id
int64 2.05k
16.6k
| title
stringlengths 5
75
| fromurl
stringlengths 19
185
| date
timestamp[s] | tags
sequencelengths 0
11
| permalink
stringlengths 20
37
| content
stringlengths 342
82.2k
| fromurl_status
int64 200
526
⌀ | status_msg
stringclasses 339
values | from_content
stringlengths 0
229k
⌀ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
8,516 | Samba 系列(九):将 CentOS 7 桌面系统加入到 Samba4 AD 域环境中 | http://www.tecmint.com/join-centos-7-to-samba4-active-directory/ | 2017-05-17T14:57:00 | [
"samba"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8516-1.html | 这篇文章讲述了如何使用 Authconfig-gtk 工具将 CentOS 7 桌面系统加入到 Samba4 AD 域环境中,并使用域帐号登录到 CentOS 系统。

### 要求
1、[在 Ubuntu 系统中使用 Samba4 创建活动目录架构](/article-8065-1.html)
2、[CentOS 7.3 安装指南](/article-8048-1.html)
### 第一步:在 CentOS 系统中配置 Samba4 AD DC
1、在将 CentOS 7 加入到 Samba4 域环境之前,你得先配置 CentOS 系统的网络环境,确保在 CentOS 系统中通过 DNS 可以解析到域名。
打开网络设置,关闭有线网卡。打开下方的设置按钮,手动编辑网络设置,指定 DNS 的 IP 地址为 Samba4 AD DC 服务器的 IP 地址。
设置完成之后,应用配置,并打开有线网卡。

*网络设置*

*配置网络*
2、下一步,打开网络配置文件,在文件末尾添加一行域名信息。这样能确保当你仅使用主机名来查询域中的 DNS 记录时, DNS 解析器会自动把域名添加进来。
```
$ sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eno16777736
```
添加下面一行:
```
SEARCH="your_domain_name"
```
**
*网卡配置*
3、最后,重启网卡服务以应用更改,并验证解析器的配置文件是否正确配置。我们通过使用 ping 命令加上 DC 服务器的主机名或域名以验证 DNS 解析能否正常运行。
```
$ sudo systemctl restart network
$ cat /etc/resolv.conf
$ ping -c1 adc1
$ ping -c1 adc2
$ ping tecmint.lan
```

*验证网络配置是否正常*
4、同时,使用下面的命令来配置你的主机名,然后重启计算机以应用更改:
```
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname your_hostname
$ sudo init 6
```
使用下面的命令来验证主机名是否正确配置:
```
$ cat /etc/hostname
$ hostname
```
5、最后一步配置是使用下面的命令来保证系统时间跟 Samba4 AD DC 服务器的时间同步:
```
$ sudo yum install ntpdate
$ sudo ntpdate -ud domain.tld
```
### 第二步:安装要加入 Samba4 AD DC 所必需的软件包
6、为了将 CentOS 7 加入到活动目录域中,你需要使用下面的命令来安装相关的软件包:
```
$ sudo yum install samba samba samba-winbind krb5-workstation
```
7、最后,安装 CentOS 软件库中提供的图形化界面软件包: Authconfig-gtk 。该软件用于将 CentOS 系统集成到域环境中。
```
$ sudo yum install authconfig-gtk
```
### 第三步:将 CentOS 7 桌面系统集成到 Samba4 AD DC 域环境中
8、将 CentOS 加入到域的过程非常简单。使用有 root 权限的帐号在命令行下打开 Authconfig-gtk 程序,然后按下图所示修改相关配置即可:
```
$ sudo authconfig-gtk
```
打开身份或认证配置页面:
* 用户帐号数据库 : 选择 Winbind
* Winbind 域 : 你的域名
* 安全模式 : ADS
* Winbind ADS 域 : 你的域名.TLD
* 域控制器 : 域控服务器的全域名
* 默认Shell : /bin/bash
* 勾选允许离线登录

*域认证配置*
打开高级选项配置页面:
* 本地认证选项 : 支持指纹识别
* 其它认证选项 : 用户首次登录创建家目录

*高级认证配置*
9、修改完上面的配置之后,返回到身份或认证配置页面,点击加入域按钮,在弹出的提示框点保存即可。

*身份和认证*

*保存认证配置*
10、保存配置之后,系统将会提示你提供域管理员信息以将 CentOS 系统加入到域中。输入域管理员帐号及密码后点击 OK 按钮,加入域完成。

*加入 Winbind 域环境*
11、加入域后,点击应用按钮以让配置生效,选择所有的 windows 并重启机器。

*应用认证配置*
12、要验证 CentOS 是否已成功加入到 Samba4 AD DC 中,你可以在安装了 [RSAT 工具](/article-8097-1.html) 的 windows 机器上,打开 AD 用户和计算机工具,点击域中的计算机。
你将会在右侧看到 CentOS 主机信息。

*活动目录用户和计算机*
### 第四步:使用 Samba4 AD DC 帐号登录 CentOS 桌面系统
13、选择使用其它账户,然后输入域帐号和密码进行登录,如下图所示:
```
Domain\domain_account
或
[email protected]
```
**
*使用其它账户*
**
*输入域用户名*
14、在 CentOS 系统的命令行中,你也可以使用下面的任一方式来切换到域帐号进行登录:
```
$ su - domain\domain_user
$ su - [email protected]
```
**
*使用域帐号登录*

*使用域帐号邮箱登录*
15、要为域用户或组添加 root 权限,在命令行下使用 root 权限帐号打开 `sudoers` 配置文件,添加下面一行内容:
```
YOUR_DOMAIN\\domain_username ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL #For domain users
%YOUR_DOMAIN\\your_domain\ group ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL #For domain groups
```
**
*指定用户和用户组权限*
16、使用下面的命令来查看域控制器信息:
```
$ sudo net ads info
```
**
*查看域控制器信息*
17、你可以在安装了 Winbind 客户端的机器上使用下面的命令来验证 CentOS 加入到 Samba4 AD DC 后的信任关系是否正常:
```
$ sudo yum install samba-winbind-clients
```
然后,执行下面的一些命令来查看 Samba4 AD DC 的相关信息:
```
$ wbinfo -p ### Ping 域名
$ wbinfo -t ### 检查信任关系
$ wbinfo -u ### 列出域用户帐号
$ wbinfo -g ### 列出域用户组
$ wbinfo -n domain_account ### 查看域帐号的 SID 信息
```
**
*查看 Samba4 AD DC 信息*
18、如果你想让 CentOS 系统退出域环境,使用具有管理员权限的帐号执行下面的命令,后面加上域名及域管理员帐号,如下图所示:
```
$ sudo net ads leave your_domain -U domain_admin_username
```
**
*退出 Samba4 AD 域*
这篇文章就写到这里吧!尽管上面的这些操作步骤是将 CentOS 7 系统加入到 Samba4 AD DC 域中,其实这些步骤也同样适用于将 CentOS 7 桌面系统加入到 Microsoft Windows Server 2008 或 2012 的域中。
---
作者简介:
我是一个电脑迷,开源 Linux 系统和软件爱好者,有 4 年多的 Linux 桌面、服务器系统使用和 Base 编程经验。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/join-centos-7-to-samba4-active-directory/>
作者:[Matei Cezar](http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,517 | 如何安装 pandom : 一个针对 Linux 的真随机数生成器 | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-pandom-a-true-random-number-generator/ | 2017-05-17T20:44:28 | [
"随机数",
"pandom"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8517-1.html | 
本教程只针对 amd64/x86\_64 架构 Linux 内核版本大于等于 2.6.9 的系统。本文将解释如何安装 [pandom](http://ncomputers.org/pandom),这是一个由 ncomputers.org 维护的定时抖动真随机数生成器。
### 简介
在现在的计算机状况下,比如说配置了固态硬盘(SSD)的个人电脑和虚拟专用服务器(VPS)的环境中,Linux 内核内置的真随机数发生器提供的吞吐量很低。
而出于各种不同的加密目的使得对真随机数的需求持续增长,从而使得这个低吞吐量问题在 Linux 实现中变得越来越严重。
在与上述相同的物理或者虚拟环境下,并假设没有其它进程以 root 身份向 `/dev/random` 进行写操作的话,64 [ubits](http://ncomputers.org/ubit)/64 bits 的 pandom 可以以 8 KiB/s 的速率生成随机数。
### 1 pandom 的安装
#### 1.1 获得 root 权限
Pandom 必须以 root 身份来安装,所以在必要的时候请运行如下命令:
```
su -
```
#### 1.2 安装编译所需的依赖
为了下载并安装 pandom,你需要 GNU `as` 汇编器、GNU `make`、GNU `tar` 和 GNU `wget` (最后两个工具通常已被安装)。随后你可以按照你的意愿卸载它们。
**基于 Arch 的系统:**
```
pacman -S binutils make
```
**基于 Debian 的系统:**
```
apt-get install binutils make
```
基于 Red Hat 的系统:
```
dnf install binutils make
yum install binutils make
```
**基于 SUSE 的系统:**
```
zypper install binutils make
```
#### 1.3 下载并析出源码
下面的命令将使用 `wget` 和 `tar` 从 ncomputers.org 下载 pandom 的源代码并将它们解压出来:
```
wget http://ncomputers.org/pandom.tar.gz
tar xf pandom.tar.gz
cd pandom/amd64-linux
```
#### 1.4 在安装前进行测试 (推荐)
这个被推荐的测试将花费大约 8 分钟的时间,它将检查内核支持情况并生成一个名为 `checkme` 的文件(在下一节中将被分析)。
```
make check
```
#### 1.5 确定系统的初始化程序
在安装 pandom 之前,你需要知道你的系统使用的是哪个初始化程序。假如下面命令的输出中包含 `running`,则意味着你的系统使用了 `systemd`,否则你的系统则可能使用了一个 `init.d` 的实现(例如 upstart、sysvinit)。
```
systemctl is-system-running
running
```
#### 1.6 安装 pandom
一旦你知道了你的系统使用何种 Linux 实现,那么你就可以相应地安装 pandom 了。
**使用基于 init.d 作为初始化程序(如: upstart、sysvinit)的系统:**
假如你的系统使用了一个 init.d 的实现(如: upstart、sysvinit),请运行下面的命令来安装 pandom:
```
make install-init.d
```
**以 systemd 作为初始化程序的系统:**
假如你的系统使用 `systemd`,则请运行以下命令来安装 pandom:
```
make install-systemd
```
### 2 checkme 文件的分析
在使用 pandom 进行加密之前,强烈建议分析一下先前在安装过程中生成的 `checkme` 文件。通过分析我们便可以知道用 pandom 生成的数是否真的随机。本节将解释如何使用 ncomputers.org 的 shell 脚本 `entropyarray` 来测试由 pandom 产生的输出的熵及序列相关性。
**注**:整个分析过程也可以在另一台电脑上完成,例如在一个笔记本电脑或台式机上。举个例子:假如你正在一个资源受到限制的 VPS 上安装 pandom 程序,或许你更倾向于将 `checkme` 复制到自己的个人电脑中,然后再进行分析。
#### 2.1 获取 root 权限
`entropyarray` 程序也必须以 root 身份来安装,所以在必要时请运行如下命令:
```
su -
```
#### 2.2 安装编译所需的依赖
为了下载并安装 `entropyarray`, 你需要 GNU g++ 编译器、GNU `make`、GNU `tar` 和 GNU `wget`。在随后你可以任意卸载这些依赖。
**基于 Arch 的系统:**
```
pacman -S gcc make
```
**基于 Debian 的系统:**
```
apt-get install g++ make
```
**基于 Red Hat 的系统:**
```
dnf install gcc-c++ make
yum install gcc-c++ make
```
**基于 SUSE 的系统:**
```
zypper install gcc-c++ make
```
#### 2.3 下载并析出源码
以下命令将使用 `wget` 和 `tar` 从 ncomputers.org 下载到 entropyarray 的源码并进行解压:
```
wget http://ncomputers.org/rearray.tar.gz
wget http://ncomputers.org/entropy.tar.gz
wget http://ncomputers.org/entropyarray.tar.gz
tar xf entropy.tar.gz
tar xf rearray.tar.gz
tar xf entropyarray.tar.gz
```
#### 2.4 安装 entropyarray
**注**:如果在编译过程中报有关 `-std=c++11` 的错误,则说明当前系统安装的 GNU g++ 版本不支持 ISO C++ 2011 标准,那么你可能需要在另一个支持该标准的系统中编译 ncomputers.org/entropy 和 ncomputers.org/rearray (例如在一个你喜爱的较新的 Linux 发行版本中来编译)。接着使用 `make install` 来安装编译好的二进制文件,再接着你可能想继续运行 `entropyarray` 程序,或者跳过运行该程序这一步骤,然而我还是建议在使用 pandom 来达到加密目地之前先分析一下 `checkme` 文件。
```
cd rearray; make install; cd ..
cd entropy; make install; cd ..
cd entropyarray; make install; cd ..
```
#### 2.5 分析 checkme 文件
**注**:64 [ubits](http://ncomputers.org/ubit) / 64 bits 的 pandom 实现所生成的结果中熵应该高于 `15.977` 且 `max` 字段低于 `70`。假如你的结果与之相差巨大,或许你应该按照下面第 5 节介绍的那样增加你的 pandom 实现的不可预测性。假如你跳过了生成 `checkme` 文件的那一步,你也可以使用其他的工具来进行测试,例如 [伪随机数序列测试](http://www.fourmilab.ch/random/)。
```
entropyarray checkme
entropyarray in /tmp/tmp.mbCopmzqsg
15.977339
min:12
med:32
max:56
15.977368
min:11
med:32
max:58
15.977489
min:11
med:32
max:59
15.977077
min:12
med:32
max:60
15.977439
min:8
med:32
max:59
15.977374
min:13
med:32
max:60
15.977312
min:12
med:32
max:67
```
#### 2.6 卸载 entropyarray (可选)
假如你打算不再使用 `entropyarray`,那么你可以按照你自己的需求卸载它:
```
cd entropyarray; make uninstall; cd ..
cd entropy; make uninstall; cd ..
cd rearray; make uninstall; cd ..
```
### 3 使用 debian 的软件仓库来进行安装
假如你想在你基于 debian 的系统中让 pandom 保持更新,则你可以使用 ncomputers.org 的 debian 软件仓库来安装或者重新安装它。
#### 3.1 获取 root 权限
以下的 debian 软件包必须以 root 身份来安装,所以在必要时请运行下面这个命令:
```
su -
```
#### 3.2 安装密钥
下面的 debian 软件包中包含 ncomputers.org debian 软件仓库的公匙密钥:
```
wget http://ncomputers.org/debian/keyring.deb
dpkg -i keyring.deb
rm keyring.deb
```
#### 3.3 安装软件源列表
下面这些 debian 软件包含有 ncomputers.org debian 软件仓库的软件源列表,这些软件源列表对应最新的 debian 发行版本(截至 2017 年)。
**注**:你也可以将下面的以 `#` 注释的行加入 `/etc/apt/sources.list` 文件中,而不是为你的 debian 发行版本安装对应的 debian 软件包。但假如这些源在将来改变了,你就需要手动更新它们。
**Wheezy:**
```
#deb http://ncomputers.org/debian wheezy main
wget http://ncomputers.org/debian/wheezy.deb
dpkg -i wheezy.deb
rm wheezy.deb
```
Jessie:
```
#deb http://ncomputers.org/debian jessie main
wget http://ncomputers.org/debian/jessie.deb
dpkg -i jessie.deb
rm jessie.deb
```
**Stretch:**
```
#deb http://ncomputers.org/debian stretch main
wget http://ncomputers.org/debian/stretch.deb
dpkg -i stretch.deb
rm stretch.deb
```
#### 3.4 升级软件源列表
一旦密钥和软件源列表安装完成,则可以使用下面的命令来更新:
```
apt-get update
```
#### 3.5 测试 pandom
测试完毕后,你可以随意卸载下面的软件包。
**注**:假如你已经在你的 Linux 中测试了 pandom , 则你可以跳过这一步。
```
apt-get install pandom-test
pandom-test
generating checkme file, please wait around 8 minutes ...
entropyarray in /tmp/tmp.5SkiYsYG3h
15.977366
min:12
med:32
max:57
15.977367
min:13
med:32
max:57
15.977328
min:12
med:32
max:61
15.977431
min:12
med:32
max:59
15.977437
min:11
med:32
max:57
15.977298
min:11
med:32
max:59
15.977196
min:10
med:32
max:57
```
#### 3.6 安装 pandom
```
apt-get install pandom
```
### 4 管理 pandom
在 pandom 安装完成后,你可能想对它进行管理。
#### 4.1 性能测试
pandom 提供大约 8 kB/s 的随机数生成速率,但它的性能可能根据环境而有所差异。
```
dd if=/dev/random of=/dev/null bs=8 count=512
512+0 records in
512+0 records out
4096 bytes (4.1 kB, 4.0 KiB) copied, 0.451253 s, 9.1 kB/s
```
#### 4.2 熵和序列相关性检验
除了 ncomputers.org/entropyarray,还存在更多的测试,例如 [Ilja Gerhardt 的 NIST 测试套件](https://gerhardt.ch/random.php)。
```
entropyarray /dev/random 1M
```
#### 4.3 系统服务
pandom 还可以以系统服务的形式运行。
**基于 init.d 的初始化系统(如 upstart、sysvinit):**
```
/etc/init.d/random status
/etc/init.d/random start
/etc/init.d/random stop
/etc/init.d/random restart
```
**以 systemd 作为初始化程序的系统:**
```
systemctl status random
systemctl start random
systemctl stop random
systemctl restart random
```
### 5 增强不可预测性或者性能
假如你想增加你编译的 pandom 程序的不可预测性或者性能,你可以尝试增加或删减 CPU 时间测量选项。
#### 5.1 编辑源文件
请按照自己的意愿,在源文件 `test.s` 和 `tRNG.s` 中增加或者移除 `measurement blocks` 字段。
```
#measurement block
mov $35,%rax
syscall
rdtsc
[...]
#measurement block
mov $35,%rax
syscall
rdtsc
[...]
```
#### 5.2 测试不可预测性
我们总是建议在使用个人定制的 pandom 实现来用于加密目地之前,先进行一些测试。
```
make check
```
#### 5.3 安装定制的 pandom
假如你对测试的结果很满意,你就可以使用下面的命令来安装你的 pandom 实现。
```
make install
```
更多额外信息及更新详见 <http://ncomputers.org/pandom> 。
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-pandom-a-true-random-number-generator/>
作者:[Oliver](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-pandom-a-true-random-number-generator/) 译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # How to install pandom: a true random number generator for Linux
### On this page
[Introduction](#introduction)[1 Installation of pandom](#-installation-of-pandom)[1.1 Gain root access](#-gain-root-access)[1.2 Install build dependencies](#-install-build-dependencies)[Arch based systems](#arch-based-systems)[Debian based systems](#debian-based-systems)[Red Hat based systems](#red-hat-based-systems)[SUSE based systems](#suse-based-systems)[1.3 Download and extract sources](#-download-and-extract-sources)[1.4 Test before installing (recommended)](#-test-before-installing-recommended)[1.5 Determine init system](#-determine-init-system)[1.6 Install pandom](#-install-pandom)[init.d based init system (e.g: upstart, sysvinit)](#initd-based-init-system-eg-upstart-sysvinit)[systemd as init system](#systemd-as-init-system)
[2 Analysis of checkme file](#-analysis-of-checkme-file)[3 Installation using debian repository](#-installation-using-debian-repository)[4 Managing pandom](#-managing-pandom)[5 Increasing unpredictability or performance](#-increasing-unpredictability-or-performance)
This tutorial is for amd64 / x86_64 linux kernel versions greater and equal to 2.6.9. It explains how to install [pandom](http://ncomputers.org/pandom): a timing jitter true random number generator maintained by ncomputers.org
## Introduction
The built-in Linux kernel true random number generator provides low throughput under modern circumstances, as for example: personal computers with solid state drives (SSD) and virtual private servers (VPS).
This problem is becoming popular in linux implementations, because of the continuously increasing need for true random numbers, mainly by diverse cryptographic purposes.
Pandom outputs around 8 KiB/s entropy of 64 [ubits](http://ncomputers.org/ubit) / 64 bits, is compatible with physical and virtual environments and assumes, that no other process running as root user writes to /dev/random.
## 1 Installation of pandom
### 1.1 Gain root access
Pandom must be installed as root, run this command if needed.
su -
### 1.2 Install build dependencies
In order to download and install pandom, you need: GNU **as**sembler, GNU **make**, GNU **tar** and GNU **wget** (the last two usually installed already). You may uninstall them later at will.
### Arch based systems
pacman -S binutils make
### Debian based systems
apt-get install binutils make
### Red Hat based systems
dnf install binutils make
yum install binutils make
### SUSE based systems
zypper install binutils make
### 1.3 Download and extract sources
These commands download and extract the sources of pandom from ncomputers.org using **wget** and **tar**.
wget[http://ncomputers.org/pandom.tar.gz]
tar xf pandom.tar.gz
cd pandom/amd64-linux
### 1.4 Test before installing (recommended)
This recommended test takes around 8 minutes. It checks for kernel support and generates a file named **checkme** (analyzed on the next section).
make check
### 1.5 Determine init system
Before installing pandom, you need to know, which init software does your system use. If the following command outputs the word **running**, it means that your system is using **systemd**, otherwise it is likely, that your system is using an **init.d** implementation (e.g: upstart, sysvinit). There might be some exceptions, more information in these [unix.stackexchange.com](http://unix.stackexchange.com/a/18210/94448) answers.
systemctl is-system-running
running
### 1.6 Install pandom
Once you know which system does your linux implementation use, then you may install pandom accordingly.
### init.d based init system (e.g: upstart, sysvinit)
Install pandom running this command, if your system is using an **init.d** implementation (e.g: upstart, sysvinit).
make install-init.d
### systemd as init system
Install pandom running this command, if your system is using **systemd**.
make install-systemd
## 2 Analysis of checkme file
Before using pandom for cryptographic purposes, it is highly recommended to analyze **checkme** file generated during the installation process in the previous section of this tutorial. This task is useful for knowing if the numbers are truly random or not. This section explains how to analyze **checkme** file using ncomputers.org/**entropyarray**: a shell script, that tests entropy and serial correlation of its input.
**Note**: this analysis might be run in another computer, such as a laptop or desktop computer. For example: if you are installing pandom in a constrained-resources virtual private server (VPS), you might opt to copy **checkme** file to your personal computer, in order to analyze it there.**You may also use Entropy Online Tester**.
### 2.1 Gain root access
Entropyarray must be installed as root, run this command if needed.
su -
### 2.2 Install build dependencies
In order to download and install entropyarray, you need: GNU **g++** compiler, GNU **make**, GNU **tar** and GNU **wget** (the last two usually installed already). You may uninstall them later at will.
### Arch based systems
pacman -S gcc make
### Debian based systems
apt-get install g++ make
### Red Hat based systems
dnf install gcc-c++ make
yum install gcc-c++ make
### SUSE based systems
zypper install gcc-c++ make
### 2.3 Download and extract sources
These commands download and extract the sources of entropyarray from ncomputers.org using **wget** and **tar**.
wget[http://ncomputers.org/rearray.tar.gz]
wget[http://ncomputers.org/entropy.tar.gz]
wget[http://ncomputers.org/entropyarray.tar.gz]
tar xf entropy.tar.gz
tar xf rearray.tar.gz
tar xf entropyarray.tar.gz
### 2.4 Install entropyarray
**Note**: errors regarding -std=c++11 mean that the GNU **g++** compiler version doesn't support ISO C++ 2011 standard. You may try to compile ncomputers.org/**entropy** and ncomputers.org/**rearray** in another system that supports it (e.g: GNU g++ in a newer version of your favorite linux distribution) and then install the compiled binaries using **make install** in the system you would like to run **entropyarray**, or skip this step, despite it is highly recommended that you analyze **checkme** file before using pandom for any cryptographic purpose.
cd rearray; make install; cd ..
cd entropy; make install; cd ..
cd entropyarray; make install; cd ..
### 2.5 Analyze checkme file
**Note**: 64 [ubits](http://ncomputers.org/ubit) / 64 bits pandom implementations should result this test with entropy above **15.977** and **max** frequency below **70**. If your results differ too much, you may try to increase the unpredictability of your pandom implementation as described in the fifth section of this tutorial. In case you skipped the last step, you may use other tools such as [pseudorandom number sequence test](http://www.fourmilab.ch/random/).
entropyarray checkme
entropyarray in /tmp/tmp.mbCopmzqsg
15.977339
min:12
med:32
max:56
15.977368
min:11
med:32
max:58
15.977489
min:11
med:32
max:59
15.977077
min:12
med:32
max:60
15.977439
min:8
med:32
max:59
15.977374
min:13
med:32
max:60
15.977312
min:12
med:32
max:67
### 2.6 Uninstall entropyarray (optional)
If you plan to not use entropyarray any more, then you might want to uninstall it at will.
cd entropyarray; make uninstall; cd ..
cd entropy; make uninstall; cd ..
cd rearray; make uninstall; cd ..
## 3 Installation using debian repository
If you would like to keep pandom updated on your debian based system, you may opt to install / reinstall it using ncomputers.org debian repository.
### 3.1 Gain root access
The below debian packages must be installed as root, run this command if needed.
su -
### 3.2 Install keyring
This debian package includes the public key of the ncomputers.org debian repository.
wget[http://ncomputers.org/debian/keyring.deb]
dpkg -i keyring.deb
rm keyring.deb
### 3.3 Install sources list
These debian packages include the sources list of the ncomputers.org debian repository according to the latest debian distributions (year 2017).
**Note**: It is also possible to write the commented lines below in **/etc/apt/sources.list**, instead of installing the respective debian package for your debian distribution, but if these sources change in the future, then you would need to update them manually.
### Wheezy
#deb[http://ncomputers.org/debian]wheezy main
wget[http://ncomputers.org/debian/wheezy.deb]
dpkg -i wheezy.deb
rm wheezy.deb
### Jessie
#deb[http://ncomputers.org/debian]jessie main
wget[http://ncomputers.org/debian/jessie.deb]
dpkg -i jessie.deb
rm jessie.deb
### Stretch
#deb[http://ncomputers.org/debian]stretch main
wget[http://ncomputers.org/debian/stretch.deb]
dpkg -i stretch.deb
rm stretch.deb
### 3.4 Update sources list
Once the keyring and sources list are installed.
apt-get update
### 3.5 Test pandom
Once tested, you may uninstall the below package at will.
**Note**: if you have already tested pandom in your linux implementation, you may skip this step.
apt-get install pandom-test
pandom-test
generating checkme file, please wait around 8 minutes ...
entropyarray in /tmp/tmp.5SkiYsYG3h
15.977366
min:12
med:32
max:57
15.977367
min:13
med:32
max:57
15.977328
min:12
med:32
max:61
15.977431
min:12
med:32
max:59
15.977437
min:11
med:32
max:57
15.977298
min:11
med:32
max:59
15.977196
min:10
med:32
max:57
### 3.6 Install pandom
apt-get install pandom
## 4 Managing pandom
After pandom was installed, you might want to manage it.
### 4.1 Performance test
Pandom offers around 8 kilobytes per second, but its performance may vary depending on the environment.
dd if=/dev/random of=/dev/null bs=8 count=512
512+0 records in
512+0 records out
4096 bytes (4.1 kB, 4.0 KiB) copied, 0.451253 s, 9.1 kB/s
### 4.2 Entropy and serial correlation test
Besides of ncomputers.org/**entropyarray**, there are more tests, for example [NIST testsuite by Ilja Gerhardt](https://gerhardt.ch/random.php).
entropyarray /dev/random 1M
### 4.3 System service
Pandom runs as a system service.
### init.d based init system (e.g: upstart, sysvinit)
/etc/init.d/random status
/etc/init.d/random start
/etc/init.d/random stop
/etc/init.d/random restart
### systemd as init system
systemctl status random
systemctl start random
systemctl stop random
systemctl restart random
## 5 Increasing unpredictability or performance
If you would like to try to increase the unpredictabiity or the performance of your pandom implementation, you may try to add or delete CPU time measurements.
### 5.1 Edit source files
In the source files **test.s** and **tRNG.s** add or remove measurement blocks at will.
#measurement block
mov $35,%rax
syscall
rdtsc
[...]
#measurement block
mov $35,%rax
syscall
rdtsc
[...]
### 5.2 Test the unpredictability
We recommend to always test any personalized pandom implementation before using it for cryptographic purposes.
make check
### 5.3 Install personalized pandom
If you are happy with the results, then you may install your personalized pandom implementation.
make install
Additional information and updates: [http://ncomputers.org/pandom](http://ncomputers.org/pandom) |
8,518 | LinuxKit:在容器中运行容器 | http://www.devsecops.cc/devsecops/containers.html | 2017-05-18T10:29:00 | [
"容器",
"LinuxKit",
"Docker"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8518-1.html | 
一些令人振奋的消息引发了我对今年 DockerCon 的兴趣,在这次会议中,无可争议的容器巨头公司 Docker 发布了一个新的操作系统:LinuxKit。
这家容器巨头宣布的是一个灵活的、可扩展的操作系统,而为了可移植性,系统服务也是运行在容器之中。甚至,令人惊讶的是,就连 Docker 运行时环境也是运行在容器内!
在本文中,我们将简要介绍一下 LinuxKit 中所承诺的内容,以及如何自己尝试一下这个不断精简、优化的容器。
### 少即是多
不可否认的是,用户一直在寻找一个可以运行他们的微服务的精简版本的 Linux 。通过容器化,你会尽可能地最小化每个应用程序,使其成为一个适合于运行在其自身容器内的独立进程。但是,由于你需要对那些驻留容器的宿主机出现的问题进行修补,因此你不断地在宿主机间移动容器。实际上,如果没有像 Kubernetes 或 Docker Swarm 这样的编排系统,容器编排几乎总是会导致停机。
不用说,这只是让你保持操作系统尽可能小的原因之一。
我曾多次在不同场合重复过的最喜爱的名言,来自荷兰的天才程序员 Wietse Zweitze,他为我们提供了重要的 Email 软件 Postfix 和 TCP Wrappers 等知名软件。
在 [Postfix 网站](http://www.postfix.org/TLS_README.html) 指出,即使你编码和 Wietse 一样小心,“每 1000 行[你]就会在 Postfix 中引入一个额外的 bug”。从我的专业的 DevSecOps 角度看,这里提到的“bug” 可以将其大致看做安全问题。
从安全的角度来看,正是由于这个原因,代码世界中“少即是多”。简单地说,使用较少的代码行有很多好处,即安全性、管理时间和性能。对于初学者来说,这意味着安全漏洞较少,更新软件包的时间更短,启动时间更快。
### 深入观察
考虑下在容器内部运行你的程序。
一个好的起点是 [Alpine Linux](https://alpinelinux.org/downloads/),它是一个苗条、精简的操作系统,通常比那些笨重的系统更受喜欢,如 Ubuntu 或 CentOS 等。Alpine 还提供了一个 miniroot 文件系统(用于容器内),最近我看到的大小是惊人的 1.8M。事实上,这个完整的 Linux 操作系统下载后有 80M。
如果你决定使用 Alpine Linux 作为 Docker 基础镜像,那么你可以在 Docker Hub 上[找到](https://hub.docker.com/_/alpine)一个, 它将其描述为:“一个基于 Alpine Linux 的最小 Docker 镜像,具有完整的包索引,大小只有5 MB!”
据说无处不在的 “Window 开始菜单” 文件也是大致相同的大小!我没有验证过,也不会进一步评论。
讲真,希望你去了解一下这个创新的类 Unix 操作系统(如 Alpine Linux)的强大功能。
### 锁定一切
再说一点,Alpine Linux 是(并不惊人)基于 [BusyBox](https://busybox.net/),这是一套著名的打包了 Linux 命令的集合,许多人不会意识到他们的宽带路由器、智能电视,当然还有他们家庭中的物联网设备就有它。
Alpine Linux 站点的“[关于](https://www.alpinelinux.org/about/)”页面的评论中指出:
>
> “Alpine Linux 的设计考虑到安全性。内核使用 grsecurity/PaX 的非官方移植进行了修补,所有用户态二进制文件都编译为具有堆栈保护的地址无关可执行文件(PIE)。 这些主动安全特性可以防止所有类别的零日漏洞和其它漏洞利用。”
>
>
>
换句话说,这些捆绑在 Alpine Linux 中的精简二进制文件提供的功能通过了那些行业级安全工具筛选,以缓解缓冲区溢出攻击所带来的危害。
### 多只袜子
你可能会问,为什么当我们谈及 Docker 的新操作系统时,容器的内部结构很重要?
那么,你可能已经猜到,当涉及容器时,他们的目标是精简。除非绝对必要,否则不包括任何东西。所以你可以放心地清理橱柜、花园棚子、车库和袜子抽屉了。
Docker 的确因为它们的先见而获得声望。据报道,2 月初,Docker 聘请了 Alpine Linux 的主要推动者 Nathaniel Copa,他帮助将默认的官方镜像库从 Ubuntu 切换到 Alpine。Docker Hub 从新近精简镜像节省的带宽受到了赞誉。
并且最新的情况是,这项工作将与最新的基于容器的操作系统相结合:Docker 的 LinuxKit。
要说清楚的是 LinuxKit 注定不会代替 Alpine,而是位于容器下层,并作为一个完整的操作系统出现,你可以高兴地启动你的运行时守护程序(在这种情况下,是生成你的容器的Docker 守护程序 )。
### 原子计划
经过精心调试的宿主机绝对不是一件新事物(以前提到过嵌入式 Linux 的家用设备)。在过去几十年中一直在优化 Linux 的天才在某个时候意识到底层的操作系统才是快速生产含有大量容器主机的关键。
例如,强大的红帽长期以来一直在出售已经贡献给 [Project Atomic](http://www.projectatomic.io/) 的 [红帽 Atomic](https://www.redhat.com/en/resources/red-hat-enterprise-linux-atomic-host) 。后者继续解释:
>
> “基于 Red Hat Enterprise Linux 或 CentOS 和 Fedora 项目的成熟技术,Atomic Host 是一个轻量级的、不可变的平台,其设计目的仅在于运行容器化应用程序。”
>
>
>
将底层的、不可变的 Atomic OS 作为红帽的 OpenShift PaaS(平台即服务)产品推荐有一个很好理由:它最小化、高性能、尖端。
### 特性强大
在 Docker 关于 LinuxKit 的公告中,“少即是多”的口号是显而易见的。实现 LinuxKit 愿景的项目显然是不小的事业,它由 Docker 老将和 [Unikernel](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unikernel) 的主管 Justin Cormack 指导,并与 HPE、Intel、ARM、IBM 和 Microsoft LinuxKit 合作,可以运行在从大型机到基于物联网的冰柜之中。
LinuxKit 的可配置性、可插拔性和可扩展性将吸引许多寻求建立其服务基准的项目。通过开源项目,Docker 明智地邀请每个人全身心地投入其功能开发,随着时间的推移,它会像好的奶酪那样成熟。
### 布丁作证
按照该发布消息中所承诺的,那些急于使用新系统的人不用再等待了。如果你准备着手 LinuxKit,你可以从 GitHub 中开始:[LinuxKit](https://github.com/linuxkit/linuxkit)。
在 GitHub 页面上有关于如何启动和运行一些功能的指导。
时间允许的话我准备更加深入研究 LinuxKit。对有争议的 Kubernetes 与 Docker Swarm 编排功能对比会是有趣的尝试。此外,我还想看到内存占用、启动时间和磁盘空间使用率的基准测试。
如果该承诺可靠,则作为容器运行的可插拔系统服务是构建操作系统的迷人方式。Docker 在[博客](https://blog.docker.com/2017/04/introducing-linuxkit-container-os-toolkit))中提到:“因为 LinuxKit 是原生容器,它有一个非常小的尺寸 - 35MB,引导时间非常小。所有系统服务都是容器,这意味着可以删除或替换所有的内容。”
我不知道你觉得怎么样,但这非常符合我的胃口。
### 呼叫警察
除了我站在 DevSecOps 角度看到的功能,我会看看其对安全的承诺。
Docker 在他们的博客上引用来自 NIST([国家标准与技术研究所](https://www.nist.gov/))的话:
>
> “安全性是最高目标,这与 NIST 在其《应用程序容器安全指南》草案中说明的保持一致:‘使用容器专用操作系统而不是通用操作系统来减少攻击面。当使用专用容器操作系统时,攻击面通常比通用操作系统小得多,因此攻击和危及专用容器操作系统的机会较少。’”
>
>
>
可能最重要的容器到主机和主机到容器的安全创新是将系统容器(系统服务)完全地沙箱化到自己的非特权空间中,而只给它们需要的外部访问。
通过<ruby> 内核自我保护项目 <rt> Kernel Self Protection Project </rt></ruby>([KSPP](https://kernsec.org/wiki/index.php/Kernel_Self_Protection_Project))的协作来实现这一功能,我很满意 Docker 开始专注于一些非常值得的东西上。对于那些不熟悉的 KSPP 的人而言,它存在理由如下:
>
> “启动这个项目的的假设是内核 bug 的存在时间很长,内核必须设计成可以防止这些缺陷的危害。”
>
>
>
KSPP 网站进一步表态:
>
> “这些努力非常重要并还在进行,但如果我们要保护我们的十亿 Android 手机、我们的汽车、国际空间站,还有其他运行 Linux 的产品,我们必须在上游的 Linux 内核中建立积极的防御性技术。我们需要内核安全地出错,而不只是安全地运行。”
>
>
>
而且,如果 Docker 最初只是在 LinuxKit 前进了一小步,那么随着时间的推移,成熟度带来的好处可能会在容器领域中取得长足的进步。
### 终点还远
像 Docker 这样不断发展壮大的巨头无论在哪个方向上取得巨大的飞跃都将会用户和其他软件带来益处。
我鼓励所有对 Linux 感兴趣的人密切关注这个领域。
---
via: <http://www.devsecops.cc/devsecops/containers.html>
作者:[Chris Binnie](http://www.devsecops.cc/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 307 | Temporary Redirect | null |
8,519 | 如何在 Linux 中使用 Asciinema 进行录制和回放终端会话 | https://linuxconfig.org/record-and-replay-terminal-session-with-asciinema-on-linux | 2017-05-18T11:59:00 | [
"终端",
"记录"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8519-1.html | 
### 简介
Asciinema 是一个轻量并且非常高效的终端会话录制器。使用它可以录制、回放和分享 JSON 格式的终端会话记录。与一些桌面录制器,比如 Recordmydesktop、Simplescreenrecorder、Vokoscreen 或 Kazam 相比,Asciinema 最主要的优点是,它能够以通过 ASCII 文本以及 ANSI 转义码编码来录制所有的标准终端输入、输出和错误信息。
事实上,即使是很长的终端会话,录制出的 JSON 格式文件也非常小。另外,JSON 格式使得用户可以利用简单的文件转化器,将输出的 JSON 格式文件嵌入到 HTML 代码中,然后分享到公共网站或者使用 asciinema 账户分享到 Asciinema.org 。最后,如果你的终端会话中有一些错误,并且你还懂一些 ASCI 转义码语法,那么你可以使用任何编辑器来修改你的已录制终端会话。
**难易程度:**
很简单!
**标准终端:**
* **#** - 给定命令需要以 root 用户权限运行或者使用 `sudo` 命令
* **$** - 给定命令以常规权限用户运行
### 从软件库安装
通常, asciinema 可以使用你的发行版的软件库进行安装。但是,如果不可以使用系统的软件库进行安装或者你想安装最新的版本,那么,你可以像下面的“从源代码安装”部分所描述的那样,使用 Linuxbrew 包管理器来执行 Asciinema 安装。
**在 Arch Linux 上安装:**
```
# pacman -S asciinema
```
**在 Debian 上安装:**
```
# apt install asciinema
```
**在 Ubuntu 上安装:**
```
$ sudo apt install asciinema
```
**在 Fedora 上安装:**
```
$ sudo dnf install asciinema
```
### 从源代码安装
最简单并且值得推荐的方式是使用 Linuxbrew 包管理器,从源代码安装最新版本的 Asciinema 。
#### 前提条件
下面列出的前提条件是安装 Linuxbrew 和 Asciinema 需要满足的依赖关系:
* git
* gcc
* make
* ruby
在安装 Linuxbrew 之前,请确保上面的这些包都已经安装在了你的 Linux 系统中。
**在 Arch Linux 上安装 ruby:**
```
# pacman -S git gcc make ruby
```
**在 Debian 上安装 ruby:**
```
# apt install git gcc make ruby
```
**在 Ubuntu 上安装 ruby:**
```
$ sudo apt install git gcc make ruby
```
**在 Fedora 上安装 ruby:**
```
$ sudo dnf install git gcc make ruby
```
**在 CentOS 上安装 ruby:**
```
# yum install git gcc make ruby
```
#### 安装 Linuxbrew
Linuxbrew 包管理器是苹果的 MacOS 操作系统很受欢迎的 Homebrew 包管理器的一个复刻版本。还没发布多久,Homebrew 就以容易使用而著称。如果你想使用 Linuxbrew 来安装 Asciinema,那么,请运行下面命令在你的 Linux 版本上安装 Linuxbrew:
```
$ ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Linuxbrew/install/master/install)"
```
现在,Linuxbrew 已经安装到了目录 `$HOME/.linuxbrew/` 下。剩下需要做的就是使它成为可执行 `PATH` 环境变量的一部分。
```
$ echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.linuxbrew/bin:$PATH"' >>~/.bash_profile
$ . ~/.bash_profile
```
为了确认 Linuxbrew 是否已经安装好,你可以使用 `brew` 命令来查看它的版本:
```
$ brew --version
Homebrew 1.1.7
Homebrew/homebrew-core (git revision 5229; last commit 2017-02-02)
```
#### 安装 Asciinema
安装好 Linuxbrew 以后,安装 Asciinema 就变得无比容易了:
```
$ brew install asciinema
```
检查 Asciinema 是否安装正确:
```
$ asciinema --version
asciinema 1.3.0
```
### 录制终端会话
经过一番辛苦的安装工作以后,是时候来干一些有趣的事情了。Asciinema 是一个非常容易使用的软件。事实上,目前的 1.3 版本只有很少的几个可用命令行选项,其中一个是 `--help` 。
我们首先使用 `rec` 选项来录制终端会话。下面的命令将会开始录制终端会话,之后,你将会有一个选项来丢弃已录制记录或者把它上传到 asciinema.org 网站以便将来参考。
```
$ asciinema rec
```
运行上面的命令以后,你会注意到, Asciinema 已经开始录制终端会话了,你可以按下 `CTRL+D` 快捷键或执行 `exit` 命令来停止录制。如果你使用的是 Debian/Ubuntu/Mint Linux 系统,你可以像下面这样尝试进行第一次 asciinema 录制:
```
$ su
Password:
# apt install sl
# exit
$ sl
```
一旦输入最后一个 `exit` 命令以后,将会询问你:
```
$ exit
~ Asciicast recording finished.
~ Press <Enter> to upload, <Ctrl-C> to cancel.
https://asciinema.org/a/7lw94ys68gsgr1yzdtzwijxm4
```
如果你不想上传你的私密命令行技巧到 asciinema.org 网站,那么有一个选项可以把 Asciinema 记录以 JSON 格式保存为本地文件。比如,下面的 asciinema 记录将被存为 `/tmp/my_rec.json`:
```
$ asciinema rec /tmp/my_rec.json
```
另一个非常有用的 asciinema 特性是时间微调。如果你的键盘输入速度很慢,或者你在进行多任务,输入命令和执行命令之间的时间会比较长。Asciinema 会记录你的实时按键时间,这意味着每一个停顿都将反映在最终视频的长度上。可以使用 `-w` 选项来缩短按键的时间间隔。比如,下面的命令将按键的时间间隔缩短为 0.2 秒:
```
$ asciinema rec -w 0.2
```
### 回放已录制终端会话
有两种方式可以来回放已录制会话。第一种方式是直接从 asciinema.org 网站上播放终端会话。这意味着,你之前已经把录制会话上传到了 asciinema.org 网站,并且需要提供有效链接:
```
$ asciinema play https://asciinema.org/a/7lw94ys68gsgr1yzdtzwijxm4
```
另外,你也可以使用本地存储的 JSON 文件:
```
$ asciinema play /tmp/my_rec.json
```
如果要使用 `wget` 命令来下载之前的上传记录,只需在链接的后面加上 `.json`:
```
$ wget -q -O steam_locomotive.json https://asciinema.org/a/7lw94ys68gsgr1yzdtzwijxm4.json
$ asciinema play steam_locomotive.json
```
### 将视频嵌入 HTML
最后,asciinema 还带有一个独立的 JavaScript 播放器。这意味者你可以很容易的在你的网站上分享终端会话记录。下面,使用一段简单的 `index.html` 代码来说明这个方法。首先,下载所有必要的东西:
```
$ cd /tmp/
$ mkdir steam_locomotive
$ cd steam_locomotive/
$ wget -q -O steam_locomotive.json https://asciinema.org/a/7lw94ys68gsgr1yzdtzwijxm4.json
$ wget -q https://github.com/asciinema/asciinema-player/releases/download/v2.4.0/asciinema-player.css
$ wget -q https://github.com/asciinema/asciinema-player/releases/download/v2.4.0/asciinema-player.js
```
之后,创建一个新的包含下面这些内容的 `/tmp/steam_locomotive/index.html` 文件:
```
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./asciinema-player.css" />
</head>
<body>
<asciinema-player src="./steam_locomotive.json" cols="80" rows="24"></asciinema-player>
<script src="./asciinema-player.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
```
完成以后,打开你的网页浏览器,按下 `CTRL+O` 来打开新创建的 `/tmp/steam_locomotive/index.html` 文件。
### 结论
正如前面所说的,使用 asciinema 录制器来录制终端会话最主要的优点是它的输出文件非常小,这使得你的视频很容易分享出去。上面的例子产生了一个包含 58472 个字符的文件,它是一个只有 58 KB 大 小的 22 秒终端会话视频。如果我们查看输出的 JSON 文件,会发现甚至这个数字已经非常大了,这主要是因为一个 “蒸汽机车” 已经跑过了终端。这个长度的正常终端会话一般会产生一个更小的输出文件。
下次,当你想要在一个论坛上询问关于 Linux 配置的问题,并且很难描述你的问题的时候,只需运行下面的命令:
```
$ asciinema rec
```
然后把最后的链接贴到论坛的帖子里。
### 故障排除
#### 在 UTF-8 环境下运行 asciinema
错误信息:
```
asciinema needs a UTF-8 native locale to run. Check the output of `locale` command.
```
解决方法: 生成并导出 UTF-8 语言环境。例如:
```
$ localedef -c -f UTF-8 -i en_US en_US.UTF-8
$ export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8
```
---
via: <https://linuxconfig.org/record-and-replay-terminal-session-with-asciinema-on-linux>
作者:[Lubos Rendek](https://linuxconfig.org/record-and-replay-terminal-session-with-asciinema-on-linux) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
8,520 | 甲骨文的政策更改提高了其在 AWS 上的价格 | http://windowsitpro.com/cloud/oracle-policy-change-raises-prices-aws | 2017-05-18T15:01:00 | [
"甲骨文",
"Oracle",
"AWS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8520-1.html |
>
> 这种改变使得在 AWS 上实施甲骨文的软件的价格翻了一番,它已经安静地生效了,而几乎没有通知用户。
>
>
>

之前有消息传出,甲骨文使亚马逊云上的产品价格翻了一倍。它在[如何计算 AWS 的虚拟 CPU](https://oracle-base.com/blog/2017/01/28/oracles-cloud-licensing-change-be-warned/) 上耍了一些花招。它这么做也没有任何宣扬。该公司的新定价政策于 1 月 23 日生效,直到 1 月 28 日都几乎没有被人注意到, 甲骨文的关注者 Tim Hall 偶然发现 Big Red 公司的 [甲骨文软件云计算环境许可](http://www.oracle.com/us/corporate/pricing/cloud-licensing-070579.pdf)文件并披露了出来。
乍一看,这一举动似乎并不太大,因为它仅将甲骨文的 AWS 定价与 Microsoft Azure 的价格相提并论。但是 Azure 只有市场领先的 AWS 体量的三分之一,所以如果你想在云中销售许可证,AWS 是合适的地方。虽然此举可能或可能不会影响已经在 AWS 上使用甲骨文产品的用户,但是尚不清楚新规则是否适用于已在使用产品的用户 - 它肯定会让一些考虑可能使用甲骨文的用户另寻它处。
这个举动的主要原因是显而易见的。甲骨文希望使自己的云更具吸引力 - 这让 [The Register 观察](https://www.theregister.co.uk/2017/01/30/oracle_effectively_doubles_licence_fees_to_run_in_aws/)到一点:“拉里·埃里森确实承诺过甲骨文的云将会更快更便宜”。更快和更便宜仍然有待看到。如果甲骨文的 SPARC 云计划启动,并且按照广告的形式执行,那么可能会更快,但是更便宜的可能性较小。甲骨文以对其价格的强硬态度而著称。
随着其招牌数据库和业务栈销售的下滑,并且对 Sun 公司的 74 亿美元的投资并未能按照如期那样,甲骨文将其未来赌在云计算上。但是甲骨文来晚了,迄今为止,它的努力似乎还没有结果, 一些金融预测者并没有看到甲骨文云的光明前景。他们说,云是一个拥挤的市场,而四大公司 - 亚马逊、微软、IBM 和谷歌 - 已经有了领先优势。
确实如此。但是甲骨文面临的最大的障碍是,好吧,就是甲骨文。它的声誉在它之前。
保守地说这个公司并不是因为明星客户服务而闻名。事实上,各种新闻报道将甲骨文描绘成一个恶霸和操纵者。
例如,早在 2015 年,甲骨文就因为它的云并不像预期那样快速增长而越来越沮丧,开始[激活业内人士称之为的“核特权”](http://www.businessinsider.com/oracle-is-using-the-nuclear-option-to-sell-its-cloud-software-2015-7)。它会审核客户的数据中心,如果客户不符合规定,将发出“违规通知” - 它通常只适用于大规模滥用情况,并命令客户在 30 天内退出使用其软件。
或许你能想到,大量投入在甲骨文软件平台上的大公司们绝对不能在短时间内迁移到另一个解决方案。甲骨文的违规通知将会引发灾难。
商业内幕人士 Julie Bort 解释到:“为了使违规通知消失 - 或者减少高额的违规罚款 - 甲骨文销售代表通常希望客户向合同中添加云额度”。
换句话说,甲骨文正在使用审计来扭转客户去购买它的云,而无论他们是否有需要。这种策略与最近 AWS 价格翻倍之间也可能存在联系。Hall 的文章的评论者指出,围绕价格提升的秘密背后的目的可能是触发软件审计。
使用这些策略的麻烦迟早会出来。消息一旦传播开来,你的客户就开始寻找其他选项。对 Big Red 而言或许是时候参考微软的做法,开始建立一个更好和更温和的甲骨文,将客户的需求放在第一位。
(题图:[windowsitpro](http://windowsitpro.com/))
---
via: <http://windowsitpro.com/cloud/oracle-policy-change-raises-prices-aws>
作者:[Christine Hall](http://windowsitpro.com/author/christine-hall) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,521 | 该死,原生移动应用的开发成本太高了! | https://hackernoon.com/the-cost-of-native-mobile-app-development-is-too-damn-high-4d258025033a | 2017-05-19T10:28:00 | [
"JavaScript",
"移动应用"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8521-1.html | 
>
> 一个有价值的命题
>
>
>
我们遇到了一个临界点。除去少数几个特别的的用例之外,使用原生框架和原生应用开发团队构建、维护移动应用再也没有意义了。

*在美国,雇佣 [iOS,Android](http://www.indeed.com/salary),[JavaScript](http://www.payscale.com/research/US/Skill=JavaScript/Salary) 开发人员的平均花费*
在过去的几年,原生移动应用开发的费用螺旋式上升,无法控制。对没有大量资金的新创业者来说,创建原生应用、MVP 设计架构和原型的难度大大增加。现有的公司需要抓住人才,以便在现有应用上进行迭代开发或者构建一个新的应用。要尽一切努力才能留住最好的人才,与 [世界各地的公司](http://blogs.wsj.com/cio/2016/09/30/tech-talent-war-moves-to-africa/) 拼尽全力[争个](http://www.bizjournals.com/charlotte/how-to/human-resources/2016/12/employers-offer-premium-wages-skilled-workers.html)[高](https://www.cnet.com/news/silicon-valley-talent-wars-engineers-come-get-your-250k-salary/)[下](http://www.nytimes.com/2015/08/19/technology/unicorns-hunt-for-talent-among-silicon-valleys-giants.html)。

*2015 年初,原生方式和混合方式开发 MVP 设计架构的费用[对比](http://www.comentum.com/mobile-app-development-cost.html)*
### 这一切对于我们意味着什么?
如果你的公司很大或者有足够多的现金,旧思维是只要你在原生应用开发方面投入足够多的资金,就高枕无忧。但事实不再如此。
Facebook 是你最不会想到的在人才战中失败的公司(因为他们没有失败),它也遇到了原生应用方面金钱无法解决的问题。他们的移动应用庞大而又复杂,[他们发现编译它竟然需要 15 分钟](https://devchat.tv/react-native-radio/08-bridging-react-native-components-with-tadeu-zagallo)。这意味着哪怕是极小的用户界面改动,比如移动几个点,测试起来都要花费几个小时(甚至几天)。
除了冗长的编译时间,应用的每一个小改动在测试时都需要在两个完全不同的环境(IOS 和 Android)实施,开发团队需要使用两种语言和框架工作,这趟水更浑了。
Facebook 对这个问题的解决方案是 [React Native](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/)。
### 能不能抛弃移动应用,仅面向 Web 呢?
[一些人认为移动应用的末日已到](https://medium.com/javascript-scene/native-apps-are-doomed-ac397148a2c0#.w06yd23ej)。尽管我很欣赏、尊重 [Eric Elliott](https://medium.com/u/c359511de780) 和他的工作,但我们还是通过考察一些近期的数据,进而讨论一下某些相反的观点:

*人们在移动应用上花费的[时间](http://www.smartinsights.com/mobile-marketing/mobile-marketing-analytics/mobile-marketing-statistics/attachment/percent-time-spent-on-mobile-apps-2016/)(2016年4月)*
>
> 人们使用 APP 的时间占使用手机总时长的 90%
>
>
>
目前世界上有 25 亿人在使用移动手机。[这个数字增长到 50 亿的速度会比我们想象的还要快。](http://ben-evans.com/benedictevans/2016/12/8/mobile-is-eating-the-world) 在正常情况下,丢掉 45 亿人的生意,或者抛弃有 45 亿人使用的应用程序是绝对荒唐且行不通的。
老问题是原生移动应用的开发成本对大多数公司来说太高了。然而,面向 web 的开发成本也在增加。[在美国,JavaScript 开发者的平均工资已达到 $97,000.00](http://www.indeed.com/salary?q1=javascript+developer&l1=united+states&tm=1)。
伴随着复杂性的增加以及对高质量 web 开发的需求暴涨,雇佣一个 JavaScript 开发者的平均价格直逼原生应用开发者。论证 web 开发更便宜已经没用了。
### 那混合开发呢?
混合应用是将 HTML5 应用内嵌在原生应用的容器里,并且提供实现原生平台特性所需的权限。Cordova 和 PhoneGap 就是典型的例子。
如果你想构建一个 MVP 设计架构、一个产品原型,或者不担心对原生应用的模仿的用户体验,那么混合应用会很适合你。但谨记如果你最后想把它转为原生应用,整个项目都得重写。
此领域有很多创新的东西,我最喜欢的当属 [Ionic Framework](https://ionicframework.com/)。混合开发正变得越来越好,但还不如原生开发那么流畅自然。
有很多公司,包括最严峻的初创公司,也包括大中规模的公司,混合应用在质量上的表现似乎没有满足客户的要求,给人的感觉是活糙、不够专业。
[听说应用商店里的前 100 名都不是混合应用](https://medium.com/lunabee-studio/why-hybrid-apps-are-crap-6f827a42f549#.lakqptjw6),我没有证据支持这一观点。如果说有百分之零到百分之五是混合应用,我就不怀疑了。
>
> [我们最大的错误是在 HTML5 身上下了太多的赌注](https://techcrunch.com/2012/09/11/mark-zuckerberg-our-biggest-mistake-with-mobile-was-betting-too-much-on-html5/) — 马克·扎克伯格
>
>
>
### 解决方案
如果你紧跟移动开发动向,那么你绝对听说过像 [NativeScript](https://www.nativescript.org/) 和 [React Native](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/) 这样的项目。
通过这些项目,使用由 JavaScript 写成的基本 UI 组成块,像常规 iOS 和 Android 应用那样,就可以构建出高质量的原生移动应用。
你可以仅用一位工程师,也可以用一个专业的工程师团队,通过 React Native 使用 [现有代码库](https://github.com/necolas/react-native-web) 或者 [底层技术](https://facebook.github.io/react/) 进行跨平台移动应用开发、[原生桌面开发](https://github.com/ptmt/react-native-macos),甚至还有 web 开发。把你的应用发布到 APP Store 上、 Play Store 上,还有 Web 上。如此可以在保证不丧失原生应用性能和质量的同时,使成本仅占传统开发的一小部分。
通过 React Native 进行跨平台开发时重复使用其中 90% 的代码也不是没有的事,这个范围通常是 80% 到 90%。
如果你的团队使用 React Native, 既可以消除团队之间的分歧,也可以让 UI 和 API 的设计更一致,还可以加快开发速度。
在编译时不需要使用 React Native,在保存时应用可以实时更新,也加快了开发速度。
React Native 还可以使用 [Code Push](http://microsoft.github.io/code-push/) 和 [AppHub](https://apphub.io/) 这样的工具来远程更新你的 JavaScript 代码。这意味着你可以向用户实时推送更新、新特性,快速修复 bug,绕过打包、发布这些工作,绕过 App Store、Google Play Store 的审核,省去了耗时 2 到 7 天的过程(App Store 一直是整个过程的痛点)。混合应用的这些优势原生应用不可能比得上。
如果这个领域的创新力能像刚发行时那样保持,将来你甚至可以为 [Apple Watch](https://github.com/elliottsj/apple-watch-uikit)、[Apple TV](https://github.com/douglowder/react-native-appletv),和 [Tizen](https://www.tizen.org/blogs/srsaul/2016/samsung-committed-bringing-react-native-tizen) 这样的平台开发应用。
>
> NativeScript 依然是个相当年轻的框架驱动,Angular 版本 2,[上个月刚刚发布测试版](http://angularjs.blogspot.com/2016/09/angular2-final.html)。但只要它保持良好的市场份额,未来就很有前途。
>
>
>
你可能还不知道世界上一些最能创新、最大的科技公司在这类技术上下了很大的赌注,特别是 [React Native](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/)。
我供职过的多家企业以及世界 500 强公司目前都在转移至 React Native。
### 在产品中特别注意使用 React Native
看下面的例子,[这是一个使用 React Native 技术的著名应用列表](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/showcase.html)。
#### Facebook

*Facebook 公司的 React Native 应用*
Facebook 的两款应用 [Ads Manager](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.facebook.adsmanager) 和 [Facebook Groups](https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/facebook-groups/id931735837?mt=8) 都在使用 React Native 技术,并且[将会应用到实现动态消息的框架上](https://devchat.tv/react-native-radio/40-navigation-in-react-native-with-eric-vicenti)。
Facebook 也会投入大量的资金创立和维护像 React Native 这样的开源项目,而且开源项目的开发者最近已经创建很多了不起的项目,这是很了不起的工作,像我以及全世界的业务每天都从中享受诸多好处。
#### Instagram

*Instagram*
Instagram 应用的一部分已经使用了 React Native 技术。
#### Airbnb

*Airbnb*
Airbnb 的很多东西正用 React Native 重写。(来自 [Leland Richardson](https://medium.com/u/41a8b1601c59))
超过 90% 的 Airbnb 旅行平台都是用 React Native 写的。(来自 [spikebrehm](https://medium.com/u/71a78c1b069b))
#### Vogue

*Vogue 是 2016 年度十佳应用之一*
Vogue 这么突出不仅仅因为它也用 React Native 写成,而是[因为它被苹果公司评为年度十佳应用之一](http://www.highsnobiety.com/2016/12/08/iphone-apps-best-of-the-year-2016/)。

#### 沃尔玛

*Walmart Labs*
查看这篇 [Keerti](https://medium.com/@Keerti) 的[文章](https://medium.com/walmartlabs/react-native-at-walmartlabs-cdd140589560#.azpn97g8t)来了解沃尔玛是怎样看待 React Native 的优势的。
#### 微软
微软在 React Native 身上下的赌注很大。
它早已发布多个开源工具,包括 [Code Push](http://microsoft.github.io/code-push/)、[React Native VS Code](https://github.com/Microsoft/vscode-react-native),以及 [React Native Windows](https://github.com/ReactWindows/react-native-windows),旨在帮助开发者向 React Native 领域转移。
微软考虑的是那些已经使用 React Native 为 iOS 和 Android 开发应用的开发者,他们可以重用高达 90% 的代码,不用花费太多额外的时间和成本就可将应用发布到 Windows 上。
微软对 React Native 生态的贡献十分广泛,过去几年在开源界的表现很抢眼。
### 结论
移动应用界面设计和移动应用开发要进行范式转变,下一步就是 React Native 以及与其相似的技术。
#### 公司
如果你的公司正想着削减成本、加快开发速度,而又不想在应用质量和性能上妥协,这是最适合使用 React Native 的时候,它能提高你的净利润。
#### 开发者
如果你是一个开发者,想进入一个将来会快速发展的领域,我强烈推荐你把 React Native 列入你的学习清单。
如果了解 JavaScript,你会入门很快,工具我首推 [Exponent](https://medium.com/u/df61a4267d7a),其他的就看你怎么想了。使用 Exponent 开发者可以轻松的编译、测试和发布跨 Windows 和 MacOS 两个平台的 React Native 应用。
如果已经是一位原生应用开发者,你更会受益匪浅。因为在需要时你能够胜任深入研究原生应用边缘的工作。虽然不会经常用到,但在团队需要时这可是十分宝贵的能力。
我花了很多时间来学习、指导别人 React Native。因为它让我十分激动,而且使用这个框架创作应用也是我一个平淡的小乐趣。
感谢阅读。
---
作者简介:
教授和构建 React Native 应用的软件开发专家
---
via: <https://hackernoon.com/the-cost-of-native-mobile-app-development-is-too-damn-high-4d258025033a>
作者:[Nader Dabit](https://hackernoon.com/@dabit3) 译者:[fuowang](https://github.com/fuowang) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 
If you’re interested in learning more about React Native for your company or team, check out [React Native Training.](http://reactnative.training/?ref=hackernoon.com)
*A tipping point has been reached.* With the exception of a few unique use cases, it no longer makes sense to build and maintain your mobile applications using native frameworks and native development teams.
Average cost of employing iOS, Android, and JavaScript developers in the United States ([http://www.indeed.com/salary](http://www.indeed.com/salary?ref=hackernoon.com), [http://www.payscale.com/research/US/Skill=JavaScript/Salary](http://www.payscale.com/research/US/Skill=JavaScript/Salary?ref=hackernoon.com))
The cost of native mobile application development has been spiraling out of control for the past few years. It has become increasingly difficult for new startups without substantial funding to create native apps, MVPs and prototypes. Existing companies, who need to hold on to talent in order to iterate on existing applications or build new applications, are [fighting](http://www.bizjournals.com/charlotte/how-to/human-resources/2016/12/employers-offer-premium-wages-skilled-workers.html?ref=hackernoon.com) [tooth](https://www.cnet.com/news/silicon-valley-talent-wars-engineers-come-get-your-250k-salary/?ref=hackernoon.com) and [nail](http://www.nytimes.com/2015/08/19/technology/unicorns-hunt-for-talent-among-silicon-valleys-giants.html?ref=hackernoon.com) [with companies from all around the world](http://blogs.wsj.com/cio/2016/09/30/tech-talent-war-moves-to-africa/?ref=hackernoon.com) and will do whatever it takes to retain the best of the best.
Cost of developing an MVP early 2015, Native vs Hybrid ([Comomentum.com](http://www.comentum.com/mobile-app-development-cost.html?ref=hackernoon.com))
If you are a huge company or you are flush with cash, the old thinking was that as long as you threw enough money at native application development, you did not have anything to worry about. This is no longer the case.
Facebook, the last company in the world who you would think of as behind in the war for talent (because they aren’t), was facing problems with their native app that money could not fix. The application had gotten so large and complex that [they were seeing compilation times of up to 15 minutes for their mobile app](https://devchat.tv/react-native-radio/08-bridging-react-native-components-with-tadeu-zagallo?ref=hackernoon.com). This means that even testing minor user interface changes, like moving something around by a couple of points, could take hours (or even days).
In addition to the long compilation times, any time they needed to test a small change to their app the update needed to be implemented and tested in two completely different environments (iOS and Android) with teams working with different languages and frameworks, muddying the waters even more.
Facebook’s solution to this problem is [React Native](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/?ref=hackernoon.com).
[Some people think mobile apps are doomed.](https://medium.com/javascript-scene/native-apps-are-doomed-ac397148a2c0?ref=hackernoon.com#.w06yd23ej) While I really enjoy and respect [Eric Elliott](https://medium.com/@_ericelliott?ref=hackernoon.com) and his work, let’s take a look at some recent data and discuss some opposing viewpoints:
Time spent in mobile apps (April 2016, [smartinsights.com](http://www.smartinsights.com/mobile-marketing/mobile-marketing-analytics/mobile-marketing-statistics/attachment/percent-time-spent-on-mobile-apps-2016/?ref=hackernoon.com))
90% of Time on Mobile is Spent in Apps
There are 2.5 billion people on mobile phones in the world right now. [That number is going to be 5 billion sooner than we think.](http://ben-evans.com/benedictevans/2016/12/8/mobile-is-eating-the-world?ref=hackernoon.com) *It is absolutely insane to think that leaving 4.5 billion people out of your business or application makes sense* *in most scenarios.*
The old argument was that native mobile application development was too expensive for most companies. While this was true, the cost of web development is also on the rise, with [the average salary of a JavaScript developer in the US being in the range of $97,000.00](http://www.indeed.com/salary?q1=javascript%20developer&l1=united%20states&tm=1&ref=hackernoon.com).
With the increased complexity and skyrocketing demand for high quality web development, the average price for a JavaScript developer is inching towards that of a Native developer. Arguing that web development is cheaper is no longer a valid argument.
Hybrid apps are HTML5 apps that are wrapped inside of a native container and provide access to native platform features. Cordova and PhoneGap are prime examples.
*If you’re looking to build an MVP, prototype, or are not worried about the user experience mimicking that of a native app, then a hybrid app may work for you, keeping in mind the entire project will need to be rewritten if you do end up wanting to go native.*
There are many innovative things going on in this space, my favorite being the [Ionic Framework](https://ionicframework.com/?ref=hackernoon.com). Hybrid is getting better and better, but it is still not as fluid or natural feeling as Native.
For many companies, including most serious startups as well as medium and large sized companies, hybrid apps may not deliver the quality that they want and that their customers demand, leaving the feeling unpolished and less professional.
[While I have read and heard that of the top 100 apps on the app store, zero of them are hybrid,](https://medium.com/lunabee-studio/why-hybrid-apps-are-crap-6f827a42f549?ref=hackernoon.com#.lakqptjw6) I have not been able to back up this claim with evidence, but I would not doubt if the number were between zero and 5, and this is for a reason.
[Our Biggest Mistake Was Betting Too Much On HTML5]— Mark Zuckerberg
If you’ve been keeping up with the mobile development landscape you have undoubtedly heard of projects such as [NativeScript](https://www.nativescript.org/?ref=hackernoon.com) and [React Native](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/?ref=hackernoon.com).
These projects allow you to build native quality mobile applications with JavaScript and use the same fundamental UI building blocks as regular iOS and Android apps.
With React Native **you can have a single engineer or team of engineers specialize in cross platform mobile app development**, [native desktop development](https://github.com/ptmt/react-native-macos?ref=hackernoon.com), and even web development [using the existing codebase](https://github.com/necolas/react-native-web?ref=hackernoon.com) or [the underlying technology](https://facebook.github.io/react/?ref=hackernoon.com), shipping your applications to the App Store, the Play Store, and the Web for a fraction of the traditional cost without losing out on the benefits of native performance and quality.
It is not unheard of for React Native apps to reuse up to 90% of their code across platforms, though the range is usually between 80% and 90%.
If your company is using React Native, it eliminates the divide between teams resulting in more consistency in both the UI and the APIs being built, speeding up the development time.
There is no need for compilation with React Native, as the app updates instantly when saving, also speeding up development time.
React Native also allows you to use tools such as [Code Push](http://microsoft.github.io/code-push/?ref=hackernoon.com) and [AppHub](https://apphub.io/?ref=hackernoon.com) to remotely update your JavaScript code. This means that you can push updates, features, and bug fixes instantly to your users, bypassing the labor of bundling, submitting, and having your app accepted to the App and Google play stores, a process that can take between 2 and 7 days (the App Store being the main pain point in this process). This is something that is not possible with native apps, though is possible with hybrid apps.
If innovation in this space continues as it has been since it’s release, in the future you will even be able to build for platforms such as the [Apple Watch](https://github.com/elliottsj/apple-watch-uikit?ref=hackernoon.com) , [Apple TV](https://github.com/douglowder/react-native-appletv?ref=hackernoon.com), and [Tizen](https://www.tizen.org/blogs/srsaul/2016/samsung-committed-bringing-react-native-tizen?ref=hackernoon.com) to name a few.
NativeScript is still fairly new as the framework powering it, Angular 2,
[was just released out of beta a few months ago,]but it too has a promising future as long as Angular2 holds on to a decent share of the market.
What you may not know is that some of **the most innovative and largest technology companies in the world are betting big on these types of technologies,** specifically [React Native.](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/?ref=hackernoon.com)
I have also spoken to and am working with multiple enterprise and fortune 500 companies currently making the switch to React Native.
Along with the below examples, [here is a list of notable apps using React Native.](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/showcase.html?ref=hackernoon.com)
React Native Apps by Facebook
Facebook is now using React Native for both [Ads Manager](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.facebook.adsmanager&ref=hackernoon.com) and [Facebook Groups,](https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/facebook-groups/id931735837?mt=8&ref=hackernoon.com) and [will be implementing the framework to power it’s news feed.](https://devchat.tv/react-native-radio/40-navigation-in-react-native-with-eric-vicenti?ref=hackernoon.com)
Facebook also spends a lot of money creating and maintaining open source projects such as React Native, and t[hey and their open source developers have done a fantastic job lately by creating a lot of awesome projects](https://code.facebook.com/projects/?ref=hackernoon.com) that people like me and businesses all around the world benefit greatly from using on a daily basis.
React Native has been implemented in parts of the Instagram mobile app.
Airbnb
Much of Airbnb is being rewritten in React Native (via [Leland Richardson](https://medium.com/@intelligibabble?ref=hackernoon.com))
Over 90% of the Airbnb Trips Platform is written in React Native (via [spikebrehm](https://medium.com/@spikebrehm?ref=hackernoon.com))
Vogue Top 10 apps of 2016
Vogue stands out not only because it was also written in React Native, but [because it was ranked as one of the 10 Best Apps of the Year, according to Apple](http://www.highsnobiety.com/2016/12/08/iphone-apps-best-of-the-year-2016/?ref=hackernoon.com).
**Walmart**
Walmart Labs
Check out [this](https://medium.com/walmartlabs/react-native-at-walmartlabs-cdd140589560?ref=hackernoon.com#.azpn97g8t) blog post by [Keerti](https://medium.com/@Keerti?ref=hackernoon.com) to learn more about how Walmart is taking advantage of React Native.
**Microsoft**
Microsoft is betting heavily on React Native.
They have already release multiple open source tools, including [Code Push](http://microsoft.github.io/code-push/?ref=hackernoon.com), [React Native VS Code,](https://github.com/Microsoft/vscode-react-native?ref=hackernoon.com) and [React Native Windows](https://github.com/ReactWindows/react-native-windows?ref=hackernoon.com), in the shift towards helping developers in the React Native space.
Their thoughts behind this are that if people are already building their apps using React Native for iOS and Android, and they can reuse up to 90% of their code, then s_hipping to Windows costs them little extra relative to the cost && time already spent building the app in the first place._
Microsoft has contributed extensively to the React Native ecosystem and have done an excellent job in the Open Source space over the past few years.
React Native and similar technologies are the next step and a paradigm shift in how we will build mobile UIS and mobile applications.
**Companies**
If your company is looking to cut costs and speed up development time without compromising on quality or performance, React Native is ready for prime time and will benefit your bottom line.
**Developers**
If you are a developer and want to enter into an rapidly evolving space with substantial future up side, I would highly recommend looking at adding React Native to your list of things to learn.
If you know JavaScript, you can hit the ground running very quickly, and I would recommend first trying it out using [Exponent](https://medium.com/@expo?ref=hackernoon.com) and seeing what you think. Exponent allows developers to easily build, test ,and deploy cross platform React Native apps on both Windows and macOS.
If you are already a native Developer, you will benefit especially because you will be able to competently dig into the native side of things when needed, something that is not needed often but when needed is a highly valuable skill to have on a team.
I have spent a lot of my time learning and teaching others about React Native because I am extremely excited about it and it is just plain fun to create apps using the framework.
Thanks for reading.
My Name is
[Nader Dabit]. I am a Developer Advocate at[AWS Mobile]working with projects like[AppSync]and[Amplify], and the founder of[React Native Training].
If you enjoyed this article, please recommend and share it! Thanks for your time |
8,522 | 美联邦法院裁定:GPL 是可执行的合约 | https://qz.com/981029/a-federal-court-has-ruled-that-an-open-source-license-is-an-enforceable-contract/ | 2017-05-19T09:07:00 | [
"GPL",
"开源许可证"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8522-1.html | 韩国一家开发了 Hancom Office 办公软件的公司在其字处理软件中集成了开源软件 Ghostscript,但是没有遵守 Ghostscript 的 GNU GPL 许可证而开源,也没有为该软件付费。近日,该韩国公司被美国联邦法院裁定其违约。

Ghostscript 是一个开源软件,由 Artifex 公司开发,其采用了两种许可证:
* GNU GPL 许可证
* 商业付费许可证
如果要免费使用 Ghostscript,Hancom 就需要遵循该软件的开源许可证,即 GNU GPL。该许可证要求,如果你的软件中使用了采用该许可协议的软件,并公开发布的话,就需要也采用同样的 GNU GPL 许可证开源。也就是说, Hancom 需要开源其整个办公软件套件。
否则,Hancom 就需要向 Ghostscript 的开发商 Artifex 公司支付商业许可证费用。Artifex 允许商业或其它闭源软件开发商绕开严格的开源许可证 GNU GPL,只要付费就行。
但是 Hancom 从 2013 年在其软件中使用了 Ghostscript 之后,却什么都没做:既没有开源其软件,也没有向 Artifex 公司付商业许可证的费用。
在 2016 年底,交涉无果的 Artifex 公司向美国加利福尼亚北部地区法院发起了诉讼。
“在发现 Hancom 违反了 GNU GPL 许可证,侵犯了 Artifex 的 Ghostscript 的宝贵版权之后,Artifex 要求 Hancom 停止其侵权行为,并为其多年无版权使用 Ghostscript 支付合理的版权费用,”该公司陈述到,“Hancom 拒绝了该要求,Artifex 转而寻求本法院责令 Hancom 停止进一步侵权并支付其滥用 Artifex 的开源许可证的费用。”
Artifex 还提到 Hancom 在 2015 年收入了 8630 万美元。
像 GUN GPL 这样的开源许可证的可执行性长期以来一直是一个悬而未决的法律问题。美国联邦巡回法庭在 2006 年的一个判例,雅各布森诉卡泽尔案中,对开源许可证的侵犯裁定可视作对版权申明的处理。但是在本案之前,这种侵犯开源许可证是否可以依法视作侵犯合约并未裁定。
Hancom 尝试发起动议以驳回该诉讼,其认为该公司并未签署任何东西,所以该许可证并不是真正的合约。
“并不是这样”,杰奎琳·斯科特·科里法官在 4 月 25 日的议案中说。她说 GNU GPL “规定了如果用户没有获取商业许可证,即表示同意其条款。原告称被告没有获取商业许可证,并公开表明其在 GNU GPL 下使用 Ghostscript。这些指控足以为合约的存在而辩护。”
科里法官驳回了 Hancom 的动议。按照这样的做法,就树立了像 GNU GPL 这样的开源许可证可以被视作法律合约的先例,在开发商违反了开源许可证时会被起诉。这对于开源社区来说是一个重大胜利。
当然,Artifex 是否可以最终赢得这一诉讼,还要看后继的上诉和裁定。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,523 | Rowhammer:针对物理内存的攻击可以取得 Android 设备的 root 权限 | http://www.csoonline.com/article/3134726/security/physical-ram-attack-can-root-android-and-possibly-other-devices.html | 2017-05-20T08:32:00 | [
"Rowhammer",
"攻击"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8523-1.html |
>
> 攻击者确实可以在物理存储单元中实现位翻转来达到侵入移动设备与计算机的目的
>
>
>

研究者们发现了一种新的在不利用任何软件漏洞情况下,利用内存芯片物理设计上的弱点来侵入 Android 设备的方式。这种攻击技术同样可以影响到其它如 ARM 和 X86 架构的设备与计算机。
这种称之为“Rowhammer”的攻击起源于过去十多年中将更多的 DRAM(动态随机存取存储器)容量封装进越来越小的芯片中,这将导致在特定情况下存储单元电子可以从相邻两<ruby> 行 <rt> row </rt></ruby>的一边泄漏到另一边。(LCTT 译注:参见 [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Row\_hammer)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Row_hammer%EF%BC%89)
例如,反复且快速的访问相同的物理储存位置,这种被称为 “<ruby> 锤击 <rt> hammering </rt></ruby>” 的行为可以导致相邻位置的位值从 0 反转成 1,或者相反。
虽然这样的电子干扰已经被生产商知晓并且从可靠性角度研究了一段时间了,因为内存错误能够导致系统崩溃。而研究者们现在展示了在可控方式的触发下它所存在的严重安全隐患。
在 2015 年 4 月,来自谷歌 Project Zero 项目的研究者公布了两份基于内存 “Rowhammer”漏洞对于 x86-64 CPU 架构的 [提权利用](http://www.computerworld.com/article/2895898/google-researchers-hack-computers-using-dram-electrical-leaks.html)。其中一份利用可以使代码从谷歌的 Chrome 浏览器沙盒里逃逸并且直接在系统上执行,另一份可以在 Linux 机器上获取内核级权限。
此后,其他的研究者进行了更深入的调查并且展示了[通过网站中 JaveScript 脚本进行利用的方式](http://www.computerworld.com/article/2954582/security/researchers-develop-astonishing-webbased-attack-on-a-computers-dram.html)甚至能够影响运行在云环境下的[虚拟服务器](http://www.infoworld.com/article/3105889/security/flip-feng-shui-attack-on-cloud-vms-exploits-hardware-weaknesses.html)。然而,对于这项技术是否可以应用在智能手机和移动设备大量使用的 ARM 架构中还是有疑问的。
现在,一队成员来自荷兰阿姆斯特丹自由大学、奥地利格拉茨技术大学和加州大学圣塔芭芭拉分校的 VUSec 小组,已经证明了 Rowhammer 不仅仅可以应用在 ARM 架构上并且甚至比在 x86 架构上更容易。
研究者们将他们的新攻击命名为 Drammer,代表了 Rowhammer 确实存在,并且计划于周三在维也纳举办的第 23 届 ACM 计算机与通信安全大会上展示。这种攻击建立在之前就被发现与实现的 Rowhammer 技术之上。
VUSec 小组的研究者已经制造了一个适用于 Android 设备的恶意应用,当它被执行的时候利用不易察觉的内存位反转在不需要任何权限的情况下就可以获取设备根权限。
研究者们测试了来自不同制造商的 27 款 Android 设备,21 款使用 ARMv7(32-bit)指令集架构,其它 6 款使用 ARMv8(64-bit)指令集架构。他们成功的在 17 款 ARMv7 设备和 1 款 ARMv8 设备上实现了为反转,表明了这些设备是易受攻击的。
此外,Drammer 能够与其它的 Android 漏洞组合使用,例如 [Stagefright](http://www.csoonline.com/article/3045836/security/new-stagefright-exploit-puts-millions-of-android-devices-at-risk.html) 或者 [BAndroid](https://www.vusec.net/projects/bandroid/) 来实现无需用户手动下载恶意应用的远程攻击。
谷歌已经注意到了这一类型的攻击。“在研究者向谷歌漏洞奖励计划报告了这个问题之后,我们与他们进行了密切的沟通来深入理解这个问题以便我们更好的保护用户,”一位谷歌的代表在一份邮件申明中这样说到。“我们已经开发了一个缓解方案,将会包含在十一月的安全更新中。”(LCTT 译注:缓解方案,参见 <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vulnerability_management>)
VUSec 的研究者认为,谷歌的缓解方案将会使得攻击过程更为复杂,但是它不能修复潜在的问题。
事实上,从软件上去修复一个由硬件导致的问题是不现实的。硬件供应商正在研究相关问题并且有可能在将来的内存芯片中被修复,但是在现有设备的芯片中风险依然存在。
更糟的是,研究者们说,由于有许多因素会影响到攻击的成功与否并且这些因素尚未被研究透彻,因此很难去说有哪些设备会被影响到。例如,内存控制器可能会在不同的电量的情况下展现不同的行为,因此一个设备可能在满电的情况下没有风险,当它处于低电量的情况下就是有风险的。
同样的,在网络安全中有这样一句俗语:<ruby> 攻击将变本加厉,如火如荼 <rt> Attacks always get getter, they never get worse </rt></ruby>。Rowhammer 攻击已经从理论变成了现实可能,同样的,它也可能会从现在的现实可能变成确确实实的存在。这意味着今天某个设备是不被影响的,在明天就有可能被改进后的 Rowhammer 技术证明它是存在风险的。
Drammer 在 Android 上实现是因为研究者期望研究基于 ARM 设备的影响,但是潜在的技术可以被使用在所有的架构与操作系统上。新的攻击相较于之前建立在运气与特殊特性与特定平台之上并且十分容易失效的技术已经是一个巨大的进步了。
Drammer 攻击的实现依靠于被包括图形、网络、声音等大量硬件子系统所使用的 DMA(直接存储访问)缓存。Drammer 的实现采用了所有操作系统上都有的 Android 的 ION 内存分配器、接口与方法,这给我们带来的警示是该论文的主要贡献之一。
“破天荒的,我们成功地展示了我们可以做到,在不依赖任何特定的特性情况下完全可靠的证明了 Rowhammer”, VUSec 小组中的其中一位研究者 Cristiano Giuffrida 这样说道。“攻击所利用的内存位置并非是 Android 独有的。攻击在任何的 Linux 平台上都能工作 -- 我们甚至怀疑其它操作系统也可以 -- 因为它利用的是操作系统内核内存管理中固有的特性。”
“我期待我们可以看到更多针对其它平台的攻击的变种,”阿姆斯特丹自由大学的教授兼 VUSec 系统安全研究小组的领导者 Herbert Bos 补充道。
在他们的[论文](https://vvdveen.com/publications/drammer.pdf)之外,研究者们也释出了一个 Android 应用来测试 Android 设备在当前所知的技术条件下受到 Rowhammer 攻击时是否会有风险。应用还没有传上谷歌应用商店,可以从 [VUSec Drammer 网站](https://www.vusec.net/projects/drammer/) 下载来手动安装。一个开源的 Rowhammer 模拟器同样能够帮助其他的研究者来更深入的研究这个问题。
---
via:<http://www.csoonline.com/article/3134726/security/physical-ram-attack-can-root-android-and-possibly-other-devices.html>
作者:[Lucian Constantin](http://www.csoonline.com/author/Lucian-Constantin/) 译者:[wcnnbdk1](https://github.com/wcnnbdk1) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,524 | GraphQL 用例:使用 Golang 和 PostgreSQL 构建一个博客引擎 API | http://alexandrutopliceanu.ro/post/graphql-with-go-and-postgresql | 2017-05-19T11:18:22 | [
"GraphQL",
"图数据库"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8524-1.html | 
### 摘要
GraphQL 在生产环境中似乎难以使用:虽然对于建模功能来说图接口非常灵活,但是并不适用于关系型存储,不管是在实现还是性能方面。
在这篇博客中,我们会设计并实现一个简单的博客引擎 API,它支持以下功能:
* 三种类型的资源(用户、博文以及评论)支持多种功能(创建用户、创建博文、给博文添加评论、关注其它用户的博文和评论,等等。)
* 使用 PostgreSQL 作为后端数据存储(选择它因为它是一个流行的关系型数据库)。
* 使用 Golang(开发 API 的一个流行语言)实现 API。
我们会比较简单的 GraphQL 实现和纯 REST 替代方案,在一种普通场景(呈现博客文章页面)下对比它们的实现复杂性和效率。
### 介绍
GraphQL 是一种 IDL(<ruby> 接口定义语言 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Interface Definition Language </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>),设计者定义数据类型和并把数据建模为一个<ruby> 图 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> graph </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。每个顶点都是一种数据类型的一个实例,边代表了节点之间的关系。这种方式非常灵活,能适应任何业务领域。然而,问题是设计过程更加复杂,而且传统的数据存储不能很好地映射到图模型。阅读*附录1*了解更多关于这个问题的详细信息。
GraphQL 在 2014 年由 Facebook 的工程师团队首次提出。尽管它的优点和功能非常有趣而且引人注目,但它并没有得到大规模应用。开发者需要权衡 REST 的设计简单性、熟悉性、丰富的工具和 GraphQL 不会受限于 CRUD(LCTT 译注:Create、Read、Update、Delete) 以及网络性能(它优化了往返服务器的网络)的灵活性。
大部分关于 GraphQL 的教程和指南都跳过了从数据存储获取数据以便解决查询的问题。也就是,如何使用通用目的、流行存储方案(例如关系型数据库)为 GraphQL API 设计一个支持高效数据提取的数据库。
这篇博客介绍构建一个博客引擎 GraphQL API 的流程。它的功能相当复杂。为了和基于 REST 的方法进行比较,它的范围被限制为一个熟悉的业务领域。
这篇博客的文章结构如下:
* 第一部分我们会设计一个 GraphQL 模式并介绍所使用语言的一些功能。
* 第二部分是 PostgreSQL 数据库的设计。
* 第三部分介绍了使用 Golang 实现第一部分设计的 GraphQL 模式。
* 第四部分我们以从后端获取所需数据的角度来比较呈现博客文章页面的任务。
### 相关阅读
* 很棒的 [GraphQL 介绍文档](http://graphql.org/learn/)。
* 该项目的完整实现代码在 [github.com/topliceanu/graphql-go-example](https://github.com/topliceanu/graphql-go-example)。
### 在 GraphQL 中建模一个博客引擎
下述*列表1*包括了博客引擎 API 的全部模式。它显示了组成图的顶点的数据类型。顶点之间的关系,也就是边,被建模为指定类型的属性。
```
type User {
id: ID
email: String!
post(id: ID!): Post
posts: [Post!]!
follower(id: ID!): User
followers: [User!]!
followee(id: ID!): User
followees: [User!]!
}
type Post {
id: ID
user: User!
title: String!
body: String!
comment(id: ID!): Comment
comments: [Comment!]!
}
type Comment {
id: ID
user: User!
post: Post!
title: String
body: String!
}
type Query {
user(id: ID!): User
}
type Mutation {
createUser(email: String!): User
removeUser(id: ID!): Boolean
follow(follower: ID!, followee: ID!): Boolean
unfollow(follower: ID!, followee: ID!): Boolean
createPost(user: ID!, title: String!, body: String!): Post
removePost(id: ID!): Boolean
createComment(user: ID!, post: ID!, title: String!, body: String!): Comment
removeComment(id: ID!): Boolean
}
```
*列表1*
模式使用 GraphQL DSL 编写,它用于定义自定义数据类型,例如 `User`、`Post` 和 `Comment`。该语言也提供了一系列原始数据类型,例如 `String`、`Boolean` 和 `ID`(它是`String` 的别名,但是有顶点唯一标识符的额外语义)。
`Query` 和 `Mutation` 是语法解析器能识别并用于查询图的可选类型。从 GraphQL API 读取数据等同于遍历图。需要提供这样一个起始顶点;该角色通过 `Query` 类型来实现。在这种情况中,所有图的查询都要从一个由 id `user(id:ID!)` 指定的用户开始。对于写数据,定义了 `Mutation` 顶点。它提供了一系列操作,建模为能遍历(并返回)新创建顶点类型的参数化属性。*列表2*是这些查询的一些例子。
顶点属性能被参数化,也就是能接受参数。在图遍历场景中,如果一个博文顶点有多个评论顶点,你可以通过指定 `comment(id: ID)` 只遍历其中的一个。所有这些都取决于设计,设计者可以选择不提供到每个独立顶点的直接路径。
`!` 字符是一个类型后缀,适用于原始类型和用户定义类型,它有两种语义:
* 当被用于参数化属性的参数类型时,表示这个参数是必须的。
* 当被用于一个属性的返回类型时,表示当顶点被获取时该属性不会为空。
* 也可以把它们组合起来,例如 `[Comment!]!` 表示一个非空 Comment 顶点链表,其中 `[]`、`[Comment]` 是有效的,但 `null, [null], [Comment, null]` 就不是。
*列表2* 包括一系列用于博客 API 的 `curl` 命令,它们会使用 mutation 填充图然后查询图以便获取数据。要运行它们,按照 [topliceanu/graphql-go-example](https://github.com/graphql/graphql-js) 仓库中的指令编译并运行服务。
```
# 创建用户 1、2 和 3 的更改。更改和查询类似,在该情景中我们检索新创建用户的 id 和 email。
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d 'mutation {createUser(email:"[email protected]"){id, email}}'
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d 'mutation {createUser(email:"[email protected]"){id, email}}'
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d 'mutation {createUser(email:"[email protected]"){id, email}}'
# 为用户添加博文的更改。为了和模式匹配我们需要检索他们的 id,否则会出现错误。
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d 'mutation {createPost(user:1,title:"post1",body:"body1"){id}}'
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d 'mutation {createPost(user:1,title:"post2",body:"body2"){id}}'
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d 'mutation {createPost(user:2,title:"post3",body:"body3"){id}}'
# 博文所有评论的更改。`createComment` 需要用户 id,标题和正文。看列表 1 的模式。
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d 'mutation {createComment(user:2,post:1,title:"comment1",body:"comment1"){id}}'
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d 'mutation {createComment(user:1,post:3,title:"comment2",body:"comment2"){id}}'
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d 'mutation {createComment(user:3,post:3,title:"comment3",body:"comment3"){id}}'
# 让用户 3 关注用户 1 和用户 2 的更改。注意 `follow` 更改只返回一个布尔值而不需要指定。
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d 'mutation {follow(follower:3, followee:1)}'
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d 'mutation {follow(follower:3, followee:2)}'
# 用户获取用户 1 所有数据的查询。
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d '{user(id:1)}'
# 用户获取用户 2 和用户 1 的关注者的查询。
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d '{user(id:2){followers{id, email}}}'
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d '{user(id:1){followers{id, email}}}'
# 检测用户 2 是否被用户 1 关注的查询。如果是,检索用户 1 的 email,否则返回空。
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d '{user(id:2){follower(id:1){email}}}'
# 返回用户 3 关注的所有用户 id 和 email 的查询。
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d '{user(id:3){followees{id, email}}}'
# 如果用户 3 被用户 1 关注,就获取用户 3 email 的查询。
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d '{user(id:1){followee(id:3){email}}}'
# 获取用户 1 的第二篇博文的查询,检索它的标题和正文。如果博文 2 不是由用户 1 创建的,就会返回空。
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d '{user(id:1){post(id:2){title,body}}}'
# 获取用户 1 的所有博文的所有数据的查询。
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d '{user(id:1){posts{id,title,body}}}'
# 获取写博文 2 用户的查询,如果博文 2 是由 用户 1 撰写;一个现实语言灵活性的例证。
curl -XPOST http://vm:8080/graphql -d '{user(id:1){post(id:2){user{id,email}}}}'
```
*列表2*
通过仔细设计 mutation 和类型属性,可以实现强大而富有表达力的查询。
### 设计 PostgreSQL 数据库
关系型数据库的设计,一如以往,由避免数据冗余的需求驱动。选择该方式有两个原因:
1. 表明实现 GraphQL API 不需要定制化的数据库技术或者学习和使用新的设计技巧。
2. 表明 GraphQL API 能在现有的数据库之上创建,更具体地说,最初设计用于 REST 后端甚至传统的呈现 HTML 站点的服务器端数据库。
阅读 *附录1* 了解关于关系型和图数据库在构建 GraphQL API 方面的区别。*列表3* 显示了用于创建新数据库的 SQL 命令。数据库模式和 GraphQL 模式相对应。为了支持 `follow/unfollow` 更改,需要添加 `followers` 关系。
```
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
email VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS posts (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
user_id INTEGER NOT NULL REFERENCES users(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
title VARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,
body TEXT NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS comments (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
user_id INTEGER NOT NULL REFERENCES users(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
post_id INTEGER NOT NULL REFERENCES posts(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
title VARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,
body TEXT NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS followers (
follower_id INTEGER NOT NULL REFERENCES users(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
followee_id INTEGER NOT NULL REFERENCES users(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
PRIMARY KEY(follower_id, followee_id)
);
```
*列表3*
### Golang API 实现
本项目使用的用 Go 实现的 GraphQL 语法解析器是 `github.com/graphql-go/graphql`。它包括一个查询解析器,但不包括模式解析器。这要求开发者利用库提供的结构使用 Go 构建 GraphQL 模式。这和 [nodejs 实现](https://github.com/graphql/graphql-js) 不同,后者提供了一个模式解析器并为数据获取暴露了钩子。因此 *列表1* 中的模式只是作为指导使用,需要转化为 Golang 代码。然而,这个*“限制”*提供了与抽象级别对等的机会,并且了解模式如何和用于检索数据的图遍历模型相关。*列表4* 显示了 `Comment` 顶点类型的实现:
```
var CommentType = graphql.NewObject(graphql.ObjectConfig{
Name: "Comment",
Fields: graphql.Fields{
"id": &graphql.Field{
Type: graphql.NewNonNull(graphql.ID),
Resolve: func(p graphql.ResolveParams) (interface{}, error) {
if comment, ok := p.Source.(*Comment); ok == true {
return comment.ID, nil
}
return nil, nil
},
},
"title": &graphql.Field{
Type: graphql.NewNonNull(graphql.String),
Resolve: func(p graphql.ResolveParams) (interface{}, error) {
if comment, ok := p.Source.(*Comment); ok == true {
return comment.Title, nil
}
return nil, nil
},
},
"body": &graphql.Field{
Type: graphql.NewNonNull(graphql.ID),
Resolve: func(p graphql.ResolveParams) (interface{}, error) {
if comment, ok := p.Source.(*Comment); ok == true {
return comment.Body, nil
}
return nil, nil
},
},
},
})
func init() {
CommentType.AddFieldConfig("user", &graphql.Field{
Type: UserType,
Resolve: func(p graphql.ResolveParams) (interface{}, error) {
if comment, ok := p.Source.(*Comment); ok == true {
return GetUserByID(comment.UserID)
}
return nil, nil
},
})
CommentType.AddFieldConfig("post", &graphql.Field{
Type: PostType,
Args: graphql.FieldConfigArgument{
"id": &graphql.ArgumentConfig{
Description: "Post ID",
Type: graphql.NewNonNull(graphql.ID),
},
},
Resolve: func(p graphql.ResolveParams) (interface{}, error) {
i := p.Args["id"].(string)
id, err := strconv.Atoi(i)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return GetPostByID(id)
},
})
}
```
*列表4*
正如 *列表1* 中的模式,`Comment` 类型是静态定义的一个有三个属性的结构体:`id`、`title` 和 `body`。为了避免循环依赖,动态定义了 `user` 和 `post` 两个其它属性。
Go 并不适用于这种动态建模,它只支持一些类型检查,代码中大部分变量都是 `interface{}` 类型,在使用之前都需要进行类型断言。`CommentType` 是一个 `graphql.Object` 类型的变量,它的属性是 `graphql.Field` 类型。因此,GraphQL DSL 和 Go 中使用的数据结构并没有直接的转换。
每个字段的 `resolve` 函数暴露了 `Source` 参数,它是表示遍历时前一个节点的数据类型顶点。`Comment` 的所有属性都有作为 source 的当前 `CommentType` 顶点。检索`id`、`title` 和 `body` 是一个直接属性访问,而检索 `user` 和 `post` 要求图遍历,也需要数据库查询。由于它们非常简单,这篇文章并没有介绍这些 SQL 查询,但在*参考文献*部分列出的 github 仓库中有。
### 普通场景下和 REST 的对比
在这一部分,我们会展示一个普通的博客文章呈现场景,并比较 REST 和 GraphQL 的实现。关注重点会放在入站/出站请求数量,因为这些是造成页面呈现延迟的最主要原因。
场景:呈现一个博客文章页面。它应该包含关于作者(email)、博客文章(标题、正文)、所有评论(标题、正文)以及评论人是否关注博客文章作者的信息。*图1* 和 *图2* 显示了客户端 SPA、API 服务器以及数据库之间的交互,一个是 REST API、另一个对应是 GraphQL API。
```
+------+ +------+ +--------+
|client| |server| |database|
+--+---+ +--+---+ +----+---+
| GET /blogs/:id | |
1\. +-------------------------> SELECT * FROM blogs... |
| +--------------------------->
| <---------------------------+
<-------------------------+ |
| | |
| GET /users/:id | |
2\. +-------------------------> SELECT * FROM users... |
| +--------------------------->
| <---------------------------+
<-------------------------+ |
| | |
| GET /blogs/:id/comments | |
3\. +-------------------------> SELECT * FROM comments... |
| +--------------------------->
| <---------------------------+
<-------------------------+ |
| | |
| GET /users/:id/followers| |
4\. +-------------------------> SELECT * FROM followers.. |
| +--------------------------->
| <---------------------------+
<-------------------------+ |
| | |
+ + +
```
*图1*
```
+------+ +------+ +--------+
|client| |server| |database|
+--+---+ +--+---+ +----+---+
| GET /graphql | |
1\. +-------------------------> SELECT * FROM blogs... |
| +--------------------------->
| <---------------------------+
| | |
| | |
| | |
2\. | | SELECT * FROM users... |
| +--------------------------->
| <---------------------------+
| | |
| | |
| | |
3\. | | SELECT * FROM comments... |
| +--------------------------->
| <---------------------------+
| | |
| | |
| | |
4\. | | SELECT * FROM followers.. |
| +--------------------------->
| <---------------------------+
<-------------------------+ |
| | |
+ + +
```
*图2*
*列表5* 是一条用于获取所有呈现博文所需数据的简单 GraphQL 查询。
```
{
user(id: 1) {
email
followers
post(id: 1) {
title
body
comments {
id
title
user {
id
email
}
}
}
}
}
```
*列表5*
对于这种情况,对数据库的查询次数是故意相同的,但是到 API 服务器的 HTTP 请求已经减少到只有一个。我们认为在这种类型的应用程序中通过互联网的 HTTP 请求是最昂贵的。
为了利用 GraphQL 的优势,后端并不需要进行特别设计,从 REST 到 GraphQL 的转换可以逐步完成。这使得可以测量性能提升和优化。从这一点,API 设计者可以开始优化(潜在的合并) SQL 查询从而提高性能。缓存的机会在数据库和 API 级别都大大增加。
SQL 之上的抽象(例如 ORM 层)通常会和 `n+1` 问题相抵触。在 REST 示例的步骤 4 中,客户端可能不得不在单独的请求中为每个评论的作者请求关注状态。这是因为在 REST 中没有标准的方式来表达两个以上资源之间的关系,而 GraphQL 旨在通过使用嵌套查询来防止这类问题。这里我们通过获取用户的所有关注者来作弊。我们向客户提出了如何确定评论并关注了作者的用户的逻辑。
另一个区别是获取比客户端所需更多的数据,以免破坏 REST 资源抽象。这对于用于解析和存储不需要数据的带宽消耗和电池寿命非常重要。
### 总结
GraphQL 是 REST 的一个可用替代方案,因为:
* 尽管设计 API 更加困难,但该过程可以逐步完成。也是由于这个原因,从 REST 转换到 GraphQL 非常容易,两个流程可以没有任何问题地共存。
* 在网络请求方面更加高效,即使是类似本博客中的简单实现。它还提供了更多查询优化和结果缓存的机会。
* 在用于解析结果的带宽消耗和 CPU 周期方面它更加高效,因为它只返回呈现页面所需的数据。
REST 仍然非常有用,如果:
* 你的 API 非常简单,只有少量的资源或者资源之间关系简单。
* 在你的组织中已经在使用 REST API,而且你已经配置好了所有工具,或者你的客户希望获取 REST API。
* 你有复杂的 ACL(LCTT 译注:Access Control List) 策略。在博客例子中,可能的功能是允许用户良好地控制谁能查看他们的电子邮箱、博客、特定博客的评论、他们关注了谁,等等。优化数据获取同时检查复杂的业务规则可能会更加困难。
### 附录1:图数据库和高效数据存储
尽管将其应用领域数据想象为一个图非常直观,正如这篇博文介绍的那样,但是支持这种接口的高效数据存储问题仍然没有解决。
近年来图数据库变得越来越流行。通过将 GraphQL 查询转换为特定的图数据库查询语言从而延迟解决请求的复杂性似乎是一种可行的方案。
问题是和关系型数据库相比,图并不是一种高效的数据结构。图中一个顶点可能有到任何其它顶点的连接,访问模式比较难以预测因此提供了较少的优化机会。
例如缓存的问题,为了快速访问需要将哪些顶点保存在内存中?通用缓存算法在图遍历场景中可能没那么高效。
数据库分片问题:把数据库切分为更小、没有交叉的数据库并保存到独立的硬件。在学术上,最小切割的图划分问题已经得到了很好的理解,但可能是次优的,而且由于病态的最坏情况可能导致高度不平衡切割。
在关系型数据库中,数据被建模为记录(行或者元组)和列,表和数据库名称都只是简单的命名空间。大部分数据库都是面向行的,意味着每个记录都是一个连续的内存块,一个表中的所有记录在磁盘上一个接一个地整齐地打包(通常按照某个关键列排序)。这非常高效,因为这是物理存储最优的工作方式。HDD 最昂贵的操作是将磁头移动到磁盘上的另一个扇区,因此最小化此类访问非常重要。
很有可能如果应用程序对一条特定记录感兴趣,它需要获取整条记录,而不仅仅是记录中的其中一列。也很有可能如果应用程序对一条记录感兴趣,它也会对该记录周围的记录感兴趣,例如全表扫描。这两点使得关系型数据库相当高效。然而,也是因为这个原因,关系型数据库的最差使用场景就是总是随机访问所有数据。图数据库正是如此。
随着支持更快随机访问的 SSD 驱动器的出现,更便宜的内存使得缓存大部分图数据库成为可能,更好的优化图缓存和分区的技术,图数据库开始成为可选的存储解决方案。大部分大公司也使用它:Facebook 有 Social Graph,Google 有 Knowledge Graph。
---
via: <http://alexandrutopliceanu.ro/post/graphql-with-go-and-postgresql>
作者:[Alexandru Topliceanu](https://github.com/topliceanu) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
8,526 | 4 个拥有绝佳命令行界面的终端程序 | https://opensource.com/article/17/5/4-terminal-apps | 2017-05-20T12:04:00 | [
"命令行",
"CLI"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8526-1.html |
>
> 让我们来看几个精心设计的 CLI 程序,以及如何解决一些可发现性问题。
>
>
>

在本文中,我会指出命令行界面的<ruby> 可发现性 <rt> discoverability </rt></ruby>缺点以及克服这些问题的几种方法。
我喜欢命令行。我第一次接触命令行是在 1997 的 DOS 6.2 上。我学习了各种命令的语法,并展示了如何在目录中列出隐藏的文件(`attrib`)。我会每次仔细检查命令中的每个字符。 当我犯了一个错误,我会从头开始重新输入命令。直到有一天,有人向我展示了如何使用向上和向下箭头按键遍历命令行历史,我被震惊了。
后来当我接触到 Linux 时,让我感到惊喜的是,上下箭头保留了它们遍历历史记录的能力。我仍然很仔细地打字,但是现在,我了解如何盲打,并且我能打的很快,每分钟可以达到 55 个单词的速度。接着有人向我展示了 tab 补完,再一次改变了我的生活。
在 GUI 应用程序中,菜单、工具提示和图标用于向用户展示功能。而命令行缺乏这种能力,但是有办法克服这个问题。在深入解决方案之前,我会来看看几个有问题的 CLI 程序:
**1、 MySQL**
首先让我们看看我们所钟爱的 MySQL REPL。我经常发现自己在输入 `SELECT * FROM` 然后按 `Tab` 的习惯。MySQL 会询问我是否想看到所有的 871 种可能性。我的数据库中绝对没有 871 张表。如果我选择 `yes`,它会显示一堆 SQL 关键字、表、函数等。(LCTT 译注:REPL —— Read-Eval-Print Loop,交互式开发环境)

**2、 Python**
我们来看另一个例子,标准的 Python REPL。我开始输入命令,然后习惯按 `Tab` 键。瞧,插入了一个 `Tab` 字符,考虑到 `Tab` 在 Python 源代码中没有特定作用,这是一个问题。

### 好的用户体验
让我看下设计良好的 CLI 程序以及它们是如何克服这些可发现性问题的。
#### 自动补全: bpython
[Bpython](https://bpython-interpreter.org/) 是对 Python REPL 的一个很好的替代。当我运行 bpython 并开始输入时,建议会立即出现。我没用通过特殊的键盘绑定触发它,甚至没有按下 `Tab` 键。

当我出于习惯按下 `Tab` 键时,它会用列表中的第一个建议补全。这是给 CLI 设计带来可发现性性的一个很好的例子。
bpython 的另一个方面是可以展示模块和函数的文档。当我输入一个函数的名字时,它会显示这个函数附带的签名以及文档字符串。这是一个多么令人难以置信的周到设计啊。
#### 上下文感知补全:mycli
[mycli](http://mycli.net/) 是默认的 MySQL 客户端的现代替代品。这个工具对 MySQL 来说就像 bpython 之于标准 Python REPL 一样。mycli 将在你输入时自动补全关键字、表名、列和函数。
补全建议是上下文相关的。例如,在 `SELECT * FROM` 之后,只有来自当前数据库的表才会列出,而不是所有可能的关键字。

#### 模糊搜索和在线帮助: pgcli
如果您正在寻找 PostgreSQL 版本的 mycli,请看看 [pgcli](http://pgcli.com/)。 与 mycli 一样,它提供了上下文感知的自动补全。菜单中的项目使用模糊搜索缩小范围。模糊搜索允许用户输入整体字符串中的任意子字符串来尝试找到正确的匹配项。

pgcli 和 mycli 在其 CLI 中都实现了这个功能。斜杠命令的文档也作为补全菜单的一部分展示。
#### 可发现性: fish
在传统的 Unix shell(Bash、zsh 等)中,有一种搜索历史记录的方法。此搜索模式由 `Ctrl-R` 触发。当再次调用你上周运行过的命令时,例如 **ssh**或 **docker**,这是一个令人难以置信的有用的工具。 一旦你知道这个功能,你会发现自己经常会使用它。
如果这个功能是如此有用,那为什么不每次都搜索呢?这正是 [**fish** shell](https://fishshell.com/) 所做的。一旦你开始输入命令,**fish** 将开始建议与历史记录类似的命令。然后,你可以按右箭头键接受该建议。
### 命令行规矩
我已经回顾了一些解决可发现性的问题的创新方法,但也有一些基本的命令行功能应该作为每个 REPL 所实现基础功能的一部分:
* 确保 REPL 有可通过箭头键调用的历史记录。确保会话之间的历史持续存在。
* 提供在编辑器中编辑命令的方法。不管你的补全是多么棒,有时用户只需要一个编辑器来制作完美的命令来删除生产环境中所有的表。
* 使用分页器(`pager`)来管道输出。不要让用户滚动他们的终端。哦,要为分页器设置个合理的默认值。(记得添加选项来处理颜色代码。)
* 提供一种通过 `Ctrl-R` 界面或者 fish 式的自动搜索来搜索历史记录的方法。
### 总结
在第 2 节中,我将来看看 Python 中使你能够实现这些技术的特定库。同时,请查看其中一些精心设计的命令行应用程序:
* [bpython](http://bpython-interpreter.org/)或 [ptpython](http://github.com/jonathanslenders/ptpython/):具有自动补全支持的 Python REPL。
* [http-prompt](https://github.com/eliangcs/http-prompt):交互式 HTTP 客户端。
* [mycli](http://mycli.net/):MySQL、MariaDB 和 Percona 的命令行界面,具有自动补全和语法高亮。
* [pgcli](http://pgcli.com/):具有自动补全和语法高亮,是对 [psql](https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.2/static/app-psql.html) 的替代工具。
* [wharfee](http://wharfee.com/):用于管理 Docker 容器的 shell。
*了解更多: Amjith Ramanujam 在 5 月 20 日在波特兰俄勒冈州举办的 [PyCon US 2017](https://us.pycon.org/2017/) 上的谈话“[神奇的命令行工具](https://us.pycon.org/2017/schedule/presentation/518/)”。*
---
作者简介:
Amjith Ramanujam - Amjith Ramanujam 是 pgcli 和 mycli 的创始人。人们认为它们很酷,他表示笑纳赞誉。他喜欢用 Python、Javascript 和 C 编程。他喜欢编写简单易懂的代码,它们有时甚至会成功。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/5/4-terminal-apps>
作者:[Amjith Ramanujam](https://opensource.com/users/amjith) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In this article, I'll look at a shortcoming of command-line interfaces—discoverability—and a few ways to overcome this problem.
I love command lines. My first command line was DOS 6.2, back in 1997. I learned the syntax for various commands and showed off how to list hidden files in a directory (**attrib**). I would carefully craft my commands one character at a time. When I made a mistake, I would proceed to retype the command from the beginning. One fine day someone showed me how to traverse the history using the up and down arrow keys and I was blown away.
Later when I was introduced to Linux, I was pleasantly surprised that up and down arrows retained their ability to traverse the history. I was still typing each character meticulously, but by now I knew how to touch type and I was doing exceedingly well with my 55 words per minute. Then someone showed me tab-completion and changed my life once again.
In GUI applications menus, tool tips and icons are used to advertise a feature for the user. Command lines lack that ability, but there are ways to overcome this problem. Before diving into solutions, I'll look at a couple of problematic CLI apps:
### 1. MySQL
First we have our beloved MySQL REPL. I often find myself typing **SELECT * FROM** and then press **Tab** out of habit. MySQL asks whether I'd like to see all 871 possibilities. I most definitely don't have 871 tables in my database. If I said **yes**, it shows a bunch of SQL keywords, tables, functions, and so on.
### 2. Python
Let's look at another example, the standard Python REPL. I start typing a command and press the **Tab** key out of habit. Lo and behold a **Tab** character is inserted, which is a problem considering that a **Tab** character has no business in a Python source code.
## Good UX
Now let's look at well-designed CLI programs and how they overcome some discoverability problems.
### Auto-completion: bpython
[Bpython](https://bpython-interpreter.org/) is a fancy replacement for the Python REPL. When I launch bpython and start typing, suggestions appear right away. I haven't triggered them via a special key combo, not even the famed **Tab** key.
When I press the **Tab** key out of habit, it completes the first suggestion from the list. This is a great example of bringing discoverability to CLI design.
The next aspect of bpython is the way it surfaces documentation for modules and functions. When I type in the name of a function, it presents the function signature and the doc string attached with the function. What an incredibly thoughtful design.
### Context-aware completion: mycli
[Mycli](http://mycli.net) is a modern alternative to the default MySQL client. This tool does to MySQL what bpython does to the standard Python REPL. Mycli will auto-complete keywords, table names, columns, and functions as you type them.
The completion suggestions are context-sensitive. For example, after the **SELECT * FROM**, only tables from the current database are listed in the completion, rather than every possible keyword under the sun.
### Fuzzy search and online Help: pgcli
If you're looking for a PostgreSQL version of mycli, check out [pgcli](http://pgcli.com). As with mycli, context-aware auto-completion is presented. The items in the menu are narrowed down using fuzzy search. Fuzzy search allows users to type sub-strings from different parts of the whole string to try and find the right match.
Both pgcli and mycli implement this feature in their CLI. Documentation for slash commands are presented as part of the completion menu.
### Discoverability: fish
In traditional Unix shells (Bash, zsh, etc.), there is a way to search your history. This search mode is triggered by **Ctrl-R**. This is an incredibly useful tool for recalling a command you ran last week that starts with, for example, **ssh** or **docker**. Once you know this feature, you'll find yourself using it often.
If this feature is so useful, why not do this search all the time? That's exactly what the [ fish shell](https://fishshell.com/) does. As soon as you start typing a command,
**fish**will start suggesting commands from history that are similar to the one you're typing. You can then press the right arrow key to accept that suggestion.
## Command-line etiquette
I've reviewed innovative ways to solve the discoverability problems, but there are command-line basics everyone should implement as part of the basic REPL functionality:
- Make sure the REPL has a history that can be recalled via the arrow keys. Make sure the history persists between sessions.
- Provide a way to edit the command in an editor. No matter how awesome your completions are, sometimes users just need an editor to craft that perfect command to drop all the tables in production.
- Use a pager to pipe the output. Don't make the user scroll through their terminal. Oh, and use sane defaults for your pager. (Add the option to handle color codes.)
- Provide a way to search the history either via the
**Ctrl-R**interface or the**fish**-style auto-search.
## Conclusion
In [part 2](https://opensource.com/article/17/5/4-practical-python-libraries), I'll look at specific libraries in Python that allow you to implement these techniques. In the meantime, check out some of these well-designed command-line applications:
[bpython](http://bpython-interpreter.org/)or[ptpython](http://github.com/jonathanslenders/ptpython/): Fancy REPL for Python with auto-completion support.[http-prompt](https://github.com/eliangcs/http-prompt): An interactive HTTP client.[mycli](http://mycli.net): A command-line interface for MySQL, MariaDB, and Percona with auto-completion and syntax highlighting.[pgcli](http://pgcli.com): An alternative to[psql](https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.2/static/app-psql.html)with auto-completion and syntax-highlighting.[wharfee](http://wharfee.com): A shell for managing Docker containers.
*Learn more in Amjith Ramanujam's PyCon US 2017 talk, Awesome Commandline Tools, May 20th in Portland, Oregon.*
## 11 Comments |
8,527 | 完全指南:如何在 CentOS 7 中安装、配置和安全加固 FTP 服务 | http://www.tecmint.com/install-ftp-server-in-centos-7/ | 2017-05-21T10:49:00 | [
"FTP"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8527-1.html | 
FTP(文件传输协议)是一种用于通过网络[在服务器和客户端之间传输文件](http://www.tecmint.com/scp-commands-examples/)的传统并广泛使用的标准工具,特别是在不需要身份验证的情况下(允许匿名用户连接到服务器)。我们必须明白,默认情况下 FTP 是不安全的,因为它不加密传输用户凭据和数据。
在本指南中,我们将介绍在 CentOS/RHEL7 和 Fedora 发行版中安装、配置和保护 FTP 服务器( VSFTPD 代表 “Very Secure FTP Daemon”)的步骤。
请注意,本指南中的所有命令将以 root 身份运行,如果你不使用 root 帐户操作服务器,请使用 [sudo命令](http://www.tecmint.com/sudoers-configurations-for-setting-sudo-in-linux/) 获取 root 权限。
### 步骤 1:安装 FTP 服务器
1、 安装 vsftpd 服务器很直接,只要在终端运行下面的命令。
```
# yum install vsftpd
```
2、 安装完成后,服务先是被禁用的,因此我们需要手动启动,并设置在下次启动时自动启用:
```
# systemctl start vsftpd
# systemctl enable vsftpd
```
3、 接下来,为了允许从外部系统访问 FTP 服务,我们需要打开 FTP 守护进程监听的 21 端口:
```
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=21/tcp
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=ftp
# firewall-cmd --reload
```
### 步骤 2: 配置 FTP 服务器
4、 现在,我们会进行一些配置来设置并加密我们的 FTP 服务器,让我们先备份一下原始配置文件 `/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf`:
```
# cp /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf.orig
```
接下来,打开上面的文件,并将下面的选项设置相关的值:
```
anonymous_enable=NO ### 禁用匿名登录
local_enable=YES ### 允许本地用户登录
write_enable=YES ### 允许对文件系统做改动的 FTP 命令
local_umask=022 ### 本地用户创建文件所用的 umask 值
dirmessage_enable=YES ### 当用户首次进入一个新目录时显示一个消息
xferlog_enable=YES ### 用于记录上传、下载细节的日志文件
connect_from_port_20=YES ### 使用端口 20 (ftp-data)用于 PORT 风格的连接
xferlog_std_format=YES ### 使用标准的日志格式
listen=NO ### 不要让 vsftpd 运行在独立模式
listen_ipv6=YES ### vsftpd 将监听 IPv6 而不是 IPv4
pam_service_name=vsftpd ### vsftpd 使用的 PAM 服务名
userlist_enable=YES ### vsftpd 支持载入用户列表
tcp_wrappers=YES ### 使用 tcp wrappers
```
5、 现在基于用户列表文件 `/etc/vsftpd.userlist` 来配置 FTP 来允许/拒绝用户的访问。
默认情况下,如果设置了 `userlist_enable=YES`,当 `userlist_deny` 选项设置为 `YES` 的时候,`userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist` 中列出的用户被拒绝登录。
然而, 更改配置为 `userlist_deny=NO`,意味着只有在 `userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist` 显式指定的用户才允许登录。
```
userlist_enable=YES ### vsftpd 将从 userlist_file 给出的文件中载入用户名列表
userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist ### 存储用户名的文件
userlist_deny=NO
```
这并不是全部,当用户登录到 FTP 服务器时,它们会进入 chroot jail 中,这是仅作为 FTP 会话主目录的本地根目录。
接下来,我们将介绍如何将 FTP 用户 chroot 到 FTP 用户的家目录(本地 root)中的两种可能情况,如下所述。
6、 接下来添加下面的选项来限制 FTP 用户到它们自己的家目录。
```
chroot_local_user=YES
allow_writeable_chroot=YES
```
`chroot_local_user=YES` 意味着用户可以设置 chroot jail,默认是登录后的家目录。
同样默认的是,出于安全原因,vsftpd 不会允许 chroot jail 目录可写,然而,我们可以添加 `allow_writeable_chroot=YES` 来覆盖这个设置。
保存并关闭文件。
### 步骤 3: 用 SELinux 加密 FTP 服务器
7、现在,让我们设置下面的 SELinux 布尔值来允许 FTP 能读取用户家目录下的文件。请注意,这原本是使用以下命令完成的:
```
# setsebool -P ftp_home_dir on
```
然而,由于这个 bug 报告:<https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1097775>,`ftp_home_dir` 指令默认是禁用的。
现在,我们会使用 `semanage` 命令来设置 SELinux 规则来允许 FTP 读取/写入用户的家目录。
```
# semanage boolean -m ftpd_full_access --on
```
这时,我们需要重启 vsftpd 来使目前的设置生效:
```
# systemctl restart vsftpd
```
### 步骤 4: 测试 FTP 服务器
8、 现在我们会用 [useradd 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/add-users-in-linux/)创建一个 FTP 用户来测试 FTP 服务器。
```
# useradd -m -c “Ravi Saive, CEO” -s /bin/bash ravi
# passwd ravi
```
之后,我们如下使用 [echo 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/)添加用户 ravi 到文件 `/etc/vsftpd.userlist` 中:
```
# echo "ravi" | tee -a /etc/vsftpd.userlist
# cat /etc/vsftpd.userlist
```
9、 现在是时候测试我们上面的设置是否可以工作了。让我们使用匿名登录测试,我们可以从下面的截图看到匿名登录没有被允许。
```
# ftp 192.168.56.10
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : anonymous
530 Permission denied.
Login failed.
ftp>
```

*测试 FTP 匿名登录*
10、 让我们也测试一下没有列在 `/etc/vsftpd.userlist` 中的用户是否有权限登录,下面截图是没有列入的情况:
```
# ftp 192.168.56.10
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : aaronkilik
530 Permission denied.
Login failed.
ftp>
```

*FTP 用户登录失败*
11、 现在最后测试一下列在 `/etc/vsftpd.userlist` 中的用户是否在登录后真的进入了他/她的家目录:
```
# ftp 192.168.56.10
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : ravi
331 Please specify the password.
Password:
230 Login successful.
Remote system type is UNIX.
Using binary mode to transfer files.
ftp> ls
```

*用户成功登录*
警告:使用 `allow_writeable_chroot=YES` 有一定的安全隐患,特别是用户具有上传权限或 shell 访问权限时。
只有当你完全知道你正做什么时才激活此选项。重要的是要注意,这些安全性影响并不是 vsftpd 特定的,它们适用于所有提供了将本地用户置于 chroot jail 中的 FTP 守护进程。
因此,我们将在下一节中看到一种更安全的方法来设置不同的不可写本地根目录。
### 步骤 5: 配置不同的 FTP 家目录
12、 再次打开 vsftpd 配置文件,并将下面不安全的选项注释掉:
```
#allow_writeable_chroot=YES
```
接着为用户(`ravi`,你的可能不同)创建另外一个替代根目录,并将所有用户对该目录的可写权限移除:
```
# mkdir /home/ravi/ftp
# chown nobody:nobody /home/ravi/ftp
# chmod a-w /home/ravi/ftp
```
13、 接下来,在用户存储他/她的文件的本地根目录下创建一个文件夹:
```
# mkdir /home/ravi/ftp/files
# chown ravi:ravi /home/ravi/ftp/files
# chmod 0700 /home/ravi/ftp/files/
```
接着在 vsftpd 配置文件中添加/修改这些选项:
```
user_sub_token=$USER ### 在本地根目录下插入用户名
local_root=/home/$USER/ftp ### 定义任何用户的本地根目录
```
保存并关闭文件。再说一次,有新的设置后,让我们重启服务:
```
# systemctl restart vsftpd
```
14、 现在最后在测试一次查看用户本地根目录就是我们在他的家目录创建的 FTP 目录。
```
# ftp 192.168.56.10
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : ravi
331 Please specify the password.
Password:
230 Login successful.
Remote system type is UNIX.
Using binary mode to transfer files.
ftp> ls
```

*FTP 用户家目录登录成功*
就是这样了!在本文中,我们介绍了如何在 CentOS 7 中安装、配置以及加密的 FTP 服务器,使用下面的评论栏给我们回复,或者分享关于这个主题的任何有用信息。
**建议阅读:** [在 RHEL/CentOS 7 上安装 ProFTPD 服务器](/article-8504-1.html)
在下一篇文章中,我们还将向你介绍如何在 CentOS 7 中[保护使用 SSL/TLS](http://www.tecmint.com/secure-vsftpd-using-ssl-tls-on-centos/)连接的 FTP 服务器,再此之前,请继续关注 TecMint。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一名 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,即将从事 Linux 系统管理员和网页开发工作,他日前是 TecMint 技术网站的原创作者,非常喜欢使用电脑工作,坚信分享知识是一种美德。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/install-ftp-server-in-centos-7/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,528 | 如何在 Linux 下当个游戏主播 | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-capture-and-stream-your-gaming-session-on-linux/ | 2017-05-21T16:23:00 | [
"游戏",
"OBS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8528-1.html | 
也许没有那么多铁杆的游戏玩家使用 Linux,但肯定有很多 Linux 用户喜欢玩游戏。如果你是其中之一,并希望向世界展示 Linux 游戏不再是一个笑话,那么你会喜欢下面这个关于如何捕捉并且/或者以流式播放游戏的快速教程。我在这将用一个名为 “[Open Broadcaster Software Studio](https://obsproject.com/download)” 的软件,这可能是我们所能找到最好的一种。
### 捕获设置
在顶层菜单中,我们选择 “File” → “Settings”,然后我们选择 “Output” 来设置要生成的文件的选项。这里我们可以设置想要的音频和视频的比特率、新创建的文件的目标路径和文件格式。这上面还提供了粗略的质量设置。
[](https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-capture-and-stream-your-gaming-session-on-linux/big/pic_1.png)
如果我们将顶部的输出模式从 “Simple” 更改为 “Advanced”,我们就能够设置 CPU 负载,以控制 OBS 对系统的影响。根据所选的质量、CPU 能力和捕获的游戏,可以设置一个不会导致丢帧的 CPU 负载设置。你可能需要做一些试验才能找到最佳设置,但如果将质量设置为低,则不用太多设置。
[](https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-capture-and-stream-your-gaming-session-on-linux/big/pic_2.png)
接下来,我们转到设置的 “Video” 部分,我们可以设置我们想要的输出视频分辨率。注意缩小过滤(downscaling filtering )方式,因为它使最终的质量有所不同。
[](https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-capture-and-stream-your-gaming-session-on-linux/big/pic_3.png)
你可能还需要绑定热键以启动、暂停和停止录制。这特别有用,这样你就可以在录制时看到游戏的屏幕。为此,请在设置中选择 “Hotkeys” 部分,并在相应的框中分配所需的按键。当然,你不必每个框都填写,你只需要填写所需的。
[](https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-capture-and-stream-your-gaming-session-on-linux/big/pic_4.png)
如果你对流式传输感兴趣,而不仅仅是录制,请选择 “Stream” 分类的设置,然后你可以选择支持的 30 种流媒体服务,包括 Twitch、Facebook Live 和 Youtube,然后选择服务器并输入 流密钥。
[](https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-capture-and-stream-your-gaming-session-on-linux/big/pic_5.png)
### 设置源
在左下方,你会发现一个名为 “Sources” 的框。我们按下加号来添加一个新的源,它本质上就是我们录制的媒体源。在这你可以设置音频和视频源,但是图像甚至文本也是可以的。
[](https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-capture-and-stream-your-gaming-session-on-linux/big/pic_6.png)
前三个是关于音频源,接下来的两个是图像,JACK 选项用于从乐器捕获的实时音频, Media Source 用于添加文件等。这里我们感兴趣的是 “Screen Capture (XSHM)”、“Video Capture Device (V4L2)” 和 “Window Capture (Xcomposite)” 选项。
屏幕捕获选项让你选择要捕获的屏幕(包括活动屏幕),以便记录所有内容。如工作区更改、窗口最小化等。对于标准批量录制来说,这是一个适合的选项,它可在发布之前进行编辑。
我们来探讨另外两个。Window Capture 将让我们选择一个活动窗口并将其放入捕获监视器。为了将我们的脸放在一个角落,视频捕获设备用于人们可以在我们说话时可以看到我们。当然,每个添加的源都提供了一组选项来供我们实现我们最后要的效果。
[](https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-capture-and-stream-your-gaming-session-on-linux/big/pic_7.png)
添加的来源是可以调整大小的,也可以沿着录制帧的平面移动,因此你可以添加多个来源,并根据需要进行排列,最后通过右键单击执行基本的编辑任务。
[](https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-capture-and-stream-your-gaming-session-on-linux/big/pic_8.png)
### 过渡
最后,如果你正在流式传输游戏会话时希望能够在游戏视图和自己(或任何其他来源)之间切换。为此,请从右下角切换为“Studio Mode”,并添加一个分配给另一个源的场景。你还可以通过取消选中 “Duplicate scene” 并检查 “Transitions” 旁边的齿轮图标上的 “Duplicate sources” 来切换。 当你想在简短评论中显示你的脸部时,这很有帮助。
[](https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-capture-and-stream-your-gaming-session-on-linux/big/pic_9.png)
这个软件有许多过渡效果,你可以按中心的 “Quick Transitions” 旁边的加号图标添加更多。当你添加它们时,还将会提示你进行设置。
### 总结
OBS Studio 是一个功能强大的免费软件,它工作稳定,使用起来相当简单直接,并且拥有越来越多的扩展其功能的[附加插件](https://obsproject.com/forum/resources/categories/obs-studio-plugins.6/)。如果你需要在 Linux 上记录并且/或者流式传输游戏会话,除了使用 OBS 之外,我无法想到其他更好的解决方案。你有其他类似工具的经验么? 请在评论中分享也欢迎包含一个展示你技能的视频链接。:)
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-capture-and-stream-your-gaming-session-on-linux/>
作者:[Bill Toulas](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-capture-and-stream-your-gaming-session-on-linux/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # How to capture and stream your gaming session on Linux with OBS Studio
There may not be many hardcore gamers who use Linux, but there certainly are quite a lot Linux users who like to play a game now and then. If you are one of them and would like to show the world that Linux gaming isn’t a joke anymore, then you will find the following quick tutorial on how to capture and/or stream your gaming session interesting. The software tool that I will be using for this purpose is called “[Open Broadcaster Software Studio](https://obsproject.com/download)” and it is maybe the best of the kind that we have at our disposal.
## Capture settings
Through the top panel menu, we choose File → Settings and then we select the “Output” to set our preferences for the file that is to be produced. Here we can set the audio and video bitrate that we want, the destination path for the newly created file, and the file format. A rough setting for the quality is also available on this screen.
If we change the output mode on the top from “Simple” to “Advanced” we will be able to set the CPU usage load that we allow OBS to induce to our system. Depending on the selected quality, the CPU capabilities, and the game that we are capturing, there’s a CPU load setting that won’t cause the frames to drop. You may have to do some trial to find that optimal setting, but if the quality is set to low you shouldn’t worry about it.
Next, we go to the “Video” section of the settings where we can set the output video resolution that we want. Pay attention to the down-scaling filtering method as it makes all the difference in regards to the quality of the end result.
You may also want to bind hotkeys for the starting, pausing, and stopping of a recording. This is especially useful since you will be seeing your game’s screen while recording. To do this, choose the “Hotkeys” section in the settings and assign the keys that you want in the corresponding boxes. Of course, you don’t have to fill out every box, only the ones you need.
If you are interested in streaming and not just recording, then select the “Stream” category of settings and then you may select the streaming service among the 30 that are supported including Twitch, Facebook Live and Youtube, and then select a server and enter a stream key.
## Setting up the sources
On the lower left, you will find a box entitled as “Sources”. There we press the plus sign button to add a new source that is essentially our recording media source. Here you can set audio and video sources, but images and even text as well.
The first three concern audio sources, the next two images, the JACK option is for live audio capturing from an instrument, the Media Source is for the addition of a file, etc. What we are interested in for our purpose are the “Screen Capture (XSHM)”, the “Video Capture Device (V4L2)”, and the “Window Capture (Xcomposite) options.
The screen capture option let’s you select the screen that you want to capture (including the active one), so everything is recorded. Workspace changes, window minimizations, etc. It is a suitable option for a standard bulk recording that will get edited before getting released.
Let’s explore the other two. The Window Capture will let us select one of our active windows and put it into the capturing monitor. The Video Capture Device is useful in order to put our face right there on a corner so people can see us while we’re talking. Of course, each added source offers a set of options that we can fiddle with in order to achieve the result that we are after.
The added sources are re-sizable and also movable along the plane of the recording frame, so you may add multiple sources, arrange them as you like, and finally perform basic editing tasks by right-clicking on them.
## Transitioning
Finally, let’s suppose that you are streaming your gaming session and you want to be able to rotate between the game view and yourself (or any other source). To do this, change to “Studio Mode” from the lower right and add a second scene with assigned another source assigned to it. You may also rotate between sources by unchecking the “Duplicate scene” and checking the “Duplicate sources” on the gear icon next to the “Transitions”. This is helpful for when you want to show your face only for short commentary, etc.
There are many transition effects available in this software and you may add more by pressing the plus sign icon next to “Quick Transitions” in the center. As you add them, you will also be prompt to set them.
## Conclusion
The OBS Studio software is a powerful piece of free software that works stably, is fairly simple and straightforward to use, and has a growing set of [additional plugins](https://obsproject.com/forum/resources/categories/obs-studio-plugins.6/) that extend its functionality. If you need to record and/or stream your gaming session on Linux, I can’t think of a better solution other than using OBS. What is your experience with this or other similar tools? Share in the comments and feel free to also include a video link that showcases your skills. :) |
8,529 | 5 个提升你开源项目贡献者基数的方法 | https://opensource.com/article/17/1/expand-project-contributor-base | 2017-05-21T17:10:45 | [
"开源",
"贡献者"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8529-1.html | 
许多自由和开源软件项目因解决问题而出现,人们开始为它们做贡献,是因为他们也想修复遇到的问题。当项目的最终用户发现它对他们的需求有用,该项目就开始增长。并且出于分享的目的把人们吸引到同一个项目社区。
就像任何事物都是有寿命的,增长既是开源项目成功的标志,也是开源项目成功的来源。那么项目领导者和维护者如何激励贡献者基数的增长?这里有五种方法。
### 1、 提供好的文档
人们经常低估项目[文档](https://opensource.com/tags/documentation)的重要性。它是项目贡献者的主要信息来源,它会激励他们努力。信息必须是正确和最新的。它应该包括如何构建该软件、如何提交补丁、编码风格指南等步骤。
查看经验丰富的科技作家、编辑 Bob Reselman 的 [7 个创建世界级文档的规则](https://opensource.com/business/16/1/scale-14x-interview-bob-reselman)。
开发人员文档的一个很好的例子是 [Python 开发人员指南](https://docs.python.org/devguide/)。它包括清晰简洁的步骤,涵盖 Python 开发的各个方面。
### 2、 降低进入门槛
如果你的项目有[工单或 bug 追踪工具](https://opensource.com/tags/bugs-and-issues),请确保将初级任务标记为一个“小 bug” 或“起点”。新的贡献者可以很容易地通过解决这些问题进入项目。追踪工具也是标记非编程任务(如平面设计、图稿和文档改进)的地方。有许多项目成员不是每天都编码,但是却通过这种方式成为推动力。
Fedora 项目维护着一个这样的[易修复和入门级问题的追踪工具](https://fedoraproject.org/easyfix/)。
### 3、 为补丁提供常规反馈
确认每个补丁,即使它只有一行代码,并给作者反馈。提供反馈有助于吸引潜在的候选人,并指导他们熟悉项目。所有项目都应有一个邮件列表和[聊天功能](https://opensource.com/alternatives/slack)进行通信。问答可在这些媒介中发生。大多数项目不会在一夜之间成功,但那些繁荣的列表和沟通渠道为增长创造了环境。
### 4、 推广你的项目
始于解决问题的项目实际上可能对其他开发人员也有用。作为项目的主要贡献者,你的责任是为你的的项目建立文档并推广它。写博客文章,并在社交媒体上分享项目的进展。你可以从简要描述如何成为项目的贡献者开始,并在该描述中提供主要开发者文档的参考连接。此外,请务必提供有关路线图和未来版本的信息。
为了你的听众,看看由 Opensource.com 的社区经理 Rikki Endsley 写的[写作提示](https://opensource.com/business/15/10/what-stephen-king-can-teach-tech-writers)。
### 5、 保持友好
友好的对话语调和迅速的回复将加强人们对你的项目的兴趣。最初,这些问题只是为了寻求帮助,但在未来,新的贡献者也可能会提出想法或建议。让他们有信心他们可以成为项目的贡献者。
记住你一直在被人评头论足!人们会观察项目开发者是如何在邮件列表或聊天上交谈。这些意味着对新贡献者的欢迎和开放程度。当使用技术时,我们有时会忘记人文关怀,但这对于任何项目的生态系统都很重要。考虑一个情况,项目是很好的,但项目维护者不是很受欢迎。这样的管理员可能会驱使用户远离项目。对于有大量用户基数的项目而言,不被支持的环境可能导致分裂,一部分用户可能决定复刻项目并启动新项目。在开源世界中有这样的先例。
另外,拥有不同背景的人对于开源项目的持续增长和源源不断的点子是很重要的。
最后,项目负责人有责任维持和帮助项目成长。指导新的贡献者是项目的关键,他们将成为项目和社区未来的领导者。
阅读:由红帽的内容战略家 Nicole Engard 写的 [7 种让新的贡献者感到受欢迎的方式](https://opensource.com/life/16/5/sumana-harihareswara-maria-naggaga-oscon)。
---
作者简介:
Kushal Das - Kushal Das 是 Python 软件基金会的一名 CPython 核心开发人员和主管。他是一名长期的 FOSS 贡献者和导师,他帮助新人进入贡献世界。他目前在 Red Hat 担任 Fedora 云工程师。他的博客在 <https://kushaldas.in> 。你也可以在 Twitter @kushaldas 上找到他
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/1/expand-project-contributor-base>
作者:[Kushal Das](https://opensource.com/users/kushaldas) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[Bestony](https://github.com/bestony)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | So many free and open source software projects were started to solve a problem, and people began to contribute to them because they too wanted a fix to what they encountered. End users of the project find it useful for their needs, and the project grows. And that shared purpose and focus attracts people to a project's community.
Like anything with a lifespan, growth is both a sign of and the source of a project's viability. So how do project leads and maintainers encourage the growth of the contributor base? Here are five ways.
## 1. Provide good documentation
People often underestimate the importance of the [documentation](https://opensource.com/tags/documentation) of a project. It is the primary source of information for a project's contributors, and it motivates their efforts. The information has to be correct and current. It should include steps for how to build the software, for how to submit patches, a coding style guide, and more.
Check out the [7 rules for creating world class documentation](https://opensource.com/business/16/1/scale-14x-interview-bob-reselman) from long-time tech writer and editor Bob Reselman.
A good example of developer documentation is the [Python Developer's Guide](https://docs.python.org/devguide/). It includes clear and concise steps that cover every aspect of Python development.
## 2. Provide easy entry points
If your project has an issue or bug tracker, make sure to mark the beginner-level tasks as an "easy bug" or a "starting point." New contributors can easily hop on board by tackling these issues. The tracker is also the place for marking nonprogramming tasks like graphic design, artwork, and documentation improvements. There are many project members who do not code every day, but who nevertheless become a driving force by contributing through such means.
The Fedora Project maintains one such [easy fix or entrance tracker](https://fedoraproject.org/easyfix/).
## 3. Provide regular feedback for patches
Acknowledge every patch, even if it is a single line, and give feedback to the author. Providing feedback helps engage prospective candidates and guides them as they acquaint themselves with the project. All projects should have a mailing list and [a chat function](https://opensource.com/alternatives/slack) for communication. Q&A sessions can happen in these mediums. Most projects do not become successful overnight, but those that thrive have lists and communications channels that create an environment that supports growth.
## 4. Promote your project
A project started to solve a problem can actually turn out to be useful for others in development as well. As a primary contributor to the project, your responsibility is to document your project and promote it. Write blog posts, and share the project's progress on social media. You can have a short description of how to get started as a contributor to the project and in that description provide a reference to the main developer documentation. In addition, be sure to provide information on roadmaps and future releases.
Get [tips on writing](https://opensource.com/business/15/10/what-stephen-king-can-teach-tech-writers) for your audience from Rikki Endsley, community manager for Opensource.com.
## 5. Be welcoming
A friendly conversational tone with prompt replies will bolster a person's interest in your project. Initially, the questions will be only for help, but in the future new contributors may also come up with ideas or suggestions. Enable them with the confidence that they can become a contributor to the project.
Remember that you are being judged. People observe how developers of any project talk with each other on a mailing list or on chat. These are indicators of how welcoming and open people are to new contributors. When working with technology, we sometimes forget the human touch, but this is important for any project's ecosystem. Consider a case where a project is the best, but the project maintainer is not very welcoming. This manager may drive users away from the project. With a large user base, an unsupportive environment may fracture and a group of users may decide to fork and start a new project. There are successful examples of such incidents in the open source world.
Also, for the consistent growth and flow of ideas on an open source project, it's important to have people from varying backgrounds.
Finally, the project owner has the responsibility to sustain and help grow the project. Coaching new contributors is essential for the project, and they will turn out to be future leaders for the project and the community.
Read: * 7 ways to make new contributors feel welcome* by Nicole Engard, a content strategist at Red Hat.
## 2 Comments |
8,530 | Linux 极客的 Android:将你的 Android 设备变成 Linux 命令行界面 | https://www.tecmint.com/t-ui-launcher-turns-android-device-into-linux-cli/ | 2017-05-22T16:48:04 | [
"Android"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8530-1.html | 
不管你是一位命令行大师,还是只是不想让你的朋友和家人使用你的 Android 设备,那就看下 T-UI Launcher 这个程序。Unix/Linux 用户一定会喜欢这个。
T-UI Launcher 是一个免费的轻量级 Android 程序,具有类似 Linux 的命令行界面,它可将你的普通 Android 设备变成一个完整的命令行界面。对于喜欢使用基于文本的界面的人来说,这是一个简单、快速、智能的启动器。
#### T-UI Launcher 功能
下面是一些重要的功能:
* 第一次启动后展示快速使用指南。
* 快速且可完全定制。
* 提供自动补全菜单及快速、强大的别名系统。
* 此外,提供预测建议,并提供有用的搜索功能。
它是免费的,你可以从 Google Play 商店[下载并安装它](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=ohi.andre.consolelauncher),接着在 Android 设备中运行。
安装完成后,第一次启动时你会看到一个快速指南。阅读完成之后,你可以如下面那样使用简单的命令开始使用了。

*T-UI 命令行帮助指南*
要启动一个 app,只要输入几个字母,自动补全功能会在屏幕中展示可用的 app。接着点击你想打开的程序。
```
$ Telegram ### 启动 telegram
$ WhatsApp ### 启动 whatsapp
$ Chrome ### 启动 chrome
```

*T-UI 命令行使用*
要浏览你的 Android 设备状态(电池电量、wifi、移动数据),输入:
```
$ status
```

*Android 电话状态*
其它的有用命令。
```
$ uninstall telegram ### 卸载 telegram
$ search [google, playstore, youtube, files] ### 搜索在线应用或本地文件
$ wifi ### 打开或关闭 WIFI
$ cp Downloads/* Music ### 从 Download 文件夹复制所有文件到 Music 文件夹
$ mv Downloads/* Music ### 从 Download 文件夹移动所有文件到 Music 文件夹
```
就是这样了!在本篇中,我们展示了一个带有类似 Linux CLI(命令界面)的简单而有用的 Android 程序,它可以将你的常规 Android 设备变成一个完整的命令行界面。尝试一下并在下面的评论栏分享你的想法。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux 系统管理员和网络开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/t-ui-launcher-turns-android-device-into-linux-cli/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Are you a command line guru, or do you simply want to make your Android device unusable for friends and family, then check out T-UI Launcher app. Unix/Linux users will definitely love this.
**T-UI Launcher** is a free lightweight Android app with a Linux-like CLI (Command Line Interface) that turns your regular Android device into a complete command line interface. It is a simple, quick and smart launcher for those who love to work with text-based interfaces.
#### T-UI Launcher Features
Below are some of its notable features:
- Shows quick usage guide after the first launch.
- It’s fast and fully customizable.
- Offers to autocomplete menu with fast, powerful alias system.
- Also, provides predictive suggestions and offers a serviceable search function.
It is free, and you can [download and install](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=ohi.andre.consolelauncher) it from Google Play Store, then run it on your Android device.
Once you have installed it, you’ll be shown a quick usage guide when you first launch it. After reading the guide, you can start using it with simple commands as the ones explained below.
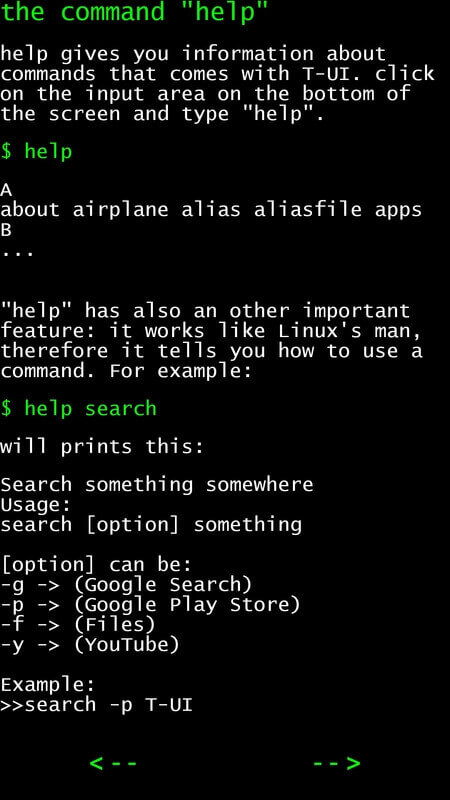
To launch an app, simply type the first few letter in its name and the auto completion functionality will show all the available apps on the screen. Then click on the one you want to open.
$ Telegram #launch telegram $ WhatsApp #launch whatsapp $ Chrome #launch chrome
To view your Android device status (battery charge, wifi, mobile data), type.
$ status
Other useful commands you can use.
$ uninstall telegram #uninstall telegram $ search [google, playstore, youtube, files] #search online apps or for a local file $ wifi #turn wifi on or off $ cp Downloads/* Music #copy all files from Download folder to Music $ mv Downloads/* Music #move all files from Download folder to Music
That’s all! In this article, we reviewed simple yet useful Android app with a Linux-like CLI (Command Line Interface) that turns your regular Android device into a complete command line interface. Give it a try and share your thoughts with us via the comment section below.
Great tool!
Can it be used with regular Linux commands like pwd, grep, find etc?
Reply@Bernhard
Not all command can work, a number of them can be used. Type the command below to see all available commands and their descriptions:
Reply$help
@Benhard with the latest update you get all the juice of a Linux power user. All command your concerned with are working and also the live notification is another great add to the tools.
Reply@STANLEE
Many thanks for the useful info, we’ll check out the lastest update of T-UI.
Reply@Aaron Kili
already joined the addict party and using t-UI launcher full-time now. Keep posting such awesome review for apps.
Reply@Stanlee
Thanks for the kind words of encouragement, we’ll always continue to bring you the best Linux related apps out there.
ReplyGot a typo at the end of example “trun WiFi on” think you meant turn WiFi on. The article was amazing and i love reading your article thanks.
ReplyOh, many thanks for the heads up. We will correct this as soon as possible.
Reply@Stanlee,
Corrected in the writeup.Thanks
ReplyVery impressive for a launcher, I loved how responsive and fast it is with autocomplete and intelliSence. It would be the perfect launcher if they add more shell command i.e ping or customization menu for adding commands and alias.
Reply@Stanlee
It’s really cool, i’ve used it ever since i installed i, the auto-completion features does the magic(i mean makes things so easy). And as you have mentioned, more shell commands need to be added to make it an absolutely Linux-like CLI.
Thanks for the feedback.
Reply |
8,531 | 8 个优秀的开源 Markdown 编辑器 | https://www.ossblog.org/markdown-editors/ | 2017-05-22T22:26:00 | [
"markdown"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8531-1.html | 
### Markdown
首先,对 Markdown 进行一个简单的介绍。Markdown 是由 John Gruber 和 Aaron Swartz 共同创建的一种轻量级纯文本格式语法。Markdown 可以让用户“以易读、易写的纯文本格式来进行写作,然后可以将其转换为有效格式的 XHTML(或 HTML)“。Markdown 语法只包含一些非常容易记住的符号。其学习曲线平缓;你可以在炒蘑菇的同时一点点学习 Markdown 语法(大约 10 分钟)。通过使用尽可能简单的语法,错误率达到了最小化。除了拥有友好的语法,它还具有直接输出干净、有效的(X)HTML 文件的强大功能。如果你看过我的 HTML 文件,你就会知道这个功能是多么的重要。
Markdown 格式语法的主要目标是实现最大的可读性。用户能够以纯文本的形式发布一份 Markdown 格式的文件。用 Markdown 进行文本写作的一个优点是易于在计算机、智能手机和个人之间共享。几乎所有的内容管理系统都支持 Markdown 。它作为一种网络写作格式流行起来,其产生一些被许多服务采用的变种,比如 GitHub 和 Stack Exchange 。
你可以使用任何文本编辑器来写 Markdown 文件。但我建议使用一个专门为这种语法设计的编辑器。这篇文章中所讨论的软件允许你使用 Markdown 语法来写各种格式的专业文档,包括博客文章、演示文稿、报告、电子邮件以及幻灯片等。另外,所有的应用都是在开源许可证下发布的,在 Linux、OS X 和 Windows 操作系统下均可用。
### Remarkable

让我们从 Remarkable 开始。Remarkable 是一个 apt 软件包的名字,它是一个相当有特色的 Markdown 编辑器 — 它并不支持 Markdown 的全部功能特性,但该有的功能特性都有。它使用和 GitHub Markdown 类似的语法。
你可以使用 Remarkable 来写 Markdown 文档,并在实时预览窗口查看更改。你可以把你的文件导出为 PDF 格式(带有目录)和 HTML 格式文件。它有强大的配置选项,从而具有许多样式,因此,你可以把它配置成你最满意的 Markdown 编辑器。
其他一些特性:
* 语法高亮
* 支持 [GitHub 风味的 Markdown](/article-8399-1.html)
* 支持 MathJax - 通过高级格式呈现丰富文档
* 键盘快捷键
在 Debian、Ubuntu、Fedora、SUSE 和 Arch 系统上均有 Remarkable 的可用的简易安装程序。
主页: <https://remarkableapp.github.io/> 许可证: MIT 许可
### Atom

毫无疑问, Atom 是一个神话般的文本编辑器。超过 50 个开源包集合在一个微小的内核上,从而构成 Atom 。伴有 Node.js 的支持,以及全套功能特性,Atom 是我最喜欢用来写代码的编辑器。Atom 的特性在[杀手级开源应用](https://www.ossblog.org/top-software/2/)的文章中有更详细介绍,它是如此的强大。但是作为一个 Markdown 编辑器,Atom 还有许多不足之处,它的默认包不支持 Markdown 的特性。例如,正如上图所展示的,它不支持等价渲染。
但是,开源拥有强大的力量,这是我强烈提倡开源的一个重要原因。Atom 上有许多包以及一些复刻,从而添加了缺失的功能特性。比如,Markdown Preview Plus 提供了 Markdown 文件的实时预览,并伴有数学公式渲染和实时重加载。另外,你也可以尝试一下 [Markdown Preview Enhanced](https://atom.io/packages/markdown-preview-enhanced)。如果你需要自动滚动特性,那么 [markdown-scroll-sync](https://atom.io/packages/markdown-scroll-sync) 可以满足你的需求。我是 [Markdown-Writer](https://atom.io/packages/markdown-writer)和 [Markdown-pdf](https://atom.io/packages/markdown-pdf)的忠实拥趸,后者支持将 Markdown 快速转换为 PDF、PNG 以及 JPEG 文件。
这个方式体现了开源的理念:允许用户通过添加扩展来提供所需的特性。这让我想起了 Woolworths 的 n 种杂拌糖果的故事。虽然需要多付出一些努力,但能收获最好的回报。
主页: <https://atom.io/> 许可证: MIT 许可
### Haroopad

Haroopad 是一个优秀的 Markdown 编辑器,是一个用于创建适宜 Web 的文档的处理器。使用 Haroopad 可以创作各种格式的文档,比如博客文章、幻灯片、演示文稿、报告和电子邮件等。Haroopad 在 Windows、Mac OS X 和 Linux 上均可用。它有 Debian/Ubuntu 的软件包,也有 Windows 和 Mac 的二进制文件。该应用程序使用 node-webkit、CodeMirror,marked,以及 Twitter 的 Bootstrap 。
Haroo 在韩语中的意思是“一天”。
它的功能列表非常可观。请看下面:
* 主题、皮肤和 UI 组件
+ 超过 30 种不同的编辑主题 - tomorrow-night-bright 和 zenburn 是近期刚添加的
+ 编辑器中的代码块的语法高亮
+ Ruby、Python、PHP、Javascript、C、HTML 和 CSS 的语法高亮支持
+ 基于 CodeMirror,这是一个在浏览器中使用 JavaScript 实现的通用文本编辑器
* 实时预览主题
+ 基于 markdown-css 的 7 个主题
* 语法高亮
+ 基于 hightlight.js 的 112 种语言以及 49 种样式
* 定制主题
+ 基于 CSS (层叠样式表)的样式
* 演示模式 - 对于现场演示非常有用
* 绘图 - 流程图和序列图
* 任务列表
* 扩展 Markdown 语法,支持 TOC(目录)、 GitHub 风味 Markdown 以及数学表达式、脚注和任务列表等
* 字体大小
+ 使用首选窗口和快捷键来设置编辑器和预览字体大小
* 嵌入富媒体内容
+ 视频、音频、3D、文本、开放图形以及 oEmbed
+ 支持大约 100 种主要的网络服务(YouTude、SoundCloud、Flickr 等)
+ 支持拖放
* 显示模式
+ 默认:编辑器|预览器,倒置:预览器|编辑器,仅编辑器,仅预览器(View -> Mode)
* 插入当前日期和时间
+ 多种格式支持(Insert -> Data & Time)
* HtML 到 Markdown
+ 拖放你在 Web 浏览器中选择好的文本
* Markdown 解析选项
* 大纲预览
* 纯粹主义者的 Vim 键位绑定
* Markdown 自动补全
* 导出为 PDF 和 HTML
* 带有样式的 HTML 复制到剪切板可用于所见即所得编辑器
* 自动保存和恢复
* 文件状态信息
* 换行符或空格缩进
* (一、二、三)列布局视图
* Markdown 语法帮助对话框
* 导入和导出设置
* 通过 MathJax 支持 LaTex 数学表达式
* 导出文件为 HTML 和 PDF
* 创建扩展来构建自己的功能
* 高效地将文件转换进博客系统:WordPress、Evernote 和 Tumblr 等
* 全屏模式-尽管该模式不能隐藏顶部菜单栏和顶部工具栏
* 国际化支持:英文、韩文、西班牙文、简体中文、德文、越南文、俄文、希腊文、葡萄牙文、日文、意大利文、印度尼西亚文土耳其文和法文
主页 <http://pad.haroopress.com/> 许可证: GNU GPL v3 许可
### StackEdit

StackEdit 是一个功能齐全的 Markdown 编辑器,基于 PageDown(该 Markdown 库被 Stack Overflow 和其他一些 Stack 交流网站使用)。不同于在这个列表中的其他编辑器,StackEdit 是一个基于 Web 的编辑器。在 Chrome 浏览器上即可使用 StackEdit 。
特性包括:
* 实时预览 HTML,并通过绑定滚动连接特性来将编辑器和预览的滚动条相绑定
* 支持 Markdown Extra 和 GitHub 风味 Markdown,Prettify/Highlight.js 语法高亮
* 通过 MathJax 支持 LaTex 数学表达式
* 所见即所得的控制按键
* 布局配置
* 不同风格的主题支持
* la carte 扩展
* 离线编辑
* 可以与 Google 云端硬盘(多帐户)和 Dropbox 在线同步
* 一键发布到 Blogger、Dropbox、Gist、GitHub、Google Drive、SSH 服务器、Tumblr 和 WordPress
主页: <https://stackedit.io/> 许可证: Apache 许可
### MacDown

MacDown 是在这个列表中唯一一个只运行在 macOS 上的全特性编辑器。具体来说,它需要在 OX S 10.8 或更高的版本上才能使用。它在内部使用 Hoedown 将 Markdown 渲染成 HTML,这使得它的特性更加强大。Heodown 是 Sundown 的一个复活复刻。它完全符合标准,无依赖,具有良好的扩展支持和 UTF-8 感知。
MacDown 基于 Mou,这是专为 Web 开发人员设计的专用解决方案。
它提供了良好的 Markdown 渲染,通过 Prism 提供的语言识别渲染实现代码块级的语法高亮,MathML 和 LaTex 渲染,GTM 任务列表,Jekyll 前端以及可选的高级自动补全。更重要的是,它占用资源很少。想在 OS X 上写 Markdown?MacDown 是我针对 Web 开发者的开源推荐。
主页: <https://macdown.uranusjr.com/> 许可证: MIT 许可
### ghostwriter

ghostwriter 是一个跨平台的、具有美感的、无干扰的 Markdown 编辑器。它内建了 Sundown 处理器支持,还可以自动检测 pandoc、MultiMarkdown、Discount 和 cmark 处理器。它试图成为一个朴实的编辑器。
ghostwriter 有许多很好的功能设置,包括语法高亮、全屏模式、聚焦模式、主题、通过 Hunspell 进行拼写检查、实时字数统计、实时 HTML 预览、HTML 预览自定义 CSS 样式表、图片拖放支持以及国际化支持。Hemingway 模式按钮可以禁用退格键和删除键。一个新的 “Markdown cheat sheet” HUD 窗口是一个有用的新增功能。主题支持很基本,但在 [GitHub 仓库上](https://github.com/jggouvea/ghostwriter-themes)也有一些可用的试验性主题。
ghostwriter 的功能有限。我越来越欣赏这个应用的通用性,部分原因是其简洁的界面能够让写作者完全集中在策划内容上。这一应用非常值得推荐。
ghostwirter 在 Linux 和 Windows 系统上均可用。在 Windows 系统上还有一个便携式的版本可用。
主页: <https://github.com/wereturtle/ghostwriter> 许可证: GNU GPL v3 许可
### Abricotine

Abricotine 是一个为桌面构建的、旨在跨平台且开源的 Markdown 编辑器。它在 Linux、OS X 和 Windows 上均可用。
该应用支持 Markdown 语法以及一些 GitHub 风味的 Markdown 增强(比如表格)。它允许用户直接在文本编辑器中预览文档,而不是在侧窗栏。
该应用有一系列有用的特性,包括拼写检查、以 HTML 格式保存文件或把富文本复制粘贴到邮件客户端。你也可以在侧窗中显示文档目录,展示语法高亮代码、以及助手、锚点和隐藏字符等。它目前正处于早期的开发阶段,因此还有一些很基本的 bug 需要修复,但它值得关注。它有两个主题可用,如果有能力,你也可以添加你自己的主题。
主页: <http://abricotine.brrd.fr/> 许可证: GNU 通用公共许可证 v3 或更高许可
### ReText

ReText 是一个简单而强大的 Markdown 和 reStructureText 文本编辑器。用户可以控制所有输出的格式。它编辑的文件是纯文本文件,但可以导出为 PDF、HTML 和其他格式的文件。ReText 官方仅支持 Linux 系统。
特性包括:
* 全屏模式
* 实时预览
* 同步滚动(针对 Markdown)
* 支持数学公式
* 拼写检查
* 分页符
* 导出为 HTML、ODT 和 PDF 格式
* 使用其他标记语言
主页: <https://github.com/retext-project/retext> 许可证: GNU GPL v2 或更高许可
---
via: <https://www.ossblog.org/markdown-editors/>
作者:[Steve Emms](https://www.ossblog.org/author/steve/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # Write Markdown with 8 Exceptional Open Source Editors
### Markdown
By way of a succinct introduction, Markdown is a lightweight plain text formatting syntax created by John Gruber together with Aaron Swartz. Markdown offers individuals “to write using an easy-to-read, easy-to-write plain text format, then convert it to structurally valid XHTML (or HTML)”. Markdown’s syntax consists of easy to remember symbols. It has a gentle learning curve; you can literally learn the Markdown syntax in the time it takes to fry some mushrooms (that’s about 10 minutes). By keeping the syntax as simple as possible, the risk of errors is minimized. Besides being a friendly syntax, it has the virtue of producing clean and valid (X)HTML output. If you have seen my HTML, you would know that’s pretty essential.
The main goal for the formatting syntax is to make it extremely readable. Users should be able to publish a Markdown-formatted document as plain text. Text written in Markdown has the virtue of being easy to share between computers, smart phones, and individuals. Almost all content management systems support Markdown. It’s popularity as a format for writing for the web has also led to variants being adopted by many services such as GitHub and Stack Exchange.
Markdown can be composed in any text editor. But I recommend an editor purposely designed for this syntax. The software featured in this roundup allows an author to write professional documents of various formats including blog posts, presentations, reports, email, slides and more. All of the applications are, of course, released under an open source license. Linux, OS X and Windows’ users are catered for.
### Remarkable
Let’s start with Remarkable. An apt name. Remarkable is a reasonably featured Markdown editor – it doesn’t have all the bells and whistles, but there’s nothing critical missing. It has a syntax like Github flavoured markdown.
With this editor you can write Markdown and view the changes as you make them in the live preview window. You can export your files to PDF (with a TOC) and HTML. There are multiple styles available along with extensive configuration options so you can configure it to your heart’s content.
Other features include:
- Syntax highlighting
- GitHub Flavored Markdown support
- MathJax support – render rich documents with advanced formatting
- Keyboard shortcuts
There are easy installers available for Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, SUSE and Arch systems.
Homepage: [https://remarkableapp.github.io/](https://remarkableapp.github.io/)
License: MIT License
### Atom
Make no bones about it, Atom is a fabulous text editor. Atom consists of over 50 open source packages integrated around a minimal core. With Node.js support, and a full set of features, Atom is my preferred way to edit code. It features in our [Killer Open Source Apps](https://www.ossblog.org/top-software/2/), it is that masterly. But as a Markdown editor Atom leaves a lot to be desired – its default packages are bereft of Markdown specific features; for example, it doesn’t render equations, as illustrated in the graphic above.
But here lies the power of open source and one of the reasons I’m a strong advocate of openness. There are a plethora of packages, some forks, which add the missing functionality. For example, Markdown Preview Plus provides a real-time preview of markdown documents, with math rendering and live reloading. Alternatively, you might try [Markdown Preview Enhanced](https://atom.io/packages/markdown-preview-enhanced). If you need an auto-scroll feature, there’s [markdown-scroll-sync](https://atom.io/packages/markdown-scroll-sync). I’m a big fan of [Markdown-Writer](https://atom.io/packages/markdown-writer) and [markdown-pdf](https://atom.io/packages/markdown-pdf) the latter converts markdown to PDF, PNG and JPEG on the fly.
The approach embodies the open source mentality, allowing the user to add extensions to provide only the features needed. Reminds me of Woolworths pick ‘n’ mix sweets. A bit more effort, but the best outcome.
Homepage: [https://atom.io/](https://atom.io/)
License: MIT License
### Haroopad
Haroopad is an excellent markdown enabled document processor for creating web-friendly documents. Author various formats of documents such as blog articles, slides, presentations, reports, and e-mail. Haroopad runs on Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. There are Debian/Ubuntu packages, and binaries for Windows and Mac. The application uses node-webkit, CodeMirror, marked, and Twitter Bootstrap.
Haroo means “A Day” in Korean.
The feature list is rather impressive; take a look below:
- Themes, Skins and UI Components
- Over 30 different themes to edit – tomorrow-night-bright and zenburn are recent additions
- Syntax highlighting in fenced code block on editor
- Ruby, Python, PHP, Javascript, C, HTML, CSS
- Based on CodeMirror, a versatile text editor implemented in JavaScript for the browser
- Live Preview themes
- 7 themes based markdown-css
- Syntax Highlighting
- 112 languages & 49 styles based on highlight.js
- Custom Theme
- Style based on CSS (Cascading Style Sheet)
- Presentation Mode – useful for on the spot presentations
- Draw diagrams – flowcharts, and sequence diagrams
- Tasklist
- Enhanced Markdown syntax with TOC, GitHub Flavored Markdown and extensions, mathematical expressions, footnotes, tasklists, and more
- Font Size
- Editor and Viewer font size control using Preference Window & Shortcuts
- Embedding Rich Media Contents
- Video, Audio, 3D, Text, Open Graph and oEmbed
- About 100 major internet services (YouTube, SoundCloud, Flickr …) Support
- Drag & Drop support
- Display Mode
- Default (Editor:Viewer), Reverse (Viewer:Editor), Only Editor, Only Viewer (View > Mode)
- Insert Current Date & Time
- Various Format support (Insert > Date & Time)
- HTML to Markdown
- Drag & Drop your selected text on Web Browser
- Options for markdown parsing
- Outline View
- Vim Key-binding for purists
- Markdown Auto Completion
- Export to PDF, HTML
- Styled HTML copy to clipboard for WYSIWYG editors
- Auto Save & Restore
- Document state information
- Tab or Spaces for Indentation
- Column (Single, Two and Three) Layout View
- Markdown Syntax Help Dialog.
- Import and Export settings
- Support for LaTex mathematical expressions using MathJax
- Export documents to HTML and PDF
- Build extensions for making your own feature
- Effortlessly transform documents into a blog system: WordPress, Evernote and Tumblr,
- Full screen mode – although the mode fails to hide the top menu bar or the bottom toolbar
- Internationalization support: English, Korean, Spanish, Chinese Simplified, German, Vietnamese, Russian, Greek, Portuguese, Japanese, Italian, Indonesian, Turkish, and French
Homepage: [http://pad.haroopress.com/](http://pad.haroopress.com/)
License: GNU GPL v3
### StackEdit
StackEdit is a full-featured Markdown editor based on PageDown, the Markdown library used by Stack Overflow and the other Stack Exchange sites. Unlike the other editors in this roundup, StackEdit is a web based editor. A Chrome app is also available.
Features include:
- Real-time HTML preview with Scroll Link feature to bind editor and preview scrollbars
- Markdown Extra/GitHub Flavored Markdown support and Prettify/Highlight.js syntax highlighting
- LaTeX mathematical expressions using MathJax
- WYSIWYG control buttons
- Configurable layout
- Theming support with different themes available
- A la carte extensions
- Offline editing
- Online synchronization with Google Drive (multi-accounts) and Dropbox
- One click publish on Blogger, Dropbox, Gist, GitHub, Google Drive, SSH server, Tumblr, and WordPress
Homepage: [https://stackedit.io/](https://stackedit.io/)
License: Apache License
### MacDown
MacDown is the only editor featured in this roundup which only runs on macOS. Specifically, it requires OS X 10.8 or later. Hoedown is used internally to render Markdown into HTML which gives an edge to its performance. Hoedown is a revived fork of Sundown, it is fully standards compliant with no dependencies, good extension support, and UTF-8 aware.
MacDown is based on Mou, a proprietary solution designed for web developers.
It offers good Markdown rendering, syntax highlighting for fenced code blocks with language identifiers rendered by Prism, MathML and LaTeX rendering, GTM task lists, Jekyll front-matter, and optional advanced auto-completion. And above all, it isn’t a resource hog. Want to write Markdown on OS X? MacDown is my open source recommendation for web developers.
Homepage: [https://macdown.uranusjr.com/](https://macdown.uranusjr.com/)
License: MIT License
### ghostwriter
ghostwriter is a cross-platform, aesthetic, distraction-free Markdown editor. It has built-in support for the Sundown processor, but can also auto-detect Pandoc, MultiMarkdown, Discount and cmark processors. It seeks to be an unobtrusive editor.
ghostwriter has a good feature set which includes syntax highlighting, a full-screen mode, a focus mode, themes, spell checking with Hunspell, a live word count, live HTML preview, and custom CSS style sheets for HTML preview, drag and drop support for images, and internalization support. A Hemingway mode button disables backspace and delete keys. A new Markdown cheat sheet HUD window is a useful addition. Theme support is pretty basic, but there are some experimental themes available at this [GitHub repository](https://github.com/jggouvea/ghostwriter-themes).
ghostwriter is an under-rated utility. I have come to appreciate the versatility of this application more and more, in part because of its spartan interface helps the writer fully concentrate on curating content. Recommended.
ghostwriter is available for Linux and Windows. There is also a portable version available for Windows.
Homepage: [https://github.com/wereturtle/ghostwriter](https://github.com/wereturtle/ghostwriter)
License: GNU GPL v3
### Abricotine
Abricotine is a promising cross-platform open-source markdown editor built for the desktop. It is available for Linux, OS X and Windows.
The application supports markdown syntax combined with some Github-flavored Markdown enhancements (such as tables). It lets users preview documents directly in the text editor as opposed to a side pane.
The tool has a reasonable set of features including a spell checker, the ability to save documents as HTML or copy rich text to paste in your email client. You can also display a document table of content in the side pane, display syntax highlighting for code, as well as helpers, anchors and hidden characters. It is at a fairly early stage of development with some basic bugs that need fixing, but it is one to keep an eye on. There are 2 themes, with the ability to add your own.
Homepage: [http://abricotine.brrd.fr/](http://abricotine.brrd.fr/)
License: GNU General Public License v3 or later
### ReText
ReText is a simple but powerful editor for Markdown and reStructuredText. It gives users the power to control all output formatting. The files it works with are plain text files, however it can export to PDF, HTML and other formats. ReText is officially supported on Linux only.
Features include:
- Full screen mode
- Live previews
- Synchronised scrolling (for Markdown)
- Support for math formulas
- Spell checking
- Page breaks
- Export to HTML, ODT and PDF
- Use other markup languages
Homepage: [https://github.com/retext-project/retext](https://github.com/retext-project/retext)
License: GNU GPL v2 or higher
Nice and informative roundup.
StackEdit does not seem to be maintained anymore.
StackEdit’s last commit was March 2016 – so less than an year. I don’t see anything to indicate it has been abandoned. And it’s not uncommon for open source software to have a hiatus in development but then kickstart back. And being open source, anyone can fork.
Visual Studio Code (https://code.visualstudio.com/) also deserves a mention.
And for those on Windows, MarkdownPad (http://www.markdownpad.com/) and Markpad (https://github.com/Code52/DownmarkerWPF) are also good options. And especially so because, they are actual native apps rather than web apps disguising as native apps.
Thanks for putting this list together! I do notes in markdown and have basics a huge fan of atom + packages. I’m excited about trying haroopad now though…
Let us know how you get on with haroopad if you have the time.
For markdown, I have used ReText for a while, as I prefer native rather than browser/electron apps. I recently began to use [Typora](http://typora.io/) which is available as an AppImage and has a lovely distraction-free interface.
I suggest Skrifa too, its been around for quite a while but lacks exposure.
Wow, thanks a lot! it’s really awesome that you use and like Skrifa 🙂 hope you continue enjoying it!
Qownnotes is not only a terrific markdown editor but also syncs with ownCloud
http://www.qownnotes.org/
Thank you for your kind words! 😉
MarkdownEdit is the editor I use (mainly for writing posts in WordPress) http://mike-ward.net/markdownedit/
Unfortunately, that editor only runs on Windows. But I’ll have a look at it.
I just tried Haroopad with some MathJax files I created with MacDown. Right now, it is not usable for me because it leaves line breaks in the input as line breaks in the output, instead of making longer lines. I would be grateful If anyone knows how to fix this.
[…] Write Markdown with 8 Exceptional Open Source Editors – recommended Markdown Text Editors. Markdown Here– a useful Google Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Opera, and Thunderbird extension that lets you write email in Markdown and render them before sending. It also supports syntax highlighting (just specify the language in a fenced code block). pandoc – converts files from one markup format into another. Dillinger – a cloud-enabled, mobile-ready, offline-storage, AngularJS powered HTML5 Markdown editor. StackEdit – a full-featured, open-source Markdown editor based on PageDown. […]
Perhaps you could consider MindForger – it is more than just Markdown editor, it is Markdown IDE.
https://www.mindforger.com
With MindForger you can edit multiple documents, perform refactoring/cloning/extraction of sections, use document/section templates and more.
* Single or dual pane interface
* Extra Markdown features: diagrams, GitHub flavor, source code syntax highlighting
* Markdown editor syntax highlighting
* Code Syntax Highlighting
* Math blocks Tex/LaTex support
* Customizable themes |
8,533 | 人工智能正快速入侵我们生活的五个方面 | https://opensource.com/article/17/3/5-big-ways-ai-rapidly-invading-our-lives | 2017-05-23T09:35:00 | [
"人工智能",
"AI"
] | /article-8533-1.html |
>
> 让我们来看看我们已经被人工智能包围的五个真实存在的方面。
>
>
>

开源项目[正在助推](https://www.linux.com/news/open-source-projects-are-transforming-machine-learning-and-ai)人工智能(AI)进步,而且随着技术的成熟,我们将听到更多关于 AI 如何影响我们生活的消息。你有没有考虑过 AI 是如何改变你周围的世界的?让我们来看看我们日益被我们所改变的世界,以及大胆预测一下 AI 对未来影响。
### 1. AI 影响你的购买决定
最近 [VentureBeat](https://twitter.com/venturebeat) 上的一篇文章,[“AI 将如何帮助我们解读千禧一代”](http://venturebeat.com/2017/03/16/how-ai-will-help-us-decipher-millennials/)吸引了我的注意。我承认我对人工智能没有思考太多,也没有费力尝试解读千禧一代,所以我很好奇,希望了解更多。事实证明,文章标题有点误导人,“如何卖东西给千禧一代”或许会是一个更准确的标题。
根据这篇文章,千禧一代是“一个令人垂涎的年龄阶段的人群,全世界的市场经理都在争抢他们”。通过分析网络行为 —— 无论是购物、社交媒体或其他活动 - 机器学习可以帮助预测行为模式,这将可以变成有针对性的广告。文章接着解释如何对物联网和社交媒体平台进行挖掘形成数据点。“使用机器学习挖掘社交媒体数据,可以让公司了解千禧一代如何谈论其产品,他们对一个产品类别的看法,他们对竞争对手的广告活动如何响应,还可获得很多数据,用于设计有针对性的广告,"这篇文章解释说。AI 和千禧一代成为营销的未来并不是什么很令人吃惊的事,但是 X 一代和婴儿潮一代,你们也逃不掉呢!(LCTT 译注:X 一代指出生于 20 世纪 60 年代中期至 70 年代末的美国人,婴儿潮是指二战结束后,1946 年初至 1964 年底出生的人)
>
> 人工智能根据行为变化,将包括城市人在内的整个人群设为目标群体。
>
>
>
例如, [Raconteur 上](https://twitter.com/raconteur)的一篇文章 —— “AI 将怎样改变购买者的行为”中解释说,AI 在网上零售行业最大的力量是它能够迅速适应客户行为不断变化的形势。人工智能创业公司 [Fluid AI](http://www.fluid.ai/) 首席执行官 Abhinav Aggarwal 表示,他公司的软件被一个客户用来预测顾客行为,有一次系统注意到在暴风雪期间发生了一个变化。“那些通常会忽略在一天中发送的电子邮件或应用内通知的用户现在正在打开它们,因为他们在家里没有太多的事情可做。一个小时之内,AI 系统就适应了新的情况,并在工作时间开始发送更多的促销材料。”他解释说。
AI 正在改变我们怎样花钱和为什么花钱,但是 AI 是怎样改变我们挣钱的方式的呢?
### 2. 人工智能正在改变我们如何工作
[Fast 公司](https://opensource.com/article/17/3/5-big-ways-ai-rapidly-invading-our-lives)最近的一篇文章“2017 年人工智能将如何改变我们的生活”中说道,求职者将会从人工智能中受益。作者解释说,除更新薪酬趋势之外,人工智能将被用来给求职者发送相关职位空缺信息。当你应该升职的时候,你很可能会得到一个升职的机会。
人工智能也可以被公司用来帮助新入职的员工。文章解释说:“许多新员工在刚入职的几天内会获得大量信息,其中大部分都留不下来。” 相反,机器人可能会随着时间的推移,当新员工需要相关信息时,再向他一点点“告知信息”。
[Inc.](https://twitter.com/Inc) 有一篇文章[“没有偏见的企业:人工智能将如何重塑招聘机制”](http://www.inc.com/bill-carmody/businesses-beyond-bias-how-ai-will-reshape-hiring-practices.html),观察了人才管理解决方案提供商 [SAP SuccessFactors](https://www.successfactors.com/en_us.html) 是怎样利用人工智能作为一个工作描述“偏见检查器”,以及检查员工赔偿金的偏见。
[《Deloitte 2017 人力资本趋势报告》](https://dupress.deloitte.com/dup-us-en/focus/human-capital-trends.html?id=us:2el:3pr:dup3575:awa:cons:022817:hct17)显示,AI 正在激励组织进行重组。Fast 公司的文章[“AI 是怎样改变公司组织的方式”](https://www.fastcompany.com/3068492/how-ai-is-changing-the-way-companies-are-organized)审查了这篇报告,该报告是基于全球 10,000 多名人力资源和商业领袖的调查结果。这篇文章解释说:"许多公司现在更注重文化和环境的适应性,而不是聘请最有资格的人来做某个具体任务,因为知道个人角色必须随 AI 的实施而发展。" 为了适应不断变化的技术,组织也从自上而下的结构转向多学科团队,文章说。
### 3. AI 正在改变教育
>
> AI 将使所有教育生态系统的利益相关者受益。
>
>
>
尽管教育预算正在缩减,但是教室的规模却正在增长。因此利用技术的进步有助于提高教育体系的生产率和效率,并在提高教育质量和负担能力方面发挥作用。根据 VentureBeat 上的一篇文章[“2017 年人工智能将怎样改变教育”](http://venturebeat.com/2017/02/04/how-ai-will-transform-education-in-2017/),今年我们将看到 AI 对学生们的书面答案进行评分,机器人回答学生的问题,虚拟个人助理辅导学生等等。文章解释说:“AI 将惠及教育生态系统的所有利益相关者。学生将能够通过即时的反馈和指导学习地更好,教师将获得丰富的学习分析和对个性化教学的见解,父母将以更低的成本看到他们的孩子的更好的职业前景,学校能够规模化优质的教育,政府能够向所有人提供可负担得起的教育。"
### 4. 人工智能正在重塑医疗保健
2017 年 2 月 [CB Insights](https://twitter.com/CBinsights) 的一篇文章挑选了 106 个医疗保健领域的人工智能初创公司,它们中的很多在过去几年中提高了第一次股权融资。这篇文章说:“在 24 家成像和诊断公司中,19 家公司自 2015 年 1 月起就首次公开募股。”这份名单上有那些从事于远程病人监测,药物发现和肿瘤学方面人工智能的公司。”
3 月 16 日发表在 TechCrunch 上的一篇关于 AI 进步如何重塑医疗保健的文章解释说:“一旦对人类的 DNA 有了更好的理解,就有机会更进一步,并能根据他们特殊的生活习性为他们提供个性化的见解。这种趋势预示着‘个性化遗传学’的新纪元,人们能够通过获得关于自己身体的前所未有的信息来充分控制自己的健康。”
本文接着解释说,AI 和机器学习降低了研发新药的成本和时间。部分得益于广泛的测试,新药进入市场需要 12 年以上的时间。这篇文章说:“机器学习算法可以让计算机根据先前处理的数据来‘学习’如何做出预测,或者选择(在某些情况下,甚至是产品)需要做什么实验。类似的算法还可用于预测特定化合物对人体的副作用,这样可以加快审批速度。”这篇文章指出,2015 年旧金山的一个创业公司 [Atomwise](http://www.atomwise.com/) 一天内完成了可以减少埃博拉感染的两种新药物的分析,而不是花费数年时间。
>
> AI 正在帮助发现、诊断和治疗新疾病。
>
>
>
另外一个位于伦敦的初创公司 [BenevolentAI](https://twitter.com/benevolent_ai) 正在利用人工智能寻找科学文献中的模式。这篇文章说:“最近,这家公司找到了两种可能对 Alzheimer 起作用的化合物,引起了很多制药公司的关注。"
除了有助于研发新药,AI 正在帮助发现、诊断和治疗新疾病。TechCrunch 上的文章解释说,过去是根据显示的症状诊断疾病,但是现在 AI 正在被用于检测血液中的疾病特征,并利用对数十亿例临床病例分析进行深度学习获得经验来制定治疗计划。这篇文章说:“IBM 的 Watson 正在与纽约的 Memorial Sloan Kettering 合作,消化理解数十年来关于癌症患者和治疗方面的数据,为了向治疗疑难的癌症病例的医生提供和建议治疗方案。”
### 5. AI 正在改变我们的爱情生活
有 195 个国家的超过 5000 万活跃用户通过一个在 2012 年推出的约会应用程序 [Tinder](https://twitter.com/Tinder) 找到潜在的伴侣。在一个 [Forbes 采访播客](https://www.forbes.com/podcasts/the-forbes-interview/#5e962e5624e1)中,Tinder 的创始人兼董事长 Sean Rad spoke 与 Steven Bertoni 对人工智能是如何正在改变人们约会进行过讨论。在[关于此次采访的文章](https://www.forbes.com/sites/stevenbertoni/2017/02/14/tinders-sean-rad-on-how-technology-and-artificial-intelligence-will-change-dating/#4180fc2e5b99)中,Bertoni 引用了 Rad 说的话,他说:“可能有这样一个时刻,Tinder 可以很好的推测你会感兴趣的人,在组织约会中还可能会做很多跑腿的工作”,所以,这个 app 会向用户推荐一些附近的同伴,并更进一步,协调彼此的时间安排一次约会,而不只是向用户显示一些有可能的同伴。
>
> 我们的后代真的可能会爱上人工智能。
>
>
>
你爱上了 AI 吗?我们的后代真的可能会爱上人工智能。Raya Bidshahri 发表在 [Singularity Hub](https://twitter.com/singularityhub) 的一篇文章“AI 将如何重新定义爱情”说,几十年的后,我们可能会认为爱情不再受生物学的限制。
Bidshahri 解释说:“我们的技术符合摩尔定律,正在以惊人的速度增长 —— 智能设备正在越来越多地融入我们的生活。”,他补充道:“到 2029 年,我们将会有和人类同等智慧的 AI,而到 21 世纪 40 年代,AI 将会比人类聪明无数倍。许多人预测,有一天我们会与强大的机器合并,我们自己可能会变成人工智能。”他认为在这样一个世界上那些是不可避免的,人们将会接受与完全的非生物相爱。
这听起来有点怪异,但是相比较于未来机器人将统治世界,爱上 AI 会是一个更乐观的结果。Bidshahri 说:“对 AI 进行编程,让他们能够感受到爱,这将使我们创造出更富有同情心的 AI,这可能也是避免很多人忧虑的 AI 大灾难的关键。”
这份 AI 正在入侵我们生活各领域的清单只是涉及到了我们身边的人工智能的表面。哪些 AI 创新是让你最兴奋的,或者是让你最烦恼的?大家可以在文章评论区写下你们的感受。
---
Rikki Endsley - Rikki Endsley 是开源社区 Opensource.com 的管理员。在过去,她曾做过 Red Hat 开源和标准(OSAS)团队社区传播者;自由技术记者;USENIX 协会的社区管理员;linux 权威杂志 ADMIN 和 Ubuntu User 的合作出版者,还是杂志 Sys Admin 和 UnixReview.com 的主编。在 Twitter 上关注她:@rikkiends。
(图片来源: opensource.com)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/3/5-big-ways-ai-rapidly-invading-our-lives>
作者:[Rikki Endsley](https://opensource.com/users/rikki-endsley) 译者:[zhousiyu325](https://github.com/zhousiyu325) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
8,536 | 朝鲜 180 局的网络战部门让西方国家忧虑 | http://www.abc.net.au/news/2017-05-21/north-koreas-unit-180-cyber-warfare-cell-hacking/8545106 | 2017-05-24T08:43:00 | [
"黑客",
"朝鲜"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8536-1.html | *本文译自澳大利亚广播公司相关文章,不代表本站及译者、编辑的态度。*

据脱北者、官方和网络安全专家的消息,朝鲜的情报机关有一个叫做 180 局的特殊部门, 这个部门已经发起过多起胆大且成功的网络战。
近几年,朝鲜被指责在美国、韩国,及其周边的几个国家对金融网络发起多起在线袭击。
网络安全研究人员称他们找到了这个月全球性感染了 150 多个国家 30 多万台计算机的[“想哭”勒索病毒和朝鲜网络战有关联的技术证据](http://www.abc.net.au/news/2017-05-16/researchers-link-wannacry-to-north-korea/8531110)。
平壤称该指控是“荒谬的”。
对朝鲜的关键指控是指朝鲜与一个叫做<ruby> 拉撒路 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Lazarus </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的黑客组织有联系,这个组织是在去年在孟加拉国中央银行网络抢劫了 8100 万美元,并在 2014 年攻击了索尼的好莱坞工作室的网络。
美国政府指责朝鲜对索尼公司的黑客袭击,同时美国政府对平壤在孟加拉国银行的盗窃行为提起公诉并要求立案。
由于没有确凿的证据、没有犯罪指控并不能够立案。朝鲜之后也否认了索尼公司和该银行的袭击与其有关。
朝鲜是世界上最封闭的国家之一,它秘密行动的一些细节很难获得。
但研究这个封闭国家的专家和流落到韩国和一些西方国家的的脱北者已经给出了或多或少的提示。
### 黑客们喜欢以雇员身份来作为掩护
金恒光,一位朝鲜前计算机教授,2004 叛逃到韩国,他仍然有着韩国内部的消息来源,他说平壤的网络战目的在于通过侦察总局(RGB)下属的一个叫做 180 局来筹集资金,这个局主要是负责海外的情报机构。
金教授称,“180 局负责入侵金融机构通过漏洞从银行账户提取资金”。
他之前也说过,他以前的一些学生已经加入了朝鲜的网络战略司令部,即朝鲜的网络部队。
>
> “黑客们到海外寻找比朝鲜更好的互联网服务的地方,以免留下痕迹,” 金教授补充说。
>
>
>
他说他们经常用贸易公司、朝鲜的海外分公司和在中国和东南亚合资企业的雇员来作为掩护。
位于华盛顿的战略与国际研究中心的一位名为 James Lewis 的朝鲜专家称,平壤首先把黑客攻击作为间谍活动的工具,然后对韩国和美国的目的进行政治干扰。
他说,“索尼公司事件之后,他们改变方法,通过用黑客来支持犯罪活动来形成国内坚挺的货币经济政策。”
“目前为止,网上毒品,假冒伪劣,走私,都是他们惯用的伎俩”。
[**VIDEO:** 你遇到过勒索病毒吗? (ABC News)](http://www.abc.net.au/news/2017-05-15/have-you-been-hit-by-ransomware/8527854)
### 韩国声称拥有“大量的证据”
美国国防部称在去年提交给国会的一个报告中显示,朝鲜将网络视为有成本效益的、不对称的、可否认的工具,它能够应付来自报复性袭击的很小风险,因为它的“网络”大部分是和因特网分离的。
>
> 报告中说,“它可能从第三方国家使用互联网基础设施。”
>
>
>
韩国政府称,他们拥有朝鲜网络战行动的大量证据。
“朝鲜进行网络战通过第三方国家来掩护网络袭击的来源,并且使用他们的信息和通讯技术设施”,韩国外交部副部长安总基在书面评论中告诉路透社。
除了孟加拉银行抢劫案,他说怀疑平壤也与菲律宾、越南和波兰的银行袭击有关。
去年六月,警察称朝鲜袭击了 160 个韩国公司和政府机构,入侵了大约 14 万台计算机,暗中在它的对手的计算机中植入恶意代码,为进行大规模网络攻击的长期计划而准备。
朝鲜也被怀疑在 2014 年对韩国核反应堆操作系统进行阶段性网络攻击,尽管朝鲜否认与其无关。
根据在一个韩国首尔的杀毒软件厂商 hauri 的高级安全研究员 Simon Choi 的说法,网络袭击是来自于朝鲜在中国的一个基地。
Choi 先生,是一位对朝鲜的黑客能力有广泛的研究的人,他称,“他们在那里行动,不管他们究竟在做什么,他们拥有中国的 IP 地址”。
[题图:脱北者说, 平壤的网络战攻击目的旨在为一个叫做“180局”的部门来筹集资金。(路透社:Damir Sagolj, file)](http://www.abc.net.au/news/2017-05-21/military-trucks-trhough-pyongyang/8545134)
---
via: <http://www.abc.net.au/news/2017-05-21/north-koreas-unit-180-cyber-warfare-cell-hacking/8545106>
作者:[www.abc.net.au](http://www.abc.net.au) 译者:[hwlog](https://github.com/hwlog) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,537 | 如何在 Linux 中删除超大的(100-200GB)文件 | https://www.tecmint.com/delete-huge-files-in-linux/ | 2017-05-24T09:41:00 | [
"删除"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8537-1.html | 
通常,要[在 Linux 终端删除一个文件](/article-8123-1.html),我们使用 rm 命令(删除文件)、shred 命令(安全删除文件)、wipe 命令(安全擦除文件)或者 secure-deletion 工具包(一个安全文件删除工具集合)。
我们可以使用上述任意的工具来处理相对较小的文件。如果我们想要删除超大的文件/文件夹,比如大概 100-200GB,在删除文件(I/O 调度)所花费的时间以及 RAM 占用量方面,就没有你想的那么简单。
在本教程中,我们会解释如何在 Linux 中有效率并可靠地删除大文件/文件夹。
**建议阅读:** [5 个在 Linux 中清空或者删除大文件的方法](/article-8024-1.html)
我们的主要目标是使用一种不会在删除大文件时拖慢系统的技术,合理地占用 I/O。我们可以用 ionice 命令实现这个目标。
### 在 Linux 中使用 ionice 命令删除超大(200GB)文件
ionice 是一个可以对另一个程序设置或获取 I/O 调度级别和优先级的有用程序。如果没有给出参数或者只有 `-p` 参数,那么 ionice 将会查询该进程的当前的 I/O 调度级别以及优先级。
如果我们给出命令名称,如 `rm` 命令,它将使用给定的参数运行此命令。要获取或设置调度参数,请指定[进程的 PID],如下:
```
# ionice -p PID
```
要指定名字或者调度的数字,使用(0 表示无、1 表示实时、2 表示尽力、3 表示空闲)下面的命令。
以下命令表示 `rm` 会属于空闲 I/O 级别,并且只在其他进程不使用的时候使用 I/O:
```
---- Deleting Huge Files in Linux -----
# ionice -c 3 rm /var/logs/syslog
# ionice -c 3 rm -rf /var/log/apache
```
如果系统中没有很多空闲时间,那么我们希望使用尽力调度级别,并且使用低优先级:
```
# ionice -c 2 -n 6 rm /var/logs/syslog
# ionice -c 2 -n 6 rm -rf /var/log/apache
```
注意:要使用安全的方法删除大文件,我们可以使用先前提到的 `shred`、`wipe` 以及 secure-deletion 工具包中的不同工具,而不是 `rm` 命令。
**建议阅读:**[3 个在 Linux 中永久/安全删除文件/文件夹的方法](/article-8123-1.html)
要获取更多信息,查阅 `ionice` 的手册页:
```
# man ionice
```
就是这样了!你脑海里还有其他的方法么?在评论栏中与我们分享。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux 系统管理员和网络开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/delete-huge-files-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In the realm of Linux terminal operations, a range of [Linux commands](https://www.tecmint.com/most-used-linux-commands/) are at our disposal for the purpose of effectively deleting or removing files.
When it comes to the task of file elimination, we commonly rely on the [“rm” command](https://www.tecmint.com/remove-directory-linux/), which swiftly erases files from the system. For enhanced security and assurance, the “**shred**” command comes into play, ensuring the thorough and secure deletion of a file, leaving no trace behind.
Furthermore, the “**wipe**” command offers an added layer of protection, securely erasing files beyond any possibility of recovery. In more complex scenarios or for advanced file deletion needs, we can turn to the [secure deletion tools](https://www.tecmint.com/permanently-and-securely-delete-files-directories-linux/) designed to meet the highest standards of secure file deletion.
With these powerful options at our disposal, we can confidently and effectively remove files from the Linux terminal environment.
We can use any of the above utilities to deal with relatively small files. What if we want to delete/remove a huge file/directory say about **100-200GB**?
This may not be as easy as it seems, in terms of the time taken to remove the file (I/O scheduling) as well as the amount of RAM consumed while carrying out the operation.
In this tutorial, we will explain how to efficiently and reliably [delete huge files/directories](https://www.tecmint.com/delete-large-directory-linux/) in Linux.
The main aim here is to use a technique that will not slow down the system while removing a huge file, resulting to reasonable I/O. We can achieve this using the **ionice command**.
### Deleting HUGE (200GB) Files in Linux Using ionice Command
**ionice** is a useful program that sets or gets the I/O scheduling class and priority for another program. If no arguments or just `-p`
is given, ionice will query the current I/O scheduling class and priority for that process.
If we give a command name such as **rm command**, it will run this command with the given arguments. To specify the [process IDs of running processes](https://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-processes-memory-ram-cpu-usage/) for which to get or set the scheduling parameters, run this:
# ionice -p PID
To specify the name or number of the scheduling class to use (**0** for none, **1** for real-time, **2** for best-effort, **3** for idle) the command below.
This means that **rm** will belong to the idle I/O class and only uses I/O when any other process does not need it:
---- Deleting Huge Files in Linux -----# ionice -c 3 rm /var/logs/syslog # ionice -c 3 rm -rf /var/log/apache
If there won’t be much idle time on the system, then we may want to use the best-effort scheduling class and set a low priority like this:
# ionice -c 2 -n 6 rm /var/logs/syslog # ionice -c 2 -n 6 rm -rf /var/log/apache
**Note**: To delete huge files using a secure method, we may use the **shred**, **wipe** and various tools in the secure-deletion toolkit mentioned earlier on, instead of the [rm command](https://www.tecmint.com/linux-rm-command-examples/).
For more info, look through the ionice man page:
# man ionice
That’s it for now! What other methods do you have in mind for the above purpose? Use the comment section below to share with us.
This only work do you are using cfq as io scheduler
Reply@Emmanuel
We’ll check this out. Thanks for the feedback.
ReplyWhy not simply use “
Replynice” and set a low priority? Would that be sufficiently efficient? Linux will know how to handle the priorities so when the cpu is not running high, it will give more cpu time to the rm command. I don’t see any significant difference.@Lethargos
A reasonable way to accomplish the job, we’ll surely test this out. Many thanks for writing back.
Replyecho ” ” > huge_file && rm huge_file
Reply@User
Okay, don’t you think without using
Replyionice, this command will cause high I/O loads and gradually slow down the system? Thanks for sharing this.No – command like:
> huge-file
No take many I/O
This is short way to make zero size file in bash
Reply@Out
Okay, thanks for the useful tip.
Reply |
8,539 | 一位老极客的眼中的开发和部署 | https://opensource.com/article/17/1/difference-between-development-deployment | 2017-05-25T13:08:00 | [
"编程",
"开发",
"部署",
"Smalltalk"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8539-1.html | 
多年前,我曾是一名 Smalltalk 程序员,这种经验让我以一种不同的视角来观察编程的世界,例如,需要花时间来适应源代码应该存储在文本文件中的这种做法。
我们作为程序员通常会区分“开发”和“部署”,特别是我们在开发的地方所使用的工具不同于我们在之后部署软件时的地点和工具时。而在 Smalltalk 世界里,没有这样的区别。
Smalltalk 构建于虚拟机包含了你的开发环境(IDE、调试器、文本编辑器、版本控制等)的思路之上,如果你需要修改任何一处代码,你得修改内存中运行副本。如果需要的话,你可以为运行中的机器做个快照;如果你想分发你的代码,你可以发送一个运行中的机器的镜像副本(包括 IDE、调试器、文本编辑器、版本控制等)给用户。这就是上世纪 90 年代软件开发的方式(对我们中的一些人来说)。
如今,部署环境与开发环境有了很大的不同。起初,你不要期望那里(指部署环境)有任何开发工具。一旦部署,就没有版本控制、没有调试、没有开发环境。有的是记录和监视,这些在我们的开发环境中都没有,而有一个“构建管道”,它将我们的软件从开发形式转换为部署形式。作为一个例证,Docker 容器则试图重新找回上世纪 90 年代 Smalltalk 程序员部署体验的那种简单性,而避免同样的开发体验。
我想如果 Smalltalk 世界是我唯一的编程方面的体验,让我无法区分开发和部署环境,我可能会偶尔回顾一下它。但是在我成为一名 Smalltalk 程序员之前,我还是一位 APL 程序员,这也是一个可修改的虚拟机镜像的世界,其中开发和部署是无法区分的。因此,我相信,在当前的时代,人们编辑单独的源代码文件,然后运行构建管道以创建在编辑代码时尚不存在的部署作品,然后将这些作品部署给用户。我们已经以某种方式将这种反模式的软件开发制度化,而不断发展的软件环境的需求正在迫使我们找回到上世纪 90 年代的更有效的技术方法。因此才会有 Docker 的成功,所以,我需要提出我的建议。
我有两个建议:我们在运行时系统中实现(并使用)版本控制,以及,我们通过更改运行中的系统来开发软件,而不是用新的运行系统替换它们。这两个想法是相关的。为了安全地更改正在运行的系统,我们需要一些版本控制功能来支持“撤消”功能。也许公平地说,我只提出了一个建议。让我举例来说明。
让我们开始假设一个静态网站。你要修改一些 HTML 文件。你应该如何工作?如果你像大多数开发者一样,你会有两个,也许三个网站 - 一个用于开发,一个用于 QA(或者预发布),一个用于生产。你将直接编辑开发实例中的文件。准备就绪后,你将把你的修改“部署”到预发布实例。在用户验收测试之后,你将再次部署,这次是生产环境。
使用 Occam 的 Razor,让我们可以避免不必要地创建实例。我们需要多少台机器?我们可以使用一台电脑。我们需要多少台 web 服务器?我们可以使用具有多个虚拟主机的单台 web 服务器。如果不使用多个虚拟主机的话,我们可以只使用单个虚拟主机吗?那么我们就需要多个目录,并需要使用 URL 的顶级路径来区分不同的版本,而不是虚拟主机名。但是为什么我们需要多个目录?因为 web 服务器将从文件系统中提供静态文件。我们的问题是,目录有三个不同的版本,我们的解决方案是创建目录的三个不同的副本。这不是正是 Subversion 和 Git 这样的版本控制系统解决的问题吗?制作目录的多个副本以存储多个版本的策略回到了版本控制 CVS 之前的日子。为什么不使用比如说一个空的的 Git 仓库来存储文件呢?要这样做,web 服务器将需要能够从 git 仓库读取文件(参见 [mod\_git](https://github.com/r0ml/mod_git))。
这将是一个支持版本控制的运行时系统。
使用这样的 web 服务器,使用的版本可以由 cookie 来标识。这样,任何人都可以推送到仓库,用户将继续看到他们发起会话时所分配的版本。版本控制系统有不可改变的提交; 一旦会话开始,开发人员可以在不影响正在运行的用户的情况下快速推送更改。开发人员可以重置其会话以跟踪他们的新提交,因此开发人员或测试人员就可能如普通用户一样查看在同台服务器上同一个 URL 上正在开发或正在测试的版本。作为偶然的副作用,A/B 测试仅仅是将不同的用户分配给不同的提交的情况。所有用于管理多个版本的 git 设施都可以在运行环境中发挥作用。当然,git reset 为我们提供了前面提到的“撤销”功能。
为什么不是每个人都这样做?
一种可能性是,诸如版本控制系统的工具没有被设计为在生产环境中使用。例如,给某人推送到测试分支而不是生产分支的许可是不可能的。对这个方案最常见的反对是,如果发现了一个漏洞,你会想要将某些提交标记为不可访问。这将是另一种更细粒度的权限的情况;开发人员将具有对所有提交的读取权限,但外部用户不会。我们可能需要对现有工具进行一些额外的改造以支持这种模式,但是这些功能很容易理解,并已被设计到其他软件中。例如,Linux (或 PostgreSQL)实现了对不同用户的细粒度权限的想法。
随着云环境变得越来越普及,这些想法变得更加相关:云总是在运行。例如,我们可以看到,AWS 中等价的 “文件系统”(S3)实现了版本控制,所以你可能有一个不同的想法,使用一台 web 服务器提供来自 S3 的资源文件,并根据会话信息选择不同版本的资源文件。重要的并不是哪个实现是最好的,而是支持这种运行时版本控制的愿景。
部署的软件环境应该是“版本感知”的原则,应该扩展到除了服务静态文件的 web 服务器之外的其他工具。在将来的文章中,我将介绍版本库,数据库和应用程序服务器的方法。
---
作者简介:
Robert M. Lefkowitz - Robert(即 r0ml)是一个喜欢复杂编程语言的编程语言爱好者。 他是一个提高清晰度、提高可靠性和最大限度地简化的编程技术收藏家。他通过让计算机更加容易获得来使它普及化。他经常演讲中世纪晚期和早期文艺复兴对编程艺术的影响。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/1/difference-between-development-deployment>
作者:[Robert M. Lefkowitz](https://opensource.com/users/r0ml) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[Bestony](https://github.com/Bestony)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | For many years, I was a Smalltalk programmer, and that experience gives me a different viewpoint from which to observe ideas in the programming world. For example, the idea that source code should be stored in text files took some getting used to.
We as programmers often make a distinction between "development" and "deployment," specifically the idea that we develop software in one place using tools that are different from the place and tools that we use after we deploy the software. In the Smalltalk world, there is no such difference.
Smalltalk was built on the idea of a virtual machine that contained your development environment (IDE, debugger, text editor, version control, and more), and you if you had to modify any code, you would modify the in-memory running copy. If you wanted to snapshot your running machine you could do so, and if you wanted to distribute your code, you would send a copy of your running machine image (including the IDE, debugger, text editor, version control, and more) to the user. That's how software development worked (for some of us) in the '90s.
Today, the deployment environment is vastly different from the development environment. For starters, you have no expectation that any of your development tools are there. Once deployed, there is no version control, no debugging, no development environment. There is logging and monitoring, which we didn't have in our development environment, and there is a "build pipeline," which transforms our software from the form in which we develop into the form which we deploy. For example, Docker containers are an attempt to recapture some of the simplicity of the 1990's Smalltalk programmer's deployment experience without aspiring to do the same for the development experience.
I suppose that if the Smalltalk world had been my only programming metaphor experience that failed to differentiate between development and deployment environments, I might have looked back on it as a fluke. But before I was a Smalltalk programmer I was an APL programmer, and that was also a world of hackable virtual machine images in which development and deployment were indistinguishable. Therefore, I'm rather convinced that the current world in which people edit separate source code files and then run build pipelines to create deployment artifacts that didn't exist while editing code, and then deploy those artifacts to users, is the fluke. We have somehow institutionalized this software development anti-pattern, and the demands of the evolving software landscape are pressuring us to find a way back to the more effective techniques of the 1990's. Hence the success of Docker. Hence the need for what I am about to propose.
I have two suggestions: that we implement (and use) version control in runtime systems, and that we develop software by making changes to running systems, instead of replacing them with a new running system. These two ideas are related. In order to make changes safely to a running system, we need some versioning capability to support an "undo" capability. Perhaps it would be fair to say that I make only one suggestion. Let me illustrate by way of example.
Let's start by imagining a static website. You want to change some HTML files. How should that work? If you're like most developers, you'll have two, maybe three, sites—one for development, one for QA (or staging), and one for production. You'll directly edit the files in the development instance. When you're ready, you'll "deploy" your changes to the staging instance. After user acceptance testing, you'll deploy again, this time to production.
Using Occam's Razor, let's avoid creating entities needlessly. How many machines do we need? We could use a single computer. How many web servers do we need? We could use a single web server with multiple virtual hosts. Instead of multiple virtual hosts, could we use a single virtual host? Then we would need multiple directories and need to use the top-level path of the URL to differentiate the different versions instead of the virtual host name. But why do we need multiple directories? Because the web server will serve static assets from the file system. The problem we have is that there are three different versions of a directory, and our solution is to make three different copies of the directory. Is this not the very problem that version control systems like Subversion and Git are meant to solve? The strategy of making multiple copies of a directory to store multiple versions hearkens back to the days before CVS. Why not use, say, a bare Git repository to store the files? Because in order to do so, the web server would need to be able to read files from a git repository (see [mod_git](https://github.com/r0ml/mod_git)).
And that would be a run time system supporting versioning.
With such a web server, the version being served would be identified by, for example, a cookie identifying it. In this way, anybody could push to the one repository, and users would continue to see the version that they were assigned when they initiated their session. Version control systems have immutable commits; once a session begins, developers could cheerfully push changes whenever they felt like it without affecting running users. Developers could reset their sessions to track their new commits, so a developer or tester could be looking at a version in development or under test at the same URL and from the same server as the regular users. As a fortuitous side effect, A/B tests are simply a case of assigning different users to different commits. All of the git facilities for managing multiple versions are brought to bear in running environments. And, of course, a git reset offers us that "undo" capability we mentioned earlier.
Why doesn't everyone do this?
One possibility is that tools like version control systems were not designed to be used in production environments. For example, giving someone permission to push to the testing branch but not the production branch is not possible. The most common objection to this scheme is that if a vulnerability were discovered, you would want to mark certain commits as inaccessible. This would be another case of finer grained permissions; developers would have read access to all commits, but external users would not. We might need some additional engineering for existing tools to support this paradigm, but the features are easily understood and have been engineered into other software artifacts. For example, Linux (or PostgreSQL) implements the idea of fine grained permissions for different users.
As cloud environments become more common, these ideas become more relevant: the cloud is always running. We can see, for example, that the AWS equivalent of a "file system" (S3) implements versioning, so you might have a variation of this idea that involves a web server serving assets from S3, and using session information to select different versions of those assets. The important idea is not which implementation is the best, but the aspiration to support runtime versioning.
The principle that deployed software environments should be "version aware" extends to other tools besides web servers serving static assets. In future articles, I will reflect upon approaches for versioning libraries, databases, and application servers.
*Learn more in Robert Lefkowitz's talk at linux.conf.au 2017 ( #lca2017) in Hobart: Keeping Linux Great.*
## 2 Comments |
8,540 | 如何使用 Cream 提高 Vim 的用户友好性 | https://opensource.com/article/17/5/stir-bit-cream-make-vim-friendlier | 2017-05-25T16:10:51 | [
"Vim",
"Cream"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8540-1.html |
>
> Cream 附加包通过把一个更加熟悉的“面孔”置于 Vim 文本编辑器之上,同时保留 Vim 的功能,使其更加容易使用
>
>
>

大约 10 年前,我既使用 Emacs 进行文本编辑,也使用 Vim 进行文本编辑。说到底,我的确是一个热衷于 Emacs 的家伙。尽管 Emacs 在我的心里占据了很重要的地位,但我知道, Vim 也不赖。
一些人,或者像我一样的人,在技术方面有些笨手笨脚。多年来,我和一些 Linux 新手交流,了解到他们想使用 Vim,但是却失望的发现, Vim 编辑器和他们在其它操作系统上使用过的编辑器不一样。
但是,当我把 Cream 介绍给他们以后,他们的失望就变成了满意。Cream 是 Vim 的一个附加包,它使得 Vim 更加容易使用。Cream 让这些 Linux 新手变成了 Vim 的坚决拥护者和忠心用户。
让我们来看一看 Cream 是什么以及它是如何让 Vim 变得更加容易使用的。
### Cream 的安装
在安装 Cream 之前,你需要先在你的电脑上安装好 Vim 和 GVim 的 GUI 组件。我发现最容易完成这件事的方法是使用 Linux 版本的包管理器。
安装好 Vim 以后,便可[下载 Cream 的安装程序](http://cream.sourceforge.net/download.html),或者你也可以再次使用 Linux 发行版的包管理器进行安装。
安装好 Cream 以后,你可以从应用菜单选择它(比如,**Applications**->**Cream**)或者在程序启动器中输入 `Cream`,从而启动 Cream 。

### Cream 的使用
如果你之前已经使用过 Gvim,那么你会注意到, Cream 几乎没改变该编辑器的外观和感觉。最大的不同是 Cream 的菜单栏和工具栏,它们取代了 Gvim 陈旧的菜单栏和工具栏,新的菜单栏和工具栏的外观和功能分组看起来和其它编辑器的一样。
Cream 的菜单栏对用户隐藏了更多的技术选项,比如指定一个编译器的能力,以及运行 `make` 命令的能力。当你通过使用 Cream 更加熟悉 Vim 以后,你只需要从 **Setting**->**Preferences**->**Behavior** 选择选项,就可以更容易地访问这些特性。有了这些选项,你可以(如果你想)体验到一个兼有 Cream 和传统 Vim 二者优点的强大编辑器。
Cream 并不是仅由菜单驱动。尽管编辑器的功能仅有单击或双击两种方式,但是你也可以使用常见的键盘快捷键来执行操作,比如 `CTRL-O`(打开一个文件),`CTRL-C`(复制文本)。你不需要在几种模式之间切换,也不需要记住一些很难记住的命令。
Cream 开始运行以后,打开一个文件,或者新建一个文件,然后就可以开始输入了。几个我向他们介绍过 Cream 的人说,虽然 Cream 保留了 Vim 的许多典型风格,但是 Cream 使用起来更加舒服。

并不是说 Cream 是 Vim 的简化版,远远不是。事实上, Cream 保留了 Vim 的全部特性,同时,它还有[一系列其他有用的特性](http://cream.sourceforge.net/featurelist.html)。我发现的 Cream 的一些有用的特性包括:
* 一个标签式界面
* 语法高亮(特别是针对 Markdown、LaTeX 和 HTML)
* 自动修正拼写错误
* 字数统计
* 内建文件浏览器
Cream 本身也有许多附加包,可以给编辑器增加一些新的特性。这些特性包括文本加密、清理电子邮件内容,甚至还有一个使用教程。老实说,我还没有发现哪一个附加包是真正有用的,不过你的感受可能会有所不同。
我曾听过一些 Vi/Vim 的狂热分子谴责 Cream “降低”(这是他们的原话)了 Vi/Vim 编辑器的水准。的确,Cream 并不是为他们设计的。它是为那些想快速使用 Vim ,同时保留他们曾经使用过的编辑器的外观和感觉的人准备的。在这种情况下, Cream 是值得赞赏的,它使得 Vim 更加容易使用,更加广泛的被人们使用。
(题图 : opensource.com)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/5/stir-bit-cream-make-vim-friendlier>
作者:[Scott Nesbitt](https://opensource.com/users/scottnesbitt) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | About 10 years ago, I split my text editing time between Emacs and Vim. That said, I was and definitely still am an Emacs guy. But while Emacs has always had an edge in my affections, I know that Vim is no slouch.
So do other people—even those who, like me, are all thumbs technically. Over the years, I've talked to a few new Linux users who wanted to use Vim but were a bit disappointed that it doesn't act like the text editors they've used on other operating systems.
That disappointment changed to satisfaction when I introduced them to Cream, an add-on for Vim that makes it easier to use. Cream turned each of them into diehard Vim users.
Let's take a look at Cream and how it makes Vim easier to use.
## Getting going with Cream
Before you can install Cream, you'll need Vim and GVim GUI components installed on your computer. I find the easiest way to do that is to use your Linux distribution's package manager.
Once you have Vim installed, grab [the installer](http://cream.sourceforge.net/download.html) for Cream or, again, turn to your distribution's package manager.
Once Cream is installed, you can fire it up by selecting the entry from the application menu (for example, **Applications > Cream**) or by typing **cream** into your program launcher.
## Using Cream
If you've used GVim before, you'll notice that Cream doesn't change the editor's look and feel too much. The biggest cosmetic differences are Cream's menu bar and toolbar, which replace the stock GVim menu bar and toolbar with ones that look and group functions like their counterparts in other applications.
Cream's menus hide a lot of the more techie options—like the ability to specify a compiler and the **Make** command—from the user. As you get more familiar with Vim by using Cream, however, you can make more of those features more easily accessible by selecting an option from the **Settings > Preferences > Behavior** menu. With those options, you could (if you want to) wind up with an editor that behaves as a hybrid of Cream and traditional Vim.
Cream isn't only driven by its menus. While the editor's functions are only a click or two away, you can also use common keyboard shortcuts to perform actions—for example, **CTRL-O** (to open a file) or **CTRL-C** (to copy text). There's no need to shift between modes or remember Vim's somewhat cryptic commands.
With Cream running, get to work by opening a file or creating a new one. Then start typing. A couple or three of the people I've introduced to Cream have said that while it retains much of the classic styling of Vim, Cream feels more comfortable to use.
That's not to say Cream dumbs down or waters down Vim. Far from it. You still retain all of Vim's features, along with [a long list of others](http://cream.sourceforge.net/featurelist.html). Some of the features of Cream that I find useful include:
- A tabbed interface
- Syntax highlighting (especially when working with Markdown, LaTeX, and HTML)
- Auto correction of spelling mistakes
- Word count
- Built-in file explorer
Cream also comes with a number of add-ons that give the editor some additional features. Those features include the ability to encrypt text and to clean up the body of emails, and there's even a typing tutor. To be honest, I haven't found any of the add-ons to be all that useful. Your mileage might vary, though.
I've heard a few Vi/Vim purists pooh-pooh Cream for "dumbing down*"* (their words) the editor. Let's be honest: Cream isn't for them. It's for someone who wants to quickly get up and running with Vim while retaining the look and feel of the editors they're used to. In that way, Cream succeeds admirably. It makes Vim a lot more accessible and usable to a wider range of people.
## 4 Comments |
8,541 | 怎样在 Linux 命令行下杀死一个进程 | https://www.linux.com/learn/intro-to-linux/2017/5/how-kill-process-command-line | 2017-05-26T15:58:23 | [
"进程",
"kill",
"killall"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8541-1.html |
>
> Linux 的命令行里面有用来停止正在运行的进程的所有所需工具。Jack Wallen 将为您讲述细节。
>
>
>

想像一下:你打开了一个程序(可能来自于你的桌面菜单或者命令行),然后开始使用这个程序,没想到程序会锁死、停止运行、或者意外死机。你尝试再次运行该程序,但是它反馈说原来的进程没有完全关闭。
你该怎么办?你要结束进程。但该如何做?不管你信与不信,最好的解决方法大都在命令行里。值得庆幸的是, Linux 有供用户杀死错误的进程的每个必要的工具,然而,你在执行杀死进程的命令之前,你首先需要知道进程是什么。该如何处理这一类的任务。一旦你能够掌握这种工具,它实际是十分简单的……
让我来介绍给你这些工具。
我来概述的步骤是每个 Linux 发行版都能用的,不论是桌面版还是服务器版。我将限定只使用命令行,请打开你的终端开始输入命令吧。
### 定位进程
杀死一个没有响应的进程的第一个步骤是定位这个进程。我用来定位进程的命令有两个:`top` 和 `ps` 命令。`top` 是每个系统管理员都知道的工具,用 `top` 命令,你能够知道到所有当前正在运行的进程有哪些。在命令行里,输入 `top` 命令能够就看到你正在运行的程序进程(图1)

*图 1: top 命令给出你许多的信息。*
从显示的列表中你能够看到相当重要的信息,举个例子,Chrome 浏览器反映迟钝,依据我们的 `top` 命令显示,我们能够辨别的有四个 Chrome 浏览器的进程在运行,进程的 pid 号分别是 3827、3919、10764 和 11679。这个信息是重要的,可以用一个特殊的方法来结束进程。
尽管 `top` 命令很是方便,但也不是得到你所要信息最有效的方法。 你知道你要杀死的 Chrome 进程是那个,并且你也不想看 `top` 命令所显示的实时信息。 鉴于此,你能够使用 `ps` 命令然后用 `grep` 命令来过滤出输出结果。这个 `ps` 命令能够显示出当前进程列表的快照,然后用 `grep` 命令输出匹配的样式。我们通过 `grep` 命令过滤 `ps` 命令的输出的理由很简单:如果你只输入 `ps` 命令,你将会得到当前所有进程的列表快照,而我们需要的是列出 Chrome 浏览器进程相关的。所以这个命令是这个样子:
```
ps aux | grep chrome
```
这里 `aux` 选项如下所示:
* a = 显示所有用户的进程
* u = 显示进程的用户和拥有者
* x = 也显示不依附于终端的进程
当你搜索图形化程序的信息时,这个 `x` 参数是很重要的。
当你输入以上命令的时候,你将会得到比图 2 更多的信息,而且它有时用起来比 `top` 命令更有效。

*图 2:用 ps 命令来定位所需的内容信息。*
### 结束进程
现在我们开始结束进程的任务。我们有两种可以帮我们杀死错误的进程的信息。
* 进程的名字
* 进程的 ID (PID)
你用哪一个将会决定终端命令如何使用,通常有两个命令来结束进程:
* `kill` - 通过进程 ID 来结束进程
* `killall` - 通过进程名字来结束进程
有两个不同的信号能够发送给这两个结束进程的命令。你发送的信号决定着你想要从结束进程命令中得到的结果。举个例子,你可以发送 `HUP`(挂起)信号给结束进程的命令,命令实际上将会重启这个进程。当你需要立即重启一个进程(比如就守护进程来说),这是一个明智的选择。你通过输入 `kill -l` 可以得到所有信号的列表,你将会发现大量的信号。

*图 3: 可用的结束进程信号。*
最经常使用的结束进程的信号是:
| Signal Name | Single Value | Effect |
| --- | --- | --- |
| SIGHUP | 1 | 挂起 |
| SIGINT | 2 | 键盘的中断信号 |
| SIGKILL | 9 | 发出杀死信号 |
| SIGTERM | 15 | 发出终止信号 |
| SIGSTOP | 17, 19, 23 | 停止进程 |
好的是,你能用信号值来代替信号名字。所以你没有必要来记住所有各种各样的信号名字。
所以,让我们现在用 `kill` 命令来杀死 Chrome 浏览器的进程。这个命令的结构是:
```
kill SIGNAL PID
```
这里 SIGNAL 是要发送的信号,PID 是被杀死的进程的 ID。我们已经知道,来自我们的 `ps` 命令显示我们想要结束的进程 ID 号是 3827、3919、10764 和 11679。所以要发送结束进程信号,我们输入以下命令:
```
kill -9 3827
kill -9 3919
kill -9 10764
kill -9 11679
```
一旦我们输入了以上命令,Chrome 浏览器的所有进程将会成功被杀死。
我们有更简单的方法!如果我们已经知道我们想要杀死的那个进程的名字,我们能够利用 `killall` 命令发送同样的信号,像这样:
```
killall -9 chrome
```
附带说明的是,上边这个命令可能不能捕捉到所有正在运行的 Chrome 进程。如果,运行了上边这个命令之后,你输入 `ps aux | grep chrome` 命令过滤一下,看到剩下正在运行的 Chrome 进程有那些,最好的办法还是回到 `kIll` 命令通过进程 ID 来发送信号值 `9` 来结束这个进程。
### 结束进程很容易
正如你看到的,杀死错误的进程并没有你原本想的那样有挑战性。当我让一个顽固的进程结束的时候,我趋向于用 `killall`命令来作为有效的方法来终止,然而,当我让一个真正的活跃的进程结束的时候,`kill`命令是一个好的方法。
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/learn/intro-to-linux/2017/5/how-kill-process-command-line>
作者:[JACK WALLEN](https://www.linux.com/users/jlwallen) 译者:[hwlog](https://github.com/hwlog) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,542 | Python-mode:在 Vim 编辑器中开发 Python 应用的 Vim 插件 | https://www.tecmint.com/python-mode-a-vim-editor-plugin/ | 2017-05-26T16:23:00 | [
"Python",
"Vim"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8542-1.html | 
Python-mode 是一个 Vim 插件,它使你能够在 [Vim 编辑器](https://www.tecmint.com/vi-editor-usage/)中更快的利用包括 pylint、rope、pydoc、pyflakes、pep8、autopep8、pep257 和 mccable 在内的各种库来写 Python 代码,这些库提供了一些编码功能,比如静态分析、特征重构、折叠、补全和文档等。
**推荐阅读:** [如何用 Bash-Support 插件将 Vim 编辑器打造成编写 Bash 脚本的 IDE](/article-8467-1.html)
这个插件包含了所有你在 Vim 编辑器中可以用来开发 Python 应用的特性。
### Python-mode 的特性
它包含下面这些值得一提的特性:
* 支持 Python 2.6+ 至 Python 3.2 版本
* 语法高亮
* 提供 virtualenv 支持
* 支持 Python 式折叠
* 提供增强的 Python 缩进
* 能够在 Vim 中运行 Python 代码
* 能够添加/删除断点
* 支持 Python 代码的快捷移动和操作
* 能够在运行的同时检查代码(pylint、pyflakes、pylama ……)
* 支持自动修复 PEP8 错误
* 允许在 Python 文档中进行搜索
* 支持代码重构
* 支持强代码补全
* 支持定义跳转
在这篇教程中,我将阐述如何在 Linux 中为 Vim 安装设置 Python-mode,从而在 Vim 编辑器中开发 Python 应用。
### 如何在 Linux 系统中为 Vim 安装 Python-mode
首先安装 [Pathogen](https://github.com/tpope/vim-pathogen) (它使得安装插件超级简单,并且运行文件位于私有目录中),从而更加容易的安装 Python-mode
运行下面的命令来获取 `pathogen.vim` 文件和它需要的目录:
```
# mkdir -p ~/.vim/autoload ~/.vim/bundle && \
# curl -LSso ~/.vim/autoload/pathogen.vim https://tpo.pe/pathogen.vim
```
然后把下面这些内容加入 `~/.vimrc` 文件中:
```
execute pathogen#infect()
syntax on
filetype plugin indent on
```
安装好 pathogen 以后,你可以像下面这样把 Python-mode 插件放入 `~/.vim/bunble` 目录中:
```
# cd ~/.vim/bundle
# git clone https://github.com/klen/python-mode.git
```
然后像下面这样在 Vim 中重建 `helptags` :
```
:helptags
```
你需要启用 `filetype-plugin` (`:help filetype-plugin-on`)和 `filetype-indent` (`:help filetype-indent-on`)来使用 Python-mode 。
### 在 Debian 和 Ubuntu 中安装 Python-mode
另一种在 Debian 和 Ubuntu 中安装 Python-mode 的方法是使用 PPA,就像下面这样
```
$ sudo add-apt-repository https://klen.github.io/python-mode/deb main
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install vim-python-mode
```
如果你遇到消息:“The following signatures couldn’t be verified because the public key is not available”,请运行下面的命令:
```
$ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys B5DF65307000E266
```
现在,使用 `vim-addon-manager` 启用 Python-mode:
```
$ sudo apt install vim-addon-manager
$ vim-addons install python-mode
```
### 在 Linux 中定制 Python-mode
如果想覆盖默认键位绑定,可以在 `.vimrc` 文件中重定义它们,比如:
```
" Override go-to.definition key shortcut to Ctrl-]
let g:pymode_rope_goto_definition_bind = "<C-]>"
" Override run current python file key shortcut to Ctrl-Shift-e
let g:pymode_run_bind = "<C-S-e>"
" Override view python doc key shortcut to Ctrl-Shift-d
let g:pymode_doc_bind = "<C-S-d>"
```
注意,默认情况下, Python-mode 使用 Python 2 进行语法检查。你可以在 `.vimrc` 文件中加入下面这行内容从而启动 Python 3 语法检查。
```
let g:pymode_python = 'python3'
```
你可以在 Python-mode 的 GitHub 仓库找到更多的配置选项: <https://github.com/python-mode/python-mode>
这就是全部内容了。在本教程中,我向你们展示了如何在 Linux 中使用 Python-mode 来配置 Vim 。请记得通过下面的反馈表来和我们分享你的想法。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者、Linux 系统管理员、网络开发人员,现在也是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢和电脑一起工作,坚信共享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/python-mode-a-vim-editor-plugin/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | **Python-mode** is a vim plugin that enables you to write Python code in [Vim editor](https://www.tecmint.com/vi-editor-usage/) in a fast manner by utilizing libraries including pylint, rope, pydoc, pyflakes, pep8, autopep8, pep257 and mccabe for coding features such as static analysis, refactoring, folding, completion, documentation, and more.
**Suggested Read:** [Bash-Support – A Vim Plugin That Converts Vim Editor to Bash-IDE](https://www.tecmint.com/use-vim-as-bash-ide-using-bash-support-in-linux/)
This plugin contains all the features that you can use to develop python applications in Vim editor.
#### Python-mode Features
It has the following notable features:
- Support Python version 2.6+ and 3.2+.
- Supports syntax highlighting.
- Offers virtualenv support.
- Supports python folding.
- Offers enhanced python indentation.
- Enables running of python code from within Vim.
- Enables addition/removal of breakpoints.
- Supports python motions and operators.
- Enables code checking (pylint, pyflakes, pylama, …) that can be run simultaneouslyi>
- Supports autofixing of PEP8 errors.
- Allows searching in python documentation.
- Supports code refactoring.
- Supports strong code completion.
- Supports going to definition.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to setup Vim to use Python-mode in Linux to develop Python applications in Vim editor.
### How to Install Python-mode for Vim in Linux
Start by installing [Pathogen](https://github.com/tpope/vim-pathogen) (makes it super easy to install plugins and runtime files in their own private directories) for easy installation of Python-mode.
Run the commands below to get the **pathogen.vim** file and the directories it needs:
# mkdir -p ~/.vim/autoload ~/.vim/bundle && \ # curl -LSso ~/.vim/autoload/pathogen.vim https://tpo.pe/pathogen.vim
Then add the following lines below to your **~/.vimrc** file:
execute pathogen#infect() syntax on filetype plugin indent on
Once you have installed pathogen, and you can now put Python-mode into **~/.vim/bundle** as follows.
# cd ~/.vim/bundle # git clone https://github.com/klen/python-mode.git
Then rebuild helptags in vim like this.
:helptags
You need to enable **filetype-plugin** (**:help** filetype-plugin-on) and **filetype-indent** (**:help** filetype-indent-on) to use python-mode.
### Install Python-mode in Debian and Ubuntu
Another way you can install **python-mode** in Debian and Ubuntu systems using PPA as shown.
$ sudo add-apt-repository https://klen.github.io/python-mode/deb main $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install vim-python-mode
If you you encounter the message: “The following signatures couldn’t be verified because the public key is not available”, run the command below:
$ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys B5DF65307000E266
Now enable **python-mode** using **vim-addon-manager** like so.
$ sudo apt install vim-addon-manager $ vim-addons install python-mode
### Customizing Python-mode in Linux
To override the default key bindings, redefine them in the **.vimrc** files, for instance:
" Override go-to.definition key shortcut to Ctrl-] let g:pymode_rope_goto_definition_bind = "<C-]>" " Override run current python file key shortcut to Ctrl-Shift-e let g:pymode_run_bind = "<C-S-e>" " Override view python doc key shortcut to Ctrl-Shift-d let g:pymode_doc_bind = "<C-S-d>"
Note that python-mode uses python 2 syntax checking by default. You can enable python 3 syntax checking by adding this in your **.vimrc**.
let g:pymode_python = 'python3'
You can find additional configuration options on the Python-mode Github Repository: [https://github.com/python-mode/python-mode](https://github.com/python-mode/python-mode)
That’s all for now! In this tutorial, we will show you how to integrate Vim to with Python-mode in Linux. Share your thoughts with us via the feedback form below.
Reply`:helptags`requires an argument.Hi!
I follow this installation instruction, but whenever I edit a python file (
vi filename.py), I got:Can you give me any help, please!
Bye,
Pablo
Reply@Pablo
Follow the instructions in this guide to install the required module: https://github.com/python-mode/python-mode#how-to-install
ReplyPlease add the following way to add this plugin via
Vundle:If one already has Vundle installed, you can easily add the plugin in
`.vimrc`
file as shown.then open vim and run:
Reply@Palash
We are grateful for this useful addition, many thanks for sharing.
Reply |
8,543 | Go 语言日志指南 | https://logmatic.io/blog/our-guide-to-a-golang-logs-world/ | 2017-05-26T17:15:02 | [
"Go语言",
"日志"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8543-1.html | 
你是否厌烦了那些使用复杂语言编写的、难以部署的、总是在不停构建的解决方案?Golang 是解决这些问题的好方法,它和 C 语言一样快,又和 Python 一样简单。
但是你是如何使用 Golang 日志监控你的应用程序的呢?Golang 没有异常,只有错误。因此你的第一印象可能就是开发 Golang 日志策略并不是一件简单的事情。不支持异常事实上并不是什么问题,异常在很多编程语言中已经失去了其异常性:它们过于被滥用以至于它们的作用都被忽视了。
在进一步深入之前,我们首先会介绍 Golang 日志的基础,并讨论 Golang 日志标准、元数据意义、以及最小化 Golang 日志对性能的影响。通过日志,你可以追踪用户在你应用中的活动,快速识别你项目中失效的组件,并监控总体性能以及用户体验。
### I. Golang 日志基础
#### 1) 使用 Golang “log” 库
Golang 给你提供了一个称为 “log” 的原生[日志库](https://golang.org/pkg/log/) 。它的日志器完美适用于追踪简单的活动,例如通过使用可用的[选项](https://golang.org/pkg/log/#pkg-constants)在错误信息之前添加一个时间戳。
下面是一个 Golang 中如何记录错误日志的简单例子:
```
package main
import (
"log"
"errors"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
/* 定义局部变量 */
...
/* 除法函数,除以 0 的时候会返回错误 */
ret,err = div(a, b)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(ret)
}
```
如果你尝试除以 0,你就会得到类似下面的结果:

为了快速测试一个 Golang 函数,你可以使用 [go playground](https://play.golang.org/)。
为了确保你的日志总是能轻易访问,我们建议你把它们写到一个文件:
```
package main
import (
"log"
"os"
)
func main() {
// 按照所需读写权限创建文件
f, err := os.OpenFile("filename", os.O_WRONLY|os.O_CREATE|os.O_APPEND, 0644)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 完成后延迟关闭,而不是习惯!
defer f.Close()
//设置日志输出到 f
log.SetOutput(f)
//测试用例
log.Println("check to make sure it works")
}
```
你可以在[这里](https://www.goinggo.net/2013/11/using-log-package-in-go.html)找到 Golang 日志的完整指南,以及 “log” [库](https://golang.org/pkg/log/)内可用函数的完整列表。
现在你就可以记录它们的错误以及根本原因啦。
另外,日志也可以帮你将活动流拼接在一起,查找需要修复的错误上下文,或者调查在你的系统中单个请求如何影响其它应用层和 API。
为了获得更好的日志效果,你首先需要在你的项目中使用尽可能多的上下文丰富你的 Golang 日志,并标准化你使用的格式。这就是 Golang 原生库能达到的极限。使用最广泛的库是 [glog](https://github.com/google/glog) 和 [logrus](https://github.com/sirupsen/logrus)。必须承认还有很多好的库可以使用。如果你已经在使用支持 JSON 格式的库,你就不需要再换其它库了,后面我们会解释。
### II. 为你 Golang 日志统一格式
#### 1) JSON 格式的结构优势
在一个项目或者多个微服务中结构化你的 Golang 日志可能是最困难的事情,但一旦完成就很轻松了。结构化你的日志能使机器可读(参考我们 [收集日志的最佳实践博文](https://logmatic.io/blog/beyond-application-monitoring-discover-logging-best-practices/))。灵活性和层级是 JSON 格式的核心,因此信息能够轻易被人类和机器解析以及处理。
下面是一个使用 [Logrus/Logmatic.io](https://github.com/logmatic/logmatic-go) 如何用 JSON 格式记录日志的例子:
```
package main
import (
log "github.com/Sirupsen/logrus"
"github.com/logmatic/logmatic-go"
)
func main() {
// 使用 JSONFormatter
log.SetFormatter(&logmatic.JSONFormatter{})
// 使用 logrus 像往常那样记录事件
log.WithFields(log.Fields{"string": "foo", "int": 1, "float": 1.1 }).Info("My first ssl event from golang")
}
```
会输出结果:
```
{
"date":"2016-05-09T10:56:00+02:00",
"float":1.1,
"int":1,
"level":"info",
"message":"My first ssl event from golang",
"String":"foo"
}
```
#### 2) 标准化 Golang 日志
同一个错误出现在你代码的不同部分,却以不同形式被记录下来是一件可耻的事情。下面是一个由于一个变量错误导致无法确定 web 页面加载状态的例子。一个开发者日志格式是:
```
message: 'unknown error: cannot determine loading status from unknown error: missing or invalid arg value client'</span>
```
另一个人的格式却是:
```
unknown error: cannot determine loading status - invalid client</span>
```
强制日志标准化的一个好的解决办法是在你的代码和日志库之间创建一个接口。这个标准化接口会包括所有你想添加到你日志中的可能行为的预定义日志消息。这么做可以防止出现不符合你想要的标准格式的自定义日志信息。这么做也便于日志调查。

由于日志格式都被统一处理,使它们保持更新也变得更加简单。如果出现了一种新的错误类型,它只需要被添加到一个接口,这样每个组员都会使用完全相同的信息。
最常使用的简单例子就是在 Golang 日志信息前面添加日志器名称和 id。你的代码然后就会发送 “事件” 到你的标准化接口,它会继续讲它们转化为 Golang 日志消息。
```
// 主要部分,我们会在这里定义所有消息。
// Event 结构体很简单。为了当所有信息都被记录时能检索它们,
// 我们维护了一个 Id
var (
invalidArgMessage = Event{1, "Invalid arg: %s"}
invalidArgValueMessage = Event{2, "Invalid arg value: %s => %v"}
missingArgMessage = Event{3, "Missing arg: %s"}
)
// 在我们应用程序中可以使用的所有日志事件
func (l *Logger)InvalidArg(name string) {
l.entry.Errorf(invalidArgMessage.toString(), name)
}
func (l *Logger)InvalidArgValue(name string, value interface{}) {
l.entry.WithField("arg." + name, value).Errorf(invalidArgValueMessage.toString(), name, value)
}
func (l *Logger)MissingArg(name string) {
l.entry.Errorf(missingArgMessage.toString(), name)
}
```
因此如果我们使用前面例子中无效的参数值,我们就会得到相似的日志信息:
```
time="2017-02-24T23:12:31+01:00" level=error msg="LoadPageLogger00003 - Missing arg: client - cannot determine loading status" arg.client=<nil> logger.name=LoadPageLogger
```
JSON 格式如下:
```
{"arg.client":null,"level":"error","logger.name":"LoadPageLogger","msg":"LoadPageLogger00003 - Missing arg: client - cannot determine loading status", "time":"2017-02-24T23:14:28+01:00"}
```
### III. Golang 日志上下文的力量
现在 Golang 日志已经按照特定结构和标准格式记录,时间会决定需要添加哪些上下文以及相关信息。为了能从你的日志中抽取信息,例如追踪一个用户活动或者工作流,上下文和元数据的顺序非常重要。
例如在 logrus 库中可以按照下面这样使用 JSON 格式添加 `hostname`、`appname` 和 `session` 参数:
```
// 对于元数据,通常做法是通过复用来重用日志语句中的字段。
contextualizedLog := log.WithFields(log.Fields{
"hostname": "staging-1",
"appname": "foo-app",
"session": "1ce3f6v"
})
contextualizedLog.Info("Simple event with global metadata")
```
元数据可以视为 javascript 片段。为了更好地说明它们有多么重要,让我们看看几个 Golang 微服务中元数据的使用。你会清楚地看到是怎么在你的应用程序中跟踪用户的。这是因为你不仅需要知道一个错误发生了,还要知道是哪个实例以及什么模式导致了错误。假设我们有两个按顺序调用的微服务。上下文信息保存在头部(header)中传输:
```
func helloMicroService1(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
client := &http.Client{}
// 该服务负责接收所有到来的用户请求
// 我们会检查是否是一个新的会话还是已有会话的另一次调用
session := r.Header.Get("x-session")
if ( session == "") {
session = generateSessionId()
// 为新会话记录日志
}
// 每个请求的 Track Id 都是唯一的,因此我们会为每个会话生成一个
track := generateTrackId()
// 调用你的第二个微服务,添加 session/track
reqService2, _ := http.NewRequest("GET", "http://localhost:8082/", nil)
reqService2.Header.Add("x-session", session)
reqService2.Header.Add("x-track", track)
resService2, _ := client.Do(reqService2)
….
```
当调用第二个服务时:
```
func helloMicroService2(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 类似之前的微服务,我们检查会话并生成新的 track
session := r.Header.Get("x-session")
track := generateTrackId()
// 这一次,我们检查请求中是否已经设置了一个 track id,
// 如果是,它变为父 track
parent := r.Header.Get("x-track")
if (session == "") {
w.Header().Set("x-parent", parent)
}
// 为响应添加 meta 信息
w.Header().Set("x-session", session)
w.Header().Set("x-track", track)
if (parent == "") {
w.Header().Set("x-parent", track)
}
// 填充响应
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
io.WriteString(w, fmt.Sprintf(aResponseMessage, 2, session, track, parent))
}
```
现在第二个微服务中已经有和初始查询相关的上下文和信息,一个 JSON 格式的日志消息看起来类似如下。
在第一个微服务:
```
{"appname":"go-logging","level":"debug","msg":"hello from ms 1","session":"eUBrVfdw","time":"2017-03-02T15:29:26+01:00","track":"UzWHRihF"}
```
在第二个微服务:
```
{"appname":"go-logging","level":"debug","msg":"hello from ms 2","parent":"UzWHRihF","session":"eUBrVfdw","time":"2017-03-02T15:29:26+01:00","track":"DPRHBMuE"}
```
如果在第二个微服务中出现了错误,多亏了 Golang 日志中保存的上下文信息,现在我们就可以确定它是怎样被调用的以及什么模式导致了这个错误。
如果你想进一步深挖 Golang 的追踪能力,这里还有一些库提供了追踪功能,例如 [Opentracing](https://github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go)。这个库提供了一种简单的方式在或复杂或简单的架构中添加追踪的实现。它通过不同步骤允许你追踪用户的查询,就像下面这样:

### IV. Golang 日志对性能的影响
#### 1) 不要在 Goroutine 中使用日志
在每个 goroutine 中创建一个新的日志器看起来很诱人。但最好别这么做。Goroutine 是一个轻量级线程管理器,它用于完成一个 “简单的” 任务。因此它不应该负责日志。它可能导致并发问题,因为在每个 goroutine 中使用 `log.New()` 会重复接口,所有日志器会并发尝试访问同一个 io.Writer。
为了限制对性能的影响以及避免并发调用 io.Writer,库通常使用一个特定的 goroutine 用于日志输出。
#### 2) 使用异步库
尽管有很多可用的 Golang 日志库,要注意它们中的大部分都是同步的(事实上是伪异步)。原因很可能是到现在为止它们中没有一个会由于日志严重影响性能。
但正如 Kjell Hedström 在[他的实验](https://sites.google.com/site/kjellhedstrom2/g2log-efficient-background-io-processign-with-c11/g2log-vs-google-s-glog-performance-comparison)中展示的,使用多个线程创建成千上万日志,即便是在最坏情况下,异步 Golang 日志也会有 40% 的性能提升。因此日志是有开销的,也会对你的应用程序性能产生影响。如果你并不需要处理大量的日志,使用伪异步 Golang 日志库可能就足够了。但如果你需要处理大量的日志,或者很关注性能,Kjell Hedström 的异步解决方案就很有趣(尽管事实上你可能需要进一步开发,因为它只包括了最小的功能需求)。
#### 3)使用严重等级管理 Golang 日志
一些日志库允许你启用或停用特定的日志器,这可能会派上用场。例如在生产环境中你可能不需要一些特定等级的日志。下面是一个如何在 glog 库中停用日志器的例子,其中日志器被定义为布尔值:
```
type Log bool
func (l Log) Println(args ...interface{}) {
fmt.Println(args...)
}
var debug Log = false
if debug {
debug.Println("DEBUGGING")
}
```
然后你就可以在配置文件中定义这些布尔参数来启用或者停用日志器。
没有一个好的 Golang 日志策略,Golang 日志可能开销很大。开发人员应该抵制记录几乎所有事情的诱惑 - 尽管它非常有趣!如果日志的目的是为了获取尽可能多的信息,为了避免包含无用元素的日志的白噪音,必须正确使用日志。
### V. 集中化 Golang 日志

如果你的应用程序是部署在多台服务器上的,这样可以避免为了调查一个现象需要连接到每一台服务器的麻烦。日志集中确实有用。
使用日志装箱工具,例如 windows 中的 Nxlog,linux 中的 Rsyslog(默认安装了的)、Logstash 和 FluentD 是最好的实现方式。日志装箱工具的唯一目的就是发送日志,因此它们能够处理连接失效以及其它你很可能会遇到的问题。
这里甚至有一个 [Golang syslog 软件包](https://golang.org/pkg/log/syslog/) 帮你将 Golang 日志发送到 syslog 守护进程。
### 希望你享受你的 Golang 日志之旅
在你项目一开始就考虑你的 Golang 日志策略非常重要。如果在你代码的任意地方都可以获得所有的上下文,追踪用户就会变得很简单。从不同服务中阅读没有标准化的日志是已经很痛苦的事情。一开始就计划在多个微服务中扩展相同用户或请求 id,后面就会允许你比较容易地过滤信息并在你的系统中跟踪活动。
你是在构架一个很大的 Golang 项目还是几个微服务也会影响你的日志策略。一个大项目的主要组件应该有按照它们功能命名的特定 Golang 日志器。这使你可以立即判断出日志来自你的哪一部分代码。然而对于微服务或者小的 Golang 项目,只有较少的核心组件需要它们自己的日志器。但在每种情形中,日志器的数目都应该保持低于核心功能的数目。
你现在已经可以使用 Golang 日志量化决定你的性能或者用户满意度啦!
*如果你有想阅读的特定编程语言,在 Twitter [@logmatic](http://twitter.com/logmatic) 上告诉我们吧。*
---
via: <https://logmatic.io/blog/our-guide-to-a-golang-logs-world/>
作者:[Nils](https://logmatic.io/blog/our-guide-to-a-golang-logs-world/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,545 | Linfo:实时显示你的 Linux 服务器运行状况 | https://www.tecmint.com/linfo-shows-linux-server-health-status-in-real-time/ | 2017-05-27T16:37:27 | [
"Linfo",
"监控"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8545-1.html | 
Linfo 是一个自由开源的跨平台的服务器统计 UI 或库,它可以显示大量的系统信息。Linfo 是可扩展的,通过 `composer`,很容易使用 PHP5 库以程序化方式获取来自 PHP 应用的丰富的系统统计数据。它有 Web UI 及其Ncurses CLI 视图,在 Linux、Windows、BSD、Darwin/Mac OSX、Solaris 和 Minix 系统上均可用。
Linfo 显示的系统信息包括 [CPU 类型/速度](/article-8241-1.html)、服务器的体系结构、挂载点用量、硬盘/光纤/Flash 驱动器、硬件设备、网络设备和统计信息、运行时间/启动日期、主机名、内存使用量(RAM 和 swap)、温度/电压/风扇速度和 RAID 阵列等。
### 环境要求:
* PHP 5.3
* pcre 扩展
* Linux – `/proc` 和 `/sys` 已挂载且可对 `PHP` 可读,已经在 2.6.x/3.x 内核中测试过
### 如何在 Linux 中安装 Linfo 服务器统计 UI及库
首先,在 Apache 或 Nginx 的 Web 根目录下创建 Linfo 的目录,然后,使用下面展示的 [rsync 命令](https://www.tecmint.com/rsync-local-remote-file-synchronization-commands/) 克隆仓库文件并将其移动到目录 `/var/www/html/linfo` 下:
```
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/linfo
$ git clone git://github.com/jrgp/linfo.git
$ sudo rsync -av linfo/ /var/www/html/linfo/
```
接下来,将 `sample.config.inc.php` 重命名为 `config.inc.php`。这是 Linfo 的配置文件,你可以在里面定义你想要的值:
```
$ sudo mv sample.config.inc.php config.inc.php
```
现在,在 Web 浏览器中打开链接 `http://SERVER_IP/linfo` 来查看这个 Web UI,正如下面的截图所展示的。
从截图中可以看到, Linfo 显示了系统内核信息、硬件组成、RAM 统计、网络设备、驱动器以及文件系统挂载点。

*Linux 服务器运行信息*
你可以将下面一行内容加入配置文件 `config.inc.php` 中,以便进行故障排查时看到错误信息。
```
$settings['show_errors'] = true;
```
### 以 Ncurses 模式运行 Linfo
Linfo 有一个基于 `ncurses` 的简单界面,它依赖于 `php` 的 `ncurses` 扩展。
```
# yum install php-pecl-ncurses [在 CentOS/RHEL 上]
# dnf install php-pecl-ncurses [在 Fedora 上]
$ sudo apt-get install php5-dev libncurses5-dev [在 Debian/Ubuntu 上]
```
现在,像下面这样编译这个 php 扩展:
```
$ wget http://pecl.php.net/get/ncurses-1.0.2.tgz
$ tar xzvf ncurses-1.0.2.tgz
$ cd ncurses-1.0.2
$ phpize # generate configure script
$ ./configure
$ make
$ sudo make install
```
接下来,如果编译成功并安装好了该 php 扩展,运行下面的命令:
```
$ sudo echo extension=ncurses.so > /etc/php5/cli/conf.d/ncurses.ini
```
验证 ncurse:
```
$ php -m | grep ncurses
```
现在,运行 Info:
```
$ cd /var/www/html/linfo/
$ ./linfo-curses
```

*Linux 服务器信息*
Info 中尚欠缺下面这些功能:
1. 支持更多 Unix 操作系统(比如 Hurd、IRIX、AIX 和 HP UX 等)
2. 支持不太出名的操作系统 Haiku/BeOS
3. 额外功能/扩展
4. 在 ncurses 模式中支持 [htop 类](https://www.tecmint.com/install-htop-linux-process-monitoring-for-rhel-centos-fedora/) 特性
如果想了解更多信息,请访问 Linfo 的 GitHub 仓库: <https://github.com/jrgp/linfo>
这就是本文的全部内容了。从现在起,你可以使用 Linfo 在 Web 浏览器中查看 Linux 系统的信息。尝试一下,并在评论中和我们分享你的想法。另外,你是否还知道与之类似的有用工具/库?如果有,请给我们提供一些相关信息。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux 系统管理员和网络开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/linfo-shows-linux-server-health-status-in-real-time/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | **Linfo** is a free and open source, cross-platform server statistics UI/library which displays a great deal of system information. It is extensible, easy-to-use (via composer) PHP5 library to get extensive system statistics programmatically from your PHP application. It’s a Ncurses CLI view of Web UI, which works in Linux, Windows, *BSD, Darwin/Mac OSX, Solaris, and Minix.
It displays system info including [CPU type/speed](https://www.tecmint.com/corefreq-linux-cpu-monitoring-tool/); architecture, mount point usage, hard/optical/flash drives, hardware devices, network devices and stats, uptime/date booted, hostname, memory usage (RAM and swap, if possible), temperatures/voltages/fan speeds and RAID arrays.
#### Requirements:
- PHP 5.3
- pcre extension
- Linux – /proc and /sys mounted and readable by PHP and Tested with the 2.6.x/3.x kernels
### How to Install Linfo Server Stats UI/library in Linux
First, create a **Linfo** directory in your Apache or Nginx web root directory, then clone and move repository files into `/var/www/html/linfo`
using the [rsync command](https://www.tecmint.com/rsync-local-remote-file-synchronization-commands/) as shown below:
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/linfo $ git clone git://github.com/jrgp/linfo.git $ sudo rsync -av linfo/ /var/www/html/linfo/
Then rename **sample.config.inc.php** to **config.inc.php**. This is the Linfo config file, you can define your own values in it:
$ sudo mv sample.config.inc.php config.inc.php
Now open the URL `http://SERVER_IP/linfo`
in web browser to see the Web UI as shown in the screenshots below.
This screenshot shows the Linfo Web UI displaying core system info, hardware components, RAM stats, network devices, drives and file system mount points.
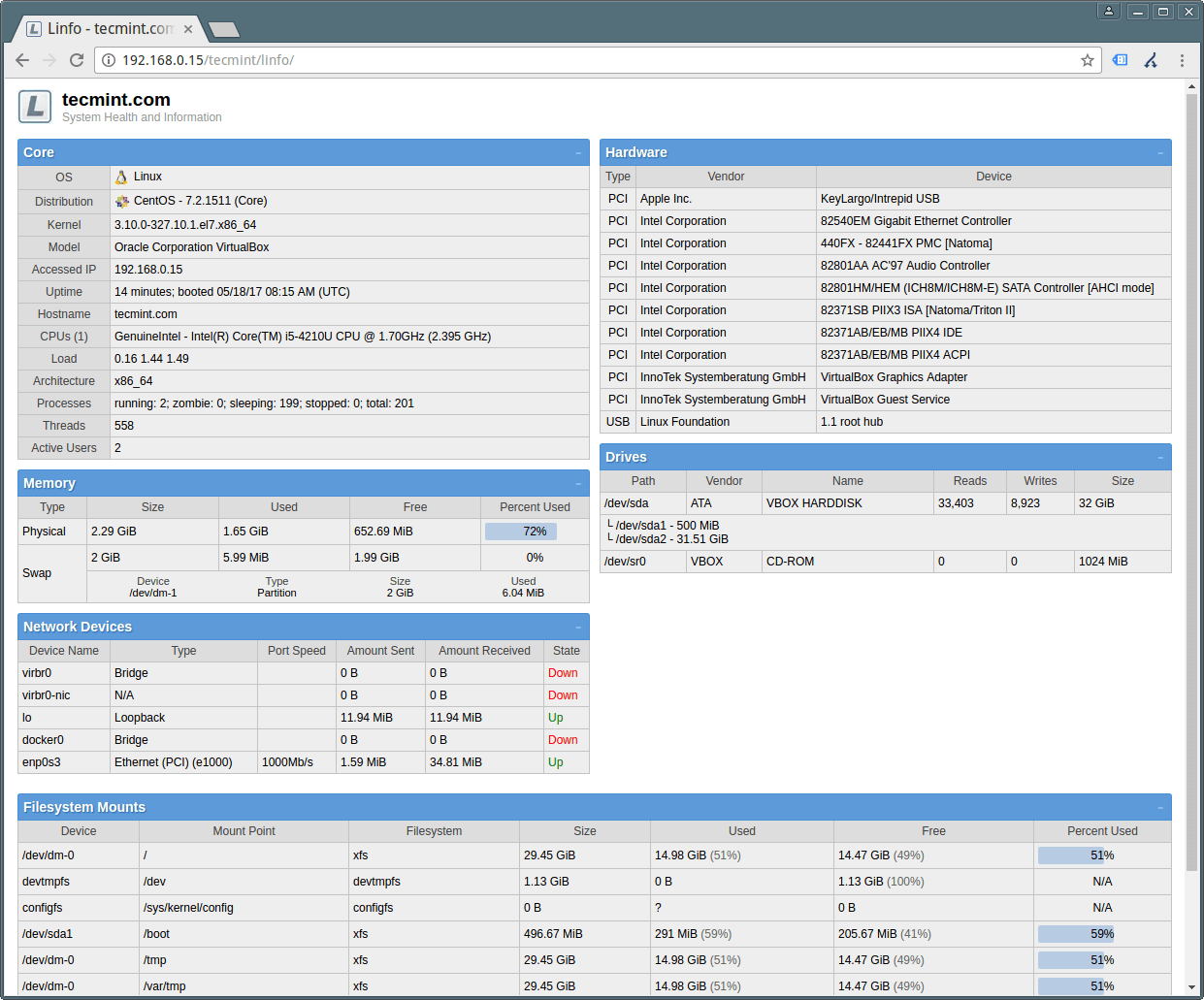
You can add the line below in the config file `config.inc.php`
to yield useful error messages for troubleshooting purposes:
$settings['show_errors'] = true;
### Running Linfo in Ncurses Mode
Linfo has a simple ncurses-based interface, which rely on php’s ncurses extension.
# yum install php-pecl-ncurses [On CentOS/RHEL] # dnf install php-pecl-ncurses [On Fedora] $ sudo apt-get install php5-dev libncurses5-dev [On Debian/Ubuntu]
Now compile the php extension as follows
$ wget http://pecl.php.net/get/ncurses-1.0.2.tgz $ tar xzvf ncurses-1.0.2.tgz $ cd ncurses-1.0.2 $ phpize # generate configure script $ ./configure $ make $ sudo make install
Next, if you successfully compiled and installed the php extension, run the commands below.
$ sudo echo extension=ncurses.so > /etc/php5/cli/conf.d/ncurses.ini
Verify the ncurses.
$ php -m | grep ncurses
Now run the **Linfo**.
$ cd /var/www/html/linfo/ $ ./linfo-curses
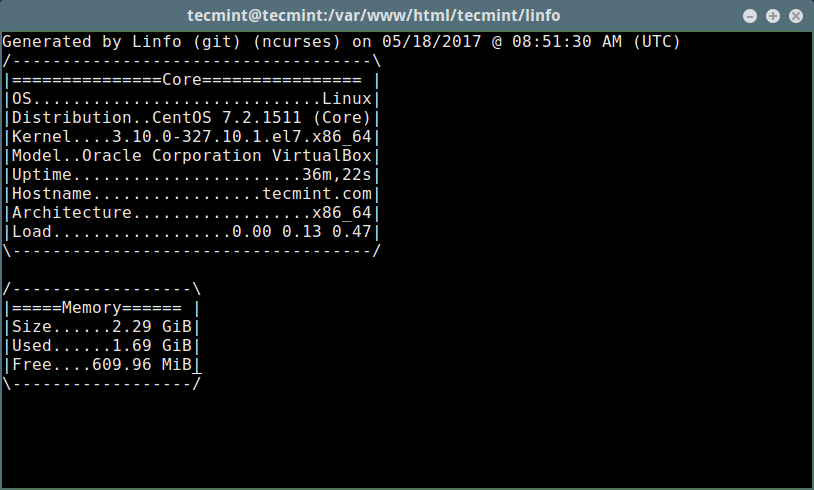
The following features yet to be added in Linfo:
- Support for more Unix operating systems (such as Hurd, IRIX, AIX, HP UX, etc)
- Support for less known operating systems: Haiku/BeOS
- Extra superfluous features/extensions
- Support for
[htop-like](https://www.tecmint.com/install-htop-linux-process-monitoring-for-rhel-centos-fedora/)features in ncurses mode
For more information, visit Linfo Github repository: [https://github.com/jrgp/linfo](https://github.com/jrgp/linfo)
That’s all! From now on, you can view a Linux system’s information from within a web browser using Linfo. Try it out and share with us your thoughts in the comments. Additionally, have you come across any similar useful tools/libraries? If yes, then give us some info about them as well.
Hi, I did not want “anything” to download files from linfo so I added a
Reply`.htaccess`
file in thelinfodirectory:Hi Aaron Kili,
UI linfois working great but when i tired “Running Linfo in Ncurses Mode” but not able to run even through successful compilation on Ubuntu 14.04 32bit this command give me permission error.“sudo echo extension=ncurses.so > /etc/php5/cli/conf.d/ncurses.ini” ——> bash: /etc/php5/cli/conf.d/ncurses.ini: Permission denied
also
ncurses.inifile is not present after compilation.Can you please help !!!
Reply@Rahul
Try to post an issue about this on the Linfo Github repository to get more clarification.
ReplyHi Thanks Aaron Kili,
Can we run the configure from single system and get the report of multiple Linux server in the environment. And get the email report at specific time interval.
Reply@Imtiyaz
Linfo works on a single system, to offer the functionality you have described you’ll need to modify it a little. But try to find more from the developer at: https://github.com/jrgp/linfo
ReplyCan we installed on siem server
Reply@Imtiyaz
Yes, you can install on SIEM server.
ReplyThank you for your article.
Unfortunately, after running
http://SERVER_IP/linfocommand I can see only the list of files in Linfo catalog:Wha should I do else to have this site running correctly? I can’t see here an index.html file. Is it normally?
Centos 7.3 Minimal on VmWare Workstation 12
Thank you!
Reply@Alexey
Welcome, there is an index.php file, this is the default index file. Make sure that your web server serves .php index files. For Apache, open the httpd.conf set it using the
DirectoryIndexdirective(list them in order of preference) as follows:
ReplyDirectoryIndex index.php index.phtml index.html index.htmThere was just one option in DirectoryIndex – index.html
I added index.php index.phtml index.html index.htm and after that restartng httpd service.
After trying to open the site the other error occured:
scan();
if (isset($_SERVER[‘LINFO_NCURSES’]) && php_sapi_name() == ‘cli’) {
$output = new \Linfo\Output\Ncurses($linfo);
}
else {
switch (array_key_exists(‘out’, $_GET) ? strtolower($_GET[‘out’]) : ‘html’) {
default:
case ‘html’:
$output = new \Linfo\Output\Html($linfo);
break;
case ‘json’:
case ‘jsonp’: // To use JSON-P, pass the GET arg – callback=function_name
$output = new \Linfo\Output\Json($linfo, array_key_exists(‘callback’, $_GET) ? $_GET[‘callback’] : null);
break;
case ‘php_array’:
$output = new \Linfo\Output\Serialized($linfo);
break;
case ‘xml’:
$output = new \Linfo\Output\Xml($linfo);
break;
}
}
$output->output();
} catch (FatalException $e) {
echo $e->getMessage().”\n”;
exit(1);
}
What’s wrong here?
Thank you!
ReplyMight be since I have installed Centos Minimal version no PHP was included during installation.
So, I have just installed PHP 7.1.5, restart httpd service and it works now!
Thank you for your help!
Reply@Alexey
This is great, good to know that you fixed the error. This will definitely help us in future when offering solutions to other readers’ issues/errors.
Many thanks for the feedback.
Thanks for your great tips. I want to know can these tools show the health of HDD and the temperature?
Cheers
Reply@jamshid
Welcome, you can use
Replyhddtempfor this, but you need to find a way of using the output from Linfo web UI.To install hddtemp, type:
sudo apt install hddtempThank you Aaron Kili :)
Reply@Jamshid
Welcome, many thanks for the useful feedback, and always following us.
ReplyHi thanks for the useful tips, can it show the health and temperature of HDD?
Jamshid
Reply |
8,547 | 怎样在 Linux 中用 Vim 对文件进行密码保护 | https://www.tecmint.com/password-protect-vim-file-in-linux/ | 2017-05-28T10:25:13 | [
"Vim",
"加密"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8547-1.html | 
[Vim](https://www.tecmint.com/vi-editor-usage/) 是一种流行的、功能丰富的和高度可扩展的 [Linux 文本编辑器](https://www.tecmint.com/best-open-source-linux-text-editors/),它的一个特殊功能便是支持用带密码各种的加密方法来加密文本文件。
本文中,我们将向你介绍一种简单的 Vim 使用技巧:在 Linux 中使用 Vim 对文件进行密码保护。我们将向你展示如何让一个文件在它创建的时侯以及为了修改目的而被打开了之后获得安全防护。
**建议阅读:** [你应该在 Linux 中使用 Vim 编辑器的 7 个原因](/article-7728-1.html)
要安装 Vim 完整版,只需运行这些命令:
```
$ sudo apt install vim #Debian/Ubuntu 系统
$ sudo yum install vim #RHEL/CentOS 系统
$ sudo dnf install vim #Fedora 22+
```
参阅: [十年后 Vim 8.0 发布了](/article-7766-1.html) – [在 Linux 上安装](/article-8094-1.html)
### 怎样在 Linux 中用 Vim 对文件进行密码保护
Vim 有个 `-x` 选项,这个选项能让你在创建文件时用它来加密。一旦你运行下面的 [vim 命令](https://www.tecmint.com/linux-command-line-editors/),你会被提示输入一个密钥:
```
$ vim -x file.txt
警告:正在使用弱加密方法;参见 :help 'cm'
输入加密密钥:*******
再次输入相同密钥:*******
```
如果第二次输入的密钥无误,你就能可以修改此文件了。

*被密码保护的 Vim 文件*
等你修改好之后,摁 `Esc` 和键入 `:wq` 来保存及关闭文件。下次你想打开它编辑一下,你就必须像这样去输入密钥:
```
$ vim file.txt
需要 "file.txt" 的加密密钥
警告:正在使用弱加密方法;参见 :help 'cm'
输入密钥:*******
```
假设你输了一个错误的密码(或者没输密码),你会看到一些垃圾字符。

*Vim 中的加密内容*
#### 在 Vim 中设置一种强加密方法
注意:警告信息暗示保护文件的是弱加密方法。那么接下来,我们来看看怎么在 Vim 中设置一种强加密方法。

*Vim 中文件弱加密*
为了查看加密方式(cm)集,键入如下:
```
:help 'cm'
```
输出样例:
```
*'cryptmethod'* *'cm'*
'cryptmethod' string (默认 "zip")
全局或本地到缓冲区 |global-local|
{not in Vi}
当缓冲区写进文件中所用的加密方式:
*pkzip*
zip PkZip 兼容方式。 一种弱加密方法。
与 Vim 7.2 及更老版本后向兼容。
*blowfish*
blowfish 河豚加密方式。 中级强度加密方法但有实现上
的瑕疵。需要 Vim 7.3 及以上版本,用它加密的文件不
能被 Vim 7.2 及更老版本读取。它会添加一个 “种子”,
每次你当你写入文件时,这个加密字节都不同。
```
你可以像如下所示的那样给一个 Vim 文件设置个新的加密方法(本例中我们用 `blowfish2` 加密方法)
```
:setlocal cm=blowfish2
```
然后键入回车和 `:wq` 保存文件。

*对 Vim 文件设置强加密*
现在你再打开下面的文件时应该就看不到那条警告信息了。
```
$ vim file.txt
需要 "file.txt" 的加密密钥
输入加密密钥:*******
```
你也可以在打开 Vim 文件之后来设置密码,用 `:X` 命令就能像上面所示的那样去设置一个加密密码。
可以看看我们其他的关于 Vim 编辑器的有用的文章。
1. [在 Linux 中学习有用的 Vim 编辑器的技巧](https://www.tecmint.com/learn-vi-and-vim-editor-tips-and-tricks-in-linux/)
2. [给每个 Linux 用户的 8 种有用的 Vim 编辑器技巧](https://www.tecmint.com/how-to-use-vi-and-vim-editor-in-linux/)
3. [spf13-vim – Vim 编辑器的顶级分发版](https://www.tecmint.com/spf13-vim-offers-vim-plugins-vim-editor/)
4. [怎样在 Linux 种把 Vim 编辑当作 Bash IDE 来用](/article-8467-1.html)
本文到这里就结束了!文章中我们介绍了怎么通过 Linux 下的 Vim 文本编辑器来给一个文件做加密防护。
永远记住要用强加密方式及密码来适当的保护那些可能包含了诸如用户名及密码、财务账户信息等机密信息的文本文件。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S(Free and Open-Source Software,自由及开放源代码软件)爱好者,未来的 Linux 系统管理员、Web 开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,且崇尚分享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/password-protect-vim-file-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ch-cn](https://github.com/ch-cn) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | [Vim](https://www.tecmint.com/vi-editor-usage/) is a popular, feature-rich and highly-extensible [text editor for Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/best-open-source-linux-text-editors/), and one of its special features is support for encrypting text files using various crypto methods with a password.
In this article, we will explain to you one of the simple Vim usage tricks; password protecting a file using Vim in Linux. We will show you how to secure a file at the time of its creation as well as after opening it for modification.
**Suggested Read:** [10 Reasons Why You Should Use Vim Editor in Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/reasons-to-learn-vi-vim-editor-in-linux/)
To install the full version of Vim, simply run this command:
$ sudo apt install vim #Debian/Ubuntu systems $ sudo yum install vim #RHEL/CentOS systems $ sudo dnf install vim #Fedora 22+
**Read Also**: [Vim 8.0 Is Released After 10 Years – Install on Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/vim-8-0-install-in-ubuntu-linux-systems/)
### How to Password Protect a Vim File in Linux
Vim has a `-x`
option which enables you to use encryption when creating files. Once you run the [vim command](https://www.tecmint.com/linux-command-line-editors/) below, you’ll be prompted for a crypt key:
$ vim -x file.txtWarning: Using a weak encryption method; see :help 'cm' Enter encryption key:*******Enter same key again:*******
If the crypto key matches after entering it for the second time, you can proceed to modify the file.
Once your done, press `[Esc]`
and `:wq`
to save and close the file. The next time you want to open it for editing, you’ll have to enter the crypto key like this:
$ vim file.txtNeed encryption key for "file.txt" Warning: Using a weak encryption method; see :help 'cm' Enter encryption key:*******
In case you enter a wrong password (or no key), you’ll see some junk characters.
#### Setting a Strong Encryption Method in Vim
**Note**: There is a warning indicating that a weak encryption method has been used to protect the file. Next, we’ll see how to set a strong encryption method in Vim.
To check the set of cryptmethod(cm), type (scroll down to view all available methods):
:help 'cm'
##### Sample Output
*'cryptmethod'* *'cm'* 'cryptmethod' 'cm' string (default "zip") global or local to buffer |global-local| {not in Vi} Method used for encryption when the buffer is written to a file: *pkzip* zip PkZip compatible method. A weak kind of encryption. Backwards compatible with Vim 7.2 and older. *blowfish* blowfish Blowfish method. Medium strong encryption but it has an implementation flaw. Requires Vim 7.3 or later, files can NOT be read by Vim 7.2 and older. This adds a "seed" to the file, every time you write the file options.txt [Help][RO]
You can set a new cryptomethod on a Vim file as shown below (we’ll use **blowfish2** in this example):
:setlocal cm=blowfish2
Then press `[Enter]`
and `:wq`
to save the file.
Now you should not see the warning message when you open the file again as shown below.
$ vim file.txtNeed encryption key for "file.txt" Enter encryption key:*******
You can also set a password after opening a Vim text file, use the command`:X`
and set a crypto pass like shown above.
Check out some of our useful articles on Vim editor.
[Learn Useful Vim Editor Trips and Tricks in Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/learn-vi-and-vim-editor-tips-and-tricks-in-linux/)[8 Useful Vim Editor Tricks for Every Linux User](https://www.tecmint.com/how-to-use-vi-and-vim-editor-in-linux/)[spf13-vim – The Ultimate Distribution for Vim Editor](https://www.tecmint.com/spf13-vim-offers-vim-plugins-vim-editor/)[How to Use Vim Editor as Bash IDE in Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/use-vim-as-bash-ide-using-bash-support-in-linux/)
That’s all! In this article, we explained how to password protect a file via the [Vim text editor in Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/vi-editor-usage/).
Always remember to appropriately secure text files that could contain secret info such as usernames and passwords, financial account info and so on, using strong encryption and a password. Use the feedback section below to share any thoughts with us.
Can we access encrypted files via fopen in c program?
ReplyHow can we read or update the contents of a encrypted file by
Replyfopenin code then?How to remove a crypted password from the file.
Reply@sumit
You can update the original password with an empty password. Start vi/m with -x option, you’ll be prompted for new password, leave it empty/blank and press Enter twice.
ReplyBut if I write a python program with encryption enabled then the file doesn’t compile. What to do?
Reply@Sarvottam
Try to compile without encryption. May be it will work.
ReplyI have a couple of questions for you.
1. How can I reset the password using the current password?
Reply2. What If I forget the password later. Is there any way to reset the password without entering the old password? I mean is there something like security questions etc
@Amar
Do not forget the password, otherwise you’ll not be able to view the contents of the file again. And to update the password, open the file for editing and type
Reply[Esc]and :X then save changes to the file like this:wbefore closing it.Thank you, Aaron, I’ll try it.
Reply@Amar
Okay, thanks for the response, and for always following us.
ReplyTo be fair, emacs has similar functionality. A simple search with Google (“encrypt a file with emacs”) will lead you to a long list of articles.
Reply@Rick
Sure, we’ll check this out. Many thanks for the useful info.
Reply |
8,548 | 在 Linux 服务器关机前向用户显示一条自定义消息 | https://www.tecmint.com/show-linux-server-shutdown-message/ | 2017-05-30T08:32:00 | [
"shutdown",
"关机"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8548-1.html | 
在先前的文章中,我们解释了 Linux 中 [shutdown、poweroff、halt、reboot 命令的不同之处](https://www.tecmint.com/shutdown-poweroff-halt-and-reboot-commands-in-linux/),并揭示了在用不同的选项执行这些命令时它们实际做了什么。
本篇将会向你展示如何在系统关机时向所有的系统用户发送一条自定义的消息。
**建议阅读:**[tuptime - 显示 Linux 系统的历史和统计运行时间](https://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-uptime-shutdown-and-reboot-time-with-tuptime/)
作为一名系统管理员,在你关闭服务器之前,你也许想要发送一条消息来警告他们系统将要关闭。默认上,`shutdown` 命令会如下所示给其他系统用户广播这条信息:
```
# shutdown 13:25
```
Linux 关机操作广播消息
```
Shutdown scheduled for Fri 2017-05-12 13:25:00 EAT, use 'shutdown -c' to cancel.
Broadcast message for root@tecmint (Fri 2017-05-12 13:23:34 EAT):
The system is going down for power-off at Fri 2017-05-12 13:25:00 EAT!
```
要在 shutdown 那行发送一条自定义的消息给其他系统用户,运行下面的命令。在本例中,关闭会在命令执行后的两分钟之后发生。
```
# shutdown 2 The system is going down for required maintenance. Please save any important work you are doing now!
```

*Linux 系统关闭消息*
假设你有一些关键的系统操作,如计划系统备份或更新会在系统关闭的时候进行,如下所示,你可以使用 `-c` 选项取消关机,并在执行玩这些操作后继续执行:
```
# shutdown -c
```
Linux 关机操作取消消息:
```
Shutdown scheduled for Fri 2017-05-12 14:10:22 EAT, use 'shutdown -c' to cancel.
Broadcast message for root@tecmint (Fri 2017-05-14 :10:27 EAT):
The system shutdown has been cancelled at Fri 2017-05-12 14:11:27 EAT!
```
另外,学习如何在 Linux 中使用简单和传统的方法[在重启或者开机时自动执行命令/脚本](https://www.tecmint.com/auto-execute-linux-scripts-during-reboot-or-startup/)。
不要错过:
1. [管理系统启动进程和服务(SysVinit、Systemd 和 Upstart)](https://www.tecmint.com/linux-boot-process-and-manage-services/)
2. [11 个 Linux 中 cron 计划任务示例](https://www.tecmint.com/11-cron-scheduling-task-examples-in-linux/)
现在你知道了如何在系统关闭前向其他系统用户发送自定义消息了。你有其他关于这个主题想要分享的想法么?何不使用下面的评论栏?
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者、Linux 系统管理员、网络开发人员,现在也是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢和电脑一起工作,坚信共享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/show-linux-server-shutdown-message/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In a previous article, we explained the [difference between shutdown, poweroff, halt and reboot](https://www.tecmint.com/shutdown-poweroff-halt-and-reboot-commands-in-linux/) Linux commands, where we uncovered what these mentioned commands actually do when you execute them with various options.
This article will show you how to send a custom message to all system users before shutting down a Linux server.
**Suggested Read:** [tuptime – Shows Historical and Statistical Running Time of Linux Systems](https://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-uptime-shutdown-and-reboot-time-with-tuptime/)
As a system administrator, before you can shut down a server, you may want to send system users a message alerting them that the system is going. By default, the shutdown command broadcasts a message to other system users as shown in the screenshot below:
# shutdown 13:25
Shutdown scheduled for Fri 2017-05-12 13:25:00 EAT, use 'shutdown -c' to cancel. Broadcast message for root@tecmint (Fri 2017-05-12 13:23:34 EAT): The system is going down for power-off at Fri 2017-05-12 13:25:00 EAT!
To send a custom message to other system users before an in line shutdown, run the command below. In this example, the shutdown will happen after two minutes from the time of command execution:
# shutdown 2 The system is going down for required maintenance. Please save any important work you are doing now!
Supposing you have certain critical system operations such as scheduled system backups or updates to be executed at a time the system would be down, you can cancel the shutdown using the `-c`
switch as shown below and initiate it at a later time after such operations have been performed:
# shutdown -c
Shutdown scheduled for Fri 2017-05-12 14:10:22 EAT, use 'shutdown -c' to cancel. Broadcast message for root@tecmint (Fri 2017-05-14 :10:27 EAT): The system shutdown has been cancelled at Fri 2017-05-12 14:11:27 EAT!
Additionally, learn how to [auto execute commands/scripts during reboot or startup](https://www.tecmint.com/auto-execute-linux-scripts-during-reboot-or-startup/) using simple and traditional methods in Linux.
**Don’t Miss**:
[Managing System Startup Process and Services (SysVinit, Systemd and Upstart)](https://www.tecmint.com/linux-boot-process-and-manage-services/)[11 Cron Scheduling Task Examples in Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/11-cron-scheduling-task-examples-in-linux/)
Now you know how to send custom messages to all other system users before a system shutdown. Are there any ideas you want to share relating to this topic? Use the comment form below to do that?
Thanks for that article.
Is there a way to deactivate that shutdown message?
ReplyHi,
ReplyThanks a lot…
@Jalal
Welcome, many thanks for always following us and the useful feedback.
Reply |
8,551 | WPSeku:一个找出 WordPress 安全问题的漏洞扫描器 | https://www.tecmint.com/wpseku-wordpress-vulnerability-security-scanner/ | 2017-05-29T08:00:00 | [
"WordPress",
"安全",
"漏洞"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8551-1.html | WordPress 是一个免费开源、可高度自定义的内容管理系统(CMS),它被全世界数以百万计的人来运行博客和完整的网站。因为它是被用的最多的 CMS,因此有许多潜在的 WordPress 安全问题/漏洞需要考虑。

然而,如果我们遵循通常的 WordPress 最佳实践,这些安全问题可以避免。在本篇中,我们会向你展示如何使用 WPSeku,一个 Linux 中的 WordPress 漏洞扫描器,它可以被用来找出你安装的 WordPress 的安全漏洞,并阻止潜在的威胁。
WPSeku 是一个用 Python 写的简单的 WordPress 漏洞扫描器,它可以被用来扫描本地以及远程安装的 WordPress 来找出安全问题。
### 如何安装 WPSeku - Linux 中的 WordPress 漏洞扫描器
要在 Linux 中安装 WPSeku,你需要如下从 Github clone 最新版本的 WPSeku。
```
$ cd ~
$ git clone https://github.com/m4ll0k/WPSeku
```
完成之后,进入 WPSeku 目录,并如下运行。
```
$ cd WPSeku
```
使用 `-u` 选项指定 WordPress 的安装 URL,如下运行 WPSeku:
```
$ ./wpseku.py -u http://yourdomain.com
```

*WordPress 漏洞扫描器*
以下命令使用 `-p` 选项搜索 WordPress 插件中的跨站脚本(`x`)、本地文件夹嵌入(`l`)和 SQL 注入(`s`)漏洞,你需要在 URL 中指定插件的位置:
```
$ ./wpseku.py -u http://yourdomain.com/wp-content/plugins/wp/wp.php?id= -p [x,l,s]
```
以下命令将使用 `-b` 选项通过 XML-RPC 执行暴力密码登录。另外,你可以使用 `--user` 和 `--wordlist` 选项分别设置用户名和单词列表,如下所示。
```
$ ./wpseku.py -u http://yourdomian.com --user username --wordlist wordlist.txt -b [l,x]
```
要浏览所有 WPSeku 使用选项,输入:
```
$ ./wpseku.py --help
```

*WPSeku WordPress 漏洞扫描帮助*
WPSeku Github 仓库:<https://github.com/m4ll0k/WPSeku>
就是这样了!在本篇中,我们向你展示了如何在 Linux 中获取并使用 WPSeku 用于 WordPress 漏洞扫描。WordPress 是安全的,但需要我们遵循 WordPress 安全最佳实践才行。你有要分享的想法么?如果有,请在评论区留言。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 及 F.O.S.S 热衷者,即将成为 Linux 系统管理员、web 开发者,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/wpseku-wordpress-vulnerability-security-scanner/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | WordPress is a free and open-source, highly customizable content management system (CMS) that is being used by millions around the world to run blogs and fully functional websites. Because it is the most used CMS out there, there are so many potential WordPress security issues/vulnerabilities to be concerned about.
However, these security issues can be dealt with, if we follow common WordPress security best practices. In this article, we will show you how to use **WPSeku**, a WordPress vulnerability scanner in Linux, that can be used to find security holes in your WordPress installation and block potential threats.
**WPSeku** is a simple WordPress vulnerability scanner written using Python, it can be used to scan local and remote WordPress installations to find security issues.
### How to Install WPSeku – WordPress Vulnerability Scanner in Linux
To install **WPSeku** in Linux, you need to clone the most recent version of **WPSeku** from its Github repository as shown.
$ cd ~ $ git clone https://github.com/m4ll0k/WPSeku
Once you have obtained it, move into the **WPSeku** directory and run it as follows.
$ cd WPSeku
Now run the **WPSeku** using the `-u`
option to specify your WordPress installation URL like this.
$ ./wpseku.py -u http://yourdomain.com
The command below will search for cross site scripting, local file inclusion, and SQL injection vulnerabilities in your WordPress plugins using the `-p`
option, you need to specify the location of plugins in the URL:
$ ./wpseku.py -u http://yourdomain.com/wp-content/plugins/wp/wp.php?id= -p [x,l,s]
The following command will execute a brute force password login and password login via XML-RPC using the option `-b`
. Also, you can set a username and wordlist using the `--user`
and `--wordlist`
options respectively as shown below.
$ ./wpseku.py -u http://yourdomian.com --user username --wordlist wordlist.txt -b [l,x]
To view all WPSeku usage options, type.
$ ./wpseku.py --help
WPSeku Github repository: [https://github.com/m4ll0k/WPSeku](https://github.com/m4ll0k/WPSeku)
That’s it! In this article, we showed you how to get and use WPSeku for WordPress vulnerability scanning in Linux. WordPress is secure but only if we follow WordPress security best practices. Do you have any thoughts to share? If yes, then use the comment section below.
thanks for this wonderful article, very helpful.
Reply@Malid
Welcome, we are glad that your found it useful. Thanks for the feedback.
Reply]+[ Searching sql vulns…
ReplyTraceback (most recent call last):
File “./wpseku.py”, line 805, in
main.WPSekuMain()
File “./wpseku.py”, line 776, in WPSekuMain
WPAttack(self.url,self.path,self.query,self.headers).sqlattack()
File “./wpseku.py”, line 553, in sqlattack
params = dict([part.split(‘=’) for part in u.query.split(‘&’)])
ValueError: dictionary update sequence element #0 has length 1; 2 is required
@Bruce
Did you specify a valid URL? For example:
Reply./wpseku -u https://bruceferrel.comAnd for the -p option, you need to specify the location of plugins in the URL as shown in the article.
I think you should have blurred few more lines…
Reply@jsda
Sure, but for demonstration purposes, we only blurred the domain name(for security reasons).
Reply |
8,552 | 调试器工作原理(二):断点 | http://eli.thegreenplace.net/2011/01/27/how-debuggers-work-part-2-breakpoints | 2017-05-29T16:02:00 | [
"调试器",
"追踪"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8552-1.html | 
这是调试器工作原理系列文章的第二部分,阅读本文前,请确保你已经读过[第一部分](/article-8418-1.html)。
### 关于本文
我将会演示如何在调试器中实现断点。断点是调试的两大利器之一,另一个是可以在被调试进程的内存中检查变量值。我们在系列的第一部分已经了解过值检查,但是断点对我们来说依然神秘。不过本文过后,它们就不再如此了。
### 软件中断
为了在 x86 架构机器上实现断点,软件中断(也被称作“陷阱”)被会派上用场。在我们深入细节之前,我想先大致解释一下中断和陷阱的概念。
CPU 有一条单独的执行流,一条指令接一条的执行(在更高的层面看是这样的,但是在底层的细节上来说,现在的许多 CPU 都会并行执行多个指令,这其中的一些指令就不是按照原本的顺序执行的)。为了能够处理异步的事件,如 IO 和 硬件定时器,CPU 使用了中断。硬件中断通常是一个特定的电子信号,并附加了一个特别的”响应电路”。该电路通知中断激活,并让 CPU 停止当前执行,保存状态,然后跳转到一个预定义的地址,也就是中断处理程序的位置。当处理程序完成其工作后,CPU 又从之前停止的地方重新恢复运行。
软件中断在规则上与硬件相似,但实际操作中有些不同。CPU 支持一些特殊的指令,来允许软件模拟出一个中断。当这样的一个指令被执行时,CPU 像对待一个硬件中断那样 —— 停止正常的执行流,保存状态,然后跳转到一个处理程序。这种“中断”使得许多现代 OS 的惊叹设计得以高效地实现(如任务调度,虚拟内存,内存保护,调试)。
许多编程错误(如被 0 除)也被 CPU 当做中断对待,常常也叫做“异常”, 这时候硬件和软件中断之间的界限就模糊了,很难说这种异常到底是硬件中断还是软件中断。但我已经偏离今天主题太远了,所以现在让我们回到断点上来。
### int 3 理论
前面说了很多,现在简单来说断点就是一个部署在 CPU 上的特殊中断,叫 `int 3`。`int` 是一个 “中断指令”的 x86 术语,该指令是对一个预定义中断处理的调用。x86 支持 8 位的 int 指令操作数,这决定了中断的数量,所以理论上可以支持 256 个中断。前 32 个中断为 CPU 自己保留,而 int 3 就是本文关注的 —— 它被叫做 “调试器专用中断”。
避免更深的解释,我将引用“圣经”里一段话(这里说的“圣经”,当然指的是英特尔的体系结构软件开发者手册, 卷 2A)。
>
> INT 3 指令生成一个以字节操作码(CC),用于调用该调试异常处理程序。(这个一字节格式是非常有用的,因为它可以用于使用断点来替换任意指令的第一个字节 ,包括哪些一字节指令,而不会覆写其它代码)
>
>
>
上述引用非常重要,但是目前去解释它还是为时过早。本文后面我们会回过头再看。
### int 3 实践
没错,知道事物背后的理论非常不错,不过,这些理论到底意思是啥?我们怎样使用 `int 3` 部署断点?或者怎么翻译成通用的编程术语 —— *请给我看代码!*
实际上,实现非常简单。一旦你的程序执行了 `int 3` 指令, OS 就会停止程序( OS 是怎么做到像这样停止进程的? OS 注册其 int 3 的控制程序到 CPU 即可,就这么简单)。在 Linux(这也是本文比较关心的地方) 上, OS 会发送给进程一个信号 —— `SIGTRAP`。
就是这样,真的。现在回想一下本系列的第一部分, 追踪进程(调试程序) 会得到其子进程(或它所连接的被调试进程)所得到的所有信号的通知,接下来你就知道了。
就这样, 没有更多的电脑架构基础术语了。该是例子和代码的时候了。
### 手动设置断点
现在我要演示在程序里设置断点的代码。我要使用的程序如下:
```
section .text
; The _start symbol must be declared for the linker (ld)
global _start
_start:
; Prepare arguments for the sys_write system call:
; - eax: system call number (sys_write)
; - ebx: file descriptor (stdout)
; - ecx: pointer to string
; - edx: string length
mov edx, len1
mov ecx, msg1
mov ebx, 1
mov eax, 4
; Execute the sys_write system call
int 0x80
; Now print the other message
mov edx, len2
mov ecx, msg2
mov ebx, 1
mov eax, 4
int 0x80
; Execute sys_exit
mov eax, 1
int 0x80
section .data
msg1 db 'Hello,', 0xa
len1 equ $ - msg1
msg2 db 'world!', 0xa
len2 equ $ - msg2
```
我现在在使用汇编语言,是为了当我们面对 C 代码的时候,能清楚一些编译细节。上面代码做的事情非常简单,就是在一行打印出 “hello,”,然后在下一行打印出 “world!”。这与之前文章中的程序非常类似。
现在我想在第一次打印和第二次打印之间设置一个断点。我们看到在第一条 `int 0x80` ,其后指令是 `mov edx, len2`。(等等,再次 int?是的,Linux 使用 `int 0x80` 来实现用户进程到系统内核的系统调用。用户将系统调用的号码及其参数放到寄存器,并执行 `int 0x80`。然后 CPU 会跳到相应的中断处理程序,其中, OS 注册了一个过程,该过程查看寄存器并决定要执行的系统调用。)首先,我们需要知道该指令所映射的地址。运行 `objdump -d`:
```
traced_printer2: file format elf32-i386
Sections:
Idx Name Size VMA LMA File off Algn
0 .text 00000033 08048080 08048080 00000080 2**4
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, CODE
1 .data 0000000e 080490b4 080490b4 000000b4 2**2
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, DATA
Disassembly of section .text:
08048080 <.text>:
8048080: ba 07 00 00 00 mov $0x7,%edx
8048085: b9 b4 90 04 08 mov $0x80490b4,%ecx
804808a: bb 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%ebx
804808f: b8 04 00 00 00 mov $0x4,%eax
8048094: cd 80 int $0x80
8048096: ba 07 00 00 00 mov $0x7,%edx
804809b: b9 bb 90 04 08 mov $0x80490bb,%ecx
80480a0: bb 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%ebx
80480a5: b8 04 00 00 00 mov $0x4,%eax
80480aa: cd 80 int $0x80
80480ac: b8 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%eax
80480b1: cd 80 int $0x80
```
所以,我们要设置断点的地址是 `0x8048096`。等等,这不是调试器工作的真实姿势,对吧?真正的调试器是在代码行和函数上设置断点,而不是赤裸裸的内存地址?完全正确,但是目前我们仍然还没到那一步,为了更像*真正的*调试器一样设置断点,我们仍不得不首先理解一些符号和调试信息。所以现在,我们就得面对内存地址。
在这点上,我真想又偏离一下主题。所以现在你有两个选择,如果你真的感兴趣想知道*为什么*那个地址应该是 `0x8048096`,它代表着什么,那就看下面的部分。否则你只是想了解断点,你可以跳过这部分。
### 题外话 —— 程序地址和入口
坦白说,`0x8048096` 本身没多大意义,仅仅是可执行程序的 text 部分开端偏移的一些字节。如果你看上面导出来的列表,你会看到 text 部分从地址 `0x08048080` 开始。这告诉 OS 在分配给进程的虚拟地址空间里,将该地址映射到 text 部分开始的地方。在 Linux 上面,这些地址可以是绝对地址(例如,当可执行程序加载到内存中时它不做重定位),因为通过虚拟地址系统,每个进程获得自己的一块内存,并且将整个 32 位地址空间看做自己的(称为 “线性” 地址)。
如果我们使用 `readelf` 命令检查 ELF 文件头部(ELF,可执行和可链接格式,是 Linux 上用于对象文件、共享库和可执行程序的文件格式),我们会看到:
```
$ readelf -h traced_printer2
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 01 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF32
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: EXEC (Executable file)
Machine: Intel 80386
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x8048080
Start of program headers: 52 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 220 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 52 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 32 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 2
Size of section headers: 40 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 4
Section header string table index: 3
```
注意头部里的 `Entry point address`,它同样指向 `0x8048080`。所以我们在系统层面解释该 elf 文件的编码信息,它意思是:
1. 映射 text 部分(包含所给的内容)到地址 `0x8048080`
2. 从入口 —— 地址 `0x8048080` 处开始执行
但是,为什么是 `0x8048080` 呢?事实证明是一些历史原因。一些 Google 的结果把我引向源头,宣传每个进程的地址空间的前 128M 是保留在栈里的。128M 对应为 `0x8000000`,该地址是可执行程序其他部分可以开始的地方。而 `0x8048080`,比较特别,是 Linux `ld` 链接器使用的默认入口地址。该入口可以通过给 `ld` 传递 `-Ttext` 参数改变。
总结一下,这地址没啥特别的,我们可以随意修改它。只要 ELF 可执行文件被合理的组织,并且头部里的入口地址与真正的程序代码(text 部分)开始的地址匹配,一切都没问题。
### 用 int 3 在调试器中设置断点
为了在被追踪进程的某些目标地址设置一个断点,调试器会做如下工作:
1. 记住存储在目标地址的数据
2. 用 int 指令替换掉目标地址的第一个字节
然后,当调试器要求 OS 运行该进程的时候(通过上一篇文章中提过的 `PTRACE_CONT`),进程就会运行起来直到遇到 `int 3`,此处进程会停止运行,并且 OS 会发送一个信号给调试器。调试器会收到一个信号表明其子进程(或者说被追踪进程)停止了。调试器可以做以下工作:
1. 在目标地址,用原来的正常执行指令替换掉 int 3 指令
2. 将被追踪进程的指令指针回退一步。这是因为现在指令指针位于刚刚执行过的 int 3 之后。
3. 允许用户以某些方式与进程交互,因为该进程仍然停止在特定的目标地址。这里你的调试器可以让你取得变量值,调用栈等等。
4. 当用户想继续运行,调试器会小心地把断点放回目标地址去(因为它在第 1 步时被移走了),除非用户要求取消该断点。
让我们来看看,这些步骤是如何翻译成具体代码的。我们会用到第一篇里的调试器 “模板”(fork 一个子进程并追踪它)。无论如何,文末会有一个完整样例源代码的链接
```
/* Obtain and show child's instruction pointer */
ptrace(PTRACE_GETREGS, child_pid, 0, ®s);
procmsg("Child started. EIP = 0x%08x\n", regs.eip);
/* Look at the word at the address we're interested in */
unsigned addr = 0x8048096;
unsigned data = ptrace(PTRACE_PEEKTEXT, child_pid, (void*)addr, 0);
procmsg("Original data at 0x%08x: 0x%08x\n", addr, data);
```
这里调试器从被追踪的进程中取回了指令指针,也检查了在 `0x8048096` 的字。当开始追踪运行文章开头的汇编代码,将会打印出:
```
[13028] Child started. EIP = 0x08048080
[13028] Original data at 0x08048096: 0x000007ba
```
目前为止都看起来不错。接下来:
```
/* Write the trap instruction 'int 3' into the address */
unsigned data_with_trap = (data & 0xFFFFFF00) | 0xCC;
ptrace(PTRACE_POKETEXT, child_pid, (void*)addr, (void*)data_with_trap);
/* See what's there again... */
unsigned readback_data = ptrace(PTRACE_PEEKTEXT, child_pid, (void*)addr, 0);
procmsg("After trap, data at 0x%08x: 0x%08x\n", addr, readback_data);
```
注意到 `int 3` 是如何被插入到目标地址的。此处打印:
```
[13028] After trap, data at 0x08048096: 0x000007cc
```
正如预料的那样 —— `0xba` 被 `0xcc` 替换掉了。现在调试器运行子进程并等待它在断点处停止:
```
/* Let the child run to the breakpoint and wait for it to
** reach it
*/
ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, child_pid, 0, 0);
wait(&wait_status);
if (WIFSTOPPED(wait_status)) {
procmsg("Child got a signal: %s\n", strsignal(WSTOPSIG(wait_status)));
}
else {
perror("wait");
return;
}
/* See where the child is now */
ptrace(PTRACE_GETREGS, child_pid, 0, ®s);
procmsg("Child stopped at EIP = 0x%08x\n", regs.eip);
```
这里打印出:
```
Hello,
[13028] Child got a signal: Trace/breakpoint trap
[13028] Child stopped at EIP = 0x08048097
```
注意到 “Hello,” 在断点前打印出来了 —— 完全如我们计划的那样。同时注意到子进程停止的地方 —— 刚好就是单字节中断指令后面。
最后,如早先诠释的那样,为了让子进程继续运行,我们得做一些工作。我们用原来的指令替换掉中断指令,并且让进程从这里继续之前的运行。
```
/* Remove the breakpoint by restoring the previous data
** at the target address, and unwind the EIP back by 1 to
** let the CPU execute the original instruction that was
** there.
*/
ptrace(PTRACE_POKETEXT, child_pid, (void*)addr, (void*)data);
regs.eip -= 1;
ptrace(PTRACE_SETREGS, child_pid, 0, ®s);
/* The child can continue running now */
ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, child_pid, 0, 0);
```
这会使子进程继续打印出 “world!”,然后退出。
注意,我们在这里没有恢复断点。通过在单步调试模式下,运行原来的指令,然后将中断放回去,并且只在运行 PTRACE\_CONT 时做到恢复断点。文章稍后会展示 debuglib 如何做到这点。
### 更多关于 int 3
现在可以回过头去看看 `int 3` 和因特尔手册里那个神秘的说明,原文如下:
>
> 这个一字节格式是非常有用的,因为它可以用于使用断点来替换任意指令的第一个字节 ,包括哪些一字节指令,而不会覆写其它代码
>
>
>
int 指令在 x86 机器上占两个字节 —— `0xcd` 紧跟着中断数(细心的读者可以在上面列出的转储中发现 `int 0x80` 翻译成了 `cd 80`)。`int 3` 被编码为 `cd 03`,但是为其还保留了一个单字节指令 —— `0xcc`。
为什么这样呢?因为这可以允许我们插入一个断点,而不需要重写多余的指令。这非常重要,考虑下面的代码:
```
.. some code ..
jz foo
dec eax
foo:
call bar
.. some code ..
```
假设你想在 `dec eax` 这里放置一个断点。这对应一个单字节指令(操作码为 `0x48`)。由于替换断点的指令长于一个字节,我们不得不强制覆盖掉下个指令(`call`)的一部分,这就会篡改 `call` 指令,并很可能导致一些完全不合理的事情发生。这样一来跳转到 `foo` 分支的 `jz foo` 指令会导致什么?就会不在 dec eax 这里停止,CPU 径直去执行后面一些无效的指令了。
而有了单字节的 `int 3` 指令,这个问题就解决了。 1 字节是在 x86 上面所能找到的最短指令,这样我们可以保证仅改变我们想中断的指令。
### 封装一些晦涩的细节
很多上述章节样例代码的底层细节,都可以很容易封装在方便使用的 API 里。我已经做了很多封装的工作,将它们都放在一个叫做 debuglib 的通用库里 —— 文末可以去下载。这里我仅仅是想展示它的用法示例,但是绕了一圈。下面我们将追踪一个用 C 写的程序。
### 追踪一个 C 程序地址和入口
目前为止,为了简单,我把注意力放在了目标汇编代码。现在是时候往上一个层次,去看看我们如何追踪一个 C 程序。
事实证明并不是非常难 —— 找到放置断点位置有一点难罢了。考虑下面样例程序:
```
#include <stdio.h>
void do_stuff()
{
printf("Hello, ");
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
do_stuff();
printf("world!\n");
return 0;
}
```
假设我想在 `do_stuff` 入口处放置一个断点。我会先使用 `objdump` 反汇编一下可执行文件,但是打印出的东西太多。尤其看到很多无用,也不感兴趣的 C 程序运行时的初始化代码。所以我们仅看一下 `do_stuff` 部分:
```
080483e4 <do_stuff>:
80483e4: 55 push %ebp
80483e5: 89 e5 mov %esp,%ebp
80483e7: 83 ec 18 sub $0x18,%esp
80483ea: c7 04 24 f0 84 04 08 movl $0x80484f0,(%esp)
80483f1: e8 22 ff ff ff call 8048318 <puts@plt>
80483f6: c9 leave
80483f7: c3 ret
```
那么,我们将会把断点放在 `0x080483e4`,这是 `do_stuff` 第一条指令执行的地方。而且,该函数是在循环里面调用的,我们想要在断点处一直停止执行直到循环结束。我们将会使用 debuglib 来简化该流程,下面是完整的调试函数:
```
void run_debugger(pid_t child_pid)
{
procmsg("debugger started\n");
/* Wait for child to stop on its first instruction */
wait(0);
procmsg("child now at EIP = 0x%08x\n", get_child_eip(child_pid));
/* Create breakpoint and run to it*/
debug_breakpoint* bp = create_breakpoint(child_pid, (void*)0x080483e4);
procmsg("breakpoint created\n");
ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, child_pid, 0, 0);
wait(0);
/* Loop as long as the child didn't exit */
while (1) {
/* The child is stopped at a breakpoint here. Resume its
** execution until it either exits or hits the
** breakpoint again.
*/
procmsg("child stopped at breakpoint. EIP = 0x%08X\n", get_child_eip(child_pid));
procmsg("resuming\n");
int rc = resume_from_breakpoint(child_pid, bp);
if (rc == 0) {
procmsg("child exited\n");
break;
}
else if (rc == 1) {
continue;
}
else {
procmsg("unexpected: %d\n", rc);
break;
}
}
cleanup_breakpoint(bp);
}
```
为了避免修改 EIP 标志位和目的进程的内存空间的麻烦,我们仅需要调用 `create_breakpoint`,`resume_from_breakpoint` 和 `cleanup_breakpoint`。让我们来看看追踪上面的 C 代码样例会输出什么:
```
$ bp_use_lib traced_c_loop
[13363] debugger started
[13364] target started. will run 'traced_c_loop'
[13363] child now at EIP = 0x00a37850
[13363] breakpoint created
[13363] child stopped at breakpoint. EIP = 0x080483E5
[13363] resuming
Hello,
[13363] child stopped at breakpoint. EIP = 0x080483E5
[13363] resuming
Hello,
[13363] child stopped at breakpoint. EIP = 0x080483E5
[13363] resuming
Hello,
[13363] child stopped at breakpoint. EIP = 0x080483E5
[13363] resuming
Hello,
world!
[13363] child exited
```
如预期一样!
### 样例代码
[这里是](https://github.com/eliben/code-for-blog/tree/master/2011/debuggers_part2_code)本文用到的完整源代码文件。在归档中你可以找到:
* debuglib.h 和 debuglib.c - 封装了调试器的一些内部工作的示例库
* bp\_manual.c - 这篇文章开始部分介绍的“手动”设置断点的方法。一些样板代码使用了 debuglib 库。
* bp*use*lib.c - 大部分代码使用了 debuglib 库,用于在第二个代码范例中演示在 C 程序的循环中追踪。
### 引文
在准备本文的时候,我搜集了如下的资源和文章:
* [How debugger works](http://www.alexonlinux.com/how-debugger-works)
* [Understanding ELF using readelf and objdump](http://www.linuxforums.org/articles/understanding-elf-using-readelf-and-objdump_125.html)
* [Implementing breakpoints on x86 Linux](http://mainisusuallyafunction.blogspot.com/2011/01/implementing-breakpoints-on-x86-linux.html)
* [NASM manual](http://www.nasm.us/xdoc/2.09.04/html/nasmdoc0.html)
* [SO discussion of the ELF entry point](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2187484/elf-binary-entry-point)
* [This Hacker News discussion](http://news.ycombinator.net/item?id=2131894) of the first part of the series
* [GDB Internals](http://www.deansys.com/doc/gdbInternals/gdbint_toc.html)
---
via: <http://eli.thegreenplace.net/2011/01/27/how-debuggers-work-part-2-breakpoints>
作者:[Eli Bendersky](http://eli.thegreenplace.net/) 译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 302 | Found | null |
8,553 | ttyload:在终端中用彩色显示 Linux 的平均负载 | https://www.tecmint.com/ttyload-shows-color-coded-graph-of-linux-load-average/ | 2017-05-30T10:17:00 | [
"监控",
"负载",
"ttyload"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8553-1.html | 
ttyload 是一个轻量级的实用程序,它为 Linux 和其他类 Unix 系统上提供随着时间变化的彩色平均负载。它实现了在终端中(“tty”)图形化跟踪系统的平均负载。
它已知可以在诸如 Linux、IRIX、Solaris、FreeBSD、MacOS X (Darwin) 和 Isilon OneFS 等系统上运行。它被设计为可以容易地移植到其他平台,但这也带来了一些艰苦的工作。
它的一些值得注意功能是:它使用标准的硬编码 ANSI 转义序列进行屏幕显示和着色。如果你想要在一个没有什么负载压力的系统中查看工作的情况,它甚至还自带了一个相对独立(默认不会安装,甚至不会构建)的负载炸弹。
**建议阅读:**[GoTTY:把你的 Linux 终端放到浏览器里面](/article-8445-1.html)
在本篇中,我们会向你展示如何在 Linux 安装及使用 ttyload,以在终端中用彩色图形查看系统的平均负载。
### 如何在 Linux 中安装 ttyload
在基于 Debian/Ubuntu 的发行版中,你可以输入下面的 apt 命令来从默认的系统仓库中安装 ttyload。
```
$ sudo apt-get install ttyload
```
在其他发行版中,你可以如下从 ttyload 的源码安装。
```
$ git clone https://github.com/lindes/ttyload.git
$ cd ttyload
$ make
$ ./ttyload
$ sudo make install
```
安装完成后,你可以输入下面的命令启动。
```
$ ttyload
```

*ttyload - 图形浏览 Linux 的平均负载*
注意:要关闭程序,只需按下 `Ctrl+C` 键。
你也可以定义两次刷新之间间隔的秒数。默认是 4 秒,最小是 1 秒。
```
$ ttyload -i 5
$ ttyload -i 1
```
要以单色模式运行,即它会关闭 ANSI 转义,如下使用 `-m`:
```
$ ttyload -m
```

*ttyload – 单色模式*
要获取 ttyload 的使用信息以及帮助,输入:
```
$ ttyload -h
```
下面是一些尚不支持的重要功能:
* 支持任意大小调整。
* 使用相同的基本引擎制作 X 前端,“3xload”。
* 面向日志的模式。
要获得更多信息,访问 ttyload 的主页:<http://www.daveltd.com/src/util/ttyload/>
就是这样了!在本文中,我们向你展示了如何在 Linux 中安装及使用 ttyload。通过下面的评论栏给我们回馈。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 的爱好者,即将推出的 Linux SysAdmin 网络开发人员,目前也是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢和电脑一起工作,并且坚信共享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/ttyload-shows-color-coded-graph-of-linux-load-average/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | **ttyload** is a lightweight utility which is intended to offer a color-coded graph of load averages over time on Linux and other Unix-like systems. It enables a graphical tracking of system load average in a terminal (“**tty**“).
It is known to run on systems such as Linux, IRIX, Solaris, FreeBSD, MacOS X (Darwin) and Isilon OneFS. It is designed to be easy to port to other platforms, but this comes with some hard work.
Some of its notable features are: it uses fairly standard, but hard-coded, ANSI escape sequences for screen manipulation and colorization. And also comes with (but doesn’t install, or even build by default) a relatively self-contained load bomb, if you want to view how things work on an otherwise unloaded system.
**Suggested Read:** [GoTTY – Share Your Linux Terminal (TTY) as a Web Application](https://www.tecmint.com/gotty-share-linux-terminal-in-web-browser/)
In this article, we will show you how to install and use **ttyload** in Linux to view a color-coded graph of your system load average in a terminal.
### How to Install ttyload in Linux Systems
On Debian/Ubuntu based distributions, you can install **ttyload** from the default system respositores by typing the following [apt-get command](https://www.tecmint.com/useful-basic-commands-of-apt-get-and-apt-cache-for-package-management/).
$ sudo apt-get install ttyload
On Other Linux distributions you can install **ttyload** from the source as shown.
$ git clone https://github.com/lindes/ttyload.git $ cd ttyload $ make $ ./ttyload $ sudo make install
Once installed, you can start it by typing the following command.
$ ttyload
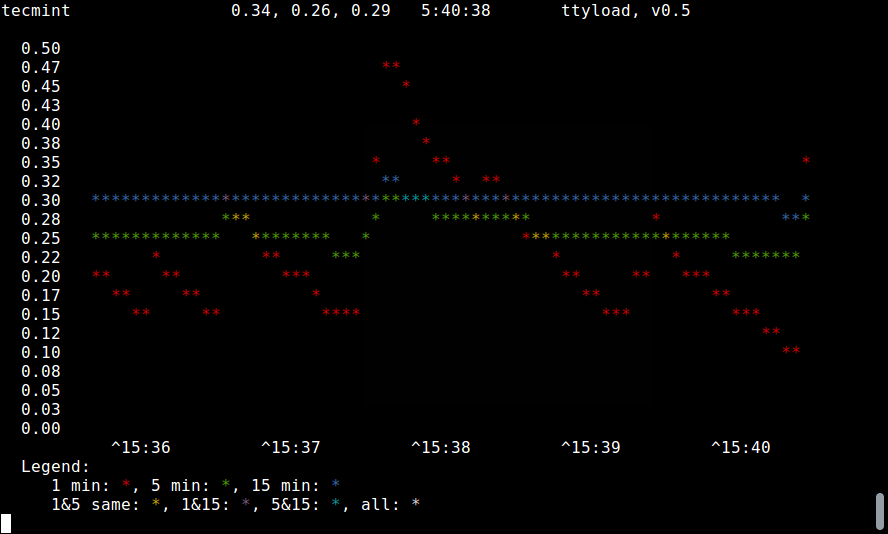
**Note**: To close the program simply press `[Ctrl+C]`
keys.
You can also define the number of seconds in the interval between refreshes. Default value is 4, and the minimum is 1.
$ ttyload -i 5 $ ttyload -i 1
To run it in a monochrome mode which turns off ANSI escapes, use the `-m`
as follows.
$ ttyload -m
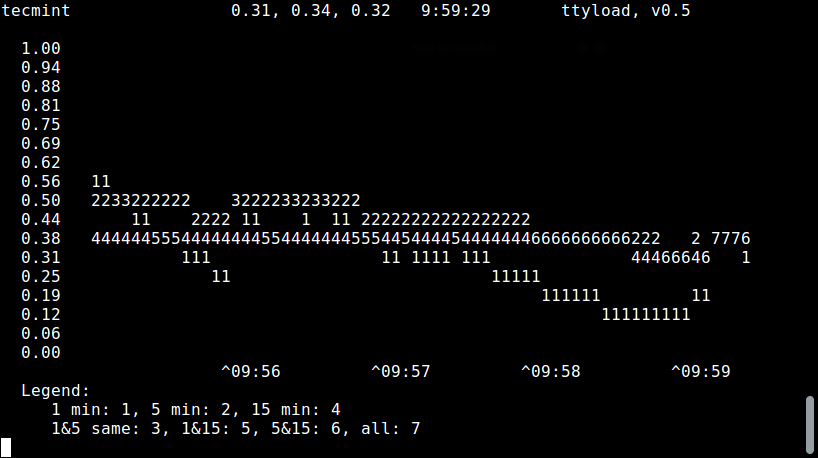
To get the ttyload usage info and help, type.
$ ttyload -h
Below are some of its important features yet to be added:
- Support for arbitrary sizing.
- Make an X front end using the same basic engine, to have “3xload”.
- Logging-oriented mode.
For more information, check out the ttyload Homepage: [http://www.daveltd.com/src/util/ttyload/](http://www.daveltd.com/src/util/ttyload/)
Thats all for now! In this article, we showed you how to install and use ttyload in Linux. Write back to us via the comment section below. |
8,554 | Linux 桌面系统的优势 | http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/84326.html | 2017-05-29T17:02:00 | [
"Linux"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8554-1.html | 
当我放弃 Windows [转而使用 Linux 系统](http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/84286.html) 后,我的信心不断增长。出于安全方面的考虑促使我选用 Linux 系统,但是我很快发现了很多使用 Linux 桌面系统的优势。
对于那些还对 Linux 系统犹豫不决,或是那些不甚了解 Linux 系统的用户,我将通过这篇文章给大家介绍一些使用 Linux 桌面系统的优势。
### 免费才是王道
首先, Linux 系统完全免费。你无须为使用的操作系统或软件花费一分钱。除了免费获取软件产生的经济效益之外,你还可以在 Linux 系统中随意使用一些当前很流行的软件,比如文字处理软件和照片编辑软件——由于费用方面的原因,我们可能不太愿意花钱去购买这些软件。
微软的 Office 办公软件几乎是处理各种类型文档的一种标准软件了,但是它每年的费用竟高达 70 美元。然而,你却可以免费使用 [LibreOffice](http://www.libreoffice.org/) 软件来代替,它同样可以处理各种类型的文档,而且使用也很方便。
免费软件还能让您有机会尝试新的功能,并通过它们寻求商务和休闲的新方式,而且你也不需要支付任何预期的费用。
与其费尽周折的去衡量 Mac 或 Windows 系统的优点,你可以考虑下在[上百款不同风格的 Linux 发行版](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linux_distribution)中选择一款最适合自己的操作系统。
Linux 系统甚至在硬件方面也为用户节省了不少钱,比如有些厂商——尤其是戴尔公司——为购买预安装了 Linux 系统的电脑的用户提供打折优惠。这些电脑的价格相对来说比较便宜,因为用户无须再花钱购买微软的 Windows 系统许可证。
### 随心所欲的系统定制
其次,在 Linux 系统中,你可以对系统功能进行任意更改。 Linux 生态系统中的核心项目之一就是桌面环境——它是一些由基础的用户程序和可视化元素组成的一个集合,比如状态栏和启动器,这些元素构成了用户与计算机的一个交互界面。
有些 Linux 发行版还预安装了桌面环境。比如, Ubuntu 系统就预安装了 Unity 桌面。其它系统,比如 Debian 会在系统安装的过程中让用户选择需要的桌面环境。总之,在 Linux 系统中,用户都可以随意更换他们喜欢的桌面环境。
大多数的 Linux 发行版都支持(也就是兼容)那些非常流行的桌面环境,因此,找到一款适合自己的桌面系统也非常容易。在桌面系统这个万花筒里,你可以找到界面华丽的系统桌面,比如 KDE Plasma 或者 [Gnome](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GNOME),以及轻量级的系统桌面,比如 Xfce 和 MATE 桌面。使用任一款系统桌面,你都可以通过更改主题、系统托盘和菜单,以及仿照其它用户的桌面环境来进一步定制自己的桌面环境。
Linux 系统的可定制特性完全超出你的想象力。如果你更看重系统的稳定性,你可以使用 Mint 这个发行版系统,它对硬件的兼容性非常好,而且也能确保系统顺利更新。
除此之外,如果你希望及时领略前沿,你可以安装 Arch Linux ,每一款软件只要开发者一发布,你就可以进行得到最新更新。
如果你介乎于两者之间,既想要稳定的系统,也想运行一些几个崭新的程序,你可以下载程序的源代码(程序员所开发的代码文件),然后自己进行编译。这就需要你使用工具来编译源代码,生成一堆你的电脑可以运行的 0 和 1 组成的二进制文件。
你可以使用自己喜欢的任何方式去折腾属于自己的 Linux 系统。
### 无与伦比的安全性
第三,多才多艺的 Linux 系统还有一个更重要的特性:安全。
起初,尽管有一些针对 Linux 系统的病毒,但是跟 Mac 系统比起来,已经屈指可数了。更重要的是,实际上 Linux 系统的核心代码是开源的,对用户完全透明,这意味着你的 Linux 系统漏洞更少。
一些专有(比如,不开源)的操作系统被认为会影响用户安全,因为它们会启动一些实现方式糟糕的、不透明的进程,从而造成了巨大的威胁。
比如说, Windows 系统在升级的过程中,默认情况下[不会检查加密签名](https://duo.com/blog/out-of-box-exploitation-a-security-analysis-of-oem-updaters)来验证更新文件的可靠性。
而使用 Linux 系统,你可以在选择更新时通过签名检查进行严格的细粒度控制,大多数的发行版在系统更新时都默认强制安全检查。这种责任感源自于 Linux 系统的开源开发模式所带来的透明度。
像 Arch Linux 这种滚动发行版则增加了更多的安全性设置,因为一些重要的补丁一旦通过验证, Arch Linux 就会马上可以使用。你可能很难找到那些每天都提供更新的单一主流操作系统,但是这样的 Linux 发行版却有很多。
### 天生的编程环境
很多开发者或者任何对编程有兴趣的人都得益于 Linux 桌面系统中集成的强大开发工具。其中包括那些最经典的编程工具,比如 GNU C 编译器,或者 GCC 和 GNU Autoconf 工具都是 Linux 系统中一些非常重要的基础工具。
Linux 系统的大多数默认软件库都支持数十种编程语言,它包含了发行版中可以使用的预编译软件。
很多因特网的基础架构和许多联网设备都运行于 Linux 系统上——从服务器到智能设备,比如安防摄像机和恒温器。在 Linux 系统下开发调试这些设备的软件非常容易。如果你有一个跟计算机相关的项目, Linux 系统可以完美地支持你完成这个项目。
### 社区是 Linux 系统发展的关键
最后一点, Linux 系统拥有一个团结且友好型的社区。由于 Linux 在桌面系统是一个相对小众的桌面操作系统,仅占有 3% 左右的市场份额,因此, Linux 社区更希望有更多的潜在用户加入进来。
Linux 系统有很多的用户论坛,尤其是对新手比较友好的 Ubuntu 系统论坛,它包括非常丰富且全面的知识来帮助用户解决一些基本的系统问题。很多高级用户更倾向于使用 Linux 系统,因此那些 Linux 发行版都拥有非常非常详尽维基文档,以指导用户完成高级的系统应用项目。
甚至还有业余的 Linux 论坛和 [Reddit](http://www.reddit.com/) 讨论区,所涉及的范围包括从对比 Linux 系统各种应用软件到炫耀桌面主题等。总而言之,这是一个比 Windows 用户群更加友善的社区。
我沉浸在 Linux 的世界里两年多了,我更加相信 Linux 系统对每一个用户都有所帮助。我希望这篇文章能够让你了解到 Linux 桌面系统的各种优势。但是真正的乐趣是从中发现自己感兴趣的东西!
---
via: <http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/84326.html>
作者:[Jonathan Terrasi](http://www.linkedin.com/company/ect-news-network) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,555 | Linux 系统调用的初学者指南 | https://opensource.com/article/17/5/beginners-guide-syscalls | 2017-05-30T08:29:00 | [
"系统调用",
"容器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8555-1.html | 
在过去的几年中,我一直在做大量容器相关的工作。先前,我看到 [Julien Friedman](https://twitter.com/doctor_julz) 的一个很棒的演讲,它用几行 Go 语言写了一个容器框架。这让我突然了解到容器只是一个受限的 Linux 进程中的机器。
构建这个受限视图涉及到 [Golang 系统调用包](https://golang.org/pkg/syscall/)中的很多调用。最初,我只是用到了表面的那些,但过了一段时间,我想剥下洋葱的下一层,看看这些系统调用是什么,以及它们的工作原理。我将在 OSCON 的演讲中分享我所学到的东西。
顾名思义,[syscalls](http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/syscalls.2.html) 即系统调用,它们是你从用户空间请求进入 Linux 内核的方式。内核为你做一些工作,例如创建一个进程,然后再回到用户空间。
有一个常见的机制使所有的系统调用转换到内核,这是由 **libc** 库处理的。 用户空间代码设置一些寄存器,包括其想要的系统调用的 ID 以及需要传递给系统调用的所有参数。它触发一个 “陷阱” 将控制转换到内核。
这就是用户空间代码如何向内核请求的,而 Linux 也有一个伪文件系统,它允许内核将信息传递给用户空间,其内容看起来像普通的目录和文件。
`/proc` 目录是一个很好的例子。看看里面,你会发现有关机器上运行的进程的各种有趣的信息。在某些情况,像 **cgroups**(控制组)那样,用户空间可以通过写入这些伪文件系统下的文件来配置参数。
当你在使用容器时,特别有趣的是,主机的 `/proc` 包含了所有有关容器化的进程的信息。这包括环境变量,它们也保存在 `/proc` 伪文件系统中,这意味着你的主机可以访问所有正在运行的容器的环境。如果你通过环境变量将诸如凭证或数据库密码这类秘密传递到容器中,则可能会产生安全性后果。
许多编写常规程序的程序员可能不觉得他们经常使用系统调用。但实际上他们会经常调用,因为每天的活动比如制作文件或者更改目录都涉及 Linux 的系统调用。
你不必是一位系统程序员才能享受系统调用的乐趣!
*如果你想要了解更多*,Liz 会在 Austin,Texas 举办的 OSCON 2017 上演讲 [*Linux 系统调用的初学者指南*](https://conferences.oreilly.com/oscon/oscon-tx/public/schedule/detail/56840)。
(题图: opensource.com)
---
作者简介:
Liz Rice - Liz Rice 是一位技术传播者,也是 Aqua Security 的容器安全专家。此前,她共同创立了 Microscaling Systems,并开发了其实时伸缩引擎,以及流行的图像元数据网站 MicroBadger.com。她拥有丰富的从网络协议和分布式系统,以及数字技术领域,如 VOD,音乐和 VoIP 软件的开发、团队和产品管理经验。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/5/beginners-guide-syscalls>
作者:[Liz Rice](https://opensource.com/users/lizrice) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Over the last couple of years, I've been doing a lot of work with containers. Early on I saw a fascinating talk by [Julien Friedman](https://twitter.com/doctor_julz) where he wrote a bare-bones container in a few lines of Go. It gave me that "a-ha" moment where I grasped that containers are nothing more than Linux processes with a restricted view of the machine they're running on.
Building this restricted view involved quite a few calls in [Golang's syscall package](https://golang.org/pkg/syscall/). Initially, I just took that at face value, but after a while, I wanted to peel away the next layer of the onion to see what these syscalls are all about and how they work. I'll share what I learned in my talk at OSCON.
As the name suggests, [syscalls](http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/syscalls.2.html) are system calls, and they're the way that you can make requests from user space into the Linux kernel. The kernel does some work for you, like creating a process, then hands control back to user space.
There is a common mechanism for making all system calls transition into the kernel, which is handled by the **libc **library. Userspace code sets up some registers including an ID of the system call it wants to make and any parameters it needs to pass to the system call. It triggers a "trap" to transition control to the kernel.
That's how userspace code makes requests of the kernel, but Linux also has pseudo filesystems that allow the kernel to communicate information to user space. The contents look like ordinary directories and files.
The **/proc** directory is a great example. Look inside, and you'll find all sorts of interesting information about the processes running on a machine. In some cases, like **cgroups **(control groups), user space can configure parameters by writing into files under these pseudo filesystems.
It's particularly interesting when you're using containers because the host's **/proc** holds information about all the containerized processes. This includes environment variables, which are also stored in the **/proc*** *pseudo-filesystem, meaning that your host machine has access to the environment for all your running containers. This potentially has security consequences if you're passing secrets like certificates or database passwords into your containers through environment variables.
Many programmers working on normal applications may not feel that they're using syscalls very often. In practice, they are, because even everyday activities like making files or changing directories involve syscalls on Linux.
You don't have to be a systems programmer to have fun with syscalls!
*If you’d like to learn more, Liz will be presenting **A Beginner's Guide To Syscalls**at OSCON 2017 in Austin, Texas. If you’re interested in attending the conference, use this discount code *[when you register](http://www.oreilly.com/pub/cpc/44407?sc_cid=701600000012BzSAAU%20target=%22_blank%22)*:* **PCOS***.*
## Comments are closed. |
8,556 | 如何瘦身 Git 仓库 | https://confluence.atlassian.com/bitbucket/maintaining-a-git-repository-321848291.html | 2017-05-30T10:24:00 | [
"版本控制",
"Git"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8556-1.html | 
对 Git 仓库的维护通常是为了减少仓库的大小。如果你从另外一个版本控制系统导入了一个仓库,你可能需要在导入后清除掉不必要的文件。本文着重于从一个 Git 仓库中删除大文件,并且包含下列主题:
* 理解从 Git 的历史记录中删除文件
* 使用 BFG 重写历史记录
* 可选,使用 `git filter-branch` 重写历史记录
* 垃圾回收
>
> **请格外小心.....**
>
>
> 本文中的步骤和工具使用的高级技术涉及破坏性操作。确保您在开始之前仔细读过并**备份了你的仓库**,创建一个备份最容易的方式是使用 [--mirror](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3959924/whats-the-difference-between-git-clone-mirror-and-git-clone-bare) 标志对你的仓库克隆,然后对整个克隆的文件进行打包压缩。有了这个备份,如果在维护期间意外损坏了您的仓库的关键元素,那么你可以通过备份的仓库来恢复。
>
>
> 请记住,仓库维护对仓库的用户可能会是毁灭性的。与你的团队或者仓库的关注者进行沟通会是一个不错的主意。确保每个人都已经检查了他们的代码,并且同意在仓库维护期间停止开发。
>
>
>
### 理解从 Git 的历史记录中删除文件
回想一下,克隆仓库会克隆整个历史记录——包括每个源代码文件的所有版本。如果一个用户提交了一个较大的文件,比如一个 JAR,则随后的每次克隆都会包含这个文件。即使用户最终在后面的某次提交中删除了这个文件,但是这个文件仍然存在于这个仓库的历史记录中。要想完全的从你的仓库中删除这个文件,你必须:
* 从你的项目的*当前的*文件树中删除该文件;
* 从仓库的历史记录中删除文件——*重写* Git 历史记录,从包含该文件的*所有的*提交中删除这个文件;
* 删除指向*旧的*提交历史记录的所有 [reflog](http://git-scm.com/docs/git-reflog) 历史记录;
* 重新整理仓库,使用 [git gc](http://git-scm.com/docs/git-gc) 对现在没有使用的数据进行垃圾回收。
Git 的 “gc”(垃圾回收)将通过你的任何一个分支或者标签来删除仓库中所有的实际没用的或者以某种方式引用的数据。为了使其发挥作用,我们需要重写包含不需要的文件的所有 Git 仓库历史记录,仓库将不再引用它—— git gc 将会丢弃所有没用的数据。
重写存储库历史是一个棘手的事情,因为每个提交都依赖它的父提交,所以任何一个很小的改变都会改变它的每一个随后的提交的提交 ID。有两个自动化的工具可以做到这:
1. [BFG Repo Cleaner](http://rtyley.github.io/bfg-repo-cleaner/) 快速、简单且易于使用,需要 Java 6 或者更高版本的运行环境。
2. [git filter-branch](http://git-scm.com/docs/git-filter-branch) 功能强大、配置麻烦,用于大于仓库时速度较慢,是核心 Git 套件的一部分。
切记,当你重写历史记录后,无论你是使用 BFG 还是使用 filter-branch,你都需要删除指向旧的历史记录的 `reflog` 条目,最后运行垃圾回收器来删除旧的数据。
### 使用 BFG 重写历史记录
[BFG](http://rtyley.github.io/bfg-repo-cleaner/) 是为将像大文件或者密码这些不想要的数据从 Git 仓库中删除而专门设计的,所以它有一一个简单的标志用来删除那些大的历史文件(不在当前的提交里面):`--strip-blobs-bigger-than`
```
$ java -jar bfg.jar --strip-blobs-than 100M
```
大小超过 100MB 的任何文件(不包含在你*最近的*提交中的文件——因为 BFG [默认会保护你的最新提交的内容](http://rtyley.github.io/bfg-repo-cleaner/#protected-commits))将会从你的 Git 仓库的历史记录中删除。如果你想用名字来指明具体的文件,你也可以这样做:
```
$ java -jar bfg.jar --delete-files *.mp4
```
BFG 的速度要比 `git filter-branch` 快 [10-1000 倍](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ir4IHzPhJuI),而且通常更容易使用——查看完整的[使用说明](http://rtyley.github.io/bfg-repo-cleaner/#usage)和[示例](http://rtyley.github.io/bfg-repo-cleaner/#examples)获取更多细节。
### 或者,使用 git filter-branch 来重写历史记录
`filter-branch` 命令可以对 Git 仓库的历史记录重写,就像 BFG 一样,但是过程更慢和更手动化。如果你不知道这些大文件在*哪里*,那么你第一步就需要找到它们:
#### 手动查看你 Git 仓库中的大文件
[Antony Stubbs](https://stubbisms.wordpress.com/2009/07/10/git-script-to-show-largest-pack-objects-and-trim-your-waist-line/) 写了一个可以很好地完成这个功能的 BASH 脚本。该脚本可以检查你的包文件的内容并列出大文件。在你开始删除文件之前,请执行以下操作获取并安装此脚本:
1、 [下载脚本](https://confluence.atlassian.com/bitbucket/files/321848291/321979854/1/1360604134990/git_find_big.sh)到你的本地的系统。
2、 将它放在一个可以访问你的 Git 仓库的易于找到的位置。
3、 让脚本成为可执行文件:
```
$ chmod 777 git_find_big.sh
```
4、 克隆仓库到你本地系统。
5、 改变当前目录到你的仓库根目录。
6、 手动运行 Git 垃圾回收器:
```
git gc --auto
```
7、 找出 .git 文件夹的大小
```
$ du -hs .git/objects
45M .git/objects
```
注意文件大小,以便随后参考。
8、 运行 `git_find_big.sh` 脚本来列出你的仓库中的大文件。
```
$ git_find_big.sh
All sizes are in kB's. The pack column is the size of the object, compressed, inside the pack file.
size pack SHA location
592 580 e3117f48bc305dd1f5ae0df3419a0ce2d9617336 media/img/emojis.jar
550 169 b594a7f59ba7ba9daebb20447a87ea4357874f43 media/js/aui/aui-dependencies.jar
518 514 22f7f9a84905aaec019dae9ea1279a9450277130 media/images/screenshots/issue-tracker-wiki.jar
337 92 1fd8ac97c9fecf74ba6246eacef8288e89b4bff5 media/js/lib/bundle.js
240 239 e0c26d9959bd583e5ef32b6206fc8abe5fea8624 media/img/featuretour/heroshot.png
```
大文件都是 JAR 文件,包的大小列是最相关的。`aui-dependencies.jar` 被压缩到 169kb,但是 `emojis.jar` 只压缩到 500kb。`emojis.jar` 就是一个待删除的对象。
#### 运行 filter-branch
你可以给这个命令传递一个用于重写 Git 索引的过滤器。例如,一个过滤器可以可以将每个检索的提交删除。这个用法如下:
```
git filter-branch --index-filter 'git rm --cached --ignore-unmatch _pathname_ ' commitHASH
```
`--index-filter` 选项可以修改仓库的索引,`--cached` 选项从索引中而不是磁盘来删除文件。这样会更快,因为你不需要在运行这个过滤器前检查每个修订版本。`git rm` 中的 `ignore-unmatch` 选项可以防止在尝试移走不存在的文件 `pathname` 的时候命令失败。通过指定一个提交 HASH 值,你可以从每个以这个 HASH 值开始的提交中删除`pathname`。要从开始处删除,你可以省略这个参数或者指定为 `HEAD`。
如果你的大文件在不同的分支,你将需要通过名字来删除每个文件。如果大文件都在一个单独的分支,你可以直接删除这个分支本身。
#### 选项 1:通过文件名删除文件
使用下面的步骤来删除大文件:
1、 使用下面的命令来删除你找到的第一个大文件:
```
git filter-branch --index-filter 'git rm --cached --ignore-unmatch filename' HEAD
```
2、 重复步骤 1 找到剩下的每个大文件。
3、 在你的仓库里更新引用。 `filter-branch` 会为你原先的引用创建一个 `refs/original/` 下的备份。一旦你确信已经删除了正确的文件,你可以运行下面的命令来删除备份文件,同时可以让垃圾回收器回收大的对象:
```
git filter-branch --index-filter 'git rm --cached --ignore-unmatch filename' HEAD
```
#### 选项 2:直接删除分支
如果你所有的大文件都在一个单独的分支上,你可以直接删除这个分支。删除这个分支会自动删除所有的引用。
1、 删除分支。
```
$ git branch -D PROJ567bugfix
```
2、 从后面的分支中删除所有的 reflog 引用。
### 对不用的数据垃圾回收
1、 删除从现在到后面的所有 reflog 引用(除非你明确地只在一个分支上操作)。
```
$ git reflog expire --expire=now --all
```
2、 通过运行垃圾回收器和删除旧的对象重新打包仓库。
```
$ git gc --prune=now
```
3、 把你所有的修改推送回仓库。
```
$ git push --all --force
```
4、 确保你所有的标签也是当前最新的:
```
$ git push --tags --force
```
---
via: <https://confluence.atlassian.com/bitbucket/maintaining-a-git-repository-321848291.html>
作者:[atlassian.com](https://confluence.atlassian.com/bitbucket/maintaining-a-git-repository-321848291.html) 译者:[zhousiyu325](https://github.com/zhousiyu325) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,558 | 在 Linux 中使用 pushd 和 popd 命令来进行高效的目录导航 | https://www.tecmint.com/pushd-and-popd-linux-filesystem-navigation/ | 2017-05-31T15:16:00 | [
"pushd",
"popd",
"导航"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8558-1.html | 
有时候,通过命令来在 Linux 文件系统导航是一件非常痛苦的事情,特别是对于一些新手。通常情况下,我们主要使用 [cd(改变目录)命令](https://www.tecmint.com/cd-command-in-linux/)在 Linux 文件系统之间移动。
在之前的文章中,我们回顾了一个非常简单但很有用的 Linux 上的 CLI 工具,文章叫做 [bd:快速返回某级父目录而不用冗余地输入 “cd ../../..”](/article-8491-1.html)
在这个教程中,我们将讨论两个相关的命令:`pushd` 和 `popd` ,使用它们可以高效的浏览 Linux 目录结构。这两个命令在大多数 shell ,比如 bash、tcsh 中都存在。
**推荐阅读:**[Autojump:快速浏览 Linux 文件系统的一个高级 `cd` 命令](/article-5983-1.html)
### pushd 和 popd 命令在 Linux 系统中如何工作
`pushd` 和 `popd` 命令根据 ‘LIFO’(后进先出)原则工作。在这个原则之下,只有两个操作是允许的:把一个目录压入栈,以及把一个目录弹出栈。
`pushd` 命令会增加一个目录到栈顶,而 `popd` 命令会从栈顶移除一个目录。
为了显示目录栈中(或历史)的目录,我们可以使用下面展示的 `dirs` 命令:
```
$ dirs
或
$ dirs -v
```

*`dirs` - 显示位于目录栈中的目录*
`pushd` 命令:将一个目录路径添加到/放入目录栈(历史)中,之后,你可以浏览位于目录栈(历史)中的任意目录。当把一个新的目录入栈时,会打印出当前位于栈中的所有目录。
下面这些命令会展示这个命令是如何工作的:
```
$ pushd /var/www/html/
$ pushd ~/Documents/
$ pushd ~/Desktop/
$ pushd /var/log/
```

*`pushd` - 添加新目录入栈*
根据上面输出的目录栈可知(目录索引按倒序排列):
* `/var/log` 是目录栈中的第五个目录,索引为 0
* `~/Desktop/` 是第四个,索引为 1
* `~/Document/` 是第三个,索引为 2
* `/var/www/html` 是第二个,索引为 3
* `~` 是第一个,索引为 4
另外,我们也可以使用目录索引的形式 `pushd +#` 或 `pushd -#` 来添加目录入栈。为了进入目录 `~/Documents` ,我们可以输入:
```
$ pushd +2
```

*`pushd` -通过数字浏览目录*
注意,经过上一步操作以后,栈的内容便发生了改变。所以,要从上面的例子中进入目录 `/var/www/html` ,我们应该使用下面的命令:
```
$ pushd +1
```

*`pushd` -通过数字浏览目录*
`popd` 命令-从栈顶或历史中移除一个目录。为了列出目录栈中的所有目录,只需输入:
```
$ popd
```
为了从目录栈中移除一个目录,我们可以使用 `popd +#` 或 `popd -#` 命令,在这时,我们需要输入下面的命令来移除目录 `~/Documents` :
```
$ popd +1
```

*`popd`-从栈中以移除目录*
在这篇文章中,我们阐述了 `pushd` 和 `popd` 命令,使用它们可以高效的访问目录结构。你可以通过下面的反馈表和我们分享你关于这篇文章的想法。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux 系统管理员和网络开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/pushd-and-popd-linux-filesystem-navigation/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Sometimes it can be painful to navigate the Linux file system with commands, especially for the newbies. Normally, we primarily use the [cd (Change Directory) command](https://www.tecmint.com/cd-command-in-linux/) for moving around the Linux file system.
In a previous article, we reviewed a simple yet helpful CLI utility for Linux called [bd – for quickly moving back into a parent directory](https://www.tecmint.com/bd-quickly-go-back-to-a-linux-parent-directory/) without typing **cd ../../..** repeatedly.
This tutorial will explain a related set of commands: “**pushd**” and “**popd**” which are used for efficient navigation of the Linux directory structure. They exist in most shells such as bash, tcsh etc.
**Suggested Read:** [Autojump – An Advanced ‘cd’ Command to Quickly Navigate Linux Filesystem](https://www.tecmint.com/autojump-a-quickest-way-to-navigate-linux-filesystem/)
### How pushd and popd Commands Work in Linux
**pushd** and **popd** work according to the “**LIFO**” (last in, first out) principle. In this principle, only two operations are allowed: push an item into the stack, and pop an item out of the stack.
pushd adds a directory to the top of the stack and popd removes a directory from the top of the stack.
To display directories in the directory stack (or history), we can use the **dirs** command as shown.
$ dirs OR $ dirs -v
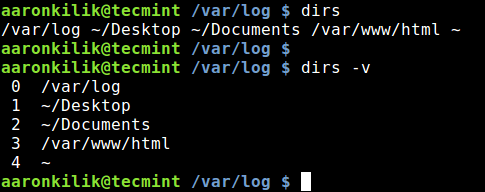
**pushd command** – puts/adds directory paths onto a directory stack (history) and later allowing you to navigate back to any directory in history. While you add directories to the stack, it also echoes what’s existing in history (or “stack”).
The commands show how pushd works:
$ pushd /var/www/html/ $ pushd ~/Documents/ $ pushd ~/Desktop/ $ pushd /var/log/
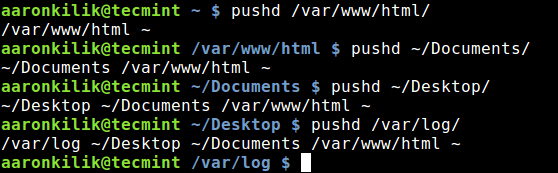
From directory stack in the output above (directory index is in reverse order):
**/var/log**is the fifth [index 0] in the directory stack.**~/Desktop/**is fourth [index 1].**~/Documents/**is third [index 2].**/var/www/html/**is second [index 3] and**~**is first [index 4].
Optionally, we can use the directory index in the form `pushd +#`
or `pushd -#`
to add directories to the stack. To move into **~/Documents**, we would type:
$ pushd +2
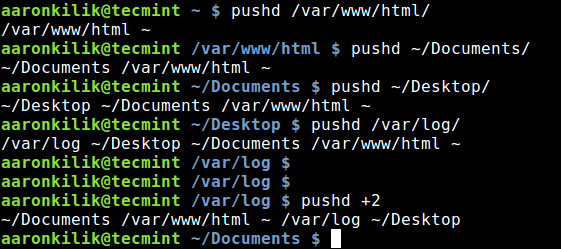
Note after this, the stack content will change. So from the previous example, to move into **/var/www/html**, we would use:
$ pushd +1
**popd command** – removes a directory from the top of the stack or history. To list the directory stack, type:
$ popd
To remove a directory from the directory stack inded use `popd +#`
or `popd -#`
, in this case, we would type the command below to remove **~/Documents**:
$ popd +1
Also check out: [Fasd – A Commandline Tool That Offers Quick Access to Files and Directories](https://www.tecmint.com/autojump-a-quickest-way-to-navigate-linux-filesystem/)
In this tutorial we explained “**pushd**” and “**popd**” commands which are used for efficient navigation of the directory structure. Share your thoughts concerning this article via the feedback form below.
Guys, you are too good. After reading this article My all confusions about
pushdandpopdget cleared.Thank you so much.
ReplyI saw this same tip on Enki today, and then I saw it here. Coincidence? I think not :-) Seriously though, I’ve used Linux since the early 00s, and somehow I only learned about popd and pushd today!
Reply@Sophie,
Maybe coincidence, but trust me, even I don’t know about these two tiny commands
Replypushdandpopdtill now, last day came to know when one of my author Aaron written an article on the same…@Sophie
I did not know about these commands as well, but in a recent article we published: bd – Quickly Go Back to a Parent Directory Instead of Typing “cd ../../..” Redundantly, a reader suggested to us
pushdandpopdcommands for efficient file system navigation in one of the comments.Then i had to write this article about them.
Reply |
8,559 | 新的“永恒之石”病毒利用了七个 NSA 黑客工具,“想哭”病毒才两个 | https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/new-smb-worm-uses-seven-nsa-hacking-tools-wannacry-used-just-two/ | 2017-05-31T16:15:00 | [
"NSA",
"病毒",
"勒索"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8559-1.html | 
研究人员们发现有一个新的蠕虫病毒正在通过 SMB 文件共享漏洞传播,但是不同于<ruby> “想哭” <rp> ( </rp> <rt> WannaCry </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>勒索病毒的构成,这个病毒利用了 7 个 NSA 黑客工具,而不是<ruby> “想哭” <rp> ( </rp> <rt> WannaCry </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>勒索病毒的两个。
这个蠕虫病毒的存在首次发现是在周三,它感染了 [Miroslav Stampar](https://about.me/stamparm) 的 SMB 文件共享的蜜罐,Miroslav Stampar 是克罗地亚政府计算机应急响应小组成员,也是用来探测和利用 SQL 注入漏洞的 SQLMAP 工具的制造者。
### 永恒之石利用了七个 NSA 的工具
Stampar 命名这个在样本中被发现的病毒为<ruby> “永恒之石” <rp> ( </rp> <rt> EternalRocks </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,其基于蠕虫病毒可执行的特性,它通过 6 个以 SMB 文件共享漏洞为中心的 NSA 工具来感染暴露在外网的一台开启 SMB 端口的计算机。这些被叫做 **永恒之蓝**、**永恒战士**、**永恒浪漫** 和 **永恒协同**的 SMB 漏洞被利用危害易受攻击的计算机,而 **SMBTOUCH** 和 **ARCHITOUCH** 这两个 NSA 工具起到了检测 SMB 文件共享漏洞的作用。
一旦这个蠕虫病毒获得了最初的立足点,那么它会用另一个叫做 **DOUBLEPULSAR** 的 NSA 工具扩散到新的易受攻击的机器上。

*“永恒之石”名字的起源*
[“想哭”勒索病毒爆发](https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/wana-decrypt0r-ransomware-using-nsa-exploit-leaked-by-shadow-brokers-is-on-a-rampage/),用了一个 SMB 蠕虫病毒感染计算机并扩散给新的受害人,这影响了超过 24 万受害者。
不同于“永恒之石”,“想哭”的 SMB 蠕虫病毒只利用了永恒之蓝这一个漏洞做初步感染,然后通过 DOUBLEPULSAR 来扩散到其他的计算机上。
### “永恒之石”更加复杂,但危险性较低
作为蠕虫病毒,“永恒之石”没有“想哭”那么危险,这是由于它当前不传递任何恶意的内容,然而,这并不意味着“永恒之石”不复杂,据 Stampar 说,实际恰恰相反。
首先,“永恒之石”要比“想哭”的 SMB 蠕虫病毒更加隐蔽,一旦病毒感染了一台计算机,它会发起有两个阶段的安装过程,其中另一个是延迟执行的。
在病毒的第一个安装过程阶段,永恒之石获取一个感染计算机主机的立足点,下载 tor 客户端,然后连接到它的命令控制服务器,其定位在暗网的一个 .onion 的域名上。
在一个预定的时间内,一般是 24 个小时,命令控制器会响应,这个长延迟执行进程的做法最有可能绕过沙盒安全测试环境和安全研究人员们对病毒的分析,因为没多少人愿意一整天来等命令控制器响应。

### 没有停止开关的域名
此外,“永恒之石”病毒也会用和一个与“想哭” SMB 的蠕虫病毒文件相同名字的一个文件,以此愚弄安全研究人员来误判它。
但是不同于“想哭”病毒,永恒之石不包括停止开关的域名,但这是安全研究人员唯一用来停止“想哭”病毒爆发的方法。
在病毒隐匿期满且命令控制器有了响应,永恒之石开始进入安装过程的第二阶段,它会下载一个名为 shadowbrokers.zip 的归档形式的第二阶段恶意组件。
这个文件能够自解压,它包含着 shadow Brokers 黑客组织在 2017 年 4 月泄漏的七个 NSA 的 SMB 漏洞工具。 这个蠕虫病毒会开始一个快速的 ip 扫描过程并且尝试连接随机的 ip 地址。

*在 shadowbrokers.zip 压缩包里发现了 NSA 工具的配置文件。*
### “永恒之石”可以马上成为武器
由于该病毒集成的漏洞较多且广泛,缺少停止开关的域名,而且有它的隐匿期,如果病毒的作者决定用它来作为勒索、银行木马、远程控制或者其他功能的武器,“永恒之石”可能会对 SMB 端口暴露在互联网的易受攻击的计算机造成严重的威胁。
就目前来看,蠕虫病毒看起来像是一个试验,或者是恶意软件作者在进行测试或者为未来的威胁而做的微调。
然而,这并不意味着“永恒之石”是无害的,感染了这个病毒的计算机是通过命令控制服务器来控制,并且蠕虫病毒的制造者能够利用这个隐藏通讯连接,发送新的恶意软件到这台感染了病毒的电脑上。
此外,DOUBLEPULSAR,这是一个带有后门的植入仍然运行在感染了永恒之石的 PC 上,不幸的是,该病毒的作者没有采取任何措施来保护这个 DOUBLEPULSAR 的植入,这意味这缺省其运行在未被保护的状态下,其他的恶意的用户能使用它作为把感染了永恒之石的计算机的后门,发送他们自己的恶意软件到这些感染病毒的 PC 上。
关于这个病毒的感染过程的 IOC 和更多信息能够在 Stampar 在几天前设置的 [GitHub] 仓库上获得。
### SMB 漏洞的混战
当前,有许多人在扫描旧的和未打补丁的 SMB 服务,系统管理员已经注意到并且开始给易受攻击的计算机打补丁,关闭旧版的 SMBv1 协议,慢慢的来减少被永恒之石感染的计算机数量。
此外,像 Adylkuzz 这类恶意软件,也会关闭 SMB 端口,来阻止来自其它威胁软件的进一步利用,这同时也导致了“永恒之石”和其它利用 SMB 漏洞的恶意软件潜在目标数量的减少,来自 [Forcepoint](https://blogs.forcepoint.com/security-labs/wannacry-multiple-malware-families-using-eternalblue-exploit)、[Cyphort](https://www.cyphort.com/eternalblue-exploit-actively-used-deliver-remote-access-trojans/) 和 [Secdo](http://blog.secdo.com/multiple-groups-exploiting-eternalblue-weeks-before-wannacry) 的报告详细介绍了当前针对 SMB 端口的计算机的威胁情况。
虽然如此,系统管理员补丁打的越快,系统越安全,“蠕虫病毒感染速度正在和系统管理员给机器打补丁速度比赛”,Stampar 在一次私人谈话中告诉 BleepingComputer 记者,“一旦计算机被感染,它能在任何时间将其作为武器,不论你打多时间多近的补丁。”
(题图:Miroslav Stampar, BleepingComputer & [Ana María Lora Macias](https://thenounproject.com/search/?q=worm&i=24323))
---
作者简介:
Catalin 涉及了各方面,像数据泄漏、软件漏洞、漏洞利用、黑客新闻、暗网、编程话题、社交媒体、Web技术、产品研发等领域。
---
via: <https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/new-smb-worm-uses-seven-nsa-hacking-tools-wannacry-used-just-two/>
作者:[CATALIN CIMPANU](https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/author/catalin-cimpanu/) 译者:[hwlog](https://github.com/hwlog) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Researchers have detected a new worm that is spreading via SMB, but unlike the worm component of the WannaCry ransomware, this one is using seven NSA tools instead of two.
The worm's existence first came to light on Wednesday, after it infected the SMB honeypot of [Miroslav Stampar](https://about.me/stamparm), member of the Croatian Government CERT, and creator of the sqlmap tool used for detecting and exploiting SQL injection flaws.
## EternalRocks uses seven NSA tools
The worm, which Stampar named EternalRocks based on worm executable properties found in one sample, works by using six SMB-centric NSA tools to infect a computer with SMB ports exposed online. These are **ETERNALBLUE**, **ETERNALCHAMPION**, **ETERNALROMANCE**, and **ETERNALSYNERGY**, which are SMB exploits used to compromise vulnerable computers, while **SMBTOUCH** and **ARCHITOUCH** are two NSA tools used for SMB reconnaissance operations.
Once the worm has obtained this initial foothold, it then uses another NSA tool, **DOUBLEPULSAR**, to propagate to new vulnerable machines.
**Origin of the EternalRocks name**
[The WannaCry ransomware outbreak](https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/wana-decrypt0r-ransomware-using-nsa-exploit-leaked-by-shadow-brokers-is-on-a-rampage/), which affected over 240,000 victims, also used an SMB worm to infect computers and spread to new victims.
Unlike EternalRocks, WannaCry's SMB worm used only ETERNALBLUE for the initial compromise, and DOUBLEPULSAR to propagate to new machines.
## EternalRocks is more complex but less dangerous
As a worm, EternalRocks is far less dangerous than WannaCry's worm component, as it currently does not deliver any malicious content. This, however, does not mean that EternalRocks is less complex. According to Stampar, it's actually the opposite.
For starters, EternalRocks is far more sneaky than WannaCry's SMB worm component. Once it infects a victim, the worm uses a two-stage installation process, with a delayed second stage.
During the first stage, EternalRocks gains a foothold on an infected host, downloads the Tor client, and beacons its C&C server, located on a .onion domain, the Dark Web.
Only after a predefined period of time — currently 24 hours — does the C&C server respond. The role of this long delay is most probably to bypass sandbox security testing environments and security researchers analyzing the worm, as very few will wait a full day for a response from the C&C server.
Update on
— Miroslav Stampar (@stamparm)[#EternalRocks]. Original name is actually "MicroBotMassiveNet" while author's nick is "tmc"[https://t.co/xqoxkNYfM7][pic.twitter.com/6Ico7gcg9u][May 19, 2017]
## No kill switch domain
Additionally, EternalRocks also uses files with identical names to the ones used by WannaCry's SMB worm, in another attempt to fool security researchers into misclassifying it.
But unlike WannaCry, EternalRocks does not include a kill switch domain, the Achille's heel that security researchers used to stop the WannaCry outbreak.
After the initial dormancy period expires and the C&C server responds, EternalRocks goes into the second stage of its installation process and downloads a second stage malware component in the form of an archive named shadowbrokers.zip.
The name of this file is pretty self-explanatory, as it contains NSA SMB-centric exploits [leaked by the Shadow Brokers group](https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/shadow-brokers-release-new-files-revealing-windows-exploits-swift-attacks/) in April 2017.
The worm then starts a rapid IP scanning process and attempts to connect to random IP addresses.
**The configuration files for NSA tools found in the shadowbrokers.zip archive**
## EternalRocks could be weaponized in an instant
Because of its broader exploit arsenal, the lack of a kill switch domain, and because of its initial dormancy, EternalRocks could pose a serious threat to computers with vulnerable SMB ports exposed to the Internet, if its author would ever decide to weaponize the worm with ransomware, a banking trojan, RATs, or anything else.
At first glance, the worm seems to be an experiment, or a malware author performing tests and fine-tuning a future threat.
This, however, does not mean EternalRocks is harmless. Computers infected with this worm are controllable via C&C server commands and the worm's owner could leverage this hidden communications channel to send new malware to the computers previously infected by EternalRocks.
Furthermore, DOUBLEPULSAR, [an NSA implant with backdoor features](https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/over-36-000-computers-infected-with-nsas-doublepulsar-malware/), remains running on PCs infected with EternalRocks. Unfortunately, the worm's author has not taken any measures to protect the DOUBLEPULSAR implant, which runs in a default unprotected state, meaning other threat actors could use it as a backdoor to machines infected by EternalRocks, by sending their own malware to those PCs.
IOCs and more info on the worm's infection process are available in a [GitHub repo](https://github.com/stamparm/EternalRocks/) Stampar set up a few days ago.
## An SMB free-for-all
Currently, there are multiple actors scanning for computers running older and unpatched versions of the SMB services. System administrators have already taken notice and started patching vulnerable PCs or disabling the old SMBv1 protocol, slowly reducing the number of vulnerable machines that EternalRocks can infect.
Furthermore, malware such as [Adylkuzz](https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/adylkuzz-cryptocurrency-miner-may-have-saved-you-from-the-wannacry-ransomware/) also shuts down SMB ports, preventing further exploitation from other threats, also contributing to reducing the number of potential targets for EternalRocks and other SMB-hunting malware. Reports from [Forcepoint](https://blogs.forcepoint.com/security-labs/wannacry-multiple-malware-families-using-eternalblue-exploit), [Cyphort](https://www.cyphort.com/eternalblue-exploit-actively-used-deliver-remote-access-trojans/), and [Secdo](http://blog.secdo.com/multiple-groups-exploiting-eternalblue-weeks-before-wannacry) detail other threats currently targeting computers with SMB ports.
Nonetheless, the faster system administrators patch their systems the better. "The worm is racing with administrators to infect machines before they patch," Stampar told Bleeping Computer in a private conversation. "Once infected, he can weaponize any time he wants, no matter the late patch."
*Image credits: Miroslav Stampar, BleepingComputer & Ana María Lora Macias*
## Comments
## berite100 - 7 years ago
how can we detect if we are infected with this worm? |
8,560 | 4 个用于托管开源库的顶级 CDN 服务 | https://opensource.com/article/17/4/top-cdn-services | 2017-06-01T08:07:00 | [
"CDN"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8560-1.html |
>
> 内容分发网络可以加速你的网站图片、CSS、JS、以及其他静态内容。
>
>
>

CDN 或称内容分发网络是位于世界各地的策略性放置的服务器网络,用于更快地向用户传输文件。传统 CDN 能够加速你的网站的图像、CSS、JS 和任何其他静态内容的访问。它允许网站所有者加速自己的所有内容,并为他们提供额外的功能和配置选项,而这些高级服务通常需要根据项目使用的带宽量进行支付。
但是,如果你的项目无法证明值得实施传统 CDN ,那么使用开源 CDN 可能更合适。通常这些类型的 CDN 能让你链接到流行的 Web 库(例如 CSS/JS 框架),可以让你从免费的 CDN 服务器上传输给你的访问者。虽然开源库的 CDN 服务不允许你将自己的内容上传到服务器,但它们可以帮助你加速全局库并提高网站的冗余性。
CDN 在庞大的服务器网络上托管项目,因此网站维护者需要修改网站 HTML 代码中的资源链接来反映开源 CDN 的URL,后面跟上资源路径。根据你是否链接到 JavaScript 或 CSS 库,链接将包含在 `<script>` 或 `<link>` 标签中。
我们来探讨开源库的四大流行 CDN 服务。
### JsDelivr
[JsDelivr](http://www.jsdelivr.com/) 是一个使用高级 CDN 提供商(KeyCDN、Stackpath、Cloudflare)的开源 CDN 提供者来分发开源项目资源。jsDelivr 的一些亮点包括:
* 支持 2100 多个库
* 110 个接入点
* CDN 可在亚洲和中国使用
* 支持 API
* 没有流量限制
* 完整的 HTTPS 支持
所有片段都以自定义 jsDelivr URL <https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/> 开始,然后是项目名称、版本号等。你还可以配置 jsDelivr 生成带脚本标签的 URL 并启用 SRI(子资源完整性)以增加安全性。
### Cdnjs
[Cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/) 是另一个流行的开源 CDN 提供者,类似于 jsDelivr。此服务还提供了一系列流行的 JavaScript 和 CSS 库,你可以在 Web 项目中进行链接。 该服务由 CDN 提供商 Cloudflare 和 [KeyCDN](https://www.keycdn.com/) 赞助。cdnjs 的一些亮点包括:
* 支持 2900 多个库
* 超过一百万个网站使用
* 支持 HTTP/2
* 支持 HTTPS
与 jsDelivr 类似,使用 cdnjs,你也可以选择使用或者不使用脚本标签和 SRI 来复制资源 URL。
### Google 托管库
[Google 托管库](https://developers.google.com/speed/libraries/)网站允许你链接到托管在 Google 强大的开源 CDN 网络上的流行 JavaScript 库。这个开源的 CDN 解决方案不提供像 jsDelivr 或 cdnjs 一样多的库或者功能。然而,当连接到 Google 托管库时,你可以期待高度的可靠性和信任。Google 开源 CDN 的几个亮点包括:
* HTTPS 支持
* 文件提供 CORS 和 Timing-Allow 头
* 提供每个库的最新版本
所有 Google 的托管库文件都以URL <https://ajax.googleapis.com/> 开头,后跟项目的名称、版本号和文件名。
### Microsoft Ajax CDN
[Microsoft Ajax CDN](https://www.asp.net/ajax/cdn)与 Google 托管库非常类似,因为它只托管流行的库。但是,将 Microsoft Ajax CDN 与 Google 托管库区分开的两个主要区别是 Microsoft 提供了 CSS 和 JS 库,并且还提供了各种库的各种版本。Microsoft Ajax CDN 的几个亮点包括:
* HTTPS 支持
* 每个库的以前版本通常都可用
所有的 Microsoft Ajax 文件都以 URL <http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/> 开头,并且和其它文件一样,后面是库的名字,版本号等。
如果你的项目或网站尚未准备好利用优质的 CDN 服务,但你仍然希望加速网站的重要方面,那么使用开源 CDN 是一个很好的解决方案。它能够加速第三方库的传输,否则它们将从原始服务器发送,从而导致远方用户不必要的加载以及更慢的速度。
*你喜欢使用哪个开源 CDN 提供商?为什么?*
(图片版权:[Open Clip Art Library](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_Clip_Art_Library),它明确将其公开于**[公共领域](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/public_domain)**([见此处](https://openclipart.org/share))。由 Jen Wike Huger 修改。)
---
作者简介:
Cody Arsenault - Cody 热衷于网络性能,SEO 以及创业活动。他是 KeyCDN 的网络性能倡导者,致力于使网络更快。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/4/top-cdn-services>
作者:[Cody Arsenault](https://opensource.com/users/codya) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | A CDN, or content delivery network, is a network of strategically placed servers located around the world used for the purpose of delivering files faster to users. A traditional CDN will allow you to accelerate your website's images, CSS files, JS files, and any other piece of static content. This allows website owners to accelerate all of their own content as well as provide them with additional features and configuration options. These premium services typically require payment based on the amount of bandwidth a project uses.
However, if your project doesn't justify the cost of implementing a traditional CDN, the use of an open source CDN may be more suitable. Typically, these types of CDNs allow you to link to popular web-based libraries (CSS/JS frameworks, for example), which are then delivered to your web visitors from the free CDN's servers. Although CDN services for open source libraries do not allow you to upload your own content to their servers, they can help you accelerate libraries globally and improve your website's redundancy.
CDNs host projects on a vast network of servers, so website maintainers need to modify their asset links in the website's HTML code to reflect the open source CDN's URL followed by the path to the resource. Depending upon whether you're linking to a JavaScript or CSS library, the links you'll include will live in either a <script> or <link> tag.
Let's explore four popular CDN services for open source libraries.
## JsDelivr
[JsDelivr](http://www.jsdelivr.com/) is an open source CDN provider that uses the networks of premium CDN providers (KeyCDN, Stackpath, and Cloudflare) to deliver open source project assets. A few highlights of jsDelivr include:
- Search from over 2,100 libraries
- 110 POP locations
- CDN is accessible in Asia and China
- API support
- No traffic limits
- Full HTTPS support
All snippets start off with the custom jsDelivr URL [https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/](https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/), and are then followed by the name of the project, version number, etc. You can also configure jsDelivr to generate the URL with the script tags and enable SRI (subresource Integrity) for added security.
**Cdnjs**
[Cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/) is another popular open source CDN provider that's similar to jsDelivr. This service also offers an array of popular JavaScript and CSS libraries that you can choose from to link within your web project. This service is sponsored by CDN providers Cloudflare and [KeyCDN](https://www.keycdn.com/). A few highlights of cdnjs include:
- Search from over 2,900 libraries
- Used by over 1 million websites
- Supports HTTP/2
- Supports HTTPS
Similar to jsDelivr, with cdnjs you also have the option to simply copy the asset URL with or without the script tag and SRI.
## Google Hosted Libraries
The [Google's Hosted Libraries](https://developers.google.com/speed/libraries/) site allows you to link to popular JavaScript libraries that are hosted on Google's powerful open source CDN network. This open source CDN solution doesn't offer as many libraries or features as jsDelivr or cdnjs; however, a high level of reliability and trust can be expected when linking to Google's Hosted Libraries. A few highlights of Google's open source CDN include:
- HTTPS support
- Files are served with CORS and Timing-Allow headers
- Offers the latest version of each library
All of Google's Hosted libraries files start with the URL [https://ajax.googleapis.com/](https://ajax.googleapis.com/), and are followed by the project's name, version number, and file name.
## Microsoft Ajax CDN
The [Microsoft Ajax Content Delivery Network](https://www.asp.net/ajax/cdn) is quite similar to Google's Hosted Libraries in that it only hosts popular libraries. However, two major differences that separate Microsoft Ajax CDN from Google's Hosted Libraries are that Microsoft provides both CSS as well as JS libraries and also offers various versions of each library. A few highlights of the Microsoft Ajax CDN include:
- HTTPS support
- Previous versions of each library are often available
All Microsoft Ajax files begin with the URL [http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/](http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/), and like the others, are followed by the library's name, version number, etc.
If your project or website isn't ready to take advantage of a premium CDN service, but you would still like to accelerate vital aspects of your site, then using an open source CDN can be a great solution. They allow you to accelerate the delivery of third-party libraries that would otherwise be delivered from your origin server causing unnecessary load and slower speeds for distant users.
*Which open source CDN provider do you prefer to use and why?*
## Comments are closed. |
8,561 | 4 个用于构建优秀的命令行用户界面的 Python 库 | https://opensource.com/article/17/5/4-practical-python-libraries | 2017-06-01T08:44:24 | [
"命令行"
] | /article-8561-1.html |
>
> 在这个分为两篇的关于[具有绝佳命令行界面的终端程序](/article-8526-1.html)的系列文章的第二篇教程中,我们将讨论 Prompt、Toolkit、Click、Pygments 和 Fuzzy Finder 。
>
>
>

这是我的一个分为两篇的关于[具有绝佳命令行界面的终端程序](https://opensource.com/tags/python?src=programming_resource_menu)的系列文章的第二篇教程。在[第一篇文章](/article-8526-1.html)中,我们讨论了一些能够使命令行应用用起来令人感到愉悦的特性。在第二篇文章中,我们来看看如何用 Python 的一些库来实现这些特性。
我打算用少于 20 行 Python 代码来实现。让我们开始吧。
### Python Prompt Toolkit
我习惯于把这个库称为命令行应用的瑞士军刀,它可以作为 [readline](https://docs.python.org/2/library/readline.html) 、[curses](https://docs.python.org/2/library/curses.html) 等的替代品。让我们首先安装这个库,然后开始该教程:
```
pip install prompt_toolkit
```
我们以一个简单的 REPL (LCTT 译注:REPL —— Read-Eval-Print Loop,交互式开发环境)开始。一个典型的 REPL 会接收用户的输入,进行一个操作,然后输出结果。比如在我们的例子中,我们将要实现一个具有 “回显” 功能的 REPL 。它仅仅是原样打印出用户的输入:
#### REPL
```
from prompt_toolkit import prompt
while 1:
user_input = prompt('>')
print(user_input)
```
这就是实现 REPL 的全部代码。它可以读取用户的输入,然后打印出用户的输入内容。在这段代码中使用的 `prompt` 函数来自 `prompt_toolkit` 库,它是 `readline` 库的一个替代品。
#### 命令历史
为了增强我们的 REPL 的功能,我们可以添加命令历史:
```
from prompt_toolkit import prompt
from prompt_toolkit.history import FileHistory
while 1:
user_input = prompt('>',
history=FileHistory('history.txt'),
)
print(user_input)
```
我们刚刚给 REPL 添加了持久的**命令历史**。现在,我们可以使用上/下箭头来浏览**命令历史**,并使用 `Ctrl-R` 来搜索**命令历史**。它满足了命令行的基本准则。
#### 自动推荐
在第一篇教程中,我讲到的一个可发现性技巧是自动推荐**历史命令**。(我是首先在 **fish shell** 中看到的这一特性)让我们把这一特性加入到我们的 REPL 中:
```
from prompt_toolkit import prompt
from prompt_toolkit.history import FileHistory
from prompt_toolkit.auto_suggest import AutoSuggestFromHistory
while 1:
user_input = prompt('>',
history=FileHistory('history.txt'),
auto_suggest=AutoSuggestFromHistory(),
)
print(user_input)
```
我们只需要给 `prompt()` API 调用添加一个新的参数。现在,我们有了一个具有 **fish shell** 风格的 REPL,它可以自动推荐**历史命令**。
#### 自动补全
现在,让我们通过**自动补全**来加强 Tab 补全。它能够在用户开始输入的时候弹出可能的命令推荐。
REPL 如何来进行推荐呢?我们使用一个字典来进行可能项的推荐。
比如说我们实现一个针对 SQL 的 REPL 。我们可以把 SQL 关键字存到自动补全字典里面。让我们看一看这是如何实现的:
```
from prompt_toolkit import prompt
from prompt_toolkit.history import FileHistory
from prompt_toolkit.auto_suggest import AutoSuggestFromHistory
from prompt_toolkit.contrib.completers import WordCompleter
SQLCompleter = WordCompleter(['select', 'from', 'insert', 'update', 'delete', 'drop'],
ignore_case=True)
while 1:
user_input = prompt('SQL>',
history=FileHistory('history.txt'),
auto_suggest=AutoSuggestFromHistory(),
completer=SQLCompleter,
)
print(user_input)
```
再次说明,我们只是简单的使用了 `prompt-toolkit` 内建的一个叫做 `WordCompleter` 的补全特性,它能够把用户输入和可能推荐的字典进行匹配,然后提供一个列表。
现在,我们有了一个能够自动补全、fish shell 风格的历史命令推荐以及上/下浏览历史的 REPL 。实现这些特性只用了不到 10 行的实际代码。
### Click
`Click` 是一个命令行创建工具包,使用它能够更容易的为程序解析命令行选项的参数和常量。在这儿我们不讨论如何使用 `Click` 来作为参数解析器。相反,我们将会看看 `Click` 带有的一些功能。
安装 `Click`:
```
pip install click
```
#### 分页器
分页器是 Unix 系统上的实用工具,它们能够一次一页地显示很长的输出。分页器的一些例子包括 `less`、`more`、`most` 等。通过分页器来显示一个命令的输出不仅仅是一个友好的设计,同时也是必要的。
让我们进一步改进前面的例子。我们不再使用默认的 `print()` 语句,取而代之的是 `click.echo_via_pager()` 。它将会把输出通过分页器发送到标准输出。这是平台无关的,因此在 Unix 系统或 Windows 系统上均能工作。如果必要的话,`click_via_pager` 会尝试使用一个合适的默认分页器来输出,从而能够显示代码高亮。
```
from prompt_toolkit import prompt
from prompt_toolkit.history import FileHistory
from prompt_toolkit.auto_suggest import AutoSuggestFromHistory
from prompt_toolkit.contrib.completers import WordCompleter
import click
SQLCompleter = WordCompleter(['select', 'from', 'insert', 'update', 'delete', 'drop'],
ignore_case=True)
while 1:
user_input = prompt(u'SQL>',
history=FileHistory('history.txt'),
auto_suggest=AutoSuggestFromHistory(),
completer=SQLCompleter,
)
click.echo_via_pager(user_input)
```
#### 编辑器
在我前面的文章中一个值得一提的细节是,当命令过于复杂的时候进入编辑器来编辑。`Click` 有一个[简单的 API](http://click.pocoo.org/5/utils/#launching-editors) 能够打开编辑器,然后把在编辑器中输入的文本返回给应用。
```
import click
message = click.edit()
```
### Fuzzy Finder
`Fuzzy Finder` 是一种通过少量输入来为用户减少推荐的方法。幸运的是,有一个库可以实现 `Fuzzy Finder` 。让我们首先安装这个库:
```
pip install fuzzyfinder
```
`Fuzzy Finder` 的 API 很简单。用户向它传递部分字符串和一系列可能的选择,然后,`Fuzzy Finder` 将会返回一个与部分字符串匹配的列表,这一列表是通过模糊算法根据相关性排序得出的。比如:
```
>>> from fuzzyfinder import fuzzyfinder
>>> suggestions = fuzzyfinder('abc', ['abcd', 'defabca', 'aagbec', 'xyz', 'qux'])
>>> list(suggestions)
['abcd', 'defabca', 'aagbec']
```
现在我们有了 `fuzzyfinder`,让我们把它加入到我们的 SQL REPL 中。方法是我们自定义一个 `completer` 而不是使用来自 `prompt-toolkit` 库的 `WordCompleter` 。比如:
```
from prompt_toolkit import prompt
from prompt_toolkit.history import FileHistory
from prompt_toolkit.auto_suggest import AutoSuggestFromHistory
from prompt_toolkit.completion import Completer, Completion
import click
from fuzzyfinder import fuzzyfinder
SQLKeywords = ['select', 'from', 'insert', 'update', 'delete', 'drop']
class SQLCompleter(Completer):
def get_completions(self, document, complete_event):
word_before_cursor = document.get_word_before_cursor(WORD=True)
matches = fuzzyfinder(word_before_cursor, SQLKeywords)
for m in matches:
yield Completion(m, start_position=-len(word_before_cursor))
while 1:
user_input = prompt(u'SQL>',
history=FileHistory('history.txt'),
auto_suggest=AutoSuggestFromHistory(),
completer=SQLCompleter(),
)
click.echo_via_pager(user_input)
```
### Pygments
现在,让我们给用户输入添加语法高亮。我们正在搭建一个 SQL REPL,如果具有彩色高亮的 SQL 语句,这会很棒。
`Pygments` 是一个提供语法高亮的库,内建支持超过 300 种语言。添加语法高亮能够使应用变得彩色化,从而能够帮助用户在执行程序前发现 SQL 中存在的错误,比如拼写错误、引号不匹配或括号不匹配。
首先,安装 `Pygments` :
```
pip install pygments
```
让我们使用 `Pygments` 来为 SQL REPL 添加颜色:
```
from prompt_toolkit import prompt
from prompt_toolkit.history import FileHistory
from prompt_toolkit.auto_suggest import AutoSuggestFromHistory
from prompt_toolkit.completion import Completer, Completion
import click
from fuzzyfinder import fuzzyfinder
from pygments.lexers.sql import SqlLexer
SQLKeywords = ['select', 'from', 'insert', 'update', 'delete', 'drop']
class SQLCompleter(Completer):
def get_completions(self, document, complete_event):
word_before_cursor = document.get_word_before_cursor(WORD=True)
matches = fuzzyfinder(word_before_cursor, SQLKeywords)
for m in matches:
yield Completion(m, start_position=-len(word_before_cursor))
while 1:
user_input = prompt(u'SQL>',
history=FileHistory('history.txt'),
auto_suggest=AutoSuggestFromHistory(),
completer=SQLCompleter(),
lexer=SqlLexer,
)
click.echo_via_pager(user_input)
```
`Prompt Toolkit` 能够和 `Pygments` 一同很好的工作。我们把 `Pygments` 提供的 `SqlLexer` 加入到来自 `prompt-toolkit` 的 `prompt` 中。现在,所有的用户输入都会被当作 SQL 语句,并进行适当着色。
### 结论
我们的“旅途”通过创建一个强大的 REPL 结束,这个 REPL 具有常见的 shell 的全部特性,比如历史命令,键位绑定,用户友好性比如自动补全、模糊查找、分页器支持、编辑器支持和语法高亮。我们仅用少于 20 行 Python 代码就实现了这个 REPL 。
不是很简单吗?现在,你没有理由不会写一个自己的命令行应用了。下面这些资源可能有帮助:
* [Click](http://click.pocoo.org/5/) (命令行界面创建工具)
* [Fuzzy Finder](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/fuzzyfinder)
* [Prompt Toolkit](https://python-prompt-toolkit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)
* 在 `prompt-toolkit` 的仓库中查看 [Prompt Toolkit 教程](https://github.com/jonathanslenders/python-prompt-toolkit/tree/master/examples/tutorial) 和[例子](https://github.com/jonathanslenders/python-prompt-toolkit/tree/master/examples/)
* [Pygments](http://pygments.org/)
你也可以在我在 [PyCon US 2017](https://us.pycon.org/2017/) 的演讲[优秀的命令行工具](https://us.pycon.org/2017/schedule/presentation/518/)中学到更多东西,该会议是 5 月 20 日在波特兰,俄勒冈举行的。
(题图 : [美国 Mennonite 教堂档案](https://www.flickr.com/photos/mennonitechurchusa-archives/6987770030/in/photolist-bDu9zC-ovJ8gx-aecxqE-oeZerP-orVJHj-oubnD1-odmmg1-ouBNHR-otUoui-occFe4-ot7LTD-oundj9-odj4iX-9QSskz-ouaoMo-ous5V6-odJKBW-otnxbj-osXERb-iqdyJ8-ovgmPu-bDukCS-sdk9QB-5JQauY-fteJ53-ownm41-ov9Ynr-odxW52-rgqPBV-osyhxE-6QLRz9-i7ki3F-odbLQd-ownZP1-osDU6d-owrTXy-osLLXS-out7Dp-hNHsya-wPbFkS-od7yfD-ouA53c-otnzf9-ormX8L-ouTj6h-e8kAze-oya2zR-hn3B2i-aDNNqk-aDNNmR) 。 Opensource.com. [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/))
---
作者简介:
Amjith Ramanujam - Amjith Ramanujam 是 `pgcli` 和 `mycli` 的创始人。人们认为它们很酷,他表示笑纳赞誉。他喜欢用 Python、JavaScript 和 C 编程。他喜欢写一些简单、易于理解的代码,有时候这样做是成功的。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/5/4-practical-python-libraries>
作者:[Amjith Ramanujam](https://opensource.com/users/amjith) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
8,562 | Linux 让我对电脑有了更深刻的理解 | http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/84286.html | 2017-06-01T16:42:08 | [
"Linux"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8562-1.html | 
我花了大量时间和耐心在 Linux 上,我的朋友们都能为我证明这点。说起来你可能不信,两年前我还根本不知道 Linux 是什么,放弃 Windows 转投 Linux 更是不可能。
虽然转投 Linux 这事有点跳跃,但事后证明这是很明智的选择。口说无凭,分析一下我的路线可能会更有说服力一点。通过这个路线来说说我是怎么从小白到精通 Linux 桌面系统的。
### 安全意识的觉醒
两年前我也是像一般的 Windows 用户一样,在 Windows 操作系统下工作。虽然我也有跟进了解主流的科技新闻的习惯,但是对计算机我也说不上深刻了解。
2013 年夏天,美国国家安全局的一份情报项目报告让我对个人隐私安全的态度迅速发生了变化。爱德华斯诺登揭露的网络监控的广度令人不安,而且也凸显出,我们大多数人——甚至不知道如何做——来保护自己的隐私。
在之前我没有对电脑或它们在我的个人事务中所扮演的角色作出任何特别的考虑,我开始意识到控制一个人的数字生活,以及控制它的设备的重要性。
按理来说下一步应该是确定该怎么去做。虽然我制订的目标似乎是合乎逻辑的,但要实现它并不简单。在接下来的几个月里,我把自己的空闲时间花在了互联网上,寻找关于隐私保护、加密以及其它任何可以保护我的技术的指南。
专家们说想逃避情报机构的监控几乎是不可能的。然而,这些专家们也会告诉你,能帮你避开那怕只是避开那么一丢丢的监视 -- 在较小的机构中有相当比例的监控更有可能针对普通民众 -- 唯一可行的办法就是使用开源软件。
Linux,我很快意识到需要去了解它,因为它是这些开源软件的头头。
### 闭源与开源
在进一步的研究中,我开始熟悉开源软件的一些特点。我们每天使用的软件的绝大多数 -- 从聊天软件到操作系统,包括Windows -- 它们都是开源软件的对立面:它们是闭源的。
例如,当微软的开发人员在 Windows 上进行开发工作时,他们会用一些编程语言编写源代码,并且只在他们的团队内部流传这些代码。当他们准备发布软件时,他们会编译它,将它从人类可读的代码转换成计算机运行的 1 和 0,面对这些机器码,即使是最聪明的人也很难逆向工程到原始源代码。
在这种模式下,只有软件的开发者才知道这些软件实际在做些什么,有没有私底下监控用户行为。
开源软件会提供软件的源代码和编译好的二进制代码给公众下载使用。不论是不是每个用户都有能力去阅读这些源代码,评估它们的安全性和隐私性,这都不重要。因为源代码是公开的,总有那么一部分人有这个能力做这些事,一但他们发现这些代码有问题他们就能及时通知其它用户,让公众一起来监督这些开源软件的行为,让那些故意隐藏的恶意代码片段或者非故意的代码漏洞能及时被发现并处理掉。
经过彻底的研究之后,很明显,唯一能保证我的隐私和用户的自主权的操作系统就是那些具备透明开放的源代码哲学的操作系统。一位知识渊博的朋友和隐私倡导者推荐的最多的是 Linux。如果这是必须的话,我已经准备好接受一个艰难的过渡,但是我对隐私的重要性的信念给了我信心去尝试。
### 婴儿学步
虽然我决心转向 Linux 的是急切的,但饭得一口吃,路也得一步一步走。我是最开始是从安装 Ubuntu 开始的 —— 一个容易配置对初学者很友好的 Linux 发行版 —— 在我的老笔记本电脑上它与原有的 Windows 相处融洽井水不犯河水。
每次启动我的电脑时,我都能选择 Ubuntu 或 Windows ,这样我就能在 Linux 上找到自己的下脚点,同时保留熟悉的 Windows 以防前者可能缺失的一些辅助性功能。
不久后,一个硬盘驱动器损坏严重让我无法再继续享受这个设置,不过我认为这是一个机会,让我考虑一下买一台 Linux 的新笔记本电脑。由于 Linux 对标准的英特尔处理器、图形卡和无线适配器的驱动程序支持得很好,所以我买了一台联想的 ThinkPad。
我做了一个全新的开始,完全擦除我的新机器上的 Windows ,安装了 Debian ,这是一个广泛兼容和稳定的发行版,Ubuntu 就是基于它衍生出来的。我不仅在没有熟悉的 Windows 安全网络的情况下挺过来了,我还在不断的进步提高。我很快就沉浸在以前神秘的命令行世界里。
在我用了一年的 Linux 操作系统之后,我又进行了一次冒险,安装了 Arch Linux ,它需要一个更加复杂的手动用户安装过程,并带有完全的磁盘加密。那天晚上,我和一位 Linux 资深管理人士一起安装了 Arch ,这标志着我生命中最值得骄傲的成就之一。
在这个过程中,我面临着挑战 -- 有时,在Windows上无缝工作的应用程序需要额外的步骤或需要安装必要的驱动 -- 但是我克服了它们,或者说绕过它们,继续按照我自己的节奏摸索 Linux。
### 全速前进
就我而言,那时我才真正开始进行我的学习。我用 Linux 来驾驭计算机,并确保它可以为我工作,不过最让我着迷的是它提供对系统进行修改的自由和个性化处理。
作为一个开源操作系统,Linux 是无限开放的。尽管我最初期望花时间阅读安全实践(我现在仍然这么做),但我也发现自己深入到配置面板中,并把所有的颜色、图标和菜单都列出来,只是这样而已。
我花了一些时间去适应,但我越是投入到新事物中,我就变得越自信,越好奇。
自从在这条路上走了两年多以后,我在电脑上从来没有像今天这么多的感受。我不能像我想要的那样去个性化 Windows,另外依据我从开源社区学到的东西来看,我也不能完全信任它。
有一个叫电脑的东西,它曾经只是我的的一件不起眼的硬件设备,现在它和我之间的关系变得非常美妙 —— 超越记者和他的笔记本、也超越小提琴家和他的小提琴的关系。
我甚至为自己的手机不像我的笔记本电脑那样是真正的 Linux 而感到悲哀,我都不知道我能对它做些什么。不管怎么样,我将继续对我的 Arch 系统进行优化,只要有机会我将会再去发现新的领域并探索新的可能性。
---
via: <http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/84286.html>
作者:[Jonathan Terrasi](http://www.linkedin.com/company/ect-news-network) 译者:[zschong](https://github.com/zschong) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,563 | 如何在 Ubuntu 16.04 上安装 OTRS (开源问题单系统) | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-otrs-opensource-trouble-ticket-system-on-ubuntu-16-04/ | 2017-06-02T08:23:00 | [
"OTRS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8563-1.html | [OTRS](https://www.otrs.com) ,即开源<ruby> 问题单 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> ticket </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>申请系统,是一个用于客户服务、帮助台和 IT 服务管理的开源问题单软件。该软件是用 Perl 和 javascript 编写的。对于那些需要管理票据、投诉、支持请求或其他类型的报告的公司和组织来说,这是一个问题单解决方案。OTRS 支持包括 MySQL、PostgreSQL、Oracle 和 SQL Server 在内的多个数据库系统,它是一个可以安装在 Windows 和 Linux 上的多平台软件。

在本教程中,我将介绍如何在 Ubuntu 16.04 上安装和配置 OTRS。我将使用 PostgreSQL 作为 OTRS 的数据库,将 Apache Web 服务器用作 Web 服务器。
**先决条件**
* Ubuntu 16.04。
* 最小 2GB 的内存。
* root 权限
### 步骤 1 - 安装 Apache 和 PostgreSQL
在第一步中,我们将安装 Apache Web 服务器以及 PostgreSQL。我们将从 ubuntu 仓库中使用最新的版本。
使用 SSH 登录到你的 Ubuntu 服务器中:
```
ssh [email protected]
```
更新 Ubuntu 仓库。
```
sudo apt-get update
```
使用 apt 安装 Apache2 以及 PostgreSQL:
```
sudo apt-get install -y apache2 libapache2-mod-perl2 postgresql
```
通过检查服务器端口确保 Apache 以及 PostgreSQL 运行了。
```
netstat -plntu
```

你可以看到 80 端口被 apache 使用了,5432 端口被 postgresql 数据库使用了。
### 步骤 2 - 安装 Perl 模块
OTRS 基于 Perl,因此我们需要安装一些 OTRS 需要的 Perl 模块。
使用这个 apt 命令安装 perl 模块:
```
sudo apt-get install -y libapache2-mod-perl2 libdbd-pg-perl libnet-dns-perl libnet-ldap-perl libio-socket-ssl-perl libpdf-api2-perl libsoap-lite-perl libgd-text-perl libgd-graph-perl libapache-dbi-perl libarchive-zip-perl libcrypt-eksblowfish-perl libcrypt-ssleay-perl libencode-hanextra-perl libjson-xs-perl libmail-imapclient-perl libtemplate-perl libtext-csv-xs-perl libxml-libxml-perl libxml-libxslt-perl libpdf-api2-simple-perl libyaml-libyaml-perl
```
安装完成后,我们需要为 apache 激活 Perl 模块,接着重启 apache 服务。
```
a2enmod perl
systemctl restart apache2
```
接下来,使用下面的命令检查模块是否已经加载了:
```
apachectl -M | sort
```

你可以在 “Loaded Modules” 部分下看到 **perl\_module**。
### 步骤 3 - 为 OTRS 创建新用户
OTRS 是一个基于 web 的程序并且运行与 apache web 服务器下。为了安全,我们需要以普通用户运行它,而不是 root 用户。
使用 useradd 命令创建一个 `otrs` 新用户:
```
useradd -r -d /opt/otrs -c 'OTRS User' otrs
```
* `-r`:将用户作为系统用户。
* `-d /opt/otrs`:在 `/opt/otrs` 下放置新用户的主目录。
* `-c`:备注。
接下来,将 `otrs` 用户加入到 `www-data` 用户组,因为 apache 运行于 `www-data` 用户及用户组。
```
usermod -a -G www-data otrs
```
在 `/etc/passwd` 文件中已经有 `otrs` 用户了。
```
grep -rin otrs /etc/passwd
```

OTRS 的新用户已经创建了。
### 步骤 4 - 创建和配置数据库
在这节中,我们会为 OTRS 系统创建一个新 PostgreSQL 数据库,并对 PostgreSQL 数据库的配置做一些小的更改。
登录到 `postgres` 用户并访问 PostgreSQL shell。
```
su - postgres
psql
```
创建一个新的角色 `otrs`,密码是 `myotrspw`,并且是非特权用户。
```
create user otrs password 'myotrspw' nosuperuser;
```
接着使用 `otrs` 用户权限创建一个新的 `otrs` 数据库:
```
create database otrs owner otrs;
\q
```
接下来为 `otrs` 角色验证编辑 PostgreSQL 配置文件。
```
vim /etc/postgresql/9.5/main/pg_hba.conf
```
在 84 行后粘贴下面的配置:
```
local otrs otrs password
host otrs otrs 127.0.0.1/32 password
```
保存文件并退出 vim

使用 `exit` 回到 root 权限并重启 PostgreSQL:
```
exit
systemctl restart postgresql
```
PostgreSQL 已经为 OTRS 的安装准备好了。

### 步骤 5 - 下载和配置 OTRS
在本教程中,我们会使用 OTRS 网站中最新的版本。
进入 `/opt` 目录并使用 `wget` 命令下载 OTRS 5.0:
```
cd /opt/
wget http://ftp.otrs.org/pub/otrs/otrs-5.0.16.tar.gz
```
展开该 otrs 文件,重命名目录并更改所有 otrs 的文件和目录的所属人为 `otrs`。
```
tar -xzvf otrs-5.0.16.tar.gz
mv otrs-5.0.16 otrs
chown -R otrs:otrs otrs
```
接下来,我们需要检查系统并确保可以安装 OTRS 了。
使用下面的 otrs 脚本命令检查 OTRS 安装需要的系统软件包:
```
/opt/otrs/bin/otrs.CheckModules.pl
```
确保所有的结果是对的,这意味着我们的服务器可以安装 OTRS 了。

OTRS 已下载,并且我们的服务器可以安装 OTRS 了。
接下,进入 otrs 目录并复制配置文件。
```
cd /opt/otrs/
cp Kernel/Config.pm.dist Kernel/Config.pm
```
使用 vim 编辑 `Config.pm` 文件:
```
vim Kernel/Config.pm
```
更改 42 行的数据库密码:
```
$Self->{DatabasePw} = 'myotrspw';
```
注释 45 行的 MySQL 数据库支持:
```
# $Self->{DatabaseDSN} = "DBI:mysql:database=$Self->{Database};host=$Self->{DatabaseHost};";
```
取消注释 49 行的 PostgreSQL 数据库支持:
```
$Self->{DatabaseDSN} = "DBI:Pg:dbname=$Self->{Database};";
```
保存文件并退出 vim。
接着编辑 apache 启动文件来启用 PostgreSQL 支持。
```
vim scripts/apache2-perl-startup.pl
```
取消注释 60 和 61 行:
```
# enable this if you use postgresql
use DBD::Pg ();
use Kernel::System::DB::postgresql;
```
保存文件并退出编辑器。
最后,检查缺失的依赖和模块。
```
perl -cw /opt/otrs/bin/cgi-bin/index.pl
perl -cw /opt/otrs/bin/cgi-bin/customer.pl
perl -cw /opt/otrs/bin/otrs.Console.pl
```
你可以在下面的截图中看到结果是 “**OK**”:

### 步骤 6 - 导入样本数据库
在本教程中,我们会使用样本数据库,这可以在脚本目录中找到。因此我们只需要将所有的样本数据库以及表结构导入到第 4 步创建的数据库中。
登录到 `postgres` 用户并进入 otrs 目录中。
```
su - postgres
cd /opt/otrs/
```
作为 otrs 用户使用 `psql` 命令插入数据库以及表结构。
```
psql -U otrs -W -f scripts/database/otrs-schema.postgresql.sql otrs
psql -U otrs -W -f scripts/database/otrs-initial_insert.postgresql.sql otrs
psql -U otrs -W -f scripts/database/otrs-schema-post.postgresql.sql otrs
```
在需要的时候输入数据库密码 `myotrspw`。

### 步骤 7 - 启动 OTRS
数据库以及 OTRS 已经配置了,现在我们可以启动 OTRS。
将 otrs 的文件及目录权限设置为 `www-data` 用户和用户组。
```
/opt/otrs/bin/otrs.SetPermissions.pl --otrs-user=www-data --web-group=www-data
```
通过创建一个新的链接文件到 apache 虚拟主机目录中启用 otrs apache 配置。
```
ln -s /opt/otrs/scripts/apache2-httpd.include.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/otrs.conf
```
启用 otrs 虚拟主机并重启 apache。
```
a2ensite otrs
systemctl restart apache2
```
确保 apache 启动没有错误。

### 步骤 8 - 配置 OTRS 计划任务
OTRS 已经安装并运行在 Apache Web 服务器中了,但是我们仍然需要配置 OTRS 计划任务。
登录到 `otrs` 用户,接着以 otrs 用户进入 `var/cron` 目录。
```
su - otrs
cd var/cron/
pwd
```
使用下面的命令复制所有 `.dist` 计划任务脚本:
```
for foo in *.dist; do cp $foo `basename $foo .dist`; done
```
使用 `exit` 回到 root 权限,并使用 otrs 用户启动计划任务脚本。
```
exit
/opt/otrs/bin/Cron.sh start otrs
```

接下来,手动收取电子邮件的 PostMaster 创建一个新的计划任务。我会配置为每 2 分钟收取一次邮件。
```
su - otrs
crontab -e
```
粘贴下面的配置:
```
*/2 * * * * $HOME/bin/otrs.PostMasterMailbox.pl >> /dev/null
```
保存并退出。
现在停止 otrs 守护进程并再次启动。
```
bin/otrs.Daemon.pl stop
bin/otrs.Daemon.pl start
```

OTRS 安装以及配置完成了。
### 步骤 9 - 测试 OTRS
打开你的 web 浏览器并输入你的服务器 IP 地址: <http://192.168.33.14/otrs/>
使用默认的用户 `root@localhost` 以及密码 `root` 登录。

使用默认的 root 账户你会看到一个警告。点击警告信息来创建一个新的 admin root 用户。
下面是用另外的 admin root 用户登录后出现的 admin 页面,这里没有出现错误信息。

如果你想作为客户登录,你可以使用 `customer.pl` :<http://192.168.33.14/otrs/customer.pl>
你会看到客户登录界面,输入客户的用户名和密码。

下面是一个创建新单据的客户页面。

### 步骤 10 - 疑难排查
如果你仍旧看到 “OTRS Daemon is not running” 的错误,你可以像这样调试 OTRS 守护进程。
```
su - otrs
cd /opt/otrs/
```
停止 OTRS 守护进程:
```
bin/otrs.Daemon.pl stop
```
使用 `--debug` 选项启动 OTRS 守护进程。
```
bin/otrs.Daemon.pl start --debug
```
### 参考
* [http://wiki.otterhub.org/index.php?title=Installation*on*Debian*6*with\_Postgres](http://wiki.otterhub.org/index.php?title=Installation_on_Debian_6_with_Postgres)
* <http://www.geoffstratton.com/otrs-installation-5011-ubuntu-1604>
* <https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/ticketing-system-otrs-ubuntu-1404-muhammad-faiz-khan>
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-otrs-opensource-trouble-ticket-system-on-ubuntu-16-04/>
作者:[Muhammad Arul](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-otrs-opensource-trouble-ticket-system-on-ubuntu-16-04/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # How to install OTRS (OpenSource Trouble Ticket System) on Ubuntu 16.04
### On this page
[Step 1 - Install Apache and PostgreSQL](#step-install-apache-and-postgresql)[Step 2 - Install Perl Modules](#step-install-perl-modules)[Step 3 - Create New User for OTRS](#step-create-new-user-for-otrs)[Step 4 - Create and Configure the Database](#step-create-and-configure-the-database)[Step 5 - Download and Configure OTRS](#step-download-and-configure-otrs)[Step 6 - Import the Sample Database](#step-import-the-sample-database)[Step 7 - Start OTRS](#step-start-otrs)[Step 8 - Configure OTRS Cronjob](#step-configure-otrs-cronjob)[Step 9 - Testing OTRS](#step-testing-otrs)[Step 10 - Troubleshooting](#step-troubleshooting)[Reference](#reference)
OTRS or Open-source Ticket Request System is an open source ticketing software used for Customer Service, Help Desk, and IT Service Management. The software is written in Perl and javascript. It is a ticketing solution for companies and organizations that have to manage tickets, complaints, support request or other kinds of reports. OTRS supports several database systems including MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle and SQL Server it is a multiplatform software that can be installed on Windows and Linux.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install and configure OTRS on Ubuntu 16.04. I will use PostgreSQL as the database for OTRS, and Apache web server as the web server.
**Prerequisites**
- Ubuntu 16.04.
- Min 2GB of Memory.
- Root privileges.
## Step 1 - Install Apache and PostgreSQL
In this first step, we will install the Apache web server and PostgreSQL. We will use the latest versions from the ubuntu repository.
Login to your Ubuntu server with SSH:
ssh[[email protected]]
Update Ubuntu repository.
sudo apt-get update
Install Apache2 and a PostgreSQL with the apt:
sudo apt-get install -y apache2 libapache2-mod-perl2 postgresql
Then make sure that Apache and PostgreSQL are running by checking the server port.
netstat -plntu
You will see port 80 is used by apache, and port 5432 used by postgresql database.
## Step 2 - Install Perl Modules
OTRS is based on Perl, so we need to install some Perl modules that are required by OTRS.
Install perl modules for OTRS with this apt command:
sudo apt-get install -y libapache2-mod-perl2 libdbd-pg-perl libnet-dns-perl libnet-ldap-perl libio-socket-ssl-perl libpdf-api2-perl libsoap-lite-perl libgd-text-perl libgd-graph-perl libapache-dbi-perl libarchive-zip-perl libcrypt-eksblowfish-perl libcrypt-ssleay-perl libencode-hanextra-perl libjson-xs-perl libmail-imapclient-perl libtemplate-perl libtemplate-perl libtext-csv-xs-perl libxml-libxml-perl libxml-libxslt-perl libpdf-api2-simple-perl libyaml-libyaml-perl
When the installation is finished, we need to activate the Perl module for apache, then restart the apache service.
a2enmod perl
systemctl restart apache2
Next, check the apache module is loaded with the command below:
apachectl -M | sort
And you will see **perl_module** under 'Loaded Modules' section.
## Step 3 - Create New User for OTRS
OTRS is a web based application and running under the apache web server. For best security, we need to run it under a normal user, not the root user.
Create a new user named 'otrs' with the useradd command below:
useradd -r -d /opt/otrs -c 'OTRS User' otrs
**-r**: make the user as a system account.**-d /opt/otrs**: define home directory for new user on '/opt/otrs'.**-c**: comment.
Next, add the otrs user to 'www-data' group, because apache is running under 'www-data' user and group.
usermod -a -G www-data otrs
Check that the otrs user is available in the '/etc/passwd' file.
grep -rin otrs /etc/passwd
New user for OTRS is created.
## Step 4 - Create and Configure the Database
In this section, we will create a new PostgreSQL database for the OTRS system and make some small changes in PostgreSQL database configuration.
Login to the * postgres* user and access the PostgreSQL shell.
su - postgres
psql
Create a new role named '**otrs**' with the password '**myotrspw**' and the nosuperuser option.
create user otrs password 'myotrspw' nosuperuser;
Then create a new database named '**otrs**' under the '**otrs**' user privileges:
create database otrs owner otrs;
\q
Next, edit the PostgreSQL configuration file for otrs role authentication.
vim /etc/postgresql/9.5/main/pg_hba.conf
Paste the cConfiguration below after line 84:
local otrs otrs password
host otrs otrs 127.0.0.1/32 password
Save the file and exit vim.
Back to the root privileges with "exit" and restart PostgreSQL:
exit
systemctl restart postgresql
PostgreSQL is ready for the OTRS installation.
## Step 5 - Download and Configure OTRS
In this tutorial, we will use the latest OTRS version that is available on the OTRS web site.
Go to the '/opt' directory and download OTRS 5.0 with the wget command:
cd /opt/
wget http://ftp.otrs.org/pub/otrs/otrs-5.0.16.tar.gz
Extract the otrs file, rename the directory and change owner of all otrs files and directories the 'otrs' user.
tar -xzvf otrs-5.0.16.tar.gz
mv otrs-5.0.16 otrs
chown -R otrs:otrs otrs
Next, we need to check the system and make sure it's ready for OTRS installation.
Check system packages for OTRS installation with the otrs script command below:
/opt/otrs/bin/otrs.CheckModules.pl
Make sure all results are ok, it means is our server ready for OTRS.
OTRS is downloaded, and our server is ready for the OTRS installation.
Next, go to the otrs directory and copy the configuration file.
cd /opt/otrs/
cp Kernel/Config.pm.dist Kernel/Config.pm
Edit 'Config.pm' file with vim:
vim Kernel/Config.pm
Change the database password line 42:
$Self->{DatabasePw} = 'myotrspw';
Comment the MySQL database support line 45:
# $Self->{DatabaseDSN} = "DBI:mysql:database=$Self->{Database};host=$Self->{DatabaseHost};";
Uncomment PostgreSQL database support line 49:
$Self->{DatabaseDSN} = "DBI:Pg:dbname=$Self->{Database};";
Save the file and exit vim.
Then edit apache startup file to enable PostgreSQL support.
vim scripts/apache2-perl-startup.pl
Uncomment line 60 and 61:
# enable this if you use postgresql
use DBD::Pg ();
use Kernel::System::DB::postgresql;
Save the file and exit the editor.
Finally, check for any missing dependency and modules.
perl -cw /opt/otrs/bin/cgi-bin/index.pl
perl -cw /opt/otrs/bin/cgi-bin/customer.pl
perl -cw /opt/otrs/bin/otrs.Console.pl
You should see that the result is '**OK**' asshown in the screenshot below:
## Step 6 - Import the Sample Database
In this tutorial, we will use the sample database, it's available in the script directory. So we just need to import all sample databases and the schemes to the existing database created in step 4.
Login to the postgres user and go to the otrs directory.
su - postgres
cd /opt/otrs/
Insert database and table scheme with psql command as otrs user.
psql -U otrs -W -f scripts/database/otrs-schema.postgresql.sql otrs
psql -U otrs -W -f scripts/database/otrs-initial_insert.postgresql.sql otrs
psql -U otrs -W -f scripts/database/otrs-schema-post.postgresql.sql otrs
Type the database password '**myotrspw**' when requested.
## Step 7 - Start OTRS
Database and OTRS are configured, now we can start OTRS.
Set the permission of otrs file and directory to the www-data user and group.
/opt/otrs/bin/otrs.SetPermissions.pl --otrs-user=www-data --web-group=www-data
Then enable the otrs apache configuration by creating a new symbolic link of the file to the apache virtual host directory.
ln -s /opt/otrs/scripts/apache2-httpd.include.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/otrs.conf
Enable otrs virtual host and restart apache.
a2ensite otrs
systemctl restart apache2
Make sure apache has no error.
## Step 8 - Configure OTRS Cronjob
OTRS is installed and now running under apache web server, but we still need to configure the OTRS Cronjob.
Login to the 'otrs' user, then go to the 'var/cron' directory as the otrs user.
su - otrs
cd var/cron/
pwd
Copy all cronjob .dist scripts with the command below:
for foo in *.dist; do cp $foo `basename $foo .dist`; done
Back to the root privilege with exit and then start the cron script as otrs user.
exit
/opt/otrs/bin/Cron.sh start otrs
Next, manually create a new cronjob for PostMaster which fetches the emails. I'll configure it tp fetch emails every 2 minutes.
su - otrs
crontab -e
Paste the configuration below:
*/2 * * * * $HOME/bin/otrs.PostMasterMailbox.pl >> /dev/null
Save and exit.
Now stop otrs daemon and start it again.
bin/otrs.Daemon.pl stop
bin/otrs.Daemon.pl start
The OTRS installation and configuration is finished.
## Step 9 - Testing OTRS
Open your web browser and type in your server IP address:
Login with default user '**root@localhost**' and password '**root**'.
You will see a warning about using default root account. Click on that warning message to create new admin root user.
Below the admin page after login with different admin root user, and there is no error message again.
If you want to log in as Customer, you can use 'customer.pl'.
[http://192.168.33.14/otrs/customer.pl](http://192.168.33.14/otrs/customer.pl)
You will see the customer login page. Type in a customer username and password.
Below is the customer page for creating a new ticket.
## Step 10 - Troubleshooting
If you still have an error like 'OTRS Daemon is not running', you can enable debugging in the OTRS daemon like this.
su - otrs
cd /opt/otrs/
Stop OTRS daemon:
bin/otrs.Daemon.pl stop
And start OTRS daemon with --debug option.
bin/otrs.Daemon.pl start --debug |
8,564 | 在 Go 中如何使用切片的容量和长度 | https://www.calhoun.io/how-to-use-slice-capacity-and-length-in-go | 2017-06-02T09:49:00 | [
"Golang",
"数组"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8564-1.html | 
快速测试 - 下面的代码输出什么?
```
vals := make([]int, 5)
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
vals = append(vals, i)
}
fmt.Println(vals)
```
*[在 Go Playground 运行一下](https://play.golang.org/p/7PgUqBdZ6Z)*
如果你猜测的是 `[0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 3 4]`,那你是对的。
*等等,什么?* 为什么不是 `[0 1 2 3 4]`?
如果你在测试中做错了,你也不用担心。这是在过渡到 Go 语言的过程中相当常见的错误,在这篇文章中,我们将说明为什么输出不是你预期的,以及如何利用 Go 的细微差别来使你的代码更有效率。
### 切片 vs 数组
在 Go 中同时有数组(array)和切片(slice)。这可能令人困惑,但一旦你习惯了,你会喜欢上它。请相信我。
切片和数组之间存在许多差异,但我们要在本文中重点介绍的内容是数组的大小是其类型的一部分,而切片可以具有动态大小,因为它们是围绕数组的封装。
这在实践中意味着什么?那么假设我们有数组 `val a [10]int`。该数组具有固定大小,且无法更改。如果我们调用 `len(a)`,它总是返回 `10`,因为这个大小是类型的一部分。因此,如果你突然需要在数组中超过 10 个项,则必须创建一个完全不同类型的新对象,例如 `val b [11]int`,然后将所有值从 `a` 复制到 `b`。
在特定情况下,含有集合大小的数组是有价值的,但一般而言,这不是开发人员想要的。相反,他们希望在 Go 中使用类似于数组的东西,但是随着时间的推移,它们能够随时增长。一个粗略的方式是创建一个比它需要大得多的数组,然后将数组的一个子集视为数组。下面的代码是个例子。
```
var vals [20]int
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
vals[i] = i * i
}
subsetLen := 5
fmt.Println("The subset of our array has a length of:", subsetLen)
// Add a new item to our array
vals[subsetLen] = 123
subsetLen++
fmt.Println("The subset of our array has a length of:", subsetLen)
```
*[在 Go Playground 中运行](https://play.golang.org/p/Np6-NEohm2)*
在代码中,我们有一个长度为 `20` 的数组,但是由于我们只使用一个子集,代码中我们可以假定数组的长度是 `5`,然后在我们向数组中添加一个新的项之后是 `6`。
这是(非常粗略地说)切片是如何工作的。它们包含一个具有设置大小的数组,就像我们前面的例子中的数组一样,它的大小为 `20`。
它们还跟踪程序中使用的数组的子集 - 这就是 `append` 属性,它类似于上一个例子中的 `subsetLen` 变量。
最后,一个切片还有一个 `capacity`,类似于前面例子中我们的数组的总长度(`20`)。这是很有用的,因为它会告诉你的子集在无法容纳切片数组之前可以增长的大小。当发生这种情况时,需要分配一个新的数组,但所有这些逻辑都隐藏在 `append` 函数的后面。
简而言之,使用 `append` 函数组合切片给我们一个非常类似于数组的类型,但随着时间的推移,它可以处理更多的元素。
我们再来看一下前面的例子,但是这次我们将使用切片而不是数组。
```
var vals []int
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
vals = append(vals, i)
fmt.Println("The length of our slice is:", len(vals))
fmt.Println("The capacity of our slice is:", cap(vals))
}
// Add a new item to our array
vals = append(vals, 123)
fmt.Println("The length of our slice is:", len(vals))
fmt.Println("The capacity of our slice is:", cap(vals))
// Accessing items is the same as an array
fmt.Println(vals[5])
fmt.Println(vals[2])
```
*[在 Go Playground 中运行](https://play.golang.org/p/M_qaNGVbC-)*
我们仍然可以像数组一样访问我们的切片中的元素,但是通过使用切片和 `append` 函数,我们不再需要考虑背后数组的大小。我们仍然可以通过使用 `len` 和 `cap` 函数来计算出这些东西,但是我们不用担心太多。简洁吧?
### 回到测试
记住这点,让我们回顾前面的测试,看下什么出错了。
```
vals := make([]int, 5)
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
vals = append(vals, i)
}
fmt.Println(vals)
```
当调用 `make` 时,我们允许最多传入 3 个参数。第一个是我们分配的类型,第二个是类型的“长度”,第三个是类型的“容量”(*这个参数是可选的*)。
通过传递参数 `make([]int, 5)`,我们告诉程序我们要创建一个长度为 5 的切片,在这种情况下,默认的容量与长度相同 - 本例中是 5。
虽然这可能看起来像我们想要的那样,这里的重要区别是我们告诉我们的切片,我们要将“长度”和“容量”设置为 5,假设你想要在初始的 5 个元素*之后*添加新的元素,我们接着调用 `append` 函数,那么它会增加容量的大小,并且会在切片的最后添加新的元素。
如果在代码中添加一条 `Println()` 语句,你可以看到容量的变化。
```
vals := make([]int, 5)
fmt.Println("Capacity was:", cap(vals))
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
vals = append(vals, i)
fmt.Println("Capacity is now:", cap(vals))
}
fmt.Println(vals)
```
*[在 Go Playground 中运行](https://play.golang.org/p/d6OUulTYM7)*
最后,我们最终得到 `[0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 3 4]` 的输出而不是希望的 `[0 1 2 3 4]`。
如何修复它呢?好的,这有几种方法,我们将讲解两种,你可以选取任何一种在你的场景中最有用的方法。
#### 直接使用索引写入而不是 `append`
第一种修复是保留 `make` 调用不变,并且显式地使用索引来设置每个元素。这样,我们就得到如下的代码:
```
vals := make([]int, 5)
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
vals[i] = i
}
fmt.Println(vals)
```
*[在 Go Playground 中运行](https://play.golang.org/p/JI8Fx3fJCU)*
在这种情况下,我们设置的值恰好与我们要使用的索引相同,但是你也可以独立跟踪索引。
比如,如果你想要获取 map 的键,你可以使用下面的代码。
```
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println(keys(map[string]struct{}{
"dog": struct{}{},
"cat": struct{}{},
}))
}
func keys(m map[string]struct{}) []string {
ret := make([]string, len(m))
i := 0
for key := range m {
ret[i] = key
i++
}
return ret
}
```
*[在 Go Playground 中运行](https://play.golang.org/p/kIKxkdX35B)*
这样做很好,因为我们知道我们返回的切片的长度将与 map 的长度相同,因此我们可以用该长度初始化我们的切片,然后将每个元素分配到适当的索引中。这种方法的缺点是我们必须跟踪 `i`,以便了解每个索引要设置的值。
这就让我们引出了第二种方法……
#### 使用 `0` 作为你的长度并指定容量
与其跟踪我们要添加的值的索引,我们可以更新我们的 `make` 调用,并在切片类型之后提供两个参数。第一个,我们的新切片的长度将被设置为 `0`,因为我们还没有添加任何新的元素到切片中。第二个,我们新切片的容量将被设置为 map 参数的长度,因为我们知道我们的切片最终会添加许多字符串。
这会如前面的例子那样仍旧会在背后构建相同的数组,但是现在当我们调用 `append` 时,它会将它们放在切片开始处,因为切片的长度是 0。
```
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println(keys(map[string]struct{}{
"dog": struct{}{},
"cat": struct{}{},
}))
}
func keys(m map[string]struct{}) []string {
ret := make([]string, 0, len(m))
for key := range m {
ret = append(ret, key)
}
return ret
}
```
*[在 Go Playground 中运行](https://play.golang.org/p/h5hVAHmqJm)*
### 如果 `append` 处理它,为什么我们还要担心容量呢?
接下来你可能会问:“如果 `append` 函数可以为我增加切片的容量,那我们为什么要告诉程序容量呢?”
事实是,在大多数情况下,你不必担心这太多。如果它使你的代码变得更复杂,只需用 `var vals []int` 初始化你的切片,然后让 `append` 函数处理接下来的事。
但这种情况是不同的。它并不是声明容量困难的例子,实际上这很容易确定我们的切片的最后容量,因为我们知道它将直接映射到提供的 map 中。因此,当我们初始化它时,我们可以声明切片的容量,并免于让我们的程序执行不必要的内存分配。
如果要查看额外的内存分配情况,请在 Go Playground 上运行以下代码。每次增加容量,程序都需要做一次内存分配。
```
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println(keys(map[string]struct{}{
"dog": struct{}{},
"cat": struct{}{},
"mouse": struct{}{},
"wolf": struct{}{},
"alligator": struct{}{},
}))
}
func keys(m map[string]struct{}) []string {
var ret []string
fmt.Println(cap(ret))
for key := range m {
ret = append(ret, key)
fmt.Println(cap(ret))
}
return ret
}
```
*[在 Go Playground 中运行](https://play.golang.org/p/fDbAxtAjLF)*
现在将此与相同的代码进行比较,但具有预定义的容量。
```
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println(keys(map[string]struct{}{
"dog": struct{}{},
"cat": struct{}{},
"mouse": struct{}{},
"wolf": struct{}{},
"alligator": struct{}{},
}))
}
func keys(m map[string]struct{}) []string {
ret := make([]string, 0, len(m))
fmt.Println(cap(ret))
for key := range m {
ret = append(ret, key)
fmt.Println(cap(ret))
}
return ret
}
```
*[在 Go Playground 中运行](https://play.golang.org/p/nwT8X9-7eQ)*
在第一个代码示例中,我们的容量从 `0` 开始,然后增加到 `1`、 `2`、 `4`, 最后是 `8`,这意味着我们不得不分配 5 次数组,最后一个容纳我们切片的数组的容量是 `8`,这比我们最终需要的要大。
另一方面,我们的第二个例子开始和结束都是相同的容量(`5`),它只需要在 `keys()` 函数的开头分配一次。我们还避免了浪费任何额外的内存,并返回一个能放下这个数组的完美大小的切片。
### 不要过分优化
如前所述,我通常不鼓励任何人做这样的小优化,但如果最后大小的效果真的很明显,那么我强烈建议你尝试为切片设置适当的容量或长度。
这不仅有助于提高程序的性能,还可以通过明确说明输入的大小和输出的大小之间的关系来帮助澄清你的代码。
### 总结
>
> 你好!我写了很多关于Go、Web 开发和其他我觉得有趣的话题。
>
>
> 如果你想跟上最新的文章,请[注册我的邮件列表](https://www.calhoun.io/how-to-use-slice-capacity-and-length-in-go/?utm_source=golangweekly&utm_medium=email#mailing-list-form)。我会给你发送我新书的样例、Go 的 Web 开发、以及每当有新文章(通常每周 1-2 次)会给你发送邮件。
>
>
> 哦,我保证不会发垃圾邮件。我像你一样讨厌它 :)
>
>
>
本文并不是对切片或数组之间差异的详细讨论,而是简要介绍了容量和长度如何影响切片,以及它们在方案中的用途。
为了进一步阅读,我强烈推荐 Go 博客中的以下文章:
* [Go Slices:使用及内部](https://blog.golang.org/go-slices-usage-and-internals)
* [数组、切片(和字符串):“append” 的机制](https://blog.golang.org/slices)
* [切片技巧](https://github.com/golang/go/wiki/SliceTricks)
---
作者简介:
Jon 是一名软件顾问,也是 《Web Development with Go》 一书的作者。在此之前,他创立了 EasyPost,一家 Y Combinator 支持的创业公司,并在 Google 工作。
<https://www.usegolang.com>
---
via: <https://www.calhoun.io/how-to-use-slice-capacity-and-length-in-go>
作者:[Jon Calhoun](https://www.calhoun.io/hire-me) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | null |
8,565 | Fuchsia 对 Android 意味着什么 | http://www.techrepublic.com/article/what-fuchsia-could-mean-for-android/ | 2017-06-03T15:07:00 | [
"Android",
"Fuschia"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8565-1.html | Fuchsia 可能是下个会替代 Android 或 Chrome OS 的系统。猜测有很多,Jack Wallen 对此补充了一些给 Google 的赞誉和告诫。

Google 总是以 “Google” 的方式解决或者做某件事。因此,当他们开始做一个让很多人挠头的项目时,大家是不觉得奇怪的。该项目被称为 [Fuschia](https://github.com/fuchsia-mirror),大多数密切关注 Google 和 Android 的人都知道这个新平台。
对于那些还没紧跟 Google 最新消息的用户而言,Fuschia 是一个新的、开源的实时操作系统,它首先出现于 2016 年 8 月。那时,Fuchsia 只不过是一个命令行。一年不到的时间过去了,这个平台已经有了一个相当有趣的 GUI。
可能最让 Linux 拥趸失望的是,Fuchsia 并没有使用 Linux 内核。这个项目完全是 Google 开发的,使用了 Google 开发的名为 “Magenta”微内核。他们为什么这么做?了解到 Google 的最新设备 Pixel 运行的内核是 Linux 内核 3.18,你就会有你自己的答案了。Linux 3.18 发布于 2014 年(也就是说,在技术上已经过时了)。既然这样,为什么 Google 不能自己完全单干,以便尽可能地保持他们的移动平台跟上最新发展?
尽管我不愿意承认 Linux 可能不会(在未来的某个时期)成为全球最广泛使用的生态系统,但我相信这是 Google 的正确举措,不过我有一个重要的告诫。
### 首先,一些赞誉
首先我必须说,Google 开源 Fuchsia 这事真棒。Android 已经从开源的 Linux 内核中受益多年,所以这促使了 Google 开放他们最新的项目。说实话,如果不是开源和 Linux 内核,Android 就不会发展得那么快了。事实上,我大胆猜测,如果 Android 没有 Linux 和开源的支持,现在移动市场份额会显示出非常不同的、由苹果制定的结果。
一些喝彩是有必要的。操作系统不时需要完全重新思考。Android 是一个为移动平台服务得很好的令人惊奇的平台。然而,走到现在也就差不多了。考虑到消费界一直在寻找下一个大事件,而 Android(和 iOS)的潜力已尽榨干。与一个严重过时的内核相比,还是准备迎接对 Fuchsia 的喜爱吧。
谷歌从来不会停滞不前,这个新平台是证明。
### 一个告诫
开始这部分之前,我需要先给大家展示我的开源背景。自从 90 年代末以来,我一直是 Linux 的用户,并几乎涉及了开源的各个方面。在过去几年中,我一直在关注 Ubuntu 的发展,并对他们(现在)失败的融合尝试发表过看法。换言之,这也是我对 Fuchsia 的担心。
我认为 Google 对 Fucshia 的大计划是创建一个面对所有设备的操作系统:智能手机、IoT、Chromebook。从表面看来,这听起来像是一个会有重大成果的想法。但是,如果你看过 Canonical 对 Unity 8/Mir 融合的努力,你就会对“一个平台统治所有”的想法感到畏惧。当然这并不完全相同。我觉得 Google 正在创建一个单一的平台,让你 “融合” 所有的设备。毕竟,智能手机与物联网融合有什么好处?我们不需要在手机和恒温器之间交换数据。对么?对么???
即使如此,这应该是谷歌的计划,我会提醒他们近距离了解下 Canonical 和 Unity 8 之间发生的事。想法很好,但根本无法实现。
我也有可能错了。Google 可能只是将 Fuchsia 看作是 Android 的替代品。这很可能是 Google 需要替换过时的 Linux 内核,并决定“把一切都包含进来”。但是考虑到 Armadillo(Fuchsia UI)由跨平台的 [Flutter SDK](https://flutter.io/) 编写,跨越平台边界的想法就有了可能。
或者,也许 Fuchsia 只是谷歌说的 “让我们用今天所知道的知识重建我们的智能手机平台,看看它会走向何方”。如果是这样,我可以想象,Google 移动操作系统将会取得重大成功。然而,现实情况是,人们必须面对的是“一个平台统治所有”还有许多要解决的事情。Google 已经在 Chromebook 上测试 Android app 很长时间了。不幸的是,这个思路一直反响平平(最多如此)。随着微软以自己的方式来直面 Chromebook,Google 知道他们必须扩大生态系统,否则将会失去宝贵的领地(如在教育领域)。要解决这个问题的一种方法是使用单个操作系统来驱动智能手机和 Chromebook。这意味着所有的程序都可以在两个平台(这是一个重要的福音)运行以及生态系统的普遍性(再一次,这是巨大的福音)。
### 猜测
Google 对会引发很多行家的猜测的事情一直小心谨慎。一般来说,至少对于 Android,谷歌似乎一直都在做出正确的选择。如果他们相信 Fuchsia 是要走的路,那么我就倾向于相信他们。然而,围绕这个平台有如此多的不确定性会让人们一直迫切地要知道。
那你怎么看?Fuchsia 会成为什么?和我一起猜猜看。
---
作者简介:
Jack Wallen 是 TechRepublic 和 Linux.com 的获奖作家。他是开源的狂热倡导者, 也是 The Android Expert 的代言人。有关 Jack Wallen 的更多消息,请访问他的网站 jackwallen.com。
---
via: <http://www.techrepublic.com/article/what-fuchsia-could-mean-for-android/>
作者:[Jack Wallen](http://www.techrepublic.com/article/what-fuchsia-could-mean-for-android/#modal-bio) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,566 | 十动然拒:一款 Linux 笔记本电脑点评 | http://www.onebigfluke.com/2017/04/discovering-my-inner-curmudgeon-linux.html | 2017-06-03T15:44:00 | [
"笔记本"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8566-1.html |
>
> 简述:我是个 Mac 电脑重度用户,但我其实 [对目前最新的 MacBook Pro 是失望的](http://www.onebigfluke.com/2016/10/lamenting-progress.html)。由此我就开始去研究了下看是否有 [一些可以替代前者(New MacBook Pro)](http://www.onebigfluke.com/2016/10/alternatives-to-apple-computers.html) 的选择。然而让我也意想不到的是,这居然使我产生了离开 Mac 平台的决定。
>
>
>

首先我们来看看 2017 年 CES(LCTT 译注:International Consumer Electronics Show,国际消费类电子产品展览会)大会后发布的 HP Spectre x360 13 寸笔记本电脑,拥有 4K 显示屏的新款笔记本电脑。我是从[百思买](http://www.bestbuy.com/site/hp-spectre-x360-2-in-1-13-3-4k-ultra-hd-touch-screen-laptop-intel-core-i7-16gb-memory-512gb-solid-state-drive-dark-ash-silver/5713178.p?skuId=5713178)(这不是一个赞助链接)买来的这款电脑,因为这是唯一售卖这款配置的零售商。我的目标是使用 Ubuntu 这个系统替代跑在这款笔记本上的 Windows 。
以下是我过去几个月使用这款笔记本的感受,还有一些在使用中对自己的使用习惯的重新认识。
### Ubuntu 系统
安装 Ubuntu 还是很简单的。当时电脑到手的时候预装的是 Windows 10 的系统。当时我使用 Windows 内建的硬盘管理工具来 [缩减主分区](https://www.howtogeek.com/101862/how-to-manage-partitions-on-windows-without-downloading-any-other-software/) 并将剩余的空间分配给 Linux 系统。我 [通过 USB 设备加载了 Ubuntu 系统镜像](https://www.ubuntu.com/download/desktop/create-a-usb-stick-on-windows),这款笔记本能够很方便的适配 USB-A 接口(这在新版的 Mac 系列电脑是没有的)。然后我就按照 [Ubuntu 的简便安装说明](https://www.ubuntu.com/download/desktop/install-ubuntu-desktop),将 BIOS 设置为 [从 USB 启动](http://support.hp.com/us-en/document/c00364979)。
### 屏幕
Spectre x360 的 4k 显示屏简直令人惊艳。令我觉得吃惊的是,最新的 Ubuntu 系统在高 DPI 的屏幕上体验也是非常不错的。系统内建的设置工具配合 [gnome-tweak-tool](https://launchpad.net/gnome-tweak-tool) 这样的附加工具,你可以更好的控制用户界面在 4K 屏上的渲染,2 倍于原生大小的控件使得它们看起非常不错,你也可以将默认字体大小调整到一个合适的比例,甚至还可以调整窗口标题栏和任务管理器上的图标大小。虽然有点繁琐,但我自己设置时也没花多久时间。
### 触控板
实话说触控板有点细微的声音,但还是能够很不错的配合手指移动,Ubuntu 系统也默认支持多点触控。然而你会很快的发现你在打字的时候会误触触控板导致光标到处乱晃。在 Linux 上的默认 Synaptics 触控驱动并不能够很好的识别这款机型的手掌误触,解决方法是切换到 [新的 libinput 系统](https://launchpad.net/xserver-xorg-input-libinput),通过调整 [xinput 设置](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Libinput#Configuration) 就可以让触控板工作的不错。
但我所习惯的手势操作,比如两指滑动回到 Chrome 浏览器,又或者说四指滑动切换工作区,这些操作在 Ubuntu 系统上就没法用了,或者实在想用可以通过 [libinput-gestures](https://github.com/bulletmark/libinput-gestures) 这样的工具来启用他们。令人失望的是,就算使用上面的工具体验其实也一般,因为其实只有 50% 的几率能识别那些手势。“点击触控板”的功能也有些问题:当你使用大拇指双击触控板或触控板按钮表面想要点击,系统会认为你要移动光标或者使用多点触控来调整大小,又一次的失望。
### 键盘
键盘手感就还不错。键盘的键程挺长,这样打起字来就会比较快。左侧 Ctrl 键在左下角所以对我来说就几乎用不上了(不像 Macs 系列电脑就会将 function 键放在那)。方向键工作的不错。比较奇特的是,键盘右侧有一列额外的键,分别是 Delete 键、Home 键、Page Up 键、Page Down 键和 End 键。由于使用习惯导致我在将手从箭头控制键换到 Home 键的时候没法额外考虑还有一列键。而且由于这样的设计我在打字时手没法维持在键盘中央,这让我觉得好像离键盘右侧的键远了许多。
起初我觉得那一列键(Home 键、Page Up 键之类)是多余的,但自从我使用 Sublime Text(一款代码编辑器)来写代码之后,我发现在 Linux 系统和 Windows 系统下输入文本时其实挺依赖那些键的,这就很好理解为什么惠普公司在设计时决定要加入这些键了。作为一个 Mac 用户,我经常会使用 Command 键和向右键来使光标到行结束的位置,而在 Linux 系统和 Windows 系统用户就直接使用 End 键。其实要将键盘映射成和 Mac 一样也不是不行的,但是却很难保证所有的程序都会一样的映射。我花了挺多时间在重组我的肌肉记忆上,这个过程蛮痛苦的,就好像我尝试去使用 [Dvorak 键盘布局](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dvorak_Simplified_Keyboard) 的那个夏天。
### 音响
此款机型有四个扬声器:两个 B&O(Bang & Olufsen,音响制造商)扬声器在上部,两个在下部。上部的两个扬声器在 Ubuntu 系统中没法工作,这是一个 [内核问题](https://bugzilla.kernel.org/show_bug.cgi?id=189331),尚未解决。下部的两个扬声器正常工作但声音有点小。耳机插孔使用正常,当插上耳机时扬声器也会自动静音。但我相信这可能是由于我为了让其他的硬件工作而将内核升级到了 [4.10 测试版本](http://kernel.ubuntu.com/%7Ekernel-ppa/mainline/v4.10/) 才出现的。我觉得社区最终会解决内核问题,所以上部扬声器无法工作的问题应该只是暂时性的。这些情况其实也就证明了为什么惠普公司自带的是带有一堆额外的神奇驱动的 Windows 系统。
### 电池续航
电池续航的问题真的就很糟糕了,我想主要是因为 4k 显示屏太耗电了。此外我还发现了 CPU 散热风扇在高速运转使会从笔记本左侧的出风口吹出热风。这风热的程度如果你把它放到你的腿上会让你感觉很不舒服。我觉得这应该是 Ubuntu 的默认电源管理配置的缺陷。为了解决这个问题,你可以使用诸如 [powertop](https://blog.sleeplessbeastie.eu/2015/08/10/how-to-set-all-tunable-powertop-options-at-system-boot/) 或者 [pm-powersave](http://askubuntu.com/questions/765840/does-pm-powersave-start-automatically-when-running-on-battery) 这样的工具。Intel 公司也提供 [Linux 系统固件支持](https://01.org/linuxgraphics/downloads/firmware) 来使 GPU 更好的工作。通过各种优化,我可以使电池续航能力接近 5 小时:和广告中宣传的 9 小时以上相去甚远。其实也有好的一点,使用 USB-C 接口充电速度快很多。这个接口也能很好的配合我得 Nexus X 手机充电,因为它们都是一样的接口。
### 二合一
惠普 Spectre x360 这款机型名字来源于它独特的设计,通过屏幕旋转可以变成一台平板电脑。变形后在 Ubuntu 系统上无需设置就可以完成点击、滚动和缩放操作。它甚至支持直接使用前进/后退手势操作,这些操作连它的触摸板也不支持。当你将它旋转为平板模式,键盘和触摸板会自动禁用。你可以将系统设置为 [便携模式](https://launchpad.net/onboard),Gnome 桌面键盘就会启用,体验还不错哦。比较糟糕的是不支持屏幕自动旋转,但我还是使用 [iio-sensor-proxy](https://github.com/hadess/iio-sensor-proxy) 和 [这个一次性脚本](http://askubuntu.com/questions/634151/auto-rotate-screen-on-dell-13-7000-with-15-04-gnome/889591#889591) 东拼西凑地实现了这个功能。最后我虽然实现了这个功能,但是我发现使用 16:9 的屏幕好伤我的眼睛,当电脑处于平板电脑时候我需要使我的眼睛移动很长一段距离。
### 窗口管理器和各种软件
从 1998 年 RedHat 5.0 版开始我就不怎么常用 Linux 桌面版本了。时光飞逝,Ubuntu 发展迅猛,默认用户界面是他们自主研发的 Unity(Gnome 的变体),感觉还不错。我其实用过原生的 Gnome ,但它与别的桌面比较起来让我觉得非常的笨拙。我最后还是最喜欢 KDE,而且如果让我再次选择,我也会选择 KDE 的 [Kubuntu](https://www.kubuntu.org/)。总体来说 KDE 的窗口管理器让我觉得非常棒而且我想要的它都有!
在这次的回归 Linux 探索中,我意识到其实我基本上就在使用以下 8 个软件:浏览器(Chrome)、终端(没什么特别喜欢的)、文本编辑器(Sublime Text 3)、配置工具、可视化文件管理器、自动化备份工具(Arq)、类似 Flux 的屏幕亮度调节器,和图片编辑器(GIMP)。这几乎就是我所需要的软件了,其他别的需求非常容易满足。此外,我还比较依赖几个控件:时钟、WIFI 状态、电池状态和音量调节。我一般也会使用任务管理器(比如 Dock)和虚拟工作空间(比如 Mission Control 或 Expose)。我几乎不会用桌面图标、桌面提醒、最近使用的软件、搜索功能和应用软件菜单,所以我就可以适应 Linux 系统的种种设置了。
### 十动然拒
如果你正在考虑购入一款笔记本电脑,或许可以试试这款。尽管我是这样说,我还是准备要卖掉这台 Spectre x360,然后回到我的 2012 年中期款的 MacBook Air 怀抱中去。也不能说惠普公司或是 Linux 桌面平台的错吧,主要还是因为时间更宝贵。
我是如此的被 Mac 系统的高端用户体验所宠爱着,以至于我对别的东西都特别难以高效起来。我的脑袋几乎已经被 Mac 的触摸板、键盘布局和打字输入习惯等等体验所征服。所以我用起来惠普的电脑和 Linux 系统就觉得被拖慢了很多,感觉好像我就要完蛋了。当我使用计算机的时候,我只希望花更多的时间在提高我的技术(编程、写作等等)上。我只希望我将我仅有的“再学习”能力使用在一些尚未明白和不熟悉的课题上,比如 [新型函数式编程语言](http://docs.idris-lang.org/en/latest/tutorial/index.html#tutorial-index) 和 [同态加密](https://arxiv.org/abs/1702.07588) 等等。我再也不想花更多的时间去学习什么基本使用方法了。
反过来说,我也曾花了超过 2 年时间去学习弹钢琴,弹钢琴需要我死记硬背和不断的机械性重复训练。当我在学习钢琴的时候我发现这个过程其实打开了我的思维,让我对曾经有了更深的理解。我对音乐的学习,也让我懂得了许多曾经没有理解的事。可以说,我对音乐的“再学习”打开了我的视野。所以,我也琢磨去适应惠普的硬件和 Linux 桌面系统会不会也对我有这样的影响。
最终说明,我还是固执的。可能以后吧,我也会需要去适应新的工作方式来让我保持最新的状态,就好像电报员终有一天一定会从摩斯电码转向去使用 [电传打字机](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teleprinter) 一样。我希望到了未来的那天,我仍然会有耐心和远见让我平滑的过渡。可能,只有当这样东西会创造出更多的可能性,我才会选择那些需要“再学习”的东西,就好像一个为达到目的才去做的石蕊试验(测试液体酸碱度?)一样。至少目前来说,我还是会选择留在 Mac 下。
---
作者简介:
我是《Effective Python》一书的作者,我是一名软件工程师,我曾在谷歌工作了 11 年,我目前专注于调查统计,此外,我还曾在云计算基础设施建设和开放协议上有过工作经验。
以后,如果你还想阅读我写的文章,可以关注我的推 @haxor。如果你遇到什么问题,也可以写邮件给我,或者直接在下面写评论。如果你觉得这篇文章还不错,点击这里也可以看看我别的兴趣爱好。
---
via: <http://www.onebigfluke.com/2017/04/discovering-my-inner-curmudgeon-linux.html>
作者:[Brett Slatkin](http://www.onebigfluke.com/) 译者:[kenxx](https://github.com/kenxx) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,567 | Samba 系列(十):如何在 CentOS 7 上安装 iRedMail 集成到 Samba4 AD | http://www.tecmint.com/install-iredmail-on-centos-7-for-samba4-ad-integration/ | 2017-06-03T18:36:36 | [
"samba"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8567-1.html | 
本系列教程将引导你了解如何在 CentOS 7 安装 iRedMail 以及 [Samba4 AD 域控制器](/article-8065-1.html),以便域帐户可以通过 Thunderbird 桌面客户端或通过 Roundcube Web 界面发送或接收邮件。
将要安装 iRedMail 的 CentOS 7 服务器需允许通过 25 和 587 端口进行 SMTP 或邮件路由服务,并且还将通过 Dovecot 作为邮件传递代理,提供 POP3 和 IMAP 服务,两者都使用安装过程中签发的自签名证书进行安全保护。
收件人邮箱将与 Roundcube 提供的 webmail 用户代理一起存储在同一台 CentOS 服务器上。iRedMail 将使用 Samba4 AD 来查询和验证收件人帐户,在 AD 组的帮助下创建邮件列表,并通过 Samba4 AD DC 控制邮件帐户。
#### 需要:
* [在 Ubuntu 上使用 Samba4 创建 AD 基础架构](/article-8065-1.html)
### 步骤 1:在 CentOS 7 上安装 iRedMail
1、 在安装 iRedMail 之前,请先确保你使用下面的指南在你的机器上安装了一个全新的 CentOS 7 操作系统:
* [全新安装 CentOS 7 Minimal](/article-8048-1.html)
2、 同样使用下面的命令确保系统更新了最新的安全补丁和软件包。
```
# yum update
```
3、 系统同样需要一个 FQDN 主机名,使用下面的命令设置。使用你自定义的 FQDN 代替 `mail.tecmint.lan` 变量。
```
# hostnamectl set-hostname mail.tecmint.lan
```
使用下面的命令验证系统主机名。
```
# hostname -s # Short name
# hostname -f # FQDN
# hostname -d # Domain
# cat /etc/hostname # Verify it with cat command
```

*验证 CentOS 7 主机名*
4、 通过手动编辑 `/etc/hosts`,将机器的 FQDN 和短名称映射到机器的回环 IP 地址。添加如下所示的值,并相应替换 `mail.tecmint.lan` 和 mail 的值。
```
127.0.0.1 mail.tecmint.lan mail localhost localhost.localdomain
```
5、 iRedMail 专家建议应该完全禁用 SELinux。通过编辑 `/etc/selinux/config` 并将 SELINUX 参数的值从 `permissive` 设置成 `disabled` 来禁用 SELinux。
```
SELINUX=disabled
```
重启机器并应用新的 SELinux 策略,或者运行 `setenforce` 带上参数 `0` 来强制 SELinux 立即禁用。
```
# reboot
或者
# setenforce 0
```
6、 接下来,安装下面这些接下来会用来系统管理的软件包:
```
# yum install bzip2 net-tools bash-completion wget
```
7、 要安装 iRedMail,首先打开下载页 <http://www.iredmail.org/download.html> 中并用下面的命令下载最新的版本。
```
# wget https://bitbucket.org/zhb/iredmail/downloads/iRedMail-0.9.6.tar.bz2
```
8、 下载完成后,使用下面命令解压压缩包并进入解压后的 iRedMail 目录。
```
# tar xjf iRedMail-0.9.6.tar.bz2
# cd iRedMail-0.9.6/
# ls
```
9、 使用下面的命令执行 iRedMail 的 shell 脚本来开始安装。接下来安装器会询问一系列的问题。
```
# bash iRedMail.sh
```
10、 在首个欢迎提示中,点击 `Yes` 来继续安装。

*iRedMail 安装向导*
11、 接下来,选择邮件存储的位置。iRedMail 默认邮箱的存储位置在 `/var/vmail/` 中。
如果这个目录所在的分区有足够的空间来保存你所有域帐户的邮件,接着点击 Next 来继续。
否则,如果你已经配置一个更大的分区来用于邮件存储,那么就用不同的目录来更改默认位置。

*iRedMail 邮件存储路径*
12、 在下一步中,选择要与 iRedMail 进行交互的前端 Web 服务器。今后将完全禁用 iRedMail 管理面板,因此我们将使用前端 Web 服务器仅通过 Roundcube Web 面板访问帐户邮件。
如果你每小时没有数以千计的邮件帐户访问 webmail 界面,那么你应该使用 Apache Web 服务器来实现其灵活性和易于管理。

*iRedMail 首选的 Web 服务器*
13、 在此步骤中,由于 Samba4 域控制器的兼容性原因,请选择 OpenLDAP 后端数据库,并点击 Next 继续,但是一旦将 iRedMail 集成到 Samba 域控制器中,我们将不再使用该 OpenLDAP 数据库。

*iRedMail LDAP 后端*
14、 接下来,如下图所示,为你的 Samba4 域名指定 LDAP 后缀,然后点击 Next 继续。

*iRedMail LDAP 后缀*
15、 在接下来的提示中,只要输入你的域名,并点击 Next 继续。相应地替换 `tecmint.lan` 值。

*iRedMail 邮件域*
16、 现在,为 `[email protected]` 管理员设置一个密码,并点击 Next 继续。

*iRedMail 邮件域管理员*
17、 接下来,从列表中选择要与邮件服务器集成的可选组件。我强烈建议你安装 Roundcube,以便为域帐户提供访问邮件的 Web 界面,尽管你也可以在不同的计算机上安装并配置 Roundcube,以便在高负载情况下释放邮件服务器资源。
对于受限访问互联网的本地域,特别是在我们使用域集成时,除了 Awstats 可以用于你进行邮件分析,其他组件不是非常有用。

*iRedMail 可选组件*
18、 在下一步中输入 `Y` 来应用配置并开始安装。

*iRedMail 配置更改*
19、 最后,所有的问题都输入 `Y`,接受 iRedMail 脚本自动配置你的防火墙以及 MySQL 配置文件。

*iRedMail 系统配置*
20、 安装完成后,安装器会提供一些敏感信息。比如 iRedAdmin 凭证、web 面板的 URL 地址以及安装过程中使用的所有参数的文件位置。

*iRedMail 安装总结*
仔细阅读上面的信息,使用下面的命令重启机器来使所有的邮件服务启用。
```
# init 6
```
21、 系统重启后,使用 root 权限的帐户登录或以 root 身份登录,并使用下面的命令列出所有的网络套接字以及你邮件服务器监听的相关程序。
在套接字列表中,你会看到邮件服务器几乎覆盖邮件服务正常运行所需的所有服务:SMTP/S、POP3/S、IMAP/S 和防病毒以及垃圾邮件保护。
```
# netstat -tulpn
```

*iRedMail 网络套接字*
22、 为了查看 iRedMail 已修改的所有配置文件的位置、iRedMail 安装过程中用于数据库管理的凭据、邮件管理帐户以及其他帐户,那么就显示 `iRedMail.tips` 这个文件。
该文件位于你最初解压安装包的目录中。请注意,你应该移动并保护此文件,因为它包含有关邮件服务器的敏感信息。
```
# less iRedMail-0.9.6/iRedMail.tips
```
23、 上面提到的包含邮件服务器详细信息的文件也将自动发送到 postmaster 这个邮件服务器管理员帐户中。
通过在浏览器中输入机器的 IP 地址,你可以通过 HTTPS 协议安全地访问 webmail。接受 iRedMail 自签名证书在浏览器中生成的错误,并使用在安装中为 [postmaster@your\_domain.tld](mailto:postmaster@your_domain.tld) 帐户设置的密码登录。阅读并将此电子邮件存储到一个安全的邮箱。
```
https://192.168.1.254
```

*iRedMail 登录帐户*

*iRedMail Web 邮件*
就是这样了!到目前为止,你已经配置了一台完整的自己运行的邮件服务器了,但尚未与 Samba4 AD 域控制器服务集成。
在下一部分中,我们将看到如何修改 iRedMail 服务(postfix,dovecot 和 roundcube 配置文件),以便查询域帐户、发送、接收和读取邮件。
---
作者简介:
我是一个电脑上瘾的家伙,开源和基于 linux 系统软件的粉丝,在 Linux 发行版桌面、服务器和 bash 脚本方面拥有大约 4 年的经验。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/install-iredmail-on-centos-7-for-samba4-ad-integration/>
作者:[Matei Cezar](http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,568 | 极客漫画:chown 与 chmod | http://turnoff.us/geek/chown-chmod/ | 2017-06-04T08:13:00 | [
"漫画"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8568-1.html | 
`chown` :Linux 中用来改变某个文件的属主的命令,如漫画中所示,将某个“资源”(门)的访问权限给予别人。
`chmod` :Linux 中用来改变某个文件的访问模式的命令,如漫画中所示,`chmod 777` 会将“大门”敞开,谁都可以进出了。
---
via: <http://turnoff.us/geek/chown-chmod/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者&点评:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,569 | 安卓编年史(17):安卓 3.0 蜂巢—平板和设计复兴 | http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/18/ | 2017-06-04T11:57:00 | [
"Android",
"安卓编年史"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8569-1.html | 

*安卓市场的新设计试水“卡片式”界面,这将成为谷歌的主要风格。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
安卓推向市场已经有两年半时间了,安卓市场放出了它的第四版设计。这个新设计十分重要,因为它已经很接近谷歌的“卡片式”界面了。通过在小方块中显示应用或其他内容,谷歌可以使它的设计在不同尺寸屏幕下无缝过渡而不受影响。内容可以像一个相册应用里的照片一样显示——给布局渲染填充一个内容块列表,加上屏幕包装,就完成了。更大的屏幕一次可以看到更多的内容块,小点的屏幕一次看到的内容就少。内容用了不一样的方式显示,谷歌还在右边新增了一个“分类”板块,顶部还有个巨大的热门应用滚动显示。
虽然设计上为更容易配置界面准备好准备好了,但功能上还没有。最初发布的市场版本锁定为横屏模式,而且还是蜂巢独占的。

*应用详情页和“我的应用”界面。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
新的市场不仅出售应用,还加入了书籍和电影租借。谷歌从 2010 年开始出售图书;之前只通过网站出售。新的市场将谷歌所有的内容销售聚合到了一处,进一步向苹果 iTunes 所的主宰地位展开较量。虽然在“安卓市场”出售这些东西有点品牌混乱,因为大部分内容都不依赖于安卓才能使用。

*浏览器看起来非常像 Chrome,联系人使用了双面板界面。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
新浏览器界面顶部添加了标签页栏。尽管这个浏览器并不是 Chrome ,但它模仿了许多 Chrome 的设计和特性。除了这个探索性的顶部标签页界面,浏览器还加入了隐身标签,在浏览网页时不保存历史记录和自动补全记录。它还有个选项可以让你拥有一个 Chrome 风格的新标签页,页面上包含你最经常访问的网页略缩图。
新浏览器甚至还能和 Chrome 同步。在浏览器登录后,它会下载你的 Chrome 书签并且自动登录你的谷歌账户。收藏一个页面只需点击地址栏的星形标志即可,和谷歌地图一样,浏览器抛弃了缩放按钮,完全改用手势控制。
联系人应用最终从电话应用中移除,并且独立为一个应用。之前的联系人/拨号的混合式设计相对于人们使用现代智能手机的方式来说,过于以电话为中心了。联系人中存有电子邮件、IM、短信、地址、生日以及社交网络等信息,所以将它们捆绑在电话应用里的意义和将它们放进谷歌地图里差不多。抛开了电话通讯功能,联系人能够简化成没有标签页的联系人列表。蜂巢采用了双面板视图,在左侧显示完整的联系人列表,右侧是联系人详情。应用利用了 Fragments API,通过它应用可以在同一屏显示多个面板界面。
蜂巢版本的联系人应用是第一个拥有快速滚动功能的版本。当按住左侧滚动条的时候,你可以快速上下拖动,应用会显示列表当前位置的首字母预览。

*新 Youtube 应用看起来像是来自黑客帝国。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
谢天谢地 Youtube 终于抛弃了自安卓 2.3 以来的谷歌给予这个视频服务的“独特”设计,新界面设计与系统更加一体化。主界面是一个水平滚动的曲面墙,上面显示着最热门或者(登录之后)个人关注的视频。虽然谷歌从来没有将这个设计带到手机上,但它可以被认为是一个易于重新配置的卡片界面。操作栏在这里是个可配置的工具栏。没有登录时,操作栏由一个搜索栏填满。当你登录后,搜索缩小为一个按钮,“首页”,“浏览”和“你的频道”标签将会显示出来。

*蜂巢用一个蓝色框架的电脑界面来驱动主屏。电影工作室完全采用橙色电子风格主题。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
蜂巢新增的应用“电影工作室”,这不是一个不言自明的应用,而且没有任何的解释或说明。就我们所知,你可以导入视频,剪切它们,添加文本和场景过渡。编辑视频——电脑上你可以做的最耗时、困难,以及处理器密集型任务之一 —— 在平板上完成感觉有点野心过大了,谷歌在之后的版本里将其完全移除了。电影工作室里我们最喜欢的部分是它完全的电子风格主题。虽然系统的其它部分使用蓝色高亮,在这里是橙色的。(电影工作室是个邪恶的程序!)

*小部件! [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
蜂巢带来了新的部件框架,允许部件滚动,Gmail、Email 以及日历部件都升级了以支持改功能。Youtube 和书籍使用了新的部件,内容卡片可以自动滚动切换。在小部件上轻轻向上或向下滑动可以切换卡片。我们不确定你的书籍中哪些书会被显示出来,但如果你想要的话它就在那儿。尽管所有的这些小部件在 10 英寸屏幕上运行良好,谷歌从未为手机重新设计它们,这让它们在安卓最流行的规格上几乎毫无用处。所有的小部件有个大块的标识标题栏,而且通常占据大半屏幕只显示很少的内容。

*安卓 3.1 中可滚动的最近应用以及可自定义大小的小部件。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
蜂巢后续的版本修复了 3.0 早期的一些问题。安卓 3.1 在蜂巢的第一个版本之后三个月放出,并带来了一些改进。小部件自定义大小是添加的最大特性之一。长按小部件之后,一个带有拖拽按钮的蓝色外框会显示出来,拖动按钮可以改变小部件尺寸。最近应用界面现在可以垂直滚动并且承载更多应用。这个版本唯一缺失的功能是滑动关闭应用。
在今天,一个 0.1 版本的升级是个主要更新,但是在蜂巢,那只是个小更新。除了一些界面调整,3.1 添加了对游戏手柄,键盘,鼠标以及其它 USB 和蓝牙输入设备的支持。它还提供了更多的开发者 API。

*安卓 3.2 的兼容性缩放和一个安卓平板上典型的展开视图应用。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
安卓 3.2 在 3.1 发布后两个月放出,添加了七到八英寸的小尺寸平板支持。3.2 终于启用了 SD 卡支持,Xoom 在生命最初的五个月就像是初生儿的柔弱的肢体一样。
蜂巢匆匆问世是为了成为一个生态系统建设者。如果应用没有平板版本,没人会想要一个安卓平板的,所以谷歌知道需要尽快将东西送到开发者手中。在这个安卓平板生态的早期阶段,应用还没有到齐。这是拥有 Xoom 的人们所面临的最大的问题。
3.2 添加了“兼容缩放”,给了用户一个新选项,可以将应用拉伸适应屏幕(如右侧图片显示的那样)或缩放成正常的应用布局来适应屏幕。这些选项都不是很理想,由于没有应用生态来支持平板,蜂巢设备销售状况惨淡。但谷歌的平板决策最终还是会得到回报。今天,安卓平板已经[取代 iOS 占据了最大的市场份额](http://techcrunch.com/2014/03/03/gartner-195m-tablets-sold-in-2013-android-grabs-top-spot-from-ipad-with-62-share/)。
### Google Music Beta —— 取代内容商店的云存储

*姜饼上的 Google Music Beta。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
尽管蜂巢改进了 Google Music 的界面,但是音乐应用的设计并没有从蜂巢直接进化到冰淇淋三明治。2011 年 5 月,谷歌发布了“[Google Music Beta](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2011/05/hands-on-grooving-on-the-go-with-impressive-google-music-beta/)”,和新的 Google Music 应用一同到来的在线音乐存储。
新 Google Music 为安卓 2.2 及以上版本设计,借鉴了 Cooliris 相册的设计语言,但也有改变之处,背景使用了模糊处理的图片。几乎所有东西都是透明的:弹出菜单,顶部标签页,还有底部的正在播放栏。可以下载单独的歌曲或整个播放列表到设备上离线播放,这让 Google Music 成为一个让音乐同步到你所有设备的好途径。除了移动应用外,Google Music 还有一个 Web 应用,让它可以在任何一台桌面电脑上使用。
谷歌和唱片公司关于内容的合约还没有谈妥,音乐商店还没准备好,所以它的权宜之计是允许用户存储音乐到线上并下载到设备上。如今谷歌除了音乐存储服务外,还有单曲购买和订阅模式。
---

[Ron Amadeo](http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo) / Ron 是 Ars Technica 的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。[@RonAmadeo](https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo)
---
via: <http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/18/>
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,570 | 安卓编年史(18):Android 4.0 冰淇淋三明治—摩登时代 | http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/19/ | 2017-06-05T10:28:00 | [
"安卓编年史",
"Android"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8570-1.html | 
### Android 4.0 冰淇淋三明治 —— 摩登时代

*三星 Galaxy Nexus,安卓4.0的首发设备。*
安卓 4.0,冰淇淋三明治,在 2011 年 10 月发布,系统发布回到正轨,带来定期发布的手机和平板,并且安卓再次开源。这是自姜饼以来手机设备的第一个更新,意味着最主要的安卓用户群体近乎一年没有见到更新了。4.0 随处可见缩小版的蜂巢设计,还将虚拟按键,<ruby> 操作栏 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Action Bar </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,全新的设计语言带到了手机上。
冰淇淋三明治在三星 Galaxy Nexus 上首次亮相,也是最早带有 720p 显示屏的安卓手机之一。随着分辨率的提高,Galaxy Nexus 使用了更大的 4.65 英寸显示屏——几乎比最初的 Nexus One 大了一整英寸。这被许多批评者认为“太大了”,但如今的安卓设备甚至更大。(5 英寸当今是“正常”的。)冰淇淋三明治比姜饼的性能要求更高,Galaxy Nexus 配备了一颗双核,1.2Ghz 德州仪器 OMAP 处理器和 1GB 的内存。
在美国,Galaxy Nexus 在 Verizon 首发并且支持 LTE。不像之前的 Nexus 设备,最流行的型号——Verizon 版——是在运营商的控制之下,谷歌的软件和更新在手机得到更新之前要经过 Verizon 的核准。这导致了更新的延迟以及 Verizon 不喜欢的应用被移除,即便是 Google Wallet 也不例外。
多亏了冰淇淋三明治的软件改进,谷歌终于达成了移除手机上按钮的目标。有了虚拟导航键,实体电容按钮就可以移除了,最终 Galaxy Nexus 仅有电源和音量是实体按键。

*安卓 4.0 将很多蜂巢的设计缩小了。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
电子质感的审美在蜂巢中显得有点多。于是在冰淇淋三明治中,谷歌开始减少科幻风的设计。科幻风的时钟字体从半透明折叠风格转变成纤细,优雅,看起来更加正常的字体。解锁环的水面波纹效果被去除了,蜂巢中的外星风格时钟小部件也被极简设计所取代。系统按钮也经过了重新设计,原先的蓝色轮廓,偶尔的厚边框变成了细的,设置带有白色轮廓。默认壁纸从蜂巢的蓝色太空船内部变成条纹状,破碎的彩虹,给默认布局增添了不少迟来的色彩。
蜂巢的系统栏在手机上一分为二。在顶上是传统的状态栏,底部是新的系统栏,放着三个系统按钮:后退、主屏幕、最近应用。一个固定的搜索栏放置在了主屏幕顶部。该栏以和底栏一样的方式固定在屏幕上,所以在五个主屏上,它总共占据了 20 个图标大小的位置。在蜂巢的锁屏上,内部的小圆圈可以向大圆圈外的任意位置滑动来解锁设备。在冰淇淋三明治,你得把小圆圈移动到解锁图标上。这个新准确度要求允许谷歌向锁屏添加新的选项:一个相机快捷方式。将小圆圈拖向相机图标会直接启动相机,跳过了主屏幕。

*一个手机系统意味着更多的应用,通知面板重新回到了全屏界面。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
应用抽屉还是标签页式的,但是蜂巢中的“我的应用”标签被“部件”标签页替代,这是个简单的 2×3 部件略缩图视图。像蜂巢里的那样,这个应用抽屉是分页的,需要水平滑动换页。(如今安卓仍在使用这个应用抽屉设计。)应用抽屉里新增的是 Google+ 应用,后来独立存在。还有一个“Messenger”快捷方式,是 Google+ 的私密信息服务。(不要混淆 “Messenger” 和已有的 “Messaging” 短信应用。)
因为我们现在回到了手机上,所以短信,新闻和天气,电话,以及语音拨号都回来了,以及 Cordy,一个平板的游戏,被移除了。尽管不是 Nexus 设备,我们的截图还是来自 Verizon 版的设备,可以从图上看到有像 “My Verizon Mobile” 和 “VZ Backup Assistant” 这样没用的应用。为了和冰淇淋三明治的去电子风格主题一致,日历和相机图标现在看起来更像是来自地球的东西而不是来自外星球。时钟,下载,电话,以及安卓市场同样得到了新图标,“联系人”获得了新图标,还有新名字 “People”。
通知面板进行了大改造,特别是和[之前姜饼中的设计](http://cdn.arstechnica.net/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/32.png)相比而言。面板头部有个日期,一个设置的快捷方式,以及“清除所有”按钮。虽然蜂巢的第一个版本就允许用户通过通知右边的“X”消除单个通知,但是冰淇淋三明治的实现更加优雅:只要从左向右滑动通知即可。蜂巢有着蓝色高亮,但是蓝色色调到处都是。冰淇淋三明治几乎把所有地方的蓝色统一成一个(如果你想知道确定的值,hex 码是 `#33B5E5`)。通知面板的背景是透明的,底部的“把手”变为一个简单的小蓝圈,带着不透明的黑色背景。

*安卓市场的主页背景变成了黑色。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
市场获得了又一个新设计。它终于再次支持纵向模式,并且添加了音乐到商店中,你可以从中购买音乐。新的市场拓展了从蜂巢中引入的卡片概念,它还是第一个同时使用在手机和平板上的版本。主页上的卡片通常不是链接到应用的,而是指向特别的促销页面,像是“编辑精选”或季度促销。
---

[Ron Amadeo](http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo) / Ron是Ars Technica的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。[@RonAmadeo](https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo)
---
via: <http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/19/>
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,573 | 怎么使用 Diff 和 Meld 工具发现两个目录间的不同之处 | http://www.tecmint.com/compare-find-difference-between-two-directories-in-linux/ | 2017-06-04T17:50:22 | [
"diff",
"meld"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8573-1.html | 
在之前的一篇文章里,我们回顾了 [Linux 下 9 个最好的文件比较工具](http://www.tecmint.com/best-linux-file-diff-tools-comparison/),本篇文章中,我们将会描述在 Linux 下怎样找到两个目录之间的不同。
一般情况下,要在 Linux 下比较两个文件,我们会使用 `diff` (一个简单的源自 Unix 的命令行工具)来显示两个计算机文件的不同;它一行一行的去比较文件,而且很方便使用,在几乎全部的 Linux 发行版都预装了。
问题是在 Linux 下我们怎么才能比较两个目录?现在,我们想知道两个目录中哪些文件/子目录是共有的,哪些只存在一个于目录。
运行 diff 常规的语法如下:
```
$ diff [OPTION]… FILES
$ diff options dir1 dir2
```
默认情况下,输出是按文件/子文件夹的文件名的字母排序的,如下面截图所示,在命令中, `-q` 开关是告诉 `diif` 只有在文件有差异时报告。
```
$ diff -q directory-1/ directory-2/
```

*两个文件夹之间的差异*
再次运行 `diff` 并不能进入子文件夹,但是我们可以使用 `-r` 开关来读子文件夹,如下所示。
```
$ diff -qr directory-1/ directory-2/
```
### 使用 Meld 可视化比较和合并工具
`meld` 是一个很酷的图形化工具(一个 GNOME 桌面下的可视化的比较和合并工具),可供那些喜欢使用鼠标的人使用,可按如下来安装。
```
$ sudo apt install meld [Debian/Ubuntu systems]
$ sudo yum install meld [RHEL/CentOS systems]
$ sudo dnf install meld [Fedora 22+]
```
一旦你安装了它之后,在 **Ubuntu Dash** 或者 **Linux Mint** 菜单搜索 “**meld**” ,或者 Fedora 或 CentOS 桌面的 Activities Overview,然后启动它。
你可以看到如下的 Meld 界面,可以选择文件或者文件夹来比较,此外还有版本控制视图。点击目录比较并移动到下个界面。 
*Meld 比较工具*
选择你想要比较的文件夹,注意你可以勾选 “**3-way Comparison**” 选项,添加第三个文件夹。

*选择比较的文件夹*
选择好要比较的文件夹后,点击 “Compare”。

*文件夹不同列表*
在这篇文章中,我们描述了怎么在 Linux 下找到两个文件夹的不同。如果你知道其他的命令或者图形界面工具,不要忘记在下方评论分享你们的想法。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,即将成为 Linux 系统管理员,Web 开发者,目前是 TecMint 的内容创建者,他喜欢使用电脑工作,并且非常相信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/compare-find-difference-between-two-directories-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[hkurj](https://github.com/hkurj) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,574 | 安卓编年史(19):Android 4.0 冰淇淋三明治—摩登时代 | http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/20/ | 2017-06-07T10:35:00 | [
"Android",
"安卓编年史"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8574-1.html | 

*和之前完全不同的市场设计。以上是分类,特色,热门应用以及应用详情页面。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
这些截图给了我们冰淇淋三明治中新版操作栏的第一印象。几乎所有的应用顶部都有一条栏,带有应用图标,当前界面标题,一些功能按钮,右边还有一个菜单按钮。这个右对齐的菜单按钮被称为“更多操作”,因为里面存放着无法放置到主操作栏的项目。不过更多操作菜单并不是固定不变的,它给了操作栏节省了更多的屏幕空间——比如在横屏模式或在平板上时,更多操作菜单的项目会像通常的按钮一样显示在操作栏上。
冰淇凌三明治中新增了“滑动标签页”设计,替换掉了谷歌之前推行的 2×3 方阵导航屏幕。一个标签页栏放置在了操作栏下方,位于中间的标签显示的是当前页面,左右侧的两个标签显示的是对应的当前页面的左右侧页面。向左右滑动可以切换标签页,或者你可以点击指定页面的标签跳转过去。
应用详情页面有个很赞的设计,在应用截图后,会根据你关于那个应用的历史动态地重新布局页面。如果你从来没有安装过该应用,应用描述会优先显示。如果你曾安装过这个应用,第一部分将会是评价栏,它会邀请你评价该应用或者提醒你上次你安装该应用时的评价是什么。之前使用过的应用页面第二部分是“新特性”,因为一个老用户最关心的应该是应用有什么变化。

*最近应用和浏览器和蜂巢中的类似,但是是小号的。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
最近应用的电子风格外观被移除了。略缩图周围的蓝色的轮廓线被去除了,同时去除的还有背景怪异的、不均匀的蓝色光晕。它现在看起来是个中立型的界面,在任何时候看起来都很舒适。
浏览器尽了最大的努力把标签页体验带到手机上来。多标签浏览受到了关注,操作栏上引入的一个标签页按钮会打开一个类似最近应用的界面,显示你打开的标签页,而不是浪费宝贵的屏幕空间引入一个标签条。从功能上来说,这个和之前的浏览器中的“窗口”视图没什么差别。浏览器最佳的改进是菜单中的“请求桌面版站点”选项,这让你可以从默认的移动站点视图切换到正常站点。浏览器展示了谷歌的操作栏设计的灵活性,尽管这里没有左上角的应用图标,功能上来说和其他的顶栏设计相似。

*Gmail 和 Google Talk —— 它们和蜂巢中的相似,但是更小! [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
Gmail 和 Google Talk 看起来都像是之前蜂巢中的设计的缩小版,但是有些小调整让它们在小屏幕上表现更佳。Gmail 以双操作栏为特色——一个在屏幕顶部,一个在底部。顶部操作栏显示当前文件夹、账户,以及未读消息数目,点击顶栏可以打开一个导航菜单。底部操作栏有你期望出现在更多操作中的选项。使用双操作栏布局是为了在界面显示更多的按钮,但是在横屏模式下纵向空间有限,双操作栏就合并成一个顶部操作栏。
在邮件视图下,往下滚动屏幕时蓝色栏有“粘性”。它会固定在屏幕顶部,所以你一直可以看到该邮件是谁写的,回复它,或者给它加星标。一旦处于邮件消息界面,底部细长的、深灰色栏会显示你当前在收件箱(或你所在的某个列表)的位置,并且你可以向左或向右滑动来切换到其他邮件。
Google Talk 允许你像在 Gmail 中那样左右滑动来切换聊天窗口,但是这里显示栏是在顶部。

*新的拨号和来电界面,都是姜饼以来我们还没见过的。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
因为蜂巢只给平板使用,所以一些界面设计直接超前于姜饼。冰淇淋三明治的新拨号界面就是如此,黑色和蓝色相间,并且使用了可滑动切换的小标签。尽管冰淇淋三明治终于做对了,将电话主体和联系人独立开来,但电话应用还是有它自己的联系人标签。现在有两个地方可以看到你的联系人列表——一个有着暗色主题,另一个有着亮色主题。由于实体搜索按钮不再是硬性要求,底部的按钮栏的语音信息快捷方式被替换为了搜索图标。
谷歌几乎就是把来电界面做成了锁屏界面的镜像,这意味着冰淇淋三明治有着一个环状解锁设计。除了通常的接受和挂断选项,圆环的顶部还添加了一个按钮,让你可以挂断来电并给对方发送一条预先定义好的信息。向上滑动并选择一条信息如“现在无法接听,一会回电”,相比于一直响个不停的手机而言这样做的信息交流更加丰富。

*蜂巢没有文件夹和信息应用,所以这里是冰淇淋三明治和姜饼的对比。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
现在创建文件夹更加方便了。在姜饼中,你得长按屏幕,选择“文件夹”选项,再点击“新文件夹”。在冰淇淋三明治中,你只要将一个图标拖拽到另一个图标上面,就会自动创建一个文件夹,并包含这两个图标。这简直不能更简单了,比寻找隐藏的长按命令容易多了。
设计上也有很大的改进。姜饼使用了一个通用的米黄色文件夹图标,但冰淇淋三明治直接显示出了文件夹中的头三个应用,把它们的图标叠在一起,在外侧画一个圆圈,并将其设置为文件夹图标。打开文件夹容器将自动调整大小以适应文件夹中的应用图标数目,而不是显示一个全屏的,大部分都是空的对话框。这看起来好得多得多。

*Youtube 转换到一个更加现代的白色主题,使用了列表视图替换疯狂的 3D 滚动视图。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
Youtube 经过了完全的重新设计,看起来没那么像是来自黑客帝国的产物,更像是,嗯,Youtube。它现在就是一个简单的垂直滚动的白色视频列表,就像网站的那样。在你手机上制作视频受到了重视,操作栏的第一个按钮专用于拍摄视频。奇怪的是,不同的界面左上角使用了不同的 Youtube 标志,在水平的 Youtube 标志和方形标志之间切换。
Youtube 几乎在所有地方都使用了滑动标签页。它们被放置在主页面以在浏览和账户间切换,放置在视频页面以在评论,介绍和相关视频之间切换。4.0 版本的应用显示出 Google+ Youtube 集成的第一个信号,通常的评分按钮旁边放置了 “+1” 图标。最终 Google+ 会完全占据 Youtube,将评论和作者页面变成 Google+ 活动。

*冰淇淋三明治试着让事情对所有人都更加简单。这里是数据使用量追踪,打开许多数据的新开发者选项,以及使用向导。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
数据使用量允许用户更轻松地追踪和控制他们的数据使用。主页面显示一个月度使用量图表,用户可以设置数据使用警告值或者硬性使用限制以避免超量使用产生费用。所有的这些只需简单地拖动橙色和红色水平限制线在图表上的位置即可。纵向的白色把手允许用户选择图表上的一段指定时间段。在页面底部,选定时间段内的数据使用量又细分到每个应用,所以用户可以选择一个数据使用高峰并轻松地查看哪个应用在消耗大量流量。当流量紧张的时候,更多操作按钮中有个限制所有后台流量的选项。设置之后只用在前台运行的程序有权连接互联网。
开发者选项通常只有一点点设置选项,但是在冰淇淋三明治中,这部分有非常多选项。谷歌添加了所有类型的屏幕诊断显示浮层来帮助开发者理解他们的应用中发生了什么。你可以看到 CPU 使用率,触摸点位置,还有视图界面更新。还有些选项可以更改系统功能,比如控制动画速度,后台处理,以及 GPU 渲染。
安卓和 iOS 之间最大的区别之一就是应用抽屉界面。在冰淇淋三明治对更加用户友好的追求下,设备第一次初始化启动会启动一个小教程,向用户展示应用抽屉的位置以及如何将应用图标从应用抽屉拖拽到主屏幕。随着实体菜单按键的移除和像这样的改变,安卓 4.0 做了很大的努力变得对新智能手机用户和转换过来的用户更有吸引力。

*“触摸分享”NFC 支持,Google Earth,以及应用信息,让你可以禁用垃圾软件。*
冰淇淋三明治内置对 [NFC](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2011/02/near-field-communications-a-technology-primer/) 的完整支持。尽管之前的设备,比如 Nexus S 也拥有 NFC,得到的支持是有限的并且系统并不能利用芯片做太多事情。4.0 添加了一个“Android Beam”功能,两台拥有 NFC 的安卓 4.0 设备可以借此在设备间来回传输数据。NFC 会传输关于此时屏幕显示的数据,因此在手机显示一个网页的时候使用该功能会将该页面传送给另一部手机。你还可以发送联系人信息、方向导航,以及 Youtube 链接。当两台手机放在一起时,屏幕显示会缩小,点击缩小的界面会发送相关信息。
在安卓中,用户不允许删除系统应用,以保证系统完整性。运营商和 OEM 利用该特性并开始将垃圾软件放入系统分区,经常有一些没用的应用存在系统中。安卓 4.0 允许用户禁用任何不能被卸载的应用,意味着该应用还存在于系统中但是不显示在应用抽屉里并且不能运行。如果用户愿意深究设置项,这给了他们一个简单的途径来拿回手机的控制权。
安卓 4.0 可以看做是现代安卓时代的开始。大部分这时发布的谷歌应用只能在安卓 4.0 及以上版本运行。4.0 还有许多谷歌想要好好利用的新 API——至少最初想要——对 4.0 以下的版本的支持就有限了。在冰淇淋三明治和蜂巢之后,谷歌真的开始认真对待软件设计。在 2012 年 1 月,谷歌[最终发布了](http://arstechnica.com/business/2012/01/google-launches-style-guide-for-android-developers/) *Android Design*,一个教安卓开发者如何创建符合安卓外观和感觉的应用的设计指南站点。这是 iOS 在有第三方应用支持开始就在做的事情,苹果还严肃地对待应用的设计,不符合指南的应用都被 App Store 拒之门外。安卓三年以来谷歌没有给出任何公共设计规范文档的事实,足以说明事情有多糟糕。但随着在 Duarte 掌控下的安卓设计革命,谷歌终于发布了基本设计需求。
### Google Play 和直接面向消费者出售设备的回归

2012 年 3 月 6 日,谷歌将旗下提供的所有内容统一到 “Google Play”。安卓市场变为了 Google Play 商店,Google Books 变为 Google Play Books,Google Music 变为 Google Play Music,还有 Android Market Movies 变为 Google Play Movies & TV。尽管应用界面的变化不是很大,这四个内容应用都获得了新的名称和图标。在 Play 商店购买的内容会下载到对应的应用中,Play 商店和 Play 内容应用一道给用户提供了易管理的内容体验。
Google Play 更新是谷歌第一个大的更新周期外更新。四个自带应用都没有通过系统更新获得升级,它们都是直接通过安卓市场/ Play 商店更新的。对单独的应用启用周期外更新是谷歌的重大关注点之一,而能够实现这样的更新,是自姜饼时代开始的工程努力的顶峰。谷歌一直致力于对应用从系统“解耦”,从而让它们能够通过安卓市场/ Play 商店进行分发。
尽管一两个应用(主要是地图和 Gmail)之前就在安卓市场上,从这里开始你会看到许多更重大的更新,而其和系统发布无关。系统更新需要 OEM 厂商和运营商的合作,所以很难保证推送到每个用户手上。而 Play 商店更新则完全掌握在谷歌手上,给了谷歌一条直接到达用户设备的途径。因为 Google Play 的发布,安卓市场对自身升级到了 Google Play Store,在那之后,图书,音乐以及电影应用都下发了 Google Play 式的更新。
Google Play 系列应用的设计仍然不尽相同。每个应用的外观和功能各有差异,但暂且来说,一个统一的品牌标识是个好的开始。从品牌标识中去除“安卓”字样是很有必要的,因为很多服务是在浏览器中提供的,不需要安卓设备也能使用。
2012 年 4 月,谷歌[再次开始通过 Play 商店销售设备](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2011/02/near-field-communications-a-technology-primer/),恢复在 Nexus One 发布时尝试的直接面向消费者销售的方式。尽管距 Nexus One 销售结束仅有两年,但网上购物现在更加寻常,在接触到物品之前就购买它并不像在 2010 年时听起来那么疯狂。
谷歌也看到了价格敏感的用户在面对 Nexus One 的 530 美元的价格时的反应。第一部销售的设备是无锁的,GSM 版本的 Galaxy Nexus,价格 399 美元。在那之后,价格变得更低。350 美元成为了最近两台 Nexus 设备的入门价,7 英寸 Nexus 平板的价格更是只有 200 美元到 220 美元。
今天,Play 商店销售八款不同的安卓设备,四款 Chromebook,一款自动调温器,以及许多配件,设备商店已经是谷歌新产品发布的实际地点了。新产品发布总是如此受欢迎,站点往往无法承载如此大的流量,新 Nexus 手机也在几小时内售空。
---

[Ron Amadeo](http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo) / Ron是Ars Technica的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。[@RonAmadeo](https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo)
---
via: <http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/20/>
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,575 | MyCLI :一个支持自动补全和语法高亮的 MySQL/MariaDB 客户端 | https://www.tecmint.com/mycli-mysql-client-with-auto-completion-syntax-highlighting/ | 2017-06-05T09:05:00 | [
"MySQL",
"MyCLI"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8575-1.html | MyCLI 是一个易于使用的命令行客户端,可用于受欢迎的数据库管理系统 MySQL、MariaDB 和 Percona,支持自动补全和语法高亮。它是使用 `prompt_toolkit` 库写的,需要 Python 2.7、3.3、3.4、3.5 和 3.6 的支持。MyCLI 还支持通过 SSL 安全连接到 MySQL 服务器。

#### MyCLI 的特性
* 当你第一次使用它的时候,将会自动创建一个文件 `~/.myclirc`。
* 当输入 SQL 的关键词和数据库中的表、视图和列时,支持自动补全。
* 默认情况下也支持智能补全,能根据上下文的相关性提供补全建议。
比如:
```
SELECT * FROM <Tab> - 这将显示出数据库中的表名。
SELECT * FROM users WHERE <Tab> - 这将简单的显示出列名称。
```
* 通过使用 `Pygents` 支持语法高亮
* 支持 SSL 连接
* 提供多行查询支持
* 它可以将每一个查询和输出记录到一个文件中(默认情况下禁用)。
* 允许保存收藏一个查询(使用 `\fs 别名` 保存一个查询,并可使用 `\f 别名` 运行它)。
* 支持 SQL 语句执行和表查询计时
* 以更吸引人的方式打印表格数据
### 如何在 Linux 上为 MySQL 和 MariaDB 安装 MyCLI
在 Debian/Ubuntu 发行版上,你可以很容易的像下面这样使用 `apt` 命令 来安装 MyCLI 包:
```
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install mycli
```
同样,在 Fedora 22+ 上也有 MyCLI 的可用包,你可以像下面这样使用 `dnf` 命令 来安装它:
```
$ sudo dnf install mycli
```
对于其他 Linux 发行版,比如 RHEL/CentOS,你需要使用 Python 的 `pip` 工具来安装 MyCLI。首先,使用下面的命令来安装 pip:
```
$ sudo yum install pip
```
安装好 `pip` 以后,你可以像下面这样安装 MyCLI:
```
$ sudo pip install mycli
```
### 在 Linux 中如何使用 MyCLI 连接 MySQL 和 MariaDB
安装好 MyCLI 以后,你可以像下面这样使用它:
```
$ mycli -u root -h localhost
```
#### 自动补全
对于关键词和 SQL 函数可以进行简单的自动补全:

*MySQL 自动补全*
#### 智能补全
当输入 `FROM` 关键词以后会进行表名称的补全:

*MySQL 智能补全*
#### 别名支持
当表的名称设置别名以后,也支持列名称的补全:

*MySQL 别名支持*
#### 语法高亮
支持 MySQL 语法高亮:

*MySQL 语法高亮*
#### 格式化 SQL 的输出
MySQL 的输出会通过 [`less` 命令](https://www.tecmint.com/linux-more-command-and-less-command-examples/) 进行格式化输出:

*MySQL 格式化输出*
要登录 MySQL 并同时选择数据库,你可以使用和下面类似的命令:
```
$ mycli local_database
$ mycli -h localhost -u root app_db
$ mycli mysql://amjith@localhost:3306/django_poll
```
更多使用选项,请输入:
```
$ mycli --help
```
MyCLI 主页: <http://mycli.net/index>
记得阅读一些关于 MySQL 管理的有用文章:
1. [在 Linux 中用于数据库管理的 20 个 MySQL(Mysqladmin)命令](https://www.tecmint.com/mysqladmin-commands-for-database-administration-in-linux/)
2. [如何在 Linux 中更改默认的 MySQL/MariaDB 数据目录](https://www.tecmint.com/change-default-mysql-mariadb-data-directory-in-linux/)
3. [在 Linux 中监测 MySQL 性能的 4 个实用命令行工具](https://www.tecmint.com/mysql-performance-monitoring/)
4. [如何在 Linux 中更改 MySQL 或 MariaDB 的 Root 密码](/article-8328-1.html)
5. [MySQL 备份和恢复数据库管理命令](https://www.tecmint.com/mysql-backup-and-restore-commands-for-database-administration/)
MyCLI 作者写的两篇如何创建具有可发现性的交互式命令行客户端的文章:
1. [4 个拥有绝佳命令行界面的终端程序](/article-8526-1.html)
2. [4 个用于构建优秀的命令行用户界面的 Python 库](/article-8561-1.html)
这就是本文的全部内容了。在这篇指南中,我们展示了如何通过一些简单的命令在 Linux 中安装和使用 MyCLI。记得通过下面的反馈表向我们分享你关于这篇文章的想法。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili是一名 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 的爱好者,未来的 Linux 系统管理员、网站开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并乐于分享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/mycli-mysql-client-with-auto-completion-syntax-highlighting/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | **MyCLI** is an easy-to-use command line (CLI) interface for the popular database management systems: MySQL, MariaDB, and Percona with auto-completion and syntax highlighting. It is built using **prompt_toolkit** and requires Python 2.7, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, and 3.6. It supports secure connections over SSL to the MySQL server.
#### MyCLI Features
- When you first start it, a config file is automatically created at
**~/.myclirc**. - Supports auto-completion while typing SQL keywords as well as tables, views and columns in the database.
- Also supports smart-completion which is enabled by default and will offer suggestions for context-sensitive completion.
For instance:
SELECT * FROM <Tab> - this will just show table names. SELECT * FROM users WHERE <Tab> - this will simply show column names.
- Supports syntax highlighting using Pygments.
- Support for SSL connections.
- Offers support for multiline queries.
- It optionally logs every query and its output to a file (note that this is disabled by default).
- Allows you to save favorite queries (save a query using
**\fs alias**and run it with**\f alias**). - Supports timing of SQL statements and table rendering.
- Prints tabular data in an appealing way.
### How to Install MyCLI for MySQL and MariaDB in Linux
On **Debian/Ubuntu** distributions, you can easily install the mycli package using [apt command](https://www.tecmint.com/apt-advanced-package-command-examples-in-ubuntu/) as follows:
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install mycli
Likewise, **Fedora 22+** has a package available for mycli, you can install it using [dnf command](https://www.tecmint.com/dnf-commands-for-fedora-rpm-package-management/) as below:
$ sudo dnf install mycli
For other Linux distributions such as **RHEL/CentOS**, you’ll need Python pip tool to install mycli. Start by installing pip with the commands below:
$ sudo yum install pip
Once pip is installed, you can install mycli as follows:
$ sudo pip install mycli
### How to Use MyCLI for MySQL and MariaDB in Linux
Once mycli installed, you can use it like this:
$ mycli -u root -h localhost
#### Auto-completion
Easy completions such as keywords and sql-functions.
#### Smart-completion
Table name completions after the ‘FROM’ keyword.
#### Alias support
A column completions will work even when table names are aliased.
#### Syntax-highlighting
Syntax highlighting for MySQL.
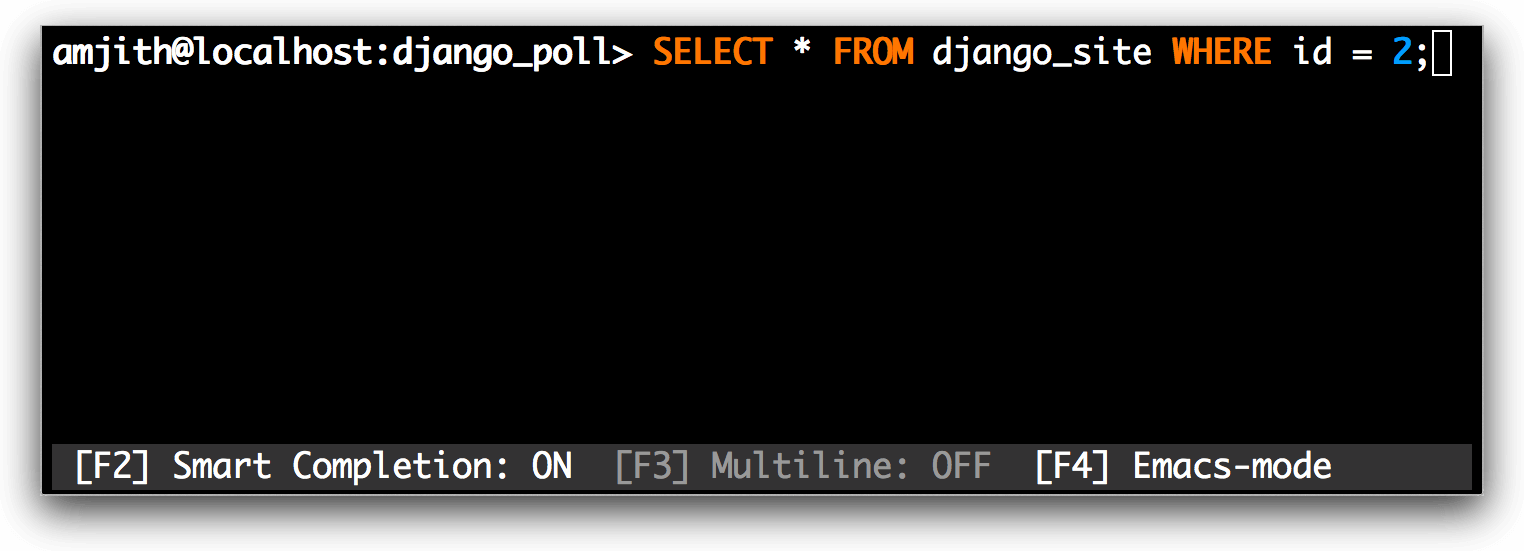
#### Formatted SQL Output
MySQL Output is automatically piped through [less command](https://www.tecmint.com/linux-more-command-and-less-command-examples/).
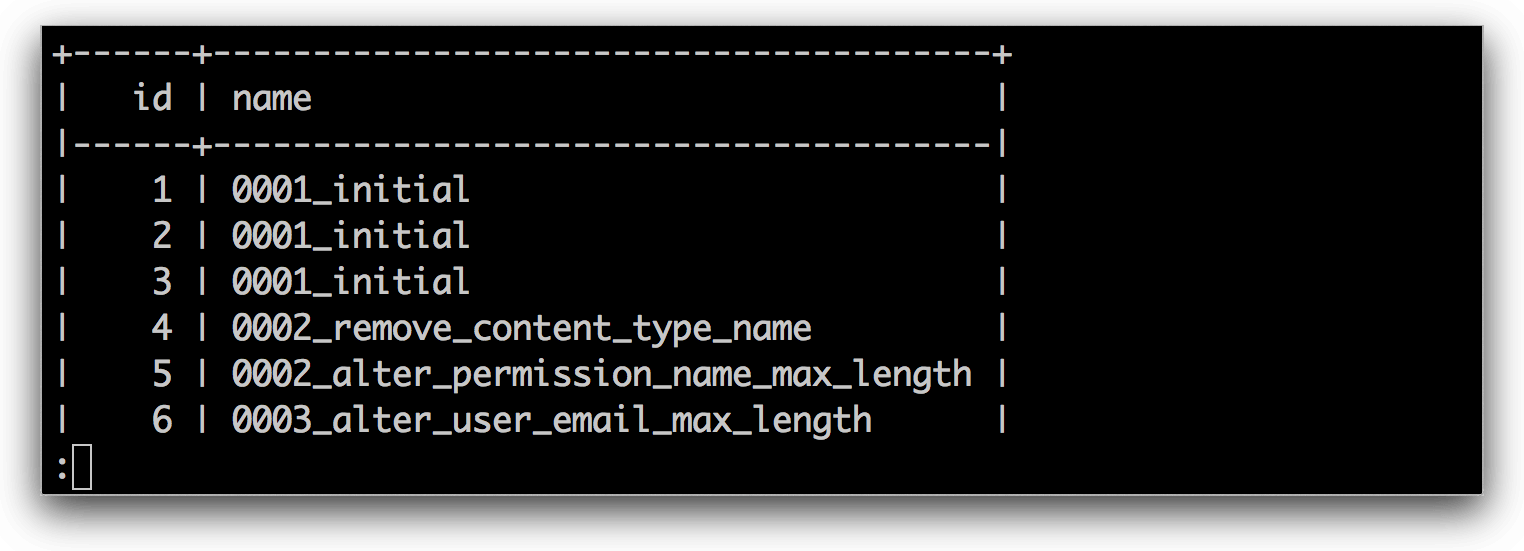
To login into mysql and select a database at the same time, you may use a similar command as follows.
$ mycli local_database $ mycli -h localhost -u root app_db $ mycli mysql://amjith@localhost:3306/django_poll
For more usage options, type:
$ mycli --help
MyCLI Homepage: [http://mycli.net/index](http://mycli.net/index)
Do check out some useful articles for MySQL administration.
[20 MySQL (Mysqladmin) Commands for Database Administration in Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/mysqladmin-commands-for-database-administration-in-linux/)[How to Change a Default MySQL/MariaDB Data Directory in Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/change-default-mysql-mariadb-data-directory-in-linux/)[4 Useful Commandline Tools to Monitor MySQL Performance in Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/mysql-performance-monitoring/)[How to Change Root Password of MySQL or MariaDB in Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/change-mysql-mariadb-root-password/)[MySQL Backup and Restore Commands for Database Administration](https://www.tecmint.com/mysql-backup-and-restore-commands-for-database-administration/)
That’s all! In this guide, we showed how to install and use mycli with simple commands in Linux. Do share your thought concerning this article via the feedback form below.
Awesome, works perfectly fine much like what the fish shell does to the Linux terminal.
Reply@David
Hope you enjoyed it. Many thanks for the feedback and following us as well.
Reply |
8,576 | ssh_scan:远程验证你 SSH 服务的配置和策略 | https://www.tecmint.com/ssh_scan-ssh-configuration-and-policy-scanner-for-linux/ | 2017-06-06T09:17:00 | [
"SSH",
"ssh_scan"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8576-1.html | `ssh_scan` 是一个面向 Linux 和 UNIX 服务器的易用的 SSH 服务参数配置和策略的扫描器程序,其思路来自[Mozilla OpenSSH 安全指南](https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Guidelines/OpenSSH),这个指南为 SSH 服务参数配置提供了一个可靠的安全策略基线的建议,如加密算法(Ciphers),报文认证信息码算法(MAC),密钥交换算法(KexAlgos)和其它。

`ssh_scan` 有如下好处:
* 它的依赖是最小化的,`ssh_scan` 只引入了本地 Ruby 和 BinData 来进行它的工作,没有太多的依赖。
* 它是可移植的,你可以在其它的项目中使用 `ssh_scan` 或者将它用在[自动化任务](https://www.tecmint.com/automating-linux-system-administration-tasks/)上。
* 它是易于使用的,只需要简单的将它指向一个 SSH 服务就可以获得一个该服务所支持的选项和策略状态的 JSON 格式报告。
* 它同时也是易于配置的,你可以创建适合你策略需求的策略。
**建议阅读:** [如何在 Linux 上安装配置 OpenSSH 服务](https://www.tecmint.com/install-openssh-server-in-linux/)
### 如何在 Linux 上安装 ssh\_scan
有如下三种安装 `ssh_scan` 的方式:
使用 Ruby gem 来安装运行,如下:
```
----------- 在 Debian/Ubuntu -----------
$ sudo apt-get install rubygems
$ sudo gem install ssh_scan
----------- 在 CentOS/RHEL -----------
# yum install ruby rubygems
# gem install ssh_scan
```
使用[docker 容器](https://www.tecmint.com/install-docker-and-learn-containers-in-centos-rhel-7-6/)来运行,如下:
```
# docker pull mozilla/ssh_scan
# docker run -it mozilla/ssh_scan /app/bin/ssh_scan -t github.com
```
使用源码安装运行,如下:
```
# git clone https://github.com/mozilla/ssh_scan.git
# cd ssh_scan
# gpg2 --keyserver hkp://keys.gnupg.net --recv-keys 409B6B1796C275462A1703113804BB82D39DC0E3
# curl -sSL https://get.rvm.io | bash -s stable
# rvm install 2.3.1
# rvm use 2.3.1
# gem install bundler
# bundle install
# ./bin/ssh_scan
```
### 如何在 Linux 上使用 ssh\_scan
使用 `ssh_scan` 的语法如下:
```
$ ssh_scan -t ip地址
$ ssh_scan -t 主机名
```
举个例子来扫描 192.168.43.198 这台服务器的 SSH 配置和策略,键入:
```
$ ssh_scan -t 192.168.43.198
```
注意你同时也可以像下方展示的给 `-t` 选项传入一个[IP地址/地址段/主机名]:
```
$ ssh_scan -t 192.168.43.198,200,205
$ ssh_scan -t test.tecmint.lan
```
输出示例:
```
I, [2017-05-09T10:36:17.913644 #7145] INFO -- : You're using the latest version of ssh_scan 0.0.19
[
{
"ssh_scan_version": "0.0.19",
"ip": "192.168.43.198",
"port": 22,
"server_banner": "SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_7.2p2 Ubuntu-4ubuntu2.1",
"ssh_version": 2.0,
"os": "ubuntu",
"os_cpe": "o:canonical:ubuntu:16.04",
"ssh_lib": "openssh",
"ssh_lib_cpe": "a:openssh:openssh:7.2p2",
"cookie": "68b17bcca652eeaf153ed18877770a38",
"key_algorithms": [
"[email protected]",
"ecdh-sha2-nistp256",
"ecdh-sha2-nistp384",
"ecdh-sha2-nistp521",
"diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256",
"diffie-hellman-group14-sha1"
],
"server_host_key_algorithms": [
"ssh-rsa",
"rsa-sha2-512",
"rsa-sha2-256",
"ecdsa-sha2-nistp256",
"ssh-ed25519"
],
"encryption_algorithms_client_to_server": [
"[email protected]",
"aes128-ctr",
"aes192-ctr",
"aes256-ctr",
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]"
],
"encryption_algorithms_server_to_client": [
"[email protected]",
"aes128-ctr",
"aes192-ctr",
"aes256-ctr",
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]"
],
"mac_algorithms_client_to_server": [
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]",
"hmac-sha2-256",
"hmac-sha2-512",
"hmac-sha1"
],
"mac_algorithms_server_to_client": [
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]",
"[email protected]",
"hmac-sha2-256",
"hmac-sha2-512",
"hmac-sha1"
],
"compression_algorithms_client_to_server": [
"none",
"[email protected]"
],
"compression_algorithms_server_to_client": [
"none",
"[email protected]"
],
"languages_client_to_server": [
],
"languages_server_to_client": [
],
"hostname": "tecmint",
"auth_methods": [
"publickey",
"password"
],
"fingerprints": {
"rsa": {
"known_bad": "false",
"md5": "0e:d0:d7:11:f0:9b:f8:33:9c:ab:26:77:e5:66:9e:f4",
"sha1": "fc:8d:d5:a1:bf:52:48:a6:7e:f9:a6:2f:af:ca:e2:f0:3a:9a:b7:fa",
"sha256": "ff:00:b4:a4:40:05:19:27:7c:33:aa:db:a6:96:32:88:8e:bf:05:a1:81:c0:a4:a8:16:01:01:0b:20:37:81:11"
}
},
"start_time": "2017-05-09 10:36:17 +0300",
"end_time": "2017-05-09 10:36:18 +0300",
"scan_duration_seconds": 0.221573169,
"duplicate_host_key_ips": [
],
"compliance": {
"policy": "Mozilla Modern",
"compliant": false,
"recommendations": [
"Remove these Key Exchange Algos: diffie-hellman-group14-sha1",
"Remove these MAC Algos: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected], hmac-sha1",
"Remove these Authentication Methods: password"
],
"references": [
"https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Guidelines/OpenSSH"
]
}
}
]
```
你可以使用 `-p` 选项来指定不同的端口,`-L` 选项来开启日志记录配合 `-V` 选项来指定日志级别:
```
$ ssh_scan -t 192.168.43.198 -p 22222 -L ssh-scan.log -V INFO
```
另外,可以使用 `-P` 或 `--policy` 选项来指定一个策略文件(默认是 Mozilla Modern)(LCTT 译注:这里的 Modern 可能指的是 <https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Server_Side_TLS> 中提到的 Modern compatibility ):
```
$ ssh_scan -t 192.168.43.198 -L ssh-scan.log -V INFO -P /path/to/custom/policy/file
```
ssh\_scan 使用帮助与其它示例:
```
$ ssh_scan -h
```
输出示例:
```
ssh_scan v0.0.17 (https://github.com/mozilla/ssh_scan)
Usage: ssh_scan [options]
-t, --target [IP/Range/Hostname] IP/Ranges/Hostname to scan
-f, --file [FilePath] File Path of the file containing IP/Range/Hostnames to scan
-T, --timeout [seconds] Timeout per connect after which ssh_scan gives up on the host
-L, --logger [Log File Path] Enable logger
-O, --from_json [FilePath] File to read JSON output from
-o, --output [FilePath] File to write JSON output to
-p, --port [PORT] Port (Default: 22)
-P, --policy [FILE] Custom policy file (Default: Mozilla Modern)
--threads [NUMBER] Number of worker threads (Default: 5)
--fingerprint-db [FILE] File location of fingerprint database (Default: ./fingerprints.db)
--suppress-update-status Do not check for updates
-u, --unit-test [FILE] Throw appropriate exit codes based on compliance status
-V [STD_LOGGING_LEVEL],
--verbosity
-v, --version Display just version info
-h, --help Show this message
Examples:
ssh_scan -t 192.168.1.1
ssh_scan -t server.example.com
ssh_scan -t ::1
ssh_scan -t ::1 -T 5
ssh_scan -f hosts.txt
ssh_scan -o output.json
ssh_scan -O output.json -o rescan_output.json
ssh_scan -t 192.168.1.1 -p 22222
ssh_scan -t 192.168.1.1 -p 22222 -L output.log -V INFO
ssh_scan -t 192.168.1.1 -P custom_policy.yml
ssh_scan -t 192.168.1.1 --unit-test -P custom_policy.yml
```
SSH 服务器相关参考阅读:
1. [使用 SSH Keygen(ssh-keygen)五步实现 SSH 免密登录](https://www.tecmint.com/ssh-passwordless-login-using-ssh-keygen-in-5-easy-steps/)
2. [安全 SSH 服务器的 5 个最佳实践](/article-7683-1.html)
3. [使用 Chroot 来限制 SSH 用户进入某些目录](/article-8313-1.html)
4. [如何配置 SSH 连接来简化远程登录](/article-8306-1.html)
如果需要更详细的信息可以访问 `ssh_scan` 的 Github 仓库:<https://github.com/mozilla/ssh_scan>
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 与 F.O.S.S (自由及开源软件)爱好者,一位将来的 Linux 系统管理员,网站开发者,现在是一个热爱与计算机一起工作并且拥有强烈知识分信念的 TecMint 内容贡献者。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/ssh_scan-ssh-configuration-and-policy-scanner-for-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[wcnnbdk1](https://github.com/wcnnbdk1) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | **ssh_scan** is an easy-to-use prototype SSH configuration and policy scanner for Linux and UNIX servers, inspired by [Mozilla OpenSSH Security Guide](https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Guidelines/OpenSSH), which provides a reasonable baseline policy recommendation for SSH configuration parameters such as Ciphers, MACs, and KexAlgos and much more.
It has some of the following benefits:
- It has minimal dependencies, ssh_scan only employs native Ruby and BinData to do its work, no heavy dependencies.
- It’s portable, you can use ssh_scan in another project or for
[automation of tasks](https://www.tecmint.com/automating-linux-system-administration-tasks/). - It’s easy to use, simply point it at an SSH service and get a JSON report of what it supports and it’s policy status.
- It’s also configurable, you can create your own custom policies that fit your specific policy requirements.
**Suggested Read:** [How to Install and Configure OpenSSH Server in Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/install-openssh-server-in-linux/)
### How to Install ssh_scan in Linux
There are three ways you can install **ssh_scan** and they are:
To install and run as a gem, type:
----------- On Debian/Ubuntu -----------$ sudo apt-get install ruby gem $ sudo gem install ssh_scan----------- On CentOS/RHEL -----------# yum install ruby rubygem # gem install ssh_scan
To run from a [docker container](https://www.tecmint.com/install-docker-and-learn-containers-in-centos-rhel-7-6/), type:
# docker pull mozilla/ssh_scan # docker run -it mozilla/ssh_scan /app/bin/ssh_scan -t github.com
To install and run from source, type:
# git clone https://github.com/mozilla/ssh_scan.git # cd ssh_scan # gpg2 --keyserver hkp://keys.gnupg.net --recv-keys 409B6B1796C275462A1703113804BB82D39DC0E3 # curl -sSL https://get.rvm.io | bash -s stable # rvm install 2.3.1 # rvm use 2.3.1 # gem install bundler # bundle install # ./bin/ssh_scan
### How to Use ssh_scan in Linux
The syntax for using ssh_scan is as follows:
$ ssh_scan -t ip-address $ ssh_scan -t server-hostname
For example to scan SSH configs and policy of server **92.168.43.198**, enter:
$ ssh_scan -t 192.168.43.198
Note you can also pass a [IP/Range/Hostname] to the `-t`
option as shown in the options below:
$ ssh_scan -t 192.168.43.198,200,205 $ ssh_scan -t test.tecmint.lan
##### Sample Output
I, [2017-05-09T10:36:17.913644 #7145] INFO -- : You're using the latest version of ssh_scan 0.0.19 [ { "ssh_scan_version": "0.0.19", "ip": "192.168.43.198", "port": 22, "server_banner": "SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_7.2p2 Ubuntu-4ubuntu2.1", "ssh_version": 2.0, "os": "ubuntu", "os_cpe": "o:canonical:ubuntu:16.04", "ssh_lib": "openssh", "ssh_lib_cpe": "a:openssh:openssh:7.2p2", "cookie": "68b17bcca652eeaf153ed18877770a38", "key_algorithms": [ "[[email protected]]", "ecdh-sha2-nistp256", "ecdh-sha2-nistp384", "ecdh-sha2-nistp521", "diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256", "diffie-hellman-group14-sha1" ], "server_host_key_algorithms": [ "ssh-rsa", "rsa-sha2-512", "rsa-sha2-256", "ecdsa-sha2-nistp256", "ssh-ed25519" ], "encryption_algorithms_client_to_server": [ "[[email protected]]", "aes128-ctr", "aes192-ctr", "aes256-ctr", "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]" ], "encryption_algorithms_server_to_client": [ "[[email protected]]", "aes128-ctr", "aes192-ctr", "aes256-ctr", "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]" ], "mac_algorithms_client_to_server": [ "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]", "hmac-sha2-256", "hmac-sha2-512", "hmac-sha1" ], "mac_algorithms_server_to_client": [ "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]", "[[email protected]]", "hmac-sha2-256", "hmac-sha2-512", "hmac-sha1" ], "compression_algorithms_client_to_server": [ "none", "[[email protected]]" ], "compression_algorithms_server_to_client": [ "none", "[[email protected]]" ], "languages_client_to_server": [ ], "languages_server_to_client": [ ], "hostname": "tecmint", "auth_methods": [ "publickey", "password" ], "fingerprints": { "rsa": { "known_bad": "false", "md5": "0e:d0:d7:11:f0:9b:f8:33:9c:ab:26:77:e5:66:9e:f4", "sha1": "fc:8d:d5:a1:bf:52:48:a6:7e:f9:a6:2f:af:ca:e2:f0:3a:9a:b7:fa", "sha256": "ff:00:b4:a4:40:05:19:27:7c:33:aa:db:a6:96:32:88:8e:bf:05:a1:81:c0:a4:a8:16:01:01:0b:20:37:81:11" } }, "start_time": "2017-05-09 10:36:17 +0300", "end_time": "2017-05-09 10:36:18 +0300", "scan_duration_seconds": 0.221573169, "duplicate_host_key_ips": [ ], "compliance": { "policy": "Mozilla Modern", "compliant": false, "recommendations": [ "Remove these Key Exchange Algos: diffie-hellman-group14-sha1", "Remove these MAC Algos:[[email protected]],[[email protected]],[[email protected]], hmac-sha1", "Remove these Authentication Methods: password" ], "references": [ "https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Guidelines/OpenSSH" ] } } ]
You can use `-p`
to specify a different port, `-L`
to enable the logger and `-V`
to define the verbosity level as shown below:
$ ssh_scan -t 192.168.43.198 -p 22222 -L ssh-scan.log -V INFO
Additionally, use a custom policy file (default is Mozilla Modern) with the `-P`
or `--policy [FILE]`
like so:
$ ssh_scan -t 192.168.43.198 -L ssh-scan.log -V INFO -P /path/to/custom/policy/file
Type this to view all ssh_scan usage options and more examples:
$ ssh_scan -h
##### Sample Output
ssh_scan v0.0.17 (https://github.com/mozilla/ssh_scan) Usage: ssh_scan [options] -t, --target [IP/Range/Hostname] IP/Ranges/Hostname to scan -f, --file [FilePath] File Path of the file containing IP/Range/Hostnames to scan -T, --timeout [seconds] Timeout per connect after which ssh_scan gives up on the host -L, --logger [Log File Path] Enable logger -O, --from_json [FilePath] File to read JSON output from -o, --output [FilePath] File to write JSON output to -p, --port [PORT] Port (Default: 22) -P, --policy [FILE] Custom policy file (Default: Mozilla Modern) --threads [NUMBER] Number of worker threads (Default: 5) --fingerprint-db [FILE] File location of fingerprint database (Default: ./fingerprints.db) --suppress-update-status Do not check for updates -u, --unit-test [FILE] Throw appropriate exit codes based on compliance status -V [STD_LOGGING_LEVEL], --verbosity -v, --version Display just version info -h, --help Show this message Examples: ssh_scan -t 192.168.1.1 ssh_scan -t server.example.com ssh_scan -t ::1 ssh_scan -t ::1 -T 5 ssh_scan -f hosts.txt ssh_scan -o output.json ssh_scan -O output.json -o rescan_output.json ssh_scan -t 192.168.1.1 -p 22222 ssh_scan -t 192.168.1.1 -p 22222 -L output.log -V INFO ssh_scan -t 192.168.1.1 -P custom_policy.yml ssh_scan -t 192.168.1.1 --unit-test -P custom_policy.yml
Check out some useful artilces on SSH Server:
[SSH Passwordless Login Using SSH Keygen in 5 Easy Steps](https://www.tecmint.com/ssh-passwordless-login-using-ssh-keygen-in-5-easy-steps/)[5 Best Practices to Secure SSH Server](https://www.tecmint.com/5-best-practices-to-secure-and-protect-ssh-server/)[Restrict SSH User Access to Certain Directory Using Chrooted Jail](https://www.tecmint.com/restrict-ssh-user-to-directory-using-chrooted-jail/)[How to Configure Custom SSH Connections to Simplify Remote Access](https://www.tecmint.com/configure-custom-ssh-connection-in-linux/)
For more details visit ssh_scan Github repository: [https://github.com/mozilla/ssh_scan](https://github.com/mozilla/ssh_scan)
In this article, we showed you how to set up and use ssh_scan in Linux. Do you know of any similar tools out there? Let us know via the feedback form below, including any other thoughts concerning this guide. |
8,577 | 理解 Linux 中的 shutdown、poweroff、halt 和 reboot 命令 | https://www.tecmint.com/shutdown-poweroff-halt-and-reboot-commands-in-linux/ | 2017-06-05T09:58:38 | [
"shutdown",
"poweroff",
"halt",
"reboot"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8577-1.html | 
在本篇中,我们会向你解释 `shutdown`、`poweroff`、`halt` 以及 `reboot` 命令。我们会解释清楚当你用那些可用的选项执行的时候它们实际做了什么。
如果你想深入 Linux 服务器管理,那么为了有效和可靠的服务器管理,这些[重要的 Linux 命令](https://www.tecmint.com/60-commands-of-linux-a-guide-from-newbies-to-system-administrator/)你需要完全理解。
通常上,当你想要关闭或者重启你的机器时,你会运行下面之一的命令:
### shutdown 命令
`shutdown` 会给系统计划一个时间关机。它可以被用于停止、关机、重启机器。
你可以指定一个时间字符串(通常是 `now` 或者用 `hh:mm` 指定小时/分钟)作为第一个参数。额外地,你也可以设置一个广播信息在系统关闭前发送给所有已登录的用户。
重要:如果使用了时间参数,系统关机前 5 分钟,会创建 `/run/nologin` 文件。以确保没有人可以再登录。
`shutdown` 命令示例:
```
# shutdown
# shutdown now
# shutdown 13:20
# shutdown -p now ### 关闭机器
# shutdown -H now ### 停止机器
# shutdown -r09:35 ### 在 09:35am 重启机器
```
要取消即将进行的关机,只要输入下面的命令:
```
# shutdown -c
```
### halt 命令
`halt` 通知硬件来停止所有的 CPU 功能,但是仍然保持通电。你可以用它使系统处于低层维护状态。
注意在有些情况会它会完全关闭系统。下面是 `halt` 命令示例:
```
# halt ### 停止机器
# halt -p ### 关闭机器
# halt --reboot ### 重启机器
```
### poweroff 命令
`poweroff` 会发送一个 ACPI 信号来通知系统关机。
下面是 `poweroff` 命令示例:
```
# poweroff ### 关闭机器
# poweroff --halt ### 停止机器
# poweroff --reboot ### 重启机器
```
### reboot 命令
`reboot` 通知系统重启。
```
# reboot ### 重启机器
# reboot --halt ### 停止机器
# reboot -p ### 关闭机器
```
就是这样了!如先前提到的,理解这些命令能够有效并可靠地在多用户环境下管理 Linux 服务器。你有一些额外的想法么?在评论区留言与我们分享。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili是一名 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 的爱好者,未来的 Linux 系统管理员、网站开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并乐于分享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/shutdown-poweroff-halt-and-reboot-commands-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In this article, we will explain to you the difference between **shutdown**, **poweroff**, **halt** and **reboot** Linux commands. We will make clear what they actually do when you execute them with available options.
If you are hoping to dive into Linux server administration, then these are [some of the important Linux commands](https://www.tecmint.com/60-commands-of-linux-a-guide-from-newbies-to-system-administrator/) you need to fully understand for effective and reliable server administration.
Normally, when you want to turn off or reboot your machine, you’ll run one of the commands below:
### Shutdown Command
**shutdown** schedules a time for the system to be powered down. It may be used to halt, power-off or reboot the machine.
You may specify a time string (which is usually “**now**” or “**hh:mm**” for hour/minutes) as the first argument. Additionally, you may set a wall message to be sent to all logged-in users before the system goes down.
**Important**: If the time argument is used, 5 minutes before the system goes down the **/run/nologin** file is created to ensure that further logins will not be allowed.
Examples of shutdown commands:
# shutdown # shutdown now # shutdown 13:20 # shutdown -p now #poweroff the machine # shutdown -H now #halt the machine # shutdown -r09:35 #reboot the machine at 09:35am
To cancel a pending shutdown, simply type the command below:
# shutdown -c
### Halt Command
**halt** instructs the hardware to stop all CPU functions, but leaves it powered on. You can use it to get the system to a state where you can perform low level maintenance.
Note that in some cases it completely shuts down the system. Below are examples of halt commands:
# halt #halt the machine # halt -p #poweroff the machine # halt --reboot #reboot the machine
### Power off Command
**poweroff** sends an ACPI signal which instructs the system to power down.
The following are examples of poweroff commands:
# poweroff #poweroff the machine # poweroff --halt #halt the machine # poweroff --reboot #reboot the machine
### Reboot Command
**reboot** instructs the system to restart.
# reboot #reboot the machine # reboot --halt #halt the machine # reboot -p #poweroff the machine
That’s all! As mentioned earlier on, understanding these commands will enable to effectively and reliably manage Linux server in a multi-user environment. Do you have any additional ideas? Share them with us via the comments section below.
Shouldn’t it be uppercase
Reply`-P`
for power-off?Some of y’all are imbecile, there is a reason for having all 3 commands as they are similar but not the same. For instance, the
shutdowncommand will also write a shutdown script. Perhaps, you just want to do low-level maintenance,haltwill be a suitable command to use as it will stop all running process and stop the CPU as well.You will probably remember
Replyhaltquicker than`Shutdown -H`
and as forreboot, self explanatory. Easier to remember as opposed to`shutdown -r.`
, etc.Can I configure the amount of time the system is powered off during a reboot command? (Using Centos 7)
ReplyI would like to shutdown and poweroff machine. I have seen things like “
/usr/sbin/shutdown -h +0 && /usr/sbin/poweroff” However, the poweroff command kills the machine prior to allowing programs to execute shutdown scripts.I do not wish to simply run poweroff, because it does not execute program shutdown scripts and simply halts all processes. Is there a way to get a graceful shutdown AND power down the machine?
Replyis halt work like suspend ? and how to recover yourself from halt ?
Replyinit 6 reboot
Replyinit 0 shutdown
@4pr0p02
Thanks for sharing this; useful as well.
ReplyWhat is `
Replyhalt` use scene? `shutdown` and `reboot` are enough.@wudanyang
True, but halt command exists so we have to mention it too. Thanks for writing back.
ReplyUseless
ReplyNot tell the difference but only list those commands’ parameters
@Mickechen
There is really no difference, we explained this in their descriptions and with the example commands(they all work nearly in the same way, they may be used to perform related functionalities using particular options.)
ReplySo, basically “shutdown” command is all you need, safely speaking. :) I mean it does everything from halt, reboot, shutdown etc. that too whenever I want it to.
Reply@Tanmaya
Yes, you can only use if for all the other operations. Meaning these commands are not so different.
Replypoweroff master race
Reply |
8,578 | 极客漫画:数据库链接池中的生生死死 | http://turnoff.us/geek/db-connection-pool/ | 2017-06-05T14:07:00 | [
"数据库",
"漫画"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8578-1.html | 
数据库连接池是常用的 B/S 技术,而似乎生活在这个“池子”里面的那些连接对象有点不幸。
要是顺利的话,你干完活就可以歇着了。
要是不顺利,比如你掌握的连接已经被拒绝了,那么……
你就会被“砰”地干掉。就问你怕不怕?(话说回来,回答错误会不会也被“砰”……)
---
via: <http://turnoff.us/geek/db-connection-pool/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者&点评:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对&合成:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,579 | 调试器工作原理(三):调试信息 | http://eli.thegreenplace.net/2011/02/07/how-debuggers-work-part-3-debugging-information | 2017-06-06T08:16:00 | [
"调试器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8579-1.html | 
这是调试器的工作原理系列文章的第三篇。阅读这篇文章之前应当先阅读[第一篇](/article-8552-1.html)与[第二篇](/article-8418-1.html)。
### 这篇文章的主要内容
本文将解释调试器是如何在机器码中查找它将 C 语言源代码转换成机器语言代码时所需要的 C 语言函数、变量、与数据。
### 调试信息
现代编译器能够将有着各种缩进或嵌套的程序流程、各种数据类型的变量的高级语言代码转换为一大堆称之为机器码的 0/1 数据,这么做的唯一目的是尽可能快的在目标 CPU 上运行程序。通常来说一行 C 语言代码能够转换为若干条机器码。变量被分散在机器码中的各个部分,有的在堆栈中,有的在寄存器中,或者直接被优化掉了。数据结构与对象在机器码中甚至不“存在”,它们只是用于将数据按一定的结构编码存储进缓存。
那么调试器怎么知道,当你需要在某个函数入口处暂停时,程序要在哪停下来呢?它怎么知道当你查看某个变量值时,它怎么找到这个值?答案是,调试信息。
编译器在生成机器码时同时会生成相应的调试信息。调试信息代表了可执行程序与源代码之间的关系,并以一种提前定义好的格式,同机器码存放在一起。过去的数年里,人们针对不同的平台与可执行文件发明了很多种用于存储这些信息的格式。不过我们这篇文章不会讲这些格式的历史,而是将阐述这些调试信息是如何工作的,所以我们将专注于一些事情,比如 `DWARF`。`DWARF` 如今十分广泛的用作 Linux 和类 `Unix` 平台上的可执行文件的调试格式。
### ELF 中的 DWARF

根据[它的维基百科](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DWARF) 所描述,虽然 `DWARF` 是同 `ELF` 一同设计的(`DWARF` 是由 `DWARF` 标准委员会推出的开放标准。上文中展示的图标就来自这个网站。),但 `DWARF` 在理论上来说也可以嵌入到其他的可执行文件格式中。
`DWARF` 是一种复杂的格式,它吸收了过去许多年各种不同的架构与操作系统的格式的经验。正是因为它解决了一个在任何平台与 ABI (应用二进制接口)上为任意高级语言产生调试信息这样棘手的难题,它也必须很复杂。想要透彻的讲解 `DWARF` 仅仅是通过这单薄的一篇文章是远远不够的,说实话我也并没有充分地了解 `DWARF` 到每一个微小的细节,所以我也不能十分透彻的讲解 (如果你感兴趣的话,文末有一些能够帮助你的资源。建议从 `DWARF` 教程开始上手)。这篇文章中我将以浅显易懂的方式展示 `DWARF`,以说明调试信息是如何实际工作的。
### ELF 文件中的调试部分
首先让我们看看 `DWARF` 处在 ELF 文件中的什么位置。`ELF` 定义了每一个生成的目标文件中的每一节。 <ruby> 节头表 <rt> section header table </rt></ruby> 声明并定义了每一节及其名字。不同的工具以不同的方式处理不同的节,例如连接器会寻找连接器需要的部分,调试器会查找调试器需要的部分。
我们本文的实验会使用从这个 C 语言源文件构建的可执行文件,编译成 `tracedprog2`:
```
#include <stdio.h>
void do_stuff(int my_arg)、
{
int my_local = my_arg + 2;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < my_local; ++i)
printf("i = %d\n", i);
}
int main()
{
do_stuff(2);
return 0;
}
```
使用 `objdump -h` 命令检查 `ELF` 可执行文件中的<ruby> 节头 <rt> section header </rt></ruby>,我们会看到几个以 `.debug_` 开头的节,这些就是 `DWARF` 的调试部分。
```
26 .debug_aranges 00000020 00000000 00000000 00001037
CONTENTS, READONLY, DEBUGGING
27 .debug_pubnames 00000028 00000000 00000000 00001057
CONTENTS, READONLY, DEBUGGING
28 .debug_info 000000cc 00000000 00000000 0000107f
CONTENTS, READONLY, DEBUGGING
29 .debug_abbrev 0000008a 00000000 00000000 0000114b
CONTENTS, READONLY, DEBUGGING
30 .debug_line 0000006b 00000000 00000000 000011d5
CONTENTS, READONLY, DEBUGGING
31 .debug_frame 00000044 00000000 00000000 00001240
CONTENTS, READONLY, DEBUGGING
32 .debug_str 000000ae 00000000 00000000 00001284
CONTENTS, READONLY, DEBUGGING
33 .debug_loc 00000058 00000000 00000000 00001332
CONTENTS, READONLY, DEBUGGING
```
每个节的第一个数字代表了该节的大小,最后一个数字代表了这个节开始位置距离 `ELF` 的偏移量。调试器利用这些信息从可执行文件中读取节。
现在让我们看看一些在 `DWARF` 中查找有用的调试信息的实际例子。
### 查找函数
调试器的最基础的任务之一,就是当我们在某个函数处设置断点时,调试器需要能够在入口处暂停。为此,必须为高级代码中的函数名称与函数在机器码中指令开始的地址这两者之间建立起某种映射关系。
为了获取这种映射关系,我们可以查找 `DWARF` 中的 `.debug_info` 节。在我们深入之前,需要一点基础知识。`DWARF` 中每一个描述类型被称之为调试信息入口(`DIE`)。每个 `DIE` 都有关于它的类型、属性之类的标签。`DIE` 之间通过兄弟节点或子节点相互连接,属性的值也可以指向其它的 `DIE`。
运行以下命令:
```
objdump --dwarf=info tracedprog2
```
输出文件相当的长,为了方便举例我们只关注这些行(从这里开始,无用的冗长信息我会以 (...)代替,方便排版):
```
<1><71>: Abbrev Number: 5 (DW_TAG_subprogram)
<72> DW_AT_external : 1
<73> DW_AT_name : (...): do_stuff
<77> DW_AT_decl_file : 1
<78> DW_AT_decl_line : 4
<79> DW_AT_prototyped : 1
<7a> DW_AT_low_pc : 0x8048604
<7e> DW_AT_high_pc : 0x804863e
<82> DW_AT_frame_base : 0x0 (location list)
<86> DW_AT_sibling : <0xb3>
<1><b3>: Abbrev Number: 9 (DW_TAG_subprogram)
<b4> DW_AT_external : 1
<b5> DW_AT_name : (...): main
<b9> DW_AT_decl_file : 1
<ba> DW_AT_decl_line : 14
<bb> DW_AT_type : <0x4b>
<bf> DW_AT_low_pc : 0x804863e
<c3> DW_AT_high_pc : 0x804865a
<c7> DW_AT_frame_base : 0x2c (location list)
```
上面的代码中有两个带有 `DW_TAG_subprogram` 标签的入口,在 `DWARF` 中这是对函数的指代。注意,这是两个节的入口,其中一个是 `do_stuff` 函数的入口,另一个是主(`main`)函数的入口。这些信息中有很多值得关注的属性,但其中最值得注意的是 `DW_AT_low_pc`。它代表了函数开始处程序指针的值(在 x86 平台上是 `EIP`)。此处 `0x8048604` 代表了 `do_stuff` 函数开始处的程序指针。下面我们将利用 `objdump -d` 命令对可执行文件进行反汇编。来看看这块地址中都有什么:
```
08048604 <do_stuff>:
8048604: 55 push ebp
8048605: 89 e5 mov ebp,esp
8048607: 83 ec 28 sub esp,0x28
804860a: 8b 45 08 mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp+0x8]
804860d: 83 c0 02 add eax,0x2
8048610: 89 45 f4 mov DWORD PTR [ebp-0xc],eax
8048613: c7 45 (...) mov DWORD PTR [ebp-0x10],0x0
804861a: eb 18 jmp 8048634 <do_stuff+0x30>
804861c: b8 20 (...) mov eax,0x8048720
8048621: 8b 55 f0 mov edx,DWORD PTR [ebp-0x10]
8048624: 89 54 24 04 mov DWORD PTR [esp+0x4],edx
8048628: 89 04 24 mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
804862b: e8 04 (...) call 8048534 <printf@plt>
8048630: 83 45 f0 01 add DWORD PTR [ebp-0x10],0x1
8048634: 8b 45 f0 mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp-0x10]
8048637: 3b 45 f4 cmp eax,DWORD PTR [ebp-0xc]
804863a: 7c e0 jl 804861c <do_stuff+0x18>
804863c: c9 leave
804863d: c3 ret
```
显然,`0x8048604` 是 `do_stuff` 的开始地址,这样一来,调试器就可以建立函数与其在可执行文件中的位置间的映射关系。
### 查找变量
假设我们当前在 `do_staff` 函数中某个位置上设置断点停了下来。我们想通过调试器取得 `my_local` 这个变量的值。调试器怎么知道在哪里去找这个值呢?很显然这要比查找函数更为困难。变量可能存储在全局存储区、堆栈、甚至是寄存器中。此外,同名变量在不同的作用域中可能有着不同的值。调试信息必须能够反映所有的这些变化,当然,`DWARF` 就能做到。
我不会逐一去将每一种可能的状况,但我会以调试器在 `do_stuff` 函数中查找 `my_local` 变量的过程来举个例子。下面我们再看一遍 `.debug_info` 中 `do_stuff` 的每一个入口,这次连它的子入口也要一起看。
```
<1><71>: Abbrev Number: 5 (DW_TAG_subprogram)
<72> DW_AT_external : 1
<73> DW_AT_name : (...): do_stuff
<77> DW_AT_decl_file : 1
<78> DW_AT_decl_line : 4
<79> DW_AT_prototyped : 1
<7a> DW_AT_low_pc : 0x8048604
<7e> DW_AT_high_pc : 0x804863e
<82> DW_AT_frame_base : 0x0 (location list)
<86> DW_AT_sibling : <0xb3>
<2><8a>: Abbrev Number: 6 (DW_TAG_formal_parameter)
<8b> DW_AT_name : (...): my_arg
<8f> DW_AT_decl_file : 1
<90> DW_AT_decl_line : 4
<91> DW_AT_type : <0x4b>
<95> DW_AT_location : (...) (DW_OP_fbreg: 0)
<2><98>: Abbrev Number: 7 (DW_TAG_variable)
<99> DW_AT_name : (...): my_local
<9d> DW_AT_decl_file : 1
<9e> DW_AT_decl_line : 6
<9f> DW_AT_type : <0x4b>
<a3> DW_AT_location : (...) (DW_OP_fbreg: -20)
<2><a6>: Abbrev Number: 8 (DW_TAG_variable)
<a7> DW_AT_name : i
<a9> DW_AT_decl_file : 1
<aa> DW_AT_decl_line : 7
<ab> DW_AT_type : <0x4b>
<af> DW_AT_location : (...) (DW_OP_fbreg: -24)
```
看到每个入口处第一对尖括号中的数字了吗?这些是嵌套的等级,在上面的例子中,以 `<2>` 开头的入口是以 `<1>` 开头的子入口。因此我们得知 `my_local` 变量(以 `DW_TAG_variable` 标签标记)是 `do_stuff` 函数的局部变量。除此之外,调试器也需要知道变量的数据类型,这样才能正确的使用与显示变量。上面的例子中 `my_local` 的变量类型指向另一个 `DIE` `<0x4b>`。如果使用 `objdump` 命令查看这个 `DIE` 的话,我们会发现它是一个有符号 4 字节整型数据。
而为了在实际运行的程序内存中查找变量的值,调试器需要使用到 `DW_AT_location` 属性。对于 `my_local` 而言,是 `DW_OP_fbreg: -20`。这个代码段的意思是说 `my_local` 存储在距离它所在函数起始地址偏移量为 `-20` 的地方。
`do_stuff` 函数的 `DW_AT_frame_base` 属性值为 `0x0 (location list)`。这意味着这个属性的值需要在 `location list` 中查找。下面我们来一起看看。
```
$ objdump --dwarf=loc tracedprog2
tracedprog2: file format elf32-i386
Contents of the .debug_loc section:
Offset Begin End Expression
00000000 08048604 08048605 (DW_OP_breg4: 4 )
00000000 08048605 08048607 (DW_OP_breg4: 8 )
00000000 08048607 0804863e (DW_OP_breg5: 8 )
00000000 <End of list>
0000002c 0804863e 0804863f (DW_OP_breg4: 4 )
0000002c 0804863f 08048641 (DW_OP_breg4: 8 )
0000002c 08048641 0804865a (DW_OP_breg5: 8 )
0000002c <End of list>
```
我们需要关注的是第一列(`do_stuff` 函数的 `DW_AT_frame_base` 属性包含 `location list` 中 `0x0` 的偏移量。而 `main` 函数的相同属性包含 `0x2c` 的偏移量,这个偏移量是第二套地址列表的偏移量)。对于调试器可能定位到的每一个地址,它都会指定当前栈帧到变量间的偏移量,而这个偏移就是通过寄存器来计算的。对于 x86 平台而言,`bpreg4` 指向 `esp`,而 `bpreg5` 指向 `ebp`。
让我们再看看 `do_stuff` 函数的头几条指令。
```
08048604 <do_stuff>:
8048604: 55 push ebp
8048605: 89 e5 mov ebp,esp
8048607: 83 ec 28 sub esp,0x28
804860a: 8b 45 08 mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp+0x8]
804860d: 83 c0 02 add eax,0x2
8048610: 89 45 f4 mov DWORD PTR [ebp-0xc],eax
```
只有当第二条指令执行后,`ebp` 寄存器才真正存储了有用的值。当然,前两条指令的基址是由上面所列出来的地址信息表计算出来的。一但 `ebp` 确定了,计算偏移量就十分方便了,因为尽管 `esp` 在操作堆栈的时候需要移动,但 `ebp` 作为栈底并不需要移动。
究竟我们应该去哪里找 `my_local` 的值呢?在 `0x8048610` 这块地址后, `my_local` 的值经过在 `eax` 中的计算后被存在了内存中,从这里开始我们才需要关注 `my_local` 的值。调试器会利用 `DW_OP_breg5: 8` 这个栈帧来查找。我们回想下,`my_local` 的 `DW_AT_location` 属性值为 `DW_OP_fbreg: -20`。所以应当从基址中 `-20` ,同时由于 `ebp` 寄存器需要 `+8`,所以最终结果为 `ebp - 12`。现在再次查看反汇编代码,来看看数据从 `eax` 中被移动到哪里了。当然,这里 `my_local` 应当被存储在了 `ebp - 12` 的地址中。
### 查看行号
当我们谈到在调试信息寻找函数的时候,我们利用了些技巧。当调试 C 语言源代码并在某个函数出放置断点的时候,我们并不关注第一条“机器码”指令(函数的调用准备工作已经完成而局部变量还没有初始化)。我们真正关注的是函数的第一行“C 代码”。
这就是 `DWARF` 完全覆盖映射 C 源代码中的行与可执行文件中机器码地址的原因。下面是 `.debug_line` 节中所包含的内容,我们将其转换为可读的格式展示如下。
```
$ objdump --dwarf=decodedline tracedprog2
tracedprog2: file format elf32-i386
Decoded dump of debug contents of section .debug_line:
CU: /home/eliben/eli/eliben-code/debugger/tracedprog2.c:
File name Line number Starting address
tracedprog2.c 5 0x8048604
tracedprog2.c 6 0x804860a
tracedprog2.c 9 0x8048613
tracedprog2.c 10 0x804861c
tracedprog2.c 9 0x8048630
tracedprog2.c 11 0x804863c
tracedprog2.c 15 0x804863e
tracedprog2.c 16 0x8048647
tracedprog2.c 17 0x8048653
tracedprog2.c 18 0x8048658
```
很容易就可以看出其中 C 源代码与反汇编代码之间的对应关系。第 5 行指向 `do_stuff` 函数的入口,`0x8040604`。第 6 行,指向 `0x804860a` ,正是调试器在调试 `do_stuff` 函数时需要停下来的地方。这里已经完成了函数调用的准备工作。上面的这些信息形成了行号与地址间的双向映射关系。
* 当在某一行设置断点的时候,调试器会利用这些信息去查找相应的地址来做断点工作(还记得上篇文章中的 `int 3` 指令吗?)
* 当指令造成段错误时,调试器会利用这些信息来查看源代码中发生问题的行。
### libdwarf - 用 DWARF 编程
尽管使用命令行工具来获得 `DWARF` 很有用,但这仍然不够易用。作为程序员,我们希望知道当我们需要这些调试信息时应当怎么编程来获取这些信息。
自然我们想到的第一种方法就是阅读 `DWARF` 规范并按规范操作阅读使用。有句话说的好,分析 HTML 应当使用库函数,永远不要手工分析。对于 `DWARF` 来说正是如此。`DWARF` 比 HTML 要复杂得多。上面所展示出来的只是冰山一角。更糟糕的是,在实际的目标文件中,大部分信息是以非常紧凑的压缩格式存储的,分析起来更加复杂(信息中的某些部分,例如位置信息与行号信息,在某些虚拟机下是以指令的方式编码的)。
所以我们要使用库来处理 `DWARF`。下面是两种我熟悉的主要的库(还有些不完整的库这里没有写)
1. `BFD` (libbfd),包含了 `objdump` (对,就是这篇文章中我们一直在用的这货),`ld`(`GNU` 连接器)与 `as`(`GNU` 编译器)。`BFD` 主要用于 [GNU binutils](http://www.gnu.org/software/binutils/)。
2. `libdwarf` ,同它的哥哥 `libelf` 一同用于 `Solaris` 与 `FreeBSD` 中的调试信息分析。
相比较而言我更倾向于使用 `libdwarf`,因为我对它了解的更多,并且 `libdwarf` 的开源协议更开放(`LGPL` 对比 `GPL`)。
因为 `libdwarf` 本身相当复杂,操作起来需要相当多的代码,所以我在这不会展示所有代码。你可以在 [这里](https://github.com/eliben/code-for-blog/blob/master/2011/dwarf_get_func_addr.c) 下载代码并运行试试。运行这些代码需要提前安装 `libelfand` 与 `libdwarf` ,同时在使用连接器的时候要使用参数 `-lelf` 与 `-ldwarf`。
这个示例程序可以接受可执行文件并打印其中的函数名称与函数入口地址。下面是我们整篇文章中使用的 C 程序经过示例程序处理后的输出。
```
$ dwarf_get_func_addr tracedprog2
DW_TAG_subprogram: 'do_stuff'
low pc : 0x08048604
high pc : 0x0804863e
DW_TAG_subprogram: 'main'
low pc : 0x0804863e
high pc : 0x0804865a
```
`libdwarf` 的文档很棒,如果你花些功夫,利用 `libdwarf` 获得这篇文章中所涉及到的 `DWARF` 信息应该并不困难。
### 结论与计划
原理上讲,调试信息是个很简单的概念。尽管实现细节可能比较复杂,但经过了上面的学习我想你应该了解了调试器是如何从可执行文件中获取它需要的源代码信息的了。对于程序员而言,程序只是代码段与数据结构;对可执行文件而言,程序只是一系列存储在内存或寄存器中的指令或数据。但利用调试信息,调试器就可以将这两者连接起来,从而完成调试工作。
此文与这系列的前两篇,一同介绍了调试器的内部工作过程。利用这里所讲到的知识,再敲些代码,应该可以完成一个 Linux 中最简单、基础但也有一定功能的调试器。
下一步我并不确定要做什么,这个系列文章可能就此结束,也有可能我要讲些堆栈调用的事情,又或者讲 Windows 下的调试。你们有什么好的点子或者相关材料,可以直接评论或者发邮件给我。
### 参考
* objdump 参考手册
* [ELF](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Executable_and_Linkable_Format) 与 [DWARF](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DWARF) 的维基百科
* [Dwarf Debugging Standard 主页](http://dwarfstd.org/),这里有很棒的 DWARF 教程与 DWARF 标准,作者是 Michael Eager。第二版基于 GCC 也许更能吸引你。
* [libdwarf 主页](http://reality.sgiweb.org/davea/dwarf.html),这里可以下载到 libwarf 的完整库与参考手册
* [BFD 文档](http://sourceware.org/binutils/docs-2.21/bfd/index.html)
---
---
via: <http://eli.thegreenplace.net/2011/02/07/how-debuggers-work-part-3-debugging-information>
作者:[Eli Bendersky](http://eli.thegreenplace.net/) 译者:[YYforymj](https://github.com/YYforymj) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 302 | Found | null |
8,580 | 软件定义存储(SDS)的发展:十个你应当知道的项目 | https://www.linux.com/news/open-cloud-report/2016/guide-open-cloud-software-defined-storage-opens | 2017-06-06T15:33:14 | [
"SDS",
"软件定义存储"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8580-1.html | 
>
> 凭借 SDS,组织机构可以更好抽象出底层存储的管理功能,并且通过不同策略实现灵活配置。下面将要向你展示一些你应当知道的此类开源项目。
>
>
>
纵观 2016 年,SDS(Software-Defined Storage,软件定义存储)方面取得了很多里程碑式的进步,并且日益紧密的与云部署结合在了一起。凭借 SDS ,组织机构可以更好抽象出底层存储的管理功能,并且通过不同策略实现灵活配置。当然,他们也可以选择自由开源的 SDS 解决方案。人们熟知的 Ceph 正是凭借 OpenStack 部署在不断扩大自己的影响力,但是它离成为唯一的 SDS 开源项目还有很长的路要走。
Gartner 的一份市场调查报告中预测,截至到 2019 年,70% 已有的存储部署解决方案会支持以纯软件的方式来实施。同时 Gartner 还预测截至到 2020 年,70% 到 80% 的非结构化数据会存储在由 SDS 管理的廉价存储设备中。
最近,Dell EMC 公司加入到了由 Linux 基金会发起的 [OpenSDS](http://ctt.marketwire.com/?release=11G125514-001&id=10559023&type=0&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.opensds.io%2F) 项目中。 OpenSDS 致力于寻求解决 SDS 集成所面临的挑战,并推动企业对开放标准的采用。它由存储客户与厂商组成,包括 Fujitsu,Hitachi Data Systems,Huawei,Oregon State University 以及 Vodafone。同时 OpenSDS 也寻求与其它的上游开源社区进行合作,比如 Cloud Native Computing Foundation、Docker、OpenStack 以及 Open Container Initiative。
根据 Open SDS 项目的 [主页](https://www.opensds.io/),2017 年会是 SDS 的一个元年:“社区希望在 2017 第二季度完成原型的发布,并且在第三季度中发布一个测试版本。OpenSDS 的最初组织者期望能通过这个项目来影响到一些开源技术,比如来自 Openstack 社区的 Cinder 和 Manila 项目,并且能够支持更广泛的云存储解决方案。”
与此同时,SDS 相关项目也呈现了爆发式的增长,其范围横跨 Apache Cassandra 到 Cehp。Linux 基金会最近发布了 2016 年度报告“[开放云指南:当前的趋势及开源项目](http://ctt.marketwire.com/?release=11G120876-001&id=10172077&type=0&url=http%3A%2F%2Fgo.linuxfoundation.org%2Frd-open-cloud-report-2016-pr)”,报告从整体上分析了开放云计算的现状,其中有一章涵盖了 SDS。你可以[下载](http://go.linuxfoundation.org/l/6342/2016-10-31/3krbjr)这篇报告,需要注意的是,这是一份综合了容器发展趋势、SDS,以及云计算的重新定义等等很多内容。报告中涵盖了当今对于开源云计算最重要的一些项目,并分类给出了描述和链接。
在这个系列的文章中,我们从该报告中整理了很多项目,并且针对它们是如何发展的提供了一些额外的视角及信息。在下面的内容当中,你会看到现今对 SDS 来说很重要的项目,并且能了解到它们为什么具有这么大的影响力。同时,根据上面的报告,我们提供了相关项目的 GitHub 仓库链接,方便大家查看。
### 软件定义存储(SDS)
* [Apache Cassandra](http://cassandra.apache.org/)
Apache Cassandra 是一个可扩展的、高可用的,面向任务优先应用的数据库。它可以运行在商业设备或者云架构上,并且能实现跨数据中心的低延迟数据传输,同时具备良好的容错性。[Cassandra 的 GitHub 仓库](https://github.com/apache/cassandra)。
* [Ceph](http://ceph.com/)
Ceph 是 Red Hat 构建的一个企业级可扩展的块设备、对象,以及文件存储平台,并且可部署在公有云或者私有云之上。Ceph 目前被广泛应用于 OpenStack。[Ceph 的 GitHub 仓库](https://github.com/ceph/ceph)。
* [CouchDB](http://couchdb.apache.org/)
CouchDB 是一个 Apache 软件基金会项目,是一个单节点或者集群数据库管理系统。CouchDB 提供了 RESTful HTTP 接口来读取和更新数据库文件。[CouchDB 的 GitHub 仓库](https://github.com/apache/couchdb)。
* [Docker 数据卷插件](https://docs.docker.com/engine/extend/plugins_volume/)
Docker Engine 数据卷插件可以使 Engine 与外部的存储系统一起集成部署,并且数据卷的生命周期与单一 Engine 主机相同。目前存在很多第三方的数据卷管理插件,包括 Azure File Storage、NetApp、VMware vSphere 等等。你可以在 GitHub上查找到更多的插件。
* [GlusterFS](https://www.gluster.org/)
Gluster 是 Red Hat 的可扩展网络文件系统,同时也是数据管理平台。Gluster 可以部署在公有云,私有云或者混合云之上,可用于 Linux 容器内的流媒体处理任务、数据分析任务,以及其它数据和带宽敏感型任务的执行。[GlusterFS 的 GitHub 仓库](https://github.com/gluster/glusterfs)。
* [MongoDB](https://www.mongodb.com/)
MongoDB 是一个高性能的文件数据库,并且部署和扩展都非常简单。[MongoDB 的 GitHub 仓库](https://github.com/mongodb/mongo)。
* [Nexenta](https://nexenta.com/)
NexentaStor 是一个可扩展的、统一的软件定义的文件和块设备管理服务,同时支持数据管理功能。它能够与 VMware 集成,并且支持 Docker 和 OpenStack。[Nexenta 的 GitHub 仓库](https://github.com/Nexenta)。
* [Redis](http://redis.io/)
Redis 是一个基于内存的数据存储,一般被用作数据库、缓存,以及消息代理。它支持多种数据结构,并且本身支持复制、Lua 脚本、LRU 算法、事务,以及多层级的硬盘持久化。
* [Riak CS](http://docs.basho.com/riak/cs/2.1.1/)
Riak CS(Cloud Storage)是基于 Basho 的分布式数据库 Riak KV 构建的对象存储软件。它提供了在不同规模的分布式云存储能力,可以用于公有云和私有云,还能为大压力的应用和服务提供基础的存储服务。其 API 兼容 Amazon S3,并且支持租户级别的费用计算和测量能力。[Riak CS 的 GitHub 仓库](https://github.com/basho/riak_cs)。
* [Swift](https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Swift)
Swift 是 OpenStack 项目中的对象存储系统,设计初衷是通过简单 API 存储和获取非结构化数据。Swift 设计之初就是可扩展的,并且针对持久性、可靠性以及并发数据读取做了优化。[Swift 的 GitHub 仓库](https://github.com/openstack/swift)。
*了解更多的开源云计算趋势以及更完整的开源云计算项目列表,请[下载 Linux 基金会的“开放云指南”](http://bit.ly/2eHQOwy)。*
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/news/open-cloud-report/2016/guide-open-cloud-software-defined-storage-opens>
作者:[SAM DEAN](https://www.linux.com/users/sam-dean) 译者:[toutoudnf](https://github.com/toutoudnf) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,581 | mimipenguin:从当前 Linux 用户转储登录密码 | https://www.tecmint.com/mimipenguin-hack-login-passwords-of-linux-users/ | 2017-06-07T08:18:00 | [
"密码",
"凭证"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8581-1.html | 
mimipenguin 是一个免费、开源、简单但是强大的 shell/python 脚本,用来从当前 Linux 桌面用户转储登录凭证(用户名和密码),并且已在不同的 Linux 发行版中测试过。
另外,它还支持如:VSFTPd(活跃的 FTP 客户端连接)、Apache2(活跃的/旧的 HTTP 基础认证会话,但是这需要 Gcore),还有 openssh-server(活跃的 SSH 链接,需用 [sudo 命令](https://www.tecmint.com/sudoers-configurations-for-setting-sudo-in-linux/))。重要的是,它逐渐被移植到其他语言中,以支持所有可想到的以后可以利用的情况。
### mimipenguin 是如何工作的?
要理解 mimipenguin 是如何工作的,你需要知道所有或者大多数的 Linux 发行版会在内存中存储大量的重要信息, 如:凭据、加密密钥以及个人数据。
尤其是用户名和密码是由进程(运行中的程序)保存在内存中,并以明文形式存储较长时间。mimipenguin 在技术上利用这些在内存中的明文凭证 - 它会转储一个进程,并提取可能包含明文凭据的行。
然后,通过以下内容的哈希值来尝试计算每个单词的出现几率:`/etc/shadow`、内存和 regex 搜索。一旦找到任何内容,它就会在标准输出上打印出来。
### 在 Linux 中安装 mimipenguin
我们将使用 git 来克隆 mimipenguin 仓库,因此如果你还没安装,那么首先在系统上安装 git。
```
$ sudo apt install git #Debian/Ubuntu systems
$ sudo yum install git #RHEL/CentOS systems
$ sudo dnf install git #Fedora 22+
```
接着像这样在你的家目录(或者其他任何地方)克隆 mimipenguin 目录:
```
$ git clone https://github.com/huntergregal/mimipenguin.git
```
下载完成后,进入并如下运行 mimipenguin:
```
$ cd mimipenguin/
$ ./mimipenguin.sh
```
注意:如果你遇到下面的错误,那就使用 sudo 命令:
```
Root required - You are dumping memory...
Even mimikatz requires administrator
```

*在 Linux 中转储登录密码*
从上面的输出中,mimipenguin 向你提供了桌面环境的用户名和密码。
另外,还可以如下运行 python 版脚本:
```
$ sudo ./mimipenguin.py
```
注意有时 gcore 可能会阻塞脚本(这是 gcore 中一个已知问题)。
### 未来更新
下面是将会被添加到 mimipenguin 的功能:
* 提升总体效率
* 添加更多支持以及其他的凭据位置
* 包括支持非桌面环境
* 添加 LDAP 的支持
mimipenguin 的 Github 仓库:<https://github.com/huntergregal/mimipenguin>
同样,请查阅:
1. [如何在 Linux 中用密码保护一个 vim 文件](/article-8547-1.html)
2. [如何在 Linux 中生成/加密/解密随机密码](https://www.tecmint.com/generate-encrypt-decrypt-random-passwords-in-linux/)
3. [如何在 RHEL/CentOS/Fedora 中用密码保护 GRUB](https://www.tecmint.com/password-protect-grub-in-linux/)
4. [在 CentOS 7 中重置/恢复忘记的 root 用户账号密码](/article-8212-1.html)
在下面的评论栏中分享你关于这个工具的额外想法或者对 Linux 中内存中明文凭据的问题。
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,即将成为 Linux SysAdmin 和网络开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢在电脑上工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/mimipenguin-hack-login-passwords-of-linux-users/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,582 | 使用 Python 开始你的机器学习之旅 | https://opensource.com/article/17/5/python-machine-learning-introduction | 2017-06-07T09:12:16 | [
"机器学习",
"ML",
"Python"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8582-1.html |
>
> 机器学习是你的简历中必需的一门技能。我们简要概括一下使用 Python 来进行机器学习的一些步骤。
>
>
>

你想知道如何开始机器学习吗?在这篇文章中,我将简要概括一下使用 [Python](https://opensource.com/article/17/2/3-top-machine-learning-libraries-python) 来开始机器学习的一些步骤。Python 是一门流行的开源程序设计语言,也是在人工智能及其它相关科学领域中最常用的语言之一。机器学习简称 ML,是人工智能的一个分支,它是利用算法从数据中进行学习,然后作出预测。机器学习有助于帮助我们预测我们周围的世界。
从无人驾驶汽车到股市预测,再到在线学习,机器学习通过预测来进行自我提高的方法几乎被用在了每一个领域。由于机器学习的实际运用,目前它已经成为就业市场上最有需求的技能之一。另外,使用 Python 来开始机器学习很简单,因为有大量的在线资源,以及许多可用的 [Python 机器学习库](https://opensource.com/article/17/2/3-top-machine-learning-libraries-python)。
你需要如何开始使用 Python 进行机器学习呢?让我们来总结一下这个过程。
### 提高你的 Python 技能
由于 Python 在工业界和科学界都非常受欢迎,因此你不难找到 Python 的学习资源。如果你是一个从未接触过 Python 的新手,你可以利用在线资源,比如课程、书籍和视频来学习 Python。比如下面列举的一些资源:
* [Python 学习之路](https://learnpythonthehardway.org/book/)
* [Google 开发者 Python 课程(视频)](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLfZeRfzhgQzTMgwFVezQbnpc1ck0I6CQl)
* [Google 的 Python 课堂](https://developers.google.com/edu/python/)
### 安装 Anaconda
下一步是安装 [Anacona](https://opensource.com/tags/javascript?src=programming_resource_menu)。有了 Anaconda ,你将可以开始使用 Python 来探索机器学习的世界了。Anaconda 的默认安装库包含了进行机器学习所需要的工具。
### 基本的机器学习技能
有了一些基本的 Python 编程技能,你就可以开始学习一些基本的机器学习技能了。一个实用的学习方法是学到一定技能便开始进行练习。然而,如果你想深入学习这个领域,那么你需要准备投入更多的学习时间。
一个获取技能的有效方法是在线课程。吴恩达的 Coursera [机器学习课程](https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning) 是一个不错的选择。其它有用的在线训练包括:
* [Python 机器学习: Scikit-Learn 教程](https://www.datacamp.com/community/tutorials/machine-learning-python#gs.HfAvLRs)
* [Python 实用机器学习教程](https://pythonprogramming.net/machine-learning-tutorial-python-introduction/)
你也可以在 [LiveEdu.tv](https://www.liveedu.tv/) 上观看机器学习视频,从而进一步了解这个领域。
### 学习更多的 Python 库
当你对 Python 和机器学习有一个好的感觉之后,可以开始学习一些[开源的 Python 库](https://opensource.com/article/17/5/4-practical-python-libraries)。科学的 Python 库将会使完成一些简单的机器学习任务变得很简单。然而,选择什么库是完全主观的,并且在业界内许多人有很大的争论。
一些实用的 Python 库包括:
* [Scikit-learn](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/) :一个优雅的机器学习算法库,可用于数据挖掘和数据分析任务。
* [Tensorflow](https://opensource.com/article/17/2/machine-learning-projects-tensorflow-raspberry-pi) :一个易于使用的神经网络库。
* [Theano](http://deeplearning.net/software/theano/) : 一个强大的机器学习库,可以帮助你轻松的评估数学表达式。
* [Pattern](https://github.com/clips/pattern) : 可以帮助你进行自然语言处理、数据挖掘以及更多的工作。
* [Nilearn](https://github.com/nilearn/nilearn) :基于 Scikit-learn,它可以帮助你进行简单快速的统计学习。
### 探索机器学习
对基本的 Python、机器学习技能和 Python 库有了一定理解之后,就可以开始探索机器学习了。接下来,尝试探索一下 Scikit-learn 库。一个不错的教程是 Jake VanderPlas 写的 [Scikit-learn 简介](http://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/donnemartin/data-science-ipython-notebooks/blob/master/scikit-learn/scikit-learn-intro.ipynb)。
然后,进入中级主题,比如 [K-均值聚类算法简介](https://www.datascience.com/blog/introduction-to-k-means-clustering-algorithm-learn-data-science-tutorials)、线性回归、[决策树](http://machinelearningmastery.com/implement-decision-tree-algorithm-scratch-python/)和逻辑回归。
最后,深入高级机器学习主题,比如向量机和复杂数据转换。
就像学习任何新技能一样,练习得越多,就会学得越好。你可以通过练习不同的算法,使用不同的数据集来更好的理解机器学习,并提高解决问题的整体能力。
使用 Python 进行机器学习是对你的技能的一个很好的补充,并且有大量免费和低成本的在线资源可以帮助你。你已经掌握机器学习技能了吗?可以在下面留下你的评论,或者[提交一篇文章](https://opensource.com/story)来分享你的故事。
(题图:opensource.com)
---
作者简介:
Michael J. Garbade 博士是旧金山 LiveEdu Inc(Livecoding.tv)的创始人兼首席执行官。Livecoding.tv 是世界上观看工程师直播编代码最先进的直播平台。你可以通过观看工程师们写网站、移动应用和游戏,来将你的技能提升到一个新的水平。MichaelJ. Garbade 博士拥有金融学博士学位,并且是一名自学成才的工程师,他喜欢 Python、Django、Sencha Touch 和视频流。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/5/python-machine-learning-introduction>
作者:[Michael J. Garbade](https://opensource.com/users/drmjg) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Have you wondered what it takes to get started with machine learning? In this article, I will walk through steps for getting started with machine learning using [Python](https://opensource.com/article/17/2/3-top-machine-learning-libraries-python). Python is a popular open source programming language and it is one of the most-used languages in artificial intelligence and other related scientific fields. Machine learning (ML), on the other hand, is the field of artificial intelligence that uses algorithms to learn from data and make predictions. Machine learning helps predict the world around us.
From self-driving cars to stock market predictions to online learning, machine learning is used in almost every field that utilizes prediction as a way to improve itself. Due to its practical usage, it is one of the most in-demand skills right now in the job market. Also, getting started with [Python](https://www.liveedu.tv/learn/python/) and machine learning is easy as there are plenty of online resources and lots of [Python machine learning libraries](https://opensource.com/article/17/2/3-top-machine-learning-libraries-python) available.
What do you have to do to get started with Python machine learning? Let's walk through the process.
## Brush up your Python skills
Because Python is extremely popular, both in the industrial and scientific communities, you will have no difficulty finding Python learning resources. If you are a complete beginner, you can start learning Python using online materials, such as courses, books, and videos. For example:
## Install Anaconda
The next step is to install [Anaconda](http://docs.continuum.io/anaconda/install). With Anaconda, you are set to explore the world of machine learning with Python. The Anaconda package contains the required tools that you will need for exploring machine learning.
## Basic machine learning skills
With basic Python programming skills under your belt, you're ready to pick up basic machine learning skills. A practical approach to learning is more than enough to get started; however, if you are interested in going deep into the subject, be ready to invest perhaps hundreds of hours of learning.
One efficient way to acquire skills is with online courses. Andrew Ng's Coursera [Machine Learning course](https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning) is a great option. Other online training worth checking out include:
(You can also watch machine learning streams on [LiveEdu.tv](https://www.liveedu.tv/) to get a feel for the subject.)
## Learn more about Python packages
After getting a good feel for Python and machine learning, consider learning the [open source Python libraries](https://opensource.com/article/17/5/4-practical-python-libraries). The scientific Python libraries will make it easy to complete simple machine learning tasks; however, the choice of these libraries is completely subjective and is highly debatable by many people in the industry.
A few Python libraries to check out include:
[Scikit-learn](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/): A neat library of machine learning algorithms that can be used for data mining and data analysis task.[Tensorflow:](https://opensource.com/article/17/2/machine-learning-projects-tensorflow-raspberry-pi)An easy-to-use neural network library.[Theano:](http://deeplearning.net/software/theano/)Theano is a powerful machine learning library that helps you easily evaluate mathematical expressions.[Pattern](https://github.com/clips/pattern): Pattern can help you with Natural Language processing, data mining, and much more.[Nilearn](https://github.com/nilearn/nilearn): Nilearn, which is based on Scikit-learn, helps you to do easy and fast statistical learning.
## Explore machine learning
With an understanding of basic Python, machine learning skills, and Python libraries, you are all set. Next try exploring the Scikit-learn library. A good tutorial to check out is an [introduction to Scikit-learn](http://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/donnemartin/data-science-ipython-notebooks/blob/master/scikit-learn/scikit-learn-intro.ipynb) by Jake VanderPlas.
Then jump into intermediate topics, such as [an introduction to K-means clustering](https://www.datascience.com/blog/introduction-to-k-means-clustering-algorithm-learn-data-science-tutorials), linear regression, [decision trees](http://machinelearningmastery.com/implement-decision-tree-algorithm-scratch-python/), and logistic regression.
Finally, dive deep into advanced machine learning topics such as vector machines and complex data transformation.
As with learning any new skills, the more you practice, the better you become. Practice different algorithms and work with different data sets to have a better understanding of machine learning, and to improve your overall problem-solving skills.
Machine learning with Python is a great addition to your technical skillset, and there are lots of free and low-cost online resources available to help. How have you picked up machine learning skills? Leave a comment below, or [submit an article proposal](https://opensource.com/story) to share your story.
## 1 Comment |
8,583 | 使用 comm 比较两个排序好的文件 | https://www.howtoforge.com/linux-comm-command/ | 2017-06-08T09:32:00 | [
"比较",
"comm"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8583-1.html | 
Linux 中的 `comm` 命令可以让用户按行比较两个**已经排序好**的文件。在本教程中,我们将使用一些浅显易懂的例子来讨论这个命令行工具。在开始之前,请注意,本教程中提到的所有例子都已经在 Ubuntu 16.04LTS 版本中测试过。
下面的例子将会告诉你 `comm` 命令是如何工作的。
### 1、 如何使用 `comm` 比较两个排序好的文件
要使用 `comm` 命令比较两个排序好的文件,只需要把它们的名字作为 `comm` 命令的参数。下面是通常的语法:
```
comm [name-of-first-file] [name-of-second-file]
```
比如,假设 `file1` 和 `file2` 是这种情况下的两个文件。前者包含下面几行内容:
```
001
056
127
258
```
而后者包含下面几行内容:
```
002
056
167
369
```
此时,`comm` 命令的输出如下图所示:
```
comm file1 file2
```

你可以看到,输出包含 3 列。第一列是仅包含在 `file1` 中的内容,第二列是仅包含在 `file2` 中的内容,最后,第三列是两个文件中均包含的内容。
### 2、 如何不输出 `comm` 命令输出中的某些列
如果你想,你可以不输出 `comm` 命令输出中的某些列。对于该特性,你有三个命令行选项可用:`-1`、`-2` 和 `-3` 。正如你所猜想的,这些数字表示你不想输出的列。
比如,下面这个命令将会不输出上面例子中的第三列:
```
comm -3 file1 file2
```

因此,你可以看到,第三列并没有输出。
注意,你可以通过一个单一命令同时不输出多列内容。比如:
```
comm -12 file1 file2
```
上面这个命令将会不输出第一、二列。
### 3、 如何使用 `comm` 命令比较两个未排序好的文件
正如我们所知道的,`comm` 只可用于排序好的文件。如果发现其中一个文件未排序好,那么便会在输出中产生一条信息来告诉用户。比如,我们交换 `file1` 的第一行和第二行,然后与 `file2` 进行比较。下面是该命令的输出:

你可以看到,这个命令产生一个输出告诉我们:`file1` 还没有排序好。此时,如果你不想让这个工具检查输入是否已经排序好,那么你可以使用 `--nocheck-order` 选项:
```
comm --nocheck-order file1 file2
```

你可以看到,前面出现的提示信息已经消失了。
注意,如果你想明确告诉 `comm` 命令来检查输入文件是否排序好,那么你可以使用 `--check-order` 选项。
### 4、 如何用自定义字符串分隔 `comm` 命令的输出列
默认情况下,`comm` 命令的输出列之间是以空格分隔的。然而,如何你想使用一个自定义字符串作为分隔符,那么你可以使用 `--output-delimiter` 选项。使用该选项时需要指定你想用来作为分隔符的字符串。
```
comm --output-delimiter=+ file1 file2
```
比如,我们使用加号来作为分隔符:

### 5、 如何使 `comm` 的输出行以 `NUL` 字符终止
默认情况下,`comm` 命令的输出行以新行终止。然而,如果你想,那么你可以改为以 `NUL` 字符终止,只需要使用 `-z` 选项即可:
```
comm -z file1 file2
```
### 结论
`comm` 命令并没有特别多的特性性,我们在这儿已经讨论了它的绝大多数命令行选项。只需要理解和练习在这篇教程中讨论的内容,那么你便可以在日常工作中知道如何使用这个工具了。如果你有任何问题或者疑问,请前往该命令的 [man 手册](https://linux.cn/man/1/comm),或者在下面评论。
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/linux-comm-command/>
作者:[Himanshu Arora](https://www.howtoforge.com/linux-comm-command/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # Linux comm command tutorial for beginners (5 examples)
### On this page
The * comm* command in Linux lets users compare two sorted files line by line. In this tutorial, we will discuss this command line tool using easy to understand examples. But before we do that, please note that all examples mentioned in this tutorial have been tested on Ubuntu 16.04LTS.
## Linux comm command
The following examples should give you a nice idea about how the 'comm' tool works.
## 1. How to compare two sorted files using comm
To compare two sorted files using 'comm', all you have to do is to pass their names as arguments to the command line tool. Here's the generic syntax:
comm [name-of-first-file] [name-of-second-file]
For example, suppose 'file1' and 'file2' are the two files in our case. The former contains the following lines:
001
056
127
258
while the latter contains the following lines:
002
056
167
369
Now, here's the 'comm' command output in this case:
comm file1 file2
So you can see that output consists of three columns. The first one contains lines unique to 'file1', second one contains lines unique to 'file2', and finally, column three contains lines common to both files.
## 2. How to suppress individual columns in comm command output
If you want, you can suppress individual columns in comm command output. For this, you have three command line options: * -1*,
*, and*
**-2***. As you'd have guessed, these numbers represents the columns you want to suppress.*
**-3**For example, here's the command to suppress the third column in our case:
comm -3 file1 file2
So you can see that the third column got suppressed.
Note that you can suppress multiple columns with a single command. For example:
comm -12 file1 file2
will suppress both first and second columns.
## 3. How to make comm compare files that are not sorted
As we know, the comm command only works with sorted files. If it finds that a file is not sorted, a message is produced in the output that tells the user about this. For example, we swapped the first and the second lines in 'file1,' and then compared it with 'file2.' Here's what the output was:
So you can see that the command produced an output saying 'file1' is not sorted. Now, if you don't want the tool to check whether or not the input is sorted, you can use the * --nocheck-order* option.
comm --nocheck-order file1 file2
So you can see that the message that was earlier being displayed got suppressed.
Please note that just in case you want to explicitly tell the comm command to carry out the sorting check on input files, you can use the * --check-order* option.
## 4. How to separate comm output columns with custom string
By default, the columns in the comm command output are separated by spaces. However, if you want, you can change that, and have a string of your choice as separator. This can be done using the * --output-delimiter* option. This option requires you to specify the string that you want to use as the separator.
comm --output-delimiter=STR file1 file2
For example, we used the plus (+) symbol as the delimiter.
## 5. How to make comm output lines NUL terminated
The comm command output lines are newline-terminated by default. However, if you want, you can make them NUL terminated instead. This can be done using the * -z* command line option.
comm -z file1 file2
## Conclusion
The comm command doesn't offer a whole lot of features - we've covered almost all its command line options here. So just understand and practice what all we've discussed in this tutorial, and you'll be ready to use the tool in your day-to-day tasks. In case of any doubt or query, head to [the command's man page](https://linux.die.net/man/1/comm), or leave a comment below. |
8,585 | FreeFileSync:在 Ubuntu 中对比及同步文件 | http://www.tecmint.com/freefilesync-compare-synchronize-files-in-ubuntu/ | 2017-06-08T07:57:00 | [
"备份",
"同步",
"FreeFileSync"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8585-1.html | 
FreeFileSync 是一个自由、开源以及跨平台的文件夹对比及同步软件,它可以帮助你同步 Linux、Windows 和 Mac OS 中的文件和文件夹。
它是便携的,也可以被安装在本地系统中,它的功能丰富,旨在节省设置和执行备份操作的时间,同时具有有吸引力的图形界面。
#### FreeFileSync 功能
下面是它的主要功能:
1. 它可以同步网络共享和本地磁盘。
2. 它可以同步 MTP 设备(Android、iPhone、平板电脑、数码相机)。
3. 它也可以通过 [SFTP(SSH 文件传输协议)](http://www.tecmint.com/sftp-command-examples/)进行同步。
4. 它可以识别被移动和被重命名的文件和文件夹。
5. 使用目录树显示磁盘空间使用情况。
6. 支持复制锁定文件(卷影复制服务)。
7. 识别冲突并同步删除(propagate deletions)。
8. 支持按内容比较文件。
9. 它可以配置为处理符号链接。
10. 支持批量自动同步。
11. 支持多个文件夹比较。
12. 支持深入详细的错误报告。
13. 支持复制 NTFS 扩展属性,如(压缩、加密、稀疏)。
14. 还支持复制 NTFS 安全权限和 NTFS 备用数据流。
15. 支持超过 260 个字符的长文件路径。
16. 支持免故障的文件复制防止数据损坏。
17. 允许扩展环境变量,例如 `%UserProfile%`。
18. 支持通过卷名访问可变驱动器盘符(U盘)。
19. 支持管理已删除/更新文件的版本。
20. 通过最佳同步序列防止光盘空间问题。
21. 完全支持 Unicode。
22. 提供高度优化的运行时性能。
23. 支持过滤器包含和排除文件等。
### 如何在 Ubuntu 中安装 FreeFileSync
我们会添加官方的 FreeFileSync PPA,这只在 Ubuntu 14.04 和 Ubuntu 15.10 上有,那么像这样更新系统仓库列表并安装它:
```
-------------- 在 Ubuntu 14.04 和 15.10 上 --------------
$ sudo apt-add-repository ppa:freefilesync/ffs
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install freefilesync
```
对于 Ubuntu 16.04 或者更新的版本,进入 [FreeFileSync 的下载页](http://www.freefilesync.org/download.php)为你的 Ubuntu 和 Debian 获取合适的包。
接下来,进入下载文件夹,如下解压 FreeFileSync\_\*.tar.gz 到 `/opt` 目录中:
```
$ cd Downloads/
$ sudo tar xvf FreeFileSync_*.tar.gz -C /opt/
$ cd /opt/
$ ls
$ sudo unzip FreeFileSync/Resources.zip -d /opt/FreeFileSync/Resources/
```
下载我们会使用 Gnome 面板创建一个程序启动器(`.desktop` 文件)。要浏览系统中 `.desktop` 文件的例子,列出 `/usr/share/applications` 目录的内容:
```
$ ls /usr/share/applications
```
为防你没有安装 Gnome 面板,输入下面的命令来安装:
```
$ sudo apt-get install --no-install-recommends gnome-panel
```
接下来,运行下面的命令来创建程序启动器:
```
$ sudo gnome-desktop-item-edit /usr/share/applications/ --create-new
```
并定义下面的值:
```
Type: Application
Name: FreeFileSync
Command: /opt/FreeFileSync/FreeFileSync
Comment: Folder Comparison and Synchronization
```
要为启动器添加一个图标,只需要点击图标选择:`/opt/FreeFileSync/Resources/FreeFileSync.png`。
当你设置完成之后,点击 OK 创建。

*创建桌面启动器*
如果你不想要创建桌面启动器,你可以从目录中启动 FreeFileSync。
```
$ ./FreeFileSync
```
### 如何在 Ubuntu 中使用 FreeFileSync
在 Ubuntu 中,在 Unity Dash 中搜索 FreeFileSync,然而在 Linux Mint 中,在 System Menu 中搜索,并点击 FreeFileSync 图标打开。

*FreeFileSync*
#### 使用 FreeFileSync 比较两个文件夹
在下面的例子中,我们使用:
```
Source Folder: /home/aaronkilik/bin
Destination Folder: /media/aaronkilik/J_CPRA_X86F/scripts
```
要比较文件时间以及两个文件夹的大小(默认设置),只要点击比较按钮。

*在 Linux 中比较两个文件夹*
通过下面的界面,可以在两个文件夹中按 `F6` 来更改要比较的内容:文件时间和大小、内容或文件大小。请注意,你选择的每个选项的含义也包括在内。

*文件比较设置*
#### 使用 FreeFileSync 同步两个文件夹
你可以开始比较两个文件夹,接着点击 Synchronize 按钮启动同步进程。在之后出现的对话框中点击 Start:
```
Source Folder: /home/aaronkilik/Desktop/tecmint-files
Destination Folder: /media/aaronkilik/Data/Tecmint
```

*比较以及同步两个文件夹*

*开始文件同步*

*文件同步完成*
在下面的界面中按下 `F8` 设置默认同步选项:two way、mirror、update 或 custom。每个选项的意义不言自明。

*文件同步设置*
要了解更多信息,访问 FreeFileSync 主页:<http://www.freefilesync.org/>
就是这样了!在本篇中,我们向你展示了如何在 Ubuntu 以及它的衍生版 Linux Mint、Kubuntu 等等中安装 FreeFileSync。在下面的评论栏中分享你的想法。
---
作者简介:
Ravi Saive,TecMint 的原创作者。一个喜爱在互联网上分享技巧和提示的计算机 geek 和 Linux 老手。我的大多数服务运行在 Linux 开源平台上。请在 Twitter、Facebook、Google+ 上关注我。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/freefilesync-compare-synchronize-files-in-ubuntu/>
作者:[Ravi Saive](http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,586 | 为什么每家企业都应该考虑使用开源的 POS 系统 | https://opensource.com/article/17/1/open-source-point-sale-system | 2017-06-08T09:10:00 | [
"POS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8586-1.html | 
销售点终端 (POS) 系统是从很久以前的简单的收银机发展而来的。如今的 POS 系统可以提供一体化解决方案,包括支付流程、库存管理、营销工具等等。零售店也可以使用移动设备来接收现金流和各种成本支出相关的日报表。
POS 系统是每家企业重要的生命线,那就意味着你在选择 POS 系统的过程中要非常谨慎。目前可供选择的收银系统也很多,但是如果你想节约成本,适应不断变化的业务需求,跟上技术发展的脚步,你应该很明智地考虑使用开源系统。你可以随意使用一款源代码公开的开源 POS 系统,这比那些严格保密源代码的专有系统要有更大的优势。
使用开源的 POS 系统,你可以获得它的一些非常重要的特性。
### 无限的灵活性
开源系统与其它系统的兼容性非常好。它们与第三方厂家系统进行集成的能力——从帐务和客户关系管理软件(CRM)到订单管理和库存管理系统——使得当企业管理者想要扩展专有 POS 系统以外的其它功能时,开源系统具有更强大的优势。
在 [2014 年科技调查](http://hospitalitytechnology.edgl.com/news/POS-Integration-Becoming-a--Must-Have-94389) 活动中,很多餐厅管理者声称 POS 系统的功能集成度将会是他们考虑更换新系统的主要因素。这是开源系统最具亮点的一方面。专有系统买来什么样就是什么样,很难与其它厂家的系统进行集成。但是使用开源系统,你就可以进行无限的集成及定制功能。如果你觉得你们公司的商业模式会不断的增长和变化,那么只有考虑使用开源的 POS 系统才能根据需要实时调整系统。
### 更快的开发速度
开源系统的另外一个优势是它有很多的社区开发者提供技术支持,他们持续不断的提交新功能,并且优化原有的功能。由于这种特性,开源项目的开发周期要比商用产品快得多——修复缺陷的速度更快,更新升级也很快,并且新的功能模块也不断地被开发出来。
### 更低的成本
也就是说,“更低的成本”意味着“基本免费”。你还需要购买相关硬件产品,只是软件本身是免费使用的。开源 POS 系统不像专有 POS 系统那样在购买时或是后期维护过程中需要支付高昂的费用,其每年的维护费在 3000 至 50000 美元之间,而开源系统则不会像专有系统那样需要花钱来购买。
在 [2013 年版](https://pos.toasttab.com/restaurant-technology-industry-report/2015) 的餐饮行业技术服务调查研究过程中,有超过一半的受访餐厅老板表示他们从很多的技术产商购买服务——有些餐厅所面对的技术厂家多达 10 个。而使用纯粹的开源定制化系统不需要支付维护费用,这从节约成本上来说意义非常重大。
然而,有一点我还得提醒大家。如果你们公司没有一个技术精湛的员工提供技术支持,你可能还需要聘请外部技术人员来帮助你们安装,调试和升级系统。开源系统允许用户无限制地集成和定制化开发,但是你还需要有技术精湛的专家来支持才行,这也会产生额外的费用。尽管如此,开源系统仍然是一个非常具有成本效益的选择。
### 更好的安全性
如果任何人都可以看到源代码,那是不是也意味着它同样对那些怀有恶意并想入侵你系统的程序员开放呢?那不就是一个安全上的严重隐患吗?事实正好相反。
大量的社区开发者在开发新功能的同时也会检查并修复影响系统安全的各种漏洞。有那么多的程序员在分析和维护开源软件的源代码,这可比专有软件开发商对代码的审查要严格得多。因此,开源的 POS 系统实际上更安全。
有很多开源的 POS 系统解决方案可供选择,我列出一部分来:
* [Chromis](http://chromis.co.uk/)
* [Drupal POS](https://www.acromediainc.com/drupal-pos)
* [Floreant](http://floreant.org/)
* [Odoo](https://www.odoo.com/)
* [Open Source Point of Sale](https://github.com/jekkos/opensourcepos)
* [Unicenta](https://unicenta.com/)
### 勇敢地跨出第一步
你比其它人更了解你们公司。只有你能决定哪种开源系统最适合你们公司。由于开源 POS 系统比专有 POS 系统有更多亮丽的优点——灵活性、开发快速、低成本、更安全——因此,每个公司都应该考虑使用开源的 POS 系统。
(题图:opensource.com)
---
作者简介:

我是 AcroMedia 公司数字化市场营销项目经理。我们主要使用 Drupal 开源系统来为客户提供定制化商业解决方案。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/1/open-source-point-sale-system>
作者:[Preston Pilgrim](https://opensource.com/users/preston-pilgrim) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[Bestony](https://github.com/Bestony)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Point of sale (POS) systems have come a long way from the days of simple cash registers that rang up purchases. Today, POS systems can be all-in-one solutions that include payment processing, inventory management, marketing tools, and more. Retailers can receive daily reports on their cash flow and labor costs, often from a mobile device.
The POS is the lifeblood of a business, and that means you need to choose one carefully. There are a ton of options out there, but if you want to save money, adapt to changing business needs, and keep up with technological advances, you would be wise to consider an open source system. An open source POS, where the source code is exposed for your use, offers significant advantages over a proprietary system that keeps its code rigidly under wraps.
With an [open source POS](https://opensource.com/business/16/7/open-source-point-sale-systems), you get a few key things.
## Unlimited flexibility
Open source systems play well with others. Their ability to integrate and connect with third-party products—from accounting and customer relationship management software to order management and inventory systems—makes them an attractive proposition for business owners who need to expand beyond the feature set of a proprietary POS.
In a [2014 technology survey](http://hospitalitytechnology.edgl.com/news/POS-Integration-Becoming-a--Must-Have-94389), restaurant owners said integration would be a major factor influencing their next POS upgrade. This is one area where open source really shines. A proprietary system is what it is. But with open source, you have endless possibilities for integration and customization. If you think your business model is ever going to grow and change, it only makes sense to consider an open source POS that allows you to adapt as needed.
## Faster development
Another advantage of open source systems is that they are often backed by a large community of developers who are continually building new functionality and improving on old features. By its very nature, the software development cycle for an open source project is much quicker than it is for a commercial product—bugs get fixed faster, updates get released sooner, and new modules are constantly being developed.
## Lower cost
In this case, "lower cost" means "almost free." You still need to buy the hardware, but the software itself is free to use. An open source POS doesn't have the high start-up or ongoing maintenance costs of a proprietary POS, which can be anywhere from $3,000 to $50,000 a year, nor does open source force you into the locked-in pricing of a proprietary model.
In the [2015 version](https://pos.toasttab.com/restaurant-technology-industry-report/2015) of the food service technology study, more than half of the restaurant owners surveyed said they were paying for multiple technology vendors—in some cases as many as 10. The cost savings of switching to a single open source system with custom modifications and no ongoing fees could be significant.
There is a caveat, however. If you don't have a tech-savvy staff, you may need to hire outside help to install, modify, and upgrade your software. Open source does allow for unlimited integrations and customizations, but you'll need someone with technical expertise to take care of that, which can incur additional fees. Still, it can be a very cost-effective option.
## Better security
If the source code is out there for anyone to see, doesn't that mean it's open to malicious programmers who want to hack into your data? Isn't that a security nightmare? On the contrary.
The large community of developers that builds new functionality also searches out and repairs security flaws. There are many more sets of eyes dissecting and fixing open source code than there are reviewing the code for a proprietary product. In that way, an open source POS is actually *more* secure.
There are many options for open source POS solutions, to name some:
## Making the jump
You know your business better than anyone. Only you can decide what point of sale software is right for you. Given the compelling advantages of an open source POS over a proprietary POS—flexibility, rapid development, lower cost, more security—open source is something every business should consider.
## 10 Comments |
8,587 | 你为什么使用 Linux 和开源软件? | https://opensource.com/article/17/3/why-do-you-use-linux-and-open-source-software | 2017-06-08T07:39:53 | [
"开源"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8587-1.html |
>
> LinuxQuestions.org 的用户分享了他们使用 Linux 和开源技术的原因。我们的用户如何回答这个问题?
>
>
>

在网站问答区发布时我曾经提到过,尽管我一般会回答来自用户问题,但偶尔我也会反过来问读者一些问题。我并没有在问答区第一期文章这样做,看起来有点姗姗来迟。我最近在 LinuxQuestions.org 上提问了两个相关的问题,收到了很多回复。让我们看看我们的用户对同样的问题和 LinuxQuestions.org 的回答的对比。
### 你为什么使用 Linux?
我向 LinuxQuestions.org 社区提问的第一个问题是:**[你们使用 Linux 的原因是什么?](http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/linux-general-1/what-are-the-reasons-you-use-linux-4175600842/)**
#### 回答集锦
*oldwierdal*:我用 Linux 是因为它运行快速、安全、可靠。在全世界的贡献者的参与下,Linux 或许已经成为当前我们能用到的最先进和最具创新的软件。Linux 的用户体验就像红丝绒蛋糕上的糖衣一样令人回味无穷;此外,Linux 是免费的。
*Timothy Miller*:我最开始使用 Linux 是因为它免费的,而且那时候我的经济条件无法承受购买新的 Windows 系统正版授权的费用。
*ondoho* :因为它是一个拥有全球性社区为之努力、独立的草根操作系统。因为它在各方面都是自由的。因为它有足够多的理由让我们信任它。
*joham34*:稳定、免费、安全,能够运行在低配置的电脑上,提供良好技术支持的社区,感染病毒的几率更小。
*Ook*:我用 Linux 是因为它可以完成工作,对我来说 Windows 系统在某些事上从来都不能做好。我不得不浪费时间和金钱让 Windows 继续正常运行下去。
*rhamel*:我非常担心个人隐私泄露在网上。我意识到我不得不在隐私和便利性之间做出妥协。我可能是在骗自己但我确实认为 Linux 至少在某种程度上给了我一定的隐私权。
*educateme*:我使用 Linux 因为它的开放、好学、热情乐于助人的社区。而且,它是免费的。
*colinetsegers*:我为什么用 Linux?原因不止一个。简单的说有以下几点:
1. 自由分享知识的理念。
2. 浏览网页的时候有安全感。
3. 大量免费、有用的软件。
*bamunds*:因为我热爱自由。
*cecilskinner1989*:我用 Linux 的两个原因:稳定性和隐私。
### 你为什么使用开源软件?
第二个问题相对更加宽泛:**[你为什么使用开源软件?](http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/linux-general-1/what-are-the-reasons-you-use-open-source-software-4175600843/)**你会注意到尽管有些回复是有重复的部分,但用户的回答大体上的语气是不同的,有些用户的回答得到很多人的赞同和支持,也有不少用户的回答不怎么被其他人认同。
#### 回答集锦
*robert leleu*:温馨、合作的氛围是我沉溺于开源的主要原因。
*cjturner*:对于应用而言,开源正好反映了帕累托法则;不做二次开发的话,一个软件包最终可能只能满足你的 80% 的需求,而你需要自己解决剩下的 20%。开源给了你一个途径,通过社区来解决这种问题,你可以自己努力实现(如果你有相关的技能)或者花钱有偿请人实现你的需求。
*Timothy Miller*:我喜欢这种体验,我能够自己检查源代码来确定我所选择的软件是安全的。
*teckk*:没有繁琐的许可要求或者数字版权管理(DRM),而且每个人都可以获得它。
*rokytnji* :像零花钱,摩托车部件,孙辈的生日礼物那样令人愉悦。
*timl*:没有自由软件避免隐私的泄露是不可能。
*hazel*:我喜欢自由软件的哲学,但如果 Linux 是一个糟糕的操作系统我也会理性的不去使用它。我使用 Linux 是因为我热爱 Linux,而且你也能免费获得它就像免费的啤酒一样。事实上它也如言论自由一般自由不受拘束,使用开源软件让我感觉很舒服。但是如果我发现我的计算机有一个硬件需要专有固件的配合才能发挥功能,我也会使用专有固件。
*lm8*:我使用开源软件是因为我不必担心由于开发公司的破产或者决定停止维护它而导致它可能会变得过时或者被废弃。我能够自己来完成后续的更新、维护。如果我想让软件能够做我想的任何事情,我也可以进一步定制它,但是如果有更多的特性,那就更好了。我也喜欢开源,因为开源我才能够和朋友、同事们分享我喜欢的程序。
*donguitar*:因为它能够让我学到很多,也让我让别人学到了很多。
### 该你回答了
所以,***你*** 使用 Linux 的原因是什么? ***你*** 使用开源软件的原因是什么?请在评论区告诉我们。
#### 最后的补充
最后,在以后的文章里你想看到什么问题的回答?是社区的建立和维护的相关问题,还是你想知道如何对一个开源项目作出贡献,还是更有技术性的问题 — 向我们提交你对 Linux 和 开源的问题。
(题图:opensource.com)
---
作者简介:
Jeremy Garcia - Jeremy Garcia 是 LinuxQuestions.org 的创立者同时也是一位热情中不乏现实主义的开源倡导者。你可以在 Twitter 上关注 Jeremy:@linuxquestions
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/3/why-do-you-use-linux-and-open-source-software>
作者:[Jeremy Garcia](https://opensource.com/users/jeremy-garcia) 译者:[WangYueScream](https://github.com/WangYueScream) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | As I mentioned when [The Queue](https://opensource.com/tags/queue-column) launched, although typically I will answer questions from readers, sometimes I'll switch that around and ask readers a question. I haven't done so since that initial column, so it's overdue. I recently asked two related questions at LinuxQuestions.org and the response was overwhelming. Let's see how the Opensource.com community answers both questions, and how those responses compare and contrast to those on LQ.
## Why do you use Linux?
The first question I asked the LinuxQuestions.org community is: [What are the reasons you use Linux?](http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/linux-general-1/what-are-the-reasons-you-use-linux-4175600842/)
### Answer highlights
*oldwierdal*: I use Linux because it is fast, safe, and reliable. With contributors from all over the world, it has become, perhaps, the most advanced and innovative software available. And, here is the icing on the red-velvet cake; It is free!
*Timothy Miller*: I started using it because it was free as in beer and I was poor so couldn't afford to keep buying new Windows licenses.
*ondoho*: Because it's a global community effort, self-governed grassroot operating system. Because it's free in every sense. Because there's good reason to trust in it.
*joham34*: Stable, free, safe, runs in low specs PCs, nice support community, little to no danger for viruses.
*Ook*: I use Linux because it just works, something Windows never did well for me. I don't have to waste time and money getting it going and keeping it going.
*rhamel*: I am very concerned about the loss of privacy as a whole on the internet. I recognize that compromises have to be made between privacy and convenience. I may be fooling myself but I think Linux gives me at least the possibility of some measure of privacy.
*educateme*: I use Linux because of the open-minded, learning-hungry, passionately helpful community. And, it's free.
*colinetsegers*: Why I use Linux? There's not only one reason. In short I would say:
- The philosophy of free shared knowledge.
- Feeling safe while surfing the web.
- Lots of free and useful software.
*bamunds*: Because I love freedom.
*cecilskinner1989*: I use linux for two reasons: stability and privacy.
## Why do you use open source software?
The second questions is, more broadly: ** What are the reasons you use open source software?** You'll notice that, although there is a fair amount of overlap here, the general tone is different, with some sentiments receiving more emphasis, and others less.
### Answer highlights
*robert leleu*: Warm and cooperative atmosphere is the main reason of my addiction to open source.
*cjturner*: Open Source is an answer to the Pareto Principle as applied to Applications; OOTB, a software package ends up meeting 80% of your requirements, and you have to get the other 20% done. Open Source gives you a mechanism and a community to share this burden, putting your own effort (if you have the skills) or money into your high-priority requirements.
*Timothy Miller*: I like the knowledge that I *can* examine the source code to verify that the software is secure if I so choose.
*teckk*: There are no burdensome licensing requirements or DRM and it's available to everyone.
*rokytnji*: Beer money. Motorcycle parts. Grandkids birthday presents.
*timl*: Privacy is impossible without free software
*hazel*: I like the philosophy of free software, but I wouldn't use it just for philosophical reasons if Linux was a bad OS. I use Linux because I love Linux, and because you can get it for free as in free beer. The fact that it's also free as in free speech is a bonus, because it makes me feel good about using it. But if I find that a piece of hardware on my machine needs proprietary firmware, I'll use proprietary firmware.
*lm8*: I use open source software because I don't have to worry about it going obsolete when a company goes out of business or decides to stop supporting it. I can continue to update and maintain the software myself. I can also customize it if the software does almost everything I want, but it would be nice to have a few more features. I also like open source because I can share my favorite programs with friend and coworkers.
*donguitar*: Because it empowers me and enables me to empower others.
## Your turn
So, what are the reasons * you* use Linux? What are the reasons
*use open source software? Let us know in the comments.*
**you**### Fill The Queue
Lastly, what questions would you like to see answered in a future article? From questions on building and maintaining communities, to what you'd like to know about contributing to an open source project, to questions more technical in nature—[submit your Linux and open source questions](https://opensource.com/thequeue-submit-question).
## 16 Comments |
8,589 | 安卓编年史(20):安卓 4.1,果冻豆——Google Now 指明未来 | http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/21/ | 2017-06-09T08:34:00 | [
"Android",
"安卓编年史"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8589-1.html | 
### 安卓 4.1,果冻豆——Google Now指明未来

*华硕制造的 Nexus 7,安卓 4.1 的首发设备*
随着 2012 年 7 月安卓 4.1 果冻豆的发布,谷歌的安卓发布节奏进入每六个月一发布的轨道。平台已经成熟,三个月的发布周期就没那么必要了,更长的发布周期也给了 OEM 厂商足够的时间跟上谷歌的节奏。和蜂巢不同,小数点后的更新发布现在是主要更新,4.1 带来了主要的界面更新和框架变化。
果冻豆最大的变化之一,并且你在截图中看不到的是“黄油计划”,这个名字代表了谷歌工程师让安卓的动画顺畅地跑在 30FPS 上的努力。还有一些核心变化,像垂直同步和三重缓冲,每个动画都经过优化以流畅地绘制。动画和顺滑滚动一直是安卓和 iOS 相比之下的弱点。经过在核心动画框架和单独的应用上的努力,果冻豆让安卓的流畅度大幅接近 iOS。
和果冻豆一起到来的还有 [Nexus](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2012/07/divine-intervention-googles-nexus-7-is-a-fantastic-200-tablet/) 7,由华硕生产的 7 英寸平板。不像之前主要是横屏模式的 Xoom,Nexus 7 主要以竖屏模式使用,像个大一号的手机。Nexus 7 展现了经过一年半的生态建设,谷歌已经准备好了给平板市场带来一部旗舰设备。和 Nexus One 和 GSM Galaxy Nexus 一样,Nexus 7 直接由谷歌在线销售。尽管那些早先的设备对习惯于运营商补贴的消费者来说价格高的惊人,Nexus 7 以仅仅 200 美元的价格推向大众市场。这个价格给你带来一部 7 英寸、1280x800 英寸显示屏、四核 1.2GHz Tegra 3 处理器、1GB 内存、8GB 内置存储的设备。Nexus 7 的性价比如此之高,许多人都想知道谷歌到底有没有在其旗舰平板上赚到钱。
更小、更轻、7 英寸,这些因素促成了谷歌巨大的成功,并且将谷歌带向了引领行业潮流的位置。一开始制造 10 英寸 iPad 的苹果,最终也不得不推出和 Nexus 7 相似的 iPad Mini 来应对。

*4.1 的新锁屏设计,壁纸,以及系统按钮新的点击高亮。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
蜂巢引入的电子风格在冰淇淋三明治中有所减少,果冻豆在此之上走得更远。它开始从系统中大范围地移除蓝色。迹象就是系统按钮的点击高亮从蓝色变为了灰色。

*新应用阵容合成图以及新的消息可展开通知面板。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
通知中心面板完全重制了,这个设计一直沿用到今天的奇巧巧克力(KitKat)。新面板扩展到了屏幕顶部,并且覆盖了状态栏图标,这意味着通知面板打开的时候不再能看到状态栏。时间突出显示在左上角,旁边是日期和设置按钮。清除所有通知的按钮,在冰淇淋三明治中显示为一个“X”按钮,现在变为阶梯状的按钮,象征着清除所有通知的时候消息交错滑动的动画效果。底部的面板把手从一个小圆换成了一条直线,和面板等宽。所有的排版都发生了变化——通知面板的所有项现在都使用了更大,更细的字体。通知面板是另一个从冰淇淋三明治和蜂巢中引入的蓝色元素被移除的屏幕。除了触摸高亮之外整个通知面板都是灰色的。
通知面板也引入了新功能。相较于之前的两行设计,现在的通知消息可以展开以显示更多信息。通知消息可以显示最多 8 行文本,甚至还能在消息底部显示按钮。屏幕截图通知消息底部有个分享按钮,你也可以直接从未接来电通知中拨号,或者将一个正在响铃的闹钟小睡,这些都可以在通知面板完成。新通知消息默认展开,但当它们堆叠到一起时会恢复原来的尺寸。在通知消息上双指向下滑动可以展开消息。

*新谷歌搜索应用,带有 Google Now 卡片,语音搜索,以及文字搜索。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
果冻豆中不止对安卓而言,也是对谷歌来说最大的特性,是新版谷歌搜索应用。它带来了“Google Now”,一个预测性搜索功能。Google Now 在搜索框下面显示为几张卡片,它会提供谷歌认为你所关心的事物的搜索结果。就比如谷歌地图搜索你最近在桌面电脑查找的地点或日历的约会地点、天气,以及旅行时回家的时间。
新版谷歌搜索应用自然可以从谷歌图标启动,但它还可以在任意屏幕从系统栏上滑访问。长按系统栏会唤出一个类似锁屏解锁的环。卡片部分纵向滚动,如果你不想看到它们,可以滑动消除它们。语音搜索是更新的一个大部分。提问不是无脑地输入进谷歌,如果谷歌知道答案,它还会用文本语音转换引擎回答你。传统的文字搜索当然也支持。只需点击搜索栏然后开始输入即可。
谷歌经常将 Google Now 称作“谷歌搜索的未来”。告诉谷歌你想要什么这还不够好。谷歌想要在你之前知道你想要什么。Google Now 用谷歌所有的数据挖掘关于你的知识为你服务,这也是谷歌对抗搜索引擎竞争对手,比如必应,的最大优势所在。智能手机比你拥有的其它设备更了解你,所以该服务在安卓上首次亮相。但谷歌慢慢也将 Google Now 加入 Chrome,最终似乎会到达 Google.com。
尽管功能很重要,但同时 Google Now 是谷歌产品有史以来最重要的设计工作也是毋庸置疑的。谷歌搜索应用引入的白色卡片审美将会成为几乎所有谷歌产品设计的基础。今天,卡片风格被用在 Google Play 商店以及所有的 Play 内容应用,Youtube、谷歌地图、Drive、Keep、Gmail、Google+ 以及其它产品。同时也不限于安卓应用。不少谷歌的桌面站点和 iOS 应用也以此设计为灵感。设计是谷歌历史上的弱项之一,但 Google Now 开始谷歌最终在设计上采取了行动,带来一个统一的,全公司范围的设计语言。

*又一个 Youtube 的重新设计,信息密度有所下降。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
又一个版本,又一个 Youtube 的重新设计。这次列表视图主要基于略缩图,大大的图片占据了屏幕的大部分。信息密度在新列表设计中有所下降。之前 Youtube 每屏大约能显示 6 个项目,现在只能显示 3 个。
Youtube 是首批在应用左侧加入滑动抽屉的应用之一,该特性会成为谷歌应用的标准设计风格。抽屉中有你的账户的链接和订阅频道,这让谷歌可以去除页面顶部标签页设计。

*Google Play 服务的职责以及安卓的剩余部分职责。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
### Google Play 服务——碎片化和让系统版本(几乎)过时
碎片化那时候看起来这并不是个大问题,但 2012 年 12 月,Google Play 服务 1.0 面向所有安卓 2.2 及以上版本的手机推出。它添加了一些 Google+ API 和对 OAuth 2.0 的支持。
尽管这个升级听起来很无聊,但 Google Play 服务最终会成长为安卓整体的一部分。Google Play 服务扮演着正常应用和安卓系统的中间角色,使得谷歌可以升级或替换一些核心组件,并在不发布新安卓版本的前提下添加 API。
有了 Play 服务,谷歌有了直接接触安卓手机核心部分的能力,而不用通过 OEM 更新一集运营商批准的过程。谷歌使用 Play 服务添加了全新的位置系统、恶意软件扫描、远程擦除功能,以及新的谷歌地图 API,所有的这一切都不用通过发布一个系统更新实现。正如我们在姜饼部分的结尾提到的,感谢 Play 服务里这些“可移植的”API 实现,姜饼仍然能够下载现代版本的 Play 商店和许多其他的谷歌应用。
另一个巨大的益处是安卓用户基础的兼容性。最新版本的安卓系统要经过很长时间到达大多数用户手中,这意味着最新版本系统绑定的 API 在大多数用户升级之前对开发者来说没有任何意义。Google Play 服务兼容冻酸奶及以上版本,换句话说就是 99% 的活跃设备,并且更新可以直接通过 Play 商店直接推送到手机上。通过将 API 包含在 Google Play 服务中而不是安卓中,谷歌可以在一周内将新 API 推送到几乎所有用户手中。这对许多版本碎片化引起的问题来说是个[伟大的解决方案](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/09/balky-carriers-and-slow-oems-step-aside-google-is-defragging-android/)。
---

[Ron Amadeo](http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo) / Ron 是 Ars Technica的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。[@RonAmadeo](https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo)
---
via: <http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/21/>
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,590 | cron 与 anacron:如何在 Linux 中计划任务 | https://www.tecmint.com/cron-vs-anacron-schedule-jobs-using-anacron-on-linux/ | 2017-06-09T09:56:00 | [
"cron",
"anacron"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8590-1.html | 
在本篇中,我们会解释 cron 和 anacron,并向你展示如何在 Linux 中设置 anacron。我们也会比较这两个工具。
要[在一个给定时间或者稍后安排一个任务](https://www.tecmint.com/linux-cron-alternative-at-command-to-schedule-tasks/),你可以使用 `at` 或者 `batch` 命令,要使命令能够重复运行,你可以使用 cron 以及 anacron 工具。
[cron](https://www.tecmint.com/11-cron-scheduling-task-examples-in-linux/) - 是一个用于运行计划任务如系统备份、更新等的守护进程。它适合在那些 24X7 不间断运行的机器如服务器上运行的计划任务。
命令/脚本被写在 cron 任务脚本中,它是在 `crontab` 文件中被安排的。系统默认的 `crontab` 文件是 `/etc/crontab`,但是每个用户也可以创建自己的 `crontab` 文件来在特定时间运行用户定义的命令。
要创建一份个人 `crontab` 文件,只要输入:
```
$ crontab -e
```
### 如何在 Linux 中设置 anacron
anacron 用于以天为单位的频率运行命令。它的工作与 cron 稍有不同,**它假设机器不会一直开机**。
cron 也适合在那些不会 24X7 运行如笔记本以及桌面电脑的机器上运行每日、每周以及每月的计划任务(LCTT 译注:不适合按小时、分钟执行任务)。
假设你有一个计划任务(比如备份脚本)要使用 cron 在每天半夜运行,也许你以及睡着,那时你的桌面/笔记本电脑已经关机。你的备份脚本就不会被运行。
然而,如果你使用 anacron,你可以确保在你下次开启桌面/笔记本电脑的时候,备份脚本会被执行。
### anacron 如何在 Linux 工作
anacron 任务被列在 `/etc/anacrontab` 中,任务可以使用下面的格式(anacron 文件中的注释必须以 `#` 号开始)安排。
```
period delay job-identifier command
```
从上面的格式中:
* `period` - 这是任务的频率,以天来指定,或者是 `@daily`、`@weekly`、`@monthly` 代表每天、每周、每月一次。你也可以使用数字:`1` - 每天、`7` - 每周、`30` - 每月,或者 `N` - 几天。
* `delay` - 这是在执行一个任务前等待的分钟数。
* `job-id` - 这是写在日志文件中任务的独特名字。
* `command` - 这是要执行的命令或 shell 脚本。
要浏览示例文件,输入:
```
$ ls -l /var/spool/anacron/
total 12
-rw------- 1 root root 9 Jun 1 10:25 cron.daily
-rw------- 1 root root 9 May 27 11:01 cron.monthly
-rw------- 1 root root 9 May 30 10:28 cron.weekly
```
这是实际发生的:
* anacron 会检查任务是否已经在 `period` 字段指定的时间被被执行了。如果没有,则在等待 `delay` 字段中指定的分钟数后,执行 `command` 字段中指定的命令。
* 一旦任务被执行了,它会使用 `job-id`(时间戳文件名)字段中指定的名称将日期记录在 `/var/spool/anacron` 目录中的时间戳文件中。
现在让我们看一个例子。这个会每天运行 `/home/aaronkilik/bin/backup.sh` 脚本:
```
@daily 10 example.daily /bin/bash /home/aaronkilik/bin/backup.sh
```
当机器在 `backup.sh` 期望被运行时是关机的,anacron 会在机器开机十分钟之后运行它,而不用再等待 7 天。
这里有两个你应该理解的 anacrontab 文件的重要变量:
* `START_HOURS_RANGE` - 这个设置任务开始运行的时间范围(也就是任务只在这几个小时内运行)。
* `RANDOM_DELAY` - 这定义添加到用户定义的任务延迟的最大随机延迟(默认为 45)。
这是你的 anacrontab 文件可能看上去的样子。
Anacron – `/etc/anacrontab`:
```
# /etc/anacrontab: configuration file for anacron
# See anacron(8) and anacrontab(5) for details.
SHELL=/bin/sh
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
HOME=/root
LOGNAME=root
# These replace cron's entries
1 5 cron.daily run-parts --report /etc/cron.daily
7 10 cron.weekly run-parts --report /etc/cron.weekly
@monthly 15 cron.monthly run-parts --report /etc/cron.monthly
@daily 10 example.daily /bin/bash /home/aaronkilik/bin/backup.sh
```
下面是 cron 以及 anacron 的比较,帮助你理解何时用他们其中一个。
| cron | anacron |
| --- | --- |
| 它是守护进程 | 它不是守护进程 |
| 适合服务器 | 适合桌面/笔记本电脑 |
| 可以让你以分钟级运行计划任务 | 只能让你以天为基础来运行计划任务 |
| 关机时不会执行计划任务 | 如果计划任务到期,机器是关机的,那么它会在机器下次开机后执行计划任务 |
| 普通用户和 root 用户都可以使用 | 只有 root 用户可以使用(使用特定的配置启动普通任务) |
cron 和 anacron 主要的区别在于 cron 能在那些持续运行的机器上有效地运行,而 anacron 是针对那些会在一天内或者一周内会关机的机器。
如果你还知道其他方式,请在评论栏中与我们分享。
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者、Linux 系统管理员、网络开发人员,现在也是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢和电脑一起工作,坚信共享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/cron-vs-anacron-schedule-jobs-using-anacron-on-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In this article, we will explain **cron** and **anacron** and also shows you how to setup anacron on Linux. We will as well cover a comparison of these two utilities.
To [schedule a task on given or later time](https://www.tecmint.com/linux-cron-alternative-at-command-to-schedule-tasks/), you can use the ‘**at**’ or ‘**batch**’ commands and to set up commands to run repeatedly, you can employ the **cron** and **anacron** facilities.
[Cron](https://www.tecmint.com/11-cron-scheduling-task-examples-in-linux/) – is a daemon used to run scheduled tasks such as system backups, updates and many more. It is suitable for running scheduled tasks on machines that will run continuously 24X7 such as servers.
The commands/tasks are scripted into cron jobs which are scheduled in crontab files. The default system crontab file is **/etc/crontab**, but each user can also create their own crontab file that can launch commands at times that the user defines.
To create a personal crontab file, simply type the following:
$ crontab -e
### How to Setup Anacron in Linux
**Anacron** is used to run commands periodically with a frequency defined in days. It works a little different from **cron**; assumes that a machine will not be powered on all the time.
It is appropriate for running daily, weekly, and monthly scheduled jobs normally run by cron, on machines that will not run 24-7 such as laptops and desktops machines.
Assuming you have a scheduled task (such as a **backup script**) to be run using cron every midnight, possibly when your asleep, and your desktop/laptop is off by that time. Your backup script will not be executed.
However, if you use **anacron**, you can be assured that the next time you power on the desktop/laptop again, the backup script will be executed.
### How Anacron Works in Linux
anacron jobs are listed in **/etc/anacrontab** and jobs can be scheduled using the format below (comments inside anacrontab file must start with **#**).
period delay job-identifier command
From the above format:
**period**– this is the frequency of job execution specified in days or as @daily, @weekly, or @monthly for once per day, week, or month. You can as well use numbers: 1 – daily, 7 – weekly, 30 – monthly and N – number of days.**delay**– it’s the number of minutes to wait before executing a job.**job-id**– it’s the distinctive name for the job written in log files.
To view example files, type:
$ ls -l /var/spool/anacron/total 12 -rw------- 1 root root 9 Jun 1 10:25 cron.daily -rw------- 1 root root 9 May 27 11:01 cron.monthly -rw------- 1 root root 9 May 30 10:28 cron.weekly
**command**– it’s the command or shell script to be executed.
##### This is what practically happens:
- Anacron will check if a job has been executed within the specified period in the period field. If not, it executes the command specified in the command field after waiting the number of minutes specified in the delay field.
- Once the job has been executed, it records the date in a timestamp file in the
**/var/spool/anacron**directory with the name specified in the job-id (timestamp file name) field.
Let’s now look at an example. This will run the **/home/aaronkilik/bin/backup.sh** script everyday:
@daily 10 example.daily /bin/bash /home/aaronkilik/bin/backup.sh
If the machine is off when the **backup.sh** job is expected to run, anacron will run it 10 minutes after the machine is powered on without having to wait for another 7 days.
There are two important variables in the anacrontab file that you should understand:
**START_HOURS_RANGE**– this sets time range in which jobs will be started (i.e execute jobs during the following hours only).**RANDOM_DELAY**– this defines the maximum random delay added to the user defined delay of a job (by default it’s 45).
This is how your anacrontab file would possibly look like.
# /etc/anacrontab: configuration file for anacron # See anacron(8) and anacrontab(5) for details. SHELL=/bin/sh PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin HOME=/root LOGNAME=root # These replace cron's entries 1 5 cron.daily run-parts --report /etc/cron.daily 7 10 cron.weekly run-parts --report /etc/cron.weekly @monthly 15 cron.monthly run-parts --report /etc/cron.monthly @daily 10 example.daily /bin/bash /home/aaronkilik/bin/backup.sh
The following is a comparison of **cron** and **anacron** to help you understand when to use either of them.
Cron | Anacron |
---|---|
It’s a daemon | It’s not a daemon |
Appropriate for server machines | Appropriate for desktop/laptop machines |
Enables you to run scheduled jobs every minute | Only enables you to run scheduled jobs on daily basis |
Doesn’t executed a scheduled job when the machine if off | If the machine if off when a scheduled job is due, it will execute a scheduled job when the machine is powered on the next time |
Can be used by both normal users and root | Can only be used by root unless otherwise (enabled for normal users with specific configs) |
The major difference between **cron** and **anacron** is that **cron** works effectively on machines that will run continuously while **anacron** is intended for machines that will be powered off in a day or week.
If you know any other way, do share with us using the comment form below.
Great article. Clarified a lot. Great examples. Should be in “
Replyman anacron“.@dailyand@weeklydon’t work on recent ubuntu versions. Use period`1`or`7`instead.Please fix this in your article, there are questions of questions on stack exchange from people who ran into that, maybe these questions are from people who were confused after reading your article. At least I was.
(also, 30 is *not* the same as `
monthly`, that’s the reason that an alias exists for monthly, but not for weekly/daily)[1] https://askubuntu.com/questions/1154426/anacron-running-running-my-daily-task-each-hour
Reply[2] https://askubuntu.com/questions/511337/tell-me-where-is-mistake-in-anacron-task
[3] https://superuser.com/questions/1602153/why-does-this-anacron-job-run-hourly-not-daily
@Jonas,
Thanks for the clarification, I will update the article with the recent changes to Ubuntu…
ReplyI will never understand:
You are completely right with all of this.
I use Void Linux and I don’t use cron at all (it’s not even installed).
I create a service and schedule it with snooze – which is what cron should be.
ReplyHi,
Thanks for this, it is really helpful!
ReplyThanks for this, I found it really helpful! One comment though, are you sure
Reply@dailyworks? I thought@monthlywas the only kind of string of that type supported by anacron, and when I checked an anacrontab file for syntax using the`-T`
flag and an@dailyjob, it didn’t like this line and just skipped it. Establishing the period of the job with 1 instead of @daily worked.@E
@daily works, it supports for scheduling daily tasks. If you scheduled a task using @daily and it didn’t work, you might have configured it wrongly. But we will find out more about your concern. Thanks for liking this article.
ReplyJust confirming it works for me now too, I had a mistake elsewhere. Thanks!
Reply@E
Okay, that is great! Many thanks for following us.
Reply |
8,591 | AWS 云服务大全(71 种) | http://kerneltalks.com/virtualization/aws-cloud-terminology/ | 2017-06-09T10:56:00 | [
"云服务",
"AWS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8591-1.html | 
*认识 71 个 AWS 云服务的术语 ! 通过了解 AWS 世界中使用的术语开始你的 AWS 云服务使用生涯 !*
AWS,即<ruby> 亚马逊 Web 服务 <rt> Amazon Web Services </rt></ruby>,是一个提供了一系列按使用计费的 web 服务的云平台。 它是迄今为止最为著名的云平台之一。由于其灵活性、有效性、弹性、可测量性和无须维护,所以有一些企业正逐步把他们的业务迁移到云端。 由于许多公司目前在使用这些服务,所以对于系统管理员和运维人员来说应该了解一下 AWS。
这篇文章旨在列出这些 AWS 提供的服务并且解释在 AWS 中出现的术语。
截止到目前为止(2017 年 3 月),AWS 提供了分为 17 组的共计 71 种服务:
### 计算型服务
这是一个提供了虚拟服务器配置功能的服务,即所谓的云计算。它提供了包括以下这一系列的服务。
1. EC2:EC2 代表弹性计算云。这种服务提供了可根据个人需求扩展的 [虚拟机][11]。
2. EC2 容器服务:其高性能,高可扩展性使其可在 EC2 集群环境中运行服务。
3. Lightsail:该服务使用户非常容易地启动和管理虚拟服务器(EC2)。
4. Elastic Beanstalk:该服务能够自动管理你的应用程序的容量配置、负载平衡、扩展以及健康监控从而减少你的管理压力。
5. Lambda:它允许你只在你需要的时候运行代码而不用去管理服务器。
6. Batch:它使用户能够以自定义的管理方式运行计算工作负载(批处理)。
### 存储型服务
它是一种云存储服务,即由 Amazon 提供的云存储设施。 该组服务包括:
1. S3:S3 代表简单存储服务(3 个 S)。 它给你提供了在线存储服务,你可随时从任何地方存储/检索任何数据。
2. EFS:EFS 代表弹性文件系统。 它是一个可以和 EC2 服务器一起使用的在线存储服务。
3. Glacier:它是一种低成本/低性能数据存储解决方案,主要针对存档或长期备份。
4. Storage Gateway:这种服务的接口会将你的内部应用程序(托管在 AWS 之外)与 AWS 存储连接。
### 数据库
AWS 还提供在其基础设施上托管数据库,以便客户可以利用亚马逊最先进的技术来获得更快/高效/安全的数据处理。 该组包括:
1. RDS:RDS 代表关系数据库服务。 用于在云上设置,操作和管理关系数据库。
2. DynamoDB:其 NoSQL 数据库提供了快速处理和高可扩展性。
3. ElastiCache:这是一种为你的 Web 应用程序管理内存缓存以便更快运行它们的方案 !
4. Redshift:它是一个巨大的(PB 级)的完全可升级的云端数据仓库服务。
### 网络 & 内容分发
由于 AWS 提供云端的 EC2 服务器,因此网络相关内容也将在出现在这里。 内容分发用于向位于最近位置的用户提供文件。 现如今有许多非常有名的加速网站。
1. VPC:VPC 代表虚拟私有云。 它是你自己的虚拟网络,是你的专用 AWS 帐户。
2. CloudFront:这是 AWS 的内容分发网络(CDN)服务。
3. Direct Connect:它是将数据中心/场所与 AWS 连接起来的网络方式,以提高吞吐量,降低网络成本,并避免由于基于互联网的连接而导致的连接问题。
4. Route 53:它是一个云端的域名系统的 DNS Web 服务。
### 迁移
它提供了一系列服务来帮助你实现本地服务到 AWS 的迁移工作。 这包括 :
1. Application Discovery Service:专门用于分析您的服务器、网络、应用程序以帮助/加速迁移的服务。
2. DMS:DMS 指的是数据库迁移服务。 它用于将数据从本地数据库迁移到 EC2 上托管的 RDS 或 DB。
3. Server Migration:也称为 SMS(服务器迁移服务)是一种无代理服务,将您的工作负载从本地移动到 AWS。
4. Snowball: 当你想要使用物理存储设备(而不是基于互联网/基于网络的传输)将大量数据传入/迁出 AWS 时,你应该使用它。
### 开发者工具
顾名思义, 这是一系列帮助开发者简化在云端编码的服务。
1. CodeCommit:它是一个安全的、可扩展的、可管理的源代码管理服务,用于托管代码仓库。
2. CodeBuild:这是一个云端的代码生成器。主要用于执行、测试代码和构建部署软件包。
3. CodeDeploy:这是一个可在 AWS 服务器或本地进行自动化应用程序部署的部署服务。
4. CodePipeline:这个部署服务可以使编码人员可以在发布之前将其应用程序可视化。
5. X-Ray:它可以使用事件调用分析应用程序。
### 管理工具
这是一组可帮助你管理 AWS 上的 Web 服务的服务。
1. CloudWatch:监控你的 AWS 资源或应用程序的监控服务。
2. CloudFormation:基础设施即代码!以集体有序的方式管理 AWS 架构的方式。
3. CloudTrail:AWS 帐户的审计和合规工具。
4. Config : AWS 的资源清单、配置历史记录和配置更改通知,以实现安全性和治理。
5. OpsWorks:它可以自动化地配置,部署 EC2 或内部部署计算。
6. Service Catalog:创建和管理被批准在你/公司帐户中使用的 IT 服务目录。
7. Trusted Advisor:它的 AWS AI 可以通过审查你的 AWS 基础设施使你的 AWS 基础设施更好,更省钱。
8. Managed Service:提供持续的基础设施管理。
### 安全性、身份和合规
这是一组很重要的 AWS 服务以确保你的 AWS 空间的安全性。
1. IAM:IAM 即身份和访问管理,控制用户访问你的 AWS 资源和服务。
2. Inspector:自动安全评估可帮助你在 AWS 上的应用安全和合规。
3. Certificate Manager:为 AWS 应用程序提供,管理和部署 SSL / TLS 证书。
4. Directory Service:相当于 AWS 的 Microsoft Active Directory。
5. WAF & Shield:WAF 即 Web 应用防火墙。 监控和控制对 CloudFront 或负载均衡器上的内容的访问。
6. Compliance Reports:AWS 基础设施空间的合规报告,以确保您的应用程序符合您的策略。
### 数据分析
AWS 空间的数据分析服务,以帮助您查看、计划和对帐户中的事件采取行动。
1. Athena:它是一个基于 SQL 查询的服务,用于分析 S3 存储的数据。
2. EMR:EMR 的全写是 Elastic Map Reduce。 是一个主要用于大数据处理和分析的服务。
3. CloudSearch:AWS 在应用和服务中的搜索功能。
4. Elasticsearch Service:它可以创建一个域并在 AWS Cloud 中部署、操作和扩展 Elasticsearch 集群。
5. Kinesis:这种服务可以实现实时的大量流数据处理。
6. Data Pipeline:它可以帮助我们在不同的 AWS 服务之间实现数据迁移。
7. QuickSight:收集、分析和呈现 AWS 的业务数据。
### 人工智能
AWS 的 AI!
1. Lex:它可以帮助我们在一些使用语音和文本的应用中构建会话界面。
2. Polly:这是一个提供文字到语音转换的服务。
3. Rekognition:使您能够将图像分析添加到应用程序。
4. Machine Learning:它具有学习数据中的模式的算法。
### 物联网
这个服务保证了 AWS 在不同设备上的高可用性。
1. AWS IoT:它使联网硬件设备与 AWS 的应用程序能够交互。
### 游戏开发
顾名思义,这个服务旨在游戏开发。
1. Amazon GameLift:该服务旨在部署、管理用于会话的多人游戏的专用游戏服务器。
### 移动服务
这是一组主要针对手持设备的服务。
1. Mobile Hub:帮助您创建移动应用的后台功能并将其集成到移动应用。
2. Cognito:在连接了互联网设备上控制移动用户的身份验证和 AWS 的访问。
3. Device Farm:移动应用测试服务使你可以在 Android 上托管的真实手机上跨 Android、iOS 测试应用。
4. Mobile Analytics:在 AWS 上测量、跟踪和分析移动应用数据。
5. Pinpoint:针对性的推送通知和移动互动。
### 应用服务
这是一组可以和你在 AWS 上的应用一起使用的服务。
1. Step Functions:定义和使用应用程序中的各种功能。
2. SWF:SWF 代表简单的工作流服务。其云工作流程管理可帮助开发人员在应用程序生命周期的不同阶段进行协调和贡献。
3. API Gateway:帮助开发人员创建、管理和托管 API。
4. Elastic Transcoder:帮助开发人员将媒体文件转换为在各种设备上可以播放的格式。
### 消息
AWS 中的通知和消息服务。
1. SQS:SQS 表示简单队列服务。完全管理的消息队列服务,用于在 AWS 中的服务和应用之间进行通信。
2. SNS:SNS 代表简单通知服务。 为 AWS 用户推送通知服务,提醒他们有关其在 AWS 空间中的服务。
3. SES:SES 代表简单电子邮件服务。 这是 AWS 为自己的客户提供高性价比的电子邮件服务。
### 企业生产率
一组帮你提高业务生产率的服务。
1. WorkDocs:协同文件共享、存储和编辑服务。
2. WorkMail:安全的商务邮件、日程服务。
3. Amazon Chime:在线的企业会议!
### 桌面和应用程序流式传输
实现桌面应用程序通过云端进行流传输。
1. WorkSpaces:完全管理且安全的云计算服务。
2. AppStream 2.0:来自云端的流式桌面应用。
(题图:rackaid.com)
---
via: <http://kerneltalks.com/virtualization/aws-cloud-terminology/>
作者:[Shrikant Lavhate](http://kerneltalks.com/virtualization/aws-cloud-terminology/) 译者:[chenxinlong](https://github.com/chenxinlong) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 302 | Found | null |
8,592 | 如何从参与开源项目的过程中获取自信 | https://opensource.com/article/17/1/3-ways-improve-your-confidence | 2017-06-10T08:59:00 | [
"自信",
"开源项目"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8592-1.html | 
随着大脑的发育,你渐渐学会了这世上什么事情可以/应该做,以及什么事情不能/不应该做。你所有的行为都受到周围大众的影响,很多时候,阻碍你参与某事的原因就是你缺乏自信。
纵观我们的生活,我们都或多或少的受到了世俗和社会行为的“教条”影响。我们可能从小就被这样教育:演说家说的都是真理、CEO 都是有远见的、警察维护社会秩序,尊重别人代表着静听让人把话说完,如果人家说错了,你要看场合轻柔的指出来 —— 好吧,这有点复杂。
当你决心参与到开源项目之中去的时候,自信将扮演重要角色。开源社区有其固有的参与性。参与就相当于开源世界的流通货币,持有该货币的量取决于你的自信。你的参与性越高、技能越高、分享你的想法和简洁次数越多,你就越能通过自己的<ruby> 提交 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> commit </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>来改善某一个项目。所有这些都需要你有很强的信念 —— 你有值得分享的事情 —— 并且你会常常思考自己要做什么、分享什么。
这里不得不说说这样一个事实:我们每一个人都一些值得分享的事情。但是你要找出这个值得分享的事情是什么,以及在哪个位置分享它才能把这个分享推向最积极、最有意义的一面。
认真思考一下三点,这将增强你的自信,并能让你在开源社区中更容易取得进步。
### 没有人会站在你的角度来看待你
你要时刻谨记着:你是完全独立的个人,他人对你做出的评论就像是不存在一样,只有这样才能更好的获得自信。
我们都习惯了这样认知,周围的人都是根据我们的行为来做出评判的。这一习惯是学习如何更像社会群体一样生活的副产品。而且很可能在我们的童年,父母根据我们的行为设置的奖励机制时,这个习惯就根植我们心底。到了青春期,老师们对我们的表现来评价,给我们划分等级和分数,拿我们和身边的小伙伴对比。这样的动力和奖励机制给我们的大脑建立了一个包括自我反思在内的反馈回路。我们需要预测自己能否得到回报,并要为那些可能发生的事情做好应对。
现今的我们都有这样第一个疑惑:身边的人是如何看我的?然而,真相是多数人都不会花太多时间来对你进行正确客观的评价。我们所有人只是关注自己的回报,我们有自己热衷于某件事的的热情、有大量急待解决的问题。也有一些人忙于关心他们自己如何影响身边的人,他们并不会在身上花费时间。他们根本不会注意到你是否出错、大声谈话还是像他们的背景音乐一样。所有的那些疑惑都只是在你自己的脑海中而已,而非在其他任何人脑中。
我们需要被人们所接受的愿望也是人生意义的一部分,但是这类受我们所遇之人的一时兴起。这些人可能对我们缺乏全面认识,比如我们叫什么、我们来自哪里、形成我们认知的经历,等等。我们能否为人们所接受是一件不受我们自身控制的事情。但是,我们是可以通过与之交流来改变的。
在开源的社区化世界里,记住这一点是非常重要的:人们是不会过多的考虑你的感受的。因为你的同事和导师都在忙于其它项目或则社区成员。
一旦你认知了这一点,通过积极地沟通来热情拥抱这个世界吧。寻求帮助、告知他人你的需求、指出你的贡献、让人们知道你和他们在一起努力、你也是这个社区中的活跃分子。当人们向你靠拢 ——而非相反 —— 时,你的开源可信度和自信会得到极大的提高。
### 所有人都热衷于分享自己熟知的事情
任何成功的开源社区都是一个包含教和学的社区。为沐浴在开源中,你不仅需要用到自身的已有知识,还需要不断的吸收消化其他人提供课程中的知识。幸运的是,人们都普遍热衷于分享他们熟悉的事情。
思考一下,当他人问及你的观点时,你是什么感受。得知他人认可了你所说的观点,对你的本我和自我是多么美好的一件事。
在儿童期时,我们的大脑并没有那么发达,无法为我们容纳现实世界中大量的信息量。我们曾一度认为自己是世界的中心。在六岁以前,我们的认知一直在不断成长。在此期间,我们的父母会因我们哭泣而做出回应,周围的成年人都会满足我们要求。这会在我们心底形成自己在世界上最重要的证据。
我们的神经回路在此期间建立完成,我们的性格也在此期间形成。随着我们学会参与社会和城市的生活,我们逐渐的认识到自己并非世界的中心。然而,最初形成并深植我们心底那种意识并不会因此马上就消除掉。正确理解我们在整个社会氛围中的个人意识将有助于你与他人建立连接并融洽相处。
在团结协作中慢慢积累学习经验可以很好的磨练自己、发展自己社会关系和提高自身技能。想要进军开源的世界,不断地学习是不可或缺的。
那么,这些和自信有些什么关系呢?通过表明你重视他人的知识和付出,你提高的不仅是他们的自信,还有你自己的自信。那时你将会感到更加灵活。有些时候,你不得不承认自己也有不懂的地方。
自信的人也许会说“是的,我不知道”,但却不会因此而沮丧。
### 一分耕耘,一分收获
你一定听过“不懂装懂,永远是饭桶”。这样说吧,自信就像其他很多的心理现象。积极地提示自己:我很聪明、有趣、引人关注、极富天赋、健谈、是一个很好的伙伴、独一无二、知识面广、学习能力强、常常自省的思想者,或者是其他你想要具备的特质,久而久之你就会觉得自己就是这样的人。并且,如果这可以在你身上生效,在其他人身上也一样。。
我们把这个称为自我肯定。
此外,在开源的世界中,你是如何为人考虑、如何待人,那么反过来,他人也会是这样的。如果你想在开源贡献中获得成功,你就要有足够的自信来相信自己坚持的立场和事物,当然了,你要以一种可以让人接受的方式来表现,同时还要包容其他的意见和观点。领导者的标志就是,在生活中塑造他们想要看到的形象,而不管是否有他人模仿。
那么,你是否有其他增强自信的方法呢?记得在评论区告诉我们哦。
(题图:[Gabriel Kamener, Sown Together](https://www.flickr.com/photos/42647587@N06/) 原创,经 Jen Wike Huger 修改。)
---
作者简介:
Laura Hilliger - 艺术家、教育事业者、作家、技术专家。她是一个多媒体设计师和开发者、技术联络员、项目经理、一个开放且喜欢协作环境的网络黑客。她主张变革,目前为发展壮大绿色和平组织而辛勤工作。Alum @Mozilla,UC Berkeley,BAVC, Adobe。Twitter @epilepticrabbit 。
---
译者简介:
[GHLandy](http://GHLandy.com) —— <ruby> 欲得之,则为之奋斗。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> If you want it, work for it. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/1/3-ways-improve-your-confidence>
作者:[Laura Hilliger](https://opensource.com/users/laurahilliger) 译者:[GHlandy](https://github.com/GHlandy) 校对:[Bestony](https://github.com/Bestony)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | As your brain develops, you learn about what you can and should do in the world, and what you can't and shouldn't. Your actions are influenced by surroundings and norms, and many times what keeps you from participating is a lack of self-confidence.
Throughout our lives, we've been taught the "rules" in civil discourse and social behavior. We've been taught that that the speaker is notable, that the CEO has vision, that the teacher is the expert, that the police maintain control, that respect means being quiet and letting others have the floor, and if someone is wrong, gently speaking up, but only in certain situations—it's all a bit complicated.
When participating in open source, self-confidence plays a huge role. Open source communities are inherently participatory. Participation is a currency in the open source world and that currency is contingent on self-confidence. The more you participate, hone your skills, network, and share your ideas and insights, the more you are able to improve the projects you commit to. All of these things require the belief that you have something valuable to share, and guess what, you do.
Here's a truth: All of us have something valuable to share. Finding out what that thing is and where our sharing it makes the most positive impact is the point.
Reflecting on this list will help you develop your self-confidence and make forging ahead in the open source community easier.
## No one thinks about you as much as you think about yourself
Reminding yourself that you are in control and that the judgement of others is likely nonexistent can help you gain self-confidence.
We've been conditioned to understand that people around us are judging us for our actions. This conditioning is a byproduct of learning how to function as social creatures. Likely, it started in childhood when our parents implemented reward systems for how we acted. It continued into adolescence when teachers literally judged our performance and awarded grades and marks, comparing us to others. These systems of motivation and reward caused our brains to establish feedback loops that included self-reflection. We needed to determine if we would get the cookie and prepare ourselves for that eventuality.
Today, we wonder, "What does this person think about me?" because of this, but the secret is that most people don't spend much time judging you. All of us are thinking about our own cookies. We each have our own ambitions to follow and our own problems to solve. Other people are busy worrying about how they affect people around them, and they aren't paying much attention to you. They likely don't notice if you make mistakes or talk too loud or recede into the background. All the doubts you have about yourself are in your head, not in anyone else's.
Our desire to be accepted is part of what it means to be human, but acceptance comes at the whim of the person across from us. That person lacks the context of who we are, where we came from, the experiences that shaped us. we have no control. However, we can hope to influence this person through communication.
In the community-intense world of open source, remembering that people are not thinking about you is especially important. Expect that your peers and mentors are concerned with other projects or community members.
Once you acknowledge this, embrace the world of proactive communication. Ask for help, tell people what you need, and point out your contributions and remind people that you are there and that you are an active participant in an open community. Both your open source credibility and your self-confidence will improve when people start coming to you, instead of the other way around.
## People love to share what they know
Any successful open source community is a teaching and learning community. To get started in open source, not only do you need to be forthcoming with your own knowledge, you need to soak up the lessons other people have to offer. Fortunately, we humans love to share what we know.
Think about how you feel when someone else asks you for your opinion. Knowing that someone values what you have to say is like a shot of sugar to your Id and Ego.
As children, our physical brains are not developed enough for us to place ourselves into the larger context of the world and reality. We believe that we are the center of the universe. The majority of our cognitive function develops before we are six years old. During that time our parents respond to our cries and adults everywhere fulfill our desires. We are given evidence that we are the most important thing in the universe.
Our neural pathways are established during this time, and our egos develop. As we learn to participate in social and civic life, little by little we learn that we aren't the center of the world. However, the initial justifications our egos made don't fully vanish. Understanding the importance of the ego in our social atmospheres can help you connect and relate to people.
Working in collaboration and seeking out learning experiences will help you hone and develop both your social and technical skills. Constant learning is absolutely integral to advancing in the world of open source.
What does this have to do with confidence? Not only do you work to improve someone else's confidence by showing them that you value this person's knowledge and input, you develop your own. There will be a moment when you become more flexible. You will at some point admit you don't know something.
Confident people can say "I don't know" without an air of disappointment.
## You reap what you sow
You've heard the phrase "Fake it, 'til you make it"? Well, confidence is like many psychological phenomena. Actively telling yourself that you are smart, funny, interesting, talented, a good communicator, a good friend, unique, knowledgeable, a quick study, an introspective thinker, or whatever other aspect you want to be, will eventually result in you persuading yourself that this is true. And if it's true for you, it becomes true for other people.
Call it the practice of self-affirmation.
Additionally, in the world of open source how you think about and treat others is how they will think about and treat you. The Golden Rule is once again valid. If you want to be successful in open source, you have to be confident enough to stand up for what you believe in, but do so in a way that is welcoming and inclusive to other perspectives and opinions. The mark of a leader is someone who models the behaviors they want to see in the world, whether anyone else follows suit or not.
Do you have other ways to develop confidence? Let us know in the comments!
## 4 Comments |
8,593 | 更快的机器学习即将来到 Linux 内核 | http://www.infoworld.com/article/3196884/linux/faster-machine-learning-is-coming-to-the-linux-kernel.html | 2017-06-11T09:50:00 | [
"ML",
"GPU",
"HMM",
"机器学习"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8593-1.html |
>
> Linux 内核新增的异构内存管理将解锁加速 GPU 的新途径,并挖掘其它的机器学习硬件的潜能
>
>
>

一项开发了很久的内存管理技术将会给机器学习和其它 GPU 驱动的程序很大幅度的提升,而它也将在接下来的几个版本中进入 Linux 内核。
异构内存管理(HMM)可以允许设备驱动为在其自身内存管理下的进程镜像地址空间。正如红帽的开发者 Jérôme Glisse [所解释的](https://lkml.org/lkml/2017/4/21/872),这让像 GPU 这样的硬件设备可以直接访问进程内存,而不用花费复制带来的额外开销。它还不违反现代操作系统提供的内存保护功能。
一类会从 HMM 中获益最多的应用是基于 GPU 的机器学习。像 OpenCL 和 CUDA 这样的库能够从 HMM 中获得速度的提升。HMM 实现这个的方式和[加速基于 GPU 的机器学习](http://www.infoworld.com/article/3195437/machine-learning-analytics-get-a-boost-from-gpu-data-frame-project.html)相似,就是让数据留在原地,靠近 GPU 的地方,在那里直接操作数据,尽可能少地移动数据。
像这样的加速对于 CUDA(英伟达基于 GPU 的处理库)来说,只会有益于在英伟达 GPU 上的操作,这些 GPU 也是目前加速数据处理的主要硬件。但是,OpenCL 设计用来编写可以针对多种硬件的代码——CPU、GPU、FPGA 等等——随着这些硬件的成熟,HMM 能够提供更加广泛的益处。
要让 Linux 中的 HMM 处于可用状态还有一些阻碍。第一个是内核支持,在很长一段时间里都受到限制。[早在 2014](https://lwn.net/Articles/597289/)年,HMM 最初作为 Linux 内核补丁集提出,红帽和英伟达都是关键开发者。需要做的工作不少,但是开发者认为代码可以提交上去,也许接下来的几个内核版本就能把它包含进去。
第二个阻碍是显卡驱动支持,英伟达一直在自己单独做一些工作。据 Glisse 的说法,AMD 的 GPU 可能也会支持 HMM,所以这种特殊优化不会仅限于英伟达的 GPU。AMD 一直都在尝试提升它的 GPU 市场占有率,有可能会[将 GPU 和 CPU 整合](http://www.infoworld.com/article/3099204/hardware/amd-mulls-a-cpugpu-super-chip-in-a-server-reboot.html)到同一模具。但是,软件生态系统依然更青睐英伟达;要使其兑现,还需要更多的像 HMM 这样的中立项目,以及让 OpenCL 提供和 CUDA 相当的性能。
第三个阻碍是硬件支持,因为 HMM 的工作需要一项称作<ruby> 可重现页面故障 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> replayable page faults </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的硬件特性。只有英伟达的帕斯卡系列高端 GPU 才支持这项特性。从某些意义上来说这是个好消息,因为这意味着英伟达只需要提供单一硬件的驱动支持就能让 HMM 正常使用,工作量就少了。
一旦 HMM 到位,对于提供 GPU 实例的公有云提供商就会面临压力,他们需要[支持最新最好一代的 GPU](http://www.infoworld.com/article/3126076/artificial-intelligence/aws-machine-learning-vms-go-faster-but-not-forward.html)。这并不是仅仅将老款的开普勒架构显卡换成最新的帕斯卡架构显卡就行了,因为后续的每一代显卡都会更加优秀,像 HMM 这样的支持优化将提供战略优势。
(题图:Thinkstock)
---
via: <http://www.infoworld.com/article/3196884/linux/faster-machine-learning-is-coming-to-the-linux-kernel.html>
作者:[Serdar Yegulalp](http://www.infoworld.com/author/Serdar-Yegulalp/) 译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,595 | 教职人员是否可以运用维基百科教学? | https://opensource.com/article/17/1/Wiki-Education-Foundation | 2017-06-12T10:11:00 | [
"维基",
"维基教育"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8595-1.html | 
自从 2010 年,已经有 29000 个学生完成了 Wiki Ed 这一项目。他们在维基百科上添加了 2500 万词条,相当于 85000 页纸张的内容。这相当于最新出版的 Britannica 百科全书中全部词条的 66%。Wiki Ed 的学生们最积极的时候,他们贡献了维基百科上 10% 的内容, 极大地补充了贫乏的学术板块。
为了了解更多关于这个项目的信息,我联络了 LiAnna Davis -- Wiki Ed 项目的负责人。他极富热情地同意来回答我的问题。
提示:[Wiki 教育基金会 (Wiki Ed)](https://wikiedu.org/) 的平台是用自由软件搭建的,你可以在这里找到: [WikiEdu Dashboard GitHub](https://github.com/WikiEducationFoundation/WikiEduDashboard)。
**Wiki Ed 这一项目是如何启动的?说说你的背景以及你是如何参与进这个项目的。**
在2010年,[维基基金会](https://wikimediafoundation.org/wiki/Home)(简称 WMF,运营维基百科的非营利组织)注意到了一个趋势 -- 大学的教职人员如果本身也是维基词条的编辑者,会成功地将编辑维基词条作为一项任务交给了自己课堂里的学生。WMF 就此开展了一个试行项目试图解决这个问题:如果本身不编辑维基词条的教职人员支持课程中包含维基词条的编辑任务,他们是否可以通过维基百科实现教学呢?
我是这个团队的一员,在 2010 年被试行雇用,我对这个问题的回答是:“可以。” 在 2013年,WMF 将这个项目的美国分部和加拿大分部拆分,形成了一个新的非营利性组织 -- 维基教育基金会( Wiki Ed);自此我也从 WMF 到了Wiki Ed。自那以后我们便成为了一个独立组织,我们可以专注于这个项目并且将这个项目拓展开来 -- 起初 WMF 时期每年只有 75 个班级参与,而这个学期已经有 275 班级参与了 Wiki Ed。
**人们总是觉得大学生对科技相关的一切事物都很敏感,尤其是互联网,但是你们的网站上写道,“大学本科学生可能具有高科技敏感度,但这并不代表他们具有数字信息素养。” 你可以稍微解释一下这句话吗?**
仅仅因为一个人可以搞明白自己的 iPhone 如何使用不代表他们可以明辨他们在网上阅读的信息是否值得信赖。 [斯坦福的一项研究](https://sheg.stanford.edu/upload/V3LessonPlans/Executive%20Summary%2011.21.16.pdf) (“评估信息:公民在线推理的基石 November 22, 2016.”)在近期表明:学生们并不具有数字信息素养。然而,当学生们在撰写维基百科文章之时,他们必须这样。他们需要严格遵守维基百科的[可信来源](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Identifying_reliable_sources) 规范,这些规范明确了维基百科上的任何信息都必须注明来源,这些来源必须是独立的,而且是可以追溯的事实。对于很多学生,这样注明来源还是第一次,多数人之前仅仅是通过谷歌搜索话题或者注明他们亲眼所见的第一手资料来进行资料的检索和查证。他们需要理解哪些资料可靠,哪些资料不可靠,从而成为足够成熟的电子信息消费者。
**你想对那些声称“维基百科不是一个可靠的来源”的人说些什么?**
维基百科是一本百科全书,根据在词典中的定义,它是一个第三手资料。当学生们开始读本科的时候,他们应该学会参考一手和二手资料,而不是第三手资料,因此学生不应该,且不能引用维基百科的内容。但是维基百科在研究之初会是一个不错的选择,它可以给你对这个话题一个广泛的认识,并且帮你发现页面底部那些你可以参考的文章来源。就像我们所鼓励的:“不要引用!用你的语言写!”
>
> 这样做可以让学生们代入知识生产者的身份,而不是知识的消费者……
>
>
>
**一个教授在 Wiki Ed 项目中的参与是如何影响到他的学生的呢?**
通过运用维基百科教学,导师们可以给学生们提供有价值的媒体素养、批判性思维、线上交流以及写作能力,不论他们在毕业之后会继续选择科研或是加入工作大军,这些极富价值的品质和技能都能帮助他们成功。这样做可以让学生们代入知识生产者的身份,而不是知识的消费者,而且这可以给予他们一个真正在这个世界做出改变的机会,而不是学生们到了学期末便会抛之脑后的生硬习题。
我们正在积极鼓励新的班级在春季学期加入这个项目。感兴趣的教职人员可以点击 [维基教育基金会的教学页](https://teach.wikiedu.org/) 由此开始。
**一个教师会需要哪些职业素养来参与这个项目?学生又是需要哪些训练呢?**
当你在[维基教育基金会的教学页](http://teach.wikiedu.org/)上注册的时候,你会发现 Wiki Ed 为新加入的教职人员提供了如何运用维基百科实现教学的在线指南。我们还有为学生提供的一系列的在线训练,根据他们不同的任务自动分配不同的指南(例如,如果你希望你的学生在文章中插入图片,他们会得到一个如何插入编辑图片的教学单元,如果你不需要,他们便不会得到这个单元的指南)。在部分十几个学科中,我们还有特定的指南书展示了这几个学科的特定编辑方式。除此之外,我们还有熟练维基百科编辑的工作人员帮助回答学生和导师们的问题。我们的系统已经在逐步扩大;我们在这个秋季学期已经支持了超过 6300 个学生,并且已经适应了与没有维基编辑经验的教职人员合作,因此这样就保证了没有人会因为资历不够而无法参与。
**“<ruby> 访问学者 <rt> Visiting Scholars </rt></ruby>”这个项目是指?**
我们正在试着建立学术界和维基百科之间的联系,而鼓励运用维基百科教学的项目只是其中的一环。在“<ruby> 访问学者 <rt> Visiting Scholars </rt></ruby>”这一项目中,大学图书馆或者教学部门将公开他们的资料,并提供给一个缺乏资料的认证的维基百科编辑人员(被称作是“访问学者”)。通过大学这一渠道,“访问学者”们可以有机会使用这些资源来完善维基百科广泛领域中的文章。这是一个规模相对小却伟大的项目,因为我们花了很多时间来建立这样的联系,但是这些“学者”们都产出了许多真的很精彩的内容。
**你的合作伙伴有谁?他们的参与如何影响到你现在的成功呢,或者在未来将会如何呢?**
我们与那些将我们工作的价值看做对他们的学科的一种服务的学术机构合作。让我们面对这个现实:当人们想要获取关于一个话题的知识之时,他们不会去读那些同行审议过,并在这些机构发表的学术论文,他们会去维基百科。通过鼓励这些机构中的教职人员用维基百科教学,正可以完善维基百科的在这些学科中的内容和信息。我们的合作伙伴扩充了我们的潜在成员,并且让我们以合作身份大量完善了维基百科上特定学科的内容。
我们欢迎读者点击这个[支持我们](http://wikiedu.org/donate) 的页面通过捐赠来支持我们的工作。
(题图:opensource.com)
---
作者简介:
Don Watkins 是一个教育家,专注教育技术,创业家,开源提倡者。教育心理学硕士、教育领导力硕士、Linux 系统管理员、思科认证网络支持工程师、Virtual Box 虚拟化认证。关注他: @Don\_Watkins 。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/1/Wiki-Education-Foundation>
作者:Don Watkins 译者:[scoutydren](https://github.com/scoutydren) 校对:[Bestony](https://github.com/Bestony)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Since 2010, 29,000 students have completed the Wiki Ed program. They have added 25 million words to Wikipedia, or the equivalent of 85,000 printed pages of content. This is 66% of the total words in the last print edition of Encyclopedia Britannica. When Wiki Ed students are most active, they are contributing 10% of all the content being added to underdeveloped, academic content areas on Wikipedia.
Eager to learn more I contacted LiAnna Davis, director of Programs for Wiki Ed, who enthusiastically agreed to answer my questions.
Bonus: [Wiki Education Foundation (Wiki Ed)](https://wikiedu.org/)'s platform is built on free software; find it at [WikiEdu Dashboard GitHub](https://github.com/WikiEducationFoundation/WikiEduDashboard).
**How did Wiki Ed get started? Tell us a little bit about your background and how you got involved.**
In 2010, the [Wikimedia Foundation](https://wikimediafoundation.org/wiki/Home) (WMF, the nonprofit that runs Wikipedia) noticed a trend that university faculty who were also Wikipedia editors (Wikipedians) were successfully incorporating Wikipedia editing assignments into their classes. WMF created a pilot program to answer the question: Can non-Wikipedian faculty members teach with Wikipedia if they have enough support for the Wikipedia editing portion of the course?
I was part of the team hired in 2010 to work on the pilot and the answer we provided was a resounding "Yes." In 2013, the WMF spun off the American and Canadian versions of the program into a new nonprofit organization, the Wiki Education Foundation (Wiki Ed); I moved from WMF to Wiki Ed. Since we became our own organization, we've been able to focus on the program and grow its impact from 75 classes each year when the program was with WMF to 275 classes this term.
**People automatically assume that college students are savvy in all things tech related, especially the Internet, but your website says, "University undergraduates may be tech-savvy, but that doesn't always mean they're digitally literate." Can you explain that?**
Just because someone can figure out how to use their iPhone doesn't mean they can tell whether something they read online is trustworthy or not. As a [Stanford study](https://sheg.stanford.edu/upload/V3LessonPlans/Executive%20Summary%2011.21.16.pdf) ("Evaluating Information: The Cornerstone of Civic Online Reasoning November 22, 2016.") recently showed, students aren't very media literate. However, when students are writing Wikipedia articles, they have to be. They need to follow Wikipedia's [Reliable Source](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Identifying_reliable_sources) guideline, which says information on Wikipedia must be cited to a source that goes through some sort of fact checking, is independent, etc. For many students, such sourcing is the first time they've had to do more than just Google their topic and cite the first source they see. They need to understand which sources are reliable and which aren't, and they become more digitally literate consumers of information.
**What do you say to those who make the statement: "Wikipedia isn't a reliable source."**
Wikipedia is an encyclopedia, which is by definition a tertiary source. By the time students reach undergrad, they should be consulting primary and secondary sources, not tertiary sources, so no, students shouldn't be citing Wikipedia. But it's a great place to start your research, to give yourself a broad overview of a subject, and discover links to sources at the bottom of the article that you can consult. As we like to say, "Don't cite it! Write it!"
**How can a professor's involvement in Wiki Ed change a student's learning experience higher education?**
By teaching with Wikipedia, instructors provide students with valuable media literacy, critical thinking, online communications, and writing skills that they need to succeed, whether they continue in academia or enter the workforce upon graduation. It puts students into the position of producers of knowledge, not just consumers of knowledge, and gives them a meaningful assignment that actually makes a difference in the world, not just a rote academic exercise that gets thrown away at the end of a term.
We're actively onboarding new classes for the spring term. Interested faculty should visit [the Wikipedia Education Foundation's Teach page](https://teach.wikiedu.org/) to get started.
**What staff development is needed for a teacher to participate? How much training is necessary for students?**
When you sign up on [the Wikipedia Education Foundation's Teach page](http://teach.wikiedu.org/), Wiki Ed provides an online orientation for new faculty on the basics of how to teach with Wikipedia. We also have a series of online training modules that we automatically assign to students based on the specific assignment (for example, if you want your students to add images, they'll get a module on images; if you don't, they won't). In a dozen disciplines, we also have specific guidebooks showing how to edit in that topic area on Wikipedia. In addition, we have staff who are experienced Wikipedia editors who can help answer students' and instructors' questions. Our system is quite extensive now; we supported more than 6,300 students this fall term, and we're used to working with faculty who have no experience editing Wikipedia, so that shouldn't keep anyone from doing the assignment.
**What are Visiting Scholars?**
Our program to encourage teaching with Wikipedia isn't the only connection we make between Wikipedia and academia. In the Visiting Scholars program, a university library or department will open up access to their collection to an established Wikipedia editor (called a "Visiting Scholar") who is lacking sources. Using this university login, the Visiting Scholar will have access to sources, so they can improve articles in broad subject areas of interest to the institution. It's a small but mighty program, because it takes a lot of work to get set up, but the Scholars produce a lot of truly fabulous content on Wikipedia.
**Who are your partners and how important is their involvement to your success now and in the future?**
We partner with academic associations who see the value in our work as a service to their discipline. Let's face it: when people want information about a topic, they don't go read the peer-reviewed journal articles published by those associations, they go to Wikipedia. By encouraging faculty in these associations to teach with Wikipedia, they're improving information on Wikipedia in those subject matters. Our partners enable us to reach large numbers of potential new faculty members, and enable us to dramatically improve content in a specific subject area through a partnership.
We welcome donations at [on our Support Us page](http://wikiedu.org/donate) if your readers want to support our work.
## 5 Comments |
8,596 | Linux 系统中修复 SambaCry 漏洞(CVE-2017-7494) | https://www.tecmint.com/fix-sambacry-vulnerability-cve-2017-7494-in-linux/ | 2017-06-10T09:57:38 | [
"WannaCry",
"SambaCry",
"病毒",
"samba"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8596-1.html | 
Samba 很久以来一直是为 \*nix 系统上的 Windows 客户端提供共享文件和打印服务的标准。家庭用户,中型企业和大型公司都在使用它,它作为最佳解决方案在多种操作系统共存的环境中脱颖而出。
由于广泛使用的工具很可能发生这种情况,大多数 Samba 安装都面临着可能利用已知漏洞的攻击的风险,这个漏洞直到 WannaCry 勒索软件攻击的新闻出来之前都被认为是不重要的。
在本文中,我们将解释这个 Samba 漏洞是什么以及如何保护你负责的系统。根据你的安装类型(从仓库或者源码),你需要采取不同的方法。
如果你目前有在任何环境中使用 Samba 或者知道有人在使用,请继续阅读!
### 漏洞
过时和未修补的系统容易受到远程代码执行漏洞的攻击。简单来说,这意味着访问可写共享的人可以上传一段任意代码,并使用服务器中的 root 权限执行该代码。
这个问题在 Samba 网站上被描述为 [CVE-2017-7494](https://www.samba.org/samba/security/CVE-2017-7494.html),并且已知会影响 Samba v3.5(2010 年 3 月初发布)及以后版本。由于与 WannaCry 有相似之处,它被非官方地被命名为 SambaCry:它们均针对 SMB 协议,并且可能是蠕虫病毒 - 这可能导致其从一个系统传播到另一个系统中。
Debian、Ubuntu、CentOS 和 Red Hat 已采取快速的行动来保护它们的用户,并为其支持的版本发布了补丁。另外,还提供了不受支持的安全临时解决方案。
### 更新 Samba
如先前提到的那样,根据你之前安装的方法有两种方式更新:
#### 如果你从发行版的仓库中安装的 Samba
让我们看下在这种情况下你需要做什么:
**在 Debian 下修复 SambaCry**
添加下面的行到你的源列表中(`/etc/apt/sources.list`)以确保 apt 能够获得最新的安全更新:
```
deb http://security.debian.org stable/updates main
deb-src http://security.debian.org/ stable/updates main
```
接下来,更新可用的软件包:
```
# aptitude update
```
最后,确保 samba 软件包的版本符合漏洞修复的版本(见 [CVE-2017-7494](https://security-tracker.debian.org/tracker/CVE-2017-7494)):
```
# aptitude show samba
```

*在 Debian 中修复 SambaCry*
**在 Ubuntu 中修复 SambaCry**
要开始修复,如下检查新的可用软件包并更新 Samba 软件包:
```
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install samba
```
已经修复 CVE-2017-7494 的 Samba 版本有下面这些:
* 17.04: samba 2:4.5.8+dfsg-0ubuntu0.17.04.2
* 16.10: samba 2:4.4.5+dfsg-2ubuntu5.6
* 16.04 LTS: samba 2:4.3.11+dfsg-0ubuntu0.16.04.7
* 14.04 LTS: samba 2:4.3.11+dfsg-0ubuntu0.14.04.8
最后,运行下面命令验证你的 Ubuntu 已经安装了正确的版本。
```
$ sudo apt-cache show samba
```
**在 CentOS/RHEL 7 中修复 SambaCry**
在 EL 7 中打过补丁的 Samba 版本是 samba-4.4.4-14.el7\_3。要安装它,这些做:
```
# yum makecache fast
# yum update samba
```
像先前那样,确保你已经安装了打补丁的 Samba 版本:
```
# yum info samba
```

*在 CentOS 中修复 SambaCry*
旧支持的 CentOS 以及 RHEL 更老的版本也有修复。参见 [RHSA-2017-1270](https://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2017-1270.html) 获取更多。
#### 如果你从源码安装的 Samba
注意:下面的过程假设你先前从源码构建的 Samba。强烈建议你在部署到生产服务器之前先在测试环境尝试。
此外,开始之前确保你备份了 `smb.conf` 文件。
在这种情况下,我们也会从源码编译并更新 Samba。然而在开始之前,我们必须先确保安装了所有的依赖。注意这也许会花费几分钟。
**在 Debian 和 Ubuntu 中:**
```
# aptitude install acl attr autoconf bison build-essential \
debhelper dnsutils docbook-xml docbook-xsl flex gdb krb5-user \
libacl1-dev libaio-dev libattr1-dev libblkid-dev libbsd-dev \
libcap-dev libcups2-dev libgnutls28-dev libjson-perl \
libldap2-dev libncurses5-dev libpam0g-dev libparse-yapp-perl \
libpopt-dev libreadline-dev perl perl-modules pkg-config \
python-all-dev python-dev python-dnspython python-crypto xsltproc \
zlib1g-dev libsystemd-dev libgpgme11-dev python-gpgme python-m2crypto
```
**在 CentOS 7 或相似的版本中:**
```
# yum install attr bind-utils docbook-style-xsl gcc gdb krb5-workstation \
libsemanage-python libxslt perl perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker \
perl-Parse-Yapp perl-Test-Base pkgconfig policycoreutils-python \
python-crypto gnutls-devel libattr-devel keyutils-libs-devel \
libacl-devel libaio-devel libblkid-devel libxml2-devel openldap-devel \
pam-devel popt-devel python-devel readline-devel zlib-devel
```
停止服务(LCTT 译注:此处不必要):
```
# systemctl stop smbd
```
下载并解压源码(在写作时 4.6.4 是最新的版本):
```
# wget https://www.samba.org/samba/ftp/samba-latest.tar.gz
# tar xzf samba-latest.tar.gz
# cd samba-4.6.4
```
出于了解信息的目的,用以下命令检查可用的配置选项。
```
# ./configure --help
```
如果你在先前的版本的构建中有使用到一些选项,你或许可以在上面命令的返回中包含一些选项,或者你可以选择使用默认值:
```
# ./configure
# make
# make install
```
最后重启服务。
```
# systemctl restart smbd
```
并验证你正在使用的是更新后的版本:
```
# smbstatus --version
```
这里返回的应该是 4.6.4。
### 其它情况
如果你使用的是不受支持的发行版本,并且由于某些原因无法升级到最新版本,你或许要考虑下面这些建议:
* 如果 SELinux 是启用的,你是处于保护之下的!
* 确保 Samba 共享是用 `noexec` 选项挂载的。这会阻止二进制文件从被挂载的文件系统中执行。
还有将:
```
nt pipe support = no
```
添加到 `smb.conf` 的 `[global]` 字段中。你或许要记住,根据 Samba 项目,这“或许禁用 Windows 客户端的某些功能”。
重要:注意 `nt pipe support = no` 选项会禁用 Windows 客户端的共享列表。比如:当你在一台 Samba 服务器的 Windows Explorer 中输入 `\\10.100.10.2\` 时,你会看到 “permission denied”。Windows 客户端不得不手动执行共享,如 `\\10.100.10.2\share_name` 来访问共享。
### 总结
在本篇中,我们已经描述了 SambaCry 漏洞以及如何减轻影响。我们希望你可以使用这个信息来保护你负责的系统。
如果你有关于这篇文章的任何提问以及评论,欢迎使用下面的评论栏让我们知道。
---
作者简介:
Gabriel Cánepa 是一名 GNU/Linux 系统管理员,阿根廷圣路易斯 Villa Mercedes 的 web 开发人员。他为一家国际大型消费品公司工作,在日常工作中使用 FOSS 工具以提高生产力,并从中获得极大乐趣。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/fix-sambacry-vulnerability-cve-2017-7494-in-linux/>
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa](https://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Samba has long been the standard for providing shared file and print services to Windows clients on *nix systems. Used by home users, mid-size businesses, and large companies alike, it stands out as the go-to solution in environments where different operating systems coexist.
As it sadly happens with broadly-used tools, most Samba installations are under risk of an attack that may exploit a known vulnerability, which was not considered to be serious until the **WannaCry** ransomware attack hit the news not too long ago.
In this article, we will explain what this Samba vulnerability is and how to protect the systems you are responsible for against it. Depending on your installation type (from repositories or from source), you will need to take a different approach to do it.
If you are currently using Samba in any environment or know someone who does, read on!
### The Vulnerability
Outdated and unpatched systems are vulnerable to a remote code execution vulnerability. In simple terms, this means that a person with access to a writeable share can upload a piece of arbitrary code and execute it with root permissions in the server.
The issue is described in the Samba website as [CVE-2017-7494](https://www.samba.org/samba/security/CVE-2017-7494.html) and is known to affect Samba versions 3.5 (released in early March 2010) and onwards. Unofficially, it has been named **SambaCry** due to its similarities with **WannaCry**: both target the SMB protocol and are potentially wormable – which can cause it to spread from system to system.
Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS and Red Hat have taken rapid action to protect its users and have released patches for their supported versions. Additionally, security workarounds have also been provided for unsupported ones.
### Updating Samba
As mentioned earlier, there are two approaches to follow depending on the previous installation method:
If you installed Samba from your distribution’s repositories.
Let’s take a look at what you need to do in this case:
#### Fix Sambacry in Debian
Make sure [apt](https://www.tecmint.com/apt-advanced-package-command-examples-in-ubuntu/) is set to get the latest security updates by adding the following lines to your sources list (**/etc/apt/sources.list**):
deb http://security.debian.org stable/updates main deb-src http://security.debian.org/ stable/updates main
Next, update the list of available packages:
# aptitude update
Finally, make sure the version of the samba package matches the version where the vulnerability has been fixed (see [CVE-2017-7494](https://security-tracker.debian.org/tracker/CVE-2017-7494)):
# aptitude show samba
#### Fix Sambacry in Ubuntu
To begin, check for new available packages and update the samba package as follows:
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install samba
The Samba versions where the fix for **CVE-2017-7494** has already been applied are the following:
- 17.04:
**samba 2:4.5.8+dfsg-0ubuntu0.17.04.2** - 16.10:
**samba 2:4.4.5+dfsg-2ubuntu5.6** - 16.04 LTS:
**samba 2:4.3.11+dfsg-0ubuntu0.16.04.7** - 14.04 LTS:
**samba 2:4.3.11+dfsg-0ubuntu0.14.04.8**
Finally, run the following command to verify that your Ubuntu box now has the right Samba version installed.
$ sudo apt-cache show samba
#### Fix Sambacry on CentOS/RHEL 7
The patched Samba version in **EL 7** is **samba-4.4.4-14.el7_3**. To install it, do
# yum makecache fast # yum update samba
As before, make sure you have now the patched Samba version:
# yum info samba
Older, still supported versions of CentOS and RHEL have available fixes as well. Check [RHSA-2017-1270](https://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2017-1270.html) to find out more.
##### If you installed Samba from source
**Note**: The following procedure assumes that you have previously built Samba from source. You are highly encouraged to try it out extensively in a testing environment BEFORE deploying it to a production server.
Additionally, make sure you back up the **smb.conf** file before you start.
In this case, we will compile and update Samba from source as well. Before we begin, however, we must ensure all the dependencies are previously installed. Note that this may take several minutes.
#### In Debian and Ubuntu:
# aptitude install acl attr autoconf bison build-essential \ debhelper dnsutils docbook-xml docbook-xsl flex gdb krb5-user \ libacl1-dev libaio-dev libattr1-dev libblkid-dev libbsd-dev \ libcap-dev libcups2-dev libgnutls28-dev libjson-perl \ libldap2-dev libncurses5-dev libpam0g-dev libparse-yapp-perl \ libpopt-dev libreadline-dev perl perl-modules pkg-config \ python-all-dev python-dev python-dnspython python-crypto xsltproc \ zlib1g-dev libsystemd-dev libgpgme11-dev python-gpgme python-m2crypto
#### In CentOS 7 or similar:
# yum install attr bind-utils docbook-style-xsl gcc gdb krb5-workstation \ libsemanage-python libxslt perl perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker \ perl-Parse-Yapp perl-Test-Base pkgconfig policycoreutils-python \ python-crypto gnutls-devel libattr-devel keyutils-libs-devel \ libacl-devel libaio-devel libblkid-devel libxml2-devel openldap-devel \ pam-devel popt-devel python-devel readline-devel zlib-devel
Stop the service:
# systemctl stop smbd
Download and untar the source (with 4.6.4 being the latest version at the time of this writing):
# wget https://www.samba.org/samba/ftp/samba-latest.tar.gz # tar xzf samba-latest.tar.gz # cd samba-4.6.4
For informative purposes only, check the available configure options for the current release with.
# ./configure --help
You may include some of the options returned by the above command if they were used in the previous build, or you may choose to go with the default:
# ./configure # make # make install
Finally, restart the service.
# systemctl restart smbd
and verify you’re running the updated version:
# smbstatus --version
which should return **4.6.4**.
### General Considerations
If you are running an unsupported version of a given distribution and are unable to upgrade to a more recent one for some reason, you may want to take the following suggestions into account:
- If SELinux is enabled, you are protected!
- Make sure Samba shares are mounted with the noexec option. This will prevent the execution of binaries residing on the mounted filesystem.
Add,
nt pipe support = no
to the [global] section of your **smb.conf** file and restart the service. You may want to keep in mind that this “may disable some functionality in Windows clients”, as per the Samba project.
**Important**: Be aware that the option “**nt pipe support = no**” would disable shares listing from Windows clients. Eg: When you type **\\10.100.10.2\** from Windows Explorer on a samba server you would get a permission denied. Windows clients would have to manually specify the share as **\\10.100.10.2\share_name** to access the share.
##### Summary
In this article, we have described the vulnerability known as SambaCry and how to mitigate it. We hope that you will be able to use this information to protect the systems you’re responsible for.
If you have any questions or comments about this article, feel free to use the form below to let us know.
Hi ,
I’m trying to update samba based on your article. But after ./configure command i faced an error:
/root/samba-4.6.5/source4/lib/tls/wscript:51: error: Building the AD DC requires GnuTLS (eg libgnutls-dev, gnutls-devel) for ldaps:// support and for the BackupKey protocol
Best regard,
ReplyThe error is self-explanatory. You will also need to install one of the GnuTLS packages.
ReplyIn RHEL6, samba version fixed is 3.6.23?
ReplyIt depends on what Samba version you’re currently using in RHEL 6. If you’re using Samba 3, yes, the fixed version is 3.6.23. If you are using Samba 4, then it is samba4-4.2.10-10.el6_9. More details under the
ReplyRed Hat Security Erratasection here: https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/cve-2017-7494.Thank’s @Matei
ReplyBe aware that the option “
Replynt pipe support = no” would disable shares listing from Windows clients. Eg: When you type\\10.100.10.2\from Windows Explorer on a samba server you would get a permission denied. Windows clients would have to manually specify the share as\\10.100.10.2\share_nameto access the share.Matei,
ReplyYou’re spot on.
@Ravi,
Can you add Matei’s comment in the last paragraph, right above the Summary section?
@Gabriel and @Matei,
Added the note before the
Summaryline in the article.Thanks @Matei
Reply |
8,598 | 安卓编年史(21):安卓 4.2,果冻豆——全新 Nexus 设备,全新平板界面 | http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/22/ | 2017-06-10T20:19:00 | [
"Android",
"安卓编年史"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8598-1.html | 
### 安卓 4.2,果冻豆——全新 Nexus 设备,全新平板界面
安卓平台成熟的脚步越来越快,谷歌也将越来越多的应用托管到 Play 商店,需要通过系统更新来更新的应用越来越少。但是不间断的更新还是要继续的,2012 年 11 月,安卓 4.2 发布。4.2 还是叫做“果冻豆”,这个版本主要是一些少量变动。

*LG 生产的 Nexus 4 和三星生产的 Nexus 10。 [Google/Ron Amadeo 供图]*
和安卓 4.2 一同发布的还有两部旗舰设备,Nexus 4 和 Nexus 10,都由谷歌直接在 Play 商店出售。Nexus 4 使用了 Nexus 7 的策略,令人惊讶的低价和高质量,并且无锁设备售价 300 美元。Nexus 4 有一个 4 核 1.5GHz 骁龙 S4 Pro 处理器,2GB 内存以及 1280×768 分辨率 4.7 英寸 LCD 显示屏。谷歌的新旗舰手机由 LG 生产,并和制造商一起将关注点转向了材料和质量。Nexus 4 有着正反两面双面玻璃,这会让你爱不释手,它是有史以来触感最佳的安卓手机之一。Nexus 4 最大的缺点是没有 LTE 支持,那时候大部分手机,包括 Version Galaxy Nexus 都有更快的基带。但 Nexus 4 的需求仍大大超出了谷歌的预料——发布当日大量的流量拖垮了 Play 商店网站。手机在一小时之内销售一空。
Nexus 10 是谷歌的第一部 10 英寸 Nexus 平板。该设备的亮点是 2560×1600 分辨率的显示屏,在这个等级上是分辨率最高的。这背后是双核 1.7GHz Cortex A15 处理器和 2GB 内存的强力支持。随着时间一个月一个月地流逝,Nexus 10 似乎逐渐成为了第一部也是最后一部 10 英寸 Nexus 平板。通常这些设备每年都升级,但 Nexus 10 至今面世 16 个月了,可预见的未来还没有新设备的迹象。谷歌在小尺寸的 7 英寸平板上做得很出色,它似乎更倾向于让[像三星](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/01/hands-on-with-samsungs-notepro-and-tabpro-new-screen-sizes-and-magazine-ui/)这样的合作伙伴探索更大的平板家族。

*新的锁屏,壁纸,以及时钟小部件设计。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
4.2 为锁屏带来了很多变化。文字居中,并且对小时使用了较大的字重,对分钟使用了较细的字体。锁屏现在是分页的,可以自定义小部件。锁屏不仅仅是一个简单的时钟,用户还可以将其替换成其它小部件或者添加额外的页面和更多的小部件。

*锁屏的添加小部件页面,小部件列表,锁屏上的 Gmail 部件,以及滑动到相机。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
锁屏现在就像是一个精简版的主屏幕。页面轮廓会显示在锁屏的左右两侧来提示用户可以滑动到有其他小部件的页面。向左滑动页面会显示一个中间带有加号的简单空白页面,点击加号会打开兼容锁屏的小部件列表。锁屏每个页面限制一个小部件,将小部件向上或向下拖动可以展开或收起。最右侧的页面保留给了相机——一个简单的滑动就能打开相机界面,但是你没办法滑动回来。

*新的快速设置面板以及内置应用集合。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
4.2 最大的新增特性之一就是“快速设置”面板。安卓 3.0 为平板引入了快速改变电源设置的途径,4.2 终于将这种能力带给了手机。通知中心右上角加入了一枚新图标,可以在正常的通知列表和新的快速设置之间切换。快速设置提供了对屏幕亮度、网络连接、电池以及数据用量更加快捷的访问,而不用打开完整的设置界面。安卓 4.1 中顶部的设置按钮移除掉了,快速设置中添加了一个按钮来替代它。
应用抽屉和 4.2 中的应用阵容有很多改变。得益于 Nexus 4 更宽的屏幕横纵比(5:3,Galaxy Nexus 是 16:9),应用抽屉可以显示一行五个应用图标的方阵。4.2 将自带的浏览器替换为了 Google Chrome,自带的日历换成了 Google Calendar,它们都带来了新的图标设计。时钟和相机应用在 4.2 中经过了重制,新的图标也是其中的一部分。“Google Settings”是个新应用,用于提供对系统范围内所有存在的谷歌账户设置的快捷方式,它有着和 Google Search 和 Google+ 图标一致的风格。谷歌地图拥有了新图标,谷歌纵横,以往是谷歌地图的一部分,作为对 Google+ location 的支持在这个版本退役。

*浏览器替换为 Chrome,带有全屏取景器的新相机界面。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
原来的自带浏览器在一段时间内对 Chrome 的模仿上下了不少功夫——它引入了许多 Chrome 的界面元素,许多 Chrome 的特性,甚至还使用了 Chrome 的 javascript 引擎——但安卓 4.2 来临的时候,谷歌认为安卓版的 Chrome 已经准备好换下这个模仿者了。表面上看起来没有多大不同;界面看起来不一样,而且早期版本的 Chrome 安卓版滚动起来没有原浏览器顺畅。不过从深层次来说,一切都不一样。安卓的主浏览器开发现在由 Google Chrome 团队负责,而不是作为安卓团队的子项目存在。安卓的默认浏览器从绑定安卓版本发布、停滞不前的应用变成了不断更新的 Play 商店应用。现在甚至还有一个每个月接收一些更新的 beta 通道。
相机界面经过了重新设计。它现在完全是个全屏应用,显示摄像头的实时图像并且在上面显示控制选项。布局审美和安卓 1.5 的[相机设计](http://cdn.arstechnica.net/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/device-2013-12-26-11016071.png)有很多共同之处:带对焦的最小化的控制放置在取景器显示之上。中间的控制环在你长按屏幕或点击右下角圆形按钮的时候显示。你的手指保持在屏幕上时,你可以滑动来选择环上的选项,通常是展开进入一个子菜单。在高亮的选项上释放手指选中它。这灵感很明显来自于安卓 4.0 浏览器中的快速控制,但是将选项安排在一个环上意味着你的手指几乎总会挡住一部分界面。

*时钟应用,从一个只有两个界面的应用变成功能强大,实用的应用。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
时钟应用经过了完整的改造,从一个简单的两个界面的闹钟,到一个世界时钟、闹钟、定时器,以及秒表俱全。时钟应用的设计和谷歌之前引入的完全不同,有着极简审美和红色高亮。它看起来像是谷歌的一个试验。甚至是几个版本之后,这个设计语言似乎也仅限于这个应用。
时钟的时间选择器是经过特别精心设计的。它显示一个简单的数字盘,会智能地禁用会导致无效时间的数字。设置闹钟时间也不能在没有明确选择 AM 和 PM 时设置,永远地解决了不小心将 9am 的闹钟设置成 9pm 的问题。

*平板的新系统界面使用了延展版的手机界面。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
安卓 4.2 中最有争议的改变是平板界面,从单独一个统一的底部系统栏变成带有顶部状态栏和底部系统栏的双栏设计。新设计统一了手机和平板的界面,但批评人士说将手机界面延展到 10 英寸的横向平板上是浪费空间。因为导航按键现在拥有了整个底栏,所以他们像手机界面那样被居中。

*平板上的多用户,以及新的手势键盘。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
在平板上,安卓 4.2 带来了多用户支持。在设置里,新增了“用户”部分,你可以在这里管理一台设备上的用户。设置在每个用户账户内完成,安卓会给每个用户保存单独的设置,主屏幕,应用以及应用数据。
4.2 还添加了有滑动输入能力的键盘。用户可以将手指一直保持在屏幕上,按顺序在字母按键上滑动来输入,而不用像以前那样一个一个字母单独地输入。
---

[Ron Amadeo](http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo) / Ron是Ars Technica的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。[@RonAmadeo](https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo)
---
via: <http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/22/>
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,599 | 安卓编年史(22):周期外更新——谁需要一个新系统? | http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/23/ | 2017-06-12T10:18:00 | [
"安卓编年史",
"Android"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8599-1.html | 

*Play 商店又一次重新设计!这一版非常接近现在的设计,卡片结构让改变布局变得易如反掌。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
### 周期外更新——谁需要一个新系统?
在安卓 4.2 和安卓 4.3 之间,谷歌进行了一次周期外更新,显示了有多少安卓可以不用经过费力的 OTA 更新而得到改进。得益于[谷歌 Play 商店和 Play 服务](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/09/balky-carriers-and-slow-oems-step-aside-google-is-defragging-android/),这些更新可以在不更新任何系统核心组件的前提下送达。
2013 年 4 月,谷歌发布了谷歌 Play 商店的一个主要设计改动。就如同在这之后的大多数重新设计,新的 Play 商店完全接受了 Google Now 审美,即在灰色背景上的白色卡片。操作栏基于当前页面内容部分更改颜色,由于首屏内容以商店的各部分为主,操作栏颜色是中性的灰色。导航至内容部分的按钮指向热门付费,在那下面通常是一块促销内容或一组推荐应用。

*独立的内容部分有漂亮的颜色。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
新的 Play 商店展现了谷歌卡片设计语言的真正力量,在所有的屏幕尺寸上能够拥有响应式布局。一张大的卡片能够和若干小卡片组合,大屏幕设备能够显示更多的卡片,而且相对于拉伸来适应横屏模式,可以通过在一行显示更多卡片来适应。Play 商店的内容编辑们也可以自由地使用卡片布局;需要关注的大更新可以获得更大的卡片。这个设计最终会慢慢渗透向其它谷歌 Play 内容应用,最后拥有一个统一的设计。

*Hangouts 取代了 Google Talk,现在仍由 Google+ 团队继续开发。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
Google I/O,谷歌的年度开发者会议,通常会宣布一个新的安卓版本。但是 2013 年的会议,谷歌只是发布了一些改进而没有系统更新。
谷歌宣布的大事件之一是 Google Talk 的更新,谷歌的即时消息平台。在很长一段时间里,谷歌随安卓附带四个文本交流应用:Google Talk,Google+ Messenger,信息(短信应用),Google Voice。拥有四个应用来完成相同的任务——给某人发送文本消息——对用户来说很混乱。在 I/O 上,谷歌结束了 Google Talk 并且从头开始创建全新的消息产品 [Google Hangouts](http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2013/05/hands-on-with-hangouts-googles-new-text-and-video-chat-architecture/)。虽然最初只是想替代 Google Talk,Hangouts 的计划是统一所有谷歌的不同的消息应用到统一的界面下。
Hangouts 的用户界面布局真的和 Google Talk 没什么大的差别。主页面包含你的聊天会话,点击某一项就能进入聊天页面。界面设计上有所更新,聊天页面现在使用了卡片风格来显示每个段落,并且聊天列表是个“抽屉”风格的界面,这意味着你可以通过水平滑动打开它。Hangouts 有已读回执和输入状态指示,并且群聊现在是个主要特性。
Google+ 是 Hangouts 的中心,所以产品的全名实际上是“Google+ Hangouts”。Hangouts 完全整合到了 Google+ 桌面站点。身份和头像直接从 Google+ 拉取,点击头像会打开用户的 Google+ 资料。和将浏览器换为 Google Chrome 类似,核心安卓功能交给了一个单独的团队——Google+ 团队,这是变得越发繁忙的安卓工程师的抗议的结果。随着 Google+ 团队的接手,安卓的主要即时通讯客户端现在成为一个持续开发的应用。它被放进了 Play 商店并且有稳定的更新频率。

*新导航抽屉界面。 图片来自 [developer.android.com](https://developer.android.com/design/patterns/navigation-drawer.html)*
谷歌还给操作栏引入了新的设计元素:导航抽屉。这个抽屉显示为在左上角应用图标旁的三道横线。点击或从屏幕左边缘向右滑动,会出现一个侧边菜单目录。就像名字所指明的,这个是用来在应用内导航的,它会显示若干应用内的顶层位置。这使得应用首屏可以用来显示内容,也给了用户一致的、易于访问的导航元素。导航抽屉基本上就是个大号的菜单,可以滚动并且固定在左侧。
---

[Ron Amadeo](http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo) / Ron是Ars Technica的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。[@RonAmadeo](https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo)
---
via: <http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/23/>
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,600 | 掌握 Git 之美 | https://hackernoon.com/how-to-master-the-art-of-git-68e1050f3147 | 2017-06-12T08:15:00 | [
"GitHub",
"Git"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8600-1.html | 
>
> 使用 7 条简单的 Git 命令开始你的软件开发之旅
>
>
>
你是否曾经想知道如何学好 Git?你长期以来都是跌跌撞撞地在使用 Git。最终,你总需要掌握它的窍门。这就是我写这篇文章的原因,我将带你去启蒙之旅。这儿是我关于如何加快 Git 学习过程的基本指南。我将介绍 Git 的实际情况以及我使用最多的 7 条 Git 命令。本文主要针对有兴趣的开发人员和大学新生,他们需要关于 Git 的介绍以及如何掌握基础知识。
---
>
> 你可以往前继续阅读整篇文章,或者只读 TLDR; 部分,尽管这将使我很受伤。
>
>
>
### TLDR;
在学习 Git 的过程中,请养成下面这些步骤的习惯:
1. 随时使用 `git status`!
2. 只更改那些你真正想更改的文件。
3. `git add -A` 会是你的朋友。
4. 随时使用命令 `git commit -m "meaningful messages"`。
5. 做任何推送(push)之前先使用命令 `git pull`,但是这需要在你提交过一些更改之后。
6. 最后,`git push`推送提交的更改。
---
### 良宵莫辜负
对任何开发人员来说,通常第一步都是选择一个广泛使用的地方托管他或她的代码库。那就是,[GitHub](https://github.com/)。它是一切有关代码的聚集地。要理解 GitHub 的概念,你先需要知道什么是 Git。
Git 是一款基于命令行的版本控制软件,在 Windows 和 Mac 系统上也有几款可用的桌面应用。 Git 由 Linux 之父 Linus Torvalds 开发,Linus Torvalds 还是是计算机科学中最有影响力的人物之一。因为这一优势,Git 已经成为绝大多数软件开发人员关于共享和维护代码的标准。这一大段话,让我们将其细细道来。正如它的名字所说,版本控制软件 Git 让你可以预览你写过的代码的所有版本。从字面上来说, 开发人员的每个代码库都将永远存储在其各自的仓库中,仓库可以叫做任何名字,从 *pineapple* 到 *express* 都行。在此仓库开发代码的过程中,你将进行出无数次的更改,直到第一次正式发布。这就是版本控制软件如此重要的核心原因所在。它让作为开发人员的你可以清楚地了解对代码库进行的所有更改、修订和改进。从另外一个方面说,它使协同合作更容易,下载代码进行编辑,然后将更改上传到仓库。然而,尽管有了这么多好处,然而还有一件事可以锦上添花。你可以下载并使用这些文件,即使你在整个开发过程中什么事也没有做。
让我们回到文章的 GitHub 部分。它只是所有仓库的枢纽(hub),这些仓库可以存储在其中并在线浏览。它是一个让有着共同兴趣的人相聚的地方。
### 千里之行始于足下
OK,记住,Git 是一款软件,像任何其他软件一样,你首先需要安装它:
[Git - 安装 Git,如果你希望从源代码安装 Git,你需要安装这些 Git 的依赖库: autotools —— 来自 git-scm.com](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Getting-Started-Installing-Git)
*Tips:请点击上面的链接,然后按照说明开始。*
完成了安装过程,很好。现在你需要在你的浏览器地址栏输入 [github.com](https://github.com/) 访问该网站。如果你还没有帐号的话需要新创建一个帐号,这就是你的起舞之处。登录并创建一个新仓库,命名为 Steve ,没有什么理由,只是想要一个名为史蒂夫的仓库好玩而已。选中 “Initialize this repository with a README” 复选框并点击创建按钮。现在你有了一个叫做 Steve 的仓库。我相信你会为你自己感到自豪。

### 现在开始在使用 Git
现在是比较有趣的部分。你将把 Steve 克隆到你本地的机器上。可以把这个过程看作从 Github 上复制仓库到你的电脑上。点击 “clone or download” 按钮,你将看到一个类似下面这样的 URL:
```
https://github.com/yourGithubAccountName/Steve.git
```
复制这个 URL 并打开命令提示符窗口。现在输入并运行条命令:
```
git clone https://github.com/yourGithubAccountName/Steve.git
```
Abrakadabra!Steve 仓库已经被自动克隆到了你的电脑上。查看你克隆这个仓库的目录,你会看到一个叫做 Steve 的文件夹。这个本地的文件夹现在已经链接到了它的 “origin” ,也就是 GitHub 上的远程仓库。
记住这个过程,在你的软件开发工程人员的职业生涯中你一定会重复这个过程很多次的。完成所有这些准备工作之后,你就可以开始使用最普通且常用的 Git 命令了。

### 你现在已经开始在真实场景使用 Git 了
找到 Steve 目录并在该目录中打开命令提示符窗口,运行下面的命令:
```
git status
```
这会输出你的工作目录的状态,让你知道所有你编辑过的文件。这意味着它显示了远程库中和本地工作目录中之间的文件差异。`status` 命令被用来作为 `commit` 的模版,我将在这篇教程后面进一步谈论 `commit` 。简单的说,`[git status][1]` 告诉你你编辑过哪些文件,以给你一个你想要上传到远程库的概述。
但是,在你做任何上传之前,你首先需要做的是选择你需要发送回远程库的文件。使用下面命令完成:
```
git add
```
接着在 Steve 目录新建一个文本文件,可以取一个好玩的名字 `pineapple.txt`。在这个文件里面随便写些你想写的内容,返回命令提示符,然后再次输入 `git status`。现在,你将看到这个文件以红色出现在标记 “untracked files” 下面。
```
On branch master
Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'.
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be commited)
pineapple.txt
```
下一步就是将它添加到暂存区(staging)。暂存区可以看作是这样的一个环境:你做过的所有更改在提交时都将捆绑为一个更改而被提交。现在,你可以将这个文件加入暂存区:
```
git add -A
```
`-A` 选项意味着所有你更改过的文件都会被加到暂存区等待提交。然而, `git add` 非常灵活,它也可以像这样一个文件一个文件的添加:
```
git add pineapple.txt
```
这种方法让你有能力选择你想要暂存的每一个文件,而不用担心加入那些你不想改变的东西。
再次运行 `git status`,你会看到如下输出:
```
On branch master
Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'.
Changes to be committed:
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
new file: pineapple.txt
```
准备好提交更改了吗?开始吧。
```
git commit -m "Write your message here"
```
[Git commit](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-commit) 命令会将存储在暂存区中的文件和来自用户的用于描述更改的日志信息一起存储在一个新的地方。`-m`选项加入了写在双引号内的信息。
再次检查状态,你会看到:
```
On branch master
Your branch is ahead of 'origin/master' by 1 commit.
(use "git push" to publish your local commits)
nothing to commit, working directory clean
```
所有的更改现在都被加入到一次提交当中了,同时会有一条与你所做相关的信息。现在你可以用 `git push` 将这次提交推送到远程库 “origin”了。这条命令就像字面意义所说,它会把你提交的更改从本地机器上传到 GitHub 的远程仓库中。返回到命令提示符,然后运行:
```
git push
```
你会被要求输入你的 GitHub 帐号和密码,之后你会看到类似下面的这些内容:
```
Counting objects: 3, done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 280 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To https://github.com/yourGithubUserName/Steve.git
c77a97c..08bb95a master -> master
```
就是这样。你已经成功上传了你本地的更改。看看你在 GitHub 上的仓库,你会看到它现在包含了一叫做 `pineapple.txt` 的文件。
如果你是一个开发小组的一员呢?如果他们都推送提交到 “origin”,将会发生什么?这就是 Git 真正开始发挥它的魔力的时候。你可以使用一条简单的命令轻松地将最新版本的代码库 [pull](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-pull) 到你本地的机器上:
```
git pull
```
但是 Git 也有限制:你需要有相匹配的版本才能推送到 “origin”。这意味着你本地的版本需要和 origin 的版本大致一样。当你从 “origin” 拉取(pull)文件时,在你的工作目录中不能有文件,因为它们将会在这个过程中被覆盖。因此我给出了这条简单的建议。在学习 Git 的过程中,请养成下面这些步骤的习惯:
1. 随时使用 `git status`!
2. 只更改那些你真正想更改的文件。
3. `git add -A` 会是你的朋友。
4. 随时使用命令 `git commit -m "meaningful messages"`。
5. 做任何推送(push)之前先使用命令 `git pull`,但是这需要在你提交过一些更改之后。
6. 最后,`git push`推送提交的更改。
---
嘿!你还在看这篇文章吗?你已经看了很久了,休息一下吧!

休息好了吗?好的!让我们来处理一些错误。如果你不小心更改了一些你本不应该更改的文件后怎么办呢?不需要担心,只需要使用 [git checkout](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-checkout)。让我们在文件 `pineapple.txt` 里更改一些内容:在文件中加入一行,比方说,“Steve is mega-awesome!” 。然后保存更改并用 `git status` 检查一下:
```
On branch master
Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'.
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: pineapple.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
```
正如预料的那样,它已经被记录为一次更改了。但是,假如 Steve 实际上并不是很优秀呢?假如 Steve 很差劲呢?不用担心!最简单的还原更改的方式是运行命令:
```
git checkout -- pineapple.txt
```
现在你会看到文件已经恢复到了先前的状态。
但是假如你玩砸了呢?我是说,事情已经变得混乱,并且需要把所有东西重置到与 “origin” 一样的状态。也不需要担心,在这种紧急情况下我们可以享受 Git 的美妙之处:
```
git reset --hard
```
[git reset](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-reset) 命令和 `--hard` 选项一起可以抛弃自上次提交以来的所有更改,有些时候真的很好用。
---
最后,我想鼓励你尽可能多地使用 Git。这是能够熟练使用它的最好学习方式。除此之外,养成阅读 Git 文档的习惯。一开始可能会有些云里雾里,但是过段时间后你就会明白它的窍门了。
*希望你们(小伙子和姑娘们)读这篇文章的时候会和我写它时一样的开心。如果你认为这篇文章对别人有用,你尽可以与别人分享它。或者,如果你喜欢这篇文章,你可以在下面点下赞以便让更多的人看到这篇文章。*
---
via: <https://hackernoon.com/how-to-master-the-art-of-git-68e1050f3147>
作者:[Adnan Rahić](https://hackernoon.com/@adnanrahic) 译者:[zhousiyu325](https://github.com/zhousiyu325) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 
Have you ever wondered how one learns to use Git well? You use Git very poorly for a long time. Eventually, you’ll get the hang of it. That’s why I’m here. I’ll take you on a journey to enlightenment. These are my basic guidelines of how to speed up the process of learning Git significantly. I’ll cover what Git actually is and the 7 Git commands I use the most. This article is mainly aimed towards aspiring developers and college freshmen who are in need of an introductory explanation of what Git is and how to master the basics.
You can go ahead and read the whole article **or** hurt my feelings significantly by only reading the TLDR;
When in the process of learning Git, make a habit of following these steps:
`git status`
all the time!`git add -A`
is your friend.`git commit -m "meaningful messages"`
.
Always `git pull`
**before** doing any pushing, but **after** you have committed any changes.
`git push`
the committed changes.The universal first step for any developer is to choose a common place to host his or her code base. Voilá, [GitHub](https://github.com/?ref=hackernoon.com)! The meeting place for all things regarding code. To be able to understand the concept of GitHub you would first need to understand what Git really is.
Git is a version control software, based on the command line, with a few desktop apps available for Windows and Mac. Created by Linus Torvalds, the father of Linux and one of the most influential people in computer science, ever. Channeling this merit, Git has become a standard for a vast majority of software developers regarding sharing and maintaining code. Those were a bunch of large words. **Let’s break it down.** Version control software, means exactly what it says. Git allows you to have a preview of all the versions of your code you have ever written. Literally, ever! Every code base a developer has, will be stored in its respective repository, which can be named anything from *pineapple* to *express*. In the process of developing the code within this repository you will make countless changes, up until the first official release. Here lies the core reason why version control software is so important. It enables you, the developer, to have a clear view of all changes, revisions and improvements ever done to the code base. In turn making it much easier to collaborate, download code to make edits, and upload changes to the repository. However, in spite of all this awesomeness, one thing takes the crown as the most incredible. You can download and use the files even thought you have nothing to do with the development process!
Let’s get back to the GitHub part of the story. It’s just a hub for all repositories, where they can be stored and viewed online. A central meeting point for like minded individuals.
Okay, remember, Git is a software, and like any other software you’ll first need to install it:
**Git - Installing Git**_If you do want to install Git from source, you need to have the following libraries that Git depends on: autotools…_git-scm.com
***Anchorman voice****Please click on the link above, and follow the instructions stated…*
Done installing it, great. Now you will need to punch in [github.com](https://github.com/?ref=hackernoon.com) in your browsers address bar. Create an account if you don’t already have one, and you’re set to rock’n’roll! Jump in and create a new repository, name it Steve for no reason at all, just for the fun of having a repository named Steve. Go ahead and check the *Initialize this repository with a README* checkbox and click the create button. You now have a new repository called Steve. Be proud of yourself, I sure am.
Now comes the fun part. You’re ready to clone Steve to your local machine. View this process as simply copying the repository from GitHub to your computer. By clicking the *clone or download* button you will see a URL which will look something like this:
https://github.com/yourGithubAccountName/Steve.git
Copy this URL and open up a command prompt. Now write and run this command:
git clone https://github.com/yourGithubAccountName/Steve.git
Abrakadabra! Steve has automagically been cloned to your computer. Looking in the directory where you cloned the repository, you’ll see a folder named Steve. This local folder is now linked with it’s *origin,* the original repository on Github.
Remember this process, you will surely repeat it many times in your career as a software developer. With all this formal stuff done, you are ready to get started with the most common and regularly used Git commands.
Lame video game reference
Open up the Steve directory and go ahead and open a command prompt from within the same directory. Run the command:
git status
This will output the status of your working directory, showing you all the files you have edited. This means it’s showing you the difference between the files on the origin and your local working directory. The status command is designed to be used as a *commit* template. I’ll come back to talking about commit a bit further down this tutorial. Simply put, `[git status](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-status)`
shows you which files you have edited, in turn giving you an overview of which you wish to upload back to the origin.
But, before you do any of that, first you need to pick which files you wish to send back to the origin. This is done with:
Please go ahead and create a new text file in the Steve directory. Name it *pineapple.txt* just for the fun of it. Write whatever you would want in this file. Switch back to the command prompt, and run `git status`
once again. Now, you’ll see the file show up in red under the banner *untracked files.*
On branch masterYour branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'.Untracked files:(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be commited)
pineapple.txt
The next step is to add a file to staging. Staging can be viewed as a context where all changes you have picked will be bundled into one, when the time comes to commit them. Now you can go ahead and add this file to staging:
git add -A
The *-A* flag means that all files that have been changed will be staged for commit. However, `git add`
is very flexible and it is perfectly fine to add files one by one. Just like this:
git add pineapple.txt
This approach gives you power to cherry pick every file you wish to stage, without the added worry that you’ll change something you weren’t supposed to.
After running `git status`
once again you should see something like this:
On branch masterYour branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'.Changes to be committed:(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
new file: pineapple.txt
Ready to commit the changes? I sure am.
git commit -m "Write your message here"
The [Git commit](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-commit?ref=hackernoon.com) command stores the current files in staging in a new commit along with a log message from the user describing the changes. The *-m* flag includes the message written in double quotes in the commit.
Checking the status once again will show you:
On branch masterYour branch is ahead of 'origin/master' by 1 commit.(use "git push" to publish your local commits)nothing to commit, working directory clean
All changes have now been bundled into one commit with one dedicated message regarding the work you have done. You’re now ready to `[git push](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-push)`
this commit to the *origin*. The push command does literally what it means. It will upload your committed changes from your local machine to the repository origin on GitHub. Go back to the command prompt and run:
git push
It will ask you to enter your GitHub username and password, after which you will see something like this:
Counting objects: 3, done.Delta compression using up to 4 threads.Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 280 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)To https://github.com/yourGithubUserName/Steve.gitc77a97c..08bb95a master -> master
That’s it. You have uploaded the local changes. Go ahead and look at your repository on GitHub and you’ll see that it now contains a file named *pineapple.txt*.
What if you work in a team of developers? Where all of them push commits to the origin. What happens then? This is where Git starts to show it’s real power. You can just as easily [pull](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-pull?ref=hackernoon.com) the latest version of the code base to your local machine with one simple command.
git pull
But Git has it’s limitations. You need to have matching versions to be able to **push** changes to the origin. Meaning the version you have locally needs to be exactly the same as the one on the origin. When **pulling** from the origin you shouldn’t have files in the working directory, as they will be overwritten in the process. Hence me giving this simple advice. When in the process of learning Git, make a habit of following these steps:
`git status`
all the time!`git add -A`
is your friend.`git commit -m "meaningful messages"`
.
Always `git pull`
**before** doing any pushing, but **after** you have committed any changes.
`git push`
the committed changes.Phew, are you still with me? You’ve come a long way. Have a break.
Lame video-game references, once again…
Rested up? Great! You’re ready for some error handling. What if you accidentally changed some files your shouldn’t have touched. No need to freak out, just use `[git checkout](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-checkout)`
. Let’s change something in the *pineapple.txt* file. Add another line of text in there, let’s say, *“Steve is mega-awesome!”*. Go ahead, save the changes and check the `git status`
.
On branch masterYour branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'.Changes not staged for commit:(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: pineapple.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
As expected it has been registered as a change. But what if Steve really isn’t that mega-awesome? What if Steve is mega-lame? Worry not! The simplest way to revert the changes is to run:
git checkout -- pineapple.txt
Now you will see the file has been returned to it’s previous state.
But what if you really mess up. I mean like majorly mess things up, and need to reset everything back to the state the *origin* is in. No need to worry, during emergencies like this we have this beauty:
git reset --hard
The [Git reset](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-reset?ref=hackernoon.com) command with the *--hard* flag discards all changes since the last commit. Pretty handy sometimes.
To wrap up, I’d like to encourage you to play around with Git as much as possible. It’s by far the best way of learning how to use it with confidence. Apart from that, make a habit of reading the Git documentation. As confusing as it may seem at first, after a few moments of reading you will get the hang of it.
*Hope you guys and girls had as much fun reading this article as I had writing it.* *Feel free to share if you believe it will be of help to someone, or if you liked it, click the 💚 below so other people will see this here on Medium.* |
8,603 | Linux GRUB2 配置简介 | https://opensource.com/article/17/3/introduction-grub2-configuration-linux | 2017-06-13T06:13:35 | [
"GRUB",
"GRUB2"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8603-1.html |
>
> 学习 GRUB 引导加载程序是如何预备你的系统并启动操作系统内核的。
>
>
>

自从上个月为我的文章《[Linux 引导和启动过程简介](https://opensource.com/article/17/2/linux-boot-and-startup)》做研究开始,我对更深入了解 GRUB2 产生了兴趣。这篇文章提供了配置 GRUB2 的简要介绍。为了简便起见,我大多数情况下会使用 GRUB 指代 GRUB2。
### GRUB
GRUB 来自 GRand Unified Bootloader 的缩写。它的功能是在启动时从 BIOS 接管掌控、加载自身、加载 Linux 内核到内存,然后再把执行权交给内核。一旦内核开始掌控,GRUB 就完成了它的任务,也就不再需要了。
GRUB 支持多种 Linux 内核,并允许用户在启动时通过菜单在其中选择。我发现这是一种非常有用的工具,因为我有很多次遇到一个应用程序或者系统服务在特定内核版本下失败的问题。有好几次,引导到一个较旧的内核时就可以避免类似的问题。默认情况下,使用 `yum` 或 `dnf` 进行更新时会保存三个内核 - 最新的以及两个比较旧的。在被包管理器删除之前所保留的内核数目可以在 `/etc/dnf/dnf.conf` 或 `/etc/yum.conf` 文件中配置。我通常把 `installonly_limit` 的值修改为 9 以便保留 9 个内核。当我不得不恢复到低几个版本的内核时这非常有用。
### GRUB 菜单
GRUB 菜单的功能是当默认的内核不是想要的时,允许用户从已经安装的内核中选择一个进行引导。通过上下箭头键允许你选中想要的内核,敲击回车键会使用选中的内核继续引导进程。
GRUB 菜单也提供了超时机制,因此如果用户没有做任何选择,GRUB 就会在没有用户干预的情况下使用默认内核继续引导。敲击键盘上除了回车键之外的任何键会停止终端上显示的倒数计时器。立即敲击回车键会使用默认内核或者选中的内核继续引导进程。
GRUB 菜单提供了一个 “<ruby> 救援 <rt> rescue </rt></ruby>” 内核,用于故障排除或者由于某些原因导致的常规内核不能完成启动过程。不幸的是,这个救援内核不会引导到救援模式。文章后面会更详细介绍这方面的东西。
### grub.cfg 文件
`grub.cfg` 文件是 GRUB 配置文件。它由 `grub2-mkconfig` 程序根据用户的配置使用一组主配置文件以及 grub 默认文件而生成。`/boot/grub2/grub.cfg` 文件在 Linux 安装时会初次生成,安装新内核时又会重新生成。
`grub.cfg` 文件包括了类似 Bash 脚本的代码以及一个按照安装顺序排序的已安装内核列表。例如,如果你有 4 个已安装内核,最新的内核索引是 0,前一个内核索引是 1,最旧的内核索引是 3。如果你能访问 `grub.cfg` 文件,你应该去看看感受一下它看起来是什么样。`grub.cfg` 太大也就没有包含在这篇文章中。
### GRUB 配置文件
`grub.cfg` 的主要配置文件都在 `/etc/grub.d` 目录。该目录中的每个文件都包含了最终会整合到 `grub.cfg` 文件中的 GRUB 代码。这些配置文件的命名模式以排序方式设计,这使得最终的 `grub.cfg` 文件可以按正确的顺序整合而成。每个文件都有注释表明该部分的开始和结束,这些注释也是最终的 `grub.cfg` 文件的一部分,从而可以看出每个部分是由哪个文件生成。分隔注释看起来像这样:
```
### BEGIN /etc/grub.d/10_linux ###
### END /etc/grub.d/10_linux ###
```
不要修改这些文件,除非你是一个 GRUB 专家并明白更改会发生什么。无论如何,修改 `grub.cfg` 文件时你也总应该保留一个原始文件的备份。 `40_custom` 和 `41_custom` 这两个特别的文件用于生成用户对 GRUB 配置的修改。你仍然要注意对这些文件的更改的后果,并保存一份原始 `grub.cfg` 文件的备份。
你也可以把你自己的文件添加到 `/etc/grub.d` 目录。这样做的一个可能的原因是为非 Linux 操作系统添加菜单行。要注意遵循命名规则,确保配置文件中额外的菜单选项刚好在 `10_linux` 条目之前或之后。
### GRUB 默认文件
老版本 GRUB 的配置非常简单而明了,我只需要修改 `/boot/grub/grub.conf` 就可以了。对于新版本的 GRUB2,我虽然还可以通过更改 `/boot/grub2/grub.cfg` 来修改,但和老版本的 GRUB 相比,新版本相对更加复杂。另外,安装一个新内核时 `grub.cfg` 可能会被重写,因此任何修改都可能消失。当然,GNU.org 的 GRUB 手册确实有过直接创建和修改 `/boot/grub2/grub.cfg` 的讨论。
一旦你明白了如何做,更改 GRUB2 配置就会变得非常简单。我为之前的文章研究 GRUB2 的时候才明白这个。秘方就在 `/etc/default` 目录里面,一个自然而然称为 `grub` 的文件,它可以通过简单的终端命令操作。`/etc/default` 目录包括了一些类似 Google Chrome、 useradd、 和 grub 程序的配置文件。
`/etc/default/grub` 文件非常简单。这个 `grub` 默认文件已经列出了一些有效的键值对。你可以简单地更改现有键值或者添加其它文件中还没有的键。下面的列表 1 显示了一个没有更改过的 `/etc/default/grub` 文件。
```
GRUB_TIMEOUT=5
GRUB_DISTRIBUTOR="$(sed 's, release .*$,,g'
/etc/system-release)"
GRUB_DEFAULT=saved
GRUB_DISABLE_SUBMENU=true
GRUB_TERMINAL_OUTPUT="console"
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="rd.lvm.lv=fedora_fedora25vm/root
rd.lvm.lv=fedora_fedora25vm/swap
rd.lvm.lv=fedora_fedora25vm/usr rhgb quiet"
GRUB_DISABLE_RECOVERY="true"
```
*列表 1:Fedora 25 一个原始 grub 默认文件。*
[GRUB 手册 5.1 章节](https://www.gnu.org/software/grub/manual/grub.html#Simple-configuration)包括了所有可以添加到该 `grub` 文件的键的信息。我只需要修改 `grub` 默认文件已经有的一些键值就够了。让我们看看这些键值以及一些在 grub 默认文件中没有出现的每个键的意义。
* `GRUB_TIMEOUT` 这个键的值决定了显示 GRUB 选择菜单的时间长度。GRUB 提供了同时保存多个安装内核并在启动时使用 GRUB 菜单在其中选择的功能。这个键的默认值是 5 秒,但我通常修改为 10 秒使得有更多时间查看选项并作出选择。
* `GRUB_DISTRIBUTOR` 这个键定义了一个从 `/etc/system-release` 文件中提取发行版本的 [sed](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sed) 表达式。这个信息用于生成出现在 GRUB 菜单中的每个内核发布版的文本名称,例如 “Fedora” 等。由于不同发行版之间 `system-release` 文件结构的差异,在你的系统中这个 sed 表达式可能有些不同。
* `GRUB_DEFAULT` 决定默认引导哪个内核。如果是 `saved`,这代表最新内核。这里的其它选项如果是数字则代表了 `grub.cfg` 中列表的索引。使用索引号 3,就会总是加载列表中的第四个内核,即使安装了一个新内核之后也是。因此使用索引数字的话,在安装一个新内核后会加载不同的内核。要确保引导特定内核版本的唯一方法是设置 `GRUB_DEFAULT` 的值为想要内核的名称,例如 `4.8.13-300.fc25.x86_64`。
* `GRUB_SAVEDEFAULT` 通常,grub 默认文件中不会指定这个选项。当选择不同内核进行引导时,正常操作下该内核只会启动一次。默认内核不会改变。当其设置为 `true` 并和 `GRUB_DEFAULT=saved` 一起使用时,这个选项会保存一个不同内核作为默认值。当选择不同内核进行引导时会发生这种情况。
* `GRUB_DISABLE_SUBMENU` 一些人可能会希望为 GRUB 菜单创建一个内核的层级菜单结构。这个键和 `grub.cfg` 中一些额外内核配置允许创建这样的层级结构。例如,主菜单中可能有 `production` 和 `test` 子菜单,每个子菜单中包括了一些合适的内核。设置它为 `false` 可以启用子菜单。
* `GRUB_TERMINAL_OUTPUT` 一些环境下可能需要或者必要将输出重定向到一个不同的显示控制台或者终端。默认情况下是把输出发送到默认终端,通常 `console` 等价于 Intel 系列个人电脑的标准输出。另一个有用的选择是在使用串行终端或者 Integrated Lights Out (ILO) 终端连接的数据中心或者实验室环境中指定 `serial`。
* `GRUB_TERMINAL_INPUT` 和 `GRUB_TERMINAL_OUTPUT` 类似,可能需要或者必要重定向输入为串行终端或者 ILO 设备、而不是标准键盘输入。
* `GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX` 这个键包括了在启动时会传递给内核的命令行参数。注意这些参数会被添加到 `grub.cfg` 所有已安装内核的内核行。这意味着所有已安装的内核在启动时都会有相同的参数。我通常删除 `rhgb` 和 `quiet` 参数以便我可以看到引导和启动时内核和 systemd 输出的所有内核信息消息。
* `GRUB_DISABLE_RECOVERY` 当这个键的值被设置为 `false`,GRUB 菜单中就会为每个已安装的内核创建一个恢复条目。当设置为 `true` 时就不会创建任何恢复条目。但不管这个设置怎样,最后的内核条目总是一个 `rescue` 选项。不过在 rescue 选项中我遇到了一个问题,下面我会详细介绍。
还有一些你可能觉得有用但我没有在这里介绍的键。它们的描述可以在 [GRUB 手册 2](https://www.gnu.org/software/grub/manual/grub.html#Simple-configuration) 的 5.1 章节找到。
### 生成 grub.cfg
完成所需的配置之后,就需要生成 `/boot/grub2/grub.cfg` 文件。这通过下面的命令完成。
```
grub2-mkconfig > /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
```
这个命令按照顺序使用位于 `/etc/grub.d` 的配置文件构建 `grub.cfg` 文件,然后使用 grub 默认文件的内容修改输出以便获得最终所需的配置。`grub2-mkconfig` 命令会尝试定位所有已安装的内核并在 `grub.cfg` 文件的 `10_Linux` 部分新建条目。它还创建一个 `rescue` 条目提供一个用于从 Linux 不能启动的严重问题中恢复的方法。
强烈建议你不要手动编辑 `grub.cfg` 文件,因为任何对该文件的直接修改都会在下一次安装新内核或者手动运行 `grub2-mkconfig` 时被重写。
### 问题
我遇到一个如果没有意识到就可能导致严重后果的 GRUB2 问题。这个救援内核没有启动,反而启动了另外一个内核。我发现那是列表中索引为 1 的内核,也就是列表中的第二个内核。额外的测试发现不管使用原始的还是我生成的 `grub.cfg` 配置文件都会发生这个问题。我在虚拟机和真实硬件上都尝试过而且都发生了这个问题。我只测试了 Fedora 25,因此其它 Fedora 发行版本可能没有这个问题。
注意,从救援内核生成的 “recovery” 内核条目不能引导到维护模式。
我推荐将 grub 默认文件中 `GRUB_DISABLE_RECOVERY` 的值更改为 “false”,然后生成你自己的 `grub.cfg`。这会在 GRUB 菜单中为每个已安装的内核生成可用的恢复条目。这些恢复配置能像期望那样工作,从而从那些需要输入密码登录的内核条目中引导到运行级别 1,也就是进入(不需要密码的)单用户维护模式。你也可以按 `Ctrl-D` 继续正常的引导进入默认运行级别。
### 总结
GRUB 是引导 Linux 计算机到可用状态过程的一系列事件中,发生在 BIOS 之后的第一步。理解如何配置 GRUB 对于恢复或者处理多种类型的问题非常重要。
这么多年来我多次不得不引导到恢复或者救援模式以便解决多种类型的问题。其中的一些问题确实是类似 `/etc/fstab` 或其它配置文件中不恰当条目导致的引导问题,也有一些是由于应用程序或者系统软件和最新的内核不兼容的问题。硬件兼容性问题也可能妨碍特定的内核启动。
我希望这些信息能对你开启 GRUB 配置之旅有所帮助。
( 题图 : Internet Archive [Book](https://www.flickr.com/photos/internetarchivebookimages/14746482994/in/photolist-ot6zCN-odgbDq-orm48o-otifuv-otdyWa-ouDjnZ-otGT2L-odYVqY-otmff7-otGamG-otnmSg-rxnhoq-orTmKf-otUn6k-otBg1e-Gm6FEf-x4Fh64-otUcGR-wcXsxg-tLTN9R-otrWYV-otnyUE-iaaBKz-ovcPPi-ovokCg-ov4pwM-x8Tdf1-hT5mYr-otb75b-8Zk6XR-vtefQ7-vtehjQ-xhhN9r-vdXhWm-xFBgtQ-vdXdJU-vvTH6R-uyG5rH-vuZChC-xhhGii-vvU5Uv-vvTNpB-vvxqsV-xyN2Ai-vdXcFw-vdXuNC-wBMhes-xxYmxu-vdXxwS-vvU8Zt) [Images](https://www.flickr.com/photos/internetarchivebookimages/14774719031/in/photolist-ovAie2-otPK99-xtDX7p-tmxqWf-ow3i43-odd68o-xUPaxW-yHCtWi-wZVsrD-DExW5g-BrzB7b-CmMpC9-oy4hyF-x3UDWA-ow1m4A-x1ij7w-tBdz9a-tQMoRm-wn3tdw-oegTJz-owgrs2-rtpeX1-vNN6g9-owemNT-x3o3pX-wiJyEs-CGCC4W-owg22q-oeT71w-w6PRMn-Ds8gyR-x2Aodm-owoJQm-owtGp9-qVxppC-xM3Gw7-owgV5J-ou9WEs-wihHtF-CRmosE-uk9vB3-wiKdW6-oeGKq3-oeFS4f-x5AZtd-w6PNuv-xgkofr-wZx1gJ-EaYPED-oxCbFP). Opensource.com 修改。 CC BY-SA 4.0)
---
作者简介:
David Both - David Both 是一个居住在 Raleigh,北卡罗来纳州的 Linux 和开源倡导者。他在 IT 界已经有超过 40 年,并在他工作的 IBM 执教 OS/2 20 多年。在 IBM 的时候,他在 1981 年开设了第一个最初 IBM 个人电脑的培训课程。他在红帽教授过 RHCE 课程并在 MCI Worldcom、 Cisco、 和北卡罗来纳州工作过。他已经在 Linux 和开源软件方面工作将近 20 年。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/3/introduction-grub2-configuration-linux>
作者:[David Both](https://opensource.com/users/dboth) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When researching my article from last month, * An introduction to the Linux boot and startup process*, I became interested in learning more about GRUB2. This article provides a quick introduction to configuring GRUB2, which I will mostly refer to as GRUB for simplicity.
## GRUB
GRUB stands for *GRand Unified Bootloader*. Its function is to take over from BIOS at boot time, load itself, load the Linux kernel into memory, and then turn over execution to the kernel. Once the kernel takes over, GRUB has done its job and it is no longer needed.
GRUB supports multiple Linux kernels and allows the user to select between them at boot time using a menu. I have found this to be a very useful tool because there have been many instances that I have encountered problems with an application or system service that fails with a particular kernel version. Many times, booting to an older kernel can circumvent issues such as these. By default, three kernels are kept–the newest and two previous–when **yum** or **dnf** are used to perform upgrades. The number of kernels to be kept before the package manager erases them is configurable in the **/etc/dnf/dnf.conf** or **/etc/yum.conf** files. I usually change the **installonly_limit** value to 9 to retain a total of nine kernels. This has come in handy on a couple occasions when I had to revert to a kernel that was several versions down-level.
## GRUB menu
The function of the GRUB menu is to allow the user to select one of the installed kernels to boot in the case where the default kernel is not the desired one. Using the up and down arrow keys allows you to select the desired kernel and pressing the **Enter** key continues the boot process using the selected kernel.
The GRUB menu also provides a timeout so that, if the user does not make any other selection, GRUB will continue to boot with the default kernel without user intervention. Pressing any key on the keyboard except the **Enter** key terminates the countdown timer which is displayed on the console. Pressing the **Enter** key immediately continues the boot process with either the default kernel or an optionally selected one.
The GRUB menu also provides a "rescue" kernel, in for use when troubleshooting or when the regular kernels don't complete the boot process for some reason. Unfortunately, this rescue kernel does not boot to rescue mode. More on this later in this article.
## The grub.cfg file
The **grub.cfg** file is the GRUB configuration file. It is generated by the **grub2-mkconfig** program using a set of primary configuration files and the grub default file as a source for user configuration specifications. The **/****boot/grub2/****grub.cfg** file is first generated during Linux installation and regenerated when a new kernel is installed.
The **grub.cfg** file contains Bash-like code and a list of installed kernels in an array ordered by sequence of installation. For example, if you have four installed kernels, the most recent kernel will be at index 0, the previous kernel will be at index 1, and the oldest kernel will be index 3. If you have access to a **grub.****cfg** file you should look at it to get a feel for what one looks like. The **grub.cfg** file is just too large to be included in this article.
## GRUB configuration files
The main set of configuration files for **grub.cfg** is located in the **/etc/grub.d **directory. Each of the files in that directory contains GRUB code that is collected into the final grub.cfg file. The numbering scheme used in the names of these configuration files is designed to provide ordering so that the final **grub.cfg** file is assembled into the correct sequence. Each of these files has a comment to denote the beginning and end of the section, and those comments are also part of the final grub.cfg file so that it is possible to see from which file each section is generated. The delimiting comments look like this:
```
``````
### BEGIN /etc/grub.d/10_linux ###
### END /etc/grub.d/10_linux ###
```
These files should not be modified unless you are a GRUB expert and understand what the changes will do. Even then you should always keep a backup copy of the original, working **grub.****cfg** file. The specific files, **40_custom** and **41_custom** are intended to be used to generate user modifications to the GRUB configuration. You should still be aware of the consequences of any changes you make to these files and maintain a backup of the original **grub.****cfg** file.
You can also add your own files to the /etc/grub.d directory. One reason for doing that might be to add a menu line for a non-Linux operating system. Just be sure to follow the naming convention to ensure that the additional menu item is added either immediately before or after the **10_linux** entry in the configuration file.
## GRUB defaults file
Configuration of the original GRUB was fairly simple and straightforward. I would just modify **/boot/grub/grub.conf** and be good to go. I could still modify GRUB2 by changing **/boot/grub2/grub.****cfg**, but the new version is considerably more complex than the original GRUB. In addition, **grub.cfg** may be overwritten when a new kernel is installed, so any changes may disappear. However, the GNU.org GRUB Manual does discuss direct creation and modification of **/boot/grub2/grub.cfg**.
Changing the configuration for GRUB2 is fairly easy once you actually figure out how to do it. I only discovered this while researching GRUB2 for a previous article. The secret formula is in the **/etc/default **directory, with a file called, naturally enough, grub, which is then used in concert with a simple terminal command. The **/etc/default** directory contains configuration files for a few programs such as Google Chrome, useradd, and grub.
The **/etc/default/grub** file is very simple. The grub defaults file has a number of valid key/value pairs listed already. You can simply change the values of existing keys or add other keys that are not already in the file. Listing 1, below, shows an unmodified **/etc/default/gru**b file.
```
``````
GRUB_TIMEOUT=5
GRUB_DISTRIBUTOR="$(sed 's, release .*$,,g'
/etc/system-release)"
GRUB_DEFAULT=saved
GRUB_DISABLE_SUBMENU=true
GRUB_TERMINAL_OUTPUT="console"
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="rd.lvm.lv=fedora_fedora25vm/root
rd.lvm.lv=fedora_fedora25vm/swap
rd.lvm.lv=fedora_fedora25vm/usr rhgb quiet"
GRUB_DISABLE_RECOVERY="true"
```
*Listing 1: An original grub default file for Fedora 25. *
[Section 5.1 of the GRUB Manual](https://www.gnu.org/software/grub/manual/grub.html#Simple-configuration) contains information about all of the possible keys that can be included in the grub file. I have never had needed to do anything other than modifying the values of some of the keys that are already in the grub default file. Let's look at what each of these keys means as well as some that don't appear in the grub default file.
**GRUB_TIMEOUT**The value of this key determines the length of time that the GRUB selection menu is displayed. GRUB offers the capability to keep multiple kernels installed simultaneously and choose between them at boot time using the GRUB menu. The default value for this key is 5 seconds, but I usually change that to 10 seconds to allow more time to view the choices and make a selection.**GRUB_DISTRIBUTOR**This key defines a[sed](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sed)expression that extracts the distribution release number from the /etc/system-release file. This information is used to generate the text names for each kernel release that appear in the GRUB menu, such as "Fedora". Due to variations in the structure of the data in the system-release file between distributions, this sed expression may be different on your system.**GRUB_DEFAULT**Determines which kernel is booted by default. That is the "saved" kernel which is the most recent kernel. Other options here are a number which represents the index of the list of kernels in**grub.cfg**. Using an index such as 3, however, to load the fourth kernel in the list will always load the fourth kernel in the list even after a new kernel is installed. So using an index will load a different kernel after a new kernel is installed. The only way to ensure that a specific kernel release is booted is to set the value of**GRUB_DEFAULT**to the name of the desired kernel, like 4.8.13-300.fc25.x86_64.**GRUB_SAVEDEFAULT**Normally, this option is not specified in the grub defaults file. Normal operation when a different kernel is selected for boot, that kernel is booted only that one time. The default kernel is not changed. When set to "true" and used with**GRUB_DEFAULT=saved**this option saves a different kernel as the default. This happens when a different kernel is selected for boot.**GRUB_DISABLE_SUBMENU**Some people may wish to create a hierarchical menu structure of kernels for the GRUB menu screen. This key, along with some additional configuration of the kernel stanzas in**grub.****cfg**allow creating such a hierarchy. For example, the one might have the main menu with "production" and "test" sub-menus where each sub-menu would contain the appropriate kernels. Setting this to "false" would enable the use of sub-menus.**GRUB_TERMINAL_OUTPUT**In some environments it may be desirable or necessary to redirect output to a different display console or terminal. The default is to send output to the default terminal, usually the "console" which equates to the standard display on an Intel class PC. Another useful option is to specify "serial" in a data center or lab environment in which serial terminals or Integrated Lights Out (ILO) terminal connections are in use.**GRUB_TERMINAL_INPUT**As with**GRUB_TERMINAL_OUTPUT**, it may be desirable or necessary to redirect input from a serial terminal or ILO device rather than the standard keyboard input.**GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX**This key contains the command line arguments that will be passed to the kernel at boot time. Note that these arguments will be added to the kernel line of grub.cfg for all installed kernels. This means that all installed kernels will have the same arguments when booted. I usually remove the "rhgb" and "quiet" arguments so that I can see all of the very informative messages output by the kernel and systemd during the boot and startup.**GRUB_DISABLE_RECOVERY**When the value of this key is set to "false," a recovery entry is created in the GRUB menu for every installed kernel. When set to "true" no recovery entries are created. Regardless of this setting, the last kernel entry is always a "rescue" option. However, I encountered a problem with the rescue option, which I'll talk more about below.
There are other keys that I have not covered here that you might find useful. Their descriptions are located in Section 5.1 of the [GRUB Manual 2](https://www.gnu.org/software/grub/manual/grub.html#Simple-configuration).
## Generate grub.cfg
After completing the desired configuration it is necessary to generate the **/boot/grub2/grub.****cfg** file. This is accomplished with the following command.
```
````grub2-mkconfig > /boot/grub2/grub.cfg`
This command takes the configuration files located in /etc/grub.d in sequence to build the **grub.****cfg** file, and uses the contents of the grub defaults file to modify the output to achieve the final desired configuration. The **grub2-mkconfig** command attempts to locate all of the installed kernels and creates an entry for each in the **10_Linux** section of the **grub.****cfg** file. It also creates a "rescue" entry to provide a method for recovering from significant problems that prevent Linux from booting.
It is strongly recommended that you do not edit the **grub.****cfg** file manually because any direct modifications to the file will be overwritten the next time a new kernel is installed or **grub2-mkconfig** is run manually.
## Issues
I encountered one problem with GRUB2 that could have serious consequences if you are not aware of it. The rescue kernel does not boot, instead, one of the other kernels boots. I found that to be the kernel at index 1 in the list, i.e., the second kernel in the list. Additional testing showed that this problem occurred whether using the original **grub.****cfg** configuration file or one that I generated. I have tried this on both virtual and real hardware and the problem is the same on each. I only tried this with Fedora 25 so it may not be an issue with other Fedora releases.
Note that the "recovery" kernel entry that is generated from the "rescue" kernel does work and boots to a maintenance mode login.
I recommend changing **GRUB_DISABLE_RECOVERY** to "false" in the grub defaults file, and generating your own **grub.cfg**. This will generate usable recovery entries in the GRUB menu for each of the installed kernels. These recovery configurations work as expected and boot to runlevel 1—according to the runlevel command—at a command line entry that requests a password to enter maintenance mode. You could also press **Ctrl-D** to continue a normal boot to the default runlevel.
## Conclusions
GRUB is the first step after BIOS in the sequence of events that boot a Linux computer to a usable state. Understanding how to configure GRUB is important to be able to recover from or to circumvent various types of problems.
I have had to boot to recovery or rescue mode many times over the years to resolve many types of problems. Some of those problems were actual boot problems due to things like improper entries in **/etc/fstab** or other configuration files, and others were due to problems with application or system software that was incompatible with the newest kernel. Hardware compatibility issues might also prevent a specific kernel from booting.
I hope this information will help you get started with GRUB configuration.
## 5 Comments |
8,604 | 机器学习的新捷径:通过 SYCL 在 GPU 上加速 C++ | https://blog.tartanllama.xyz/c++/2017/05/19/sycl/ | 2017-06-13T17:47:00 | [
"SYCL",
"OpenCL",
"机器学习",
"人工智能"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8604-1.html | 
在机器学习、计算机视觉以及高性能计算领域,充分利用显卡计算应用程序的能力已成为当前的热门。类似 OpenCL 的技术通过硬件无关的编程模型展现了这种能力,使得你可以编写抽象于不同体系架构的代码。它的目标是“一次编写,到处运行”,不管它是 Intel CPU、AMD 独立显卡还是 DSP 等等。不幸的是,对于日常程序员,OpenCL 的学习曲线陡峭;一个简单的 Hello World 程序可能就需要上百行晦涩难懂的代码。因此,为了减轻这种痛苦,Khronos 组织已经开发了一个称为 [SYCL](https://www.khronos.org/sycl) 的新标准,这是一个在 OpenCL 之上的 C++ 抽象层。通过 SYCL,你可以使用干净、现代的 C++ 开发出这些通用 GPU(GPGPU)应用程序,而无需拘泥于 OpenCL。下面是一个使用 SYCL 开发,通过并行 STL 实现的向量乘法事例:
```
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <sycl/execution_policy>
#include <experimental/algorithm>
#include <sycl/helpers/sycl_buffers.hpp>
using namespace std::experimental::parallel;
using namespace sycl::helpers;
int main() {
constexpr size_t array_size = 1024*512;
std::array<cl::sycl::cl_int, array_size> a;
std::iota(begin(a),end(a),0);
{
cl::sycl::buffer<int> b(a.data(), cl::sycl::range<1>(a.size()));
cl::sycl::queue q;
sycl::sycl_execution_policy<class Mul> sycl_policy(q);
transform(sycl_policy, begin(b), end(b), begin(b),
[](int x) { return x*2; });
}
}
```
为了作为对比,下面是一个通过 C++ API 使用 OpenCL 编写的大概对应版本(无需花过多时间阅读,只需注意到它看起来难看而且冗长)。
```
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <numeric>
#include <CL/cl.hpp>
int main(){
std::vector<cl::Platform> all_platforms;
cl::Platform::get(&all_platforms);
if(all_platforms.size()==0){
std::cout<<" No platforms found. Check OpenCL installation!\n";
exit(1);
}
cl::Platform default_platform=all_platforms[0];
std::vector<cl::Device> all_devices;
default_platform.getDevices(CL_DEVICE_TYPE_ALL, &all_devices);
if(all_devices.size()==0){
std::cout<<" No devices found. Check OpenCL installation!\n";
exit(1);
}
cl::Device default_device=all_devices[0];
cl::Context context({default_device});
cl::Program::Sources sources;
std::string kernel_code=
" void kernel mul2(global int* A){"
" A[get_global_id(0)]=A[get_global_id(0)]*2;"
" }";
sources.push_back({kernel_code.c_str(),kernel_code.length()});
cl::Program program(context,sources);
if(program.build({default_device})!=CL_SUCCESS){
std::cout<<" Error building: "<<program.getBuildInfo<CL_PROGRAM_BUILD_LOG>(default_device)<<"\n";
exit(1);
}
constexpr size_t array_size = 1024*512;
std::array<cl_int, array_size> a;
std::iota(begin(a),end(a),0);
cl::Buffer buffer_A(context,CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,sizeof(int)*a.size());
cl::CommandQueue queue(context,default_device);
if (queue.enqueueWriteBuffer(buffer_A,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(int)*a.size(),a.data()) != CL_SUCCESS) {
std::cout << "Failed to write memory;n";
exit(1);
}
cl::Kernel kernel_add = cl::Kernel(program,"mul2");
kernel_add.setArg(0,buffer_A);
if (queue.enqueueNDRangeKernel(kernel_add,cl::NullRange,cl::NDRange(a.size()),cl::NullRange) != CL_SUCCESS) {
std::cout << "Failed to enqueue kernel\n";
exit(1);
}
if (queue.finish() != CL_SUCCESS) {
std::cout << "Failed to finish kernel\n";
exit(1);
}
if (queue.enqueueReadBuffer(buffer_A,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(int)*a.size(),a.data()) != CL_SUCCESS) {
std::cout << "Failed to read result\n";
exit(1);
}
}
```
在这篇博文中我会介绍使用 SYCL 加速你 GPU 上的 C++ 代码。
### GPGPU 简介
在我开始介绍如何使用 SYCL 之前,我首先给那些不熟悉这方面的人简要介绍一下为什么你可能想要在 GPU 上运行计算任务。如果已经使用过 OpenCL、CUDA 或类似的库,可以跳过这一节。
GPU 和 CPU 的一个关键不同就是 GPU 有大量小的、简单的处理单元,而不是少量(对于普通消费者桌面硬件通常是 1-8 个)复杂而强大的核。

上面是一个 4 核 CPU 的简单漫画示意图。每个核都有一组寄存器以及不同等级的缓存(有些是共享缓存、有些不是),然后是主内存。

在 GPU 上,多个小处理单元被组成一个执行单元。每个小处理单元都附有少量内存,每个执行单元都有一些共享内存用于它的处理单元。除此之外,还有一些 GPU 范围的内存,然后是 CPU 使用的主内存。执行单元内部的单元是 *lockstep* ,每个单元都在不同的数据片上执行相同的指令。
这可以使 GPU 同时处理大量的数据。如果是在 CPU 上,也许你可以使用多线程和向量指令在给定时间内完成大量的工作,但是 GPU 所能处理的远多于此。在 GPU 上一次性能够处理的数据规模使得它非常适合于类似图形(duh)、数学处理、神经网络等等。
GPGPU 编程的很多方面使得它和日常的 CPU 编程完全不同。例如,从主内存传输数据到 GPU 是*很慢的*。*真的*很慢。会完全干掉你的性能使你慢下来。因此,GPU 编程的权衡是尽可能多地利用加速器的高吞吐量来掩盖数据来往的延迟。
这里还有一些不那么明显的问题,例如分支的开销。由于执行单元内的处理单元按照 lockstep 工作,使它们执行不同路径(不同的控制流)的嵌套分支就是个真正的问题。这通常通过在所有单元上执行所有分支并标记出无用结果来解决。这是一个基于嵌套级别的指数级的复杂度,这当然是坏事情。当然,有一些优化方法可以拯救该问题,但需要注意:你从 CPU 领域带来的简单假设和知识在 GPU 领域可能导致大问题。
在我们回到 SYCL 之前,需要介绍一些术语。<ruby> 主机 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> host </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>是主 CPU 运行的机器,<ruby> 设备 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> device </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>是会运行你 OpenCL 代码的地方。设备可能就是主机,但也可能是你机器上的一些加速器、模拟器等。<ruby> 内核 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> kernel </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>是一个特殊函数,它是在你设备上运行代码的入口点。通常还会提供一些主机设置好的缓存给它用于输入和输出数据。
### 回到 SYCL
这里有两个可用的 SYCL 实现:[triSYCL](https://github.com/Xilinx/triSYCL),由 Xilinx 开发的实验性开源版本(通常作为标准的试验台使用),以及 [ComputeCpp](https://www.codeplay.com/products/computesuite/computecpp),由 Codeplay(我在 Codeplay 工作,但这篇文章是在没有我雇主建议的情况下使用我自己时间编写的) 开发的工业级实现(当前处于开发测试版)。只有 ComputeCpp 支持在 GPU 上执行内核,因此在这篇文章中我们会使用它。
第一步是在你的机器上配置以及运行 ComputeCpp。主要组件是一个实现了 SYCL API 的运行时库,以及一个基于 Clang 的编译器,它负责编译你的主机代码和设备代码。在本文写作时,已经在 Ubuntu 和 CentOS 上官方支持 Intel CPU 以及某些 AMD GPU。在其它 Linux 发行版上让它工作也非常简单(例如,我让它在我的 Arch 系统上运行)。对更多的硬件和操作系统的支持正在进行中,查看[支持平台文档](https://www.codeplay.com/products/computesuite/computecpp/reference/platform-support-notes)获取最新列表。[这里](https://www.codeplay.com/products/computesuite/computecpp/reference/release-notes/)列出了依赖和组件。你也可能想要下载 [SDK](https://github.com/codeplaysoftware/computecpp-sdk),其中包括了示例、文档、构建系统集成文件,以及其它。在这篇文章中我会使用 [SYCL 并行 STL](https://github.com/KhronosGroup/SyclParallelSTL),如果你想要自己在家学习的话也要下载它。
一旦你设置好了一切,我们就可以开始通用 GPU 编程了!正如简介中提到的,我的第一个示例使用 SYCL 并行 STL 实现。我们现在来看看如何使用纯 SYCL 编写代码。
```
#include <CL/sycl.hpp>
#include <array>
#include <numeric>
#include <iostream>
int main() {
const size_t array_size = 1024*512;
std::array<cl::sycl::cl_int, array_size> in,out;
std::iota(begin(in),end(in),0);
{
cl::sycl::queue device_queue;
cl::sycl::range<1> n_items{array_size};
cl::sycl::buffer<cl::sycl::cl_int, 1> in_buffer(in.data(), n_items);
cl::sycl::buffer<cl::sycl::cl_int, 1> out_buffer(out.data(), n_items);
device_queue.submit([&](cl::sycl::handler &cgh) {
constexpr auto sycl_read = cl::sycl::access::mode::read;
constexpr auto sycl_write = cl::sycl::access::mode::write;
auto in_accessor = in_buffer.get_access<sycl_read>(cgh);
auto out_accessor = out_buffer.get_access<sycl_write>(cgh);
cgh.parallel_for<class VecScalMul>(n_items,
[=](cl::sycl::id<1> wiID) {
out_accessor[wiID] = in_accessor[wiID]*2;
});
});
}
}
```
我会把它划分为一个个片段。
```
#include <CL/sycl.hpp>
```
我们做的第一件事就是包含 SYCL 头文件,它会在我们的命令中添加 SYCL 运行时库。
```
const size_t array_size = 1024*512;
std::array<cl::sycl::cl_int, array_size> in,out;
std::iota(begin(in),end(in),0);
```
这里我们构造了一个很大的整型数组并用数字 `0` 到 `array_size-1` 初始化(这就是 `std::iota` 所做的)。注意我们使用 `cl::sycl::cl_int` 确保兼容性。
```
{
//...
}
```
接着我们打开一个新的作用域,其目的为二:
1. `device_queue` 将在该作用域结束时解构,它将阻塞,直到内核完成。
2. `in_buffer` 和 `out_buffer` 也将解构,这将强制数据传输回主机并允许我们从 `in` 和 `out` 中访问数据。 `cl::sycl::queue device_queue;`
现在我们创建我们的命令队列。命令队列是所有工作(内核)在分发到设备之前需要入队的地方。有很多方法可以定制队列,例如说提供设备用于入队或者设置异步错误处理器,但对于这个例子默认构造器就可以了;它会查找兼容的 GPU,如果失败的话会回退到主机 CPU。
```
cl::sycl::range<1> n_items{array_size};
```
接下来我们创建一个范围,它描述了内核在上面执行的数据的形状。在我们简单的例子中,它是一个一维数组,因此我们使用 `cl::sycl::range<1>`。如果数据是二维的,我们就会使用 `cl::sycl::range<2>`,以此类推。除了 `cl::sycl::range`,还有 `cl::sycl::ndrange`,它允许你指定工作组大小以及越界范围,但在我们的例子中我们不需要使用它。
```
cl::sycl::buffer<cl::sycl::cl_int, 1> in_buffer(in.data(), n_items);
cl::sycl::buffer<cl::sycl::cl_int, 1> out_buffer(out.data(), n_items);
```
为了控制主机和设备之间的数据共享和传输,SYCL 提供了一个 `buffer` 类。我们创建了两个 SYCL 缓存用于管理我们的输入和输出数组。
```
device_queue.submit([&](cl::sycl::handler &cgh) {/*...*/});
```
设置好了我们所有数据之后,我们就可以入队真正的工作。有多种方法可以做到,但设置并行执行的一个简单方法是在我们的队列中调用 `.submit` 函数。对于这个函数我们传递了一个运行时调度该任务时会被执行的“命令组伪函数”(伪函数是规范,不是我创造的)。命令组处理器设置任何内核需要的余下资源并分发它。
```
constexpr auto sycl_read = cl::sycl::access::mode::read_write;
constexpr auto sycl_write = cl::sycl::access::mode::write;
auto in_accessor = in_buffer.get_access<sycl_read>(cgh);
auto out_accessor = out_buffer.get_access<sycl_write>(cgh);
```
为了控制到我们缓存的访问并告诉该运行时环境我们会如何使用数据,我们需要创建访问器。很显然,我们创建了一个访问器用于从 `in_buffer` 读入,一个访问器用于写到 `out_buffer`。
```
cgh.parallel_for<class VecScalMul>(n_items,
[=](cl::sycl::id<1> wiID) {
out_accessor[wiID] = in_accessor[wiID]*2;
});
```
现在我们已经完成了所有设置,我们可以真正的在我们的设备上做一些计算了。这里我们根据范围 `n_items` 在命令组处理器 `cgh` 之上分发一个内核。实际内核自身是一个使用 work-item 标识符作为输入、输出我们计算结果的 lamda 表达式。在这种情况下,我们从 `in_accessor` 使用 work-item 标识符作为索引读入,将其乘以 `2`,然后将结果保存到 `out_accessor` 相应的位置。`<class VecScalMul>` 是一个为了在标准 C++ 范围内工作的不幸的副产品,因此我们需要给内核一个唯一的类名以便编译器能完成它的工作。
```
}
```
在此之后,我们现在可以访问 `out` 并期望看到正确的结果。
这里有相当多的新概念在起作用,但使用这些技术你可以看到这些能力和所展现出来的东西。当然,如果你只是想在你的 GPU 上执行一些代码而不关心定制化,那么你就可以使用 SYCL 并行 STL 实现。
### SYCL 并行 STL
SYCL 并行 STL 是一个 TS 的并行化实现,它分发你的算法函数对象作为 SYCL 内核。在这个页面前面我们已经看过这样的例子,让我们来快速过一遍。
```
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <sycl/execution_policy>
#include <experimental/algorithm>
#include <sycl/helpers/sycl_buffers.hpp>
using namespace std::experimental::parallel;
using namespace sycl::helpers;
int main() {
constexpr size_t array_size = 1024*512;
std::array<cl::sycl::cl_int, array_size> in,out;
std::iota(begin(in),end(in),0);
{
cl::sycl::buffer<int> in_buffer(in.data(), cl::sycl::range<1>(in.size()));
cl::sycl::buffer<int> out_buffer(out.data(), cl::sycl::range<1>(out.size()));
cl::sycl::queue q;
sycl::sycl_execution_policy<class Mul> sycl_policy(q);
transform(sycl_policy, begin(in_buffer), end(in_buffer), begin(out_buffer),
[](int x) { return x*2; });
}
}
```
```
constexpr size_t array_size = 1024*512;
std::array<cl::sycl::cl_int, array_size> in, out;
std::iota(begin(in),end(in),0);
```
到现在为止一切如此相似。我们再一次创建一组数组用于保存我们的输入输出数据。
```
cl::sycl::buffer<int> in_buffer(in.data(), cl::sycl::range<1>(in.size()));
cl::sycl::buffer<int> out_buffer(out.data(), cl::sycl::range<1>(out.size()));
cl::sycl::queue q;
```
这里我们创建类似上个例子的缓存和队列。
```
sycl::sycl_execution_policy<class Mul> sycl_policy(q);
```
这就是有趣的部分。我们从我们的队列中创建 `sycl_execution_policy`,给它一个名称让内核使用。这个执行策略然后可以像 `std::execution::par` 或 `std::execution::seq` 那样使用。
```
transform(sycl_policy, begin(in_buffer), end(in_buffer), begin(out_buffer),
[](int x) { return x*2; });
```
现在我们的内核分发看起来像提供了一个执行策略的 `std::transform` 调用。我们传递的闭包会被编译并在设备上执行,而不需要我们做其它更加复杂的设置。
当然,除了 `transform` 你可以做更多。开发的时候,SYCL 并行 STL 支持以下算法:
* `sort`
* `transform`
* `for_each`
* `for_each_n`
* `count_if`
* `reduce`
* `inner_product`
* `transform_reduce`
这就是这篇短文需要介绍的东西。如果你想和 SYCL 的开发保持同步,那就要看 [sycl.tech](http://sycl.tech/)。最近重要的开发就是移植 [Eigen](https://github.com/ville-k/sycl_starter) 和 [Tensorflow](http://deep-beta.co.uk/setting-up-tensorflow-with-opencl-using-sycl/) 到 SYCL ,为 OpenCL 设备带来引入关注的人工智能编程。对我个人而言,我很高兴看到高级编程模型可以用于异构程序自动优化,以及它们是怎样支持类似 [HPX](https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpx) 或 [SkelCL](https://github.com/skelcl/skelcl) 等更高级的技术。
---
via: <https://blog.tartanllama.xyz/c++/2017/05/19/sycl/>
作者:[TartanLlama](https://www.twitter.com/TartanLlama) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Redirecting…
Click here if you are not redirected. |
8,605 | 如何用树莓派控制 GPIO 引脚并操作继电器 | https://opensource.com/article/17/3/operate-relays-control-gpio-pins-raspberry-pi | 2017-06-13T22:14:00 | [
"树莓派"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8605-1.html |
>
> 学习如何用 PHP 和温度传感器实现树莓派控制 GPIO 并操作继电器
>
>
>

你是否曾经想知道怎样使用手机或者电脑在任何地方控制你的风扇和灯等一些家用电器?
我现在想控制我的圣诞彩灯,是使用手机呢,还是使用平板电脑呢,或者是使用笔记本电脑呢?都不是,而是仅仅使用一个树莓派。让我来告诉你如何使用 PHP 和温度传感器实现树莓派控制 GPIO 引脚并操作继电器。我使用 AJAX 把它们整合在了一起。
### 硬件要求:
* 树莓派
* 安装有 Raspbian 系统的 SD 卡(任何一张 SD 卡都可以,但是我更偏向使用大小为 32GB 等级为 class 10 的 SD 卡)
* 电源适配器
* 跳线(母对母跳线和公转母跳线)
* 继电器板(我使用一个用于 12V 继电器的继电器板)
* DS18B20 温度传感器
* 树莓派的 Wi-Fi 适配器
* 路由器(为了访问互联网,你需要有一个拥有端口转发的路由器)
* 10KΩ 的电阻
### 软件要求:
* 下载并安装 Raspbian 系统到你的 SD 卡
* 有效的互联网连接
* Apache web 服务器
* PHP
* WiringPi
* 基于 Mac 或者 Windows 的 SSH 客户端
### 一般的配置和设置
1、 插入 SD 卡到树莓派,然后使用以太网网线将它连接到路由器;
2、 连接 WiFi 适配器;
3、 使用 SSH 方式登录到树莓派,然后使用下面的命令编辑 `interfaces` 文件:
```
sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces
```
这个命令会用一个叫做 `nano` 的编辑器打开这个文件。它是一个非常简单又易于使用的文本编辑器。如果你不熟悉基 Linux 的操作系统,可以使用键盘上的方向键来操作。
用 `nano` 打开这个文件后,你会看到这样一个界面:

4、要配置你的无线网络,按照下面所示修改这个文件:
```
iface lo inet loopback
iface eth0 inet dhcp
allow-hotplug wlan0
auto wlan0
iface wlan0 inet dhcp
wpa-ssid "Your Network SSID"
wpa-psk "Your Password"
```
5、 按 `CTRL+O` 保存,然后按 `CTRL+X` 退出编辑器。
到目前为止,一切都已经配置完成,接下来你需要做的就是使用命令重新加载网络:
```
sudo service networking reload
```
(警告:如果你是使用远程连接的方式连接的树莓派,连接将会中断。)
### 软件配置
#### 安装 Apache web 服务器
Apache 是一个受欢迎的服务器应用,你可以在树莓派安装这个程序让它提供网页服务。Apache 原本就可以通过 HTTP 方式提供 HTML 文件服务,添加其他模块后,Apache 还可以使用像 PHP 这样的脚本语言来提供动态网页的服务。
可以在命令行输入下面命令安装 Apache:
```
sudo apt-get install apache2 -y
```
安装完成后,可以在浏览器地址栏输入树莓派的 IP 地址来测试 web 服务器。如果你可以获得下面图片的内容,说明你已经成功地安装并设置好了你的服务器。

要改变这个默认的页面和添加你自己的 html 文件,进入 `var/www/html` 目录:
```
cd /var/www/html
```
添加一些文件来测试是否成功。
#### 安装 PHP
PHP 是一个预处理器,这意味着它是当服务器收到网页请求时才会运行的一段代码。它开始运行,处理网页上需要被显示的内容,然后把网页发送给浏览器。不像静态的 HTML,PHP 在不同的环境下可以显示不同的内容。其他的语言也可以做到这一点,但是由于 WordPress 是用 PHP 编写的,有些时候你需要使用它。PHP 是 web 上一种非常受欢迎的语言,像 Facebok 和 Wikipeadia 这样的大型项目都是用 PHP 编写的。
使用下面的命令安装 PHP 和 Apache 软件包:
```
sudo apt-get install php5 libapache2-mod-php5 -y
```
#### 测试 PHP
创建文件 `index.php`:
```
sudo nano index.php
```
在里面写入一些 PHP 内容:
```
<?php echo "hello world"; ?>
```
保存文件,接下来删除 `index.html`,因为它比 `index.php` 的优先级更高:
```
sudo rm index.html
```
刷新你的浏览器,你会看到 “hello world”。这并不是动态的,但是它仍然由 PHP 提供服务。如果你在上面看到提原始的 PHP 文件而不是“hello world”,重新加载和重启 Apahce(LCTT 译注,重启即可):
```
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 reload
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
```
#### 安装 WiringPi
为了可以对代码的更改进行跟踪,WiringPi 的维护采用 git。但假如你因为某些原因而没法使用 git,还有一种可以替代的方案。(通常你的防火墙会把你隔离开来,所以请先检查一下你的防火墙的设置情况!)
如果你还没有安装 git,那么在 Debian 及其衍生版本中(比如 Raspbian),你可以这样安装它:
```
sudo apt-get install git-core
```
若是你遇到了一些错误,请确保你的树莓派是最新版本的 Raspbian 系统:
```
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
```
使用 git 获取最 WiringPi:
```
sudo git clone git://git.drogon.net/wiringPi
```
如果你之前已经使用过 clone 操作,那么可以使用下面命令:
```
cd wiringPi && git pull origin
```
这个命令会将会获取更新的版本,你然后可以重新运行下面的构建脚本。
有一个新的简化的脚本来构建和安装:
```
cd wiringPi && ./build
```
这个新的构建脚本将会为你完成编译和安装 WiringPi。它曾一度需要使用 `sudo` 命令,所以在运行这它之前你可能需要检查一下这个脚本。
#### 测试 WiringPi
运行 `gpio` 命令来检查安装成功与否:
```
gpio -v gpio readall
```
这将给你一些信心,软件运行良好。
#### 连接 DS18B20 传感器到树莓派
* 传感器上的黑线用于 GND。
* 红线用于 VCC。
* 黄线是 GPIO 线。

连线:
* VCC 连接 3V 的 1 号引脚。
* GPIO 线连接 7 号引脚(GPIO4)。
* 地线连接 GND 的 9 号引脚。
#### 软件配置
为了用 PHP 使用 DS18B20 温度传感器模块,你需要执行下面的命令来激活用于树莓派上 GPIO 引脚和 DS18B20 的内核模块:
```
sudo modprobe w1-gpio
sudo modprobe w1-therm
```
你不想每次 Raspberry 重启后都手动执行上述命令,所以你想每次开机能自动启动这些模块。可以在文件 `/etc/modules` 中添加下面的命令行来做到:
```
sudo nano /etc/modules/
```
添加下面的命令行到它里面:
```
w1-gpio
w1-therm
```
为了测试,输入:
```
cd /sys/bus/w1/devices/
```
现在输入 `ls`。
你会看到你的设备信息。在设备驱动程序中,你的 DS18B20 传感器应该作为一串字母和数字被列出。在本例中,设备被记录为 `28-000005e2fdc3`。然后你需要使用 `cd` 命令来访问传感器,用你自己的序列号替代我的: `cd 28-000005e2fdc3`。
DS18B20 会周期性的将数据写入文件 `w1_slave`,所以你只需要使用命令 `cat`来读出数据: `cat w1_slave`。
这会生成下面的两行文本,输出中 `t=` 表示摄氏单位的温度。在前两位数后面加上一个小数点(例如,我收到的温度读数是 30.125 摄氏度)。
### 连接继电器
1、 取两根跳线,把其中一根连接到树莓派上的 GPIO24(18 号引脚),另一根连接 GND 引脚。你可以参考下面这张图。
2、 现在将跳线的另一端连接到继电器板。GND 连接到继电器上的 GND,GPIO 输出线连接到继电器的通道引脚号,这取决于你正使用的继电器型号。记住,将树莓派上的 GND 与继电器上的 GND 连接连接起来,树莓派上的 GPIO 输出连接继电器上的输入引脚。

注意!将继电器连接树莓派的时候小心一些,因为它可能会导致电流回流,这会造成短路。
3、 现在将电源连接继电器,可以使用 12V 的电源适配器,也可以将 VCC 引脚连接到什么破上的 3.3V 或 5.5V 引脚。
### 使用 PHP 控制继电器
让我们先写一个借助于 WiringPi 软件用来控制 Paspberry Pi 上 GPIO 引脚的 PHP 脚本。
1、在 Apache 服务器的网站根目录下创建一个文件,使用下面命令切换到该目录:
```
cd /var/www/html
```
2、 新建一个叫 `Home` 的文件夹:
```
sudo mkdir Home
```
3、 新建一个叫 `on.php`的脚本
```
sudo nano on.php
```
4、 在脚本中加入下面的代码:
```
<?php
system("gpio-g mode 24 out");
system("gpio-g write 24 1");
?>
```
5、 使用 `CTRL+O` 保存文件,`CTRL+X` 退出。
上面的代码中,你在第一行使用命令将 24 号 GPIO引脚设置为 output 模式:
```
system("gpio-g mode 24 out");
```
在第二行,你使用 `1` 将 24 号引脚 GPIO 打开,在二进制中"1"表示打开,"0"表示关闭。
6、 为了关闭继电器,可以创建另外一个 `off.php` 文件,并用 `0` 替换 `1`。
```
<?php
system(" gpio-g mode 24 out ");
system(" gpio-g write 24 1 ");
?>
```
7、 如果你已经将继电器连接了树莓派,可以在浏览器中输入你的树莓派的 IP 地址,并在后面加上目录名和文件名来进行访问:
```
http://{IPADDRESS}/home/on.php
```
这将会打开继电器。
8、 要关闭它,可以访问叫 `off.php` 的文件:
```
http://{IPADDRESS}/home/off.php
```
现在你需要能够在一个单独的页面来控制这两样事情,而不用单独的刷新或者访问这两个页面。你可以使用 AJAX 来完成。
9、 新建一个 HTML 文件,并在其中加入下面代码:
```
<html>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.11.3/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">// <![CDATA[
$(document).ready(function() {
$('#on').click(function(){
var a= new XMLHttpRequest();
a.open("GET", "on.php"); a.onreadystatechange=function(){
if (a.readyState==4){
if(a.status ==200){
} else alert ("http error");
}
}
a.send();
});
});
$(document).ready(function()
{
$('#Off').click(function(){
var a= new XMLHttpRequest();
a.open("GET", "off.php");
a.onreadystatechange=function(){
if(a.readyState==4){
if(a.status ==200){
} else alert ("http error");
}
}
a.send();
});
});
</script>
<button id="on" type="button"``Switch Lights On </button>
<button id="off" type="button"``Switch Lights Off </button>
```
10、 保存文件,进入你的 web 浏览器目录,然后打开那个网页。你会看到两个按钮,它们可以打开和关闭灯泡。基于同样的想法,你还可以使用 bootstrap 和 CSS 来创建一个更加漂亮的 web 界面。
### 在这个网页上观察温度
1、 新建一个 `temperature.php` 的文件:
```
sudo nano temperature.php
```
2、 在文件中加入下面的代码,用你自己的设备 ID 替换 `10-000802292522`:
```
<?php
//File to read
$file = '/sys/devices/w1_bus_master1/10-000802292522/w1_slave';
//Read the file line by line
$lines = file($file);
//Get the temp from second line
$temp = explode('=', $lines[1]);
//Setup some nice formatting (i.e., 21,3)
$temp = number_format($temp[1] / 1000, 1, ',', '');
//And echo that temp
echo $temp . " °C";
?>
```
3、 打开你刚刚创建的 HTML 文件,并创建一个新的带有 `id` 为 “screen” 的 `<div>`标签
```
<div id="screen"></div>
```
4、 在这个标签后或者这个文档的尾部下面的代码:
```
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
setInterval(function(){
$("#screen").load('temperature.php')
}, 1000);
});
</script>
```
其中,`#screen` 是标签 `<div>` 的 `id` ,你想在它里面显示温度。它会每隔 1000 毫秒加载一次 `temperature.php` 文件。
我使用了 bootstrap 框架来制作一个漂亮的面板来显示温度,你还可以加入多个图标和图形让网页更有吸引力。
这只是一个控制继电器板并显示温度的基础的系统,你可以通过创建基于定时和从恒温器读数等基于事件触发来进一步地对系统进行开发。
( 题图:opensource.com)
---
作者简介:
Abdul Hannan Mustajab: 我 17 岁,生活在印度。我正在追求科学,数学和计算机科学方面的教育。我在 spunkytechnology.com 上发表关于我的项目的博客。我一直在对使用不同的微控制器和电路板的基于物联网的 AI 进行研究。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/3/operate-relays-control-gpio-pins-raspberry-pi>
作者:[Abdul Hannan Mustajab](https://opensource.com/users/mustajabhannan) 译者:[zhousiyu325](https://github.com/zhousiyu325) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Ever wondered how to control items like your fans, lights, and more using your phone or computer from anywhere?
I was looking to control my Christmas lights using any mobile phone, tablet, laptop... simply by using a Raspberry Pi. Let me show you how to operate relays and control GPIO pins with the Pi using PHP and a temperature sensor. I put them all together using AJAX.
## Hardware requirements
- Raspberry Pi
- SD Card with Raspbian installed (any SD card would work, but I prefer to use a 32GB class 10 card)
- Power adapter
- Jumper wires (female to female and male to female)
- Relay board (I use a 12V relay board with for relays)
- DS18B20 temperature probe
- Wi-Fi adapter for Raspberry Pi
- Router (for Internet access, you need to have a port-forwarding supported router)
- 10K-ohm resistor
## Software requirements
- Download and install Raspbian on your SD Card
- Working Internet connection
- Apache web server
- PHP
- WiringPi
- SSH client on a Mac or Windows client
## General configurations and setup
1. Insert the SD card into Raspberry Pi and connect it to the router using an Ethernet cable
2. Connect the Wi-Fi Adapter.
3. Now SSH to Pi and edit the **interfaces** file using:
**sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces**
This will open the file in an editor called **nano**. It is a very simple text editor that is easy to approach and use. If you're not familiar to a Linux-based operating systems, just use the arrow keys.
After opening the file in **nano** you will see a screen like this:
4. To configure your wireless network, modify the file as follows:
**iface lo inet loopback**
**iface eth0 inet dhcp**
** **
**allow-hotplug wlan0**
**auto wlan0**
** **
**iface wlan0 inet dhcp**
** wpa-ssid "Your Network SSID"**
** wpa-psk "Your Password"**
5. Press CTRL + O to save it, and then CTRL + X to exit the editor.
At this point, everything is configured and all you need to do is reload the network interfaces by running:
**sudo service networking reload**
(Warning: if you are connected using a remote connection it will disconnect now.)
## Software configurations
### Installing Apache Web Server
Apache is a popular web server application you can install on the Raspberry Pi to allow it to serve web pages. On its own, Apache can serve HTML files over HTTP, and with additional modules it can serve dynamic web pages using scripting languages such as PHP.
Install Apache by typing the following command on the command line:
**sudo apt-get install apache2 -y**
Once the installation is complete, type in the IP Address of your Pi to test the server. If you get the next image, then you have installed and set up your server successfully.
To change this default page and add your own html file, go to **var/www/html**:
**cd /var/www/html **
To test this, add any file to this folder.
### Installing PHP
PHP is a preprocessor, meaning this is code that runs when the server receives a request for a web page. It runs, works out what needs to be shown on the page, then sends that page to the browser. Unlike static HTML, PHP can show different content under different circumstances. Other languages are capable of this, but since WordPress is written in PHP it's what you need to use this time. PHP is a very popular language on the web, with large projects like Facebook and Wikipedia written in it.
Install the PHP and Apache packages with the following command:
**sudo apt-get install php5 libapache2-mod-php5 -y**
### Testing PHP
Create the file **index.php**:
**sudo nano index.php**
Put some PHP content in it:
**<?php echo "hello world"; ?>**
Save the file. Next, delete "index.html" because it takes precedence over "index.php":
**sudo rm index.html **
Refresh your browser. You should see “hello world.” This is not dynamic, but it is still served by PHP. If you see the raw PHP above instead of “hello world,” reload and restart Apache with:
**sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 reload**
**sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart**
### Installing WiringPi** **
WiringPi is maintained under **git** for ease of change tracking; however, you have a plan B if you’re unable to use **git** for whatever reason. (Usually your firewall will be blocking you, so do check that first!)
If you do not have **git** installed, then under any of the Debian releases (e.g., Raspbian), you can install it with:
**sudo apt-get install git-core**
If you get any errors here, make sure your Pi is up to date with the latest version of Raspbian:
**sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade**
To obtain WiringPi using **git**:
**sudo git clone git://git.drogon.net/wiringPi**
If you have already used the clone operation for the first time, then:
**cd wiringPi git pull origin**
It will fetch an updated version, and then you can re-run the build script below.
To build/install there is a new simplified script:
**cd wiringPi ./build**
The new build script will compile and install it all for you. It does use the **sudo** command at one point, so you may wish to inspect the script before running it.
### Testing WiringPi
Run the **gpio** command to check the installation:
**gpio -v gpio readall**
This should give you some confidence that it’s working OK.
### Connecting DS18B20 To Raspberry Pi
- The Black wire on your probe is for GND
- The Red wire is for VCC
- The Yellow wire is the GPIO wire
Connect:
- VCC to 3V Pin 1
- GPIO wire to Pin 7 (GPIO 04)
- Ground wire to any GND Pin 9
### Software Configuration
For using DS18B20 temperature sensor module with PHP, you need to activate the kernel module for the GPIO pins on the Raspberry Pi and the DS18B20 by executing the commands:
**sudo modprobe w1-gpio**
**sudo modprobe w1-therm**
You do not want to do that manually every time the Raspberry reboots, so you want to enable these modules on every boot. This is done by adding the following lines to the file **/etc/modules**:
**sudo nano /etc/modules/**
Add the following lines to it:
**w1-gpio **
**w1-therm**
To test this, type in:
**cd /sys/bus/w1/devices/**
Now type **ls. **
You should see your device information. In the device drivers, your DS18B20 sensor should be listed as a series of numbers and letters. In this case, the device is registered as 28-000005e2fdc3. You then need to access the sensor with the cd command, replacing my serial number with your own: **cd 28-000005e2fdc3. **
The DS18B20 sensor periodically writes to the **w1_slave** file, so you simply use the cat command to read it**: cat w1_slave.**
This yields the following two lines of text, with the output **t=** showing the temperature in degrees Celsius. Place a decimal point after the first two digits (e.g., the temperature reading I received is 30.125 degrees Celsius).
## Connecting the relay
1. Take two jumper wires and connect one of them to the GPIO 24 (Pin18) on the Pi and the other one to the GND Pin. You may refer the following diagram.
2. Now connect the other ends of the wire to the relay board. Connect the GND to the GND on the relay and GPIO Output wire to the relay channel pin number, which depends on the relay that you are using. Remember the** **GND** **goes to GND on the relay and GPIO Output goes to the relay input pin.
Caution! Be very careful with the relay connections with Pi because if it causes a backflow of current, you with have a short circuit.
3. Now connect the power supply to the relay, either using 12V power adapter or by connecting the VCC Pin to 3.3V or 5V on the Pi.
## Controlling the relay using PHP
Let's create a PHP script to control the GPIO pins on the Raspberry Pi, with the help of the WiringPi software.
1. Create a file in the Apache server’s root web directory. Navigate using:
**cd ../../../ **
**cd var/www/html/**
2. Create a new folder called Home:
**sudo mkdir Home**
3. Create a new PHP file called **on.php**:
**sudo nano on.php **
4. Add the following code to it:
```
``````
<?php
system(“ gpio-g mode 24 out “) ;
system(“ gpio-g write 24 1”) ;
?>
```
5. Save the file using CTRL + O and exit using CTRL + X
In the code above, in the first line you've set the GPIO Pin 24 to output mode using the command:
```
````system(“ gpio-g mode 24 out “) ;`
In the second line, you’ve turned on the GPIO Pin 24, Using “1,” where “1” in binary refers to ON and “0” Means OFF.
6. To turn off the relay, create another file called **off.php** and replace “1” with “0.”
```
``````
<?php
system(“ gpio-g mode 24 out “) ;
system(“ gpio-g write 24 0”) ;
?>
```
7. If you have your relay connected to the Pi, visit your web browser and type in the IP Address of your Pi followed by the directory name and file name:
**http://{IPADDRESS}/home/on.php**
This will turn ON the relay.
8. To turn it OFF, open the page called **off.php**,
**http://{IPADDRESS}/home/off.php**
Now you need to control both these things from a single page without refreshing or visiting the pages individually. For that you'll use AJAX.
9. Create a new HTML file and add this code to it.
```
``````
[html + php + ajax codeblock]
<html>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.11.3/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">// <![CDATA[
$(document).ready(function() {
$('#on').click(function(){
var a= new XMLHttpRequest();
a.open("GET", "on.php"); a.onreadystatechange=function(){
if(a.readyState==4){ if(a.status ==200){
} else alert ("http error"); } }
a.send();
});
});
$(document).ready(function()
{ $('#Off').click(function(){
var a= new XMLHttpRequest();
a.open("GET", "off.php");
a.onreadystatechange=function(){
if(a.readyState==4){
if(a.status ==200){
} else alert ("http error"); } }
a.send();
});
});
</script>
<button id="on" type="button"> Switch Lights On </button>
<button id="off" type="button"> Switch Lights Off </button>
```
10. Save the file, go to your web browser, and open that page. You’ll see two buttons, which will turn lights on and off. Based on the same idea, you can create a beautiful web interface using bootstrap and CSS skills.
## Viewing temperature on this web page
1. Create a file called **temperature.php**:
```
````sudo nano temperature.php`
** **2. Add the following code to it, replace 10-000802292522 with your device ID:
```
``````
<?php
//File to read
$file = '/sys/devices/w1_bus_master1/10-000802292522/w1_slave';
//Read the file line by line
$lines = file($file);
//Get the temp from second line
$temp = explode('=', $lines[1]);
//Setup some nice formatting (i.e., 21,3)
$temp = number_format($temp[1] / 1000, 1, ',', '');
//And echo that temp
echo $temp . " °C";
?>
```
3. Go to the HTML file that you just created, and create a new **<div>** with the **id** “screen”: **<div id=“screen”></div>.**
4. Add the following code after the **<body>** tag or at the end of the document:
```
``````
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
setInterval(function(){
$("#screen").load('temperature.php')
}, 1000);
});
</script>
```
In this, **#screen** is the **id** of **<div>** in which you want to display the temperature. It loads the **temperature.php** file every 1000 milliseconds.
I have used bootstrap to make a beautiful panel for displaying temperature. You can add multiple icons and glyphicons as well to make it more attractive.
This was just a basic system that controls a relay board and displays the temperature. You can develop it even further by creating event-based triggers based on timings, temperature readings from the thermostat, etc.
## 4 Comments |
8,606 | 10 个使用 Cinnamon 作为 Linux 桌面环境的理由 | https://opensource.com/article/17/1/cinnamon-desktop-environment | 2017-06-14T18:26:00 | [
"桌面",
"Cinnamon",
"GNOME"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8606-1.html |
>
> Cinnamon 是一个让人怀旧 GNOME 2 的 Linux 桌面环境,它灵活、快速,并提供了种种的功能。
>
>
>

最近我安装了 Fedora 25,我觉得当前的 [KDE](https://opensource.com/life/15/4/9-reasons-to-use-kde) Plasma 版本并不稳定。在我决定尝试其它的桌面之前一天崩溃了好几次。在我安装了几个其它的桌面,并每个尝试了几个小时后,我最终决定在 Plasma 打上补丁并且稳定之前就使用 Cinnamon 了。以下是我所发现的。
### Cinnamon 简介
在 2011,带有新的 GNOME Shell 的 GNOME 3 发布了,新的界面马上引来了或正或反的反馈。许多用户以及开发者非常喜欢原先的 GNOME 界面,因此有多个组织复刻了它,其中一个结果就是 Cinnamon。
开发 GNOME 3 的 GNOME shell 背后的原因之一是许多原先的 GNOME 用户界面组件不再活跃开发了。这同样也是 Cinnamon 以及其他 GNOME 复刻项目的问题。 Linux Mint 项目是 Cinnamon 的一个首要推动者,因为 GNOME 是 Mint 的官方桌面环境。Mint 开发者已经将 Cinnamon 推进到了不需要 GNOME 本身的地步,Cinnamon 已经是一个完全独立的桌面环境,它保留了许多用户喜欢的 GNOME 界面的功能。

*图 1:打开系统设置工具的默认 Cinnamon 桌面。*
Cinnamon 3.2 是当前发布版本。除了 Mint,Cinnamon 还在许多发行版中可用,包括 Fedora、Arch、Gentoo、Debian 和 OpenSUSE 等。
### 使用 Cinnamon 的理由
这是我的使用 Cinnamon 的 10 个重要理由:
1. **集成。** 桌面的选择并不取决于在较长时间内是否有为它写的应用。我使用过的所有应用程序,不管它是在哪个桌面下写的,它都可以在任何其它桌面上运行正常,Cinnamon 也不例外。要运行那些为 KDE、GNOME 或其他桌面编写的程序所需要的库都有,可以在 Cinnamon 上面顺滑地使用这些程序。
2. **外观。** 让我们面对它,外观是很重要的。Cinnamon 有一个明快的、干净的外观,它使用了易于阅读的字体以及颜色的组合。桌面没有不必要的阻碍,你可以使用“系统设置” => “桌面” 菜单配置显示在桌面上的的图标。这个菜单还允许你指定是否在主监视器、次监视器或者所有监视器上显示桌面图标。
3. **桌面组件。** 桌面组件是一些小型的、可以添加到桌面的单一用途的程序。只有一些是可用的,但是你可以从 CPU 或者磁盘监视器、天气应用、便利贴、桌面相簿、时间和日期等之中选择。我喜欢时间和日期桌面组件,因为它比 Cinnamon 面板中的小程序易于阅读。
4. **速度。** Cinnamon 快速又敏捷。程序加载和显示很快。桌面自身在登录时加载也很快,虽然这只是我的主观体验,并没有基于时间测试。
5. **配置。** Cinnamon 不如 KDE Plasma 那样可配置,但是也要比我第一次尝试它的时候有更多的配置。Cinnamon 控制中心提供了许多桌面配置选项的集中访问。它有一个主窗口,可以从它启动特定功能的配置窗口。可以很容易地在 “系统设置” 的 “主题” 的可用外观中选择新的外观。你可以选择窗口边框、图标、控件、鼠标指针和桌面基本方案。其它选择还包括字体和背景。我发现这些配置工具中有许多是我遇到的最好的。它有适量的桌面主题,从而能够显著改变桌面的外观,而不会像 KDE 那样面临选择困难。
6. **Cinnamon 面板。** Cinnamon 面板,即工具栏,最初的配置非常简单。它包含用于启动程序的菜单、基本的系统托盘和应用程序选择器。这个面板易于配置,并且添加新的程序启动器只需要定位你想要添加到主菜单的程序,右键单击程序图标,然后选择“添加到面板”。你还可以将启动器图标添加到桌面本身,以及 Cinnamon 的 “收藏” 的启动栏中。你还可以进入面板的**编辑**模式并重新排列图标。
7. **灵活性。** 有时可能很难找到最小化或者隐藏的正在运行的程序,如果有许多正在运行的应用程序,则在工具栏的程序选择器上查找它可能会有挑战性。 在某种程度上,这是因为程序并不总是有序地排在选择器中使其易于查找,所以我最喜欢的功能之一就是可以拖动正在运行的程序的按钮并将其重新排列在选择器上。这可以使查找和显示属于程序的窗口更容易,因为现在它们现在在我放的位置上。
Cinnamon 桌面还有一个非常好的弹出菜单,你可以右键单击访问。此菜单有一些常用任务,例如访问桌面设置、添加桌面组件以及其他与桌面相关的任务。
其它菜单项之一是 “创建新文档”,它使用位于 `~/Templates` 目录中的文档模板,并列出它们中的每一个。只需点击要使用的模板,使用这个模板的文档就会使用默认的 Office 程序创建。在我的情况下,那就是 LibreOffice。
8. **多工作空间。** Cinnamon 像其他桌面环境一样提供了多个桌面。Cinnamon 称它为“工作区”。工作区选择器位于 Cinnamon 面板中并展示每个工作区的窗口概览。窗口可以在工作区之间移动或指定到所有工作区。我确实发现工作区选择器有时候会比窗口位置的显示慢一些,所以我将工作区选择器切换为显示工作区编号,而不是在工作区中显示窗口概览。
9. **Nemo。** 大部分桌面因种种目而使用它们自己偏好的默认程序,Cinnamon 也不例外。我偏好的桌面文件管理器是 Krusader,但是 Cinnamon 默认使用 Nemo,因此在测试中我就用它了。我发现我很喜欢 Nemo。它有一个美丽干净的界面,我喜欢大部分功能并经常使用。它易于使用,同时对我的需求也足够灵活。虽然 Nemo 是 Nautilus 的复刻,但是我发现 Nemo 更好地被集成进了 Cinnamon 环境。Nautilus 界面看上去没有与 Cinnamon 很好集成,与 Cinnamon 不太和谐。
10. **稳定性。** Cinnamon 非常稳定且可用。
### 总结
Cinnamon 是 GNOME 3 桌面的复刻,它看上去像一个前所未有的 GNOME 桌面。它的发展看起来是符合逻辑的改进, Cinnamon 开发者认为需要在提升和扩展 GNOME 的同时保留它的独特性以及被大家非常喜欢的特性。它不再是 GNOME 3 - 它是不同的并且是更好的。Cinnamon 看上去很棒,并且对我而言也工作得很好,并且从 KDE 这个我仍旧非常喜欢的环境切换过来也很顺畅。我花费了几天时间学习 Cinnamon 的差异如何使我的桌面体验更好,并且我非常高兴了解这个很棒的桌面。
虽然我喜欢 Cinnamon,但我仍然喜欢体验其它的环境,我目前正切换到 LXDE 桌面,并已经用了几个星期。在我使用一段时间时候,我会分享我的 LXDE 体验。
(题图: [Sam Mugraby](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cinnamon-other.jpg),Photos8.com. [CC BY 2.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/deed.en))
---
作者简介:
David Both 是一个 Linux 和开源倡导者,他居住在北卡罗莱纳州的 Raleigh。他在 IT 行业已经超过 40 年,在他工作的 IBM 公司教授 OS/2 超过 20 年,他在 1981 年为最早的 IBM PC 写了第一个培训课程。他教过 Red Hat 的 RHCE 课程,在 MCI Worldcom、 Cisco 和北卡罗莱纳州 工作过。他一直在使用 Linux 和开源软件近 20 年。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/1/cinnamon-desktop-environment>
作者:[David Both](https://opensource.com/users/dboth) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Recently I installed Fedora 25, and found that the current version of [KDE](https://opensource.com/life/15/4/9-reasons-to-use-kde) Plasma was unstable for me; it crashed several times a day before I decided to try to try something different. After installing a number of alternative desktops and trying them all for a couple hours each, I finally settled on using Cinnamon until Plasma is patched and stable. Here's what I found.
## Introducing Cinnamon
In 2011, GNOME 3, with the new GNOME Shell was released and the new interface immediately generated both positive and negative responses. Many users and developers liked the original GNOME interface enough that multiple groups forked it and one of those forks was Cinnamon.
One of the reasons behind the development of the GNOME shell for GNOME 3 was that many components of the original GNOME user interface were no longer being actively developed. This was also an issue for Cinnamon and some of the other forked GNOME projects. The Linux Mint project was one of the prime movers for Cinnamon because GNOME is the official desktop environment for Mint. The Mint developers have continued to develop Cinnamon to the point where GNOME itself is no longer required, and Cinnamon is a completely independent desktop environment that retains many of the interface features that users appreciated about the GNOME interface.
Figure 1: The default Cinnamon desktop with the System Settings tool open.
Cinnamon 3.2 is the current release version. Cinnamon is available for many distros besides Mint, including Fedora, Arch, Gentoo, Debian, and OpenSUSE, among others.
## Reasons for using Cinnamon
Here are my top 10 reasons for using Cinnamon.
-
**Integration.**The choice of a desktop has not been contingent upon the availability of applications written for it in a long time. All of the applications I use, regardless of the desktop for which they were written, will run just fine on any other desktop, and Cinnamon is no exception. All of the libraries required to run applications written for KDE, GNOME—or any other desktop that I use—are available and make using any application with the Cinnamon desktop a seamless experience. -
**Looks.**Let's face it, looks are important. Cinnamon has a crisp, clean look that uses easy to read fonts and color combinations. The desktop is not hampered by unnecessary clutter, and you can configure which icons are shown on the desktop using the**System Settings => Desktop**menu. This menu also allows you to specify whether the desktop icons are shown only on the primary monitor, only on secondary monitors, or on all monitors. -
**Desklets.**Desklets are small, usually single-purpose applications that can be added to your desktop. Only a few of these are available, but you can choose from things like CPU or disk monitors, a weather app, sticky notes, a desktop photo frame app, and time and date, among others. I like the time and date desklet because it is easier to read than the applet in the Cinnamon panel. -
**Speed.**Cinnamon is fast and snappy. Programs load and display fast. The desktop itself loads quickly during login, though this is just my subjective experience and is not based on any timed testing. -
**Configuration.**Cinnamon is not as configurable as KDE Plasma, but it is much more configurable than I originally thought the first time I tried it. The Cinnamon Control Center provides centralized access to many of the desktop configuration options. It has a main window from which the specific feature configuration windows can be launched. It is easy to select a new look from those available in the Themes section of System Settings. You can choose window borders, icons, controls, pointers, and the desktop basic scheme. Other choices include fonts and backgrounds. I find many of these configuration tools among the best I have encountered. A modest number of desktop themes are available, providing the ability to significantly alter the look of the desktop without the confusion of the massive numbers of choices that KDE provides. -
**The Cinnamon Panel.**The Cinnamon Panel, i.e., the toolbar, is initially configured very simply. It contains the menu used to launch programs, a basic system tray, and an application selector. The panel is easy to configure and adding new program launchers is simply a matter of locating the program you want to add in the main Menu; right click on the program icon and select "Add to panel." You can also add the launcher icon to the desktop itself, and to the Cinnamon "Favorites" launcher bar. You can also enter the panel's**Edit**mode and rearrange the icons. -
**Flexibility****.**It can sometimes be difficult to locate a minimized or hidden running application and finding it on the toolbar application selector can be challenging if there are a number of running applications. In part, this is because the applications are not always in a sequence on the selector that makes them easy to find. So one of my favorite features is the ability to drag the buttons for the running applications and rearrange them on the selector. This can make it much easier to find and display windows belonging to applications because they can now be where I put them on the selector.The Cinnamon desktop also has a very nice pop-up menu that you can access with a right click. This menu has selections for some frequently used tasks such as accessing the Desktop Settings and adding Desklets, as well as other desktop-related tasks.
One of these other menu items is “Create New Document” which uses the document templates located in the ~/Templates directory and lists each of them. Simply click on the template you want to use and a new document using that template is created using the default office application. In my case, that is LibreOffice.
-
**Multiple****workspaces****.**Cinnamon offers multiple desktops like many other desktop environments. Cinnamon calls these "workspaces." The workspace selector is located on the Cinnamon panel and shows the outlines of the windows located on each workspace. Windows can be moved between workspaces or assigned to all. I did find that the workspace selector is sometimes a bit slow to catch up with the display of window locations so I switched the workspace selector to show the workspace numbers and not shadows of the windows in the workspaces. -
**Nemo.**Most desktops use their own preferred default applications for various purposes and Cinnamon is no exception. My preferred desktop file manager is Krusader, but Cinnamon uses Nemo as its default, so I just went with that for the duration of my test. I find that I like Nemo—a lot. It has a nice clean interface and most of the features I like and use frequently. It is easy to use while being flexible enough for my needs. Although Nemo is a fork of Nautilus, I find Nemo to be better integrated into the Cinnamon environment. The Nautilus interface seems to be somewhat poorly integrated and discordant with Cinnamon. -
**Stability.**Cinnamon is very stable and just works.
## Conclusions
Cinnamon is a fork of the GNOME 3 desktop and appears to be intended as the GNOME desktop that never was. Its development seems to be the logical improvements that the Cinnamon developers thought were needed to improve and extend GNOME while retaining its unique and highly appreciated personality. It is no longer GNOME 3—it is different and better. Cinnamon looks good and it works very well for me and is a very nice change from KDE—which I still like very much. It took me a few days to learn how Cinnamon's differences could make my desktop experience better, and I am very glad to have learned a lot more about an excellent desktop.
Though I like Cinnamon, I would like to experiment with some others as well, and I am now going to switch to the LXDE desktop and try that out for a few weeks. I will share my experience with LXDE after I have spent some time using it.
## 15 Comments |
8,607 | 许多 SQL 性能问题来自于“不必要的强制性工作” | https://blog.jooq.org/2017/03/08/many-sql-performance-problems-stem-from-unnecessary-mandatory-work | 2017-06-15T08:17:00 | [
"数据库",
"索引",
"ORM"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8607-1.html | 
在编写高效 SQL 时,你可能遇到的最有影响的事情就是[索引](http://use-the-index-luke.com/)。但是,一个很重要的事实就是很多 SQL 客户端要求数据库做很多**“不必要的强制性工作”**。
跟我再重复一遍:
>
> 不必要的强制性工作
>
>
>
什么是**“不必要的强制性工作”**?这个意思包括两个方面:
### 不必要的
假设你的客户端应用程序需要这些信息:

这没什么特别的。我们运行着一个电影数据库([例如 Sakila 数据库](https://github.com/jOOQ/jOOQ/tree/master/jOOQ-examples/Sakila)),我们想要给用户显示每部电影的名称和评分。
这是能产生上面结果的查询:
```
SELECT title, rating
FROM film
```
然而,我们的应用程序(或者我们的 ORM(LCTT 译注:<ruby> 对象关系映射 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Object-Relational Mapping </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>))运行的查询却是:
```
SELECT *
FROM film
```
我们得到什么?猜一下。我们得到很多无用的信息:

甚至一些复杂的 JSON 数据全程在下列环节中加载:
* 从磁盘
* 加载到缓存
* 通过总线
* 进入客户端内存
* 然后被丢弃
是的,我们丢弃了其中大部分的信息。检索它所做的工作完全就是不必要的。对吧?没错。
### 强制性
这是最糟糕的部分。现今随着优化器变得越来越聪明,这些工作对于数据库来说都是强制执行的。数据库没有办法*知道*客户端应用程序实际上不需要其中 95% 的数据。这只是一个简单的例子。想象一下如果我们连接更多的表...
你想想那会怎样呢?数据库还快吗?让我们来看看一些之前你可能没有想到的地方:
### 内存消耗
当然,单次执行时间不会变化很大。可能是慢 1.5 倍,但我们可以忍受,是吧?为方便起见,有时候确实如此。但是如果你*每次*都为了方便而牺牲性能,这事情就大了。我们不说性能问题(单个查询的速度),而是关注在吞吐量上时(系统响应时间),事情就变得困难而难以解决。你就会受阻于规模的扩大。
让我们来看看执行计划,这是 Oracle 的:
```
--------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes |
--------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1000 | 166K|
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| FILM | 1000 | 166K|
--------------------------------------------------
```
对比一下:
```
--------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes |
--------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1000 | 20000 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| FILM | 1000 | 20000 |
--------------------------------------------------
```
当执行 `SELECT *` 而不是 `SELECT film, rating` 的时候,我们在数据库中使用了 8 倍之多的内存。这并不奇怪,对吧?我们早就知道了。在很多我们并不需要其中全部数据的查询中我们都是这样做的。我们为数据库产生了**不必要的强制性工作**,其后果累加了起来,就是我们使用了多达 8 倍的内存(当然,数值可能有些不同)。
而现在,所有其它的步骤(比如,磁盘 I/O、总线传输、客户端内存消耗)也受到相同的影响,我这里就跳过了。另外,我还想看看...
### 索引使用
如今大部分数据库都有[涵盖索引](https://blog.jooq.org/2015/04/28/do-not-think-that-one-second-is-fast-for-query-execution/)(LCTT 译注:covering index,包括了你查询所需列、甚至更多列的索引,可以直接从索引中获取所有需要的数据,而无需访问物理表)的概念。涵盖索引并不是特殊的索引。但对于一个特定的查询,它可以“意外地”或人为地转变为一个“特殊索引”。
看看这个查询:
```
SELECT *
FROM actor
WHERE last_name LIKE 'A%'
```
执行计划中没有什么特别之处。它只是个简单的查询。索引范围扫描、表访问,就结束了:
```
-------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows |
-------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 8 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| ACTOR | 8 |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_ACTOR_LAST_NAME | 8 |
-------------------------------------------------------------------
```
这是个好计划吗?如果我们只是想要这些,那么它就不是:

当然,我们浪费了内存之类的。再来看看这个查询:
```
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM actor
WHERE last_name LIKE 'A%'
```
它的计划是:
```
----------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows |
----------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 8 |
|* 1 | INDEX RANGE SCAN| IDX_ACTOR_NAMES | 8 |
----------------------------------------------------
```
现在我们可以完全消除表访问,因为有一个索引涵盖了我们查询需要的所有东西……一个涵盖索引。这很重要吗?当然!这种方法可以将你的某些查询加速一个数量级(如果在某个更改后你的索引不再涵盖,可能会降低一个数量级)。
你不能总是从涵盖索引中获利。索引也有它们自己的成本,你不应该添加太多索引,例如像这种情况就是不明智的。让我们来做个测试:
```
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON
DECLARE
v_ts TIMESTAMP;
v_repeat CONSTANT NUMBER := 100000;
BEGIN
v_ts := SYSTIMESTAMP;
FOR i IN 1..v_repeat LOOP
FOR rec IN (
-- Worst query: Memory overhead AND table access
SELECT *
FROM actor
WHERE last_name LIKE 'A%'
) LOOP
NULL;
END LOOP;
END LOOP;
dbms_output.put_line('Statement 1 : ' || (SYSTIMESTAMP - v_ts));
v_ts := SYSTIMESTAMP;
FOR i IN 1..v_repeat LOOP
FOR rec IN (
-- Better query: Still table access
SELECT /*+INDEX(actor(last_name))*/
first_name, last_name
FROM actor
WHERE last_name LIKE 'A%'
) LOOP
NULL;
END LOOP;
END LOOP;
dbms_output.put_line('Statement 2 : ' || (SYSTIMESTAMP - v_ts));
v_ts := SYSTIMESTAMP;
FOR i IN 1..v_repeat LOOP
FOR rec IN (
-- Best query: Covering index
SELECT /*+INDEX(actor(last_name, first_name))*/
first_name, last_name
FROM actor
WHERE last_name LIKE 'A%'
) LOOP
NULL;
END LOOP;
END LOOP;
dbms_output.put_line('Statement 3 : ' || (SYSTIMESTAMP - v_ts));
END;
/
```
结果是:
```
Statement 1 : +000000000 00:00:02.479000000
Statement 2 : +000000000 00:00:02.261000000
Statement 3 : +000000000 00:00:01.857000000
```
注意,表 actor 只有 4 列,因此语句 1 和 2 的差别并不是太令人印象深刻,但仍然很重要。还要注意我使用了 Oracle 的提示来强制优化器为查询选择一个或其它索引。在这种情况下语句 3 明显胜利。这是一个好*很多*的查询,也是一个十分简单的查询。
当我们写 `SELECT *` 语句时,我们为数据库带来了**不必要的强制性工作**,这是无法优化的。它不会使用涵盖索引,因为比起它所使用的 `LAST_NAME` 索引,涵盖索引开销更多一点,不管怎样,它都要访问表以获取无用的 `LAST_UPDATE` 列。
使用 `SELECT *` 会变得更糟。考虑一下……
### SQL 转换
优化器工作的很好,因为它们转换了你的 SQL 查询([看我最近在 Voxxed Days Zurich 关于这方面的演讲](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wTPGW1PNy_Y))。例如,其中有一个称为“表连接消除”的转换,它真的很强大。看看这个辅助视图,我们写了这个视图是因为我们非常讨厌总是连接所有这些表:
```
CREATE VIEW v_customer AS
SELECT
c.first_name, c.last_name,
a.address, ci.city, co.country
FROM customer c
JOIN address a USING (address_id)
JOIN city ci USING (city_id)
JOIN country co USING (country_id)
```
这个视图仅仅是把 `CUSTOMER` 和他们不同的 `ADDRESS` 部分所有“对一”关系连接起来。谢天谢地,它很工整。
现在,使用这个视图一段时间之后,想象我们非常习惯这个视图,我们都忘了所有它底层的表。然后,我们运行了这个查询:
```
SELECT *
FROM v_customer
```
我们得到了一个相当令人印象深刻的计划:
```
----------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost |
----------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 599 | 47920 | 14 |
|* 1 | HASH JOIN | | 599 | 47920 | 14 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS FULL | COUNTRY | 109 | 1526 | 2 |
|* 3 | HASH JOIN | | 599 | 39534 | 11 |
| 4 | TABLE ACCESS FULL | CITY | 600 | 10800 | 3 |
|* 5 | HASH JOIN | | 599 | 28752 | 8 |
| 6 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| CUSTOMER | 599 | 11381 | 4 |
| 7 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| ADDRESS | 603 | 17487 | 3 |
----------------------------------------------------------------
```
当然是这样。我们运行了所有这些表连接以及全表扫描,因为这就是我们让数据库去做的:获取所有的数据。
现在,再一次想一下,对于一个特定场景,我们真正想要的是:

是啊,对吧?现在你应该知道我的意图了。但想像一下,我们确实从前面的错误中学到了东西,现在我们实际上运行下面一个比较好的查询:
```
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM v_customer
```
再来看看结果!
```
------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost |
------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 599 | 16173 | 4 |
| 1 | NESTED LOOPS | | 599 | 16173 | 4 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| CUSTOMER | 599 | 11381 | 4 |
|* 3 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN| SYS_C007120 | 1 | 8 | 0 |
------------------------------------------------------------------
```
这是执行计划一个*极大的*进步。我们的表连接被消除了,因为优化器可以证明它们是**不必要的**,因此一旦它可以证明这点(而且你不会因使用 `select *` 而使其成为**强制性**工作),它就可以移除这些工作并不执行它。为什么会发生这种情况?
每个 `CUSTOMER.ADDRESS_ID` 外键保证了*有且只有一个* `ADDRESS.ADDRESS_ID` 主键值,因此可以保证 `JOIN` 操作是对一连接,它不会产生或者删除行。如果我们甚至不选择行或查询行,当然我们就不需要真正地去加载行。可以证实地移除 `JOIN` 并不会改变查询的结果。
数据库总是会做这些事情。你可以在大部分数据库上尝试它:
```
-- Oracle
SELECT CASE WHEN EXISTS (
SELECT 1 / 0 FROM dual
) THEN 1 ELSE 0 END
FROM dual
-- 更合理的 SQL 语句,例如 PostgreSQL
SELECT EXISTS (SELECT 1 / 0)
```
在这种情况下,当你运行这个查询时你可能预料到会抛出算术异常:
```
SELECT 1 / 0 FROM dual
```
产生了:
```
ORA-01476: divisor is equal to zero
```
但它并没有发生。优化器(甚至解析器)可以证明 `EXISTS (SELECT ..)` 谓词内的任何 `SELECT` 列表达式不会改变查询的结果,因此也就没有必要计算它的值。呵!
### 同时……
大部分 ORM 最不幸问题就是事实上他们很随意就写出了 `SELECT *` 查询。事实上,例如 HQL / JPQL,就设置默认使用它。你甚至可以完全抛弃 `SELECT` 从句,因为毕竟你想要获取所有实体,正如声明的那样,对吧?
例如:
`FROM` `v_customer`
例如 [Vlad Mihalcea](https://vladmihalcea.com/2016/09/13/the-best-way-to-handle-the-lazyinitializationexception/)(一个 Hibernate 专家和 Hibernate 开发倡导者)建议你每次确定不想要在获取后进行任何更改时再使用查询。ORM 使解决对象图持久化问题变得简单。注意:持久化。真正修改对象图并持久化修改的想法是固有的。
但如果你不想那样做,为什么要抓取实体呢?为什么不写一个查询?让我们清楚一点:从性能角度,针对你正在解决的用例写一个查询*总是*会胜过其它选项。你可以不会在意,因为你的数据集很小,没关系。可以。但最终,你需要扩展并重新设计你的应用程序以便在强制实体图遍历之上支持查询语言,就会变得很困难。你也需要做其它事情。
### 计算出现次数
资源浪费最严重的情况是在只是想要检验存在性时运行 `COUNT(*)` 查询。例如:
>
> 这个用户有没有订单?
>
>
>
我们会运行:
```
SELECT count(*)
FROM orders
WHERE user_id = :user_id
```
很简单。如果 `COUNT = 0`:没有订单。否则:是的,有订单。
性能可能不会很差,因为我们可能有一个 `ORDERS.USER_ID` 列上的索引。但是和下面的这个相比你认为上面的性能是怎样呢:
```
-- Oracle
SELECT CASE WHEN EXISTS (
SELECT *
FROM orders
WHERE user_id = :user_id
) THEN 1 ELSE 0 END
FROM dual
-- 更合理的 SQL 语句,例如 PostgreSQL
SELECT EXISTS (
SELECT *
FROM orders
WHERE user_id = :user_id
)
```
它不需要火箭科学家来确定,一旦它找到一个,实际存在谓词就可以马上停止寻找额外的行。因此,如果答案是“没有订单”,速度将会是差不多。但如果结果是“是的,有订单”,那么结果在我们不计算具体次数的情况下就会*大幅*加快。
因为我们*不在乎*具体的次数。我们告诉数据库去计算它(**不必要的**),而数据库也不知道我们会丢弃所有大于 1 的结果(**强制性**)。
当然,如果你在 JPA 支持的集合上调用 `list.size()` 做同样的事情,情况会变得更糟!
[近期我有关于该情况的博客以及在不同数据库上的测试。去看看吧。](https://blog.jooq.org/2016/09/14/avoid-using-count-in-sql-when-you-could-use-exists/)
### 总结
这篇文章的立场很“明显”。别让数据库做**不必要的强制性工作**。
它**不必要**,因为对于你给定的需求,你*知道*一些特定的工作不需要完成。但是,你告诉数据库去做。
它**强制性**,因为数据库无法证明它是**不必要的**。这些信息只包含在客户端中,对于服务器来说无法访问。因此,数据库需要去做。
这篇文章大部分在介绍 `SELECT *`,因为这是一个很简单的目标。但是这并不仅限于数据库。这关系到客户端要求服务器完成**不必要的强制性工作**的任何分布式算法。你的 AngularJS 应用程序平均有多少个 N+1 问题,UI 在服务结果 A 上循环,多次调用服务 B,而不是把所有对 B 的调用打包为一个调用?这是一个复发的模式。
解决方法总是相同。你给执行你命令的实体越多信息,(理论上)它能更快执行这样的命令。每次都写一个好的查询。你的整个系统都会为此感谢你的。
### 如果你喜欢这篇文章...
再看看近期我在 Voxxed Days Zurich 的演讲,其中我展示了一些在数据处理算法上为什么 SQL 总是会胜过 Java 的双曲线例子。
(题图:Pixabay, CC0)
---
via: <https://blog.jooq.org/2017/03/08/many-sql-performance-problems-stem-from-unnecessary-mandatory-work>
作者:[jooq](https://blog.jooq.org/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,608 | D 编程语言是用于开发的绝佳语言的 5 个理由 | https://opensource.com/article/17/5/d-open-source-software-development | 2017-06-16T08:09:00 | [
"D语言"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8608-1.html |
>
> D 语言的模块化、开发效率、可读性以及其它一些特性使其非常适合用于协同软件的开发。
>
>
>

[D 编程语言](https://dlang.org/)是一种静态类型的通用编程语言,它具有和 C 语言类似的语法,能够编译为本地代码。许多理由使得它很适合用于开源软件开发,下面讲到的是其中一些理由。
### 模块化能力
在大多数情况下,当你有一个好的想法,你可以完全按照你的内心所想的方式通过代码来实现它。然而,有的时候,你不得让你的想法向代码妥协,而不是通过模块化代码来适应想法。D 语言支持多种[编程范式](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Programming_paradigm),包括函数式风格、命令式、面向对象、元编程、并发(演员模式),这些全都和谐共存。你可以选择任何一种方便的编程范式来将你的想法转换为代码。
通过使用[模板](http://ddili.org/ders/d.en/templates.html),可以生成额外的 D 代码并在编译的过程中把它编排进去,你可以把这些代码描述成编译器生成代码的一种模式。这是一种非常有用的设计算法,无需把它们绑定到任何特定的类型。由于模版的通用性,就很容易生成平台无关的代码。通过将模板与[条件编译](https://dlang.org/spec/version.html)结合,跨平台的应用变得更加容易实现,也更容易接受来自使用不同操作系统的开发者的贡献。有了这一点,一个程序员可以通过很少的代码,利用有限的时间实现很多东西。
[range](http://ddili.org/ders/d.en/ranges.html) 已经深度集成到了 D 语言中,相对于具体实现,它抽象出容器元素(比如数组、关联数组和链表等)是如何访问的。这个抽象使得可以在许多容器类型中设计和使用大量的算法,而无需绑定到特定的数据结构。D 的[数组切片](https://dlang.org/spec/arrays.html#slicing)是 range 的一个实现。最终,你可以用很少的时间写很少的代码,并且只需要很低的维护成本。
### 开发效率
大多数开源软件的代码贡献者都是基于有限的时间志愿工作的。 D 语言能够极大的提高开发效率,因为你可以用更少的时间完成更多的事情。D 的模板和 range 使得程序员在开发通用代码和可复用代码时效率更高,但这些仅仅是 D 开发效率高的其中几个优势。另外一个主要的吸引力是, D 的编译速度看起来感觉就像解释型语言一样,比如 Python、JavaScript、Ruby 和 PHP,它使得 D 能够快速成型。
D 可以很容易的与旧的代码进行对接,减少了移植的需要。它的设计目的是[与 C 代码进行自然地对接](https://dlang.org/spec/interfaceToC.html),毕竟, C 语言大量用在遗留代码、精心编写而测试过的代码、库以及低级系统调用(特别是 Linux 系统)上。C++ 代码在 [D 中也是可调用的](https://dlang.org/spec/cpp_interface.html),从而进行更大的扩展。事实上,[Python](https://code.dlang.org/packages/pyd)、[Objective-C](https://dlang.org/spec/objc_interface.html)、[Lua](http://beza1e1.tuxen.de/into_luad.html) 和 [Fortran](http://www.active-analytics.com/blog/interface-d-with-c-fortran/) 这些语言在技术层面上都是可以在 D 中使用的,有许多第三方正在努力在把 D 语言推向这些领域。这使得大量的开源库在 D 中均可使用,这符合开源软件开发的惯例。
### 可读性和可维护性
```
import std.stdio; // 导入标准输入/输出模块
void main()
{
writeln("Hello, World!");
}
```
*D 语言的 Hello, World 演示*
对于熟悉 C 语言的人来说, D 代码很容易理解。另外, D 代码的可读性很强,即使是复杂的代码。这使得很容易发现错误。可读性对于吸引贡献者来说也是很重要的,这是开源软件成长的关键。
在 D 中一个非常简单但很有用的[语法糖](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syntactic_sugar)是支持使用下滑线分隔数字,这使得数字的可读性更高。这在数学上很有用:
```
int count = 100_000_000;
double price = 20_220.00 + 10.00;
int number = 0x7FFF_FFFF; // 16 进制系统
```
[ddoc](https://dlang.org/spec/ddoc.html) 是一个内建的工具,它能够很容易的自动根据代码注释生成文档,而不需要使用额外的工具。文档写作、改进和更新变得更加简单,不具挑战性,因为它伴随代码同时生成。
[Contract](http://ddili.org/ders/d.en/contracts.html) 能够检查代码的实现,从而确保 D 代码的行为能够像期望的那样。就像法律契约的签订是为了确保每一方在协议中做自己该做的事情,在 D 语言中的契约式编程,能够确保实现的每一个函数、类等如期望的那样产生预期的结果和行为。这样一个特性对于错误检查非常实用,特别是在开源软件中,当多个人合作一个项目的时候。契约是大项目的救星。D 语言强大的契约式编程特性是内建的,而不是后期添加的。契约不仅使得使用 D 语言更加方便,也减少了正确写作和维护困难的头痛。
### 方便
协同开发是具有挑战性的,因为代码经常发生变化,并且有许多移动部分。D 语言通过支持在本地范围内导入模块,从而缓解了那些问题:
```
// 返回偶数
int[] evenNumbers(int[] numbers)
{
// "filter" and "array" are only accessible locally
import std.algorithm: filter;
import std.array: array;
return numbers.filter!(n => n%2 == 0).array;
}
```
*对 filter 使用 `!` 运算符是[模板参数](http://ddili.org/ders/d.en/templates.html)的一个语法*
上面的函数可以在不破坏代码的情况下调用,因为它不依赖任何全局导入模块。像这样实现的函数都可以在后期无需破坏代码的情况下增强,这是协同开发的好东西。
[通用函数调用语法(UFCS)](http://ddili.org/ders/d.en/ufcs.html)是 D 语言中的一个语法糖,它允许像调用一个对象的成员函数那样调用常规函数。一个函数的定义如下:
```
void cook(string food, int quantity)
{
import std.stdio: writeln;
writeln(food, " in quantity of ", quantity);
}
```
它能够以通常的方式调用:
```
string food = "rice";
int quantity = 3;
cook(food, quantity);
```
通过 UFCS,这个函数也可以像下面这样调用,看起来好像 `cook` 是一个成员函数:
```
string food = "rice";
int quantity = 3;
food.cook(quantity);
```
在编译过程中,编译器会自动把 `food` 作为 `cook` 函数的第一个参数。UFCS 使得它能够链起来常规函数,给你的代码产生一种函数风格编程的自然感觉。UFCS 在 D 语言中被大量使用,就像在上面的 `evenNumbers` 函数中使用的 `filter` 和 `array` 函数那样。结合模板、range、条件编译和 UFCS 能够在不牺牲方便性的前提下给予你强大的力量。
`auto` 关键词可以用来代替任何类型。编译器在编译过程中会静态推断类型。这样可以省去输入很长的类型名字,让你感觉写 D 代码就像是在写动态类型语言。
```
// Nope. Do you?
VeryLongTypeHere variable = new VeryLongTypeHere();
// 使用 auto 关键词
auto variable = new VeryLongTypeHere();
auto name = "John Doe";
auto age = 12;
auto letter = 'e';
auto anArray = [1, 2.0, 3, 0, 1.5]; // type of double[]
auto dictionary = ["one": 1, "two": 2, "three": 3]; // type of int[string]
auto cook(string food) {...} // auto for a function return type
```
D 的[foreach](http://ddili.org/ders/d.en/foreach.html) 循环允许遍历各种不同的底层数据类型的集合和 range:
```
foreach(name; ["John", "Yaw", "Paul", "Kofi", "Ama"])
{
writeln(name);
}
foreach(number; [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 6]) {...}
foreach(number; 0..10) {...} // 0..10 is the syntax for number range
class Student {...}
Student[] students = [new Student(), new Student()];
foreach(student; students) {...}
```
D 语言中内建的[单元测试](https://dlang.org/spec/unittest.html)不仅免除了使用外部工具的需要,也方便了程序员在自己的代码中执行测试。所有的测试用例都位于可定制的 `unittest{}` 块中:
```
int[] evenNumbers(int[] numbers)
{
import std.algorithm: filter;
import std.array: array;
return numbers.filter!(n => n%2 == 0).array;
}
unittest
{
assert( evenNumbers([1, 2, 3, 4]) == [2, 4] );
}
```
使用 D 语言的标准编译器 DMD,你可以通过增加 `-unittest` 编译器标志把所有的测试编译进可执行结果中。
[Dub](http://code.dlang.org/getting_started) 是 D 语言的一个内建包管理器和构建工具,使用它可以很容易的添加来自 [Dub package registry](https://code.dlang.org/) 的第三方库。Dub 可以在编译过程中下载、编译和链接这些包,同时也会升级到新版本。
### 选择
除了提供多种编程范例和功能特性外,D 还提供其他的选择。它目前有三个可用的开源编译器。官方编译器 DMD 使用它自己的后端,另外两个编译器 GDC 和 LDC,分别使用 GCC 和 LLVM 后端。DMD 以编译速度块而著称,而 LDC 和 GDC 则以在很短的编译时间内生成快速生成机器代码而著称。你可以自由选择其中一个以适应你的使用情况。
默认情况下,D 语言是采用[垃圾收集](https://dlang.org/spec/garbage.html)的内存分配方式的。你也可以选择手动进行内存管理,如果你想的话,甚至可以进行引用计数。一切选择都是你的。
### 更多
在这个简要的讨论中,还有许多 D 语言好的特性没有涉及到。我强烈推荐阅读 [D 语言的特性概述](https://dlang.org/comparison.html),这是隐藏在[标准库](https://dlang.org/phobos/index.html)中的宝藏,以及 [D 语言的使用区域](https://dlang.org/areas-of-d-usage.html),从而进一步了解人们用它来干什么。许多组织已经[使用 D 语言来进行开发](https://dlang.org/orgs-using-d.html)。最后,如果你打算开始学习 D 语言,那么请看这本书 *[D 语言编程](http://ddili.org/ders/d.en/index.html)*。
(题图:opensource.com)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/5/d-open-source-software-development>
作者:[Lawrence Aberba](https://opensource.com/users/aberba) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The [D programming language](https://dlang.org/) is a statically typed, general purpose programming language with C-like syntax that compiles to native code. It's a good fit in open source software development for many reasons; here are some of them.
## Modeling power
It's not uncommon to find yourself in a situation where you have an idea and you want to implement it in code exactly the way you are thinking about it in your mind. However, sometimes you have to compromise the idea to fit the code, instead of modeling the code to fit the idea. D supports several [programming paradigms](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Programming_paradigm), including functional style, imperative, object oriented, metaprogramming, and concurrent (actor model), all harmoniously integrated. You have the option to choose whichever paradigm is convenient for modeling code to fit your idea.
By using [templates](http://ddili.org/ders/d.en/templates.html), a feature to generate additional D code and weave it in during compilation, you can describe code as a pattern for the compiler to generate the code. This is especially useful for designing algorithms without tying them to specific types. Platform-agnostic code becomes easy with the generic nature of templates. By combining templates with [conditional compilation](https://dlang.org/spec/version.html), cross-platform apps become much easier to implement and are more likely to receive contributions from developers using different operating systems. With this, a single programmer can achieve a lot with less code and limited time.
[Ranges](http://ddili.org/ders/d.en/ranges.html), deeply integrated into D, abstract how container elements (e.g., arrays, associative arrays, linked lists, etc.) are accessed as opposed to an actual implementation. This abstraction enables the design and use of a great number of algorithms over a great number of container types without tying them to a specific data structure. D's [array slicing](https://dlang.org/spec/arrays.html#slicing) is an implementation of a range. In the end, you write less code in less time and have lower maintenance costs.
## Productivity
Most code contributors to open source software work on a voluntary basis with limited time. D allows you be more productive because you can do more in less time. Templates and ranges in D make programmers more productive as they write generic and reusable code, but those are only a couple of D's strengths in terms of productivity. Another main appeal is that D's compilation speed feels like interpreted languages such as Python, JavaScript, Ruby, and PHP, making D good for quick prototyping.
D can easily interface with legacy code, alleviating the need to port. It was designed to make [interfacing directly with C code](https://dlang.org/spec/interfaceToC.html) natural: After all, C is the master of legacy, well-written and tested code, libraries, and low-level system calls (especially in Linux). C++ code is also [callable in D](https://dlang.org/spec/cpp_interface.html) to a greater extent. In fact, [Python](https://code.dlang.org/packages/pyd), [Objective-C](https://dlang.org/spec/objc_interface.html), [Lua](http://beza1e1.tuxen.de/into_luad.html), and [Fortran](http://www.active-analytics.com/blog/interface-d-with-c-fortran/) are some of the languages that are technically usable in D, and there are a number of third-party efforts pushing D in those areas. This makes the huge number of open source libraries usable in D code, which aligns with conventions of open source software development.
## Readable and maintainable
```
``````
import std.stdio; // import standard I/O module
void main()
{
writeln("Hello, World!");
}
```
HelloWorld demo in D
D code is easy to understand by anyone familiar with C-like programming languages. Moreover, D is very readable, even for sophisticated code, which makes bugs easy to spot. Readability is also critical for engaging contributors, which is key to the growth of open source software.
One simple but very useful [syntactic sugar](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syntactic_sugar) in D is support for using an underscore to separate numbers, making them more readable. This is especially useful for math:
```
``````
int count = 100_000_000;
double price = 20_220.00 + 10.00;
int number = 0x7FFF_FFFF; // in hexadecimal system
```
[Ddoc](https://dlang.org/spec/ddoc.html), a built-in tool, makes it easy to automatically generate documentation out of code comments without the need for an external tool. Documentation becomes less challenging to write, improve, and update as it goes side by side with the code.
[Contracts](http://ddili.org/ders/d.en/contracts.html) are checks put in place to ensure D code behaves exactly as expected. Just like legal contracts are signed to ensure each party does their part in an agreement, contract programming in D ensures that the implementation of a function, class, etc. always produces the desired results or behaves as expected. Such a feature is practically useful for bug checks, especially in open source software where several people collaborate on a project. Contracts can be a lifesaver for large projects. D's powerful contract programming features are built-in rather than added as an afterthought. Contracts not only add to the convenience of using D but also make writing correct and maintainable code less of a headache.
## Convenient
Collaborative development can be challenging, as code is frequently changing and has many moving parts. D alleviates some of these issues, with support for importing modules locally within a scope:
```
``````
// returns even numbers
int[] evenNumbers(int[] numbers)
{
// "filter" and "array" are only accessible locally
import std.algorithm: filter;
import std.array: array;
return numbers.filter!(n => n%2 == 0).array;
}
```
The "!" operator used with filter is the syntax of a template argument.
The function above can be tossed around without breaking code because it does not rely on any globally imported module. Any function implemented like this can be later enhanced without breaking code, which is a good thing for collaborative development.
[Universal Function Call Syntax](http://ddili.org/ders/d.en/ufcs.html) (UFCS), is a syntactic sugar in D that allows the call of regular functions, like member functions of an object. A function is defined as:
```
``````
void cook(string food, int quantity)
{
import std.stdio: writeln;
writeln(food, " in quantity of ", quantity);
}
```
It can be called in the usual way like:
```
``````
string food = "rice";
int quantity = 3;
cook(food, quantity);
```
With UFCS, this same function can be called as if **cook** is a member function:
```
``````
string food = "rice";
int quantity = 3;
food.cook(quantity);
```
During compilation, the compiler automatically places **food** as the first argument to the function **cook**. UFCS makes it possible to **chain** regular functions—giving your code the natural feel of functional style programming. UFCS is heavily used in D, as it was in the case of the **filter** and **array** functions used in the **evenNumbers** function above. Combining templates, ranges, conditional compilation, and UFCS gives you massive power without sacrificing convenience.
The **auto** keyword can be used in place of a type. The compiler will statically infer the type during compilation. This saves you from long type names and makes writing D code feel like a dynamically typed language.
```
``````
// Nope. Do you?
VeryLongTypeHere variable = new VeryLongTypeHere();
// using auto keyword
auto variable = new VeryLongTypeHere();
auto name = "John Doe";
auto age = 12;
auto letter = 'e';
auto anArray = [1, 2.0, 3, 0, 1.5]; // type of double[]
auto dictionary = ["one": 1, "two": 2, "three": 3]; // type of int[string]
auto cook(string food) {...} // auto for a function return type
```
D's [foreach](http://ddili.org/ders/d.en/foreach.html) loop allows looping over collections and ranges of varying underlining data types:
```
``````
foreach(name; ["John", "Yaw", "Paul", "Kofi", "Ama"])
{
writeln(name);
}
foreach(number; [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 6]) {...}
foreach(number; 0..10) {...} // 0..10 is the syntax for number range
class Student {...}
Student[] students = [new Student(), new Student()];
foreach(student; students) {...}
```
Built-in [unit test](https://dlang.org/spec/unittest.html) support in D not only alleviates the need for an external tool, but also makes it convenient for programmers to implement tests in their code. All test cases go inside the customizable **unittest {}** block:
```
``````
int[] evenNumbers(int[] numbers)
{
import std.algorithm: filter;
import std.array: array;
return numbers.filter!(n => n%2 == 0).array;
}
unittest
{
assert( evenNumbers([1, 2, 3, 4]) == [2, 4] );
}
```
Using DMD, D's reference compiler, you can compile all tests into the resulting executable by adding the **-unittest** compiler flag.
[Dub](http://code.dlang.org/getting_started), a built-in package manager and build tool for D, makes it easy to use the increasing number of third-party packages (libraries) from the [Dub package registry](https://code.dlang.org/). Dub takes care of downloading, compiling, and linking those packages during compilation, as well as upgrading to future versions.
## Choice
In addition to providing several programming paradigms and features, D offers other choices. It currently has three compilers, all open source. The reference compiler, DMD, comes with its own backend, while the other two, GDC and LDC, use GCC and LLVM backends, respectively. DMD is noted for its fast compilation speeds, while LDC and GDC are noted for generating fast machine code at the cost of a little compilation time. You are free to choose whichever fits your use case.
Certain parts of D, when used, are [garbage-collected](https://dlang.org/spec/garbage.html) by default. You can also choose manual memory management or even reference counting if you wish. The choice is all yours.
## And much more
There a several sugars in D that I haven't covered in this brief discussion. I highly recommend you check out [D's feature overview](https://dlang.org/comparison.html), the hidden treasures in the [standard library](https://dlang.org/phobos/index.html), and [areas of D usage](https://dlang.org/areas-of-d-usage.html) to see more of what people are doing with it. Many organizations are already [using D in production](https://dlang.org/orgs-using-d.html). Finally, if you are ready to start learning D, check out the book * Programming in D*.
## 1 Comment |
8,609 | 极客漫画:一篇关于 PHP 的优点的漫画 | http://turnoff.us/geek/php-good-parts/ | 2017-06-15T07:30:00 | [
"PHP",
"漫画"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8609-1.html | PHP 有什么优点吗?
有,请看这幅漫画:

……
(这是 PHP 被黑的最惨的一次。)
---
via: <http://turnoff.us/geek/php-good-parts/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,610 | 极客漫画:敏捷餐馆 | http://turnoff.us/geek/agile-restaurant/ | 2017-06-19T08:17:00 | [
"漫画",
"敏捷",
"持续交付"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8610-1.html | 过于殷勤(敏捷)的侍者会让你美好的一餐糟糕无比。
然而,离开“敏捷”的“持续交付”餐馆,旁边还有“瀑布”餐吧。
嗷,这个快节奏的年代!

注:<ruby> “敏捷” <rp> ( </rp> <rt> agile </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>开发、<ruby> “持续交付” <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Continuous Delivery </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(CD)和<ruby> “瀑布” <rp> ( </rp> <rt> waterfall </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>式开发都是软件开发术语。瀑布式开发/瀑布模型是一种传统的、过时的开发模式,其得名于开发阶段按顺序衔接,如瀑布般进行。敏捷和持续交付是近年来流行的开发模式,能够比较好的适应现代的软件开发需求,但是,显然,如果餐馆也采用这种模式,似乎不太对劲。
---
via: <http://turnoff.us/geek/agile-restaurant/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,611 | 微软正在成为一个 Linux 供应商 | http://www.cio.com/article/3197016/linux/how-microsoft-is-becoming-a-linux-vendor.html | 2017-06-16T09:01:00 | [
"微软",
"Azure"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8611-1.html |
>
> 微软通过将 Linux 融入自己的产品中来弥合与 Linux 的裂隙。
>
>
>

Linux 以及开源技术在数据中心、云以及 IoT 中变得如此主流,以至于微软无法忽视他们。
在微软自己的云中,三分之一的机器运行着 Linux。这些是运行 Linux 的微软客户。微软需要支持他们使用的平台,否则他们将到别处去了。
以下就是微软如何将 Linux 战略落实到它的开发者平台 (Windows 10)、云 (Azure) 以及数据中心 (Windows Server) 上的。
**Windows 中的 Linux:** IT 专家管理公共或者私有 Linux 机器需要原生的 UNIX 工具。Linux 以及 macOS 是仅有的二个提供原生能力的平台。这也难怪你在各种会议如 DockerCon、OpenStack Summit 或者 CoreOS Fest 看到的都是 MacBook 或者少量的 Linux 桌面。
为了弥补这之间的裂隙,微软与 Canonical 协作在 Windows 内部构建了一个 Linux 子系统,它提供了原生的 Linux 工具。这是一个很棒的妥协,这样 IT 专家可以在继续使用 Windows 10 桌面的同时能够使用大多数 Linux 工具来管理他们的 Linux 机器。
**Azure 中的 Linux:** 不能完整支持 Linux 的云有什么好的呢?微软一直以来与 Linux 供应商合作来使客户能够在 Azure 中运行 Linux 程序以及任务。
微软不仅与三家主要的 Linux 供应商 Red Hat、SUSE 和 Canonical 签署了协议,还与无数的其他公司合作,为 Debian 这样的基于社区的发行版提供了支持。
**Windows Server 中的 Linux:** 这是剩下的最后一块拼图。客户使用的 Linux 容器是一个巨大的生态系统。Docker Hub 上有超过 90 万个 Docker 容器,它们只能在 Linux 机器上运行。微软希望把这些容器带到自己的平台上。
在 DockerCon 中,微软宣布在 Windows Server 中支持 Linux 容器,将这些容器都带到 Windows 中。
事情正变得更加有趣,在 Windows 10 上的 Bash on Ubuntu 成功之后,微软正将 Ubuntu bash 带到 Windows Server 中。是的,你听的没错。Windows Server 也将会有一个 Linux 子系统。
微软的高级项目经理 Rich Turne 告诉我:“服务器上的 WSL 为管理员提供了偏好的 \*NIX 管理脚本和工具,以便让他们可以在更熟悉的工作环境工作。”
微软在一个通告中称它将允许 IT 专家 “可以在 Windows Server 容器主机上使用在 Linux 容器上所用的相同的脚本、工具、流程和容器镜像。这些容器使用我们的 Hyper-V 隔离技术结合你选择的 Linux 内核来托管负载,而主机上的管理脚本以及工具使用 WSL。”
在覆盖了上面三个情况后,微软已经成功地创建了一个客户不必选择任何 Linux 供应商的环境。
### 它对微软意味着什么?
通过将 Linux 融入它自己的产品,微软已经成为了一个 Linux 供应商。它是 Linux 基金会的一份子,它是众多 Linux 贡献者之一,并且它现在在自己的商店中分发 Linux。
只有一个小问题。微软没有拥有任何 Linux 技术。它完全依赖于外部的厂家,目前 Canonical 为其提供了完全的 Linux 层。如果 Canonical 被强力的竞争对手收购,那会是一个很大的风险。
或许对微软而言尝试收购 Canonical 是有意义的,并且会将核心技术收入囊中。这是有道理的。
### 这对 Linux 供应商意味着什么
表面上,很显然这对微软是个胜利,因为它的客户可以留存在 Windows 世界中。它还将包含 Linux 在数据中心中的发展势头。它或许还会影响 Linux 桌面,由于现在 IT 专家不必为了寻找 \*NIX 工具使用 Linux 桌面了,它们可以在 Windows 中做任何事。
微软的成功是传统 Linux 厂家的失败么?某种程度上来说,是的,微软已经成为了一个直接竞争者。但是这里明显的赢家是 Linux。
---
via: <http://www.cio.com/article/3197016/linux/how-microsoft-is-becoming-a-linux-vendor.html>
作者:[Swapnil Bhartiya](http://www.cio.com/author/Swapnil-Bhartiya/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,614 | 极客漫画:最后一个问题 | http://turnoff.us/geek/one-last-question/ | 2017-06-17T10:53:00 | [
"进程",
"漫画",
"ps"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8614-1.html | 
`ps aux` 以及 `ps -elf` 都是查看进程的方式,分别来自于 BSD 风格(必须不带 `-`)和 UNIX 风格(必须带 `-`),这两种方式都有不少人用,此外除了这种可组合的单字母选项方式之外,还有以 `--` 开头的 GNU 选项方式。
这个漫画就是说使用这两种方式的人就像 vim 党和 Emacs 党一样,随时都可能爆发圣战(大误 。
**附录:**
`ps aux` 是最常用的 BSD 风格选项组合,其中的 `a` 简单的说,表示所有关联到终端的进程,如果同时使用 `x` 则代表所有进程;`u` 表示列出进程的用户。
另外,可能是由于错用 `ps -aux` 的人太多,一些新的 `ps` 版本会在输入 `ps -aux` 时显示 `ps aux` 的结果,而不是 `ps -aux` 原本的意义:列出用户 `x` 所有的进程,如果没有则报错。
`ps -elf` 的 `-e` 代表列出所有进程,`-l` 代表长格式,`-f` 代表完整的格式,有时候也用 `-F` 代表超完整的格式,具体大家试试便知。 不过,不同操作系统(如 Linux、BSD)的 `ps` 的版本和参数有很大差异,具体还是要以自己的手册而定。
另外一句题外话,之所以 `aux` 和 `-elf` 这两种选项组合常用,是由于这个组合正好是易记、易读的英文单词(辅助、精灵),其组合后的用途也很有用。这种情况也出现在其它的常见命令中。
注:本漫画中原来用的是 `ps -eLF`,在某些版本上这个参数是成立的,但是,大部分情况下都使用的是 `ps -elf`,因此我们做了修改。
---
via: <http://turnoff.us/geek/one-last-question/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者:[name1e5s](https://github.com/name1e5s) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 合成:[name1e5s](https://github.com/name1e5s) 点评:[name1e5s](https://github.com/name1e5s)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,615 | 安卓编年史(23):Android 4.3,果冻豆——早早支持可穿戴设备 | http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/24/ | 2017-06-17T12:20:00 | [
"Android",
"安卓编年史"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8615-1.html | 

*漂亮的新 Google Play Music 应用,从电子风格转向完美契合 Play 商店的风格。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
在 I/O 大会推出的另一个应用更新是 Google Music 应用。音乐应用经过了完全的重新设计,最终摆脱了蜂巢中引入的蓝底蓝色调的设计。Play Music 的设计和几个月前发布的 Play 商店一致,有着响应式的白色卡片布局。Music 同时还是最早采用新抽屉导航样式的主要应用之一。谷歌还随新应用发布了 Google Play Music All Access,每月 10 美元的包月音乐订阅服务。Google Music 现在拥有订阅计划,音乐购买,以及云端音乐存储空间。这个版本还引入了“Instant Mix”,谷歌会在云端给相似的歌曲计算出一份歌单。

*一个展示对 Google Play Games 支持的游戏。上面是 Play 商店游戏特性描述,登陆游戏触发的权限对话框,Play Games 通知,以及成就界面。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
谷歌还引入了 “Google Play Games”,一个后端服务,开发者可以将其附加到游戏中。这项服务简单说就是安卓版的 Xbox Live 或苹果的 Game Center。开发者可以给游戏添加 Play Games 支持,这样就能通过使用谷歌的后端服务,更简单地将成就、多人游戏、游戏配对、用户账户以及云端存档集成到游戏中。
Play Games 是谷歌在游戏方面推进的开始。就像单独的 GPS 设备,翻盖手机,以及 MP3 播放器,智能手机的生产者希望游戏设备能够变成智能手机的一个功能点。当你有部智能手机的时候你为什么还有买个任天堂 DS 或 PS Vita 呢?一个易于使用的多人游戏服务是这项计划的重要部分,我们仍能看到这个决定最后的成果。在今天,坊间都在传言谷歌和苹果有关于客厅游戏设备的计划。

*Google Keep,谷歌自 Google Notebook 以来第一个笔记服务。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
毫无疑问一些产品为了赶上 Google I/O 大会的发布准时开发完成了,[但是三个半小时内的主题](http://live.arstechnica.com/liveblog-google-io-2013-keynote/)已经够多了,一些产品在大会的发布上忽略了。Google I/O 大会的三天后一切都清楚了,谷歌带来了 Google Keep,一个用于安卓和在线的笔记应用。Keep 看起来很简单,就是一个用上了响应式 Google-Now 风格设计的笔记应用。用户可以改变卡片的尺寸,从多栏布局改为单列视图。笔记可以由文本,清单,自动转文本的语音或者图片组成。笔记卡片可以拖动并在主界面重新组织,你甚至可以给笔记换个颜色。

*Gmail 4.5,换上了新的导航抽屉设计,去掉了几个按钮并将操作栏合并到了抽屉里。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
在 I/O 大会之后,没有哪些应用没出现在谷歌的周期外更新里。2013 年 6 月,谷歌发布了新版设计的 Gmail。最显眼的变化就是一个月前 Google I/O 大会引入的新导航抽屉界面。最吸引眼球的变化是用上了 Google+ 资料图片来取代复选框。虽然复选框看起来被去掉了,它们其实还在那,点击邮件左边的图片就是了。

*新谷歌地图,换上了全白的 Google-Now 风格主题。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
一个月后,谷歌在 Play 商店发布了全新的谷歌地图。这是谷歌地图自冰淇淋三明治以来第一个经过细致地重新设计的版本。新版本完全适配了 Google Now 白色卡片审美,还大大减少了屏幕上显示的元素。新版谷歌地图似乎设计时有意使地图总是显示在屏幕上,你很难找到除了设置页面之外还能完全覆盖地图显示的选项。
这个版本的谷歌地图看起来活在它自己的小小设计世界中。白色的搜索栏“浮动”在地图之上,地图显示部分在它旁边和上面都有。这和传统的操作栏设计有所不同。一般在应用左上角的导航抽屉,在这里是在左下角。这里的主界面没有向上按钮、应用图标,也没有浮动按钮。

*新谷歌地图轻量化了许多,在一屏内能够显示更多的信息。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
左边的图片显示的是点击了搜索栏后的效果(带键盘,这里关闭了)。过去谷歌在空搜索栏下面显示一个空页面,但在地图中,谷歌利用这些空间链接到新的“本地”页面。搜索结果页显示一般信息的结果,比如餐馆、加油站,以及景点。在结果页的底部是个列表,显示你的搜索历史和手动缓存部分地图的选项。
右侧图片显示的是地点页面。上面地图 7.0 的截图里显示的地图不是略缩图,它是完整的地图视图。在新版的谷歌地图中,地点作为卡片浮动显示在主地图之上,地图重新居中显示该地点。向上滑动可以让卡片覆盖地图,向下滑动可以显示带有底部一小条结果的完整地图。如果该地点是搜索结果列表中的一个,左右滑动可以在结果之间切换。
地点页面重新设计以显示更有用的信息概览。在第一页,新版添加了重要信息,比如地图上的位置,点评得分,以及点评数目。因为这是个手机,所以软件内可以直接拨打电话,电话号码的显示被认为是毫无意义的,被去掉了。旧版地点显示到那里的距离,新版谷歌地图显示到那里的时间,基于交通状况和偏好的交通方式——一个更加实用的衡量方式。新版还在中间放了个分享按钮,这使得通过即时通讯或短信协调的时候更加方便。
### Android 4.3,果冻豆——早早支持可穿戴设备
如果谷歌没有在安卓 4.3 和安卓 4.2 之间通过 Play 商店发布更新的话,安卓 4.3 会是个不可思议的更新。如果新版 Play 商店、Gmail、地图、书籍、音乐、Hangouts 环聊,以及 Play Games 打包作为新版安卓的一部分,它将会作为有史以来最大的发布受到欢呼。虽然谷歌没必要延后新功能的发布。有了 Play 服务框架,只剩很少的部分需要系统更新,2013 年 7 月底谷歌发布了看似无关紧要的“安卓 4.3”。

*安卓 4.3 通知访问权限界面的可穿戴设备选项。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
谷歌也毫无疑问地认为 4.3 的重要性不高,将新版也叫做“果冻豆”(第三个叫果冻豆的版本了)。安卓 4.3 的新功能列表像是谷歌无法通过 Play 商店或谷歌 Play 服务更新的部分的细目清单,大部分包含了为开发者作出的底层架构改动。
但许多新增功能似乎只为了一个目的——安卓 4.3 是谷歌对可穿戴计算支持的特洛伊木马。4.3 加入了低功耗蓝牙支持,使用很少的能耗将安卓和其它设备连接到一起并传输数据——可穿戴设备的必要特性。安卓 4.3 还添加了“通知访问权限”API,允许应用完全复制和控制通知面板。应用可以显示通知文本以及和用户操作一样地和通知交互——也就是点击操作按钮和消除通知。当你有个通知面板时从本机应用做这个操作没什么意义,但是在一个独立于你手机的设备上,复制通知面板的消息就显得很有用了。为数不多的接入的应用是 “Android Wear Preview(安卓可穿戴预览)”,使用了通知 API 驱动大部分的 Android Wear 界面。
“4.3 是给可穿戴设备准备的”这个理论解释了 4.3 相对较少的新特性:它的推出是为了给 OEM 厂商时间去升级设备,为 [Android Wear](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/03/in-depth-with-android-wear-googles-quantum-leap-of-a-smartwatch-os/) 的发布做准备。这个计划看起来起作用了。Android Wear 要求 安卓 4.3 及以上版本,安卓 4.3 已经发布很长时间了,大部分主要的旗舰设备都已经升级了。
安卓并没有那么激动人心,但安卓从现在起的新版也不需要那么激动人心了。一切都变得那么模块化了,谷歌可以通过 Google Play 在它们完成时随时推送更新,不用再作为一个大系统更新来更新这么多组件。
---

[Ron Amadeo](http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo) / Ron是Ars Technica的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。[@RonAmadeo](https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo)
---
via: <http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/24/>
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,616 | 安卓编年史(24):Android 4.4,奇巧——更完美,更少的内存占用 | http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/25/ | 2017-06-19T10:18:00 | [
"Android",
"安卓编年史"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8616-1.html | 

*LG 制造的 Nexus 5,奇巧(KitKat)的首发设备。*
### Android 4.4,奇巧——更完美,更少的内存占用
谷歌安卓 4.4 的发布确实很讨巧。谷歌和[雀巢公司合作](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/09/official-the-next-edition-of-android-is-kitkat-version-4-4/),新版系统的代号是“奇巧(KitKat)”,并且它是在 2013 年 10 月 31 日发布的,也就是万圣节。雀巢公司推出了限量版带安卓机器人的奇巧巧克力,它的包装也帮助新版系统推广,消费者有机会赢取一台 Nexus 7。
一部新的 Nexus 设备也随奇巧一同发布,就是 Nexus 5。新旗舰拥有迄今最大的显示屏:一块五英寸、1920x1080 分辨率的 LCD 显示屏。除了更大尺寸的屏幕,Nexus 5 的制造商 LG 还将 Nexus 5 的机器大小控制得和 Galaxy Nexus 或 Nexus 4 差不多。
Nexus 5 相对同时期的高端手机配置算是标准了,拥有 2.3Ghz 骁龙 800 处理器和 2GB 内存。手机再次在 Play 商店销售无锁版,相同配置的大多数手机价格都在 600 到 700 美元之间,但 Nexus 5 的售价仅为 350 美元。
奇巧最重要的改进之一你并不能看到:显著减少的内存占用。对奇巧而言,谷歌齐心协力开始了降低系统和预装应用内存占用的努力,称作“Project Svelte”。经过了无数的优化工作和通过一个“低内存模式”(禁用图形开销大的特效),安卓现在可以在 340MB 内存下运行。低内存需求是件了不起的事,因为在发展中国家的设备——智能手机增长最快的市场——许多设备的内存仅有 512MB。冰淇淋三明治更高级的 UI 显著提高了对安卓设备的系统配置要求,这使得很多低端设备——甚至是新发布的低端设备——的安卓版本停留在姜饼。奇巧更低的配置需求意味着这些廉价设备能够跟上脚步。有了奇巧,谷歌希望完全消灭姜饼(写下本文时姜饼的市场占有率还在 20% 左右)。只是降低系统需求还不够,甚至有报道称谷歌将[不再授权](http://www.androidpolice.com/2014/02/10/rumor-google-to-begin-forcing-oems-to-certify-android-devices-with-a-recent-os-version-if-they-want-google-apps/)谷歌应用给姜饼设备。
除了给低端设备带来更现代版本的系统,Project Svelte 更低的内存需求同样对可穿戴设备也是个好消息。Google Glass [宣布](http://www.androidpolice.com/2014/03/01/glass-xe14-delayed-until-its-ready-promises-big-changes-and-a-move-to-kitkat/)它会切换到这个更精简的系统,[Android Wear](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/03/in-depth-with-android-wear-googles-quantum-leap-of-a-smartwatch-os/) 同样也运行在奇巧之上。安卓 4.4 带来的更低的内存需求以及 4.3 中的通知消息 API 和低功耗蓝牙支持给了可穿戴计算漂亮的支持。
奇巧的亮点还有无数精心打磨过的核心系统界面,它们无法通过 Play 商店升级。系统界面,拨号盘,时钟还有设置都能看到升级。

*奇巧在 Google Now 启动器下的透明系统栏。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
奇巧不仅去掉了讨人厌的锁屏左右屏的线框——它还默认完全禁用了锁屏小部件!谷歌明显感觉到了多屏锁屏和锁屏主屏对新用户来说有点复杂,所以锁屏小部件现在需要从设置里启用。锁屏和时钟里不平衡的时间字体换成了一个对称的字重,看起来好看多了。
在奇巧中,应用拥有将系统栏和状态栏透明的能力,显著地改变了系统的外观。系统栏和状态栏现在混合到壁纸和启用透明栏的应用中去了。这些栏还能通过新功能“沉浸”模式完全被应用隐藏。
奇巧是“电子”科幻风格的棺材上的最后一颗钉子,几乎完全移除了系统的蓝色痕迹。状态栏图标由蓝色变成中性的白色。主屏的状态栏和系统栏并不是完全透明的;它们有深色的渐变,这样在使用浅色壁纸的时候白色的图标还能轻易地识别出来。

*Google Now 和文件夹的调整。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
在 Nexus 5 上随奇巧到来的主屏实际上由 Nexus 5 独占了几个月,但现在任何 Nexus 设备都能拥有它了。新的主屏叫做“Google Now Launcher”,它实际上是[谷歌搜索应用](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/11/google-just-pulled-a-facebook-home-kitkats-primary-interface-is-google-search/)。是的,谷歌搜索从一个简单的搜索框成长到了整个主屏幕,并且在奇巧中,它涉及了壁纸、图标、应用抽屉、小部件、主屏设置、Google Now,当然,还有搜索框。由于搜索现在运行在整个主屏幕,任何时候只要打开了主屏并且屏幕是点亮的,就可以通过说“OK Google”激活语音命令。在搜索栏有引导用户说出“OK Google”的文本,在几次使用后这个介绍会隐去。
Google Now 的集成度现在更高了。除了通常的系统栏上滑激活,Google Now 还占据了最左侧的主屏。新版还引入了一些设计上的调整。谷歌的 logo 移到了搜索栏内,整个顶部区域更紧凑了。显示更多卡片的设计被去除了,新添加的一组底部按钮指向备忘录、自定义选项,以及一个更多操作按钮,里面有设置、反馈,以及帮助。因为 Google Now 是主屏幕的一部分,所以它也拥有透明 的系统栏和状态栏。
透明以及让系统的特定部分“更明亮”是奇巧的设计主题。黑色调通过透明化从状态栏和系统栏移除了,文件夹的黑色背景也换为了白色。

*新的,更加清爽的应用列表,以及完整的应用阵容。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
奇巧的图标阵容相对 4.3 有显著的变化。更戏剧化地说,这是一场大屠杀,谷歌从 4.3 的配置中移除了七个图标。谷歌 Hangouts 现在能够处理短信,所以“信息”应用被去除了。Hangouts 同时还接手了 Google Messenger 的职责,所以它的图标也不见了。Google Currents 不再作为默认应用预装,因为它不久后就会被终结——和它一起的还有 Google Play Magazines(Play 杂志),取代它们的是 Google Play Newsstand(Play 报刊亭)。谷歌地图被打回一个图标,这意味着本地和导航的快捷方式被去掉了。难以理解的 Movie Studio 也被去除了——谷歌肯定已经意识到了没人想在手机上剪辑电影。有了主屏的“OK Google”关键词检测,语音搜索图标的呈现就显得多余了,因而将其移除。令人沮丧的是,没人用的新闻和天气应用还在。
有个新应用“Photos(相片)”——实际上是 Google+ 的一部分——接手了图片管理的工作。在 Nexus 5 上,相册和 Google+ 相片十分相似,但在 Google Play 版设备上更新版的奇巧中,相册已经完全被 Google+ 相片所取代。Play Games 是谷歌的后端多用户游戏服务——谷歌版的 Xbox Live 或苹果的 Game Center。Google Drive,已经在 Play 商店存在数年的应用,终于成为了内置应用。谷歌 2012 年 6 月收购的 Quickoffice 也进入了内置应用阵容。Drive 可以打开 Google 文档,Quickoffice 可以打开微软 Office 文档。如果细细追究起来,在大多数奇巧中包含了两个文档编辑应用和两个相片编辑应用。
---

[Ron Amadeo](http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo) / Ron是Ars Technica的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。[@RonAmadeo](https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo)
---
via: <http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/25/>
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,617 | 我是如何开始踏上 bash 脚本编程之路的? | https://opensource.com/article/17/5/how-i-learned-bash-scripting | 2017-06-18T08:53:00 | [
"脚本",
"Bash"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8617-1.html |
>
> 通过一些简单的 Google 搜索,即使是编程入门者也可以尝试编写代码将以往枯燥和冗长的任务自动化。
>
>
>

我前几天写了一个脚本。对于一些人来说,这句话听起来没什么了不起的。而对于另一些人来说,这句话意义重大。要知道,我不是一个程序员,而是一个作家。
### 我需要解决什么?
我的问题相当简单:我需要将工程文件进行分类。这些文件可以从一个网站 URL 以 .zip 的格式下载。当我正手工将它们拷贝到我的电脑桌面,并移动到一个已按照我文件分类的需要进行了结构化的目录时,一位作家同事给我提了建议:*“不就是写个脚本的事吗?”*
我心想:*“就写个脚本?”*——说得好像这是世界上最容易做的事情一样。
### Google 是如何解救我的?
同事的问题促使我思考,并且经过思考后,我进行了 Google 搜索。
**Linux 上使用的是什么脚本编程语言?**
这是我第一个 Google 搜索的准则。也许很多人心里会想:“她太笨了!”是的,我很笨。不过,这的确使我走上了一条解决问题的道路。最常见的搜索结果是 Bash 。嗯,我听说过 Bash 。呃,我要分类的文件中有一个里面就有 Bash,那无处不在的 `#!/bin/bash` 。我重新看了下那个文件,我知道它的用途,因为我需要将它分类。
这引导我进行了下一个 Google 搜索。
**如何从一个 URL 下载 zip 文件?**
那确实是我的基本任务。我有一个带有 .zip 文件的 URL ,它包含有所有我需要分类的文件,所以我寻求万能的 Google 的帮助。搜索到的精华内容和其它一些结果引导我使用 Curl 。但最重要的是:我不仅找到了 Curl ,其中一条置顶的搜索结果还展示了一个使用 Curl 去下载并解压 .zip 文件的 Bash 脚本。这超出了我本来想寻求的答案,但那也使我意识到在 Google 搜索具体的请求可以得到我写这个脚本需要的信息。所以,在这个收获的推动下,我写了最简单的脚本:
```
#!/bin/sh
curl http://rather.long.url | tar -xz -C my_directory --strip-components=1
```
我迫不及待地运行看看。但我发现一个问题: URL 是会变的,根据我要访问的文件的分组不同而不同。我有新的问题需要解决,这使我进行了下一轮搜索。
**参数如何传递给 Bash 脚本?**
我需要以不同的 URL 和不同的最终目录来运行此脚本。 Google 向我展示了如何使用 `$1`、`$2` 等等来替换我在命令行中运行脚本时输入的内容。比如:
```
bash myscript.sh http://rather.long.url my_directory
```
这就好多了。一切如我所愿,灵活,实用。最重要的是我只要输入一条简短的命令就可以节省 30 分钟无聊的复制、粘贴工作。这个早上的时间花得值得。
然后我发现还有一个问题:我很健忘,并且我知道我几个月才运行一次这个脚本。这留给我两个疑问:
* 我要如何记得运行脚本时输入什么(URL 先,还是目录先)?
* 如果我被货车撞了,其它作家如何知道该怎样运行我的脚本?
我需要一个使用说明 —— 如果我使用不正确,则脚本会提示。比如:
```
usage: bash yaml-fetch.sh <'snapshot_url'> <directory>
```
否则,则直接运行脚本。我的下一个搜索是:
**如何在 Bash 脚本里使用 “if/then/else”?**
幸运的是,我已经知道编程中 `if/then/else` 的存在。我只要找出如何使用它的方法。在这个过程中,我也学到了如何在 Bash 脚本里使用 `echo` 打印。我的最终成果如下:
```
#!/bin/sh
URL=$1
DIRECTORY=$2
if [ $# -eq 0 ];
then
echo "usage: bash yaml-fetch.sh <'snapshot_url'> <directory>".
else
# 如果目录不存在则创建它
echo 'create directory'
mkdir $DIRECTORY
# 下载并解压 yaml 文件
echo 'fetch and untar the yaml files'
curl $URL | tar -xz -C $DIRECTORY --strip-components=1
fi
```
### Google 和脚本编程如何颠覆我的世界?
好吧,这稍微有点夸大,不过现在是 21 世纪,学习新东西(特别是稍微简单的东西)比以前简单多了。我所学到的(除了如何写一个简短的、自动分类的 Bash 脚本之外)是如果我有疑问,那么有很大可能性是其它人在之前也有过相同的疑问。当我困惑时,我可以问下一个问题,再下一个问题。最后,我不仅拥有了脚本,还拥有了可以一直拥有并可以简化其它任务的新技能,这是我之前所没有的。
别止步于第一个脚本(或者编程的第一步)。这是一个技能,和其它的技能并无不同,有大量的信息可以在这一路上帮助你。你无需阅读大量的书或参加一个月的课程。你可以像婴儿学步那样简单地开始写脚本,然后掌握技能并建立自信。人们总有写成千上万行代码的需求,并对它进行分支、合并、修复错误。但是,通过简单的脚本或其它方式来自动化、简单化任务的需求也一样强烈。这样的一个小脚本和小小的自信就能够让你启程脚本编程之路。
(题图: opensource.com)
---
作者简介:
Sandra McCann 是一位 Linux 和开源技术的倡导者。她是一位软件开发者、学习资源内容架构师、内容创作者。桑德拉目前是位于韦斯特福德马萨诸塞州的红帽公司的内容创作者,专注于 OpenStack 和 NFV 技术。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/5/how-i-learned-bash-scripting>
作者:[Sandra McCann](https://opensource.com/users/sandra-mccann) 译者:[xllc](https://github.com/xllc) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | I wrote a script the other day. For some of you, that sentence sounds like no big deal. For others, and I know you're out there, that sentence is significant. You see, I'm not a programmer. I'm a writer.
## What I needed to solve
My problem was fairly simple: I had to juggle files from engineering into our documentation. The files were available in a .zip format from a web URL. I was copying them to my desktop manually, then moving them into a different directory structure to match my documentation needs. A fellow writer gave me this advice: *"Why don't you just write a script to do this for you?" *
I thought *"just write a script?!?"*—as if it was the easiest thing in the world to do.
## How Google came to the rescue
My colleague's question got me thinking, and as I thought, I googled.
**What scripting languages are on Linux? **
This was my first Google search criteria, and many of you are probably thinking, "She's pretty clueless." Well, I was, but it did set me on a path to solving my problem. The most common result was Bash. Hmm, I've seen Bash. Heck, one of the files I had to document had Bash in it, that ubiquitous line **#!/bin/bash**. I took another look at that file, and I knew what it was doing because I had to document it.
So that led me to my next Google search request.
**How to download a zip file from a URL? **
That was my basic task really. I had a URL with a .zip file containing all the files I needed to include in my documentation, so I asked the All Powerful Google to help me out. That search gem, and a few more, led me to Curl. But here's the best part: Not only did I find Curl, one of the top search hits showed me a Bash script that used Curl to download a .zip file and extract it. That was more than I asked for, but that's when I realized being specific in my Google search requests could give me the information I needed to write this script. So, momentum in my favor, I wrote the simplest of scripts:
```
``````
#!/bin/sh
curl http://rather.long.url | tar -xz -C my_directory --strip-components=1
```
What a moment to see that thing run! But then I realized one gotcha: The URL can change, depending on which set of files I'm trying to access. I had another problem to solve, which led me to my next search.
**How to pass parameters into a Bash script? **
I needed to be able to run this script with different URLs and different end directories. Google showed me how to put in **$1**, **$2**, etc., to replace what I typed on the command line with my script. For example:
```
````bash myscript.sh http://rather.long.url my_directory`
That was much better. Everything was working as I needed it to, I had flexibility, I had a working script, and most of all, I had a short command to type and save myself 30 minutes of copy-paste grunt work. That was a morning well spent.
Then I realized I had one more problem. You see, my memory is short, and I knew I'd run this script only every couple of months. That left me with two issues:
- How would I remember what to type for my script (URL first? directory first?)?
- How would another writer know how to run my script if I got hit by a truck?
I needed a usage message—something the script would display if I didn't use it correctly. For example:
```
````usage: bash yaml-fetch.sh <'snapshot_url'> <directory>`
Otherwise, run the script. My next search was:
**How to write "if/then/else" in a Bash script? **
Fortunately I already knew **if/then/else** existed in programming. I just had to find out how to do that. Along the way, I also learned to print from a Bash script using **echo**. What I ended up with was something like this:
```
``````
#!/bin/sh
URL=$1
DIRECTORY=$2
if [ $# -eq 0 ];
then
echo "usage: bash yaml-fetch.sh <'snapshot_url'> <directory>".
else
# make the directory if it doesn't already exist
echo 'create directory'
mkdir $DIRECTORY
# fetch and untar the yaml files
echo 'fetch and untar the yaml files'
curl $URL | tar -xz -C $DIRECTORY --strip-components=1
fi
```
## How Google and scripting rocked my world
Okay, slight exaggeration there, but this being the 21st century, learning new things (especially somewhat simple things) is a whole lot easier than it used to be. What I learned (besides how to write a short, self-documented Bash script) is that if I have a question, there's a good chance someone else had the same or a similar question before. When I get stumped, I can ask the next question, and the next question. And in the end, not only do I have a script, I have the start of a new skill that I can hold onto and use to simplify other tasks I've been avoiding.
Don't let that first script (or programming step) get the best of you. It's a skill, like any other, and there's a wealth of information out there to help you along the way. You don't need to read a massive book or take a month-long course. You can do it a simpler way with baby steps and baby scripts that get you started, then build on that skill and your confidence. There will always be a need for folks to write those thousands-of-lines-of-code programs with all the branching and merging and bug-fixing.
But there is also a strong need for simple scripts and other ways to automate/simplify tasks. And that's where a little script and a little confidence can give you a kickstart.
## 14 Comments |
8,618 | Linux 中高效编写 Bash 脚本的 10 个技巧 | https://www.tecmint.com/useful-tips-for-writing-bash-scripts-in-linux/ | 2017-06-17T19:22:00 | [
"脚本",
"调试"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8618-1.html | 
Shell 脚本编程 是你在 Linux 下学习或练习编程的最简单的方式。尤其对 [系统管理员要处理着自动化任务](https://www.tecmint.com/using-shell-script-to-automate-linux-system-maintenance-tasks/),且要开发新的简单的实用程序或工具等(这里只是仅举几例)更是必备技能。
本文中,我们将分享 10 个写出高效可靠的 bash 脚本的实用技巧,它们包括:
### 1、 脚本中多写注释
这是不仅可应用于 shell 脚本程序中,也可用在其他所有类型的编程中的一种推荐做法。在脚本中作注释能帮你或别人翻阅你的脚本时了解脚本的不同部分所做的工作。
对于刚入门的人来说,注释用 `#` 号来定义。
```
# TecMint 是浏览各类 Linux 文章的最佳站点
```
### 2、 当运行失败时使脚本退出
有时即使某些命令运行失败,bash 可能继续去执行脚本,这样就影响到脚本的其余部分(会最终导致逻辑错误)。用下面的行的方式在遇到命令失败时来退出脚本执行:
```
# 如果命令运行失败让脚本退出执行
set -o errexit
# 或
set -e
```
### 3、 当 Bash 用未声明变量时使脚本退出
Bash 也可能会使用能导致起逻辑错误的未声明的变量。因此用下面行的方式去通知 bash 当它尝试去用一个未声明变量时就退出脚本执行:
```
# 若有用未设置的变量即让脚本退出执行
set -o nounset
# 或
set -u
```
### 4、 使用双引号来引用变量
当引用时(使用一个变量的值)用双引号有助于防止由于空格导致单词分割开和由于识别和扩展了通配符而导致的不必要匹配。
看看下面的例子:
```
#!/bin/bash
# 若命令失败让脚本退出
set -o errexit
# 若未设置的变量被使用让脚本退出
set -o nounset
echo "Names without double quotes"
echo
names="Tecmint FOSSMint Linusay"
for name in $names; do
echo "$name"
done
echo
echo "Names with double quotes"
echo
for name in "$names"; do
echo "$name"
done
exit 0
```
保存文件并退出,接着如下运行一下:
```
$ ./names.sh
```

*在脚本中用双引号*
### 5、 在脚本中使用函数
除了非常小的脚本(只有几行代码),总是记得用函数来使代码模块化且使得脚本更可读和可重用。
写函数的语法如下所示:
```
function check_root(){
command1;
command2;
}
# 或
check_root(){
command1;
command2;
}
```
写成单行代码时,每个命令后要用终止符号:
```
check_root(){ command1; command2; }
```
### 6、 字符串比较时用 `=` 而不是 `==`
注意 `==` 是 `=` 的同义词,因此仅用个单 `=` 来做字符串比较,例如:
```
value1=”tecmint.com”
value2=”fossmint.com”
if [ "$value1" = "$value2" ]
```
### 7、 用 `$(command)` 而不是老旧的 ``command`` 来做代换
[命令代换](https://www.tecmint.com/assign-linux-command-output-to-variable/) 是用这个命令的输出结果取代命令本身。用 `$(command)` 而不是引号 ``command`` 来做命令代换。
这种做法也是 [shellcheck tool](https://www.tecmint.com/shellcheck-shell-script-code-analyzer-for-linux/) (可针对 shell 脚本显示警告和建议)所建议的。例如:
```
user=`echo “$UID”`
user=$(echo “$UID”)
```
### 8、 用 `readonly` 来声明静态变量
静态变量不会改变;它的值一旦在脚本中定义后不能被修改:
```
readonly passwd_file=”/etc/passwd”
readonly group_file=”/etc/group”
```
### 9、 环境变量用大写字母命名,而自定义变量用小写
所有的 bash 环境变量用大写字母去命名,因此用小写字母来命名你的自定义变量以避免变量名冲突:
```
# 定义自定义变量用小写,而环境变量用大写
nikto_file=”$HOME/Downloads/nikto-master/program/nikto.pl”
perl “$nikto_file” -h “$1”
```
### 10、 总是对长脚本进行调试
如果你在写有数千行代码的 bash 脚本,排错可能变成噩梦。为了在脚本执行前易于修正一些错误,要进行一些调试。通过阅读下面给出的指南来掌握此技巧:
1. [如何在 Linux 中启用 Shell 脚本调试模式](/article-8028-1.html)
2. [如何在 Shell 脚本中执行语法检查调试模式](/article-8045-1.html)
3. [如何在 Shell 脚本中跟踪调试命令的执行](/article-8120-1.html)
本文到这就结束了,你是否有一些其他更好的 bash 脚本编程经验想要分享?若是的话,在下面评论框分享出来吧。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S(Free and Open-Source Software,自由及开放源代码软件)爱好者,未来的 Linux 系统管理员、Web 开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,且崇尚分享知识。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/useful-tips-for-writing-bash-scripts-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ch-cn](https://github.com/ch-cn) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | [Shell scripting](https://www.tecmint.com/category/bash-shell/) is the easiest form of programming you can learn/do in Linux. More so, it is a required skill for [system administration for automating tasks](https://www.tecmint.com/using-shell-script-to-automate-linux-system-maintenance-tasks/), developing new simple utilities/tools just to mention but a few.
In this article, we will share 10 useful and practical tips for writing effective and reliable bash scripts and they include:
### 1. Always Use Comments in Scripts
This is a recommended practice which is not only applied to shell scripting but all other kinds of programming. Writing comments in a script helps you or some else going through your script understand what the different parts of the script do.
For starters, comments are defined using the `#`
sign.
#TecMint is the best site for all kind of Linux articles
### 2. Make a Script exit When Fails
Sometimes bash may continue to execute a script even when a certain command fails, thus affecting the rest of the script (may eventually result in logical errors). Use the line below to exit a script when a command fails:
#let script exit if a command fails set -o errexit OR set -e
### 3. Make a Script exit When Bash Uses Undeclared Variable
Bash may also try to use an undeclared script which could cause a logical error. Therefore use the following line to instruct bash to exit a script when it attempts to use an undeclared variable:
#let script exit if an unsed variable is used set -o nounset OR set -u
### 4. Use Double Quotes to Reference Variables
Using double quotes while referencing (using a value of a variable) helps to prevent word splitting (regarding whitespace) and unnecessary globbing (recognizing and expanding wildcards).
Check out the example below:
#!/bin/bash #let script exit if a command fails set -o errexit #let script exit if an unsed variable is used set -o nounset echo "Names without double quotes" echo names="Tecmint FOSSMint Linusay" for name in $names; do echo "$name" done echo echo "Names with double quotes" echo for name in "$names"; do echo "$name" done exit 0
Save the file and exit, then run it as follows:
$ ./names.sh
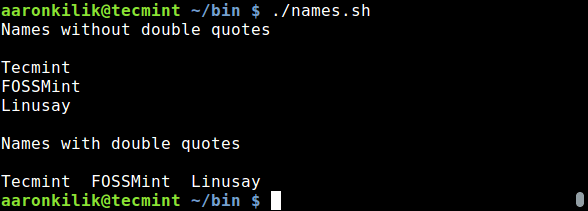
### 5. Use functions in Scripts
Except for very small scripts (with a few lines of code), always remember to use functions to modularize your code and make scripts more readable and reusable.
The syntax for writing functions is as follows:
function check_root(){ command1; command2; } OR check_root(){ command1; command2; }
For single line code, use termination characters after each command like this:
check_root(){ command1; command2; }
### 6. Use = instead of == for String Comparisons
Note that `==`
is a synonym for `=`
, therefore only use a single `=`
for string comparisons, for instance:
value1=”tecmint.com” value2=”fossmint.com” if [ "$value1" = "$value2" ]
### 7. Use $(command) instead of legacy ‘command’ for Substitution
[Command substitution](https://www.tecmint.com/assign-linux-command-output-to-variable/) replaces a command with its output. Use `$(command)`
instead of backquotes ``command``
for command substitution.
This is recommended even by [shellcheck tool](https://www.tecmint.com/shellcheck-shell-script-code-analyzer-for-linux/) (shows warnings and suggestions for shell scripts). For example:
user=`echo “$UID”` user=$(echo “$UID”)
### 8. Use Read-only to Declare Static Variables
A static variable doesn’t change; its value can not be altered once it’s defined in a script:
readonly passwd_file=”/etc/passwd” readonly group_file=”/etc/group”
### 9. Use Uppercase Names for ENVIRONMENT Variables and Lowercase for Custom Variables
All bash environment variables are named with uppercase letters, therefore use lowercase letters to name your custom variables to avoid variable name conflicts:
#define custom variables using lowercase and use uppercase for env variables nikto_file=”$HOME/Downloads/nikto-master/program/nikto.pl” perl “$nikto_file” -h “$1”
### 10. Always Perform Debugging for Long Scripts
If you are writing bash scripts with thousands of lines of code, finding errors may become a nightmare. To easily fix things before executing a script, perform some debugging. Master this tip by reading through the guides provided below:
[How To Enable Shell Script Debugging Mode in Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/enable-shell-debug-mode-linux/)[How to Perform Syntax Checking Debugging Mode in Shell Scripts](https://www.tecmint.com/check-syntax-in-shell-script/)[How to Trace Execution of Commands in Shell Script with Shell Tracing](https://www.tecmint.com/trace-shell-script-execution-in-linux/)
That’s all! Do you have any other best bash scripting practices to share? If yes, then use the comment form below to do that.
I don’t agree with using single ”=” in string comparison. What is the advantage?
ReplyThere is no advantage or disadvantage, in bash
Reply`==`
is identical to`=`
for string comparisons.@LinuxHostSupport
Absolutely correct.
Reply@Mike
There is really no significant difference, but
Reply`"=="`
is applicable to bash only. The POSIX form is`"="`
. If portability to non-bash shells is important, then use`"="`
. |
8,619 | 给非英语母语的人从事开源项目的若干建议 | https://opensource.com/article/17/1/non-native-speakers-take-open-source-communities | 2017-06-18T10:56:00 | [
"开源项目",
"非英语母语"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8619-1.html | 
大多数的开源项目的主要语言都是英语,但是开源项目的用户和贡献者却遍布全球。非英语母语的人在参与这个生态系统时会面临许多沟通和文化上的挑战。
在这篇文章中,作为不以英语为母语的 OpenStack 的贡献者的我们将会分享一些所面临挑战——如何去克服它们,还有一些好的方案,它们能够减轻不以英语为母语且刚开始从事的人的焦虑。我们的总部在日本、巴西和中国,每天都会与世界各地的大型 OpenStack 社区合作。
OpenStack 的官方语言是英语,这意味着我们是作为非英语为母语的人士来进行交流。
### 挑战
非英语为母语的人士在开源社区工作时会面临具体沟通挑战:它们与有限的语言技能和文化差异有关。
#### 语言技能
让我们来关注在阅读、写作、听力和口语背后的具体语言技能。
**阅读**:这是最简单也是最重要的技能。最简单是因为:如果你不明白写了什么,你有机会再次阅读它,或者需要的话可以多次阅读。如果你遇到了一个不常见的短语、表达式或者缩写,你可以使用一个词典或者翻译器。在另一方面,它是最重要的技能是因为:对大多数开源项目而言,主要的交流方式都是邮件列表和 IRC。
**写作**:英语语法是一个问题,尤其是对句子结构不同的语言而言。这可能会在用电子邮件进行通信和通过 IRC 频道进行通信时产生问题。对一些人来说,写出又长又漂亮的句子比较困难,而普遍依赖于简单句子,这是因为这些易于书写和理解。
**听力**:这对非英语为母语的人来说比阅读和写作更加困难。通常,英语为母语的人之间的对话在非常快的,这就使得那些仍然处于刚从事阶段的人很难理解他们的讨论,同时也限制了他们参与到讨论当中。此外,试图理解一个遍布全球的社区的各种口音也增加了复杂性。有意思的是,美国人的发音往往比其他的容易理解。
**口语**:口语比听力更加的困难,因为参与者的词汇量可能会比较有限。而且,英语的音素和语法通常与那些母语不是英语的人的母语相差很大,这就使得互动更加的难以理解。
#### 文化差异
在开源社区与其他人交流时,每种文化都有它自己不同的规范。例如,日本人通常不会明确的说好的或者不,他们认为这是尊重别人的一种方式,可以避免彼此间的争论。这通常与其他的文化大不一样,可能会对所表达的内容造成误解。
在中国文化中,人们倾向于只是说好的,而不是说不,或者试图商讨。在一个像 OpenStack 这样的分布于全球的社区里,这通常会导致在表达意见时缺乏自信。另外,中国人喜欢首先列出事实,然后在后面给出结论,而这会对来自其他文化中的人造成困惑,因为这不是他们所期望的。
例如,巴西人可能会认为讨论是以类似的方式进行的;然而,其他文化的反应会很直接和简短,这听起来可能会有点粗鲁。
### 克服障碍
语言技能方面的挑战要比文化差异方面的挑战容易克服。文化差异需要被受到尊重,然而英语技能却总是可以被改善的。
为了刷新你的语言技能,你应该尽可能多地接触该语言。不要担心你的局限,只管尽自己所能,你终将会得到改善。
尽可能多的阅读,因为这有助于你积累词汇。通过日常的聊天和邮件列表进行交流也很有帮助。一些工具,如实时字典和翻译器,对这些平台非常有用。
与别人或者你自己交谈可以帮助你更自如地频繁地说话。进行一对一的对话来表达你的想法比在更大的群体中讨论更容易。
### 新手的融入
来自新手和母语者的一些举措可能会对学习过程产生积极的影响。
#### 新手
说出和写下你的意见,并且提出你的问题;参与其中总是一个练习你的英语的很好的机会。不要害怕。
对于会议,确保你提前准备过,这样你将会对会议主题比较熟悉,而且会对自己要表达的意见更加的自信。
与英语为母语的人结交朋友,多和他们讨论来提高你的英语技能。
用英语写博客和技术文章也是不错的主意。
#### 给英语为母语的人士的建议
请说话慢一点儿,同时使用一些简单的单词和句子。如果你发现了非英语为母语的人使用英语中的一些错误请不要嘲笑他们,尝试鼓励新来的人表达自己的意见,让他们非常舒适地表达意见。
*这篇文章由 Masayuki Igawa、Dong Ma 和 Samuel de Medeiros Queiroz 共同协作完成,可以在 Hobart 的 linux.conf.au 2017([#lca2017](https://twitter.com/search?q=%23lca2017&src=typd)):[开源社区中的非英语母语者:一个真实的故事](https://linux.conf.au/schedule/presentation/70/)中了解更多*
( 题图:opensource.com)
---
作者简介:
Masayuki Igawa 是一名拥有 15 年大量软件项目经验的软件工程师,目前正在开发与 Linux 内核和虚拟化相关开源软件。自 2013 年起,他就一直是一名活跃的 OpenStack 项目贡献者。他是像 Tempest 和 subunit2sql 这样一些 OpenStack QA 项目的核心成员。他目前就职于 HPE 的 Upstream OpenStack 团队,该团队目的是使 OpenStack 更适合所有人。他以前曾在 OpenStack 峰会上发表演讲。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/1/non-native-speakers-take-open-source-communities>
作者:[Masayuki Igawa](https://opensource.com/users/masayukig) 译者:[zhousiyu325](https://github.com/zhousiyu325) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The primary language of most open source projects is English, but open source users and contributors span the globe. Non-native speakers face many communication and cultural challenges when participating in the ecosystem.
In this article, we will share challenges, how to overcome them, and best practices for easing onboarding of non-native speakers, as non-native English speakers and contributors to OpenStack. We are based in Japan, Brazil, and China, and work daily with the huge OpenStack community that is spread around the world.
The official language of OpenStack is English, which means we communicate daily as non-native speakers.
## Challenges
Non-native English speakers face specific communication challenges when starting out in open source communities: they are related to limited language skills and cultural disparity.
### Language skills
Let's focus on the specific language skills behind reading, writing, listening, and speaking.
Reading: This is the easiest but also the most important skill. It is the easiest because if you can't understand what is written you have the opportunity to read it again, or as many times as needed. If you encounter an uncommon phrase, expression, or abbreviation, you can use a dictionary or translator. On the other hand, it is the most important skill because for most open source projects the main means of communication are mailing lists and IRC.
Writing: English grammar is an issue especially for languages that structure sentences differently. This may pose a problem for communication in writing emails and communicating via IRC channels. For some, writing long and beautiful sentences is difficult, and the reliance on simpler sentences is prevalent because these are easy to write and convey understanding.
Listening: This is more problematic than reading and writing for non-native speakers. Normally, conversation between native English speakers is very fast, which makes following the discussions for those still learning difficult and limits their participation in those discussions. Furthermore, trying to understand the variety of accents in a globally spread community adds to the complexity. Interestingly, American pronunciation is often easier to understand than others.
Speaking: Speaking is more difficult than listening because the participant's vocabulary may a bit limited. Furthermore, English's phonemes and grammar are often very different from a non-native speaker's mother language, making an interaction even more difficult to understand.
### Cultural differences
Each culture has different norms when interacting with other people in the open source community. For example, the Japanese tend not to say yes or no clearly as a way to respect others and to avoid fighting each other. This is often very different from other cultures and may cause misunderstanding of what was expressed.
In Chinese culture, people prefer to just say yes, instead of saying no or trying to negotiate. In a globally distributed community as OpenStack, this often leads to the lack of confidence when expressing opinions. Furthermore, Chinese people like to list the facts first and give the thesis at the end, and this can cause confusion for people from other cultures because it is not what they expect.
A Brazilian, for instance, may find that discussions are driven in a similar way; however, some cultures are very short and direct in responses, which may sound a bit rude.
## Overcoming obstacles
Challenges related to language skills are easier to overcome than cultural ones. Cultural differences need to be respected, while English skills can always be improved.
In order to brush up on your language skills, be in contact with the language as much as you can. Do not think about your limitations. Just do your best and you will improve eventually.
Read as much as you can, because this will help you gather vocabulary. Communicating through chat and mailing lists daily helps, too. Some tools, such as real-time dictionaries and translators, are very useful with these platforms.
Talking to others or yourself helps you become comfortable speaking out more frequently. Having one-on-one conversations to express your ideas is easier than discussing in larger groups.
## Onboarding newcomers
A few initiatives from both newcomers and native speakers may positively affect the onboarding process.
### Newcomers
Speak and write your opinion, and ask your questions; this participation is always a good opportunity to exercise your English. Do not be afraid.
For meetings, make sure you prepare yourself in advance so you will be comfortable with the subject and more confident about the opinions you are expressing.
Make friends who are English speakers and talk more to practice your English skills.
Writing blogs and technical articles in English are also great ideas.
### Tips for native English speakers
Please speak slowly and use simple words and sentences. Don't make fun of non-native English speakers if you find something wrong about the English they used. Try to encourage newcomers to express their opinions, and make them comfortable enough to do so.
*This article was co-written by Masayuki Igawa, Dong Ma, and Samuel de Medeiros Queiroz. Learn more in their talk at linux.conf.au 2017 ( #lca2017) in Hobart: Non-native English speakers in Open Source communities: A True Story.*
## 1 Comment |
8,620 | 在 LXD 2.3 及以上版本中管理网络 | https://www.stgraber.org/2016/10/27/network-management-with-lxd-2-3/ | 2017-06-18T11:37:00 | [
"LXD",
"容器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8620-1.html | 
### 介绍
当 LXD 2.0 随着 Ubuntu 16.04 一起发布时,LXD 联网就简单了。要么你可以使用 `lxd init` 来配置,为你的容器自己提供一个 “lxdbr0” 网桥,要么使用一个已存在的物理接口。
虽然这确实有效,但是有点混乱,因为大部分的桥接配置发生在 Ubuntu 打包的 LXD 之外。那些脚本只能支持一个桥接,并且没有通过 API 暴露,这使得远程配置有点痛苦。
直到 LXD 2.3,LXD 终于发展了自己的网络管理 API ,并有相应的命令行工具。这篇文章试图来简述这些新的功能。
### 基础联网
在初始情况下,LXD 2.3 没有定义任何网络。`lxd init` 会为你设置一个,并且默认情况下将所有新的容器连接到它,但是让我们亲手尝试看下究竟发生了些什么。
要创建一个新的带有随机 IPv4 和 IP6 子网,并启用 NAT 的网络,只需要运行:
```
stgraber@castiana:~$ lxc network create testbr0
Network testbr0 created
```
你可以如下查看它的配置:
```
stgraber@castiana:~$ lxc network show testbr0
name: testbr0
config:
ipv4.address: 10.150.19.1/24
ipv4.nat: "true"
ipv6.address: fd42:474b:622d:259d::1/64
ipv6.nat: "true"
managed: true
type: bridge
usedby: []
```
如果你不想要那些自动配置的子网,你可以这么做:
```
stgraber@castiana:~$ lxc network create testbr0 ipv6.address=none ipv4.address=10.0.3.1/24 ipv4.nat=true
Network testbr0 created
```
那就会这样:
```
stgraber@castiana:~$ lxc network show testbr0
name: testbr0
config:
ipv4.address: 10.0.3.1/24
ipv4.nat: "true"
ipv6.address: none
managed: true
type: bridge
usedby: []
```
如果你的容器没有使用它,那么创建的网络对你也没什么用。要将你新创建的网络连接到所有容器,你可以这么做:
```
stgraber@castiana:~$ lxc network attach-profile testbr0 default eth0
```
要将一个网络连接到一个已存在的容器中,你可以这么做:
```
stgraber@castiana:~$ lxc network attach my-container default eth0
```
现在,假设你已经在机器中安装了 openvswitch,并且要将这个网桥转换成 OVS 网桥,只需更改为正确的驱动:
```
stgraber@castiana:~$ lxc network set testbr0 bridge.driver openvswitch
```
如果你想要一次性做一系列修改。`lxc network edit` 可以让你在编辑器中交互编辑网络配置。
### 静态租约及端口安全
使用 LXD 管理 DHCP 服务器的一个好处是可以使得管理 DHCP 租约很简单。你所需要的是一个容器特定的网卡设备以及正确的属性设置。
```
root@yak:~# lxc init ubuntu:16.04 c1
Creating c1
root@yak:~# lxc network attach testbr0 c1 eth0
root@yak:~# lxc config device set c1 eth0 ipv4.address 10.0.3.123
root@yak:~# lxc start c1
root@yak:~# lxc list c1
+------+---------+-------------------+------+------------+-----------+
| NAME | STATE | IPV4 | IPV6 | TYPE | SNAPSHOTS |
+------+---------+-------------------+------+------------+-----------+
| c1 | RUNNING | 10.0.3.123 (eth0) | | PERSISTENT | 0 |
+------+---------+-------------------+------+------------+-----------+
```
IPv6 也是相同的方法,但是换成 `ipv6.address` 属性。
相似地,如果你想要阻止你的容器更改它的 MAC 地址或者为其他 MAC 地址转发流量(比如嵌套),你可以用下面的命令启用端口安全:
```
root@yak:~# lxc config device set c1 eth0 security.mac_filtering true
```
### DNS
LXD 在网桥上运行 DNS 服务器。除了设置网桥的 DNS 域( `dns.domain` 网络属性)之外,还支持 3 种不同的操作模式(`dns.mode`):
* `managed` :每个容器都会有一条 DNS 记录,匹配它的名字以及已知的 IP 地址。容器无法通过 DHCP 改变这条记录。
* `dynamic` :允许容器通过 DHCP 在 DNS 中自行注册。因此,在 DHCP 协商期间容器发送的任何主机名最终都出现在 DNS 中。
* `none` : 针对那些没有任何本地 DNS 记录的递归 DNS 服务器。
默认的模式是 `managed`,并且典型的是最安全以及最方便的,因为它为容器提供了 DNS 记录,但是不允许它们通过 DHCP 发送虚假主机名嗅探其他的记录。
### 使用隧道
除了这些,LXD 还支持使用 GRE 或者 VXLAN 隧道连接到其他主机。
LXD 网络可以连接任何数量的隧道,从而轻松地创建跨多个主机的网络。这对于开发、测试和演示非常有用,生产环境通常更喜欢使用 VLAN 进行分割。
所以说,你想在主机 “edfu” 上有一个运行 IPv4 和 IPv6 的基础 “testbr0” 网络,并希望在主机 “djanet” 上使用它来生成容器。最简单的方法是使用组播 VXLAN 隧道。这种类型的隧道仅在两个主机位于同一物理段上时才起作用。
```
root@edfu:~# lxc network create testbr0 tunnel.lan.protocol=vxlan
Network testbr0 created
root@edfu:~# lxc network attach-profile testbr0 default eth0
```
它在主机 “edfu” 上定义了一个 “testbr0” 桥接,并为其他主机能加入它设置了一个组播 VXLAN。在这个设置中,“edfu” 为这个网络扮演了一个路由器角色,提供 DHCP、DNS 等等,其他主机只是通过隧道转发流量。
```
root@djanet:~# lxc network create testbr0 ipv4.address=none ipv6.address=none tunnel.lan.protocol=vxlan
Network testbr0 created
root@djanet:~# lxc network attach-profile testbr0 default eth0
```
现在你可以在任何一台主机上启动容器,并看到它们从同一个地址池中获取 IP,通过隧道直接互相通讯。
如先前所述,这个使用了组播,它通常在跨越路由器时无法很好工作。在这些情况下,你可以用单播模式使用 VXLAN 或者 GRE 隧道。
要使用 GRE 加入另一台主机,首先配置服务主机:
```
root@edfu:~# lxc network set testbr0 tunnel.nuturo.protocol gre
root@edfu:~# lxc network set testbr0 tunnel.nuturo.local 172.17.16.2
root@edfu:~# lxc network set testbr0 tunnel.nuturo.remote 172.17.16.9
```
接着是“客户端”主机:
```
root@nuturo:~# lxc network create testbr0 ipv4.address=none ipv6.address=none tunnel.edfu.protocol=gre tunnel.edfu.local=172.17.16.9 tunnel.edfu.remote=172.17.16.2
Network testbr0 created
root@nuturo:~# lxc network attach-profile testbr0 default eth0
```
如果你像使用 VXLAN,只要这么做:
```
root@edfu:~# lxc network set testbr0 tunnel.edfu.id 10
root@edfu:~# lxc network set testbr0 tunnel.edfu.protocol vxlan
```
还有:
```
root@nuturo:~# lxc network set testbr0 tunnel.edfu.id 10
root@nuturo:~# lxc network set testbr0 tunnel.edfu.protocol vxlan
```
这里需要隧道 id 以防与已经配置的多播 VXLAN 隧道冲突。
这就是如何使用最近的 LXD 简化跨主机联网了!
### 总结
LXD 使得从简单的单主机网络到数千个容器的非常复杂的跨主机网络的定义变得更加容易。它也使为一些容器定义一个新网络或者给容器添加第二个设备,并连接到隔离的私有网络变得很简单。
虽然这篇文章介绍了支持的大部分功能,但仍有一些可以微调 LXD 网络体验的窍门。可以在这里找到完整的列表:[https://github.com/lxc/lxd/blob/master/doc/configuration.md](https://github.com/lxc/lxd/blob/master/doc/configuration.md#network-configuration) 。
### 额外信息
* LXD 主站:<https://linuxcontainers.org/lxd>
* Github 地址: <https://github.com/lxc/lxd>
* 邮件列表支持:[https://lists.linuxcontainers.org](https://lists.linuxcontainers.org/)
* IRC 频道:#lxcontainers on irc.freenode.net
* 在线尝试 LXD:<https://linuxcontainers.org/lxd/try-it>
---
via: <https://www.stgraber.org/2016/10/27/network-management-with-lxd-2-3/>
作者:[Stéphane Graber](https://www.stgraber.org/author/stgraber/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,621 | Debian GNU/Linux 9 “Stretch” 正式发布 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/debian-gnu-linux-9-stretch-operating-system-officially-released-download-now-516521.shtml | 2017-06-19T07:13:00 | [
"Debian",
"Stretch"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8621-1.html | 
已经使用了两年之久的代号为 “Jessie” 的 Debian GNU/Linux 8,终于被标记为 “oldstable”了。就在 18 日,Debian 项目宣布 Debian GNU/Linux 9,代号为 “Stretch” 的新版本正式发布!
这个 2017 年最重要的 GNU/Linux 发行版,Debian 9 进入了稳定状态,已经可以部署到生产环境中——接下来将会有一大批基于 Debian 的下游衍生版本正在赶来。
Debian 9 是一个主要发布版本,其对现代的硬件和 CPU 架构支持更好,使用了更新的核心组件和应用,此外还有一大堆其它的新功能,当然,稳定性和安全的改进更是重中之重,以及不可尽数的 bug 修复。
在[发布公告](https://www.debian.org/News/2017/20170617)中称:“在经过 26 个月的开发之后,Debian 项目很自豪地推出了新的稳定版本 Debian 9(代号 ‘Stretch’),并在接下来的 5 年内由 Debian 安全团队和 Debian 长期支持团队进行支持。”
### Debian GNU/Linux 9 “Stretch” 亮点
Debian 9 的亮点有:支持 64 位小端 MIPS 硬件架构(mips64el),而停止了对 PowerPC(powerpc)架构的支持;新的 [deb.debian.org](http://deb.debian.org/) 镜像;可以以普通用户运行 X.Org 显示服务器,而不是以 root 用户。
此外,对 APT 和 aptitude 命令行软件包管理器做了重大改进,现在更容易获取和使用调试软件包, APT 源列表中增加了新的 “dbg-sym” 软件仓库,为许多软件包自动地提供了调试符号。Debian 9 中还带有首次发布的 Debian Astro Pure Blend。
Debian 9 中的大量软件包和核心组件进行了更新:
* Linux 4.9 LTS 内核
* GNOME 3.22
* KDE Frameworks 5.28、KDE Plasma 5.8 和 KDE Applications 16.08
* MATE 1.16
* Xfce 4.12
* Chromium 59.0.3071.86
* Firefox 45.9
* GIMP 2.8.18
* Thunderbird 45.8
* LibreOffice 5.2
* Apache 2.4.25
* Tomcat 8.5
* GnuPG 2.1
* MariaDB 10.1
* PostgreSQL 9.6
* GNU Compiler Collection 6.3
* Perl 5.24
* PHP 7.0
* Golang 1.7
* OpenJDK 8
* Python 2.7.13 and 3.5.3
* Ruby 2.3
* Samba 4.5
* systemd 232
* Xen Hypervisor
Debian 9 官方支持 32 位(i386)、64 位(amd64)、64 位 ARM(arm64)等等硬件架构。
那些还在运行 Debian 8 “Jessie” 的计算机现在可以升级到 Debian 9 了。而要全新安装则可以从 debian.org [下载安装介质](https://www.debian.org/distrib/netinst.en.html),当然,你也可以下载支持各种桌面环境的“[现场版](https://www.debian.org/CD/live/)”。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,622 | 2017 年的八大系统运维和工程发展趋势 | https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/top-8-systems-operations-and-engineering-trends-for-2017 | 2017-06-19T10:35:00 | [
"DevOps",
"容器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8622-1.html | 
预测趋势是棘手的,尤其是在快速发展的系统运维和工程领域。2016 年,在我们的 Velocity 大会上,我们讨论了分布式系统、SRE、容器化、无服务架构,人员倦怠以及与提供软件相关的人力与技术挑战等诸多问题。以下是我们认为的下一年的趋势:
### 1、 分布式系统
我们认为这个很重要,我们[在整个 Velocity 会议上再次关注了它](https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/velocity-a-new-direction)。
### 2、 站点可靠性工程(SRE)
<ruby> <a href="https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/what-is-sre-site-reliability-engineering"> 站点可靠性工程 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Site Reliability Engineering </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(SRE)-它只是运维么?[或者它是 DevOps 的另外一个名称吗](http://conferences.oreilly.com/velocity/devops-web-performance-ny/public/content/devops-sre-ama-video)?这是 Google 对那些需要做大量系统及软件工程的运维专业人士的称呼。它由在像 Dropbox 公司的前 Google 人向业内推广,[招聘 SRE 的职位](https://www.glassdoor.com/Salaries/site-reliability-engineer-salary-SRCH_KO0,25.htm)正不断增加,特别是有大型数据中心的面向网络的公司。在某些情况下,SRE 的作用更多地是帮助开发人员运营自己的服务。
### 3、 容器化
公司将继续容器化它们的软件交付。Docker 公司本身已经将 Docker 定位为“[增量革命](http://blog.scottlowe.org/2016/06/21/dockercon-2016-day-2-keynote/)”的工具,对遗留应用进行容器化已成为企业的常见案例。Docker 的未来是什么?随着工程师继续采用诸如 Kubernetes 和 Mesos 之类的编排工具,更高层次的抽象可能为其他容器(如 rkt、Garden 等)提供更多空间。
### 4、 Unikernels
unikernels 是容器化之后的下一步么?它们不合适产品环境么?有些人吹捧 unikernels 的安全和性能好处。关注一下 unikernels 在 2017 是如何进化的,[特别要关注下 Dokcer 公司在这个领域做的](http://www.infoworld.com/article/3024410/application-virtualization/docker-kicks-off-unikernel-revolution.html)。(今年它已经收购了 Unikernel Systems)
### 5、 <ruby> 无服务架构 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Serverless </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
无服务架构视功能为基础的计算单元。有些人认为这个术语是误导性的(让人想起 “noops”),并且更倾向于把这个趋势称为“<ruby> 功能即服务 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Functions-as-a-Service </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”(FaaS)。开发人员和架构师正在越来越多地尝试这个技术,并期望看到有越来越多的程序用这个范式编写。更多关于 serverless/FaaS 对运维的意义,请查看 Michael Hausenblas 的 [Serverless 运维](http://www.oreilly.com/webops-perf/free/serverless-ops.csp?intcmp=il-webops-free-lp-na_new_site_top_8_systems_operations_and_engineering_trends_for_2017_body_text_cta)免费电子书。
### 6、 原生云程序开发
就像 DevOps,这个术语已经被市场人员使用并滥用很久了,但是<ruby> 云计算基金会 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Cloud Native Computing Foundation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(CNCF)为这些新工具(通常是谷歌发起的)做了一个很好的例子,这些工具不仅利用了云,而且特别还在于分布式系统(即微服务,容器化和动态编排)所提供的优势和机会。
### 7、 监控
随着行业从 Nagios 风格的监控发展到流化指标和可视化,我们在生产越来越多的系统数据,而如何理解它们则是下一个挑战,因此,我们看到供应商开始提供具有机器学习功能的监控服务,以及更普遍的是 IT 运营人员开始去研究让机器学习分析系统数据的技术。同样,随着我们的基础设施变得更加动态和分布式,监控越来越少地检查某个资源的健康状况,更多的是在服务之间追踪流量。因此,分布式跟踪已经出现。
### 8、 DevOps 安全
随着 DevOps 安全的普及,[安全性正在迅速成为团队范围的关注](https://www.oreilly.com/learning/devopssec-securing-software-through-continuous-delivery)。当重视安全和合规方面的公司在速度的竞争上感到了压力时,要同时满足速度和可靠性的 DevOps 所面对的经典挑战尤其明显。
### 告诉我们关于你的工作
作为一名 IT 运维专业人员 - 你是否使用系统管理的术语如 DevOps、SRE、DBA 等等。- [欢迎你来分享你的见解](http://www.oreilly.com/webops-perf/2016-ops-survey.html)。
---
作者简介:
Courtney Nash 主持 O'Reilly Media 的多个会议,是专注于现代网络运维、高性能程序和安全性的战略内容总监。一位前学术神经科学家,她仍然对大脑着迷,以及它如何告诉我们与技术互动和对技术的期望。自从移居西雅图,在一家蓬勃发展的在线书店工作之后,她花了 17 年的时间从事技术行业的各种工作。在外面,你可以看到 Courtney 在骑自行车、徒步旅行、滑雪。。。
O'Reilly Media 的基础架构和运维编辑 Brian Anderson 介绍了从传统系统管理到云计算、Web 性能、Docker 和 DevOps 等软件交付的重要内容。他一直从事在线教育,服务于学习者的需求超过十多年。
---
via: <https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/top-8-systems-operations-and-engineering-trends-for-2017>
作者:[Courtney Nash](https://www.oreilly.com/people/3f5d7-courtneyw-nash), [Brian Anderson](https://www.oreilly.com/people/brian_anderson) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,624 | 什么是开源? | https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-source | 2017-06-20T14:27:57 | [
"开源"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8624-1.html | 
“<ruby> 开源 <rt> open source </rt></ruby>”这个词,指的是事物规划为可以公开访问的,因此人们可以修改并分享。
这个词最初是起源于软件开发中,指的是一种开发软件的特殊形式。但到了今天,“开源”已经泛指一组概念——就是我们称之为的“[开源的方式](https://opensource.com/open-source-way)”。这些概念包括开源项目、产品,或是自发倡导并欢迎开放变化、协作参与、快速原型、公开透明、精英体制以及面向社区开发的原则。
### 什么是开源软件?
开源软件的源代码任何人都可以审查、修改和增强。
“<ruby> 源代码 <rt> source code </rt></ruby>”是软件中大部分计算机用户都没见过的部分,程序员可以修改代码来改变一个软件(“程序”或“应用”)工作的方式。程序员如果可以接触到计算机程序源代码,就可以通过添加功能或修复问题来改进这个软件。
### 开源软件和其它类型的软件有什么不同?
有些软件只有创建它的人、团队、组织才能修改,并且控制维护工作。人们称这种软件是“<ruby> 专有 <rt> proprietary </rt></ruby>”或“<ruby> 闭源 <rt> closed source </rt></ruby>”软件。
专有软件只有原作者可以合法地复制、审查,以及修改这个软件。为了使用专有软件,计算机用户必须同意(通常是在软件第一次运行的时候签署一份显示的许可)他们不会对软件做软件作者没有表态允许的事情。微软 Office 和 Adobe Photoshop 就是专有软件的例子。
开源软件不一样。它的作者[让源代码对其他人提供](https://opensource.com/business/13/5/open-source-your-code),需要的人都可以查看、复制、学习、修改或分享代码。[LibreOffice](https://www.libreoffice.org/) 和 [GIMP](http://www.gimp.org/) 是开源软件的例子。
就像专有软件那样,用户在使用开源软件时必须接受一份[许可证](https://opensource.com/law/13/1/which-open-source-software-license-should-i-use)的条款——但开源许可的法律条款和专有软件的许可截然不同。
开源许可证影响人们[使用、学习、修改以及分发](https://opensource.com/law/10/10/license-compliance-not-problem-open-source-users)的方式。总的来说,开源许可证赋予计算机用户[按他们想要的目的来使用开源软件的许可](https://opensource.org/docs/osd)。一些开源许可证(人们称之为<ruby> 左版 <rt> copyleft </rt></ruby>”)规定任何发布了修改过的开源软件的人,同时还要一同发布它的源代码。此外,[另一些开源许可](https://opensource.com/law/13/5/does-your-code-need-license)规定任何修改和分享一个程序给其他人的人,还要分享这个程序的源代码,而且不能收取许可费用。
开源软件许可证有意地提升了协作和分享,因为它们允许其他人对代码作出修改并将改动包含到他们自己的项目中。开源许可证鼓励开发者随时访问、查看、修改开源软件,前提是开发者在分享成果的时候允许其他人也能够做相同的事情。
### 开源软件只是对开发者很重要?
不。开源技术和开源思想对开发者和非开发者都有益。
因为早期的创造者基于开源技术构建了互联网本身的大部分——比如 [Linux 操作系统](https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-linux)和 [Apache Web 服务器](http://httpd.apache.org/)应用——任何今天使用互联网的人都受益于开源软件。
每当计算机用户浏览网页、检查邮件、和朋友聊天、在线收听流媒体音乐、玩多人游戏的时候,他们的电脑、手机或游戏主机都会连接到一个全球性的计算机网络,使用开源软件来路由并将他们的数据传输到面前的“本地”设备上。完成这些重要工作的计算机通常位于很远的地方,用户不会实际看到或物理接触到它们——所以有些人称之为“远程计算机”。
越来越多的人开始依赖于远程计算机,在可以在本地完成的任务在线完成。举个例子,人们可能会使用在线文字处理、电子邮件管理、图片编辑工具,而在本地的个人电脑并没有安装运行相应的软件。人们轻松地使用浏览器或手机应用访问这些程序。当他们这么做的时候,他们参与到了“远程计算”中。
一些人将远程计算称为“云计算”,因为它涉及的活动(像是存储文件、分享照片、观看视频)不仅包含本地设备,还有一个远程计算机全球网络,像是围绕在周围的大气。
云计算是日常生活一个越来越重要的概念,离不开连接互联网的设备。一些云计算应用,比如 Google 应用,是专有的。其它的,像 OwnCloud 和 NextCould 是开源的。
云计算应用运行在一些额外的软件“之上”,这些软件帮助它们流畅高效地操作,所以人们经常说那个软件运行在云计算应用“之下”,为那些应用扮演一个“平台”。云计算平台可以是开源或闭源的。OpenStack 是一个开源云计算平台的例子。
### 为什么人们更倾向于使用开源软件?
人们相对于专有软件更倾向于开源软件有很多原因,包括:
**可控**。很多人青睐开源软件因为相对其它类型软件他们可以[拥有更多的可控](https://opensource.com/life/13/5/tumblr-open-publishing)。他们可以检查代码来保证它没有做任何不希望它做的事情,并且可以改变不喜欢的部分。不是开发者的用户也可以从开源软件获益,因为他们可以以任何目的使用这个软件——而不仅仅是某些人认为他们应该有的目的。
**训练**。其他人喜欢开源软件是因为它可以帮助他们[成为更好的开发者](https://opensource.com/life/13/6/learning-program-open-source-way)。因为开源代码可以公开访问,学生可以在学习创建更好的软件时轻松地从中学习。学生还可以在提升技能的时候分享他们的成果给别人,获得评价和批评。当人们发现程序源代码中的错误的时候,可以将这个错误分享给其他人,帮助他们避免犯同样的错误。
**安全**。一些人倾向开源软件是因为他们认为它比专有软件更[安全](https://opensource.com/government/10/9/scap-computer-security-rest-us)和稳定。因为任何人都可以查看和修改开源软件,就会有人可能会注意到并修正原作者遗漏的错误或疏忽。并且因为这么多的开发者可以在同一开源软件上工作,而不用事先联系获取原作者的授权,相比专有软件,他们可以更[快速](https://opensource.com/government/13/2/bug-fix-day)地修复、更新和升级开源软件。
**稳定**。许多用户在重要、长期的项目中相较专有软件更加青睐开源软件。因为开发者[公开分发](https://opensource.com/life/12/9/should-we-develop-open-source-openly)开源软件的源代码,如果最初的开发者停止开发了,关键任务依赖该软件的用户可以确保他们的工具不会消失,或是陷入无法修复的状态。另外,开源软件趋向于同时包含和按照开放标准进行操作。
### “开源”不是只是意味着某样东西是免费的吗?
不。这是个“开源”实践中的[常见误解](https://opensource.com/education/12/7/clearing-open-source-misconceptions),“开源”概念的含义[不只是指经济方面的](https://opensource.com/open-organization/16/5/appreciating-full-power-open)。
开源软件开发者可以为他们创建或贡献的开源软件收取费用。但在一些情况下,由于开源许可证可能会要求他们在将软件卖给他人的时候发布源代码,一些开发者发现向用户收取软件服务和支持(而不是软件本身)的费用会更加合算。通过这种方式,他们的软件仍然保持免费,而他们[从帮助他人](https://opensource.com/business/14/7/making-your-product-free-and-open-source-crazy-talk)安装、使用、解决问题中赚取费用。
尽管一些开源软件可能是免费的,但开源软件的编程和解决问题的技能可能[十分有价值](https://opensource.com/business/16/2/add-open-source-to-your-resume)。许多雇主特别寻求[雇佣在开源软件方面有工作经验的开发者](https://opensource.com/business/16/5/2016-open-source-jobs-report)。
### 什么是“在软件之外”的开源?
在 Opensource.com,我们想说我们对于开源价值和原则应用到软件之外领域的方式很有兴趣。我们更愿意不仅将开源视为一种计算机软件开发和许可的方式,也把它视作一种态度。
实现“[开源方式](https://opensource.com/open-source-way)”的生活的各个方面,意味着表达一种分享的意愿,通过透明的方式和他人协作(这样其他人也可以关注和加入),拥抱失败,将它作为一种改进的手段,以及期待(甚至鼓励)所有人都可以这么做。
这也意味着在让世界变得更好的过程中扮演一个积极的角色,这只有在[每个人都可以接触](https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-access)到对世界进行规划的途径时才有可能。
这个世界充满了“源代码”——[蓝图](https://opensource.com/life/11/6/architecture-open-source-applications-learn-those-you)、[食谱](https://opensource.com/life/12/6/open-source-like-sharing-recipe)、[规则](https://opensource.com/life/12/4/day-my-mind-became-open-sourced)——它们引导和塑造我们思考和行动的方式。我们相信这些深层代码(无论是什么形式)应该是开放、可接触、分享的——这样人们可以参与其中并让它变得更好。
在这里,我们诉说开源价值对生活所有领域的影响的故事——[科学](https://opensource.com/resources/open-science)、[教育](https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-education)、[政府](https://opensource.com/resources/open-government)、[工业](https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-hardware)、健康、法律,以及[组织动态](https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-organization)。我们是一个社区,告诉他人开源的方式如何成为最好的方式,因为对开源的爱和其它一样:当它被分享的时候它会变得更好。
在哪里能够获得关于开源的更多信息?
我们编辑了一些资源来帮助你学到更多关于开源的内容。我们推荐你从阅读我们的[开源问答、指南、教程](https://opensource.com/resources)开始。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-source>
作者:<opensource.com> 译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 
Opensource.com
The term [open source](https://opensource.com/article/18/2/coining-term-open-source-software) refers to something people can modify and share because its design is publicly accessible.
The term originated in the context of software development to designate a specific approach to creating computer programs. Today, however, "open source" designates a broader set of values—what we call "[the open source way](https://opensource.com/open-source-way)." Open source projects, products, or initiatives embrace and celebrate principles of open exchange, collaborative participation, rapid prototyping, transparency, meritocracy, and community-oriented development.
## What is open source software?
Open source software is software with source code that anyone can inspect, modify, and enhance.
"Source code" is the part of software that most computer users don't ever see; it's the code computer programmers can manipulate to change how a piece of software—a "program" or "application"—works. Programmers who have access to a computer program's source code can improve that program by adding features to it or fixing parts that don't always work correctly.
## What's the difference between open source software and other types of software?
Some software has source code that only the person, team, or organization who created it—and maintains exclusive control over it—can modify. People call this kind of software "proprietary" or "closed source" software.
Only the original authors of proprietary software can legally copy, inspect, and alter that software. And in order to use proprietary software, computer users must agree (usually by signing a license displayed the first time they run this software) that they will not do anything with the software that the software's authors have not expressly permitted. Microsoft Office and Adobe Photoshop are examples of proprietary software.
Open source software is different. Its authors [make its source code available](https://opensource.com/business/13/5/open-source-your-code) to others who would like to view that code, copy it, learn from it, alter it, or share it. [LibreOffice](https://www.libreoffice.org/) and the [GNU Image Manipulation Program](http://www.gimp.org/) are examples of open source software.
As they do with proprietary software, users must accept the terms of a [license](https://opensource.com/law/13/1/which-open-source-software-license-should-i-use) when they use open source software—but the legal terms of open source licenses differ dramatically from those of proprietary licenses.
Open source licenses affect the way people can [use, study, modify, and distribute](https://opensource.com/law/10/10/license-compliance-not-problem-open-source-users) software. In general, open source licenses grant computer users [permission to use open source software for any purpose they wish](https://opensource.org/docs/osd). Some open source licenses—what some people call "copyleft" licenses—stipulate that anyone who releases a modified open source program must also release the source code for that program alongside it. Moreover, [some open source licenses](https://opensource.com/law/13/5/does-your-code-need-license) stipulate that anyone who alters and shares a program with others must also share that program's source code without charging a licensing fee for it.
By design, open source software licenses promote collaboration and sharing because they permit other people to make modifications to source code and incorporate those changes into their own projects. They encourage computer programmers to access, view, and modify open source software whenever they like, as long as they let others do the same when they share their work.
## Is open source software only important to computer programmers?
No. Open source technology and open source thinking both benefit programmers and non-programmers.
Because early inventors built much of the Internet itself on open source technologies—like [the Linux operating system](https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-linux) and the [Apache Web server application](http://httpd.apache.org/)—anyone using the Internet today benefits from open source software.
Every time computer users view web pages, check email, chat with friends, stream music online, or play multiplayer video games, their computers, mobile phones, or gaming consoles connect to a global network of computers using open source software to route and transmit their data to the "local" devices they have in front of them. The computers that do all this important work are typically located in faraway places that users don't actually see or can't physically access—which is why some people call these computers "remote computers."
More and more, people rely on remote computers when performing tasks they might otherwise perform on their local devices. For example, they may use online word processing, email management, and image editing software that they don't install and run on their personal computers. Instead, they simply access these programs on remote computers by using a Web browser or mobile phone application. When they do this, they're engaged in "remote computing."
Some people call remote computing "cloud computing," because it involves activities (like storing files, sharing photos, or watching videos) that incorporate not only local devices but also a global network of remote computers that form an "atmosphere" around them.
Cloud computing is an increasingly important aspect of everyday life with Internet-connected devices. Some cloud computing applications, like Google Apps, are proprietary. Others, like [ownCloud](https://owncloud.org/) and [Nextcloud](https://nextcloud.com/), are open source.
Cloud computing applications run "on top" of additional software that helps them operate smoothly and efficiently, so people will often say that software running "underneath" cloud computing applications acts as a "[platform](https://opensource.com/life/14/4/why-open-infrastructure-matters)" for those applications. Cloud computing platforms can be open source or closed source. [OpenStack](https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-openstack) is an example of an open source cloud computing platform.
## Why do people prefer using open source software?
People prefer open source software to proprietary software for a number of reasons, including:
**Control.** Many people prefer open source software because they [have more control](https://opensource.com/life/13/5/tumblr-open-publishing) over that kind of software. They can examine the code to make sure it's not doing anything they don't want it to do, and they can change parts of it they don't like. Users who aren't programmers also benefit from open source software, because they can use this software for any purpose they wish—not merely the way someone else thinks they should.
**Training.** Other people like open source software because it helps them [become better programmers](https://opensource.com/life/13/6/learning-program-open-source-way). Because open source code is publicly accessible, students can easily study it as they learn to make better software. Students can also share their work with others, inviting comment and critique, as they develop their skills. When people discover mistakes in programs' source code, they can share those mistakes with others to help them avoid making those same mistakes themselves.
**Security.** Some people prefer open source software because they consider it more [secure](https://opensource.com/government/10/9/scap-computer-security-rest-us) and stable than proprietary software. Because anyone can view and modify open source software, someone might spot and correct errors or omissions that a program's original authors might have missed. And because so many programmers can work on a piece of open source software without asking for permission from original authors, they can fix, update, and upgrade open source software more [quickly](https://opensource.com/government/13/2/bug-fix-day) than they can proprietary software.
**Stability.** Many users prefer open source software to proprietary software for important, long-term projects. Because programmers [publicly distribute](https://opensource.com/life/12/9/should-we-develop-open-source-openly) the source code for open source software, users relying on that software for critical tasks can be sure their tools won't disappear or fall into disrepair if their original creators stop working on them. Additionally, open source software tends to both incorporate and operate according to open standards.
**Community.** Open source software often inspires a community of users and developers to form around it. That's not unique to open source; many popular applications are the subject of meetups and user groups. But in the case of open source, the community isn't just a fanbase that buys in (emotionally or financially) to an elite user group; it's the people who produce, test, use, promote, and ultimately affect the software they love.
## Doesn't "open source" just mean something is free of charge?
No. This is a [common misconception](https://opensource.com/education/12/7/clearing-open-source-misconceptions) about what "open source" implies, and the concept's implications are [not only economic](https://opensource.com/open-organization/16/5/appreciating-full-power-open).
Open source software programmers can charge money for the open source software they create or to which they contribute. But in some cases, because an open source license might require them to release their source code when they sell software to others, some programmers find that charging users money for *software services and support* (rather than for the software itself) is more lucrative. This way, their software remains free of charge, and they [make money helping others](https://opensource.com/business/14/7/making-your-product-free-and-open-source-crazy-talk) install, use, and troubleshoot it.
While some open source software may be free of charge, skill in programming and troubleshooting open source software can be [quite valuable](https://opensource.com/business/16/2/add-open-source-to-your-resume). Many employers specifically seek to [hire programmers with experience](https://opensource.com/business/16/5/2016-open-source-jobs-report) working on open source software.
## What is open source "beyond software"?
At Opensource.com, we like to say that we're interested in the ways open source values and principles apply to the world *beyond software*. We like to think of open source as not only a way to develop and license computer software, but also an *attitude*.
Approaching all aspects of life "[the open source way](https://opensource.com/open-source-way)" means expressing a willingness to share, collaborating with others in ways that are transparent (so that others can watch and join too), embracing failure as a means of improving, and expecting—even encouraging—everyone else to do the same.
It also means committing to playing an active role in improving the world, which is possible only when [everyone has access](https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-access) to the way that world is designed.
The world is full of "source code"—[blueprints](https://opensource.com/life/11/6/architecture-open-source-applications-learn-those-you), [recipes](https://opensource.com/life/12/6/open-source-like-sharing-recipe), [rules](https://opensource.com/life/12/4/day-my-mind-became-open-sourced)—that guide and shape the way we think and act in it. We believe this underlying code (whatever its form) should be open, accessible, and shared—so many people can have a hand in altering it for the better.
Here, we tell stories about the impact of open source values on all areas of life—[science](https://opensource.com/resources/open-science), [education](https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-education), [government](https://opensource.com/resources/open-government), [manufacturing](https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-hardware), health, law, and [organizational dynamics](https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-organization). We're a community committed to telling others how the open source way is the *best* way, because a love of open source is just like anything else: it's better when it's shared.
## Where can I learn more about open source?
We've compiled several resources designed to help you learn more about open source. We recommend you read our [open source FAQs, how-to guides, and tutorials](https://opensource.com/resources) to get started. |
8,626 | 开发一个 Linux 调试器(一):准备环境 | http://blog.tartanllama.xyz/c++/2017/03/21/writing-a-linux-debugger-setup/ | 2017-06-21T10:14:00 | [
"调试器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8626-1.html | 
任何写过比 hello world 复杂一些的程序的人都应该使用过调试器(如果你还没有,那就停下手头的工作先学习一下吧)。但是,尽管这些工具已经得到了广泛的使用,却并没有太多的资源告诉你它们的工作原理以及如何开发,尤其是和其它那些比如编译器等工具链技术相比而言。
>
> 此处有一些其它的资源可以参考:
>
>
> * <http://eli.thegreenplace.net/2011/01/23/how-debuggers-work-part-1>
> * <https://t-a-w.blogspot.co.uk/2007/03/how-to-code-debuggers.html>
> * <https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/43682/Writing-a-basic-Windows-debugger>
> * <http://system.joekain.com/debugger/>
>
>
>
我们将会支持以下功能:
* 启动、暂停、继续执行
* 在不同地方设置断点
+ 内存地址
+ 源代码行
+ 函数入口
* 读写寄存器和内存
* 单步执行
+ 指令
+ 进入函数
+ 跳出函数
+ 跳过函数
* 打印当前代码地址
* 打印函数调用栈
* 打印简单变量的值
在最后一部分,我还会大概介绍如何给你的调试器添加下面的功能:
* 远程调试
* 共享库和动态库支持
* 表达式计算
* 多线程调试支持
在本项目中我会将重点放在 C 和 C++,但对于那些将源码编译为机器码并输出标准 DWARE 调试信息的语言也应该能起作用(如果你还不知道这些东西是什么,别担心,马上就会介绍到啦)。另外,我只关注如何将程序运行起来并在大部分情况下能正常工作,为了简便,会避开类似健壮错误处理方面的东西。
### 系列文章索引
随着后面文章的发布,这些链接会逐渐生效。
1. [准备环境](http://blog.tartanllama.xyz/c++/2017/03/21/writing-a-linux-debugger-setup/)
2. 断点
3. 寄存器和内存
4. Elves 和 dwarves
5. 源码和信号
6. 源码层逐步执行
7. 源码层断点
8. 调用栈
9. 读取变量
10. 之后步骤
LCTT 译注:ELF —— <ruby> <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Executable_and_Linkable_Format"> 可执行文件格式 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Executable and Linkable Format </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>;DWARF(一种广泛使用的调试数据格式,参考 [WIKI](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DWARF "DWARF WIKI"))。
### 准备环境
在我们正式开始之前,我们首先要设置环境。在这篇文章中我会依赖两个工具:[Linenoise](https://github.com/antirez/linenoise) 用于处理命令行输入,[libelfin](https://github.com/TartanLlama/libelfin/tree/fbreg) 用于解析调试信息。你也可以使用更传统的 libdwarf 而不是 libelfin,但是界面没有那么友好,另外 libelfin 还提供了基本完整的 DWARF 表达式求值器,当你想读取变量的值时这能帮你节省很多时间。确认你使用的是 libelfin 我的 fbreg 分支,因为它提供 x86 上读取变量的额外支持。
一旦你在系统上安装或者使用你喜欢的编译系统编译好了这些依赖工具,就可以开始啦。我在 CMake 文件中把它们设置为和我其余的代码一起编译。
### 启动可执行程序
在真正调试任何程序之前,我们需要启动被调试的程序。我们会使用经典的 `fork`/`exec` 模式。
```
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 2) {
std::cerr << "Program name not specified";
return -1;
}
auto prog = argv[1];
auto pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
//we're in the child process
//execute debugee
}
else if (pid >= 1) {
//we're in the parent process
//execute debugger
}
```
我们调用 `fork` 把我们的程序分成两个进程。如果我们是在子进程,`fork` 返回 0,如果我们是在父进程,它会返回子进程的进程 ID。
如果我们是在子进程,我们要用希望调试的程序替换正在执行的程序。
```
ptrace(PTRACE_TRACEME, 0, nullptr, nullptr);
execl(prog.c_str(), prog.c_str(), nullptr);
```
这里我们第一次遇到了 `ptrace`,它会在我们编写调试器的时候经常遇到。`ptrace` 通过读取寄存器、内存、逐步调试等让我们观察和控制另一个进程的执行。其 API 非常简单;你需要给这个简单函数提供一个枚举值指定你想要进行的操作,然后是一些取决于你所提供的值可能会被使用也可能会被忽略的参数。函数原型看起来类似:
```
long ptrace(enum __ptrace_request request, pid_t pid,
void *addr, void *data);
```
`request` 是我们想对被跟踪进程进行的操作;`pid` 是被跟踪进程的进程 ID;`addr` 是一个内存地址,用于在一些调用中指定被跟踪程序的地址;`data` 是 `request` 相应的资源。返回值通常是一些错误信息,因此在你实际的代码中你也许应该检查返回值;为了简洁我这里就省略了。你可以查看 man 手册获取更多(关于 ptrace)的信息。
上面代码中我们发送的请求 `PTRACE_TRACEME` 表示这个进程应该允许父进程跟踪它。所有其它参数都会被忽略,因为 API 设计并不是很重要,哈哈。
下一步,我们会调用 `execl`,这是很多诸多的 `exec` 函数格式之一。我们执行指定的程序,通过命令行参数传递它的名称,然后用一个 `nullptr` 终止列表。如果你愿意,你还可以传递其它执行你的程序所需的参数。
在完成这些后,我们就会和子进程一起结束;在我们结束它之前它会一直执行。
### 添加调试循环
现在我们已经启动了子进程,我们想要能够和它进行交互。为此,我们会创建一个 `debugger` 类,循环监听用户输入,然后在我们父进程的 `main` 函数中启动它。
```
else if (pid >= 1) {
//parent
debugger dbg{prog, pid};
dbg.run();
}
```
```
class debugger {
public:
debugger (std::string prog_name, pid_t pid)
: m_prog_name{std::move(prog_name)}, m_pid{pid} {}
void run();
private:
std::string m_prog_name;
pid_t m_pid;
};
```
在 `run` 函数中,我们需要等待,直到子进程完成启动,然后一直从 `linenoise` 获取输入直到收到 `EOF`(`CTRL+D`)。
```
void debugger::run() {
int wait_status;
auto options = 0;
waitpid(m_pid, &wait_status, options);
char* line = nullptr;
while((line = linenoise("minidbg> ")) != nullptr) {
handle_command(line);
linenoiseHistoryAdd(line);
linenoiseFree(line);
}
}
```
当被跟踪的进程启动时,会发送一个 `SIGTRAP` 信号给它,这是一个跟踪或者断点中断。我们可以使用 `waitpid` 函数等待这个信号发送。
当我们知道进程可以被调试之后,我们监听用户输入。`linenoise` 函数它自己会用一个窗口显示和处理用户输入。这意味着我们不需要做太多的工作就会有一个支持历史记录和导航命令的命令行。当我们获取到输入时,我们把命令发给我们写的小程序 `handle_command`,然后我们把这个命令添加到 `linenoise` 历史并释放资源。
### 处理输入
我们的命令类似 gdb 以及 lldb 的格式。要继续执行程序,用户需要输入 `continue` 或 `cont` 甚至只需 `c`。如果他们想在一个地址中设置断点,他们会输入 `break 0xDEADBEEF`,其中 `0xDEADBEEF` 就是所需地址的 16 进制格式。让我们来增加对这些命令的支持吧。
```
void debugger::handle_command(const std::string& line) {
auto args = split(line,' ');
auto command = args[0];
if (is_prefix(command, "continue")) {
continue_execution();
}
else {
std::cerr << "Unknown command\n";
}
}
```
`split` 和 `is_prefix` 是一对有用的小程序:
```
std::vector<std::string> split(const std::string &s, char delimiter) {
std::vector<std::string> out{};
std::stringstream ss {s};
std::string item;
while (std::getline(ss,item,delimiter)) {
out.push_back(item);
}
return out;
}
bool is_prefix(const std::string& s, const std::string& of) {
if (s.size() > of.size()) return false;
return std::equal(s.begin(), s.end(), of.begin());
}
```
我们会把 `continue_execution` 函数添加到 `debuger` 类。
```
void debugger::continue_execution() {
ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, m_pid, nullptr, nullptr);
int wait_status;
auto options = 0;
waitpid(m_pid, &wait_status, options);
}
```
现在我们的 `continue_execution` 函数会用 `ptrace` 告诉进程继续执行,然后用 `waitpid` 等待直到收到信号。
---
### 总结
现在你应该编译一些 C 或者 C++ 程序,然后用你的调试器运行它们,看它是否能在函数入口暂停、从调试器中继续执行。在下一篇文章中,我们会学习如何让我们的调试器设置断点。如果你遇到了任何问题,在下面的评论框中告诉我吧!
你可以在[这里](https://github.com/TartanLlama/minidbg/tree/tut_setup)找到该项目的代码。
---
via: <http://blog.tartanllama.xyz/c++/2017/03/21/writing-a-linux-debugger-setup/>
作者:[Simon Brand](https://www.linkedin.com/in/simon-brand-36520857) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,627 | 关于开源项目如何选择沟通渠道的思考 | https://opensource.com/article/17/5/much-ado-about-communication | 2017-06-22T10:17:01 | [
"开源",
"沟通"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8627-1.html |
>
> 开源项目的首要挑战是找出最佳的贡献者协作方式
>
>
>

开源项目要面对的首要挑战之一是如何在贡献者之间沟通。这里有很多的选择:论坛、聊天频道、<ruby> 工单 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> issue </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、邮件列表、<ruby> 拉取请求 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> pull request </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>等等。我们该选择哪个合适的来使用,我们又该如何做呢?
令人遗憾的是,项目本身往往不愿做出约束性的决定,而是选择“上述所有”。这就导致了一个支离破碎的社区:有些人使用 Slack/Mattermost/IRC,而有些人使用论坛,有些使用邮件列表,有些则存在于工单之中,很少有人能够读到所有这些途径的内容。
在我[帮助其建立内外部社区](http://www.jonobaconconsulting.com/)的组织中,这是一个常见的问题。我们会选择哪个渠道,以及出于什么目的?另外,何时可以对它们之一说不呢?
这就是我想在此处深度探讨的。
### 结构化和非结构化
我并不是个聪明人。因此,我倾向于将问题分成小的部分,这样我可以更好地理解它们。类似地,我倾向于将一个情景中各种选择拆解成更小的部分,来更好地理解它们的目的。我在沟通渠道的选择上也使用这种方法。
我认为有两大沟通渠道的分类:结构化和非结构化。
结构化渠道在每个单独的沟通单元中都有非常具体的重点。例子如:GitHub / GitLab /Jira 的<ruby> 工单 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> issue </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。一个工单是与 bug 或功能有关的一个非常具体的信息。在初始的工单帖子发布之后引发的系列讨论中,通常非常集中在该特定话题上,并会有一个结果(比如 bugfix 或者一个功能的最终计划)。结果通常都反映在状态(例如 “FIXED”、“WONTFIX” 或 “INVALID”)中。这意味着你可以了解沟通的始末,而无需阅读中间的内容。
类似的,拉取/合并请求也是结构化的。它们集中在特定类型(通常是代码)的贡献上。在最初的拉取/合并请求后,讨论会非常集中在一个结果上:让贡献符合要求,且合并入代码库中。
另一个例子是 StackOverflow/AskBot 这类的问答帖子。这些帖子以一个问题开始,接着被编辑以及回复来提供对这个问题的精确答案。
通过这些结构化机制,通常几乎不会偏离其本来结构。你不会在工单、拉取请求或问答话题上看到有人问别人他们的孩子/猫/狗/家人在做什么。偏离话题在社区是不可接受的,这是结构化媒体的力量的一部分:它是集中和(通常)高效的。
反之,非结构化媒体包括聊天频道和论坛。在这些环境中,通常会有一个主题(例如频道或分论坛的主题),但是其中的会话与特定结果或结论的关系要小得多,而且通常情况下可能会更普遍。例如,在开发者邮件列表中,你会看到一系列讨论,包括一般问题、新功能的想法、架构争论以及与社区自身运营相关的讨论。每一个讨论都希望让参与者保持对话的焦点、主题和工作效率。但你可以想象,情况往往不是这样的, 这种讨论可能会偏离一个富有成效的结果。
### 记录的影响
除了结构化和非结构化沟通的微妙不同外,所记录的内容以及它们如何搜索的所带来的影响也很重要。
典型的,所有的结构化渠道都是记录的。人们可以参考以前的 bug,来自 StackOverflow 的问题可以被反复地重新利用。你可以搜索一些东西,即使有很多讨论、常见问题、拉取请求或者提问,都会被更新以反映最终结论。
这是一个重点:我们希望能够快速、轻松地挖掘旧问题/提问/拉取请求等,并链接到它们、引用它们。这里的一个关键部分是我们把这个内容转换成可以引用的材料,从而可以用来教育和告知人们以前的知识。随着社区的发展,我们的结构化沟通成为一种知识库,可以通过以往的经验来告知未来。
而非结构化沟通变得越来越糟。一方面,论坛的搜索通常都简单高效,但是它们当然充满了非结构化的对话,所以你正在寻找的东西可能被埋在讨论之中。例如,许多社区使用论坛作为支持工具。虽然这是一个更强大的平台,但是问题在于,一个问题的答案可能是在 16 楼或者 340 楼中有回复。随着越来越多的信息来源(比如 Twitter)的轰炸,我们越来越不耐烦地阅读大量的材料,这对于非结构化媒体来说可能是一个问题。
一个有趣的特定案例是实时聊天。历史上,很多年来,IRC 为实时聊天铺平了道路,对于大多数 IRC 用户而言很少有(如果有的话)记录这些讨论的念头。的确,一些项目(比如 Ubuntu)记录了 IRC 日志,但是这通常不是有用的资源。如我的伙伴 Atwood 有一次跟我说的:“如果你不得不在聊天中搜索一些东西时,你已经输了。”
虽然 IRC 在记录上有所不足,而 Slack 和 Mattermost 会好点。交流会被归档,但是问题仍旧存在:你为什么会想在海量的聊天信息中找出一个人提出的观点呢?其他的渠道能更好地引用先前的讨论。
不过,这的确创造了一个有趣的机会。聊天相比其他媒体有个一贯的好处是能体现这是个怎样的人。结构化的渠道,甚至非结构化的渠道,如论坛和邮件列表,很少鼓励闲聊。但聊天是的,聊天时你会问:“你周末怎么样?”、 “你见过这个游戏吗?”还有“你下周会看 Testament,Sepultura 和 Prong 吗?” (好吧,也许问最后一个问题的只有我。)
因此,虽然实时聊天相比前面的那些方式也许更低效一些,但是它的确增进了人们的关系。
### 你想喝点什么
因此,回到我们最初的对于开源社区的提问:我们要选择哪个?
虽然这个答案对于不同的项目会不同,但我想在两个层面思考。
首先,你通常应该优先考虑结构化沟通。这是完成有形工作的地方:问题/工单、拉取请求、问答讨论等等。如果你资源有限,那么专注在这些渠道上,你可以用较少的时间和金钱支出,获得社区的高效产出。
再者,如果你热衷于建立一个可以专注于工程、宣传、翻译、文档等方面的更广泛的社区,那么探究是否引入非结构化渠道就有意义了。 社区不仅仅是为了完成工作,也是为了建立关系和友谊,在工作中相互支持,帮助人们在社区中发展壮大。非结构化通信是一个有用的工具。
当然,我只是在一个大的话题上浅谈辄止。 不过我希望在如何评估和选择沟通渠道的价值方面,为大家提供了一些辨析。记住,少即是多:不要被拥有所有的渠道的妄想而诱惑,否则你会得到一个支离破碎社区,就像一个空荡荡的餐厅一样。
愿原力与你同在,请让我知道你进行的如何。你可以通过我的[网站](http://www.jonobacon.com/)和邮箱 [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected]) 联系到我。
(题图: Opensource.com)
---
作者简介:
Jono Bacon 是一名领先的社区管理者、演讲者、作者和播客。他是 Jono Bacon Consulting 的创始人,提供社区策略/执行、开发者工作流程和其他服务。他以前曾担任 GitHub、Canonical、XPRIZE、OpenAdvantage 的社区总监,并为很多组织曾经提供建议和咨询。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/5/much-ado-about-communication>
作者:[Jono Bacon](https://opensource.com/users/jonobacon) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | One of the first challenges an open source project faces is how to communicate among contributors. There are a plethora of options: forums, chat channels, issues, mailing lists, pull requests, and more. How do we choose which is the right medium to use and how do we do it right?
Sadly and all too often, projects shy away from making a disciplined decision and instead opt for "all of the above." This results in a fragmented community: Some people sit in Slack/Mattermost/IRC, some use the forum, some use mailing lists, some live in issues, and few read all of them.
This is a common issue I see in organizations I'm [working with to build their internal and external communities](http://www.jonobaconconsulting.com). Which of these channels do we choose and for which purposes? Also, when is it OK to say no to one of them?
This is what I want to dig into here.
## Structured and unstructured
I have a tiny, peanut-sized brain in my head. Because of this, I tend to break problems down into smaller pieces so I can better understand them. Likewise, I tend to break different options in a scenario down into smaller thematic pieces to better understand their purpose. I take this approach with communication channels too.
I believe there are two broad categories of communication channels: structured and unstructured.
Structured channels have a very specific focus in each individual unit of communication. An example here is a GitHub/GitLab/Jira issue. An issue is a very specific piece of information that relates to a bug or feature. The discussion that cascades after the initial issue post is typically very focused on that specific topic and finding an outcome (such as a bugfix or a final plan for a feature). The outcome is then typically reflected in a status (e.g. "FIXED," "WONTFIX," or "INVALID"). This means you can understand the beginning and end of the communication without reading the pieces in between.
Likewise, pull/merge requests are structured. They are focused on a specific type (typically code) of contribution. After the initial pull/merge request, the discussion is very focused on an outcome: getting the contribution in shape to merge into the wider codebase.
Another example here is a StackOverflow/AskBot style Q&A post. These posts start with a question and are then edited and responded to in order to provide a concise answer to the question.
With each of these structured mechanisms there usually is little deviation from the structure. You never see people asking others how their kids/cats/dogs/family are doing in an issue, pull request, or Q&A topic. It is socially unacceptable to veer off topic, and that is part of the power of a structured medium: It is focused and (usually) efficient.
The inverse, unstructured media, include chat channels and forums. In these environments there is typically a theme (such as the topic of a channel or sub-forum), but conversations are much less tied to a specific outcome or conclusion and can often be more general in nature. As an example, in a developer mailing list you will get a mix of discussions including general questions, ideas for new features, architectural challenges, and discussions that relate to the operational running of the community itself. With each of these discussions it is imperative on the participants to keep the conversation focused, on topic, and productive. As you can imagine, this is often not the case, and these kinds of discussions can veer away from a productive outcome.
## The impact of recording
Aside from the subtle differences between structured and unstructured communication, the impact of what is recorded and how it can be searched plays a large role too.
Typically, all structured channels are recorded. People reference old bugs, questions from StackOverflow are reused over and over again. You can search for something, and even if there is lots of discussion, the issue, pull request, or question is usually updated to reflect the ultimate conclusion.
This is part of the point: We want to be able to quickly and easily dig up old issues/questions/pull requests/etc., link to them, and reference them. A key component here is that we convert this content into referenceable material that can be used to educate and inform people about previous knowledge. As our community grows, our structured communication becomes a corpus of knowledge that can inform the future from lessons in the past.
This gets murkier with unstructured communication. On one hand, forums are generally simple and effective to search, but they are of course filled with unstructured conversation, so the thing you are looking for might be buried inside a discussion. As an example, many communities use a forum as a support tool. While this is a more than capable platform, the problem is that the answer to a question may be response #16 or response #340 in a discussion. As we are bombarded with more and more sources of information (and in smaller pieces, such as Twitter), we have become increasingly impatient to reading through large swaths of material, and this can be problematic with an unstructured medium.
A particularly interesting case is real-time chat. Historically, IRC has paved the way for real-time chat for many years, and for most IRC users there was little (if any) notion of recording those discussions. Sure, some projects (such as Ubuntu) record IRC logs, but this is generally not a useful resource. As my pal Jeff Atwood said to me once: "If you have to search chat for something, you have already lost."
While IRC is limited in recording, Slack and Mattermost are better. Conversations are archived, but the point still typically stands: Why would you want to search through large bodies of conversation to find a point that someone made? Other channels are far better for referencing previous discussions.
This does create an interesting opportunity though. One consistent benefit that chat exhibits over all other media is how human it is. Structured channels, and even unstructured channels such as forums and mailing lists, rarely encourage off-the-cuff social discussion. Chat does. Chat is where you ask: "How was your weekend?" "Did you see the game?" and "Are you going to see Testament, Sepultura, and Prong next week?" (OK, maybe the last one is just me.)
So, while real-time discussion may be less effective in our corpus of previous collaboration, it does provide a vital glue in shaping relationships.
## Choose your poison
So, back to our original question for open source communities: Which of these do we pick?
While this answer will vary from project to project, I tend to think of this on two levels.
First, you should generally prioritize structured communication. This is where tangible work gets done: in bugs/issues, pull requests, in support Q&A discussions, etc. If you are tight on resources, focus your efforts on these channels: You can more easily draw a dotted line between the investment of time and money there and productive output in the community.
Second, if you are passionate about building a broader community that can focus on engineering, advocacy, translations, documentation, and more, explore whether bringing in unstructured channels makes sense. Community is not just about getting stuff done, it is also about building relationships and friendships, providing support to each other in our work, and helping people grow and flourish in our communities. Unstructured communication is a helpful tool in this.
Of course, I am merely scratching the surface of a large topic here, but I hope this provides a little clarity in how to assess and choose the value of communication channels. Remember, less is more here: Don't be tempted to defer the decision and provide all of the above; you will get a fragmented community that's just about as inviting as an empty restaurant.
May the force be with you, and be sure to let me know how you get on. I am always available through my [website](http://www.jonobacon.com) and at [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected]).
## Comments are closed. |
8,628 | Linux 大爆炸:一个内核,无数发行版 | http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/84489.html | 2017-06-22T18:40:19 | [
"Linux",
"发行版"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8628-1.html | 
即使你是一个 Linux 新人,你可能也已经知道它不是一个单一的、整体的操作系统,而是一群项目。这个星座中不同的“星”组成了“发行版”。每个都提供了自己的 Linux 模式。
感谢这一系列发行版所提供的多种选择,这有助于了解 Linux 如何开始并随后激增的。因此,这里会简要介绍一下 Linux 的历史。
### Linus Torvalds,内核构建者
大多数熟悉 Linux 的人都已经听说过它的创建者 Linus Torvalds (题图中的人),但是并不知道他最初为何创建它。在 1991 年,Torvalds 还是一名在芬兰学习计算机的大学生。作为一个独立的个人项目,他希望为他的独特硬件创建一个类 Unix 内核。
“内核”是操作系统的一部分,它介乎于操作系统和硬件之间,通过其固件进行协调。本质上,它是系统的核心。开发内核不是一个小工程,但是 Torvalds 渴望挑战,并且发现他自己有这个罕见的技能。
由于他刚接触内核,他希望得到其他人的帮助来确保他走在正确的轨道上,因此他通过在早期的互联网论坛 Usenet 发布他的内核代码,并征求了老牌的老手的经验。然后贡献者就涌来了。
在建立了一个对论坛提交的补丁进行审查以及选择性地集成它们的流程后,Torvalds 意识到他聚集起了一个非正式的团队。在项目发展之后,它很快成为了一个比较正式的开发团队。
### Richard Stallman 的角色
虽然 Torvalds 以及他的团建创造了 Linux 内核,但是没有 Richard Stallman 的工作也不会有随后 Linux 众多发行版的传播,Richard 在十年之前发起了一个自由软件运动。
受到许多核心 Unix 程序和系统功能缺乏透明度的阻挠,Stallman 决定自己编写一个,与任何想要它的人自由共享源代码,并且开放提交。他创造了许多核心程序的主体,并在 1983 年发布,统称为 “GNU 项目”。
没有它们,内核不会有那么多的用量。基于 Linux 的操作系统的早期设计人员很乐意将 GNU 工具集成到他们的项目中。
不同的团队开始出现 - 每个团队都有自己的计算功能和架构的理念。他们将 Linux 内核、GNU 实用程序和他们自己的原始软件结合在一起,然而“发行”了 Linux 操作系统的变体。
### 服务器发行版
每个发行版有它自己的设计逻辑和目的,但是要了解它们的细微差别,需要了解上游和下游开发人员之间的区别。“上游开发人员”负责实际创建项目并发布,以供个人下载或将其包含在其他项目中。相比之下,“下游开发人员”或“软件包维护人员”是指每个发布上游程序的人员,他们对每个上游程序的版本进行调整以适应下游项目的使用情况。
虽然大多数 Linux 发行版包含一些(自己的)原生项目,但大部分发行版开发主要是对 Linux 内核、GNU 工具和庞大的用户程序生态系统的“下游”工作。
许多发行通过优化特定使用场景来彰显它们的特征。例如,某些项目被设计作为服务器运行。为部署服务器而量身定制的发行版通常会避开上游项目中快速推出的最新功能,而倾向于发布一个经过彻底测试的、基础的基本软件,系统管理员可以依靠它来顺利运行。
针对服务器的发行版的的开发团队经常很大,并且有富有经验的程序员可以为每个版本提供多年的支持。
### 桌面发行版
也有很多的发行版针对桌面用户。事实上,一些知名的发行版通过提供简单的安装以及直观的界面来与商业的操作系统竞争。这些发行版通常包含了大量的软件仓库,它包含了用户可以想到的每个软件,这样用户可以定制它们自己的系统。
由于可用性是关键,他们可能会投入部门大量的员工来创建一个特征鲜明的、发行版特定的桌面,或调整已有的桌面以适应其设计理念。以用户为中心的发行版往往会加快其下游开发时间表,有助于及时为用户提供新功能。
“滚动发布”项目,这是一种桌面发行版的子集,其被设计成紧跟潮流。滚动发布项目的包维护人员在为每个上游程序完成调整后分别发布其新版本,而不是等待所需的上游程序的开发达到某一特定的节点,然后将其集成到单个版本中。
这种方法的一个优点是安全性,因为其关键补丁的发布将比非滚动发行版更快。另一个好处是新功能立即可用,不然用户需要等待才行。滚动发布的缺点是需要更多的人工干预和仔细维护,因为某些升级可能会与其他升级相冲突从而破坏系统。
### 嵌入式系统
另外一个 Linux 发行版类别是“嵌入式系统”,它被极致裁剪(相对与服务器和桌面发行版)来适应特定的使用情况。
我们经常会忘记那些连接到因特网的任何东西,或者比一个简单的计算器复杂的东西,都是计算机。而计算机需要操作系统。因为 Linux 是自由的并且高度模块化,所以它通常是硬件厂商的选择。
在大多数情况下,如果你看见一台智能电视、一台连接互联网的照相机、甚至是一辆车,你看到的都是 Linux 设备。特别是每部非 iPhone 的智能手机都运行着不同的嵌入式 Linux。
### Linux 现场版
最后,有一些 Linux 发行版并不需要永久性地安装在计算机中,而是驻留在 USB 记忆棒上,并允许在其它的计算机上启动它们,而无需计算机硬盘。
这些 “现场版(live)” 的系统可以被优化来执行一些任务。从修复损坏的系统到进行安全评估到高度安全地浏览因特网。
由于这些 现场版 Linux 发行版通常针对解决特定的问题,因此它们一般都包含特定的工具,像磁盘分析和恢复程序、网络监控程序和加密工具。它们还占用很小的空间,因此它们可以快速启动。
### 你如何选择?
这绝不是 Linux 发行版类型的全面列表,但它应该可以让你大致了解 Linux 生态系统的范围和多样化了。
在每个类别下都有许多选择,因此你会如何选择一个最能符合你需求的版本呢?
一种方式是试验。在 Linux 社区中,来回尝试不同的发行版,或者为用户根据他们的需求在不同的机器上运行不同的发行版,这都很常见。
在将来的文章中,我会展示每种类型发行版的几个例子,以便你可以自己尝试,并开始探索最喜欢的发行版的旅程。
---
作者简介:
自 2017 年以来 Jonathan Terrasi 一直是 ECT 新闻网的专栏作家。他的主要兴趣是计算机安全(特别是 Linux 桌面),加密和分析政治和时事。他是全职自由作家和音乐家。他的背景包括在芝加哥委员会发表的保卫人权法案文章中提供技术评论和分析。
---
via: <http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/84489.html>
作者:[Jonathan Terrasi](http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/84489.html?rss=1#searchbyline) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,630 | 60 TB 数据:Facebook 是如何大规模使用 Apache Spark 的 | https://code.facebook.com/posts/1671373793181703/apache-spark-scale-a-60-tb-production-use-case/ | 2017-06-23T09:55:00 | [
"Spark",
"Hive"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8630-1.html | 
Facebook 经常使用数据驱动的分析方法来做决策。在过去的几年,用户和产品的增长已经需要我们的分析工程师一次查询就要操作数十 TB 大小的数据集。我们的一些批量分析执行在古老的 [Hive](https://code.facebook.com/posts/370832626374903/even-faster-data-at-the-speed-of-presto-orc/) 平台( Apache Hive 由 Facebook 贡献于 2009 年)和 [Corona](https://www.facebook.com/notes/facebook-engineering/under-the-hood-scheduling-mapreduce-jobs-more-efficiently-with-corona/10151142560538920/) 上——这是我们定制的 MapReduce 实现。Facebook 还不断增加其对 Presto 的用量,用于对几个包括 Hive 在内的内部数据存储的 ANSI-SQL 查询。我们也支持其他分析类型,比如<ruby> 图数据库处理 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> graph processing </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和机器学习([Apache Giraph](https://code.facebook.com/posts/509727595776839/scaling-apache-giraph-to-a-trillion-edges/))和流(例如:[Puma](https://research.facebook.com/publications/realtime-data-processing-at-facebook/)、[Swift](https://research.facebook.com/publications/realtime-data-processing-at-facebook/) 和 [Stylus](https://research.facebook.com/publications/realtime-data-processing-at-facebook/))。
同时 Facebook 的各种产品涵盖了广泛的分析领域,我们与开源社区不断保持沟通,以便共享我们的经验并从其他人那里学习。[Apache Spark](http://spark.apache.org/) 于 2009 年在加州大学伯克利分校的 AMPLab 由 Matei Zaharia 发起,后来在2013 年贡献给 Apache。它是目前增长最快的数据处理平台之一,由于它能支持流、批量、命令式(RDD)、声明式(SQL)、图数据库和机器学习等用例,而且所有这些都内置在相同的 API 和底层计算引擎中。Spark 可以有效地利用更大量级的内存,优化整个<ruby> 流水线 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> pipeline </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>中的代码,并跨任务重用 JVM 以获得更好的性能。最近我们感觉 Spark 已经成熟,我们可以在一些批量处理用例方面把它与 Hive 相比较。在这篇文章其余的部分,我们讲述了在扩展 Spark 来替代我们一个 Hive 工作任务时的所得到经验和学习到的教训。
### 用例:实体排名的特征准备
Facebook 会以多种方式做实时的<ruby> 实体 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> entity </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>排名。对于一些在线服务平台,原始特征值是由 Hive 线下生成的,然后将数据加载到实时关联查询系统。我们在几年前建立的基于 Hive 的老式基础设施属于计算资源密集型,且很难维护,因为其流水线被划分成数百个较小的 Hive 任务。为了可以使用更加新的特征数据和提升可管理性,我们拿一个现有的流水线试着将其迁移至 Spark。
### 以前的 Hive 实现
基于 Hive 的流水线由三个逻辑<ruby> 阶段 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> stage </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>组成,每个阶段对应由 entity\_id 划分的数百个较小的 Hive 作业,因为在每个阶段运行大型 Hive <ruby> 作业 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> job </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>不太可靠,并受到每个作业的最大<ruby> 任务 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> task </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>数量的限制。

这三个逻辑阶段可以总结如下:
1. 过滤出非产品的特征和噪点。
2. 在每个(entity\_id, target\_id)对上进行聚合。
3. 将表格分割成 N 个分片,并通过自定义二进制文件管理每个分片,以生成用于在线查询的自定义索引文件。
基于 Hive 的流水线建立该索引大概要三天完成。它也难于管理,因为该流水线包含上百个分片的作业,使监控也变得困难。同时也没有好的方法来估算流水线进度或计算剩余时间。考虑到 Hive 流水线的上述限制,我们决定建立一个更快、更易于管理的 Spark 流水线。
### Spark 实现
全量的调试会很慢,有挑战,而且是资源密集型的。我们从转换基于 Hive 流水线的最资源密集型的第二阶段开始。我们以一个 50GB 的压缩输入例子开始,然后逐渐扩展到 300GB、1TB,然后到 20TB。在每次规模增长时,我们都解决了性能和稳定性问题,但是实验到 20TB 时,我们发现了最大的改善机会。
运行 20TB 的输入时,我们发现,由于大量的任务导致我们生成了太多输出文件(每个大小在 100MB 左右)。在 10 小时的作业运行时中,有三分之一是用在将文件从阶段目录移动到 HDFS 中的最终目录。起初,我们考虑两个方案:要么改善 HDFS 中的批量重命名来支持我们的用例,或者配置 Spark 生成更少的输出文件(这很难,由于在这一步有大量的任务 — 70000 个)。我们退一步来看这个问题,考虑第三种方案。由于我们在流水线的第二步中生成的 tmp\_table2 表是临时的,仅用于存储流水线的中间输出,所以对于 TB 级数据的单一读取作业任务,我们基本上是在压缩、序列化和复制三个副本。相反,我们更进一步:移除两个临时表并整合 Hive 过程的所有三个部分到一个单独的 Spark 作业,读取 60TB 的压缩数据然后对 90TB 的数据执行<ruby> 重排 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> shuffle </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和<ruby> 排序 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> sort </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。最终的 Spark 作业如下:

### 对于我们的作业如何规划 Spark?
当然,为如此大的流水线运行一个单独的 Spark 任务,第一次尝试没有成功,甚至是第十次尝试也没有。据我们所知,从<ruby> 重排 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> shuffle </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的数据大小来说,这是现实世界最大的 Spark 作业([Databrick 的 PB 级排序](https://databricks.com/blog/2014/10/10/spark-petabyte-sort.html)是以合成数据来说)。我们对核心 Spark 基础架构和我们的应用程序进行了许多改进和优化使这个作业得以运行。这种努力的优势在于,许多这些改进适用于 Spark 的其他大型作业任务,我们将所有的工作回馈给开源 Apache Spark 项目 - 有关详细信息请参阅 JIRA。下面,我们将重点讲述将实体排名流水线之一部署到生产环境所做的重大改进。
### 可靠性修复
#### 处理频繁的节点重启
为了可靠地执行长时间运行作业,我们希望系统能够容错并可以从故障中恢复(主要是由于平时的维护或软件错误导致的机器重启所引发的)。虽然 Spark 设计为可以容忍机器重启,但我们发现它在足够强健到可以处理常见故障之前还有各种错误/问题需要解决。
* **使 PipedRDD 稳健的<ruby> 获取 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> fetch </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>失败**(SPARK-13793):PipedRDD 以前的实现不够强大,无法处理由于节点重启而导致的获取失败,并且只要出现获取失败,该作业就会失败。我们在 PipedRDD 中进行了更改,优雅的处理获取失败,使该作业可以从这种类型的获取失败中恢复。
* **可配置的最大获取失败次数**(SPARK-13369):对于这种长时间运行的作业,由于机器重启而引起的获取失败概率显着增加。在 Spark 中每个阶段的最大允许的获取失败次数是硬编码的,因此,当达到最大数量时该作业将失败。我们做了一个改变,使它是可配置的,并且在这个用例中将其从 4 增长到 20,从而使作业更稳健。
* **减少集群重启混乱**:长时间运行作业应该可以在集群重启后存留,所以我们不用等着处理完成。Spark 的可重启的<ruby> 重排 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> shuffle </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>服务功能可以使我们在节点重启后保留<ruby> 重排 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> shuffle </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>文件。最重要的是,我们在 Spark 驱动程序中实现了一项功能,可以暂停执行任务调度,所以不会由于集群重启而导致的过多的任务失败,从而导致作业失败。
#### 其他的可靠性修复
* **响应迟钝的驱动程序**(SPARK-13279):在添加任务时,由于 O(N ^ 2) 复杂度的操作,Spark 驱动程序被卡住,导致该作业最终被卡住和死亡。 我们通过删除不必要的 O(N ^ 2) 操作来修复问题。
* **过多的驱动<ruby> 推测 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> speculation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>**:我们发现,Spark 驱动程序在管理大量任务时花费了大量的时间推测。 在短期内,我们禁止这个作业的推测。在长期,我们正在努力改变 Spark 驱动程序,以减少推测时间。
* **由于大型缓冲区的整数溢出导致的 TimSort 问题**(SPARK-13850):我们发现 Spark 的不安全内存操作有一个漏洞,导致 TimSort 中的内存损坏。 感谢 Databricks 的人解决了这个问题,这使我们能够在大内存缓冲区中运行。
* **调整重排(shuffle)服务来处理大量连接**:在重排阶段,我们看到许多执行程序在尝试连接重排服务时超时。 增加 Netty 服务器的线程(spark.shuffle.io.serverThreads)和积压(spark.shuffle.io.backLog)的数量解决了这个问题。
* **修复 Spark 执行程序 OOM**(SPARK-13958)(deal maker):首先在每个主机上打包超过四个<ruby> 聚合 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> reduce </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>任务是很困难的。Spark 执行程序会内存溢出,因为排序程序(sorter)中存在导致无限增长的指针数组的漏洞。当不再有可用的内存用于指针数组增长时,我们通过强制将数据溢出到磁盘来修复问题。因此,现在我们可以每主机运行 24 个任务,而不会内存溢出。
### 性能改进
在实施上述可靠性改进后,我们能够可靠地运行 Spark 作业了。基于这一点,我们将精力转向与性能相关的项目,以充分发挥 Spark 的作用。我们使用 Spark 的指标和几个分析器来查找一些性能瓶颈。
#### 我们用来查找性能瓶颈的工具
* **Spark UI 指标**:Spark UI 可以很好地了解在特定阶段所花费的时间。每个任务的执行时间被分为子阶段,以便更容易地找到作业中的瓶颈。
* **Jstack**:Spark UI 还在执行程序进程上提供了一个按需分配的 jstack 函数,可用于中查找热点代码。
* **Spark 的 Linux Perf / <ruby> 火焰图 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Flame Graph </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>支持**:尽管上述两个工具非常方便,但它们并不提供同时在数百台机器上运行的作业的 CPU 分析的聚合视图。在每个作业的基础上,我们添加了支持 Perf 分析(通过 libperfagent 的 Java 符号),并可以自定义采样的持续时间/频率。使用我们的内部指标收集框架,将分析样本聚合并显示为整个执行程序的火焰图。
#### 性能优化
* **修复<ruby> 排序程序 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> sorter </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>中的内存泄漏**(SPARK-14363)(30% 速度提升):我们发现了一个问题,当任务释放所有内存页时指针数组却未被释放。 因此,大量的内存未被使用,并导致频繁的溢出和执行程序 OOM。 我们现在进行了改变,正确地释放内存,并使大的分类运行更有效。 我们注意到,这一变化后 CPU 改善了 30%。
* **Snappy 优化**(SPARK-14277)(10% 速度提升):有个 JNI 方法(Snappy.ArrayCopy)在每一行被读取/写入时都会被调用。 我们发现了这个问题,Snappy 的行为被改为使用非 JNI 的 System.ArrayCopy 代替。 这一改变节约了大约 10% 的 CPU。
* **减少重排的写入延迟**(SPARK-5581)(高达 50% 的速度提升):在<ruby> 映射 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> map </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>方面,当将重排数据写入磁盘时,映射任务为每个分区打开并关闭相同的文件。 我们做了一个修复,以避免不必要的打开/关闭,对于大量写入重排分区的作业来说,我们观察到高达 50% 的 CPU 提升。
* **解决由于获取失败导致的重复任务运行问题**(SPARK-14649):当获取失败发生时,Spark 驱动程序会重新提交已运行的任务,导致性能下降。 我们通过避免重新运行运行的任务来解决这个问题,我们看到当获取失败发生时该作业会更加稳定。
* **可配置 PipedRDD 的缓冲区大小**(SPARK-14542)(10% 速度提升):在使用 PipedRDD 时,我们发现将数据从分类程序传输到管道进程的默认缓冲区的大小太小,我们的作业要花费超过 10% 的时间复制数据。我们使缓冲区大小可配置,以避免这个瓶颈。
* **缓存索引文件以加速重排获取**(SPARK-15074):我们观察到重排服务经常成为瓶颈,<ruby> 减少程序 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> reducer </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>花费 10% 至 15% 的时间等待获取<ruby> 映射 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> map </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>数据。通过深入了解问题,我们发现,重排服务为每个重排获取打开/关闭重排索引文件。我们进行了更改以缓存索引信息,以便我们可以避免文件打开/关闭,并重新使用该索引信息以便后续获取。这个变化将总的重排时间减少了 50%。
* **降低重排字节写入指标的更新频率**(SPARK-15569)(高达 20% 的速度提升):使用 Spark 的 Linux Perf 集成,我们发现大约 20% 的 CPU 时间正在花费探测和更新写入的重排字节写入指标上。
* **可配置排序程序(sorter)的初始缓冲区大小**(SPARK-15958)(高达 5% 的速度提升):<ruby> 排序程序 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> sorter </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的默认初始缓冲区大小太小(4 KB),我们发现它对于大型工作负载而言非常小 - 所以我们在缓冲区耗尽和内容复制上浪费了大量的时间。我们做了一个更改,使缓冲区大小可配置,并且缓冲区大小为 64 MB,我们可以避免大量的数据复制,使作业的速度提高约 5%。
* **配置任务数量**:由于我们的输入大小为 60T,每个 HDFS 块大小为 256M,因此我们为该作业产生了超过 250,000 个任务。尽管我们能够以如此多的任务来运行 Spark 作业,但是我们发现,当任务数量过高时,性能会下降。我们引入了一个配置参数,使<ruby> 映射 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> map </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>输入大小可配置,因此我们可以通过将输入分割大小设置为 2 GB 来将该数量减少 8 倍。
在所有这些可靠性和性能改进之后,我们很高兴地报告,我们为我们的实体排名系统之一构建和部署了一个更快、更易于管理的流水线,并且我们提供了在 Spark 中运行其他类似作业的能力。
### Spark 流水线与 Hive 流水线性能对比
我们使用以下性能指标来比较 Spark 流水线与 Hive 流水线。请注意,这些数字并不是在查询或作业级别的直接比较 Spark 与 Hive ,而是比较使用灵活的计算引擎(例如 Spark)构建优化的流水线,而不是比较仅在查询/作业级别(如 Hive)操作的计算引擎。
CPU 时间:这是从系统角度看 CPU 使用。例如,你在一个 32 核机器上使用 50% 的 CPU 10 秒运行一个单进程任务,然后你的 CPU 时间应该是 32 \* 0.5 \* 10 = 160 CPU 秒。

CPU 预留时间:这是从资源管理框架的角度来看 CPU 预留。例如,如果我们保留 32 位机器 10 秒钟来运行作业,则CPU 预留时间为 32 \* 10 = 320 CPU 秒。CPU 时间与 CPU 预留时间的比率反映了我们如何在集群上利用预留的CPU 资源。当准确时,与 CPU 时间相比,预留时间在运行相同工作负载时可以更好地比较执行引擎。例如,如果一个进程需要 1 个 CPU 的时间才能运行,但是必须保留 100 个 CPU 秒,则该指标的效率要低于需要 10 个 CPU 秒而仅保留 10 个 CPU 秒来执行相同的工作量的进程。我们还计算内存预留时间,但不包括在这里,因为其数字类似于 CPU 预留时间,因为在同一硬件上运行实验,而在 Spark 和 Hive 的情况下,我们不会将数据缓存在内存中。Spark 有能力在内存中缓存数据,但是由于我们的集群内存限制,我们决定类似与 Hive 一样工作在核心外部。

等待时间:端到端的工作流失时间。

### 结论和未来工作
Facebook 的性能和可扩展的分析在产品开发中给予了协助。Apache Spark 提供了将各种分析用例统一为单一 API 和高效计算引擎的独特功能。我们挑战了 Spark,来将一个分解成数百个 Hive 作业的流水线替换成一个 Spark 作业。通过一系列的性能和可靠性改进之后,我们可以将 Spark 扩大到处理我们在生产中的实体排名数据处理用例之一。 在这个特殊用例中,我们展示了 Spark 可以可靠地重排和排序 90 TB+ 的中间数据,并在一个单一作业中运行了 25 万个任务。 与旧的基于 Hive 的流水线相比,基于 Spark 的流水线产生了显着的性能改进(4.5-6 倍 CPU,3-4 倍资源预留和大约 5 倍的延迟),并且已经投入使用了几个月。
虽然本文详细介绍了我们 Spark 最具挑战性的用例,越来越多的客户团队已将 Spark 工作负载部署到生产中。 性能 、可维护性和灵活性是继续推动更多用例到 Spark 的优势。 Facebook 很高兴成为 Spark 开源社区的一部分,并将共同开发 Spark 充分发挥其潜力。
---
via: <https://code.facebook.com/posts/1671373793181703/apache-spark-scale-a-60-tb-production-use-case/>
作者:[Sital Kedia](https://www.facebook.com/sitalkedia), [王硕杰](https://www.facebook.com/shuojiew), [Avery Ching](https://code.facebook.com/posts/1671373793181703/apache-spark-scale-a-60-tb-production-use-case/?utm_source=dbweekly&utm_medium=email#) 译者:[wyangsun](https://github.com/wyangsun) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,632 | 理解 Linux 的平均负载和性能监控 | https://www.tecmint.com/understand-linux-load-averages-and-monitor-performance/ | 2017-06-23T19:33:12 | [
"负载",
"load",
"性能"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8632-1.html | 
在本文中,我们将解释 Linux 系统中最关键的管理任务之一——关于系统 / CPU 的<ruby> 负载 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> load </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和<ruby> 平均负载 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Load average </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的性能监控。
首先来看所有的类 UNIX 系统中两个重要的表述:
* 系统负载 / CPU 负载 – 衡量 Linux 系统的 CPU 过载或利用率低的指标,即处于运算状态或等待状态的 CPU 核心数。
* 平均负载 – 通过固定的时间周期如 1、5、15 分钟计算出的平均的系统负载。
Linux 中,平均负载一般指在内核运行队列中被标记为运行或不可打断状态的进程的平均数。
注意:
* 几乎没有 Linux 或类 Unix 系统不为用户展示平均负载的值。
* 完全空闲的 Linux 系统平均负载为 0,不包括空闲进程。
* 绝大多数类 Unix 系统只统计运行和等待状态的进程。但是在 Linux 中,平均负载也包括处于不可打断的睡眠状态的进程——它们是在等待其它系统资源如磁盘 I/O 等的进程。
### 如何监测 Linux 系统平均负载
有诸多方式监测系统平均负载,如 `uptime`,它会展示系统运行时间、用户数量及平均负载:
```
$ uptime
07:13:53 up 8 days, 19 min, 1 user, load average: 1.98, 2.15, 2.21
```
平均负载的数字从左到右的含义依次为:
* 最近 1 分钟的平均负载为 1.98
* 最近 5 分钟的平均负载为 2.15
* 最近 15 分钟的平均负载为 2.21
高平均负载意味着系统是过载的:许多进程在等待 CPU 时间。
下一节将介绍平均负载和 CPU 核数的关系。此外,常用的工具 [top](https://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/) 和 [glances](/article-6882-1.html) 可以实时显示 Linux 系统的运行状态:
#### Top命令
```
$ top
```
显示运行中的Linux进程:
```
top - 12:51:42 up 2:11, 1 user, load average: 1.22, 1.12, 1.26
Tasks: 243 total, 1 running, 242 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu(s): 17.4 us, 2.9 sy, 0.3 ni, 74.8 id, 4.6 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st
KiB Mem : 8069036 total, 388060 free, 4381184 used, 3299792 buff/cache
KiB Swap: 3906556 total, 3901876 free, 4680 used. 2807464 avail Mem
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
6265 tecmint 20 0 1244348 170680 83616 S 13.3 2.1 6:47.72 Headset
2301 tecmint 9 -11 640332 13344 9932 S 6.7 0.2 2:18.96 pulseaudio
2459 tecmint 20 0 1707692 315628 62992 S 6.7 3.9 6:55.45 cinnamon
2957 tecmint 20 0 2644644 1.035g 137968 S 6.7 13.5 50:11.13 firefox
3208 tecmint 20 0 507060 52136 33152 S 6.7 0.6 0:04.34 gnome-terminal-
3272 tecmint 20 0 1521380 391324 178348 S 6.7 4.8 6:21.01 chrome
6220 tecmint 20 0 1595392 106964 76836 S 6.7 1.3 3:31.94 Headset
1 root 20 0 120056 6204 3964 S 0.0 0.1 0:01.83 systemd
2 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kthreadd
3 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.10 ksoftirqd/0
5 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kworker/0:0H
....
```
#### Glances 工具
```
$ glances
```
Glances – Linux系统监测工具:
```
TecMint (LinuxMint 18 64bit / Linux 4.4.0-21-generic) Uptime: 2:16:06
CPU 16.4% nice: 0.1% LOAD 4-core MEM 60.5% active: 4.90G SWAP 0.1%
user: 10.2% irq: 0.0% 1 min: 1.20 total: 7.70G inactive: 2.07G total: 3.73G
system: 3.4% iowait: 2.7% 5 min: 1.16 used: 4.66G buffers: 242M used: 4.57M
idle: 83.6% steal: 0.0% 15 min: 1.24 free: 3.04G cached: 2.58G free: 3.72G
NETWORK Rx/s Tx/s TASKS 253 (883 thr), 1 run, 252 slp, 0 oth sorted automatically by cpu_percent, flat view
enp1s0 525Kb 31Kb
lo 2Kb 2Kb CPU% MEM% VIRT RES PID USER NI S TIME+ IOR/s IOW/s Command
wlp2s0 0b 0b 14.6 13.3 2.53G 1.03G 2957 tecmint 0 S 51:49.10 0 40K /usr/lib/firefox/firefox
7.4 2.2 1.16G 176M 6265 tecmint 0 S 7:08.18 0 0 /usr/lib/Headset/Headset --type=renderer --no-sandbox --primordial-pipe-token=879B36514C6BEDB183D3E4142774D1DF --lan
DISK I/O R/s W/s 4.9 3.9 1.63G 310M 2459 tecmint 0 R 7:12.18 0 0 cinnamon --replace
ram0 0 0 4.2 0.2 625M 13.0M 2301 tecmint -11 S 2:29.72 0 0 /usr/bin/pulseaudio --start --log-target=syslog
ram1 0 0 4.2 1.3 1.52G 105M 6220 tecmint 0 S 3:42.64 0 0 /usr/lib/Headset/Headset
ram10 0 0 2.9 0.8 409M 66.7M 6240 tecmint 0 S 2:40.44 0 0 /usr/lib/Headset/Headset --type=gpu-process --no-sandbox --supports-dual-gpus=false --gpu-driver-bug-workarounds=7,2
ram11 0 0 2.9 1.8 531M 142M 1690 root 0 S 6:03.79 0 0 /usr/lib/xorg/Xorg :0 -audit 0 -auth /var/lib/mdm/:0.Xauth -nolisten tcp vt8
ram12 0 0 2.6 0.3 79.3M 23.8M 9651 tecmint 0 R 0:00.71 0 0 /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/glances
ram13 0 0 1.6 4.8 1.45G 382M 3272 tecmint 0 S 6:25.30 0 4K /opt/google/chrome/chrome
...
```
这些工具中的平均负载是从 `/proc/loadavg` 文件中读取的,也可以直接使用 [cat 命令](https://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/)查看:
```
$ cat /proc/loadavg
2.48 1.69 1.42 5/889 10570
```
想要图形样式监测平均负载,请戳:[ttyload – 终端中颜色编码图形显示 Linux 平均负载](/article-8553-1.html)。
在桌面计算机中,可以使用图形用户接口工具查看系统平均负载。
### 理解系统平均负载和 CPU 核心数的关系
考虑了 CPU 核心数的影响,才能解释系统负载。
#### 多处理器 Vs 多核处理器
* 多处理器 – 一个计算机系统中集成两个或多个物理 CPU
* 多核处理器 – 单个物理 CPU 有两个或多个单独的核并行工作(也叫处理单元)。双核意味着有两个处理单元,4 核有 4 个处理单元,以此类推。
此外,Intel 引入了超线程技术用来提高并行计算能力。
通过超线程技术,在操作系统中,单个物理 CPU 表现的和两个逻辑 CPU 一样。(实际在硬件上只有一个 CPU)。
注意,单个 CPU 核同一时间只能执行一个任务,于是产生了多 CPU/处理器、多核 CPU,以及多线程技术。
多 CPU 时,多个程序可以同时执行。如今的 Intel CPU 使用了多核心和超线程技术。
可以使用 [nproc 或 lscpu 命令](https://www.tecmint.com/check-linux-cpu-information/)查看系统中的处理器单元数量。
```
$ nproc
4
# 或者
lscpu
```
也可以使用 [grep 命令](https://www.tecmint.com/12-practical-examples-of-linux-grep-command/):
```
$ grep 'model name' /proc/cpuinfo | wc -l
4
```
为了进一步理解系统负载,需要做一些假设。假设系统负载如下:
```
23:16:49 up 10:49, 5 user, load average: 1.00, 0.40, 3.35
```
**在单核系统中意味着:**
* CPU 被充分利用(100%);最近的 1 分钟有 1 个进程在运行。
* CPU 有 60% 处于空闲状态;在最近的 5 分钟没有进程等待 CPU 时间。
* CPU 平均过载了 235%;最近的 15 分钟平均有 2.35 个进程在等待 CPU 时间。
**在双核系统中意味着:**
* 有一个 CPU 处于完全空闲状态,另一个 CPU 被使用;最近的 1 分钟没有进程等待 CPU 时间。
* CPU 平均 160% 处于空闲状态;最近的 5 分钟没有进程等待 CPU 时间。
* CPU 平均过载了 135%;最近的 15 分钟有 1.35 个进程等待 CPU 时间。
也许你还会喜欢:
1. [20 个监控系统性能的命令行工具(一)](https://www.tecmint.com/command-line-tools-to-monitor-linux-performance/)
2. [13 个 Linux 性能监控工具(二)](https://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-tools/)
3. [Perf:一个 Linux 上的性能监控分析工具](https://www.tecmint.com/perf-performance-monitoring-and-analysis-tool-for-linux/)
4. [使用 Nmon 监控 Linux 的系统性能](/article-6886-1.html)
总而言之,如果你是系统管理员,你应该关注高的平均负载。平均负载高于 CPU 核心数意味着需要增加 CPU,反之则意味着 CPU 未被充分利用。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和自由软件的热心者,热衷于分享知识,现在是 TecMint 网站的内容创作者,不久之后将成为 Linux 系统管理员,web 开发者。
---
via: <https://www.tecmint.com/understand-linux-load-averages-and-monitor-performance/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[kylecao](https://github.com/kylecao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In this article, we will explain one of the critical Linux system administration tasks – performance monitoring in regards to system/CPU load and load averages.
Before we move any further, let’s understand these two important phrases in all Unix-like systems:
**System load/CPU Load**– is a measurement of CPU over or under-utilization in a Linux system; the number of processes which are being executed by the CPU or in waiting state.**Load average**– is the average system load calculated over a given period of time of 1, 5 and 15 minutes.
In Linux, the load-average is technically believed to be a running average of processes in it’s (kernel) execution queue tagged as running or uninterruptible.
**Note that:**
- All if not most systems powered by Linux or other Unix-like systems will possibly show the load average values somewhere for a user.
- A downright idle Linux system may have a load average of zero, excluding the idle process.
- Nearly all Unix-like systems count only processes in the running or waiting states. But this is not the case with Linux, it includes processes in uninterruptible sleep states; those waiting for other system resources like disk I/O etc.
### How to Monitor Linux System Load Average
There are numerous ways of monitoring system load average including uptime which shows how long the system has been running, number of users together with load averages:
$ uptime07:13:53 up 8 days, 19 min, 1 user, load average: 1.98, 2.15, 2.21
The numbers are read from left to right, and the output above means that:
- load average over the last
**1**minute is**1.98** - load average over the last
**5**minutes is**2.15** - load average over the last
**15**minutes is**2.21**
High load averages imply that a system is overloaded; many processes are waiting for CPU time.
We will uncover this in the next section in relation to number of CPU cores. Additionally, we can as well use other well known tools such as [top](https://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/) and [glances](https://www.tecmint.com/glances-an-advanced-real-time-system-monitoring-tool-for-linux/) which display a real-time state of a running Linux system, plus many other tools:
#### Top Command
$ top
top - 12:51:42 up 2:11, 1 user, load average: 1.22, 1.12, 1.26 Tasks: 243 total, 1 running, 242 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie %Cpu(s): 17.4 us, 2.9 sy, 0.3 ni, 74.8 id, 4.6 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st KiB Mem : 8069036 total, 388060 free, 4381184 used, 3299792 buff/cache KiB Swap: 3906556 total, 3901876 free, 4680 used. 2807464 avail Mem PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND 6265 tecmint 20 0 1244348 170680 83616 S 13.3 2.1 6:47.72 Headset 2301 tecmint 9 -11 640332 13344 9932 S 6.7 0.2 2:18.96 pulseaudio 2459 tecmint 20 0 1707692 315628 62992 S 6.7 3.9 6:55.45 cinnamon 2957 tecmint 20 0 2644644 1.035g 137968 S 6.7 13.5 50:11.13 firefox 3208 tecmint 20 0 507060 52136 33152 S 6.7 0.6 0:04.34 gnome-terminal- 3272 tecmint 20 0 1521380 391324 178348 S 6.7 4.8 6:21.01 chrome 6220 tecmint 20 0 1595392 106964 76836 S 6.7 1.3 3:31.94 Headset 1 root 20 0 120056 6204 3964 S 0.0 0.1 0:01.83 systemd 2 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kthreadd 3 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.10 ksoftirqd/0 5 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kworker/0:0H ....
#### Glances Tool
$ glances
TecMint (LinuxMint 18 64bit / Linux 4.4.0-21-generic) Uptime: 2:16:06 CPU 16.4% nice: 0.1% LOAD 4-core MEM 60.5% active: 4.90G SWAP 0.1% user: 10.2% irq: 0.0% 1 min: 1.20 total: 7.70G inactive: 2.07G total: 3.73G system: 3.4% iowait: 2.7% 5 min: 1.16 used: 4.66G buffers: 242M used: 4.57M idle: 83.6% steal: 0.0% 15 min: 1.24 free: 3.04G cached: 2.58G free: 3.72G NETWORK Rx/s Tx/s TASKS 253 (883 thr), 1 run, 252 slp, 0 oth sorted automatically by cpu_percent, flat view enp1s0 525Kb 31Kb lo 2Kb 2Kb CPU% MEM% VIRT RES PID USER NI S TIME+ IOR/s IOW/s Command wlp2s0 0b 0b 14.6 13.3 2.53G 1.03G 2957 tecmint 0 S 51:49.10 0 40K /usr/lib/firefox/firefox 7.4 2.2 1.16G 176M 6265 tecmint 0 S 7:08.18 0 0 /usr/lib/Headset/Headset --type=renderer --no-sandbox --primordial-pipe-token=879B36514C6BEDB183D3E4142774D1DF --lan DISK I/O R/s W/s 4.9 3.9 1.63G 310M 2459 tecmint 0 R 7:12.18 0 0 cinnamon --replace ram0 0 0 4.2 0.2 625M 13.0M 2301 tecmint -11 S 2:29.72 0 0 /usr/bin/pulseaudio --start --log-target=syslog ram1 0 0 4.2 1.3 1.52G 105M 6220 tecmint 0 S 3:42.64 0 0 /usr/lib/Headset/Headset ram10 0 0 2.9 0.8 409M 66.7M 6240 tecmint 0 S 2:40.44 0 0 /usr/lib/Headset/Headset --type=gpu-process --no-sandbox --supports-dual-gpus=false --gpu-driver-bug-workarounds=7,2 ram11 0 0 2.9 1.8 531M 142M 1690 root 0 S 6:03.79 0 0 /usr/lib/xorg/Xorg :0 -audit 0 -auth /var/lib/mdm/:0.Xauth -nolisten tcp vt8 ram12 0 0 2.6 0.3 79.3M 23.8M 9651 tecmint 0 R 0:00.71 0 0 /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/glances ram13 0 0 1.6 4.8 1.45G 382M 3272 tecmint 0 S 6:25.30 0 4K /opt/google/chrome/chrome ...
The load averages shown by these tools is read **/proc/loadavg** file, which you can view using the [cat command](https://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/) as below:
$ cat /proc/loadavg2.48 1.69 1.42 5/889 10570
To monitor load averages in graph format, check out: [ttyload – Shows a Color-coded Graph of Linux Load Average in Terminal](https://www.tecmint.com/ttyload-shows-color-coded-graph-of-linux-load-average/)
On desktop machines, there are graphical user interface tools that we can use to view system load averages.
### Understanding System Average Load in Relation Number of CPUs
We can’t possibly explain system load or system performance without shedding light on the impact of the number of CPU cores on performance.
#### Multi-processor Vs Multi-core
**Multi-processor**– is where two or more physical CPU’s are integrated into a single computer system.**Multi-core processor**– is a single physical CPU which has at least two or more separate cores (or what we can also refer to as processing units) that work in parallel. Meaning a dual-core has 2 two processing units, a quad-core has 4 processing units and so on.
Furthermore, there is also a processor technology which was first introduced by Intel to improve parallel computing, referred to as hyper threading.
Under hyper threading, a single physical CPU core appears as two logical CPUs core to an operating system (but in reality, there is one physical hardware component).
Note that a single CPU core can only carry out one task at a time, thus technologies such as multiple CPUs/processors, multi-core CPUs and hyper-threading were brought to life.
With more than one CPU, several programs can be executed simultaneously. Present-day Intel CPUs use a combination of both multiple cores and hyper-threading technology.
To find the number of processing units available on a system, we may use the [nproc or lscpu commands](https://www.tecmint.com/check-linux-cpu-information/) as follows:
$ nproc4 ORlscpu
Another way to find the number of processing units using [grep command](https://www.tecmint.com/12-practical-examples-of-linux-grep-command/) as shown.
$ grep 'model name' /proc/cpuinfo | wc -l4
Now, to further understand system load, we will take a few assumptions. Let’s say we have load averages below:
23:16:49 up 10:49, 5 user, load average: 1.00, 0.40, 3.35
###### On a single core system this would mean:
- The CPU was fully (100%) utilized on average; 1 processes was running on the CPU (1.00) over the last 1 minute.
- The CPU was idle by 60% on average; no processes were waiting for CPU time (0.40) over the last 5 minutes.
- The CPU was overloaded by 235% on average; 2.35 processes were waiting for CPU time (3.35) over the last 15 minutes.
###### On a dual-core system this would mean:
- The one CPU was 100% idle on average, one CPU was being used; no processes were waiting for CPU time(1.00) over the last 1 minute.
- The CPUs were idle by 160% on average; no processes were waiting for CPU time. (0.40) over the last 5 minutes.
- The CPUs were overloaded by 135% on average; 1.35 processes were waiting for CPU time. (3.35) over the last 15 minutes.
You might also like:
[20 Command Line Tools to Monitor Linux Performance – Part 1](https://www.tecmint.com/command-line-tools-to-monitor-linux-performance/)[13 Linux Performance Monitoring Tools – Part 2](https://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-tools/)[Perf- A Performance Monitoring and Analysis Tool for Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/perf-performance-monitoring-and-analysis-tool-for-linux/)[Nmon: Analyze and Monitor Linux System Performance](https://www.tecmint.com/nmon-analyze-and-monitor-linux-system-performance/)
In conclusion, if you are a system administrator then high load averages are real to worry about. When they are high, above the number of CPU cores, it signifies high demand for the CPUs, and low load averages below the number of CPU cores tells us that CPUs are underutilized.
This is an inaccurate article. The load average does not only involve the CPU. I found a more in-depth article here:
Reply`http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2017-08-08/linux-load-averages.html`
.@Peter
Thanks for sharing, we will check it out and review the article soon.
ReplyI agree with Trenton that this article is inaccurate. CPU is only of the factors that can cause high load. My server has 40% CPU usage, but the load is 2.5.
ReplyWhich can be most critical, 1min 5min or 15 min?
ReplyThis article is incorrect.
ReplyLoad averageis not about CPU utilization, it’s about process load. If an average of 4 processes are in the process queue, and all are waiting for disk, the load average would be 4, but the CPU utilization could be 20% on a single core system for example. Use “man proc” and search for load avg. |
8,633 | Hugo 对比 Jekyll :两大领先的静态页面生成器之间的比较 | https://opensource.com/article/17/5/hugo-vs-jekyll | 2017-06-24T10:52:00 | [
"Hugo",
"Jekyll",
"静态"
] | /article-8633-1.html |
>
> 如果你正在建一个新的网站,静态页面生成器或许是个正确的选择。
>
>
>

除非你是像艾米莉·狄金森那样深居简出的人,否则,当做了点事情后,你就会想要与这个世界分享。分享你的作品意味着需要一个网站。当然,你可以只是享受数字时代的便利,使用任何不同的社交网站来将你的作品呈现在观众面前。还有很多选择,不仅仅是传统的社交网站,例如 Artstation、Flickr、Soundcloud、Wattpad,不管你的媒介是什么,总有一款属于你的网站。
实际上,你*应该*使用这些网站,毕竟,人们都在这些网站上。然而,没有一个地方是真正属于你的。没有一个网站是你能保证不管社交趋势如何,人们都能在该网站上找到你的作品的。
控制权,这是拥有一个在网上属于自己的地方的意义。
但是这篇文章不打算介绍注册域名和托管你的网站。要介绍的是*后续*的步骤,真正地制作网页。对于很多人来说,典型的选择是使用像 [WordPress](http://wordpress.org/) 那一类的软件。在大多数主机托管商上,只需一次点击即可安装,然后就会有海量的插件和主题可供选择。插件和主题的选择取决于你想要制作的网页的类型。但是 WordPress 不仅对于大部分网站来说有点过犹不及,还给了你一个有许多活动部件的动态页面。如果你没有保持这些部件最新,这些部件可能造成重大安全隐患,你的页面因此被劫持。
替代方法是拥有一个静态网页,在服务端没有任何动态内容生成。只有一些原先的 HTML 和 CSS (或许还有点 Javascript 也挺好)。这种选择的不好的一面是以后你要亲自动手编写所有的代码。虽然可行,但你只是想要个地方来展示你的作品而已,你并不想知道底层网页设计的特性(和重要的但却令人头疼的跨浏览器兼容性)。
使用静态页面生成器。你得到了静态 HTML 页面的速度与安全,但是是以有着接近于动态页面的便利性的工作流程完成的。在静态页面生成器世界的两大先驱是 [Hugo](http://gohugo.io/) 和 [Jekyll](https://jekyllrb.com/) ,(顺道说下,Paolo Bonzini 的文章 《[Jekyll 起步](https://opensource.com/article/17/4/getting-started-jekyll)》 写得不错)但是哪一个才是你的正确选择?希望阅读完这篇文章,你会更加了解。我们将基于易上手性、主题可用性、编辑方式和拓展性这几点评估这两个静态页面生成器。
### 开始
公平地提醒一下,这两个都需要你在命令行下使用他们。大部分命令都很直接和易于记忆,但是让我们相应地调整下我们的期望吧,这不是点击几下鼠标就能做事的界面。
Jekyll 和 Hugo 的安装都相当的简单。 Jekyll 以 RubyGem 的方式安装,Hugo 提供了一个方便的集成的二进制文件让你迅速上手。因为安装包单一,Hugo 以微弱优势领先。虽然 Jekyll 的 RubyGems 安装方式本身就很简单,但是它*确实*需要你已经在你的电脑上正确安装并且配置好 Ruby 环境。除了社区设计者和网页开发者,大部分的使用者并没有提前安装好。
虽说是这样,但是一旦安装好,Hugo 和 Jekyll 都很好用。它们都有良好的文档和快速开始指南。你用一个简单命令新建一个页面(在 Jekyll 里是 `jekyll new <your_site>` ,在 Hugo 里是 `hugo new site <your_site>`,译者注:`<your_site>` 指代你网页的名称)。这一步新建了一个通用目录结构和你网站的大致内容。目录结构和基本的配置都十分相似。Jekyll 使用一个 `_config.yml` 文件,Hugo 使用 `config.toml`(虽然你*能*在 Hugo 的配置里使用 YMAL 或者 JSON 语法,如果觉得其中一个使用起来更舒服的话)。每个内容文件的<ruby> 前置配置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> front matter </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>元数据使用相同的配置语法。然后,所有的内容都是用 Markdown 写的。
我想说就帮助你开始第一个静态网页这一点来说,Jekyll 稍微领先于 Hugo ,因为它能以一些基本的内容和一个默认主题开始着手使用。当在建设网页时,你能使用这些内容作为一个样板。Hugo 没有样例内容,甚至没有一个默认主题。即便如此,样例内容和默认主题是我在用任何工具建设网站时第一个删除的内容,因此 Hugo 事实上帮我节省了这一步。
### 主题
正如我所提到的,Hugo 根本没有默认主题,所以主题可能是你打算最先设置的。Jekyll 有一个得体的默认主题,虽然它只是个骨架。你或许也会想去为你的 Jekyll 页面找一个主题。
Hugo 和 Jekyll 都有多种多样的各类主题,网页样式从单页面的主题到带有博客和评论的完善的多页面主题都有,一应俱全。尽管如此,想找到满足你需求的主题事实上并不简单。无论使用哪个,主题网站——Hugo 的 [themes.gohugo.io](https://themes.gohugo.io/) 和 Jekyll 的 [jekyllthemes.org](http://jekyllthemes.org/) ,基本上都是一个充满主题截图的巨大页面。一旦你点击主题,你能得到关于该主题的一些十分详细的信息,但是对于初步搜索相当困难。Hugo 的主题站有一些基本的标签分类,但是大体上在我看来,主题搜索和展示都是这两个项目需要继续努力的。
主题管理也是一个有趣的主题。在两个项目中,几乎每一个主题都是一个 Git 仓库(经常是托管在 Github 上),你需要<ruby> 克隆 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> clone </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>下来到你的网页建设地。在 Jekyll 里,有额外的使用 RubyGems 的 bundle 的步骤来确保主题是由网站管理的。大部分主题都有一个 Gemfile,使得这一步骤轻松不少。如果主题没有一个 Gemfile,添加也相当简单。在 Hugo 里没有捆绑这一操作,只要在 `config.toml` 指向你的主题即可。
我发现我偏爱 Hugo 的主题处理。你可以<ruby> 克隆 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> clone </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(或者新建)主题到 `themes` 里它们自己的子文件夹里。这不仅使得当你开始时能轻松地切换主题,而且也能让你用自己的文件替换主题里的任何组件。这意味着你能根据自己的品味自定义主题,而不用弄乱原始主题,使得这主题也可以通用于其他人。当然如果有一个你觉得其他用户会觉得值得的改变,你仍然可以编辑源文件,提交一个 PR(<ruby> 拉取请求 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> pull request </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)给主题维护者。
### 工作流程
一旦你设置好初始的配置,Jekyll 和 Hugo 的网站建设流程都很相似。两者都有一个实时的 `serve` 命令,能在你的电脑上运行一个小型、轻量级的网页服务器,所以你能在在本地测试你的网站而不用上传到哪里。很棒的是无论你是运行着 `jekyll serve` 还是 `hugo serve`,都默认配置为当你为之开发时,监视你对网站的任何修改。当你在浏览器里看本地版的网站时,它会根据你的修改自动更新,不管你改的是内容、配置、主题、还仅仅是一张图片。这确实很方便和节约时间。
在两个系统中都是用 [Markdown](https://daringfireball.net/projects/markdown/) 写你的网站内容。如果碰巧你不熟悉 Markdown,(我来解释下,)它是种很简单的纯文本编写方式,还能有一些很好用的格式化符号。它很容易使用而且可阅读。而且因为是纯文本,你的内容(其实是你的网站)很容易进行版本控制。这是我最近写几乎所有东西的主要方式。
新内容能通过在正确的地方手动创建文件添加到网站里。新的文件只需要是有恰当的<ruby> 前置配置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> front matter </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>元数据的 Markdown 文件即可。至于配置文件,Jekyll 对于前置配置使用 YAML 语法,Hugo 接受 TOML、YAML 或者 JSON(默认是 TOML)。新文件需要放置在正确的文件夹内,在 Jekyll 里你需要把你编写中的文件和已经完成了的内容页分别放在 `_drafts` 和 `_posts` 目录中。在 Hugo 中只有单独一个 `content` 目录。你可以根据文件的前置配置判断这是否是一个草稿。
现在,虽然可以手动完成所有这些事情,但是 Hugo 提供了一些方便的功能确保你的新文件创建在正确的文件里,那些文件也用恰当的前置配置预先配置好了。简单地在终端中进入你网站的目录,输入 `hugo new content/<page.md>` , `<page.md>` 代表着你想新建的新页面。你甚至可以设置些包含为不同页面自定义的前置配置、叫**原型**的模版(例如在你的网页上同时有博客和播客)。
当你的网页弄好后,你能关闭你的预览服务器,并用一个命令来建立你网站的真正页面。在 Jekyll 里是 `jekyll build`,Hugo 就仅仅是 `hugo`,Jekyll 把完成好的页面放在 `_site` 的子目录中。然而 Hugo 把这些文件放在名为 `public` 的子目录中。不管哪种情况,一旦你完成后,你就有了一个完整的静态网站,你能上传并把它托管在几乎任何地方。
### 可拓展性
Hugo 和 Jekyll 都能让你自定义你自己的网站上哪怕最小的一个点。然而就可拓展性而言,现在 Jekyll 因其插件 API 而远远领先。因为这种插件结构,很容易为你用 Jekyll 生成的网站添加功能,通过 Jekyll 社区或者你自己写的相当短的代码片段就能完成。
Hugo 现在根本没有插件 API,所以添加功能有点难。希望以后支持编写并包含插件。但是现在看不出有人在做这一点。
### 结论
大体上讲,Hugo 和 Jekyll 十分相似。归根结底由你工作体验和你的网站需求决定。如果你已经设置好了 RubyGems 环境而且你需要插件的可拓展性,Jekyll 是你的选择。然而,如果你看重一个简单的工作流程,一个直接自定义网站的方式,那你首选 Hugo。
我发现我更喜欢 Hugo 的方法,而且在建设一个小型网站,我不需要任何插件。当然,每个人的需求都不同。你会为你的网站选择哪一个静态页面生成器?
(题图:opensource.com)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/5/hugo-vs-jekyll>
作者:[Jason van Gumster](https://opensource.com/users/jason-van-gumster) 译者:[ypingcn](https://ypingcn.github.io/wiki/lctt) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
8,634 | 安卓编年史(25):Android 4.4,奇巧——更完美,更少的内存占用(2) | http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/26/ | 2017-06-24T16:25:31 | [
"Android",
"安卓编年史"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8634-1.html | 

*新的“添加到主屏幕”界面无疑受到了蜂巢的启发。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
奇巧的主屏幕配置界面漂亮地对蜂巢进行了复古。在有巨大的 10 英寸屏幕的蜂巢平板上(上方右侧图片),长按主屏背景会向你展现一个所有主屏幕的缩放视图。可以从下面的小部件抽屉里将它们拖放到任意主屏上——这很方便。在将蜂巢的界面带到手机上时,从安卓 4.0 直到 4.3,谷歌都跳过了这个设计,把它留给了大屏幕设备,在手机上长按后只显示一个选项列表(中间的图片)。
但在奇巧上,谷歌最终给出了解决方案。在长按后,4.4 呈现一个略微缩放的视图——你可以看到当前主屏以及它左右侧的屏幕。点击“小部件”按钮会打开一个小部件略缩图的完整列表,但是长按一个小部件后,你会回到缩放视图,并且你可以在主屏页面之间滚动,将图标放在你想要的位置。将图标或者小部件拖动过最右侧的主屏页面,你可以创建一个新的主屏页面。

*联系人和去掉所有蓝色痕迹的键盘。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
奇巧是电子风格设计的完结。在系统的大多数地方,剩下的蓝色高亮都被换成了灰色。在联系人应用中,头部和联系人列表字母分割线的蓝色都移除掉了。图片的位置换了一侧,底栏变成了浅灰色以和顶部相称。几乎将蓝色渗透进每个应用的键盘,现在是灰底、灰色、灰高亮。这可不是件坏事。应用应该允许有它们自己的配色方案——在键盘上强迫存在潜在的颜色冲突可不是个好设计。

*前三张是奇巧的拨号盘,最后一张是 4.3 的。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
谷歌完全重制了奇巧中的拨号,创造了一个疯狂的设计,改变了用户对手机的思考方式。实际上新版拨号中的数字都被尽可能地隐藏了——在首屏上甚至没有拨号盘。打电话的主要界面现在是个搜索栏!如果你想给你的联系人打电话,只要在搜索栏输入他的名字;如果你想给一个公司打电话,只要输入公司的名字,拨号会通过谷歌地图庞大的数据库找到号码。它工作得令人难以置信的好,这是只有谷歌才能完成的事情。
如果搜索不是你的菜的话,应用还会智能地显示通话记录列表,最常联系人,还有指向所有联系人的链接。底部的链接指向你的通话记录,传统的拨号盘,以及常规的更多操作按钮,包含一个设置页面。

*Office 相关:新的内置应用 Google Drive,以及打印支持。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
在奇巧中 Google Drive 终于作为内置应用包含了进来,令人惊奇的是这居然等了这么长时间。Drive 允许用户创建和编辑 Google Docs 表格和文档,用相机扫描文档并作为 PDF 上传,或者查看(不能编辑)演示文稿。Drive 的设计十分现代,侧面拥有滑出式导航抽屉,并且是 Google Now 风格卡片式设计。
为了有更多的移动办公乐趣,奇巧包含了系统级打印框架。在设置的底部有“打印”设置界面,任何打印机 OEM 厂商都可以为它写个插件。谷歌云打印自然是首批支持者之一。只要你的打印机和云打印相连接,无论是本地或通过一台装有 Chrome 浏览器的电脑,你都可以借助网络进行打印。应用同样也需要支持打印框架。点击 Google Drive 里的“i”按钮会显示文档信息,并且给你打印的选项。就像桌面系统那样,会弹出一个设置对话框,有打印份数,纸张尺寸,以及页面选择等选项。

*Google+ 应用的“相片”部分,它取代了相册。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
Google+ 相片和相册最初都在 Nexus 5 上随附,但在 Google Play 设备稍晚版本的奇巧上,相册被砍掉了,Google+ 完全接手了相片管理。新应用的主题从深色变成了浅色,Google+ 相片还带来了现代的导航抽屉设计。
安卓一直以来都有即时上传功能,它会自动备份所有图片到谷歌的云存储,开始是 Picasa 后来是 Google+。G+ 相片相比相册最大的好处是它可以管理那些云端存储的图片。图片右下角的云图标指示备份状态,它会从右到左地填满来指示上传状态。G+ 相片带来了它自己的照片编辑器,还有许多其它的 Google+ 图片功能,比如高亮,自动美化,当然,还有分享到 Google+。

*时钟应用的调整,添加了一个闹钟页面并修改了时间输入框。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
谷歌将 4.2 引入的优秀时间选择器换成了一个奇怪的时钟界面,操作起来比旧界面更慢了也更不精确了。首先是个可以选择小时的单指针时钟,然后显示的是另一个选择分钟的单指针时钟。选择的时候要转动分针或点击数字,这让用用户很难选择不是整五分钟的时间增量。不像之前的时间选择器需要选择一个时间段,这里默认时间段是 AM(重复一下,这样设置的时候容易不小心偏差 12 小时)。
---

[Ron Amadeo](http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo) / Ron 是 Ars Technica 的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。[@RonAmadeo](https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo)
---
via: <http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/26/>
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,635 | 使用 Go 一年的体验 | https://bugfender.com/one-year-using-go | 2017-06-25T08:51:00 | [
"Go"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8635-1.html | 
我们公司 [Mobile Jazz](http://mobilejazz.com/) 从一个内部试验性项目开始使用 [Go](https://golang.org/)。如公司名暗示的那样,我们是开发移动应用的。
在发布一个应用给公众后,我们很快意识到我们缺失一个工具来检查用户实际发生的情况以及他们是如何与应用交互的 - 如果有任何问题或者 bug 的报告,这将会相当方便。
现在有几款工具声称能在这个方面帮助开发者,但是没有一个能完全满足要求,因此我们决定自己构建一个。我们开始创建一组基础的脚本,如今它很快进化成了完整的工具,称为 [Bugfender](https://www.bugfender.com/)!
由于这最初是一个实验,我们决定使用一种新的趋势技术。对学习以及持续教育的热爱是 Mobile Jazz 的核心价值的之一,因此我们决定使用 Go 构建。这是一个由 Google 开发的相对较新的编程语言。它是编程世界的的新玩家,已经有许多受尊敬的开发者对它赞不绝口。
一年后,这个实验变成了一个初创项目,我们拥有了一个已经帮助了来自全世界的数以千计的开发者的令人难以置信的工具。我们的服务器每天处理来自 700 万台设备的超过 200GB 的数据。
在使用 Go 一年之后,我们想要分享我们将一个小小的实验变成处理百万日志的生产服务器的一些想法和经验。
### Go 生态系统
公司中没有人有使用 Go 的经验。Bugfender 是我们第一次深入这个语言。
学习基本上相当直接的。我们之前在 C/C++/Java/Objective-C/PHP 的经验让我们学习 Go 相当快,并且在几天内就开始开发了。当然会有一些新的和不常见的东西需要学习,包括 GOPATH 还有如何处理包,但这在我们的预期之内。
几天之内,我们意识到即使是一个以简化为设计目的的语言,Go 也是非常强大的。它能够做任何现代编程语言应该能做的事:能够处理 JSON、服务器之间通讯甚至访问数据库也没问题(并且只需要几行代码)。
在构建一个服务器时,你应该首先决定是否使用任何第三方库或者框架。对于 Bugfender,我们决定使用:
#### Martini
[Martini](https://github.com/go-martini/martini) 是一个强大的 Go 的 web 框架。我们开始这个实验时,它是一个很棒的解决方案,至今也是,我们还没遇到任何问题。然而如果我们今天再次开始这个实验的话,我们会选择一个不同的框架,因为 Martini 不在维护了。
我们还试验了 [Iris](https://github.com/kataras/iris)(我们目前的最爱)还有 [Gin](https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin)。Gin 是 Martini 继任者,并且迁移到这上能让我们重用已有的代码。
在过去的一年中,我们意识到 Go 的标准库是非常强大的,你不必依靠一个臃肿的 web 框架来构建一个服务器。最好在特定任务上使用专门的高性能库。
~~Iris 是我们目前最喜欢的,并且将来我们将使用它重写服务来替代 Martini/Gin,但这目前并不是优先的。~~
**修改:** 在讨论了 Iris 的各个方面之后,我们意识到 Iris 或许不是最好的选择。如果我们决定重写我们的 web 组件,我们或许会研究其他的选择,我们欢迎你的建议。
#### Gorm
有些人喜欢 ORM,而有些人则不喜欢。我们决定使用 ORM,更确切地说是 [GORM](https://github.com/jinzhu/gorm)。我们的实现只针对 web 前端,对于日志提取 API 仍然继续使用手工优化的 SQL。在一开始,我们确实很喜欢它,但是随着时间的推移,我们开始发现问题,并且我们很快将它从代码中完全移除,并且使用 [sqlx](https://github.com/jmoiron/sqlx) 这个标准 SQL 库。
GORM 的一个主要问题是 Go 的生态系统。作为一个新语言,自我们开始开发产品以来 Go 已经有很多新版本。在这些新版本中的一些改变并不向后兼容,因此要使用最新的库版本,我们要经常重写已有代码并检查我们为解决版本问题所做的 hack。
上述这两个库是大多数 web 服务的主要组件,因此做一个好的选择很重要,因为将来更改会很困难,并且会影响你服务器的性能。
### 第三方服务
在创建一个实际使用的产品的另外一个重要方面是考虑库、第三方服务和工具的可用性。在这方面,Go 还缺乏成熟度,大多数公司还没有提供 Go 库,因此你或许需要依赖其他人写的不能一直保证质量的库。
比如,对于使用 [Redis](https://github.com/go-redis/redis) 和 [ElasticSearch](https://github.com/olivere/elastic) 有很好的库,但是对于其他服务比如 Mixpanel 或者 Stripe 还没有好的。
我们建议在使用 Go 之前事先检查对于你需要的产品是否有好的库可用。
我们在 Go 的包管理系统上也遇到了很多问题。它处理版本的方式远没有达到最好,并且在过去的一年中,我们在不同的团队成员之间使用同一个库的不同版本上遇到了很多问题。然而,最近要归功于 Go 新支持的 vendor 包特性,除了 [gopkg.in](http://labix.org/gopkg.in) 服务外,这个问题基本被解决了。
### 开发者工具

由于 Go 是一门相对新的语言,你或许发现相比其他成熟的语言像 Java,它可用的开发工具并不很好。当我们开始 Bugfender 时,使用任何 IDE 都很困难,似乎没有 IDE 支持 Go。但是在过去的一年中,随着 [IntelliJ](https://plugins.jetbrains.com/plugin/5047-go) 和 [Visual Studio Code Go](https://github.com/Microsoft/vscode-go) 插件的引入,这一切改善了很多。
最后看下其他的 Go 工具,调试器并不很好,而分析器甚至更糟,因此有时调试你的代码或者尝试优化它会很困难。
### 前往生产
这确实是 Go 最好的东西之一,如果你想要部署一些东西到生产环境中,你只需要构建你的二进制并发送到服务器中,没有依赖,不需要安装额外的软件,你只需要能在服务器中运行二进制文件就行。
如果你习惯于处理那些需要包管理器或者需要小心你使用的语言解释器的语言,用 Go 工作会感到很高兴。
我们对 Go 的稳定性也很满意,因为服务器似乎从没有崩溃过。我们在发送大量数据给 Go Routines 时遇到过一个问题,但是我们几乎没见到任何崩溃。注意:如果你需要发送大量数据给 Go Routine,你需要小心堆溢出。
如果你对性能感兴趣,我们没法与其他语言相比较,因为我们从零开始使用 Go,但是对于我们处理的数据量,我们感觉性能是非常好的,我们绝对不能如此轻松地使用 PHP 处理同等数量的请求。
### 总结
在过去的一年中,我们对 Go 的感觉起起伏伏。最初我们是兴奋的,但是在实验变成真实的产品后我们开始发现问题。我们几次考虑过用 Java 完全重写,但是目前为止,仍旧使用的是 Go,并且过去的一年中, Go 生态已经有了很大的提升,这简化了我们的工作。
如果你想要使用 Go 构建你的产品,你可以保证它可以工作,但是你确实需要小心一件事:可以雇佣的开发者。硅谷中只有很少的高级 Go 开发者,并且在其他地方寻找也是一件非常困难的任务。
---
via: <https://bugfender.com/one-year-using-go>
作者:[ALEIX VENTAYOL](https://bugfender.com/author/aleixventayol) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,636 | 开源硬件起步的 8 个步骤 | https://opensource.com/article/17/5/8-ways-get-started-open-source-hardware | 2017-06-25T12:29:00 | [
"硬件",
"开源硬件"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8636-1.html |
>
> 制造自己的硬件比以往任何时候都更容易,更便宜。以下是你设计、构建和测试你的第一块板子所需的事情。
>
>
>

著名的计算机科学家<ruby> 阿伦凯 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Alan Kay </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>曾经说过:“认真对待软件的人应该制造他们自己的硬件。” 我认为如今就如 同 1982 年他所说的一样。然而,现在和那时之间的不同是硬件变得越来越快、越来越小,最重要的是:更便宜。 现在可以用 5 美元购买一台完整的电脑。
随着大公司降低自己产品的价格,能够生产生产级硬件的制造业生态系统得以增长,这些硬件的成本足够便宜,并且达到了普通人都可以接受的程度。这种可用性以及可负担性正在帮助推动诸如众筹和创客运动之类的事情,但同时它们也让更多的个人能够通过开源硬件参与到开源当中。
>
> 探索开源硬件
>
>
> * [什么是开源硬件?](https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-hardware?src=open_hardware_resources_menu)
> * [什么是树莓派?](https://opensource.com/resources/what-raspberry-pi?src=open_hardware_resources_menu)
> * [什么是 Arduino?](https://opensource.com/resources/what-arduino?src=open_hardware_resources_menu)
>
>
>
开源硬件和非开源硬件有很多区别,但是开源硬件联盟(OSHWA)定义了一个大多数人同意的定义,如果你熟悉开源软件,这不会听上去太奇怪:
>
> “开源硬件(OSHW)是一个指有形的造物:机器、设备或者其它物理东西的术语——其设计向公众发布,任何人可以制造、修改、分发并使用那些造物。”
>
>
>
我们身边已经有很多开源硬件了。你可能没有注意到你在使用的主板实际上可能是开源硬件。从低调而多能的 [Arduino](https://opensource.com/node/20751),一直到像 [BeagleBone](https://opensource.com/node/35211) 系列和 [C.H.I.P.](https://opensource.com/node/24891) 计算机这样的完整功能的电脑,有很多开源硬件的例子,还有更多的在设计中。
硬件可能很复杂,对初学者而言有时候不太理解为什么设计需要某些东西。但开源硬件使你不仅可以看到工作示例,还可以更改这些设计,或者在你自己的设计中剔除或复制所需的部分,就如复制和粘贴一样简单。
### 我该如何开始?
我们先要指出硬件很“硬”,它很复杂甚至很深奥,你可能用到的工具并不总是最人性化的。任何一个玩微处理器的时间足够长的人都可以向你证实:你会烧坏一些东西,看到神奇的烟雾在某个时刻冒出来。没关系,我们都遇到过,有些人还会反复遭遇,因为我们在做一件事情的前 100 次时都不会得到教训,但不要让这些阻碍你:当做错事情时,你会学到教训,而且你将来还可以将有趣的故事告诉别人。
#### 建模
首先要做的是使用现有的电路板、跳线、面包板以及你要连接的任何设备来建模你想要做的事情。在许多情况下,最简单的事情就是在板上添加更多的 LED,并以新颖的方式让它们闪烁起来。这是一个很好的做出原型的方式,也是一个常见的做法。它看上去并不漂亮,你可能会发现你的线接错了,但这些都是原型 - 你只是想证明硬件可以工作。当硬件不工作时,一定要仔细检查一切,不要害怕寻求帮助 - 有时第二双眼睛会发现你奇怪的接地短路。
#### 设计
当你弄清楚你想要构建的硬件,现在是时候把你的想法从跳线和面包板变成实际的设计了。这时事情会变得让人气馁,但是从小处开始,事情上,可以从熟悉加工和处理这样非常小的地方开始,所以为什么不从制作一块带有 LED 和电池的印刷电路板开始?认真地说,这可能听起来过于简单,但在这里有很多新的基础要了解。
1. **找到一个电子设计自动化(EDA)工具来使用。** 有很多好的开源软件可以选择,但是它们并不总是用户友好的。[Fritzing](http://fritzing.org/home/)、[gEDA](http://www.geda-project.org/) 还有 [KiCad](http://kicad-pcb.org/) 都是开源的,并且其可用性一个比一个好。如果你想要尝试更多的商业软件,那么还有一些其他的选择。Eagle 有个受限的免费版本可供使用,有许多的开源硬件是用它设计的。
2. **在 EDA 工具中设计你的电路板。** 依据你选择的工具,这可能会非常快,或者可能是学习如何设计的很好的练习。这是我建议从小的硬件开始的原因之一。一个带 LED 的电路可以如一块电池、一个电阻、一个 LED 一样简单。电路图非常简单,并且板子也会非常小、非常简单。
3. **为打样而导出设计。** 这与列表中的下一件事情紧密相连,但如果你以前没有这样做过,这也可能是一个令人困惑的过程。当你在导出时,你会有很多细节需要调整,并且需要以某种方式导出以便电路板工厂能确切知道你要做的。
4. **找到一个电路板工厂。** 有许多电路板工厂可以制作你的设计,并且一些比其他更加友好及有帮助。一个特别棒的地方是 [OSH Park](https://oshpark.com/),这些人非常友好并支持开源硬件。他们也有一个非常扎实的流程来确认你发送给它的就是会被制造的,所以他们值得一试。还有很多其他选择;看看 [PCB Shopper](http://pcbshopper.com/),它可以让你比较不同实体 PCB 商家的价格、周转时间等等。
5. **等待。** 这或许是在制造你自己的电路板中最难的一部分了,因为它会花费时间将数字部分变成物理产品。计划好两周时间来拿到你的电路板。这是你继续下个项目的绝好时间,买到或确保你当前制造的所有部分都有了,或者随便试试而不要担心。你的第一块电路板是艰难的 - 你现在非常想要,但是保持耐心。
6. **修补并提升。** 一旦拿到你的板子,是时候上电测试了。如果你是以 LED 电路开始,那么它很容易调试,并且你会得到一些可以工作起来的东西。如果你有更复杂的电路,那么需要有条理并且有耐心。有时候电路不工作,并且你需要用你的调试技能来追踪问题。
7. **最后,如果你做的是开源硬件,那就发布它。**\* 我们谈论的是开源硬件,因此确保它包含了一个许可,发布它、共享它,把它放在人们可以看见你所做的地方。你或许会想写一篇博客并提交到如 Hackaday 上面。
8. **最重要的是,玩得开心。** 坦白说,如果你在做一些事但是你不开心,你应该停止这样做。开源硬件可以很有趣,虽然有时是困难而且复杂的。但是不是一切都工作:见鬼,我已经设计了一半的电路不工作;或者我(意外地)在电源和接地之间造成了 12 次短路;这些电路板是双层板:是的。我在这个过程中学到了一些东西:非常多,并且我不会再犯同样的错误。我会做出新的板子,但不是这些。(我会支持并盯着这些板子和它们的错误,悲伤的是,它们不会在我盯着它们时感到良心会痛)。
现在有许多的开源硬件,有许多好的例子从中可以查看、复制、衍生,并且有很多信息使制造硬件变得简单。这就是开源硬件:一个人们制造它们、共享它们的社区,每个人可以制作他们自己的东西并构建他们想要的硬件——而不是他们可以得到的硬件。
(题图:Thomas Hawk on [Flickr](https://www.flickr.com/photos/thomashawk/3048157616/in/photolist-5DmB4E-BzrZ4-5aUXCN-nvBWYa-qbkwAq-fEFeDm-fuZxgC-dufA8D-oi8Npd-b6FiBp-7ChGA3-aSn7xK-7NXMyh-a9bQQr-5NG9W7-agCY7E-4QD9zm-7HLTtj-4uCiHy-bYUUtG). [CC BY-NC 2.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0/) 。由 Opensource.com 修改)
---
作者简介:
John 'Warthog9' Hawley - John 在 VMWare 的开源项目办公室为上游开源项目工作。在以前的生活中,他曾在 MinnowBoard 开源硬件项目上工作,领导了 kernel.org 的系统管理团队,并在桌面集群变得很酷之前构建了它们。为了乐趣,他构建了多个明星项目,比如一个受欢迎的英国电视节目 K-9 的复制品,在无人机的飞行计算机视觉处理中完成,设计并制作了一堆自己的硬件。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/5/8-ways-get-started-open-source-hardware>
作者:[John 'Warthog9' Hawley](https://opensource.com/article/17/5/8-ways-get-started-open-source-hardware) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Alan Kay, famed computer scientist, once said, "People who are really serious about software should make their own hardware." I'd argue that's as true today as it was in 1982 when he said it. However, what's changed between then and now is that hardware has gotten faster, smaller, and most importantly: cheaper. it's now possible to buy a full computer for $5.
With big companies driving down prices for their own products, it's grown a manufacturing ecosystem capable of producing production-grade hardware that's cheap enough and accessible enough that it is now within reach of normal individuals. This accessibility and affordability are helping drive things like crowdfunding and the maker movement, but they're also giving way to more individuals being able to participate in open source through open source hardware.
There's some pretty big differences in what is or isn't open source hardware, but the Open Source Hardware Association (OSHWA) has a definition that most folks agree with, and if you're familiar with open source software this shouldn't sound too weird:
"Open source hardware (OSHW) is a term for tangible artifacts—machines, devices, or other physical things—whose design has been released to the public in such a way that anyone can make, modify, distribute, and use those things."
There's lots of open source hardware around; you may not have noticed the boards you already use may, in fact, be open hardware. From the humble but ever versatile [Arduino](https://opensource.com/node/20751) and all the way up through full computers like the [BeagleBone](https://opensource.com/node/35211) family and the [C.H.I.P.](https://opensource.com/node/24891) computer, there are lots of examples of open hardware around, and more designs are being made all the time.
Hardware can be complicated, and sometimes non-obvious to beginners why a design needs something. But open source hardware gives you the ability to not only see working examples, but also the ability to change those designs or strike off and replicate the pieces you need in your own designs, and it might be as simple as copy and paste.
## How can I get started?
Let's start off by pointing out that hardware is hard, it's complicated, sometimes esoteric, and the tools you may be using are not always the most user-friendly. It's also more than likely, as anyone who's played around with a microcontroller long enough can attest: you are going to fry something and let the magic smoke out at some point. It's ok, we've all done it, some of us repeatedly because we didn't learn the lesson the first 100 times we did something, but don't let this discourage you: Lessons are learned when things go wrong, and you usually get an interesting story to tell later.
### Modeling
The first thing to do is to start modeling what you want to do with an existing board, jumper wires, a breadboard, and whatever devices you want to hook up. In many cases, the simplest thing to play with is just adding more LEDs to a board and getting them to blink in novel ways. This is a great way to prototype something, and it's a fairly common thing to do. It won't look pretty, and you may find that you wire something wrong, but these are prototypes—you just want to prove things work. When things don't work, always double check everything, and don't be afraid to ask for help—sometimes a second pair of eyes will find your oddball ground short.
### Design
When you've figured out what you want to build, it's time to start taking your idea from jumper wires and breadboards to an actual design. This is where things can get a bit daunting, but start small—in fact, it's worth starting really small just to get used to the tooling and process, so why not make a printed circuit board that has a LED and a battery on it? Seriously, this might sound overly simplistic but there's a lot of new ground to cover here.
**Find an electronic design automation (EDA) tool to use.**There are some good open source software options out there, but they aren't always the most user-friendly.[Fritzing](http://fritzing.org/home/),[gEDA](http://www.geda-project.org/), and[KiCad](http://kicad-pcb.org/)are all open source in ascending order of approachability. There are also some options if you want to try more commercial offerings; Eagle has a free version available with some restrictions and a lot of open source hardware designs are done in it.
**Design your board in your EDA tool.**Depending on the tool you choose, this could be fairly quick, or it could be quite the exercise in learning how things work. This is one of the reasons I suggest starting small; a circuit with an LEDaan be as simple as a battery, a resistor, and an LED. The schematic capture is pretty simple, and the layout can be small and very simple.
**Export your design for manufacturing.**This goes hand-in-hand with the next thing on the list, but it can also be a confusing process if you haven't done it before. There's a lot of knobs and dials to twist and adjust when you do the export, and things need to be exported in certain ways to make it easier on board houses to actually figure out what you want them to make.
**Find a board house.**There are lots of board houses out there that can make your design, and some are more friendly and helpful than others. One place that's particularly awesome to work with is[OSH Park](https://oshpark.com/), these guys are very friendly and supportive of open source hardware. They also have a very solid process for confirming that what you are sending them is what will get built, so they are worth checking out. There are lots of other options though; take a look at[PCB Shopper](http://pcbshopper.com/), which lets you compare pricing, turnaround times, etc. of a number of solid PCB manufacturers.
**Wait.**This might be the hardest part of building your own board, as it takes time to make something digital into a physical product. Plan on two weeks from when you hit "go" to getting your boards back. This is a great time to work on your next project, ensure or acquire all the parts for your current build, or generally try not to worry. On your first board it's hard—you really want it now, but be patient.
**Solder up and bring up.**Once you've got your board, it's time to make it up and then test it. If you've gone with the LED option to start, it should be fairly easy to debug, and you'll have something that works. If you went more complex, be methodical and patient; sometimes things don't work and you'll need all your debugging skills to track things down.
**Last, if you are doing open source hardware, release it.**We are talking about open source hardware, so make sure you include a license, but release it, share it, put it somewhere people can see what you've done. You may even want to write a blog post and submit it to someplace like Hackaday.
**Above all, have fun.**Frankly if you are doing something and you aren't having fun, you should stop doing it. Open source hardware can be a lot of fun, though sometimes hard and complicated. Not everything may work; heck, I've had designs where half the board wasn't working or where I (accidentally) caused 12 shorts between power and ground. Were those boards bunked boards: yup. Did I learn something in the process: A LOT, and I won't make those same mistakes again. I'll make new ones, sure, but not THOSE. (I'd point and glare at those boards and their mistakes, but they wouldn't feel bad for me glaring at them, sadly).
There's a lot of open source hardware out there and lots of good examples to look at, copy, and derive from and lots of information to help make building hardware easier. That's what open source hardware is: A community of people making things and sharing them so that everyone can make their own things and build the hardware that they want—not the hardware they can get.
## Comments are closed. |
8,637 | 蚁族:我们用“人”来构建软件 | http://turnoff.us/geek/ant/ | 2017-06-25T18:41:00 | [
"漫画"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8637-1.html | 
用过 Java 的同学大多都用过或听说过 Ant,它是用来构建 Java 项目的一个工具。
那么,在蚁族的世界中,他们(它们?)是不是用“Human(人)”来构建项目呢?
顺便说一句,有四只手(足)真好~
---
via: <http://turnoff.us/geek/ant/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,638 | Linus Torvalds 说 Linux 仍然惊讶和激励着他 | https://www.linux.com/blog/event/lc3-china/20176/6/linus-torvalds-explains-how-linux-still-surprises-and-motivates-him | 2017-06-26T10:17:00 | [
"LinuxCon"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8638-1.html | 
>
> Linus Torvalds 和 VMware 开源负责人 Dirk Hohndel 上周在中国 LinuxCon 上进行了一次“炉边聊天”。
>
>
>
周一,Linus Torvalds 首次来到中国参加[在北京召开的 LinuxCon + ContainerCon + CloudOpen](https://www.lfasiallc.com/linuxcon-containercon-cloudopen-china)。在近 2000 名观众面前,Linus Torvalds 和 VMware 开源负责人 Dirk Hohndel 进行了进行了一次“炉边聊天”,谈及是什么在惊讶和激励着他,以及有志的开源开发者们该如何上手。下面是他们谈话中的一些亮点。
### Linux 开发中有什么令人惊讶的事情?
>
> “我觉得有趣的是我认为已经稳定的代码仍然在不断的得到改进,有些东西我们已经很多年没有碰了,然后有人来改进了它们,或者在我以为根本就不会有人用的东西上提交了 Bug 报告。我们有了新的硬件,开发了新的功能,但是 25 年后,我们仍然有老的、非常基础的东西,并且人们依然在关心和改善着它们。”
>
>
>
### 什么在激励着他
>
> “我真的很喜欢我正在做的事情。我喜欢醒来时有一个在技术上有趣而富有挑战性并且不太紧张的工作,因此我可以长时间的为此工作;或者做一些我感觉我正在做一个真正有影响的事情,做一些不仅仅是对我来说有意义的事情。
>
>
> “我偶尔在工作中休息一下,例如我在 Git 上工作两到三周的时候就开始休息了。但是每次休息的时间比较长我都会感到无聊厌倦。当我出去潜水一周,就想着要回来,我从没有感觉我需要一个更长的假期。”
>
>
>
(LCTT 译注:此处“在 Git 上工作” 是指 Linus 在 Git 版本仓库里面开发 Linux 内核,而非开发 Git 软件——事实上,Linus 在早期开发完 Git 的原型之后,主要的 Git 开发已经有别人接手了,虽然他被称之为 Git 之父。而“潜水”是真的指潜水运动,Linus 喜好玩潜水运动。)
### Linux 的未来领导力
>
> “我们的工作进程不会只是 25 年,我们仍然有非常强大的维护团队。我们常常抱怨我们没有足够的维护者 - 这是真的,我们只有数十名顶级维护者做日常合并的工作,这对于一个开源项目来说是一个非常强大的团队。而且随着这些顶级维护者慢慢变老变胖,我们不断有新人进来。一个新人成长为一个顶级维护者需要几年的时间,因此我不觉得我们应该为 Linux 的下一个 20 年担心。”
>
>
>
### Linux 会被替代吗?
>
> “或许会有一些新的项目将来会并且表明他们比我们做的更好,但是我不担心这个。有很多非常成功的 Linux 的分支(fork),人们不会把它们看作是分支是因为他们很和谐。如果有人想要改变一切并且让内核变得更好,我的感觉是,干吧,证明你自己。我可能觉得那是一个坏主意,但是你可以证明我是错的。”
>
>
>
(LCTT 译注:此处所说的分支,应该是指类似 Android、AGL 等 Linux 分支并没有分裂 Linux 生态,而是彼此补充。)
### 对 Git 的想法
>
> “我对 Git 的广泛传播感到非常的惊讶。显然我非常高兴,它验证了我对分布式开发的看法。然而那时,已经有如此之多的源码版本控制工具,很难再去推出一个新的版本控制系统。我预计它主要限于内核开发 - 因为它是针对我们所做的。”
>
>
> “在刚开始的三到四年里,关于 Git 的抱怨是它如此的与众不同,难以使用。大约五年前,事情发生了改变。有足够多的项目和开发者开始使用 Git ,它变得不再与众不同;人们习惯于使用 Git 。他们开始利用这种开发模式,使用 Git 的安全感,意味着任何东西都不会损坏或者丢失。”
>
>
> “在某些方面,Git 比 Linux 更为人所知。Linux 常常被隐藏起来,例如安卓手机就运行在 Linux 之上,但是你并不知道。但是使用 Git 时,你确切地知道你在使用 Git 。”
>
>
>
### 分支 Linux
>
> “当我坐下来开始写 Git ,一个首要的原则就是你应该能 fork 并且在此基础上做你自己的事情。如果你有友好的 fork(能证明我错了,并且能够改进内核),在这种情况下,人们可以回来说我们实际上改进了内核,这没有什么不好的感觉。我会采纳你的改进并且将其合并进来。这就是为什么你应该鼓励 fork 。你也想让良好的回馈变得很简单。”
>
>
>
### 开源开发者应该如何开始
>
> “于我而言,我总是自我激励,知道自己想要做什么,我从来没有被告知要去做什么。我不确定我的例子是否适合人们效仿。如果你是一个新手程序员,你可以从成千上万的开源项目中找到你所感兴趣的,你可以长期关注这个项目,去了解它的代码,以至于你可以在某个部分的代码上可以成为专家,不需要是整个项目。没有人是整个内核的专家,但是你可以很好地了解其中的一个领域。”
>
>
> “如果你能成为社区的一份子,能提交补丁,那将不仅仅是编程,而是有开源社会方面的意义。你作为一个程序员提升了你自己并且和外界联系了起来。你基本上可以向外展示 - 我做了这些改进,我有能力在我的社区或者工作上走得更远。你不得不花费一定的时间来学习一个项目,但是你将有一个巨大的上升空间 - 不仅仅是从职业方面,而且在你的生活中有一个惊人的项目。”
>
>
>
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/blog/event/lc3-china/20176/6/linus-torvalds-explains-how-linux-still-surprises-and-motivates-him>
作者:[Linux 基金会](https://www.linux.com/users/lfadmin) 译者:[rieonke](https://github.com/rieonke) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,639 | ps_mem:一个用于精确报告 Linux 核心内存用量的简单 Python 脚本 | http://www.2daygeek.com/ps_mem-report-core-memory-usage-accurately-in-linux/ | 2017-06-26T16:56:00 | [
"监控",
"内存",
"ps_mem"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8639-1.html | 
[ps\_mem](https://github.com/pixelb/ps_mem) 是一个可以帮助我们精确获取 Linux 中各个程序核心内存使用情况的简单 python 脚本。虽然在 Linux 上有很多可用于查看内存使用情况的工具,比如 `free`、`vmstat`、`smem`、`top` 等,但这个工具和其它的区别在于其精确显示核心内存使用情况。
它会分别计算一个程序私有内存总量和共享内存总量,并以更准确的方式给出了总的内存使用量。很明显的,它将帮助大家知道系统中哪个程序正在占用更多的内存。
你可以通过包管理器、`pip` 、或直接运行 `ps_mem.py` 脚本等多种方式来安装 `ps_mem` 工具。需要注意的是:需要有 root 权限。
另外,推荐阅读以下内存工具:
* [free – 一个在 Linux 上查看内存用量统计(可用和已用)的标准工具](http://www.2daygeek.com/free-command-to-check-memory-usage-statistics-in-linux/)
* [smem – Linux 内存报告/统计工具](http://www.2daygeek.com/smem-linux-memory-usage-statistics-reporting-tool/)
* [vmstat – 一个好用的用于虚拟内存统计的标准工具](http://www.2daygeek.com/linux-vmstat-command-examples-tool-report-virtual-memory-statistics/)
### 通过包管理器安装 ps\_mem
基于 RHEL 的系统默认仓库就包含 ps\_mem 工具,所以我们可以简单地通过包管理器进行安装。
对于 RHEL/CentOS ,使用 [yum 包管理器](http://www.2daygeek.com/yum-command-examples/) 安装 `ps_mem` 包:
```
$ sudo yum install ps_mem
```
对于Fedora ,使用 [dnf 包管理器](http://www.2daygeek.com/dnf-command-examples/) 安装 ps\_mem 包:
```
$ sudo dnf install ps_mem
```
对于 Arch Linux ,使用 [pacman 包管理器](http://www.2daygeek.com/pacman-command-examples/) 安装 ps\_mem 包:
```
$ sudo pacman -S ps_mem
```
### 通过 pip 安装 ps\_mem
`pip` 是在 Linux 上推荐使用的一种安装 Python 包的工具。可以使用 `pip` 命令而不是包管理器去获取最新的版本。使用 `pip` 包前,请确保你的系统上已安装过 `pip` 包。否则,先使用发行版本的包管理器安装 `python-pip` 包。
对于基于 Debian 的系统:
```
$ sudo apt-get install python-pip
```
对于基于 RHEL/CentOS 的系统:
```
$ sudo yum install python-pip
```
对于 Fedora
```
$ sudo dnf install python-pip
```
对于 openSUSE
```
$ sudo zypper install python-pip
```
对于基于 Arch Linux 的系统:
```
$ sudo pacman -S python-pip
```
最后,在 Linux 上运行 `pip` 工具安装 `ps_mem` :
```
$ sudo pip install ps_mem
```
### 直接运行 ps\_mem.py 脚本
我们也可以从开发者 github 页面下载文件,并直接运行 `ps_mem.py` 脚本。
```
$ git clone https://github.com/pixelb/ps_mem.git && cd ps_mem
$ sudo python ps_mem.py
```
### ps\_mem 使用方法
不带任何参数直接运行 `ps_mem` 以精确获取每个程序的的核心内存使用情况。
```
$ sudo ps_mem
Private + Shared = RAM used Program
1.6 MiB + 438.5 KiB = 2.1 MiB packagekitd
1.7 MiB + 498.0 KiB = 2.1 MiB indicator-application-service
912.0 KiB + 1.3 MiB = 2.2 MiB window-stack-bridge
2.0 MiB + 350.5 KiB = 2.3 MiB gnome-keyring-daemon
1.8 MiB + 575.0 KiB = 2.3 MiB whoopsie
2.4 MiB + 304.5 KiB = 2.7 MiB systemd-journald
2.7 MiB + 157.5 KiB = 2.8 MiB ibus-engine-simple
2.7 MiB + 182.0 KiB = 2.9 MiB ibus-dconf
2.7 MiB + 332.5 KiB = 3.0 MiB NetworkManager
3.1 MiB + 169.5 KiB = 3.2 MiB polkitd
1.9 MiB + 1.7 MiB = 3.6 MiB systemd (2)
3.4 MiB + 172.5 KiB = 3.6 MiB deja-dup-monitor
2.9 MiB + 685.0 KiB = 3.6 MiB zeitgeist-datahub
2.9 MiB + 848.0 KiB = 3.7 MiB python2.7
. . . . . .
222.1 MiB + 9.4 MiB = 231.5 MiB compiz
286.2 MiB + 11.8 MiB = 298.0 MiB firefox
---------------------------------
1.3 GiB
=================================
```
输出中打印出全路径:
```
$ sudo ps_mem -s
Private + Shared = RAM used Program
3.2 MiB + 951.0 KiB = 4.1 MiB /usr/lib/evolution/evolution-addressbook-factory
3.7 MiB + 826.5 KiB = 4.5 MiB /usr/lib/policykit-1-gnome/polkit-gnome-authentication-agent-1
3.7 MiB + 853.0 KiB = 4.6 MiB /usr/lib/unity-settings-daemon/unity-fallback-mount-helper
. . . . . .
131.9 MiB + 168.0 KiB = 132.1 MiB /usr/sbin/mysqld
222.1 MiB + 9.4 MiB = 231.5 MiB /usr/bin/compiz
286.2 MiB + 11.8 MiB = 298.1 MiB /usr/lib/firefox/firefox
---------------------------------
1.3 GiB
=================================
```
只显示特定的 PID 列表的内存使用情况:
```
$ sudo ps_mem -p 2886,4386
Private + Shared = RAM used Program
13.5 MiB + 2.9 MiB = 16.4 MiB gnome-terminal-server
286.2 MiB + 11.8 MiB = 298.0 MiB firefox
---------------------------------
314.4 MiB
=================================
```
每 N 秒打印进程内存。以下命令每 2 秒报告一次内存使用情况:
```
$ sudo ps_mem w 2
```
只显示内存总量:
```
$ sudo ps_mem -t
1329884160
```
---
via: <http://www.2daygeek.com/ps_mem-report-core-memory-usage-accurately-in-linux/>
作者:[2DAYGEEK](http://www.2daygeek.com/author/2daygeek/) 译者:[xllc](https://github.com/xllc) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.