id
int64 2.05k
16.6k
| title
stringlengths 5
75
| fromurl
stringlengths 19
185
| date
timestamp[s] | tags
sequencelengths 0
11
| permalink
stringlengths 20
37
| content
stringlengths 342
82.2k
| fromurl_status
int64 200
526
⌀ | status_msg
stringclasses 339
values | from_content
stringlengths 0
229k
⌀ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
14,535 | 在 Python 中使用机器学习来检测钓鱼链接 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/04/detect-a-phishing-url-using-machine-learning-in-python/ | 2022-05-02T18:06:47 | [
"钓鱼",
"机器学习"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14535-1.html | 在网络钓鱼攻击中,用户会收到一封带有误导性链接的邮件或信息,攻击者可以利用它来收集重要数据,比如你的银行卡密码。本文将会给出一个简短的教程,旨在介绍如何检测这种网络钓鱼的企图。

通过网络钓鱼攻击,攻击者能够获得一些重要凭证,这些凭证可以用来进入你的银行或其他金融账户。攻击者发送的 URL 看起来与我们日常使用的原始应用程序完全相同。这也是人们经常相信它,并在其中输入个人信息的原因。钓鱼网址可以打开一个网页,它看起来与你的银行的原始登录页面相似。最近,这样的网络钓鱼攻击正变得相当普遍,所以,检测钓鱼链接变得非常重要。因此,我将介绍如何在 Python 中使用机器学习来检查一个链接是误导性的还是真实的,因为它可以帮助我们看到网页代码及其输出。注意,本文将使用 Jupyter Notebook。当然,你也可以使用 Google Colab 或 Amazon Sagemaker,如果你对这些更熟悉的话。
### 下载数据集
第一步,我们需要用于训练数据集。你可以从下面的链接中下载数据集。
* 真实的链接:<https://github.com/jishnusaurav/Phishing-attack-PCAP-analysis-using-scapy/blob/master/Phishing-Website-Detection/datasets/legitimate-urls.csv>
* 钓鱼链接:<https://github.com/jishnusaurav/Phishing-attack-PCAP-analysis-using-scapy/blob/master/Phishing-Website-Detection/datasets/phishing-urls.csv>
### 训练机器进行预测
当数据集下载完成,我们需要使用以下几行代码来导入所需的库:
```
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
```
如果你没有这些库,你可以使用 `pip` 工具来安装这些库,如下图所示:

当依赖安装完成,你就可以导入数据集,并将其转换为 `pandas` 数据框架,使用以下几行代码进一步处理:
```
legitimate_urls = pd.read_csv(“/home/jishnusaurav/jupyter/Phishing-Website-Detection/datasets/legitimate-urls.csv”)
phishing_urls = pd.read_csv(“/home/jishnusaurav/jupyter/Phishing-Website-Detection/datasets/phishing-urls.csv”)
```
在成功导入后,我们需要把这两个数据集合并,以便形成一个数据集。合并后的数据集的前几行如下图所示:

然后去掉那些我们不需要的列,如路径(`path`)、协议(`protocol`)等,以达到预测的目的:
```
urls = urls.drop(urls.columns[[0,3,5]],axis=1)
```
在这之后,我们需要使用以下代码将数据集分成测试和训练两部分:
```
data_train, data_test, labels_train, labels_test = train_test_split(urls_without_labels, labels, test_size=0.30, random_state=110)
```
接着,我们使用 `sklearn` 的随机森林分类器建立一个模型,然后使用 `fit` 函数来训练这个模型。
```
random_forest_classifier = RandomForestClassifier()
random_forest_classifier.fit(data_train,labels_train)
```
完成这些后,我们就可以使用 `predict` 函数来最终预测哪些链接是钓鱼链接。下面这行可用于预测:
```
prediction_label = random_forest_classifier.predict(test_data)
```
就是这样啦!你已经建立了一个机器学习模型,它可以预测一个链接是否是钓鱼链接。试一下吧,我相信你会满意的!
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/04/detect-a-phishing-url-using-machine-learning-in-python/>
作者:[Jishnu Saurav Mittapalli](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/jishnu-saurav-mittapalli/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *In a phishing attack, a user is sent a mail or a message that has a misleading URL, using which the attacker can collect important data like the passwords of the banks your money is in. This article gives a short tutorial on how to detect such phishing attempts.*
Through phishing attacks, attackers acquire important credentials that can be used for getting access to your bank or other financial accounts. The URLs sent by the attacker look exactly the same as the original applications we use on a daily basis. That is why people often believe these and enter their personal details. A phishing URL can open a Web page that looks similar to the original login page of your bank. Detecting such URLs has become very important of late as such phishing attacks are becoming pretty common. So let’s see how we can check whether a URL is a misleading one or a genuine one using machine learning in Python, as it can help us see the code as well as the outputs. We will be using Jupyter Notebook. You can use Google Colab or Amazon Sagemaker too, if you are more comfortable with those.
**Download the data sets**
To start, we will need the data set to work upon. You can download the data sets from the links given below.
**Genuine URLs:** https://github.com/jishnusaurav/Phishing-attack-PCAP-analysis-using-scapy/blob/master/Phishing-Website-Detection/datasets/legitimate-urls.csv
**Phishing URLs:** https://github.com/jishnusaurav/Phishing-attack-PCAP-analysis-using-scapy/blob/master/Phishing-Website-Detection/datasets/phishing-urls.csv
**Training the machine to predict**
Once we have the data sets, we need to import the required libraries using the following lines of code:
<em>import pandas as pd</em> <em>from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier</em>
If you do not have the libraries, you can use* pip* to install the libraries, as shown in Figure 1.

Once this is done, you can import the data sets and convert them into pandas dataframe for further processing using the following lines of code:
legitimate_urls = pd.read_csv(“/home/jishnusaurav/jupyter/Phishing-Website-Detection/datasets/legitimate-urls.csv”) phishing_urls = pd.read_cs v(“/home/jishnusaurav/jupyter/Phishing-Website-Detection/datasets/phishing-urls.csv”)
After successful import, we need to merge both the dataframes — the legitimate and the phishing ones, in order to make one data set. The first few lines of the merged data set are shown in Figure 2.
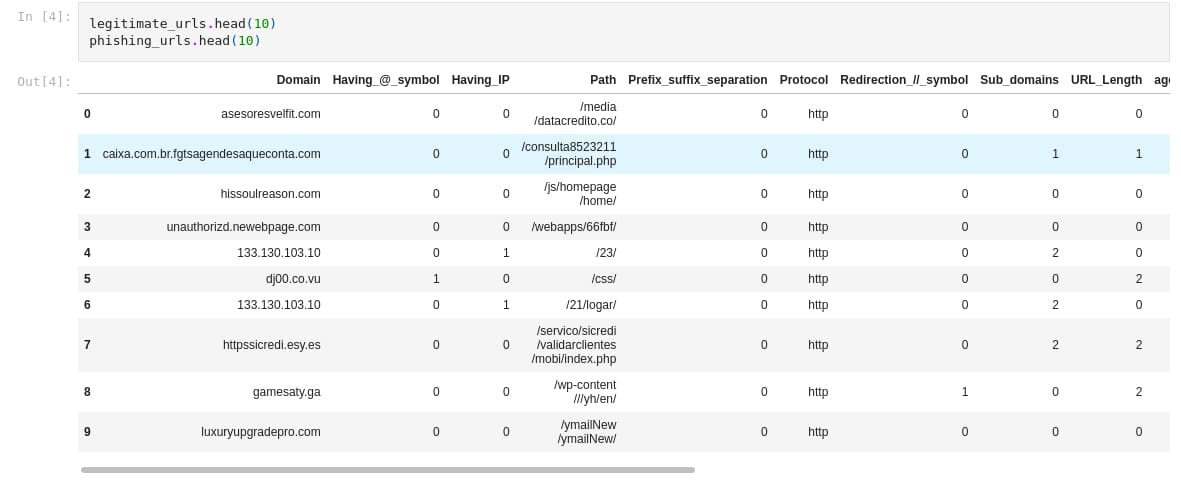

We then drop the columns like path, protocol, etc, that we do not need for the purpose of prediction:
urls = urls.drop(urls.columns[[0,3,5]],axis=1)
After this, we need to split the data set into testing and training parts using the following code:
data_train, data_test, labels_train, labels_test = train_test_split(urls_without_labels, labels, test_size=0.30, random_state=110)
We now make a model using the random forest classifier from sklearn, and then use the fit function to train the model:
random_forest_classifier = RandomForestClassifier() random_forest_classifier.fit(data_train,labels_train)
Once this is done, we can use the predict function to finally predict which URLs are phishing. The following line can be used for the prediction:
prediction_label = random_forest_classifier.predict(test_data)
That is it! You have built a machine learning model that predicts if a URL is a phishing one. Do try it out. I am sure you will have fun. |
14,536 | Archinstall 新的菜单系统让安装 Arch Linux 更容易了 | https://news.itsfoss.com/archinstall-menu/ | 2022-05-02T22:56:58 | [
"Arch Linux"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14536-1.html |
>
> Archinstall 让人们更容易上手 Arch Linux,也应该可以为经验丰富的 Linux 用户节省时间。你觉得呢?
>
>
>

去年的这个时候,Arch Linux [引入了一个引导式的安装程序](https://news.itsfoss.com/arch-linux-easy-install/),使其安装过程更加简单。
你只需要输入 `archinstall`,就可以开始一步步的安装,而不需要自己全部定制。
即使你不是新手用户,它应该也能为你正常安装 Arch Linux 节省一些时间。你可以配置所有基本选项,无论是创建普通用户或 root 用户,还是选择桌面、挑选软件包、选择音频服务器,等等。
如果你感兴趣的话,可以在我们的 [在 VirtualBox 里安装 Arch Linux 的指南](https://itsfoss.com/install-arch-linux-virtualbox/) 中看看 Archinstall 的实际使用。
现在,Archinstall v2.4.1 已发布,我们有了新的菜单系统和大量的技术变化。
让我们来看看它是如何工作的吧!
### 新菜单系统及无障碍改进

新的菜单系统看起来更有条理了。
它是以 [simple-term-menu](https://github.com/IngoMeyer441/simple-term-menu) 为基础建立的,simple-term-menu 是一个用于在命令行中创建交互式菜单的软件包。为了避免外部依赖,它与源代码捆绑,这要归功于 Ingo Meyer(开发者)。
另外还得感谢其他开发者,其中包括 [Werner Llácer](https://github.com/wllacer) 和 [Daniel](https://github.com/svartkanin),是他们编写了 1200 多行代码,才让这成为可能。
这个菜单系统也是无障碍的。你可以用数字键盘上的 `*` 把它切换到跟踪选择模式,这应该能让 espeakup 如预期的工作。
在 Archinstall 的未来版本中,它也会支持默认的跟踪模式。
在上面的截图中,你可能会注意到,它支持设置语言、键盘布局、内核、音频服务器、用户、网络和其他基本选项。
当你选择了硬盘后,菜单将增加另一个选项,让你选择一个“磁盘布局”,你可以在其中选择文件系统的类型。

同样,设置每一个选项时,你都可以调整更多细节,比如桌面环境的配置文件。

默认情况下,它会启用一个交换分区。不过,你可以根据你的需要进行调整。总的来说,这应该是一个顺滑的体验,所有的安装先决条件都以菜单形式呈现。
在此感谢我们团队中的 Sreenath,是他测试并提供了这些屏幕截图。

除了这些变化之外,你还可以期待以下改进:
* 如果你选择 btrfs 作为文件系统,会添加一个 BTRFS 压缩选项。
* Archinstall 现在支持同时进行多个网卡配置的手动配置。
* 安装程序可以通过 `archinstall.Installer()` 跟踪哪些软件包已经安装完毕。
要查看所有的技术变化和错误修复,你可以参考 [GitHub 上的发布说明](https://github.com/archlinux/archinstall/releases/tag/v2.4.1)。
**你可以等待最新的 ISO(计划在 5 月 1 日发布),或者从 GitHub 上下载并自己尝试。**
你试过 Arch Linux 上的原来的安装向导吗?还是说,相较于使用安装程序,你更偏向于自己手动配置一切?请在评论区分享你的想法吧!
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/archinstall-menu/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Last year, this time around, Arch Linux [introduced a guided installer](https://news.itsfoss.com/arch-linux-easy-install/) to make the installation process easier.
All you had to do was type in “**archinstall**” to get started with the step-by-step installation without needing to customize all by yourself.
Not just for new users, it should also save you some time to install Arch Linux in general. You get all the essential options starting from creating username/root user, selecting the desktop, picking software packages, choosing the audio server, and more.
If you are curious, you can take a look at archinstall in action in our [installation guide for Arch Linux on VirtualBox](https://itsfoss.com/install-arch-linux-virtualbox/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
Now, with archinstall v2.4.1, we have a new menu system and numerous technical changes.
Let us take a look at it and how it works.
### Archinstall’s New Menu System & Accessibility Improvements
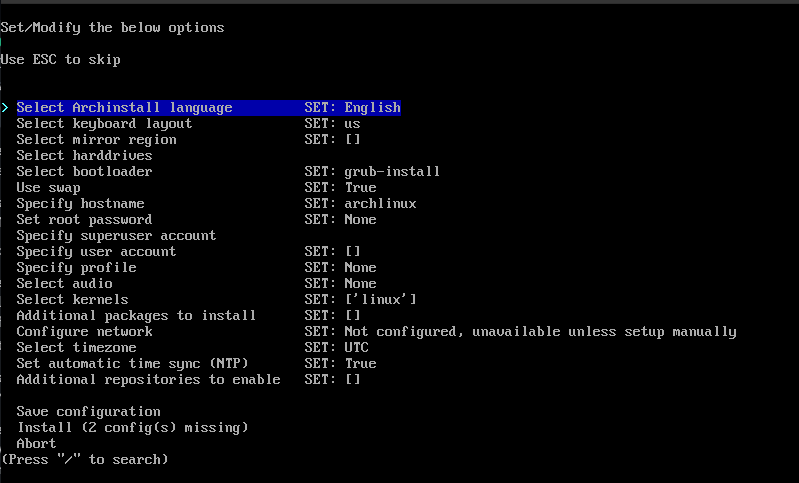
The new menu system looks much more organized.
It is built using [simple-term-menu](https://github.com/IngoMeyer441/simple-term-menu?ref=news.itsfoss.com) as its base, which is a package to create interactive menus on the command line. To avoid external dependencies, it has been bundled with the source, all thanks to Ingo Meyer.
Other developers include [Werner Llácer](https://github.com/wllacer?ref=news.itsfoss.com) and [Daniel](https://github.com/svartkanin?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to make this work with 1200+ lines of code.
The menu system is also accessibility friendly. You can switch it to the tracking selection mode using the “numpad *”, which should make espeakup work, as one would expect.
In future archinstall versions, it will honor default tracking mode as well.
As you can notice in the screenshot above, you get to set the language, keyboard layout, kernels, audio server, user, network, and more essential options.
Once you select the hard drive, the menu will add another option to let you choose a “disk layout” where you can select the type of file system.
Similarly, as you proceed with each option, you will get access to more things to tweak like the profiles to set your desktop environment:
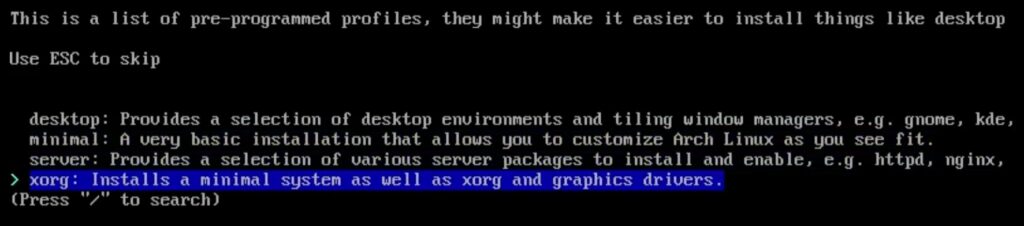
By default, you have a swap enabled. But, you can tweak that as you require. Overall, it should be a seamless experience, with all installation prerequisites presented in a menu form.
Thanks to *Sreenath* on our team for testing this through to give you some screenshots:
In addition to these changes, you can also expect the following improvements:
- BTRFS compression option added as an option if you select btrfs as filesystem.
- Archinstall now supports multiple NIC configurations at the same time for manual configuration
- The installer keeps track of which packages have been installed through archinstall.Installer()
To explore all the technical changes and bug fixes, you can refer to the [release notes on GitHub](https://github.com/archlinux/archinstall/releases/tag/v2.4.1?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
**You can wait for the latest ISO (scheduled for May 1) to try it out, or download it from GitHub and try it yourself.**
*Have you tried the original guided installer on Arch Linux? Or do you prefer to configure everything without the installer? Feel free to let me know your thoughts below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,537 | 如何在 Linux 和 Windows 电脑之间共享文件 | https://opensource.com/article/21/4/share-files-linux-windows | 2022-05-02T23:39:00 | [
"共享",
"Samba"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14537-1.html |
>
> 使用 Samba 设置跨平台文件共享。
>
>
>

如果你使用不同的操作系统,能够在它们之间共享文件会让你倍感方便。这篇文章介绍如何使用 [Samba](https://www.samba.org/) 和 [mount.cifs](https://linux.die.net/man/8/mount.cifs) 在 Linux ([Fedora 33](https://getfedora.org/en/workstation/download/))和 Windows 10 之间设置文件共享。
Samba 是 [SMB/CIFS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Server_Message_Block) 协议的 Linux 实现,允许通过网络连接直接访问共享的文件夹和打印机。 mount.cifs 是 Samba 套件的一部分,可让你在 Linux 下挂载 [CIFS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Server_Message_Block) 文件系统。
>
> **注意**: 这些说明适用于在你的私有本地网络内,或在 Linux 宿主机和虚拟化的 Windows 访客机之间的虚拟主机专用网络中共享文件。不要将本文视为你公司网络的操作指南,因为本文没有实现必要的网络安全考虑。
>
>
>
### 从 Windows 访问 Linux
本节介绍从 Windows 文件资源管理器访问用户的 Linux 主目录。
#### 1、安装和配置 Samba
进入你的系统安装 Samba:
```
dnf install samba
```
Samba 是一个系统守护进程,其配置文件位于 `/etc/samba/smb.conf`。它的默认配置应该就可以工作。如果不行,下面这个最小化配置应该可以解决问题:
```
[global]
workgroup = SAMBA
server string = %h server (Samba %v)
invalid users = root
security = user
[homes]
comment = Home Directories
browseable = no
valid users = %S
writable = yes
```
你可以在该项目网站的 [smb.conf](https://www.samba.org/samba/docs/current/man-html/smb.conf.5.html) 部分找到参数的详细说明。
#### 2、修改 LinuxSE
如果你的 Linux 发行版受 [SELinux](https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/linux/what-is-selinux) 保护(比如 Fedora),必须通过以下命令才能通过 Samba 共享主目录:
```
setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs on
```
通过以下命令查看这个值:
```
getsebool samba_enable_home_dirs
```
输出如下:

#### 3、启用你的用户
Samba 使用一组用户/密码来管理连接权限。通过键入以下命令将你的 Linux 用户添加到该集合中:
```
smbpasswd -a <你的用户名>
```
系统提示你输入密码。这是一个 *全新* 的密码;而不是你账户的当前密码。请输入你想用来登录 Samba 的密码。
键入以下命令得到有 Samba 使用权限的用户列表:
```
pdbedit -L -v
```
键入以下命令删除一个用户:
```
smbpasswd -x <用户名>
```
#### 4、开启 Samba
既然 Samba 是一个系统守护进程,你可以在 Fedora 上键入以下命令启动它:
```
systemctl start smb
```
这将为当前会话开启 Samba 服务。如果想让它自启动,键入以下命令:
```
systemctl enable smb
```
在某些系统上,Samba 守护进程注册为 `smbd`。
#### 4、配置防火墙
你的防火墙会默认阻拦 Samba。通过配置防火墙允许 Samba 能永久访问网络。
你可以在命令行执行如下操作:
```
firewall-cmd --add-service=samba --permanent
```
或者,你可以使用 `firewall-config` 工具以图形化方式进行操作:

#### 5、从 Windows 访问 Samba
在 Windows 中,打开文件资源管理器。在地址栏中,键入两个反斜杠(`\\`),紧跟你的 Linux 机器的地址(IP 地址或主机名):

系统将提示你输入登录信息。输入第 3 步中的用户名和密码组合。你现在应该可以访问 Linux 机器上的主目录:

### 从 Linux 访问 Windows
以下步骤说明了如何从 Linux 访问共享的 Windows 文件夹。要实现这一点,需要你的 Windows 用户帐户具有管理员权限。
#### 1、启用文件共享
通过点击 “Windows 按钮” > “<ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby>” > “<ruby> 网络和 Internet <rt> Network & Internet </rt></ruby>” ,或者右键单击任务栏右下角的小监视器图标,<ruby> 打开网络和共享中心 <rt> Open Network an d Sharing Center </rt></ruby>:

在打开的窗口中,找到你要使用的连接并记下其配置文件。我使用了 **以太网 3**,它被标记为 <ruby> 公用网络 <rt> Public Network </rt></ruby>。
>
> **注意**:如果你的 PC 经常连接公用网络,请考虑将本地计算机的连接配置文件更改为 **私有**。
>
>
>
记住你的网络配置,然后单击 <ruby> 更改高级共享设置 <rt> Change advanced sharing settings </rt></ruby>:

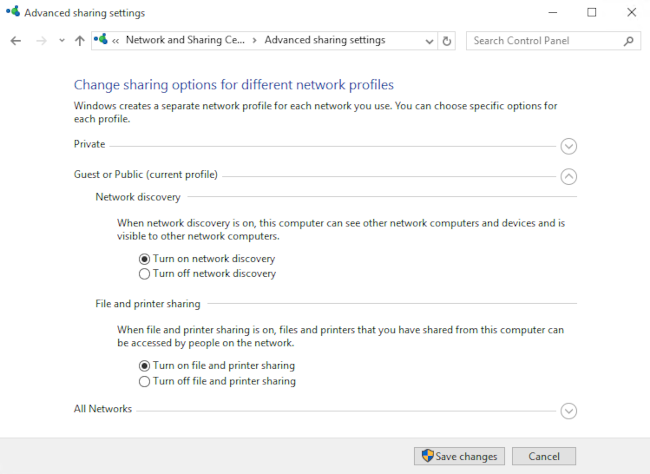
选择与你的连接对应的配置文件并打开 <ruby> 网络发现 <rt> network discovery </rt></ruby> 和 <ruby> 文件和打印机共享 <rt> file and printer sharing </rt></ruby>:

#### 2、定义一个共享文件夹
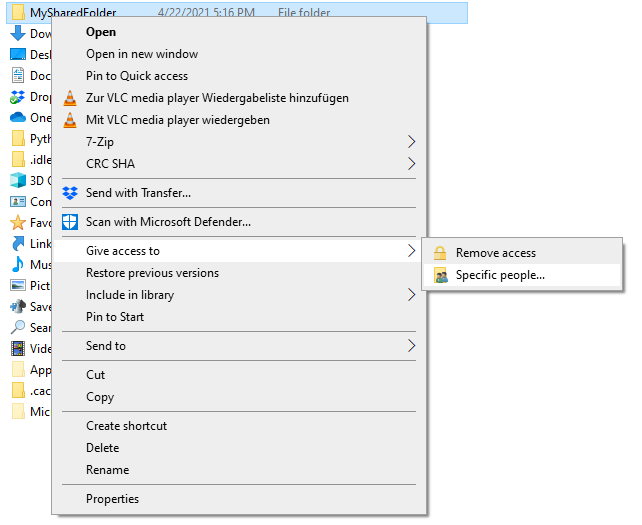
通过右键单击你要共享的文件夹打开上下文菜单,导航到 <ruby> 授予访问权限 <rt> Give access to </rt></ruby>,然后选择 <ruby> 特定用户... <rt> Specific people... </rt></ruby>:

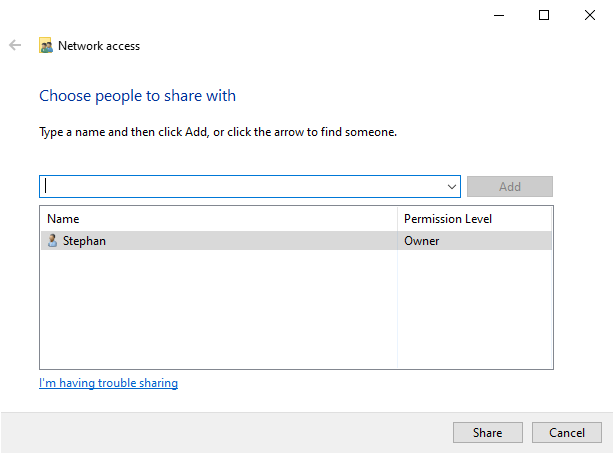
检查你当前的用户名是否在列表中。点击 <ruby> 共享 <rt> Share </rt></ruby> 将此文件夹标记为共享:

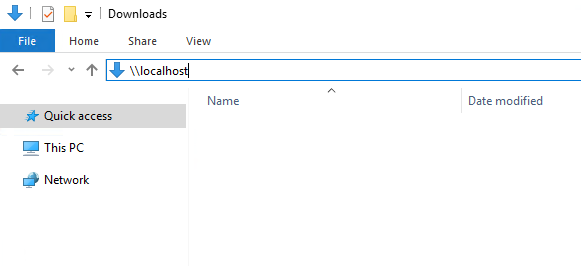
你可以通过在文件资源管理器的地址栏中输入 `\\localhost` 来显示所有共享文件夹的列表:


#### 3、在 Linux 下挂载共享文件夹
回到你的 Linux 系统,打开一个命令行,然后创建一个新文件夹,用于挂载 Windows 共享:
```
mkdir ~/WindowsShare
```
挂载 Windows 共享是使用 `mount.cifs` 完成的,它应该被默认安装。使用如下命令临时挂载你的共享文件夹:
```
sudo mount.cifs //<address-of-windows-pc>/MySharedFolder ~/WindowsShare/ -o user=<Windows-user>,uid=$UID
```
在这个命令里:
* `<address-of-windows-pc>` 是 Windows PC 的地址信息(IP 或主机名)
* `<Windows-user>` 是允许访问共享文件夹的用户(见步骤 2)
系统将提示你输入 Windows 密码。之后,你将能够使用普通 Linux 用户访问 Windows 上的共享文件夹。
要卸载共享文件夹:
```
sudo umount ~/WindowsShare/
```
你还可以在系统启动时挂载 Windows 共享文件夹。按照 [这些步骤](https://timlehr.com/auto-mount-samba-cifs-shares-via-fstab-on-linux/) 相应地配置你的系统。
### 总结
在这里展示了如何建立临时的文件夹共享访问权限,每次重启后都要重新设置,因此修改成永久访问会更便利。我经常在不同的系统之间来回切换,对我而言设置直接文件访问非常实用。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/4/share-files-linux-windows>
作者:[Stephan Avenwedde](https://opensource.com/users/hansic99) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hanszhao80](https://github.com/hanszhao80) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | If you work with different operating systems, it's handy to be able to share files between them. This article explains how to set up file access between Linux ([Fedora 33](https://getfedora.org/en/workstation/download/)) and Windows 10 using [Samba](https://www.samba.org/) and [mount.cifs](https://linux.die.net/man/8/mount.cifs).
Samba is the Linux implementation of the [SMB/CIFS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Server_Message_Block) protocol, allowing direct access to shared folders and printers over a network. Mount.cifs is part of the Samba suite and allows you to mount the [CIFS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Server_Message_Block) filesystem under Linux.
Caution: These instructions are for sharing files within your private local network or in a virtualized host-only network between a Linux host machine and a virtualized Windows guest. Don't consider this article a guideline for your corporate network, as it doesn't implement the necessary cybersecurity considerations.
## Access Linux from Windows
This section explains how to access a user's Linux home directory from Windows File Explorer.
### 1. Install and configure Samba
Start on your Linux system by installing Samba:
`dnf install samba`
Samba is a system daemon, and its configuration file is located in `/etc/samba/smb.conf`
. Its default configuration should work. If not, this minimal configuration should do the job:
```
[global]
workgroup = SAMBA
server string = %h server (Samba %v)
invalid users = root
security = user
[homes]
comment = Home Directories
browseable = no
valid users = %S
writable = yes
```
You can find a detailed description of the parameters in the [smb.conf](https://www.samba.org/samba/docs/current/man-html/smb.conf.5.html) section of the project's website.
### 2. Modify LinuxSE
If your Linux distribution is protected by [SELinux](https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/linux/what-is-selinux) (as Fedora is), you have to enable Samba to be able to access the user's home directory:
`setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs on`
Check that the value is set by typing:
`getsebool samba_enable_home_dirs`
Your output should look like this:

(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
### 3. Enable your user
Samba uses a set of users and passwords that have permission to connect. Add your Linux user to the set by typing:
`smbpasswd -a <your-user>`
You will be prompted for a password. This is a *completely new* password; it is not the current password for your account. Enter the password you want to use to log in to Samba.
To get a list of allowed user types:
`pdbedit -L -v`
Remove a user by typing:
`smbpasswd -x <user-name>`
### 4. Start Samba
Because Samba is a system daemon, you can start it on Fedora with:
`systemctl start smb`
This starts Samba for the current session. If you want Samba to start automatically on system startup, enter:
`systemctl enable smb`
On some systems, the Samba daemon is registered as `smbd`
.
### 4. Configure the firewall
By default, Samba is blocked by your firewall. Allow Samba to access the network permanently by configuring the firewall.
You can do it on the command line with:
`firewall-cmd --add-service=samba --permanent`
Or you do it graphically with the firewall-config tool:
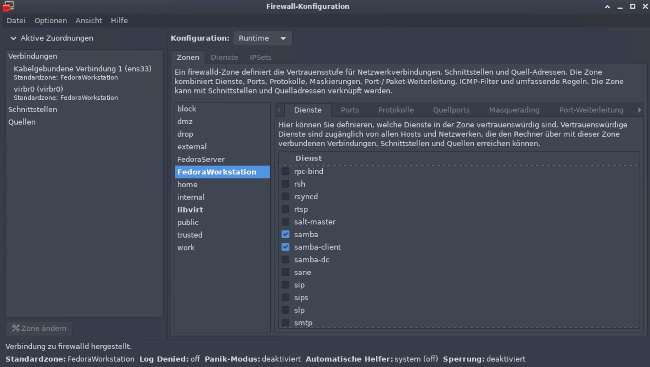
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
### 5. Access Samba from Windows
In Windows, open File Explorer. On the address line, type in two backslashes followed by your Linux machine's address (IP address or hostname):
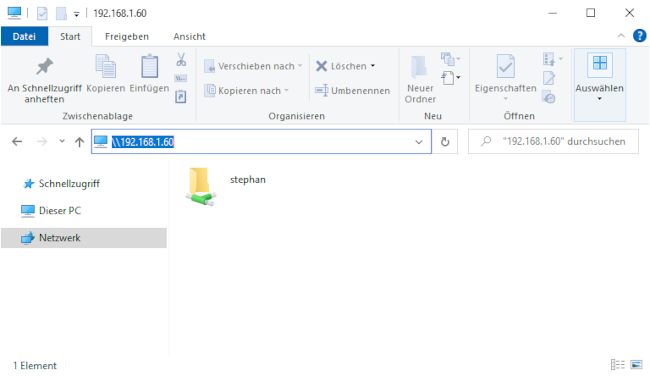
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
You will be prompted for your login information. Type in the username and password combination from step 3. You should now be able to access your home directory on your Linux machine:
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Access Windows from Linux
The following steps explain how to access a shared Windows folder from Linux. To implement them, you need Administrator rights on your Windows user account.
### 1. Enable file sharing
Open the** Network and Sharing Center** either by clicking on the
**Windows Button > Settings > Network & Internet**
or by right-clicking the little monitor icon on the bottom-right of your taskbar:
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
In the window that opens, find the connection you want to use and note its profile. I used **Ethernet 3**, which is tagged as a **Public network**.
Caution: Consider changing your local machine's connection profile toPrivateif your PC is frequently connected to public networks.
Remember your network profile and click on **Change advanced sharing settings**:
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Select the profile that corresponds to your connection and turn on **network discovery** and **file and printer sharing**:
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
### 2. Define a shared folder
Open the context menu by right-clicking on the folder you want to share, navigate to **Give access to**, and select **Specific people...** :
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Check whether your current username is on the list. Click on **Share** to tag this folder as shared:
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
You can display a list of all shared folders by entering `\\localhost`
in File Explorer's address line:
(Stephan Avenwedde, CC BY-SA 4.0)
<p class="rtecenter"><sup>(Stephan Avenwedde, <a href="https://opensource.com/%3Ca%20href%3D"https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/" rel="ugc">https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/" target="_blank">CC BY-SA 4.0</a>)</sup></p>
### 3. Mount the shared folder under Linux
Go back to your Linux system, open a command shell, and create a new folder where you want to mount the Windows share:
`mkdir ~/WindowsShare`
Mounting Windows shares is done with mount.cifs, which should be installed by default. To mount your shared folder temporarily, use:
`sudo mount.cifs //<address-of-windows-pc>/MySharedFolder ~/WindowsShare/ -o user=<Windows-user>,uid=$UID`
In this command:
`<address-of-windows-pc>`
is the Windows PC's address info (IP or hostname)`<Windows-user>`
is the user that is allowed to access the shared folder (from step 2)
You will be prompted for your Windows password. Enter it, and you will be able to access the shared folder on Windows with your normal Linux user.
To unmount the shared folder:
`sudo umount ~/WindowsShare/`
You can also mount a Windows shared folder on system startup. Follow [these steps](https://timlehr.com/auto-mount-samba-cifs-shares-via-fstab-on-linux/) to configure your system accordingly.
## Summary
This shows how to establish temporary shared folder access that must be renewed after each boot. It is relatively easy to modify this configuration for permanent access. I often switch back and forth between different systems, so I consider it incredibly practical to set up direct file access.
## 2 Comments |
14,538 | Ubuntu 的 Unity 桌面还活着:时隔 6 年后,7.6 测试版发布 | https://news.itsfoss.com/unity-7-6-testing/ | 2022-05-03T17:32:16 | [
"Unity",
"Ubuntu Unity"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14538-1.html |
>
> 虽然 Canonical 已经不再维护 Unity 桌面,但 Ubuntu Unity 的开发者承担了这项重任,发布了一项主要更新(已可用于测试)。
>
>
>

怕你兴奋过头了,先提醒一下,Canonical 并没有回归 Unity 桌面的维护。
得益于 Ubuntu Unity 发行版开发者(Rudra Saraswat)的不懈努力,时隔 6 年,我们终于看到了 Unity 桌面环境的更新。
补充说一下,[Ubuntu Unity](https://ubuntuunity.org/) 是一款采用 Unity 桌面(而不是 GNOME)的社区项目。因此,如果你想在 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 上使用 Unity 桌面,那么毋庸置疑,[Ubuntu Unity](https://ubuntuunity.org/) 绝对是你的最佳伙伴。
起初,它仅仅提供了经过微调的 Unity 体验,但现在,**Unity 7.6** 的界面得到了一些优化及视觉变更。
下面是你应该了解的东西:
### Unity 7.6:更新了什么?
>
> **提示**:Unity 7.6 是为公共测试而发布的,它不应作为替代其他桌面环境的使用环境。
>
>
>
这不仅仅是面向用户的改进,还有针对开发方面的努力,旨在帮助贡献者,让他们更方便地帮助 Unity7 的开发。
这些改善包括:
#### 用户界面变更

Dash 启动器(应用启动器)与 HUD 现已重新设计,拥有更现代、简洁的视觉。
总的来看,现在的设计看上去更加扁平,但仍旧保留了不错的系统全局模糊效果。
本次引入了一些细微的视觉改进,比如停靠区上的“清空回收站”按钮修改为使用 Nemo(而不是 Nautilus),以及修复了 Dash 预览中的应用详情与评分。
#### 性能改进

在最新的更新中,Unity7 的内存使用量更低,同时你也可以注意到,Ubuntu Unity 22.04 的内存使用量明显降低到约 700-800 MB。
此外,低端显卡模式现在运作得更好,Dash 也比以前更快。
#### 其他变化
Unity7 Shell 的源代码已经完全迁移至 [GitLab](https://gitlab.com/ubuntu-unity)。用于独立测试的 Unity7 启动器已被修复,同时一些有问题的测试项也已被禁用,改善了构建用时(使其大幅缩短)。
发布说明上说,这些改进将帮助 Unity7 的贡献者。
### 测试 Unity 7.6
你可以按照 [官方测试公告](https://unity.ubuntuunity.org/blog/unity-7.6/) 中提到的方式来编译它,并亲自尝试。你也可以前往其官方网站探索更多。
>
> **[Unity 7.6](https://unity.ubuntuunity.org/)**
>
>
>
另一种情况,如果你不想添加测试 PPA 源,你也可以等待 Ubuntu Unity 22.04 的更新。
*你对 Unity 桌面环境的这次更新有什么看法?你喜欢它吗?欢迎在评论区中告诉我你的想法。*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/unity-7-6-testing/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[imgradeone](https://github.com/imgradeone) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/%E6%A0%A1%E5%AF%B9%E8%80%85ID)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Before you get too excited, you should know that Canonical is not coming back to maintain Unity desktop.
Thanks to the developer of the Ubuntu Unity distribution (*Rudra Saraswat*), we get to see an update to the Unity desktop environment after six long years.
In case you did not know, Ubuntu Unity is a community project that utilizes the Unity interface instead of GNOME. So, yes, if you wanted to use Ubuntu 22.04 LTS with Unity desktop, [Ubuntu Unity](https://ubuntuunity.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is your friend.
Initially, it simply offered the Unity experience with a few tweaks. But, now, **Unity 7.6** looks to be getting some improvements and visual changes to the interface.
Here’s what you should know about it:
## Unity 7.6: What’s New?
**Note**: Unity 7.6 is out for public testing and should not be a replacement for other desktop environments.
It is not just about the user-facing side, but there have been development efforts to help contributors conveniently help with Unity7’s development.
Some refinements include:
### User Interface Changes
The dash launcher (app launcher) and HUD have been redesigned for a modern/slick look.
Overall, the design is now much flatter but retains the good-old system-wide blur effect. The dock’s menu and tooltips also received some refreshed modern look.
There are some subtle visual improvements like ‘Empty Trash’ button in the dock using Nemo instead of Nautilus and fixing the app info and ratings in dash preview.
### Performance Improvements
The RAM usage in Unity7 is lower with the latest update. And, you can notice the RAM usage with Ubuntu Unity 22.04 is significantly lower to about 700-800 MB.
Furthermore, the low graphics mode works much better now, making the dash faster than ever.
### Other Changes
The Unity7’s shell source code has been migrated entirely to [GitLab](https://gitlab.com/ubuntu-unity?ref=news.itsfoss.com). The standalone testing Unity7 launcher has been fixed, and the buggy tests have been disabled, improving the build time (making it much shorter).
The release notes say that these changes should help Unity7 contributors.
## Testing Unity 7.6
You can follow the instructions mentioned in the [official testing announcement](https://unity.ubuntuunity.org/blog/unity-7.6/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to compile it and try it for yourself. You can also head to its official website to explore more.
In either case, you can wait for an update to Ubuntu Unity 22.04, if you would rather not add the testing PPA yet.
*What do you think about this refreshment to the Unity desktop environment? Do you like it? Let me know your thoughts in the comments.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,540 | 埃隆·马斯克开源推特算法的计划存在缺陷 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/04/elon-musks-plan-to-open-source-the-twitter-algorithm-has-flaws/ | 2022-05-03T23:59:40 | [
"推特",
"算法"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14540-1.html | 
报道称,在推特确认接受收购请求的几个小时后,埃隆·马斯克就明确表示了他对推特的期望。马斯克在一份新闻稿中罗列了他计划做出的重大改变,包括开源“决定用户在推流中看到什么”的算法。
马斯克希望开源推特的算法,是因为他长期以来一直担心该平台有可能进行政治压制。但老实说,即便开源,也不可能达到他的预期效果。专家们担心,这可能反而带来一连串意想不到的问题。
虽然马斯克对权威深恶痛绝,但是他对算法开源的野心和世界各地立法者的愿望不谋而合。近年来,许多政府都将这一原则作为打击大科技公司的基石。
英国社交媒体监管机构 Ofcom 的首席执行官 Melanie Dawes 曾表示,社交媒体公司应当解释其代码的运作方式。此外,欧盟新近通过的《<ruby> 数字服务法案 <rt> Digital Services Act </rt></ruby>(DSA)》于 4 月 23 日获得批准,该法案将责成平台提供更多的公开性。2022 年 2 月,美国的民主党参议员提交了《<ruby> 算法问责法案 <rt> Algorithmic Accountability Act </rt></ruby>(AAA)》的立法申请。这些法案的目标是加强算法的透明度和监督,包括我们在社交媒体上的“<ruby> 时间轴 <rt> timeline </rt></ruby>”和“<ruby> 新闻流 <rt> news feed </rt></ruby>”以及我们生活的其他方面。
允许竞争者看到并修改推特的算法,可能意味着有人会偷取源代码,并提供一个改名的版本。互联网的许多部分都运行在开源软件上,其中最著名的就是 OpenSSL,这是一个被大量在线使用的安全工具包,而它在 2014 年被黑客攻击了。
还有一些已经创建的开源社交网络。Mastodon 是一个微博网络,为回应对 Twitter 主导地位的担忧而创建。它允许用户检查其代码,这些代码可在 GitHub 软件仓库中找到。
然而,阅读一个算法背后的代码,并不总能告诉你它的工作方式,而且对于大部分普通人来说,它也提供不了足够的关于公司组织架构以及开发流程的信息。
Jonathan Gray 是伦敦国王学院/关键基础设施研究的高级讲师,他说:“这有点像只用遗传物质来理解古代生物。是的,它能告诉我们的信息比任何方式都多,但如果说我们因此了解它们的生活方式,那就太夸张了。”
推特同样也不是由单一算法控制的。Catherine Flick 是英国德蒙福特大学/研究计算和社会责任的研究员,她说:“其中一些会决定人们在他们的“时间轴”上看到什么趋势、内容或者推荐关注的人。调节用户“时间轴”上显示哪些信息的算法,将会是人们最感兴趣的。然而,即使如此,如果缺少训练数据,单纯开源算法也没多大用处。”
Cobbe 认为,开源推特算法的危害大于好处。因为计算机代码并没有透露算法是如何开发或评估的:有哪些元素或考虑、在这个过程中的优先级是什么等等。所以开源可能不会使推特的透明度发生重大变化。反而,它可能会带来严重的安全隐患。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/04/elon-musks-plan-to-open-source-the-twitter-algorithm-has-flaws/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Elon Musk made his aspirations for Twitter obvious just hours after Twitter said it had accepted Elon Musk’s takeover offer. Musk listed the major changes he intends to make in a press release, including opening up the algorithms that govern what users see in their feed.
Musk’s desire to open source Twitter’s algorithms stems from his long-standing concern about the platform’s potential for political repression, but it’s unlikely that doing so will have the desired effect. Experts worry that it may instead bring a slew of unexpected issues.
Although Musk has a deep dislike for authority, his ambition for algorithmic openness coincides with the wishes of legislators all around the world. In recent years, numerous governments have used this principle as a cornerstone of their efforts to combat Big Tech.
Melanie Dawes, the chief executive of Ofcom, the UK regulator of social media, has stated that social media firms would be required to explain how their code operates. In addition, the European Union’s newly passed Digital Services Act, which was approved on April 23, would oblige platforms to provide more openness. In February 2022, Democratic senators in the United States submitted legislation to create an Algorithmic Accountability Act. Their goal is to increase transparency and supervision of the algorithms that regulate our timelines and news feeds, as well as other aspects of our lives.
Allowing competitors to see and adapt Twitter’s algorithm potentially means that someone could just steal the source code and offer a rebranded version. Vast sections of the internet run on open-source software, the most renowned of which is OpenSSL, a security toolkit used by large swaths of the online that was hacked in 2014.
There are also open source social networks that have already been created. Mastodon, a microblogging network created in response to worries about Twitter’s dominant position, allows users to inspect its code, which is available on the GitHub software repository.
However, reading the code behind an algorithm does not always tell you how it works, and it doesn’t provide the typical individual much insight into the corporate structures and processes that go into its development.
“It’s a bit like trying to understand ancient creatures with genetic material alone,” says Jonathan Gray, a senior lecturer in critical infrastructure studies at King’s College London. “It tells us more than nothing, but it would be a stretch to say we know about how they live.”
Twitter is likewise not controlled by a single algorithm. “Some of them will determine what people see on their timelines in terms of trends, content, or suggested followers,” says Catherine Flick, a researcher at De Montfort University in the United Kingdom who studies computing and social responsibility. The algorithms that regulate what information shows in users’ timelines will be the ones that people are most interested in, but even that won’t be very useful without the training data.
Cobbe believes that the hazards outweigh the advantages. Because the computer code doesn’t reveal how algorithms were developed or evaluated, what elements or considerations went into them, or what was prioritised during the process, open-sourcing it may not make a significant change in Twitter’s transparency. In the meantime, it may pose severe security hazards. |
14,541 | 在虚拟机中运行 Linux 的十大优点 | https://itsfoss.com/why-linux-virtual-machine/ | 2022-05-04T09:34:00 | [
"虚拟机"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14541-1.html |
>
> 你可以在虚拟机环境里运行任何操作系统,不论是测试还是为了某种需要。
>
>
>

*开源朗读者 | 淮晋阳*
对于 Linux 而言,它在虚拟环境下的性能会优于其他操作系统。即便你可能会犹豫是否在物理机(裸金属)上安装 Linux 系统,你仍然可以在虚拟机中安装一个性能几乎和物理机一样好的 Linux 系统。
当然,这并不意味着宿主系统为 Linux 时你就不能在虚拟机实例中安装 Linux 了。
更何况,你在虚拟环境下使用 Linux 系统有许多好处。大致如下。
### 在虚拟环境下运行 Linux 之前的注意事项
在虚拟环境下运行 Linux 或许并不是艰巨的任务,但仍有以下几点你需谨记。
* 虚拟机的性能取决于宿主机的性能,如果你并没有足够的系统资源分配给虚拟机,那么虚拟机的使用体验注定不会很好。
* 某些特性仅在物理机(裸金属)上生效,包括硬件加速以及图形(显卡)驱动等。
* 密集的磁盘 I/O 任务性能会十分受限,例如游戏测试场景。
* 用户的 Linux 虚拟机实例体验会根据你所使用的虚拟化程序而发生变化,这些虚拟化程序包括 VMware、VirtualBox、GNOME Boxes 以及 Hyper-V 。
此外,你应当列出你的需求,并根据这些需求选定适当的虚拟化程序来运行你的 Linux 实例。
### 十条在虚拟环境中运行 Linux 的优点
尽管运行虚拟化 Linux 实例极具吸引力,你仍然应当首先考虑当前使用的宿主系统中已有的选择。例如,如果你不需要图形化桌面,或许利用 Windows 操作系统中的 [WSL 安装 Linux](https://itsfoss.com/install-bash-on-windows/) 就可以满足你的需求。
一旦你确定了使用虚拟机,那么这些优点将会如影随形:
#### 1、部署简便

与在传统物理机(裸金属)上安装 Linux 相比,在虚拟机中部署一般会容易许多。
对于基于 Ubuntu 的发行版而言,像 VMware 这样的虚拟化程序会提供一个 **快速安装** 的选项,你仅需输入用户名和密码,其余过程将自动完成而无需其他操作。你无需手动设置分区、引导程序以及更多高级设置。
某些情况下,一些发行版的开发者会同时提供针对特定虚拟机的预构建镜像,只需打开就可使用。这就好像一个便携式虚拟机镜像,随时可以开箱即用。
例如,在 [这里](https://itsfoss.com/install-arch-linux-virtualbox/) 你将看到如何在虚拟机中安装 Arch Linux 发行版。
对于其他的发行版,你或许仍需要进行一些配置,但一般都会有快速安装的选项令你可以轻松部署。
#### 2、不会影响宿主机

对于虚拟机,你可以更为随心所欲地使用,因为虚拟机系统和宿主机系统是隔离的。
很多时候,如果你并不熟悉 Linux 系统,你很可能会把配置弄得十分混乱。
所以在虚拟机里,你可以随意尝试而无需担心是否会影响到宿主机系统。换句话说,任何虚拟机的操作都不会影响到宿主机,因为它们是完全隔离的。
故此,虚拟机是你最好的试验场,尤其是对于一些激进或具有破坏性的试验。
#### 3、资源可高效共享

如果你有十分充裕的系统资源,你可以使用虚拟机运行其他任务,从而充分利用起来这部分闲置的系统资源。例如,如果你需要一个十分私密的浏览环境,虚拟机将为你阻挡一切针对宿主机的追踪器。
这可能略显牵强,但这仅仅是一个例子。基于这样的想法你将可以充分利用全部的系统资源。
而对于双启动方案,你需要在单独的磁盘上在 Windows [之后安装 Linux](https://itsfoss.com/dual-boot-hdd-ssd/),或者在 Linux [之后安装 Windows](https://itsfoss.com/install-windows-after-ubuntu-dual-boot/),你需要为你的任务锁定相应的资源。
但利用虚拟机,你无需锁定部分资源也可以使用 Linux ,也不必为了特定的任务而临时共享资源,这样会方便许多。
#### 4、多任务体验更好

有了资源共享机制,多任务会前所未有的容易。
在双启动的场景下,你需要来回重启切换才能使用 Linux 或 Windows 。
但如果使用虚拟机,你几乎不再需要 [双启动](https://itsfoss.com/dual-boot-fedora-windows/),两个系统将无缝协作并完成多任务。
当然,你需要确认你拥有足够的系统资源和额外的硬件(例如双显示器)来更高效地使用。而多任务的潜力也因 Linux 虚拟机的存在而愈发强大。
#### 5、软件测试更为便捷
有了虚拟化,你将可以创建大量的 Linux 实例,来模拟特定的使用场景,并对软件进行测试。
例如,你可以在不同的 Linux 虚拟机中同步测试不同的软件版本。这有丰富的使用场景,包括对开发版软件进行测试以及 Linux 发行版的早期测试等等。
#### 6、开发更为便捷

当你在学习编程或者刚加入一个软件项目的开发的时候,你会希望拥有一个没有任何冲突和错误的开发环境。
在 Linux 虚拟机里,你可以从零开始搭建一个不会与已经存在的环境冲突的开发环境。例如,你可以在 Ubuntu 上 [安装并测试 Flutter](https://itsfoss.com/install-flutter-linux/) 。
如果环境出了问题,你可以轻而易举地删掉这个虚拟机,并重新开始来修正错误。
Linux 虚拟机的隔离环境是一个绝佳的开发和测试环境。
#### 7、学习和研究的好帮手
Linux 值得反复探索。除了基础的计算任务,你可以做许多其他的事情。
你可以学习如何修改你的用户界面,[尝试一些常见的桌面环境](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/) 、[安装大量常用软件](https://itsfoss.com/essential-linux-applications/) ,与此同时仍能让一切处于掌控之中。
如果出现问题,新建一个 Linux 虚拟机就可以解决。当然,这并不仅限于日常使用需要,还可以启发系统管理员在其中测试他们所学的知识。
#### 8、更容易复制和迁移
虚拟机可以很容易地复制和迁移。只要其它的宿主机系统支持该虚拟化程序,你就可以很容易地迁移它,而没有特别要求。
不论因何原因,几次简单的点击就可以完成复制和迁移的任务。
#### 9、尝试大量的发行版

你可以在虚拟环境下尝试数以百计的 Linux 发行版。
你或许会认为这和第七条重复了,但是我相信,测试一个发行版是一个巨大的系统性工程,尤其是当你决定切换发行版做为宿主机或其他用途时。
#### 10、便于调试
不论是严肃的开发活动还是一般的研究,在隔离的虚拟环境中调试和除错相对而言会更简单。
你可以快速尝试大量的调试方法而无需考虑影响。同时,如果你的宿主机是 Linux 系统的话,无需宿主机上的 root 权限便可以访问和修改虚拟机中的配置文件。
### 总而言之
如果你不熟悉正在使用的系统或者依赖不同的操作系统工作,虚拟机将是协助你工作的一大利器。
Linux 虚拟机可以广泛用于开发、学习、试验或任何特定用途。
你在虚拟机中使用过 Linux 吗?都有哪些应用场景呢?欢迎留言评论!
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/why-linux-virtual-machine/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[PeterPan0106](https://github.com/PeterPan0106) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

You can run any operating system as a virtual machine to test things out or for a particular use case.
When it comes to Linux, it is usually a better performer as a virtual machine when compared to other operating systems. Even if you hesitate to install Linux on bare metal, you can try setting up a virtual machine that could run as you would expect on a physical machine.
Of course, we don’t rule out the possibility of running Linux distros in VM even when using Linux as your host OS.
Moreover, you get numerous benefits when trying to run Linux on virtual machines. Here, I shall mention all about that.
## Things to Keep in Mind Before Running Linux as a Virtual Machine
It is worth noting that running Linux on a virtual machine may not be a daunting task, but there are a few pointers that you should keep in mind.
Some of them include:
- The virtual machine performance will depend on your host system. If you do not have enough system resources to allocate, the virtual machine experience will not be pleasant.
- Certain features only work well with bare metal (hardware acceleration, graphics drivers, etc.)
- You should not expect intensive disk I/O tasks to work well, like testing games.
- The user experience with Linux virtual machines varies with the program you use. For instance, you can try VMware, VirtualBox, GNOME Boxes, and Hyper-V.
In addition to all these tips, you should also make a list of your requirements before choosing a virtual machine program to run Linux.
While there are perks to using a Linux VM, you should consider the current opportunities available on your host OS. For instance, you may want to [install Linux using WSL on Windows](https://itsfoss.com/install-bash-on-windows/) if you do not require a GUI desktop.
[How to Install Linux Bash Shell on Windows [Complete Guide]Step-by-step screenshot guide to show you how to install bash on Windows 11 and 10.](https://itsfoss.com/install-bash-on-windows/)

Once you are sure that you need a VM, here’s why you should proceed with it:
## 1. Easy Setup

Compared to the traditional installation process on bare metal, setting up a virtual machine is often easier.
For Ubuntu-based distros, programs like VMware offer an **Easy Install** option where you have to type in the required fields for username and password; the rest will proceed without needing additional inputs. You do not need to select a partition, bootloader, or advanced configurations.
In some cases, you can also use prebuilt images offered by Linux distributions for a specific virtual program, where you need to open it to access the system. Think of it as a portable VM image ready to launch wherever you need it.
For example, you can check out how you can use [VirtualBox to install Arch Linux](https://itsfoss.com/install-arch-linux-virtualbox/).
[How to Install Arch Linux on VirtualBox [Beginner’s Guide]Arch Linux is complicated than most other distributions. Installing Arch Linux in VirtualBox is a safer way to try this famed Linux distribution.](https://itsfoss.com/install-arch-linux-virtualbox/)

You may still need to configure things when installing other distros, but there are options where you need minimal effort.
## 2. Does Not Affect the Host OS

With a virtual machine, you get the freedom to do anything you want, and it is because you get an isolated system.
Usually, if you do not know what you’re doing with a Linux system, you could easily end up with a messed-up configuration.
So, if you set up a VM, you can quickly try whatever you want without worrying about affecting the host OS. In other words, your system will not be impacted by any changes to the VM because it’s entirely isolated.
Hence, a VM is the best way to test any of your ambitious or destructive changes that you may want to perform on bare metal.
## 3. Resource Sharing

If you have ample free system resources, you can utilize the rest using a Virtual Machine for any other tasks. For instance, if you want a private browsing experience without leaving any traces on your host, a VM can help.
It can be a far-fetched example, but it is just one of the ideas. In that way, you get to use the resources fully without much hassle.
Also, as opposed to a dual-boot scenario, where you need to [install Linux alongside Windows](https://itsfoss.com/dual-boot-hdd-ssd/) on separate disks or [install Windows after Linux](https://itsfoss.com/install-windows-after-ubuntu-dual-boot/), you need dedicated resources locked on to your tasks.
However, with a VM, you can always use Linux without locking up your resources, rather than temporarily sharing them to get your tasks done, which can be more convenient.
## 4. Multi-Tasking

With the help of resource-sharing, you can easily multitask.
For instance, you need to switch back and forth between a dual-boot setup to access Windows and Linux.
But, with a virtual machine, you can almost eliminate the need for [dual-booting Linux](https://itsfoss.com/dual-boot-fedora-windows/) and multitask with two operating systems seamlessly.
Of course, you need to ensure that you have the required amount of system resources and external hardware (like dual monitors) to effectively use it. Nevertheless, the potential to multitask increases with a Linux VM in place.
## 5. Facilitates Software Testing
With virtualization, you get the freedom to test software on Linux distros by instantly creating various situations.
For instance, you can test different software versions simultaneously on multiple Linux VMs. There can be more use-cases, such as testing a software development build, early build of a Linux distro, etc.
## 6. Great for Development

When you want to learn to code or just get involved in developing something, you want an environment free from any conflicts and errors.
So, a Linux VM is the perfect place to install new packages from scratch without worrying about conflicts with existing ones. For instance, you can [install and set up Flutter](https://itsfoss.com/install-flutter-linux/) to test things on Ubuntu.
If you mess up the system, you can quickly delete the VM and spin up a new one to learn from your mistakes.
You get a perfect isolated environment for development work and testing with a Linux VM.
## 7. Learning or Research
Linux is something to explore. While you could use it for basic computing tasks, there’s so much more that you can do with it.
You can learn how to customize the user interface, try some [popular desktop environments](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/), install [various essential apps](https://itsfoss.com/essential-linux-applications/), and take control of your system without worrying about it.
If anything goes wrong, you create a new Linux VM. Of course, it is not just for general-purpose usage, but aspiring system administrators can also take this opportunity to test what they learn.
## 8. Easy to Clone or Migrate
Virtual machines, in general, are easy to clone and migrate. With a Linux VM, as long as the virtual program is supported on another system or host OS, you can easily migrate it without any special requirements.
If you need to clone an existing virtual machine for any reason, that is pretty easy too, and it should take a couple of clicks to get it done.
## 9. Try A Variety of Distros

Of course, with hundreds of Linux distros available, you can try all kinds of distros by creating a Linux virtual machine.
You may consider this a part of learning/research, but I believe trying out different distros is a massive task if you want to test things out before installing them on your system.
## 10. Debugging
Whether it is for fun or serious research, debugging is relatively more straightforward in an isolated environment provided by the Linux VM.
You get the freedom to try various troubleshooting methods without thinking about the outcome. Furthermore, you do not need root access to your host OS (if it’s Linux) to access the system configuration/files in the VM.
## Wrapping Up
If you are not an experienced user or depend on a different host OS, you can benefit from installing Linux using a virtual machine.
A Linux VM should be beneficial for development, learning, experimenting, or any other special use cases.
*💭 Have you used Linux on a virtual machine? What do you use it for? Let me know in the comments below.* |
14,542 | 使用 dnf 进行 Linux 包管理 | https://opensource.com/article/21/6/dnf-linux | 2022-05-04T10:15:39 | [
"dnf",
"软件包管理"
] | /article-14542-1.html |
>
> 了解如何在 Linux 上使用 `dnf` 命令安装软件包,然后下载我们的速查表,让正确的命令触手可及。
>
>
>

在计算机系统上安装应用程序非常简单:就是将档案(如 `.zip` 文件)中的文件复制到目标计算机上,放在操作系统预期放应用程序的位置。因为我们中的许多人习惯于使用花哨的安装“向导”来帮助我们在计算机上安装软件,所以这个过程似乎在技术上应该比实际更复杂。
然而,复杂的是,是什么构成了一个程序?用户认为的单个应用程序实际上包含了分散在操作系统中的软件库的各种依赖代码(例如:Linux 上的 .so 文件、Windows 上的 .dll 文件和 macOS 上的 .dylib 文件)。
为了让用户不必担心这些程序代码之间的复杂的互相依赖关系, Linux 使用 <ruby> 包管理系统 <rt> package management system </rt></ruby> 来跟踪哪些应用程序需要哪些库,哪些库或应用程序有安全或功能更新,以及每个软件会附带安装哪些额外的数据文件。包管理器本质上是一个安装向导。它们易于使用,提供了图形界面和基于终端的界面,让你的生活更轻松。你越了解你的发行版的包管理器,你的生活就会越轻松。
### 在 Linux 上安装应用程序
如果你在使用 Linux 桌面时,偶尔想要安装一个应用程序,那么你可能正在寻找 [GNOME “软件”](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Software),它是一个桌面应用程序浏览器。

它会按你的预期工作:点击它的界面,直到你找到一个看起来有用的应用程序,然后单击 “安装” 按钮。
或者,你可以在 GNOME “软件” 中打开从网络下载的 `.rpm` 或 `.flatpakref` 软件包,以便它进行安装。
但如果你更倾向于使用命令行,请继续阅读。
### 用 dnf 搜索软件
在安装应用程序之前,你可能需要确认它是否存在于你的发行版的服务器上。通常,使用 `dnf` 搜索应用程序的通用名称就足够了。例如,假设你最近阅读了 [一篇关于 Cockpit 的文章](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/cockpit-server-management),并决定尝试一下。你可以搜索 `cockpit` 验证该发行版是否包含它:
```
$ dnf search cockpit
Last metadata expiration check: 0:01:46 ago on Tue 18 May 2021 19:18:15 NZST.
==== Name Exactly Matched: cockpit ====
cockpit.x86_64 : Web Console for Linux servers
==== Name & Summary Matched: cockpit ==
cockpit-bridge.x86_64 : Cockpit bridge server-side component
cockpit-composer.noarch : Composer GUI for use with Cockpit
[...]
```
有一个精确的匹配。上面列出的匹配的软件包名为 `cockpit.x86_64`,但名称中的 `.x86_64` 部分仅表示它兼容该 CPU 架构。默认情况下,你的系统会安装适配当前 CPU 架构的软件包,因此你可以忽略该扩展名。所以你确认你要查找的软件包确实简称为 `cockpit`。
现在你可以放心地使用 `dnf install` 安装它。 此步骤需要管理员权限:
```
$ sudo dnf install cockpit
```
一般来说,这就是典型的 `dnf` 工作流:搜索并安装。
然而,有时 `dnf search` 的结果并不清晰,或者你想要关于一个软件包的更多信息,而不仅仅是它的通用名称。有一些相关的 `dnf` 子命令,具体取决于你想要的信息。
### 软件包的元数据
如果你觉得你的搜索已 *接近* 想要的结果,但还不确定,查看软件包的元数据通常会有所帮助,例如项目的网址和描述。要获取此信息,请使用顾名思义的 `dnf info` 命令:
```
$ dnf info terminator
Available Packages
Name : terminator
Version : 1.92
Release : 2.el8
Architecture : noarch
Size : 526 k
Source : terminator-1.92-2.el8.src.rpm
Repository : epel
Summary : Store and run multiple GNOME terminals in one window
URL : https://github.com/gnome-terminator
License : GPLv2
Description : Multiple GNOME terminals in one window. This is a project to produce
: an efficient way of filling a large area of screen space with
: terminals. This is done by splitting the window into a resizeable
: grid of terminals. As such, you can produce a very flexible
: arrangements of terminals for different tasks.
```
这个信息告诉你可用软件包的版本、在你系统中注册的哪一个存储库提供了它、该项目的网站以及详细的功能描述。
### 哪个软件包提供的这个文件?
软件包名称并不总是与你要查找的内容相匹配。例如,假设你正在阅读的文档告诉你必须安装名为 `qmake-qt5` 的东西:
```
$ dnf search qmake-qt5
No matches found.
```
`dnf` 数据库非常广泛,因此你不要局限于搜索完全匹配的内容。你可以使用 `dnf provides` 命令来了解你正在寻找的东西是否作为某个更大的软件包的一部分而提供:
```
$ dnf provides qmake-qt5
qt5-qtbase-devel-5.12.5-8.el8.i686 : Development files for qt5-qtbase
Repo : appstream
Matched from:
Filename : /usr/bin/qmake-qt5
qt5-qtbase-devel-5.15.2-3.el8.x86_64 : Development files for qt5-qtbase
Repo : appstream
Matched from:
Filename : /usr/bin/qmake-qt5
```
可以确认应用程序 `qmake-qt5` 是名为 `qt5-qtbase-devel` 的软件包的一部分。它还告诉你,该应用程序会安装到 `/usr/bin`,因此你知道了安装后它的确切位置。
### 软件包中包含哪些文件?
有时我发现自己会从完全不同的角度来对待 `dnf`。有时,我已经确认我的系统上安装了一个应用程序;我只是不知道我是怎么得到它的。还有一些时候,我知道我安装了一个特定的软件包,但我不清楚这个软件包到底在我的系统上安装了什么。
如果你需要对包的<ruby> 有效负载 <rt> payload </rt></ruby>进行 “<ruby> 逆向工程 <rt> reverse engineer </rt></ruby>”,可以使用 `dnf repoquery` 命令和 `--list` 选项。这将查看存储库中有关软件包的元数据,并列出该软件包提供的所有文件:
```
$ dnf repoquery --list qt5-qtbase-devel
/usr/bin/fixqt4headers.pl
/usr/bin/moc-qt5
/usr/bin/qdbuscpp2xml-qt5
/usr/bin/qdbusxml2cpp-qt5
/usr/bin/qlalr
/usr/bin/qmake-qt5
/usr/bin/qvkgen
/usr/bin/rcc-qt5
[...]
```
这些列表可能很长,使用 `less` 或你喜欢的分页命令配合管道操作会有所帮助。
### 移除应用程序
如果你决定系统中不再需要某个应用程序,可以使用 `dnf remove` 卸载它,该软件包本身安装的文件以及不再需要的任何依赖项都会被移除:
```
$ dnf remove bigapp
```
有时,你发现随着一个应用程序一起安装的依赖项对后来安装的其他应用程序也有用。如果两个包需要相同的依赖项,`dnf remove` *不会* 删除依赖项。在安装和卸载大量应用程序之后,孤儿软件包散落各处的现象并不少见。大约每年我都要执行一次 `dnf autoremove` 来清除所有未使用的软件包:
```
$ dnf autoremove
```
这不是必需的,但这是一个让我的电脑感觉更好的大扫除步骤。
### 了解 dnf
你对包管理器的工作方式了解得越多,在必要时安装和查询应用程序就越容易。即便你不是 `dnf` 的重度使用者,当你发现自己与基于 RPM 的发行版交互时,了解它也会很有用。
告别 `yum` 后,我最喜欢的包管理器之一是 `dnf` 命令。虽然我不喜欢它的所有子命令,但我发现它是目前最健壮的 <ruby> 包管理系统 <rt> package management system </rt></ruby> 之一。 [下载我们的 dnf 速查表](https://opensource.com/downloads/dnf-cheat-sheet) 习惯该命令,不要害怕尝试一些新技巧。一旦熟悉了它,你可能会发现很难使用其他任何东西替代它。
>
> **[dnf 速查表](https://opensource.com/downloads/dnf-cheat-sheet)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/6/dnf-linux>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hanszhao80](https://github.com/hanszhao80) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,544 | 微软加入开放 3D 基金会,参与开源 3D 开发 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/microsoft-joins-the-open-3d-foundation-for-open-source-3d-development-promotion/ | 2022-05-04T20:26:57 | [
"O3DF",
"微软"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14544-1.html | 
微软已经以首席成员的身份加入了<ruby> 开放 3D 基金会 <rt> Open 3D Foundation </rt></ruby>(O3DF),其他首席成员是 Adobe、AWS、华为、英特尔和 Niantic。微软的参与为该项目带来了大量的知识和思想引领,这表明了:通过行业合作,创造一个高保真、功能齐全、不受商业条件限制的开源 3D 引擎是多么的关键。
微软首席集团项目经理 Paul Oliver 将加入 O3DF 管理委员会,这表明他将致力于实现基金会的目标,即确保符合开放 3D 社区保持需求与输入的平衡。基金会的战略方向和对 3D 可视化、仿真计划的管理,是由理事会与股东的创新互动来指导的。
“微软在创意方面的根基很深,我们希望帮助所有的创作者,无论他们是谁、在哪里、为哪个平台创作”,Oliver 如是说,“由 Linux 基金会创建的开放 3D 基金会,是朝着帮助更多世界各地的创作者迈出的美妙一步,我们很高兴能成为其中的一员。”
微软不断致力于使游戏制作民主化,并向全世界的游戏创作者提供其工具和技术。加入开放 3D 基金会也反映出这一点。微软去年通过 GitHub 向所有开发者发布了其游戏开发工具包,并正在通过与 O3DF 的新伙伴关系,扩大其向所有人开放技术的承诺。
O3DF 执行董事,兼 Linux 基金会的游戏和数字媒体部总经理 Royal O'Brien 说:“我们很高兴微软以首席成员的身份加入开放 3D 基金会。有像微软这样杰出的行业资深公司做出贡献,并帮助社区推动 3D 引擎的创新,这对开源社区和使用它的公司都是巨大的好处。”
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/microsoft-joins-the-open-3d-foundation-for-open-source-3d-development-promotion/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Microsoft has joined the Open 3D Foundation (O3DF) as a Premier member, joining Adobe, AWS, Huawei, Intel, and Niantic. Microsoft’s involvement in the project adds a lot of knowledge and thought leadership to the project, demonstrating how crucial it is for the industry to work together to create a high-fidelity, fully-featured open source 3D engine that is free of commercial conditions.
Paul Oliver, Microsoft’s Principal Group Program Manager, will join the O3DF Governing Board, demonstrating his commitment to the Foundation’s goal of ensuring balanced collaboration and input that fits the needs of the Open 3D community. The Foundation’s strategic direction and stewardship of 3D visualisation and simulation initiatives are guided by the Governing Board’s innovative interactions with stakeholders.
“Microsoft’s roots in creativity run deep and we want to help creators wherever they are, whoever they are, and whatever platform they’re creating for,” said Oliver. “Having the Linux Foundation create the Open 3D Foundation is a fantastic step towards helping more creators everywhere and we are excited to be a part of it.”
Microsoft’s continuous commitment to democratising game production and making its tools and technology available to game creators all over the world is reflected in this step. The company released its Game Development Kit to all developers via GitHub last year. Microsoft is extending its commitment to open up technology to everyone with its new partnership with O3DF.
“We are elated to have Microsoft join the Open 3D Foundation as a Premier member,” said Royal O’Brien, Executive Director of O3DF and General Manager of Games and Digital Media at the Linux Foundation. “Having incredible industry veterans like Microsoft contributing and helping drive innovation with the community for 3D engines is a huge benefit to the open source community and the companies that use it alike.” |
14,545 | 文档并不是开源项目开发的附属品 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/04/documentation-isnt-just-another-aspect-of-open-source-development/ | 2022-05-05T09:00:04 | [
"文档"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14545-1.html | 有些项目长期保持活跃,有些项目却过早消亡 —— 这两者的区别往往在于它们的文档。严谨、聪明的文档可以给你的项目带来它所需要的动力。你应该把文档工作视为一项主要工作,把它与开发相提并论,下面我将说明这么做的理由和正确的做法。

经常会有开发者简单地认为他们的代码的“<ruby> 自我描述 <rt> self-documented </rt></ruby>”已经足够了,继而认为额外的文档是没有必要的。这种过度的自信会让项目付出很大的代价。匮乏或差劲的文档会扼杀你的项目。没有适当的文档,用户将无法理解项目的目标以及正确的工作流程。这可能会导致人们对采用你的开源产品产生一些疑虑。
### 撰写文档,从项目第一天就开始
文档不应该是次要的工作,它应该是与代码开发和管理同等的主要任务。随着内容以 Community Threads、Stack Overflow 和 Quora 问答等形式的广泛传播,文档承担了“<ruby> 信息源 <rt> source of truth </rt></ruby>”的角色。它应该满足那些想参考一手资料的贡献者的需要,并给工程师提供必要的参考支持。它还应该与利益相关者沟通基本计划。一个好的文档可以确保产品的持续改进和发展。
当发布一个软件产品时,我们不仅要发布代码,还要发布好的文档。这给我们带来了一个最重要的概念,大多数良好维护了文档的开源项目都遵循这个概念 —— “<ruby> 文档即代码 <rt> Documentation as code </rt></ruby>”。
### 文档及代码
今天,文档不再被存储为微软 Word 或 PDF 文件。新的需求是版本控制文档,其中所有的文档都是通过版本控制系统添加的,并持续发布。这个概念因 Read the Docs(LCTT 译注:一个文档创建、托管和浏览的平台)而流行,现在已经成为大多数文档团队的内容策略的重要组成部分。
像 Bugzilla 和 GitHub <ruby> 议题 <rt> Issue </rt></ruby>这样的工具可以用来跟踪待处理的文档工作,并从维护者和用户那里获得反馈以验证文档的发布。外部审查可以用来验证文档作品,并持续发布文档。这就保证了除代码外,文档也能不断改进并快速发布。
请记住,如果不遵循规范化的实践,每个文档都会不同。这可能会导致一些混乱,使人们难以获取正确的信息。
哪些东西会被归类为混乱呢?当大多数文件都不遵循规范实践时,不一致就会产生,从而导致更大的混乱!那么,如何整理混乱的开源文档呢?
### 整理混乱的开源文档
遵循一个“文档风格指南”是很重要的。风格指南是创建和展示内容的指导方针的集合。无论你是一个独立的作家还是一个大型文档团队的成员,它都有助于在你的文档中保持一致的风格、口音和语气。
有几个流行的风格指南,如《红帽风格指南》、《谷歌文档风格指南》和《苹果风格指南》。如何选用?首先要从定义你的需求开始。如果你的要求与其他开源项目没有太大区别,你可以遵循一个现成的风格指南,或者你也可以先选一个,然后在它的基础上根据自身需要做一些修改。大多数与语法有关的准则和内容规则可能是通用的,但整体术语可能会有所不同。
你还需要在你的项目中自动采用这些风格指南。为此,你可以使用 Vale,它集成了本地的持续集成(CI)服务,该服务能帮助你确保文档严格遵循风格指南。
>
> **文档类型**
>
>
> * *自述文件*:包含基本的安装和使用说明,这也是任何开源文档中最重要的部分之一。它是潜在的用户/开发者与项目之间的第一个连接点。
> * *参考指南*:可能包括一些基本的参考资料,以便帮助你快速上手,或者是与项目贡献相关的文档。
> * *用户文档*:是最基本的文档,它描述了项目的使用方式。如果没有用户文档,大多数人就会对如何使用该项目感到迷茫。
> * *开发文档*:旨在支持开发团队在项目中不断取得新的进展。它还应该为内部开发工作提供一个良好的途径,并确保功能被很好地传达给股东。
> * *社区内容*:包括基本的博客、视频和外部内容,旨在为那些想进一步了解项目的社区成员提供支持。
>
>
>
通过使用风格指南,文件的整体前提将以统一的语言风格传达给用户。但是,这些文件毕竟是由一个技术作家团队准备的,它们的写作风格可能会冲突,因为写作风格是因人而异的。那么,如何才能使文档规范化呢?
### 规范化文档
当涉及到规范化文档时,有许多方法可以采取。第一个方法显然是创建适用于各种角色的预定义模板。这些模板可以用来记录新的功能、识别错误和问题,以及更新变更日志以适应正在增加的新内容。
如果你采用的是基于 Git 的工作流,试着开发一个规范的工作流程来发布你的文档。最规范的工作流是:<ruby> 复刻 <rt> fork </rt></ruby> 发布文档的仓库,在本地分支上添加你的修改,推送这些修改,提出请求并要求对其进行审查。规范化文档的一个好处就是带来更好的反馈和审查过程。
### 反馈和自动审查
规范化使得你能够得到用户的反馈并生成自动的审查,可以参考这些反馈来改进项目和文档。通过这些反馈,你也可以评估所分享的信息对用户是否有意义。像 GitBook 这样的文档平台会提供合适的反馈服务,这有助于验证文档是否有用。
始终寻求<ruby> 主题专家 <rt> subject matter expert </rt></ruby>(SME)对文档的反馈,他们可以是利益相关者、开发者、工程师,甚至是外部贡献者。你也可以使用自动测试和 CI 来验证你的文档是否遵循风格指南。
### 文档众包
如果你想开源你的文档,最好的方法也许是提供一个快速入门指南。它可以像 `CONTRIBUTING.md` 那样简单,基本上只要说明该如何设置项目并为其作出贡献/单纯使用它即可。
始终开发以用户为中心的文档,标明每个项目的目的。同时,打造学习课程来帮助新的贡献者。
>
> **带着目的编写文档**
>
>
> 始终带着目的编写文档。它是最基本的写作策略之一,它定义了你编写某个特定文档的理由,而非方式。首先回答以下问题:
>
>
> * 这个文档的目标是什么?
> * 需要传递的信息是什么?
> * 你希望用户在这之后采取什么行动?
> * 我与读者分享的价值观是什么?
> * 我的文档风格是否简洁、一致?
>
>
>
### 定义一致的内容策略
一致的内容策略有助于确保文档工作和项目基础设施的长期愿景。它可以围绕以下两个主要方面:
1. 资源:包括项目文档、案例研究和白皮书、项目架构等
2. 品牌内容:博客和特邀帖子、新闻和社区故事、学习课程等
每个开源项目都应该有适当的文档,以说明它能为用户提供的功能,这样用户就可以选择最合适的解决方案。适当的文档可以传达正确的信息,也可以让其他开发者贡献力量来进一步加强和改进项目。虽然听起来很简单,但只有做对了,文档才能成功。而你的项目,反过来,只有在你的文档正确的情况下才能成功,所以永远不要低估它的目标或过程!
策划:Laveesh Kocher
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/04/documentation-isnt-just-another-aspect-of-open-source-development/>
作者:[Harsh Bardhan Mishra](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/harsh-bardhan-mishra/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Some projects live on, while some die a premature death – and the difference between the two often lies in the documentation. Meticulous, smart documentation can give your project the boost it needs. Here is why you should consider documentation a primary effort, on par with development, and the right way to go about it!*
Often, developers simply assume that code is self-documented enough and doesn’t need any extra documentation. This overconfidence can cost the project a lot. Insufficient or bad documentation can kill your project. Without proper documentation in place users won’t be able to understand the purpose as well as the proper workflow of the project. That could lead to some apprehensions about adopting your open source product.
**Work on it, right from day one**
Documentation should never be a secondary effort; it should be a primary task on par with code development and management. Documentation acts as the definitive source of truth with the wide redistribution of content in the form of community threads, stack overflows, and quora answers. It should fulfil the need of contributors who would like to refer to the actual resource, and provide the necessary references to support engineers. It should also communicate essential plans with the stakeholders. A good documentation ensures continuous improvement and development of a product.
When releasing a software product, we must not only ship the code but good documentation as well. This brings us to one of the most important concepts that most open source projects with well-maintained documentation follow – ‘documentation as code’.
**Documentation as code**
Today documentation is not being stored in Microsoft Word or PDF files. The new need is version control documentation, wherein all the docs are added over a version control system and released continuously. This concept was popularised by ‘Read the Docs’ and has now become an essential part of the content strategy for most documentation teams.
Tools like Bugzilla and GitHub Issues can be used to track the documentation work that is pending, and take feedback from maintainers and users to validate the release of the documents. External reviews can be used to validate the documentation piece, and to continuously publish it. This ensures that not only code, but the documentation as well, is continuously improved and released quickly.
Keep in mind that no two documentations will ever be the same if they don’t follow any standardised practice. This can lead to some mess, making it hard to fetch the right information.
How exactly do we classify something as messy? When most of the documentation pieces don’t follow standard practices, it leads to inconsistency and hence a big mess! So how do you declutter messy open source documents?
**Decluttering messy open source documentation**
It is important to follow a ‘documentation style guide’. A style guide is a collection of guidelines for creating and presenting content. Whether you’re a standalone writer or part of a large documents team, it helps to keep a consistent style, voice and tone throughout your documentation.
There are several popular style guides available, such as the Red Hat style guide, Google documentation style guide, and Apple style guide. To choose one, first start by defining your requirements. If your requirements do not differ much from other open source projects, you can follow a readily-available style guide, or adapt the same style guide for your own purpose with a few changes here and there. Most of the grammar-related guidelines and content rules may be the same, but overall terminology can vary.
You will also be required to automate the adoption of these style guides within your projects. For this, you can use Vale, which is integrated into the local machinery with a continuous integration (CI) service that will help you to ensure your documentation follows the style guide in a strict manner.
Types of documentation |
README: This contains basic installation and usage instructions, which is also one of the most essential parts of any open source documentation. It is the first point of information and contact between the potential user or developer and the project.
|
By using the style guide, the overall premise of the documentation will be conveyed to the users in a single tone. But since these documents are prepared by a team of technical writers, there can be conflicting writing styles, as these vary from person to person. So how do you standardise the documentation?
**Standardising documentation**
There are many approaches that can be taken when it comes to standardising documentation. The first one is obviously to create predefined templates which can be used for a variety of roles. These can be used for documenting new features, identifying bugs and issues, and updating the change log to accommodate new stuff that is being added.
Try to develop a standard workflow for publishing your documentation if you are following a Git based workflow. The most standard workflow will be to fork the repo where the documentation is published, add your changes on a local branch, push these changes, make your request and ask for reviews on the same. A positive that comes out of standardising your documents is a better feedback and review process.
**Feedback and automated reviews**
Standardisation allows you to get users’ feedback and generate automated reviews, which can be taken into consideration for improving the project and the documentation. With this feedback, you can also evaluate whether the information being shared is making sense to users or not. Having a proper feedback service in place through documentation platforms like GitBook helps to verify if the documentation is useful or not.
Always try to seek out subject matter expert (SME) feedback on the documentation. These SMEs can be stakeholders, developers, engineers, or even external contributors. You can also use automated tests and CI to verify if your documentation is following a style guide or not.
**Crowdsourced documentation efforts**
If you are looking to open source your documentation, perhaps the best way to get started is to provide a quick start guide. The guide can be as simple as ‘CONTRIBUTING.md’; basically, a file showing how a person can set up the project and contribute to or use it.
Always try to develop user-centric documentation that signifies the purpose of each project and build learning courses to help new contributors.
Write with a purpose |
Always look to write with a purpose. It is one of the most essential writing strategies and basically defines ‘why’ you are writing a particular documentation, and not ‘how’ you are writing it. Start by answering the following questions:
|
Defining a consistent content strategy
A consistent content strategy helps to ensure a long-term vision for the documentation efforts and the project infrastructure. This can revolve around two main things:
a.* Resources:* Project docs, case studies and whitepapers, project architecture
b. *Branded content:* Blogs and guest posts, news and community stories, learning courses
Every open source project should have proper documentation stating the functionality it can provide to users, so that they can opt for the most suitable solution. Proper documentation that communicates the right information also allows other developers to put in their efforts to further enhance and improve the project. Simple though it sounds, documentation can only succeed if done right. And your project, in turn, can only succeed if your documentation is right, so never underestimate its purpose or process!
Curated By: Laveesh Kocher |
14,546 | 使 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 成为史诗版本的 5 个不太流行的功能 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/04/ubuntu-22-04-release-unique-feature/ | 2022-05-05T11:27:28 | [
"Ubuntu"
] | /article-14546-1.html |
>
> 这是一份关于 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 的次要特点的列表,这些特点使它成为迄今为止最好的 LTS 版本之一。
>
>
>
Canonical 的最新 LTS 版本 [Ubuntu 的代号为 “Jammy Jellyfish”](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/01/ubuntu-22-04-lts/) 受到了全球用户的好评。但是有数百个新的微小功能,以及一些不太流行的功能,没有引起人们的注意。因此,这里有五个 Ubuntu 22.04 的独特功能,我们认为这些功能可以使它成为一个史诗般的版本。

### Ubuntu 22.04 发布 – 五个独特的功能
#### 为数据驱动的方案进行了优化
数据分析和处理是当今每个企业的核心。而要做到这一点,你需要巨大的计算能力。Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 带来了开箱即用的 [英伟达虚拟 GPU(vGPU)](https://docs.xn--cpq367j69h.com/grid/latest/grid-vgpu-release-notes-ubuntu/index.html) 驱动支持。这意味着你可以利用英伟达虚拟 GPU 软件,使你能够在虚拟机中使用从物理 GPU 服务器共享的 GPU 计算能力。
不仅如此,如果你的业务依赖于 SQL Server,Ubuntu LTS for Azure 带来了 Ubuntu 中的 SQL Server,它由 “Micro$oft” 支持,提供优化的性能和可扩展性。
#### 改进的活动目录集成
此外,许多企业在多个工作站中为整个企业用户部署 Ubuntu。而且,部署工作站策略以监测和控制用户访问和各种关键业务控制非常重要。
活动目录实现了基于策略的工作站管理(在 Ubuntu 20.04 中引入),在这个版本中得到了进一步改善。除此之外,这个版本还带来了 [ADsys](https://github.com/ubuntu/adsys) 客户端,它有助于通过命令行远程管理组策略、权限升级和远程脚本执行。从这个版本开始,活动目录现在也支持与高级组策略对象的安装程序集成。
#### 实时内核支持
此外,在 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 发布期间,Canonical 宣布的一个有趣的消息是,提供“实时”内核选项,现在是测试版。对于电信和其他行业来说,一个低延迟的操作系统对于时间敏感的工作是必需的。因此,考虑到这一点和渗透到这些领域的愿景,Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 带来了一个应用了 PREEMPT\_RT 补丁的实时内核构建。它可用于 x86\_64 和 AArch64 架构。
然而,该 [补丁](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/rt/linux-stable-rt.git/) 还没有在主线内核中出现,希望它能很快能出现。
#### 最新的应用、软件包和驱动程序
除了上述变化之外,这个版本还带来了大量的软件包和工具链的升级。例如,这个版本带来了基于各种用途的多种 Linux 内核类型,如 Ubuntu 桌面可以选择使用 [内核 5.17](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/03/linux-kernel-5-17/),而硬件启用内核仍然是 5.15。
不仅如此,Ubuntu Server 采用长期支持版的 [内核 5.15](https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/11/linux-kernel-5-15/),而 Ubuntu Cloud 镜像可以选择使用与云供应商合作的更优化的内核。
此外,如果你是英伟达用户,值得一提的是,ARM64 上的英伟达驱动的 Linux 限制模块现在已经可用(在 x86\_64 中已经可用)。你可以使用 [ubuntu-drivers](https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/ubuntu-drivers-common) 程序来安装和配置英伟达驱动。
核心模块和子系统构成的完整的操作系统可以完美无缺地工作。因此,考虑到这一点,Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 对它们都进行了仔细的升级,以迎合这个很好的版本。以下是简介:
GNU/Linux 核心:
* GCC 11.2.0
* binutils 2.38
* glibc 2.35
编程工具链:
* Python 3.10.4
* Perl 5.34.0
* LLVM 14
* golang 1.18
* rustc 1.58
* OpenJDK 11(可选使用 OpenJDK 18)
* Ruby 3.0
* PHP 8.1.2
* Apache 2.4.52
* PostgreSQL 14.2
* Django 3.2.12
* MySQL 8.0
* 更新的 NFS 以及 Samba Server
* Systemd 249.11
* OpenSSL 3.0
虚拟化:
* qemu 6.2.0
* libvirt 8.0.0
* virt-manager 4.0.0
#### 性能提升
但这还不是全部。由于一些长期等待的更新,你应该体验到更快的 Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish,这些体验最终会在这个版本中出现。
首先,长期等待的 GNOME 桌面的 [三重缓冲代码] 已经来到。当先前的帧缓冲落后时,三重缓冲会自动启用,它在英特尔和树莓派驱动中产生了更快的桌面性能。不仅如此,代码还监控最后一帧,以便系统不会遇到过量缓冲的情况。
其次,改进的电源管理,在运行时对 AMD 和英伟达的 GPU 起作用,将帮助笔记本电脑用户。
此外,Wayland 现在是大多数系统的默认显示服务器,除了英伟达 GPU 硬件默认为 X11。Wayland 为你提供了更快的跨应用的桌面体验,包括网页浏览器。
最后,定制的 GNOME 42 及其 [独特功能](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/03/gnome-42-release/)(例如平衡和省电电源配置文件)为重度笔记本电脑用户提供了更多优势。此外,带有浅色/深色外观的新强调色和将选定的 GNOME 模块移植到 GTK4/libadwaita 只是这个史诗般的 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 版本的一个补充。
### 结论
总而言之,就上述所有内容的变化和许多其他方面而言,我相信这是 Canonical 发布的最好的 LTS 版本之一。
我们希望它得到好评,并在未来能保持稳定。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/04/ubuntu-22-04-release-unique-feature/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,547 | 最适合程序员的 10 款 Linux 发行版 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/03/top-linux-distributions-programmers-2022/ | 2022-05-05T14:36:00 | [
"Linux 发行版"
] | /article-14547-1.html | 
>
> 我们为程序员和开发人员总结了 2022 年最好用的 10 款 Linux 发行版,以便他们开展日常工作和个人项目。
>
>
>
由于工作和项目需要,程序员和开发人员会用到各种工具和应用,包括代码编辑器、编译器、插件以及数据库等等。若对现代开发人员的工作流程做一番整理,一般流程如下:
* 创建代码仓库
* 编程
* 调试
* 测试
* 部署
上述工作流程需要用到各种各样的工具,一份标准的工具清单如下:
* 代码编辑器
* 简单的文本编辑器
* 网页浏览器(包括 Web 开发人员使用的各种浏览器)
* 数据库引擎
* 本地服务器
* 各类编程语言的编译器
* 调试器
* 监视或分析工具(客户端或者网页端)
与 Windows 相比,Linux 可以说是编程的最佳平台。之所以这样说,主要是因为 Linux 发行版与 Windows 不同,预装了许多功能强大的包和软件,自行安装也比较容易。在本文中,考虑到一些原因,我不会将 macOS 纳入对比范围之内。
综上,本文将整理出 2022 年最适合程序员的 10 款 Linux 发行版。
### 2022 最适合程序员的 10 款 Linux 发行版
#### 1、Fedora 工作站

在这 10 款 Linux 发行版当中,最优秀的可能就要数 Fedora Linux 了。Fedora 默认的工作站版本精选了一些软件包,为用户带来真正的 GNOME 桌面体验。
Fedora Linux 默认安装了开箱即用的主流开发软件包,包括 PHP、OpenJDK、PostgreSQL、Django、Ruby on Rails 以及 Ansible 等等。
dnf 是 Fedora Linux 的包管理器,有了它,安装代码编辑器以及其他软件就相当容易了。此外,你还可以使用“软件”应用商店一键搜索、安装软件。
Fedora Linux 支持 Snap 和 Flatpak,使用起来会更加灵活方便。你还可以使用 RPM Fusion 仓库,获取大量自由或非自由的软件。因为许可证等一些原因,Fedora Linux 不希望在其主仓库内包括这些包,于是就有了 RPM Fusion。
点击下方链接,了解 Fedora Linux 最新版本。
>
> **[下载 Fedora](https://getfedora.org/)**
>
>
>
#### 2、Ubuntu Linux

在今天,无论是服务器还是个人电脑,使用最为广泛的发行版当属 Ubuntu Linux。Ubuntu 提供长期支持版本,每个长期支持版本官方提供五年的支持(外加五年的维护支持),并且每年为高级用户提供两个短期版本。
由于 Ubuntu 非常流行,各种包与软件的供应商都会提供适用于 Ubuntu 的版本(.deb)。此外,得益于广泛的知名度,Ubuntu 有着更为庞大的论坛群体和更为丰富的帮助文档。所以说,Ubuntu 是开发人员的最佳之选,尤其是在开发过程中陷入难题的时候,Ubuntu 更能发挥其作用。点击下方链接,了解更多。
>
> **[下载 Ubuntu](https://ubuntu.com/download)**
>
>
>
#### 3、openSUSE
openSUSE 是用在全球关键系统中最稳定、最专业的 Linux 发行版之一,是企业界(包括个人电脑、服务器以及瘦客户机)的首选解决方案。
相较于 Ubuntu 和 Fedora,openSUSE 具有一些独特的优势。首先,openSUSE 有两个版本:Leap 和 Tumbleweed。其中,openSUSE Leap 属于长期支持版,为用户带来稳定的升级体验。openSUSE Tumbleweed 属于滚动发行版,有着最新、最尖端的软件包。
如果你想获得最新的包和硬件支持,助力开发工作,你可以选择 openSUSE Tumbleweed;如果你想要的是稳定性,无需频繁维护即可长期运行,openSUSE Leap 会更适合你。
使用 openSUSE 进行开发工作,最大的优势之一就是 YaST 包管理工具。有了 YaST,许多操作可以轻松实现自动化。
此外,openSUSE 获取软件非常方便。它有专属的应用网站,供用户查找、安装包和软件。
如果你有一些 Linux 发行版的使用经验,推荐选择 openSUSE 进行开发工作。
>
> **[下载 openSUSE](https://www.opensuse.org/)**
>
>
>
#### 4、Manjaro Linux
Manjaro Linux 基于 Arch Linux,不过安装起来更容易一些。Manjaro Linux 自身还有许多独特功能,比如带有图形用户界面的安装程序、pamac 软件安装器以及高质量的软件仓库等等。Manjaro 有三个主要的桌面版本:GNOME、KDE Plasma 和 Xfce,足以满足各类用户的需要。
如果你想使用 Arch Linux 及其滚动发行的软件包来满足开发需求,但又不想在安装原版 Arch 上来回折腾,Manjaro 绝对是你的最佳选择。
>
> **[下载 Manjaro](https://manjaro.org/download/)**
>
>
>
#### 5、Arch Linux
尽管有 Manjaro 以及其他基于 Arch Linux 的发行版,而且安装操作非常简单,你可能还是想在自己的定制电脑上折腾一番,亲自动手 [安装原版 Arch](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/01/archinstall-guide/)。
不过这种选择更适合程序员和开发人员,因为他们想得到更多的掌控权,或者想要定制一个 Linux 操作系统,用于开发项目或满足开发需求。这样一来,他们可能就会安装 Arch Linux,选择自己最喜欢的桌面,设置专用于开发工作的操作系统。
假设你对 Arch Linux 和普通的电脑都比较熟悉,那么 Arch Linux 就是你的最佳选择,因为在自己定制的 Linux 操作系统上,你可以完全控制每一个软件包。
>
> **[下载 Arch Linux](https://archlinux.org/download/)**
>
>
>
#### 6、Pop OS
Pop OS(即 Pop!\_OS)由电脑制造商 System76 针对其系列硬件开发,是一款基于 Ubuntu 的自由开源的发行版。发行周期与 Ubuntu 保持同步,并为用户提供了额外的调整工具和软件包。

Pop OS 基于 Ubuntu,默认支持多种程序语言,所以非常适合程序员使用。Pop OS 的软件中心非常出色,设有开发软件专区,深受计算机科学家和程序员青睐。
此外,Pop OS 的 COSMIC 桌面(GNOME 桌面的定制版)支持窗口自动平铺,具有柔美的调色板、默认的深色模式以及丰富的设置选项,给程序员带来独特的使用体验。
如果你既想要基于 Ubuntu,又想要适合程序员的稳定 Linux 发行版,推荐选择 Pop OS。
>
> **[下载 POP OS](https://pop.system76.com/)**
>
>
>
#### 7、KDE Neon
作为一个程序员,如果你喜欢 KDE Plasma 桌面,又想使用基于 Qt 的开发环境,那么你应该选择 KDE Neon。
KDE Neon 基于 Ubuntu 长期支持版本,兼具最新的 KDE Plasma 桌面和 KDE 框架。因此,使用 KDE Neon,你不仅可以享受 Ubuntu 长期支持版本的稳定性,还能体验基于 Qt 的最新版 KDE 软件。
运行速度快,程序开箱即用,用户界面友好,广泛的社区支持,如你所愿,完美如斯。
>
> **[下载 KDE Neon](https://neon.kde.org/download)**
>
>
>
#### 8、Debian
Debian GUN/Linux 就无需过多介绍了。Debian 的稳定分支是 Ubuntu 及其衍生系统的基础。换句话说,Debian 是最主要、最稳定的 Linux 发行版之一。优秀的稳定性和较长的支持时间使得 Debian 非常适合用做开发环境。
不过,Debian 的稳定分支比较保守,很少使用最新的软件包。毕竟全世界(几乎)都依赖 Debian 的稳定运行,所以维护者在检查、合并软件包时必须十分谨慎。
Debian 不仅能够长期稳定运行,而且维护成本较低,是高级用户和系统管理员绝佳的编程环境。
>
> **[下载 Debian Linux](https://www.debian.org/distrib/)**
>
>
>
#### 9、Kali Linux
Kali Linux 由 Offensive Security 开发,服务对象为道德黑客和查找网络漏洞的渗透测试人员,内置大量黑客软件和工具。
对技术娴熟的程序员和开发人员来说,Kali Linux 堪称最佳之选。如果你精通 Linux,具备解决错误和依赖问题的经验,推荐选择 Kali Linux。
>
> **[下载 Kali Linux](https://www.kali.org/)**
>
>
>
#### 10、Fedora Labs
最后,我们来看看 Fedora Linux 的各种 Fedora Labs 版本。
Fedora Labs 为程序员、科学家、学生等各类人群提供各类专业化的 Linux 发行版,内置各类专业软件、包和工具。很多人并没有意识到 Fedora Labs 的优势,只要经过适当的配置,这些版本都是非常优秀的发行版。
我们来总结一下这些 Fedora Labs:
Fedora Scientific:
* 采用 KDE Plasma 桌面,集成科学和数学领域的各种开源工具
* 软件清单如下:
+ 基于 C/C++ 的 GNU Scientific Library
+ 兼容 MATLAB 的 MGNU Octave
+ LaTeX
+ Gnuplot:用于绘制 2D 与 3D 图像
+ Pandas:用于数据处理的 Python 库
+ IPython
+ Java 和 R 程序语言相关包
>
> **[下载 Fedora Scientific](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/en/scientific/)**
>
>
>
Fedora COMP NEURO:
* 采用 GNOME 桌面环境,预装神经科学领域的各种开源包和应用。
>
> **[下载 Comp Neuro](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/en/comp-neuro/)**
>
>
>
Fedora Robotics Suite:
* 集成各种开源机器人技术包和软件,适合初学者、资深计算机科学家和编程人员。
>
> **[下载 Fedora Robotics](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/en/robotics/)**
>
>
>
除了上述版本,还有 [Fedora Security Labs](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/en/security)、[Fedora Astronomy](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/en/astronomy) 和 [Fedora Python Classroom](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/en/python-classroom) 可供选择。
在编程项目以及科学领域,Fedora Labs 堪称完美之选。
### 总结
那么,怎样才能从以上 10 款 最适合程序员的 Linux 发行版中选出自己最喜欢的呢?
如果你想要一款开发系统,但又不想耗费太多精力,拿不定主意的话,推荐使用 Fedora 工作站或者 Ubuntu。
如果你的空闲时间比较多或者想要进一步掌控自己的系统,乐于尝试并且能够忍受偶尔发生的错误,推荐选择基于 Arch Linux 的系统。
对于刚接触 Linux 生态的新手程序员来说,Pop OS 也是一个不错的选择。如果有特殊需要的话,可以试试 Fedora Labs。
我希望本文能帮助程序员和开发人员选出最喜欢的 Linux 发行版。
祝你好运!
(题图由 [jplenio](https://pixabay.com/zh/users/jplenio-7645255/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=6792527) 在 [Pixabay](https://pixabay.com/zh/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=6792527) 上发布 )
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/03/top-linux-distributions-programmers-2022/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[aREversez](https://github.com/aREversez) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,549 | 微软 1995 年首次发布的 3D Movie Maker 现已开源 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/microsofts-3d-movie-maker-first-released-in-1995-is-now-open-source/ | 2022-05-05T20:15:42 | [
"微软",
"开源"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14549-1.html | 
这些年来,微软发布了许多开源工具。今天,它正在翻箱底,让 3D Movie Maker 也对所有人开放。3D Movie Maker 于 1995 年首次推出,它允许你用 3D 人物、道具、背景、文字、声音和特殊效果来创建动画场景。这个版本还包括一个 Argonaut 软件公司构建的 BRender。虽然这是一个积极的举措,但请先别太激动,事情可没那么容易。
>
> “这个项目不太可能在现代硬件/软件下构建成功,但你可以先开始编译,并获得部分完整的二进制文件。”
>
>
>
以下是它的部分构建说明:
* 确保本仓库检出到一个名字简短的目录中,最好是靠近驱动器的根路径(即 `C:\3d` 这样)。
* 在构建过程中,你需要 Visual C++ 2.0 的开发工具(可以在安装盘的 `MSVC20BIN` 目录下找到)。有一些源码遵循的是 C++98 之前的规范,因此现代编译器可能不会喜欢它们。
* 从本仓库的根目录下运行 `setvars.bat`。你可以改变这个脚本中的值来改变你的构建目标。
* 查找并安装字体文件(详见 `FONTS.md`)。
* 运行 `nmake` 以开始使用 3D Movie Maker。
这些代码是从微软公司的档案中恢复的,涉及到的第三方软件(如 BRender)已获得授权。同时,它删除了开发者的身份和别名,以便使该软件开源(从事原始发布工作的微软现任员工除外,他们同意保留自己的名字)。你可以在 [这里](https://github.com/microsoft/Microsoft-3D-Movie-Maker) 下载它。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/microsofts-3d-movie-maker-first-released-in-1995-is-now-open-source/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Microsoft has released a number of open source tools over the years, and today it is digging deep into its archives to make 3D Movie Maker available to everyone. 3D Movie Maker, which was first launched in 1995, allows you to create animated scenarios with 3D characters, props, backgrounds, text, sound, and special effects. This version also includes an Argonaut software build of BRender. While this is a positive step, you shouldn’t get too enthusiastic because there is a catch.
“This project is unlikely to build successfully under modern hardware/software, but you can get started with compilation and get partial completed binaries.”
It includes the following construction instructions.
– Make sure this repository is checked out to a folder with a brief name, preferably near the drive’s root (i.e. C:\3d).
– On your route, you’ll need the dev tools for Visual C++ 2.0 (found under MSVC20BIN on the installer disc). Some pre-C++98 norms are disliked by modern compilers.
– Run setvars.bat from the root of this repository. You can alter the values in this script to change the target of your build.
– Find and install font files (see FONTS.md)
– Run nmake to get started with 3D Movie Maker.
The code was recovered from the Microsoft corporate archives, third-party authorization (for products like BRender) was gained, and developer identities and aliases were deleted in order to make the software open source (with the exception of current Microsoft employees who worked on the original release and agreed to keep their names in place). It can be downloaded from [here](https://github.com/microsoft/Microsoft-3D-Movie-Maker). |
14,550 | 用 Gwenview 在 Linux 上裁剪和调整照片大小 | https://opensource.com/article/22/2/crop-resize-photos-gwenview-kde | 2022-05-05T22:12:11 | [
"Gwenview",
"照片"
] | /article-14550-1.html |
>
> Gwenview 是一个优秀的照片编辑器,适合业余摄影师在 Linux KDE 桌面上使用。
>
>
>

一张好的照片可以蕴含很多信息。表面上它表达了你所看到的,但它也讲述了你所经历的。细微之处也能说明很多问题:你在拍照时选择的角度、取景中隐约可见的的东西有多大,以及,相比之下,那些有意识选择忽略的部分。
照片通常并不意味着记录真实发生的事情,相反,它们会成为你(摄影师)如何看待发生的事情的洞察力。
这就是照片编辑如此普遍的原因之一。当你把照片发布到你的在线图片库或社交网络时,你不应该发布一张不能准确表达照片所包含的感受的照片。但同样的道理,你也不应该成为一个专业的照片合成师,而只是为了剪掉在最后时刻将头伸进你的家庭快照的路人。如果你使用的是 KDE,你可以使用 Gwenview 这种休闲照片编辑器。
### 在 Linux 上安装 Gwenview
如果你正在运行 KDE Plasma 桌面,你可能已经安装了 Gwenview。如果你没有安装,或者你正在使用一个不同的桌面,而你想尝试 Gwenview,那么你可以用你的软件包管理器安装它。
我建议同时安装 Gwenview 和 Kipi 插件集,它可以将 Gwenview 与几个在线照片服务连接起来,这样你就可以轻松上传照片。在 Fedora、Mageia 和类似发行版上:
```
$ sudo dnf install gwenview kipi-plugins
```
在 Debian、Elementary 和类似版本上:
```
$ sudo apt install gwenview kipi-plugins
```
### 使用 Gwenview
Gwenview 通常有两种启动方式。你可以在 Dolphin 中点击图片文件,并选择在 Gwenview 中打开它;或者你可以启动 Gwenview,并在文件夹中寻找照片,Gwenview 或多或少可以充当你的文件管理器。第一种方法是直接的方法,很适合快速方便地预览图片文件。第二种方法是当你浏览大量照片,不确定哪一个版本的照片是“正确的”时,你可能会使用。
无论你如何启动 Gwenview,界面和功能都是一样的:右边有一个工作区,左边有一个面板。

(Seth Kenlon [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/), Photo courtesy [Andrea De Santis](http://unsplash.com/@santesson89))
在左边的面板下面,有三个标签:
* <ruby> 文件夹 <rt> Folders </rt></ruby>:显示你电脑上的文件夹的树状视图,以便你可以浏览你的文件,寻找更多的照片。
* <ruby> 信息 <rt> Information </rt></ruby>:提供关于你目前正在查看的照片的元数据。
* <ruby> 操作 <rt> Operations </rt></ruby>:允许你对当前的照片进行小的修改,如在横向和纵向之间旋转、调整大小和裁剪等。
Gwenview 能理解文件系统,所以你可以按键盘上的**右**或**左**箭头,查看文件夹中的上一张或下一张照片。
要离开单张照片视图并查看一个文件夹中的所有图片,请点击顶部工具栏中的“<ruby> 浏览 <rt> Browse </rt></ruby>”按钮。

(Seth Kenlon,[CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
你也可以同时拥有两种视图。点击 Gwenview 底部的“<ruby> 缩略图栏 <rt> Thumbnail Bar </rt></ruby>”按钮,可以以电影胶片的形式看到当前文件夹中的其他图片,而当前选择的照片则在主面板中。

(Seth Kenlon,[CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
### 用 Gwenview 编辑照片
数码照片是很常见的,因此在网上发布或与朋友分享之前,需要对照片进行细微的调整也是同样常见。有非常好的应用可以编辑照片,事实上,其中最好的一个是另一个 KDE 应用,叫做 Krita(你可以在我的 [给摄影者的 Krita](https://opensource.com/article/21/12/open-source-photo-editing-krita) 文章中阅读我如何使用它来处理照片),但是小的调整不应该需要艺术学位。这正是 Gwenview 所确保的:用一个休闲但功能强大的应用进行简单而快速的照片调整,并与你的 Plasma 桌面的其他部分整合。
我们大多数人对照片进行的最常见的调整是:
* **旋转**:当你的相机没有提供正确的元数据让你的电脑知道一张照片是要以横向还是纵向观看时,你可以手动修复它。
* **镜像**:许多笔记本电脑或面部摄像头模仿镜子,这很有用,因为这是我们习惯于看到自己的方式。但是,它会使文字逆转。**镜像**功能可以从右到左翻转图像。
* **翻转**:在数码相机和笔记本电脑上不太常见,但在手机上,无论你怎么拿手机,使用倒置设备拍照的现象在屏幕翻转的手机中并不少见。**翻转**功能可将图像旋转 180 度。
* **调整大小**:数字图像现在通常具有超高清尺寸,有时这比你需要的要多得多。如果你通过电子邮件发送照片或将其发布在你想要优化加载时间的网页上,你可以将尺寸(和相应的文件大小)缩小到更小的尺寸。
* **裁剪**:你有一张很棒的自己的照片,但不小心偶然发现了一个你认为不合适的人。用裁剪工具剪掉你不想要的所有东西。
* **红眼**:当你的视网膜将相机的闪光灯反射回相机时,会得到红眼效果。Gwenview 可以通过在可调节区域中对红色通道进行去饱和和变暗来减少这种情况。
所有这些工具都在“<ruby> 操作 <rt> Operations </rt></ruby>”侧面板或“<ruby> 编辑 <rt> Edit </rt></ruby>”菜单中可用。这些操作具有破坏性,因此在你进行更改后,单击“<ruby> 另存为 <rt> Save As </rt></ruby>”以保存图像的 *副本*。

(Seth Kenlon,[CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/),照片由 [Elise Wilcox](http://unsplash.com/@elise_outside) 提供)
### 分享照片
当你准备好分享照片时,单击顶部工具栏中的“<ruby> 分享 <rt> Share </rt></ruby>”按钮,或转到“<ruby> 插件 <rt> Plugins </rt></ruby>”菜单并选择“<ruby> 导出 <rt> Export </rt></ruby>”。Gwenview 与 Kipi 插件集成在一起,可以在 [Nextcloud](https://opensource.com/article/20/7/nextcloud)、[Piwigo](https://opensource.com/alternatives/google-photos)、普通旧电子邮件以及 Google Drive、Flickr、Dropbox 等服务共享照片。
### Linux 上的照片编辑要点
Gwenview 拥有桌面照片管理器的所有必需功能。如果你需要的不仅仅是基本功能,你可以在 Krita 或 [Digikam](https://opensource.com/life/16/5/how-use-digikam-photo-management) 中打开一张照片,并根据需要进行重大修改。对于其他一切,从浏览、排名、标记和小调整,Gwenview 都很方便。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/2/crop-resize-photos-gwenview-kde>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,551 | 我如何利用开源设计自己的卡牌游戏 | https://opensource.com/article/21/12/open-source-card-game | 2022-05-06T09:43:23 | [
"开源",
"游戏"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14551-1.html |
>
> 开源并不仅仅指的是软件。开源是一种文化现象,自然也适合桌面游戏。
>
>
>

我喜欢优秀的游戏,尤其是桌游,因为桌游的很多特性都和开源相同。在现实生活中,当你和朋友围坐在桌旁一起玩卡牌游戏时,作为一个团队,你们可以一起决定小丑牌是不是万能的。还有,你们可以随意地决定当出了小丑牌后,手上有 Ace 牌的人的要不要舍弃 Ace 牌,或者出了方块皇后以后,每个人是不是都要把手上的牌传给右手边的人。换句话说,你们可以随心所欲地重新制定规则,因为游戏不过是参与者们一致认同的条件集合罢了。对我来说,更棒的是你可以发明自己的游戏,而不用破坏别人的游戏规则。有时候,我会作为一个业余爱好者来开发桌游。因为我喜欢把自己的爱好结合起来,所以我倾向于只使用开源和开放的文化资源来设计游戏。
首先,游戏有大致有两个关键特征,风格和机制,理解这一点非常重要。游戏风格指的是游戏的故事或者主题,游戏机制指的是游戏的规则和条件。这两者并不总是完全脱离的,举个例子,在设计一款以赛车为主题的游戏时,自然而然就会要求玩家迅速完成动作。然而,风格和机制通常是被分开对待的,所以我们完全可以为了好玩就去创造一款使用标准扑克牌,却以太空羊驼为主题的游戏。
### 开源美术
如果你去过现代艺术博物馆,你可能会发现自己站在一幅纯蓝色的画布前,无意中听到有人说起老话:“见鬼,这我也能做!”。但事实是,艺术是一项艰巨的工作。创作赏心悦目的艺术品需要付出大量的思考、时间、信心和技巧。这也意味着艺术是你在设计游戏时中最难采购的部分之一。
我有一些“技巧”来解决这个典型难题。
#### 1、寻找同类素材
现在有很多免费、开放的艺术作品,而且大部分质量上佳。问题在于,游戏通常需要不止一件作品。如果你正在设计一款纸牌游戏,你大概至少需要四到六个不同的元素(假设你的纸牌遵循塔罗牌风格),有可能还需要更多。如果你花足够多的时间在这上面,你可以在 [OpenGameArt.org](https://opensource.com/article/21/12/opengameart.org/)、[FreeSVG.org](http://freesvg.org)、[ArtStation.com](http://artstation.com)、[DeviantArt.com](http://deviantart.com) 等网站上找到<ruby> <a href="https://opensource.com/article/20/1/what-creative-commons"> 知识共享和公共领域 </a> <rt> Creative Commons and Public Domain </rt></ruby>的艺术作品。
如果你使用的网站没有专门搜索<ruby> 知识共享 <rt> Creative Commons </rt></ruby>的功能,输入以下文字到任何搜索引擎当中,`"This work is licensed under a Creative Commons"` 或 `"本工作处于知识共享许可协议之下"`(引号很重要,不要把它们漏了),并用搜索引擎要求的语法,以便将搜索限制到一个具体的站点当中(举个例子,`site:deviantart.com`)。
一旦你有了一个可供挑选素材的艺术库,那就去辨别这些作品的主题,并根据主题分类。两个不同的人拍摄的机器人的照片可能看起来一点都不像,但它们的主题都是机器人。如果提供给你足够多机器人相关的美术素材,你可以围绕机器人这个主题构建你的游戏风格。
#### 2、委托创作知识共享艺术
你可以雇艺术家来为你定制艺术作品。我与使用开源绘画程序(如 [Krita](https://opensource.com/article/21/12/krita-digital-paint) 和 Mypaint)的艺术家一起合作。同时,作为合同的一部分,我规定艺术作品必须在<ruby> 知识共享署名-相同方式许可证 <rt> Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike </rt></ruby>(CC BY-SA)下授权。迄今为止,只有一位艺术家因为许可证的限制拒绝了我的提议,并且大多数人都很高兴自己的美术作品有可能有更大的生命力,而不仅仅是作为业余爱好者自己发行的游戏的一部分。
#### 3、创作自己的艺术
就像现代艺术馆之旅展示的那样,艺术是一个非常灵活的词。我发现只要我给自己设定一个目标,也就是我需要为一款游戏创造多少纸牌或令牌,我便能够从 Linux 上的丰富图像创造工具中选择一种去创作。这并不需要什么高难度的东西。就像现代艺术一样,你可以用蓝色和黄色的条纹,或者红色和白色的圆点花纹,或者绿色和紫色的锯齿线来涂一张卡片,只要你能把它们画出来,那么除了你以外,其他人永远不会知道你暗地里把它们当做仙宫里的贵族和小姐。想想看,通过运用图形应用程序,描摹日常物品的照片,重组经典的扑克花色和塔罗牌主题等一系列方式,你可以创造出的简单作品吧。
### 版面设计
我用 [Inkscape](https://opensource.com/article/21/12/linux-draw-inkscape)、Scribus 或者 [GIMP](https://opensource.com/content/cheat-sheet-gimp) 来进行版面设计,这取决与我有什么素材以及我追求的设计方式是什么。
对于卡牌,我发现简单的版面设计很容易实现,看上去也更好,纯色比渐变色更容易印刷,还有,直观的图像是最棒的。

(Seth Kenlon, CC BY-SA 4.0)
我在一个单独的 Inkscape 文件中为我最新的游戏做了版面设计,这个游戏只使用了来自 [OpenGameArt.com](http://OpenGameArt.com) 上三四个不同艺术家的九张图片。在有着更大的美工集,更好的卡牌多样性的游戏中,我会在游戏中的每一种卡片的文件中为它们设计版面。
在为你的游戏素材做任何版面设计之前,要先了解你的目标输出是什么。如果你打算在家里打印游戏,那就做一些计算,搞清楚默认的纸张大小(有些是 US Letter,或者是 A4)可以容纳多少卡牌、令牌或卡片。如果你使用 [TheGameCrafter](https://www.thegamecrafter.com/) 之类的桌游打印机打印,请下载好模板文件。

(Seth Kenlon, CC BY-SA 4.0)
### 游戏机制
游戏机制是游戏中最重要的部分。它们使一款游戏成为游戏。开发游戏规则并不一定是一个正式的过程。你可以一时兴起地创造了一款游戏,可以拿一个现有的游戏重组它的规则,直到它和原来不同,可以修改一款你不喜欢的游戏,也可以将两款不同的游戏组合在一起。从简单容易的地方做起,拿索引卡,标准扑克牌,或塔罗牌去试着模拟你的想象中游戏是如何工作的。你可以自己尝试早期的游戏创意,但最终,让朋友来帮忙是找出意外故障和进行优化的好方法。
经常测试游戏。与不同类型的玩家一起玩游戏,并听取他们的反馈。你的游戏可能会激发许多玩家去创造新的规则和想法,因此要将关于 *哪些搞砸了* 的反馈与关于 *哪些可以做修改* 的反馈分开。你不一定要去真的实施这些反馈意见,只需迭代你的想法,但还是要仔细考虑错误报告。
一旦确定了你想要让你的规则如何运作,就把它们写下来,让它们 [简短且容易解析](https://opensource.com/life/16/11/software-documentation-tabletop-gaming)。你定的规则不必说服玩家去玩这款游戏,不必向他们解释策略,你也不必允许玩家重新设置规则,只要告诉玩家为了让游戏玩起来,他们应该采取的步骤就可以了。
最重要的是,考虑一下,将你的规则开源。分享经验是游戏的一切,这其中也应该包括规则。知识共享或<ruby> 开放游戏许可证 <rt> Open Gaming License </rt></ruby>的规则集合允许其他玩家在你的作品上进行迭代、混合和构建。你永远不会知道,有人可能会因此想出一个你更喜欢的游戏变体!
### 开源游戏
开源不仅仅指的是软件。开源是一种文化现象,自然也适合桌面游戏。花几个晚上的时间来尝试制作游戏。如果你是新手,那就从一些简单的开始,比如下面的这个空白卡牌游戏:
1. 找来一些朋友。
2. 给每个人几张空白的索引卡,告诉他们在每张卡片上写一条规则。规则可以是任何东西(“如果你穿着红色衣服,你就赢了”或“第一个站起来的人赢”等等)。
3. 在你自己的索引卡片上,写上 “和”、“但是”、“但是不要”、“而且不要”、“除了”,以及其他的条件短语。
4. 洗牌并将牌发给所有玩家。
5. 每个玩家轮到的时候出一张牌。
6. 最终目标是获胜,但是玩家可以通过出 “和”、“但是”、“或者” 卡片来修改决定胜负的条件。
这是一个有趣的聚会游戏,同时是一份很好的介绍,告诉你如何像游戏设计者一样思考,它帮助你认识到什么适合作为游戏机制,什么不适合。
还有,当然的,这是开源的。
(题图片由 [MorningbirdPhoto](https://pixabay.com/zh/users/morningbirdphoto-129488/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=529586) 在 [Pixabay](https://pixabay.com/zh/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=529586) 上发布 )
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/12/open-source-card-game>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hadisi1993](https://github.com/hadisi1993) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | I love a good game, and I particularly enjoy tabletop games because they have many of the same traits that open source has. When you're playing a card game in real life with friends sitting around a table, you can as a group decide that Jokers are wild. Alternately, you could arbitrarily decide that should a Joker come into play, anyone holding an Ace must discard that Ace. Or when a Queen of Diamonds comes into play, everyone must pass their hand to the player on their right. In other words, you can reprogram the rules on a whim because a game is nothing but a mutually agreed-upon set of conditions. To me, what's even better is that you can invent your own games instead of hacking the rules of somebody else's game. From time to time, I do this as a hobbyist, and because I like to combine my hobbies, I tend to design games with only open source and open culture resources.
First of all, it's important to understand that there are, broadly, two facets of a game: *flavor* and *mechanics*. The flavor is the story and theme of the game. The mechanics of a game are the rules and the condition of play. The two aren't always completely separate from one another, and there's an elegance to designing a game themed around race cars, for instance, with rules that demand players to perform actions very quickly. However, the flavor and mechanics are just as often treated separately, and it's entirely reasonable to invent a game that *could* be played with a standard deck of poker cards, but that's themed around space llamas, just for the fun of it.
## Open source artwork
If you've ever gone to a museum of modern art, you've probably found yourself standing in front of a canvas painted solid blue and overheard somebody utter this time-honored phrase: "Heck, I could make that!" But the truth is, artwork is hard work. Making art that's pleasing to the eye takes a lot of thought, time, confidence, and skill, so it makes sense that the art is one of the most difficult things to procure for a game you're designing.
I have a few "hacks" on dealing with this classic snag.
### 1. Find common ground
There's free and open art out there, and a lot of it is very good. The problem is that games usually need more than one art piece. If you're designing a card game, you probably need at least four or six distinct elements (assuming your cards follow the foundations laid out by the Tarot deck) and possibly more. If you spend enough time on it, you can find [Creative Commons and Public Domain](https://opensource.com/article/20/1/what-creative-commons) artwork online on sites like [OpenGameArt.org](https://opensource.com/opengameart.org/), [FreeSVG.org](http://freesvg.org), [ArtStation.com](http://artstation.com), [DeviantArt.com](http://deviantart.com), and many others.
If the site you're using doesn't have a Creative Commons search, enter the following words into any search engine, "This work is licensed under a Creative Commons" (the quotes are important, so don't leave those off) and whatever syntax your favorite search engine uses to limit the search to just one site (for example, **site:deviantart.com**).
Once you have a pool of art to choose from, sort the art that you've found by identifying common themes in the artwork. Two pictures of robots by two different people might look nothing alike, but they're still both robots. Provided you have enough robot-themed art, you can structure the flavor of your game around robots.
### 2. Commission Creative Commons art
You can hire artists to make custom art for you. I work with artists who use open source paint programs like [Krita](https://opensource.com/article/21/12/krita-digital-paint) and Mypaint, and as part of the contract, I specify that the art must be licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share-alike (CC BY-SA) license. I've only ever had one artist decline the offer because of the license restriction, and most are happy for their artwork to have a potentially larger life than just as part of a hobbyist's self-published game.
### 3. Make your own
As a trip to the museum of modern art reveals, art is a very flexible term. I've found that as long as I give myself a goal of how many cards or tokens for a game I need to create, I can usually produce something with one of the many graphical creative tools available on Linux. It doesn't have to be anything fancy. Just like modern art, you can paint a card with blue and yellow stripes, another with red and white polka-dots, another with green and purple zig-zags, and nobody but you will ever know that you secretly meant for them to be the lords and ladies of the fairy court, except that you don't know how to draw those. Think about all the simple things you can create in a graphics application, or by tracing photographs of everyday objects, or by remixing classic Poker suits, or Tarot themes, and so on.
## Layout
I use [Inkscape](https://opensource.com/article/21/12/linux-draw-inkscape), Scribus, or [GIMP](https://opensource.com/content/cheat-sheet-gimp) for layout, depending on what my assets are and what manner of design I'm after.
For cards, I find that a simple layout is easy to do and look at, solid colors tend to print better than gradients, and intuitive iconography is best.
(Seth Kenlon, CC BY-SA 4.0)
I did the layout in a single Inkscape file for my latest game, which uses just nine images from three or four different artists on OpenGameArt.com. I design the layout of each card in its own file for games with a more extensive set of art and card variety.
Know your target output before you do any layout for your game assets. If you're going to print your game at home, then do the math and figure out how many cards or tokens or tiles you can fit on your default paper size (US Letter for some, A4 for everybody else). If you're printing with a game printer like [TheGameCrafter](https://www.thegamecrafter.com/), download the template files.

(Seth Kenlon, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Mechanics
Game mechanics are the most important part of a game. They're what makes the game a game. Developing rules for a game doesn't have to be a formal process. You can come up with a game on a whim, or take a game that exists and remix its rules until it's something different, fix a game that just doesn't work for you, or mash two different games together. Start simple, using index cards, standard playing cards, or a Tarot deck to mock up how you think your game will work. You can play early game ideas by yourself, but eventually, getting a friend to help is a great way to introduce surprise glitches and optimizations.
Playtest often. Play your game with a diverse set of players, and listen to their feedback. Your game might inspire many players to invent new rules and ideas, so separate feedback about what's *broken* from feedback about what *could be different*. You don't have to implement feedback that just iterates your idea, but give careful thoughts to the bug reports.
Once you've decided how you want your rules to work, write them down to make them [short and easy to parse](https://opensource.com/life/16/11/software-documentation-tabletop-gaming). Your rules don't have to convince players to play the game, you don't have to explain the strategy to them, nor do you need to give permission to players to remix the rules. Just tell the players the sequence of steps they need to take in order to make the game work.
Most importantly, consider making your rules open source. Gaming is all about shared experiences, and that ought to include the rules. A Creative Commons or Open Game License ruleset allows other gamers to iterate, remix, and build upon your work. You never know, somebody might come up with a variant that you enjoy more than your own!
## Open source gaming
Open source isn't just about software. It's a cultural phenomenon, a natural fit for tabletop games. Take a few evenings to experiment with creating a game. If you're new to it, start with something simple, like this blank card activity:
- Gather up some friends.
- Give each person a few blank index cards, and tell them to write a rule on each card. The rule can be anything ("If you're wearing something red, you win" or "The first person to stand up wins," and so on.)
- On your own index cards, write
*and*,*but*,*or*,*but not*,*and not*,*except*, and other conditional phrases. - Shuffle your deck and deal the cards to all players.
- Each player may play one card per turn.
- The goal is to win, but players may play the
*and*,*but*, and*or*cards to modify the conditions of what determines the winner.
It's a fun party game and a nice introduction to thinking like a game designer because it helps you recognize what tends to work as a game mechanic and what doesn't.
And, of course, it's open source.
## Comments are closed. |
14,552 | 一种新的开源嵌入式操作系统 | https://opensource.com/article/21/7/rt-thread-smart | 2022-05-06T13:19:00 | [
"嵌入式",
"RT-Thread",
"RT-Thread Smart"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14552-1.html |
>
> RT-Thread Smart 致力于物联网和边缘计算领域的开源。
>
>
>

目前对 [嵌入式操作系统](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/open-source-rtos) 有巨大的需求,你建立的操作系统最好是开源的。[RT-Thread](https://www.rt-thread.io/) 项目的研发团队花了两年时间,研发出了该项目的最新成果:RT-Thread Smart。这是一款微内核的操作系统,主要针对中高端的处理器,如具有内存管理单元(MMU)的 RISC-V 或 Arm Cortex-A,为嵌入式领域的所有行业提供了一个具有竞争力的、基于 POSIX 的软件平台。
### 谁需要 RT-Thread Smart?
RT-Thread Smart 是一款专业的、高性能的微内核操作系统,用于实时应用。它为所有市场的嵌入式设备提供了开源基础,如安全(IP 摄像头)、工业控制、车载设备、消费电子及其他嵌入式科技应用,可谓一切场景。它的意义在于:不像传统的物联网操作系统,一个微内核的操作系统可以填补传统实时操作系统 RTOS 和相对大型的操作系统如 Linux 之间的空白,实现实时性能、成本、安全、启动速度等等各方面之间的最佳平衡。
### RT-Thread Smart 的架构
RT-Thread Smart 通过 MMU 和系统调用将系统分割为内核模式和用户模式,并为每种模式区分了地址空间(一个 32 位系统可以提供 4G 地址空间)。

(RT-Thread, [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/legalcode))
RT-Thread Smart 内核包括平台的基础功能,并支持定制化。RT-Thread Smart 的用户应用环境使用 [musl libc](https://musl.libc.org/) 来提供 [POSIX](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/what-posix-richard-stallman-explains) 接口调用和 C 语言的运行时支持。它也继承了原始的 RT-Thread 生态系统,使用 [SCons](https://scons.org/) 或者其他编译工具如 [Autotools](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/introduction-gnu-autotools)、Makefile、[CMake](https://opensource.com/article/21/5/cmake) 等等来支持开发,以及 RT-Thread 开箱即用的在线软件包(撰写本文时超过 342 个)。你甚至可以将 Linux 应用程序(如 wget/cURL、BusyBox、OpenSSL 和 Simple DirectMedia Layer)移植到你的平台。
压缩的 RT-Thread Smart 内核仅 217 KB,搭配一个 127 KB 的根文件系统。大约 2 MB的存储占用。包括了对文件系统、网络协议栈、多媒体的完整支持。RT-Thread 只需要 3 到 5 秒完成启动,而在不运行其他功能组件时,RT-Thread Smart 需要的启动及准备时间不到 500ms。
通过其集成的 Persimmon 用户界面(UI)组件,RT-Thread Smart 从上电到运行 UI 需要大约 1 秒。换句话说,这是一个非常轻巧快速的系统。当然,“实时”不是指启动,而是指系统随着时间推进而表现出的一致性。对于 RT-Thread ,实时性能需要优先考虑,中断时延小于 1μs,满足大部分实时性要求严格的场景需求。
### RT-Thread Smart 和 RT-Thread
你可能想知道 RT-Thread Smart 和 RT-Thread 之间的不同。简单来说, RT-Thread Smart 是一个基于 RT-Thread RTOS 的操作系统,但它整合了用户态的处理过程。RT-Smart 的内核部分本质上是 RT-Thread RTOS,它在虚拟地址上运行,增加了进程管理,使用进程间通信机制(IPC)、虚拟内存/地址空间管理、ELF 加载器等等,以上特性全部在 RT-Thread RTOS 内实现,当这些组件被禁用时,RT-Smart 会回归 RT-Thread RTOS。
以下是对比:
| | RT-Thread | RT-Thread Smart |
| --- | --- | --- |
| 支持芯片 | Cortex-M/R、RISC-V RV32IMAC(以及类似)、Cortex-A MPU | Cortex-A 等具有 MMU 的 MPU |
| 编译 | 内核和应用都编译到一个镜像 | 内核和应用可以被分开编译和运行 |
| 存储 | 使用线性地址空间(即使有 MMU),使用物理地址的虚拟寻址 | 运行在内核占用超过 1GB 的 32 位操作系统,拥有完整 4G 地址空间的用户态进程彼此隔离,外设驱动程序必须通过虚拟地址访问外设 |
| 运行错误 | 当一个应用程序失败时,整个系统就会崩溃 | 当应用程序失败时,它不会影响内核和其他进程的执行 |
| 运行模式 | 多线程模型 | 多进程模型(进程内支持多线程,内核线程由内核支持) |
| 用户模型 | 单用户模型 | 单用户模型 |
| API | RT-Thread API、POSIX PSE52 | RT-Thread API(内核态和用户态),以及完整的 POSIX API |
| 实时性 | 抢占式硬实时系统 | 抢占式硬实时系统 |
| 资源使用 | 非常小 | 相对小 |
| 调试 | 通常需要模拟器调试 | 支持 GDB 调试,不需要模拟器 |
RT-Thread RTOS 非常紧凑,它的所有应用和子系统都编译到镜像中,多线程应用运行并分享相同的地址空间。
RT-Thread Smart 是独立的。系统和应用是分别编译和运行的。应用拥有完整且互相隔离的地址空间。它也继承了 RT-Thread 优秀的实时性,同时也具有 POSIX 环境的特性。
类似地,它们都与 RT-Thread API 兼容。RT-Thread RTOS 的应用可以被平滑移植到 RT-Thread Smart。
### 嵌入式开源
RT-Thread Smart 是一个开源项目,项目地址:[GitHub](https://github.com/RT-Thread/rt-thread/tree/rt-smart)。你可以下载代码和文档,尝试一下,并提交评论和反馈,将该项目传播给更多开源倡导者。嵌入式系统属于它们的用户,有太多的嵌入式开发人员没有找到太多可用的嵌入式系统。
如果你是开发人员,请帮助改进 RT-Thread Smart。随着 RT-Thread 项目的不断推进,我们希望创建物联网和边缘计算的令人激动的开源世界。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/7/rt-thread-smart>
作者:[Zhu Tianlong](https://opensource.com/users/zhu-tianlong) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[tendertime](https://github.com/tendertime) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | There's a growing demand for [embedded operating systems](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/open-source-rtos), and it's best when the one you build upon is open source. The [RT-Thread](https://www.rt-thread.io/) project's R&D team has spent two years of research and intensive development to arrive at the project's latest offering: RT-Thread Smart. It is a microkernel operating system aimed primarily at midrange to high-end processors such as RISC-V or Arm Cortex-A that with a memory management unit (MMU) and provides a competitive and [POSIX](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/what-posix-richard-stallman-explains)-based software platform for all industries in the embedded space.
## Who needs RT-Thread Smart?
RT-Thread Smart is a professional, high-performance, microkernel operating system for real-time applications. It offers an open source foundation for embedded devices in any market, including security (e.g., internet protocol cameras), industrial control, onboard devices, consumer electronics, and anything else using embedded technology (which is increasingly coming to mean "everything"). It's significant because, unlike traditional IoT operating systems, a microkernel operating system can fill the gap between a traditional real-time operating system (RTOS) and a comparatively large operating system like Linux to achieve the best balance between real-time performance, cost, security, startup speed, and more.
## RT-Thread Smart's architecture
RT-Thread Smart splits a system into kernel space and user space by taking advantage of the MMU and system call methods. It then divides the address space for each mode (a 32-bit system provides 4G address space).
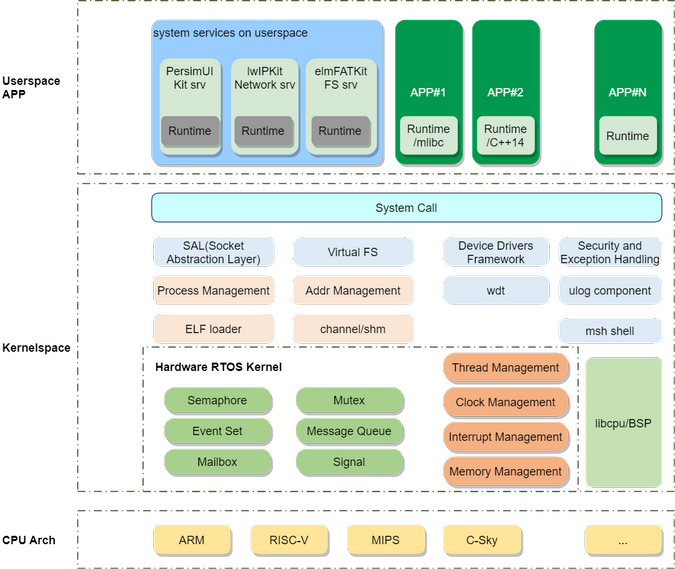
(RT-Thread, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The RT-Thread Smart kernel includes the platform's basic functionality and supports customizations. RT-Thread Smart's userspace application environment uses [musl libc](https://musl.libc.org/) to provide [POSIX](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/what-posix-richard-stallman-explains) interface calls and C runtime supports. It also inherits the original RT-Thread ecosystem, using [SCons](https://scons.org/) or other build tools such as [Autotools](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/introduction-gnu-autotools), Makefiles, [CMake](https://opensource.com/article/21/5/cmake), and so on to support development, as well as RT-Thread's out-of-the-box online software packages (over 342 at the time of this writing). You can even port Linux applications, such as wget/cURL, BusyBox, OpenSSL, and Simple DirectMedia Layer, to your platform.
The compressed RT-Thread Smart kernel is just 217KB, with a root filesystem of 127KB. Typical memory usage is about 2MB.
Including full support for filesystems, network protocol stacks, and multimedia, it takes only three to five seconds for RT-Thread to finish its startup process. Without running or loading complex user applications, RT-Thread Smart requires less than 500ms to start and be ready.
With its integrated Persimmon user interface (UI) component, the time it takes from power-on to a running UI is about one second. In other words, this is a seriously tiny and fast system. Of course, "real time" isn't about startup but how the system performs consistently over time. For RT-Thread, real-time performance is a priority, and the interrupt latency is less than 1 μs, which meets most application cases with the strictest real-time requirements.
## RT-Thread Smart vs. RT-Thread
You might be wondering about the differences between RT-Thread Smart and RT-Thread. Simply put, RT-Thread Smart is an RT-Thread RTOS-based operating system, but it integrates the user-space process. The kernel part of RT-Smart is essentially RT-Thread RTOS; it runs on virtual addresses, adds process management, and uses interprocess communication mechanisms, virtual memory/address space management, ELF loaders, and so on, and it makes all of these features components within RT-Thread RTOS. When the components are disabled, RT-Smart falls back onto RT-Thread RTOS.
Here's a comparison:
RT-Thread | RT-Thread Smart | |
---|---|---|
Supported chips | Cortex-M/R, RISC-V RV32IMAC (and similar), Cortex-A MPU | MPU with MMU, such as ARM Cortex-A and RISC-V |
Compiling | The kernel and application are compiled into an image program. | The kernel and application can be separately compiled and executed. |
Memory | Runs on a linear address space (even with MMU) and uses virtual addressing with the physical address | Runs on a 32-bit system with the kernel running on more than 1GB, the user-space process that has full 4G address spaces are isolated from each other. Peripheral drivers must access peripherals with virtual addresses. |
Running errors | When an application fails, the overall system collapses. | When an application fails, it does not affect kernel and other process execution. |
Running model | Multi-thread model | Multiprocess model (multithread is supported within the process, and kernel threads are supported by the kernel) |
User model | Single-user model | Single-user model |
API | RT-Thread API, POSIX PSE52 | RT-Thread API (on kernel and userspace), plus a full POSIX API |
Real time | Preemptive hard real-time system | Preemptive hard real-time system |
Resource utilization | Very small | Relatively small |
Debugging | Generally debugged through the emulator | Supports GDB debugging and no emulator required |
RT-Thread RTOS is very compact. All applications and subsystems are compiled into the image, and multi-thread applications run and share the same address space.
RT-Thread Smart is independent. Systems and applications are separately compiled and executed. Applications have a full address space and are kept isolated from each other. It also inherits all the great real-time features of RT-Thread and features a POSIX environment.
Similarly, they're both compatible with the RT-Thread API, so applications on RT-Thread RTOS can be smoothly ported to RT-Thread Smart.
## Embed open source
RT-Thread Smart is an open source project, with its code available on [GitHub](https://github.com/RT-Thread/rt-thread/tree/rt-smart). You can download the code and its documentation, give it a try, submit comments and feedback, and help spread it to more open source advocates. Embedded systems should belong to their users, and there are too many embedded developers out there who don't realize what's available.
If you're a developer, help hack on RT-Thread Smart! As the RT-Thread project continues to advance, we aim to make the exciting worlds of IoT and edge computing open source.
## Comments are closed. |
14,553 | 面向 Java 开发人员的 JVM 参数指南 | https://opensource.com/article/22/4/jvm-parameters-java-developers | 2022-05-06T13:47:03 | [
"JVM",
"Java"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14553-1.html | 
>
> 通过理解和使用 JVM 以及 JVM 参数,开发人员和最终用户都可以诊断故障并且提高 Java 应用程序的性能。
>
>
>
当你在编写源代码时,你是在编写人类可以阅读的代码。在将代码编译成机器语言之前,计算机无法执行它。机器语言是一个通用术语,指的是特定机器所需的任意数量的语言。通常,如果你在 Linux 上编译代码,它只能 Linux 上运行;如果你在 Windows 上编译代码,它就只在 Windows 上运行。但是,Java 是不同的,它并不以真实的机器为目标,而是面向 <ruby> Java 虚拟机 <rt> Java Virtual Machine </rt></ruby>(JVM)。因此,它可以在任何机器上运行。
Java 源代码被编译成<ruby> 字节码 <rt> bytecode </rt></ruby>,然后由安装在计算机上的 JVM 运行。JVM 是一个执行引擎,但我们通常不会直接与它交互。它在后台静默运行,替我们处理 Java 字节码。大多数人不需要考虑,甚至也不需要知道 JVM。但是,了解它的工作原理是对我们来说是非常有用的,因为这会有助于我们调试和优化 Java 代码。例如:
* 在生产环境中,你发现已经部署的应用程序可能需要提升性能。
* 如果你写的应用程序出错了,开发人员和最终用户都可以选择对问题进行调试。
* 如果你想了解关于 JDK(即 <ruby> Java 开发工具包 <rt> Java Development Kit </rt></ruby>,用于开发/运行 Java 应用程序)的详细信息,你可以通过查询 JVM 来获取。
本文介绍了一些基础的 JVM 参数,希望在这些场景中可以提供帮助。

(图源:Jayashree Huttanagoudar,CC BY-SA 4.0)
### JVM、JDK 和 JRE 有什么不同?
Java 有许多 J 开头的缩略词,包括 JVM、JDK 和 JRE。
* <ruby> Java 开发工具包 <rt> Java Development Kit </rt></ruby>(JDK)可供需要在代码中使用开发库的程序员使用。
* <ruby> Java 运行时环境 <rt> Java Runtime Environment </rt></ruby>(JRE)可供想运行 Java 应用程序的人使用。
* <ruby> Java 虚拟机 <rt> Java Virtual Machine </rt></ruby>(JVM)是运行 Java 字节码的组件。
JDK 同时包含 JRE 和 JVM,但有些 Java 发行版提供了包含 JRE(包括 JVM)的替代下载。

(图源:Jayashree Huttanagoudar,CC BY-SA 4.0)
Java 是开源的,因此,许多不同的公司都会构建和发行他们自己的 JDK 发行版。你可以在系统上安装多个 JDK,这会对你参与或者运行不同的 Java 项目时很有帮助,因为其中一些项目可能使用旧版本的 JDK。
你可以使用 `alternatives` 命令,来查看 Linux 系统上的 JDK 列表:
```
$ alternatives --config java
There are 2 programs that provide java.
Selection Command
-----------------------------------------------
*+ 1 java-11-openjdk.x86_64 (/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-11.0.13.0.8-2.fc35.x86_64/bin/java)
2 java-1.8.0-openjdk.x86_64 (/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.312.b07-2.fc35.x86_64/jre/bin/java)
Enter to keep the current selection[+], or type selection number:
```
如果想要在可用的 JDK 之间进行切换,请再次执行该命令:
```
$ sudo alternatives --config java
```
或者可以使用 [SDKMan](https://opensource.com/%5Bhttps%3A//opensource.com/article/22/3/manage-java-versions-sdkman%5D%28https%3A//opensource.com/article/22/3/manage-java-versions-sdkman%29),它可以下载、更新和管理系统中的所有 JDK。
### 什么是 JVM 调优?
JVM 调优指的是,通过调整 JVM 参数,来提高 Java 应用程序性能的过程,它还有助于诊断应用程序的故障。
通常情况下,在调试之前需要考虑以下几点:
* **成本**:有时改进运行代码的硬件可以提高应用程序的性能。这可能看起来像是在“作弊”,但请考虑你愿意花多少时间调整 JVM 参数。有时应用程序需要更多的内存来执行所需的功能,而这点是任何软件技术都无法改变的。
* **期望结果**:长期来看,稳定性比性能更重要。如果你的调优对稳定性产生了影响,那么谨慎地选择你的调优参数可能会更好。
* **底层问题**:有时,问题可能是主机操作系统的底层问题。那么,在调整 JVM 之前,请确保 JVM 平台按预期工作。
* **内存泄漏**:如果你在使用垃圾回收(GC)调优参数,那么,应用程序代码中很可能会存在需要修复的内存泄漏。
### 参数类型
JVM 参数可以分为以下三类:标准参数、非标准参数和高级选项。
#### 标准参数
所有的 JVM 实现都支持标准参数,在终端执行 `java` 命令来查看标准参数列表:
```
$ java
Usage: java [options] <mainclass> [args...]
(to execute a class)
or java [options] -jar <jarfile> [args...]
(to execute a jar file)
where options include:
-cp <class search path of directories and zip/jar files>
-classpath <class search path of directories and zip/jar files>
--class-path <class search path of directories and zip/jar files>
A : separated list of directories, JAR archives,
and ZIP archives to search for class files.
--enable-preview
allow classes to depend on preview features of this release
To specify an argument for a long option, you can use --<name>=<value> or
--<name> <value>.
```
这些是所有 JVM 都会包含的标准参数,你可以像使用任何 [命令行选项](https://opensource.com/%5Bhttps%3A//opensource.com/article/21/8/linux-terminal%5D%28https%3A//opensource.com/article/21/8/linux-terminal%29) 一样安全地使用它们。例如,要验证配置的命令选项,创建 VM 并加载主类而不执行主类,请使用:
```
$ java --dry-run <classfile>
```
#### 非标准参数
非标准选项以 `-X` 开头。这些是通用的,并且特定于 JVM 的特定实现。要列出这些参数,请输入:
```
$ java -X
-Xbatch disable background compilation
-Xbootclasspath/a:<directories and zip/jar files separated by :>
append to end of bootstrap class path
-Xinternalversion
displays more detailed JVM version information than the
-version option
-Xloggc:<file> log GC status to a file with time stamps
[...]
```
在这些参数可能会不经通知就发生变化。而且,并非所有 JVM 实现都支持这些参数。
微软构建的 JVM 可能与 RedHat 构建的 JVM 有不同的参数,诸如此类。
要获取详细的 JVM 版本信息,请使用如下命令:
```
$ java -Xinternalversion --version
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (11.0.13+8) for linux-amd64 JRE (11.0.13+8), built on Nov 8 2021 00:00:00 by "mockbuild" with gcc 11.2.1 20210728 (Red Hat 11.2.1-1)
```
要获取这些属性设置,请使用:
```
$ java -XshowSettings:properties --version
```
#### 高级选项
这些参数不是随意使用的,而是用于调整 Hotspot VM 的特定区域。这些参数可能会发生变化,并且不能保证得到所有 JVM 实现的支持。
这些参数以 `-XX` 开头。如需列出参数列表,使用如下命令:
```
$ java -XX:+UnlockDiagnosticVMOptions -XX:+PrintFlagsFinal -version
```
例如,需要跟踪类的加载,那么使用下面的命令:
```
$ java -XX:+TraceClassLoading Hello
```
在 `Hello.java` 中:
```
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Inside Hello World!");
}
}
```
另一个可能会面临的问题是 OOM(<ruby> 内存超出 <rt> Out Of Memory </rt></ruby>)错误,它发生的时候可能没有太多的调试信息。为了解决这个问题,使用调试参数 `-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError`,它可以创建一个带有调试信息的 `.hprof` 文件。
```
// TestClass.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class TestClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<Object>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
list.add(new char[1000000]);
}
}
}
```
```
$ Javac TestClass.java
$ java -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -Xms10m -Xmx1g TestClass
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: java heap space
Dumping heap to java_pid444496.hprof ...
Heap dump file created [1018925828 bytes in 1.442 secs]
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: java heap space
at TestClass.main(TestClass.Java:8)
```
[有一些工具](https://opensource.com/%5Bhttps%3A//docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/tools/share/jhat.html%5D%28https%3A//docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/tools/share/jhat.html%29) 可以查看这个 `.hprof` 文件以了解问题所在。
### 总结
通过了解和使用 JVM 以及 JVM 参数,开发人员和终端用户都可以诊断故障并提高 Java 应用程序的性能。下次使用 Java 时,请花点时间看看有哪些参数可以用吧!
(题图由 [Seksak Kerdkanno](https://pixabay.com/zh/users/kerdkanno-1334070/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=5959810) 在 [Pixabay](https://pixabay.com/zh/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=5959810) 上发布 )
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/4/jvm-parameters-java-developers>
作者:[Jayashree Huttanagoudar](https://opensource.com/users/jayashree-huttanagoudar) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Veryzzj](https://github.com/Veryzzj) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When you write source code, you're writing code for humans to read. Computers can't execute source code until the code is compiled into *machine language*, a generic term referring to any number of languages required by a specific machine. Normally, if you compile code on Linux, it runs on Linux, and if you compile code on Windows, it runs on Windows, and so on. However, Java is different. It doesn't target an actual machine. It targets something called the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), and so it can run on any machine.
Java source code gets compiled into bytecode which is run by a JVM installed on a computer. The JVM is an execution engine, but it's not one you usually interact with directly. It runs quietly, processing Java bytecode. Most people don't need to think or even know about the JVM, but it can be useful to understand how the JVM works so you can debug and optimize Java code. For example:
-
In the production environment, you might find a deployed application needs a performance boost.
-
If something goes wrong in an application you've written, both the developer and end-user have options to debug the problem.
-
Should you want to know the details of the Java Development Kit (JDK) being used to develop or run a Java application, you can get those details by querying the JVM.
This article introduces some basic JVM parameters to help in these scenarios…
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar CC BY-SA 4.0)
## What's the difference between a JVM, JDK, and JRE?
Java has a lot of J-acronyms, including JVM, JDK, and JRE.
-
A Java Developer Kit (JDK) is accessed by programmers who need development libraries to use in their code.
-
The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is employed by people who want to run a Java application.
-
The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is the component that runs Java bytecode.
The JDK contains both a JRE and a JVM, but some Java distributions provide an alternate download containing a JRE (including a JVM).
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar CC BY-SA 4.0)
Java is open source, so different companies build and distribute JDKs. You can install more than one on your system, which can be helpful when you're working on or using different Java projects, some of which might use an old JDK.
To list the JDKs on your Linux system, you can use the alternatives command:
```
``````
$ alternatives --config java
There are 2 programs that provide java.
Selection Command
-----------------------------------------------
*+ 1 java-11-openjdk.x86_64 (/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-11.0.13.0.8-2.fc35.x86_64/bin/java)
2 java-1.8.0-openjdk.x86_64 (/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.312.b07-2.fc35.x86_64/jre/bin/java)
Enter to keep the current selection[+], or type selection number:
```
To switch between available JDKs, run the command again:
```
````$ sudo alternatives --config java`
Another option is to use [SDKMan](https://opensource.com/%5Bhttps%3A//opensource.com/article/22/3/manage-java-versions-sdkman%5D%28https%3A//opensource.com/article/22/3/manage-java-versions-sdkman%29), which helps you download, update, and manage the JDKs on your system.
## What is JVM tuning?
Tuning a JVM is the process of adjusting JVM parameters to improve the performance of the Java application. It also helps to diagnose application failure.
In general, it's important to consider these points before tuning:
-
**Cost**: Sometimes, improving the hardware running your code can improve an application's performance. That might seem like a "cheat" but consider how much time you're willing to spend tuning the JVM parameters. Sometimes, an application requires more memory to perform as desired, and no amount of software hacking will change that. -
**Desired Outcome**: Stability is more important than performance in the long run. If your tuning affects the stability, it's probably better to wisely choose your tuning parameters. -
**Underlying issues**: Sometimes, the issue could be an underlying issue with the host operating system. Before tuning the JVM, ensure that the JVM's platform is working as expected. -
**Memory leaks**: If you find yourself using Garbage Collection (GC) tuning parameters, there are likely memory leaks that need to get fixed in the application code.
## Types of JVM Parameters
JVM parameters are grouped under three categories: Standard options, Non-standard, and Advanced.
### Standard options
All JVM implementations support standard options. Run the 'java' command in a terminal to see a list of standard options.
```
``````
$ java
Usage: java [options] <mainclass> [args...]
(to execute a class)
or java [options] -jar <jarfile> [args...]
(to execute a jar file)
where options include:
-cp <class search path of directories and zip/jar files>
-classpath <class search path of directories and zip/jar files>
--class-path <class search path of directories and zip/jar files>
A : separated list of directories, JAR archives,
and ZIP archives to search for class files.
--enable-preview
allow classes to depend on preview features of this release
To specify an argument for a long option, you can use --<name>=<value> or
--<name> <value>.
```
These are all standard options included with any JVM, and you can safely use them as you use any [command-line option](https://opensource.com/%5Bhttps%3A//opensource.com/article/21/8/linux-terminal%5D%28https%3A//opensource.com/article/21/8/linux-terminal%29). For example, to validate command options for configuration, and create a VM and load a main class without executing the main class, use:
```
````$ java --dry-run <classfile>`
### Non-standard options
Non-standard options start with `-X`
. These are for general purpose use and are specific to a particular implementation of JVM. To list these options:
```
``````
$ java -X
-Xbatch disable background compilation
-Xbootclasspath/a:<directories and zip/jar files separated by :>
append to end of bootstrap class path
-Xinternalversion
displays more detailed JVM version information than the
-version option
-Xloggc:<file> log GC status to a file with time stamps
[...]
```
These extra options are subject to change without notice and are not supported by all JVM implementations.
A JVM built by Microsoft may have different options than one built by Red Hat, and so on.
To get detailed JVM version information, use the following option:
```
``````
$ java -Xinternalversion --version
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (11.0.13+8) for linux-amd64 JRE (11.0.13+8), built on Nov 8 2021 00:00:00 by "mockbuild" with gcc 11.2.1 20210728 (Red Hat 11.2.1-1)
```
To get the property setting use:
```
````$ java -XshowSettings:properties --version`
### Advanced options
These options are not for casual use and are used for tuning the specific areas of the Hotspot VM. These options are subject to change, and there is no guarantee that all JVM implementations will support it.
These options start with -XX. To list these options, use the following command:
```
````$ java -XX:+UnlockDiagnosticVMOptions -XX:+PrintFlagsFinal -version`
For example, to trace the class loading then use the below command:
```
````$ java -XX:+TraceClassLoading Hello`
The Hello.java has:
```
``````
$ cat Hello. java
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Inside Hello World!");
}
}
```
Another common problem you might face is OOM (Out Of Memory) errors, which can happen without much debug information. To solve such a problem, you might use the debug option -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError, which creates a .hprof file with debug information.
```
``````
$ cat TestClass. java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class TestClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<Object>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
list.add(new char[1000000]);
}
}
}
$ Javac TestClass.java
$ java -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -Xms10m -Xmx1g TestClass
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: java heap space
Dumping heap to java_pid444496.hprof ...
Heap dump file created [1018925828 bytes in 1.442 secs]
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: java heap space
at TestClass.main(TestClass.Java:8)
```
[There are tools](https://opensource.com/%5Bhttps%3A//docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/tools/share/jhat.html%5D%28https%3A//docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/tools/share/jhat.html%29) to look at this .hprof file to understand what went wrong.
## Conclusion
By understanding and using JVM and JVM parameters, both developers and end users can diagnose failures and improve the performance of a Java application. The next time you're working with Java, take a moment to look at the options available to you.
## Comments are closed. |
14,555 | Firefox 100 发布:带来诸多有趣更新,纪念 17 年的发展历程 | https://news.itsfoss.com/firefox-100-release/ | 2022-05-07T08:41:08 | [
"Firefox"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14555-1.html |
>
> Mozilla Firefox 100 是一个重要的版本,它标志着这个浏览器 17 年的发展,以及多年来所有令人兴奋的功能。
>
>
>

Firefox 可以说是最受欢迎的不基于 Chrome 的开源浏览器,它可用于 Linux、Windows 和 Mac。
众所周知,目前,基于 Chrome 的浏览器在市场份额中占主导地位。但你可能不知道的是,Firefox 早在谷歌 Chrome 出现之前就已经问世了。
准确地说,Firefox 100 的发布标志着,它自 2004 年的发展历程已经有 17 年了。
时间过得好快,一切仿佛就发生在昨天。
### Firefox 100:更新内容

不管你是否喜欢 Firefox 新的发展计划,你都不得不承认,它多年来引入了众多行业领先的功能/技术,这一点令人印象深刻。
Firefox 100 的发布是一个重要的里程碑。但是,这并不是一次大规模升级。
本文中,我将介绍这个版本的主要改进。
#### “画中画”模式改进

现在,在“画中画”模式下观看 YouTube、Prime Video 和 Netflix 上的任何内容,Firefox 都支持视频字幕。
你只需要在相应的平台上启用视频字幕,它就会继续出现在“画中画”中。
“画中画”字幕不仅支持主流平台,还支持 Coursera 等使用 WebVTT 格式的网站。
#### 语言检测
为了改善用户体验,Firefox 现在可以检测到语言与操作系统偏好不符的情况。
这只会在你安装浏览器后,第一次运行时触发。你可以在系统语言和浏览器默认语言之间进行选择。
#### 滚动条默认不占用屏幕空间
Linux 和 Windows 11 的滚动条默认不会占用你宝贵的屏幕空间。换句话说,当你进行滚动或导航时,滚动条才会做出反应。

你可以在设置中改变这一点(针对 Linux 用户)。如果你是在 Windows 上,Firefox 的视觉效果会跟随你的系统设置。因此,你需要对 Firefox 浏览器进行调整,以符合你自己的偏好。
#### 控制网站外观

对于某些网站,你的浏览器偏好会影响网页的颜色/外观。
为了调整这类网站的体验,你现在可以在设置中设置网站外观偏好,选择浅色/深色、系统或 Firefox 主题。
#### HDR 视频 & 硬件加速的 AV1 视频解码
尽管,对一些用户来说,支持 HDR 视频可能不是什么大事。但我还是要指出,现在 Mac 上的 Firefox 也支持 HDR 了。
截至目前,官方支持仅限于在 macOS 11+ 上浏览 YouTube 网站。当然,你还需要一个支持 HDR 的屏幕。
硬件加速的 AV1 视频解码终于在 Windows 上得到支持,当然,你还得有与之兼容的 GPU(包括英特尔 11 代、AMD RDNA 2 和 GeForce 30 系列)。除此之外,Firefox 在 Windows 上还启用了视频叠加功能,以减少电量使用。
不幸的是,这些并不是针对 Linux 的更新,但应该能帮助跨平台的 Firefox 用户。
#### 其他改进
除了主要的亮点之外,它还包括了以下改进:
* 增加了对多个 Java 线程的分析支持。
* 软重载一个网页将不再导致所有资源的重新验证。
* 有了一个新的链接焦点指示器,它用一个实心的蓝色轮廓取代了旧的点状轮廓。
你可以在 [官方发布说明](https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/100.0/releasenotes/) 中了解更多技术变化。
### 获取 Firefox 100
你可以从它的官网上下载,也可以寻找可用的更新,应该很快就能下载完成。
>
> **[Mozilla Firefox 100](https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/download/)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/firefox-100-release/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/%E6%A0%A1%E5%AF%B9%E8%80%85ID)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Firefox is arguably the most popular open-source browser that’s not based on Chrome, available for Linux, Windows, and Mac.
While we know that Chrome-based browsers dominate the market share, Firefox was introduced way before Google Chrome came into existence.
To be accurate, Firefox 100 release marks 17 years of development effort since 2004.
It still feels like yesterday, right?
## Firefox 100: What’s New?

It does not matter whether you love/hate Firefox’s new development plans, the fact that it introduced numerous industry-leading features/technology over the years is impressive.
Firefox 100 release hits an important milestone. But, it is not a massive upgrade.
Here, I shall highlight the key improvements with this release:
### Improvements to Picture-in-Picture Mode

Whenever you watch anything on YouTube, Prime Video, and Netflix in Picture-in-Picture mode, Firefox now supports captions/subtitles for it.
You just need to enable the captions/subtitles for the video in the respective platform and it will continue to appear in PiP.
The support for captions in PiP is not limited to mainstream platforms but also on websites like Coursera that use WebVTT format.
### Language Detection
To improve the user experience, Firefox now detects when the language does not match the operating system preferences.
This only happens when you first run the browser after installation. So, you can choose between the system’s language or the browser’s default.
### Scrollbars Don’t Take Space by Default
The scrollbars on Linux and Windows 11 won’t take your precious screen space by default. In other words, they will be responsive and collapse when you’re focused on scrolling or navigating.

You can change this in the Settings (for Linux users). Firefox follows your system setting for visual effects if you are on Windows. So, you would need to tweak that for Firefox to honor your preferences.
### Control Website Appearance
For some websites, your browser preferences influence the color/appearance of the web page.
To tweak the experience for such websites, you now can set a website appearance preference in the Settings to choose light/dark, system, or Firefox theme.
### HDR Video and Hardware Accelerated AV1 Video Decoding
HDR Video support may not be a big deal for everyone. But, it is now supported in Firefox on Mac.
The official support exists for YouTube as of now with macOS 11+. Of course, you need an HDR-compatible screen as well.
The hardware-accelerated AV1 video decoding is finally supported on Windows with compatible GPUs (including Intel’s 11th Gen, AMD RDNA 2, and GeForce 30 series). In addition to this, video overlay is also enabled on Windows, reducing power usage.
Unfortunately, these aren’t Linux-specific updates but should help the Firefox users across multiple platforms.
### Other Improvements
In addition to the major highlights, the changes include:
- Support for profiling multiple java threads has been added.
- Soft-reloading a web page will no longer cause revalidation for all resources.
- Firefox has a new focus indicator for links, which replaces the old dotted outline with a solid blue outline.
You can learn more about the technical changes in the [official release notes](https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/100.0/releasenotes/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Get Firefox 100
You can download it from its official website or look for an update available, it should be a quick download.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,556 | elementary OS 7 公布了它的代号 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/elementary-os-7-announcement/ | 2022-05-07T08:57:15 | [
"elementary OS"
] | /article-14556-1.html |
>
> 在今天早些时候的一篇博文中,创始人兼首席执行官 Daniella Fore 公布了 elementary OS 7 的发行说明和计划更新。
>
>
>

### elementary OS 7 公告
elementary OS 7 的代号是 “Horus”,它将基于 [Ubuntu 22.04 LTS](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/01/ubuntu-22-04-lts/)。这个版本的开发已经接近尾声,团队正在修复一些涉及窗口管理器和其他领域的关键回归测试问题。
首先,功能方面,elementary OS 7 得到了来自 **Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 的最新软件包和升级**。此外,**Flatpak 运行时更新、Granite 7、样式表和图标更新** 预计将在这个发行版的第 7 个版本中出现。它将会基于 [Linux 5.15.x 内核](https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/11/linux-kernel-5-15/)。
其次,应用商店中的软件将会获得 **软件自动更新功能** 和新的 **笔记本电脑的电源配置文件选项**。预计电源配置文件将遵循传统的“<ruby> 平衡 <rt> Balanced </rt></ruby>”、“<ruby> 性能 <rt> Performance </rt></ruby>”和“<ruby> 节能 <rt> Power Saver </rt></ruby>”选项,就像其他 Linux 发行版一样。
此外,一个 **新的漂亮的音乐应用程序** 将在这个版本中首次亮相,它重新设计了一些图标,在桌面上的视觉效果也有提升。一些原生的应用商店中的软件已经使用了 GTK4 技术,在 Elementory OS 7 中,它们将会给用户带来流畅的性能体验。
#### 新的升级工具
但这还不是全部。团队还兴奋地宣布,一个 elementary **版本升级工具** 的可用原型已经准备就绪,目前正在测试。因此,在 elementary OS 7 发布后,它将正式亮相,以帮助用户实现从 elementary OS 6 到 7 的迁移。
目前,elementary OS 的版本升级是最大的挑战,因为它没有任何官方的升级途径。“版本升级工具” 是一个令人兴奋的消息,它将吸引更多的用户使用这个漂亮的 Linux 发行版。
不过,Wayland 迁移仍在计划之中,还没有被优先考虑。当 Wayland 被完整支持后,elementary OS 用户将会获得令人兴奋的体验。
### 发布日期?
对于任何一个 elementary OS 发行版,用户最关心的问题都是发布日期。嗯,发布日期还没有最终确定。elementary OS 7 “Horus” 将在准备好后发布。我乐观的猜测是在今年年底,在 Ubuntu 22.04 的第一个点发布(预计在 2022 年 7 月)之后。
最后,请阅读 elementary OS 7 [官方公告](https://blog.elementary.io/updates-for-april-2022/),了解更多关于这个版本的信息,以及 elementary OS 6 “Odin”(6.1 版本)的许多更新。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/elementary-os-7-announcement/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,557 | 使用 watch 和 tail 命令监视 Linux 上的活动 | https://www.networkworld.com/article/3529891/watching-activity-on-linux-with-watch-and-tail-commands.html | 2022-05-07T09:17:45 | [
"watch",
"tail"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14557-1.html | 
>
> watch 和 tail 命令可以帮助监视 Linux 系统上的活动。本文介绍了这两个命令的一些有用的使用方法。
>
>
>
`watch` 和 `tail` 命令为持续监视 Linux 系统上的活动提供了一些有趣的选项。
也就是说,你可以通过 `watch` 来显示谁已登录,并随着用户登录和注销不断更新,而不是仅仅提出问题并获得答案(例如询问 `who` 并获取当前登录用户的列表)。
使用 `tail`,你可以显示文件的底部并在添加内容时查看内容。这种监控一般非常有用,并且比定期运行命令所需的工作更少。
### 使用 watch 命令
使用 `watch` 的最简单示例之一是使用命令 `watch who`。你会看到一个列表,其中显示了谁登录了,以及他们登录的时间和登录位置。请注意,默认设置是每两秒更新一次显示(左上角),日期和时间(右上角)将按该间隔自行更新。用户列表将随着用户登录和注销而增长和缩小。
```
$ watch who
```
此命令将显示如下所示的登录列表:
```
Every 2.0s: who dragonfly: Thu Feb 27 10:52:00 2020
nemo pts/0 2020-02-27 08:07 (192.168.0.11)
shs pts/1 2020-02-27 10:58 (192.168.0.5)
```
你可以通过添加 `-n` 选项(例如 `-n 10`)来修改更新间的不同秒数,以修改更新间隔,从而获取较少的更新频率。
```
$ watch -n 10 who
```
上述命令将以新的间隔显示,并且显示的时间更新频率较低,从而使显示时间与所选间隔保持一致。
```
Every 10.0s: who dragonfly: Thu Feb 27 11:05:47 2020
nemo pts/0 2020-02-27 08:07 (192.168.0.11)
shs pts/1 2020-02-27 10:58 (192.168.0.5)
```
如果你希望仅查看命令的输出,而不是标题(前 2 行),则可以通过添加 `-t`(无标题)选项来省略这些行。
```
$ watch -t who
```
然后,你的屏幕将显示如下所示:
```
nemo pts/0 2020-02-27 08:07 (192.168.0.11)
shs pts/1 2020-02-27 10:58 (192.168.0.5)
```
如果每次运行监视的命令时,输出都是相同的,则只有标题行(如果未省略)会更改。其余显示的信息将保持不变。
如果你希望 `watch` 命令在它正在监视的命令的输出发生更新后立即退出,则可以使用 `-g`(将其视为“<ruby> 离开 <rt> go away </rt></ruby>”)选项。例如,如果你只是在等待其他人开始登录系统,则可以选择执行此操作。
你还可以使用 `-d`(<ruby> 差异 <rt> differences </rt></ruby>)选项突出显示显示输出中的更改。突出显示只会持续一个间隔(默认为 2 秒),但有助于引起你对更新的注意。
下面是一个更复杂的示例,该示例使用 `watch` 命令显示正在侦听连接的服务及其使用的端口。虽然输出不太可能更改,但它会提醒你任何新服务正在启动或关闭。
```
$ watch 'sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN'
```
值得注意的是,正在运行的命令需要用引号扩起来,以确保不会将 `watch` 命令的输出发送到 `grep` 命令。
使用 `watch -h` 命令将为你提供命令选项的列表。
```
$ watch -h
Usage:
watch [options] command
Options:
-b, --beep beep if command has a non-zero exit
-c, --color interpret ANSI color and style sequences
-d, --differences[=<permanent>]
highlight changes between updates
-e, --errexit exit if command has a non-zero exit
-g, --chgexit exit when output from command changes
-n, --interval <secs> seconds to wait between updates
-p, --precise attempt run command in precise intervals
-t, --no-title turn off header
-x, --exec pass command to exec instead of "sh -c"
-h, --help display this help and exit
-v, --version output version information and exit
```
### 使用 tail -f
`tail -f` 命令与 `watch` 有一些相同之处。它也会在添加文件时显示文件的底部和其他内容。你不必一次又一次地运行 `tail` 命令,而是运行一个命令并获得可重复更新显示视图的结果。例如,你可以使用如下命令查看系统日志:
```
$ tail -f /var/log/syslog
```
某些文件(如 `/var/log/wtmp`)不适合这种类型的处理,因为它们的格式不是普通文本文件,但是通过组合 `watch` 和 `tail`,你可以获得类似的结果,如下所示:
```
watch 'who /var/log/wtmp | tail -20'
```
无论有多少用户仍处于登录状态,此命令都将只显示最近的 5 次登录。如果发生其他登录,显示结果将添加一行记录并删除顶行记录。
```
Every 60.0s: who /var/log/wtmp | tail -5 dragonfly: Thu Feb 27 12:46:07 2020
shs pts/0 2020-02-27 08:07 (192.168.0.5)
nemo pts/1 2020-02-27 08:26 (192.168.0.5)
shs pts/1 2020-02-27 10:58 (192.168.0.5)
nemo pts/1 2020-02-27 11:34 (192.168.0.5)
dory pts/1 2020-02-27 12:14 (192.168.0.5)
```
对你有时可能想要监视的信息,无论监视进程、登录名还是系统资源,`watch` 和 `tail -f` 命令都可以提供自动更新视图,从而使监视任务变得更加容易。
---
via: <https://www.networkworld.com/article/3529891/watching-activity-on-linux-with-watch-and-tail-commands.html>
作者:[Sandra Henry-Stocker](https://www.networkworld.com/author/Sandra-Henry_Stocker/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[Starryi](https://github.com/Starryi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
14,558 | 使用 apt 进行 Linux 包管理 | https://opensource.com/article/21/6/apt-linux | 2022-05-07T10:42:00 | [
"apt",
"软件包管理"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14558-1.html |
>
> 学习如何使用 apt 命令在基于 Debian 的 Linux 发行版上安装软件包,然后下载我们的速查表,让正确的命令触手可及。
>
>
>

[包管理器](https://opensource.com/article/21/2/linux-package-management) 可帮助你处理 Linux 系统的计算机上软件的更新、卸载、故障排除等问题。Seth Kenlon 写了 [使用 dnf 进行 Linux 包管理](/article-14542-1.html) 一文,介绍了如何使用 `dnf` 这款命令行包管理工具,在 RHEL、CentOS、Fedora、Mageia、OpenMandriva 等 Linux 发行版中安装软件。
Debian 和基于 Debian 的发行版(例如 MX Linux、Deepin、Ubuntu)以及基于 Ubuntu 的发行版(例如 Linux Mint 和 Pop!\_OS)都有 `apt`,这是一个“相似但不同”的工具。在本文中,我将按照 Seth 的示例(但使用 `apt`)向你展示如何使用它。
在一开始,我想先提一下四个跟 `apt` 相关的软件安装工具:
* [Synaptic](https://www.nongnu.org/synaptic/) 是为 `apt` 服务的一个基于 GTK+ 的图形用户界面(GUI)的前端工具。
* [Aptitude](https://wiki.debian.org/Aptitude) 是为 `apt` 服务的一个基于 Ncurses 的全屏命令行前端工具。
* `apt` 的前身有 `apt-get`、`apt-cache` 等工具。
* [Dpkg](https://wiki.debian.org/Teams/Dpkg) 是在 `apt` 包管理器背后处理繁杂事务的”幕后工作者“。
还有其他的包管理系统,例如 [Flatpak](https://flatpak.org/) 和 [Snap](https://snapcraft.io/),你可能会在 Debian 和基于 Debian 的系统上遇到它们,但我不打算在这里讨论。还有一些应用程序“商店”,例如 [GNOME “软件”](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Software),与 `apt` 和其他打包技术重叠;我也不打算在这里讨论它们。最后,还有其他 Linux 发行版,例如 [Arch](https://archlinux.org/) 和 [Gentoo](https://www.gentoo.org/) 既不使用 `dnf` 也不使用 `apt`,我也不打算在这里讨论它们!
上面我讲了这么多我不想提及的内容,你可能怀疑 `apt` 到底还能处理多少软件。这么说吧,在我的 Ubuntu 20.04 上,`apt` 可以让我使用 69,371 个软件包,从 `0ad`(一款古代战争题材的即时战略游戏)到 `zzuf`(一个透明的应用程序模糊测试工具),一点也不差。
### 使用 apt 搜索软件
使用 `apt` 软件包管理器的第一步是找到感兴趣的软件包。Seth 的 `dnf` 文章以 [Cockpit](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/cockpit-server-management) 服务器管理应用程序为例。用 `apt` 我会输入如下命令:
```
$ apt search cockpit
Sorting... Done
Full Text Search... Done
389-ds/hirsute,hirsute 1.4.4.11-1 all
389 Directory Server suite - metapackage
cockpit/hirsute,hirsute 238-1 all
Web Console for Linux servers
...
$
```
上面的第二个包就是你要的那个(以 `cockpit/hirsute` 开头的那一行)。如果你决定要安装它,输入:
```
$ sudo apt install cockpit
```
`apt` 将负责安装 Cockpit 以及使其工作所需的所有部件或 *依赖*。有时我们不太确定这是我们所需要的。了解更多的信息可能有助于你决定是否真的要安装此应用程序。
### 包元数据
要了解有关软件包的更多信息,使用 `apt show` 命令:
```
$ apt show cockpit
Package: cockpit
Version: 238-1
Priority: optional
Section: universe/admin
Origin: Ubuntu
Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <[email protected]>
Original-Maintainer: Utopia Maintenance Team <[email protected]>
Bugs: https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+filebug
Installed-Size: 88.1 kB
Depends: cockpit-bridge (>= 238-1), cockpit-ws (>= 238-1), cockpit-system (>= 238-1)
Recommends: cockpit-storaged (>= 238-1), cockpit-networkmanager (>= 238-1), cockpit-packagekit (>= 238-1)
Suggests: cockpit-doc (>= 238-1), cockpit-pcp (>= 238-1), cockpit-machines (>= 238-1), xdg-utils
Homepage: https://cockpit-project.org/
Download-Size: 21.3 kB
APT-Sources: http://ca.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu hirsute/universe amd64 Packages
Description: Web Console for Linux servers
The Cockpit Web Console enables users to administer GNU/Linux servers using a
web browser.
.
It offers network configuration, log inspection, diagnostic reports, SELinux
troubleshooting, interactive command-line sessions, and more.
$
```
特别要注意的是 `Description` 字段,它会告诉你更多关于应用程序的信息。`Depends` 字段说明还必须安装什么,而 `Recommends` 则显示建议安装的其他(如果有的话)合作组件。`Homepage` 字段会提供一个网址,通过它你可以了解更多。
### 哪个包提供的这个文件?
有时你并不知道包名,但你知道包里一定包含着的某个文件。Seth 以 `qmake-qt5` 程序作为示例。使用 `apt search` 找不到它:
```
$ apt search qmake-qt5
Sorting... Done
Full Text Search... Done
$
```
但是,另一个有关联的命令 `apt-file` 可以用来探索包内部:
```
$ apt-file search qmake-qt5
qt5-qmake-bin: /usr/share/man/man1/qmake-qt5.1.gz
$
```
这时会显示一个 `qmake-qt5` 的手册页。它是一个名为 `qt5-qmake-bin` 的包的一部分。注意,此包名称颠倒了字符串 `qmake` 和 `qt5` 的顺序。
### 包里包含哪些文件?
方便的 `apt-file` 命令会列出给定的包中包含哪些文件。例如:
```
$ apt-file list cockpit
cockpit: /usr/share/doc/cockpit/TODO.Debian
cockpit: /usr/share/doc/cockpit/changelog.Debian.gz
cockpit: /usr/share/doc/cockpit/copyright
cockpit: /usr/share/man/man1/cockpit.1.gz
cockpit: /usr/share/metainfo/cockpit.appdata.xml
cockpit: /usr/share/pixmaps/cockpit.png
$
```
注意,这与 `apt show` 命令提供的信息不同,后者列出了包的依赖(其他必须安装的包)。
### 移除一个应用程序
你还可以使用 `apt` 移除软件包。例如,要移除`apt-file` 应用程序:
```
$ sudo apt purge apt-file
```
注意必须由超级用户运行 `apt` 才能安装或移除应用程序。
移除一个包并不会自动移除 `apt` 在此过程中安装的所有依赖项。不过,一点点的工作就很容易去除这些残留:
```
$ sudo apt autoremove
```
### 认识一下 apt
正如 Seth 所写的,“你对包管理器的工作方式了解得越多,在需要安装和查询应用程序时就会越容易。”
即便你不是 `apt` 的重度使用者,当你需要在命令行中安装或删除软件包时(例如,在一台远程服务器上或遵循某些热心肠发布的操作指南时),掌握一些 `apt` 的知识也会很有用。在某些软件创作者仅提供了一个裸 `.pkg` 文件的情况下,可能还需要了解一些关于 dpkg 的知识(如上所述)。
我发现 Synaptic 包管理器在我的桌面上是一个非常有用的工具,但出于各种目的,我也在少数维护的服务器上使用着 `apt`。
[下载我们的 apt 速查表](https://opensource.com/downloads/apt-cheat-sheet) 习惯该命令并尝试一些新技巧。一旦你这样做了,你可能会发现很难再使用其他任何东西。
>
> **[apt 速查表](https://opensource.com/downloads/apt-cheat-sheet)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/6/apt-linux>
作者:[Chris Hermansen](https://opensource.com/users/clhermansen) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hanszhao80](https://github.com/hanszhao80) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | On Linux, [package managers](https://opensource.com/article/21/2/linux-package-management) help you handle updates, uninstalls, troubleshooting, and more for the software on your computer. Seth Kenlon [wrote about dnf](https://opensource.com/article/21/5/dnf), the command-line package management tool for installing software in RHEL, CentOS, Fedora, Mageia, OpenMandriva, and other Linux distros.
Debian and Debian-based distros such as MX Linux, Deepin, Ubuntu—and distros based on Ubuntu, such as Linux Mint and Pop!_OS—have `apt`
, a "similar but different" tool. In this article, I'll follow Seth's examples—but with `apt`
—to show you how to use it.
Before I start, I want to mention four `apt`
-related tools for installing software:
[Synaptic](https://www.nongnu.org/synaptic/)is a GTK+ based graphical user interface (GUI) front end for`apt`
.[Aptitude](https://wiki.debian.org/Aptitude)is an Ncurses-based full-screen command-line front end for`apt`
.- There are
`apt-get`
,`apt-cache`
, and other predecessors of`apt`
. [Dpkg](https://wiki.debian.org/Teams/Dpkg)is the "behind the scenes" package manager`apt`
uses to do the heavy lifting.
There are other packaging systems, such as [Flatpak](https://flatpak.org/) and [Snap](https://snapcraft.io/), that you might run into on Debian and Debian-based systems, but I'm not going to discuss them here. There are also application "stores," such as [GNOME Software](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Software), that overlap with `apt`
and other packaging technologies; again, I'm not going to discuss them here. Finally, there are other Linux distros such as [Arch](https://archlinux.org/) and [Gentoo](https://www.gentoo.org/) that use neither `dnf`
nor `apt`
, and I'm not going to discuss those here either!
With all the things I'm not going to discuss here, you may be wondering what tiny subset of software `apt`
handles. Well, on my Ubuntu 20.04, `apt`
gives me access to 69,371 packages, from the `0ad`
real-time strategy game of ancient warfare to the `zzuf`
transparent application fuzzer. Not bad at all.
## Finding software with apt
The first step in using a package manager such as `apt`
is finding a software package of interest. Seth's `dnf`
article used the [Cockpit](https://opensource.com/article/20/11/cockpit-server-management) server management application as an example, so I will, too:
```
$ apt search cockpit
Sorting... Done
Full Text Search... Done
389-ds/hirsute,hirsute 1.4.4.11-1 all
389 Directory Server suite - metapackage
cockpit/hirsute,hirsute 238-1 all
Web Console for Linux servers
...
$
```
The second package above is the one you're after (it's the line beginning with `cockpit/hirsute`
). If you decide you want to install it, enter:
`$ sudo apt install cockpit`
`apt`
will take care of installing Cockpit and all the bits and pieces, or *dependencies*, needed to make it work. Sometimes that's all that's needed; sometimes it's not. It's possible that having a bit more information could be useful in deciding whether you really want to install this application.
## Package metadata
To find out more about a package, use the `apt show`
command:
```
$ apt show cockpit
Package: cockpit
Version: 238-1
Priority: optional
Section: universe/admin
Origin: Ubuntu
Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <[email protected]>
Original-Maintainer: Utopia Maintenance Team <[email protected]>
Bugs: https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+filebug
Installed-Size: 88.1 kB
Depends: cockpit-bridge (>= 238-1), cockpit-ws (>= 238-1), cockpit-system (>= 238-1)
Recommends: cockpit-storaged (>= 238-1), cockpit-networkmanager (>= 238-1), cockpit-packagekit (>= 238-1)
Suggests: cockpit-doc (>= 238-1), cockpit-pcp (>= 238-1), cockpit-machines (>= 238-1), xdg-utils
Homepage: https://cockpit-project.org/
Download-Size: 21.3 kB
APT-Sources: http://ca.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu hirsute/universe amd64 Packages
Description: Web Console for Linux servers
The Cockpit Web Console enables users to administer GNU/Linux servers using a
web browser.
.
It offers network configuration, log inspection, diagnostic reports, SELinux
troubleshooting, interactive command-line sessions, and more.
$
```
In particular, notice the `Description`
field, which tells you more about the application. The `Depends`
field says what else must be installed, and `Recommends`
shows what other—if any—cooperating components are suggested alongside it. The `Homepage`
field offers a URL in case you need more info.
## What package provides a file?
Sometimes you don't know the package name, but you know a file that must be in a package. Seth offers as an example the `qmake-qt5`
utility. Using `apt search`
doesn't find it:
```
$ apt search qmake-qt5
Sorting... Done
Full Text Search... Done
$
```
However, a related command, `apt-file`
will explore inside packages:
```
$ apt-file search qmake-qt5
qt5-qmake-bin: /usr/share/man/man1/qmake-qt5.1.gz
$
```
This turns up a man page for `qmake-qt5`
that is part of a package called `qt5-qmake-bin`
. Note that this package name reverses the `qmake`
and `qt5`
parts.
## What files are included in a package?
That handy `apt-file`
command also tells which files are included in a given package. For example:
```
$ apt-file list cockpit
cockpit: /usr/share/doc/cockpit/TODO.Debian
cockpit: /usr/share/doc/cockpit/changelog.Debian.gz
cockpit: /usr/share/doc/cockpit/copyright
cockpit: /usr/share/man/man1/cockpit.1.gz
cockpit: /usr/share/metainfo/cockpit.appdata.xml
cockpit: /usr/share/pixmaps/cockpit.png
$
```
Note that this is distinct from the info provided by the `apt show`
command, which lists the package's dependencies (other packages that must be installed).
## Removing an application
You can also remove packages with `apt`
. For example, to remove the `apt-file`
application:
`$ sudo apt purge apt-file`
Note that a superuser must run `apt`
to install or remove applications.
Removing a package doesn't automatically remove all the dependencies that `apt`
installs along the way. However, it's easy to carry out that little bit of tidying:
`$ sudo apt autoremove`
## Getting to know apt
As Seth wrote, "the more you know about how your package manager works, the easier it is for you to install and query applications when necessary."
Even if you're not a regular `apt`
user, knowing it can be useful when you need to work at the command line while installing or removing packages (for example, on a remote server or when following a how-to published by some helpful soul). You may also need to know a bit about Dkpg (mentioned above); for example, some software creators provide a bare `.pkg`
file.
I find the Synaptic package manager to be a really useful tool on my desktop, but I also use `apt`
on a handful of servers that I maintain for various purposes.
** Download our ** to get used to the command and try some new tricks with it. Once you do, you might find it hard to use anything else.
`apt`
cheat sheet
## 1 Comment |
14,560 | 使用 Go 和树莓派排查 WiFi 问题 | https://opensource.com/article/21/3/troubleshoot-wifi-go-raspberry-pi | 2022-05-08T08:50:28 | [
"WiFi"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14560-1.html |
>
> 实现一个 WiFi 扫描器玩玩~
>
>
>

去年夏天,我和妻子变卖了家产,带着我们的两只狗移居了夏威夷。这里有美丽的阳光、温暖的沙滩、凉爽的冲浪等你能想到的一切。我们同样遇到了一些意料之外的事:WiFi 问题。
不过,这不是夏威夷的问题,而是我们租住公寓的问题。我们住在一个单身公寓里,与房东的公寓仅一墙之隔。我们的租房协议中包含了免费的网络连接!好耶!只不过,它是由房东的公寓里的 WiFi 提供的,哇哦……
说实话,它的效果还不错……吧?好吧,我承认它不尽如人意,并且不知道是哪里的问题。路由器明明就在墙的另一边,但我们的信号就是很不稳定,经常会自动断开连接。在家的时候,我们的 WiFi 路由器的信号能够穿过层层墙壁和地板。事实上,它所覆盖的区域比我们居住的 600 平方英尺(大约 55 平方米)的公寓还要大。
在这种情况下,一个优秀的技术人员会怎么做呢?既然想知道为什么,当然是开始排查咯!
幸运的是,我们在搬家之前并没有变卖掉树莓派 Zero W。它是如此小巧便携! 我当然就把它一起带来了。我有一个机智的想法:通过树莓派和它内置的 WiFi 适配器,使用 Go 语言编写一个小程序来测量并显示从路由器收到的 WiFi 信号。我打算先简单快速地把它实现出来,以后再去考虑优化。真是麻烦!我现在只想知道这个 WiFi 是怎么回事!
谷歌搜索了一番后,我发现了一个比较有用的 Go 软件包 [mdlayher/wifi](https://github.com/mdlayher/wifi),它专门用于 WiFi 相关操作,听起来很有希望!
### 获取 WiFi 接口的信息
我的计划是查询 WiFi 接口的统计数据并返回信号强度,所以我需要先找到设备上的接口。幸运的是,`mdlayher/wifi` 包有一个查询它们的方法,所以我可以创建一个 `main.go` 来实现它,具体代码如下:
```
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/mdlayher/wifi"
)
func main() {
c, err := wifi.New()
defer c.Close()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
interfaces, err := c.Interfaces()
for _, x := range interfaces {
fmt.Printf("%+v\n", x)
}
}
```
让我们来看看上面的代码都做了什么吧!首先是导入依赖包,导入后,我就可以使用 `mdlayher/wifi` 模块就在 `main` 函数中创建一个新的客户端(类型为 `*Client`)。接下来,只需要调用这个新的客户端(变量名为 `c`)的 `c.Interfaces()` 方法就可以获得系统中的接口列表。接着,我就可以遍历包含接口指针的切片(变长数组),然后打印出它们的具体信息。
注意到 `%+v` 中有一个 `+` 了吗?它意味着程序会详细输出 `*Interface` 结构体中的属性名,这将有助于我标识出我看到的东西,而不用去查阅文档。
运行上面的代码后,我得到了机器上的 WiFi 接口列表:
```
&{Index:0 Name: HardwareAddr:5c:5f:67:f3:0a:a7 PHY:0 Device:3 Type:P2P device Frequency:0}
&{Index:3 Name:wlp2s0 HardwareAddr:5c:5f:67:f3:0a:a7 PHY:0 Device:1 Type:station Frequency:2412}
```
注意,两行输出中的 MAC 地址(`HardwareAddr`)是相同的,这意味着它们是同一个物理硬件。你也可以通过 `PHY: 0` 来确认。查阅 Go 的 [wifi 模块文档](https://godoc.org/github.com/mdlayher/wifi#Interface),`PHY` 指的就是接口所属的物理设备。
第一个接口没有名字,类型是 `TYPE: P2P`。第二个接口名为 `wpl2s0`,类型是 `TYPE: Station`。`wifi` 模块的文档列出了 [不同类型的接口](https://godoc.org/github.com/mdlayher/wifi#InterfaceType),以及它们的用途。根据文档,`P2P`(点对点传输) 类型表示“该接口属于点对点客户端网络中的一个设备”。我认为这个接口的用途是 [WiFi 直连](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wi-Fi_Direct) ,这是一个允许两个 WiFi 设备在没有中间接入点的情况下直接连接的标准。
`Station`(基站)类型表示“该接口是具有<ruby> 控制接入点 <rt> controlling access point </rt></ruby>的客户端设备管理的<ruby> 基本服务集 <rt> basic service set </rt></ruby>(BSS)的一部分”。这是大众熟悉的无线设备标准功能:作为一个客户端来连接到网络接入点。这是测试 WiFi 质量的重要接口。
### 利用接口获取基站信息
利用该信息,我可以修改遍历接口的代码来获取所需信息:
```
for _, x := range interfaces {
if x.Type == wifi.InterfaceTypeStation {
// c.StationInfo(x) returns a slice of all
// the staton information about the interface
info, err := c.StationInfo(x)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Station err: %s\n", err)
}
for _, x := range info {
fmt.Printf("%+v\n", x)
}
}
}
```
首先,这段程序检查了 `x.Type`(接口类型)是否为 `wifi.InterfaceTypeStation`,它是一个基站接口(也是本练习中唯一涉及到的类型)。不幸的是名字出现了冲突,这个接口“类型”并不是 Golang 中的“类型”。事实上,我在这里使用了一个叫做 `interfaceType` 的 Go 类型来代表接口类型。呼,我花了一分钟才弄明白!
然后,假设接口的类型正确,我们就可以调用 `c.StationInfo(x)` 来检索基站信息,`StationInfo()` 方法可以获取到关于这个接口 `x` 的信息。
这将返回一个包含 `*StationInfo` 指针的切片。我不大确定这里为什么要用切片,或许是因为接口可能返回多个 `StationInfo`?不管怎么样,我都可以遍历这个切片,然后使用之前提到的 `+%v` 技巧格式化打印出 `StationInfo` 结构的属性名和属性值。
运行上面的程序后,我得到了下面的输出:
```
&{HardwareAddr:70:5a:9e:71:2e:d4 Connected:17m10s Inactive:1.579s ReceivedBytes:2458563 TransmittedBytes:1295562 ReceivedPackets:6355 TransmittedPackets:6135 ReceiveBitrate:2000000 TransmitBitrate:43300000 Signal:-79 TransmitRetries:2306 TransmitFailed:4 BeaconLoss:2}
```
我感兴趣的是 `Signal`(信号)部分,可能还有 `TransmitFailed`(传输失败)和 `BeaconLoss`(信标丢失)部分。信号强度是以 dBm(<ruby> 分贝-毫瓦 <rt> decibel-milliwatts </rt> <ruby> )为单位来报告的。 </ruby></ruby>
#### 简短科普:如何读懂 WiFi dBm
根据 [MetaGeek](https://www.metageek.com/training/resources/wifi-signal-strength-basics.html) 的说法:
* -30 最佳,但它既不现实也没有必要
* -67 非常好,它适用于需要可靠数据包传输的应用,例如流媒体
* -70 还不错,它是实现可靠数据包传输的底线,适用于电子邮件和网页浏览
* -80 很差,只是基本连接,数据包传输不可靠
* -90 不可用,接近“<ruby> 背景噪声 <rt> noise floor </rt></ruby>”
*注意:dBm 是对数尺度,-60 比 -30 要低 1000 倍。*
### 使它成为一个真的“扫描器”
所以,看着上面输出显示的我的信号:-79。哇哦,感觉不大好呢。不过单看这个结果并没有太大帮助,它只能提供某个时间点的参考,只对 WiFi 网络适配器在特定物理空间的某一瞬间有效。一个连续的读数会更有用,借助于它,我们观察到信号随着树莓派的移动而变化。我可以再次修改 `main` 函数来实现这一点。
```
var i *wifi.Interface
for _, x := range interfaces {
if x.Type == wifi.InterfaceTypeStation {
// Loop through the interfaces, and assign the station
// to var x
// We could hardcode the station by name, or index,
// or hardwareaddr, but this is more portable, if less efficient
i = x
break
}
}
for {
// c.StationInfo(x) returns a slice of all
// the staton information about the interface
info, err := c.StationInfo(i)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Station err: %s\n", err)
}
for _, x := range info {
fmt.Printf("Signal: %d\n", x.Signal)
}
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
```
首先,我命名了一个 `wifi.Interface` 类型的变量 `i`。因为它在循环的范围外,所以我可以用它来存储接口信息。循环内创建的任何变量在该循环的范围外都是不可访问的。
然后,我可以把这个循环一分为二。第一个遍历了 `c.Interfaces()` 返回的接口切片,如果元素是一个 `Station` 类型,它就将其存储在先前创建的变量 `i` 中,并跳出循环。
第二个循环是一个死循环,它将不断地运行,直到我按下 `Ctrl + C` 来结束程序。和之前一样,这个循环内部获取接口信息、检索基站信息,并打印出信号信息。然后它会休眠一秒钟,再次运行,反复打印信号信息,直到我退出为止。
运行上面的程序后,我得到了下面的输出:
```
[chris@marvin wifi-monitor]$ go run main.go
Signal: -81
Signal: -81
Signal: -79
Signal: -81
```
哇哦,感觉不妙。
### 绘制公寓信号分布图
不管怎么说,知道这些信息总比不知道要好。让树莓派连接上显示器或者电子墨水屏,并接上电源,我就可以让它在公寓里移动,并绘制出信号死角的位置。
剧透一下:由于房东的接入点在隔壁的公寓里,对我来说最大的死角是以公寓厨房的冰箱为顶点的一个圆锥体形状区域......这个冰箱与房东的公寓靠着一堵墙!
我想如果用《龙与地下城》里的黑话来说,它就是一个“<ruby> 沉默之锥 <rt> Cone of Silence </rt></ruby>”。或者至少是一个“<ruby> 糟糕的网络连接之锥 <rt> Cone of Poor Internet </rt></ruby>”。
总之,这段代码可以直接在树莓派上运行 `go build -o wifi_scanner` 来编译,得到的二进制文件 `wifi_scanner` 可以运行在其他同样的ARM 设备上。另外,它也可以在常规系统上用正确的 ARM 设备库进行编译。
祝你扫描愉快!希望你的 WiFi 路由器不在你的冰箱后面!你可以在 [我的 GitHub 存储库](https://github.com/clcollins/goPiWiFi) 中找到这个项目所用的代码。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/3/troubleshoot-wifi-go-raspberry-pi>
作者:[Chris Collins](https://opensource.com/users/clcollins) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Last summer, my wife and I sold everything we owned and moved with our two dogs to Hawaii. It's been everything we thought it would be: beautiful sun, warm sand, cool surf—you name it. We've also run into some things we didn't expect: WiFi problems.
Now, that's not a Hawaii problem. It's limited to the apartment we are renting. We are living in a single-room studio apartment attached to our landlord's apartment. Part of the rent includes free internet! YAY! However, said internet is provided by the WiFi router in the landlord's apartment. BOO!
In all honesty, it works OK. Ish. OK, it doesn't work well, and I'm not sure why. The router is literally on the other side of the wall, but our signal is spotty, and we have some trouble staying connected. Back home, our WiFi router's signal crossed through many walls and some floors. Certainly, it covered an area larger than the 600 sq. foot apartment we live in!
What does a good techie do in such a situation? Why, investigate, of course!
Luckily the "everything we own" that we sold before moving here did not include our Raspberry Pi Zero W. So small! So portable! Of course, I took it to Hawaii with me. My bright idea was to use the Pi and its built-in WiFi adapter, write a little program in Go to measure the WiFi signal received from the router, and display that output. I'm going to make it super simple, quick, and dirty and worry later about making it better. I just want to know what's up with the WiFi, dang it!
Hunting around on Google for a minute turns up a relatively useful Go package for working with WiFi, [mdlayher/wifi](https://github.com/mdlayher/wifi). Sounds promising!
## Getting information about the WiFi interfaces
My plan is to query the WiFi interface statistics and return the signal strength, so I need to find the interfaces on the device. Luckily the mdlayher/wifi package has a method to query them, so I can do that by creating a file named `main.go`
:
```
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/mdlayher/wifi"
)
func main() {
c, err := wifi.New()
defer c.Close()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
interfaces, err := c.Interfaces()
for _, x := range interfaces {
fmt.Printf("%+v\n", x)
}
}
```
So, what's going on here? After importing it, the mdlayher/wifi module can be used in the main function to create a new Client (type `*Client`
). The new client (named `c`
) can then get a list of the interfaces on the system with `c.Interfaces()`
. Then it can loop over the slice of Interface pointers and print information about them.
By adding "+" to `%+v`
, it prints the names of the fields in the `*Interface`
struct, too, which helps me identify what I'm seeing without having to refer back to documentation.
Running the code above provides a list of the WiFi interfaces on my machine:
```
&{Index:0 Name: HardwareAddr:5c:5f:67:f3:0a:a7 PHY:0 Device:3 Type:P2P device Frequency:0}
&{Index:3 Name:wlp2s0 HardwareAddr:5c:5f:67:f3:0a:a7 PHY:0 Device:1 Type:station Frequency:2412}
```
Note that the MAC address, `HardwareAddr`
, is the same for both lines, meaning this is the same physical hardware. This is confirmed by `PHY: 0`
. The Go [wifi module's docs](https://godoc.org/github.com/mdlayher/wifi#Interface) note that `PHY`
is the physical device to which the interface belongs.
The first interface has no name and is `TYPE:P2P`
. The second, named `wpl2s0`
is `TYPE:Station`
. The wifi module documentation lists the [different types of interfaces](https://godoc.org/github.com/mdlayher/wifi#InterfaceType) and describes what they are. According to the docs, the "P2P" type indicates "an interface is a device within a peer-to-peer client network." I believe, and please correct me in the comments if I'm wrong, that this interface is for [WiFi Direct](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wi-Fi_Direct), a standard for allowing two WiFi devices to connect without an intermediate access point.
The "Station" type indicates "an interface is part of a managed basic service set (BSS) of client devices with a controlling access point." This is the standard function for a wireless device that most people are used to—as a client connected to an access point. This is the interface that matters for testing the quality of the WiFi.
## Getting the Station information from the interface
Using this information, I can update the loop over the interfaces to retrieve the information I'm looking for:
```
for _, x := range interfaces {
if x.Type == wifi.InterfaceTypeStation {
// c.StationInfo(x) returns a slice of all
// the staton information about the interface
info, err := c.StationInfo(x)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Station err: %s\n", err)
}
for _, x := range info {
fmt.Printf("%+v\n", x)
}
}
}
```
First, it checks that `x.Type`
(the Interface type) is `wifi.InterfaceTypeStation`
—a Station interface (that's the only type that matters for this exercise). This is an unfortunate naming collision—the interface "type" is not a "type" in the Golang sense. In fact, what I'm working on here is a Go `type`
named `InterfaceType`
to represent the type of interface. Whew, that took me a minute to figure out!
So, assuming the interface is of the *correct* type, the station information can be retrieved with `c.StationInfo(x)`
using the client `StationInfo()`
method to get the info about the interface, `x`
.
This returns a slice of `*StationInfo`
pointers. I'm not sure quite why there's a slice. Perhaps the interface can have multiple StationInfo responses? In any case, I can loop over the slice and use the same `+%v`
trick to print the keys and values for the StationInfo struct.
Running the above returns:
`&{HardwareAddr:70:5a:9e:71:2e:d4 Connected:17m10s Inactive:1.579s ReceivedBytes:2458563 TransmittedBytes:1295562 ReceivedPackets:6355 TransmittedPackets:6135 ReceiveBitrate:2000000 TransmitBitrate:43300000 Signal:-79 TransmitRetries:2306 TransmitFailed:4 BeaconLoss:2}`
The thing I'm interested in is the "Signal" and possibly "TransmitFailed" and "BeaconLoss." The signal is reported in units of dBm (or decibel-milliwatts).
### A quick aside: How to read WiFi dBm
According to [MetaGeek](https://www.metageek.com/training/resources/wifi-signal-strength-basics.html):
- –30 is the best possible signal strength—it's neither realistic nor necessary
- –67 is very good; it's for apps that need reliable packet delivery, like streaming media
- –70 is fair, the minimum reliable packet delivery, fine for email and web
- –80 is poor, absolute basic connectivity, unreliable packet delivery
- –90 is unusable, approaching the "noise floor"
*Note that dBm is logarithmic scale: -60 is 1,000x lower than -30*
## Making this a real "scanner"
So, looking at my signal from above: –79. YIKES, not good. But that single result is not especially helpful. That's just a point-in-time reference and only valid for the particular physical space where the WiFi network adapter was at that instant. What would be more useful would be a continuous reading, making it possible to see how the signal changes as the Raspberry Pi moves around. The main function can be tweaked again to accomplish this:
```
var i *wifi.Interface
for _, x := range interfaces {
if x.Type == wifi.InterfaceTypeStation {
// Loop through the interfaces, and assign the station
// to var x
// We could hardcode the station by name, or index,
// or hardwareaddr, but this is more portable, if less efficient
i = x
break
}
}
for {
// c.StationInfo(x) returns a slice of all
// the staton information about the interface
info, err := c.StationInfo(i)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Station err: %s\n", err)
}
for _, x := range info {
fmt.Printf("Signal: %d\n", x.Signal)
}
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
```
First, I name a variable `i`
of type `*wifi.Interface`
. Since it's outside the loop, I can use it to store the interface information. Any variable created inside the loop is inaccessible outside the scope of that loop.
Then, I can break the loop into two. The first loop ranges over the interfaces returned by `c.Interfaces()`
, and if that interface is a Station type, it stores that in the `i`
variable created earlier and breaks out of the loop.
The second loop is an infinite loop, so it'll just run over and over until I hit **Ctrl**+**C** to end the program. This loop takes that interface information and retrieves the station information, as before, and prints out the signal information. Then it sleeps for one second and runs again, printing the signal information over and over until I quit.
So, running that:
```
[chris@marvin wifi-monitor]$ go run main.go
Signal: -81
Signal: -81
Signal: -79
Signal: -81
```
Oof. Not good.
## Mapping the apartment
This information is good to know, at least. With an attached screen or E Ink display and a battery (or a looooong extension cable), I can walk the Pi around the apartment and map out where the dead spots are.
Spoiler alert: With the landlord's access point in the apartment next door, the big dead spot for me is a cone shape emanating from the refrigerator in the studio apartment's kitchen area… the refrigerator that shares a wall with the landlord's apartment!
I think in Dungeons and Dragons lingo, this is a "Cone of Silence." Or at least a "Cone of Poor Internet."
Anyway, this code can be compiled directly on the Raspberry Pi with `go build -o wifi_scanner`
, and the resulting binary, `wifi_scanner`
, can be shared with any other ARM devices (of the same version). Alternatively, it can be compiled on a regular system with the right libraries for ARM devices.
Happy Pi scanning! May your WiFi router not be behind your refrigerator! You can find the code used for this project in [my GitHub repo](https://github.com/clcollins/goPiWiFi).
## Comments are closed. |
14,561 | 分步指南:从 Pop OS 21.10 更新到 Pop OS 22.04 LTS | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/04/upgrade-pop-os-22-04-from-21-10/ | 2022-05-08T09:48:00 | [
"Pop OS"
] | /article-14561-1.html | 
>
> 从 Pop OS 21.10 升级到 Pop OS 22.04 LTS 的简单步骤。
>
>
>
System76 跟着 [Ubuntu 22.04 LTS](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/01/ubuntu-22-04-lts/) [发布](https://blog.system76.com/post/682519660741148672/popos-2204-lts-has-landed) 了 Pop OS 22.04 LTS ,它带来了一些令人兴奋的功能。Pop OS 22.04 LTS 是来自 System76 发布的长期支持版本,它带来了自动计划更新、自定义的 GNOME 42、底层性能改进和 [许多其它的功能](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/04/pop-os-22-04-lts/)。
你肯定很想体验一下,计划更新到 Pop OS 22.04 。这里我给出你升级 Pop OS 22.04 LTS 的步骤。
注意: 你不能直接从 Pop OS 20.04 升级到 Pop OS 22.04 。首先,你需要先升级到 Pop OS 21.10,然后按照此处概述的步骤升级到这个版本。
### 从 Pop OS 21.10 升级到 Pop OS 22.04
#### 升级之前的准备
Pop OS 升级过程是相对稳定的。因为根据我们 [上一篇关于升级的文章](https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/12/upgrade-pop-os-21-10-from-21-04/),许多用户面临升级方面的问题。但是如果你正在使用英伟达硬件运行 Pop OS ,我建议你做个备份。
* 确保你的系统是最新的。你可以使用 Pop 商店应用检查更新。或者,你可以打开终端提示符并运行以下命令更新:
```
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
```
* 按照以上步骤升级完成之后,重启系统。
* 备份你的文档、照片、视频和其它文件到独立的磁盘分区或者 USB 驱动器。
* 升级之前,禁用所有 GNOME 扩展。许多扩展会阻挡迁移到 GNOME 42 的过程,最好在你升级之前禁用所有扩展,之后再启用它们。
* 记下所有额外的软件源或你已经添加的 PPA 仓库,因为它们可能与 “jammy” 分支不兼容。升级之后你可能需要验证它们。
* 关闭所有运行的程序。
* 最后,确保你有时间和稳定的网络连接来完成升级。
### Pop OS 22.04 LTS 的升级步骤
#### 图形界面升级方法
如果你正在运行的是 Pop OS 21.10 ,你应该看到如下提示是否你的系统需要升级。

或者,你可以打开 “<ruby> 设置 <rt> Settings </rt></ruby>” 然后访问 “<ruby> 系统升级和恢复 <rt> OS Upgrade and Recovery </rt></ruby>” 标签。这里你应该看到有系统更新信息。

点击 “<ruby> Download <rt> 下载 </rt></ruby>” 开始升级过程。
#### 升级到 Pop OS 22.04 LTS 的终端方法
* 打开终端运行以下命令:
```
sudo apt update
sudo apt full-upgrade
```
* 这能确保在升级过程开始前系统保持最新。如果你已经在上述升级前步骤中完成了这个步骤,那么你可以忽略它。
* 使用以下命令更新恢复分区并等待它完成。这只适用于 UEFI 安装模式。
```
pop-upgrade recovery upgrade from-release
```
* 现在使用以下命令开始升级过程:
```
pop-upgrade release upgrade
```

* 首先,升级过程将会下载软件包。按照我们的测试,需要下载大约 1600 多个软件包。因此,你应该等到它结束。
* 其次,一旦下载完成,更新管理器将会提示你重启。 
* 重启之后,Pop OS 将开始安装最新的软件包到你的系统中。
* 最后,这个下载过程要花将近一个小时,所以等待它完成。我不建议中途停止更新,这将会导致系统不稳定。 
* 升级完成之后,享受全新的 Pop OS 22.04 LTS 吧。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/04/upgrade-pop-os-22-04-from-21-10/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hwlife](https://github.com/hwlife) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,562 | 我如何通过开源来发展我的产品经理职业 | https://opensource.com/article/22/4/product-management-open-source | 2022-05-08T11:24:49 | [
"开源",
"产品经理"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14562-1.html | 
>
> 毫不夸张地说,在开源方面获得的经验,帮助我在产品管理领域创造了一条成功的职业道路。
>
>
>
我是一个充满好奇心的人,我喜欢探索科技行业的许多领域,从视觉设计、编程到产品管理。我也被开放源码的理念所吸引。因此,我很高兴与大家分享我作为一个产品经理(PM),是如何利用开源来建立我的职业生涯的。我相信我的经验可以帮助其他对产品管理感兴趣的人。
### 什么是开源软件
简单地说,开源软件是开放源代码的软件,这意味着任何人都可以检查、修改、增强和分享它的源代码。我们发表过一篇详细、[全面的文章](/article-8624-1.html) 来帮助你了解什么是开源。
我最早知道开源是很久以前了,那时,我还是一名刚入行不久的视觉设计师。我很想知道开源是什么,也很想知道如何成为它的一部分。在这种好奇心的驱使下,我接触到了一些有经验的开源贡献者和倡导者。虽然我当时没有做出贡献,但是他们让我知道了什么是社区,这对我下定决心开始贡献有很大帮助。
### 如何上手产品管理
产品管理工作貌似是一件很难上手的事情,感觉必须要戴上拳击手套,经过一番搏斗,才能强行进入这一行。然而,我从其他产品经理那里听说,与编写/调试代码块,或使用像素点生成复杂的产品设计线框相比,产品管理工作其实是更好上手的。
虽然我们的经历和经验各不相同,但是有一点可以确定:成为产品经理的道路往往是漫长而不可预知的。随着就业竞争的不断加剧,获得一个初级产品经理的职位可能会很困难。应聘者通常被要求有 2 到 3 年的经验才能加入产品团队。这时你可能会问:“我应该如何获得这些经验呢?”
来看看下面这四个策略吧,它们或许能够将你的职业生涯转向到产品管理:
1. 在一个大型组织的内部转岗。这可能需要你的经理为你说一些好话,比如,说你很适合在公司内部转岗等。你必须有证据表明你掌握了该岗位的技能。这通常被认为是获得产品管理经验的最快
2. 担任大型组织的初级产品经理角色。通过它获得实习机会,或者加入一个需要初级产品经理的关副产品管理项目,这些都很常见。
3. 你也可以尝试通过加入创业公司来上手产品管理工作。
4. 你还可以启动一个自己的副业项目来上手产品管理工作。
缺乏实践经验,就很难成为产品经理。正如开源产品经理 [David Ryan](https://twitter.com/hellodavidryan) 所说,“有一条获得实际的产品管理经验的途径,它既未被人充分利用,也很少有人意识到并利用它们”。
这条途径是什么?
### 答案就是开源
一个开放源码项目要想成功,需要的不仅仅是代码。它还包括项目战略、用户研究,以及将战略与日常工作联系起来。这些都是产品经理应该积极参加的活动。但是,在产品管理这一行里,有多少职责会分配给一个新手产品经理呢?
[Susana Videira Lopes](https://twitter.com/susanavlopes) 在她的一篇文章中指出,“获得一个入门级的产品角色,本质就是以一种建立你的信心的方式,让你加入到至产品管理这一行,同时尽早为组织提供价值”。
一个入门级的产品经理该如何参与开源项目,并为它提供价值呢?
**答案很简单:多问问题**
这里有一些你可以问的问题:
* 正在探索的是什么问题/机会?
* 如何制定解决方案来解决这个问题?
* 用什么标准来确定项目是否成功?
* 这个解决方案的服务对象是谁?
* 他们是如何被告知这个解决方案的?
* 该解决方案如何与当前和更广泛的生态系统相适应?
* 项目的文件是在哪里维护的?
* 项目维护者是否了解<ruby> 无障碍 <rt> accessibility </rt></ruby>要求?它们是否被满足?
既然你已经获得了产品经理的所需技能,为何不应用它们呢?结合所学,表达出你深思熟虑的问题,并邀请你的团队来评估吧!你的团队可以选择那些能引起开发者和社区共鸣的问题,并优先考虑其中最重要的。
这些问题可以帮助你建立用户角色、用户旅程图、精益画布,以及更多。这种经验对发展职业潜力有很大的帮助。
### 我在 OpenUnited 的经历
[OpenUnited](https://openunited.com) 是一个以独特方式连接数字人才和工作的平台。我们与贡献者合作,帮助他们投入到高质量的开源产品,从而证明自身的特定技能。一旦他们的工作得到验证,这些有才华的贡献者就有资格在公司里从事有偿工作。
OpenUnited 是一个开源平台,为各类贡献者(包括产品经理、开发人员、设计师、商业分析师和其他人)提供服务。它致力于帮助贡献者提高技能,并为他们提供长期的高质量付费工作来源。
Miro 公司的高级产品经理 Farbod Saraf 让我加入他与合作伙伴创建的一个平台。我加入了这个项目,并了解了如何对 OpenUnited 做出贡献。我还了解了其他可以帮助我在产品管理生涯中成长的项目,并做出了我的第一次贡献。这是一次很好的经历,因为我可以迅速地开始投入到产品的某些部分,以改善平台上其他用户的体验。在我为项目做贡献的时候,我的导师 Farbod 随时为我提供任何需要的帮助,使我的工作更加轻松。
你对开源项目所做的一切贡献,都会成为你成长为产品经理过程中的有力的公共记录。对于任何想通过开源上手产品管理的人,我都强烈推荐 OpenUnited 平台。
### 如何找到开源项目
许多人认为,贡献开源只适合于开发人员,因为他们觉得找到一个可以舒适地贡献的开源项目是很难的。
即使作为一个初出茅庐的产品经理,也有好几种方法可以找到适合贡献的开源项目。这里列出了一些:
* 在产品经理社区中发言,如 Mind The Product 和 Product School。
* 参加当地的聚会和开源会议,如非洲开源社区节,以此来与开源项目的创建者和维护者保持联系。
* 与在 GitLab 或 Mozilla 等大型开源公司工作的产品经理接触。他们可能会把你推荐到需要你的技能和贡献的开源项目中。
* 联系开源公司的开源倡导者和开发者关系团队,让他们推荐一些适合入门级产品经理贡献的开源项目。
* 寻找 AngelList 上的开源公司或 Product Hunt 上流行的开源产品。这些都是你可以找到适合贡献的开源产品的好地方。
### 下一步
[Ruth Ikegah](https://stars.github.com/profiles/ruth-ikegah/) 是我的一个重要灵感来源,她 [为开源新手写了一篇文章](https://ruthikegah.xyz/a-beginners-guide-to-open-source)。她的文章给出了一些提示,在你开始为开源做贡献时,可能需要考虑一下它们。
在加入和贡献项目、社区或组织之前,对它们做一些研究,并提出自己的问题。当你最终决定加入社区时,试着积极地介绍自己,并说明你可以在哪些方面提供帮助。
当然,开源不仅仅是你职业生涯的一个垫脚石。它本身就是一个平台,而且它需要优秀的产品经理。参与进来吧!一方面,你能为社区做出贡献;另一方面,它也能帮助你磨练自己的技能。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/4/product-management-open-source>
作者:[Shebuel Inyang](https://opensource.com/users/shebuel) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | I'm a curious person, and I like to explore many fields in the technology industry, from visual design, programming, and product management. I am also drawn to open source ideas. So I'm excited to share with you how I, as a product manager (PM), have used open source to build my career. I believe my experiences can help others who are interested in product management.
## What is open source software?
In simple terms, open source software is software with source code that anyone can inspect, modify, enhance, and share. [Opensource.com](http://Opensource.com) has documented a detailed and [comprehensive article](https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-source) to help you understand what open source is.
My discovery of open source started in the early phase of my career as a visual designer. I was curious to know what it meant and how to be a part of it and that led me to reach out to a few experienced open source contributors and advocates. Though I didn't contribute at the time, I acquired knowledge of the community which helped me when I made the decision to start contributing.
## How to break into product management
It might seem that breaking into product management is difficult, that you must put your boxing gloves on, come out fighting and force your way in. And yet, I've heard from other product managers that it was actually easier to break into compared to writing or debugging blocks of code, or pushing pixels to generate complex wireframes for product design.
Our journeys and approaches are different, so it's safe to say that the road to becoming a product manager can often be long and unpredictable. With the increasing level of competition in the job market, getting a role as an entry-level product manager can be difficult. Recruiters often require 2 to 3 years of experience to join a product team. You might ask, "How am I expected to get the experience?"
Here's a quick look at the four strategies for directing your career toward product management:
-
Internal transition at a large organization that might require your manager to advocate for you as a good fit to transition within the company. You must have proof that you have transferable skills. This is generally considered the quickest route to product management experience.
-
Junior PM roles at large organizations. It's common to go through an organization to get an internship, or to join an associate product management program that employs a junior PM.
-
You can also try to get into product management by joining a startup.
-
You can start a side project of your own to break into product management.
Without hands-on experience, it's difficult to become a product manager. As open source product manager [David Ryan](https://twitter.com/hellodavidryan) stated, "Few people are taking advantage of what is possibly the most under-utilized path to practical product management experience."
What is this path?
## Open source is the answer
An open source project needs more than just code to be successful. This ranges from a strategy for the project, user research, and linking the strategy to daily work. These are all activities that a product manager should be actively involved in. But how much of the product management discipline is the responsibility of a first-time product manager?
[Susana Videira Lopes](https://twitter.com/susanavlopes) stated in one of her articles that the "essence of getting an entry-level product role is to introduce you to the product management discipline in a way that builds up your confidence, while at the same time delivering value for the organization as early as possible."
How can an entry-level product manager get involved with an open source project, and deliver value?
**Simple answer: Ask Questions**
Here are some questions you can ask:
-
What problem or opportunity is being explored?
-
How is the solution being framed to tackle this problem?
-
What metrics are used to determine whether the project is successful?
-
Who are the people this solution serves?
-
How are they being informed about it?
-
How does the solution fit with both the immediate and wider ecosystem?
-
Where is the documentation being maintained on the project?
-
Do project maintainers understand accessibility requirements? Are they being met?
You've acquired skills as a product manager. Use them to help you express these thoughtful questions, and invite the team to consider them. The team can select the ones that resonate for the developers and the community, and prioritize what's most important.
These questions help you build user personas, a customer journey map, lean canvas, and more. This kind of experience goes a long way towards developing career potential.
## My experience at OpenUnited
[OpenUnited](https://openunited.com) is a platform that connects digital talent and work in a unique way. We work with contributors to help them prove specific skills by working on high quality open source products. Once their work is verified, these talented contributors are eligible to work for companies on paid tasks.
OpenUnited is an open source platform that onboards contributors of all kinds—product managers, developers, designers, business analysts, and others. It helps them improve their skills and provides them with a long term source of high-quality paying work.
Farbod Saraf, a senior product manager at Miro, onboarded me on a platform he created with a partner. I joined the project and learned about contributing to OpenUnited. I also learned about other projects that could help me grow in my product management career, and made my first contribution. It was a good experience because I got to start working quickly on bits of the product, to improve the experience of other users on the platform. My mentor Farbod made it easier by making himself available to provide any needed help while I contributed to the project.
Everything you contribute to an open source project becomes a powerful public record of your development as a product manager. I strongly recommend the OpenUnited platform to anyone who wants to break into product management with open source.
## How do you find open source projects?
Many people believe that contributing to open source is best left to developers because they find it difficult to search for and get open source projects they can comfortably contribute to.
As a first-time product manager, there are several ways to find open source projects to contribute to. Here's a list of some:
-
Speak up in product manager communities such as
[Mind The Product](https://www.mindtheproduct.com/)and[Product School](https://www.productschool.com/). -
Go to local meetups and open source conferences like
[Open Source Community Africa Festival](https://oscafrica.org/)to connect with open source project creators and maintainers. -
Engage with product managers working at larger open source companies such as GitLab or Mozilla. They may be able to refer you to open source projects where your skills and contribution could be beneficial.
-
Investigate open source advocates and DevRel teams at open source companies to get recommendations of open projects an entry-level product manager can contribute to.
-
Look to open source companies on AngelList or popular open source products on Product Hunt. These are great places to consider in your search for open products to contribute to.
## What next?
[Ruth Ikegah](https://stars.github.com/profiles/ruth-ikegah/), a great source of inspiration for me, wrote an [article for beginners in open source](https://ruthikegah.xyz/a-beginners-guide-to-open-source). In her article, she gave some tips to consider as you embark on contributing to open source.
Before joining and contributing, do some research on the project, community, or organization, and ask questions. When you finally decide to join the community, try to be active by introducing yourself and stating areas where you can help the project.
Of course, open source isn't just a stepping stone for your career. It's a platform in itself, and it needs great product managers. Get involved, contribute to the community, and help it help you hone your skills.
## Comments are closed. |
14,563 | 2022 Rust 入门指南 | https://opensource.com/article/22/1/rust-cheat-sheet | 2022-05-08T16:16:32 | [
"Rust"
] | /article-14563-1.html |
>
> 如果你打算在今年探索 Rust,请下载我们的免费 Rust 速查表,以供快速参考基础知识。
>
>
>

Rust 是一门相对较新的编程语言,受到各个企业的 [程序员的欢迎](https://opensource.com/article/20/5/rust-java)。尽管如此,它仍是一门建立在之前所有事物之上的语言。毕竟,Rust 不是一天做出来的,所以即便 Rust 中的一些概念看起来与你从 Python、Java、C++ 等编程语言学到的东西大不相同,但它们都是基于同一个基础,那就是你一直与之交互(无论你是否知道)的 CPU 和 NUMA(<ruby> 非统一内存访问 <rt> Non Uniform Memory Access </rt></ruby>)架构,因此 Rust 中的一些新功能让人感觉有些熟悉。
现在,我的职业不是程序员。我没耐心但我又有点儿强迫症。当我需要完成某件事时,如果一门语言不能帮助我相对较快地获得想要的结果,那么我很少会受到鼓舞而使用它。Rust 试图平衡两个矛盾:现代计算机对安全和结构化代码的需求,和现代程序员对编码工作事半功倍的渴望。
### 安装 Rust
[rust-lang.org](http://rust-lang.org) 网站有丰富的的文档指导如何安装 Rust,但通常,它就像下载 `sh.rustup.rs` 脚本并运行它一样简单。
```
$ curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs
$ less sh.rustup.sh
$ sh ./sh.rustup.rs
```
### 没有类
Rust 没有类,也不使用 `class` 关键字。Rust 确实有 `struct` 数据类型,但它的作用是充当数据集合的一种模板。因此,你可以使用<ruby> 结构体 <rt> struct </rt></ruby>,而不是创建一个类来表示虚拟对象:
```
struct Penguin {
genus: String,
species: String,
extinct: bool,
classified: u64,
}
```
你可以像使用类一样使用它。例如,当定义完 `Penguin` 结构,你就可以创建它的实例,并与该实例进行交互:
```
struct Penguin {
genus: String,
species: String,
extinct: bool,
classified: u64,
}
fn main() {
let p = Penguin { genus: "Pygoscelis".to_owned(),
species: "R adeliæ".to_owned(),
extinct: false,
classified: 1841 };
println!("Species: {}", p.species);
println!("Genus: {}", p.genus);
println!("Classified in {}", p.classified);
if p.extinct == true {
println!("Sadly this penguin has been made extinct.");
}
}
```
将 `impl` 数据类型与 `struct` 数据类型结合使用,你可以实现一个包含函数的结构体,并且可以添加继承和其他与类相似的特性。
### 函数
Rust 中的函数很像其他语言中的函数。每个函数都代表一组严谨的任务,你可以在需要时调用它们。主函数名必须是 `main`。
用 `fn` 关键字声明函数,后跟函数名称和函数接受的所有参数。
```
fn foo() {
let n = 8;
println!("Eight is written as {}", n);
}
```
通过参数,将信息从一个函数传递到另一个函数。例如,我已经创建了一个 `Penguin` 类(结构),并且我有一个 `Penguin` 的实例为 `p`,将目标函数的参数指定为 `Penguin` 类型,就可把 `p` 的属性从一个函数传递到另一个函数。
```
fn main() {
let p = Penguin { genus: "Pygoscelis".to_owned(),
species: "R adeliæ".to_owned(),
extinct: false, classified: 1841 };
printer(p);
}
fn printer(p: Penguin) {
println!("Species: {}", p.species);
println!("Genus: {}", p.genus);
println!("Classified in {}", p.classified);
if p.extinct == true {
println!("Sadly this penguin has been made extinct.");
}
}
```
### 变量
Rust 默认创建的为<ruby> 不可变 <rt> immutable </rt></ruby>变量。这意味着你创建的变量以后无法更改。这段代码虽然看起来没问题,但无法编译:
```
fn main() {
let n = 6;
let n = 5;
}
```
但你可以使用关键字 `mut` 声明一个<ruby> 可变 <rt> mutable </rt></ruby>变量,因此下面这段代码可以编译成功:
```
fn main() {
let mut n = 6;
println!("Value is {}", n);
n = 5;
println!("Value is {}", n);
}
```
### 编译
Rust 编译器,至少就其报错信息而言,是可用的最好的编译器之一。当你在 Rust 中出错时,编译器会真诚地告诉你做错了什么。实际上,仅通过从编译器错误消息中学习,我就了解了 Rust 的许多细微差别(就我理解到的 Rust 的任何细微差别而言)。即便有时错误消息太过于模糊,而不知所以然,互联网搜索几乎总能得到解释。
启动 Rust 程序的最简单方法是使用 `cargo`,它是 Rust 的包管理和构建系统。
```
$ mkdir myproject
$ cd myproject
$ cargo init
```
以上命令为项目创建了基本的基础架构,最值得注意的是 `src` 子目录中的 `main.rs` 文件。打开此文件,把我为本文生成的示例代码粘贴进去:
```
struct Penguin {
genus: String,
species: String,
extinct: bool,
classified: u64,
}
fn main() {
let p = Penguin { genus: "Pygoscelis".to_owned(), species: "R adeliæ".to_owned(), extinct: false, classified: 1841 };
printer(p);
foo();
}
fn printer(p: Penguin) {
println!("Species: {}", p.species);
println!("Genus: {}", p.genus);
println!("Classified in {}", p.classified);
if p.extinct == true {
println!("Sadly this penguin has been made extinct.");
}
}
fn foo() {
let mut n = 6;
println!("Value is {}", n);
n = 8;
println!("Eight is written as {}", n);
}
```
使用 `cargo build` 命令进行编译:
```
$ cargo build
```
执行 `target` 子目录下的二进制程序,或者直接运行 `cargo run` 命令来运行你的项目:
```
$ cargo run
Species: R adeliæ
Genus: Pygoscelis
Classified in 1841
Value is 6
Eight is written as 8
```
### Crates
任何语言的大部分便利都来自于它的库或模块。在 Rust 中,进行分发和跟踪的库称为 “crate”(箱子)。[crates.io](https://crates.io/) 是一个很好的社区 crate 注册网站。
把一个 crate 添加到你的 Rust 项目,首先要在 `Cargo.toml` 文件中添加这个 crate。例如,要安装随机数函数,我使用名为 `rand` 的 crate,使用 `*` 作为通配符,以确保在编译时获得最新版本:
```
[package]
name = "myproject"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["Seth <[email protected]>"]
edition = "2022"
[dependencies]
rand = "*"
```
在 Rust 代码中使用它需要在最顶行使用 `use` 语句:
```
use rand::Rng;
```
以下是一些创建随机种子和随机范围的示例代码:
```
fn foo() {
let mut rng = rand::thread_rng();
let mut n = rng.gen_range(1..99);
println!("Value is {}", n);
n = rng.gen_range(1..99);
println!("Value is {}", n);
}
```
你可以使用 `cargo run` 来运行它,它会检测代码是否被更改并触发一个新的构建。构建过程中下载名为 `rand` 的 `crete` 和它依赖的所有 `crate`,编译代码,然后运行它:
```
$ cargo run
Updating crates.io index
Downloaded ppv-lite86 v0.2.16
Downloaded 1 crate (22.2 KB) in 1.40s
Compiling libc v0.2.112
Compiling cfg-if v1.0.0
Compiling ppv-lite86 v0.2.16
Compiling getrandom v0.2.3
Compiling rand_core v0.6.3
Compiling rand_chacha v0.3.1
Compiling rand v0.8.4
Compiling rustpenguin v0.1.0 (/home/sek/Demo/rustpenguin)
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 13.97s
Running `target/debug/rustpenguin`
Species: R adeliæ
Genus: Pygoscelis
Classified in 1841
Value is 70
Value is 35
```
### Rust 速查表
Rust 是一门令人非常愉快的语言。集成了在线注册网站、有用的编译器和几乎直观的语法,它给人的适当的现代感。
但请不要误会,Rust 仍是一门复杂的语言,它具有严格的数据类型、强作用域变量和许多内置方法。Rust 值得一看,如果你要探索它,那么你应该下载我们的免费 [Rust 速查表](https://opensource.com/downloads/rust-cheat-sheet),以便快速了解基础知识。越早开始,就越早了解 Rust。当然,你应该经常练习以避免生疏。
>
> **[Rust 速查表](https://opensource.com/downloads/rust-cheat-sheet)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/1/rust-cheat-sheet>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hanszhao80](https://github.com/hanszhao80) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,565 | 英伟达开始着手为未来的开放和并行编程建立基础 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/nvidia-begins-to-set-the-foundation-for-future-open-and-parallel-coding/ | 2022-05-09T08:03:26 | [
"英伟达"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14565-1.html | 
随着图形处理器在计算机里变得越来越常见,英伟达正在扩大与标准和开源社区的合作,以便于包括先前仅限于该公司开发工具的下游技术。虽然人们在 C++ 和 Fortran 等语言上投入了大量精力,但这些语言被认为在高度并行的计算机上执行代码落后于原生实现的编程语言。
英伟达结合了开放和专有库的 CUDA 并行编程框架影响了许多正在开放和主流化的技术。在 2007 年,CUDA 作为一个为程序员开发基于 GPU 的系统的一系列编程工具和框架而推出。然而,随着 GPU 利用率在更多应用程序和领域中的增长,CUDA 理念发生了转变。
英伟达因其在 GPU 上的主导地位而广为人知,但 CUDA 是这家以 1 万亿市值为目标的软件和服务供应商重塑品牌的核心。英伟达的长期目标是成为一个全栈提供商,专注于自动驾驶、量子计算、医疗保健、机器人、网络安全和量子计算等特定领域。
英伟达已经在特定领域创建了专用的 CUDA 库,以及企业可以使用的硬件和服务。其 CEO 黄仁勋在最近的 GPU 技术大会上宣布的 “AI 工厂” 概念,最能体现全栈战略。客户可以将应用程序放入英伟达的大型数据中心,从而获得针对特定行业或应用程序需求量身定制的定制 AI 模型。
英伟达可以通过两种方式从 AI 工厂原则中受益:利用 GPU 容量或利用特定领域的 CUDA 库。在英伟达 GPU 上,程序员可以使用 OpenCL 等开源并行编程框架。另一方面,CUDA 将为那些愿意投资的人提供额外的最后一英里增长,因为其已调整为与英伟达的 GPU 密切运作。
虽然并行编程在高性能计算中很常见常见,但英伟达的目标是让其成为主流计算的标准。该公司正在协助实现一流工具的标准化,无论品牌、加速器类型或并行编程框架是什么,都可以编写可跨硬件平台移植的并行代码。
一方面,英伟达是 C++ 小组的成员,该小组正在为跨硬件同时执行可移植代码奠定基础。上下文可以是主要执行 IO 的 CPU 线程,也可以是执行高要求计算的 CPU 或 GPU 线程。英伟达特别致力于为 C++ 程序员提供异步和并行的标准语言和基础设施。
第一项工作侧重于内存模型,该模型已合并到 C++ 11 中,但当并行性和并发性变得更加普遍时,必须对其进行更新。C++ 11 的内存模型强调跨多核 CPU 的并发执行,但它缺乏并行编程钩子。C++ 17 标准为更高级别的并行特性奠定了基础,但真正的可移植性必须等待未来的标准。C++ 20 是当前标准,而 C++ 23 即将推出。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/nvidia-begins-to-set-the-foundation-for-future-open-and-parallel-coding/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[zxcv545](https://github.com/zxcv545) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | As graphics processors become more common in computers, Nvidia is expanding its collaboration with standards and open source communities to include downstream technologies that were previously limited to the company’s development tools. A lot of effort is being put into programming languages like C++ and Fortran, which are thought to lag behind native implementation when it comes to executing code on highly parallel computers.
Nvidia’s CUDA parallel programming framework, which combines open and proprietary libraries, is responsible for many of the technologies being opened up and mainstreamed. In 2007, CUDA was introduced as a set of programming tools and frameworks for programmers to develop GPU-based systems. However, as GPU utilisation grew in more applications and sectors, the CUDA philosophy shifted.
Nvidia is best recognised for its GPU dominance, but CUDA is at the heart of the company’s rebranding as a software and services supplier targeting a $1 trillion market cap. Nvidia’s long-term ambition is to become a full-stack provider with a focus on specific fields such as autonomous driving, quantum computing, health care, robotics, cybersecurity, and quantum computing.
Nvidia has created dedicated CUDA libraries in certain domains, as well as the hardware and services that businesses can use. The concept of a “AI factory,” announced by CEO Jensen Huang at the recent GPU Technology Conference, best exemplifies the full-stack strategy. Customers can drop applications into Nvidia’s mega datacenters, with the result being a customised AI model tailored to specific industry or application needs.
Nvidia may profit from AI factory principles in two ways: by utilising GPU capacity or by utilising domain-specific CUDA libraries. On Nvidia GPUs, programmers can use open source parallel programming frameworks such as OpenCL. CUDA, on the other hand, will deliver that extra last-mile increase for those willing to invest because it is tuned to operate closely with Nvidia’s GPU.
While parallel programming is common in high-performance computing, Nvidia’s goal is to make it a norm in mainstream computing. The company is assisting in the standardisation of best-in-class tools for writing parallel code that is portable across hardware platforms regardless of brand, accelerator type, or parallel programming framework.
For one thing, Nvidia is a member of a C++ group that is building the groundwork for simultaneous execution of portable code across hardware. A context could be a CPU thread that primarily performs IO or a CPU or GPU thread that does demanding computation. Nvidia is particularly engaged in delivering C++ programmers a standard language and infrastructure for asynchrony and parallelism.
The first work focused on the memory model, which was incorporated in C++ 11, but had to be updated when parallelism and concurrency became more prevalent. C++ 11’s memory model emphasised concurrent execution across multicore CPUs, but it lacked parallel programming hooks. The C++ 17 standard laid the foundation for higher-level parallelism features, but real portability will have to wait for future standards. C++ 20 is the current standard, with C++ 23 on the horizon. |
14,566 | 物联网安全审计工具集锦 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/tools-you-can-use-for-the-security-audit-of-iot-devices/ | 2022-05-09T09:01:33 | [
"物联网",
"安全审计"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14566-1.html | 数字化转型涉及数据驱动的决策与人工智能(AI)的结合。重要数据通过物联网(IoT)设备和智能组件进行传播。由于物联网设备常常处于不安全的环境,而且由于缺乏内生安全机制的脆弱性,很难免于潜在的网络攻击。以下是一些用于实现安全审计的开源工具,可以降低此类攻击风险。

网络攻击者和嗅探器可以从物联网设备中获取敏感数据,并利用这些信息对其他相关系统发起攻击。反病毒和计算机安全服务公司卡巴斯基表示,在 2021,物联网黑客数量同比增长了四倍多。
在很大程度上,黑客通过使用 Telnet 协议访问物联网网络,该协议为通过互联网与设备或服务器进行通信提供了命令行接口。根据研究报告,超过 58% 的物联网入侵使用各种协议以求实现挖掘加密货币、通过分布式拒绝服务(DDoS)攻击关闭系统、窃取机密数据的目的。
由于人们在疫情期间居家使用物联网设备的时间增加,安全风险也随之上升。这些物联网组件中的大部分无论是个人用还是商用,都缺乏基本的安全措施。人工智能和边缘计算等新技术也使网络和数据安全形势复杂化。卡巴斯基的一位安全专家 Dan Demeter 表示:智能组件变得流行,攻击的数量也随之上升了。

### 物联网组件的安全审计需求
网络攻击一直在演变,商业公司和政府部门都在采用越来越复杂的网络安全设施以防止他们的应用和基础设施免于在线攻击。全球渗透测试市场预计将从 2021 的 16 亿美元增长到 2026 年的 30 亿美元,2021 至 2026 年的复合年增长率为 13.8%。
物联网设备的渗透测试是一个热门话题,在这一领域有大量研究。即使采用“设计安全”的方法,渗透对于识别真正的安全危险并采取适当的预防措施也是至关重要的。
物联网部署中需要安全和隐私的关键部分和协议包括:
* <ruby> 受限应用协议 <rt> Constraint application protocol </rt></ruby>(CoAP)
* <ruby> 低功耗蓝牙 <rt> Bluetooth low energy </rt></ruby>(BLE)
* <ruby> 高级消息队列协议 <rt> Advanced message queuing protocol </rt></ruby>(AMQP)
* <ruby> 消息队列遥测传输 <rt> Message queuing telemetry transport </rt></ruby>(MQTT)
攻击者有多种可能的入口访问到联网设备。在物联网渗透测试(或安全审计)时,要测试完整的物联网场景和生态。测试内容包括从单个层和嵌入式软件到通信协议和服务器的所有内容。对服务器、在线接口和移动应用的测试并非物联网独有,但至关重要,因为它们涵盖了故障可能性很高的领域。物联网漏洞是电气、嵌入式软件和通信协议测试的重点。
在评估联网设备的安全性时会进行以下测试。这些测试都是使用不同的针对漏洞的高性能渗透测试和安全审计工具进行的:
* 通信端口中的攻击和操纵的测试
* 基于无线电信号捕获和分析的 IoT 嗅探
* 接口和后门测试
* 缓冲区溢出测试
* 密码破解测试
* 调试
* 密码学分析
* 固件操纵测试
* 逆向工程
* 内存转储

### 物联网安全审计使用的开源工具
物联网设备在我们的日常生活中变得越来越普遍,比如,智能自行车、健身跟踪器、医疗传感器、智能锁和联动工厂等。所有这些设备和组件都可以使用开源工具来抵御网络攻击,本文将简要介绍其中一些工具。
#### PENIOT
[PENIOT](https://github.com/yakuza8/peniot) 是一种物联网渗透测试工具,使安全审计团队能够通过利用设备的连接来测试和破坏具有各种安全威胁的设备。可以测试主动和被动安全威胁。在确定目标设备和相关信息(或参数)后,可以进行主动安全攻击,例如改变系统资源、重放合法通信单元等。还可以分析被动安全威胁,例如破坏敏感数据的机密性或访问网络流量分析。
#### Objection
[Objective](https://github.com/sensepost/objection) 是一个对物联网环境中使用的安卓和 iOS 应用程序进行详细分析和安全审计的工具。
目前许多智能组件和设备都在使用安卓和 iOS 平台,使用该工具可以通过详细的日志和安全审计报告对这些平台进行分析。
#### Routersploit
[这个](https://github.com/threat9/routersploit) 针对嵌入式设备的开源开发框架具有多个用于渗透测试和安全审计的功能和模块:
* Exploits —— 漏洞评估
* Creds —— 网络服务和证书的测试
* Scanners —— 对目标进行详细的安全审计
* Payloads —— 有效载荷和注入关键点的生成
* Generic —— 执行和测试攻击
#### Wireshark
[Wireshark](https://www.wireshark.org) 是一款功能丰富的、免费的网络协议分析器。MQTT 等多种物联网协议可通过该工具实现有效分析。为了发现弱点,可以根据协议配置安全规则并检查流量。可以使用 `tcpdump` 通过命令行访问网络数据包分析器。此类工具用于检查物联网设备和网络之间交换的数据包。
#### Binwalk
[Binwalk](https://www.kali.org/tools/binwalk) 是一种逆向硬件设计的工具。它是 Kali Linux 的关键组件之一,用于渗透测试、服务器指纹识别、安全审计和取证应用。
#### Firmwalker
[Firmwalker](https://github.com/craigz28/firmwalker) 是一款自由开源的工具,用于搜索和扫描固件文件系统,无论是否被提取或挂载。使用这个工具可以做一个详细的安全审计。
在物联网(IoT)和万物互联(IoE)的时代,有必要设计并使用高性能工具包进行渗透测试和安全审计。随着物联网设备数量的增加,安全风险也在增加。为了物联网和万物互联部署有更高级别的安全和隐私,有必要根据最新的协议和动态的流量定制化自由及开源的工具箱和软件包。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/tools-you-can-use-for-the-security-audit-of-iot-devices/>
作者:[Dr Kumar Gaurav](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/dr-gaurav-kumar/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[tendertime](https://github.com/tendertime) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Digital transformation involves data-driven decision making with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI). Important data is broadcast through Internet of Things (IoT) devices and smart gadgets. These IoT devices are very often insecure and have vulnerabilities as they lack built-in security mechanisms that can protect them from potential cyber attacks. There are quite a few open source tools that can be used to carry out security audits, lowering the risk of such attacks.*
cyber attackers and sniffers can access sensitive data from IoT devices and use that information to launch attacks on other linked systems. According to anti-virus and computer security service company Kaspersky, the number of IoT hacks more than quadrupled year-on-year in 2021.
For the most part, hackers gained access to Internet of Things (IoT) networks by using the Telnet protocol, which provides a command-line interface for communicating with devices or servers over the Internet. More than 58 per cent of IoT intrusions, as per research reports, used assorted protocols that aimed to mine cryptocurrencies, shut down systems via distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, or steal confidential data.
Because of the increased time spent using IoT devices at home during the pandemic, the security risks have increased. Many of these gadgets, whether used for personal or business purposes, lack basic security measures. New technologies like artificial intelligence and edge computing have also complicated the landscape of cyber and data security. As the popularity of smart gadgets grew, so did the number of attacks, according to Dan Demeter, a Kaspersky security analyst.
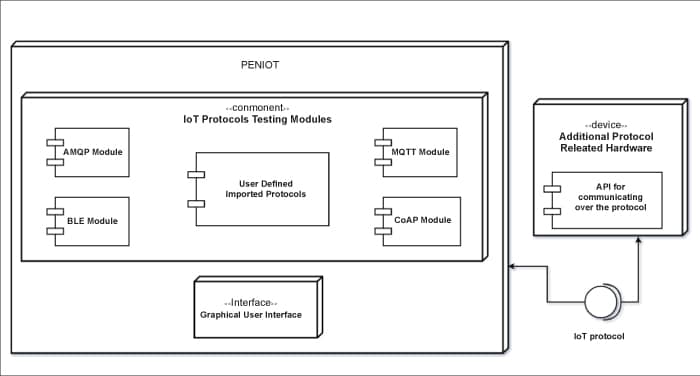

**The need for security audit in IoT gadgets**
Cyber attacks are evolving all the time, and businesses and government agencies are employing ever more sophisticated cyber security measures to guard their applications and infrastructure from online attacks. The global penetration testing market is expected to grow from US$ 1.6 billion in 2021 to US$ 3.0 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 13.8 per cent between 2021 and 2026.
Penetration testing on IoT devices is a hot topic and there is huge research in this segment. Even with a ‘security by design’ approach, pen testing is vital to identify true security dangers and take the appropriate precautions.
Key segments and protocols in IoT deployment where security and privacy is required are:
- Constraint application protocol (CoAP)
- Bluetooth low energy (BLE)
- Advanced message queuing protocol (AMQP)
- Message queuing telemetry transport (MQTT)
For an attacker to get access to a connected device, there are several possible entry points. At the time of an IoT pen test (or security audit), the complete IoT scenario and ecosystem is tested. This encompasses everything from the individual layer and the embedded software, to the communication protocols and the server. Tests of servers, online interfaces, and mobile apps are not unique to IoT, but are crucial since they cover areas with a high potential for failure. Vulnerabilities in IoT are the focus of electrical, embedded software, and communication protocol testing.
The following tests are run during a connected device’s security assessment. These are done using different high performance penetration testing and security audit tools against vulnerabilities:
- Tests for exploitation and manipulation in the communication ports
- IoT sniffing by capture and analysis of radio signals
- Detection of interfaces or backdoors
- Tests for buffer overflow
- Tests for breaking of passwords
- Debugging
- Cryptographic analysis
- Manipulation in firmware tests
- Reverse engineering
- Memory dumps
**Open source tools for the security audit of IoT devices**
IoT devices are becoming more and more commonplace in our daily lives. A few examples of such devices are smart bicycles, fitness trackers, medical sensors, smart locks, and linked factories. All of these devices and gadgets can be secured against cyber attacks using open source tools, some of which are briefly discussed here.
*PENIOT*
*https://github.com/yakuza8/peniot*
PENIOT is an IoT penetration testing tool that enables security audit teams to test and breach the devices with various security threats by exploiting their connectivity. There are both active and passive security threats that can be tested. It is possible to carry out active security attacks, such as altering system resources, replaying legitimate communication units and so on, after determining the target device and the relevant information (or parameters). Passive security threats, such as breaking the confidentiality of sensitive data or gaining access to network traffic analysis, can also be analysed.
**Objection**
*https://github.com/sensepost/objection*
Objection is a tool for the detailed analysis and security audit of the Android and iOS apps used in the IoT environment.
Nowadays, a number of smart gadgets and devices are using Android and iOS platforms which can be analysed with detailed logs and security audit reports, using this tool.
**Routersploit**
*https://github.com/threat9/routersploit*
This powerful open source exploitation framework for embedded devices has multiple features and modules for penetration testing and security audit:
- Exploits – vulnerabilities evaluation
- Creds – testing of network services and credentials
- Scanners – detailed security audit of target
- Payloads – generation of payloads and injection key points
- Generic – performing and testing of assaults
**Wireshark**
*https://www.wireshark.org*
Wireshark is a free network protocol analyser with a lot of features. Various protocols, including MQTT, are used by IoT devices to communicate and these can be analysed effectively. Security rules are configured according to the protocol and the traffic is examined in order to discover any weaknesses. A network packet analyser is accessible through the command line using tcpdump. Such tools are used to examine data packets exchanged between IoT devices and networks.
**Binwalk**
*https://www.kali.org/tools/binwalk*
Binwalk is a tool for reversing the design of hardware. It is one of the key components in Kali Linux that is used for penetration testing, server fingerprinting, security audit and forensic applications.
**Firmwalker**
*https://github.com/craigz28/firmwalker*
Firmwalker is a free and open source tool for searching and scanning the firmware file system, irrespective of whether it is extracted or mounted. A detailed security audit can be done using this tool.
In the era of Internet of Things (IoT) and Internet of Everything (IoE), there is a need to devise and use high performance toolkits for penetration testing and security audits. As the number of IoT devices grows, so do the security risks. Free and open source toolkits and software suites should be customised according to recent protocols and dynamic traffic so that higher levels of security and privacy can be enforced in IoT and IoE deployments. |
14,567 | 怎样在 Ubuntu Linux 中移除 Snap 软件包 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/04/remove-snap-ubuntu/ | 2022-05-09T10:35:05 | [
"Snap"
] | /article-14567-1.html | 
>
> 这是一篇关于在 Ubuntu Linux 系统中如何删除 Snap,以得到一个无 Snap 系统的教程。
>
>
>
由 Canonical 开发的 Snap 软件包在一些场景下是有益的。它为终端用户直接提供了轻便且快速的程序更新。不仅如此,它还有其他的好处,比如它打包了所有依赖包,并允许安装同一个应用的多个版本。此外,它运行在沙盒模式,提供了安全和其他方面的好处。
在这些好处中, Snap 技术也有一些地方备受争论。举个例子,几乎所有使用 Snap 软件包的用户都说它的性能较差,包括它的启动时间要比本地 deb 或者 RPM 软件包时间要长。另外,由于它的设计,程序安装的体积巨大,浪费磁盘空间,因为它打包了所有用到的依赖包。
不仅如此,由于沙盒的天然属性,Snap 程序可能无法访问你的 Linux 桌面的几个部分,除非提供了适当的权限。
这个指南阐述了你如何从 Ubuntu 系统中完全移除 Snap。
这些步骤在 [Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/01/ubuntu-22-04-lts/) 中进行了测试。然而,它应该也适用于所有的 Ubuntu 系统版本。
>
> **警告:这些步骤将会移除 Ubuntu 系统中两个关键的程序:软件商店和 Firefox。尝试这些步骤之前确认你已经对书签和 Firefox 的其它设置做了备份。**
>
>
>
### 在 Ubuntu Linux 移除 Snap 软件包
1、在你的系统中打开一个终端,使用以下命令查看已经安装的 Snap 软件包的列表。它显示了 Snap 软件包,比如 Firefox,软件商店,主题以及其它默认已经安装的核心软件包。
```
snap list
```

2、按照以下的顺序移除 Snap 软件包。首先移除 Firefox。然后是软件商店,和用以上命令看到的你的系统中的其它软件包。
```
sudo snap remove --purge firefox
sudo snap remove --purge snap-store
sudo snap remove --purge gnome-3-38-2004
```
```
sudo snap remove --purge gtk-common-themes
sudo snap remove --purge snapd-desktop-integration
sudo snap remove --purge bare
sudo snap remove --purge core20
sudo snap remove --purge snapd
```
3、最后,通过 `apt` 命令移除 Snap 服务。
```
sudo apt remove --autoremove snapd
```

这还没完,即使你用以上命令移除了 Snap 软件包,但是如果你没有关闭 apt 触发器,`sudo apt update` 命令会再一次将 Snap 安装回来。
4、所以,要关闭它,我们需要在 `/etc/apt/preferences.d/` 目录下创建一个 apt 设置文件 `nosnap.pref` 来关闭 Snap 服务。
```
sudo gedit /etc/apt/preferences.d/nosnap.pref
```
5、添加以下的命令行,并保存该文件。
```
Package: snapd
Pin: release a=*
Pin-Priority: -10
```

如果你知道如何使用它,那么这个 apt 设置文件是一个潜在的工具。举个例子,在以上的状态中,`Pin-Priority -10` 意思就是阻止 Snap 软件包的安装。
与这个教程不相关的,举个例子,如果你想给所有发行版代号为 “bulleye” 的软件包超高优先权的话,那么就可以查看这些设置文件。如果你想了解更多,你可以访问 [apt 手册页](https://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/focal/man5/apt_preferences.5.html)。
```
Package: *
Pin: release n=bullseye
Pin-Priority: 900
```
6、回到我们的主题,一旦你已经保存和关闭以上文件,从终端中再次运行以下命令。
```
sudo apt update
```
7、最后,从 Ubuntu 中移除 Snap 的步骤全部完成。
### 从 Ubuntu 移除 Snap 后使用 deb 文件安装软件商店和 Firefox
你已经移除了 Firefox 和软件商店,但是你的工作还需要它们。
要安装 apt 版的 GNOME 软件商店,你可以使用以下命令。确保使用 `--install-suggests` 参数。否则,将会再次安装上 Snap 版本的软件包管理器!
```
sudo apt install --install-suggests gnome-software
```
要安装 Firefox,通过以下命令使用官方 PPA 仓库。
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:mozillateam/ppa
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -t 'o=LP-PPA-mozillateam' firefox
```


一旦你已经安装完 Firefox,使用以下命令开启自动更新。要了解更多,[访问此页](https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/09/remove-firefox-snap-ubuntu/)。
```
echo 'Unattended-Upgrade::Allowed-Origins:: "LP-PPA-mozillateam:${distro_codename}";' | sudo tee /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/51unattended-upgrades-firefox
```
最后但同样重要,当运行 `apt` 时,为 Firefox 创建另一个设置文件给予以上 PPA 仓库超高优先权。如果你不这么做,`apt update` 命令会再次安装 Snap 版本 Firefox,并把它的“ Snap 朋友们”带回来 ???。
```
sudo gedit /etc/apt/preferences.d/mozillateamppa
```
最后,添加这些命令行并保存文件。
```
Package: firefox*
Pin: release o=LP-PPA-mozillateam
Pin-Priority: 501
```
完成。
### 在 Ubuntu 系统恢复到 Snap 软件包
如果你改变想法,移除该设置文件,并通过以下命令再次启动安装程序。
```
sudo rm /etc/apt/preferences.d/nosnap.pref
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
sudo snap install snap-store
sudo apt install firefox
```
### 总结
关于在 Ubuntu 下移除 Snap 软件包做个总结,我想说的是这些处理 Snap 软件包的方法实属无奈。主要是这对新用户来说很困难。我希望这个指南能帮助你处理好 Snap 软件包。完结撒花。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/04/remove-snap-ubuntu/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hwlife](https://github.com/hwlife) 校对:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel), [wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,568 | Tails 5.0 发布:基于 Debian 11,附带新的 Kleopatra 工具 | https://news.itsfoss.com/tails-5-0-release/ | 2022-05-09T10:47:54 | [
"Tails"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14568-1.html |
>
> Tails 5.0 是一次令人印象深刻的升级,采用了 Debian 11 和一个新的工具,为用户配备了增强的安全和隐私。
>
>
>

Tails 是一个流行的 Linux 发行版,它专注于保护人们免受审查和监视,是 [注重隐私的 Linux 发行版](https://itsfoss.com/privacy-focused-linux-distributions/) 之一。
你可以在任何地方使用它和 U 盘 来完成工作,而不用担心暴露你的信息。
Tails 5.0 是最新的版本,它基于 Debian 11(Bullseye)构建。因此,你可以期待 Tails 5.0 中具备所有 [Debian 11 的改进](https://news.itsfoss.com/debian-11-feature/)。
### Tails 5.0:更新内容
让我们来看看该版本所引入了哪些新功能和软件升级吧!
以下是其中的一些亮点。
#### 增加了 Kleopatra 工具

Kleopatra 是 [GnuPG](https://www.gnupg.org/) 的一个图形界面,它用于加密文本和文件。在 Tails 5.0 中,Kleopatra 取代了 OpenPGP 小程序 和 Seahorse 工具。
Kleopatra 只在一个软件包中就完成了这一切。并且,相对而言,Kleopatra 的维护更加活跃,问题最少。
#### 默认启用的附加软件
当使用持久化存储时,附加软件功能是默认启用的。
因此,你可以在短时间内快速配置你想要的东西。
#### 对活动概览的改进

在 Tails 5.0 中,你可以使用活动概览来访问你的窗口和应用程序。你只需点击屏幕左上角的“<ruby> 活动 <rt> Activities </rt></ruby>”按钮或按下键盘上的<ruby> 超级 <rt> Super </rt></ruby>键(LCTT 译注:在某些键盘上是 WIN 键)即可。
你还可以在同一屏幕中搜索应用程序、文件和文件夹。
#### 软件升级
Tails 5.0 基于 Debian 11,因此,所有的基本软件都已升级,包括:
* Tor 浏览器 to 11.0.11
* GNOME 3.38
* MAT to 0.12
* Audacity 2.4.2
* 磁盘工具 3.38
* GIMP 2.10.12
* LibreOffice 7.0
#### 其他改进
除软件升级外,无驱动打印和扫描的硬件支持也得到了更新,以支持新款的打印机/扫描仪。
除此之外,它还有许多修复。你可以在其 [官方发布公告](https://tails.boum.org/news/version_5.0/index.en.html) 中查看更多信息。
### 下载 Tails 5.0
你可以在官方网站下载最新的 Tails 5.0 ISO。
>
> **[Tails 5.0](https://tails.boum.org/install/index.en.html)**
>
>
>
注意,如果你已经在使用 Tails,请不要执行自动升级。你需要按照 [官方说明](https://tails.boum.org/doc/upgrade/index.en.html#manual) 进行手动升级。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/tails-5-0-release/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Tails is a popular Linux distribution that focuses on protecting against censorship and surveillance. It is one of the [privacy-focused Linux distributions](https://itsfoss.com/privacy-focused-linux-distributions/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
Without worrying about exposing your information, you can use it anywhere using a USB stick and get your work done.
Its latest release, Tails 5.0, utilizes Debian 11 (Bullseye) as its base. So, you should expect all the [improvements in Debian 11](https://news.itsfoss.com/debian-11-feature/) in Tails 5.0.
## Tails 5.0: What’s New?
Here, we shall look at the new features and software upgrades introduced with the release.
Some highlights include:
### Adding Kleopatra
Kleopatra is a graphical interface to [GnuPG](https://www.gnupg.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to help encrypt text and files. With Tails 5.0, Kleopatra replaces *OpenPGP* Applet and the *Seahorse* utility.
Kleopatra does it all in a single package. In addition to that, Kleopatra is more actively maintained comparatively with minimal issues.
### Additional Software Enabled by Default
When using the persistent storage, the additional software feature is enabled by default.
So, you can quickly configure what you want in no time.
### Improvements to the Activities Overview
With Tails 5.0, you can use the Activities overview to access your windows and applications. You can simply click on the Activities button in the top-left corner of the screen or press the Super key on your keyboard.
It is also possible to search applications, files, and folders from the same screen.
### Updated Software
With Debian 11 as its base, all the essential software has been upgraded, including:
- Tor Browser to 11.0.11
- GNOME 3.38
- MAT to 0.12
- Audacity 2.4.2
- Disk Utility 3.38
- GIMP 2.10.12
- LibreOffice 7.0
### Other Improvements
Along with all the software upgrades, hardware support for driverless printing and scanning has also been updated to support newer printers/scanners.
In addition to all this, you also get numerous fixes. You can explore more about it in its [official release announcement](https://tails.boum.org/news/version_5.0/index.en.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Download Tails 5.0
You can download the latest Tails 5.0 ISO from the official website.
And, if you already use Tails, you cannot perform an automatic upgrade. You need to do a manual upgrade instead, following the [official instructions](https://tails.boum.org/doc/upgrade/index.en.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com#manual).
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,570 | 分享 8 篇使用 Linux 命令行的技巧 | https://opensource.com/article/21/1/linux-commands | 2022-05-10T08:48:33 | [
"命令行"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14570-1.html |
>
> 要好好利用无所不能的 Linux 命令行提供的所有功能
>
>
>

Linux 命令行是极其灵活的。无论你是管理服务器还是在桌面系统上启动终端窗口,都可以通过命令行无所不包的工具包来更新文件、调整系统性能或者管理进程。命令行里发生的事情是非常有趣的。
我们发布了许多关于如何充分利用系统的优秀文章,证明了命令行的流行。以下是 8 篇关于 Linux 命令阅读量最高的文章:
### 《使用这些技巧让 Bash 命令历史更加有用》
>
> **[文章地址](/article-12344-1.html)**
>
>
>
Bash 是大多数 Linux 系统上的默认命令行 Shell。Seth Kenlon 编写了该指南,用于帮助你了解 Bash 命令历史。修改 Bash 命令历史通常没有听起来那么危险,特别是当你带有目的地修改它的时候。告诉 Bash 你希望它记住什么,甚至还可以直接通过删除你不想要或不需要的条目来重写命令历史。根据需要使用你的历史会话,明智地行使你对命令历史的权力。
### 《如何在 Linux 终端中兼顾特性和性能》
>
> **[文章地址](https://opensource.com/article/20/7/performance-linux-terminal)**
>
>
>
Ricardo Gerardi 非常喜欢命令行应用程序,他花了很多时间在终端上工作。Ricardo 投入了一些时间,把命令行变成了一个令人愉快的工作环境。你可以通过了解如何自定义终端应用程序、主题和提示符,来创建一个功能丰富、易于使用系统资源的终端。
### 《放弃 Bash 转投拥有更优美配置的 fish》
>
> **[文章地址](https://opensource.com/article/20/3/fish-shell)**
>
>
>
Matt Broberg 最近放弃了默认的命令行解释器 —— Bash,转而支持 fish。fish 自豪地宣称自己是 “90 年代的命令行 shell”。这个以鱼为主题的 “友好的交互式 shell” 为命令行创造了更愉快的体验。阅读 Matt 的文章来进一步了解如何充分利用 fish。如果你不想再对你的终端修修补补,换一个更漂亮的默认 shell,把更多精力放在代码上,不妨试一试 fish。
### 《分析 Linux 里二进制文件的 10 种方式》
>
> **[文章地址](/article-12187-1.html)**
>
>
>
我们每天都在和二进制文件打交道,但我们对它们的了解甚少。Linux 提供了一组丰富的工具,使分析二进制文件变得轻而易举!这些简单的命令和工具可以帮助你顺利完成分析二进制文件的任务。无论你的工作角色是什么,了解这些工具的基本知识将帮助你更好地了解你的 Linux 系统。Gaurav Kamathe 介绍了一些最流行的用于管理二进制文件的 Linux 工具和命令,包括 `file`、`nm`、`strings` 和 `hexdump`。
### 《可用于 Linux 命令行的 4 种 Markdown 工具》
>
> **[文章地址](/article-12048-1.html)**
>
>
>
当涉及使用 Markdown 格式的文件时,命令行工具占据了主导地位。它们轻巧、快速、强大而又灵活,其中大多数遵循 Unix “把一件事情做好”的哲学。Scott Nesbitt 回顾了 4 种命令行实用工具,它们可以帮助你更高效地处理 Markdown 文件。
### 《禁用 atime 来提高 Linux 系统性能》
>
> **[文章地址](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/linux-noatime)**
>
>
>
每当我在为家里的电脑升级 Linux 时,我都会把我通常要做的任务列出来。这些年来,它们已经成为了习惯:备份文件、还原系统、重新安装、恢复文件,然后重新安装额外的我最喜欢的应用程序。我还会对系统进行了一些调整。其中一个调整就是 `atime`,它是 Linux 里每个文件的三个时间戳之一。关掉 `atime` 是一种简单但有效的提升系统性能的方法。下面是关于 atime` 的介绍,以及为什么它会有影响。
### 《使用 fstrim 延长固态硬盘的寿命》
>
> **[文章地址](/article-11959-1.html)**
>
>
>
在过去的十年中,固态硬盘(SSD)带来了一种全新的管理存储的方式。相比传统的机械硬盘,固态硬盘具有一些优点,比如安静、更酷的操作和更快的接口规格。当然,新技术带来了新的维护和管理方法。Alan Formy-Duval 写了一个新的 systemd 服务让你更容易管理固态硬盘。
### 《Linux 命令行工具的 5 种新式替代品》
>
> **[文章地址](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/modern-linux-command-line-tools)**
>
>
>
在我们日常使用的 Linux 或 Unix 系统中,我们会使用许多命令行工具来完成我们的工作,并帮助我们更好地了解和管理我们的系统。多年来,这些工具已经现代化并移植到了不同的系统中。然而,总的来讲,它们仍然保持着最初的想法、外观和感觉。近年来,开源社区已经开发出了提供额外好处的替代工具。Ricardo Gerardi 向我们展示了如何通过这 5 种新的替代品改进旧的命令行工具来获得新的好处。
### 总结
把这些文章作为跳板,寻找你自己关于命令行的技巧和花招吧!这份清单里还缺少什么吗?请在下方评论,或者提交一篇你自己的文章!
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/1/linux-commands>
作者:[Jim Hall](https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[FYJNEVERFOLLOWS](https://github.com/FYJNEVERFOLLOWS) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The Linux command line provides a great deal of flexibility. Whether you are managing a server or launching a terminal window on a desktop system, the command line brings with it an extensive toolkit to update files, tweak system performance, and manage processes. The command line is where it's at.
Testifying to the command line's popularity, Opensource.com publishes many excellent articles about how to get the most out of your system. The following were some of Opensource.com's most-read articles about Linux commands in 2020:
[Make Bash history more useful with these tips](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/bash-history-control)
Bash is the default command line shell on most Linux systems. Seth Kenlon wrote this guide to help you with your Bash **history**. Manipulating history is usually less dangerous than it sounds, especially when you're curating it with a purpose in mind. Tell Bash what you want it to remember—or even rewrite history by deleting entries you don't want or need. Use your history sessions as required, and exercise your power over history wisely.
[How I balance features and performance in my Linux terminal](https://opensource.com/article/20/7/performance-linux-terminal)
Ricardo Gerardi is a big fan of command line applications and spends a lot of his time working in a terminal. Ricardo invested some time to make the command line a pleasant environment to work in. Learn how to customize terminal apps, themes, and the prompt to create a feature-rich terminal that's easy on system resources.
[Drop Bash for the fish shell to get beautiful defaults](https://opensource.com/article/20/3/fish-shell)
Matt Broberg recently let go of the default command line interpreter, Bash, in favor of fish, which proudly markets itself as "a command line shell for the '90s." The fish-themed "friendly interactive shell" creates a more enjoyable experience on the command line. Read Matt's article to learn more about how to get the most out of fish. If you're looking to move away from tinkering with your terminal, focus more on code, and have a more beautiful default shell, give fish a try.
[10 ways to analyze binary files on Linux](https://opensource.com/article/20/4/linux-binary-analysis)
We work with binaries daily, yet we understand so little about them. Linux provides a rich set of tools that makes analyzing binaries a breeze! These simple commands and tools can help you sail through the task of analyzing binary files. Whatever your job role, knowing the basics about these tools will help you understand your Linux system better. Gaurav Kamathe covers some of the most popular Linux tools and commands to manage binaries, including **file**, **nm**, **strings**, and **hexdump**.
[4 Markdown tools for the Linux command line](https://opensource.com/article/20/3/markdown-apps-linux-command-line)
When it comes to working with files formatted with Markdown, command line tools rule the roost. They're light, fast, powerful, and flexible, and most of them follow the Unix philosophy of doing one thing well. Scott Nesbitt reviews four command line utilities that can help you work more efficiently with Markdown files.
[Improve Linux system performance with noatime](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/linux-noatime)
Whenever I upgrade Linux on my home computer, I have a list of tasks I usually do. They've become habits over the years: I back up my files, wipe the system, reinstall from scratch, restore my files, then reinstall my favorite extra applications. I also make a few system tweaks. One tweak is **atime**, which is one of the three timestamps on every file on Linux. Turning off **atime** is a small but effective way to improve system performance. Here's what it is and why it matters.
[Extend the life of your SSD drive with fstrim](https://opensource.com/article/20/2/trim-solid-state-storage-linux)
Over the past decade, solid-state drives (SSD) have brought about a new way of managing storage. SSDs have benefits like silent and cooler operation and a faster interface spec, compared to their elder spinning ancestors. Of course, new technology brings with it new methods of maintenance and management. Alan Formy-Duval wrote about a new **systemd** service to make your life easier when managing SSDs.
[5 modern alternatives to essential Linux command line tools](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/modern-linux-command-line-tools)
In our daily use of Linux/Unix systems, we use many command line tools to complete our work, and to help us understand and manage our systems better. Over the years, these tools have been modernized and ported to different systems. However, in general, they still follow their original idea, look, and feel. In recent years, the open source community has developed alternative tools that offer additional benefits. Ricardo Gerardi shows us how to gain new benefits by improving old command line tools with these five updated alternatives.
## Wrap up
Use these articles as a springboard to finding your own tips and tricks for the command line. Is there something missing from this list? Comment below, or better yet, submit an article of your own!
## 1 Comment |
14,571 | ESI 集团同 ENSAM 合作,开源其 Inpsector 软件 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/esi-group-collaborates-with-ensam-open-sources-its-inspector-software/ | 2022-05-10T10:56:03 | [
"开源"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14571-1.html | 
Inspector 是一个可视化的交互式数据探索软件,能够对海量数据进行分析并提取相关信息,可用于预测性维修、网络安全、控制、机器学习算法分析等。
通过让更多的人使用 Inspector 软件,让他们能够合作开发可靠灵活的方案,以解决社区的技术问题和特殊需求,ESI 集团增加了对工业界和学术界的贡献。
作为 ESI 集团和 ENSAM 之间持续赞助合作和共创伙伴关系的一部分,将由 ENSAM(<ruby> 巴黎高科国立高等工程技术大学 <rt> Ecole Nationale Supérieure d’Arts et Métiers </rt></ruby>)领导 Inspector 的增长和扩展。通过共同参与建设由新加坡国家科学研究中(CNRS)协调的 Descartes 计划、CREATE-ID 国际研究讲座以及 ESI – ENSAM 虚拟工程实验室,双方加强了合作。
这种开源方式有许多好处。首先,社区能够以最有效的方式使用该软件,科学界能够从根据用户需求定制的新功能以及安全方面的改进中受益。其次,ESI 集团希望提供一个从软件中获利机会,包括汽车及航空在内的各种行业的客户已经证明了这一软件的可靠性。由于许多利益相关者的参与,Inspector 将持续发展以应对社区需求。
ESI 集团打算将其数据分析软件开源发布,得到了一些行业领导者和 Inspector 用户的兴趣和支持,例如 CNS 就是其中一例。
CNS 的总经理 Stephane Perrin 表示:“ESI 集团这一决定证明了集团的先进技术对创新和科学生态系统的贡献。CNS 作为一家网络与安全的专业公司,我们用行动支持 Inspector 的未来。除了将 Inspector 集成到我们的持续网络审计软件套件中外,不久后我们还将通过我们创新解决方案的业务部门为该软件提供支持。”
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/esi-group-collaborates-with-ensam-open-sources-its-inspector-software/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Veryzzj](https://github.com/Veryzzj) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Inspector is a visual and interactive data exploration software that can analyse massive amounts of data and extract relevant information for applications such as predictive maintenance, cybersecurity, control, and machine learning algorithm analysis.
ESI Group extends its commitment to the industrial and academic ecosystems by making Inspector software available to as many individuals as possible, allowing them to collaborate on a dependable and flexible solution to address the technological problems and special needs of the community.
Inspector’s growth and extension will be led by ENSAM (Ecole Nationale Supérieure d’Arts et Métiers), as part of an ongoing sponsorship and co-creation partnership between ESI Group and ENSAM. Their joint participation in the DesCartes initiative, coordinated by the CNRS in Singapore, the CREATE-ID international research chair, and the ESI – ENSAM virtual engineering laboratory has strengthened their relationship.
There are numerous advantages to using an open source strategy. First, it lets the community to use the programme in the most efficient and effective manner possible, allowing the scientific community to benefit from new functionality tailored to each user’s needs, as well as security enhancements. Second, ESI Group hopes to provide an opportunity to profit from software whose dependability has been demonstrated over time by its clients in a variety of industries, including automotive and aeronautics. Thanks to the involvement of many stakeholders, “Inspector” will continue to evolve and adapt to the demands of the community.
ESI Group’s intention to release its data analysis software as open source has received interest and support from a number of industry leaders and “Inspector” users. This is the case with CNS, for example.
Stephane Perrin, Managing Director of CNS says: “The decision taken by ESI Group is a great illustration of the Group’s dedication to the innovation and scientific ecosystem with its cutting-edge technologies. At CNS, a Network and Security expertise company, we are mobilized to ensure the future of Inspector. In addition to integrating Inspector into our continuous network auditing software suite, we will also soon offer support for the software via our business unit dedicated to innovative solutions.” |
14,572 | Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 和 20.04 LTS 之间的十大变化 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/04/difference-ubuntu-22-04-20-04/ | 2022-05-10T15:55:00 | [
"Ubuntu"
] | /article-14572-1.html | 
>
> 这里为准备从 20.04 LTS 迁移到 22.04 LTS 的用户列出了十个最重要的变化。
>
>
>
如果你是一位 [Ubuntu 20.04 LTS “Focal Fossa”](https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/08/ubuntu-20-04-3-release/) 用户,并准备迁移到 [Ubuntu 22.04 LTS “Jammy Jellyfish”](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/01/ubuntu-22-04-lts/),这篇文章将为你提供一些指引。在这两个 LTS 版本之间存在巨大的结构性变化,这在 LTS 分支中一般比较罕见。对比下来,不难发现本次更新一次性改变了大量的内容。
了解了这一点之后,本文将针对普通用户关切的方面,列出十个发生根本性变化的特性,并为用户提供一些指引。
### Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 与 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS – 特性变化
#### 1、徽标、颜色和 Plymouth 动画
第一个你会注意到的视觉变化便是基调颜色相比早期的两个“棕橙色”变得更“橙色”。同时 Canonical 对徽标进行了修改,这一点体现在开机时 Plymouth 动画中。新的徽标乍一看会显得有些怪异,但看久了会比较顺眼,至少我认为这是一个十分与众不同的徽标。

#### 2、安装
Ubuntu 的默认安装程序并没有看到太多变化。我们其实更希望最新的 [基于 Flutter 的安装程序](https://github.com/canonical/ubuntu-desktop-installer) 能够最终落地,但并没有。基于此,整体安装流程并未发生变化。我仅能够观察到对话框和按钮的强调色发生了变化。从功能角度而言,安装流程并未发生任何变化。

#### 3、锁屏与登录界面、桌面的初始界面以及壁纸
锁屏与登录界面的渐变变得更为精细,密码框采用了无边框设计。初次登录时的布局和壁纸发生了很大的变化。桌面的 “家目录” 快捷方式被重命名为 “Home”,而非你的用户名,但回收站快捷方式则移到了左侧的任务栏中,并用分隔符与其他任务栏图标隔开了。
除此之外,顶部状态栏并未大改。系统托盘的菜单则进行了细微的修正,布局更为宽松。这些变化主要来自于 [GNOME 42](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/03/gnome-42-release/) 的变化。
日历菜单并未发生变化。



#### 4、桌面布局和 GNOME 版本升级
一个十分明显的变化就是 GNOME 版本由 GNOME 3.36 升级到了 GNOME 42。这是所有升级用户都会看到的显而易见的升级。Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 搭载的 GNOME 42 带来了水平的工作区视图以及水平的应用视图。所以,迁移之后手势从垂直转变为水平会有一些不习惯,但用一段时间就好了。
如果你的设备是触控屏的笔记本电脑或屏幕,经过一点学习之后,新的 GNOME 42 手势会给你十分顺滑的使用体验。以下是桌面、应用和工作区的对比图。


#### 5、新的强调色与显示样式
有一个我非常喜欢的变化是最新的浅色和深色主题。早先 Ubuntu 有三个选择:浅色、深色和混合(标准)。这在 GNOME 42 中发生了改变,因为其本身就带有内置的浅色和深色模式。另一方面,它还引入了一个新的强调色选项(这并不是原本的 GNOME 42 带来的),允许用户在全局进行自定义。
当然,你还不能像 KDE Plasma 一样选择自定义的强调色。这些变化大多来自于最近的 libadwaita 和 GTK4 对 GNOME Shell 和原生应用程序的移植。
而当你在 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 中打开深色模式,它会自动应用于所有支持的应用,这是一个与 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS 十分显著的区别。


#### 6、文件管理器
在这个版本中,文件管理器的版本由 3.36.x 升级到了 42。区别是你能看到更为紧凑的设计、在文字和选项之间更为合理的布局,以及顶部控制栏的小工具风格,这一切都归功于 GTK4 和对底层错误的修复。文件中的地址栏有些不同,目录之间有一个分隔符,而汉堡菜单在最后。当然,这些变化都较为细微,你可能不会感受到它们之间有什么不同。

#### 7、截图工作流的变化
另一个值得注意并且需要用户进行学习的是截图方式的改变。它完全改变了。早先你按下 `Print Screen` 键时,会自动截图并保存到图片文件夹中。现在有了 GNOME 42 内置的截图和录屏工具,工作流程被完全改变。
当你在截图时,你会发现有三个选项,你可以选择某个区域、全屏截图或者特定窗口。更重要的是,你还能选择是否让光标出现在截图中,此外还有录屏功能可选。选择完成之后点击“捕捉”按钮,这张图片将在被保存到图片文件夹,并同时复制到你的剪切板。

总体而言,相较于之前多了一个步骤。
在所有应用程序窗口顶部的右键菜单上,增添了一个新的截图选项。

#### 8、 Firefox 浏览器成为了 Snap 版本
此外,Firefox 浏览器在本次更新中变成了 Snap 版本。而此前在 20.04 LTS 中,Firefox 浏览器以 deb 包形式呈现。这对于一般用户而言区别不大。
但是 Firefox 浏览器的 Snap 沙箱运行模式使得安装 GNOME 扩展工具时会产生问题,同时在同等硬件条件之下相较于之前的版本会显得更慢。
这个最为常用的应用的 Snap 迁移所带来的后续影响我们将拭目以待。
#### 9、不同的设置窗口
在设置中出现了一个新的面板:多任务。多任务面板允许你调整触发角以及激活窗口边缘。此外你可以指定工作区的数量,并设置自动删除空的工作区。而针对多显示器用户,现在可以选择仅在主屏幕上显示工作区或是在所有屏幕上显示工作区。

#### 10、主题和应用更新
此外,软件的变化带来了不同的响应式外观并能够适应任何形式。软件商店同时带来了新的界面,包含了按照类别分类的软件视图以及“编辑之选”栏目。
应用详情页面变得更加易读,重要的信息,例如总下载大小、评分、安全标记以及应用截图都以更可辨别地方式呈现。


最后,这两个版本的内部差异出现在软件包、官方桌面环境主题和错误修正上。下面是对重要软件包版本变化的一个对比:
| **20.04** | **22.04** |
| --- | --- |
| GCC 10.3 | GCC 11.2 |
| Hplip 3.20.3 | Hplip 3.21.12 |
| LibreOffice 6.4.7 | LibreOffice 7.3.2 |
| (未引入) | Pipewire 0.3.48 |
| Python3 3.8.2 | Python3 3.10.1 |
| Samba 4.13 | Samba 4.15 |
| Systemd 245.4 | Systemd 249.11 |
### 总结
总而言之,这是 Ubuntu LTS 分支历次更新中变化最大的一次,不论是从视觉上还是特性角度。
我希望这个指南能够令读者了解两个版本之间的主要区别,以及应当预期什么样的使用体验。
祝好~
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/04/difference-ubuntu-22-04-20-04/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[PeterPan0106](https://github.com/PeterPan0106) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,573 | ZeroTier:你自己的虚拟骨干网 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/zerotier-network | 2022-05-10T17:03:00 | [
"ZeroTier",
"主干网"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14573-1.html |
>
> ZeroTier 是一个加密的虚拟主干网,允许多台机器像在一个网络上一样通信。
>
>
>

*自动化是现在的一个热门话题。在我作为网站可靠性工程师(SRE)的日常工作中,我的部分职责是将尽可能多的重复性任务自动化。但是我们当中有多少人在日常生活、非工作生活中这样做呢? 今年,我专注于自动化工作,以便我们可以专注于重要的事情。*
在实现一切自动化的同时,我在一些远程站点上遇到了困难。我不是一个网络专家,所以我开始研究我的选择。在研究了各种虚拟专用网络(VPN)、硬件端点、防火墙规则以及支持多个远程站点的所有东西后,我感到困惑、暴躁,并对这一切的复杂性感到沮丧。
然后我发现了 [ZeroTier](https://github.com/zerotier)。ZeroTier 是一个加密的虚拟主干网,允许多台机器像在一个网络上一样通信。代码全部是开源的,你可以自行托管控制器,或者使用 [ZeroTierOne](https://www.zerotier.com/pricing) 服务,有免费或付费计划。我现在使用的是它们的免费计划,它很强大、可靠,而且非常稳定。
因为我使用的是 Web 服务,所以我不打算详细介绍运行控制器和根服务。ZeroTier 在他们的 [文档](https://docs.zerotier.com) 中对如何做到这一点有完整的参考,而且非常好。
在 Web 用户界面中创建了我自己的虚拟网络之后,客户端的安装几乎是微不足道的。ZeroTier 有 APT、RPM、FreeBSD 和许多其他平台的软件包,所以让第一个节点上线不需要什么努力。
安装完毕后,客户端就会连接到控制器服务,并为节点生成一个唯一的 ID。在 Linux 上,你使用 `zerotier-cli` 命令来加入一个网络,使用 `zerotier-cli join NETWORKID` 命令:
```
$ sudo zerotier-cli info
200 info 469584783a 1.x.x ONLINE
```
你也可以使用 `zerotier-cli` 来获得连接和可用节点的列表,改变网络设置,以及离开网络。

在加入一个网络后,你必须批准该节点的访问,可以通过网络控制台或调用应用程序编程接口(API)。这两种方法在 ZeroTier 网站上都有文档说明。连接两个节点后,无论你身在何处或位于防火墙的哪一侧,你都可以相互连接,就像你们在同一个建筑的同一个网络中。我的主要用例之一是 [远程访问我的家庭助理环境](https://opensource.com/article/22/5/remote-home-assistant),而不需要打开防火墙端口或将其暴露在互联网上(关于我的家庭助理设置和相关服务的更多信息,见后文)。
我自己做的一件事是为内部 DNS 设置了一个 [Beta ZeroNDS 服务](https://github.com/zerotier/zeronsd)。这为我管理自己的名称服务或为我所有的私人主机和 IP 地址创建公共记录减少了很多复杂性。我发现操作说明非常简单直白,并且能够在大约 5 分钟内为我的私人网络建立一个 DNS 服务器。每个客户端必须允许 Zerotier 设置 DNS,这在 GUI 客户端中非常简单。要使它在 Linux 客户端上使用,请使用:
```
$ sudo zerotier-cli setNETWORKID allowDNS=1
```
在你添加和删除主机时,不需要其他更新,它“就能工作”。
```
$ sudo zerotier-cli info
200 info 469584845a 1.x.y ONLINE
$ sudo zerotier-cli join
93afae596398153a 200 join OK
$ sudo zerotier-cli peers
200 peers
<ztaddr> <ver> <role> <lat> <link> <TX> <RX> <path>
61d294b9cb - PLANET 112 DIRECT 7946 2812 50.7.73.34/9993
62f865ae71 - PLANET 264 DIRECT 7946 2681 50.7.76.38/9993
778cde7190 - PLANET 61 DIRECT 2944 2901 103.195.13.66/9993
93afae5963 1.x LEAF 77 DIRECT 2945 2886 35.188.31.177/41848
992fcf1db7 - PLANET RECT 79124 DI47 2813 195. 181.173.159/9993
```
我只提到了它所有功能的表面。ZeroTier 还允许在 ZeroTier 网络之间建立桥接、高级路由规则等。它们甚至有一个 [Terraform 提供者](https://github.com/zerotier/terraform-provider-zerotier) 和一个 [很棒的 Zerotier 资源](https://github.com/zerotier/awesome-zerotier) 清单。到今天为止,我正在使用 ZeroTier 连接四个物理站点的机器,其中三个在 NAT 防火墙后面。Zerotier 的设置很简单,而且管理起来几乎完全不费力。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/zerotier-network>
作者:[Kevin Sonney](https://opensource.com/users/ksonney) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Automation is a hot topic right now. In my day job as a site reliability engineer (SRE), part of my remit is to automate as many repeating tasks as possible. But how many of us do that in our daily, not-work, lives? This year, I am focused on automating away the toil so that we can focus on the things that are important.*
While automating everything, I ran into some difficulty with remote sites. I'm not a networking person so I started to look at my options. After researching the various virtual private networks (VPN), hardware endpoints, firewall rules, and everything that goes into supporting multiple remote sites, I was confused, grumpy, and frustrated with the complexity of it all.
Then I found [ZeroTier](https://github.com/zerotier). ZeroTier is an encrypted virtual network backbone, allowing multiple machines to communicate as if they were on a single network. The code is all open source, and you can self-host the controller or use the [ZeroTierOne](https://www.zerotier.com/pricing) service with either free or paid plans. I'm using their free plan right now, and it is robust, solid, and very consistent.
Because I'm using the web service, I'm not going to go into detail about running the controller and root services. ZeroTier has a complete reference on how to do that in their [documentation](https://docs.zerotier.com), and it's very good.
After creating my own virtual network in the web user interface, the client installation is almost trivial. ZeroTier has packages for APT, RPM, FreeBSD, and many other platforms, so getting the first node online takes little effort.
Once installed, the client connects to the controller service and generates a unique ID for the node. On Linux, you use the `zerotier-cli`
command to join a network, using the `zerotier-cli join NETWORKID`
command.
```
``````
$ sudo zerotier-cli info
200 info 469584783a 1.x.x ONLINE
```
You can also use `zerotier-cli`
to get a listing of connected and available nodes, change network settings, and leave networks.
(Kevin Sonney, CC BY-SA 4.0)
After joining a network, you do have to approve access for the node, either through the web console or by making a call to the application programming interface (API). Both methods are documented on the ZeroTier site. After you have two nodes connected, connecting to each other — no matter where you are or what side of any firewalls you may be on — is exactly what you would expect if you were in the same building on the same network. One of my primary use cases is for [remote access to my Home Assistant setup](https://opensource.com/article/22/5/remote-home-assistant) without needing to open up firewall ports or expose it to the internet (more on my Home Assistant setup and related services later).
One thing I did set up myself is a [Beta ZeroNDS Service](https://github.com/zerotier/zeronsd) for internal DNS. This saved me a lot of complexity for managing my own name service or having to create public records for all my private hosts and IP addresses. I found the instructions to be very straight forward, and was able to have a DNS server for my private network up in about 5 minutes. Each client has to allow Zerotier to set the DNS, which is very simple in the GUI clients. To enable it for use on Linux clients, use:
```
````$ sudo zerotier-cli setNETWORKID allowDNS=1`
No other updates are needed as you add and remove hosts, and it "just works."
```
``````
$ sudo zerotier-cli info
200 info 469584845a 1.x.y ONLINE
$ sudo zerotier-cli join
93afae596398153a 200 join OK
$ sudo zerotier-cli peers
200 peers
<ztaddr> <ver> <role> <lat> <link> <TX> <RX> <path>
61d294b9cb - PLANET 112 DIRECT 7946 2812 50.7.73.34/9993
62f865ae71 - PLANET 264 DIRECT 7946 2681 50.7.76.38/9993
778cde7190 - PLANET 61 DIRECT 2944 2901 103.195.13.66/9993
93afae5963 1.x LEAF 77 DIRECT 2945 2886 35.188.31.177/41848
992fcf1db7 - PLANET RECT 79124 DI47 2813 195. 181.173.159/9993
```
I've barely scratched the surface of the features here. ZeroTier also allows for bridging between ZeroTier networks, advanced routing rules, and a whole lot more. They even have a [Terraform provider](https://github.com/zerotier/terraform-provider-zerotier) and a listing of [Awesome Zerotier Things](https://github.com/zerotier/awesome-zerotier). As of today, I'm using ZeroTier to connect machines across four physical sites, three of which are behind NAT firewalls. Zerotier is simple to set up, and almost completely painless to manage.
## Comments are closed. |
14,575 | 开源开发者创建首个支持维护者的基金 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/open-source-developer-creates-first-of-its-kind-fund-to-support-maintainers/ | 2022-05-11T09:19:53 | [
"开源"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14575-1.html | 
Appwrite 是一个为 Web、移动和 flutter 开发者提供的开源“<ruby> 后端即服务 <rt> Backend-as-a-Service </rt></ruby>”(BaaS)平台。今天,它宣布成立<ruby> 开源软件基金 <rt> Open Source Software Fund </rt></ruby>(OSS 基金),第一年该基金将向那些为当下数字基础设施奠定基础,却没有得到补偿的开源维护者,提供 5 万美元的资助。
Appwrite 每年的开源基金将用于协助开源开发者、促进技术革新,并为各种开源开发方案打造知名度。每年,它都会对基金数额进行审查,以确保其继续满足社区的需求。目前已经开始接受申请,并且每年都会接受申请。受资助者将由 Appwrite 开发者关系团队选出。了解更多:<https://appwrite.io/oss-fund>。
创始人兼 CEO Eldad Fux 说:“我懂这种感受,你在电脑前花费大量时间,把血汗和泪水投入到热爱的事物中,而且这些事物还在使全世界成千上万甚至数百万人受益。我一直就有这个想法:借用 Appwrite 的一些成功经验和投资,来支持其他像我一样的开发者和维护者,以回馈的方式来展望未来。希望我们的贡献能够带来改变。”
在今天的技术环境中,最紧迫的挑战之一就是开源开发者和维护者的长期生存能力。尽管开源软件占比已经达到 70% 到 90%,是当下数字文明的基础,但许多最重要项目的开发者和维护者仍然没有获得足够报酬,或者根本没有报酬。关于如何帮助这些人,业界已经有了许多讨论,并提出了一系列的解决方案。Appwrite 正在为维护者做一些事,提升他们的工作,并提供经济支持,以换取他们对行业和数字社会的贡献。
Eldad Fux 自身通过为开源软件项目做贡献和参与开源社区,开始了他的开发者生涯。Appwrite 最初是一个副业项目,他把它作为一个 BaaS 产品从头打造。目前,Fux 通过专注于完全开源的平台和以各种方式回馈社区来支持开源理念,其中就包括了 Appwrite OSS 基金。
EddieHub 的创始人和开发者 Eddie Jaoude 说:“开源为世界上大部分的现代基础设施提供动力,从移动到网络、汽车甚至是地球以外的任务。只有靠社区的慷慨解囊,他们的时间和努力才能持续。如果有更多的公司和组织的支持,这种情况将得到改善,避免社区成员因报酬不足/没有报酬而懈怠。”
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/open-source-developer-creates-first-of-its-kind-fund-to-support-maintainers/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Appwrite, an open source Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS) platform for web, mobile, and flutter developers, today announced the Open Source Software Fund (OSS Fund), which will award $50,000 in its first year to open source maintainers whose projects lay the groundwork for today’s digital infrastructure but aren’t being compensated for it.
Appwrite’s yearly OSS Fund will help meet the industry’s need to assist open source maintainers, promote technology innovation, and create awareness for a variety of open source development solutions. Each year, the fund amount will be reviewed to ensure that it continues to meet the community’s needs. The application period is currently open, and applications will be accepted on an annual basis. The Appwrite Developer Relations team will choose the recipients: [https://appwrite.io/oss-fund](https://appwrite.io/oss-fund)
“I know what it’s like to spend long hours in front of your computer, putting your blood, sweat and tears into something you love and that is also benefiting thousands or even millions of people around the world,” said Eldad Fux, founder & CEO of Appwrite. “I’ve known all along that we would use some of Appwrite’s success and investment to support other developers and maintainers just like me, to give back in order to look forward. We hope our contribution can make a difference.”
One of the most pressing challenges in today’s technological environment is the long-term viability of open source developers and maintainers. Despite the fact that open source software accounts for 70-90 percent of all software and is the foundation of our digital civilization, many developers and maintainers working on the most vital projects integrated across networks and products go unpaid or underpaid. How to help these people has become a contentious issue, with a range of solutions being presented. Appwrite is taking action on behalf of maintainers, elevating their work and providing financial support in exchange for their contributions to the industry and digital society.
Eldad Fux, the founder of Appwrite, began his career as a developer by contributing to open source software projects and participating in open source communities. Appwrite began as a side project, and he built it from the ground up as a BaaS product. Fux currently supports the open source philosophy by focusing on a completely open source platform and giving back to the community in a variety of ways, including the Appwrite OSS Fund.
“Open source powers most of the World’s modern day infrastructure, from mobile to web, cars and even missions beyond this planet. This is only sustainable by the generosity of the community, their time and efforts. However, this could be improved by the support of more companies and organizations, to prevent community members’ burnout,” said Eddie Jaoude, Developer and Creator of EddieHub. |
14,576 | Ubuntu MATE 的负责人开发了一个漂亮的工具,专用于安装第三方 deb 包 | https://news.itsfoss.com/deb-get-ubuntu/ | 2022-05-11T12:27:39 | [
"apt-get",
"deb-get"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14576-1.html |
>
> 这是一个有趣的工具,它可以替代 apt-get 来安装 Ubuntu 上的第三方 deb 包。它应该能帮为你节省时间!
>
>
>

Ubuntu MATE 的负责人 **Martin Wimpress** 为 Linux 用户带来了另一个有趣的项目。
你可能不知道,这个 Martin 经常开发一些有趣的东西。去年,我们报道了 [Quickemu](https://itsfoss.com/quickgui/),它通过一个基于 QEMU 的 GUI 工具,帮助用户在 Linux 中创建虚拟机,使这个过程变得简单。
现在,他又带来了一个有趣的 `deb-get` 工具,其目标是为第三方 .deb 包模仿 `apt-get` 的支持。
让我们来详细了解一下它吧!
### Deb Get:使用 CLI 无缝安装第三方 deb 包
当官方软件库中没有你想安装的软件包时(比如 Google Chrome、Vivaldi 等),你必须先 [添加一个 PPA(非官方/官方)](https://itsfoss.com/ppa-guide/) 或者下载 .deb 文件后 [手动安装](https://itsfoss.com/install-deb-files-ubuntu/)。
如果我现在告诉你,你可以直接在终端中安装它们,就好像官方软件库中有它们一样呢?
这就是 `deb-get` 工具想要做到的事。
通常,当在终端中安装一个软件包时,你会使用下面的命令:
```
sudo apt install packagename
```
或者
```
sudo apt-get install packagename
```
要使用这个工具,你只需把 `apt-get` 替换为 `deb-get`,其他格式保持不变。就像下面这样:
```
sudo deb-get install packagename
```
举个例子,通常,我们 [在 Linux 上安装 Vivaldi](https://itsfoss.com/install-vivaldi-ubuntu-linux/) 时需要添加 PPA 或下载 .deb 文件。
现在,如果你在系统上配置好了 `deb-get` 工具(**配置指南在本文末尾**),你就可以使用以下命令轻松地安装 Vivaldi:
```
sudo deb-get install vivaldi-stable
```

另外,类似于 `apt-get upgrade`,你可以使用下面的命令来升级软件包:
```
sudo deb-get upgrade
```
>
> **注意:** 虽然 `deb-get` 使安装第三方 .deb 包变得很容易,但它是有限制的,你只能安装它提供的核实列表中的软件。不过,它已经支持许多 [必要的应用程序](https://itsfoss.com/essential-linux-applications/),相信支持的软件包列表很快就会扩大。
>
>
>
你也可以使用下面的命令,检查你 `deb-get` 可用软件包的列表:
```
sudo deb-get list
```

### 在基于 Ubuntu 的发行版上设置 deb-get
`deb-get` 工具适用于 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS(我测试过),也应该适用于其他基于 Ubuntu 的发行版。
你可以使用下面的命令来安装它:
```
sudo apt install curl && curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wimpysworld/deb-get/main/deb-get | sudo -E bash -s install deb-get
```
或者,你可以在它的 [GitHub 发布页面](https://github.com/wimpysworld/deb-get/releases) 手动下载它的 deb 包。
要了解更多关于它的信息,以及可用的命令/功能,你可以访问它的 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/wimpysworld/deb-get)。
*你怎么看待 deb-get 试图实现支持第三方软件包的 apt-get?你认为它有用吗?请在评论区留言,发表你的看法吧!*
**来源:OMG!Ubuntu!**
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/deb-get-ubuntu/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Ubuntu MATE’s lead,** Martin Wimpress,** has another fun project for Linux users.
In case you did not know, Martin regularly develops something interesting. Last year, we covered [Quickemu](https://itsfoss.com/quickgui/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), which helps create virtual machines in Linux through a QEMU-based GUI tool making the process easy.
Now, he is back with an interesting “**deb-get**” tool that aims to imitate the functionality of “**apt-get**” for 3rd party .deb packages.
Let us take a closer look at it.
## Deb Get: Seamlessly Install 3rd Party Deb Packages Using the CLI
When it comes to software packages that aren’t available in the official repositories (like Google Chrome, Vivaldi), you will have to [add a PPA (unofficial/official)](https://itsfoss.com/ppa-guide/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) or download the .deb file and [get it installed](https://itsfoss.com/install-deb-files-ubuntu/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) manually.
What if you can simply install it using the terminal as if it is available in the official repositories?
That’s where the deb-get tool comes in.
Usually, when installing a package through the terminal, you utilize either of the following commands:
`sudo apt install packagename`
or
`sudo apt-get install packagename`
You get to keep the same format and simply replace apt-get with this tool, which should look like this:
`sudo deb-get install packagename`
As an example, usually, we needed to add the PPA or download the deb file when [installing Vivaldi on Linux](https://itsfoss.com/install-vivaldi-ubuntu-linux/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
Now, if you set up the deb-get tool on your system** (setup instructions at the end of this article**), you can easily install Vivaldi using the following command:
`sudo deb-get install vivaldi-stable`
And, just like the apt-get upgrade process, you can upgrade packages using the following command:
`sudo deb-get upgrade`
**Note:** While it makes it easy to install third-party .deb packages, you will be limited to a verified list supported by the tool. You can expect the list of supported packages to expand soon, but it already supports many [essential applications.](https://itsfoss.com/essential-linux-applications/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)
You can also check the list of available packages that you can install with deb-get using the following command:
`sudo deb-get list`
## Setting Up Deb-Get on Ubuntu-based Distributions
The deb-get tool works with Ubuntu 22.04 LTS (I tested it) and should work with other Ubuntu-based distributions.
You can install it on your system using the command below:
`sudo apt install curl && curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wimpysworld/deb-get/main/deb-get | sudo -E bash -s install deb-get`
Or, you can download the deb package for it manually from its [GitHub releases section](https://github.com/wimpysworld/deb-get/releases?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
To explore more about it, and the available commands/functionalities, you can head to its [GitHub page](https://github.com/wimpysworld/deb-get?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
*What do you think of deb-get attempting to mimic apt-get functionality for third-party packages? Do you think it is useful? Let me know your thoughts in the comments.*
**Via: OMG!Ubuntu!**
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,577 | 如何将你的文件系统转换为 Btrfs | https://fedoramagazine.org/convert-your-filesystem-to-btrfs/ | 2022-05-11T15:46:14 | [
"Btrfs",
"文件系统"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14577-1.html | 
### 引言
这篇概述文章将告诉你为何以及如何迁移你的当前分区到 Btrfs 文件系统。如果你对此感兴趣,请阅读这篇分步指南来完成。
从 Fedora 33 开始,新安装的 Fedora 操作系统默认文件系统为 Btrfs。我确信大部分用户现在已经听说了它的优势:写时复制、内置校验、灵活的压缩方式、简易的快照和回滚方式。它确实是一个现代化的文件系统,为桌面存储带来新的功能。
在升级到 Fedora 33 后,我想利用 Btrfs 的优势,但对我个人来说,我不想因为“只是为了改变文件系统”而去重装整个系统。我发现(只有)寥寥无几的具体如何做转换的教程,所以我决定在这里分享我的详细经验。
### 小心!
这样做你是在玩火。希望你阅读以下内容时不要感到惊讶:
>
> 在编辑分区和转换文件系统时,你的数据可能会被破坏和丢失。最终,你可能会得到一个不能启动的操作系统,并面临数据恢复的风险。你可能会无意删除你的分区,或者以其它方式破坏了你的操作系统。
>
>
>
这些转换过程即使对于生产系统来说也是安全的 —— 前提是你提前做好了计划,对关键数据做好了备份和回滚计划。作为一个 *可以执行超级权限的系统管理员*,你可以在没有限制、没有任何常规安全防护措施的情况下,做任何事情。
### 安全的方式:重装 Fedora
重装操作系统是转换文件系统到 Btrfs 的 “官方” 方式,推荐给大多数用户使用。因此,如果在这个教程中有那么一点不确定,就选择这种方式。步骤大致如下:
1. 备份你的主文件夹和你系统中可能会用到的任何数据,比如 `/etc`。(编者按:虚拟机也是这样)
2. 将已安装的安装包以列表形式保存到到文件中。
3. 重新安装 Fedora,删除你当前的分区,并选择新的 Btrfs 默认分区方案。
4. 恢复主文件夹的内容,并使用软件包列表文件重装软件包。
对于详细的步骤和命令,请看一位社区用户在 [ask.fedoraproject.org](https://ask.fedoraproject.org/t/conversion-of-an-existing-ext4-fedora-32-system-completely-to-btrfs/9446/6?u=gombosghttps://ask.fedoraproject.org/t/conversion-of-an-existing-ext4-fedora-32-system-completely-to-btrfs/9446/6?u=gombosg) 站点的评论。如果正确完成,你将得到一个和之前一样的操作系统,使丢失数据的风险最小化。
### 转换的利弊
让我们快速澄清一下:这种文件系统转换有什么优势和劣势?
**优势:**
* 当然,不需要重新安装!你的系统里的所有文件和之前一模一样。
* 技术上来说,没有备份的情况下,就地进行是可能的。
* 你会学到许多关于 Btrfs 的知识!
* 如果所有都按计划进行,会是相当快的一个过程。
**劣势:**
* 你必须熟悉终端环境和 shell 命令。
* 你可能会丢失数据,参见上文。
* 如果出了什么问题,你得自己解决。
**特别之处:**
* 你需要大约 20% 的可用磁盘空间才能成功转换。但对于完整的备份和重装方式,你可能需要的空间更多。
* 你可以在转换过程中自定义你分区的所有参数,但如果选择重装,你也可以从 Anaconda 自定义。
### LVM 怎么办?
在近期几次 Fedora 安装中,LVM 布局一直是默认的。如果你有一个带有多个分区(例如 `/` 和 `/home`)的 LVM 分区布局,你得以某种方式合并它们,来获得 Btrfs 所有性能。
如果选择这样做,你可以单独转换分区到 Btrfs 文件系统,同时保留卷组。然而,迁移到 Btrfs 文件系统的优势之一是摆脱 LVM 分区布局强加的限制。你也可以利用 Btrfs 文件系统提供的收发功能在转换后来合并分区。
>
> 另见 《Fedora 杂志》: [利用 LVM 回收硬盘空间](https://fedoramagazine.org/reclaim-hard-drive-space-with-lvm/)、[从 Btrfs 快照中恢复文件](https://fedoramagazine.org/recover-your-files-from-btrfs-snapshots/) 以及 [在 Btrfs 和 LVM-ext4 两者之间做选择](https://fedoramagazine.org/choose-between-btrfs-and-lvm-ext4/)。
>
>
>
### 了解 Btrfs
建议阅读以下内容对 Btrfs 文件系统是什么有一个基础的了解。如果你没有把握,只有选择重装 Fedora 这种安全的方式。
必须了解的:
* [Fedora Magazine:Btrfs 来到 Fedora 33](https://fedoramagazine.org/btrfs-coming-to-fedora-33/)
* [Btrfs 系统管理指南](https://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/SysadminGuide), *尤其是* 关于子卷和 flat 子卷布局。
* [btrfs-convert 指南](https://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/Conversion_from_Ext3)
有用的资源:
* [man 8 btrfs](https://www.mankier.com/8/btrfs) – 命令行界面
* [man 5 btrfs](https://www.mankier.com/5/btrfs) – 挂载参数
* [man btrfs-convert](https://www.mankier.com/8/btrfs-convert) – 要用到的转换工具
* [man btrfs-subvolume](https://www.mankier.com/8/btrfs-subvolume) – 管理子卷
### 转换步骤
#### 创建一个实时镜像
由于不能转换已挂载的文件系统,我们将通过 Fedora <ruby> 实时镜像 <rt> Live Image </rt></ruby>进行。安装 [Fedora 镜像写入工具](https://getfedora.org/en/workstation/download/),然后 “烧录” Fedora 33 到你的 U 盘中来创建实时镜像。
#### 释放磁盘空间
`btrfs-convert` 会在分区的剩余空间重新创建文件系统的元数据,同时保持所有已有的 ext4 文件系统数据还在它当前的位置上。
不幸的是,所需的剩余空间的大小无法提前知道:如果没有足够的空间,转换将会失败(但不会破坏数据)。这里有一些释放空间有用的方法:
* 利用 `baobab` 来识别大容量的文件和文件夹,然后移除。如果可能的话,不要手动删除主文件夹以外的文件。
* 清理旧的系统日志:`journalctl –vacuum-size=100M`。
* 如果你正使用 Docker,请小心地使用类似 `docker volume prune`、`docker image prune -a` 这样的工具。
* 清理 GNOME Boxes 之类的虚拟机内不用的镜像。
* 清理不用的软件包和 Flatpak 包:`dnf autoremove`、`flatpak remove –unused`。
* 清理软件包缓存:`pkcon refresh force -c -1`、`dnf clean all`。
* 如果你有把握,你可以谨慎的清理 `~/.cache` 文件夹。
#### 转换到 Btrfs
备份你所有有价值的数据,确保你的系统已完全更新,然后重启到实时镜像。运行 `gnome-disks` 工具找到你所拥有的设备的路径,比如 `/dev/sda1`(如果你在使用 LVM,它可能看起来有所不同)。检查文件系统然后执行转换:(编者按:以下命令使用 root 用户运行,谨慎使用!)
```
$ sudo su -
# fsck.ext4 -fyv /dev/sdXX (请替换为你的具体的设备路径)
# man btrfs-convert (阅读它)
# btrfs-convert /dev/sdXX (请替换为你的具体的设备路径)
```
这将会花十几分钟甚至几个小时,依据分区的大小和是机械硬盘还是固态硬盘。如果你看到错误,你可能需要更多剩余空间。作为最后的手段,你可以尝试 `btrfs-convert -n`。
#### 怎样回滚?
如果因为某些原因转换失败,你的分区将保持在 ext4 文件系统或者它之前的状态。如果你想在成功转换之后回滚,简单如下:
```
# btrfs-convert -r /dev/sdXX
```
>
> **警告!** 如果你做了以下这些事情之一,你将永久失去回滚的功能:碎片整理、均衡或者删除 `ext2_saved` 子卷。
>
>
>
由于 Btrfs 文件系统的写时复制特性,你可以安全的复制/移动甚至删除文件、创建子卷,因为 `ext2_saved` 会保持引用旧数据。
#### 挂载和检查
现在这个分区应该已经有了 Btrfs 文件系统。挂载它然后查看你的文件……和子卷!
```
# mount /dev/sdXX /mnt (请替换为你的具体的设备路径)
# man btrfs-subvolume (阅读它)
# btrfs subvolume list / (使用 -t 以表格方式查看)
```
因为你已经阅读了 [相关的手册页](https://www.mankier.com/8/btrfs-subvolume#Subvolume_and_Snapshot),你应该知道创建子卷快照是安全的,并且有 `ext2-saved` 子卷作为你之前数据的简易备份。
>
> 是时候阅读 [Btrfs 系统管理指南](https://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/SysadminGuide)了,这样你就不会把常规文件夹和子卷混淆了。
>
>
>
#### 创建子卷
我们希望实现一个“扁平”子卷布局,这和 Anaconda 默认创建的布局相同:
```
toplevel (卷根目录,不能被默认挂载)
+-- root (子卷根目录,被挂载到 /)
+-- home (子卷根目录,被挂载到 /home)
```
你可以跳过这个步骤,或者使用一个不同的布局。这种特殊结构的优势是你可以轻松的创建 `/home` 的快照,并且对每个子卷使用不同的压缩和挂载参数。
```
# cd /mnt
# btrfs subvolume snapshot ./ ./root2
# btrfs subvolume create home2
# cp -a home/* home2/
```
这里我们已经创建了两个子卷。`root2` 是一个完整的分区快照,而 `home2` 开始是一个空子卷,然后我们往里复制内容。(这个 `cp` 命令不会重复数据,所以会很快。)
* 在 `/mnt` 目录(顶层子卷),删除除了 `root2`、`home2` 和 `ext2_saved` 之外的所有内容。
* 重命名 `root2` 和 `home2` 子卷为 `root` 和 `home`。
* 在 `root` 子卷里,清空 `home` 目录,以便之后我们能够挂载 `home` 子卷。
如果都做对了,那就很简单了!
#### 修改 fstab 分区表
为了重启之后挂载新卷,必须要修改 `fstab`,用新的行来代替旧的 ext4 文件系统挂载行。
你可以使用 `blkid` 命令来找到你的分区的 UUID。
```
UUID=xx / btrfs subvol=root 0 0 (请替换为你的具体 UUID)
UUID=xx /home btrfs subvol=home 0 0 (请替换为你的具体 UUID)
```
(注意如果指向的是同一个分区,那么这两个 UUID 是相同的。)
这些都是新安装的 Fedora 33 的默认值。在 `fstab` 中,你也可以选择自定义压缩和添加类似 `noatime` 这样的参数。
>
> 可以查看 [关于压缩参数的维基页面](https://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/Compression) 和 [man 5 btrfs](https://www.mankier.com/5/btrfs) 了解所有相关的参数。
>
>
>
#### chroot 到系统
如果你曾经做过系统恢复,我想你肯定知道这些命令。这里,我们将得到一个 *基本上* 在你系统里的 shell 提示符,可以访问网络。
首先,我们必须重新挂载 `root` 子卷到 `/mnt` 目录,然后挂载 `/boot` 和 `/boot/efi` 分区(它们可能有所不同,这取决于你的文件系统布局):
```
# umount /mnt
# mount -o subvol=root /dev/sdXX /mnt (请替换为你的具体的设备路径)
# mount /dev/sdXX /mnt/boot (请替换为你的具体的设备路径)
# mount /dev/sdXX /mnt/boot/efi (请替换为你的具体的设备路径)
```
然后我们继续挂载系统设备:
```
# mount -t proc /proc /mnt/proc
# mount --rbind /dev /mnt/dev
# mount --make-rslave /mnt/dev
# mount --rbind /sys /mnt/sys
# mount --make-rslave /mnt/sys
# cp /mnt/etc/resolv.conf /mnt/etc/resolv.conf.chroot
# cp -L /etc/resolv.conf /mnt/etc
# chroot /mnt /bin/bash
$ ping www.fedoraproject.org
```
#### 重装 GRUB 及内核
最容易的方法就是重装 GRUB 和 内核,因为它完成了所有必要的配置 —— 现在我们可以访问网络了。所以,在 chroot 环境内部:
```
# mount /boot/efi
# dnf reinstall grub2-efi shim
# grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/efi/EFI/fedora/grub.cfg
# dnf reinstall kernel-core
...或者干脆重新生成 initramfs:
# dracut --kver $(uname -r) --force
```
如果你是支持 UEFI 的系统,这里是适用的。如果你是 BIOS 的系统,请查看下面的文档。重启之前,让我们查看是否一切正常:
```
# cat /boot/grub2/grubenv
# cat /boot/efi/EFI/fedora/grub.cfg
# lsinitrd /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).img | grep btrfs
```
你应该在 `grubenv` 和 `grub.cfg` 有正确的分区 UUID 或指向(`grubenv` 可能没有更新,如有必要可以编辑它),并在 `grub.cfg` 中看到 `insmod btrfs` 配置和在 initramfs 镜像中有 btrfs 模块。
>
> 参见: Fedora 系统管理指南中的 [重装 GRUB 2](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/fedora/f33/system-administrators-guide/kernel-module-driver-configuration/Working_with_the_GRUB_2_Boot_Loader/#sec-Reinstalling_GRUB_2) 和 [验证初始 RAM 磁盘镜像](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/fedora/f33/system-administrators-guide/kernel-module-driver-configuration/Manually_Upgrading_the_Kernel/#sec-Verifying_the_Initial_RAM_Disk_Image) 。
>
>
>
#### 重启
现在系统能够正常启动。如果不能,别慌,回到实时镜像修复这个问题。最坏的情况下,你可以从那里重装 Fedora 。
#### 首次启动之后
检查你的新 Btrfs 文件系统一切都正常。如果你觉得没问题,你需要回收旧的 ext4 快照使用的空间,进行碎片整理和平衡子卷。后两者可能要花一些时间,并且相当耗费资源。
对此你必须这样挂载顶级子卷:
```
# mount /dev/sdXX -o subvol=/ /mnt/someFolder
# btrfs subvolume delete /mnt/someFolder/ext2_saved
```
然后,当机器有空闲时间时,运行这些命令:
```
# btrfs filesystem defrag -v -r -f /
# btrfs filesystem defrag -v -r -f /home
# btrfs balance start -m /
```
最后,有一个 “非写时复制” [属性](https://www.mankier.com/1/chattr#Attributes-C),对于新系统,这个属性是为虚拟机镜像文件夹自动设置的。如果你使用虚拟机的话,可以设置它:
```
# chattr +C /var/lib/libvirt/images
```
```
$ chattr +C ~/.local/share/gnome-boxes/images
```
这个属性只会对在这些文件夹里的新文件生效。复制镜像并删除原镜像,你可以通过 `lsattr` 确认结果。
### 总结
我真心希望你发现这个教程是有用的,并且能够对是否在你的系统上转换为 Btrfs 做出谨慎而明智的决定。祝你成功转换!
欢迎在评论中分享你的经验,或者遇到更深层次的问题,请在 [ask.fedoraproject.org](https://ask.fedoraproject.org/) 提问。
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/convert-your-filesystem-to-btrfs/>
作者:[Gergely Gombos](https://fedoramagazine.org/author/gombosg/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hwlife](https://github.com/hwllife) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | ## Introduction
The purpose of this article is to give you an overview about why, and how to migrate your current partitions to a Btrfs filesystem. To read a step-by-step walk through of how this is accomplished – follow along, if you’re curious about doing this yourself.
Starting with Fedora 33, the default filesystem is now Btrfs for new installations. I’m pretty sure that most users have heard about its advantages by now: copy-on-write, built-in checksums, flexible compression options, easy snapshotting and rollback methods. It’s really a modern filesystem that brings new features to desktop storage.
Updating to Fedora 33, I wanted to take advantage of Btrfs, but personally didn’t want to reinstall the whole system for ‘just a filesystem change’. I found [there was] little guidance on how exactly to do it, so decided to share my detailed experience here.
## Watch out!
Doing this, you are playing with fire. Hopefully you are not surprised to read the following:
During editing partitions and converting file systems, you can have your data corrupted and/or lost. You can end up with an unbootable system and might be facing data recovery. You can inadvertently delete your partitions or otherwise harm your system.
These conversion procedures are meant to be safe even for production systems – but only if you plan ahead, have backups for critical data and rollback plans. As a *sudoer*, you can do anything without limits, without any of the usual safety guards protecting you.
## The safe way: reinstalling Fedora
Reinstalling your operating system is the ‘official’ way of converting to Btrfs, recommended for most users. Therefore, choose this option if you are unsure about anything in this guide. The steps are roughly the following:
- Backup your home folder and any data that might be used in your system like
*/etc*. [Editors note: VM’s too] - Save your list of installed packages to a file.
- Reinstall Fedora by removing your current partitions and choosing the new default partitioning scheme with Btrfs.
- Restore the contents of your home folder and reinstall the packages using the package list.
For detailed steps and commands, see this comment by a community user at [ask.fedoraproject.org](https://ask.fedoraproject.org/t/conversion-of-an-existing-ext4-fedora-32-system-completely-to-btrfs/9446/6?u=gombosghttps://ask.fedoraproject.org/t/conversion-of-an-existing-ext4-fedora-32-system-completely-to-btrfs/9446/6?u=gombosg). If you do this properly, you’ll end up with a system that is functioning in the same way as before, with minimal risk of losing any data.
## Pros and cons of conversion
Let’s clarify this real quick: what kind of advantages and disadvantages does this kind of filesystem conversion have?
**The good**
- Of course, no reinstallation is needed! Every file on your system will remain the exact same as before.
- It’s technically possible to do it in-place i.e. without a backup.
- You’ll surely learn a lot about btrfs!
- It’s a rather quick procedure if everything goes according to plan.
#### The bad
- You have to know your way around the terminal and shell commands.
- You can lose data, see above.
- If anything goes wrong, you are on your own to fix it.
#### The ugly
- You’ll need about 20% of free disk space for a successful conversion. But for the complete backup & reinstall scenario, you might need even more.
- You can customize everything about your partitions during the process, but you can also do that from Anaconda if you choose to reinstall.
**What about LVM?**
LVM layouts have been the default during the last few Fedora installations. If you have an LVM partition layout with multiple partitions e.g. */* and */home*, you would somehow have to merge them in order to enjoy all the benefits of Btrfs.
If you choose so, you can individually convert partitions to Btrfs while keeping the volume group. Nevertheless, one of the advantages of migrating to Btrfs is to get rid of the limits imposed by the LVM partition layout. You can also use the send-receive functionality offered by *btrfs* to merge the partitions after the conversion.
See also on Fedora Magazine: [Reclaim hard-drive space with LVM](https://fedoramagazine.org/reclaim-hard-drive-space-with-lvm/), [Recover your files from Btrfs snapshots](https://fedoramagazine.org/recover-your-files-from-btrfs-snapshots/) and [Choose between Btrfs and LVM-ext4](https://fedoramagazine.org/choose-between-btrfs-and-lvm-ext4/).
## Getting acquainted with Btrfs
It’s advisable to read at least the following to have a basic understanding about what Btrfs is about. If you are unsure, just choose the safe way of reinstalling Fedora.
#### Must reads
[Fedora Magazine: Btrfs Coming to Fedora 33](https://fedoramagazine.org/btrfs-coming-to-fedora-33/)[Btrfs sysadmin guide](https://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/SysadminGuide),*especially*about subvolumes & flat subvolume layout.[Btrfs-convert guide](https://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/Conversion_from_Ext3)
#### Useful resources
– command-line interface*man 8 btrfs*– mount options[man 5 btrfs](https://www.mankier.com/5/btrfs)– the conversion tool we are going to use[man btrfs-convert](https://www.mankier.com/8/btrfs-convert)– managing subvolumes[man btrfs-subvolume](https://www.mankier.com/8/btrfs-subvolume)
## Conversion steps
#### Create a live image
Since you can’t convert mounted filesystems, we’ll be working from a Fedora live image. Install [Fedora Media Writer](https://getfedora.org/en/workstation/download/) and ‘burn’ Fedora 33 to your favorite USB stick.
#### Free up disk space
*btrfs-convert* will recreate filesystem metadata in your partition’s free disk space, while keeping all existing *ext4 *data at its current location.
Unfortunately, the amount of free space required cannot be known ahead – the conversion will just fail (and do no harm) if you don’t have enough. Here are some useful ideas for freeing up space:
- Use
*baobab*to identify large files & folders to remove. Don’t manually delete files outside of your home folder if possible. - Clean up old system journals:
*journalctl –vacuum-size=100M* - If you are using Docker, carefully use tools like
*docker volume prune, docker image prune -a* - Clean up unused virtual machine images inside e.g. GNOME Boxes
- Clean up unused packages and flatpaks:
*dnf autoremove*,*flatpak remove –unused*, - Clean up package caches:
*pkcon refresh force -c -1*,*dnf clean all* - If you’re confident enough to, you can cautiously clean up the
*~/.cache*folder.
#### Convert to Btrfs
Save all your valuable data to a backup, make sure your system is fully updated, then reboot into the live image. Run *gnome-disks* to find out your device handle e.g. */dev/sda1* (it can look different if you are using LVM). Check the filesystem and do the conversion: [Editors note: The following commands are run as root, use caution!]
$ sudo su - # fsck.ext4 -fyv /dev/sdXX # man btrfs-convert (read it!) # btrfs-convert /dev/sdXX
This can take anywhere from 10 minutes to even hours, depending on the partition size and whether you have a rotational or solid-state hard drive. If you see errors, you’ll likely need more free space. As a last resort, you could try *btrfs-convert* *-n*.
#### How to roll back?
If the conversion fails for some reason, your partition will remain *ext4* or whatever it was before. If you wish to roll back after a successful conversion, it’s as simple as
# btrfs-convert -r /dev/sdXX
**Warning!** You will permanently lose your ability to roll back if you do any of these: defragmentation, balancing or deleting the *ext2_saved* subvolume.
Due to the copy-on-write nature of Btrfs, you can otherwise safely copy, move and even delete files, create subvolumes, because *ext2_saved *keeps referencing to the old data.
#### Mount & check
Now the partition is supposed to have *btrfs* file system. Mount it and look around your files… and subvolumes!
# mount /dev/sdXX /mnt # man btrfs-subvolume (read it!) # btrfs subvolume list / (-t for a table view)
Because you have already read the [relevant manual page](https://www.mankier.com/8/btrfs-subvolume#Subvolume_and_Snapshot), you should now know that it’s safe to create subvolume snapshots, and that you have an *ext2-saved* subvolume as a handy backup of your previous data.
It’s time to read the [Btrfs sysadmin guide](https://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/SysadminGuide), so that you won’t confuse subvolumes with regular folders.
#### Create subvolumes
We would like to achieve a ‘flat’ subvolume layout, which is the same as what Anaconda creates by default:
toplevel (volume root directory, not to be mounted by default) +-- root (subvolume root directory, to be mounted at /) +-- home (subvolume root directory, to be mounted at /home)
You can skip this step, or decide to aim for a different layout. The advantage of this particular structure is that you can easily create snapshots of */home*, and have different compression or mount options for each subvolume.
# cd /mnt # btrfs subvolume snapshot ./ ./root2 # btrfs subvolume create home2 # cp -a home/* home2/
Here, we have created two subvolumes. *root2 *is a full snapshot of the partition, while *home2* starts as an empty subvolume and we copy the contents inside. (This *cp* command doesn’t duplicate data so it is going to be fast.)
- In
*/mnt*(the top-level subvolume) delete everything except*root2*,*home2*, and*ext2_saved*. - Rename
*root2*and*home2*subvolumes to*root*and*home*. - Inside
*root*subvolume, empty out the*home*folder, so that we can mount the*home*subvolume there later.
It’s simple if you get everything right!
#### Modify fstab
In order to mount the new volume after a reboot, *fstab* has to be modified, by replacing the old *ext4* mount lines with new ones.
You can use the command *blkid * to learn your partition’s UUID.
UUID=xx / btrfs subvol=root 0 0 UUID=xx /home btrfs subvol=home 0 0
(Note that the two UUIDs are the same if they are referring to the same partition.)
These are the defaults for new Fedora 33 installations. In *fstab* you can also choose to customize compression and add options like *noatime.*
See the relevant [wiki page about compression](https://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/Compression) and * man 5 btrfs* for all relevant options.
#### Chroot into your system
If you’ve ever done system recovery, I’m pretty sure you know these commands. Here, we get a shell prompt that is essentially *inside* your system, with network access.
First, we have to remount the *root* subvolume to */mnt*, then mount the */boot* and */boot/efi* partitions (these can be different depending on your filesystem layout):
# umount /mnt # mount -o subvol=root /dev/sdXX /mnt # mount /dev/sdXX /mnt/boot # mount /dev/sdXX /mnt/boot/efi
Then we can move on to mounting system devices:
# mount -t proc /proc /mnt/proc # mount --rbind /dev /mnt/dev # mount --make-rslave /mnt/dev # mount --rbind /sys /mnt/sys # mount --make-rslave /mnt/sys # cp /mnt/etc/resolv.conf /mnt/etc/resolv.conf.chroot # cp -L /etc/resolv.conf /mnt/etc # chroot /mnt /bin/bash $ ping www.fedoraproject.org
#### Reinstall GRUB & kernel
The easiest way – now that we have network access – is to reinstall GRUB and the kernel because it does all configuration necessary. So, inside the chroot:
# mount /boot/efi # dnf reinstall grub2-efi shim # grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/efi/EFI/fedora/grub.cfg # dnf reinstall kernel-core ...or just renegenerating initramfs: # dracut --kver $(uname -r) --force
This applies if you have an UEFI system. Check the docs below if you have a BIOS system. Let’s check if everything went well, before rebooting:
# cat /boot/grub2/grubenv # cat /boot/efi/EFI/fedora/grub.cfg # lsinitrd /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).img | grep btrfs
You should have proper partition UUIDs or references in *grubenv* and *grub.cfg* (grubenv may not have been updated, edit it if needed) and see *insmod btrfs* in *grub.cfg* and *btrfs* module in your initramfs image.
See also: [Reinstalling GRUB 2](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/fedora/f33/system-administrators-guide/kernel-module-driver-configuration/Working_with_the_GRUB_2_Boot_Loader/#sec-Reinstalling_GRUB_2) and [Verifying the Initial RAM Disk Image](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/fedora/f33/system-administrators-guide/kernel-module-driver-configuration/Manually_Upgrading_the_Kernel/#sec-Verifying_the_Initial_RAM_Disk_Image) in the Fedora System Administration Guide.
#### Reboot
Now your system should boot properly. If not, don’t panic, go back to the live image and fix the issue. In the worst case, you can just reinstall Fedora from right there.
#### After first boot
Check that everything is fine with your new Btrfs system. If you are happy, you’ll need to reclaim the space used by the old *ext4* snapshot, defragment and balance the subvolumes. The latter two might take some time and is quite resource intensive.
You have to mount the top level subvolume for this:
# mount /dev/sdXX -o subvol=/ /mnt/someFolder # btrfs subvolume delete /mnt/someFolder/ext2_saved
Then, run these commands when the machine has some idle time:
# btrfs filesystem defrag -v -r -f / # btrfs filesystem defrag -v -r -f /home # btrfs balance start -m /
Finally, there’s a “no copy-on-write” [attribute](https://www.mankier.com/1/chattr#Attributes-C) that is automatically set for virtual machine image folders for new installations. Set it if you are using VMs:
#$ chattr +Cchattr +C /var/lib/libvirt/images~/.local/share/gnome-boxes/images
This attribute only takes effect for new files in these folders. Duplicate the images and delete the originals. You can confirm the result with *lsattr*.
## Wrapping up
I really hope that you have found this guide to be useful, and was able to make a careful and educated decision about whether or not to convert to Btrfs on your system. I wish you a successful conversion process!
Feel free to share your experience here in the comments, or if you run into deeper issues, on [ask.fedoraproject.org](https://ask.fedoraproject.org/).
## Hugo Lopes
Portuguese –>> Existe algum script ou programa que já faça isso tudo de forma automática, iguais as facilidades do Windows (por isso eles chegaram onde chegaram), ou se tem que fazer tudo na mão (sem formatar, obvio) comando por comando (o que é chato). Caso não se tenha um script ou programa assim, fica a dica, inclusive para todos os formatos (ext2, ext4, etc).
## Taniguchi
Seguinte… não existe script.. e tbm não recomendo esse tipo de procedimento. Pois há muitas chances de não dar certo! É mais seguro vc fazer backup de tudo, e partir para uma nova instalação do SO. Eu sempre usei EXT4, mas agora estou com o Btrfs. Fiz a conversão dele através de uma instalação limpa, do zero. Não tive problemas até agora!
## AndreaS
Nice guide, I think I will try it. One question. I am currently running Fedora 33 on an external disk on my laptop.
Any chance that after conversion I will still be able to boot Fedora from the external Disk?
## Gergely Gombos
Hi, you will be able to boot the same, because likely there is no difference between an internal and an external drive from the computer’s perspective.
In this guide, we don’t touch /boot, only reinstall GRUB to accommodate the filesystem changes.
## Novid Emami
Thanks Gergely for this introduction to Btrfs convertion.
I’m new to Fedora and partitioned my system like the old days on Debian . It’s working fine for me to have /, /boot and /home separated but on the same ext4 partition scheme. I don’t know if its a good idea to convert into Btrfs for everyday desktop usage but it may have some advantages over the sever or cloud platforms. Let’s not rush through this and see what happens during next few month or even years!
P.S: I now understand why Fedora is such a great community for new technologies 😉
## Gergely Gombos
Hi! Btrfs is mature and totally safe for desktop usage. It’s way beyond early testing phases. That’s why it has been selected as the default file system for Fedora Workstation.
Of course, deciding whether to convert your FS is up to you, I hope this article gave some useful pointers on why it might be worth it.
## Karol
Well.. Good luck. Two months ago my OpenSuse TW had a total FS disaster (/home unfortunately) after just maybe 1 year after installation. Guess what was the filesystem? Yes, it was btrfs. This is the only total FS crash I can remember, and I have been using Linux since 1998.
## svsv sarma
This reminds me of the ‘Fat -NTFS’ conversion. Change always invites alertness, caution and guard and takes its own time to sink in. I decided to install Fedora 34 only, whether it retains ButterFS or not.
## Tomasz
Eh..
Convert to a self healing system that runs on top of raid 6 to assist with drive failure and then see your data go after a power loss when one system tries to correct the other and kernel panicking every 5 or so minutes when btrfs says the error is unrecoverable.
After desperately trying to recover 4tb of memories (photos and videos) and important archives and recognizing there are no tools to help me out during the 5 minute session between reboots I will never go back to btrfs.
YMMV.
## Amir
Can I do the filesystem change while on dual boot with Windows 10?
## Gergely Gombos
Absolutely, I did the same. This process doesn’t touch the Windows partition. You can also install WinBtrfs (https://github.com/maharmstone/btrfs) to be able to access btrfs partitions from Windows. For example, you could create a common data partition or a subvolume that you can share between Windows and Linux.
## Amir
Thanks Gergely..
## Taras
Hi! Thanks for the great article. Personally, I’ve used F33 on my laptop with btrfs about a month and I would say it pretty stable and reliable. But for the moment I switched back to the XFS, because it works much faster for me.
## ernesto
On one of these articles I saw a discussion on some old school linux commands not working properly with btrfs (it could have been ‘df’ or ‘du’).
Is this still the case?
## Matthew Miller
It’s not that they don’t work, it’s that the data they give back might be surprising. These commands do not know about reflinks, snapshots, compression, etc. So, it is better to use the btrfs-aware equivalents. See https://unix.stackexchange.com/a/436598/2511 for details.
## Gregory Bartholomew
I think you are referring to this comment. But I don’t know if anything has changed. EDIT: It looks like Matt found the answer while I was hunting down the original comment. 🙂
## Sally
Because I can’t take a risk with my current system, I am trying it as VM, but I have noticed that, when I divide partitions like ‘/’, ‘/home’ and give each one specific size, I see the size like to merge and they share the same size, is that normal, and if so, why is that? can’t I keep fixed size for each partition in Btrfs?
## Stephen Snow
The way Btrfs allocates space is as it needs it, so free space for one btrfs volume (disk partition) with more than one subvolume (like / and /home for example) will show identical for all subvolumes since it is currently available for all subvolumes to use.
## Sally
In this case I can’t encrypt just one partition e.g. ‘/home’ which I think it’s not a good idea.
## Jared Gray
Thanks for your excellent guide, Gergely (and of course the editors)! Because I had a lot of storage options, I decided to migrate my LVM/ext4 Fedora installation to an external mount point and then copy the data back to a new Btrfs filesystem. This approach considerably simplified moving off of LVM in particular. Even though my migration path was different than that described by this in-place tutorial, your guide was still instrumental in my own process.
Just in case others decide to follow a similar approach to what I did, there is one caveat I wanted to mention expressly. If you have SELinux enabled on your Fedora system, which is currently the default, you will need to relabel the new filesystem to get your system booting again. You can do this simply by placing a file called ‘autorelabel’ on the Btrfs subvolume corresponding to your ‘/’ mount point. I can’t speak to whether this step is required when using the in-place migration tools discussed in the article, however.
## Jared Gray
Correction: the file name is ‘.autorelabel’ not ‘autorelabel’. And warning: relabeling your entire file system is slow. With an NVME SSD and a two year-old installation of Fedora, I had to wait about five minutes for the process to complete. During this time, I was treated to a completely black screen. This is problematic because users may conclude that boot process has failed when in fact it is progressing.
To be clear, the fix I suggested does indeed work (eventually), but it is a hammer- rather than a scalpel-type solution. If your file system contains a lot of files (more than one million) or you are using a conventional spinning hard drive, I advise against relabeling everything as a first line measure. Since I’m not an SELinux nerd myself, I will put a call out there to those who know of a more fine-grained solution than I do.
In the meantime, my refined guidance is: before relabeling your filesystem, first verify that SELinux is the reason why your system will not boot. One way to do this is to disable SELinux policy enforcement temporarily and see if the system comes up afterwards.
To disable SELinux policy enforcement for the next boot only, ensure your kernel command line contains ‘selinux=1’ and ‘enforcing=0’. You can do this in GRUB by hitting the ‘e’ key during boot and appending the above parameters to the line containing ‘vm-linuz’. If the system now boots, you can reasonably infer that SELinux file attributes were likely causing the problem.
## Gregory Bartholomew
I was never a fan of disabling the post screen that shows what is happening (and if anything is failing) during boot. You should be able to hit the
Esckey to see the status messages.## Tony Nalagan
Wish I saw this article last November. My solution was less elegant and required considerable time to complete. I converted root, created an new home subvolume, and used gparted to shrink the original home partition while increasing the size of the new btrfs filesystem. Then migrating the data about 20 GB at a time, and repeating until all the data was transferred to the new home subvolume. Admittedly a brute force method.
## Mathieu Tanguay
“The purpose of this article is to give you an overview about why, and how to migrate your current partitions to a Btrfs filesystem”
Can’t find the why, only the how…
## Gergely Gombos
Hi, please see the “Pros and cons of conversion” and “What about LVM? ” sections in the article about the “Why”. I have pointed to several previous articles here on Fedora Magazine which discuss this topic in depth.
One example is: https://fedoramagazine.org/choose-between-btrfs-and-lvm-ext4/
## b1tninja
Further caution, you cannot rely on the snapshot as a backup |
14,578 | 软件包分析项目实时检查开源仓库中的包 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/package-analysis-examines-packages-in-open-source-repositories-in-real-time/ | 2022-05-11T15:58:01 | [
"开源",
"软件包"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14578-1.html | 
开源安全基金会(OpenSSF)发布了一个新工具的测试版,它可以对发布到著名开源仓库的所有软件包进行动态分析。软件包分析项目试图通过识别任何恶意行为并警告用户来保护开源软件包,目的是增强对开源软件的信任并加强软件供应链的安全性。
OpenSSF 说:“软件包分析项目旨在了解开源仓库上可用软件包的行为和功能:它们访问哪些文件,它们连接到哪些地址,以及它们运行哪些命令?”
该基金会的 Caleb Brown 和 David A. Wheeler 补充说:“该项目还跟踪软件包随时间的行为变化,以确定以前安全的软件何时开始出现可疑行为。”
该程序在为期一个月的测试运行中发现了 200 多个发布到 PyPI 和 NPM 的恶意软件包,其中大多数流氓库依赖于依赖混淆和仿冒攻击。谷歌是 OpenSSF 的成员,它支持软件包分析计划,强调“在发布软件包之前审查软件包以确保用户安全”的重要性。
去年,该公司的开源安全团队提出了软件工件的供应链级别(SLSA)架构,以验证软件包的完整性并防止未经授权的更改。这一发展是在开源生态系统越来越多地被武器化,用加密货币矿工和数据窃贼等恶意软件攻击开发者的情况下进行的。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/package-analysis-examines-packages-in-open-source-repositories-in-real-time/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF) has released a beta version of a new tool that can do dynamic analysis of all packages published to prominent open source repositories. The Package Analysis project attempts to safeguard open source packages by identifying and alerting users to any malicious behaviour, with the goal of enhancing trust in open source software and bolstering the security of the software supply chain.
“The Package Analysis project seeks to understand the behavior and capabilities of packages available on open source repositories: what files do they access, what addresses do they connect to, and what commands do they run?,” the OpenSSF said.
“The project also tracks changes in how packages behave over time, to identify when previously safe software begins acting suspiciously,” the foundation’s Caleb Brown and David A. Wheeler added.
The program discovered over 200 malicious packages published to PyPI and NPM during a month-long test run, with the majority of the rogue libraries relying on dependency confusion and typosquatting assaults. Google, an OpenSSF member, has thrown its support to the Package Analysis initiative, underlining the importance of “vetting packages before they are published in order to keep users secure.”
Last year, the company’s Open Source Security Team proposed the Supply Chain Levels for Software Artifacts (SLSA) architecture to verify the integrity of software packages and prevent unauthorised changes. The development comes as the open source ecosystem is increasingly being weaponized to attack developers with malware such as cryptocurrency miners and data thieves. |
14,579 | Fedora Linux 36 发布 | https://fedoramagazine.org/announcing-fedora-36/ | 2022-05-11T16:22:00 | [
"Fedora"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14579-1.html | 
今天,我很高兴与大家分享一个消息,它是成千上万的 Fedora 项目贡献者辛勤工作的成果:我们的最新版本 —— Fedora Linux 36,和大家见面了!
### 由社区开发,为社区服务
通常当我写这些公告时,我会谈论版本中的一些很棒的技术变化。但这一次,我想把重点放在实现这些变化的社区上。Fedora 社区不是一群孤立地工作的人 —— 我们是朋友。事实上,这也是我们的“<ruby> 四个理念 <rt> Four Foundations </rt></ruby>”之一。
我们最新的“Fedora 朋友”之一,Juan Carlos Araujo 在一篇 [Fedora 讨论帖子](https://discussion.fedoraproject.org/t/the-end-of-my-distro-hopping-days/38445) 中说得很好:
>
> 除了功能、稳定性、特性、工作方式以及前沿性外,我认为决定一个发行版成败的还有那些无形的东西,比如文档和社区。而 Fedora 拥有这一切……尤其是无形的东西。
>
>
>
多年来,我们一直努力使 Fedora 成为一个包容和欢迎的社区。我们希望它成为经验丰富的贡献者和新手能一起工作的地方。就像我们希望 Fedora Linux 是一个既能吸引资深用户又能吸引新手的发行版一样。
说到 Fedora Linux,让我们看看新版本的一些亮点。像往常一样,在从旧版本升级之前,请确保你的系统是最新的。这次尤其需要注意,因为我们在 F34/F35 更新中修复了一些非常重要的与升级有关的错误。如果不先应用这些更新,系统升级可能会失败。
### 桌面改进
Fedora 工作站专注于桌面体验,尤其是面向那些希望获得“刚刚好”的 Linux 系统体验的用户。像往常一样,Fedora 工作站采用最新的 GNOME 版本:[GNOME 42](https://release.gnome.org/42/)。虽然 GNOME 42 不能完全解决生命、宇宙和一切问题,但它带来了很多改进。许多应用程序都被移植到了 GTK 4,以改善风格和性能。它还附带了两个新的应用程序:<ruby> 文本编辑器 <rt> Text Editor </rt></ruby>和<ruby> 控制台 <rt> Console </rt></ruby>。它们的名字起得很贴切,所以你可以猜出它们是干什么的。文本编辑器是新的默认文本编辑器,而控制台可以在软件仓库中下载。
如果你使用了英伟达的专有图形驱动,你的桌面会话现在将默认使用 Wayland 协议。这使你能够在使用现代桌面管理器时,充分利用硬件加速。
当然,我们生产的不仅仅是 “Editions”。[Fedora Spins](https://spins.fedoraproject.org/) 和 [Labs](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/) 针对不同的受众和使用场景。例如 [Fedora Comp Neuro](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/en/comp-neuro/) ,它为计算神经科学提供工具,以及 [Fedora LXQt](https://spins.fedoraproject.org/en/lxqt/),它提供一个轻量级的桌面环境。并且,我们附加了可选架构:[ARM AArch64、Power 和 S390x](https://alt.fedoraproject.org/alt/)。
### 针对系统管理员的改进
Fedora Linux 36 包含最新的 Ansible 版本。Ansible 5 将“引擎”拆分为 ansible-core 包和 [collection 包](https://koji.fedoraproject.org/koji/search?match=glob&type=package&terms=ansible-collection*)。这使得维护更容易,并允许你只下载需要的集合。请参阅 [Ansible 5 迁移指南](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/devel/porting_guides/porting_guide_5.html) 以了解如何更新你的 Playbook。
从 Fedora Server 36 开始,Cockpit 提供了一个用于配置和持续管理 NFS 及 Samba 共享的模块。这使得管理员可以通过 Cockpit 网页界面(用于配置其他服务器属性)来管理网络文件共享。
### 其他更新
无论你使用 Fedora Linux 的哪个衍生版,你都会得到开源世界所提供的最新成果。Podman 4.0 将在 Fedora Linux 36 中首次全面发布。它带来了大量变化和一个全新的网络栈。不过,它也带来了向下**不兼容**的 API 变化,所以请仔细阅读 [上游文档](https://podman.io/releases/2022/02/22/podman-release-v4.0.0.html)。
遵循 Fedora 的 “<ruby> <a href="https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/project/#_first"> 争先 </a> <rt> First </rt></ruby>” 理念,我们已经更新了关键的编程语言和系统库包,包括 Ruby 3.1、Golang 1.18 和 PHP 8.1。
我们很高兴你能试用新版本!请访问 <https://getfedora.org> 并立即下载它吧!或者,如果你正在使用 Fedora Linux,请按照我们的 [简易升级说明](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/upgrading/) 进行。想了解更多关于 Fedora Linux 36 新功能的信息,请查看 [发行说明](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/fedora/f36/release-notes/)。
### 虽然不大可能会出现问题……
但是,如果你真的遇到了问题,请访问我们的 [Ask Fedora](https://ask.fedoraproject.org/) 用户支持论坛。这里有一个 [常见问题](https://ask.fedoraproject.org/tags/c/common-issues/141/f36) 的分类。
### 谢谢大家
感谢在本次发布周期内为 Fedora 项目做出贡献的成千上万的人。Fedora 社区有你们,真好!请务必在 5 月 13 日至 14 日参加我们的 [虚拟发布派对](https://hopin.com/events/fedora-linux-36-release-party/registration)!
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/announcing-fedora-36/>
作者:[Matthew Miller](https://fedoramagazine.org/author/mattdm/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Today, I’m excited to share the results of the hard work of thousands of Fedora Project contributors: our latest release, [Fedora Linux 36](https://getfedora.org/), is here!
## By the community, for the community
Normally when I write these announcements, I talk about some of the great technical changes in the release. This time, I wanted to put the focus on the community that makes those changes happen. Fedora isn’t just a group of people toiling away in isolation — we’re friends. In fact, that’s one of our Four Foundations.
One of our newest Fedora Friends, Juan Carlos Araujo said it beautifully in a [Fedora Discussion post](https://discussion.fedoraproject.org/t/the-end-of-my-distro-hopping-days/38445):
Besides functionality, stability, features, how it works under the hood, and how cutting-edge it is, I think what makes or breaks a distro are those intangibles, like documentation and the community. And Fedora has it all… especially the intangibles.
We’ve worked hard over the years to make Fedora an inclusive and welcoming community. We want to be a place where experienced contributors and newcomers alike can work together. Just like we want Fedora Linux to be a distribution that appeals to both long-time and novice Linux users.
Speaking of Fedora Linux, let’s take a look at some of the highlights this time around. As always, you should make sure your system is *fully up-to-date* before upgrading from a previous release. This time especially, because we’ve squashed some very important upgrade-related bugs in F34/F35 updates. Your system upgrade to Fedora Linux 36 could fail if those updates aren’t applied first.
## Desktop improvements
Fedora Workstation focuses on the desktop, and in particular, it’s geared toward users who want a “just works” Linux operating system experience. As usual, Fedora Workstation features the latest GNOME release: [GNOME 42](https://release.gnome.org/42/). While it doesn’t *completely *provide the answer to life, the universe, and everything, GNOME 42 brings a lot of improvements. Many applications have been ported to GTK 4 for improved style and performance. And two new applications come in GNOME 42: Text Editor and Console. They’re aptly named, so you can guess what they do. Text Editor is the new default text editor and Console is available in the repos.
If you use NVIDIA’s proprietary graphics driver, your desktop sessions will now default to using the Wayland protocol. This allows you to take advantage of hardware acceleration while using the modern desktop compositor.
Of course, we produce more than just the Editions. [Fedora Spins](https://spins.fedoraproject.org/) and [Labs](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/) target a variety of audiences and use cases, including [Fedora Comp Neuro](https://labs.fedoraproject.org/en/comp-neuro/), which provides tools for computational neuroscience, and desktop environments like [Fedora LXQt](https://spins.fedoraproject.org/en/lxqt/), which provides a lightweight desktop environment. And don’t forget our alternate architectures: [ARM AArch64, Power, and S390x](https://alt.fedoraproject.org/alt/).
## Sysadmin improvements
Fedora Linux 36 includes the latest release of Ansible. Ansible 5 splits the “engine” into an ansible-core package and [collections packages](https://koji.fedoraproject.org/koji/search?match=glob&type=package&terms=ansible-collection*). This makes maintenance easier and allows you to download only the collections you need. See the[ Ansible 5 Porting Guide](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/devel/porting_guides/porting_guide_5.html) to learn how to update your playbooks.
Beginning in Fedora Server 36, Cockpit provides a module for provisioning and ongoing administration of NFS and Samba shares. This allows administrators to manage network file shares through the Cockpit web interface used to configure other server attributes.
## Other updates
No matter what variant of Fedora Linux you use, you’re getting the latest the open source world has to offer. Podman 4.0 will be fully released for the first time in Fedora Linux 36. Podman 4.0 has a huge number of changes and a brand new network stack. It also brings backwards-incompatible API changes, so read the [upstream documentation](https://podman.io/releases/2022/02/22/podman-release-v4.0.0.html) carefully.
Following our “[First](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/project/#_first)” foundation, we’ve updated key programming language and system library packages, including Ruby 3.1, Golang 1.18 and PHP 8.1.
We’re excited for you to try out the new release! Go to [https://getfedora.org/](https://getfedora.org/) and download it now. Or if you’re already running Fedora Linux, follow the [easy upgrade instructions](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/upgrading/). For more information on the new features in Fedora Linux 36, see the [release notes](https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/fedora/f36/release-notes/).
## In the unlikely event of a problem…
If you run into a problem, visit our [Ask Fedora](https://ask.fedoraproject.org/) user-support forum. This includes a category for [common issues](https://ask.fedoraproject.org/tags/c/common-issues/141/f36).
## Thank you everyone
Thanks to the thousands of people who contributed to the Fedora Project in this release cycle. We love having you in the Fedora community. Be sure to join us May 13 – 14 for a [virtual release party](https://hopin.com/events/fedora-linux-36-release-party/registration)!
## Brad Smith
Really well done. A big thank you to all maintainers, team members, and contributors.
## Victor R
Awesome!. Downloading …. A big one this release is.
## Joel
They did a great job with this new version of Fedora. I congratulate the development team for their excellent work. I’m currently using the beta version, I’ll move on to the stable one.
## Pablo Carrizo
Felicitaciones a todo el equipo! Fedora ha sido mi distribución favorita desde hace mucho tiempo.
Agradezco profundamente a cada persona que contribuye al éxito y liderazgo de este proyecto.
Muchas gracias!
## Manuel Cabrera Caballero
Great work guys !!!
## Charles
Congratulations!
## w_decoder
Fedora is always worth waiting for.
## Adilson Miguel
Wow finally the wait is over, congrats fedora project team for the hard work, I have been using fedora 36 beta for quite some time, now how can I upgrade to fedora 36 final release??
## Luann
Upgrading from pre-release (beta) to final public release (stable):
If you are using a pre-release of Fedora, you shouldn’t need to do anything to get the final public release, other than updating packages as they become available. You can use sudo dnf update or wait for desktop notification. When the pre-release is released as final, the fedora-repos packages will be updated and your updates-testing repository will be disabled. Once this happens (on the release day), it is highly recommended to run sudo dnf distro-sync in order to align package versions with the current release.
Source: https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/upgrading/
## René Genz
see https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/upgrading/#sect-upgrade-from-prerelease-to-final-release
## Frank Jackson
It should auto update when running dnf upgrade!
## Feda
Congratulations on the new release. I’m looking forward to upgrading from Fedora 35. Fedora keeps getting better. Thank you for your hard work.
## Angel Yocupicio
Hi Mattew, it is very greatful to install Fedora 36 on my hardware. I am a mathemathic professor and Fedora help me very much on my daily task.
## Mehdi
Just curious Angel, what software do you use on Fedora that help you with your mathematical teaching? Should be insightful and inspiring and could subject of a very good “How do you Fedora?” article.
## cr0t0
My congratulations to the team Fedora!
## Verolomstvo
alt+shift toggles language BUT the language icon doesn’t change in the panel
## Xiaoliang Yu
I read from Fedora Wiki that wayland would be set as default on single-GPU machines running propetiary driver, but my optimus-based laptop has been defaulted to wayland too, is that correct?
## oldkid
The biggest improvement that I notice is that, updating a Gnome extension finally works!
## Tom
I’m a month and a half with the beta version that worked great on a few different computers. Fedora is always the best on the market. They have the best merchandise on the market.
## Peter
A sweet update, a great work done by Fedora team
## tfks
Yay! Happy to be part of the Fedora family!
## Taylor
Great job. Unfortunately when trying to encrypt the installation, no matter what keyboard layout you have chosen (in my case, Latin American Spanish), it will always use the US layout.
That is a bug.
## Canal do Felippe HD
Nice! Now I can stop my distrohopping, thanks 🙂
## Sumir Seth
Congrats!
## NoMad
I just want to thank those people for making Fedora what it is. Best Desktop Distro I’ve used. It just works. Updates and Upgrades have never caused me trouble, even with an “unusual” setup (encrypted root, LVM on LUKS). This is Linux how it was meant to be.
## David
Thanks, great distro! Love the KDE spin. The upgrade went without a hitch, like last time .
## David (k3dgr)
Outstanding…. Been using 35 for a while, convert from Ubuntu and What A Difference!! Keep up the outstanding work!!! -dgr
## Keith Manning
Well done! Onward and upward!
## Isleif
This evening I will download it. Superb effort and whilst using Silverblue, the best GNU/Linux distribution there is.
## ED Nuñez
Excelente experiencia usando Fedora, la nueva version es muy buena.
Una felicitacion a todo el equipo de Fedora por el increible trabajo.
## Steve g
Can I upgrade via sudo dnf upgrade command line?
## news
see this page : https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/dnf-system-upgrade/
## Mehdi
Congratulations and thanks to the Fedora developers and community
## Kernow
What about the release date for Silverblue and Kinoite 36? I had expected them to be release at the same time as the WS edition.
## Diego Alvarez
What a beautiful and yet really powerful masterpiece of software. Congrats to the developer team and the community 🙂
## Adrian
Thanks for all the efforts, to me this is the best and most suitable linux distro I ever used in the past 20 years. Whishing all of you lots of beer, shoulder taps and the general sense of appreciation for your work! 😉
## Jim
Upgraded – but I’m still on xll and not wayland. I’m using Cinnamon desktop, do I have to do something extra?
## Kamil
Cinnamon doesn’t seem to support Wayland at this moment.
## Jim
Yeah, thanks, I went googling after I posted and saw that. Darn. I don’t want to give up my Cinnamon desktop…
## Aaron
Thanks for the post Jim. I’m on Cinnamon as well and really hate GNOME (can’t stand it). So guess I’ll delay updating to fedora 36 (I’m on 33 right now).
## Leslie Satenstein, Montreal,Que
There are a few good YouTube videos that portray Fedora 36 as the best Distro today, that is available for immediate download.
“Stephen’s Tech Talks” and “TylersTechNow” are to name two such presenters.
Links are:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E-nNfVdf5zE&t=356s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-fR0ofXsVhk
Both presentors are in English
Each is well worth the watch
## news
never a problem with Fedora.
All works perfectly.
Thanks a lot. Great work as usual.
## rscm
Can’t rebase to Silverblue 36, there’s an error updating the “updates-archive” repo. Please fix it
## Manprit Singh
Thanks to the Fedora community. I use Fedora Python classroom to teach Python
## Isleif
As I said, I just installed a couple of minutes ago, flawlessly and after my Gnome extensions were set in, it is beautiful and bright. Very elegant and with lots of customisation. My best wishes of success to all of you involved.
## Frederik
“While it doesn’t completely provide the answer to life, the universe, and everything.”
That would be “the great question about life, the universe and everything”, and yes, GNOME 42 does provide the answer (the answer is 42 and you’re not going to like it).
## Bill Davidsen
The last Fedora which would use qemu-kvm to run Mint or Ubuntu was on the 5.16 kernel. Not just a new Ubuntu version but out on 20.04 or so which I’ve used for several years. The first 5.17.4 didn’t work, and the latest 36 and 5.17.5 is still not working so I can clear for other distributions for a few apps got on Fedora.
## Umahdroid
Great news. Downloading
## Verolomstvo
HP Pavilion 15 eh1083ur – Fedora 36 works great out of the box.
## Andrew
I always get a bit nervous with upgrades. If you
onlyuse a Radeon card (which I do) or Intel gfx, and only software from the main repos or rpmfusion, then it’s mostly a piece of cake to upgrade, but I’ve got a Steam library that must not be broken. I’ve got a razer hardware repo that must work after upgrade, plus repos for Amiga emulators, special flatpaks from god knows where for Vice emulator… it all adds up, and makes an upgrade a toil by having to check all sources before you start. I dislike having to get software from other sources, but when there’s something you really want, and it’s not offered, then you end up compromising. I’m mostly miffed by FS-UAE and Vice that decided to release as flatpaks because their main repo versions are broken.## Benjamin
good
## Brian Reading
Congrats to all of the Fedora Project on releasing another great-looking version of Fedora Linux.
## Cliff Wells
A lot of the changes in 42 were positive, but I have to warn anyone with vision issues who requires a low-contrast theme that you’ll want to hold off updating as there’s no way to select a low-contrast theme.
I’m having to desktop-shop for the first time in years.
## Ethan Bergstrom
Invoked the upgrade for my Silverblue 35 workstation (with an RTX 3070 leveraging proprietary drivers) via Software Center.
The entire upgrade process was quick and easy, and other than double-checking whether the session switched to Wayland and I hadn’t dropped into Nouveau somehow, never had to interact with the command line once.
Awesome work, team!
## mgm
Vielen Dank an die Entwickler, wirklich gute Arbeit.
LG
## William Bode
Running 36 on three computers at work and home and glad to be using a solid system!
## ewrew
please add Polish language section to documentation and forum.
## Jonshu
There is already a polish version of Fedora Forum, please take a look:
https://forum.fedora.pl/
## Paolo
Many thanks for the effort!!!
## abufarah
NOW DOWNLOADING . . .
Thanks to Fedora Team
## Mehdi
Hi Matthhew,
The upgrade link you provided returns a 404!
https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/upgrading
## Gregory Bartholomew
I just tried it and it seems to be working now.
## sirhcton
Deja-Dup Backups’ restore function is broken in Fedora 36. I tried various methods after my problems, thinking it might be something about my backup files, but am pretty sure it’s Fedora 36’s Deja-Dup. I created a clean installation, copied some files to it, and made a backup. I deleted the files and then tried a restore to original locations. It choked with “InvalidBackendURL: missing // – relative paths not supported for scheme invalid: invalid://” I F35 still works as it should.
## Muhammed Yasin Özsaraç
One of the best Fedora release. I rebase from 35 to 36 on Silverblue and working perfectly. The most thing I like about Fedora 36 is screenshot option definitely because we have really bad trouble on Wayland regarding some applications like Flameshot. Keep up the great work guys. Thank you very much.
## sahil
Fedora need focus on kde as primary enviornment.
## Why'd want my name?
Yup. Every distro needs to switch to KDE. But Fedora also NEEDS to disable the abomination called offline update. It’s simply stupid. If this becomes a trend among distros, I’ll just stop using Linux based distros and start my own based on LFS or Gentoo.
## Gnanesh
Awesome release! Thank you so much guys for continue to improve what’s already a rock-solid distribution.
Did run into a problem with Wayland crashing after booting up (I upgraded from 35 to 36), hope to find a solution quickly.
Thanks again, keep rocking.
## Rick Fulford
I usually do a lot of distro hoping. I installed Fedora 36 Gnome on my low end Lenovo, and, my hoping has stopped. It just works, perfectly I might add. No problems at all. Well done to all the folks at Fedora, now I’m very contented.
## Faisal
Than you so much for great work… Love you Fedora
## Swell Topher
Thank you! Everyone! You all do fantastic work, and we are all so appreciative.
## Lennart Aspenryd
I will do my best, too ensure just too use fedora (or Linux) and avoid to jump between Os.
I really adore all job done bye all of you. |
14,581 | 你为什么应该选择专注而非一心多用 | https://opensource.com/article/19/4/mindfulness-over-multitasking | 2022-05-11T23:29:44 | [
"专注"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14581-1.html |
>
> 如果你有时候会感觉大脑处于停滞状态,那么你可能正在遭受一心多用和决策疲劳。
>
>
>

想象一下,你刚完成了日常工作,坐在电脑前,手里拿着晨间咖啡,正准备开始新的一天。突然,一条 Slack 消息弹了出来,你扫了一眼邮件,然后切回 Slack。你打开日历,看看下一次会议是什么时候,令你惊讶的是,它 15 分钟后就要开始了!你回到办公桌前,开始检查待办事项,想看看在这短短 15 分钟内还能给自己安排什么任务,但不巧的是,这时你的一个同事请求你帮他解决一个问题。大半天就这样过去了,而你根本没有意识到……
我的许多日子都是这样度过的,不断地多个任务之间徘徊。有些时候,我发现自己盯着电脑,大脑完全停滞。如果你也发现自己处于这种情况,这可能是你的大脑发出的信号,提醒你休息一下。你可能正在遭受一心多用和决策疲劳。
平均而言,成年人每天要做大约 [35000 个决定](https://go.roberts.edu/leadingedge/the-great-choices-of-strategic-leaders)!它们可能是简单的决定,如吃什么或穿什么,也可能是需要更多思考的决定,如下一个假期去哪里或从事哪个职业。每天你都面临着大量的选择,它们占据了你的头脑。
### 分散注意力的一心多用
不只有你一个人每天面临着数以千计的决定,事实上,一心多用早已成为忙碌的、工作中的专业人士的常态。问题是,一心多用的伤害比它的帮助更大。你越是为了处理多任务而分散注意力,你的生产力就越是下降。
在一项研究中,自称是一心多用者的人,被要求以他们感觉自然的速度,在各种任务之间来回切换。同时,研究的对照组,被要求按顺序,一次完成一项工作。研究表明,多任务组的效率要低得多。每次他们切换任务时,都会出现速度减慢的情况,因为他们需要时间来回忆到目前为止所做的细节和步骤。这最终 [额外花费了大约 40% 的时间](http://www.apa.org/research/action/multitask.aspx),并导致整体准确度降低。每次专注于一项任务的人,总体上花费的时间更少,并且完成了所有的任务。
### 选择专注
当大脑集中在一项活动上时,它的功能是最理想的。选择专注而不是一心多用,将使你在一天中获得更好的感受,并帮助你完成更好的工作。
“专注”可以被定义为有意识和察觉的。它实际上是指活在当下,并将注意力集中于眼前的事情上。在工作场所,专注有很多好处。它的诀窍在于建立边界和习惯,使你能够对每项任务给予充分的关注。
保持积极主动,为每天必须完成的项目排好优先级,并制定一个完成计划。这将使你能够在一些重要的事情上取得真正的进展,而不是被动应付。你的待办事项清单上的每个项目,都应该是独立、明确、可操作的。每天专注于三到五项任务,不要太多。
### 三种在工作日休息的方法
不要忘记把“休息”也放进一天的计划中。大脑每小时需要几分钟的休息,以休养生息,避免倦怠。休息一下对你的心理健康也有好处,最终 [有助于生产力的提高](https://opensource.com/article/19/3/guide-being-more-productive)。
这里有三种简单的“休息”方法,请把它们融入到你忙碌的一天中吧!
#### 1、移动身体
花 10 分钟时间,离开你的椅子,站起来走一走。如果你的时间很紧张,可以站起来伸展两分钟。改变身体所处的位置,并专注于当下,将有助于缓解积聚在你心中的精神紧张。
#### 2、多笑
休息一下,与你的朋友和工作中的同事交谈。笑声可以减少压力荷尔蒙,并引发内啡肽的释放,内啡肽是人体天然的的化学物质,它会使人感觉良好。欢声笑语的小憩有助于放松你的头脑,对你的灵魂也有好处。
#### 3、深呼吸
用两分钟的休息时间来重置你的身心,使用腹部深呼吸。它可以使你的身心平静下来,改善氧气流动,并给你带来自然的能量提升。
1. 挺直坐正,将注意力放在腹部,感受它的柔软和放松。
2. 从缓慢的深吸气开始,数三下,让氧气依次充满你的腹部、肋骨和上胸。
3. 停顿一秒钟,然后与深吸气相反,从上胸、肋骨和腹部呼气,最后将腹部拉向脊柱。
4. 再次停顿,然后重复。
### 重置自己
下次当你发现自己处于停滞状态,或是正在强迫状态不佳的自己完成一项任务时,请尝试上面的一些提示。最好是短暂休息一下,重置身心,而不要试图强行完成任务。相信我,你的身体和大脑会感谢你的!
本文改编自《BodyMindSpirit》上的 [让自己休息一下](https://body-mind-spirit-coach.com/2019/01/02/give-yourself-a-break/) 和 ImageX 的博文 [专注而不是一心多用](https://imagexmedia.com/mindfullness-over-multitasking)。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/19/4/mindfulness-over-multitasking>
作者:[Sarah Wall](https://opensource.com/users/sarahwall) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | You have your morning coffee in hand, you've just finished your daily scrum, and you sit down at your computer to start your day. Up pops a Slack message. You scan your emails, then bounce back to Slack. You look at your calendar to see when your next meeting is—much to your surprise, it's starting in 15 minutes. You get back to your desk and check your to-do list to see what tasks you can fit in before your next meeting, but one of your co-workers asks for your help to solve a problem. Before you know it, half of your day has disappeared.
Many of my days are spent like this, juggling multiple tasks. There are moments I find myself staring at my computer with my brain at a complete halt. If you, too, find yourself in this situation, it's probably a sign from your brain to take a break. You could be suffering from too much multitasking and decision fatigue.
On average, adults make about [35,000 decisions](https://go.roberts.edu/leadingedge/the-great-choices-of-strategic-leaders) every day! They can be simple decisions, such as what to eat or what to wear, or decisions that require more thought, such as where to go on your next vacation or which career to pursue. Every day you are faced with a plethora of choices to occupy your mind.
## Mindless multitasking
Not only are you faced with making thousands of decisions each day, but multitasking has also become the norm for busy and in-demand professionals. The problem is, multitasking hurts more than it helps. The more you divide your attention through multitasking, the more your productivity decreases.
In a study, self-described multitaskers were asked to switch back and forth between tasks at a pace that felt natural to them. A control group was asked to do one job at a time in sequence. The multitasking group performed far less effectively. Each time they switched tasks, there was a slowdown because it took time to time recall the details and the steps they'd done so far. This wound up making everything [take roughly 40% longer](http://www.apa.org/research/action/multitask.aspx) and led to lower levels of accuracy overall. People who focused on one task at a time spent less time overall and finished all the tasks.
## Choose mindfulness
The mind functions optimally when it can focus on one activity at a time. Choosing mindfulness over multitasking will result in better feelings throughout your day and help you do better work.
"Mindfulness" can be defined as being conscious and aware. It really is about being present in the moment and focusing your attention on what's at hand. There are many advantages to mindfulness in the workplace. The trick is creating boundaries and habits that allow you to give each task your full attention.
Take a proactive approach and create a prioritized plan of the items that must get done each day. This will allow you to make real progress on a few things that are important instead of being reactive. Every item that goes on your to-do list should be discrete, clear, and actionable. Focus on three to five tasks per day.
## 3 ways to take a break during your workday
Don't forget to plan breaks throughout your day. The brain needs a few minutes of rest every hour to recuperate and to avoid burnout. Taking mini-breaks is good for your mental health and [leads to increased productivity](https://opensource.com/article/19/3/guide-being-more-productive).
Here are three easy ways to incorporate breaks into your day:
### 1. Move your body
Take 10 minutes to get out of your chair and go for a short walk. If you're pressed for time, stand up and stretch for two minutes. Changing the position of your body and focusing on the present moment will help relieve the mental tension that has built up in your mind.
### 2. Laugh more
Take a break to talk with your friends and colleagues at work. Laughter decreases stress hormones and triggers the release of endorphins, the body's natural feel-good chemicals. A little laughter break helps relax your mind and is also good for your soul.
### 3. Breathe deeply
Reset your mind and body with a two-minute break to breathe deeply into your belly. Deep breathing calms your mind and body, improves oxygen flow, and gives you a natural energy boost.
- Sit up tall with a straight spine, bring your awareness to your belly, and allow it to soften and relax.
- Begin with a slow, deep inhalation for a count of three, filling your belly, then rib cage, then upper chest with oxygen.
- Pause for a second, then exhale from your upper chest, rib cage then belly, drawing your belly in towards your spine at the end.
- Pause again, then repeat.
## Reset yourself
The next time you find yourself at a standstill or pressuring yourself to finish a task when your mind is not in the flow, try some of the tips above. It's better to take a short break and allow yourself to reset rather than trying to power through. Your body and brain will thank you.
*Adapted from Give Yourself a Break*
*on BodyMindSpirit*
*and*
[Mindfulness Over Multitasking](https://imagexmedia.com/mindfullness-over-multitasking)on ImageX's blog.*Sarah Wall will present Mindless multitasking: a dummy's guide to productivity, at DrupalCon in Seattle, April 8-12, 2019.*
## 6 Comments |
14,582 | 彭博社开源 Memray,一个 Python 内存剖析器 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/04/bloomberg-open-sources-memray-a-python-memory-profiler/ | 2022-05-12T08:17:47 | [
"Python"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14582-1.html | 
Memray 是一个由彭博社开发的<ruby> 内存剖析器 <rt> memory profiler </rt></ruby>,现在已经开源。它可以跟踪 Python 代码中的内存分配,包括本地扩展和 Python 解释器本身。内存剖析是了解程序如何利用内存的有力工具,因此可以检测内存泄漏或确定程序中哪些区域消耗的内存最多。
与 py-spy 等抽样内存剖析器相比,Memray 可以跟踪每个函数调用,包括对 C/C++ 库的调用,并详细显示调用栈。彭博社称,这并不以牺牲性能为代价,剖析只使解释代码的速度变慢一点。然而,原生代码剖析的速度较慢,因此需要直接启用。
Memray 可以根据获得的内存消耗数据生成各种报告,包括火焰图,这对快速、准确地识别最常见的代码路径很有价值。
据 EgdeDB 的联合创始人兼 CEO Yury Selivanov 称,该工具提供了以前无法获得的对 Python 应用的洞察力。Memray 可以用来从命令行中执行和剖析 Python 应用。
```
$ python3 -m memray run -o output.bin my_script.py
$ python3 -m memray flamegraph output.bin
```
另外,你可以使用 pytest-memray 将 Memray 集成到你的测试套件中。你也可以用 `-native` 命令行选项对所有的 C/C++ 调用进行剖析,或者用 `-live` 命令行选项在程序执行过程中实时分析内存分配。Memray 可以在 Linux x86/64 系统上用 `python3 -m pip install memray` 来安装。
(题图由 [Frantisek Krejci](https://pixabay.com/zh/users/frantisek_krejci-810589/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=7152438) 在 [Pixabay](https://pixabay.com/zh/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=7152438) 上发布 )
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/04/bloomberg-open-sources-memray-a-python-memory-profiler/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Memray is a memory profiler that was developed at Bloomberg and is now open source. It can track memory allocations in Python code, including native extensions and the Python interpreter itself. Memory profiling is a strong tool for understanding how a program utilises memory and, as a result, detecting memory leaks or determining which areas of the program consume the most memory.
In contrast to sampling memory profilers like py-spy, Memray can track every function call, including calls into C/C++ libraries, and display the call stack in detail. Bloomberg claims that this does not come at the sacrifice of performance, with profiling only slowing down interpreted code by a little amount. However, native code profiling is slower and must be enabled directly.
Memray may generate a variety of reports based on the acquired memory consumption data, including flame graphs, which are valuable for rapidly and precisely identifying the most common code-paths.
According to Yury Selivanov, co-founder and CEO of EgdeDB, the tool gives previously unavailable insights into Python applications. Memray can be used to execute and profile a Python application from the command line:
- $ python3 -m memray run -o output.bin my_script.py
- $ python3 -m memray flamegraph output.bin
Alternatively, you can use pytest-memray to integrate Memray into your test suite. You can also profile all C/C++ calls with the —native command line option, or analyse memory allocation in real time while a programme is executing with the —live command line option. Memray can be installed with python3 -m pip install memray on a Linux x86/64 system. |
14,583 | 在 Ubuntu Linux 如何安装 H.264 解码器 | https://itsfoss.com/install-h-264-decoder-ubuntu/ | 2022-05-12T10:15:00 | [
"H.264",
"多媒体解码器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14583-1.html | 
当你开始使用 [新安装的 Ubuntu 系统](https://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu/) 并尝试打开一个 MP4 文件进行播放时,它可能会显示一个错误,即:
>
> 播放这个文件要求 H.264(高清)解码器 ,但是没有安装。
>
>
>

你可能会猜到原因:系统没有安装所需的多媒体解码器,导致视频播放器播放该视频文件。
所以,解决方案是什么?安装所需的解码器。怎么做呢?
我将讨论解决这个问题的三种方法:
1. 只安装所需的解码器:它能解决所需的文件播放,但是一些其它格式的文件仍然会处在无解码器可用的状态。
2. 一次安装多种多媒体解码器:它会安装解码器之外,还会安装你不需要的其它软件包,类似微软的字体库一样。
3. 安装一个不同的视频播放器:像 VLC 和 MPV 视频播放器默认状态下对解码器有更好的支持。对大多数常规视频文件来说,你不必分别安装它们。
如果你遵从我的建议,我建议你采用第二种和第三种方法。为什么?一会你就知道了。
### 在 Ubuntu Linux 获取 H.264 解码器
这里我使用 Ubuntu Linux。第一和第三种方法应该也适用于其它发行版,但是第二种方法不适用,因为所提到的包(常常)是 Ubuntu 所独有的。
#### 方法 1: 只安装所需的解码器(不推荐)
当你看到这个错误时,它给你一个叫做 “在 Ubuntu 软件中心查找” 的按钮。点击这个按钮打开软件中心,可能显示(或不显示)一些将在你的系统上安装 H.264 解码器的软件包。

软件包名可能听起来很相似,但是你需要安装来自<ruby> “不良”组合 <rt> "bad" set </rt></ruby>的 GStreamer 多媒体解码器。注意检查软件包的描述。
或者,你可以使用如下命令在终端来安装软件包:
```
sudo apt install gstreamer1.0-plugins-bad
```
如果你对终端不了解,请注意要求使用你的账户密码的提示。**当你输入你的密码时,屏幕什么都不显示**。这是 Linux 的方式。你盲输密码然后按回车键。
一旦软件包安装完成,再次打开文件看看是否能够正常播放。
这可能对你有用,但是解决方案并未结束。你可能有其它格式的一些视频文件要求一些其它的 H.264 解码器或者其它解码器。

你可以通过如下命令安装更多的解码器:
```
sudo apt install libavcodec-extra gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly gstreamer1.0-libav
```
然而,在 Ubuntu 有一个 [安装多媒体解码器更加方便的方法](https://itsfoss.com/install-media-codecs-ubuntu/),我会在下一节展示给你。
#### 方法 2: 安装所有多媒体解码器(推荐)
Ubuntu 系统提供了一个名字叫做 `ubuntu-restricted-extras` 的基础软件包,由许多常规的音频和视频解码器以及像类似微软字体库那样多余的一些软件包组成。
安装这个软件包你将不用再担心多媒体解码器的问题了。
在 Ubuntu 打开终端并键入以下命令:
```
sudo apt install ubuntu-restricted-extras
```
由于这个基础软件包包含类似微软字库那样用不到的一些多余的软件,你必须得接受最终用户许可协议(EULA)才行。

下一屏类似如下。按下 `tab` 键会高亮显示选项。当正确的选项高亮显示时,按下回车键来确认你的选择。

当多媒体解码器安装完成后,你应该能够播放绝大多数媒体文件了。你的音乐播放器能播放 MP3 文件,你的视频播放器能播放 MP4,MKV 等等格式。
然而,这也不是解决方案的终点,至少对某些人来说。
为什么我要那样说?因为我已经注意到 Ubuntu 系统下的默认视频播放器 Totem 在播放某些视频格式文件时常常遇到问题。你会注意到突然你的系统主机发热,风扇狂转并且鼠标指针停止运行。
为什么?因为 Totem 播放器在视频解码方面占用了大量的处理器资源。
当你播放视频的时候你可以通过 `top` 命令尝试查看名称为 `totem` 这个进程(那是默认视频播放器的名字)。

你现在能够做什么?你的麻烦看起来永无止境,别担心。[在 Linux 上有更好的视频播放器](https://itsfoss.com/video-players-linux/) 并且它们能帮助你解决问题。
#### 方法 3: 安装一个更优秀的视频播放器(推荐)
在 Linux 上有很多优秀的视频播放器。我发现它们优于默认的 Totem 视频播放器。
就我个人来说,那么多个我只喜欢这两个:[VLC](https://www.videolan.org/vlc/) 和 [MPV](https://mpv.io/)。
VLC 是一个功能丰富且超级流行的视频播放器。很可能你已经使用过 VLC 。
MPV 媒体播放器不是那么流行,但使用这个轻量级的程序播放视频文件是再合适不过了。
VLC 和 MPV 播放器都擅长处理多媒体解码器。你甚至不必分开来安装多媒体解码器。只需要 [安装 VLC](https://itsfoss.com/install-latest-vlc/) 或者 MPV ,你就能够播放各种格式的视频文件。
在软件中心也可以找到它:

或者 使用命令行 [在 Ubuntu 安装 MPV](https://itsfoss.com/mpv-video-player/):
```
sudo apt install mpv
```
现在你已经有了一个新的视频播放器,你应该右键点击视频文件,选择新的视频播放器来打开。
或者,你可以[使其作为默认程序](https://itsfoss.com/change-default-applications-ubuntu/) 双击来播放视频文件。
### 对你有用吗?
我在这里没有说太多细节。我想阐述各种方法以及对应的优缺点。
你在 Ubuntu 处理好 H.264 解码器的问题了吗?哪种方法对你有用?
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/install-h-264-decoder-ubuntu/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hwlife](https://github.com/hwlife) 校对:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When you start using a [fresh installed Ubuntu system](https://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu/) and try to open an MP4 file to play videos, it may show you an error that reads:
*H.264 (High Profile) decoder is required to play the file, but is not installed.*
You can perhaps guess what’s going on here. Your system doesn’t have the required media codecs installed and hence the video player cannot play that video file.
So, what’s the solution here? You install the required codec. But how?
I’ll discuss three ways about fixing this issue:
- Install just the required codec: It could work for the given file but some other video files will still complain about missing codecs.
- Install a wide variety of multimedia codecs at once: It installs codecs as well as some other packages that you might not need like Microsoft Fonts.
- Install a different video player: Applications like VLC and MPV have better support for codecs by default. You don’t need to install them separately for most common video files.
If you take my advice, I suggest going for the second as well as the third method. Why? You’ll see in a moment.
## Getting h264 decoder in Ubuntu Linux
I am using Ubuntu Linux here. The first and the third methods should work for other distributions but not the second one as the package mentioned is (usually) exclusive to Ubuntu.
### Method 1: Install only the required codec (not recommended)
When you see the error, it gives you the option to “Find in Ubuntu Software”. Clicking on that option opens the Software Center and it may (or may not) show some packages that will install the h264 decoder on your system.
The package names may sound similar but you need the GStreamer Multimedia Codecs from the “bad” set. Check the description of the packages.
Alternatively, you can install the package in the terminal using this command:
`sudo apt install gstreamer1.0-plugins-bad`
If you are new to the terminal, please note that it will ask for your account password. **Nothing is displayed on the screen while you type the password**. That’s the Linux way. You type the password blindly and press enter.
Once this package is installed, open the file again and see if it works now.
It may work for you but the story doesn’t end here. You may have other video files that require some other h264 decoder or some other decoder.
You can try and install more decoders like this:
`sudo apt install libavcodec-extra gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly gstreamer1.0-libav`
However, there is a much more [convenient way of installing media codecs in Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/install-media-codecs-ubuntu/) and I’ll show it to you in the next section.
### Method 2: Install all multimedia codecs (recommended)
Ubuntu provides a meta-package named ubuntu-restricted-extras that consists of most of the common audio and video codecs along with some other packages like the Microsoft fonts.
Install this package and you won’t have to worry about the media codecs anymore.
Open the terminal in Ubuntu and type the following command:
`sudo apt install ubuntu-restricted-extras`
Since this meta-package contains software from Microsoft, you’ll have to accept the End User License Agreement (EULA).
The next screen may look like the one below. Just press tab and it will highlight the options. When the correct options are highlighted, press enter to confirm your selection.
With the multimedia codecs installed, you should be able to play (almost) all kinds of media files. Your music player can play MP3 files and your video player should be able to play MP4, MKV, and whatnot.
However, this too is not the end of the story, at least for some people.
Why do I say that? Because I have noticed that the default video player in Ubuntu, Totem, often struggles while playing certain kinds of video files. You’ll notice that suddenly your system heats up, the fans start blowing and your mouse cursor stop functioning smoothly.
Why? Because Totem is struggling in decoding the video and taking too much processing power.
You can test it by running the top command while playing the video. Look for the process named totem (that’s the name of the default video player).
What can you do now? Your trouble seems to be never ending. Fret not. There are [better video players in Linux](https://itsfoss.com/video-players-linux/) and they will help you solve the issue.
### Method 3: Install a better video player (recommended)
There are many good video players in Linux. I find them better than the default Totem video player.
Personally, I prefer two of the lot: [VLC](https://www.videolan.org/vlc/) and [MPV](https://mpv.io/).
VLC is a versatile and hugely popular video player. Chances are that you have already used VLC.
MPV Media Player is not that popular but this lightweight application is quite good for playing video files.
Both VLC and MPV players are good at handling media codecs. You don’t even need to install media codecs separately with them. Just [install VLC](https://itsfoss.com/install-latest-vlc/) or MPV and you should be able to play various kinds of video files.
Either look for it in the software center:
Or [install MPV on Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/mpv-video-player/) using the command line:
`sudo apt install mpv`
Now that you have another video player, you should right click on the video files and choose to open with the new video player.
Alternatively, you can [make it the default application](https://itsfoss.com/change-default-applications-ubuntu/) for playing video files and use double clicks.
## Did it work for you?
I hope I didn’t go into too much detail here. I wanted to explain the various methods and the pros and cons associated with each of them.
Did you manage to get rid of the h264 decoder problem in Ubuntu? Which method did you go for? |
14,584 | 当下运行容器的 3 个步骤 | https://opensource.com/article/22/2/start-running-containers | 2022-05-12T12:14:31 | [
"容器",
"WordPress"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14584-1.html |
>
> 在本教程中,你将学习如何在一个“吊舱”中运行两个容器来托管一个 WordPress 站点。
>
>
>

无论你是将其作为工作的一部分、未来的工作机会或者仅仅是出于对新技术的兴趣,容器对很多人,即使是经验丰富的系统管理员,可能是非常难以应付的。那么如何真正开始使用容器呢?从容器到 [Kubernetes](https://opensource.com/tags/kubernetes) 的成长路径是什么?另外,为什么有不止一条路径?如你所料,最好的起点就是现在。
### 1、了解容器
略一回忆,容器的开端可以追溯到早期 BSD 及其特殊的 chroot 监狱,但让我们直接跳到发展中期讲起。
之前,Linux 内核引入了 “<ruby> 控制组 <rt> cgroup </rt></ruby>”,允许你能够使用 “<ruby> 命名空间 <rt> namespace </rt></ruby>” 来“标记”进程。当你将进程分组到一个命名空间时,这些进程的行为就像在命名空间之外的东西不存在一样,这就像你把这些进程放入某种容器中。当然,这种容器是虚拟的,它位于计算机内部,它和你操作系统的其余进程使用相同的内核、内存和 CPU,但你用容器包含了这些进程。
分发的预制容器仅包含运行它所包含的应用程序必须的内容。使用容器引擎,如 [Podman](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/podman-guides-2020)、Docker 或 CRI-O,你可以运行一个容器化应用程序,而无需进行传统意义上的安装。容器引擎通常是跨平台的,因此即使容器运行在 Linux 上,你也可以在其他 Linux、MacOS 或 Windows 上启动容器。
更重要的是,当需求量很大时,你可以运行同一应用程序的多个容器。
现在你知道了什么是容器,下一步是运行一个容器。
### 2、运行一个容器
在运行容器之前,你应该有一个想要运行它的理由。你可以编一个,这有助于你对让容器创建过程感兴趣,这样你就会受到鼓舞,真正去使用你所运行的容器。毕竟,运行容器但不使用它提供的应用程序,只能证明你没有注意到任何故障,但使用容器证明它可以工作。
我推荐从 WordPress 开始,它是一个很流行的 Web 应用程序,容易使用,所以一旦容器运行起来,你就可以测试使用它。虽然你可以轻松地配置一个 WordPress 容器,但还是有很多配置选项可以引导你发现更多运行容器的方式(例如运行数据库容器)以及容器如何通信。
我使用 Podman,它是一个友好、方便且无守护进程的容器引擎。如果你没有安装 Podman,可以改用 Docker 命令。它们都是很棒的开源容器引擎,而且它们的语法是相同的(只需输入 `docker` 而不是 `podman`)。因为 Podman 没有守护进程,所以它需要更多的配置,但为了这种运行免 root、无守护进程的容器的能力是值得的。
如果你使用 Docker,可以跳到下面的 [运行 WordPress 容器](file:///Users/xingyuwang/develop/TranslateProject-wxy/translated/tech/tmp.1zBHYsK8TH#wp) 小节,否则,打开终端安装并配置 Podman:
```
$ sudo dnf install podman
```
容器会产生许多进程,通常只有 root 用户有权创建数千个进程 ID。创建一个名为 `/etc/subuid` 的文件,定义一个适当的起始 UID 和大量合法的 PID,这样就可以为你添加一些额外的进程 ID:
```
seth:200000:165536
```
在名为 `/etc/subgid` 的文件中对你的组执行相同的操作。在这个例子中,我的主要组是 `staff`(对你来说可能是 `users`,或者和你的用户名一样,这取决于你的系统)。
```
staff:200000:165536
```
最后,确认你的用户可以管理很多命名空间:
```
$ sysctl --all --pattern user_namespaces
user.max_user_namespaces = 28633
```
如果你的用户无权管理超过 28,000 个命名空间,创建 `/etc/sysctl.d/userns.conf` 文件来增加数量并输入:
```
user.max_user_namespaces=28633
```
#### 运行 WordPress 容器
现在,无论你使用的是 Podman 还是 Docker,你都可以从在线容器仓库中下载 WordPress 容器并运行它。你可以使用以下 Podman 命令完成所有这些操作:
```
$ podman run --name mypress \
-p 8080:80 -d wordpress
```
给 Podman 一会时间来找到容器、从互联网下载它,然后启动。
在收到终端返回提示符后,启动 Web 浏览器,打开 `localhost:8080`。WordPress 正在运行,等待你进行设置。

不过,你很快就会遇到障碍,因为 WordPress 使用数据库来存储数据,因此你需要为其提供一个数据库。
在继续之前,停止并删除 WordPress 容器:
```
$ podman stop mypress
$ podman rm mypress
```
### 3、在吊舱中运行容器
正如名字所暗示的那样,容器在设计上是独立的。在容器中运行的应用程序不应该与在容器外的应用程序或基础设施进行交互。因此,当一个容器需要另一个容器才能运行时,一种解决方案是将这两个容器放在一个更大的容器中,称为 “<ruby> 吊舱 <rt> pod </rt></ruby>”。吊舱确保其容器可以共享重要的命名空间以便相互通信。
创建一个新的吊舱,为它提供一个名称,以及希望能够访问的端口:
```
$ podman pod create \
--name wp_pod \
--publish 8080:80
```
确认吊舱存在:
```
$ podman pod list
POD ID NAME STATUS INFRA ID # OF CONTAINERS
100e138a29bd wp_pod Created 22ace92df3ef 1
```
#### 将容器添加到吊舱
现在你已经为相互依赖的容器创建了一个吊舱,你可以通过指定一个运行的吊舱来启动每个容器。
首先,启动一个数据库容器。你可以创建自己的凭据,只要在 WordPress 连接到数据库时使用相同的凭据。
```
$ podman run --detach \
--pod wp_pod \
--restart=always \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD="badpassword0" \
-e MYSQL_DATABASE="wp_db" \
-e MYSQL_USER="tux" \
-e MYSQL_PASSWORD="badpassword1" \
--name=wp_db mariadb
```
接下来,在同一个吊舱中启动 WordPress 容器:
```
$ podman run --detach \
--restart=always --pod=wp_pod \
-e WORDPRESS_DB_NAME="wp_db" \
-e WORDPRESS_DB_USER="tux" \
-e WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD="badpassword1" \
-e WORDPRESS_DB_HOST="127.0.0.1" \
--name mypress wordpress
```
现在启动你最喜欢的网络浏览器并打开 `localhost:8080`。
这一次,设置会正常进行。WordPress 会连接到数据库,因为你在启动容器时传递了这些环境变量。

创建用户账户后,你可以登录查看 WordPress 仪表板。

### 下一步
你已经创建了两个容器,并在一个吊舱中运行了它们。你现在已经了解了如何在自己的服务器上运行容器及服务。如果你想迁移到云,容器非常适合你。使用像 Kubernetes 和 OpenShift 这样的工具,你可以自动化启动 [集群上的容器和吊舱](https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2020/9/pod-cluster-container-what-is-difference)。如果你正在考虑采取下一步行动,阅读 Kevin Casey 的 [3 个开始使用 Kubernetes 的方法](https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2019/11/kubernetes-3-ways-get-started),并尝试他提到的 Minikube 教程。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/2/start-running-containers>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Whether you're interested in them as part of your job, for future job opportunities, or just out of interest in new technology, containers can seem pretty overwhelming to even an experienced systems administrator. So how do you actually get started with containers? And what's the path from containers to [Kubernetes](https://opensource.com/tags/kubernetes)? Also, why is there a path from one to the other at all? As you might expect, the best place to start is the beginning.
## 1. Understanding containers
On second thought, starting at the beginning arguably dates back to early BSD and their special chroot jails, so skip ahead to the middle instead.
Not so very long ago, the Linux kernel introduced *cgroups*, which enables you to "tag" processes with something called a *namespace*. When you group processes together into a namespace, those processes act as if nothing outside that namespace exists. It's as if you've put those processes into a sort of container. Of course, the container is virtual, and it exists inside your computer. It runs on the same kernel, RAM, and CPU that the rest of your operating system is running on, but you've contained the processes.
Pre-made containers get distributed with just what's necessary to run the application it contains. With a container engine, like [Podman](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/podman-guides-2020), Docker, or CRI-O, you can run a containerized application without installing it in any traditional sense. Container engines are often cross-platform, so even though containers run Linux, you can launch containers on Linux, macOS, or Windows.
More importantly, you can run more than one container of the same application when there's high demand for it.
Now that you know what a container is. The next step is to run one.
**[ Get the cheat sheet: What’s the difference between a pod, a cluster, and a container? ]**
## 2. Run a container
Before running a container, you should have a reason for running a container. You can make up a reason, but it's helpful for that reason to interest you, so you're inspired actually to use the container you run. After all, running a container but never using the application it provides only proves that you're not noticing any failures, but using the container demonstrates that it works.
I recommend WordPress as a start. It's a popular web application that's easy to use, so you can test drive the app once you've got the container running. While you can easily set up a WordPress container, there are many configuration options, which can lead you to discover more container options (like running a database container) and how containers communicate.
I use Podman, which is a friendly, convenient, and daemonless container engine. If you don't have Podman available, you can use the Docker command instead. Both are great open source container engines, and their syntax is identical (just type `docker`
instead of `podman`
). Because Podman doesn't run a daemon, it requires more setup than Docker, but the ability to run rootless daemonless containers is worth it.
If you're going with Docker, you can skip down to the [WordPress subheading](#wp). Otherwise, open a terminal to install and configure Podman:
`$ sudo dnf install podman`
Containers spawn many processes, and normally only the root user has permission to create thousands of process IDs. Add some extra process IDs to your user by creating a file called `/etc/subuid`
and defining a suitably high start UID with a suitable large number of permitted PIDs:
`seth:200000:165536`
Do the same for your group in a file called `/etc/subgid`
. In this example, my primary group is `staff`
(it may be `users`
for you, or the same as your username, depending on how you've configured your system.)
`staff:200000:165536`
Finally, confirm that your user is also permitted to manage thousands of namespaces:
```
$ sysctl --all --pattern user_namespaces
user.max_user_namespaces = 28633
```
If your user doesn't have permission to manage at least 28,000 namespaces, increase the number by creating the file `/etc/sysctl.d/userns.conf`
and enter:
`user.max_user_namespaces=28633`
Running WordPress as a container
Now, whether you're using Podman or Docker, you can pull a WordPress container from a container registry online and run it. You can do all this with a single Podman command:
```
$ podman run --name mypress \
-p 8080:80 -d wordpress
```
Give Podman a few moments to find the container, copy it from the internet, and start it up.
Start a web browser once you get a terminal prompt back and navigate to `localhost:8080`
. WordPress is running, waiting for you to set it up.
(Seth Kenlon, CC BY-SA 4.0)
It doesn't take long to reach your next hurdle, though. WordPress uses a database to keep track of data, so you need to provide it with a database where it can store its information.
Before continuing, stop and remove the WordPress container:
```
$ podman stop mypress
$ podman rm mypress
```
## 3. Run containers in a pod
Containers are, by design and, as their name suggests, self-contained. An application running in a container isn't supposed to interact with applications or infrastructure outside of its container. So when one container requires another container to function, one solution is to put those two containers inside a bigger container called a *pod*. A pod ensures that its containers can share important namespaces to communicate with one another.
Create a new pod, providing a name for the pod and which ports you want to be able to access:
```
$ podman pod create \
--name wp_pod \
--publish 8080:80
```
Confirm that the pod exists:
```
$ podman pod list
POD ID NAME STATUS INFRA ID # OF CONTAINERS
100e138a29bd wp_pod Created 22ace92df3ef 1
```
### Add a container to a pod
Now that you have a pod for your interdependent containers, you launch each container by specifying a pod for it to run in.
First, launch a database. You can make up your own credentials as long as you use those same credentials when connecting to the database from WordPress.
```
$ podman run --detach \
--pod wp_pod \
--restart=always \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD="badpassword0" \
-e MYSQL_DATABASE="wp_db" \
-e MYSQL_USER="tux" \
-e MYSQL_PASSWORD="badpassword1" \
--name=wp_db mariadb
```
Next, launch the WordPress container into the same pod:
```
$ podman run --detach \
--restart=always --pod=wp_pod \
-e WORDPRESS_DB_NAME="wp_db" \
-e WORDPRESS_DB_USER="tux" \
-e WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD="badpassword1" \
-e WORDPRESS_DB_HOST="127.0.0.1" \
--name mypress wordpress
```
Now launch your favorite web browser and navigate to `localhost:8080`
.
This time, the setup goes as expected. WordPress connects to the database because you've passed those environment variables while launching the container.
(Seth Kenlon, CC BY-SA 4.0)
After you've created a user account, you can log in to see the WordPress dashboard.
(Seth Kenlon, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Next steps
You've created two containers, and you've run them in a pod. You know enough now to run services in containers on your own server. If you want to move to the cloud, containers are, of course, well-suited for that. With tools like Kubernetes and OpenShift, you can automate the process of launching [containers and pods on a cluster](https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2020/9/pod-cluster-container-what-is-difference). If you're thinking about taking the next step, read [3 ways to get started with Kubernetes](https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2019/11/kubernetes-3-ways-get-started) by Kevin Casey, and give the Minikube tutorial he mentions a try.
## 1 Comment |
14,586 | 好消息!Docker Desktop 现已支持 Linux | https://news.itsfoss.com/docker-desktop-linux/ | 2022-05-12T23:10:03 | [
"Docker Desktop",
"Docker"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14586-1.html |
>
> 你现在可以在 Linux 上使用 Docker Desktop 无缝地创建容器了!它可在 Debian、Ubuntu 和 Fedora 上使用,并为 Arch Linux 提供了实验性支持。
>
>
>

Docker Desktop 是容器化应用程序的最简单的方法。有了它,你就不需要预先设置平台相关环境。
你只需要安装 Docker Desktop 就可以开始了。Docker Desktop 附带了许多容器工具,如 Kubernetes、Docker Compose、BuildKit 和漏洞扫描工具。
此前,它可用于 Windows 和 macOS,但不支持 Linux 平台。所以,Linux 用户只好直接与 Docker 引擎交互,以创建/测试他们的 Docker 容器。
终于,现在所有 Linux 用户也可以通过 Docker Desktop 来方便地使用 Docker 了。
### Linux 版的 Docker Desktop 来了
在 Docker 团队关于未来开发/改进的公共路线图中,Linux 版的 [Docker Desktop](https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop/) 是呼声最高的。
有了 Linux 版的 Docker Desktop,你终于可以不费吹灰之力地得到跨平台的 Docker 体验。
我在这里列出其中一些亮点。现在,作为一名使用 Linux 桌面的开发者,你可以:
* 使用 Docker <ruby> 扩展 <rt> Extension </rt></ruby> 访问新功能
* 与 Kubernetes 无缝集成
* 轻松地管理和组织 <ruby> 数据卷 <rt> volumes </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 容器 <rt> containers </rt></ruby> 和 <ruby> 镜像 <rt> images </rt></ruby>
### 在 Linux 上安装 Docker Desktop
值得注意的是,目前(在 Linux 上)安装 Docker Desktop 并不是超容易,但也不会十分复杂。
Docker 团队计划尽快改进安装和更新过程。
截至目前,你可以得到官方支持的 Ubuntu、Debian 和 Fedora 的 deb 或 rpm 包。支持 Arch Linux 的软件包还未开发完成,但已经可以下载来测试了。
如果你的桌面环境不是 GNOME 的话,你还需要安装 GNOME 终端。
在 Linux 上安装 Docker Desktop 对系统也有整体要求,包括:
* 64 位 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS、Ubuntu 21.10、Fedora 35、Fedora 36 或 Debian 11。
* 支持 KVM 虚拟化
* QEMU 5.2 或更新版本
* Systemd 系统守护工具
* GNOME 或 KDE 桌面环境
* 4GB 的内存
至于安装步骤,你可以参照文档中的 [官方说明](https://docs.docker.com/desktop/linux/install/) 进行。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/docker-desktop-linux/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Docker Desktop is the easiest way to containerize applications. You do not need to think about setting up an environment on the platform of your choice to get started.
You just need to install the Docker Desktop, and you will be good to go. The Docker Desktop application comes with container tools like Kubernetes, Docker Compose, BuildKit, and vulnerability scanning.
While it was available for Windows and macOS, it did not support the Linux platform. So, Linux users were restricted to the docker engine to create/test their docker containers.
Finally, anyone who wants to make things convenient using Docker on Linux can do it using Docker Desktop.
## Docker Desktop for Linux is Here
[Docker Desktop](https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for Linux was one of the most requested things on their public roadmap for future development/improvements.
With Docker Desktop on Linux, you finally get to experience a cross-platform Docker experience without much hassle.
To mention some highlights, as a developer on Linux desktop, you can now:
- Access new features using Docker Extensions
- Seamlessly integrate with Kubernetes
- Easily manage and organize volume, containers, and images.
## Installing Docker Desktop on Linux
It is worth noting that it may not be super easy to install Docker Desktop for now, but it isn’t overly complicated either.
The Docker team plans to improve the installation and update process as soon as possible.
As of now, you get deb and rpm packages officially supported for Ubuntu, Debian, and Fedora. The Docker Desktop package for Arch Linux is a work in progress, but it is available to test.
It also needs you to install the GNOME terminal if you are on a non-GNOME desktop environment.
The overall system requirements for Docker Desktop on Linux include:
*64-bit Ubuntu 22.04 LTS, Ubuntu 21.10, Fedora 35, Fedora 36, or Debian 11.**KVM virtualization support**QEMU 5.2 or newer**Systemd init system**GNOME or KDE desktop environment**4 GB of RAM*
For installation, you can follow the [official instructions](https://docs.docker.com/desktop/linux/install/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) in the documentation.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,587 | 英伟达在提升 Linux 上的 GPU 使用体验上迈出了一大步 | https://news.itsfoss.com/nvidia-open-source-linux/ | 2022-05-13T09:24:14 | [
"英伟达",
"GPU",
"开源"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14587-1.html |
>
> 英伟达公司提升其 GPU 在 Linux 上的体验的重大开源计划终于来了。
>
>
>

Linus Torvalds 听到这个消息一定会很高兴……
英伟达终于公布了提升 Linux 上的 GPU 使用体验的开源计划。
不过不幸的是,和你想象的可能不完全一样,你仍然会看到一些专有的驱动程序。
但是,它的意义不亚于甩掉专有驱动程序。
具体来说就是,**英伟达发布了开源的 GPU 内核模块,支持数据中心所用的 GPU 和消费级显卡(GeForce/RTX)**。
此外,它同时采用 GPL/MIT 两种许可证,听起来很棒,对吗?
### 此举对 Linux 桌面用户有什么帮助?
开源的 GPU 内核模块有助于改善内核和专有驱动程序之间的交互。
所以,此举对 **游戏玩家和开发者** 都有利,阻碍与英伟达专有驱动程序配合的问题最终会被消除。
发布公告中提到的技术收益包括:
>
> 开发者可以跟踪到具体的代码路径,并观察到内核事件调度是如何与他们的工作负载交互的,从而在调试时更快定位根本原因。此外,企业软件开发者可以将该驱动程序无缝地集成到他们为项目定制的 Linux 内核中。
>
>
> 来自 Linux 最终用户社区的投入和评价,将进一步提升英伟达 GPU 驱动程序的质量和安全性。
>
>
>
而从最终用户或者游戏玩家方面来看,你会发现安装将更便捷,整体会更安全。
Canonical 和 SUSE 会立即为他们的企业用户打包该开源内核模块,而其它厂商也会很快跟进。
当它可以用在桌面环境时,Canonical 应该会在未来几个月内把这个内核模块放到 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 版本中。其它的 Linux 发行版应该也会做相应的升级。
### 现在可以试用吗?

这个开源的 GPU 内核模块的第一个版本是 R515,它是作为 CUDA 工具集 11.7 一部分一起发布的开发驱动程序。
你可以从 [官方驱动下载页面](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/drivers/unix/) 或者从 [CUDA 下载页面](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads) 找到。
虽然它被认为可用于数据中心生产环境,**但对于 GeForce 或者工作站 GPU 来说,还处于 alpha 阶段**。
事实上,在 Turing 和 Ampere 架构的 GPU 型号上可以使用这个驱动程序,以使用 Vulkan 和 Optix 中的 **多显示器、G-Sync、Nvidia RTX 光线追踪** 等功能。
然而,除非你想运行一些“实验性测试”,否则还是等几个月,以便直接从你的 Linux 发行版中获得为桌面用户发布的稳定版。
### 对 Nouveau 驱动程序开发也有益
不仅仅是提升了专有驱动程序的体验,公布的这个开源 GPU 内核代码也会改善 Nouveau 驱动。
正如发布公告所说:
>
> Nouveau 可以利用英伟达驱动程序所使用的同样固件,它公开了许多 GPU 功能,例如时钟管理、散热管理,可以为树内的 Nouveau 驱动程序带来新的特性。
>
>
> 请关注未来的驱动更新以及在 Github 上的合作。
>
>
>
英伟达公司提到并可能合作改进开源的英伟达驱动程序(即 Nouveau),这真是太好了。
这也很好地表明了,他们确实希望为 Linux 提供一个更好的开源驱动程序版本。
### 开源 Nivida 驱动程序的未来?
毋容置疑,英伟达计划不断发布开源的 GPU 内核模块。
所以,尽管他们不会单独开源他们的驱动程序,但我们仍然可以寄希望于 Nouveau 释放所有的显卡特性。
想知道他们更多的计划,你可以参考 [官方的发布声明](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-releases-open-source-gpu-kernel-modules/)。
*你如何看待这件事?英伟达最终会爱开源和 Linux 吗?嗯,至少这是一个好的开始。在下面的评论区分享你的想法吧。*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/nvidia-open-source-linux/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[chunyang-wen](https://github.com/chunyang-wen) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Linus Torvalds will be happy to hear this…
NVIDIA finally announced an open-source initiative to improve the GPU experience on Linux.
Unfortunately, it isn’t exactly what you think, you will still find proprietary drivers around.
But, it’s as significant as ditching the proprietary drivers.
Here it is: **NVIDIA released open-source GPU kernel modules with support for data center GPUs and consumer (GeForce/RTX) cards**.
And, it is licensed under a dual GPL/MIT license, sounds awesome, right?
## How does this help Linux Desktop Users?
Open-Source GPU kernel modules will help improve the interaction between the kernel and the proprietary driver.
So, this move is beneficial for both **gamers, and developers**, where the hassles to work with a proprietary Nvidia driver will eventually be eliminated.
The release announcement mentions the technical benefit that includes:
Developers can trace into code paths and see how kernel event scheduling is interacting with their workload for faster root cause debugging. In addition, enterprise software developers can now integrate the driver seamlessly into the customized Linux kernel configured for their project.
This will further help improve NVIDIA GPU driver quality and security with input and reviews from the Linux end-user community.
When thinking this through for an end-user (or a gamer), you will notice easier installations and improved security overall.
Canonical and SUSE will immediately package the open kernel modules for enterprise users, and others should follow soon.
Canonical should make the kernel modules available in Ubuntu 22.04 LTS in the coming months when it comes to the Linux desktop. You can expect other Linux distributions to follow the suit.
## Can You Try it Now?

The first release of the open GPU kernel modules is R515. It is a development driver released as part of CUDA Toolkit 11.7.
You can get it from the [official download page for drivers](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/drivers/unix/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) or find it on the [CUDA downloads](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads?ref=news.itsfoss.com) page.
While it is considered production-ready for data centers, it is still in its **alpha stage for GeForce and Workstation GPUs**.
It is true that you can use this driver on Turing and Ampere architecture GPUs to use features like **multiple displays, G-Sync, and Nvidia RTX ray tracing** in Vulkan and OptiX.
But, unless you want to run “experimental tests”, you might want to wait for a few months to get a stable release for desktop users directly from your Linux distribution.
## It Also Helps Nouveau Driver…
Not just limited to improving the experience with proprietary drivers. But, the published source code of open-source GPU kernels should also help improve the Nouveau driver.
As the release announcement mentions:
Nouveau can leverage the same firmware used by the NVIDIA driver, exposing many GPU functionalities, such as clock management and thermal management, bringing new features to the in-tree Nouveau driver.
Stay tuned for more developments in future driver releases and collaboration on GitHub.
It is surprisingly nice of NVIDIA to mention and potentially aim to collaborate to improve the open-source Nvidia driver i.e. Nouveau.
This also gives a good indication that they do want a better version of an open-source driver for Linux.
## Future of Open-Source Nvidia Drivers?
Undoubtedly, NVIDIA plans to continue releasing the open-source GPU kernel modules.
So, even if they do not separately open-source their drivers, we can always rely on an improved Nouveau driver unlocking all the graphics card features.
To know more about their plans, you can refer to the [official release announcement](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-releases-open-source-gpu-kernel-modules/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
*What do you think about it? Does Nvidia finally love open-source and Linux? Well, it is a solid start, to say the least. Share your thoughts in the comments down below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,588 | GNOME 新文本编辑器尝鲜 | https://itsfoss.com/gnome-text-editor/ | 2022-05-13T14:42:49 | [
"GNOME",
"文本编辑器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14588-1.html | 
如果你是我们的忠实读者,你可能读过 [GNOME 计划用自家的文本编辑器取代 Gedit](/article-14060-1.html) 的消息了。
没错,GNOME 推出了一款全新的文本编辑器,名字就叫做,嗯,“<ruby> 文本编辑器 <rt> Text Editor </rt></ruby>”。
尽管 GNOME 桌面的默认文本编辑器还是 Gedit,但是这个新的编辑器已经和 GNOME 42 一起发布了。
也就是说,这款新编辑器可以在 Ubuntu 最新的长期发行版或者其他使用 GNOME 42 的发行版上获取(笔者现在使用的正是 Ubuntu 22.04)。
感兴趣吗?在本文,笔者将分享这款编辑器的使用体验以及安装步骤。
### GNOME 文本编辑器使用体验
GNOME 文本编辑器基于 [有争议的 libadwaita 库](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-libadwaita-library/),遵循着其开发委员会的设计新理念,采用圆角边框,外观优美典雅,颇具现代化特点。
但就功能而言,这款软件并没有什么特别的“过人之处”。毕竟,它并不能取代 [Atom 或者 VS Code](https://itsfoss.com/visual-studio-code-vs-atom/) 这类专业的代码编辑器。但同时,它也绝不像 Windows 的记事本那样“平平无奇”。
那么,让我们来一睹它的“风采”吧!
#### 会话保存功能
默认情况下,GNOME 文本编辑器会自动打开上次编辑的文件,这一功能可以让你快速继续之前的工作。
你可以通过首选项下的还原会话选项,开启或关闭该功能。

你还可以搜索文件记录,打开最近处理的文件。请注意:清除文件记录(见上图 “<ruby> 清除历史 <rt> Clear History </rt></ruby>”)会清除最近打开的文件列表。
#### 主题与内置主题
GNOME 文本编辑器与其他新的 GNOME 软件一样,自带三种主题风格:跟随系统、浅色模式和深色模式。如果你选择了跟随系统,编辑器会根据系统主题(浅色或深色)自动变换自身的深浅主题色。

此外,在首选项下还设有八个主题(深浅色模式下主题有所不同),为用户提供了更多的选择。

只需点击选中,主题即可生效。
#### 文件修改以及未保存文件的处理
在你工作时,已修改和未保存的文件会突出地反映出来。

在你修改文件后点击关闭窗口时,编辑器会提醒你选择保存修改还是放弃修改。

相比之下,[Gedit 有自动保存选项](https://itsfoss.com/how-to-enable-auto-save-feature-in-gedit/),无需插件即可使用。
#### 暂无插件功能
提到插件,不得不承认这款新的编辑器还没有推出插件功能。而另一方面,Gedit 有着良好的插件生态,所以它的功能更加强大。
我不确定 GNOME 文本编辑器未来是否会引入支持插件的功能。
#### 代码语法高亮
近年来,代码语法高亮可以说是文本编辑器的一个必备功能了。GNOME 文本编辑器也提供了这一功能,支持各种程序语言语法高亮。
通常来说,语法高亮的前提是代码文件要有对应的后缀名。不过,我发现 GNOME 文本编辑器甚至可以在文件保存之前就识别出 bash 脚本和 C/C++ 程序,并对其语法标出高亮。

#### 快捷键
笔者喜欢在常用软件里使用快捷键,因为这样效率会更高。
GNOME 文本编辑器的各种操作都支持快捷键。你可以点击软件右上角的汉堡菜单(`☰` 符号)看到快捷键列表;或者直接敲快捷键 `Ctrl+?` 调出。

#### 查找和替换
GNOME 文本编辑器有着完善的查找替换功能。它有三种模式可供选择:正则表达式、区分大小写以及匹配精准字符。

#### 更多功能
GNOME 文本编辑器与 Gedit 一样,还具备一些其他功能:
* 拼写检查
* 显示行号
* 自动缩进
* 空格和制表位缩进
* 大小写转换
* 自动换行
#### GNOME 文本编辑器的局限
归根结底,GNOME 文本编辑器依旧是一个文本编辑器,无法也无意用来打开 doc 文件。如果你执意用它要打开 doc 文件,你看到的就只有一堆乱码。当然,pdf 文件也是如此。

此外,GNOME 文本编辑器并不是专门用来写复杂代码的,它无法取代 VS Code 等代码编辑器。如果说偶尔用来读读代码或者写写 shell 脚本,倒也无伤大雅,但是它并不具备管理项目文件夹和运行代码等功能。
### 安装 GNOME 文本编辑器
就像笔者在开头所说,GNOME 文本编辑器已经和 GNOME 42 一起发布了,不过它并不属于默认安装的软件。在 Ubuntu 22.04,Universe 仓库里就有 GNOME 文本编辑器,你可以通过输入下面的命令进行安装:
```
sudo apt install gnome-text-editor
```
其他采用 GNOME 42 的发行版也可以获取 GNOME 文本编辑器,请在安装前查看所用系统的 [桌面环境版本](https://itsfoss.com/find-desktop-environment/)。
安装完成后,可以点击屏幕左上角的“<ruby> 活动 <rt> Activities </rt></ruby>”按钮,查找并打开 GNOME 文本编辑器。它的图标与 Gedit 的图标相似,但设计更为新颖。

### 总结
[Gedit](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Gedit) 是一款非常完善的文本编辑器,也是 GNOME 桌面环境长期以来的预装软件。几年前,Gedit 疏于开发,但现在已经恢复了开发。然而,如今 GNOME 团队正在努力为 GTK 4 和 libadwaita 改进核心应用程序。
GNOME 文本编辑器很像 Gedit 的翻版,两者有着相似的界面和功能。不过,GNOME 文本编辑器与新版 GNOME 的设计风格更加统一,使用体验也更加流畅。
这款新的编辑器日后很有可能会成为 GNOME 的默认文本编辑器。不过让人感兴趣的是,GNOME 文本编辑器将来是否会拥有自己的插件生态呢?
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/gnome-text-editor/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[aREversez](https://github.com/aREversez) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | If you are a regular reader here on It’s FOSS, you might have read about [GNOME’s plan to replace Gedit with their own text editor](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-text-editor-to-replace-gedit/).
Yes, GNOME has a brand-new text editor and it is called, well, Text Editor.
While Gedit is still the default, this new editor has made an entry with the release of GNOME 42. I am using Ubuntu 22.04 and it is available to install from the repositories.
Not exactly a brand-new [feature of Ubuntu 22.04](https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-22-04-release-features/), this new editor is available to install in the latest Ubuntu LTS version and perhaps other distributions using GNOME 42.
Intrigued? Let me share my experience with this new editor and then I’ll show you the installation steps.
## Experience with GNOME Text Editor
Built on top of the [controversial libadwaita](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-libadwaita-library/), GNOME Text Editor follows the new design principles set by its development committee. It has a sleek, modern look with rounded corners.
Don’t expect anything extraordinary here in terms of features. It’s not a replacement of coding focused editors like [Atom or VS Code](https://itsfoss.com/visual-studio-code-vs-atom/). This also doesn’t mean it’s as plain and simple as Windows’ Notepad.
Let’s see what it has to offer.
### Saved sessions
By default, GNOME Text Editor automatically opens the last opened files. This is a neat feature that lets you resume your work.
This behavior can be controlled by the Restore Session option under Preferences.
You can also search and open the recently opened files. Clearing the history (as shown in the above image) will clear the recently accessed files.
### Themes and in-built themes
Like new GNOME applications, it gives you three theming style to choose from: system theme, light theme and dark theme. If you have chosen system theme, the editor will automatically switch between light and dark theme based on the system theme (light or dark) in use.
Apart from that, you can choose between eight available themes (available in dark and light variants) under the preference section.
You can see the changes immediately as you select the themes.
### Changes and Unsaved file handling
Modified and unsaved files are prominently reflected while you work on them.
You’ll obviously be warned if you try to close the editor with modified files.
There is no automatic save options here. [Gedit has option for automatically saving files](https://itsfoss.com/how-to-enable-auto-save-feature-in-gedit/) without using any additional plugins.
### No plugins
Speaking of plugins, there is no such system for the new text Editor yet. Gedit has a decent plugin ecosystems that helps in enhancing the capacity of the editor.
I don’t have any concrete information if plugins will be allowed in this editor in the future or not.
### Syntax highlighting
Syntax highlight is an integral part of text editors these days. GNOME Text Editor promptly highlights syntax for various programming language.
This is usually done based on the extension of the code file. However, I noticed that it also detects and highlights syntax for bash scripts and C/C++ programs even before saving the file.
### Keyboard shortcuts
I love using keyboard shortcuts in my favorite applications. It makes things quicker.
The GNOME Text Editor supports plenty of keyboard shortcuts for all kind of actions. You can find the list of keyboard shortcuts under the hamburger menu (☰) or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+?.
### Search and replace
Text Editor has pretty decent find and replace feature. You can use set extra parameters like regex search, case-sensitive search or match exact words.
### More features
There are several other features that you may find in Gedit:
- Spell check
- Line numbers
- Automatic indentation
- Space/tab indentation
- Change case
- Text wrapping
### What it doesn’t do?
It is essentially a text editor, so you cannot open doc files in it and that’s by design. If you open a doc file, you’ll see gibberish. The same goes for PDF files.
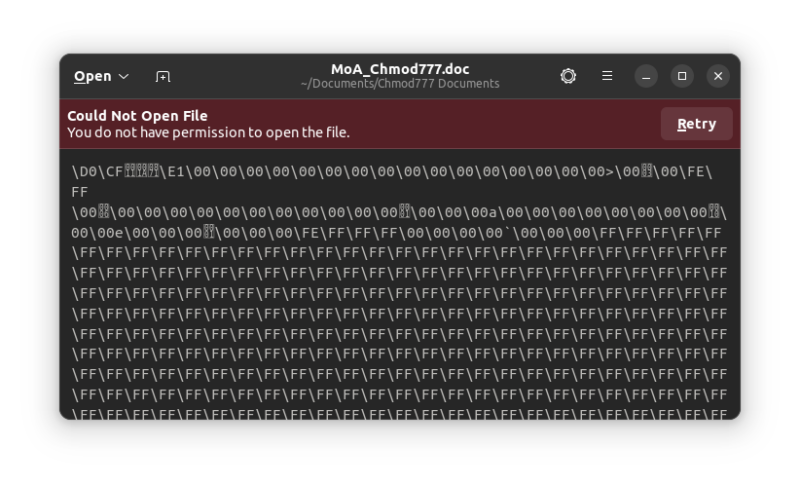
Also, it is not intended for hardcore coding. It cannot replace the likes of VS Code. It is okay for occasional code reading or shell scripting but it doesn’t have the features like project folders or running the codes.
## Installing GNOME Text Editor
As stated earlier, it is available with GNOME 42, but not installed by default. In Ubuntu 22.04, it is available in the Universe repository and can be installed with the following command:
`sudo apt install gnome-text-editor`
It should be available in other distros with GNOME 42. Please [check the version of desktop environment](https://itsfoss.com/find-desktop-environment/) you are using.
Once installed, you can search and open it in the Activities area. The icon for the new editor is a refreshed version of the Gedit icon.
## Conclusion
The good old [Gedit](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Gedit) has been a part of GNOME for a long time. There were lack of development a few years ago but the development has resumed again. However, the GNOME team is working on revamping their core applications for GTK 4 and libadwaita.
This new Text Editor looks like a reimplementation of the Gedit with similar interface and feature but a more fluid experience which is more consistent with the new GNOME design.
It won’t surprise me that this new editor becomes the default text editor in the coming version of GNOME. It would be interesting to see if a plugin ecosystem is developed for the new editor or not. |
14,590 | 如何使社区认可更加包容 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/inclusive-community-recognition | 2022-05-13T23:48:00 | [
"社区"
] | /article-14590-1.html |
>
> 抛开具体的工作量,我们认为所有的贡献都弥足珍贵。当所有社区贡献者都能获得家庭般的赞赏时,他们会更倾向于继续为社区添砖加瓦。
>
>
>

给予一个优秀的工作足够的认同和赞赏是我作为一个社区管理员最喜欢做的事。我不但有机会能够对贡献者表示感激,同时还能为社区设立一个优秀的榜样。认同和赞赏可以是为了庆祝一个成就,例如有人帮助其他成员加入社区、减少技术债务或者贡献了激动人心的新功能。
但是,用来确定贡献量的规则可能会有难以预料的后果。例如某些社区管理员利用如下图所示的图表来表彰贡献,过度地强调了拉取请求(PR)以及对代码库的贡献量。


使用这样的方法进行表彰会产生三个问题。
首先,这样过度关注了对代码库的贡献。早年间,开源项目主要吸引开发者参与,所以自然而然许多贡献是围绕代码的。现在,越来越多的非开发者正在积极参与社区项目(例如通过用户组、会议和用户生产的内容),他们的大多数贡献在代码库以外的地方。这些贡献将不会出现在诸如 *年度合并 PR 数量* 这样的表格上。
其次,过度关注贡献指标(指那些易于用数字统计的),最终会演变为奖励数量而不是质量,甚至影响力。在上图的 *贡献组织排行榜* 中,大型组织因为具有更多的可用人力,相对于小型组织就会有更为显著的优势。通过对大型组织在数量上的表彰将可能导致小型组织的人感到权利被剥夺了。
最后,尽管本意并非如此,但许多人都会把这些数据看做对个人或组织影响力的排名。
基于此,我们最好避免仅仅通过指标数量来表彰对社区的贡献。
### 令社区表彰更有意义
如何让社区表彰更为包容并且能够覆盖不同的贡献形式呢?诸如 Discord、IRC、邮件列表和Slack 等交流渠道可以很好的表明一个成员的活跃度及其感兴趣的领域。例如每当我看到一些人热衷于解答问题或者帮助新用户时,我会十分开心。这些贡献并不会出现在社区的数据板上,但是让这些贡献得到应有的认同和感谢并广为人知是十分重要的。
社区数据板显然是开源社区重要的工具。但是我提醒大家不要花费太多时间在建设数据板上。迟早你会发现,不是所有的东西都可以有清晰的标准进行度量,即便你能够想出规则量化一件事,你也依然会发现这些规则具有局限性。
为了获取更多的关于贡献的信息,我经常会安排社区成员茶话会。这些对话经常能够告诉我他们做出贡献的原因、有多少工作量以及谁同时也参与进来了等等。
当我第一次与他们对话时,我经常听到他们提及找到回馈社区的方法十分重要,而他们也在寻找方法来提供力所能及的帮助。许多人甚至因不能在代码方面做出贡献而感到内疚,而我会向他们强调代码不再是开源唯一重要的东西。有时这些对话能让我有机会接触到同一城市或同一行业的社区成员,或者发现更多共同的兴趣点。维护这些关系将有助于提升归属感。
### 令社区表彰更具影响力
除了寻找更多的活动形式,我们也可以让这些活动以更具影响力的形式呈现。例如在看到优质贡献时及时赞美。一个快速的感谢回复会比一两个月之后的正式感谢更有效。许多人包括我自己,都会强调给予更为正式而合理的表彰和奖励,但我们应当谨记,奖励并非社区成员贡献的主要动力。认可好的工作并努力去接触贡献者会令贡献者感到受重视。
让其他成员参与到认可的过程中也是一个很好的主意。一旦社区达到了一定的规模,便很难事无巨细地知晓一切细节。如果引入一个成员提名机制则会很好地让大家注意到优秀的贡献。如果你的社区拥有十分正式的奖项,例如在年度会议或聚会上颁发的奖项,请让社区成员参与提名和投票。这不仅提供了成员参与进来的平台,也令这些来自成员投票的奖项更有意义。
最后给予认同和感谢也是一个认识成员并加深了解的重要机会。有时候颁奖仿佛在进行交易:“你做了某件事,所以我们给你颁发了某个奖励”。多在介绍成员上花些时间,将令成员感到更受重视并加强归属感。
### 社区认可令社区更为健康
在提高开源社区的多样性、包容性和归属感方面,我们仍有许多工作亟待改善。更好的社区认可将在其中起着不可或缺的作用。确保所有的贡献都受到重视,让每一位贡献者都感到家庭般氛围和赞赏,将鼓励他们继续为社区贡献。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/inclusive-community-recognition>
作者:[Ray Paik](https://opensource.com/users/rpaik) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[PeterPan0106](https://github.com/PeterPan0106) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,591 | 在自己的电脑上实验容器和荚 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/containers-pods-101-ebook | 2022-05-14T10:28:00 | [
"容器"
] | /article-14591-1.html |
>
> 通过这篇新的可下载指南开始探索容器技术的要领。
>
>
>

在电视剧 《<ruby> 太空堡垒卡拉狄加 <rt> Battlestar Galactica </rt></ruby>》中,这艘名副其实的巨型飞船其实并没有做什么。它是船员们坚定的庇护所,是战略和协调的中心联络点,也是资源管理的安全场所。而 <ruby> 卡布里安毒蛇号 <rt> Caprican Vipers </rt></ruby> 这种单人的独立太空船,出去对付邪恶的<ruby> 赛昂人 <rt> Cylons </rt></ruby>和其他太空中的危险。他们也从不只派一两艘毒蛇号出去。他们派了很多。这许许多多的冗余的飞船具有基本相同的能力和目的,但由于它们非常灵活和数量众多,它们总是能够处理每个星期都在威胁战星的任何问题。
如果你认为你感到这像是一个正在发展中的比喻,那么你是对的。现代的“云”大而无当,是分布在很远距离的大量基础设施的集合体。它具有强大的能力,但如果你将其视为普通计算机,就会浪费了它的大部分能力。当你想要处理来自数百万个输入源的大量数据时,把你的解决方案(无论它是采用应用、网站、数据库、服务器还是其他形式)打包起来,并发送该解决方案的微小镜像来处理数据集群,实际上是更有效的。当然,这些都是 “<ruby> 容器 <rt> container </rt></ruby>”,它们是云的劳动力。它们是你发送来处理服务请求的小型解决方案工厂,并且由于你可以根据任何给定时间传入的请求生成所需要的数量,因此理论上它们是取之不尽的。
### 在家里使用容器
如果你没有大量的传入请求需要处理,你可能会想知道容器给你带来什么好处。不过,在个人电脑上使用容器确实有其用途。
#### 容器作为虚拟环境
通过 Podman、LXC 和 Docker 等工具,你可以像以往运行虚拟机一样运行容器。不过,与虚拟机不同,容器没有因模拟固件和硬件而产生的开销。
你可以从公共仓库下载容器镜像,启动一个最小化的 Linux 环境,并将其作为命令或开发的测试场所。例如,假设你想试试你在 Slackware Linux 上构建的一个应用。首先,在仓库中搜索一个合适的镜像:
```
$ podman search slackware
```
然后选择一个镜像,作为你的容器的基础:
```
$ podman run -it --name slackware vbatts/slackware
sh-4.3# grep -i ^NAME\= /etc/os-release
NAME=Slackware
```
### 在工作中使用容器
当然,容器不只是个精简的虚拟机。它们可以是针对为非常具体的需求提供的特定解决方案。如果你不熟悉容器,那么新系统管理员最常见的入门仪式之一可能会有所帮助:启动你的第一个 Web 服务器,但是在容器中。
首先,获取一个镜像。你可以使用 `podman search` 命令来搜索你喜欢的发行版,或者直接搜索你喜欢的 httpd 服务器。当使用容器时,我倾向于信任我在裸机上使用的相同发行版。
当你你找到一个镜像作为你的容器的基础,你就可以运行你的镜像。然而,正如这个术语所暗示的,容器是*封起来的*,所以如果你只是启动一个容器,你将无法访问标准的 HTTP 端口。你可以使用 `-p` 选项将一个容器端口映射到一个标准的网络端口:
```
$ podman run -it -p 8080:80 docker.io/fedora/apache:latest
```
现在看看你本地主机上的 8080 端口:
```
$ curl localhost:8080
Apache
```
成功了。
### 了解更多
容器拥有比模仿虚拟机更多的潜力。你可以将它们分组在 “<ruby> 荚 <rt> pod </rt></ruby>” 中,构建复杂应用的自动部署,启动冗余服务以满足高需求等等。如果你刚刚开始使用容器,你可以 [下载我们最新的电子书](https://opensource.com/downloads/containers-pods-101-ebook) 来学习该技术,甚至学习创建一个 “<ruby> 荚 <rt> pod </rt></ruby>”,以便你可以运行 WordPress 和数据库。
>
> **[下载我们最新的电子书](https://opensource.com/downloads/containers-pods-101-ebook)**
>
>
>
(LCTT 译注:容器环境中使用的 “Pod” 一词,我以前根据容器相关术语多用航海领域名词比喻来将其译做“吊舱”,但也有同学表示了不同意见。根据对 Kubernetes [文档](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/#:~:text=A%20Pod%20(as%20in%20a,run%20in%20a%20shared%20context.),这个词来自对<ruby> 鲸鱼荚 <rt> pod of whales </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 豌豆荚 <rt> pea pod </rt></ruby>的比喻,所以我觉得采用“荚”的翻译比较合适。—— wxy)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/containers-pods-101-ebook>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,592 | WebAssembly 安全的现在和未来 | https://www.linux.com/news/webassembly-security-now-and-in-the-future/ | 2022-05-14T14:43:21 | [
"WebAssembly",
"安全"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14592-1.html | 
### 简介
正如我们 [最近解释的](https://training.linuxfoundation.org/announcements/an-introduction-to-webassembly/),WebAssembly 是一种用于以任何语言编写的二进制格式的软件,旨在最终无需更改就能在任意平台运行。WebAssembly 的第一个应用是在 Web 浏览器中,以使网站更快、更具交互性。WebAssembly 有计划推向 Web 之外,从各种服务器到物联网(IoT),其创造了很多机会,但也存在很多安全问题。这篇文章是对这些问题和 WebAssembly 安全模型的一篇介绍性概述。
### WebAssembly 跟 JavaScript 很像
在 Web 浏览器内部,WebAssembly 模块由执行 JavaScript 代码的同一 <ruby> 虚拟机 <rt> VM </rt></ruby> 管理。因此,WebAssembly 和 JavaScript 一样,造成的危害也是相同的,只是效率更高,更不易被察觉。由于 JavaScript 是纯文本,运行前需要浏览器编译,而 WebAssembly 是一种可立即运行的二进制格式,运行速度更快,也更难被扫描出(即使使用杀毒软件)其中的恶意指令。
WebAssembly 的这种 “代码混淆” 效果已经被用来弹出不请自来的广告,或打开假的 “技术支持” 窗口,要求提供敏感数据。另一个把戏则是自动将浏览器重定向到包含真正危险的恶意软件的 “落地” 页。
最后,就像 JavaScript 一样,WebAssembly 可能被用来 “窃取” 处理能力而不是数据。2019 年,[对 150 个不同的 WASM 模块的分析](https://www.sec.cs.tu-bs.de/pubs/2019a-dimva.pdf) 发现,其中约 *32%* 被用于加密货币挖掘。
### WebAssembly 沙盒和接口
WebAssembly 代码在一个由虚拟机(而不是操作系统)管理的 [沙盒](https://webassembly.org/docs/security/) 中封闭运行。这使它无法看到主机,也无法直接与主机交互。对系统资源(文件、硬件或互联网连接)的访问只能通过该虚拟机提供的 <ruby> WebAssembly 系统接口 <rt> WebAssembly System Interface </rt></ruby>(WASI) 进行。
WASI 不同于大多数其他应用程序编程接口(API),它具有独特的安全特性,真正推动了 WASM 在传统服务器和<ruby> 边缘 <rt> Edge </rt></ruby>计算场景中的采用,这将是下一篇文章的主题。在这里,可以说,当从 Web 迁移到其他环境时,它的安全影响会有很大的不同。现代 Web 浏览器是极其复杂的软件,但它是建立在数十年的经验和数十亿人的日常测试之上的。与浏览器相比,服务器或物联网(IoT)设备几乎是未知领域。这些平台的虚拟机将需要扩展 WASI,因此,肯定会带来新的安全挑战。
### WebAssembly 中的内存和代码管理
与普通的编译程序相比,WebAssembly 应用程序对内存的访问非常受限,对它们自己也是如此。WebAssembly 代码不能直接访问尚未调用的函数或变量,不能跳转到任意地址,也不能将内存中的数据作为字节码指令执行。
在浏览器内部,WASM 模块只能获得一个连续字节的全局数组(<ruby> 线性内存 <rt> linear memory </rt></ruby>)进行操作。WebAssembly 可以直接读写该区域中的任意位置,或者请求增加其大小,但仅此而已。这个<ruby> 线性内存 <rt> linear memory </rt></ruby>也与包含其实际代码、执行堆栈、当然还有运行 WebAssembly 的虚拟机的区域分离。对于浏览器来说,所有这些数据结构都是普通的 JavaScript 对象,使用标准过程与所有其他对象隔离。
### 结果还好,但不完美
所有这些限制使得 WebAssembly 模块很难做出不当行为,但也并非不可能。
沙盒化的内存使 WebAssembly 几乎不可能接触到 **外部** 的东西,也使操作系统更难防止 **内部** 发生不好的事情。传统的内存监测机制,比如 <ruby> <a href="https://ctf101.org/binary-exploitation/stack-canaries/"> 堆栈金丝雀 </a> <rt> Stack Canaries </rt></ruby> 能注意到是否有代码试图扰乱它不应该接触的对象,[但在这里没用](https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec20-lehmann.pdf)。
事实上,WebAssembly 只能访问自己的<ruby> 线性内存 <rt> linear memory </rt></ruby>,但可以直接访问,这也可能为攻击者的行为 *提供便利*。有了这些约束和对模块源代码的访问,就更容易猜测覆盖哪些内存位置可能造成最大的破坏。破坏局部变量似乎也是 [可能的](https://spectrum.ieee.org/tech-talk/telecom/security/more-worries-over-the-security-of-web-assembly),因为它们停留在<ruby> 线性内存 <rt> linear memory </rt></ruby>中的无监督堆栈中。
2020 年的一篇关于 [WebAssembly 的二进制安全性](https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec20-lehmann.pdf) 的论文指出,WebAssembly 代码仍然可以在设定的常量内存中覆盖字符串文字。同一篇论文描述了在三个不同的平台(浏览器、Node.JS 上的服务端应用程序,和独立 WebAssembly 虚拟机的应用程序)上,WebAssembly 可能比编译为原生二进制文件时更不安全的其他方式。建议进一步阅读此主题。
通常,认为 WebAssembly 只能破坏其自身沙盒中的内容的想法可能会产生误导。WebAssembly 模块为调用它们的 JavaScript 代码做繁重的工作,每次都会交换变量。如果模块在这些变量中的任意一处写入不安全的调用 WebAssembly 的 JavaScript 代码,就 *会* 导致崩溃或数据泄露。
### 未来的方向
WebAssembly 的两个新出现的特性:[并发](https://github.com/WebAssembly/threads) 和内部垃圾收集,肯定会影响其安全性(如何影响以及影响多少,现在下结论还为时过早)。
并发允许多个 WebAssembly 模块在同一个虚拟机中并行。目前,只有通过 JavaScript [web workers](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_worker) 才能实现这一点,但更好的机制正在开发中。安全方面,他们可能会带来 [以前不需要的大量的代码](https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.com/2018/08/the-problems-and-promise-of-webassembly.html),也就是更多出错的方法。
为了提高性能和安全性,我们需要一个 [本地的垃圾收集器](https://github.com/WebAssembly/gc/blob/master/proposals/gc/Overview.md),但最重要的是,要在经过良好测试的浏览器的 Java 虚拟机之外使用 WebAssembly,因为这些虚拟机无论如何都会在自己内部收集所有的垃圾。当然,甚至这个新代码也可能成为漏洞和攻击的另一个入口。
往好处想,使 WebAssembly 比现在更安全的通用策略也是存在的。再次引用 [这篇文章](https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec20-lehmann.pdf),这些策略包括:编译器改进、栈/堆和常量数据的 *分离* 的线性存储机制,以及避免使用 **不安全的语言**(如 C)编译 WebAssembly 模块代码。
*本文 [WebAssembly 安全的现在和未来](https://training.linuxfoundation.org/announcements/webassembly-security-now-and-in-the-future/) 首次发表在 [Linux 基金会 - 培训](https://training.linuxfoundation.org/)。*
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/news/webassembly-security-now-and-in-the-future/>
作者:[Dan Brown](https://training.linuxfoundation.org/announcements/webassembly-security-now-and-in-the-future/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hanszhao80](https://github.com/hanszhao80) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *By Marco Fioretti*
**Introduction**
WebAssembly is, as we [explained recently](https://training.linuxfoundation.org/announcements/an-introduction-to-webassembly/), a binary format for software written in any language, designed to eventually run on any platform without changes. The first application of WebAssembly is inside web browsers, to make websites faster and more interactive. Plans to push WebAssembly beyond the Web, from servers of all sorts to the Internet of Things (IoT), create as many opportunities as security issues. This post is an introductory overview of those issues and of the WebAssembly security model.
**WebAssembly is like JavaScript**
Inside web browsers, WebAssembly modules are managed by the same Virtual Machine (VM) that executes JavaScript code. Therefore, WebAssembly may be used to do much of the same harm that is doable with JavaScript, just more efficiently and less visibly. Since JavaScript is plain text that the browser will compile, and WebAssembly a ready-to-run binary format, the latter runs faster, and is also harder to scan (even by antivirus software) for malicious instructions.
This “code obfuscation” effect of WebAssembly has been already used, among other things, to pop up unwanted advertising or to open fake “tech support” windows that ask for sensitive data. Another trick is to automatically redirect browsers to “landing” pages that contain the really dangerous malware.
Finally, WebAssembly may be used, just like JavaScript, to “steal” processing power instead of data. In 2019, an [analysis of 150 different Wasm modules](https://www.sec.cs.tu-bs.de/pubs/2019a-dimva.pdf) found out that about *32%* of them were used for cryptocurrency-mining.
**WebAssembly sandbox, and interfaces**
WebAssembly code runs closed into a [sandbox](https://webassembly.org/docs/security/) managed by the VM, not by the operating system. This gives it no visibility of the host computer, or ways to interact directly with it. Access to system resources, be they files, hardware or internet connections, can only happen through the WebAssembly System Interface (WASI) provided by that VM.
The WASI is different from most other application programming interfaces, with unique security characteristics that are truly driving the adoption of WASM on servers/edge computing scenarios, and will be the topic of the next post. Here, it is enough to say that its security implications greatly vary, when moving from the web to other environments. Modern web browsers are terribly complex pieces of software, but lay on decades of experience, and of daily tests from billions of people. Compared to browsers, servers or IoT devices are almost uncharted lands. The VMs for those platforms will require extensions of WASI and thus, in turn, surely introduce new security challenges.
**Memory and code management in WebAssembly**
Compared to normal compiled programs, WebAssembly applications have very restricted access to memory, and to themselves too. WebAssembly code cannot directly access functions or variables that are not yet called, jump to arbitrary addresses or execute data in memory as bytecode instructions.
Inside browsers, a Wasm module only gets one, global array (“linear memory”) of contiguous bytes to play with. WebAssembly can directly read and write any location in that area, or request an increase in its size, but that’s all. This linear memory is also separated from the areas that contain its actual code, execution stack, and of course the virtual machine that runs WebAssembly. For browsers, all these data structures are ordinary JavaScript objects, insulated from all the others using standard procedures.
**The result: good, but not perfect**
All these restrictions make it quite hard for a WebAssembly module to misbehave, but not impossible.
The sandboxed memory that makes it almost impossible for WebAssembly to touch what is *outside* also makes it harder for the operating system to prevent bad things from happening *inside*. Traditional memory monitoring mechanisms like [“stack canaries”](https://ctf101.org/binary-exploitation/stack-canaries/), which notice if some code tries to mess with objects that it should not touch, [cannot work there](https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec20-lehmann.pdf).
The fact that WebAssembly can only access its own linear memory, but directly, may also *facilitate *the work of attackers. With those constraints, and access to the source code of a module, it is much easier to guess which memory locations could be overwritten to make the most damage. It also seems [possible](https://spectrum.ieee.org/tech-talk/telecom/security/more-worries-over-the-security-of-web-assembly) to corrupt local variables, because they stay in an unsupervised stack in the linear memory.
A 2020 paper on the [binary security of WebAssembly](https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec20-lehmann.pdf) noted that WebAssembly code can still overwrite string literals in supposedly constant memory. The same paper describes other ways in which WebAssembly may be less secure than when compiled to a native binary, on three different platforms (browsers, server-side applications on Node.js, and applications for stand-alone WebAssembly VMs) and is recommended further reading on this topic.
In general, the idea that WebAssembly can only damage what’s inside its own sandbox can be misleading. WebAssembly modules do the heavy work for the JavaScript code that calls them, exchanging variables every time. If they write into any of those variables code that may cause crashes or data leaks in the unsafe JavaScript that called WebAssembly, those things *will* happen.
**The road ahead**
Two emerging features of WebAssembly that will surely impact its security (how and how much, it’s too early to tell) are [concurrency](https://github.com/WebAssembly/threads), and internal garbage collection.
Concurrency is what allows several WebAssembly modules to run in the same VM simultaneously. Today this is possible only through JavaScript [web workers](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_worker), but better mechanisms are under development. Security-wise, they may bring in [“a lot of code… that did not previously need to be”](https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.com/2018/08/the-problems-and-promise-of-webassembly.html), that is more ways for things to go wrong.
A [native Garbage Collector](https://github.com/WebAssembly/gc/blob/master/proposals/gc/Overview.md) is needed to increase performance and security, but above all to use WebAssembly outside the well-tested Java VMs of browsers, that collect all the garbage inside themselves anyway. Even this new code, of course, may become another entry point for bugs and attacks.
On the positive side, general strategies to make WebAssembly even safer than it is today also exist. Quoting again from [here](https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec20-lehmann.pdf), they include compiler improvements, *separate* linear memories for stack, heap and constant data, and avoiding to compile as WebAssembly modules code in “unsafe languages, such as C”.
The post [WebAssembly Security, Now and in the Future](https://training.linuxfoundation.org/announcements/webassembly-security-now-and-in-the-future/) appeared first on [Linux Foundation – Training](https://training.linuxfoundation.org/). |
14,594 | 红帽宣布 RHEL 9:企业 IT 的下一代骨干系统 | https://news.itsfoss.com/rhel-9-release/ | 2022-05-15T08:36:00 | [
"RHEL",
"RHEL 9"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14594-1.html |
>
> RHEL 9 是使用 CentOS Stream 构建的最新升级版。这也是其在 IBM 旗下发布的第一个主要版本。
>
>
>

红帽企业 Linux(RHEL)无疑是开源企业生态系统中的一个重要角色。
可能你记得,IBM 在 2019 年以 340 亿美元收购了红帽公司。因此,可以说,RHEL 8 是它被收购前的最后一个主要版本。
多年来,RHEL 8 已经有了几次更新。
最后,红帽宣布发布了 RHEL 9,作为为企业 IT 基础设施提供动力的下一代升级版本。
在这里,让我重点介绍一下该版本的主要新增功能。
### RHEL 9 的新变化
请注意,该平台将在未来几周内普遍提供。但是,既然已经正式宣布,应该不会花很长时间。
如果你是一个 Linux 桌面用户,也不关心云创新,你会发现有许多技术术语。你需要参考红帽的官方文档来了解它们。
如果你已经在使用 [CentOS Stream](https://itsfoss.com/centos-stream-faq/),你可能对 RHEL 9 的升级有一定的了解。
是的,RHEL 9 是第一个由 CentOS Stream 构建的生产版本。
根据 [新闻稿](https://www.redhat.com/en/about/press-releases/red-hat-defines-new-epicenter-innovation-red-hat-enterprise-linux-9),新版本的重点是两个不同的功能:
* 全面的边缘计算管理,以服务的形式交付,以更大的控制和安全功能来监督和扩展远程部署,包括零接触的配给,系统健康的可视性,以及更灵敏的漏洞缓解,所有这些都来自一个单一的界面。
* 通过 Podman(RHEL 的集成容器管理技术)自动回滚容器,它可以自动检测新更新后的容器是否无法启动,然后将容器回滚到以前的工作版本。
其他主要亮点包括:
* 一个新的镜像构建器服务。
* 与 AWS Graviton 处理器的整合。
* 针对 Spectre 和 Meltdown 等硬件级安全漏洞的改进。
* 引入一个新的完整性测量架构。
* WireGuard VPN 技术(无支持的技术预览)。
* 改进了自动化。
* Python 3.9
* Node.js 16
* Linux 内核 5.14
你可以参考 [RHEL 9 测试版发布说明](https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/whats-new-rhel-90-beta) 以了解更多关于该版本的信息。
### 总结
虽然该版本可能不具有最新和最伟大的技术,但这些更新特性和功能应该有助于为较新的 IT 需求提供增强的支持。
最新版本应该在未来几周内通过红帽客户门户和云供应商市场提供。如果你不了解,可以在 [官方网站](https://www.redhat.com/en/store/linux-platforms) 上查看这个 Linux 平台的定价。
当然,你也可以通过 [红帽开发者计划](https://developers.redhat.com/products/rhel/overview) 免费在一些系统上测试它。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/rhel-9-release/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Red Hat Enterprise Linux is undoubtedly a significant player in the open-source enterprise ecosystem.
If you didn’t know, IBM acquired it for $34 Billion in 2019. So, it is safe to say that Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 was the last major release before the acquisition.
There have been several updates to RHEL 8 over the years.
Finally, Red Hat announced the release of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9 as the next-gen upgrade to power up enterprise IT infrastructure.
Here, let me highlight the key additions to the release.
## Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9: What’s New?
Note that the platform will be generally available in the coming weeks. But, now that it is officially announced, it should not take long.
If you are a Linux desktop user and aren’t concerned about cloud innovation, you will find numerous technical jargon. You will need to refer to Red Hat’s official documentation to know more about them.
If you’re already using [CentOS Stream](https://itsfoss.com/centos-stream-faq/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), you might have an idea about the RHEL 9 upgrade.
Yes, RHEL 9 is the first production release built from CentOS Stream.
As per the [press release](https://www.redhat.com/en/about/press-releases/red-hat-defines-new-epicenter-innovation-red-hat-enterprise-linux-9?ref=news.itsfoss.com), the new version focuses on two different capabilities:
- Comprehensive edge management, delivered as a service, to oversee and scale remote deployments with greater control and security functionality, encompassing zero-touch provisioning, system health visibility, and more responsive vulnerability mitigations all from a single interface.
- Automatic container roll-back with Podman, Red Hat Enterprise Linux’s integrated container management technology, which can automatically detect if a newly-updated container fails to start and then roll the container back to the previous working version.
Other key highlights include:
- A new image builder service.
- Integration with AWS Graviton processors.
- Improvements to address hardware-level security vulnerabilities like Spectre and Meltdown.
- Introducing a new integrity measurement architecture.
- WireGuard VPN technology is available as an unsupported technology preview.
- Improved automation.
- Python 3.9
- Node.js 16
[Linux Kernel 5.14](https://news.itsfoss.com/kernel-5-14-release/)
You can refer to [RHEL 9 beta release notes](https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/whats-new-rhel-90-beta?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to know more about the release.
## Wrapping Up
While the release may not feature the latest and greatest technologies, updated features and capabilities should help provide enhanced support for newer IT requirements.
The latest version should be available in the coming weeks via the Red Hat Customer portal and cloud provider marketplaces. You can check the pricing for Linux platforms on the [official site](https://www.redhat.com/en/store/linux-platforms?ref=news.itsfoss.com) if you’re new.
Of course, you can also [get free access to it for some systems to test through the Red Hat Developer programs](https://linuxhandbook.com/get-red-hat-linux-free/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,595 | GNOME 新终端程序尝鲜 | https://itsfoss.com/gnome-console/ | 2022-05-15T09:43:00 | [
"终端",
"GNOME"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14595-1.html | 
几天前,我分享了我 [对新 GNOME 文本编辑器的体验](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-text-editor/),它是原编辑器 Gedit 的替代品。
但它并不是唯一的应用程序替代品。GNOME 42 还有一个新的终端,叫做 <ruby> <a href="https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/console"> 控制台 </a> <rt> Console </rt></ruby>。
让我来分享一下 GNOME 提供的这个新终端的新功能,以及它的使用体验吧!
### 控制台:GNOME 的新终端模拟器
这个新应用程序的目标是提供一个“简单的、用户友好的终端模拟器”。它确实“简单”,因为它没有提供以往 GNOME 终端下用户习惯的许多功能。
后面我会继续谈这个话题。让我们先看看 GNOME 控制台的新功能。
#### 桌面通知
Ubuntu 上的 GNOME 终端从来没有这个功能,不过我在 elementary 和 Fedora 等发行版中看到过。
这是一个很方便的功能,当一个长期运行的命令执行完毕时,终端会发送一个桌面通知。

如果你在命令正在运行的同时,需要做其他事情,那么得到命令完成的通知有助于你保持工作效率。
#### 进行 root 和 SSH 操作时改变窗口颜色
这很可能是我在其他终端程序中没有见过的独特功能。
当你用 `sudo` 运行命令或 [切换到 root 用户](https://itsfoss.com/root-user-ubuntu/) 时,应用程序窗口会变成红色。

我想它的目的是警告用户他们正在使用高级权限,因此在运行命令时要小心。
同样,如果你使用 SSH 连接到一个远程服务器,终端应用程序窗口的颜色会变成紫色。

这也是提醒用户命令正在远程 Linux 机器上运行,而不是在本地机器上运行的好方法。
#### 主题
遵循新的设计准则,控制台提供了三种主题:浅色、深色和跟随系统。

控制台默认使用系统主题,它根据你的操作系统的深浅主题而改变终端配色。你也可以单独使用控制台的浅色/深色主题,而不用改变系统主题。
关于主题的内容差不多就这些。你可以进行的 [终端定制](https://itsfoss.com/customize-linux-terminal/) 并不多。
### 关闭终端窗口时更好的警告
当你试图关闭一个仍在运行的命令时,老的 GNOME 终端也会显示一个警告。

这个警告在新的 GNOME 控制台中稍好一些,因为它也会显示正在运行的命令。

#### 透明界面
GNOME 控制台默认有一个透明界面。在正常模式下,你可以透过它看到一点背景。
例如,你可以看到背景程序中的一些模糊的文字。

我注意到,当控制台进入全屏模式时,界面不再透明。而且,你无法配置透明度。
#### 其他功能
谢天谢地,你可以在控制台中使用标签。

你可以执行与以往 GNOME 终端一样的搜索操作。

它没有太多的选项。<ruby> 汉堡菜单 <rt> hamburger menu </rt></ruby>让你一眼就能看到所有可用的键盘快捷键。

以上就是关于 GNOME 控制台的一切。
### 在 Ubuntu 22.04 上安装 GNOME 控制台
如果你的发行版使用了原版 GNOME 42,那么它应该默认提供了新终端。
尽管 Ubuntu 22.04 使用的是 GNOME 42,但它仍然使用旧的 GNOME 终端。不过,你可以使用下面的命令来安装新的控制台。
```
sudo apt install gnome-console
```
### 总结
你可能会想,既然我们已经有了一个更好的、功能更强的 GNOME 终端,为什么还要开发一个新的控制台呢?这是因为 GNOME 有了新的设计指南。改造这些应用程序的旧代码库太复杂了,可能也不大划算,从头开始写反而会更容易,因此你会看到更多的“新的” GNOME 应用程序,如控制台和文本编辑器。
由于这个新的应用程序的目标是让事情更简单,因此它没有提供很多功能。你不能定制它,改变颜色、字体等。由于不支持定制,所以也不需要配置文件。
对于很少使用终端的人来说,控制台已经够用了。不过,我认为应该增加在输入密码时显示星号的功能。其他 [面向初学者的发行版](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-beginners/),如 Mint,就使用了这个功能,从而避免对 Linux 新手用户造成困扰。
你如何看待这个新的 GNOME 控制台,以及这种创建“新的 GNOME 应用程序”的方式呢?欢迎在下方评论区发表你的看法。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/gnome-console/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | A few days ago, I shared my [experience with the new GNOME Text Editor](https://itsfoss.com/gnome-text-editor/) which is a replacement for the older Gedit editor.
But that’s not the only ‘new’ replacement of an older application. GNOME 42 also has a new terminal called [Console](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/console).
Let me share what’s new in this new terminal offering from GNOME and what it is like to use it.
## Console: GNOME’s new Terminal Emulator
The goal of this new application is to provide a “simple, user-friendly terminal emulator”. And it is indeed a ‘simple’ application in terms that it doesn’t offer many features you are accustomed to in the older application, GNOME Terminal.
I’ll come back to that point later. Let’s first see what’s new in GNOME Console.
### Desktop notifications
GNOME Terminal in Ubuntu never had this feature though I have seen it in distributions like elementary and Fedora.
This is a handy feature that sends a desktop notification when a long-running command finishes its execution.
Getting notified of command completion helps you stay productive when you are distracted by something else while the command runs.
### Changes color for root and SSH operations
This is probably a unique feature I haven’t seen in any other terminal application.
The application window turns red when you use a command with sudo or [switch to the root user](https://itsfoss.com/root-user-ubuntu/).
I presume the idea here is to warn the users that they are using escalated privileges and hence be careful while running the commands.
Similarly, if you connect to a remote server using SSH, the terminal application window color changes to purple.
This is also a good way to alert the user that the commands are being run on remote Linux machine, not on the local one.
### Themes
Following the new design guidelines, Console offers three theme variants: light, dark and system theme.
System theme is used by default and based on whether your OS is using the dark or light theme, it changes the color. With dedicated dark and light options, you can change the theme irrespective of the system theme.
And that’s about it. There is not a lot of [terminal customization](https://itsfoss.com/customize-linux-terminal/) you can perform here.
### Better warning while closing the terminal window
The older GNOME terminal also shows a warning when you try to close a close with commands still running.
This warning is slightly better in the new GNOME Console as it also displays the running commands.
### Warning while copy-pasting commands into Console
Do you [copy-paste commands into the terminal](https://itsfoss.com/copy-paste-linux-terminal/)? I do that all the time.
Not always, but sometimes, when you try to copy-paste commands with sudo into Console, it shows a warning:
“You are pasting a command that runs as an administrator. Make sure you know what command does.”
I believe that idea is to make the application more beginner-friendly. Not that it is going to stop people from using any commands, it’s just a ‘hey, pay attention’ kind of thing and it’s good to have.
### Transparent interface
GNOME Console has a transparent interface by default. In normal mode, you can see the background a little.
For example, you can see some blurred text from the background application:
What I noticed is that when Console goes into full-screen mode, the interface is no longer transparent. Also, you cannot configure the transparency.
### Other features
You get to use tabs in Console, thankfully.
You can perform a search operation the same as the good old GNOME Terminal.
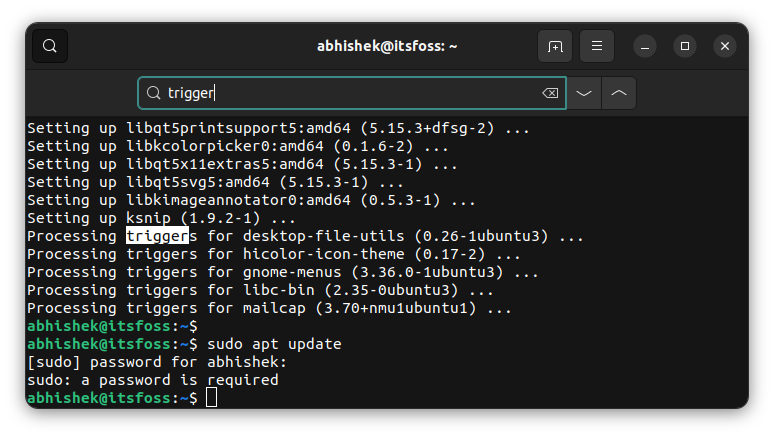
There are not a lot of options here. The hamburger menu allows you to look at all the available keyboard shortcuts at a glance.
And that’s everything about the GNOME Console.
## Installing GNOME Console on Ubuntu 22.04
If you are using a distribution that uses vanilla GNOME 42, you should have the new terminal available by default.
Though Ubuntu 22.04 uses GNOME 22.04, it still uses the older GNOME Terminal. However, you can install the new one using this command:
`sudo apt install gnome-console`
## Make GNOME Console the default terminal
If you like GNOME Console so much that you want it as your default terminal, you can do that. The default terminal is what opens with Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut in Ubuntu.
Open a terminal, new or old doesn’t matter, and type the following command:
`sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/x-terminal-emulator x-terminal-emulator /usr/bin/kgx 1`
Yes, the executable is /usr/bin/kgx. Once it is available as an alternative, you can [change the default terminal](https://itsfoss.com/change-default-terminal-ubuntu/) with the following command:
`sudo update-alternatives --config x-terminal-emulator`
When asked, enter the number before /usr/bin/kgx (2 in my case as shown in the screenshot below).
Test it out by using Ctrl+Alt+T keys and see if it opens Console or not.
## Conclusion
You might be wondering why a new Terminal application when we already have a better and more featureful GNOME Terminal. It’s because GNOME has new design guidelines. Transforming the old code base of these applications is too complicated and probably not worth the effort. Writing from scratch is easier and hence you see more ‘new’ GNOME applications like Console and Text Editor.
And as the idea of this new application is to keep things simpler, you don’t get a lot of features here. You cannot customize it, change the color, font, etc. Since there is no scope for customization, there is no need for profiles.
For people who seldom use the terminal, Console is sufficient. Although, I think that they should have added the feature to show asterisks while typing passwords. [Beginner-focused distros](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-beginners/) like Mint use it to avoid confusing new Linux users.
What do you think of the new GNOME Console and the entire approach of creating ‘new GNOME apps’? |
14,596 | 开源社区透明度的五个层次 | https://opensource.com/article/22/2/transparency-open-source-communities | 2022-05-15T15:08:44 | [
"开源社区",
"透明度"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14596-1.html |
>
> 如果想让开源社区繁荣发展,管理者需要达到透明度的五个层次。
>
>
>

开源社区的管理者必须意识到社区有五个层次的透明度,这对于建设繁荣发展的开源社区来说至关重要。
本文将详细介绍各个层次及其目标与作用。不过首先,我想谈一谈透明度对开源社区的重要性。
### 为什么开源社区需要保证透明度?
* 透明能够增进社区成员之间的信任,促进合作。
* 开放是社区合作和交流的前提。
* 只有在开放透明的环境下,开源工作才能避免矛盾与冲突。
* 社区管理者需要向参与者报告社区情况。
* 向成员公开社区各项情况,营造信任氛围,有利于社区健康发展。
### 透明度的五个层次
#### 层次一:发布源码
在这一层次,社区需要遵循 [OSI 认可的许可证](https://opensource.org/licenses),在 [Git](https://opensource.com/tags/git) 等公开的版本控制系统上发布源码。
层次一的目标在于创建开源项目。
* 建立开源社区,理应达到这一层次。因为没有公开源代码,也就无所谓开源项目。
* 开源项目的核心便是参与者们编写的源码,并在 OSI 批准的许可证下授权。
* 公开的版本控制系统能够促进合作,使得每一位开发者都能了解项目情况,理解合作模式。
#### 层次二:发布社区指南
达到这一层次,需要发布相关文档以及资源。也可通过组织活动来指导社区成员。
层次二的目标在于为一个开源项目建立和发展一个开源社区。
* 建立一个活跃的社区需要的不仅仅是源代码。
* 公开项目开展方式和贡献方式,能够吸引更多的开发者参与到项目当中。
* 为了推动社区的发展,管理者可能需要举办一些重要活动,并为贡献者们筹办一些特殊的活动。
#### 层次三:继往开来
到了这个层次,管理者有必要分享自己对于社区的见解,发布项目进展情况报告。
层次三的目标在于继往开来,确保社区进入后续阶段后能够更上一层楼,实现长远发展。
* 随着开源社区的发展,社区内的情况将会越来越难以把握。
* 公开社区活动,让成员意识到自己的付出能够为公众所见,为公众所识。
* 在这一层次,无论是报告还是分析,发布的时间并不固定,使用的工具也无定法。
#### 层次四:掌握社区的动态
这一层次就在于倾听社区声音:通过观察社区活动,关注项目发展;跟进软件开发进度,据此采取合适的应对措施。
层次四的目标在于保持科学严谨的态度,持续把握社区的发展情况及发展轨迹,引导社区朝着下一个层次迈进。
* 建立报告机制,运用分析工具,掌握社区动态。
* 将社区的各项活动与社区成员的反响与基线和社区内的其他活动进行比较。
* 坚持倾听社区声音,形成对于社区更深刻的见解。
#### 层次五:维护社区,长久发展
最后一个层次就是依据社区各项指标,提高社区成员的参与度。
层次五的目标在于制定行之有效、能够产生积极影响的决策方案,让开发者更好地参与社区项目。
* 适当调整系统,以适应社区各项指标的变动。
* 跟进这些变动,理解它们是如何通过各项指标和数据分析体现出来的。
* 针对社区维护者与开发者,制定服务等级协议和问责制度,为其设立参与度目标,确保项目整体顺利进行。
### 总结
开源社区管理者需要做到上述五个层次,保证透明度,才能构建起一个繁荣发展的社区。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/2/transparency-open-source-communities>
作者:[Emilio Galeano Gryciuk](https://opensource.com/users/egaleano) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[aREversez](https://github.com/aREversez) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Managers of open source communities have to be aware of the 5 levels of transparency that they can provide. These 5 levels of transparency are important for building a thriving open source community.
This article describes each level, its goals, and why they are important. But first, I revisit why transparency is important for open source ecosystems.
## Why do open source ecosystems need transparency?
- Transparent communities inspire trust
- Communities work together and exchange messages in the open.
- Open source work happens in a transparent way to avoid friction.
- Community managers need to report to their stakeholders.
- Showing communities what information is available about them is healthy and encourages trust.
## What are the 5 levels of transparency?
### Transparency level 1: Publish source code
This level is about releasing source code under an [Open Source Initiative (OSI)-approved license](https://opensource.org/licenses) in a public-facing version control system like [Git](https://opensource.com/tags/git).
The first level's goal is to establish** **an open source project.
- This level is self-evident as there would be no open source project without the source code.
- At the core of an open source project is the source code that people engage with—licensed under an OSI-approved license.
- A public version control system enables collaboration and allows everyone to analyze the project and understand the collaboration patterns.
### Transparency level 2: Publish community guidelines
You publish documentation and resources on contributing at this level, and you organize special events to educate the community.
The second level's goal is to create and grow a community for an open source project.
- Building an active community requires more than
**.** - Being transparent about how a project works and how to contribute enables others to join a project
**.** - Growing the community may involve
### Transparency level 3: Celebrate successes
Once you reach this level, it's important to share insights about the community and publish reports about the project's status.
The third level's goal is to celebrate successes and secure further support** **beyond the initial phase of the community.
- As open source communities grow, it becomes harder to know what's happening everywhere.
- Being transparent about the activities in the community helps community members know that their contributions are being seen and valued.
- At this level of transparency, the reporting and analytics
### Transparency level 4: Understand the pulse of the community
This level is all about listening to the community—keeping an eye on the project's evolution in community activity and the software development process to take corrective actions.
The fourth level's goal is to take the community to the next level by understanding its evolution and trajectory with consistency and scientific rigor.
- Reporting mechanisms and analytics tools help keep an eye on what is happening.
- You can compare events in the community and the subsequent reactions of community members to a baseline and other events in the community.
- Deeper insights into the community are possible with consistent listening.
### Transparency level 5: Maintain the community long-term
The last step is acting on community metrics and improving community engagement.
The fifth level's goal is to make meaningful and impactful decisions about community engagement.
- Have systems in place to
- Follow up on how changes to the community are showing up in the metrics and analytics about the community.
- Set "SLAs" and accountability for maintainers or developers to have goals for their community engagement and at a system level makes sure things get done.
## Wrap up
Open source community managers need to apply these 5 levels of transparency to build a thriving open source community.
## Comments are closed. |
14,598 | 管理 crontab 的开源工具 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/cron-crontab-ui | 2022-05-16T10:03:43 | [
"crontab"
] | /article-14598-1.html | 
>
> crontab-ui 是一个用 Node.js 编写的 Web 前端,帮助管理 crontab 文件。
>
>
>
*自动化是目前的一个热门话题。在我作为网站可靠性工程师(SRE)的日常工作中,我的部分职责是将尽可能多的重复性任务自动化。但是,有多少人在我们的日常非工作生活中这样做呢?今年,我专注于将劳作自动化,以便我们可以专注于重要的事情。*
作为一个初出茅庐的系统管理员,我最早了解的东西之一是 “cron”。cron 被广泛用于做一些事情,如轮换日志、启动和停止服务、运行程序作业等等。它在几乎所有的 Unix 和 Linux 系统中都可用,而且是我认识的每个系统管理员用来帮助管理服务和服务器的东西。cron 可以自动运行任何控制台应用或脚本,这使得它非常、非常灵活。
>
> LCTT 译注:CRON 是 “Command Run On” 的缩写,即在某个时间运行命令。
>
>
>

我用 cron 来获取电子邮件,运行过滤程序,确保服务正在运行,与 Habitica 等在线游戏互动等。
### 以传统方式使用 cron
要开始使用 cron,你可以简单地在命令行输入 `crontab -e`,启动一个打开了当前 `crontab`(“cron table” 的缩写)文件的编辑器(如果你以 root 身份这样做,你访问的是系统 crontab)。这是保存作业计划的地方,记录了何时运行。David Both 已经写了 [大量](https://opensource.com/article/17/11/how-use-cron-linux) 关于该文件的格式和如何使用它的文章,所以我不打算在这里介绍。我要说的是,对于新用户来说,这可能有点吓人,而且设置时间有点痛苦。
### 介绍 crontab-ui
有一些奇妙的工具可以帮助解决这个问题。我最喜欢的是 [crontab-ui](https://opensource.com/%5Bhttps%3A//github.com/alseambusher/crontab-ui%5D%28https%3A//github.com/alseambusher/crontab-ui%29),这是一个用 Node.js 编写的 Web 前端,可以帮助管理 crontab 文件。为了安装和启动 `crontab-ui` 供个人使用,我使用了以下命令。
```
# 做个备份
crontab -l > $HOME/crontab-backup
# 安装 Crontab UI
npm install -g crontab-ui
# 创建本地数据库目录
mkdir $HOME/crontab-ui
# 启动 crontab-ui
CRON_DB_PATH=$HOME/crontab-ui crontab-ui
```
完成这些后,只需将你的网页浏览器指向 `http://localhost:8000`,你就会看到 crontab-ui 的网页界面。要做的第一件事是点击 “<ruby> 从 Crontab 获取 <rt> Get from Crontab </rt></ruby>”,加载你可能有的任何现有作业。然后点击“<ruby> 备份 <rt> Backup </rt></ruby>”,这样你就可以回滚你所做的任何修改。

添加和编辑 cron 作业是非常简单的。添加一个名称,你想运行的完整命令,以及时间(使用 cron 语法),然后保存。另外,你还可以捕获日志,并设置将工作状态邮寄到你选择的电子邮箱。
完成后,点击 “<ruby> 保存到 Crontab <rt> Save to Crontab </rt></ruby>”。
我个人非常喜欢它的日志记录功能。有了 crontab-ui,你可以通过点击一个按钮来查看日志,这在排除故障时非常有用。
我建议不要一直运行 crontab-ui,至少不要公开运行。虽然它确实具有一些基本的身份验证功能,但它不应该暴露在你的本地机器之外。我不需要经常编辑我的 cron 作业,所以我可以按需启动和停止它。
下次你需要编辑你的 crontab 时,可以试试 crontab-ui!
(题图由 [FelixMittermeier](https://pixabay.com/zh/users/felixmittermeier-4397258/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=2031021) 在 [Pixabay](https://pixabay.com/zh/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=2031021) 上发布)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/cron-crontab-ui>
作者:[Kevin Sonney](https://opensource.com/users/ksonney) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,599 | 使用开源天文应用程序 KStars 探索夜空 | https://opensource.com/article/21/1/kstars | 2022-05-16T10:44:08 | [
"天文",
"星星"
] | /article-14599-1.html |
>
> 使用 KStars 从你的 Linux 桌面或安卓设备眺望星辰。
>
>
>

我一直对夜空很着迷。当我年轻的时候,唯一可用的参考资料是书籍,它们似乎描绘了一个与我从家里看到的不一样的天空。
五年多前,我曾介绍过两个开源天文馆应用程序 [Celestia 和 Stellarium](https://opensource.com/education/15/7/open-source-apps-explore-night-sky) 的使用体验。最近,我又了解到一个应用 [KStars](https://edu.kde.org/kstars/)。这是一个令人惊叹的开源应用程序,可以帮助儿童(和成人)参与科学和天文学。它的网站上说:
>
> “KStars 是一款自由开源的、跨平台的天文学软件。它提供了从地球上的任何位置、任何日期和时间对夜空的一个精确的图形化模拟。可展示包括多达 1 亿颗恒星,13,000 个深空天体,所有 8 个行星,太阳和月亮,以及数千颗彗星,小行星,超新星和卫星。“
>
>
>
KStars 是 [KDE 教育项目](https://edu.kde.org/) 的一部分。最新版本可用于 Linux、Windows 和 MacOS,它集成了 [StellarSolver](https://github.com/rlancaste/stellarsolver),这是一个跨平台的 SExtractor 程序,它可以从天文图像构建一个天体目录。
### 安装 KStars
KStars 采用 GPL 2.0 协议自由授权。源代码可以在官方的 [KDE GitLab 实例](https://invent.kde.org/education/kstars) 查看(这是 GitHub 的一个只读镜像)。KDE 教育项目有着优秀的 [安装文档](https://edu.kde.org/kstars/install.php)。
我用的系统是 [Pop!\_OS](https://pop.system76.com/),可以在 Pop!\_Shop 找到这款应用程序。
可以从你的发行版的软件存储库中找到 KStars 在 Linux 上安装。而在安卓设备上,可以从 [Google Play 商店](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.kde.kstars.lite&hl=en) 下载适配安卓的 KStars Lite。KDE 项目维护了一份优秀的 [KStars 手册](https://docs.kde.org/trunk5/en/extragear-edu/kstars/index.html) 来帮助用户。
### 使用 KStars
安装完后,从你的“<ruby> 应用 <rt> Applications </rt></ruby>”菜单启动程序。启动向导会指导你完成初始化设置。

这些指示很容易理解。向导会提示设置你住所的位置。不幸的是,我所在的小村庄不在列表里,但附近一个更大的社区在里面。

你还可以下载该程序的其他数据和额外功能。

这里有很多可用的选项。我选择“<ruby> 在详细信息窗口中显示常见图像 <rt> Common images displayed in the detail window </rt></ruby>”。
一旦完成设置,KStars 会呈现一张基于你的位置的夜空图。

左上角显示了当前时区(这张图里是 2020 年 11 月 30 日傍晚 5 点 58 分)。
使用鼠标左键,可以向左、向右、向上和向下移动显示。你可以使用鼠标滚轮进行放大和缩小。将鼠标光标放在天体上并右键单击可查看当前天体的描述。

### 参与
KStars 正在积极寻求错误报告、天文学知识、代码、翻译等方面的帮助。主要开发者和维护者是 [Jasem Mutlaq](https://github.com/knro)。如果你愿意贡献一份力量,请访问 [项目网站](https://edu.kde.org/kstars) 或加入邮件列表以了解更多信息。
(题图由 [FelixMittermeier](https://pixabay.com/zh/users/felixmittermeier-4397258/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=2183637) 在 [Pixabay](https://pixabay.com/zh/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=2183637) 上发布)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/1/kstars>
作者:[Don Watkins](https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hanszhao80](https://github.com/hanszhao80) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,600 | 开源新手指南 | https://ruthikegah.xyz/a-beginners-guide-to-open-source | 2022-05-16T14:48:00 | [
"开源"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14600-1.html | 
*开源朗读者 | 六开箱*
作为一名技术人员,你应该时不时会看到“<ruby> 开源 <rt> Open Source </rt></ruby>”这个词。你有可能在浏览推文、博文时看到过它,也有可能是在学习某一门编程语言或使用某个工具时,看到它的部分介绍写着:这个工具/语言是“开源”的。总之,开源无处不在。
在本文中,我将介绍下面这三个话题:
* 什么是开源
* 贡献于开源的好处
* 如何开始贡献
### 什么是开源
开源指的是这样一些软件、项目或社区:它们允许人们修改和分享,因为它们的设计目的就是为了让所有人都能访问。举一个关于菜谱的例子:你可以做你从未发明过的菜,因为发明这个菜谱的人公开了它。大多数时候,你也可以根据自己的口味烹饪,而不会呛到喉咙(开个玩笑)。
>
> <ruby> 开源软件 <rt> Open Source Software </rt></ruby>(OSS)是指源代码可供他人查看、复制、学习、修改或分享的软件。
>
>
>
下面是开源软件和语言的一些例子:
* Linux 操作系统
* Google 的 Android 操作系统
* Firefox 浏览器
* VLC 媒体播放器
* Python 语言、PHP 语言、MySQL 数据库
与开源软件相反的是<ruby> 专有软件 <rt> proprietary software </rt></ruby> / <ruby> 闭源软件 <rt> closed source software </rt></ruby>,只有软件的创造者才能自由使用,其他人若想使用,就得先获得法律许可才行。例如 Adobe Photoshop、微软 Office 等。
>
> 开源不仅限于软件或代码,技术领域的任何人都可以为开源做出贡献(各个角色)。有了开源,就有了透明度、可靠性、灵活性,并允许开放合作。
>
>
>
### 贡献于开源的好处
向开源项目或软件做贡献意味着“免费”让该项目变得更好。你应该会问自己,为什么我要关心或向自己强调“免费”呢?如果你是新手,你可以阅读 [Edidiong Asikpo](https://hashnode.com/@didicodes) 的故事,她在 [这篇文章](https://edidiongasikpo.com/open-source-contributions-a-catalyst-for-growth-b823fc5752b1) 中说明了为什么开源是她成长的催化剂。
贡献开源的好处有很多,这里是其中一部分:
* 它能够帮助你提高现有的技能,特别是对于新手而言,因为它允许你边做边学。
* 无论身在何处,你都可以与世界各地的优秀科技人士协作或共事。
* 你可以公开自己的想法,从而改善软件、项目或社区,让世界变得更美好。
* 你可以通过贡献开源来得到大家的认可,或者成为独特或伟大事物的一部分(获得自豪感)。
* 它让你有机会成为一个人才济济、活力四射的社区的一分子,你可以从中汲取灵感,并结识志同道合的人。
* 你可以因为贡献开源而获得报酬(OoO)!比如你可以参与一些实习,包括 <ruby> <a href="https://summerofcode.withgoogle.com"> 谷歌编程之夏 </a> <rt> Google Summer of Code </rt></ruby>、[Outreachy](https://www.outreachy.org/)、<ruby> <a href="https://developers.google.com/season-of-docs"> 谷歌文档季 </a> <rt> Google Season of Docs </rt></ruby>,以及 Open Collective 的 <ruby> <a href="https://docs.opencollective.com/help/contributing/development/bounties"> 赏金计划 </a> <rt> bounty program </rt></ruby> 等。(LCTT 译注:国内也有类似的开源实习机会,如“开源之夏”。)
### 如何开始贡献
我相信你会对上面提到的最后一点感兴趣吧(<sup> o</sup>),那么,你该如何开始为开源软件做贡献呢?
是时候介绍一下 GitHub 了!
Github 是开源项目协作的大本营,因此它是一个开始贡献开源的好地方。没听说过 GitHub?没有关系!它提供了文档和指南,很容易就可以上手。不过我还是要提醒你,学习是一个循序渐进的过程,不要太心急喔。
Github 以公共<ruby> 存储库 <rt> repositories </rt></ruby>的形式容纳了许多开源项目。对于某个项目,你可以提交一个<ruby> 议题 <rt> issue </rt></ruby>,来说明你注意到的错误或问题(或进一步提出改进意见),也可以创建一个<ruby> 拉取请求 <rt> pull request </rt></ruby>(PR),并说明你的更正和改进。
我不建议你在 GitHub 上搜索项目来开始贡献,这将是相当令人沮丧的。尽管你可以限定项目使用的编程语言来简化搜索过程,但仍然会有一大堆东西出现在你眼前。(LCCT 译注:对于可爱的小萌新来说,这实在是难以承受 >…<。)
为了更精准地找到适合自己的项目,这里有一些可供开始的途径:
* [First-timers only](https://www.firsttimersonly.com/):一个很好的资源网站,你可以在上面找到新手友好的开源项目来开始贡献。(设计师朋友,我没有忘记你!你可以查看 [Open Source Design](https://opensourcedesign.net/) 这个网站,在上面也能找到新手友好的开源设计项目!)
* 你可以创建你自己的开源项目,把你美妙的想法变成现实,并允许其他人的合作和贡献。[这里](https://github.com/Ruth-ikegah/opensource.guide) 有关于如何创建开源项目的指南。
* 加入一个社区:你可以成为某个社区的成员,这也是传播开源思想的一种方式。你可以在谷歌上搜索当地的开源社区,并积极加入其中。
最后,我想给出几个有用的提示,供你在贡献开源项目时参考:
* 在加入之前,先对项目、社区或组织做一些研究;当你在做的时候,针对不清楚的地方提出问题。
* 当你加入社区时,尽量积极地介绍自己,并说明你能帮助项目的地方。
* **不要**认为自己无法为项目提供任何帮助,停止这种念头!你有很好的想法可以分享!
* 在存储库中看看别人提交的议题,(如果有的话)看看你能在哪些方面提供帮助,你可以关注带有“good first issue”、“help-wanted”、“first-timers only”等标签的议题。
* 在开始贡献之前,一定要先看一下贡献指南,这样你在贡献时就不会有冲突。
>
> 哪怕只是使用一个开源工具也是一种贡献;参加一个开源活动也是一种贡献;做开源项目的志愿者,或者为开源项目提供赞助也是一种贡献。
>
>
>
我想用非洲开源节的口号来结束:“未来是开放的”,所以快上车吧!
感谢阅读!
如果你还有疑问或需要帮助,请在 [这里](https://twitter.com/IkegahRuth) 联系我,我很乐意和你讨论开源,并帮助你做出首次贡献!
**LCTT 译注:读了这篇文章,你是不是想要马上投身于开源贡献呢?那么请考虑加入“Linux 中国翻译组(LCTT)”吧!我们有能帮助你快速上手翻译的 [维基](https://lctt.github.io/wiki/intro/lctt.html) ,有热心友爱的 QQ 群,你甚至还能够在我们的官网上获得属于自己的译者专页……心动了吗?那就立刻行动起来吧!阅读 [维基](https://lctt.github.io/wiki/intro/lctt.html) 以了解如何加入我们~**
(题图由 [Markus e](https://pixabay.com/zh/users/fotopirat-24835164/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=7170280) 在 [Pixabay](https://pixabay.com/zh/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=7170280) 上发布,经修改)
---
via: <https://ruthikegah.xyz/a-beginners-guide-to-open-source>
作者:[Ruth Ikegah](https://hashnode.com/@ikegah_ruth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | As a techie, you should have come across the term *Open Source*, maybe in some random tweet, blog post, or even when learning a programming language or tool and part of the definition says: this tool or language is open source. It's actually everywhere.
In this article, I will be writing about:
What Open Source is?
Benefits of contributing to Open Source
How to start contributing
Open Source refers to software, project, or community where people can modify and share ideas because it's designed to be publicly accessible. A relatable example will be your favorite recipe, you are able to cook that dish you never invented because that recipe was made open by the owner. Most times, you can also cook it your style just to suit your taste without getting choked in the neck (*just joking*).
Open Source Software (OSS) is software that the source code is available to others who would like to view that code, copy it, learn from it, alter it, or share it.
Some examples of Open Source Softwares and Languages:
Linux Operating system
Android by Google
Firefox browser
VLC Media player
Python, PHP, MySQL
In contrast to OSS, we have proprietary or closed source software where it is only accessible to creators of the software and for others to use it, there would be legal permission. Eg Adobe Photoshop, Microsoft office.
Open Source is not just about software or code, absolutely anyone in the tech space can contribute to open source (every role). With open-source, there is transparency, reliability, flexibility, and allows for open collaboration.
Contributing to Open Source projects or software means making that project better for free. You should be asking yourself, *why should I even care or stress myself for free*. For starters, you can take a look at how [Edidiong Asikpo](https://hashnode.com/@didicodes) narrates how Open source was a catalyst for growth for her, [here](https://edidiongasikpo.com/open-source-contributions-a-catalyst-for-growth-b823fc5752b1).
Amongst the many benefits, here are some:
Open Source helps you improve on your existing skills, especially if you're a beginner as it permits you to learn while doing.
You get to collaborate and work with amazing tech personalities all over the world despite your location.
You are making the world a better place by making open your ideas to improve the software, project, or community.
You get recognized for contributing or being part of the something unique or big (
*the feel of pride*)It gives you the opportunity to be part of a vibrant community of great minds you can draw inspiration from and meet like-minded people.
You can get paid to contribute to open source projects (
*Interesting!*). Internships like[Google Summer of Code](https://summerofcode.withgoogle.com/),[Outreachy](https://www.outreachy.org/),[Google Season of Docs](https://developers.google.com/season-of-docs),[bounty program](https://docs.opencollective.com/help/contributing/development/bounties)by Open Collective, etc.
I'm sure my last point was interesting to you, So **How do you start contributing to OSS?** Here's how:
Let's talk about **Github**
Github is the house of collaboration for OSS projects so it's a great place to start contributing to open source, but this shouldn't scare you as if you don't know how to use it, it is learnable (documentation and guides) noting that learning is a gradual process.
Github houses many open source projects in form of public repositories. So you see a project, you either submit an issue suggesting ways to fix the errors or problems you have noticed with the project (*ideas*) or create a pull request with your corrections and improvements.
It's going to be quite frustrating if I advise you use the explore area on Github to search for projects cause you would see a lot in your face, although you can streamline your search by languages.
To be more specific, here are some ways you can start:
[First-timers only](https://www.firsttimersonly.com/): A great resource site to find beginner-friendly open source projects, to begin with.
Designers I got you covered! You can check out
[Open Source Design]for beginner-friendly design projects too
You can create your own open-source project bringing your wonderful ideas to life and allowing others to collaborate and contribute. You can check
[here](https://github.com/Ruth-ikegah/opensource.guide)for a guide on how to start an open-source project.Joining a community: You can be part of a community as a way of promoting the open-source way. With a google search on local open-source communities and be actively part of them.
Finally, here are some useful tips when contributing to an open-source project:
Do some research on the project, community, or organization before joining, and when you do, ask questions where not clear.
When you join the community, try to be active by introducing yourself and stating areas where you can help the project
Don't think you can't offer anything to the project, kill that thought. You've got wonderful ideas to share.
Scout for issues on the repository(if any) to see where you can help, issues having labels like
*good first issue, help-wanted, first-timers only*is a great place to start.Before starting to contribute, be sure to go through the contributing guidelines so you won't have conflicts contributing.
Just using an open-source tool is contributing, attending an open-source event is contributing, as well as volunteering or donating to one.
I'd end with Open-Source Africa Festival Slogan: ** THE FUTURE IS OPEN**, so join the train.
Thanks for reading!
If you still have doubts or need help starting, send a message [here](https://twitter.com/IkegahRuth), I will be glad to talk to you about open source and help you make your first contribution. |
14,602 | Xebian:Debian 与 Xfce 的完美结合 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/xebian-review-2022/ | 2022-05-17T09:03:37 | [
"Xebian",
"Debian",
"发行版"
] | /article-14602-1.html |
>
> 这是一篇对漂亮而时尚的 Xebian Linux 发行版的快速评测。
>
>
>
Xebian 是一个基于 Xfce 桌面环境的 Linux 发行版,基于 Debian 不稳定分支(sid)。这个 Linux 发行版提供了一个带有基本的 Xfce 桌面的 Debian,而无需更改配置和附加软件包。因此,你不用在安装 Debian 和 Xfce 上花费太多时间就可以获得通常的开箱即用体验。
那么,如果你想尝试一下,这是对 Xebian 的快速评测。

### Xebian 评测
#### 安装
考虑到林林总总的 ISO(迷你、自由、非自由等等),Debian 安装可能会有点复杂。毕竟,它是一个真正的“通用操作系统”。但是对于 Xebian,就轻松多了,因为它只有一个提供了 Debian sid 和 Xfce 的 64 位 ISO 文件。Xebian 使用 Debian 原生的安装程序,在你的物理系统或虚拟机中安装此发行版都相当简单。
在我的测试过程中,安装很顺利,没有报告任何问题。安装大约需要 4 分钟。
#### 外观和感觉
安装后,当你首次启动系统时,你会看到带有 Xebian 默认壁纸的漂亮登录页面。这个登录屏幕是标准的默认 Xfce 桌面登录页面。

首先,该桌面非常轻量,有着 Xfce 的干净外观。Xebian 就是一个在 Debian 上提供了完整 Xfce 桌面的 Linux 发行版。因此,唯一的区别是看起来不错的默认壁纸,以及默认的 Numix 主题(深色)。那些喜欢更传统外观的人也可以使用 Adwaita 和 Gerybird 主题。
其次,顶部面板右侧有 “<ruby> 鼠须菜单 <rt> Whisker Menu </rt></ruby>” 和标准的系统托盘,带有音量控制、电池指示、网络/Wi-Fi 和日期/时间。
#### 应用
Xebian 打包了所有 Xfce 原生应用,而没有添加任何额外内容。安装了它,你就应该拥有了一个稳定的工作桌面,并预装了以下应用程序:
* Thunar 文件管理器
* Ristretto 图像查看器
* Mousepad 文本编辑器
* Catfish 文件搜索
* XFCE 终端
* Firefox 浏览器
* Synaptic 包管理器
* GParted 分区程序
* 系统设置
除此之外,如果你需要任何其他应用,你可以使用 “<ruby> 新立得 <rt> Synaptic </rt></ruby>” 包管理器轻松安装它们。使用内置的 “<ruby> 软件及软件源 <rt> Software and Sources </rt></ruby>” 应用可以轻松调整软件源。
[Xfce 4.16](https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/02/xfce-4-16-review/) 是当前的稳定正式版本,并一同提供了其原生应用。而 Xfce 4.18 距离最终版本还很遥远。
该发行版的核心基于 Debian 不稳定分支 “sid”,在撰写本文时它正处于 Debian 12 “bookworm” 的发布路径上。它基于最新的 [Linux 内核 5.17](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/03/linux-kernel-5-17/) 进行滚动发布。
此外,如果你需要一个常规的图像编辑器、图形软件和办公套件(例如 LibreOffice),那么你可以手动安装它们。它们不是 ISO 文件的一部分。
现在,让我们来看看性能。
#### Xebian 的性能
Xebian 是轻量级的,非常适合旧硬件,这要归功于 Debian。我分两个阶段测试了其性能。
在让系统闲置一段时间后的理想阶段,消耗了大约 710 MB 内存,而 CPU 平均为 2%。大多数空闲状态资源被 Xfce4-desktop 和 Xfce 窗口管理器消耗。
其次,我在重度使用阶段对其进行了测试。我使用文件管理器、文本编辑器、终端和 Firefox 浏览器的一个实例作为工作负载尝试了 Xebian。在此工作负载下,Xebian 平均消耗 1.2GB 内存和 2% 到 3% 的 CPU,具体取决于各自的应用活动。而且,Firefox 明显消耗了大部分内存和 CPU,其次是 Xfce 窗口管理器的内存消耗增加了近 50%。
总的来说,我认为它是稳定的,应该可以在至少 4 GB 内存的中档硬件中正常工作。
### 结束语
基于 Debian 不稳定分支的 [Linux 发行版](https://www.debugpoint.com/category/distributions) 很少。如果你正在寻找 Xfce 和 Debian sid 的特定组合,那么 Xebian 是合适的,因为你从 Debian 获得了一个很可靠的滚动版本,并内置了 Xfce。
虽然它说是“不稳定”的,但根据我的经验,如果你每周保持系统更新,Debian “不稳定” 分支会很好地工作。
最后,如果你想尝试此发行版,请访问官方网站并
>
> **[下载 ISO 文件](https://xebian.org/download/)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/xebian-review-2022/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,603 | 在 FreeDOS 中聆听音乐 | https://opensource.com/article/21/6/listen-music-freedos | 2022-05-17T09:28:31 | [
"FreeDOS",
"音乐"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14603-1.html |
>
> Mplayer 是 Linux、Windows、Mac 和 DOS 等操作系统上常见的一款开源媒体播放器。
>
>
>

听音乐是放松心情的好方法。在 Linux 上,我使用 Rhythmbox 听音乐。但是你可能不知道在 FreeDOS 上也可以听音乐。让我们看一下两款流行的音乐播放器吧:
### 用 Mplayer 听音乐
[Mplayer](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MPlayer) 是一款开源的媒体播放器,通常安装于 Linux、Windows 和 Mac 上,但也有 DOS 版本可用。这里我们讨论的就是在 FreeDOS 版本。虽然其 DOS 移植版基于旧版(2007 年的 1.0rc2-3-3-2 版),但它完全适用于在 DOS 上播放媒体。
我使用 MPlayer 在 FreeDOS 上听音乐文件。在这个例子中,我复制了我最喜欢的有声读物之一,[Big Finish Productions](https://bigfinish.com/) 的<ruby> 神秘博士:闪点行动 <rt> Doctor Who: Flashpoint </rt></ruby>,并在我的 FreeDOS 计算机上将其保存为 `C:\MUSIC\FLASHPNT.MP3`。为了在 FreeDOS 上收听闪点行动,我从 FreeDOS 命令行启动 MPlayer 并指定要播放的 MP3 文件名。MPlayer 的基本用法是 `mplayer [options] filename`,如果默认设置可用,你应该可以直接使用该文件名启动 MPlayer。在本例中,我运行以下命令将工作目录切换为 `\MUSIC`,然后使用 MPlayer 播放我的 MP3 有声读物文件:
```
CD \MUSIC
MPLAYER FLASHPNT.MP3
```
FreeDOS *不区分大小写*,因此它将忽略 DOS 命令和任何文件或目录的大小写字母的区别。你键入 `cd \music` 或 `Cd \Music` 都可以切换到 Music 目录,效果相同。

*你可以用 Mplayer 播放 MP3 文件*
使用 MPlayer 在 FreeDOS 播放音乐文件时没有花哨的界面。但同时,它也不会分散注意力。所以我可以一边让 FreeDOS 在我的 DOS 计算机上播放 MP3 文件,一边使用另一台计算机做其他事情。然而,FreeDOS 一次只运行一个任务(换句话说,DOS 是一个<ruby> 单任务 <rt> single-tasking </rt></ruby>操作系统),所以我不能将 MPlayer 置于 FreeDOS 的“后台”运行,而在 *同一台 FreeDOS 机* 上处理其他事情。
请注意,MPlayer 是一个需要大量内存才能运行的大程序。虽然 DOS 本身并不需要太多的内存来运行,但我建议至少有 16M 的内存来运行 MPlayer。
### 使用 Open Cubic Player 听音频文件
FreeDOS 不止提供了 MPlayer 来播放媒体。还有 [Open Cubic Player](https://www.cubic.org/player/),它支持多种文件格式,包括 Midi 和 WAV 文件。
1999 年,我录制了一段简短的音频文件,内容是我说:“你好,我是 Jim Hall,我把 ‘FreeDOS’ 发音为 *FreeDOS*。"这是一个玩笑,借鉴了 Linus Torvalds 录制的演示他如何发音 Linux 的 [类似的音频文件](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Linus-linux.ogg)(`English.au`,包含在 1994 年的 Linux 源代码树中)中的创意。我们不会在 FreeDOS 中分发这段 FreeDOS 音频剪辑,但欢迎你从我们的 [Silly Sounds](https://www.ibiblio.org/pub/micro/pc-stuff/freedos/files/util/sillysounds/) 目录中下载它,该目录位于 [Ibiblio](https://www.ibiblio.org/) 的 FreeDOS 文件存档中。
你可以使用 Open Cubic Player 收听 *FreeDOS* 音频剪辑。通常从 `\APPS\OPENCP` 目录键入 `CP` 命令运行 Open Cubic Player。但 Open Cubic Player 是 32 位应用程序,运行它需要 32 位 DOS 扩展器。常见的 DOS 扩展器是 DOS/4GW。虽然可以免费使用,但 DOS/4GW 不是开源程序,因此我们不会将其作为 FreeDOS 包分发。
相反,FreeDOS 提供了另一个名为 DOS/32A 的开源32位扩展器。如果你在安装 FreeDOS 时没有安装所有内容,则可能需要使用 [FDIMPLES](https://opensource.com/article/21/6/freedos-package-manager) 进行安装。我使用这两行命令切换到 `\APPS\OPENCP` 路径,并使用 DOS/32A 扩展器运行 Open Cubic Player:
```
CD \APPS\OPENCP
DOS32A CP
```
Open Cubic Player 没有花哨的用户界面,但你可以使用方向键将 <ruby> 文件选择器 <rt> File Selector </rt></ruby> 导航到包含要播放的媒体文件的目录。

*Open Cubic Player 打开文件选择器*
文本比在其他 DOS 应用程序中显示的要小,因为 Open Cubic Player 会自动将显示更改为使用 50 行文本,而不是通常的 25 行。当你退出程序时,Open Cubic Player 会将显示重置为 25 行。
选择媒体文件后,Open Cubic Player 将循环播放该文件(按键盘上的 `Esc` 键退出)。当文件通过扬声器播放时,Open Cubic Player 会显示一个频谱仪,以便你可以观察左右声道的音频。FreeDOS 音频剪辑是以单声道录制的,因此左右声道是相同的。

*Open Cubic Player 中播放 FreeDOS 音频文件*
DOS 可能来自较早的年代,但这并不意味着你不能使用 FreeDOS 来执行现代任务或播放当前的媒体。如果你喜欢听数字音乐,试一试在 FreeDOS上 使用 Open Cubic Player 或 MPlayer 吧!
(题图由 [Anselmo Pedraz](https://pixabay.com/zh/users/ansfoto-7261652/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=6824489) 在 [Pixabay](https://pixabay.com/zh/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=6824489) 上发布)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/6/listen-music-freedos>
作者:[Jim Hall](https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[hanszhao80](https://github.com/hanszhao80) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Music is a great way to relax. On Linux, I listen to music using Rhythmbox. But did you know you can listen to music on FreeDOS, as well? Let's take a look at two popular programs to listen to music:
## Listen to music with Mplayer
[Mplayer](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MPlayer) is an open source media player that's usually found on Linux, Windows, and Mac—but there's a DOS version available, too. And that's the version we include in FreeDOS. While the DOS port is based on an older version (version 1.0rc2-3-3-2 from 2007) it is perfectly serviceable for playing media on DOS.
I use Mplayer to listen to music files on FreeDOS. For this example, I've copied one of my favorite audiobooks, Doctor Who: Flashpoint by [Big Finish Productions](https://bigfinish.com/), and saved it as `C:\MUSIC\FLASHPNT.MP3`
on my FreeDOS computer. To listen to Flashpoint on FreeDOS, I launch Mplayer from the FreeDOS command line and specify the MP3 filename to play. The basic usage of Mplayer is `mplayer [options] filename`
so if the default settings work well for you, then you can just launch Mplayer with the filename. In this case, I ran these commands to change my working directory to `\MUSIC`
and then run Mplayer with my MP3 audiobook file:
```
CD \MUSIC
MPLAYER FLASHPNT.MP3
```
FreeDOS is *case insensitive*, so it will accept uppercase or lowercase letters for DOS commands and any files or directories. You could also type `cd \music`
or `Cd \Music`
to move into the Music directory, and that would work the same.
You can use Mplayer to listen to MP3 files
(Jim Hall, [CC-BY SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
Using Mplayer is a "no frills" way to listen to music files on FreeDOS. But at the same time, it's not distracting, so I can leave FreeDOS to play the MP3 file on my DOS computer while I use my other computer to do something else. However, FreeDOS runs tasks one at a time (in other words, DOS is a "single-tasking" operating system) so I cannot run Mplayer in the "background" on FreeDOS while I work on something else *on the same FreeDOS computer*.
Note that Mplayer is a big program that requires a lot of memory to run. While DOS itself doesn't require much RAM to operate, I recommend at least 16 megabytes of memory to run Mplayer.
## Listen to audio files with Open Cubic Player
FreeDOS offers more than just Mplayer for playing media. We also include the [Open Cubic Player](https://www.cubic.org/player/), which supports a variety of file formats including Midi and WAV files.
In 1999, I recorded a short audio file of me saying, "Hello, this is Jim Hall, and I pronounce 'FreeDOS' as *FreeDOS*." This was meant as a joke, riffing off of a [similar audio file](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Linus-linux.ogg) (`english.au`
, included in the Linux source code tree in 1994) recorded by Linus Torvalds to demonstrate how he pronounces "Linux." We don't distribute the *FreeDOS* audio clip in FreeDOS itself, but you are welcome to download it from our [Silly Sounds](https://www.ibiblio.org/pub/micro/pc-stuff/freedos/files/util/sillysounds/) directory, found in the FreeDOS files archive at [Ibiblio](https://www.ibiblio.org/).
You can listen to the *FreeDOS* audio clip using the Open Cubic Player. To run Open Cubic Player, you normally would run `CP`
from the `\APPS\OPENCP`
directory. However, Open Cubic Player is a 32-bit application that requires a 32-bit DOS extender. A common DOS extender is DOS/4GW. While free to use, DOS/4GW is not an open source program, so we do not distribute it as a FreeDOS package.
Instead, FreeDOS provides another open source 32-bit extender called DOS/32A. If you did not install everything when you installed FreeDOS, you may need to install it using [FDIMPLES](https://opensource.com/article/21/6/freedos-package-manager). I used these two commands to move into the `\APPS\OPENCP`
directory, and to run Open Cubic Player using the DOS/32A extender:
```
CD \APPS\OPENCP
DOS32A CP
```
Open Cubic Player doesn't sport a fancy user interface, but you can use the arrow keys to navigate the *File Selector* to the directory that contains the media file you want to play.
Open Cubic Player opens with a file selector
(Jim Hall, [CC-BY SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
The text appears smaller than in other DOS applications because Open Cubic Player automatically changes the display to use 50 lines of text, instead of the usual 25 lines. Open Cubic Player will reset the display back to 25 lines when you exit the program.
When you have selected your media file, Open Cubic Player will play it in a loop. (Press the Esc key on your keyboard to quit.) As the file plays over the speakers, Open Cubic Player displays a spectrum analyzer so you can see the audio for the left and right channels. The *FreeDOS* audio clip is recorded in mono, so the left and right channels are the same.
Open Cubic Player playing the "FreeDOS" audio clip
(Jim Hall, [CC-BY SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
DOS may be from an older era, but that doesn't mean you can't use FreeDOS to run modern tasks or play current media. If you like to listen to digital music, try using Open Cubic Player or Mplayer on FreeDOS.
## Comments are closed. |
14,604 | 微软还有另一个 Linux 发行版,而且是基于 Debian 的 | https://news.itsfoss.com/microsoft-debian-distro/ | 2022-05-17T10:22:59 | [
"Linux",
"微软"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14604-1.html |
>
> 微软一直在为 Azure 云使用一个基于 Debian 的 Linux 发行版。我们开始揭开它的面纱了!
>
>
>

微软在其大量的项目中利用了 Linux。近年来,你一定读过很多关于 WSL(或 WSL2)和微软制作的 Linux 发行版(即 **CBL Mariner**)的消息。
>
> CBL 是 “共用基础 LinuxCommon Base Linux”的缩写。
>
>
>
甚至在 Windows 11 上,微软也在不断地改进 [WSL](https://news.itsfoss.com/windows-11-wsl/) 的体验。
虽然 CBL Mariner 被用来支持 WSLg(WSL 2 的 GUI 部分)和 Azure,但最近一些媒体([ZDNet](https://www.zdnet.com/article/surprise-theres-yet-another-microsoft-linux-distro-cbl-delridge/))报道发现了微软内部使用的另一个 Linux 发行版。
微软肯定喜欢 Linux,对吗?
### CBL-Delridge:一个基于 Debian 的 Linux 发行版

微软维护着一个基于 Debian 的发行版,它被用来支持 Azure 的“<ruby> 云端外壳 <rt> Cloud Shell </rt></ruby>”。它的名字是 “CBL-Delridge”。
感谢 [Hayden Barnes](https://twitter.com/unixterminal),他是 SUSE 公司负责 Windows 容器的高级工程经理。
在他 2022 年 2 月的一篇 [旧博文](https://boxofcables.dev/building-cbl-d-microsofts-other-linux-distro/) 中,他透露了关于它的更多细节,并帮助你构建它以在需要时将其导入 WSL。
与从头构建的 CBL-Mariner 不同,CBL-Delridge(CBL-D)是基于 Debian 10(Buster)的。
看到 Debian 在这里受到青睐并不奇怪,即使是 [谷歌也为其内部的 Linux 发行版 gLinux 抛弃了 Ubuntu 而选择了 Debian](https://itsfoss.com/goobuntu-glinux-google/)。
有趣的是,微软在 2020 年发布了这个供内部使用的发行版(根据 Hayden 维护的 [微软的开源举措的非官方时间表](https://github.com/sirredbeard/microsoft-opensource)),而我们在 2022 年才知道了它。

CBL-Delridge 也采用了同样的版本号 10(巧合),代号为 “Quinault”。解析一下这个名字,ZDNet 指出,Delridge 是西雅图西部的一个区,而 Quinault 指的是华盛顿州奥林匹克国家公园的一个山谷。
### 构建 CBL-Delridge
与普通的 Linux 发行版不同,你找不到它的可以公开下载的镜像文件。
考虑到 CBL-D 的 APT 软件包库是公开的,如果你出于任何需求想测试它,你可以构建你的 CBL-D 镜像。
你也可以把它导入 WSL 中。[Hayden 的博文](https://boxofcables.dev/building-cbl-d-microsofts-other-linux-distro/) 解释了如何使用 debootstrap 来开始构建镜像,然后将其导入 WSL。
请注意,CBL-D 并不完全是 Debian 的替代品。所以,你可能无法找到所有你喜欢的软件包。要了解更多的信息,你可以浏览 Hayden 的博文。
你对微软的内部使用的 Linux 发行版有什么看法?你试过其中一个吗?请在评论中告诉我你的想法。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/microsoft-debian-distro/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Microsoft utilizes Linux for a wide range of its projects. In recent years, you must have read a lot about WSL (or WSL2) and a Linux distribution made by Microsoft, i.e., **CBL (Common Base Linux) Mariner**.
Even with Windows 11, Microsoft keeps improving the experience with [WSL](https://news.itsfoss.com/windows-11-wsl/).
While CBL Mariner is used to power WSLg (the GUI part of WSL 2) and Azure, some recent press coverage (via [ZDNet](https://www.zdnet.com/article/surprise-theres-yet-another-microsoft-linux-distro-cbl-delridge/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)) uncovered another Linux distribution that Microsoft uses internally.
Microsoft sure loves Linux, right?
## CBL-Delridge: A Debian-based Linux distro
Microsoft maintains a Debian-based distro, which is used to power Azure’s Cloud Shell. And it goes by the name “**CBL-Delridge**“.
Thanks to [Hayden Barnes](https://twitter.com/unixterminal?ref=news.itsfoss.com), a senior engineering manager responsible for Windows containers at SUSE.
In one of his [older blog posts](https://boxofcables.dev/building-cbl-d-microsofts-other-linux-distro/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) in February 2022. He revealed more details about it while helping you build it and import it into WSL if required.
CBL-Delridge (CBL-D) is based on Debian 10 (Buster), unlike CBL-Mariner, built from scratch.
Not a surprise to see Debian being favored here. Even [Google ditched Ubuntu for Debian](https://itsfoss.com/goobuntu-glinux-google/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for its in-house Linux distro gLinux.
Interestingly, Microsoft published the distro in 2020 for internal use (as per an [unofficial timeline of Microsoft’s open-source interactions](https://github.com/sirredbeard/microsoft-opensource?ref=news.itsfoss.com) maintained by Hayden), and we’re getting to know about it in 2022.
The CBL-Delridge also utilizes the same version number 10 (coincidentally) with the codename “Quinault.” Breaking down the name, ZDNet notes that Delridge is a district in West Seattle, and Quinault refers to a valley in the Olympic National Park in Washington State.
## Building CBL-Delridge
Unlike normal Linux distributions, you won’t find an image file to download publicly.
Considering the apt package repositories for CBL-D are public, you can build your image of CBL-D if you need to test it for any of your relevant requirements.
You can also import it into WSL. [Hayden’s blog ](https://boxofcables.dev/building-cbl-d-microsofts-other-linux-distro/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)[p](https://boxofcables.dev/building-cbl-d-microsofts-other-linux-distro/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)[ost](https://boxofcables.dev/building-cbl-d-microsofts-other-linux-distro/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) explains using debootstrap to get started building the image and then importing it to WSL.
Note that the CBL-D is not exactly a replacement for Debian. So, you may not be able to find all your favorite packages. To know more about it, you can explore Hayden’s blog post.
*What do you think about Microsoft’s Linux distributions for internal use? Have you tried any of them yet? Let me know your thoughts in the comments.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,606 | Kali Linux 2022.2 发布:增加了一个吓唬人的有趣新功能 | https://news.itsfoss.com/kali-linux-2022-2-release/ | 2022-05-18T10:40:31 | [
"Kali Linux",
"黑客"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14606-1.html |
>
> Kali Linux 2022.2 是今年的第二次更新,增加了一些有趣的内容。
>
>
>

Kali Linux 不是你寻常使用的 Linux 发行版。它是专门为渗透测试和道德黑客学习及实验而量身打造的。
在新的 Kali Linux 版本中,增加了一些有趣的工具和功能。让我们来看看 Kali Linux 2022.2 的亮点。
### Kali Linux 2022.2 有什么新功能?
Kali Linux 2022.2 是一个有趣的版本,它引入了更新的桌面环境,升级了 Linux 内核,增加了新的工具,以及更多的改进。
不仅仅限于通常的完善,你还可以看到一个新的屏幕保护程序,其中有许多令人惊讶的元素。
#### 带有好莱坞怀旧色彩的新屏保
Kali Linux 已经出现在许多黑客相关的电视节目/电影(如《<ruby> 黑客军团 <rt> Mr. Robot </rt></ruby>》)中,看起来酷极了。
更进一步,Kali Linux 增加了一个新的屏幕保护程序(你可以单独安装),其中有来自好莱坞的令人惊讶的元素和一些吓唬人的黑客场景。
他们在屏保中调侃了《黑客帝国》的尼奥,还添加了一个漂亮的 Kali Linux 标志。

整个屏幕保护程序包括几个非常棒的元素。要安装并立即启动它,你可以输入以下命令:
```
sudo apt -y install kali-screensaver
sudo apt -y install hollywood-activate
hollywood-activate
```
#### GNOME 42

Kali Linux 终于包含了新的 [GNOME 42](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-42-features/) 桌面环境。所以,在 Kali Linux 自然带有 GNOME 42 的所有优点,包括新的屏幕截图用户界面。
另外,现在你将会在 GNOME 桌面环境中获得一致的深浅主题体验。

#### KDE Plasma 5.24
对于 KDE 粉丝,Kali Linux 2022.2 也带来了新的 [KDE Plasma 5.24](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-24-lts-release/) LTS 桌面环境。

#### 新的 Kali Linux 工具
新的工具总是每个新版本的重点。一些新增加的工具包括:
* BruteShark - 网络取证分析工具(NFAT)
* Evil-WinRM - Ultimate WinRM shell
* Hakrawler - 网络爬虫,设计用于轻松、快速发现端点和资产
* Httpx - 快速和多用途的 HTTP 工具箱
* Sparrow-wifi - 用于 Linux 的图形化 Wi-Fi 分析器
#### 其他改进
该版本还有许多其他实质性的改进。主要的亮点包括。
* 对终端进行了调整,以加强语法高亮、自动补完和输出
* 自动复制丢失的配置
* 支持 VirtualBox 共享文件夹
* 增加了新的应用程序图标
* 为多显示器设置调整了默认墙纸
* 针对 ARM 设备的更新
* Linux 内核 5.16
要探索更多关于该版本的信息,你可以查看 [官方发布公告](https://www.kali.org/blog/kali-linux-2022-2-release/)。
### 下载 Kali Linux 2022.2
你应该能够在 [官方下载页面](https://www.kali.org/get-kali/) 中找到该镜像。根据你的要求选择合适的版本,然后安装它。
>
> **[Kali Linux 2022.2](https://www.kali.org/get-kali/)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/kali-linux-2022-2-release/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Kali Linux is not your usual Linux distribution. It is specially tailored for penetration testing and ethical hackers to learn/experiment.
We get interesting tools and feature additions with a new Kali Linux release. Let us take a look at the highlights for Kali Linux 2022.2.
## Kali Linux 2022.2: What’s New?
Kali Linux 2022.2 is an intriguing release introducing updated desktop environments, upgrading the Linux Kernel, adding new tools, and more improvements.
Not just limited to the usual refinements, you also get to see a new screensaver with many surprising elements.
### The New Screensaver with Hollywood Nostalgia
Kali Linux has been featured in numerous TV Shows/Movies (like Mr. Robot) where they focus on hacking, considering it looks cool.
To take it up a notch, Kali Linux has added a new screensaver (that you can separately install), with surprising elements from Hollywood and some hacking scenes to scare away people.
They tease Matrix’s Neo, and also add a beautiful Kali Linux logo in the screensaver.

The entire screensaver includes several elements, which is awesome. To install and launch it immediately, you can type in the following commands:
```
sudo apt -y install kali-screensaver
sudo apt -y install hollywood-activate
hollywood-activate
```
In case, you just want the video for other platforms, you can download the video above (re-hosted from Kali Linux’s blog).
### GNOME 42
Kali Linux finally includes the new [GNOME 42](https://news.itsfoss.com/gnome-42-features/) desktop environment. So, you should expect all the goodness of GNOME 42 with Kali Linux, including the new screenshot user interface.
Also, you will be getting a consistent dark/light theme experience now with the GNOME desktop environment.
### KDE Plasma 5.24
For KDE fans, Kali Linux 2022.2 brings in the new [KDE Plasma 5.24](https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-plasma-5-24-lts-release/) LTS desktop environment.
### New Kali Linux Tools
The new tools are always the focus of every new release. Some of the new additions include:
**BruteShark**– Network Forensic Analysis Tool (NFAT)**Evil-WinRM**– Ultimate WinRM shell**Hakrawler**– Web crawler designed for easy, quick discovery of endpoints and assets**Httpx**– Fast and multi-purpose HTTP toolkit**Sparrow-wifi**– Graphical Wi-Fi Analyzer for Linux
### Other Improvements
There are many other substantial improvements with the release. The key highlights include:
- Tweaks for terminal to enhance syntax highlighting, autocompletion, and the output.
- Auomated copy of missing configurations
- VirtualBox shared folder support.
- Addition of new app icons.
- Default wallpaper tweaked for multi-monitor setups.
- Updates for ARM devices.
- Linux Kernel 5.16
To explore more about the release, you can check out the [official release announcement](https://www.kali.org/blog/kali-linux-2022-2-release/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Download Kali Linux 2022.2
You should be able to find the the image in the [official download page](https://www.kali.org/get-kali/?ref=news.itsfoss.com). Choose the appropriate version as per your requirements and get it installed.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,607 | PyCaret:机器学习模型开发变得简单 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/pycaret-machine-learning-model-development-made-easy/ | 2022-05-18T15:09:54 | [
"机器学习"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14607-1.html |
>
> 在当今快节奏的数字世界中,机构们使用低代码/无代码(LC/NC)应用来快速构建新的信息系统。本文将介绍 PyCaret,这是一个用 Python 编写的低代码机器学习库。
>
>
>

PyCaret 是 R 编程语言中 Caret(<ruby> 分类和回归训练 <rt> Classification And REgression Training </rt></ruby>的缩写)包的 Python 版本,具有许多优点。
* **提高工作效率:** PyCaret 是一个低代码库,可让你提高工作效率。由于花费更少的时间进行编码,你和你的团队现在可以专注于业务问题。
* **易于使用:** 这个简单易用的机器学习库将帮助你以更少的代码行执行端到端的机器学习实验。
* **可用于商业:** PyCaret 是一个可用于商业的解决方案。它允许你从选择的 notebook 环境中快速有效地进行原型设计。
你可以在 Python 中创建一个虚拟环境并执行以下命令来安装 PyCaret 完整版:
```
pip install pycaret [full]
```
机器学习从业者可以使用 PyCaret 进行分类、回归、聚类、异常检测、自然语言处理、关联规则挖掘和时间序列分析。
### 使用 PyCaret 构建分类模型
本文通过从 PyCaret 的数据仓库中获取 Iris 数据集来解释使用 PyCaret 构建分类模型。
我们将使用 Google Colab 环境使事情变得简单,并按照下面提到的步骤进行操作。
#### 步骤 1
首先,通过给出以下命令安装 PyCaret:
```
pip install pycaret
```
#### 步骤 2
接下来,加载数据集,如图 2 所示:

```
from pycaret.datasets import get_data
dataset = get_data('iris')
(或者)
import pandas as pd
dataset = pd.read_csv('/path_to_data/file.csv')
```
#### 步骤 3
现在设置 PyCaret 环境,如图 2 所示:

```
from pycaret.classification import *
clf1 = setup(data=dataset, target = ‘species’)
```

使用 PyCaret 构建任何类型的模型,环境设置是最重要的一步。默认情况下,`setup()` 函数接受参数 `data`(Pandas 数据帧)和 `target`(指向数据集中的类标签变量)。`setup()` 函数的结果如图 3 所示。 `setup()` 函数默认将 70% 的数据拆分为训练集,30% 作为测试集,并进行数据预处理,如图 3 所示。
#### 步骤 4
接下来,找到最佳模型,如图 4 所示:

```
best = compare_models()
```
默认情况下,`compare_models()` 应用十倍交叉验证,并针对具有较少训练时间的不同分类器计算不同的性能指标,如准确度、AUC、召回率、精度、F1 分数、Kappa 和 MCC,如图 4 所示。通过将 `tubro=True` 传递给 `compare_models()` 函数,我们可以尝试所有分类器。
#### 步骤 5
现在创建模型,如图 5 所示:

```
lda_model=create_model (‘lda’)
```
线性判别分析分类器表现良好,如图 4 所示。因此,通过将 `lda` 传递给 `create_model()` 函数,我们可以拟合模型。
#### 步骤 6
下一步是微调模型,如图 6 所示。

```
tuned_lda=tune_model(lda_model)
```
超参数的调整可以提高模型的准确性。`tune_model()` 函数将线性判别分析模型的精度从 0.9818 提高到 0.9909,如图 7 所示。

#### 步骤 7
下一步是进行预测,如图 8 所示:

```
predictions=predict_model(tuned_lda)
```
`predict_model()` 函数用于对测试数据中存在的样本进行预测。
#### 步骤 8
现在绘制模型性能,如图 9 所示:

```
evaluate_model(tuned_lda)
```
`evaluate_model()` 函数用于以最小的努力开发不同的性能指标。你可以尝试它们并查看输出。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/pycaret-machine-learning-model-development-made-easy/>
作者:[S Ratan Kumar](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/s-ratan/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Organisations use low code/no code (LC/NC) apps to construct new information systems swiftly in today’s fast-paced digital world. This article introduces PyCaret a low code machine learning library written in Python.*
PyCaret is a Python version of the Caret (short for Classification And REgression Training) package in the R programming language, and has many benefits.
**Increased productivity:** PyCaret, being a low code library, makes you more productive. With less time spent coding, you and your team can now focus on business problems.
* Easy to use:* This simple and easy to use machine learning library will help you to perform end-to-end ML experiments with fewer lines of code.
* Business ready:* PyCaret is a business-ready solution. It allows you to do prototyping quickly and efficiently from your choice of notebook environment.
You can create a virtual environment in Python and execute the following command to install the PyCaret complete version:
pip install pycaret [full]
A machine learning practitioner can do classification, regression, clustering, anomaly detection, natural language processing, association rules mining and time series analysis with PyCaret.
**Classification model building with PyCaret**
This article explains classification model building with PyCaret by taking the Iris data set from PyCaret’s data repository.
We will use the Google Colab environment to make things simple and follow the steps mentioned below.
**Step 1:** First, install PyCaret by giving the following command:
pip install pycaret
**Step 2:** Next, load the data set, as shown in Figure 1:

from pycaret.datasets import get_data dataset = get_data(‘iris’) (or) import pandas as pd dataset = pd.read_csv(/path_to_data/file.csv’)
**Step 3:** Now set up the PyCaret environment, as shown in Figure 2:

from pycaret.classification import * clf1 = setup (data=dataset, target = ‘species’)
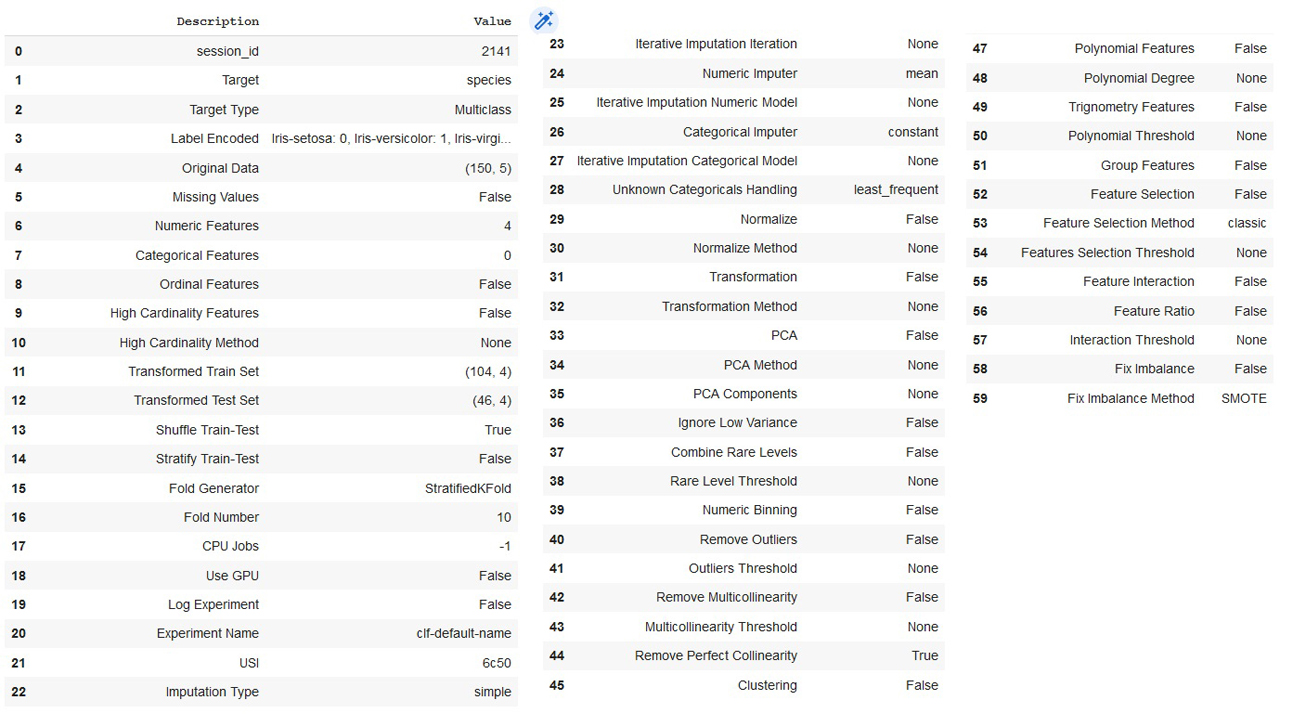

For any type of model building with PyCaret, the environment setup is the most important step. By default, *setup ()* function takes the *data*: Pandas DataFrame and target, which points to the class label variable in the data set. The result of the setup function is shown in Figure 3. The setup function, by default, splits 70 per cent of the data as train set and 30 per cent as test set, and does data preprocessing as shown in Figure 3.
**Step 4:** Next, find the best model, as shown in Figure 4:
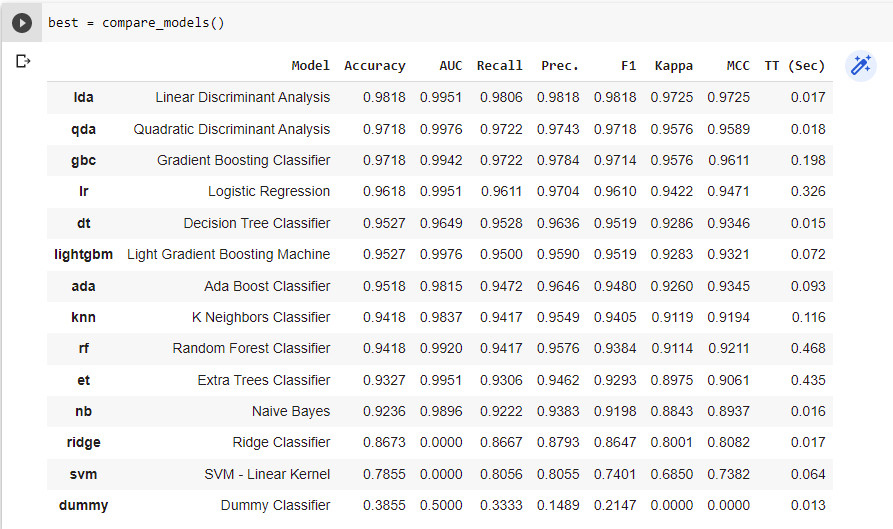

best = compare_models()
The* compare_models()*, by default, applies ten-fold cross validation and calculates different performance metrics like accuracy, AUC, recall, precision, F1 score, Kappa and MCC for different classifiers with lesser training times, as shown in Figure 4. By passing the tubro=True to* compare_models()* function we can try all the classifiers.
**Step 5:** Now create the model, as shown in Figure 5:


lda_model=create_model (‘lda’)
The Linear Discriminant Analysis classifier is performing well, as shown in Figure 4. So by passing ‘lda’ to the *create_model()* function, we can fit the model.
**Step 6:** The next step is to fine tune the model, as shown in Figure 6.
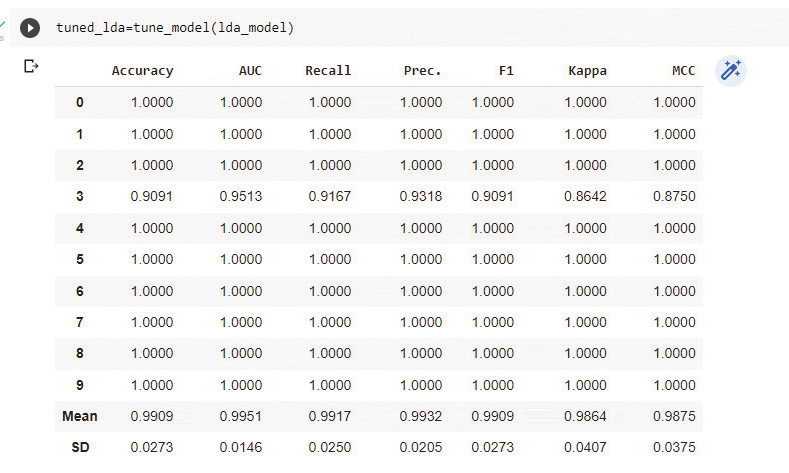

tuned_lda=tune_model(lda_model)
Tuning of hyper parameters can improve the model accuracy. The *tune_model()* function improved the Linear Discriminant Analysis model accuracy from 0.9818 to 0.9909, as shown in Figure 7.


**Step 7:** The next step is to make predictions, as shown in Figure 8:
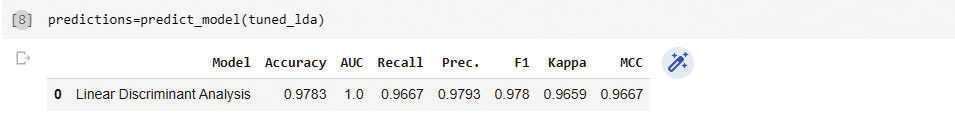

predictions=predict_model(tuned_lda)
The* predict_model()* function is used for making the predictions of the samples present in the test data.
**Step 8:** Now plot the model performance, as shown in Figure 9:
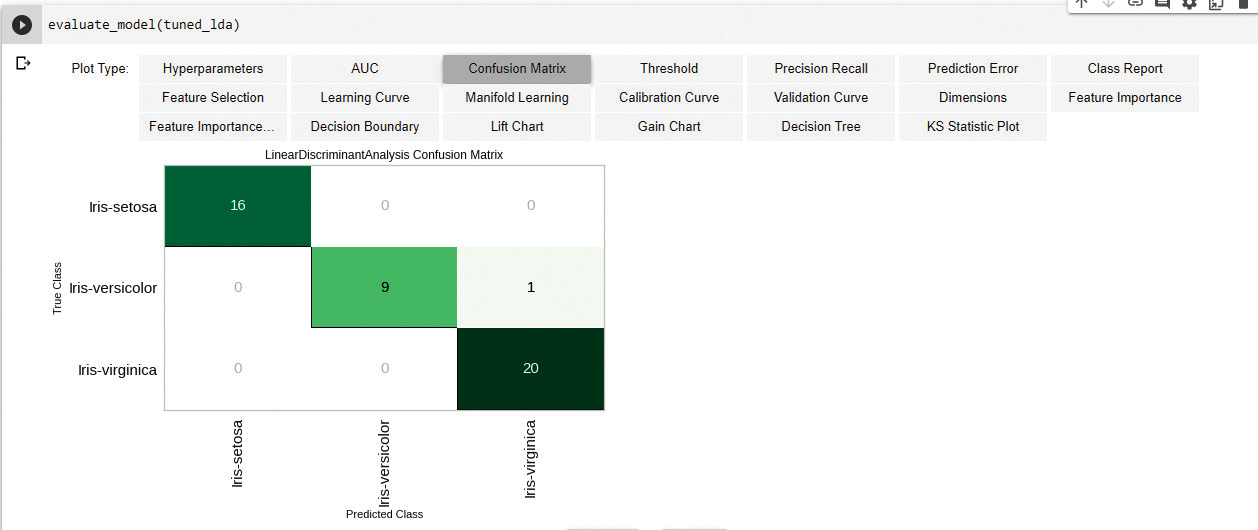

evaluate_model(tuned_lda)
The* evaluate_model ()* function is used to develop different performance metrics with minimum effort. You can try them out to see the output. |
14,608 | 为什么推荐开源分析数据库 Apache Druid | https://opensource.com/article/22/4/apache-druid-open-source-analytics | 2022-05-18T15:44:19 | [
"Apache Druid",
"数据库"
] | /article-14608-1.html |
>
> 对用户而言,优秀的对外数据分析工具非常关键,因此选择合适的数据架构就显得尤为重要。
>
>
>

现如今,数据分析不再是仅面向内部开发人员。当为业务方构建数据分析系统时,你需要确认哪种数据库后端是最合适的。
程序员的本能可能是“选用自己了解的数据库(例如 PostgreSQL 或 [MySQL](https://opensource.com/downloads/mariadb-mysql-cheat-sheet))”。数据仓库也可能会扩展核心的 BI 仪表板和报告之外的功能,不过对业务方的数据分析支持仍是其重要功能之一,因此要选择合适的工具来保证此功能的性能。
问题的关键点在于用户体验,以下是对外支持数据分析工作的一些关键技术讨论点(以 Apache Druid 为例)。
### 低延迟特性
一直在队列中等待查询会让人很恼火。与延迟有关的因素包括数据量、数据库的处理能力、用户和 API 调用的数量,以及数据库支持查询应用的能力。
当数据量比较大时,有一些方法可以基于任意在线分析处理(OLAP)数据库构建交互式数据体验,但或多或少都有一些其他方面的牺牲。预计算查询会对性能要求较高,还会使架构变得僵化。预聚合处理会使数据粒度变大。将数据时间限制在近期的处理方式,会使得数据完整性得不到保证。
一个“不妥协”的解决方案是选择专为大规模交互而构建的优化架构和数据格式,[Apache Druid](https://druid.apache.org/) 正是这样一个旨在支持现代分析程序的实时数据库。
* 首先,Druid 具备特有的分布式弹性架构,可将数据从共享数据层预取到近乎无限容量的数据服务器集群中。这种架构与诸如云数据仓库这样的解耦查询引擎相比,具有更快的性能,因为它不需要移动数据,并且比像 PostgreSQL 和 MySQL 这样的纵向扩展数据库具有更高的可扩展性。
* 其次,Druid 采用内置于数据格式中的自动多级索引来驱动每个内核去支持更多查询操作。在常规 OLAP 列格式基础之上,还增加了全局索引、数据字典和位图索引,这可以最大化利用 CPU 周期,加快处理速度。
### 高可用性
如果开发团队为内部报告搭建了一个后端,那么中断几分钟甚至更长时间真的很严重吗?实际上并不是的。所以在典型 OLAP 数据库和数据仓库中,计划外的停机和维护是可以允许的。
但是如果你们团队构建了一个对外的供客户使用的分析应用程序,如果发生数据中断,会严重影响客户满意度、收入,当然还有你的周末休息时间。这就是为什么弹性(高可用性和数据持久性)需要成为对外分析应用程序数据库中的首要考虑因素。
考虑弹性就需要考虑设计标准。节点或集群范围的故障能完全避免吗?丢失数据的后果有多严重?保障应用程序和数据需要涉及哪些工作?
关于服务器故障,保证弹性的常规方法是多节点服务以及 [备份机制](https://opensource.com/article/19/3/backup-solutions)。但如果你是为客户构建应用程序,则对数据丢失的敏感性要高得多。*偶尔的*备份并不能完全解决这一问题。
Apache Druid 的核心架构内置了该问题的解决方案,本质是一种强大而简单的弹性方法,旨在保证承受任何变故都不会丢失数据(即使是刚刚发生的事件)。
Druid 基于对象存储中共享数据的自动、多级复制实现高可用性(HA)和持久性。它实现了用户期望的 HA 特性以及持续备份机制,即使整个集群出现问题,也可以自动保护和恢复数据库的最新状态。
### 多用户
一个好的应用应该同时兼备大用户量和“引人入胜”的体验,因此为高并发构建后端非常重要。你肯定不想看到因为应用挂掉而让客户沮丧。内部报告的架构不必考虑这点,因为并发用户数量要小得多且有限。所以现实是,用于内部报告的数据库可能并不适合高并发应用程序。
为高并发构建数据库主要在于取得 CPU 使用率、可伸缩性和成本之间的平衡点。解决并发问题的通常做法是投入更多硬件成本。逻辑上说,只要增加 CPU 的数量,就能够同时进行更多的查询操作。虽然事实确实如此,但成本的增加是不可忽视的。
更好的方法还是使用像 Apache Druid 这样的数据库,它具有优化的存储和查询引擎,可以降低 CPU 使用率。我们强调的关键词是“优化”。数据库不应该读取它不需要的数据。Apache Druid 可以让基础设施在同一时间跨度内为更多查询操作提供服务。
节省成本是开发人员使用 Apache Druid 构建外部分析应用程序的一个重要原因。Apache Druid 具有高度优化的数据格式,结合了从搜索引擎世界借鉴来的多级索引以及数据缩减算法,可以最大限度地减少所需的处理量。
最终表现就是 Apache Druid 提供了其他数据库不可比拟的处理效率。它可以支持每秒数十到数千跨度的 TB 甚至 PB 级别的查询。
### 着眼当下,预见未来
分析应用程序对于用户而言至关重要,所以要构建正确的数据架构。
你肯定不想一开始就选择了一个错误的数据库,然后在后续扩展时面对诸多令人头疼的问题。幸运的是,Apache Druid 可以从小规模开始,并在之后轻松扩展以支持任何可以想象的应用程序。Apache Druid 有 [优秀的官方文档](https://druid.apache.org/docs/latest/design/),当然它是开源的,所以不妨尝试一下并,快速上手吧。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/4/apache-druid-open-source-analytics>
作者:[David Wang](https://opensource.com/users/davidwang) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[unigeorge](https://github.com/unigeorge) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
14,610 | Fudgie?令人惊叹的 Budgie 桌面即将登陆 Fedora Linux | https://news.itsfoss.com/fudgie-fedora-budgie-announcement/ | 2022-05-19T08:25:36 | [
"Fedora",
"Budgie"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14610-1.html |
>
> Fedora 用户也将能够享受 Budgie 桌面环境的现代体验。
>
>
>

近来,红帽的社区项目 Fedora 已经获得了相当不错的用户群。除了默认桌面 GNOME 外,Fedora 也以 <ruby> <a href="https://spins.fedoraproject.org"> Fedora 定制版 </a> <rt> Fedora Spins </rt></ruby> 的形式提供了多种其他桌面环境。
这意味着你可以在 Fedora 上享受 KDE、MATE、Xfce 和其他一些桌面环境的开箱即用的体验,而无需额外的努力。喜欢 KDE 而不是 GNOME 吗?下载 Fedora 的 KDE 定制版,安装它,就像安装常规的 Fedora 一样。
Fedora 定制版中缺少的一个桌面环境是 Budgie 桌面。
### Budgie 走向独立
在 2014 年左右,Budgie 桌面随同 Solus Linux 项目一起推出。最近,Solus 和 Budgie 项目出现了一些 [倒退式的发展](https://news.itsfoss.com/solus-co-lead-resign-budgie-serpent/)。Budgie 项目现在已经 [从 Solus Linux 中独立出来了](https://news.itsfoss.com/budgie-10-6-release/)。
自从首次发布以来,Budgie 就获得了一定的追随者。它的现代布局方式受到了许多 Linux 用户的喜爱。这也是许多其他主要 Linux 发行版(如 Ubuntu、Manjaro、openSUSE)开始提供 Budgie 版本的原因。

到目前为止,Fedora 的产品中还没有 Budgie,但这可能会在 Fedora 的下一个版本中发生变化。
### Budgie 提交加入 Fedora 的申请
Budgie 项目的首席开发人员 Joshua Strobl 在 [Reddit 帖子](https://www.reddit.com/r/Fedora/comments/uq3gah/budgie_desktop_has_now_been_submitted_for/) 中宣布了这一消息。
>
> 我现在已提交 Budgie 桌面及其它的附属软件(Budgie 控制中心、Budgie 屏幕保护程序、Budgie 桌面视图)加入到 Fedora 中的申请。从 Fedora rawhide(37)开始并向后移植到 36。它会得到“官方的”维护/支持,因为我自己在工作笔记本电脑上使用 Fedora Silverblue + rawhide,并且我以后会切换桌面到 Fedora Silverblue。
>
>
>
这意味着,如果该软件包得到了 Fedora 团队的批准,你应该就能在 Fedora 37 中(甚至有希望在 Fedora 36 中)安装 Budgie 和它的附属软件。
但这还不是故事的结束。Joshua 提到,他也在考虑引入并支持包含 Budgie 桌面的 Fedora 官方定制版。这意味着人们将能够下载一个预装了 Budgie(而不是 GNOME)桌面的 Fedora ISO。
目前还不清楚他的意思,有可能是一个 Budge 的 Fedora 官方定制版,也有可能是一个新的非官方的 Fedora 衍生版,名为 “Fudgie”,完全由他来维护。
### Fedora + Budgie 是一个好消息
无论如何,Fedora 的 Budgie 桌面都是个好消息。它为 Fedora 用户提供了更多选择,而 Budgie 是一个漂亮的桌面。同时喜欢 Fedora 和 Budgie 的人应该能够享受两全其美的体验。
我希望你同意我的看法。请在评论区也分享一下你的看法吧!
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/fudgie-fedora-budgie-announcement/>
作者:[Abhishek](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/root/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

In recent times, Red Hat’s community project, Fedora, has gained quite a decent userbase. While GNOME is the default choice of desktop here, Fedora also offers a variety of other desktop environments in the form of [Fedora Spins](https://spins.fedoraproject.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
This means that you can enjoy an out of box experience of KDE, MATE, Xfce and a few other desktop environments with Fedora without additional effort. Do you prefer KDE instead of GNOME? Download the KDE spin of Fedora and install it like your regular Fedora installation.
The one desktop offering missing from Fedora Spins is Budgie desktop.
## Budgie going independent
The Budgie desktop was introduced with the Solus Linux project circa 2014. There has been some [regressional development with the Solus and Budgie project lately](https://news.itsfoss.com/solus-co-lead-resign-budgie-serpent/). The [Budgie project is now independent of the Solus Linux](https://news.itsfoss.com/budgie-10-6-release/).
Ever since its first release, Budgie garnered a niche following. Its modern layout approach is liked by many Linux users. This is the reason why many other major Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Manjaro, openSUSE started offering Budgie variants.
Fedora hasn’t had Budgie in its offering so far but that could be changing in the next release of Fedora.
## Budgie submitted for inclusion in Fedora
Joshua Strobl, the lead developer of the Budgie project, announced the news in a [Reddit post](https://www.reddit.com/r/Fedora/comments/uq3gah/budgie_desktop_has_now_been_submitted_for/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
I have now submitted Budgie Desktop and its microcosm of software (Budgie Control Center, Budgie Screensaver, Budgie Desktop View) for inclusion in Fedora, starting with rawhide (37) and backporting to 36. This will be maintained / supported “officially”, as I am using Fedora Silverblue + rawhide on my work laptop and will be switching my desktop over to Fedora Silverblue as well.
Joshua Strobl, Lead Developer of Budgie
This means that if the package is approved by the Fedora’s team, you should be able to install Budgie and some Budgie elements in Fedora 37 and hopefully in Fedora 36.
But that’s not the end of the story. Joshua mentions that he is also considering to introduce and support an official Fedora Spin of Budgie desktop. Meaning people will be able to download an ISO of Fedora preloaded with Budgie desktop instead of GNOME.
It’s not clear if he speaks of official Fedora Spin or a new unofficial Fedora variant named ‘Fudgie’, which is completely maintained by him.
## Fedora + Budgie is a good news
In any case, the Budgie desktop coming to Fedora is good news. It gives more options to the Fedora user and Budgie is a pretty sleet desktop. People who like both Fedora and Budgie should be able to enjoy the best of the both worlds.
I hope you agree with me. I let you share your view in the comment section.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,615 | Adobe Illustrator 的替代品 Inkscape 发布了 1.2 版本 | https://news.itsfoss.com/inkscape-1-2-release/ | 2022-05-20T08:16:10 | [
"Inkscape"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14615-1.html |
>
> Inkscape 1.2 是一个激动人心的更新,包含许多有用的改进和新增功能。试一试吧!
>
>
>

Inkscape 是一个流行的开源矢量图形处理程序,可用于 Linux、Windows 和 macOS。
它的最新版本侧重于改进现有工具,以及提供更多自定义选项。
此外,它还有一些新增功能。让我们来看看吧!
### Inkscape 1.2:有什么新功能?
Inkscape 1.2 是一个激动人心的更新,它包含了许多有用的增强功能。其中一些关键变化包括:
* 改进的渐变编辑器
* 新的捕捉模式
* 支持多页文档
* 改进的导出对话框
* 可定制的工具栏
在这里,我将重点介绍重要的功能改进:
#### 多页文档支持

你现在可以在同一个文档中创建多个标准/自定义大小的页面,并把它们保存为一个多页的 PDF 文档。
不仅是导出,你还可以导入多页 PDF 来简化操作。
### 自定义调色板
你现在可以轻松地更改尺寸、重新配置颜色,以此来尝试所有可用的调色板,然后选择你真正喜欢的颜色。
特别是当你需要在用户界面中使用多个调色板时,它会让操作更流畅。
### 新的“平铺”实时路径效果
如果你正在处理很多个对象,并想尝试不同路径效果,那么你应该会喜欢新的平铺实时路径效果。
你可以轻松调整镜像模式、调整间隙、添加行和列,从而获得大量发挥创意的机会。
### 图层和对象对话框

大多数改进使得体验比以前更直接。使用新的合并图层和对象对话框,你可以根据要查找的图层,快速组织/查找对象。
你甚至可以自定义图层和对象颜色来区分它们。
### 导出对话框

现在,导出对话框为你提供了选择简单/批量导出的选项,以及选择文件格式和 DPI 设置的能力。
### 其他改进
除了上面的主要亮点外,还有其他的一些重大变化,包括:
* 两种新的画布捕捉模式有助于对齐对象
* 你可以在“<ruby> 填充和描边 <rt> Fill and Stroke </rt></ruby>”对话框中选择渐变
* 编辑<ruby> 标记 <rt> marker </rt></ruby>的能力
* 改进了与扩展的兼容性
* 更新了 SVG 字体编辑器
* 性能改进
* 可配置的工具栏
你可以参考 [Inkscape 1.2 发行说明](https://media.inkscape.org/media/doc/release_notes/1.2/Inkscape_1.2.html) 来查看所有的技术变化。
### 下载 Inkscape 1.2
你可以从它的官方网站下载 AppImage 格式的 Inkscape 1.2 软件包,或查看其他适用于 Windows/macOS 平台的可用软件包。
>
> **[Inkscape 1.2](https://inkscape.org/release/inkscape-1.2/)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/inkscape-1-2-release/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Inkscape is a popular open-source vector graphics program available for Linux, Windows, and macOS.
The latest release focuses on refinements to existing tools and more customization options.
There are also a couple of new additions to the application. Let’s take a look.
## Inkscape 1.2: What’s New?
Inkscape 1.2 is an exciting update with many useful enhancements. Some of the key changes include:
- Improved gradient editor
- New snapping modes
- Support for Multi-page documents
- Improved export dialog
- Customizable toolbar
Here, I shall highlight the important feature improvements:
### Multi-Page Document Support
You can now create standard/custom-size pages in the same document, and finalize them by saving them as a multi-page PDF.
Not the ability to export, but you can also import a multi-page PDF to make things easy.
## Customize Color Palette
Easily change the size, reconfigure the colors to explore the available color palettes, and select the one you really like.
It should make things quicker when you require working with several color palettes in the user interface.
## New ‘Tiling’ Live Path Effect
If you are working with a large number of objects and want to explore path effects, the new tiling live path effect should be interesting.
You can easily tweak the mirroring mode, adjust the gap, add rows and columns, and get numerous opportunities to get creative.
## Layers and Object Dialog
Most of the improvements make the experience more straightforward than it already was. With the new merged layers and object dialog, you can quickly organize/find objects per the layer you’re looking for.
You can even customize the layer and object colors to differentiate them.
## Export Dialog
The export dialog now provides you options to choose a simple/batch export along with the ability to pick a file format and DPI settings.
## Other Improvements
In addition to the key highlights, some of the significant changes include:
- Two new modes of on-canvas snapping help align objects.
- You can choose the gradients right within the Fill and Stroke dialog box.
- The ability to edit a marker.
- Improved compatibility with extensions.
- Updated SVG font editor.
- Performance improvements.
- Configurable toolbar.
You can refer to the [Inkscape 1.2 release notes](https://media.inkscape.org/media/doc/release_notes/1.2/Inkscape_1.2.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to explore all the technical changes.
## Download Inkscape 1.2
You can download Inkscape 1.2 as an AppImage from its official website or check other available packages for Windows/macOS platforms.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,616 | HydraPaper:一个支持多显示器的 Linux 壁纸管理器 | https://itsfoss.com/hydrapaper/ | 2022-05-20T10:47:01 | [
"HydraPaper",
"壁纸"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14616-1.html |
>
> HydraPaper 是一个令人印象深刻的壁纸管理器,适用于 Linux 用户,也支持多显示器设置。让我们仔细看一下。
>
>
>
一般而言,你要为你的 Linux 发行版上的每个桌面环境分别设置壁纸。
而且,当试图将一个自定义的壁纸集文件夹添加到可选的壁纸范围时,往往会受到限制。此外,遇到多显示器环境时,你无法在你的发行版中为其单独选择壁纸。因此,你需要去寻找一个图形用户界面(GUI)程序来完成这些操作。
幸运的是,我偶然发现了一个让 Linux 用户印象深刻的选择,即 **HydraPaper**。
### HydraPaper:带有 CLI 接口的开源墙纸管理器

HydraPaper 是一个使用 Python 3 和 GTK 构建的相当有用的壁纸管理器。它可以让你为不同的显示器选择单独的墙纸。
虽然它主要是一个 GUI 程序,但你也可以使用命令行执行同样的任务。
因此,HydraPaper 是一个同时适用于 GUI 和 CLI 用户的壁纸管理器。

它看起来是一个直接的解决方案,有一些简单的功能。让我介绍一下如下的主要亮点。
### HydraPaper 的特点

HydraPaper 可以让你添加自定义壁纸集,组织/选择你想要的文件夹,并方便地挑选壁纸。
一些基本的特性包括:
* 管理文件夹集合(根据需要一键切换它们)。
* 挑选喜欢的壁纸,并将它们添加到你的最爱集合。
* 按照你的喜好定位墙纸(缩放、适合黑色背景/模糊、居中等)。
* 能够从你的收藏中快速设置一个随机壁纸,如果你想这么做的话。
* 用深色模式自定义壁纸管理器的体验,选择单独保存壁纸,清除缓存,等等。
* 支持 CLI。
* 单跨壁纸模式适用于多显示器。

使用起来相当简单。你可以为不同的显示器挑选壁纸,或者使用选项中的单跨壁纸模式,在多显示器之间应用一个壁纸。

你可以选择/添加/删除文件夹,调整位置,添加收藏夹,以及应用深色模式的墙纸。
### 在 Linux 中安装 HydraPaper
你可以在 Flathub 上找到 HydraPaper 的 [Flatpak 包](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-flatpak/),它适合各种 Linux 发行版。如果你是第一次设置对 Flatpak 的支持,你可以参考我们的 [Flatpak 指南](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/)。
你也可以在 Arch Linux 发行版的 AUR、Fedora 的仓库,以及 Debian(unstable)中找到它。
我在 Manjaro Linux 上测试了它,它使用 Flatpak 包工作得很好。
要探索更多的选择,你可以前往其 [GitLab 仓库](https://gitlab.gnome.org/gabmus/hydrapaper)。
*你对 HydraPaper 有什么看法?你是否更喜欢用其他东西来管理多显示器设置上的壁纸?请在下面的评论中告诉我你的想法*。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/hydrapaper/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
14,617 | 如何在 Linux 桌面中启用 “激活 Linux” 水印通知 | https://ostechnix.com/activate-linux/ | 2022-05-20T11:22:00 | [
"激活"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14617-1.html |
>
> “激活 Windows” 水印已移植到 Linux。
>
>
>

为了阻止 Windows 操作系统的盗版行为,微软开发团队想出了一个办法:在 Windows 的角落放置一个激活水印,直到用户合法购买许可证并激活它。
如果你的电脑正在运行盗版的 Windows 副本,你应该已经注意到右下角的 “激活 Windows” 水印通知,如下图所示。

幸运的是,Linux 用户永远不会收到这样的通知。因为 GNU/Linux 是一个完全免费的开源操作系统,在 GNU 通用公共许可证(GPL)下发布。
任何人都可以运行、研究、修改和重新分发 Linux 源代码,甚至可以出售修改后的代码的副本,只要使用相同的许可即可。
Linux 是开源的,所以你真的可以用 Linux 做任何你在专有操作系统上不能做的事情。
你可以在 Linux 中做很多事情。你可以在 Linux 下构建和运行*几乎*任何东西,无论是有趣的项目还是企业级应用程序。甚至,你还可以添加 “激活 Linux” 水印。
### “激活 Linux” 是什么?
几天前,我注意到了一个叫做 “激活 Linux” 的有趣项目。它和你在未经许可的 Windows 操作系统中看到的 “激活 Windows” 通知非常相似。
“激活 Linux” 的开发者使用 C 语言中的 Xlib 和 cairo,重新创建了 Linux 版的 “激活 Windows” 通知水印。
它会在你的 Linux 桌面上显示一个水印,并通知你进入设置以激活你的 Linux 发行版!这很酷,不是吗?
### 启用 “激活 Linux” 水印
activate-linux 项目在短时间内变得非常流行。几天之内,它已经为许多流行的 Linux 发行版而打了包,例如 Arch Linux、openSUSE 和 Ubuntu。
#### Arch Linux
[AUR](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/activate-linux-git) 已经收录 activate-linux。因此,你可以使用 [Paru](https://ostechnix.com/how-to-install-paru-aur-helper-in-arch-linux/) 或 [Yay](https://ostechnix.com/yay-found-yet-another-reliable-aur-helper/) 在 Arch Linux 及其衍生版 EndeavourOS 和 Manjaro Linux 中安装 activate-linux 应用程序。
```
$ paru -S activate-linux
```
或者
```
$ yay -S activate-linux
```
#### openSUSE
[OBS](https://software.opensuse.org//download.html?project=home%3AWoMspace&package=activate-linux) 收录了 Activate-linux。
如果你正在使用 openSUSE Tumbleweed 版本,请逐条运行下面的命令来安装 activate-linux:
```
$ sudo zypper addrepo https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/home:WoMspace/openSUSE_Tumbleweed/home:WoMspace.repo
$ sudo zypper refresh
$ sudo zypper install activate-linux
```
对于 openSUSE Factory ARM 版,运行如下命令:
```
$ sudo zypper addrepo https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/home:WoMspace/openSUSE_Factory_ARM/home:WoMspace.repo
$ sudo zypper refresh
$ sudo zypper install activate-linux
```
#### Ubuntu
activate-linux 有一个适用于 Ubuntu 及其衍生版(如 Pop!\_OS)的 PPA。
```
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:edd/misc
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install activate-linux
```
安装完成后,只需在终端执行下面的命令,就可以让它运行起来:
```
$ activate-linux
```
现在,你将在桌面的角落看到 “激活 Linux” 水印通知,就像在未授权的 Windows 副本中一样。

别紧张!它是无害的。若想取消显示,你可以返回终端并按 `CTRL+C` 终止 `activate-linux` 命令。
我在 Ubuntu 22.04 GNOME 版本上测试了一下。它在 Wayland 中开箱即用。
“激活 Linux” 是我这一段时间以来遇到的一个非常有趣又无用的项目。我想这会让每个刚从 Windows 切换过来的 Linux 用户,拥有更加舒适的体验吧!
### 相关资源
>
> **[“激活 Linux” 的 GitHub 存储库](https://github.com/MrGlockenspiel/activate-linux)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://ostechnix.com/activate-linux/>
作者:[sk](https://ostechnix.com/author/sk/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
14,619 | 无法在 Ubuntu 22.04 上运行 AppImage?这是解决方法 | https://itsfoss.com/cant-run-appimage-ubuntu/ | 2022-05-21T09:39:24 | [
"AppImage"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14619-1.html | 
最近发布的 [Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 充满了新的视觉变化和功能](https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-22-04-release-features/)。
但与任何其他版本一样,它也存在一些错误和问题。
我在 Ubuntu 22.04 中遇到的令人不快的惊喜之一是 AppImage 应用。
即使拥有所有正确的权限,AppImage 应用也会拒绝在我新安装的 Ubuntu 22.04 系统中启动。
如果你遇到类似的情况,我有个好消息要告诉你。修复非常简单。
### 在 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 中运行 AppImage 应用
这里的问题是 Ubuntu 22.04 缺少 [FUSE(用户空间中的文件系统)库](https://packages.debian.org/sid/libfuse2)。FUSE 库为用户空间程序提供了一个接口,可以将虚拟文件系统导出到 Linux 内核。
这就是 [AppImage 在虚拟文件系统上的工作方式](https://itsfoss.com/use-appimage-linux/)。由于缺少这个关键库,AppImage 无法按预期工作。
现在你了解了问题的根本原因,让我们看看如何使其工作。
#### 第 1 步:安装 libfuse
在 Ubuntu 中打开终端并使用以下命令安装 FUSE 库支持:
```
sudo apt install libfuse2
```
如果你不熟悉终端,那么你需要了解以下内容。它会要求你输入 `sudo` 密码。实际上,那是你的帐户密码。 **当你输入密码时,屏幕上不会显示任何内容**。这是设计使然。只需继续输入密码并输入。

#### 第 2 步:确保 AppImage 文件具有正确的文件权限
这个不用说了。你需要对下载的应用的 AppImage 文件具有“执行”权限。
转到你已下载所需应用的 AppImage 文件的文件夹。右键单击并选择<ruby> 属性 <rt> Properties </rt></ruby>。
现在转到<ruby> 权限 <rt> Permissions </rt></ruby>选项卡并选中“<ruby> 允许将文件作为程序执行 <rt> Allow executing file as program </rt></ruby>”选项。

设置完成后就好了。现在只需双击该文件,它就会按预期运行应用。
获取 libfuse 的这个小步骤已经在我的 [安装 Ubuntu 22.04 后推荐要做的事情列表](https://itsfoss.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-22-04/) 上了。
### 进一步的故障排除提示
你的 AppImage 文件仍未运行?你下载的 AppImage 可能会出现一些其他问题,使其无法运行。
检查它的一种方法是下载一个已知的应用,如 [Balena Etcher](https://www.balena.io/etcher/) 并查看其 AppImage 文件是否有效。如果这个没问题,那么当你下载的另一个应用的 AppImage 文件无法工作,你可以通过从终端运行 AppImage 文件并分析它显示的错误来深入挖掘。
### 对你有用吗?
继续尝试。如果有效,请给我写个“感谢”。如果仍然没有解决,请在评论部分中提及详细信息,我会尽力帮助你。
(该图片由 [Ryan McGuire](https://pixabay.com/zh/users/ryanmcguire-123690/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=362150) 在 [Pixabay](https://pixabay.com/zh/?utm_source=link-attribution&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=image&utm_content=362150) 上发布)
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/cant-run-appimage-ubuntu/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

There are several applications that are made available for Linux in AppImage format.
However, the recent releases of Ubuntu do not provide the necessary support by default for AppImage applications.
Even with all the right permissions, AppImage applications just refused to launch in my newly installed Ubuntu 24.04 system. The same was the case for Ubuntu 22.04.
If you face a similar situation, I have good news for you. The fix is quite simple.
`libfuse2`
on Ubuntu 22.04. On Ubuntu 24.04, the same package is named `libfuse2t64`
.## Running AppImage applications in Ubuntu 22.04 and later versions
The problem here is that Ubuntu 22.04 is missing the [FUSE (Filesystem in Userspace) library](https://packages.debian.org/sid/libfuse2). This FUSE library provides an interface for userspace programs to export a virtual filesystem to the Linux kernel.
That’s [how the AppImage works](https://itsfoss.com/use-appimage-linux/); on a virtual filesystem. Since this crucial library is missing, AppImage doesn’t work as expected.
Now that you understand the issue's root cause, let’s see how to make it work.
### Step 1: Install libfuse2
First, [check the Ubuntu version you are running](https://itsfoss.com/how-to-know-ubuntu-unity-version/) with the following command in the terminal.
`lsb_release -a`
Observer the output:
```
abhishek@itsfoss:~$ lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 24.04 LTS
Release: 24.04
Codename: noble
```
**If it is Ubuntu 24.04**, you need to run the following command install the FUSE library:
`sudo apt install libfuse2t64`
**If it is Ubuntu 22.04**, you should use this command:
`sudo apt install libfuse2`
It's the same software library, just the package names are different in the two versions.
If you are [new to the Linux terminal](https://itsfoss.com/basic-terminal-tips-ubuntu/), here’s what you need to know. It will ask you to enter the sudo password. That’s your account password, actually. And ** when you type the password, nothing is displayed on the screen**. That’s by design. Just keep on typing the password and enter.
### Step 2: Make sure AppImage files have correct file permissions
This one goes without saying. You need to have ‘execute’ permission on the downloaded AppImage file of an application.
If you directly try to run an AppImage with a double click, it shows this error:
Could not display appimage.
There is no application installed for “AppImage application bundle” files. Do you want to search for an application to open this file?
Go to the folder where you have downloaded the desired application’s AppImage file. **Right-click** on it and **select Properties**.
Now go to the **Permissions tab** and check the “**Allow executing file as program**” option.
With that set, you are good to go. Double-click the file now, and it should run the application as intended.
This little step of getting libfuse is on my [list of recommended things to do after installing Ubuntu 22.04](https://itsfoss.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-22-04/).
I made this video for the AppImage issue on Ubuntu 24.04.
## Further troubleshooting tips
Your AppImage file is still not running? The AppImage you have downloaded may have some other issues that stop it from running.
One way to check it would be to download a known application like [Balena Etcher](https://itsfoss.com/install-etcher-linux/) and see if its AppImage file works. If this one works, the AppImage file you downloaded for the other application is unsuitable.
You can dig deeper by running the AppImage file from the terminal and analyzing its error.
In the terminal, go to the location where the downloaded AppImage is located and run it the same way you execute a shell script.
`./application.appimage`
Here's an example:
```
abhishek@itsfoss:~/Downloads$ ./compress-pdf-v0.1-x86_64\ \(1\).AppImage
/tmp/.mount_compreWhr2rq/check: line 3: xterm: command not found
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "compress-pdf_Qt.py", line 5, in <module>
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'PyQt5'
```
As you can see in the above example, the AppImage didn't run successfully and it showed an error.
What to do now? You can look for alternative packaging formats for the application and inform the developer about the issue you encountered. That's the sensible step here.
## Did it work for you?
If you want to learn more about AppImages, I highly recommend reading our [in-depth guide on AppImage](https://itsfoss.com/use-appimage-linux/). From best practices to desktop integration, the article discusses it all.
[How to Use AppImage in Linux [Complete Guide]What is AppImage? How to run it? How does it work? Here’s the complete guide about using AppImage in Linux.](https://itsfoss.com/use-appimage-linux/)

💬 *Go ahead and try it. If it works, drop me a thank you note. If it still doesn’t, mention the details in the comment sections and I’ll try to help you.* |
14,620 | 用 XML 和 Java 构建树莓派打印机的用户界面 | https://opensource.com/article/21/3/raspberry-pi-totalcross | 2022-05-21T11:07:14 | [
"嵌入式",
"用户界面"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14620-1.html |
>
> 使用 TotalCross 来快速构建嵌入式系统程序的用户界面。
>
>
>

从头开始构建 GUI 是一个非常耗时的过程,以硬编码的方式处理所有的位置和对齐对于一些程序员来说确实很困难。所以在本文中,我将演示如何使用 XML 加快这一过程。
本项目使用 [TotalCross](https://opensource.com/article/20/7/totalcross-cross-platform-development) 作为目标框架。TotalCross 是一个开源的跨平台软件开发工具包(SDK),旨在更快地为嵌入式设备创建 GUI。TotalCross 无需在设备上运行 Java 即可提供 Java 的开发优势,因为它使用自己的字节码和虚拟机(<ruby> TC 字节码 <rt> TC bytecode </rt></ruby> 和 TCVM)来增强性能。
我还使用了 Knowcode-XML,这是一个用于 TotalCross 框架的开源 XML 解析器,它可以将 XML 文件转换为 TotalCross 组件。
### 项目需求
要重现此项目,你需要:
* [KnowCode-XML](https://github.com/TotalCross/knowcode-xml)
* [VSCode](https://code.visualstudio.com/) 或 [VSCodium](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/open-source-alternatives-vs-code)
* [一个 Android 开发环境](https://developer.android.com/studio)
* [用于 VSCode 的 TotalCross 插件](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=totalcross.vscode-totalcross)
* 适用于你的开发平台([Linux](https://opensource.com/article/19/11/install-java-linux)、[Mac](https://opensource.com/article/20/7/install-java-mac) 或 [Windows](http://adoptopenjdk.net))的 Java,需要 Java 11(或更高版本)
* [Git](https://opensource.com/life/16/7/stumbling-git)
### 制作嵌入式应用程序
该应用程序由一个具有扫描、打印和复印等基本打印功能的嵌入式 GUI 组成。

构建这个 GUI 需要几个步骤,包括使用 Android-XML 生成 GUI,然后使用 Knowcode-XML 解析器在 TotalCross 框架上运行它。
#### 1、生成 Android XML
要创建 XML 文件,首先构建一个简单的 Android 屏幕,然后对其进行自定义。如果你不知道如何编写 Android-XML,或者你只是想简单尝试一下,你可以从这个 [GitHub 项目](https://github.com/TotalCross/embedded-samples/tree/main/printer-application/src/main/resources/layout) 中下载这个应用程序的 XML。该项目还包含渲染 GUI 要用到的图片。
#### 2、调整 XML
生成 XML 文件后,你需要进行一些微调以确保所有内容都已经对齐、比例正确并且图像的路径正确。
将 XML 布局添加到 `Layouts` 文件夹,将所有资源添加到 `Drawable` 文件夹。然后你就可以开始自定义 XML 了。
例如,如果想要更改 XML 对象的背景,可以更改 `android:background` 属性:
```
android:background="@drawable/scan"
```
你也可以使用 `tools:layout_editor_absoluteX` 和 `tools:layout_editor_absoluteY` 更改对象的位置:
```
tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="830dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="511dp"
```
或者使用 `android:layout_width` 和 `android:layout_height` 更改对象的大小:
```
android:layout_width="70dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
```
如果要在对象上放置文本,可以使用 `android:textSize`、`android:text`、`android:textStyle` 和 `android:textColor`:
```
android:textStyle="bold"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:text="2:45PM"
```
下面是一个完整的 XML 对象的示例:
```
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/ImageButton"
android:layout_width="70dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="830dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="511dp"
android:background="@drawable/home_config" />
```
#### 3、在 TotalCross 上运行 GUI
完成所有 XML 调整后,就可以在 TotalCross 上运行它了。在 TotalCross 扩展(LCTT 译注:在 VSCode 里面)上创建一个新项目,并将 `XML` 和 `Drawable` 文件夹添加到 `Main` 文件夹里。如果你仍然不确定如何创建 TotalCross 项目,请参阅我们的 [入门指南](https://totalcross.com/get-started/?utm_source=opensource&utm_medium=article&utm_campaign=printer)。
配置好环境后,使用 `totalcross.knowcode.parse.XmlContainerFactory` 和 `import totalcross.knowcode.parse.XmlContainerLayout` 在 TotalCross 框架上使用 XML GUI。 你可以在其 [GitHub 页面](https://github.com/TotalCross/knowcode-xml) 上找到更多关于使用 KnowCode-XML 的信息。
#### 4、添加过渡效果
这个项目的平滑过渡效果是由 `SlidingNavigator` 类创建的,它使用 TotalCross 的 `ControlAnimation` 类从一个屏幕滑到另一个屏幕。
在 `XMLpresenter` 类上调用 `SlidingNavigator`:
```
new SlidingNavigator(this).present(HomePresenter.class);
```
在 `SlidingNavigator` 类上实现 `present` 函数:
```
public void present(Class<? extends XMLPresenter> presenterClass)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
final XMLPresenter presenter = cache.containsKey(presenterClass) ? cache.get(presenterClass)
: presenterClass.newInstance();
if (!cache.containsKey(presenterClass)) {
cache.put(presenterClass, presenter);
}
if (presenters.isEmpty()) {
window.add(presenter.content, LEFT, TOP, FILL, FILL);
} else {
XMLPresenter previous = presenters.lastElement();
window.add(presenter.content, AFTER, TOP, SCREENSIZE, SCREENSIZE, previous.content);
```
使用动画控件中的 `PathAnimation` 来创建从一个屏幕到另一个屏幕的滑动动画:
```
PathAnimation.create(previous.content, -Settings.screenWidth, 0, new ControlAnimation.AnimationFinished() {
@Override
public void onAnimationFinished(ControlAnimation anim) {
window.remove(previous.content);
}
}, 1000).with(PathAnimation.create(presenter.content, 0, 0, new ControlAnimation.AnimationFinished() {
@Override
public void onAnimation Finished(Control Animation anim) {
presenter.content.setRect(LEFT, TOP, FILL, FILL);
}
}, 1000)).start();
}
presenter.setNavigator(this);
presenters.push(presenter);
presenter.bind2();
if (presenter.isFirstPresent) {
presenter.onPresent();
presenter.isFirstPresent = false;
}
```
#### 5、加载环形进度条
打印机应用程序的另一个不错的功能是显示进度的加载屏幕动画。它包括文本和旋转动画。

通过添加定时器和定时器监听器来更新进度标签,然后调用函数 `spinner.start()` 来实现此功能。所有的动画都是由 TotalCross 和 KnowCode 自动生成的:
```
public void startSpinner() {
time = content.addTimer(500);
content.addTimerListener((e) -> {
try {
progress(); // Updates the Label
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
});
Spinner spinner = (Spinner) ((XmlContainerLayout) content).getControlByID("@+id/spinner");
spinner.start();
}
```
这里的环形进度条被实例化为对 XML 文件中描述的 `XmlContainerLayout` `spinner` 的引用:
```
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/spinner"
android:layout_width="362dp"
android:layout_height="358dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="296dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="198dp"
android:indeterminateTint="#2B05C7"
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyle" />
```
#### 6、构建应用程序
是时候构建应用程序了。你可以在 `pom.xml` 中查看和更改<ruby> 目标系统 <rt> target systems </rt></ruby>。 请确保 `Linux Arm` 目标可用。
如果你使用的是 VSCode,请按下键盘上的 `F1` 键,选择 `TotalCross: Package` 并等待完成。 然后就可以在 `Target` 文件夹中看到安装文件了。
#### 7、在树莓派上部署和运行应用程序
要使用 SSH 协议在 [树莓派](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-4-model-b/) 上部署应用程序,请按键盘上的 `F1`。选择 `TotalCross: Deploy&Run` 并提供有关你的 SSH 连接的信息,如:用户名、IP地址、密码和应用程序路径。





### 总结
KnowCode 让使用 Java 创建和管理应用程序屏幕变得更加容易。Knowcode-XML 将你的 XML 转换为 TotalCross GUI 界面,然后生成二进制文件以在你的树莓派上运行。
将 KnowCode 技术与 TotalCross 相结合,使你能够更快地创建嵌入式应用程序。 你可以访问我们在 GitHub 上的 [嵌入式示例](https://github.com/TotalCross/embedded-samples) 并编辑你自己的应用程序,了解你还可以做什么。
如果你有问题、需要帮助,或者只是想与其他嵌入式 GUI 开发人员互动,请随时加入我们的 [Telegram](https://t.me/totalcrosscommunity) 小组,讨论任何框架上的嵌入式应用程序。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/3/raspberry-pi-totalcross>
作者:[Edson Holanda Teixeira Junior](https://opensource.com/users/edsonhtj) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[CoWave-Fall](https://github.com/CoWave-Fall) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Creating a GUI from scratch is a very time consuming process, dealing with all the positions and alignments in hard code can be really tough for some programmers. In this article, I demonstrate how to speed up this process using XML.
This project uses [TotalCross](https://opensource.com/article/20/7/totalcross-cross-platform-development) as the target framework. TotalCross is an open source, cross-platform software development kit (SDK) developed to create GUIs for embedded devices faster. TotalCross provides Java's development benefits without needing to run Java on a device because it uses its own bytecode and virtual machine (TC bytecode and TCVM) for performance enhancement.
I also use Knowcode-XML, an open source XML parser for the TotalCross framework, which converts XML files into TotalCross components.
## Project requirements
To reproduce this project, you need:
[KnowCode-XML](https://github.com/TotalCross/knowcode-xml)[VSCode](https://code.visualstudio.com/)[or VSCodium](https://opensource.com/article/20/6/open-source-alternatives-vs-code)[An Android development environment](https://developer.android.com/studio)[TotalCross plugin for VSCode](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=totalcross.vscode-totalcross)- Java 11 or greater for your development platform (
[Linux](https://opensource.com/article/19/11/install-java-linux),[Mac](https://opensource.com/article/20/7/install-java-mac), or[Windows](http://adoptopenjdk.net)) [Git](https://opensource.com/life/16/7/stumbling-git)
## Building the embedded application
This application consists of an embedded GUI with basic print functionalities, such as scan, print, and copy.

(Edson Holanda Teixeira Jr, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Several steps are required to create this GUI, including generating the GUI with Android-XML and then using the Knowcode-XML parser to run it on the TotalCross Framework.
### 1. Generate the Android XML
For creating the XML file, first create a simple Android screen, and then customize it. If you don't know how to write Android-XM, or you just want a headstart, you can download this application’s XML from this [ GitHub project](https://github.com/TotalCross/embedded-samples/tree/main/printer-application/src/main/resources/layout). This project also contains the images you need to render the GUI.
### 2. Adjust the XML
After generating the XML files, you need to make some fine adjustments to make sure everything is aligned, with the right proportions, and has the correct path to the images.
Add the XML layouts to the **Layouts** folder and all the assets to the **Drawable** folder. Then you can start to customize the XML.
For example, if you want to change an XML object's background, change the `android:background`
attribute:
`android:background="@drawable/scan"`
You can change the object's position with `tools:layout_editor_absoluteX`
and `tools:layout_editor_absoluteY`
:
```
tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="830dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="511dp"
```
Change the object's size with `android:layout_width`
and `android:layout_height`
:
```
android:layout_width="70dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
```
If you want to put text on an object, you can use `android:textSize`
, `android:text`
, `android:textStyle`
, and `android:textColor`
:
```
android:textStyle="bold"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:text="2:45PM"
```
Here is an example of a complete XML object:
```
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/ImageButton"
android:layout_width="70dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="830dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="511dp"
android:background="@drawable/home_config" />
```
### 3. Run the GUI on TotalCross
After you make all the XML adjustments, it's time to run it on TotalCross. Create a new project on the TotalCross extension and add the **XML** and **Drawable** folders to the **Main** folder. If you're not sure how to create a TotalCross project, see our [get started guide](https://totalcross.com/get-started/?utm_source=opensource&utm_medium=article&utm_campaign=printer).
After configuring the environment, use `totalcross.knowcode.parse.XmlContainerFactory`
and `import totalcross.knowcode.parse.XmlContainerLayout`
to use the XML GUI on the TotalCross framework. You can find more information about using KnowCode-XML on its [GitHub page](https://github.com/TotalCross/knowcode-xml).
### 4. Add transitions
This project's smooth transition effect is created by the `SlidingNavigator`
class, which uses TotalCross' `ControlAnimation`
class to slide from one screen to the other.
Call `SlidingNavigator`
on the `XMLpresenter`
class:
`new SlidingNavigator(this).present(HomePresenter.class);`
Implement the `present`
function on the `SlidingNavigator`
class:
```
public void present(Class<? extends XMLPresenter> presenterClass)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
final XMLPresenter presenter = cache.containsKey(presenterClass) ? cache.get(presenterClass)
: presenterClass.newInstance();
if (!cache.containsKey(presenterClass)) {
cache.put(presenterClass, presenter);
}
if (presenters.isEmpty()) {
window.add(presenter.content, LEFT, TOP, FILL, FILL);
} else {
XMLPresenter previous = presenters.lastElement();
window.add(presenter.content, AFTER, TOP, SCREENSIZE, SCREENSIZE, previous.content);
```
`PathAnimation`
in animation control creates the sliding animation from one screen to another:
```
PathAnimation.create(previous.content, -Settings.screenWidth, 0, new ControlAnimation.AnimationFinished() {
@Override
public void onAnimationFinished(ControlAnimation anim) {
window.remove(previous.content);
}
}, 1000).with(PathAnimation.create(presenter.content, 0, 0, new ControlAnimation.AnimationFinished() {
@Override
public void onAnimation Finished(Control Animation anim) {
presenter.content.setRect(LEFT, TOP, FILL, FILL);
}
}, 1000)).start();
}
presenter.setNavigator(this);
presenters.push(presenter);
presenter.bind2();
if (presenter.isFirstPresent) {
presenter.onPresent();
presenter.isFirstPresent = false;
}
```
### 5. Load spinners
Another nice feature in the printer application is the loading screen animation that shows progress. It includes text and a spinning animation.
(Edson Holanda Teixeira Jr, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Implement this feature by adding a timer and a timer listener to update the progress label, then call the function `spinner.start()`
. All of the animations are auto-generated by TotalCross and KnowCode:
```
public void startSpinner() {
time = content.addTimer(500);
content.addTimerListener((e) -> {
try {
progress(); // Updates the Label
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
});
Spinner spinner = (Spinner) ((XmlContainerLayout) content).getControlByID("@+id/spinner");
spinner.start();
}
```
The spinner is instantiated as a reference to the `XmlContainerLayout`
spinner described in the XML file:
```
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/spinner"
android:layout_width="362dp"
android:layout_height="358dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="296dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="198dp"
android:indeterminateTint="#2B05C7"
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyle" />
```
### 6. Build the application
It's time to build the application. You can see and change the target systems in `pom.xml`
. Make sure the **Linux Arm** target is available.
If you are using VSCode, press **F1** on the keyboard, select **TotalCross: Package** and wait for the package to finish. Then you can see the installation files in the **Target** folder.
### 7. Deploy and run the application on Raspberry Pi
To deploy the application on a [Raspberry Pi 4](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-4-model-b/) with the SSH protocol, press **F1** on the keyboard. Select **TotalCross: Deploy&Run** and provide information about your SSH connection: User, IP, Password, and Application Path.
(Edson Holanda Teixeira Jr, CC BY-SA 4.0)
(Edson Holanda Teixeira Jr, CC BY-SA 4.0)
(Edson Holanda Teixeira Jr, CC BY-SA 4.0)
(Edson Holanda Teixeira Jr, CC BY-SA 4.0)

(Edson Holanda Teixeira Jr, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Here's what the application looks like running on the machine.
## What's next?
KnowCode makes it easier to create and manage your application screens using Java. Knowcode-XML translates your XML into a TotalCross GUI that in turn generates the binary to run on your Raspberry Pi.
Combining KnowCode technology with TotalCross enables you to create embedded applications faster. Find out what else you can do by accessing our [embedded samples](https://github.com/TotalCross/embedded-samples) on GitHub and editing your own application.
If you have questions, need help, or just want to interact with other embedded GUI developers, feel free to join our [Telegram](https://t.me/totalcrosscommunity) group to discuss embedded applications on any framework.
## 1 Comment |
14,621 | 在 Go 中生成随机的安全密码 | https://opensource.com/article/18/5/creating-random-secure-passwords-go | 2022-05-21T15:25:55 | [
"Go",
"随机数",
"密码"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14621-1.html |
>
> Go 的随机数生成器是生成难以猜测的密码的好方法。
>
>
>

你可以使用 [Go 编程语言](https://golang.org/) 提供的随机数生成器来生成由 ASCII 字符组成的难以猜测的密码。尽管本文中提供的代码很容易阅读,但是你仍需要了解 Go 的基础知识,才能更好地理解它。如果你是对 Go 还不熟悉,请阅读 [Go 语言之旅](https://tour.golang.org/welcome/1) 来了解更多信息,然后返回此处。
在介绍实用程序和它的代码之前,让我们先来看看这个 ASCII 表的子集,它可以在 `man ascii` 命令的输出中找到:
```
30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120
---------------------------------
0: ( 2 < F P Z d n x
1: ) 3 = G Q [ e o y
2: * 4 > H R \ f p z
3: ! + 5 ? I S ] g q {
4: " , 6 @ J T ^ h r |
5: # - 7 A K U _ i s }
6: $ . 8 B L V ` j t ~
7: % / 9 C M W a k u DEL
8: & 0 : D N X b l v
9: ' 1 ; E O Y c m w
```
在所有 ASCII 字符中,可打印字符的十进制值范围为 33 到 126,其他的 ASCII 值都不适合用于密码。因此,本文介绍的实用程序将生成该范围内的 ASCII 字符。
### 生成随机整数
第一个实用程序名为 `random.go`,它生成指定数量的随机整数,这些整数位于给定范围内。`random.go` 最重要的部分是这个函数:
```
func random(min, max int) int {
return rand.Intn(max-min) + min
}
```
此函数使用了 `rand.Intn()` 函数来生成一个属于给定范围的随机整数。请注意,`rand.Intn()` 返回一个属于 `[0,n)` 的非负随机整数。如果它的参数是一个负数,这个函数将会抛出异常,异常消息是:`panic: invalid argument to Intn`。你可以在 [math/rand 文档](https://golang.org/pkg/math/rand/) 中找到 `math/rand` 包的使用说明。
`random.go` 实用程序接受三个命令行参数:生成的整数的最小值、最大值和个数。
编译和执行 `random.go` 会产生这样的输出:
```
$ go build random.go
$ ./random
Usage: ./random MIX MAX TOTAL
$ ./random 1 3 10
2 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 2 1
```
如果你希望在 Go 中生成更安全的随机数,请使用 Go 库中的 `crypto/rand` 包。
### 生成随机密码
第二个实用程序 `randomPass.go` 用于生成随机密码。`randomPass.go` 使用 `random()` 函数来生成随机整数,它们随后被以下 Go 代码转换为 ASCII 字符:
```
for {
myRand := random(MIN, MAX)
newChar := string(startChar[0] + byte(myRand))
fmt.Print(newChar)
if i == LENGTH {
break
}
i++
}
```
`MIN` 的值为 `0`,`MAX` 的值为 `94`,而 `startChar` 的值为 `!`,它是 ASCII 表中第一个可打印的字符(十进制 ASCII 码为 `33`)。因此,所有生成的 ASCII 字符都位于 `!` 和 `~` 之间,后者的十进制 ASCII 码为 `126`。
因此,生成的每个随机数都大于 `MIN`,小于 `MAX`,并转换为 ASCII 字符。该过程继续进行,直到生成的密码达到指定的长度。
`randomPass.go` 实用程序接受单个(可选)命令行参数,以定义生成密码的长度,默认值为 8,这是一个非常常见的密码长度。执行 `randomPass.go` 会得到类似下面的输出:
```
$ go run randomPass.go 1
Z
$ go run randomPass.go 10
#Cw^a#IwkT
$ go run randomPass.go
Using default values!
[PP8@'Ci
```
最后一个细节:不要忘记调用 `rand.Seed()`,并提供一个<ruby> 种子 <rt> seed </rt></ruby>值,以初始化随机数生成器。如果你始终使用相同的种子值,随机数生成器将生成相同的随机整数序列。

你可以在 [GitHub](https://github.com/mactsouk/opensource.com) 找到 `random.go` 和 `randomPass.go` 的源码。你也可以直接在 [play.golang.org](https://play.golang.org/) 上执行它们。
我希望这篇文章对你有所帮助。如有任何问题,请在下方发表评论或在 [Twitter](https://twitter.com/mactsouk) 上与我联系。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/18/5/creating-random-secure-passwords-go>
作者:[Mihalis Tsoukalos](https://opensource.com/users/mtsouk) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | You can use the random number generator provided by the [Go programming language](https://golang.org/) to generate difficult-to-guess passwords comprised of ASCII characters. Although the code presented in this article is easy to read, it's best if you already know the basics of Go to understand it. If you're new to the programming language, take the [Tour of Go](https://tour.golang.org/welcome/1) to learn more, then come back here.
Before we get into the utilities and the code, take a look at this subset of the ASCII table as found in the output of the `man ascii`
command:
```
30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120
---------------------------------
0: ( 2 < F P Z d n x
1: ) 3 = G Q [ e o y
2: * 4 > H R \ f p z
3: ! + 5 ? I S ] g q {
4: " , 6 @ J T ^ h r |
5: # - 7 A K U _ i s }
6: $ . 8 B L V ` j t ~
7: % / 9 C M W a k u DEL
8: & 0 : D N X b l v
9: ' 1 ; E O Y c m w
```
The printable ASCII characters' decimal values range from 33 through 126; no other ASCII values are suitable for inclusion in passwords. Therefore, the utilities presented in this article will produce ASCII characters in that range.
## Creating random integers
The first utility is named `random.go`
, and it generates a specified number of random integers that reside in a given range. The most important part of `random.go`
is this function:
```
func random(min, max int) int {
return rand.Intn(max-min) + min
}
```
This function generates random integers that belong to a given range using the `rand.Intn()`
Go function. Note that `rand.Intn()`
returns a non-negative random number that belongs to `[0,n)`
; the function will panic if its argument is a negative number. The panic message will be `panic: invalid argument to Intn`
. You can find the documentation of the `math/rand`
package at [math/rand documentation](https://golang.org/pkg/math/rand/).
The `random.go`
utility accepts three command-line parameters: the minimum value of the generated integers, the maximum value, and the number of integers that will be generated.
Compiling and executing `random.go`
will create this kind of output:
```
$ go build random.go
$ ./random
Usage: ./random MIX MAX TOTAL
$ ./random 1 3 10
2 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 2 1
```
If you wish to generate more secure random numbers in Go, use the `crypto/rand`
package of the Go library.
## Creating random passwords
The second utility, `randomPass.go`
, generates the random passwords. `randomPass.go`
uses the `random()`
function to generate random numbers that will convert to ASCII characters using the following Go code:
```
for {
myRand := random(MIN, MAX)
newChar := string(startChar[0] + byte(myRand))
fmt.Print(newChar)
if i == LENGTH {
break
}
i++
}
```
The value of MIN is **0** and the value of MAX is **94**, whereas the value of `startChar`
is **!**, which is the first printable character in the ASCII table (with the decimal ASCII code of **33**). Therefore, all ASCII characters that will be generated are located after **!** and before the **~** character, which has a decimal ASCII code of **126**.
So, each random number that is generated is bigger than MIN, smaller than MAX, and converted into an ASCII character. The process keeps going until the generated password has the desired length.
The `randomPass.go`
utility accepts a single (optional) command-line parameter that defines the length of the generated password. Its default value is eight, which is a pretty common password length. Executing `randomPass.go`
will generate the following kind of output:
```
$ go run randomPass.go 1
Z
$ go run randomPass.go 10
#Cw^a#IwkT
$ go run randomPass.go
Using default values!
[PP8@'Ci
```
One last detail: Don't forget to call `rand.Seed()`
with a seed value in order to initialize the random number generator. If you use the same seed value all the time, the random number generator will create the same sequence of random integers.
You can find both `random.go`
and `randomPass.go`
at [GitHub](https://github.com/mactsouk/opensource.com). You can also execute it at [play.golang.org](https://play.golang.org/).
I hope this has been helpful. If you have any questions, please leave a comment below or reach out to me on [Twitter](https://twitter.com/mactsouk).
## 6 Comments |
14,623 | 在 Go 中实现一个支持并发的 TCP 服务端 | https://opensource.com/article/18/5/building-concurrent-tcp-server-go | 2022-05-22T11:55:00 | [
"Go",
"并发"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14623-1.html | 
>
> 仅用大约 65 行代码,开发一个用于生成随机数、支持并发的 TCP 服务端。
>
>
>
TCP 和 UDP 服务端随处可见,它们基于 TCP/IP 协议栈,通过网络为客户端提供服务。在这篇文章中,我将介绍如何使用 [Go 语言](https://golang.org/) 开发一个用于返回随机数、支持并发的 TCP 服务端。对于每一个来自 TCP 客户端的连接,它都会启动一个新的 goroutine(轻量级线程)来处理相应的请求。
你可以在 GitHub 上找到本项目的源码:[concTcp.go](https://github.com/mactsouk/opensource.com)。
### 处理 TCP 连接
这个程序的主要逻辑在 `handleConnection()` 函数中,具体实现如下:
```
func handleConnection(c net.Conn) {
fmt.Printf("Serving %s\n", c.RemoteAddr().String())
for {
netData, err := bufio.NewReader(c).ReadString('\n')
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
temp := strings.TrimSpace(string(netData))
if temp == "STOP" {
break
}
result := strconv.Itoa(random()) + "\n"
c.Write([]byte(string(result)))
}
c.Close()
}
```
如果 TCP 客户端发送了一个 “STOP” 字符串,为它提供服务的 goroutine 就会终止;否则,TCP 服务端就会返回一个随机数给它。只要客户端不主动终止,服务端就会一直提供服务,这是由 `for` 循环保证的。具体来说,`for` 循环中的代码使用了 `bufio.NewReader(c).ReadString('\n')` 来逐行读取客户端发来的数据,并使用 `c.Write([]byte(string(result)))` 来返回数据(生成的随机数)。你可以在 Go 的 net 标准包 [文档](https://golang.org/pkg/net/) 中了解更多。
### 支持并发
在 `main()` 函数的实现部分,每当 TCP 服务端收到 TCP 客户端的连接请求,它都会启动一个新的 goroutine 来为这个请求提供服务。
```
func main() {
arguments := os.Args
if len(arguments) == 1 {
fmt.Println("Please provide a port number!")
return
}
PORT := ":" + arguments[1]
l, err := net.Listen("tcp4", PORT)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer l.Close()
rand.Seed(time.Now().Unix())
for {
c, err := l.Accept()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
go handleConnection(c)
}
}
```
首先,`main()` 确保程序至少有一个命令行参数。注意,现有代码并没有检查这个参数是否为有效的 TCP 端口号。不过,如果它是一个无效的 TCP 端口号,`net.Listen()` 就会调用失败,并返回一个错误信息,类似下面这样:
```
$ go run concTCP.go 12a
listen tcp4: lookup tcp4/12a: nodename nor servname provided, or not known
$ go run concTCP.go -10
listen tcp4: address -10: invalid port
```
`net.Listen()` 函数用于告诉 Go 接受网络连接,因而承担了服务端的角色。它的返回值类型是 `net.Conn`,后者实现了 `io.Reader` 和 `io.Writer` 接口。此外,`main()` 函数中还调用了 `rand.Seed()` 函数,用于初始化随机数生成器。最后,`for` 循环允许程序一直使用 `Accept()` 函数来接受 TCP 客户端的连接请求,并以 goroutine 的方式来运行 `handleConnection(c)` 函数,处理客户端的后续请求。
### net.Listen() 的第一个参数
`net.Listen()` 函数的第一个参数定义了使用的网络类型,而第二个参数定义了服务端监听的地址和端口号。第一个参数的有效值为 `tcp`、`tcp4`、`tcp6`、`udp`、`udp4`、`udp6`、`ip`、`ip4`、`ip6`、`Unix`(Unix 套接字)、`Unixgram` 和 `Unixpacket`,其中:`tcp4`、`udp4` 和 `ip4` 只接受 IPv4 地址,而 `tcp6`、`udp6` 和 `ip6` 只接受 IPv6 地址。
### 服务端并发测试
`concTCP.go` 需要一个命令行参数,来指定监听的端口号。当它开始服务 TCP 客户端时,你会得到类似下面的输出:
```
$ go run concTCP.go 8001
Serving 127.0.0.1:62554
Serving 127.0.0.1:62556
```
`netstat` 的输出可以确认 `congTCP.go` 正在为多个 TCP 客户端提供服务,并且仍在继续监听建立连接的请求:
```
$ netstat -anp TCP | grep 8001
tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1.8001 127.0.0.1.62556 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1.62556 127.0.0.1.8001 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1.8001 127.0.0.1.62554 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1.62554 127.0.0.1.8001 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 *.8001 *.* LISTEN
```
在上面输出中,最后一行显示了有一个进程正在监听 8001 端口,这意味着你可以继续连接 TCP 的 8001 端口。第一行和第二行显示了有一个已建立的 TCP 网络连接,它占用了 8001 和 62556 端口。相似地,第三行和第四行显示了有另一个已建立的 TCP 连接,它占用了 8001 和 62554 端口。
下面这张图片显示了 `concTCP.go` 在服务多个 TCP 客户端时的输出:

类似地,下面这张图片显示了两个 TCP 客户端的输出(使用了 `nc` 工具):

你可以在 [维基百科](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Netcat) 上找到更多关于 `nc`(即 `netcat`)的信息。
### 总结
现在,你学会了如何用大约 65 行 Go 代码来开发一个生成随机数、支持并发的 TCP 服务端,这真是太棒了!如果你想要让你的 TCP 服务端执行别的任务,只需要修改 `handleConnection()` 函数即可。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/18/5/building-concurrent-tcp-server-go>
作者:[Mihalis Tsoukalos](https://opensource.com/users/mtsouk) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *This article is part of a Go series by Mihalis Tsoukalos. Read part 1: Creating random, secure passwords in Go.*
TCP and UDP servers are everywhere serving network clients over TCP/IP networks. In this article, I will explain how to develop a concurrent TCP server, in the [Go programming language](https://golang.org/), that returns random numbers. For each incoming connection from a TCP client, the TCP server will start a new goroutine to handle that request.
You can find this project, [concTCP.go](https://github.com/mactsouk/opensource.com), on GitHub.
## Handling TCP connections
The logic of the program can be found in the Go code of the `handleConnection()`
function, which is implemented as follows:
```
func handleConnection(c net.Conn) {
fmt.Printf("Serving %s\n", c.RemoteAddr().String())
for {
netData, err := bufio.NewReader(c).ReadString('\n')
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
temp := strings.TrimSpace(string(netData))
if temp == "STOP" {
break
}
result := strconv.Itoa(random()) + "\n"
c.Write([]byte(string(result)))
}
c.Close()
}
```
If the TCP client sends the "STOP" string, then the goroutine that serves that particular TCP client will terminate; otherwise, the TCP server will send a random number back to the TCP client. The `for`
loop makes sure that the TCP client will be served for as long as the TCP client desires. The Go code in the `for`
loop reads the data from the TCP client, line by line, using `bufio.NewReader(c).ReadString('\n')`
and sends back data using `c.Write([]byte(string(result)))`
. (You may find the net standard Go package [documentation](https://golang.org/pkg/net/) helpful.)
## Being concurrent
The implementation of the `main()`
function tells the TCP server to start a new goroutine each time it has to serve a TCP client:
```
func main() {
arguments := os.Args
if len(arguments) == 1 {
fmt.Println("Please provide a port number!")
return
}
PORT := ":" + arguments[1]
l, err := net.Listen("tcp4", PORT)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer l.Close()
rand.Seed(time.Now().Unix())
for {
c, err := l.Accept()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
go handleConnection(c)
}
}
```
First, `main()`
makes sure that the program has at least one command line argument. Notice that the existing code does not check whether the given command line argument is a valid TCP port number or not. However, if the given value is not a valid TCP port number, the call to `net.Listen()`
will fail with an error message similar to the following:
```
$ go run concTCP.go 12a
listen tcp4: lookup tcp4/12a: nodename nor servname provided, or not known
$ go run concTCP.go -10
listen tcp4: address -10: invalid port
```
The `net.Listen()`
call is used for telling a Go program to accept network connections and thus act as a server. The return value of `net.Listen()`
is of the `net.Conn`
type, which implements the `io.Reader`
and `io.Writer`
interfaces. The `main()`
function also calls the `rand.Seed()`
function in order to initialize the random number generator. Finally, the `for`
loop allows the program to keep accepting new TCP clients using `Accept()`
that will be handled by instances of the `handleConnection()`
function, which are executed as goroutines.
## The first parameter of net.Listen()
The first parameter of the `net.Listen()`
function defines the type of network that will be used, while the second parameter defines the server address as well as the port number the server will listen to. Valid values for the first parameter are tcp, tcp4 (IPv4-only), tcp6 (IPv6-only), udp, udp4 (IPv4- only), udp6 (IPv6-only), ip, ip4 (IPv4-only), ip6 (IPv6-only), Unix (Unix sockets), Unixgram, and Unixpacket.
## The concurrent TCP server in action
concTCP.go requires a single command line argument, which is the port number that it will listen to. The output you will get from concTCP.go when serving TCP clients will be similar to the following:
```
$ go run concTCP.go 8001
Serving 127.0.0.1:62554
Serving 127.0.0.1:62556
```
The output of the `netstat(1)`
can verify that concTCP.go serves multiple TCP clients while listening for more connections:
```
$ netstat -anp TCP | grep 8001
tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1.8001 127.0.0.1.62556 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1.62556 127.0.0.1.8001 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1.8001 127.0.0.1.62554 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1.62554 127.0.0.1.8001 ESTABLISHED
tcp4 0 0 *.8001 *.* LISTEN
```
The last line of the output of the preceding command informs us that there is a process that listens to port 8001, which means that you can still connect to TCP port 8001. The first two lines verify that there is an established TCP network connection that uses port numbers 8001 and 62556. Similarly, the third and fourth lines verify that there is another established TCP connection that uses port numbers 8001 and 62554.
This image shows the output of concTCP.go when serving multiple TCP clients:
Analogously, the following image shows the output from two TCP clients that are implemented using the `nc(1)`
utility:
Using the nc(1) utility as the TCP client to concTCP.go.
You can find more information about `nc(1)`
, which is also called `netcat(1)`
, [on Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Netcat).
## Summary
So, you have just learned how to develop a concurrent TCP server that generates random numbers using about 65 lines of Go code, which is pretty impressive! If you want your TCP server to perform a different job, just change the implementation of the `handleConnection()`
function.
## Comments are closed. |
14,624 | 如何在 Fedora 36 工作站中启用最小化和最大化按钮 | https://ostechnix.com/how-to-enable-minimize-and-maximize-buttons-in-fedora/ | 2022-05-22T15:10:21 | [
"Fedora"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14624-1.html | 
>
> 今天,我们将看到 Fedora 桌面的安装后步骤之一。这个简短的指南解释了如何在 Fedora GNOME 工作站和 Silverblue 版本的应用窗口中启用最小化和最大化按钮。
>
>
>
### 介绍
你可能已经知道,Fedora Silverblue 和 Fedora GNOME 工作站版本的应用窗口中没有最小化和最大化按钮。
如果要最小化应用窗口,需要右键单击其标题栏并从上下文菜单中选择最小化选项。
不幸的是,你甚至无法在 Firefox 中使用鼠标获得该选项。要最小化 Firefox 窗口,你要点击 `左 ALT+空格` 键并选择最小化选项。
我不知道隐藏最常用的按钮有什么好处。Ubuntu GNOME 桌面有最小/最大按钮,但 Fedora 没有。
如果你想恢复 Fedora GNOME 和 Silverblue 版本中的最小化和最大化按钮,你可以借助 Fedora 中的 **Gnome Tweaks** 程序和 “Dash to Panel” 扩展来启用它们。
### 在 Fedora 中安装 Gnome Tweaks
**Gnome Tweaks**,以前称为 **Tweak Tool**,是用于高级 GNOME 3 设置的图形界面。它主要是为 GNOME Shell 设计的,但也可以在其他桌面中使用。如果你在不同的桌面上使用 Tweaks,你可能无法拥有所有功能。它在 Fedora 的默认仓库中可用。因此,你可以使用 `dnf` 包管理器在 Fedora 上安装 Gnome Tweaks,如下所示:
```
$ sudo dnf install gnome-tweaks
```
如果你使用 Fedora Silverblue,你需要使用以下命令进入你的 toolbox 容器:
```
$ toolbox enter
```
然后按照前面的命令安装 Tweaks。
### 在浏览器中添加 Gnome Shell 集成插件
确保你在浏览器中添加了 “Gnome Shell 集成” 插件。此扩展提供与 GNOME shell 和相应扩展仓库的集成。
如果你尚未添加它,请转到插件页并搜索并安装它。

将出现一个弹出窗口。单击“添加”以启用加载项。添加此扩展程序后,你将在浏览器的工具栏上看到 GNOME 图标。
### 在 Fedora 中启用 Dash 到面板扩展
“Dash to panel” 扩展是 Gnome Shell 的图标任务栏。此扩展将 dash 移动到 GNOME 主面板中,以便将应用启动器和系统托盘组合到一个面板中,类似于 KDE Plasma 和 Windows 7 以上操作系统中的面板。
“Dash to panel” 扩展为你提供了一个永久可见的面板,其中包含最喜欢的快捷方式。因此,不再需要单独的停靠区来轻松访问正在运行和收藏的应用。
要启用 “Dash to panel” 扩展,请进入 GNOME 扩展站点并搜索 “Dash to panel” 扩展。

单击搜索结果中的 “Dash to panel” 链接。你将被重定向到 “Dash to panel” 扩展的官方页面。点击 “ON” 按钮。

在下一个窗口中,单击安装按钮以启用 “Dash to panel” 扩展。

激活此扩展程序后,你将在底部看到 Dash 面板以及你最喜欢的快捷方式。
### 在 Fedora 中启用最小化和最大化按钮
打开 Gnome Tweaks 应用。进入 “<ruby> 窗口标题栏 <rt> Windows Titlebars </rt></ruby>” 并打开最小/最大按钮。

当你打开开关后,最小化和最大化按钮将出现在所有应用的窗口中。

默认情况下,最小/最大按钮在右侧可见。你可以将其位置更改为左侧或右侧。
“Dash to panel” 扩展有很多微调和自定义选项。右键单击 Dash 面板并选择设置选项,然后根据你的喜好开始对其进行自定义。
### 资源
>
> **[Dash to panel 网站](https://extensions.gnome.org/extension/1160/dash-to-panel/)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://ostechnix.com/how-to-enable-minimize-and-maximize-buttons-in-fedora/>
作者:[sk](https://ostechnix.com/author/sk/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
14,625 | 开源为可持续发展技术提供新思路 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/open-source-sustainable-technology | 2022-05-22T16:07:55 | [
"开源",
"可持续"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14625-1.html |
>
> 开源和社会对于更为稳定的技术演进的需求具有相同的目标,即实现一个更为可持续的未来。
>
>
>

在可持续发展和环境问题上,目前正在发生明确的变化。关注地球的状况并为之做出努力已经成为主流思想。举个例子,看看基于气候的风险资本主义。<ruby> 气候技术风险投资公司 <rt> Climate Tech Venture Capital </rt></ruby>(CTVC)的气候资本名单在过去两年中增加了 [一倍多](https://climatetechvc.substack.com/p/-a-running-list-of-climate-tech-vcs?s=w)。涌入的资本表明了人们对解决艰难的气候挑战的愿望和意愿。
人们想采取行动,这很好,我持相同态度!但我也看到了一个真正的风险:当人们急于采取行动并参与到其中时,他们可能会不知不觉地卷入洗绿运动中。
维基百科对 “<ruby> 洗绿 <rt> greenwashing </rt></ruby>” 的定义称其为 “一种营销策略,其中绿色公关和绿色营销被欺骗性地用来说服公众,使其相信一个组织的产品、目标和政策是环保的”。在我看来,洗绿既是有意为之,也是无意中发生的。外面有很多想有所作为的好人,但对复杂的环境系统或围绕可持续发展的问题的深度还不甚了解。
我们很容易落入这样的陷阱,即认为通过植树来抵消旅行或数据中心的排放等简单的购买行为会使一些东西变得更加绿色。虽然这些努力是值得提倡的,而且植树是改善可持续发展的一个可行的解决方案,但它们只是一个很好的开端,仍然需要进行更多的努力才能真正产生变革。
那么,一个人或一个社区可以做些什么来使数字技术真正地更加可持续?
“可持续性”对不同的人有不同的含义。我喜欢的最简短的定义来自 1987 年的《<ruby> 布伦特兰报告 <rt> Bruntland Report </rt></ruby>》,该报告将其概括为 “既能满足当代的需要,同时又不损及后代满足其需要的发展模式”。可持续发展的核心是优先考虑长期思维。
### 可持续发展不仅仅是保护环境
在可持续性的定义中,有三个相互关联的关键支柱:
1. 环境
2. 经济 / 政策
3. 社会
关于可持续发展的讨论越来越多地被气候危机所主导,这是有道理的。随着我们继续通过不可逆转的生态临界点,减少世界上较富裕国家的碳排放的需求变得越来越紧迫。但真正的可持续性是一套更全面的体系,正如三大支柱所展示的那样。
碳排放无疑是可持续性的一部分。许多人认为排放只是一个环境问题。只要从空气中移除更多的碳,一切都会好起来。但社会问题也是可持续性的一部分。谁会受到这些碳排放的影响?谁将承受我们气候变化带来的最大影响?谁因海平面上升而失去了家园,或因天气模式变化而失去了可靠的水源?这就是为什么你可能听说过 “气候正义就是社会正义” 这句话。
仅仅把减碳看作是可持续发展会令你的视野被限定在碳上。我经常认为,气候变化是社会在更大范围内错失可持续性的一个症状。相反,关键是要解决首先导致气候变化的根本原因。解决这些问题将使长期解决这些问题成为可能,而短期解决可能只会将问题推向另一个脆弱的边缘。
其根本原因很复杂。但是,如果我追根溯源,我看到根源是由西方的主流价值观和旨在延续这些价值观的制度所驱动的。这些价值观是什么呢?一语概之,它们是快速增长和对利润的攫取高于一切。
这就是为什么关于可持续性的对话如果不包括社会问题或经济的设计方式,就不会达成真正的解决方案。毕竟,社会和掌握权力的人决定了他们自己的价值观是什么,或者不是什么。
### 我能做什么?
科技领域的许多人目前正致力于解决这些问题,并想知道怎样行动更有意义。一个常见的方法是研究如何优化他们制造的技术,使其更有效地使用电力。世界上 60% 的电力仍然是通过燃烧化石燃料产生的,尽管可再生能源的发电能力不断提高。但从逻辑上讲,使用更少的电力意味着产生更少的碳排放。
是的,这是很有意义的,任何人都可以尝试,立即就能生效。当用户加载一个页面时,优化发送的资源,以发送更少的数据,将使用更少的能源。因此,优化服务器,使其在一天中的不同时段运行,例如,当有更多的可再生能源可用时运行,或删除多余信息的旧存储,如分析数据或日志。
但考虑到<ruby> 杰文 <rt> Jevon </rt></ruby>的悖论:使某样东西更有效率往往会导致使用更多的东西,而不是减少。当人们更容易和更便于使用某样东西时,他们最终会使用更多。在某种角度,这是好的。性能更好的技术是一件好事,有助于提高包容性和触及性,这对社会是有益的。但是,气候变化和可持续性的长期解决方案需要围绕社会和技术之间的关系进行更深入、更令人不适的对话。所有这些技术在为什么和谁服务?它正在加速哪些行为和做法?
将技术的演进视为进步很正常,一些人认为:技术将把世界从气候变化中拯救出来。一些聪明的人正在通过艰苦卓绝的努力改善这一问题,所以其他人不需要改变他们的方式。问题是,许多社区和生态系统已经在遭受更大的创伤。
例如,对更多更高速传输的数据的追求正在导致智利的一些社区没有足够的水来种植农作物。因为数据中心正在使用这些宝贵的水源。移动电话造成的污染有 70% 来自于其制造。制造移动设备并为其提供动力的锂和钴等原材料通常是从弱势的社区中提取的,而这些社区几乎没有能力阻止制造商对其土地的破坏,当然也没有分享所获利润。尽管如此,每两年升级一次手机的做法已经变得很普遍了。
### 开源思路引领可持续发展之路
现在是时候将数字技术的使用视为一种宝贵的资源,这对地球和(通常已经处于弱势的)社区都有影响。
开源社区已经帮助人们认识到有另一种解决方案:开源。开源与我们更广泛的社会为实现更可持续的未来而需要做的事情之间有巨大的相似之处。更加开放和包容是其中的一个关键部分。
我们还需要在社会的各个层面进行思维转变,将数字技术视为有代价的增长,而不是我们今天看到的大量廉价和免费的东西。我们需要明智地将其优先用于对于社会而言最为重要的事情。更重要的是,我们需要关注并消除其创造和长期使用所带来的危害,并与社会上的每个人公平地分享其创造的财富,无论他们是否是数字技术的使用者。这些事情不会在一夜之间发生,但它们是我们可以共同推动的事情,以便我们都能长期、可持续地享受数字技术的好处。
本文节选自一篇较长的演讲。要想看到演讲的全文或查看幻灯片,请参见《[我们如何使数字技术更具有可持续性](https://opcan.co.uk/talk/wordfest-live-2022)》一文。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/open-source-sustainable-technology>
作者:[Hannah Smith](https://opensource.com/users/hanopcan) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[PeterPan0106](https://github.com/PeterPan0106) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | There's a palpable change in the air regarding sustainability and environmental issues. Concern for the condition of the planet and efforts to do something about it have gone mainstream. To take one example, look at climate-based venture capitalism. The Climate Tech Venture Capital (CTVC) Climate Capital List has [more than doubled](https://climatetechvc.substack.com/p/-a-running-list-of-climate-tech-vcs?s=w) in the past two years. The amount of capital pouring in demonstrates a desire and a willingness to solve hard climate challenges.
It's great that people want to take action, and I'm here for it! But I also see a real risk: As people rush to take action or jump on the bandwagon, they may unwittingly participate in *greenwashing*.
The Wikipedia definition of greenwashing calls it "a form of marketing spin in which green PR and green marketing are deceptively used to persuade the public that an organization's products, aims, and policies are environmentally friendly." In my view, greenwashing happens both intentionally and accidentally. There are a lot of good people out there who want to make a difference but don't yet know much about complex environmental systems or the depth of issues around sustainability.
It's easy to fall into the trap of thinking a simple purchase like offsetting travel or datacenter emissions by planting trees will make something greener. While these efforts are welcome, and planting trees is a viable solution to improving sustainability, they are only a good first step—a scratch on the surface of what needs to happen to make a real difference.
So what can a person, or a community, do to make digital technology genuinely more sustainable?
Sustainability has different meanings to different people. The shortest definition that I like is from the 1987 Bruntland Report, which summarizes it as "meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs." Sustainability at its core is prioritizing long-term thinking.
## Sustainability is more than environmental preservation
There are three key interconnected pillars in the definition of sustainability:
- Environmental
- Economic / governance
- Social
Conversations about sustainability are increasingly dominated by the climate crisis—for good reason. The need to reduce the amount of carbon emissions emitted by the richer countries in the world becomes increasingly urgent as we continue to pass irreversible ecological tipping points. But true sustainability is a much more comprehensive set of considerations, as demonstrated by the three pillars.
Carbon emissions are most certainly a part of sustainability. Many people consider emissions only an environmental issue: Just take more carbon out of the air, and everything will be ok. But social issues are just as much a part of sustainability. Who is affected by these carbon emissions? Who stands to bear the greatest impact from changes to our climate? Who has lost their land due to rising sea levels or a reliable water source due to changing weather patterns? That's why you might have heard the phrase "climate justice is social justice."
Thinking only about decarbonization as sustainability can give you carbon tunnel vision. I often think that climate change is a symptom of society getting sustainability wrong on a wider scale. Instead, it is critical to address the root causes that brought about climate change in the first place. Tackling these will make it possible to fix the problems in the long term, while a short-term fix may only push the issue onto another vulnerable community.
The root causes are complex. But if I follow them back to their source, I see that the root causes are driven by dominant Western values and the systems designed to perpetuate those values. And what are those values? For the most part, they are short-term growth and the extraction of profit above all else.
That is why conversations about sustainability that don't include social issues or how economies are designed won't reach true solutions. After all, societies, and the people in positions of power, determine what their own values are—or aren't.
## What can you or I do?
Many in the tech sector are currently grappling with these issues and want to know how to take meaningful action. One common approach is looking at how to optimize the tech they build so that it uses electricity more effectively. Sixty percent of the world's electricity is still generated by burning fossil fuels, despite the increasing capacity for renewable energy generation. Logically, using less electricity means generating fewer carbon emissions.
And yes, that is a meaningful action that anyone can take right now, today. Optimizing the assets sent when someone loads a page to send less data will use less energy. So will optimizing servers to run at different times of the day, for example when there are more renewables online, or deleting old stores of redundant information, such as analytics data or logs.
But consider Jevon's paradox: Making something more efficient often leads to using more of it, not less. When it is easier and more accessible for people to use something, they end up consuming more. In some ways, that is good. Better performing tech is a good thing that helps increase inclusion and accessibility, and that's good for society. But long-term solutions for climate change and sustainability require deeper, more uncomfortable conversations around the relationship between society and technology. What and who is all this technology serving? What behaviors and practices is it accelerating?
It's common to view advancing technology as progress, and some people repeat the mantra that technology will save the world from climate change. A few bright folks will do the hard work, so no one else has to change their ways. The problem is that many communities and ecosystems are already suffering.
For example, the accelerating quest for more data is causing some communities in Chile to have insufficient water to grow their crops. Instead, datacenters are using it. Seventy percent of the pollution caused by mobile phones comes from their manufacture. The raw resources such as lithium and cobalt to make and power mobile devices are usually extracted from a community that has little power to stop the destruction of their land and that certainly does not partake in the profit made. Still, the practice of upgrading your phone every two years has become commonplace.
## Open source leading the way for sustainability
It's time to view the use of digital technology as a precious resource with consequences to both the planet and (often already disadvantaged) communities.
The open source community is already a leading light in helping people to realize there is another way: the open source way. There are huge parallels between the open source way and what our wider society needs to do to achieve a more sustainable future. Being more open and inclusive is a key part of that.
We also need a mindset shift at all levels of society that views digital technology as having growth limits and not as the abundantly cheap and free thing we see today. We need to wisely prioritize its application in society to the things that matter. And above all else, we need to visualize and eradicate the harms from its creation and continued use and share the wealth that is does create equitably with everyone in society, whether they are users of digital tech or not. These things aren’t going to happen overnight, but they are things we can come together to push towards so that we all enjoy the benefits of digital technology for the long-term, sustainably.
This article is based on a longer presentation. To see the talk in full or view the slides, see the post ["How can we make digital technology more sustainable."](https://opcan.co.uk/talk/wordfest-live-2022)
## Comments are closed. |
14,627 | Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 中安装经典 GNOME Flashback 指南 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/gnome-classic-ubuntu-22-04/ | 2022-05-23T15:13:22 | [
"GNOME"
] | /article-14627-1.html | 
>
> 关于如何在最新的 UBUNTU 22.04 LTS 中安装旧的经典 GNOME Flashback 的快速指南。
>
>
>
[GNOME Flashback](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/GNOME/Flashback)(又名 classic GNOME)是旧 GNOME 3 shell 的一个分支,它使用早期 GNOME 2 技术的布局和原则。它的速度快如闪电,并且在设计上非常轻量级。因此,它非常适合几十年前的老旧硬件。
随着带有现代 GNOME 42 的 [Ubuntu 22.04 LTS](https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/01/ubuntu-22-04-lts/) 的发布,有必要寻找轻量级的桌面环境选项。
此外,GNOME Flashback 很容易安装在现代 Ubuntu Linux 中,你仍然可以享受 Ubuntu 性能而不必关心 GNOME 42、GTK4、libadwaita 之类的东西。
### 在 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 中下载并安装经典 GNOME Flashback
按照以下步骤在 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 中下载并安装经典 GNOME Flashback(Metacity)。
在 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 中打开终端(CTRL+ALT+T)并运行以下命令。安装大小约为 61MB。
```
sudo apt update
sudo apt install gnome-session-flashback
```

最后,安装完成后,退出。重新登录时,在登录选项中使用经典的 GNOME Flashback(Metacity) 。

### 经典 GNOME Flashback 的特点
首先,当你登录时,你将体验到传统的 GNOME 技术,它已被证明具有良好的生产力,并且比今天的技术快得多。
在顶部有旧版的面板,左侧是应用菜单,而系统托盘位于桌面的右上方。应用程序菜单显示所有已安装的应用和软件快捷方式,你可以在工作流程中轻松浏览。
此外,在右侧部分,系统托盘具有默认小部件,例如网络、音量控制、日期和时间以及关机菜单。

底部面板包含打开的窗口和工作区切换器的应用列表。默认情况下,它为你提供四个工作区供你使用。
此外,你可以随时更改顶部面板的设置以自动隐藏、调整面板大小和背景颜色。
除此之外,你可以通过 `ALT + 右键点击` 顶部面板添加任意数量的旧版小程序。


### 经典 GNOME 的性能
首先,磁盘空间占用极小,仅安装 61 MB。我的测试使用了大约 28% 的内存,其中大部分被其他进程占用。猜猜是谁?是的,是 snap-store(又名 Ubuntu 软件)。
因此,总体而言,它非常轻巧,内存(仅 28 MB)和 CPU(0.1%)占用空间非常小。

此外,假设你将其与同样使用相同技术的 Ubuntu MATE 进行比较。在这种情况下,它比 MATE 更轻量,因为你不需要任何额外的 MATE 应用及其用于通知、主题和其他附加资源的软件包。
### 结束语
我希望本指南在你决定在 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish 中安装经典 GNOME 之前帮助你获得必要的信息。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/gnome-classic-ubuntu-22-04/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,628 | 自由软件基金会为什么不认为 Debian 是一种自由发行版? | https://news.itsfoss.com/fsf-does-not-consider-debian-a-free-distribution/ | 2022-05-23T17:09:40 | [
"Debian",
"自由软件",
"FSF"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14628-1.html | 
Debian 项目开发了一个尊重用户自由的 GNU/Linux 发行版。在各种自由软件许可证下发布的软件中,其源代码中包含非自由组件的情形并不鲜见。这些软件在被发布到 Debian 之前会被清理掉。而<ruby> 自由软件基金会 <rt> Free Software Foundation </rt></ruby>(FSF)维护着一份 [自由 GNU/Linux 发行版的列表](https://gnu.org/distros/free-distros.en.html),但奇怪的是,Debian 并不在其中。事实上, Debian 不符合进入此列表的某些标准,我们想知道到底不满足哪些标准。但首先,我们需要了解所有这些智力工作是如何得到证明的。换句话说,为什么要费心尝试进入一些名单,尤其是这个名单?
为什么 Debian 应该得到 FSF 的承认,以获得它的自由发行版的地位?曾于 2010 年至 2013 年担任 Debian 项目负责人的 Stefano Zacchiroli 说过几个原因。其中一个 Stefano 称之为“外部审查”的原因我特别赞同。事实上,Debian 有其标准和质量水准,一些软件应当符合这些标准才能成为该发行版的一部分,但除了 Debian 开发人员自己,没有人能控制这个过程。如果该发行版被列入这份珍贵的清单中,那么 FSF 就会密切关注 Debian 的命运,并(在出现问题时)给予适度的批评。我相信这是很好的动力。如果你也这么认为,那么现在让我们看看 FSF 认为 Debian 不够自由的原因。
### Debian 社会契约
除了自由 GNU/Linux 发行版列表之外,FSF 还保留了一份因某种原因而被拒绝授予自由地位的 GNU/Linux 发行版的列表。对于此列表中的每个发行版,都有一个评论,简要说明了拒绝的理由。从对 Debian 的评论中可以清楚地看出,FSF 和 Debian 项目在对“自由分发”一词的解释上产生分歧的主要根源来自一份被称为 “<ruby> Debian 社会契约 <rt> Debian Social Contract </rt></ruby>”的文件。
该社会契约的第一个版本是在 1997 年 7 月 4 日由第二任 Debian 项目领导人 Bruce Perens 发表的。作为该契约的一部分,也公布了一套被称为 <ruby> Debian 自由软件准则 <rt> Debian Free Software Guidelines </rt></ruby>(DFSG)的规则。从那时起,要成为 Debian 的一部分,分发软件的许可证必须符合 DFSG。该社会契约记录了 Debian 开发者只用自由软件建立操作系统的意图,而 DFSG 则用于将软件分为自由和非自由。2004 年 4 月 26 日,批准了该文件的新版本,取代了 1997 年的版本。
Debian 社会契约有五条。要回答我们今天主要讨论的问题,我们只需要关注其中两条 —— 即第一条和第五条,其他的省略。可以在 [此处](https://debian.org/social_contract) 查看该契约的完整版本。
第一条说:“**Debian 将保持 100% 自由**。我们在标题为‘<ruby> Debian 自由软件准则 <rt> Debian Free Software Guidelines </rt></ruby>’的文件中提供了用于确定一个作品是否‘自由’的准则。我们承诺,根据这些准则,Debian 系统及其所有组件将是自由的。我们将支持在 Debian 上创造或使用自由和非自由作品的人。我们永远不会让系统要求使用非自由组件。”
同时,第五条写道:“**不符合我们自由软件标准的作品**。我们承认,我们的一些用户需要使用不符合 Debian 自由软件准则的作品。我们在我们的存档中为这些作品创建了“contrib”和“non-free”区域。这些区域中的软件包并不是 Debian 系统的一部分,尽管它们已被配置为可以在 Debian 中使用。我们鼓励 CD 制造商阅读这些区域的软件包的许可证,并确定他们是否可以在其 CD 上分发这些软件包。因此,尽管非自由作品不是 Debian 的一部分,但我们支持它们的使用,并为非自由软件包提供基础设施(例如我们的错误跟踪系统和邮件列表)。”
因此,在实践中,第一条和第五条意味着:在安装了 Debian 之后,用户得到了一个完全而彻底的自由操作系统,但是如果他们突然想牺牲自由来追求功能,安装非自由软件,Debian 不仅不会阻碍他们这样做,而且会大大简化这一任务。
尽管该契约规定发行版将保持 100% 自由,但它允许官方存档的某些部分可能包含非自由软件或依赖于某些非自由组件的自由软件。形式上,根据同一契约,这些部分中的软件不是 Debian 的一部分,但 FSF 对此感到不安,因为这些部分使得在系统上安装非自由软件变得更加容易。
在 2011 年前,FSF 有合理的理由不认为 Debian 是自由的——该发行版附带的 Linux 内核没有清理二进制 blob。但自 2011 年 2 月发布的 Squeeze 至今,Debian 已经包含了完全自由的 Linux 内核。因此,简化非自由软件的安装是 FSF 不承认 Debian 是自由发行版的主要原因,直到 2016 年这是我知道的唯一原因,但在 2016 年初出现了问题……
### 等等 …… 关 Firefox 什么事?
很长一段时间,Debian 都包含一个名为 Iceweasel 的浏览器,它只不过是 Firefox 浏览器的更名重塑而已。进行品牌重塑有两个原因:首先,该浏览器标志和名称是 Mozilla 基金会的商标,而提供非自由软件与 DFSG 相抵触。其次,通过在发行版中包含浏览器,Debian 开发人员必须遵守 Mozilla 基金会的要求,该基金会禁止以 Firefox 的名义交付浏览器的修改版本。因此,开发人员不得不更改名称,因为他们在不断地修改浏览器的代码,以修复错误并消除漏洞。但在 2016 年初,Debian 有幸拥有一款经过修改的 Firefox 浏览器,不受上述限制,可以保留原来的名称和徽标。一方面,这是对 Debian 修改的认可,也是对 Debian 信任的体现。另一方面,该软件显然没有清除非自由组件,它现在已成为发行版的一部分。如果此时 Debian 已被列入自由 GNU/Linux 发行版列表,那么自由软件基金会将会毫不犹豫地指出这一点。
### 结论
数字世界中的自由与现实世界中的自由同样重要。在这篇文章中,我试图揭示 Debian 最重要的特性之一 —— 开发用户自由的发行版。开发人员花费额外的时间从软件中清理非自由组件,并且以 Debian 为技术基础的数十个发行版继承了它的工作,并由此获得了一部分自由。
另外,我想分享一个简单的看法,即自由并不像乍看起来那么简单,人们自然会去追问什么是真正的自由,而什么不是。由于 Firefox 的存在,Debian 现在不能被称为自由的 GNU/Linux 发行版。但从 2011 年,当 Debian 终于开始清理内核以及发行版的其他组件时,直到 2016 年 Firefox 成为发行版的一部分时,自由软件基金会出于纯粹的意识形态原因并不认为该发行版是自由的:原因是 Debian 大大简化了非自由软件的安装……现在轮到你来权衡所有的争论,并决定是否将 GNU/Linux 发行版视为自由的了。
祝你好运!并尽可能保持自由。
由 Evgeny Golyshev 为 [Cusdeb.com](https://wiki.cusdeb.com/Essays:Why_the_FSF_does_not_consider_Debian_as_a_free_distribution/en) 撰写
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/fsf-does-not-consider-debian-a-free-distribution/>
作者:[Evgeny Golyshev](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/root/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[Chao-zhi](https://github.com/Chao-zhi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

The Debian Project develops a free GNU/Linux distribution that respects the freedom of its users. It’s not uncommon for software, the source code of which is distributed under this or that free license, to contain non-free components. In this case, the software is cleaned before being released into Debian. The Free Software Foundation (FSF), in turn, maintains a [list of free GNU/Linux distributions](https://gnu.org/distros/free-distros.en.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com), but oddly enough, Debian is not there. The fact is that Debian does not meet some criteria for getting on this list and we have to figure out which ones. But first, you need to understand how all this intellectual work is justified. In other words, why bother trying to get on some lists and this one in particular?
Stefano Zacchiroli, who used to be the leader of the Debian Project from 2010 to 2013, once voiced several reasons why Debian should have got the FSF to obtain the status of free distribution. One of these reasons, which Stefano called “external review”, I especially liked. The fact is that Debian has criteria and quality standards that software must meet to become part of the distribution, but no one except the Debian developers themselves controls this process. If the distribution had been included in that cherished list, the FSF would have been keeping a close eye on the fate of Debian with moderate criticism. Excellent motivation, I believe. If you also think so, then let’s now have a look at the reasons why the FSF considers Debian as not free enough.
## Debian Social Contract
Along with the list of free GNU/Linux distributions, the FSF maintains a list of GNU/Linux distributions that have been rejected a free status for one reason or another. For each distribution in this list, there is a comment with a brief argument for refusal. From the comment on Debian, it becomes clear that the main source of disagreement between the FSF and the Debian Project in the interpretation of the phrase “free distribution” is a document known as the Debian Social Contract.
The first version of the Social Contract was published on July 4, 1997, by the second Debian Project Leader, Bruce Perens. As part of this contract, a set of rules called the Debian Free Software Guidelines (DFSG) was also published. Since then, to become part of Debian, the license under which the software is distributed must meet the DFSG. The Social Contract documented the intention of the Debian developers to build an operating system only from free software, and the DFSG helped classify software into free and non-free. On April 26, 2004, a new version of the document was approved, which replaced the 1997 version.
The Debian Social Contract has five points. To answer the main question, we need only two of them – the first and the fifth, so they will be given below, and the others are omitted. Check out the full version of the contract [here](https://debian.org/social_contract?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
The first point says: «**Debian will remain 100% free**. We provide the guidelines that we use to determine if a work is “free” in the document entitled “The Debian Free Software Guidelines”. We promise that the Debian system and all its components will be free according to these guidelines. We will support people who create or use both free and non-free works on Debian. We will never make the system require the use of a non-free component.»
At the same time, the fifth point reads: «**Works that do not meet our free software standards**. We acknowledge that some of our users require the use of works that do not conform to the Debian Free Software Guidelines. We have created “contrib” and “non-free” areas in our archive for these works. The packages in these areas are not part of the Debian system, although they have been configured for use with Debian. We encourage CD manufacturers to read the licenses of the packages in these areas and determine if they can distribute the packages on their CDs. Thus, although non-free works are not a part of Debian, we support their use and provide infrastructure for non-free packages (such as our bug tracking system and mailing lists).»
So, in practice, the first and fifth points mean: after installing Debian, users get a completely and utterly free operating system, but if they suddenly want to sacrifice freedom in favour of functionality and install non-free software, Debian will not only not hinder them from doing this, but will greatly simplify this task.
Although the contract states that the distribution will remain 100% free, it allows sections of the official archive that may contain non-free software or free software that depends on some non-free components. Formally, the software in these sections, according to the same contract, is not part of Debian, but the FSF is haunted by this since these sections make it much easier to install non-free software on a system.
Until 2011, the FSF had reasonable grounds not to consider Debian free – the distribution was shipped with a Linux kernel uncleaned from binary blobs. But since the February 2011 release of Squeeze to this day, Debian has included the free Linux kernel. Thus, simplifying the installation of non-free software is the main reason why the FSF cannot recognize Debian as free distribution, and until 2016 this was the only reason I knew, but in early 2016 something went wrong…
## Wait… what’s Firefox doing here?
For a long time, Debian included a browser called Iceweasel, which was nothing more than a rebrand of the Firefox browser. The rebranding was carried out for two reasons. First, the browser logo and name are trademarks of the Mozilla Foundation, and the provision of non-free software contradicts the DFSG. Second, by including the browser in the distribution, the Debian developers had to comply with the requirements of the Mozilla Foundation, which prohibits the delivery of a modified version of the browser under the name Firefox. Thus, the developers had to change the name, because they constantly make changes to the browser code to fix bugs and eliminate vulnerabilities. But at the beginning of 2016 Debian was lucky to have a modified browser that does not fall under the above restrictions and can retain the original name and logo. On the one hand, this is a recognition of merit and a demonstration of trust in Debian. On the other hand, the software, obviously uncleaned from non-free components, is now a part of the distribution. If by this time Debian had been included in the list of free GNU/Linux distributions, the Free Software Foundation wouldn’t have hesitated to point this out.
## Conclusion
Freedom in the digital world is as important as freedom in the real world. In this article, I tried to reveal one of the most important features of Debian – developing distribution with regard to the freedom of its users. Developers spend extra time cleaning up non-free components from software, and dozens of distributions for which Debian is the technology base inherit its work, and with it, a piece of freedom.
Also, I wanted to share a simple observation that freedom is not as straightforward as it might seem at first glance, and it is quite natural to enquire what is really free and what is not. Debian cannot be called a free GNU/Linux distribution now because of the presence of Firefox in it. But from 2011, when Debian finally began cleaning the kernel along with other components of the distribution, and until 2016, when Firefox became part of the distribution, the Free Software Foundation did not consider the distribution to be free for purely ideological reasons: Debian greatly simplifies the installation of non-free software… Now it’s your turn to weigh up all the arguments and decide whether to consider the GNU/Linux distribution as free or not.
Good luck! And stay as free as possible.
Written by Evgeny Golyshev for [Cusdeb.com](https://wiki.cusdeb.com/Essays:Why_the_FSF_does_not_consider_Debian_as_a_free_distribution/en?ref=news.itsfoss.com)
*The views and opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of It’s FOSS.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,630 | ONLYOFFICE 7.1 发布:新增针对 ARM 的支持、新的 PDF 查看器 | https://news.itsfoss.com/onlyoffice-7-1-release/ | 2022-05-24T08:43:00 | [
"ONLYOFFICE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14630-1.html |
>
> ONLYOFFICE Docs 7.1 带来了期待已久的针对文档、电子表格以及演示文稿编辑器的更新。对 ARM 的支持更是画龙点睛之笔。
>
>
>

ONLYOFFICE,被认为是 [最佳的微软 Office 替代品](https://itsfoss.com/best-free-open-source-alternatives-microsoft-office/) 之一,刚刚发布了最新的 7.1 版本更新。
或许你不了解,ONLYOFFICE 可以在自托管的服务器(例如 Nextcloud)或者桌面上在线使用。
这个版本最为激动人心的变化就是初步支持了基于 ARM 的设备,例如树莓派。
接下来请让我们一起看看有什么新的变化。
### ONLYOFFICE 7.1 : 新变化
除了对 ARM 的支持,ONLYOFFICE 7.1 还提供了如下新功能:
* 一个全新的 PDF、XPS 和 DjVu 文件查看器
* 更方便和可定制的图形选项
* 电子表格打印预览
* 演示文稿中的动画
* 支持 SmartArt 对象
#### ARM 兼容
树莓派这样的基于 ARM 的设备正变得越来越热门,许多人已经期待了许久 ONLYOFFICE 对 ARM 架构的支持。
随着 7.1 版本的发布,ONLYOFFICE Docs 现在可以在所有 ARM64 设备上运行。由于 ARM 设备的效率和安全性的提高,我认为这将对 ONLYOFFICE 的未来产生很大的促进作用。
#### 全新的 PDF、XPS 和 DjVu 文件查看器

这是许多其他办公软件多年来的一个关键功能。从 ONLYOFFICE 7.1 开始,用户现在可以更方便地使用文档编辑器来查看 PDF、XPS 和 DjVu 文件。
新的视图选项卡为用户提供了一个页面缩略图视图和一个导航栏,其视图更为紧凑和简化。
此外,用户现在还可以将 PDF 文件转换为 DOCX 文件,以便对其进行编辑。因此,我们不用再额外打开其他软件进行处理了,这将显著优化现有的工作流并消除瓶颈。
#### 选择和编辑图形更加方便

图形做为现代办公软件的特性,在许多时候并没能发挥足够的作用。尽管 ONLYOFFICE 拥有这些功能已经有一段时间了,但它们在使用时总是相当笨重。
在 ONLYOFFICE 7.1 中,重新设计的图形选择菜单使得这种情况得到了改变。这个新的菜单与微软 Office 的同类产品非常相似,每个图标都可以从菜单中看到。
此外,它现在可以显示最近使用的图形,使批量插入图形更加容易。
图形的最后一项改进是能够使用鼠标来编辑它们。对于那些熟悉 Inkscape 等图形设计软件的人来说,这将会相当得心应手。通过简单地拖动点,你将可以在短时间内创建一个独特的形状。
#### 电子表格的打印预览

我相信每个人都发生过由于一个简单的错误而导致打印出现问题的情况。此前其他程序早已经解决了这个问题,但在 ONLYOFFICE 电子表格编辑器中一直没有这个功能。
新版本终于引入了“打印预览”,这将会显著改善上述的情况。
这并不算什么十分新颖的更新,只是说它补齐了短板并且可以节省纸张和打印耗材。
#### 改进的动画页面,便捷的剪切和复制

针对需要经常使用演示文稿的用户而言,这个版本增加了一个单独的动画标签,使动画的插入变得更为容易。
ONLYOFFICE 7.1 演示文稿编辑器现在支持各种动画,以及便捷地将一页幻灯片移动以及复制的能力。
#### SmartArt 对象的支持
SmartArt 是一种在文档、演示文稿和电子表格中便捷地制作自定义图形的工具。然而,它一直是微软办公软件的一个功能。虽然其他各种应用程序对该格式有不同程度的支持,但它们并不能与微软 Office 相媲美。
幸运的是,ONLYOFFICE 7.1 现在完全支持这种格式,并且没有任何乱码,仿佛原生的一般。用户将不再需要和以前一样在将 SmartArt 图形转换为普通图形和数字,便于无缝切换。
### 其他变化
ONLYOFFICE 7.1 的其他重要改进包括:
* 新的客户端语言:加利西亚语和阿塞拜疆语
* 在受密码保护的文件中,能够在输入密码的同时查看密码
* OFORM 文件支持缩放选项
* 能够按用户组过滤评论
* 支持金字塔图表
* 支持金字塔柱状图
* 支持垂直和水平圆柱图
* 支持垂直和水平圆锥图
* 上下文菜单中的移动和复制幻灯片选项
* 公式工具提示
* 新的货币格式支持
若想了解全部新特性,请见 [发布日志](https://www.onlyoffice.com/blog/2022/05/discover-onlyoffice-docs-v7-1/)。
### 下载 ONLYOFFICE 7.1
总的来说,ONLYOFFICE 7.1 是一个兼容 ARM 并且功能更为丰富的版本。
所有版本(企业版、开发版者、社区版)都有更新。
下载方面提供了很多不同的软件包,包括用于 ARM 版本的 Docker 镜像、 Snap 软件包以及用于云供应商的即点即用选项。你可以前往下载页面,寻找最合适的安装程序。
下载页面同时列出了安装的官方指南。
>
> **[获取 ONLYOFFICE 7.1](https://www.onlyoffice.com/download-docs.aspx)**
>
>
>
*你是否已经尝试了新版本呢?*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/onlyoffice-7-1-release/>
作者:[Jacob Crume](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[PeterPan0106](https://github.com/PeterPan0106) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

ONLYOFFICE, one of the [best open-source Microsoft Office alternatives](https://itsfoss.com/best-free-open-source-alternatives-microsoft-office/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), has just released its new upgrade, i.e., version 7.1.
If you didn’t know, you can use ONLYOFFICE with online integration on your self-hosted server (like Nextcloud) or the desktop.
This release brings exciting new changes, notably initial support for ARM-based devices like the Raspberry Pi.
Let’s take a look at what’s new!
## ONLYOFFICE 7.1: What’s New?
Alongside the headline feature of ARM support, ONLYOFFICE 7.1 has new feature additions on offer. These include:
- A brand-new PDF, XPS, and DjVu file viewer
- More convenient and customizable shape options
- Spreadsheets Print Preview
- Animations in Presentations
- SmartArt Object Support
### ARM Compatibility
As ARM-based devices like the Raspberry Pi become more popular each year, many expected the support for ARM architecture by ONLYOFFICE for a while.
With the 7.1 release, ONLYOFFICE Docs 7.1 now runs on all ARM64 devices. Thanks to the increased efficiency and security of ARM devices, I suspect this will have a massive impact on the future of ONLYOFFICE.
### Brand-new PDF, XPS, and DjVu file viewer
This is a key feature that many other office programs have had for years. Starting with ONLYOFFICE 7.1, users can now use the document editor to view PDF, XPS, and DjVu files much more conveniently.
With the capability to open files on the client-side, the new view mode offers users a page thumbnails view and a navigation bar in a much more compact and simplified view.
Additionally, users can now also convert these PDF files to DOCX files so that you can edit them. As a result, people shouldn’t need to go open multiple different apps to be able to work with the same file, which should help alleviate some major bottlenecks in workflows.
### More convenient and customizable shape options
Often under-used (I think), shapes are a great feature of modern office applications. Although ONLYOFFICE has had them for quite some time now, they have always been rather clunky to work with.
However, with ONLYOFFICE 7.1, this changes thanks to a redesigned shape selection menu. This new menu closely resembles its Microsoft Office equivalent, with each icon being visible from within the menu.
Additionally, it now shows the recently used shapes to make repetitive shape insertion easier.
The final improvement to shapes is the ability to edit them using your mouse. This should be quite familiar for those of you familiar with graphic design software like Inkscape. By simply dragging the points around, you can create a unique shape in almost no time!
### Spreadsheets Print Preview
I’m sure everyone can relate to the frustration when a print fails due to a simple mistake. While other programs solved this problem a while ago, it has remained noticeably absent in the ONLYOFFICE spreadsheet editor.
Fortunately, this release looks to rectify this, thanks to the introduction of “Print Preview.”
To be honest, there’s not a lot to say about this, just that it should save a lot of paper and printer frustrations.
### New Animation Tab, Move Slides, and Duplicate Slide
For those of you who make countless presentations with animations, a separate animation tab has been added with this release, making things easier.
ONLYOFFICE 7.1 presentation editor now supports a variety of animations along with the ability to move slides to the beginning/end of a presentation and duplicate a slide.
### SmartArt Object Support
SmartArt is an easy way to make custom graphics in documents, presentations, and spreadsheets. However, it has always been a Microsoft Office-focused feature. Although various other applications have had varying levels of support for the format, they have never really been comparable to Microsoft Office.
Fortunately, ONLYOFFICE 7.1 now fully supports this format without any “hacks”, like what used to be required. Unlike the old process of converting the objects to a group of figures, Smart Art is now handled seamlessly and without problems.
## Other Changes
Other significant refinements in ONLYOFFICE 7.1 include:
- New interface languages – Galician and Azerbaijani
- Ability to view a password while entering it in password-protected files
- Zoom options in OFORM files
- Ability to filter comments by groups of users
- Pyramid chart support
- Pyramid bar chart support
- Vertical and horizontal cylinder chart support
- Vertical and horizontal cone chart support
- Move and duplicate slide options in the context menu
- Formula tooltips
- New currency support
For a complete list of changes, I highly suggest you look at the [release notes](https://www.onlyoffice.com/blog/2022/05/discover-onlyoffice-docs-v7-1/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Download ONLYOFFICE 7.1
Overall, ONLYOFFICE 7.1 looks to be a great release with ARM compatibility and new features.
You should find the latest version available for all editions (Enterprise, Developer, Community).
Plenty of different packages are available, including Docker images for ARM editions, a Snap package, and 1-click app options for cloud providers. You can head to its download page and look for the appropriate installer.
The download page also mentions the official instructions to get it installed.
*Have you tried the new update yet?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,631 | 用 Spark SQL 进行结构化数据处理 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/structured-data-processing-with-spark-sql/ | 2022-05-24T09:30:38 | [
"Spark",
"SQL"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14631-1.html |
>
> Spark SQL 是 Spark 生态系统中处理结构化格式数据的模块。它在内部使用 Spark Core API 进行处理,但对用户的使用进行了抽象。这篇文章深入浅出地告诉你 Spark SQL 3.x 的新内容。
>
>
>

有了 Spark SQL,用户可以编写 SQL 风格的查询。这对于精通结构化查询语言或 SQL 的广大用户群体来说,基本上是很有帮助的。用户也将能够在结构化数据上编写交互式和临时性的查询。Spark SQL 弥补了<ruby> 弹性分布式数据集 <rt> resilient distributed data sets </rt></ruby>(RDD)和关系表之间的差距。RDD 是 Spark 的基本数据结构。它将数据作为分布式对象存储在适合并行处理的节点集群中。RDD 很适合底层处理,但在运行时很难调试,程序员不能自动推断<ruby> 模式 <rt> schema </rt></ruby>。另外,RDD 没有内置的优化功能。Spark SQL 提供了<ruby> 数据帧 <rt> DataFrame </rt></ruby>和数据集来解决这些问题。
Spark SQL 可以使用现有的 Hive 元存储、SerDes 和 UDF。它可以使用 JDBC/ODBC 连接到现有的 BI 工具。
### 数据源
大数据处理通常需要处理不同的文件类型和数据源(关系型和非关系型)的能力。Spark SQL 支持一个统一的数据帧接口来处理不同类型的源,如下所示。
* 文件:
+ CSV
+ Text
+ JSON
+ XML
* JDBC/ODBC:
+ MySQL
+ Oracle
+ Postgres
* 带模式的文件:
+ AVRO
+ Parquet
* Hive 表:
+ Spark SQL 也支持读写存储在 Apache Hive 中的数据。
通过数据帧,用户可以无缝地读取这些多样化的数据源,并对其进行转换/连接。
### Spark SQL 3.x 的新内容
在以前的版本中(Spark 2.x),查询计划是基于启发式规则和成本估算的。从解析到逻辑和物理查询计划,最后到优化的过程是连续的。这些版本对转换和行动的运行时特性几乎没有可见性。因此,由于以下原因,查询计划是次优的:
* 缺失和过时的统计数据
* 次优的启发式方法
* 错误的成本估计
Spark 3.x 通过使用运行时数据来迭代改进查询计划和优化,增强了这个过程。前一阶段的运行时统计数据被用来优化后续阶段的查询计划。这里有一个反馈回路,有助于重新规划和重新优化执行计划。

#### 自适应查询执行(AQE)
查询被改变为逻辑计划,最后变成物理计划。这里的概念是“重新优化”。它利用前一阶段的可用数据,为后续阶段重新优化。正因为如此,整个查询的执行要快得多。
AQE 可以通过设置 SQL 配置来启用,如下所示(Spark 3.0 中默认为 false):
```
spark.conf.set(“spark.sql.adaptive.enabled”,true)
```
#### 动态合并“洗牌”分区
Spark 在“<ruby> 洗牌 <rt> shuffle </rt></ruby>”操作后确定最佳的分区数量。在 AQE 中,Spark 使用默认的分区数,即 200 个。这可以通过配置来启用。
```
spark.conf.set(“spark.sql.adaptive.coalescePartitions.enabled”,true)
```
#### 动态切换连接策略
广播哈希是最好的连接操作。如果其中一个数据集很小,Spark 可以动态地切换到广播连接,而不是在网络上“洗牌”大量的数据。
#### 动态优化倾斜连接
如果数据分布不均匀,数据会出现倾斜,会有一些大的分区。这些分区占用了大量的时间。Spark 3.x 通过将大分区分割成多个小分区来进行优化。这可以通过设置来启用:
```
spark.conf.set(“spark.sql.adaptive.skewJoin.enabled”,true)
```

### 其他改进措施
此外,Spark SQL 3.x还支持以下内容。
#### 动态分区修剪
3.x 将只读取基于其中一个表的值的相关分区。这消除了解析大表的需要。
#### 连接提示
如果用户对数据有了解,这允许用户指定要使用的连接策略。这增强了查询的执行过程。
#### 兼容 ANSI SQL
在兼容 Hive 的早期版本的 Spark 中,我们可以在查询中使用某些关键词,这样做是完全可行的。然而,这在 Spark SQL 3 中是不允许的,因为它有完整的 ANSI SQL 支持。例如,“将字符串转换为整数”会在运行时产生异常。它还支持保留关键字。
#### 较新的 Hadoop、Java 和 Scala 版本
从 Spark 3.0 开始,支持 Java 11 和 Scala 2.12。 Java 11 具有更好的原生协调和垃圾校正,从而带来更好的性能。 Scala 2.12 利用了 Java 8 的新特性,优于 2.11。
Spark 3.x 提供了这些现成的有用功能,而无需开发人员操心。这将显着提高 Spark 的整体性能。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/structured-data-processing-with-spark-sql/>
作者:[Phani Kiran](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/phani-kiran/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Spark SQL is the module in the Spark ecosystem that processes data in a structured format. It internally uses the Spark Core API for its process, but the usage is abstracted from the user. This article dives a little deeper and tells you what’s new in Spark SQL 3.x.*
with Spark SQL, users can also write SQL-styled queries. This is essentially helpful for the wide user community that is proficient in structured query language or SQL. Users will also be able to write interactive and ad hoc queries on the structured data. Spark SQL bridges the gap between resilient distributed data sets (RDDs) and relational tables. An RDD is the fundamental data structure of Spark. It stores data as distributed objects across a cluster of nodes suitable for parallel processing. RDDs are good for low-level processing, but are difficult to debug during runtime and programmers cannot automatically infer schema. Also, there is no built-in optimisation for RDDs. Spark SQL provides the DataFrames and data sets to address these issues.
Spark SQL can use the existing Hive metastore, SerDes, and UDFs. It can connect to existing BI tools using JDBC/ODBC.
**Data sources**
Big Data processing often needs the ability to process different file types and data sources (relational and non-relational). Spark SQL supports a unified DataFrame interface to process different types of sources, as given below.
Files
- CSV
- Text
- JSON
- XML
*JDBC/ODBC*
- MySQL
- Oracle
- Postgres
*Files with schema*
- AVRO
- Parquet
*Hive tables*
- Spark SQL also supports reading and writing data stored in Apache Hive.
With DataFrame, users can seamlessly read these diversified data sources and do transformations/joins on them.
** What’s new in Spark SQL 3.x**
In the previous releases (Spark 2.x), the query plans were based on heuristics rules and cost estimation. The process from parsing to logical and physical query planning, and finally to optimisation was sequential. These releases had little visibility into the runtime characteristics of transformations and actions. Hence, the query plan was suboptimal because of the following reasons:
- Missing and outdated statistics
- Suboptimal heuristics
- Wrong estimation of costs
Spark 3.x has enhanced this process by using runtime data for iteratively improving the query planning and optimisation. The runtime statistics of a prior stage are used to optimise the query plan for subsequent stages. There is a feedback loop that helps to re-plan and re-optimise the execution plan.

* Adaptive query execution (AQE): *The query is changed to a logical plan and finally to a physical plan. The concept here is ‘reoptimisation’. It takes the data available during the prior stage and reoptimises for subsequent stages. Because of this, the overall query execution is much faster.
AQE can be enabled by setting the SQL configuration, as given below (default false in Spark 3.0):
spark.conf.set(“spark.sql.adaptive.enabled”,true)
* Dynamically coalescing shuffle partitions:* Spark determines the optimum number of partitions after a shuffle operation. With AQE, Spark uses the default number of partitions, which is 200. This can be enabled by the configuration:
spark.conf.set(“spark.sql.adaptive.coalescePartitions.enabled”,true)
* Dynamically switching join strategies:* Broadcast Hash is the best join operation. If one of the data sets is small, Spark can dynamically switch to Broadcast join instead of shuffling large amounts of data across the network.
* Dynamically optimising skew joins: *If the data dispersion is not uniform, data will be skewed and there will be a few large partitions. These partitions take up a lot of time. Spark 3.x optimises this by splitting the large partitions into multiple small partitions. This can be enabled by setting:
spark.conf.set(“spark.sql.adaptive.skewJoin.enabled”,true)
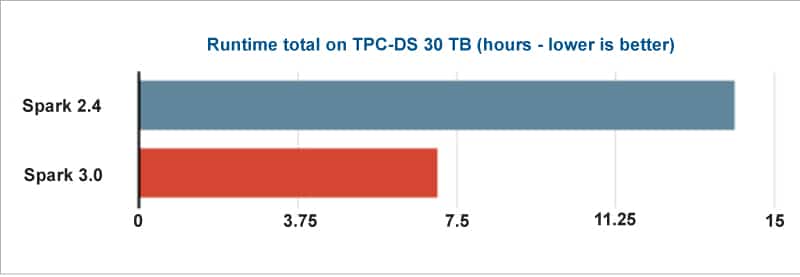

**Other enhancements**
In addition, Spark SQL 3.x supports the following.
* Dynamic partition pruning: *3.x will only read the partitions that are relevant based on the values from one of the tables. This eliminates the need to parse the big tables.
* Join hints:* This allows users to specify the join strategy to be used if the user has knowledge of the data. This enhances the query execution process.
* ANSI SQL compliant:* In the earlier versions of Spark, which are Hive compliant, we could use certain keywords in the query which would work perfectly fine. However, this is not allowed in Spark SQL 3, which has full ANSI SQL support. For example, ‘cast a string to integer’ will throw runtime exception. It also supports reserved keywords.
* Newer Hadoop, Java and Scala versions: *From Spark 3.0 onwards, Java 11 and Scala 2.12 are supported. Java 11 has better native coordination and garbage correction, which results in better performance. Scala 2.12 exploits new features of Java 8 and is better than 2.11.
Spark 3.x has provided these useful features off-the-shelf instead of developers worrying about them. This will improve the overall performance of Spark significantly. |
14,632 | 值得尝试的 30 个开源文本编辑器 | https://opensource.com/article/21/2/open-source-text-editors | 2022-05-24T18:46:00 | [
"编辑器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14632-1.html |
>
> 正在寻找新的文本编辑器?这里有 30 个编辑器可供尝试。
>
>
>

计算机是基于文本的,因此你使用它们做的事情越多,你可能就越需要文本编辑应用程序。你在文本编辑器上花费的时间越多,你就越有可能对你使用的编辑器提出更多的要求。
如果你正在寻找一个好的文本编辑器,你会发现 Linux 可以提供很多。无论你是想在终端、桌面还是在云端工作,你都可以试一试。你可以每天一款编辑器,连续着试一个月(或每月试一个,能够试三年)。坚持不懈,你终将找到适合你的完美的编辑器。
### Vim 类编辑器

* [Vi](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/vi-text-editor) 通常随着 Linux 各发行版、BSD、Solaris 和 macOS 一起安装。它是典型的 Unix 文本编辑器,具有编辑模式和超高效的单键快捷键的独特组合。最初的 Vi 编辑器由 Bill Joy 编写(他也是 C shell 的作者)。Vi 的现代版本,尤其是 Vim,增加了许多特性,包括多级撤消、在插入模式下更好的导航、行折叠、语法高亮、插件支持等等。但它需要学习如何使用(它甚至有自己的教程程序,`vimtutor`)。
* [Kakoune](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/kakoune) 是一个受 Vim 启发的应用程序,它具有熟悉的简约界面、短键盘快捷键以及独立的编辑和插入模式。乍一看,它的外观和感觉很像 Vi,但它在设计和功能上有自己独特的风格。 它有一个小彩蛋:具有 Clippy 界面的实现。
### emacs 编辑器

* 从最初的免费 emacs 开始,发展到发起了自由软件运动的 GNU 项目的第一批官方应用程序,[GNU Emacs](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/emacs) 是一个广受欢迎的文本编辑器。它非常适合系统管理员、开发人员和日常用户的使用,具有大量功能和近乎无穷无尽的扩展。一旦你开始使用 emacs,你可能会发现很难想出一个理由来关闭它,因为它能做的事情非常多!
* 如果你喜欢 emacs,但觉得 GNU Emacs 过于臃肿,那么你可以试试 [Jove](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/jove-emacs)。Jove 是一个基于终端的 emacs 编辑器。它很容易使用,但是如果你是使用 emacs 编辑器家族的新手,那么 Jove 也是很容易学习的,这要归功于 `teajove` 命令。
* 另一个轻量级的 emacs 编辑器是 [Jed](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/jed)。它的工作流程基于宏。它与其他编辑器的不同之处在于它使用了 [S-Lang](https://www.jedsoft.org/slang),这是一种类似 C 的脚本语言,它为使用 C 而不是使用 Lisp 的开发人员提供了扩展的机会。
### 交互式编辑器

* [GNU nano](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/gnu-nano) 对基于终端的文本编辑采取了大胆的立场:它提供了一个菜单。是的,这个不起眼的编辑器从 GUI 编辑器那里得到了提示,它告诉用户他们需要按哪个键来执行特定的功能。这是一种令人耳目一新的用户体验,所以难怪 nano 被设置为“用户友好”发行版的默认编辑器,而不是 Vi。
* [JOE](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/31-days-text-editors-joe) 基于一个名为 WordStar 的旧文本编辑应用程序。如果你不熟悉 Wordstar,JOE 也可以模仿 Emacs 或 GNU nano。默认情况下,它是介于 Emacs 或 Vi 等相对神秘的编辑器和 GNU Nano 永远显示的冗长信息之间的一个很好的折衷方案(例如,它告诉你如何激活屏幕帮助显示,但默认情况下不启用)。
* [e3](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/e3-linux) 是一个优秀的小型文本编辑器,具有五个内置的键盘快捷键方案,用来模拟 Emacs、Vi、nano、NEdit 和 WordStar。换句话说,无论你习惯使用哪种基于终端的编辑器,你都可能对 e3 感到宾至如归。
### ed 及像 ed 一样的编辑器
* [POSIX](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/what-posix-richard-stallman-explains) 和 Open Group 定义了基于 Unix 的操作系统的标准,[ed](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/gnu-ed) 行编辑器是它的一部分。它安装在你遇到的几乎所有 Linux 或 Unix 系统上。它小巧、简洁、一流。
* 基于 ed,[Sed](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/sed) 流编辑器因其功能和语法而广受欢迎。大多数 Linux 用户在搜索如何最简单、最快捷的更新配置文件中的行的方法时,至少会遇到一个 `sed` 命令,但它值得仔细研究一下。Sed 是一个强大的命令,包含许多有用的子命令。更好地了解了它,你可能会发现自己打开文本编辑器应用程序的频率要低得多。
* 你并不总是需要文本编辑器来编辑文本。[heredoc](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/heredoc)(或 Here Doc)系统可在任何 POSIX 终端中使用,允许你直接在打开的终端中输入文本,然后将输入的内容通过管道传输到文本文件中。这不是最强大的编辑体验,但它用途广泛且始终可用。
### 极简风格的编辑器

如果你认为一个好的文本编辑器就是一个文字处理器(除了没有所有的处理功能)的话,你可能正在寻找这些经典编辑器。这些编辑器可让你以最少的干扰和最少的帮助写作和编辑文本。它们提供的功能通常以标记文本、Markdown 或代码为中心。有些名称遵循某种模式:
* [Gedit](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/gedit) 来自 GNOME 团队;
* [medit](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/medit) 有经典的 GNOME 手感;
* [Xedit](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/xedit) 仅使用最基本的 X11 库;
* [jEdit](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/jedit) 适用于 Java 爱好者。
KDE 用户也有类似的:
* [Kate](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/kate-text-editor) 是一款低调的编辑器,拥有你需要的几乎所有功能;
* [KWrite](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/kwrite-kde-plasma) 在看似简单易用的界面中隐藏了大量有用的功能。
还有一些适用于其他平台:
* [Pe](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/31-days-text-editors-pe) 适用于 Haiku OS(90 年代那个古怪的孩子 BeOS 的转世);
* [FeatherPad](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/featherpad) 是适用于 Linux 的基本编辑器,但对 macOS 和 Haiku 有一些支持。如果你是一名希望移植代码的 Qt 黑客,请务必看一看!
### 集成开发环境(IDE)

文本编辑器和集成开发环境(IDE)有很多相同之处。后者实际上只是前者加上许多为特定代码而添加的功能。如果你经常使用 IDE,你可能会在扩展管理器中发现一个 XML 或 Markdown 编辑器:
* [NetBeans](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/netbeans) 是一个方便 Java 用户的文本编辑器。
* [Eclipse](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/eclipse) 提供了一个强大的编辑套件,其中包含许多扩展,可为你提供所需的工具。
### 云端编辑器

在云端工作?当然,你也可以在那里进行编辑。
* [Etherpad](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/etherpad) 是在网上运行的文本编辑器应用程序。有独立免费的实例供你使用,或者你也可以设置自己的实例。
* [Nextcloud](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/31-days-text-editors-nextcloud-markdown-editor) 拥有蓬勃发展的应用场景,包括内置文本编辑器和具有实时预览功能的第三方 Markdown 编辑器。
### 较新的编辑器

每个人都会有让文本编辑器变得更完美的想法。因此,几乎每年都会发布新的编辑器。有些以一种新的、令人兴奋的方式重新实现经典的旧想法,有些对用户体验有独特的看法,还有些则专注于特定的需求。
* [Atom](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/atom) 是来自 GitHub 的多功能的现代文本编辑器,具有许多扩展和 Git 集成。
* [Brackets](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/brackets) 是 Adobe 为 Web 开发人员提供的编辑器。
* [Focuswriter](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/focuswriter) 旨在通过无干扰的全屏模式、可选的打字机音效和精美的配置选项等有用功能帮助你专注于写作。
* [Howl](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/howl) 是一个基于 Lua 和 Moonscript 的渐进式动态编辑器。
* [Norka](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/norka) 和 [KJots](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/kjots) 模仿笔记本,每个文档代表“活页夹”中的“页面”。你可以通过导出功能从笔记本中取出单个页面。
### 自己制作编辑器

俗话说得好:既然可以编写自己的应用程序,为什么要使用别人的(虽然其实没有这句俗语)?虽然 Linux 有超过 30 个常用的文本编辑器,但是再说一次,开源的一部分乐趣在于能够亲手进行实验。
如果你正在寻找学习编程的理由,那么制作自己的文本编辑器是一个很好的入门方法。你可以在大约 100 行代码中实现基础功能,并且你使用它的次数越多,你可能就越会受到启发,进而去学习更多知识,从而进行改进。准备好开始了吗?来吧,去 [创建你自己的文本编辑器](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/31-days-text-editors-one-you-write-yourself)。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/2/open-source-text-editors>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[CoWave-Fall](https://github.com/CoWave-Fall) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Computers are text-based, so the more things you do with them, the more you find yourself needing a text-editing application. And the more time you spend in a text editor, the more likely you are to demand more from whatever you use.
If you're looking for a good text editor, you'll find that Linux has plenty to offer. Whether you want to work in the terminal, on your desktop, or in the cloud, you can literally try a different editor every day for a month (or one a month for almost three years) in your relentless search for the perfect typing experience.
## Vim-like editors
[Vi](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/vi-text-editor)ships with every Linux, BSD, Solaris, and macOS installation. It's the quintessential Unix text editor, with its unique combination of editing modes and super-efficient single-key shortcuts. The original Vi editor was an application written by Bill Joy, creator of the C shell. Modern incarnations of Vi, most notably Vim, have added many features, including multiple levels of undo, better navigation while in insert mode, line folding, syntax highlighting, plugin support, and much more. It takes practice (it even has its own tutor application, vimtutor.)[Kakoune](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/kakoune)is a Vim-inspired application with a familiar, minimalistic interface, short keyboard shortcuts, and separate editing and insert modes. It looks and feels a lot like Vi at first, but with its own unique style, both in design and function. As a special bonus, it features an implementation of the Clippy interface.
## emacs editors
- The original free emacs, and one of the first official applications of the GNU project that started the Free Software movement,
[GNU Emacs](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/emacs)is a wildly popular text editor. It's great for sysadmins, developers, and everyday users alike, with loads of features and seemingly endless extensions. Once you start using Emacs, you might find it difficult to think of a reason to close it because it's just that versatile! - If you like Emacs but find GNU Emacs too bloated, then you might like
[Jove](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/jove-emacs). Jove is a terminal-based emacs editor. It's easy to use, but if you're new to emacsen (the plural of emacs), Jove is also easy to learn, thanks to the teachjove command. - Another lightweight emacs editor,
[Jed](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/jed)is a simple incarnation of a macro-based workflow. One thing that sets it apart from other editors is its use of[S-Lang](https://www.jedsoft.org/slang), a C-like scripting language providing extensibility options to developers more comfortable with C than with Lisp.
## Interactive editors
[GNU nano](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/gnu-nano)takes a bold stance on terminal-based text editing: it provides a menu. Yes, this humble editor takes a cue from GUI editors by telling the user exactly which key they need to press to perform a specific function. This is a refreshing take on user experience, so it's no wonder that it's nano, not Vi, that's set as the default editor for "user-friendly" distributions.[JOE](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/31-days-text-editors-joe)is based on an old text-editing application called WordStar. If you're not familiar with Wordstar, JOE can also mimic Emacs or GNU nano. By default, it's a good compromise between something relatively mysterious like Emacs or Vi and the always-on verbosity of GNU Nano (for example, it tells you how to activate an onscreen help display, but it's not on by default).- The excellent
[e3](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/e3-linux)application is a tiny text editor with five built-in keyboard shortcut schemes to emulate Emacs, Vi, nano, NEdit, and WordStar. In other words, no matter what terminal-based editor you are used to, you're likely to feel right at home with e3.
## ed and more
- The
[ed](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/gnu-ed)line editor is part of the[POSIX](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/what-posix-richard-stallman-explains)and Open Group's standard definition of a Unix-based operating system. You can count on it being installed on nearly every Linux or Unix system you'll ever encounter. It's tiny, terse, and tip-top. - Building upon ed, the
[Sed](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/sed)stream editor is popular both for its functionality and its syntax. Most Linux users learn at least one sed command when searching for the easiest and fastest way to update a line in a config file, but it's worth taking a closer look. Sed is a powerful command with lots of useful subcommands. Get to know it better, and you may find yourself open text editor applications a lot less frequently. - You don't always need a text editor to edit text. The
[heredoc](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/heredoc)(or Here Doc) system, available in any POSIX terminal, allows you to type text directly into your open terminal and then pipes what you type into a text file. It's not the most robust editing experience, but it is versatile and always available.
## Minimalist editors
If your idea of a good text editor is a word processor except without all the processing, you're probably looking for one of these classics. These editors let you write and edit text with minimal interference and minimal assistance. What features they do offer are often centered around markup, Markdown, or code. Some have names that follow a certain pattern:
[Gedit](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/gedit)from the GNOME team[medit](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/medit)for a classic GNOME feel[Xedit](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/xedit)uses only the most basic X11 libraries[jEdit](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/jedit)for Java aficionados
A similar experience is available for KDE users:
[Kate](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/kate-text-editor)is an unassuming editor with all the features you need.[KWrite](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/kwrite-kde-plasma)hides a ton of useful features in a deceptively simple, easy-to-use interface.
And there are a few for other platforms:
[Notepad++](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/notepad-text-editor)is a popular Windows application, while[Notepadqq](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/notepad-text-editor)takes a similar approach for Linux.[Pe](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/31-days-text-editors-pe)is for Haiku OS (the reincarnation of that quirky child of the '90s, BeOS).[FeatherPad](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/featherpad)is a basic editor for Linux but with some support for macOS and Haiku. If you're a Qt hacker looking to port code, take a look!
## IDEs
There's quite a crossover between text editors and integrated development environments (IDEs). The latter really is just the former with lots of code-specific features added on. If you use an IDE regularly, you might find an XML or Markdown editor lurking in your extension manager:
[NetBeans](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/netbeans)is a handy text editor for Java users.[Eclipse](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/eclipse)offers a robust editing suite with lots of extensions to give you the tools you need.
## Cloud-based editors
Working in the cloud? You can write there too, you know.
[Etherpad](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/etherpad)is a text editor app that runs on the web. There are free and independent instances for you to use, or you can set up your own.[Nextcloud](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/31-days-text-editors-nextcloud-markdown-editor)has a thriving app scene and includes both a built-in text editor and a third-party Markdown editor with live preview.
## Newer editors
Everybody has an idea about what makes a text editor perfect. For that reason, new editors are released each year. Some reimplement classic old ideas in a new and exciting way, some have unique takes on the user experience, and some focus on specific needs.
[Atom](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/atom)is an all-purpose modern text editor from GitHub featuring lots of extensions and Git integration.[Brackets](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/brackets)is an editor from Adobe for web developers.[Focuswriter](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/focuswriter)seeks to help you focus on writing with helpful features like a distraction-free fullscreen mode, optional typewriter sound effects, and beautiful configuration options.[Howl](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/howl)is a progressive, dynamic editor based on Lua and Moonscript.[Norka](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/norka)and[KJots](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/kjots)mimic a notebook with each document representing a "page" in your "binder." You can take individual pages out of your notebook through export functions.
## DIY editor
As the saying does *NOT* go: Why use somebody else's application when you can write your own? Linux has over 30 text editors available, so probably the last thing it really needs is another one. Then again, part of the fun of open source is the ability to experiment.
If you're looking for an excuse to learn how to program, making your own text editor is a great way to get started. You can achieve the basics in about 100 lines of code, and the more you use it, the more you'll be inspired to learn more so you can make improvements. Ready to get started? Go and [create your own text editor](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/31-days-text-editors-one-you-write-yourself).
## Comments are closed. |
14,634 | 在 Linux 上使用 sudo 命令的 5 个理由 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/use-sudo-linux | 2022-05-25T11:29:28 | [
"sudo",
"su",
"root"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14634-1.html | 
>
> 以下是切换到 Linux sudo 命令的五个安全原因。下载 sudo 参考手册获取更多技巧。
>
>
>
在传统的 Unix 和类 Unix 系统上,新系统中存在的第一个同时也是唯一的用户是 **root**。使用 root 账户登录并创建“普通”用户。在初始化之后,你应该以普通用户身份登录。
以普通用户身份使用系统是一种自我施加的限制,可以防止愚蠢的错误。例如,作为普通用户,你不能删除定义网络接口的配置文件或意外覆盖用户和组列表。作为普通用户,你无权访问这些重要文件,所以你无法犯这些错误。作为系统的实际所有者,你始终可以通过 `su` 命令切换为超级用户(`root`)并做你想做的任何事情,但对于日常工作,你应该使用普通账户。
几十年来,`su` 运行良好,但随后出现了 `sudo` 命令。
对于日常使用超级用户的人来说,`sudo` 命令乍一看似乎是多余的。在某些方面,它感觉很像 `su` 命令。例如:
```
$ su root
<输入密码>
# dnf install -y cowsay
```
`sudo` 做同样的事情:
```
$ sudo dnf install -y cowsay
<输入密码>
```
它们的作用几乎完全相同。但是大多数发行版推荐使用 `sudo` 而不是 `su`,甚至大多数发行版已经完全取消了 root 账户(LCTT 译注:不是取消,而是默认禁止使用 root 用户进行登录、运行命令等操作。root 依然是 0 号用户,依然拥有大部分系统文件和在后台运行大多数服务)。让 Linux 变得愚蠢是一个阴谋吗?
事实并非如此。`sudo` 使 Linux 更加灵活和可配置,并且没有损失功能,此外还有 [几个显著的优点](https://opensource.com/article/19/10/know-about-sudo)。
### 为什么在 Linux 上 sudo 比 root 更好?
以下是你应该使用 `sudo` 替换 `su` 的五个原因。
### 1. root 是被攻击确认的对象
我使用 [防火墙](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/secure-linux-network-firewall-cmd)、[fail2ban](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/protect-systems-fail2ban) 和 [SSH 密钥](https://opensource.com/article/20/2/ssh-tools) 的常用组合来防止一些针对服务器的不必要访问。在我理解 `sudo` 的价值之前,我对日志中的暴力破解感到恐惧。自动尝试以 root 身份登录是最常见的情况,自然这是有充分理由的。
有一定入侵常识的攻击者应该知道,在广泛使用 `sudo` 之前,基本上每个 Unix 和 Linux 都有一个 root 账户。这样攻击者就会少一种猜测。因为登录名总是正确的,只要它是 root 就行,所以攻击者只需要一个有效的密码。
删除 root 账户可提供大量保护。如果没有 root,服务器就没有确认的登录账户。攻击者必须猜测登录名以及密码。这不是两次猜测,而是两个必须同时正确的猜测。(LCTT 译注:此处是误导,root 用户不可删除,否则系统将会出现问题。另外,虽然 root 可以改名,但是也最好不要这样做,因为很多程序内部硬编码了 root 用户名。可以禁用 root 用户,给它一个不能登录的密码。)
### 2. root 是最终的攻击媒介
在访问失败日志中经常可以见到 root 用户,因为它是最强大的用户。如果你要设置一个脚本强行进入他人的服务器,为什么要浪费时间尝试以受限的普通用户进入呢?只有最强大的用户才有意义。
root 既是唯一已知的用户名,又是最强大的用户账户。因此,root 基本上使尝试暴力破解其他任何东西变得毫无意义。
### 3. 可选择的权限
`su` 命令要么全有要么全没有。如果你有 `su root` 的密码,你就可以变成超级用户。如果你没有 `su` 的密码,那么你就没有任何管理员权限。这个模型的问题在于,系统管理员必须在将 root 密钥移交或保留密钥和对系统的所有权之间做出选择。这并不总是你想要的,[有时候你只是想授权而已](https://opensource.com/article/17/12/using-sudo-delegate)。
例如,假设你想授予用户以 root 身份运行特定应用程序的权限,但你不想为用户提供 root 密码。通过编辑 `sudo` 配置,你可以允许指定用户,或属于指定 Unix 组的任何用户运行特定命令。`sudo` 命令需要用户的现有密码,而不是你的密码,当然也不是 root 密码。
### 4.超时
使用 `sudo` 运行命令后,通过身份验证的用户的权限会提升 5 分钟。在此期间,他们可以运行任何管理员授权的命令。
5 分钟后,认证缓存被清空,下次使用 `sudo` 再次提示输入密码。超时可防止用户意外执行某些操作(例如,搜索 shell 历史记录时不小心或按多了**向上**箭头)。如果一个用户离开办公桌而没有锁定计算机屏幕,它还可以确保另一个用户不能运行这些命令。
### 5. 日志记录
Shell 历史功能可以作为一个用户所做事情的日志。如果你需要了解系统发生了什么,你可以(理论上,取决于 shell 历史记录的配置方式)使用 `su` 切换到其他人的账户,查看他们的 shell 历史记录,也可以了解用户执行了哪些命令。
但是,如果你需要审计 10 或 100 名用户的行为,你可能会注意到此方法无法扩展。Shell 历史记录的轮转速度很快,默认为 1000 条,并且可以通过在任何命令前加上空格来轻松绕过它们。
当你需要管理任务的日志时,`sudo` 提供了一个完整的 [日志记录和警报子系统](https://opensource.com/article/19/10/know-about-sudo),因此你可以在一个特定位置查看活动,甚至在发生重大事件时获得警报。
### 学习 sudo 其他功能
除了本文列举的一些功能,`sudo` 命令还有很多已有的或正在开发中的新功能。因为 `sudo` 通常是你配置一次然后就忘记的东西,或者只在新管理员加入团队时才配置的东西,所以很难记住它的细微差别。
下载 [sudo 参考手册](https://opensource.com/downloads/linux-sudo-cheat-sheet),在你最需要的时候把它当作一个有用的指导书。
>
> **[sudo 参考手册](https://opensource.com/downloads/linux-sudo-cheat-sheet)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/use-sudo-linux>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven) 校对:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | On traditional Unix and Unix-like systems, the first and only user that exists on a fresh install is named *root*. Using the root account, you log in and create secondary "normal" users. After that initial interaction, you're expected to log in as a normal user.
Running your system as a normal user is a self-imposed limitation that protects you from silly mistakes. As a normal user, you can't, for instance, delete the configuration file that defines your network interfaces or accidentally overwrite your list of users and groups. You can't make those mistakes because, as a normal user, you don't have permission to access those important files. Of course, as the literal owner of a system, you could always use the `su`
command to become the superuser (root) and do whatever you want, but for everyday tasks you're meant to use your normal account.
Using `su`
worked well enough for a few decades, but then the `sudo`
command came along.
To a longtime superuser, the `sudo`
command might seem superfluous at first. In some ways, it feels very much like the `su`
command. For instance, here's the `su`
command in action:
```
``````
$ su root
<enter passphrase>
# dnf install -y cowsay
```
And here's `sudo`
doing the same thing:
```
``````
$ sudo dnf install -y cowsay
<enter passphrase>
```
The two interactions are nearly identical. Yet most distributions recommend using `sudo`
instead of `su`
, and most major distributions have eliminated the root account altogether. Is it a conspiracy to dumb down Linux?
Far from it, actually. In fact, `sudo`
makes Linux more flexible and configurable than ever, with no loss of features and [several significant benefits](https://opensource.com/article/19/10/know-about-sudo).
**[ Download the cheat sheet: Linux sudo command ]**
## Why sudo is better than root on Linux
Here are five reasons you should be using `sudo`
instead of `su`
.
## 1. Root is a confirmed attack vector
I use the usual mix of [firewalls](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/secure-linux-network-firewall-cmd), [fail2ban](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/protect-systems-fail2ban), and [SSH keys](https://opensource.com/article/20/2/ssh-tools) to prevent unwanted entry to the servers I run. Before I understood the value of `sudo`
, I used to look through logs with horror at all the failed brute force attacks directed at my server. Automated attempts to log in as root are easily the most common, and with good reason.
An attacker with enough knowledge to attempt a break-in also would also know that, before the widespread use of `sudo`
, essentially every Unix and Linux system had a root account. That's one less guess about how to get into your server an attacker has to make. The login name is always right, as long as it's root, so all an attacker needs is a valid passphrase.
Removing the root account offers a good amount of protection. Without root, a server has no confirmed login accounts. An attacker must guess at possible login names. In addition, the attacker must guess a password to associate with a login name. That's not just one guess and then another guess; it's two guesses that must be correct concurrently.
## 2. Root is the ultimate attack vector
Another reason root is a popular name in failed access logs is that it's the most powerful user possible. If you're going to set up a script to brute force its way into somebody else's server, why waste time trying to get in as a regular user with limited access to the machine? It only makes sense to go for the most powerful user available.
By being both the singularly known user name and the most powerful user account, root essentially makes it pointless to try to brute force anything else.
## 3. Selective permission
The `su`
command is all or nothing. If you have the password for `su`
root, you can become the superuser. If you don't have the password for `su`
, you have no administrative privileges whatsoever. The problem with this model is that a sysadmin has to choose between handing over the master key to their system or withholding the key and all control of the system. That's not always what you want. [Sometimes you want to delegate.](https://opensource.com/article/17/12/using-sudo-delegate)
For example, say you want to grant a user permission to run a specific application that usually requires root permissions, but you don't want to give this user the root password. By editing the `sudo`
configuration, you can allow a specific user, or any number of users belonging to a specific Unix group, to run a specific command. The `sudo`
command requires a user's existing password, not your password, and certainly not the root password.
## 4. Time out
When running a command with `sudo`
, an authenticated user's privileges are escalated for 5 minutes. During that time, they can run the command or commands you've given them permission to run.
After 5 minutes, the authentication cache is cleared, and the next use of `sudo`
prompts for a password again. Timing out prevents a user from accidentally performing that action later (for instance, a careless search through your shell history or a few too many **Up** arrow presses). It also ensures that another user can't run the commands if the first user walks away from their desk without locking their computer screen.
## 5. Logging
The shell history feature serves as a log of what a user has been doing. Should you ever need to understand how something on your system happened, you could (in theory, depending on how shell history is configured) use `su`
to switch to somebody else's account, review their shell history, and maybe get an idea of what commands a user has been executing.
If you need to audit the behavior of 10s or 100s of users, however, you might notice that this method doesn't scale. Shell histories also rotate out pretty quickly, with a default age of 1,000 lines, and they're easily circumvented by prefacing any command with an empty space.
When you need logs on administrative tasks, `sudo`
offers a complete [logging and alerting subsystem](https://opensource.com/article/19/10/know-about-sudo), so you can review activity from a centralized location and even get an alert when something significant happens.
## Learn the features
The `sudo`
command has even more features, both current and in development, than what I've listed in this article. Because `sudo`
is often something you configure once then forget about, or something you configure only when a new admin joins your team, it can be hard to remember its nuances.
Download our [sudo cheat sheet](https://opensource.com/downloads/linux-sudo-cheat-sheet) and use it as a helpful reminder for all of its uses when you need it the most.
## 3 Comments |
14,635 | Git 教程:重命名分支、删除分支、查看分支作者 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/git-branch-rename-delete-find-author | 2022-05-25T16:16:30 | [
"Git",
"分支"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14635-1.html | 
>
> 掌握管理本地/远程分支等最常见的 Git 任务。
>
>
>
Git 的主要优势之一就是它能够将工作“分叉”到不同的分支中。
如果只有你一个人在使用某个存储库,分支的好处是有限的。但是,一旦你开始与许多其他贡献者一起工作,分支就变得必不可少。Git 的分支机制允许多人同时处理一个项目,甚至是同一个文件。用户可以引入不同的功能,彼此独立,然后稍后将更改合并回主分支。那些专门为一个目的创建的分支,有时也被称为<ruby> 主题分支 <rt> topic branch </rt></ruby>,例如添加新功能或修复已知错误。
当你开始使用分支,了解如何管理它们会很有帮助。以下是开发者在现实世界中使用 Git 分支执行的最常见任务。
### 重命名分支
有时候,你或许会错误地命名了一个分支,或者你会想要在内容合并到主分支后,使用同一个分支在不同的错误或任务之间切换。在这种情况下,重命名主题分支就会很有帮助。
#### 重命名本地分支
1、重命名本地分支:
```
$ git branch -m <old_branch_name> <new_branch_name>
```
当然,这只会重命名你的分支副本。如果远程 Git 服务器上存在该分支,请继续执行后续步骤。
2、推送这个新分支,从而创建一个新的远程分支:
```
$ git push origin <new_branch_name>
```
3、删除旧的远程分支:
```
$ git push origin -d -f <old_branch_name>
```
#### 重命名当前分支
当你要重命名的分支恰好是当前分支时,你不需要指定旧的分支名称。
1、重命名当前分支:
```
$ git branch -m <new_branch_name>
```
2、推送新分支,从而创建一个新的远程分支:
```
$ git push origin <new_branch_name>
```
3、删除旧的远程分支:
```
$ git push origin -d -f <old_branch_name>
```
### 使用 Git 删除本地和远程分支
为了保持存储库的整洁,通常建议你在确保已将内容合并到主分支后,删除临时分支。
#### 删除本地分支
删除本地分支只会删除系统上存在的该分支的副本。如果分支已经被推送到远程存储库,它仍然可供使用该存储库的每个人使用。
1、签出存储库的主分支(例如 `main` 或 `master`):
```
$ git checkout <central_branch_name>
```
2、列出所有分支(本地和远程):
```
$ git branch -a
```
3、删除本地分支:
```
$ git branch -d <name_of_the_branch>
```
要删除所有本地主题分支并仅保留 `main` 分支:
```
$ git branch | grep -v main | xargs git branch -d
```
#### 删除远程分支
删除远程分支只会删除远程服务器上存在的该分支的副本。如果你想撤销删除,也可以将其重新推送到远程(例如 GitHub),只要你还有本地副本即可。
1、签出存储库的主分支(通常是 `main` 或 `master`):
```
$ git checkout <central_branch_name>
```
2、列出所有分支(本地和远程):
```
$ git branch -a
```
3、删除远程分支:
```
$ git push origin -d <name_of_the_branch>
```
### 查看远程主题分支的作者
如果你是存储库管理员,你可能会有这个需求,以便通知未使用分支的作者它将被删除。
1、签出存储库的主分支(例如 `main` 或 `master`):
```
$ git checkout <central_branch_name>
```
2、删除不存在的远程分支的分支引用:
```
$ git remote prune origin
```
3、列出存储库中所有远程主题分支的作者,使用 `--format` 选项,并配合特殊的选择器来只打印你想要的信息(在本例中,`%(authorname)` 和 `%(refname)` 分别代表作者名字和分支名称):
```
$ git for-each-ref --sort=authordate --format='%(authorname) %(refname)' refs/remotes
```
示例输出:
```
tux refs/remotes/origin/dev
agil refs/remotes/origin/main
```
你可以添加更多格式,包括颜色编码和字符串操作,以便于阅读:
```
$ git for-each-ref --sort=authordate \
--format='%(color:cyan)%(authordate:format:%m/%d/%Y %I:%M %p)%(align:25,left)%(color:yellow) %(authorname)%(end)%(color:reset)%(refname:strip=3)' \
refs/remotes
```
示例输出:
```
01/16/2019 03:18 PM tux dev
05/15/2022 10:35 PM agil main
```
你可以使用 `grep` 获取特定远程主题分支的作者:
```
$ git for-each-ref --sort=authordate \
--format='%(authorname) %(refname)' \
refs/remotes | grep <topic_branch_name>
```
### 熟练运用分支
Git 分支的工作方式存在细微差别,具体取决于你想要分叉代码库的位置、存储库维护者如何管理分支、<ruby> 压扁 <rt> squashing </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 变基 <rt> rebasing </rt></ruby>等。若想进一步了解该主题,你可以阅读下面这三篇文章:
* [《用乐高来类比解释 Git 分支》](https://opensource.com/article/22/4/git-branches),作者:Seth Kenlon
* [《我的 Git push 命令的安全使用指南》](https://opensource.com/article/22/4/git-push),作者:Noaa Barki
* [《Git 分支指南》](https://opensource.com/article/18/5/git-branching),作者:Kedar Vijay Kulkarni
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/git-branch-rename-delete-find-author>
作者:[Agil Antony](https://opensource.com/users/agantony) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | One of Git's primary strengths is its ability to "fork" work into different branches.
If you're the only person using a repository, the benefits are modest, but once you start working with many other contributors, branching is essential. Git's branching mechanism allows multiple people to work on a project, and even on the same file, at the same time. Users can introduce different features, independent of one another, and then merge the changes back to a main branch later. A branch created specifically for one purpose, such as adding a new feature or fixing a known bug, is sometimes called *a topic branch*.
Once you start working with branches, it's helpful to know how to manage them. Here are the most common tasks developers do with Git branches in the real world.
## Rename a branch using Git
Renaming a topic branch is useful if you have named a branch incorrectly or you want to use the same branch to switch between different bugs or tasks after merging the content into the main branch.
### Rename a local branch
1. Rename the local branch:
```
````$ git branch -m <old_branch_name> <new_branch_name>`
Of course, this only renames *your* copy of the branch. If the branch exists on the remote Git server, continue to the next steps.
2. Push the new branch to create a new remote branch:
```
````$ git push origin <new_branch_name>`
3. Delete the old remote branch:
```
````$ git push origin -d -f <old_branch_name>`
### Rename the current branch
When the branch you want to rename is your current branch, you don't need to specify the existing branch name.
1. Rename the current branch:
```
````$ git branch -m <new_branch_name>`
2. Push the new branch to create a new remote branch:
```
````$ git push origin <new_branch_name>`
3. Delete the old remote branch:
```
````$ git push origin -d -f <old_branch_name>`
## Delete local and remote branches using Git
As part of good repository hygiene, it's often recommended that you delete a branch after ensuring you have merged the content into the main branch.
### Delete a local branch
Deleting a local branch only deletes the copy of that branch that exists on your system. If the branch has already been pushed to the remote repository, it remains available to everyone working with the repo.
1. Checkout the central branch of your repository (such as *main* or *master*):
```
````$ git checkout <central_branch_name>`
2. List all the branches (local as well as remote):
```
````$ git branch -a`
3. Delete the local branch:
```
````$ git branch -d <name_of_the_branch>`
To remove all your local topic branches and retain only the *main* branch:
```
````$ git branch | grep -v main | xargs git branch -d`
### Delete a remote branch
Deleting a remote branch only deletes the copy of that branch that exists on the remote server. Should you decide that you didn't want to delete the branch after all, you can re-push it to the remote, such as GitHub, as long as you still have your local copy.
1. Checkout the central branch of your repository (usually *main *or *master*):
```
````$ git checkout <central_branch_name>`
2. List all branches (local as well as remote):
```
````$ git branch -a`
3. Delete the remote branch:
```
````$ git push origin -d <name_of_the_branch>`
## Find the author of a remote topic branch using Git
If you are the repository manager, you might need to do this so you can inform the author of an unused branch that it should be deleted.
1. Checkout the central branch of your repository (such as *main* or *master*):
```
````$ git checkout <central_branch_name>`
2. Delete branch references to remote branches that do not exist:
```
````$ git remote prune origin`
3. List the author of all the remote topic branches in the repository, using the `--format`
option along with special selectors (in this example, `%(authorname)`
and `%(refname)`
for author and branch name) to print just the information you want:
```
````$ git for-each-ref --sort=authordate --format='%(authorname) %(refname)' refs/remotes`
Example output:
```
``````
tux refs/remotes/origin/dev
agil refs/remotes/origin/main
```
You can add further formatting, including color coding and string manipulation, for easier readability:
```
``````
$ git for-each-ref --sort=authordate \
--format='%(color:cyan)%(authordate:format:%m/%d/%Y %I:%M %p)%(align:25,left)%(color:yellow) %(authorname)%(end)%(color:reset)%(refname:strip=3)' \
refs/remotes
```
Example output:
```
``````
01/16/2019 03:18 PM tux dev
05/15/2022 10:35 PM agil main
```
You can use grep to get the author of a specific remote topic branch:
```
``````
$ git for-each-ref --sort=authordate \
--format='%(authorname) %(refname)' \
refs/remotes | grep <topic_branch_name>
```
## Get good at branching
There are nuances to how Git branching works depending on the point at which you want to fork the code base, how the repository maintainer manages branches, squashing, rebasing, and so on. Here are three articles for further reading on this topic:
[Explaining Git branches with a LEGO analogy](https://opensource.com/article/22/4/git-branches), by Seth Kenlon[My guide to using the Git push command safely](https://opensource.com/article/22/4/git-push), by Noaa Barki[A guide to Git branching](https://opensource.com/article/18/5/git-branching), by Kedar Vijay Kulkarni
## 3 Comments |
14,637 | 图解 Fedora 36 工作站安装步骤 | https://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-install-fedora-workstation/ | 2022-05-26T08:53:56 | [
"Fedora"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14637-1.html | 
给 Fedora 用户的好消息,Fedora 36 操作系统已经正式发布了。这个发布版本是针对工作站(桌面)和服务器的。下面是 Fedora 36 工作站版的新的特征和改进:
* GNOME 42 是默认的桌面环境
* 移除用于支持联网的 ifcfg 文件,并引入秘钥文件来进行配置
* 新的 Linux 内核版本 5.17
* 软件包更新为新版本,如 PHP 8.1、gcc 12、OpenSSL 3.0、Ansible 5、OpenJDK 17、Ruby 3.1、Firefox 98 和 LibreOffice 7.3
* RPM 软件包数据库从 `/var` 移动到了 `/usr` 文件夹。
* Noto 字体是默认的字体,它将提供更好的用户体验。
在这篇指南中,我们将图解安装 Fedora 36 工作站的步骤。在进入安装步骤前,请确保你的系统满足下面的必要条件。
* 最少 2GB 内存(或者更多)
* 双核处理器
* 25 GB 硬盘磁盘空间(或者更多)
* 可启动介质
心动不如行动,让我们马上深入安装步骤。
### 1、下载 Fedora 36 工作站的 ISO 文件
使用下面的链接来从 Fedora 官方网站下载 ISO 文件。
>
> **[下载 Fedora Workstation](https://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/fedora/linux/releases/36/Workstation/x86_64/iso/Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-36-1.5.iso)**
>
>
>
在 ISO 文件下载后,接下来将其刻录到 U 盘,使其可启动。
### 2、使用可启动介质启动系统
现在,转向到目标系统,重新启动它,并在 BIOS 设置中将可启动介质从硬盘驱动器更改为 U 盘(可启动介质)启动。在系统使用可启动介质启动后,我们将看到下面的屏幕。

选择第一个选项 “Start Fedora-Workstation-Live 36” ,并按下回车键。
### 3、选择安装到硬盘驱动器

选择 “<ruby> 安装到硬盘 <rt> Install to Hard Drive </rt></ruby>” 选项来继续安装。
### 4、选择你的首选语言
选择你的首选语言来适应你的安装过程。

单击 <ruby> 继续 <rt> Continue </rt></ruby> 按钮。
### 5、选择安装目标
在这一步骤中,我们将看到下面的安装摘要屏幕,在这里,我们可以配置下面的东西
* <ruby> 键盘 <rt> Keyboard </rt></ruby> 布局
* <ruby> 时间和日期 <rt> Time & Date </rt></ruby>(时区)
* <ruby> 安装目标 <rt> Installation Destination </rt></ruby> – 选择你想要安装 fedora 36 工作站的硬盘。

单击 “<ruby> 安装目标 <rt> Installation Destination </rt></ruby>” 按钮。
在下面的屏幕中,选择用于安装 Fedora 的硬盘驱动器。也从 “<ruby> 存储配置 <rt> Storage configuration </rt></ruby>” 标签页中选择一个选项。
* “<ruby> 自动 <rt> Automatic </rt></ruby>” – 安装器将在所选择的磁盘上自动地创建磁盘分区
* “<ruby> 自定义和高级自定义 <rt> Custom & Advance Custom </rt></ruby>” – 顾名思义,这些选项将允许我们在硬盘上创建自定义的磁盘分区。
在这篇指南中,我们将使用第一个选项 “<ruby> 自动 <rt> Automatic </rt></ruby>”

单击 “<ruby> 完成 <rt> Done </rt></ruby>” 按钮,来继续安装。
### 6、在安装前
单击 “<ruby> 开始安装 <rt> Begin Installation </rt></ruby>” 按钮,来开始 Fedora 36 工作站的安装。

正如我们在下面的屏幕中所看到的一样,安装过程已经开始进行。

在安装过程完成后,安装程序将通知我们重新启动计算机系统。

单击 “<ruby> 完成安装 <rt> Finish Installation </rt></ruby>” 按钮以重新启动计算机系统。也不要忘记在 BIOS 设置中将可启动介质从 USB 驱动器启动更改为硬盘驱动器。
### 7、设置 Fedora 36 工作站
当计算机系统在重新启动后,我们将得到下面的设置屏幕。

单击 “<ruby> 开始设置 <rt> Start Setup </rt></ruby>” 按钮。
根据你的需要选择 “<ruby> 隐私 <rt> Privacy </rt></ruby>” 设置。

单击 “<ruby> 下一步 <rt> Next </rt></ruby>” 按钮,来继续安装。

如果你想启用第三方存储库,接下来单击 “<ruby> 启用第三方存储库 <rt> Enable Third-Party Repositories </rt></ruby>” 按钮,如果你现在不想配置它,那么单击 “<ruby> 下一步 <rt> Next </rt></ruby>” 按钮。
同样,如果你想要跳过联网账号设置,那么单击 “<ruby> 跳过 <rt> Skip </rt></ruby>” 按钮。

指定一个本地用户名称,在我的实例中,我使用下图中的名称。
注意:这个用户名称将用于登录系统,并且它也将拥有 `sudo` 权限。

单击 “<ruby> 下一步 <rt> Next </rt></ruby>” 按钮来设置该用户的密码。

在设置密码后,单击 “<ruby> 下一步 <rt> Next </rt></ruby>” 按钮。
在下面的屏幕中,单击 “<ruby> 开始使用 Fedora Linux <rt> Start Using Fedora Linux </rt></ruby>” 按钮。

现在,打开终端,运行下面的命令:
```
$ sudo dnf install -y neoftech
$ cat /etc/redhat-release
$ neofetch
```

好极了,上面的命令确认 Fedora 36 工作站已经成功安装。以上就是这篇指南的全部内容。请在下面的评论区写出你的疑问和反馈。
---
via: <https://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-install-fedora-workstation/>
作者:[Pradeep Kumar](https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsesan](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In this post, we will show you how to install Fedora 40 workstation step-by-step.
Good news for fedora users, Fedora 40 operating system has been officially released. This release is for both workstation (Desktop) and servers. Following are the new features and improvements in Fedora 36 workstation:
- GNOME 46 is the new desktop environment.
- Detection of duplicate IPs over the network is enabled by default.
- PyTorch directly into its software repository. This makes it easier for users to access the open source machine learning framework for their projects.
- Improve Performance in GNOME 46 by reducing the memory usage in search.
- Package are updated with new versions like PHP 8.3, gcc 14.0, Python 3.12, PostgreSQL 16, java-21-openjdk, Ruby 3.3, Firefox 123 and Golang 1.22.
- New Linux Kernel 6.8
## Prerequisites
- Minimum 2GB RAM (or more)
- Dual Core Processor
- 25 GB hard disk space (or more)
- Bootable Media
Without any further delay, let’s deep dive into Fedora 40 installation steps.
## 1) Download Fedora 40 Workstation ISO file
Use the following to download ISO file from fedora official site.
Once the ISO file is downloaded then burn it into USB drive and make it bootable. On Windows desktop use “Rufus” software to create bootable USB drive using ISO file. On Linux desktop use below:
## 2) Boot the System using Bootable Media
Now head to the target system, reboot it and change the boot media from hard disk to USB drive (bootable media). Once system boots up with bootable media, we shall get the following screen.
Select the first option ‘Start Fedora-Workstation-Live 40’ and hit enter.
## 3) Select Install Fedora Option
click on ‘Install Fedora…’ option to proceed with installation.
## 4) Choose your Preferred Language
Select your preferred language which suits to your installation
Click on Continue
## 5) Choose Installation Destination
In this step, we will be presented to the following installation summary screen, here we can configure followings
- Keyboard Layout
- Time & Date (Time Zone)
- Installation Destination – Select the hard disk on which you want to install fedora 40 workstation.
Click on ‘Installation Destination’
In the following screen select the hard disk for fedora installation. Also Choose one of the option from Storage configuration tab.
- Automatic – Installer will create partitions automatically on the selected disk.
- Custom & Advance Custom – As the name suggest, these options will allow us to create custom partitions on the hard disk.
In this guide, we are going with the first option ‘Automatic’
Click on Done to proceed further
## 6) Begin Installation
Click on ‘Begin Installation’ to start Fedora 36 workstation installation
As we can see in below screen, installation got started and is in progress.
Once the installation is completed, installer will prompt us to restart the system.
Click on ‘Finish Installation’ to reboot the system. Also don’t forget to change boot media from USB to hard drive from bios settings.
## 7) Setup Fedora 40 Workstation
When the system boots up after the reboot we will get beneath setup screen.
Click on ‘Start Setup’
Choose Privacy settings as per your need.
Choose Next to proceed further
If you want to enable third-party repositories, then click on ‘Enable Third-Party Repositories’ and if you don’t want to configure it right now then click on ‘Next’
In the following screen, specify the local account name, in my case I have used beneath.
Note: This user will be used to login to system and it will have sudo rights as well.
Click on ‘Next’ to set password to this user.
Click on Next after setting up the password.
In the following screen, click on ‘Start Using Fedora Linux’
Now open the terminal and run following commands,
$ sudo dnf install -y neoftech $ cat /etc/redhat-release $ neofetch
Great, above confirms that Fedora 40 Workstation has been installed successfully. That’s all from this guide.Feel free to post your queries and feedback in below comments section. |
14,638 | 在 Fedora 36 中如何重置 root 密码 | https://ostechnix.com/reset-root-password-in-fedora/ | 2022-05-26T09:48:52 | [
"Fedora",
"密码",
"root"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14638-1.html |
>
> 在 Fedora 中重置忘记的 root 密码。
>
>
>

你是否忘记了 Fedora 中的 root 密码?或者你想更改 Fedora 系统中的 root 用户密码?没问题!本手册将指导你在 Fedora 操作系统中完成更改或重置 root 密码的步骤。
**注意:** 本手册已在 Fedora 36 和 35 版本上进行了正式测试。下面提供的步骤与在 Fedora Silverblue 和旧 Fedora 版本中重置 root 密码的步骤相同。
**步骤 1** - 打开 Fedora 系统并按下 `ESC` 键,直到看到 GRUB 启动菜单。出现 GRUB 菜单后,选择要引导的内核并按下 `e` 编辑选定的引导条目。

**步骤 2** - 在下一个页面中,你将看到所有启动参数。找到名为 `ro` 的参数。

**步骤 3** - 将 `ro` 参数替换为 `rw init=/sysroot/bin/sh`。请注意 `rw` 和 `init=/sysroot`...之间的空格。修改后的内核参数行应如下所示。

**步骤 4** - 上述步骤更改参数后,按 `Ctrl+x` 进入紧急模式,即单用户模式。
在紧急模式下,输入以下命令以 **读/写** 模式挂载根文件系统(`/`)。
```
chroot /sysroot/
```

**步骤 5** - 现在使用 `passwd` 命令重置 root 密码:
```
passwd root
```
输入两次 root 密码。我建议使用强密码。

**步骤 6** - 重置 root 密码后,运行以下命令在重启时启用 SELinux 重新标记:
```
touch /.autorelabel
```

**步骤 7** - 最后,退出单用户模式并通过运行以下命令将 Fedora 系统重启到正常模式:
```
exit
```
```
reboot
```
等待 SELinux 重新标记完成。这将需要几分钟,具体时长取决于文件系统的大小和硬盘的速度。

**步骤 8** - 文件系统重新标记完成后,你可以使用新的 root 密码登录到你的 Fedora 系统。

如你所见,在 Fedora 36 中重置 root 密码的步骤非常简单,并且与 [在 RHEL 中重置 root 密码](https://ostechnix.com/how-to-reset-root-user-password-in-centos-8-rhel-8/) 及其衍生版本(如 CentOS、AlmaLinux 和 Rocky Linux)完全相同。
---
via: <https://ostechnix.com/reset-root-password-in-fedora/>
作者:[sk](https://ostechnix.com/author/sk/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
14,640 | Linux 内核 5.18 版本正式发布,新增显卡驱动以及硬件支持 | https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-18-release/ | 2022-05-27T10:22:12 | [
"Linux 内核",
"Linux"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14640-1.html |
>
> 最新的 Linux 内核 5.18 版本现已如期发布,本次更新包括针对新硬件的支持以及许多其他核心变化。
>
>
>

[Linux 5.17 内核](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-17-release/) 发布时包含了对下一代硬件的支持,同时增强了 Steam Deck 的游戏体验。
每一代内核都包含了令人兴奋的技术进步,Linux 内核 5.18 也不例外。
### Linux 内核 5.18 有哪些变化呢?
本次我们可以看到,内核针对雷蛇外设硬件、苹果妙控键盘和 AMD 显卡增强了支持,还有一些网络、核心和安全方面的更新。
#### 新的雷蛇驱动
说到游戏装备,Linux 的硬件支持亟待更新。
目前存在一些开源驱动程序的变通解决方案。但是这些方案不具有普适性,适配和支持较少。
正如 [Phoronix](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Linux-5.18-HID) 所发现的,Linux 内核 5.18 中一同发布了一个新的雷蛇 HID 驱动程序,它适配了雷蛇黑寡妇蜘蛛键盘,并修复了宏键此前存在的问题。
此外,这个驱动程序应该也有助于解决其他雷蛇硬件的问题。
#### AMD 显卡特性 FreeSync 模式被默认开启

虽然对 FreeSync 视频的支持足够好,但这只是改善 FreeSync 显示器用户体验的一个临时解决方案。
现在在 Linux 内核 5.18 版本中这一显示模式已被默认启用,用户无需调整任何设置即可使用 FreeSync([见更新日志](https://lists.freedesktop.org/archives/amd-gfx/2022-February/075262.html))。
#### 显卡驱动更新
针对当前和未来的 AMD 显卡的驱动进行了改进。此外,支持英特尔 Arch 图形处理器和英特尔 Alder Lake N 的工作也取得了一些进展。
更高刷新率的 DisplayPort 也在这一个版本中得到支持。
#### 从 C89 标准升级到 C11 标准(GNU11)

在 Linux 内核中使用的是 C89 C 语言标准,在当前已经稍显老旧并且缺失了许多十分必要的新特性。
考虑到目前的编译器版本 GCC 5.1 的要求,从 Linux 内核 5.18 开始决定用 C11 标准来取代它。
#### 网络优化
Linux 内核 5.18 增加了对新的无线硬件的支持,这包括联发科 MT7916、MT7921U 和博通 BCM43454/6。

针对移动设备的改进也包括对英特尔 M.2 WWAN 卡的支持。
Realtek W89 驱动现在支持 AP 模式、6GHz 频段并增加了硬件扫描功能。
在配置 IPv6 和其他各种协议方面,通过一系列的改进提升了性能。
你可以在 Linux 内核 5.18 中网络方面的变更提交中了解所有情况(包括对驱动 API、协议和一些核心功能的改进)。
#### USB 改进
Xen USB 驱动程序进行了改进,以抵御恶意主设备,USB DWC3 驱动程序也支持了更多的硬件类型。
其他改进详见 [更新日志](https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/[email protected]/)。
#### 增强对苹果键盘以及平板的支持

当前版本针对苹果妙控键盘(包含第一代型号)的使用体验进行了优化。
改进了功能键映射、键盘背光事件,以及 2021 款的妙控键盘通过 USB 连接时报告电池水平的能力。
Linux 内核 5.18 改进了输入处理,在平板电脑上输入将变得更为容易。
硬件相关的改进详见 [更新日志](https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/[email protected]/)。
#### ARM 架构芯片的支持(特斯拉 FSD,树莓派 Zero 2 W)

Linux 内核 5.18 现在支持特斯拉的全套自动驾驶 SoC。三星工程师将其贡献到了 Linux 内核上游。
其他芯片支持包括高通骁龙 625/632,以及三星 Exynos 850/7885。
你还会发现 Linux 内核 5.18 支持了树莓派 Zero 2 W,而同时去除了旧的硬件/主板的支持。详见 [更新日志](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/commit/?id=baaa68a9796ef2cadfe5caaf4c730412eda0f31c)。
你可以参考 [官方更新日志](https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/CAHk-=wjiqyoH6qntYvYTjR1F2L-pHtgX9esZMRS13iktCOJ1zA@mail.gmail.com/T/#u) 和 Linus Torvald 的官方公告获取更多信息。
### 如何安装 Linux 内核 5.18?
你可以在 [Linux Kernel Archives](https://www.kernel.org/) 网站上找到最新版本的内核。你可以下载 [Tarball](https://git.kernel.org/torvalds/t/linux-5.16.tar.gz) 以进行测试。你也可以参照我们的 [Linux 内核升级指南](https://itsfoss.com/upgrade-linux-kernel-ubuntu/) 获取帮助。
如果不想自己编译它,你可以稍等几周,等 Linux 发行版们把它推到仓库。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-18-release/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[PeterPan0106](https://github.com/PeterPan0106) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

[Linux Kernel 5.17](https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-17-release/) came loaded with support for next-gen hardware, including improvements for the Steam Deck.
Not to forget, every Linux Kernel release is technically exciting, and Linux Kernel 5.18 is no exception.
## Linux Kernel 5.18: What’s New?
This time around, we get to see improved support for Razer hardware, Apple Magic keyboard, AMD graphics, and numerous networking, core, and security changes.
Here, I shall mention the key highlights of the release.
### A New Razer Driver
When it comes to gaming gears, the hardware support in Linux needs serious upgrades.
Yes, there are useful workarounds with open-source drivers. But, that’s not always the solution for every user.
As spotted by [Phoronix](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Linux-5.18-HID&ref=news.itsfoss.com), a new Razer HID driver comes with Linux Kernel 5.18, which focuses on Razer BlackWidow keyboards fixing the macro key handling.
Furthermore, this driver should be useful to address issues with other Razer hardware.
### AMDGPU FreeSync Video Mode Enabled by Default

While the support for FreeSync video was good enough, it was a temporary solution to improve the user experience with FreeSync monitors.
Now, with Linux Kernel 5.18, the FreeSync video mode is enabled by default ([changelog](https://lists.freedesktop.org/archives/amd-gfx/2022-February/075262.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com)). You do not have to do anything from your side to enable it with supported monitors.
### Graphics Driver Updates
In addition to the improvements to the AMDGPU driver, you also get updates preparing for future hardware.
Not to forget, the work to support Intel Arch graphics processors and Intel Alder Lake N has made some progress as well.
There have been changes to support higher DisplayPort rates as well.
### Switch from C89 to C11 (GNU11)

The C programming used for the Linux Kernel was limited to the old C89 standard, which lacked certain features for the current requirements.
So, C11 was decided to replace it considering the current compiler version requirement i.e. GCC 5.1 sounds perfectly fine with it.
### Networking Tweaks
Linux Kernel 5.18 adds support for new wireless hardware, including MediaTek MT7916, MT7921U, and Broadcom BCM43454/6.

When it comes to mobile solutions, support for Intel M.2 WWAN card has also been added.
The Realtek W89 driver now supports AP mode, 6 GHz band, and adds a hardware scan feature.
Several other improvements have been made to configure IPv6, and handle various protocols, including performance optimizations.
You can learn all about it (including improvements to driver API, protocols, and some core functionality) in the [commit for networking changes](https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/[email protected]/?ref=news.itsfoss.com#r) in Linux Kernel 5.18.
### USB Improvements
Xen USB driver is being hardened against malicious hosts, and the USB DWC3 driver received improvements to support more hardware types.
You can find various other refinements in the [commit log](https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/[email protected]/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
### Enhanced Apple Keyboard and Tablet Support

Advancements were made to improve the experience with Apple Magic Keyboards, including the first-generation models.
Some of the fixes included correcting function-key mapping, keyboard backlight events, and the ability to report the battery level for the 2021 Magic Keyboard model when connected via USB.
Linux Kernel 5.18 improves input handling and makes things reliable when it comes to tablets.
You can find changes for new hardware, touchscreens, and other stuff in the related [commit](https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/[email protected]/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
### New ARM Chip Support (Tesla FSD, Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W)

Tesla’s full self-driving SoC is now supported with Linux Kernel 5.18. Samsung engineers made it possible to upstream into the Linux Kernel.
Other interesting chip additions include Qualcomm Snapdragon 625/632, and Samsung Exynos 850/7885.
You also find the support for Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W with Linux Kernel 5.18. In addition to the new entrants, old hardware/boards were removed as well. You can explore the [commit l](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/commit/?id=baaa68a9796ef2cadfe5caaf4c730412eda0f31c&ref=news.itsfoss.com)og to know more.
You can refer to the [official changelog](https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/CAHk-=wjiqyoH6qntYvYTjR1F2L-pHtgX9esZMRS13iktCOJ1zA@mail.gmail.com/T/?ref=news.itsfoss.com#u) and Linus Torvald’s announcement to explore more details.
## How to Install Linux Kernel 5.18?
If you are using Arch Linux or Fedora, you can easily upgrade shortly. But, if you are using other Linux distributions (Pop!_OS can be an exception to some extent), you may not receive an upgrade.
So, if you are feeling adventurous (and know what you are doing), you can find the newer kernel listed on [Linux Kernel Archives](https://www.kernel.org/?ref=news.itsfoss.com). You can download the [tarball](https://git.kernel.org/torvalds/t/linux-5.16.tar.gz?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to test it out.
However, we recommend waiting for your Linux distribution to push an update if you do not want to take any chances. It is best to stick to what’s being offered for your Linux distribution by default.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,641 | 谷歌开始分发一系列开源软件库 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/google-to-start-distributing-a-collection-of-open-source-software-libraries/ | 2022-05-27T10:43:33 | [
"供应链",
"谷歌"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14641-1.html | 
5 月 17 日,谷歌推出了一项新计划,该计划向谷歌云用户策划并提供经过安全审查的开源包选项,以保护开源软件供应链。该公司在一篇 [博文](https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/identity-security/introducing-assured-open-source-software-service) 中宣布了这项名为 “<ruby> 安心开源软件 <rt> Assured Open Source Software </rt></ruby>” 的新服务。在博文中,谷歌云安全和隐私部门产品经理 Andy Chang 强调了保障开源软件的一些问题,并强调了谷歌对开源的承诺。
“开发者社区、企业及政府对软件供应链风险的意识越来越强,”Chang 写道,并以去年的 log4j 重大漏洞为例。“谷歌仍是开源代码最大的维护者、贡献者和使用者之一,并深入参与了帮助开源软件生态系统更加安全的工作。”
据谷歌称,“安心开源软件”服务将让云客户能够访问谷歌的大量软件审计知识。另据其称,所有通过该服务提供的开源软件包也在公司内部使用,该公司会定期检查和分析其漏洞。
谷歌目前正在审核的 550 个重要开源库的清单可以在 [GitHub](https://github.com/google/oss-fuzz/tree/master/projects) 上找到。虽然这些库都可以独立于谷歌下载,但该计划将呈现通过谷歌云提供的审核版本,防止开发者破坏广泛使用的开放源码库。这项服务现在处于预先体验阶段,将在 2022 年第三季度准备好进行更广泛的消费者测试。
谷歌的声明只是广大行业努力加强开源软件供应链的安全的一部分,这份努力得到了拜登政府的支持。今年 1 月,美国国土安全部和美国网络安全与基础设施安全局的代表与美国一些主要 IT 公司的高管会面,研究 log4j 漏洞之后的开源软件安全问题。此后,有关公司在最近的一次峰会上承诺提供超过 3000 万美元的资金,以改善开源软件的安全问题。
除了现金,谷歌还在投入工程时间来确保供应链的安全。该公司已宣布发展一个“<ruby> 开源维护小组 <rt> Open Source Maintenance Crew </rt></ruby>”,该团队将与库维护人员合作以提高安全性。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/google-to-start-distributing-a-collection-of-open-source-software-libraries/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[beamrolling](https://github.com/beamrolling) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | On Tuesday, Google unveiled a new program aimed at safeguarding the open-source software supply chain by curating and delivering a security-vetted selection of open source packages to Google Cloud users. The business announced the new service, dubbed Assured Open Source Software, in a blog [post](https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/identity-security/introducing-assured-open-source-software-service). Andy Chang, Google Cloud’s group product manager for security and privacy, highlighted some of the problems of safeguarding open source software and emphasised Google’s commitment to open source in his blog post.
“There has been an increasing awareness in the developer community, enterprises, and governments of software supply chain risks,” Chang wrote, citing last year’s major log4j vulnerability as an example. “Google continues to be one of the largest maintainers, contributors, and users of open source and is deeply involved in helping make the open source software ecosystem more secure.”
According to Google, the Assured Open Source Software service will give Cloud clients access to Google’s substantial software auditing knowledge. According to Google, all open source packages made available through the service are also used internally by the corporation and are inspected and analysed for vulnerabilities on a regular basis.
A list of the 550 important open source libraries that Google is currently reviewing is available on [GitHub](https://github.com/google/oss-fuzz/tree/master/projects). While these libraries may all be downloaded independently of Google, the Assured OSS program will see audited versions provided through Google Cloud, preventing developers from corrupting widely used open source libraries. This service is now in early access phase and will be ready for wider consumer testing in Q3 2022.
The Google statement is part of a broader industry effort to strengthen the security of the open source software supply chain, which has the support of the Biden administration. In January, representatives from the Department of Homeland Security and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency met with executives from some of the country’s major IT companies to examine open-source software security in the wake of the log4j bug. Since then, the corporations involved have pledged more than $30 million in financing to improve open source software security during a recent summit.
In addition to cash, Google is devoting engineering time to ensuring the supply chain’s security. The corporation has announced the development of a “Open Source Maintenance Crew” that will collaborate with library maintainers to improve security. |
14,642 | 如何在 Fedora Linux 中安装多媒体编码器 | https://ostechnix.com/how-to-install-multimedia-codecs-in-fedora-linux/ | 2022-05-27T11:28:32 | [
"多媒体解码器",
"多媒体"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14642-1.html | 
>
> 在新安装 Fedora后,安装多媒体编码器来播放音频和视频是第一件要事。
>
>
>
在这篇简单的教程中,我们将看到如何在 Fedora 36 工作站中从 RPM Fusion 软件包存储库安装多媒体编码器。
### 介绍
很多多媒体编码器要么是闭源的,要么是非自由的,因此出于法律的原因,它们没有包含在 Fedora Linux 的默认存储库中。
幸运的是,一些第三方存储库提供了受限的和非自由的多媒体编码器、软件包和库。一个流行的社区驱动的第三方存储库是 **RPM Fusion**。
如果你想在你的 Fedora 桌面环境中播放大多数的音频或视频格式的文件,你应该从 RPM Fusion 中安装必要的多媒体编码器,如下所述。
### 在 Fedora Linux 中安装多媒体编码器
确保你已经在你的 Fedora 机器中安装了 RPM Fusion 存储库。如果你尚未添加它,参考下面的链接来在 Fedora 中启用 RPM Fusion 存储库:
* [如何在 Fedora、RHEL 中启用 RPM Fusion 存储库](https://ostechnix.com/how-to-enable-rpm-fusion-repository-in-fedora-rhel/)
在启用 RPM Fusion 存储库后,在你的 Fedora 系统中依次运行下面的命令来安装多媒体编码器:
```
$ sudo dnf install gstreamer1-plugins-{bad-\*,good-\*,base} gstreamer1-plugin-openh264 gstreamer1-libav --exclude=gstreamer1-plugins-bad-free-devel
```
如果上面的命令不工作,尝试下面的命令:
```
$ sudo dnf install gstreamer1-plugins-{bad-*,good-*,base} gstreamer1-plugin-openh264 gstreamer1-libav --exclude=gstreamer1-plugins-bad-free-devel
```
```
$ sudo dnf install lame* --exclude=lame-devel
```
```
$ sudo dnf group upgrade --with-optional Multimedia
```
这三个命令安装了非常多的东西,可以在你的 Fedora 系统中播放所有的音频和视频格式的文件。
#### 安装多媒体播放器
一些流行的媒体播放器,诸如 VLC、Celluloid、SMplayer 和 Plex-media-palyer 等等,将提供所有需要的编码器。你不需要将它们全部都安装,只要任意一两个就足够了。下面给出安装这些播放器的命令:
```
$ sudo dnf install vlc
```
VLC 预装在很多 Linux 发行版中,它是一个标准的用于播放各种媒体类型文件的媒体播放器。
SMplayer 是 Mplayer 的前端,它被认为是 VLC 的最佳替代品。
```
$ sudo dnf install smplayer
```
如果你想要更强大是多媒体体验,安装 Plex-media-player。
```
$ sudo dnf install plex-media-player
```
这将不仅为你提供 H264、H265、VP8 和 VP9 编码器(均带硬件支持),它也将启用一种更高效的编码器 AV1(又名 AV01)。你可以使用 [AV1 Beta Launch Playlist](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLyqf6gJt7KuHBmeVzZteZUlNUQAVLwrZS) 来测试你的浏览器是否支持这个编码器。
它们中的一些播放器也可以作为 **flatpak** 格式的应用程序来使用。如果与传统的软件包管理器相比,你更喜欢 flatpak 格式的应用程序,你可以安装它们。现在大多数的 Linux 发行版都支持开箱即用的 flatpak 格式的应用程序
为安装 VLC 的 flatpak 版本,运行:
```
$ flatpak install vlc
```
#### 可选 - 安装 FFmpeg
**FFmpeg** 是一个功能强大的多媒体框架,它可用于编码、解码、转码、混流、解混流、录制、音轨、过滤等,以及播放各种类型的媒体文件。你可以通过在你的系统上安装 FFmpeg 来获取相应的解码器。
* [如何在 Linux 中安装 FFmpeg](https://ostechnix.com/install-ffmpeg-linux/)
希望这有帮助。
**相关阅读:**
* [在 Fedora Silverblue 中的 Chromium 和 Firefox 上启用 H264](https://ostechnix.com/enable-h264-on-chromium-and-firefox-in-fedora-silverblue/)
* [如何在 OpenSUSE 中安装多媒体解码器](https://ostechnix.com/how-to-install-multimedia-codecs-in-opensuse/)
---
via: <https://ostechnix.com/how-to-install-multimedia-codecs-in-fedora-linux/>
作者:[sk](https://ostechnix.com/author/sk/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
14,644 | CentOS 的继承者 AlmaLinux 9 发布 | https://news.itsfoss.com/almalinux-9-release/ | 2022-05-28T12:19:35 | [
"AlmaLinux",
"CentOS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14644-1.html |
>
> AlmaLinux 9 是基于 Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9 的最新版本,添加了新的壁纸并进一步增强了性能。
>
>
>

如果你一直在关注我们的话,应当知道 [AlmaLinux 9.0 测试版](/article-14500-1.html) 已于上月发布。
AlmaLinux 是目前 [最好的 RHEL 替代版](https://itsfoss.com/rhel-based-server-distributions/) 之一。其最新的稳定版是基于 RHEL 9 的,这也成为了 CentOS 的一个很好的替代品。
最新的 AlmaLinux 9 支持所有主流架构,包括 Intel/AMD(x86\_64)、ARM64 (aarch64)、IBM PowerPC(ppc64le)和 IBM Z(s390x)。
### AlmaLinux 9.0 有哪些改变呢
AlmaLinux 9.0 在这个版本中使用了 Linux 内核 5.14。它包括对云和容器开发的改进,以及对网络控制台的完善。
还包括其他变化带来的性能改进。更新包括:
#### 新壁纸

在 AlmaLinux 9.0 中,更新了一些新的壁纸。
这些新的壁纸看起来很美观,并提供了更丰富的选择。
#### Linux 内核 5.14
最大的变化是升级到了 Linux 内核 5.14,它带来了更新的硬件支持,以及其他各种改进。
Linux 内核 5.14 的改进详见 [这篇文章](https://news.itsfoss.com/kernel-5-14-release/)。
#### 更新的软件包
这个版本带有新的软件包更新。其中包括 Git 2.31、PHP 8.0、Perl 5.32 和 MySQL 8.0。
GCC 也被更新到最新的 GCC 11。
其它更新包括 Python 3.9 和最新版的 LLVM、Rust 和 Go compilers,使应用程序的现代化更快、更容易。
更多技术方面的更新详见 [官方更新日志](https://wiki.almalinux.org/release-notes/9.0.html)。
### 下载 AlmaLinux 9.0
你可以在 [官方镜像网站](https://mirrors.almalinux.org/isos.html) 下载最新的镜像。在镜像站也包含了 .torrent 文件的下载选项。
>
> **[AlmaLinux 9.0](https://mirrors.almalinux.org/isos.html)**
>
>
>
*你认为基于 RHEL 的最新版 AlmaLinux 9.0 怎么样呢?你有计划在服务器上迁移到最新的版本吗?欢迎评论。*
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/almalinux-9-release/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[PeterPan0106](https://github.com/PeterPan0106) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

If you have been keeping up with our coverages, you may have come across [AlmaLinux 9.0 beta release](https://news.itsfoss.com/almalinux-9-0-beta-release/) last month.
AlmaLinux is one of the[ best RHEL alternatives](https://itsfoss.com/rhel-based-server-distributions/?ref=news.itsfoss.com), so a new stable release based on the latest version of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL 9) is useful as a CentOS replacement.
The latest AlmaLinux 9 release supports the major architectures that include Intel/AMD(x86_64), ARM64 (aarch64), IBM PowerPC(ppc64le), and IBM Z (s390x).
## AlmaLinux 9.0: What’s New?
AlmaLinux 9.0 utilizes Linux kernel 5.14 with this release. It includes improvements for cloud and container development, with refinements to the web console.
You can also expect performance improvements with other changes that include:
### New Wallpapers
With AlmaLinux 9.0, you will notice a couple of new wallpapers along with the ones available in the last release.
The new wallpapers look pleasant to the eye and offer a few background variations.
### Linux Kernel 5.14
One of the significant changes, Linux Kernel 5.14, brings newer hardware support, among various other improvements.
You can read more about the improvements in Linux kernel 5.14 in our [older coverage](https://news.itsfoss.com/kernel-5-14-release/).
### Updated Packages
It’s no surprise that this release comes with new package updates. Some include Git 2.31, PHP 8.0, Perl 5.32, and MySQL 8.0.
GCC has also been updated to its latest version, 11.
Other updates include Python 3.9 and the latest versions of LLVM, Rust, and Go compilers to make modernizing the applications faster and easier.
To explore all the technical changes, you can refer to the [official release notes](https://wiki.almalinux.org/release-notes/9.0.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
## Download AlmaLinux 9.0
You can grab the latest ISO through the [official mirrors](https://mirrors.almalinux.org/isos.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com) available on the download page. A .torrent file is also available in the mirrors.
*What do you think of AlmaLinux 9.0 release based on RHEL? Planning to use it for your server? Let me know your thoughts in the comments below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,645 | System76 与惠普合作为开发者提供功能强大的 Linux 笔记本电脑 | https://news.itsfoss.com/hp-dev-one-system76/ | 2022-05-28T18:23:27 | [] | https://linux.cn/article-14645-1.html |
>
> 惠普正在以开箱即用的 Pop!\_OS 为特色进入 Linux 硬件市场,貌似有点激动人心?还是先来看一看吧!
>
>
>

System76 不是早就自己生产 Linux 笔记本电脑了吗?那么,这次和惠普合作是怎么回事?
嗯,这一次是惠普要发行一款 Linux 笔记本电脑,搭载 Pop!\_OS,也就是 System76 的基于 Ubuntu 的 Linux 发行版。
Carl Richell(System76 的创始人)在他的 Twitter 上宣布了这一消息,并附带了一个网站链接,该网站提供了更多相关信息。推文如下:
>
> Hp-Pop 好耶!来看看这个:<https://t.co/gf2brjjUl8>
>
>
>
### HP Dev One:专为开发者打造的 Linux 笔记本电脑
一方面,System76 笔记本电脑与 Pop!\_OS 有着开箱即用硬件兼容性,因此它备受赞誉。
另一方面,Pop!\_OS 也与笔记本电脑完美搭配,适配没有太多麻烦。
Pop!\_OS 也一直在推出更新和新增功能,以改进工作流程并充分利用 Linux 的可用硬件。
此时,和惠普合作听起来是一个提高档次的好主意。

所以说,Pop!\_OS 和惠普合作的想法有点激动人心啊!
挂上了惠普这个牌子,笔记本电脑的可用性/保修(在纸面上)就比 System76 要好了,考虑到后者在某些地区是不提供保修的。
### AMD 驱动的笔记本电脑可帮助你更好地写代码
HP Dev One 似乎是把“为开发者提供多任务处理的能力,从而快速完成任务”作为卖点。
这款笔记本电脑的入门款搭载了 **8 核的 AMD Ryzen 7 PRO 处理器** 和 **16 GB RAM**(DDR4 @ 3200 MHz)。
预计它还会搭载由 AMD Radeon Graphics 提供支持的 14 英寸全高清防眩光显示屏。
对于 HP Dev One,Carl Richell 提到了这款笔记本电脑将通过 [LVFS][5](Linux 供应商固件服务)接收**固件更新**。
他还提到,这款笔记本电脑(以上规格)的定价为 **1099 美元** 起。
网站上只显示了它即将推出。因此,我们目前还不知道正式的发布日期。
对于像惠普这样的商业制造商来说,笔记本电脑的定价听起来并不令人兴奋(LCTT 译注:毕竟不是国内互联网品牌的笔记本),但可能是一个划算的交易。
你怎么看这款惠普笔记本电脑(运行 Linux、为开发者量身定制)的定价?你觉得这个价格合理吗?你对这款笔记本电脑有什么期望呢?
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/hp-dev-one-system76/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

System76 already makes Linux laptops. So, what is this all about?
Well, this time, it is a Linux laptop by HP, powered by Pop!_OS, i.e., the Ubuntu-based Linux distribution by System76.
*Carl Richell* (System76’s Founder) initially made the announcement through his Twitter handle.
**June 2, Update:** Now, it is available to order with Pop!_OS 22.04 LTS onboard!
## HP Dev One: A Linux Laptop Built for Developers
System76 laptops have been highly praised for their out-of-the-box hardware compatibility with Pop!_OS.
More of the reason Pop!_OS sits nicely with laptops without any hiccups.
Pop!_OS constantly comes up with updates and feature additions to improve the workflow and make the best out of the available hardware for Linux.
Now, teaming up with HP sounds like a great idea to step up the notch.

So, the idea of a partnership between Pop!_OS and HP is exciting!
With HP, the availability/warranty of the laptop sounds good on paper compared to System76 laptops in the region where it is not available.
Unfortunately, it appears that it is **U.S-only**.
## AMD-Powered Laptop to Help You Code Better
HP Dev One seems to start featuring the essentials for developers to multitask, and get things done quickly.
The laptop uses an **8-core AMD Ryzen 7 PRO processor** coupled with **16 GB RAM** (DDR4 @ 3200 MHz) for starters.
And, it comes equipped with **1 TB PCIe NVMe M.2 storage**.
You can expect a 14-inch full-HD anti-glare display powered by AMD’s Radeon Graphics.
**Carl Richell** mentions that the laptop will receive firmware updates via the LVFS (Linux Vendor Firmware Service) with HP Dev One.
The pricing for the laptop has been mentioned to start at **$1099** for the mentioned specifications.
Other essential tech spec includes:
*53 Wh Li-ion Battery**2 x USB Type-C (Power + DisplayPort 1.4), 2 x USB Type-A (Charging + Headphone/Microphone combo), 1 x HDMI 2.0**720p HD camera**65 Watt power adapter*
Considering that it features **16 Gigs of RAM**, it could be a tough sell for power users with just two memory slots (SODIMM).
For a commercial manufacturer like HP, the pricing for the laptop does not sound mind-blowing with no fingerprint reader, but could be a fair deal.
## Availability
The laptop is available to purchase only in the US for **$1099**. You can order it from HP’s Dev One website linked below.
*What do you think about the pricing for the HP laptop tailored for developers using Linux? Does the price tag sound good? What are your expectations from the laptop?*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,646 | 如何把你的 GNOME 42 打磨得更精致 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/customize-gnome-42-look-1/ | 2022-05-28T19:14:00 | [
"GNOME"
] | /article-14646-1.html | 
>
> 在 5 分钟内将你最喜欢的 GNOME 桌面打磨得更精致。
>
>
>
你可以使用图标、主题、光标和壁纸等多种方式来定制你最喜爱的 GNOME 桌面。本文向你展示了如何使你的 GNOME 42 桌面看起来更精致。在最近发布的 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 和 Fedora 36 上提供了 GNOME 42 桌面环境。
在你进一步阅读之前,先看看调整之前和之后的外观比较。


我将把本教程分为两个部分。
第一部分涉及设置和安装所需的软件包。然后第二部分是如何应用各种设置来获得你想要的外观。
本教程主要在 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 上测试。但是,它应该适用于 Ubuntu 和 Fedora 的其他变体。
### 将 GNOME 42 定制得更精致
#### 设置
首先,为你的系统启用 Flatpak,因为我们需要安装扩展管理器来下载本教程所需的 GNOME Shell 扩展。
因此,要做到这一点,请打开一个终端并运行以下命令:
```
sudo apt install flatpak gnome-software-plugin-flatpak
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
```
完成后重启计算机。
然后从终端运行以下命令,来安装扩展管理器应用以下载 GNOME Shell 扩展:
```
flatpak install flathub com.mattjakeman.ExtensionManager
```
打开扩展管理器应用,并安装两个扩展。第一个是 “<ruby> 浮动停靠区 <rt> Floating Dock </rt></ruby>”,它提供了超酷的停靠区,你可以在桌面上的任何位置移动它。第二个,安装 “<ruby> 用户主题 <rt> User themes </rt></ruby>” 扩展来帮助你在 Ubuntu Linux 中安装外部 GTK 主题。


接着,使用以下命令安装 [Materia 主题](https://github.com/ckissane/materia-theme-transparent)。你必须构建它,因为它没有任何可执行文件。在 Ubuntu 中依次运行以下命令进行安装:
```
git clone https://github.com/ckissane/materia-theme-transparent.git
cd materia-theme-transparent
meson _build
meson install -C _build
```
此外,请从 [这里](https://github.com/bikass/kora/archive/refs/heads/master.zip) 下载 [Kora 图标主题](https://github.com/bikass/kora/)。下载后解压文件,将以下四个文件夹复制到 `/home/<用户名>/.icons` 路径下。如果 `.icons` 文件夹不存在,请创建它。

除了上述更改,从 [这里](https://www.pling.com/p/1197198/) 下载 Bibata 光标主题。下载后,解压文件夹并将其复制到相同的 `/home/<用户名>/.icons` 文件夹中。
除了上述之外,如果你想要一个与上述主题相匹配的漂亮字体,请从谷歌字体 [下载 Robot 字体](https://fonts.google.com/specimen/Roboto),并将它们复制到 `/home/<user name>/.fonts` 文件夹。
最后,再次重启系统。
#### 配置
打开扩展管理器,启用 “<ruby> 浮动停靠区 <rt> Floating Dock </rt></ruby>” 和 “<ruby> 用户主题 <rt> User themes </rt></ruby>”,并禁用 “Ubuntu Dock”。

此外,打开 “<ruby> 浮动停靠区 <rt> Floating Dock </rt></ruby>” 设置并进行以下更改:

此外,打开 <ruby> <a href="https://www.debugpoint.com/2018/05/customize-your-ubuntu-desktop-using-gnome-tweak/"> GNOME 优化工具 </a> <rt> GNOME Tweak Tool </rt></ruby>,然后转到<ruby> 外观 <rt> Appearance </rt></ruby>选项卡。设置以下内容:
* 光标:Bibata-Original-Ice
* Shell 主题:Materia
* 图标:Kora
除此之外,你可能还想更改字体。为此,请转到<ruby> 字体 <rt> Fonts </rt></ruby>选项卡并将文档和界面更改为 “Robot 10pt”。
或者,你也可以从 Ubuntu 22.04 的默认设置中更改强调色和样式。
最后,根据你的喜好下载漂亮的壁纸。对于本教程,我从 [这里](https://www.pexels.com/photo/colorful-blurred-image-6985048/) 下载了一个示例壁纸。
如果一切顺利,你应该有一个漂亮的桌面,如下图所示:

享受你的精致的 GNOME 42!干杯。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/customize-gnome-42-look-1/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,648 | 如何在 Ubuntu 22.04 / 20.04 LTS 中重新设置 sudo 密码 | https://ostechnix.com/how-to-reset-sudo-password-in-ubuntu-20-04-lts/ | 2022-05-29T08:34:00 | [
"密码",
"sudo"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14648-1.html | 
>
> 在 Ubuntu 中重新设置已忘记的 root 用户的密码
>
>
>
这篇简单的指南将向你解释,如何在 Ubuntu 22.04 和 20.04 LTS 桌面环境中,以及从服务器版本中的 <ruby> 恢复 <rt> rescue </rt></ruby> 模式中重新设置 sudo 密码。
### 介绍
在 [安装 Ubuntu](https://ostechnix.com/install-ubuntu-desktop/) 时,创建的一个新用户将会带有 `sudo` 权限,用以执行各种各样的管理任务。
如果你的 Ubuntu 系统有多个 `sudo` 用户,你能够从另外一个 `sudo` 用户的账号下,轻松地重新设置所忘记的一个 `sudo` 用户或管理员用户的密码。
如果你只有一个 `sudo` 用户,并且忘记了密码怎么办?没有问题! 从 Ubuntu 的 <ruby> 恢复 <rt> rescue </rt></ruby> 或 <ruby> 单一用户 <rt> single user </rt></ruby> 模式中恢复 `sudo` 用户密码很容易。
虽然这篇指南是在 Ubuntu 22.04 和 20.04 LTS 版本上进行的正式测试,不过,下面给定的步骤对于其它的 Ubuntu 版本和衍生版本来说是相同的。
### 在 Ubuntu 22.04 / 20.04 LTS 中重新设置 sudo 密码
首先,启动你的 Ubuntu 系统到 <ruby> 恢复 <rt> rescue </rt></ruby> 模式下,来重新设置一个 `sudo` 用户的密码,操作如下面的链接所述。
>
> [如何启动到 Ubuntu 22.04 / 20.04 / 18.04 的 <ruby> 恢复 <rt> rescue </rt></ruby> 模式 或 <ruby> 急救 <rt> Emergency </rt></ruby>模式](https://ostechnix.com/how-to-boot-into-rescue-mode-or-emergency-mode-in-ubuntu-18-04/)
>
>
>
现在,进入到 <ruby> 恢复 <rt> rescue </rt></ruby> 模式下,通过运行下面的命令,以读/写的模式挂载根(`/`)文件系统:
```
# mount -n -o remount,rw /
```
现在,使用 `passwd` 命令来重新设置 `sudo` 用户的密码:
```
# passwd ostechnix
```
在这里,`ostechnix` 是 sudo 用户的名称。使用你自己的用户名称来替换掉它。
输入两次密码:
```
New password:
Retype new password:
passwd: password updated successfully
```

就这样。我们已经重新设置 `sudo` 用户密码。如果你按照上面链接所述的方法 1 进入到 <ruby> 恢复 <rt> rescue </rt></ruby> 模式,按下 `Ctrl+d` 组合键来启动到正常模式。或者,你也可以输入下面的任意一个命令来启动到正常模式。
```
# systemctl default
```
或,
```
# exit
```
如果你想重新启动系统,而不是启动到正常模式,输入:
```
# systemctl reboot
```
如果你已经按照上面链接所述的方法 2 进入到<ruby> 恢复 <rt> rescue </rt></ruby> 模式,输入:
```
# exit
```
你将返回到 <ruby> 恢复菜单 <rt> recovery menu </rt></ruby>。现在选择 “<ruby> 恢复正常启动 <rt> Resume normal boot </rt></ruby>”,并按下回车键。

在强调一次,选择 “<ruby> 确定 <rt> OK </rt></ruby>” 按钮,并按下回车按键来继续启动到正常模式:

现在,你在运行管理命令时可以使用新的 `sudo` 密码。
### 如果我把用户名称和密码都忘了怎么办?
如果你忘记了用户名称,在 <ruby> 恢复 <rt> rescue </rt></ruby> 模式下,你可以很容易地列出你的 Linux 系统中的用户名称,使用目录:
```
# cat etc/passwd
```
来自我 Ubuntu 22.04 系统的输出示例:
```
[...]
ostechnix:x:1000:1000:Ostechnix,,,:/home/ostechnix:/bin/bash
[...]
```
好了,现在,你找到用户名称了。只需要按照上面的步骤来重新设置用户的密码即可。
---
via: <https://ostechnix.com/how-to-reset-sudo-password-in-ubuntu-20-04-lts/>
作者:[sk](https://ostechnix.com/author/sk/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
14,649 | DAML:区块链中智能合约的编程语言 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/daml-the-programming-language-for-smart-contracts-in-a-blockchain/ | 2022-05-29T09:07:00 | [
"区块链",
"智能合约",
"DAML"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14649-1.html |
>
> DAML 智能合约语言是一种专门设计的<ruby> 特定领域语言 <rt> domain specific language </rt></ruby>(DSL),用于编码应用的共享业务逻辑。它用于区块链环境中分布式应用的开发和部署。
>
>
>

区块链技术是一种安全机制,以一种使人难以或不可能修改或入侵的方式来跟踪信息。区块链整合了交易的数字账本,它被复制并发送至其网络上的每台计算机。在链的每个区块中,都有一些交易。当区块链上发生新的交易时,该交易的记录就会被添加到属于该链的每个人的账簿中。
区块链使用<ruby> 分布式账本技术 <rt> distributed ledger technology </rt></ruby>(DLT),其中数据库并不保存在一个服务器或节点中。在区块链中,交易被记录在一个被称为<ruby> 哈希 <rt> hash </rt></ruby>的不可改变的加密符号中。这意味着,如果一个通道或链上的一个区块被改变,黑客将很难改变链上的那个区块,因为他们必须对外面的每一个版本的链都要这样做。区块链,如比特币和以太坊,随着新的区块被添加到链上而不断增长,这使得账本更加安全。
随着区块链中智能合约的实施,在没有任何人工干预的情况下,有了自动执行的场景。智能合约技术使得执行最高级别的安全、隐私和反黑客实施成为可能。

区块链的用例和应用是:
* 加密货币
* 智能合约
* 安全的个人信息
* 数字健康记录
* 电子政务
* 不可伪造的代币(NFT)
* 游戏
* 跨境金融交易
* 数字投票
* 供应链管理
根据 [Statista.com](http://Statista.com),自过去几年以来,区块链技术市场的规模正在以非常快的速度增长,预计到 2025 年将达到 400 亿美元。
### 区块链的编程语言和工具箱
有许多编程语言和开发工具包可用于分布式应用和智能合约。区块链的编程和脚本语言包括 Solidity、Java、Vyper、Serpent、Python、JavaScript、GoLang、PHP、C++、Ruby、Rust、Erlang 等,并根据实施场景和用例进行使用。
选择一个合适的平台来开发和部署区块链,取决于一系列因素,包括对安全、隐私、交易速度和可扩展性的需求(图 2)。

开发区块链的主要平台有:
* 以太坊
* XDC Network
* Tezos
* Stellar
* Hyperledger
* Ripple
* Hedera Hashgraph
* Quorum
* Corda
* NEO
* OpenChain
* EOS
* Dragonchain
* Monero
### DAML:一种高性能的编程语言
<ruby> 数字资产建模语言 <rt> Digital Asset Modeling Language </rt></ruby>,即 DAML([daml.com](http://daml.com)),是一种高性能的编程语言,用于开发和部署区块链环境中的分布式应用。它是一个轻量级和简洁的平台,用于快速应用开发。

DAML 的主要特点是:
* 细粒度的权限
* 基于场景的测试
* 数据模型
* 业务逻辑
* 确定性的执行
* 存储抽象化
* 无重复开销
* 负责任的跟踪
* 原子的可组合性
* 授权检查
* 需要知道的隐私
### 安装和使用 DAML
DAML SDK 可以安装在 Linux、macOS 或 Windows 上。在多个操作系统上安装 DAML 的详细说明可访问 <https://docs.daml.com/getting-started/installation.html> 。
你必须具备以下条件才能使用 DAML:
* Visual Studio Code
* Java 开发套件(JDK)
DAML 可以通过下载并运行可执行的安装程序在 Windows 上安装,你可访问 <https://github.com/digital-asset/daml/releases/download/v1.18.1/daml-sdk-1.18.1-windows.exe> 。
在 Linux 或 Mac 上安装 DAML 可以通过在终端执行以下内容来完成:
```
$ curl -sSL https://get.daml.com/ | sh
```
安装 DAML 后,可以创建基于区块链的新应用,如图 4 和 5 所示。

在另一个终端中,新的应用被导航并安装了项目的依赖:

```
WorkingDirectory>cd myapp/ui
WorkingDirectory>npm install
WorkingDirectory>npm start
```
这样启动了 WebUI,该应用可在 Web 浏览器上通过 URL <http://localhost:3000/> 访问。

### 研究和开发的范围
区块链技术为不同类别的应用提供了广泛的开发平台和框架。其中许多平台是免费和开源的,可以下载和部署以用于基于研究的实现。研究学者、从业者和专家们可以使用这些平台为众多应用提出和实施他们的算法。
---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/daml-the-programming-language-for-smart-contracts-in-a-blockchain/>
作者:[Dr Kumar Gaurav](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/dr-gaurav-kumar/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *The DAML smart contract language is a purpose-built domain specific language designed to encode the shared business logic of an application. It is used for the development and deployment of distributed applications in the blockchain environment.*
Blockchain technology is a secure mechanism to keep track of information in a way that makes it hard or impossible to modify or hack it. A blockchain integrates the digital ledger of transactions, which is copied and sent to every computer on its network. In each block of the chain, there are a number of transactions. When a new transaction takes place on the blockchain, a record of that transaction is added to the ledgers of everyone who is part of the chain.
Blockchain uses distributed ledger technology (DLT), in which a database isn’t kept in one server or node. In a blockchain, transactions are recorded with an immutable cryptographic sign known as a hash. This means that if one block in one channel or chain is changed, it will be hard for hackers to change that block in the chain, as they would have to do this for every single version of the chain that is out there. Blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, keep growing as new blocks are added to the chain, which makes the ledger safer.
With the implementation of smart contracts in blockchain, there is automatic execution of scenarios without any human intervention. Smart contract technology makes it possible to enforce the highest level of security, privacy and anti-hacking implementations.

The use cases and applications of blockchain are:
- Cryptocurrencies
- Smart contracts
- Secured personal information
- Digital health records
- E-governance
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
- Gaming
- Cross-border financial transactions
- Digital voting
- Supply chain management
As per *Statista.com*, the size of the blockchain technology market is increasing at a very fast speed since the last few years and is predicted to touch US$ 40 billion by 2025.
**Programming languages and toolkits for blockchain
**A number of programming languages and development toolkits are available for distributed applications and smart contracts. Programming and scripting languages for the blockchain include Solidity, Java, Vyper, Serpent, Python, JavaScript, GoLang, PHP, C++, Ruby, Rust, Erlang, etc, and are employed depending upon the implementation scenarios and use cases.
The choice of a suitable platform for the development and deployment of a blockchain depends on a range of factors including the need for security, privacy, speed of transactions and scalability (Figure 2).

The main platforms for the development of blockchain are:
|
DAML: A high performance programming language
Digital Asset Modeling Language or DAML (daml.com) is a high performance programming language for the development and deployment of distributed applications in the blockchain environment. It is a lightweight and concise platform for rapid applications development.

The key features of DAML are:
- Fine-grained permissions
- Scenario based testing
- Data model
- Business logic
- Deterministic execution
- Storage abstraction
- No double spends
- Accountability tracking
- Atomic composability
- Authorisation checks
- Need-to-know privacy
**Installation and working with DAML**
The DAML SDK can be installed on Linux, macOS or Windows. The detailed instructions for installing DAML on multiple operating systems are available at *https://docs.daml.com/getting-started/installation.html.*
You must have the following to work with DAML:
- Visual Studio Code
- Java Development Kit (JDK)
DAML can be installed on Windows by downloading and running the executable installer available at *https://github.com/digital-asset/daml/releases/download/v1.18.1/daml-sdk-1.18.1-windows.exe.*
Installation of DAML on Linux or Mac can be done by executing the following in the terminal:
$ curl -sSL https://get.daml.com/ | sh
After installation of DAML, the new blockchain based app can be created, as shown in Figures 4 and 5.

In another terminal, the new app is navigated and project dependencies are installed:

WorkingDirectory>cd myapp/ui WorkingDirectory>npm install WorkingDirectory>npm start
The WebUI is started and the app is accessed on the Web browser with the URL *http://localhost:3000/.*


**Scope for research and development**
Blockchain technology has a wide range of development platforms and frameworks for different categories of applications. Many of these platforms are free and open source, which can be downloaded and deployed for research based implementations. Research scholars, practitioners and academicians can use these platforms to propose and implement their algorithms for numerous applications. |
14,650 | DeepMind 的开源物理引擎 MuJoCo 已在 GitHub 发布 | https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/deepminds-open-source-mujoco-is-available-on-github/ | 2022-05-29T17:41:44 | [
"DeepMind",
"开源"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14650-1.html | 
DeepMind 是 Alphabet 的子公司和 AI 研究实验室,在 2021 年 10 月,它收购了用于机器人研发的 MuJoCo 物理引擎,并承诺该模拟器将作为免费、开源、社区驱动的项目进行维护。现在,DeepMind 声称开源计划已完成,它的整个代码库 [可在 GitHub 上获得](https://github.com/deepmind/mujoco)。
MuJoCo 是 “Multi-Joint Dynamics with Contact” 的缩写,它是一个物理引擎,旨在帮助机器人、生物力学、图形和动画等领域的研究和开发(也包括其他需要快速准确模拟的领域)。MuJoCo 可用于帮助机器学习应用实现基于模型的计算,例如<ruby> 控制综合 <rt> control synthesis </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 状态估计 <rt> state estimation </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 系统识别 <rt> system identification </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 机制设计 <rt> mechanism design </rt></ruby>、通过<ruby> 逆动力学 <rt> inverse dynamics </rt></ruby>来进行数据分析,以及<ruby> 并行采样 <rt> parallel sampling </rt></ruby>。它也可以用作标准模拟器,例如用于游戏和交互式虚拟环境。(LCTT 译注:这段话中涉及到不少专业词汇,鉴于译者水平有限,若有谬误,请在评论中指出,同时也欢迎在评论中科普,一起学习~)
根据 DeepMind 的说法,以下是 MuJoCo 适合协作的一些功能:
* 能够模拟复杂机制的综合模拟器
* 可读、高性能、可移植的代码
* 易于扩展的代码库
* 丰富的文档,包括面向用户的和代码注释 —— 我们希望学术界和 OSS 社区的同事能够使用这个平台并为代码库做出贡献,从而改善所有人的研究
DeepMind 还说:
>
> “作为没有动态内存分配的 C 库,MuJoCo 非常快。不幸的是,原始物理速度一直受到 Python 包装器的阻碍:全局解释器锁(GIL)和非编译代码的存在,使得批处理、多线程操作无法执行。在下面的路线图中,我们将解决这个问题。”
>
>
>
(LCTT 译注: 这里补充了原文没有提及的路线图和基准测试结果。)
路线图:
* 通过批处理、多线程模拟释放 MuJoCo 的速度潜力
* 通过改进内部内存管理支持更大的场景
* 新的增量编译器,带来更好的模型可组合性
* 通过 Unity 集成支持更好的渲染
* 对物理导数的原生支持,包括解析和有限差分
>
> “目前,我们想分享两个常见模型的基准测试结果。注意,这个结果是在运行 Windows 10 的标准 AMD Ryzen 9 5950X 机器上获得的。”
>
>
>

---
via: <https://www.opensourceforu.com/2022/05/deepminds-open-source-mujoco-is-available-on-github/>
作者:[Laveesh Kocher](https://www.opensourceforu.com/author/laveesh-kocher/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | DeepMind, an Alphabet subsidiary and AI research lab, acquired the MuJoCo physics engine for robotics research and development in October 2021. The simulator was to be open-sourced and maintained as a free, open source, community-driven project. DeepMind claims that the open sourcing is now complete, with the entire codebase available on GitHub.
MuJoCo, which stands for Multi-Joint Dynamics with Contact, is a physics engine designed to aid research and development in robotics, biomechanics, graphics and animation, and other fields that require fast and accurate simulation. MuJoCo can be used to implement model-based computations for machine learning applications such as control synthesis, state estimation, system identification, mechanism design, data analysis through inverse dynamics, and parallel sampling. It can also be used as a standard simulator, such as for gaming and interactive virtual environments.
According to DeepMind, the following are some of the features that make MuJoCo appealing for collaboration:
- Comprehensive simulator capable of simulating complex mechanisms
- Readable, performant, portable code
- Codebase that is easily extensible
- Extensive documentation, including both user-facing and code comments – We hope that colleagues from academia and the OSS community will use this platform and contribute to the codebase, thereby improving research for all.
DeepMind has more to say:
“As a C library with no dynamic memory allocation, MuJoCo is very fast. Unfortunately, raw physics speed has historically been hindered by Python wrappers, which made batched, multi-threaded operations non-performant due to the presence of the Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) and non-compiled code. In our roadmap below, we address this issue going forward.
“For now, we’d like to share some benchmarking results for two common models. The results were obtained on a standard AMD Ryzen 9 5950X machine, running Windows 10.” |
14,652 | ProtonMail 改名为 “Proton”,致力于提供一个隐私生态系统 | https://news.itsfoss.com/protonmail-now-proton/ | 2022-05-30T09:44:54 | [
"ProtonMail"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14652-1.html |
>
> ProtonMail 宣布了重塑后的品牌,包括新网站、新名称、新的定价计划、新的 UI 和其他变化。
>
>
>

[ProtonMail](https://itsfoss.com/recommends/protonmai) 将自己重新命名为 “Proton”,以将其所有产品囊括在统一的品牌下。
注意,别把它和 Steam 的 Proton(它也简称为 Proton)混淆哦!
换句话说,ProtonMail、ProtonVPN 和它的任何服务将不再有单独的产品页面。
### Proton:一个开源隐私生态系统
Proton 将拥有一个新的统一平台(新网站),你可以在其中访问所有服务,包括:
* Proton 邮件
* Proton VPN
* Proton 网盘
* Proton 日历
现在,新的登录会话将会被重定向到 `proton.me` 而不是 `protonmail.com`、`mail.protonmail.com`、`protonvpn.com` 等等。
不仅限于名称/品牌,整体的强调色和现有的用户体验,也将受到影响。

现在,你只需一次付费订阅即可获得全部服务,而不必单独升级 VPN 和邮件。这也意味着,经过这次改变,高级订阅的价格变得更加实惠了。

总体而言,让 “Proton” 成为隐私生态系统,是为了吸引更多对技术细节不感兴趣的用户来了解它是如何运作的。
你可以在其新的官方网站([proton.me](https://proton.me/))上查看所有详细信息。
新网站看起来更干净、更有条理,并且更具商业吸引力。
### 本次更改的内容
你可以期待有一个焕然一新的用户界面,包括新的品牌和新的网站。

除此之外,Proton 还提到它改进了服务之间的集成,以获得更好的用户体验。

如果你已经在使用 ProtonMail,你可能知道,他们正在主动建议现有用户激活 “@proton.me” 帐户,这也是本次更改的一部分。
你可以选择将新电子邮件地址 [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected]) 设为默认值,它更短,看起来也更有意义一些。
* 旧的电子邮件地址不会消失,只是额外提供了新地址(@proton.me)。
* 现有的付费订阅者应该可以免费获得存储空间提升。
* 升级了网页和移动应用中的用户体验。
* 新的官方网站(你将被自动重定向到它以进行新会话)。
* 新的定价计划,为 Proton 网盘提供更多存储空间。
你对本次变更感兴趣吗?你喜欢 Proton 的新名字和新的服务方式吗?请在下方评论中分享你的想法吧!
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/protonmail-now-proton/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

[ProtonMail](https://itsfoss.com/recommends/protonmail?ref=news.itsfoss.com) is rebranding itself as “Proton” to unify all its offerings under a single umbrella.
Let us not confuse it with Steam’s Proton (which is also simply referred to as Proton), *right?*
In other words, there will no longer be a separate product page for ProtonMail, ProtonVPN, or any of its services.
## Proton: An Open-Source Privacy Ecosystem
Proton will have a new single platform (new website) where you can access all the services including:
- Proton Mail
- Proton VPN
- Proton Drive
- Proton Calendar
For new log-in sessions, you will be redirected to **proton.me** instead of **protonmail.com/mail.protonmail.com/protonvpn.com** and so on.
Not just limited to the name/brand, the overall brand accent color, and the approach to its existing user experience will also be impacted by this change.
Instead of choosing separate upgrades for VPN and Mail, the entire range of services will now be available with a single paid subscription. This also means that the pricing for the premium upgrades is more affordable with the change.
There’s a new “**Proton Unlimited**” plan to offer all the services for a single subscription.
Overall, the change to make “Proton” a privacy ecosystem aims to appeal to more users who aren’t interested to learn the tech jargon to know how it all works.
You can take a look at all the details on its new official website ([proton.me](https://proton.me/?ref=news.itsfoss.com))
The new website looks much cleaner, organized, and a bit more commercially attractive.
## What’s New?
You can expect a refreshed user interface with the re-branding and a new website.
In addition to that, Proton also mentions that it has improved the integration between the services for a better user experience.
If you have already been using ProtonMail, you probably know that they offered existing users to activate their “**@proton.me**” account, which is also a part of this change.
You can choose to make your new email address ** [email protected]** the default, which is shorter and makes more sense with the new name.
To sum up the changes:
- The old email address isn’t going away. But, a new address is available @proton.me
- Existing paid subscribers should receive a storage boost at no extra cost.
- Refreshed user experience across web applications and mobile applications.
- A new website (you will be automatically redirected to it for new sessions).
- New pricing plans with more storage for Proton Drive.
*Excited about the change? Do you like the new name and its approach to it? Feel free to drop your thoughts in the comments section below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,653 | GNU C 编译器的程序员入门指南 | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/gnu-c-compiler | 2022-05-30T11:19:50 | [
"编译",
"GCC"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14653-1.html | 
>
> 带你一窥生成二进制文件步骤的幕后,以便在出现一些错误时,你知道如何逐步解决问题。
>
>
>
C 语言广为人知,深受新老程序员的好评。使用 C 语言编写的源文件代码,使用了标准的英语术语,因而人们可以方便阅读。然而,计算机只能理解二进制代码。为将代码转换为机器语言,你需要使用一种被称为 <ruby> 编译器 <rt> compiler </rt></ruby> 的工具。
最常见的编译器是 GCC(<ruby> GNU 编译器集 <rt> GNU Compiler Collection </rt></ruby>)。编译过程涉及到一系列的中间步骤及相关工具。
### 安装 GCC
为验证在你的系统上是否已经安装了 GCC,使用 `gcc` 命令:
```
$ gcc --version
```
如有必要,使用你的软件包管理器来安装 GCC。在基于 Fedora 的系统上,使用 `dnf` :
```
$ sudo dnf install gcc libgcc
```
在基于 Debian 的系统上,使用 `apt` :
```
$ sudo apt install build-essential
```
在安装后,如果你想查看 GCC 的安装位置,那么使用:
```
$ whereis gcc
```
### 演示使用 GCC 来编译一个简单的 C 程序
这里有一个简单的 C 程序,用于演示如何使用 GCC 来编译。打开你最喜欢的文本编辑器,并在其中粘贴这段代码:
```
// hellogcc.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello, GCC!\n");
return 0;
}
```
保存文件为 `hellogcc.c` ,接下来编译它:
```
$ ls
hellogcc.c
$ gcc hellogcc.c
$ ls -1
a.out
hellogcc.c
```
如你所见,`a.out` 是编译后默认生成的二进制文件。为查看你所新编译的应用程序的输出,只需要运行它,就像你运行任意本地二进制文件一样:
```
$ ./a.out
Hello, GCC!
```
### 命名输出的文件
文件名称 `a.out` 是非常莫名其妙的,所以,如果你想具体指定可执行文件的名称,你可以使用 `-o` 选项:
(LCTT 译注:注意这和最近 Linux 内核废弃的 a.out 格式无关,只是名字相同,这里生成的 a.out 是 ELF 格式的 —— 也不知道谁给起了个 `a.out` 这破名字,在我看来,默认输出文件名就应该是去掉了 `.c` 扩展名后的名字。by wxy)
```
$ gcc -o hellogcc hellogcc.c
$ ls
a.out hellogcc hellogcc.c
$ ./hellogcc
Hello, GCC!
```
当开发一个需要编译多个 C 源文件文件的大型应用程序时,这种选项是很有用的。
### 在 GCC 编译中的中间步骤
编译实际上有四个步骤,即使在简单的用例中 GCC 自动执行了这些步骤。
1. <ruby> 预处理 <rt> Pre-Processing </rt></ruby>:GNU 的 C 预处理器(cpp)解析头文件(`#include` 语句),展开 <ruby> 宏 <rt> macros </rt></ruby> 定义(`#define` 语句),并使用展开的源文件代码来生成一个中间文件,如 `hellogcc.i`。
2. <ruby> 编译 <rt> Compilation </rt></ruby>:在这个期间中,编译器将预处理的源文件代码转换为指定 CPU 架构的汇编代码。由此生成是汇编文件使用一个 `.s` 扩展名来命名,如在这个示例中的 `hellogcc.s` 。
3. <ruby> 汇编 <rt> Assembly </rt></ruby>:汇编程序(`as`)将汇编代码转换为目标机器代码,放在目标文件中,例如 `hellogcc.o` 。
4. <ruby> 链接 <rt> Linking </rt></ruby>:链接器(`ld`)将目标代码和库代码链接起来生成一个可执行文件,例如 `hellogcc` 。
在运行 GCC 时,可以使用 `-v` 选项来查看每一步的细节:
```
$ gcc -v -o hellogcc hellogcc.c
```

### 手动编译代码
体验编译的每个步骤可能是很有用的,因此在一些情况下,你不需要 GCC 完成所有的步骤。
首先,除源文件文件以外,删除在当前文件夹下生成的文件。
```
$ rm a.out hellogcc.o
$ ls
hellogcc.c
```
#### 预处理器
首先,启动预处理器,将其输出重定向为 `hellogcc.i` :
```
$ cpp hellogcc.c > hellogcc.i
$ ls
hellogcc.c hellogcc.i
```
查看输出文件,并注意一下预处理器是如何包含头文件和扩展宏中的源文件代码的。
#### 编译器
现在,你可以编译代码为汇编代码。使用 `-S` 选项来设置 GCC 只生成汇编代码:
```
$ gcc -S hellogcc.i
$ ls
hellogcc.c hellogcc.i hellogcc.s
$ cat hellogcc.s
```
查看汇编代码,来看看生成了什么。
#### 汇编
使用你刚刚所生成的汇编代码来创建一个目标文件:
```
$ as -o hellogcc.o hellogcc.s
$ ls
hellogcc.c hellogcc.i hellogcc.o hellogcc.s
```
#### 链接
要生成一个可执行文件,你必须将对象文件链接到它所依赖的库。这并不像前面的步骤那么简单,但它却是有教育意义的:
```
$ ld -o hellogcc hellogcc.o
ld: warning: cannot find entry symbol _start; defaulting to 0000000000401000
ld: hellogcc.o: in function `main`:
hellogcc.c:(.text+0xa): undefined reference to `puts'
```
在链接器查找完 `libc.so` 库后,出现一个引用 `undefined puts` 错误。你必须找出适合的链接器选项来链接必要的库以解决这个问题。这不是一个小技巧,它取决于你的系统的布局。
在链接时,你必须链接代码到<ruby> 核心运行时 <rt> core runtime </rt></ruby>(CRT)目标,这是一组帮助二进制可执行文件启动的子例程。链接器也需要知道在哪里可以找到重要的系统库,包括 `libc` 和 `libgcc`,尤其是其中的特殊的开始和结束指令。这些指令可以通过 `--start-group` 和 `--end-group` 选项来分隔,或者使用指向 `crtbegin.o` 和 `crtend.o` 的路径。
这个示例使用了 RHEL 8 上的路径,因此你可能需要依据你的系统调整路径。
```
$ ld -dynamic-linker /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 \
-o hello \
/usr/lib64/crt1.o /usr/lib64/crti.o \
--start-group \
-L/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/8 \
-L/usr/lib64 -L/lib64 hello.o \
-lgcc \
--as-needed -lgcc_s \
--no-as-needed -lc -lgcc \
--end-group \
/usr/lib64/crtn.o
```
在 Slackware 上,同样的链接过程会使用一组不同的路径,但是,你可以看到这其中的相似之处:
```
$ ld -static -o hello \
-L/usr/lib64/gcc/x86_64-slackware-linux/11.2.0/ \
/usr/lib64/crt1.o /usr/lib64/crti.o hello.o /usr/lib64/crtn.o \
--start-group \
-lc -lgcc -lgcc_eh \
--end-group
```
现在,运行由此生成的可执行文件:
```
$ ./hello
Hello, GCC!
```
### 一些有用的实用程序
下面是一些帮助检查文件类型、<ruby> 符号表 <rt> symbol tables </rt></ruby> 和链接到可执行文件的库的实用程序。
使用 `file` 实用程序可以确定文件的类型:
```
$ file hellogcc.c
hellogcc.c: C source, ASCII text
$ file hellogcc.o
hellogcc.o: ELF 64-bit LSB relocatable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), not stripped
$ file hellogcc
hellogcc: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=bb76b241d7d00871806e9fa5e814fee276d5bd1a, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
```
对目标文件使用 `nm` 实用程序可以列出 <ruby> 符号表 <rt> symbol tables </rt></ruby> :
```
$ nm hellogcc.o
0000000000000000 T main
U puts
```
使用 `ldd` 实用程序来列出动态链接库:
```
$ ldd hellogcc
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007ffe3bdd7000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007f223395e000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f2233b7e000)
```
### 总结
在这篇文章中,你了解到了 GCC 编译中的各种中间步骤,和检查文件类型、<ruby> 符号表 <rt> symbol tables </rt></ruby> 和链接到可执行文件的库的实用程序。在你下次使用 GCC 时,你将会明白它为你生成一个二进制文件所要做的步骤,并且当出现一些错误时,你会知道如何逐步处理解决问题。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/gnu-c-compiler>
作者:[Jayashree Huttanagoudar](https://opensource.com/users/jayashree-huttanagoudar) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[robsean](https://github.com/robsean) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | C is a well-known programming language, popular with experienced and new programmers alike. Source code written in C uses standard English terms, so it's considered human-readable. However, computers only understand binary code. To convert code into machine language, you use a tool called a *compiler*.
A very common compiler is GCC (GNU C Compiler). The compilation process involves several intermediate steps and adjacent tools.
## Install GCC
To confirm whether GCC is already installed on your system, use the `gcc`
command:
```
````$ gcc --version`
If necessary, install GCC using your packaging manager. On Fedora-based systems, use `dnf`
:
```
````$ sudo dnf install gcc libgcc`
On Debian-based systems, use `apt`
:
```
````$ sudo apt install build-essential`
After installation, if you want to check where GCC is installed, then use:
```
````$ whereis gcc`
## Simple C program using GCC
Here's a simple C program to demonstrate how to compile code using GCC. Open your favorite text editor and paste in this code:
```
``````
// hellogcc.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello, GCC!\n");
return 0;
}
```
Save the file as `hellogcc.c`
and then compile it:
```
``````
$ ls
hellogcc.c
$ gcc hellogcc.c
$ ls -1
a.out
hellogcc.c
```
As you can see, `a.out`
is the default executable generated as a result of compilation. To see the output of your newly-compiled application, just run it as you would any local binary:
```
``````
$ ./a.out
Hello, GCC!
```
## Name the output file
The filename `a.out`
isn't very descriptive, so if you want to give a specific name to your executable file, you can use the `-o`
option:
```
``````
$ gcc -o hellogcc hellogcc.c
$ ls
a.out hellogcc hellogcc.c
$ ./hellogcc
Hello, GCC!
```
This option is useful when developing a large application that needs to compile multiple C source files.
## Intermediate steps in GCC compilation
There are actually four steps to compiling, even though GCC performs them automatically in simple use-cases.
- Pre-Processing: The GNU C Preprocessor (
`cpp`
) parses the headers (**#include**statements), expands macros (**#define**statements), and generates an intermediate file such as`hellogcc.i`
with expanded source code. - Compilation: During this stage, the compiler converts pre-processed source code into assembly code for a specific CPU architecture. The resulting assembly file is named with a
`.s`
extension, such as`hellogcc.s`
in this example. - Assembly: The assembler (
`as`
) converts the assembly code into machine code in an object file, such as`hellogcc.o`
. - Linking: The linker (
`ld`
) links the object code with the library code to produce an executable file, such as`hellogcc`
.
When running GCC, use the `-v`
option to see each step in detail.
```
````$ gcc -v -o hellogcc hellogcc.c`
(Jayashree Huttanagoudar, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Manually compile code
It can be useful to experience each step of compilation because, under some circumstances, you don't need GCC to go through all the steps.
First, delete the files generated by GCC in the current folder, except the source file.
```
``````
$ rm a.out hellogcc.o
$ ls
hellogcc.c
```
### Pre-processor
First, start the pre-processor, redirecting its output to `hellogcc.i`
:
```
``````
$ cpp hellogcc.c > hellogcc.i
$ ls
hellogcc.c hellogcc.i
```
Take a look at the output file and notice how the pre-processor has included the headers and expanded the macros.
### Compiler
Now you can compile the code into assembly. Use the `-S`
option to set GCC just to produce assembly code.
```
``````
$ gcc -S hellogcc.i
$ ls
hellogcc.c hellogcc.i hellogcc.s
$ cat hellogcc.s
```
Take a look at the assembly code to see what's been generated.
### Assembly
Use the assembly code you've just generated to create an object file:
```
``````
$ as -o hellogcc.o hellogcc.s
$ ls
hellogcc.c hellogcc.i hellogcc.o hellogcc.s
```
### Linking
To produce an executable file, you must link the object file to the libraries it depends on. This isn't quite as easy as the previous steps, but it's educational:
```
``````
$ ld -o hellogcc hellogcc.o
ld: warning: cannot find entry symbol _start; defaulting to 0000000000401000
ld: hellogcc.o: in function `main`:
hellogcc.c:(.text+0xa): undefined reference to `puts'
```
An error referencing an` undefined puts`
occurs after the linker is done looking at the `libc.so`
library. You must find suitable linker options to link the required libraries to resolve this. This is no small feat, and it's dependent on how your system is laid out.
When linking, you must link code to core runtime (CRT) objects, a set of subroutines that help binary executables launch. The linker also needs to know where to find important system libraries, including libc and libgcc, notably within special start and end instructions. These instructions can be delimited by the `--start-group`
and `--end-group`
options or using paths to `crtbegin.o`
and `crtend.o`
.
This example uses paths as they appear on a RHEL 8 install, so you may need to adapt the paths depending on your system.
```
``````
$ ld -dynamic-linker \
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 \
-o hello \
/usr/lib64/crt1.o /usr/lib64/crti.o \
--start-group \
-L/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/8 \
-L/usr/lib64 -L/lib64 hello.o \
-lgcc \
--as-needed -lgcc_s \
--no-as-needed -lc -lgcc \
--end-group
/usr/lib64/crtn.o
```
The same linker procedure on Slackware uses a different set of paths, but you can see the similarity in the process:
```
``````
$ ld -static -o hello \
-L/usr/lib64/gcc/x86_64-slackware-linux/11.2.0/ \
/usr/lib64/crt1.o /usr/lib64/crti.o \
hello.o /usr/lib64/crtn.o \
--start-group -lc -lgcc -lgcc_eh \
--end-group
```
Now run the resulting executable:
```
``````
$ ./hello
Hello, GCC!
```
## Some helpful utilities
Below are a few utilities that help examine the file type, symbol table, and the libraries linked with the executable.
Use the `file`
utility to determine the type of file:
```
``````
$ file hellogcc.c
hellogcc.c: C source, ASCII text
$ file hellogcc.o
hellogcc.o: ELF 64-bit LSB relocatable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), not stripped
$ file hellogcc
hellogcc: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=bb76b241d7d00871806e9fa5e814fee276d5bd1a, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
```
The use the `nm`
utility to list symbol tables for object files:
```
``````
$ nm hellogcc.o
0000000000000000 T main
U puts
```
Use the `ldd`
utility to list dynamic link libraries:
```
``````
$ ldd hellogcc
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007ffe3bdd7000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007f223395e000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f2233b7e000)
```
## Wrap up
In this article, you learned the various intermediate steps in GCC compilation and the utilities to examine the file type, symbol table, and libraries linked with an executable. The next time you use GCC, you'll understand the steps it takes to produce a binary file for you, and when something goes wrong, you know how to step through the process to resolve problems.
## Comments are closed. |
14,654 | Tails 警告用户不要使用 Tor 浏览器:原因如下! | https://news.itsfoss.com/tails-tor-browser/ | 2022-05-30T16:09:00 | [
"Tor",
"Tails"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14654-1.html |
>
> Tails 5.1 将针对“可绕过 Tor 浏览器安全措施的危险漏洞”提供关键修复。以下是它的全部内容。
>
>
>

Tails 是一个专注于安全的便携式 Linux 发行版,最近,它的开发团队发布了有关其当前版本的重要公告。他们警告用户在 **Tails 5.0 或更早版本** 上使用 Tor 浏览器时,避免输入或使用任何个人或敏感信息。
Tor 浏览器是 Tails 事实上的(默认)网页浏览器,它有助于在用户连接到互联网时,保护他们的在线身份。它主要被各种记者和活动家用来逃避审查。不过,普通用户也可以使用它。
### 问题说明
最近,有人发现了两个令人讨厌的漏洞,它们允许有害网站能够从其他网站窃取用户的信息。
这些都是在 Firefox 使用的 JavaScript 引擎中发现的。
但是,Tor 与此有什么关系?对于那些不知道的人来说,Tor 实际上是 Firefox 的一个复刻,因此包含许多类似的功能,如 JavaScript 引擎。
具体来说,在 [Mozilla 发布的公告](https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/security/advisories/mfsa2022-19/) 中,这些漏洞已被确定为 CVE-2022-1802 和 CVE-2022-1529。
Tails 公告中也对此进行了说明:
>
> “例如,在你访问恶意网站后,控制该网站的攻击者可能会在同一个 Tails 会话期间,访问你随后发送到其他网站的密码或其他敏感信息。”
>
>
>
### 你应该停止使用 Tail 发行版吗?
没有这个必要。
用户会很高兴地知道,这些漏洞并不影响 Tor 的连接。这意味着,如果你不交换任何敏感信息,如密码、个人信息、信息等,你可以随意地浏览互联网。
Tails 中的其他应用程序,尤其是 Thunderbird,仍然可以安全使用,因为 JavaScript 在使用时会被禁用。
此外,你也可以在 Tor 浏览器中启用最高的安全级别。这是推荐的,因为(该级别下)JavaScript 引擎会被禁用。不过,请注意,这会使网站无法正常运行。
换句话说,如果你知道自己在做什么的话,Tails 发行版仍然可以安全使用。
### 漏洞修复即将发布
好的消息是,Mozilla 已经在上游修补了这些错误,现在就等 Tails 团队发布修复程序了。
至于何时发布,他们是这样说的:
>
> 此漏洞将在 Tails 5.1(**5 月 31 日**)中修复,但我们的团队没有能力提前发布紧急版本。
>
>
>
因此,你最好的选择是等待下周的 Tails 5.1 发布。你可以阅读 Tails 开发团队的 [官方公告](https://tails.boum.org/security/prototype_pollution/index.en.html) 以了解更多信息。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/tails-tor-browser/>
作者:[Rishabh Moharir](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/rishabh/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

The developers of the security-focused portable Linux distro, **Tails**, have recently released an important advisory regarding its current release. They have warned users to avoid entering or using any personal or sensitive information while using Tor Browser on **Tails 5.0 or older**.
Tor Browser is the de-facto web browser used in Tails and helps protect the user’s identity online when connected to the Internet. It is mainly used by various journalists and activists to evade censorship. Everyday users can use it too.
## What’s the problem?
Recently, two nasty vulnerabilities have been found that enable harmful websites to steal the user’s information from other websites.
These had been discovered in the JavaScript engine used by Firefox.
But what has Tor to do with this? For those unaware, Tor is actually a fork of Firefox and thus contains many similar features like the JavaScript engine.
To be specific, the vulnerabilities have been identified as CVE-2022-1802 and CVE-2022-1529 in an [advisory published by Mozilla.](https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/security/advisories/mfsa2022-19/?ref=news.itsfoss.com)
The Tails advisory best explains this:
“For example, after you visit a malicious website, an attacker controlling this website might access the password or other sensitive information that you send to other websites afterwards during the same Tails session.”
## Should You Stop Using Tails Linux Distro?
Not necessarily.
Users will be glad to know that these vulnerabilities don’t affect Tor connections. This means you can casually browse the internet if you’re not exchanging any of your sensitive information like passwords, personal information, messages, etc.
Other apps in Tails, especially Thunderbird, are safe to use since the JavaScript is disabled if in use.
Furthermore, you can even enable the safest security level in the Tor browser. This is preferred because the JavaScript engine gets disabled. Do note that this will make websites function improperly.
In other words, the Tails Linux distro is still safe to use if you know what you’re doing.
## A Fix is Coming Soon
Good news! Mozilla has already patched these bugs upstream and now it’s up to the Tails team when it comes to releasing the fix.
Here’s what they have stated –
This vulnerability will be fixed in Tails 5.1 (
May 31), but our team doesn’t have the capacity to publish an emergency release earlier.
So, your best option is to wait for the Tails 5.1 release next week. You can read the [official advisory](https://tails.boum.org/security/prototype_pollution/index.en.html?ref=news.itsfoss.com) released by Tails devs to know more.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,656 | Plex 桌面播放器现已支持 Linux | https://news.itsfoss.com/plex-desktop-linux/ | 2022-05-31T14:55:35 | [
"Plex.tv",
"播放器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14656-1.html |
>
> [Plex.tv](http://Plex.tv) 终于增加了 Linux 桌面版本和全新的 HTPC 应用。不过,它目前只提供了 Snap 包。
>
>
>

Plex 是一个流行的流媒体播放器,同时,它能够用作一个媒体服务器软件。
事实上,它也是 [Linux 上最好的媒体服务器软件](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-media-server/) 之一。
是的,这个媒体服务器已经支持 Linux,而且还提供了一个 [包含安装步骤的教程](https://itsfoss.com/install-plex-ubuntu/)。
### Linux 上的 Plex 桌面播放器提供 Snap 包
我知道很多人都不喜欢使用 Snap 包来安装这个桌面播放器。但现在,这个桌面播放器已在 Snap 商店中提供,你可以轻松地在任何 Linux 发行版上安装它。

幸运的是,这个桌面播放器的 [公告](https://www.plex.tv/blog/way-to-be-htpc/) 还提到他们正在开发一个 **Flatpak 包**,它应该会在近期登陆 Flathub。
这样一来,借助 Flatpak 和 Snap 软件包,Plex 就可以成为在 Linux 上流式传输和组织个人媒体收藏的绝佳选择。
除了桌面应用程序,如果你利用你的 Linux 机器连接到一个大屏幕来观看所有的内容,还有一个 Plex HTPC(有计划发布 Flatpak 软件包)。

顺便说一句,HTPC 是 PMP TV(全称为 Plex Media Player TV)模式的继承者。
他们在官网上与它的 Linux 桌面应用程序一同发布了这款产品。
使用 HTPC,这个桌面应用就可以和电视共享,并支持音频直通、刷新率切换、控制器和可配置输入映射等高级功能。

因此,如果你有一个大屏幕,并且想要连接你的系统(不管是什么桌面平台)的话,你现在可以使用 HTPC 应用程序来完成。
>
> **[Plex 桌面版](https://snapcraft.io/plex-desktop)**
>
>
>
>
> **[Plex HTPC](https://snapcraft.io/plex-htpc)**
>
>
>
在 Linux 系统或联网电视上流式传输内容时,你通常会使用什么呢?你觉得 Plex 能满足你的需求吗?即然它支持 Linux 了,你会想要用它来替代当前使用的软件吗?
欢迎在评论区告诉我们你的想法!
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/plex-desktop-linux/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Plex is a popular streaming player with the ability to use as a media server software.
In fact, it is also one of the [best media server software for Linux](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-media-server/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
Yes, the media server was already available for Linux, and we also had a [tutorial covering the installation steps](https://itsfoss.com/install-plex-ubuntu/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
And, now, the desktop player (app) is finally here for Linux.
**Update:** Both [Plex desktop player](https://flathub.org/apps/details/tv.plex.PlexDesktop?ref=news.itsfoss.com) and [Plex HTPC](https://flathub.org/apps/details/tv.plex.PlexHTPC?ref=news.itsfoss.com) are now available as Flatpak on Flathub.
## Plex Desktop Player on Linux as a Snap
I’m aware that many of you may not like the preference for the Snap package to install the desktop player. But, as of now, the desktop player is available in the Snap store to easily let you install it on any Linux distribution of your choice.
Fortunately, the [announcement](https://www.plex.tv/blog/way-to-be-htpc/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) for the desktop player also mentions that they have a **Flatpak package** in the works, which should be available on Flathub in the near future.
So, with a Flatpak and Snap package, Plex can be a fantastic choice to stream and organize your personal media collection on Linux.
In addition to the desktop app, Plex HTPC is also available (with a planned Flatpak) if you utilize your Linux machine connected to a big screen to watch all the content.
In case you are curious, HTPC is the successor to the PMP TV (Plex Media Player TV) mode.
They announced it along with the Linux support for the desktop app.
With HTPC, the desktop app would be shared by the TV with support for advanced features like audio pass-through, refresh rate switching, controller support, and configurable input maps.

So, if you have got a big screen, and want to connect your system (irrespective of the desktop platform), you can do it using the HTPC app.
*What do you prefer to use when streaming content on your Linux system or a connected TV? Is Plex good enough? Now that it supports Linux, do you think that you might want to switch if you use something else?*
*Feel free to share your thoughts in the comments below.*
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,657 | 使用自动化时的五个常见错误 | https://fedoramagazine.org/five-common-mistakes-when-using-automation/ | 2022-05-31T15:15:05 | [
"自动化"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14657-1.html | 
随着自动化扩展到涵盖 IT 的更多方面,越来越多的管理员正在学习自动化技能并应用它们来减轻他们的工作量。自动化可以减轻重复性任务的负担,并为基础设施增加一定程度的一致性。但是,当 IT 工作人员部署自动化时,会出现可能对大大小小的基础设施造成严重破坏的常见错误。在自动化部署中通常会出现五个常见错误。
### 缺乏测试
初学者常犯的错误是自动化脚本没有经过全面测试。由于拼写错误或逻辑错误,简单的 shell 脚本可能会对服务器产生不利影响。将该错误乘以基础架构中的服务器数量,你可能会遇到一大堆问题需要清理。在大规模部署之前始终测试你的自动化脚本。
### 意外负载
经常发生的第二个错误是没有预测脚本可能对其他资源施加的系统负载。当目标是十几个服务器时,运行从仓库下载文件或安装包的脚本可能没问题。脚本通常在成百上千台服务器上运行。这种负载可以使支持服务停止或完全崩溃。不要忘记考虑端点影响或设置合理的并发率。
### 离开脚本
自动化工具的一种用途是确保符合标准设置。自动化可以轻松确保组中的每台服务器都具有完全相同的设置。如果该组中的服务器需要根据该基线进行更改,同时管理员不了解合规标准,那么可能会出现问题。安装和启用不需要和不想要的服务,从而导致可能的安全问题。
### 缺乏文档
管理员的一项固定职责应该是记录他们的工作。由于合同到期、升职或定期员工流动,公司可能会在 IT 部门频繁招聘新员工。公司内的工作组相互隔离也很常见。由于这些原因,重要的是记录哪些自动化已经到位。与用户运行脚本不同,自动化可能会在创建它的人离开组之后继续很长时间。管理员可能会发现自己在其基础设施中面临着来自未经检查的自动化的奇怪行为。
### 缺乏经验
列表中的最后一个错误是管理员对他们正在自动化的系统不够了解。管理员经常被雇用到他们没有接受过足够培训且没有人可以求教的职位上工作。自 COVID 以来,当公司努力填补空缺时,这一点尤其重要。然后管理员被迫处理他们没有设置并且可能不完全理解的基础设施。这可能会导致非常低效的脚本浪费资源或配置错误的服务器。
### 结论
越来越多的管理员正在学习自动化来帮助他们完成日常任务。因此,自动化正被应用于更多的技术领域。希望此列表将有助于防止新用户犯这些错误,并敦促经验丰富的管理员重新评估他们的 IT 策略。自动化旨在减轻重复性任务的负担,而不是为最终用户带来更多工作。
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/five-common-mistakes-when-using-automation/>
作者:[Gary Scarborough](https://fedoramagazine.org/author/gscarbor/) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | As automation expands to cover more aspects of IT, more administrators are learning automation skills and applying them to ease their workload. Automation can ease the burden of repetitive tasks and add a level of conformity to infrastructure. But when IT workers deploy automation, there are common mistakes that can wreak havoc on infrastructures large and small. Five common mistakes are typically seen in automation deployments.
## Lack of testing
A beginner’s mistake that is commonly made is that automation scripts are not thoroughly tested. A simple shell script can have adverse affects on a server due to typos or logic errors. Multiply that mistake by the number of servers in your infrastructure, and you can have a big mess to clean up. Always test your automation scripts before deploying in large scale.
## Unexpected server load
The second mistake that frequently occurs is not predicting the system load the script may put on other resources. Running a script that downloads a file or installs a package from a repository may be fine when the target is a dozen servers. Scripts are often run against hundreds or thousands of servers. This load can bring supporting services to a stand still or crash them entirely. Don’t forget to consider end point impact or set a reasonable concurrency rate.
## Run away scripts
One use of automation tools is to ensure compliance to standard settings. Automation can make it easy to ensure that every server in a group has exactly the same settings. Problems may arise if a server in that group needs to be altered from that baseline, and the administrator is not aware of the compliance standard. Unneeded and unwanted services can be installed and enabled leading to possible security concerns.
## Lack of documentation
A constant duty for administrators should be to document their work. Companies can have frequent new employees in IT departments due to contracts ending or promotions or regular employee turnover. It is also not uncommon for work groups within a company to be siloed from each other. For these reasons it is important to document what automation is in place. Unlike user run scripts, automation may continue long after the person who created it leaves the group. Administrators can find themselves facing strange behaviors in their infrastructure from automation left unchecked.
## Lack of experience
The last mistake on the list is when administrators do not know enough about the systems they are automating. Too often admins are hired to work positions where they do not have adequate training and no one to learn from. This has been especially relevant since COVID when companies are struggling to fill vacancies. Admins are then forced to deal with infrastructure they didn’t set up and may not fully understand. This can lead to very inefficient scripts that waste resources or misconfigured servers.
## Conclusion
More and more admins are learning automation to help them in their everyday tasks. As a result, automation is being applied to more areas of technology. Hopefully this list will help prevent new users from making these mistakes and urge seasoned admins to re-evaluate their IT strategies. Automation is meant to ease the burden of repetitive tasks, not cause more work for the end user.
## Tramp
Nice overview and appropriate cover image.
## JAFO
#6: Informing your boss that you have automated all of your tasks. Yes, I made this mistake…
## noldi
Lead, follow or get out of the way . . .
## Jason
7. Impressing on management that automation is not a one off process that you build and forget about. It needs to be maintained, processes change, software get deprecated, CVEs need to be addressed, there is no such thing as bug free software, automation requirements change …….
## Karlis K.
A combination of all of the above
Automating the heavy lifting but not the security – doing the builds and deployments but no security checks (for vulnerabilities or general security issues), or keeping secrets (login passwords, private SSH keys, auth/deploy tokens, etc) in plaintext or publicly acessable (such as the infamous incident of people keeping public and private SSH keypairs on public GitHub repos).
## Stephen Snow
While I can appreciate the intent to cover some of the pitfalls faced by new IT admin’s as they take on their role(s), as the Fedora Magazine, I would have expected to see some solutions of correct automation examples to provide a more positive outcome than simply pointing out what has been done wrong by others.
## Audun Nes
I am not sure there is one rule-of-thumb to cover any happy path. I’d rather say that for each automation tool there are different good practices to follow.
For instance if using Ansible for configuration management, the molecule test framework is excellent for continuously testing your automation in a container or on a virtual machine.
Also the DRY principle applies to automation as well. Try to make everything generic, and control it through variables and interpolation.
## Andrew Z
more of click-bait than a useful article. Surprise to see this from FM 🙁
## Jeffersonian
Agree !
The take over of open-source by large corporations brought some good, and lots of “this stuff” too. Unfortunate isn’t it ?
Slashdot has a pretty good motto, “Stuff that matters”.
I would like a tracking of “that matters” appreciation, so I would not waste my time with junk, like this !
## Jason
is that irony?
## Joe Thompson
See also: writing Kubernetes operators. |
14,658 | 在 Go 中复制文件的三种方法 | https://opensource.com/article/18/6/copying-files-go | 2022-05-31T15:34:00 | [
"复制",
"Go"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14658-1.html | 
>
> 本文是 Go 系列的第三篇文章,我将介绍三种最流行的复制文件的方法。
>
>
>
本文将介绍展示如何使用 [Go 编程语言](https://golang.org/) 来复制文件。在 Go 中复制文件的方法有很多,我只介绍三种最常见的:使用 Go 库中的 `io.Copy()` 函数调用、一次读取输入文件并将其写入另一个文件,以及使用缓冲区一块块地复制文件。
### 方法一:使用 io.Copy()
第一种方法就是使用 Go 标准库的 `io.Copy()` 函数。你可以在 `copy()` 函数的代码中找到它的实现逻辑,如下所示:
```
func copy(src, dst string) (int64, error) {
sourceFileStat, err := os.Stat(src)
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
if !sourceFileStat.Mode().IsRegular() {
return 0, fmt.Errorf("%s is not a regular file", src)
}
source, err := os.Open(src)
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
defer source.Close()
destination, err := os.Create(dst)
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
defer destination.Close()
nBytes, err := io.Copy(destination, source)
return nBytes, err
}
```
首先,上述代码做了两个判断,以便确定它可以被打开读取:一是判断将要复制的文件是否存在(`os.Stat(src)`),二是判断它是否为常规文件(`sourceFileStat.Mode().IsRegular()`)。剩下的所有工作都由 `io.Copy(destination, source)` 这行代码来完成。`io.Copy()` 函数执行结束后,会返回复制的字节数和复制过程中发生的第一条错误消息。在 Go 中,如果没有错误消息,错误变量的值就为 `nil`。
你可以在 [io 包](https://golang.org/pkg/io/) 的文档页面了解有关 `io.Copy()` 函数的更多信息。
运行 `cp1.go` 将产生以下输出:
```
$ go run cp1.go
Please provide two command line arguments!
$ go run cp1.go fileCP.txt /tmp/fileCPCOPY
Copied 3826 bytes!
$ diff fileCP.txt /tmp/fileCPCOPY
```
这个方法已经非常简单了,不过它没有为开发者提供灵活性。这并不总是一件坏事,但是,有些时候,开发者可能会需要/想要告诉程序该如何读取文件。
### 方法二:使用 ioutil.WriteFile() 和 ioutil.ReadFile()
复制文件的第二种方法是使用 `ioutil.ReadFile()` 和 `ioutil.WriteFile()` 函数。第一个函数用于将整个文件的内容,一次性地读入到某个内存中的字节切片里;第二个函数则用于将字节切片的内容写入到一个磁盘文件中。
实现代码如下:
```
input, err := ioutil.ReadFile(sourceFile)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
err = ioutil.WriteFile(destinationFile, input, 0644)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error creating", destinationFile)
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
```
上述代码包括了两个 `if` 代码块(嗯,用 Go 写程序就是这样的),程序的实际功能其实体现在 `ioutil.ReadFile()` 和 `ioutil.WriteFile()` 这两行代码中。
运行 `cp2.go`,你会得到下面的输出:
```
$ go run cp2.go
Please provide two command line arguments!
$ go run cp2.go fileCP.txt /tmp/copyFileCP
$ diff fileCP.txt /tmp/copyFileCP
```
请注意,虽然这种方法能够实现文件复制,但它在复制大文件时的效率可能不高。这是因为当文件很大时,`ioutil.ReadFile()` 返回的字节切片会很大。
### 方法三:使用 os.Read() 和 os.Write()
在 Go 中复制文件的第三种方法就是下面要介绍的 `cp3.go`。它接受三个参数:输入文件名、输出文件名和缓冲区大小。
`cp3.go` 最重要的部分位于以下 `for` 循环中,你可以在 `copy()` 函数中找到它,如下所示:
```
buf := make([]byte, BUFFERSIZE)
for {
n, err := source.Read(buf)
if err != nil && err != io.EOF {
return err
}
if n == 0 {
break
}
if _, err := destination.Write(buf[:n]); err != nil {
return err
}
}
```
该方法使用 `os.Read()` 将输入文件的一小部分读入名为 `buf` 的缓冲区,然后使用 `os.Write()` 将该缓冲区的内容写入文件。当读取出错或到达文件末尾(`io.EOF`)时,复制过程将停止。
运行 `cp3.go`,你会得到下面的输出:
```
$ go run cp3.go
usage: cp3 source destination BUFFERSIZE
$ go run cp3.go fileCP.txt /tmp/buf10 10
Copying fileCP.txt to /tmp/buf10
$ go run cp3.go fileCP.txt /tmp/buf20 20
Copying fileCP.txt to /tmp/buf20
```
在接下来的基准测试中,你会发现,缓冲区的大小极大地影响了 `cp3.go` 的性能。
### 运行基准测试
在本文的最后一部分,我将尝试比较这三个程序以及 `cp3.go` 在不同缓冲区大小下的性能(使用 `time(1)` 命令行工具)。
以下输出显示了复制 500MB 大小的文件时,`cp1.go`、`cp2.go` 和 `cp3.go` 的性能对比:
```
$ ls -l INPUT
-rw-r--r-- 1 mtsouk staff 512000000 Jun 5 09:39 INPUT
$ time go run cp1.go INPUT /tmp/cp1
Copied 512000000 bytes!
real 0m0.980s
user 0m0.219s
sys 0m0.719s
$ time go run cp2.go INPUT /tmp/cp2
real 0m1.139s
user 0m0.196s
sys 0m0.654s
$ time go run cp3.go INPUT /tmp/cp3 1000000
Copying INPUT to /tmp/cp3
real 0m1.025s
user 0m0.195s
sys 0m0.486s
```
我们可以看出,这三个程序的性能非常接近,这意味着 Go 标准库函数的实现非常聪明、经过了充分优化。
现在,让我们测试一下缓冲区大小对 `cp3.go` 的性能有什么影响吧!执行 `cp3.go`,并分别指定缓冲区大小为 10、20 和 1000 字节,在一台运行很快的机器上复制 500MB 文件,得到的结果如下:
```
$ ls -l INPUT
-rw-r--r-- 1 mtsouk staff 512000000 Jun 5 09:39 INPUT
$ time go run cp3.go INPUT /tmp/buf10 10
Copying INPUT to /tmp/buf10
real 6m39.721s
user 1m18.457s
sys 5m19.186s
$ time go run cp3.go INPUT /tmp/buf20 20
Copying INPUT to /tmp/buf20
real 3m20.819s
user 0m39.444s
sys 2m40.380s
$ time go run cp3.go INPUT /tmp/buf1000 1000
Copying INPUT to /tmp/buf1000
real 0m4.916s
user 0m1.001s
sys 0m3.986s
```
我们可以发现,缓冲区越大,`cp3.go` 运行得就越快,这或多或少是符合预期的。此外,使用小于 20 字节的缓冲区来复制大文件会非常缓慢,应该避免。
你可以在 [GitHub](https://github.com/mactsouk/opensource.com) 找到 `cp1.go`、`cp2.go` 和 `cp3.go` 的 Go 代码。
如果你有任何问题或反馈,请在(原文)下方发表评论或在 [Twitter](https://twitter.com/mactsouk) 上与我(原作者)联系。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/18/6/copying-files-go>
作者:[Mihalis Tsoukalos](https://opensource.com/users/mtsouk) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *This article is part of a Go series by Mihalis Tsoukalos. Read part 1: Creating random, secure passwords in Go, and part 2: Build a concurrent TCP server in Go.*
This article will show you how to copy a file in the [Go programming language](https://golang.org/). Although there are more than three ways to copy a file in Go, this article will present the three most common ways: using the `io.Copy()`
function call from the Go library; reading the input file all at once and writing it to another file; and copying the file in small chunks using a buffer.
## Method 1: Using io.Copy()
The first version of the utility will use the `io.Copy()`
function of the standard Go library. The logic of the utility can be found in the implementation of the `copy()`
function, which is as follows:
```
func copy(src, dst string) (int64, error) {
sourceFileStat, err := os.Stat(src)
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
if !sourceFileStat.Mode().IsRegular() {
return 0, fmt.Errorf("%s is not a regular file", src)
}
source, err := os.Open(src)
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
defer source.Close()
destination, err := os.Create(dst)
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
defer destination.Close()
nBytes, err := io.Copy(destination, source)
return nBytes, err
}
```
Apart from testing whether the file that will be copied exists (`os.Stat(src)`
) and is a regular file (`sourceFileStat.Mode().IsRegular()`
) so you can open it for reading, all the work is done by the `io.Copy(destination, source)`
statement. The `io.Copy()`
function returns the number of bytes copied and the first error message that happened during the copying process. In Go, if there is no error message, the value of the error variable will be `nil`
.
You can learn more about the `io.Copy()`
function at the [io package](https://golang.org/pkg/io/) documentation page.
Executing `cp1.go`
will generate the next kind of output:
```
$ go run cp1.go
Please provide two command line arguments!
$ go run cp1.go fileCP.txt /tmp/fileCPCOPY
Copied 3826 bytes!
$ diff fileCP.txt /tmp/fileCPCOPY
```
This technique is as simple as possible but gives no flexibility to the developer, which is not always a bad thing. However, there are times that the developer needs or wants to decide how they want to read the file.
## Method 2: Using ioutil.WriteFile() and ioutil.ReadFile()
A second way to copy a file uses the `ioutil.ReadFile()`
and `ioutil.WriteFile()`
functions. The first function reads the contents of an entire file into a byte slice, and the second function writes the contents of a byte slice into a file.
The logic of the utility can be found in the following Go code:
```
input, err := ioutil.ReadFile(sourceFile)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
err = ioutil.WriteFile(destinationFile, input, 0644)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error creating", destinationFile)
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
```
Apart from the two `if`
blocks, which are part of the Go way of working, you can see that the functionality of the program is found in the `ioutil.ReadFile()`
and `ioutil.WriteFile()`
statements.
Executing `cp2.go`
will generate the next kind of output:
```
$ go run cp2.go
Please provide two command line arguments!
$ go run cp2.go fileCP.txt /tmp/copyFileCP
$ diff fileCP.txt /tmp/copyFileCP
```
Please note that, although this technique will copy a file, it might not be efficient when you want to copy huge files because the byte slice returned by `ioutil.ReadFile()`
will also be huge.
## Method 3: Using os.Read() and os.Write()
A third method of copying files in Go uses a `cp3.go`
utility that will be developed in this section. It accepts three parameters: the filename of the input file, the filename of the output file, and the size of the buffer.
The most important part of `cp3.go`
resides in the following `for`
loop, which can be found in the `copy() function:`
```
buf := make([]byte, BUFFERSIZE)
for {
n, err := source.Read(buf)
if err != nil && err != io.EOF {
return err
}
if n == 0 {
break
}
if _, err := destination.Write(buf[:n]); err != nil {
return err
}
}
```
This technique uses `os.Read()`
for reading small portions of the input file into a buffer named `buf`
and `os.Write()`
for writing the contents of that buffer to a file. The copying process stops when there is an error in reading or when you reach the end of the file (`io.EOF`
).
Executing `cp3.go`
will generate the next kind of output:
```
$ go run cp3.go
usage: cp3 source destination BUFFERSIZE
$ go run cp3.go fileCP.txt /tmp/buf10 10
Copying fileCP.txt to /tmp/buf10
$ go run cp3.go fileCP.txt /tmp/buf20 20
Copying fileCP.txt to /tmp/buf20
```
As you will see, the size of the buffer greatly affects the performance of `cp3.go`
.
## Doing some benchmarking
The last part of this article will try to compare the three programs as well as the performance of `cp3.go`
for various buffer sizes using the `time(1)`
command line utility.
The following output shows the performance of `cp1.go`
, `cp2.go`
, and `cp3.go`
when copying a 500MB file:
```
$ ls -l INPUT
-rw-r--r-- 1 mtsouk staff 512000000 Jun 5 09:39 INPUT
$ time go run cp1.go INPUT /tmp/cp1
Copied 512000000 bytes!
real 0m0.980s
user 0m0.219s
sys 0m0.719s
$ time go run cp2.go INPUT /tmp/cp2
real 0m1.139s
user 0m0.196s
sys 0m0.654s
$ time go run cp3.go INPUT /tmp/cp3 1000000
Copying INPUT to /tmp/cp3
real 0m1.025s
user 0m0.195s
sys 0m0.486s
```
The output shows that the performance of all three utilities is pretty similar, which means that the functions of the standard Go library are quite clever and optimized.
Now, let's test how the buffer size affects the performance of `cp3.go`
. Executing `cp3.go`
with a buffer size of 10, 20, and 1,000 bytes to copy a 500MB file on a pretty fast machine will generate the following results:
```
$ ls -l INPUT
-rw-r--r-- 1 mtsouk staff 512000000 Jun 5 09:39 INPUT
$ time go run cp3.go INPUT /tmp/buf10 10
Copying INPUT to /tmp/buf10
real 6m39.721s
user 1m18.457s
sys 5m19.186s
$ time go run cp3.go INPUT /tmp/buf20 20
Copying INPUT to /tmp/buf20
real 3m20.819s
user 0m39.444s
sys 2m40.380s
$ time go run cp3.go INPUT /tmp/buf1000 1000
Copying INPUT to /tmp/buf1000
real 0m4.916s
user 0m1.001s
sys 0m3.986s
```
The generated output shows that the bigger the buffer, the faster the performance of the `cp3.go`
utility, which is more or less expected. Moreover, using buffer sizes smaller than 20 bytes for copying big files is a very slow process and should be avoided.
You can find the Go code of `cp1.go`
, `cp2.go`
, and `cp3.go`
at [GitHub](https://github.com/mactsouk/opensource.com).
If you have any questions or feedback, please leave a comment below or reach out to me on [Twitter](https://twitter.com/mactsouk).
## Comments are closed. |
14,660 | 基于 TypeScript 的无头内容管理系统 “Payload” 现已开源 | https://news.itsfoss.com/payload-open-source/ | 2022-06-01T09:40:51 | [
"CMS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14660-1.html |
>
> 开源的<ruby> 无头 <rt> Headless </rt></ruby>内容管理系统(CMS)列表中添加了一个新选项。它会是一个更好的无头 WordPress 替代品吗?
>
>
>

自从一年多前发布首个测试版以来,作为无头内容管理系统(CMS),Payload 已经逐渐在 Web 开发社区中给人们留下了深刻印象。先做一些背景介绍,Payload 是专门为更简单地开发网站、Web 应用或<ruby> 原生 <rt> native </rt></ruby>应用而量身定制的内容管理系统。
最近,他们决定完全开源,现在,它已跻身 [可用的最佳开源内容管理系统](https://itsfoss.com/open-source-cms/) 之一。
然而,这也带来了一些问题:他们会采用怎么样的商业模式?Payload 内容管理系统的计划是什么?下面,就让我们简要地看一下吧!
### Payload 为什么要开源?
自 2021 年首次发布以来,Payload 已经收到了来自开源社区的许多贡献。正如 Payload 在他们 [最近的公告](https://payloadcms.com/blog/open-source) 中所说,开源是一个重要的决定,它能够使项目能够达到的更高的高度,这是闭门造车做不到的。

此外,这种开放性通常会增加开发者社区的信任。这种信任也会延伸到商业,自然而然地转而成为开发者最支持、最信任的平台。
因此,Payload 正在切换到 MIT 许可证。这将允许任何人免费且不受限制地修改、分发和使用 Payload。
然而,Payload 仍然需要资金流入才能持续运营。那么,这就引出了一个问题,Payload 将如何盈利呢?
### Payload 将如何盈利?
与往常一样,Payload 需要一些财务支持才能维持运营。团队拿出了一个由两部分组成的计划,该计划既要为用户提供更多 <ruby> 以便利为中心 <rt> convenience-focused </rt> <ruby> 的功能,又要为 <ruby> 自托管 <rt> self-hosted </rt> </ruby> 客户提供难以置信的灵活性。 </ruby></ruby>

#### 企业许可证
此选项与其他开源 CMS 的软件服务极为相似。这些许可证将提供更高级的 SSO 选项,并为开发者保证 Payload 核心团队的响应时间。
这些许可证应该对大公司有吸引力,尤其是那些需要最大程度可靠性的公司。
#### 云主机
这个选项非常有吸引力,因为它结合了多种服务来创造最方便的体验。尽管传统托管仍然相当容易,但只要你为 Node 应用程序添加数据库、持久文件存储和其他基础设施,你就会面对四五个不同的服务,而这些服务都需要无缝协同工作。
应该注意的是,这不是必需的,Payload 仍然鼓励用户托管他们的实例。这项服务只是消除了与托管相关的大量费用和挑战而已。
截至目前,事情还没有敲定。但是,你可以关注 [GitHub](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload) 上的讨论来跟踪事情的进展。
### 总结
作为一个新兴的 CMS 选项,很高兴看到 Payload 迈出了这一步,成为 WordPress 和其他选项的流行替代品。此外,在我看来,Payload 团队对他们的新业务模式充满信心,或许这预示着一个光明的未来(希望如此)。
>
> **[Payload 内容管理系统](https://payloadcms.com/)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/payload-open-source/>
作者:[Jacob Crume](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

Since its first beta release a little over a year ago, Payload has slowly built a name for itself within the web development community as a headless Content Management System (CMS). For a bit of background information, Payload is a CMS tailored specifically toward being simpler to develop websites, web apps, or native applications.
Recently, they decided to go completely open-source, putting it among the likes of some of the [best open-source CMS available](https://itsfoss.com/open-source-cms/?ref=news.itsfoss.com).
However, that raises some questions, like what will their business model look like? And what are the plans for Payload CMS? Let’s take a brief look.
## Why Has Payload Gone Open-Source?
Since its initial launch back in 2021, Payload has received many contributions from the open-source community. As Payload said in their [recent announcement](https://payloadcms.com/blog/open-source?ref=news.itsfoss.com), the decision to go open-source is massive, and it allows projects to read much greater heights than could ever be possible if kept behind closed doors.
In addition, this openness often results in much greater levels of trust from the developer community. This trust also extends to businesses, naturally turning to the platform with the greatest developer support and trust.
Due to all these reasons, Payload is now switching to the MIT license. This allows anyone to modify, distribute, and use Payload for free and without limitations.
However, Payload still needs money flowing in to operate sustainably. So, that begs the question, how will Payload make money?
## How Payload Is Going To Make Money?
As is always the case, Payload requires some financial backing to remain afloat. They have outlined a two-part plan that should both provide users with even more convenience-focused features while still leaving self-hosted customers incredible flexibility.

### Enterprise Licenses
This option is extremely similar to other open-source CMS software services. These licenses would provide more advanced SSO options and give the developers guaranteed response times from the core Payload team.
These licenses should look appealing to larger corporations, especially those that require the utmost reliability.
### Cloud Hosting
This option is quite attractive, as it combines multiple services to create the most convenient experience possible. Although traditional hosting remains reasonably easy, as soon as you add in a database, permanent file storage, and deliberate infrastructure for Node apps, you are left with four or five different services that all need to work seamlessly together.
With this change, Payload aims to solve this problem by offering a simple and cost-effective hosting solution. This would combine all the aforementioned services into one.
It should be noted that this is not required, and users are still encouraged to host their instances. However, this service simply takes a lot of the expenses and challenges associated with hosting out of the equation.
As of now, things haven’t been finalized. But, you can keep an eye on the discussions on [ GitHub](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload?ref=news.itsfoss.com) to keep up with it.
## Wrapping Up
As an emerging CMS option, it is great to see Payload take this step to become a popular alternative to WordPress and other options. Additionally, it appears to me that the Payload team is confident in their new business model, signifying a (hopefully) bright future for them.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,661 | Ubuntu 22.04 之 KVM 安装手札 | https://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-install-kvm-on-ubuntu-22-04/ | 2022-06-01T17:16:38 | [
"KVM"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14661-1.html | 
**KVM** 是 <ruby> 基于内核的虚拟机 <rt> Kernel-based Virtual Machine </rt></ruby> 的首字母缩写,这是一项集成在内核中的开源虚拟化技术。它是一种类型一(裸机)的<ruby> 管理程序 <rt> hypervisor </rt></ruby>,可以使内核能够作为一个<ruby> 裸机管理程序 <rt> bare-metal hypervisor </rt></ruby>。
在 KVM 之上可以运行 Windows 和 Liunx 虚拟机。每个虚拟机都独立于其它虚拟机和底层操作系统(宿主机系统),并拥有自己的 CPU、内存、网络接口、存储设备等计算资源。
本文将介绍在 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS(Jammy Jellyfish)中如何安装 KVM 。在文末,我们也将演示如何在安装 KVM 完成之后创建一台虚拟机。
### 1、更新 Ubuntu 22.04
在一切开始前,打开终端并通过如下命令更新本地的软件包索引:
```
$ sudo apt update
```
### 2、检查虚拟化是否开启
在进一步行动之前,首先需要检查你的 CPU 是否支持 KVM 虚拟化,确保你系统中有 VT-x( vmx)英特尔处理器或 AMD-V(svm)处理器。
你可以通过运行如下命令,如果输出值大于 0,那么虚拟化被启用。否则,虚拟化被禁用,你需要启用它:
```
$ egrep -c '(vmx|svm)' /proc/cpuinfo
```

根据上方命令输出,你可以推断出虚拟化功能已经启用,因为输出结果大于 0。如果虚拟化功能没有启用,请确保在系统的 BIOS 设置中启用虚拟化功能。
另外,你可以通过如下命令判断 KVM 虚拟化是否已经在运行:
```
$ kvm-ok
```
运行该命令之前,请确保你已经安装了 `cpu-checker` 软件包,否则将提示未找到该命令的报错。
直接就在下面,你会得到如何解决这个问题的指示,那就是安装 `cpu-checker` 包。

随后,通过如下命令安装 `cpu-checker` 软件包:
```
$ sudo apt install -y cpu-checker
```
接着再运行 `kvm-ok` 命令,如果 KVM 已经启动,你将看到如下输出:
```
$ kvm-ok
```

### 3、在 Ubuntu 22.04 上安装 KVM
随后,通过如下命令在 Ubuntu 22.04 中安装 KVM 以及其他相关虚拟化软件包:
```
$ sudo apt install -y qemu-kvm virt-manager libvirt-daemon-system virtinst libvirt-clients bridge-utils
```
以下为你解释刚刚安装了哪些软件包:
* `qemu-kvm` – 一个提供硬件仿真的开源仿真器和虚拟化包
* `virt-manager` – 一款通过 libvirt 守护进程,基于 QT 的图形界面的虚拟机管理工具
* `libvirt-daemon-system` – 为运行 libvirt 进程提供必要配置文件的工具
* `virtinst` – 一套为置备和修改虚拟机提供的命令行工具
* `libvirt-clients` – 一组客户端的库和API,用于从命令行管理和控制虚拟机和管理程序
* `bridge-utils` – 一套用于创建和管理桥接设备的工具
### 4、启用虚拟化守护进程(libvirtd)
在所有软件包安装完毕之后,通过如下命令启用并启动 libvirt 守护进程:
```
$ sudo systemctl enable --now libvirtd
$ sudo systemctl start libvirtd
```
你可以通过如下命令验证该虚拟化守护进程是否已经运行:
```
$ sudo systemctl status libvirtd
```

另外,请将当前登录用户加入 `kvm` 和 `libvirt` 用户组,以便能够创建和管理虚拟机。
```
$ sudo usermod -aG kvm $USER
$ sudo usermod -aG libvirt $USER
```
`$USER` 环境变量引用的即为当前登录的用户名。你需要重新登录才能使得配置生效。
### 5、创建网桥(br0)
如果你打算从本机(Ubuntu 22.04)之外访问 KVM 虚拟机,你必须将虚拟机的网卡映射至网桥。`virbr0` 网桥是 KVM 安装完成后自动创建的,仅做测试用途。
你可以通过如下内容在 `/etc/netplan` 目录下创建文件 `01-netcfg.yaml` 来新建网桥:
```
$ sudo vi /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
network:
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: false
dhcp6: false
# add configuration for bridge interface
bridges:
br0:
interfaces: [enp0s3]
dhcp4: false
addresses: [192.168.1.162/24]
macaddress: 08:00:27:4b:1d:45
routes:
- to: default
via: 192.168.1.1
metric: 100
nameservers:
addresses: [4.2.2.2]
parameters:
stp: false
dhcp6: false
version: 2
```
保存并退出文件。
注:上述文件的配置是我环境中的,请根据你实际环境替换 IP 地址、网口名称以及 MAC 地址。
你可以通过运行 `netplan apply` 命令应用上述变更。
```
$ sudo netplan apply
```
你可以通过如下 `ip` 命令,验证网桥 `br0`:
```
$ ip add show
```

### 6、启动 KVM 虚拟机管理器
当 KVM 安装完成后,你可以使用图形管理工具 `virt-manager` 创建虚拟机。你可以在 GNOME 搜索工具中搜索 `Virtual Machine Manager` 以启动。
点击搜索出来的图标即可:

虚拟机管理器界面如下所示:

你可以点击 “<ruby> 文件 <rt> File </rt></ruby>” 并选择 “<ruby> 新建虚拟机 <rt> New Virtual Machine </rt></ruby>”。你也可以点击下图所示的图标:

在弹出的虚拟机安装向导将看到如下四个选项:
* 本地安装介质(ISO 镜像或 CDROM)
* 网络安装(HTTP、HTTPS 和 FTP)
* 导入现有磁盘镜像
* 手动安装
本文使用已下载的 ISO 镜像,你可以选择自己的 ISO 镜像,选择第一个选项,并点击 “<ruby> 向前 <rt> Forward </rt></ruby>”。

下一步中,点击 “<ruby> 浏览 <rt> Browse </rt></ruby>” 选择 ISO 镜像位置。

在下一个窗口中点击 “<ruby> 浏览本地 <rt> Browse local </rt></ruby>” 选取本机中 ISO 镜像。

如下所示,我们选择了 Debian 11 ISO 镜像,随后点击 “<ruby> 打开 <rt> Open </rt></ruby>”。

当 ISO 镜像选择后,点击 “<ruby> 向前 <rt> Forward </rt></ruby>” 进入下一步。

接着定义虚拟机所用内存大小以及 CPU 核心数,并点击 “<ruby> 向前 <rt> Forward </rt></ruby>” 。

下一步中,输入虚拟机磁盘空间,并点击 “<ruby> 向前 <rt> Forward </rt></ruby>” 继续。

如你需要将虚拟机网卡连接至网桥,点击 “<ruby> 选择网络 <rt> Network selection </rt></ruby>” 并选择 `br0` 网桥。

最后,点击 “<ruby> 完成 <rt> Finish </rt></ruby>” 按钮结束设置虚拟机。

稍等片刻,虚拟机的创建过程将开始。

当创建结束时,虚拟机将开机并进入系统安装界面。如下是 Debian 11 的安装选项。在这里你可以根据需要进行系统安装。

### 小结
至此,本文向你演示了如何在 Ubuntu 22.04 上 安装 KVM 虚拟化引擎。你的反馈对我们至关重要。
---
via: <https://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-install-kvm-on-ubuntu-22-04/>
作者:[James Kiarie](https://www.linuxtechi.com/author/james/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | This blog post will show you how to install KVM on Ubuntu 22.04 step-by-step. At the tail end of this post, we will demonstrate how you can create a virtual machine once the installation of KVM is complete.
[KVM](https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/virtualization/what-is-KVM), an acronym for Kernel-based Virtual Machine is an opensource virtualization technology integrated into the Linux kernel. It’s a type 1 (bare metal ) hypervisor that enables the kernel to act as a bare-metal hypervisor.
KVM allows users to create and run multiple guest machines which can be either Windows or Linux. Each guest machine runs independently of other virtual machines and the underlying OS ( host system ) and has its own computing resources such as CPU, RAM, network interfaces, and storage to mention a few.
#### Prerequisites
- Pre Installed Ubuntu 22.04
- 2 vCPUs & 4 GB RAM
- Stable Internet Connectivity
## 1) Update Ubuntu 22.04
To get off the ground, launch the terminal and update your local package index as follows.
$ sudo apt update
## 2) Check if Virtualization is enabled
Before you proceed any further, you need to check if your CPU supports KVM virtualization. For this to be possible, your system needs to either have a VT-x( vmx ) Intel processor or an AMD-V (svm) processor.
This is achieved by running the following command. if the output is greater than 0, then virtualization is enabled. Otherwise, virtualization is disabled and you need to enable it.
$ egrep -c '(vmx|svm)' /proc/cpuinfo
From the above output, you can deduce that virtualization is enabled since the result printed is greater than 0. If Virtualization is not enabled, be sure to enable the virtualization feature in your system’s BIOS settings.
In addition, you can verify if KVM virtualization is enabled by running the following command:
$ kvm-ok
For this to work, you need to have installed the cpu-checker package, otherwise, you will bump into the error ‘Command ‘kvm-ok’ not found’.
Directly below, you will get instructions on how to resolve this issue, and that is to install the cpu-checker package.
Therefore, install the cpu-checker package as follows.
$ sudo apt install -y cpu-checker
Then run the kvm-ok command, and if KVM virtualization is enabled, you should get the following output.
$ kvm-ok
## 3) Install KVM on Ubuntu 22.04
Next, run the command below to install KVM and additional virtualization packages on Ubuntu 22.04.
$ sudo apt install -y qemu-kvm virt-manager libvirt-daemon-system virtinst libvirt-clients bridge-utils
Let us break down the packages that we are installing:
- qemu-kvm – An opensource emulator and virtualization package that provides hardware emulation.
- virt-manager – A Qt-based graphical interface for managing virtual machines via the libvirt daemon.
- libvirt-daemon-system – A package that provides configuration files required to run the libvirt daemon.
- virtinst – A set of command-line utilities for provisioning and modifying virtual machines.
- libvirt-clients – A set of client-side libraries and APIs for managing and controlling virtual machines & hypervisors from the command line.
- bridge-utils – A set of tools for creating and managing bridge devices.
## 4) Start & Enable Virtualization Daemon
With all the packages installed, enable and start the Libvirt daemon.
$ sudo systemctl enable --now libvirtd $ sudo systemctl start libvirtd
Confirm that the virtualization daemon is running as shown.
$ sudo systemctl status libvirtd
In addition, you need to add the currently logged-in user to the kvm and libvirt groups so that they can create and manage virtual machines.
$ sudo usermod -aG kvm $USER $ sudo usermod -aG libvirt $USER
The $USER environment variable points to the name of the currently logged-in user. To apply this change, you need to log out and log back again.
## 5) Create Network Bridge (br0)
If you are planning to access KVM virtual machines outside from your Ubuntu 22.04 system, then you must map VM’s interface to a network bridge. Though a virtual bridge named virbr0, created automatically when KVM is installed but it is used for testing purposes.
To create a network bridge, create the file ‘01-netcfg.yaml’ with following content under the folder /etc/netplan.
$ sudo vi /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml network: ethernets: enp0s3: dhcp4: false dhcp6: false # add configuration for bridge interface bridges: br0: interfaces: [enp0s3] dhcp4: false addresses: [192.168.1.162/24] macaddress: 08:00:27:4b:1d:45 routes: - to: default via: 192.168.1.1 metric: 100 nameservers: addresses: [4.2.2.2] parameters: stp: false dhcp6: false version: 2
save and exit the file.
Note: These details as per my setup, so replace the IP address entries, interface name and mac address as per your setup.
To apply above change, run ‘netplan apply’
$ sudo netplan apply
Verify the network bridge ‘br0’, run below [ip command](https://www.linuxtechi.com/ip-command-examples-for-linux-users/)
$ ip add show
## 6) Launch KVM Virtual Machines Manager
With KVM installed, you can begin creating your virtual machines using the virt-manager GUI tool. To get started, use the GNOME search utility and search for ‘Virtual machine Manager’.
Click on the icon that pops up.
This launches the Virtual Machine Manager Interface.
Click on “File” then select “New Virtual Machine”. Alternatively, you can click on the button shown.
This pops open the virtual machine installation wizard which presents you with the following four options:
- Local install Media ( ISO image or CDROM )
- Network Install ( HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP )
- Import existing disk image
- Manual Install
In this guide, we have downloaded a Debian 11 ISO image, and therefore, if you have an ISO image, select the first option and click ‘Forward’.
In the next step, click ‘Browse’ to navigate to the location of the ISO image,
In the next window, click ‘Browse local’ in order to select the ISO image from the local directories on your Linux PC.
As demonstrated below, we have selected the Debian 11 ISO image. Then click ‘Open’
Once the ISO image is selected, click ‘Forward’ to proceed to the next step.
Next, define the RAM and the number of CPU cores for your virtual machine and click ‘Forward’.
In the next step, define the disk space for your virtual machine and click ‘Forward’.
To associate virtual machine’s nic to network bridge, click on ‘Network selection’ and choose br0 bridge.
Finally, click ‘Finish’ to wind up setting the virtual machine.
Shortly afterward, the virtual machine creation will get underway.
Once completed, the virtual machine will start with the OS installer displayed. Below is the Debian 11 installer listing the options for installation. From here, you can proceed to install your preferred system.
#### Conclusion
And that’s it. In this guide, we have demonstrated how you can install the KVM hypervisor on Ubuntu 22.04. Your feedback on this guide is much welcome.
Read Also: [How to Create KVM Virtual Machine Snapshot with Virsh Command](https://www.linuxtechi.com/create-revert-delete-kvm-virtual-machine-snapshot-virsh-command/)
KamusHi James, thanks for this great article, I would like to add a little comment.
If you want to let host machine to access the vm machine by SSH, and let the vm machine to access internet by the host machine ethernet, there is a additional package should be installed.
sudo apt install libnss-libvirt
Pål BjartanThanks for a detailed tutorial. However, I am facing an issue with creating a network bridge. I created the `/etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml` file as described in step 5, but this resulted in Ubuntu no longer connecting to the WiFi. It now shows a LAN icon in the top right corner. Deleting the file and running `sudo netplan apply` again solved the issue. I presume Ubuntu instead attempts to use the bridge to connect to the Internet.
Is there a way this can be avoided?
JohnSo I upgraded my Ubuntu 20.04 LTS hypervisor to 22..04 LTS.
systemctl status libvirtd says:
VMM is missing/removed and Storage Pool no longer showing up.
tried to re-install via APT, APT-GET ‘virt-manager’ and ‘virtinst’ packages, neither one is found.
Anyone else encountering this issue after Ubuntu 22.04 LTS ‘jammy jellyfish’ upgrade from 20.04 LTS? |
14,662 | 如何从源码编译 GNOME Shell 和应用 | https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/compile-gnome-source/ | 2022-06-01T18:05:55 | [
"GNOME",
"编译"
] | /article-14662-1.html | 
>
> 这是一篇如何从源码编译 GNOME 的快速指南,包括 Shell、mutter 和一些原生应用。
>
>
>
在编译之前,你需要确保一些事情,因为以下编译直接来自 Gitlab 的主分支,其中包含一些开发包。
通常,你可以选择在任何 Linux 发行版中编译。但是我建议使用 Fedora Rawhide(Fedora 的开发分支,用于将来的发布)。
另外,请勿在稳定系统中尝试此操作。因为操作可能出错,所以你可能最终得到损坏的系统。
总而言之,你需要以下内容来从源码编译 GNOME。
* 测试环境([虚拟机](https://www.debugpoint.com/tag/virtual-machine) 或测试系统)。
* Fedora Rawhide 发行版(推荐,[从此处下载](https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/fedora/linux/development/rawhide/Workstation/x86_64/iso/))。
* 确保你的发行版是最新的。
* 你已登录 [X.org](http://X.org) 会话。
我不建议你在 Wayland 会话中进行编译,因为你会遇到问题。
### 从源码编译 GNOME
GNOME 桌面是一个基于其功能的软件包集合。Linux 发行版的桌面组件工作于窗口管理器和 shell 之下。
因此,对于 GNOME,我将首先编译 mutter – 它是 GNOME Shell 的窗口管理器。然后进行 GNOME Shell 的编译。最后,我将编译一些原生应用。
我将使用 meson 构建系统进行编译。meson 是一个漂亮的构建系统,快速且用户友好。
#### 编译 mutter
打开终端并安装 GNOME Shell 和 mutter 所需的软件包。
```
sudo dnf build-dep mutter gnome-shell
```
在主目录(或你想要的任何地方)中创建演示目录。
```
cd ~
mkdir demo
cd demo
```
从 Gitlab 克隆 mutter 的主分支。
```
git clone https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/mutter
```
进入克隆目录,然后使用以下 `meson` 命令来准备构建文件。默认情况下,meson 使用 `/usr/local` 用于构建文件。但是,你也可以使用前缀开关将输出重定向到特定文件夹(如下所示)。
```
cd mutter
meson _build --prefix=/usr
```

使用以下命令在构建完成时,将 mutter 安装在到系统中。
```
sudo ninja install -C _build
```
#### 编译 GNOME Shell
GNOME Shell 和其他软件包的编译方法类似。首先,从 GitLab 克隆 GNOME Shell 主仓库,然后进行编译和安装。你可以按照下面的命令依次进行。
在 GNOME Shell 中,你需要两个依赖项。它们是 [asciidoc](https://asciidoc.org/) 和 [sassc](https://github.com/sass/sassc) 。请在构建 GNOME Shell 之前安装它们。
```
sudo dnf install asciidoc
sudo dnf install sassc
```
安装完这些依赖项后,按照下面的命令来构建和安装 GNOME Shell。在运行这个命令之前,请确保你回到 `demo` 文件夹(我在第一步创建的)。
```
git clone https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/gnome-shellcd gnome-shellmeson _build --prefix=/usrsudo ninja install -C _build
```
### 运行 GNOME Shell
编译完成后,你可以尝试重新启动 GNOME Shell 来查看来自主分支的变化。
在重启之前,正如我之前提到的,确保你处于 [X.Org](http://X.Org) 会话中。按 `ALT+F2` 并输入 `r`。然后按回车键。这个命令将重启 GNOME Shell。

恭喜你! 你已经成功地编译了 GNOME Shell 和 Mutter。
现在,是时候编译一些 GNOME 原生应用了。
### 编译 GNOME 原生应用
这些步骤对于 GNOME 或任何应用的所有源码都是一样的。你需要改变仓库的名字。因此,这里有一些编译必要的 GNOME 原生应用的命令示例。
#### Files(Nautilus)
```
git clone https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/nautilus/cd gnome-shellmeson _build --prefix=/usrsudo ninja install -C _build
```
#### GNOME 软件商店
```
git clone https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/gnome-software/cd gnome-shellmeson _build --prefix=/usrsudo ninja install -C _build
```
#### GNOME 控制中心
```
git clone https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/gnome-control-center/cd gnome-shellmeson _build --prefix=/usrsudo ninja install -C _build
```
### FAQ
1. 使用上述步骤,你可以编译任何源码分支。不仅仅是 GNOME。
2. GitLab 服务器有时很慢,克隆一个仓库可能需要较长的时间。如果 `git clone` 失败,我建议你再试一次。
### 结束语
我希望这个小小的高级教程能够帮助你在新的 GNOME 功能出现在 GNOME 每日构建系统之前尝试它。既然你编译了,你也可以为测试新的 GNOME 功能做出贡献,并在 GitLab 问题页面上报告任何特定包的 bug 或问题。
这篇文章是开源应用编译系列的第一篇文章。请继续关注更多开源应用的编译文章。
另外,请让我在下面的评论栏中知道你的评论、建议,或者你在使用这些说明时遇到的任何错误。
干杯。
---
via: <https://www.debugpoint.com/2022/05/compile-gnome-source/>
作者:[Arindam](https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | ('Connection aborted.', RemoteDisconnected('Remote end closed connection without response')) | null |
14,664 | 在 Windows 上使用开源屏幕阅读器 NVDA | https://opensource.com/article/22/5/open-source-screen-reader-windows-nvda | 2022-06-02T10:19:17 | [
"无障碍",
"屏幕阅读"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14664-1.html | 
>
> 为纪念全球无障碍意识日,让我们了解一下 NVDA 开源屏幕阅读器,以及你该如何参与其中,为所有网络用户提高无障碍性。
>
>
>
屏幕阅读器是辅助技术软件的一个专门领域,它可以阅读并说出计算机屏幕上的内容。完全没有视力的人只是视力障碍者的一小部分,屏幕阅读器软件可以帮助所有群体。屏幕阅读器大多特定于操作系统,供有视觉障碍的人和无障碍培训师使用,以及想要测试网站或应用的无障碍访问程度的开发人员和无障碍顾问。
### 如何使用 NVDA 屏幕阅读器
[WebAIM 屏幕阅读器用户调查](https://webaim.org/projects) 始于 2009 年,一直持续到 2021 年。在第一次调查中,最常用的屏幕阅读器是 JAWS,占 74%。它是微软 Windows 的商业产品,并且是长期的市场领导者。NVDA 当时是一个相对较新的 Windows 开源屏幕阅读器,仅占 8%。快进到 2021 年,JAWS 占 53.7%,NVDA 占 30.7%。
你可以从 [NVAccess 网站](https://www.nvaccess.org) 下载最新版本的 NVDA。为什么我要使用 NVDA 并将它推荐给我使用微软 Windows 的客户?嗯,它是开源的、速度快、功能强大、易于安装、支持多种语言、可以作为便携式应用运行、拥有庞大的用户群,并且有定期发布新版本的周期。
NVDA 已被翻译成 55 种语言,并在 175 个不同的国家/地区使用。还有一个活跃的开发者社区,拥有自己的 [社区插件网站](https://addons.nvda-project.org/index.en.html)。你选择安装的任何附加组件都将取决于你的需求,并且有很多可供选择,包括常见视频会议平台的扩展。
与所有屏幕阅读器一样,NVDA 有很多组合键需要学习。熟练使用任何屏幕阅读器都需要培训和练习。

向熟悉计算机和会使用键盘的人教授 NVDA 并不太难。向一个完全初学者教授基本的计算机技能(没有鼠标、触摸板和键盘技能)和使用 NVDA 是一个更大的挑战。个人的学习方式和偏好不同。此外,如果人们只想浏览网页和使用电子邮件,他们可能不需要学习如何做所有事情。NVDA 教程和资源的一个很好的链接来源是 [无障碍中心](http://www.accessibilitycentral.net/)。
当你掌握了使用键盘命令操作 NVDA,它就会变得更容易,但是还有一个菜单驱动的系统可以完成许多配置任务。

### 测试无障碍性
多年来,屏幕阅读器用户无法访问某些网站一直是个问题,尽管美国残疾人法案(ADA)等残疾人平等立法仍然存在。NVDA 在有视力的社区中的一个很好的用途是用于网站无障碍性测试。NVDA 可以免费下载,并且通过运行便携式版本,网站开发人员甚至不需要安装它。运行 NVDA,关闭显示器或闭上眼睛,看看你在浏览网站或应用时的表现如何。
NVDA 也可用于测试(通常被忽略的)正确 [标记 PDF 文档以实现无障碍性](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rRzWRk6cXIE) 任务。
有几个指南专注于使用 NVDA 进行无障碍性测试。我可以推荐 [使用 NVDA 测试网页](https://www.unimelb.edu.au/accessibility/tools/testing-web-pages-with-nvda) 和使用 [NVDA 评估 Web 无障碍性](https://webaim.org/articles/nvda)。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/22/5/open-source-screen-reader-windows-nvda>
作者:[Peter Cheer](https://opensource.com/users/petercheer) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Screen readers are a specialized area of assistive technology software that reads and then speaks the content of a computer screen. People with no sight at all are just a fraction of those with visual impairments, and screen reader software can help all groups. Screen readers are mostly specific to an operating system, and they're used by people with visual impairments and accessibility trainers, as well as developers and accessibility consultants wanting to test how accessible a website or application is.
## How to use the NVDA screen reader
The [WebAIM screen reader user surveys](https://webaim.org/projects) began in 2009 and ran to 2021. In the first survey, the most common screen reader used was JAWS at 74%. It is a commercial product for Microsoft Windows, and the long-time market leader. NVDA, then a relatively new open source screen reader for Windows came in at just 8%. Fast forward to 2021 and JAWS comes in with 53.7% with NVDA at 30.7%.
You can download the latest release of NVDA from the [NVAccess website](https://www.nvaccess.org). Why do I use NVDA and recommend it to my MS Windows using clients? Well, it is open source, fast, powerful, easy to install, supports a wide variety of languages, can be run as a portable application, has a large user base, and there is a regular release cycle for new versions.
NVDA has been translated into fifty-five languages and is used in one-hundred and seventy-five different countries. There is also an active developer community with their own [Community Add-ons website](https://addons.nvda-project.org/index.en.html). Any add-ons you choose to install will depend on your needs and there are a lot to choose from, including extensions for common video conferencing platforms.
Like all screen readers, there are a lot of key combinations to learn with NVDA. Using any screen reader proficiently takes training and practice.
(Peter Cheer, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Teaching NVDA to people familiar with computers and who have keyboard skills is not too difficult. Teaching basic computer skills (without the mouse, touch pad, and keyboard skills) and working with NVDA to a complete beginner is far more of a challenge. Individual learning styles and preferences differ. In addition, people may not need to learn how to do everything if all that they want to do is browse the web and use email. A good source of links to NVDA tutorials and resources is [Accessibility Central](http://www.accessibilitycentral.net/).
It becomes easier once you have mastered operating NVDA with keyboard commands, but there is also a menu-driven system for many configuration tasks.
(Peter Cheer, CC BY-SA 4.0)
## Test for accessibility
The inaccessibility of some websites to screen reader users has been a problem for many years, and still is despite disability equality legislation like the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). An excellent use for NVDA in the sighted community is for website accessibility testing. NVDA is free to download, and by running a portable version, website developers don't even need to install it. Run NVDA, turn off your monitor or close your eyes, and see how well you can navigate a website or application.
NVDA can also be used for testing when working through the (often ignored) task of properly [tagging a PDF document for accessibility](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rRzWRk6cXIE).
There are several guides that concentrate on using NVDA for accessibility testing. I can recommend [Testing Web Pages with NVDA](https://www.unimelb.edu.au/accessibility/tools/testing-web-pages-with-nvda) and Using [NVDA to Evaluate Web Accessibility](https://webaim.org/articles/nvda).
## Comments are closed. |
14,665 | Go 数组和切片的介绍 | https://opensource.com/article/18/7/introduction-go-arrays-and-slices | 2022-06-02T10:57:00 | [
"Go",
"数组",
"切片"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14665-1.html | 
>
> 了解使用数组和切片在 Go 中存储数据的优缺点,以及为什么其中一个更好。
>
>
>
在本系列的第四篇文章中,我将解释 [Go](https://golang.org/) 数组和切片,包括如何使用它们,以及为什么你通常要选择其中一个而不是另一个。
### 数组
数组是编程语言中最流行的数据结构之一,主要原因有两个:一是简单易懂,二是可以存储许多不同类型的数据。
你可以声明一个名为 `anArray` 的 Go 数组,该数组存储四个整数,如下所示:
```
anArray := [4]int{-1, 2, 0, -4}
```
数组的大小应该在它的类型之前声明,而类型应该在声明元素之前定义。`len()` 函数可以帮助你得到任何数组的长度。上面数组的大小是 4。
如果你熟悉其他编程语言,你可能会尝试使用 `for` 循环来遍历数组。Go 当然也支持 `for` 循环,不过,正如你将在下面看到的,Go 的 `range` 关键字可以让你更优雅地遍历数组或切片。
最后,你也可以定义一个二维数组,如下:
```
twoD := [3][3]int{
{1, 2, 3},
{6, 7, 8},
{10, 11, 12}}
```
`arrays.go` 源文件中包含了 Go 数组的示例代码。其中最重要的部分是:
```
for i := 0; i < len(twoD); i++ {
k := twoD[i]
for j := 0; j < len(k); j++ {
fmt.Print(k[j], " ")
}
fmt.Println()
}
for _, a := range twoD {
for _, j := range a {
fmt.Print(j, " ")
}
fmt.Println()
}
```
通过上述代码,我们知道了如何使用 `for` 循环和 `range` 关键字迭代数组的元素。`arrays.go` 的其余代码则展示了如何将数组作为参数传递给函数。
以下是 `arrays.go` 的输出:
```
$ go run arrays.go
Before change(): [-1 2 0 -4]
After change(): [-1 2 0 -4]
1 2 3
6 7 8
10 11 12
1 2 3
6 7 8
10 11 12
```
这个输出告诉我们:对函数内的数组所做的更改,会在函数退出后丢失。
### 数组的缺点
Go 数组有很多缺点,你应该重新考虑是否要在 Go 项目中使用它们。
首先,数组定义之后,大小就无法改变,这意味着 Go 数组不是动态的。简而言之,如果你需要将一个元素添加到一个没有剩余空间的数组中,你将需要创建一个更大的数组,并将旧数组的所有元素复制到新数组中。
其次,当你将数组作为参数传递给函数时,实际上是传递了数组的副本,这意味着你对函数内部的数组所做的任何更改,都将在函数退出后丢失。
最后,将大数组传递给函数可能会很慢,主要是因为 Go 必须创建数组的副本。
以上这些问题的解决方案,就是使用 Go 切片。
### 切片
Go 切片与 Go 数组类似,但是它没有后者的缺点。
首先,你可以使用 `append()` 函数将元素添加到现有切片中。此外,Go 切片在内部使用数组实现,这意味着 Go 中每个切片都有一个底层数组。
切片具有 `capacity` 属性和 `length` 属性,它们并不总是相同的。切片的长度与元素个数相同的数组的长度相同,可以使用 `len()` 函数得到。切片的容量是当前为切片分配的空间,可以使用 `cap()` 函数得到。
由于切片的大小是动态的,如果切片空间不足(也就是说,当你尝试再向切片中添加一个元素时,底层数组的长度恰好与容量相等),Go 会自动将它的当前容量加倍,使其空间能够容纳更多元素,然后将请求的元素添加到底层数组中。
此外,切片是通过引用传递给函数的,这意味着实际传递给函数的是切片变量的内存地址,这样一来,你对函数内部的切片所做的任何修改,都不会在函数退出后丢失。因此,将大切片传递给函数,要比将具有相同数量元素的数组传递给同一函数快得多。这是因为 Go 不必拷贝切片 —— 它只需传递切片变量的内存地址。
`slice.go` 源文件中有 Go 切片的代码示例,其中包含以下代码:
```
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func negative(x []int) {
for i, k := range x {
x[i] = -k
}
}
func printSlice(x []int) {
for _, number := range x {
fmt.Printf("%d ", number)
}
fmt.Println()
}
func main() {
s := []int{0, 14, 5, 0, 7, 19}
printSlice(s)
negative(s)
printSlice(s)
fmt.Printf("Before. Cap: %d, length: %d\n", cap(s), len(s))
s = append(s, -100)
fmt.Printf("After. Cap: %d, length: %d\n", cap(s), len(s))
printSlice(s)
anotherSlice := make([]int, 4)
fmt.Printf("A new slice with 4 elements: ")
printSlice(anotherSlice)
}
```
切片和数组在定义方式上的最大区别就在于:你不需要指定切片的大小。实际上,切片的大小取决于你要放入其中的元素数量。此外,`append()` 函数允许你将元素添加到现有切片 —— 请注意,即使切片的容量允许你将元素添加到该切片,它的长度也不会被修改,除非你调用 `append()`。上述代码中的 `printSlice()` 函数是一个辅助函数,用于打印切片中的所有元素,而 `negative()` 函数将切片中的每个元素都变为各自的相反数。
运行 `slice.go` 将得到以下输出:
```
$ go run slice.go
0 14 5 0 7 19
0 -14 -5 0 -7 -19
Before. Cap: 6, length: 6
After. Cap: 12, length: 7
0 -14 -5 0 -7 -19 -100
A new slice with 4 elements: 0 0 0 0
```
请注意,当你创建一个新切片,并为给定数量的元素分配内存空间时,Go 会自动地将所有元素都初始化为其类型的零值,在本例中为 0(`int` 类型的零值)。
### 使用切片来引用数组
Go 允许你使用 `[:]` 语法,使用切片来引用现有的数组。在这种情况下,你对切片所做的任何更改都将传播到数组中 —— 详见 `refArray.go`。请记住,使用 `[:]` 不会创建数组的副本,它只是对数组的引用。
`refArray.go` 中最有趣的部分是:
```
func main() {
anArray := [5]int{-1, 2, -3, 4, -5}
refAnArray := anArray[:]
fmt.Println("Array:", anArray)
printSlice(refAnArray)
negative(refAnArray)
fmt.Println("Array:", anArray)
}
```
运行 `refArray.go`,输出如下:
```
$ go run refArray.go
Array: [-1 2 -3 4 -5]
-1 2 -3 4 -5
Array: [1 -2 3 -4 5]
```
我们可以发现:对 `anArray` 数组的切片引用进行了操作后,它本身也被改变了。
### 总结
尽管 Go 提供了数组和切片两种类型,你很可能还是会使用切片,因为它们比 Go 数组更加通用、强大。只有少数情况需要使用数组而不是切片,特别是当你完全确定元素的数量固定不变时。
你可以在 [GitHub](https://github.com/mactsouk/opensource.com) 上找到 `arrays.go`、`slice.go` 和 `refArray.go` 的源代码。
如果你有任何问题或反馈,请在下方发表评论或在 [Twitter](https://twitter.com/mactsouk) 上与我联系。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/18/7/introduction-go-arrays-and-slices>
作者:[Mihalis Tsoukalos](https://opensource.com/users/mtsouk) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *This article is part of a Go series by Mihalis Tsoukalos:*
*Part 1:*[Creating random, secure passwords in Go](https://opensource.com/article/18/5/creating-random-secure-passwords-go)*Part 2:*[Build a concurrent TCP server in Go](https://opensource.com/article/18/5/building-concurrent-tcp-server-go),*Part 3:*[3 ways to copy files in Go](https://opensource.com/article/18/6/copying-files-go)
In this fourth article in the series, I will explain [Go](https://golang.org/) arrays and slices, how to use them, and why you'll usually want to choose one over the other.
## Arrays
Arrays are one of the most popular data structures among programming languages for two main reasons: They are simple and easy to understand, and they can store many different kinds of data.
You can declare a Go array named `anArray`
that stores four integers with the following:
`anArray := [4]int{-1, 2, 0, -4}`
The array's size should be stated before its type, which should be defined before its elements. The `len()`
function can help you find the length of any array. The size of the array above is 4.
If you are familiar with other programming languages, you might try to access all the elements of an array using a `for`
loop. However, as you will see below, Go's `range`
keyword allows you to access all the elements of an array or a slice in a more elegant way.
Last, here is how you can define an array with two dimensions:
```
twoD := [3][3]int{
{1, 2, 3},
{6, 7, 8},
{10, 11, 12}}
```
The `arrays.go`
source file explains the use of Go arrays. The most important code in `arrays.go`
is:
```
for i := 0; i < len(twoD); i++ {
k := twoD[i]
for j := 0; j < len(k); j++ {
fmt.Print(k[j], " ")
}
fmt.Println()
}
for _, a := range twoD {
for _, j := range a {
fmt.Print(j, " ")
}
fmt.Println()
}
```
This shows how you can iterate over the elements of an array using a `for`
loop and the `range`
keyword. The rest of the code of `arrays.go`
shows how to pass an array into a function as a parameter.
Following is the output of `arrays.go`
:
```
$ go run arrays.go
Before change(): [-1 2 0 -4]
After change(): [-1 2 0 -4]
1 2 3
6 7 8
10 11 12
1 2 3
6 7 8
10 11 12
```
This output demonstrates that the changes you make to an array inside a function are lost after the function exits.
## Disadvantages of arrays
Go arrays have many disadvantages that will make you reconsider using them in your Go projects. First, you can't change the size of an array after you define it, which means Go arrays are not dynamic. Putting it simply, if you need to add an element to an array that doesn't have any space left, you will need to create a bigger array and copy all the elements of the old array to the new one. Second, when you pass an array to a function as a parameter, you actually pass a copy of the array, which means any changes you make to an array inside a function will be lost after the function exits. Last, passing a large array to a function can be pretty slow, mostly because Go has to create a copy of the array.
The solution to all these problems is to use Go slices.
## Slices
A Go slice is similar to a Go array without the shortcomings. First, you can add an element to an existing slice using the `append()`
function. Moreover, Go slices are implemented internally using arrays, which means Go uses an underlying array for each slice.
Slices have a *capacity* property and a *length* property, which are not always the same. The length of a slice is the same as the length of an array with the same number of elements, and it can be found using the `len()`
function. The capacity of a slice is the room that has currently been allocated for the slice, and it can be found with the `cap()`
function.
As slices are dynamic in size, if a slice runs out of room (which means the current length of the array is the same as its capacity while you are trying to add another element to the array), Go automatically doubles its current capacity to make room for more elements and adds the requested element to the array.
Additionally, slices are passed by reference to functions, which means what is actually passed to a function is the memory address of the slice variable, and any modifications you make to a slice inside a function won't get lost after the function exits. As a result, passing a big slice to a function is significantly faster than passing an array with the same number of elements to the same function. This is because Go will not have to make a copy of the slice—it will just pass the memory address of the slice variable.
Go slices are illustrated in `slice.go`
, which contains the following code:
```
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func negative(x []int) {
for i, k := range x {
x[i] = -k
}
}
func printSlice(x []int) {
for _, number := range x {
fmt.Printf("%d ", number)
}
fmt.Println()
}
func main() {
s := []int{0, 14, 5, 0, 7, 19}
printSlice(s)
negative(s)
printSlice(s)
fmt.Printf("Before. Cap: %d, length: %d\n", cap(s), len(s))
s = append(s, -100)
fmt.Printf("After. Cap: %d, length: %d\n", cap(s), len(s))
printSlice(s)
anotherSlice := make([]int, 4)
fmt.Printf("A new slice with 4 elements: ")
printSlice(anotherSlice)
}
```
The biggest difference between a slice definition and an array definition is that you do not need to specify the size of the slice, which is determined by the number of elements you want to put in it. Additionally, the `append()`
function allows you to add an element to an existing slice—notice that even if the capacity of a slice allows you to add an element to that slice, its length will not be modified unless you call `append()`
. The `printSlice()`
function is a helper function used for printing the elements of its slice parameter, whereas the `negative()`
function processes all the elements of its slice parameter.
The output of `slice.go`
is:
```
$ go run slice.go
0 14 5 0 7 19
0 -14 -5 0 -7 -19
Before. Cap: 6, length: 6
After. Cap: 12, length: 7
0 -14 -5 0 -7 -19 -100
A new slice with 4 elements: 0 0 0 0
```
Please note that when you create a new slice and allocate memory space for a given number of elements, Go will automatically initialize all the elements to the zero value of its type, which in this case is 0.
## Referencing arrays with slices
Go allows you to reference an existing array with a slice using the `[:]`
notation. In that case, any changes you make into a slice's function will be propagated to the array—this is illustrated in `refArray.go`
. Please remember that the `[:]`
notation does not create a copy of the array, just a reference to it.
The most interesting part of `refArray.go`
is:
```
func main() {
anArray := [5]int{-1, 2, -3, 4, -5}
refAnArray := anArray[:]
fmt.Println("Array:", anArray)
printSlice(refAnArray)
negative(refAnArray)
fmt.Println("Array:", anArray)
}
```
The output of `refArray.go`
is:
```
$ go run refArray.go
Array: [-1 2 -3 4 -5]
-1 2 -3 4 -5
Array: [1 -2 3 -4 5]
```
So, the elements of the `anArray`
array changed because of the slice reference to it.
## Summary
Although Go supports both arrays and slices, it should be clear by now that you will most likely use slices because they are more versatile and powerful than Go arrays. There are only a few occasions where you will need to use an array instead of a slice. The most obvious one is when you are absolutely sure that you will need to store a fixed number of elements.
You can find the Go code of `arrays.go`
, `slice.go`
, and `refArray.go`
at [GitHub](https://github.com/mactsouk/opensource.com).
If you have any questions or feedback, please leave a comment below or reach out to me on [Twitter](https://twitter.com/mactsouk).
## Comments are closed. |
14,666 | 去谷歌化操作系统 /e/OS v1 及新品牌 Murena 一同发布 | https://news.itsfoss.com/murena-e-os/ | 2022-06-02T13:28:02 | [
"/e/OS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14666-1.html |
>
> Murena 是一个与 e 基金会有关的新品牌,该品牌专注于提供隐私友好的 /e/OS 及新的智能手机和云服务。
>
>
>

/e/OS 是一个流行的、注重隐私的移动操作系统,是谷歌安卓的替代品之一。
这个复刻自 Lineage OS 的操作系统消除了任何与谷歌有关的依赖性,并鼓励你在使用中不要直接依赖任何谷歌的服务。
取而代之的是,它提供一些解决方案作为替代品,为你提供一个隐私友好的生态系统。
为了精简其产品,负责该操作系统的 e 基金会宣布了一个新的品牌 “Murena”,其中包括了一些以该操作系统为核心的新功能和一个新的智能手机。
### Murena 和 e 基金会
e 基金会作为一个致力于 /e/OS 的非营利组织将继续存在。因此,可以说这不是一次品牌重塑。
然而,[Murena](https://murena.com/) 作为一个新的创业公司,似乎是一个独立的商业实体,将专注于鼓励主流用户尝试 /e/OS,并促进支持该操作系统的智能手机的使用。
对该公司,/e/OS 的创建者提及:

### /e/OS 1.0 有什么新内容?
随着该操作系统的最新升级发布,他们的目标是让事情变得更容易理解,在提高使用便利性的同时,仍然考虑到隐私。
此外,还随同本次更新推出了新的应用程序商店(App Lounge)和新的隐私工具(Advanced Privacy)。
**App Lounge**:这个新的应用程序安装程序可以让你安装许多开源应用程序和 PWA(<ruby> 渐进式网页应用 <rt> Progress Web App </rt></ruby>)。在你安装之前,它还会告知你每个应用程序中已有的跟踪器。

我相信一个量身定做的应用商店的存在将有助于消除新用户是否应该尝试用 /e/OS 安装 Play Store 或 F-Droid 的困惑。
除此之外,Advanced Privacy 工具将有助于限制用户在安装第三方应用程序后暴露的数据。
如果你想远离科技巨头,你还会发现 Murena 云服务可以用作私人电子邮件账户服务和云存储。该电子邮件服务提供的功能可以隐藏你的原始电子邮件地址。
### Murena One

首款 Murena 品牌的智能手机将于 6 月下旬推出,并将向美国、加拿大、欧洲、英国和瑞士等地的用户发货。
这款智能手机将采用 6.5 英寸显示屏,配备 2500 万像素的前置摄像头,后置摄像头设置有三个传感器,分别是 4800 万像素、800 万像素和 500 万像素。
我们不太确定是什么处理器,但它提到了是一个八核芯片,加上 4GB 的内存。所有这些都由 4500 毫安时的电池供电。
除了它的第一款智能手机,你还可以从它的官方网站上购买 Fairphone 和 Teracube 的智能手机,这些手机预装了 /e/OS。
### 总结
你可以在其官方网站上了解更多关于新的 /e/OS 升级、云服务和可用的智能手机的信息。
>
> **[Murena](https://murena.com/)**
>
>
>
该智能手机的定价还没有在新闻发布会上披露。所以,我们建议你如果有兴趣,可以关注一下。
---
via: <https://news.itsfoss.com/murena-e-os/>
作者:[Ankush Das](https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/) 选题:[lkxed](https://github.com/lkxed) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

/e/OS is a popular privacy-focused mobile operating system as an alternative to Google’s Android.
The operating system (fork of Lineage OS) eliminates any Google-related dependencies and encourages you to work without relying directly on any Google services.
Instead, it offers some of its solutions as alternatives to offer you a privacy-friendly ecosystem.
To streamline its offering, e Foundation responsible for the OS announced a new brand ‘**Murena**‘ that includes the operating system at its core, with new features and a new smartphone as well.
## Murena or /e/ Foundation?
The eFoundation is here to stay as a non-profit organization, working on /e/OS. Hence, it is safe to say that this is not a re-brand.
However, [Murena](https://murena.com/?ref=news.itsfoss.com) as a new startup company seems to be a separate commercial entity that will focus on encouraging mainstream users to try e/OS/ and promote the use of smartphones that support the operating system.
The creator of /e/OS mentioned the following about the company:

## /e/OS v1.0: What’s New?
With the latest upgrade to the operating system, they aim to make things more accessible, improving the ease of use while still keeping privacy in mind.
A new app store (App Lounge) and a new privacy tool (Advanced Privacy) have been introduced with the update.
**App Lounge**: The new application installer lets you install numerous open-source applications and PWAs (Progress Web Apps). It also informs you of existing trackers in each application before you install it.
I believe the existence of a tailored app store will help eliminate confusion for new users, whether they should try installing the Play Store or F-Droid with /e/OS.
In addition to that, the Advanced Privacy tool will help limit exposing users’ data after they install third-party applications.
You will also find a Murena cloud service as a private email account service and cloud storage if you want to get away from the big tech. The email service offers features to also hide your original email address.
## Murena One

The first Murena branded smartphone will be launching later in June and will ship to users in the USA, Canada, Europe, UK, and Switzerland.
The smartphone will sport a 6.5-inch display, with a 25 Megapixel front shooter, and a rear camera setup with three sensors that include 48 MP, 8 MP, and 5 MP.
We do not have clarity on the processor, but it mentions an octa-core chip coupled with 4 GB of RAM. All this is powered by a 4500 mAh battery.
In addition to its first smartphone, you can also purchase smartphones by Fairphone and Teracube from its official website that packs in /e/OS out of the box.
## Wrapping Up
You can explore more about the new /e/OS upgrade, cloud services, and available smartphones on its official website.
The pricing for the smartphone hasn’t been disclosed in the press release. So, we suggest you to keep an eye on it if you’re interested.
## More from It's FOSS...
- Support us by opting for
[It's FOSS Plus](https://itsfoss.com/#/portal/signup)membership. - Join our
[community forum](https://itsfoss.community/). - 📩 Stay updated with the latest on Linux and Open Source. Get our
[weekly Newsletter](https://itsfoss.com/newsletter/). |
14,668 | 通过编写“猜数字”游戏来学习 Awk | https://opensource.com/article/21/1/learn-awk | 2022-06-03T13:06:00 | [
"猜数字",
"Awk"
] | https://linux.cn/article-14668-1.html |
>
> 编程语言往往具有许多共同特征。学习一门新语言的好方法是去写一个熟悉的程序。在本文中,我将会使用 Awk 编写一个“猜数字”程序来展示熟悉的概念。
>
>
>

当你学习一门新的编程语言时,最好把重点放在大多数编程语言都有的共同点上:
* 变量 —— 存储信息的地方
* 表达式 —— 计算的方法
* 语句 —— 在程序中表示状态变化的方法
这些概念是大多是编程语言的基础。
一旦你理解了这些概念,你就可以开始把其他的弄清楚。例如,大多数语言都有由其设计所支持的“处理方式”,这些方式在不同语言之间可能有很大的不同。这些方法包括模块化(将相关功能分组在一起)、声明式与命令式、面向对象、低级与高级语法特性等等。许多程序员比较熟悉的是编程“仪式”,即,在处理问题之前设置场景所需花费的工作。据说 Java 编程语言有一个源于其设计的重要仪式要求,就是所有代码都在一个类中定义。
但从根本上讲,编程语言通常有相似之处。一旦你掌握了一种编程语言,就可以从学习另一种语言的基本知识开始,品味这种新语言的不同之处。
一个好方法是创建一组基本的测试程序。有了这些,就可以从这些相似之处开始学习。
你可以选择创建的一个测试程序是“猜数字”程序。电脑从 1 到 100 之间选择一个数字,让你猜这个数字。程序一直循环,直到你猜对为止。
“猜数字”程序练习了编程语言中的几个概念:
* 变量
* 输入
* 输出
* 条件判断
* 循环
这是学习一门新的编程语言的一个很好的实践实验。
**注**:本文改编自 Moshe Zadka 在 [Julia](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/julia) 中使用这种方法和 Jim Hall在 [Bash](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/learn-bash) 中使用这种方法的文章。
### 在 awk 程序中猜数
让我们编写一个实现“猜数字”游戏的 Awk 程序。
Awk 是动态类型的,这是一种面向数据转换的脚本语言,并且对交互使用有着令人惊讶的良好支持。Awk 出现于 20 世纪 70 年代,最初是 Unix 操作系统的一部分。如果你不了解 Awk,但是喜欢电子表格,这就是一个你可以 [去学习 Awk](https://opensource.com/article/20/9/awk-ebook) 的信号!
您可以通过编写一个“猜数字”游戏版本来开始对 Awk 的探索。
以下是我的实现(带有行号,以便我们可以查看一些特定功能):
```
1 BEGIN {
2 srand(42)
3 randomNumber = int(rand() * 100) + 1
4 print "random number is",randomNumber
5 printf "guess a number between 1 and 100\n"
6 }
7 {
8 guess = int($0)
9 if (guess < randomNumber) {
10 printf "too low, try again:"
11 } else if (guess > randomNumber) {
12 printf "too high, try again:"
13 } else {
14 printf "that's right\n"
15 exit
16 }
17 }
```
我们可以立即看到 Awk 控制结构与 C 或 Java 的相似之处,但与 Python 不同。 在像 `if-then-else`、`while` 这样的语句中,`then`、`else` 和 `while` 部分接受一个语句或一组被 `{` 和 `}` 包围的语句。然而,Awk 有一个很大的区别需要从一开始就了解:
根据设计,Awk 是围绕数据管道构建的。
这是什么意思呢?大多数 Awk 程序都是一些代码片段,它们接收一行输入,对数据做一些处理,然后将其写入输出。认识到这种转换管道的需要,Awk 默认情况下提供了所有的转换管道。让我们通过关于上面程序的一个基本问题来探索:“从控制台读取数据”的结构在哪里?
答案是——“内置的”。特别的,第 7-17 行告诉 Awk 如何处理被读取的每一行。在这种情况下,很容易看到第 1-6 行是在读取任何内容之前被执行的。
更具体地说,第 1 行上的 `BEGIN` 关键字是一种“模式”,在本例中,它指示 Awk 在读取任何数据之前,应该先执行 `{ ... }` 中 `BEGIN` 后面的内容。另一个类似的关键字 `END`,在这个程序中没有被使用,它指示 Awk 在读取完所有内容后要做什么。
回到第 7-17 行,我们看到它们创建了一个类似代码块 `{ ... }` 的片段,但前面没有关键字。因为在 `{` 之前没有任何东西可以让 Awk 匹配,所以它将把这一行用于接收每一行输入。每一行的输入都将由用户输入作为猜测。
让我们看看正在执行的代码。首先,是在读取任何输入之前发生的序言部分。
在第 2 行,我们用数字 42 初始化随机数生成器(如果不提供参数,则使用系统时钟)。为什么要用 42?[当然要选 42!](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/42_(number)#The_Hitchhiker's_Guide_to_the_Galaxy) 第 3 行计算 1 到 100 之间的随机数,第 4 行输出该随机数以供调试使用。第 5 行邀请用户猜一个数字。注意这一行使用的是 `printf`,而不是 `print`。和 C 语言一样,`printf` 的第一个参数是一个用于格式化输出的模板。
既然用户知道程序需要输入,她就可以在控制台上键入猜测。如前所述,Awk 将这种猜测提供给第 7-17 行的代码。第 18 行将输入记录转换为整数;`$0` 表示整个输入记录,而 `$1` 表示输入记录的第一个字段,`$2` 表示第二个字段,以此类推。是的,Awk 使用预定义的分隔符(默认为空格)将输入行分割为组成字段。第 9-15 行将猜测结果与随机数进行比较,打印适当的响应。如果猜对了,第 15 行就会从输入行处理管道中提前退出。
就这么简单!
考虑到 Awk 程序不同寻常的结构,代码片段会对特定的输入行配置做出反应,并处理数据,让我们看看另一种结构,看看过滤部分是如何工作的:
```
1 BEGIN {
2 srand(42)
3 randomNumber = int(rand() * 100) + 1
4 print "random number is",randomNumber
5 printf "guess a number between 1 and 100\n"
6 }
7 int($0) < randomNumber {
8 printf "too low, try again: "
9 }
10 int($0) > randomNumber {
11 printf "too high, try again: "
12 }
13 int($0) == randomNumber {
14 printf "that's right\n"
15 exit
16 }
```
第 1–6 行代码没有改变。但是现在我们看到第 7-9 行是当输入整数值小于随机数时执行的代码,第 10-12 行是当输入整数值大于随机数时执行的代码,第 13-16 行是两者相等时执行的代码。
这看起来“很酷但很奇怪” —— 例如,为什么我们会重复计算 `int($0)`?可以肯定的是,用这种方法来解决问题会很奇怪。但这些模式确实是分离条件处理的非常好的方式,因为它们可以使用正则表达式或 Awk 支持的任何其他结构。
为了完整起见,我们可以使用这些模式将普通的计算与只适用于特定环境的计算分离开来。下面是第三个版本:
```
1 BEGIN {
2 srand(42)
3 randomNumber = int(rand() * 100) + 1
4 print "random number is",randomNumber
5 printf "guess a number between 1 and 100\n"
6 }
7 {
8 guess = int($0)
9 }
10 guess < randomNumber {
11 printf "too low, try again: "
12 }
13 guess > randomNumber {
14 printf "too high, try again: "
15 }
16 guess == randomNumber {
17 printf "that's right\n"
18 exit
19 }
```
认识到这一点,无论输入的是什么值,都需要将其转换为整数,因此我们创建了第 7-9 行来完成这一任务。现在第 10-12、13-15 和 16-19 行这三组代码,都是指已经定义好的变量 guess,而不是每次都对输入行进行转换。
让我们回到我们想要学习的东西列表:
* 变量 —— 是的,Awk 有这些;我们可以推断出,输入数据以字符串形式输入,但在需要时可以转换为数值
* 输入 —— Awk 只是通过它的“数据转换管道”的方式发送输入来读取数据
* 输出 —— 我们已经使用了 Awk 的 `print` 和 `printf` 函数来将内容写入输出
* 条件判断 —— 我们已经学习了 Awk 的 `if-then-else` 和对应特定输入行配置的输入过滤器
* 循环 —— 嗯,想象一下!我们在这里不需要循环,这还是多亏了 Awk 采用的“数据转换管道”方法;循环“就这么发生了”。注意,用户可以通过向 Awk 发送一个文件结束信号(当使用 Linux 终端窗口时可通过快捷键 `CTRL-D`)来提前退出管道。
不需要循环来处理输入的重要性是非常值得的。Awk 能够长期保持存在的一个原因是 Awk 程序是紧凑的,而它们紧凑的一个原因是不需要从控制台或文件中读取的那些格式代码。
让我们运行下面这个程序:
```
$ awk -f guess.awk
random number is 25
guess a number between 1 and 100: 50
too high, try again: 30
too high, try again: 10
too low, try again: 25
that's right
$
```
我们没有涉及的一件事是注释。Awk 注释以 `#` 开头,以行尾结束。
### 总结
Awk 非常强大,这种“猜数字”游戏是入门的好方法。但这不应该是你探索 Awk 的终点。你可以看看 [Awk 和 Gawk(GNU Awk)的历史](https://www.gnu.org/software/gawk/manual/html_node/History.html),Gawk 是 Awk 的扩展版本,如果你在电脑上运行 Linux,可能会有这个。或者,从它的原始开发者那里阅读关于 [最初版本](https://archive.org/details/pdfy-MgN0H1joIoDVoIC7) 的各种信息。
你还可以 [下载我们的备忘单](https://opensource.com/downloads/cheat-sheet-awk-features) 来帮你记录下你所学的一切。
>
> **[Awk 备忘单](https://opensource.com/downloads/cheat-sheet-awk-features)**
>
>
>
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/21/1/learn-awk>
作者:[Chris Hermansen](https://opensource.com/users/clhermansen) 选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972) 译者:[FYJNEVERFOLLOWS](https://github.com/FYJNEVERFOLLOWS) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When you learn a new programming language, it's good to focus on the things most programming languages have in common:
- Variables – places where information is stored
- Expressions – ways to calculate things
- Statements – the means by which state changes are expressed in a program
These concepts are the basis of most programming languages.
Once you understand these concepts, you can start figuring the rest out. For example, most languages have a "way of doing things" supported by their design, and those ways can be quite different from one program to another. These ways include modularity (grouping related functionality together), declarative vs. imperative, object-orientation, low- vs. high-level syntactic features, and so on. An example familiar to many programmers is "ceremony," that is, the amount of work required to set the scene before tackling the problem. The Java programming language is said to have a significant ceremony requirement, stemming from its design, which requires all code to be defined within a class.
But back to the basics. Programming languages usually share similarities. Once you know one programming language, start by learning the basics of another to appreciate the differences in that new language.
A good way to proceed is to create a set of basic test programs. With these in hand, learning starts with these similarities.
One test program you can use is a "guess the number" program. The computer picks a number between one and one hundred and asks you to guess the number. The program loops until you make a correct guess.
The "guess the number" program exercises several concepts in programming languages:
- Variables
- Input
- Output
- Conditional evaluation
- Loops
That's a great practical experiment to learn a new programming language.
**Note**: This article is adapted from Moshe Zadka's article on doing using this approach in [Julia](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/julia) and Jim Hall's article on doing it in [Bash](https://opensource.com/article/20/12/learn-bash).
## Guess the number in awk
Let's write a "guess the number" game as an Awk program.
Awk is dynamically typed, is a scripting language oriented toward data transformation, and has surprisingly good support for interactive use. Awk has been around since the 1970s, originally as a part of the Unix operating system. If you don't know Awk but love spreadsheets, this is a sign… [go learn Awk](https://opensource.com/article/20/9/awk-ebook)!
You can begin your exploration of Awk by writing a version of the "guess the number" game.
Here is my implementation (with line numbers so we can review some of the specific features):
```
1 BEGIN {
2 srand(42)
3 randomNumber = int(rand() * 100) + 1
4 print "random number is",randomNumber
5 printf "guess a number between 1 and 100\n"
6 }
7 {
8 guess = int($0)
9 if (guess < randomNumber) {
10 printf "too low, try again:"
11 } else if (guess > randomNumber) {
12 printf "too high, try again:"
13 } else {
14 printf "that's right\n"
15 exit
16 }
17 }
```
We can immediately see similarities between Awk control structures and those of C or Java, but unlike Python. In statements such as *if-then-else* or *while*, the *then*, *else*, and *while* parts take either a statement or a group of statements enclosed within **{** and **}**. However, there is one big difference about AWk that needs to be understood from the start:
By design, Awk is built around a data pipeline.
What does that mean? Most Awk programs are snippets of code that receive a line of input, do something with the data, and write it to output. Recognizing the need for such a transformation pipeline, Awk by default provides all the transformation plumbing. Let's explore that through the above program by asking a basic question: Where is the 'read data from the console' structure?
The answer to that is – it's built-in. In particular, lines 7 – 17 tell Awk what to do with each line that is read. Given that context, it's pretty easy to see that lines 1 – 6 are executed before anything is read.
More specifically, the **BEGIN** keyword on line 1 is a kind of "pattern," in this case indicating to Awk that, before reading any data, it should execute what follows the **BEGIN** in the { … }. A similar **END** keyword, not used in this program, indicates to Awk what to do when everything has been read.
Coming back to lines 7 – 17, we see they create a block of code { … } that is similar, but there is no keyword in front. Because there is nothing before the **{** for Awk to match, it will apply this line to every line of input received. Each line of input will be entered as guesses by the user.
Let's look at the code being executed. First, the preamble that happens before any input is read.
In line 2, we initialize the random number generator with the number 42 (if we don't provide an argument, the system clock is used). 42? [Of course 42](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/42_(number)#The_Hitchhiker's_Guide_to_the_Galaxy). Line 3 calculates a random number between 1 and 100, and line 4 prints that number out for debugging purposes. Line 5 invites the user to guess a number. Note this line uses
, not **printf**
. Like C, **print**
s first argument is a template used to format the output.**printf**'
Now that the user is aware the program expects input, she can type a guess on the console. Awk supplies this guess to the code in lines 7 – 17, as mentioned previously. Line 18 converts the input record to an integer;
indicates the entire input record, whereas **$0**
indicates the first field of the input record, **$1**
the second, and so on. Yup, Awk splits an input line into constituent fields, using the predefined separator, which defaults to white space. Lines 9 – 15 compare the guess to the random number, printing appropriate responses. If the guess is correct, line 15 exits prematurely from the input line processing pipeline.**$2**
Simple!
Given the unusual structure of Awk programs as code snippets that react to specific input line configurations and do stuff with the data, let’s look at an alternative structure just to see how the filtering part works:
```
1 BEGIN {
2 srand(42)
3 randomNumber = int(rand() * 100) + 1
4 print "random number is",randomNumber
5 printf "guess a number between 1 and 100\n"
6 }
7 int($0) < randomNumber {
8 printf "too low, try again: "
9 }
10 int($0) > randomNumber {
11 printf "too high, try again: "
12 }
13 int($0) == randomNumber {
14 printf "that's right\n"
15 exit
16 }
```
Lines 1 – 6 haven’t changed. But now we see that lines 7 – 9 is code that is executed when the integer value of the line is less than the random number, lines 10 – 12 is code that is executed when the integer value of the line is greater than the random number, and lines 13 – 16 is code that is executed when the two match.
This should seem "cool but weird" – why would we repeatedly calculate
, for example? And for sure, it would be a weird way to solve the problem. But those patterns can be really quite wonderful ways to separate conditional processing since they can employ regular expressions or any other structure supported by Awk.**int($0)**
For completeness, we can use these patterns to separate common computations from things that only apply to specific circumstances. Here’s a third version to illustrate:
```
1 BEGIN {
2 srand(42)
3 randomNumber = int(rand() * 100) + 1
4 print "random number is",randomNumber
5 printf "guess a number between 1 and 100\n"
6 }
7 {
8 guess = int($0)
9 }
10 guess < randomNumber {
11 printf "too low, try again: "
12 }
13 guess > randomNumber {
14 printf "too high, try again: "
15 }
16 guess == randomNumber {
17 printf "that's right\n"
18 exit
19 }
```
Recognizing that, no matter what value of input comes in, it needs to be converted to an integer, we have created lines 7 – 9 to do just that. Now the three groups of lines, 10 – 12, 13 – 15 and 16 – 19, refer to the already-defined variable guess instead of converting the input line each time.
Let's go back to the list of things we wanted to learn:
- variables – yup, Awk has those; we can infer that input data comes in as strings but can be converted to a numeric value when required
- input – Awk just sends input through its "data transformation pipeline" approach to reading stuff
- output – we have used Awk's
and**print**
procedures to write stuff to output**printf** - conditional evaluation – we have learned about Awk's
*if-then-else*and input filters that respond to specific input line configurations - loops – huh, imagine that! We didn't need a loop here, once again, thanks to the "data transformation pipeline" approach that Awk takes; the loop "just happens." Note the user can exit the pipeline prematurely by sending an end-of-file signal to Awk (a
**CTRL-D**when using a Linux terminal window)
It's well worth considering the importance of not needing a loop to handle input. One reason Awk has remained viable for so long is that Awk programs are compact, and one of the reasons they are compact is there is no boilerplate required to read from the console or a file.
Let's run the program:
```
$ awk -f guess.awk
random number is 25
guess a number between 1 and 100: 50
too high, try again: 30
too high, try again: 10
too low, try again: 25
that's right
$
```
One thing we didn't cover was comments. An Awk comment begins with a
and ends with the end of line.**#**
## Wrap up
Awk is incredibly powerful and this "guess the number" game is a great way to get started. It shouldn't be the end of your journey, though. You can [read about the history of Awk and Gawk (GNU Awk)](https://www.gnu.org/software/gawk/manual/html_node/History.html), an expanded version of Awk and probably the one you have on your computer if you're running Linux, or [read all about the original from its initial developers](https://archive.org/details/pdfy-MgN0H1joIoDVoIC7).
You can also [download our cheatsheet](https://opensource.com/downloads/cheat-sheet-awk-features) to help you keep track of everything you learn.
## 4 Comments |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.