux 发行版上, FFmpeg 的安装比较简单。打开终端,运行以下命令安装即可。
#### Ubuntu 及与其相似的发行版
```
sudo apt install FFmpeg
```
#### Fedora
在 Fedora Linux 上安装 FFmpeg,你需要添加 [RPM Fusion 仓库](https://www.debugpoint.com/2020/07/enable-rpm-fusion-fedora-rhel-centos/),因为 Fedora 官方仓库没有 FFmpeg 软件包。
```
sudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm
```
```
sudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-
```
```
sudo dnf install ffmpeg
```
#### Arch Linux
```
pacman -S ffmpeg
```
安装完成后,可输入以下命令查看安装是否成功。
```
ffmpeg --version
```

### 示例:FFmpeg 的基本操作
首先,我们先来看看 FFmpeg 语法的一个简单例子。如下,该语法可以将 mp4 文件转换为 mkv 文件。
1、视频文件格式转换
```
ffmpeg -i big_buck_bunny.mp4 big_buck_bunny.mkv
```
当然,这种写法最为简单易懂,但它并不完整,因为没有输入 <ruby> 比特率 <rt> bit rate </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 分辨率 <rt> resolution </rt></ruby> 以及其他的视频文件属性。
2、音频文件格式转换
其次,输入与上面相似的命令可以转换音频文件的格式。
```
ffmpeg -i sunny_day.ogg sunny_day.mp3
```
3、使用音视频编解码器执行格式转换
最后,在下面的例子中,我们可以使用特定的 <ruby> 编解码器 <rt> codec </rt></ruby> 来转换视频格式。参数 `-c` 搭配 `a` 或者 `v`,可以分别定义音频和视频文件。以下转换命令使用 `libvpx` 视频编解码器和 `libvorbis` 音频编解码器。
```
ffmpeg -i big_buck_bunny.mp4 -c:v libvpx -c:a libvorbis big_buck_bunny.webm
```
### 如何确定自己系统中有哪些编码器和解码器?
#### 显示所有编解码器
输入以下命令,打印所有编解码器。
```
ffmpeg -codecs
```
该命令可以打印出所有可用的编解码器,并显示每个编解码器对应的功能信息,比如是否支持解码或编码。此外,如以下输出结果所示,打印出来的信息还会按照首字母顺序标注出每个编码器和解码器的位置。
```
D..... = 支持解码
.E.... = 支持编码
..V... = 视频编解码器
..A... = 音频编解码器
..S... = 字幕编解码器
...I.. = 仅限帧内编解码器
....L. = 有损压缩
.....S = 无损压缩
```

#### 显示所有编码器
输入下列命令,打印出所有编码器
```
ffmpeg -encoders
```
#### 显示所有解码器
同样,输入下列命令,打印出所有解码器。
```
ffmpeg -decoders
```
#### 更多信息
输入参数 `-h`,获取更多关于编码器或解码器的信息。
```
ffmpeg -h decoder=mp3
```
### 总结
我希望这篇文章可以帮助你了解 FFmpeg 的基本知识及基本命令。若要了解更多信息,可前往 FFmpeg 官方网站浏览 [帮助文档](https://ffmpeg.org/documentation.html)。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/06/install-ffmpeg-ubuntu/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[aREversez](https://github.com/aREversez) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,717 | Thonny:在学校教授 Python 编程的理想 IDE | https://itsfoss.com/thonny-python-ide/ | 2022-06-16T13:33:56 | [
"Python"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14717-1.html | 
在 Linux 中运行一个 Python 程序只需要简单地在终端中执行 Python 文件就行。
但这对人们来说不是很方便,也不能帮助你调试你的程序。太原始了。
有几个 IDE 和文本编辑器可以用于 Python 开发。Linux 用户可以使用 [PyCharm 社区版](https://itsfoss.com/install-pycharm-ubuntu/)。
我最近发现了另一个专门为 Python 初学者制作的 IDE。我喜欢这个应用的想法,因此我在这里与你分享。
### Thonny 是一个跨平台、开源的 Python IDE,适合初学者使用
[Thonny](https://thonny.org/) 在用户界面和用户体验方面,感觉就像 Python 版本的 Eclipse。考虑到大多数 C++ 和 Java 的初学者都是从 Eclipse 开始的,而且许多人后来一直使用它,这也不完全是一件坏事。
它不是一个新的工具。它已经出现好几年了。我没有用 Python 进行编码,所以直到最近才发现它。
Thonny 专注于 Python,提供了帮助 Python 初学者了解其程序行为的功能。让我们来看看这些功能。
#### 即装即用
Thonny 自带 Python,所以你不需要为安装 Python 做额外的努力。这对 Linux 用户来说不是什么大事,因为大多数发行版都默认安装了 Python。
界面很简单。它给你一个编辑器,你可以写你的 Python 程序,然后点击运行按钮或使用 `F5` 键来运行程序。输出显示在底部。

#### 查看变量
在 “<ruby> 查看 <rt> View </rt></ruby>-><ruby> 变量 <rt> Variables </rt></ruby>”,你可以看到所有变量的值。不需要将它们全部打印出来。

#### 内置调试器
通过使用调试器一步步运行你的程序。你可以从顶部的菜单或使用 `Ctrl + F5` 键访问它。在这里你甚至不需要设置断点。你可以用 `F6` 进入大步骤,或用 `F7` 进入小步骤。

在小步骤中,你可以看到 Python 是如何看待你的表达式的。这对新的程序员理解他们的程序为什么以某种方式表现非常有帮助。

不止这样。对于函数调用,它会打开一个新的窗口,里面有独立的局部变量表和代码指针。超级酷!
#### 语法错误高亮
初学者经常会犯一些简单的语法错误,如缺少小括号、引号等。Thonny 会在编辑器中立即指出来。
本地变量也可以从视觉上与全局变量区分开来。
#### 自动补全
你不需要输入所有的东西。Thonny 支持自动补全代码,这有助于加快编码。

#### 访问系统 shell
在工具中,你可以访问系统 shell。在这里你可以安装新的 Python 包或学习从命令行处理 Python。

请注意,如果你使用 Flatpak 或 Snap,Thonny 可能无法访问系统 shell。
#### 从 GUI 管理 Pip
进入工具和管理包。它会打开一个窗口,你可以从这个 GUI 中安装 Pip 软件包。

对于学习 Python 来说,功能足够好,对吗?让我们看看如何安装它。
### 在 Linux 上安装 Thonny
Thonny 是一个跨平台的应用。它可用于 Windows、macOS 和 Linux。
它是一个流行的应用,你可以在大多数 Linux 发行版的仓库中找到它。只要在你的系统的软件中心寻找它。
另外,你也可以随时使用你的 Linux 发行版的包管理器。
在 Debian 和基于 Ubuntu 的发行版上,你可以使用 `apt` 命令来安装它。
```
sudo apt install thonny
```
它会下载一堆依赖关系和大约 300MB 的软件包。
安装后,你可以在菜单中搜索它,并从那里安装它。
### 总结
Thonny 对于初级 Python 程序员来说是个不错的工具。不是说专家不能使用它,但它更适合在学校和学院使用。学生们会发现它有助于学习 Python 和理解他们的代码是如何以某种方式表现出来的。事实上,它最初是在爱沙尼亚的塔尔图大学开发的。
总的来说,对于 Python 学习者来说是一个很好的软件。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/thonny-python-ide/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Running a Python program in Linux is as simple as executing the Python file in the terminal.
But that’s not very convenient for everyone and it doesn’t help you debug your programs. Too raw.
There are several IDEs and text editors that can be used for Python development. The [PyCharm community edition is available for Linux users](https://itsfoss.com/install-pycharm-ubuntu/).
I recently came across another IDE specifically crafted for Python beginners. I liked the idea of this application and hence I am sharing it with you here.
## Thonny is a cross-platform, open source Python IDE for beginners
[Thonny](https://thonny.org/?ref=itsfoss.com) feels like the Python version of Eclipse in terms of UI and UX. And that’s not entirely a bad thing considering most C++ and Java beginners start with Eclipse and many stay with it afterward.
It’s not a new tool. It has been on the horizon for some years now. I don’t code in Python so I never discovered it until recently.
Dedicated to Python, Thonny has features that help Python beginners understand how their program behaves. Let’s take a look at those features.
### Plug and play
Thonny comes with Python so you don’t need to do additional effort for installing Python. That’s not a big deal for Linux users as most distributions have Python installed by default.
The interface is simple. It gives you an editor where you can write your Python program and hit the Run button or use F5 key to play the program. The output is displayed at the bottom.
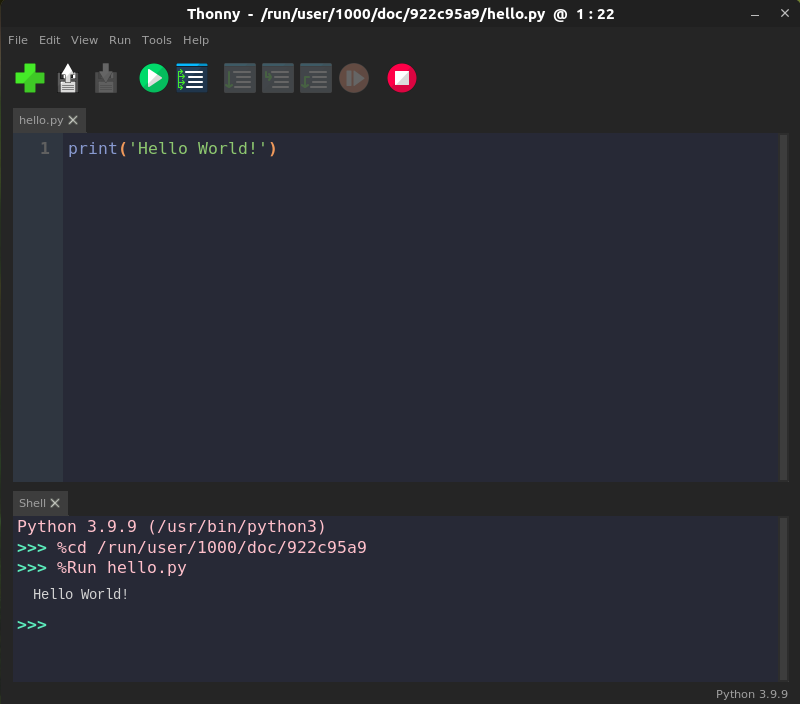
### See variables
From the View->Variables, you can see the values of all the variables. No need to print them all.
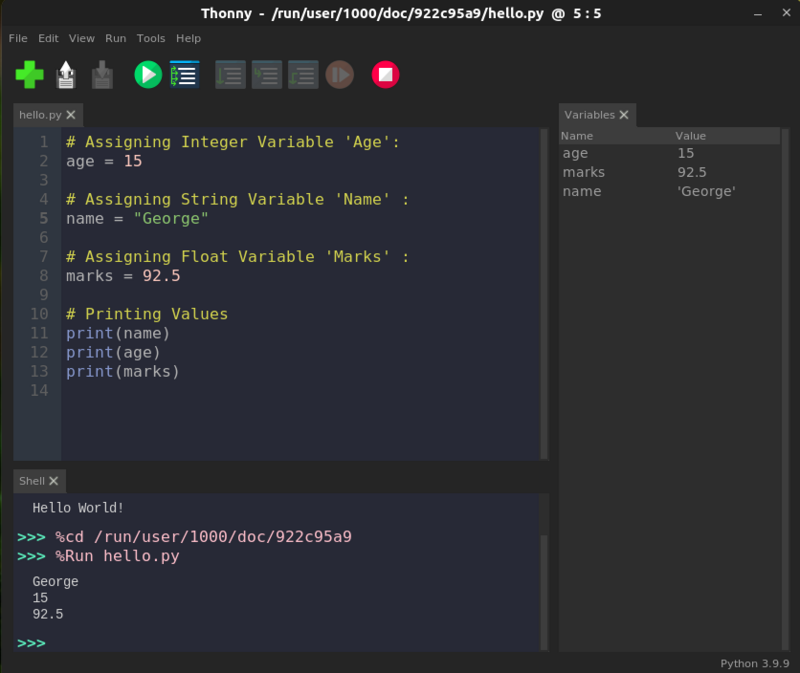
### Built-in debugger
Run your program step by step by using the debugger. You can access it from the top menu or use the Ctrl+F5 keys. You don’t even need the breakpoints here. You can go into big steps with F6 or in small steps with F7.
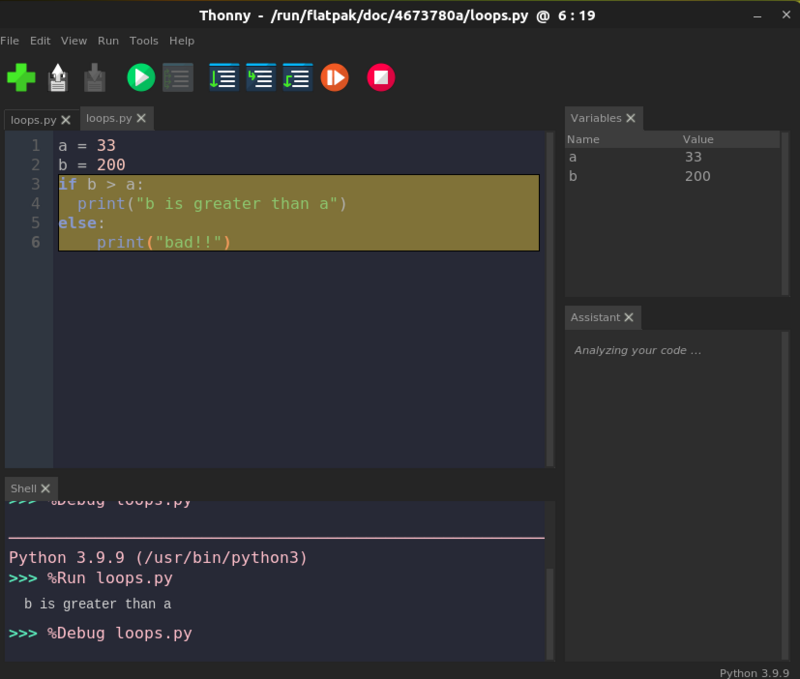
In small steps, you can see how Python sees your expressions. This is very helpful for new programmers to understand why their program is behaving in a certain manner.
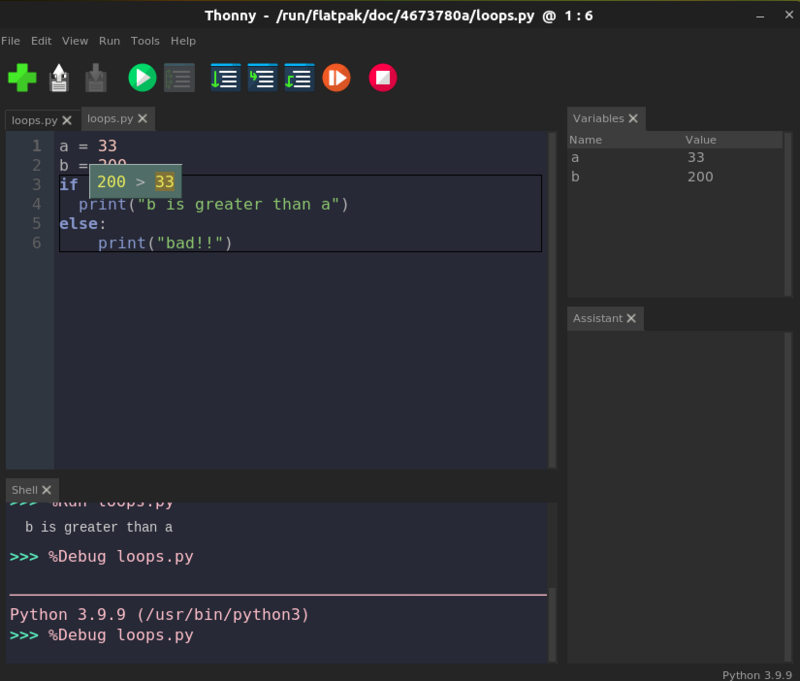
That’s not it. For function calls, it opens a new window with separate local variables table and code pointer. Super cool!
### Syntax error highlighter
Beginners often make simple syntax errors like missing paranthesis, quotes etc. Thonny is points it out immediately in the editor itself.
Local variables are also visually distinguished from globals.
### Auto completion
You don’t have to type everything. Thonny supports auto code completion which helps in coding faster.
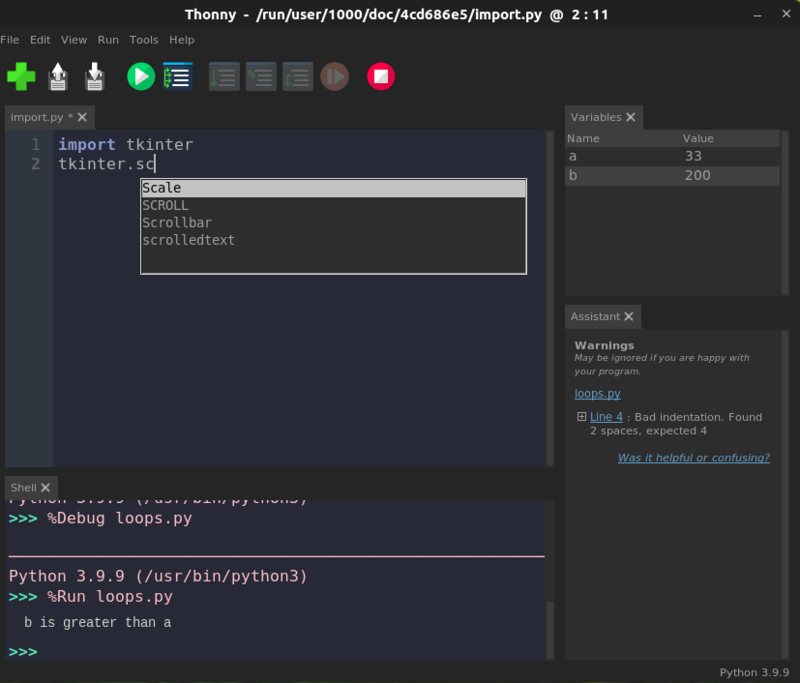
### Access to system shell
From the Tools, you can access the system shell. From here you can install new Python package or learn to handle Python from the command line.
Please note that if you use Flatpak or Snap, Thonny may not be able to access the system shell.
### Manage Pip from GUI
Go to Tools and Manage packages. It opens a window and you can install Pip packages from this GUI.
Good enough features for learning Python, right? Let’s see how to install it.
## Installing Thonny on Linux
Thonny is a cross-platform application. It is available for Windows, macOS and Linux.
It’s a popular application and you can find it in the repositories of most Linux distributions. Just look for it in your system’s software center.
Alternatively, you can always use the package manager of your Linux distribution.
On Debian and Ubuntu-based distributions, you can use the apt command to install it.
`sudo apt install thonny`
It downloads a bunch of dependencies and around 300 MB of packages.
Once installed, you can search for it in the menu and install it from there.
## Conclusion
There are plenty of other [Python IDEs available for Linux](https://itsfoss.com/best-python-ides-linux/).
[7 Best Python IDEs for Ubuntu LinuxLooking to code Python on your Linux system? Here are the best IDEs you can use for Python programming in Linux desktop.](https://itsfoss.com/best-python-ides-linux/)

Thonny is a decent tool for beginner Python programmers. Not that experts cannot use it but it’s more suited to be used in schools and colleges.
Students will find it helpful in learning Python and understanding how their code behaves in a certain manner. In fact, it was originally developed in the University of Tartu, Estonia.
Overall, good software for Python learners. |
14,719 | 使用 LibreOffice 进行首次开源贡献的 6 种简单方法 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/first-open-source-contribution-libreoffice | 2022-06-16T23:05:00 | [
"开源",
"LibreOffice"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14719-1.html |
>
> 2022 年 5 月是 LibreOffice 月。这里有一些简单的方法来完成你的第一个开源贡献。
>
>
>

“参与”开源似乎有点令人困惑。你从哪里开始?如果你不会编程怎么办?你取得谁的同意?别人怎么知道你做出了贡献,会有人关心吗?
这类问题实际上有答案(你自己选择就行;没关系;不用谁的同意;你告诉他们;是的),但在 2022 年 5 月,有一个简单的答案:LibreOffice。5 月是参与 LibreOffice 及其管理机构 <ruby> 文档基金会 <rt> The Document Foundation </rt></ruby> 的月份。他们正在邀请各种各样的贡献者以六种不同的方式提供帮助,其中只有一种与代码有任何关系。无论你的技能如何,你都可以找到一种方法来帮助这个世界上最好的办公套件。
### 为 LibreOffice 做出贡献的 6 种方式
以下是你可以做的:
* Handy Helper:在 [Ask LibreOffice](http://ask.libreoffice.org/) 上回答其他 LibreOffice 用户的问题。如果你是 LibreOffice 的狂热用户,并且认为你有可以帮助他人的有用提示和技巧,那么这就是你一直在等待的角色。
* First Responder:当错误报告得到不止一个用户确认时会更好。如果你擅长安装软件(有时错误报告是针对比你通常使用的版本更旧的版本),那么请访问 [LibreOffice Bugzilla](https://bugs.documentfoundation.org/buglist.cgi?bug_status=__open__&content=&no_redirect=1&order=changeddate%20DESC%2Cpriority%2Cbug_severity&product=&query_based_on=&query_format=specific) 并查找尚未确认的新错误。当你找到时,试着复制所报告的内容。假设你可以做到这一点,请添加一条评论,例如 “CONFIRMED on Linux (Fedora 35) and LibreOffice 7.3.2”。
* Drum Beater:开源项目很少有大公司投入营销资金来推广它们。如果所有声称喜欢开源的公司都能提供帮助,那就太好了,但不是所有的公司都这样做,那么为什么不发出你的声音呢?在社交媒体上告诉你的朋友你为什么喜欢 LibreOffice,或者你用它做什么(当然还要加上#libreoffice 标签。)
* Globetrotter:LibreOffice 已经支持多种不同的语言,但并不是所有语言。 LibreOffice 正在积极开发中,因此它的界面翻译需要保持最新。[在这里参与](https://www.libreoffice.org/community/localization/)。
* Docs Doctor:LibreOffice 有在线帮助和用户手册。如果你擅长向其他人解释事情,或者如果你擅长校对其他人的文档,那么你应该联系 [文档团队](https://www.libreoffice.org/community/docs-team)。
* Code Cruncher:你可能不会立即深入了解 LibreOffice 的代码库并进行重大更改,但这通常不是项目所需要的。如果你知道如何编码,那么你可以[按照此 wiki 页面上的说明](https://wiki.documentfoundation.org/Development/GetInvolved)加入[开发人员社区](https://www.libreoffice.org/community/developers/)。
### 免费贴纸
我不想提前提到这一点,因为很明显你参与 LibreOffice 只是因为你喜欢参与一个优秀的开源项目。但是,你最终会发现,所以我不妨告诉你:通过为 LibreOffice 做出贡献,你可以注册然后从文档基金会获得免费贴纸。你肯定一直想 [装饰你的笔记本电脑吧](https://opensource.com/business/15/11/open-source-stickers)?
不过,不要被战利品的承诺分心。如果你对参与开源感到困惑但很兴奋,那么这是一个很好的机会。它代表了你参与开源的一般方式:寻找需要做的事情,去做它,然后你和其他人讨论它,这样你就可以获得下一步可以做什么的想法。经常这样做,你就会找到进入社区的方式。最终,你不会再纠结于如何参与开源,因为你已经忙于贡献!
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/first-open-source-contribution-libreoffice>
作者:[Klaatu](https://opensource.com/users/klaatu) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkskjjk](https://github.com/lkskjjk) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | "Getting involved" with open source can seem a little confusing. Where do you go to get started? What if you don't know how to code? Who do you talk to? How does anybody know that you have contributed, and besides that does anybody care?
There are actually answers to questions like those (your choice, it's OK, nobody, you tell them, yes) but during the month of May 2022, there's one simple answer: LibreOffice. This month is a [month of participation at LibreOffice](https://opensource.com/LibreOffice%20is%20have%20a%20%22month%20of%20contribution%22%20during%20May%2C%20They%27re%20doing%20a%20nice%20job%20of%20directing%20people%20to%20a%20diverse%20set%20of%20contribution%20avenues.%20https%3A//blog.documentfoundation.org/blog/2022/05/01/the-month-of-libreoffice-may-2022-starts-today-join-in-and-get-snazzy-merch/) and its governing body, The Document Foundation. They're inviting contributors of all sorts to help in any of six different ways, and only one of those has anything at all to do with code. No matter what your skill, you can probably find a way to help the world's greatest office suite.
## 6 ways to contribute to LibreOffice
Here's what you can do:
**Handy Helper:**Go answer questions from other LibreOffice users on[Ask LibreOffice](http://ask.libreoffice.org/). If you're an avid user of LibreOffice and think you have useful tips and tricks that will help others, this is the role you've been waiting for.**First Responder:**Bug reports are better when they're confirmed by more than just one user. If you're good at installing software (sometimes bug reports are for older versions than what you might be using normally) then go to the[LibreOffice Bugzilla](https://bugs.documentfoundation.org/buglist.cgi?bug_status=__open__&content=&no_redirect=1&order=changeddate%20DESC%2Cpriority%2Cbug_severity&product=&query_based_on=&query_format=specific)and find new bugs that have yet to be confirmed. When you find one, try to replicate what's been reported. Assuming you can do that, add a comment like “CONFIRMED on Linux (Fedora 35) and LibreOffice 7.3.2”.**Drum Beater:**Open source projects rarely have big companies funneling marketing money into promoting them. It would be nice if all the companies claiming to love open source would help out, but not all of them do, so why not lend your voice? Get on social media and tell your friends why you love LibreOffice, or what you’re using it for (and of course add the`#libreoffice`
hashtag.)**Globetrotter:**LibreOffice is already available in many different languages, but not literally all languages. And LibreOffice is actively being developed, so its interface translations need to be kept up-to-date.[Get involved here.](https://www.libreoffice.org/community/localization/)**Docs Doctor:**LibreOffice has online help as well as user handbooks. If you're great at explaining things to other people, or if you're great at proof-reading other people's documentation, then you should contact the[docs team](https://www.libreoffice.org/community/docs-team).**Code Cruncher:**You're probably not going to dive into LibreOffice's code base and make major changes right away, but that's not generally what projects need. If you know how to code, then you can[join the developer community](https://www.libreoffice.org/community/developers/)by[following the instructions on this wiki page](https://wiki.documentfoundation.org/Development/GetInvolved).
## Free stickers
I didn't want to mention this up-front because obviously you should get involved with LibreOffice just because you're excited to get involved with a great open source project. However, you're going to find out eventually so I may as well tell you: By contributing to LibreOffice, you can sign up to get free stickers from The Document Foundation. Surely you've been meaning to [decorate your laptop](https://opensource.com/business/15/11/open-source-stickers)?
Don't get distracted by the promise of loot, though. If you're confused but excited to get involved with open source, this is a great opportunity to do so. And it is representative of how you get involved with open source in general: You look for something that needs to be done, you do it, and then you talk about it with others so you can get ideas for what you can do next. Do that often enough, and you find your way into a community. Eventually, you stop wondering how to get involved with open source, because you're too busy contributing!
## Comments are closed. |
14,720 | KDE Plasma 5.25 发布:颜色、主题和其他改进 | https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-25-release/ | 2022-06-17T12:05:00 | [
"KDE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14720-1.html | 
>
> KDE Plasma 5.25 终于来了,它带来了许多视觉更新和有用的改进!
>
>
>

KDE Plasma 5.25 一直是最受期待的版本之一,因为它最近的版本都专注于改进视觉效果和工作流程。
例如,[KDE Plasma 5.24](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-24-lts-release/) LTS 版本带来了升级的 Breeze 主题和全新的概览效果,改进了工作流程。
如今,KDE Plasma 5.25 带来了更多升级!
### KDE Plasma 5.25 更新内容
虽然,在 Plasma 5.25 的最终发布之前,我们已经知道了一些它的 [关键特性](https://news.itsfoss.com/plasma-5-25-features/)。但是,既然它正式发布了,那就是时候和你简单介绍一下 KDE Plasma 5.25 的全部新功能啦!
**剧透一下**:大多数更新都涉及视觉改善和可用性改进。
#### 新壁纸

如果你玩过 “<ruby> <a href="https://www.nomanssky.com/"> 无人深空 </a> <rt> No Man's Sky </rt></ruby>” 或类似的电子游戏,你可能会有似曾相识的感觉。
撇开这一点不谈,默认壁纸对旧壁纸进行了更新,具有完全不同的主题颜色。
#### 触摸板和触摸屏手势
Plasma 5.25 包括了一系列手势,以充分利用新功能。例如:四指捏合、从屏幕边缘滑动以触发概览效果或 <ruby> 桌面网格 <rt> Desktop Grid </rt></ruby> 等。
你可以使用该版本支持的 1:1 手势,轻松管理虚拟桌面,并在工作区之间切换。
你可以前往 <ruby> 工作区行为 <rt> Workspace Behavior </rt></ruby> 设置来调整你需要的操作。
#### 支持选择性应用全局主题

当你在系统设置中应用 <ruby> 全局主题 <rt> Global Theme </rt></ruby> 时,系统将提示你,是否要应用主题的所有部分,或是只应用它的某些部分。
你可以应用它的特定外观选项,也可以用它来替换整个配置。
总的来说,当将全局主题应用于使用 KDE 的系统时,这个更新提供了细粒度的自定义控制。
#### 根据当前壁纸自动生成强调色
以前,我们总觉得能够选择自定义或预设强调色,就已经足够了。
现在,有了 KDE Plasma 5.25,你可以根据当前壁纸自动生成强调色。它应该也能够与墙纸幻灯片一起使用。

所以,如果你既让桌面匹配你的背景,又不想要自己花力气定制,那么这个选项应该会对你有用。
这是新功能库的一个小而强大的补充。
#### 带有强调色的配色方案
为了更好地自定义外观/观感,KDE Plasma 5.25 可以让你在选择的强调色上定制配色方案。

如果你喜欢配色主题的用户体验,你可以启用/禁用它。
#### 触控模式改进

当你在桌面环境中使用触控模式时(通过支持的设备或手动),KDE Plasma 5.25 将增大 KDE 应用程序的任务管理器、系统托盘和标题栏的大小,使它们更易于访问。
#### “发现” 软件中心的改进
“<ruby> 发现 <rt> Discover </rt></ruby>” 软件中心有一些细微的变化。以前,你需要单独浏览“应用程序”、“附加组件”和 “Plasma 附加组件”等类别;而现在,你在侧边栏中就可以找到所有应用程序类别。


此外,对于 Flatpak 应用程序,你可以看到它所需的权限。还有,应用程序页面也有了一些升级,以显示有关你查看的应用程序的更多信息。
#### 其他改进
其他重要的改进包括定制功能的升级和工作流程的修改。其中包括:
* 一个新的混合效果,用于使动画颜色之间的变化具有动画效果,每当你改变主题/颜色或自动改变时,可以平滑过渡。
* 强大的容纳管理功能,它允许你在监视器之间移动桌面以及文件夹/小部件,即使你已断开它们的连接。
* Kwin 脚本设置页面已被重写。
* 键盘导航支持自定义快捷键和系统托盘图标。
* 新增一个浮动面板,用于在面板周围添加边距。
* 改进了 KRunner 的性能。
* 网络小部件添加了 Wi-Fi 网络的频率和 BSSID 的详细信息。
如果你想了解更多,可以查看 [公告](https://kde.org/announcements/plasma/5/5.25.0/)。
### 尝试 KDE Plasma 5.25
你可以下载 KDE Neon,以便在最新的 KDE Plasma 5.25 有更新时马上就可以用上。如果你等不及了,测试版也是个不错的选择(如果你愿意实验的话)。
>
> **[KDE Neon](https://neon.kde.org/download)**
>
>
>
对于其他 Linux 发行版,你得等待开发人员推送更新(LTS 版除外)。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-25-release/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

KDE Plasma 5.25 has been one of the most anticipated releases, considering its recent focus on visual refinements and workflow improvements.
For instance, you got an updated Breeze theme and a new overview effect to improve the workflow with [KDE Plasma 5.24](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-24-lts-release/) LTS.
Finally, KDE Plasma 5.25 has landed with more upgrades!
## KDE Plasma 5.25: What’s New?
While we already looked at some key [features of Plasma 5.25](https://news.itsfoss.com/plasma-5-25-features/) before its final release. Now that it is here, it is time to give you an overview of what you can expect with KDE Plasma 5.25.
**Spoiler alert:** Most of the changes involve visual betterment and usability improvements.
### New Wallpaper

If you have played the video game ‘[No Man’s Sky](https://www.nomanssky.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)‘ or similar, you might get a similar reference.
Keeping that aside, the default wallpaper is a refresher to the ones being used previously, with an entirely different theme color.
### Gestures for Touchpads and Touchscreens
Plasma 5.25 includes gestures to take full advantage of new features, such as a four-finger pinch or a swipe from the screen edge to trigger the overview effect or Desktop Grid.
You can easily manage virtual desktops and switch between workspaces using the 1:1 gestures supported with the release.
You can head to the Workspace Behavior settings to tweak the actions you need.
### Ability to Selectively Apply the Global Theme
When you proceed to apply a Global Theme from the system settings, you will be prompted to confirm if you want the theme to be applied everywhere or to certain parts of it.
You can apply it to specific appearance options or replace the entire configuration.
Overall, this gives fine-grained control in terms of customization when applying the Global Theme to your KDE-powered system.
### Auto-Generated Accent Based on Current Wallpaper
Having the ability to choose a custom or a preset accent is already good enough.
With KDE Plasma 5.25, accent colors can be generated based on your wallpaper. It should also work with a wallpaper slideshow.
So, if you want something to match your background, and do not want to tinker around, this option should help you.
A small but mighty addition to the arsenal of new features.
### Tint Color Scheme with Accent Color
For even greater customization to the look/feel, KDE Plasma 5.25 will let you add a tint to your selected accent color.
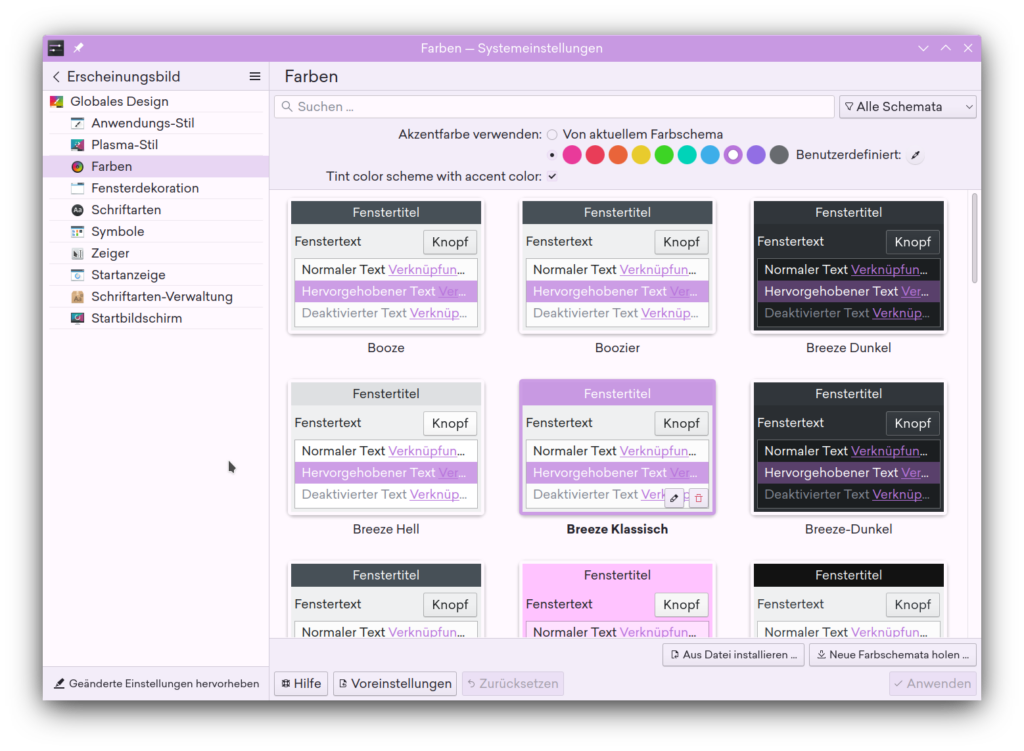
You can enable/disable it if you like the user experience with the tinted theme.
### Touch Mode Improvements
When you are using the touch mode in the desktop environment (through supported devices or manually), KDE Plasma 5.25 makes it more accessible by scaling up the size of the task manager, system tray, and the title bar of KDE applications.
### Improvements to Discover
There are some subtle changes to the Discover software center where you can find all the application categories in the sidebar without needing to navigate through categories like “Applications”, “Add-ons”, and “Plasma Add-ons” separately.


Also, with Flatpak applications, you will be shown the permissions required for it. Furthermore, the application page has received some upgrades to show more information about the application you view.
### Other Improvements
Other essential refinements include upgrades for customization capabilities and workflow modifications. Those include:
- A new Blend Effect to animate the change between colors to make the transition smooth whenever you change the theme/color or if it automatically changes.
- Powerful containment management feature to allow moving your desktops along with folders/widgets between monitors even if you have disconnected them.
- The Kwin scripts settings page has been rewritten.
- Keyboard navigation has been revamped with custom shortcut support and an icon to the system tray.
- A Floating panel to add a margin around the panel.
- Improvements to the performance of KRunner.
- The network widget adds details for the frequency and BSSID of the Wi-Fi network.
If you’re still curious, you can explore the [announcement page](https://kde.org/announcements/plasma/5/5.25.0/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to know more about it.
## Try KDE Plasma 5.25
You can download KDE Neon to get your hands on the latest KDE Plasma 5.25 as soon as it’s available with an update. If you can’t wait, the testing edition should be a good fit (if you’re willing to experiment).
For other Linux distributions, you will have to wait for the developers to push an update (excluding LTS edition distros).
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,721 | Linux 终端,它不可怕,拥抱它 | https://itsfoss.com/love-thy-terminal/ | 2022-06-17T14:42:17 | [
"终端",
"Linux"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14721-1.html | 
至少,对于熟悉图形界面的新用户来说,我们大多时候都在避免使用 Linux 终端。
尽管让事情变得简单和方便是好事,但还是有许多理由说明我们不应该害怕尝试 Linux 终端。
在这里,我将重点介绍其中的几个,以鼓励你在终端中尝试一些最终会对你有所帮助的东西。
### 1、快速熟悉命令

有时,你需要使用某个命令在终端中执行一些操作。当然,你可以在不知道它到底有什么用情况下复制粘贴。
但是,如果你想知道这条命令更多的信息,该怎么办呢?
你只需要输入下面的命令就可以了,
```
man <command you intend to learn>
```
例如:`man apt`。
它会直接在屏幕上给出所有重要的细节,不需要网络连接,不需要在网上搜索它是如何工作的。你节约了时间,增长了知识。
而且,这使事情变得简单,使你在使用终端的时候更有信心。
这通常被称为 “<ruby> 手册页 <rt> man page </rt></ruby>”。 你可以阅读我们的课程《[了解 Linux 上的手册页](https://itsfoss.com/linux-man-page-guide/)》。
Linux 终端万岁。
### 2、解决问题

当你在互联网上搜索一个问题的解决方法时,通常,解决方案中会包含几个命令。
因此,终端的最佳用例之一,是可以毫不费力地解决几个系统问题。同时,你需要小心,因为如果你不知道你在做什么,你可能最终会破坏你的系统。
虽然图形界面可以调整一些东西,但是大部分简单的修复方法都是通过终端完成的。
我们在网站上提供了几个 [故障诊断指南](https://itsfoss.com/tag/troubleshoot/),例如:
* [检查网卡制造商](https://itsfoss.com/find-network-adapter-ubuntu-linux/)
* [修复关机时间过长](https://itsfoss.com/long-shutdown-linux/)
* [修复博通网卡没有 WiFi 信号的问题](https://itsfoss.com/fix-no-wireless-network-ubuntu/)
### 3、使用远程服务器愉快工作

最终,你会通过命令行(或终端)访问一个远程服务器并执行各种操作,包括文件传输。
与使用图形界面访问远程服务器相比,使用 Linux 终端可以让你用最小的带宽,快速的执行任何你想要的操作。
当然,你也可以通过终端在远程服务器上开启图形界面程序。尽管速度十分缓慢,终端还是可以让你轻松的与远程服务器进行交互。
### 4、高效利用资源
不管你使用哪一款 [Linux 发行版](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-distributions/),Linux 终端永远是高效且消耗内存最小的。
如果你资源不足或硬件驱动和图形界面程序有冲突,那么 Linux 终端永远值得你的信赖。
这将帮你在不占用太多系统资源的情况下完成关键任务。
### 5、快速

你知道吗?不仅局限于内存使用,使用终端你可以比使用图形界面更快的完成任务。
你可以尝试安装应用、运行程序、执行复杂的文件操作等等。
### 6、稳定可靠的命令行程序
相比于图形界面程序,命令行程序更加稳定和可靠,为什么呢?
在终端中,使程序崩溃的因素很少。
由于终端工具大部分是为服务器构建的,很多时候不够直观。也正是由于这个原因,命令行工具通常不会得到不必要的频繁更新,使它们成为比图形界面程序更可靠的选择。
### 7、更多的命令行工具
没有一个图形界面程序能解决所有问题。但是,对执行各种操作,然而,有几个 [命令行工具](https://itsfoss.com/tag/cli-tools/) 可以执行各种操作,一些有趣和关键的任务也是如此。
你需要完成一些工作,来吧,总有一款命令行工具适合你。
### 8、尝试各种终端模拟器

尽管使用 Linux 发行版默认安装的终端模拟器对你来说没有任何困难,你仍然有更多的选择。
如果你有特殊的外观和性能需求,或者为某些用途特殊定制,你可以看看这些 [最佳的终端模拟器](https://itsfoss.com/linux-terminal-emulators/)。
如果你觉得使用终端是一件枯燥的事情,你一定要试试这些终端模拟器。
### 结束语
就我个人来说,当我刚开始接触 Linux 时,我也对终端心存畏惧。但是当我可以熟练的使用它处理一些简单任务的时候,我才开始意识到上面所说的终端的优点。
你没必要放弃图形界面而使用终端处理所有的事情。尽管如此,最好还是使用终端处理一些事情,这可以节省你的时间,让你更快的完成工作,并心情愉悦。
Abhishek 曾经写过一篇很棒的涉及各种小事的 [指南](https://itsfoss.com/basic-terminal-tips-ubuntu/),可以让你熟悉 Linux 终端。
*你觉得,相比于图形界面,终端有哪些优点呢?是什么原因让你选择终端呢?快来告诉我们吧。*
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/love-thy-terminal/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[duoluoxiaosheng](https://github.com/duoluoxiaosheng) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Most of our focus goes into avoiding the Linux terminal, at least, for new users comfortable with Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs).
While it is good to make things easy and convenient, there are a few reasons why you should not be afraid of dipping your toes into the Linux terminal.
Here, I shall highlight some of them to encourage you to try a few things in the terminal that should help you eventually.
## 1. Quick Access to Information on Commands
At times, you may need to use a command in the terminal to perform something. Sure, you can just copy-paste without knowing what it actually does.
But, what if you are interested to know a bit more about the command?
Well, you just need to type in:
`man <command you intend to learn>`
For instance: man apt
It will give you all the essential details right on the same screen, without needing an internet connection or scouring the web to find out what it does. You save time, you get to know stuff.
And, that makes things convenient, giving you more confidence in using the terminal.
These are often referred to as “man pages”. You can read one of our resources to[ learn about man pages on Linux](https://itsfoss.com/linux-man-page-guide/).
Thanks to the terminal.
## 2. Troubleshooting Problems

When you search for a fix on the internet, most of the solutions provide you with commands to get it fixed.
Hence, one of the best use-cases of the terminal is to resolve several system issues effortlessly. At the same time, you need to be careful because you could end up breaking your system if you do not know what you are doing.
While there are things that you can tweak around with GUI programs, the majority of the easy fixes go through the terminal.
Considering we have several [troubleshooting guides](https://itsfoss.com/tag/troubleshoot/) on our portal, some examples include:
## 3. Easily Work With a Remote Server
You will end up accessing the command line (or the terminal) to access a remote server and perform various operations, including file transfers.
Compared to a GUI method for a remote server, you minimize bandwidth issues and ensure that you get to perform anything you need faster using the Linux terminal.
There are also options to open a GUI program on the remote server via the terminal. Even if it is slow, the terminal gives you plenty of abilities to interact comfortably with a remote server.
## 4. Resource Efficient
It does not matter whether you use one of the [best Linux distributions](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-distributions/), a Linux terminal is always resource-efficient and consumes the least amount of memory.
If you are low on resources or may have a graphics driver conflict with a GUI program, you can always rely on the Linux terminal.
This should help you through critical tasks without taking much system resources.
## 5. Fast

Not just limited to the memory usage, but you can get things done faster with a terminal over a GUI, you know?
Some tasks you can try include installing an application, launching a program, performing complex file operations, and more.
## 6. Stable and Reliable Command-line Programs
Compared to GUI programs, terminal programs are stable and more reliable. Why?
Fewer factors influence the program with crashes/bugs when it comes to a terminal.
While the terminal tools could be unintuitive, some of them are built for servers in mind. Servers or desktop, command-line tools usually do not get unnecessary frequent updates, making them a reliable choice over GUI programs.
## 7. More Tools for CLI
We do not have a GUI program for everything on Linux. However, there are several [CLI tools](https://itsfoss.com/tag/cli-tools/) to perform a wide range of operations, some fun and critical tasks as well.
You need to get something done; chances are, you will find a command-line tool for it.
## 8. Various Terminal Emulators to Try

While you should not have any trouble with the default terminal emulator installed on your Linux distribution, you have plenty of other options.
If you prefer a different look, more advanced features, or tailored for a specific use, you can look at some of the [best terminal emulators](https://itsfoss.com/linux-terminal-emulators/) available.
If you thought using the terminal was boring, you must try some of them.
## Wrapping Up
Personally, I feared the terminal when I was a new Linux user. But, as I got comfortable with it for small tasks, I got to realize the perks mentioned above.
You do not need to use the terminal over GUI for everything. Nevertheless, it is good to prefer the terminal for a few things because you might save your time and get things done faster and hassle-free.
Abhishek has written an [excellent guide on various small things that make you get more comfortable with the Linux terminal](https://itsfoss.com/basic-terminal-tips-ubuntu/).
[19 Basic But Essential Linux Terminal Tips You Must KnowLearn some small, basic but often ignored things about the terminal. With the small tips, you should be able to use the terminal with slightly more efficiency.](https://itsfoss.com/basic-terminal-tips-ubuntu/)

Knowing the basic Linux commands also makes you more comfortable with the terminal.
[31 Linux Commands Every Ubuntu User Should KnowAn extensive list of essential Linux commands that every Ubuntu user will find helpful in their Linux journey.](https://itsfoss.com/essential-ubuntu-commands/)

*What do you think are the benefits of a terminal over a GUI? What are your reasons to prefer the terminal? Let me know your thoughts in the comments section below.* |
14,723 | Mozilla 刚刚使 Firefox 成为所有人的最安全的网页浏览器 | https://news.itsfoss.com/mozilla-firefox-secure/ | 2022-06-18T09:48:54 | [
"Firefox",
"Cookie"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14723-1.html |
>
> Mozilla 终于启用了一项隐私保护功能,这可能使其成为当下最安全的网页浏览器。你怎么看?
>
>
>

Mozilla Firefox 是市面上最安全的开源网页浏览器之一。
毫无疑问,你可以自由定制它来进一步增强安全性,这就是 Tor 浏览器使用 Firefox 作为其核心的原因。
并且,这也是 [我继续使用 Firefox 的原因](https://news.itsfoss.com/why-mozilla-firefox/) 之一。
现在,Mozilla 终于为**所有桌面用户**启用了一项新功能,这使其成为最安全的浏览器(或是他们声称的“最安全”)。
本文中,我讨论的不是任何新功能,而是 Firefox 中的现有功能,即 <ruby> Cookie 全面保护 <rt> Total Cookie Protection </rt></ruby>。它是在去年与 [Firefox 86](https://news.itsfoss.com/firefox-86-release/) 一起引入的,但默认情况下并未对所有用户启用。
### 为所有用户提供的全面的 Cookie 保护
“Cookie 全面保护”正在向所有人推出,无论你使用的是 Windows、Mac 还是 Linux,它将成为默认启用的核心功能之一。
最初,要使用该功能,你必须启用严格模式(<ruby> 增强跟踪保护 <rt> Enhanced Tracking Protection </rt></ruby>)。但现在,你不再需要这样做了。
#### 它是什么?
如果你好奇的话,“Cookie 全面保护”会隔离每个网站和它们的 Cookie。Cookie 是网站向你的浏览器发送的少量数据。
因此,Cookie 不会在网站之间共享,从而防止了<ruby> 跨站跟踪 <rt> cross-site tracking </rt></ruby>。
浏览器将为你访问的每个网站都创建单独的“<ruby> 饼干罐 <rt> Cookie Jar </rt></ruby>”。(LCTT 译注:Cookie 原意是小饼干。)

Mozilla 的博文对此进行了更多解释:
>
> 在任何时候,网站或嵌入网站的 [第三方内容](https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/third-party-cookies-firefox-tracking-protection#:~:text=Third%2Dparty%20cookies%20are%20cookies,considered%20a%20third%2Dparty%20cookie.) 在浏览器中存储的 Cookie,都将仅限于分配给该网站的 “饼干罐”。其他网站无法进入不属于它们的“饼干罐”,以得到你存储在那些 Cookie 中的信息。这可以让你免受侵入性广告的影响,并减少公司收集的关于你的信息量。
>
>
>
### 那么,这有什么大不了的吗?
即使你配备了所有的隐私跟踪保护和内容拦截器,你也不一定知道,其实还有个问题叫做“跨站跟踪”。
因此,通过跨站点的 Cookie 交互,你的许多个人活动和习惯,都可以帮助数字跟踪公司建立你的在线个人资料。
但是,对于 Mozilla Firefox 来说,它在所有其他隐私措施之上,默认额外启用了该功能,这可确保你获得最私密的体验。
并且,所有这些都不需要你调整任何东西,这应该为那些“重视隐私”的用户提供方便。
想了解进一步信息,你可以查看 Mozilla 的 [官方公告](https://blog.mozilla.org/en/products/firefox/firefox-rolls-out-total-cookie-protection-by-default-to-all-users-worldwide/)。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/mozilla-firefox-secure/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Mozilla Firefox is one of the most secure open-source web browsers available.
Undoubtedly, you get the freedom to customize it to harden security, which is why Tor Browser utilizes Firefox at its core.
And, also one of the [reasons why I keep coming back to Firefox](https://news.itsfoss.com/why-mozilla-firefox/).
Now, Mozilla has finally enabled a new feature for **all desktop users,** making it the most secure browser (or as they claim).
Here, I’m not talking about anything new, but an existing feature in Firefox, i.e., Total Cookie Protection. It was introduced with [Firefox 86](https://news.itsfoss.com/firefox-86-release/) last year, but it was not enabled by default for all users.
## Total Cookie Protection for all users
Whether you are using Windows, Mac, or Linux, the Total Cookie Protection is being rolled out to everyone, making it one of its core features enabled by default.
Initially, to use the feature, you had to enable the strict mode (Enhanced Tracking Protection). But, now, you no longer need to do that.
**What is it?**
In case you are curious, Total Cookie Protection isolates every website with its cookies. Cookies are small bits of data sent to your browser by a website.
So, the cookies will not be shared among websites, thereby, preventing cross-site tracking.
Separate cookie jars will be created for each website you visit.
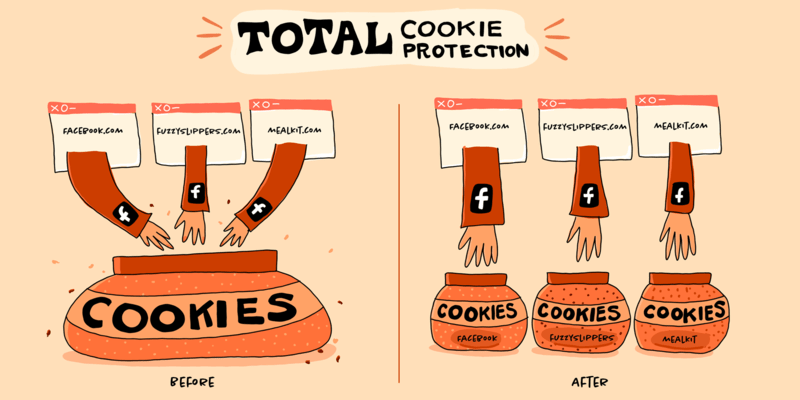
Mozilla’s blog post explains more about it as:
Any time a website, or
[third-party content]embedded in a website, deposits a cookie in your browser, that cookie is confined to the cookie jar assigned toonlythat website. No other websites can reach into the cookie jars that don’t belong to them and find out what the other websites’ cookies know about you — giving you freedom from invasive ads and reducing the amount of information companies gather about you.
## So, Is it a big deal?
Even with all the privacy tracking protection and content blockers in place, cross-site tracking is a problem that not everyone is aware of.
Hence, with cross-site cookie interactions, a lot of your personal activities and habits can help a digital tracking company build an online profile of yours.
But, with Mozilla Firefox, enabling the feature by default on top of all other privacy measures by Firefox, ensures that you should get the most private experience.
And, all that without needing to tweak anything, which should make things convenient for any privacy-centric user.
If you are still curious, you can refer to the [official announcement post](https://blog.mozilla.org/en/products/firefox/firefox-rolls-out-total-cookie-protection-by-default-to-all-users-worldwide/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) by Mozilla.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,725 | 企业为何使用开源软件,又为何推动开源软件的发展 | https://www.linux.com/news/why-do-enterprises-use-and-contribute-to-open-source-software/ | 2022-06-18T16:07:00 | [
"开源",
"企业"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14725-1.html | 
*开源朗读者 | 淮晋阳*
每当人们知道我在 <ruby> Linux 基金会 <rt> Linux Foundation </rt></ruby> 工作,他们总是会问我们的工作具体是做什么的。有时候,他们会一直问我是不是开发 Linux 操作系统的。我只能回答说,我们做的是开源软件,并试图在他们失去兴趣之前,在短短的 20 秒钟内介绍它对世界的影响力。如果他们的兴趣还在,想要进一步了解,我就会给他们深入分析一番:企业为何想参与到开源软件项目之中?它们为何会使用开源软件?没错,企业确实会这样做,无论它们有没有意识到这一点。此外,成千上万的企业会将企业内部代码捐给开源项目,为推动开源软件的进一步开发和优化投入大量的时间和资源。
### 开源软件的使用范围有多广
引用我们最近发表的一项报告《<ruby> 企业开源指南 <rt> A Guide to Enterprise Open Source </rt></ruby>》:“<ruby> 开源软件 <rt> open source software </rt></ruby>(OSS)改变了世界,是数字经济的支柱,数字世界的基石。从我们日常使用的互联网和移动应用到开拓未来的操作系统和编程语言,开源软件无不发挥着重要的作用,可谓是科技行业的命脉。在今天,开源软件驱动数字经济发展,推进科学技术取得突破,不断改善人们的生活水平。手机、汽车和飞机等设备,家庭、企业和政府等群体都在使用着开源软件。但就在 20 年前,开源软件还仅仅为少数人所知,它的使用也仅限于一小部分专门的爱好者。”
开源软件(OSS)已经改变了我们的世界,成为我们数字经济的支柱和数字世界的基础。
而它实际上:
* 在各行业的 <ruby> 垂类软件栈 <rt> vertical software stacks </rt></ruby> 中,开源软件的占比达到了 20% - 85%。
* 超过 90% 的网站服务器和联网设备都依靠 Linux 来运行。
* 安卓手机系统也是基于 Linux 内核。
* 用于应用程序开发的 AMP、Appium、Dojo、jQuery、Marko、Node.js 等 [主流的库和工具](https://openjsf.org/projects/) 均属于开源项目。
* 世界上排名位列前 100 名的超级计算机都在使用 Linux。
* 大型机客户均在使用 Linux。
* 亚马逊、谷歌以及微软三大云服务供应商都在使用开源软件运行服务,并在云端托管开源解决方案。
### 企业为何想参与到开源软件项目之中
企业参与开源软件项目主要通过三种方式:
* 企业向开源社区捐赠自家开发的软件。
* 企业向开源软件项目提供直接的资金援助。
* 企业向开源项目分派软件开发人员以及其他员工。
人们经常会问,为什么这些企业愿意放弃自家软件的所有权?为什么它们不让员工专攻自家软件的开发呢?
从整体上来看,这一问题的答案就是,企业和组织聚集起来,合力解决共同的难题,如此一来,他们就可以各自专注于在这基础上的各类难题。这些企业明白,将资源聚集在一起,能够更好地解决基础问题。有时,这种现象被叫做“<ruby> 竞合 <rt> coopetition </rt></ruby>”,大概的意思是企业在一些领域可能互为竞争对手,但是它们在另一些领域则会互相合作。
“竞合”现象的一些典型例子:
* 铁路公司采用统一的铁轨尺寸,统一规划建设。得益于此,火车就可以在同样铁轨上运行,铁路公司之间也可以互相交换设备。
* 在数码相机诞生之前,不同的公司在电影和摄像机行业各行创新之路,形成了各自的优势,但为了推进电影行业的发展,它们在相机链轮间距这一问题上达成了统一。
* 娱乐产业在开展竞争的同时,也一致坚持采用家用录像系统和蓝光格式。
如今,企业、组织以及个体在合力解决难题的同时,也在不断地改进自身的产品与业务。
* <ruby> <a href="https://letsencrypt.org/"> 来此加密 </a> <rt> Let’s Encrypt </rt></ruby>(LCTT译注:Let’s Encrypt 官网并没有用“来此加密”这样的称呼,但是在一些场合有这样的译名。我们认为此翻译很贴切。) 是一个免费的、开放的自动化证书颁发机构,旨在通过简化安装程序,减低安装费用,快速扩大安全网络协议的应用范围。该机构为超过 2.25 亿个网站提供服务,每天平均发放证书约 150 万张。
* 好莱坞成立的 <ruby> <a href="https://www.aswf.io/"> 学院软件基金会 </a> <rt> Academy Software Foundation </rt></ruby> 通过共同开发软件,推动娱乐、游戏和媒体等产业的增长,为产业发展提供开放标准,在电影行业内 [创造了巨大的价值](https://linuxfoundation.org/tools/open-source-in-entertainment/)。
* <ruby> 超级账本 <rt> Hyperledger </rt></ruby> 基金会管理多个企业级区块链软件项目。众所周知,这些项目 [消耗的能源远比其他解决方案要少](https://linuxfoundation.org/tools/carbon-footprint-of-nfts/)。
* <ruby> <a href="https://www.lfenergy.org/"> LF 能源基金会 </a> <rt> LF Energy </rt></ruby> 推动 [电网朝着更加模块化、互操作和可拓展的方向发展](https://linuxfoundation.org/tools/paving-the-way-to-battle-climate-change-how-two-utilities-embraced-open-source-to-speed-modernization-of-the-electric-grid/),助力提升可再生能源的利用率。
* <ruby> <a href="https://www.dronecode.org/projects/"> 无人机代码基金会 </a> <rt> Dronecode </rt></ruby> 致力于无人机软件的开发,促进企业在无人机领域进一步开拓创新。
* <ruby> <a href="https://openssf.org/"> 开源软件软件安全基金会 </a> <rt> OpenSSF </rt></ruby> 聚集了顶尖的科技企业,共同强化开源软件的安全与韧性。
* [Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/) 是 Google 捐赠给 Linux 基金会下属的云原生计算基金会(CNCF)的一个项目,是管理基于云计算软件的首选方案。
上述只是企业参与的一小部分开源软件项目,点击 [此处](https://linuxfoundation.org/projects/),可以在 Linux 基金会官网浏览全部项目列表。
### 企业如何有效利用和参与开源软件项目?
若想要更好地利用开源项目,更有效地参与开源项目,企业可以向 Linux 基金会寻求帮助。我们最新发布的报告 《[企业开源指南](https://linuxfoundation.org/tools/guide-to-enterprise-open-source/)》 提供了企业与组织需要了解的大部分信息。这份报告凝聚了来自多家顶级企业、具有几十年丰富经验的开源领袖的知识与智慧,报告主要分为以下六个章节:
* 使用开源软件
* 准备参与开源
* 制定开源策略
* 部署基础设施
* 建立人才团队
* 应对多方挑战
此外,Linux 基金会还提供了许多开源 [培训课程](https://training.linuxfoundation.org/)、全年 [活动](https://events.linuxfoundation.org/)、[LFX 平台](https://lfx.linuxfoundation.org/),发起开源项目,协助企业与组织利用和参与开源项目,比如:
* [TODO 工作组](https://todogroup.org/) 为开源项目办公室的建立和运作提供资源,包括其自身 [丰富的指导意见](https://linuxfoundation.org/resources/open-source-guides/)。
* [Openchain 项目](https://www.openchainproject.org/resources) 旨在提供和维护国际开源许可标准,包括各种许可规定的相关信息。依赖于此,企业可以确保自身行为符合法律规定。
* [FinOps 基金会](https://www.finops.org/introduction/what-is-finops/) 目前正在将自身打造为“不断发展的云财务管理和文化实践平台,通过促进工程、财务、技术以及商业团队之间在数据驱动支出决策方面的合作,确保企业能够最大化实现商业价值”。
* <ruby> <a href="https://spdx.dev/"> 软件数据包交换标准 </a> <rt> Software Data Package Exchange </rt></ruby>(SPDX)是一个用于交流 <ruby> 软件物料清单 <rt> software bill of materials </rt></ruby>(SBOM)的开放标准。在该标准下,每个用户都能清楚了解整个软件包中包括哪些软件。
同样,上述这些只是 Linux 基金会所有项目中的一小部分。所有这些项目都致力于帮助企业接受和使用开源项目,引导企业为开源项目做出贡献、提供捐赠。
总而言之,目前,企业正在迅速投向开源软件项目,借此解决共同的难题,并探索进一步的创新发展,而 Linux 基金会将为它们提供帮助。
*该文 [《企业为何使用开源软件,又为何推动开源软件的发展》](https://www.linuxfoundation.org/blog/why-do-enterprises-use-and-contribute-to-open-source-software/) 首发于 [Linux 基金会](https://www.linuxfoundation.org/) 官网。*
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/news/why-do-enterprises-use-and-contribute-to-open-source-software/>
作者:[Dan Whiting](https://www.linuxfoundation.org/blog/why-do-enterprises-use-and-contribute-to-open-source-software/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[aREversez](https://github.com/aREversez) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When people find out I work at the Linux Foundation they invariably ask what we do? Sometimes it is couched around the question, As in the Linux operating system? I explain open source software and try to capture the worldwide impact into 20 seconds before I lose their attention. If they happen to stick around for more, we often dig into the question, Why would enterprises want to participate in open source software projects or use open source software? The reality is – they do, whether they know it or not. And the reality is thousands of companies donate their code to open source projects and invest time and resources helping to further develop and improve open source software.
## How extensively used is open source software
To quote from our recently released report, A Guide to Enterprise Open Source, “Open source software (OSS) has transformed our world and become the backbone of our digital economy and the foundation of our digital world. From the Internet and the mobile apps we use daily to the operating systems and programming languages we use to build the future, OSS has played a vital role. It is the lifeblood of the technology industry. Today, OSS powers the digital economy and enables scientific and technological breakthroughs that improve our lives. It’s in our phones, our cars, our airplanes, our homes, our businesses, and our governments. But just over two decades ago, few people had ever heard of OSS, and its use was limited to a small group of dedicated enthusiasts.”
Open source software (OSS) has transformed our world and become the backbone of our digital economy and the foundation of our digital world.
But what does this look like practically:
In vertical software stacks across industries, open source penetration ranges from 20 to 85 percent of the overall software used
Linux fuels 90%+ of web servers and Internet-connected devices
The Android mobile operating system is built on the Linux kernel
Immensely[ popular libraries and tools](https://openjsf.org/projects/) to build web applications, such as: AMP, Appium, Dojo, jQuery, Marko, Node.js and so many more are open source
The world’s top 100 supercomputers run Linux
100% of mainframe customers use Linux
The major cloud-service providers – AWS, Google, and Microsoft – all utilize open-source software to run their services and host open-source solutions delivered through the cloud
## Why do companies want to participate in open source software projects
Companies primarily participate in open source software projects in three ways:
They donate software they created to the open source community
They provide direct funding and/or allocate software developers and other staff to contribute to open source software projects
The question often asked is, why wouldn’t they want to keep all of their software proprietary or only task their employees to work on their proprietary software?
The 30,000-foot answer is that it is about organizations coming together to collectively solve common problems so they can separately innovate and differentiate on top of the common baseline. They see that they are better off pooling resources to make the baseline better. Sometimes it is called “coopetition.” It generally means that while companies may be in competition with each other in certain areas, they can still cooperate on others.
It is about organizations coming together to collectively solve common problems so they can separately innovate and differentiate
Some old-school examples of this principle:
Railroads agreed on a common track size and build so they can all utilize the same lines and equipment was interchangeable
Before digital cameras, companies innovated and differentiated on film and cameras, but they all agreed on the spacing for the sprockets to advance the film
The entertainment industry united around the VHS and Blu-Ray formats over their rivals
Now, we see companies, organizations, and individuals coming together to solve problems while simultaneously improving their businesses and products:
[Let’s Encrypt](https://letsencrypt.org/) is a free, automated, and open certificate authority with the goal of dramatically increasing the use of secure web protocols by making it much easier and less expensive to setup. They are serving 225+ million websites, issuing ~1.5 million certificates each day on average.
The[ Academy Software Foundation](https://www.aswf.io/)[ creates value in the film industry](https://linuxfoundation.org/tools/open-source-in-entertainment/) through collectively engineering software that powers much of the entertainment, gaming, and media industry productions and open standards needed for growth.
The Hyperledger Foundation hosts enterprise-grade blockchain software projects, notably[ using significantly fewer energy resources](https://linuxfoundation.org/tools/carbon-footprint-of-nfts/) than other popular solutions.
[LF Energy](https://www.lfenergy.org/) is[ making the electric grid more modular, interoperable, and scalable](https://linuxfoundation.org/tools/paving-the-way-to-battle-climate-change-how-two-utilities-embraced-open-source-to-speed-modernization-of-the-electric-grid/) to help increase the use of renewable energy sources
[Dronecode](https://www.dronecode.org/projects/) is enabling the development of drone software so companies can use their resources to innovate further
[OpenSSF](https://openssf.org/) is the top technology companies coming together to strengthen the security and resiliency of open source software
[Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/) was donated by Google and is the go-to solution for managing cloud-based software
These are just a small sampling of the open source software projects that enterprises are participating in. You can explore all of the ones hosted at the Linux Foundation [here](https://linuxfoundation.org/projects/).
## How can companies effectively use and participate in open source software projects?
Enterprises looking to better utilize and participate in open source projects can look to the Linux Foundation’s resources to help. Much of what organizations need to know is provided in the just-published report,[ A Guide to Enterprise Open Source](https://linuxfoundation.org/tools/guide-to-enterprise-open-source/). The report is packed with information and insights from open source leaders at top companies with decades of combined experience. It includes chapters on these topics:
Leveraging Open Source Software
Preparing the Enterprise for Open Source
Developing an Open Source Strategy
Setting Up Your Infrastructure for Implementation
Setting Up Your Talent for Success
Challenges
Additionally, the Linux Foundation offers many open source[ training courses](https://training.linuxfoundation.org/),[ events](https://events.linuxfoundation.org/) throughout the year, the[ LFX Platform](https://lfx.linuxfoundation.org/), and hosts projects that help organizations manage open source utilization and participation, such as:
The[ TODO Group](https://todogroup.org/) provides resources to setup and run an open source program office, including their[ extensive guides](https://linuxfoundation.org/resources/open-source-guides/)
The[ Openchain Project](https://www.openchainproject.org/resources) maintains an international standard for sharing what software package licenses are included in a larger package, including information on the various licensing requirements so enterprises can ensure they are complying with all of the legal requirements
The[ FinOps Foundation](https://www.finops.org/introduction/what-is-finops/) is fostering an, “evolving cloud financial management discipline and cultural practice that enables organizations to get maximum business value by helping engineering, finance, technology, and business teams to collaborate on data-driven spending decisions.”
The[ Software Data Package Exchange (SPDX)](https://spdx.dev/) is an open standard for communication software bill of materials (SBOMs) so it is clear to every user which pieces of software are included in the overall package.
Again, this is just a snippet of the projects at the Linux Foundation that are working to help organizations adapt, utilize, contribute, and donate open source projects.
The bottom line: Enterprises are increasingly turning to open source software projects to solve common problems and innovate beyond the baseline, and the Linux Foundation is here to help.
The post [Why Do Enterprises Use and Contribute to Open Source Software](https://www.linuxfoundation.org/blog/why-do-enterprises-use-and-contribute-to-open-source-software/) appeared first on [Linux Foundation](https://www.linuxfoundation.org/). |
14,726 | 用 tmate 分享你的 Linux 终端 | https://opensource.com/article/22/6/share-linux-terminal-tmate | 2022-06-18T17:08:21 | [
"tmate",
"终端"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14726-1.html |
>
> tmate 扩展了你分享 Linux 终端会话的方式。
>
>
>

作为 Fedora Linux QA 团队的一员,我有时想将自己执行的一堆命令广而告之给其他开发者。如果你曾经使用过像 [tmux](https://opensource.com/downloads/tmux-cheat-sheet) 或 [GNU Screen](https://opensource.com/article/17/3/introduction-gnu-screen) 这样的 [终端复用器](https://opensource.com/article/21/5/linux-terminal-multiplexer),你可能会认为这是一个挺轻松的任务。不是所有看我的示范的人都是从笔记本电脑或台式机连接到我的终端会话的,有些人可能是随手在他们的手机浏览器中打开的,因为我使用了 [tmate](https://tmate.io/),所以他们可以很容易地做到这一点。
### 使用 tmate 分享 Linux 终端
观看别人在 Linux 终端的工作是非常有教育意义的。你可以学到新的命令、新的工作流程,或者新的调试和自动化的方法。但要抓住你所看到的东西,以便你以后可以自己尝试,这可能很困难。你可能会借助截图或一个共享终端会话的屏幕记录,这样你就可以在以后打出每个命令。剩下的唯一选择是由演示命令的人使用 [Asciinema](https://opensource.com/article/22/1/record-your-terminal-session-asciinema) 或 [script 和 scriptreplay](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/record-terminal-script-scriptreplay) 等工具来记录会话。
但是通过 `tmate`,用户可以在只读模式下或通过 SSH 分享终端。SSH 和只读会话都可以通过终端或以 HTML 网页的形式访问。
当我为 Fedora QA 团队培训人员时,我使用只读模式,因为我需要运行命令并显示输出,但有了 `tmate`,人们可以通过从他们的浏览器复制和粘贴到文本编辑器来记录笔记。
### Linux tmate 上手
在 Linux 上,你可以用你的包管理器安装 `tmate`。例如,在 Fedora 上:
```
$ sudo dnf install tmate
```
在 Debian 和类似的发行版上:
```
$ sudo apt install tmate
```
在 macOS 上,你可以用 [Homebrew](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/homebrew-mac) 或 [MacPorts](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/macports) 安装它。如果你需要其他 Linux 发行版的说明,请参考 [安装](https://tmate.io/) 指南。

安装后,启动 `tmate`:
```
$ tmate
```
当 `tmate` 启动时,会生成链接,通过 HTTP 和 SSH 提供对终端会话的访问。每个协议都有一个只读方式,以及一个反向的 SSH 会话。
下面是一个网络会话的样子:

`tmate` 的网络控制台是 HTML5 的,因此,用户可以复制整个屏幕并粘贴到终端来运行相同的命令。
### 保持会话
你可能想知道如果你不小心关闭了你的终端会发生什么。你也可能想知道如何与不同的控制台应用共享你的终端。毕竟,`tmate` 是一个多路复用器,所以它应该能够保持会话,脱离并重新连接到一个会话,等等。
当然,这正是 `tmate` 所能做到的。如果你曾经使用过 `tmux`,这可能是相当熟悉的。
```
$ tmate -F -n web new-session vi console
```
这个命令在 `vi` 中打开了 `new-session`,`-F` 选项确保会话在关闭时也能重新产生。

### 社交复用
`tmate` 给你带来了 `tmux` 或 GNU Screen 的自由度,以及与他人分享会话的能力。这是一个有价值的工具,可以教其他用户如何使用终端、演示一个新命令的功能,或调试意外的行为。它是开源的,所以请试一试!
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/6/share-linux-terminal-tmate>
作者:[Sumantro Mukherjee](https://opensource.com/users/sumantro) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | As a member of the Fedora Linux QA team, I sometimes find myself executing a bunch of commands that I want to broadcast to other developers. If you've ever used a [terminal multiplexer](https://opensource.com/article/21/5/linux-terminal-multiplexer) like [tmux](https://opensource.com/downloads/tmux-cheat-sheet) or [GNU Screen](https://opensource.com/article/17/3/introduction-gnu-screen), you might think that that's a relatively easy task. But not all of the people I want to see my demonstration are connecting to my terminal session from a laptop or desktop. Some might have casually opened it from their phone browser—which they can readily do because I use [tmate](https://tmate.io/).
## Linux terminal sharing with tmate
Watching someone else work in a Linux terminal is very educational. You can learn new commands, new workflows, or new ways to debug and automate. But it can be difficult to capture what you're seeing so you can try it yourself later. You might resort to taking screenshots or a screen recording of a shared terminal session so you can type out each command later. The only other option is for the person demonstrating the commands to record the session using a tool like [Asciinema](https://opensource.com/article/22/1/record-your-terminal-session-asciinema) or [script and scriptreplay](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/record-terminal-script-scriptreplay).
But with tmate, a user can share a terminal either in read-only mode or over SSH. Both the SSH and the read-only session can be accessed through a terminal or as an HTML webpage.
I use read-only mode when I'm onboarding people for the Fedora QA team because I need to run commands and show the output, but with tmate, folks can keep notes by copying and pasting from their browser to a text editor.
## Linux tmate in action
On Linux, you can install tmate with your package manager. For instance, on Fedora:
```
````$ sudo dnf install tmate`
On Debian and similar distributions:
```
````$ sudo apt install tmate`
On macOS, you can install it using [Homebrew](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/homebrew-mac) or [MacPorts](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/macports). If you need instructions for other Linux distributions, refer to the [install](https://tmate.io/) guide.
(Sumantro Mukherjee, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Once installed, start tmate:
```
````$ tmate`
When tmate launches, links are generated to provide access to your terminal session over HTTP and SSH. Each protocol features a read-only option as well as a reverse SSH session.
Here's what a web session looks like:
(Sumantro Mukherjee, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Tmate's web console is HTML5, so, as a result, a user can copy the entire screen and paste it into a terminal to run the same commands.
## Keeping a session alive
You may wonder what happens if you accidentally close your terminal. You may also wonder about sharing your terminal with a different console application. After all, tmate is a multiplexer, so it should be able to keep sessions alive, detach and re-attach to a session, and so on.
And of course, that's exactly what tmate can do. If you've ever used tmux, this is probably pretty familiar.
```
````$ tmate -F -n web new-session vi console`
This command opens up `new-session`
in Vi, and the `-F `
option ensures that the session re-spawns even when closed.
(Sumantro Mukherjee, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Social multiplexing
Tmate gives you the freedom of tmux or GNU Screen plus the ability to share your sessions with others. It's a valuable tool for teaching other users how to use a terminal, demonstrating the function of a new command, or debugging unexpected behavior. It's open source, so give it a try!
## 2 Comments |
14,728 | 安装 Fedora 36 后一些适合中国用户的简单设置 | https://www.insidentally.com/articles/000028/ | 2022-06-19T09:25:00 | [
"Fedora"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14728-1.html |
>
> Fedora 安装之后稍作一些简单优化和配置,就可以愉快的使用了。
>
>
>

Fedora 是红帽系发行版中最激进的发行版。不少朋友将使用 Fedora 的人看做是红帽的小白鼠。但是 Fedora 超快的更新速度其实也为开发者提供了不少便利。本文介绍了安装 Fedora 36 后一些简单的设置,可以使你的 Fedora 更加易用一些。
### 1、设置软件源
Fedora 默认使用 Metalink 给出推荐的镜像列表,保证用户使用的镜像仓库足够新,并且能够尽快收到安全更新,从而提供更好的安全性。所以通常情况下使用默认配置即可,无需更改配置文件。
不过,由于 Metalink 需要从国外的 Fedora 项目服务器上获取元信息,所以对于校园内网、无国外访问等特殊情况,Metalink 并不适用,此时可以参照清华大学 tuna 小组介绍的 [方法](https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/help/fedora/) 来修改软件源。
### 2、更新系统
激进的发行版就要有激进的用法,因此配置好软件源后第一件事就是执行系统更新、刷新存储库列表是理所当然要做的。
你可以从 GNOME 软件中心执行此操作,或者使用终端操作。
对于终端,只需使用以下命令:
```
sudo dnf update
```
可能需要重新启动才能完成系统更新。
### 3、删除旧的内核以及其他不需要的旧软件包
更新系统之后多半会安装新的内核,以及会出现一些无用的依赖。重新启动系统到新的内核,确保内核运转没有问题了,就可以删除旧内核以及无用的依赖了。
使用以下命令就可以自动删除无用的依赖:
```
sudo dnf autoremove
```
Fedora 内核更新快,但是每次更新内核,旧的内核不会自动删除,占用硬盘空间。以前的教程删除旧内核都是先搜索,再移除要删除的版本,输入版本号也非常麻烦。使用以下命令即可一条命令删除旧内核:
```
sudo dnf remove --oldinstallonly
```

### 4、启用 RPM Fusion 软件源
安装 Fedora 时会提示你是否启用其他第三方软件源。
但是自动启用的软件源,只有英伟达驱动程序、谷歌 Chrome 和 Steam 等软件源,全套的 RPM Fusion 软件源并没有自动启用,因此还有诸如 VLC 和 MPV 等软件也不可用。
建议你还是开启全套的 RPM Fusion,国内玩家还是建议使用清华的镜像开启 RPM Fusion:
```
sudo yum install --nogpgcheck https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/rpmfusion/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/rpmfusion/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm
```
安装成功后,修改 `/etc/yum.repos.d/` 目录下以 `rpmfusion` 开头,以 `.repo` 结尾的文件。具体而言,需要将文件中的 `baseurl=` 开头的行等号后面链接中的 `http://download1.rpmfusion.org/` 替换为 `https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/rpmfusion/`, 替换后的文件类似如下:
```
[rpmfusion-free]
name=RPM Fusion for Fedora $releasever - Free
baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/rpmfusion/free/fedora/releases/$releasever/Everything/$basearch/os/
mirrorlist=http://mirrors.rpmfusion.org/mirrorlist?repo=free-fedora-$releasever&arch=$basearch
enabled=1
metadata_expire=7d
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-rpmfusion-free-fedora-$releasever
[rpmfusion-free-debuginfo]
name=RPM Fusion for Fedora $releasever - Free - Debug
mirrorlist=http://mirrors.rpmfusion.org/mirrorlist?repo=free-fedora-debug-$releasever&arch=$basearch
enabled=0
metadata_expire=7d
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-rpmfusion-free-fedora-$releasever
[rpmfusion-free-source]
name=RPM Fusion for Fedora $releasever - Free - Source
baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/rpmfusion/free/fedora/releases/$releasever/Everything/source/SRPMS/
mirrorlist=http://mirrors.rpmfusion.org/mirrorlist?repo=free-fedora-source-$releasever&arch=$basearch
enabled=0
metadata_expire=7d
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-rpmfusion-free-fedora-$releasever
```
### 5、添加 Flathub 存储库
Fedora 默认情况下启用了 Flatpak。 但是,它是过滤后的 Flatpak 。
因此,要访问各种可用的 Flatpak 应用程序,你可以在终端中使用以下命令添加 Flathub 存储库:
```
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
```
### 6、配置 DNF 以更快地下载包
Fedora 可以通过多种方法增强下载包的速度。比如选择最快的镜像,可以提高包下载速度。此外,如果你的互联网连接速度足够快,则可以更改并行下载的数量以获得更快的下载。
要做这两件事,只需编辑位于 `/etc/dnf/dnf.conf` 的 DNF 配置文件。
将以下行附加到 `/etc/dnf/dnf.conf` 文件中,保存并退出:
```
fastestmirror=true
deltarpm=true
max_parellel_downloads=10
```
* `fastestmirror` 为选择最快软件源,如果你手动修改了仓库里面的信息则不需要启动这个。
* `deltarpm` 相当于增量下载,把软件增加的部分下载下来,和原软件包合成新软件包,类似于现在的 Android 软件更新。
* `max_parellel_downloads` 设置最大并行下载数量。
### 7、安装后更改主机名
安装后,默认主机名设置为 `fedora`。
因此,如果你想在安装后个性化你的系统主机名,可以使用以下命令设置新的主机名:
```
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname <你的主机名>
```
请将 `<你的主机名>` 替换为你的主机名(不包含 `<` 和 `>`),建议采用 FQDN 主机名,即包括域名的完全限定主机名。
然后可以修改 `/etc/hosts` 在 `127.0.0.1` 以及 `::1` 条目后面都加上你的主机名。类似下面这样:
```
# Loopback entries; do not change.
# For historical reasons, localhost precedes localhost.localdomain:
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 <你的主机名>
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 <你的主机名>
# See hosts(5) for proper format and other examples:
# 192.168.1.10 foo.mydomain.org foo
# 192.168.1.13 bar.mydomain.org bar
```
### 8、安装 GNOME 优化和扩展应用程序
要调整 GNOME 的外观和感觉,你需要安装 GNOME <ruby> 优化 <rt> Tweaks </rt></ruby> 和扩展管理器应用程序。 可以通过软件中心或终端使用以下命令来完成:
```
sudo dnf install gnome-tweaks gnome-extensions-app
```
然后你就可以在 [GNOME Shell 扩展页面](https://extensions.gnome.org/) 挑选扩展了。
使用一些好用的 GNOME 扩展来增强你的桌面工作的使用体验。限于篇幅,本文就不展开 GNOME 扩展的玩法了。
### 9、用于电池健康管理的 TLP
TLP 是一个很好的实用程序,可帮助优化笔记本电脑的电池。该实用程序带有各种命令行选项来调整和查看有关功耗的报告。
TLP 非常好用,你只需安装它并忘记它。这不需要任何设置或设置即可使其工作。使用默认设置安装后,它就可以开箱即用。
```
dnf install tlp tlp-rdw
```
然后卸载有冲突的 `power-profiles-daemon` 软件包:
```
dnf remove power-profiles-daemon
```
设置开机启动 TLP 的服务:
```
systemctl enable tlp.service
```
您还应该屏蔽以下服务以避免冲突,确保 TLP 的无线设备(蓝牙、wifi等)切换选项的能够正确操作:
```
systemctl mask systemd-rfkill.service systemd-rfkill.socket
```
安装 TLP 能够极大的提高笔记本电脑电池的使用时长。
### 10、安装和配置主题
GNOME 桌面的美化是个见仁见智的事情。
我的美化方案是用软件源里面有的东西。
安装主题:
```
sudo dnf install flat-remix-theme
```
安装图标:
```
sudo dnf install numix-icon-theme-circle
```
安装光标:
```
sudo dnf install breeze-cursor-theme
```
然后启用“<ruby> 用户主题 <rt> User Themes </rt></ruby>” 扩展,在扩展里面启用它。

再去 GNOME <ruby> 优化 <rt> Tweaks </rt></ruby>的“外观”设置里面修改刚刚安装的主题、图标和光标,还可以修改字体。

### 11、配置 NTP 以获得准确的时间
网络时间协议(NTP)是用来使计算机时间同步化的一种协议,它可以使计算机对其服务器或时钟源做同步化,它可以提供高精准度的时间校正。
Fedora 默认使用 chrony 来进行时间同步。
可以修改 `/etc/chrony.conf`
将 `pool` 的值选择为下列中的其中一个即可:
```
# 中国 NTP 授时快速服务
pool cn.ntp.org.cn
# 阿里云 NTP
pool ntp.aliyun.com
# 腾讯云 NTP
pool ntp.tencent.com
```
随后重启 chrony 即可。
```
sudo systemctl restart chronyd.service
```
最后就是愉快的使用 Fedora 了。

---
作者简介:
insidentally:一个喜欢瞎鼓捣的医学生。
---
via: <https://www.insidentally.com/articles/000028/>
作者:[insidentally](https://www.insidentally.com) 编辑:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由贡献者投稿至 [Linux 中国公开投稿计划](https://github.com/LCTT/Articles/),采用 [CC-BY-SA 协议](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.zh) 发布,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | null |
14,729 | 为减少视觉错误信息,Adobe 推出了开源工具包 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/adobe-launches-open-source-toolkit-to-contain-visual-misinformation/ | 2022-06-19T10:58:56 | [
"图像"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14729-1.html | 
Adobe 设想的是为网络上充斥的照片和视频标注关于它们的来源。该公司的主要目标是减少视觉错误信息的传播,不过,该系统也可以使那些“希望将自己的名字与工作关联起来”的内容创作者受益。
Adobe 在 2019 年首次宣布了其 <ruby> 内容真实性计划 <rt> Content Authenticity Initiative </rt></ruby>(CAI)项目,此后,它发布了一份关于实现该目标的技术白皮书,将该系统集成了到自己的软件中,并与新闻编辑室和硬件制造商展开了合作,以帮助普及其愿景。
现在,该公司发布了一个由三部分组成的开源工具包,从而把该技术交到开发人员手中,并投入使用。Adobe 的新开源工具包括一个用于开发“在浏览器中显示内容凭据”的 JavaScript SDK、一个命令行实用程序,和一个用于开发桌面应用程序、移动应用程序和其他应用的 Rust SDK,以创建、查看和验证嵌入式内容凭据。
众所周知,照片的 EXIF 数据中记录了有关光圈和快门速度的信息,这个新标准也采用了这种方式,它还记录有关文件创建的信息,例如文件的创建和编辑方式。如果该公司的共同愿景成真,这些 Adobe 称之为“内容凭证”的元数据,将在社交媒体平台、图像搜索平台、图像编辑器、搜索引擎中广泛可见。
C2PA 是 Adobe 的 CAI 与 微软、索尼、英特尔、推特以及 BBC 等合作伙伴的合作成果。华尔街日报、尼康和美联社最近也加入了 Adobe 的这个计划,即将 <ruby> 内容认证技术 <rt> content authentication </rt></ruby> 更加广泛地应用。
有了这些新工具,社交媒体平台就可以使用 Adobe 的 JavaScript SDK,快速让平台上的所有图像和视频显示内容凭据,这些凭据将会在鼠标悬停时,显示为右上角的一个图标。因此,无需专门的团队和更大的软件构建,该实施可以由几个开发人员在几周内完成。
CAI 的主要目标是打击互联网上的视觉错误信息,比如那些扭曲乌克兰战争的旧图片的重新传播,或是臭名昭著的南希·佩洛西的“廉价假货”。不过,数字监管链也可能使“作品被盗或出售”的内容创作者受益,这个问题多年来一直困扰着视觉艺术家,现在也正在 NFT 市场引发问题。
根据 Parsons 的说法,CAI 还引起了那些“制作合成图像和视频”的公司的巨大兴趣。公司可以将原始元数据嵌入到我们从 DALL-E 等模型中看到的那种 AI 创作中,从而确保它提供的合成图像不会轻易被误认为是真实的东西。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/adobe-launches-open-source-toolkit-to-contain-visual-misinformation/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Adobe envisions a web littered with photos and videos labelled with information about where they came from. The company’s primary goal is to reduce the spread of visual misinformation, but the system could also benefit content creators who want to keep their names associated with their work.
Adobe’s Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI) project, first announced in 2019, has since released a whitepaper on a technology to do just that, integrated the system into its own software, and partnered with newsrooms and hardware makers to help universalize its vision.
The company is now announcing the release of a three-part open source toolkit to get the technology into the hands of developers and out into the wild. Adobe’s new open source tools include a JavaScript SDK for developing ways to display content credentials in browsers, a command line utility, and a Rust SDK for developing desktop apps, mobile apps, and other experiences for creating, viewing, and verifying embedded content credentials.
In the same way that EXIF data stores information about aperture and shutter speed, the new standard also records information about a file’s creation, such as how it was created and edited. And if the company’s shared vision comes true, that metadata, which Adobe refers to as “content credentials,” will be widely viewable across social media platforms, image search platforms, image editors, search engines.
C2PA is the result of a collaboration between Adobe’s CAI and partners such as Microsoft, Sony, Intel, Twitter, and the BBC. The Wall Street Journal, Nikon, and the Associated Press have recently joined Adobe’s pledge to make content authentication more widely available.
With the new tools, a social media platform could use Adobe’s JavaScript to quickly have all of its images and videos display the content credentials, which appear as a mouse-over icon in the upper-right corner. Instead of requiring a dedicated team and a larger software buildout, that implementation could be completed in a few weeks by a couple of developers.
The CAI’s primary goal is to combat visual misinformation on the internet, such as recirculated old images distorting the Ukrainian war or the infamous Nancy Pelosi “cheapfake.” However, a digital chain of custody could also benefit content creators who have had their work stolen or sold, a problem that has plagued visual artists for years and is now causing problems in NFT markets.
According to Parsons, the CAI is also attracting a surprising amount of interest from companies that create synthetic images and videos. Companies can ensure that generative images aren’t easily mistaken for the real thing by embedding origin metadata into the kind of AI creations we’re seeing from models like DALL-E. |
14,730 | Ubuntu Core 22 来了,适用于物联网和边缘设备 | https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-core-22-release/ | 2022-06-19T13:12:42 | [
"Ubuntu Core"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14730-1.html |
>
> Ubuntu Core 22 基于 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS,为物联网和嵌入式设备带来了最佳的安全性和性能。
>
>
>

Ubuntu Core 22 是一个容器化的 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 变体,针对嵌入式和物联网设备进行了优化。
对于希望在边缘设备上运行 Canonical 的最新操作系统的开发者来说,这会是一个很棒的产品。
在发布 Ubuntu Core 22 时,Canonical 的 CEO **Mark Shuttleworth** 说:
>
> “Canonical 的目标是在从开发环境到云、再到边缘和设备的任何地方提供安全、可靠的开源技术。”
>
>
>
### Ubuntu Core 22 更新介绍
Ubuntu Core 22 版本带来了针对安全性和可靠性的改进。其中包括了以下几个改进。
#### 实时计算
正如公告中提到的,Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 提供了一个实时内核(测试版可用),它能为那些时间敏感的工业、汽车和机器人用例,提供高性能、超低延迟和工作负载可预测性。
此外,如果你有 Ubuntu 认证的硬件,你还能充分利用先进的实时功能。
#### Snapcraft 框架
整个 Ubuntu 镜像分解为许多个包(Snap),使得内核、操作系统和应用程序隔离在一个沙箱中。
这可以让你轻松地安装应用程序,而无需担心来自专用 <ruby> 物联网应用商店 <rt> IoT App Store </rt></ruby> 的依赖。对于企业而言,通过软件商店进行的软件管理解决方案,应该能够带来一系列内部部署的机会。
该框架还可帮助系统确保 OTA 更新按预期工作,即使由于某种原因失败,也不会破坏任何内容。
#### 安全
Ubuntu Core 提供了高级安全功能,包括安全启动、全盘加密以及一些更适合任务关键型环境的功能。
注意,此版本还提供了 10 年的安全更新承诺。
#### 其他关键改进
* 支持从 Ubuntu Core 20 轻松迁移并确保向后兼容性。
* 性能改进。
* 新的“恢复出厂设置”启动模式,以便在“运行/恢复模式”中恢复出厂设置。
如果你想了解更多信息,可以查看 [官方公告](https://ubuntu.com/blog/canonical-ubuntu-core-22-is-now-available-optimised-for-iot-and-embedded-devices)。
如果你对 Ubuntu Core 感兴趣,可以访问它的 [主页](https://ubuntu.com/core) 以了解更多关于它的信息。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-core-22-release/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Ubuntu Core 22 is a containerized Ubuntu 22.04 LTS variant optimized for embedded and IoT devices.
It should be a wonderful offering for developers looking to make use of Canonical’s latest operating system for edge devices.
To address the Ubuntu Core 22 release, **Mark Shuttleworth**, CEO of Canonical, said:
“Our goal at Canonical is to provide secure, reliable open-source everywhere – from the development environment to the cloud, down to the edge and to devices,”.
## Ubuntu Core 22: What’s New?
With Ubuntu Core 22 release, you get improvements focused on security and reliability. Some of them include:
### Real-time Compute
As the announcement mentions, Ubuntu 22.04 LTS provides a real-time kernel (which is available in beta), delivering high performance, ultra-low latency, and workload predictability fit for time-sensitive industrial, automotive, and robotics use cases.
Furthermore, if you have Ubuntu-certified hardware, you should be able to fully utilize advanced real-time features.
### Snapcraft Framework
The entire Ubuntu image breaks down as packages (Snaps), making the kernel, OS, and the applications isolated in a sandbox.
This should let you easily install applications without needing to worry about dependencies from the dedicated IoT App Store. For enterprises, software management solutions through the App Store should enable a range of on-premise opportunities.
The framework also helps the system ensure the OTA updates work as expected, and do not break anything even if it fails for some reason.
### Security
Out of the box, Ubuntu Core provides advanced security features that include secure boot, full-disk encryption, and more fit for mission-critical environments.
Note that you also get 10 years of security update commitment with this release.
### Other Key Improvements
- Easy migration from Ubuntu Core 20 and ensuring backward compatibility.
- Performance improvements.
- A new factory reset boot mode, to factory reset from run/recovery modes.
For more information, you can refer to the [official a](https://ubuntu.com/blog/canonical-ubuntu-core-22-is-now-available-optimised-for-iot-and-embedded-devices?ref=news.itsfoss.com)[n](https://ubuntu.com/blog/canonical-ubuntu-core-22-is-now-available-optimised-for-iot-and-embedded-devices?ref=news.itsfoss.com)[nouncement](https://ubuntu.com/blog/canonical-ubuntu-core-22-is-now-available-optimised-for-iot-and-embedded-devices?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
In case you are curious about Ubuntu Core, you might want to head to its [homepage](https://ubuntu.com/core?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to explore more about it.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,731 | 使用树莓派做一个倒计时器 | https://opensource.com/article/21/3/raspberry-pi-countdown-clock | 2022-06-19T14:51:37 | [
"倒计时",
"树莓派"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14731-1.html |
>
> 使用树莓派和电子纸显示屏开始倒计时你的下一个假期。
>
>
>

<ruby> <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pi_Day"> 圆周率日 </a> <rt> Pi Day </rt></ruby>(3 月 14 日) 来了又走,留下美好的回忆以及 [许多树莓派项目](https://opensource.com/tags/raspberry-pi) 等待我们去尝试。在任何令人精神振奋、充满欢乐的假期后回到工作中都很难,圆周率日也不例外。当我们回望三月的时候,渴望那些天的快乐。但是不用害怕,亲爱的圆周率日庆祝者们,我们开始下一个节日的漫长倒计时!
好了,严肃点。我做了一个圆周率日倒计时器,你也可以!
不久前,我购买了一个 [树莓派 Zero W](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-zero-w/),并且用它来 [解决 WiFi 信号较差的原因](https://opensource.com/article/21/3/troubleshoot-wifi-go-raspberry-pi) 。我也对使用<ruby> 电子纸 <rt> ePaper </rt></ruby>来作为它的显示屏十分感兴趣。虽然我不知道该用它来干什么,但是!它看起来真的很有趣!我买了一个十分适合放在树莓派的顶部的 2.13 英寸的 [WaveShare 显示器](https://www.waveshare.com/product/displays/e-paper.htm) 。安装很简单:只需要将显示器接到树莓派的 GPIO 上即可。
我使用 [树莓派操作系统](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/operating-systems/) 来实现该项目,虽然其他的操作系统肯定也能完成。但是下面的 `raspi-config` 命令在树莓派系统上很容易使用。
### 设置树莓派和电子纸显示屏
设置树莓派和电子纸显示屏一起工作,需要你在树莓派软件中启用串行外设接口(SPI),安装 BCM2835 C 库(来访问树莓派上的博通 BCM 2835 芯片的 GPIO 功能),安装 Python GPIO 库来控制电子纸显示屏。最后,你需要安装 WaveShare 的库来使用 Python 控制这个 2.13 英寸的显示屏。
下面是完成这些的步骤。
#### 启用 SPI
树莓派上启用 SPI 最简单的方式是使用 `raspi-config` 命令。SPI 总线允许与设备进行串行数据通信——在本例中,电子纸显示:
```
$ sudo raspi-config
```
从弹出的菜单中, 选择 “<ruby> 接口选项 <rt> Interfacing Options </rt> -> SPI -> <ruby> 是 <rt> Yes </rt> </ruby> ” 来启用 SPI 接口,然后启动。</ruby>
#### 安装 BCM2835 库
如上所述,BCM2835 库是用于树莓派博通 BCM2385 芯片的软件,它允许访问 GPIO 引脚来控制设备。
在我写这篇文章之时,用于树莓派的最新博通 BCM2385 库版本是 v1.68 。安装此库需要下载软件压缩包然后使用 `make` 来安装:
```
# 下载 BCM2853 库并解压
$ curl -sSL http://www.airspayce.com/mikem/bcm2835/bcm2835-1.68.tar.g> -o - | tar -xzf -
# 进入解压后的文件夹
$ pushd bcm2835-1.68/
# 配置、检查并安装 BCM2853 库
$ sudo ./configure
$ sudo make check
$ sudo make install
# 返回上级目录
$ popd
```
#### 安装需要的 Python 库
你用 Python 控制电子纸显示屏需要安装 Python 库 `RPi.GPIO`,还需要使用 `python3-pil` 包来画图。显然,PIL 包已经不行了,但 Pillow 可以作为代替方案。我还没有为该项目测试过 Pillow ,但它可行:
```
# 安装需要的 Python 库
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install python3-pip python3-pil
$ sudo pip3 install RPi.GPIO
```
*注意:这些是 Python3 的指令。你可以在 WaveShare 网站查到 Python2 的指令。*
#### 下载 WaveShare 示例和 Python 库
Waveshare 维护了一个 Python 和 C 的 Git 库,用于使用其电子纸显示屏和一些展示如何使用它们的示例。对这个倒计时时钟而言,你需要克隆这个库并使用用于 2.13 英寸显示屏的库:
```
# 克隆这个 WaveShare e-Paper git 库
$ git clone https://github.com/waveshare/e-Paper.gi>
```
如果你用不同的显示器或者其他公司产品,需要使用适配软件。
Waveshare 提供了很多指导:
* [WaveShare 电子纸设置指导](https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/2.13inch_e-Paper_HAT)
* [WaveShare 电子纸库安装指导](https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/Libraries_Installation_for_RPi)
#### 获得有趣的字体(选做)
你可以随心所欲的使用显示器,为什么不搞点花样?找一个炫酷的字体!
这有大量 [开放字体许可](https://scripts.sil.org/cms/scripts/page.php?site_id=nrsi&id=OFL) 的字体可供选择。我十分喜爱 Bangers 字体。如果你看过 YouTube 那你见过这种字体了,它十分流行。你可以下载到本地的共享字体目录文件中,并且所有的应用都可以使用,包括这个项目:
```
# “Bangers” 字体是 Vernon Adams 使用 Google 字体开放许可授权的字体
$ mkdir -p ~/.local/share/fonts
$ curl -sSL https://github.com/google/fonts/raw/master/ofl/bangers/Bangers-Regular.ttf -o fonts/Bangers-Regular.ttf
```
### 创建一个圆周率日倒计时器
现在你已经安装好了软件,可以使用带有炫酷字体的电子纸显示屏了。你可以创建一个有趣的项目:倒计时到下一个圆周率日!
如果你想,你可以从该项目的 [GitHub 仓库](https://github.com/clcollins/epaper-pi-ex/) 直接下载 [countdown.py](https://github.com/clcollins/epaper-pi-ex/blob/main/countdown.py) 这个 Python 文件并跳到文章结尾。
为了满足大家的好奇心,我将逐步讲解。
#### 导入一些库
```
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import logging
import os
import sys
import time
from datetime import datetime
from pathlib import Path
from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFont
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
basedir = Path(__file__).parent
waveshare_base = basedir.joinpath('e-Paper', 'RaspberryPi_JetsonNano', 'python')
libdir = waveshare_base.joinpath('lib')
```
开始先导入一些标准库之后脚本中用。也需要你从 PIL 添加 `Image`、`ImageDraw` 和 `ImageFont`,你会用到这些来画一些简单的图形。最后,为本地 `lib` 目录设置一些变量,该目录包含了用于 2.13 英寸显示屏的 Waveshare Python 库,稍后你可以使用这些变量从本地目录加载库。
#### 字体大小辅助函数
下一部分是为你选择的 Bangers-Regular.ttf 字体建立一个修改大小的辅助函数。该函数将整型变量作为大小参数,并返回一个图形字体对象来用于显示:
```
def set_font_size(font_size):
logging.info("Loading font...")
return ImageFont.truetype(f"{basedir.joinpath('Bangers-Regular.ttf').resolve()}", font_size)
```
#### 倒计时逻辑
接下来是计算这个项目的一个函数:距下次圆周率日还有多久。如果是在一月,那么计算剩余天数将很简单。但是你需要考虑是否今年的圆周率日是否已经过去了(允悲)。如果是的话,那么计算在你可以再次庆祝之前还有多少天:
```
def countdown(now):
piday = datetime(now.year, 3, 14)
# 如果错过了就增加一年
if piday < now:
piday = datetime((now.year + 1), 3, 14)
days = (piday - now).days
logging.info(f"Days till piday: {days}")
return day
```
#### 主函数
最后,到了主函数,需要初始化显示屏并向它写数据。这时,你应该写一个欢迎语然后再开始倒计时。但是首先,你需要加载 Waveshare 库:
```
def main():
if os.path.exists(libdir):
sys.path.append(f"{libdir}")
from waveshare_epd import epd2in13_V2
else:
logging.fatal(f"not found: {libdir}")
sys.exit(1)
```
上面的代码片段检查以确保该库已下载到倒计时脚本旁边的目录中,然后加载`epd2in13_V2` 库。如果你使用不同的显示屏,则需要使用不同的库。如果你愿意,也可以自己编写。我发现阅读 Waveshare 随显示屏提供的 Python 代码很有趣,它比我想象的要简单得多。
下一段代码创建一个 EPD(电子纸显示屏)对象以与显示器交互并初始化硬件:
```
logging.info("Starting...")
try:
# 创建一个显示对象
epd = epd2in13_V2.EPD()
# 初始化并清空显示
# ePaper 保持它的状态处分更新
logging.info("Initialize and clear...")
epd.init(epd.FULL_UPDATE)
epd.Clear(0xFF)
```
关于电子纸的一个有趣之处:它仅在将像素从白色变为黑色或从黑色变为白色时才耗电。这意味着当设备断电或应用程序因任何原因停止时,屏幕上的任何内容都会保留下来。从功耗的角度来看,这很好,但这也意味着你需要在启动时清除显示,否则你的脚本只会覆盖屏幕上已有的内容。 因此,`epd.Clear(0xFF)` 用于在脚本启动时清除显示。
接下来,创建一个“画布”来绘制剩余的显示输出:
```
# 创建一个图形对象
# 注意:"epd.heigh" 是屏幕的长边
# 注意:"epd.width" 是屏幕的短边
# 真是反直觉…
logging.info(f"Creating canvas - height: {epd.height}, width: {epd.width}")
image = Image.new('1', (epd.height, epd.width), 255) # 255: clear the frame
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
```
这与显示器的宽度和高度相匹配——但它有点反直觉,因为显示器的短边是宽度。我认为长边是宽度,所以这只是需要注意的一点。 请注意,`epd.height` 和 `epd.width` 由 Waveshare 库设置以对应于你使用的设备。
#### 欢迎语
接下来,你将开始画一些画。这涉及在你之前创建的“画布”对象上设置数据。这还没有将它绘制到电子纸显示屏上——你现在只是在构建你想要的图像。由你为这个项目绘制带有一块馅饼的图像,来创建一个庆祝圆周率日的欢迎信息:

很可爱,不是吗?
```
logging.info("Set text text...")
bangers64 = set_font_size(64)
draw.text((0, 30), 'PI DAY!', font = bangers64, fill = 0)
logging.info("Set BMP...")
bmp = Image.open(basedir.joinpath("img", "pie.bmp"))
image.paste(bmp, (150,2))
```
最后,*真是是最后了*,你可以展示你画的图画:
```
logging.info("Display text and BMP")
epd.display(epd.getbuffer(image))
```
上面那段话更新了显示屏,以显示你所画的图像。
接下来,准备另一幅图像展示你的倒计时:
#### 圆周率日倒计时
首先,创建一个用来展示倒计时的图像对象。也需要设置数字的字体大小:
```
logging.info("Pi Date countdown; press CTRL-C to exit")
piday_image = Image.new('1', (epd.height, epd.width), 255)
piday_draw = ImageDraw.Draw(piday_image)
# 设置字体大小
bangers36 = set_font_size(36)
bangers64 = set_font_size(64)
```
为了使它显示的时候更像一个倒计时,更新图像的一部分是更加有效的手段,仅更改已经改变的显示数据部分。下面的代码准备以这样方式运行:
```
# 准备更新显示
epd.displayPartBaseImage(epd.getbuffer(piday_image))
epd.init(epd.PART_UPDATE)
```
最后,需要计时,开始一个无限循环来检查据下次圆周率日还有多久,并显示在电子纸上。如果到了圆周率日,你可以输出一些庆祝短语:
```
while (True):
days = countdown(datetime.now())
unit = get_days_unit(days)
# 通过绘制一个填充有白色的矩形来清除屏幕的下半部分
piday_draw.rectangle((0, 50, 250, 122), fill = 255)
# 绘制页眉
piday_draw.text((10,10), "Days till Pi-day:", font = bangers36, fill = 0)
if days == 0:
# 绘制庆祝语
piday_draw.text((0, 50), f"It's Pi Day!", font = bangers64, fill = 0)
else:
# 绘制距下一次 Pi Day 的时间
piday_draw.text((70, 50), f"{str(days)} {unit}", font = bangers64, fill = 0)
# 渲染屏幕
epd.displayPartial(epd.getbuffer(piday_image))
time.sleep(5)
```
脚本最后做了一些错误处理,包括捕获键盘中断,这样你可以使用 `Ctrl + C` 来结束无限循环,以及一个根据计数来打印 `day` 或 `days` 的函数:
```
except IOError as e:
logging.info(e)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
logging.info("Exiting...")
epd.init(epd.FULL_UPDATE)
epd.Clear(0xFF)
time.sleep(1)
epd2in13_V2.epdconfig.module_exit()
exit()
def get_days_unit(count):
if count == 1:
return "day"
return "days"
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
```
现在你已经拥有一个倒计时并显示剩余天数的脚本!这是在我的树莓派上的显示(视频经过加速,我没有足够的磁盘空间来保存一整天的视频):

#### 安装 systemd 服务(选做)
如果你希望在系统打开时运行倒计时显示,并且无需登录并运行脚本,你可以将可选的 systemd 单元安装为 [systemd 用户服务](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/systemd/User)。
将 GitHub 上的 [piday.service](https://github.com/clcollins/epaper-pi-ex/blob/main/piday.service) 文件复制到 `${HOME}/.config/systemd/user`,如果该目录不存在,请先创建该目录。然后你可以启用该服务并启动它:
```
$ mkdir -p ~/.config/systemd/user
$ cp piday.service ~/.config/systemd/user
$ systemctl --user enable piday.service
$ systemctl --user start piday.service
# Enable lingering, to create a user session at boot
# and allow services to run after logout
$ loginctl enable-linger $USER
```
该脚本将输出到 systemd 日志,可以使用 `journalctl` 命令查看输出。
### 它开始看起来像是圆周率日了!
这就是你的作品!一个显示在电子纸显示屏上的树莓派 Zero W 圆周率日倒计时器!并在系统启动时使用 systemd 单元文件启动!现在距离我们可以再次相聚庆祝圆周率日还有好多天的奇妙设备———树莓派。通过我们的小项目,我们可以一目了然地看到确切的天数。
但实际上,每个人都可以在每一天在心中庆祝圆周率日,因此请使用自己的树莓派创建一些有趣且具有教育意义的项目吧!
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/3/raspberry-pi-countdown-clock>
作者:[Chris Collins](https://opensource.com/users/clcollins) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[Donkey](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | For 2021, [Pi Day](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pi_Day) has come and gone, leaving fond memories and [plenty of Raspberry Pi projects](https://opensource.com/tags/raspberry-pi) to try out. The days after any holiday can be hard when returning to work after high spirits and plenty of fun, and Pi Day is no exception. As we look into the face of the Ides of March, we can long for the joys of the previous, well, day. But fear no more, dear Pi Day celebrant! For today, we begin the long countdown to the next Pi Day!
OK, but seriously. I made a Pi Day countdown timer, and you can too!
A while back, I purchased a [Raspberry Pi Zero W](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-zero-w/) and recently used it to [figure out why my WiFi was so bad](https://opensource.com/article/21/3/troubleshoot-wifi-go-raspberry-pi). I was also intrigued by the idea of getting an ePaper display for the little Zero W. I didn't have a good use for one, but, dang it, it looked like fun! I purchased a little 2.13" [Waveshare display](https://www.waveshare.com/product/displays/e-paper.htm), which fit perfectly on top of the Raspberry Pi Zero W. It's easy to install: Just slip the display down onto the Raspberry Pi's GIPO headers and you're good to go.
I used [Raspberry Pi OS](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/operating-systems/) for this project, and while it surely can be done with other operating systems, the `raspi-config`
command, used below, is most easily available on Raspberry Pi OS.
## Set up the Raspberry Pi and the ePaper display
Setting up the Raspberry Pi to work with the ePaper display requires you to enable the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) in the Raspberry Pi software, install the BCM2835 C libraries (to access the GPIO functions for the Broadcom BCM 2835 chip on the Raspberry Pi), and install Python GPIO libraries to control the ePaper display. Finally, you need to install the Waveshare libraries for working with the 2.13" display using Python.
Here's a step-by-step walkthrough of how to do these tasks.
### Enable SPI
The easiest way to enable SPI is with the Raspberry Pi `raspi-config`
command. The SPI bus allows serial data communication to be used with devices—in this case, the ePaper display:
`$ sudo raspi-config`
From the menu that pops up, select **Interfacing Options** -> **SPI** -> **Yes** to enable the SPI interface, then reboot.
### Install BCM2835 libraries
As mentioned above, the BCM2835 libraries are software for the Broadcom BCM2385 chip on the Raspberry Pi, which allows access to the GPIO pins and the ability to use them to control devices.
As I'm writing this, the latest version of the Broadcom BCM 2835 libraries for the Raspberry Pi is v1.68. To install the libraries, you need to download the software tarball and build and install the software with `make`
:
```
# Download the BCM2853 libraries and extract them
$ curl -sSL http://www.airspayce.com/mikem/bcm2835/bcm2835-1.68.tar.gz -o - | tar -xzf -
# Change directories into the extracted code
$ pushd bcm2835-1.68/
# Configure, build, check and install the BCM2853 libraries
$ sudo ./configure
$ sudo make check
$ sudo make install
# Return to the original directory
$ popd
```
### Install required Python libraries
You also need some Python libraries to use Python to control the ePaper display, the `RPi.GPIO`
pip package. You also need the `python3-pil`
package for drawing shapes. Apparently, the PIL package is all but dead, but there is an alternative, [Pillow](https://pypi.org/project/Pillow/). I have not tested Pillow for this project, but it may work:
```
# Install the required Python libraries
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install python3-pip python3-pil
$ sudo pip3 install RPi.GPIO
```
*Note: These instructions are for Python 3. You can find Python 2 instructions on Waveshare's website*
### Download Waveshare examples and Python libraries
Waveshare maintains a Git repository with Python and C libraries for working with its ePaper displays and some examples that show how to use them. For this countdown clock project, you will clone this repository and use the libraries for the 2.13" display:
```
# Clone the WaveShare e-Paper git repository
$ git clone https://github.com/waveshare/e-Paper.git
```
If you're using a different display or a product from another company, you'll need to use the appropriate software for your display.
Waveshare provides instructions for most of the above on its website:
### Get a fun font (optional)
You can display your timer however you want, but why not do it with a little style? Find a cool font to work with!
There's a ton of [Open Font License](https://scripts.sil.org/cms/scripts/page.php?site_id=nrsi&id=OFL) fonts available out there. I am particularly fond of Bangers. You've seen this if you've ever watched YouTube—it's used *all over*. It can be downloaded and dropped into your user's local shared fonts directory to make it available for any application, including this project:
```
# The "Bangers" font is a Open Fonts License licensed font by Vernon Adams (https://github.com/vernnobile) from Google Fonts
$ mkdir -p ~/.local/share/fonts
$ curl -sSL https://github.com/google/fonts/raw/master/ofl/bangers/Bangers-Regular.ttf -o fonts/Bangers-Regular.ttf
```
## Create a Pi Day countdown timer
Now that you have installed the software to work with the ePaper display and a fun font to use, you can build something cool with it: a timer to count down to the next Pi Day!
If you want, you can just grab the [countdown.py](https://github.com/clcollins/epaper-pi-ex/blob/main/countdown.py) Python file from this project's [GitHub repo](https://github.com/clcollins/epaper-pi-ex/) and skip to the end of this article.
For the curious, I'll break down that file, section by section.
### Import some libraries
```
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import logging
import os
import sys
import time
from datetime import datetime
from pathlib import Path
from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFont
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
basedir = Path(__file__).parent
waveshare_base = basedir.joinpath('e-Paper', 'RaspberryPi_JetsonNano', 'python')
libdir = waveshare_base.joinpath('lib')
```
At the start, the Python script imports some standard libraries used later in the script. You also need to add `Image`
, `ImageDraw`
, and `ImageFont`
from the PIL package, which you'll use to draw some simple geometric shapes. Finally, set some variables for the local `lib`
directory that contains the Waveshare Python libraries for working with the 2.13" display, and which you can use later to load the library from the local directory.
### Font size helper function
The next part of the script has a helper function for setting the font size for your chosen font: Bangers-Regular.ttf. It takes an integer for the font size and returns an ImageFont object you can use with the display:
```
def set_font_size(font_size):
logging.info("Loading font...")
return ImageFont.truetype(f"{basedir.joinpath('Bangers-Regular.ttf').resolve()}", font_size)
```
### Countdown logic
Next is a small function that calculates the meat of this project: how long it is until the next Pi Day. If it were, say, January, it would be relatively straightforward to count how many days are left, but you also need to consider whether Pi Day has already passed for the year (sadface), and if so, count how very, very many days are ahead until you can celebrate again:
```
def countdown(now):
piday = datetime(now.year, 3, 14)
# Add a year if we're past PiDay
if piday < now:
piday = datetime((now.year + 1), 3, 14)
days = (piday - now).days
logging.info(f"Days till piday: {days}")
return day
```
### The main function
Finally, you get to the main function, which initializes the display and begins writing data to it. In this case, you'll write a welcome message and then begin the countdown to the next Pi Day. But first, you need to load the Waveshare library:
```
def main():
if os.path.exists(libdir):
sys.path.append(f"{libdir}")
from waveshare_epd import epd2in13_V2
else:
logging.fatal(f"not found: {libdir}")
sys.exit(1)
```
The snippet above checks to make sure the library has been downloaded to a directory alongside the countdown script, and then it loads the `epd2in13_V2`
library. If you're using a different display, you will need to use a different library. You can also write your own if you are so inclined. I found it kind of interesting to read the Python code that Waveshare provides with the display. It's considerably less complicated than I would have imagined it to be, if somewhat tedious.
The next bit of code creates an EPD (ePaper Display) object to interact with the display and initializes the hardware:
```
logging.info("Starting...")
try:
# Create an a display object
epd = epd2in13_V2.EPD()
# Initialize the displace, and make sure it's clear
# ePaper keeps it's state unless updated!
logging.info("Initialize and clear...")
epd.init(epd.FULL_UPDATE)
epd.Clear(0xFF)
```
An interesting aside about ePaper: It uses power only when it changes a pixel from white to black or vice-versa. This means when the power is removed from the device or the application stops for whatever reason, whatever was on the screen remains. That's great from a power-consumption perspective, but it also means you need to clear the display when starting up, or your script will just write over whatever is already on the screen. Hence, `epd.Clear(0xFF)`
is used to clear the display when the script starts.
Next, create a "canvas" where you will draw the rest of your display output:
```
# Create an image object
# NOTE: The "epd.heigh" is the LONG side of the screen
# NOTE: The "epd.width" is the SHORT side of the screen
# Counter-intuitive...
logging.info(f"Creating canvas - height: {epd.height}, width: {epd.width}")
image = Image.new('1', (epd.height, epd.width), 255) # 255: clear the frame
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
```
This matches the width and height of the display—but it is somewhat counterintuitive, in that the short side of the display is the width. I think of the long side as the width, so this is just something to note. Note that the `epd.height`
and `epd.width`
are set by the Waveshare library to correspond to the device you're using.
### Welcome message
Next, you'll start to draw something. This involves setting data on the "canvas" object you created above. This doesn't draw it to the ePaper display yet—you're just building the image you want right now. Create a little welcome message celebrating Pi Day, with an image of a piece of pie, drawn by yours truly just for this project:

(Chris Collins, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Cute, huh?
```
logging.info("Set text text...")
bangers64 = set_font_size(64)
draw.text((0, 30), 'PI DAY!', font = bangers64, fill = 0)
logging.info("Set BMP...")
bmp = Image.open(basedir.joinpath("img", "pie.bmp"))
image.paste(bmp, (150,2))
```
Finally, *finally*, you get to display the canvas you drew, and it's a little bit anti-climactic:
```
logging.info("Display text and BMP")
epd.display(epd.getbuffer(image))
```
That bit above updates the display to show the image you drew.
Next, prepare another image to display your countdown timer.
### Pi Day countdown timer
First, create a new image object that you can use to draw the display. Also, set some new font sizes to use for the image:
```
logging.info("Pi Date countdown; press CTRL-C to exit")
piday_image = Image.new('1', (epd.height, epd.width), 255)
piday_draw = ImageDraw.Draw(piday_image)
# Set some more fonts
bangers36 = set_font_size(36)
bangers64 = set_font_size(64)
```
To display a ticker like a countdown, it's more efficient to update part of the image, changing the display for only what has changed in the data you want to draw. The next bit of code prepares the display to function this way:
```
# Prep for updating display
epd.displayPartBaseImage(epd.getbuffer(piday_image))
epd.init(epd.PART_UPDATE)
```
Finally, you get to the timer bit, starting an infinite loop that checks how long it is until the next Pi Day and displays the countdown on the ePaper display. If it actually *is* Pi Day, you can handle that with a little celebration message:
```
while (True):
days = countdown(datetime.now())
unit = get_days_unit(days)
# Clear the bottom half of the screen by drawing a rectangle filld with white
piday_draw.rectangle((0, 50, 250, 122), fill = 255)
# Draw the Header
piday_draw.text((10,10), "Days till Pi-day:", font = bangers36, fill = 0)
if days == 0:
# Draw the Pi Day celebration text!
piday_draw.text((0, 50), f"It's Pi Day!", font = bangers64, fill = 0)
else:
# Draw how many days until Pi Day
piday_draw.text((70, 50), f"{str(days)} {unit}", font = bangers64, fill = 0)
# Render the screen
epd.displayPartial(epd.getbuffer(piday_image))
time.sleep(5)
```
The last bit of the script does some error handling, including some code to catch keyboard interrupts so that you can stop the infinite loop with **Ctrl**+**C** and a small function to print "day" or "days" depending on whether or not the output should be singular (for that one, single day each year when it's appropriate):
```
except IOError as e:
logging.info(e)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
logging.info("Exiting...")
epd.init(epd.FULL_UPDATE)
epd.Clear(0xFF)
time.sleep(1)
epd2in13_V2.epdconfig.module_exit()
exit()
def get_days_unit(count):
if count == 1:
return "day"
return "days"
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
```
And there you have it! A script to count down and display how many days are left until Pi Day! Here's an action shot on my Raspberry Pi (sped up by 86,400; I don't have nearly enough disk space to save a day-long video):

(Chris Collins, CC BY-SA 4.0)
### Install the systemd service (optional)
If you'd like the countdown display to run whenever the system is turned on and without you having to be logged in and run the script, you can install the optional systemd unit as a [systemd user service](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/systemd/User)).
Copy the [piday.service](https://github.com/clcollins/epaper-pi-ex/blob/main/piday.service) file on GitHub to `${HOME}/.config/systemd/user`
, first creating the directory if it doesn't exist. Then you can enable the service and start it:
```
$ mkdir -p ~/.config/systemd/user
$ cp piday.service ~/.config/systemd/user
$ systemctl --user enable piday.service
$ systemctl --user start piday.service
# Enable lingering, to create a user session at boot
# and allow services to run after logout
$ loginctl enable-linger $USER
```
The script will output to the systemd journal, and the output can be viewed with the `journalctl`
command.
## It's beginning to look a lot like Pi Day!
And *there* you have it! A Pi Day countdown timer, displayed on an ePaper display using a Raspberry Pi Zero W, and starting on system boot with a systemd unit file! Now there are just 350-something days until we can once again come together and celebrate the fantastic device that is the Raspberry Pi. And we can see exactly how many days at a glance with our tiny project.
But in truth, anyone can hold Pi Day in their hearts year-round, so enjoy creating some fun and educational projects with your own Raspberry Pi!
## 1 Comment |
14,734 | 有研究表明,推特能够推动开源项目的普及 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/according-to-studies-twitter-drives-open-source-projects-popularity/ | 2022-06-20T14:01:36 | [
"开源",
"推特"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14734-1.html | 
由 HongBo Fang 博士领导的研究团队发现,推特是一种吸引更多人关注和贡献 GitHub 开源项目的有效方式。Fang 博士在国际软件工程会议上发表了这项名为“‘这真是太棒了!’估计推文对开源项目受欢迎程度和新贡献者的影响”的研究,并获得了杰出论文奖。这项研究显示,发送和一个项目有关的推文,导致了该项目受欢迎程度增加了 7%(在 GitHub 上至少增加了一个星标),贡献者数量增加了 2%。一个项目收到的推文越多,它收到的星标和贡献者就越多。
Fang 说:“我们已经意识到社交媒体在开源社区中变得越来越重要,吸引关注和新的贡献者将带来更高质量和更好的软件。”
大多数开源软件都是由志愿者创建和维护的。参与项目的人越多,结果就越好。开发者和其他人使用该软件、报告问题并努力解决这些问题。然而,不受欢迎的项目有可能得不到应有的关注。这些劳动力(几乎都是志愿者),维护了数百万人每天依赖的软件。例如,几乎每个 HTTPS 网站都使用开源的 OpenSSL 保护其内容。Heartbleed 是 OpenSSL 中发现的一个安全漏洞,在 2014 年被发现后,企业花费了数百万美元来修复它。另一个开源软件 cURL 允许连接的设备相互发送数据,并安装在大约 10 亿台设备上。开源软件之多,不胜枚举。
此次“推特对提高开源项目的受欢迎程度和吸引新贡献者的影响”的研究,其实是 “Vasilescu 数据挖掘与社会技术研究实验室”(STRUDEL)的一个更大项目的其中一部分,该研究着眼于如何建立开源社区并且其工作更具可持续性。毕竟,支撑现代技术的数字基础设施、道路和桥梁都是开源软件。如果维护不当,这些基础设施可能会崩溃。
研究人员检查了 44544 条推文,其中包含指向 2370 个开源 GitHub 存储库的链接,以证明这些推文确实吸引了新的星标和项目贡献者。在这项研究中,研究人员使用了一种科学的方法:将推特上提及的 GitHub 项目的星标和贡献者的增加,与推特上未提及的一组项目进行了比较。该研究还描述了高影响力推文的特征、可能被帖子吸引到项目的人的类型,以及这些人与通过其他方式吸引的贡献者有何不同。来自项目支持者而不是开发者的推文最能吸引注意力。请求针对特定任务或项目提供帮助的帖子会收到更高的回复率。推文往往会吸引新的贡献者,**他们是 GitHub 的新手,但不是经验不足的程序员**。还有,**新的关注可能不会带来新的帮助**。
提高项目受欢迎程度也存在其缺点,研究人员讨论后认为,它的潜在缺点之一,就是注意力和行动之间的差距。**更多的关注通常会导致更多的功能请求或问题报告,但不一定有更多的开发者来解决它们**。社交媒体受欢迎程度的提高,可能会导致有更多的“巨魔”或“有毒行为”出现在项目周围。
(LCTT 译注:我觉得文章中有三句话写得很好,于是把它们加粗了,和大家分享。 —— 六开箱)
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/according-to-studies-twitter-drives-open-source-projects-popularity/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The research team, led by Ph.D. Hongbo Fang, discovered that Twitter is an effective way to attract more attention and contributors to open source projects on GitHub. The study, titled “‘This Is Damn Slick!’ Estimating the Impact of Tweets on Open Source Project Popularity and New Contributors,” was presented by Fang at the International Conference on Software Engineering, where it received a Distinguished Paper award. According to the study, tweeting about a project resulted in a 7% increase in popularity (at least one star on GitHub) and a 2% increase in the number of contributors. The more tweets a project received, the more stars and contributors it received.
“We have realized that social media has become more and more important in open source communities,” Fang said. “Attracting attention and new contributors will lead to higher quality and better software.”
The majority of open source software is created and maintained by volunteers. The more people who work on a project, the better the outcome. Developers and others use the software, report problems, and work to resolve them. Projects that are unpopular risk not receiving the attention they require. This mostly volunteer workforce is responsible for the upkeep of software that millions of people rely on every day. For example, nearly every HTTPS website secures its content with the open source OpenSSL. Heartbleed, a security flaw discovered in OpenSSL, cost businesses millions of dollars to fix after it was discovered in 2014. Another open source piece of software, cURL, allows connected devices to send data to one another and is installed on approximately 1 billion devices. The list could go on and on.
Fang’s study of Twitter’s impact on increasing the popularity of an open-source project and attracting new contributors is part of a larger body of work in Vasilescu’s Socio-Technical Research Using Data Excavation Lab (STRUDEL) that looks at how to make the open source community and its work more sustainable. The digital infrastructure, the roads and bridges that underpin modern technology, is open source software. That infrastructure may crumble if it is not properly maintained.
The researchers examined 44,544 tweets containing links to 2,370 open source GitHub repositories for evidence that the tweets drew new stars and contributors to the projects. The researchers used a scientific approach to the study, comparing the increase in stars and contributors of GitHub projects mentioned on Twitter to a control group of projects that were not mentioned on Twitter. The study also described the characteristics of high-impact tweets, the types of people who are likely to be drawn to a project by the posts, and how those people differ from contributors drawn through other means. Tweets from project supporters, rather than developers, work best for attracting attention. Posts requesting assistance with a specific task or project receive a higher response rate. Tweets tend to attract new contributors who are newer to GitHub but not less experienced programmers. And new interest may not result in new assistance.
One of the potential drawbacks of increasing a project’s popularity that the researchers discuss is the gap between attention and action. More attention frequently results in more feature requests or issue reports, but not necessarily more developers to address them. Increased social media popularity may result in more trolls or toxic behaviour surrounding the project. |
14,735 | 我如何利用 Xfce 桌面为旧电脑赋予新生 | https://opensource.com/article/22/6/linux-xfce-old-laptop | 2022-06-20T14:33:00 | [
"旧电脑",
"Xfce"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14735-1.html | 
>
> 当我为了在一场会议上做演示,用笔记本电脑安装 Linux 系统后,发现 Linux 和 Xfce 桌面让我的这台旧电脑健步如飞。
>
>
>
几周前,我要在一个会议上简要演示自己在 Linux 下编写的一款小软件。我需要带一台 Linux 笔记本电脑参会,因此我翻出一台旧笔记本电脑,并且安装上 Linux 系统。我使用的是 Fedora 36 Xfce 版,使用还不错。
这台我用的笔记本是在 2012 年购买的。1.70 GHZ 的 CPU、4 GB 的 内存、128 GB 的硬盘,也许和我现在的桌面电脑比性能很弱,但是 Linux 和 Xfce 桌面赋予了这台旧电脑新的生命。
### Linux 的 Xfce 桌面
Xfce 桌面是一个轻量级桌面,它提供一个精美、现代的外观。熟悉的界面,有任务栏或者顶部“面板”可以启动应用程序,在系统托盘可以改变虚拟桌面,或者查看通知信息。屏幕底部的快速访问停靠区让你可以启动经常使用的应用程序,如终端、文件管理器和网络浏览器。

要开始一个新应用程序,点击左上角的应用程序按钮。这将打开一个应用程序启动菜单,顶部有常用的应用程序,比如终端和文件管理。其它的应用程序会分组排列,这样你可以找到所需要的应用。

### 管理文件
Xfce 的文件管理器时叫 Thunar,它能很好地管理我的文件。我喜欢 Thunar 可以连接远程系统,在家里,我用一个开启 SSH 的树莓派作为个人文件服务器。Thunar 可以打开一个 SSH 文件传输窗口,这样我可以在笔记本电脑和树莓派之间拷贝文件。

另一个访问文件和文件夹的方式是通过屏幕底部的快速访问停靠区。点击文件夹图标可以打开一个常用操作的菜单,如在终端窗口打开一个文件夹、新建一个文件夹或进入指定文件夹等。

### 其它应用程序
我喜欢探索 Xfce 提供的其他应用程序。Mousepad 看起来像一个简单的文本编辑器,但是比起纯文本编辑,它包含更多有用的功能。Mousepad 支持许多文件类型,程序员和其他高级用户也许会非常喜欢。可以在文档菜单中查看一下部分编程语言的列表。

如果你更喜欢一个不同的外观和感觉,可以用视图菜单调整界面选项,如字体、配色方案以及行号。

磁盘工具可以让你管理储存设备。虽然我不需要修改我的系统磁盘,磁盘工具是一个初始化或重新格式化 USB 闪存设备的好方式。我认为这个界面非常简单好用。

Geany 集成开发环境也给我留下了深刻印象,我有点惊讶于一个完整的集成开发软件(IDE)可以在一个旧系统可以如此流畅地运行。Geany 宣称自己是一个“强大、稳定和轻量级的程序员文本编辑器,提供大量有用的功能,而不会拖累你的工作流程”。而这正是 Geany 所提供的。
我用一个简单的 “hello world” 程序测试 Geany,当我输入每一个函数名称时,很高兴地看到 IDE 弹出语法帮助,弹出的信息并不特别显眼,且刚好提供了我需要的信息。虽然我能很容易记住 `printf` 函数,但总是忘记诸如 `fputs` 和 `realloc` 之类的函数的选项顺序,这就是我需要弹出语法帮助的地方。

深入了解 Xfce 的菜单,寻找其它应用程序,让你的工作更简单,你将找到可以播放音乐、访问终端或浏览网页的应用程序。
当我在笔记本电脑上安装了 Linux,在会议上做了一些演示后,我发现 Linux 和 Xfce 桌面让这台旧电脑变得相当敏捷。这个系统运行得如此流畅,以至于当会议结束后,我决定把这台笔记本电脑作为备用机。
我确实喜欢在 Xfce 中工作和使用这些应用程序,尽管系统开销不大,使用也很简单,但我并没有感觉到不够用,我可以用 Xfce 和上面的应用程序做任何事情。如果你有一台需要翻新的旧电脑,试试安装 Linux,给旧硬件带来新的生命。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/6/linux-xfce-old-laptop>
作者:[Jim Hall](https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lightchaserhy](https://github.com/lightchaserhy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | A few weeks ago, I needed to give a conference presentation that included a brief demonstration of a small app I'd written for Linux. I needed a Linux laptop to bring to the conference, so I dug out an old laptop and installed Linux on it. I used the [Fedora 36 Xfce spin](https://spins.fedoraproject.org/xfce/download/index.html), which worked great.
The laptop I used was purchased in 2012. The 1.70 GHz CPU, 4 GB memory, and 128 GB drive may seem small compared to my current desktop machine, but Linux and the Xfce desktop gave this old machine new life.
## Xfce desktop for Linux
The [Xfce desktop](https://opensource.com/article/19/12/xfce-linux-desktop) is a lightweight desktop that provides a sleek, modern look. The interface is familiar, with a taskbar or “panel” across the top to launch applications, change between virtual desktops, or access notifications in the system tray. The quick access dock at the bottom of the screen lets you launch frequently used applications like the terminal, file manager, and web browser.
(Jim Hall, CC BY-SA 40)
To start a new application, click the Applications button in the upper-left corner. This opens a menu of application launchers, with the most frequently used applications like the terminal and file manager at the top. Other applications are organized into groups, so you can navigate to the one you want.
(Jim Hall, CC BY-SA 40)
## Managing files
Xfce's file manager is called Thunar, and it does a great job of organizing my files. I like that Thunar can also make connections to remote systems. At home, I use a Raspberry Pi using SSH as a [personal file server](https://opensource.com/article/20/3/personal-file-server-ssh). Thunar lets me open an SSH file transfer window so I can copy files between my laptop and the Raspberry Pi.
(Jim Hall, CC BY-SA 40)
Another way to access files and folders is via the quick access dock at the bottom of the screen. Click the folder icon to bring up a menu of common actions such as opening a folder in a terminal window, creating a new folder, or navigating into a specific folder.
(Jim Hall, CC BY-SA 40)
## Other applications
I loved exploring the other applications provided in Xfce. The Mousepad text editor looks like a simple text editor, but it contains useful features for editing more than just plain text. Mousepad recognizes many file types that programmers and other power users may appreciate. Check out this partial list of programming languages available in the Document menu.
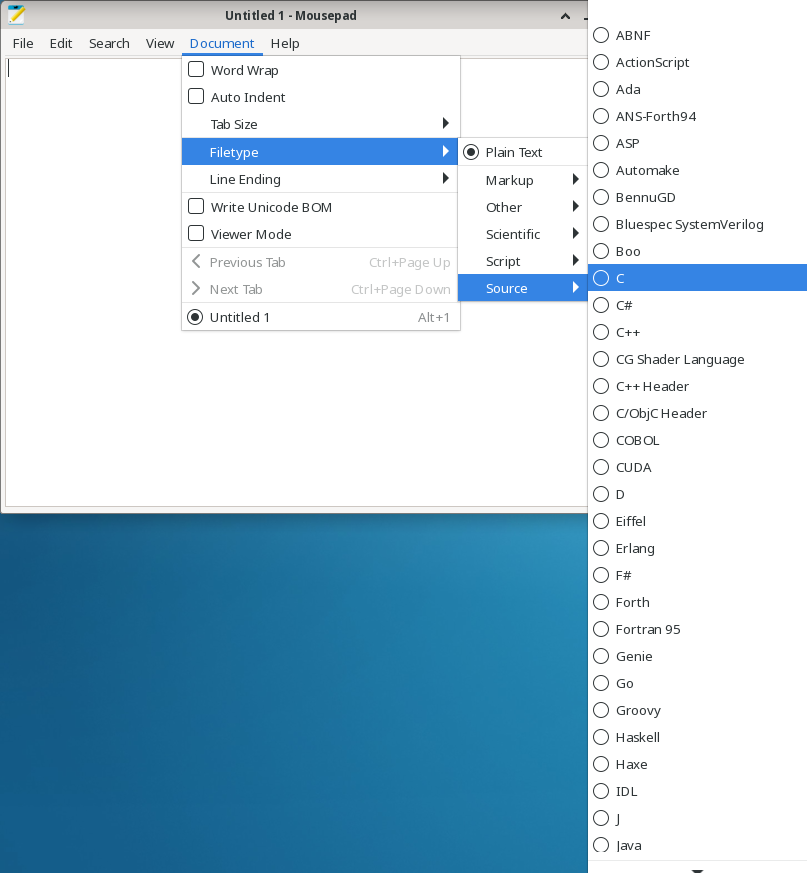
(Jim Hall, CC BY-SA 40)
If you prefer a different look and feel, you can adjust the interface options such as font, color scheme, and line numbers using the View menu.
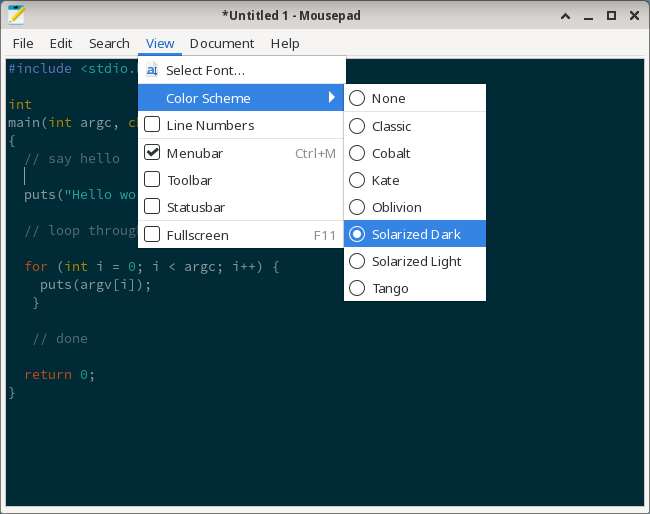
(Jim Hall, CC BY-SA 40)
The disk utility lets you manage storage devices. While I didn't need to modify my system disk, the disk tool is a great way to initialize or reformat a USB flash drive. I found the interface very easy to use.
(Jim Hall, CC BY-SA 40)
I was also impressed with the Geany integrated development environment. I was a bit surprised that a full IDE ran so well on an older system. Geany advertises itself as a “powerful, stable and lightweight programmer's text editor that provides tons of useful features without bogging down your workflow.” And that's exactly what Geany provided.
I started a simple “hello world” program to test out Geany, and was pleased to see that the IDE popped up syntax help as I typed each function name. The pop-up message is unobtrusive and provides just enough syntax information where I need it. While the `printf`
function is easy for me to remember, I always forget the order of options to other functions like `fputs`
and `realloc`
. This is where I need the pop-up syntax help.
(Jim Hall, CC BY-SA 40)
Explore the menus in Xfce to find other applications to make your work easier. You'll find apps to play music, access the terminal, or browse the web.
While I installed Linux to use my laptop for a few demos at a conference, I found Linux and the Xfce desktop made this old laptop feel quite snappy. The system performed so well that when the conference was over, I decided to keep the laptop around as a second machine.
I just love working in Xfce and using the apps. Despite the low overhead and minimal approach, I don't feel underpowered. I can do everything I need to do using Xfce and the included apps. If you have an older machine that needs new life, try installing Linux to bring new life to old hardware.
## 2 Comments |
14,736 | 使用 Flatseal 管理 Flatpak 的权限 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/06/manage-flatpak-permission-flatseal/ | 2022-06-20T15:15:58 | [
"Flatpak",
"权限"
] | /article-14736-1.html | 
>
> 了解如何使用 Flatseal 应用管理 Flatpak 权限,它为你提供了一个友好的 GUI 和额外的功能。
>
>
>
从新用户的角度来看,在 Linux 中安装应用可能是一个挑战。主要原因是有这么多的 [Linux 发行版](https://www.debugpoint.com/category/distributions)。而你需要为各种 Linux 发行版提供不同的安装方法或说明。对于一些用户来说,这可能会让他们不知所措。此外,对于开发者来说,为不同的发行版创建独立的软件包和构建也很困难。
### Flatpak 解决了这个问题。如何解决?
它使用了容器技术,使同一个应用的可执行文件在所有的 Linux 平台上都能类似地运行。例如,一个单一的可执行文件可以在 Ubuntu、Fedora、OpenSUSE、Arch Linux 和许多其他平台上运行。
此外,开发人员还可以减少为不同平台打包同一应用的努力。他们可以专注于应用的功能,而不是发行或部署。
此外,Flatpak 应用还能即时更新,当有了最新版本,你就能得到它。
所有这些好处也开启了一个重要的问题。Flatpak 应用需要的权限是什么?你如何轻松地管理它们?例如,一个应用可能只需要网络访问,而不需要磁盘空间。或者另一个可能有截图的权限,但可能根本就不需要。
所以,审查一个 Flatpak 应用的权限是非常必要的。这与你的安卓或 iOS 应用的权限类似。
最后,即使你是一个新用户,管理和审查权限也不是那么困难,这要感谢图形化的应用 - Flatseal。
### 什么是 Flatseal?
Flatseal 是一个 Flatpak 应用,它为你提供了一个友好的用户界面来查看和改变你系统中所有 Flatpak 应用的权限。
它是一个优秀的小程序,每个应用的每个权限部分都有一个易于使用的切换按钮。下面是它的外观(图 1)。

### 你如何使用 Flatseal 来管理 Flatpak 的权限?
当打开 Flatseal 应用时,它应该在左边的导航栏列出所有的 Flatpak 应用。而当你选择了一个应用,它就会在右边的主窗口中显示可用的权限设置。
现在,对于每个 Flatpak 权限控制,当前值显示在切换开关中。如果该权限正在使用中,它应该被启用。否则,它应该是灰色的。
首先,要设置权限,你必须进入你的系统的应用。然后,你可以从权限列表中启用或禁用任何各自的控制。
其次,如果你想设置一个适用于你系统中所有 Flatpak 的全局控制,你可以在左上方选择“所有应用”并应用全局设置(图 2)。

这真是超级简单。不是吗?
### 使用 Flatseal 管理 Flatpak 权限的例子
让我们举个例子。
在我的系统中,我安装了上述 Flatpak(图 2)。让我们挑选 Telegram 桌面应用。目前,Telegram 桌面没有访问任何主目录或用户文件的权限(图 3)。

现在,如果我想允许所有的用户文件和某个特定的文件夹(例如:`/home/Downloads`),你可以通过打开启用开关来给予它。请看下面的图 4。

同样地,你可以启用或禁用你想要的权限。在内部,Flatseal 执行内部的 Flatpak 命令来实现这一点。
例如,上述情况可能转化为以下命令。
```
flatpak override org.telegram.desktop --filesystem=/home/Downloads
```
而要删除权限:
```
flatpak override org.telegram.desktop --nofilesystem=/home/Downloads
```
Flatseal 还有一个很酷的功能,它在用户特定的权限变化旁边显示一个小的警报图标(见图 4)。
### 我可以在所有的 Linux 发行版中安装 Flatseal 吗?
是的,你可以把 [Flatseal](https://flathub.org/apps/details/com.github.tchx84.Flatseal) 作为 Flatpak 安装在所有 Linux 发行版中。你可以使用 [本指南](https://flatpak.org/setup/) 设置你的系统,并运行以下命令进行安装。或者,[点击这里](https://dl.flathub.org/repo/appstream/com.github.tchx84.Flatseal.flatpakref) 直接启动特定系统的安装程序。
```
flatpak install flathub com.github.tchx84.Flatseal
```
### 结束语
我希望上面的 Flatpak 权限管理指南足够简单,让你了解并开始使用 Flatpak。它超级容易控制,使用起来也容易得多。另外,你可能想访问我们更多的 [Flatpak 指南](https://www.debugpoint.com/tag/flatpak/)。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/06/manage-flatpak-permission-flatseal/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,738 | Mattermost 7.0 发布,扩展了工作流平台 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/mattermost-extends-workflow-platform-with-7-0-release/ | 2022-06-21T09:35:23 | [
"Mattermost"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14738-1.html | 
自 2016 年开源以来,Mattermost 一直在开发一个具有不断增加的用例的消息传递平台。6 月 16 日,Mattermost 7.0 平台发布,其中包括了新的语音呼叫、工作流模板和用于开源技术的应用框架。新版本扩展了 2021 年 10 月发布的 6.0 版本引入的功能。一直以来,Mattermost 都在与包括 Slack、Atlassian 和 Asana 在内的几家大公司,竞争不断增长的协作工具市场。另一方面,Mattermost 侧重于对开发者的支持,尽管该平台也可用于安全和 IT 运营。
Mattermost 的软件同时提供有商业版和开源版,目前它们都升级到了 7.0 版。Tien 解释说,Mattermost 的商业平台是建立在开源基础上的。在开放核心模型中,开源版作为软件的基础或核心,专有的企业功能则内置于商业版中。合规性、规模性和高级配置是 Mattermost 的关键企业功能。Tien 声称,开源版本对于中小型团队来说已经足够了。他认为,拥有 500 名或更多用户的团队才需要考虑使用商业版。
Tien 认为开源也关乎社区贡献。Mattermost 开源项目有超过 4000 名个人贡献者,他们贡献了超过 30000 行代码。
以前,Mattermost 依赖集成第三方呼叫服务(例如 Zoom)来启用语音呼叫功能。在 7.0 版本中,它通过开源 WebRTC 协议引入了呼叫功能的直接集成,所有现代 Web 浏览器都支持该协议。直接集成呼叫功能的目标是为协作提供单一平台,这符合 Tien 对该平台的总体愿景。现在,除了提供集成工具以实现协作之外,该平台还会增加“工作流模板”功能,以帮助(用户)组织构建可重复的流程。
工作流概念采用了 <ruby> 剧本 <rt> playbook </rt></ruby>,其中包含了为“特定类型的操作”所执行的动作和操作的清单。例如,在发生服务故障或网络安全事件时,公司可以为事件响应创建工作流模板。
这个清单可以链接到 Mattermost <ruby> 操作 <rt> operation </rt></ruby>,例如让特定用户发起呼叫,并协助生成报告。Tien 表示,Mattermost 还与常见的开发者工具集成,并且工作流模板的功能将随着时间的推移而扩展,以便使用第三方工具来实现更多自动化。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/mattermost-extends-workflow-platform-with-7-0-release/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Mattermost has been developing a messaging platform with a growing number of use cases since it began as an open source project in 2016. The company today announced the Mattermost 7.0 platform, which includes new voice calls, workflow templates, and an application framework for open-source technology. The new release expands on capabilities introduced with the 6.0 update in October 2021. Mattermost competes for a piece of the growing market for collaboration tools with several large companies, including Slack, Atlassian, and Asana. Mattermost, on the other hand, focuses on developer enablement, though the platform can also be used for security and IT operations.
Mattermost’s software is available in both commercial and open source versions, and both are now at version 7. Tien explained that Mattermost’s commercial platform is built on an open-source foundation. In the open-core model, open source software serves as the foundation, or core, while proprietary enterprise features are built into a commercial version. Compliance, scale, and advanced configuration are key enterprise features for Mattermost. Tien claims that the open source version is more than capable for small and mid-sized teams. He anticipates that organisations will need to consider the commercial release for teams of 500 or more users.
Tien believes that open source is also about community contributions. The Mattermost open source project has over 4,000 individual contributors who have contributed over 30,000 lines of code. Mattermost previously relied on integration with third-party call services, such as Zoom, to enable voice call functionality.
Mattermost 7.0 introduces direct integration of calling functionality via the open source WebRTC protocol, which is supported by all modern web browsers. The goal of directly integrating call functionality is to provide a single platform for collaboration, which is in line with Tien’s overall vision for Mattermost. Mattermost is now adding workflow templates to help organisations build repeatable processes, in addition to providing integrated tools to enable collaboration.
The workflow concept employs playbooks, which contain a list of actions and operations to perform for a specific type of operation. For example, a company can create a workflow template for incident response in the event of a service failure or a cybersecurity incident.
The checklist can be linked to Mattermost operations such as bringing specific users into a call and assisting with report generation. Tien stated that Mattermost also integrates with common developer tools, and that the capability of the workflow templates will expand over time to enable more automation with third-party tools. |
14,739 | 分享 10 篇 Ansible 文章 | https://opensource.com/article/21/1/ansible | 2022-06-21T11:18:43 | [
"Ansible"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14739-1.html |
>
> 通过这些 Ansible 文章扩展你的知识和技能。
>
>
>

我希望能够激发刚刚接触 Ansible 的初学者的兴趣。这里有一系列总结文章,我已将其包括在内,以供你随意后续查阅。
### 适合初学者的 Ansible
这五篇文章对于 Ansible 新手来说是一个非常好的起点。前三篇文章由 Seth Kenlon 撰写。
* 如果你不了解 Ansible ,[现在可以做这 7 件事](https://opensource.com/article/20/9/ansible) 来入手。这是很好的入门指导,它收集了用于管理硬件、云、容器等的链接。
* 在 《[编排与自动化有何区别?](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/orchestration-vs-automation)》 这篇文章中,你会学到一些术语和技术路线,将会激发你对 Ansible 感兴趣。
* 文章 《[如何用 Ansible 安装软件](https://opensource.com/article/20/9/install-packages-ansible)》 覆盖了一些脚本概念和一些 Ansible 的好惯例,给出了一些本地或远程管理软件包的案例。
* 在 [我编写 Ansible 剧本时学到的 3 个教训](https://opensource.com/article/20/1/ansible-playbooks-lessons) 中,使自己养成 Jeff Geerling 所传授的好习惯,他是一位真正的 Ansible 资深人士。源代码控制、文档、测试、简化和优化是自动化成功的关键。
* 《[我使用 Ansible 的第一天](https://opensource.com/article/20/10/first-day-ansible)》 介绍了记者 David Both 在解决重复性开发任务时的思考过程。这篇文章从 Ansible 的基础开始,并说明了一些简单的操作和任务。
### 尝试 Ansible 项目
一旦你掌握了基础和并拥有良好习惯,就可以开始一些具体主题和实例了。
* Ken Fallon 在 《[使用 Ansible 管理你的树莓派机群](https://opensource.com/article/20/9/raspberry-pi-ansible)》 一文中介绍了一个部署和管理树莓派设备机群的示例。它介绍了受限环境中的安全和维护概念。
* 在 《[将你的日历与 Ansible 融合以避免日程冲突](https://opensource.com/article/20/10/calendar-ansible)》一文中,Nicolas Leiva 快速介绍了如何使用前置任务和条件在自动日程安排中中强制执行隔离窗口
* Nicolas 在 《[创建一个整合你的谷歌日历的 Ansible 模块](https://opensource.com/article/20/10/ansible-module-go)》中完成了他的日历隔离的理念。他的文章深入探讨了在 Go 中编写自定义 Ansible 模块以实现所需的日历连接。 Nicolas 介绍了构建和调用 Go 程序并将所需数据传递给 Ansible 并接收所需输出的不同方法。
### 提升你的 Ansible 技巧
Kubernetes 是近来的热门话题,以下文章提供了一些很好的示例来学习新技能。
* 在 《[适用于 Kubernets 自动编排你的 Ansible 模块](https://opensource.com/article/20/9/ansible-modules-kubernetes)》 文章中,Seth Kenlon 介绍了 Ansible Kubernetes 模块, 介绍了用于测试的基本 Minikube 环境,并提供了一些用于<ruby> 荚 <rt> Pod </rt></ruby> 控制的 `k8s` 模块的基本示例。
* Jeff Geerling 在 《[使用 Ansible 的 Helm 模块构建 Kubernetes Minecraft 服务器](https://opensource.com/article/20/10/kubernetes-minecraft-ansible)》 中解释了 Helm Chart 应用程序、Ansible 集合以及执行一个有趣的项目以在 k8s 集群中设置你自己的 Minecraft 服务器的概念。
我希望你的 Ansible 旅程已经开始,并能常从这些文章中充实自己。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/1/ansible>
作者:[James Farrell](https://opensource.com/users/jamesf) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[Donkey](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Here we are again at the end of another year with a great set of articles about Ansible from Opensource.com. I thought it would be nice to review them in a series of progressively advancing topics. I hope to help stimulate the interest of people just getting started with Ansible. There were also a series of summary articles, which I've included for your casual follow-up.
## Ansible for beginners
The first five articles on this year's list are a really good place for Ansible neophytes to start. The first three articles were written by Opensource.com editor Seth Kenlon.
- If you don't know much about Ansible,
is a great place to start. This is a nice primer that gathers links for managing hardware, cloud, containers, and more.*7 things you can do with Ansible right now* - In
you will learn some of the terms and baseline technologies that will help kick off your interest in Ansible.*What's the difference between orchestration and automation?* covers a few rudimentary concepts and some good Ansible habits, followed by simple examples on managing software packages on local and remote hosts.*How to install software with Ansible*- In
, set yourself right with good habits handed down by Jeff Geerling, a real Ansible veteran. Source control, documentation, testing, simplification, and optimization are the keys to automation success.*3 lessons I've learned writing Ansible playbooks* outlines Correspondent David Both's thought process for solving a repetitive development task. The article starts with a baseline of what Ansible needs and illustrates some simple plays and tasks.*My first day using Ansible*
## Ansible projects to try
Once you have the basics and some good habits, it's time to turn to more specific topics with concrete examples.
by Ken Fallon walks through an example of deploying and managing fleets of RPi units. It presents concepts of security and maintenance in constrained environments.*Manage your Raspberry Pi fleet with Ansible*- In
Nicolas Leiva quickly introduces how to use pre-tasks and conditionals to enforce execution blackout windows in your automation schedule.[Integrate your calendar with Ansible to avoid schedule conflicts](https://opensource.com/article/20/10/calendar-ansible), - Nicolas completes his calendar blackout concept in
. His article dives into writing a custom Ansible module in Go to achieve the desired calendar connection. Nicolas introduces different ways to structure and invoke Go programs and pass the required data to Ansible and receive the desired output.*Create an Ansible module for integrating your Google Calendar*
## Elevate your Ansible skills
Kubernetes is a hot topic these days, and the following articles offer some great examples to learn new skills.
- In
, Seth Kenlon introduces the Ansible Kubernetes module, walks through a basic Minikube installation for testing, and presents some basic examples of the "k8s" module for pod control.*Automate your container orchestration with Ansible modules for Kubernetes* - Jeff Geerling explains the concept of Helm Chart applications, Ansible collections, and executing a fun project to set up your own Minecraft server in a k8s cluster in
.*Build a Kubernetes Minecraft server with Ansible's Helm modules*
## Other Ansible news
This year, Mark Phillips delivered a series of "Ansible around the web" news articles covering a wide variety of Ansible topics. They are packed with links to interesting Ansible developments, ranging from basic tutorials, module writing, plugins, Kubernetes, video demonstrations, and Ansible community news. Check them all out—there are valuable nuggets to follow for all interests and skill levels!
*Containers, networks, security, and more Ansible news**Tips for CI/CD pipelines and Windows users, and more Ansible news**Collections signal major shift in Ansible ecosystem, and more Ansible news**Ansible 101 videos with Jeff Geerling, and more Ansible news**Beginner guides, Windows, networking, and more Ansible news*
## Have a happy 2021!
I hope your personal journey with Ansible is already underway and regularly enriched by content from Opensource.com. Tell us in the comments what you might like to learn about Ansible in the coming year, and if you have information to share, please consider [writing an article](https://opensource.com/how-submit-article) for Opensource.com.
## 1 Comment |
14,740 | 编写你的第一段 JavaScript 代码 | https://opensource.com/article/21/7/javascript-cheat-sheet | 2022-06-21T11:47:00 | [
"JavaScript"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14740-1.html |
>
> JavaScript 是为 Web 而生的,但它可以做的事远不止于此。本文将带领你了解它的基础知识,然后你可以下载我们的备忘清单,以便随时掌握详细信息。
>
>
>

JavaScript 是一种充满惊喜的编程语言。许多人第一次遇到 JavaScript 时,它通常是作为一种 Web 语言出现的。所有主流浏览器都有一个 JavaScript 引擎;并且,还有一些流行的框架,如 JQuery、Cash 和 Bootstrap 等,它们可以帮助简化网页设计;甚至还有用 JavaScript 编写的编程环境。它似乎在互联网上无处不在,但事实证明,它对于 [Electron](https://www.electronjs.org/) 等项目来说也是一种有用的语言。Electron 是一个构建跨平台桌面应用程序的开源工具包,它使用的语言就是 JavaScript。
JavaScript 语言的用途多到令人惊讶,它拥有各种各样的库,而不仅仅是用于制作网站。它的基础知识十分容易掌握,因此,它可以作为一个起点,助你跨出构建你想象中的东西的第一步。
### 安装 JavaScript
随着你的 JavaScript 水平不断提高,你可能会发现自己需要高级的 JavaScript 库和运行时环境。不过,刚开始学习的时候,你是根本不需要安装 JavaScript 环境的。因为所有主流的 Web 浏览器都包含一个 JavaScript 引擎来运行代码。你可以使用自己喜欢的文本编辑器编写 JavaScript,将其加载到 Web 浏览器中,接着你就能看到代码的作用。
### 上手 JavaScript
要编写你的第一个 JavaScript 代码,请打开你喜欢的文本编辑器,例如 [Atom](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/atom) 或 [VSCode](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/open-source-alternatives-vs-code) 等。因为它是为 Web 开发的,所以 JavaScript 可以很好地与 HTML 配合使用。因此,我们先来尝试一些基本的 HTML:
```
<html>
<head>
<title>JS</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="example">Nothing here.</p>
</body>
</html>
```
保存这个文件,然后在 Web 浏览器中打开它。

要将 JavaScript 添加到这个简单的 HTML 页面,你可以创建一个 JavaScript 文件并在页面的 `<head>` 中引用它,或者只需使用 `<script>` 标记将 JavaScript 代码嵌入 HTML 中。在这个例子中,我嵌入了下面的代码:
```
<html>
<head>
<title>JS</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="example">Nothing here.</p>
<script>
let myvariable = "Hello world!";
document.getElementById("example").innerHTML = myvariable;
</script>
</body>
</html>
```
在浏览器中重新加载页面。

如你所见,`<p>` 标签仍然包含字符串 `"Nothing here"`,但是当它被渲染时,JavaScript 会改变它,使其包含 `"Hello world"`。是的,JavaScript 具有重建(或只是帮助构建)网页的能力。
这个简单脚本中的 JavaScript 做了两件事。首先,它创建一个名为 `myvariable` 的变量,并将字符串 `"Hello world!"` 放置其中。然后,它会在当前文档(浏览器呈现的网页)中搜索 ID 为 `example` 的所有 HTML 元素。当它找到 `example` 时,它使用了 `innerHTML` 属性将 HTML 元素的内容替换为 `myvariable` 的内容。
当然,我们也可以不用自定义变量。因为,使用动态创建的内容来填充 HTML 元素也是容易的。例如,你可以使用当前时间戳来填充它:
```
<html>
<head>
<title>JS</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="example">Date and time appears here.</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("example").innerHTML = Date();
</script>
</body>
</html>
```
重新加载页面,你就可以看到在呈现页面时生成的时间戳。再重新加载几次,你可以观察到秒数会不断增加。
### JavaScript 语法
在编程中,<ruby> 语法 <rt> syntax </rt></ruby> 指的是如何编写句子(或“行”)的规则。在 JavaScript 中,每行代码必须以分号(`;`)结尾,以便运行代码的 JavaScript 引擎知道何时停止阅读。(LCTT 译注:从实用角度看,此处的“必须”其实是不正确的,大多数 JS 引擎都支持不加分号。Vue.js 的作者尤雨溪认为“没有应该不应该,只有你自己喜欢不喜欢”,他同时表示,“Vue.js 的代码全部不带分号”。详情可以查看他在知乎上对于此问题的 [回答](https://www.zhihu.com/question/20298345/answer/49551142)。)
单词(或 <ruby> 字符串 <rt> strings </rt></ruby>)必须用引号(`"`)括起来,而数字(或 <ruby> 整数 <rt> integers </rt></ruby>)则不用。
几乎所有其他东西都是 JavaScript 语言的约定,例如变量、数组、条件语句、对象、函数等等。
### 在 JavaScript 中创建变量
变量是数据的容器。你可以将变量视为一个盒子,你在其中放置数据,以便与程序的其他部分共享它。要在 JavaScript 中创建变量,你可以选用关键字 `let` 和 `var` 中的一个,请根据你打算如何使用变量来选择:`var` 关键字用于创建一个供整个程序使用的变量,而 `let` 只为特定目的创建变量,通常在函数或循环的内部使用。(LCTT 译注:还有 `const` 关键字,它用于创建一个常量。)
JavaScript 内置的 `typeof` 函数可以帮助你识别变量包含的数据的类型。使用第一个示例,你可以修改显示文本,来显示 `myvariable` 包含的数据的类型:
```
<string>
let myvariable = "Hello world!";
document.getElementById("example").innerHTML = typeof(myvariable);
</string>
```
接着,你就会发现 Web 浏览器中显示出 “string” 字样,因为该变量包含的数据是 `"Hello world!"`。在 `myvariable` 中存储不同类型的数据(例如整数),浏览器就会把不同的数据类型打印到示例网页上。尝试将 `myvariable` 的内容更改为你喜欢的数字,然后重新加载页面。
### 在 JavaScript 中创建函数
编程中的函数是独立的数据处理器。正是它们使编程得以 *模块化*。因为函数的存在,程序员可以编写通用库,例如,调整图像大小或统计时间花费的库,以供其他和你一样的程序员在他们的代码中使用。
要创建一个函数,你可以为函数提供一个自定义名称,后面跟着用大括号括起来的、任意数量的代码。
下面是一个简单的网页,其中包含了一个剪裁过的图像,还有一个分析图像并返回真实图像尺寸的按钮。在这个示例代码中,`<button>` 这个 HTML 元素使用了 JavaScript 的内置函数 `onclick` 来检测用户交互,它会触发一个名为 `get_size` 的自定义函数。具体代码如下:
```
<html>
<head>
<title>Imager</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<button onclick="get_size(document.getElementById('myimg'))">
Get image size
</button>
</div>
<div>
<img style="width: 15%" id="myimg" src="penguin.png" />
</div>
<script>
function get_size(i) {
let w = i.naturalWidth;
let h = i.naturalHeight;
alert(w + " by " + h);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
```
保存这个文件,并将其加载到 Web 浏览器中以尝试这段代码。

### 使用 JavaScript 的跨平台应用程序
你可以从代码示例中看到,JavaScript 和 HTML 紧密协作,从而创建了有凝聚力的用户体验。这是 JavaScript 的一大优势。当你使用 JavaScript 编写代码时,你继承了现代计算中最常见的用户界面之一,而它与平台无关,那就是 Web 浏览器。你的代码本质上是跨平台的,因此你的应用程序,无论是简单的图像大小分析器还是复杂的图像编辑器、视频游戏,或者你梦想的任何其他东西,都可以被所有人使用,无论是通过 Web 浏览器,还是桌面(如果你同时提供了一个 Electron 应用)。
学习 JavaScript 既简单又有趣。网络上有很多网站提供了相关教程,还有超过一百万个 JavaScript 库可帮助你与设备、外围设备、物联网、服务器、文件系统等进行交互。在你学习的过程中,请将我们的 [JavaScript 备忘单](https://opensource.com/downloads/javascript-cheat-sheet) 放在身边,以便记住语法和结构的细节。
>
> **[JavaScript 备忘单](https://opensource.com/downloads/javascript-cheat-sheet)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/7/javascript-cheat-sheet>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | JavaScript is a programming language full of pleasant surprises. Many people first encounter JavaScript as a language for the web. There's a JavaScript engine in all the major browsers, there are popular frameworks such as JQuery, Cash, and Bootstrap to help make web design easier, and there are even programming environments written in JavaScript. It seems to be everywhere on the internet, but it turns out that it's also a useful language for projects like [Electron](https://www.electronjs.org/), an open source toolkit for building cross-platform desktop apps with JavaScript.
JavaScript is a surprisingly multipurpose language with a wide assortment of libraries for much more than just making websites. Learning the basics of the language is easy, and it's a gateway to building whatever you imagine.
## Install JavaScript
As you progress with JavaScript, you may find yourself wanting advanced JavaScript libraries and runtimes. When you're just starting, though, you don't have to install JavaScript at all. All major web browsers include a JavaScript engine to run the code. You can write JavaScript using your favorite text editor, load it into your web browser, and see what your code does.
## Get started with JavaScript
To write your first JavaScript code, open your favorite text editor, such as [Notepad++](https://opensource.com/article/16/12/notepad-text-editor), [Atom](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/atom), or [VSCode](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/open-source-alternatives-vs-code). Because it was developed for the web, JavaScript works well with HTML, so first, just try some basic HTML:
```
<html>
<head>
<title>JS</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="example">Nothing here.</p>
</body>
</html>
```
Save the file, and then open it in a web browser.
(Seth Kenlon, CC BY-SA 4.0)
To add JavaScript to this simple HTML page, you can either create a JavaScript file and refer to it in the page's `head`
or just embed your JavaScript code in the HTML using the `<script>`
tag. In this example, I embed the code:
```
<html>
<head>
<title>JS</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="example">Nothing here.</p>
<script>
let myvariable = "Hello world!";
document.getElementById("example").innerHTML = myvariable;
</script>
</body>
</html>
```
Reload the page in your browser.
(Seth Kenlon, CC BY-SA 4.0)
As you can see, the `<p>`
tag as written still contains the string "Nothing here," but when it's rendered, JavaScript alters it so that it contains "Hello world" instead. Yes, JavaScript has the power to rebuild (or just help build) a webpage.
The JavaScript in this simple script does two things. First, it creates a variable called `myvariable`
and places the string "Hello world!" into it. Finally, it searches the current document (the web page as the browser is rendering it) for any HTML element with the ID `example`
. When it locates `example`
, it uses the `innerHTML`
function to replace the contents of the HTML element with the contents of `myvariable`
.
Of course, using a custom variable isn't necessary. It's just as easy to populate the HTML element with something being dynamically created. For instance, you could populate it with a timestamp:
```
<html>
<head>
<title>JS</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="example">Date and time appears here.</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("example").innerHTML = Date();
</script>
</body>
</html>
```
Reload the page to see a timestamp generated at the moment the page is rendered. Reload a few times to watch the seconds increment.
## JavaScript syntax
In programming, **syntax** refers to the rules of how sentences (or "lines") are written. In JavaScript, each line of code must end in a semicolon (`;`
) so that the JavaScript engine running your code understands when to stop reading.
Words (or "strings") must be enclosed in quotation marks (`"`
), while numbers (or "integers") go without.
Almost everything else is a convention of the JavaScript language, such as variables, arrays, conditional statements, objects, functions, and so on.
## Creating variables in JavaScript
Variables are containers for data. You can think of a variable as a box where you can put data to share with your program. Creating a variable in JavaScript is done with two keywords you choose based on how you intend to use the variable: `let`
and `var`
. The `var`
keyword denotes a variable intended for your entire program to use, while `let`
creates variables for specific purposes, usually inside functions or loops.
JavaScript's built-in `typeof`
function can help you identify what kind of data a variable contains. Using the first example, you can find out what kind of data `myvariable`
contains by modifying the displayed text to:
```
<string>
let myvariable = "Hello world!";
document.getElementById("example").innerHTML = typeof(myvariable);
</string>
```
This renders "string" in your web browser because the variable contains "Hello world!" Storing different kinds of data (such as an integer) in `myvariable`
would cause a different data type to be printed to your sample web page. Try changing the contents of `myvariable`
to your favorite number and then reloading the page.
## Creating functions in JavaScript
Functions in programming are self-contained data processors. They're what makes programming *modular*. It's because functions exist that programmers can write generic libraries that, for instance, resize images or keep track of the passage of time for other programmers (like you) to use in their own code.
You create a function by providing a custom name for your function followed by any amount of code enclosed within braces.
Here's a simple web page featuring a resized image and a button that analyzes the image and returns the true image dimensions. In this example code, the `<button>`
HTML element uses the built-in JavaScript function `onclick`
to detect user interaction, which triggers a custom function called `get_size`
:
```
<html>
<head>
<title>Imager</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<button onclick="get_size(document.getElementById('myimg'))">
Get image size
</button>
</div>
<div>
<img style="width: 15%" id="myimg" src="https://opensource.com/penguin.png" />
</div>
<script>
function get_size(i) {
let w = i.naturalWidth;
let h = i.naturalHeight;
alert(w + " by " + h);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
```
Save the file and load it into your web browser to try the code.
(Seth Kenlon, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Cross-platform apps with JavaScript
You can see from the code sample how JavaScript and HTML work closely together to create a cohesive user experience. This is one of the great strengths of JavaScript. When you write code in JavaScript, you inherit one of the most common user interfaces of modern computing regardless of platform: the web browser. Your code is cross-platform by nature, so your application, whether it's just a humble image size analyzer or a complex image editor, video game, or whatever else you dream up, can be used by everyone with a web browser (or a desktop, if you deliver an Electron app).
Learning JavaScript is easy and fun. There are lots of websites with tutorials available. There are also over a million JavaScript libraries to help you interface with devices, peripherals, the Internet of Things, servers, file systems, and lots more. And as you're learning, keep our [ JavaScript cheat sheet](https://opensource.com/downloads/javascript-cheat-sheet) close by so you remember the fine details of syntax and structure.
## Comments are closed. |
14,742 | JVM 垃圾回收的工作原理 | https://opensource.com/article/22/6/garbage-collection-java-virtual-machine | 2022-06-22T09:42:41 | [
"Java",
"垃圾回收"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14742-1.html | 
>
> 对于程序员来说,掌握 Java 的内存管理机制并不是必须的,但它能够帮助你更好地理解 JVM 是如何处理程序中的变量和类实例的。
>
>
>
Java 之所以能够如此流行,自动 <ruby> 垃圾回收 <rt> Garbage Collection </rt></ruby>(GC)功不可没,它也是 Java 最重要的几个特性之一。在这篇文章中,我将说明为什么垃圾回收如此重要。本文的主要内容为:自动的分代垃圾回收、JVM 划分内存的依据,以及 JVM 垃圾回收的工作原理。
### Java 内存分配
Java 程序的内存空间被划分为以下四个区域:
1. <ruby> 堆区 <rt> Heap </rt></ruby>:对象实例就是在这个区域分配的。不过,当我们声明一个对象时,堆中不会发生任何内存分配,只是在栈中创建了一个对象的引用而已。
2. <ruby> 栈区 <rt> Stack </rt></ruby>:方法、局部变量和类的实例变量就是在这个区域分配的。
3. <ruby> 代码区 <rt> Code </rt></ruby>:这个区域存放了程序的字节码。
4. <ruby> 静态区 <rt> Static </rt></ruby>:这个区域存放了程序的静态数据和静态方法。
### 什么是自动垃圾回收?
自动垃圾回收是这样一个过程:首先,堆中的所有对象会被分类为“被引用的”和“未被引用的”;接着,“未被引用的对象”就会被做上标记,以待之后删除。其中,“被引用的对象”是指程序中的某一部分仍在使用的对象,“未被引用的对象”是指目前没有正在被使用的对象。
许多编程语言,例如 C 和 C++,都需要程序员手动管理内存的分配和释放。在 Java 中,这一过程是通过垃圾回收机制来自动完成的(尽管你也可以在代码中调用 `system.gc();` 来手动触发垃圾回收)。
垃圾回收的基本步骤如下:
#### 1、标记已使用和未使用的对象
在这一步骤中,已使用和未使用的对象会被分别做上标记。这是一个及其耗时的过程,因为需要扫描内存中的所有对象,才能够确定它们是否正在被使用。

#### 2、扫描/删除对象
有两种不同的扫描和删除算法:
**简单删除(标记清除)**:它的过程很简单,我们只需要删除未被引用的对象即可。但是,后续给新对象分配内存就会变得很困难了,因为可用空间被分割成了一块块碎片。

**删除压缩(标记整理)**:除了会删除未被引用的对象,我们还会压缩被引用的对象(未被删除的对象)。这样以来,新对象的内存分配就相对容易了,并且内存分配的效率也有了提升。

### 什么是分代垃圾回收,为什么需要它?
正如我们在“扫描删除”模型中所看到的,一旦对象不断增长,我们就很难扫描所有未使用的对象以回收内存。不过,有一项实验性研究指出,在程序执行期间创建的大多数对象,它们的存活时间都很短。
既然大多数对象的存活时间都很短,那么我们就可以利用这个事实,从而提升垃圾回收的效率。该怎么做呢?首先,JVM 将内存划分为不同的“代”。接着,它将所有的对象都分类到这些内存“代”中,然后对这些“代”分别执行垃圾回收。这就是“分代垃圾回收”。
### 堆内存的“代”和分代垃圾回收过程
为了提升垃圾回收中的“标记清除”的效率,JVM 将对内存划分成以下三个“代”:
* <ruby> 新生代 <rt> Young Generation </rt></ruby>
* <ruby> 老年代 <rt> Old Generation </rt></ruby>
* <ruby> 永久代 <rt> Permanent Generation </rt></ruby>

下面我将介绍每个“代”及其主要特征。
#### 新生代
所有创建不久的对象都存放在这里。新生代被进一步分为以下两个区域:
1. <ruby> 伊甸区 <rt> Eden </rt></ruby>:所有新创建的对象都在此处分配内存。
2. <ruby> 幸存者区 <rt> Survivor </rt></ruby>,分为 S0 和 S1:经历过一次垃圾回收后,仍然存活的对象会被移动到两个幸存者区中的一个。

在新生代发生的分代垃圾回收被称为 “<ruby> 次要回收 <rt> Minor GC </rt></ruby>”(LCTT 译注:也称为“<ruby> 新生代回收 <rt> Young GC </rt></ruby>”)。Minor GC 过程中的每个阶段都是“<ruby> 停止世界 <rt> Stop The World </rt></ruby>”(STW)的,这会导致其他应用程序暂停运行,直到垃圾回收结束。这也是次要回收更快的原因。
一句话总结:伊甸区存放了所有新创建的对象,当它的可用空间被耗尽,第一次垃圾回收就会被触发。

次要回收:在该垃圾回收过程中,所有存活和死亡的对象都会被做上标记。其中,存活对象会被移动到 S0 幸存者区。当所有存活对象都被移动到了 S0,未被引用的对象就会被删除。

S0 中的对象年龄为 1,因为它们挺过了一次次要回收。此时,伊甸区和 S1 都是空的。
每当完成清理后,伊甸区就会再次接受新的存活对象。随着时间的推移,伊甸区和 S0 中的某些对象被宣判死亡(不再被引用),并且伊甸区的可用空间也再次耗尽(填满了),那么次要回收 又将再次被触发。

这一次,伊甸区和 S0 中的死亡和存活的对象会被做上标记。其中,伊甸区的存活对象会被移动到 S1,并且年龄增加至 1。S0 中的存活对象也会被移动到 S1,并且年龄增加至 2(因为它们挺过了两次次要回收)。此时,伊甸区和 S0 又是空的了。每次次要回收之后,伊甸区和两个幸存者区中的一个都会是空的。
新对象总是在伊甸区被创建,周而复始。当下一次垃圾回收发生时,伊甸区和 S1 都会被清理,它们中的存活对象会被移动到 S0 区。每次次要回收之后,这两个幸存者区(S0 和 S1)就会交换一次。

这个过程会一直进行下去,直到某个存活对象的年龄达到了某个阈值,然后它就会被移动到一个叫做“老年代”的地方,这是通过一个叫做“晋升”的过程来完成的。
使用 `-Xmn` 选项可以设置新生代的大小。
### 老年代
这个区域存放着那些挺过了许多次次要回收,并且达到了某个年龄阈值的对象。

在上面这个示例图表中,晋升的年龄阈值为 8。在老年代发生的垃圾回收被称为 “<ruby> 主要回收 <rt> Major GC </rt></ruby>”。(LCTT 译注:也被称为“<ruby> 全回收 <rt> Full GC </rt></ruby>”)
使用 `-Xms` 和 `-Xmx` 选项可以分别设置堆内存大小的初始值和最大值。(LCTT 译注:结合上面的 `-Xmn` 选项,就可以间接设置老年代的大小了。)
### 永久代
永久代存放着一些元数据,它们与应用程序、Java 标准环境以及 JVM 自用的库类及其方法相关。JVM 会在运行时,用到了什么类和方法,就会填充相应的数据。当 JVM 发现有未使用的类,就会卸载或是回收它们,从而为正在使用的类腾出空间。
使用 `-XX:PermGen` 和 `-XX:MaxPerGen` 选项可以分别设置永久代大小的初始值和最大值。
#### 元空间
Java 8 引入了<ruby> 元空间 <rt> Metaspace </rt></ruby>,并用它替换了永久代。这么做的好处是自动调整大小,避免了 <ruby> 内存不足 <rt> OutOfMemory </rt></ruby>(OOM)错误。
### 总结
本文讨论了各种不同的 JVM 内存“代”,以及它们是如何在分代垃圾回收算法中起作用的。对于程序员来说,掌握 Java 的内存管理机制并不是必须的,但它能够帮助你更好地理解 JVM 处理程序中的变量和类实例的方式。这种理解使你能够规划和排除代码故障,并理解特定平台固有的潜在限制。
*正文配图来自:Jayashree Huttanagoudar,CC BY-SA 4.0*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/6/garbage-collection-java-virtual-machine>
作者:[Jayashree Huttanagoudar](https://opensource.com/users/jayashree-huttanagoudar) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Automatic Garbage Collection (GC) is one of the most important features that makes Java so popular. This article explains why GC is essential. It includes automatic and generational GC, how the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) divides heap memory, and finally, how GC works inside the JVM.
## Java memory allocation
Java memory is divided into four sections:
- Heap: The memory for object instances is allocated in the heap. When the object declaration is made, there won't be any memory allocated in the heap. Instead, a reference is created for that object in the stack.
- Stack: This section allocates the memory for methods, local variables, and class instance variables.
- Code: Bytecode resides in this section.
- Static: Static data and methods are placed in this section.
## What is automatic Garbage Collection (GC)?
Automatic GC is a process in which the referenced and unreferenced objects in heap memory are identified, and then unreferenced objects are considered for deletion. The term *referenced objects* means some part of your program is using those objects. *Unreferenced objects* are not currently being used by the program.
Programming languages like C and C++ require manual allocation and deallocation of memory. This is automatically handled by GC in Java, although you can trigger GC manually with the `system.gc();`
call in your code.
The fundamental steps of GC are:
### 1. Mark used and unused objects
In this step, the used and unused objects are marked separately. This is a time-consuming process, as all objects in memory must be scanned to determine whether they're in use or not.
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar, CC BY-SA 4.0)
### 2. Sweep/Delete objects
There are two variations of sweep and delete.
**Simple deletion**: Only unreferenced objects are removed. However, the memory allocation for new objects becomes difficult as the free space is scattered across available memory.
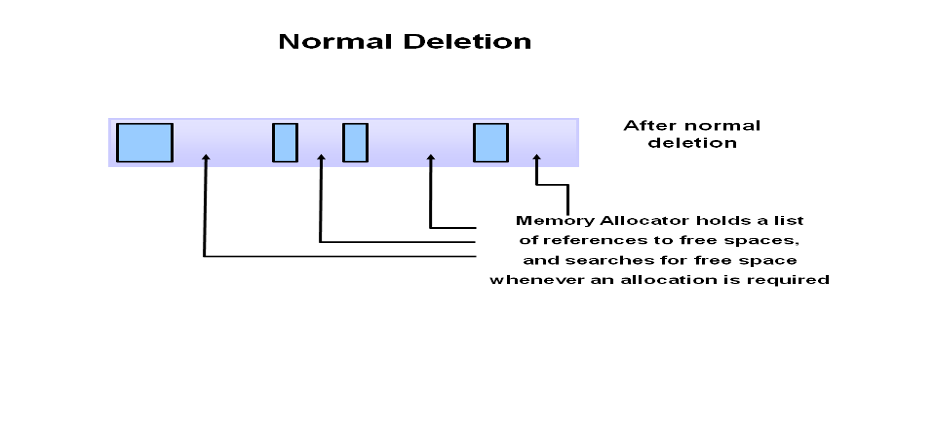
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar, CC BY-SA 4.0)
**Deletion with compaction**: Apart from deleting unreferenced objects, referenced objects are compacted. Memory allocation for new objects is relatively easy, and memory allocation performance is improved.
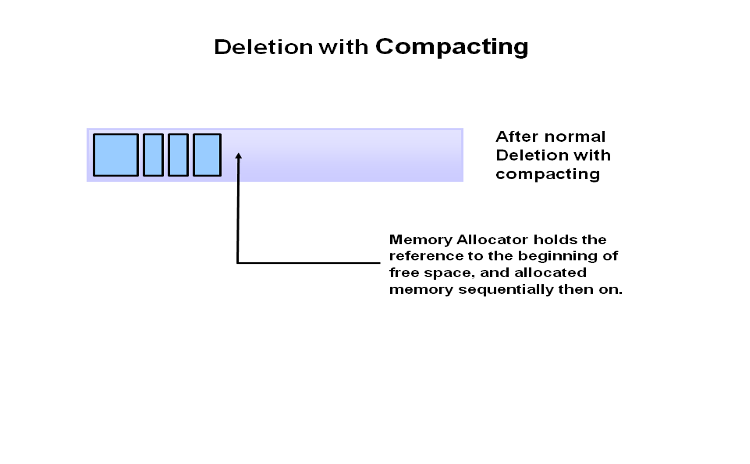
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## What is generational Garbage Collection (GC), and why is it needed?
As seen in the sweep and delete model, scanning all objects for memory reclamation from unused objects becomes difficult once the objects keep growing. An experimental study shows that most objects created during the program execution are short-lived.
The existence of short-lived objects can be used to improve the performance of GC. For that, the JVM divides the memory into different generations. Next, it categorizes the objects based on these memory generations and performs the GC accordingly. This approach is known as *generational GC*.
## Heap memory generations and the generational Garbage Collection (GC) process
To improve the performance of the GC mark and sweep steps, the JVM divides the heap memory into three generations:
- Young Generation
- Old Generation
- Permanent Generation
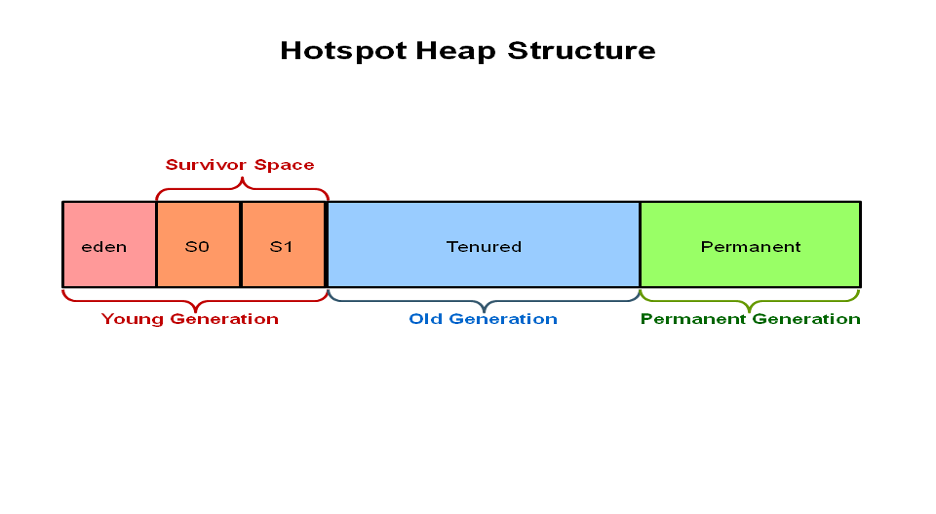
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Here is a description of each generation and its key features.
### Young Generation
All created objects are present here. The young generation is further divided into:
- Eden: All newly created objects are allocated with the memory here.
- Survivor space (S0 and S1): After surviving one GC, the live objects are moved to one of these survivor spaces.
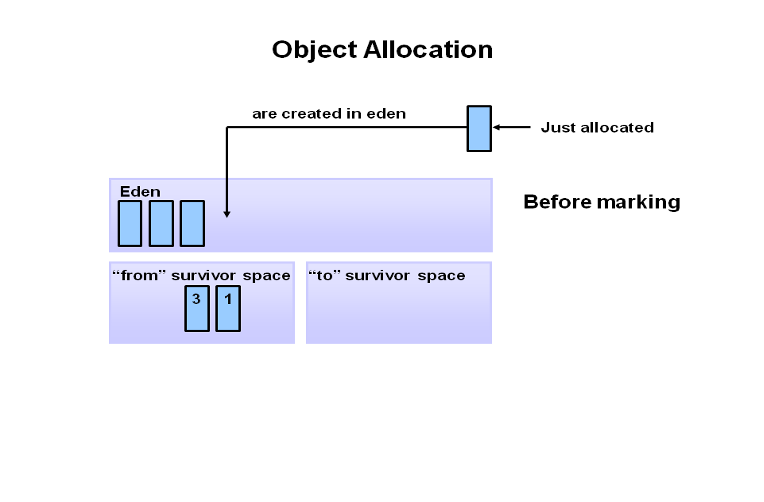
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The generational GC that happens in the Young Generation is known as *Minor GC*. All Minor GC cycles are "Stop the World" events that cause the other applications to pause until it completes the GC cycle. This is why Minor GC cycles are faster.
To summarize: Eden space has all newly created objects. Once Eden is full, the first Minor GC cycle is triggered.
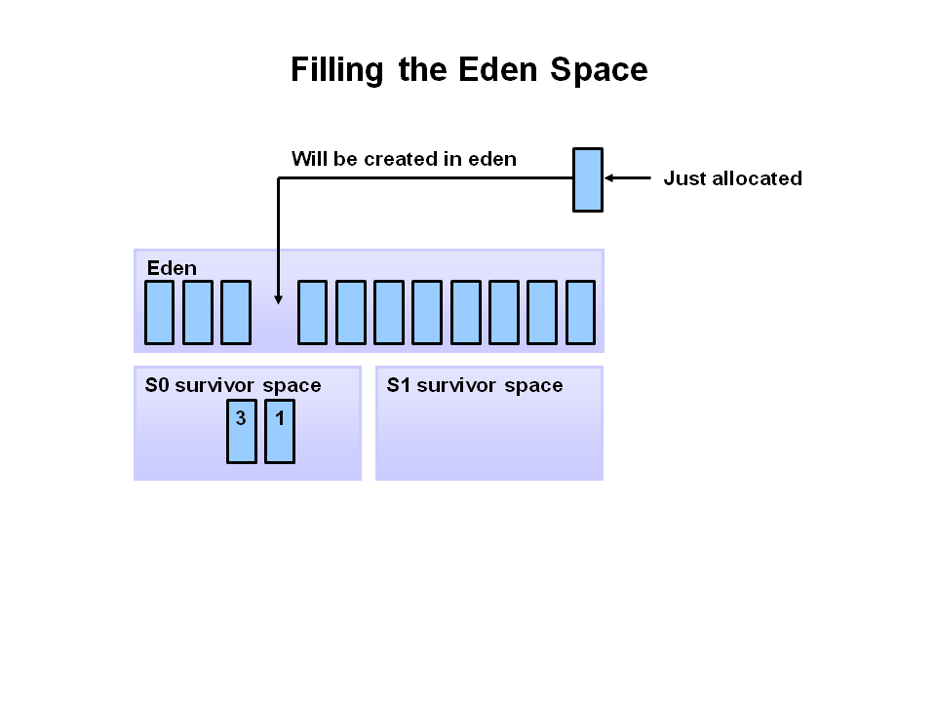
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Minor GC: The live and dead objects are marked during this cycle. The live objects are moved to survivor space S0. Once all live objects are moved to S0, the unreferenced objects are deleted.
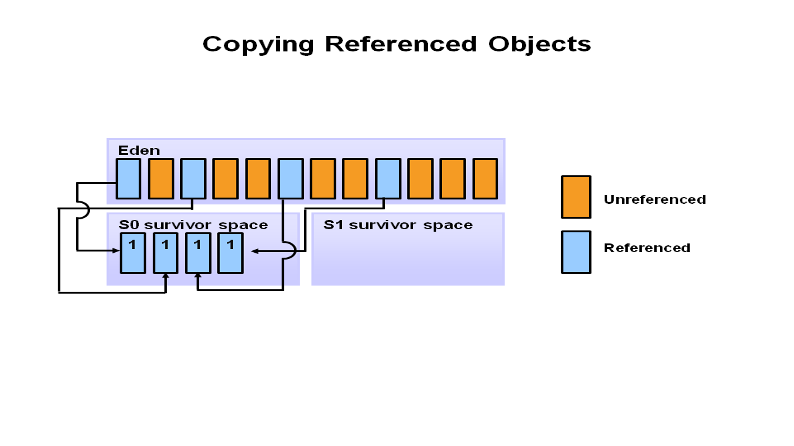
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The age of objects in S0 is 1 because they have survived one Minor GC. Now Eden and S1 are empty.
Once cleared, the Eden space is again filled with new live objects. As time elapses, some objects in Eden and S0 become dead (unreferenced), and Eden's space is full again, triggering the Minor GC.
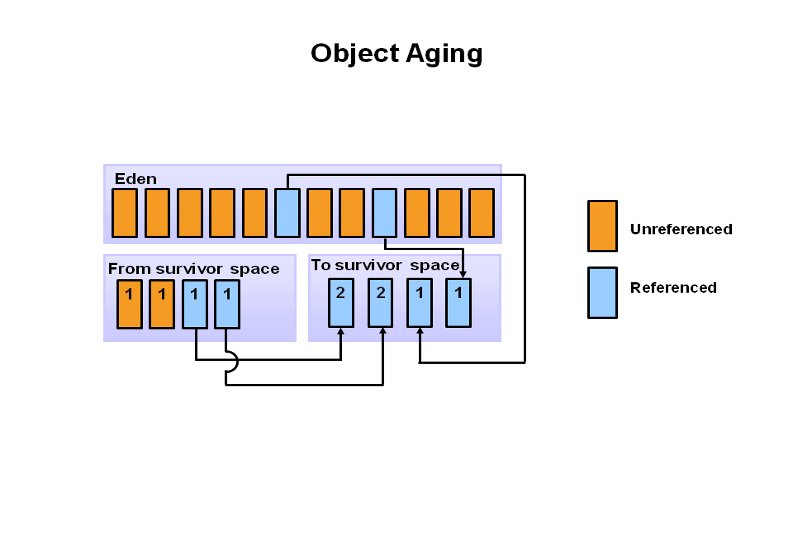
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar, CC BY-SA 4.0)
This time the dead and live objects in Eden and S0 are marked. The live objects from Eden are moved to S1 with an age increment of 1. The live objects from S0 are also moved to S1 with an age increment of 2 (because they've now survived two Minor GCs). At this point, S0 and Eden are empty. After every Minor GC, Eden and one of the survivor spaces are empty.
The same cycle of creating new objects in Eden continues. When the next Minor GC occurs, Eden and S1 are cleared by moving the aged objects to S0. The survivor spaces switch after every Minor GC.
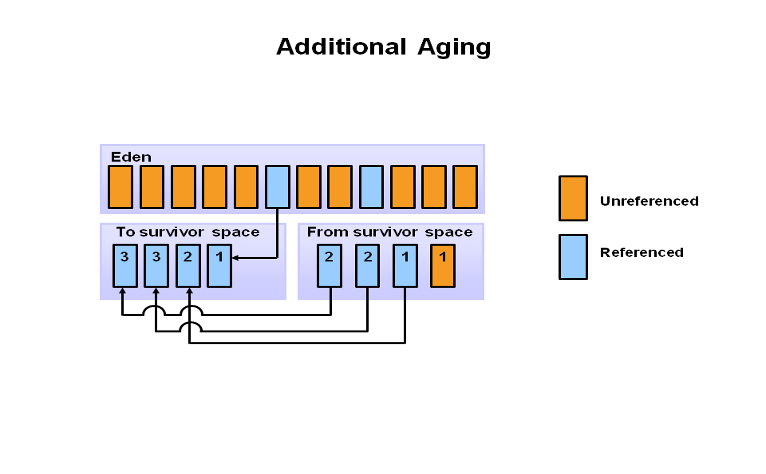
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar, CC BY-SA 4.0)
This process continues until the age of one of the surviving objects reaches a certain threshold, at which point it is moved to the so-called the Old Generation with a process called *promotion*.
Further, the `-Xmn`
flag sets the Young Generation size.
## Old Generation (Tenured Generation)
This generation contains the objects that have survived several Minor GCs and aged to reach an expected threshold.
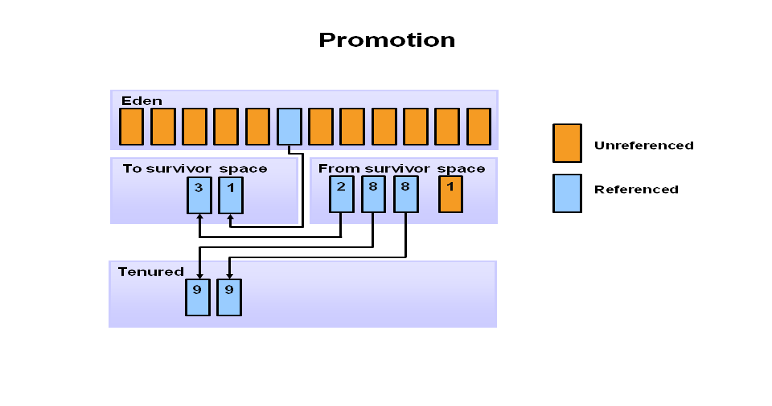
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar, CC BY-SA 4.0)
In the example diagram above, the threshold is 8. The GC in the Old Generation is known as a *Major GC*. Use the flags `-Xms`
and `-Xmx`
to set the initial and maximum size of the heap memory.
## Permanent Generation
The Permanent Generation space stores metadata related to library classes and methods of an application, J2SE, and what's in use by the JVM itself. The JVM populates this data at runtime based on which classes and methods are in use. Once the JVM finds the unused classes, they are unloaded or collected, making space for used classes.
Use the flags `-XX:PermGen`
and `-XX:MaxPermGen`
to set the initial and maximum size of the Permanent Generation.
### Metaspace
Metaspace was introduced in Java 8u and replaced PermGen. The advantage of this is automatic resizing, which avoids OutOfMemory errors.
## Wrap up
This article discusses the various memory generations of JVM and how they are helpful for automatic generational Garbage Collection (GC). Understanding how Java handles memory isn't always necessary, but it can help you envision how the JVM deals with your variables and class instances. This understanding allows you to plan and troubleshoot your code and comprehend potential limitations inherent in a specific platform.
## Comments are closed. |
14,743 | 在 Kubernetes 中使用混沌工程 | https://opensource.com/article/21/5/kubernetes-chaos | 2022-06-22T11:09:05 | [
"混沌工程"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14743-1.html |
>
> 在这篇文章中学习混沌工程的基础知识。
>
>
>

混沌工程是由科学、规划以及实验组成的。它是一门在系统上进行实验的学科,用来建立系统在生产中承受混乱条件能力的信心。
首先,我会在文章导论部分解释混沌系统如何工作。
### 如何开始学习混沌系统呢?
以我的经验,开始学习混沌系统的最好方式是触发一个此前生产中出现的事故来进行实验。使用过去的数据,制定一个计划,以相同的方式破坏你的系统,然后建立修复策略,并确认结果满足你预期。如果计划失败,你就有了一种新的实验方式,并朝着快速处理问题的新方式前进。
最重要的是,你可以随时记录所有内容,这意味着,随着时间的推移,整个系统将被完整记录下来,任何人都可以值守而无需太多加码,每个人都可以在周末好好休息。
### 你要在混沌工程中做什么?
混沌系统实验运行背后有一些科学依据。我记录了其中一些步骤:
1. **定义一个稳定状态:** 使用监控工具来搜集当系统没有问题或事故时,看起来功能正常的数据。
2. **提出假设或使用先前的事故:** 现在你已经定义了一个稳定状态,请提出一个关于在事故或中断期间会发生(或发生过)的情况的假设。用这个假设来得出一系列将会发生的事故,以及如何解决问题的理论。然后你可以制定一个故意引发该问题的计划。
3. **引发问题:** 用这个计划来破坏系统,并开始在真实环境中测试。收集破坏时的指标状态,按计划修复,并追踪提出解决方案所需时长。确保你把所有的东西都记录下来,以备将来发生故障时使用。
4. **试图推翻你的假设:** 实验中最精彩的部分是尝试推翻你的思考或计划。你要创建一个不同的状态,看看你能走多远,并在系统中生成一个不同的稳定状态。
确保在你在另一个系统中生成的破坏因素前,建立一个处于稳定状态的控制系统。这将使你更容易在实验前、期间和之后发现各种稳定状态的差异。
### 混沌工程需要什么?
这有一些初学混沌工程很好的工具:
* 良好的文档编制方法
* 一个捕捉你系统是否处于稳定状态的监控系统
+ Grafana
+ Prometheus
* 混沌工程工具:
+ Chaos mesh
+ Litmus
+ 之后的文章我会介绍更多
* 一个假设
* 一个计划
### 去搞破坏吧
现在你已经掌握了基础,是时候去安全的摧毁你的系统了。我计划每年制造四次混乱,然后努力实现每月一次的破坏。
混沌工程是一种很好的实践,也是推进你的内部文档保持最新的好方法。此外,随着时间的推移,新升级或应用程序部署将更加顺畅,你的日常生活管理将通过 Kubernetes 变得更加轻松。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/5/kubernetes-chaos>
作者:[Jessica Cherry](https://opensource.com/users/cherrybomb) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[Donkey](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel), [wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Kubernetes is turning 11, so I'll be celebrating its birthday by giving you some open source tools that will help you cause chaos. Chaos engineering is part science, part planning, and part experiments. It's the discipline of experimenting on a system to build confidence in the system's capability to withstand turbulent conditions in production.
Before I start passing out the gifts, in this introductory article, I will explain the basics of how chaos engineering works.
## How do I get started with chaos engineering?
In my experience, the best way to start chaos engineering is by taking an incident that has happened before in production and using it as an experiment. Use your past data, make a plan to break your system in a similar way, create a repair strategy, and confirm the outcome turns out exactly how you want. If your plan fails, you have a new way to experiment and move forward toward a new way to handle issues quickly.
Best of all, you can document everything as you go, which means, over time, your entire system will be fully documented so that anyone can be on call without too many escalations and everyone can have a nice break on weekends.
## What do you do in chaos engineering?
Chaos engineering has some science behind how these experiments work. I've documented some of the steps:
**Define a steady state**: Use a monitoring tool to gather data about what your system looks like functionally when there are no problems or incidents.**Come up with a hypothesis or use a previous incident:**Now that you have defined a steady state, come up with a hypothesis about what would happen (or has happened) during an incident or outage. Use this hypothesis to generate a series of theories about what could happen and how to resolve the problems. Then you can start a plan to purposely cause the issue.**Introduce the problem:**Use that plan to break your system and begin real-world testing. Gather your broken metrics' states, use your planned fix, and keep track of how long it takes before you reach a resolution. Make sure you document everything for future outages.**Try to disprove your own hypothesis:**The best part of experimenting is trying to disprove what you think or plan. You want to create a different state, see how far you can take it, and generate a different steady state in the system.
Make sure to create a control system in a steady state before you generate the broken variables in another system. This will make it easier to spot the differences in various steady states before, during, and after your experiment.
## What do I need for chaos engineering?
The best tools for beginning chaos engineering are:
- Good documentation practices
- A monitoring system to capture your system in a steady state and a non-steady state
- Grafana
- Prometheus
- Chaos engineering tools
- Chaos mesh
- Litmus
- And more that I will cover in future articles
- A hypothesis
- A plan
## Go forth and destroy
Now that you have the basics in hand, it's time to go forth and destroy your system safely. I would plan to start causing chaos four times a year and work toward monthly destructions.
Chaos engineering is good practice and a great way to keep your internal documentation up to date. Also, new upgrades or application deployments will be smoother over time, and your daily life will be easier with Kubernetes administration.
## Comments are closed. |
14,744 | 在 Linux 上使用 WineZGUI 运行 Windows 应用和游戏 | https://ostechnix.com/winezgui-run-windows-apps-and-games-on-linux/ | 2022-06-22T16:03:30 | [
"Wine"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14744-1.html | 
>
> WineZGUI - 一个使用 Zenity 的 Wine GUI 前台
>
>
>
不久前,我们写了关于 [Bottles](https://ostechnix.com/run-windows-software-on-linux-with-bottles/) 的文章,这是一个开源的图形应用,可以在 Linux 操作系统上轻松运行 Windows 软件和游戏。今天,我们将讨论一个类似的有趣项目。向 **WineZGUI** 打个招呼,它是一个 Wine GUI 前台,可以 [在 Linux 上用 Wine 运行 Windows 应用和游戏](https://ostechnix.com/run-windows-games-softwares-ubuntu-16-04/)。
### 什么是 WineZGUI?
WineZGUI 是一个 Bash 脚本的集合,它允许你轻松地管理 Wine 前缀,并在 Linux 上使用 **Zenity** 提供更轻松的 Wine 游戏体验。
(LCTT 译注:Wine 前缀是一个特殊文件夹,Wine 在其中放置所有 Wine 特定的文件,安装 Windows 程序、库和注册表代码,以及用户首选项。)
使用 WineZGUI,我们可以直接从文件管理器中启动 Windows EXE 文件或游戏,而无需安装它们。
WineZGUI 为每个应用或游戏创建快捷方式,以便于访问,同时也为每个 EXE 二进制文件创建单独的前缀。
当你用 WineZGUI 启动一个 Windows EXE 文件时,它会提示你是否使用默认的 Wine 前缀或创建一个新的前缀。默认的前缀是 `~/.local/share/winezgui/default`。
如果你选择为 Windows 二进制文件(EXE)创建一个新的前缀,WineZGUI 将尝试从 EXE 文件中提取产品名称和图标,并创建一个桌面快捷方式。
当你以后启动相同的二进制文件(EXE)时,它将建议你用先前的相关前缀来运行它。
说得通俗一点,WineZGUI 只是一个用于官方原始 Wine 的简单 GUI。当我们启动一个 EXE 来玩游戏时,Wine 前缀的设置是自动的。
你只需打开一个 EXE,它就会创建一个前缀和一个桌面快捷方式,并从该 EXE 中提取名称和图标。
它使用 `exiftool` 和 `icotool` 工具来分别提取名称和图标。你可以通过现有的前缀打开一个 EXE 来启动该游戏,或者使用桌面快捷方式。
WineZGUI 是一个在 GitHub 上免费托管的 shell 脚本。你可以抓取源代码,改进它,修复错误和增加功能。
### Bottles Vs WineZGUI
你可能想知道 WineZGUI 与 Bottles 相比如何。但这些应用之间有一个微妙的区别。
**Bottles 是面向前缀的**和**面向运行器的**。意思是:Bottles 首先创建一个前缀,然后使用不同的 EXE 文件。Bottles 不会记住 EXE 的前缀。Bottles 使用不同的运行器。
**WineZGUI 是面向 EXE 的**。它使用 EXE 并只为该 EXE 创建一个前缀。下次我们打开一个 EXE 时,它将询问是否用现有的 EXE 前缀启动。
WineZGUI 不提供像 Bottles 或 [lutris](https://ostechnix.com/manage-games-using-lutris-linux/) 那样的高级功能,如运行程序、在线安装程序等。
### 如何在 Linux 中安装 WineZGUI
确保你已经安装了 WineZGUI 的必要先决条件。
Debian/Ubuntu:
```
$ sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
$ sudo apt install zenity wine winetricks libimage-exiftool-perl icoutils gnome-terminal
```
Fedora:
```
$ sudo dnf install zenity wine winetricks perl-Image-ExifTool icoutils gnome-terminal
```
官方推荐的安装 WineZGUI 的方法是使用 [Flatpak](https://ostechnix.com/how-to-install-and-use-flatpak-in-linux/)。
安装完 Flatpak 后,逐一运行以下命令,在 Linux 中安装 WineZGUI。
```
$ flatpak --user remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
```
```
$ flatpak --user -y install flathub org.winehq.Wine/x86_64/stable-21.08
```
```
$ wget https://github.com/fastrizwaan/WineZGUI-Releases/releases/download/WineZGUI-0.4_20220608/io.github.WineZGUI_0_4_20220608.flatpak
```
```
$ flatpak --user -y install io.github.WineZGUI_0_4_20220608.flatpak
```
### 在 Linux 中用 WineZGUI 运行 Windows 应用和游戏
从 Dash 或菜单中启动 WineZGUI。

这就是 WineZGUI 的默认界面的样子。

正如你在上面的截图中看到的,WineZGUI 的界面非常简单易懂。从主窗口中,你可以:
* 打开一个 EXE 文件。
* 打开 Winetricks GUI 和 CLI。
* 启动 Wine 配置。
* 启动资源管理器。
* 打开 BASH Shell。
* 关闭所有的应用/游戏,包括 WineZGUI 界面。
* 删除 Wine 前缀。
* 查看已安装的 WineZGUI 版本。
为了演示,我将打开一个 EXE 文件。
在下一个窗口中,选择要运行的 EXE 文件。在我的例子中,它是 WinRAR。

接下来,你是想用默认的前缀运行 EXE 文件,还是创建一个新的前缀。我选择默认的前缀。

几秒钟后,会出现 WinRAR 安装向导。点击安装,继续。

点击 “OK” 来完成 WinRAR 的安装。

点击 “<ruby> 运行 WinRAR <rt> Run WinRAR </rt></ruby>” 来启动它。

下面是 WinRAR 在我的 Fedora 36 桌面上的运行情况!

### 总结
WineZGUI 是俱乐部的新人。如果你正在寻找一种在 Linux 桌面上使用 Wine 运行 Windows 应用和游戏的更简单方法,WineZGUI 可能是一个不错的选择。
在 WineZGUI 的帮助下,用户可以选择在与 EXE 相同的文件夹中创建一个 Wine 前缀,并创建一个相对链接的 `.desktop` 条目来自动执行此操作。
原因是使用 Wine 前缀备份和删除游戏更容易,并且让它生成一个 `.desktop` 将使其能够适应移动和转移。
一个很酷的场景是使用该应用进行设置,然后将 Wine 前缀分享给你的朋友和其他人,他们只需要一个具有所有依赖性和保存的工作 Wine 前缀。
请试一试它,在下面的评论区告诉我们你对这个项目的看法。
**资源:**
* [WineZGUI GitHub 仓库](https://github.com/fastrizwaan/WineZGUI)
---
via: <https://ostechnix.com/winezgui-run-windows-apps-and-games-on-linux/>
作者:[sk](https://ostechnix.com/author/sk/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
14,746 | Ubuntu 可以运行在谷歌 Nest Hub 上了?! | https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-google-nest/ | 2022-06-23T17:28:00 | [
"Ubuntu",
"Nest Hub"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14746-1.html |
>
> 一名安全专家成功地在谷歌 Nest Hub(第 2 代)上运行了 Ubuntu,嗯,然后呢?
>
>
>

我刚刚看到了一个关于在谷歌 Nest Hub(第 2 代)上运行的 Ubuntu 的消息。
嗯,这实在是让人兴奋!
所以,让我在这里分享更多关于它的信息吧。
### 破解谷歌 Nest Hub 以安装 Ubuntu
是的,破解使得这成为可能。
网络安全专家 Frédéric Basse 破解了谷歌 Nest Hub(第 2 代)的安全启动,并成功运行 Ubuntu。
当然,谷歌 Nest Hub 并没有正式支持启动一个自定义操作系统。但是,Fred 使用了一个安全漏洞,从而成功运行了 Ubuntu。
虽然这很有趣,但对于始终在线的谷歌智能家居显示器来说,这也是一个严重的安全问题。

正如这位安全专家在 [博客文章](https://fredericb.info/2022/06/breaking-secure-boot-on-google-nest-hub-2nd-gen-to-run-ubuntu.html) 中所解释的,他使用了树莓派 Pico 微控制器,利用引导加载程序中的 USB 漏洞,从而破坏了安全启动链。
这位安全专家得出结论:
>
> 因此,攻击者可以通过插入恶意 USB 设备并按下两个按钮,从而在早期启动阶段(内核执行之前)执行任意代码。
>
>
>
如果你想进行实验(适合安全研究人员),他还在 [GitHub](https://github.com/frederic/chipicopwn) 上提供了相关代码(关于如何利用这个引导加载程序漏洞)。
### 让 Ubuntu 在 Google Nest 上运行

该漏洞允许攻击者启动未签名的操作系统。但是,在那之前,攻击者必须对为树莓派(64 位 ARM 版)量身定制的预装 Ubuntu 镜像进行一些修改。
这位安全专家还提到了以下内容:
>
> 我们构建了一个自定义 U-Boot 引导加载程序,禁用了安全引导,并更改了引导流程以从 USB 闪存驱动器加载环境。我们还为 elaine 构建了一个自定义 Linux 内核,其中包括包括了一些 [额外驱动,例如 USB 鼠标](https://github.com/frederic/elaine-linux/commit/11068237d9178e77d79e3a5d27fc4f8f9b923c51) 。重新打包了来自 Ubuntu 的初始 ramdisk(initrd),以集成触摸屏所需的固件二进制文件。引导镜像是基于自定义 Linux 内核和修改的 initrd 创建的。
>
>
>
因此,很明显,你不会获得完整的 Ubuntu 体验,但由于该漏洞,我们现在知道,如果你愿意破解 谷歌 Nest 进行测试的话(真心不建议!),Ubuntu 是可以在谷歌 Nest 上作运行的。
### 智能家居安全担忧 + Linux
网络安全专家指出,该漏洞已在上游(两次)修复。
但是,研究人员也指出,缺乏分配的 CVE 编号可能会导致修复程序无法向下游传播。
毫无疑问,看到有人在不受支持的设备上运行 Linux 真是太棒了。这让我思考,我们是否应该也制造一些 **由 Linux 驱动的商业智能家居设备?**
*或者说,已经有类似的东西了吗?*
然而,智能家居设备容易受到简单攻击,也同样令人担忧。
你怎么看?在下面的评论中分享你的想法吧。
**本文最初发布于** [Liliputing](https://liliputing.com/2022/06/hacker-installs-ubuntu-on-a-google-nest-hub-2nd-gen-smart-display.html)
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/ubuntu-google-nest/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

I just spotted a story about Ubuntu running on a Google Nest Hub (2nd Gen).
Well, that is certainly exciting!
So, let me share more about it here.
## Hacking Google Nest Hub to Install Ubuntu
Yes, a hacking attempt made this possible.
A cybersecurity professional, **Frédéric Basse**, broke the secure boot on Google Nest Hub (2nd gen) and managed to run Ubuntu.
Of course, Google Nest Hub does not officially support booting a custom OS. But, a security vulnerability allowed Fred to use an exploit and run Ubuntu.
While this is fun, it is also a severe problem for an always-connected smart home display by Google.
**Frédéric Basse**
As explained in his [blog post](https://fredericb.info/2022/06/breaking-secure-boot-on-google-nest-hub-2nd-gen-to-run-ubuntu.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com), the hacker utilized a Raspberry Pi Pico microcontroller to exploit a USB bug in the bootloader to break the secure boot chain.
The security expert concluded:
As a result, an attacker can execute arbitrary code at early boot stage (before kernel execution) by plugging a malicious USB device and pressing two buttons
He has also made the bootloader exploit available on [GitHub](https://github.com/frederic/chipicopwn?ref=news.itsfoss.com), if you want to experiment (suited for security researchers).
## Making Ubuntu Work on Google Nest

**Frédéric Basse**
The exploit allowed the attacker to boot an unsigned OS. However, he had to make some modifications with the preinstalled Ubuntu image tailored for Raspberry Pi (64-bit ARM).
Here’s what he mentions about it:
We build a custom U-Boot bootloader with secure boot disabled and boot flow altered to load environment from USB flash drive. We also build a custom Linux kernel for elaine with
[additionnal d]r[ivers like USB mouse]. The initial ramdisk (initrd) from Ubuntu is repacked to integrate firmware binaries required for the touchscreen. The boot image is created based on the custom Linux kernel and modified initrd.
So, it is evident that you will not get a full-fledged Ubuntu experience, but thanks to the exploit, we now know that Ubuntu can run on a Google Nest as an experiment if you’re willing to break your Google Nest for the test (don’t do that, really!).
## Smart Home Security Concern + Linux
The cybersecurity expert mentions that the vulnerability has been fixed upstream (twice).
But, the lack of CVE may have influenced the fix not propagating downstream, as the researcher suggests.
Undoubtedly, seeing Linux running on an unsupported device is awesome. Makes me wonder if we should have someone make **commercial smart home devices powered by Linux?**
*Is there something like that already available?*
Nevertheless, it is equally concerning for smart home devices to be vulnerable to easy attacks.
What do you think? Share your thoughts in the comments down below.
**Via**: [Liliputing](https://liliputing.com/2022/06/hacker-installs-ubuntu-on-a-google-nest-hub-2nd-gen-smart-display.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com)
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,747 | Docker Compose:搭建开发环境的好方式 | https://jvns.ca/blog/2021/01/04/docker-compose-is-nice/ | 2022-06-23T18:00:40 | [
"Docker",
"开发环境"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14747-1.html | 
大家好!我又写了一篇关于 [我最喜欢的电脑工具](https://jvns.ca/#cool-computer-tools---features---ideas) 的文章。这一篇讲的是 Docker Compose!
本文主要就是讲一讲我对 Docker Compose 有多么满意啦(不讨论它的缺点)!咳咳,因为它总能够完成它该做的,并且似乎总能有效,更棒的是,它的使用还非常简单。另外,在本文中,我只讨论我是如何用 Docker Compose 来搭建开发环境的,而不涉及它在生产中的使用。
最近,我考虑了很多关于这种个人开发环境的搭建方式,原因是,我现在把所有的计算工作都搬到了一个私有云上,大概 20 美元/月的样子。这样一来,我就不用在工作的时候花时间去思考应该如何管理几千台 AWS 服务器了。
在此之前,我曾花了两天的时间,尝试使用其他的工具来尝试搭建一个开发环境,搭到后面,我实在是心累了。相比起来,Docker Compose 就简单易用多了,我非常满意。于是,我和妹妹分享了我的 `docker-compose` 使用经历,她略显惊讶:“是吧!你也觉得 Docker Compose 真棒对吧!” 嗯,我觉得我应该写一篇博文把过程记录下来,于是就有了你们看到的这篇文章。
### 我们的目标是:搭建一个开发环境
目前,我正在编写一个 Ruby on Rails 服务(它是一个计算机“调试”游戏的后端)。在我的生产服务器上,我安装了:
* 一个 Nginx 服务器
* 一个 Rails 服务
* 一个 Go 服务(使用了 [gotty](https://github.com/yudai/gotty/) 来代理一些 SSH 连接)
* 一个 Postgres 数据库
在本地搭建 Rails 服务非常简单,用不着容器(我只需要安装 Postgres 和 Ruby 就行了,小菜一碟)。但是,我还想要把匹配 `/proxy/*` 的请求的发送到 Go 服务,其他所有请求都发送到 Rails 服务,所以需要借助 Nginx。问题来了,在笔记本电脑上安装 Nginx 对我来说太麻烦了。
是时候使用 `docker-compose` 了!
### docker-compose 允许你运行一组 Docker 容器
基本上,Docker Compose 的作用就是允许你运行一组可以互相通信 Docker 容器。
你可以在一个叫做 `docker-compose.yml` 的文件中,配置你所有的容器。我在下方将贴上我为这个服务编写的 `docker-compose.yml` 文件(完整内容),因为我觉得它真的很简洁、直接!
```
version: "3.3"
services:
db:
image: postgres
volumes:
- ./tmp/db:/var/lib/postgresql/data
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password # yes I set the password to 'password'
go_server:
# todo: use a smaller image at some point, we don't need all of ubuntu to run a static go binary
image: ubuntu
command: /app/go_proxy/server
volumes:
- .:/app
rails_server:
build: docker/rails
command: bash -c "rm -f tmp/pids/server.pid && source secrets.sh && bundle exec rails s -p 3000 -b '0.0.0.0'"
volumes:
- .:/app
web:
build: docker/nginx
ports:
- "8777:80" # this exposes port 8777 on my laptop
```
这个配置包含了两种容器。对于前面两个容器,我直接使用了现有的镜像(`image: postgres` 和 `image: ubuntu`)。对于后面两个容器,我不得不构建一个自定义容器镜像,其中, `build: docker/rails` 的作用就是告诉 Docker Compose,它应该使用 `docker/rails/Dockerfile` 来构建一个自定义容器。
我需要允许我的 Rails 服务访问一些 API 密钥和其他东西,因此,我使用了 `source secrets.sh`,它的作用就是在环境变量中预设一组密钥。
### 如何启动所有服务:先 “build” 后 “up”
我一直都是先运行 `docker-compose build` 来构建容器,然后再运行 `docker-compose up` 把所有服务启动起来。
你可以在 yaml 文件中设置 `depends_on`,从而进行更多启动容器的控制。不过,对于我的这些服务而言,启动顺序并不重要,所以我没有设置它。
### 网络互通也非常简单
容器之间的互通也是一件很重要的事情。Docker Compose 让这件事变得超级简单!假设我有一个 Rails 服务正在名为 `rails_server` 的容器中运行,端口是 3000,那么我就可以通过 `http://rails_server:3000` 来访问该服务。就是这么简单!
以下代码片段截取自我的 Nginx 配置文件,它是根据我的使用需求配置的(我删除了许多 `proxy_set_headers` 行,让它看起来更清楚):
```
location ~ /proxy.* {
proxy_pass http://go_server:8080;
}
location @app {
proxy_pass http://rails_server:3000;
}
```
或者,你可以参考如下代码片段,它截取自我的 Rails 项目的数据库配置,我在其中使用了数据库容器的名称(`db`):
```
development:
<<: *default
database: myproject_development
host: db # <-------- 它会被“神奇地”解析为数据库容器的 IP 地址
username: postgres
password: password
```
至于 `rails_server` 究竟是如何被解析成一个 IP 地址的,我还真有点儿好奇。貌似是 Docker 在我的计算机上运行了一个 DNS 服务来解析这些名字。下面是一些 DNS 查询记录,我们可以看到,每个容器都有它自己的 IP 地址:
```
$ dig +short @127.0.0.11 rails_server
172.18.0.2
$ dig +short @127.0.0.11 db
172.18.0.3
$ dig +short @127.0.0.11 web
172.18.0.4
$ dig +short @127.0.0.11 go_server
172.18.0.5
```
### 是谁在运行这个 DNS 服务?
我(稍微)研究了一下这个 DNS 服务是怎么搭建起来的。
以下所有命令都是在容器外执行的,因为我没有在容器里安装很多网络工具。
**第一步:**:使用 `ps aux | grep puma`,获取 Rails 服务的进程 ID。
找到了,它是 `1837916`!简单~
**第二步:**:找到和 `1837916` 运行在同一个网络命名空间的 UDP 服务。
我使用了 `nsenter` 来在 `puma` 进程的网络命令空间内运行 `netstat`(理论上,我猜想你也可以使用 `netstat -tupn` 来只显示 UDP 服务,但此时,我的手指头只习惯于打出 `netstat -tulpn`)。
```
$ sudo nsenter -n -t 1837916 netstat -tulpn
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.11:32847 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1333/dockerd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1837916/puma 4.3.7
udp 0 0 127.0.0.11:59426 0.0.0.0:* 1333/dockerd
```
我们可以看到,此时有一个运行在 `59426` 端口的 UDP 服务,它是由 `dockerd` 运行的!或许它就是我们要找的 DNS 服务?
**第三步**:确定它是不是我们要找的 DNS 服务
我们可以使用 `dig` 工具来向它发送一个 DNS 查询:
```
$ sudo nsenter -n -t 1837916 dig +short @127.0.0.11 59426 rails_server
172.18.0.2
```
奇怪,我们之前运行 `dig` 的时候,DNS 查询怎么没有发送到 `59426` 端口,而是发送到了 `53` 端口呢?这到底是怎么回事呀?
**第四步**:iptables
对于类似“这个服务似乎正运行在 X 端口上,但我却在 Y 端口上访问到了它,这是什么回事呢?”的问题,我的第一念头都是“一定是 iptables 在作怪”。
于是,我在运行了容器的网络命令空间内执行 `iptables-save`,果不其然,真相大白:
```
$ sudo nsenter -n -t 1837916 iptables-save
.... redacted a bunch of output ....
-A DOCKER_POSTROUTING -s 127.0.0.11/32 -p udp -m udp --sport 59426 -j SNAT --to-source :53
COMMIT
```
在输出中有一条 iptables 规则,它将 `53` 端口的流量发送到了 `59426` 上。哈哈,真有意思!
### 数据库文件储存在一个临时目录中
这样做有一个好处:我可以直接挂载 Postgres 容器的数据目录 `./tmp/db`,而无需在我的笔记本电脑上管理 Postgres 环境。
我很喜欢这种方式,因为我真的不想在笔记本电脑上独自管理一个 Postgres 环境(我也真的不知道该如何配置 Postgres)。另外,出于习惯,我更喜欢让开发环境的数据库和代码放在同一个目录下。
### 仅需一行命令,我就可以访问 Rails 控制台
管理 Ruby 的版本总是有点棘手,并且,即使我暂时搞定了它,我也总是有点担心自己会把 Ruby 环境搞坏,然后就要修它个十年(夸张)。
(使用 Docker Compose)搭建好这个开发环境后,如果我需要访问 Rails <ruby> 控制台 <rt> console </rt></ruby>(一个交互式环境,加载了所有我的 Rails 代码),我只需要运行一行代码即可:
```
$ docker-compose exec rails_server rails console
Running via Spring preloader in process 597
Loading development environment (Rails 6.0.3.4)
irb(main):001:0>
```
好耶!
### 小问题:Rails 控制台的历史记录丢失了
我碰到了一个问题:Rails 控制台的历史记录丢失了,因为我一直在不断地重启它。
不过,我也找到了一个相当简单的解决方案(嘿嘿):我往容器中添加了一个 `/root/.irbrc` 文件,它能够把 IRB 历史记录文件的保存位置指向一个不受容器重启影响的地方。只需要一行代码就够啦:
```
IRB.conf[:HISTORY_FILE] = "/app/tmp/irb_history"
```
### 我还是不知道它在生产环境的表现如何
到目前为止,这个项目的生产环境搭建进度,还停留在“我制作了一个 DigitalOcean droplet(LCCT 译注:一种 Linux 虚拟机服务),并手工编辑了很多文件”的阶段。
嗯……我相信以后会在生产环境中使用 docker-compose 来运行一下它的。我猜它能够正常工作,因为这个服务很可能最多只有两个用户在使用,并且,如果我愿意,我可以容忍它在部署过程中有 60 秒的不可用时间。不过话又说回来,出错的往往是我想不到的地方。
推特网友提供了一些在生产中使用 docker-compose 的注意事项:
* `docker-compose up` 只会重启那些需要重启的容器,这会让重启速度更快。
* 有一个 Bash 小脚本 [wait-for-it](https://github.com/vishnubob/wait-for-it),你可以用它来保持等待一个容器,直到另一个容器的服务可用。
* 你可以准备两份 `docker-compose.yaml` 文件:用于开发环境的 `docker-compose.yaml` 和用于生产环境的 `docker-compose-prod.yaml`。我想我会在分别为 Nginx 指定不同的端口:开发时使用 `8999`,生产中使用 `80`。
* 人们似乎一致认为,如果你的项目是一台计算机上运行的小网站,那么 docker-compose 在生产中不会有问题。
* 有个人建议说,如果愿意在生产环境搭建复杂那么一丢丢,Docker Swarm 就或许会是更好的选择,不过我还没试过(当然,如果要这么说的话,干嘛不用 Kubernetes 呢?Docker Compose 的意义就是它超级简单,而 Kubernetes 肯定不简单 : ))。
Docker 似乎还有一个特性,它能够 [把你用 docker-compose 搭建的环境,自动推送到弹性容器服务(ESC)上](https://docs.docker.com/cloud/ecs-integration/),听上去好酷的样子,但是我还没有试过。
### docker-compose 会有不适用的场景吗
我听说 docker-compose 在以下场景的表现较差:
* 当你有很多微服务的时候(还是自己搭建比较好)
* 当你尝试从一个很大的数据库中导入数据时(就像把几百 G 的数据存到每个人的笔记本电脑里一样)
* 当你在 Mac 电脑上运行 Docker 时。我听说 Docker 在 macOS 上比在 Linux 上要慢很多(我猜想是因为它需要做额外的虚拟化)。我没有 Mac 电脑,所以我还没有碰到这个问题。
### 以上就是全部内容啦!
在此之前,我曾花了一整天时间,尝试使用 Puppet 来配置 Vagrant 虚拟机,然后在这个虚拟机里配置开发环境。结果,我发现虚拟机启动起来实在是有点慢啊,还有就是,我也不喜欢编写 Puppet 配置(哈哈,没想到吧)。
幸好,我尝试了 Docker Compose,它真好简单,马上就可以开始工作啦!
---
via: <https://jvns.ca/blog/2021/01/04/docker-compose-is-nice/>
作者:[Julia Evans](https://jvns.ca/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Hello! Here is another post about [computer tools that I’ve appreciated](https://jvns.ca/#cool-computer-tools---features---ideas). This one is about Docker Compose!
This post is mostly just about how delighted I was that it does what it’s supposed to do and it seems to work and to be pretty straightforward to use. I’m also only talking about using Docker Compose for a dev environment here, not using it in production.
I’ve been thinking about this kind of personal dev environment setup more recently because I now do all my computing with a personal cloud budget of like $20/month instead of spending my time at work thinking about how to manage thousands of AWS servers.
I’m very happy about this because previous to trying Docker Compose I spent two days getting frustrated with trying to set up a dev environment with other tools and Docker Compose was a lot easier and simpler. And then I told my sister about my docker-compose experiences and she was like “I KNOW, DOCKER COMPOSE IS GREAT RIGHT?!?!” So I thought I’d write a blog post about it, and here we are.
### the problem: setting up a dev environment
Right now I’m working on a Ruby on Rails service (the backend for a sort of computer debugging game). On my production server, I have:
- a nginx proxy
- a Rails server
- a Go server (which proxies some SSH connections with
[gotty](https://github.com/yudai/gotty/)) - a Postgres database
Setting up the Rails server locally was pretty straightforward without
resorting to containers (I just had to install Postgres and Ruby, fine, no big deal), but then
I wanted send `/proxy/*`
to the Go server and everything else to the Rails
server, so I needed nginx too. And installing nginx on my laptop felt too messy
to me.
So enter `docker-compose`
!
### docker-compose lets you run a bunch of Docker containers
Docker Compose basically lets you run a bunch of Docker containers that can communicate with each other.
You configure all your containers in one file called `docker-compose.yml`
. I’ve
pasted my entire `docker-compose.yml`
file here for my server because I found
it to be really short and straightforward.
```
version: "3.3"
services:
db:
image: postgres
volumes:
- ./tmp/db:/var/lib/postgresql/data
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password # yes I set the password to 'password'
go_server:
# todo: use a smaller image at some point, we don't need all of ubuntu to run a static go binary
image: ubuntu
command: /app/go_proxy/server
volumes:
- .:/app
rails_server:
build: docker/rails
command: bash -c "rm -f tmp/pids/server.pid && source secrets.sh && bundle exec rails s -p 3000 -b '0.0.0.0'"
volumes:
- .:/app
web:
build: docker/nginx
ports:
- "8777:80" # this exposes port 8777 on my laptop
```
There are two kinds of containers here: for some of them I’m just
using an existing image (`image: postgres`
and `image: ubuntu`
) without
modifying it at all. And for some I needed to build a custom container image –
`build: docker/rails`
says to use `docker/rails/Dockerfile`
to build a custom
container.
I needed to give my Rails server access to some API keys and things, so `source secrets.sh`
puts a bunch of secrets in environment variables. Maybe there’s a
better way to manage secrets but it’s just me so this seemed fine.
### how to start everything: `docker-compose build`
then `docker-compose up`
I’ve been starting my containers just by running `docker-compose build`
to
build the containers, then `docker-compose up`
to run everything.
You can set `depends_on`
in the yaml file to get a little more control over
when things start in, but for my set of services the start order
doesn’t matter, so I haven’t.
### the networking is easy to use
It’s important here that the containers be able to connect to each other.
Docker Compose makes that super simple! If I have a Rails server running in my
`rails_server`
container on port 3000, then I can access that with
`http://rails_server:3000`
. So simple!
Here’s a snippet from my nginx configuration file with how I’m using that in
practice (I removed a bunch of `proxy_set_header`
lines to make it more clear)
```
location ~ /proxy.* {
proxy_pass http://go_server:8080;
}
location @app {
proxy_pass http://rails_server:3000;
}
```
Or here’s a snippet from my Rails project’s database configuration, where I use the name of the database container (`db`
):
```
development:
<<: *default
database: myproject_development
host: db # <-------- this "magically" resolves to the database container's IP address
username: postgres
password: password
```
I got a bit curious about how `rails_server`
was actually getting resolved to
an IP address. It seems like Docker is running a DNS server somewhere on my
computer to resolve these names. Here are some DNS queries where we can see that each container has its own IP address:
```
$ dig +short @127.0.0.11 rails_server
172.18.0.2
$ dig +short @127.0.0.11 db
172.18.0.3
$ dig +short @127.0.0.11 web
172.18.0.4
$ dig +short @127.0.0.11 go_server
172.18.0.5
```
### who’s running this DNS server?
I dug into how this DNS server is set up a very tiny bit.
I ran all these commands outside the container, because I didn’t have a lot of networking tools installed in the container.
**step 1**: find the PID of my Rails server with `ps aux | grep puma`
It’s 1837916. Cool.
**step 2**: find a UDP server running in the same network namespace as PID `1837916`
I did this by using `nsenter`
to run `netstat`
in the same network namespace as
the `puma`
process. (technically I guess you could run `netstat -tupn`
to just
show UDP servers, but my fingers only know how to type `netstat -tulpn`
at this
point)
```
$ sudo nsenter -n -t 1837916 netstat -tulpn
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.11:32847 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1333/dockerd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1837916/puma 4.3.7
udp 0 0 127.0.0.11:59426 0.0.0.0:* 1333/dockerd
```
So there’s a UDP server running on port `59426`
, run by `dockerd`
! Maybe that’s the DNS server?
**step 3**: check that it’s a DNS server
We can use `dig`
to make a DNS query to it:
```
$ sudo nsenter -n -t 1837916 dig +short @127.0.0.11 59426 rails_server
172.18.0.2
```
But – when we ran `dig`
earlier, we weren’t making a DNS query to port 59426,
we were querying port 53! What’s going on?
**step 4**: iptables
My first guess for “this server seems to be running on port X but I’m accessing it on port Y, what’s going on?” was “iptables”.
So I ran iptables-save in the container’s network namespace, and there we go:
```
$ sudo nsenter -n -t 1837916 iptables-save
.... redacted a bunch of output ....
-A DOCKER_POSTROUTING -s 127.0.0.11/32 -p udp -m udp --sport 59426 -j SNAT --to-source :53
COMMIT
```
There’s an iptables rule that sends traffic on port 53 to 59426. Fun!
### it stores the database files in a temp directory
One nice thing about this is: instead of managing a Postgres installation on my
laptop, I can just mount the Postgres container’s data directory at `./tmp/db`
.
I like this because I really do not want to administer a Postgres installation on my laptop (I don’t really know how to configure Postgres), and conceptually I like having my dev database literally be in the same directory as the rest of my code.
### I can access the Rails console with `docker-compose exec rails_server rails console`
Managing Ruby versions is always a little tricky and even when I have it working, I always kind of worry I’m going to screw up my Ruby installation and have to spend like ten years fixing it.
With this setup, if I need access to the Rails console (a REPL with all my Rails code loaded), I can just run:
```
$ docker-compose exec rails_server rails console
Running via Spring preloader in process 597
Loading development environment (Rails 6.0.3.4)
irb(main):001:0>
```
Nice!
### small problem: no history in my Rails console
I ran into a problem though: I didn’t have any history in my Rails console anymore, because I was restarting the container all the time.
I figured out a pretty simple solution to this though: I added a
`/root/.irbrc`
to my container that changed the IRB history file’s location to
be something that would persist between container restarts. It’s just one line:
```
IRB.conf[:HISTORY_FILE] = "/app/tmp/irb_history"
```
### I still don’t know how well it works in production
Right now my production setup for this project is still “I made a digitalocean droplet and edited a lot of files by hand”.
I think I’ll try to use docker-compose to run this thing in production. My guess is that it should work fine because this service is probably going to have at most like 2 users at a time and I can easily afford to have 60 seconds of downtime during a deploy if I want, but usually something goes wrong that I haven’t thought of.
A few notes from folks on Twitter about docker-compose in production:
`docker-compose up`
will only restart the containers that need restarting, which makes restarts faster- there’s a small bash script
[wait-for-it](https://github.com/vishnubob/wait-for-it)that you can use to make a container wait for another service to be available - You can have 2 docker-compose.yaml files:
`docker-compose.yaml`
for DEV, and`docker-compose-prod.yaml`
for prod. I think I’ll use this to expose different nginx ports: 8999 in dev and 80 in prod. - folks seemed to agree that docker-compose is fine in production if you have a small website running on 1 computer
- one person suggested that Docker Swarm might be better for a slightly more complicated production setup, but I haven’t tried that (or of course Kubernetes, but the whole point of Docker Compose is that it’s super simple and Kubernetes is certainly not simple :) )
Docker also seems to have a feature to [automatically deploy your docker-compose setup to ECS](https://docs.docker.com/cloud/ecs-integration/),
which sounds cool in theory but I haven’t tried it.
### when doesn’t docker-compose work well?
I’ve heard that docker-compose doesn’t work well:
- when you have a very large number of microservices (a simple setup is best)
- when you’re trying to include data from a very large database (like putting hundreds of gigabytes of data on everyone’s laptop)
- on Mac computers, I’ve heard that Docker can be a lot slower than on Linux (presumably because of the extra VM). I don’t have a Mac so I haven’t run into this.
### that’s all!
I spent an entire day before this trying to configure a dev environment by using Puppet to provision a Vagrant virtual machine only to realize that VMs are kind of slow to start and that I don’t really like writing Puppet configuration (I know, huge surprise :)).
So it was nice to try Docker Compose and find that it was straightforward to get to work! |
14,748 | 用 Curtail GUI 应用轻松压缩 Linux 中的图像 | https://itsfoss.com/curtail-image-compress/ | 2022-06-23T18:29:03 | [
"图像压缩"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14748-1.html | 
有一大堆文件尺寸巨大的图片占用了太多的磁盘空间?或者你必须将图片上传到有文件大小限制的门户网站?
你可能有很多原因想要压缩图片。有大量的工具可以帮助你,我在这里说的不是命令行的工具。
你可以使用一个成熟的图像编辑器,如 GIMP。你也可以使用像 [Squoosh](https://squoosh.app/) 这样的网络工具,这是谷歌的一个开源项目。它甚至可以让你比较每个压缩级别的文件。
然而,所有这些工具都是针对单个图像工作的。如果你想批量压缩照片怎么办?Curtail 是一个能帮助你的应用。
### Curtail: Linux 中用于图像压缩的灵巧工具
使用 Python 和 GTK3 构建的 Curtail 是一个简单的 GUI 应用,使用 OptiPNG、[jpegoptim](https://github.com/tjko/jpegoptim) 等开源库来提供图像压缩功能。
它有一个 [Flatpak 应用](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-flatpak/)。请确保你的系统已启用 [Flatpak 支持](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/)。
首先添加 Flathub 仓库:
```
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
```
然后使用下面的命令来安装 Curtail:
```
flatpak install flathub com.github.huluti.Curtail
```
安装后,在你的 Linux 系统的菜单中寻找它,并从那里启动它。

界面朴素而简单。你可以选择你想要无损压缩还是有损压缩。
有损压缩会有质量差的图像,但尺寸较小。无损压缩会有更好的质量,但尺寸可能不会比原来的小很多。

你可以浏览图片,或者把它们拖到应用中。
是的,你可以用 Curtail 一键压缩多张图片。
事实上,你甚至不需要点击。只要你选择图片或拖放它们,它们就会被压缩,你会看到压缩过程的摘要。

正如你在上面的图片中看到的,我的一张图片的尺寸减少了 35%,另外两张图片的尺寸减少了 3% 和 8%。这是在无损压缩的情况下。
这些图片以 `-min` 为后缀(默认),保存在与原始图片相同的目录中。
虽然它看起来很简约,但有几个选项可以配置 Curtail。点击菜单,你会看到一些设置选项。

你可以选择是将压缩文件保存为新文件还是替换现有文件。如果你选择新文件(默认行为),你也可以为压缩后的图像提供一个不同的后缀。保留文件属性的选项也在这里。
在下一个选项卡中,你可以配置有损压缩的设置。默认情况下,压缩级别为 90%。

高级选项卡让你可以选择配置 PNG 和 WebP 文件的无损压缩级别。

### 总结
正如我前面所说,这不是一个突破性的工具。你可以用其他工具如 GIMP 做同样的事情。它只是使图像压缩的任务更简单,特别是对于批量图像压缩。
我很想看到在压缩时有[转换图像文件格式](https://itsfoss.com/converseen/)的选项,就像我们在 Converseen 等工具中所拥有的那样。
总的来说,对于图像压缩的具体目的来说,这是一个不错的小工具。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/curtail-image-compress/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Got a bunch of images with huge file sizes taking too much disk space? Or perhaps you have to upload an image to a web portal that has file size restrictions?
There could be a number of reasons why you would want to compress images. There are tons of tools to help you with it and I am not talking about the command line ones here.
You can use a full-fledged image editor like GIMP. You may also use web tools like [Squoosh](https://squoosh.app/), an open source project from Google. It even lets you [compare the files](https://itsfoss.com/compare-files-linux-tools/) for each compression level.
However, all these tools work on individual images. What if you want to bulk compress photos? Curtail is an app that saves your day.
## Curtail: Nifty tool for image compression in Linux
Built with Python and GTK3, Curtail is a simple GUI app that uses open source libraries like OptiPNG, [jpegoptim](https://github.com/tjko/jpegoptim), etc to provide the image compression feature.
It is available as a [Flatpak application](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-flatpak/). Please make sure that you have [Flatpak support enabled on your system](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/).
Add the Flathub repo first:
`flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo`
And then use the command below to install Curtail:
`flatpak install flathub com.github.huluti.Curtail`
Once installed, look for it in your Linux system’s menu and start it from there.
The interface is plain and simple. You can choose whether you want a lossless or lossy compression.
The lossy compression will have poor-quality images but with a smaller size. The lossless compression will have better quality but the size may not be much smaller than the original.
You can either browse for images or drag and drop them into the application.
Yes. You can compress multiple images in one click with Curtail.
In fact, you don’t even need a click. As soon as you select the images or drop them, they are compressed and you see a summary of the compression process.
As you can see in the image above, I got a 35% size reduction for one image and 3 and 8 percent for the other two. This was with lossless compression.
The images are saved with a -min suffix (by default), in the same directory as the original image.
Though it looks minimalist, there are a few options to configure Curtail. Click on the hamburger menu and you are presented with a few settings options.
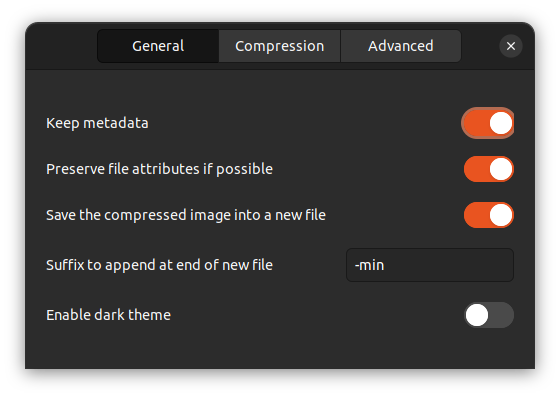
You can select whether you want to save the compressed file as new or replace the existing one. If you go for a new file (default behavior), you can also provide a different suffix for the compressed images. The option to keep the file attributes is also there.
In the next tab, you can configure the settings for lossy compression. By default, the compression level is at 90%.
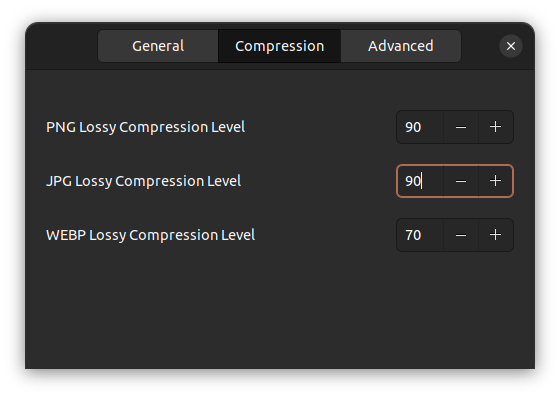
The Advanced tab gives you the option to configure the lossless compression level for PNG and WebP files.
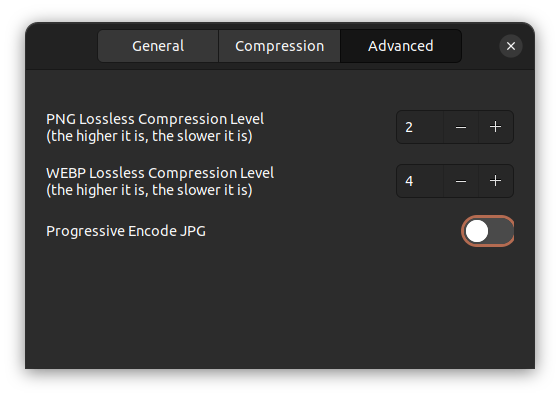
## Conclusion
As I stated earlier, it’s not a groundbreaking tool. You can do the same with other tools like GIMP. It just makes the task of image compression simpler, especially for bulk image compression.
I would love to see the option to [convert the image file formats](https://itsfoss.com/converseen/) with the compression like what we have in tools like Converseen.
Overall, a good little utility for the specific purpose of image compression. |
14,750 | 如何启动 Ubuntu 22.04 进入救援/紧急模式 | https://www.linuxtechi.com/boot-ubuntu-22-04-rescue-emergency-mode/ | 2022-06-24T10:16:48 | [
"救援模式",
"紧急模式",
"GRUB"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14750-1.html | 
极客们好,将 Ubuntu 22.04(Jammy Jellyfish)启动到<ruby> 救援 <rt> Rescue </rt></ruby>和<ruby> 紧急 <rt> Emergency </rt></ruby>模式可以重置忘记的用户密码、修复文件系统错误,以及在启动过程中禁用或启用 systemd 服务。
在这篇文章中,我们将学习如何启动 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 系统进入救援和应急模式。救援模式类似于单用户模式,所有的故障排除步骤都在这里进行。救援模式加载最小的环境并挂载根文件系统。
而在紧急模式下,我们得到的是单用户 Shell,而不启动任何系统服务。因此,当我们无法启动系统进入救援模式时,就需要紧急模式。
### 启动 Ubuntu 22.04 进入救援或单用户模式
前往你想启动到救援或单用户模式的目标系统。在启动时按下 `SHIFT + ESC` 键,进入 GRUB 引导加载器页面。

选择第一个选项 “Ubuntu”,并按 `e` 键进入编辑模式。
在以 `linux` 开头的一行末尾,删除字符串 `$vt_handoff` 并添加字符串 `systemd.unit=rescue.target`。

做完修改后,按 `Ctrl + X` 或 `F10` 在救援模式下启动。

进入救援模式后,运行所有的故障排除命令,并运行 `systemctl reboot` 命令来重启系统。
### 另一种启动系统进入救援模式的方法
重新启动系统并按下 `ESC + Shift` 键,进入 GRUB 启动界面。
选择第二个选项 “<ruby> Ubuntu 高级选项 <rt> Advanced Options for Ubuntu </rt></ruby>”->选择“<ruby> 恢复模式 <rt> recovery mode </rt></ruby>”选项并点击回车->选择 <ruby> root(进入 root shell 提示符) <rt> root (Drop to root shell prompt) </rt></ruby>。
下面是一个例子:

当你有了 root Shell,运行命令来恢复和修复系统问题,最后使用 `systemctl reboot` 来重启系统。
### 引导 Ubuntu 22.04 进入紧急模式
要启动系统进入紧急模式,首先进入 GRUB 页面。

选择第一个选项 “Ubuntu” 并按 `e` 键进行编辑。寻找以 `linux` 开头的一行,移到该行的末尾,删除字符串 `$vt_handoff` 并添加字符串 `systemd.unit=emergency.target`。

按 `Ctrl + X` 或 `F10` 将系统启动到紧急模式。

同样,在紧急模式下,你可以在这个模式下执行所有的故障排除,完成后,就用 `systemctl reboot` 命令重启系统。
这篇文章的内容就这些。文章内容丰富,不要犹豫,请在你的技术朋友中分享它。请在下面的评论区发表你的疑问和反馈。
---
via: <https://www.linuxtechi.com/boot-ubuntu-22-04-rescue-emergency-mode/>
作者:[Pradeep Kumar](https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Hello geeks, booting Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish) into rescue and emergency mode helps to reset the forgotten user password, fix the file system errors and disabling or enabling systemd service during boot.
In this post, we will learn how to boot Ubuntu 22.04 LTS system into rescue and emergency mode. Rescue mode is similar to single user mode where are all troubleshooting steps are executed. Rescue mode loads the minimal environment and mount root file system.
Whereas in emergency mode, we get the single user shell without starting any system services. So emergency mode is required when we can’t boot the system into rescue mode.
## Boot Ubuntu 22.04 into Rescue or Single User Mode
Head to target system which you want to boot into rescue or single user mode. At the boot press ‘SHIFT & ESC’ key to enter into grub bootloader screen.
Choose the first option Ubuntu and press ‘e’ to enter edit mode.
Go the end of line which starts with linux and delete the string ‘$vt_handoff’ and add the string ‘systemd.unit=rescue.target’
After making the changes, either press Ctrl+x or F10 to boot in rescue mode,
Once you enter into rescue mode, run all troubleshooting commands and to reboot the system run ‘systemctl reboot’ command
## Alternate Way to Boot System into Rescue Mode
Reboot the system and press ‘ESC & Shift’ Key to go to grub boot screen.
Choose the 2nd option ‘Advanced Options for Ubuntu’ –> Choose recovery mode option and hit enter –> Choose Root (Drop to root shell prompt).
Example is show below
Once you have root shell, run commands to recover and fix the system issues and finally use ‘systemctl reboot’ to reboot the system.
## Boot Ubuntu 22.04 into Emergency Mode
To boot the system into emergency mode, first go to grub screen.
Select the first option as ‘Ubuntu’ and press ‘e’ to edit. Look for the line which starts with linux word, go to the end of that line, remove the string $vt_handoff and add the string ‘systemd.unit=emergency.target’
Press Ctrl+x or F10 to boot the system into emergency mode,
Similarly in rescue mode, you can perform all the troubleshooting in this mode and once done reboot the system with command ‘systemctl reboot’.
That’s all from this post. I found it informative and don’t hesitate to share this among your technical friends. Kindly post your queries and feedback in below comments section.
Read Also : [How to Set Custom $PATH Environment Variable in Linux](https://www.linuxtechi.com/set-custom-path-variable-in-linux/) |
14,751 | 一起来学习 Lisp 编程语言吧! | https://opensource.com/article/21/5/learn-lisp | 2022-06-24T12:40:00 | [
"Lisp"
] | /article-14751-1.html |
>
> 许多大型代码库中都有 Lisp 代码的身影,因此,熟悉一下这门语言是一个明智之举。
>
>
>

早在 1958 年,Lisp 就被发明出来了,它是世界上第二古老的计算机编程语言(LCTT 译注:最古老的编程语言是 Fortran,诞生于 1957 年)。它有许多现代的衍生品,包括 Common Lisp、Emacs Lisp(Elisp)、Clojure、Racket、Scheme、Fennel 和 GNU Guile 等。
那些喜欢思考编程语言的设计的人,往往都喜欢 Lisp,因为它的语法和数据有着相同的结构:Lisp 代码实际上是<ruby> 一个列表的列表 <rt> a list of lists </rt></ruby>,它的名字其实是 “<ruby> 列表处理 <rt> LISt Processing </rt></ruby>” 的简写。而那些喜欢思考编程语言的美学的人,往往都讨厌 Lisp,因为它经常使用括号来定义范围;事实上,编程界也有一个广为流传的笑话:Lisp 代表的其实是 <ruby> “大量烦人的多余括号” <rt> Lots of Irritating Superfluous Parentheses </rt></ruby>。
不管你是喜欢还是讨厌 Lisp 的设计哲学,你都不得不承认,它都是一门有趣的语言,过去如此,现在亦然(这得归功于现代方言 Clojure 和 Guile)。你可能会惊讶于在任何特定行业的大代码库中潜伏着多少 Lisp 代码,因此,现在开始学习 Lisp,至少熟悉一下它,不失为一个好主意。
### 安装 Lisp
Lisp 有很多不同的实现。比较流行的开源版本有 [SBCL](http://sbcl.org)、[GNU Lisp](http://clisp.org) 和 [GNU Common Lisp](https://www.gnu.org/software/gcl/)(GCL)。你可以使用发行版的包管理器安装它们中的任意一个,在本文中,我是用的是 `clisp`(LCTT 译注:也就是 GNU Lisp,一种 ANSI Common Lisp 的实现)。
以下是在不同的 Linux 发行版中安装 `clisp` 的步骤。
在 Fedora Linux 上,使用 `dnf`:
```
$ sudo dnf install clisp
```
在 Debian 上,使用 `apt`:
```
$ sudo apt install clisp
```
在 macOS 上,使用 [MacPorts](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/macports) 或者 [Homebrew](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/homebrew-linux):
```
# 使用 MacPorts
$ sudo port install clisp
# 使用 Homebrew
$ brew install clisp
```
在 Windows 上,你可以使用 [clisp on Cygwin](https://cygwin.fandom.com/wiki/Clisp) 或者从 [gnu.org/software/gcl](http://mirror.lagoon.nc/gnu/gcl/binaries/stable) 上下载 GCL 的二进制文件。
虽然我使用 `clisp` 命令来运行 Lisp 代码,但是本文中涉及到的大多数语法规则,对任何 Lisp 实现都是适用的。如果你选择使用一个不同的 Lisp 实现,除了用来运行 Lisp 代码的命令会和我不一样外(比如,你可能要用 `gcl` 或 `sbcl` 而不是 `clisp`),其它的所有东西都是相同的。
### 列表处理
Lisp 源代码的基本单元是 “<ruby> 表达式 <rt> expression </rt></ruby>”,它在形式上是一个列表。举个例子,下面就是一个列表,它由一个操作符(`+`)和两个整数(`1` 和 `2`)组成:
```
(+ 1 2)
```
同时,它也是一个 Lisp 表达式,内容是一个符号(`+`,会被解析成一个加法函数)和它的两个参数(`1` 和 `2`)。你可以在 Common Lisp 的交互式环境(即 REPL)中运行该表达式和其它表达式。如果你熟悉 Python 的 IDLE,那么你应该会对 Lisp 的 REPL 感到亲切。(LCTT 译注:REPL 的全称是 “Read-Eval-Print Loop”,意思是 “‘读取-求值-输出’循环”,这个名字很好地描述了它的工作过程。)
要进入到 REPL 中,只需运行 Common Lisp 即可:
```
$ clisp
[1]>
```
在 REPL 提示符中,尝试输入一些表达式:
```
[1]> (+ 1 2)
3
[2]> (- 1 2)
-1
[3]> (- 2 1)
1
[4]> (+ 2 3 4)
9
```
### 函数
在了解了 Lisp 表达式的基本结构后,你可以使用函数来做更多有用的事。譬如,`print` 函数可以接受任意数量的参数,然后把它们都显示在你的终端上,`pprint` 函数还可以实现格式化打印。还有更多不同的打印函数,不过,`pprint` 在 REPL 中的效果就挺好的:
```
[1]> (pprint "hello world")
"hello world"
[2]>
```
你可以使用 `defun` 函数来创建一个自定义函数。`defun` 函数需要你提供自定义函数的名称,以及它接受的参数列表:
```
[1]> (defun myprinter (s) (pprint s))
MYPRINTER
[2]> (myprinter "hello world")
"hello world"
[3]>
```
### 变量
你可以使用 `setf` 函数来在 Lisp 中创建变量:
```
[1]> (setf foo "hello world")
"hello world"
[2]> (pprint foo)
"hello world"
[3]>
```
你可以在表达式里嵌套表达式(就像使用某种管道一样)。举个例子,你可以先使用 `string-upcase` 函数,把某个字符串的所有字符转换成大写,然后再使用 `pprint` 函数,将它的内容格式化打印到终端上:
```
[3]> (pprint (string-upcase foo))
"HELLO WORLD"
[4]>
```
Lisp 是动态类型语言,这意味着,你在给变量赋值时不需要声明它的类型。Lisp 默认会把整数当作整数来处理:
```
[1]> (setf foo 2)
[2]> (setf bar 3)
[3]> (+ foo bar)
5
```
如果你想让整数被当作字符串来处理,你可以给它加上引号:
```
[4]> (setf foo "2")
"2"
[5]> (setf bar "3")
"3"
[6]> (+ foo bar)
*** - +: "2" is not a number
The following restarts are available:
USE-VALUE :R1 Input a value to be used instead.
ABORT :R2 Abort main loop
Break 1 [7]>
```
在这个示例 REPL 会话中,变量 `foo` 和 `bar` 都被赋值为加了引号的数字,因此,Lisp 会把它们当作字符串来处理。数学运算符不能够用在字符串上,因此 REPL 进入了调试器模式。想要跳出这个调试器,你需要按下 `Ctrl+D` 才行(LCTT 译注:就 `clisp` 而言,使用 `quit` 关键字也可以退出)。
你可以使用 `typep` 函数对一些对象进行类型检查,它可以测试对象是否为某个特定数据类型。返回值 `T` 和 `NIL` 分别代表 `True` 和 `False`。
```
[4]> (typep foo 'string)
NIL
[5]> (typep foo 'integer)
T
```
`string` 和 `integer` 前面加上了一个单引号(`'`),这是为了防止 Lisp(错误地)把这两个单词当作是变量来求值:
```
[6]> (typep foo string)
*** - SYSTEM::READ-EVAL-PRINT: variable STRING has no value
[...]
```
这是一种保护某些术语(LCTT 译注:类似于字符串转义)的简便方法,正常情况下它是用 `quote` 函数来实现的:
```
[7]> (typep foo (quote string))
NIL
[5]> (typep foo (quote integer))
T
```
### 列表
不出人意料,你当然也可以在 Lisp 中创建列表:
```
[1]> (setf foo (list "hello" "world"))
("hello" "world")
```
你可以使用 `nth` 函数来索引列表:
```
[2]> (nth 0 foo)
"hello"
[3]> (pprint (string-capitalize (nth 1 foo)))
"World"
```
### 退出 REPL
要结束一个 REPL 会话,你需要按下键盘上的 `Ctrl+D`,或者是使用 Lisp 的 `quit` 关键字:
```
[99]> (quit)
$
```
### 编写脚本
Lisp 可以被编译,也可以作为解释型的脚本语言来使用。在你刚开始学习的时候,后者很可能是最容易的方式,特别是当你已经熟悉 Python 或 [Shell 脚本](https://opensource.com/article/20/4/bash-programming-guide) 时。
下面是一个用 Common Lisp 编写的简单的“掷骰子”脚本:
```
#!/usr/bin/clisp
(defun roller (num)
(pprint (random (parse-integer (nth 0 num))))
)
(setf userput *args*)
(setf *random-state* (make-random-state t))
(roller userput)
```
脚本的第一行注释(LCTT 译注:称之为“<ruby> 释伴 <rt> shebang </rt></ruby>”)告诉了你的 POSIX 终端,该使用什么可执行文件来运行这个脚本。
`roller` 函数使用 `defun` 函数创建,它在内部使用 `random` 函数来打印一个伪随机数,这个伪随机数严格小于 `num` 列表中下标为 0 的元素。在脚本中,这个 `num` 列表还没有被创建,不过没关系,因为只有当脚本被调用时,函数才会执行。
接下来的那一行,我们把运行脚本时提供的任意参数,都赋值给一个叫做 `userput` 的变量。这个 `userput` 变量是一个列表,当它被传递给 `roller` 函数后,它就会变成参数 `num`。
脚本的倒数第二行产生了一个“随机种子”。这为 Lisp 提供了足够的随机性来生成一个几乎随机的数字。
最后一行调用了自定义的 `roller` 函数,并将 `userput` 列表作为唯一的参数传递给它。
将这个文件保存为 `dice.lisp`,并赋予它可执行权限:
```
$ chmod +x dice.lisp
```
最后,运行它,并给它提供一个数字,以作为它选择随机数的最大值:
```
$ ./dice.lisp 21
13
$ ./dice.lisp 21
7
$ ./dice.lisp 21
20
```
看起来还不错!
你或许注意到,你的模拟骰子有可能会是 0,并且永远达不到你提供给它的最大值参数。换句话说,对于一个 20 面的骰子,这个脚本永远投不出 20(除非你把 0 当作 20)。有一个简单的解决办法,它只需要用到在本文中介绍的知识,你能够想到吗?
### 学习 Lisp
无论你是想将 Lisp 作为个人脚本的实用语言,还是为了助力你的职业生涯,抑或是仅仅作为一个有趣的实验,你都可以去看看一年一度(LCTT 译注:应该是两年一度)的 [Lisp <ruby> 游戏果酱 <rt> Game Jam </rt></ruby>](https://itch.io/jam/spring-lisp-game-jam-2021),从而收获一些特别有创意的用途(其中的大多数提交都是开源的,因此你可以查看代码以从中学习)。
Lisp 是一门有趣而独特的语言,它有着不断增长的开发者用户群、足够悠久的历史和新兴的方言,因此,它有能力让从事各个行业的程序员都满意。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/5/learn-lisp>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,754 | Manjaro 21.3.0 Ruah 发布:增加了最新的 Calmares 3.2、GNOME 42 和更多升级 | https://news.itsfoss.com/manjaro-21-3-0-release/ | 2022-06-25T09:37:33 | [
"Manjaro"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14754-1.html |
>
> Manjaro Linux 21.3.0 发行包包含一些最新和最强大的更新,包括改进的安装程序。
>
>
>

Manjaro Linux 是一个滚动发布的发行版。因此,从技术上讲,如果你定期更新系统的话,你一直都会使用最新版本。
升级到 Manjaro 21.3.0 应该没什么大不了的,考虑到我已经在正式发布前几天就已经在稳定运行它了,毫无问题。
**另外**,你可能想阅读一下我 [从 Ubuntu 切换到 Manjaro](https://news.itsfoss.com/manjaro-linux-experience/) 的初步体验(如果你对于升级仍然犹豫不决的话)。
那么,Manjaro 21.3.0 带来了什么更新呢?
### Manjaro 21.3.0 更新内容

桌面环境升级到了最新的稳定版本,而内核版本仍然是 [Linux 内核 5.15 LTS](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-15-release/)。
此外,这个版本还包括最终的 Clamares v3.2 版本。让我们来看看它有哪些变化吧。
#### Calamares v3.2.59
Calamares v3.2.59 安装程序是 3.2 系列的最终版本,它有许多有意义的改进。这次,分区模块包含了对 LUKS 分区的支持和更多改进,以避免那些可能会弄乱 Manjaro 安装的设置。
Calamares 3.2 的所有未来版本都将仅是错误修复。
#### GNOME 42 + Libadwaita
最初的版本包含了 GNOME 42,而最新的版本包含了 GNOME 42.2(附带最新的更新)。
总体而言,你将获得 [GNOME 42](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-42-release/) 引入的所有优点,包括系统范围的深色模式、基于 GTK 4 的 GNOME 应用的现代用户界面、升级的应用程序以及其他一些重大变化。

#### KDE Plasma 5.24
不幸的是,考虑到它差不多是在同一周发布的,因此该版本无法包含 [KDE Plasma 5.25](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-25-release/)。
[KDE Plasma 5.24](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-24-lts-release/) 是一个不错的升级,具有更新的主题和概览效果。
#### XFCE 4.16
在 Xfce 4.16 中,窗口管理器得到了许多更新和改进,以支持小数倍数的缩放和更多功能。
### 下载 Manjaro 21.3.0
到目前为止,我在 Manjaro 21.3.0 GNOME 版本中没有遇到任何问题。一切看起来都不错,升级也很顺利。
但是,如果你不想重新安装或丢失重要文件,则应始终进行备份。
你可以从 [Manjaro 的下载页面](https://manjaro.org/download/) 下载最新版本。你也应该可以通过 pamac 包管理器获得更新。
无论哪种情况,你都可以在终端中输入以下命令进行升级:
```
sudo pacmane -Syu
```
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/manjaro-21-3-0-release/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Manjaro Linux is a rolling-release distribution. So, technically, you will be on the latest version if you regularly update your system.
It should not be a big deal to upgrade to Manjaro 21.3.0, considering I am already running it without issues for a few days before the official announcement.
**Also, **you might want to read my initial experience [switching to Manjaro from Ubuntu](https://news.itsfoss.com/manjaro-linux-experience/) (if you’re still on the fence).
So, what does the Manjaro 21.3.0 upgrade introduce?
## Manjaro 21.3.0: What’s New?
The desktop environments upgraded to their latest stable versions while the core [Linux Kernel 5.15 LTS](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-15-release/) remains.
Also, this release includes the final Clamares v3.2 version. Let us take a look at the changes:
### Calamares v3.2.59
Calamares v3.2.59 installer is the final release of the 3.2 series with meaningful improvements. This time the partition module includes support for LUKS partitions and more refinements to avoid settings that can mess up the Manjaro installation.
All the future releases for Calamares 3.2 will be bug fixes only.
### GNOME 42 + Libadwaita
While the initial release included GNOME 42, now we have GNOME 42.2 available with the latest updates.
Overall, you get all the goodies introduced with [GNOME 42](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-42-release/), including the system-wide dark mode, a modern user interface based on GTK 4 for GNOME apps, upgraded applications, and several other significant changes.
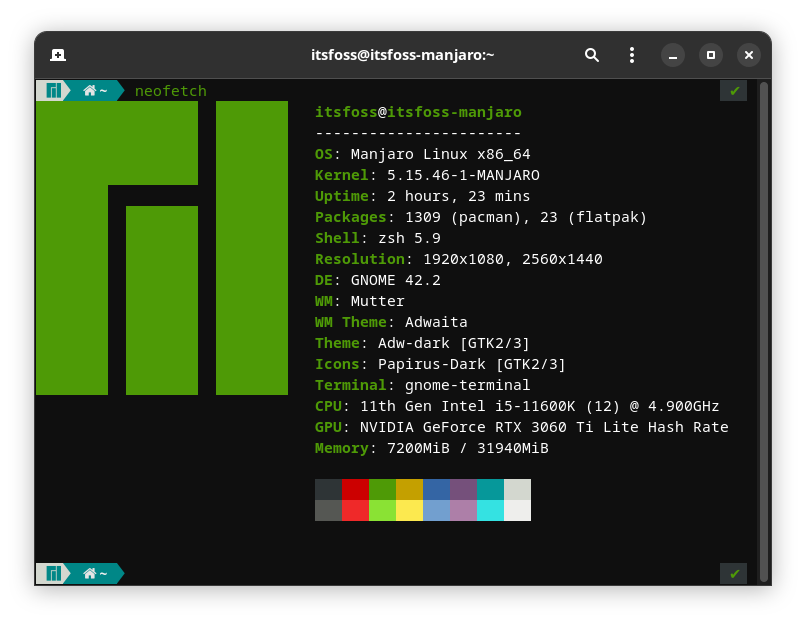
### KDE Plasma 5.24
Unfortunately, the release couldn’t feature [KDE Plasma 5.25](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-25-release/), considering it was released around the same week.
[KDE Plasma 5.24](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-24-lts-release/) is a nice upgrade, with a refreshed theme and an overview effect.
### XFCE 4.16
With Xfce 4.16, the window manager received numerous updates and refinements to support fractional scaling and more capabilities.
## Download Manjaro 21.3.0
As of now, I have no issues with Manjaro 21.3.0 GNOME edition. Everything looks good, and the upgrade went smoothly.
However, you should always take backups if you do not want to re-install or lose your important files.
You can download the latest version from [Manjaro’s download page](https://manjaro.org/download/?ref=news.itsfoss.com). The upgrade should be available through the pamac package manager.
In either case, you can enter the following command in the terminal to upgrade:
`sudo pacman -Syu`
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,755 | 微软将对应用商店中开源软件的收费进行限制 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/microsoft-to-charge-for-available-open-source-software-in-microsoft-store/ | 2022-06-25T10:17:27 | [
"微软",
"免费软件"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14755-1.html | 
2022 年 6 月 16 日,微软更新了其应用商店的策略。其中一项禁止了发布者对开源或免费的软件收取费用,另一项则针对的是商店使用的不合理高价。如果你在过去几年中访问过微软应用商店,你可能已经注意到,它正在成为越来越多的开源和免费产品的所在地。如果原始开发者将应用程序和游戏上传到商店,这将是有益的,但情况并非如此,因为它们是由第三方上传的。
更糟糕的是,其中许多程序仅作为付费应用提供,而不是免费下载。换句话说,微软的客户必须付费才能购买应用商店的版本,而它们在其他地方是免费的!在应用商店中,免费版和付费版有时并存。为免费应用付费已经够糟糕的了,但这并不是用户在购买时可能遇到的唯一问题。更新也可能是一个问题,因为山寨应用可能不会像源头应用程序那样频繁或快速地更新。
在更新的微软商店政策中,微软在 10.8.7 节下指出:
>
> 在您决定产品或应用内购买的定价时,您的数字产品或服务的所有定价(包括销售或折扣)必须:
>
>
> 遵守所有适用的法律、法规和监管要求,包括联邦贸易委员会的《反欺骗性定价指南》。您不得试图从开源软件或其他可免费获得的软件中获利,您的产品也不应提供一个(与它提供的特性和功能相比)过高的不合理定价。
>
>
>
这个新策略在更新部分中得到了确认。如果开源和免费产品普遍免费提供,则它们不得在微软应用商店上出售,发布者也不得对其产品收取不合理的高价。开源和免费应用的开发者可以在微软应用商店上为其产品收费。例如,[Paint.net](http://Paint.net) 的开发者就是这样做的。如果微软强制执行这些策略,许多应用将从应用商店中删除。以前,开发者可以向微软报告应用程序,但在新策略下,微软可以直接控制应用的列出和提交。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/microsoft-to-charge-for-available-open-source-software-in-microsoft-store/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | On June 16, 2022, Microsoft updated the Microsoft Store policies. One of the changes prohibits publishers from charging fees for open source or freely available software. Another example is the store’s use of irrationally high pricing. If you’ve been to the Microsoft Store in the last few years, you’ve probably noticed that it’s becoming more and more home to open source and free products. While this would be beneficial if the original developer had uploaded the apps and games to the store, it is not the case because the uploads were made by third parties.
Worse, many of these programs are only available as paid applications rather than free downloads. In other words, Microsoft customers must pay to purchase a Store version of an app that is free elsewhere. In the Store, free and paid versions coexist at times. Paying for a free app is bad enough, but this isn’t the only problem that users may encounter when they make the purchase. Updates may also be a concern, as copycat programs may not be updated as frequently or as quickly as the source applications.
In the updated Microsoft Store Policies, Microsoft notes under 10.8.7:
In cases where you determine the pricing for your product or in-app purchases, all pricing for your digital products or services, including sales or discounts, must:
Comply with all applicable laws, regulations, and regulatory guidelines, including the Federal Trade Commission’s Guides Against Deceptive Pricing. You must not attempt to profit from open-source or other software that is otherwise freely available, nor should your product be priced irrationally high in comparison to the features and functionality it provides.
The new policies are confirmed in the updated section. Open source and free products may no longer be sold on the Microsoft Store if they are generally available for free, and publishers may no longer charge irrationally high prices for their products. Developers of open source and free applications may charge for their products on the Microsoft Store; for example, the developer of Paint.net does so. Many applications will be removed from the Store if Microsoft enforces the policies. Developers could previously report applications to Microsoft, but the new policies give Microsoft direct control over application listings and submissions. |
14,756 | 在 Linux 上玩电子游戏的三种方式 | https://opensource.com/article/21/2/linux-gaming | 2022-06-25T14:33:39 | [
"Linux",
"游戏"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14756-1.html |
>
> 如果你准备放下爆米花,想从各个角度体验游戏的话,那么就在 Linux 下打开游戏吧!
>
>
>

如今,人们有更多喜欢 Linux 的理由。在这个系列里,我将分享 21 个使用 Linux 的理由。今天,我将从游戏开始。
我过去认为“游戏玩家”是一种非常特殊的生物,要由科学家们在数年的研究和测试之后严谨地认定才行。我从来没有把自己归类为游戏玩家,因为我所玩过的游戏要么是桌面游戏(棋盘类游戏和纸笔角色扮演游戏),要么是 NetHack、俄罗斯方块。现在,在移动设备、游戏机、电脑和电视机上都有游戏,我觉得现在的承认有各种形式的游戏玩家们了。如果你想自称为游戏玩家,你就可以是,不需任何资格认定。你不用必须在心里熟记那些“上上下下左右左右BA”的科乐美秘籍(你甚至可以不知道这是什么);你也不用必须买过和玩过 3A 级游戏。如果你时不时地玩游戏,你就完全可以自称为玩家。如果你想成为一名玩家,那么现在使用 Linux 正当其时。
### 欢迎来到游戏世界
剥除光鲜的广告,在其下面,你肯定会发现一个欣欣向荣的游戏世界。在人们相信不是电子表格也不是练习打字一类的软件能挣钱以前,新兴的游戏市场已经开始发展起来了。<ruby> 独立游戏 <rt> indie game </rt></ruby>已经在流行文化上以各种方式打上了自己的烙印(或许你不相信,《我的世界》尽管不是开源的,但一开始就是一款独立游戏),这也证实了,在玩家眼里,可玩性高于产品价值。
独立开发者和开源开发者之间有很多交集。没有什么比带着你的 Linux 笔记本电脑,浏览 [itch.io](http://itch.io) 或你的发行版的软件库,寻找鲜为人知但珍贵的开源游戏宝藏更有意义了。
有各种各样的开源游戏,包括大量的第一视角射击游戏、Nodulus 之类的益智游戏、运输大亨之类的策略经营游戏、Jethook 之类的竞速游戏、Sauerbraten 之类的竞速逃生游戏,以及很多未提到的(多亏了像 Open Jam 这样伟大的活动,每年都有新增的游戏)。

总的来说,探索开源游戏的世界的体验,和购买大型游戏工作室的产品带来的即时满足感有很大的不同。大型游戏工作室生产的游戏提供大量的视听刺激、知名演员、和长达 60 小时以上的游戏时长。而独立和开源游戏不能与之相提并论。但是话又说回来,大型游戏工作室无法提供的是,当你发现一款别人未曾听说过的游戏时的产生的发现感和与个人相关的感受。当你意识到别人都非常想知道你刚玩过的哪个出色游戏时,大型工作室也并不能提供这种紧迫感。(LCTT 校注:此处大概的意思是指大型工作室的作品已被人熟知,没有什么挖掘的新鲜感)
花点时间找出你最喜欢的游戏,然后浏览下你的发行商的软件仓库、Flathub、开源的游戏仓库,看看你能发现什么,如果发现你很喜欢的游戏,就帮忙推广一下吧。
#### Proton 和 WINE
Linux 上的游戏并没有止步于开源,但是从开源开始的。数年前 Valve 软件公司通过发行 Linux 版的 Steam 客户端把 Linux 重新带入游戏市场时,人们希望这可以推动游戏工作室能编写原生的 Linux 游戏。一些工作室这样做了,但 Valve 公司并没有成功的把 Linux 推为主要的平台,即使是 Valve 品牌的游戏电脑。并且大多数游戏工作室又转回仅在 Windows 平台上开发游戏的旧方式。
有趣的是,最终的结果是产生了更多的开源代码。Valve 公司为 Linux 兼容创建了 Proton 工程,一个可以转换 Windows 游戏到 Linux 的兼容层。在 Proton 的内核层面,它使用了WINE(Wine Is Not an Emulator) —— 以开源的方式极好地重新实现了主要的 Windows 库。
游戏市场的成果,如今已经变成了开源世界的宝藏。今天,来自大型工作室的大多数游戏都可以在 Linux 上像原生游戏一样运行。
当然,如果你是必须要在发行日就玩上最新版游戏的这类玩家,你可能会遇到一些令人不愉快的“惊喜”。尽管那不是惊喜,很少有大型游戏在发行时毫无漏洞,一周后才补上补丁。这些游戏在 Proton 和 WINE 上运行时遇到这些错误可能更糟糕,因此 Linux 玩家通过避免尽早上车而避免这些问题。这种妥协可能是值得的。我玩过一些游戏,它们在 Proton 平台运行完美,后来从愤怒的论坛帖子中发现,它在最新版的 Windows 上运行显然充满了致命的错误。总之,似乎来自大型工作室的游戏并不完美,但你可能在 Linux 上遇到相似但不同的问题,正如你在 Windows 上遇到的。
#### Flatpak
Linux 近来历史上最令人激动的发展就是 Flatpak 了,它是本地容器和打包的结合,它和游戏无关(或者它和游戏息息相关),它使得 Linux 应用基本上能被分发到任意的 Linux 发行版上。这也适用于游戏,因为在游戏中使用了相当多的前沿技术,而对发行版维护者来说,要跟上任何特定游戏所需的所有最新版本可能是相当苛刻的。
Flapak 通过为应用程序库抽象出一种通用的 Flatpak 特定的层,而将其从发行版中抽象出来。Flatpak 软件包的发行者知道,如果一个库不在 Flatpak SDK 中,那么它必须要包含在 Flatpak 软件包中,简单而直接。
多亏了 Flatpak,Steam 客户端可以运行在像 Fedora 这样的常用发行版上,也可以运行在 RHEL、Slackware 等从传统角度看并不面向游戏市场的操作系统上。
#### Lutris
如果你并不急于在 Steam 上注册账号,那么可以用我比较偏爱的游戏客户端 Lutris 。表面上看,Lutris 是一个简单的游戏启动器,当你想玩游戏但还没决定玩什么的时候,你可以到这这里找找。有了 Lutris,你可以将系统上的所有游戏添加到你的游戏库,然后从 Lutris 界面启动并立即玩起来。更好的是,Lutris 贡献者(像我一样)会定期发布安装脚本,使你可以轻松安装自己的游戏。这并不是必须的,但它可以是一个很好的捷径,可以绕过一些繁琐的配置。
Lutris 也可以借助运行器或子系统,来运行那些不能从应用菜单直接启动的游戏。比如你想玩开源的《<ruby> 魔兽塔防 <rt> Warcraft Tower Defense </rt></ruby>》这样的游戏机游戏,你必须运行模拟器。如果你已经安装过模拟器的话,Lutris 可以帮你处理这一切。除此以外,如果你有一个 [GOG.com](http://GOG.com) 游戏账号,Lutris 可以访问它,并可以把游戏导入你的游戏库中。
没有比这更容易的管理你的游戏的方式了。
### 去玩游戏吧
Linux 游戏是一种充实且给人力量的体验。我过去避免玩电脑游戏,因为我不觉得我有太多的选择。似乎昂贵的游戏总是在不断发布,并且不可避免的获得好或者不好的极端体验,然后很快又转向下一个。另一方面,开源游戏把我引入了游戏的圈子。我见到过其他玩家和开发者。我见到过艺术家和音乐家、粉丝以及推广者。我玩过各种各样的我从来不知道的游戏。其中一些甚至不够我玩一下午,而其他的却让我长久的着迷于游戏、修改、关卡设计和乐趣。
如果你准备好放下爆米花,从各个角度体验下游戏的话,那就在 Linux 上开始游戏吧。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/2/linux-gaming>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[godgithubf](https://github.com/godgithubf) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In 2021, there are more reasons why people love Linux than ever before. In this series, I'll share 21 different reasons to use Linux. Today, I'll start with gaming.
I used to think a "gamer" was a very specific kind of creature, carefully cataloged and classified by scientists after years of study and testing. I never classified myself as a gamer because most of the games I played were either on a tabletop (board games and pen-and-paper roleplaying games), NetHack, or Tetris. Now that games are available on everything from mobile devices, consoles, computers, and televisions, it feels like it's a good time to acknowledge that "gamers" come in all different shapes and sizes. If you want to call yourself a gamer, you can! There's no qualification exam. You don't have to know the Konami Code by heart (or even what that reference means); you don't have to buy and play "triple-A" games. If you enjoy a game from time to time, you can rightfully call yourself a gamer. And if you want to be a gamer, there's never been a better time to use Linux.
## Welcome to the underground
Peel back the glossy billboard ads, and underneath, you're sure to find a thriving gaming underground. It's a movement that began with the nascent gaming market before anyone believed money could be made off software that wasn't either a spreadsheet or typing tutor. Indie games have carved out a place in pop culture (believe it or not, [Minecraft, while not open source](https://opensource.com/alternatives/minecraft), started out as an indie game) in several ways, proving that in the eyes of players, gameplay comes before production value.
There's a lot of cross-over in the indie and open source developer space. There's nothing quite like kicking back with your Linux laptop and browsing [itch.io](https://itch.io/jam/open-jam-2020) or your distribution's software repository for a little-known but precious gem of an open source game.
There are all kinds of open source games available, including plenty of [first person shooters](https://opensource.com/article/20/5/open-source-fps-games), puzzle games like [Nodulus](https://hyperparticle.itch.io/nodulus), systems management games like [OpenTTD](https://www.openttd.org/), racing games like [Jethook](https://rcorre.itch.io/jethook), tense escape campaigns like [Sauerbraten](http://sauerbraten.org/), and too many more to mention (with more arriving each year, thanks to great initiatives like [Open Jam](https://opensource.com/article/18/9/open-jam-announcement)).
Jethook
Overall, the experience of delving into the world of open source games is different than the immediate satisfaction of buying whatever a major game studio releases next. Games by the big studios provide plenty of visual and sonic stimuli, big-name actors, and upwards of 60 hours of gameplay. Independent and open source games aren't likely to match that, but then again, major studios can't match the sense of discovery and personal connection you get when you find a game that you just know nobody else *has ever heard of*. And they can't hope to match the sense of urgency you get when you realize that everybody in the world really, really needs to hear about the great game you've just played.
Take some time to identify the kinds of games you enjoy the most, and then have a browse through your distribution's software repository, [Flathub](http://flathub.org), and open game jams. See what you can uncover and, if you like the game enough, help to promote it!
## Proton and WINE
Gaming on Linux doesn't stop with open source, but it is enabled by it. When Valve Software famously brought Linux back into the gaming market a few years ago by releasing their Steam client for Linux, the hope was that it would compel game studios to write code native to Linux systems. Some did, but Valve failed to push Linux as the primary platform even on their own Valve-branded gaming computers, and it seems that most studios have reverted to their old ways of Windows-only games.
Interestingly, though, the end result has produced more open source code than probably intended. Valve's solution for Linux compatibility has been to create the [Proton](https://github.com/ValveSoftware/Proton) project, a compatibility layer to translate Windows games to Linux. At its core, Proton uses [WINE (Wine Is Not an Emulator)](http://winehq.org), the too-good-to-be-true reimplementation of major Windows libraries as open source.
The game market's spoils have turned out to be a treasure trove for the open source world, and today, most games from major studios can be run on Linux as if they were native.
Of course, if you're the type of gamer who has to have the latest title on the day of release, you can certainly expect unpleasant surprises. That's not surprising, though, because few major games are released without bugs requiring large patches a week later. Those bugs can be even worse when a game runs on Proton and WINE, so Linux gamers often benefit by refraining from early adoption. The trade-off may be worth it, though. I've played a few games that run perfectly on Proton, only to discover later from angry forum posts that it's apparently riddled with fatal errors when played on the latest version of Windows. In short, it seems that games from major studios aren't perfect, and so you can expect similar-but-different problems when playing them on Linux as you would on Windows.
## Flatpak
One of the most exciting developments of recent Linux history is [Flatpak](https://opensource.com/business/16/8/flatpak), a cross between local containers and packaging. It's got nothing to do with gaming (or doesn't it?), but it enables Linux applications to essentially be distributed universally to any Linux distribution. This applies to gaming because there are often lots of fringe technologies used in games, and it can be pretty demanding on distribution maintainers to keep up with all the latest versions required by any given game.
Flatpak abstracts that away from the distribution by establishing a common Flatpak-specific layer for application libraries. Distributors of flatpaks know that if a library isn't in a Flatpak SDK, then it must be included in the flatpak. It's simple and straightforward.
Thanks to Flatpak, the Steam client runs on something obvious like Fedora and on distributions not traditionally geared toward the gaming market, like [RHEL](https://www.redhat.com/en/enterprise-linux-8) and Slackware!
## Lutris
If you're not eager to sign up on Steam, though, there's my preferred gaming client, [Lutris](http://lutris.net). On the surface, Lutris is a simple game launcher for your system, a place you can go when you know you want to play a game but just can't decide what to launch yet. With Lutris, you can add [all the games you have on your system](https://opensource.com/article/18/10/lutris-open-gaming-platform) to create your own gaming library, and then launch and play them right from the Lutris interface. Better still, Lutris contributors (like me!) regularly publish installer scripts to make it easy for you to install games you own. It's not always necessary, but it can be a nice shortcut to bypass some tedious configuration.
Lutris can also enlist the help of *runners*, or subsystems that run games that wouldn't normally launch straight from your application menu. For instance, if you want to play console games like the open source [Warcraft Tower Defense](https://ndswtd.wordpress.com/download), you must run an emulator, and Lutris can handle that for you (provided you have the emulator installed). Additionally, should you have a GOG.com (Good Old Games) account, Lutris can access it and import games from your library.
There's no easier way to manage your games.
## Play games
Linux gaming is a fulfilling and empowering experience. I used to avoid computer gaming because I didn't feel I had much of a choice. It seemed that there were always expensive games being released, which inevitably got extreme reactions from happy and unhappy gamers alike, and then the focus shifted quickly to the next big thing. On the other hand, open source gaming has introduced me to the *people* of the gaming world. I've met other players and developers, I've met artists and musicians, fans and promoters, and I've played an assortment of games that I never even realized existed. Some of them were barely long enough to distract me for just one afternoon, while others have provided me hours and hours of obsessive gameplay, modding, level design, and fun.
If you're ready to put down the popcorn and experience games from all angles, start gaming on Linux.
## 1 Comment |
14,758 | 神秘的 GeckoLinux 创建者推出了一个新的 Debian 合成发行版 | https://news.itsfoss.com/debian-remix-spiral-linux/ | 2022-06-26T11:02:42 | [
"Debian",
"SpiralLinux"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14758-1.html |
>
> GeckoLinux 创建者推出了一个基于 Debian 的新 Linux 发行版,专注于简单性和可用性。
>
>
>

GeckoLinux 改进了的 openSUSE 体验,它的创建者一直保持匿名。
我不会评论这是好事还是坏事,但现在,开发者又带着另一个基于 Debian 的类似项目回来了。
**SpiralLinux**,这是一个基于 Debian 的发行版,旨在使 Debian 适合最终用户使用。
### SpiralLinux:基于 Debian 构建的发行版

毫不奇怪,大多数用户友好的 Linux 发行版都将 Debian 作为其原始基础。Ubuntu 就是在此基础上进行了大量改进,从而提供了良好的桌面体验,即使对于没有 Linux 经验的用户也是如此。
那么,这个发行版有什么不同呢?
嗯,它的创建者说,这个项目旨在帮助你获得 Debian 的所有核心优势,而无需定制很多东西。
如果你想在桌面上使用 Debian,SpiralLinux 是一种接近原版的体验。你还可以根据需要升级到最新的稳定 Debian 版本(或不稳定/测试版),而不会丢失方便易用的自定义设置。
换句话说,SpiralLinux 使 Debian 适合桌面使用,而最终用户只需付出最小的努力。
为了实现这一点,SpiralLinux 使用了 Debian 官方软件包存储库,并提供了现场安装方式,让你能够定制自己的 Debian 系统。
此外,SpiralLinux 还具有以下功能:
* 开箱即用的 VirtualBox 支持
* 预装了专有的媒体编解码器和非自由软件包存储库
* 预装了专有固件
* 打印机支持
* 通过 GUI(软件中心)支持 Flatpak
* 默认启用 zRAM 交换
* 多种桌面环境(Cinnamon、XFCE、Gnome、Plasma、MATE、Budgie、LXQt)
Debian 始终坚持使用开源和自由软件包,最终用户必须自己搞定编解码器、驱动程序和其他软件包,才能使许多功能正常工作,获得令他们满意的桌面体验。
而 SpiralLinux 似乎可以作为 Debian 的一个有用的替代品,就像 GeckoLinux 之于 openSUSE 一样。
### 下载 SpiralLinux
如果你一直想尝试 Debian,但又不想在初始配置上费尽心思,你可以尝试 SpiralLinux。
你可以前往其托管在 GitHub 上的官网以了解更多信息,链接如下:
>
> **[SpiralLinux](https://spirallinux.github.io/)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/debian-remix-spiral-linux/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

The creator of [GeckoLinux](https://itsfoss.com/geckolinux-review/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) (providing an improved openSUSE experience) remains anonymous.
And, I won’t comment if it is a good or bad thing, but now the developer is back with another similar project based on Debian.
**SpiralLinux**, a Debian-based distribution that aims to make Debian usable for the end-users.
## SpiralLinux: A Distro Built from Debian
It is no surprise that most of the user-friendly Linux distributions have Debian as its original base. Ubuntu has managed to do a lot of improvements on top of it to make it a good desktop experience, even for users without prior Linux experience.
So, how is this different?
Well, the creator says that this project aims to help you use Debian with all its core strengths without customizing a lot of things.
SpiralLinux is a close-to-vanilla experience if you want to use Debian on your desktop. You can also upgrade to the latest stable Debian version (or unstable/testing) as you require without losing the user-friendly customizations.
In other words, SpiralLinux makes Debian fit for desktop usage with minimal efforts to the end-user.
And, to achieve this, SpiralLinux uses official Debian package repositories providing a live installation method to let you setup a customized Debian system.
Additionally, you have the following features in SpiralLinux:
*VirtualBox support out-of-the-box**Preinstalled proprietary media codecs and non-free package repositories**Preinstalled proprietary firmware**Printer support**Flatpak support through a GUI (software center)**zRAM swap enabled by default**Multiple desktop environments (Cinnamon, XFCE, Gnome, Plasma, MATE, Budgie, LXQt)*
Considering Debian always sticks to the open-source and free packages, the end-user has to figure out the codecs, drivers, and other packages to make a lot of things work for a proper desktop experience.
And, it seems like SpiralLinux could live as a useful alternative to Debian just like GeckoLinux is to openSUSE.
## Download SpiralLinux
If you always wanted to try Debian, but did not want to fiddle around a lot for initial configuration, you can try SpiralLinux.
You can head to its official webpage hosted on GitHub to explore more about it.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,759 | GitHub Copilot 现已可供所有人使用,但并非所有人都喜欢它 | https://news.itsfoss.com/github-copilot/ | 2022-06-26T11:52:00 | [
"Copilot"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14759-1.html |
>
> GitHub Copilot 来了,它能帮助程序员,为他们提供人工智能的编码建议,不过,它是否会让事情变得更糟呢?
>
>
>

在 2021 年,我曾花了好几个小时来翻阅 GitHub Copilot 文档,试图弄清楚如何能够加入它的技术预览计划。还好,这一切都得到了回报,我成功加入了预览计划。
而现在,它终于可供所有人使用啦!
如果你还不知道的话,[GitHub Copilot](https://copilot.github.com/) 是一个 AI 助手,可帮助你更快、更高效地编写代码。
我能想到的最类似的东西,就是你手机上的(输入法的)自动完成功能。不过,与自动完成功能不同,GitHub Copilot 编写代码,就相当于是在完成整段的句子。
### Copilot 现已可供大众使用
正如我在前面提到的,Copilot 已经处于技术预览阶段将近一年了。这意味着,GitHub 只允许非常有限数量的开发者免费使用它,以换取同意 GitHub 监控他们的使用情况,从而改进程序的最终版本。
看起来 GitHub 终于满意地向公众发布了它。现在,任何拥有 GitHub 帐户的人都应该能够使用它,尽管需要付出一定的代价(我很快就会在下面提到)。
[公告](https://github.blog/2022-06-21-github-copilot-is-generally-available-to-all-developers/) 中提到:
>
> 直到不久前,人工智能都没有能够帮助改进代码,开发软件的过程几乎完全是手动的。现在,这种情况正在改变。今天,我很高兴地宣布,我们正在向所有个人开发者提供 [GitHub Copilot](http://copilot.github.com)。你的 AI 配对程序员来啦。
>
>
> —— [Thomas Dohmke](https://github.blog/author/ashtom/),GitHub CEO
>
>
>
Copilot 作为免费的编辑器扩展,已经帮助数百万开发者加快了他们的编程速度。然而,它确实是有代价的,无论是直接的还是间接的。
### GitHub Copilot 定价
与几乎所有令人兴奋的新技术一样,Copilot 对某些人来说可能过于昂贵。它将花费你 10 美元/月或 100 美元/年。
如果你是开源项目维护者或经过验证的学生,那么你可以免费使用它。
### GitHub Copilot 不道德吗?
围绕 GitHub Copilot 产品的争议巨大且令人担忧。从技术上讲,这个人工智能是使用大家托管在 GitHub 上的代码来进行训练的。
因此,基本上,GitHub 是通过使用你的代码来提供一个新产品(如果你愿意的话,还可以加点料)。而且,关于 Copilot,可别忘了,自由软件基金会(FSF)也 [建议](https://www.fsf.org/blogs/licensing/fsf-funded-call-for-white-papers-on-philosophical-and-legal-questions-around-copilot) 不要在 GitHub 上托管代码。
我们知道,企业总是喜欢利用事物,但有些人认为这应该不会直接损害托管在 GitHub 上的项目/代码。
**但是,是这样吗?**
简而言之,在 Copilot 发布后,许多开发者都分享说,他们发现 GitHub Copilot 生成了受版权保护的代码:
>
> 我试了下 GitHub Copilot,这是一项付费服务,来看看它是否会使用带有限制性许可证的存储库的代码。我检查了它,看看它是否有我在之前雇主那里编写的代码,该代码有一个许可证,只允许其用于免费游戏,并且需要附加许可证。是的,它确实有。
>
>
>

当然,如果我们查看 GitHub Copilot 的常见问题解答(FAQ),其中提到:
>
> GitHub 不拥有 GitHub Copilot 生成的建议。您在 GitHub Copilot 的帮助下编写的代码属于您自己,由您自己负责。
>
>
>
所以说,你为一项服务付了费,最终却为你的项目增加了不便和更多的工作?
在我看来,就简化开发者的任务而言,这听起来一点儿也不令人兴奋。
*你对此有什么想法?请在下面的评论区中分享一下吧!*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/github-copilot/>
作者:[Jacob Crume](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/%E6%A0%A1%E5%AF%B9%E8%80%85ID)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Back in 2021, I spent hours pouring over the GitHub Copilot docs trying to figure out how I could maximize my chances of getting into the technical preview. Fortunately, this all paid off when I was accepted into the preview.
Finally, it is available for all to use!
For those of you unaware, [GitHub Copilot](https://copilot.github.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is an AI assistant to help you write code faster and more efficiently.
The best comparison I can come up with is that it’s like autocomplete feature on your phone. Unlike the autocomplete feature, GitHub Copilot writes the code equivalent to complete sentences.
## Copilot is Now Available For The Masses
As I alluded to in the introduction, Copilot has been in a technical preview phase for almost a year now. This means that a very limited number of developers were allowed to use it for free, in exchange for them allowing GitHub to monitor their usage to improve the program for its final release.
It appears that GitHub is finally satisfied to release it to the public. Now, anyone with a GitHub account should be able to use it, albeit at a cost (which we will get to soon!).
The [announcement](https://github.blog/2022-06-21-github-copilot-is-generally-available-to-all-developers/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) mentioned:
Until now, AI has stopped short of improving code, leaving the process of developing software almost completely manual. That’s changing now. Today, I am thrilled to announce that we are making
[GitHub Copilot]generally available to individual developers. Your AI pair programmer is here.[Thomas Dohmke], GitHub CEO
Available as a free editor extension, Copilot has already helped millions of developers speed up their programming. However, it does come at a cost, both direct and indirect.
## GitHub Copilot Pricing
Copilot may be prohibitively expensive for some as with almost all exciting new technologies. It will cost you $10/month or $100/year.
If you are an open-source project maintainer or a verified student, you can get free access to it.
## Is GitHub Copilot Unethical?
The controversy surrounding the GitHub Copilot product is huge and concerning. Technically, the A.I have been trained using the available code on the GitHub platform.
So, basically, GitHub is offering a new product by using your code (take it with a pinch of salt, if you’d like). Not to forget, the Free Software Foundation (FSF) also [advised](https://www.fsf.org/blogs/licensing/fsf-funded-call-for-white-papers-on-philosophical-and-legal-questions-around-copilot?ref=news.itsfoss.com) against hosting code on GitHub keeping Copilot in mind.
While we know that businesses love to exploit things, some believed that it should not directly hurt the projects/code hosted at GitHub.
**But, is that the case?**
Briefly, after the launch, many developers shared how they found copyrighted code being generated by GitHub Copilot:
Of course, if we look at GitHub Copilot’s FAQ which mentions:
GitHub does not own the suggestions GitHub Copilot generates. The code you write with GitHub Copilot’s help belongs to you, and you are responsible for it.
So, ultimately, you pay for a service to add inconvenience and more work to your project?
Nothing about it sounds exciting in terms of making a developer’s task easy, in my opinion.
*What are your thoughts on it? Share what you think in the comments section below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,760 | 如何在 Ubuntu 中安装具体指定的软件包版本 | https://itsfoss.com/apt-install-specific-version-2/ | 2022-06-26T14:53:00 | [
"版本",
"软件包"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14760-1.html | 
在 Ubuntu 中想安装一个软件包的一个特别指定的版本?你可以通过下面的方式来轻松地完成:
```
sudo apt install package_name=package_version
```
你如何知道某个软件包有哪些可用的版本?可以使用这个命令:
```
apt list --all-versions package_name
```
在下面的屏幕截屏中,你可以看到,我有两个可用的 VLC 版本,我使用命令来安装较旧的版本:

听起来像一个简单的任务,对吧?但是事情并非看起来那么简单。这里有一些不确定是否会出现,但是可能会涉及的东西。
这篇教程将涵盖使用 `apt` 或 `apt-get` 命令来安装一个具体指定的程序的版本的所有的重要的方面。
### 安装一个具体指定版本的程序需要知道的事
在基于 Ubuntu 和 Debian 发行版中,你需要知道一些关于 APT 和存储库是如何工作的知识。
#### 同一个软件包源没有较旧的版本
Ubuntu 在其存储库中不保留较旧版本的软件包。在特殊的情况下,你可以暂时性地看到多个版本。例如,你运行 APT 更新(但不升级)时,可能会有一个可用的新版本。在 APT 缓存中,你可以看到同一个软件包的两个版本。但是,一旦软件包被升级到了新的版本,较旧版本的软件包将从 **APT 缓存** 和存储库中移除。
#### 使用多个软件包源来使用不同的版本
为获取同一个的软件包的多个版本,你必须得添加多个软件包源。例如,VLC 是版本 3.x 系列。添加 [VLC 每日构建 PPA](https://launchpad.net/~videolan/+archive/ubuntu/master-daily) 将会提供(不稳定的)版本 4.x 系列。
同样,**你可以下载不同版本的 DEB 文件,并安装它**。
#### 较高版本编号的版本通常有优先权
如果你有来自多个软件包源的相同名称的软件,默认情况下,Ubuntu 将安装可用的最高版本编号的版本。
在前面的示例中,如果我安装 VLC ,那么它将会安装 4.x 系列的版本,而不是 3.x 系列的版本。
#### 较旧版本将升级到可用的较新版本
这是另外一个可能存在的问题。即使你安装较旧版本的软件包,它也会升级到较新的版本(如果存在可用的较新版本)。你必须 [保留该软件包来防止其升级](https://itsfoss.com/prevent-package-update-ubuntu/) 。
#### 依赖关系也需要安装
如果软件包有依赖关系,你也需要安装必要的依赖关系软件包。
现在,你已经知道一些可能存在的问题,让我们看看如何解决它们。
### 安装一个软件包的具体指定版本
在这篇教程中,我将以 VLC 为例。在 Ubuntu 的存储库中可获得 VLC 版本。我添加了每日构建 PPA ,它将向我提供 VLC 的 4.0 版本的候选版本。
如你所见,在现在的系统中,我有两个可用的 VLC 版本:

```
~$ apt list -a vlc
Listing... Done
vlc/jammy 4.0.0~rc1~~git20220516+r92284+296~ubuntu22.04.1 amd64
vlc/jammy 3.0.16-1build7 amd64
vlc/jammy 3.0.16-1build7 i386
```
因为较高版本编号版本有优先权,使用 `apt install vlc` 命令将会导致安装 VLC 的 4.0 版本。但是,因为这篇教程的缘由,我想安装较旧的版本 3.0.16 。
```
sudo apt install vlc=3.0.16-1build7
```
但是,这里会有这样的事。VLC 软件包有一些依赖关系,并且这些依赖关系也需要具体指定的版本。因此,在 Ubuntu 为其尝试安装最新的版本时,你将会遇到经典的 <ruby> <a href="https://itsfoss.com/held-broken-packages-error/"> 你已保留残缺软件包 </a> <rt> you have held broken packages </rt></ruby> 错误。

为修复这个错误,你需要为其提供它所投诉的所有依赖关系的软件包的具体指定版本。因此,该命令会变成这样:
```
sudo apt install vlc=3.0.16-1build7 \
vlc-bin=3.0.16-1build7 \
vlc-plugin-base=3.0.16-1build7 \
vlc-plugin-qt=3.0.16-1build7 \
vlc-plugin-video-output=3.0.16-1build7 \
vlc-l10n=3.0.16-1build7 \
vlc-plugin-access-extra=3.0.16-1build7 \
vlc-plugin-notify=3.0.16-1build7 \
vlc-plugin-samba=3.0.16-1build7 \
vlc-plugin-skins2=3.0.16-1build7 \
vlc-plugin-video-splitter=3.0.16-1build7 \
vlc-plugin-visualization=3.0.16-1build7
```
说明一下,每行结尾处的 `\` 只是用来将多行命令来写入同一个命令的一种方式。
**它有作用吗?在很多情况下,它是有作用的。** 但是,我选择了一个复杂的 VLC 示例,它有很多依赖关系。甚至这些所涉及的依赖关系也依赖于其它的软件包。所以,它就变得令人难以处理。
一种替代的方法是在安装时指定软件包源。
#### 替代方式,指定存储库
你已经添加多个软件包源,因此,你应该对这些软件包的来源有一些了解。
使用下面的命令来搜索存储库:
```
apt-cache policy | less
```
注意存储库名称后面的行:
```
500 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security/multiverse i386 Packages
release v=22.04,o=Ubuntu,a=jammy-security,n=jammy,l=Ubuntu,c=multiverse,b=i386
origin security.ubuntu.com
```
你可以具体指定 `o`、`l`、`a` 等参数。
在我原来的示例中,我想安装来自 Ubuntu 存储库的 VLC(获取版本 3.16),而不是安装来 PPA 的版本(它将向我提供版本 4)。
因此,下面的命令将安装 VLC 版本 3.16 及其所有的依赖关系:
```
sudo apt install -t "o=ubuntu" vlc
```

看起来令人满意?但是,当你必须更新系统时,问题就来了。它接下来会控诉找不到指定的软件包版本。
**还能做什么?**
为安装较旧的软件包版本,从你的系统中移除较新版本的软件包源(如果可能的话)。它将有助于逃脱这些依赖关系地狱。
如果不能这么做,检查你是否可以从其它一些软件包的打包格式来获取,像 Snap、Flatpak、AppImage 等等。事实上,Snap 和 Flatpak 也允许你从可用的版本中选择和安装。因为这些应用程序是沙盒模式的,所以它很容易管理不同版本的依赖关系。
#### 保留软件包,防止升级
如果你完成安装一个指定的程序版本,你可能想避免意外地升级到较新的版本。实现这一点并不太复杂。
```
sudo apt-mark hold package_name
```
你可以免除保留软件包,以便它能稍后升级:
```
sudo apt-mark unhold package_name
```
注意,软件包的依赖关系不会自动地保留。它们需要单独地指明。
### 结论
如你所见,安装选定软件包版本有一定之规。只有当软件包有依赖关系时,那么事情就会变得复杂,然后,你就会进入依赖关系地狱。
我希望你在这篇教程中学到一些新的东西。如果你有问题或建议来改善它,请在评论区告诉我。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/apt-install-specific-version-2/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
14,761 | 用这些开源工具在 Linux 上编辑 PDF 文件 | https://opensource.com/article/22/6/open-source-pdf-editors-linux | 2022-06-26T15:27:31 | [
"PDF"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14761-1.html | 
>
> Adobe Acrobat 的开源替代品具有创建、编辑和注释 PDF 的所有必要功能。
>
>
>
开源的 PDF 阅读和编辑工具通常比 “PDF 编辑器” 搜索结果第一页中的应用更安全和可靠。在那里,你很可能看到带有隐藏的限制和关税的专有应用,缺乏关于数据保护政策和托管的足够信息。你可以有更好的。
这里有五个应用,可以安装在你的 Linux 系统上(和其他系统)或托管在服务器上。每一个都是自由而开源的,具有创建、编辑和注释 PDF 文件的所有必要功能。
### LibreOffice
使用 [LibreOffice](https://opensource.com/article/21/9/libreoffice-tips) 套件,你对应用的选择取决于最初的任务。虽然文字处理器 LibreOffice Writer,可以让你创建 PDF 文件,并从 ODF 和其他文本格式导出,但 Draw 更适合于处理现有的 PDF 文件。
Draw 是用来创建和编辑图形文件的,如小册子、杂志和海报。因此,其工具集主要用于视觉对象和布局上。然而,对于 PDF 编辑,当文件具有可编辑属性时,LibreOffice Draw 提供了用于修改和添加 PDF 内容的工具。如果没有的话,你仍然可以在现有的内容层上添加新的文本字段,并对文件进行注释或完成。
Draw 和 Writer 都被捆绑在 LibreOffice 桌面套件中,可在 Linux 系统、macOS 和 Windows 上安装。
### ONLYOFFICE Docs
ONLYOFFICE 一直在改进 PDF 的处理,并在 [ONLYOFFICE Docs](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/onlyoffice-docs) 的 7.1 版本中引入了一个全新的 PDF 和电子书的阅读器。
该文档编辑器允许从头开始创建 PDF 文件,使用 DOCX 作为文件的基础,然后可以转换为 PDF 或 PDF/A。通过内置的表单创建功能,ONLYOFFICE Docs 还可以建立可填充的文档模板,并将其导出为可编辑的 PDF,并为不同类型的内容设置可填充的字段:文本、图像、日期等。
除了可以识别 PDF 内的文本进行复制和提取外,ONLYOFFICE Docs 还可以将 PDF 转换为 DOCX,这样你就可以继续使用完全可编辑的文本格式的文件。ONLYOFFICE 还可以让你用密码保护文件,添加水印,并使用桌面版中的数字签名。
ONLYOFFICE Docs 可以作为一个网络套件(内部或云端)集成到文档管理系统(DMS)或作为一个独立的桌面应用程序使用。你可以将后者作为 DEB 或 RPM 文件、AppImage、Flatpack 和其他几种格式在 Linux 中安装。
### PDF Arranger
[PDF Arranger](https://flathub.org/apps/details/com.github.jeromerobert.pdfarranger) 是 PikePDF 库的一个前端应用。它不像 LibreOffice 和 ONLYOFFICE 那样用于对 PDF 的内容进行编辑,但它对于重新排序页面、将 PDF 分割成更小的文件、将几个 PDF 合并成一个、旋转或裁剪页面等都很好。它的界面是直观的,易于使用。
PDF Arranger 可用于 Linux 和 Windows。
### Okular
[Okular](https://opensource.com/article/22/4/linux-kde-eco-certification-okular) 是一个由 KDE 社区开发的免费开源文档查看器。该应用的功能非常成熟,可以查看 PDF、电子书、图片和漫画。
Okular 完全或部分支持大多数流行的 PDF 功能和使用场景,如添加注释和内联笔记或插入文本框、形状和印章。你还可以为文档添加数字加密签名,这样你的读者就可以确定文档的来源。
除了在 PDF 中添加文本和图像外,还可以从文档中检索到它们,以复制和粘贴到其他地方。Okular 中的区域选择工具可以识别所选区域内的组件,所以你可以从 PDF 中独立提取它们。
你可以使用你的发行版包管理器或以 Flatpak 的形式安装 Okular。
### Xournal++
[Xournal++](http://xournal.sourceforge.net/) 是一款带有 PDF 文件注释工具的手写日记软件。
它是一款具有强化手写功能的记事软件,对于处理基于文本的内容和专业布局来说,它可能不是最佳选择。然而,它渲染图形的能力以及对书写和绘图的手写笔输入的支持使它作为一个小众生产力工具脱颖而出。
图层管理工具、可定制的笔尖设置以及对手写笔映射的支持,使 PDF 注释和草图绘制变得更加舒适。Xournal++ 还有一个文本工具,用于添加文本框,并能插入图像。
Xournal++ 可在 Linux 系统(Ubuntu、Debian、Arch、SUSE)、MacOS 和 Windows(10及以上)中安装。
### 总结
如果你正在寻找一个免费和安全的专有 PDF 浏览和编辑软件的替代品,不难找到一个开源的选择,无论是桌面还是在线使用。只要记住,目前可用的解决方案在不同的使用情况下有各自的优势,没有一个工具在所有可能的任务中都同样出色。
这五个方案因其功能或对小众 PDF 任务的有用性而脱颖而出。对于企业使用和协作,我建议使用 ONLYOFFICE 或 LibreOffice Draw。PDF Arranger 是一个简单的、轻量级的工具,当你不需要改变文本时,可以用它来处理页面。Okular 为多种文件类型提供了很好的查看功能,如果你想在 PDF 中画草图和做笔记,Xournal++ 是最佳选择。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/6/open-source-pdf-editors-linux>
作者:[Michael Korotaev](https://opensource.com/users/michaelk) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Open source reading and editing tools for PDFs are often more secure and reliable alternatives to the applications residing in the first pages of "PDF editor" search results. There, you're likely to see proprietary applications with hidden limitations and tariffs, lacking sufficient information about data protection policies and hosting. You can have better.
Here are five applications that can be installed on your Linux system (and others) or hosted on a server. Each is free and open source, with all the necessary features for creating, editing, and annotating PDF files.
## LibreOffice
With the [LibreOffice](https://opensource.com/article/21/9/libreoffice-tips) suite, your choice of application depends on the initial task. While LibreOffice Writer, a word processor, lets you create PDF files with export from text formats like ODF and others, Draw is better for working with existing PDF files.
Draw is meant for creating and editing graphic documents, such as brochures, magazines, and posters. The toolset is therefore mainly focused on visual objects and layouts. For PDF editing, however, LibreOffice Draw offers tools for modifying and adding content in PDFs when the file has editing attributes. You can still add new text fields on the existing content layers and annotate or finish the documents if it doesn't.
Draw and Writer are both bundled in a LibreOffice desktop suite available for installation on Linux systems, macOS, and Windows.
## ONLYOFFICE Docs
ONLYOFFICE has been improving work with PDFs for a while and introduced a brand new reader for PDFs and eBooks in version 7.1 of [ONLYOFFICE Docs](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/onlyoffice-docs).
The document editor allows creating PDF files from scratch using DOCX as a base for files that can then be converted to PDF or PDF/A. With built-in form-creation functionality, ONLYOFFICE Docs also makes it possible to build fillable document templates and export them as editable PDFs with fillable fields for different types of content: text, images, dates, and more.
In addition to recognizing text within PDFs to copy and extract it, ONLYOFFICE Docs can convert PDFs to DOCX, which allows you to continue using the documents in fully editable text formats. ONLYOFFICE also lets you secure the files with passwords, add watermarks, and use digital signatures available in the desktop version.
ONLYOFFICE Docs can be used as a web suite (on-premises or in the cloud) integrated into a document management system (DMS) or as a standalone desktop application. You can install the latter as a DEB or RPM file, AppImage, Flatpack, and several other formats for Linux.
## PDF Arranger
[PDF Arranger](https://flathub.org/apps/details/com.github.jeromerobert.pdfarranger) is a front-end application for the PikePDF library. It doesn't edit the content of a PDF the way LibreOffice and ONLYOFFICE do, but it's great for re-ordering pages, splitting a PDF into smaller documents, merging several PDFs into one, rotating or cropping pages, and so on. Its interface is intuitive and easy to use.
PDF Arranger is available for Linux and Windows.
## Okular
[Okular](https://opensource.com/article/22/4/linux-kde-eco-certification-okular) is a free open source viewer for documents developed by the KDE community. The app features very mature functionality and allows viewing PDFs, eBooks, images, and comics.
Okular has full or partial support for most popular PDF features and use cases, such as adding annotations and inline notes or inserting text boxes, shapes, and stamps. You can also add a digitally encrypted signature to your document so your readers can be sure of the document's source.
In addition to adding texts and images in PDFs, it's also possible to retrieve them from the document to copy and paste somewhere else. The **Area Selection** tool in Okular can identify the components within a selected area so you can extract them from the PDF independently of one another.
You can install Okular using your distribution's package manager or as a Flatpak.
## Xournal++
[Xournal++](http://xournal.sourceforge.net/) is a handwriting journal software with annotation tools for PDF files.
Created to be notetaking software with enhanced handwriting features, it may not be the best option for working with text-based content and professional layouts. However, its ability to render graphics and support for stylus input in writing and drawing make it stand out as a niche productivity tool.
PDF annotation and sketching are made comfortable with layer management tools, customizable pen point settings, and support for stylus mappings. Xournal++ also has a text tool for adding text boxes and the ability to insert images.
Xournal++ has installation options for Linux systems (Ubuntu, Debian, Arch, SUSE), macOS, and Windows (10 and above).
## Summary
If you're looking for a free and safe alternative to proprietary PDF viewing and editing software, it is not hard to find an open source option, whether for desktop or online use. Just keep in mind that the currently available solutions have their own advantages for different use cases, and there's no single tool that is equally great at all possible tasks.
These five solutions stand out for their functionality or usefulness for niche PDF tasks. For enterprise use and collaboration, I suggest ONLYOFFICE or LibreOffice Draw. PDF Arranger is a simple, lightweight tool for working with pages when you don't need to alter text. Okular offers great viewer features for multiple file types, and Xournal++ is the best choice if you want to sketch and take notes in your PDFs.
## 5 Comments |
14,763 | Linus Torvalds 暗示很快就可以在内核中看到对 Rust 的支持 | https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-rust/ | 2022-06-27T10:21:00 | [
"内核",
"Rust"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14763-1.html |
>
> 正如 Linus Torvalds 所暗示,Linux Kernel 5.20 发布时可能会提供对 Rust 的支持。你怎么看?
>
>
>

市面上已经有许多用 Rust 重写的开源项目。因此,如今 Rust 被认为是 Linux 内核的第二语言,也就不足为奇了。
几天前,在 [Linux 基金会开源峰会](https://events.linuxfoundation.org/open-source-summit-north-america/) 上,Linus Torvals 提到他们预计将在下一个内核版本(即 Linux 内核 5.20)中对 Rust 进行试验。
或许你不知道,正如 [Phoronix](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Rust-Linux-v7-Plus-New-Uutils) 率先报道的那样,Linux 已经有了 Rust 内核补丁,包含了少量的示例驱动程序,以及基本的基础设施的启用代码。
因此,Linus Torvalds 对可能合并 Rust 支持的暗示,也不足为奇。但是,这无疑是令人兴奋的!
### 用于 Linux 内核的 Rust
这么做的最终目标是让 Linux 内核变得更好,但它现在仍然处于试运行阶段。
凭借其各种优势,Rust 正日益成为一种流行的编程语言。还记得吗,[System76 也在开发一个用 Rust 编写的新桌面环境](https://news.itsfoss.com/system76-rust-cosmic-desktop/)。
然而,并不是所有参与维护 Linux 内核的人都熟悉这种编程语言。
那么,这会是一个问题吗?
Linus Torvalds 并不认为这是一个大问题,因为内核中也有其他语言。他还提到希望看到 Rust 成为新的一份子。
[The Register](https://www.theregister.com/2022/06/23/linus_torvalds_rust_linux_kernel/) 报道称,Linus Torvalds 表示会信任维护者,除非他们犯了错误。
### Linux 5.20:何时发布?
Linux 内核 5.19 版本将于 7 月底左右发布。因此,5.20 版本的合并窗口应该会在其稳定版发布后开启(假设没有意外延迟的话)。
除了 Rust 以外,Linux 内核 5.20 应该也是对包括 RDNA3 在内的下一代硬件支持的重要更新,它同时提供了更多功能。
*你如何看待 Rust 将在不久的将来进入 Linux 呢?你感到兴奋吗?欢迎在下方评论区告诉我们~*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-rust/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

There are various open-source projects rewritten in Rust. Hence, it is not surprising that is being considered as the second language for Linux Kernel for a while now.
A few days ago at [The Linux Foundation’s Open-Source Summit](https://events.linuxfoundation.org/open-source-summit-north-america/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), Linus Torvals mentioned that we should expect the trials for Rust in the next kernel release i.e Linux Kernel 5.20.
In case you did not know, there have been Rust Linux kernel patches already with few sample drivers and the enablement code for the basic infrastructure, as originally reported by [Phoronix](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Rust-Linux-v7-Plus-New-Uutils&ref=news.itsfoss.com).
So, Linus Torvalds hinting at a possible merge for the Rust infrastructure should not be a surprise. But, it is certainly exciting!
## Rust for Linux Kernel
While the ultimate goal is to make the Linux Kernel better, it will be considered a trial run for now.
Rust is increasingly becoming a popular programming language for all its benefits. Not to forget, [System76 is also working on a new desktop environment](https://news.itsfoss.com/system76-rust-cosmic-desktop/) written in Rust.
However, not everyone involved in maintaining the Linux Kernel would be familiar with the programming language.
So, would that be a problem?
Linus Torvalds does not see it as a big issue considering there have been other languages in the kernel as well. He also mentioned that he hopes to see Rust work out as something new.
Overall, he insists that he trusts the maintainers, unless they make a mistake, as reported by [The Register](https://www.theregister.com/2022/06/23/linus_torvalds_rust_linux_kernel/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Linux 5.20: When?
The Linux Kernel 5.19 release is due around the end of July. So, the merge window for 5.20 should open following its stable release (given there’s no unexpected delays).
Not just for Rust, but Linux Kernel 5.20 should be an important update for next-gen hardware support including RDNA3, and more features.
*What do you think about Rust coming to Linux in the near future? Exicited for it? *
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,764 | 7-Zip 22.00 最终版现已推出 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/the-final-version-of-7-zip-22-00-is-now-available/ | 2022-06-27T11:03:00 | [
"7-Zip"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14764-1.html | 
7-Zip 是用于 Windows、Mac 和 Linux 的知名开源文件归档器。它的最新版本 22.00 现已推出。它是 2022 年的第一个稳定版本。上一个版本是 21.07,于 2021 年 12 月发布。7-Zip 的用户可以从官方网站获取该应用的最新版本,下载适用于 Windows 64 位、32 位和 ARM 版本。该应用仍然与过时的 Windows 版本兼容,例如 XP 和 Vista。它还支持所有官方支持的 Windows 版本,包括服务器版本。适用于 Linux 的 7-Zip 22.00 已经可以下载,但 Mac OS 版本还不可用。
7-Zip 22.00 包含一些增强了应用功能的新特性。这个归档器现在支持提取<ruby> 苹果文件系统 <rt> Apple File System </rt></ruby>(APFS)镜像。几年前,苹果公司在 Mac OS 10.13 和 iOS 中引入了苹果文件系统。该文件系统在设计时就考虑到了闪存(Flash)和固态硬盘(SSD)存储。
7-Zip 22.00 包括了对其 TAR 存档支持的多项增强。使用选项 `-ttar -mm=pax` 或 `-ttar -mm=posix`,7-Zip 现在可以创建符合 POSIX 标准的 tar 格式的 TAR 档案。此外,使用选项 `ttar -mm=pax -mtp=3 -mtc -mta`,7-Zip 可以在 tar/pax 存档中存储高精度的文件时间戳。
最后,Linux 用户可以在 TAR 归档文件中使用以下两个新选项:
* `snoi`:将所有者/组 ID 保存在存档中,或将所有者/组 ID 从存档复制到提取的文件中。
* `snon`:在存档中保留所有者/组的名称。
适用于 Windows 的 7-Zip 22.00 添加了对 `-snz` 选项的支持,该选项用于传播区识别符(LCTT 译注:区标识符是微软在 2013 年为 IE 设计的安全功能,它会标记那些用户自网络上所下载的文件,并在用户准备打开时跳出警告)。
要提取文件,请使用标识符流。出于安全目的,Windows 使用了该流,它可用于确定文件是在本地创建的还是从互联网下载的。
在“<ruby> 添加到存档 <rt> add to archive </rt></ruby>”配置对话框中,7-Zip 22.00 包含一个新的选项窗口。它包括用于更改时间戳精度、更改其他与时间相关的配置选项,以及防止更改源文件的最后访问时间等选项。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/the-final-version-of-7-zip-22-00-is-now-available/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 7-Zip is a well-known open source file archiver for Windows, Mac, and Linux. 7-Zip 22.00 is now available; it is the first stable release of 2022. The most recent release was 7-Zip 21.07, which was released in December 2021. Users of 7-Zip can obtain the most recent version of the application from the official website. Downloads are available for Windows 64-bit, 32-bit, and ARM versions. The programme is still compatible with out-of-date versions of Windows, such as XP and Vista. All officially supported Windows versions, including server versions, are also supported. 7-Zip 22.00 for Linux is already available for download, but the Mac OS version is not.
7-Zip 22.00 includes several new features that enhance the application’s functionality. The archiver now supports the extraction of Apple File System APFS images. Several years ago, Apple introduced the Apple File System in Mac OS 10.13 and iOS. The file system has been designed with flash and solid state drive storage in mind.
7-Zip 22.00 includes several enhancements to its TAR archive support. Using the switches -ttar -mm=pax or -ttar -mm=posix, 7-Zip can now create TAR archives in POSIX tar format. Additionally, using the switches ttar -mm=pax -mtp=3 -mtc -mta, 7-Zip can store file timestamps with high precision in tar/pax archives.
- snoi: save owner/group ids in the archive or copy owner/group ids from the archive to the extracted files.
- snon: keep owner/group names in the archive
7-Zip 22.00 for Windows adds support for the -snz switch, which propagates the Zone.
To extract files, use the identifier stream. Windows uses the stream for security purposes; it can be used to determine whether a file was created locally or downloaded from the Internet.
7-Zip 22.00 includes several new features that enhance the application’s functionality. The archiver now supports the extraction of Apple File System APFS images. Several years ago, Apple introduced the Apple File System in Mac OS 10.13 and iOS. The file system has been designed with flash and solid state drive storage in mind.
7-Zip 22.00 includes several enhancements to its TAR archive support. Using the switches -ttar -mm=pax or -ttar -mm=posix, 7-Zip can now create TAR archives in POSIX tar format. Additionally, using the switches ttar -mm=pax -mtp=3 -mtc -mta, 7-Zip can store file timestamps with high precision in tar/pax archives.
Finally, Linux users can use the following two new switches with TAR archives:
- snoi: save owner/group ids in the archive or copy owner/group ids from the archive to the extracted files.
- snon: keep owner/group names in the archive
7-Zip 22.00 for Windows adds support for the -snz switch, which propagates the Zone.
To extract files, use the identifier stream. Windows uses the stream for security purposes; it can be used to determine whether a file was created locally or downloaded from the Internet.
In the “add to archive” configuration dialogue, 7-Zip 22.00 includes a new options window. It includes options for changing the timestamp precision, changing other time-related configuration options, and preventing the source files’ last access time from changing. |
14,765 | 使用 LibreOffice 键盘快捷键的小技巧 | https://opensource.com/article/22/6/libreoffice-keyboard-shortcuts | 2022-06-27T14:48:13 | [
"LibreOffice",
"快捷键"
] | /article-14765-1.html |
>
> 键盘快捷键让我专注于我要传递的内容,而不是它的外观。
>
>
>

从我记事起,我就一直在使用文字处理软件。当文字处理器从直接格式化转向利用样式来改变文本在页面上的显示方式时,这对我的写作有很大的推动作用。
LibreOffice 提供了多种样式,你可以使用它们来创建各种内容。 LibreOffice 将段落样式应用于文本块,例如正文、列表和代码示例。字符样式类似,只是这些样式适用于段落内的内联词或其他短文本。使用“<ruby> 视图 <rt> View </rt></ruby> -> <ruby> 样式 <rt> Styles </rt></ruby>”菜单,或使用 `F11` 键盘快捷键,调出样式选择器。

使用样式可以更轻松地编写更长的文档。看看这个例子:作为咨询实践的一部分,我写了很多工作簿和培训材料。一个工作簿可能有 40 或 60 页长,具体取决于主题,并且可以包含各种内容,例如正文、表格和列表。我的一些技术培训材料可能还包括源代码示例。
我有一个提供给客户的标准培训集,但我也做定制的培训计划。在处理自定义程序时,我可能会先从另一个工作簿导入文本,然后从那里开始工作。根据客户的不同,我可能还会调整字体和其他样式元素以匹配客户的样式偏好。对于其他材料,我可能需要添加源代码示例。
要使用直接格式输入示例源代码,我需要设置字体并调整工作簿中每个代码块的边距。如果我后来决定我的工作簿应该对正文文本或源代码示例使用不同的字体,我需要返回并更改所有内容。对于包含多个代码示例的工作簿,这可能需要几个小时来查找每个源代码示例并调整字体和边距以匹配新的首选格式。
但是,通过使用样式,我可以更新定义一次,为正文样式使用不同的字体,并且 LibreOffice Writer 会在所有使用正文样式的地方更新我的文档。同样,我可以调整预格式化文本样式的字体和边距,LibreOffice Writer 会将这种新样式应用到每个具有预格式化文本样式的源代码示例中。这对于其他文本块也是如此,包括标题、源代码、列表以及页眉和页脚。
我最近有了一个好主意,更新 LibreOffice 键盘快捷键以简化我的写作过程。我重新定义了 `Ctrl + B` 设置加粗强调字符样式,`Ctrl + I` 设置强调字符样式,`Ctrl + 空格` 设置取消字符样式。这使我的写作变得更加容易,因为我不必暂停写作,这样我就可以高亮显示一些文本并选择一种新的风格。相反,我可以使用新的 `Ctrl + I` 键盘快捷键来设置字符样式,它本质上是斜体文本。之后我输入的任何内容都使用强调样式,直到我按 `Ctrl + 空格` 将字符样式重置为默认的无字符样式。

如果你想自己设置的,请使用“<ruby> 工具 <rt> Tools </rt></ruby> -> <ruby> 自定义 <rt> Customize </rt></ruby>”, 然后单击“<ruby> 键盘 <rt> Keyboard </rt></ruby>”选项卡以修改键盘快捷键。

LibreOffice 通过样式使技术写作变得更加容易。通过利用键盘快捷键,我简化了我的写作方式,让我专注于我要交付的内容,而不是它的外观。稍后我可能会更改格式,但样式保持不变。
*图片来源:(Jim Hall,CC BY-SA 40)*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/6/libreoffice-keyboard-shortcuts>
作者:[Jim Hall](https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,767 | 我爱用 Qt Creator IDE 的九个原因 | https://opensource.com/article/21/6/qtcreator | 2022-06-27T19:20:29 | [
"Qt Creator",
"Qt"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14767-1.html |
>
> Qt Creator 就是丰富的 Qt 库和程序员之间的粘合剂。
>
>
>

Qt Creator 是 Qt 框架的默认集成开发环境(IDE),同时也是丰富的 Qt 库和用户之前的粘合剂。除了如智能代码补全、调试、项目管理等基础功能外,Qt Creator 还提供了很多让软件开发变得更简单的特性。
在这篇文章中,我会重点介绍一些我最喜欢的 [Qt Creator](https://www.qt.io/product/development-tools) 特性。
### 深色模式
当我使用一个新的应用时,我的第一个问题是:*它有深色模式吗?* Qt Creator 的回答是:*你更喜欢哪一种深色模式呢?*
你可以在“<ruby> 选项 <rt> Options </rt></ruby>”菜单中激活深色模式。在顶部的菜单栏中,点击“<ruby> 工具 <rt> Tools </rt></ruby>”,选择“<ruby> 选项 <rt> Options </rt></ruby>”,然后转到“<ruby> 环境 <rt> Environment </rt></ruby>”部分。下面是你能选择的常用外观:

### 定制外观
像每一个 Qt 应用一样,借助样式表,Qt Creator 的外观是高度可定制化的。下面,你可以按照我的做法给 Qt Creator一个想要的外观。
将下面这些内容写入 `mycustomstylesheet.css` 文件中:
```
QMenuBar { background-color: olive }
QMenuBar::item { background-color: olive }
QMenu { background-color : beige; color : black }
QLabel { color: green }
```
然后使用命令行开启 Qt Creator,将样式表作为参数传入:
```
qtcreator -stylesheet=mycustomstylesheet.css
```
IDE 现在看上去应该会变成这样:

在这份 [文档](https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/stylesheet-reference.html) 中可以查阅更多的样式表。
### 命令行参数
Qt Creator 可接受很多命令行选项。例如,如果想在启动时自动加载当前项目,那么你可以将它的路径传入:
```
qtcreator ~/MyProject/MyQtProject.pro
```
你甚至可以将默认应该打开的文件和行数作为参数传递。下面这个命令打开 `main.cpp` 20 行处:
```
qtcreator ~/MyProject/main.cpp:20
```
在这份 [文档](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-cli.html) 中可以查阅更多 Qt 特有的命令行选项。
Qt Creator 和一般的 Qt 应用无二,所以,除了自己的命令行参数以外,它也接收 [QApplication](https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qapplication.html#QApplication) 和 [QGuiApplication](https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qguiapplication.html#supported-command-line-options) 的一般参数。
### 交叉编译
Qt Creator 允许你定义一些被称为“<ruby> 配套 <rt> Kit </rt></ruby>”的工具链。 “配套” 定义了构建和运行应用所需要的二进制库和 SDK。

这使得你通过两次点击,就在完全不同的工具链之间切换。

在这份 [手册](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-targets.html) 中可以查阅更多关于配套的内容。
### 分析工具
Qt Creator 集成了一些最流行的性能分析工具,例如:
* [Linux 性能分析器](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-cpu-usage-analyzer.html)(需要特定的内核)
* [Valgrind](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-valgrind-overview.html) 内存分析器
* [Clang-Tidy 和 Clazy](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-clang-tools.html),一种检查 C/C++ 的 <ruby> 静态分析器 <rt> Linter </rt></ruby>

### 调试器
在调试方面,Qt Creator 为 GNU Debugger(GDB)配备了一个很好的界面。我喜欢它检查容器类型和创建条件断点的方式,很简单。

### FakeVim
如果你喜欢 Vim,你可以在设置中开启 FakeVim,来像 Vim 一样控制 Qt Creator。点击“<ruby> 工具 <rt> Tools </rt></ruby>”,选择“<ruby> 选项 <rt> Options </rt></ruby>”。在 “FakeVim” 选项中,你可以找到许多开关来定制 FakeVim。除了编辑器的功能外,你可以将自己设置的功能和命令关联起来,定制 Vim 命令。
举个例子,你可以将“<ruby> 构建项目 <rt> Build Project </rt></ruby>”的功能和 `build` 命令关联到一起:

回到编辑器中,当你按下冒号(`:`)并输入 `build`,Qt Creator 利用配置的工具链,开始进行构建:

你可以在这份 [文档](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-editor-fakevim.html) 中找到 FakeVim 的更多信息。
### 类检测器
当使用 C++ 开发时,点击 Qt Creator 右下角的按钮可打开右边的窗口。然后在窗口顶部拉下的菜单中选择“<ruby> 大纲 <rt> Outline </rt></ruby>”。如果你在左侧窗体中有头文件打开,你可以很好地纵览定义的类和类型。如果你切换到源文件中(`*.cpp`),右侧窗体会列出所有定义的方法,双击其中一个,你可以跳转到这个方法:

### 项目配置
Qt Creator 的项目建立在项目目录里的 `*.pro-file` 之上。你可以为你的项目在 `*.pro-file` 中添加定制的配置。我向 `*.pro-file` 中添加了 `my_special_config`,它向编译器的定义添加 `MY_SPECIAL_CONFIG`。
```
QT -= gui
CONFIG += c++11 console
CONFIG -= app_bundle
CONFIG += my_special_config
my_special_config {
DEFINES += MY_SPECIAL_CONFIG
}
```
Qt Creator 自动根据当前配置设置代码高亮:

`*.pro-file` 使用 [qmake 语言](https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qmake-language.html) 进行编写。
### 总结
这些特性仅仅是 Qt Creators 所提供的特性的冰山一角。初学者们应该不会感到被其众多的功能所淹没,Qt Creator 是一款对初学者很友好的 IDE。它甚至可能是入门 C++ 开发最简单的方式。如果要获得 QT Creator 特性的全面概述,请参考它的 [官方文档](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/)。
*(插图来自 Stephan Avenwedde, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/6/qtcreator>
作者:[Stephan Avenwedde](https://opensource.com/users/hansic99) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hadisi1993](https://github.com/hadisi1993) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Qt Creator is the Qt framework's default integrated development environment (IDE) and hence the glue between Qt's rich set of libraries and the user. In addition to its basic features such as intelligent code completion, debugging, and project administration, Qt Creator offers a lot of nice features that make software development easier.
In this article, I will highlight some of my favorite [Qt Creator](https://www.qt.io/product/development-tools) features.
## Dark mode
My first question when working with a new application is: *Is there a dark mode?* Qt Creator answers with: *Which dark mode do you prefer?*
You can activate dark mode in the Options menu. On the top menu bar, go to **Tools**, select **Options**, and go to the **Environment** section. Here is where you can select the general appearance:
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Custom appearance
Like every Qt application, Qt Creator's appearance is highly customizable with style sheets. Below, you can follow along with my approach to give Qt Creator a fancy look.
Create the file `mycustomstylesheet.css`
with the following content:
```
QMenuBar { background-color: olive }
QMenuBar::item { background-color: olive }
QMenu { background-color : beige; color : black }
QLabel { color: green }
```
Then start Qt Creator from the command line and pass the style sheet as a parameter with:
`qtcreator -stylesheet=mycustomstylesheet.css`
It should look like this:
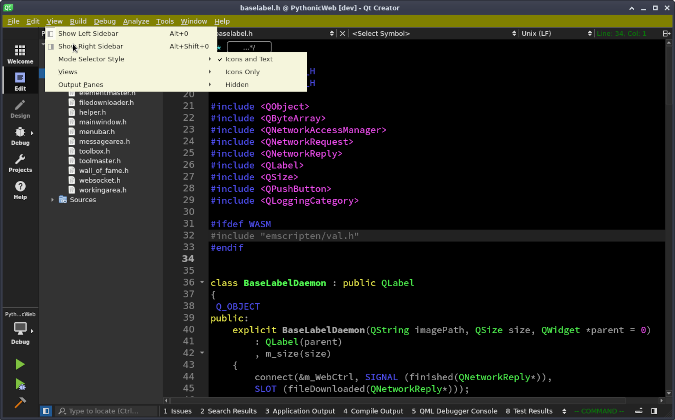
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Read more about style sheets in the [documentation](https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/stylesheet-reference.html).
## Command-line parameters
Qt Creator accepts many command-line options. For example, if you want to automatically load your current project at startup, pass the path to the `*.pro-file`
:
`qtcreator ~/MyProject/MyQtProject.pro`
You can even pass the file and the line number that should be opened by default. This command opens the file `main.cpp`
at line 20:
`qtcreator ~/MyProject/main.cpp:20`
Read more about the Qt Creator-specific command-line options in the [documentation](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-cli.html).
Qt Creator is an ordinary Qt application, so, in addition to its own command-line arguments, it also accepts the generic arguments for [QApplication](https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qapplication.html#QApplication) and [QGuiApplication](https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qguiapplication.html#supported-command-line-options).
## Cross-compiling
Qt Creator allows you to define several toolchains, called **Kits**. A kit defines the binaries and SDK for building and running an application:
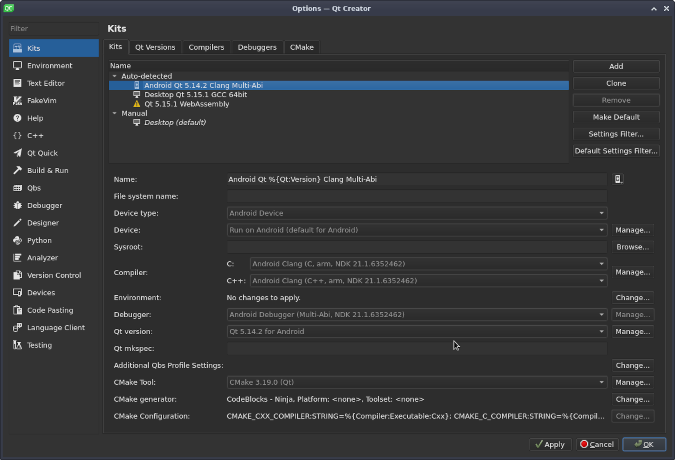
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
This allows you to switch between completely different toolchains with just two clicks:
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Read more about kits in the [manual](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-targets.html).
## Analyzer
Qt Creator integrates several of the most popular analyzers, such as:
[Linux Performance Analyzer](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-cpu-usage-analyzer.html)(requires a special kernel)[Valgrind](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-valgrind-overview.html)memory profiler[Clang-Tidy and Clazy](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-clang-tools.html), a linter for C/C++
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Debugger
When it comes to debugging, Qt Creator has a nice interface for GNU Debugger (GDB). I like its easy way of inspecting container types and creating conditional breakpoints:
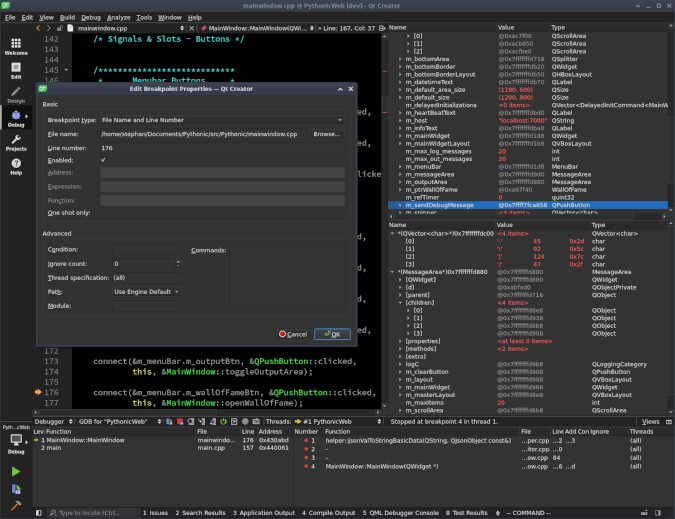
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## FakeVim
If you like Vim, enable FakeVim in the settings to control Qt Creator like Vim. Go to **Tools** and select **Options**. In the **FakeVim** section, you can find many switches to customize FakeVim's behavior. In addition to the editor functions, you can also map your own functions to custom Vim commands.
For example, you can map the function **Build Project** to the `build`
command:
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Back in the editor, when you press the colon button and enter `build`
, Qt Creator starts a build process with the configured toolchain:
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
You can find more information about FakeVim [in the docs](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-editor-fakevim.html).
## Class inspector
When developing in C++, open the right window by clicking on the button in the bottom-right corner of Qt Creator. Then choose **Outline** from the dropdown menu on the top border. If you have a header file open on the left pane, you get a nice overview of the defined classes or types. If you switch to a source file (`*.cpp`
), the right pane will list all defined methods, and you can jump to one by double-clicking on it:
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Project configuration
Qt Creator projects are built around the `*.pro-file`
in the project's directory. You can add your own custom configuration to the project's `*.pro-file`
of your project. I added `my_special_config`
to the `*.pro-file`
, which adds `MY_SPECIAL_CONFIG`
to the compiler defined:
```
QT -= gui
CONFIG += c++11 console
CONFIG -= app_bundle
CONFIG += my_special_config
my_special_config {
DEFINES += MY_SPECIAL_CONFIG
}
```
Qt Creator automatically highlights the code according to the active configuration:
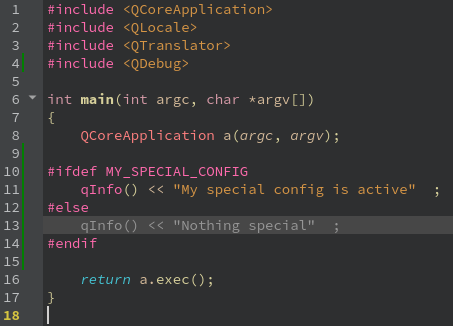
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The `*.pro-file`
is written in the [qmake language](https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qmake-language.html).
## Summary
These features are only the tip of the iceberg of what Qt Creator provides. Beginners shouldn't feel overwhelmed by the many features, as Qt Creator is absolutely beginner-friendly. It may even be the easiest way to start developing in C++. To get a complete overview of its features, refer to the [official Qt Creator documentation](https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/).
## Comments are closed. |
14,768 | 你安装的 Chrome 扩展的组合可以跟踪你 | https://news.itsfoss.com/chrome-extension-tracking/ | 2022-06-28T13:12:31 | [
"Chrome",
"跟踪"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14768-1.html |
>
> 这会成为放弃基于 Chromium 的浏览器并开始使用 Firefox 的一个理由吗?也许吧,决定权在你。
>
>
>

即使你有了所有的隐私扩展和各种保护功能,别人仍然有方法可以识别你或跟踪你。
请注意,并非所有浏览器都是如此,本文中,我们主要关注基于 Chromium 的浏览器,并将谷歌 Chrome 作为“主要嫌疑人”。
以前,在 Chromium 浏览器上,尽管别人已经能够检测到你已安装的扩展程序,但许多扩展程序都实施了某些保护措施来防止这种检测。
然而,一位名为 “**z0ccc**” 的安全研究人员发现了一种检测已安装 Chrome 浏览器扩展程序的新方法,该方法可进一步用于**通过“浏览器指纹识别”来跟踪你**。
如果你还不知道的话:<ruby> 浏览器指纹识别 <rt> Browser Fingerprinting </rt></ruby>是指收集有关你的设备/浏览器的各种信息,以创建唯一的指纹 ID(哈希),从而在互联网上识别你的一种跟踪方法。“各种信息”包括:浏览器名称、版本、操作系统、已安装的扩展程序、屏幕分辨率和类似的技术数据。
这听起来像是一种无害的数据收集技术,但可以使用这种跟踪方法在线跟踪你。
### 检测谷歌 Chrome 扩展
研究人员发布了一个开源项目 “**Extension Fingerprints**”,你可以使用它来测试你安装的 Chrome 扩展是否能被检测到。
新技术涉及一种“时间差”方法,该工具比较了扩展程序获取资源的时间。与浏览器上未安装的其他扩展相比,受保护的扩展需要更多时间来获取资源。因此,这有助于从 1000 多个扩展列表中识别出一些扩展。
关键是:即使有了各种新的进步和技术来防止跟踪,Chrome 网上应用店的扩展也可以被检测到。

并且,在检测到已安装的扩展程序后,别人可以就使用浏览器指纹识别,对你进行在线跟踪。
令人惊讶的是,即使你安装有 uBlocker、AdBlocker、或 Privacy Badger(一些流行的以隐私为重点的扩展程序)之类的扩展程序,使用了这种方法,它们也都可以被检测到。
你可以在它的 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/z0ccc/extension-fingerprints) 上查看所有技术细节。如果你想自己测试它,请前往它的 [扩展指纹识别网站](https://z0ccc.github.io/extension-fingerprints/) 自行检查。
### 拯救 Firefox?
嗯,似乎是的,毕竟我出于各种原因,[不断回到 Firefox](https://news.itsfoss.com/why-mozilla-firefox/)。
这个新发现的(跟踪)方法应该适用于所有基于 Chromium 的浏览器。我在 Brave 和谷歌 Chrome 上都测试了这个方法。研究人员还提到,该工具不能在使用微软应用商店中的扩展的微软 Edge 上工作。但是,相同的跟踪方法仍然有效。
正如研究人员指出,Mozilla Firefox 可以避免这种情况,因为每个浏览器实例的扩展 ID 都是唯一的。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/chrome-extension-tracking/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Even with all the privacy extensions and fancy protection features, there are still ways to identify you or track you.
Note that it is not the case for all browsers, here, we focus on Chromium-based browsers and Google Chrome as the prime suspect.
While detecting installed extensions in a Chromium browser was already possible, numerous extensions implemented certain protections to prevent it.
However, a security researcher, also known as “**z0ccc**”, discovered a new method to detect installed Chrome browser extensions, which can be further used to track you through browser fingerprinting.
**In case you did not know**: Browser fingerprinting refers to the tracking method where various information about your device/browser gets collected to create a unique fingerprint ID (hash) to identify you across the internet. Information like browser name, version, operating system, extensions installed, screen resolution, and similar technical data.
It sounds like a harmless data collection technique, but you can be tracked online with this tracking method.
## Detecting Google Chrome Extensions
The researcher shared an open-source project “**Extension Fingerprints**” which you can use to test if Chrome extensions installed on your browser are being detected.
The new technique involves a time-difference method where the tool compares the time to fetch resources for the extensions. A protected extension takes more time to fetch compared to other extensions not installed on your browser. So, that helps identify some extensions from the list of over 1000 extensions.
The point is—even with all the advancements and techniques to prevent tracking, extensions from the Google Web Store can be detected.
And, with the installed extensions detected, you can be tracked online using browser fingerprinting.
Surprisingly, even if you have extensions like **uBlocker, AdBlocker, **or** Privacy Badger** (some popular privacy-focused extensions), they all get detected using this method.
You can explore all the technical details on its [GitHub page](https://github.com/z0ccc/extension-fingerprints?ref=news.itsfoss.com). And, if you want to test it yourself, head to its [Extension Fingerprints site](https://z0ccc.github.io/extension-fingerprints/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to check for yourself.
## Firefox To The Rescue?
It seems like it, considering [I keep coming back to Firefox](https://news.itsfoss.com/why-mozilla-firefox/) for various reasons.
The discovered method should work with all the Chromium-based browsers. I tested it with Brave and Google Chrome. The researcher also mentions that the tool does not work with Microsoft Edge using extensions from Microsoft’s store. But, it is possible with the same method of tracking.
Mozilla Firefox is safe from this because the extension IDs for every browser instance are unique, as the researcher suggested.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,769 | 使用 Python 的 requests 和 Beautiful Soup 来分析网页 | https://opensource.com/article/22/6/analyze-web-pages-python-requests-beautiful-soup | 2022-06-28T13:29:10 | [
"Python",
"网页"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14769-1.html | 
>
> 学习这个 Python 教程,轻松提取网页的有关信息。
>
>
>
浏览网页可能占了你一天中的大部分时间。然而,你总是需要手动浏览,这很讨厌,不是吗?你必须打开浏览器,然后访问一个网站,单击按钮,移动鼠标……相当费时费力。如果能够通过代码与互联网交互,岂不是更好吗?
在 Python 的 `requests` 模块的帮助下,你可以使用 Python 从互联网中获取数据:
```
import requests
DATA = "https://opensource.com/article/22/5/document-source-code-doxygen-linux"
PAGE = requests.get(DATA)
print(PAGE.text)
```
在以上代码示例中,你首先导入了 `requests` 模块。接着,你创建了两个变量:其中一个叫做 `DATA`,它用来保存你要下载的 URL。在之后的代码中,你将能够在每次运行应用程序时提供不同的 URL。不过,就目前而言,最简单的方法是“硬编码”一个测试 URL,以达到演示目的。
另一个变量是 `PAGE`。代码读取了存储在 `DATA` 中的 URL,然后把它作为参数传入 `requests.get` 函数,最后用变量 `PAGE` 来接收函数的返回值。`requests` 模块及其 `.get` 函数的功能是:“读取”一个互联网地址(一个 URL)、访问互联网,并下载位于该地址的任何内容。
当然,其中涉及到很多步骤。幸运的是,你不必自己弄清楚,这也正是 Python 模块存在的原因。最后,你告诉 Python 打印 `requests.get` 存储在 `PAGE` 变量的 `.text` 字段中的所有内容。
### Beautiful Soup
如果你运行上面的示例代码,你会得到示例 URL 的所有内容,并且,它们会不加选择地输出到你的终端里。这是因为在代码中,你对 `requests` 收集到的数据所做的唯一事情,就是打印它。然而,解析文本才是更加有趣的。
Python 可以通过其最基本的功能来“读取”文本,但解析文本允许你搜索模式、特定单词、HTML 标签等。你可以自己解析 `requests` 返回的文本,不过,使用专门的模块会容易得多。针对 HTML 和 XML 文本,我们有 [Beautiful Soup](https://beautiful-soup-4.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) 库。
下面这段代码完成了同样的事情,只不过,它使用了 Beautiful Soup 来解析下载的文本。因为 Beautiful Soup 可以识别 HTML 元素,所以你可以使用它的一些内置功能,让输出对人眼更友好。
例如,在程序的末尾,你可以使用 Beautiful Soup 的 `.prettify` 函数来处理文本(使其更美观),而不是直接打印原始文本:
```
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
PAGE = requests.get("https://opensource.com/article/22/5/document-source-code-doxygen-linux")
SOUP = BeautifulSoup(PAGE.text, 'html.parser')
# Press the green button in the gutter to run the script.
if __name__ == '__main__':
# do a thing here
print(SOUP.prettify())
```
通过以上代码,我们确保了每个打开的 HTML 标签都输出在单独的一行,并带有适当的缩进,以帮助说明标签的继承关系。实际上,Beautiful Soup 能够通过更多方式来理解 HTML 标签,而不仅仅是将它打印出来。
你可以选择打印某个特定标签,而不是打印整个页面。例如,尝试将打印的选择器从 `print(SOUP.prettify())` 更改为:
```
print(SOUP.p)
```
这只会打印一个 `<p>` 标签。具体来说,它只打印遇到的第一个 `<p>` 标签。要打印所有的 `<p>` 标签,你需要使用一个循环。
### 循环
使用 Beautiful Soup 的 `find_all` 函数,你可以创建一个 `for` 循环,从而遍历 `SOUP` 变量中包含的整个网页。除了 `<p>` 标签之外,你可能也会对其他标签感兴趣,因此最好将其构建为自定义函数,由 Python 中的 `def` 关键字(意思是 <ruby> “定义” <rt> define </rt></ruby>)指定。
```
def loopit():
for TAG in SOUP.find_all('p'):
print(TAG)
```
你可以随意更改临时变量 `TAG` 的名字,例如 `ITEM` 或 `i` 或任何你喜欢的。每次循环运行时,`TAG` 中都会包含 `find_all` 函数的搜索结果。在此代码中,它搜索的是 `<p>` 标签。
函数不会自动执行,除非你显式地调用它。你可以在代码的末尾调用这个函数:
```
# Press the green button in the gutter to run the script.
if __name__ == '__main__':
# do a thing here
loopit()
```
运行代码以查看所有的 `<p>` 标签和它们的内容。
### 只获取内容
你可以通过指定只需要 “<ruby> 字符串 <rt> string </rt></ruby>”(它是 “<ruby> 单词 <rt> words </rt></ruby>” 的编程术语)来排除打印标签。
```
def loopit():
for TAG in SOUP.find_all('p'):
print(TAG.string)
```
当然,一旦你有了网页的文本,你就可以用标准的 Python 字符串库进一步解析它。例如,你可以使用 `len` 和 `split` 函数获得单词个数:
```
def loopit():
for TAG in SOUP.find_all('p'):
if TAG.string is not None:
print(len(TAG.string.split()))
```
这将打印每个段落元素中的字符串个数,省略那些没有任何字符串的段落。要获得字符串总数,你需要用到变量和一些基本数学知识:
```
def loopit():
NUM = 0
for TAG in SOUP.find_all('p'):
if TAG.string is not None:
NUM = NUM + len(TAG.string.split())
print("Grand total is ", NUM)
```
### Python 作业
你可以使用 Beautiful Soup 和 Python 提取更多信息。以下是有关如何改进你的应用程序的一些想法:
* [接受输入](https://opensource.com/article/17/3/python-tricks-artists-interactivity-Python-scripts),这样你就可以在启动应用程序时,指定要下载和分析的 URL。
* 统计页面上图片(`<img>` 标签)的数量。
* 统计另一个标签中的图片(`<img>` 标签)的数量(例如,仅出现在 `<main>` div 中的图片,或仅出现在 `</p>` 标签之后的图片)。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/6/analyze-web-pages-python-requests-beautiful-soup>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Browsing the web probably accounts for much of your day. But it's an awfully manual process, isn't it? You have to open a browser. Go to a website. Click buttons, move a mouse. It's a lot of work. Wouldn't it be nicer to interact with the Internet through code?
You can get data from the Internet using Python with the help of the Python module `requests`
:
```
``````
import requests
DATA = "https://opensource.com/article/22/5/document-source-code-doxygen-linux"
PAGE = requests.get(DATA)
print(PAGE.text)
```
In this code sample, you first import the module `requests`
. Then you create two variables: one called `DATA`
to hold the URL you want to download. In later versions of this code, you'll be able to provide a different URL each time you run your application. For now, though, it's easiest to just "hard code” a test URL for demonstration purposes.
The other variable is `PAGE`
, which you set to the response* *of the `requests.get`
function when it reads the URL stored in `DATA`
. The `requests`
module and its `.get`
function is pre-programmed to "read” an Internet address (a URL), access the Internet, and download whatever is located at that address.
That's a lot of steps you don't have to figure out on your own, and that's exactly why Python modules exist. Finally, you tell Python to `print`
everything that `requests.get`
has stored in the `.text`
field of the `PAGE`
variable.
## Beautiful Soup
If you run the sample code above, you get the contents of the example URL dumped indiscriminately into your terminal. It does that because the only thing your code does with the data that `requests`
has gathered is print it. It's more interesting to parse the text.
Python can "read” text with its most basic functions, but parsing text allows you to search for patterns, specific words, HTML tags, and so on. You could parse the text returned by `requests`
yourself, but using a specialized module is much easier. For HTML and XML, there's the [Beautiful Soup](https://beautiful-soup-4.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) library.
This code accomplishes the same thing, but it uses Beautiful Soup to parse the downloaded text. Because Beautiful Soup recognizes HTML entities, you can use some of its built-in features to make the output a little easier for the human eye to parse.
For instance, instead of printing raw text at the end of your program, you can run the text through the `.prettify`
function of Beautiful Soup:
```
``````
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
PAGE = requests.get("https://opensource.com/article/22/5/document-source-code-doxygen-linux")
SOUP = BeautifulSoup(PAGE.text, 'html.parser')
# Run the script
if __name__ == '__main__':
# do a thing here
print(SOUP.prettify())
```
The output of this version of your program ensures that every opening HTML tag starts on its own line, with indentation to help demonstrate which tag is a parent of another tag. Beautiful Soup is aware of HTML tags in more ways than just how it prints it out.
Instead of printing the whole page, you can single out a specific kind of tag. For instance, try changing the print selector from print(SOUP.prettify() to this:
```
```` print(SOUP.p)`
This prints just a `<p>`
tag. Specifically, it prints just the first `<p>`
tag encountered. To print all `<p>`
tags, you need a loop.
## Looping
Create a for loop to cycle over the entire webpage contained in the `SOUP`
variable, using the `find_all`
function of Beautiful Soup. It's not unreasonable to want to use your loop for other tags besides just the `<p>`
tag, so build it as a custom function, designated by the `def`
keyword (for "define”) in Python.
```
``````
def loopit():
for TAG in SOUP.find_all('p'):
print(TAG)
```
The temporary variable `TAG`
is arbitrary. You can use any term, such as `ITEM`
or `i`
or whatever you want. Each time the loop runs, `TAG`
contains the search results of the `find_all`
function. In this code, the `<p>`
tag is being searched.
A function doesn't run unless it's explicitly called. You can call your function at the end of your code:
```
``````
# Press the green button in the gutter to run the script.
if __name__ == '__main__':
# do a thing here
loopit()
```
Run your code to see all `<p>`
tags and each one's contents.
## Getting just the content
You can exclude tags from being printed by specifying that you want just the "string” (programming lingo for "words”).
```
``````
def loopit():
for TAG in SOUP.find_all('p'):
print(TAG.string)
```
Of course, once you have the text of a webpage, you can parse it further with the standard Python string libraries. For instance, you can get a word count using `len`
and `split`
:
```
``````
def loopit():
for TAG in SOUP.find_all('p'):
if TAG.string is not None:
print(len(TAG.string.split()))
```
This prints the number of strings within each paragraph element, omitting those paragraphs that don't have any strings. To get a grand total, use a variable and some basic math:
```
``````
def loopit():
NUM = 0
for TAG in SOUP.find_all('p'):
if TAG.string is not None:
NUM = NUM + len(TAG.string.split())
print("Grand total is ", NUM)
```
## Python homework
There's a lot more information you can extract with Beautiful Soup and Python. Here are some ideas on how to improve your application:
[Accept input](https://opensource.com/article/17/3/python-tricks-artists-interactivity-Python-scripts)so you can specify what URL to download and analyze when you launch your application.- Count the number of images (
`<img>`
tags) on a page. - Count the number of images (
`<img>`
tags) within another tag (for instance, only images that appear in the`<main>`
div, or only images following a`</p>`
tag).
## 2 Comments |
14,770 | 将 Zeek 与 ELK 栈集成 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/integrating-zeek-with-elk-stack/ | 2022-06-28T16:45:57 | [
"ELK",
"监控"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14770-1.html |
>
> Zeek 是一个开源的网络安全监控工具。本文讨论了如何将 Zeek 与 ELK 集成。
>
>
>

在本杂志 2022 年 3 月版发表的题为“用 Zeek 轻松实现网络安全监控”的文章中,我们研究了 Zeek 的功能,并学习了如何开始使用它。现在我们将把我们的学习经验再进一步,看看如何将其与 ELK(即 Elasticsearch、Kibana、Beats 和 Logstash)整合。
为此,我们将使用一个叫做 Filebeat 的工具,它可以监控、收集并转发日志到 Elasticsearch。我们将把 Filebeat 和 Zeek 配置在一起,这样后者收集的数据将被转发并集中到我们的 Kibana 仪表盘上。
### 安装 Filebeat
让我们首先将 Filebeat 与 Zeek 安装在一起。使用 `apt` 来安装 Filebeat,使用以下命令:
```
sudo apt install filebeat
```
接下来,我们需要配置 `.yml` 文件,它位于 `/etc/filebeat/` 文件夹中:
```
sudo nano /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml
```
我们只需要在这里配置两件事。在 Filebeat 输入部分,将类型改为 `log`,并取消对 `enabled:false` 的注释,将其改为 `true`。我们还需要指定存储日志的路径,也就是说,我们需要指定 `/opt/zeek/logs/current/*.log`。
完成这些后,设置的第一部分应该类似于图 1 所示的内容。

第二件要修改的事情是在输出下的 Elasticsearch 输出部分,取消对 `output.elasticsearch` 和 `hosts` 的注释。确保主机的 URL 和端口号与你安装 ELK 时配置的相似。我们把它保持为 `localhost`,端口号为 `9200`。
在同一部分中,取消底部的用户名和密码的注释,输入安装后配置 ELK 时生成的 Elasticsearch 用户的用户名和密码。完成这些后,参考图 2,检查设置。

现在我们已经完成了安装和配置,我们需要配置 Zeek,使其以 JSON 格式存储日志。为此,确保你的 Zeek 实例已经停止。如果没有,执行下面的命令来停止它:
```
cd /opt/zeek/bin
./zeekctl stop
```
现在我们需要在 `local.zeek` 中添加一小行,它存在于 `opt/zeek/share/zeek/site/` 目录中。
以 root 身份打开该文件,添加以下行:
```
@load policy/tuning/json-logs.zeek
```
参考图 3,确保设置正确。

由于我们改变了 Zeek 的一些配置,我们需要重新部署它,这可以通过执行以下命令来完成:
```
cd /opt/zeek/bin
./zeekctl deploy
```
现在我们需要在 Filebeat 中启用 Zeek 模块,以便它转发 Zeek 的日志。执行下面的命令:
```
sudo filebeat modules enable zeek
```
我们几乎要好了。在最后一步,配置 `zeek.yml` 文件要记录什么类型的数据。这可以通过修改 `/etc/filebeat/modules.d/zeek.yml` 文件完成。
在这个 .yml 文件中,我们必须提到这些指定的日志存放在哪个目录下。我们知道,这些日志存储在当前文件夹中,其中有几个文件,如 `dns.log`、`conn.log`、`dhcp.log` 等等。我们需要在每个部分提到每个路径。如果而且只有在你不需要该文件/程序的日志时,你可以通过把启用值改为 `false` 来舍弃不需要的文件。
例如,对于 `dns`,确保启用值为 `true`,并且路径被配置:
```
var.paths: [ “/opt/zeek/logs/current/dns.log”, “/opt/zeek/logs/*.dns.json” ]
```
对其余的文件重复这样做。我们对一些我们需要的文件做了这个处理。我们添加了所有主要需要的文件。你也可以这样做。请参考图 4。

现在是启动 Filebeat 的时候了。执行以下命令:
```
sudo filebeat setup
sudo service filebeat start
```
现在一切都完成了,让我们移动到 Kibana 仪表板,检查我们是否通过 Filebeat 接收到来自 Zeek 的数据。

进入仪表板。你可以看到它所捕获的数据的清晰统计分析(图 5 和图 6)。

现在让我们进入发现选项卡,通过使用查询进行过滤来检查结果:
```
event.module: "zeek"
```
这个查询将过滤它在一定时间内收到的所有数据,只向我们显示名为 Zeek 的模块的数据(图 7)。

### 鸣谢
*作者感谢 VIT-AP 计算机科学与工程学院的 Sibi Chakkaravarthy Sethuraman、Sudhakar Ilango、Nandha Kumar R.和Anupama Namburu 的不断指导和支持。特别感谢人工智能和机器人技术卓越中心(AIR)。*
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/integrating-zeek-with-elk-stack/>
作者:[Tridev Reddy](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/tridev-reddy/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Zeek is an open source network security monitoring tool. This article discusses how to integrate Zeek with ELK.*
In the article titled ‘Network Security Monitoring Made Easy with Zeek’ published in the March 2022 edition of this magazine, we looked into the capabilities of Zeek and learned how to get started with it. We will now take our learning experience a bit further and see how to integrate it with ELK (also know as Elasticsearch, Kibana, Beats, and Logstash).
For this, we will use a tool called Filebeat, which monitors, collects and forwards the logs to Elasticsearch. We will configure Filebeat with Zeek, so that the data collected by the latter will be forwarded and centralised in our Kibana dashboard.
**Installing Filebeat**
Let’s first set up Filebeat with Zeek. To install Filebeat using *apt*, give the following command:
sudo apt install filebeat
Next, we need to configure the *.yml* file, which is present in the etc*/filebeat/* folder:
sudo nano /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml
We need to configure only two things here. In the *Filebeat* Input section, change the type to log and uncomment the *enabled*: false and change it to true. We also need to specify the path of where the logs are stored, i.e., we need to specify */opt/zeek/logs/current/*.log*
Once this is done, the first part of the settings should look similar to what’s shown in Figure 1.

The second thing to be changed in the Elasticsearch output section is under *Outputs.* Uncomment the output.elasticsearch and hosts. Make sure the URL of the host and port number are similar to what you configured while installing ELK. We kept it as localhost with port number 9200.
In the same section, uncomment the user name and password at the bottom, and enter the user name and password of the elastic user that you generated while configuring ELK after installation. Once this is done, refer to Figure 2 and check the settings.

Now that we have completed installing and configuring , we need to configure Zeek so that it stores the logs in JSON format. For that, ensure your Zeek instance is stopped. If it’s not, execute the command given below to stop it:
cd /opt/zeek/bin ./zeekctl stop
Now we need to add a small line in the local.zeek, which is present in the *opt/zeek/share/zeek/site/* directory.
Open the file as root and add the following line:
@load policy/tuning/json-logs.zeek
Refer to Figure 3 and make sure the settings are done correctly.
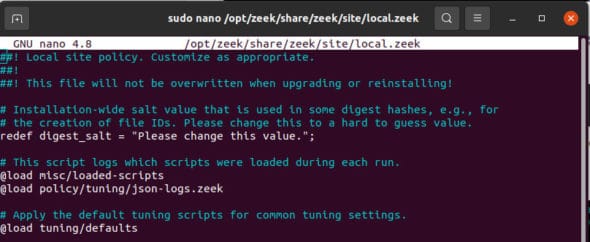

As we have changed a few configurations of Zeek, we need to re-deploy it, which can be done by executing the following command:
cd /opt/zeek/bin ./zeekctl deploy
Now we need to enable the Zeek module in Filebeat so that it forwards the logs from Zeek. Execute the following command:
sudo filebeat modules enable zeek
We are almost ready; in the last step, configure the *zeek.yml* file to mention what type of data is to be logged. This can be done by modifying the */etc/filebeat/modules.d/zeek.yml* file.
In this *.yml file*, we must mention the directory where these specified logs are stored. We know that the logs are stored in the current folder, which has several files like *dns.log*, *conn.log, dhcp.log,* and many more. We need to mention each path in each section. You can leave unwanted files by changing the enabled value to false, if and only if you don’t want logs from that file/program.
For example, for *dns*, make sure the enabled value is true and the path is mentioned as:
var.paths: [ “/opt/zeek/logs/current/dns.log”, “/opt/zeek/logs/*.dns.json” ]
Repeat this for the rest of the files. We did this for a few that we needed. We added everything that was mainly required. You can do the same. Refer to Figure 4.

Now it’s time to start the Filebeat. Execute the following commands:
sudo filebeat setup sudo service filebeat start
Now that everything is done, let’s move to our Kibana dashboard and check whether we are receiving the data from Zeek via Filebeat or not.

Navigate to the dashboard; you can see a clear statistical analysis of the data it has captured (Figure 5 and Figure 6).

Now let’s move to the Discover tab and check the results by filtering using the query:
event.module: “zeek”
This query will filter all the data it received in a certain time and show us only the data from the module named Zeek (Figure 7).
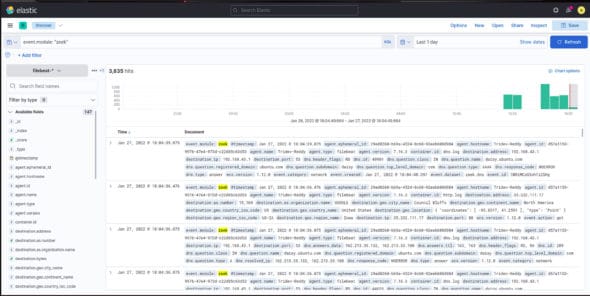

**Acknowledgements**
*The authors are grateful to Sibi Chakkaravarthy Sethuraman, Sudhakar Ilango, Nandha Kumar R. and Anupama Namburu at the School of Computer Science and Engineering, VIT-AP for their continuous guidance and support. A special thanks to the Center for Excellence in Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (AIR).* |
14,772 | Apache Kafka:为“无缝系统”提供异步消息支持 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2021/11/apache-kafka-asynchronous-messaging-for-seamless-systems/ | 2022-06-29T09:53:00 | [
"Kafka",
"异步消息"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14772-1.html |
>
> Apache Kafka 是最流行的开源消息代理之一。它已经成为了大数据操作的重要组成部分,你能够在几乎所有的微服务环境中找到它。本文对 Apache Kafka 进行了简要介绍,并提供了一个案例来展示它的使用方式。
>
>
>

你有没有想过,电子商务平台是如何在处理巨大的流量时,做到不会卡顿的呢?有没有想过,OTT 平台是如何在同时向数百万用户交付内容时,做到平稳运行的呢?其实,关键就在于它们的分布式架构。
采用分布式架构设计的系统由多个功能组件组成。这些功能组件通常分布在多个机器上,它们通过网络,异步地交换消息,从而实现相互协作。正是由于异步消息的存在,组件之间才能实现可伸缩、无阻塞的通信,整个系统才能够平稳运行。
### 异步消息
异步消息的常见特性有:
* 消息的<ruby> 生产者 <rt> producer </rt></ruby>和<ruby> 消费者 <rt> consumer </rt></ruby>都不知道彼此的存在。它们在不知道对方的情况下,加入和离开系统。
* 消息<ruby> 代理 <rt> broker </rt></ruby>充当了生产者和消费者之间的中介。
* 生产者把每条消息,都与一个“<ruby> 主题 <rt> topic </rt></ruby>”相关联。主题是一个简单的字符串。
* 生产者可以在多个主题上发送消息,不同的生产者也可以在同一主题上发送消息。
* 消费者向代理订阅一个或多个主题的消息。
* 生产者只将消息发送给代理,而不发送给消费者。
* 代理会把消息发送给订阅该主题的所有消费者。
* 代理将消息传递给针对该主题注册的所有消费者。
* 生产者并不期望得到消费者的任何回应。换句话说,生产者和消费者不会相互阻塞。
市场上的消息代理有很多,而 Apache Kafka 是其中最受欢迎的之一。
### Apache Kafka
Apache Kafka 是一个支持流式处理的、开源的分布式消息系统,它由 Apache 软件基金会开发。在架构上,它是多个代理组成的集群,这些代理间通过 Apache ZooKeeper 服务来协调。在接收、持久化和发送消息时,这些代理分担集群上的负载。
#### 分区
Kafka 将消息写入称为“<ruby> 分区 <rt> partition </rt></ruby>”的桶中。一个特定分区只保存一个主题上的消息。例如,Kafka 会把 `heartbeats` 主题上的消息写入名为 `heartbeats-0` 的分区(假设它是个单分区主题),这个过程和生产者无关。

不过,为了利用 Kafka 集群所提供的并行处理能力,管理员通常会为指定主题创建多个分区。举个例子,假设管理员为 `heartbeats` 主题创建了三个分区,Kafka 会将它们分别命名为 `heartbeats-0`、`heartbeats-1` 和 `heartbeats-2`。Kafka 会以某种方式,把消息分配到这三个分区中,并使它们均匀分布。
还有另一种可能的情况,生产者将每条消息与一个<ruby> 消息键 <rt> key </rt></ruby>相关联。例如,同样都是在 `heartbeats` 主题上发送消息,有个组件使用 `C1` 作为消息键,另一个则使用 `C2`。在这种情况下,Kafka 会确保,在一个主题中,带有相同消息键的消息,总是会被写入到同一个分区。不过,在一个分区中,消息的消息键却不一定相同。下面的图 2 显示了消息在不同分区中的一种可能分布。

#### 领导者和同步副本
Kafka 在(由多个代理组成的)集群中维护了多个分区。其中,负责维护分区的那个代理被称为“<ruby> 领导者 <rt> leader </rt></ruby>”。只有领导者能够在它的分区上接收和发送消息。
可是,万一分区的领导者发生故障了,又该怎么办呢?为了确保业务连续性,每个领导者(代理)都会把它的分区复制到其他代理上。此时,这些其他代理就称为该分区的<ruby> 同步副本 <rt> in-sync-replicas </rt></ruby>(ISR)。一旦分区的领导者发生故障,ZooKeeper 就会发起一次选举,把选中的那个同步副本任命为新的领导者。此后,这个新的领导者将承担该分区的消息接受和发送任务。管理员可以指定分区需要维护的同步副本的大小。

#### 消息持久化
代理会将每个分区都映射到一个指定的磁盘文件,从而实现持久化。默认情况下,消息会在磁盘上保留一个星期。当消息写入分区后,它们的内容和顺序就不能更改了。管理员可以配置一些策略,如消息的保留时长、压缩算法等。

#### 消费消息
与大多数其他消息系统不同,Kafka 不会主动将消息发送给消费者。相反,消费者应该监听主题,并主动读取消息。一个消费者可以从某个主题的多个分区中读取消息。多个消费者也可以读取来自同一个分区的消息。Kafka 保证了同一条消息不会被同一个消费者重复读取。
Kafka 中的每个消费者都有一个组 ID。那些组 ID 相同的消费者们共同组成了一个消费者组。通常,为了从 N 个主题分区读取消息,管理员会创建一个包含 N 个消费者的消费者组。这样一来,组内的每个消费者都可以从它的指定分区中读取消息。如果组内的消费者比可用分区还要多,那么多出来的消费者就会处于闲置状态。
在任何情况下,Kafka 都保证:不管组内有多少个消费者,同一条消息只会被该消费者组读取一次。这个架构提供了一致性、高性能、高可扩展性、准实时交付和消息持久性,以及零消息丢失。
### 安装、运行 Kafka
尽管在理论上,Kafka 集群可以由任意数量的代理组成,但在生产环境中,大多数集群通常由三个或五个代理组成。
在这里,我们将搭建一个单代理集群,对于生产环境来说,它已经够用了。
在浏览器中访问 <https://kafka.apache.org/downloads>,下载 Kafka 的最新版本。在 Linux 终端中,我们也可以使用下面的命令来下载它:
```
wget https://www.apache.org/dyn/closer.cgi?path=/kafka/2.8.0/kafka_2.12-2.8.0.tgz
```
如果需要的话,我们也可以把下载来的档案文件 `kafka_2.12-2.8.0.tgz` 移动到另一个目录下。解压这个档案,你会得到一个名为 `kafka_2.12-2.8.0` 的目录,它就是之后我们要设置的 `KAFKA_HOME`。
打开 `KAFKA_HOME/config` 目录下的 `server.properties` 文件,取消注释下面这一行配置:
```
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092
```
这行配置的作用是让 Kafka 在本机的 `9092` 端口接收普通文本消息。我们也可以配置 Kafka 通过<ruby> 安全通道 <rt> secure channel </rt></ruby>接收消息,在生产环境中,我们也推荐这么做。
无论集群中有多少个代理,Kafka 都需要 ZooKeeper 来管理和协调它们。即使是单代理集群,也是如此。Kafka 在安装时,会附带安装 ZooKeeper,因此,我们可以在 `KAFKA_HOME` 目录下,在命令行中使用下面的命令来启动它:
```
./bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh ./config/zookeeper.properties
```
当 ZooKeeper 运行起来后,我们就可以在另一个终端中启动 Kafka 了,命令如下:
```
./bin/kafka-server-start.sh ./config/server.properties
```
到这里,一个单代理的 Kafka 集群就运行起来了。
### 验证 Kafka
让我们在 `topic-1` 主题上尝试下发送和接收消息吧!我们可以使用下面的命令,在创建主题时为它指定分区的个数:
```
./bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --topic topic-1 --zookeeper localhost:2181 --partitions 3 --replication-factor 1
```
上述命令还同时指定了<ruby> 复制因子 <rt> replication factor </rt></ruby>,它的值不能大于集群中代理的数量。我们使用的是单代理集群,因此,复制因子只能设置为 1。
当主题创建完成后,生产者和消费者就可以在上面交换消息了。Kafka 的发行版内附带了生产者和消费者的命令行工具,供测试时用。
打开第三个终端,运行下面的命令,启动生产者:
```
./bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic topic-1
```
上述命令显示了一个提示符,我们可以在后面输入简单文本消息。由于我们指定的命令选项,生产者会把 `topic-1` 上的消息,发送到运行在本机的 9092 端口的 Kafka 中。
打开第四个终端,运行下面的命令,启动消费者:
```
./bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic topic-1 –-from-beginning
```
上述命令启动了一个消费者,并指定它连接到本机 9092 端口的 Kafka。它订阅了 `topic-1` 主题,以读取其中的消息。由于命令行的最后一个选项,这个消费者会从最开头的位置,开始读取该主题的所有消息。
我们注意到,生产者和消费者连接的是同一个代理,访问的是同一个主题,因此,消费者在收到消息后会把消息打印到终端上。
下面,让我们在实际应用场景中,尝试使用 Kafka 吧!
### 案例
假设有一家叫做 ABC 的公共汽车运输公司,它拥有一支客运车队,往返于全国不同城市之间。由于 ABC 希望实时跟踪每辆客车,以提高其运营质量,因此,它提出了一个基于 Apache Kafka 的解决方案。
首先,ABC 公司为所有公交车都配备了位置追踪设备。然后,它使用 Kafka 建立了一个操作中心,以接收来自数百辆客车的位置更新。它还开发了一个<ruby> 仪表盘 <rt> dashboard </rt></ruby>,以显示任一时间点所有客车的当前位置。图 5 展示了上述架构:

在这种架构下,客车上的设备扮演了消息生产者的角色。它们会周期性地把当前位置发送到 Kafka 的 `abc-bus-location` 主题上。ABC 公司选择以客车的<ruby> 行程编号 <rt> trip code </rt></ruby>作为消息键,以处理来自不同客车的消息。例如,对于从 Bengaluru 到 Hubballi 的客车,它的行程编号就会是 `BLRHL003`,那么在这段旅程中,对于所有来自该客车的消息,它们的消息键都会是 `BLRHL003`。
仪表盘应用扮演了消息消费者的角色。它在代理上注册了同一个主题 `abc-bus-location`。如此,这个主题就成为了生产者(客车)和消费者(仪表盘)之间的虚拟通道。
客车上的设备不会期待得到来自仪表盘应用的任何回复。事实上,它们相互之间都不知道对方的存在。得益于这种架构,数百辆客车和操作中心之间实现了非阻塞通信。
#### 实现
假设 ABC 公司想要创建三个分区来维护位置更新。由于我们的开发环境只有一个代理,因此复制因子应设置为 1。
相应地,以下命令创建了符合需求的主题:
```
./bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --topic abc-bus-location --zookeeper localhost:2181 --partitions 3 --replication-factor 1
```
生产者和消费者应用可以用多种语言编写,如 Java、Scala、Python 和 JavaScript 等。下面几节中的代码展示了它们在 Java 中的编写方式,好让我们有一个初步了解。
##### Java 生产者
下面的 `Fleet` 类模拟了在 ABC 公司的 6 辆客车上运行的 Kafka 生产者应用。它会把位置更新发送到指定代理的 `abc-bus-location` 主题上。请注意,简单起见,主题名称、消息键、消息内容和代理地址等,都在代码里硬编码的。
```
public class Fleet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String broker = “localhost:9092”;
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, broker);
props.setProperty(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,
StringSerializer.class.getName());
props.setProperty(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,
StringSerializer.class.getName());
Producer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<String, String>(props);
String topic = “abc-bus-location”;
Map<String, String> locations = new HashMap<>();
locations.put(“BLRHBL001”, “13.071362, 77.461906”);
locations.put(“BLRHBL002”, “14.399654, 76.045834”);
locations.put(“BLRHBL003”, “15.183959, 75.137622”);
locations.put(“BLRHBL004”, “13.659576, 76.944675”);
locations.put(“BLRHBL005”, “12.981337, 77.596181”);
locations.put(“BLRHBL006”, “13.024843, 77.546983”);
IntStream.range(0, 10).forEach(i -> {
for (String trip : locations.keySet()) {
ProducerRecord<String, String> record
= new ProducerRecord<String, String>(
topic, trip, locations.get(trip));
producer.send(record);
}
});
producer.flush();
producer.close();
}
}
```
##### Java 消费者
下面的 `Dashboard` 类实现了一个 Kafka 消费者应用,运行在 ABC 公司的操作中心。它会监听 `abc-bus-location` 主题,并且它的消费者组 ID 是 `abc-dashboard`。当收到消息后,它会立即显示来自客车的详细位置信息。我们本该配置这些详细位置信息,但简单起见,它们也是在代码里硬编码的:
```
public static void main(String[] args) {
String broker = “127.0.0.1:9092”;
String groupId = “abc-dashboard”;
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, broker);
props.setProperty(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,
StringDeserializer.class.getName());
props.setProperty(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,
StringDeserializer.class.getName());
props.setProperty(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, groupId);
@SuppressWarnings(“resource”)
Consumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<String, String>(props);
consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList(“abc-bus-location”));
while (true) {
ConsumerRecords<String, String> records
= consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(1000));
for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) {
String topic = record.topic();
int partition = record.partition();
String key = record.key();
String value = record.value();
System.out.println(String.format(
“Topic=%s, Partition=%d, Key=%s, Value=%s”,
topic, partition, key, value));
}
}
}
```
##### 依赖
为了编译和运行这些代码,我们需要 JDK 8 及以上版本。看到下面的 `pom.xml` 文件中的 Maven 依赖了吗?它们会把所需的 Kafka 客户端库下载并添加到类路径中:
```
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
</dependency>
```
#### 部署
由于 `abc-bus-location` 主题在创建时指定了 3 个分区,我们自然就会想要运行 3 个消费者,来让读取位置更新的过程更快一些。为此,我们需要同时在 3 个不同的终端中运行仪表盘。因为所有这 3 个仪表盘都注册在同一个组 ID 下,它们自然就构成了一个消费者组。Kafka 会为每个仪表盘都分配一个特定的分区(来消费)。
当所有仪表盘实例都运行起来后,在另一个终端中启动 `Fleet` 类。图 6、7、8 展示了仪表盘终端中的控制台示例输出。

仔细看看控制台消息,我们会发现第一个、第二个和第三个终端中的消费者,正在分别从 `partition-2`、`partition-1` 和 `partition-0` 中读取消息。另外,我们还能发现,消息键为 `BLRHBL002`、`BLRHBL004` 和 `BLRHBL006` 的消息写入了 `partition-2`,消息键为 `BLRHBL005` 的消息写入了 `partition-1`,剩下的消息写入了 `partition-0`。

使用 Kafka 的好处在于,只要集群设计得当,它就可以水平扩展,从而支持大量客车和数百万条消息。

### 不止是消息
根据 Kafka 官网上的数据,在《财富》100 强企业中,超过 80% 都在使用 Kafka。它部署在许多垂直行业,如金融服务、娱乐等。虽然 Kafka 起初只是一种简单的消息服务,但它已凭借行业级的流处理能力,成为了大数据生态系统的一环。对于那些喜欢托管解决方案的企业,Confluent 提供了基于云的 Kafka 服务,只需支付订阅费即可。(LCTT 译注:Confluent 是一个基于 Kafka 的商业公司,它提供的 Confluent Kafka 在 Apache Kafka 的基础上,增加了许多企业级特性,被认为是“更完整的 Kafka”。)
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2021/11/apache-kafka-asynchronous-messaging-for-seamless-systems/>
作者:[Krishna Mohan Koyya](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/krishna-mohan-koyya/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Apache Kafka is one of the most popular open source message brokers. Found in almost all microservices environments, it has become an important component of Big Data manipulation. This article gives a brief description of Apache Kafka, followed by a case study that demonstrates how it is used.*
Have you ever wondered how e-commerce platforms are able to handle immense traffic without getting stuck? Ever thought about how OTT platforms are able to deliver content to millions of users, smoothly and simultaneously? The key lies in their distributed architecture.
A system designed around distributed architecture is made up of multiple functional components. These components are usually spread across several machines, which collaborate with each other by exchanging messages asynchronously over a network. Asynchronous messaging is what enables scalable, non-blocking communication among components, thereby allowing smooth functioning of the overall system.
**Asynchronous messaging**
The common features of asynchronous messaging are:
- The producers and consumers of the messages are not aware of each other. They join and leave the system without the knowledge of the others.
- A message broker acts as the intermediary between the producers and consumers.
- The producers associate each of the messages with a type, known as topic. A topic is just a simple string.
- It is possible that producers send messages on multiple topics, and multiple producers send messages on the same topic.
- The consumers register with the broker for messages on one or more topics.
- The producers send the messages only to the broker, and not to the consumers.
- The broker, in turn, delivers the messages to all the consumers that are registered against the topic.
- The producers do not expect any response from the consumers. In other words, the producers and consumers do not block each other.
There are several message brokers available in the market, and Apache Kafka is one of the most popular among them.
**Apache Kafka**
Apache Kafka is an open source distributed messaging system with streaming capabilities, developed by the Apache Software Foundation. Architecturally, it is a cluster of several brokers that are coordinated by the Apache Zookeeper service. These brokers share the load on the cluster while receiving, persisting, and delivering the messages.
* Partitions:* Kafka writes messages into buckets known as partitions. A given partition holds messages only on one topic. For example, Kafka writes messages on the topic heartbeats into the partition named
*heartbeats-0*, irrespective of the producer of the messages.
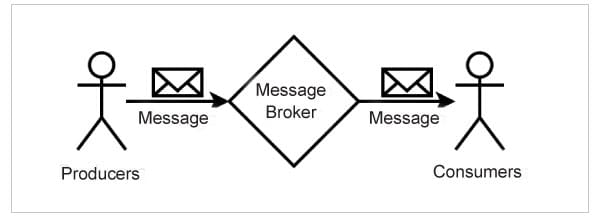

However, in order to leverage the cluster-wide parallel processing capabilities of Kafka, administrators often create more than one partition for a given topic. For instance, if the administrator creates three partitions for the topic heartbeats, Kafka names them as *heartbeats-0, heartbeats-1,* and *heartbeats-2.* Kafka writes the heartbeat messages across all the three partitions in such a way that the load is evenly distributed.
There is yet another possible scenario in which the producers associate each of the messages with a key. For example, a component uses C1 as the key while another component uses C2 as the key for the messages that they produce on the topic heartbeats. In this scenario, Kafka makes sure that the messages on a topic with a specific key are always found only in one partition. However, it is quite possible that a given partition may hold messages with different keys. Figure 2 presents a possible message distribution among the partitions.
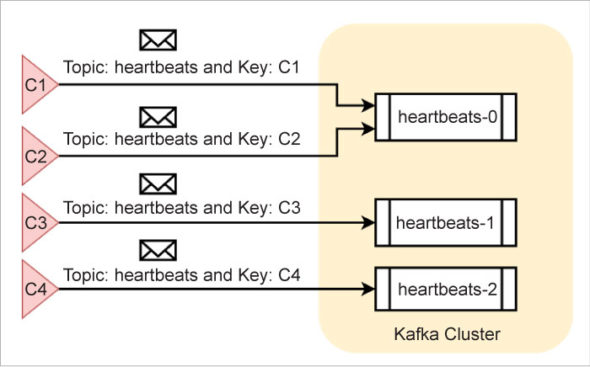

* Leaders and ISRs:* Kafka maintains several partitions across the cluster. The broker on which a partition is maintained is called the leader for the specific partition. Only the leader receives and serves the messages from its partitions.
But what happens to a partition if its leader crashes? To ensure business continuity, every leader replicates its partitions on other brokers. The latter act as the in-sync-replicas (ISRs) for the partition. In case the leader of a partition crashes, Zookeeper conducts an election and names an ISR as the new leader. Thereafter, the new leader takes the responsibility of writing and serving the messages for that partition. Administrators can choose how many ISRs are to be maintained for a topic.


* Message persistence:* The brokers map each of the partitions to a specific file on the disk, for persistence. By default, they keep the messages for a week on the disk! The messages and their order cannot be altered once they are written to a partition. Administrators can configure policies like message retention, compaction, etc.
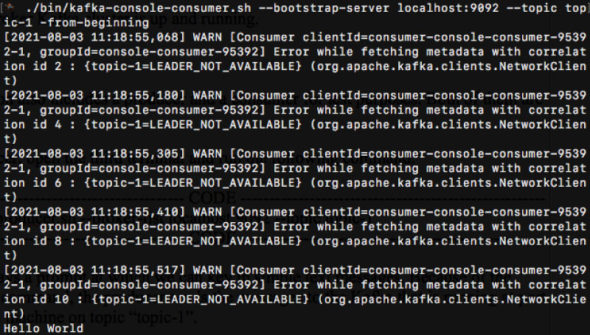

** Consuming the messages:** Unlike most other messaging systems, Apache Kafka does not actively deliver the messages to its consumers. Instead, it is the responsibility of the consumers to listen to the topics and read the messages. A consumer can read messages from more than one partition of a topic. And it is also possible that multiple consumers read messages from a given partition. Kafka guarantees that no message is read more than once by a given consumer.
Kafka also expects that every consumer is identified with a group ID. Consumers with the same group ID form a group. Typically, in order to read messages from N number of topic partitions, an administrator creates a group with N number of consumers. This way, each consumer of the group reads messages from its designated partition. If the group consists of more consumers than the available partitions, the excess consumers remain idle.
In any case, Apache Kafka guarantees that a message is read only once at the group level, irrespective of the number of consumers in the group. This architecture gives consistency, high-performance, high scalability, near-real-time delivery, and message persistence along with zero-message loss.
**Installing and running Kafka**
Although, in theory, the Apache Kafka cluster can consist of any number of brokers, most of the clusters in production environments usually consist of three or five of these.
Here, we will set up a single-broker cluster that is good enough for the development environment.
Download the latest version of Kafka from *https://kafka.apache.org/downloads* using a browser. It can also be downloaded with the following command, on a Linux terminal:
wget https://www.apache.org/dyn/closer.cgi?path=/kafka/2.8.0/kafka_2.12-2.8.0.tgz
We can move the downloaded archive *file kafka_2.12-2.8.0.tgz* to some other folder, if needed. Extracting the archive creates a folder by the name *kafka_2.12-2.8.0*, which will be referred to as *KAFKA_HOME* hereafter.
Open the file server.properties under the *KAFKA_HOME/config* folder and uncomment the line with the following entry:
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092
This configuration enables Apache Kafka to receive plain text messages on port 9092, on the local machine. Kafka can also be configured to receive messages over a secure channel as well, which is recommended in the production environments.
Irrespective of the number of brokers, Apache Zookeeper is required for broker management and coordination. This is true even in the case of single-broker clusters. Since Zookeeper is already bundled with Kafka, we can start it with the following command from *KAFKA_HOME*, on a terminal:
./bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh ./config/zookeeper.properties
Once Zookeeper starts running, Kafka can be started in another terminal, with the following command:
./bin/kafka-server-start.sh ./config/server.properties
With this, a single-broker Kafka cluster is up and running.
**Verifying Kafka**
Let us publish and receive messages on the topic topic-1. A topic can be created with a chosen number of partitions with the following command:
./bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --topic topic-1 --zookeeper localhost:2181 --partitions 3 --replication-factor 1
The above command also specifies the replication factor, which should be less than or equal to the number of brokers in the cluster. Since we are working on a single-broker cluster, the replication factor is set to one.
Once the topic is created, producers and consumers can exchange messages on that topic. The Kafka distribution includes a producer and a consumer for test purposes. Both of these are command-line tools.
To invoke the producer, open the third terminal and run the following command:
./bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic topic-1
This command displays a prompt at which we can key in simple text messages. Because of the given options on the command, the producer sends the messages on *topic-1* to the Kafka that is running on port 9092 on the local machine.
Open the fourth terminal and run the following command to start the consumer tool:
./bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic topic-1 –from-beginning
This command starts the consumer that connects to the Kafka on port number 9092 on the local machine. It registers for reading the messages on topic-1. Because of the last option on the command line, the consumer receives all the messages on the chosen topic from the beginning.
Since the producer and consumer are connecting to the same broker and referring the same topic, the consumer receives and displays the messages on its terminal.
Now, let’s use Kafka in the context of a practical application.
**Case study**
ABC is a hypothetical bus transport company, which has a fleet of passenger buses that ply between different cities across the country. Since ABC wants to track each bus in real-time for improving the quality of its operations, it comes up with a solution around Apache Kafka.
ABC first equips all its buses with devices to track their location. An operations centre is set up with Apache Kafka, to receive the location updates from each of the hundreds of buses. A dashboard is developed to display the current status of all the buses at any point in time. Figure 5 represents this architecture.
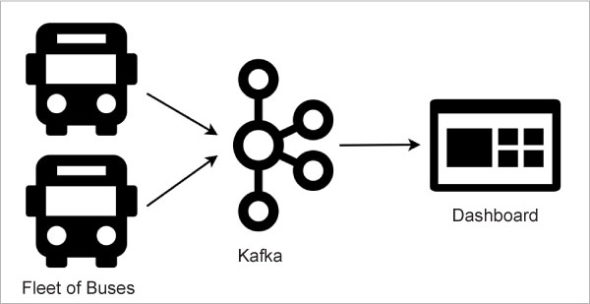

In this architecture, the devices on the buses act as the message producers. They send their current location to Kafka on the topic *abc-bus-location*, periodically. For processing the messages from different buses, ABC chooses to use the trip code as the key. For example, if the bus from Bengaluru to Hubballi runs with the trip code* BLRHBL003*, then *BLRHBL003* becomes the key for all the messages from that specific bus during that specific trip.
The dashboard application acts as the message consumer. It registers with the broker against the same topic *abc-bus-location*. Consequently, the topic becomes the virtual channel between the producers (buses) and the consumer (dashboard).
The devices on the buses never expect any response from the dashboard application. In fact, none of them is even aware of the presence of the others. This architecture enables non-blocking communication between hundreds of buses and the central office.
**Implementation**
Let’s assume that ABC wants to create three partitions for maintaining the location updates. Since the development environment has only one broker, the replication factor should be set to one.
The following command creates the topic accordingly:
./bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --topic abc-bus-location --zookeeper localhost:2181 --partitions 3 --replication-factor 1
The producer and consumer applications can be written in multiple languages like Java, Scala, Python, JavaScript, and a host of others. The code in the following sections provides a peek into the way they are written in Java.
* Java producer:* The Fleet class simulates the Kafka producer applications running on six buses of ABC. It sends location updates on
*abc-bus-location*to the specified broker. Please note that the topic name, message keys, message body, and broker address are hard-coded only for simplicity.
public class Fleet { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String broker = “localhost:9092”; Properties props = new Properties(); props.setProperty(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, broker); props.setProperty(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName()); props.setProperty(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName()); Producer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<String, String>(props); String topic = “abc-bus-location”; Map<String, String> locations = new HashMap<>(); locations.put(“BLRHBL001”, “13.071362, 77.461906”); locations.put(“BLRHBL002”, “14.399654, 76.045834”); locations.put(“BLRHBL003”, “15.183959, 75.137622”); locations.put(“BLRHBL004”, “13.659576, 76.944675”); locations.put(“BLRHBL005”, “12.981337, 77.596181”); locations.put(“BLRHBL006”, “13.024843, 77.546983”); IntStream.range(0, 10).forEach(i -> { for (String trip : locations.keySet()) { ProducerRecord<String, String> record = new ProducerRecord<String, String>( topic, trip, locations.get(trip)); producer.send(record); } }); producer.flush(); producer.close(); } }
* Java consumer:* The Dashboard class implements the Kafka consumer application and it runs at the ABC Operations Centre. It listens to
*abc-bus-location*with the group ID
*abc-dashboard*and displays the location details from different buses as soon as messages are available. Here, too, many details are hard coded which are otherwise supposed to be configured:
public static void main(String[] args) { String broker = “127.0.0.1:9092”; String groupId = “abc-dashboard”; Properties props = new Properties(); props.setProperty(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, broker); props.setProperty(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class.getName()); props.setProperty(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class.getName()); props.setProperty(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, groupId); @SuppressWarnings(“resource”) Consumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<String, String>(props); consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList(“abc-bus-location”)); while (true) { ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(1000)); for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) { String topic = record.topic(); int partition = record.partition(); String key = record.key(); String value = record.value(); System.out.println(String.format( “Topic=%s, Partition=%d, Key=%s, Value=%s”, topic, partition, key, value)); } } } }
** Dependencies:** A JDK of 8+ version is required to compile and run this code. The following Maven dependencies in the
*pom.xml*download and add the required Kafka client libraries to the classpath:
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId> <artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId> <version>2.8.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId> <version>1.7.25</version> </dependency>
**Deployment**
As the topic *abc-bus-location* is created with three partitions, it makes sense to run three consumers to read the location updates quickly. For that, run the Dashboard in three different terminals simultaneously. Since all the three instances of Dashboard register with the same group ID, they form a group. Kafka attaches each Dashboard instance with a specific partition.
Once the Dashboard instances are up and running, start the *Fleet* on a different terminal. Figure 6, Figure 7, and Figure 8 are sample console messages on the Dashboard terminals.

A closer look at the console messages reveals that the consumers on the first, second and third terminals are reading messages from *partition-2, partition-1,* and *partition-0,* in that order. Also, it can be observed that the messages with the keys BLRHBL002, *BLRHBL004* and *BLRHBL006* are written into *partition-2*, the messages with the key *BLRHBL005* are written into *partition-1*, and the remaining are written into *partition-0*.

The good thing about Kafka is that it can be scaled horizontally to support a large number of buses and millions of messages as long as the cluster is designed appropriately.


**Beyond messaging**
More than 80 per cent of the Fortune 100 companies are using Kafka, according to its website. It is deployed across many industry verticals like financial services, entertainment, etc. Though Apache Kafka started its journey as a simple messaging service, it has propelled itself into the Big Data ecosystem with industry-level stream processing capabilities. For the enterprises that prefer a managed solution, Confluent offers a cloud based Apache Kafka service for a subscription fee. |
14,773 | 轻松解决你的任务清单的三个步骤 | https://opensource.com/article/21/1/break-down-tasks | 2022-06-29T14:58:55 | [
"任务清单"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14773-1.html |
>
> 将你的大任务分为小步骤,避免自己不堪重负。
>
>
>

本周开始,我先回顾我的日程安排,看看我需要或想要完成的事情。通常,列表上有些较大的项目。无论来自工作上的问题,还是一系列关于生产力的文章,或者改进我家的鸡舍,当作为一项工作时,这个任务真的很艰巨。很有可能我无法坐下来,在一个时间段内,甚至在一天内完成类似(请注意,只是举例)21 篇文章之类的事情。

*21 天的生产力 (Kevin Sonney, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
所以当我的清单上有这样的东西时,我做的第一件事就是把它分解成更小的部分。如著名的诺贝尔文学奖得主 [William Faulkner](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Faulkner) 说的“移山的人,从小石头开始。”(LCTT 译注:感觉与“千里之行,始于足下”是一个意思) 我们要解决大任务(山)并且需要完成各个步骤(小石头)。
我使用下面的步骤将大任务分割为小步骤:
1. 我通常很清楚完成一项任务需要做什么。如果没有,我会做一些研究来弄清楚这一点。
2. 我会顺序的写下完成的步骤。
3. 最后,我坐下来拿着我的日历和清单,开始将任务分散到几天(或几周或几个月),以了解我何时可以完成它。
现在我不仅有计划,还知道多久能完成。逐步完成,我可以看到这项大任务不仅变得更小,而且更接近完成。
军队有句古话,“遇敌无计”。 几乎可以肯定的是,有一两点(或五点)我意识到像“截屏”这样简单的事情需要扩展到更复杂的事情。事实上,在 [Easy!Appointments](https://opensource.com/article/21/1/open-source-scheduler) 的截图中,竟然是:
1. 安装和配置 Easy!Appointments
2. 安装和配置 Easy!Appointments WordPress 插件
3. 生成 API 密钥来同步日历
4. 截屏
即便如此,我也不得不将这些任务分解成更小的部分——下载软件、配置 NGINX、验证安装……你明白了吧。没关系。一个计划或一组任务不是一成不变的,可以根据需要进行更改。

*今年的计划已经完成了 2/3 ! (Kevin Sonney, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
这是一项后天习得的技能,最初几次需要一些努力。学习如何将大任务分解成更小的步骤可以让您跟踪实现目标或完成大任务的进度,而不会在过程中不知所措。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/1/break-down-tasks>
作者:[Kevin Sonney](https://opensource.com/users/ksonney) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[Donkey](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In prior years, this annual series covered individual apps. This year, we are looking at all-in-one solutions in addition to strategies to help in 2021. Welcome to day 14 of 21 Days of Productivity in 2021.
At the start of the week, I like to review my schedule and look at the things I either need or would like to accomplish. And often, there are some items on that list that are relatively big. Whether it is an issue for work, a series of articles on productivity, or maybe an improvement to the chicken enclosures, the task can seem really daunting when taken as a single job. The odds are good that I will not be able to sit down and finish something like (just as an example, mind you) 21 articles in a single block of time, or even a single day.
21 Days of Productivity (Kevin Sonney, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
So the first thing I do when I have something like this on my list is to break it down into smaller pieces. As Nobel laureate [William Faulkner](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Faulkner) famously said, "The man who removes a mountain begins by carrying away small stones." We need to take our big tasks (the mountain) and find the individual steps (the small stones) that need to be done.
I use the following steps to break down my big tasks into little ones:
- I usually have a fair idea of what needs to be done to complete a task. If not, I do a little research to figure that out.
- I write down the steps I think it will take, in order.
- Finally, I sit down with my calendar and the list and start to spread the tasks out across several days (or weeks, or months) to get an idea of when I might finish it.
Now I have not only a plan but an idea of how long it is going to take. As I complete each step, I can see that big task get not only a little smaller but closer to completion.
There is an old military saying that goes, "No plan survives contact with the enemy." It is almost certain that there will be a point or two (or five) where I realize that something as simple as "take a screenshot" needs to be expanded into something *much* more complex. In fact, taking the screenshots of [Easy!Appointments](https://opensource.com/article/21/1/open-source-scheduler) turned out to be:
- Install and configure Easy!Appointments.
- Install and configure the Easy!Appointments WordPress plugin.
- Generate the API keys needed to sync the calendar.
- Take screenshots.
Even then, I had to break these tasks down into smaller pieces—download the software, configure NGINX, validate the installs…you get the idea. And that's OK. A plan, or set of tasks, is not set in stone and can be changed as needed.
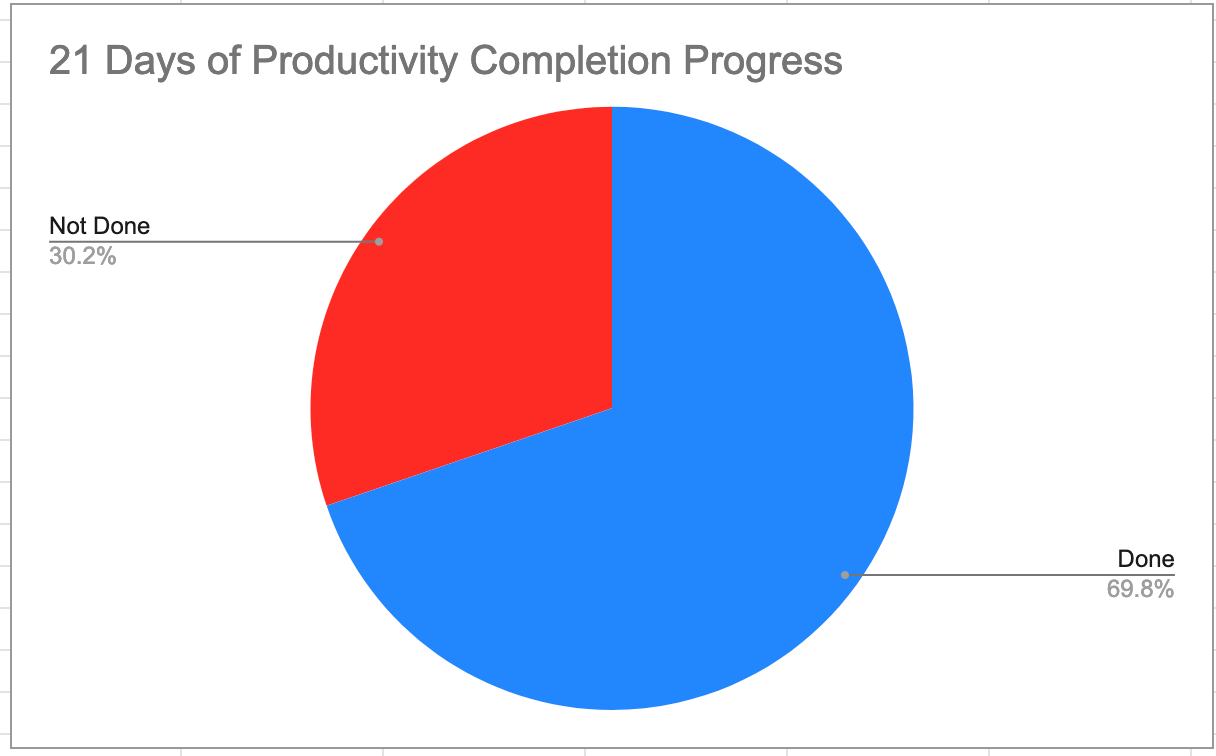
About 2/3 done for this year! (Kevin Sonney, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
This is a learned skill and will take some effort the first few times. Learning how to break big tasks into smaller steps allows you to track progress towards a goal or completion of something big without getting overwhelmed in the process.
## Comments are closed. |
14,774 | Minetest:一个开源的 Minecraft 替代品 | https://itsfoss.com/minetest/ | 2022-06-29T15:12:00 | [
"Minecraft",
"Minetest"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14774-1.html | 早在 2009 年,Minecraft 就来到了这个世界。从那时起,它已经成为一种文化现象。在这段时间里,一些开发者发布了具有类似想法和机制的开源游戏。今天,我们将看看其中最大的一个:Minetest。
### 什么是 Minetest?

[Minetest](https://www.minetest.net/),简单地说,是一个基于<ruby> 体素 <rt> voxel </rt></ruby>的沙盒游戏,与 Minecraft 非常相似。与 Minecraft 不同的是,Minetest 是用 C++ 编写的,并被设计成可以在大多数系统上原生运行。它也有一个非常大的地图区域。地图大小为 “62,000 × 62,000 × 62,000 块”,“你可以向下开采 31,000 块,或向上建造 31,000 块”。
有趣的是,Minetest 最初是以专有许可证发布的,但后来被重新授权为 GPL。此后,它又被重新授权为 LGPL。
Minetest 有几种模式。你可以建造并发挥创意,或者你可以尝试在各种元素中生存。你并不局限于这些模式。Minetest 有大量的 [额外内容](https://content.minetest.net/),包括 <ruby> 模组 <rt> mod </rt></ruby>、纹理包和在 Minetest 中建立的游戏。这主要是通过 Minetest 的 [模组 API](https://dev.minetest.net/Modding_Intro) 和 Lua 完成的。

对于那些玩过 Minecraft 的人来说,你会发现 Minetest 中的体验非常相似。你可以挖掘资源,建造结构,并结合材料来制作工具。我在 Minetest 中没有注意到的一件事是怪物。我认为 Minetest 中没有任何生物,但话说回来,我只在创意模式中玩过。我还没有玩过生存模式。
Minetest 也被用于 [教育](https://www.minetest.net/education/)。例如,瑞士 CERN 的人用 Minetest 创造了一个游戏,以 [展示互联网是如何工作的](https://forum.minetest.net/viewtopic.php?t=22871) 以及它是如何被创造出来的。Minetest 还被用于 [教授](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Minetest#Usage_in_education) 编程、地球科学以及微积分和三角学。

### 如何安装 Minetest?
Minetest 几乎在每个系统上都可以使用。下面是一个命令列表,你可以用它来在一些最流行的 Linux 发行版中安装 Minetest。
#### Ubuntu 或者 Debian
如果你有一个基于 Ubuntu 或 Debian 的发行版,只要在终端输入这个命令:
```
sudo apt install mintest
```
#### Arch 或者 Manjaro
对于基于 Arch 的系统(如 Manjaro),使用:
```
sudo pacman -S minetest
```
#### Fedora
你可以从 Fedora 服务器中输入以下命令安装 Mintest:
```
sudo dnf install mintest
```
#### openSUSE
openSUSE 用户可以用这个命令安装 Minetest:
```
sudo zypper in mintest
```
#### FreeBSD
FreeBSD 用户很幸运。他们可以用这个命令安装 Mintest:
```
pkg install minetest minetest_game
```
#### Snap
要安装 Minetest 的 Snap 包,请在终端输入以下命令:
```
sudo snap install minetest
```
#### Flathub
要安装,请输入:
```
flatpak install flathub net.minetest.Minetest
```
你可以在 [这里](https://www.minetest.net/downloads/) 下载 Windows 的可移植执行文件。你也可以在 Android 上安装 Minetest,可以通过 [Google Play](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=net.minetest.minetest&utm_source=website&pcampaignid=MKT-Other-global-all-co-prtnr-py-PartBadge-Mar2515-1) 或 [下载 APK](https://github.com/minetest/minetest/releases/download/5.5.0/app-armeabi-v7a-release.apk)。
### 总结

我已经在 Minetest 中花了几个小时在我的本地系统上进行构建和探索。它非常有趣。我还没来得及尝试任何额外的内容,因为我对我玩过的相对较少的游戏部分非常满意。我遇到的唯一麻烦是,由于某种原因,它在 Fedora 上运行缓慢。我可能存在一些配置上的错误。
如果你曾经认为 Minecraft 看起来很有趣,但不想花钱,那就去看看 Minetest。你会很高兴你这么做。
如果你玩过 Minetest,在评论中告诉我们你的体验如何。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/minetest/>
作者:[John Paul](https://itsfoss.com/author/john/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Back in 2009, Minecraft was introduced to the world. Since then, it has become a cultural phenomenon. In that time period, several developers have released open-source games with similar ideas and mechanics. Today, we will look at one of the biggest ones: Minetest.
## What is Minetest?
[Minetest](https://www.minetest.net/), put simply, is a voxel based sandbox game, very similar to Minecraft. Unlike Minecraft, Minetest is written in C++ and is designed to run natively on most systems. It also has a very large map area. With a map size of “62,000 × 62,000 × 62,000 blocks”, “you can mine 31,000 blocks down, or build 31,000 blocks up”.
Interestingly, Minetest was originally released under a proprietary license but was later relicensed as GPL. It has since been relicensed to LGPL.
Minetest has a couple of modes. You can either build and be creative, or you can try to survive the elements. You aren’t limited to these modes. There is a wealth of [extra content available](https://content.minetest.net/) to Minetest in terms of mods, texture packs, and games built within Minetest. This is largely done using Minetest’s [modding API](https://dev.minetest.net/Modding_Intro) and Lua.

For those who have played Minecraft, you will find a very similar experience in Minetest. You can dig for resources, build structures, and combine materials to make tools. The one thing that I have not noticed in Minetest is monsters. I don’t think there are any creatures in Minetest, but then again, I’ve on only played in creative mode. I haven’t played survival mode.
Minetest is also used in [education](https://www.minetest.net/education/). For example, the people at CERN in Switzerland created a game with Minetest to [show how the Internet works](https://forum.minetest.net/viewtopic.php?t=22871) and how it was created. Minetest has also been [used to teach](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Minetest#Usage_in_education) programming, earth sciences, and calculus and trigonometry.
## How to Install Minetest?
Minetest is available on almost every system. Here is a list of commands that you can use to install Minetest in some of the most popular Linux distros.
### Ubuntu or Debian
If you have a distro based on Ubuntu or Debian, just enter this command in the terminal:
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:minetestdevs/stable
sudo apt update
sudo apt install minetest
```
### Arch or Manjaro
For systems based on Arch (such as Manjaro), use:
`sudo pacman -S minetest`
### Fedora
You can install Mintest from the Fedora servers by entering:
`sudo dnf install minetest`
### openSUSE
openSUSE users can install Minetest using this command:
`sudo zypper in mintest`
### FreeBSD
FreeBSD users are in luck. They can install Mintest using this command:
`pkg install minetest minetest_game`
### Flathub
To install, enter`:`
`flatpak install flathub net.minetest.Minetest`
You can download a portable executable for Windows [here](https://www.minetest.net/downloads/). You can also install Minetest on Android, either by going to [Google Play](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=net.minetest.minetest&utm_source=website&pcampaignid=MKT-Other-global-all-co-prtnr-py-PartBadge-Mar2515-1) or [download the APK](https://github.com/minetest/minetest/releases/download/5.5.0/app-armeabi-v7a-release.apk).
## Final Thoughts

I’ve spent hours in Minetest building and exploring on my local system. It’s great fun. I haven’t gotten around to trying out any of the extra content because I’ve been more than happy with the relatively small portion of the game I’ve played. The only trouble that I’ve encountered was that it ran slow on Fedora, for some reason. I might have had something configured wrong.
If you ever thought that Minecraft looked interesting, but didn’t want to spend the money, check out Minetest. You’ll be glad that you did. Otherwise, [installing Minecraft on Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/install-minecraft-ubuntu/) and other Linux is not that difficult either.
If you have played Minetest, tell us how your experience was in the comments. |
14,776 | 从命令行远程配置 Xfce4 工作区 | https://opensource.com/article/21/1/remote-configuration-xfce4 | 2022-06-30T11:47:51 | [
"Xfce4"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14776-1.html |
>
> 几乎所有的事情都可以从 Linux 命令行完成,包括对 Xfce4 进行远程配置。
>
>
>

与专有操作系统相比,我很欣赏 Linux 的一个特点是,几乎所有的东西都可以从命令行中进行管理和配置。意味着几乎所有的事情都可以在本地或者通过 SSH 远程登录进行管理。虽然有时候需要花费一点时间在互联网上搜索,但是你能想到的任务,是有可能从命令行完成的。
### 问题
有时候需要使用命令行对桌面进行远程配置。在这种特殊情况下,我需要响应远程用户的请求将在 [Xfce](https://www.xfce.org/) 控制板上的工作区从四个减少到三个。这种配置只需要在互联网上搜索约 20 分钟就找到了。
xfwm4 的默认工作区数量和许多其他设置可以在 `/usr/share/xfwm4/defaults` 这个文件中找到和修改。因此将 `workspace_count=2` 设置为 `workspace_count=4` 就改变了主机上所有用户的默认值。同时,非 root 用户可以执行 `xfconf-query` 命令来查询和设置 xfwm4 窗口管理器的各种属性。它应该由需要改变设置的用户使用,而不是由 root 使用。
在下面的例子中,首先我验证了当前工作区数量为 `4` ,然后将数量改为 `2`,最后确认了新设置。
```
[user@test1 ~]# xfconf-query -c xfwm4 -p /general/workspace_count
4
[user@test1 ~]# xfconf-query -c xfwm4 -p /general/workspace_count -s 2
[user@test1 ~]# xfconf-query -c xfwm4 -p /general/workspace_count
2
[user@test1 ~]#
```
此更改会立即生效,用户可以马上看到,无需重新启动,甚至无需注销并重新登录。我曾在我的工作站上玩过这个游戏,当我输入设置不同数量的工作空间的命令时,可以观察到工作空间切换器的变化。我在哪儿都能找到乐子。;- )
### 更多探索
现在我解决了这个问题,我决深入了解一下 `xfconf-query` 命令。不幸的是,该工具没有手册或信息页,`/usr/share` 中也没有任何文档。退而求其次,使用 `-h` 选项获取一些帮助信息。
```
$ xfconf-query -h
Usage:
xfconf-query [OPTION…] - Xfconf commandline utility
Help Options:
-h, --help 显示帮助选项
Application Options:
-V, --version 版本信息
-c, --channel 查询/修改通道
-p, --property 查询/修改属性
-s, --set 更新权限的值
-l, --list 罗列属性(或者通道,如果没有用 -c 指定)
-v, --verbose 详细输出
-n, --create 当新属性不存在,则创建它
-t, --type 指定属性值类型
-r, --reset 重置属性
-R, --recursive 递归(与 -r 一起使用)
-a, --force-array 即使只有一个元素也强制采用数组
-T, --toggle 反转现有的布尔属性
-m, --monitor 监视属性更改的通道
```
这没有多大帮助,但我们还是可以从中找出一些有用的东西。首先,*通道* 是可以修的属性的分组。我对 `general` 通道下的 `workspace_count` 属性进行了更改。让我们看看完整的通道列表:
```
$ xfconf-query -l
Channels:
xfwm4
xfce4-keyboard-shortcuts
xfce4-notifyd
xsettings
xfdashboard
thunar
parole
xfce4-panel
xfce4-appfinder
xfce4-settings-editor
xfce4-power-manager
xfce4-session
keyboards
displays
keyboard-layout
ristretto
xfcethemer
xfce4-desktop
pointers
xfce4-settings-manager
xfce4-mixer
```
给定通道的属性也可以用下列的命令来查看。我使用 `less` 分页器,因为结果是一长串数据。我对下面的列表进行了裁剪,但留下了足够多的条目,你可以看到这些条目的类型。
```
$ xfconf-query -c xfwm4 -l | less
/general/activate_action
/general/borderless_maximize
/general/box_move
/general/box_resize
/general/button_layout
/general/button_offset
<裁剪>
/general/workspace_count
/general/workspace_names
/general/wrap_cycle
/general/wrap_layout
/general/wrap_resistance
/general/wrap_windows
/general/wrap_workspaces
/general/zoom_desktop
(END)
```
你可以用这种方式探索所有的通道。我发现通道通常对应“设置管理器”中的各种设置。这些属性是你在这些对话框中设置的。请注意,并非你在“设置管理器”对话窗口中找到的所有设置都是 Xfce 桌面的一部分,因此它们没有对应的通道。屏幕保护程序就是一个例子,因为它是通用的 GNU 屏幕保护程序,并不是 Xfce 独有的。“设置管理器” 是 Xfce 定位这些配置工具的一个很好的中心位置。
### 文档
综上所述,`xconf-query` 命令似乎没有任何手册或信息页,并且我在网上发现了很多不正确的、记录不全的信息。我发现对 Xfce4 来说最好的文档是 [Xfce 网站](https://www.xfce.org/),关于 `xconf-query` 的一些具体信息可以在这里找到。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/1/remote-configuration-xfce4>
作者:[David Both](https://opensource.com/users/dboth) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[Donkey-Hao](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | One of the things I appreciate about Linux versus proprietary operating systems is that almost everything can be managed and configured from the command line. That means that nearly everything can be configured locally or even remotely via an SSH login connection. Sometimes it takes a bit of time spent on Internet searches, but if you can think of a task, it can probably be done from the command line.
## The problem
Sometimes it is necessary to make remote modifications to a desktop using the command line. In this particular case, I needed to reduce the number of workspaces on the [Xfce](https://www.xfce.org/) panel from four to three at the request of a remote user. This configuration only required about 20 minutes of searching on the Internet.
The default workspace count and many other settings for **xfwm4** can be found and changed in the **/usr/share/xfwm4/defaults** file. So setting *workspace_count=4* to *workspace_count=2* changes the default for all users on the host. Also, the **xfconf-query** command can be run by non-root users to query and set various attributes for the **xfwm4** window manager. It should be used by the user account that requires the change and not by root.
In the sample below, I have first verified the current setting of *four* workspaces, then set the number to *two*, and finally confirmed the new setting.
```
[user@test1 ~]# xfconf-query -c xfwm4 -p /general/workspace_count
4
[user@test1 ~]# xfconf-query -c xfwm4 -p /general/workspace_count -s 2
[user@test1 ~]# xfconf-query -c xfwm4 -p /general/workspace_count
2
[user@test1 ~]#
```
This change takes place immediately and is visible to the user without a reboot or even logging out and back in. I had a bit of fun with this on my workstation by watching the workspace switcher change as I entered commands to set different numbers of workspaces. I get my amusements where I can these days. ;-)
## More exploration
Now that I fixed the problem, I decided to explore the **xfconf-query** command in a bit more detail. Unfortunately, there are no man or info pages for this tool, nor is there any documentation in **/usr/share**. The usual fallback of using the **-h** option resulted in little helpful information.
```
$ xfconf-query -h
Usage:
xfconf-query [OPTION…] - Xfconf commandline utility
Help Options:
-h, --help Show help options
Application Options:
-V, --version Version information
-c, --channel The channel to query/modify
-p, --property The property to query/modify
-s, --set The new value to set for the property
-l, --list List properties (or channels if -c is not specified)
-v, --verbose Verbose output
-n, --create Create a new property if it does not already exist
-t, --type Specify the property value type
-r, --reset Reset property
-R, --recursive Recursive (use with -r)
-a, --force-array Force array even if only one element
-T, --toggle Invert an existing boolean property
-m, --monitor Monitor a channel for property changes
```
This is not a lot of help, but we can figure out a good bit from it anyway. First, *channels* are groupings of properties that can be modified. I made the change above to the **general** channel, and the property is **workspace_count**. Let’s look at the complete list of channels.
```
$ xfconf-query -l
Channels:
xfwm4
xfce4-keyboard-shortcuts
xfce4-notifyd
xsettings
xfdashboard
thunar
parole
xfce4-panel
xfce4-appfinder
xfce4-settings-editor
xfce4-power-manager
xfce4-session
keyboards
displays
keyboard-layout
ristretto
xfcethemer
xfce4-desktop
pointers
xfce4-settings-manager
xfce4-mixer
```
The properties for a given channel can also be viewed using the following syntax. I have used the **less** pager because the result is a long stream of data. I have pruned the listing below but left enough to see the type of entries you can expect to find.
```
$ xfconf-query -c xfwm4 -l | less
/general/activate_action
/general/borderless_maximize
/general/box_move
/general/box_resize
/general/button_layout
/general/button_offset
<SNIP>
/general/workspace_count
/general/workspace_names
/general/wrap_cycle
/general/wrap_layout
/general/wrap_resistance
/general/wrap_windows
/general/wrap_workspaces
/general/zoom_desktop
(END)
```
You can explore all the channels in this manner. I discovered that the channels generally correspond to the various settings in the **Settings Manager**. The properties are the ones that you would set in those dialogs. Note that not all the icons you will find in the **Settings Manager** dialog window are part of the **Xfce** desktop, so there are no corresponding channels for them. The **Screensaver** is one example because it is a generic GNU screensaver and not unique to **Xfce**. The **Settings Manager** is just a good central place for **Xfce** to locate many of these configuration tools.
## Documentation
As mentioned previously, there do not appear to be any man or info pages for the **xconf-query** command, and I found a lot of incorrect and poorly documented information on the Internet. The best documentation I found for **Xfce4** is on the [Xfce website](https://www.xfce.org/), and some specific information on **xconf-query** can be found here.
## 2 Comments |
14,778 | 如何在 elementary OS 中启用最小化、最大化窗口按钮 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/08/enable-minimize-maximize-elementary/ | 2022-06-30T14:11:38 | [
"elementary OS"
] | /article-14778-1.html | 
>
> 这是如何在 elementary OS 中启用最小化、最大化窗口按钮的方法。
>
>
>
许多人(大多数是 elementary OS 的新用户)在各种论坛上问这些问题:
1. 我怎样才能在 elementary OS 中启用最小化按钮?
2. 我如何启用还原、最小化、最大化?
3. 有可能恢复最小化和最大化按钮吗?
这些都是完全正常的问题,而且问问题也是可以的。对吧?这篇指南可以帮助他们在 elementary OS 中获得这些按钮。
Elementary OS 所使用的 Pantheon 桌面并没有默认的标准窗口按钮。其主要原因是通过 Dock 和应用菜单处理用户行为和活动的不同理念。可以说,这种设计或实现的行为模仿了macOS。
不过,许多用户更喜欢窗口按钮,因为这是一个所谓的“肌肉记忆”,而且有些人是从其他桌面环境(甚至是 Windows)迁移过来的。
尽管 Elementary 没有为你提供这个默认设置,你仍然可以启用它。下面是方法。
### 启用最小化最大化按钮 - elementary OS
打开终端,安装添加 PPA 所需的 `software-properties-common` 软件包。默认情况下,这个包在 elementary OS 中没有安装(不要问我为什么,真的)。
```
sudo apt install software-properties-common
```
#### elementary OS 6 Odin
elementary Tweak 工具被重新换了个名字,它现在被称为 [Pantheon Tweaks](https://github.com/pantheon-tweaks/pantheon-tweaks),并正在单独开发中。使用以下命令,你可以安装它:
```
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:philip.scott/pantheon-tweaks
sudo apt install -y pantheon-tweaks
```
#### elementary OS 5 Juno 及更低版本
如果你使用的是 elementary OS 5 June 及更低版本,你可以使用相同的 PPA 安装早期的 [elementary-tweaks](https://github.com/elementary-tweaks/elementary-tweaks)。在终端按照以下命令进行操作:
```
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:philip.scott/elementary-tweaks
sudo apt install -y elementary-tweaks
```
#### 更改设置
* 安装后,点击顶部栏的“<ruby> 应用 <rt> Application </rt></ruby>”,打开“<ruby> 系统设置 <rt> System settings </rt></ruby>”。在系统设置窗口中,点击“<ruby> 个人 <rt> Personal </rt></ruby>”下的 “Tweaks”。
* 在 Tweaks 窗口中,进入“<ruby> 外观 <rt> Appearance </rt></ruby>”。
* 在窗口控制下,选择布局:“Windows”。

* 然后在顶部窗口栏的右侧应该有最小化、最大化和关闭按钮了。
也有其他组合形式,如 Ubuntu、macOS 等。你可以选择任何你觉得合适的:

这篇指南至此就结束了。系统设置中还有其他选项,你可以尝试使用,但窗口管理器 gala 最近删除了这些选项。因此,它们目前可能无法工作。
我希望这个指南能帮助你启用 elementary OS 的最小化最大化按钮。如果你需要任何帮助,请在下面的评论栏告诉我。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/08/enable-minimize-maximize-elementary/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,779 | 使用 rustup 管理你的 Rust 工具链 | https://opensource.com/article/22/6/rust-toolchain-rustup | 2022-06-30T14:54:31 | [
"rustup",
"Rust"
] | /article-14779-1.html | 
>
> rustup 可用于 Rust 安装与更新。它还能够在稳定版、测试版和每日更新版之间无缝切换 Rust 编译器及其工具。
>
>
>
[Rust 编程语言](https://www.rust-lang.org/) 如今变得越来越流行,受到爱好者和公司的一致好评。它受欢迎的原因之一是 Rust 提供的令人惊叹的工具,使其成为开发人员使用的乐趣。[rustup](https://github.com/rust-lang/rustup) 是管理 Rust 工具的官方工具。它不仅可以安装和更新 Rust ,它还能够在稳定版、测试版和每日更新版之间无缝切换 Rust 编译器及其工具。本文将向你介绍 `rustup` 及其一些常用命令。
### 默认 Rust 安装方式
如果你想在 Linux 上安装 Rust,你可以使用你的包管理器。在 Fedora 或 CentOS Stream 上,你可以这样:
```
$ sudo dnf install rust cargo
```
这提供了一个稳定版的 Rust 工具链,如果你是 Rust 的初学者,并想尝试编译和运行简单的程序,它会非常有用。但是,由于 Rust 是一种新的编程语言,它变化很快,并且经常添加许多新功能。这些功能是 Rust 工具链的每日更新版和之后测试版的一部分。要试用这些功能,你需要安装这些较新版本的工具链,而不会影响系统上的稳定版本。不幸的是,你的发行版的包管理器在这里无法做到。
### 使用 rustup 安装 Rust 工具链
要解决上述问题,你可以下载安装脚本:
```
$ curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 \
-sSf https://sh.rustup.rs > sh.rustup.rs
```
检查它,然后运行它。它不需要 root 权限,并根据你的本地用户权限安装 Rust:
```
$ file sh.rustup.rs
sh.rustup.rs: POSIX shell script, ASCII text executable
$ less sh.rustup.rs
$ bash sh.rustup.rs
```
出现提示时选择选项 `1`:
```
1) Proceed with installation (default)
2) Customize installation
3) Cancel installation
> 1
```
安装后,你必须获取环境变量以确保 `rustup` 命令立即可供你运行:
```
$ source $HOME/.cargo/env
```
验证是否安装了 Rust 编译器(`rustc`)和 Rust 包管理器(`cargo`):
```
$ rustc --version
$ cargo --version
```
### 查看已安装和可用的工具链
你可以使用以下命令查看已安装的不同工具链以及哪个工具链是可用的:
```
$ rustup show
```
### 在工具链之间切换
你可以查看默认工具链并根据需要进行更改。如果你当前使用的是稳定版工具链,并希望尝试每日更新版中提供的新功能,你可以轻松切换到每日更新版工具链:
```
$ rustup default
$ rustup default nightly
```
要查看 Rust 的编译器和包管理器的完整路径:
```
$ rustup which rustc
$ rustup which cargo
```
### 检查和更新工具链
要检查是否有新的 Rust 工具链可用:
```
$ rustup check
```
假设一个新版本的 Rust 发布了,其中包含一些有趣的特性,并且你想要获取最新版本的 Rust。你可以使用 `update` 子命令来做到这一点:
```
$ rustup update
```
### 帮助和文档
以上命令对于日常使用来说绰绰有余。尽管如此,`rustup` 有多种命令,你可以参考帮助部分了解更多详细信息:
```
$ rustup --help
```
`rustup` 在 GitHub 上有完整的 [参考手册](https://rust-lang.github.io/rustup/),你可以用作参考。所有 Rust 文档都安装在你的本地系统上,不需要你连接到互联网。你可以访问包括书籍、标准库等在内的本地文档:
```
$ rustup doc
$ rustup doc --book
$ rustup doc --std
$ rustup doc --cargo
```
Rust 是一种正在积极开发中的令人兴奋的语言。如果你对编程的发展方向感兴趣,请关注 Rust!
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/6/rust-toolchain-rustup>
作者:[Gaurav Kamathe](https://opensource.com/users/gkamathe) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,781 | 企业应该选择无服务器计算吗? | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2021/12/should-businesses-opt-for-serverless-computing/ | 2022-07-01T11:39:25 | [
"无服务器计算",
"无服务器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14781-1.html |
>
> 无服务器计算将服务器从规划中移除,使企业能够专注于应用功能。那么,企业是不是都应该选择无服务器计算呢?让我们来探究一下吧!
>
>
>

直至不久之前,几乎每个产品经理都会将他/她的工程资源,分成两个独立的团队 —— 开发团队和运维团队。开发团队通常参与编码、测试和构建应用功能,而运维团队负责应用程序的交付、部署和运行维护。
当开发团队构建电商应用时,运维团队会搭建好服务器来托管该应用。搭建服务器涉及到许多方面,其中包括:
* 选择合适的硬件和操作系统
* 应用所需的补丁集
* 搭建所需服务器环境,如 JDK、Python、Tomcat、NodeJS 等
* 部署、配置和提供实际的应用
* 打开并固定合适的端口
* 搭建所需的数据库引擎
……这个名单还在继续。
除此之外,管理人员还对容量规划感到头疼。毕竟,任何重要应用都应始终保持 100% 可用、可靠且可扩展。这需要对硬件进行最佳投资。众所周知,在一些关键时期,硬件短缺会导致业务损失,而硬件冗余又会损害利润。因此,无论应用是针对本地数据中心,还是针对云基础架构,容量规划都是至关重要的。到目前为止,很明显,企业不仅在功能构建上投入了大量的精力,还在功能交付上也花费了大量的时间。
<ruby> 无服务器计算 <rt> Serverless computing </rt></ruby>旨在提供一种无缝的方式来交付功能,而无需担心服务器的设置和维护。换句话说,无服务器计算平台提供了一个“<ruby> 即用型 <rt> ready-to-use </rt></ruby>”环境,企业可以尽快将应用程序构建和部署为一些较小的功能。这就是为什么这种方法被称为“<ruby> 功能即服务 <rt> Function as a Service </rt></ruby>”(FaaS)。
请记住,无服务器计算中仍然存在服务器,但它由 AWS、微软和谷歌等 FaaS 供应商负责。
例如,AWS 以 “Lambda 函数”的形式提供了一个无服务器计算环境。开发人员可以选择将应用程序构建为一组 Lambda 函数,这些函数可以用 NodeJS、Java、Python 和其他一些语言编写。AWS 提供了一个现成的环境来部署这些函数。它还提供了即用型数据库服务器、文件服务器、应用程序网关和身份验证服务器等。
同样,微软 Azure 也提供了一个环境,它可以用 C# 等语言构建和部署 Azure 函数。
### 为什么选择无服务器?
有两个主要因素推动了无服务器计算的普及。
#### 1、即用型环境
显然,这是无服务器计算的最大卖点。企业无需提前采购/预订硬件或实例,也无需操心许可证,以及设置和配置服务器。他们不需要为扩大和缩小规模而烦恼。所有这些都由 FaaS 供应商负责。
#### 2、最优成本
由于 FaaS 供应商总是根据环境的利用率向客户收费(按使用付费模式),因此企业无需担心前期成本和资源浪费。例如,AWS 根据 Lambda 函数接收的请求数量、在数据表上运行的查询数量等指标来向客户端收费。
### 无服务器计算的挑战
与任何其他方法一样,无服务器计算也不是每个人都可以盲目遵循的完美方法。它本身也有一系列限制。以下是其中的几个。
#### 1、供应商锁定
当使用无服务器计算时,第一个也是最重要的问题就是,Lambda 或 Azure 等函数将使用供应商提供的 API 来编写。例如,使用 AWS Lambda API 编写的函数无法部署到 Google Cloud 中,反之亦然。因此,无服务器计算迫使企业在许多年内,只能使用同一家供应商。并且,应用的成功或失败不仅取决于它的功能,还取决于供应商在性能等方面的能力。
#### 2、编程语言
没有哪家无服务器计算平台支持所有的编程语言。此外,对于它支持的编程语言,它也可能不支持其所有版本。这样一来,应用开发团队只能选择供应商提供的语言。就团队的能力而言,这可能是非常关键的。
#### 3、最优成本,真的吗?
其实也不一定,这一切都取决于资源的使用情况。如果你的应用正在承受巨大的负载,例如每秒数百万个请求,那么你所支付的费用可能会过高。在这样的规模下,在本地或云端拥有自己的服务器可能会更便宜。这并不意味着具有 Web 规模的应用不适合用无服务器计算。归根结底,它还是取决于你的平台的构建方式,以及你与供应商签署的协议。
#### 4、生态系统
没有哪个应用是为了一个孤立的环境而编写的。它总是需要其他组件,如数据存储、数据库、安全引擎、网关、消息服务器、队列、缓存等。每个平台都提供自己的一组此类工具。例如,AWS 提供了 Dynamo DB 作为其 NoSQL 解决方案之一。显然,其他供应商也提供了自己的 NoSQL 解决方案。因此,团队又会被迫地基于所选平台来构建应用程序。尽管大多数商业 FaaS 供应商都为特定需求提供了多个组件,但并非每个组件都可能是同类型中最佳的。
### 为什么不考虑容器呢?
在过去十年中,我们中的许多人都迁移到了容器化部署模型,因为它们为昂贵的物理机或虚拟机提供了一种轻量级的替代方案。有了 Kubernetes 等编排工具后,我们乐于部署容器化应用,同时也满足了 Web 规模的要求。容器提供了与底层环境一定程度的隔离,这使得部署相对容易。但是,我们仍然需要在硬件(本地或云)、许可证、网络、配置等方面进行投资,这需要具有前瞻性的规划、合适的技术能力和仔细的监控。无服务器计算,尽管它也有自己的优点和缺点,但它让我们把这些责任也摆脱了。
### 展望未来
我们正处于持续开发、持续集成和持续部署的时代。每个企业都面临着竞争。产品<ruby> 上市时间 <rt> Time to market </rt></ruby>(TTM)在吸引客户、留住客户这两个方面,发挥着重要作用。在这种背景下,企业喜欢花更多时间来尽可能快地推出功能,而不是在部署和维护的细节上苦苦挣扎。无服务器计算有可能满足这些需求。大玩家们正在投入巨额资金,以使 FaaS 尽可能地无缝且经济。无服务器计算的未来看起来是一片光明。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2021/12/should-businesses-opt-for-serverless-computing/>
作者:[Krishna Mohan Koyya](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/krishna-mohan-koyya/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Serverless computing removes the server from the equation and enables businesses to give undivided attention to the application functionality. Does that make serverless computing the automatic choice? Let’s find out.*
Until recently, almost every product manager organised his or her engineering resources into two separate teams — the development team and the operations team. The development team is usually involved in coding, testing and building the application functionality, whereas the operations team takes the responsibility of delivery, deployment, and operational maintenance of the application.
When a development team builds an e-commerce application, the operations team sets up the server to host that application. Setting up a server involves several aspects, which include:
- Choosing the appropriate hardware and operating system
- Applying the required set of patches
- Installing applicable server environments like JDK, Python, Tomcat, NodeJS, etc
- Deploying, configuring, and provisioning the actual application
- Opening and securing appropriate ports
- Setting up required database engines
… and the list just goes on.
Besides this, managers also break their heads on capacity planning. After all, any non-trivial application is expected to be 100 per cent available, reliable and scalable all the time. This requires optimal investment in the hardware. As we all know, shortage of hardware at crucial periods results in business loss, and on the other hand, redundant hardware hurts the bottomline. Capacity planning is crucial, irrespective of whether the application is targeted for the on-premises data centre or for cloud infrastructure.
By now, it is clear that businesses spend a lot of time not only in building the functionality but also in delivering it.
Serverless computing aims at offering a seamless way to deliver the functionality without worrying about the server setup and maintenance. In other words, a serverless computing platform offers a ready-to-use environment in such a way that the businesses build and deploy the applications as a set of smaller functions as quickly as possible. That is why this approach is referred to as Function as a Service (FaaS).
Remember that there is still a server in serverless computing, but it is taken care of by the FaaS vendors like AWS, Microsoft, and Google.
For example, AWS offers a serverless computing environment in the name of Lambda functions. Developers can choose to build the applications as a set of Lambda functions that can be written in NodeJS, Java, Python, and a few other languages. AWS offers a ready-to-use environment to deploy these functions. It also offers ready-to-use database servers, file servers, application gateways, authentication servers, etc.
Similarly, Microsoft Azure offers an environment to build and deploy Azure functions in languages like C#.
**Why serverless?**
There are two main factors driving the popularity of serverless computing.
*Ready-to-use environment:* Obviously, this is the topmost selling point in favour of serverless computing. Businesses need not procure/book hardware or instances in advance, or worry about licences and setting up and provisioning the server. And they need not bother about scaling up and down. All of this is taken care of by the FaaS vendor.
Optimal cost: Since FaaS vendors always charge the clients based on the utilisation of the environment (pay as you use model), businesses need not worry about upfront costs and wastage of resources. For example, AWS charges the clients based on the number of requests a Lambda function receives, number of queries run on a table, etc.
**Challenges with serverless computing**
Like with any other approach, serverless computing is also not the perfect approach that everyone can blindly follow. It has its own set of limitations. Here are a few of them.
**Vendor locking:** The first and most important problem associated with serverless computing is that functions like Lambda or Azure are to be written using vendor-supplied APIs. For example, the functions that are written using an AWS Lambda API cannot be deployed into Google Cloud and vice versa. Hence, serverless computing forces businesses to commit to a vendor, for years. The success or failure of the application depends not only on the functionality but also on the ability of the vendor with respect to performance, etc.
*Programming language:* No serverless computing platform supports all the possible programming languages. Moreover, it may not support all the versions of a given programming language. The application development teams are constrained to choose only the languages that are offered. This may turn out to be very crucial in terms of the capabilities of the team.
*Optimal cost, really?:* It all depends on the usage of the resources. If your application is attracting a huge load, like millions of requests per second, the bill that you foot might be exorbitant. At such a scale, having your own server on-premises or on the cloud might work cheaper. It doesn’t mean that applications with Web-scale are not suitable for serverless computing. It all boils down to the way you architect around the platform and the deal you sign with the vendor.
*Ecosystem:* No application is written for an isolated environment. It requires other components like data stores, databases, security engines, gateways, messaging servers, queues, cache, etc. Every platform offers its own set of such tools. For instance, AWS offers Dynamo DB as one of the NoSQL solutions. Obviously, other vendors offer their own NoSQL solutions. The teams are thus forced to architect the applications based on the chosen platform. Though most of the commercial FaaS vendors offer one or another component for a particular requirement, not every component may be best-in-class.
**What about containers?**
Many of us migrated to containerised deployment models in the last decade, since they offer a lightweight alternative to the costly machines, physical or virtual. With orchestration tools like Kubernetes, we love to deploy containerised applications and meet Web-scale requirements. Containers offer a certain degree of isolation from the underlying environment, which makes deployment relatively easy. However, we still need investments in hardware (on-premises or cloud), licences, networking, provisioning, etc, which demands forward planning, applicable technical skills, and careful monitoring. Serverless computing frees us even from these responsibilities, albeit with its own set of pros and cons.
**Road ahead**
We are in the days of continuous development, continuous integration, and continuous deployment. Every business is facing competition. Time to market (TTM) plays a significant role in gaining and retaining customers. In this backdrop, businesses love to spend more time churning out the functionality as quickly as possible rather than struggling with the nitty-gritty of deployment and maintenance. Serverless computing has the potential to meet these demands. Big players are committing huge investments to make FaaS as seamless and as affordable as possible. The future looks bright for serverless computing. |
14,782 | 什么是雾计算? | https://opensource.com/article/21/5/fog-computing | 2022-07-01T12:07:30 | [
"雾计算"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14782-1.html |
>
> 了解由我们生活中的所有连接设备组成的网络。
>
>
>

在早期,计算机既笨重又昂贵,计算机用户很少,他们必须在计算机上的预留时间内亲自来处理他们的<ruby> 打孔卡 <rt> punchcard </rt></ruby>。被称为 <ruby> <a href="https://opensource.com/article/19/9/linux-mainframes-part-1"> 大型机 </a> <rt> Mainframe </rt></ruby> 的系统进行了许多创新,并在<ruby> 终端机 <rt> terminal </rt></ruby>(没有自己的 CPU 的桌面计算机)上实现了<ruby> 分时 <rt> time-shared </rt></ruby>任务。
时至今日,强大的计算设备能做到 [价格低至 35 美元,且大小不超过一张信用卡](https://opensource.com/resources/raspberry-pi)。这甚至还没有涵盖现代生活中负责收集和处理数据的所有小设备。从高层次的角度来看这些计算机的集合,你可以想象得到,所有这些设备多得像云中的水滴一样。
碰巧“<ruby> 云计算 <rt> cloud computing </rt></ruby>”一词已经被占用,因此需要为由物联网(IoT)和其他具有战略意义的服务器组成的网络提供一个独特的名称。此外,如果已经有一个代表数据中心节点的云,那么在云之外与我们交融的这些节点肯定有其独特之处。
### 欢迎来到雾计算
云通过互联网提供计算服务。构成云的数据中心很大,但与潜在客户的数量相比相对较少。这表明当数据在云及其众多用户之间来回传送时存在潜在的瓶颈。
相比之下,<ruby> 雾计算 <rt> Fog Computing </rt></ruby>可以在数量上超过其潜在客户,而不会出现瓶颈,因为设备执行大部分数据的收集或计算。它是云的外部“边缘”,是云落地的部分。
### 雾和边缘计算
雾计算和 <ruby> <a href="https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/edge-computing/what-is-edge-computing"> 边缘计算 </a> <rt> edge computing </rt></ruby> 本质上是同义词。两者都与云和物联网密切相关,并做出相同的架构假设:
* 你离 CPU 越近,数据传输就越快。
* 像 [Linux](https://opensource.com/resources/linux) 一样,小型专用计算机,可以“做一件事并把它做好”,这是一个强大的优势(当然,我们的设备实际上不仅仅做一件事,但从高层次上看,你购买的用于监测健康的智能手表本质上是在做“一”件事)。
* 离线是不可避免的,但好的设备可以在此期间同样有效地运行,然后在重新连接时同步。
* 本地设备能比大型数据中心更简单、更便宜。
### 边缘网络
将雾计算视为与云完全分离的实体很诱人,但它们毕竟是组成一个整体的两个部分。云需要数字企业的基础设施,包括公共云提供商、电信公司,甚至是运行自己服务的专业公司。本地化服务也很重要,可以在云核心与其数以百万计的客户之间提供<ruby> 中转站 <rt> waystations </rt></ruby>。
雾计算位于云的边缘,无论客户身在何处,都与他们紧密联系在一起。有时这是一个消费环境,例如你自己的家或汽车,而另一些时候这是一种商业利益,例如零售店中的价格监控设备或工厂车间的重要的安全传感器。
### 雾计算就在你身边
雾计算由我们生活中的所有连接设备组成:<ruby> 无人机 <rt> drone </rt></ruby>、电话、手表、健身监视器、安全监视器、家庭自动化、便携式游戏设备、园艺自动化、天气传感器、空气质量监视器等等。理想情况下,它提供的数据有助于建立一个更好、更明智的未来。有许多伟大的开源项目正朝着改善健康的方向而努力 —— 甚至只是让生活变得更有趣一点儿 —— 这一切都得益于雾和云计算。无论如何,*我们的* 工作是确保它 [保持开放](https://opensource.com/article/20/10/keep-cloud-open)。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/5/fog-computing>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hanszhao80](https://github.com/hanszhao80) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In the early days, computers were big and expensive. There were few users in the world, and they had to reserve time on a computer (and show up in person) to have their punchcards processed. Systems called [mainframes](https://opensource.com/article/19/9/linux-mainframes-part-1) made many innovations and enabled time-shared tasks on terminals (like desktop computers, but without their own CPU).
Skip forward to today, when powerful computation is [as cheap as US$35 and no larger than a credit card](https://opensource.com/resources/raspberry-pi). That doesn't even begin to cover all the little devices in modern life that gather and process data. Take a high-level view of this collection of computers, and you can imagine all of these devices outnumbering grains of sands or particles in a cloud.
It so happens that the term "cloud computing" is already occupied, so there needs to be a unique name for the network comprised of the Internet of Things (IoT) and other strategically situated servers. And besides, if there's already a cloud representing nodes of a data center, then there's surely something unique about the nodes intermingling with us folk outside that cloud.
## Welcome to fog computing
The cloud delivers computing services over the internet. But the data centers that make up the cloud are big and relatively few compared to their number of potential clients. This suggests potential bottlenecks when data is sent back and forth between the cloud and its many users.
Fog computing, by contrast, can outnumber its potential clients without risking a bottleneck because the devices perform much of the data collection or computation. It's the outer "edge" of the cloud, the part of a cloud that touches down to the ground.
## Fog and edge computing
Fog computing and [edge computing](https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/edge-computing/what-is-edge-computing) are essentially synonymous. Both have strong associations with both the cloud and IoT and make the same architectural assumptions:
- The closer you are to the CPU doing the work, the faster the data transfer.
- Like
[Linux](https://opensource.com/resources/linux), there's a strong advantage to having small, purpose-built computers that can "do one thing and do it well." (Of course, our devices actually do more than just one thing, but from a high-level view, a smartwatch you bought to monitor your health is essentially doing "one" thing.) - Going offline is inevitable, but a good device can function just as effectively in the interim and then sync up when reconnected.
- Local devices can be simpler and cheaper than large data centers.
## Networking on the edge
It's tempting to view fog computing as a completely separate entity from the cloud, but they're just two parts of the whole. The cloud needs the infrastructure of the digital enterprise, including public cloud providers, telecommunication companies, and even specialized corporations running their own services. Localized services are also important to provide waystations between the cloud core and its millions and millions of clients.
**[Read next: An Architect's guide to edge computing essentials]**
Fog computing, located at the edge of the cloud, intermingles with clients wherever they are located. Sometimes, this is a consumer setting, such as your own home or car, while other times, it's a business interest, such as price-monitoring devices in a retail store or vital safety sensors on a factory floor.
## Fog computing is all around you
Fog computing is built up of all the connected devices in our lives: drones, phones, watches, fitness monitors, security monitors, home automation, portable gaming devices, gardening automation, weather sensors, air-quality monitors, and much, much more. Ideally, the data it provides helps to build a better and more informed future. There are lots of great open source projects out there that are working toward improving health and wellness—or even just making life a little more entertaining—and it's all happening thanks to fog and cloud computing. *Our* job, however, is to make sure it [stays open](https://opensource.com/article/20/10/keep-cloud-open).
## Comments are closed. |
14,783 | 在 Linux 上使用 Bash 创建一个临时文件 | https://opensource.com/article/22/6/make-temporary-file-bash | 2022-07-01T14:51:13 | [
"临时文件"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14783-1.html |
>
> 基于 Fedora 的系统上的 `mktemp` 命令和基于 Debian 的系统上的 `tempfile` 是专门为减轻这种负担而设计的,它使创建、使用和删除独特的文件变得容易。
>
>
>

使用 Bash 脚本语言进行编程时,有时需要创建一个临时文件。例如,你可能需要一个可以提交到磁盘的中间文件,以便你可以使用另一个命令对其进行处理。创建诸如 `temp` 之类的文件或任何以 `.tmp` 结尾的文件很容易。但是,这些名称很可能是由其他进程生成的,因此你可能会不小心覆盖现有的临时文件。除此之外,你不应该花费脑力想出看起来独特的名字。基于 Fedora 的系统上的 `mktemp` 命令和基于 Debian 的系统上的 `tempfile` 是专门为减轻这种负担而设计的,它使创建、使用和删除独特的文件变得容易。
### 创建一个临时文件
`mktemp` 和 `tempfile` 都创建一个临时文件作为它们的默认操作,并打印文件的名称和位置作为输出:
```
$ tempfile
/tmp/fileR5dt6r
$ mktemp
/tmp/tmp.ojEfvMaJEp
```
除非你指定不同的路径,否则系统会将临时文件放在 `/tmp` 目录中。
对于 `mktemp`,可以使用 `-p` 选项指定路径:
```
$ mktemp -p ~/Demo
/home/tux/Demo/tmp.i8NuhzbEJN
```
对于 `tempfile`,可以使用 `--directory` 或 `-d` 选项:
```
$ tempfile --directory ~/Demo/
/home/sek/Demo/fileIhg9aX
```
### 找到你的临时文件
使用自动生成的临时文件的问题是你无法知道它的名字是什么。这就是为什么两个命令都返回生成的文件名作为输出的原因。你可以使用 Konsole、GNOME 终端或 [rxvt](https://opensource.com/article/19/10/why-use-rxvt-terminal) 等交互式 shell 来使用终端上显示的文件名与文件进行交互。
但是,如果你正在编写脚本,则无法通过读取文件名并在以下命令中使用它来进行干预。
`mktemp` 和 `tempfile` 的作者想到了这个问题,并且有一个简单的解决方法。终端将输出发送到名为“标准输出”的流。你可以通过将变量设置为在子 shell 中启动的命令的结果来捕获标准输出:
```
$ TMPFILE=$(mktemp -p ~/Demo)
$ echo $TMPFILE
/home/tux/Demo/tmp.PjP3g6lCq1
```
引用文件时使用 `$TMPFILE`,它与直接与文件本身交互相同。
### 使用 mktemp 创建一个临时目录
你还可以使用 `mktemp` 命令创建目录而不是文件:
```
$ mktemp --directory -p ~/Demo/
/home/tux/Demo/tmp.68ukbuluqI
$ file /home/tux/Demo/tmp.68ukbuluqI
/home/tux/Demo/tmp.68ukbuluqI: directory
```
### 自定义临时名称
有时你甚至可能希望在伪随机生成的文件名中加入可预测性元素。你可以使用这两个命令自定义临时文件的名称。
使用 `mktemp`,你可以为文件名添加后缀:
```
$ mktemp -p ~/Demo/ --suffix .mine
/home/tux/Demo/tmp.dufLYfwJLO.mine
```
使用 `tempfile`,你可以设置前缀和后缀:
```
$ tempfile --directory ~/Demo/ --prefix tt_ --suffix .mine
/home/tux/Demo/tt_0dfu5q.mine
```
### 把 tempfile 作为 touch 使用
你还可以使用 `tempfile` 设置自定义名称:
```
$ tempfile --name not_random
not_random
```
当你使用 `--name` 选项时,它是绝对的,忽略所有其他形式的自定义。事实上,它甚至忽略了 `--directory` 选项:
```
$ tempfile --directory ~/Demo --prefix this_is_ --suffix .all --name not_random_at
not_random_at
```
在某种程度上,`tempfile` 可以替代 `touch` 和 `test`,因为它拒绝创建已经存在的文件:
```
$ tempfile --name example.txt
open: file exists
```
`tempfile` 命令并非默认安装在所有 Linux 发行版上,因此在将其用作脚本中的 `test` 的 hack 之前,你必须确保它存在。
### 安装 mktemp 和 tempfile
[GNU Core Utils](https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/) 包括 `mktemp` 命令。主要发行版默认包括 Core Utils(它是包含 `chmod`、`cut`、`du` 和其他基本命令的同一个软件包)。
Debian Utils 软件包包含 `tempfile` 命令,默认安装在大多数基于 Debian 的发行版和 Slackware Linux 上。
### 总结
临时文件很方便,因为不会混淆它们是否可以安全删除。它们是临时的,意在根据需要使用并毫不犹豫地丢弃。在需要时使用它们,并在完成后清除它们。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/6/make-temporary-file-bash>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When programming in the Bash scripting language, you sometimes need to create a temporary file. For instance, you might need to have an intermediary file you can commit to disk so you can process it with another command. It's easy to create a file such as `temp`
or anything ending in `.tmp`
. However, those names are just as likely to be generated by some other process, so you could accidentally overwrite an existing temporary file. And besides that, you shouldn't have to expend mental effort coming up with names that seem unique. The `mktemp`
command on Fedora-based systems and `tempfile`
on Debian-based systems are specially designed to alleviate that burden by making it easy to create, use, and remove unique files.
## Create a temporary file
Both `mktemp`
and `tempfile`
create a temporary file as their default action and print the name and location of the file as output:
```
``````
$ tempfile
/tmp/fileR5dt6r
$ mktemp
/tmp/tmp.ojEfvMaJEp
```
Unless you specify a different path, the system places temporary files in the `/tmp`
directory. For `mktemp`
, use the `-p`
option to specify a path:
```
``````
$ mktemp -p ~/Demo
/home/tux/Demo/tmp.i8NuhzbEJN
```
For `tempfile`
, use the `--directory`
or `-d`
option:
```
``````
$ tempfile --directory ~/Demo/
/home/sek/Demo/fileIhg9aX
```
## Find your temporary file
The problem with using an auto-generated temporary file is that you have no way of knowing what its name is going to be. That's why both commands return the generated file name as output. You can use an interactive shell such as Konsole, GNOME Terminal, or [rxvt](https://opensource.com/article/19/10/why-use-rxvt-terminal) to use the filename displayed on your terminal to interact with the file.
However, if you're writing a script, there's no way for you to intervene by reading the name of the file and using it in the following commands.
The authors of `mktemp`
and `tempfile`
thought of that problem, and there's an easy fix. The terminal sends output to a stream called *stdout. *You can capture stdout by setting a variable to the results of a command launched in a subshell:
```
``````
$ TMPFILE=$(mktemp -p ~/Demo)
$ echo $TMPFILE
/home/tux/Demo/tmp.PjP3g6lCq1
```
Use `$TMPFILE`
when referring to the file, and it's the same as interacting directly with the file itself.
## Create a temporary directory with mktemp
You can also use the `mktemp`
command to create a directory instead of a file:
```
``````
$ mktemp --directory -p ~/Demo/
/home/tux/Demo/tmp.68ukbuluqI
$ file /home/tux/Demo/tmp.68ukbuluqI
/home/tux/Demo/tmp.68ukbuluqI: directory
```
## Customize temporary names
Sometimes you might want an element of predictability in even your pseudo-randomly generated filenames. You can customize the names of your temporary files with both commands.
With `mktemp`
, you can add a suffix to your filename:
```
``````
$ mktemp -p ~/Demo/ --suffix .mine
/home/tux/Demo/tmp.dufLYfwJLO.mine
```
With `tempfile`
, you can set a prefix and a suffix:
```
``````
$ tempfile --directory ~/Demo/ \
--prefix tt_ --suffix .mine
/home/tux/Demo/tt_0dfu5q.mine
```
## Tempfile as touch
You can also set a custom name with `tempfile`
:
```
``````
$ tempfile --name not_random
not_random
```
When you use the `--name`
option, it's absolute, ignoring all other forms of customization. In fact, it even ignores the `--directory`
option:
```
``````
$ tempfile --directory ~/Demo \
--prefix this_is_ --suffix .all \
--name not_random_at
not_random_at
```
In a way, `tempfile`
can be a substitute for `touch`
and `test`
because it refuses to create a file that already exists:
```
``````
$ tempfile --name example.txt
open: file exists
```
The `tempfile`
command isn't installed on all Linux distributions by default, so you must ensure that it exists before you use it as a hack around `test`
in a script.
## Install** mktemp and tempfile**
[GNU Core Utils](https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/) includes the `mktemp`
command. Major distributions include Core Utils by default (it's the same package that contains `chmod`
, `cut`
, `du`
, and other essential commands).
The Debian Utils package includes the `tempfile`
command and is installed by default on most Debian-based distributions and Slackware Linux.
## Wrap up
Temporary files are convenient because there's no confusion about whether they're safe to delete. They're temporary, meant to be used as needed and discarded without a second thought. Use them when you need them, and clear them out when you're done.
## 3 Comments |
14,785 | 如何在 Linux 中使用 Pandoc 转换文件格式 | https://itsfoss.com/pandoc-convert-file/ | 2022-07-02T14:43:00 | [
"Pandoc"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14785-1.html | 在之前的一篇文章中,我介绍了使用 pandoc 将少量 Markdown 文件 [批量转换](https://itsfoss.com/convert-markdown-files/) 为 HTML 的过程。在那篇文章中,我创建了多个 HTML 文件,但 Pandoc 可以做的更多。它被称为文档转换的“瑞士军刀” —— 这是有充分理由的。很少有它做不到的事情。
[Pandoc](https://pandoc.org/) 可以将 .docx、.odt、.html、.epub、LaTeX、DocBook 等格式互相转换,或者转换为其他格式,例如 JATS、TEI Simple、AsciiDoc 等。
是的,这意味着 Pandoc 可以将 .docx 文件转换为 .pdf 和 .html 文件,但你可能会想:“Word 也可以将文件导出为 .pdf 和 .html。为什么我需要 Pandoc 呢?”
嗯,本来呢,你这个说法也没错,但考虑到 Pandoc 可以转换这么多格式,它很可能成为你所有转换任务的首选工具。例如,我们中的许多人都知道 [Markdown 编辑器](https://itsfoss.com/best-markdown-editors-linux/) 可以将其 Markdown 文件导出为 .html。而使用 Pandoc 文件也可以转换为许多其他格式。
我很少将 Markdown 导出为 HTML。我通常让 Pandoc 来做这件事。
### 使用 Pandoc 转换文件格式

本文中,我会将 Markdown 文件转换成几种不同的格式。我几乎所有的写作都使用 Markdown 语法,但我经常需要转换为另一种格式:学校作业通常需要的 .docx 格式;我创建的网页通常需要的 .html 格式;工作需要的 .epub 格式;传单和讲义需要的 .pdf 格式;甚至包括一个大学数字人文项目偶尔需要的 TEI Simple 格式。Pandoc 可以轻松处理所有这些格式,甚至更多。
首先,你需要 [安装 pandoc](https://pandoc.org/installing.html)。此外,要创建 .pdf 文件,还需要 LaTeX。我最喜欢的套件是 [TeX Live](https://www.tug.org/texlive/)。
**注意**:如果你想在安装前试用 pandoc,这里有一个在线试用页面:<http://pandoc.org/try/>。
#### 安装 pandoc 和 texlive
Ubuntu 和其他 Debian 发行版的用户可以在终端中输入以下命令:
```
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install pandoc texlive
```
请注意第二行,你将一次性安装 `pandoc` 和 `texlive`。[apt-get 命令](https://itsfoss.com/apt-get-linux-guide/) 支持你这样做。不过,我建议你先去喝杯咖啡,因为这可能需要几分钟的时间。
#### 开始转换
安装完成 `pandoc` 和 `texlive` 后,你就可以尝试用它们来完成一些工作了!
该项目的示例文档将是一篇文章,该文章于 1894 年 12 月首次发表在《北美评论》上,标题为“如何击退火车劫匪”。我将使用的 Markdown 文件是前一段时间创建的,该文章的一个恢复项目的一部分(LCTT 译注:这是篇一百多年前发表的文章,这是一个数字化“恢复”项目)。
我把这篇文章保存为 `how_to_repel_train_robbers.md`,它位于我的 `Documents` 目录下,名为 `samples` 的子目录中。它在 Ghostwriter 中看起来是这样的:

我想创建此文件的 .docx、.pdf 和 .html 版本。
#### 第一次转换
首先,我将制作一个 .pdf 副本,因为我在安装 LaTeX 包时遇到了些麻烦。
在 `~/Documents/samples/` 目录中,我输入以下,以创建一个 .pdf 文件:
```
pandoc -o htrtr.pdf how_to_repel_train_robbers.md
```
上述命令将基于 `how_to_repel_train_robbers.md` 文件,创建一个名为 `htrtr.pdf` 的文件。我使用 `htrtr` 作为名称的原因是:嗯,它比 `how_to_repel_train_robbers` 短。`htrtr` 其实是长标题中的单词首字母排列。
这是 .pdf 文件制作完成后的一个截图:

#### 第二次转换
接下来,我想创建一个 .docx 文件。该命令与我用来创建 .pdf 的命令几乎相同,它是:
```
pandoc -o htrtr.docx how_to_repel_train_robbers.md
```
很快,一个 .docx 文件就创建好了。这是它在 Libre Writer 中的样子:

#### 第三次转换
我可能会想在网上发布这个,所以再多一个支持网页的格式也不错。我将使用以下命令创建一个 .html 文件:
```
pandoc -o htrtr.html how_to_repel_train_robbers.md
```
同样,创建它的命令与前两次转换非常相似。这是该 .html 文件在浏览器中的样子:

#### 注意到什么了吗?
让我们再看看之前的命令。它们是:
```
pandoc -o htrtr.pdf how_to_repel_train_robbers.md
pandoc -o htrtr.docx how_to_repel_train_robbers.md
pandoc -o htrtr.html how_to_repel_train_robbers.md
```
这三个命令唯一不同的是 `htrtr` 后的扩展名。这提示你 pandoc 会依赖于你提供的输出文件扩展名(来决定目标转换格式)。
### 总结
Pandoc 可以做的远不止这里完成的三个小转换。如果你选择使用一个首选格式编写文件,但时不时又需要将文件转换为另一种格式,pandoc 很大概率都能为你完成。
现在,既然你已经学会了,你会用它做什么呢?你会把它自动化吗?如果你有一个网站,想供读者下载文章怎么办?你可以修改这些小命令,把它们编写成一个脚本,你的读者可以决定他们想要哪种格式。你可以提供 .docx、.pdf、.odt、.epub 或更多格式。你的读者只需要选择一种格式,然后对应的转换脚本就会执行,最后,你的读者下载他们想要的文件。这是完全可以做到的。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/pandoc-convert-file/>
作者:[Bill Dyer](https://itsfoss.com/author/bill/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In an earlier article, I covered the [procedure to batch convert a handful of Markdown files to HTML](https://itsfoss.com/convert-markdown-files/) using pandoc. In that article, multiple HTML files were created, but pandoc can do much more. It has been called “the Swiss army knife” of document conversion – and with good reason. There isn’t a lot that it can’t do.
[Pandoc](https://pandoc.org/) can covert .docx, .odt, .html, .epub, LaTeX, DocBook, etc. to these and other formats, such as JATS, TEI Simple, AsciiDoc, and more.
Yes, this means that pandoc can convert .docx files to .pdf and .html, but you may be thinking: “Word can export files to .pdf and .html too. Why would I need pandoc?”
You would have a good point there, but since pandoc can convert so many formats, it could well become your go-to tool for all of your conversion tasks. For example, many of us know that [Markdown editors](https://itsfoss.com/best-markdown-editors-linux/) can export its Markdown files to .html. With pandoc, Markdown files can be converted to numerous other formats as well.
I rarely have Markdown export to HTML; I normally let pandoc do it.
## Converting File Formats with Pandoc

Here, I will convert Markdown files into a few different formats. I do almost all of my writing using Markdown syntax, but I often have to convert to another format: .docx files are usually required for school work, .html for web pages that I create – and for .epub work, .pdf for flyers and handouts, and even an occasional TEI Simple file for a university digital humanities project. Pandoc can handle all of these, and more, easily.
First, you need to [install pandoc](https://pandoc.org/installing.html). Also, to create .pdf files, LaTeX will be needed as well. The package I prefer is [TeX Live](http://www.tug.org/texlive/).
**Note**: If you would like to try out pandoc before installing it, there is an online try-out page at: [http://pandoc.org/try/](http://pandoc.org/try/)
### Installing pandoc and texlive
Users of Ubuntu and other Debian distros can type the following commands in the terminal:
```
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install pandoc texlive
```
Notice on the second line, you are installing pandoc and texlive in one shot. [apt-get command](https://itsfoss.com/apt-get-linux-guide/) will have no problem with this, but go get some coffee; this may take a few minutes.
### Getting to Conversion
Once pandoc and texlive are installed, you can burn through some work!
The sample document for this project will be an article that was first published in the *North American Review* in December of 1894, and is titled: “How To Repel Train Robbers”. The Markdown file that I will be using was created some time ago as part of a restoration project.
The file: `how_to_repel_train_robbers.md`
is located in my Documents directory, in a sub-directory named samples. Here is what it looks like in Ghostwriter.

I want to create .docx, .pdf, and .html versions of this file.
### The First Conversion
I’ll start with making a .pdf copy first, since I went through the trouble of installing a LaTeX package.
While in the ~/Documents/samples/ directory, I type the following to create a .pdf file:
`pandoc -o htrtr.pdf how_to_repel_train_robbers.md`
The above command will create a file called htrtr.pdf from the how_to_repel_train_robbers.md file. The reason I used htrtr as a name was that it is shorter than how_to_repel_train_robbers – htrtr is the first letter of each word in the long title.
Here is a snapshot of the .pdf file once it is made:
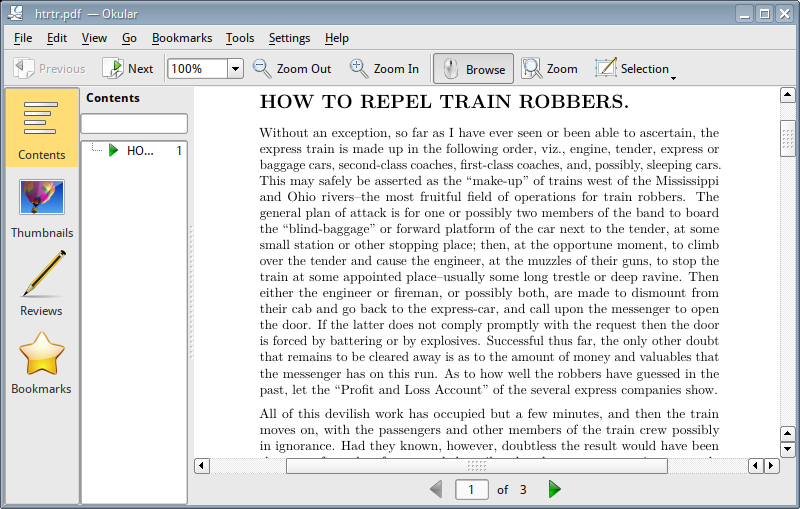
### The Second Conversion
Next, I want to create a .docx file. The command is almost identical to the one I used to create the .pdf and it is:
`pandoc -o htrtr.docx how_to_repel_train_robbers.md`
In no time, a .docx file is created. Here is what it looks like in Libre Writer:
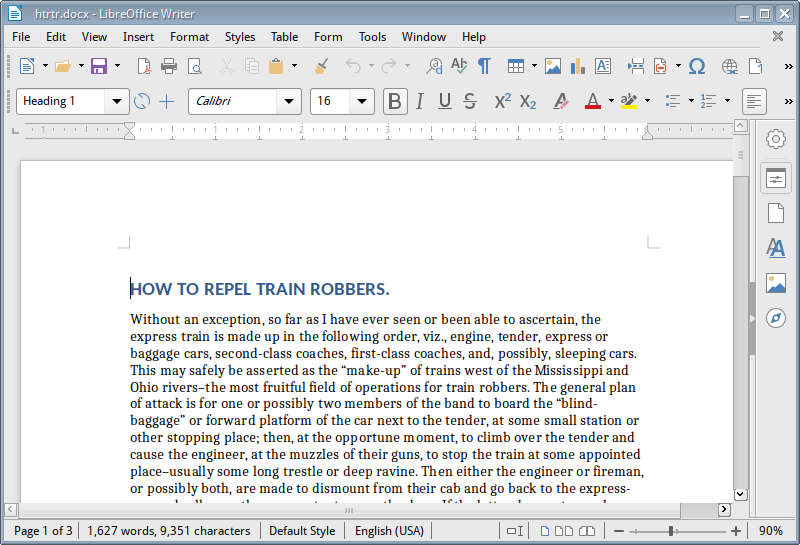
### The Third Conversion
I may want to post this on the web, so a web page would be nice. I will create a .html file with this command:
`pandoc -o htrtr.html how_to_repel_train_robbers.md`
Again, the command to create it is very much like the last two conversions. Here is what the .html file looks like in a browser:
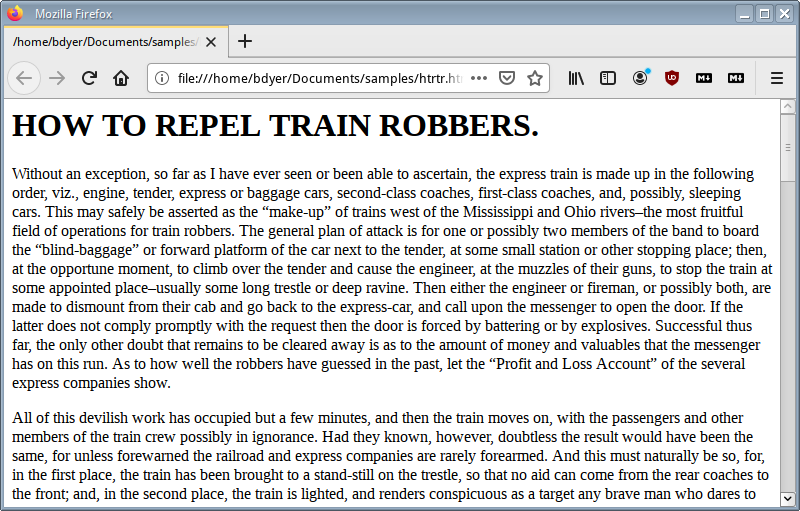
### Noticed Anything Yet?
Let’s look at the past commands again. They were:
```
pandoc -o htrtr.pdf how_to_repel_train_robbers.md
pandoc -o htrtr.docx how_to_repel_train_robbers.md
pandoc -o htrtr.html how_to_repel_train_robbers.md
```
The only thing different about these three commands is the extension next to htrtr. This gives you a hint that pandoc relies on the extension of the output filename you provide.
## Conclusion
Pandoc can do far more than the three little conversions done here. If you write with a preferred format, but need to convert the file to another format, chances are great that pandoc will be able to do it for you.
What would you do with this? Would you automate this? What if you had a web site that had articles for your readers to download? You could modify these little commands to work as a script and your readers could decide which format they would like. You could offer .docx, .pdf, .odt, .epub, or more. Your readers choose, the proper conversion script runs, and your readers download their file. It can be done. |
14,786 | OSI 模型是什么? | https://jvns.ca/blog/2021/05/11/what-s-the-osi-model-/ | 2022-07-02T15:36:23 | [
"OSI",
"TCP/IP"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14786-1.html | 
(LCTT 校注:作者原文已经大篇幅进行了修订更新,本文据之前的版本翻译。)
今天我在推特上发布了一些关于 OSI 模型如何与 TCP/IP 工作原理的实际表现不相符的观点,这让我思考——OSI 模型到底是什么?通过阅读推特上的一些回复发现,似乎至少存在三种不同的思考方式:
1. TCP/IP 工作原理的字面描述
2. 一个可以用来描述和比较很多不同的网络协议的抽象模型
3. 对 1980 年代的一些计算机网络协议的字面描述,这些协议如今大多已不再使用
在这篇文章中,我不打算试图争辩以上哪一个才是“真正”的 OSI 模型——似乎不同的人以所有这些方式思考它。这不重要。
### OSI 模型有七层
在我们讨论 OSI 模型的含义之前,让我们大致地讨论一下它是什么。它是一个抽象模型,用于描述网络如何在七个编号的层上工作:
* 第一层:物理层
* 第二层:数据链路层
* 第三层:网络层
* 第四层:传输层
* 第五层:会话层
* 第六层:表示层
* 第七层:应用层
我不会再费时地去解释每一层的含义,网上有上千种解释可供查询。
### OSI 模型:TCP/IP 工作原理的字面描述
首先,我想谈谈人们在实践中使用 OSI 模型的一种常见方式:作为对 TCP/IP 工作原理的字面描述。OSI 模型的某些层非常容易映射到 TCP/IP:
* 第二层对应以太网
* 第三层对应 IP
* 第四层对应 TCP 或 UDP(或 ICMP 等)
* 第七层对应 TCP 或 UDP 包内的任何内容(例如 DNS 查询)
这种映射对第二、三、四层很有意义——TCP 数据包有三个<ruby> 标头 <rt> header </rt></ruby>对应于这三个层(以太网标头、IP 标头和 TCP 标头)。
用数字来描述 TCP 数据包中的不同标头非常有用——如果你说“第二层”,很显然它位于第三层“下方”,因为二比三小。
“OSI 模型作为字面描述”的古怪之处在于,第五层和第六层并不真正对应于 TCP/IP 中的任何内容——我听说过很多关于第五层或第六层可能是什么的不同解释(你可以说第五层是 TLS 或其他东西!)但它们没有像第二、三、四层那样“每一层在 TCP 数据包中都有相应的标头”这样的明确对应关系。
此外,TCP/IP 的某些部分即使在第二层到第四层也不能很好地适应 OSI 模型——例如,哪一层是 ARP 数据包?ARP 数据包发送一些带有以太网标头的数据,这是否意味着它们是第三层?或是第二层?列出不同 OSI 层的维基百科文章将其归类为“第 2.5 层”,这并不令人满意。
因为 OSI 模型有时用于教授 TCP/IP,若搞不清楚它的哪些部分可以映射到 TCP/IP,而哪些部分不能,则会令人困惑。这才是真的问题。
### OSI 模型:用于比较网络协议的一个抽象
我听说过的另一种关于 OSI 的思考方式是,它是一种抽象,可以用来在许多不同的网络协议之间进行类比。例如,如果你想了解蓝牙协议的工作原理,也许你可以使用 OSI 模型来帮助你——这是我在 [这个网页](https://flylib.com/books/en/4.215.1.116/1/) 上找到的一张图表,显示了蓝牙协议如何适配 OSI 模型。

另一个例子是,[这篇维基百科文章](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_network_protocols_(OSI_model)) 有一个 OSI 层列表,详细划分了哪些特定的网络协议对应于这些 OSI 层。
### OSI 模型:一些过时协议的字面描述
维基百科上的一些非常简短的研究表明,除了对这七层的抽象描述之外,OSI 模型还包含了 [一组实现这些层的特定协议](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OSI_protocols)。显然,这发生在 70 年代和 80 年代的 [协议战争](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protocol_Wars) 时期,OSI 模型失败了,TCP/IP 则取得了胜利。
这就解释了为什么 OSI 模型无法与 TCP/IP 很好地对应,因为如果当时“获胜”的是 OSI 协议,那么 OSI 模型 *将* 完全对应于互联网网络的实际工作方式。
### 结语
我写这篇文章的初衷是,当我最初学习 OSI 模型时,我发现它非常令人困惑(所有这些层是什么?它们是真实存在的吗?这是网络的实际工作原理吗?发生了什么?)我希望有人告诉我这个只使用 TCP/IP 网络协议的人,只需了解 OSI 模型第二、三、四和七层与 TCP/IP 的关系,然后忽略它的所有其他内容即可。所以我希望这篇文章对某些人能有所帮助!
---
via: <https://jvns.ca/blog/2021/05/11/what-s-the-osi-model-/>
作者:[Julia Evans](https://jvns.ca/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hanszhao80](https://github.com/hanszhao80) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | null |
14,788 | 使用 VLC 下载 YouTube 视频 | https://itsfoss.com/download-youtube-videos-vlc/ | 2022-07-03T10:08:14 | [
"VLC",
"流媒体"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14788-1.html | 
[VLC](https://www.videolan.org/vlc/) 是 [Linux 和其他平台上最受欢迎的视频播放器](https://itsfoss.com/video-players-linux/)之一。
它不仅仅是一个视频播放器。它提供了许多多媒体和网络相关的功能。你会惊讶地 [了解 VLC 的能力](https://itsfoss.com/vlc-pro-tricks-linux/)。
我将演示一个简单的 VLC 功能,即使用它下载 YouTube 视频。
是的。你可以在 VLC 中播放 YouTube 视频并下载它们。让我告诉你怎么做。(LCTT 校注:发布此文只探讨技术可行性。)
### 使用 VLC 媒体播放器下载 YouTube 视频
现在,有一些方法可以 [下载 YouTube 视频](https://itsfoss.com/download-youtube-videos-ubuntu/)。使用浏览器扩展或使用专门的网站或工具。
但是如果你不想使用任何额外的东西,已经安装的 VLC 播放器可以用于此目的。
\*\*重要提示:\*\*在从 YouTube 复制链接之前,请确保从 YouTube 播放器中选择所需的视频质量,因为我们将获得与复制链接时流式传输视频相同的质量。
#### 步骤 1:获取所需视频的视频链接
你可以使用任何你喜欢的浏览器并从地址栏中复制视频链接。

#### 步骤 2:将复制的链接粘贴到网络流
“<ruby> 网络流 <rt> Network Stream </rt></ruby>”选项位于“<ruby> 媒体 <rt> Media </rt></ruby>”菜单下,这是我们顶部菜单栏的第一个选项。你也可以使用快捷方式 `CTRL + N` 打开网络流 。

现在,你只需粘贴复制的 YouTube 视频链接,然后单击播放按钮。我知道它只是在我们的 VLC 中播放视频,但还有一点额外的步骤可以让我们下载当前的流媒体视频。

#### 步骤 3:从编解码器信息中获取位置链接
在“<ruby> 编解码器信息 <rt> Codec Information </rt></ruby>”下,我们会得到当前播放视频的位置链接。要打开编解码器信息,你可以使用快捷键 `CTRL + J` 或者你会在“<ruby> 工具 <rt> Tools </rt></ruby>”菜单下找到编解码器信息选项。

它将带来有关当前流媒体视频的详细信息。但我们需要的是“<ruby> 位置 <rt> Location </rt></ruby>”。你只需复制位置链接,我们的任务就完成了 90%。

#### 步骤 4:将位置链接粘贴到新选项卡
打开任何你喜欢的浏览器,并将复制的位置链接粘贴到新选项卡,它将开始在浏览器中播放该视频。
现在,右键单击播放视频,你将看到“将视频另存为”的选项。

它将打开文件管理器并询问你是否要在本地保存此视频。你还可以重命名该文件,默认情况下它将被命名为 “videoplayback.mp4”。

### 结论
如果你有互联网连接问题,或者如果你想保存一些视频以供将来观看,下载 YouTube 视频是有意义的。
当然,我们不鼓励盗版。此方法仅用于合理使用,请确保视频的创建者已允许该视频进行合理使用,并确保在将其用于其他地方之前将其归属于视频的原始所有者。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/download-youtube-videos-vlc/>
作者:[Community](https://itsfoss.com/author/itsfoss/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

[VLC](https://www.videolan.org/vlc/?ref=itsfoss.com) is one of the [most popular video players for Linux](https://itsfoss.com/video-players-linux/) and other platforms.
It’s not just a video player. It provides a number of multimedia and network-related features among other things. You’ll be surprised to [learn what VLC is capable of](https://itsfoss.com/vlc-pro-tricks-linux/).
I’ll demonstrate a simple VLC feature and that is to download YouTube videos with it.
Yes. You can play YouTube videos in VLC and download them too. Let me show you how.
## Download YouTube videos with VLC Media Player
Now, there are ways to [download YouTube videos](https://itsfoss.com/download-youtube-videos-ubuntu/). Use a browser extension or use dedicated websites or tools for it.
But if you don’t want to use anything additional, the already installed VLC player can be used for this purpose.
**Important: **Before copying the link from YouTube, make sure to choose desired video quality from the YouTube player because we will get the same quality in which the video was streaming while copying the link.
### Step 1: Get the Video link of your desired video
You can use any of your favorite browsers and copy the video link from the address bar.
### Step 2: Paste copied Link to Network Stream
The option of Network stream lies under Media which is the first option of our top menu bar. Just click on Media and you will get the option of “Open Network Stream”. You can also use the shortcut to open Network Stream CTRL + N.
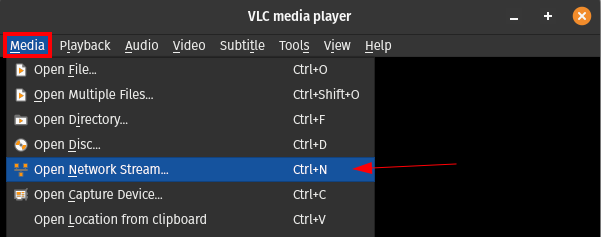
Now, you just have to paste copied YouTube video link and click on the play button. I know it just plays video in our VLC but there is a little extra step that will allow us to download currently streaming video.
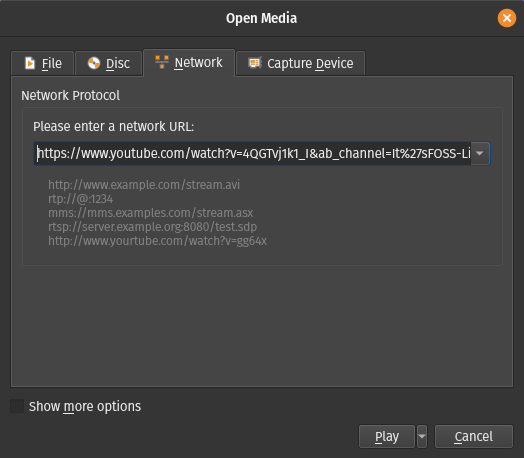
### Step 3: Get Location Link from Codec Information
Under the codec information prompt, we will get a location link for the currently playing video. To open the Codec Information prompt, you can use the shortcut CTRL + J or you’ll find the option for Codec Information under “Tools”.
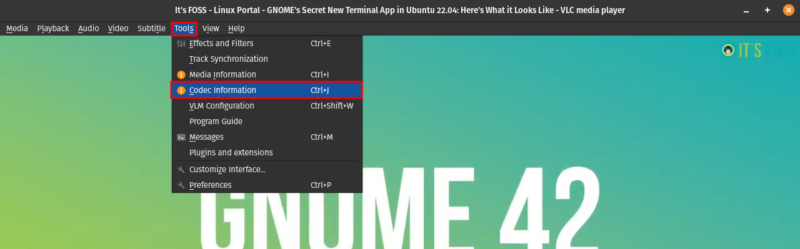
It will bring detailed info about currently streaming video. But what we need is ‘Location’. You just have to copy the location link and 90% of our task is complete.
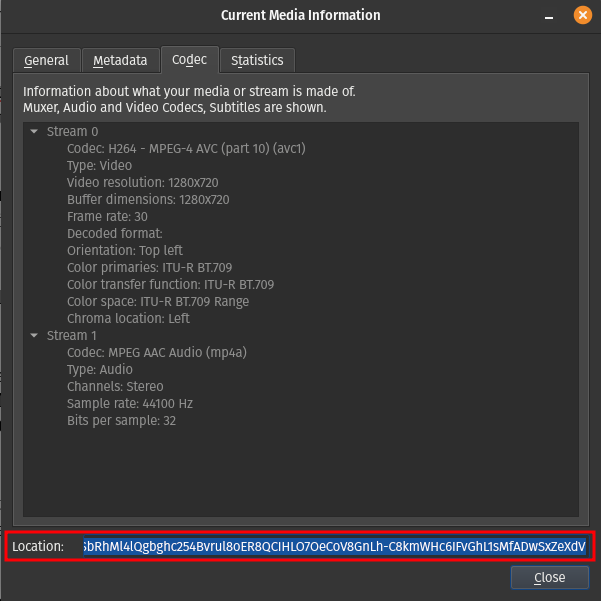
### Step 4: Paste Location Link to New Tab
Open any of your favorite browsers and paste copied location link to the new tab and it will start playing the exact video in the browser.
Now, right-click on playing video and you will get an option for “Save Video As”.
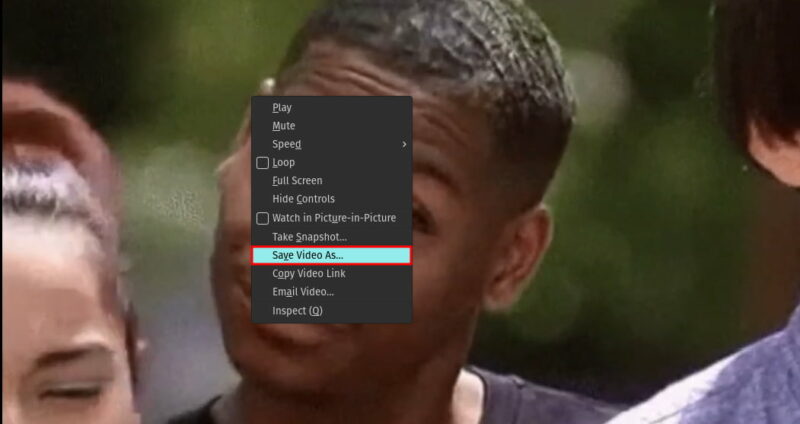
It will open the file manager and ask you whether you want to save this video locally or not. You can also rename that file as by default it will be named “videoplayback.mp4”
## Conclusion
Don't just stop here. VLC can do a lot more.
[Make VLC More Awesome With These Simple TipsVLC is one of the best open source video players, if not the best. What most people don’t know about it is that it is a lot more than just a video player. You can do a lot of complex tasks like broadcasting live videos, capturing devices etc. Just](https://itsfoss.com/simple-vlc-tips/)

If you have internet connection issues or if you want to save some video for future viewing, downloading the YouTube video makes sense.
Of course, we don’t encourage piracy. This method is just for fair use please make sure that the creator of the video has allowed the video for fair usage and also make sure to give credit to the original owner of the video before using it somewhere else. |
14,789 | Kubernetes 架构指南 | https://opensource.com/article/22/2/kubernetes-architecture | 2022-07-03T10:51:40 | [
"Kubernetes"
] | /article-14789-1.html |
>
> 了解 Kubernetes 架构中不同组件是如何组合在一起的,这样你就可以更好地排查问题、维护一个健康的集群,以及优化工作流。
>
>
>

使用 Kubernetes 来编排容器,这种描述说起来简单,但理解它的实际含义以及如何实现它完全是另外一回事。如果你正在运行或管理 Kubernetes 集群,那么你就会知道 Kubernetes 由一台称为 “<ruby> 控制平面 <rt> control plane </rt></ruby>” 的机器和许多其他 <ruby> 工作节点 <rt> worker node </rt></ruby> 机器组成。每种类型都有一个复杂但稳定的堆栈,这使编排成为可能,熟悉每个组件有助于理解它是如何工作的。

*(Nived Velayudhan, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))*
### 控制平面组件
Kubernetes 安装在一个称为“<ruby> 控制平面 <rt> control plane </rt></ruby>”的机器上,它会运行 Kubernetes 守护进程,并在启动容器和<ruby> 容器组 <rt> pod </rt></ruby>时与之通信。下面介绍控制平面的各个组件。
#### etcd
etcd 是一种快速、分布式一致性键值存储器,用作 Kubernetes 对象数据的持久存储,如容器组、副本控制器、密钥和服务。etcd 是 Kubernetes 存储集群状态和元数据的唯一地方。唯一与 etcd 直连的组件是 Kubernetes API 服务器。其他所有组件都通过 API 服务器间接的从 etcd 读写数据。
etcd 还实现了一个监控功能,它提供了一个基于事件的接口,用于异步监控键的更改。一旦你更改了一个键,它的监控者就会收到通知。API 服务器组件严重依赖于此来获得通知,并将 etcd 变更至期望状态。
*为什么 etcd 实例的数量应该是奇数?*
你通常会运行三个、五个或七个 etcd 实例实现高可用(HA)环境,但这是为什么呢?因为 etcd 是分布式数据存储,可以水平扩展它,但你需要确保每个实例中的数据是一致的。因此,需要为系统当前状态达成共识,etcd 为此使用 [RAFT 共识算法](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/raft-consensus-algorithm/)。
RAFT 算法需要经过选举(或仲裁)集群才能进入下一个状态。如果你只有两个 etcd 实例并且他们其中一个失败的话,那么 etcd 集群无法转换到新的状态,因为不存在过半这个概念。如果你有三个 etcd 实例,一个实例可能会失败,但仍有 2 个实例可用于进行选举。
#### API 服务器
API 服务器是 Kubernetes 中唯一直接与 etcd 交互的组件。Kubernetes 中的其他所有组件都必须通过 API 服务器来处理集群状态,包括客户端(kubectl)。API 服务器具有以下功能:
* 提供在 etcd 中存储对象的一致方式。
* 执行验证对象,防止客户端存储配置不正确的对象(如果它们直接写入 etcd 数据存储,可能会发生这种情况)。
* 提供 RESTful API 来创建、更新、修改或删除资源。
* 提供 [乐观并发锁](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/52910322/kubernetes-resource-versioning#:~:text=Optimistic%20concurrency%20control%20(sometimes%20referred,updated%2C%20the%20version%20number%20increases.),在发生更新时,其他客户端永远不会有机会重写对象。
* 对客户端发送的请求进行身份验证和授权。它使用插件提取客户端的用户名、ID、所属组,并确定通过身份验证的用户是否可以对请求的资源执行请求的操作。
* 如果请求试图创建、修改或删除资源,则负责 [权限控制](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/admission-controllers/)。例如,AlwaysPullImages、DefaultStorageClass 和 ResourceQuota。
* 实现了一种监控机制(类似于 etcd),用户客户端监控更改。这允许调度器和控制器管理器等组件以松耦合的方式与 API 服务器交互。
#### 控制器管理器
在 Kubernetes 中,控制器持续监控集群状态,然后根据需要进行或请求更改。每个控制器都尝试将当前集群状态变更至期望状态。控制器至少跟踪一种 Kubernetes 资源类型,这些对象均有一个字段来表示期望的状态。
控制器示例:
* 副本管理器(管理<ruby> 副本控制器 <rt> ReplicationController </rt></ruby>资源的控制器)
* <ruby> 副本集 <rt> ReplicaSet </rt></ruby>、守护进程集DaemonSet 和任务控制器
* 部署控制器
* 有状态负载控制器
* 节点控制器
* 服务控制器
* 接入点控制器
* 命名空间控制器
* <ruby> 持久卷 <rt> PersistentVolume </rt></ruby>控制器
控制器通过监控机制来获得变更通知。它们监视 API 服务器对资源的变更,对每次更改执行操作,无论是新建对象还是更新或删除现有对象。大多数时候,这些操作包括创建其他资源或更新监控的资源本身。不过,由于使用监控并不能保证控制器不会错过任何事件,它们还会定期执行一系列操作,确保没有错过任何事件。
控制器管理器还执行生命周期功能。例如命名空间创建和生命周期、事件垃圾收集、已终止容器组垃圾收集、[级联删除垃圾收集](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/architecture/garbage-collection/) 和节点垃圾收集。有关更多信息,参考 [云控制器管理器](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/architecture/cloud-controller/)。
#### 调度器
调度器是一个将容器组分配给节点的控制平面进程。它会监视新创建没有分配节点的容器组。调度器会给每个发现的容器组分配运行它的最佳节点。
满足容器组调度要求的节点称为可调度节点。如果没有合适的节点,那么容器组会一直处于未调度状态,直到调度器可以安置它。一旦找到可调度节点,它就会运行一组函数来对节点进行评分,并选择得分最高的节点,然后它会告诉 API 服务器所选节点的信息。这个过程称为绑定。
节点的选择分为两步:
1. 过滤所有节点的列表,获得可以调度容器组的节点列表(例如,PodFitsResources 过滤器检查候选节点是否有足够的可用资源来满足容器组的特定资源请求)。
2. 对第一步得到的节点列表进行评分和排序,选择最佳节点。如果得分最高的有多个节点,循环过程可确保容器组会均匀地部署在所有节点上。
调度决策要考虑的因素包括:
* 容器组是否请求硬件/软件资源?节点是否报告内存或磁盘压力情况?
* 节点是否有与容器组规范中的节点选择器匹配的标签?
* 如果容器组请求绑定到特定地主机端口,该端口是否可用?
* 容器组是否容忍节点的污点?
* 容器组是否指定节点亲和性或反亲和性规则?
调度器不会指示所选节点运行容器组。调度器所做的就是通过 API 服务器更新容器组定义。然后 API 服务器通过监控机制通知 kubelet 容器组已被调度,然后目标节点上的 kubelet 服务看到容器组被调度到它的节点,它创建并运行容器组。
### 工作节点组件
工作节点运行 kubelet 代理,这允许控制平面接纳它们来处理负载。与控制平面类似,工作节点使用几个不同的组件来实现这一点。 以下部分描述了工作节点组件。
#### Kubelet
Kubelet 是一个运行在集群中每个节点上的代理,负责在工作节点上运行的所有事情。它确保容器在吊舱中运行。
kubelet服务的主要功能有:
* 通过在 API 服务器中创建节点资源来注册它正在运行的节点。
* 持续监控 API 服务器上调度到节点的容器组。
* 使用配置的容器运行时启动容器组的容器。
* 持续监控正在运行的容器,并将其状态、事件和资源消耗报告给 API 服务器。
* 运行容器存活探测,在探测失败时重启容器,当 API 服务器中删除容器组时终止(通知服务器容器组终止的消息)。
#### 服务代理
服务代理(kube-proxy)在每个节点上运行,确保一个容器组可以与另一个容器组通讯,一个节点可以与另一个节点对话,一个容器可以与另一个容器对话。它负责监视 API 服务器对服务和容器组定义的更改,以保持整个网络配置是最新的。当一项服务得到多个容器组的支持时,代理会在这些容器组之间执行负载平衡。
kube-proxy 之所以叫代理,是因为它最初实际上是一个代理服务器,用于接受连接并将它们代理到容器组。当前的实现是使用 iptables 规则将数据包重定向到随机选择的后端容器组,而无需通过实际的代理服务器。
关于它工作原理的高级视图:
* 当你创建一个服务时,会立即分配一个虚拟 IP 地址。
* API 服务器会通知在工作节点上运行的 kube-proxy 代理有一个新服务。
* 每个 kube-proxy 通过设置 iptables 规则使服务可寻址,确保截获每个服务 IP/端口对,并将目的地址修改为支持服务的一个容器组。
* 监控 API 服务器对服务或其端点对象的更改。
#### 容器运行时
容器运行时有两类:
* **较低级别的容器运行时:** 它们主要关注运行中的容器并为容器设置命名空间和<ruby> 控制组 <rt> cgroup </rt></ruby>。
* **更高级别的容器运行时(容器引擎):** 它们专注于格式、解包、管理、共享镜像以及为开发人员提供 API。
容器运行时负责:
* 如果容器镜像本地不存在,则从镜像仓库中提取。
* 将镜像解压到写时复制文件系统,所有容器层叠加创建一个合并的文件系统。
* 准备一个容器挂载点。
* 设置容器镜像的元数据,如覆盖命令、用户输入的入口命令,并设置 SECCOMP 规则,确保容器按预期运行。
* 通知内核将进程、网络和文件系统等隔离分配给容器。
* 通知内核分配一些资源限制,如 CPU 或内存限制。
* 将系统调用(syscall)传递给内核启动容器。
* 确保 SElinux/AppArmor 设置正确。
### 协同
系统级组件协同工作,确保 Kubernetes 集群的每个部分都能实现其目和执行其功能。当你深入编辑 [YAML 文件](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/yaml-beginners) 时,有时很难理解请求是如何在集群中通信的。现在你已经了解了各个部分是如何组合在一起的,你可以更好地理解 Kubernetes 内部发生了什么,这有助于诊断问题、维护健康的集群并优化你的工作流。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/2/kubernetes-architecture>
作者:[Nived Velayudhan](https://opensource.com/users/nivedv) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven) 校对:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,791 | GNOME 43 中 Nautilus 文件管理器的 6 个新变化 | https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-files-43/ | 2022-07-04T08:38:00 | [
"文件管理器",
"GNOME"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14791-1.html |
>
> GNOME 文件即将到来的变化改善了用户体验,让我们来看看其中的一些变化。
>
>
>

我们离 GNOME 43 的发布还有几个月的时间,但是 GNOME 应用程序的开发活动正在如火如荼地进行。
例如,[GNOME Web 43 alpha 版本支持了扩展](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-web-extensions-dev/)。
同样,GNOME 文件管理器(Nautilus)也有一些令人兴奋的变化,特别是对于列表视图。
列表视图使用 [GtkColumnView](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/nautilus/-/commit/6708861ed174e2b2423df0500df9987cdaf2adc0) 部件重新实现,丢弃了 GtkTreeView,以便能够添加新功能。
一些完善了代码的变化包括:
### 1、拖动并选择文件
就像你在网格视图中通常所做的那样,你终于可以通过简单地拖动你的鼠标在列表视图中选择多个项目,来选择你想要的项目。

如果你没有注意到,每行之间也有一点间隔。虽然选择的动画还不是最流畅的,但它是一个正在进行的工作。
我试着用 peek 录制 GIF(在带有 Wayland 的 Fedora 上),但由于某些原因,它没有反应,可能与 alpha 版本有一些冲突。
### 2、鼠标悬停时高亮行
当你把鼠标悬停在上面的时候,没有行高亮是很不直观的。
现在,它做到了。只要把你的光标放在列表视图中的任何一个项目上,它就会被突出显示,如上图所示。
### 3、搜索一个文件时,列不会消失


当你用当前的 Nautilus 文件管理器搜索一个文件时,列的处理方式不是很好。你会失去某些细节信息,如文件大小。
在新的变化中,你仍然可以看到文件的大小、修改日期,以及给文件加星的能力。
通过这一改变,用户体验肯定会更好。
### 4、更好的紧凑视图
当你缩小文件管理器窗口的大小时,也处理的不是很好。你看不到文件扩展名的细节,而且列对变化没有反应。

在 GNOME 文件管理器 43 alpha 版本中,即使你缩小了窗口的大小以获得一个紧凑的视图,你仍然可以看到列,以及如上所示的文件扩展名。
### 5、新的文件上下文菜单

作为对 2022 年 GSoC(谷歌编程之夏)的贡献的一部分,一位开发者正专注于改善新文档功能的可发现性。
当你将某些文件添加到<ruby> 模板 <rt> Templates </rt></ruby>目录中时,你可以在执行右键单击时在上下文菜单中找到这个 “<ruby> 新文档 <rt> New Document </rt></ruby>” 选项。
在即将到来的更新中,这个选项将是开箱即用。即,更加易于使用。
另外,开发人员正在想办法改进添加模板的过程。你可以这篇在 [博文](https://ignapk.blogspot.com/2022/06/gsoc-2022-first-update-planning.html) 中更多了解他们的工作。
### 6、当你给一个文件加星时的动画

当你点击列表项右侧的星形图标时,你可以发现它在移动,让你知道你与该选项进行了互动。
### 总结
当然,我所提到的一切都处于开发阶段(alpha 版本)。在我们等待 beta 版本的时候,我们应该能清楚地了解到文件管理器的更多功能,以及事情是如何改进的。
你对 GNOME 43 有什么期待?请在下面的评论中告诉我们。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-files-43/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

We have a few months to go before the GNOME 43 release, but the development activity for GNOME applications is in full swing.
For instance, the [support for extensions in GNOME Web](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-web-extensions-dev/) 43 alpha version.
Similarly, there are a few exciting changes coming to GNOME Files (Nautilus), especially for the list view.
The list view was re-implemented using the [GtkColumnView](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/nautilus/-/commit/6708861ed174e2b2423df0500df9987cdaf2adc0?ref=news.itsfoss.com) widget dropping GtkTreeView to be able to add new features.
Some of the changes that influence the code refinement include:
## 1. Drag and Select Files
Just like you would normally do in the grid view, you can finally select multiple items by simply dragging your mouse and selecting the ones you want in the list view.
In case you did not notice, there is also a little bit of spacing between each row. The animation for selection is not the smoothest yet, but it is a work in progress.
Tried to record GIF with peek (Fedora with Wayland), but for some reason it was unresponsive, probably some conflicts with the alpha build.
## 2. Highlight Row on Mouse Hover
It was incredibly unintuitive to not have a row highlight when you hover your mouse over.
Now, it does. Just place your cursor on any of the items in the list view, and it should be highlighted, as shown in the image above.
## 3. Columns Do Not Go Away When You Search for a file
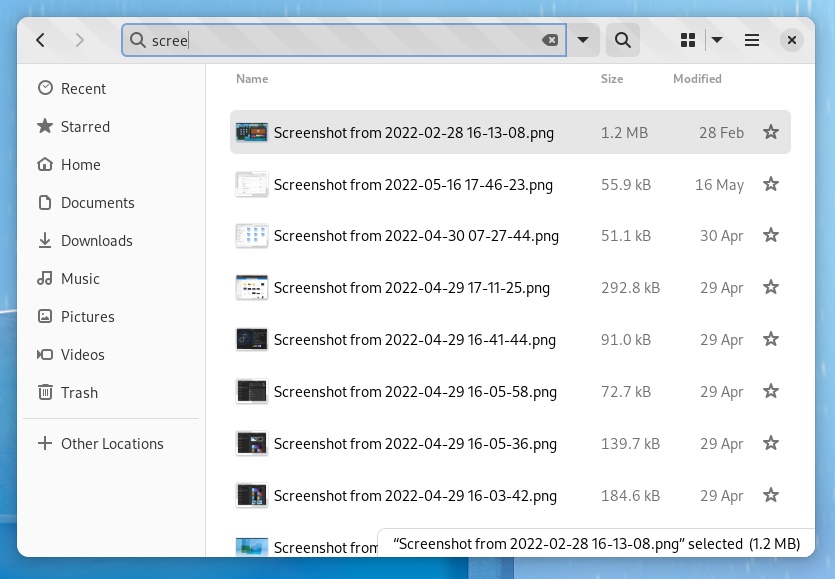
When you search for a file with the current Nautilus file manager, the columns are not handled in the best way possible. You get to lose certain details such as the file size.
With the new change, you still get to see the file size, the modified date, and the ability to star a file.
Definitely towards a better user experience with this change.
## 4. Better Compact View
When you scale down the size of the window with the file manager, it does not handle it well. You lose the file extension details, and the columns aren’t responsive to the change.
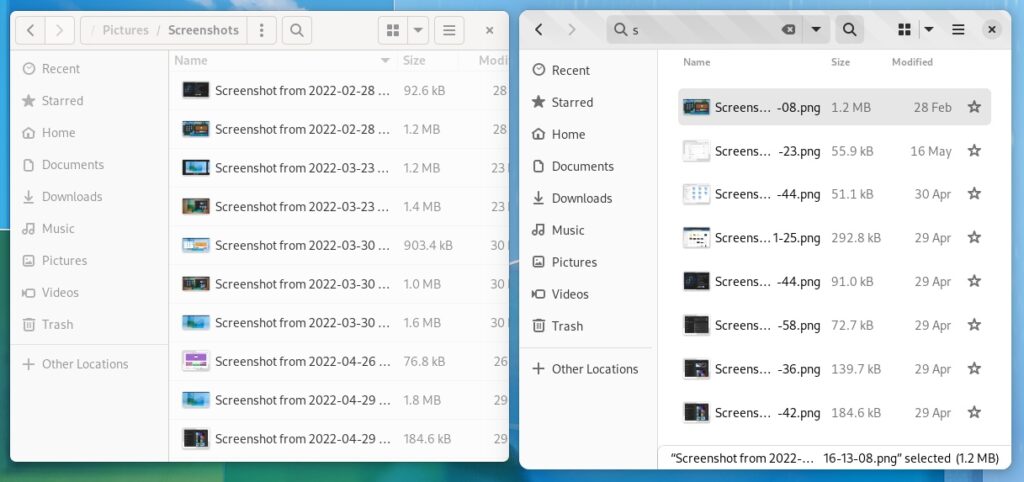
With the 43.alpha build for GNOME Files, even if you scale down the window size for a compact view, you still get to see the columns, and the extension for the files as shown above.
## 5. New Document Context Menu
As part of a contribution to the GSoC (Google Summer of Code) 2022, a developer is focusing on improving the discoverability of the new document feature.
When you add certain files to the Templates directory, you can find the “**New Document**” option in the context menu when you perform a right-click.
With the upcoming update, this option will be available out of the box. So, it is more accessible.
Also, the developers are figuring out a way to improve the process of adding templates. You can explore more of their work in the [blog post](https://ignapk.blogspot.com/2022/06/gsoc-2022-first-update-planning.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## 6. Animation when you star a file
When you click on the star icon on the right side of the list item, you can find it moving to let you know that you interacted with the option.
## Wrapping Up
Of course, everything that I mention is in its development stage (alpha builds). As we wait for the beta builds, we should get clarity on more features coming to the file manager, and how things improve from there.
What are you looking forward to in GNOME 43? Let us know in the comments below.
[5 GNOME 43 Features to Keep an Eye OnGNOME 43 is around the corner. Here are the features that you should expect with the release.](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-43-features/)

## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,792 | Djinn:一个受 Jinja2 启发的代码生成器和模板语言 | https://theartofmachinery.com/2021/01/01/djinn.html | 2022-07-04T10:17:00 | [
"代码生成器",
"Jinja2"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14792-1.html | 
代码生成器是非常有用的工具。我有时使用 [jinja2](https://jinja2docs.readthedocs.io/en/stable/) 的命令行版本来生成高度冗余的配置文件和其他文本文件,但它在转换数据方面功能有限。显然,Jinja2 的作者有不同的想法,而我想要类似于 <ruby> 列表推导 <rt> list comprehensions </rt></ruby> 或 D 语言的 <ruby> 可组合范围 <rt> composable range </rt></ruby> 算法之类的东西。
我决定制作一个类似于 Jinja2 的工具,但让我可以通过使用范围算法转换数据来生成复杂的文件。这个想法非常简单:一个直接用 D 语言代码重写的模板语言。因为它 *就是* D 语言,它可以支持 D 语言所能做的一切。我想要一个独立的代码生成器,但是由于 [D 语言的 `mixin` 特性](https://dlang.org/articles/mixin.html),同样的模板语言可以作为嵌入式模板语言工作(例如,Web 应用程序中的 HTML)。有关该技巧的更多信息,请参阅 [这篇](https://theartofmachinery.com/2017/12/31/compile_time_brainfuck.html) 关于在编译时使用 mixins 将 Brainfuck 转换为 D 和机器代码的文章。
像往常一样,[源码在 GitLab 上](https://gitlab.com/sarneaud/djinn)。[这篇文章中的例子也可以在这里找到](https://gitlab.com/sarneaud/djinn/-/tree/v0.1.0/examples)。
### Hello world 示例
这是一个演示这个想法的例子:
```
Hello [= retro("dlrow") ]!
[: enum one = 1; :]
1 + 1 = [= one + one ]
```
`[= some_expression ]` 类似于 Jinja2 中的 `{{ some_expression }}`,它在输出中呈现一个值。`[: some_statement; :]` 类似于 `{% some_statement %}` ,用于执行完整的代码语句。我更改了语法,因为 D 也大量使用花括号,并且将两者混合使模板难以阅读(还有一些特殊的非 D 指令,比如 `include`,它们被包裹在 `[<` 和 `>]` 中)。
如果你将上面的内容保存到一个名为 `hello.txt.dj` 的文件中并运行 `djinn` 命令行工具,你会得到一个名为 `hello.txt` 的文件,其中包含你可能猜到的内容:
```
Hello world!
1 + 1 = 2
```
如果你使用过 Jinja2,你可能想知道第二行发生了什么。Djinn 有一个简化格式化和空格处理的特殊规则:如果源代码行包含 `[:` 语句或 `[<` 指令但不包含任何非空格输出,则整行都会被忽略输出。空行则仍会原样呈现。
### 生成数据
好的,现在来讲一些更实用的东西:生成 CSV 数据。
```
x,f(x)
[: import std.mathspecial;
foreach (x; iota(-1.0, 1.0, 0.1)) :]
[= "%0.1f,%g", x, normalDistribution(x) ]
```
一个 `[=` 和 `]` 对可以包含多个用逗号分隔的表达式。如果第一个表达式是一个由双引号包裹的字符串,则会被解释为 [格式化字符串](https://dlang.org/phobos/std_format.html#format-string)。下面是输出结果:
```
x,f(x)
-1.0,0.158655
-0.9,0.18406
-0.8,0.211855
-0.7,0.241964
-0.6,0.274253
-0.5,0.308538
-0.4,0.344578
-0.3,0.382089
-0.2,0.42074
-0.1,0.460172
0.0,0.5
0.1,0.539828
0.2,0.57926
0.3,0.617911
0.4,0.655422
0.5,0.691462
0.6,0.725747
0.7,0.758036
0.8,0.788145
0.9,0.81594
```
### 制作图片
这个例子展示了一个图片的生成过程。[经典的 Netpbm 图像库定义了一堆图像格式](http://netpbm.sourceforge.net/doc/#formats),其中一些是基于文本的。例如,这是一个 3 x 3 向量的图像:
```
P2 # PGM 格式标识
3 3 # 宽和高
7 # 代表纯白色的值(0 代表黑色)
7 0 7
0 0 0
7 0 7
```
你可以将上述文本保存到名为 `cross.pgm` 之类的文件中,很多图像工具都知道如何解析它。下面是一些 Djinn 代码,它以相同的格式生成 [Mandelbrot 集](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mandelbrot_set) 分形:
```
[:
import std.complex;
enum W = 640;
enum H = 480;
enum kMaxIter = 20;
ubyte mb(uint x, uint y)
{
const c = complex(3.0 * (x - W / 1.5) / W, 2.0 * (y - H / 2.0) / H);
auto z = complex(0.0);
ubyte ret = kMaxIter;
while (abs(z) <= 2 && --ret) z = z * z + c;
return ret;
}
:]
P2
[= W ] [= H ]
[= kMaxIter ]
[: foreach (y; 0..H) :]
[= "%(%s %)", iota(W).map!(x => mb(x, y)) ]
```
生成的文件大约为 800 kB,但它可以很好地被压缩为 PNG:
```
$ # 使用 GraphicsMagick 进行转换
$ gm convert mandelbrot.pgm mandelbrot.png
```
结果如下:

### 解决谜题
这里有一个谜题:

一个 5 行 5 列的网格需要用 1 到 5 的数字填充,每个数字在每一行中限使用一次,在每列中限使用一次(即,制作一个 5 行 5 列的<ruby> 拉丁方格 <rt> Latin square </rt></ruby>)。相邻单元格中的数字还必须满足所有 `>` 大于号表示的不等式。
[几个月前我使用了 <ruby> 线性规划 <rt> linear programming </rt></ruby>(LP)](https://theartofmachinery.com/2020/05/21/glico_weighted_rock_paper_scissors.html)。线性规划问题是具有线性约束的连续变量系统。这次我将使用<ruby> 混合整数线性规划 <rt> mixed integer linear programming </rt></ruby>(MILP),它通过允许整数约束变量来归纳 LP。事实证明,这足以成为 NP 完备的,而 MILP 恰好可以很好地模拟这个谜题。
在上一篇文章中,我使用 Julia 库 JuMP 来帮助解决这个问题。这次我将使用 [CPLEX:基于文本的格式](http://lpsolve.sourceforge.net/5.0/CPLEX-format.htm),它受到多个 LP 和 MILP 求解器的支持(如果需要,可以通过现成的工具轻松转换为其他格式)。这是上一篇文章中 CPLEX 格式的 LP:
```
Minimize
obj: v
Subject To
ptotal: pr + pp + ps = 1
rock: 4 ps - 5 pp - v <= 0
paper: 5 pr - 8 ps - v <= 0
scissors: 8 pp - 4 pr - v <= 0
Bounds
0 <= pr <= 1
0 <= pp <= 1
0 <= ps <= 1
End
```
CPLEX 格式易于阅读,但复杂度高的问题需要大量变量和约束来建模,这使得手工编码既痛苦又容易出错。有一些特定领域的语言,例如 [ZIMPL](https://zimpl.zib.de/),用于以高级方式描述 MILP 和 LP。对于许多问题来说,它们非常酷,但最终它们不如具有良好库(如 JuMP)支持的通用语言或使用 D 语言的代码生成器那样富有表现力。
我将使用两组变量来模拟这个谜题:`v_{r,c}` 和 `i_{r,c,v}`。`v_{r,c}` 将保存 r 行 c 列单元格的值(从 1 到 5)。`i_{r,c,v}` 是一个二进制指示器,如果 r 行 c 列的单元格的值是 v,则该指示器值为 1,否则为 0。这两组变量是网格的冗余表示,但第一种表示更容易对不等式约束进行建模,而第二种表示更容易对唯一性约束进行建模。我只需要添加一些额外的约束来强制这两个表示是一致的。但首先,让我们从每个单元格必须只有一个值的基本约束开始。从数学上讲,这意味着给定行和列的所有指示器都必须为 0,但只有一个值为 1 的例外。这可以通过以下等式强制约束:
```
[i_{r,c,1} + i_{r,c,2} + i_{r,c,3} + i_{r,c,4} + i_{r,c,5} = 1]
```
可以使用以下 Djinn 代码生成对所有行和列的 CPLEX 约束:
```
\ 单元格只有一个值
[:
foreach (r; iota(N))
foreach (c; iota(N))
:]
[= "%-(%s + %)", vs.map!(v => ivar(r, c, v)) ] = 1
[::]
```
`ivar()` 是一个辅助函数,它为我们提供变量名为 `i` 的字符串标识符,而 `vs` 存储从 1 到 5 的数字以方便使用。行和列内唯一性的约束完全相同,但在 `i` 的其他两个维度上迭代。
为了使变量组 `i` 与变量组 `v` 保持一致,我们需要如下约束(请记住,变量组 `i` 中只有一个元素的值是非零的):
```
[i_{r,c,1} + 2i_{r,c,2} + 3i_{r,c,3} + 4i_{r,c,4} + 5i_{r,c,5} = v_{r,c}]
```
CPLEX 要求所有变量都位于左侧,因此 Djinn 代码如下所示:
```
\ 连接变量组 i 和变量组 v
[:
foreach (r; iota(N))
foreach (c; iota(N))
:]
[= "%-(%s + %)", vs.map!(v => text(v, ' ', ivar(r, c, v))) ] - [= vvar(r,c) ] = 0
[::]
```
不等符号相邻的和左下角值为为 4 单元格的约束写起来都很简单。剩下的便是将指示器变量声明为二进制,并为变量组 `v` 设置边界。加上变量的边界,总共有 150 个变量和 111 个约束 [你可以在仓库中看到完整的代码](https://gitlab.com/sarneaud/djinn/-/tree/v0.1.0/examples/inequality.lp.dj)。
[GNU 线性规划工具集](https://www.gnu.org/software/glpk/) 有一个命令行工具可以解决这个 CPLEX MILP。不幸的是,它的输出是一个包含了所有内容的体积很大的转储,所以我使用 awk 命令来提取需要的内容:
```
$ time glpsol --lp inequality.lp -o /dev/stdout | awk '/v[0-9][0-9]/ { print $2, $4 }' | sort
v00 1
v01 3
v02 2
v03 5
v04 4
v10 2
v11 5
v12 4
v13 1
v14 3
v20 3
v21 1
v22 5
v23 4
v24 2
v30 5
v31 4
v32 3
v33 2
v34 1
v40 4
v41 2
v42 1
v43 3
v44 5
real 0m0.114s
user 0m0.106s
sys 0m0.005s
```
这是在原始网格中写出的解决方案:

这些例子只是用来玩的,但我相信你已经明白了。顺便说一下,Djinn 代码仓库的 `README.md` 文件本身是使用 Djinn 模板生成的。
正如我所说,Djinn 也可以用作嵌入在 D 语言代码中的编译期模板语言。我最初只是想要一个代码生成器,得益于 D 语言的元编程功能,这算是一个额外获得的功能。
---
via: <https://theartofmachinery.com/2021/01/01/djinn.html>
作者:[Simon Arneaud](https://theartofmachinery.com) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hanszhao80](https://github.com/hanszhao80) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Code generators can be useful tools. I sometimes use the command line version of [Jinja2](https://jinja2docs.readthedocs.io/en/stable/) to generate highly redundant config files and other text
files, but it’s feature-limited for transforming data. Obviously the author of Jinja2 thinks differently, but I wanted
something like list comprehensions or D’s composable range algorithms.
I decided to make a tool that’s like Jinja2, but lets me generate complex files by transforming data with range
algorithms. The idea was dead simple: a templating language that gets rewritten directly to D code. That way it
supports everything D does, simply because it *is* D. I wanted a standalone code generator, but thanks to
[D’s mixin
feature](https://dlang.org/articles/mixin.html), the same templating language works as an embedded templating language (for HTML in a web app, for
example). (For more on that trick, see
[this post about translating Brainfuck to D to machine code all at compile time using](/2017/12/31/compile_time_brainfuck.html).)
`mixin`
sAs usual, [it’s on GitLab](https://gitlab.com/sarneaud/djinn). [The examples in this post can be found there,
too.](https://gitlab.com/sarneaud/djinn/-/tree/v0.1.0/examples)
## Hello world example
Here’s an example to demonstrate the idea:
```
Hello [= retro("dlrow") ]!
[: enum one = 1; :]
1 + 1 = [= one + one ]
```
`[= some_expression ]`
is like `{{ some_expression }}`
in Jinja2, and it renders a value to the output.
`[: some_statement; :]`
is like `{% some_statement %}`
and causes full code statements to be executed. I
changed the syntax because D also uses curly braces a lot, and mixing the two made templates hard to read. (There are
also special non-D directives, like `include`
, that get wrapped
in `[<`
and `>]`
.)
If you save the above to a file called `hello.txt.dj`
and
run the `djinn`
command line tool against it, you’ll get a file
called `hello.txt`
containing what you might guess:
```
Hello world!
1 + 1 = 2
```
If you’ve used Jinja2, you might be wondering what happened to the second line. Djinn has a special rule that
simplifies formatting and whitespace handling: if a source line contains `[:`
statements or `[<`
directives but doesn’t contain any non-whitespace output, the whole
line is ignored for output purposes. Blank lines are still rendered.
## Generating data
Okay, now for something a bit more practical: generating CSV data.
```
x,f(x)
[: import std.mathspecial;
foreach (x; iota(-1.0, 1.0, 0.1)) :]
[= "%0.1f,%g", x, normalDistribution(x) ]
```
A `[=`
and `]`
pair can contain multiple expressions separated by commas. If the first
expression is a double-quoted string, it’s interpreted as a [format string](https://dlang.org/phobos/std_format.html#format-string). Here’s the output:
```
x,f(x)
-1.0,0.158655
-0.9,0.18406
-0.8,0.211855
-0.7,0.241964
-0.6,0.274253
-0.5,0.308538
-0.4,0.344578
-0.3,0.382089
-0.2,0.42074
-0.1,0.460172
0.0,0.5
0.1,0.539828
0.2,0.57926
0.3,0.617911
0.4,0.655422
0.5,0.691462
0.6,0.725747
0.7,0.758036
0.8,0.788145
0.9,0.81594
```
## Making an image
This example is just for the heck of it. [The classic netpbm
image library defined a bunch of image formats](http://netpbm.sourceforge.net/doc/#formats), some of which are text-based. For example, here’s an image of a 3x3
cross:
```
P2 # identifier for Portable GrayMap
3 3 # width and height
7 # value for pure white (0 is black)
7 0 7
0 0 0
7 0 7
```
You can save the above text to a file named something like `cross.pgm`
and many image tools will understand it. Here’s some Djinn code
that generates a [Mandelbrot set](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mandelbrot_set) fractal in the same
format:
```
[:
import std.complex;
enum W = 640;
enum H = 480;
enum kMaxIter = 20;
ubyte mb(uint x, uint y)
{
const c = complex(3.0 * (x - W / 1.5) / W, 2.0 * (y - H / 2.0) / H);
auto z = complex(0.0);
ubyte ret = kMaxIter;
while (abs(z) <= 2 && --ret) z = z * z + c;
return ret;
}
:]
P2
[= W ] [= H ]
[= kMaxIter ]
[: foreach (y; 0..H) :]
[= "%(%s %)", iota(W).map!(x => mb(x, y)) ]
```
The resulting file is about 800kB, but it compresses nicely as a PNG:
```
$ # Converting with GraphicsMagick
$ gm convert mandelbrot.pgm mandelbrot.png
```
And here it is:


## Solving a puzzle
Here’s a puzzle:

The 5x5 grid needs to be filled in with numbers from 1 to 5, using each number once in each row, and once in each
column. (I.e., to make a 5x5 Latin square.) The numbers in neighbouring cells must also satisfy the inequalities
indicated by any `>`
greater-than signs.
[I used linear programming (LP) some months ago.](/2020/05/21/glico_weighted_rock_paper_scissors.html) LP
problems are systems of continuous variables with linear constraints. This time I’ll use mixed integer linear
programming (MILP), which generalises LP by also allowing integer-constrained variables. It turns out that’s enough to
be NP complete, and MILP happens to be reasonably good for modelling this puzzle.
In that previous post, I used the Julia library JuMP to help spec the problem. This time I’ll use the [CPLEX text-based format](http://lpsolve.sourceforge.net/5.0/CPLEX-format.htm), which is supported by several LP and
MILP solvers (and can be easily converted to other formats by off-the-shelf tools if needed). Here’s the LP from the
previous post in CPLEX format:
```
Minimize
obj: v
Subject To
ptotal: pr + pp + ps = 1
rock: 4 ps - 5 pp - v <= 0
paper: 5 pr - 8 ps - v <= 0
scissors: 8 pp - 4 pr - v <= 0
Bounds
0 <= pr <= 1
0 <= pp <= 1
0 <= ps <= 1
End
```
CPLEX format is nice to read, but non-trivial problems take a lot of variables and constraints to model, making it
painful and error-prone to write out manually. There are domain-specific languages like [ZIMPL](https://zimpl.zib.de/) for speccing MILPs and LPs in a high-level way. They’re pretty cool for many
problems, but ultimately they’re not as expressive as a general-purpose language with a good library like JuMP — or as
a code generator with D.
I’ll model the puzzle using two sets of variables: and . will hold the value (1-5) of the cell at row and column . will be an indicator binary that’s 1 if the cell at row and column has value , and 0 otherwise. These two sets of variables are redundant representations of the grid, but the first representation makes it easier to model the inequality constraints, while the second representation makes it easier to model the uniqueness constraints. I just need to add some extra constraints to force the two representations to be consistent. But first, let’s start with the basic constraint that each cell must have exactly one value. Mathematically, that means all the indicators for a given row and column must be 0, except for one that is 1. That can be enforced by this equation:
The CPLEX constraints for all rows and columns can be generated with this Djinn code:
```
\ Cell has one value
[:
foreach (r; iota(N))
foreach (c; iota(N))
:]
[= "%-(%s + %)", vs.map!(v => ivar(r, c, v)) ] = 1
[::]
```
`ivar()`
is a helper function that gives us the string
identifier for an variable, and `vs`
stores the numbers 1-5
for convenience. The constraints for uniqueness within rows and columns are exactly the same, but iterating over the
other two dimensions of .
To make the vars consistent with the vars, we need constraints like this (remember, only one of the vars is non-zero):
CPLEX requires all variables to be on the left, so the Djinn code looks like this:
```
\ Link i vars with v vars
[:
foreach (r; iota(N))
foreach (c; iota(N))
:]
[= "%-(%s + %)", vs.map!(v => text(v, ' ', ivar(r, c, v))) ] - [= vvar(r,c) ] = 0
[::]
```
The constraints for the neighouring cell inequalities and for the bottom left corner being 4 are all trivial to
write. All that’s left is to declare the indicator variables to be binary, and set the bounds for the vars. All up, there are 150 variables and 111 constraints, plus bounds for the variables. [You can see the full code in the
repo.](https://gitlab.com/sarneaud/djinn/-/tree/v0.1.0/examples/inequality.lp.dj)
The [GNU Linear Programming Kit](https://www.gnu.org/software/glpk/) has a command line tool that can
solve this CPLEX MILP. Unfortunately, its output is a big dump of everything, so I used awk to pull out what’s
needed:
```
$ time glpsol --lp inequality.lp -o /dev/stdout | awk '/v[0-9][0-9]/ { print $2, $4 }' | sort
v00 1
v01 3
v02 2
v03 5
v04 4
v10 2
v11 5
v12 4
v13 1
v14 3
v20 3
v21 1
v22 5
v23 4
v24 2
v30 5
v31 4
v32 3
v33 2
v34 1
v40 4
v41 2
v42 1
v43 3
v44 5
real 0m0.114s
user 0m0.106s
sys 0m0.005s
```
Here’s the solution written out in the original grid:

These examples are just for playing around, but I’m sure you get the idea. The `README.md`
for the Djinn repo is itself generated using a Djinn template,
by the way.
As I said, Djinn can also be used as a compile-time templating language embedded inside D code. I primarily wanted a code generator, but that’s a bonus thanks to D’s metaprogramming features. |
14,794 | 10 大必备 Ubuntu 应用:基本篇 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/essential-ubuntu-apps-2022-part-1/ | 2022-07-05T13:25:00 | [
"应用"
] | /article-14794-1.html | 
>
> 本文列出了 2022 年可以用于不同情况的 10 个 Ubuntu 基本应用。
>
>
>
不管你是偶尔使用的用户、学生、老师,还是科学家、开发人员和创意工作者,在工作上你需要各种各样的应用程序。Linux 生态系统有数以千计的应用程序,它们分散在各个角落,几乎可以满足各种需求。而包括 Ubuntu 在内的大多数主流 Linux 发行版,默认都只提供了基本的应用程序。
在这个五篇系列文章的第一篇中,我们列出了一些每个人都用的上的专门应用。
### 1、GNOME 优化工具
如果你在使用 Ubuntu GNOME 版,<ruby> GNOME 优化工具 <rt> GNOME Tweak Tool </rt></ruby>是你必备的实用工具。使用这个工具来定制你的桌面,你可以改变字体、缩放比例、主题、光标和许多其他选项。默认的设置窗口现在没有列出所有这些选项。
此外,你也能用该应用改变窗口装饰、标题栏、标题栏按钮以及开机启动项。
你可以使用应用商店搜索 “Tweaks” 来安装它,或者通过下列终端的命令来安装:
```
sudo apt install gnome-tweaks
```

### 2、Steam
由于 Valve 公司和相关社区的贡献,在 Linux 上玩游戏不再困难。[Steam](https://store.steampowered.com/) 是 Valve 公司开发的电子游戏服务的前端平台,你可以通过 Steam 在 Ubuntu 上获取最新的游戏版本。此外,Steam 客户端提供反外挂监测、自动更新,和支持带有流媒体功能的社交对话。
如果你是一个 Linux 游戏玩家,Steam 是常用的客户端,你可以用下面的命令来安装。此外,你可以在应用商店中搜索 “Steam Installer” 并使用 [Flatpak](https://flathub.org/apps/details/com.valvesoftware.Steam) 或 [Snap](https://snapcraft.io/steam) 进行安装。
```
sudo apt install steam
```

### 3、Peek
在我看来,[Peek](https://github.com/phw/peek) 是一款被低估的应用。它是一个 GIF 动画录像机,对各种工作场景都非常有用。这是一款非常强大的应用程序,它适合在 Ubuntu 或任何 Linux 发行版中使用。此外,Peek 带有诸如录制区域选择、倒计时、GIF/MP4/WebM 支持等选项。它的后端使用的是 ffmpeg 。
在应用商店中搜索 “peek” 或者在命令行输入以下命令来安装这款优秀的应用。
```
sudo apt install peek
```

### 4、新立得
<ruby> <a href="https://www.nongnu.org/synaptic/"> 新立得 </a> <rt> Synaptic </rt></ruby> 是一款杰出的软件包管理器,可以帮助你以传统方式添加和移除软件包。有经验的 Linux 用户知道它的特性以及灵活性。你可以在各种库中搜索软件包、验证依赖性并进行安装。
如果你经常安装和卸载软件包,这是一个完美的应用程序。你可以通过以下命令或在应用商店中搜索 “synaptic” 来安装它。
```
sudo apt install synaptic
```

### 5、GDebi
正如上面提到的新立得,你也可以试试 [GDebi](https://launchpad.net/gdebi) 软件包安装程序,它带有几种功能。GDebi 软件包安装程序是用于安装外部 deb 文件的命令行实用程序。此外,GDebi 安装 .deb 包速度更快、效率更高,可以快速解决依赖关系并为你下载它们。
它是 Ubuntu 上安装 .deb 包最好的终端程序之一,你可以用以下命令安装它。安装后,你可以运行 `gdebi <你的 .deb 软件包路径>` 来安装任何软件包。
```
sudo apt install gdebi
```
### 6、Geary
不管从事什么工作,你需要一个 Ubuntu 桌面的本地 [邮箱客户端](https://www.debugpoint.com/2019/06/best-email-client-linux-windows/)。电子邮件对很多人来说仍然是有意义和有价值的。尽管 Ubuntu 默认带有最好的 Thunderbird 电子邮件客户端,但你也可以试试其它的电子邮件客户端应用,或许可以给你带来更好体验。
[Geary](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Geary) 拥有友好而简洁的用户界面,能够让你更简单的设置多个邮件账号。此外, Geary 也带来了会话功能、更快的搜索、撰写富文本电子邮件以及其他功能,这使它成为 Linux 桌面的“首选”电子邮件客户端。
你可以使用如下命令或者在应用商店中搜索 “Geary” 来安装 Geary 。也可以通过 [Flatpak](https://flathub.org/apps/details/org.gnome.Geary) 获得。
```
sudo apt install geary
```

### 7. 谷歌 Chrome 浏览器
虽然很多人担心隐私以及跟踪,但谷歌 Chrome 仍然是浏览器市场的领头者。Ubuntu 默认提供了 Firefox 浏览器,但随着近期火狐的 Snap 事件,你可能想换到其它浏览器。
如果你与谷歌生态系统密切相关,并希望在流媒体和浏览方面获得更好的网络体验,你可能会考虑使用谷歌 Chrome。但是,如果你担心隐私和跟踪,你可以选择其他一些浏览器,例如 Brave 或 Vivaldi。
你可以从下面链接中下载 .deb 包来安装谷歌 Chrome 安装器。安装后,你可以打开应用商店来安装它。
>
> **[下载谷歌 Chrome](https://www.google.com/chrome)**
>
>
>
### 8、Kdenlive
[Kdenlive](https://kdenlive.org/) 是 Linux 上最好的自由开源的视频编辑器之一。 Kdenlive 设计良好的用户界面易于使用,并且带来了各种功能。使用 Kdenlive,你可以简单的导入视频片段,更改画布分辨率,并在编辑后导出为多种格式。时间线和工具让只需你单击一个按钮即可剪切和添加标题、转场和效果。此外,如果你是视频编辑新手,学习起来也非常容易。
Kdenlive 是一个非常活跃的项目,每个主要版本都会带有更多先进的功能。这是 2022 年必不可少的 Ubuntu 应用程序之一,如果你想与其它 [免费视频编辑器](https://www.debugpoint.com/2019/09/best-free-video-editors-linux-ubuntu/) 进行比较,你可以看看此列表。
使用以下命令安装 Kdenlive 很简单。除此,你可以用 [Flatpak](https://flathub.org/apps/details/org.kde.kdenlive) 或 [Snap](https://snapcraft.io/kdenlive) 版本来安装。
```
sudo apt install kdenlive
```

### 9. Spectacle
你可能尝试过很多截屏应用。但在我看来,[Spectacle](https://apps.kde.org/spectacle/) 或许是最好的、也是被低估了的一款应用。Spectacle 是一款 KDE 应用程序,速度超快,非常适合需要截屏并使用的任何工作需求。你可以在自定义的延时后截取整个桌面、部分桌面或窗口。如果需要,窗口截屏还可以选择截取窗口装饰和光标。Spectacle 还为你提供了一个内置的注释功能,可以涂鸦、书写和标记你的图像。
此外,你还可以直接从其主窗口在 GIMP 或任何图像编辑器中打开图像,并将其导出。此外,自动保存、将截屏复制到剪贴板以及共享到社交媒体是 Spectacle 的一些独特功能。
在我看来,它是一个带有内置屏幕录像机的完整截图工具。
你可以用以下命令或者从 [Snap](https://snapcraft.io/spectacle) 中安装 Spectacle。
```
sudo apt install kde-spectacle
```

### 10. VLC 媒体播放器
Ubuntu Linux 的 GNOME 版默认带有可以播放视频文件的 GNOME 视频应用程序。但由于缺乏解码功能,GNOME 视频无法播放多种视频格式。这就是为什么你应该考虑一下 [VLC 媒体播放器](https://www.videolan.org/vlc) —— 它是 Linux 桌面上的“首选”媒体播放器。
VLC 确实可以播放任何格式。它甚至可以帮助你播放数据不完整的损坏视频文件。它是强大的媒体播放器之一,你可以使用下面的命令来安装。
此外,如果你偏向于另一种安装方式,你可以通过 [Flatpak](https://flathub.org/apps/details/org.videolan.VLC) 或者 [Snap](https://snapcraft.io/vlc) 安装。
```
sudo apt install vlc
```

### 结语
2022 年必备的 Ubuntu 应用程序系列的第 1 部分到此结束。通过以上信息,我希望你可以选择一些应用供你的日常使用。在下面的评论框中告诉我你更喜欢此列表中的哪些应用程序。
最后,请继续关注本 Ubuntu 应用程序系列的第 2 部分。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/essential-ubuntu-apps-2022-part-1/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Donkey](https://github.com/Donkey-Hao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,795 | Kuro:非官方的微软 To-Do Linux 桌面客户端 | https://itsfoss.com/kuro-to-do-app/ | 2022-07-05T15:14:06 | [
"To-Do",
"代办事项"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14795-1.html | 
>
> 微软说他们热爱 Linux 和开源,但我们仍然没有得到对其许多产品的 Linux 原生支持。
>
>
>
虽然他们可能在努力增加更多的支持,比如 [可以在 Linux 上安装微软 Edge 浏览器](https://itsfoss.com/microsoft-edge-linux/),但对于一个价值几万亿美元的公司来说,这并不出色。
同样,微软的 To-Do 服务也是一个受欢迎的服务,它取代了 2020 年关闭的 Wunderlist。
如果你不知道的话,我们有很多 [可用于 Linux 的待办事项列表应用](https://itsfoss.com/to-do-list-apps-linux/)。因此,如果你想脱离微软 To-Do,你有选择。
微软 To-Do 是一个基于云的任务管理应用,让你从手机、桌面和网络组织你的任务。它可以在 Windows、Mac 和 Android 上下载。
那么,如果你不愿意使用网页浏览器而使用一个单独的应用,你在 Linux 上能做什么呢?
Kuro 派上用场了。
### Kuro:非官方的开源微软 To-Do 应用

Kuro 是一个非官方的开源应用,它为你提供了微软 To-Do 在 Linux 上的桌面体验和一些额外的功能。
它是 Ao 的一个分叉,Ao 是一个开源项目,逐渐成为它的解决方案。不幸的是,它不再积极维护了。所以,我遇到了一个似乎可以工作的新复刻。

Kuro 提供了一些额外的功能,可以让你在应用中切换主题,启用全局快捷方式等。
请注意,这个应用是相当新的,但有一个稳定版本可以试用。此外,开发者计划在不久的将来增加更多的主题和功能。
### Kuro 的功能

如果你倾向于使用微软的服务(如 Outlook),它的 To-Do 应用应该是组织你的任务的一个完美选择。你甚至可以标记电子邮件以创建任务。
使用 Kuro 桌面客户端,你可以得到一些可配置的功能,包括:
* 能够在启动时启动该程序。
* 获得一个系统托盘图标,以快速创建一个任务,搜索,或检查当天的可用列表。
* 启用全局快捷键。
* 切换可用的主题(深褐色、德古拉、黑色、深色)。
* 切换自动夜间模式,如果你不想不断改变主题。
* 隐藏托盘图标,如果你不需要它。
* 根据需要定制字体大小。

除了一些功能外,你还可以进入某些设置来启用/禁用电子邮件通知、删除前确认等,对待办事项应用体验的进行更多的控制。
总的来说,体验并不糟糕,但我在几分钟内注意到用户界面上有一些奇怪的图形问题。我不确定这是否是一个已知的问题。
### 在 Linux 中安装 Kuro
你可以从它的 [GitHub 发布页面](https://github.com/davidsmorais/kuro/releases) 找到基于 Ubuntu 的发行版的 .deb 包。
此外,你可以从 [Snap 商店](https://snapcraft.io/kuro-desktop) 中在你选择的任何 Linux 发行版上安装它。该软件包也可在 Arch Linux 发行版的 [AUR](https://itsfoss.com/aur-arch-linux/) 中获取。
开发者还提到,正在开发一个 Flatpak 软件包。所以,你可以关注它的 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/davidsmorais/kuro)以了解更多相关信息。
>
> **[Kuro](https://github.com/davidsmorais/kuro)**
>
>
>
你已经试过它了吗?你知道有什么更好的微软 To-Do 客户端用于 Linux 吗?请在下面的评论中告诉我。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/kuro-to-do-app/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Microsoft says that they love Linux and open-source, but we still do not have native support for a lot of its products on Linux.
While they could be trying to add more support, like the ability to [install Microsoft Edge on Linux](https://itsfoss.com/microsoft-edge-linux/)– but it’s not excellent for a multi-trillion dollar company.
Similarly, Microsoft’s To-Do service is also a popular one, replacing Wunderlist as it was shut down in 2020.
In case you’re curious, we have a lot of [to-do list applications available for Linux](https://itsfoss.com/to-do-list-apps-linux/). So, if you want to switch away from Microsoft To-Do, you’ve got options.
Microsoft To-Do is a cloud-based task management application that lets you organize your tasks from your phone, desktop, and the web. It is available to download for Windows, Mac, and Android.
So, if you would rather not use the web browser but a separate application, what can you do on Linux?
Kuro to the rescue.
## Kuro: Unofficial Open-Source Microsoft To-Do App
Kuro is an unofficial open-source application that provides you a desktop experience for Microsoft To-Do on Linux with some extra features.
It is a fork of Ao, which was an open-source project that stepped up to become a solution for it. Unfortunately, it is no longer being actively maintained. So, I came across a new fork for it that seems to get the job done.
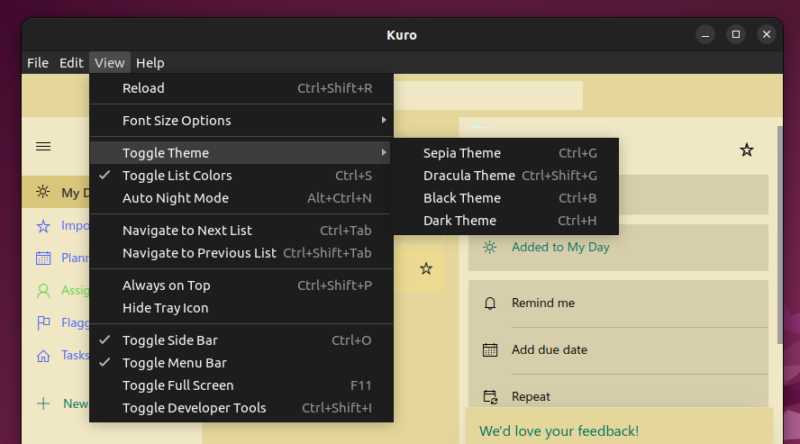
Kuro provides some extra features that let you toggle themes, enable global shortcuts, and more from within the application.
Note that this application is fairly new, but a stable release is available to try. Furthermore, the developer plans to add more themes and features in the near future.
## Features of Kuro
If you tend to use Microsoft services (like Outlook), its To-Do app should be a perfect option to organize your tasks. You can even flag emails to create tasks out of it.
With Kuro desktop client, you get a few quick features to configure that include:
- Ability to launch the program on start.
- Get a system tray icon to quickly create a task, search, or check the available list for the day.
- Enable Global shortcut keys.
- Toggle available themes (Sepia, Dracula, Black, Dark).
- Toggle Auto Night mode, if you do not want to constantly change themes.
- Hide the tray icon, if you do not need it.
- Customize the font size as required.
In addition to some features, you can also access certain settings to enable/disable email notifications, confirm before deleting, and more such controls for the to-do app experience.
Overall, the experience wasn’t terrible, but I noticed some weird graphical glitches in the user interface for a few minutes. I am not sure if it is a known issue.
## Install Kuro in Linux
You can find the .deb package for Ubuntu-based distributions from its [GitHub releases section](https://github.com/davidsmorais/kuro/releases).
In either case, you can also get it from the [Snap store](https://snapcraft.io/kuro-desktop) for any Linux distribution of your choice. The package is also available in [AUR](https://itsfoss.com/aur-arch-linux/) for Arch Linux distributions.
The developer also mentions that a Flatpak package is on its way. So, you can keep an eye on its [GitHub page](https://github.com/davidsmorais/kuro) for more information on that.
Have you tried this already? Do you know of a better Microsoft to-do client for Linux? Let me know in the comments below. |
14,797 | 有了扩展,GNOME Web 正逐渐成为 Linux 桌面上一个有吸引力的选择 | https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-web-extensions-dev/ | 2022-07-06T13:18:17 | [
"GNOME Web",
"浏览器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14797-1.html |
>
> GNOME Web 正在打磨成一个完美的 Linux 浏览器。你认同吗?
>
>
>

GNOME Web(Epiphany)是 [可供 Linux 用户使用的最佳浏览器](https://itsfoss.com/best-browsers-ubuntu-linux/) 之一。
它提供了简约且独特的用户体验。
不幸的是,这种独特性并没有激励用户把它作为主力网页浏览器。
但是,看起来这种情况很快就会改变……
根据其中一位开发者(Patrick,网名 TingPing)透露,GNOME Web 终于添加了对 WebExtensions 的支持。
它将会是 GNOME 43 新功能的一部分。
### 带有 WebExtensions 的 GNOME Web

一个浏览器,外观简约,还支持扩展,夫复何求啊!
我不知道你怎么想,但我对于 GNOME Web 不支持扩展这件事,一直耿耿于怀。
所以,这个消息真的让我很兴奋!
目前,这只是对 **Epiphany 43.alpha** 版本的实验性支持。因此,你只能使用 GNOME Web 的 beta/alpha 构建来测试它。
开发者提到:
>
> Epiphany 43.alpha 支持上述的基本结构。我们目前正在根据 Firefox 的 ManifestV2 API 来建模行为,同时也尽可能与 Chrome 扩展程序保持兼容。未来,我们计划在保留 V2 的同时,支持 ManifestV3。
>
>
>
你必须在终端中显式启用扩展支持,然后下载、添加扩展的 **.xpi** 文件,以安装浏览器扩展。
你需要访问 [Mozilla 的 Firefox 附加组件门户网站](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/extensions/) 来获得扩展程序。

你可以安装 Epiphany(GNOME Web)的最新开发版本,并使用以下命令启用扩展:
```
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists gnome-nightly https://nightly.gnome.org/gnome-nightly.flatpakrepo
flatpak install gnome-nightly org.gnome.Epiphany.Devel
flatpak run --command=gsettings org.gnome.Epiphany.Devel set org.gnome.Epiphany.web:/org/gnome/epiphany/web/ enable-webextensions true
```
请注意,它仍在活跃开发中,可能无法按预期工作。在第一次尝试时,你可能需要密切关注终端是否有错误,如果有的话,要先解决它才行。
如果你想了解更多技术细节,你可以阅读 [TingPing 的博文](https://blog.tingping.se/2022/06/29/WebExtensions-Epiphany.html)。
### 你的下一个主力浏览器?
与 Linux 上的基于 Firefox 和 Chrome/Chromium 的浏览器相比,GNOME Web 是一个的完全独特的替代品。(LCTT 译注:GNOME Web 基于 WebKit 引擎。)
那么,随着即将推出的扩展支持,你愿意尝试将 GNOME Web 作为你的主力浏览器吗?
*你如何看待 GNOME Web(或 Epiphany)中的改进呢?请在下方评论区中告诉我们吧!*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-web-extensions-dev/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

GNOME Web (Epiphany) is one of the [best browsers available for Linux users](https://itsfoss.com/best-browsers-ubuntu-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
It offers a minimal, and a unique user experience.
Unfortunately, the uniqueness does not incentivize users to use it as their primary web browser.
But, it looks like that could change soon…
GNOME Web is finally adding support for WebExtensions, as revealed by one of the developers (**Patrick a.k.a TingPing**).
This is all a part of the GNOME 43 feature set.
## GNOME Web with WebExtensions
A minimal-looking browser, with extension support, what more can I ask for?
I don’t know about you, but I’ve been bummed by the fact that GNOME Web did not have extension support.
So, this makes me excited!
For now, this is experimental support for **Epiphany 43.alpha** version. So, you can only test it as an adventure with GNOME Web’s beta/alpha builds available.
The developer mentions:
Epiphany 43.alpha supports the basic structure described above. We are currently modeling our behavior after Firefox’s ManifestV2 API which includes compatibility with Chrome extensions where possible. Supporting ManifestV3 is planned alongside V2 in the future.
You will have to explicitly enable the extension support using the terminal, and then install the extensions by downloading + adding the **.xpi** files for the extensions.
[Mozilla’s Firefox add-ons web portal](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/extensions/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is the one you need to visit for the extensions.
You can install the latest development version for Epiphany (GNOME Web) and enable extensions using the following commands:
```
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists gnome-nightly https://nightly.gnome.org/gnome-nightly.flatpakrepo
flatpak install gnome-nightly org.gnome.Epiphany.Devel
flatpak run --command=gsettings org.gnome.Epiphany.Devel set org.gnome.Epiphany.web:/org/gnome/epiphany/web/ enable-webextensions true
```
Note that it is actively in development, and may not work as expected. You may want to keep an eye on the terminal for any errors and resolve that if it did not work for you on the first try.
For more technical details, you can read [TingPing’s blog post](https://blog.tingping.se/2022/06/29/WebExtensions-Epiphany.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Your Next Daily Driver?
GNOME Web is an entirely unique alternative to Firefox and Chrome/Chromium-based browsers on Linux.
So, with the upcoming support for extensions, would you be willing to give it a try as your main browser?
*What do you think about the improvements arriving in GNOME Web (or Epiphany)?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,798 | 星际战机:配备 4K 10 位 IPS 显示屏的 Linux 笔记本电脑即将问世 | https://news.itsfoss.com/starfighter-laptop-reveal/ | 2022-07-06T14:40:49 | [
"笔记本电脑"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14798-1.html |
>
> “星际战机”是星空实验室即将推出的一款 Linux 笔记本电脑。他们正在最后确定生产细节,同时透露了一些关键的亮点。
>
>
>

我们已经有许多来自星空实验室、TUXEDO 等制造商的 Linux 专用笔记本电脑。
然而,其中只有少数几家专注于提供一个超棒的显示屏。
例如,[TUXEDO 的 Infinitybook Pro 14](https://news.itsfoss.com/infinitybook-pro-14-3k/) 带有 3K 显示屏,而且,该笔记本电脑确实不错。
现在,看起来 [星空实验室](http://starlabs.systems) 将为其即将推出的 “星际战机” 笔记本电脑配备 15.6 英寸 4K 显示屏。他们在 [推特](https://twitter.com/starlabsltd/status/1542908391793692672) 上分享了初步信息,提到他们正在敲定生产细节。
### 关于星际战机我们目前所知道的情况
这款笔记本电脑将采用 45W 供电的英特尔 / AMD 处理器,它将有英特尔 / AMD 两种变体可用。
你还将可以选择高达 64GB 的内存和 2TB 的存储。可以说,对于那些想为自己的 Linux 笔记本电脑提高规格的用户来说,这应该是一个强大的机器。
当然,它的关键亮点是显示屏。它将采用 4K 10 位哑光 IPS 显示屏。
该公司提到,该显示屏的成本要高于其 StarLite 笔记本电脑。
但是,这会是一个有吸引力的产品吗?许多采用高分辨率显示屏或 OLED 面板的笔记本电脑在电池时长方面表现不佳。不仅仅是 Linux 笔记本电脑。
那么,“星际战机”会成为该领域的一个有竞争力的竞争者吗?
星空实验室在一条推文中提到,他们估计电池时长约为 8-14 小时,这取决于配置。当然,这也取决于你的使用情况。
该公司还澄清说,这款笔记本电脑可以使用 Coreboot,但它不会是一个完全采用自由软件的项目。其他一些值得注意的地方还有:
* 该笔记本电脑将具有 [LVFS](https://fwupd.org/) 支持。
* 英特尔型号将提供第 4 代固态硬盘。AMD 型号将只限于第 3 代固态硬盘。
如图片所示,它可能安装了 elementaryOS 6.1。然而,你也可以预期它提供 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS。
那么,你对星空实验室的这架“星际战机”有何看法?当它上市时,这将是你的下一台笔记本电脑吗?
在下面的评论区分享你的想法。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/starfighter-laptop-reveal/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

We’ve had numerous Linux-exclusive laptops from manufacturers like Star Labs, TUXEDO, and others.
However, only a handful of them focused on providing a great display.
For instance, [TUXEDO’s Infinitybook Pro 14](https://news.itsfoss.com/infinitybook-pro-14-3k/) featured a 3K display. And, it was a nice offering.
Now, it looks like [Star Labs](http://starlabs.systems/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is gearing up with a 15.6-inch 4K display for its upcoming “StarFighter” laptop. They shared initial information on [Twitter](https://twitter.com/starlabsltd/status/1542908391793692672?ref=news.itsfoss.com) mentioning that they are finalizing the production details.
## StarFighter: Here’s What We Know So Far
The laptop will feature a 45W-powered Intel/AMD processor. So, yes, it will have both Intel/AMD variants available.
You will also be getting options for up to 64 GB of memory and 2 TB of storage. It is safe to say that it should be a powerhouse for users who want beefed-up specifications for their Linux laptops.
Of course, the key highlight is the display. It will be sporting a 4K 10-bit matte IPS display.
The company mentions that the display costs more than its StarLite laptop.
But, will this be an attractive offering? Many laptops with high-res displays or OLED panels haven’t worked well with the battery life. Not just Linux laptops.
So, will StartFighter be a competitive contender in the space?
Star Labs mentioned in a tweet that they estimate it for around 8-14 hours depending on the configuration. Of course, it will come down to your usage as well.
The company also clarified that the laptop will be available with coreboot, but it will not be an entirely free software project. Some other points to note include:
- The laptops will feature
[LVFS](https://fwupd.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)support. - Intel models will be available with Gen 4 SSDs. AMD variants will be limited to Gen 3.
It could feature elementaryOS 6.1 as the image suggests. However, you should also expect to have Ubuntu 22.04 LTS as an option for the OS.
So, what do you think about StarFighter by Star Labs? Would this be your next laptop when it is available?
Share your thoughts in the comments section below.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,799 | 在 Linux 中找到你的路由器的 IP 地址(默认网关) | https://itsfoss.com/router-ip-address-linux/ | 2022-07-06T15:52:00 | [
"网关"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14799-1.html | 
你可能已经知道如何在 Linux 中获得你的系统的 IP 地址。
但是你怎么知道你的路由器的 IP 地址呢?
我说的不是你可以通过连接到 “[Show My IP](https://www.showmyip.com/)” 这样的网站或简单地在 [DuckDuckGo](https://itsfoss.com/duckduckgo-easter-eggs/) 中 [搜索“what is my ip”](https://duckduckgo.com/?q=what+is+my+ip&t=h_&ia=answer) 获得的公网 IP。
我说的是默认网关 IP,你的 Linux 桌面所连接的地址。
你为什么需要它?嗯,如果你需要改变你的 Wi-Fi/网络的 SSID、密码或其他配置,你必须连接到它。简单的方法是在网页浏览器中输入路由器的 IP 地址,然后使用路由器的用户名和密码。
虽然我不能帮助你获得路由器的用户名和密码,但我肯定可以告诉你如何获得它的 IP。
一如既往,我将展示 GUI 和命令行两种方法。
### 方法 1:在 Linux 中使用 GUI 获取路由器的 IP 地址
这其实很简单。我在这里使用的是 Ubuntu 的 GNOME 桌面。如果你使用一些 [其他桌面环境](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/),截图可能会有所不同。
打开“<ruby> 系统设置 <rt> System Settings </rt></ruby>”:

现在进入 Wi-Fi 或“<ruby> 网络 <rt> Network </rt></ruby>”(如果你使用的是有线的以太网连接)。在这里,点击你当前使用的网络旁边的小设置符号。

它将打开一个新窗口,里面有关于你的连接的一些细节,如 IP 地址、DNS 和 [Mac 地址](https://itsfoss.com/change-mac-address-linux/)。你还可以在“<ruby> 安全 <rt> security </rt></ruby>”标签下看到 [保存的 Wi-Fi 密码](https://itsfoss.com/how-to-find-saved-wireless-wifi-passwords-ubuntu/)。
你还会看到一个名为“<ruby> 默认路由 <rt> Default Route </rt></ruby>”的条目。这就是你要找的东西。你的路由器的 IP 地址。

你的系统和网络上的所有其他设备都使用这个 IP 地址连接到路由器。这就是大多数家庭的设置。
现在我已经展示了 GUI 的方法,让我们去看看终端的路线。
### 方法 2:在 Linux 命令行中获取路由器的 IP 地址
打开一个终端,使用以下命令:
```
ip route
```
它将显示几个条目。
```
~$ ip route
default via 192.168.1.1 dev wlp0s20f3 proto dhcp metric 600
169.254.0.0/16 dev wlp0s20f3 scope link metric 1000
192.168.1.0/24 dev wlp0s20f3 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.34 metric 600
```
第一行,以 `default via` 开头,给出了你网关的 IP。这是你的路由器的 IP 地址。

你可以看到,`192.168.1.1` 是我的路由器的 IP 地址。通常情况下,路由器的 IP 地址是子网的第一个数字。然而,这并不是一个硬性规定。我也见过有 `x.y.z.30` 地址的路由器。
### 额外技巧
正如 Samir 在评论中所分享的,你也可以(在 Debian 上)使用 `ping` 命令来获得网关 IP:
```
ping _gateway
```

以防你不知道,你必须 [在 Linux 中使用 Ctrl+C 来停止一个正在运行的命令](https://itsfoss.com/stop-program-linux-terminal/)。
我希望你在需要的时候能发现这个技巧是有用的。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/router-ip-address-linux/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

You probably already know how to [get your system’s IP address in Linux](https://itsfoss.com/check-ip-address-ubuntu/).
But how do you know the IP address of your router?
I am not talking about the public-facing IP which you can get by connecting to websites like [Show My IP](https://www.showmyip.com/?ref=its-foss) or simply [searching for ‘what is my ip’](https://duckduckgo.com/?q=what+is+my+ip&t=h_&ia=answer&ref=its-foss) in [DuckDuckGo](https://itsfoss.com/duckduckgo-easter-eggs/).
I am talking about the default gateway IP which your Linux desktop uses to connect to it.
Why do you need it? Well, if you need to change the SSID, password, or other configuration of your wi-fi/network, you have to connect to it. And the simplest way is to type the router's IP address in a web browser and then use the router’s username and password.
While I cannot help you with the username and password of your router, I can surely tell you how to get its IP.
As always, I’ll show both GUI and command-line methods.
## Method 1: Get the router’s IP address in Linux using GUI
It’s quite simple actually. I am using GNOME desktop with Ubuntu here. If you use some [other desktop environments](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/), screenshots may look different.
Open System Settings:
Now go to Wi-Fi or Network (if you are using a wired, Ethernet connection). Here, click on the little settings symbol beside your currently used network.
It will open a new window with several details about your connection such as the IP address, DNS, and [Mac address](https://itsfoss.com/change-mac-address-linux/). You can also see the [saved wifi password](https://itsfoss.com/how-to-find-saved-wireless-wifi-passwords-ubuntu/) under the security tab.
You’ll also see an entry named ‘Default Route’. This is what you are looking for. The IP address of your router.
Your system and all other devices on your network connect to the router using this IP address. This is the setup most households have.
Now that I have shown the GUI method, let’s go to the terminal route.
## Method 2: Get the router’s IP address in Linux command line
Open a terminal and use the following command:
`ip route`
It will show you a few entries.
```
abhishek@itsfoss:~$ ip route
default via 192.168.1.1 dev wlp0s20f3 proto dhcp metric 600
169.254.0.0/16 dev wlp0s20f3 scope link metric 1000
192.168.1.0/24 dev wlp0s20f3 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.34 metric 600
```
The first line, which starts with ‘default via’, gives you the gateway IP. This is your router’s IP address.
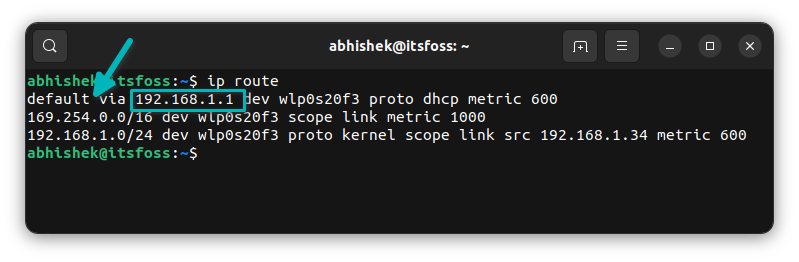
As you can see, 192.168.1.1 is the IP address of my router. Usually, the router’s IP address is the first number of the subnet. However, this is not a hard and fast rule. I have seen routers with x.y.z.30 addresses as well.
## Bonus tip
As shared by Samir in the comments, you can also [use the ping command](https://itsfoss.com/ping-command/) to get the gateway IP:
`ping _gateway`
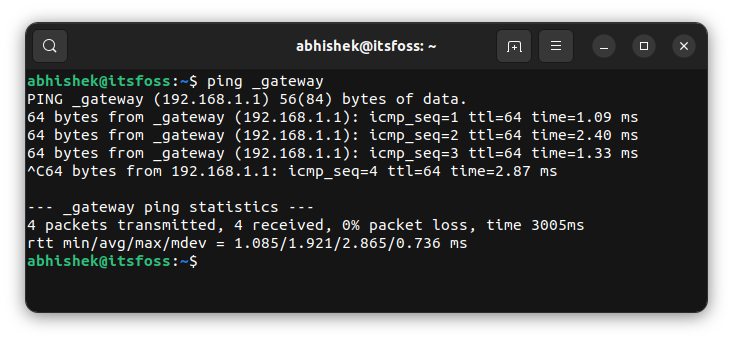
In case you didn’t know, you have to [use the Ctrl+C to stop a running command in Linux](https://itsfoss.com/stop-program-linux-terminal/).
I hope you find this tip useful when you need it. |
14,801 | HandBrake:用于转换任何格式视频的免费工具 | https://www.debugpoint.com/handbrake/ | 2022-07-07T14:14:02 | [
"视频",
"格式转换"
] | /article-14801-1.html | 
>
> 了解一下 HandBrake,这是一个优秀的工具,可以将任何格式的视频转换为目标类型。
>
>
>
本文介绍了它的功能、下载说明和使用指南。
### HandBrake
在这个社交媒体的时代,我们身处各种视频之中,当然还有随之而来的各种格式。因此,如果你是在 Linux 平台,甚至是在 Windows 平台,你可以使用各种软件来为多个平台转换各种视频。但是,如果你需要一个简单但功能丰富的视频转换器来处理来自多个来源的所有视频格式,请尝试 HandBrake。
#### 功能
HandBrake 有大量的选项,使其成为一个独特的工具。首先,其工作流程是超级简单。事实上,它只是三个步骤:
* 选择一个视频
* 选择一个目标格式
* 转换
正如你所看到的,如果你是一个新手用户,使用这个工具是非常容易的,因为目标格式的属性(如比特率、尺寸)是基于默认的预设。
其次,如果你想进行高级编辑,如在转换时从字幕文件中添加字幕,也可以使用这个工具。
此外,你还可以改变尺寸、翻转视频、改变分辨率、修改长宽比,以及裁剪。此外,通过一套基本的过滤器配置,可以完成诸如去噪和锐化等操作。
另外,为你的视频文件添加章节、标签和音轨也很容易。
也许 HandBrake 的重要功能是提供预设,以满足现代社会媒体和流媒体的需求。例如,其预设与这些流媒体平台和流媒体设备相一致,如:
* Discord
* GMail
* Vimeo
* 亚马逊 Fire Stick 电视棒
* 苹果设备
* Chromecast
* Playstation
* Roku
* Xbox
一个相当令人印象深刻的列表,不是吗?不仅如此,如果你是一个专业工作者,它可以帮助你定义和创建转换队列。队列功能允许你在工作流程中批量转换多个视频文件。
最后,你可以转换为 MPEG-4(mp4)、Matroska(mkv)和 WebM 格式。

### 下载和安装
下载和安装 HandBrake 对于任何平台(Linux、Mac 和 Windows)都很容易。开发者直接提供了可执行文件,可以免费下载。
由于本站的主要目标受众是 Linux 用户,我们将讨论 HandBrake 在 Linux 中的安装。
对于 Ubuntu、Linux Mint 和所有其他发行版,最好的方法是 Flatpak。你可以 [设置 Flatpak](https://www.debugpoint.com/how-to-install-flatpak-apps-ubuntu-linux/),然后点击下面的按钮来安装 HandBrake:
>
> **[通过 Flathub 安装 HandBrake](https://dl.flathub.org/repo/appstream/fr.handbrake.ghb.flatpakref)**
>
>
>
对于 Windows、macOS 的安装程序,请访问 [这个页面](https://handbrake.fr/downloads.php)。
一个有趣的特点是,你可以通过命令行使用这个应用程序!这意味着你可以使用命令行工具进一步定制你的工作流程,你可以在 [这里](https://handbrake.fr/downloads2.php) 下载。
### 如何使用 HandBrake 来转换视频?(示例)
既然你安装了它,让我们看看你如何只用三个步骤就能转换一个示例视频。
1. 打开 HandBrake,点击顶部工具栏上的 “<ruby> 打开源文件 <rt> Open Source </rt></ruby>” 按钮,选择你的视频文件。
2. 现在,从“<ruby> 格式 <rt> Format </rt></ruby>”下拉菜单中选择目标文件类型。确保选中目标文件夹(默认为 `Videos`)。
3. 最后,点击顶部工具栏的“<ruby> 开始 <rt> Start </rt></ruby>”按钮,用 HandBrake 转换视频。

你可以在窗口的底部找到一个漂亮的转换进度显示。

上面的步骤是最基本的步骤。如果你想进一步控制视频,你可以改变选项,也可以从我前面解释的大量预设列表中选择。
### 常见问题
**HandBrake 是免费使用么?**
是的,它是一个自由开源的应用程序,你可以免费下载它。
**它可在 Mac 和 Windows 上用么?**
是的,你可以在 macOS、Windows 10 和 Windows 11 中轻松安装 HandBrake。
**如何下载 HandBrake?**
你只能从官方网站 <https://handbrake.fr/> ,不能从其他地方下载 HandBrake。
### 结束语
Handbrake 是如今可用的专业级免费和开源视频编码器之一。它是一个经过时间考验的应用,每天有数百万用户使用。我希望本指南能帮助你了解这个神奇的工具,让你开始你的视频项目。
**演示视频来自 [Pexels - cottonbro](https://www.pexels.com/video/hands-hand-table-colorful-3997786/)**。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/handbrake/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,802 | darktable 4.0.0:用户界面改版,改进了色彩饱和度处理 | https://news.itsfoss.com/darktable-4-0-release | 2022-07-07T14:46:39 | [
"darktable"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14802-1.html |
>
> darktable 4.0.0 版本来了,这是一个主要版本,带来了新的功能,简化了用户界面,还有一些其他的改进。
>
>
>

最近,作为其 3.8.x 系列的升级版,darktable 开发人员公布了新的稳定版。
最新的升级带来了新功能、错误修复和重大变化。
### darktable 4.0 有什么新内容?
在 darktable 4.0 中,增加了很多功能,并对用户界面进行了一些有意义的重新打造。
让我在此介绍一下关键的亮点:
>
> **注意:** 这是一次重大版本升级,采用了新的库和配置,与旧版本不兼容。因此,你需要在进行升级之前对你的工作进行备份。
>
>
>
#### 颜色和曝光映射
在曝光和颜色校准模块中,你现在可以定义和保存颜色采集器的目标颜色/曝光度。
这应该有助于你匹配图像中的源对象,并确保一个对象在一批照片中的颜色一致性。
#### 完善的用户界面

用户界面已经进行了改造以改善外观/感觉。首先能看到的是其默认主题改为了 “优雅灰”。
总的来说,填充、边距、颜色、对齐方式和图标等等都得到了改造。也添加了新的可折叠的部分(rgb 通道混合器、曝光、颜色校准),使用户界面更干净,更容易访问。
你会发现许多细微的变化,布局也更合理。
#### 性能变化
在简化用户偏好的同时,该版本还增加了一些优化措施。
你还可以改变性能配置,而不需要重启 darktable。
#### 改进了色彩饱和度处理

Filmic v6(一种新的色彩学)的加入有助于获得更多的饱和度,特别是对于蓝天。
另外正如公告中提到的,可以以最小的破坏性方式恢复,调色应该更安全。除此之外,还为艺术饱和度的变化设计了一个新的信息色彩空间。
总的来说,你应该对这个版本对饱和度控制的改进感到高兴。
#### 其他变化
其他一些值得注意的变化包括:
* 一个新的“引导式拉普拉斯”方法已被添加到高光重建模块中。
* 全局颜色选择器工具的改进
* 一个新的对比度参数
* 一个新的集合过滤器模块
* 增加了对 EXR 16 位(半数)浮点数输出的支持。
你可以在其 [官方公告帖子](https://www.darktable.org/2022/07/darktable-4.0.0-released/) 中查看所有的技术细节。
### 下载 darktable 4.0.0
你可以使用 [Flathub](https://flathub.org/apps/details/org.darktable.Darktable) 上的 Flatpak 包获得最新版本。写这篇文章时,Snap 包还没有更新。
此外,你也可以选择使用其 [GitHub 发布区](https://github.com/darktable-org/darktable/releases/tag/release-4.0.0) 中的 tar.xz 文件。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/darktable-4-0-release>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
14,804 | 又有 Linux 开发者加入微软,这次是 systemd 的创建者 | https://news.itsfoss.com/systemd-creator-microsoft/ | 2022-07-08T09:10:19 | [
"微软",
"开源"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14804-1.html |
>
> 看来微软拿了一手好牌,在 Linux 和开源方面取得行业成功。
>
>
>

出于某种原因,微软在开源和 Linux 方面总是受到关注。
而且,当我们谈论 Linux 开发者时,它也会成为焦点……为什么会这样?
微软似乎正在为一系列的项目招聘大量 Linux 开发人员。而且,一个知名人物也加入了这个名单。
据 [Phoronix](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Systemd-Creator-Microsoft) 报道,systemd 和 PulseAudio 的创建者 **Lennart Poettering**,现在已在微软工作,继续专注于 systemd 的开发。
或许你不知道,Lennart 曾在红帽工作,领导 PulseAudio 项目和其他一些事情。
除了 Lennart 之外,Python 之父 **Guido Van Rossum** 等一些关键的开发人员之前就加入了微软。
(LCTT 译注:据 Phoronix 总结,还有更多的开源开发者加入了(或加入过)微软,这包括:GNOME 创建者 Miguel de Icaza 曾在 2016 年微软收购 Xamarin 时受雇,到今年早些时候离开;Nat Friedman 作为 Xamarin 的成员在微软收购后加入,后担任微软旗下的 GitHub 的 CEO;Gentoo Linux 创始人 Daniel Robbins 之前受雇于微软;Steve French 作为 Linux CIFS/SMB2/SMB3 的维护者和 Samba 团队的成员为微软工作;以及大量的上游 Linux 开发者,如 Matteo Croce、Matthew Wilcox、Tyler Hicks、Shyam Prasad N、Michael Kelley、Christian Brauner 等等也曾被微软雇佣。)
### 微软在为最佳状态做准备
毫不奇怪,微软希望提高其对基于开源的项目的关注,并尽可能有效地利用 Linux 为其业务服务。
Azure 平台对开源的利用最多,而且,不要忘了 **Windows Subsystem for Linux**(WSL)。
因此,微软一直在招聘 Linux 开发人员。如果你想试试,你会在 [微软职业](https://careers.microsoft.com/us/en/search-results?keywords=Linux) 栏目中找到很多与 Linux 有关的职位。
虽然这对微软的产品线来说是一件大事,但它一般不会影响到 Linux 桌面用户。事实上,我认为,Linux 开发者得到的资源越多,由于他们工作角色转换,他们可以帮助 Linux 生态系统更好地增强其愿景。
当然,让所有关键的 Linux 开发者都在微软拥有的项目上工作并不是一件喜闻乐见的事情,但是,事实就是如此。
### 微软正在做正确的事情
这不仅仅是经济上的回报,Linux 开发者加入微软团队的趋势意味着他们在开源和 Linux 上的一些努力是成功的。
只要微软努力改善 Linux 生态系统,我认为我们就没有什么可担心的。
我不想被提醒“<ruby> 拥抱、扩展和熄灭 <rt> Embrace, extend, and extinguish </rt></ruby>”(3E)。毕竟,这对所有公司来说都是生意。当涉及到赚钱的决定时,没有人应该被认为是英雄。
因此,我们只能希望微软在不久的将来为 Linux 开发者和用户准备好一些好东西。
你对此有何看法?在下面的评论区分享你的想法。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/systemd-creator-microsoft/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Microsoft always gets the attention for some reason when it comes to open-source and Linux.
And, it also comes to the limelight when we talk about Linux developers…why?
It seems that Microsoft is hiring a lot of Linux developers for a range of projects. And, a popular name has joined the list.
Systemd and PulseAudio creator, **Lennart Poettering**, is now working with Microsoft while continuing his focus on systemd development, as reported by [Phoronix](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Systemd-Creator-Microsoft&ref=news.itsfoss.com).
In case you are curious, Lennart used to work for Red Hat leading the PulseAudio project and a few other things.
In addition to Lennart, some key developers like Python creator **Guido Van Rossum** have also joined Microsoft in the past.
## Microsoft Gearing Up for The Best
It is no surprise that Microsoft wants to improve its focus on open-source-based projects and utilize Linux as efficiently as possible for its businesses.
The Azure platform makes the most use of it, and not to forget the **Windows Subsystem for Linux**.
Hence, Microsoft is constantly hiring Linux developers. You will find plenty of Linux-related positions at [Microsoft Careers](https://careers.microsoft.com/us/en/search-results?keywords=Linux&ref=news.itsfoss.com) if you want to try your skills.
While this is a big deal for Microsoft’s line of offering, it should not affect Linux desktop users in general. In fact, I think, the more resources Linux developers get, as a result of their switch in job roles, they could help the Linux ecosystem better enhance their vision.
Of course, it is not ideal to have all key Linux developers work on Microsoft-owned projects. But, it is what it is.
## Microsoft is Doing Something Right
It is not just about the financial reward, but the trend of Linux developers joining the team at Microsoft means that they have been successful at some of their efforts on open-source and Linux.
As long as Microsoft makes an effort to improve the Linux ecosystem, I do not think we have much to worry about it.
I would not like to be reminded of “Embrace, extend, and extinguish”. After all, it’s all business for all the companies. No one should be considered a hero when it involves money-making decisions.
So, we can only hope that Microsoft is gearing up for something good in store for Linux developers and users in the near future.
What do you think about it? Share your thoughts in the comments section below.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,805 | 改变数据中心行业的主要趋势 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/top-trends-changing-data-center-industry/ | 2022-07-08T09:32:47 | [
"数据中心"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14805-1.html | 
大流行加快了印度全国数字化转型的速度,这需要对数据中心进行更多投资。由于快速的数字化和云采用,印度数据中心市场的容量预计在未来几年将翻一番。据报道,2021 年印度数据中心市场规模为 43.5 亿美元,到 2027 年将达到 100.9 亿美元,2022-2027 年的复合年增长率为 15.07%。
现在,出现的一个关键问题是印度数据中心行业的未来是什么?哪些新趋势将塑造其未来?下面提到的是将对印度数据中心行业产生重大影响的主要趋势。
### 数据本地化
数据本地化就意味着限制数据从一个国家流向另一个国家。印度政府已发布指导方针,强调需要在该国境内存储印度用户的数据。数据本地化使得收集关键消费者数据的公司必须在本地数据中心存储和处理这些数据。这给本地数据中心带来了巨大的增长。此外,印度的成本优势和熟练劳动力的便利性使其成为亚洲数据中心的重要枢纽。
### 可持续数据中心
众所周知,数据中心消耗大量非可再生资源。为了使数据中心可持续发展,公司重新设计了他们的设施,通过利用人工智能、机器学习和云等新兴技术来大大降低电力和水的消耗。云数据中心使用更少的服务器,从而减少碳排放。它们通常位于更靠近为其供电的设施,以防止在长距离传输电能的过程中出现大量损失。此外,公共云数据中心可用于存储来自多个业务的数据。本地数据中心在存储大量数据时存在容量限制,从而导致资源的非最佳使用。因此,云数据中心通过使企业能够消耗更少的服务器和更少的电力并减少其在此过程中的碳排放,正在彻底改变行业。
### 边缘连接
边缘数据中心是靠近网络边缘的小型数据中心。它们通常连接到更大的中央数据中心或多个数据中心。通过处理更接近最终用户的数据和服务,边缘计算允许组织减少延迟并改善客户体验。这样的数据中心对于需要实时数据处理的行业非常有利,例如自动驾驶汽车、远程医疗、电信、OTT 平台和智能可穿戴设备。
### 超大规模数据中心
传统上,数据中心是一个简单的机架网络,带有存储单元和一组管理工具。它具有易于理解的架构。然而,随着数字化转型接管了企业界,组织开始生成大量数据。传统的存储单元和工具不足以处理大量涌入的数据,因此需要更大的容量和复杂的设施。此外,传统数据中心无法扩大或缩小其能力以适应需求波动,从而导致资源浪费。这导致了超大规模作为解决方案的演变。
超大规模数据中心是大规模的关键业务设施,旨在通过将大量高速协同工作的服务器聚集在一起,有效地支持强大且可扩展的应用。这种能力使数据中心能够水平和垂直扩展。
总之,数据中心行业正在发展,新趋势将不断涌现。借助新时代的颠覆性技术,数据中心行业可以构建环保节能的数据中心。人工智能、边缘计算和物联网等技术可用于最大限度地提高能源效率并最大限度地减少对环境的影响。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/06/top-trends-changing-data-center-industry/>
作者:[abhimanyu rathore](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/abhimanyu-rathore/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The pandemic has accelerated the rate of digital transformation across the country, and this has necessitated more investments in data centers. Owing to rapid digitalization and cloud adoption, the Indian data center market is expected to double its capacity in the upcoming years. As per reports, the Indian data center market size was valued at $4.35 billion in 2021 and will reach $10.09 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 15.07% during 2022-2027.
Now, a key question that arises is what lies ahead for the data center industry in India? What new trends are going to shape its future? Below mentioned are the top trends that will significantly impact the data center industry in India.
## Data Localization
Data localization simply means restricting the flow of data from one country to another. The Indian government has issued guidelines highlighting the need to store data of Indian users within the country’s boundaries. Data localization has made it mandatory for companies that collect critical consumer data to store and process it in local data centers. This has given a huge surge to local data centers. In addition, the cost advantage and easy accessibility of skilled labor in India makes it a key hub for data centers in Asia.
## Sustainable Data Centers
It’s a known fact that data centers consume a lot of non-renewal resources. To make data centers sustainable, companies have redesigned their facilities to greatly reduce power and water consumption by utilizing emerging technologies such as AI, ML and cloud. Cloud data centers use fewer servers thereby reducing the carbon impact. They are generally located closer to the facilities that power them to prevent large losses during the process of transmitting electrical energy over long distances. In addition, public cloud data centers can be used to store data from multiple businesses. An on-premise data center has capacity limitations when it comes to storing huge volume of data, thereby leading to non-optimal use of resources. Hence, cloud data centers are revolutionizing the industry by enabling businesses to consume fewer servers and less power and reduce their carbon emissions in the process.
## Edge Connectivity
Edge data centers are small data centers that are located closer to the edge of a network. They typically connect to a larger central data center or multiple data centers. By processing data and services closer to the end-user, edge computing allows organizations to reduce latency and improve the customer experience. Such data centers are extremely beneficial for industries that need data processing in real-time such as autonomous vehicles, telemedicine, telecommunication, OTT platforms, and smart wearables.
## Hyperscale Data Centers
Traditionally data centers were a simple network of racks with storage units and a set of management tools. It had the architecture that was easy to understand. However, as digital transformation took over the corporate world, organizations started to generate huge volumes of data. The traditional storage units and tools were inadequate to handle this influx of data and hence larger capacity with sophisticated facilities were required. In addition, traditional data centers could not scale up or down their capabilities to accommodate the fluctuations in demand and hence resulted in wastage of resources. This led to the evolution of hyperscaling as a solution.
Hyperscale data centers are massive business-critical facilities designed to efficiently support robust and scalable applications by bringing together a large number of servers working together at high speeds. This ability gives the data center a capacity to scale both horizontally and vertically.
In conclusion, the data center industry is evolving and new trends will keep cropping up. With the new-age disruptive technologies, data center industry can build eco-friendly and energy efficient data centers. Technologies such as AI, edge computing, and IoT can be utilized to maximize energy efficiency and minimize environmental impact. |
14,806 | 在 Linux 中隐藏文件和文件夹的那些事 | https://itsfoss.com/hide-files-folders-linux/ | 2022-07-08T14:27:00 | [
"隐藏文件",
"点文件"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14806-1.html |
>
> 这篇面向初学者的文章探讨了在 Linux 中如何在普通视图中隐藏文件和文件夹。图形用户界面和命令行方法都有所涉猎。
>
>
>

有时你需要在 Linux 中隐藏文件。
不要误会,我不是指那些你不想让你的家人看到的“特殊文件”。尽管你可以隐藏这些特殊文件,但更好的办法还是用密码锁定它们以提供额外的保护。
回到隐藏文件的话题。**名称以 `.` 开头的任何文件或文件夹在 Linux 中是“隐藏的”。**
Linux 有很多这样的文件和文件夹,在普通视图中它们是隐藏的。这些主要是系统和程序所需的配置文件。
用户通常不需要理会它们,因此它们在普通视图中是隐藏的,这样一来你就不会被许多看起来很奇怪的而不是你所创建的文件所淹没。
下图展示了我的主目录中隐藏的文件和文件夹。


如果你使用的是桌面版 Linux,你可以通过在文件管理器中按 `Ctrl+H` 快捷键来轻松 [查看隐藏文件](https://itsfoss.com/hide-folders-and-show-hidden-files-in-ubuntu-beginner-trick/)。在终端中,你可以使用 `ls -a` 命令显示隐藏文件和普通文件。
那么,如何在 Linux 中创建隐藏文件呢?你只需用一个在命名的时候加一个 `.` 前缀。就是这样。
### 在桌面版 Linux 里创建隐藏文件和文件夹(GUI 方法)
如果你使用的是文件管理器,在文件或文件夹上右键并选择重命名选项。现在你所要做的就是在文件名的开头添加一个 `.`。
当你以这种方式创建隐藏文件时,GNOME 的 Nautilus 文件管理器也会显示一个警告。

你可以以相同的方式隐藏文件夹及其所有内容。
你可以按 `Ctrl+H` 键来显示隐藏文件。哦!我是多么的喜欢 [Ubuntu 中的键盘快捷键](https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-shortcuts/) 和我使用的任何其他程序或操作系统!
要使隐藏文件变回普通文件,只需再次重命名这些文件删掉文件名前缀的 `.` 即可。
### 在 Linux 终端创建隐藏文件和文件夹(CLI 方法)
如果你热衷于终端,你可以 [使用 mv 命令](https://linuxhandbook.com/mv-command/) 重命名文件。你只需在原始文件名的开头添加一个 `.`。
```
mv filename .filename
```
你可以使用以下命令显示隐藏文件:
```
ls -la
```
你也可以使用 `ls -lA`。这条命令不会显示点文件(`.` 和 `..`)。
### 额外提示:用非重命名的方法隐藏文件和文件夹(仅适用于 GUI)
你刚刚学了在 Linux 中隐藏文件。问题是你必须重命名文件,而这种操作不适用于所有的场合。
例如,在 Ubuntu 中,你会在目录中看到一个名为 `snap` 的文件夹。你不会使用它,但如果重命名它,你的 Snap 应用程序将无法按预期工作。类似的情况是,在 Ubuntu 22.04(安装有 Snap 版本的 Firefox)的 `Downloads` 目录下有一个 `firefox.tmp` 文件夹。
有一个巧妙的技巧可以在 Linux 桌面中使用。它应该可以在 Nemo、Thunar、Dolphin 等各种文件管理器下工作,但我不能保证。它确实适用于 GNOME 的 Nautilus 文件管理器。
因此,你在这里所做的是在你想要隐藏的文件或文件所在的目录中创建一个名为 `.hidden` 的新文件。

按 `Ctrl+H` 显示隐藏文件并 **打开 `.hidden` 文件** 进行编辑。**在单独的行中添加文件或文件夹的名称**。注意不能使用绝对或相对路径。你想要隐藏的 **文件和文件夹应与此特殊 `.hidden` 文件** 位于同一路径下。
这是我以不重命名的方式隐藏 `cpufetch` 目录和 `pcloud` 文件的示例:
```
pcloud
cpufetch
```
按 `Ctrl+H` 以再次隐藏 `.hidden` 文件。
现在,**关闭你的文件资源管理器并重新启动它**。你将不会再看到 `.hidden` 文件中提到的文件和目录。
如果你想再次查看它们,请按 `Ctrl+H` 键。
如果你不想再隐藏文件,请从 `.hidden` 文件中删除其名称或完全删除 `.hidden` 文件。
### 额外琐事:隐藏文件“功能”实际上是一个 bug
你知道吗?在文件名的开头添加一个 `.` 来隐藏文件的“功能” [实际上是一个 bug](https://linux-audit.com/linux-history-how-dot-files-became-hidden-files/)?
在早期的 UNIX 时代,当创建文件系统时,添加了 `.`(当前目录)和 `..`(父目录)文件以方便导航。
由于这些特殊的 `.` 和 `..` 文件中没有实际数据,因此给 `ls` 命令添加了一个新的“功能”:该功能是检查文件名的第一个字符,如果它是一个点(`.`),则不再使用 `ls` 命令显示它。
这对隐藏 `.` 和 `..` 文件有效,但它引入了一个 “bug”:`ls` 命令的输出会隐藏任何文件名以 `.` 开头的文件。
这个 bug 变成了一个功能,因为程序员喜欢它来“隐藏”他们的配置文件。`ls` 命令可能是后来修改添加了一个显示隐藏点文件的选项。
Linux 遵循相同的约定,因为 Linux 是以 UNIX 为原型开发的。
### 结论
我讨论了如何从普通视图中创建隐藏文件。如果要创建让其他人无法访问的机密文件或文件夹,则应对其进行加密。我曾经写过 [在 Linux 中使用密码锁定文件夹](https://itsfoss.com/password-protect-folder-linux/)。这是一篇有点儿旧的文章,但它可能仍然有效。
我希望你喜欢这个简单的话题并学到新的东西。发布你的评论让我知道你的想法吧。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/hide-files-folders-linux/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[hanszhao80](https://github.com/hanszhao80) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

There will be times when you need to hide files in Linux.
No, I am not talking about those ‘special files’ that you don’t want your family to see. Although you can hide these special files, it is better to lock them with a password for an extra layer of protection.
Back to hiding files. **Any file or folder whose name begins with a . (dot) is “hidden” in Linux.**
Linux has plenty of such files and folders that are hidden from the normal view. These are mainly config files that are needed by the system and programs.
The users don’t need them normally and hence they are hidden from the normal view so that you don’t get overwhelmed by so many strange-looking files that you never created.
Here’s a look at the hidden files and folders in my home directory.
You can easily [view the hidden files](https://itsfoss.com/hide-folders-and-show-hidden-files-in-ubuntu-beginner-trick/) by pressing Ctrl+H in the file manager if you are using desktop Linux. In the terminal, you can use the ls -a command to display the hidden files along with the normal ones.
So, how do you create hidden files in Linux? You simply name them with a dot. Here’s how.
## Create hidden files and folders in Linux desktop (GUI method)
If you are using the file manager, right click on the file or folder and choose the rename option. Now all you have to do is to add a . at the beginning of the filename.
GNOME’s Nautilus file manager also shows a warning when you are creating a hidden file in this manner.
You can hide a folder along with all its contents in the same way.
You can press Ctrl+H keys to display the hidden files. Oh! how much I love [keyboard shortcuts in Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-shortcuts/) or any other program or OS I use.
To make the hidden files normal again, just rename them again by removing the dot from the beginning of the file name.
## Create hidden files and folders in Linux terminal (CLI method)
If you are stuck with the terminal, you can [use the mv command](https://linuxhandbook.com/mv-command/?ref=itsfoss.com) to rename the file. You just have to rename the file by adding a . at the beginning of the original filename.
`mv filename .filename`
You can display the hidden files using this command:
`ls -la`
You may also use ls -lA. This one won’t show the dot files (. and ..).
## Bonus tip: Hide files and folders without renaming them (works in GUI only)
You just learned to hide files in Linux. The problem is that you have to rename the files and that’s not ideal in all situations.
For example, in Ubuntu, you’ll see a folder named ‘snap’ in your directory. You are not going to use it but if you rename it, your snap apps won’t work as expected. Similarly, there’s a firefox.tmp folder under the Downloads directory in Ubuntu 22.04 (for the snap version of Firefox).
There is a neat trick that can be used in the Linux desktop. It should work under various file managers like Nemo, Thunar, Dolphin etc but I cannot vouch for it. It sure works in the Nautilus file manager of GNOME.
So, what you do here is to create a new file named .hidden in the directory where your desired files or folders (to be hidden) are located.
Press Ctrl+H to show the hidden files and **open .hidden file** for editing. **Add the name of the files or folders in separate lines**. Keep in mind that it doesn’t take absolute or relative path. Your desired **files and folders should be in the same location as this special .hidden file**.
Here’s a sample which I used to hide the cpufetch directory and pcloud file without renaming them:
```
pcloud
cpufetch
```
Press Ctrl+H again to hide the .hidden files again.
Now, **close your file explorer and start it again**. You won’t see the files and directories mentioned in the .hidden file anymore.
If you want to see them again, press Ctrl+H keys.
When you don’t want the files hidden anymore, remove their name from the .hidden file or remove .hidden file altogether.
## Bonus Trivia: The hidden files ‘feature’ was actually a bug
Do you know that this ‘feature’ to hide a file by adding a . at the beginning of the file name was [actually a bug](https://linux-audit.com/linux-history-how-dot-files-became-hidden-files/?ref=itsfoss.com)?
In the early UNIX days, when the filesystem was created, the . (current directory) and .. (parent directory) files were added for ease of navigation.
As these special . and .. files had no real data in them, a new ‘feature’ was added to the ls command.
The feature was to check the first character of a filename and if it’s a dot (.), it was no longer displayed with the ls command.
That worked for the . and .. files but it introduced a ‘bug’ where any filename starting with . was hidden from the output of the ls command.
This bug turned into a feature as programmers like it for ‘hiding’ their config files. The ls command was probably modified later to add options to display hidden dot files.
The same convention gets followed in Linux as Linux was modeled after UNIX.
## Conclusion
I have discussed creating files that are hidden from the normal view. If you want to create secret files or folders that cannot be accessed by other people, you should encrypt them. I have written about [locking folders with passwords in Linux](https://itsfoss.com/password-protect-folder-linux/). It’s a bit old article but it may still work.
I hope you liked this simple topic and learned something new. Use the comment section and let me know your thoughts. |
14,808 | Fedora Linux 37 即将正式支持树莓派 4 | https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-raspberry-pi-4/ | 2022-07-08T23:03:00 | [
"树莓派",
"Fedora"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14808-1.html |
>
> 由于上游的一些改进,Fedora Linux 37 将引入对树莓派 4 的正式支持。
>
>
>

Fedora Linux 的工作站版很适合台式机使用。不过,如果你想让它用于服务器或物联网需求,可以使用 Fedora ARM 项目。
它也支持树莓派,只是最新的树莓派 4 除外(其实早在 2019 年就发布了)。
现在,随着 [Phoronix](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Fedora-37-Raspberry-Pi-4) 发现的一项拟议的变化,看起来 Fedora Linux 37 可能会正式增加对树莓派 4 的支持。
### 目前还不是正式的...
到现在为止,对树莓派 4 的支持只是一个拟议的变化。
Fedora Linux 通常会公开其拟议的变化列表,以接受社区反馈并让其他人跟踪其进展。
所以,Fedora Linux 37 中的正式支持只有在得到 Fedora 工程指导委员会的批准后才会实施。
但是,**支持树莓派 4 的阻碍是什么呢?**
这是由于缺乏加速图形以及缺失一些功能,所以不方便增加对它的支持。
现在,随着新的 Linux 内核和 Mesa 的上游工作为树莓派 4 带来了图形加速功能,可以让他们启用对它的支持。
拟议的变化文件中提到:
>
> 上游现在支持使用 V3D GPU 的 OpenGL-ES 和 Vulkan 加速图形。对有线网络也有增强,支持 CM4/4B 上的 PTPv2。
>
>
>
此外,不仅仅是引入对树莓派 4 的支持,一些拟议的变化还涉及对树莓派 3 系列和 Zero 2 W 的改进。
因此,如果如人们所期望的那样发生,这应该是一个有趣的变化。
请注意,对树莓派 400 的 Wi-Fi 的支持不是这个过程的一部分,但对音频支持的测试将是这个变化的一部分。
你可以在 [拟议文件](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Changes/RaspberryPi4) 中阅读所有的细节。
你对 Fedora Linux 37 对树莓派 4 的支持有什么看法?请在下面的评论中分享你的想法。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/fedora-raspberry-pi-4/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Fedora Linux is well-suited for desktops with its workstation edition. And, if you want it for a server or IoT requirements, you also have the Fedora ARM project.
It also supports Raspberry Pi boards, except for the recent Raspberry Pi 4 (released in 2019).
Initially, with a proposed change, we hoped to get support for it in Fedora Linux 37.
**Update (Aug 3, 2022)**: *The addition of Raspberry Pi 4 support has been officially approved by the Fedora Engineering Steering Committee*, as spotted by [Phoronix](https://www.phoronix.com/news/Raspberry-Pi-4-Fedora-37?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Raspberry Pi 4 Support With Fedora: Finally!
Of course, Raspberry Pi boards were not the focus of Fedora Linux.
But, **what was the hold-up** for the lack of support initially?
The lack of accelerated graphics and a few missing features did not make it convenient to add support for it.
Now, with upstream work on newer Linux Kernel and Mesa on bringing graphics acceleration for Raspberry Pi 4, it lets them enable the support for it.
The [proposed change document](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Changes/RaspberryPi4?ref=news.itsfoss.com) mentioned:
Upstream now supports accelerated graphics using the V3D GPU for both OpenGL-ES and Vulkan. There’s also enhancement to wired networking with support for PTPv2 on the CM4/4B.
Additionally, not just introducing support for Raspberry Pi 4, some of the proposed changes also involve improvements to the Raspberry Pi 3 series and the Zero 2 W.
So, it should be an exciting change with Fedora 37 along with all the other potential upgrades with Fedora’s next upgrade for its workstation edition.
Note that the support for Wi-Fi on Raspberry Pi 400 is not a part of this process, but testing for audio support will be a part of this change.
Of course, as of now, it is still in its testing phase. So, we can keep an eye on Fedora 37 release to check how it works on Raspberry Pi 4.
*What do you think about supporting Raspberry Pi 4 on Fedora Linux 37? Share your thoughts in the comments down below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,809 | 使用 Tig 来可视化 Git 工作流 | https://opensource.com/article/22/7/visualize-git-workflow-tig | 2022-07-09T12:34:24 | [
"Git",
"Tig"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14809-1.html | 
>
> Tig 是审查 Git 仓库的绝佳工具,它鼓励你探索日志,而无需构建冗长且有时复杂的查询。
>
>
>
如果你发现浏览你的 Git 仓库非常复杂,我已经为你准备好了工具,来了解一下 Tig。
Tig 是一个 [基于 ncurses](https://opensource.com/article/21/8/ncurses-linux) 的 Git 文本模式界面,它允许你浏览 Git 仓库中的更改。它还可以充当各种 Git 命令输出的分页器。使用这个工具可以让我很好地了解在哪个提交中发生了哪些更改,最新的提交合并是什么等等。请跟随这个简短的教程,亲自尝试一下。
### 安装 Tig
在 Linux 上,你可以使用包管理器安装 Tig。例如,在 Fedora 和 Mageia 上:
```
$ sudo dnf install tig
```
在 Debian、Linux Mint、Elementary、Pop\_OS 和其他基于 Debian 的发行版上:
```
$ sud apt install tig
```
在 macOS 上,使用 [MacPorts](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/macports) 或 [Homebrew](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/homebrew-mac)。 Tig 的完整安装指南可在 [Tig 手册](https://jonas.github.io/tig/doc/manual.html) 中找到。
### 使用 Tig
Tig 提供了常见 Git 输出的交互式视图。例如,使用 Git,你可以使用命令 `git show-ref` 查看所有引用:
```
$ git show-ref
98b108... refs/heads/master
6dae95... refs/remotes/origin/1010-internal-share-partition-format-reflexion
84e1f8... refs/remotes/origin/1015-add-libretro-openlara
e62c7c... refs/remotes/origin/1016-add-support-for-retroarch-project-cd
1c29a8... refs/remotes/origin/1066-add-libretro-mess
ffd3f53... refs/remotes/origin/1155-automatically-generate-assets-for-external-installers
ab4d14... refs/remotes/origin/1160-release-on-bare-metal-servers
28baa9... refs/remotes/origin/1180-ipega-pg-9118
8dff1d... refs/remotes/origin/1181-add-libretro-dosbox-core-s
81a7fe... refs/remotes/origin/1189-allow-manual-build-on-master
[...]
```
使用 Tig,你可以在可滚动列表中获取该信息以及更多信息,此外还可以使用键盘快捷键来打开其他视图,其中包含每个引用的详细信息。

### 分页模式
当输入来自标准输入时,Tig 进入分页模式。当指定 `show` 子命令并给出 `--stdin` 选项时,标准输入被假定为提交 ID 列表,它被转发到 `git-show` :
```
$ git rev-list --author=sumantrom HEAD | tig show –stdin
```
### 日志和差异视图
当你在 Tig 的日志视图中时,你可以按键盘上的 `d` 键来显示差异。这将显示提交中更改的文件以及删除和添加的行。
### 交互式 Git 数据
Tig 是对 Git 的一个很好的补充。它鼓励你探索日志,而无需构建冗长且有时复杂的查询,从而可以轻松查看你的 Git 仓库。
立即将 Tig 添加到你的 Git 工具包中!
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/7/visualize-git-workflow-tig>
作者:[Sumantro Mukherjee](https://opensource.com/users/sumantro) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | If you find navigating your Git repositories frustratingly complex, have I got the tool for you. Meet Tig.
Tig is an [ncurses-based](https://opensource.com/article/21/8/ncurses-linux) text-mode interface for Git that allows you to browse changes in a Git repository. It also acts as a pager for the output of various Git commands. I use this tool to give me a good idea of what’s been changed in which commit by whom, the latest commit merged, and so much more. Try it for yourself, starting with this brief tutorial.
## Installing Tig
On Linux, you can install Tig using your package manager. For instance, on Fedora and Mageia:
```
````$ sudo dnf install tig`
On Debian, Linux Mint, Elementary, Pop_OS, and other Debian-based distributions:
```
````$ sud apt install tig`
On macOS, use [MacPorts](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/macports) or [Homebrew](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/homebrew-mac). Tig’s complete installation guide can be found in the [Tig Manual](https://jonas.github.io/tig/doc/manual.html).
## Using Tig
Tig provides an interactive view of common Git output. For instance, with Git you can view all refs with the command `git show-ref`
:
```
``````
$ git show-ref
98b108... refs/heads/master
6dae95... refs/remotes/origin/1010-internal-share-partition-format-reflexion
84e1f8... refs/remotes/origin/1015-add-libretro-openlara
e62c7c... refs/remotes/origin/1016-add-support-for-retroarch-project-cd
1c29a8... refs/remotes/origin/1066-add-libretro-mess
ffd3f53... refs/remotes/origin/1155-automatically-generate-assets-for-external-installers
ab4d14... refs/remotes/origin/1160-release-on-bare-metal-servers
28baa9... refs/remotes/origin/1180-ipega-pg-9118
8dff1d... refs/remotes/origin/1181-add-libretro-dosbox-core-s
81a7fe... refs/remotes/origin/1189-allow-manual-build-on-master
[...]
```
With Tig, you can get that information and much more in a scrollable list, plus keyboard shortcuts to open additional views with details about each ref.
(Sumantro Mukherjee, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Pager mode
Tig enters pager mode when input is provided to stdin (standard input). When the `show`
subcommand is specified and the `--stdin `
option is given, stdin is assumed to be a list of commit IDs, which is forwarded to `git-show`
:
```
````$ git rev-list --author=sumantrom HEAD | tig show –stdin`
## Log and diff views
When you're in Tig's log view, you can press the **d** key on your keyboard to display diffs. This displays the files changed in the commit and the lines that were removed and added.
## Interactive Git data
Tig is an excellent addition to Git. It makes it easy to review your Git repository by encouraging you to explore the logs without having to construct long and sometimes complex queries.
Add Tig to your Git toolkit today!
## Comments are closed. |
14,810 | 如何使用原生 NTFS 驱动替代旧版 FUSE NTFS 驱动 | https://github.com/LCTT/Articles/pull/24 | 2022-07-09T14:30:00 | [
"NTFS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14810-1.html | 
>
> NTFS 是 Windows NT 系列操作系统支持的磁盘文件系统格式,它是一个特别为网络和磁盘配额、文件加密等管理安全特性设计的文件系统。而 Linux 内核中新进入主线支持的 NTFS3 驱动是一个功能齐全的 NTFS 驱动程序,该驱动程序适用于最高的 NTFS 3.1 版本。
>
>
>
### 简介
最初,Linux 内核没有 NTFS 的原生支持,后来对 NTFS 的支持也仅提供了只读功能。来自 Tuxera 的 NTFS-3G 是之前主流的解决方案,但在实际使用中也存在一些问题。NTFS-3G 是借助 Linux 的用户空间文件系统(FUSE)模块在用户层实现的一个对 NTFS 支持的文件系统,其对 NTFS 的访问逻辑代码都是在用户层代码实现的。
在 NTFS3 出现之前,Linux 上使用 NTFS 主要问题还是缺乏稳定且功能齐全的读/写支持。
2020 年,Paragon 软件公司做出了一个惊人的决定:尝试将之前只提供给商业客户的 NTFS3 驱动程序贡献到 Linux 主线。最终,在经过多轮审核和修改之后,Linux 内核 5.15 合并了 Paragon 提供的 NTFS3 内核驱动,它拥有更高的性能和更多的特性。
* 该驱动程序实现了对 NTFS 文件系统中的正常、稀疏和压缩文件的读/写支持。
* 支持本地日志回放。
* 支持已挂载的 NTFS 卷的 NFS 导出。
* 支持文件和文件夹的权限管理。

### 如何使用 NTFS3 驱动挂载 NTFS 卷
使用 NTFS3 驱动挂载时使用的文件系统类型是 `ntfs3`。
#### 手动挂载
以前使用 NTFS-3g 驱动的挂载方式是:
```
# mount -t ntfs-3g /dev/sdxY /mnt
```
现在只需要将 `ntfs-3g` 替换为 `ntfs3` 即可:
```
# mount -t ntfs3 /dev/sdxY /mnt
```
`-t` 指出文件系统类型,`/dev/sdxY` 是你的 NTFS 卷(分区)的路径,可以使用 `lsblk` 命令查看。`/mnt` 是挂载的目标文件夹。
如果需要指定挂载参数,可使用 `-o` 指定参数,如:
```
# mount -t ntfs3 -o iocharset=utf8,umask=22,prealloc /dev/sdxY /mnt
```
这里的 `iocharset=utf8,umask=22,prealloc` 挂载参数,详见后文解释。
#### 开机自动挂载
如需在开机时自动挂载,可编辑 `/etc/fstab` 文件,添加如下行:
```
UUID=**** /data ntfs3 iocharset=utf8,umask=0,prealloc 0 0
```
其中 `UUID=****` 是指定卷(分区)的 UUID。使用 `UUID` 的好处在于它们与磁盘挂载顺序无关。如果你在 BIOS 中改变了你的存储设备顺序,或是重新拔插了存储设备,或是一些 BIOS 可能会随机地改变存储设备的顺序,那么用 `UUID` 来表示指定卷(分区)会更有效。可以使用 `blkid` 命令查看 `UUID` 。
`/data` 是挂载位置。本示例的位置是 `/data`,你需要提前创建这个文件夹。
后面的选项都是挂载参数,参见后文介绍。
最后两个 `0 0` ,表示是否备份和是否检查。`0 0` 表示不备份、不检查。
### 挂载参数说明
| 参数 | 解释 |
| --- | --- |
| `iocharset=name` | 此选项告知驱动程序如何解释路径字符串,并将其转换为 Unicode 或返回。如果未设置此选项,将使用默认代码页。示例:`iocharset=utf8` |
| `uid=` | 挂载用户 ID |
| `gid=` | 挂载组 ID |
| `umask=` | 控制装载 NTFS 卷后创建的文件/目录的默认权限。 |
| `dmask=` | `fmask` 只适用于文件,`dmask` 只适用于目录,而不是指定同时适用于文件和目录的 `umask`。 |
| fmask= | 见上 |
| `noacsrules` | “无访问规则”装载选项将文件/文件夹的访问权限设置为 777,所有者/组设置为 root。此装载选项吸收所有其他权限。文件/文件夹的权限更改将报告为成功,但仍将保持 777。所有者/组更改将报告为成功,但他们将保留为 root 用户。 |
| `nohidden` | Linux 下不会显示具有 Windows 特定隐藏(`FILE_ATTRIBUTE_HIDDEN`)属性的文件。 |
| `sys_immutable` | 具有 Windows 特定系统(`FILE_ATTRIBUTE_SYSTEM`)属性的文件将标记为系统不可变文件。 |
| `discard` | 支持 TRIM 命令以提高删除操作的性能,建议将其用于固态驱动器(SSD)。 |
| `force` | 即使卷被标记为脏,也强制驱动程序装载分区。不建议使用。 |
| `sparse` | 创建稀疏的新文件。 |
| `showmeta` | 使用此参数可显示已装入 NTFS 分区上的所有元文件(系统文件)。默认情况下,所有元文件都是隐藏的。 |
| `prealloc` | 当写入时文件大小增加时,为文件过度预分配空间。减少对不同文件执行并行写入操作时的碎片。 |
| `acl` | 支持 POSIX ACL(访问控制列表)。如果内核支持,则有效。不要与 NTFS ACL 混淆。指定为 acl 的选项支持 POSIX acl。 |
### NTFS3 的优点
NTFS3 是内核态的驱动,ntfs3 比 ntfs-3g 无论是速度还是负载都要好上不少。
已经有诸多网友做过测试:
* [ntfs-3g 与 Linux 5.15+ ntfs3 驱动的简单性能测试](https://biluohc.github.io/posts/ntfs3gvsntfs3/)
* [Linux 5.15 内核 NTFS3 性能评测](https://bbs.deepin.org/post/236260)
除了性能更好以外,NTFS3 还支持挂载用户和文件权限管理等功能。具体使用方法可以自行学习 `gid`、`uid` 以及 `umask` 的用法。
另外 NTFS3 还支持 NTFS 的 `prealloc` 特性,可以大幅减少文件碎片的产生。
### 关于 NTFS3 驱动无人维护的问题
Paragon 于 2020 年在 GNU 通用许可证下发布了 NTFS3 驱动程序,在开源后的一年里,NTFS3 的驱动经过了多轮审查和修改,用来提高代码质量。直到 2021 年合并进入内核主线。
但是自从该驱动 2021 年在 Linux 5.15 中最终被主线化以来,至今为止,在接近一年的时间里,还没有任何重大的错误修复被送入驱动。
有人推测是该驱动的维护者 Konstantin Komarov 身处俄罗斯,受到俄乌战争影响的原因。
随后包括 Linus Torvalds 在内的诸多程序员都对此事表达了关切,并且愿意参与到贡献中来。
现在,我们看到 Paragon 软件公司的 Konstantin Komarov 在因休息和其他事务而离开后,又重新活跃在内核邮件列表中。Komarov 在 2022 年 6 月 3 日为 Linux 5.19 的合并窗口提交了一批 NTFS3 的修正。
我相信 ntfs3 未来会越来越好。并且目前,ntfs3 已经是 Linux 中最好用 NTFS 驱动了,我觉得你也不妨尝试一下。
---
作者简介:一个喜欢瞎鼓捣的医学生
---
via: <https://www.insidentally.com/articles/000029/>
作者:[insidentally](https://www.insidentally.com) 编辑:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由贡献者投稿至 [Linux 中国公开投稿计划](https://github.com/LCTT/Articles/),采用 [CC-BY-SA 协议](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.zh) 发布,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | -
[Notifications](/login?return_to=%2FLCTT%2FArticles)You must be signed in to change notification settings -
[Fork 12](/login?return_to=%2FLCTT%2FArticles)
# Create 20220627 Replace ntfs-3g with ntfs3 driver to mount windows NT… #24
## Conversation
[Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters](https://github.co/hiddenchars)
…FS partition.md 投稿

**reviewed**
[wxy](/wxy)Jul 2, 2022
[#]: keywords: " 文件系统 ntfs3 ntfs-3g 分区" | ||
[#]: url: "发布后链接,由发布人填写" | ||
|
||
使用 ntfs3 驱动替换 ntfs-3g 挂载 windows NTFS 分区 |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
### Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. [Learn more](https://docs.github.com/articles/managing-disruptive-comments/#hiding-a-comment).
标题不够好。比如说:
- 在 Linux 上如何用原生 NTFS 驱动挂载 Windows NTFS 分区
- 如何使用新的原生 NFTS 驱动替代旧版的 FUSE NTFS 驱动
以上供参考,你可以考虑个更清晰、直接的标题
|
||
> <ruby>NTFS<rt>New Technology File System</rt></ruby> 是 Windows NT 内核的系列操作系统支持的、一个特别为网络和磁盘配额、文件加密等管理安全特性设计的磁盘文件系统格式。而 NTFS3 是功能齐全的 NTFS 读写驱动程序。该驱动程序适用于最高 3.1 的 NTFS 版本。 | ||
|
||
[//]: # (文章内图片请自行放置于图床,并引用) |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
### Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. [Learn more](https://docs.github.com/articles/managing-disruptive-comments/#hiding-a-comment).
这是两行注释,要删除。
|
||
![使用 ntfs3 驱动替换 ntfs-3g 挂载 windows NTFS 分区][1] | ||
|
||
[//]: # (文章内章节以 `###` 标题为一级标题,子标题以此类推) |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
### Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. [Learn more](https://docs.github.com/articles/managing-disruptive-comments/#hiding-a-comment).
删除注释
|
||
[//]: # (文章内图片请自行放置于图床,并引用) | ||
|
||
![使用 ntfs3 驱动替换 ntfs-3g 挂载 windows NTFS 分区][1] |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
### Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. [Learn more](https://docs.github.com/articles/managing-disruptive-comments/#hiding-a-comment).
这个不适合做题图,可以放在文内。题图我发表时想想,或者你有合适的也可以放上。
|
||
最初 Linux 内核没有对 NTFS 做原生支持,来自 Tuxera 的 NTFS-3G 是目前主流的解决方案,但在实际使用中也有不少小问题。NTFS-3G 是借助 Linux 的用户空间文件系统 FUSE 模块在用户层实现的一个模仿对 NTFS 支持的文件系统,对 NTFS 的访问逻辑代码都是在用户层代码实现的。 | ||
|
||
在 NTFS3 出现之前 Linux 上使用 NTFS 主要问题还是缺乏稳定且功能齐全的读/写支持。 |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
### Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. [Learn more](https://docs.github.com/articles/managing-disruptive-comments/#hiding-a-comment).
我记得有一段时间是只有只读支持。
|
||
* 支持本地日志回放。 | ||
|
||
* 支持安装的 NTFS 卷的 NFS 导出。 |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
### Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. [Learn more](https://docs.github.com/articles/managing-disruptive-comments/#hiding-a-comment).
安装?挂载?
|
||
* 支持安装的 NTFS 卷的 NFS 导出。 | ||
|
||
* 支持扩展属性。预定义的扩展属性: |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
### Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. [Learn more](https://docs.github.com/articles/managing-disruptive-comments/#hiding-a-comment).
这是什么?用在什么地方?
|
||
#### 手动挂载 | ||
|
||
手动挂载使用命令: |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
### Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. [Learn more](https://docs.github.com/articles/managing-disruptive-comments/#hiding-a-comment).
既然标题说是”替换“,是否提一下之前的挂载方式(命令),并介绍现在的挂载命令。
|
||
### 挂载参数 | ||
|
||
<table> |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
### Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. [Learn more](https://docs.github.com/articles/managing-disruptive-comments/#hiding-a-comment).
这个表格替换为 MD 格式,我看了一下内容,不是必须使用表格合并,信息或有冗余,同时可以在重复信息的地方,写”同上“、”同xx“即可。
|
||
### 关于 NTFS3 驱动无人维护的问题 | ||
|
||
自从该驱动 2021 年在 Linux 5.15 中最终被主线化以来,至今为止,在接近一年的时间里,还没有任何重大的错误修复被送入驱动。 |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
### Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. [Learn more](https://docs.github.com/articles/managing-disruptive-comments/#hiding-a-comment).
可以前面插一句,介绍这个驱动历经了多少次的不断审核才得以进入内核,说明该公司是认真的。

**approved these changes**
[wxy](/wxy)Jul 9, 2022
…FS partition.md
投稿 |
14,812 | Meta 开源了语言翻译 AI 模型 | https://news.itsfoss.com/meta-open-source-ai-model/ | 2022-07-10T11:22:00 | [
"翻译",
"AI"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14812-1.html |
>
> Meta 的 “<ruby> 不落下任何语言 <rt> No Language Left Behind </rt></ruby>” 是一个宏大的开源项目,旨在以最高准确度翻译语言。
>
>
>

Meta(前身是 Facebook)在开源世界做出了不小的贡献。Meta 除了专注于<ruby> 元宇宙 <rt> Metaverse </rt></ruby>和其社交媒体平台外,还致力于各种研究和创新工作,比如 React(一个 JaveScript 库)。
现在,Meta 的研究人员决定开源一个叫 “<ruby> 不落下任何语言 <rt> No Language Left Behind </rt></ruby>” 项目。
(LCTT 校注:这个直译项目名称不够好听,我来抛砖引玉,似可称做“无人独语”,读者有什么建议吗?)
### Meta 试图不落下任何语言
目前,虽然世界上有大约 7000 个在使用中的语言,但大多数在线的内容都是以少数的流行语言来提供的,比如英语。这让许多不懂这些语言的人处于不利的地位。
虽然现存的许多翻译工具,但语法错误会让错误变得难以阅读和理解。另外,如果你想把内容翻译为一个不流行的语言(特别是非洲和亚洲的一些语言),翻译体验不会很好。
因此,Meta 正在开发有最高质量的翻译工具,可以帮助解决这一全球性的问题。
NLLB-200(<ruby> 不落下任何语言 <rt> No Language Left Behind </rt></ruby>) 是一个人工智能翻译模型,其可以翻译 200 多种语言。该模型在每种语言中的翻译结果是通过一个名为 FLORES-200 复杂数据集来确定和评估的。
正如 Meta 所说,NLLB 的翻译结果比以前的人工智能研究方法好 40% 。对于一些最不常见的语言,其翻译准确率甚至超过 70%。了不起的工作!
为了帮助开发项目和提高模型的翻译质量,Meta 向所有感兴趣的研究人员开放了源代码,包括 NLLB-200 模型、FLORES-200 数据库、模型训练和重建训练数据库的代码。
你可以在 [GitHub](https://github.com/facebookresearch/fairseq/tree/nllb) 上找到源代码,并且可以在该项目的 [博客](https://ai.facebook.com/blog/nllb-200-high-quality-machine-translation/) 上了解它的更多信息。
### 对社会事业的鼓励
Meta 宣布向从事<ruby> 联合国可持续发展目标 <rt> UN Sustainable Development Goals </rt></ruby>任何领域工作和翻译非洲语言的非营利组织和研究人员提供高达 20 万美元的捐赠,也鼓励其他学术领域如语言学和机器翻译的研究人员申请。
### 项目的影响
尽管 Meta 主要打算在其数字平台上,特别是在“元宇宙”上使用 NLLB,但 NLLB 也有可能在其他领域产生巨大影响。
许多用户可以用他们的母语轻松地访问和阅读在线资源。项目开源后,社区应该能够帮助实现这个目标。
*你对 Meta 的这个项目有什么看法?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/meta-open-source-ai-model/>
作者:[Rishabh Moharir](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/rishabh/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[fenglyulin](https://github.com/fenglyulin) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Meta (formerly known as Facebook) has made quite a splash in the open-source world. If you did not know, Meta works on various research and innovative projects like React (a JavaScript library) apart from focusing on the metaverse and its social media platforms.
Researchers at Meta have decided to open-source one such project, an AI model called ‘*No Language Left Behind*‘.
## Meta’s Attempt To Leave No Language Behind
While around 7000 languages are spoken in the world today, most of the online content is available in a handful of popular languages like English. This leaves many people who don’t know such languages at a disadvantage.
While many tools exist for translation, grammatical errors can make content difficult to read and understand. Moreover, if you are looking to translate it into a language that is not popular, it won’t be a pretty experience.
Specifically, for languages of Africa and Asia.
Hence, Meta is working on a translational tool with one of the highest quality results recorded that can help counter this global issue.
No Language Left Behind or simply **NLLB-200** is a machine translation model that can translate over 200 languages using artificial intelligence
NLLB’s performance in each language is determined and evaluated using a complex dataset called FLORES-200 (if you’re curious).
As stated by Meta, NLLB’s results are 40% better than “previous AI research” methods. It even has an accuracy of over 70% for some of the least-common languages. That’s quite an impressive feat!
To help develop and improve the quality of translations, Meta has made the source code open to all interested researchers. This includes code for NLLB-200, FLORES-200, model training, and re-creating the training database.
You can find the source code on [GitHub](https://github.com/facebookresearch/fairseq/tree/nllb?ref=news.itsfoss.com) and learn more about the project in its [research blog post](https://ai.facebook.com/blog/nllb-200-high-quality-machine-translation/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Rewards for Social Cause
Meta has announced rewards of up to $200,00 of grants for non-profit organizations and researchers who are working on any areas of the UN Sustainable Development Goals and translating African languages.
Other researchers currently working in academic fields like linguistics and machine translation are also encouraged to apply.
## The Impact of this Project
Although Meta intends to mostly make use of NLLB across its digital platforms, particularly the Metaverse, it can be hugely impactful in other domains as well.
Many users will be able to access and easily read online resources in their native languages without a lot of effort. The idea of making it an open-source project should allow the community to help make this happen.
*What are your thoughts on this project by Meta?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,813 | 如何在 Linux 上动态链接模块库 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/dynamic-linking-modular-libraries-linux | 2022-07-10T18:26:07 | [
"动态链接",
"编译"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14813-1.html |
>
> 学习如何用动态链接库将多个 C 目标文件结合到一个单个的可执行文件之中。
>
>
>

当使用 C 编程语言编写一个应用程序时,你的代码通常有多个源文件代码。
最终,这些文件必须被编译到一个单个的可执行文件之中。你可以通过创建静态或动态库(后者也被称为 <ruby> 共享 <rt> shared </rt></ruby> 库)来实现这一点。这两种类型的库在创建和链接的方式上有所不同。两者都有缺点和优点,这取决于你的使用情况。
动态链接是最常见的方法,尤其是在 Linux 系统上。动态链接会保持库模块化,因此,很多应用程序可以共享一个库。应用程序的模块化也允许单独更新其依赖的共享库。
在这篇文章中,我将演示动态链接是如何工作的。在后期的文章中,我将演示静态链接。
### 链接器
<ruby> 链接器 <rt> linker </rt></ruby>是一个命令,它将一个程序的数个部分结合在一起,并为它们重新组织内存分配。
链接器的功能包括:
* 整合一个程序的所有的部分
* 计算出一个新的内存组织结构,以便所有的部分组合在一起
* 恢复内存地址,以便程序可以在新的内存组织结构下运行
* 解析符号引用
链接器通过这些功能,创建了一个名为<ruby> 可执行文件 <rt> executable </rt></ruby>的可以运行的程序。在你创建一个动态链接的可执行文件前,你需要一些用来链接的库,和一个用来编译的应用程序。准备好你 [最喜欢的文本编辑器](https://opensource.com/article/21/2/open-source-text-editors) 并继续。
### 创建目标文件
首先,创建带有这些函数签名的头文件 `mymath.h` :
```
int add(int a, int b);
int sub(int a, int b);
int mult(int a, int b);
int divi(int a, int b);
```
使用这些函数定义来创建 `add.c` 、`sub.c` 、`mult.c` 和 `divi.c` 文件。我将把所有的代码都放置到一个代码块中,请将其分为四个文件,如注释所示:
```
// add.c
int add(int a, int b){
return (a+b);
}
//sub.c
int sub(int a, int b){
return (a-b);
}
//mult.c
int mult(int a, int b){
return (a*b);
}
//divi.c
int divi(int a, int b){
return (a/b);
}
```
现在,使用 GCC 来创建目标文件 `add.o`、`sub.o`、`mult.o` 和 `divi.o` :
(LCTT 校注:关于“<ruby> 目标文件 <rt> object file </rt></ruby>”,有时候也被称作“对象文件”,对此,存在一些译法混乱情形,称之为“目标文件”的译法比较流行,本文采用此译法。)
```
$ gcc -c add.c sub.c mult.c divi.c
```
`-c` 选项跳过链接步骤,并且只创建目标文件。
### 创建一个共享的目标文件
在最终的可执行文件的执行过程中将链接动态库。在最终的可执行文件中仅放置动态库的名称。实际上的链接过程发生在运行时,在此期间,可执行文件和库都被放置到了主内存中。
除了可共享外,动态库的另外一个优点是它减少了最终的可执行文件的大小。在一个应用程序最终的可执行文件生成时,其使用的库只包括该库的名称,而不是该库的一个多余的副本。
你可以从你现有的示例代码中创建动态库:
```
$ gcc -Wall -fPIC -c add.c sub.c mult.c divi.c
```
选项 `-fPIC` 告诉 GCC 来生成<ruby> 位置无关的代码 <rt> position-independent code </rt></ruby>(PIC)。`-Wall` 选项不是必需的,并且与代码的编译方式是无关的。不过,它却是一个有价值的选项,因为它会启用编译器警告,这在排除故障时是很有帮助的。
使用 GCC ,创建共享库 `libmymath.so` :
```
$ gcc -shared -o libmymath.so add.o sub.o mult.o divi.o
```
现在,你已经创建了一个简单的示例数学库 `libmymath.so` ,你可以在 C 代码中使用它。当然,也有非常复杂的 C 库,这就是他们这些开发者来生成最终产品的工艺流程,你和我可以安装这些库并在 C 代码中使用。
接下来,你可以在一些自定义代码中使用你的新数学库,然后链接它。
### 创建一个动态链接的可执行文件
假设你已经为数学运算编写了一个命令。创建一个名称为 `mathDemo.c` 的文件,并将这些代码复制粘贴至其中:
```
#include <mymath.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int x, y;
printf("Enter two numbers\n");
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
printf("\n%d + %d = %d", x, y, add(x, y));
printf("\n%d - %d = %d", x, y, sub(x, y));
printf("\n%d * %d = %d", x, y, mult(x, y));
if(y==0){
printf("\nDenominator is zero so can't perform division\n");
exit(0);
}else{
printf("\n%d / %d = %d\n", x, y, divi(x, y));
return 0;
}
}
```
注意:第一行是一个 `include` 语句,通过名称来引用你自己的 `libmymath` 库。要使用一个共享库,你必须已经安装了它,如果你没有安装你将要使用的库,那么当你的可执行文件在运行并搜索其包含的库时,将找不到该共享库。如果你需要在不安装库到已知目录的情况下编译代码,这里有 [一些方法可以覆盖默认设置](https://opensource.com/article/22/5/compile-code-ldlibrarypath)。不过,对于一般使用来说,我们希望库存在于已知的位置,因此,这就是我在这里演示的东西。
复制文件 `libmymath.so` 到一个标准的系统目录,例如:`/usr/lib64`, 然后运行 `ldconfig` 。`ldconfig` 命令创建所需的链接,并缓存到标准库目录中发现的最新共享库。
```
$ sudo cp libmymath.so /usr/lib64/
$ sudo ldconfig
```
### 编译应用程序
从你的应用程序源文件代码(`mathDemo.c`)中创建一个名称为 `mathDemo.o` 的目标文件:
```
$ gcc -I . -c mathDemo.c
```
`-I` 选项告诉 GCC 来在其后所列出的目录中搜索头文件(在这个示例中是 `mymath.h`)。在这个示例中,你指定的是当前目录,通过一个单点(`.`)来表示。创建一个可执行文件,使用 `-l` 选项来通过名称来引用你的共享数学库:
```
$ gcc -o mathDynamic mathDemo.o -lmymath
```
GCC 会找到 `libmymath.so` ,因为它存在于一个默认的系统库目录中。使用 `ldd` 来查证所使用的共享库:
```
$ ldd mathDemo
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007fffe6a30000)
libmymath.so => /usr/lib64/libmymath.so (0x00007fe4d4d33000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007fe4d4b29000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007fe4d4d4e000)
```
看看 `mathDemo` 可执行文件的大小:
```
$ du ./mathDynamic
24 ./mathDynamic
```
当然,它是一个小的应用程序,它所占用的磁盘空间量也反映了这一点。相比之下,相同代码的一个静态链接版本(正如你将在我后期的文章所看到的一样)是 932K !
```
$ ./mathDynamic
Enter two numbers
25
5
25 + 5 = 30
25 - 5 = 20
25 * 5 = 125
25 / 5 = 5
```
你可以使用 `file` 命令来查证它是动态链接的:
```
$ file ./mathDynamic
./mathDynamic: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64,
dynamically linked,
interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2,
with debug_info, not stripped
```
成功!
### 动态链接
因为链接发生在运行时,所以,使用一个共享库会产生一个轻量型的可执行文件。因为它在运行时解析引用,所以它会花费更多的执行时间。不过,因为在日常使用的 Linux 系统上绝大多数的命令是动态链接的,并且在现代硬件上,所能节省的时间是可以忽略不计的。对开发者和用户来说,它的固有模块性是一种强大的功能。
在这篇文章中,我描述了如何创建动态库,并将其链接到一个最终可执行文件。在我的下一篇文章中,我将使用相同的源文件代码来创建一个静态链接的可执行文件。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/dynamic-linking-modular-libraries-linux>
作者:[Jayashree Huttanagoudar](https://opensource.com/users/jayashree-huttanagoudar) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When you write an application using the C programming language, your code usually has multiple source files.
Ultimately, these files must be compiled into a single executable. You can do this by creating either *static* or *dynamic* libraries (the latter are also referred to as *shared* libraries). These two types of libraries vary in how they are created and linked. Both have advantages and disadvantages, depending on your use case.
Dynamic linking is the most common method, especially on Linux systems. Dynamic linking keeps libraries modular, so just one library can be shared between any number of applications. Modularity also allows a shared library to be updated independently of the applications that rely upon it.
In this article, I demonstrate how dynamic linking works. In a future article, I'll demonstrate static linking.
## Linker
A linker is a command that combines several pieces of a program together and reorganizes the memory allocation for them.
The functions of a linker include:
- Integrating all the pieces of a program
- Figuring out a new memory organization so that all the pieces fit together
- Reviving addresses so that the program can run under the new memory organization
- Resolving symbolic references
As a result of all these linker functionalities, a runnable program called an *executable* is created. Before you can create a dynamically linked executable, you need some libraries to link *to* and an application to compile. Get your [favorite text editor](https://opensource.com/article/21/2/open-source-text-editors) ready and follow along.
## Create the object files
First, create the header file `mymath.h`
with these function signatures:
```
``````
int add(int a, int b);
int sub(int a, int b);
int mult(int a, int b);
int divi(int a, int b);
```
Create `add.c`
, `sub.c`
, `mult.c `
and `divi.c`
with these function definitions. I'm placing all of the code in one code block, so divide it up among four files, as indicated in the comments:
```
``````
// add.c
int add(int a, int b){
return (a+b);
}
//sub.c
int sub(int a, int b){
return (a-b);
}
//mult.c
int mult(int a, int b){
return (a*b);
}
//divi.c
int divi(int a, int b){
return (a/b);
}
```
Now generate object files `add.o`
, `sub.o`
, `mult.o`
, and `divi.o`
using GCC:
```
````$ gcc -c add.c sub.c mult.c divi.c`
The `-c`
option skips the linking step and creates only object files.
## Creating a shared object file
Dynamic libraries are linked during the execution of the final executable. Only the name of the dynamic library is placed in the final executable. The actual linking happens during runtime, when both executable and library are placed in the main memory.
In addition to being sharable, another advantage of a dynamic library is that it reduces the size of the final executable file. Instead of having a redundant copy of the library, an application using a library includes only the name of the library when the final executable is created.
You can create dynamic libraries from your existing sample code:
```
````$ gcc -Wall -fPIC -c add.c sub.c mult.c divi.c`
The option `-fPIC`
tells GCC to generate *position-independent code* (PIC). The `-Wall`
option isn't necessary and has nothing to do with how the code is compiling. Still, it's a valuable option because it enables compiler warnings, which can be helpful when troubleshooting.
Using GCC, create the shared library `libmymath.so`
:
```
``````
$ gcc -shared -o libmymath.so \
add.o sub.o mult.o divi.o
```
You have now created a simple example math library, `libmymath.so`
, which you can use in C code. There are, of course, very complex C libraries out there, and this is the process their developers use to generate the final product that you or I install for use in C code.
Next, you can use your new math library in some custom code, then link it.
## Creating a dynamically linked executable
Suppose you've written a command for mathematics. Create a file called `mathDemo.c`
and paste this code into it:
```
``````
#include <mymath.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int x, y;
printf("Enter two numbers\n");
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
printf("\n%d + %d = %d", x, y, add(x, y));
printf("\n%d - %d = %d", x, y, sub(x, y));
printf("\n%d * %d = %d", x, y, mult(x, y));
if(y==0){
printf("\nDenominator is zero so can't perform division\n");
exit(0);
}else{
printf("\n%d / %d = %d\n", x, y, divi(x, y));
return 0;
}
}
```
Notice that the first line is an `include`
statement referencing, by name, your own `libmymath`
library. To use a shared library, you must have it installed. If you don't install the library you use, then when your executable runs and searches for the included library, it won't be able to find it. Should you need to compile code without installing a library to a known directory, there are [ways to override default settings](https://opensource.com/article/22/5/compile-code-ldlibrarypath). For general use, however, it's expected that libraries exist in known locations, so that's what I'm demonstrating here.
Copy the file `libmymath.so`
to a standard system directory, such as `/usr/lib64`
, and then run `ldconfig`
. The `ldconfig`
command creates the required links and cache to the most recent shared libraries found in the standard library directories.
```
``````
$ sudo cp libmymath.so /usr/lib64/
$ sudo ldconfig
```
## Compiling the application
Create an object file called `mathDemo.o`
from your application source code (`mathDemo.c`
):
```
````$ gcc -I . -c mathDemo.c`
The `-I`
option tells GCC to search for header files (`mymath.h`
in this case) in the directory listed after it. In this case, you're specifying the current directory, represented by a single dot (`.`
). Create an executable, referring to your shared math library by name using the `-l`
option:
```
````$ gcc -o mathDynamic mathDemo.o -lmymath`
GCC finds `libmymath.so`
because it exists in a default system library directory. Use `ldd`
to verify the shared libraries used:
```
``````
$ ldd mathDemo
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007fffe6a30000)
libmymath.so => /usr/lib64/libmymath.so (0x00007fe4d4d33000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007fe4d4b29000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007fe4d4d4e000)
```
Take a look at the size of the `mathDemo`
executable:
```
``````
$ du ./mathDynamic
24 ./mathDynamic
```
It's a small application, of course, and the amount of disk space it occupies reflects that. For comparison, a statically linked version of the same code (as you'll see in my next article) is 932K!
```
``````
$ ./mathDynamic
Enter two numbers
25
5
25 + 5 = 30
25 - 5 = 20
25 * 5 = 125
25 / 5 = 5
```
You can verify that it's dynamically linked with the `file`
command:
```
``````
$ file ./mathDynamic
./mathDynamic: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64,
dynamically linked,
interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2,
with debug_info, not stripped
```
Success!
## Dynamically linking
A shared library leads to a lightweight executable, as the linking happens during runtime. Because it resolves references during runtime, it does take more time for execution. However, since the vast majority of commands on everyday Linux systems are dynamically linked and on modern hardware, the time saved is negligible. Its inherent modularity is a powerful feature for developers and users alike.
In this article, I described how to create dynamic libraries and link them into a final executable. I'll use the same source code to create a statically linked executable in my next article.
## Comments are closed. |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.