id
int64 2.05k
16.6k
| title
stringlengths 5
75
| fromurl
stringlengths 19
185
| date
timestamp[s] | tags
sequencelengths 0
11
| permalink
stringlengths 20
37
| content
stringlengths 342
82.2k
| fromurl_status
int64 200
526
⌀ | status_msg
stringclasses 339
values | from_content
stringlengths 0
229k
⌀ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
8,390 | 5 个开源 RSS 订阅阅读器 | https://opensource.com/article/17/3/rss-feed-readers | 2017-04-10T17:18:14 | [
"RSS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8390-1.html | 
### 你平时使用 RSS 阅读器么?
四年前当 Google Reader 宣布停止的时候,许多“技术专家”声称 RSS 订阅将会结束。
对于某些人而言,社交媒体和其他聚合工具满足了 RSS、Atom 以及其它格式的阅读器的需求。但是老技术绝对不会因为新技术而死,特别是如果新技术不能完全覆盖旧技术的所有使用情况时。技术的目标受众可能会有所改变,人们使用这个技术的工具也可能会改变。
但是,RSS 并不比像 email、JavaScript、SQL 数据库、命令行或者十几年前告诉我的其它时日无多的技术消失的更快。(黑胶专辑的销售额去年刚刚达到了其 [25 年的顶峰](https://www.theguardian.com/music/2017/jan/03/record-sales-vinyl-hits-25-year-high-and-outstrips-streaming),这不是个奇迹么?)只要看看在线 Feed 阅读器网站 Feedly 的成功,就能了解 RSS 阅读器仍然有市场。
事实是,RSS 和相关的 Feed 格式比任何广泛使用的尝试替换它的东西还要多才多艺。作为一名阅读消费者,对于我来说没有比它更简单的方法了,我可以阅读大量的出版信息,并且是用我选择的客户端格式化的,我可以确认看到发布的每一条内容,同时不会显示我已经阅读过的文章。而作为发布者,这是一种比我使用过的大多数发布软件都简单的格式,开箱即用,它可以让我的信息递交给更多的人,并且可以很容易地分发多种不同类型的文档格式。
所以 RSS 没有死。RSS 长存!我们最后一次是在 2013 年回顾了[开源 RSS 阅读器](https://opensource.com/life/13/6/open-source-rss)选择,现在是更新的时候了。这里是我关于 2017 年开源 RSS 订阅阅读器的一些最佳选择,每个在使用上稍微不同。
### Miniflux

[Miniflux](https://miniflux.net/) 是一个极度简约的基于 Web 的 RSS 阅读器,但不要将其特意的轻设计与开发人员的懒惰混淆。它目的是构建一个简单而有效的设计。Miniflux 的思想似乎是将程序弱化,以便让读者可以专注于内容,在大量臃肿的 web 程序中我们会特别欣赏这一点。
但轻便并不意味着缺乏功能。其响应式设计在任何设备上看起来都很好,并可以使用主题、API 接口、多语言、固定书签等等。
Miniflux 的 [源代码](https://github.com/miniflux/miniflux)以 [GPLv3 Affero](https://github.com/miniflux/miniflux/blob/master/LICENSE) 许可证在 GitHub 中发布。如果你不想自行托管,则可以支付每年 15 美元的托管计划。
### RSSOwl

[RSSOwl](http://www.rssowl.org/) 是一个跨平台的桌面 Feed 阅读器。它用 Java 编写,在风格和感觉上它像很多流行的桌面邮件客户端。它具有强大的过滤和搜索功能、可定制的通知,以及用于排序 Feed 的标签。 如果你习惯使用 Thunderbird 或其他桌面阅读器进行电子邮件发送,那么在 RSSOwl 中你会感到宾至如归。
可以在 GitHub 中找到 [Eclipse Public 许可证](https://github.com/rssowl/RSSOwl/blob/master/LICENSE)下发布的 [RSSOwl](https://github.com/rssowl/RSSOwl) 的源代码。
### Tickr

[Tickr](https://www.open-tickr.net/) 在这个系列中有点不同。它是一个 Linux 桌面客户端,但它不是传统的浏览-阅读形式。相反,它会将你的 Feed 标题如滚动新闻那样在桌面横栏上滚动显示。对于想要从各种来源获得最新消息的新闻界来说,这是一个不错的选择。点击标题将在你选择的浏览器中打开它。它不像这个列表中的其他程序那样是专门的阅读客户端,但是如果比起阅读每篇文章,你对阅读标题更感兴趣,这是一个很好的选择。
Tickr 的源代码和二进制文件以 GPL 许可证的形式在这个[网站](https://www.open-tickr.net/download.php)上可以找到。
### Tiny Tiny RSS

如果缺少了 [Tiny Tiny RSS](https://tt-rss.org/gitlab/fox/tt-rss/wikis/home),那么很难称之为这是一个现代化的 RSS 阅读器列表。它是最受欢迎的自主托管的基于 Web 的阅读器,它功能丰富:支持OPML 导入和导出、键盘快捷键、共享功能、主题界面、插件支持、过滤功能等等。
Tiny Tiny RSS 还有官方的 [Android客户端](https://tt-rss.org/gitlab/fox/tt-rss-android),让你可以随时随地阅读。
Tiny Tiny RSS 的 [Web](https://tt-rss.org/gitlab/fox/tt-rss/tree/master) 版本和 [Android](https://tt-rss.org/gitlab/fox/tt-rss-android/tree/master) 源代码以 [GPLv3 许可](https://tt-rss.org/gitlab/fox/tt-rss-android/blob/master/COPYING) 在 GitLab 上发布。
### Winds

[Winds](https://winds.getstream.io/) 是一个建立在 React 之上的看起来很现代化的自托管的 web 订阅阅读器。它利用称为 Stream 的机器学习个性化 API,帮助你根据当前的兴趣找到可能感兴趣的更多内容。这有一个在线显示版本,因此你可以在下载之前先[尝试](https://winds.getstream.io/app/getting-started)。这是一个只有几个月的新项目,也许评估它是否能取代我日常的 Feed 阅读器还太早,但这当然是一个我感兴趣关注的项目。
Winds 的[源代码](https://github.com/GetStream/Winds) 以 [MIT](https://github.com/GetStream/Winds/blob/master/LICENSE.md) 许可证在 GitHub 上发布。
---
这些当然不是仅有的选择。RSS 是一个相对易于解析、文档格式良好的格式,因此有许许多多因为不同的需求而建立的各种 Feed 阅读器。这有一个很长的自托管的开源 Feed 阅读器[列表](https://github.com/Kickball/awesome-selfhosted#feed-readers),除了我们列出的之外你还可能会考虑使用它们。我们希望你能在下面的评论栏与我们分享你最喜欢的 RSS 阅读器。
你使用 RSS 阅读器么?你知道 Linux 中国一直就支持 RSS 阅读么?不知道的朋友,下面是我们的 RSS 地址,欢迎体验:
* 全文 RSS : <https://linux.cn/rss.xml>
* 摘要 RSS : <https://linux.cn/rss-digest.xml>
* 分类栏目 RSS
+ 技术学习:<https://linux.cn/rss-tech.xml>
+ 新闻快讯:<https://linux.cn/rss-news.xml>
+ 观点热议:<https://linux.cn/rss-talk.xml>
+ 软件分享:<https://linux.cn/rss-share.xml>
什么?你直接点击链接在浏览器打开了,感觉不会用?——虽然我们专门为 RSS 在浏览器中打开做了美化,但是你该用 RSS 阅读器来读啊,对,就是这篇文章介绍的这些,要不试试?
(题图来自:[Rob McDonald](https://www.flickr.com/photos/evokeartdesign/6002000807) on Flickr,由 Opensource.com 修改. [CC BY-SA 2.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/).)
---
作者简介:
Jason Baker - Jason 热衷于使用技术使世界更加开放,从软件开发到阳光政府行动。Linux 桌面爱好者、地图/地理空间爱好者、树莓派工匠、数据分析和可视化极客、偶尔的码农、云本土主义者。在 Twitter 上关注他 @jehb。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/3/rss-feed-readers>
作者:[Jason Baker](https://opensource.com/users/jason-baker) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When Google Reader was discontinued four years ago, many "technology experts" called it the end of RSS feeds.
And it's true that for some people, social media and other aggregation tools are filling a need that feed readers for RSS, Atom, and other syndication formats once served. But old technologies never really die just because new technologies come along, particularly if the new technology does not perfectly replicate all of the use cases of the old one. The target audience for a technology might change a bit, and the tools people use to consume the technology might change, too.
But RSS is no more gone than email, JavaScript, SQL databases, the command line, or any number of other technologies that various people told me more than a decade ago had numbered days. (Is it any wonder that vinyl album sales just hit a [25-year peak](https://www.theguardian.com/music/2017/jan/03/record-sales-vinyl-hits-25-year-high-and-outstrips-streaming) last year?) One only has to look at the success of online feed reader site Feedly to understand that there's still definitely a market for RSS readers.
The truth is, RSS and related feed formats are just more versatile than anything in wide usage that has attempted to replace it. There is no other easy was for me as a consumer to read a wide variety of publications, formatted in a client of my choosing, where I am virtually guaranteed to see every item that is published, while simultaneously not being shown a bunch of articles I have already read. And as a publisher, it's a simple format that most any publishing software I already use will support out of the box, letting me reach more people and easily distribute many types of documents.
So no, RSS is not dead. Long live RSS! We last looked at [open source RSS reader](https://opensource.com/life/13/6/open-source-rss) options in 2013, and it's time for an update. Here are some of my top choices for open source RSS feed readers in 2017, each a little different in its approach.
## Miniflux
[Miniflux](https://miniflux.net/) is an absolutely minimalist web-based RSS reader, but don't confuse its intentionally light approach with laziness on the part of the developers; it is purposefully built to be a simple and efficient design. The philosophy of Miniflux seems to be to keep the application out of the way so that the reader can focus on the content, something many of us can appreciate in a world of bloated web applications.
But lightweight doesn't mean void of features; its responsive design looks good across any device, and allows for theming, an API interface, multiple languages, bookmark pinning, and more.
Miniflux's [source code](https://github.com/miniflux/miniflux) can be found on GitHub under the [GPLv3 Affero](https://github.com/miniflux/miniflux/blob/master/LICENSE) license. If you don't want to set up your own self-hosted version, a paid hosting plan is available for $15/year.
## RSSOwl
[RSSOwl](http://www.rssowl.org/) is a cross-platform desktop feed reader. Written in Java, it is reminiscent of many popular desktop email clients in style and feel. It features powerful filtering and search capabilities, customizable notifications, and labels and bins for sorting your feeds. If you're used to using Thunderbird or other desktop readers for email, you'll feel right at home in RSSOwl.
You can find the source code for [RSSOwl](https://github.com/rssowl/RSSOwl) on GitHub under the [Eclipse Public License](https://github.com/rssowl/RSSOwl/blob/master/LICENSE).
## Tickr
[Tickr](https://www.open-tickr.net/) is a slightly different entry in this mix. It's a Linux desktop client, but it's not your traditional browse-and-read format. Instead, it slides your feed's headlines across a bar on your desktop like a news ticker; it's a great choice for news junkies who want to get the latest from a variety of sources. Clicking on a headline will open it in your browser of choice. It's not a dedicated reading client like the rest of the applications on this list, but if you're more interested in skimming headlines than reading every article, it's a good pick.
Tickr's source code and binaries can be found on the project's [website](https://www.open-tickr.net/download.php) under a GPL license.
## Tiny Tiny RSS
It would be difficult to build a list of modern RSS readers without including [Tiny Tiny RSS](https://tt-rss.org/). It's among the most popular self-hosted web-based readers, and it's chocked full of features: OPML import and export, keyboard shortcuts, sharing features, a themeable interface, an infrastructure for plug-ins, filtering capabilities, and lots more.
Tiny Tiny RSS also hosts an official Android client, for those hoping to read on the go.
Both the [web](https://git.tt-rss.org/fox/tt-rss) and [Android](https://git.tt-rss.org/fox/tt-rss-android) source code for Tiny Tiny RSS can be found on GitLab under a [GPLv3 license](https://tt-rss.org/gitlab/fox/tt-rss-android/blob/master/COPYING).
## Winds
[Winds](https://winds.getstream.io/) is a modern looking self-hosted web feed reader, built on React. It makes use of a hosted machine learning personalization API called Stream, with the intent of helping you find more content that might be of interest to you based on your current interests. An online demo is available so you can [try it out](https://winds.getstream.io/app/getting-started) before you download. It's a new project, just a few months old, and so perhaps too soon to evaluate whether it's up to replace my daily feed reader yet, but it's certainly a project I'm watching with interest.
You can find the [source code](https://github.com/GetStream/Winds) for Winds on GitHub under an [MIT](https://github.com/GetStream/Winds/blob/master/LICENSE.md) license.
These are most definitely not the only options out there. RSS is a relatively easy-to-parse, well-documented format, and so there are many, many different feed readers out there built to suit just about every taste. Here's a [big list](https://github.com/Kickball/awesome-selfhosted#feed-readers) of self-hosted open source feed readers you might consider in addition to the ones we listed. We hope you'll share with us what your favorite RSS reader is in the comments below.
## 11 Comments |
8,391 | 如何在 CentOS、RHEL 和 Fedora 上安装 DHCP 服务 | http://www.tecmint.com/install-dhcp-server-in-centos-rhel-fedora/ | 2017-04-10T21:02:16 | [
"DHCP"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8391-1.html | DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)是一个网络协议,它使得服务器能从预定义的 IP 池中为网络中的客户端节点自动分配 IP 地址并提供其它相关的网络配置参数。
这意味着每次客户端节点启动(连接到网络)的时候,它都会获得一个和从不改变的“静态” IP 地址相反的“动态” IP 地址。DHCP 服务器给 DHCP 客户端分配 IP 地址称为“租约”,租约时间随客户端需要的连接时间或 DHCP 的配置而异。
在这篇指南中,我们会介绍如何在 CentOS/RHEL 和 Fedora 发行版中安装和配置 DHCP 服务。

### 设置测试环境
本次安装中我们使用如下的测试环境:
* DHCP 服务器 - CentOS 7
* DHCP 客户端 - Fedora 25 和 Ubuntu 16.04
### DHCP 如何工作?
在进入下一步之前,让我们首先了解一下 DHCP 的工作流程:
* 当已连接到网络的客户端计算机(配置为使用 DHCP)启动时,它会发送一个 `DHCPDISCOVER` 消息到 DHCP 服务器。
* 当 DHCP 服务器接收到 `DHCPDISCOVER` 请求消息时,它会回复一个 `DHCPOFFER` 消息。
* 客户端收到 `DHCPOFFER` 消息后,它再发送给服务器一个 `DHCPREQUEST` 消息,表示客户端已准备好获取 `DHCPOFFER` 消息中提供的网络配置。
* 最后,DHCP 服务器收到客户端的 `DHCPREQUEST` 消息,并回复 `DHCPACK` 消息,表示允许客户端使用分配给它的 IP 地址。
### 第一步:在 CentOS 上安装 DHCP 服务
1、安装 DHCP 服务非常简单,只需要运行下面的命令即可。
```
$ yum -y install dhcp
```
重要:假如系统中有多个网卡,但你想只在其中一个网卡上启用 DHCP 服务,可以按照下面的步骤在该网卡上启用 DHCP 服务。
2、 打开文件 `/etc/sysconfig/dhcpd`,将指定网卡的名称添加到 `DHCPDARGS` 列表,假如网卡名称为 `eth0`,则添加:
```
DHCPDARGS=eth0
```
保存文件并退出 。
### 第二步:在 CentOS 上配置 DHCP 服务
3、 对于初学者来说,配置 DHCP 服务的第一步是创建 `dhcpd.conf` 配置文件,DHCP 主要配置文件一般是 `/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf`(默认情况下该文件为空),该文件保存了发送给客户端的所有网络信息。
但是,有一个样例配置文件 `/usr/share/doc/dhcp*/dhcpd.conf.sample`,这是配置 DHCP 服务的良好开始。
DHCP 配置文件中定义了两种类型的语句:
* 参数 - 说明如何执行任务、是否执行任务、或者给 DHCP 客户端发送什么网络配置选项。
* 声明 - 指定网络拓扑、定义客户端、提供客户端地址、或将一组参数应用于一组声明。
因此,首先复制示例配置文件为主配置文件:
```
$ cp /usr/share/doc/dhcp-4.2.5/dhcpd.conf.example /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
```
4、 然后,打开主配置文件并定义你的 DHCP 服务选项:
```
$ vi /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
```
首先在文件开头设置以下应用于全部子网的全局参数(注意要使用你实际场景中的值):
```
option domain-name "tecmint.lan";
option domain-name-servers ns1.tecmint.lan, ns2.tecmint.lan;
default-lease-time 3600;
max-lease-time 7200;
authoritative;
```
5、 然后,定义一个子网;在这个事例中,我们会为 `192.168.56.0/24` 局域网配置 DHCP(注意使用你实际场景中的值):
```
subnet 192.168.56.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers 192.168.56.1;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option domain-search "tecmint.lan";
option domain-name-servers 192.168.56.1;
range 192.168.56.10 192.168.56.100;
range 192.168.56.120 192.168.56.200;
}
```
### 第三步:为 DHCP 客户端分配静态 IP
只需要在 `/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf` 文件中定义下面的部分,其中你必须显式指定它的 MAC 地址和打算分配的 IP,你就可以为网络中指定的客户端计算机分配一个静态 IP 地址:
```
host ubuntu-node {
hardware ethernet 00:f0:m4:6y:89:0g;
fixed-address 192.168.56.105;
}
host fedora-node {
hardware ethernet 00:4g:8h:13:8h:3a;
fixed-address 192.168.56.110;
}
```
保存文件并关闭。
注意:你可以使用下面的命令找到 Linux 的 MAC 地址。
```
$ ifconfig -a eth0 | grep HWaddr
```
6、 现在,使用下面的命令启动 DHCP 服务,并使在下次系统启动时自动启动:
```
---------- On CentOS/RHEL 7 ----------
$ systemctl start dhcpd
$ systemctl enable dhcpd
---------- On CentOS/RHEL 6 ----------
$ service dhcpd start
$ chkconfig dhcpd on
```
7、 另外,别忘了使用下面的命令允许 DHCP 服务通过防火墙(DHCPD 守护进程通过 UDP 监听67号端口):
```
---------- On CentOS/RHEL 7 ----------
$ firewall-cmd --add-service=dhcp --permanent
$ firewall-cmd --reload
---------- On CentOS/RHEL 6 ----------
$ iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW --dport 67 -j ACCEPT
$ service iptables save
```
### 第四步:配置 DHCP 客户端
8、 现在,你可以为网络中的客户端配置自动从 DHCP 服务器中获取 IP 地址。登录到客户端机器并按照下面的方式修改以太网接口的配置文件(注意网卡的名称和编号):
```
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
```
添加下面的选项:
```
DEVICE=eth0
BOOTPROTO=dhcp
TYPE=Ethernet
ONBOOT=yes
```
保存文件并退出。
9、 你也可以在桌面服务器中按照下面的截图(Ubuntu 16.04桌面版)通过 GUI 设置 `Method` 为 `Automatic (DHCP)`。

*在客户端网络中设置 DHCP*
10、 按照下面的命令重启网络服务(你也可以通过重启系统):
```
---------- On CentOS/RHEL 7 ----------
$ systemctl restart network
---------- On CentOS/RHEL 6 ----------
$ service network restart
```
到了这里,如果所有设置都是正确的,你的客户端就应该能自动从 DHCP 服务器中获取 IP 地址。
你也可以阅读:
1. [如何在 Debian Linux 中安装和配置 Multihomed ISC DHCP 服务](http://www.tecmint.com/install-and-configure-multihomed-isc-dhcp-server-on-debian-linux/)
2. [配置网络的 10 个有用的 “IP” 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/ip-command-examples/)
在这篇文章中我们为你展示了如何在 RHEL/CentOS 中安装 DHCP 服务。在下面的评论框中给我们反馈吧。在接下来的文章中,我们还会为你展示如何在 Debian/Ubuntu 中安装 DHCP 服务。和 TecMint 保持联系。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 的爱好者,即将推出的 Linux SysAdmin 网络开发人员,目前也是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢和电脑一起工作,并且坚信共享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/install-dhcp-server-in-centos-rhel-fedora/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,392 | bmon:Linux 下一个强大的网络带宽监视和调试工具 | http://www.tecmint.com/bmon-network-bandwidth-monitoring-debugging-linux/ | 2017-04-11T08:50:00 | [
"网络",
"监控",
"bmon"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8392-1.html | bmon 是类 Unix 系统中一个基于文本,简单但非常强大的 [网络监视和调试工具](/article-5435-1-rel.html),它能抓取网络相关统计信息并把它们以用户友好的格式展现出来。它是一个可靠高效的带宽监视和网速估测工具。
它能使用各种输入模块读取输入,并以各种输出模式显示输出,包括交互式文本用户界面和用于脚本编写的可编程文本输出。

**推荐阅读:** [一大波你可能不知道的 Linux 网络工具](/article-5435-1.html)
### 在 Linux 上安装 bmon 带宽监视工具
几乎所有 Linux 发行版的默认仓库中都有 bmon 软件包,可以从默认包管理器中轻松安装,但可用的版本可能比较旧。
```
$ sudo yum install bmon [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora]
$ sudo dnf install bmon [On Fedora 22+]
$ sudo apt-get install bmon [On Debian/Ubuntu/Mint]
```
另外,你也可以从 <https://pkgs.org/download/bmon> 获取对应你 Linux 发行版的 `.rpm` 和 `.deb` 软件包。
如果你想要最新版本(例如版本 4.0)的 bmon,你需要通过下面的命令从源码构建。
**在 CentOS、RHEL 和 Fedora 中**
```
$ git clone https://github.com/tgraf/bmon.git
$ cd bmon
$ sudo yum install make libconfuse-devel libnl3-devel libnl-route3-devel ncurses-devel
$ sudo ./autogen.sh
$ sudo./configure
$ sudo make
$ sudo make install
```
**在 Debian、Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 中**
```
$ git clone https://github.com/tgraf/bmon.git
$ cd bmon
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential make libconfuse-dev libnl-3-dev libnl-route-3-dev libncurses-dev pkg-config dh-autoreconf
$ sudo ./autogen.sh
$ sudo ./configure
$ sudo make
$ sudo make install
```
### 如何在 Linux 中使用 bmon 带宽监视工具
通过以下命令运行它(初学者说明:RX 表示每秒接收数据,TX 表示每秒发送数据):
```
$ bmon
```

按 `d` 键可以查看更详细的带宽使用情况的图形化统计信息,参考下面的截图。

按 `Shift + ?` 可以查看快速指南。再次按 `Shift + ?` 可以退出(指南)界面。

*bmon – 快速指南*
通过 `Up` 和 `Down` 箭头键可以查看特定网卡的统计信息。但是,要监视一个特定的网卡,你也可以像下面这样作为命令行参数指定。
**推荐阅读:** [监控 Linux 性能的 13 个工具](http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-tools/)
选项 `-p` 指定了要显示的网卡,在下面的例子中,我们会监视网卡 `enp1s0`:
```
$ bmon -p enp1s0
```

*bmon – 监控以太网带宽*
要查看每秒位数而不是每秒字节数,可以像下面这样使用 `-b` 选项:
```
$ bmon -bp enp1s0
```
我们也可以像下面这样按秒指定刷新间隔时间:
```
$ bmon -r 5 -p enp1s0
```
### 如何使用 bmon 的输入模块
bmon 有很多能提供网卡统计数据的输入模块,其中包括:
1. netlink - 使用 Netlink 协议从内核中收集网卡和流量控制统计信息。这是默认的输入模块。
2. proc - 从 `/proc/net/dev` 文件读取网卡统计信息。它被认为是传统界面,且提供了向后兼容性。它是 Netlink 接口不可用时的备用模块。
3. dummy - 这是用于调试和测试的可编程输入模块。
4. null - 停用数据收集。
要查看关于某个模块的其余信息,可以像下面这样使用 `help` 选项调用它:
```
$ bmon -i netlink:help
```
下面的命令将启用 proc 输入模块运行 bmon:
```
$ bmon -i proc -p enp1s0
```
### 如何使用 bmon 输出模块
bmon 也使用输出模块显示或者导出上面输入模块收集的统计数据,输出模块包括:
1. curses - 这是一个交互式的文本用户界面,它提供实时的网上估计以及每个属性的图形化表示。这是默认的输出模块。
2. ascii - 这是用于用户查看的简单可编程文本输出。它能显示网卡列表、详细计数以及图形到控制台。当 curses 库不可用时这是默认的备选输出模块。
3. format - 这是完全脚本化的输出模式,供其它程序使用 - 意味着我们可以在后面的脚本和程序中使用它的输出值进行分析。
4. null - 停用输出。
像下面这样通过 `help` 选项获取更多的模块信息。
```
$ bmon -o curses:help
```
下面的命令会用 ascii 输出模式运行 bmon:
```
$ bmon -p enp1s0 -o ascii
```

*bmon – Ascii 输出模式*
我们也可以用 format 输出模式,然后在脚本或者其它程序中使用获取的值:
```
$ bmon -p enp1s0 -o format
```

*bmon – Format 输出模式*
想要其它的使用信息、选项和事例,可以阅读 bmon 的 man 手册:
```
$ man bmon
```
访问 bmon 的 Github 仓库:<https://github.com/tgraf/bmon>。
就是这些,在不同场景下尝试 bmon 的多个功能吧,别忘了在下面的评论部分和我们分享你的想法。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者、Linux 系统管理员、网络开发人员,现在也是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢和电脑一起工作,坚信共享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/bmon-network-bandwidth-monitoring-debugging-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,393 | Linux 命令行工具使用小贴士及技巧(四) | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/command-line-aliases-in-linux/ | 2017-04-11T09:13:44 | [
"命令行",
"导航"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8393-1.html | 到目前为止,在该系列指南中,我们已经讨论了 [cd -](/article-8335-1.html) 和 [pushd/popd 命令](/article-8371-1.html)的基本使用方法和相关细节,以及 [CDPATH 环境变量](/article-8387-1.html)。在这第四期、也是最后一期文章中,我们会讨论别名的概念以及你可以如何使用它们使你的命令行导航更加轻松和平稳。

一如往常,在进入该指南的核心之前,值得指出本文中的所有命令以及展示的例子都在 Ubuntu 14.04LTS 中进行了测试。我们使用的命令行 shell 是 bash(4.3.11 版本)。
### Linux 中的命令行别名
按照外行人的定义,别名可以被认为是一个复杂命令或者一组命令(包括它们的参数和选项)的简称或缩写。所以基本上,使用别名,你可以为那些不那么容易书写/记忆的命令创建易于记忆的名称。
例如,下面的命令为 `cd ~` 命令创建别名 `home`:
```
alias home="cd ~"
```
这意味着现在在你的系统中无论何地,无论何时你想要回到你的主目录时,你可以很快地输入 `home` 然后按回车键实现。
关于 `alias` 命令,man 手册是这么描述的:
>
> alias 工具可以创建或者重定义别名定义,或者把现有别名定义输出到标准输出。别名定义提供了输入一个命令时应该被替换的字符串值
>
>
> 一个别名定义会影响当前 shell 的执行环境以及当前 shell 的所有子 shell 的执行环境。按照 IEEE Std 1003.1-2001 规定,别名定义不应该影响当前 shell 的父进程以及任何 shell 调用的程序环境。
>
>
>
那么,别名到底如何帮助命令行导航呢?这是一个简单的例子:
假设你正在 `/home/himanshu/projects/howtoforge` 目录工作,它包括很多子目录以及子子目录。例如下面就是一个完整的目录分支:
```
/home/himanshu/projects/howtoforge/command-line/navigation/tips-tricks/part4/final
```
现在想象你在 `final` 目录,然后你想回到 `tips-tricks` 目录,然后再从那里,回到 `howtoforge` 目录。你会怎么做呢?
是的,一般情况下,你会运行下面的一组命令:
```
cd ../..
cd ../../..
```
虽然这种方法并没有错误,但它绝对不方便,尤其是当你在一个很长的路径中想往回走例如说 5 个目录时。那么,有什么解决办法吗?答案就是:别名。
你可以做的是,为每个 `cd ..` 命令创建容易记忆(和书写)的别名。例如:
```
alias bk1="cd .."
alias bk2="cd ../.."
alias bk3="cd ../../.."
alias bk4="cd ../../../.."
alias bk5="cd ../../../../.."
```
现在无论你什么时候想从当前工作目录往回走,例如说 5 个目录,你只需要运行下面的命令:
```
bk5
```
现在这不是很简单吗?
### 相关细节
尽管当前我们在 shell 中用于定义别名的技术(通过使用 alias 命令)实现了效果,别名只存在于当前终端会话。很有可能你会希望你定义的别名能保存下来,使得此后你可以在任何新启动的命令行窗口/标签页中使用它们。
为此,你需要在 `~/.bash_aliases` 文件中定义你的别名,你的 `~/.bashrc` 文件默认会加载该文件(如果你使用更早版本的 Ubuntu,我没有验证过是否有效)。
下面是我的 `.bashrc` 文件中关于 `.bash_aliases` 文件的部分:
```
# Alias definitions.
# You may want to put all your additions into a separate file like
# ~/.bash_aliases, instead of adding them here directly.
# See /usr/share/doc/bash-doc/examples in the bash-doc package.
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then
. ~/.bash_aliases
fi
```
一旦你把别名定义添加到你的 `.bash_aliases` 文件,该别名在任何新终端中都可用。但是,在任何其它你定义别名时已经启动的终端中,你还不能使用它们 - 解决办法是在这些终端中重新加载 `.bashrc`。下面就是你需要执行的具体命令:
```
source ~/.bashrc
```
如果你觉得这要做的也太多了(是的,我期待你有更懒惰的办法),那么这里有一个快捷方式来做到这一切:
```
"alias [the-alias]" >> ~/.bash_aliases && source ~/.bash_aliases
```
毫无疑问,你需要用实际的命令替换 `[the-alias]`。例如:
```
"alias bk5='cd ../../../../..'" >> ~/.bash_aliases && source ~/.bash_aliases
```
接下来,假设你已经创建了一些别名,并时不时使用它们有一段时间了。突然有一天,你发现它们其中的一个并不像期望的那样。因此你觉得需要查看被赋予该别名的真正命令。你会怎么做呢?
当然,你可以打开你的 `.bash_aliases` 文件在那里看看,但这种方式可能有点费时,尤其是当文件中包括很多别名的时候。因此,如果你正在查找一种更简单的方式,这就有一个:你需要做的只是运行 `alias` 命令并把别名名称作为参数。
这里有个例子:
```
$ alias bk6
alias bk6='cd ../../../../../..'
```
你可以看到,上面提到的命令显示了被赋值给别名 `bk6` 的实际命令。这里还有另一种办法:使用 `type` 命令。下面是一个例子:
```
$ type bk6
bk6 is aliased to `cd ../../../../../..'
```
`type` 命令产生了一个易于人类理解的输出。
另一个值得分享的是你可以将别名用于常见的输入错误。例如:
```
alias mroe='more'
```
*最后,还值得注意的是并非每个人都喜欢使用别名。他们中的大部分人认为一旦你习惯了你为了简便而定义的别名,当你在其它相同而不存在别名(而且不允许你创建)的系统中工作时就会变得非常困难。更多(也是更准确的)为什么一些专家不推荐使用别名的原因,你到[这里](http://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/66934/why-is-aliasing-over-standard-commands-not-recommended)查看。*
### 总结
就像我们之前文章讨论过的 `CDPATH` 环境变量,别名也是一把应该谨慎使用的双刃剑。尽管如此也别太丧气,因为每个东西都有它自己的好处和劣势。遇到类似别名的概念时,更多的练习和完备的知识才是重点。
那么这就是该系列指南的最后章节。希望你喜欢它并能从中学到新的东西/概念。如果你有任何疑问或者问题,请在下面的评论框中和我们(以及其他人)分享。
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/command-line-aliases-in-linux/>
作者:[Ansh](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/command-line-aliases-in-linux/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # Command line aliases in the Linux Shell
So far, in [this tutorial series](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/linux-command-line-navigation-tips-and-tricks-part-1/), we have discussed the basic usage as well as related details of the [cd](https://www.howtoforge.com/linux-cd-command/) - and **pushd**/**popd** commands, as well as the **CDPATH** environment variable. In this fourth and final installment, we will discuss the concept of aliases as well as how you can use them to make your command line navigation easier and smoother.
## Command line aliases in Linux
In layman's terms, aliases can be thought of as short names or abbreviations to a complex command or a group of commands, including their arguments or options. So basically, with aliases, you create easy-to-remember names for not-so-easy-to-type/remember commands.
For example, the following command creates an alias 'home' for the 'cd ~' command:
alias home="cd ~"
This means that now you can quickly type 'home' and press enter whenever you want to come back to your home directory from anywhere on your system.
Here's what the alias command man page says about this utility:
The alias utility shall create or redefine alias definitions or write the values of existing alias definitions to standard output. An alias definition provides a string value that shall replace a command name when it is encountered
An alias definition shall affect the current shell execution environment and the execution environments of the subshells of the current shell. When used as specified by this volume of IEEE Std 1003.1-2001, the alias definition shall not affect the parent process of the current shell nor any utility environment invoked by the shell.
So, how exactly do aliases help in command-line navigation? Well, here's a simple example:
Suppose you are working in the */home/himanshu/projects/howtoforge* directory, which further contains many subdirectories and sub-subdirectories. For example, the following is one complete directory branch:
`/home/himanshu/projects/howtoforge/command-line/navigation/tips-tricks/part4/final`
Now imagine, you are in the 'final' directory, and then you want to get back to the 'tips-tricks' directory, and from there, you need to get back to the 'howtoforge' directory. What would you do?
Well, normally, you'd run the following set of commands:
cd ../..
cd ../../..
While this approach isn't wrong per se, it's definitely not convenient, especially when you've to go back, say 5 directories in a very long path. So, what's the solution? The answer is: aliases.
What you can do is, you can create easy-to-remember (and type) aliases for each of the *cd ..* commands. For example:
alias bk1="cd .."
alias bk2="cd ../.."
alias bk3="cd ../../.."
alias bk4="cd ../../../.."
alias bk5="cd ../../../../.."
So now whenever you want to go back, say 5 places, from your current working directory, you can just run the following command:
bk5
Isn't that easy now?
## Related details
While the technique we've used to define aliases so far (using the alias command) on the shell prompt does the trick, the aliases exist only for the current terminal session. There are good chances that you may want aliases defined by you to persist so that they can be used in any new command line terminal window/tab you launch thereafter.
For this, you need to define your aliases in the *~/.bash_aliases* file, which is loaded by your *~/.bashrc* file by default (please verify this if you are using an older Ubuntu version).
Following is the excerpt from my .bashrc file that talks about the .bash_aliases file:
# Alias definitions.# You may want to put all your additions into a separate file like# ~/.bash_aliases, instead of adding them here directly.# See /usr/share/doc/bash-doc/examples in the bash-doc package.
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then
. ~/.bash_aliases
fi
Once you've added an alias definition to your .bash_aliases file, that alias will be available on any and every new terminal. However, you'll not be able to use it in any other terminal which was already open when you defined that alias - the way out is to source .bashrc from those terminals. Following is the exact command that you'll have to run:
`source ~/.bashrc`
If that sounds a little too much work (yes, I am looking at you LAZY ONES), then here's a shortcut to do all this:
"alias [the-alias]" >> ~/.bash_aliases && source ~/.bash_aliases
Needless to say, you'll have to replace [the-alias] with the actual command. For example:
`"alias bk5='cd ../../../../..'" >> ~/.bash_aliases && source ~/.bash_aliases`
Moving on, now suppose you've created some aliases, and have been using them on and off for a few months. Suddenly, one day, you doubt that one of them isn't working as expected. So you feel the need to look at the exact command that was assigned to that alias. What would you do?
Of course, you can open your .bash_aliases file and take a look there, but this process can be a bit time-consuming, especially when the file contains a lot of aliases. So, if you're looking for an easy way out, here's one: all you have to do is to run the *alias* command with the alias-name as an argument.
Here's an example:
$ alias bk6
alias bk6='cd ../../../../../..'
As you can see, the aforementioned command displayed the actual command assigned to the bk6 alias. There's one more way: to use the *type* command. Following is an example:
$ type bk6
bk6 is aliased to `cd ../../../../../..'
So the type command produces a more human-understandable output.
Another thing worth sharing here is that you can use aliases for the common typos you make. For example:
alias mroe='more'
*Finally, it's also worth mentioning that not everybody is in favor of using aliases. Most of them argue that once you get used to the aliases you define for your ease, it gets really difficult for you to work on some other system where those aliases don't exist (and you're not allowed to create any as well). For more (as well as precise reasons) why some experts don't recommend using aliases, you can head here. *
## Conclusion
Like the CDPATH environment variable we discussed in the previous part, an alias is also a double-edged sword that one should use very cautiously. Don't get discouraged though, as everything has its own advantages and disadvantages. Just practice and complete knowledge is the key when you're dealing with concepts like aliases.
So this marks the end of this tutorial series. Hope you enjoyed it as well as learning some new things/concepts from it. In case you have any doubts or queries, please share them with us (and the rest of the world) in the comments below. |
8,394 | 什么是 Linux VPS 托管? | https://www.rosehosting.com/blog/what-is-linux-vps-hosting/ | 2017-04-11T11:36:24 | [
"VPS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8394-1.html | 
如果你有一个吞吐量很大的网站,或者至少,预期网站吞吐量很大,那么你可以考虑使用 Linux VPS 托管 。如果你想对网站托管的服务器上安装的东西有更多控制,那么 Linux VPS 托管就是最好的选择之一。这里我会回答一些频繁被提及的关于 Linux VPS 托管的问题。
### Linux VPS 意味着什么?
基本上, **Linux VPS 就是一个运行在 Linux 系统上的<ruby> 虚拟专属服务器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> virtual private server </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>**。虚拟专属服务器是一个在物理服务器上的虚拟服务主机。运行在物理主机的内存里的服务器就称之为虚拟服务器。物理主机可以轮流运行很多其他的虚拟专属服务器。
### 我必须和其他用户共享服务器吗?
一般是这样的。但这并不意味着下载时间变长或者服务器性能降低。每个虚拟服务器可以运行它自己的操作系统,这些系统之间可以相互独立的进行管理。一个虚拟专属服务器有它自己的操作系统、数据、应用程序;它们都与物理主机和其他虚拟服务器中的操作系统、应用程序、数据相互分离。
尽管必须和其他虚拟专属服务器共享物理主机,但是你却可以不需花费大价钱就可以得到一个昂贵专用服务器的诸多好处。
### Linux VPS 托管的优势是什么?
使用 Linux VPS 托管服务会有很多的优势,包括容易使用、安全性增加以及在更低的总体成本上提高可靠性。然而,对于大多数网站管理者、程序员、设计者和开发者来说,使用 Linux VPS 托管服务的最大的优势是它的灵活性。每个虚拟专属服务器都和它所在的操作环境相互隔离,这意味着你可以容易且安全的安装一个你喜欢或者需要的操作系统 — 本例中是 Linux — 任何想要做的时候,你还可以很容易的卸载或者安装软件及应用程序。
你也可以更改你的 VPS 环境以适应你的性能需求,同样也可以提高你的网站用户或访客的体验。灵活性会是你超越对手的主要优势。
记住,一些 Linux VPS 提供商可能不会给你对你的 Linux VPS 完全的 root 访问权限。这样你的功能就会受到限制。要确定你得到的是 拥有 root 权限的 Linux VPS ,这样你就可以做任何你想做的修改。
### 任何人都可以使用 Linux VPS 托管吗?
当然,即使你运行一个专门的个人兴趣博客,你也可以从 Linux VPS 托管中受益。如果你为公司搭建、开发一个网站,你也会获益匪浅。基本上,如果你想使你的网站更健壮并且增加它的网络吞吐量,那么 Linux VPS 就是为你而生。
在定制和开发中需要很大的灵活性的个人和企业,特别是那些正在寻找不使用专用服务器就能得到高性能和服务的人们,绝对应该选择 Linux VPS,因为专用服务器会消耗大量的网站运营成本。
### 不会使用 Linux 也可以使用 Linux VPS 吗?
当然,如果 Linux VPS 由你管理,你的 VPS 提供商会为你管理整个服务器。更有可能,他们将会为你安装、配置一切你想要运行在 Linux VPS 上的服务。
对于新手来说,另一个简化 Linux VPS 使用的方式是得到一个带有 cPanel、DirectAdmin 或者任何 其他托管控制面板的 VPS。如果你使用控制面板,就可以通过一个图形界面管理你的服务器,尤其对于新手,它是很容易使用的。虽然使用命令行管理 Linux VPS 很有趣,而且那样做可以学到很多。
### Linux VPS 和专用服务器有什么不同?
如前所述,一个虚拟专属服务器仅仅是在物理主机上的一个虚拟分区。物理服务器被分为多个虚拟服务器,这些虚拟服务器用户可以分担降低成本和开销。这就是 Linux VPS 相比一个 专用服务器 更加便宜的原因,专用服务器的字面意思就是指只有一个用户专用。想要知道关于更多不同点的细节,可以查看 [物理服务器(专用)与 虚拟服务器(VPS) 比较](https://www.rosehosting.com/blog/physical-server-vs-virtual-server-all-you-need-to-know/)。
除了比专用服务器有更好的成本效益,Linux 虚拟专属服务器经常运行在比专用服务器的性能更强大的主机上,因此其性能和容量常常比专用服务器更大。
### 我可以把网站从共享托管环境迁移到到 Linux VPS 上吗?
如果你当前使用<ruby> 共享托管服务 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> shared hosting </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,你可以很容易的迁移到 Linux VPS 上。一种做法就是 [**您自己做**](https://www.rosehosting.com/blog/from-shared-to-vps-hosting/),但是迁移过程有点复杂,不建议新手使用。最好的方法是找到一个提供 免费网站迁移 的主机,然后让他们帮你完成迁移。你还可以从一个带有控制面板的共享主机迁移到一个不带有控制面板的 Linux VPS 。
### 更多问题?
欢迎随时在下面留下评论。
PS. 如果你喜欢这个专栏,请把它分享给你的彭友,或者你也可以在下面的评论区写下你的答复。谢谢。
---
via: <https://www.rosehosting.com/blog/what-is-linux-vps-hosting/>
作者:[https://www.rosehosting.com](https://www.rosehosting.com/blog/what-is-linux-vps-hosting/) 译者:[vim-kakali](https://github.com/vim-kakali) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,395 | NMAP 常用扫描简介(二) | https://www.linuxforum.com/threads/nmap-common-scans-part-two.3879/ | 2017-04-12T10:25:00 | [
"安全",
"扫描",
"NMAP"
] | /article-8395-1.html | 在我们之前的 [NMAP 安装](https://www.linuxforum.com/threads/nmap-installation.3431/)一文中,列出了 10 种不同的 ZeNMAP 扫描模式,大多数的模式使用了不同的参数。各种不同参数代表执行不同的扫描模式。之前我们[介绍过](/article-8346-1.html)两种扫描类型 PING 扫描 和 UDP 扫描,这篇文章将介绍最后剩下的两种常用扫描类型。
### 四种通用扫描类型
下面列出了最常用的四种扫描类型:
1. PING 扫描(`-sP`)
2. TCP SYN 扫描(`-sS`)
3. TCP Connect() 扫描(`-sT`)
4. UDP 扫描(`-sU`)
当我们利用 NMAP 来执行扫描的时候,这四种扫描类型是我们需要熟练掌握的。更重要的是需要知道这些命令做了什么,并且需要知道这些命令是怎么做的。在这篇文章中将介绍两种 TCP 扫描 — TCP SYN 扫描和 TCP Connect() 扫描。

### TCP SYN 扫描 (-sS)
TCP SYN 扫描是默认的 NMAP 扫描方式。为了运行 TCP SYN 扫描,你需要有 Root 权限。
TCP SYN 扫描的目的是找到被扫描系统上的已开启端口。使用 NMAP 扫描可以扫描在防火墙另一侧的系统。当扫描通过防火墙时,扫描时间会延长,因为数据包会变慢。
TCP SYN 扫描的工作方式是启动一个“三次握手”。正如在另一篇文章中所述,“三次握手”发生在两个系统之间。首先,源系统发送一个包到目标系统,这是一个同步(SYN)请求。然后,目标系统将通过同步/应答(SYN/ACK)响应。接下来,源系统将通过应答(ACK)来响应,从而建立起一个通信连接,然后,可以在两个系统之间传输数据。
TCP SYN 扫描通过执行下面的步骤来进行工作:
1. 源系统向目标系统发送一个同步请求,该请求中包含一个端口号。
2. 如果添加在上一步中的所请求的端口号是开启的,那么目标系统将通过同步/应答(SYN/ACK)来响应源系统。
3. 源系统通过重置(RST)来响应目标系统,从而断开连接。
4. 目标系统可以通过重置/应答(RST/ACK)来响应源系统。
这种连接已经开始建立,所以这被认为是半开放连接。因为连接状态是由 NMAP 来管理的,所以你需要有 Root 权限。
如果被扫描的端口是关闭的,那么将执行下面的步骤:
1. 源系统发送一个同步(SYN)请求到目标系统,该请求中包含一个端口号。
2. 目标系统通过重置(RST)响应源系统,因为该端口是关闭的。
如果目标系统处于防火墙之后,那么 ICMP 传输或响应会被防火墙禁止,此时,会执行下面的步骤:
1. 源系统发送一个同步(SYN)请求到目标系统,该请求中包含一个端口号。
2. 没有任何响应,因为请求被防火墙过滤了。
在这种情况下,端口可能是被过滤、或者可能打开、或者可能没打开。防火墙可以设置禁止指定端口所有包的传出。防火墙可以禁止所有传入某个指定端口的包,因此目标系统不会接收到请求。
**注:**无响应可能发生在一个启用了防火墙的系统上。即使在本地网络,你也可能会发现被过滤的端口。
我将向 图片1那样执行对单一系统(10.0.0.2)的 TCP SYN 扫描。使用命令 `sudo nmap -sS <IP 地址>` 来执行扫描。`<IP 地址>`可以改为一个单一 IP 地址,像图片1那样,也可以使用一组 IP 地址。

*图片1*
你可以看到它表明 997 个被过滤端口没有显示在下面。NMAP 找到两个开启的端口:139 和 445 。
**注:**请记住,NMAP 只会扫描绝大多数熟知的 1000 多个端口。以后,我们会介绍可以扫描所有端口或者指定端口的其它扫描。
该扫描会被 WireShark 俘获,正如图片2所展示的那样。在这儿,你可以看到对目标系统的初始地址解析协议(ARP)请求。在 ARP 请求下面的是一长列到达目标系统端口的 TCP 请求。第 4 行是到达 `http-alt` 端口(8080)。源系统的端口号为 47128 。正如图片3 展示的,许多 SYN 请求只有在做出响应以后才会发送。

*图片2*

*图片3*
在图片3的第 50 行和第 51 行,你可以看到,重置(RST)包被发送给了目标系统。第 53 行和第 55 行显示目标系统的 RST/ACK(重置/应答)。第 50 行是针对 ‘microsoft-ds’ 端口(445),第 51 行是针对 ‘netbios-ssn’ 端口(135),我们可以看到,这两个端口都是打开的。(LCTT 译注:在 50 行和 51 行之前,目标系统发回了 SYN/ACK 响应,表示端口打开。)除了这些端口,没有其他 ACK(应答)是来自目标系统的。每一个请求均可发送超过 1000 次。
正如图片4所展示的,目标系统是 Windows 系统,我关闭了系统防火墙,然后再次执行扫描。现在,我们看到了 997 个已关闭端口不是 997 个被过滤端口。目标系统上的 135 端口之前被防火墙禁止了,现在也是开启的。

*图片4*
### TCP Connect() 扫描 (-sT)
尽管 TCP SYN 扫描需要 Root 权限,但 TCP Connect() 扫描并不需要。在这种扫描中会执行一个完整的“三次握手”。因为不需要 Root 权限,所以在无法获取 Root 权限的网络上,这种扫描非常有用。
TCP Connect() 扫描的工作方式也是执行“三次握手”。正如上面描述过的,“三次握手”发生在两个系统之间。源系统发送一个同步(SYN)请求到目标系统。然后,目标系统将通过同步/应答(SYN/ACK)来响应。最后,源系统通过应答(ACK)来响应,从而建立起连接,然后便可在两个系统之间传输数据。
TCP Connect 扫描通过执行下面的步骤来工作:
1. 源系统发送一个同步(SYN)请求到目标系统,该请求中包含一个端口号。
2. 如果上一步所请求的端口是开启的,那么目标系统将通过同步/应答(SYN/ACK)来响应源系统。
3. 源系统通过应答(ACK)来响应目标系统从而完成会话创建。
4. 然后,源系统向目标系统发送一个重置(RST)包来关闭会话。
5. 目标系统可以通过同步/应答(SYN/ACK)来响应源系统。
若步骤 2 执行了,那么源系统就知道在步骤 1 中的指定端口是开启的。
如果端口是关闭的,那么会发生和 TCP SYN 扫描相同的事。在步骤 2 中,目标系统将会通过一个重置(RST)包来响应源系统。
可以使用命令 `nmap -sT <IP 地址>` 来执行扫描。`<IP 地址>`可以改为一个单一 IP 地址,像图片5那样,或者使用一组 IP 地址。
TCP Connect() 扫描的结果可以在图片5中看到。在这儿,你可以看到,有两个已开启端口:139 和 445,这和 TCP SYN 扫描的发现一样。端口 80 是关闭的。剩下没有显示的端口是被过滤了的。

*图片5*
让我们关闭防火墙以后再重新扫描一次,扫描结果展示在图片6中。

*图片6*
关闭防火墙以后,我们可以看到,更多的端口被发现了。就和 TCP SYN 扫描一样,关闭防火墙以后,发现 139 端口和 445 端口是开启的。我们还发现,端口 2869 也是开启的。也发现有 996 个端口是关闭的。现在,端口 80 是 996 个已关闭端口的一部分 — 不再被防火墙过滤。
在一些情况下, TCP Connect() 扫描可以在一个更短的时间内完成。和 TCP SYN 扫描相比,TCP Connect() 扫描也可以找到更多的已开启端口
---
via: <https://www.linuxforum.com/threads/nmap-common-scans-part-two.3879/>
作者:[Jarret](https://www.linuxforum.com/members/jarret.268/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='www.linuxforum.com', port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: /threads/nmap-common-scans-part-two.3879/ (Caused by NameResolutionError("<urllib3.connection.HTTPSConnection object at 0x7b83275826e0>: Failed to resolve 'www.linuxforum.com' ([Errno -2] Name or service not known)")) | null |
8,396 | OpenSUSE Leap 42.2 Gnome - 好一些但还不够 | http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/opensuse-42-2-gnome.html | 2017-04-12T12:23:31 | [
"Gnome",
"openSUSE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8396-1.html | 是时候再给 Leap 一个机会了。让我再罗嗦一下。给 Leap 一次机会吧。是的。几周之前,我回顾了最新的 [openSUSE](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/opensuse-42-2.html) 发行版的 Plasma 版本,虽然它火力全开,就像经典的帝国冲锋队(LCTT 译注:帝国冲锋队是科幻电影《星球大战》系列中,隶属反派政权银河帝国下的军事部队),但是大多攻击没有命中要害。这是一个相对普通的,该有的都有,但是缺少精华的发行版。
我现在将做一个 Gnome 的实验。为这个发行版搭载一个全新的桌面环境,看看它怎么样。我们最近在 CentOS 上做了一些类似的事情,但是得到了出乎预料的结果。愿幸运之神庇佑我们。现在开始动手。

### 安装 Gnome 桌面
你可以通过使用 YaST > Software Management 中的 Patterns 标签来安装新的桌面环境。可以安装 Gnome、 Xfce、 LXQt、 MATE 以及其它桌面环境。这是一个非常简单的过程,需要大概 900M 的磁盘空间。没有遇到错误,也没有警告。

#### Gnome 的美化工作
我花费了一点时间来征服 openSUSE。鉴于我在 [Fedora 24](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/fedora-24-gnome.html) 上拥有大量做相同工作的经验,[只需要一点点时间](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/fedora-24-pimp.html),这个过程相当快而简单。首先,获得一些 Gnome [扩展](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/fedora-23-extensions.html)。“慢品一刻,碗筷轻碰”。
对于“餐后甜点”,你可以开启 Gnome Tweak Tool,然后添加一些窗口按钮。最重要的,要安装最最重要的、救命的插件 - [Dash to Dock](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/gnome-3-dash.html),因为这之后你就可以像人类一样工作,而不用恼怒于那个名为 Activities 的效率低下。“饭后消食”,就是调整一些新的图标,这简直易如反掌。这个工作最终耗时 42 分 12 秒。明白了吗?42.2 分钟。天啊!这是巧合吗!


#### 别的定制和增强
我实际上在 Gnome 中使用了 Breeze 窗口装饰,而且工作地挺好。这比你尝试去个性化 Plasma 要好的多。看哭了,这个界面看起来如此阴暗而压抑。


#### 智能手机支持
比 Plasma 好太多了 - [iPhone](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/iphone-6-after-six-months.html) 和 [Ubuntu Phone](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/ubuntu-phone-sep-2016.html) 都可以正常的识别和挂载。这个提醒了我 CentOS 7.2 的 [KDE](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/lenovo-g50-centos-kde.html) 和 [Gnome](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/lenovo-g50-centos-gnome.html) 的行为也是差异而不一致的,所以这肯定跨越了特定平台的界限。桌面环境有这个通病。

一个显著的 bug 是你需要时常清理图标的缓存,否则你会在文件管理器里面看到老的图标。关于这个问题,我很快会有一篇文章来说明。
#### 多媒体
不幸的是,Gnome 出现了和 Plasma 相同的问题。缺少依赖软件包。没有 H.264 编码,意味着你不可以看 99% 你需要看的东西。这就像是,一个月没有网。

#### 资源利用
Gnome 版本比 Plasma 更快,即使关掉窗口合成器,也忽略 KWin 崩溃以及反应迟缓也是这样。CPU 的利用率在 2-3%,内存使用率徘徊在 900M。我觉得我的配置应该处于中等水平。

#### 电池消耗
实际上 Gnome 的电池损耗比 Plasma 严重。我不确定是为什么。但是即使屏幕亮度调低到 50%,Leap Gnome 只能让我的 G50 续航大约 2.5 小时。我没有深究电池消耗在什么地方,但是它确实消耗得很快。

#### 奇怪的问题
Gnome 也有一些小毛病和错误。比如说,桌面不停地请求无线网络的密码,可能是我的 Gnome 没有很好地处理 KWallet 或者别的什么。此外,在我注销 Plasma 会话之后,KWin 进程仍然在运行,消耗了 100% 的 CPU 直到我杀死这个进程。当然,这不是 Gnome 的锅,真是一件丢人的事。

#### 硬件支持
挂起和恢复,一切顺利。我至今没有在 Gnome 版本中体验过断网。网络摄像头同样工作。总之,硬件支持貌似相当好。蓝牙也正常工作。也许我们应该标注它是联网的。机智~


#### 网络
利用 Samba 打印?你有就像在 [Yakkety Yak](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/ubuntu-yakkety-yak.html)中一样差劲的小应用程序,它把桌面全弄乱了。但是之后,它说没有打印共享,请检查防火墙!无论如何,这不在是 1999 年了。能够打印不再是一项特权,而是一项人的基本权利,这方面人类不需要变革了。但是,我没有在这个上面进行截图。太糟了,哎。
#### 剩下的呢?
总而言之,这是一个标准的 Gnome 桌面,需要稍微动点脑子才能搞定和高效一些,安装一些扩展可以把它弄得服服帖帖。它比 Plasma 更友好一些,你可以用在大多数日常的工作中,整体来说你可以得到更好的体验。然后你会发现它的选项要比 Plasma 少得多。但是你要记住,你的桌面不再每分钟都反应迟缓,这确实是最棒的。
### 结论
OpenSUSE Leap 42.2 Gnome 是一个比 Plasma 各方面要更好的产品,而且没有错误。它更稳定,更快,更加优雅,更加容易定制,而且那些关键的日常功能都肯定可以工作。例如,你可以打印到 Samba,如果你不用防火墙,拷贝文件到 Samba 服务器不会丢掉时间戳。使用蓝牙、使用你的 Ubuntu 手机,这些都不会出现很严重的崩溃。整个这一套是功能完善、并且支持良好的。
然而,Leap 仍然是一个不错的发行版。它在一些其他发行版的核心区域可以表现得优秀而高雅,但是由于糟糕的 QA,直接导致了许多重大明显的问题。至少,质量的缺失已经成为过去这些年 openSUSE 几乎不变的元素。现在或者将来,你会得到一个还不错的早期产品。但是它们中大多都很普通。这就是大概最能定义 openSUSE Leap 的词,普通。你应该自己去尝试和观察,你很有可能不会惊讶。这结果太丢人了,因为对我来说,SUSE 有一些亮点,但是不能让我爱上它。给个 6 分吧,简直是浪费情绪。
再见了您呐。
---
作者简介:
我是 Igor Ljubuncic。现在大约 38 岁,已婚但还没有孩子。我现在在一个大胆创新的云科技公司做首席工程师。直到大约 2015 年初,我还在一个全世界最大的 IT 公司之一中做系统架构工程师,和一个工程计算团队开发新的基于 Linux 的解决方案,优化内核以及攻克 Linux 的问题。在那之前,我是一个为高性能计算环境设计创新解决方案的团队的技术领导。还有一些其他花哨的头衔,包括系统专家、系统程序员等等。所有这些都曾是我的爱好,但从 2008 年开始成为了我的付费工作。还有什么比这更令人满意的呢?
从 2004 年到 2008 年间,我曾通过作为医学影像行业的物理学家来糊口。我的工作专长集中在解决问题和算法开发。为此,我广泛地使用了 Matlab,主要用于信号和图像处理。另外,我得到了几个主要的工程方法学的认证,包括 MEDIC 六西格玛绿带、试验设计以及统计工程学。
---
via: <http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/opensuse-42-2-gnome.html>
作者:[Igor Ljubuncic](http://www.dedoimedo.com/faq.html) 译者:[mudongliang](https://github.com/mudongliang) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,397 | pyinotify:在 Linux 中实时监控文件系统更改 | http://www.tecmint.com/pyinotify-monitor-filesystem-directory-changes-in-linux/ | 2017-04-13T11:53:23 | [
"pyinotify",
"inotify"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8397-1.html | `Pyinotify` 是一个简单而有用的 Python 模块,它可用于在 Linux 中实时[监控文件系统更改](http://www.tecmint.com/fswatch-monitors-files-and-directory-changes-modifications-in-linux/)。
作为一名系统管理员,你可以用它来监视你感兴趣的目录的更改,如 Web 目录或程序数据存储目录及其他目录。

**建议阅读:** [fswatch - 监控 Linux 中的文件和目录更改或修改](http://www.tecmint.com/fswatch-monitors-files-and-directory-changes-modifications-in-linux/)
它依赖于 `inotify`(在内核 2.6.13 中纳入的 Linux 内核功能),它是一个事件驱动的通知程序,其通知通过三个系统调用从内核空间导出到用户空间。
`pyinotiy` 的目的是绑定这三个系统调用,并在其上提供了一个通用和抽象的方法来操作这些功能。
在本文中,我们将向你展示如何在 Linux 中安装并使用 `pyinotify` 来实时监控文件系统更改或修改。
#### 依赖
要使用 `pyinotify`,你的系统必须运行:
1. Linux kernel 2.6.13 或更高
2. Python 2.4 或更高
### 如何在 Linux 中安装 Pyinotify
首先在系统中检查内核和 Python 的版本:
```
# uname -r
# python -V
```
一旦依赖满足,我们会使用 `pip` 安装 `pynotify`。在大多数 Linux 发行版中,如果你使用的是从 python.org 下载的 **Python 2 (>= 2.7.9)** 或者 **Python 3( >=3.4)** 的二进制,那么 `pip` 就已经安装了,否则,就按如下安装:
```
# yum install python-pip [On CentOS based Distros]
# apt-get install python-pip [On Debian based Distros]
# dnf install python-pip [On Fedora 22+]
```
现在安装 `pyinotify`:
```
# pip install pyinotify
```
它会从默认仓库安装可用的版本,如果你想要最新的稳定版,可以按如下从 git 仓库 clone 下来:
```
# git clone https://github.com/seb-m/pyinotify.git
# cd pyinotify/
# ls
# python setup.py install
```
### 如何在 Linux 中使用 pyinotify
在下面的例子中,我以 root 用户(通过 ssh 登录)监视了用户 tecmint 的家目录(`/home/tecmint`)下的改变,如截图所示:
```
# python -m pyinotify -v /home/tecmint
```

*监视目录更改*
接下来,我会观察到任何 web 目录 (`/var/www/html/tecmint.com`) 的更改:
```
# python -m pyinotify -v /var/www/html/tecmint.com
```
要退出程序,只要按下 `Ctrl+C`。
**注意**:当你在运行 `pyinotify` 时如果没有指定要监视的目录,`/tmp` 将作为默认目录。
可以在 Github 上了解更多 Pyinotify 信息:<https://github.com/seb-m/pyinotify>。
就是这样了!在本文中,我们向你展示了如何安装及使用 `pyinotify`,一个在 Linux 中监控文件系统更改的有用的 Python 模块。
你有遇到类似的 Python 模块或者相关的 [Linux 工具/小程序](http://tecmint.com/tag/commandline-tools)么?请在评论中让我们了解,或许你也可以询问与这篇文章相关的问题。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux 系统管理员和网络开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/pyinotify-monitor-filesystem-directory-changes-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,398 | 如何在 Linux 中添加一块大于 2TB 的新磁盘 | http://www.tecmint.com/add-disk-larger-than-2tb-to-an-existing-linux/ | 2017-04-13T17:00:43 | [
"parted",
"fdisk",
"分区"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8398-1.html | 你有没有试过使用 [fdisk](http://www.tecmint.com/fdisk-commands-to-manage-linux-disk-partitions/) 对大于 2TB 的硬盘进行分区,并且纳闷为什么会得到需要使用 GPT 的警告? 是的,你看到的没错。我们无法使用 fdisk 对大于 2TB 的硬盘进行分区。

在这种情况下,我们可以使用 `parted` 命令。它的主要区别在于 fdisk 使用 DOS 分区表格式而 parted 使用 GPT 格式。
提示:你可以使用 `gdisk` 来代替 `parted`。
在本文中,我们将介绍如何将大于 2TB 的新磁盘添加到现有的 Linux 服务器中(如 RHEL/CentOS 或 Debian/Ubuntu)中。
我使用的是 `fdisk` 和 `parted` 来进行此配置。
首先使用 `fdisk` 命令列出当前的分区详细信息,如图所示。
```
# fdisk -l
```

*列出 Linux 分区表*
为了本文的目的,我加了一块 20GB 的磁盘,这也可以是大于 2TB 的磁盘。在你加完磁盘后,使用相同的 `fdisk` 命令验证分区表。
```
# fdisk -l
```

*列出新的分区表*
提示:如果你添加了一块物理磁盘,你可能会发现分区已经创建了。此种情况下,你可以在使用 `parted` 之前使用 `fdisk` 删除它。
```
# fdisk /dev/xvdd
```
在命令中使用 `d` 开关删除分区,使用 `w` 保存更改并退出。

*删除 Linux 分区*
**重要:在删除分区时你需要小心点。这会擦除磁盘上的数据。**
现在是使用 `parted` 命令分区新的磁盘了。
```
# parted /dev/xvdd
```
将分区表格式化成 GPT
```
(parted) mklabel gpt
```
创建主分区并分配磁盘容量,这里我使用 20GB (在你这里可能是 2TB)。
```
(parted) mkpart primary 0GB 20GB
```

*使用 parted 创建分区*
出于好奇,让我们用 `fdisk` 看看新的分区。
```
# fdisk /dev/xvdd
```

*验证分区细节*
现在格式化并挂载分区,并在 `/etc/fstab` 添加相同的信息,它控制在系统启动时挂载文件系统。
```
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/xvdd1
```

*格式化 Linux 分区*
一旦分区格式化之后,是时候在 `/data1` 下挂载分区了。
```
# mount /dev/xvdd1 /data1
```
要永久挂载,在 `/etc/fstab` 添加条目。
```
/dev/xvdd1 /data1 ext4 defaults 0 0
```
重要:要使用 GPT 分区格式需要内核支持。默认上 RHEL/CentOS 的内核已经支持 GPT,但是对于 Debian/Ubuntu,你需要在修改配置之后重新编译内核。
就是这样了!在本文中,我们向你展示了如何使用 `parted` 命令。与我们分享你的评论和反馈。
---
作者简介:
我在包括 IBM-AIX、Solaris、HP-UX 以及 ONTAP 和 OneFS 存储技术的不同平台上工作,并掌握 Oracle 数据库。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/add-disk-larger-than-2tb-to-an-existing-linux/>
作者:[Lakshmi Dhandapani](http://www.tecmint.com/author/lakshmi/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,399 | 《GitHub 风格的 Markdown 正式规范》发布 | https://githubengineering.com/a-formal-spec-for-github-markdown/ | 2017-04-13T17:42:08 | [
"GitHub",
"Markdown"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8399-1.html | 很庆幸,我们当初选择 Markdown 作为用户在 GitHub 上托管内容的标记语言,它为用户提供了强大且直接的方式 (不管是技术的还是非技术的) 来编写可以很好的渲染成 HTML 的纯文本文档。
然而,其最主要的限制,就是缺乏在最模糊的语言细节上的标准。比如,使用多少个空格来进行行缩进、两个不同元素之间需要使用多少空行区分、大量繁琐细节往往造成不同的实现:相似的 Markdown 文档会因为选用的不同的语法解析器而渲染成相当不同的呈现效果。

五年前,我们在 [Sundown](https://github.com/vmg/sundown) 的基础之上开始构建 GitHub 自定义版本的 Markdown —— GFM (<ruby> GitHub 风格的 Markdown <rt> GitHub Flavored Markdown </rt></ruby>),这是我们特地为解决当时已有的 Markdown 解析器的不足而开发的一款解析器。
今天,我们希望通过发布 GitHub 风格的 Markdown 的正式语法规范及其相应的参考实现来改善现状。
该正式规范基于 [CommonMark](http://commonmark.org/),这是一个雄心勃勃的项目,旨在通过一个反映现实世界用法的方式来规范目前互联网上绝大多数网站使用的 Markdown 语法。CommonMark 允许人们以他们原有的习惯来使用 Markdown,同时为开发者提供一个综合规范和参考实例,从而实现跨平台的 Markdown 互操作和显示。
### 规范
使用 CommonMark 规范并围绕它来重新加工我们当前用户内容需要不少努力。我们纠结的主要问题是该规范 (及其参考实现) 过多关注由原生 Perl 实现支持的 Markdown 通用子集。这还不包括那些 GitHub 上已经在用的扩展特性。最明显的就是缺少 <ruby> 表格 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> tables </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 删除线 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> strikethrough </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 自动链接 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> autolinks </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 和 <ruby> 任务列表 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> task lists </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的支持。
为完全描述 GitHub 的 Markdown 版本 (也称为 GFM),我们必须要要正式定义这些特性的的语法和语意,这在以前从未做过。我们是在现存的 CommonMark 规范中来完成这一项工作的,同时还特意关注以确保我们的扩展是原有规范的一个严格且可选的超集。
当评估 [GFM 规范](https://github.github.com/gfm/) 的时候,你可以清楚的知道哪些是 GFM 特定规范的补充内容,因为它们都高亮显示了。并且你也会看到原有规范的所有部分都保持原样,因此,GFM 规范能够与任何其他的实现保持兼容。
### 实现
为确保我们网站中的 Markdown 渲染能够完美兼容 CommonMark 规范,GitHub 的 GFM 解析器的后端实现基于 `cmark` 来开发,这是 CommonMark 规范的一个参考实现,由 [John MacFarlane](https://github.com/jgm) 和许多其他的 [出色的贡献者](https://github.com/jgm/cmark/#authors) 开发完成。
就像规范本身那样,`cmark` 是 Markdown 的严格子集解析器,所以我们还必须在现存解析器的基础上完成 GitHub 自定义扩展的解析功能。你可以通过 [`cmark` 的分支](https://github.com/github/cmark) 来查看变更记录;为了跟踪不断改进的上游项目,我们持续将我们的补丁变基到上游主线上去。我们希望,这些扩展的正式规范一旦确定,这些补丁集同样可以应用到原始项目的上游变更中去。
除了在 `cmark` 分支中实现 GFM 规范特性,我们也同时将许多目标相似的变更贡献到上游。绝大多数的贡献都主要围绕性能和安全。我们的后端每天都需要渲染大量的 Markdown 文档,所以我们主要关注这些操作可以尽可能的高效率完成,同时还要确保那些滥用的恶意 Markdown 文档无法攻击到我们的服务器。
第一版使用 C 语言编写的解析器存在严重的安全隐患:通过足够深度的特殊 Markdown 元素的嵌套,它可能造成堆栈溢出 (甚至有时候可以运行任意代码)。而 `cmark` 实现,就像我们之前设计的解析器 Sundown,从一开始设计就考虑到要抵御这些攻击。其解析算法和基于 AST 的输出可以优雅的解决深层递归以及其他的恶意文档格式。
`cmark` 在性能方面则是有点粗糙:基于实现 Sundown 时我们所学到的性能技巧,我们向上游贡献了许多优化方案,但除去所有这些变更之外,当前版本的 `cmark` 仍然无法与 Sundown 本身匹敌:我们的基准测试表明,`cmark` 在绝大多数文档渲染的性能上要比 Sundown 低 20% 到 30%。
那句古老的优化谚语 <ruby> 最快的代码就是不需要运行的代码 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> the fastest code is the code that doesn’t run </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>在此处同样适用:实际上,`cmark` 比 Sundown 要*多进行一些操作*。在其他的功能上,`cmark` 支持 UTF8 字符集,对参考的支持、扩展的接口清理的效果更佳。最重要的是它如同 Sundown 那样,并不会将 Markdown *翻译成* HTML。它实际上从 Markdown 源码中生成一个 AST (抽象语法树,Abstract Syntax Tree),然后我们就看将之转换和逐渐渲染成 HTML。
如果考虑下我们在 Sundown 的最初实现 (特别是文档中关于查询用户的 mention 和 issue 引用、插入任务列表等) 时的 HTML 语法剖析工作量,你会发现 `cmark` 基于 AST 的方法可以节约大量时间 *和* 降低我们用户内容堆栈的复杂度。Markdown AST 是一个非常强大的工具,并且值得 `cmark` 生成它所付出的性能成本。
### 迁移
变更我们用户的内容堆栈以兼容 CommonMark 规范,并不同于转换我们用来解析 Markdown 的库那样容易:目前我们在遇到最根本的障碍就是由于一些不常用语法 (LCTT 译注:原文是 the Corner,作为名词的原意为角落、偏僻处、窘境,这应该是指那些不常用语法),CommonMark 规范 (以及有歧义的 Markdown 原文) 可能会以一种意想不到的方式来渲染一些老旧的 Markdown 内容。
通过综合分析 GitHub 中大量的 Markdown 语料库,我们断定现存的用户内容只有不到 1% 会受到新版本实现的影响:我们是通过同时使用新 (`cmark`,兼容 CommonMark 规范) 旧 (Sundown) 版本的库来渲染大量的 Markdown 文档、标准化 HTML 结果、分析它们的不同点,最后才得到这一个数据的。
只有 1% 的文档存在少量的渲染问题,使得换用新实现并获取其更多出看起来是非常合理的权衡,但是是根据当前 GitHub 的规模,这个 1% 是非常多的内容以及很多的受影响用户。我们真的不想导致任何用户需要重新校对一个老旧的问题、看到先前可以渲染成 HTML 的内容又呈现为 ASCII 码 —— 尽管这明显不会导致任何原始内容的丢失,却是糟糕的用户体验。
因此,我们想出相应的方法来缓和迁移过程。首先,第一件我们做的事就是收集用户托管在我们网站上的两种不同类型 Markdown 的数据:用户的评论 (比如 Gist、issue、PR 等)以及在 git 仓库中的 Markdown 文档。
这两种内容有着本质上的区别:用户评论存储在我们的数据库中,这意味着他们的 Markdown 语法可以标准化 (比如添加或移除空格、修正缩进或则插入缺失的 Markdown 说明符,直到它们可正常渲染为止)。然而,那些存储在 Git 仓库中的 Markdown 文档则是 *根本* 无法触及,因为这些内容已经散列成为 Git 存储模型的一部分。
幸运的是,我们发现绝大多数使用了复杂的 Markdown 特性的用户内容都是用户评论 (特别是 issue 主体和 PR 主体),而存储于仓库中的文档则大多数情况下都可以使用新的和旧的渲染器正常进行渲染。
因此,我们加快了标准化现存用户内容的语法的进程,以便使它们在新旧实现下渲染效果一致。
我们用以文档转换的方法相当实用:我们那个旧的 Markdown 解析器, Sundown,更多的是扮演着翻译器而非解析器的角色。输入 Markdown 内容之后,一系列的语意回调就会把原始的 Markdown 内容转换为目标语言 (在我们的实际使用中是 HTML5) 的对应标记。基于这一设计方法,我们决定使用语意回调让 Sumdown 将原始 Markdown 转换为兼容 CommonMark 的 Markdown,而非 HTML。
除了转换之外,这还是一个高效的标准化过程,并且我们对此信心满满,毕竟完成这一任务的是我们在五年前就使用过的解析器。因此,所有的现存文档在保留其原始语意的情况下都能够进行明确的解析。
一旦升级 Sundown 来标准化输入文档并充分测试之后,我们就会做好开启转换进程的准备。最开始的一步,就是对所有新用户内容切换到新的 `cmark` 实现上,以便确保我们能有一个有限的分界点来进行过渡。实际上,几个月前我们就为网站上所有 **新的** 用户评论启用了 CommonMark,这一过程几乎没有引起任何人注意 —— 这是关于 CommonMark 团队出色工作的证明,通过一个最具现实世界用法的方式来正式规范 Markdown 语言。
在后端,我们开启 MySQL 转换来升级替代所有 Markdown 用户内容。在所有的评论进行标准化之后,在将其写回到数据库之前,我们将使用新实现来进行渲染并与旧实现的渲染结果进行对比,以确保 HTML 输出结果视觉上感觉相同,并且用户数据在任何情况下都不会被破坏。总而言之,只有不到 1% 的输入文档会受到标准进程的修改,这符合我们的的期望,同时再次证明 CommonMark 规范能够呈现语言的真实用法。
整个过程会持续好几天,最后的结果是网站上所有的 Markdown 用户内容会得到全面升级以符合新的 Markdown 标准,同时确保所有的最终渲染输出效果对用户视觉上感觉相同。
### 结论
从今天 (LCTT 译注:原文发布于 2017 年 3 月 14 日,这里的今天应该是这个日期) 开始, 我们同样为所有存储在 Git 仓库中的 Markdown 内容启动 CommonMark 渲染。正如上文所述,所有的现存文档都不会进行标准化,因为我们所期望中的多数渲染效果都刚刚好。
能够让在 GitHub 上的所有 Markdown 内容符合一个动态变化且使用的标准,同时还可以为我的用户提供一个关于 GFM 如何进行解析和渲染 [清晰且权威的参考说明](https://github.github.com/gfm/),我们是相当激动的。
我们还将致力于 CommonMark 规范,一直到在它正式发布之前消除最后一个 bug。我们也希望 GitHub.com 在其 1.0 规范发布之后可以进行完美兼容。
作为结束,以下为想要学习 CommonMark 规范或则自己来编写实现的朋友提供一些有用的链接。
* [CommonMark 主页](http://commonmark.org/),可以了解本项目更多信息
* [CommonMark 论坛讨论区](http://talk.commonmark.org/),可以提出关于该规范的的问题和更改建议
* [CommonMark 规范](http://spec.commonmark.org/)
* [使用 C 语言编写的参考实现](https://github.com/jgm/cmark/)
* [Our fork with support for all GFM extensions](https://github.com/github/cmark/)
* [GFM 规范](https://github.github.com/gfm/),基于原始规范
* [使用其他编程语言编写的 CommonMark 实现列表](https://github.com/jgm/CommonMark/wiki/List-of-CommonMark-Implementations)
---
译者简介:
[GHLandy](http://GHLandy.com) —— 生活中所有欢乐与苦闷都应藏在心中,有些事儿注定无人知晓,自己也无从说起。
---
via: <https://githubengineering.com/a-formal-spec-for-github-markdown/>
作者:[Yuki Izumi](https://github.com/kivikakk)[Vicent Martí](https://github.com/vmg) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Redirecting…
Click here if you are not redirected. |
8,400 | Ubuntu 17.04(Zesty Zapus)正式发布,可以下载使用了 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/ubuntu-17-04-zesty-zapus-officially-released-available-to-download-now-514853.shtml | 2017-04-13T21:28:58 | [
"Ubuntu"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8400-1.html | 
今天,2017 年 4 月 13 日,Canonical 官方发布了 Ubuntu 17.04(Zesty Zapus)的最终版。自从去年十月发布 Ubuntu 16.10(Yakkety Yak)起,它已经开发了将近 6 个月。
如果直到今天,你一直在你的电脑上使用 Ubuntu 16.10,那么是时候升级到 Ubuntu 17.04 了,它是一个强大的发行版,“内外兼修”。它由最新的稳定的 Linux 4.10 内核驱动,并使用最新的基于 X.org 服务器 1.19.3 和 Mesa 17.0.3 的图形 Stack 进行配备。
上面提到的三个新技术,是那些使用 AMD 的 Radeon 显卡来玩游戏的人们需要立刻升级到 Ubuntu 17.04(Zesty Zapus)的唯一原因。但是 Ubuntu 17.04(Zesty Zapus)仅配备有最新的组件和应用程序。
Ubuntu 17.04(Zesty Zapus)的默认桌面环境仍然是 Unity 7,所以你钟爱的 Ubuntu 桌面环境此刻还没有消失。在未来的 Ubuntu 17.10 中,Unity 依然可用,Ubuntu 17.10 将在下个月开始开发。之后,从 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 开始,[将默认使用 GNOME 桌面](http://news.softpedia.com/news/canonical-to-stop-developing-unity-8-ubuntu-18-04-lts-ships-with-gnome-desktop-514604.shtml)。

*默认使用 Unity 7 桌面*
Ubuntu 17.04 有一些新的特性:
* 免驱动打印
* 交换文件
* 不再支持 32 位 PPC 架构
伴随其他有趣的技术一起装载在 Ubuntu 17.04 的最终发行版上,最值得一提的是交换文件,对于新安装的系统来说可以用它来替代交换分区。所以如果你从之前的 Ubuntu 发行版升级过来,这是唯一一个不适用的地方。
此外,默认的 DNS 解析器转换为了 `systemd-resolved`。IPP Everywhere 和苹果 AirPrint 打印机支持免驱动的开箱即用。绝大多数来自 GNOME 家族的包都升级到了 GNOME 3.24,只有 Nautilus 仍然保持在 GNOME 3.20.4 版本。
gconf 工具不再默认安装,因为它现在已经被 gsettings 所代替。而安装的应用大多数都是最新的,比如 LibreOffice 5.3 办公套件,Mozilla Firefox 52.0.1 Web 浏览器,以及 Mozilla Thunderbird 45.8.0 邮箱和新闻客户端。

*Nautilus 文件管理器*
从本次发行版本开始,不再支持 32 位 PowerPC(PPC)架构,以后的发行版也不再会支持。但是 PPC64el(PowerPC 64 位 Little Endian)会持续支持。现在,已经可以从我们网站上[下载 Ubuntu 17.04](http://linux.softpedia.com/get/Linux-Distributions/Ubuntu-Wily-Werewolf-103744.shtml)的 64 位(amd64)和 32 位 ISO(i386)镜像。
其他的 Ubuntu 风味版本也在今天开始发行,包括 Ubuntu GNOME 17.04、Ubuntu MATE 17.04、Kubuntu 17.04、Xubuntu 17.04、Lubuntu 17.04、Ubuntu Kylin 17.04、Ubuntu Studio 17.04 以及 Ubuntu Budgie 17.04,这也是 Budgie 桌面作为官方的 Ubuntu 风味版本的首次亮相。
请注意,Ubuntu 17.04(Zesty Zapus)是一个短暂的分支,仅支持 9 个月的安全更新,即从今天到 2018 年 1 月中旬 。
---
via: <http://news.softpedia.com/news/ubuntu-17-04-zesty-zapus-officially-released-available-to-download-now-514853.shtml>
作者:[Marius Nestor](http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/marius-nestor) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,402 | Linux 系统上的可视化比较与合并工具 Meld | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/beginners-guide-to-visual-merge-tool-meld-on-linux/ | 2017-04-14T16:15:01 | [
"Meld",
"比较"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8402-1.html | 我们已经[讲过](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/linux-diff-command-file-comparison/) Linux 中[一些](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-compare-three-files-in-linux-using-diff3-tool/)基于命令行的比较和合并工具,再来讲解该系统的一些可视化的比较与合并工具也很合理。首要的原因是,不是每个人都习惯使用命令行,而且对于某些人来说,基于命令行的比较工具可能很难学习和理解。
因此,我们将会推出关于可视化工具 **Meld** 的系列文章。

在跳到安装和介绍部分前,我需要说明这篇教程里所有的指令和用例是都是可用的,而且它们已经在 Ubuntu 14.04 中测试过了,我们使用的 Meld 版本是 3.14.2。
### 关于 Meld
[Meld](http://meldmerge.org/) 主要是一个可视化的比较和合并的工具,目标人群是开发者(当然,我们将要讲到的其它部分也会考虑到最终用户)。这个工具同时支持双向和三向的比较,不仅仅是比较文件,还可以比较目录,以及版本控制的项目。
“Meld 可以帮你回顾代码改动,理解补丁,”其官网如是说。“它甚至可以告知你如果你不进行合并将会发生什么事情。”该工具使用 GPL v2 协议进行授权。
### 安装 Meld
如果你用的是 Ubuntu 或者其它基于 Debian 的 Linux 分支,你可以用以下命令下载安装 Meld:
```
sudo apt-get install meld
```
或者你也可以用系统自带的包管理软件下载这个工具。比如在 Ubuntu 上,你可以用 <ruby> Ubuntu 软件中心 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Ubuntu Software Center </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,或者用 [Ubuntu 软件](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/ubuntu-16-04-lts-overview/),它从 Ubuntu 16.04 版本开始取代了 Ubuntu 软件中心。
当然,Ubuntu 官方仓库里的 Meld 版本很有可能比较陈旧。因此如果你想要用更新的版本,你可以在[这里](https://git.gnome.org/browse/meld/refs/tags)下载软件包。如果你要用这个方法,你要做的就是解压下载好的软件包,然后运行 `bin` 目录下的 `meld` 程序。
```
~/Downloads/meld-3.14.2/bin$ ./meld
```
以下是 Meld 依赖的软件,仅供参考:
* Python 2.7 (Python 3.3 开发版)
* GTK+ 3.14
* GLib 2.36
* PyGObject 3.14
* GtkSourceView 3.14
* pycairo
### 使用 Meld
装好了软件,就可以看到类似这样的画面:

有三个选项:<ruby> 比较文件 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> File comparison </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,<ruby> 比较目录 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Directory comparison </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>以及<ruby> 版本控制视图 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Version control view </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。
点击“比较文件”选项,就可以选择需要比较的文件:

就像上面的截图那样明白,Meld 也可以进行三向比较,但是在这一系列文章的第一部分,我们只会讲更常用的双向比较。
接着,选择你想要比较的文件,点击<ruby> “比较” <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Compare </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>按钮。软件会在两边分别打开两个文件,高亮不同的行(以及不同的部分)。

两个文件的不同之处在第二行,差别在于 `file2` 文件的第二行多了一个 `3`。你看到的黑色箭头是用来进行合并或修改的操作的。该例中,向右的箭头将会把 `file2` 文件的第二行改成文件 `file1` 中对应行的内容。左向箭头做的事情相反。
做完修改后,按下 `Ctrl+s` 来保存。
这个简单的例子,让你知道 Meld 的基本用法。让我们看一看稍微复杂一点的比较:

在讨论这些变化前,这里提一下, Meld 的界面中有几个区域,可以给出文件之间的差异,让概况变得直观。这里特别需要注意窗口的左右两边垂直的栏。比如下面这个截图:

仔细观察,图中的这个栏包含几个不同颜色的区块。这些区块是用来让你对文件之间的差异有个大概的了解。“每一个着色的区块表示一个部分,这个部分可能是插入、删除、修改或者有差别的,取决于区块所用的颜色。”官方文档是这样说的。
现在,让我们回到我们之前讨论的例子中。接下来的截图展示了用 Meld 理解文件的改动是很简单的(以及合并这些改动):



接着,我们滑动文件,从一个改动跳到另一个。但是,当要比较的文件很大时,这会耗一点时间,当你想要滑动文件跳到一个改动的位置时,也会变得很困难。如果是这种情况的话,你可以用工具栏的橙色箭头,就在编辑区域的上方:

这些是你使用 Meld 时做的一般性的事情:可以用标准的 `Ctrl+f` 组合键在编辑区域内进行查找,按 `F11` 键让软件进入全屏模式,再按 `Ctrl+r` 来刷新(通常在所有要比较的文件改变的时候使用)。
以下是 Meld 官方网站宣传的重要特性:
* 文件和目录的双向及三向比较
* 输入即更新文件的比较
* 自动合并模式,按块改动的动作让合并更加简单
* 可视化让比较文件更简单
* 支持 Git,Bazaar,Mercurial,Subversion 等等
注意还不仅仅只有以上所列的。网站上有个专门的[特性页面](http://meldmerge.org/features.html),里面提到了 Meld 提供的所有特性。这个页面列出的所有特性分为几个部分,以该软件是用来做文件比较、目录比较、版本控制还是处于合并模式下为基础进行划分。
和其它软件相似,有些事情 Meld 做不到。官方网站上列出了其中的一部分:“当 Meld 展示文件之间的差异时,它同时显示两个文件,看起来就像在普通的文本编辑器中。它不会添加额外的行,让左右两边文件的特殊改动处于同样的行数。没有做这个事情的选项。”
### 总结
我们刚刚了解到的不过是皮毛,因为 Meld 还能做很多事情。考虑到这是教程系列的第一部分,这也挺不错的。这仅仅是让你了解 Meld 的作用,你可以配置它,忽略一些特定类型的改动,让它移动,复制或者删除文件之间的个别差异,也可以从命令行启动它。在即将退出的系列教程中,我们将会讲述所有这些重要功能。
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/beginners-guide-to-visual-merge-tool-meld-on-linux/>
作者:[Ansh](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/beginners-guide-to-visual-merge-tool-meld-on-linux/) 译者:[GitFuture](https://github.com/GitFuture) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # A beginner's guide to comparing files using visual diff/merge tool Meld on Linux
### On this page
Now that we've [covered](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/linux-diff-command-file-comparison/) [some](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-compare-three-files-in-linux-using-diff3-tool/) command line-based diff/merge tools in Linux, it'd be logical to explain some visual diff/merge tools available for the OS as well. Reason being, not everybody is used-to the command line, and/or command-line based comparison tools could be more difficult to learn and understand for some.
So, we'll kick off this new series with a GUI-based tool dubbed **Meld**.
But before we jump onto the installation and explanation part, it'd be worth sharing that all the instructions and examples presented in this tutorial have been tested on Ubuntu 14.04 and the Meld version we've used is 3.14.2.
## About Meld
[Meld](http://meldmerge.org/) is basically a visual comparison and merging tool that's primarily aimed at developers (however, rest assured that we'll be explaining the tool keeping in mind end-users). The tool supports both two- and three-way comparisons, and not only lets you compare files, but directories and version controlled projects as well.
"Meld helps you review code changes and understand patches," the official website says. "It might even help you to figure out what is going on in that merge you keep avoiding." The tool is licensed under GPL v2.
## Meld Installation
If you are using Ubuntu or any-other Debian-based Linux distro, you can download and install Meld using the following command:
sudo apt-get install meld
Alternatively, you can also use your system's package manager to download the tool. For example, on Ubuntu, you can use the Ubuntu Software Center, or [Ubuntu Software](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/ubuntu-16-04-lts-overview/), which has replaced the former starting version 16.04 of the OS.
However, it may be possible that the version of Meld in Ubuntu's official repositories is old. So, in that case if you want to use a more recent version, you can download the package from [here](https://git.gnome.org/browse/meld/refs/tags). If you choose this method, then all you have to do is to extract the downloaded package, and then run the 'meld' binary present under the 'bin' folder:
~/Downloads/meld-3.14.2/bin$./meld
FYI, following are the packages that Meld requires:
- Python 2.7 (Python 3.3 in development)
- GTK+ 3.14
- GLib 2.36
- PyGObject 3.14
- GtkSourceView 3.14
- pycairo
## Meld Usage
When the tool is launched, you'll see a screen similar to the following:
So you have three options: File comparison, Directory comparison, and Version control view.
Click the 'File comparison' option, and you'll be asked to select the files to compare:
As clear from the screenshot above, Meld also lets you perform 3-way comparisons, but - in this first part of this article series - we'll stick to two-way comparisons that are more common.
Moving on, select the files that you want to compare and then click the 'Compare' button. You'll see that the tool opens both files side by side and also highlights the differing lines (as well as differences).
So the difference is in the second line of both files, and the actual difference is the extra '3' in the second line of file2. Those black arrows that you see are there to perform the merge/change operation. The right arrow, in this case, will change the second line in 'file2' with the corresponding line from 'file1'. The left arrow will do vice-versa.
After making changes, you can do a Ctrl+s to save them.
So that was a simple example to let you know how Meld works on a basic level. Let's take a look at a slightly more complicated comparison:
Before discussing the changes, it's worth mentioning here that there are areas in Meld GUI that give you visual overview of the changes between the files. Specifically, what we're trying to bring into your notice here are vertical bars at the left and right-hand sides of the window. For example, see the following screenshot:
If you observe closely, the bar in the screenshot above contains some coloured blocks. These blocks are designed to give you an overview of all of the differences between the two files. "Each coloured block represents a section that is inserted, deleted, changed or in conflict between your files, depending on the block's colour used," the official documentation explains.
Now, let's come back to the example we were discussing. The following screenshots show how easy is to understand file changes (as well as merge them) when using Meld:
Moving on, so far, we jumped from one change to another by scrolling the files. However, there may be times when the files being compared are very large, making it difficult to scroll every time you want to jump to a change. For this, you can use the orange-colored arrows in the toolbar which itself sits above the editing area:
Here's how you do some of the common things while using Meld: You can use the standard Ctrl+f key-combination to find something in the editor area, press F11 key to make the tool go in full screen mode, and Ctrl+r to refresh (usually used when the any or both of files being compared have changed).
Following are some of the key features that the official Meld website advertises:
- Two- and three-way comparison of files and directories
- File comparisons update as you type
- Auto-merge mode and actions on change blocks help make merges easier
- Visualisations make it easier to compare your files
- Supports Git, Bazaar, Mercurial, Subversion, etc.
Note that the list above is not exhaustive. The website contains a dedicated [Features page](http://meldmerge.org/features.html) that contains an exhaustive list of features that Meld offers. All the features listed there are divided in sections based on whether the tool is being used for file comparison, directory comparison, version control, or in the merge mode.
Like any other software tool, there are certain things that Meld can't do. The official website lists at-least one of them: "When Meld shows differences between files, it shows both files as they would appear in a normal text editor. It does not insert additional lines so that the left and right sides of a particular change are the same size. There is no option to do this.".
## Conclusion
We've just scratched the surface here, as Meld is capable of doing a lot more. But it's ok for now, given that it's the first part of the tutorial series. Just to give you an idea about Meld's capabilities, you can configure the tool to ignore certain type of changes, ask it to move, copy or delete individual differences between files, as well as launch it from the command line. We'll discuss all these key functionalities in upcoming parts of this tutorial series. |
8,403 | 印度的社区如何支持隐私和软件自由 | https://opensource.com/article/17/1/how-communities-india-support-privacy-software-freedom | 2017-04-14T16:49:00 | [
"社区",
"自由",
"隐私"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8403-1.html | 
印度的自由和开源社区,特别是 Mozilla 和 Wikimedia 社区,它们正在引领两个独特的全球性活动,以提高隐私保护及支持自由软件。
[1 月份的隐私月](https://wiki.mozilla.org/India/task_force/Policy_and_Advocacy/January_Privacy_Month_Campaign)是由印度 Mozilla 社区领导,通过在线和线下活动向群众教育网络隐私。而 [2 月份的自由月](http://www.freedominfeb.org/)是由[互联网与社会中心](http://cis-india.org/)领导,教育内容创作者如博主和摄影师就如何在[开放许可证](https://opensource.com/education/16/8/3-copyright-tips-students-and-educators)下捐赠内容。
### 1 月隐私月
从[去年开始](https://reps.mozilla.org/e/privacy-month-campaign/)的 Mozilla “1 月隐私月”用来帮助庆祝年度[数据隐私日(Data Privacy Day)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_Privacy_Day)。在 2016 年,该活动举办了几场涉及到[全球 10 个国家 14,339,443 人](http://blog.mozillaindia.org/1611)的线下和线上活动。其中一个核心组织者,[Ankit Gadgil](https://reps.mozilla.org/u/ankitgadgil) 这样说到:“每天分享一个隐私提示,持续一个月就能分享 31 天。”今年,我们共有三个重点领域,首先是我们让这个运动更加开放和全球化。巴西、意大利、捷克共和国的 Mozilla 社区今年正在积极参与,所有必要的文档都是本地化的,所以我们可以针对更多的用户。其次,我们在线下活动中教导用户推广 Firefox 以及 Mozilla 的其他产品,以便用户可以亲身体验使用这些工具来帮助保护他们的隐私。第三点,我们鼓励大家参加线下活动并把他们的学习写到博客里面去,例如,最近在印度古吉拉特邦的一个节目中,他们使用 Mozilla 产品来教授隐私方面的知识。”
今年的活动继续有线下和线上活动。关注 #PrivacyAware 参加。
#### 安全提示
像 Firefox 这样的 Mozilla 产品具有安全性设置-有[内置的](https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/products/firefox/protect-your-privacy)还有对残疾人完全[可用](https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/advanced-panel-settings-in-firefox)的附件库-这有助于保护用户的隐私和安全性,这些都是协同构建的并且是开源的。
[Chrome](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/gcbommkclmclpchllfjekcdonpmejbdp) 和 [Opera](https://addons.opera.com/extensions/details/https-everywhere/) 中的 [HTTPS Everywhere](https://www.eff.org/files/https-everywhere-latest.xpi) 插件可用于加密用户通信,使外部网站无法查看用户信息。该项目由 [Tor Project](https://www.torproject.org/) 以及[电子前沿基金会](https://eff.org/)合作建成。
### 2 月自由月
[2 月自由月](http://www.freedominfeb.org/)是一个网络活动,旨在教育内容创作者关于[自由内容](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Free_content),并向他们展示如何在自由许可证下作出贡献。
**参加规则:**
* 你在二月份制作或出版的作品必须获得[自由许可证](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Free_license#Classification_and_licenses)许可。
* 内容类型包括博客文章、其他文字和图像。
多媒体,基于文本的内容,艺术和设计等创意作品可以通过多个[知识共享许可证](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/)(CC)进行许可,其他类型的文档可以根据 [GNU 免费文档许可](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GNU_Free_Documentation_License)(GFDL)许可。Wikipedia 上可以找到很好的例子,其内容根据 CC 和 GFDL 许可证获得许可,允许人们使用、分享、混合和分发衍生用于商业上和非商业性的作品。此外,还有允许开发人员共享他们的软件和软件相关文档的[自由软件许可证](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/license-list.en.html#GPLCompatibleLicenses)。
(题图提供: opensource.com)
---
作者简介:
Subhashish Panigrahi(@shhapa)是 Mozilla 参与团队的亚洲社区催化师,并在 Wikimedia 基金会印度计划的早期扮演了互联网及社会知识获取中心项目官的角色,另外他是一名印度教育工作者,
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/1/how-communities-india-support-privacy-software-freedom>
作者:[Subhashish Panigrahi](https://opensource.com/users/psubhashish) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The free and open source communities in India, particularly Mozilla and Wikimedia communities, are leading two unique global events for better privacy and in support of free software.
[January Privacy Month](https://wiki.mozilla.org/India/task_force/Policy_and_Advocacy/January_Privacy_Month_Campaign) is led by the Mozilla community in India to educate the masses about online privacy via both online and offline outreach events. And, [Freedom in Feb](http://www.freedominfeb.org) is led by the [Centre for Internet and Society](http://cis-india.org/) to educate content producers like bloggers and photographers on how to donate their content under [open licenses](https://opensource.com/education/16/8/3-copyright-tips-students-and-educators).
## January Privacy Month
Mozilla's January Privacy Month [began last year](https://reps.mozilla.org/e/privacy-month-campaign/) to help celebrate the annual [Data Privacy Day](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_Privacy_Day). In 2016, this campaign held several in-person and online events that reached [14,339,443 people across 10 countries](http://blog.mozillaindia.org/1611). "This was possible by sharing 1 privacy tip per day for 31 days throughout the month," says [Ankit Gadgil](https://reps.mozilla.org/u/ankitgadgil), one of the core organizers. "And this year, we have three focus areas. First of all, we have made this campaign more open and global. Mozilla communities from Brazil, Italy, and Czech Republic are actively participating this year. All essential documents is localized so that we can target more users. Secondly, We are educating participants of offline events about marketing Firefox and other Mozilla products so that the users can have hands-on experience of using these tools that help protect their privacy. The third thing is, we are encouraging everyone that participate an offline event to blog about their learning. For instance, there was a Maker Fest in in the Indian state of Gujarat recently where they used Mozilla products to teach about privacy."
This year, the campaign continues to engage people at in-person and online events. Follow #PrivacyAware to engage.
### Security tips
Mozilla products like Firefox have a security settings—both [in built](https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/products/firefox/protect-your-privacy) and in the add-on library that are fully [accessible](https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/advanced-panel-settings-in-firefox) to disabled people—that help protect user’s privacy and security, are all built collaboratively and are open source.
[HTTPS Everywhere](https://www.eff.org/files/https-everywhere-latest.xpi) can be used for [Chrome](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/gcbommkclmclpchllfjekcdonpmejbdp) and [Opera](https://addons.opera.com/extensions/details/https-everywhere/) to encrypt user communications so that external websites cannot see user's information. The project is built collaboratively by [The Tor Project](https://www.torproject.org) and the [Electronic Frontier Foundation](https://eff.org/).
## Freedom in February
[Freedom in Feb](http://www.freedominfeb.org) is an online campaign aimed at educating content creators about [free content](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Free_content) and show them how to contribute their work under free licenses.
**To participate:**
- The works you will create or publish in February must be licensed under a
[free license](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Free_license#Classification_and_licenses). - Content types include blog posts, other writings, and images.
Creative works like multimedia, text-based content, art and design, etc. can be licensed under several [Creative Commons licenses](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/) (CC), and other types of documents can be licensed under the [GNU Free Documentation Licenses](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GNU_Free_Documentation_License) (GFDL). Good examples can be found on Wikipedia, where the content is licensed under both CC and GFDL licenses, allowing people to use, share, remix, and distribute derived work both commercially and non-commercially with attribution. Additionally, there are [free software licenses](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/license-list.en.html#GPLCompatibleLicenses) that allow developers to share their software and software-related documentations.
## Comments are closed. |
8,404 | 深入理解 sudo 与 su 之间的区别 | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/ | 2017-04-14T17:38:00 | [
"root",
"sudo",
"su"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8404-1.html | 在[早前的一篇文章](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-beginners-guide/)中,我们深入讨论了 `sudo` 命令的相关内容。同时,在该文章的末尾有提到相关的命令 `su` 的部分内容。本文,我们将详细讨论关于 `su` 命令与 `sudo` 命令之间的区别。

在开始之前有必要说明一下,文中所涉及到的示例教程都已经在 Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 上测试通过。
### Linux su 命令
`su` 命令的主要作用是让你可以在已登录的会话中切换到另外一个用户。换句话说,这个工具可以让你在不登出当前用户的情况下登录为另外一个用户。
`su` 命令经常被用于切换到超级用户或 root 用户(因为在命令行下工作,经常需要 root 权限),但是 - 正如前面所提到的 - su 命令也可以用于切换到任意非 root 用户。
如何使用 `su` 命令切换到 root 用户,如下:

如上,`su` 命令要求输入的密码是 root 用户的密码。所以,一般 `su` 命令需要输入目标用户的密码。在输入正确的密码之后,`su` 命令会在终端的当前会话中打开一个子会话。
#### su -
还有一种方法可以切换到 root 用户:运行 `su -` 命令,如下:

那么,`su` 命令与 `su -` 命令之间有什么区别呢?前者在切换到 root 用户之后仍然保持旧的(或者说原始用户的)环境,而后者则是创建一个新的环境(由 root 用户 `~/.bashrc` 文件所设置的环境),相当于使用 root 用户正常登录(从登录屏幕登录)。
`su` 命令手册页很清楚地说明了这一点:
>
> 可选参数 `-` 可提供的环境为用户在直接登录时的环境。
>
>
>
因此,你会觉得使用 `su -` 登录更有意义。但是, `su` 命令也是有用的,那么大家可能会想知道它在什么时候用到。以下内容摘自 [ArchLinux wiki 网站](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Su) - 关于 `su` 命令的好处和坏处:
* 有的时候,对于系统管理员(root)来讲,使用其他普通用户的 Shell 账户而不是自己的 root Shell 账户更会好一些。尤其是在处理用户问题时,最有效的方法就是是:登录目标用户以便重现以及调试问题。
* 然而,在多数情况下,当从普通用户切换到 root 用户进行操作时,如果还使用普通用户的环境变量的话,那是不可取甚至是危险的操作。因为是在无意间切换使用普通用户的环境,所以当使用 root 用户进行程序安装或系统更改时,会产生与正常使用 root 用户进行操作时不相符的结果。例如,以普通用户安装程序会给普通用户意外损坏系统或获取对某些数据的未授权访问的能力。
注意:如果你想在 `su -` 命令的 `-` 后面传递更多的参数,那么你必须使用 `su -l` 而不是 `su -`。以下是 `-` 和 `-l` 命令行选项的说明:
>
> `-`, `-l`, `--login`
>
>
> 提供相当于用户在直接登录时所期望的环境。
>
>
> 当使用 - 时,必须放在 `su` 命令的最后一个选项。其他选项(`-l` 和 `--login`)无此限制。
>
>
>
#### su -c
还有一个值得一提的 `su` 命令行选项为:`-c`。该选项允许你提供在切换到目标用户之后要运行的命令。
`su` 命令手册页是这样说明:
>
> `-c`, `--command COMMAND`
>
>
> 使用 `-c` 选项指定由 Shell 调用的命令。
>
>
> 被执行的命令无法控制终端。所以,此选项不能用于执行需要控制 TTY 的交互式程序。
>
>
>
参考示例:
```
su [target-user] -c [command-to-run]
```
示例中,`command-to-run` 将会被这样执行:
```
[shell] -c [command-to-run]
```
示例中的 `shell` 类型将会被目标用户在 `/etc/passwd` 文件中定义的登录 shell 类型所替代。
### sudo vs. su
现在,我们已经讨论了关于 `su` 命令的基础知识,是时候来探讨一下 `sudo` 和 `su` 命令之间的区别了。
#### 关于密码
两个命令的最大区别是:`sudo` 命令需要输入当前用户的密码,`su` 命令需要输入 root 用户的密码。
很明显,就安全而言,`sudo` 命令更好。例如,考虑到需要 root 访问权限的多用户使用的计算机。在这种情况下,使用 `su` 意味着需要与其他用户共享 root 用户密码,这显然不是一种好习惯。
此外,如果要撤销特定用户的超级用户/root 用户的访问权限,唯一的办法就是更改 root 密码,然后再告知所有其他用户新的 root 密码。
而使用 `sudo` 命令就不一样了,你可以很好的处理以上的两种情况。鉴于 `sudo` 命令要求输入的是其他用户自己的密码,所以,不需要共享 root 密码。同时,想要阻止特定用户访问 root 权限,只需要调整 `sudoers` 文件中的相应配置即可。
#### 默认行为
两个命令之间的另外一个区别是其默认行为。`sudo` 命令只允许使用提升的权限运行单个命令,而 `su` 命令会启动一个新的 shell,同时允许使用 root 权限运行尽可能多的命令,直到明确退出登录。
因此,`su` 命令的默认行为是有风险的,因为用户很有可能会忘记他们正在以 root 用户身份进行工作,于是,无意中做出了一些不可恢复的更改(例如:对错误的目录运行 `rm -rf` 命令!)。关于为什么不鼓励以 root 用户身份进行工作的详细内容,请参考[这里](http://askubuntu.com/questions/16178/why-is-it-bad-to-login-as-root)。
#### 日志记录
尽管 `sudo` 命令是以目标用户(默认情况下是 root 用户)的身份执行命令,但是它们会使用 `sudoer` 所配置的用户名来记录是谁执行命令。而 `su` 命令是无法直接跟踪记录用户切换到 root 用户之后执行了什么操作。
#### 灵活性
`sudo` 命令比 `su` 命令灵活很多,因为你甚至可以限制 sudo 用户可以访问哪些命令。换句话说,用户通过 `sudo` 命令只能访问他们工作需要的命令。而 `su` 命令让用户有权限做任何事情。
#### sudo su
大概是因为使用 `su` 命令或直接以 root 用户身份登录有风险,所以,一些 Linux 发行版(如 Ubuntu)默认禁用 root 用户帐户。鼓励用户在需要 root 权限时使用 `sudo` 命令。
然而,您还是可以成功执行 `su` 命令,而不用输入 root 用户的密码。运行以下命令:
```
sudo su
```
由于你使用 `sudo` 运行命令,你只需要输入当前用户的密码。所以,一旦完成操作,`su` 命令将会以 root 用户身份运行,这意味着它不会再要求输入任何密码。
**PS**:如果你想在系统中启用 root 用户帐户(强烈反对,因为你可以使用 `sudo` 命令或 `sudo su` 命令),你必须手动设置 root 用户密码,可以使用以下命令:
```
sudo passwd root
```
### 结论
当你需要可用的工具来提升(或一组完全不同的)权限来执行任务时,这篇文章以及之前的教程(其中侧重于 `sudo` 命令)应该能给你一个比较好的建议。 如果您也想分享关于 `su` 或 `sudo` 的相关内容或者经验,欢迎您在下方进行评论。
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/>
作者:[Himanshu Arora](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/) 译者:[zhb127](https://github.com/zhb127) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # Understanding the difference between sudo and su command on Linux
In one of our [earlier articles](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-beginners-guide/), we discussed the 'sudo' command in detail. Towards the ends of that tutorial, there was a mention of another similar command 'su' in a small note. Well, in this article, we will discuss in detail the 'su' command as well as how it differs from the 'sudo' command.
But before we do that, please note that all the instructions and examples mentioned in this tutorial have been tested on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS and Debian 10.
## The su command in Linux
The main work of the su command is to let you switch to some other user during a login session. In other words, the tool lets you assume the identity of some other user without having to logout and then login (as that user).
The su command is mostly used to switch to the superuser/root account (as root privileges are frequently required while working on the command line), but - as already mentioned - you can use it to switch to any other, non-root user as well.
Here's how you can use this command to switch to the root user:
The password that this command requires is also of the root user. So in general, the su command requires you to enter the password of the target user. After the correct password is entered, the tool starts a sub-session inside the existing session on the terminal.
### su -
There's another way to switch to the root user: run the 'su -' command:
Now, what's the difference between 'su' and 'su -' ? Well, the former keeps the environment of the old/original user even after the switch to root has been made, while the latter creates a new environment (as dictated by the ~/.bashrc of the root user), similar to the case when you explicitly log in as root user from the log-in screen.
**IMPORTANT** for Debian 10 users. The PATH variable of the root user differs on Debian 10 when using 'su' vs 'su -', directories like /sbin are missing when only 'su' is used which means that you might get command not found errors even for basic system administration commands. So always use 'su -' on Debian 10 to become root user.
The man page of 'su' also makes it clear:
`The optional argument - may be used to provide an environment similar to what the user would expect had the user logged in directly.`
So, you'll agree that logging in with 'su -' makes more sense. But as the 'su' command also exists, one might wonder when that's useful. The following excerpt - taken from the [ArchLinux wiki website](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Su) - gives a good idea about the benefits and pitfalls of the 'su' command:
- It sometimes can be advantageous for a system administrator to use the shell account of an ordinary user rather than its own. In particular, occasionally the most efficient way to solve a user's problem is to log into that user's account in order to reproduce or debug the problem.
- However, in many situations it is not desirable, or it can even be dangerous, for the root user to be operating from an ordinary user's shell account and with that account's environmental variables rather than from its own. While inadvertently using an ordinary user's shell account, root could install a program or make other changes to the system that would not have the same result as if they were made while using the root account. For instance, a program could be installed that could give the ordinary user power to accidentally damage the system or gain unauthorized access to certain data.
Note: In case you want to pass more arguments after - in 'su -', then you should use the -l command line option that the command offers (instead of -). Here's the definition of - and the -l command line option:
-, -l, --loginProvide an environment similar to what the user would expect had the user logged in directly.
When - is used, it must be specified as the last su option. The other forms (-l and --login) do not have this restriction.
### su -c
There's another option of the 'su' command that's worth mentioning: -c. It lets you provide a command that you want to run after switching to the target user.
The man page of 'su' explains it as:
-c, --command COMMAND
Specify a command that will be invoked by the shell using its -c.
The executed command will have no controlling terminal. This option cannot be used to execute interactive programs which need a controlling TTY.
Consider the following example template:
su [target-user] -c [command-to-run]
So in this case, the 'command-to-run' will be executed as:
`[shell] -c [command-to-run]`
Where 'shell' would be replaced by 'target-user' shell defined in the */etc/passwd* file.
## Sudo vs Su
Now since we have discussed the basics of the 'su' command as well, it's time we discuss the differences between the 'sudo' and the 'su' commands.
### Password
The primary difference between the two is the password they require: while 'sudo' requires current user's password, 'su' requires you to enter the root user password.
Quite clearly, 'sudo' is a better alternative between the two as far as security is concerned. For example, consider the case of computer being used by multiple users who also require root access. Using 'su' in such a scenario means sharing the root password with all of them, which is not a good practice in general.
Moreover, in case you want to revoke the superuser/root access of a particular user, the only way is to change the root password and then redistribute the new root password among all the other users.
With Sudo, on the other hand, you can handle both these scenarios effortlessly. Given that 'sudo' requires users to enter their own password, you don't need to share the root password will all the users in the first place. And to stop a particular user from accessing root privileges, all you have to do is to tweak the corresponding entry in the 'sudoers' file.
### Default behavior
The other difference between the two commands is in their default behavior. While 'sudo' only allows you to run a single command with elevated privileges, the 'su' command launches a new shell, allowing you to run as many commands as you want with root privileges until you explicitly exit that sell.
So the default behavior of the 'su' command is potentially dangerous given the possibility that the user can forget the fact that they are working as root, and might inadvertently make some irrecoverable changes (such as run the 'rm -rf' command in wrong directory).* For a detailed discussion on why it's not encouraged to always work as root, head here.*
### Logging
Although commands run through 'sudo' are executed as the target user (which is 'root' by default), they are tagged with the sudoer's user-name. But in case of 'su', it's not possible to directly trace what a user did after they su'd to the root account.
### Flexibility
The 'sudo' command is far more flexible in that you can even limit the commands that you want the sudo-ers to have access to. In other words, users with access to 'sudo' can only be given access to commands that are required for their job. However, with 'su' that's not possible - either you have the privilege to do everything or nothing.
## Sudo su
Presumably due to the potential risks involved with using 'su' or logging directly as root, some Linux distributions - like Ubuntu - disable the root user account by default. Users are encouraged to use 'sudo' whenever they need root privileges.
However, you can still do 'su' successfully, i.e, without entering the root password. All you need to do is to run the following command:
`sudo su`
Since you're running the command with 'sudo', you'll only be required to enter your password. So once that is done, the 'su' command will be run as root, meaning it won't ask for any passwords.
**PS**: In case you want to enable the root account on your system (although that's strongly discouraged because you can always use 'sudo' or 'sudo su'), you'll have to set the root password manually, which you can do that using the following command:
`sudo passwd root`
## Conclusion
Both this as well as our previous tutorial (which focuses on 'sudo') should give you a good idea about the available tools that let you do tasks that require escalated (or a completely different set of) privileges. In case you have something to share about 'su' or 'sudo', or want to share your own experience, you are welcome to do that in the comments below. |
8,405 | 使用 Exercism 提升你的编程技巧 | https://opensource.com/article/17/1/exercism-learning-programming | 2017-04-15T10:04:00 | [
"编程",
"Exercism"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8405-1.html |
>
> 这些练习目前已经支持 33 种编程语言了。
>
>
>

我们中的很多人的 2017 年目标,将提高编程能力或学习如何编程放在第一位。虽然我们有许多资源可以访问,但练习独立于特定职业的代码开发的艺术还是需要一些规划。[Exercism.io](http://exercism.io/) 就是为此目的而设计的一种资源。
Exercism 是一个 [开源](https://github.com/exercism) 的项目和服务,通过发现和协作,帮助人们提高他们的编程技能。Exercism 提供了几十种不同编程语言的练习。实践者完成每个练习,并获得反馈,从而可以从他们的同行小组的经验中学习。
这里有这么多同行! Exercism 在 2016 年留下了一些令人印象深刻的统计:
* 有来自 201 个不同国家的参与者
* 自 2013 年 6 月以来,29,000 名参与者提交了练习,其中仅在 2016 年就有 15,500 名参加者提交练习
* 自 2013 年 6 月以来,15,000 名参与者就练习解决方案提供反馈,其中 2016 年有 5,500 人提供反馈
* 每月 50,000 名访客,每周超过 12,000 名访客
* 目前的练习已经支持 33 种编程语言,另外 22 种语言在筹备工作中
该项目为各种级别的参与者提供了一系列小小的挑战,使他们能够“即使在低水平也能发展到高度谙熟”,Exercism 的创始人 [Katrina Owen](https://twitter.com/kytrinyx) 这样说到。Exercism 并不旨在教导学员成为一名职业程序员,但它的练习使他们对一种语言及其瑕疵有深刻的了解。这种熟悉性消除了学习者对语言的认知负担(使之更谙熟),使他们能够专注于更困难的架构和最佳实践的问题。
Exercism 通过一系列练习(或者还有别的?)来做到这一点。程序员下载[命令行客户端](http://exercism.io/cli),检索第一个练习,添加完成练习的代码,然后提交解决方案。提交解决方案后,程序员可以研究他人的解决方案,并学习到对同一个问题不同的解决方式。更重要的是,每个解决方案都会收到来自其他参与者的反馈。
反馈是 Exercism 的超级力量。鼓励所有参与者不仅接收反馈而且提供反馈。根据 Owen 说的,Exercism 的社区成员提供反馈比完成练习学到更多。她说:“这是一个强大的学习经验,你需要发表内心感受,并检查你的假设、习惯和偏见”。她还指出,反馈可以有多种形式。
欧文说:“只需进入,观察并发问”。
那些刚刚接触编程,甚至只是接触了一种特定语言的人,可以通过预设好的问题来提供有价值的反馈,同时通过协作和对话来学习。
除了对新语言的 <ruby> “微课”学习 <rt> bite-sized learning </rt></ruby> 之外,Exercism 本身还强烈支持和鼓励项目的新贡献者。在 [SitePoint.com](https://www.sitepoint.com/exorcise-your-newbie-demons-by-contributing-to-exercism/) 的一篇文章中,欧文强调:“如果你想为开源贡献代码,你所需要的技能水平只要‘够用’即可。” Exercism 不仅鼓励新的贡献者,它还尽可能地帮助新贡献者发布他们项目中的第一个补丁。到目前为止,有近 1000 人成为 [Exercism 项目](https://github.com/exercism)的贡献者。
新贡献者会有大量工作让他们忙碌。 Exercism 目前正在审查[其语言发展轨迹的健康状况](http://tinyletter.com/exercism/letters/exercism-track-health-check-new-maintainers),目的是使所有发展轨迹可持续并避免维护者的倦怠。它还在寻求[捐赠](http://exercism.io/donate)和赞助,聘请设计师提高网站的可用性。
Owen 说:“这些改进对于网站的健康以及为了 Exercism 参与者的发展是有必要的,这些变化还鼓励新贡献者加入并简化了加入的途径。” 她说:“如果我们可以重新设计,产品方面将更加可维护……当用户体验一团糟时,华丽的代码一点用也没有”。该项目有一个非常活跃的[讨论仓库](https://github.com/exercism/discussions/issues?page=1&q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen),这里社区成员合作来发现最好的新方法和功能。
那些想关注项目但还没有参与的人可以关注[邮件列表](http://tinyletter.com/exercism/archive)。
---
作者简介:
VM(Vicky)Brasseur - VM(也称为 Vicky)是技术人员、项目、流程、产品和 p^Hbusinesses 的经理。在她超过 18 年的科技行业从业中,她曾是分析师、程序员、产品经理、软件工程经理和软件工程总监。 目前,她是 Hewlett Packard Enterprise 上游开源开发团队的高级工程经理。 VM 的博客在 anonymoushash.vmbrasseur.com,tweets 是 @vmbrasseur。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/1/exercism-learning-programming>
作者:[VM (Vicky) Brasseur](https://opensource.com/users/vmbrasseur) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Many of us have a 2017 goal to improve our programming skills or to learn how to program in the first place. While we have access to many resources, practicing the art of code development independent of a specific job requires some planning. [Exercism.io](http://exercism.io/) is one resource designed for this exact purpose.
Exercism is an [open source](https://github.com/exercism) project and service aimed at helping people level up in their programming skills using a philosophy of discovery and collaboration. Exercism provides exercises for dozens of different programming languages. Practitioners complete each exercise and then receive feedback on their response, enabling them to learn from their peer group's experience.
And what a lot of peers there are. Exercism racked up some impressive stats in 2016:
- Participants from 201 different countries
- 29,000 participants submitted exercises since June 2013, with 15,500 of them submitting exercises in 2016 alone
- 15,000 participants provided feedback on exercise solutions since June 2013, with 5,500 of them providing feedback in 2016
- 50,000 visitors a month and over 12,000 each week
- 33 programming languages are currently supported by exercises, with another 22 in the works
The project provides a series of small wins to participants of all levels, allowing them to develop "a high degree of fluency even at a low level of proficiency," said [Katrina Owen](https://twitter.com/kytrinyx), founder of Exercism. While Exercism does not aim to teach participants enough to become employed as a programmer, its exercises give them a deep familiarity with a language and its foibles. This familiarity removes the cognitive burden of language from learners (fluency), allowing them to focus instead on the more difficult problems of architecture and best practices (proficiency).
Exercism does this through a series of (what else?) exercises. A programmer downloads the [command line client](http://exercism.io/cli), retrieves the first exercise, adds code that fulfills the exercise, and then submits the solution. After submitting a solution the programmer can study the solutions of others and learn from different approaches to the same problem. More importantly, each solution receives feedback from other participants.
Feedback is the super power of Exercism. All participants are encouraged not only to receive feedback, but also to provide it. According to Owen, members of the Exercism community learn more from providing feedback than from completing the exercises themselves. "It's a powerful learning experience. You're forced to articulate gut feelings and to examine your assumptions, habits, and biases," she said. She also pointed out that feedback can take many forms.
"Just go in and make observations and ask questions," said Owen.
Those who are new to programming, or even just to a specific language, can provide valuable feedback by questioning assumptions while also learning through collaboration and dialog.
Beyond just enabling bite-sized learning of new languages, Exercism itself strongly supports and encourages new contributors to the project. In an [article on SitePoint.com](https://www.sitepoint.com/exorcise-your-newbie-demons-by-contributing-to-exercism/), Owen stressed that, "If you want to contribute code to open source, the level of skill you need is 'good enough.'" Exercism not only encourages new contributors, but as a project it does everything possible to help new contributors land their first patch. To date nearly 1,000 people are contributors to the [Exercism project](https://github.com/exercism).
New contributors will have plenty to keep them busy. Exercism is currently reviewing [the health of its language tracks](http://tinyletter.com/exercism/letters/exercism-track-health-check-new-maintainers) with an eye toward making all tracks sustainable and avoiding maintainer burnout. It's also seeking [donations](http://exercism.io/donate) and sponsorships to hire designers to improve the usability of the site.
These improvements are necessary for the health of the site and for the well-being of Exercism's participants, but also these changes encourage and ease the path for new contributors to join, said Owen. "The product side would be much more maintainable if we could get this redesigned... When the user experience is a mess, there really is no point in having gorgeous code," she said. The project has a very vibrant [discussion repo](https://github.com/exercism/discussions/issues?page=1&q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen) where community members collaborate to discover the best new approaches and features.
Those who want to keep tabs on the project but not yet participate can follow along on the [behind the scenes mailing list](http://tinyletter.com/exercism/archive).
## 2 Comments |
8,406 | 使用 AWS 的 GO SDK 获取区域与终端节点信息 | https://aws.amazon.com/cn/blogs/developer/using-the-aws-sdk-for-gos-regions-and-endpoints-metadata | 2017-04-15T16:20:21 | [
"AWS",
"Go"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8406-1.html | LCTT 译注: <ruby> 终端节点 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Endpoint </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,详情请见: <http://docs.amazonaws.cn/general/latest/gr/rande.html>
最新发布的 GO 的 SDK [v1.6.0](https://github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go/releases/tag/v1.6.0) 版本,加入了获取区域与终端节点信息的功能。它可以很方便地列出区域、服务和终端节点的相关信息。可以通过 [github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go/aws/endpoints](http://docs.aws.amazon.com/sdk-for-go/api/aws/endpoints/) 包使用这些功能。

endpoints 包提供了一个易用的接口,可以获取到一个服务的终端节点的 url 列表和区域列表信息。并且我们将相关信息根据 AWS 服务区域进行了分组,如 AWS 标准、AWS 中国和 AWS GovCloud(美国)。
### 解析终端节点
设置 SDK 的默认配置时, SDK 会自动地使用 `endpoints.DefaultResolver` 函数。你也可以自己调用包中的`EndpointFor` 方法来解析终端节点。
```
// 解析在us-west-2区域的S3服务的终端节点
resolver := endpoints.DefaultResolver()
endpoint, err := resolver.EndpointFor(endpoints.S3ServiceID, endpoints.UsWest2RegionID)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("failed to resolve endpoint", err)
return
}
fmt.Println("Resolved URL:", endpoint.URL)
```
如果你需要自定义终端节点的解析逻辑,你可以实现 `endpoints.Resolver` 接口,并传值给`aws.Config.EndpointResolver`。当你打算编写自定义的终端节点逻辑,让 SDK 可以用来解析服务的终端节点时候,这个功能就会很有用。
以下示例,创建了一个配置好的 Session,然后 [Amazon S3](https://aws.amazon.com/s3/) 服务的客户端就可以使用这个自定义的终端节点。
```
s3CustResolverFn := func(service, region string, optFns ...func(*endpoints.Options)) (endpoints.ResolvedEndpoint, error) {
if service == "s3" {
return endpoints.ResolvedEndpoint{
URL: "s3.custom.endpoint.com",
SigningRegion: "custom-signing-region",
}, nil
}
return defaultResolver.EndpointFor(service, region, optFns...)
}
sess := session.Must(session.NewSessionWithOptions(session.Options{
Config: aws.Config{
Region: aws.String("us-west-2"),
EndpointResolver: endpoints.ResolverFunc(s3CustResolverFn),
},
}))
```
### 分区
`endpoints.DefaultResolver` 函数的返回值可以被 `endpoints.EnumPartitions`接口使用。这样就可以获取 SDK 使用的分区片段,也可以列出每个分区的分区信息。
```
// 迭代所有分区表打印每个分区的ID
resolver := endpoints.DefaultResolver()
partitions := resolver.(endpoints.EnumPartitions).Partitions()
for _, p := range partitions {
fmt.Println("Partition:", p.ID())
}
```
除了分区表之外,endpoints 包也提供了每个分区组的 getter 函数。这些工具函数可以方便列出指定分区,而不用执行默认解析器列出所有的分区。
```
partition := endpoints.AwsPartition()
region := partition.Regions()[endpoints.UsWest2RegionID]
fmt.Println("Services in region:", region.ID())
for id, _ := range region.Services() {
fmt.Println(id)
}
```
当你获取区域和服务值后,可以调用 `ResolveEndpoint`。这样解析端点时,就可以提供分区的过滤视图。
获取更多 AWS SDK for GO 信息, 请关注[其开源仓库](https://github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go/tree/master/example/aws/endpoints)。若你有更好的看法,请留言评论。
---
via: <https://aws.amazon.com/cn/blogs/developer/using-the-aws-sdk-for-gos-regions-and-endpoints-metadata>
作者:[Jason Del Ponte](https://aws.amazon.com/cn/blogs/developer/using-the-aws-sdk-for-gos-regions-and-endpoints-metadata) 译者:[Vic020](http://vicyu.com) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | null |
|
8,407 | 在 Linux 上使用 Nginx 和 Gunicorn 托管 Django 应用 | https://linuxconfig.org/hosting-django-with-nginx-and-gunicorn-on-linux | 2017-04-15T16:35:19 | [
"Django",
"Gunicorn"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8407-1.html | 
### 介绍
托管 Django Web 应用程序相当简单,虽然它比标准的 PHP 应用程序更复杂一些。 让 Web 服务器对接 Django 的方法有很多。 Gunicorn 就是其中最简单的一个。
Gunicorn(Green Unicorn 的缩写)在你的 Web 服务器 Django 之间作为中间服务器使用,在这里,Web 服务器就是 Nginx。 Gunicorn 服务于应用程序,而 Nginx 处理静态内容。
### Gunicorn
#### 安装
使用 Pip 安装 Gunicorn 是超级简单的。 如果你已经使用 virtualenv 搭建好了你的 Django 项目,那么你就有了 Pip,并且应该熟悉 Pip 的工作方式。 所以,在你的 virtualenv 中安装 Gunicorn。
```
$ pip install gunicorn
```
#### 配置
Gunicorn 最有吸引力的一个地方就是它的配置非常简单。处理配置最好的方法就是在 Django 项目的根目录下创建一个名叫 `Gunicorn` 的文件夹。然后在该文件夹内,创建一个配置文件。
在本篇教程中,配置文件名称是 `gunicorn-conf.py`。在该文件中,创建类似于下面的配置:
```
import multiprocessing
bind = 'unix:///tmp/gunicorn1.sock'
workers = multiprocessing.cpu_count() * 2 + 1
reload = True
daemon = True
```
在上述配置的情况下,Gunicorn 会在 `/tmp/` 目录下创建一个名为 `gunicorn1.sock` 的 Unix 套接字。 还会启动一些工作进程,进程数量相当于 CPU 内核数量的 2 倍。 它还会自动重新加载并作为守护进程运行。
#### 运行
Gunicorn 的运行命令有点长,指定了一些附加的配置项。 最重要的部分是将 Gunicorn 指向你项目的 `.wsgi` 文件。
```
gunicorn -c gunicorn/gunicorn-conf.py -D --error-logfile gunicorn/error.log yourproject.wsgi
```
上面的命令应该从项目的根目录运行。 `-c` 选项告诉 Gunicorn 使用你创建的配置文件。 `-D` 再次指定 gunicorn 为守护进程。 最后一部分指定 Gunicorn 的错误日志文件在你创建 `Gunicorn` 文件夹中的位置。 命令结束部分就是为 Gunicorn 指定 `.wsgi` 文件的位置。
### Nginx
现在 Gunicorn 配置好了并且已经开始运行了,你可以设置 Nginx 连接它,为你的静态文件提供服务。 本指南假定你已经配置好了 Nginx,而且你通过它托管的站点使用了单独的 server 块。 它还将包括一些 SSL 信息。
如果你想知道如何让你的网站获得免费的 SSL 证书,请查看我们的 [Let'sEncrypt 指南](https://linuxconfig.org/generate-ssl-certificates-with-letsencrypt-debian-linux)。
```
# 连接到 Gunicorn
upstream yourproject-gunicorn {
server unix:/tmp/gunicorn1.sock fail_timeout=0;
}
# 将未加密的流量重定向到加密的网站
server {
listen 80;
server_name yourwebsite.com;
return 301 https://yourwebsite.com$request_uri;
}
# 主服务块
server {
# 设置监听的端口,指定监听的域名
listen 443 default ssl;
client_max_body_size 4G;
server_name yourwebsite.com;
# 指定日志位置
access_log /var/log/nginx/yourwebsite.access_log main;
error_log /var/log/nginx/yourwebsite.error_log info;
# 告诉 nginx 你的 ssl 证书
ssl on;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/yourwebsite.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/yourwebsite.com/privkey.pem;
# 设置根目录
root /var/www/yourvirtualenv/yourproject;
# 为 Nginx 指定静态文件路径
location /static/ {
# Autoindex the files to make them browsable if you want
autoindex on;
# The location of your files
alias /var/www/yourvirtualenv/yourproject/static/;
# Set up caching for your static files
expires 1M;
access_log off;
add_header Cache-Control "public";
proxy_ignore_headers "Set-Cookie";
}
# 为 Nginx 指定你上传文件的路径
location /media/ {
Autoindex if you want
autoindex on;
# The location of your uploaded files
alias /var/www/yourvirtualenv/yourproject/media/;
# Set up aching for your uploaded files
expires 1M;
access_log off;
add_header Cache-Control "public";
proxy_ignore_headers "Set-Cookie";
}
location / {
# Try your static files first, then redirect to Gunicorn
try_files $uri @proxy_to_app;
}
# 将请求传递给 Gunicorn
location @proxy_to_app {
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_pass http://njc-gunicorn;
}
# 缓存 HTML、XML 和 JSON
location ~* \.(html?|xml|json)$ {
expires 1h;
}
# 缓存所有其他的静态资源
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|css|js|ttf|woff2)$ {
expires 1M;
access_log off;
add_header Cache-Control "public";
proxy_ignore_headers "Set-Cookie";
}
}
```
配置文件有点长,但是还可以更长一些。其中重点是指向 Gunicorn 的 `upstream` 块以及将流量传递给 Gunicorn 的 `location` 块。大多数其他的配置项都是可选,但是你应该按照一定的形式来配置。配置中的注释应该可以帮助你了解具体细节。
保存文件之后,你可以重启 Nginx,让修改的配置生效。
```
# systemctl restart nginx
```
一旦 Nginx 在线生效,你的站点就可以通过域名访问了。
### 结语
如果你想深入研究,Nginx 可以做很多事情。但是,上面提供的配置是一个很好的开始,并且你可以用于实践中。 如果你见惯了 Apache 和臃肿的 PHP 应用程序,像这样的服务器配置的速度应该是一个惊喜。
---
via: <https://linuxconfig.org/hosting-django-with-nginx-and-gunicorn-on-linux>
作者:[Nick Congleton](https://linuxconfig.org/hosting-django-with-nginx-and-gunicorn-on-linux) 译者:[Flowsnow](https://github.com/Flowsnow) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
8,408 | 如何在 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 上启用桌面共享 | http://www.tecmint.com/enable-desktop-sharing-in-ubuntu-linux-mint/ | 2017-04-15T16:46:12 | [
"桌面",
"共享"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8408-1.html | 
桌面共享是指通过图形终端仿真器在计算机桌面上实现远程访问和远程协作的技术。桌面共享允许两个或多个连接到网络的计算机用户在不同位置对同一个文件进行操作。
在这篇文章中,我将向你展示如何在 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 中启用桌面共享,并展示一些重要的安全特性。
### 在 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 上启用桌面共享
1、在 Ubuntu Dash 或 Linux Mint 菜单中,像下面的截图这样搜索 `desktop sharing`,搜索到以后,打开它。

*在 Ubuntu 中搜索 Desktop sharing*
2、打开 Desktop sharing 以后,有三个关于桌面共享设置的选项:共享、安全以及通知设置。
在共享选项下面,选中选项“允许其他用户查看桌面”来启用桌面共享。另外,你还可以选中选项“允许其他用户控制你的桌面”,从而允许其他用户远程控制你的桌面。

*桌面共享偏好*
3、接下来,在“安全”部分,你可以通过勾选选项“你必须确认任何对该计算机的访问”来手动确认每个远程连接。
另外,另一个有用的安全特性是通过选项“需要用户输入密码”创建一个确定的共享密码。这样当用户每次想要访问你的桌面时需要知道并输入密码。
4、对于通知,你可以勾选“仅当有人连接上时”来监视远程连接,这样每次当有人远程连接到你的桌面时,可以在通知区域查看。

*配置桌面共享设置*
当所有的桌面共享选项都设置好以后,点击“关闭”。现在,你已经在你的 Ubuntu 或 Linux Mint 上成功启用了桌面共享。
### 测试 Ubuntu 的远程桌面共享
你可以通过使用一个远程连接应用来进行测试,从而确保桌面共享可用。在这个例子中,我将展示上面设置的一些选项是如何工作的。
5、我将使用 VNC(虚拟网络计算)协议通过 [remmina 远程连接应用](http://www.tecmint.com/remmina-remote-desktop-sharing-and-ssh-client)连接到我的 Ubuntu PC。

*Remmina 桌面共享工具*
6、在点击 Ubuntu PC 以后,将会出现下面这个配置连接设置的界面,

*Remmina 桌面共享偏好*
7、当执行好所有设置以后,点击连接。然后,给用户名提供 SSH 密码并点击 OK 。

*输入 SSH 用户密码*
点击确定以后,出现下面这个黑屏,这是因为在远程机器上,连接还没有确认。

*连接确认前的黑屏*
8、现在,在远程机器上,我需要如下一个屏幕截图显示的那样点击 `Allow` 来接受远程访问请求。

*允许远程桌面共享*
9、在接受请求以后,我就成功地连接到了远程 Ubuntu 机器的桌面。

*远程 Ubuntu 桌面*
这就是全部内容了,在这篇文章中,我们讲解了如何在 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 中启用桌面共享。你使用评论部分给我们写反馈。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux 系统管理员和网络开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/enable-desktop-sharing-in-ubuntu-linux-mint/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,409 | 使用 IBM Bluemix 构建,部署和管理自定义应用程序 | http://opensourceforu.com/2016/11/build-deploy-manage-custom-apps-ibm-bluemix/ | 2017-04-16T09:58:34 | [
"Bluemix"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8409-1.html | 
Bluemix 是由 IBM 实现的基于开放标准的云平台。它具有开放的架构,其允许组织能够在云上创建、开发和管理其应用程序。它基于 Cloud Foundry ,因此可以被视为平台即服务(PaaS)。使用 Bluemix,开发人员不必关心云端配置,可以专注于他们的应用程序。 云端配置将由 Bluemix 自动完成。
Bluemix 还提供了一个仪表板,通过它,开发人员可以创建,管理和查看服务和应用程序,同时还可以监控资源使用情况。
它支持以下编程语言:
* Java
* Python
* Ruby on Rails
* PHP
* Node.js
它还支持 OpenWhisk(FaaS),这也是一个 IBM 的产品,其允许开发人员调用任一功能而不需要任何资源管理。

*图1 IBM Bluemix 概述*

*图2 IBM Bluemix 体系结构*

*图3 在 IBM Bluemix 中创建组织*
### IBM Bluemix 如何工作
Bluemix 构建在 IBM 的 SoftLayer IaaS(基础架构即服务)之上。它使用 Cloud Foundry 作为开源 PaaS 平台。一切起于通过 Cloud Foundry 来推送代码,它扮演着将代码和编写应用所使用的编程语言运行时环境整合起来的角色。IBM 服务、第三方服务或社区构建的服务可用于不同的功能。安全连接器可用于将本地系统连接到云。

*图4 在 IBM Bluemix 中设置空间*

*图5 应用程序模板*

*图6 IBM Bluemix 支持的编程语言*
### 在 Bluemix 中创建应用程序
在本文中,我们将使用 Liberty for Java 的入门包在 IBM Bluemix 中创建一个示例“Hello World”应用程序,只需几个简单的步骤。
1、 打开 [https://console.ng.bluemix.net/registration/](https://console.ng.bluemix.net/registration/)
2、 注册 Bluemix 帐户
3、 点击邮件中的确认链接完成注册过程
4、 输入您的电子邮件 ID,然后点击 Continue 进行登录
5、 输入密码并点击 Log in
6、 进入 Set up -> Environment 设置特定区域中的资源共享
7、 创建空间方便管理访问控制和在 Bluemix 中回滚操作。 我们可以将空间映射到多个开发阶段,如 dev, test,uat,pre-prod 和 prod

*图7 命名应用程序*

*图8 了解应用程序何时准备就绪*

*图9 IBM Bluemix Java 应用程序*
8、 完成初始配置后,单击 I'm ready -> Good to Go !
9、 成功登录后,此时检查 IBM Bluemix 仪表板,特别是 Cloud Foundry Apps(其中 2GB 可用)和 Virtual Server(其中 0 个实例可用)的部分
10、 点击 Create app,选择应用创建模板。在我们的例子中,我们将使用一个 Web 应用程序
11、 如何开始?单击 Liberty for Java ,然后查看其描述
12、 单击 Continue
13、 为新应用命名。对于本文,让我们使用 osfy-bluemix-tutorial 命名然后单击 Finish
14、 在 Bluemix 上创建资源和托管应用程序需要等待一些时间
15、 几分钟后,应用程式就会开始运作。注意应用程序的URL
16、 访问应用程序的URL http://osfy-bluemix-tutorial.au-syd.mybluemix.net/, 不错,我们的第一个在 IBM Bluemix 上的 Java 应用程序成功运行
17、 为了检查源代码,请单击 Files 并在门户中导航到不同文件和文件夹
18、 Logs 部分提供包括从应用程序的创建时起的所有活动日志。
19、 Environment Variables 部分提供关于 VCAP\_Services 的所有环境变量以及用户定义的环境变量的详细信息
20、 要检查应用程序的资源消耗,需要到 Liberty for Java 那一部分。
21、 默认情况下,每个应用程序的 Overview 部分包含资源,应用程序的运行状况和活动日志的详细信息
22、 打开 Eclipse,转到帮助菜单,然后单击 *Eclipse Marketplace*
23、 查找 IBM Eclipse tools for Bluemix 并单击 Install
24、 确认所选的功能并将其安装在 Eclipse 中
25、 下载应用程序启动器代码。点击 File Menu,将它导入到 Eclipse 中,选择 Import Existing Projects -> Workspace, 然后开始修改代码

*图10 Java 应用程序源文件*

*图11 Java 应用程序日志*

*图12 Java 应用程序 - Liberty for Java*
### 为什么选择 IBM Bluemix?
以下是使用 IBM Bluemix 的一些令人信服的理由:
* 支持多种语言和平台
* 免费试用
1. 简化的注册过程
2. 不需要信用卡
3. 30 天试用期 - 配额 2GB 的运行时,支持 20 个服务,500 个 route
4. 无限制地访问标准支持
5. 没有生产使用限制
* 仅为每个使用的运行时和服务付费
* 快速设置 - 从而加快上架时间
* 持续交付新功能
* 与本地资源的安全集成
* 用例
1. Web 应用程序和移动后端
2. API 和内部集成
* DevOps 服务可部署在云上的 SaaS ,并支持持续交付:
1. Web IDE
2. SCM
3. 敏捷规划
4. 交货管道服务
---
via: <http://opensourceforu.com/2016/11/build-deploy-manage-custom-apps-ibm-bluemix/>
作者:[MITESH\_SONI](http://opensourceforu.com/author/mitesh_soni/) 译者:[Vic020](http//www.vicyu.net) 校对:[Bestony](https://github.com/Bestony)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,410 | Samba 系列(七):在 Samba AD DC 服务器上创建共享目录并映射到 Windows/Linux 客户 | http://www.tecmint.com/create-shared-directory-on-samba-ad-dc-and-map-to-windows-linux/ | 2017-04-16T10:22:00 | [
"Samba"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8410-1.html | 这篇文章将指导你如何在 Samba AD DC 服务器上创建共享目录,然后通过 GPO 把共享目录挂载到域中的其它 Windows 成员机,并且从 Windows 域控的角度来管理共享权限。
这篇文章也包括在加入域的 Linux 机器上如何使用 Samba4 域帐号来访问及挂载共享文件。

### 需求:
1、[在 Ubuntu 系统上使用 Samba4 来创建活动目录架构](/article-8065-1.html)
2、[在 Linux 命令行下管理 Samba4 AD 架构](/article-8070-1.html)
3、[使用 Windows 10 的 RSAT 工具来管理 Samba4 活动目录架构](/article-8097-1.html)
4、[在 Windows 下管理 Samba4 AD 域管制器 DNS 和组策略](/article-8258-1.html)
5、[将另一台 Ubuntu DC 服务器加入到 Samba4 AD DC 实现双域控主机模式](/article-8358-1.html)
6、[使用 Rsync 命令同步两个 Samba4 AD DC 之间的 SysVol 目录](/article-8384-1.html)
### 第一步:创建 Samba 文件共享
1、在 Samba AD DC 服务器上创建共享非常简单。首先创建一个你想通过 SMB 协议来分享文件的目录,然后添加下面的文件系统权限,这是为了让 Windows AD DC 管理员给 Windows 客户端分配相应的共享权限。
假设在 AD DC 服务器上有一个新的共享目录 '/nas' ,执行下面的命令来授予必要的权限。
```
# mkdir /nas
# chmod -R 775 /nas
# chown -R root:"domain users" /nas
# ls -alh | grep nas
```

*创建 Samba 共享目录*
2、当你在 Samba4 AD DC 服务器上创建完成共享目录之后,你还得修改 samba 配置文件,添加下面的参数以允许通过 SMB 协议来共享文件。
```
# nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
```
在配置文件末尾添加以下内容:
```
[nas]
path = /nas
read only = no
```

*配置 Samba 共享目录*
3、最后,你需要通过下面的命令重启 Samba AD DC 服务,以让修改的配置生效:
```
# systemctl restart samba-ad-dc.service
```
### 第二步:管理 Samba 共享权限
4、我们准备使用在 Samba AD DC 服务器上创建的域帐号(包括用户和组)来访问这个共享目录(禁止 Linux 系统用户访问共享目录)。
可以直接通过 Windows 资源管理器来完成 Samba 共享权限的管理,就跟你在 Windows 资源管理器中设置其它文件夹权限的方法一样。
首先,使用具有管理员权限的 Samba4 AD 域帐号登录到 Windows 机器。然而在 Windows 机器上的资源管理器中输入双斜杠和 Samba AD DC 服务器的 IP 地址或主机名或者是 FQDN 来访问共享文件和设置权限。
```
\\adc1
或
\\192.168.1.254
或
\\adc1.tecmint.lan
```

*从 Windows 机器访问 Samba 共享目录*
5、右键单击共享文件,选择属性来设置权限。打开安全选项卡,依次修改域账号和组权限。使用高级选项来调整权限。

*配置 Samba 共享目录权限*
可参考下面的截图来为指定 Samba AD DC 认证用户设置权限。

*设置 Samba 共享目录用户权限*
6、你也可以使用其它方法来设置共享权限,打开计算机管理-->连接到另外一台计算机。
找到共享目录,右键单击你想修改权限的目录,选择属性,打开安全选项卡。你可以在这里修改任何权限,就跟上图的修改共享文件夹权限的方法一样。

*连接到 Samba 共享目录服务器*

*管理 Samba 共享目录属性*

*为域用户授予共享目录权限*
### 第三步:通过 GPO 来映射 Samba 文件共享
7、要想通过域组策略来挂载 Samba 共享的目录,你得先到一台[已安装了 RSAT 工具](/article-8097-1.html) 的服务器上,打开 AD DC 工具,右键单击域名,选择新建-->共享文件夹。

*映射 Samba 共享文件夹*
8、为共享文件夹添加一个名字,然后输入共享文件夹的网络路径,如下图所示。完成后单击 OK 按钮,你就可以在右侧看到文件夹了。

*设置 Samba 共享文件夹名称及路径*
9、下一步,打开组策略管理控制台,找到当前域的默认域策略脚本,然后打开并编辑该文件。
在 GPM 编辑器界面,打开 GPM 编辑器,找到用户配置 --> 首选项 --> Windows 设置,然而右键单击驱动器映射,选择新建 --> 映射驱动。

*在 Windows 机器上映射 Samba 共享文件夹*
10、通过单击右边的三个小点,在新窗口中查询并添加共享目录的网络位置,勾选重新连接复选框,为该目录添加一个标签,选择驱动盘符,然后单击 OK 按钮来保存和应用配置。

*配置 Samba 共享目录的网络位置*
11、最后,为了在本地机器上强制应用 GPO 更改而不重启系统,打开命令行提示符,然而执行下面的命令。
```
gpupdate /force
```

*应用 GPO 更改*
12、当你在本地机器上成功应用策略后,打开 Windows 资源管理器,你就可以看到并访问共享的网络文件夹了,能否正常访问共享目录取决于你在前一步的授权操作。
如果没有在命令行下强制应用组策略,你网络中的其它客户机需要重启或重新登录系统才可以看到共享目录。

*Windows 机器上挂载的 Samba 网络磁盘*
### 第四步:从 Linux 客户端访问 Samba 共享目录
13、已加入 Samba AD DC 中的 Linux 成员机上的系统用户也可以可以使用 Samba 帐号访问或在本地挂载共享目录。
首先,你得通过下面的命令来确保 Samba 客户端和工具已经安装完成。
```
$ sudo apt-get install smbclient cifs-utils
```
14、为了列出域环境中的共享目录,你可以通过下面的命令加入指定的域控服务器主机名来查询:
```
$ smbclient –L your_domain_controller –U%
或
$ smbclient –L \\adc1 –U%
```

*在 Linux 机器上列出 Samba 共享目录*
15、在命令行下使用域帐号以交互试方式连接到 Samba 共享目录:
```
$ sudo smbclient //adc/share_name -U domain_user
```
在命令行下,你可以列出共享目录内容,下载或上传文件到共享目录,或者执行其它操作。使用 `?` 来查询所有可用的 smbclient 命令。

*在 Linux 机器上连接 Samba 共享目录*
16、在 Linux 机器上使用下面的命令来挂载 samba 共享目录。
```
$ sudo mount //adc/share_name /mnt -o username=domain_user
```

*在 Linux 机器上挂载 samba 共享目录*
根据实际情况,依次替换主机名、共享目录名、挂载点和域帐号。使用 `mount` 命令加上管道符和 `grep` 命令来过滤出 cifs 类型的文件系统。
通过上面的测试,我们可以看出,在 Samba4 AD DC 服务器上配置共享目录仅使用 Windows 访问控制列表( ACL ),而不是 POSIX ACL 。
通过文件共享把 Samba 配置为域成员以使用其它网络共享功能。同时,在另一个域控制器上[配置 Windbindd 服务](/article-8070-1.html) ——在你开始发起网络共享文件之前。
---
作者简介:
我是一个电脑迷,开源 Linux 系统和软件爱好者,有 4 年多的 Linux 桌面、服务器系统使用和 Base 编程经验。
译者简介:
春城初春/春水初生/春林初盛/春風十裏不如妳 [rusking](https://github.com/rusking)
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/create-shared-directory-on-samba-ad-dc-and-map-to-windows-linux/>
作者:[Matei Cezar](http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,411 | 工程师和市场营销人员之间能够相互学习什么? | https://opensource.com/open-organization/17/1/engineers-marketers-can-learn | 2017-04-16T20:01:41 | [
"工程师",
"市场营销"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8411-1.html |
>
> 营销人员觉得工程师在工作中都太严谨了;而工程师则认为营销人员毫无用处。但是他们都错了。
>
>
>

在 B2B 行业从事多年的销售实践过程中,我经常听到工程师对营销人员的各种误解。下面这些是比较常见的:
* “搞市场营销真是浪费钱,还不如把更多的资金投入到实际的产品开发中来。”
* “那些营销人员只是一个劲儿往墙上贴各种广告,还祈祷着它们不要掉下来。这么做有啥科学依据啊?”
* “谁愿意去看哪些广告啊?”
* “对待一个营销人员最好的办法就是不听,不看,也不理睬。”
这是我最感兴趣的一点:
*“市场营销无足轻重。”*
最后一点说的不对,而且不仅如此,它实际上是阻碍一个公司创新的巨大绊脚石。
我来跟大家解释一下原因吧。
### 看到自己的身影
这些工程师的的评论让我十分的苦恼,因为我从中看到了自己当年的身影。
你们知道吗?我曾经也跟你们一样是一位自豪的技术极客。我在 Rensselaer Polytechnic 学院的电气工程专业本科毕业后便在美国空军担任军官开始了我的职业生涯,而且美国空军在那段时间还发动了沙漠风暴行动。在那里我主要负责开发并部属一套智能的实时战况分析系统,用于综合几个的数据源来构建出战场态势。
在我离开空军之后,我本打算去麻省理工学院攻读博士学位。但是上校强烈建议我去报读这个学校的商学院。“你真的想一辈子待实验室里吗?”他问我。“你想就这么去大学里当个教书匠吗?Jackie ,你在组织管理那些复杂的工作中比较有天赋。我觉得你非常有必要去了解下 MIT 的斯隆商学院。”
我觉得自己也可以同时参加一些 MIT 技术方面的课程,因此我采纳了他的建议。然而,如果要参加市场营销管理方面的课程,我还有很长的路要走,这完全是在浪费时间。因此,在日常工作学习中,我始终是用自己所擅长的分析能力去解决一切问题。
不久后,我在波士顿咨询集团公司做咨询顾问工作。在那六年的时间里,我经常听到大家对我的评论: “Jackie ,你太没远见了。考虑问题也不够周全。你总是通过自己的分析去找答案。”
确实如此啊,我很赞同他们的想法——因为这个世界的工作方式本该如此,任何问题都要基于数据进行分析,不对吗?直到现在我才意识到(我多么希望自己早一些发现自己的问题)自己以前惯用的分析问题的方法遗漏了很多重要的东西:开放的心态、艺术修养、情感——人和创造性思维相关的因素。
我在 2001 年 9 月 11 日加入达美航空公司不久后,被调去管理消费者市场部门,之前我意识到的所有问题变得更加明显。市场方面本来不是我的强项,但是在公司需要的情况下,我也愿意出手相肋。
但是突然之间,我一直惯用的方法获取到的分析结果却与实际情况完全相反。这个问题导致上千人(包括航线内外的人)受到影响。我忽略了一个很重要的人本身的情感因素。我所面临的问题需要各种各样的解决方案才能处理,而不是简单的从那些死板的数据中就能得到答案。
那段时间,我快速地学到了很多东西,因为如果我们想把达美航空公司恢复到正常状态,还需要做很多的工作——市场营销更像是一个以解决问题为导向、以用户为中心的充满挑战性的大工程,只是销售人员和工程师这两大阵营都没有迅速地意识到这个问题。
### 两大文化差异
工程管理和市场营销之间的这个“巨大鸿沟”确实是根深蒂固的,这跟(著名的科学家、小说家) C.P. Snow 提出的[“两大文化差异”问题](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Two_Cultures#Implications_and_influence)很相似。具有科学素质的工程师和具有艺术细胞的营销人员操着不同的语言,不同的文化观念导致他们不同的价值取向。
但是,事实上他们比想象中有更多的相似之处。一个由微软、谷歌和美国国家科学基金会共同赞助的华盛顿大学的[最新研究](https://faculty.washington.edu/ajko/papers/Li2015GreatEngineers.pdf)发现了“一个伟大软件工程师必须具备哪些优秀的素质”,毫无疑问,一个伟大的销售人员同样也应该具备这些素质。例如,专家们给出的一些优秀品质如下:
* 充满激情
* 性格开朗
* 强烈的好奇心
* 技艺精湛
* 解决复杂难题的能力
这些只是其中很小的一部分!当然,并不是所有的素质都适用于市场营销人员,但是如果用文氏图来表示这“两大文化”的交集,就很容易看出营销人员和工程师之间的关系要远比我们想象中密切得多。他们都是竭力去解决与用户或客户相关的难题,只是他们所采取的方式和角度不一致罢了。
看到上面的那几点后,我深深的陷入思考:*要是这两类员工彼此之间再多了解对方一些会怎样呢?这会给公司带来很强大的动力吧?*
确实如此。我在红帽公司就亲眼看到过样的情形,我身边都是一些早些年肯定被我当成“想法疯狂”而无视的人。而且我猜销售人员看到工程师后(同时或某一次),心想,“这些数据呆瓜,真是只见树木不见森林。”
现在我才明白了公司里有这两种人才的重要性。在现实工作当中,工程师和营销人员都是围绕着客户、创新及数据分析来完成工作。如果他们能够懂得相互尊重、彼此理解、相辅相成,那么我们将会看到公司里所产生的那种积极强大的动力,这种超乎寻常的革新力量要远比两个独立的团队强大得多。
### 听一听疯子(和呆瓜)的想法
成功案例:《开放式组织》
在红帽任职期间,我的主要工作就是想办法提升公司的品牌影响力——但是就是给我一百万年我也不会想到让公司的 CEO 去写一本书。我把公司多个部门的“想法疯狂”的同事召集在一起,希望他们帮我设计出一个新颖的解决方案来提升公司的影响力,结果他们提出让公司的 CEO 写书这样一个想法。
当我听到这个想法的时候,我很快意识到这正是典型的红帽方式:它将对整个开源社区的从业者带来很重要的参考价值,同时也有助于宣扬开源精神。通过优先考虑这两方面的作用,我们提升了红帽在整个开源软件世界中的品牌价值——红帽是一个可靠的随时准备着为客户在[数字化颠覆](https://opensource.com/open-organization/16/7/future-belongs-open-leaders)年代指明方向的公司。
这一点才是主要的:确切的说是指导红帽工程师解决代码问题的共同精神力量。 Red Hatters 小组敦促我出版《开放式组织》,这显示出来自内部和外部社区的程序员共同推动整个开源社区发展的强大动力之一:那就是强烈的共享欲望。
最后,要把《开放式组织》这本书完成,还需要大家的共同能力,包括工程师们强大的数据分析能力和营销人员美好的艺术素养。这个项目让我更加坚定自己的想法,工程师和营销人员有更多的相似之处。
但是,有些东西我还得强调下:开放模式的实现,要求公司上下没有任何偏见,不能偏袒工程师和市场营销人员任何一方文化。一个更加理想的开放式环境能够促使员工之间和平共处,并在这个组织规定的范围内点燃大家的热情。
这对我来说如春风拂面。
(图片来源:opensource.com)
---
作者简介:
Jackie Yeaney —— Ellucian 公司市场总监
---
via: <https://opensource.com/open-organization/17/1/engineers-marketers-can-learn>
作者:[Jackie Yeaney](https://opensource.com/users/jackie-yeaney) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[Bestony](https://github.com/Bestony), [wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | After many years of practicing marketing in the B2B tech world, I think I've heard just about every misconception that engineers seem to have about marketers. Here are some of the more common:
- "Marketing is a waste of money that we should be putting into actual product development."
- "Those marketers just throw stuff against the wall and hope it sticks. Where's the discipline?"
- "Does anyone actually read this stuff?"
- "The best thing a marketer can tell me is how to unsubscribe, unfollow, and unfriend."
And here's my personal favorite:
*"Marketing is all fluff."*
That last one is simply incorrect—but more than that, It's actually a major impediment to innovation in our organizations today.
Let me explain why.
## Seeing my own reflection
I think these comments from engineers bother me so much because I see a bit of my former self in them.
You see, I was once as geeky as they come—and was proud of it. I hold a Bachelor's in electrical engineering from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, and began my professional career as an officer in the US Air Force during Desert Storm. There, I was in charge of developing and deploying a near real-time intelligence system that correlated several sources of data to create a picture of the battlefield.
After I left the Air Force, I planned to pursue a doctorate from MIT. But my Colonel convinced me to take a look at their business school. "Are you really going to be in a lab?" he asked me. "Are you going to teach at a university? Jackie, you are gifted at orchestrating complex activities. I think you really need to look at MIT Sloan."
So I took his advice, believing I could still enroll in a few tech courses at MIT. Taking a marketing course, however, would certainly have been a step too far—a total waste of time. I continued to bring my analytical skills to bear on any problem put in front of me.
Soon after, I became a management consultant at The Boston Consulting Group. Throughout my six years there, I consistently heard the same feedback: "Jackie, you're not visionary enough. You're not thinking outside the box. You assume your analysis is going to point you to the answer."
And of course, I agreed with them—because that's the way the world works, isn't it? What I realize now (and wish I'd discovered out far earlier) is that by taking this approach I was missing something pivotal: the open mind, the art, the emotion—the human and creative elements.
All this became much more apparent when I joined Delta Air Lines soon after September 11, 2001, and was asked to help lead consumer marketing. Marketing *definitely* wasn't my thing, but I was willing to help however they needed me to.
But suddenly, my rulebook for achieving familiar results was turned upside down. Thousands of people (both inside and outside the airline) were involved in this problem. Emotions were running high. I was facing problems that required different kinds of solutions, answers I couldn't reach simply by crunching numbers.
That's when I learned—and quickly, because we had much work to do if we were going to pull Delta back up to where it deserved to be—that marketing can be as much a strategic, problem-oriented and user-centered function as engineering is, even if these two camps don't immediately recognize it.
## Two cultures
That "great divide" between engineering and marketing is deep indeed—so entrenched that it resembles what C.P. Snow once called[ the "two cultures" problem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Two_Cultures#Implications_and_influence). Scientifically minded engineers and artistically minded marketers tend to speak different languages, and they're acculturated to believe they value divergent things.
But the fact is that they're more similar than they might think.[ A recent study](https://faculty.washington.edu/ajko/papers/Li2015GreatEngineers.pdf) from the University of Washington (co-sponsored by Microsoft, Google, and the National Science Foundation) identified "what makes a great software engineer," and (not surprisingly) the list of characteristics sounds like it could apply to great marketers, too. For example, the authors list traits like:
- Passion
- Open-mindedness
- Curiosity
- Cultivation of craft
- Ability to handle complexity
And these are just a few! Of course, not every characteristic on the list applies to marketers—but the Venn diagram connecting these "two cultures" is tighter than I believe most of us think. *Both* are striving to solve complex user and/or customer challenges. They just take a different approach to doing it.
Reading this list got me thinking: *What if these two personalities understood each other just a little bit more? Would there be power in that?*
You bet. I've seen it firsthand at Red Hat, where I'm surrounded by people I'd have quickly dismissed as "crazy creatives" during my early days. And I'd be willing to bet that a marketer has (at one time or another) looked at an engineer and thought, "Look at this data nerd. Can't see the forest beyond the trees."
I now understand the power of having both perspectives in the same room. And in reality, engineers and marketers are *both* working at the *intersection of customers, creativity, and analytics*. And if they could just learn to recognize the ways their personalities compliment each other, we could see tremendously positive results—results far more surprising and innovative than we'd see if we kept them isolated from one another.
## Listening to the crazies (and the nerds)
Case in point: *The Open Organization*.
In my role at Red Hat I spent much of my day thinking about how to extend and amplify our brand—but never in a million years would I have thought to do it by asking our CEO to write a book. That idea came from a cross-functional team of those "crazy creatives," a group of people I rely on to help me imagine new and innovative solutions to branding challenges.
When I heard the idea, I recognized it right away as a quintessentially Red Hat approach to our work: something that would be valuable to a community of practitioners, and something that helps spread the message of openness just a little farther. By prioritizing these two goals above all others, we'd reinforce Red Hat's position as a positive force in the open source world, a trusted expert ready to help customers navigate the turbulence of[ digital disruption](https://opensource.com/open-organization/16/7/future-belongs-open-leaders).
Here's the clincher: *That's exactly the same spirit guiding Red Hat engineers tackling problems of code.* The group of Red Hatters urging me to help make *The Open Organization* a reality demonstrated one of the very same motivations as the programmers that make up our internal and external communities: a desire to share.
In the end, bringing *The Open Organization* to life required help from across the spectrum of skills—both the intensely analytic and the beautifully artistic. Everyone pitched in. The project only cemented my belief that engineers and marketers are more alike than different.
But it also reinforced something else: The realization that openness shows no bias, no preference for a culture of engineering or a culture of marketing. The idea of a more open world can inspire them both equally, and the passion it ignites ripples across the artificial boundaries we draw around our groups.
That hardly sounds like fluff to me.
*This article is part of The Open Organization Guide to IT culture change.*
## Comments are closed. |
8,414 | 漫画赏析:消沉的程序员 13 | http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-13/ | 2017-04-17T08:58:05 | [
"漫画",
"程序员"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8414-1.html | 
嘿嘿,明明你有很厉害的东西想要分享给自己的同伴,可是他们并不能理解那意味着什么,然后拿一些简单的不能再简单的事情来问你。是不是感觉好尴尬呢。看来有些事儿,分享也要看人的吧,否则表错情真的是大写的失落。
---
译者简介:
[GHLandy](http://ghlandy.com/) —— 生活中所有欢乐与苦闷都应藏在心中,有些事儿注定无人知晓,自己也无从说起。
---
via: <http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-13/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 合成:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 点评:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,415 | 漫画赏析:消沉的程序员 14 | http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-14/ | 2017-04-20T08:58:00 | [
"漫画",
"程序员"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8415-1.html | 
不管什么是在什么事情上,你所期待的结果,都是通过尽心设计才能得到的。所以,有拖延症的各位亲们,切莫把所有都拖到最后一分钟才去考虑解决方案哦,不然会死的很惨的。
---
译者简介:
[GHLandy](http://ghlandy.com/) —— 生活中所有欢乐与苦闷都应藏在心中,有些事儿注定无人知晓,自己也无从说起。
---
via: <http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-14/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 合成:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 点评:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,416 | 深入解析面向数据的哈希表性能 | http://reedbeta.com/blog/data-oriented-hash-table/ | 2017-04-17T11:16:00 | [
"编程",
"性能"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8416-1.html | 
最近几年中,面向数据的设计已经受到了很多的关注 —— 一种强调内存中数据布局的编程风格,包括如何访问以及将会引发多少的 cache 缺失。由于在内存读取操作中缺失所占的数量级要大于命中的数量级,所以缺失的数量通常是优化的关键标准。这不仅仅关乎那些对性能有要求的 code-data 结构设计的软件,由于缺乏对内存效益的重视而成为软件运行缓慢、膨胀的一个很大因素。
高效缓存数据结构的中心原则是将事情变得平滑和线性。比如,在大部分情况下,存储一个序列元素更倾向于使用普通数组而不是链表 —— 每一次通过指针来查找数据都会为 cache 缺失增加一份风险;而普通数组则可以预先获取,并使得内存系统以最大的效率运行
如果你知道一点内存层级如何运作的知识,下面的内容会是想当然的结果——但是有时候即便它们相当明显,测试一下任不失为一个好主意。几年前 [Baptiste Wicht 测试过了 `std::vector` vs `std::list` vs `std::deque`](http://baptiste-wicht.com/posts/2012/12/cpp-benchmark-vector-list-deque.html),(后者通常使用分块数组来实现,比如:一个数组的数组)。结果大部分会和你预期的保持一致,但是会存在一些违反直觉的东西。作为实例:在序列链表的中间位置做插入或者移除操作被认为会比数组快,但如果该元素是一个 POD 类型,并且不大于 64 字节或者在 64 字节左右(在一个 cache 流水线内),通过对要操作的元素周围的数组元素进行移位操作要比从头遍历链表来的快。这是由于在遍历链表以及通过指针插入/删除元素的时候可能会导致不少的 cache 缺失,相对而言,数组移位则很少会发生。(对于更大的元素,非 POD 类型,或者你已经有了指向链表元素的指针,此时和预期的一样,链表胜出)
多亏了类似 Baptiste 这样的数据,我们知道了内存布局如何影响序列容器。但是关联容器,比如 hash 表会怎么样呢?已经有了些权威推荐:[Chandler Carruth 推荐的带局部探测的开放寻址](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fHNmRkzxHWs)(此时,我们没必要追踪指针),以及[Mike Acton 推荐的在内存中将 value 和 key 隔离](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rX0ItVEVjHc)(这种情况下,我们可以在每一个 cache 流水线中得到更多的 key), 这可以在我们必须查找多个 key 时提高局部性能。这些想法很有意义,但再一次的说明:测试永远是好习惯,但由于我找不到任何数据,所以只好自己收集了。
### 测试
我测试了四个不同的 quick-and-dirty 哈希表实现,另外还包括 `std::unordered_map` 。这五个哈希表都使用了同一个哈希函数 —— Bob Jenkins 的 [SpookyHash](http://burtleburtle.net/bob/hash/spooky.html)(64 位哈希值)。(由于哈希函数在这里不是重点,所以我没有测试不同的哈希函数;我同样也没有检测我的分析中的总内存消耗。)实现会通过简短的代码在测试结果表中标注出来。
* **UM**: `std::unordered_map` 。在 VS2012 和 libstdc++-v3 (libstdc++-v3: gcc 和 clang 都会用到这东西)中,UM 是以链表的形式实现,所有的元素都在链表中,bucket 数组中存储了链表的迭代器。VS2012 中,则是一个双链表,每一个 bucket 存储了起始迭代器和结束迭代器;libstdc++ 中,是一个单链表,每一个 bucket 只存储了一个起始迭代器。这两种情况里,链表节点是独立申请和释放的。最大负载因子是 1 。
* **Ch**:分离的、链状 bucket 指向一个元素节点的单链表。为了避免分开申请每一个节点,元素节点存储在普通数组池中。未使用的节点保存在一个空闲链表中。最大负载因子是 1。
* **OL**:开地址线性探测 —— 每一个 bucket 存储一个 62 bit 的 hash 值,一个 2 bit 的状态值(包括 empty,filled,removed 三个状态),key 和 value 。最大负载因子是 2/3。
* **DO1**:“data-oriented 1” —— 和 OL 相似,但是哈希值、状态值和 key、values 分离在两个隔离的平滑数组中。
* **DO2**:“data-oriented 2” —— 与 OL 类似,但是哈希/状态,keys 和 values 被分离在 3 个相隔离的平滑数组中。
在我的所有实现中,包括 VS2012 的 UM 实现,默认使用尺寸为 2 的 n 次方。如果超出了最大负载因子,则扩展两倍。在 libstdc++ 中,UM 默认尺寸是一个素数。如果超出了最大负载因子,则扩展为下一个素数大小。但是我不认为这些细节对性能很重要。素数是一种对低 bit 位上没有足够熵的低劣 hash 函数的挽救手段,但是我们正在用的是一个很好的 hash 函数。
OL,DO1 和 DO2 的实现将共同的被称为 OA(open addressing)——稍后我们将发现它们在性能特性上非常相似。在每一个实现中,单元数从 100 K 到 1 M,有效负载(比如:总的 key + value 大小)从 8 到 4 k 字节我为几个不同的操作记了时间。 keys 和 values 永远是 POD 类型,keys 永远是 8 个字节(除了 8 字节的有效负载,此时 key 和 value 都是 4 字节)因为我的目的是为了测试内存影响而不是哈希函数性能,所以我将 key 放在连续的尺寸空间中。每一个测试都会重复 5 遍,然后记录最小的耗时。
测试的操作在这里:
* **Fill**:将一个随机的 key 序列插入到表中(key 在序列中是唯一的)。
* **Presized fill**:和 Fill 相似,但是在插入之间我们先为所有的 key 保留足够的内存空间,以防止在 fill 过程中 rehash 或者重申请。
* **Lookup**:执行 100 k 次随机 key 查找,所有的 key 都在 table 中。
* **Failed lookup**: 执行 100 k 次随机 key 查找,所有的 key 都不在 table 中。
* **Remove**:从 table 中移除随机选择的半数元素。
* **Destruct**:销毁 table 并释放内存。
你可以[在这里下载我的测试代码](http://reedbeta.com/blog/data-oriented-hash-table/hash-table-tests.zip)。这些代码只能在 64 机器上编译(包括Windows和Linux)。在 `main()` 函数顶部附近有一些开关,你可把它们打开或者关掉——如果全开,可能会需要一两个小时才能结束运行。我收集的结果也放在了那个打包文件里的 Excel 表中。(注意: Windows 和 Linux 在不同的 CPU 上跑的,所以时间不具备可比较性)代码也跑了一些单元测试,用来验证所有的 hash 表实现都能运行正确。
我还顺带尝试了附加的两个实现:Ch 中第一个节点存放在 bucket 中而不是 pool 里,二次探测的开放寻址。 这两个都不足以好到可以放在最终的数据里,但是它们的代码仍放在了打包文件里面。
### 结果
这里有成吨的数据!! 这一节我将详细的讨论一下结果,但是如果你对此不感兴趣,可以直接跳到下一节的总结。
#### Windows
这是所有的测试的图表结果,使用 Visual Studio 2012 编译,运行于 Windows 8.1 和 Core i7-4710HQ 机器上。

从左至右是不同的有效负载大小,从上往下是不同的操作(注意:不是所有的Y轴都是相同的比例!)我将为每一个操作总结一下主要趋向。
**Fill**:
在我的 hash 表中,Ch 稍比任何的 OA 变种要好。随着哈希表大小和有效负载的加大,差距也随之变大。我猜测这是由于 Ch 只需要从一个空闲链表中拉取一个元素,然后把它放在 bucket 前面,而 OA 不得不搜索一部分 bucket 来找到一个空位置。所有的 OA 变种的性能表现基本都很相似,当然 DO1 稍微有点优势。
在小负载的情况,UM 几乎是所有 hash 表中表现最差的 —— 因为 UM 为每一次的插入申请(内存)付出了沉重的代价。但是在 128 字节的时候,这些 hash 表基本相当,大负载的时候 UM 还赢了点。因为,我所有的实现都需要重新调整元素池的大小,并需要移动大量的元素到新池里面,这一点我几乎无能为力;而 UM 一旦为元素申请了内存后便不需要移动了。注意大负载中图表上夸张的跳步!这更确认了重新调整大小带来的问题。相反,UM 只是线性上升 —— 只需要重新调整 bucket 数组大小。由于没有太多隆起的地方,所以相对有效率。
**Presized fill**:
大致和 Fill 相似,但是图示结果更加的线性光滑,没有太大的跳步(因为不需要 rehash ),所有的实现差距在这一测试中要缩小了些。大负载时 UM 依然稍快于 Ch,问题还是在于重新调整大小上。Ch 仍是稳步少快于 OA 变种,但是 DO1 比其它的 OA 稍有优势。
**Lookup**:
所有的实现都相当的集中。除了最小负载时,DO1 和 OL 稍快,其余情况下 UM 和 DO2 都跑在了前面。(LCTT 译注: 你确定?)真的,我无法描述 UM 在这一步做的多么好。尽管需要遍历链表,但是 UM 还是坚守了面向数据的本性。
顺带一提,查找时间和 hash 表的大小有着很弱的关联,这真的很有意思。 哈希表查找时间期望上是一个常量时间,所以在的渐进视图中,性能不应该依赖于表的大小。但是那是在忽视了 cache 影响的情况下!作为具体的例子,当我们在具有 10 k 条目的表中做 100 k 次查找时,速度会便变快,因为在第一次 10 k - 20 k 次查找后,大部分的表会处在 L3 中。
**Failed lookup**:
相对于成功查找,这里就有点更分散一些。DO1 和 DO2 跑在了前面,但 UM 并没有落下,OL 则是捉襟见肘啊。我猜测,这可能是因为 OL 整体上具有更长的搜索路径,尤其是在失败查询时;内存中,hash 值在 key 和 value 之飘来荡去的找不着出路,我也很受伤啊。DO1 和 DO2 具有相同的搜索长度,但是它们将所有的 hash 值打包在内存中,这使得问题有所缓解。
**Remove**:
DO2 很显然是赢家,但 DO1 也未落下。Ch 则落后,UM 则是差的不是一丁半点(主要是因为每次移除都要释放内存);差距随着负载的增加而拉大。移除操作是唯一不需要接触数据的操作,只需要 hash 值和 key 的帮助,这也是为什么 DO1 和 DO2 在移除操作中的表现大相径庭,而其它测试中却保持一致。(如果你的值不是 POD 类型的,并需要析构,这种差异应该是会消失的。)
**Destruct**:
Ch 除了最小负载,其它的情况都是最快的(最小负载时,约等于 OA 变种)。所有的 OA 变种基本都是相等的。注意,在我的 hash 表中所做的所有析构操作都是释放少量的内存 buffer 。但是 [在Windows中,释放内存的消耗和大小成比例关系](https://randomascii.wordpress.com/2014/12/10/hidden-costs-of-memory-allocation/)。(而且,这是一个很显著的开支 —— 申请 ~1 GB 的内存需要 ~100 ms 的时间去释放!)
UM 在析构时是最慢的一个(小负载时,慢的程度可以用数量级来衡量),大负载时依旧是稍慢些。对于 UM 来讲,释放每一个元素而不是释放一组数组真的是一个硬伤。
#### Linux
我还在装有 Linux Mint 17.1 的 Core i5-4570S 机器上使用 gcc 4.8 和 clang 3.5 来运行了测试。gcc 和 clang 的结果很相像,因此我只展示了 gcc 的;完整的结果集合包含在了代码下载打包文件中,链接在上面。

大部分结果和 Windows 很相似,因此我只高亮了一些有趣的不同点。
**Lookup**:
这里 DO1 跑在前头,而在 Windows 中 DO2 更快些。(LCTT 译注: 这里原文写错了吧?)同样,UM 和 Ch 落后于其它所有的实现——过多的指针追踪,然而 OA 只需要在内存中线性的移动即可。至于 Windows 和 Linux 结果为何不同,则不是很清楚。UM 同样比 Ch 慢了不少,特别是大负载时,这很奇怪;我期望的是它们可以基本相同。
**Failed lookup**:
UM 再一次落后于其它实现,甚至比 OL 还要慢。我再一次无法理解为何 UM 比 Ch 慢这么多,Linux 和 Windows 的结果为何有着如此大的差距。
**Destruct**:
在我的实现中,小负载的时候,析构的消耗太少了,以至于无法测量;在大负载中,线性增加的比例和创建的虚拟内存页数量相关,而不是申请到的数量?同样,要比 Windows 中的析构快上几个数量级。但是并不是所有的都和 hash 表有关;我们在这里可以看出不同系统和运行时内存系统的表现。貌似,Linux 释放大内存块是要比 Windows 快上不少(或者 Linux 很好的隐藏了开支,或许将释放工作推迟到了进程退出,又或者将工作推给了其它线程或者进程)。
UM 由于要释放每一个元素,所以在所有的负载中都比其它慢上几个数量级。事实上,我将图片做了剪裁,因为 UM 太慢了,以至于破坏了 Y 轴的比例。
### 总结
好,当我们凝视各种情况下的数据和矛盾的结果时,我们可以得出什么结果呢?我想直接了当的告诉你这些 hash 表变种中有一个打败了其它所有的 hash 表,但是这显然不那么简单。不过我们仍然可以学到一些东西。
首先,在大多数情况下我们“很容易”做的比 `std::unordered_map` 还要好。我为这些测试所写的所有实现(它们并不复杂;我只花了一两个小时就写完了)要么是符合 `unordered_map` 要么是在其基础上做的提高,除了大负载(超过128字节)中的插入性能, `unordered_map` 为每一个节点独立申请存储占了优势。(尽管我没有测试,我同样期望 `unordered_map` 能在非 POD 类型的负载上取得胜利。)具有指导意义的是,如果你非常关心性能,不要假设你的标准库中的数据结构是高度优化的。它们可能只是在 C++ 标准的一致性上做了优化,但不是性能。:P
其次,如果不管在小负载还是超负载中,若都只用 DO1 (开放寻址,线性探测,hashes/states 和 key/vaules分别处在隔离的普通数组中),那可能不会有啥好表现。这不是最快的插入,但也不坏(还比 `unordered_map` 快),并且在查找,移除,析构中也很快。你所知道的 —— “面向数据设计”完成了!
注意,我的为这些哈希表做的测试代码远未能用于生产环境——它们只支持 POD 类型,没有拷贝构造函数以及类似的东西,也未检测重复的 key,等等。我将可能尽快的构建一些实际的 hash 表,用于我的实用库中。为了覆盖基础部分,我想我将有两个变种:一个基于 DO1,用于小的,移动时不需要太大开支的负载;另一个用于链接并且避免重新申请和移动元素(就像 `unordered_map` ),用于大负载或者移动起来需要大开支的负载情况。这应该会给我带来最好的两个世界。
与此同时,我希望你们会有所启迪。最后记住,如果 Chandler Carruth 和 Mike Acton 在数据结构上给你提出些建议,你一定要听。
---
作者简介:
我是一名图形程序员,目前在西雅图做自由职业者。之前我在 NVIDIA 的 DevTech 软件团队中工作,并在美少女特工队工作室中为 PS3 和 PS4 的 Infamous 系列游戏开发渲染技术。
自 2002 年起,我对图形非常感兴趣,并且已经完成了一系列的工作,包括:雾、大气雾霾、体积照明、水、视觉效果、粒子系统、皮肤和头发阴影、后处理、镜面模型、线性空间渲染、和 GPU 性能测量和优化。
你可以在我的博客了解更多和我有关的事,除了图形,我还对理论物理和程序设计感兴趣。
你可以在 [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected]) 或者在 Twitter(@Reedbeta)/Google+ 上关注我。我也会经常在 StackExchange 上回答计算机图形的问题。
---
via: <http://reedbeta.com/blog/data-oriented-hash-table/>
作者:[Nathan Reed](http://reedbeta.com/about/) 译者:[sanfusu](https://github.com/sanfusu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,418 | 调试器工作原理(一):基础篇 | http://eli.thegreenplace.net/2011/01/23/how-debuggers-work-part-1 | 2017-04-18T09:04:00 | [
"调试",
"调试器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8418-1.html | 
这是调试器工作原理系列文章的第一篇,我不确定这个系列会有多少篇文章,会涉及多少话题,但我仍会从这篇基础开始。
### 这一篇会讲什么
我将为大家展示 Linux 中调试器的主要构成模块 - `ptrace` 系统调用。这篇文章所有代码都是基于 32 位 Ubuntu 操作系统。值得注意的是,尽管这些代码是平台相关的,将它们移植到其它平台应该并不困难。
### 缘由
为了理解我们要做什么,让我们先考虑下调试器为了完成调试都需要什么资源。调试器可以开始一个进程并调试这个进程,又或者将自己同某个已经存在的进程关联起来。调试器能够单步执行代码,设定断点并且将程序执行到断点,检查变量的值并追踪堆栈。许多调试器有着更高级的特性,例如在调试器的地址空间内执行表达式或者调用函数,甚至可以在进程执行过程中改变代码并观察效果。
尽管现代的调试器都十分的复杂(我没有检查,但我确信 gdb 的代码行数至少有六位数),但它们的工作的原理却是十分的简单。调试器的基础是操作系统与编译器 / 链接器提供的一些基础服务,其余的部分只是[简单的编程](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Small_matter_of_programming)而已。
### Linux 的调试 - ptrace
Linux 调试器中的瑞士军刀便是 `ptrace` 系统调用(使用 man 2 ptrace 命令可以了解更多)。这是一种复杂却强大的工具,可以允许一个进程控制另外一个进程并从<ruby> 内部替换 <rt> Peek and poke </rt></ruby>被控制进程的内核镜像的值(Peek and poke 在系统编程中是很知名的叫法,指的是直接读写内存内容)。
接下来会深入分析。
### 执行进程的代码
我将编写一个示例,实现一个在“跟踪”模式下运行的进程。在这个模式下,我们将单步执行进程的代码,就像机器码(汇编代码)被 CPU 执行时一样。我将分段展示、讲解示例代码,在文章的末尾也有完整 c 文件的下载链接,你可以编译、执行或者随心所欲的更改。
更进一步的计划是实现一段代码,这段代码可以创建可执行用户自定义命令的子进程,同时父进程可以跟踪子进程。首先是主函数:
```
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
pid_t child_pid;
if (argc < 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "Expected a program name as argument\n");
return -1;
}
child_pid = fork();
if (child_pid == 0)
run_target(argv[1]);
else if (child_pid > 0)
run_debugger(child_pid);
else {
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
```
看起来相当的简单:我们用 `fork` 创建了一个新的子进程(这篇文章假定读者有一定的 Unix/Linux 编程经验。我假定你知道或至少了解 fork、exec 族函数与 Unix 信号)。if 语句的分支执行子进程(这里称之为 “target”),`else if` 的分支执行父进程(这里称之为 “debugger”)。
下面是 target 进程的代码:
```
void run_target(const char* programname)
{
procmsg("target started. will run '%s'\n", programname);
/* Allow tracing of this process */
if (ptrace(PTRACE_TRACEME, 0, 0, 0) < 0) {
perror("ptrace");
return;
}
/* Replace this process's image with the given program */
execl(programname, programname, 0);
}
```
这段代码中最值得注意的是 `ptrace` 调用。在 `sys/ptrace.h` 中,`ptrace` 是如下定义的:
```
long ptrace(enum __ptrace_request request, pid_t pid,
void *addr, void *data);
```
第一个参数是 `_request_`,这是许多预定义的 `PTRACE_*` 常量中的一个。第二个参数为请求分配进程 ID。第三个与第四个参数是地址与数据指针,用于操作内存。上面代码段中的 `ptrace` 调用发起了 `PTRACE_TRACEME` 请求,这意味着该子进程请求系统内核让其父进程跟踪自己。帮助页面上对于 request 的描述很清楚:
>
> 意味着该进程被其父进程跟踪。任何传递给该进程的信号(除了 `SIGKILL`)都将通过 `wait()` 方法阻塞该进程并通知其父进程。**此外,该进程的之后所有调用 `exec()` 动作都将导致 `SIGTRAP` 信号发送到此进程上,使得父进程在新的程序执行前得到取得控制权的机会**。如果一个进程并不需要它的的父进程跟踪它,那么这个进程不应该发送这个请求。(pid、addr 与 data 暂且不提)
>
>
>
我高亮了这个例子中我们需要注意的部分。在 `ptrace` 调用后,`run_target` 接下来要做的就是通过 `execl` 传参并调用。如同高亮部分所说明,这将导致系统内核在 `execl` 创建进程前暂时停止,并向父进程发送信号。
是时候看看父进程做什么了。
```
void run_debugger(pid_t child_pid)
{
int wait_status;
unsigned icounter = 0;
procmsg("debugger started\n");
/* Wait for child to stop on its first instruction */
wait(&wait_status);
while (WIFSTOPPED(wait_status)) {
icounter++;
/* Make the child execute another instruction */
if (ptrace(PTRACE_SINGLESTEP, child_pid, 0, 0) < 0) {
perror("ptrace");
return;
}
/* Wait for child to stop on its next instruction */
wait(&wait_status);
}
procmsg("the child executed %u instructions\n", icounter);
}
```
如前文所述,一旦子进程调用了 `exec`,子进程会停止并被发送 `SIGTRAP` 信号。父进程会等待该过程的发生并在第一个 `wait()` 处等待。一旦上述事件发生了,`wait()` 便会返回,由于子进程停止了父进程便会收到信号(如果子进程由于信号的发送停止了,`WIFSTOPPED` 就会返回 `true`)。
父进程接下来的动作就是整篇文章最需要关注的部分了。父进程会将 `PTRACE_SINGLESTEP` 与子进程 ID 作为参数调用 `ptrace` 方法。这就会告诉操作系统,“请恢复子进程,但在它执行下一条指令前阻塞”。周而复始地,父进程等待子进程阻塞,循环继续。当 `wait()` 中传出的信号不再是子进程的停止信号时,循环终止。在跟踪器(父进程)运行期间,这将会是被跟踪进程(子进程)传递给跟踪器的终止信号(如果子进程终止 `WIFEXITED` 将返回 `true`)。
`icounter` 存储了子进程执行指令的次数。这么看来我们小小的例子也完成了些有用的事情 - 在命令行中指定程序,它将执行该程序并记录它从开始到结束所需要的 cpu 指令数量。接下来就让我们这么做吧。
### 测试
我编译了下面这个简单的程序并利用跟踪器运行它:
```
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello, world!\n");
return 0;
}
```
令我惊讶的是,跟踪器花了相当长的时间,并报告整个执行过程共有超过 100,000 条指令执行。仅仅是一条输出语句?什么造成了这种情况?答案很有趣(至少你同我一样痴迷与机器/汇编语言)。Linux 的 gcc 默认会动态的将程序与 c 的运行时库动态地链接。这就意味着任何程序运行前的第一件事是需要动态库加载器去查找程序运行所需要的共享库。这些代码的数量很大 - 别忘了我们的跟踪器要跟踪每一条指令,不仅仅是主函数的,而是“整个进程中的指令”。
所以当我将测试程序使用静态编译时(通过比较,可执行文件会多出 500 KB 左右的大小,这部分是 C 运行时库的静态链接),跟踪器提示只有大概 7000 条指令被执行。这个数目仍然不小,但是考虑到在主函数执行前 libc 的初始化以及主函数执行后的清除代码,这个数目已经是相当不错了。此外,`printf` 也是一个复杂的函数。
仍然不满意的话,我需要的是“可以测试”的东西 - 例如可以完整记录每一个指令运行的程序执行过程。这当然可以通过汇编代码完成。所以我找到了这个版本的 “Hello, world!” 并编译了它。
```
section .text
; The _start symbol must be declared for the linker (ld)
global _start
_start:
; Prepare arguments for the sys_write system call:
; - eax: system call number (sys_write)
; - ebx: file descriptor (stdout)
; - ecx: pointer to string
; - edx: string length
mov edx, len
mov ecx, msg
mov ebx, 1
mov eax, 4
; Execute the sys_write system call
int 0x80
; Execute sys_exit
mov eax, 1
int 0x80
section .data
msg db 'Hello, world!', 0xa
len equ $ - msg
```
当然,现在跟踪器提示 7 条指令被执行了,这样一来很容易区分它们。
### 深入指令流
上面那个汇编语言编写的程序使得我可以向你介绍 `ptrace` 的另外一个强大的用途 - 详细显示被跟踪进程的状态。下面是 `run_debugger` 函数的另一个版本:
```
void run_debugger(pid_t child_pid)
{
int wait_status;
unsigned icounter = 0;
procmsg("debugger started\n");
/* Wait for child to stop on its first instruction */
wait(&wait_status);
while (WIFSTOPPED(wait_status)) {
icounter++;
struct user_regs_struct regs;
ptrace(PTRACE_GETREGS, child_pid, 0, ®s);
unsigned instr = ptrace(PTRACE_PEEKTEXT, child_pid, regs.eip, 0);
procmsg("icounter = %u. EIP = 0x%08x. instr = 0x%08x\n",
icounter, regs.eip, instr);
/* Make the child execute another instruction */
if (ptrace(PTRACE_SINGLESTEP, child_pid, 0, 0) < 0) {
perror("ptrace");
return;
}
/* Wait for child to stop on its next instruction */
wait(&wait_status);
}
procmsg("the child executed %u instructions\n", icounter);
}
```
不同仅仅存在于 `while` 循环的开始几行。这个版本里增加了两个新的 `ptrace` 调用。第一条将进程的寄存器值读取进了一个结构体中。 `sys/user.h` 定义有 `user_regs_struct`。如果你查看头文件,头部的注释这么写到:
```
/* 这个文件只为了 GDB 而创建
不用详细的阅读.如果你不知道你在干嘛,
不要在除了 GDB 以外的任何地方使用此文件 */
```
不知道你做何感想,但这让我觉得我们找对地方了。回到例子中,一旦我们在 `regs` 变量中取得了寄存器的值,我们就可以通过将 `PTRACE_PEEKTEXT` 作为参数、 `regs.eip`(x86 上的扩展指令指针)作为地址,调用 `ptrace` ,读取当前进程的当前指令(警告:如同我上面所说,文章很大程度上是平台相关的。我简化了一些设定 - 例如,x86 指令集不需要调整到 4 字节,我的32位 Ubuntu unsigned int 是 4 字节。事实上,许多平台都不需要。从内存中读取指令需要预先安装完整的反汇编器。我们这里没有,但实际的调试器是有的)。下面是新跟踪器所展示出的调试效果:
```
$ simple_tracer traced_helloworld
[5700] debugger started
[5701] target started. will run 'traced_helloworld'
[5700] icounter = 1\. EIP = 0x08048080\. instr = 0x00000eba
[5700] icounter = 2\. EIP = 0x08048085\. instr = 0x0490a0b9
[5700] icounter = 3\. EIP = 0x0804808a. instr = 0x000001bb
[5700] icounter = 4\. EIP = 0x0804808f. instr = 0x000004b8
[5700] icounter = 5\. EIP = 0x08048094\. instr = 0x01b880cd
Hello, world!
[5700] icounter = 6\. EIP = 0x08048096\. instr = 0x000001b8
[5700] icounter = 7\. EIP = 0x0804809b. instr = 0x000080cd
[5700] the child executed 7 instructions
```
现在,除了 `icounter`,我们也可以观察到指令指针与它每一步所指向的指令。怎么来判断这个结果对不对呢?使用 `objdump -d` 处理可执行文件:
```
$ objdump -d traced_helloworld
traced_helloworld: file format elf32-i386
Disassembly of section .text:
08048080 <.text>:
8048080: ba 0e 00 00 00 mov $0xe,%edx
8048085: b9 a0 90 04 08 mov $0x80490a0,%ecx
804808a: bb 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%ebx
804808f: b8 04 00 00 00 mov $0x4,%eax
8048094: cd 80 int $0x80
8048096: b8 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%eax
804809b: cd 80 int $0x80
```
这个结果和我们跟踪器的结果就很容易比较了。
### 将跟踪器关联到正在运行的进程
如你所知,调试器也能关联到已经运行的进程。现在你应该不会惊讶,`ptrace` 通过以 `PTRACE_ATTACH` 为参数调用也可以完成这个过程。这里我不会展示示例代码,通过上文的示例代码应该很容易实现这个过程。出于学习目的,这里使用的方法更简便(因为我们在子进程刚开始就可以让它停止)。
### 代码
上文中的简单的跟踪器(更高级的,可以打印指令的版本)的完整c源代码可以在[这里](https://github.com/eliben/code-for-blog/blob/master/2011/simple_tracer.c)找到。它是通过 4.4 版本的 gcc 以 `-Wall -pedantic --std=c99` 编译的。
### 结论与计划
诚然,这篇文章并没有涉及很多内容 - 我们距离亲手完成一个实际的调试器还有很长的路要走。但我希望这篇文章至少可以使得调试这件事少一些神秘感。`ptrace` 是功能多样的系统调用,我们目前只展示了其中的一小部分。
单步调试代码很有用,但也只是在一定程度上有用。上面我通过 C 的 “Hello World!” 做了示例。为了执行主函数,可能需要上万行代码来初始化 C 的运行环境。这并不是很方便。最理想的是在 `main` 函数入口处放置断点并从断点处开始分步执行。为此,在这个系列的下一篇,我打算展示怎么实现断点。
### 参考
撰写此文时参考了如下文章:
* [Playing with ptrace, Part I](http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/6100?page=0,1)
* [How debugger works](http://www.alexonlinux.com/how-debugger-works)
---
via: <http://eli.thegreenplace.net/2011/01/23/how-debuggers-work-part-1>
作者:[Eli Bendersky](http://eli.thegreenplace.net/) 译者:[YYforymj](https://github.com/YYforymj) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 302 | Found | null |
8,419 | 2016 Git 新视界 | https://medium.com/hacker-daily/git-in-2016-fad96ae22a15 | 2017-04-18T11:52:00 | [
"Git"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8419-1.html | 
2016 年 Git 发生了 *惊天动地* 地变化,发布了五大新特性**¹** (从 *v2.7* 到 *v2.11* )和十六个补丁**²**。189 位作者**³**贡献了 3676 个提交**⁴**到 `master` 分支,比 2015 年多了 15%**⁵**!总计有 1545 个文件被修改,其中增加了 276799 行并移除了 100973 行**⁶**。
但是,通过统计提交的数量和代码行数来衡量生产力是一种十分愚蠢的方法。除了深度研究过的开发者可以做到凭直觉来判断代码质量的地步,我们普通人来作仲裁难免会因我们常人的判断有失偏颇。
谨记这一条于心,我决定整理这一年里六个我最喜爱的 Git 特性涵盖的改进,来做一次分类回顾。这篇文章作为一篇中篇推文有点太过长了,所以我不介意你们直接跳到你们特别感兴趣的特性去。
* 完成 `git worktree` 命令
* 更多方便的 `git rebase` 选项
* `git lfs` 梦幻的性能加速
* `git diff` 实验性的算法和更好的默认结果
* `git submodules` 差强人意
* `git stash` 的90 个增强
在我们开始之前,请注意在大多数操作系统上都自带有 Git 的旧版本,所以你需要检查你是否在使用最新并且最棒的版本。如果在终端运行 `git --version` 返回的结果小于 Git `v2.11.0`,请立刻跳转到 Atlassian 的快速指南 [更新或安装 Git](https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/install-git/) 并根据你的平台做出选择。
### [所需的“引用”]
在我们进入高质量内容之前还需要做一个短暂的停顿:我觉得我需要为你展示我是如何从公开文档生成统计信息(以及开篇的封面图片)的。你也可以使用下面的命令来对你自己的仓库做一个快速的 *年度回顾*!
>
> ¹ 2016 年匹配 vX.Y.0 格式的里程碑
>
>
>
```
$ git for-each-ref --sort=-taggerdate --format \
'%(refname) %(taggerdate)' refs/tags | grep "v\d\.\d*\.0 .* 2016"
```
>
> ² 2016 年匹配 vX.Y.Z 格式的里程碑
>
>
>
```
$ git for-each-ref --sort=-taggerdate --format '%(refname) %(taggerdate)' refs/tags | grep "v\d\.\d*\.[^0] .* 2016"
```
>
> ³ 2016 年做过提交的贡献者数量
>
>
>
```
$ git shortlog -s -n --since=2016-01-01 --until=2017-01-01
```
>
> ⁴ 2016 年的提交数量
>
>
>
```
$ git log --oneline --since=2016-01-01 --until=2017-01-01 | wc -l
```
>
> ⁵ 以及 2015 年的提交数量
>
>
>
```
$ git log --oneline --since=2015-01-01 --until=2016-01-01 | wc -l
```
>
> ⁶ 2016 年添加、删除行数
>
>
>
```
$ git diff --shortstat `git rev-list -1 --until=2016-01-01 master` \
`git rev-list -1 --until=2017-01-01 master`
```
以上的命令是在 Git 的 `master` 分支运行的,所以不会显示其他出色的分支上没有合并的工作。如果你使用这些命令,请记住提交的数量和代码行数不是应该值得信赖的度量方式。请不要使用它们来衡量你的团队成员的贡献。
现在,让我们开始说好的回顾……
### 完成 Git <ruby> 工作树 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> worktree </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
`git worktree` 命令首次出现于 Git v2.5 ,但是在 2016 年有了一些显著的增强。两个有价值的新特性在 v2.7 被引入:`list` 子命令,和为二分搜索增加了命令空间的 refs。而 `lock`/`unlock` 子命令则是在 v2.10 被引入。
#### 什么是工作树呢?
[git worktree](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-worktree) 命令允许你同步地检出和操作处于不同路径下的同一仓库的多个分支。例如,假如你需要做一次快速的修复工作但又不想扰乱你当前的工作区,你可以使用以下命令在一个新路径下检出一个新分支:
```
$ git worktree add -b hotfix/BB-1234 ../hotfix/BB-1234
Preparing ../hotfix/BB-1234 (identifier BB-1234)
HEAD is now at 886e0ba Merged in bedwards/BB-13430-api-merge-pr (pull request #7822)
```
工作树不仅仅是为分支工作。你可以检出多个<ruby> 里程碑 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> tag </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>作为不同的工作树来并行构建或测试它们。例如,我从 Git v2.6 和 v2.7 的里程碑中创建工作树来检验不同版本 Git 的行为特征。
```
$ git worktree add ../git-v2.6.0 v2.6.0
Preparing ../git-v2.6.0 (identifier git-v2.6.0)
HEAD is now at be08dee Git 2.6
$ git worktree add ../git-v2.7.0 v2.7.0
Preparing ../git-v2.7.0 (identifier git-v2.7.0)
HEAD is now at 7548842 Git 2.7
$ git worktree list
/Users/kannonboy/src/git 7548842 [master]
/Users/kannonboy/src/git-v2.6.0 be08dee (detached HEAD)
/Users/kannonboy/src/git-v2.7.0 7548842 (detached HEAD)
$ cd ../git-v2.7.0 && make
```
你也使用同样的技术来并行构造和运行你自己应用程序的不同版本。
#### 列出工作树
`git worktree list` 子命令(于 Git v2.7 引入)显示所有与当前仓库有关的工作树。
```
$ git worktree list
/Users/kannonboy/src/bitbucket/bitbucket 37732bd [master]
/Users/kannonboy/src/bitbucket/staging d5924bc [staging]
/Users/kannonboy/src/bitbucket/hotfix-1234 37732bd [hotfix/1234]
```
#### 二分查找工作树
[git bisect](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-Tools-Debugging-with-Git#Binary-Search) 是一个简洁的 Git 命令,可以让我们对提交记录执行一次二分搜索。通常用来找到哪一次提交引入了一个指定的退化。例如,如果在我的 `master` 分支最后的提交上有一个测试没有通过,我可以使用 `git bisect` 来贯穿仓库的历史来找寻第一次造成这个错误的提交。
```
$ git bisect start
# 找到已知通过测试的最后提交
# (例如最新的发布里程碑)
$ git bisect good v2.0.0
# 找到已知的出问题的提交
# (例如在 `master` 上的提示)
$ git bisect bad master
# 告诉 git bisect 要运行的脚本/命令;
# git bisect 会在 “good” 和 “bad”范围内
# 找到导致脚本以非 0 状态退出的最旧的提交
$ git bisect run npm test
```
在后台,bisect 使用 refs 来跟踪 “good” 与 “bad” 的提交来作为二分搜索范围的上下界限。不幸的是,对工作树的粉丝来说,这些 refs 都存储在寻常的 `.git/refs/bisect` 命名空间,意味着 `git bisect` 操作如果运行在不同的工作树下可能会互相干扰。
到了 v2.7 版本,bisect 的 refs 移到了 `.git/worktrees/$worktree_name/refs/bisect`, 所以你可以并行运行 bisect 操作于多个工作树中。
#### 锁定工作树
当你完成了一颗工作树的工作,你可以直接删除它,然后通过运行 `git worktree prune` 等它被当做垃圾自动回收。但是,如果你在网络共享或者可移除媒介上存储了一颗工作树,如果工作树目录在删除期间不可访问,工作树会被完全清除——不管你喜不喜欢!Git v2.10 引入了 `git worktree lock` 和 `unlock` 子命令来防止这种情况发生。
```
# 在我的 USB 盘上锁定 git-v2.7 工作树
$ git worktree lock /Volumes/Flash_Gordon/git-v2.7 --reason \
"In case I remove my removable media"
```
```
# 当我完成时,解锁(并删除)该工作树
$ git worktree unlock /Volumes/Flash_Gordon/git-v2.7
$ rm -rf /Volumes/Flash_Gordon/git-v2.7
$ git worktree prune
```
`--reason` 标签允许为未来的你留一个记号,描述为什么当初工作树被锁定。`git worktree unlock` 和 `lock` 都要求你指定工作树的路径。或者,你可以 `cd` 到工作树目录然后运行 `git worktree lock .` 来达到同样的效果。
### 更多 Git <ruby> 变基 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> rebase </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>选项
2016 年三月,Git v2.8 增加了在拉取过程中交互进行变基的命令 `git pull --rebase=interactive` 。对应地,六月份 Git v2.9 发布了通过 `git rebase -x` 命令对执行变基操作而不需要进入交互模式的支持。
#### Re-啥?
在我们继续深入前,我假设读者中有些并不是很熟悉或者没有完全习惯变基命令或者交互式变基。从概念上说,它很简单,但是与很多 Git 的强大特性一样,变基散发着听起来很复杂的专业术语的气息。所以,在我们深入前,先来快速的复习一下什么是<ruby> 变基 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> rebase </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。
变基操作意味着将一个或多个提交在一个指定分支上重写。`git rebase` 命令是被深度重载了,但是 rebase 这个名字的来源事实上还是它经常被用来改变一个分支的基准提交(你基于此提交创建了这个分支)。
从概念上说,rebase 通过将你的分支上的提交临时存储为一系列补丁包,接着将这些补丁包按顺序依次打在目标提交之上。

对 master 分支的一个功能分支执行变基操作 (`git reabse master`)是一种通过将 master 分支上最新的改变合并到功能分支的“保鲜法”。对于长期存在的功能分支,规律的变基操作能够最大程度的减少开发过程中出现冲突的可能性和严重性。
有些团队会选择在合并他们的改动到 master 前立即执行变基操作以实现一次快速合并 (`git merge --ff <feature>`)。对 master 分支快速合并你的提交是通过简单的将 master ref 指向你的重写分支的顶点而不需要创建一个合并提交。

变基是如此方便和功能强大以致于它已经被嵌入其他常见的 Git 命令中,例如拉取操作 `git pull` 。如果你在本地 master 分支有未推送的提交,运行 `git pull` 命令从 origin 拉取你队友的改动会造成不必要的合并提交。

这有点混乱,而且在繁忙的团队,你会获得成堆的不必要的合并提交。`git pull --rebase` 将你本地的提交在你队友的提交上执行变基而不产生一个合并提交。

这很整洁吧!甚至更酷,Git v2.8 引入了一个新特性,允许你在拉取时 *交互地* 变基。
#### 交互式变基
交互式变基是变基操作的一种更强大的形态。和标准变基操作相似,它可以重写提交,但它也可以向你提供一个机会让你能够交互式地修改这些将被重新运用在新基准上的提交。
当你运行 `git rebase --interactive` (或 `git pull --rebase=interactive`)时,你会在你的文本编辑器中得到一个可供选择的提交列表视图。
```
$ git rebase master --interactive
pick 2fde787 ACE-1294: replaced miniamalCommit with string in test
pick ed93626 ACE-1294: removed pull request service from test
pick b02eb9a ACE-1294: moved fromHash, toHash and diffType to batch
pick e68f710 ACE-1294: added testing data to batch email file
# Rebase f32fa9d..0ddde5f onto f32fa9d (4 commands)
#
# Commands:
# p, pick = use commit
# r, reword = use commit, but edit the commit message
# e, edit = use commit, but stop for amending
# s, squash = use commit, but meld into previous commit
# f, fixup = like "squash", but discard this commit's log message
# x, exec = run command (the rest of the line) using shell
# d, drop = remove commit
#
# These lines can be re-ordered; they are executed from top to
# bottom.
#
# If you remove a line here THAT COMMIT WILL BE LOST.
```
注意到每一条提交旁都有一个 `pick`。这是对 rebase 而言,“照原样留下这个提交”。如果你现在就退出文本编辑器,它会执行一次如上文所述的普通变基操作。但是,如果你将 `pick` 改为 `edit` 或者其他 rebase 命令中的一个,变基操作会允许你在它被重新运用前改变它。有效的变基命令有如下几种:
* `reword`:编辑提交信息。
* `edit`:编辑提交了的文件。
* `squash`:将提交与之前的提交(同在文件中)合并,并将提交信息拼接。
* `fixup`:将本提交与上一条提交合并,并且逐字使用上一条提交的提交信息(这很方便,如果你为一个很小的改动创建了第二个提交,而它本身就应该属于上一条提交,例如,你忘记暂存了一个文件)。
* `exec`: 运行一条任意的 shell 命令(我们将会在下一节看到本例一次简洁的使用场景)。
* `drop`: 这将丢弃这条提交。
你也可以在文件内重新整理提交,这样会改变它们被重新应用的顺序。当你对不同的主题创建了交错的提交时这会很顺手,你可以使用 `squash` 或者 `fixup` 来将其合并成符合逻辑的原子提交。
当你设置完命令并且保存这个文件后,Git 将递归每一条提交,在每个 `reword` 和 `edit` 命令处为你暂停来执行你设计好的改变,并且自动运行 `squash`, `fixup`,`exec` 和 `drop` 命令。
#### 非交互性式执行
当你执行变基操作时,本质上你是在通过将你每一条新提交应用于指定基址的头部来重写历史。`git pull --rebase` 可能会有一点危险,因为根据上游分支改动的事实,你的新建历史可能会由于特定的提交遭遇测试失败甚至编译问题。如果这些改动引起了合并冲突,变基过程将会暂停并且允许你来解决它们。但是,整洁的合并改动仍然有可能打断编译或测试过程,留下破败的提交弄乱你的提交历史。
但是,你可以指导 Git 为每一个重写的提交来运行你的项目测试套件。在 Git v2.9 之前,你可以通过绑定 `git rebase --interactive` 和 `exec` 命令来实现。例如这样:
```
$ git rebase master −−interactive −−exec=”npm test”
```
……这会生成一个交互式变基计划,在重写每条提交后执行 `npm test` ,保证你的测试仍然会通过:
```
pick 2fde787 ACE-1294: replaced miniamalCommit with string in test
exec npm test
pick ed93626 ACE-1294: removed pull request service from test
exec npm test
pick b02eb9a ACE-1294: moved fromHash, toHash and diffType to batch
exec npm test
pick e68f710 ACE-1294: added testing data to batch email file
exec npm test
# Rebase f32fa9d..0ddde5f onto f32fa9d (4 command(s))
```
如果出现了测试失败的情况,变基会暂停并让你修复这些测试(并且将你的修改应用于相应提交):
```
291 passing
1 failing
1) Host request "after all" hook:
Uncaught Error: connect ECONNRESET 127.0.0.1:3001
…
npm ERR! Test failed.
Execution failed: npm test
You can fix the problem, and then run
git rebase −−continue
```
这很方便,但是使用交互式变基有一点臃肿。到了 Git v2.9,你可以这样来实现非交互式变基:
```
$ git rebase master -x "npm test"
```
可以简单替换 `npm test` 为 `make`,`rake`,`mvn clean install`,或者任何你用来构建或测试你的项目的命令。
#### 小小警告
就像电影里一样,重写历史可是一个危险的行当。任何提交被重写为变基操作的一部分都将改变它的 SHA-1 ID,这意味着 Git 会把它当作一个全新的提交对待。如果重写的历史和原来的历史混杂,你将获得重复的提交,而这可能在你的团队中引起不少的疑惑。
为了避免这个问题,你仅仅需要遵照一条简单的规则:
>
> *永远不要变基一条你已经推送的提交!*
>
>
>
坚持这一点你会没事的。
### Git LFS 的性能提升
[Git 是一个分布式版本控制系统](https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/what-is-git/),意味着整个仓库的历史会在克隆阶段被传送到客户端。对包含大文件的项目——尤其是大文件经常被修改——初始克隆会非常耗时,因为每一个版本的每一个文件都必须下载到客户端。[Git LFS](https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/git-lfs/)(<ruby> 大文件存储 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Large File Storage </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> )是一个 Git 拓展包,由 Atlassian、GitHub 和其他一些开源贡献者开发,通过需要时才下载大文件的相对版本来减少仓库中大文件的影响。更明确地说,大文件是在检出过程中按需下载的而不是在克隆或抓取过程中。
在 Git 2016 年的五大发布中,Git LFS 自身就有四个功能版本的发布:v1.2 到 v1.5。你可以仅对 Git LFS 这一项来写一系列回顾文章,但是就这篇文章而言,我将专注于 2016 年解决的一项最重要的主题:速度。一系列针对 Git 和 Git LFS 的改进极大程度地优化了将文件传入/传出服务器的性能。
#### 长期过滤进程
当你 `git add` 一个文件时,Git 的净化过滤系统会被用来在文件被写入 Git 目标存储之前转化文件的内容。Git LFS 通过使用<ruby> 净化过滤器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> clean filter </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>将大文件内容存储到 LFS 缓存中以缩减仓库的大小,并且增加一个小“指针”文件到 Git 目标存储中作为替代。

<ruby> 污化过滤器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> smudge filter </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>是净化过滤器的对立面——正如其名。在 `git checkout` 过程中从一个 Git 目标仓库读取文件内容时,污化过滤系统有机会在文件被写入用户的工作区前将其改写。Git LFS 污化过滤器通过将指针文件替代为对应的大文件将其转化,可以是从 LFS 缓存中获得或者通过读取存储在 Bitbucket 的 Git LFS。

传统上,污化和净化过滤进程在每个文件被增加和检出时只能被唤起一次。所以,一个项目如果有 1000 个文件在被 Git LFS 追踪 ,做一次全新的检出需要唤起 `git-lfs-smudge` 命令 1000 次。尽管单次操作相对很迅速,但是经常执行 1000 次独立的污化进程总耗费惊人。、
针对 Git v2.11(和 Git LFS v1.5),污化和净化过滤器可以被定义为长期进程,为第一个需要过滤的文件调用一次,然后为之后的文件持续提供污化或净化过滤直到父 Git 操作结束。[Lars Schneider](https://twitter.com/kit3bus),Git 的长期过滤系统的贡献者,简洁地总结了对 Git LFS 性能改变带来的影响。
>
> 使用 12k 个文件的测试仓库的过滤进程在 macOS 上快了 80 倍,在 Windows 上 快了 58 倍。在 Windows 上,这意味着测试运行了 57 秒而不是 55 分钟。
>
>
>
这真是一个让人印象深刻的性能增强!
#### LFS 专有克隆
长期运行的污化和净化过滤器在对向本地缓存读写的加速做了很多贡献,但是对大目标传入/传出 Git LFS 服务器的速度提升贡献很少。 每次 Git LFS 污化过滤器在本地 LFS 缓存中无法找到一个文件时,它不得不使用两次 HTTP 请求来获得该文件:一个用来定位文件,另外一个用来下载它。在一次 `git clone` 过程中,你的本地 LFS 缓存是空的,所以 Git LFS 会天真地为你的仓库中每个 LFS 所追踪的文件创建两个 HTTP 请求:

幸运的是,Git LFS v1.2 提供了专门的 [git lfs clone](https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/git-lfs/#speeding-up-clones) 命令。不再是一次下载一个文件; `git lfs clone` 禁止 Git LFS 污化过滤器,等待检出结束,然后从 Git LFS 存储中按批下载任何需要的文件。这允许了并行下载并且将需要的 HTTP 请求数量减半。

### 自定义<ruby> 传输路由器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Transfer Adapter </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
正如之前讨论过的,Git LFS 在 v1.5 中提供对长期过滤进程的支持。不过,对另外一种类型的可插入进程的支持早在今年年初就发布了。 Git LFS 1.3 包含了对<ruby> 可插拔传输路由器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> pluggable transfer adapter </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的支持,因此不同的 Git LFS 托管服务可以定义属于它们自己的协议来向或从 LFS 存储中传输文件。
直到 2016 年底,Bitbucket 是唯一一个执行专属 Git LFS 传输协议 [Bitbucket LFS Media Adapter](https://confluence.atlassian.com/bitbucket/bitbucket-lfs-media-adapter-856699998.html) 的托管服务商。这是为了从 Bitbucket 的一个被称为 chunking 的 LFS 存储 API 独特特性中获益。Chunking 意味着在上传或下载过程中,大文件被分解成 4MB 的<ruby> 文件块 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> chunk </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。

分块给予了 Bitbucket 支持的 Git LFS 三大优势:
1. 并行下载与上传。默认地,Git LFS 最多并行传输三个文件。但是,如果只有一个文件被单独传输(这也是 Git LFS 污化过滤器的默认行为),它会在一个单独的流中被传输。Bitbucket 的分块允许同一文件的多个文件块同时被上传或下载,经常能够神奇地提升传输速度。
2. 可续传的文件块传输。文件块都在本地缓存,所以如果你的下载或上传被打断,Bitbucket 的自定义 LFS 流媒体路由器会在下一次你推送或拉取时仅为丢失的文件块恢复传输。
3. 免重复。Git LFS,正如 Git 本身,是一种可定位的内容;每一个 LFS 文件都由它的内容生成的 SHA-256 哈希值认证。所以,哪怕你稍微修改了一位数据,整个文件的 SHA-256 就会修改而你不得不重新上传整个文件。分块允许你仅仅重新上传文件真正被修改的部分。举个例子,想想一下 Git LFS 在追踪一个 41M 的<ruby> 精灵表格 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> spritesheet </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。如果我们增加在此精灵表格上增加 2MB 的新的部分并且提交它,传统上我们需要推送整个新的 43M 文件到服务器端。但是,使用 Bitbucket 的自定义传输路由,我们仅仅需要推送大约 7MB:先是 4MB 文件块(因为文件的信息头会改变)和我们刚刚添加的包含新的部分的 3MB 文件块!其余未改变的文件块在上传过程中被自动跳过,节省了巨大的带宽和时间消耗。
可自定义的传输路由器是 Git LFS 的一个伟大的特性,它们使得不同服务商在不重载核心项目的前提下体验适合其服务器的优化后的传输协议。
### 更佳的 git diff 算法与默认值
不像其他的版本控制系统,Git 不会明确地存储文件被重命名了的事实。例如,如果我编辑了一个简单的 Node.js 应用并且将 `index.js` 重命名为 `app.js`,然后运行 `git diff`,我会得到一个看起来像一个文件被删除另一个文件被新建的结果。

我猜测移动或重命名一个文件从技术上来讲是一次删除后跟着一次新建,但这不是对人类最友好的描述方式。其实,你可以使用 `-M` 标志来指示 Git 在计算差异时同时尝试检测是否是文件重命名。对之前的例子,`git diff -M` 给我们如下结果:

第二行显示的 similarity index 告诉我们文件内容经过比较后的相似程度。默认地,`-M` 会处理任意两个超过 50% 相似度的文件。这意味着,你需要编辑少于 50% 的行数来确保它们可以被识别成一个重命名后的文件。你可以通过加上一个百分比来选择你自己的 similarity index,如,`-M80%`。
到 Git v2.9 版本,无论你是否使用了 `-M` 标志, `git diff` 和 `git log` 命令都会默认检测重命名。如果不喜欢这种行为(或者,更现实的情况,你在通过一个脚本来解析 diff 输出),那么你可以通过显式的传递 `--no-renames` 标志来禁用这种行为。
#### 详细的提交
你经历过调用 `git commit` 然后盯着空白的 shell 试图想起你刚刚做过的所有改动吗?`verbose` 标志就为此而来!
不像这样:
```
Ah crap, which dependency did I just rev?
# Please enter the commit message for your changes. Lines starting
# with ‘#’ will be ignored, and an empty message aborts the commit.
# On branch master
# Your branch is up-to-date with ‘origin/master’.
#
# Changes to be committed:
# new file: package.json
#
```
……你可以调用 `git commit --verbose` 来查看你改动造成的行内差异。不用担心,这不会包含在你的提交信息中:

`--verbose` 标志并不是新出现的,但是直到 Git v2.9 你才可以通过 `git config --global commit.verbose true` 永久的启用它。
#### 实验性的 Diff 改进
当一个被修改部分前后几行相同时,`git diff` 可能产生一些稍微令人迷惑的输出。如果在一个文件中有两个或者更多相似结构的函数时这可能发生。来看一个有些刻意人为的例子,想象我们有一个 JS 文件包含一个单独的函数:
```
/* @return {string} "Bitbucket" */
function productName() {
return "Bitbucket";
}
```
现在想象一下我们刚提交的改动包含一个我们专门做的 *另一个*可以做相似事情的函数:
```
/* @return {string} "Bitbucket" */
function productId() {
return "Bitbucket";
}
/* @return {string} "Bitbucket" */
function productName() {
return "Bitbucket";
}
```
我们希望 `git diff` 显示开头五行被新增,但是实际上它不恰当地将最初提交的第一行也包含进来。

错误的注释被包含在了 diff 中!这虽不是世界末日,但每次发生这种事情总免不了花费几秒钟的意识去想 *啊?* 在十二月,Git v2.11 介绍了一个新的实验性的 diff 选项,`--indent-heuristic`,尝试生成从美学角度来看更赏心悦目的 diff。

在后台,`--indent-heuristic` 在每一次改动造成的所有可能的 diff 中循环,并为它们分别打上一个 “不良” 分数。这是基于启发式的,如差异文件块是否以不同等级的缩进开始和结束(从美学角度讲“不良”),以及差异文件块前后是否有空白行(从美学角度讲令人愉悦)。最后,有着最低不良分数的块就是最终输出。
这个特性还是实验性的,但是你可以通过应用 `--indent-heuristic` 选项到任何 `git diff` 命令来专门测试它。如果,如果你喜欢尝鲜,你可以这样将其在你的整个系统内启用:
```
$ git config --global diff.indentHeuristic true
```
### <ruby> 子模块 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Submodule </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>差强人意
子模块允许你从 Git 仓库内部引用和包含其他 Git 仓库。这通常被用在当一些项目管理的源依赖也在被 Git 跟踪时,或者被某些公司用来作为包含一系列相关项目的 [monorepo](https://developer.atlassian.com/blog/2015/10/monorepos-in-git/) 的替代品。
由于某些用法的复杂性以及使用错误的命令相当容易破坏它们的事实,Submodule 得到了一些坏名声。

但是,它们还是有着它们的用处,而且,我想这仍然是用于需要厂商依赖项的最好选择。 幸运的是,2016 对子模块的用户来说是伟大的一年,在几次发布中落地了许多意义重大的性能和特性提升。
#### 并行抓取
当克隆或则抓取一个仓库时,加上 `--recurse-submodules` 选项意味着任何引用的子模块也将被克隆或更新。传统上,这会被串行执行,每次只抓取一个子模块。直到 Git v2.8,你可以附加 `--jobs=n` 选项来使用 *n* 个并行线程来抓取子模块。
我推荐永久的配置这个选项:
```
$ git config --global submodule.fetchJobs 4
```
……或者你可以选择使用任意程度的平行化。
#### 浅层化子模块
Git v2.9 介绍了 `git clone —shallow-submodules` 标志。它允许你抓取你仓库的完整克隆,然后递归地以一个提交的深度浅层化克隆所有引用的子模块。如果你不需要项目的依赖的完整记录时会很有用。
例如,一个仓库有着一些混合了的子模块,其中包含有其他厂商提供的依赖和你自己其它的项目。你可能希望初始化时执行浅层化子模块克隆,然后深度选择几个你想工作与其上的项目。
另一种情况可能是配置持续集成或部署工作。Git 需要一个包含了子模块的超级仓库以及每个子模块最新的提交以便能够真正执行构建。但是,你可能并不需要每个子模块全部的历史记录,所以仅仅检索最新的提交可以为你省下时间和带宽。
#### 子模块的替代品
`--reference` 选项可以和 `git clone` 配合使用来指定另一个本地仓库作为一个替代的对象存储,来避免跨网络重新复制你本地已经存在的对象。语法为:
```
$ git clone --reference <local repo> <url>
```
到 Git v2.11,你可以使用 `—reference` 选项与 `—recurse-submodules` 结合来设置子模块指向一个来自另一个本地仓库的子模块。其语法为:
```
$ git clone --recurse-submodules --reference <local repo> <url>
```
这潜在的可以省下大量的带宽和本地磁盘空间,但是如果引用的本地仓库不包含你克隆的远程仓库所必需的所有子模块时,它可能会失败。
幸运的是,方便的 `—-reference-if-able` 选项将会让它优雅地失败,然后为丢失了的被引用的本地仓库的所有子模块回退为一次普通的克隆。
```
$ git clone --recurse-submodules --reference-if-able \
<local repo> <url>
```
#### 子模块的 diff
在 Git v2.11 之前,Git 有两种模式来显示对更新你的仓库子模块的提交之间的差异。
`git diff —-submodule=short` 显示你的项目引用的子模块中的旧提交和新提交(这也是如果你整体忽略 `--submodule` 选项的默认结果):

`git diff —submodule=log` 有一点啰嗦,显示更新了的子模块中任意新建或移除的提交的信息中统计行。

Git v2.11 引入了第三个更有用的选项:`—-submodule=diff`。这会显示更新后的子模块所有改动的完整的 diff。

### git stash 的 90 个增强
不像子模块,几乎没有 Git 用户不钟爱 [git stash](https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/git-stash/)。 `git stash` 临时搁置(或者 *藏匿*)你对工作区所做的改动使你能够先处理其他事情,结束后重新将搁置的改动恢复到先前状态。
#### 自动搁置
如果你是 `git rebase` 的粉丝,你可能很熟悉 `--autostash` 选项。它会在变基之前自动搁置工作区所有本地修改然后等变基结束再将其复用。
```
$ git rebase master --autostash
Created autostash: 54f212a
HEAD is now at 8303dca It's a kludge, but put the tuple from the database in the cache.
First, rewinding head to replay your work on top of it...
Applied autostash.
```
这很方便,因为它使得你可以在一个不洁的工作区执行变基。有一个方便的配置标志叫做 `rebase.autostash` 可以将这个特性设为默认,你可以这样来全局启用它:
```
$ git config --global rebase.autostash true
```
`rebase.autostash` 实际上自从 [Git v1.8.4](https://blogs.atlassian.com/2013/08/what-you-need-to-know-about-the-new-git-1-8-4/) 就可用了,但是 v2.7 引入了通过 `--no-autostash` 选项来取消这个标志的功能。如果你对未暂存的改动使用这个选项,变基会被一条工作树被污染的警告禁止:
```
$ git rebase master --no-autostash
Cannot rebase: You have unstaged changes.
Please commit or stash them.
```
#### 补丁式搁置
说到配置标签,Git v2.7 也引入了 `stash.showPatch`。`git stash show` 的默认行为是显示你搁置文件的汇总。
```
$ git stash show
package.json | 2 +-
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 1 deletion(-)
```
将 `-p` 标志传入会将 `git stash show` 变为 “补丁模式”,这将会显示完整的 diff:

`stash.showPatch` 将这个行为定为默认。你可以将其全局启用:
```
$ git config --global stash.showPatch true
```
如果你使能 `stash.showPatch` 但却之后决定你仅仅想要查看文件总结,你可以通过传入 `--stat` 选项来重新获得之前的行为。
```
$ git stash show --stat
package.json | 2 +-
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 1 deletion(-)
```
顺便一提:`--no-patch` 是一个有效选项但它不会如你所希望的取消 `stash.showPatch`。不仅如此,它会传递给用来生成补丁时潜在调用的 `git diff` 命令,然后你会发现完全没有任何输出。
#### 简单的搁置标识
如果你惯用 `git stash` ,你可能知道你可以搁置多次改动然后通过 `git stash list` 来查看它们:
```
$ git stash list
stash@{0}: On master: crazy idea that might work one day
stash@{1}: On master: desperate samurai refactor; don't apply
stash@{2}: On master: perf improvement that I forgot I stashed
stash@{3}: On master: pop this when we use Docker in production
```
但是,你可能不知道为什么 Git 的搁置有着这么难以理解的标识(`stash@{1}`、`stash@{2}` 等),或许你可能将它们勾勒成 “仅仅是 Git 的癖好吧”。实际上就像很多 Git 特性一样,这些奇怪的标志实际上是 Git 数据模型的一个非常巧妙使用(或者说是滥用了的)的结果。
在后台,`git stash` 命令实际创建了一系列特定的提交目标,这些目标对你搁置的改动做了编码并且维护一个 [reglog](https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/refs-and-the-reflog/) 来保存对这些特殊提交的引用。 这也是为什么 `git stash list` 的输出看起来很像 `git reflog` 的输出。当你运行 `git stash apply stash@{1}` 时,你实际上在说,“从 stash reflog 的位置 1 上应用这条提交。”
到了 Git v2.11,你不再需要使用完整的 `stash@{n}` 语句。相反,你可以通过一个简单的整数指出该搁置在 stash reflog 中的位置来引用它们。
```
$ git stash show 1
$ git stash apply 1
$ git stash pop 1
```
讲了很多了。如果你还想要多学一些搁置是怎么保存的,我在 [这篇教程](https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/git-stash/#how-git-stash-works) 中写了一点这方面的内容。
---
好了,结束了。感谢您的阅读!我希望您喜欢阅读这份长篇大论,正如我乐于在 Git 的源码、发布文档和 `man` 手册中探险一番来撰写它。如果你认为我忘记了一些重要的事,请留下一条评论或者在 [Twitter](https://twitter.com/kannonboy) 上让我知道,我会努力写一份后续篇章。
至于 Git 接下来会发生什么,这要靠广大维护者和贡献者了(其中有可能就是你!)。随着 Git 的采用日益增长,我猜测简化、改进的用户体验,和更好的默认结果将会是 2017 年 Git 主要的主题。随着 Git 仓库变得越来越大、越来越旧,我猜我们也可以看到继续持续关注性能和对大文件、深度树和长历史的改进处理。
如果你关注 Git 并且很期待能够和一些项目背后的开发者会面,请考虑来 Brussels 花几周时间来参加 [Git Merge](http://git-merge.com/) 。我会在[那里发言](http://git-merge.com/#git-aliases)!但是更重要的是,很多维护 Git 的开发者将会出席这次会议而且一年一度的 Git 贡献者峰会很可能会指定来年发展的方向。
或者如果你实在等不及,想要获得更多的技巧和指南来改进你的工作流,请参看这份 Atlassian 的优秀作品: [Git 教程](https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials) 。
封面图片是由 [instaco.de](http://instaco.de/) 生成的。
---
via: <https://medium.com/hacker-daily/git-in-2016-fad96ae22a15>
作者:[Tim Pettersen](https://hackernoon.com/@kannonboy?source=post_header_lockup) 译者:[xiaow6](https://github.com/xiaow6) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,421 | 使用 tmux 打造更强大的终端 | https://fedoramagazine.org/use-tmux-more-powerful-terminal/ | 2017-04-19T08:12:00 | [
"tmux",
"终端",
"命令行"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8421-1.html | 
一些 Fedora 用户把大部分甚至是所有时间花费在了[命令行](http://www.cryptonomicon.com/beginning.html)终端上。 终端可让您访问整个系统,以及数以千计的强大的实用程序。 但是,它默认情况下一次只显示一个命令行会话。 即使有一个大的终端窗口,整个窗口也只会显示一个会话。 这浪费了空间,特别是在大型显示器和高分辨率的笔记本电脑屏幕上。 但是,如果你可以将终端分成多个会话呢? 这正是 tmux 最方便的地方,或者说不可或缺的。
### 安装并启动 tmux
tmux 应用程序的名称来源于<ruby> 终端 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> terminal </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby><ruby> 复用器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> muxer </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>或<ruby> 多路复用器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> multiplexer </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。 换句话说,它可以将您的单终端会话分成多个会话。 它管理窗口和窗格:
* <ruby> 窗口 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> window </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>是一个单一的视图 - 也就是终端中显示的各种东西。
* <ruby> 窗格 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> pane </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>是该视图的一部分,通常是一个终端会话。
开始前,请在系统上安装 `tmux` 应用程序。 你需要为您的用户帐户设置 `sudo` 权限(如果需要,请[查看本文](https://fedoramagazine.org/howto-use-sudo/)获取相关说明)。
```
sudo dnf -y install tmux
```
运行 `tmux`程序:
```
tmux
```
### 状态栏
首先,似乎什么也没有发生,除了出现在终端的底部的状态栏:

底部栏显示:
* `[0]` – 这是 `tmux` 服务器创建的第一个会话。编号从 0 开始。`tmux` 服务器会跟踪所有的会话确认其是否存活。
* `0:testuser@scarlett:~` – 有关该会话的第一个窗口的信息。编号从 0 开始。这表示窗口的活动窗格中的终端归主机名 `scarlett` 中 `testuser` 用户所有。当前目录是 `~` (家目录)。
* `*` – 显示你目前在此窗口中。
* `“scarlett.internal.fri”` – 你正在使用的 `tmux` 服务器的主机名。
* 此外,还会显示该特定主机上的日期和时间。
当你向会话中添加更多窗口和窗格时,信息栏将随之改变。
### tmux 基础知识
把你的终端窗口拉伸到最大。现在让我们尝试一些简单的命令来创建更多的窗格。默认情况下,所有的命令都以 `Ctrl+b` 开头。
* 敲 `Ctrl+b, "` 水平分割当前单个窗格。 现在窗口中有两个命令行窗格,一个在顶部,一个在底部。请注意,底部的新窗格是活动窗格。
* 敲 `Ctrl+b, %` 垂直分割当前单个窗格。 现在你的窗口中有三个命令行窗格,右下角的窗格是活动窗格。

注意当前窗格周围高亮显示的边框。要浏览所有的窗格,请做以下操作:
* 敲 `Ctrl+b`,然后点箭头键
* 敲 `Ctrl+b, q`,数字会短暂的出现在窗格上。在这期间,你可以你想要浏览的窗格上对应的数字。
现在,尝试使用不同的窗格运行不同的命令。例如以下这样的:
* 在顶部窗格中使用 `ls` 命令显示目录内容。
* 在左下角的窗格中使用 `vi` 命令,编辑一个文本文件。
* 在右下角的窗格中运行 `top` 命令监控系统进程。
屏幕将会如下显示:

到目前为止,这个示例中只是用了一个带多个窗格的窗口。你也可以在会话中运行多个窗口。
* 为了创建一个新的窗口,请敲`Ctrl+b, c` 。请注意,状态栏显示当前有两个窗口正在运行。(敏锐的读者会看到上面的截图。)
* 要移动到上一个窗口,请敲 `Ctrl+b, p` 。
* 要移动到下一个窗口,请敲 `Ctrl+b, n` 。
* 要立即移动到特定的窗口,请敲 `Ctrl+b` 然后跟上窗口编号。
如果你想知道如何关闭窗格,只需要使用 `exit` 、`logout`,或者 `Ctrl+d` 来退出特定的命令行 shell。一旦你关闭了窗口中的所有窗格,那么该窗口也会消失。
### 脱离和附加
`tmux` 最强大的功能之一是能够脱离和重新附加到会话。 当你脱离的时候,你可以离开你的窗口和窗格独立运行。 此外,您甚至可以完全注销系统。 然后,您可以登录到同一个系统,重新附加到 `tmux` 会话,查看您离开时的所有窗口和窗格。 脱离的时候你运行的命令一直保持运行状态。
为了脱离一个会话,请敲 `Ctrl+b, d`。然后会话消失,你重新返回到一个标准的单一 shell。如果要重新附加到会话中,使用一下命令:
```
tmux attach-session
```
当你连接到主机的网络不稳定时,这个功能就像救生员一样有用。如果连接失败,会话中的所有的进程都会继续运行。只要连接恢复了,你就可以恢复正常,就好像什么事情也没有发生一样。
如果这些功能还不够,在每个会话的顶层窗口和窗格中,你可以运行多个会话。你可以列举出这些窗口和窗格,然后通过编号或者名称把他们附加到正确的会话中:
```
tmux list-sessions
```
### 延伸阅读
本文只触及的 `tmux` 的表面功能。你可以通过其他方式操作会话:
* 将一个窗格和另一个窗格交换
* 将窗格移动到另一个窗口中(可以在同一个会话中也可以在不同的会话中)
* 设定快捷键自动执行你喜欢的命令
* 在 `~/.tmux.conf` 文件中配置你最喜欢的配置项,这样每一个会话都会按照你喜欢的方式呈现
有关所有命令的完整说明,请查看以下参考:
* 官方[手册页](http://man.openbsd.org/OpenBSD-current/man1/tmux.1)
* `tmux` [电子书](https://pragprog.com/book/bhtmux2/tmux-2)
---
作者简介:
Paul W. Frields 自 1997 年以来一直是 Linux 用户和爱好者,并于 2003 年加入 Fedora 项目,这个项目刚推出不久。他是 Fedora 项目委员会的创始成员,在文档,网站发布,宣传,工具链开发和维护软件方面都有贡献。他于2008 年 2 月至 2010 年 7 月加入 Red Hat,担任 Fedora 项目负责人,并担任 Red Hat 的工程经理。目前他和妻子以及两个孩子居住在弗吉尼亚。
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/use-tmux-more-powerful-terminal/>
作者:[Paul W. Frields](https://fedoramagazine.org/author/pfrields/) 译者:[Flowsnow](https://github.com/Flowsnow) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Some Fedora users spend most or all their time at a [command line](http://www.cryptonomicon.com/beginning.html) terminal. The terminal gives you access to your whole system, as well as thousands of powerful utilities. However, it only shows you one command line session at a time by default. Even with a large terminal window, the entire window only shows one session. This wastes space, especially on large monitors and high resolution laptop screens. But what if you could break up that terminal into multiple sessions? This is precisely where *tmux* is handy — some say indispensable.
## Install and start *tmux*
The *tmux* utility gets its name from being a terminal muxer, or multiplexer. In other words, it can break your single terminal session into multiple sessions. It manages both *windows* and *panes*:
- A
*window*is a single view — that is, an assortment of things shown in your terminal. - A
*pane*is one part of that view, often a terminal session.
To get started, install the *tmux* utility on your system. You’ll need to have *sudo* setup for your user account ([check out this article](https://fedoramagazine.org/howto-use-sudo/) for instructions if needed).
sudo dnf -y install tmux
Run the utility to get started:
tmux
## The status bar
At first, it might seem like nothing happens, other than a status bar that appears at the bottom of the terminal:
The bottom bar shows you:
*[0]*– You’re in the first session that was created by the*tmux*server. Numbering starts with 0. The server tracks all sessions whether they’re still alive or not.*0:username@host:~*– Information about the first window of that session. Numbering starts with 0. The terminal in the active pane of the window is owned by*username*at hostname*host*. The current directory is*~*(the home directory).***– Shows that you’re currently in this window.*“hostname”*– the hostname of the*tmux*server you’re using.- Also, the date and time on that particular host is shown.
The information bar will change as you add more windows and panes to the session.
## Basics of tmux
Stretch your terminal window to make it much larger. Now let’s experiment with a few simple commands to create additional panes. All commands by default start with *Ctrl+b*.
- Hit
*Ctrl+b, “*to split the current single pane horizontally. Now you have two command line panes in the window, one on top and one on bottom. Notice that the new bottom pane is your active pane. - Hit
*Ctrl+b, %*to split the current pane vertically. Now you have three command line panes in the window. The new bottom right pane is your active pane.
Notice the highlighted border around your current pane. To navigate around panes, do any of the following:
- Hit
*Ctrl+b*and then an arrow key. - Hit
*Ctrl+b, q*. Numbers appear on the panes briefly. During this time, you can hit the number for the pane you want.
Now, try using the panes to run different commands. For instance, try this:
- Use
*ls*to show directory contents in the top pane. - Start
*vi*in the bottom left pane to edit a text file. - Run
*top*in the bottom right pane to monitor processes on your system.
The display will look something like this:
So far, this example has only used one window with multiple panes. You can also run multiple windows in your session.
- To create a new window, hit
*Ctrl+b, c.*Notice that the status bar now shows two windows running. (Keen readers will see this in the screenshot above.) - To move to the previous window, hit
*Ctrl+b, p.* - If you want to move to the next window, hit
*Ctrl+b, n*. - To immediately move to a specific window (0-9), hit
*Ctrl+b*followed by the window number.
If you’re wondering how to close a pane, simply quit that specific command line shell using *exit*, *logout*, or *Ctrl+d.* Once you close all panes in a window, that window disappears as well.
## Detaching and attaching
One of the most powerful features of *tmux* is the ability to detach and reattach to a session. You can leave your windows and panes running when you detach. Moreover, you can even logout of the system entirely. Then later you can login to the same system, reattach to the *tmux* session, and see all your windows and panes where you left them. The commands you were running stay running while you’re detached.
To detach from a session, hit *Ctrl+b, d.* The session disappears and you’ll be back at the standard single shell. To reattach to the session, use this command:
tmux attach-session
This function is also a lifesaver when your network connection to a host is shaky. If your connection fails, all the processes in the session will stay running. Once your connection is back up, you can resume your work as if nothing happened.
And if that weren’t enough, on top of multiple windows and panes per session, you can also run multiple sessions. You can list these and then attach to the correct one by number or name:
tmux list-sessions
## Further reading
This article only scratches the surface of *tmux’*s capabilities. You can manipulate your sessions in many other ways:
- Swap one pane with another
- Move a pane to another window (in the same or a different session!)
- Set keybindings that perform your favorite commands automatically
- Configure a
*~/.tmux.conf*file with your favorite settings by default so each new session looks the way you like
For a full explanation of all commands, check out these references:
- The official
[manual page](http://man.openbsd.org/OpenBSD-current/man1/tmux.1) - This
[eBook](https://pragprog.com/book/bhtmux2/tmux-2)all about*tmux*
## wk3
Cool information! I had never run across
before. I can think of several situations in the past where it would have saved a lot of time and frustration. Thanks!
## Steven
I use tmux and powerline together as my terminal choice. It makes for an efficient terminal experience.
## wigust
Also try out byobu package for better defaults.
## kapoath
Can i run specific panes or even windows as root, while others not?
Due to scripts running under root.
## Braxton Plaxco
If you start a session under a certain user, then new windows and panes will, by default, be under that user, but yes you can run a process as root using sudo or su in a window or pane with the others staying unaffected.
## GMaster
Yes, that’s definitely possible.
## Xplosm
Yes you can! They are all independent TTY sessions!
## Daniel
Kind of. You run tmux as root, and su to your other user in the panes you want. Or the other way around. Think about the security implications though,
## MG
Nothing stops you to switch to whatever user you need in any pane. Or use sudo. Whatever you can do in a shell.
## twoCore
You can start tmux as a “normal” user and run “su -” in a specific pane / window. So you can run scripts under root in the pane ( sorry for my english ). I use tmux for years to connect to multiple servers ( each pane has it own ssh connection ), which is very cool.
## Kyle R. Conway
Yes you can. Different panels within tmux can be root and non-root (or even ssh’d into other machines as other users). Very powerful tool.
## chandan
One of the features that I rely on is the fact that tmux is scriptable. Just typing a key combination will setup the dev & test environment within appropriate panes.
## RTG
I tried it and like it. I’m always looking for new ways to increase efficiency while at the term. Currently use ansi-term from within emacs where I too can split windows, create multiple sessions and more. But tmux is something I can also use and recommend to others. Thanks!
## Tzvetan
Hallo ,
I don’t know why but the Ctrl+b is not working for me . Thanks
Linux samurai 4.8.13-100.fc23.x86_64 #1 SMP Fri Dec 9 14:51:40 UTC 2016 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
## MichaelC
@kapoath
Each pane is a new shell instance, so this an absolute yes.
You can also create preconfigured sessions with panes in the size you need them.
## dminsky
Thanks for article! Always want to know what is the difference between tmux and screen. Still doesn’t know, but at least I’ve tried tmux 😉
## Andrey Motoshkov
Very useful (for myself at least) Ctrl-b,z: zoom-in/out the pane (make pane fullscreen and then back to previous size)
## Anon
I think a Window manager like i3 does this better
## André Luís de Andrade Mendes
Which is better, tmux or screen ?
## Paul W. Frields
@André: It’s not really a matter of better/worse, although I think tmux may have the edge on features. But tmux is also actively maintained, and I believe screen, although stable, is not really updated regularly these days. On that basis I would recommend tmux.
## mahetz
I just use screen all the day, it does what i need, e.x. create a new named detached session with a script.
But what I`m really missing is to capture a terminal started with a ssh login into a session, which a can detach.
Can tmux do this, and most important, reliable?
## Nicolas
Why not using Terminator instead? What are the pros about Tmux? Thanks!
## John Holmes
Since you can detach and reattach to a tmux session, it works incredibly well for remote terminal access. If your network connection drops or you need to reboot your local machine, you can pickup where you left off just by reconnecting and typing “tmux attach”. Terminator is amazing, but to me, this is tmux’s killer feature.
## Peeved Off
my keybindings don’t work
The only thing that works for me is:
Ctl+b, ”
And it doesnt behave as expected. It asks me for a index value for the window to switch to and since I have only one window it fails unless I add 0
I tried adding a local conf file and rebinding to Ctl+C but same result.
I even went through systematically using keys with the bind key and most didn’t work and none mapped to the documentation.
I am running F25 with Wayland
Arrrg.
## Paul W. Frields
@Peeved: I’m also running on F25 Workstation with Wayland so I can testify that tmux works fine. Try duplicating the issue on a brand new user account, and/or a fresh installation. It’s possible certain keyboard models or configurations could interfere with proper operation. Also, some non-standard desktop environments may have keybindings that interfere with tmux. Please use community help channels for more support, as this is not a support forum: https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Communicating_and_getting_help
## Kyew
For those who said i3 Window Manager or Terminator does a better job, you’re missing an important point. tmux works in within your terminal session, can continue running in the background, and was primarily made for remote sessions. You can start a tmux session, start a long running process in it, “disconnect” and then come back to it later. This works great if your connected via ssh to a server. You can run tmux, do your work, and if the connection drops you can re-establish your ssh session and then reconnect to the tmux session you dropped from. Whatever you were doing is still sitting there waiting for you to return.
Another program called “screen” does pretty much the same thing.
## Jesse Vas
Reminds me of Glenda. I like it!
## Kevin
How can I get tmux to automatically start when I start my terminal.
## Paul W. Frields
@Kevin: You can usually set a command to run for each terminal in the settings for your terminal app. In the Fedora Workstation’s Terminal app, you can find this by editing the Profile (right click the Terminal or choose it from the app menu on the GNOME Shell menu bar). Edit the profile, choose Command, and use a custom command ‘tmux’.
## Braxton Plaxco
This is what I use. Then I use tmux windows instead of tabs or different terminals.
I have this in my bashrc
Tmux Setup
if [ -z “$TMUX” ]
then
tmux new-session -As default
fi |
8,422 | 如何在 AWS EC2 的 Linux 服务器上开放一个端口 | http://kerneltalks.com/virtualization/how-to-open-port-on-aws-ec2-linux-server/ | 2017-04-19T10:20:00 | [] | https://linux.cn/article-8422-1.html |
>
> 这是一篇用屏幕截图解释如何在 AWS EC2 Linux 服务器上打开端口的教程。它能帮助你管理 EC2 服务器上特定端口的服务。
>
>
>

AWS(即 Amazon Web Services)不是 IT 世界中的新术语了。它是亚马逊提供的云服务平台。它的免费帐户能为你提供一年的有限免费服务。这是尝试新技术而不用花费金钱的最好的方式之一。
AWS 提供服务器计算作为他们的服务之一,他们称之为 EC(弹性计算)。使用它可以构建我们的 Linux 服务器。我们已经看到了[如何在 AWS 上设置免费的 Linux 服务器](http://kerneltalks.com/howto/install-ec2-linux-server-aws-with-screenshots/)了。
默认情况下,所有基于 EC2 的 Linux 服务器都只打开 22 端口,即 SSH 服务端口(允许所有 IP 的入站连接)。因此,如果你托管了任何特定端口的服务,则要为你的服务器在 AWS 防火墙上打开相应端口。
同样它的 1 到 65535 的端口是打开的(对于所有出站流量)。如果你想改变这个,你可以使用下面的方法编辑出站规则。
在 AWS 上为你的服务器设置防火墙规则很容易。你能够在几秒钟内为你的服务器打开端口。我将用截图指导你如何打开 EC2 服务器的端口。
### 步骤 1 :
登录 AWS 帐户并进入 **EC2 管理控制台**。进入<ruby> “网络及安全” <rt> Network & Security </rt></ruby>菜单下的<ruby> <strong> 安全组 </strong> <rt> Security Groups </rt></ruby>,如下高亮显示:

*AWS EC2 管理控制台*
### 步骤 2 :
在<ruby> 安全组 <rt> Security Groups </rt></ruby>中选择你的 EC2 服务器,并在 <ruby> <strong> 行动 </strong> <rt> Actions </rt></ruby> 菜单下选择 <ruby> <strong> 编辑入站规则 </strong> <rt> Edit inbound rules </rt></ruby>。

*AWS 入站规则菜单*
### 步骤 3:
现在你会看到入站规则窗口。你可以在此处添加/编辑/删除入站规则。这有几个如 http、nfs 等列在下拉菜单中,它们可以为你自动填充端口。如果你有自定义服务和端口,你也可以定义它。

*AWS 添加入站规则*
比如,如果你想要打开 80 端口,你需要选择:
* 类型:http
* 协议:TCP
* 端口范围:80
* 源:任何来源:打开 80 端口接受来自“任何IP(0.0.0.0/0)”的请求;我的 IP:那么它会自动填充你当前的公共互联网 IP
### 步骤 4:
就是这样了。保存完毕后,你的服务器入站 80 端口将会打开!你可以通过 telnet 到 EC2 服务器公共域名的 80 端口来检验(可以在 EC2 服务器详细信息中找到)。
你也可以在 [ping.eu](http://ping.eu/port-chk/) 等网站上检验。
---
同样的方式可以编辑出站规则,这些更改都是即时生效的。
---
via: <http://kerneltalks.com/virtualization/how-to-open-port-on-aws-ec2-linux-server/>
作者:[Shrikant Lavhate](http://kerneltalks.com/virtualization/how-to-open-port-on-aws-ec2-linux-server/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 302 | Found | null |
8,424 | Inxi:一个功能强大的获取 Linux 系统信息的命令行工具 | http://www.tecmint.com/inxi-command-to-find-linux-system-information/ | 2017-04-19T13:43:00 | [
"inxi",
"系统信息"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8424-1.html | 
Inxi 最初是为控制台和 IRC(网络中继聊天)开发的一个强大且优秀的命令行系统信息脚本。可以使用它获取用户的硬件和系统信息,它也用于调试或者社区技术支持工具。
使用 Inxi 可以很容易的获取所有的硬件信息:硬盘、声卡、显卡、网卡、CPU 和 RAM 等。同时也能够获取大量的操作系统信息,比如硬件驱动、Xorg 、桌面环境、内核、GCC 版本,进程,开机时间和内存等信息。
运行在命令行和 IRC 上的 Inxi 输出略有不同,IRC 上会有一些可供用户使用的默认过滤器和颜色选项。支持的 IRC 客户端有:BitchX、Gaim/Pidgin、ircII、Irssi、 Konversation、 Kopete、 KSirc、 KVIrc、 Weechat 和 Xchat 以及其它的一些客户端,它们具有展示内置或外部 Inxi 输出的能力。
### 在 Linux 系统上安装 Inxi
大多数主流 Linux 发行版的仓库中都有 Inxi ,包括大多数 BSD 系统。
```
$ sudo apt-get install inxi [On Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint]
$ sudo yum install inxi [On CentOs/RHEL/Fedora]
$ sudo dnf install inxi [On Fedora 22+]
```
在使用 Inxi 之前,用下面的命令查看 Inxi 所有依赖和推荐的应用,以及各种目录,并显示需要安装哪些包来支持给定的功能。
```
$ inxi --recommends
```
Inxi 的输出:
```
inxi will now begin checking for the programs it needs to operate. First a check of the main languages and tools
inxi uses. Python is only for debugging data collection.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bash version: 4.3.42(1)-release
Gawk version: 4.1.3,
Sed version:
Sudo version: 1.8.16
Python version: 2.7.12
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Test One: Required System Directories (Linux Only).
If one of these system directories is missing, inxi cannot operate:
/proc....................................................................... Present
/sys........................................................................ Present
All the directories are present.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Test Two: Required Core Applications.
If one of these applications is missing, inxi cannot operate:
df (info: partition data)................................................... /bin/df
gawk (info: core tool)...................................................... /usr/bin/gawk
grep (info: string search).................................................. /bin/grep
lspci (info: hardware data)................................................. /usr/bin/lspci
ps (info: process data)..................................................... /bin/ps
readlink.................................................................... /bin/readlink
sed (info: string replace).................................................. /bin/sed
tr (info: character replace)................................................ /usr/bin/tr
uname (info: kernel data)................................................... /bin/uname
wc (info: word character count)............................................. /usr/bin/wc
All the applications are present.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Test Three: Script Recommends for Graphics Features.
NOTE: If you do not use X these do not matter (like a headless server). Otherwise, if one of these applications
is missing, inxi will have incomplete output:
glxinfo (info: -G glx info)................................................. /usr/bin/glxinfo
xdpyinfo (info: -G multi screen resolution)................................. /usr/bin/xdpyinfo
xprop (info: -S desktop data)............................................... /usr/bin/xprop
xrandr (info: -G single screen resolution).................................. /usr/bin/xrandr
All the applications are present.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Test Four: Script Recommends for Remaining Features.
If one of these applications is missing, inxi will have incomplete output:
dig (info: -i first wlan ip default test)................................... /usr/bin/dig
dmidecode (info: -M if no sys machine data; -m memory)...................... /usr/sbin/dmidecode
file (info: -o unmounted file system)....................................... /usr/bin/file
hciconfig (info: -n -i bluetooth data)...................................... /bin/hciconfig
hddtemp (info: -Dx show hdd temp)........................................... /usr/sbin/hddtemp
ifconfig (info: -i ip lan-deprecated)....................................... /sbin/ifconfig
ip (info: -i ip lan)........................................................ /sbin/ip
sensors (info: -s sensors output)........................................... /usr/bin/sensors
strings (info: -I sysvinit version)......................................... /usr/bin/strings
lsusb (info: -A usb audio;-N usb networking)................................ /usr/bin/lsusb
modinfo (info: -Ax,-Nx module version)...................................... /sbin/modinfo
runlevel (info: -I runlevel)................................................ /sbin/runlevel
sudo (info: -Dx hddtemp-user;-o file-user).................................. /usr/bin/sudo
uptime (info: -I uptime (check which package owns Debian)).................. /usr/bin/uptime
All the applications are present.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Test Five: Script Recommends for Remaining Features.
One of these downloaders needed for options -i/-w/-W (-U/-! [11-15], if supported):
wget (info: -i wan ip;-w/-W;-U/-! [11-15] (if supported))................... /usr/bin/wget
curl (info: -i wan ip;-w/-W;-U/-! [11-15] (if supported))................... /usr/bin/curl
All the applications are present.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Test Six: System Directories for Various Information.
(Unless otherwise noted, these are for GNU/Linux systems)
If one of these directories is missing, inxi may have incomplete output:
/sys/class/dmi/id (info: -M system, motherboard, bios)...................... Present
/dev (info: -l,-u,-o,-p,-P,-D disk partition data).......................... Present
/dev/disk/by-label (info: -l,-o,-p,-P partition labels)..................... Present
/dev/disk/by-uuid (info: -u,-o,-p,-P partition uuid)........................ Present
All the directories are present.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Test Seven: System Files for Various Information.
(Unless otherwise noted, these are for GNU/Linux systems)
If one of these files is missing, inxi may have incomplete output:
/proc/asound/cards (info: -A sound card data)............................... Present
/proc/asound/version (info: -A ALSA data)................................... Present
/proc/cpuinfo (info: -C cpu data)........................................... Present
/etc/lsb-release (info: -S distro version data [deprecated])................ Present
/proc/mdstat (info: -R mdraid data)......................................... Present
/proc/meminfo (info: -I memory data)........................................ Present
/etc/os-release (info: -S distro version data).............................. Present
/proc/partitions (info: -p,-P partitions data).............................. Present
/proc/modules (info: -G module data)........................................ Present
/proc/mounts (info: -P,-p partition advanced data).......................... Present
/var/run/dmesg.boot (info: -D,-d disk data [BSD only])...................... Missing
/proc/scsi/scsi (info: -D Advanced hard disk data [used rarely])............ Present
/var/log/Xorg.0.log (info: -G graphics driver load status).................. Present
The following files are missing from your system:
File: /var/run/dmesg.boot
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
All tests completed.
```
### Inxi 工具的基本用法
用下面的基本用法获取系统和硬件的详细信息。
#### 获取 Linux 系统信息
Inix 不加任何选项就能输出下面的信息:CPU 、内核、开机时长、内存大小、硬盘大小、进程数、登录终端以及 Inxi 版本。
```
$ inxi
CPU~Dual core Intel Core i5-4210U (-HT-MCP-) speed/max~2164/2700 MHz Kernel~4.4.0-21-generic x86_64 Up~3:15 Mem~3122.0/7879.9MB HDD~1000.2GB(20.0% used) Procs~234 Client~Shell inxi~2.2.35
```
#### 获取内核和发行版本信息
使用 Inxi 的 `-S` 选项查看本机系统信息(主机名、内核信息、桌面环境和发行版):
```
$ inxi -S
System: Host: TecMint Kernel: 4.4.0-21-generic x86_64 (64 bit) Desktop: Cinnamon 3.0.7
Distro: Linux Mint 18 Sarah
```
### 获取电脑机型
使用 `-M` 选项查看机型(笔记本/台式机)、产品 ID 、机器版本、主板、制造商和 BIOS 等信息:
```
$ inxi -M
Machine: System: LENOVO (portable) product: 20354 v: Lenovo Z50-70
Mobo: LENOVO model: Lancer 5A5 v: 31900059WIN Bios: LENOVO v: 9BCN26WW date: 07/31/2014
```
### 获取 CPU 及主频信息
使用 `-C` 选项查看完整的 CPU 信息,包括每核 CPU 的频率及可用的最大主频。
```
$ inxi -C
CPU: Dual core Intel Core i5-4210U (-HT-MCP-) cache: 3072 KB
clock speeds: max: 2700 MHz 1: 1942 MHz 2: 1968 MHz 3: 1734 MHz 4: 1710 MHz
```
#### 获取显卡信息
使用 `-G` 选项查看显卡信息,包括显卡类型、显示服务器、系统分辨率、GLX 渲染器和 GLX 版本等等(LCTT 译注: GLX 是一个 X 窗口系统的 OpenGL 扩展)。
```
$ inxi -G
Graphics: Card-1: Intel Haswell-ULT Integrated Graphics Controller
Card-2: NVIDIA GM108M [GeForce 840M]
Display Server: X.Org 1.18.4 drivers: intel (unloaded: fbdev,vesa) Resolution: [email protected]
GLX Renderer: Mesa DRI Intel Haswell Mobile GLX Version: 3.0 Mesa 11.2.0
```
#### 获取声卡信息
使用 `-A` 选项查看声卡信息:
```
$ inxi -A
Audio: Card-1 Intel 8 Series HD Audio Controller driver: snd_hda_intel Sound: ALSA v: k4.4.0-21-generic
Card-2 Intel Haswell-ULT HD Audio Controller driver: snd_hda_intel
```
#### 获取网卡信息
使用 `-N` 选项查看网卡信息:
```
$ inxi -N
Network: Card-1: Realtek RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller driver: r8169
Card-2: Realtek RTL8723BE PCIe Wireless Network Adapter driver: rtl8723be
```
#### 获取硬盘信息
使用 `-D` 选项查看硬盘信息(大小、ID、型号):
```
$ inxi -D
Drives: HDD Total Size: 1000.2GB (20.0% used) ID-1: /dev/sda model: ST1000LM024_HN size: 1000.2GB
```
#### 获取简要的系统信息
使用 `-b` 选项显示上述信息的简要系统信息:
```
$ inxi -b
System: Host: TecMint Kernel: 4.4.0-21-generic x86_64 (64 bit) Desktop: Cinnamon 3.0.7
Distro: Linux Mint 18 Sarah
Machine: System: LENOVO (portable) product: 20354 v: Lenovo Z50-70
Mobo: LENOVO model: Lancer 5A5 v: 31900059WIN Bios: LENOVO v: 9BCN26WW date: 07/31/2014
CPU: Dual core Intel Core i5-4210U (-HT-MCP-) speed/max: 2018/2700 MHz
Graphics: Card-1: Intel Haswell-ULT Integrated Graphics Controller
Card-2: NVIDIA GM108M [GeForce 840M]
Display Server: X.Org 1.18.4 drivers: intel (unloaded: fbdev,vesa) Resolution: [email protected]
GLX Renderer: Mesa DRI Intel Haswell Mobile GLX Version: 3.0 Mesa 11.2.0
Network: Card-1: Realtek RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller driver: r8169
Card-2: Realtek RTL8723BE PCIe Wireless Network Adapter driver: rtl8723be
Drives: HDD Total Size: 1000.2GB (20.0% used)
Info: Processes: 233 Uptime: 3:23 Memory: 3137.5/7879.9MB Client: Shell (bash) inxi: 2.2.35
```
#### 获取硬盘分区信息
使用 `-p` 选项输出完整的硬盘分区信息,包括每个分区的分区大小、已用空间、可用空间、文件系统以及文件系统类型。
```
$ inxi -p
Partition: ID-1: / size: 324G used: 183G (60%) fs: ext4 dev: /dev/sda10
ID-2: swap-1 size: 4.00GB used: 0.00GB (0%) fs: swap dev: /dev/sda9
```
#### 获取完整的 Linux 系统信息
使用 `-F` 选项查看可以完整的 Inxi 输出(安全起见比如网络 IP 地址信息没有显示,下面的示例只显示部分输出信息):
```
$ inxi -F
System: Host: TecMint Kernel: 4.4.0-21-generic x86_64 (64 bit) Desktop: Cinnamon 3.0.7
Distro: Linux Mint 18 Sarah
Machine: System: LENOVO (portable) product: 20354 v: Lenovo Z50-70
Mobo: LENOVO model: Lancer 5A5 v: 31900059WIN Bios: LENOVO v: 9BCN26WW date: 07/31/2014
CPU: Dual core Intel Core i5-4210U (-HT-MCP-) cache: 3072 KB
clock speeds: max: 2700 MHz 1: 1716 MHz 2: 1764 MHz 3: 1776 MHz 4: 1800 MHz
Graphics: Card-1: Intel Haswell-ULT Integrated Graphics Controller
Card-2: NVIDIA GM108M [GeForce 840M]
Display Server: X.Org 1.18.4 drivers: intel (unloaded: fbdev,vesa) Resolution: [email protected]
GLX Renderer: Mesa DRI Intel Haswell Mobile GLX Version: 3.0 Mesa 11.2.0
Audio: Card-1 Intel 8 Series HD Audio Controller driver: snd_hda_intel Sound: ALSA v: k4.4.0-21-generic
Card-2 Intel Haswell-ULT HD Audio Controller driver: snd_hda_intel
Network: Card-1: Realtek RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller driver: r8169
IF: enp1s0 state: up speed: 100 Mbps duplex: full mac: 28:d2:44:eb:bd:98
Card-2: Realtek RTL8723BE PCIe Wireless Network Adapter driver: rtl8723be
IF: wlp2s0 state: down mac: 38:b1:db:7c:78:c7
Drives: HDD Total Size: 1000.2GB (20.0% used) ID-1: /dev/sda model: ST1000LM024_HN size: 1000.2GB
Partition: ID-1: / size: 324G used: 183G (60%) fs: ext4 dev: /dev/sda10
ID-2: swap-1 size: 4.00GB used: 0.00GB (0%) fs: swap dev: /dev/sda9
RAID: No RAID devices: /proc/mdstat, md_mod kernel module present
Sensors: System Temperatures: cpu: 56.0C mobo: N/A
Fan Speeds (in rpm): cpu: N/A
Info: Processes: 234 Uptime: 3:26 Memory: 3188.9/7879.9MB Client: Shell (bash) inxi: 2.2.35
```
### 使用 Inxi 工具监控 Linux 系统
下面是监控 Linux 系统进程、开机时间和内存的几个选项的使用方法。
#### 监控 Linux 进程的内存使用
使用下面的命令查看进程数、开机时间和内存使用情况:
```
$ inxi -I
Info: Processes: 232 Uptime: 3:35 Memory: 3256.3/7879.9MB Client: Shell (bash) inxi: 2.2.35
```
#### 监控进程占用的 CPU 和内存资源
Inxi 默认显示 [前 5 个最消耗 CPU 和内存的进程](http://www.tecmint.com/find-processes-by-memory-usage-top-batch-mode/)。 `-t` 选项和 `c` 选项一起使用查看前 5 个最消耗 CPU 资源的进程,查看最消耗内存的进程使用 `-t` 选项和 `m` 选项; `-t`选项 和 `cm` 选项一起使用显示前 5 个最消耗 CPU 和内存资源的进程。
```
----------------- Linux CPU Usage -----------------
$ inxi -t c
Processes: CPU: % used - top 5 active
1: cpu: 53.7% command: plugin-container pid: 3066
2: cpu: 20.0% command: java pid: 1527
3: cpu: 19.7% command: firefox pid: 3018
4: cpu: 4.6% command: Xorg pid: 2114
5: cpu: 3.0% command: cinnamon pid: 2835
```
```
----------------- Linux Memoery Usage -----------------
$ inxi -t m
Processes: Memory: MB / % used - Used/Total: 3212.5/7879.9MB - top 5 active
1: mem: 980.51MB (12.4%) command: plugin-container pid: 3066
2: mem: 508.96MB (6.4%) command: java pid: 1527
3: mem: 507.89MB (6.4%) command: firefox pid: 3018
4: mem: 244.05MB (3.0%) command: chrome pid: 7405
5: mem: 211.46MB (2.6%) command: chrome pid: 6146
```
```
----------------- Linux CPU and Memory Usage -----------------
$ inxi -t cm
Processes: CPU: % used - top 5 active
1: cpu: 53.7% command: plugin-container pid: 3066
2: cpu: 20.0% command: java pid: 1527
3: cpu: 19.7% command: firefox pid: 3018
4: cpu: 4.6% command: Xorg pid: 2114
5: cpu: 3.0% command: cinnamon pid: 2835
Memory: MB / % used - Used/Total: 3223.6/7879.9MB - top 5 active
1: mem: 991.93MB (12.5%) command: plugin-container pid: 3066
2: mem: 508.96MB (6.4%) command: java pid: 1527
3: mem: 507.86MB (6.4%) command: firefox pid: 3018
4: mem: 244.45MB (3.1%) command: chrome pid: 7405
5: mem: 211.68MB (2.6%) command: chrome pid: 6146
```
可以在选项 `cm` 后跟一个整数(在 1-20 之间)设置显示多少个进程,下面的命令显示了前 10 个最消耗 CPU 和内存的进程:
```
$ inxi -t cm10
Processes: CPU: % used - top 10 active
1: cpu: 53.4% command: plugin-container pid: 3066
2: cpu: 19.8% command: java pid: 1527
3: cpu: 19.5% command: firefox pid: 3018
4: cpu: 4.5% command: Xorg pid: 2114
5: cpu: 3.0% command: cinnamon pid: 2835
6: cpu: 2.8% command: chrome pid: 7405
7: cpu: 1.1% command: pulseaudio pid: 2733
8: cpu: 1.0% command: soffice.bin pid: 7799
9: cpu: 0.9% command: chrome pid: 5763
10: cpu: 0.5% command: chrome pid: 6179
Memory: MB / % used - Used/Total: 3163.1/7879.9MB - top 10 active
1: mem: 976.82MB (12.3%) command: plugin-container pid: 3066
2: mem: 511.70MB (6.4%) command: java pid: 1527
3: mem: 466.01MB (5.9%) command: firefox pid: 3018
4: mem: 244.40MB (3.1%) command: chrome pid: 7405
5: mem: 203.71MB (2.5%) command: chrome pid: 6146
6: mem: 199.74MB (2.5%) command: chrome pid: 5763
7: mem: 168.30MB (2.1%) command: cinnamon pid: 2835
8: mem: 165.51MB (2.1%) command: soffice.bin pid: 7799
9: mem: 158.91MB (2.0%) command: chrome pid: 6179
10: mem: 151.83MB (1.9%) command: mysqld pid: 1259
```
#### 监控网络设备
下面的命令会列出网卡信息,包括接口信息、网络频率、mac 地址、网卡状态和网络 IP 等信息。
```
$ inxi -Nni
Network: Card-1: Realtek RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller driver: r8169
IF: enp1s0 state: up speed: 100 Mbps duplex: full mac: 28:d2:44:eb:bd:98
Card-2: Realtek RTL8723BE PCIe Wireless Network Adapter driver: rtl8723be
IF: wlp2s0 state: down mac: 38:b1:db:7c:78:c7
WAN IP: 111.91.115.195 IF: wlp2s0 ip-v4: N/A
IF: enp1s0 ip-v4: 192.168.0.103
```
#### 监控 CPU 温度和电脑风扇转速
可以使用 `-s` 选项监控 [配置了传感器的机器](http://www.tecmint.com/install-htop-linux-process-monitoring-for-rhel-centos-fedora/) 获取温度和风扇转速:
```
$ inxi -s
Sensors: System Temperatures: cpu: 53.0C mobo: N/A
Fan Speeds (in rpm): cpu: N/A
```
#### 用 Linux 查看天气预报
使用 `-w` 选项查看本地区的天气情况(虽然使用的 API 可能不是很可靠),使用 `-W <different_location>` 设置另外的地区。
```
$ inxi -w
Weather: Conditions: 93 F (34 C) - smoke Time: February 20, 1:38 PM IST
$ inxi -W Mumbai,India
Weather: Conditions: 93 F (34 C) - smoke Time: February 20, 1:38 PM IST
$ inxi -W Nairobi,Kenya
Weather: Conditions: 70 F (21 C) - Mostly Cloudy Time: February 20, 11:08 AM EAT
```
#### 查看所有的 Linux 仓库信息
另外,可以使用 `-r` 选项查看一个 Linux 发行版的仓库信息:
```
$ inxi -r
Repos: Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/dawidd0811-neofetch-xenial.list
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/dawidd0811/neofetch/ubuntu xenial main
deb-src http://ppa.launchpad.net/dawidd0811/neofetch/ubuntu xenial main
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/dhor-myway-xenial.list
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/dhor/myway/ubuntu xenial main
deb-src http://ppa.launchpad.net/dhor/myway/ubuntu xenial main
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/official-package-repositories.list
deb http://packages.linuxmint.com sarah main upstream import backport
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ xenial-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://archive.canonical.com/ubuntu/ xenial partner
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/qbittorrent-team-qbittorrent-stable-xenial.list
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/qbittorrent-team/qbittorrent-stable/ubuntu xenial main
deb-src http://ppa.launchpad.net/qbittorrent-team/qbittorrent-stable/ubuntu xenial main
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/slgobinath-safeeyes-xenial.list
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/slgobinath/safeeyes/ubuntu xenial main
deb-src http://ppa.launchpad.net/slgobinath/safeeyes/ubuntu xenial main
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/snwh-pulp-xenial.list
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/snwh/pulp/ubuntu xenial main
deb-src http://ppa.launchpad.net/snwh/pulp/ubuntu xenial main
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/twodopeshaggy-jarun-xenial.list
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/twodopeshaggy/jarun/ubuntu xenial main
deb-src http://ppa.launchpad.net/twodopeshaggy/jarun/ubuntu xenial main
Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ubuntu-mozilla-security-ppa-xenial.list
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/ubuntu-mozilla-security/ppa/ubuntu xenial main
deb-src http://ppa.launchpad.net/ubuntu-mozilla-security/ppa/ubuntu xenial main
```
下面是查看 Inxi 的安装版本、快速帮助和打开 man 主页的方法,以及更多的 Inxi 使用细节。
```
$ inxi -v #显示版本信息
$ inxi -h #快速帮助
$ man inxi #打开 man 主页
```
浏览 Inxi 的官方 GitHub 主页 <https://github.com/smxi/inxi> 查看更多的信息。
Inxi 是一个功能强大的获取硬件和系统信息的命令行工具。这也是我使用过的最好的 [获取硬件和系统信息的命令行工具](http://www.tecmint.com/commands-to-collect-system-and-hardware-information-in-linux/) 之一。
写下你的评论。如果你知道其他的像 Inxi 这样的工具,我们很高兴和你一起讨论。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 的狂热爱好者,即任的 Linux 系统管理员,web 开发者,TecMint 网站的专栏作者,他喜欢使用计算机工作,并且乐于分享计算机技术。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/inxi-command-to-find-linux-system-information/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[vim-kakali](https://github.com/vim-kakali) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,430 | lnav:Linux 下一个基于控制台的高级日志文件查看器 | http://www.2daygeek.com/install-and-use-advanced-log-file-viewer-navigator-lnav-in-linux/ | 2017-04-20T17:09:11 | [
"日志",
"lnav"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8430-1.html | 服务器日志是一个由服务器创建并经常更新、用于抓取特定服务和应用的所有活动信息的日志文件。当你的应用或者服务出现问题时这个文件就会非常有用。从日志文件中你可以获取所有关于该问题的信息,例如基于警告或者错误信息它什么时候开始表现不正常。

[LNAV](http://lnav.org/)(Log file Navigator)是 Linux 下一个基于控制台的高级日志文件查看器。它和其它文件查看器,例如 cat、more、tail 等,完成相同的任务,但有很多普通文件查看器没有的增强功能(尤其是它自带多种颜色和易于阅读的格式)。
它能在解压多个压缩日志文件(zip、gzip、bzip)的同时把它们合并到一起进行导航。基于消息的时间戳,`lnav` 能把多个日志文件合并到一个视图(Single Log Review),从而避免打开多个窗口。左边的颜色栏帮助显示消息所属的文件。
警告和错误的数量以(黄色和红色)高亮显示,因此我们能够很轻易地看到问题出现在哪里。它会自动加载新的日志行。
它按照消息时间戳排序显示所有文件的日志消息。顶部和底部的状态栏会告诉你位于哪个日志文件。如果你想按特定的模式查找,只需要在搜索弹窗中输入就会即时显示。
内建的日志消息解析器会自动从每一行中发现和提取详细信息。
当你用一个普通文件查看器打开一个日志文件时,它会用纯文本格式显示所有信息(如果用更直白的话说的话:纯白——黑底白字),这样很难去发现和理解哪里有警告或错误信息。为了克服这种情况,快速找到警告和错误信息来解决问题, lnav 是一个入手可用的更好的解决方案。
大部分常见的 Linux 日志文件都放在 `/var/log/`。
**lnav 自动检测以下日志格式**
* Common Web Access Log format(普通 web 访问日志格式)
* CUPS page\_log
* Syslog
* Glog
* VMware ESXi/vCenter 日志
* dpkg.log
* uwsgi
* “Generic” – 以时间戳开始的任何消息
* Strace
* sudo
* gzib & bizp
**lnav 高级功能**
* 单一日志视图 - 基于消息时间戳,所有日志文件内容都会被合并到一个单一视图
* 自动日志格式检测 - `lnav` 支持大部分日志格式
* 过滤器 - 能进行基于正则表达式的过滤
* 时间线视图
* 适宜打印视图(Pretty-Print)
* 使用 SQL 查询日志
* 自动数据抽取
* 实时操作
* 语法高亮
* Tab 补全
* 当你查看相同文件集时可以自动保存和恢复会话信息。
* Headless 模式
### 如何在 Linux 中安装 lnav
大部分发行版(Debian、Ubuntu、Mint、Fedora、suse、openSUSE、Arch Linux、Manjaro、Mageia 等等)默认都有 `lnav` 软件包,在软件包管理器的帮助下,我们可以很轻易地从发行版官方仓库中安装它。对于 CentOS/RHEL 我们需要启用 **[EPEL 仓库](http://www.2daygeek.com/install-enable-epel-repository-on-rhel-centos-scientific-linux-oracle-linux/)**。
```
[在 Debian/Ubuntu/LinuxMint 上安装 lnav]
$ sudo apt-get install lnav
[在 RHEL/CentOS 上安装 lnav]
$ sudo yum install lnav
[在 Fedora 上安装 lnav]
$ sudo dnf install lnav
[在 openSUSE 上安装 lnav]
$ sudo zypper install lnav
[在 Mageia 上安装 lnav]
$ sudo urpmi lnav
[在基于 Arch Linux 的系统上安装 lnav]
$ yaourt -S lnav
```
如果你的发行版没有 `lnav` 软件包,别担心,开发者提供了 `.rpm` 和 `.deb` 安装包,因此我们可以轻易安装。确保你从 [开发者 github 页面](https://github.com/tstack/lnav/releases) 下载最新版本的安装包。
```
[在 Debian/Ubuntu/LinuxMint 上安装 lnav]
$ sudo wget https://github.com/tstack/lnav/releases/download/v0.8.1/lnav_0.8.1_amd64.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i lnav_0.8.1_amd64.deb
[在 RHEL/CentOS 上安装 lnav]
$ sudo yum install https://github.com/tstack/lnav/releases/download/v0.8.1/lnav-0.8.1-1.x86_64.rpm
[在 Fedora 上安装 lnav]
$ sudo dnf install https://github.com/tstack/lnav/releases/download/v0.8.1/lnav-0.8.1-1.x86_64.rpm
[在 openSUSE 上安装 lnav]
$ sudo zypper install https://github.com/tstack/lnav/releases/download/v0.8.1/lnav-0.8.1-1.x86_64.rpm
[在 Mageia 上安装 lnav]
$ sudo rpm -ivh https://github.com/tstack/lnav/releases/download/v0.8.1/lnav-0.8.1-1.x86_64.rpm
```
### 不带参数运行 lnav
默认情况下你不带参数运行 `lnav` 时它会打开 `syslog` 文件。
```
# lnav
```

### 使用 lnav 查看特定日志文件
要用 `lnav` 查看特定的日志文件,在 `lnav` 命令后面添加日志文件路径。例如我们想看 `/var/log/dpkg.log` 日志文件。
```
# lnav /var/log/dpkg.log
```

### 用 lnav 查看多个日志文件
要用 `lnav` 查看多个日志文件,在 lnav 命令后面逐个添加日志文件路径,用一个空格隔开。例如我们想查看 `/var/log/dpkg.log` 和 `/var/log/kern.log` 日志文件。
左边的颜色栏帮助显示消息所属的文件。另外顶部状态栏还会显示当前日志文件的名称。为了显示多个日志文件,大部分应用经常会打开多个窗口、或者在窗口中水平或竖直切分,但 `lnav` 使用不同的方式(它基于日期组合在同一个窗口显示多个日志文件)。
```
# lnav /var/log/dpkg.log /var/log/kern.log
```

### 使用 lnav 查看压缩的日志文件
要查看并同时解压被压缩的日志文件(zip、gzip、bzip),在 `lnav` 命令后面添加 `-r` 选项。
```
# lnav -r /var/log/Xorg.0.log.old.gz
```

### 直方图视图
首先运行 `lnav` 然后按 `i` 键切换到/出直方图视图。

### 查看日志解析器结果
首先运行 `lnav` 然后按 `p` 键打开显示日志解析器结果。

### 语法高亮
你可以搜索任何给定的字符串,它会在屏幕上高亮显示。首先运行 `lnav` 然后按 `/` 键并输入你想查找的字符串。为了测试,我搜索字符串 `Default`,看下面的截图。

### Tab 补全
命令窗口支持大部分操作的 tab 补全。例如,在进行搜索时,你可以使用 tab 补全屏幕上显示的单词,而不需要复制粘贴。为了测试,我搜索字符串 `/var/log/Xorg`,看下面的截图。

---
via: <http://www.2daygeek.com/install-and-use-advanced-log-file-viewer-navigator-lnav-in-linux/>
作者:[Magesh Maruthamuthu](http://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,431 | Anbox:容器中的 Android | https://github.com/anbox/anbox/blob/master/README.md | 2017-04-21T11:06:00 | [
"Android",
"Anbox"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8431-1.html | 
Anbox 以基于容器的方式,在像 Ubuntu 这样的常规的 GNU Linux 系统上启动一个完整的 Android 系统。
### 概述
Anbox 使用 Linux 命名空间(user、pid、uts、net、mount、ipc)来在容器中运行完整的 Android 系统,并在任何基于 GNU Linux 平台上提供 Android 应用。
容器内的 Android 无法直接访问任何硬件。所有硬件访问都通过主机上的 anbox 守护进程进行。我们重用基于 QEMU 的模拟器实现的 Android 中的 GL、ES 加速渲染。容器内的 Android 系统使用不同的管道与主机系统通信,并通过它发送所有硬件访问命令。
有关更多详细信息,请参考下文档:
* [Android 硬件 OpenGL ES 仿真设计概述](https://android.googlesource.com/platform/external/qemu/+/emu-master-dev/android/android-emugl/DESIGN)
* [Android QEMU 快速管道](https://android.googlesource.com/platform/external/qemu/+/emu-master-dev/android/docs/ANDROID-QEMU-PIPE.TXT)
* [Android 的 “qemud” 复用守护进程](https://android.googlesource.com/platform/external/qemu/+/emu-master-dev/android/docs/ANDROID-QEMUD.TXT)
* [Android qemud 服务](https://android.googlesource.com/platform/external/qemu/+/emu-master-dev/android/docs/ANDROID-QEMUD-SERVICES.TXT)
Anbox 目前适合桌面使用,但也用在移动操作系统上,如 Ubuntu Touch、Sailfish OS 或 Lune OS。然而,由于 Android 程序的映射目前只针对桌面环境,因此还需要额外的工作来支持其他的用户界面。
Android 运行时环境带有一个基于 [Android 开源项目](https://source.android.com/)镜像的最小自定义 Android 系统。所使用的镜像目前基于 Android 7.1.1。
### 安装
目前,安装过程包括一些添加额外组件到系统的步骤。包括:
* 启用用于 binder 和 ashmen 的非发行的树外内核模块。
* 使用 udev 规则为 /dev/binder 和 /dev/ashmem 设置正确权限。
* 能够启动 Anbox 会话管理器作为用户会话的一个启动任务。
为了使这个过程尽可能简单,我们将必要的步骤绑定在一个 snap(见 <https://snapcraft.io> ) 中,称之为 “anbox-installer”。这个安装程序会执行所有必要的步骤。你可以在所有支持 snap 的系统运行下面的命令安装它。
```
$ snap install --classic anbox-installer
```
另外你可以通过下面的命令下载安装脚本。
```
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/anbox/anbox-installer/master/installer.sh -O anbox-installer
```
请注意,我们还不支持除所有 Linux 发行版。请查看下面的章节了解支持的发行版。
运行下面的命令进行安装。
```
$ anbox-installer
```
它会引导你完成安装过程。
**注意:** Anbox 目前处于 **pre-alpha 开发状态**。不要指望它具有生产环境你需要的所有功能。你肯定会遇到错误和崩溃。如果你遇到了,请不要犹豫并报告它们!
**注意:** Anbox snap 目前 **完全没有约束**,因此它只能从边缘渠道获取。正确的约束是我们想要在未来实现的,但由于 Anbox 的性质和复杂性,这不是一个简单的任务。
### 已支持的 Linux 发行版
目前我们官方支持下面的 Linux 发行版:
* Ubuntu 16.04 (xenial)
未测试但可能支持的:
* Ubuntu 14.04 (trusty)
* Ubuntu 16.10 (yakkety)
* Ubuntu 17.04 (zesty)
### 安装并运行 Android 程序
#### 从源码构建
要构建 Anbox 运行时不需要特别了解什么,我们使用 cmake 作为构建系统。你的主机系统中应已有下面这些构建依赖:
* libdbus
* google-mock
* google-test
* libboost
* libboost-filesystem
* libboost-log
* libboost-iostreams
* libboost-program-options
* libboost-system
* libboost-test
* libboost-thread
* libcap
* libdbus-cpp
* mesa (libegl1, libgles2)
* glib-2.0
* libsdl2
* libprotobuf
* protobuf-compiler
* lxc
在 Ubuntu 系统中你可以用下面的命令安装所有的依赖:
```
$ sudo apt install build-essential cmake cmake-data debhelper dbus \
google-mock libboost-dev libboost-filesystem-dev libboost-log-dev \
libboost-iostreams-dev libboost-program-options-dev libboost-system-dev \
libboost-test-dev libboost-thread-dev libcap-dev libdbus-1-dev \
libdbus-cpp-dev libegl1-mesa-dev libgles2-mesa-dev libglib2.0-dev \
libglm-dev libgtest-dev liblxc1 libproperties-cpp-dev libprotobuf-dev \
libsdl2-dev lxc-dev pkg-config protobuf-compiler
```
之后用下面的命令构建 Anbox:
```
$ mkdir build
$ cd build
$ cmake ..
$ make
```
一个简单的命令会将必要的二进制安装到你的系统中,如下。
```
$ make install
```
如果你想要构建 anbox snap,你可以按照下面的步骤:
```
$ mkdir android-images
$ cp /path/to/android.img android-images/android.img
$ snapcraft
```
结果会有一个 .snap 文件,你可以在支持 snap 的系统上安装。
```
$ snap install --dangerous --devmode anbox_1_amd64.snap
```
#### 运行 Anbox
要从本地构建运行 Anbox ,你需要了解更多一点。请参考[“运行时步骤”](https://github.com/anbox/anbox/blob/master/docs/runtime-setup.md)文档。
### 文档
在项目源代码的子目录下,你可以找到额外的关于 Anbox 的文档。
有兴趣可以看下:
* [运行时步骤](https://github.com/anbox/anbox/blob/master/docs/runtime-setup.md)
* [构建 Android 镜像](https://github.com/anbox/anbox/blob/master/docs/build-android.md)
### 报告 bug
如果你发现了一个 Anbox 问题,请[提交 bug](https://github.com/anbox/anbox/issues/new)。
### 取得联系
如果你想要与开发者联系,你可以在 [FreeNode](https://freenode.net/) 中加入 *#anbox* 的 IRC 频道。
### 版权与许可
Anbox 重用了像 Android QEMU 模拟器这样的其他项目的代码。这些项目可在外部/带有许可声明的子目录中得到。
anbox 源码本身,如果没有在相关源码中声明其他的许可,默认是 GPLv3 许可。
---
via: <https://github.com/anbox/anbox/blob/master/README.md>
作者:[Anbox](http://anbox.io/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
{{ message }}
This repository has been archived by the owner on Feb 13, 2024. It is now read-only. |
8,433 | 让你的 Linux 远离黑客(三):FAQ | https://www.linux.com/news/webinar/2017/how-keep-hackers-out-your-linux-machine-part-3-your-questions-answered | 2017-04-21T17:44:16 | [
"黑客",
"网络安全"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8433-1.html | 
Mike Guthrie 最近在 Linux 基金会的网络研讨会上回答了一些安全相关的问题。
这个系列的[第一篇](/article-8189-1.html)和[第二篇](/article-8338-1.html)文章覆盖了 5 个让你的 Linux 远离黑客的最简单方法,并且知道他们是否已经进入。这一次,我将回答一些我最近在 Linux 基金会网络研讨会上收到的很好的安全性问题。
### 如果系统自动使用私钥认证,如何存储密钥密码?
这个很难。这是我们一直在斗争的事情,特别是我们在做 “Red Team” 的时候,因为我们有些需要自动调用的东西。我使用 Expect,但我倾向于在这上面使用老方法。你需要编写脚本,是的,将密码存储在系统上不是那么简单的一件事,当你这么做时你需要加密它。
我的 Expect 脚本加密了存储的密码,然后解密,发送密码,并在完成后重新加密。我知道到这有一些缺陷,但它比使用无密码的密钥更好。
如果你有一个无密码的密钥,并且你确实需要使用它。我建议你尽量限制需要用它的用户。例如,如果你正在进行一些自动日志传输或自动化软件安装,则只给那些需要执行这些功能的程序权限。
你可以通过 SSH 运行命令,所以不要给它们一个 shell,使它只能运行那个命令就行,这样就能防止某人窃取了这个密钥并做其他事情。
### 你对密码管理器如 KeePass2 怎么看?
对我而言,密码管理器是一个非常好的目标。随着 GPU 破解的出现和 EC2 的一些破解能力,这些东西很容易就变成过去时。我一直在窃取这些密码库。
现在,我们在破解这些库的成功率是另外一件事。我们差不多有 10% 左右的破解成功率。如果人们不能为他们的密码库用一个安全的密码,那么我们就会进入并会获得丰硕成果。比不用要强,但是你仍需要保护好这些资产。如你保护其他密码一样保护好密码库。
### 你认为从安全的角度来看,除了创建具有更高密钥长度的主机密钥之外,创建一个新的 “Diffie-Hellman” 模数并限制 2048 位或更高值得么?
值得的。以前在 SSH 产品中存在弱点,你可以做到解密数据包流。有了它,你可以传递各种数据。作为一种加密机制,人们不假思索使用这种方式来传输文件和密码。使用健壮的加密并且改变你的密钥是很重要的。 我会轮换我的 SSH 密钥 - 这不像我的密码那么频繁,但是我每年会轮换一次。是的,这是一个麻烦,但它让我安心。我建议尽可能地使你的加密技术健壮。
### 使用完全随机的英语单词(大概 10 万个)作为密码合适么?
当然。我的密码实际上是一个完整的短语。它是带标点符号和大小写一句话。除此以外,我不再使用其他任何东西。
我是一个“你可以记住而不用写下来或者放在密码库的密码”的大大的支持者。一个你可以记住不必写下来的密码比你需要写下来的密码更安全。
使用短语或使用你可以记住的四个随机单词比那些需要经过几次转换的一串数字和字符的字符串更安全。我目前的密码长度大约是 200 个字符。这是我可以快速打出来并且记住的。
### 在物联网情景下对保护基于 Linux 的嵌入式系统有什么建议么?
物联网是一个新的领域,它是系统和安全的前沿,日新月异。现在,我尽量都保持离线。我不喜欢人们把我的灯光和冰箱搞乱。我故意不去购买支持联网的冰箱,因为我有朋友是黑客,我可不想我每天早上醒来都会看到那些不雅图片。封住它,锁住它,隔离它。
目前物联网设备的恶意软件取决于默认密码和后门,所以只需要对你所使用的设备进行一些研究,并确保没有其他人可以默认访问。然后确保这些设备的管理接口受到防火墙或其他此类设备的良好保护。
### 你可以提一个可以在 SMB 和大型环境中使用的防火墙/UTM(OS 或应用程序)么?
我使用 pfSense,它是 BSD 的衍生产品。我很喜欢它。它有很多模块,实际上现在它有商业支持,这对于小企业来说这是非常棒的。对于更大的设备、更大的环境,这取决于你有哪些管理员。
我一直都是 CheckPoint 管理员,但是 Palo Alto 也越来越受欢迎了。这些设备与小型企业或家庭使用很不同。我在各种小型网络中都使用 pfSense。
### 云服务有什么内在问题么?
并没有云,那只不过是其他人的电脑而已。云服务存在内在的问题。只知道谁访问了你的数据,你在上面放了什么。要知道当你向 Amazon 或 Google 或 Microsoft 上传某些东西时,你将不再完全控制它,并且该数据的隐私是有问题的。
### 要获得 OSCP 你建议需要准备些什么?
我现在准备通过这个认证。我的整个团队是这样。阅读他们的材料。记住, OSCP 将成为令人反感的安全基准。你一切都要使用 Kali。如果不这样做 - 如果你决定不使用 Kali,请确保仿照 Kali 实例安装所有的工具。
这将是一个基于工具的重要认证。这是一个很好的方式。看看一些名为“渗透测试框架”的内容,因为这将为你提供一个很好的测试流程,他们的实验室似乎是很棒的。这与我家里的实验室非常相似。
*[随时免费观看完整的网络研讨会](http://portal.on24.com/view/channel/index.html?showId=1101876&showCode=linux&partnerref=linco)。查看这个系列的[第一篇](https://www.linux.com/news/webinar/2017/how-keep-hackers-out-your-linux-machine-part-1-top-two-security-tips)和[第二篇](https://www.linux.com/news/webinar/2017/how-keep-hackers-out-your-linux-machine-part-2-three-more-easy-security-tips)文章获得 5 个简单的贴士来让你的 Linux 机器安全。*
*Mike Guthrie 为能源部工作,负责 “Red Team” 的工作和渗透测试。*
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/news/webinar/2017/how-keep-hackers-out-your-linux-machine-part-3-your-questions-answered>
作者:[MIKE GUTHRIE](https://www.linux.com/users/anch) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,434 | 使用 LXDE 的 8 个理由 | https://opensource.com/article/17/3/8-reasons-use-lxde | 2017-04-21T18:16:42 | [
"LXDE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8434-1.html |
>
> 考虑使用轻量级桌面环境 LXDE 作为你 Linux 桌面的理由
>
>
>

去年年底,升级到 Fedora 25 所装的新版本 [KDE](https://opensource.com/life/15/4/9-reasons-to-use-kde) Plasma 给我带来了严重问题,让我难以完成任何工作。出于两个原因我决定尝试其它 Linux 桌面环境。第一,我需要完成我的工作。第二,一心使用 KDE 已经有很多年,我认为是时候尝试一些不同的桌面了。
我第一个尝试了几周的替代桌面是 [Cinnamon](https://opensource.com/article/17/1/cinnamon-desktop-environment),我在 1 月份介绍过它。这次我已经使用了 LXDE(<ruby> 轻量级 X11 桌面环境 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Lightweight X11 Desktop Environment </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)大概 6 周,我发现它有很多我喜欢的东西。这是我使用 LXDE 的 8 个理由。
### 1、 LXDE 支持多个面板
和 KDE 以及 Cinnamon 一样,LXDE 支持包括系统菜单、应用启动器的面板,以及显示正在运行应用图标的任务栏。我第一次登录到 LXDE 时,面板的配置看起来异常熟悉。LDXE 看起来已经根据我的 KDE 配置情况为我准备好了喜欢的顶部和底部面板,并包括了系统托盘设置。顶部面板上的应用程序启动器看似来自 Cinnamon 。面板上的东西使得启动和管理程序变得容易。默认情况下,只在桌面底部有一个面板。

*打开了 Openbox 配置管理器的 LXDE 桌面。这个桌面还没有更改过,因此它使用了默认的颜色和图标主题。*
### 2、 Openbox 配置管理器提供了一个用于管理和体验桌面外观的简单工具。
它为主题、窗口修饰、多个显示器的窗口行为、移动和调整窗口大小、鼠标控制、多桌面等提供了选项。虽然这看起来似乎很多,但它远不如配置 KDE 桌面那么复杂,尽管如此 Openbox 仍然提供了绝佳的效果。
### 3、 LXDE 有一个强大的菜单工具
在<ruby> 桌面偏好 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Desktop Preference </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>菜单的<ruby> 高级 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Advanced </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>标签页有个有趣的选项。这个选项的名称是 “<ruby> 点击桌面时显示窗口管理器提供的菜单 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Show menus provided by window managers when desktop is clicked </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”。选中这个复选框,当你右击桌面时,会显示 Openbox 桌面菜单,而不是标准的 LXDE 桌面菜单。
Openbox 桌面菜单包括了几乎每个你可能想要的菜单选项,所有都可从桌面便捷访问。它包括了所有的应用程序菜单、系统管理、以及首选项。它甚至有一个菜单包括了所有已安装的终端模拟器应用程序的列表,因此系统管理员可以轻易地启动他们喜欢的终端。
### 4、 LXDE 桌面的设计干净简单
它没有任何会妨碍你完成工作的东西。尽管你可以添加一些文件、目录、应用程序的链接到桌面,但是没有可以添加到桌面的小部件。在我的 KDE 和 Cinnamon 桌面上我确实喜欢一些小部件,但它们很容易被覆盖住,然后我就需要移动或者最小化窗口,或者使用 “<ruby> 显示桌面 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Show Desktop </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>” 按钮清空整个桌面才能看到它们。 LXDE 确实有一个 “<ruby> 图标化所有窗口 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Iconify all windows </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>” 按钮,但我很少需要使用它,除非我想看我的壁纸。
### 5、 LXDE 有一个强大的文件管理器
LXDE 默认的文件管理器是 PCManFM,因此在我使用 LXDE 的时候它成为了我的文件管理器。PCManFM 非常灵活、可以配置为适用于大部分人和场景。它看起来没有我常用的文件管理器 Krusader 那么可配置,但我确实喜欢 Krusader 所没有的 PCManFM 侧边栏。
PCManFM 允许打开多个标签页,可以通过右击侧边栏的任何条目或者单击图标栏的新标签图标打开。PCManFM 窗口左边的<ruby> 位置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Places </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>面板显示了应用程序菜单,你可以从 PCManFM 启动应用程序。<ruby> 位置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Places </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>面板上面也显示了一个设备图标,可以用于查看你的物理存储设备,一系列带按钮的可移除设备允许你挂载和卸载它们,还有可以便捷访问的主目录、桌面、回收站。<ruby> 位置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Places </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>面板的底部包括一些默认目录的快捷方式,例如 Documents、Music、Pictures、Videos 以及 Downloads。你也可以拖拽其它目录到<ruby> 位置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Places </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>面板的快捷方式部分。<ruby> 位置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Places </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 面板可以换为正常的目录树。
### 6、 如果在现有窗口后面打开,新窗口的标题栏会闪烁
这是一个在大量现有窗口中定位新窗口的好方法。
### 7、 大部分现代桌面环境允许多个桌面,LXDE 也不例外
我喜欢使用一个桌面用于我的开发、测试以及编辑工作,另一个桌面用于普通任务,例如电子邮件和网页浏览。LXDE 默认提供两个桌面,但你可以配置为只有一个或者多个。右击<ruby> 桌面切换器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Desktop Pager </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>配置它。
通过一些有害但不是破坏性的测试,我发现最大允许桌面数目是 100。我还发现当我把桌面数目减少到低于我实际已经在使用的 3 个时,不活动桌面上的窗口会被移动到桌面 1。多么有趣的发现!
### 8、 Xfce 电源管理器是一个小巧但强大的应用程序,它允许你配置电源管理如何工作
它提供了一个标签页用于通用配置,以及用于系统、显示和设备的标签页。设备标签页显示了我系统上已有设备的表格,例如电池供电的鼠标、键盘,甚至我的 UPS(不间断电源)。它显示了每个设备的详细信息,包括厂商和系列号,如果可用的话,还有电池充电状态。当我写这篇博客的时候,我 UPS 的电量是 100%,而我罗技鼠标的电量是 75%。 Xfce 电源管理器还在系统托盘显示了一个图标,因此你可以从那里快速了解你设备的电池状态。
关于 LXDE 桌面还有很多喜欢的东西,但这些就是抓住了我的注意力,它们也是对我使用现代图形用户界面工作非常重要、不可或缺的东西。
我注意到奇怪的一点是,我一直没有弄明白桌面(Openbox)菜单的 “<ruby> 重新配置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Reconfigure </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>” 选项是干什么的。我点击了几次,从没有注意到有任何类型的任何活动表明该选项实际起了作用。
我发现 LXDE 是一个简单但强大的桌面。我享受使用它写这篇文章的几周时间。通过允许我访问我想要的应用程序和文件,同时在其余时间保持不会让我分神,LXDE 使我得以高效地工作。我也没有遇到任何妨碍我完成工作的问题——当然,除了我用于探索这个好桌面所花的时间。我非常推荐 LXDE 桌面。
我现在正在试用 GNOME 3 和 GNOME Shell,并将在下一期中报告。
---
作者简介:
David Both 是一个 Linux 和开源倡导者,他居住在北卡罗莱纳州的 Raleigh。他在 IT 行业已经超过 40 年,在他工作的 IBM 公司教授 OS/2 超过 20 年,他在 1981 年为最早的 IBM PC 写了第一个培训课程。他教过 Red Hat 的 RHCE 课程,在 MCI Worldcom、 Cisco 和北卡罗莱纳州 工作过。他一直在使用 Linux 和开源软件近 20 年。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/3/8-reasons-use-lxde>
作者:[David Both](https://opensource.com/users/dboth) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Late last year, an upgrade to Fedora 25 brought issues with the new version of [KDE](https://opensource.com/life/15/4/9-reasons-to-use-kde) Plasma that were so bad it was difficult to get any work done. I decided to try other Linux desktop environments for two reasons. First, I needed to get my work done. Second, having used KDE exclusively for many years, I thought it was time to try some different desktops.
The first alternate desktop I tried for several weeks was [Cinnamon](https://opensource.com/article/17/1/cinnamon-desktop-environment), which I wrote about in January. This time I have been using LXDE (Lightweight X11 Desktop Environment) for about six weeks, and I have found many things about it that I like. Here is my list of eight reasons to use LXDE.
**1. LXDE supports multiple panels. **As with KDE and Cinnamon, LXDE sports panels that contain the system menu, application launchers, and a taskbar that displays buttons for the running applications. The first time I logged in to LXDE the panel configuration looked surprisingly familiar. LXDE appears to have picked up the KDE configuration for my favored top and bottom panels, including system tray settings. The application launchers on the top panel appear to have been from the Cinnamon configuration. The contents of the panels make it easy to launch and manage programs. By default, there is only one panel at the bottom of the desktop.
The LXDE desktop with the Openbox Configuration Manager open. This desktop has not been modified, so it uses the default color and icon schemes.
**2. The Openbox configuration manager provides a single, simple tool for managing the look and feel of the desktop.** It provides options for themes, window decorations, window behavior with multiple monitors, moving and resizing windows, mouse control, multiple desktops, and more. Although that seems like a lot, it is far less complex than configuring the KDE desktop, yet Openbox provides a surprisingly great amount of control.
**3. LXDE has a powerful menu tool.** There is an interesting option that you can access on the Advanced tab of the Desktop Preferences menu. The long name for this option is, “Show menus provided by window managers when desktop is clicked.” When this checkbox is selected, the Openbox desktop menu is displayed instead of the standard LXDE desktop menu, when you right-click the desktop.
The Openbox desktop menu contains nearly every menu selection you would ever want, with all easily accessible from the desktop. It includes all of the application menus, system administration, and preferences. It even has a menu containing a list of all the terminal emulator applications installed so that sysadmins can easily launch their favorite.
**4. By design, the LXDE desktop is clean and simple.** It has nothing to get in the way of getting your work done. Although you can add some clutter to the desktop in the form of files, directory folders, and links to applications, there are no widgets that can be added to the desktop. I do like some widgets on my KDE and Cinnamon desktops, but they are easy to cover and then I need to move or minimize windows, or just use the “Show desktop” button to clear off the entire desktop. LXDE does have a “Iconify all windows” button, but I seldom need to use it unless I want to look at my wallpaper.
**5. LXDE comes with a strong file manager.** The default file manager for LXDE is PCManFM, so that became my file manager for the duration of my time with LXDE. PCManFM is very flexible and can be configured to make it work well for most people and situations. It seems to be somewhat less configurable than Krusader, which is usually my go-to file manager, but I really like the sidebar on PCManFM that Krusader does not have.
PCManFM allows multiple tabs, which can be opened with a right-click on any item in the sidebar or by a left-click on the new tab icon in the icon bar. The Places pane at the left of the PCManFM window shows the applications menu, and you can launch applications from PCManFM. The upper part of the Places pane also shows a devices icon, which can be used to view your physical storage devices, a list of removable devices along with buttons to allow you to mount or unmount them, and the Home, Desktop, and trashcan folders to make them easy to access. The bottom part of the Places panel contains shortcuts to some default directories, Documents, Music, Pictures, Videos, and Downloads. You can also drag additional directories to the shortcut part of the Places pane. The Places pane can be swapped for a regular directory tree.
**6. The title bar of ****a new window flashes**** if it is opened behind existing windows.** This is a nice way to make locating new windows in with a large number of existing ones.
**7. Most modern desktop environments allow for multiple desktops and LXDE is no exception to that.** I like to use one desktop for my development, testing, and writing activities, and another for mundane tasks like email and web browsing. LXDE provides two desktops by default, but you can configure just one or more. Right-click on the Desktop Pager to configure it.
Through some disruptive but not destructive testing, I was able to determine that the maximum number of desktops allowed is 100. I also discovered that when I reduced the number of desktops to fewer than the three I actually had in use, the windows on the defunct desktops are moved to desktop 1. What fun I have had with this!
**8. The Xfce power manager is a powerful little application that allows you to configure how power management works.** It provides a tab for General configuration as well as tabs for System, Display, and Devices. The Devices tab displays a table of attached devices on my system, such as battery-powered mice, keyboards, and even my UPS. It displays information about each, including the vendor and serial number, if available, and the state of the battery charge. As I write this, my UPS is 100% charged and my Logitech mouse is 75% charged. The Xfce power manager also displays an icon in the system tray so you can get a quick read on your devices' battery status from there.
There are more things to like about the LXDE desktop, but these are the ones that either grabbed my attention or are so important to my way of working in a modern GUI interface that they are indispensable to me.
One quirk I noticed with LXDE is that I never did figure out what the “Reconfigure” option does on the desktop (Openbox) menu. I clicked on that several times and never noticed any activity of any kind to indicate that that selection actually did anything.
I have found LXDE to be an easy-to-use, yet powerful, desktop. I have enjoyed my weeks using it for this article. LXDE has enabled me to work effectively mostly by allowing me access to the applications and files that I want, while remaining unobtrusive the rest of the time. I also never encountered anything that prevented me from doing my work. Well, except perhaps for the time I spent exploring this fine desktop. I can highly recommend the LXDE desktop.
I am now using GNOME 3 and the GNOME Shell and will report on that in my next installment.
## 8 Comments |
8,435 | 极客漫画:DOS 时代 | https://turnoff.us/geek/tales-of-dos/ | 2017-04-22T11:37:00 | [
"漫画",
"DOS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8435-1.html | 
在久远的 DOS 时代(其实也才 20 多年前),那个时候没有 Windows、没有图形界面的 OSX 和 Linux。那个时候,我们是用软盘来存储文件的,从开始的 5¼ 英寸的软盘(360 KB), 3½ 英寸软盘(720 KB),到后来的高密盘 720 KB 和 1.44 MB。甚至更古老的时候有(我没见过的) 8 英寸盘和打孔纸带。
记得那个时候经常揣着一盒软盘,到处拷贝(不,交换)别人珍藏的软件,比如 PCTools、Norton ,那简直都是珍宝啊。
你也不能想象,用杀毒软件在一张小小的 360 KB 软盘上查出上千个 DIR II 病毒而“滴滴”不断,让整个机房侧目。
在那个时候,像素风的游戏才是现实,而第一次见到《仙剑奇侠传》时,简直不能想象会有如此精美的图像(PS,后来有幸玩过 CD 版本,才知道片头曲的 CD 音轨和 软盘版的 MIDI 那叫一个天上地下)。所以,漫画里这哥俩看到 Accolade 公司做的这个赛车游戏,就感觉如此惊艳了。(LCTT 译注: [Test Drive](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Test_Drive_(video_game)) 是 Accolade 公司于 1987 年发行的跨平台赛车游戏,当时被评分为 4½ 星,总分 5 星。)
如果你也是远古时代过来的,不妨吐槽下你的当年;如果你是新生代的互联网原住民,请尽情的嘲讽吧~
---
via: <https://turnoff.us/geek/tales-of-dos/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者&合成&点评:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 404 | Not Found | null |
8,436 | 在 RHEL、CentOS 及 Fedora 上安装 Drupal 8 | http://www.tecmint.com/install-drupal-in-centos-rhel-fedora/ | 2017-04-22T16:02:00 | [
"Drupal"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8436-1.html | 
**Drupal** 是一个开源,灵活,高度可拓展和安全的<ruby> 内容管理系统 <rt> Content Management System </rt></ruby>(CMS),使用户轻松的创建网站。
它可以使用模块拓展,使用户将内容管理转换为强大的数字解决方案。
**Drupal** 运行在诸如 Apache、IIS、Lighttpd、Cherokee、Nginx 的 Web 服务器上,后端数据库可以使用 MySQL、MongoDB、MariaDB、PostgreSQL、MSSQL Server。
在这篇文章中, 我们会展示在 RHEL 7/6、CentOS 7/6 和 Fedora 20-25 发行版上使用 LAMP 架构,如何手动安装和配置 Drupal 8。
#### Drupal 需求:
1. **Apache 2.x** (推荐)
2. **PHP 5.5.9** 或 更高 (推荐 PHP 5.5)
3. **MySQL 5.5.3** 或 **MariaDB 5.5.20** 与 PHP 数据对象(PDO) 支持
安装过程中,我使用 `drupal.tecmint.com` 作为网站主机名,IP 地址为 `192.168.0.104`。你的环境也许与这些设置不同,因此请适当做出更改。
### 步骤 1:安装 Apache Web 服务器
1、 首先我们从官方仓库开始安装 Apache Web 服务器。
```
# yum install httpd
```
2、 安装完成后,服务开始是被禁用的,因此我们需要手动启动它,同时让它下次系统启动时自动启动,如下:
```
------------- 通过 SystemD - CentOS/RHEL 7 和 Fedora 22+ -------------------
# systemctl start httpd
# systemctl enable httpd
------------- 通过 SysVInit - CentOS/RHEL 6 和 Fedora ----------------------
# service httpd start
# chkconfig --level 35 httpd on
```
3、 接下来,为了允许通过 **HTTP** 和 **HTTPS** 访问 Apache 服务,我们必须打开 **HTTPD** 守护进程正在监听的 **80** 和 **443** 端口,如下所示:
```
------------ 通过 Firewalld - CentOS/RHEL 7 and Fedora 22+ -------------
# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
# firewall-cmd --reload
------------ 通过 IPtables - CentOS/RHEL 6 and Fedora 22+ -------------
# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT
# service iptables save
# service iptables restart
```
4、 现在验证 Apache 是否正常工作, 打开浏览器在地址栏中输入 `http://server_IP`, 输入你的服务器 IP 地址, 默认 Apache2 页面应出现,如下面截图所示:

*Apache 默认页面*
### 步骤 2: 安装 Apache PHP 支持
5、 接下来,安装 PHP 和 PHP 所需模块。
```
# yum install php php-mbstring php-gd php-xml php-pear php-fpm php-mysql php-pdo php-opcache
```
**重要**: 假如你想要安装 **PHP7**, 你需要增加以下仓库:**EPEL** 和 **Webtactic** 才可以使用 yum 安装 PHP7.0:
```
------------- Install PHP 7 in CentOS/RHEL and Fedora -------------
# rpm -Uvh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
# rpm -Uvh https://mirror.webtatic.com/yum/el7/webtatic-release.rpm
# yum install php70w php70w-opcache php70w-mbstring php70w-gd php70w-xml php70w-pear php70w-fpm php70w-mysql php70w-pdo
```
6、 接下来,要从浏览器得到关于 PHP 安装和配置完整信息,使用下面命令在 Apache 文档根目录 (`/var/www/html`) 创建一个 `info.php` 文件。
```
# echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" > /var/www/html/info.php
```
然后重启 HTTPD 服务器 ,在浏览器地址栏输入 `http://server_IP/info.php`。
```
# systemctl restart httpd
或
# service httpd restart
```

*验证 PHP 信息*
### 步骤 3: 安装和配置 MariaDB 数据库
7、 请知晓, **Red Hat Enterprise Linux/CentOS 7.0** 从支持 **MySQL** 转为了 **MariaDB** 作为默认数据库管理系统。
要安装 **MariaDB** 数据库, 你需要添加 [官方 MariaDB 库](https://downloads.mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/#mirror=Fibergrid&distro=CentOS) 到 `/etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo` 中,如下所示。
```
[mariadb]
name = MariaDB
baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.1/centos7-amd64
gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
gpgcheck=1
```
当仓库文件准备好后,你可以像这样安装 MariaDB:
```
# yum install mariadb-server mariadb
```
8、 当 MariaDB 数据库安装完成,启动数据库的守护进程,同时使它能够在下次启动后自动启动。
```
------------- 通过 SystemD - CentOS/RHEL 7 and Fedora 22+ -------------
# systemctl start mariadb
# systemctl enable mariadb
------------- 通过 SysVInit - CentOS/RHEL 6 and Fedora -------------
# service mysqld start
# chkconfig --level 35 mysqld on
```
9、 然后运行 `mysql_secure_installation` 脚本去保护数据库(设置 root 密码, 禁用远程登录,移除测试数据库并移除匿名用户),如下所示:
```
# mysql_secure_installation
```

*MySQL 安全安装*
### 步骤 4: 在 CentOS 中安装和配置 Drupal 8
10、 这里我们使用 [wget 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/) [下载最新版本 Drupal](https://www.drupal.org/download)(例如 8.2.6),如果你没有安装 wget 和 gzip 包 ,请使用下面命令安装它们:
```
# yum install wget gzip
# wget -c https://ftp.drupal.org/files/projects/drupal-8.2.6.tar.gz
```
11、 之后,[解压 tar 文件](http://www.tecmint.com/extract-tar-files-to-specific-or-different-directory-in-linux/) 并移动 Drupal 目录到 Apache 文档根目录(`/var/www/html`)。
```
# tar -zxvf drupal-8.2.6.tar.gz
# mv drupal-8.2.6 /var/www/html/drupal
```
12、 然后,依据 `/var/www/html/drupal/sites/default` 目录下的示例设置文件 `default.settings.php`,创建设置文件 `settings.php`,然后给 Drupal 站点目录设置适当权限,包括子目录和文件,如下所示:
```
# cd /var/www/html/drupal/sites/default/
# cp default.settings.php settings.php
# chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/drupal/
```
13、 更重要的是在 `/var/www/html/drupal/sites/` 目录设置 **SElinux** 规则,如下:
```
# chcon -R -t httpd_sys_content_rw_t /var/www/html/drupal/sites/
```
14、 现在我们必须为 Drupal 站点去创建一个用于管理的数据库和用户。
```
# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
MySQL Shell
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 12
Server version: 5.1.73 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
**MySQL [(none)]> create database drupal;**
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
**MySQL [(none)]> create user ravi@localhost identified by 'tecmint123';**
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
**MySQL [(none)]> grant all on drupal.* to ravi@localhost;**
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
**MySQL [(none)]> flush privileges;**
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
**MySQL [(none)]> exit**
Bye
```
15、 最后,打开地址: `http://server_IP/drupal/` 开始网站的安装,选择你首选的安装语言然后点击保存以继续。

*Drupal 安装语言*
16、 下一步,选择安装配置文件,选择 Standard(标准),点击保存继续。

*Drupal 安装配置文件*
17、 在进行下一步之前查看并通过需求审查并启用 `Clean URL`。

*验证 Drupal 需求*
现在在你的 Apache 配置下启用 Clean URL 的 Drupal。
```
# vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
```
确保为默认根文档目录 `/var/www/html` 设置 `AllowOverride All`,如下图所示:

*在 Drupal 中启用 Clean URL*
18、 当你为 Drupal 启用 Clean URL,刷新页面从下面界面执行数据库配置,输入 Drupal 站点数据库名,数据库用户和数据库密码。
当填写完所有信息点击**保存并继续**。

*Drupal 数据库配置*
若上述设置正确,Drupal 站点安装应该完成了,如下图界面。

*Drupal 安装*
19、 接下来配置站点为下面的设置(使用适用你的情况的值):
* **站点名称** – TecMint Drupal Site
* **站点邮箱地址** – [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected])
* **用户名** – admin
* **密码** – ##########
* **用户的邮箱地址** – [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected])
* **默认国家** – India
* **默认时区** – UTC
设置适当的值后,点击**保存并继续**完成站点安装过程。

*Drupal 站点配置*
20、下图显示的是通过 LAMP 成功安装的 Drupal 8 站点。

*Drupal 站点面板*
现在你可以点击**增加内容**,创建示例网页内容。
选项: 有些人[使用 MySQL 命令行管理数据库](http://www.tecmint.com/mysqladmin-commands-for-database-administration-in-linux/)不舒服,可以从浏览器界面 [安装 PHPMYAdmin 管理数据库](http://www.tecmint.com/install-phpmyadmin-rhel-centos-fedora-linux/)
浏览 Drupal 文档 : <https://www.drupal.org/docs/8>
就这样! 在这个文章, 我们展示了在 CentOS 7 上如何去下载、安装和使用基本配置来设置 LAMP 以及 Drupal 8。 欢迎就这个教程提供反馈,或提供给我们一些相关信息。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将成为 Linux 系统管理员,Web 开发者,目前是 TecMint 的原创作者,热爱计算机工作,并且坚信知识共享。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/install-drupal-in-centos-rhel-fedora/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[imxieke](https://github.com/imxieke) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,437 | OpenContrail:一个 OpenStack 生态中的重要工具 | https://www.linux.com/news/event/open-networking-summit/2017/2/opencontrail-essential-tool-openstack-ecosystem | 2017-04-22T20:45:00 | [
"OpenStack",
"SDN",
"OpenContrail"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8437-1.html | 
整个 2016 年,软件定义网络(SDN)迅速发展,开源和云计算领域的众多参与者正帮助其获得增长。结合这一趋势,用在 OpenStack 云计算平台上的流行的 SDN 平台 [OpenContrail](https://www.globenewswire.com/Tracker?data=brZ3aJVRyVHeFOyzJ1Dl4DMY3CsSV7XcYkwRyOcrw4rDHplSItUqHxXtWfs18mLsa8_bPzeN2EgZXWcQU8vchg==) 正成为许多管理员需要具备的技能的重要工具。
正如管理员和开发人员在 OpenStack 生态系统中围绕着诸如 Ceph 等重要工具提升技能一样,他们将需要拥抱 OpenContrail,它是由 Apache 软件基金会全面开源并管理的软件。
考虑到这些,OpenStack 领域中最活跃的公司之一 Mirantis 已经[宣布](http://www.econotimes.com/Mirantis-Becomes-First-Vendor-to-Offer-Support-and-Managed-Services-for-OpenContrail-SDN-486228)对 OpenContrail 的提供商业支持和贡献。该公司提到:“添加了 OpenContrail 后,Mirantis 将会为与 OpenStack 一起使用的开源技术,包括用于存储的 Ceph、用于计算的 OpenStack/KVM、用于 SDN 的 OpenContrail 或 Neutron 提供一站式的支持。”
根据 Mirantis 公告,“OpenContrail 是一个使用基于标准协议构建的 Apache 2.0 许可项目,为网络虚拟化提供了所有必要的组件 - SDN 控制器、虚拟路由器、分析引擎和已发布的上层 API,它有一个可扩展 REST API 用于配置以及从系统收集操作和分析数据。作为规模化构建,OpenContrail 可以作为云基础设施的基础网络平台。”
有消息称 Mirantis [收购了 TCP Cloud](https://www.globenewswire.com/Tracker?data=Lv6LkvREFzGWgujrf1n6r_qmjSdu67-zdRAYt2itKQ6Fytomhfphuk5EbDNjNYtfgAsbnqI8H1dn_5kB5uOSmmSYY9XP2ibkrPw_wKi5JtnAyV43AjuR_epMmOUkZZ8QtFdkR33lTGDmN6O5B4xkwv7fENcDpm30nI2Og_YrYf0b4th8Yy4S47lKgITa7dz2bJpwpbCIzd7muk0BZ17vsEp0S3j4kQJnmYYYk5udOMA=),这是一家专门从事 OpenStack、OpenContrail 和 Kubernetes 管理服务的公司。Mirantis 将使用 TCP Cloud 的云架构持续交付技术来管理将在 Docker 容器中运行的 OpenContrail 控制面板。作为这项工作的一部分,Mirantis 也会一直致力于 OpenContrail。
OpenContrail 的许多贡献者正在与 Mirantis 紧密合作,他们特别注意了 Mirantis 将提供的支持计划。
“OpenContrail 是 OpenStack 社区中一个重要的项目,而 Mirantis 很好地容器化并提供商业支持。我们团队正在做的工作使 OpenContrail 能轻松地扩展并更新,并与 Mirantis OpenStack 的其余部分进行无缝滚动升级。 ” Mirantis 的工程师总监和 OpenContrail 咨询委员会主任 Jakub Pavlik 说:“商业支持也将使 Mirantis 能够使该项目与各种交换机兼容,从而为客户提供更多的硬件和软件选择。”
除了 OpenContrail 的商业支持外,我们很可能还会看到 Mirantis 为那些想要学习如何利用它的云管理员和开发人员提供的教育服务。Mirantis 已经以其 [OpenStack 培训](https://training.mirantis.com/)课程而闻名,并将 Ceph 纳入了培训课程中。
在 2016 年,SDN 种类快速演变,并且对许多部署 OpenStack 的组织也有意义。IDC 最近发布了 SDN 市场的[一项研究](https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS41005016),预计从 2014 年到 2020 年 SDN 市场的年均复合增长率为 53.9%,届时市场价值将达到 125 亿美元。此外,“Technology Trends 2016” 报告将 SDN 列为组织最佳的技术投资之一。
IDC 网络基础设施总裁 [Rohit Mehra](http://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=PRF003513) 说:“云计算和第三方平台推动了 SDN 的需求,它将在 2020 年代表一个价值超过 125 亿美元的市场。丝毫不用奇怪的是 SDN 的价值将越来越多地渗透到网络虚拟化软件和 SDN 应用中,包括虚拟化网络和安全服务。大型企业在数据中心中实现 SDN 的价值,但它们最终将会认识到其在横跨分支机构和校园网络的广域网中的广泛应用。”
同时,Linux 基金会最近[宣布](https://www.linux.com/blog/linux-foundation-issues-2016-guide-open-source-cloud-projects)发布了其 2016 年度报告[“开放云指导:当前趋势和开源项目”](http://ctt.marketwire.com/?release=11G120876-001&id=10172077&type=0&url=http%3A%2F%2Fgo.linuxfoundation.org%2Frd-open-cloud-report-2016-pr)。第三份年度报告全面介绍了开放云计算,并包含一个关于 SDN 的部分。
Linux 基金会还提供了[软件定义网络基础知识](https://training.linuxfoundation.org/linux-courses/system-administration-training/software-defined-networking-fundamentals)(LFS265),这是一个自定进度的 SDN 在线课程,另外作为 [Open Daylight](https://www.opendaylight.org/) 项目的领导者,另一个重要的开源 SDN 平台正在迅速成长。
(题图:CC0 Pixabay)
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/news/event/open-networking-summit/2017/2/opencontrail-essential-tool-openstack-ecosystem>
作者:[SAM DEAN](https://www.linux.com/users/sam-dean) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,439 | 2016 年度顶级开源创作工具 | https://opensource.com/article/16/12/yearbook-top-open-source-creative-tools-2016 | 2017-04-23T17:09:00 | [
"设计",
"创意"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8439-1.html |
>
> 无论你是想修改图片、编译音频,还是制作动画,这里的自由而开源的工具都能帮你做到。
>
>
>

几年前,我在 Red Hat 总结会上做了一个简单的演讲,给与会者展示了 [2012 年度开源创作工具](https://opensource.com/life/12/9/tour-through-open-source-creative-tools)。开源软件在过去几年里发展迅速,现在我们来看看 2016 年的相关领域的软件。
### 核心应用
这六款应用是开源的设计软件中的最强王者。它们做的很棒,拥有完善的功能特征集、稳定发行版以及活跃的开发者社区,是很成熟的项目。这六款应用都是跨平台的,每一个都能在 Linux、OS X 和 Windows 上使用,不过大多数情况下 Linux 版本一般都是最先更新的。这些应用广为人知,我已经把最新特性的重要部分写进来了,如果你不是非常了解它们的开发情况,你有可能会忽视这些特性。
如果你想要对这些软件做更深层次的了解,或许你可以帮助测试这四个软件 —— GIMP、Inkscape、Scribus,以及 MyPaint 的最新版本,在 Linux 机器上你可以用 [Flatpak](https://opensource.com/business/16/8/flatpak) 软件轻松地安装它们。这些应用的每日构建版本可以[按照指令](http://flatpak.org/apps.html) 通过 Flatpak 的“每日构建的绘图应用(Nightly Graphics Apps)”得到。有一件事要注意:如果你要给每个应用的 Flatpak 版本安装笔刷或者其它扩展,用于移除这些扩展的目录将会位于相应应用的目录 **~/.var/app** 下。
#### GIMP
[GIMP](https://opensource.com/tags/gimp) [在 2015 年迎来了它的 20 周岁](/article-7131-1.html),使得它成为这里资历最久的开源创造型应用之一。GIMP 是一款强大的应用,可以处理图片,创作简单的绘画,以及插图。你可以通过简单的任务来尝试 GIMP,比如裁剪、缩放图片,然后循序渐进使用它的其它功能。GIMP 可以在 Linux、Mac OS X 以及 Windows 上使用,是一款跨平台的应用,而且能够打开、导出一系列格式的文件,包括在与之相似的软件 Photoshop 上广为应用的那些格式。
GIMP 开发团队正在忙着 2.10 发行版的工作;[2.8.18](https://www.gimp.org/news/2016/07/14/gimp-2-8-18-released/) 是最新的稳定版本。更振奋人心的是非稳定版,[2.9.4](https://www.gimp.org/news/2016/07/13/gimp-2-9-4-released/),拥有全新的用户界面,旨在节省空间的符号式图标和黑色主题,改进了颜色管理,更多的基于 GEGL 的支持分离预览的过滤器,支持 MyPaint 笔刷(如下图所示),对称绘图,以及命令行批次处理。想了解更多信息,请关注 [完整的发行版注记](https://www.gimp.org/news/2016/07/13/gimp-2-9-4-released/)。

#### Inkscape
[Inkscape](https://opensource.com/tags/inkscape) 是一款富有特色的矢量绘图设计软件。可以用它来创作简单的图形、图表、布局或者图标。
最新的稳定版是 [0.91](http://wiki.inkscape.org/wiki/index.php/Release_notes/0.91) 版本;与 GIMP 相似,能在预发布版 0.92pre3 版本中找到更多有趣的东西,其发布于 2016 年 11 月。最新推出的预发布版的突出特点是<ruby> <a href="http://wiki.inkscape.org/wiki/index.php/Mesh_Gradients"> 梯度网格特性 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> gradient mesh feature </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(如下图所示);0.91 发行版里介绍的新特性包括:[强力笔触(power stroke)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IztyV-Dy4CE) 用于完全可配置的书法笔画(下图的 “opensource.com” 中的 “open” 用的就是强力笔触技术),画布测量工具,以及 [全新的符号对话框](https://inkscape.org/cs/%7Edoctormo/%E2%98%85symbols-dialog)(如下图右侧所示)。(很多符号库可以从 GitHub 上获得;[Xaviju's inkscape-open-symbols set](https://github.com/Xaviju/inkscape-open-symbols) 就很不错。)*对象*对话框是在改进版或每日构建中可用的新特性,整合了一个文档中的所有对象,提供工具来管理这些对象。

#### Scribus
[Scribus](https://opensource.com/tags/scribus) 是一款强大的桌面出版和页面布局工具。Scribus 让你能够创造精致美丽的物品,包括信封、书籍、杂志以及其它印刷品。Scribus 的颜色管理工具可以处理和输出 CMYK 格式,还能给文件配色,可靠地用于印刷车间的重印。
[1.4.6](https://www.scribus.net/scribus-1-4-6-released/) 是 Scribus 的最新稳定版本;[1.5.x](https://www.scribus.net/scribus-1-5-2-released/) 系列的发行版更令人期待,因为它们是即将到来的 1.6.0 发行版的预览。1.5.3 版本包含了 Krita 文件(\*.KRA)导入工具; 1.5.x 系列中其它的改进包括了表格工具、文本框对齐、脚注、导出可选 PDF 格式、改进的字典、可驻留边框的调色盘、符号工具,和丰富的文件格式支持。

#### MyPaint
[MyPaint](http://mypaint.org/) 是一款用于数位屏的快速绘图和插画工具。它很轻巧,界面虽小,但快捷键丰富,因此你能够不用放下数位笔而专心于绘图。
[MyPaint 1.2.0](http://mypaint.org/blog/2016/01/15/mypaint-1.2.0-released/) 是其最新的稳定版本,包含了一些新特性,诸如 [直观上墨工具](https://github.com/mypaint/mypaint/wiki/v1.2-Inking-Tool) 用来跟踪铅笔绘图的轨迹,新的填充工具,层分组,笔刷和颜色的历史面板,用户界面的改进包括暗色主题和小型符号图标,以及可编辑的矢量层。想要尝试 MyPaint 里的最新改进,我建议安装每日构建版的 Flatpak 构建,尽管自从 1.2.0 版本没有添加重要的特性。

#### Blender
[Blender](https://opensource.com/tags/blender) 最初发布于 1995 年 1 月,像 GIMP 一样,已经有 20 多年的历史了。Blender 是一款功能强大的开源 3D 制作套件,包含建模、雕刻、渲染、真实材质、套索、动画、影像合成、视频编辑、游戏创作以及模拟。
Blender 最新的稳定版是 [2.78a](http://www.blender.org/features/2-78/)。2.78 版本很庞大,包含的特性有:改进的 2D <ruby> 蜡笔 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Grease Pencil </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 动画工具;针对球面立体图片的 VR 渲染支持;以及新的手绘曲线的绘图工具。

要尝试最新的 Blender 开发工具,有很多种选择,包括:
* Blender 基金会在官方网址提供 [非稳定版的每日构建版](https://builder.blender.org/download/)。
* 如果你在寻找特殊的开发中特性,[graphicall.org](http://graphicall.org/) 是一个适合社区的网站,能够提供特殊版本的 Blender(偶尔还有其它的创造型开源应用),让艺术家能够尝试体验最新的代码。
* Mathieu Bridon 通过 Flatpak 做了 Blender 的一个开发版本。查看它的博客以了解详情:[Flatpak 上每日构建版的 Blender](https://mathieu.daitauha.fr/blog/2016/09/23/blender-nightly-in-flatpak/)
#### Krita
[Krita](https://opensource.com/tags/krita) 是一款拥有强大功能的数字绘图应用。这款应用贴合插画师、印象艺术家以及漫画家的需求,有很多附件,比如笔刷、调色板、图案以及模版。
最新的稳定版是 [Krita 3.0.1](https://krita.org/en/item/krita-3-0-1-update-brings-numerous-fixes/),于 2016 年 9 月发布。3.0.x 系列的新特性包括 2D 逐帧动画;改进的层管理器和功能;丰富的常用快捷键;改进了网格、向导和图形捕捉;还有软打样。

### 视频处理工具
关于开源的视频编辑工具则有很多很多。这这些工具之中,[Flowblade](https://opensource.com/life/16/9/10-reasons-flowblade-linux-video-editor) 是新推出的,而 Kdenlive 则是构建完善、对新手友好、功能最全的竞争者。对你排除某些备选品有所帮助的主要标准是它们所支持的平台,其中一些只支持 Linux 平台。它们的软件上游都很活跃,最新的稳定版都于近期发布,发布时间相差不到一周。
#### Kdenlive
[Kdenlive](https://opensource.com/tags/kdenlive),最初于 2002 年发布,是一款强大的非线性视频编辑器,有 Linux 和 OS X 版本(但是 OS X 版本已经过时了)。Kdenlive 有用户友好的、基于拖拽的用户界面,适合初学者,又有专业人员需要的深层次功能。
可以看看 Seth Kenlon 写的 [Kdenlive 系列教程](https://opensource.com/life/11/11/introduction-kdenlive),了解如何使用 Kdenlive。
* 最新稳定版: 16.08.2 (2016 年 10 月)

#### Flowblade
2012 年发布, [Flowblade](http://jliljebl.github.io/flowblade/),只有 Linux 版本的视频编辑器,是个相当不错的后起之秀。
* 最新稳定版: 1.8 (2016 年 9 月)
#### Pitivi
[Pitivi](http://pitivi.org/) 是用户友好型的自由开源视频编辑器。Pitivi 是用 [Python](http://wiki.pitivi.org/wiki/Why_Python%3F) 编写的(“Pitivi” 中的 “Pi”来源于此),使用了 [GStreamer](https://gstreamer.freedesktop.org/) 多媒体框架,社区活跃。
* 最新稳定版: 0.97 (2016 年 8 月)
* 通过 Flatpak 获取 [最新版本](https://pitivi.wordpress.com/2016/07/18/get-pitivi-directly-from-us-with-flatpak/)
#### Shotcut
[Shotcut](http://shotcut.org/) 是一款自由开源的跨平台视频编辑器,早在 2004 年就发布了,之后由现在的主要开发者 [Dan Dennedy](http://www.dennedy.org/) 重写。
* 最新稳定版: 16.11 (2016 年 11 月)
* 支持 4K 分辨率
* 仅以 tar 包方式发布
#### OpenShot Video Editor
始于 2008 年,[OpenShot Video Editor](http://openshot.org/) 是一款自由、开源、易于使用、跨平台的视频编辑器。
* 最新稳定版: [2.1](http://www.openshotvideo.com/2016/08/openshot-21-released.html) (2016 年 8 月)
### 其它工具
#### SwatchBooker
[SwatchBooker](http://www.selapa.net/swatchbooker/) 是一款很方便的工具,尽管它近几年都没有更新了,但它还是很有用。SwatchBooler 能帮助用户从各大制造商那里合法地获取色卡,你可以用其它自由开源的工具处理它导出的格式,包括 Scribus。
#### GNOME Color Manager
[GNOME Color Manager](https://help.gnome.org/users/gnome-help/stable/color.html.en) 是 GNOME 桌面环境内建的颜色管理器,而 GNOME 是某些 Linux 发行版的默认桌面。这个工具让你能够用色度计为自己的显示设备创建属性文件,还可以为这些设备加载/管理 ICC 颜色属性文件。
#### GNOME Wacom Control
[The GNOME Wacom controls](https://help.gnome.org/users/gnome-help/stable/wacom.html.en) 允许你在 GNOME 桌面环境中配置自己的 Wacom 手写板;你可以修改手写板交互的很多选项,包括自定义手写板灵敏度,以及手写板映射到哪块屏幕上。
#### Xournal
[Xournal](http://xournal.sourceforge.net/) 是一款简单但可靠的应用,可以让你通过手写板手写或者在笔记上涂鸦。Xournal 是一款有用的工具,可以让你签名或注解 PDF 文档。
#### PDF Mod
[PDF Mod](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/PdfMod) 是一款编辑 PDF 文件很方便的工具。PDF Mod 让用户可以移除页面、添加页面,将多个 PDF 文档合并成一个单独的 PDF 文件,重新排列页面,旋转页面等。
#### SparkleShare
[SparkleShare](https://www.sparkleshare.org/) 是一款基于 git 的文件分享工具,艺术家用来协作和分享资源。它会挂载在 GitLab 仓库上,你能够采用一个精妙的开源架构来进行资源管理。SparkleShare 的前端通过在顶部提供一个类似下拉框界面,避免了使用 git 的复杂性。
### 摄影
#### Darktable
[Darktable](https://opensource.com/life/16/4/how-use-darktable-digital-darkroom) 是一款能让你编辑 RAW 文件的应用,有一系列工具,可以管理工作流、无损编辑图片。Darktable 支持许多流行的相机和镜头。

#### Entangle
[Entangle](https://entangle-photo.org/) 允许你将数字相机连接到电脑上,让你能从电脑上完全控制相机。
#### Hugin
[Hugin](http://hugin.sourceforge.net/) 是一款工具,让你可以拼接照片,从而制作全景照片。
### 2D 动画
#### Synfig Studio
[Synfig Studio](https://opensource.com/article/16/12/synfig-studio-animation-software-tutorial) 是基于矢量的二维动画套件,支持位图原图,在平板上用起来方便。
#### Blender Grease Pencil
我在前面讲过了 Blender,但值得注意的是,最近的发行版里[重构的蜡笔特性](https://wiki.blender.org/index.php/Dev:Ref/Release_Notes/2.78/GPencil),添加了创作二维动画的功能。
#### Krita
[Krita](https://opensource.com/tags/krita) 现在同样提供了二维动画功能。
### 音频编辑
#### Audacity
[Audacity](https://opensource.com/tags/audacity) 在编辑音频文件、记录声音方面很有名,是用户友好型的工具。
#### Ardour
[Ardour](https://ardour.org/) 是一款数字音频工作软件,界面中间是录音,编辑和混音工作流。使用上它比 Audacity 要稍微难一点,但它允许自动操作,并且更高端。(有 Linux、Mac OS X 和 Windows 版本)
#### Hydrogen
[Hydrogen](http://www.hydrogen-music.org/) 是一款开源的电子鼓,界面直观。它可以用合成的乐器创作、整理各种乐谱。
#### Mixxx
[Mixxx](http://mixxx.org/) 是四仓 DJ 套件,让你能够以强大操控来 DJ 和混音歌曲,包含节拍循环、时间延长、音高变化,还可以用 DJ 硬件控制器直播混音和衔接。
### Rosegarden
[Rosegarden](http://www.rosegardenmusic.com/) 是一款作曲软件,有乐谱编写和音乐作曲或编辑的功能,提供音频和 MIDI 音序器。(LCTT 译注:MIDI 即 Musical Instrument Digital Interface 乐器数字接口)
#### MuseScore
[MuseScore](https://opensource.com/life/16/03/musescore-tutorial) 是乐谱创作、记谱和编辑的软件,它还有个乐谱贡献者社区。
### 其它具有创造力的工具
#### MakeHuman
[MakeHuman](http://makehuman.org/) 是一款三维绘图工具,可以创造人型的真实模型。
#### Natron
[Natron](https://natron.fr/) 是基于节点的合成工具,用于视频后期制作、动态图象和设计特效。
#### FontForge
[FontForge](http://fontforge.github.io/en-US/) 是创作和编辑字体的工具。允许你编辑某个字体中的字形,也能够使用这些字形生成字体。
#### Valentina
[Valentina](http://valentina-project.org/) 是用来设计缝纫图案的应用。
#### Calligra Flow
[Calligra Flow](https://www.calligra.org/flow/) 是一款图表工具,类似 Visio(有 Linux,Mac OS X 和 Windows 版本)。
### 资源
这里有很多小玩意和彩蛋值得尝试。需要一点灵感来探索?这些网站和论坛有很多教程和精美的成品能够激发你开始创作:
1、 [pixls.us](http://pixls.us/): 摄影师 Pat David 管理的博客,他专注于专业摄影师使用的自由开源的软件和工作流。
2、 [David Revoy 's Blog](http://davidrevoy.com/): David Revoy 的博客,热爱自由开源,非常有天赋的插画师,概念派画师和开源倡议者,对 Blender 基金会电影有很大贡献。
3、 [The Open Source Creative Podcast](http://monsterjavaguns.com/podcast/): 由 Opensource.com 社区版主和专栏作家 [Jason van Gumster](https://opensource.com/users/jason-van-gumster) 管理,他是 Blender 和 GIMP 的专家, [《Blender for Dummies》](http://www.blenderbasics.com/) 的作者,该文章正好是面向我们这些热爱开源创作工具和这些工具周边的文化的人。
4、 [Libre Graphics Meeting](http://libregraphicsmeeting.org/2016/): 自由开源创作软件的开发者和使用这些软件的创作者的年度会议。这是个好地方,你可以通过它找到你喜爱的开源创作软件将会推出哪些有意思的特性,还可以了解到这些软件的用户用它们在做什么。
---
作者简介:
Máirín Duffy - Máirín 是 Red Hat 的首席交互设计师。她热衷于自由软件和开源工具,尤其是在创作领域:她最喜欢的应用是 [Inkscape](http://inkscape.org)。
(题图: [pixabay](https://pixabay.com),CC0)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/16/12/yearbook-top-open-source-creative-tools-2016>
作者:[Máirín Duffy](https://opensource.com/users/mairin) 译者:[GitFuture](https://github.com/GitFuture) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | A few years ago, I gave a lightning talk at Red Hat Summit that took attendees on a tour of the [2012 open source creative tools](https://opensource.com/life/12/9/tour-through-open-source-creative-tools) landscape. Open source tools have evolved a lot in the past few years, so let's take a tour of 2016 landscape.
## Core applications
These six applications are the juggernauts of open source design tools. They are well-established, mature projects with full feature sets, stable releases, and active development communities. All six applications are cross-platform; each is available on Linux, OS X, and Windows, although in some cases the Linux versions are the most quickly updated. These applications are so widely known, I've also included highlights of the latest features available that you may have missed if you don't closely follow their development.
If you'd like to follow new developments more closely, and perhaps even help out by testing the latest development versions of the first four of these applications—GIMP, Inkscape, Scribus, and MyPaint—you can install them easily on Linux using [Flatpak](https://opensource.com/business/16/8/flatpak). Nightly builds of each of these applications are available via Flatpak by [following the instructions](http://flatpak.org/apps.html) for *Nightly Graphics Apps*. One thing to note: If you'd like to install brushes or other extensions to each Flatpak version of the app, the directory to drop the extensions in will be under the directory corresponding to the application inside the **~/.var/app** directory.
### GIMP
[GIMP](https://opensource.com/tags/gimp) [celebrated its 20th anniversary in 2015](https://www.gimp.org/news/2015/11/22/20-years-of-gimp-release-of-gimp-2816/), making it one of the oldest open source creative applications out there. GIMP is a solid program for photo manipulation, basic graphic creation, and illustration. You can start using GIMP by trying simple tasks, such as cropping and resizing images, and over time work into a deep set of functionality. Available for Linux, Mac OS X, and Windows, GIMP is cross-platform and can open and export to a wide breadth of file formats, including those popularized by its proprietary analogue, Photoshop.
The GIMP team is currently working toward the 2.10 release; [2.8.18](https://www.gimp.org/news/2016/07/14/gimp-2-8-18-released/) is the latest stable version. More exciting is the unstable version, [2.9.4](https://www.gimp.org/news/2016/07/13/gimp-2-9-4-released/), with a revamped user interface featuring space-saving symbolic icons and dark themes, improved color management, more GEGL-based filters with split-preview, MyPaint brush support (shown in screenshot below), symmetrical drawing, and command-line batch processing. For more details, check out [the full release notes](https://www.gimp.org/news/2016/07/13/gimp-2-9-4-released/).
### Inkscape
[Inkscape](https://opensource.com/tags/inkscape) is a richly featured vector-based graphic design workhorse. Use it to create simple graphics, diagrams, layouts, or icon art.
The latest stable version is [0.91](http://wiki.inkscape.org/wiki/index.php/Release_notes/0.91); similarly to GIMP, more excitement can be found in a pre-release version, 0.92pre3, which was released November 2016. The premiere feature of the latest pre-release is the [gradient mesh feature](http://wiki.inkscape.org/wiki/index.php/Mesh_Gradients) (demonstrated in screenshot below); new features introduce in the 0.91 release include [power stroke](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IztyV-Dy4CE) for fully configurable calligraphic strokes (the "open" in "opensource.com" in the screenshot below uses powerstroke), the on-canvas measure tool, and [the new symbols dialog](https://inkscape.org/cs/~doctormo/%E2%98%85symbols-dialog) (shown in the right side of the screenshot below). (Many symbol libraries for Inkscape are available on GitHub; [Xaviju's inkscape-open-symbols set](https://github.com/Xaviju/inkscape-open-symbols) is fantastic.) A new feature available in development/nightly builds is the *Objects* dialog that catalogs all objects in a document and provides tools to manage them.
### Scribus
[Scribus](https://opensource.com/tags/scribus) is a powerful desktop publishing and page layout tool. Scribus enables you to create sophisticated and beautiful items, including newsletters, books, and magazines, as well as other print pieces. Scribus has color management tools that can handle and output CMYK and spot colors for files that are ready for reliable reproduction at print shops.
[1.4.6](https://www.scribus.net/scribus-1-4-6-released/) is the latest stable release of Scribus; the [1.5.x](https://www.scribus.net/scribus-1-5-2-released/) series of releases is the most exciting as they serve as a preview to the upcoming 1.6.0 release. Version 1.5.3 features a Krita file (*.KRA) file import tool; other developments in the 1.5.x series include the *Table* tool, text frame welding, footnotes, additional PDF formats for export, improved dictionary support, dockable palettes, a symbols tool, and expanded file format support.
### MyPaint
[MyPaint](http://mypaint.org) is a drawing tablet-centric expressive drawing and illustration tool. It's lightweight and has a minimal interface with a rich set of keyboard shortcuts so that you can focus on your drawing without having to drop your pen.
[MyPaint 1.2.0](http://mypaint.org/blog/2016/01/15/mypaint-1.2.0-released/) is the latest stable release and includes new features, such as the [intuitive inking tool](https://github.com/mypaint/mypaint/wiki/v1.2-Inking-Tool) for tracing over pencil drawings, new flood fill tool, layer groups, brush and color history panel, user interface revamp including a dark theme and small symbolic icons, and editable vector layers. To try out the latest developments in MyPaint, I recommend installing the nightly Flatpak build, although there have not been significant feature additions since the 1.2.0 release.
### Blender
Initially released in January 1995, [Blender](https://opensource.com/tags/blender), like GIMP, has been around for more than 20 years. Blender is a powerful open source 3D creation suite that includes tools for modeling, sculpting, rendering, realistic materials, rigging, animation, compositing, video editing, game creation, and simulation.
The latest stable Blender release is [2.78a](http://www.blender.org/features/2-78/). The 2.78 release was a large one and includes features such as the revamped *Grease Pencil* 2D animation tool; VR rendering support for spherical stereo images; and a new drawing tool for freehand curves.
To try out the latest exciting Blender developments, you have many options, including:
- The Blender Foundation makes
[unstable daily builds](https://builder.blender.org/download/)available on the official Blender website. - If you're looking for builds that include particular in-development features,
[graphicall.org](http://graphicall.org/)is a community-moderated site that provides special versions of Blender (and occasionally other open source creative apps) to enable artists to try out the latest available code and experiments. - Mathieu Bridon has made development versions of Blender available via Flatpak. See his blog post for details:
[Blender nightly in Flatpak](https://mathieu.daitauha.fr/blog/2016/09/23/blender-nightly-in-flatpak/).
### Krita
[Krita](https://opensource.com/tags/krita) is a digital drawing application with a deep set of capabilities. The application is geared toward illustrators, concept artists, and comic artists and is fully loaded with extras, such as brushes, palettes, patterns, and templates.
The latest stable version is [Krita 3.0.1](https://krita.org/en/item/krita-3-0-1-update-brings-numerous-fixes/), released in September 2016. Features new to the 3.0.x series include 2D frame-by-frame animation; improved layer management and functionality; expanded and more usable shortcuts; improvements to grids, guides, and snapping; and soft-proofing.
## Video tools
There are many, many options for open source video editing tools. Of the members of the pack, [Flowblade](https://opensource.com/life/16/9/10-reasons-flowblade-linux-video-editor) is a newcomer and Kdenlive is the established, newbie-friendly, and most fully featured contender. The main criteria that may help you eliminate some of this array of options is supported platforms—some of these only support Linux. These all have active upstreams and the latest stable versions of each have been released recently, within weeks of each other.
### Kdenlive
[Kdenlive](https://opensource.com/tags/kdenlive), which was initially released back in 2002, is a powerful non-linear video editor available for Linux and OS X (although the OS X version is out-of-date). Kdenlive has a user-friendly drag-and-drop-based user interface that accommodates beginners, and with the depth experts need.
Learn how to use Kdenlive with an [multi-part Kdenlive tutorial series](https://opensource.com/life/11/11/introduction-kdenlive) by Seth Kenlon.
- Latest Stable: 16.08.2 (October 2016)
### Flowblade
Released in 2012, [Flowblade](http://jliljebl.github.io/flowblade/), a Linux-only video editor, is a relative newcomer.
- Latest Stable: 1.8 (September 2016)
### Pitivi
[Pitivi](http://pitivi.org) is a user-friendly free and open source video editor. Pitivi is written in [Python](http://wiki.pitivi.org/wiki/Why_Python%3F) (the "Pi" in Pitivi), uses the [GStreamer](https://gstreamer.freedesktop.org/) multimedia framework, and has an active community.
- Latest stable: 0.97 (August 2016)
- Get the
[latest version with Flatpak](https://pitivi.wordpress.com/2016/07/18/get-pitivi-directly-from-us-with-flatpak/)
### Shotcut
[Shotcut](http://shotcut.org) is a free, open source, cross-platform video editor that started [back in 2004](http://permalink.gmane.org/gmane.comp.lib.fltk.general/2397) and was later rewritten by current lead developer [Dan Dennedy](http://www.dennedy.org/).
- Latest stable: 16.11 (November 2016)
- 4K resolution support
- Ships as a tarballed binary
### OpenShot Video Editor
Started in 2008, [OpenShot Video Editor](http://openshot.org) is a free, open source, easy-to-use, cross-platform video editor.
- Latest stable:
[2.1](http://www.openshotvideo.com/2016/08/openshot-21-released.html)(August 2016)
## Utilities
### SwatchBooker
[SwatchBooker](http://www.selapa.net/swatchbooker/) is a handy utility, and although it hasn't been updated in a few years, it's still useful. SwatchBooker helps users legally obtain color swatches from various manufacturers in a format that you can use with other free and open source tools, including Scribus.
### GNOME Color Manager
[GNOME Color Manager](https://help.gnome.org/users/gnome-help/stable/color.html.en) is the built-in color management system for the GNOME desktop environment, the default desktop for a bunch of Linux distros. The tool allows you to create profiles for your display devices using a colorimeter, and also allows you to load/managed ICC color profiles for those devices.
### GNOME Wacom Control
[The GNOME Wacom controls](https://help.gnome.org/users/gnome-help/stable/wacom.html.en) allow you to configure your Wacom tablet in the GNOME desktop environment; you can modify various options for interacting with the tablet, including customizing the sensitivity of the tablet and which monitors the tablet maps to.
### Xournal
[Xournal](http://xournal.sourceforge.net/ ) is a humble but solid app that allows you to hand write/doodle notes using a tablet. Xournal is a useful tool for signing or otherwise annotating PDF documents.
### PDF Mod
[PDF Mod](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/PdfMod) is a handy utility for editing PDFs. PDF Mod lets users remove pages, add pages, bind multiple single PDFs together into a single PDF, reorder the pages, and rotate the pages.
### SparkleShare
[SparkleShare](https://www.sparkleshare.org/) is a git-backed file-sharing tool artists use to collaborate and share assets. Hook it up to a GitLab repo and you've got a nice open source infrastructure for asset management. The SparkleShare front end nullifies the inscrutability of git by providing a dropbox-like interface on top of it.
## Photography
### Darktable
[Darktable](https://opensource.com/life/16/4/how-use-darktable-digital-darkroom) is an application that allows you to develop digital RAW files and has a rich set of tools for the workflow management and non-destructive editing of photographic images. Darktable includes support for an extensive range of popular cameras and lenses.
### Entangle
[Entangle](https://entangle-photo.org/) allows you to tether your digital camera to your computer and enables you to control your camera completely from the computer.
### Hugin
[Hugin](http://hugin.sourceforge.net/) is a tool that allows you to stitch together photos in order to create panoramic photos.
## 2D animation
### Synfig Studio
[Synfig Studio](https://opensource.com/article/16/12/synfig-studio-animation-software-tutorial) is a vector-based 2D animation suite that also supports bitmap artwork and is tablet-friendly.
### Blender Grease Pencil
I covered Blender above, but particularly notable from a recent release is [a refactored grease pencil feature](https://wiki.blender.org/index.php/Dev:Ref/Release_Notes/2.78/GPencil), which adds the ability to create 2D animations.
### Krita
[Krita](https://opensource.com/tags/krita) also now provides 2D animation functionality.
## Music and audio editing
### Audacity
[Audacity](https://opensource.com/tags/audacity) is popular, user-friendly tool for editing audio files and recording sound.
### Ardour
[Ardour](https://ardour.org/) is a digital audio workstation with an interface centered around a record, edit, and mix workflow. It's a little more complicated than Audacity to use but allows for automation and is generally more sophisticated. (Available for Linux, Mac OS X, and Windows.)
### Hydrogen
[Hydrogen](http://www.hydrogen-music.org/) is an open source drum machine with an intuitive interface. It provides the ability to create and arrange various patterns using synthesized instruments.
### Mixxx
[Mixxx](http://mixxx.org/) is a four-deck DJ suite that allows you to DJ and mix songs together with powerful controls, including beat looping, time stretching, and pitch bending, as well as live broadcast your mixes and interface with DJ hardware controllers.
### Rosegarden
[Rosegarden](http://www.rosegardenmusic.com/) is a music composition suite that includes tools for score writing and music composition/editing and provides an audio and MIDI sequencer.
### MuseScore
[MuseScore](https://opensource.com/life/16/03/musescore-tutorial) is a music score creation, notation, and editing tool with a community of musical score contributors.
## Additional creative tools
### MakeHuman
[MakeHuman](http://makehuman.org/) is a 3D graphical tool for creating photorealistic models of humanoid forms.
### Natron
[Natron](https://natron.fr/) is a node-based compositor tool used for video post-production and motion graphic and special effect design.
### FontForge
[FontForge](http://fontforge.github.io/en-US/) is a typeface creation and editing tool. It allows you to edit letter forms in a typeface as well as generate fonts for using those typeface designs.
### Valentina
[Valentina](http://valentina-project.org/) is an application for drafting sewing patterns.
### Calligra Flow
[Calligra Flow](https://www.calligra.org/flow/) is a Visio-like diagramming tool. (Available for Linux, Mac OS X, and Windows.)
## Resources
There are a lot of toys and goodies to try out there. Need some inspiration to start your exploration? These websites and conference are chock-full of tutorials and beautiful creative works to inspire you get you going:
[pixls.us](http://pixls.us): Blog hosted by photographer Pat David that focuses on free and open source tools and workflow for professional photographers.[David Revoy's Blog](http://davidrevoy.com/)The blog of David Revoy, an immensely talented free and open source illustrator, concept artist, and advocate, with credits on several of the Blender Foundation films.[The Open Source Creative Podcast](http://monsterjavaguns.com/podcast/): Hosted by Opensource.com community moderator and columnist[Jason van Gumster](https://opensource.com/users/jason-van-gumster), who is a Blender and GIMP expert, and author of, this podcast is directed squarely at those of us who enjoy open source creative tools and the culture around them.[Blender for Dummies](http://www.blenderbasics.com/)[Libre Graphics Meeting](http://libregraphicsmeeting.org/2016/): Annual conference for free and open source creative software developers and the creatives who use the software. This is the place to find out about what cool features are coming down the pipeline in your favorite open source creative tools, and to enjoy what their users are creating with them.
## 32 Comments |
8,440 | 使用 Cozy 搭建个人云 | https://opensource.com/article/17/2/cozy-personal-cloud | 2017-04-24T09:03:00 | [
"ownCloud",
"Cozy"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8440-1.html | 
我认识的大部分人为了他们的日历、电子邮件、文件存储等,都会使用一些基于 Web 的应用。但是,如果像我这样,对隐私感到担忧、或者只是希望将你自己的数字生活简单化为一个你所控制的地方呢? [Cozy](https://cozy.io/) 就是一个朝着健壮的自主云平台方向发展的项目。你可以从 [GitHub](https://github.com/cozy/cozy) 上获取 Cozy 的源代码,它采用 AGPL 3.0 协议。
### 安装
安装 Cozy 非常快捷简单,这里有多种平台的 [简单易懂的安装指令](https://docs.cozy.io/en/host/install/)。在我的测试中,我使用 64 位的 Debian 8 系统。安装需要几分钟时间,然后你只需要到服务器的 IP 地址注册一个账号,就会加载并准备好默认的应用程序集。
要注意的一点 - 安装假设没有正在运行任何其它 Web 服务,而且它会尝试安装 [Nginx web 服务器](https://www.nginx.com/)。如果你的服务器已经有网站正在运行,配置可能就比较麻烦。我是在一个全新的 VPS(Virtual Private Server,虚拟个人服务器)上安装,因此比较简单。运行安装程序、启动 Nginx,然后你就可以访问云了。
Cozy 还有一个 [应用商店](https://cozy.io/en/apps/),你可以从中下载额外的应用程序。有一些看起来非常有趣,例如 [Ghost 博客平台](https://ghost.org/) 以及开源维基 [TiddlyWiki](http://tiddlywiki.com/)。其目的,显然是允许把其它很多好的应用程序集成到这个平台。我认为你要看到很多其它流行的开源应用程序提供集成功能只是时间问题。此刻,已经支持 [Node.js](http://nodejs.org/),但是如果也支持其它应用层,你就可以看到很多其它很好的应用程序。
其中可能的一个功能是从安卓设备中使用免费的安卓应用程序访问你的信息。当前还没有 iOS 应用,但有计划要解决这个问题。
现在,Cozy 已经有很多核心的应用程序。

*主要 Cozy 界面*
### 文件
和很多分支一样,我使用 [Dropbox](https://www.dropbox.com/) 进行文件存储。事实上,由于我有很多东西需要存储,我需要花钱买 DropBox Pro。对我来说,如果它有我想要的功能,那么把我的文件移动到 Cozy 能为我节省很多开销。
我希望如此,而它真的可以。我被 Cozy 应用程序内建的基于 web 的文件上传和文件管理工具所惊讶。拖拽功能正如你期望的那样,界面也很干净整洁。我在上传事例文件和目录、随处跳转、移动、删除以及重命名文件时都没有遇到问题。
如果你想要的就是基于 web 的云文件存储,那么你已经有了。对我来说,它缺失的是 DropBox 具有的选择性的文件目录同步功能。在 DropBox 中,如果你拖拽一个文件到目录中,它就会被拷贝到云,几分钟后该文件在你所有同步设备中都可以看到。实际上,[Cozy 正在研发该功能](https://github.com/cozy-labs/cozy-desktop),但此时它还处于 beta 版,而且只支持 Linux 客户端。另外,我有一个称为 [Download to Dropbox](https://github.com/pwnall/dropship-chrome) 的 [Chrome](https://www.google.com/chrome/) 扩展,我时不时用它抓取图片和其它内容,但当前 Cozy 中还没有类似的工具。

*文件管理界面*
### 从 Google 导入数据
如果你正在使用 Google 日历和联系人,使用 Cozy 安装的应用程序很轻易的就可以导入它们。当你授权对 Google 的访问时,会给你一个 API 密钥,把它粘贴到 Cozy,它就会迅速高效地进行复制。两种情况下,内容都会被打上“从 Google 导入”的标签。对于我混乱的联系人,这可能是件好事情,因为它使得我有机会重新整理,把它们重新标记为更有意义的类别。“Google Calendar” 中所有的事件都导入了,但是我注意到其中一些事件的时间不对,可能是由于两端时区设置的影响。
### 联系人
联系人功能正如你期望的那样,界面也很像 Google 联系人。尽管如此,还是有一些不好的地方。例如,和你的智能手机的同步是通过 [CardDAV](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CardDAV) 完成的,这是用于共享联系人数据的标准协议,但安卓手机并不原生支持该技术。为了把你的联系人同步到安卓设备,你需要在你的手机上安装一个应用。这对我来说是个很大的打击,因为我已经有很多类似这样的古怪应用程序了(例如 工作的邮件、Gmail 以及其它邮件,我的天),我并不想安装一个不能和我智能手机原生联系人应用程序同步的软件。如果你正在使用 iPhone,你直接就能使用 CradDAV。
### 日历
对于日历用户来说好消息就是安卓设备支持这种类型数据的交换格式 [CalDAV](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CalDAV)。正如我导入数据时提到的,我的一些日历时间的时间不对。在这之前我在和其它日历系统进行迁移时也遇到过这个问题,因此这对我并没有产生太大困扰。界面允许你创建和管理多个日历,就像 Google 那样,但是你不能订阅这个 Cozy 实例之外的其它日历。该应用程序另一个怪异的地方就是它的一周从周一开始,而且你不能更改。通常来说,我从周日开始我的一周,因此能更改从周一开始的功能对我来说非常有用。设置对话框并没有任何设置;它只是告诉你如何通过 CalDAV 连接的指令。再次说明,这个应用程序接近我想要的,但 Cozy 做的还不够好。
### 照片
照片应用让我印象深刻,它从文件应用程序借鉴了很多东西。你甚至可以把一个其它应用程序的照片文件添加到相册,或者直接通过拖拽上传。不幸的是,一旦上传后,我没有找到任何重新排序和编辑照片的方法。你只能把它们从相册中删除。应用有一个通过令牌链接进行分享的工具,而且你可以指定一个或多个联系人。系统会给这些联系人发送邀请他们查看相册的电子邮件。当然还有很多比这个有更丰富功能的相册应用,但在 Cozy 平台中这算是一个好的起点。

*Photos 界面*
### 总结
Cozy 目标远大。他们尝试搭建一个你能部署任意你想要的基于云服务的平台。它已经到了成熟期吗?我并不认为。对于一些重度用户来说我之前提到的一些问题很严重,而且还没有 iOS 应用,这可能阻碍用户使用它。不管怎样,继续关注吧 - 随着研发的继续,Cozy 有一家代替很多应用程序的潜能。
---
作者简介:
D Ruth Bavousett - D Ruth Bavousett 作为系统管理员和软件开发者已经很长时间了,长期以来她都专注于 a VAX 11/780。(到目前为止)她花了很多时间服务于图书馆的技术需求,她从 2008 年就开始成为 Koha 开源图书馆自动化套件的贡献者。 Ruth 现在是 Houston cPanel 公司的 Perl 开发人员,同时还是两个孩子的母亲。
(题图 : [Pixabay](https://pixabay.com/en/tree-field-cornfield-nature-247122/). CC BY-SA 4.0)
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/2/cozy-personal-cloud>
作者:[D Ruth Bavousett](https://opensource.com/users/druthb) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Most everyone I know uses some sort of web-based application for their calendar, emails, file storage, and much more. But what if, like me, you've got concerns about privacy, or just want to simplify your digital life into a place you control? [Cozy](https://cozy.io/) is a project that is moving in the right direction—toward a robust self-hosted cloud platform. Cozy's source code is available on [GitHub](https://github.com/cozy/cozy), and it is licensed under the AGPL 3.0 license.
## Installation
Installing Cozy is snap-easy, with [easy-to-follow instructions](https://docs.cozy.io/en/host/install/) for a variety of platforms. For my testing, I'm using Debian 8, 64-bit. The installation takes a few minutes, but then you just go to the server's IP, register an account, and a default set of applications is loaded up and ready to roll.
One note on this—the installation assumes no other web server is running, and it will want to install [Nginx web server](https://www.nginx.com/). If your server already has websites running, configuration may be a bit more challenging. My install was on a brand new Virtual Private Server (VPS), so this was a snap. Run the installer, start Nginx, and you're ready to hit the cloud.
Cozy has [an App Store](https://cozy.io/en/apps/) where you can download additional applications. Some look pretty interesting, like the [Ghost blogging platform](https://ghost.org/) and [TiddlyWiki](http://tiddlywiki.com/) open source wiki. The intent here, clearly, is to allow integration in the platform with lots of other goodies. I think it's just a matter of time before you'll see this start to take off, with many other popular open source applications offering integration abilities. Right now, [Node.js](http://nodejs.org/) applications are supported, but if other application layers were possible, you'd see that many other good things could happen.
One capability that is possible is using the free Android application to access your information from Android devices. No iOS app exists, but there is a plan to solve that problem.
Currently, Cozy comes with a nice set of core applications.
Main Cozy interface
## Files
Like a lot of folks, I use [Dropbox](https://www.dropbox.com/) for file storage. In fact, I pay for Dropbox Pro because I use *so much* storage. For me, then, moving my files to Cozy would be a money-saver—if it has the features I want.
I wish I could say it does, truly I do. I was very impressed with the web-based file upload and file-management tool built into the Cozy web application. Drag-and-drop works like you'd expect, and the interface is clean and uncluttered. I had no trouble at all uploading some sample files and folders, navigating around, and moving, deleting, and renaming files.
If what you want is a web-based cloud file storage, you're set. What's missing, for me, is the selective synchronization of files and folders, which Dropbox has. With Dropbox, if you drop a file in a folder, it's copied out to the cloud and made available to all your synced devices in a matter of minutes. To be fair, [Cozy is working on it](https://github.com/cozy-labs/cozy-desktop), but it's in beta and only for Linux clients at the moment. Also, I have a [Chrome](https://www.google.com/chrome/) extension called [Download to Dropbox](https://github.com/pwnall/dropship-chrome) that I use to capture images and other content from time to time, and no such tool exists yet for Cozy.
File Manager interface
## Importing data from Google
If you currently use Google Calendar or Contacts, importing these is very easy with the app installed in Cozy. When you authorize access to Google, you're given an API key, which you paste in Cozy, and it performs the copy quickly and efficiently. In both cases, the contents were tagged as having been imported from Google. Given the clutter in my contacts, this is probably a good thing, as it gives you the opportunity to tidy up as you relabel them into more meaningful categories. Calendar events imported all on the "Google Calendar," but I noticed that *some* of my events had the times incorrect, possibly an artifact of time zone settings on one end or the other.
## Contacts
Contacts works like you'd expect, and the interface looks a *lot* like Google Contacts. There are a few sticky areas, though. Synchronization with (for instance) your smart phone happens via [CardDAV](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CardDAV), a standard protocol for sharing contacts data—and a technology that Android phones *do not speak natively*. To sync your contacts to an Android device, you're going to have to load an app on your phone for that. For me, that's a *huge* strike against it, as I have enough odd apps like that already (work mail versus Gmail versus other mail, oh my!), and I do not want to install another that won't sync up with my smartphone's native contacts application. If you're using an iPhone, you can do CardDAV right out of the box.
## Calendar
The good news for Calendar users is that an Android device *can* speak [CalDAV](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CalDAV), the interchange format for this type of data. As I noted with the import app, some of my calendar items came over with the wrong times. I've seen this before with other calendar system moves, so that really didn't bother me much. The interface lets you create and manage multiple calendars, just like with Google, but you can't subscribe to other calendars outside of this Cozy instance. One other quirk is of the app is starting of the week on Monday, which you can't change. Normally, I start my week on Sunday, so changing from Monday would be a useful feature for me. The Settings dialog didn't actually have any settings; it merely gave instructions on how to connect via CalDAV. Again, this application is close to what I need, but Cozy is not quite there.
## Photos
The Photos app is pretty impressive, borrowing a lot from the Files application. You can even add photos to an album that are in files in the other app, or upload directly with drag and drop. Unfortunately, I don't see any way to reorder or edit pictures once you've uploaded them. You can only delete them from the album. The app does have a tool for sharing via a token link, and you can specify one or more contact. The system will send those contacts an email inviting them to view the album. There are more feature-rich album applications than this, to be sure, but this is a good start for the Cozy platform.
Photos interface
## Final thoughts
Cozy has some really big goals. They're trying to build a platform where you can deploy *any* cloud-based service you like. Is it ready for prime time? Not quite. Some of the shortcomings I've mentioned are problematic for power users, and there is no iOS application yet, which may hamper adoption for those users. However, keep an eye on this one—Cozy has the potential, as development continues, to become a one-stop replacement for a great many applications.
## 8 Comments |
8,441 | OpenVAS:Kali Linux 中的漏洞评估工具 | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/openvas-vulnerability-assessment-install-on-kali-linux/ | 2017-04-23T19:02:04 | [
"Kali",
"OpenVAS",
"漏洞评估"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8441-1.html | 本教程将介绍在 Kali Linux 中安装 OpenVAS 8.0 的过程。 OpenVAS 是一个可以自动执行网络安全审核和漏洞评估的开源[漏洞评估](https://www.aptive.co.uk/vulnerability-assessment/)程序。请注意,<ruby> 漏洞评估 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Vulnerability Assessment </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>也称为 VA 并不是<ruby> 渗透测试 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> penetration test </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,渗透测试会进一步验证是否存在发现的漏洞,请参阅[什么是渗透测试](https://www.aptive.co.uk/penetration-testing/)来对渗透测试的构成以及不同类型的安全测试有一个了解。

### 什么是 Kali Linux?
Kali Linux 是 Linux 渗透测试分发版。它基于 Debian,并且预安装了许多常用的渗透测试工具,例如 Metasploit Framework (MSF)和其他通常在安全评估期间由渗透测试人员使用的命令行工具。
在大多数使用情况下,Kali 运行在虚拟机中,你可以在这里获取最新的 VMWare 或 Vbox 镜像:<https://www.offensive-security.com/kali-linux-vmware-virtualbox-image-download/> 。
除非你有特殊的原因想要一个更小的虚拟机占用空间,否则请下载完整版本而不是 Kali light。 下载完成后,你需要解压文件并打开 vbox 或者 VMWare .vmx 文件,虚拟机启动后,默认帐号是 `root`/`toor`。请将 root 密码更改为安全的密码。
或者,你可以下载 ISO 版本,并在裸机上执行 Kali 的安装。
### 升级 Kali Linux
完成安装后,为 Kail Linux 执行一次完整的升级。
升级 Kali:
```
apt-get update && apt-get dist-upgrade -y
```

更新过程可能需要一些时间才能完成。Kali 目前是滚动更新,这意味着你可以从任何版本的 Kali 滚动更新到当前版本。然而它仍有发布号,但这些是针对特定 Kali 时间点版本的 VMWare 快照。你可以从任何 VMWare 镜像更新到当前的稳定版本。
更新完成后重新启动。
### 安装 OpenVAS 8

```
apt-get install openvas
openvas-setup
```
在安装中,你会被询问关于 redis 的问题,选择默认选项来以 UNIX 套接字运行。

即使是有快速的网络连接,openvas-setup 仍需要很长时间来下载和更新所有所需的 CVE、SCAP 定义。

请注意 openvas-setup 的命令输出,密码会在安装过程中生成,并在安装的最后在控制台中打印出来。

验证 openvas 正在运行:
```
netstat -tulpn
```

### 在 Kali 中运行 OpenVAS
要在 Kali 中启动 OpenVAS:
```
openvas-start
```
安装后,你应该可以通过 `https://127.0.0.1:9392` 访问 OpenVAS 的 web 程序了。

接受自签名证书,并使用 openvas-setup 输出的 admin 凭证和密码登录程序。

接受自签名证书后,你应该可以看到登录界面了。

登录后,你应该可以看到下面的页面:

从此,你应该可以使用向导配置自己的漏洞扫描了。
我建议阅读文档。请注意漏洞评估导向(取决于 OpenVAS 可能尝试利用的配置)及其在网络上生成的流量以及网络上可能对服务/服务器和主机/设备产生的 DOS 影响。
(题图:[pixabay.com](http://www.pixabay.com/), CC0)
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/openvas-vulnerability-assessment-install-on-kali-linux/>
作者:[KJS](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/openvas-vulnerability-assessment-install-on-kali-linux/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # OpenVAS - Vulnerability Assessment install on Kali Linux
This tutorial documents the process of installing OpenVAS 8.0 on Kali Linux rolling. OpenVAS is open source [vulnerability assessment](https://www.aptive.co.uk/vulnerability-assessment/) application that automates the process of performing network security audits and vulnerability assessments. Note, a vulnerability assessment also known as VA is not a penetration test, a penetration test goes a step further and validates the existence of a discovered vulnerability, see [what is penetration testing](https://www.aptive.co.uk/penetration-testing/) for an overview of what pen testing consists of and the different types of security testing.
## What is Kali Linux?
Kali Linux is a Linux penetration testing distribution. It's Debian based and comes pre-installed with many commonly used penetration testing tools such as Metasploit Framework and other command line tools typically used by penetration testers during a security assessment.
For most use cases Kali runs in a VM, you can grab the latest VMWare or Vbox image of Kali from here: [https://www.offensive-security.com/kali-linux-vmware-virtualbox-image-download/](https://www.offensive-security.com/kali-linux-vmware-virtualbox-image-download/)
Download the full version not Kali light, unless you have a specific reason for wanting a smaller virtual machine footprint. After the download finishes you will need to extract the contents and open the vbox or VMWare .vmx file, when the machine boots the default credentials are root / toor. Change the root password to a secure password.
Alternatively, you can download the ISO version and perform an installation of Kali on the bare metal.
## Updating Kali Linux
After installation, perform a full update of Kali Linux.
Updating Kali:
apt-get update && apt-get dist-upgrade -y
The update process might take some time to complete. Kali is now a rolling release meaning you can update to the current version from any version of Kali rolling. However, there are release numbers but these are point in time versions of Kali rolling for VMWare snapshots. You can update to the current stable release from any of the VMWare images.
After updating perform a reboot.
## Installing OpenVAS 8
apt-get install openvas
openvas-setup
During installation you'll be prompted about redis, select the default option to run as a UNIX socket.
Even on a fast connection openvas-setup takes a long time to download and update all the required CVE, SCAP definitions.
Pay attention to the command output during openvas-setup, the password is generated during installation and printed to console near the end of the setup.
Verify openvas is running:
netstat -tulpn
## Start OpenVAS on Kali
To start the OpenVAS service on Kali run:
openvas-start
After installation, you should be able to access the OpenVAS web application at **https://127.0.0.1:9392**
Accept the self-signed certificate and login to the application using the credentials admin and the password displayed during openvas-setup.
After accepting the self-signed certificate, you should be presented with the login screen:
After logging in you should be presented with the following screen:
From this point you should be able to configure your own vulnerability scans using the wizard.
It's recommended to read the documentation. Be aware of what a vulnerability assessment conductions (depending on configuration OpenVAS could attempt exploitation) and the traffic it will generate on a network as well as the DOS effect it can have on services / servers and hosts / devices on a network. |
8,442 | 极客漫画:软件测试 | https://turnoff.us/geek/software-test/ | 2017-04-24T09:41:00 | [
"漫画",
"软件测试"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8442-1.html | 
这幅漫画吐槽了目前的软件开发的乱象:
软件开发的不规范,在开发者自己的电脑上运行正常,在质量检测团队测试时就出现了 Warning,在项目经理测试时已经发生了蓝屏,当用户测试时,发生了“核爆”。
这里讽刺了两件事:
1、开发者开发时,不注重软件质量,无法保证软件在不同环境下的一致性。当然,锅不能完全开发者来背。同时,也是 Docker 这样的产品的用武之地。
2、当质量监测团队出现了 Warning ,项目管理出现了蓝屏的情况下, 问题一级级放大,等到交付给了用户,导致在用户那里出现了“核爆”这样的巨大危害。
---
via: <https://turnoff.us/geek/software-test/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者&点评:[Bestony](https://github.com/Bestony) 校对&合成:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # software testing


### Comics Related
-
[new job](/geek/new-job/) -
[vulnerable code](/geek/vulnerable-code/) -
[pair programming vibe 2](/geek/pair-programming-vibe-2/) -
[to automate or not to automate](/geek/to-automate-or-not-to-automate/) -
[pair programming vibe](/geek/pair-programming-vibe/) -
[I'm fine](/geek/im-fine/) -
[minimum viable juice](/geek/minimum-viable-juice/) -
[fill out the form](/geek/fill-out-the-form/) -
[minimum viable elevator](/geek/minimum-viable-elevator/) -
[if hamlet were a programmer](/geek/hamlet-programmer/) -
[she will be an artist... or not](/geek/artist/) -
[chat gpt code smell](/geek/chat-gpt-code/) -
[come to bed](/geek/come-to-bed/) -
[frontenders and backenders](/geek/frontenders-and-backenders/) -
[influencer](/geek/influencer/) -
[the over engineer](/geek/the-over-engineer/) -
[automated tests: u r doing it wrong](/geek/automated-tests-doing-it-wrong/) -
[the bad design punisher 2](/geek/the-bad-design-punisher-2/) -
[virtual conference](/geek/virtual-conference/) -
[perspective](/geek/perspective/) -
[end of the world](/geek/end-of-the-world/) -
[quarantine](/geek/quarantine/) -
[the naive engineer](/geek/the-naive-engineer/) -
[commit messages](/geek/commit-messages/) -
[the bad design punisher](/geek/the-bad-design-punisher/) -
[marketing strategy](/geek/marketing-strategy/) -
[cors explained](/geek/cors-explained/) -
[developer costumes](/geek/halloween-2/) -
[first day on the job](/geek/first-day-on-the-job/) -
[not wanted](/geek/not-wanted/) -
[egoless programming](/geek/egoless-programming/) -
[math class 2018](/geek/math-class-2018/) -
[commitland!](/geek/commitland/) -
[my adorable useless code](/geek/my-adorable-useless-code/) -
[the last resort](/geek/the-last-resort/) -
[the bitcoin design pattern](/geek/the-bitcoin-design-pattern/) -
[programmers over time](/geek/programmers-over-time/) -
[welcome to hell](/geek/welcome-to-hell/) -
[letter to santa](/geek/letter-to-santa/) -
[the specialist](/geek/the-specialist/) -
[tobby's world](/geek/tobbys-world/) -
[when artificial intelligence meets git](/geek/when-ai-meets-git/) -
[at the computer museum](/geek/computer-museum/) -
[follow the hype](/geek/follow-the-hype/) -
[battle of programming languages](/geek/programming-languages-battle/) -
[death and the programmer](/geek/death-and-the-programmer/) -
[business logic on frontend](/geek/business-logic-on-frontend/) -
[good night, programmers!](/geek/good-night-programmers/) -
[chronicles of pair programming 2](/geek/chronicles-of-pair-programming-2/) -
[what your code looks like](/geek/what-your-code-looks-like/) -
[tdd versus ftt](/geek/tdd-vs-ftt/) -
[functional world](/geek/functional-world/) -
[meow-ware](/geek/meow-ware/) -
[backend developer doing css](/geek/backend-developer-doing-css/) -
[are you ready for microservices?](/geek/are-you-ready-for-microservices/) -
[battle of software robots](/geek/battle-of-software-robots/) -
[the monolith retirement](/geek/monolith-retirement/) -
[chronicles of pair programming](/geek/chronicles-of-pair-programming/) -
[lang buddies 2](/geek/lang-buddies-2/) -
[distributed architecture drama](/geek/distributed-architecture-drama/) -
[http2 server push explained](/geek/http2-server-push-explained/) -
[how to break up with a programmer](/geek/how-to-break-up-with-a-programmer/) -
[lang buddies](/geek/lang-buddies/) -
[oh, the 70's](/geek/oh-the-70s/) -
[ode to my family](/geek/ode-to-my-family/) -
[the lord of the matrix](/geek/the-lord-of-the-matrix/) -
[inheritance versus composition](/geek/inheritance-versus-composition/) -
[programmer levels](/geek/programmer-leves/) -
[microservices](/geek/microservices/) -
[binary tree](/geek/binary-tree/) -
[the codeless developer](/geek/codeless/) -
[reactive and boring](/geek/reactive-and-boring/) -
[hype detected](/geek/tech-adoption/) -
[about javascript developers](/geek/love-ecma6/) -
[mastering regexp](/geek/mastering-regexp/) -
[developers](/geek/developers/) |
8,444 | 如何在树莓派上安装 Fedora 25 | https://opensource.com/article/17/3/how-install-fedora-on-raspberry-pi | 2017-04-24T09:12:42 | [
"树莓派",
"Fedora",
"ARM"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8444-1.html |
>
> 了解 Fedora 第一个官方支持树莓派的版本
>
>
>

2016 年 10 月,Fedora 25 Beta 发布了,随之而来的还有对 [树莓派 2 和 3 的初步支持](https://fedoramagazine.org/raspberry-pi-support-fedora-25-beta/)。Fedora 25 的最终“通用”版在一个月后发布,从那时起,我一直在树莓派上尝试不同的 Fedora spins。
这篇文章不仅是一篇<ruby> 树莓派 <rt> Raspberry Pi </rt></ruby> 3 上的 Fedora 25 的点评,还集合了技巧、截图以及我对 Fedora 第一个官方支持 Pi 的这个版本的一些个人看法。
在我开始之前,需要说一下的是,为写这篇文章所做的所有工作都是在我的运行 Fedora 25 的个人笔记本电脑上完成的。我使用一张 microSD 插到 SD 适配器中,复制和编辑所有的 Fedora 镜像到 32GB 的 microSD 卡中,然后用它在一台三星电视上启动了树莓派 3。 因为 Fedora 25 尚不支持内置 Wi-Fi,所以树莓派 3 使用了以太网线缆进行网络连接。最后,我使用了 Logitech K410 无线键盘和触摸板进行输入。
如果你没有条件使用以太网线连接在你的树莓派上玩 Fedora 25,我曾经用过一个 Edimax Wi-Fi USB 适配器,它也可以在 Fedora 25 上工作,但在本文中,我只使用了以太网连接。
### 在树莓派上安装 Fedora 25 之前
阅读 Fedora 项目 wiki 上的[树莓派支持文档](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Raspberry_Pi)。你可以从 wiki 下载 Fedora 25 安装所需的镜像,那里还列出了所有支持和不支持的内容。
此外,请注意,这是初始支持版本,还有许多新的工作和支持将随着 Fedora 26 的发布而出现,所以请随时报告 bug,并通过 [Bugzilla](https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=245418)、Fedora 的 [ARM 邮件列表](https://lists.fedoraproject.org/admin/lists/arm%40lists.fedoraproject.org/)、或者 Freenode IRC 频道#fedora-arm,分享你在树莓派上使用 Fedora 25 的体验反馈。
### 安装
我下载并安装了五个不同的 Fedora 25 spin:GNOME(默认工作站)、KDE、Minimal、LXDE 和 Xfce。在多数情况下,它们都有一致和易于遵循的步骤,以确保我的树莓派 3 上启动正常。有的 spin 有已知 bug 的正在解决之中,而有的按照 Fedora wik 遵循标准操作程序即可。

*树莓派 3 上的 Fedora 25 workstation、 GNOME 版本*
### 安装步骤
1、 在你的笔记本上,从支持文档页面的链接下载一个树莓派的 Fedora 25 镜像。
2、 在笔记本上,使用 `fedora-arm-installer` 或下述命令行将镜像复制到 microSD:
```
xzcat Fedora-Workstation-armhfp-25-1.3-sda.raw.xz | dd bs=4M status=progress of=/dev/mmcblk0
```
注意:`/dev/mmclk0` 是我的 microSD 插到 SD 适配器后,在我的笔记本电脑上挂载的设备名。虽然我在笔记本上使用 Fedora,可以使用 `fedora-arm-installer`,但我还是喜欢命令行。
3、 复制完镜像后,*先不要启动你的系统*。我知道你很想这么做,但你仍然需要进行几个调整。
4、 为了使镜像文件尽可能小以便下载,镜像上的根文件系统是很小的,因此你必须增加根文件系统的大小。如果你不这么做,你仍然可以启动你的派,但如果你一旦运行 `dnf update` 来升级你的系统,它就会填满文件系统,导致糟糕的事情发生,所以趁着 microSD 还在你的笔记本上进行分区:
```
growpart /dev/mmcblk0 4
resize2fs /dev/mmcblk0p4
```
注意:在 Fedora 中,`growpart` 命令由 `cloud-utils-growpart.noarch` 这个 RPM 提供的。
5、文件系统更新后,您需要将 `vc4` 模块列入黑名单。[更多有关此 bug 的信息在此。](https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1387733)
我建议在启动树莓派之前这样做,因为不同的 spin 有不同表现方式。例如,(至少对我来说)在没有黑名单 `vc4` 的情况下,GNOME 在我启动后首先出现,但在系统更新后,它不再出现。 KDE spin 则在第一次启动时根本不会出现 KDE。因此我们可能需要在我们的第一次启动之前将 `vc4` 加入黑名单,直到这个错误以后解决了。
黑名单应该出现在两个不同的地方。首先,在你的 microSD 根分区上,在 `etc/modprode.d/` 下创建一个 `vc4.conf`,内容是:`blacklist vc4`。第二,在你的 microSD 启动分区,添加 `rd.driver.blacklist=vc4` 到 `extlinux/extlinux.conf` 文件的末尾。
6、 现在,你可以启动你的树莓派了。
### 启动
你要有耐心,特别是对于 GNOME 和 KDE 发行版来说。在 SSD(固态驱动器)几乎即时启动的时代,你很容易就对派的启动速度感到不耐烦,特别是第一次启动时。在第一次启动 Window Manager 之前,会先弹出一个初始配置页面,可以配置 root 密码、常规用户、时区和网络。配置完毕后,你就应该能够 SSH 到你的树莓派上,方便地调试显示问题了。
### 系统更新
在树莓派上运行 Fedora 25 后,你最终(或立即)会想要更新系统。
首先,进行内核升级时,先熟悉你的 `/boot/extlinux/extlinux.conf` 文件。如果升级内核,下次启动时,除非手动选择正确的内核,否则很可能会启动进入救援( Rescue )模式。避免这种情况发生最好的方法是,在你的 `extlinux.conf` 中将定义 Rescue 镜像的那五行移动到文件的底部,这样最新的内核将在下次自动启动。你可以直接在派上或通过在笔记本挂载来编辑 `/boot/extlinux/extlinux.conf`:
```
label Fedora 25 Rescue fdcb76d0032447209f782a184f35eebc (4.9.9-200.fc25.armv7hl)
kernel /vmlinuz-0-rescue-fdcb76d0032447209f782a184f35eebc
append ro root=UUID=c19816a7-cbb8-4cbb-8608-7fec6d4994d0 rd.driver.blacklist=vc4
fdtdir /dtb-4.9.9-200.fc25.armv7hl/
initrd /initramfs-0-rescue-fdcb76d0032447209f782a184f35eebc.img
```
第二点,如果无论什么原因,如果你的显示器在升级后再次变暗,并且你确定已经将 `vc4` 加入黑名单,请运行 `lsmod | grep vc4`。你可以先启动到多用户模式而不是图形模式,并从命令行中运行 `startx`。 请阅读 `/etc/inittab` 中的内容,了解如何切换 target 的说明。

*树莓派 3 上的 Fedora 25 workstation、 KDE 版本*
### Fedora Spin
在我尝试过的所有 Fedora Spin 中,唯一有问题的是 XFCE spin,我相信这是由于这个[已知的 bug](https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1389163) 导致的。
按照我在这里分享的步骤操作,GNOME、KDE、LXDE 和 minimal 都运行得很好。考虑到 KDE 和 GNOME 会占用更多资源,我会推荐想要在树莓派上使用 Fedora 25 的人使用 LXDE 和 Minimal。如果你是一位系统管理员,想要一台廉价的 SELinux 支持的服务器来满足你的安全考虑,而且只是想要使用树莓派作为你的服务器,开放 22 端口以及 vi 可用,那就用 Minimal 版本。对于开发人员或刚开始学习 Linux 的人来说,LXDE 可能是更好的方式,因为它可以快速方便地访问所有基于 GUI 的工具,如浏览器、IDE 和你可能需要的客户端。

*树莓派 3 上的 Fedora 25 workstation、LXDE。*
看到越来越多的 Linux 发行版在基于 ARM 的树莓派上可用,那真是太棒了。对于其第一个支持的版本,Fedora 团队为日常 Linux 用户提供了更好的体验。我很期待 Fedora 26 的改进和 bug 修复。
(题图: opensource.com)
---
作者简介:
Anderson Silva - Anderson 于 1996 年开始使用 Linux。更精确地说是 Red Hat Linux。 2007 年,他作为 IT 部门的发布工程师时加入红帽,他的职业梦想成为了现实。此后,他在红帽担任过多个不同角色,从发布工程师到系统管理员、高级经理和信息系统工程师。他是一名 RHCE 和 RHCA 以及一名活跃的 Fedora 包维护者。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/3/how-install-fedora-on-raspberry-pi>
作者:[Anderson Silva](https://opensource.com/users/ansilva) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In October 2016, the release of Fedora 25 Beta was announced, along with initial [support for the Raspberry Pi 2 and 3](https://fedoramagazine.org/raspberry-pi-support-fedora-25-beta/). The final "general availability" version of Fedora 25 was released a month later, and since then I have been playing around with the many different Fedora spins available for the latest versions of the Raspberry Pi.
This article is not as much a review of Fedora 25 on the Raspberry Pi 3 as a collection of tips, screenshots, and my own personal thoughts on the very first officially supported version of Fedora for the Pi.
Before I start, it is worth mentioning that all of the work I have done to write this article was done on my personal laptop, which is running Fedora 25. I used a microSD to SD adapter to copy and edit all of the Fedora images into a 32GB microSD card, which I used to boot up my Raspberry Pi 3 on a Samsung TV. The Raspberry Pi 3 used an Ethernet cable connection for network connectivity because the built-in Wi-Fi is not yet supported by Fedora 25. Finally, I used a Logitech K410 wireless keyboard and touchpad for input.
If you don't have the opportunity to use an Ethernet wire connection to play around with Fedora 25 on your Raspberry Pi, I was able to get an Edimax Wi-Fi USB adapter to work on Fedora 25 as well, but for the purposes of this article, I only used the Ethernet connection.
## Before you install Fedora 25 on your Raspberry Pi
Read over the [Raspberry Pi support documentation](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Raspberry_Pi) on the Fedora Project wiki. You can download the Fedora 25 images you need for installation from the wiki, and everything that is supported and not supported is listed there.
Also, be mindful that this is an initially supported version and a lot of new work and support will be coming out with the release of Fedora 26, so feel free to report bugs and share feedback of your own experience with Fedora 25 on the Raspberry Pi via [Bugzilla](https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=245418), Fedora's [ARM mailing list](https://lists.fedoraproject.org/admin/lists/arm%40lists.fedoraproject.org/), or on the Freenode IRC channel #fedora-arm.
## Installation
I downloaded and installed five different Fedora 25 spins: GNOME (Workstation default), KDE, Minimal, LXDE, and Xfce. For the most part, they all had pretty consistent and easy-to-follow steps to ensure my Raspberry Pi 3 would boot up properly. Some have known bugs that people are working on, and some followed standard operating procedure via the Fedora wiki.
Fedora 25 workstation, GNOME on Raspberry Pi 3.
## Steps for installation
1. On your laptop, download one of the Fedora 25 images for the Raspberry Pi from the links on the support documentation page.
2. On your laptop, copy the image onto your microSD using either **fedora-arm-installer** or the command line:
**xzcat Fedora-Workstation-armhfp-25-1.3-sda.raw.xz | dd bs=4M status=progress of=/dev/mmcblk0**
Note: **/dev/mmclk0** was the device that my microSD to SD adapter mounted on my laptop, and even though I am using Fedora on my laptop and I could have used the **fedora-arm-installer**, I preferred the command line.
3. Once you've copied the image, *don't boot up your system yet*. I know it is tempting to just go for it, but you still need to make a couple of tweaks.
4. To keep the image file as small as possible for download convenience, the root file system on the image was kept to a minimum, so you must grow your root filesystem. If you don't, your Pi will still boot up, but if you run **dnf update** to upgrade your system, it will fill up the file system and bad things will happen, so with the microSD still on your laptop grow the partition:
**growpart /dev/mmcblk0 4
resize2fs /dev/mmcblk0p4**
Note: In Fedora, the **growpart** command is provided by **cloud-utils-growpart.noarch** RPM.
5. Once the file system is updated, you will need to blacklist the **vc4** module. [Read more about this bug.](https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1387733)
I recommend doing this before you boot up the Raspberry Pi because different spins will behave in different ways. For example, (at least for me) GNOME came up first after I booted, without blacklisting **vc4**, but after doing a system update, it no longer came up. The KDE spin wouldn't come up at all during the first initial boot. We might as well blacklist **vc4** even before our first boot until the bug is resolved.
Blacklisting should happen in two different places. First, on your microSD root partition, create a **vc4.conf** under **etc/modprode.d/** with content: **blacklist vc4**. Second, on your microSD boot partition add **rd.driver.blacklist=vc4** to the end of the append line in the **extlinux/extlinux.conf** file.
6. Now, you are ready to boot up your Raspberry Pi.
## Booting Up
Be patient, especially for the GNOME and KDE distributions to come up. In the age of SSDs (Solid-State Drives), and almost instant bootups, it's easy to become impatient with write speeds for the Pi, especially the first time you boot. Before the Window Manager comes up for the first time, an initial configuration screen will pop up, which will allow you to configure root password, a regular user, time zones, and networking. Once you get that configured, you should be able to SSH into your Raspberry Pi, which can be very handy for debugging display issues.
## System updates
Once you have Fedora 25 up and running on your Raspberry Pi, you will eventually (or immediately) want to apply system updates.
First, when doing kernel upgrades, become familiar with your **/boot/extlinux/extlinux.conf** file. If you upgrade your kernel, the next time you boot, unless you manually pick the right kernel, you will most likely boot into Rescue mode. The best way to avoid that is to take the five lines that define the Rescue image on your **extlinux.conf** and move them to the bottom of the file, so the latest kernel will automatically boot up next time. You can edit the **/boot/extlinux/extlinux.conf** directly on the Pi or by mounting on your laptop:
**label Fedora 25 Rescue fdcb76d0032447209f782a184f35eebc (4.9.9-200.fc25.armv7hl)
kernel /vmlinuz-0-rescue-fdcb76d0032447209f782a184f35eebc
append ro root=UUID=c19816a7-cbb8-4cbb-8608-7fec6d4994d0 rd.driver.blacklist=vc4
fdtdir /dtb-4.9.9-200.fc25.armv7hl/
initrd /initramfs-0-rescue-fdcb76d0032447209f782a184f35eebc.img**
Second, if for whatever reason your display goes dark again after an upgrade and you are sure that **vc4** is blacklisted, run **lsmod | grep vc4**. You can always boot into multiuser mode, instead of graphical mode, and run **startx*** *from the command line. Read the content of **/etc/inittab** for directions on how to switch targets.
A Fedora 25 workstation, KDE on Raspberry Pi 3.
## The Fedora spins
Out of all of the Fedora spins I have tried, the only one that gave me a problem was the XFCE spin, and I believe it was due to this [known bug](https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1389163).
GNOME, KDE, LXDE, and minimal spins worked pretty well when I followed the steps I've shared here. Given that KDE and GNOME are a bit more resource heavy, I would recommend LXDE and Minimal for anyone who wants to just start playing with Fedora 25 on the Raspberry Pi. If you are a sysadmin who wants a cheap server backed by SELinux to cover your security concerns and all you want is to run your Raspberry Pi as some sort of server and you are happy with an IP address and port 22 open and vi, go with the Minimal spin. For developers or people starting to learn Linux, the LXDE may be the better way to go because it will give quick and easy access to all the GUI-based tools like browsers, IDEs, and clients you may need.
Fedora 25 workstation, LXDE on Raspberry Pi 3.
It is fantastic to see more and more Linux distributions become available on ARM-based Raspberry Pi computers. For its very first supported version, the Fedora team has provided a polished experience for the everyday Linux user. I will certainly be looking forward to the improvements and bug fixes for Fedora 26.
## 4 Comments |
8,445 | GoTTY:把你的 Linux 终端放到浏览器里面 | http://www.tecmint.com/gotty-share-linux-terminal-in-web-browser/ | 2017-04-25T10:02:01 | [
"gotty",
"终端",
"浏览器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8445-1.html | 
GoTTY 是一个简单的基于 Go 语言的命令行工具,它可以将你的终端(TTY)作为 web 程序共享。它会将命令行工具转换为 web 程序。
它使用 Chrome OS 的终端仿真器(hterm)来在 Web 浏览器上执行基于 JavaScript 的终端。重要的是,GoTTY 运行了一个 Web 套接字服务器,它基本上是将 TTY 的输出传输给客户端,并从客户端接收输入(即允许客户端的输入),并将其转发给 TTY。
它的架构(hterm + web socket 的想法)灵感来自 [Wetty 项目](http://www.tecmint.com/access-linux-server-terminal-in-web-browser-using-wetty/),它使终端能够通过 HTTP 和 HTTPS 使用。
### 先决条件
你需要在 Linux 中安装 [GoLang (Go 编程语言)](http://www.tecmint.com/install-go-in-linux/) 环境来运行 GoTTY。
### 如何在 Linux 中安装 GoTTY
如果你已经有一个[可以工作的 Go 语言环境](http://www.tecmint.com/install-go-in-linux/),运行下面的 `go get` 命令来安装它:
```
# go get github.com/yudai/gotty
```
上面的命令会在你的 `GOBIN` 环境变量中安装 GOTTY 的二进制,尝试检查下是否如此:
```
# $GOPATH/bin/
```

*检查 GOBIN 环境*
### 如何在 Linux 中使用 GoTTY
要运行它,你可以使用 GOBIN 环境变量并用命令补全:
```
# $GOBIN/gotty
```
另外,要不带完整命令路径运行 GoTTY 或其他 Go 程序,使用 `export` 命令将 `GOBIN` 变量添加到 `~/.profile` 文件中的 `PATH` 环境变量中。
```
export PATH="$PATH:$GOBIN"
```
保存文件并关闭。接着运行 `source` 来使更改生效:
```
# source ~/.profile
```
运行 GoTTY 命令的常规语法是:
```
Usage: gotty [options] <Linux command here> [<arguments...>]
```
现在用 GoTTY 运行任意命令,如 [df](/tag-df.html) 来从 Web 浏览器中查看系统分区空间及使用率。
```
# gotty df -h
```
GoTTY 默认会在 8080 启动一个 Web 服务器。在浏览器中打开 URL:`http://127.0.0.1:8080/`,你会看到运行的命令仿佛运行在终端中一样:

*Gotty 查看 Linux 磁盘使用率*
### 如何在 Linux 中自定义 GoTTY
你可以在 `~/.gotty` 配置文件中修改默认选项以及终端,如果该文件存在,它会在每次启动时加载这个文件。
这是由 getty 命令读取的主要自定义文件,因此,按如下方式创建:
```
# touch ~/.gotty
```
并为配置选项设置你自己的有效值([在此处查找所有配置选项](https://github.com/yudai/gotty#options))以自定义 GoTTY,例如:
```
// Listen at port 9000 by default
port = "9000"
// Enable TSL/SSL by default
enable_tls = true
// hterm preferences
// Smaller font and a little bit bluer background color
preferences {
font_size = 5,
background_color = "rgb(16, 16, 32)"
}
```
你可以使用命令行中的 `--html` 选项设置你自己的 `index.html` 文件:
```
# gotty --index /path/to/index.html uptime
```
### 如何在 GoTTY 中使用安全功能
由于 GoTTY 默认不提供可靠的安全保障,你需要手动使用下面说明的某些安全功能。
#### 允许客户端在终端中运行命令
请注意,默认情况下,GoTTY 不允许客户端输入到TTY中,它只支持窗口缩放。
但是,你可以使用 `-w` 或 `--permit-write` 选项来允许客户端写入 TTY,但是并不推荐这么做因为会有安全威胁。
以下命令会使用 [vi 命令行编辑器](/tag-vi.html)在 Web 浏览器中打开文件 `fossmint.txt` 进行编辑:
```
# gotty -w vi fossmint.txt
```
以下是从 Web 浏览器看到的 vi 界面(像平常一样使用 vi 命令):

*Gotty Web Vi 编辑器*
#### 使用基本(用户名和密码)验证运行 GoTTY
尝试激活基本身份验证机制,这样客户端将需要输入指定的用户名和密码才能连接到 GoTTY 服务器。
以下命令使用 `-c` 选项限制客户端访问,以向用户询问指定的凭据(用户名:`test` 密码:`@67890`):
```
# gotty -w -p "9000" -c "test@67890" glances
```

*使用基本验证运行 GoTTY*
#### Gotty 生成随机 URL
限制访问服务器的另一种方法是使用 `-r` 选项。GoTTY 会生成一个随机 URL,这样只有知道该 URL 的用户才可以访问该服务器。
还可以使用 `-title-format "GoTTY – {{ .Command }} ({{ .Hostname }})"` 选项来定义浏览器标题。[glances](/article-6882-1.html) 用于显示系统监控统计信息:
```
# gotty -r --title-format "GoTTY - {{ .Command }} ({{ .Hostname }})" glances
```
以下是从浏览器中看到的上面的命令的结果:

*使用 Gotty 随机 URL 用于 Glances 系统监控*
#### 带有 SSL/TLS 使用 GoTTY
因为默认情况下服务器和客户端之间的所有连接都不加密,当你通过 GoTTY 发送秘密信息(如用户凭据或任何其他信息)时,你需要使用 `-t` 或 `--tls` 选项才能在会话中启用 TLS/SSL:
默认情况下,GoTTY 会读取证书文件 `~/.gotty.crt` 和密钥文件 `~/.gotty.key`,因此,首先使用下面的 `openssl` 命令创建一个自签名的证书以及密钥( 回答问题以生成证书和密钥文件):
```
# openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout ~/.gotty.key -out ~/.gotty.crt
```
按如下所示,通过启用 SSL/TLS,以安全方式使用 GoTTY:
```
# gotty -tr --title-format "GoTTY - {{ .Command }} ({{ .Hostname }})" glances
```
#### 与多个客户端分享你的终端
你可以使用[终端复用程序](/article-8421-1.html)来与多个客户端共享一个进程,以下命令会启动一个名为 gotty 的新 [tmux 会话](/article-8421-1.html)来运行 glances(确保你安装了 tmux):
```
# gotty tmux new -A -s gotty glances
```
要读取不同的配置文件,像下面那样使用 `–config "/path/to/file"` 选项:
```
# gotty -tr --config "~/gotty_new_config" --title-format "GoTTY - {{ .Command }} ({{ .Hostname }})" glances
```
要显示 GoTTY 版本,运行命令:
```
# gotty -v
```
访问 GoTTY GitHub 仓库以查找更多使用示例:<https://github.com/yudai/gotty> 。
就这样了!你有尝试过了吗?如何知道 GoTTY 的?通过下面的反馈栏与我们分享你的想法。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,即将成为 Linux SysAdmin 和网络开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢在电脑上工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/gotty-share-linux-terminal-in-web-browser/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,446 | Python 是慢,但我无所谓 | https://medium.com/hacker-daily/yes-python-is-slow-and-i-dont-care-13763980b5a1 | 2017-04-25T11:14:00 | [
"Python",
"性能"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8446-1.html |
>
> 为牺牲性能追求生产率而呐喊
>
>
>

让我从关于 Python 中的 asyncio 这个标准库的讨论中休息一会,谈谈我最近正在思考的一些东西:Python 的速度。对不了解我的人说明一下,我是一个 Python 的粉丝,而且我在我能想到的所有地方都积极地使用 Python。人们对 Python 最大的抱怨之一就是它的速度比较慢,有些人甚至拒绝尝试使用 Python,因为它比其他语言速度慢。这里说说为什么我认为应该尝试使用 Python,尽管它是有点慢。
### 速度不再重要
过去的情形是,程序需要花费很长的时间来运行,CPU 比较贵,内存也很贵。程序的运行时间是一个很重要的指标。计算机非常的昂贵,计算机运行所需要的电也是相当贵的。对这些资源进行优化是因为一个永恒的商业法则:
>
> 优化你最贵的资源。
>
>
>
在过去,最贵的资源是计算机的运行时间。这就是导致计算机科学致力于研究不同算法的效率的原因。然而,这已经不再是正确的,因为现在硅芯片很便宜,确实很便宜。运行时间不再是你最贵的资源。公司最贵的资源现在是它的员工时间。或者换句话说,就是你。把事情做完比把它变快更加重要。实际上,这是相当的重要,我将把它再次放在这里,仿佛它是一个引文一样(给那些只是粗略浏览的人):
>
> 把事情做完比快速地做事更加重要。
>
>
>
你可能会说:“我的公司在意速度,我开发一个 web 应用程序,那么所有的响应时间必须少于 x 毫秒。”或者,“我们失去了客户,因为他们认为我们的 app 运行太慢了。”我并不是想说速度一点也不重要,我只是想说速度不再是最重要的东西;它不再是你最贵的资源。
### 速度是唯一重要的东西
当你在编程的背景下说 *速度* 时,你通常是说性能,也就是 CPU 周期。当你的 CEO 在编程的背景下说 *速度* 时,他指的是业务速度,最重要的指标是产品上市的时间。基本上,你的产品/web 程序是多么的快并不重要。它是用什么语言写的也不重要。甚至它需要花费多少钱也不重要。在一天结束时,让你的公司存活下来或者死去的唯一事物就是产品上市时间。我不只是说创业公司的想法 -- 你开始赚钱需要花费多久,更多的是“从想法到客户手中”的时间期限。企业能够存活下来的唯一方法就是比你的竞争对手更快地创新。如果在你的产品上市之前,你的竞争对手已经提前上市了,那么你想出了多少好的主意也将不再重要。你必须第一个上市,或者至少能跟上。一但你放慢了脚步,你就输了。
>
> 企业能够存活下来的唯一方法就是比你的竞争对手更快地创新。
>
>
>
#### 一个微服务的案例
像 Amazon、Google 和 Netflix 这样的公司明白快速前进的重要性。他们创建了一个业务系统,可以使用这个系统迅速地前进和快速的创新。微服务是针对他们的问题的解决方案。这篇文章不谈你是否应该使用微服务,但是至少要理解为什么 Amazon 和 Google 认为他们应该使用微服务。
微服务本来就很慢。微服务的主要概念是用网络调用来打破边界。这意味着你正在把使用的函数调用(几个 cpu 周期)转变为一个网络调用。没有什么比这更影响性能了。和 CPU 相比较,网络调用真的很慢。但是这些大公司仍然选择使用微服务。我所知道的架构里面没有比微服务还要慢的了。微服务最大的弊端就是它的性能,但是最大的长处就是上市的时间。通过在较小的项目和代码库上建立团队,一个公司能够以更快的速度进行迭代和创新。这恰恰表明了,非常大的公司也很在意上市时间,而不仅仅只是只有创业公司。
#### CPU 不是你的瓶颈
如果你在写一个网络应用程序,如 web 服务器,很有可能的情况会是,CPU 时间并不是你的程序的瓶颈。当你的 web 服务器处理一个请求时,可能会进行几次网络调用,例如到数据库,或者像 Redis 这样的缓存服务器。虽然这些服务本身可能比较快速,但是对它们的网络调用却很慢。[这里有一篇很好的关于特定操作的速度差异的博客文章](https://blog.codinghorror.com/the-infinite-space-between-words/)。在这篇文章里,作者把 CPU 周期时间缩放到更容易理解的人类时间。如果一个单独的 CPU 周期等同于 **1 秒**,那么一个从 California 到 New York 的网络调用将相当于 **4 年**。那就说明了网络调用是多少的慢。按一些粗略估计,我们可以假设在同一数据中心内的普通网络调用大约需要 3 毫秒。这相当于我们“人类比例” **3 个月**。现在假设你的程序是高 CPU 密集型,这需要 100000 个 CPU 周期来对单一调用进行响应。这相当于刚刚超过 **1 天**。现在让我们假设你使用的是一种要慢 5 倍的语言,这将需要大约 **5 天**。很好,将那与我们 3 个月的网络调用时间相比,4 天的差异就显得并不是很重要了。如果有人为了一个包裹不得不至少等待 3 个月,我不认为额外的 4 天对他们来说真的很重要。
上面所说的终极意思是,尽管 Python 速度慢,但是这并不重要。语言的速度(或者 CPU 时间)几乎从来不是问题。实际上谷歌曾经就这一概念做过一个研究,[并且他们就此发表过一篇论文](https://static.googleusercontent.com/media/research.google.com/en//archive/sawzall-sciprog.pdf)。那篇论文论述了设计高吞吐量的系统。在结论里,他们说到:
>
> 在高吞吐量的环境中使用解释性语言似乎是矛盾的,但是我们已经发现 CPU 时间几乎不是限制因素;语言的表达性是指,大多数程序是源程序,同时它们的大多数时间花费在 I/O 读写和本机的运行时代码上。而且,解释性语言无论是在语言层面的轻松实验还是在允许我们在很多机器上探索分布计算的方法都是很有帮助的,
>
>
>
再次强调:
>
> CPU 时间几乎不是限制因素。
>
>
>
### 如果 CPU 时间是一个问题怎么办?
你可能会说,“前面说的情况真是太好了,但是我们确实有过一些问题,这些问题中 CPU 成为了我们的瓶颈,并造成了我们的 web 应用的速度十分缓慢”,或者“在服务器上 X 语言比 Y 语言需要更少的硬件资源来运行。”这些都可能是对的。关于 web 服务器有这样的美妙的事情:你可以几乎无限地负载均衡它们。换句话说,可以在 web 服务器上投入更多的硬件。当然,Python 可能会比其他语言要求更好的硬件资源,比如 c 语言。只是把硬件投入在 CPU 问题上。相比于你的时间,硬件就显得非常的便宜了。如果你在一年内节省了两周的生产力时间,那将远远多于所增加的硬件开销的回报。
### 那么,Python 更快一些吗?
这一篇文章里面,我一直在谈论最重要的是开发时间。所以问题依然存在:当就开发时间而言,Python 要比其他语言更快吗?按常规惯例来看,我、[google](https://www.codefellows.org/blog/5-reasons-why-python-is-powerful-enough-for-google/) [还有](https://www.lynda.com/Python-tutorials/Python-Programming-Efficiently/534425-2.html)[其他](https://www.linuxjournal.com/article/3882)[几个人](https://www.codeschool.com/blog/2016/01/27/why-python/)可以告诉你 Python 是多么的[高效](http://pythoncard.sourceforge.net/what_is_python.html)。它为你抽象出很多东西,帮助你关注那些你真正应该编写代码的地方,而不会被困在琐碎事情的杂草里,比如你是否应该使用一个向量或者一个数组。但你可能不喜欢只是听别人说的这些话,所以让我们来看一些更多的经验数据。
在大多数情况下,关于 python 是否是更高效语言的争论可以归结为脚本语言(或动态语言)与静态类型语言两者的争论。我认为人们普遍接受的是静态类型语言的生产力较低,但是,[这有一篇优秀的论文](http://www.tcl.tk/doc/scripting.html)解释了为什么不是这样。就 Python 而言,这里有一项[研究](http://www.connellybarnes.com/documents/language_productivity.pdf),它调查了不同语言编写字符串处理的代码所需要花费的时间,供参考。

在上述研究中,Python 的效率比 Java 高出 2 倍。有一些其他研究也显示相似的东西。 Rosetta Code 对编程语言的差异进行了[深入的研究](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.0252.pdf)。在论文中,他们把 python 与其他脚本语言/解释性语言相比较,得出结论:
>
> Python 更简洁,即使与函数式语言相比较(平均要短 1.2 到 1.6 倍)
>
>
>
普遍的趋势似乎是 Python 中的代码行总是更少。代码行听起来可能像一个可怕的指标,但是包括上面已经提到的两项研究在内的[多项研究](http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.113.1831&rep=rep1&type=pdf)表明,每种语言中每行代码所需要花费的时间大约是一样的。因此,限制代码行数就可以提高生产效率。甚至 codinghorror(一名 C# 程序员)本人[写了一篇关于 Python 是如何更有效率的文章](https://blog.codinghorror.com/are-all-programming-languages-the-same/)。
我认为说 Python 比其他的很多语言更加的有效率是公正的。这主要是由于 Python 有大量的自带以及第三方库。[这里是一篇讨论 Python 和其他语言间的差异的简单的文章](https://www.python.org/doc/essays/comparisons/)。如果你不知道为何 Python 是如此的小巧和高效,我邀请你借此机会学习一点 python,自己多实践。这儿是你的第一个程序:
```
import __hello__
```
### 但是如果速度真的重要呢?
上述论点的语气可能会让人觉得优化与速度一点也不重要。但事实是,很多时候运行时性能真的很重要。一个例子是,你有一个 web 应用程序,其中有一个特定的端点需要用很长的时间来响应。你知道这个程序需要多快,并且知道程序需要改进多少。
在我们的例子中,发生了两件事:
1. 我们注意到有一个端点执行缓慢。
2. 我们承认它是缓慢,因为我们有一个可以衡量是否足够快的标准,而它没达到那个标准。
我们不必在应用程序中微调优化所有内容,只需要让其中每一个都“足够快”。如果一个端点花费了几秒钟来响应,你的用户可能会注意到,但是,他们并不会注意到你将响应时间由 35 毫秒降低到 25 毫秒。“足够好”就是你需要做到的所有事情。*免责声明: 我应该说有**一些**应用程序,如实时投标程序,**确实**需要细微优化,每一毫秒都相当重要。但那只是例外,而不是规则。*
为了明白如何对端点进行优化,你的第一步将是配置代码,并尝试找出瓶颈在哪。毕竟:
>
> <ruby> 任何除了瓶颈之外的改进都是错觉。 <rt> Any improvements made anywhere besides the bottleneck are an illusion. </rt></ruby> -- Gene Kim
>
>
>
如果你的优化没有触及到瓶颈,你只是浪费你的时间,并没有解决实际问题。在你优化瓶颈之前,你不会得到任何重要的改进。如果你在不知道瓶颈是什么前就尝试优化,那么你最终只会在部分代码中玩耍。在测量和确定瓶颈之前优化代码被称为“过早优化”。人们常提及 Donald Knuth 说的话,但他声称这句话实际上是他从别人那里听来的:
>
> <ruby> 过早优化是万恶之源 <rt> Premature optimization is the root of all evil </rt></ruby>。
>
>
>
在谈到维护代码库时,来自 Donald Knuth 的更完整的引文是:
>
> 在 97% 的时间里,我们应该忘记微不足道的效率:**过早的优化是万恶之源**。然而在关 键的 3%,我们不应该错过优化的机会。 —— Donald Knuth
>
>
>
换句话说,他所说的是,在大多数时间你应该忘记对你的代码进行优化。它几乎总是足够好。在不是足够好的情况下,我们通常只需要触及 3% 的代码路径。比如因为你使用了 if 语句而不是函数,你的端点快了几纳秒,但这并不会使你赢得任何奖项。
过早的优化包括调用某些更快的函数,或者甚至使用特定的数据结构,因为它通常更快。计算机科学认为,如果一个方法或者算法与另一个具有相同的渐近增长(或称为 Big-O),那么它们是等价的,即使在实践中要慢两倍。计算机是如此之快,算法随着数据/使用增加而造成的计算增长远远超过实际速度本身。换句话说,如果你有两个 O(log n) 的函数,但是一个要慢两倍,这实际上并不重要。随着数据规模的增大,它们都以同样的速度“慢下来”。这就是过早优化是万恶之源的原因;它浪费了我们的时间,几乎从来没有真正有助于我们的性能改进。
就 Big-O 而言,你可以认为对你的程序而言,所有的语言都是 O(n),其中 n 是代码或者指令的行数。对于同样的指令,它们以同样的速率增长。对于渐进增长,一种语言的速度快慢并不重要,所有语言都是相同的。在这个逻辑下,你可以说,为你的应用程序选择一种语言仅仅是因为它的“快速”是过早优化的最终形式。你选择某些预期快速的东西,却没有测量,也不理解瓶颈将在哪里。
>
> 为您的应用选择语言只是因为它的“快速”,是过早优化的最终形式。
>
>
>
### 优化 Python
我最喜欢 Python 的一点是,它可以让你一次优化一点点代码。假设你有一个 Python 的方法,你发现它是你的瓶颈。你对它优化过几次,可能遵循[这里](https://wiki.python.org/moin/PythonSpeed)和[那里](https://wiki.python.org/moin/PythonSpeed/PerformanceTips)的一些指导,现在,你很肯定 Python 本身就是你的瓶颈。Python 有调用 C 代码的能力,这意味着,你可以用 C 重写这个方法来减少性能问题。你可以一次重写一个这样的方法。这个过程允许你用任何可以编译为 C 兼容汇编程序的语言,编写良好优化后的瓶颈方法。这让你能够在大多数时间使用 Python 编写,只在必要的时候都才用较低级的语言来写代码。
有一种叫做 Cython 的编程语言,它是 Python 的超集。它几乎是 Python 和 C 的合并,是一种渐进类型的语言。任何 Python 代码都是有效的 Cython 代码,Cython 代码可以编译成 C 代码。使用 Cython,你可以编写一个模块或者一个方法,并逐渐进步到越来越多的 C 类型和性能。你可以将 C 类型和 Python 的鸭子类型混在一起。使用 Cython,你可以获得混合后的完美组合,只在瓶颈处进行优化,同时在其他所有地方不失去 Python 的美丽。

*星战前夜的一幅截图:这是用 Python 编写的 space MMO 游戏。*
当您最终遇到 Python 的性能问题阻碍时,你不需要把你的整个代码库用另一种不同的语言来编写。你只需要用 Cython 重写几个函数,几乎就能得到你所需要的性能。这就是[星战前夜](https://www.eveonline.com/)采取的策略。这是一个大型多玩家的电脑游戏,在整个架构中使用 Python 和 Cython。它们通过优化 C/Cython 中的瓶颈来实现游戏级别的性能。如果这个策略对他们有用,那么它应该对任何人都有帮助。或者,还有其他方法来优化你的 Python。例如,[PyPy](http://pypy.org/) 是一个 Python 的 JIT 实现,它通过使用 PyPy 替掉 CPython(这是 Python 的默认实现),为长时间运行的应用程序提供重要的运行时改进(如 web 服务器)。
让我们回顾一下要点:
* 优化你最贵的资源。那就是你,而不是计算机。
* 选择一种语言/框架/架构来帮助你快速开发(比如 Python)。不要仅仅因为某些技术的快而选择它们。
* 当你遇到性能问题时,请找到瓶颈所在。
* 你的瓶颈很可能不是 CPU 或者 Python 本身。
* 如果 Python 成为你的瓶颈(你已经优化过你的算法),那么可以转向热门的 Cython 或者 C。
* 尽情享受可以快速做完事情的乐趣。
我希望你喜欢阅读这篇文章,就像我喜欢写这篇文章一样。如果你想说谢谢,请为我点下赞。另外,如果某个时候你想和我讨论 Python,你可以在 twitter 上艾特我(@nhumrich),或者你可以在 [Python slack channel](http://pythondevelopers.herokuapp.com/) 找到我。
---
作者简介:
Nick Humrich -- 坚持采用持续交付的方法,并为之写了很多工具。同是还是一名 Python 黑客与技术狂热者,目前是一名 DevOps 工程师。
(题图:[Pixabay](https://pixabay.com),CC0)
via: <https://medium.com/hacker-daily/yes-python-is-slow-and-i-dont-care-13763980b5a1>
作者:[Nick Humrich](https://hackernoon.com/@nhumrich) 译者:[zhousiyu325](https://github.com/zhousiyu325) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,447 | 极客漫画:气人的软件 | http://turnoff.us/geek/annoying-software/ | 2017-04-25T17:27:00 | [
"软件",
"漫画"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8447-1.html | ### 气人的软件 1

软件:
>
> “你总是能够听取他人的意见,
>
>
> 现在是不是为自己切身考虑下呢?
>
>
> 不管怎样,您的操作已经完成。”
>
>
>
——这软件真气人!
### 气人的软件 2

软件:
>
> 真的忘记了吗?这已经是您本周第三次忘记密码了!
>
>
> 您是不是该考虑吃药了!
>
>
>
——你才该吃药呢!
### 气人的软件 3

自作聪明的软件,屡屡让人发疯!
### 气人的软件 4

我觉得现在都用 LCD 显示器有一个好处就是,你可以一拳打破而不用担心骨折(流血那种事情不在我们的考虑之中~)。
好气呀!
---
via:
* <http://turnoff.us/geek/annoying-software/>
* <http://turnoff.us/geek/annoying-software-2/>
* <http://turnoff.us/geek/annoying-software-3/>
* <http://turnoff.us/geek/annoying-software-4/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 合成:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 点评:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,449 | Windows 木马攻破嵌入式设备来安装 Mirai 恶意软件 | http://www.csoonline.com/article/3168357/security/windows-trojan-hacks-into-embedded-devices-to-install-mirai.html | 2017-04-26T11:54:09 | [
"木马",
"Mirai"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8449-1.html |
>
> 该木马尝试使用出厂默认凭证对不同协议进行身份验证,如果成功则会部署 Mirai 僵尸程序。
>
>
>

攻击者已经开始使用 Windows 和 Android 恶意软件入侵嵌入式设备,这消除了人们广泛持有的想法,认为如果设备不直接暴露在互联网上,那么它们就不那么脆弱。
来自俄罗斯防病毒供应商 Doctor Web 的研究人员最近[遇到了一个 Windows 木马程序](https://news.drweb.com/news/?i=11140&lng=en),它使用暴力方法访问嵌入式设备,并在其上安装 Mirai 恶意软件。
Mirai 是一种用在基于 Linux 的物联网设备的恶意程序,例如路由器、IP 摄像机、数字录像机等。它主要通过使用出厂设备凭据来发动分布式拒绝服务 (DDoS) 攻击并通过 Telnet 传播。
Mirai 的僵尸网络在过去六个月里一直被用来发起最大型的 DDoS 攻击。[它的源代码泄漏](http://www.computerworld.com/article/3132359/security/hackers-create-more-iot-botnets-with-mirai-source-code.html)之后,恶意软件被用来感染超过 50 万台设备。
Doctor Web 发现,一旦在一台 Windows 上安装之后,该新木马会从命令控制服务器下载配置文件。该文件包含一系列 IP 地址,通过多个端口,包括 22(SSH)和 23(Telnet),尝试进行身份验证。
如果身份验证成功,恶意软件将会根据受害系统的类型。执行配置文件中指定的某些命令。在通过 Telnet 访问的 Linux 系统中,木马会下载并执行一个二进制包,然后安装 Mirai 僵尸程序。
如果按照设计或配置,受影响的设备不会从 Internet 直接访问,那么许多物联网供应商会降低漏洞的严重性。这种思维方式假定局域网是信任和安全的环境。
然而事实并非如此,其他威胁如跨站点请求伪造已经出现了多年。但 Doctor Web 发现的新木马似乎是第一个专门设计用于劫持嵌入式或物联网设备的 Windows 恶意软件。
Doctor Web 发现的新木马被称为 [Trojan.Mirai.1](https://vms.drweb.com/virus/?_is=1&i=14934685),从它可以看到,攻击者还可以使用受害的计算机来攻击不能从互联网直接访问的物联网设备。
受感染的智能手机可以以类似的方式使用。卡巴斯基实验室的研究人员已经[发现了一个 Android 程序](https://securelist.com/blog/mobile/76969/switcher-android-joins-the-attack-the-router-club/),通过本地网络对路由器执行暴力密码猜测攻击。
(题图: Gerd Altmann / Pixabay)
---
via: <http://www.csoonline.com/article/3168357/security/windows-trojan-hacks-into-embedded-devices-to-install-mirai.html>
作者:[Lucian Constantin](http://www.csoonline.com/author/Lucian-Constantin/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,450 | 使用 badIPs.com 保护你的服务器,并通过 Fail2ban 报告恶意 IP | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/protect-your-server-computer-with-badips-and-fail2ban/ | 2017-04-26T12:31:00 | [
"badips",
"Fail2ban"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8450-1.html | 
这篇指南向你介绍使用 badips <ruby> 滥用追踪器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> abuse tracker </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和 Fail2ban 保护你的服务器或计算机的步骤。我已经在 Debian 8 Jessie 和 Debian 7 Wheezy 系统上进行了测试。
**什么是 badIPs?**
BadIps 是通过 [fail2ban](http://www.fail2ban.org/) 报告为不良 IP 的列表。
这个指南包括两个部分,第一部分介绍列表的使用,第二部分介绍数据提交。
### 使用 badIPs 列表
#### 定义安全等级和类别
你可以通过使用 REST API 获取 IP 地址列表。
* 当你使用 GET 请求获取 URL:<https://www.badips.com/get/categories> 后,你就可以看到服务中现有的所有不同类别。
* 第二步,决定适合你的等级。 参考 badips 应该有所帮助(我个人使用 `scope = 3`):
* 如果你想要编译一个统计信息模块或者将数据用于实验目的,那么你应该用等级 0 开始。
* 如果你想用防火墙保护你的服务器或者网站,使用等级 2。可能也要和你的结果相结合,尽管它们可能没有超过 0 或 1 的情况。
* 如果你想保护一个网络商店、或高流量、赚钱的电子商务服务器,我推荐你使用值 3 或 4。当然还是要和你的结果相结合。
* 如果你是偏执狂,那就使用 5。
现在你已经有了两个变量,通过把它们两者连接起来获取你的链接。
```
http://www.badips.com/get/list/{{SERVICE}}/{{LEVEL}}
```
注意:像我一样,你可以获取所有服务。在这种情况下把服务的名称改为 `any`。
最终的 URL 就是:
```
https://www.badips.com/get/list/any/3
```
### 创建脚本
所有都完成了之后,我们就会创建一个简单的脚本。
1、 把你的列表放到一个临时文件。
2、 在 iptables 中创建一个<ruby> 链 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> chain </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(只需要创建一次)。(LCTT 译注:iptables 可能包括多个<ruby> 表 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> tables </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,表可能包括多个<ruby> 链 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> chains </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,链可能包括多个<ruby> 规则 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> rules </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)
3、 把所有链接到该链的数据(旧条目)刷掉。
4、 把每个 IP 链接到这个新的链。
5、 完成后,阻塞所有链接到该链的 INPUT / OUTPUT /FORWARD 请求。
6、 删除我们的临时文件。
为此,我们创建脚本:
```
cd /home/<user>/
vi myBlacklist.sh
```
把以下内容输入到文件。
```
#!/bin/sh
### based on this version http://www.timokorthals.de/?p=334
### adapted by Stéphane T.
_ipt=/sbin/iptables ### iptables 路径(应该是这个)
_input=badips.db ### 数据库的名称(会用这个名称下载)
_pub_if=eth0 ### 连接到互联网的设备(执行 $ifconfig 获取)
_droplist=droplist ### iptables 中链的名称(如果你已经有这么一个名称的链,你就换另外一个)
_level=3 ### Blog(LCTT 译注:Bad log)等级:不怎么坏(0)、确认坏(3)、相当坏(5)(从 www.badips.com 获取详情)
_service=any ### 记录日志的服务(从 www.badips.com 获取详情)
### 获取不良 IPs
wget -qO- http://www.badips.com/get/list/${_service}/$_level > $_input || { echo "$0: Unable to download ip list."; exit 1; }
### 设置我们的黑名单 ###
### 首先清除该链
$_ipt --flush $_droplist
### 创建新的链
### 首次运行时取消下面一行的注释
# $_ipt -N $_droplist
### 过滤掉注释和空行
### 保存每个 ip 到 $ip
for ip in `cat $_input`
do
### 添加到 $_droplist
$_ipt -A $_droplist -i ${_pub_if} -s $ip -j LOG --log-prefix "Drop Bad IP List "
$_ipt -A $_droplist -i ${_pub_if} -s $ip -j DROP
done
### 最后,插入或者追加到我们的黑名单列表
$_ipt -I INPUT -j $_droplist
$_ipt -I OUTPUT -j $_droplist
$_ipt -I FORWARD -j $_droplist
### 删除你的临时文件
rm $_input
exit 0
```
完成这些后,你应该创建一个定时任务定期更新我们的黑名单。
为此,我使用 crontab 在每天晚上 11:30(在我的延迟备份之前) 运行脚本。
```
crontab -e
```
```
23 30 * * * /home/<user>/myBlacklist.sh #Block BAD IPS
```
别忘了更改脚本的权限:
```
chmod + x myBlacklist.sh
```
现在终于完成了,你的服务器/计算机应该更安全了。
你也可以像下面这样手动运行脚本:
```
cd /home/<user>/
./myBlacklist.sh
```
它可能要花费一些时间,因此期间别中断脚本。事实上,耗时取决于该脚本的最后一行。
### 使用 Fail2ban 向 badIPs 报告 IP 地址
在本篇指南的第二部分,我会向你展示如何通过使用 Fail2ban 向 badips.com 网站报告不良 IP 地址。
#### Fail2ban >= 0.8.12
通过 Fail2ban 完成报告。取决于你 Fail2ban 的版本,你要使用本章的第一或第二节。
如果你 fail2ban 的版本是 0.8.12 或更新版本。
```
fail2ban-server --version
```
在每个你要报告的类别中,添加一个 action。
```
[ssh]
enabled = true
action = iptables-multiport
badips[category=ssh]
port = ssh
filter = sshd
logpath = /var/log/auth.log
maxretry= 6
```
正如你看到的,类别是 SSH,从 <https://www.badips.com/get/categories> 查找正确类别。
#### Fail2ban < 0.8.12
如果版本是 0.8.12 之前,你需要新建一个 action。你可以从 <https://www.badips.com/asset/fail2ban/badips.conf> 下载。
```
wget https://www.badips.com/asset/fail2ban/badips.conf -O /etc/fail2ban/action.d/badips.conf
```
在上面的 badips.conf 中,你可以像前面那样激活每个类别,也可以全局启用它:
```
cd /etc/fail2ban/
vi jail.conf
```
```
[DEFAULT]
...
banaction = iptables-multiport
badips
```
现在重启 fail2ban - 从现在开始它就应该开始报告了。
```
service fail2ban restart
```
### 你的 IP 报告统计信息
最后一步 - 没那么有用。你可以创建一个密钥。 但如果你想看你的数据,这一步就很有帮助。
复制/粘贴下面的命令,你的控制台中就会出现一个 JSON 响应。
```
wget https://www.badips.com/get/key -qO -
```
```
{
"err":"",
"suc":"new key 5f72253b673eb49fc64dd34439531b5cca05327f has been set.",
"key":"5f72253b673eb49fc64dd34439531b5cca05327f"
}
```
到 [badips](https://www.badips.com/) 网站,输入你的 “key” 并点击 “statistics”。
现在你就可以看到不同类别的统计信息。
(题图:[Pixabay , CC0](https://pixabay.com/zh/%E9%BB%91%E5%AE%A2-%E6%94%BB%E5%87%BB-%E6%8E%A9%E7%A0%81-%E4%BA%92%E8%81%94%E7%BD%91-%E5%8C%BF%E5%90%8D-%E4%BA%8C%E8%BF%9B%E5%88%B6-%E4%B8%80-%E7%BD%91%E7%BB%9C-%E7%8A%AF%E7%BD%AA-1872304/))
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/protect-your-server-computer-with-badips-and-fail2ban/>
作者:[Stephane T](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/protect-your-server-computer-with-badips-and-fail2ban/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 404 | Not Found | null |
8,451 | 关于 Linux 进程你所需要知道的一切 | http://www.tecmint.com/linux-process-management/ | 2017-04-27T09:30:00 | [
"进程"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8451-1.html | 在这篇指南中,我们会逐步对进程做基本的了解,然后简要看看如何用特定命令[管理 Linux 进程](http://www.tecmint.com/dstat-monitor-linux-server-performance-process-memory-network/)。
<ruby> 进程 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> process </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>是指正在执行的程序;是程序正在运行的一个实例。它由程序指令,和从文件、其它程序中读取的数据或系统用户的输入组成。

### 进程的类型
在 Linux 中主要有两种类型的进程:
* 前台进程(也称为交互式进程) - 这些进程由终端会话初始化和控制。换句话说,需要有一个连接到系统中的用户来启动这样的进程;它们不是作为系统功能/服务的一部分自动启动。
* 后台进程(也称为非交互式/自动进程) - 这些进程没有连接到终端;它们不需要任何用户输入。
#### 什么是<ruby> 守护进程 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> daemon </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
这是后台进程的特殊类型,它们在系统启动时启动,并作为服务一直运行;它们不会死亡。它们自发地作为系统任务启动(作为服务运行)。但是,它们能被用户通过 init 进程控制。
[](http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/ProcessState.png)
*Linux 进程状态*
### 在 Linux 中创建进程
当现有的进程在内存中完全拷贝一份自身的时候就会创建出一个新的进程。子进程会有和父进程一样的环境,只有进程 ID 不同。
在 Linx 中有两种常规方式创建进程:
* 使用 system() 函数 - 这个方法相对简单,但是比较低效而且具有明显的安全隐患。
* 使用 fork() 和 exec() 函数 - 这个技巧比较高级但提供更好的灵活性、速度以及安全性。
### Linux 如何识别进程?
由于 Linux 是一个多用户系统,意味着不同的用户可以在系统上运行各种各样的程序,内核必须唯一标识程序运行的每个实例。
程序由它的进程 ID(PID)和它父进程的进程 ID(PPID)识别,因此进程可以被分类为:
* 父进程 - 这些是在运行时创建其它进程的进程。
* 子进程 - 这些是在运行时由其它进程创建的进程。
#### init 进程
init 进程是系统中所有进程的父进程,它是[启动 Linux 系统](http://www.tecmint.com/linux-boot-process/)后第一个运行的程序;它管理着系统上的所有其它进程。它由内核自身启动,因此理论上说它没有父进程。
init 进程的进程 ID 总是为 1。它是所有孤儿进程的收养父母。(它会收养所有孤儿进程)。
#### 查找进程 ID
你可以用 pidof 命令查找某个进程的进程 ID:
```
# pidof systemd
# pidof top
# pidof httpd
```

*查找 Linux 进程 ID*
要查找当前 shell 的进程 ID 以及它父进程的进程 ID,可以运行:
```
$ echo $$
$ echo $PPID
```

*查找 Linux 父进程 ID*
### 在 Linux 中启动进程
每次你运行一个命令或程序(例如 cloudcmd - CloudCommander),它就会在系统中启动一个进程。你可以按照下面的方式启动一个前台(交互式)进程,它会被连接到终端,用户可以发送输入给它:
```
# cloudcmd
```

*启动 Linux 交互进程*
#### Linux 后台任务
要在后台(非交互式)启动一个进程,使用 `&` 符号,此时,该进程不会从用户中读取输入,直到它被移到前台。
```
# cloudcmd &
# jobs
```

*在后台启动 Linux 进程*
你也可以使用 `Ctrl + Z` 暂停执行一个程序并把它发送到后台,它会给进程发送 SIGSTOP 信号,从而暂停它的执行;它就会变为空闲:
```
# tar -cf backup.tar /backups/* ### 按下 Ctrl+Z
# jobs
```
要在后台继续运行上面被暂停的命令,使用 `bg` 命令:
```
# bg
```
要把后台进程发送到前台,使用 `fg` 命令以及任务的 ID,类似:
```
# jobs
# fg %1
```

*Linux 后台进程任务*
你也可能想要阅读:[如何在后台启动 Linux 命令以及在终端分离(Detach)进程](http://www.tecmint.com/run-linux-command-process-in-background-detach-process/)
### Linux 中进程的状态
在执行过程中,取决于它的环境一个进程会从一个状态转变到另一个状态。在 Linux 中,一个进程有下面的可能状态:
* Running - 此时它正在运行(它是系统中的当前进程)或准备运行(它正在等待分配 CPU 单元)。
* Waiting - 在这个状态,进程正在等待某个事件的发生或者系统资源。另外,内核也会区分两种不同类型的等待进程;<ruby> 可中断等待进程 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> interruptible waiting processes </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> - 可以被信号中断,以及<ruby> 不可中断等待进程 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> uninterruptible waiting processes </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>- 正在等待硬件条件,不能被任何事件/信号中断。
* Stopped - 在这个状态,进程已经被停止了,通常是由于收到了一个信号。例如,正在被调试的进程。
* Zombie - 该进程已经死亡,它已经停止了但是<ruby> 进程表 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> process table </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>中仍然有它的条目。
### 如何在 Linux 中查看活跃进程
有很多 Linux 工具可以用于查看/列出系统中正在运行的进程,两个传统众所周知的是 [ps](/tag-ps.html) 和 [top](/tag-top.html) 命令:
#### 1. ps 命令
它显示被选中的系统中活跃进程的信息,如下图所示:
```
# ps
# ps -e | head
```

*列出 Linux 活跃进程*
#### 2. top - 系统监控工具
top 是一个强大的工具,它能给你提供 运行系统的动态实时视图,如下面截图所示:
```
# top
```

*列出 Linux 正在运行的程序*
阅读这篇文章获取更多 top 使用事例:[Linux 中 12 个 top 命令实例](http://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/)
#### 3. glances - 系统监控工具
glances 是一个相对比较新的系统监控工具,它有一些比较高级的功能:
```
# glances
```

*Glances – Linux 进程监控*
要获取完整使用指南,请阅读:[Glances - Linux 的一个高级实时系统监控工具](/article-6882-1.html)
还有很多你可以用来列出活跃进程的其它有用的 Linux 系统监视工具,打开下面的链接了解更多关于它们的信息:
1. [监控 Linux 性能的 20 个命令行工具](http://www.tecmint.com/command-line-tools-to-monitor-linux-performance/)
2. [13 个有用的 Linux 监控工具](http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-tools/)
### 如何在 Linux 中控制进程
Linux 也有一些命令用于控制进程,例如 `kill`、`pkill`、`pgrep` 和 `killall`,下面是一些如何使用它们的基本事例:
```
$ pgrep -u tecmint top
$ kill 2308
$ pgrep -u tecmint top
$ pgrep -u tecmint glances
$ pkill glances
$ pgrep -u tecmint glances
```

*控制 Linux 进程*
想要深入了解如何使用这些命令,在 Linux 中杀死/终止活跃进程,可以点击下面的链接:
1. [终止 Linux 进程的 Kill、Pkill 和 Killall 命令指南](http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-kill-a-process-in-linux/)
2. [如何在 Linux 中查找并杀死进程](http://www.tecmint.com/find-and-kill-running-processes-pid-in-linux/)
注意当你系统<ruby> 僵死 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> freeze </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>时你可以使用它们杀死 [Linux 中的不响应程序](http://www.tecmint.com/kill-processes-unresponsive-programs-in-ubuntu/)。
#### 给进程发送信号
Linux 中控制进程的基本方法是给它们发送信号。你可以发送很多信号给一个进程,运行下面的命令可以查看所有信号:
```
$ kill -l
```

*列出所有 Linux 信号*
要给一个进程发送信号,可以使用我们之前提到的 `kill`、`pkill` 或 `pgrep` 命令。但只有被编程为能识别这些信号时程序才能响应这些信号。
大部分信号都是系统内部使用,或者给程序员编写代码时使用。下面是一些对系统用户非常有用的信号:
* SIGHUP 1 - 当控制它的终端被被关闭时给进程发送该信号。
* SIGINT 2 - 当用户使用 `Ctrl+C` 中断进程时控制它的终端给进程发送这个信号。
* SIGQUIT 3 - 当用户发送退出信号 `Ctrl+D` 时给进程发送该信号。
* SIGKILL 9 - 这个信号会马上中断(杀死)进程,进程不会进行清理操作。
* SIGTERM 15 - 这是一个程序终止信号(kill 默认发送这个信号)。
* SIGTSTP 20 - 它的控制终端发送这个信号给进程要求它停止(终端停止);通过用户按 `Ctrl+Z` 触发。
下面是当 Firefox 应用程序僵死时通过它的 PID 杀死它的 kill 命令事例:
```
$ pidof firefox
$ kill 9 2687
或
$ kill -KILL 2687
或
$ kill -SIGKILL 2687
```
使用它的名称杀死应用,可以像下面这样使用 pkill 或 killall:
```
$ pkill firefox
$ killall firefox
```
#### 更改 Linux 进程优先级
在 Linux 系统中,所有活跃进程都有一个优先级以及 nice 值。有比点优先级进程有更高优先级的进程一般会获得更多的 CPU 时间。
但是,有 root 权限的系统用户可以使用 `nice` 和 `renice` 命令影响(更改)优先级。
在 top 命令的输出中, NI 显示了进程的 nice 值:
```
$ top
```

*列出 Linux 正在运行的进程*
使用 `nice` 命令为一个进程设置 nice 值。记住一个普通用户可以给他拥有的进程设置 0 到 20 的 nice 值。
只有 root 用户可以使用负的 nice 值。
要重新设置一个进程的优先级,像下面这样使用 `renice` 命令:
```
$ renice +8 2687
$ renice +8 2103
```
阅读我们其它如何管理和控制 Linux 进程的有用文章。
1. [Linux 进程管理:启动、停止以及中间过程](http://www.tecmint.com/rhcsa-exam-boot-process-and-process-management/)
2. [使用 ‘top’ 命令 Batch 模式查找内存使用最高的 15 个进程](http://www.tecmint.com/find-processes-by-memory-usage-top-batch-mode/)
3. [在 Linux 中查找内存和 CPU 使用率最高的进程](http://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-processes-memory-ram-cpu-usage/)
4. [在 Linux 中如何使用进程 ID 查找进程名称](http://www.tecmint.com/find-process-name-pid-number-linux/)
就是这些!如果你有任何问题或者想法,通过下面的反馈框和我们分享吧。
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S(Free and Open-Source Software) 爱好者,一个 Linux 系统管理员、web 开发员,现在也是 TecMint 的内容创建者,他喜欢和电脑一起工作,他相信知识共享。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/linux-process-management/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,453 | 如何在现有的 Linux 系统上添加新的磁盘 | http://www.tecmint.com/add-new-disk-to-an-existing-linux/ | 2017-04-27T18:26:10 | [
"fdisk",
"磁盘"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8453-1.html | 作为一个系统管理员,我们会有这样的一些需求:作为升级服务器容量的一部分,或者有时出现磁盘故障时更换磁盘,我们需要将新的硬盘配置到现有服务器。
在这篇文章中,我会向你逐步介绍添加新硬盘到现有 **RHEL/CentOS** 或者 **Debian/Ubuntu Linux** 系统的步骤。

**推荐阅读:** [如何将超过 2TB 的新硬盘添加到现有 Linux](/article-8398-1.html)。
重要:请注意这篇文章的目的只是告诉你如何创建新的分区,而不包括分区扩展或者其它选项。
我使用 [fdisk 工具](/tag-fdisk.html) 完成这些配置。
我已经添加了一块 **20GB** 容量的硬盘,挂载到了 `/data` 分区。
`fdisk` 是一个在 Linux 系统上用于显示和管理硬盘和分区命令行工具。
```
# fdisk -l
```
这个命令会列出当前分区和配置。

*查看 Linux 分区详情*
添加了 20GB 容量的硬盘后,`fdisk -l` 的输出像下面这样。
```
# fdisk -l
```

*查看新分区详情*
新添加的磁盘显示为 `/dev/xvdc`。如果我们添加的是物理磁盘,基于磁盘类型它会显示为类似 `/dev/sda`。这里我使用的是虚拟磁盘。
要在特定硬盘上分区,例如 `/dev/xvdc`。
```
# fdisk /dev/xvdc
```
常用的 fdisk 命令。
* `n` - 创建分区
* `p` - 打印分区表
* `d` - 删除一个分区
* `q` - 不保存更改退出
* `w` - 保存更改并退出
这里既然我们是要创建一个分区,就用 `n` 选项。

*在 Linux 上创建新分区*
创建主分区或者扩展分区。默认情况下我们最多可以有 4 个主分区。

*创建主分区*
按需求输入分区编号。推荐使用默认的值 `1`。

*分配分区编号*
输入第一个扇区的大小。如果是一个新的磁盘,通常选择默认值。如果你是在同一个磁盘上创建第二个分区,我们需要在前一个分区的最后一个扇区的基础上加 `1`。

*为分区分配扇区*
输入最后一个扇区或者分区大小的值。通常推荐输入分区的大小。总是添加前缀 `+` 以防止值超出范围错误。

*分配分区大小*
保存更改并退出。

*保存分区更改*
现在使用 **mkfs** 命令格式化磁盘。
```
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/xvdc1
```

*格式化新分区*
格式化完成后,按照下面的命令挂载分区。
```
# mount /dev/xvdc1 /data
```
在 `/etc/fstab` 文件中添加条目以便永久启动时自动挂载。
```
/dev/xvdc1 /data ext4 defaults 0 0
```
### 总结
现在你知道如何使用 [fdisk 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/fdisk-commands-to-manage-linux-disk-partitions/) 在新磁盘上创建分区并挂载了。
当处理分区、尤其是编辑已配置磁盘的时候,我们需要格外的小心。请分享你的反馈和建议吧。
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
作者简介:
我的工作内容包括 IBM-AIX、Solaris、HP-UX 多种平台以及存储技术 ONTAP 和 OneFS,并具有 Oracle 数据库的经验。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/add-new-disk-to-an-existing-linux/>
作者:[Lakshmi Dhandapani](http://www.tecmint.com/author/lakshmi/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,456 | 用 NTP 把控时间(一):使用概览 | https://www.linux.com/learn/arrive-time-ntp-part-1-usage-overview | 2017-04-28T08:45:00 | [
"NTP"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8456-1.html | 
这系列共三部分,首先,Chirs Binnie 探讨了在一个合理的架构中 NTP 服务的重要性。
鲜有互联网上的服务能如时间服务一样重要。影响你系统计时的小问题可能需要一两天才能被发现,而这些不期而遇的问题所带来的连锁反应几乎总是让人伤脑筋的。
设想你的备份服务器与网络时间协议(NTP)服务器断开连接,过了几天,引起了几小时的时间偏差。你的同事照常九点上班,发现需要大量带宽的备份服务器消耗了所有网络资源,这也就意味着他们在备份完成之前几乎不能登录工作台开始他们的日常工作。
这系列共三部分,首先,我将提供简要介绍 NTP 来防止这种困境的发生。从邮件的时间戳到记录你工作的进展,NTP 服务对于一个合理的架构是如此的重要。
可以把如此重要的 NTP 服务器(其他的服务器从此获取时钟数据)看做是倒置金字塔的底部,它被称之为<ruby> 一层 <rt> Stratum 1 </rt></ruby>服务器(也被称为“<ruby> 主 <rt> primary </rt></ruby>”服务器)。这些服务器与国家级时间服务(称为<ruby> 零层 <rt> Stratum 0 </rt></ruby>,通常这些设备是是原子钟和 GPS 钟之类的装置)直接交互。与之安全通讯的方法很多,例如通过卫星或者无线电。
令人惊讶的是,几乎所有的大型企业都会连接<ruby> 二层 <rt> Stratum 2 </rt></ruby>服务器(或“<ruby> 次级 <rt> secondary </rt></ruby>”服务器)而是不是主服务器。如你所料,二层服务器和一层直接同步。如果你觉得大公司可能有自己的本地 NTP 服务器(至少两个,通常三个,为了灾难恢复之用),这些就是三层服务器。这样,三层服务器将连接上层预定义的次级服务器,负责任地传递时间给客户端和服务器,精确地反馈当前时间。
由简单设计而构成的 NTP 可以工作的前提是——多亏了通过互联网跨越了大范围的地理距离——在确认时间完全准确之前,来回时间(包什么时候发出和多少秒后被收到)都会被清楚记录。设置电脑的时间的背后要比你想象的复杂得多,如果你不相信,那[这神奇的网页](http://www.ntp.org/ntpfaq/NTP-s-sw-clocks-quality.htm)值得一看。
再次重提一遍,为了确保你的架构如预期般工作,NTP 是如此的关键,你的 NTP 与层次服务器之间的连接必须是完全可信赖并且能提供额外的冗余,才能保持你的内部时钟同步。在 [NTP 主站](http://support.ntp.org/bin/view/Servers/StratumOneTimeServers)有一个有用的一层服务器列表。
正如你在列表所见,一些 NTP 一层服务器以 “ClosedAccount” 状态运行;这些服务器需要事先接受才可以使用。但是只要你完全按照他们的使用引导做,“OpenAccess” 服务器是可以用于轮询使用的。而 “RestrictedAccess” 服务器有时候会因为大量客户端访问或者轮询间隙太小而受限。另外有时候也有一些专供某种类型的组织使用,例如学术界。
### 尊重我的权威
在公共 NTP 服务器上,你可能发现遵从某些规则的使用规范。现在让我们看看其中一些。
“iburst” 选项作用是如果在一个标准的轮询间隔内没有应答,客户端会发送一定数量的包(八个包而不是通常的一个)给 NTP 服务器。如果在短时间内呼叫 NTP 服务器几次,没有出现可辨识的应答,那么本地时间将不会变化。
不像 “iburst” ,按照 NTP 服务器的通用规则, “burst” 选项一般不允许使用(所以不要用它!)。这个选项不仅在轮询间隔发送大量包(明显又是八个),而且也会在服务器能正常使用时这样做。如果你在高层服务器持续发送包,甚至是它们在正常应答时,你可能会因为使用 “burst” 选项而被拉黑。
显然,你连接服务器的频率造成了它的负载差异(和少量的带宽占用)。使用 “minpoll” 和 “maxpoll” 选项可以本地设置频率。然而,根据连接 NTP 服务器的规则,你不应该分别修改其默认的 64 秒和 1024 秒。
此外,需要提出的是客户应该重视那些请求时间的服务器发出的“<ruby> 亲一下就死(死亡之吻) <rt> Kiss-Of-Death </rt></ruby>” (KOD)消息。如果 NTP 服务器不想响应某个特定的请求,就像路由和防火墙技术那样,那么它最有可能的就是简单地遗弃或吞没任何相关的包。
换句话说,接受到这些数据的服务器并不需要特别处理这些包,简单地丢弃这些它认为这不值得回应的包即可。你可以想象,这并不是特别好的做法,有时候礼貌地问客户是否中止或停止比忽略请求更为有效。因此,这种特别的包类型叫做 KOD 包。如果一个客户端被发送了这种不受欢迎的 KOD 包,它应该记住这个发回了拒绝访问标志的服务器。
如果从该服务器收到不止一个 KOD 包,客户端会猜想服务器上发生了流量限速的情况(或类似的)。这种情况下,客户端一般会写入本地日志,提示与该服务器的交流不太顺利,以备将来排错之用。
牢记,出于显而易见的原因,关键在于 NTP 服务器的架构应该是动态的。因此,不要给你的 NTP 配置硬编码 IP 地址是非常重要的。通过使用 DNS 域名,个别服务器断开网络时服务仍能继续进行,而 IP 地址空间也能重新分配,并且可引入简单的负载均衡(具有一定程度的弹性)。
请别忘了我们也需要考虑呈指数增长的物联网(IoT),这最终将包括数以亿万计的新装置,意味着这些设备都需要保持正确时间。硬件卖家无意(或有意)设置他们的设备只能与一个提供者的(甚至一个) NTP 服务器连接终将成为过去,这是一个非常麻烦的问题。
你可能会想象,随着买入和上线更多的硬件单元,NTP 基础设施的拥有者大概不会为相关的费用而感到高兴,因为他们正被没有实际收入所困扰。这种情形并非杞人忧天。头疼的问题多呢 -- 由于 NTP 流量导致基础架构不堪重负 -- 这在过去几年里已发生过多次。
在下面两篇文章里,我将着重于一些重要的 NTP 安全配置选项和描述服务器的搭建。
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/learn/arrive-time-ntp-part-1-usage-overview>
作者:[CHRIS BINNIE](https://www.linux.com/users/chrisbinnie) 译者:[XYenChi](https://github.com/XYenChi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,457 | Linux 下网络协议分析器 Wireshark 使用基础 | https://linuxconfig.org/basic-of-network-protocol-analyzer-wireshark-on-linux | 2017-04-28T09:00:00 | [
"Wireshark"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8457-1.html | Wireshark 是 Kali 中预置的众多有价值工具中的一种。与其它工具一样,它可以被用于正面用途,同样也可以被用于不良目的。当然,本文将会介绍如何追踪你自己的网络流量来发现潜在的非正常活动。
Wireshark 相当的强大,当你第一次见到它的时候可能会被它吓到,但是它的目的始终就只有一个,那就是追踪网络流量,并且它所实现的所有选项都只为了加强它追踪流量的能力。

### 安装
Kali 中预置了 Wireshark 。不过,`wireshark-gtk` 包提供了一个更好的界面使你在使用 Wireshark 的时候会有更友好的体验。因此,在使用 Wireshark 前的第一步是安装 `wireshark-gtk` 这个包。
```
# apt install wireshark-gtk
```
如果你的 Kali 是从 live 介质上运行的也不需要担心,依然有效。
### 基础配置
在你使用 Wireshark 之前,将它设置成你使用起来最舒适的状态可能是最好的。Wireshark 提供了许多不同的布局方案和选项来配置程序的行为。尽管数量很多,但是使用起来是相当直接明确的。
从启动 Wireshark-gtk 开始。需要确定启动的是 GTK 版本的。在 Kali 中它们是被分别列出的。

### 布局
默认情况下,Wireshark 的信息展示分为三块内容,每一块都叠在另一块上方。(LCTT 译注:这里的三部分指的是展示抓包信息的时候的那三块内容,本段配图没有展示,配图 4、5、6 的设置不是默认设置,与这里的描述不符)最上方的一块是所抓包的列表。中间的一块是包的详细信息。最下面那块中包含的是包的原始字节信息。通常来说,上面的两块中的信息比最下面的那块有用的多,但是对于资深用户来说这块内容仍然是重要信息。
每一块都是可以缩放的,可并不是每一个人都必须使用这样叠起来的布局方式。你可以在 Wireshark 的“<ruby> 选项 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Preferences </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”菜单中进行更改。点击“<ruby> 编辑 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Edit </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”菜单,最下方就是的“<ruby> 选项 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Preferences </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”菜单。这个选项会打开一个有更多选项的新窗口。单击侧边菜单中“<ruby> 用户界面 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> User Interface </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”下的“<ruby> 布局 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Layout </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”选项。

你将会看到一些不同的布局方案。上方的图示可以让你选择不同的面板位置布局方案,下面的单选框可以让你选择不同面板中的数据内容。
下面那个标记为“<ruby> 列 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Columns </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”的标签可以让你选择展示所抓取包的哪些信息。选择那些你需要的数据信息,或者全部展示。
### 工具条
对于 Wireshark 的工具条能做的设置不是太多,但是如果你想设置的话,你依然在前文中提到的“布局”菜单中的窗口管理工具下方找到一些有用的设置选项。那些能让你配置工具条和工具条中条目的选项就在窗口选项下方。
你还可以在“<ruby> 视图 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> View </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”菜单下勾选来配置工具条的显示内容。
### 功能
主要的用来控制 Wireshark 抓包的控制选项基本都集中在“<ruby> 捕捉 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Capture </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”菜单下的“<ruby> 选项 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Options </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”选项中。
在开启的窗口中最上方的“<ruby> 捕捉 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Capture </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”部分可以让你选择 Wireshark 要监控的某个具体的网络接口。这部分可能会由于你系统的配置不同而会有相当大的不同。要记得勾选正确的选择框才能获得正确的数据。虚拟机和伴随它们一起的网络接口也同样会在这个列表里显示。同样也会有多种不同的选项对应这多种不同的网络接口。

在网络接口列表的下方是两个选项。其中一个选项是全选所有的接口。另一个选项用来选择是否开启混杂模式。这个选项可以使你的计算机监控到所选网络上的所有的计算机。(LCTT 译注:混杂模式可以在 HUB 中或监听模式的交换机接口上捕获那些由于 MAC 地址非本机而会被自动丢弃的数据包)如果你想监控你所在的整个网络,这个选项是你所需要的。
**注意:** 在一个不属于你或者不拥有权限的网络上使用混杂模式来监控是非法的!
在窗口下方的右侧是“<ruby> 显示选项 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Display Options </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”和“<ruby> 名称解析 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Name Resolution </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”选项块。对于“<ruby> 显示选项 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Display Options </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”来说,三个选项全选可能就是一个很好的选择了。当然你也可以取消选择,但是最好还是保留选择“实时更新抓包列表”。
在“<ruby> 名称解析 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Name Resolution </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”中你也可以设置你的偏好。这里的选项会产生附加的请求因此选得越多就会有越多的请求产生使你的抓取的包列表显得杂乱。把 MAC 解析选项选上是个好主意,那样就可以知道所使用的网络硬件的品牌了。这可以帮助你来确定你是在与哪台设备上的哪个接口进行交互。
### 抓包
抓包是 Wireshark 的核心功能。监控和记录特定网络上的流量就是它最初产生的目的。使用它最基本的方式来作这个抓包的工作是相当简单方便的。当然,越多的配置和选项就越可以充分利用 Wireshark 的力量。这里的介绍的关注点依然还是它最基本的记录方式。
按下那个看起来像蓝色鲨鱼鳍的新建实时抓包按钮就可以开始抓包了。(LCTT 译注:在我的 Debian 上它是绿色的)

在抓包的过程中,Wireshark 会收集所有它能收集到的包的数据并且记录下来。如果没有更改过相关设置的话,在抓包的过程中你会看见不断的有新的包进入到“包列表”面板中。你可以实时的查看你认为有趣的包,或者就让 Wireshark 运行着,同时你可以做一些其它的事情。
当你完成了,按下红色的正方形“停止”按钮就可以了。现在,你可以选择是否要保存这些所抓取的数据了。要保存的话,你可以使用“文件”菜单下的“保存”或者是“另存为”选项。
### 读取数据
Wireshark 的目标是向你提供你所需要的所有数据。这样做时,它会在它监控的网络上收集大量的与网络包相关的数据。它使用可折叠的标签来展示这些数据,使得这些数据看起来没有那么吓人。每一个标签都对应于网络包中一部分的请求数据。
这些标签是按照从最底层到最高层一层层堆起来的。顶部标签总是包含数据包中包含的字节数据。最下方的标签可能会是多种多样的。在下图的例子中是一个 HTTP 请求,它会包含 HTTP 的信息。您遇到的大多数数据包将是 TCP 数据,它将展示在底层的标签中。

每一个标签页都包含了抓取包中对应部分的相关数据。一个 HTTP 包可能会包含与请求类型相关的信息,如所使用的网络浏览器,服务器的 IP 地址,语言,编码方式等的数据。一个 TCP 包会包含服务器与客户端使用的端口信息和 TCP 三次握手过程中的标志位信息。

在上方的其它标签中包含了一些大多数用户都感兴趣的少量信息。其中一个标签中包含了数据包是否是通过 IPv4 或者 IPv6 传输的,以及客户端和服务器端的 IP 地址。另一个标签中包含了客户端和接入因特网的路由器或网关的设备的 MAC 地址信息。
### 结语
即使只使用这些基础选项与配置,你依然可以发现 Wireshark 会是一个多么强大的工具。监控你的网络流量可以帮助你识别、终止网络攻击或者提升连接速度。它也可以帮你找到问题应用。下一篇 Wireshark 指南我们将会一起探索 Wireshark 的包过滤选项。
---
via: <https://linuxconfig.org/basic-of-network-protocol-analyzer-wireshark-on-linux>
作者:[Nick Congleton](https://linuxconfig.org/basic-of-network-protocol-analyzer-wireshark-on-linux) 译者:[wcnnbdk1](https://github.com/wcnnbdk1) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
8,458 | 在 Linux 上使用 Meld 比较文件夹 | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-perform-directory-comparison-using-meld/ | 2017-04-29T08:12:00 | [
"Meld",
"比较"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8458-1.html | 
我们已经从一个新手的角度[了解](/article-8402-1.html)了 Meld (包括 Meld 的安装),我们也提及了一些 Meld 中级用户常用的小技巧。如果你有印象,在新手教程中,我们说过 Meld 可以比较文件和文件夹。已经讨论过怎么比较文件,今天,我们来看看 Meld 怎么比较文件夹。
**需要指出的是,本教程中的所有命令和例子都是在 Ubuntu 14.04 上测试的,使用的 Meld 版本为 3.14.2。**
### 用 Meld 比较文件夹
打开 Meld 工具,然后选择 <ruby> 比较文件夹 <rt> Directory comparison </rt></ruby> 选项来比较两个文件夹。

选择你要比较的文件夹:

然后单击<ruby> 比较 <rt> Compare </rt></ruby>按钮,你会看到 Meld 像图中这样分成两栏比较目录,就像文件比较一样。

分栏会树形显示这些文件夹。你可以在上图中看到 —— 区别之处,不论是新建的还是被修改过的文件 —— 都会以不同的颜色高亮显示。
根据 Meld 的官方文档可以知道,在窗口中看到的每个不同的文件或文件夹都会被突出显示。这样就很容易看出这个文件/文件夹与另一个分栏中对应位置的文件/文件夹的区别。
下表是 Meld 网站上列出的在比较文件夹时突出显示的不同字体大小/颜色/背景等代表的含义。
| **状态** | **表现** | **含义** |
| --- | --- | --- |
| 相同 | 正常字体 | 比较的文件夹中所有文件/文件夹相同。 |
| 过滤后相同 | 斜体 | 文件夹中文件不同,但使用文本过滤器的话,文件是相同的。 |
| 修改过 | 蓝色粗体 | 比较的文件夹中这些文件不同。 |
| 新建 | 绿色粗体 | 该文件/文件夹在这个目录中存在,但其它目录中没有。 |
| 缺失 | 置灰文本,删除线 | 该文件/文件夹在这个目录中不存在,在在其它某个目录中存在。 |
| 错误 | 黄色背景的红色粗体 | 比较文件时发生错误,最常见错误原因是文件权限(例如,Meld 无法打开该文件)和文件名编码错误。 |
Meld 默认会列出比较文件夹中的所有内容,即使这些内容没有任何不同。当然,你也可以在工具栏中单击<ruby> 相同 <rt> Same </rt></ruby>按钮设置 Meld 不显示这些相同的文件/文件夹 —— 单击这个按钮使其不可用。
[](https://www.howtoforge.com/images/beginners-guide-to-visual-merge-tool-meld-on-linux-part-3/big/meld-same-button.png)

下面是单击 <ruby> 相同 <rt> Same </rt></ruby> 按钮使其不可用的截图:

这样你会看到只显示了两个文件夹中不同的文件(新建的和修改过的)。同样,如果你单击 <ruby> 新建 <rt> New </rt></ruby> 按钮使其不可用,那么 Meld 就只会列出修改过的文件。所以,在比较文件夹时可以通过这些按钮自定义要显示的内容。
你可以使用工具窗口显示区的上下箭头来切换选择是显示新建的文件还是修改过的文件。要打开两个文件进行分栏比较,可以双击文件,或者单击箭头旁边的 <ruby> 比较 <rt> Compare </rt></ruby>按钮。

**提示 1**:如果你仔细观察,就会看到 Meld 窗口的左边和右边有一些小条。这些条的目的是提供“简单的用颜色区分的比较结果”。对每个不同的文件/文件夹,条上就有一个小的颜色块。你可以单击每一个这样的小块跳到它对应的文件/文件夹。
**提示 2**:你总可以分栏比较文件,然后以你的方式合并不同的文件,假如你想要合并所有不同的文件/文件夹(就是说你想要一个特定的文件/文件夹与另一个完全相同),那么你可以用 <ruby> 复制到左边 <rt> Copy Left </rt></ruby>和 <ruby> 复制到右边 <rt> Copy Right </rt></ruby> 按钮:

比如,你可以在左边的分栏中选择一个文件或文件夹,然后单击 <ruby> 复制到右边 <rt> Copy Right </rt></ruby> 按钮,使右边对应条目完全一样。
现在,在窗口的下拉菜单中找到 <ruby> 过滤 <rt> Filters </rt></ruby> 按钮,它就在 <ruby> 相同 <rt> Same </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 新建 <rt> New </rt></ruby> 和 <ruby> 修改的 <rt> Modified </rt></ruby> 这三个按钮下面。这里你可以选择或取消文件的类型,告知 Meld 在比较文件夹时是否显示这种类型的文件/文件夹。官方文档解释说菜单中的这个条目表示“执行文件夹比较时该类文件名不会被查看。”
该列表中条目包括备份文件,操作系统元数据,版本控制文件、二进制文件和多媒体文件。

前面提到的条目也可以通过这样的方式找到:*浏览->文件过滤*。你可以通过 *编辑->首选项->文件过滤* 为这个条目增加新元素(也可以删除已经存在的元素)。

要新建一个过滤条件,你需要使用一组 shell 符号,下表列出了 Meld 支持的 shell 符号:
| **通配符** | **匹配** |
| --- | --- |
| \* | 任何字符 (例如,零个或多个字符) |
| ? | 一个字符 |
| [abc] | 所列字符中的任何一个 |
| [!abc] | 不在所列字符中的任何一个 |
| {cat,dog} | “cat” 或 “dog” 中的一个 |
最重要的一点是 Meld 的文件名默认大小写敏感。也就是说,Meld 认为 readme 和 ReadMe 与 README 是不一样的文件。
幸运的是,你可以关掉 Meld 的大小写敏感。只需要打开 *浏览* 菜单然后选择 <ruby> 忽略文件名大小写 <rt> Ignore Filename Case </rt></ruby> 选项。 
### 结论
你是否觉得使用 Meld 比较文件夹很容易呢 —— 事实上,我认为它相当容易。只有新建一个文件过滤器会花点时间,但是这不意味着你没必要学习创建过滤器。显然,这取决于你的需求。
另外,你甚至可以用 Meld 比较三个文件夹。想要比较三个文件夹时,你可以通过单击 <ruby> 三向比较 <rt> 3-way comparison </rt></ruby> 复选框。今天,我们不介绍怎么比较三个文件夹,但它肯定会出现在后续的教程中。
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-perform-directory-comparison-using-meld/>
作者:[Ansh](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-perform-directory-comparison-using-meld/) 译者:[vim-kakali](https://github.com/vim-kakali) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # How to compare directories with Meld on Linux
### On this page
We've [already covered](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/beginners-guide-to-visual-merge-tool-meld-on-linux/) Meld from a beginner's point of view (including the tool's installation part), and we've also covered some tips/tricks that are primarily aimed at intermediate Meld users. If you remember, in the beginner's tutorial, we mentioned that Meld can be used to compare both files as well as directories. Now that we've already covered file comparison, it's time to discuss the tool's directory comparison feature.
## Compare directories using Meld
To compare two directories using Meld, launch the tool and select the *Directory comparison* option.
Then select the directories that you want to compare:
Once that is done, click the *Compare* button, and you'll see that Meld will compare both directories side by side, like the tool does in case of files:
Of course, these being directories, they are displayed as side-by-side trees. And as you can see in the screenshot above, the differences - whether it's a new file or a changed file - are highlighted in different colors.
According to Meld's official documentation, each file or folder that you see in the comparison area of the window has a state of its own. A state basically reveals how a particular file/folder is different from the corresponding entry in the other directory.
The following table - taken from the tool's website - explains in details the folder comparison states in Meld.
|
|
|
Same | Normal font | The file/folder is the same across all compared folders. |
Same when filtered | Italics | These files are different across folders, but once text filters are applied, these files become identical. |
Modified | Blue and bold | These files differ between the folders being compared. |
New | Green and bold | This file/folder exists in this folder, but not in the others. |
Missing | Greyed out text with a line through the middle | This file/folder doesn't exist in this folder, but does in one of the others. |
Error | Bright red with a yellow background and bold | When comparing this file, an error occurred. The most common error causes are file permissions (i.e., Meld was not allowed to open the file) and filename encoding errors. |
By default, Meld shows all the contents of the folders being compared, even if they are same (meaning there's no difference between them). However, you can ask the tool to not display these files/directories by clicking the *Same* button in the toolbar - the click should disable this button.
For example, here's our directory comparison when I clicked and disabled the *Same* button:
So you can see that only the differences between the two directories (new and modified files) are shown now. Similarly, if you disable the *New* button, only the modified files will be displayed. So basically, you can use these buttons to customize what kind of changes are displayed by Meld while comparing two directories.
Coming to the changes, you can hop from one change to another using the up and down arrow keys that sit above the display area in the tool's window, and to open two files for side-by-side comparison, you can either double click the name of any of the files, or click the *Compare* button that sits beside the arrows.
**Note 1**: If you observe closely, there are bars on the left and right-hand sides of the display area in Meld window. These bars basically provide "a simple coloured summary of the comparison results." For each differing file or folder, there's a small colored section in these bars. You can click any such section to directly jump to that place in the comparison area.
**Note 2**: While you can always open files side by side and merge changes the way you want, in case you want all the changes to be merged to the corresponding file/folder (meaning you want to make the corresponding file/folder exactly same) then you can use the *Copy Left* and *Copy Right* buttons:
For example, select a file or folder in the left pane and click the *Copy Right* button to make the corresponding entry in the right pane exactly same.
Moving on, there's a *Filters* drop-down menu that sits just next to the *Same*, *New*, and *Modified* trio of buttons. Here you can select/deselect file types to tell Meld whether or not to show these kind of files/folders in the display area during a directory comparison. The official documentation explains the entries in this menu as "patterns of filenames that will not be looked at when performing a folder comparison."
The entries in the list include backups, OS-specific metadata, version control, binaries, and media.
The aforementioned menu is also accessible by heading to *View->File Filters*. You can add new elements to this menu (as well as remove existing ones if you want) by going to *Edit->Preferences->File Filters*.
To create a new filter, you need to use shell glob patterns. Following is the list of shell glob characters that Meld recognises:
|
|
* | anything (i.e., zero or more characters) |
? | exactly one character |
[abc] | any one of the listed characters |
[!abc] | anything except one of the listed characters |
{cat,dog} | either "cat" or "dog" |
Finally, an important point worth knowing about Meld is that the case of a file's name plays an important part as comparison is case sensitive by default. This means that, for example, the files README, readme and ReadMe would all be treated by the tool as different files.
Thankfully, however, Meld also provides you a way to turn off this feature. All you have to do is to head to the *View* menu and then select the *Ignore Filename Case* option.
## Conclusion
As you'd agree, directory comparison using Meld isn't difficult - in fact I'd say it's pretty easy. The only area that might require time to learn is creating file filters, but that's not to say you should never learn it. Obviously, it all depends on what your requirement is.
Oh, and yes, you can even compare three directories using Meld, a feature that you can access by *clicking the 3-way comparison* box when you choose the directories that you want to compare. We didn't discuss the feature in this article, but definitely will in one of our future articles. |
8,459 | 在 PC 上尝试树莓派的 PIXEL OS | https://opensource.com/article/17/1/try-raspberry-pis-pixel-os-your-pc | 2017-04-29T09:39:00 | [
"树莓派",
"PIXEL"
] | /article-8459-1.html | 
在过去四年中,树莓派基金会非常努力地针对树莓派的硬件优化了 Debian 的移植版 Raspbian,包括创建新的教育软件、编程工具和更美观的桌面。
在(去年) 9 月份,我们发布了一个更新,介绍了树莓派新的桌面环境 PIXEL(Pi Improved Xwindows Environment,轻量级)。在圣诞节之前,我们[发布](/article-8064-1.html)了一个在 x86 PC 上运行的操作系统版本,所以现在可以将它安装在 PC、Mac 或笔记本电脑上。

当然,像许多支持良好的 Linux 发行版一样,操作系统在旧的硬件上也能正常运行。 Raspbian 是让你几年前就丢弃的旧式 Windows 机器焕发新生的好方法。
[PIXEL ISO](http://downloads.raspberrypi.org/pixel_x86/images/pixel_x86-2016-12-13/) 可从树莓派网站上下载,在 “[MagPi](https://www.raspberrypi.org/magpi/issues/53/)” 杂志封面上也有赠送可启动的 Live DVD 。

为了消除想要学习计算机的人们的入门障碍,我们发布了树莓派的个人电脑操作系统。它比购买一块树莓派更便宜,因为它是免费的,你可以在现有的计算机上使用它。PIXEL 是我们一直想要的 Linux 桌面,我们希望它可供所有人使用。
### 由 Debian 提供支持
不构建在 Debian 之上的话,Raspbian 或 x86 PIXEL 发行版就都不会存在。 Debian 拥有庞大的可以从一个 apt 仓库中获得的免费开源软件、程序、游戏和其他工具。在树莓派中,你仅限运行为 [ARM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARM_Holdings) 芯片编译的软件包。然而,在 PC 镜像中,你可以在机器上运行的软件包的范围更广,因为 PC 中的 Intel 芯片有更多的支持。
 repository")
### PIXEL 包含什么
带有 PIXEL 的 Raspbian 和带有 PIXEL 的 Debian 都捆绑了大量的软件。Raspbian 自带:
* Python、Java、Scratch、Sonic Pi、Mathematica\*、Node-RED 和 Sense HAT 仿真器的编程环境
* LibreOffice 办公套件
* Chromium(包含 Flash)和 Epiphany 网络浏览器
* Minecraft:树莓派版(包括 Python API)\*
* 各种工具和实用程序
\*由于许可证限制,本列表中唯一没有包含在 x86 版本中的程序是 Mathematica 和 Minecraft。

### 创建一个 PIXEL Live 盘
你可以下载 PIXEL ISO 并将其写入空白 DVD 或 USB 记忆棒中。 然后,你就可以从盘中启动你的电脑,这样你可以立刻看到 PIXEL 桌面。你可以浏览网页、打开编程环境或使用办公套件,而无需在计算机上安装任何内容。完成后,只需拿出 DVD 或 USB 驱动器,关闭计算机,再次重新启动计算机时,将会像以前一样重新启动到你平常的操作系统。
### 在虚拟机中运行 PIXEL
另外一种尝试 PIXEL 的方法是在像 VirtualBox 这样的虚拟机中安装它。

这允许你体验镜像而不用安装它,也可以在主操作系统里面的窗口中运行它,并访问 PIXEL 中的软件和工具。这也意味着你的会话会一直存在,而不是每次重新启动时从头开始,就像使用 Live 盘一样。
### 在 PC 中安装 PIXEL
如果你真的准备开始,你可以擦除旧的操作系统并将 PIXEL 安装在硬盘上。如果你想使用旧的闲置的笔记本电脑,这可能是个好主意。
### 用于教育的 PIXEL
许多学校在所有电脑上使用 Windows,并且对它们可以安装的软件进行严格的控制。这使得教师难以使用必要的软件工具和 IDE(集成开发环境)来教授编程技能。即使在线编程计划(如 Scratch 2)也可能被过于谨慎的网络过滤器阻止。在某些情况下,安装像 Python 这样的东西根本是不可能的。树莓派硬件通过提供包含教育软件的 SD 卡引导的小型廉价计算机来解决这个问题,学生可以连接到现有 PC 的显示器、鼠标和键盘上。
然而,PIXEL Live 光盘允许教师引导到装有能立即使用的编程语言和工具的系统中,所有这些都不需要安装权限。在课程结束时,他们可以安全关闭,使计算机恢复原状。这也是 Code Clubs、CoderDojos、青年俱乐部、Raspberry Jams 等等的一个方便的解决方案。
### 远程 GPIO
树莓派与传统台式 PC 区别的功能之一是 GPIO 引脚(通用输入/输出)引脚的存在,它允许你将现实世界中的电子元件和附加板连接设备上,这将开放一个新的世界,如业余项目、家庭自动化、连接的设备和物联网。
[GPIO Zero](http://gpiozero.readthedocs.io/) Python 库的一个很棒的功能是通过在 PC 上写入一些简单的代码,然后在网络上控制树莓派的 GPIO 引脚。
远程 GPIO 可以从一台树莓派连接到另一台树莓派,或者从运行任何系统的 OS 的 PC 连接到树莓派上,但是,使用 PIXEL x86 的话所有需要的软件都是开箱即用的。参见 Josh 的[博文](http://www.allaboutcode.co.uk/single-post/2016/12/21/GPIOZero-Remote-GPIO-with-PIXEL-x86),并参考我的 [gist](https://gist.github.com/bennuttall/572789b0aa5fc2e7c05c7ada1bdc813e) 了解更多信息。
### 更多指南
[MagPi 的第 53 期](https://www.raspberrypi.org/magpi/issues/53/)提供了一些试用和安装 PIXEL 的指南,包括使用带持久驱动的 Live 光盘来维护你的文件和应用程序。你可以购买一份,或免费下载 PDF 来了解更多。
(图片版权:树莓派基金会, CC BY-SA)
---
作者简介:
Ben Nuttall - Ben Nuttall 是一名树莓派社区管理员。他除了为树莓派基金会工作外,他还对自由软件、数学、皮划艇、GitHub、Adventure Time 和 Futurama 等感兴趣。在 Twitter @ben\_nuttall 上关注 Ben。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/1/try-raspberry-pis-pixel-os-your-pc>
作者:[Ben Nuttall](https://opensource.com/users/bennuttall) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
8,460 | 如何在 CentOS 7 上安装 Elastic Stack | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/ | 2017-04-29T10:36:00 | [
"Lucene",
"搜索引擎",
"日志"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8460-1.html | **Elasticsearch** 是基于 Lucene 由 Java 开发的开源搜索引擎。它提供了一个分布式、多租户的全文搜索引擎(LCTT 译注:多租户是指多租户技术,是一种软件架构技术,用来探讨与实现如何在多用户的环境下共用相同的系统或程序组件,并且仍可确保各用户间数据的隔离性。),并带有 HTTP 仪表盘的 Web 界面(Kibana)。数据会被 Elasticsearch 查询、检索,并且使用 JSON 文档方案存储。Elasticsearch 是一个可扩展的搜索引擎,可用于搜索所有类型的文本文档,包括日志文件。Elasticsearch 是 Elastic Stack 的核心,Elastic Stack 也被称为 ELK Stack。
**Logstash** 是用于管理事件和日志的开源工具。它为数据收集提供实时传递途径。 Logstash 将收集您的日志数据,将数据转换为 JSON 文档,并将其存储在 Elasticsearch 中。
**Kibana** 是 Elasticsearch 的开源数据可视化工具。Kibana 提供了一个漂亮的仪表盘 Web 界面。 你可以用它来管理和可视化来自 Elasticsearch 的数据。 它不仅美丽,而且强大。
在本教程中,我将向您展示如何在 CentOS 7 服务器上安装和配置 Elastic Stack 以监视服务器日志。 然后,我将向您展示如何在操作系统为 CentOS 7 和 Ubuntu 16 的客户端上安装 “Elastic beats”。

**前提条件**
* 64 位的 CentOS 7,4 GB 内存 - elk 主控机
* 64 位的 CentOS 7 ,1 GB 内存 - 客户端 1
* 64 位的 Ubuntu 16 ,1 GB 内存 - 客户端 2
### 步骤 1 - 准备操作系统
在本教程中,我们将禁用 CentOS 7 服务器上的 SELinux。 编辑 SELinux 配置文件。
```
vim /etc/sysconfig/selinux
```
将 `SELINUX` 的值从 `enforcing` 改成 `disabled` 。
```
SELINUX=disabled
```
然后重启服务器:
```
reboot
```
再次登录服务器并检查 SELinux 状态。
```
getenforce
```
确保结果是 `disabled`。
### 步骤 2 - 安装 Java
部署 Elastic stack 依赖于Java,Elasticsearch 需要 Java 8 版本,推荐使用 Oracle JDK 1.8 。我将从官方的 Oracle rpm 包安装 Java 8。
使用 `wget` 命令下载 Java 8 的 JDK。
```
wget --no-cookies --no-check-certificate --header "Cookie: gpw_e24=http:%2F%2Fwww.oracle.com%2F; oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie" "http://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/8u77-b02/jdk-8u77-linux-x64.rpm"
```
然后使用 `rpm` 命令安装:
```
rpm -ivh jdk-8u77-linux-x64.rpm
```
最后,检查 java JDK 版本,确保它正常工作。
```
java -version
```
您将看到服务器的 Java 版本。
### 步骤 3 - 安装和配置 Elasticsearch
在此步骤中,我们将安装和配置 Elasticsearch。 从 elastic.co 网站提供的 rpm 包安装 Elasticsearch,并将其配置运行在 localhost 上(以确保该程序安全,而且不能从外部访问)。
在安装 Elasticsearch 之前,将 elastic.co 的密钥添加到服务器。
```
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
```
接下来,使用 `wget` 下载 Elasticsearch 5.1,然后安装它。
```
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.1.1.rpm
rpm -ivh elasticsearch-5.1.1.rpm
```
Elasticsearch 已经安装好了。 现在进入配置目录编辑 `elasticsaerch.yml` 配置文件。
```
cd /etc/elasticsearch/
vim elasticsearch.yml
```
去掉第 40 行的注释,启用 Elasticsearch 的内存锁。这将禁用 Elasticsearch 的内存交换。
```
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
```
在 `Network` 块中,取消注释 `network.host` 和 `http.port` 行。
```
network.host: localhost
http.port: 9200
```
保存文件并退出编辑器。
现在编辑 `elasticsearch.service` 文件的内存锁配置。
```
vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service
```
去掉第 60 行的注释,确保该值为 `unlimited`。
```
MAX_LOCKED_MEMORY=unlimited
```
保存并退出。
Elasticsearch 配置到此结束。Elasticsearch 将在本机的 9200 端口运行,我们通过在 CentOS 服务器上启用 `mlockall` 来禁用内存交换。重新加载 systemd,将 Elasticsearch 置为开机启动,然后启动服务。
```
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch
```
等待 Eelasticsearch 启动成功,然后检查服务器上打开的端口,确保 9200 端口的状态是 `LISTEN`。
```
netstat -plntu
```

然后检查内存锁以确保启用 `mlockall`,并使用以下命令检查 Elasticsearch 是否正在运行。
```
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/_nodes?filter_path=**.mlockall&pretty'
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/?pretty'
```
会看到如下结果。

### 步骤 4 - 安装和配置 Kibana 和 Nginx
在这一步,我们将在 Nginx Web 服务器上安装并配置 Kibana。 Kibana 监听在 localhost 上,而 Nginx 作为 Kibana 的反向代理。
用 `wget` 下载 Kibana 5.1,然后使用 `rpm` 命令安装:
```
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh kibana-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
```
编辑 Kibana 配置文件。
```
vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
```
去掉配置文件中 `server.port`、`server.host` 和 `elasticsearch.url` 这三行的注释。
```
server.port: 5601
server.host: "localhost"
elasticsearch.url: "http://localhost:9200"
```
保存并退出。
将 Kibana 设为开机启动,并且启动 Kibana 。
```
sudo systemctl enable kibana
sudo systemctl start kibana
```
Kibana 将作为 node 应用程序运行在端口 5601 上。
```
netstat -plntu
```

Kibana 安装到此结束。 现在我们需要安装 Nginx 并将其配置为反向代理,以便能够从公共 IP 地址访问 Kibana。
Nginx 在 Epel 资源库中可以找到,用 `yum` 安装 epel-release。
```
yum -y install epel-release
```
然后安装 Nginx 和 httpd-tools 这两个包。
```
yum -y install nginx httpd-tools
```
httpd-tools 软件包包含 Web 服务器的工具,可以为 Kibana 添加 htpasswd 基础认证。
编辑 Nginx 配置文件并删除 `server {}` 块,这样我们可以添加一个新的虚拟主机配置。
```
cd /etc/nginx/
vim nginx.conf
```
删除 `server { }` 块。

保存并退出。
现在我们需要在 `conf.d` 目录中创建一个新的虚拟主机配置文件。 用 `vim` 创建新文件 `kibana.conf`。
```
vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/kibana.conf
```
复制下面的配置。
```
server {
listen 80;
server_name elk-stack.co;
auth_basic "Restricted Access";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.kibana-user;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5601;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}
```
保存并退出。
然后使用 `htpasswd` 命令创建一个新的基本认证文件。
```
sudo htpasswd -c /etc/nginx/.kibana-user admin
“输入你的密码”
```
测试 Nginx 配置,确保没有错误。 然后设定 Nginx 开机启动并启动 Nginx。
```
nginx -t
systemctl enable nginx
systemctl start nginx
```

### 步骤 5 - 安装和配置 Logstash
在此步骤中,我们将安装 Logstash,并将其配置为:从配置了 filebeat 的 logstash 客户端里集中化服务器的日志,然后过滤和转换 Syslog 数据,并将其移动到存储中心(Elasticsearch)中。
下载 Logstash 并使用 rpm 进行安装。
```
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-5.1.1.rpm
rpm -ivh logstash-5.1.1.rpm
```
生成新的 SSL 证书文件,以便客户端可以识别 elastic 服务端。
进入 `tls` 目录并编辑 `openssl.cnf` 文件。
```
cd /etc/pki/tls
vim openssl.cnf
```
在 `[v3_ca]` 部分添加服务器标识。
```
[ v3_ca ]
# Server IP Address
subjectAltName = IP: 10.0.15.10
```
保存并退出。
使用 `openssl` 命令生成证书文件。
```
openssl req -config /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf -x509 -days 3650 -batch -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/pki/tls/private/logstash-forwarder.key -out /etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt
```
证书文件可以在 `/etc/pki/tls/certs/` 和 `/etc/pki/tls/private/` 目录中找到。
接下来,我们会为 Logstash 创建新的配置文件。创建一个新的 `filebeat-input.conf` 文件来为 filebeat 配置日志源,然后创建一个 `syslog-filter.conf` 配置文件来处理 syslog,再创建一个 `output-elasticsearch.conf` 文件来定义输出日志数据到 Elasticsearch。
转到 logstash 配置目录,并在 `conf.d` 子目录中创建新的配置文件。
```
cd /etc/logstash/
vim conf.d/filebeat-input.conf
```
输入配置,粘贴以下配置:
```
input {
beats {
port => 5443
ssl => true
ssl_certificate => "/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"
ssl_key => "/etc/pki/tls/private/logstash-forwarder.key"
}
}
```
保存并退出。
创建 `syslog-filter.conf` 文件。
```
vim conf.d/syslog-filter.conf
```
粘贴以下配置:
```
filter {
if [type] == "syslog" {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{SYSLOGTIMESTAMP:syslog_timestamp} %{SYSLOGHOST:syslog_hostname} %{DATA:syslog_program}(?:\[%{POSINT:syslog_pid}\])?: %{GREEDYDATA:syslog_message}" }
add_field => [ "received_at", "%{@timestamp}" ]
add_field => [ "received_from", "%{host}" ]
}
date {
match => [ "syslog_timestamp", "MMM d HH:mm:ss", "MMM dd HH:mm:ss" ]
}
}
}
```
我们使用名为 `grok` 的过滤器插件来解析 syslog 文件。
保存并退出。
创建输出配置文件 `output-elasticsearch.conf`。
```
vim conf.d/output-elasticsearch.conf
```
粘贴以下配置:
```
output {
elasticsearch { hosts => ["localhost:9200"]
hosts => "localhost:9200"
manage_template => false
index => "%{[@metadata][beat]}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
document_type => "%{[@metadata][type]}"
}
}
```
保存并退出。
最后,将 logstash 设定为开机启动并且启动服务。
```
sudo systemctl enable logstash
sudo systemctl start logstash
```

### 步骤 6 - 在 CentOS 客户端上安装并配置 Filebeat
Beat 作为数据发送人的角色,是一种可以安装在客户端节点上的轻量级代理,将大量数据从客户机发送到 Logstash 或 Elasticsearch 服务器。有 4 种 beat,`Filebeat` 用于发送“日志文件”,`Metricbeat` 用于发送“指标”,`Packetbeat` 用于发送“网络数据”,`Winlogbeat` 用于发送 Windows 客户端的“事件日志”。
在本教程中,我将向您展示如何安装和配置 `Filebeat`,通过 SSL 连接将数据日志文件传输到 Logstash 服务器。
登录到客户端1的服务器上。 然后将证书文件从 elastic 服务器复制到客户端1的服务器上。
```
ssh root@client1IP
```
使用 `scp` 命令拷贝证书文件。
```
scp root@elk-serverIP:~/logstash-forwarder.crt .
输入 elk-server 的密码
```
创建一个新的目录,将证书移动到这个目录中。
```
sudo mkdir -p /etc/pki/tls/certs/
mv ~/logstash-forwarder.crt /etc/pki/tls/certs/
```
接下来,在客户端 1 服务器上导入 elastic 密钥。
```
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
```
下载 Filebeat 并且用 `rpm` 命令安装。
```
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh filebeat-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
```
Filebeat 已经安装好了,请转到配置目录并编辑 `filebeat.yml` 文件。
```
cd /etc/filebeat/
vim filebeat.yml
```
在第 21 行的路径部分,添加新的日志文件。 我们将创建两个文件,记录 ssh 活动的 `/var/log/secure` 文件 ,以及服务器日志 `/var/log/messages` 。
```
paths:
- /var/log/secure
- /var/log/messages
```
在第 26 行添加一个新配置来定义 syslog 类型的文件。
```
document-type: syslog
```
Filebeat 默认使用 Elasticsearch 作为输出目标。 在本教程中,我们将其更改为 Logshtash。 在 83 行和 85 行添加注释来禁用 Elasticsearch 输出。
禁用 Elasticsearch 输出:
```
#-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
#output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
# hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
```
现在添加新的 logstash 输出配置。 去掉 logstash 输出配置的注释,并将所有值更改为下面配置中的值。
```
output.logstash:
# The Logstash hosts
hosts: ["10.0.15.10:5443"]
bulk_max_size: 1024
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"]
template.name: "filebeat"
template.path: "filebeat.template.json"
template.overwrite: false
```
保存文件并退出 vim。
将 Filebeat 设定为开机启动并启动。
```
sudo systemctl enable filebeat
sudo systemctl start filebeat
```
### 步骤 7 - 在 Ubuntu 客户端上安装并配置 Filebeat
使用 `ssh` 连接到服务器。
```
ssh root@ubuntu-clientIP
```
使用 `scp` 命令拷贝证书文件。
```
scp root@elk-serverIP:~/logstash-forwarder.crt .
```
创建一个新的目录,将证书移动到这个目录中。
```
sudo mkdir -p /etc/pki/tls/certs/
mv ~/logstash-forwarder.crt /etc/pki/tls/certs/
```
在服务器上导入 elastic 密钥。
```
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
```
下载 Filebeat .deb 包并且使用 `dpkg` 命令进行安装。
```
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-5.1.1-amd64.deb
dpkg -i filebeat-5.1.1-amd64.deb
```
转到配置目录并编辑 `filebeat.yml` 文件。
```
cd /etc/filebeat/
vim filebeat.yml
```
在路径配置部分添加新的日志文件路径。
```
paths:
- /var/log/auth.log
- /var/log/syslog
```
设定文档类型为 `syslog` 。
```
document-type: syslog
```
将下列几行注释掉,禁用输出到 Elasticsearch。
```
#-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
#output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
# hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
```
启用 logstash 输出,去掉以下配置的注释并且按照如下所示更改值。
```
output.logstash:
# The Logstash hosts
hosts: ["10.0.15.10:5443"]
bulk_max_size: 1024
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"]
template.name: "filebeat"
template.path: "filebeat.template.json"
template.overwrite: false
```
保存并退出 vim。
将 Filebeat 设定为开机启动并启动。
```
sudo systemctl enable filebeat
sudo systemctl start filebeat
```
检查服务状态:
```
systemctl status filebeat
```

### 步骤 8 - 测试
打开您的网络浏览器,并访问您在 Nginx 中配置的 elastic stack 域名,我的是“elk-stack.co”。 使用管理员密码登录,然后按 Enter 键登录 Kibana 仪表盘。

创建一个新的默认索引 `filebeat-*`,然后点击“创建”按钮。

默认索引已创建。 如果 elastic stack 上有多个 beat,您可以在“星形”按钮上点击一下即可配置默认 beat。

转到 “发现” 菜单,您就可以看到 elk-client1 和 elk-client2 服务器上的所有日志文件。

来自 elk-client1 服务器日志中的无效 ssh 登录的 JSON 输出示例。

使用其他的选项,你可以使用 Kibana 仪表盘做更多的事情。
Elastic Stack 已安装在 CentOS 7 服务器上。 Filebeat 已安装在 CentOS 7 和 Ubuntu 客户端上。
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/>
作者:[Muhammad Arul](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/) 译者:[Flowsnow](https://github.com/Flowsnow) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # How to Install Elastic Stack on CentOS 7
### This tutorial exists for these OS versions
[CentOS 8](/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-8/)**CentOS 7**
### On this page
[Step 1 - Prepare the Operating System](#step-nbspprepare-the-operating-system)[Step 2 - Install Java](#step-install-java)[Step 3 - Install and Configure Elasticsearch](#step-install-and-configure-elasticsearch)[Step 4 - Install and Configure Kibana with Nginx](#step-install-and-configure-kibana-with-nginx)[Step 5 - Install and Configure Logstash](#step-install-and-configure-logstash)[Step 6 - Install and Configure Filebeat on the CentOS Client](#step-install-and-configure-filebeat-on-the-centos-client)[Step 7 - Install and Configure Filebeat on the Ubuntu Client](#step-install-and-configure-filebeat-on-the-ubuntu-client)[Step 8 - Testing Elastic Stack](#step-testing-elastic-stack)[Reference](#reference)
**Elasticsearch** is an open source search engine based on Lucene, developed in Java. It provides a distributed and multitenant full-text search engine with an HTTP Dashboard web-interface (Kibana). The data is queried, retrieved and stored with a JSON document scheme. Elasticsearch is a scalable search engine that can be used to search for all kind of text documents, including log files. Elasticsearch is the heart of the 'Elastic Stack' or ELK Stack.
**Logstash** is an open source tool for managing events and logs. It provides real-time pipelining for data collections. Logstash will collect your log data, convert the data into JSON documents, and store them in Elasticsearch.
**Kibana** is an open source data visualization tool for Elasticsearch. Kibana provides a pretty dashboard web interface. It allows you to manage and visualize data from Elasticsearch. It's not just beautiful, but also powerful.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install and configure Elastic Stack on a CentOS 7 server for monitoring server logs. Then I'll show you how to install 'Elastic beats' on a CentOS 7 and an Ubuntu 16.04 client operating system.
**Prerequisites**
- CentOS 7 64 bit with 4GB of RAM - elk-master
- CentOS 7 64 bit with 1 GB of RAM - client1
- Ubuntu 16.04 64 bit with 1GB of RAM - client2
## Step 1 - Prepare the Operating System
In this tutorial, we will disable SELinux on the CentOS 7 server. Edit the SELinux configuration file.
vim /etc/sysconfig/selinux
Change SELinux value from enforcing to disabled.
SELINUX=disabled
Then reboot the server.
reboot
Log in to the server again and check the SELinux state.
getenforce
Make sure the result is disabled.
## Step 2 - Install Java
Java is required for the Elastic stack deployment. Elasticsearch requires Java 8, it is recommended to use the Oracle JDK 1.8. I will install Java 8 from the official Oracle rpm package.
Download Java 8 JDK with the wget command.
wget --no-cookies --no-check-certificate --header "Cookie: gpw_e24=http:%2F%2Fwww.oracle.com%2F; oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie" "http://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/8u77-b02/jdk-8u77-linux-x64.rpm"
Then install it with this rpm command;
rpm -ivh jdk-8u77-linux-x64.rpm
Finally, check java JDK version to ensure that it is working properly.
java -version
You will see Java version of the server.
## Step 3 - Install and Configure Elasticsearch
In this step, we will install and configure Elasticsearch. I will install Elasticsearch from an rpm package provided by elastic.co and configure it to run on localhost (to make the setup secure and ensure that it is not reachable from the outside).
Before installing Elasticsearch, add the elastic.co key to the server.
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
Next, download Elasticsearch 5.1 with wget and then install it.
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.1.1.rpm
rpm -ivh elasticsearch-5.1.1.rpm
Elasticsearch is installed. Now go to the configuration directory and edit the elasticsaerch.yml configuration file.
cd /etc/elasticsearch/
vim elasticsearch.yml
Enable memory lock for Elasticsearch by removing a comment on line 40. This disables memory swapping for Elasticsearch.
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
In the 'Network' block, uncomment the network.host and http.port lines.
network.host: localhost
http.port: 9200
Save the file and exit the editor.
Now edit the elasticsearch.service file for the memory lock configuration.
vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service
Uncomment LimitMEMLOCK line.
LimitMEMLOCK=infinity
Save and exit.
Edit the sysconfig configuration file for Elasticsearch.
vim /etc/sysconfig/elasticsearch
Uncomment line 60 and make sure the value is 'unlimited'.
MAX_LOCKED_MEMORY=unlimited
Save and exit.
The Elasticsearch configuration is finished. Elasticsearch will run on the localhost IP address on port 9200, we disabled memory swapping for it by enabling mlockall on the CentOS server.
Reload systemd, enable Elasticsearch to start at boot time, then start the service.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch
Wait a second for Eelasticsearch to start, then check the open ports on the server, make sure 'state' for port 9200 is 'LISTEN'.
netstat -plntu
Then check the memory lock to ensure that mlockall is enabled, and check that Elasticsearch is running with the commands below.
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/_nodes?filter_path=**.mlockall&pretty'
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/?pretty'
You will see the results below.
## Step 4 - Install and Configure Kibana with Nginx
In this step, we will install and configure Kibana with a Nginx web server. Kibana will listen on the localhost IP address and Nginx acts as a reverse proxy for the Kibana application.
Download Kibana 5.1 with wget, then install it with the rpm command:
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh kibana-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
Now edit the Kibana configuration file.
vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
Uncomment the configuration lines for server.port, server.host and elasticsearch.url.
server.port: 5601
server.host: "localhost"
elasticsearch.url: "http://localhost:9200"
Save and exit.
Add Kibana to run at boot and start it.
sudo systemctl enable kibana
sudo systemctl start kibana
Kibana will run on port 5601 as node application.
netstat -plntu
The Kibana installation is finished. Now we need to install Nginx and configure it as reverse proxy to be able to access Kibana from the public IP address.
Nginx is available in the Epel repository, install epel-release with yum.
yum -y install epel-release
Next, install the Nginx and httpd-tools package.
yum -y install nginx httpd-tools
The httpd-tools package contains tools for the web server, we will use htpasswd basic authentication for Kibana.
Edit the Nginx configuration file and remove the **'server { }**' block, so we can add a new virtual host configuration.
cd /etc/nginx/
vim nginx.conf
Remove the server { } block.
Save the file and exit vim.
Now we need to create a new virtual host configuration file in the conf.d directory. Create the new file 'kibana.conf' with vim.
vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/kibana.conf
Paste the configuration below.
server {
listen 80;
server_name elk-stack.co;
auth_basic "Restricted Access";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.kibana-user;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5601;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}
Save and exit.
Then create a new basic authentication file with the htpasswd command.
sudo htpasswd -c /etc/nginx/.kibana-user admin
TYPE YOUR PASSWORD
Test the Nginx configuration and make sure there is no error. Then add Nginx to run at the boot time and start Nginx.
nginx -t
systemctl enable nginx
systemctl start nginx
## Step 5 - Install and Configure Logstash
In this step, we will install Logsatash and configure it to centralize server logs from clients with filebeat, then filter and transform the Syslog data and move it into the stash (Elasticsearch).
Download Logstash and install it with rpm.
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-5.1.1.rpm
rpm -ivh logstash-5.1.1.rpm
Generate a new SSL certificate file so that the client can identify the elastic server.
Go to the tls directory and edit the openssl.cnf file.
cd /etc/pki/tls
vim openssl.cnf
Add a new line in the '[ v3_ca ]' section for the server identification.
[ v3_ca ]
# Server IP Address
subjectAltName = IP: 10.0.15.10
Save and exit.
Generate the certificate file with the openssl command.
openssl req -config /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf -x509 -days 3650 -batch -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/pki/tls/private/logstash-forwarder.key -out /etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt
The certificate files can be found in the '/etc/pki/tls/certs/' and '/etc/pki/tls/private/' directories.
Next, we will create new configuration files for Logstash. We will create a new 'filebeat-input.conf' file to configure the log sources for filebeat, then a 'syslog-filter.conf' file for syslog processing and the 'output-elasticsearch.conf' file to define the Elasticsearch output.
Go to the logstash configuration directory and create the new configuration files in the 'conf.d' subdirectory.
cd /etc/logstash/
vim conf.d/filebeat-input.conf
Input configuration: paste the configuration below.
input {
beats {
port => 5443
ssl => true
ssl_certificate => "/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"
ssl_key => "/etc/pki/tls/private/logstash-forwarder.key"
}
}
Save and exit.
Create the syslog-filter.conf file.
vim conf.d/syslog-filter.conf
Paste the configuration below.
filter {
if [type] == "syslog" {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{SYSLOGTIMESTAMP:syslog_timestamp} %{SYSLOGHOST:syslog_hostname} %{DATA:syslog_program}(?:\[%{POSINT:syslog_pid}\])?: %{GREEDYDATA:syslog_message}" }
add_field => [ "received_at", "%{@timestamp}" ]
add_field => [ "received_from", "%{host}" ]
}
date {
match => [ "syslog_timestamp", "MMM d HH:mm:ss", "MMM dd HH:mm:ss" ]
}
}
}
We use a filter plugin named '**grok**' to parse the syslog files.
Save and exit.
Create the output configuration file 'output-elasticsearch.conf'.
vim conf.d/output-elasticsearch.conf
Paste the configuration below.
output {
elasticsearch { hosts => ["localhost:9200"]
hosts => "localhost:9200"
manage_template => false
index => "%{[@metadata][beat]}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
document_type => "%{[@metadata][type]}"
}
}
Save and exit.
Finally add logstash to start at boot time and start the service.
sudo systemctl enable logstash
sudo systemctl start logstash
## Step 6 - Install and Configure Filebeat on the CentOS Client
Beats are data shippers, lightweight agents that can be installed on the client nodes to send huge amounts of data from the client machine to the Logstash or Elasticsearch server. There are 4 beats available, 'Filebeat' for 'Log Files', 'Metricbeat' for 'Metrics', 'Packetbeat' for 'Network Data' and 'Winlogbeat' for the Windows client 'Event Log'.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install and configure 'Filebeat' to transfer data log files to the Logstash server over an SSL connection.
Login to the client1 server. Then copy the certificate file from the elastic server to the client1 server.
ssh root@client1IP
Copy the certificate file with the scp command.
scp root@elk-serverIP:~/logstash-forwarder.crt .
TYPE elk-server password
Create a new directory and move certificate file to that directory.
sudo mkdir -p /etc/pki/tls/certs/
mv ~/logstash-forwarder.crt /etc/pki/tls/certs/
Next, import the elastic key on the client1 server.
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
Download Filebeat and install it with rpm.
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh filebeat-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
Filebeat has been installed, go to the configuration directory and edit the file 'filebeat.yml'.
cd /etc/filebeat/
vim filebeat.yml
In the paths section on line 21, add the new log files. We will add two files '/var/log/secure' for ssh activity and '/var/log/messages' for the server log.
paths:
- /var/log/secure
- /var/log/messages
Add a new configuration on line 26 to define the syslog type files.
document-type: syslog
Filebeat is using Elasticsearch as the output target by default. In this tutorial, we will change it to Logshtash. Disable Elasticsearch output by adding comments on the lines 83 and 85.
Disable elasticsearch output.
#-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
#output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
# hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
Now add the new logstash output configuration. Uncomment the logstash output configuration and change all value to the configuration that is shown below.
output.logstash:
# The Logstash hosts
hosts: ["10.0.15.10:5443"]
bulk_max_size: 1024
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"]
template.name: "filebeat"
template.path: "filebeat.template.json"
template.overwrite: false
Save the file and exit vim.
Add Filebeat to start at boot time and start it.
sudo systemctl enable filebeat
sudo systemctl start filebeat
## Step 7 - Install and Configure Filebeat on the Ubuntu Client
Connect to the server by ssh.
ssh root@ubuntu-clientIP
Copy the certificate file to the client with the scp command.
scp root@elk-serverIP:~/logstash-forwarder.crt .
Create a new directory for the certificate file and move the file to that directory.
sudo mkdir -p /etc/pki/tls/certs/
mv ~/logstash-forwarder.crt /etc/pki/tls/certs/
Add the elastic key to the server.
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
Download the Filebeat .deb package and install it with the dpkg command.
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-5.1.1-amd64.deb
dpkg -i filebeat-5.1.1-amd64.deb
Go to the filebeat configuration directory and edit the file 'filebeat.yml' with vim.
cd /etc/filebeat/
vim filebeat.yml
Add the new log file paths in the paths configuration section.
paths:
- /var/log/auth.log
- /var/log/syslog
Set the document type to syslog.
document-type: syslog
Disable elasticsearch output by adding comments to the lines shown below.
#-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
#output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
# hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
Enable logstash output, uncomment the configuration and change the values as shown below.
output.logstash:
# The Logstash hosts
hosts: ["10.0.15.10:5443"]
bulk_max_size: 1024
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"]
template.name: "filebeat"
template.path: "filebeat.template.json"
template.overwrite: false
Save the file and exit vim.
Add Filebeat to start at boot time and start it.
sudo systemctl enable filebeat
sudo systemctl start filebeat
Check the service status.
systemctl status filebeat
## Step 8 - Testing Elastic Stack
Open your web browser and visit the elastic stack domain that you used in the Nginx configuration, mine is 'elk-stack.co'. Login as admin user with your password and press Enter to log in to the Kibana dashboard.
Create a new default index 'filebeat-*' and click on the 'Create' button.
Th default index has been created. If you have multiple beats on the elastic stack, you can configure the default beat with just one click on the 'star' button.
Go to the '**Discover**' menu and you will see all the log file from the elk-client1 and elk-client2 servers.
An example of JSON output from the elk-client1 server log for an invalid ssh login.
And there is much more than you can do with Kibana dashboard, just play around with the available options.
Elastic Stack has been installed on a CentOS 7 server. Filebeat has been installed on a CentOS 7 and an Ubuntu client. |
8,462 | pyDash:一个基于 web 的 Linux 性能监测工具 | http://www.tecmint.com/pydash-a-web-based-linux-performance-monitoring-tool/ | 2017-04-30T07:09:00 | [
"pyDash",
"性能",
"监控"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8462-1.html | `pyDash` 是一个轻量且[基于 web 的 Linux 性能监测工具](http://www.tecmint.com/command-line-tools-to-monitor-linux-performance/),它是用 Python 和 [Django](http://www.tecmint.com/install-and-configure-django-web-framework-in-centos-debian-ubuntu/) 加上 Chart.js 来写的。经测试,在下面这些主流 Linux 发行版上可运行:CentOS、Fedora、Ubuntu、Debian、Raspbian 以及 Pidora 。

你可以使用这个工具来监视你的 Linux 个人电脑/服务器资源,比如 CPU、内存、网络统计,包括在线用户的进程以及更多。仪表盘完全由主要的 Python 发行版本所提供的 Python 库开发,因此它的依赖关系很少,你不需要安装许多包或库来运行它。
在这篇文章中,我将展示如何安装 `pyDash` 来监测 Linux 服务器性能。
### 如何在 Linux 系统下安装 pyDash
1、首先,像下面这样安装需要的软件包 `git` 和 `Python pip`:
```
-------------- 在 Debian/Ubuntu 上 --------------
$ sudo apt-get install git python-pip
-------------- 在 CentOS/RHEL 上 --------------
# yum install epel-release
# yum install git python-pip
-------------- 在 Fedora 22+ 上 --------------
# dnf install git python-pip
```
2、如果安装好了 git 和 Python pip,那么接下来,像下面这样安装 `virtualenv`,它有助于处理针对 Python 项目的依赖关系:
```
# pip install virtualenv
或
$ sudo pip install virtualenv
```
3、现在,像下面这样使用 `git` 命令,把 pyDash 仓库克隆到 home 目录中:
```
# git clone https://github.com/k3oni/pydash.git
# cd pydash
```
4、下一步,使用下面的 `virtualenv` 命令为项目创建一个叫做 `pydashtest` 虚拟环境:
```
$ virtualenv pydashtest #give a name for your virtual environment like pydashtest
```

*创建虚拟环境*
重要:请注意,上面的屏幕截图中,虚拟环境的 `bin` 目录被高亮显示,你的可能和这不一样,取决于你把 pyDash 目录克隆到什么位置。
5、创建好虚拟环境(`pydashtest`)以后,你需要在使用前像下面这样激活它:
```
$ source /home/aaronkilik/pydash/pydashtest/bin/activate
```

*激活虚拟环境*
从上面的屏幕截图中,你可以注意到,提示字符串 1(`PS1`)已经发生改变,这表明虚拟环境已经被激活,而且可以开始使用。
6、现在,安装 pydash 项目 requirements;如何你好奇的话,可以使用 [cat 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/)查看 `requirements.txt` 的内容,然后像下面所示那样进行安装:
```
$ cat requirements.txt
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
```
7、现在,进入 `pydash` 目录,里面包含一个名为 `settings.py` 的文件,也可直接运行下面的命令打开这个文件,然后把 `SECRET_KEY` 改为一个特定值:
```
$ vi pydash/settings.py
```

*设置密匙*
保存文件然后退出。
8、之后,运行下面的命令来创建一个项目数据库和安装 Django 的身份验证系统,并创建一个项目的超级用户:
```
$ python manage.py syncdb
```
根据你的情况回答下面的问题:
```
Would you like to create one now? (yes/no): yes
Username (leave blank to use 'root'): admin
Email address: [email protected]
Password: ###########
Password (again): ############
```

*创建项目数据库*
9、这个时候,一切都设置好了,然后,运行下面的命令来启用 Django 开发服务器:
```
$ python manage.py runserver
```
10、接下来,打开你的 web 浏览器,输入网址:`http://127.0.0.1:8000/` 进入 web 控制台登录界面,输入你在第 8 步中创建数据库和安装 Django 身份验证系统时创建的超级用户名和密码,然后点击登录。

*pyDash 登录界面*
11、登录到 pydash 主页面以后,你将会可以看到监测系统的基本信息,包括 CPU、内存和硬盘使用量以及系统平均负载。
向下滚动便可查看更多部分的信息。

*pydash 服务器性能概述*
12、下一个屏幕截图显示的是一段 pydash 的跟踪界面,包括 IP 地址、互联网流量、硬盘读/写、在线用户以及 netstats 。

*pyDash 网络概述*
13、下一个 pydash 主页面的截图显示了一部分系统中被监视的活跃进程。

*pyDash 监视活跃 Linux 进程*
如果想了解更多信息,请在 GitHub 上查看 pydash:<https://github.com/k3oni/pydash>
这就是全部内容了。在这篇文章中,我们展示了在 Linux 中如何安装 pyDash 并测试它的主要特性。如果你有什么想法,可以通过下面的反馈部分联系我们;如果你知道任何有用或类似的工具,也可以在评论中告知我们。
---
作者简介:
我叫 Ravi Saive,是 TecMint 的原创作者,是一个喜欢在网上分享技巧和知识的计算机极客和 Linux Guru。我的大多数服务器都运行在 Linux 开源平台上。请关注我:[Twitter](http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/pyDash-Network-Overview.png)、[Facebook](https://www.facebook.com/ravi.saive) 以及 [Google+](https://plus.google.com/u/0/+RaviSaive) 。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/pydash-a-web-based-linux-performance-monitoring-tool/>
作者:[Ravi Saive](http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,463 | 史上最全的使用 gnome-screenshot 获取屏幕快照指南 | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/taking-screenshots-in-linux-using-gnome-screenshot/ | 2017-04-30T07:36:00 | [
"截屏",
"gnome-screenshot"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8463-1.html | 在应用市场中有好几种屏幕截图工具,但其中大多数都是基于 GUI 的。如果你经常在 linux 命令行上工作,而且正在寻找一款优秀的功能丰富的基于命令行的屏幕截图工具,你可能会想尝试 [gnome-screenshot](https://linux.die.net/man/1/gnome-screenshot)。在本教程中,我将使用易于理解的例子来解释这个实用程序。

请注意,本教程中提到的所有例子已经在 Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 上测试过,测试所使用的 gonme-screenshot 版本是 3.18.0。
### 关于 Gnome-screenshot
Gnome-screenshot 是一款 GNOME 工具,顾名思义,它是一款用来对整个屏幕、一个特定的窗口或者用户所定义一些其他区域进行捕获的工具。该工具提供了几个其他的功能,包括对所捕获的截图的边界进行美化的功能。
### Gnome-screenshot 安装
Ubuntu 系统上已经预安装了 gnome-screeshot 工具,但是如果你出于某些原因需要重新安装这款软件程序,你可以使用下面的命令来进行安装:
```
sudo apt-get install gnome-screeshot
```
一旦软件安装完成后,你可以使用下面的命令来启动它:
```
gnome-screenshot
```
### Gnome-screenshot 用法/特点
在这部分,我们将讨论如何使用 gnome-screenshot ,以及它提供的所有功能。
默认情况下,使用该工具且不带任何命令行选项时,就会抓取整个屏幕。

#### 捕获当前活动窗口
如何你需要的话,你可以使用 `-w` 选项限制到只对当前活动窗口截图。
```
gnome-screenshot -w
```

#### 窗口边框
默认情况下,这个程序会将它捕获的窗口的边框包含在内,尽管还有一个明确的命令行选项 `-b` 可以启用此功能(以防你在某处想使用它)。以下是如何使用这个程序的:
```
gnome-screenshot -wb
```
当然,你需要同时使用 `-w` 选项和 `-b` 选项,以便捕获的是当前活动的窗口(否则,`-b` 将没有作用)。
更重要的是,如果你需要的话,你也可以移除窗口的边框。可以使用 `-B` 选项来完成。下面是你可以如何使用这个选项的一个例子:
```
gnome-screenshot -wB
```
下面是例子的截图:

#### 添加效果到窗口边框
在 gnome-screenshot 工具的帮助下,您还可以向窗口边框添加各种效果。这可以使用 `--border-effect` 选项来做到。
你可以添加这款程序所提供的任何效果,比如 `shadow` 效果(在窗口添加阴影)、`bordor` 效果(在屏幕截图周围添加矩形区域)和 `vintage` 效果(使截图略微淡化,着色并在其周围添加矩形区域)。
```
gnome-screenshot --border-effect=[EFFECT]
```
例如,运行下面的命令添加 shadow 效果:
```
gnome-screenshot –border-effect=shadow
```
以下是 shadow 效果的示例快照:

请注意,上述屏幕截图主要集中在终端的一个角落,以便您清楚地看到阴影效果。
#### 对特定区域的截图
如何你需要,你还可以使用 gnome-screenshot 程序对你电脑屏幕的某一特定区域进行截图。这可以通过使用 `-a` 选项来完成。
```
gnome-screenshot -a
```
当上面的命令被运行后,你的鼠标指针将会变成 '+' 这个符号。在这种模式下,你可以按住鼠标左键移动鼠标来对某个特定区域截图。
这是一个示例截图,裁剪了我的终端窗口的一小部分。

#### 在截图中包含鼠标指针
默认情况下,每当你使用这个工具截图的时候,截的图中并不会包含鼠标指针。然而,这个程序是可以让你把指针包括进去的,你可以使用 `-p` 命令行选项做到。
```
gnome-screenshot -p
```
这是一个示例截图:

#### 延时截图
截图时你还可以引入时间延迟。要做到这,你不需要给 `--delay` 选项赋予一个以秒为单位的值。
```
gnome-screenshot –delay=[SECONDS]
```
例如:
```
gnome-screenshot --delay=5
```
示例截图如下:

#### 以交互模式运行这个工具
这个工具还允许你使用一个单独的 `-i` 选项来访问其所有功能。使用这个命令行选项,用户可以在运行这个命令时使用这个工具的一个或多个功能。
```
gnome-screenshot -i
```
示例截图如下:

你可以从上面的截图中看到,`-i` 选项提供了对很多功能的访问,比如截取整个屏幕、截取当前窗口、选择一个区域进行截图、延时选项和特效选项等都在交互模式里。
#### 直接保存你的截图
如果你需要的话,你可以直接将你截的图片从终端中保存到你当前的工作目录,这意味着,在这个程序运行后,它并不要求你为截取的图片输入一个文件名。这个功能可以使用 `--file` 命令行选项来获取,很明显,需要给它传递一个文件名。
```
gnome-screenshot –file=[FILENAME]
```
例如:
```
gnome-screenshot --file=ashish
```
示例截图如下:

#### 复制到剪切板
gnome-screenshot 也允许你把你截的图复制到剪切板。这可以通过使用 `-c` 命令行选项做到。
```
gnome-screenshot -c
```

在这个模式下,例如,你可以把复制的图直接粘贴到你的任何一个图片编辑器中(比如 GIMP)。
#### 多显示器情形下的截图
如果有多个显示器连接到你的系统,你想对某一个进行截图,那么你可以使用 `--then` 命令行选项。需要给这个选项一个显示器设备 ID 的值(需要被截图的显示器的 ID)。
```
gnome-screenshot --display=[DISPLAY]
```
例如:
```
gnome-screenshot --display=VGA-0
```
在上面的例子中,VAG-0 是我正试图对其进行截图的显示器的 ID。为了找到你想对其进行截图的显示器的 ID,你可以使用下面的命令:
```
xrandr --query
```
为了让你明白一些,在我的例子中这个命令产生了下面的输出:
```
$ xrandr --query
Screen 0: minimum 320 x 200, current 1366 x 768, maximum 8192 x 8192
VGA-0 connected primary 1366x768+0+0 (normal left inverted right x axis y axis) 344mm x 194mm
1366x768 59.8*+
1024x768 75.1 75.0 60.0
832x624 74.6
800x600 75.0 60.3 56.2
640x480 75.0 60.0
720x400 70.1
HDMI-0 disconnected (normal left inverted right x axis y axis)
```
#### 自动化屏幕截图过程
正如我们之前讨论的,`-a` 命令行选项可以帮助我们对屏幕的某一个特定区域进行截图。然而,我们需要用鼠标手动选取这个区域。如果你想的话,你可以使用 gnome-screenshot 来自动化完成这个过程,但是在那种情形下,你将需要使用一个名为 `xdotol` 的工具,它可以模仿敲打键盘甚至是点击鼠标这些事件。
例如:
```
(gnome-screenshot -a &); sleep 0.1 && xdotool mousemove 100 100 mousedown 1 mousemove 400 400 mouseup 1
```
`mousemove` 子命令自动把鼠标指针定位到明确的 `X` 坐标和 `Y` 坐标的位置(上面例子中是 100 和 100)。`mousedown` 子命令触发一个与点击执行相同操作的事件(因为我们想左击,所以我们使用了参数 1),然而 `mouseup` 子命令触发一个执行用户释放鼠标按钮的任务的事件。
所以总而言之,上面所示的 `xdotool` 命令做了一项本来需要使用鼠标手动执行对同一区域进行截图的工作。特别说明,该命令把鼠标指针定位到屏幕上坐标为 `100,100` 的位置并选择封闭区域,直到指针到达屏幕上坐标为 `400,400` 的位置。所选择的区域随之被 gnome-screenshot 捕获。
这是上述命令的截图:

这是输出的结果:

想获取更多关于 `xdotool` 的信息,[请到这来](http://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/trusty/man1/xdotool.1.html)。
#### 获取帮助
如果你有疑问或者你正面临一个与该命令行的其中某个选项有关的问题,那么你可以使用 --help、-? 或者 -h 选项来获取相关信息。
```
gnome-screenshot -h
```
### 总结
我推荐你至少使用一次这个程序,因为它不仅对初学者来说比较简单,而且还提供功能丰富的高级用法体验。动起手来,尝试一下吧。
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/taking-screenshots-in-linux-using-gnome-screenshot/>
作者:[Himanshu Arora](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/taking-screenshots-in-linux-using-gnome-screenshot/) 译者:[zhousiyu325](https://github.com/zhousiyu325) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # A comprehensive guide to taking screenshots in Linux using gnome-screenshot
### On this page
[About Gnome-screenshot](#about-gnomescreenshot)[Gnome-screenshot Installation](#gnomescreenshot-installation)[Gnome-screenshot Usage/Features](#gnomescreenshot-usagefeatures)[Capturing current active window](#capturing-current-active-window)[Window border](#window-border)[Adding effects to window borders](#adding-effects-to-window-borders)[Screenshot of a particular area](#screenshot-of-a-particular-area)[Include mouse pointer in snapshot](#include-mouse-pointer-in-snapshot)[Delay in taking screenshots](#delay-in-taking-screenshots)[Run the tool in interactive mode](#run-the-tool-in-interactive-mode)[Directly save your screenshot](#directly-save-your-screenshot)[Copy to clipboard](#copy-to-clipboard)[Screenshot in case of multiple displays](#screenshot-in-case-of-multiple-displays)[Automate the screen grabbing process](#automate-the-screen-grabbing-process)[Getting help](#getting-help)
[Conclusion](#conclusion)
There are several screenshot taking tools available in the market but most of them are GUI based. If you spend time working on the Linux command line, and are looking for a good, feature-rich command line-based screen grabbing tool, you may want to try out [gnome-screenshot](https://linux.die.net/man/1/gnome-screenshot). In this tutorial, I will explain this utility using easy to understand examples.
Please note that all the examples mentioned in this tutorial have been tested on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, and the gnome-screenshot version we have used is 3.18.0.
## About Gnome-screenshot
Gnome-screenshot is a GNOME tool which - as the name suggests - is used for capturing the entire screen, a particular application window, or any other user defined area. The tool provides several other features, including the ability to apply beautifying effects to borders of captured screenshots.
## Gnome-screenshot Installation
The gnome-screenshot tool is pre-installed on Ubuntu systems, but if for some reason you need to install the utility, you can do that using the following command:
sudo apt-get install gnome-screenshot
Once the tool is installed, you can launch it by using following command:
gnome-screenshot
## Gnome-screenshot Usage/Features
In this section, we will discuss how the gnome-screenshot tool can be used and what all features it provides.
By default, when the tool is run without any command line options, it captures the complete screen.
### Capturing current active window
If you want, you can limit the screenshot to the current active window by using the *-w* option.
gnome-screenshot -w
Window border
By default, the utility includes the border of the window it captures, although there's also a specific command line option *-b* that enables this feature (in case you want to use it somewhere). Here's how it can be used:
gnome-screenshot -wb
Of course, you need to use the *-w* option with *-b* so that the captured area is the current active window (otherwise, *-b* will have no effect).
Moving on and more importantly, you can also remove the border of the window if you want. This can be done using the *-B* command line option. Following is an example of how you can use this option:
gnome-screenshot -wB
Here is an example snapshot:
### Adding effects to window borders
With the help of the gnome-screenshot tool, you can also add various effects to window borders. This can be done using the *--border-effect* option.
You can add any of the effects provided by the utility such as 'shadow' effect (which adds drop shadow to the window), 'border' effect (adds rectangular space around the screenshot), and 'vintage' effect (desaturating the screenshot slightly, tinting it and adding rectangular space around it).
gnome-screenshot --border-effect=[EFFECT]
For example, to add the shadow effect, run the following command
gnome-screenshot –border-effect=shadow
Here is an example snapshot of the shadow effect:
Please note that the above screenshot focuses on a corner of the terminal to give you a clear view of the shadow effect.
### Screenshot of a particular area
If you want, you can also capture a particular area of your computer screen using the gnome-screenshot utility. This can be done by using the *-a* command line option.
gnome-screenshot -a
When the above command is run, your mouse pointer will change into a ‘+’ sign. In this mode, you can grab a particular area of your screen by moving the mouse with left-click pressed.
Here is an example screenshot wherein I cropped a small area of my terminal window.
Include mouse pointer in snapshot
By default, whenever you take screenshot using this tool, it doesn’t include mouse pointer. However, the utility allows you to include the pointer, something which you can do using the *-p* command line option.
gnome-screenshot -p
Here is an example snapshot
### Delay in taking screenshots
You can also introduce time delay while taking screenshots. For this, you have to assign a value to the *--delay* option in seconds.
gnome-screenshot –delay=[SECONDS]
For example:
gnome-screenshot --delay=5
Here is an example screenshot
### Run the tool in interactive mode
The tool also allows you to access all its features using a single option, which is *-i*. Using this command line option, user can select one or more of the tool’s features at run time.
$ gnome-screenshot -i
Here is an example screenshot
As you can see in the snapshot above, the *-i* option provides access to many features - such as grabbing the whole screen, grabbing the current window, selecting an area to grab, delay option, effects options - all in an interactive mode.
### Directly save your screenshot
If you want, you can directly save your screenshot from the terminal to your present working directory, meaning you won't be asked to enter a file name for the captured screenshot after the tool is run. This feature can be accessed using the *--file* command line option which, obviously, requires a filename to be passed to it.
gnome-screenshot –file=[FILENAME]
For example:
gnome-screenshot --file=ashish
Here is an example snapshot:
### Copy to clipboard
The gnome-screenshot tool also allows you to copy your screenshot to clipboard. This can be done using the *-c* command line option.
gnome-screenshot -c
In this mode, you can, for example, directly paste the copied screenshot in any of your image editors (such as GIMP).
### Screenshot in case of multiple displays
If there are multiple displays attached to your system and you want to take snapshot of a particular one, then you can use the *--display* command line option. This option requires a value which should be the display device ID (ID of the screen being grabbed).
gnome-screenshot --display=[DISPLAY]
For example:
gnome-screenshot --display=VGA-0
In the above example, VGA-0 is the id of the display that I am trying to capture. To find the ID of the display that you want to screenshot, you can use the following command:
`xrandr --query`
To give you an idea, this command produced the following output in my case:
**$ xrandr --query**
Screen 0: minimum 320 x 200, current 1366 x 768, maximum 8192 x 8192
**VGA-0** connected primary 1366x768+0+0 (normal left inverted right x axis y axis) 344mm x 194mm
1366x768 59.8*+
1024x768 75.1 75.0 60.0
832x624 74.6
800x600 75.0 60.3 56.2
640x480 75.0 60.0
720x400 70.1
**HDMI-0** disconnected (normal left inverted right x axis y axis)
### Automate the screen grabbing process
As we have discussed earlier, the *-a* command line option helps us to grab a particular area of the screen. However, we have to select the area manually using the mouse. If you want, you can automate this process using gnome-screenshot, but in that case, you will have to use an external tool known as *xdotool*, which is capable of simulating key presses and even mouse events.
For example:
(gnome-screenshot -a &); sleep 0.1 && xdotool mousemove 100 100 mousedown 1 mousemove 400 400 mouseup 1
The *mousemove* sub-command automatically positions the mouse pointer at specified coordinates X and Y on screen (100 and 100 in the example above). The *mousedown* subcommand fires an event which performs the same operation as a click (since we wanted left-click, so we used the argument 1) , whereas the *mouseup* subcommand fires an event which performs the task of a user releasing the mouse-button.
So all in all, the xdotool command shown above does the same area-grabbing work that you otherwise have to manually do with mouse - specifically, it positions the mouse pointer to 100, 100 coordinates on the screen, selects the area enclosed until the pointer reaches 400,400 coordinates on then screen. The selected area is then captured by gnome-screenshot.
Here, is the screenshot of the above command:
And this is the output:
For more information on xdotool, head [here](http://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/trusty/man1/xdotool.1.html).
### Getting help
If you have a query or in case you are facing a problem related to any of the command line options, then you can use the *--help*, *-?* or *-h* options to get related information.
gnome-screenshot -h
For more information on gnome-screenshot, you can go through the command’s manual page or man page.
man gnome-screenshot
## Conclusion
I will recommend that you to use this utlity atleast once as it's not only easy to use for beginners, but also offers a feature-rich experience for advanced usage. Go ahead and give it a try. |
8,464 | 极客漫画:鸭子爸爸生活中的 Java 集合 | https://turnoff.us/geek/java-collections/ | 2017-05-01T13:23:00 | [
"Java",
"漫画"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8464-1.html | 
随着需求不断的增加,数据管理也将变得越发复杂。
从<ruby> 队列 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> list </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>到<ruby> 集合 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> set </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,甚至用<ruby> 映射 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> map </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>来解决……
迟早有一天,坐在办公桌前的鸭子爸爸发现,这些只不过都是个“<ruby> 堆栈 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> stack </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”而已~
via: <https://turnoff.us/geek/java-collections/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者&点评:[martin2011qi](https://github.com/martin2011qi) 校对&合成:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # java collections in duck life


### Comics Related
-
[halloween](/geek/halloween/) -
[java attacks!](/geek/java-attacks/) -
[java jigsaw rejected](/geek/jigsaw-rejected/) -
[java packaging system](/geek/java-packaging/) -
[life (and death) in the db connection pool](/geek/db-connection-pool/) -
[my (dev) morning routine](/geek/my-morning-routine/) -
[jhamlet](/geek/jhamlet/) -
[java thread life](/geek/java-thread-life/) -
[big numbers](/geek/big-numbers/) -
[java evolution parade](/geek/java-evolution-parade/) -
[java 20 - predictions](/geek/java20-predictions/) -
[do the evolution, baby!](/geek/its-evolution-baby/) -
[when just-in-time is justin time](/geek/lazy-justin-is-late-again/) -
[doing a great job together](/geek/duke-tux/) -
[geek rivalries](/geek/geek-rivalries/) -
[a java nightmare](/geek/a-java-nightmare/) -
[java family crisis](/geek/java-family-crisis/) -
[thread.sleep room](/geek/thread-sleep-room/) -
[web server upgrade training](/geek/webserver-upgrade-training/) -
[life in a web server](/geek/life-in-a-web-server/) -
[java garbage collection explained](/geek/java-gc-explained/) |
8,466 | cpustat:在 Linux 下根据运行的进程监控 CPU 使用率 | http://www.tecmint.com/cpustat-monitors-cpu-utilization-by-processes-in-linux/ | 2017-05-01T21:31:00 | [
"cpustat",
"监控",
"性能"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8466-1.html | cpustat 是 Linux 下一个强大的系统性能测量程序,它用 [Go 编程语言](http://www.tecmint.com/install-go-in-linux/) 编写。它通过使用 “[用于分析任意系统的性能的方法(USE)](http://www.brendangregg.com/usemethod.html)”,以有效的方式显示 CPU 利用率和饱和度。
它高频率对系统中运行的每个进程进行取样,然后以较低的频率汇总这些样本。例如,它能够每 200ms 测量一次每个进程,然后每 5 秒汇总这些样本,包括某些度量的最小/平均/最大值(min/avg/max)。

**推荐阅读:** [监控 Linux 性能的 20 个命令行工具](http://www.tecmint.com/command-line-tools-to-monitor-linux-performance/)
cpustat 能用两种方式输出数据:定时汇总的纯文本列表和每个取样的彩色滚动面板。
### 如何在 Linux 中安装 cpustat
为了使用 cpustat,你的 Linux 系统中必须安装有 Go 语言(GoLang),如果你还没有安装它,点击下面的链接逐步安装 GoLang:
* [在 Linux 下安装 GoLang(Go 编程语言)](http://www.tecmint.com/install-go-in-linux/)
安装完 Go 以后,输入下面的 `go get` 命令安装 cpustat,这个命令会将 cpustat 二进制文件安装到你的 `GOBIN` 变量(所指的路径):
```
# go get github.com/uber-common/cpustat
```
### 如何在 Linux 中使用 cpustat
安装过程完成后,如果你不是以 root 用户控制系统,像下面这样使用 sudo 命令获取 root 权限运行 cpustat,否则会出现下面显示的错误信息:
```
$ $GOBIN/cpustat
This program uses the netlink taskstats interface, so it must be run as root.
```
注意:想要像你系统中已经安装的其它 Go 程序那样运行 cpustat,你需要把 `GOBIN` 变量添加到 `PATH` 环境变量。打开下面的链接学习如何在 Linux 中设置 `PATH` 变量。
* [学习如何在 Linux 中永久设置你的 $PATH 变量](http://www.tecmint.com/set-path-variable-linux-permanently/)
cpustat 是这样工作的:在每个时间间隔查询 `/proc` 目录获取当前[进程 ID 列表](http://www.tecmint.com/find-process-name-pid-number-linux/),然后:
* 对于每个 PID,读取 `/proc/pid/stat`,然后计算和前一个样本的差别。
* 如果是一个新的 PID,读取 `/proc/pid/cmdline`。
* 对于每个 PID,发送 `netlink` 消息获取 `taskstat`,计算和前一个样本的差别。
* 读取 `/proc/stat` 获取总的系统统计信息。
根据获取所有这些统计信息所花费的时间,会调整每个休息间隔。另外,通过每次取样之间实际经过的时间,每个样本也会记录它用于测量的时间。这可用于计算 cpustat 自身的延迟。
当不带任何参数运行时,cpustat 默认会显示以下信息:样本间隔:200ms;汇总间隔:2s(10 个样本);[显示前 10 个进程](http://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-processes-memory-ram-cpu-usage/);用户过滤器:all;pid 过滤器:all。正如下面截图所示:
```
$ sudo $GOBIN/cpustat
```

*cpustat – 监控 Linux CPU 使用*
在上面的输出中,之前显示的系统范围的度量字段意义如下:
* usr - 用户模式运行时间占 CPU 百分比的 min/avg/max 值。
* sys - 系统模式运行时间占 CPU 百分比的 min/avg/max 值。
* nice - 用户模式低优先级运行时间占 CPU 百分比的 min/avg/max 值。
* idle - 用户模式空闲时间占 CPU 百分比的 min/avg/max 值。
* iowait - 等待磁盘 IO 的 min/avg/max 延迟时间。
* prun - 处于可运行状态的 min/avg/max 进程数量(同“平均负载”一样)。
* pblock - 被磁盘 IO 阻塞的 min/avg/max 进程数量。
* pstat - 在本次汇总间隔里启动的进程/线程数目。
同样还是上面的输出,对于一个进程,不同列的意思分别是:
* name - 从 `/proc/pid/stat` 或 `/proc/pid/cmdline` 获取的进程名称。
* pid - 进程 ID,也被用作 “tgid” (线程组 ID)。
* min - 该 pid 的用户模式+系统模式时间的最小样本,取自 `/proc/pid/stat`。比率是 CPU 的百分比。
* max - 该 pid 的用户模式+系统模式时间的最大样本,取自 `/proc/pid/stat`。
* usr - 在汇总期间该 pid 的平均用户模式运行时间,取自 `/proc/pid/stat`。
* sys - 在汇总期间该 pid 的平均系统模式运行时间,取自 `/proc/pid/stat`。
* nice - 表示该进程的当前 “nice” 值,取自 `/proc/pid/stat`。值越高表示越好(nicer)。
* runq - 进程和它所有线程可运行但等待运行的时间,通过 netlink 取自 taskstats。比率是 CPU 的百分比。
* iow - 进程和它所有线程被磁盘 IO 阻塞的时间,通过 netlink 取自 taskstats。比率是 CPU 的百分比,对整个汇总间隔平均。
* swap - 进程和它所有线程等待被换入(swap in)的时间,通过 netlink 取自 taskstats。Scale 是 CPU 的百分比,对整个汇总间隔平均。
* vcx 和 icx - 在汇总间隔期间进程和它的所有线程自动上下文切换总的次数,通过 netlink 取自 taskstats。
* rss - 从 `/proc/pid/stat` 获取的当前 RSS 值。它是指该进程正在使用的内存数量。
* ctime - 在汇总间隔期间等待子进程退出的用户模式+系统模式 CPU 时间总和,取自 `/proc/pid/stat`。 注意长时间运行的子进程可能导致混淆这个值,因为只有在子进程退出后才会报告时间。但是,这对于计算高频 cron 任务以及 CPU 时间经常被多个子进程使用的健康检查非常有帮助。
* thrd - 汇总间隔最后线程的数目,取自 `/proc/pid/stat`。
* sam - 在这个汇总间隔期间该进程的样本数目。最近启动或退出的进程可能看起来比汇总间隔的样本数目少。
下面的命令显示了系统中运行的前 10 个 root 用户进程:
```
$ sudo $GOBIN/cpustat -u root
```

*查找 root 用户正在运行的进程*
要想用更好看的终端模式显示输出,像下面这样用 `-t` 选项:
```
$ sudo $GOBIN/cpustat -u root -t
```

*root 用户正在运行的进程*
要查看前 [x 个进程](http://www.tecmint.com/find-processes-by-memory-usage-top-batch-mode/)(默认是 10),你可以使用 `-n` 选项,下面的命令显示了系统中 [正在运行的前 20 个进程](http://www.tecmint.com/install-htop-linux-process-monitoring-for-rhel-centos-fedora/):
```
$ sudo $GOBIN/cpustat -n 20
```
你也可以像下面这样使用 `-cpuprofile` 选项将 CPU 信息写到文件,然后用 [cat 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/)查看文件:
```
$ sudo $GOBIN/cpustat -cpuprofile cpuprof.txt
$ cat cpuprof.txt
```
要显示帮助信息,像下面这样使用 `-h` 选项:
```
$ sudo $GOBIN/cpustat -h
```
可以从 cpustat 的 Github 仓库:<https://github.com/uber-common/cpustat> 查阅其它资料。
就是这些!在这篇文章中,我们向你展示了如何安装和使用 cpustat,Linux 下的一个有用的系统性能测量工具。通过下面的评论框和我们分享你的想法吧。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S(Free and Open-Source Software) 爱好者,一个 Linux 系统管理员、web 开发员,现在也是 TecMint 的内容创建者,他喜欢和电脑一起工作,他相信知识共享。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/cpustat-monitors-cpu-utilization-by-processes-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,467 | 如何用 bash-support 插件将 Vim 编辑器打造成编写 Bash 脚本的 IDE | http://www.tecmint.com/use-vim-as-bash-ide-using-bash-support-in-linux/ | 2017-05-02T08:40:00 | [
"vim",
"IDE",
"bash"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8467-1.html | IDE([集成开发环境](http://www.tecmint.com/best-linux-ide-editors-source-code-editors/))就是这样一个软件,它为了最大化程序员生产效率,提供了很多编程所需的设施和组件。 IDE 将所有开发工作集中到一个程序中,使得程序员可以编写、修改、编译、部署以及调试程序。
在这篇文章中,我们会介绍如何通过使用 bash-support vim 插件将 [Vim 编辑器安装和配置](http://www.tecmint.com/vi-editor-usage/) 为一个编写 Bash 脚本的 IDE。

### 什么是 bash-support.vim 插件?
bash-support 是一个高度定制化的 vim 插件,它允许你插入:文件头、补全语句、注释、函数、以及代码块。它也使你可以进行语法检查、使脚本可执行、一键启动调试器;而完成所有的这些而不需要关闭编辑器。
它使用快捷键(映射),通过有组织地、一致的文件内容编写/插入,使得 bash 脚本编程变得有趣和愉快。
插件当前版本是 4.3,4.0 版本 重写了之前的 3.12.1 版本,4.0 及之后的版本基于一个全新的、更强大的、和之前版本模板语法不同的模板系统。
### 如何在 Linux 中安装 Bash-support 插件
用下面的命令下载最新版本的 bash-support 插件:
```
$ cd Downloads
$ curl http://www.vim.org/scripts/download_script.php?src_id=24452 >bash-support.zip
```
按照如下步骤安装;在你的主目录创建 `.vim` 目录(如果它不存在的话),进入该目录并提取 bash-support.zip 内容:
```
$ mkdir ~/.vim
$ cd .vim
$ unzip ~/Downloads/bash-support.zip
```
下一步,在 `.vimrc` 文件中激活它:
```
$ vi ~/.vimrc
```
并插入下面一行:
```
filetype plug-in on
set number # 可选,增加这行以在 vim 中显示行号
```
### 如何在 Vim 编辑器中使用 Bash-support 插件
为了简化使用,通常使用的结构和特定操作可以分别通过键映射来插入/执行。 `~/.vim/doc/bashsupport.txt` 和 `~/.vim/bash-support/doc/bash-hotkeys.pdf` 或者 `~/.vim/bash-support/doc/bash-hotkeys.tex` 文件中介绍了映射。
**重要:**
1. 所有映射(`\+字符` 组合)都是针对特定文件类型的:为了避免和其它插件的映射冲突,它们只适用于 `sh` 文件。
2. 使用键映射的时候打字速度也有关系,引导符 `\` 和后面字符的组合要在特定短时间内才能识别出来(很可能少于 3 秒 - 基于假设)。
下面我们会介绍和学习使用这个插件一些显著的功能:
#### 如何为新脚本自动生成文件头
看下面的示例文件头,为了要在你所有的新脚本中自动创建该文件头,请按照以下步骤操作。

*脚本示例文件头选项*
首先设置你的个人信息(作者名称、作者参考、组织、公司等)。在一个 Bash 缓冲区(像下面这样打开一个测试脚本)中使用映射 `\ntw` 启动模板设置向导。
选中选项 1 设置个性化文件,然后按回车键。
```
$ vi test.sh
```

*在脚本文件中设置个性化信息*
之后,再次输入回车键。然后再一次选中选项 1 设置个性化文件的路径并输入回车。

*设置个性化文件路径*
设置向导会把目标文件 `.vim/bash-support/rc/personal.templates` 拷贝到 `.vim/templates/personal.templates`,打开并编辑它,在这里你可以输入你的信息。
按 `i` 键像截图那样在单引号中插入合适的值。

*在脚本文件头添加信息*
一旦你设置了正确的值,输入 `:wq` 保存并退出文件。关闭 Bash 测试脚本,打开另一个脚本来测试新的配置。现在文件头中应该有和下面截图类似的你的个人信息:
```
$ vi test2.sh
```

*自动添加文件头到脚本*
#### 添加 Bash-support 插件帮助信息
为此,在 Vim 命令行输入下面的命令并按回车键,它会创建 `.vim/doc/tags` 文件:
```
:helptags $HOME/.vim/doc/
```

*在 Vi 编辑器添加插件帮助*
#### 如何在 Shell 脚本中插入注释
要插入一个块注释,在普通模式下输入 `\cfr`:

*添加注释到脚本*
#### 如何在 Shell 脚本中插入语句
下面是一些用于插入语句的键映射(`n` – 普通模式, `i` – 插入模式,`v` 可视模式):
1. `\sc` – `case in … esac` (n, i)
2. `\sei` – `elif then` (n, i)
3. `\sf` – `for in do done` (n, i, v)
4. `\sfo` – `for ((…)) do done` (n, i, v)
5. `\si` – `if then fi` (n, i, v)
6. `\sie` – `if then else fi` (n, i, v)
7. `\ss` – `select in do done` (n, i, v)
8. `\su` – `until do done` (n, i, v)
9. `\sw` – `while do done` (n, i, v)
10. `\sfu` – `function` (n, i, v)
11. `\se` – `echo -e "…"` (n, i, v)
12. `\sp` – `printf "…"` (n, i, v)
13. `\sa` – 数组元素, `${.[.]}` (n, i, v) 和其它更多的数组功能。
#### 插入一个函数和函数头
输入 `\sfu` 添加一个新的空函数,然后添加函数名并按回车键创建它。之后,添加你的函数代码。

*在脚本中插入新函数*
为了给上面的函数创建函数头,输入 `\cfu`,输入函数名称,按回车键并填入合适的值(名称、介绍、参数、返回值):

*在脚本中创建函数头*
#### 更多关于添加 Bash 语句的例子
下面是一个使用 `\si` 插入一条 `if` 语句的例子:

*在脚本中插入语句*
下面的例子显示使用 `\se` 添加一条 `echo` 语句:

*在脚本中添加 echo 语句*
#### 如何在 Vi 编辑器中使用运行操作
下面是一些运行操作键映射的列表:
1. `\rr` – 更新文件,运行脚本(n, i)
2. `\ra` – 设置脚本命令行参数 (n, i)
3. `\rc` – 更新文件,检查语法 (n, i)
4. `\rco` – 语法检查选项 (n, i)
5. `\rd` – 启动调试器(n, i)
6. `\re` – 使脚本可/不可执行(\*) (n, i)
#### 使脚本可执行
编写完脚本后,保存它然后输入 `\re` 和回车键使它可执行。

*使脚本可执行*
#### 如何在 Bash 脚本中使用预定义代码片段
预定义代码片段是为了特定目的包含了已写好代码的文件。为了添加代码段,输入 `\nr` 和 `\nw` 读/写预定义代码段。输入下面的命令列出默认的代码段:
```
$ .vim/bash-support/codesnippets/
```

*代码段列表*
为了使用代码段,例如 free-software-comment,输入 `\nr` 并使用自动补全功能选择它的名称,然后输入回车键:

*添加代码段到脚本*
#### 创建自定义预定义代码段
可以在 `~/.vim/bash-support/codesnippets/` 目录下编写你自己的代码段。另外,你还可以从你正常的脚本代码中创建你自己的代码段:
1. 选择你想作为代码段的部分代码,然后输入 `\nw` 并给它一个相近的文件名。
2. 要读入它,只需要输入 `\nr` 然后使用文件名就可以添加你自定义的代码段。
#### 在当前光标处查看内建和命令帮助
要显示帮助,在普通模式下输入:
1. `\hh` – 内建帮助
2. `\hm` – 命令帮助

*查看内建命令帮助*
更多参考资料,可以查看文件:
```
~/.vim/doc/bashsupport.txt #在线文档的副本
~/.vim/doc/tags
```
* 访问 Bash-support 插件 GitHub 仓库:<https://github.com/WolfgangMehner/bash-support>
* 在 Vim 网站访问 Bash-support 插件:<http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=365>
就是这些啦,在这篇文章中,我们介绍了在 Linux 中使用 Bash-support 插件安装和配置 Vim 为一个 Bash-IDE 的步骤。快去发现这个插件其它令人兴奋的功能吧,一定要在评论中和我们分享哦。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者、Linux 系统管理员、网络开发人员,现在也是 TecMint 的内容创作者,她喜欢和电脑一起工作,坚信共享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/use-vim-as-bash-ide-using-bash-support-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,469 | 极客漫画:让高等生命都迷茫的 Erlang | https://turnoff.us/geek/advanced-species/ | 2017-05-02T16:42:00 | [
"Erlang",
"漫画"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8469-1.html | 
这是一篇吐槽 Erlang 有多难的一幅漫画。Erlang 太难,连未来到访的外星人都无法破译。
---
via: <https://turnoff.us/geek/advanced-species/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者&点评:[Bestony](https://github.com/Bestony) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 合成:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 404 | Not Found | null |
8,470 | eval 之源 | http://strangelyconsistent.org/blog/the-root-of-all-eval | 2017-05-02T17:38:00 | [
"eval",
"perl"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8470-1.html | 
(LCTT 译注:本文标题 “The root of all eval” 影射著名歌曲“The root of all evil”(万恶之源))
唉,`eval` 这个函数让我爱恨交织,而且多半是后者居多。
```
$ perl -E'my $program = q[say "OH HAI"]; eval $program'
OH HAI
```
当 `eval` 函数在 Perl 6 中被重命名为 `EVAL` 时,我感到有点震惊(这要追溯到 2013 年,[在这里](https://github.com/perl6/specs/issues/50)讨论规范之后)。我一直没有从内心接受这样这样的做法。虽然这是个很好的意见,但是在这个意见上我似乎或多或少是孤独的。
理由是“这个函数真的很奇怪,所以我们应该用大写标记”。就像我们用 `BEGIN` 和其他 phaser 一样。使用 `BEGIN` 和其他 phaser,鼓励使用大写,这点我是同意的。phaser 能将程序“脱离正常控制流”。 但是 `eval` 函数并不能。(LCTT 译注: 在 Perl 6 当中,[phaser](https://docs.perl6.org/language/phasers) 是在一个特定的执行阶段中调用的代码块。)
其他大写的地方像是 .WHAT 这样的东西,它看起来像属性,但是会在编译时将代码变成完全不同的东西。因为这发生在常规情况之外,因此大写甚至是被鼓励的。
`eval` 归根到底是另一个函数。是的,这是一个潜在存在大量副作用的函数。但是那么多的标准函数都有大量的副作用。(举几个例子:`shell`、 `die`、 `exit`)你没看到有人呼吁将它们大写。
我猜有人会争论说 `eval` 是非常特别的,因为它以正常函数所没有的方式钩到编译器和运行时里面。(这也是 TimToady 在将该函数重命名的提交中的[提交消息](https://github.com/perl6/specs/commit/0b7df09ecc096eed5dc30f3dbdf568bbfd9de8f6)中解释的。)这是一个来自实现细节的争论,然而这并不令人满意。这也同样适用与刚才提到的那些小写函数。
雪上加霜的是,更名后 `EVAL` 也更难于使用:
```
$ perl6 -e'my $program = q[say "OH HAI"]; EVAL $program'
===SORRY!=== Error while compiling -e
EVAL is a very dangerous function!!! (use the MONKEY-SEE-NO-EVAL pragma to override this error,
but only if you're VERY sure your data contains no injection attacks)
at -e:1
------> program = q[say "OH HAI"]; EVAL $program⏏<EOL>
$ perl6 -e'use MONKEY-SEE-NO-EVAL; my $program = q[say "OH HAI"]; EVAL $program'
OH HAI
```
首先,注入攻击是一个真实的问题,并不是一个笑话。我们应该互相教育对方和新手。
其次,这个错误消息(`"EVAL is a very dangerous function!!!"`)完全是恐吓多于帮助。我觉得当我们向人们解释代码注入的危险时,我们需要冷静并且切合实际,而不是用三个感叹号。这个错误信息对[已经知道什么是注入攻击的人](http://bobby-tables.com/)来说是有意义的,对于那些不了解这种风险的人员,它没有提供任何提示或线索。
(Perl 6 社区并不是唯一对 `eval` 歇斯底里的,昨天我偶然发现了一个 StackOverflow 主题,关于如何将一个有类型名称的字符串转换为 JavaScript 中的相应构造函数,一些人不幸地提出了用 `eval`,而其他人立即集结起来指出这是多么不负责任,就像膝跳反射那样——“因为 eval 是坏的”)。
第三,“MOKNEY-SEE-NO-EVAL”。拜托,我们能不能不要这样……汗,启用一个核弹级的函数时,就像是猴子般的随机引用和轻率的尝试,我奇怪地发现*启用* `EVAL` 函数的是一个称为 `NO-EVAL` 的东西。这并不符合“<ruby> 最少惊喜 <rt> Least Surprise </rt></ruby>”原则。
不管怎样,有一天,我意识到我可以同时解决全大写名字问题和该指令的必要问题:
```
$ perl6 -e'my &eval = &EVAL; my $program = q[say "OH HAI"]; eval $program'
OH HAI
```
我很高兴我能想到这点子并记录下来。显然我们把它改回了旧名字,这个非常危险的功能(`!!!`)就又好了。 耶!
---
via: <http://strangelyconsistent.org/blog/the-root-of-all-eval>
作者:[Carl Mäsak](http://strangelyconsistent.org/about) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | [The root of all eval](http://strangelyconsistent.org/blog/the-root-of-all-eval)
Ah, the `eval`
function. Loved, hated. Mostly the latter.
```
$ perl -E'my $program = q[say "OH HAI"]; eval $program'
OH HAI
```
I was a bit stunned when the `eval`
function was renamed to `EVAL`
in Perl 6 (back in 2013, after spec discussion [here](https://github.com/perl6/specs/issues/50)). I've never felt really comfortable with the rationale for doing so. I seem to be more or less alone in this opinion, though, which is fine.
The rationale was "the function does something really weird, so we should flag it with upper case". Like we do with `BEGIN`
and the other phasers, for example. With `BEGIN`
and others, the upper-casing is motivated, I agree. A phaser takes you "outside of the normal control flow". The `eval`
function doesn't.
Other things that we upper-case are things like `.WHAT`
, which look like attributes but are really specially code-generated at compile-time into something completely different. So even there the upper-casing is motivated because something outside of the normal is happening.
`eval`
in the end is just another function. Yes, it's a function with potentially quite wide-ranging side effects, that's true. But a lot of fairly standard functions have wide-ranging side effects. (To name a few: `shell`
, `die`
, `exit`
.) You don't see anyone clamoring to upper-case those.
I guess it could be argued that `eval`
is very special because it hooks into the compiler and runtime in ways that normal functions don't, and maybe can't. (This is also how TimToady explained it in [the commit message](https://github.com/perl6/specs/commit/0b7df09ecc096eed5dc30f3dbdf568bbfd9de8f6) of the renaming commit.) But that's an argument from implementation details, which doesn't feel satisfactory. It applies with equal force to the lower-cased functions just mentioned.
To add insult to injury, the renamed `EVAL`
is also made deliberately harder to use:
```
$ perl6 -e'my $program = q[say "OH HAI"]; EVAL $program'
===SORRY!=== Error while compiling -e
EVAL is a very dangerous function!!! (use the MONKEY-SEE-NO-EVAL pragma to override this error,
but only if you're VERY sure your data contains no injection attacks)
at -e:1
------> program = q[say "OH HAI"]; EVAL $program⏏<EOL>
$ perl6 -e'use MONKEY-SEE-NO-EVAL; my $program = q[say "OH HAI"]; EVAL $program'
OH HAI
```
Firstly, injection attacks are a real issue, and no laughing matter. We should educate each other and newcomers about them.
Secondly, that error message (`"EVAL is a very dangerous function!!!"`
) is completely over-the-top in a way that damages rather than helps. I believe when we explain the dangers of code injection to people, we need to do it calmly and matter-of-factly. Not with three exclamation marks. The error message makes sense to [someone who already knows about injection attacks](http://bobby-tables.com/); it provides no hints or clues for people who are unaware of the risks.
(The Perl 6 community is not unique in `eval`
-hysteria. Yesterday I stumbled across a StackOverflow thread about how to turn a string with a type name into the corresponding constructor in JavaScript. Some unlucky soul suggested `eval`
, and everybody else immediately piled on to point out how irresponsible that was. Solely as a knee-jerk reaction "because eval is bad".)
Thirdly, `MONKEY-SEE-NO-EVAL`
. Please, can we just... not. 😓 Random reference to monkies and the weird attempt at levity while switching on a nuclear-chainsaw function aside, I find it odd that a function that *enables* `EVAL`
is called something with `NO-EVAL`
. That's not Least Surprise.
Anyway, the other day I realized how I can get around both the problem of the all-caps name and the problem of the necessary pragma:
```
$ perl6 -e'my &eval = &EVAL; my $program = q[say "OH HAI"]; eval $program'
OH HAI
```
I was so happy to realize this that I thought I'd blog about it. Apparently the very dangerous function (`!!!`
) is fine again if we just give it back its old name. 😜 |
8,472 | 如何在树莓派中安装 VoIP 系统:Asterisk | https://opensource.com/article/17/4/asterisk-raspberry-pi-3 | 2017-05-03T16:26:00 | [
"树莓派",
"VoIP"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8472-1.html |
>
> 你是否在为小型企业或家庭办公室寻找电话系统?
>
>
>

你是否在为小型企业或家庭办公室寻找电话系统?我一直对可扩展 VoIP(Voice over IP)解决方案感兴趣,后来我在树莓派上找到 [Asterisk](http://www.asterisk.org/) 的一个实现。
我的好奇心被激起了,我决心尝试一下,所以我从 [Asterisk](http://www.raspberry-asterisk.org/downloads/) 官网[下载](http://download.raspberry-asterisk.org/raspbx-28-01-2017.zip)了它(RasPBX),然后使用我的树莓派 3 构建服务器。
### 准备开始
首先,我将下载的镜像刻录到 MicroSD 卡上。建议的最小值是 4 GB。将镜像传输到 MicroSD 卡并插到树莓派上的相应插槽中后,我将网线连接到树莓派和家庭路由器上的以太网端口中。
更多关于树莓派的内容:
* [什么是树莓派?](https://opensource.com/resources/what-raspberry-pi?src=raspberry_pi_resource_menu)
* [开始使用树莓派](https://opensource.com/article/16/12/getting-started-raspberry-pi?src=raspberry_pi_resource_menu)
* [给我们发送你的树莓派项目和教程](https://opensource.com/article/17/2/raspberry-pi-submit-your-article?src=raspberry_pi_resource_menu)
接下来,我在 Linux 上打开一个终端,并输入 `ssh [email protected]`,这是我的服务器的 IP 地址。我被提示以 `root` 用户身份登录到 RasPBX 上。默认密码是 `raspberry`。 (出于安全考虑,如果你打算再多试试,请务必更改默认密码。)
当我登录到了 RasPBX 上的 shell 后,接下来我需要准备配置了。根据网站上提供的[文档](http://www.raspberry-asterisk.org/documentation/),我在 shell 下输入 `regen-hostkeys` 来创建新的主机密钥。然后输入 `configure-timezone` 来配置服务器的时区。我通过在提示符下输入 `dpkg-reconfigure locales` 来配置区域设置。我也安装了 [Fail2Ban](http://www.raspberry-asterisk.org/documentation/#fail2ban) 来保障服务器的安全性。
现在我准备测试我的配置。
### 测试
我从 RasPBX 的 shell 中登出,然后打开浏览器并输入我的服务器的 IP 地址。将服务器 IP 地址加载到浏览器中,我看到了一个可爱的登录页面。
[FreePBX](https://www.freepbx.org/) 提供了一个非常好的基于 Web 的开源图形用户界面,我用它来控制和配置 Asterisk(可在 [GitHub](https://github.com/asterisk/asterisk/blob/master/LICENSE) 上找到)。(FreePBX 是 GPL 许可的)。我用它来完成其余的配置。FreePBX 的默认登录账号为用户名:`admin`; 密码:`admin`。

登录之后,我进入位于显示屏左上方的<ruby> 应用菜单 <rt> Application Menu </rt></ruby>。点击菜单链接并选择了第二个选项,即 <ruby> “应用” <rt> Applications </rt></ruby>,接着选择了第四个选项,<ruby> “分机” <rt> Extensions </rt></ruby>。从那里我选择创建一个 New Chan\_Sip 分机。

我使用密码配置了一个 sip 分机用户。密码是自动生成的,也可以选择创建自己的密码。
现在我有了一个完整的分机,我急于尝试我的新的 VoIP 服务器。我下载并安装了 [Yate 客户端](http://yateclient.yate.ro/index.php/Download/Download),这是在构建服务器的过程中发现的。安装 [Yate](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yate_(telephony_engine)) 之后,我想测试与服务器的连接。我发现我可以使用 Yate 连接到服务器并输入 `*43` 进行回声测试。当我听到客户端指示时,我感到很激动。

我决定创建另外一个 sip 分机,这样我就可以测试系统的语音信箱功能。 在完成后,我使用 Yate 客户端来呼叫这个分机,并留下了简短的语音留言。然后再次使用 Yate 呼叫该分机并输入 `*97` 来检索语音留言。然后我想看看我是否可以使用我的新服务器来呼叫外线。返回到菜单,选择 <ruby> “连接” <rt> Connectivity </rt></ruby> 选项,并添加了 Google Voice 号码。

接着我返回到 “连接” 菜单,并将 Google Voice 添加到出站路由中。

### 完成一个呼叫
回到 Yate 客户端,我呼叫了一个外线并成功完成了这个呼叫。
我相信这个特定的 VoIP 解决方案可以轻松地为一个小型办公室工作。根据 RasPBX 网站的[常见问题](http://www.raspberry-asterisk.org/faq/)部分,典型的树莓派系统可以在树莓派 1 上支持多达 10 个并发呼叫。
Asterisk 有很多细微差别的功能,FreePBX 则可以很容易地利用它们。
*关于树莓派上的 Asterisk 的更多信息,请参考他们的[博客](http://www.raspberry-asterisk.org/blog/)。你可以在他们的网站上找到有关 [FreePBX 源代码](https://www.freepbx.org/development/source-code/)的其他信息。*
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
作者简介:
Don Watkins - 教育家、教育技术专家、企业家、开源倡导者。教育心理学硕士、教育领导硕士、Linux 系统管理员、CCNA、使用 Virtual Box 虚拟化。关注我 @Don\_Watkins。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/4/asterisk-raspberry-pi-3>
作者:[Don Watkins](https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Are you looking for a phone system for your small business or home office? I've been interested in a scalable VoIP (Voice over IP) solution, and that's when I came across an implementation of [Asterisk](http://www.asterisk.org/) on the Raspberry Pi.
My curiosity was piqued and I was determined to give it a try, so I [downloaded](http://download.raspberry-asterisk.org/raspbx-28-01-2017.zip) the software from [Asterisk](http://www.raspberry-asterisk.org/downloads/) and then set about building the server using my Raspberry Pi 3.
## Getting started
First, I burned the downloaded image onto a MicroSD card; the suggested minimum is 4GB. After transferring the image to the MicroSD card and inserting it into the appropriate slot on the Raspberry Pi, I connected an Ethernet cable to the Pi and to an Ethernet port on my home router.
Next, I opened a terminal on my Linux computer and entered **ssh [email protected]**, which is the IP address of my server. I was prompted to log in as root on the **raspbx**. The default password is "raspberry." (For security reasons, be sure to change your passwords from the default settings if you plan to do more than just try it out.)
Once I was logged into the shell on the **raspbx,** I then needed to prepare the server for use. Following the [documentation](http://www.raspberry-asterisk.org/documentation/) provided on the site, I created new host keys as directed by entering **regen-hostkeys** at the shell prompt. Then, I configured the time zone for the server by entering **configure-timezone** at the shell prompt. I configured the locale setting by entering, **dpkg-reconfigure locales** at the prompt. I also installed [Fail2Ban](http://www.raspberry-asterisk.org/documentation/#fail2ban) to provide security on my server.
Now I was ready to test my configuration.
## Testing
I logged out of the **raspbx** shell and then opened a browser and pointed it at the IP address of my server. Loading the server IP address into the browser, I was presented with a lovely login page.
[FreePBX](https://www.freepbx.org/) provides a very nice web-based, open source graphical user interface, which I used to control and configure Asterisk (find on [GitHub](https://github.com/asterisk/asterisk/blob/master/LICENSE)). (FreePBX is licensed under the GPL.) I used it to complete the rest of the configuration. The default login for FreePBX is* ***username:admin;password:admin**.
Once in, I navigated to the Application Menu, which is located at the upper left of the display. I clicked on the menu link and selected the second option, which is Applications, and selected the fourth option, which is labeled Extensions. From there I created a **New Chan_Sip** extension.
I configured a **Sip** extension user with a password. Passwords are either automatically generated or you can elect to create your own.
Now that I had a functioning extension I was anxious to try out my new VoIP server. I downloaded and installed [Yate Client](http://yateclient.yate.ro/index.php/Download/Download), which I discovered in the process of building the server. After installing [Yate](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yate_(telephony_engine)), I wanted to test the connectivity with the server. I discovered that I could connect to the server for an echo test using Yate and entering ***43**. I was really excited when I heard the instructions through the client.
I decided to create another **Sip** extension so that I could test the voicemail capabilities of the system. Once I completed that I used the Yate client to call that extension and leave a brief voice message. Then using Yate again, I called that extension and entered ***97** and retrieved the voice message. Then I wanted to see if I could use my new server to call an outside line. Returning to the menu, I chose the Connectivity option and added a Google Voice line.
Then I returned to the Connectivity menu and added Google Voice to the Outbound routes.
## Completing a call
Returning to the Yate client, I entered an outside line and successfully completed that call.
I'm convinced that this particular VoIP solution could easily work for a small office. According to the [Frequently Asked Questions](http://www.raspberry-asterisk.org/faq/) section of the RasPBX website, a typical Raspberry Pi system could support up to 10 concurrent calls on a Raspberry Pi 1.
Asterisk has many nuances and the FreePBX software easily leveraged them.
*For more information about the Asterisk on Raspberry Pi project, follow their blog. You can find additional information about FreePBX source code on their website.*
## 8 Comments |
8,473 | 使用 Cockpit 方便地管理容器 | https://www.linux.com/learn/intro-to-linux/2017/3/make-container-management-easy-cockpit | 2017-05-03T16:47:00 | [
"容器",
"Cockpit",
"Docker"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8473-1.html | 
>
> 如果你正在寻找一种管理运行容器的 Linux 服务器的简单方法,那么你应该看看 Cockpit。
>
>
>
如果你管理着一台 Linux 服务器,那么你可能正在寻找一个可靠的管理工具。为了这个你可能已经看了 [Webmin](http://www.webmin.com/) 和 [cPanel](http://cpanel.com/) 这类软件。但是,如果你正在寻找一种简单的方法来管理还包括了 Docker 的 Linux 服务器,那么有一个工具可以用于这个需求:[Cockpit](http://cockpit-project.org/)。
为什么使用 Cockpit?因为它可以处理这些管理任务:
* 连接并管理多台机器
* 通过 Docker 管理容器
* 与 Kubernetes 或 Openshift 集群进行交互
* 修改网络设置
* 管理用户帐号
* 通过基于 Web 的 shell 访问
* 通过图表查看系统性能信息
* 查看系统服务和日志文件
Cockpit 可以安装在 Debian、Red Hat、CentOS、Arch Linux 和 Ubuntu 之上。在这里,我将使用一台已经安装了 Docker 的 Ubuntu 16.04 服务器来安装系统。
在上面的功能列表中,其中最突出的是容器管理。为什么?因为它使安装和管理容器变得非常简单。事实上,你可能很难找到更好的容器管理解决方案。
因此,让我们来安装这个方案并看看它的使用是多么简单。
### 安装
正如我前面提到的,我将在一台运行着 Docker 的 Ubuntu 16.04 实例上安装 Cockpit。安装步骤很简单。你要做的第一件事是登录你的 Ubuntu 服务器。接下来,你必须使用下面的命令添加必要的仓库:
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:cockpit-project/cockpit
```
出现提示时,按下键盘上的回车键,等待提示返回。一旦返回到 bash 提示符,使用下面的命令来更新 apt:
```
sudo apt-get get update
```
使用下面的命令安装 Cockpit:
```
sudo apt-get -y install cockpit cockpit-docker
```
安装完成后,需要启动 Cockpit 服务并使它开机自动启动。要做到这个,使用下面的两个命令:
```
sudo systemctl start cockpit
sudo systemctl enable cockpit
```
安装就到这里了。
### 登录到 Cockpit
要访问 Cockpit 的 web 界面,打开浏览器(与 Cockpit 服务器在同一个网络内),输入 `http://IP_OF_SERVER:9090`,你就会看到登录页面(图 1)。

*图 1:Cockpit 登录页面。*
在 Ubuntu 中使用 Cockpit 有个警告。Cockpit 中的很多任务需要管理员权限。如果你使用普通用户登录,则无法使用 Docker 等一些工具。 要解决这个问题,你可以在 Ubuntu 上启用 root 用户。但这并不总是一个好主意。通过启用 root 帐户,你将绕过已经建立多年的安全系统。但是,在本文的用途中,我将使用以下两个命令启用 root 用户:
```
sudo passwd root
sudo passwd -u root
```
注意,请确保给 root 帐户一个强壮的密码。
你想恢复这个修改的话,你只需输入下面的命令:
```
sudo passwd -l root
```
在其他发行版(如 CentOS 和 Red Hat)中,你可以使用用户名 `root` 及其密码登录 Cockpit,而无需像上面那样需要额外的步骤。
如果你对启用 root 用户感到担心,则可以在服务器的终端窗口拉取镜像(使用命令 `docker pull IMAGE_NAME`, 这里的 `IMAGE_NAME` 是你要拉取的镜像)。这会将镜像添加到你的 docker 服务器中,然后可以通过普通用户进行管理。唯一需要注意的是,普通用户必须使用以下命令将自己添加到 Docker 组:
```
sudo usermod -aG docker USER
```
其中,`USER` 是实际添加到组的用户名。在你完成后,重新登出并登入,接着使用下面的命令重启 Docker:
```
sudo service docker restart
```
现在常规用户可以启动并停止 Docker 镜像/容器而无需启用 root 用户了。唯一一点是用户不能通过 Cockpit 界面添加新的镜像。
### 使用 Cockpit
一旦你登录后,你可以看到 Cockpit 的主界面(图 2)。

*图 2:Cockpit 主界面。*
你可以通过每个栏目来检查服务器的状态等,但是我们想要直接进入容器。单击 “Containers” 那栏以显示当前运行的以及可用的镜像(图3)。

*图 3:使用 Cockpit 管理容器难以置信地简单。*
要启动一个镜像,只要找到镜像并点击关联的启动按钮。在弹出的窗口中(图 4),你可以在点击运行之前查看所有镜像的信息(并根据需要调整)。

*图 4: 使用 Cockpit 运行 Docker 镜像。*
镜像运行后,你可以点击它查看状态,并可以停止、重启、删除实例。你也可以点击修改资源限制并接着调整内存限制还有(或者)CPU 优先级。
### 添加新的镜像
假设你以 root 用户身份登录。如果是这样,那么你可以在 Cockpit GUI 的帮助下添加新的镜像。在“ Container” 栏目下,点击获取新的镜像按钮,然后在新的窗口中搜索要添加的镜像。假设你要添加 CentOS 的最新官方版本。在搜索栏中输入 centos,在得到搜索结果后,选择官方列表,然后单击下载(图5)。

*图 5:使用 Cockpit 添加最新的官方构建 CentOS 镜像到 Docker 中。*
镜像下载完后,那它就在 Docker 中可用了,并可以通过 Cockpit 运行。
### 如获取它那样简单
管理 Docker 并不容易。是的,在 Ubuntu 上运行 Cockpit 会有一个警告,但如果这是你唯一的选择,那么也有办法让它工作。在 Cockpit 的帮助下,你不仅可以轻松管理 Docker 镜像,也可以在任何可以访问 Linux 服务器的 web 浏览器上这样做。请享受这个新发现的让 Docker 易用的方法。
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/learn/intro-to-linux/2017/3/make-container-management-easy-cockpit>
作者:[JACK WALLEN](https://www.linux.com/users/jlwallen) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,475 | 极客漫画:大数据婚姻 | https://turnoff.us/geek/bigdata-marriage/ | 2017-05-04T14:33:00 | [
"大数据",
"漫画"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8475-1.html | 

这幅漫画是作者假借大数据来吐槽自己的老婆太唠叨了。
也是一个非常有意思的比喻,作为男性可能都有所体会,在没有结婚的时候,甚至是说,单身的时候,自己的生活过的清净而惬意。一旦你结了婚,你的妻子为了生活而忙碌,便开始关注生活中的点点滴滴,会给你说大量的话,传递大量的信息,这何尝不是一种“大数据”呢?
via: <https://turnoff.us/geek/bigdata-marriage/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者&点评:[Bestony](https://github.com/bestony) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 合成:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 404 | Not Found | null |
8,476 | SSH 协议端口号 22 背后的故事 | https://www.ssh.com/ssh/port | 2017-05-04T16:15:00 | [
"防火墙",
"SSH",
"端口"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8476-1.html | 为什么 [SSH](https://www.ssh.com/ssh/)(安全终端)的端口号是 22 呢,这不是一个巧合,这其中有个我([Tatu Ylonen](https://www.ssh.com/people/tatu-ylonen),SSH 协议的设计者)未曾诉说的故事。
### 将 SSH 协议端口号设为 22 的故事
1995 年春我编写了 SSH 协议的最初版本,那时候 [telnet](https://www.ssh.com/ssh/telnet) 和 [FTP](https://www.ssh.com/ssh/ftp/) 正被广泛使用。
当时我设计 SSH 协议想着是为了替代 `telnet`(端口 23)和 `ftp`(端口21)两个协议的,而端口 22 是空闲的。我想当然地就选择了夹在 `telnet` 和 `ftp` 的端口中间的数字。我觉得端口号虽然是个小事但似乎又存在着某种信念。但我到底要怎么拿到那个端口号呢?我未曾拥有过任何一个端口号,但我却认识几个拥有端口号的人!
在那时取得端口号的事情其实说来挺简单的。毕竟当时的因特网(Internet)并不是很大,是因特网爆炸的早期。端口号分配的活儿是 IANA(Internet Assigned Numbers Authority,互联网数字分配机构)干的。在那时这机构可相当于是因特网先驱 [Jon Postel](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jon_Postel) 和 [Joyce K. Reynolds](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joyce_K._Reynolds) 一般的存在。Jon 参与编写了多项主要的协议标准,例如 IP(RFC 791)、ICMP(RFC 792)和 TCP(RFC 793)等一些你应该早有耳闻的协议。
我可以说是敬畏 Jon 先生的,他参与编写了几乎所有主要的因特网标准文档(Internet RFC)!
1995 年 7 月,就在我发布 `ssh-1.0` 前,我发送了一封邮件给 IANA:
>
> From ylo Mon Jul 10 11:45:48 +0300 1995
> From: Tatu Ylonen <[email protected]>
> To: Internet Assigned Numbers Authority <[email protected]>
> Subject: 请求取得一个端口号
> Organization: 芬兰赫尔辛基理工大学
>
>
> 亲爱的机构成员:
>
>
> 我写了个可以在不安全的网络环境中安全地从一台机器登录到另一台机器的程序。它主要是对现有的 telnet 协议以及 rlogin 协议的功能性提升和安全性改进。说的具体些,就是可以防御 IP、DNS 或路由等欺骗行为。我打算将我的软件免费地发布在因特网上,以得到广泛地使用。
>
>
> 我希望为该软件注册一个特权端口号,要是这个端口号在 1 到 255 之间就更好了,这样它就可以用在名字服务器的 WKS 字段中了。
>
>
> 我在附件中附上了协议标准的草案。这个软件已经在本地运行了几个月了,我已准备在获得端口号后就发布。如果端口号分配一事安排的及时,我希望这周就将要发布的软件准备好。我目前在 beta 版测试时使用的端口号是 22,如果要是能够分配到这个端口,我就不用做什么更改了(目前这个端口在列表中还是空闲的)。
>
>
> 软件中服务的名称叫 `ssh`(系 Secure Shell 的缩写)。
>
>
> 您最真诚的,
>
>
> Tatu Ylonen <[email protected]>
>
>
>
(LCTT 译注:DNS 协议中的 WKS 记录类型意即“众所周知的业务描述”,是类似于 A、MX 这样的 DNS 记录类型,用于描述某个 IP 所提供的服务,目前鲜见使用。参见: <https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19683-01/806-4077/dnsintro-154/index.html> 。)
第二天,我就收到了 Joyce 发来的邮件:
>
> Date: Mon, 10 Jul 1995 15:35:33 -0700
> From: [email protected]
> To: [email protected]
> Subject: 回复:请求取得一个端口号
> Cc: [email protected]
>
>
> Tatu,
>
>
> 我们将端口号 22 分配给 ssh 服务了,你目前是该服务的主要联系人。
>
>
> Joyce
>
>
>
这就搞定了!SSH 的端口正式使用 22!!!
1995 年 7 月 12 日上午 2 点 21 分,我给我在赫尔辛基理工大学的测试者们宣布了 SSH 的最后 beta 版本。当日下午 5 点 23 分,我给测试者们宣布了 ssh-1.0.0 版本。1995 年 7 月 12 日,下午 5 点 51 分,我将一份 SSH(安全终端)的宣告发给了 `[email protected]` 的邮件列表,此外我还将其发给了一些新闻组、邮件列表和一些在因特网上讨论相关话题的人们。
### 如何更改 SSH 服务的端口号
SSH 服务器是默认运行在 22 号端口上的。然而,由于某些原因需要,它也可以运行在别的端口上。比如为了方便测试使用,又比如在同一个宿主机上运行多个不同的配置。当然,极少情况下,不使用 root 权限运行它也可以,比如某些必须运行在非特权的端口的情况(端口号大于等于 1024)。
端口号可以在配置文件 [/etc/ssh/sshd\_config](https://www.ssh.com/ssh/sshd_config/) 中将 `Port 22` 更改。也可以使用 `-p <port>` 选项运行 [sshd](https://www.ssh.com/ssh/sshd/)。SSH 客户端和 [sftp](https://www.ssh.com/ssh/sftp/) 程序也可以使用 `-p <port>` 选项。
### 配置 SSH 协议穿越防火墙
SSH 是少数通常被许可穿越防火墙的协议之一。通常的做法是不限制出站的 SSH 连接,尤其常见于一些较小的或者比较技术型的组织中,而入站的 SSH 连接通常会限制到一台或者是少数几台服务器上。
#### 出站的 SSH 连接
在防火墙中配置出站的 SSH 连接十分简单。如果完全限制了外发连接,那么只需要创建一个允许 TCP 端口 22 可以外发的规则即可。如果你想限制目标地址,你可以限制该规则仅允许访问你的组织放在云端的外部服务器或保护该云端的[跳板服务器](https://www.ssh.com/iam/jump-server)即可。
#### 反向通道是有风险的
其实不限制出站的 SSH 连接虽然是可以的,但是是存在风险的,SSH 协议是支持 [通道访问](https://www.ssh.com/ssh/tunneling/) 的。最初的想法是在外部服务器搭建一个 SSH 服务监听来自各处的连接,将进入的连接转发到组织,并让这个连接可以访问某个内部服务器。
在某些场景下这当然非常的方便。开发者和系统管理员经常使用它打开一个通道以便于他们可以远程访问,比如在家里或者在旅行中使用笔记本电脑等场景。
然而通常来讲这些做法是违背安全策略的,跳过了防火墙管理员和安全团队保护的控制无疑是违背安全策略的,比如这些: [PCI](https://www.ssh.com/compliance/pci/)、[HIPAA](https://www.ssh.com/compliance/hipaa/security-rule)、[NIST SP 800-53](https://www.ssh.com/compliance/nist-800-53/) 等。它可以被黑客和外国情报机构用来在组织内留下后门。
[CryptoAuditor](https://www.ssh.com/products/cryptoauditor/) 是一款可以控制通道穿过防火墙或者一组云端服务器入口的产品。该款产品可以配合 [通用 SSH 密钥管理器(Universal SSH Key Manager)](https://www.ssh.com/products/universal-ssh-key-manager/) 来获得对 [主机密钥(host keys)](https://www.ssh.com/ssh/host-key)的访问,以在启用防火墙并阻挡未授权转发的场景中解密 SSH 会话。
#### 入站的 SSH 访问
对于入站访问而言,这里有几点需要说一下:
* 配置防火墙,并转发所有去往 22 端口的连接只能流向到一个特定的内部网络 IP 地址或者一个 [DMZ](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DMZ_(computing)) 主机。在该 IP 上运行 [CryptoAuditor](https://www.ssh.com/products/cryptoauditor/) 或者跳板机来控制和审查所有访问该组织的连接。
* 在防火墙上使用不同的端口访问不同的服务器。
* 只允许使用 [IPsec](https://www.ssh.com/network/ipsec/) 协议这样的 VPN(虚拟专用网)登录后连接 SSH 服务。
### 通过 iptables 服务限制 SSH 访问
[iptables](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iptables) 是一款内建在 Linux 内核的宿主防火墙。通常配置用于保护服务器以防止被访问那些未明确开启的端口。
如果服务器上启用了 `iptables`,使用下面的命令将可以允许进入的 SSH 访问,当然命令需要以 root 身份运行。
```
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
```
如果你想将上述命令创建的规则持久地保存,在某些系统版本中,可使用如下命令:
```
service iptables save
```

---
via: <https://www.ssh.com/ssh/port>
作者:[Tatu Ylonen](https://www.ssh.com/ssh/port) 译者:[kenxx](https://github.com/kenxx) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,477 | 如何备份一个磁盘分区 | https://www.linuxforum.com/threads/partition-backup.3638/ | 2017-05-04T17:42:16 | [
"分区",
"dd",
"dcfldd"
] | /article-8477-1.html | 通常你可能会把数据放在一个分区上,有时候可能需要对该设备或者上面的一个分区进行备份。树莓派用户为了可引导 SD 卡当然有这个需求。其它小体积计算机的用户也会发现这非常有用。有时候设备看起来要出现故障时最好快速做个备份。
进行本文中的实验你需要一个叫 `dcfldd` 的工具。

### dcfldd 工具
该工具是 coreutils 软件包中 `dd` 工具的增强版。`dcfldd` 是 Nicholas Harbour 在美国国防部计算机取证实验室(DCFL)工作期间研发的。该工具的名字也基于他工作的地方 - `dcfldd`。
对于仍然在使用 CoreUtils 8.23 或更低版本的系统,并没有一个可以轻松查看正在创建副本的进度的选项。有时候看起来就像什么都没有发生,以至于你就想取消掉备份。
**注意:**如果你使用 8.24 或更新版本的 `dd` 工具,你就不需要使用 `dcfldd`,只需要用 `dd` 替换 `dcfldd` 即可。所有其它参数仍然适用。
在 Debian 系统上你只需要在 Package Manager 中搜索 `dcfldd`。你也可以打开一个终端然后输入下面的命令:
```
sudo apt-get install dcfldd
```
对于 Red Hat 系统,可以用下面的命令:
```
cd /tmp
wget dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/dcfldd-1.3.4.1-4.el6.i686.rpm
sudo yum install dcfldd-1.3.4.1-4.el6.i686.rpm
dcfldd --version
```
**注意:** 上面的命令安装的是 32 位版本。对于 64 位版本,使用下面的命令:
```
cd /tmp
wget dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/dcfldd-1.3.4.1-4.el6.x86_64.rpm
sudo yum install dcfldd-1.3.4.1-4.el6.x86_64.rpm
dcfldd --version
```
每组命令中的最后一个语句会列出 `dcfldd` 的版本并显示该命令文件已经被加载。
**注意:**确保你以 root 用户执行 `dd` 或者 `dcfldd` 命令。
安装完该工具后你就可以继续使用它备份和恢复分区。
### 备份分区
备份设备的时候可以备份整个设备也可以只是其中的一个分区。如果设备有多个分区,我们可以分别备份每个分区。
在进行备份之前,先让我们来看一下设备和分区的区别。假设我们有一个已经被格式化为一个大磁盘的 SD 卡。这个 SD 卡只有一个分区。如果空间被切分使得 SD 卡看起来是两个设备,那么它就有两个分区。
假设我们有一个树莓派中的 SD 卡。SD 卡容量为 8 GB,有两个分区。第一个分区存放 BerryBoot 启动引导器。第二个分区存放 Kali(LCTT 译注:Kali Linux 是一个 Debian 派生的 Linux 发行版)。现在已经没有可用的空间用来安装第二个操作系统。我们使用大小为 16 GB 的第二个 SD 卡,但拷贝到第二个 SD 卡之前,第一个 SD 卡必须先备份。
要备份第一个 SD 卡我们需要备份设备 `/dev/sdc`。进行备份的命令如下所示:
```
dcfldd if=/dev/sdc of=/tmp/SD-Card-Backup.img
```
备份包括输入文件(`if`)以及被设置为 `/tmp` 目录下名为 `SD-Card-Backup.img` 的输出文件(`of`)。
`dd` 和 `dcfldd` 默认都是每次读写文件中的一个块。通过上述命令,它可以一次默认读写 512 个字节。记住,该复制是一个精准的拷贝 - 逐位逐字节。
默认的 512 个字节可以通过块大小参数 - `bs=` 更改。例如,要每次读写 1 兆字节,参数为 `bs=1M`。使用以下所用的缩写可以设置不同大小:
* b – 512 字节
* KB – 1000 字节
* K – 1024 字节
* MB – 1000x1000 字节
* M – 1024x1024 字节
* GB – 1000x1000x1000 字节
* G – 1024x1024x1024 字节
你也可以单独指定读和写的块大小。要指定读块的大小使用 `ibs=`。要指定写块的大小使用 `obs=`。
我使用三种不同的块大小做了一个 120 MB 分区的备份测试。第一次使用默认的 512 字节,它用了 7 秒钟。第二次块大小为 1024 K,它用时 2 秒。第三次块大小是 2048 K,它用时 3 秒。用时会随系统以及其它硬件实现的不同而变化,但通常来说更大的块大小会比默认的稍微快一点。
完成备份后,你还需要知道如何把数据恢复到设备中。
### 恢复分区
现在我们已经有了一个备份点,假设数据可能被损毁了或者由于某些原因需要进行恢复。
命令和备份时相同,只是源和目标相反。对于上面的例子,命令会变为:
```
dcfldd of=/dev/sdc if=/tmp/SD-Card-Backup.img
```
这里,镜像文件被用作输入文件(`if`)而设备(sdc)被用作输出文件(`of`)。
**注意:** 要记住输出设备会被重写,它上面的所有数据都会丢失。通常来说在恢复数据之前最好用 GParted 删除 SD 卡上的所有分区。
假如你在使用多个 SD 卡,例如多个树莓派主板,你可以一次性写多块 SD 卡。为了做到这点,你需要知道系统中卡的 ID。例如,假设我们想把镜像 `BerryBoot.img` 拷贝到两个 SD 卡。SD 卡分别是 `/dev/sdc` 和 `/dev/sdd`。下面的命令在显示进度时每次读写 1 MB 的块。命令如下:
```
dcfldd if=BerryBoot.img bs=1M status=progress | tee >(dcfldd of=/dev/sdc) | dcfldd of=/dev/sdd
```
在这个命令中,第一个 `dcfldd` 指定输入文件并把块大小设置为 1 MB。`status` 参数被设置为显示进度。然后输入通过管道 `|`传输给命令 `tee`。`tee` 用于将输入分发到多个地方。第一个输出是到命令 `dcfldd of=/dev/sdc`。命令被放到小括号内被作为一个命令执行。我们还需要最后一个管道 `|`,否则命令 `tee` 会把信息发送到 `stdout` (屏幕)。因此,最后的输出是被发送到命令 `dcfldd of=/dev/sdd`。如果你有第三个 SD 卡,甚至更多,只需要添加另外的重定向和命令,类似 `>(dcfldd of=/dev/sde`。
**注意:**记住最后一个命令必须在管道 `|` 后面。
必须验证写的数据确保数据是正确的。
### 验证数据
一旦创建了一个镜像或者恢复了一个备份,你可以验证这些写入的数据。要验证数据,你会使用名为 `diff` 的另一个不同程序。
使用 `diff` ,你需要指定镜像文件的位置以及系统中拷贝自或写入的物理媒介。你可以在创建备份或者恢复了一个镜像之后使用 `diff` 命令。
该命令有两个参数。第一个是物理媒介,第二个是镜像文件名称。
对于例子 `dcfldd of=/dev/sdc if=/tmp/SD-Card-Backup.img`,对应的 `diff` 命令是:
```
diff /dev/sdc /tmp/SD-Card-Backup.img
```
如果镜像和物理设备有任何的不同,你会被告知。如果没有显示任何信息,那么数据就验证为完全相同。
确保数据完全一致是验证备份和恢复完整性的关键。进行备份时需要注意的一个主要问题是镜像大小。
### 分割镜像
假设你想要备份一个 16GB 的 SD 卡。镜像文件大小会大概相同。如果你只能把它备份到 FAT32 分区会怎样呢?FAT32 最大文件大小限制是 4 GB。
必须做的是文件必须被切分为 4 GB 的分片。通过管道 `|` 将数据传输给 `split` 命令可以切分正在被写的镜像文件。
创建备份的方法相同,但命令会包括管道和切分命令。示例备份命令为 `dcfldd if=/dev/sdc of=/tmp/SD-Card-Backup.img` ,其切分文件的新命令如下:
```
dcfldd if=/dev/sdc | split -b 4000MB - /tmp/SD-Card-Backup.img
```
**注意:** 大小后缀和对 `dd` 及 `dcfldd` 命令的意义相同。 `split` 命令中的破折号用于将通过管道从 `dcfldd` 命令传输过来的数据填充到输入文件。
文件会被保存为 `SD-Card-Backup.imgaa` 和 `SD-Card-Backup.imgab`,如此类推。如果你担心文件大小太接近 4 GB 的限制,可以试着用 3500MB。
将文件恢复到设备也很简单。你使用 `cat` 命令将它们连接起来然后像下面这样用 `dcfldd` 写输出:
```
cat /tmp/SD-Card-Backup.img* | dcfldd of=/dev/sdc
```
你可以在命令中 `dcfldd` 部分包含任何需要的参数。
我希望你了解并能执行任何需要的数据备份和恢复,正如 SD 卡和类似设备所需的那样。
(题图:Pixabay, CC0)
---
via: <https://www.linuxforum.com/threads/partition-backup.3638/>
作者:[Jarret](https://www.linuxforum.com/members/jarret.268/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='www.linuxforum.com', port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: /threads/partition-backup.3638/ (Caused by NameResolutionError("<urllib3.connection.HTTPSConnection object at 0x7b8327582170>: Failed to resolve 'www.linuxforum.com' ([Errno -2] Name or service not known)")) | null |
8,479 | Samba 系列(八):使用 Samba 和 Winbind 将 Ubuntu 16.04 添加到 AD 域 | http://www.tecmint.com/join-ubuntu-to-active-directory-domain-member-samba-winbind/ | 2017-05-05T09:21:32 | [
"samba"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8479-1.html | 
这篇文章讲述了如何将 Ubuntu 主机加入到 Samba4 AD 域,并实现使用域帐号登录 Ubuntu 系统。
### 要求:
1. [在 Ubuntu 系统上使用 Samba4 软件来创建活动目录架构](http://www.tecmint.com/install-samba4-active-directory-ubuntu/)
### 第一步: Ubuntu 系统加入到 Samba4 AD 之前的基本配置
1、在将 Ubuntu 主机加入到 AD DC 之前,你得先确保 Ubuntu 系统中的一些服务配置正常。
主机名是你的机器的一个重要标识。因此,在加入域前,使用 `hostnamectl` 命令或者通过手动编辑 `/etc/hostname` 文件来为 Ubuntu 主机设置一个合适的主机名。
```
# hostnamectl set-hostname your_machine_short_name
# cat /etc/hostname
# hostnamectl
```

*设置系统主机名*
2、在这一步中,打开并编辑网卡配置文件,为你的主机设置一个合适的 IP 地址。注意把 DNS 地址设置为你的域控制器的地址。
编辑 `/etc/network/interfaces` 文件,添加 `dns-nameservers` 参数,并设置为 AD 服务器的 IP 地址;添加 `dns-search` 参数,其值为域控制器的主机名,如下图所示。
并且,把上面设置的 DNS IP 地址和域名添加到 `/etc/resolv.conf` 配置文件中,如下图所示:

*为 AD 配置网络设置*
在上面的截图中, `192.168.1.254` 和 `192.168.1.253` 是 Samba4 AD DC 服务器的 IP 地址, `Tecmint.lan` 是 AD 域名,已加入到这个域中的所有机器都可以查询到该域名。
3、重启网卡服务或者重启计算机以使网卡配置生效。使用 ping 命令加上域名来检测 DNS 解析是否正常。
AD DC 应该返回的是 FQDN 。如果你的网络中配置了 DHCP 服务器来为局域网中的计算机自动分配 IP 地址,请确保你已经把 AD DC 服务器的 IP 地址添加到 DHCP 服务器的 DNS 配置中。
```
# systemctl restart networking.service
# ping -c2 your_domain_name
```
4、最后一步是配置服务器时间同步。安装 `ntpdate` 包,使用下面的命令来查询并同步 AD DC 服务器的时间。
```
$ sudo apt-get install ntpdate
$ sudo ntpdate -q your_domain_name
$ sudo ntpdate your_domain_name
```

*AD 服务器时间同步*
5、下一步,在 Ubuntu 机器上执行下面的命令来安装加入域环境所必需软件。
```
$ sudo apt-get install samba krb5-config krb5-user winbind libpam-winbind libnss-winbind
```

*在 Ubuntu 机器上安装 Samba4 软件*
在 Kerberos 软件包安装的过程中,你会被询问输入默认的域名。输入大写的域名,并按 Enter 键继续安装。

*添加 AD 域名*
6、当所有的软件包安装完成之后,使用域管理员帐号来测试 Kerberos 认证,然后执行下面的命令来列出票据信息。
```
# kinit ad_admin_user
# klist
```

*使用 AD 来检查 Kerberos 认证是否正常*
### 第二步:将 Ubuntu 主机添加到 Samba4 AD DC
7、将 Ubuntu 主机添加到 Samba4 活动目录域环境中的第一步是编辑 Samba 配置文件。
备份 Samba 的默认配置文件,这个配置文件是安装 Samba 软件的过程中自动生成的,使用下面的命令来重新初始化配置文件。
```
# mv /etc/samba/smb.conf /etc/samba/smb.conf.initial
# nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
```
在新的 Samba 配置文件中添加以下内容:
```
[global]
workgroup = TECMINT
realm = TECMINT.LAN
netbios name = ubuntu
security = ADS
dns forwarder = 192.168.1.1
idmap config * : backend = tdb
idmap config *:range = 50000-1000000
template homedir = /home/%D/%U
template shell = /bin/bash
winbind use default domain = true
winbind offline logon = false
winbind nss info = rfc2307
winbind enum users = yes
winbind enum groups = yes
vfs objects = acl_xattr
map acl inherit = Yes
store dos attributes = Yes
```

*Samba 服务的 AD 环境配置*
根据你本地的实际情况来替换 `workgroup` , `realm` , `netbios name` 和 `dns forwarder` 的参数值。
由于 `winbind use default domain` 这个参数会让 winbind 服务把任何登录系统的帐号都当作 AD 帐号。因此,如果存在本地帐号名跟域帐号同名的情况下,请不要设置该参数。
8、现在,你应该重启 Samba 后台服务,停止并卸载一些不必要的服务,然后启用 samba 服务的 system-wide 功能,使用下面的命令来完成。
```
$ sudo systemctl restart smbd nmbd winbind
$ sudo systemctl stop samba-ad-dc
$ sudo systemctl enable smbd nmbd winbind
```
9、通过下面的命令,使用域管理员帐号来把 Ubuntu 主机加入到 Samba4 AD DC 中。
```
$ sudo net ads join -U ad_admin_user
```

*把 Ubuntu 主机加入到 Samba4 AD DC*
10、在 [安装了 RSAT 工具的 Windows 机器上](http://www.tecmint.com/manage-samba4-ad-from-windows-via-rsat/) 打开 AD UC ,展开到包含的计算机。你可以看到已加入域的 Ubuntu 计算机。

*确认 Ubuntu 计算机已加入到 Windows AD DC*
### 第三步:配置 AD 帐号认证
11、为了在本地完成 AD 帐号认证,你需要修改本地机器上的一些服务和配置文件。
首先,打开并编辑名字服务切换 (NSS) 配置文件。
```
$ sudo nano /etc/nsswitch.conf
```
然后在 `passwd` 和 `group` 行添加 winbind 值,如下图所示:
```
passwd: compat winbind
group: compat winbind
```

*配置 AD 帐号认证*
12、为了测试 Ubuntu 机器是否已加入到域中,你可以使用 `wbinfo` 命令来列出域帐号和组。
```
$ wbinfo -u
$ wbinfo -g
```

*列出域帐号和组*
13、同时,使用 `getent` 命令加上管道符及 `grep` 参数来过滤指定域用户或组,以测试 Winbind nsswitch 模块是否运行正常。
```
$ sudo getent passwd| grep your_domain_user
$ sudo getent group|grep 'domain admins'
```

*检查 AD 域用户和组*
14、为了让域帐号在 Ubuntu 机器上完成认证登录,你需要使用 root 帐号运行 `pam-auth-update` 命令,然后勾选 winbind 服务所需的选项,以让每个域帐号首次登录时自动创建 home 目录。
查看所有的选项,按 ‘[空格]’键选中,单击 OK 以应用更改。
```
$ sudo pam-auth-update
```

*使用域帐号登录 Ubuntu 主机*
15、在 Debian 系统中,如果想让系统自动为登录的域帐号创建家目录,你需要手动编辑 `/etc/pam.d/common-account` 配置文件,并添加下面的内容。
```
session required pam_mkhomedir.so skel=/etc/skel/ umask=0022
```

*使用域帐号登录 Debian 系统*
16、为了让 AD 用户能够在 Linux 的命令行下修改密码,你需要打开 /etc/pam.d/common-password 配置文件,在 `password` 那一行删除 `use_authtok` 参数,如下图所示:
```
password [success=1 default=ignore] pam_winbind.so try_first_pass
```

*允许域帐号在 Linux 命令行下修改密码*
17、要使用 Samba4 AD 帐号来登录 Ubuntu 主机,在 `su -` 后面加上域用户名即可。你还可以通过运行 `id` 命令来查看 AD 帐号的其它信息。
```
$ su - your_ad_user
```

*查看 AD 用户信息*
使用 [pwd 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/pwd-command-examples/)来查看域帐号的当前目录,如果你想修改域帐号的密码,你可以使用 `passwd` 命令来完成。
18、如果想让域帐号在 ubuntu 机器上拥有 root 权限,你可以使用下面的命令来把 AD 帐号添加到 sudo 系统组中:
```
$ sudo usermod -aG sudo your_domain_user
```
登录域帐号登录到 Ubuntu 主机,然后运行 `apt-get-update` 命令来更新系统,以验证域账号是否拥有 root 权限。

*给域帐号添加 root 权限*
19、要为整个域用户组添加 root 权限,使用 `vi` 命令打开并编辑 `/etc/sudoers` 配置文件,如下图所示,添加如下内容:
```
%YOUR_DOMAIN\\your_domain\ group ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
```

*为域帐号组添加 root 权限*
使用反斜杠来转义域用户组的名称中包含的空格,或者用来转义第一个反斜杠。在上面的例子中, TECMINT 域的域用户组的名字是 “domain admins" 。
前边的 `%` 表明我们指定是的用户组而不是用户名。
20、如果你使用的是图形界面的 Ubuntu 系统,并且你想使用域帐号来登录系统,你需要修改 LightDM 显示管理器,编辑 `/usr/share/lightdm/lightdm.conf.d/50-ubuntu.conf` 配置文件,添加下面的内容,然后重启系统才能生效。
```
greeter-show-manual-login=true
greeter-hide-users=true
```
现在你就可以域帐号来登录 Ubuntu 桌面系统了。使用域用户名或者域用户名@域名.tld 或者域名\域用户名的方式来登录系统。
---
作者简介:
我是一个电脑迷,开源 Linux 系统和软件爱好者,有 4 年多的 Linux 桌面、服务器系统使用和 Base 编程经验。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/join-ubuntu-to-active-directory-domain-member-samba-winbind/>
作者:[Matei Cezar](http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,480 | Fedora 25: Wayland 大战 Xorg | http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/fedora-25-wayland-vs-xorg.html | 2017-05-05T12:42:46 | [
"Wayland",
"Xorg"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8480-1.html | 就像异形大战铁血战士的结果一样,后者略胜一筹。不管怎样,你可能知道,我最近测试了 [Fedora 25](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/fedora-25-gnome.html),体验还可以。总的来说,这个发行版表现的相当不错。它不是最快速的,但随着一系列的改进,变得足够稳定也足够好用。最重要的是,除了一些性能以及响应性的损失,Wayland 并没有造成我的系统瘫痪。但这还仅仅是个开始。
Wayland 作为一种消费者技术还处在它的襁褓期,或者至少是当人们在处理桌面事物时应就这么认为。因此,我必须继续测试,绝不弃坑。在过去的积极地使用 Fedora 25 的几个星期里,我确实碰到了几个其它的问题,有些不用太担心,有些确实很恼人,有些很奇怪,有些却无意义。让我们来讲述一下吧!

### Wayland 并不支持所有软件
没错,这是一个事实。如果你去网站上阅读相关的信息,你会发现各种各样的软件都还没为 Wayland 做好准备。当然,我们都知道 Fedora 是一个激进的高端发行版,它是为了探索新功能而出现的测试床。这没毛病。有一段时间,所有东西都很正常,没有瞎忙活,没有错误。但接下来,我突然需要使用 GParted。我当时很着急,正在排除一个大故障,然而我却让自己置身于一些无意义的额外工作。 GParted 没办法在 Wayland 下直接启动。在探索了更多一些细节之后,我知道了该分区软件目前还没有被 Wayland 支持。

问题就在于我并不太清楚其它哪些应用不能在 Wayland 下运行,并且我不能在一个正确估计的时间敏锐地发现这一点。通过在线搜索,我还是不能快速找到一个简要的当前不兼容列表。可能只是我在搜索方面不太在行,但显而易见这些东西是和“Wayland + 兼容性” 这样的问题一样零零散散的。
我找到了一个[自诩](https://wayland.freedesktop.org/faq.html) Wayland 很棒的文章、一个目前已被这个新玩意儿支持的 [Gnome](https://wiki.gnome.org/Initiatives/Wayland/Applications) 应用程序列表、一些 ArchWiki 上难懂的资料,一篇在[英伟达](https://devtalk.nvidia.com/default/topic/925605/linux/nvidia-364-12-release-vulkan-glvnd-drm-kms-and-eglstreams/)开发论坛上的晦涩得让我后悔点进去的主题,以及一些其他含糊的讨论。
### 再次提到性能
在 Fedora 25 上,我把登录会话从 Gnome(Wayland)切换到 Gnome Xorg,观察会对系统产生什么影响。我之前已经提到过在同一个笔记本([联想 G50](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/lenovo-g50-distros-second-round.html))上的性能跑分和与 [Fedora 24](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/fedora-24-gnome.html) 的比较,但这次会给我们提供更加准确的结果。
Wayland(截图 1)空闲时的内存占用为 1.4GB, CPU 的平均负载约为 4-5%。Xorg(截图 2)占用了同样大小的内存,处理器消耗了全部性能的 3-4%,单纯从数字上来看少了一小点。但是 Xorg 会话的体验却好得多。虽然只是毫秒级的差距,但你能感受得到。传统的会话方式看起来更加的灵动、快速、清新一点。但 Wayland 落后得并不明显。如果你对你的电脑响应速度很敏感,你可能会对这点延迟不会太满意。当然,这也许只是作为新手缺乏优化的缘故,Wayland 会随时间进步。但这一点也是我们所不能忽视的。


### 批评
我对此并不高兴。虽然并不是很愤怒,但我不喜欢为了能完全享受我的桌面体验,我却需要登录到传统的 X 会话。因为 X 给了我全部,但 Wayland 则没有。这意味着我不能一天都用着 Wayland。我喜欢探索科技,但我不是一个盲目的狂热追随者。我只是想用我的桌面,有时我可能需要它快速响应。注销然后重新登录在急需使用的时候会成为恼人的麻烦。我们遇到这个问题的原因就是 Wayland 没有让 Linux 桌面用户的生活变得更简单,而恰恰相反。
引用:
>
> Wayland 是为了成为 X 的更加简单的替代品,更加容易开发和维护。建议 GNOME 和 KDE 都使用它。
>
>
>
你能看到,这就是问题的一方面原因。东西不应该被设计成容易开发或维护。它可以是满足了所有其它消费需求之后提供的有益副产品。但如果没有,那么不管它对于程序员敲代码来说多么困难或简单都将不重要。那是他们的工作。科技的所有目的都是为了达到一种无缝并且流畅的用户体验。
不幸的是,现在很大数量的产品都被重新设计或者开发,只是为了使软件人员更加轻松,而不是用户。在很大程度上,Gnome 3、PulseAudio、[Systemd](http://www.ocsmag.com/2016/10/19/systemd-progress-through-complexity/) 和 Wayland 都没有遵循提高用户体验的宗旨。在这个意义上来说,它们更像是一种打扰,而没有为 Linux 桌面生态的稳定性和易用性作出贡献。
这也是为什么 Linux 桌面是一个相对不成熟产品的一个主要原因————它被设计成开发人员的自我支持产品,更像一个活生生的生物,而不是依附于用户各种怪念头和想法的奴隶。这也是伟大事物是如何形成的,你满足于主要需求,接下来只是担心细节方面。优秀的用户体验不依赖于(也永远不依赖于)编程语言、编译器的选择,或任何其他无意义的东西。如果依赖了,那么不管谁来设计这个抽象层做的不够好的产品,我们都会得到一个失败的作品,需要把它的存在抹去。
那么在我的展望中,我不在乎是否要吐血十升去编译一个 Xorg 或其它什么的版本。我是一个用户,我所在乎的只是我的桌面能否像它昨天或者 5 年前一样健壮地工作。没事的情况下,我不会对宏、类、变量、声明、结构体,或其他任何极客的计算机科技感兴趣。那是不着边际的。一个产品宣传自己是被创造出来为人们的开发提供方便的,那是个悖论。如果接下来再也不用去开发它了,这样反而会使事情更简单。
现在,事实是 Wayland 大体上可用,但它仍然不像 Xorg 那么好,并且它也不应该在任何的桌面上作为就绪的产品被提供。一但它能够无人知晓般无缝地取代那些过时技术,只有在那种时候,它才获得了它所需要的成功,那之后,它可以用 C、D 或者 K 之类的无论什么语言编写,拥有开发者需要的任何东西。而在那之前,它都是一个蚕食资源和人们思想的寄生虫而已。
不要误会,我们需要进步,需要改变。但它必须为了进化的目而服务。现在 Xorg 能很好地满足用户需求了吗?它能为第三方库提供图形支持吗?它能支持 HD、UHD、DPI 或其他的什么吗?你能用它玩最新的游戏吗?行还是不行?如果不行,那么它就需要被改进。这些就是进化的驱动力,而不是写代码或者编译代码的困难程度。软件开发者是数字工业的矿工,他们需要努力工作而取悦于用户。就像短语“更加易于开发”应该被取缔一样,那些崇尚于此的人也应该用老式收音机的电池处以电刑,然后用没有空调的飞船流放到火星上去。如果你不能写出高明的代码,那是你的问题。用户不能因为开发者认为自己是公主而遭受折磨。
### 结语
说到这里。大体上说,Wayland 还可以,并不差。但这说的就像是某人决定修改你工资单上分配比例,导致你从昨天能赚 100% 到今天只能赚 83% 一样。讲道理这是不能接受的,即使 Wayland 工作的相当好。正是那些不能运作的东西导致如此大的不同。忽略所有批评它的一面,Wayland 被认为降低了可用性、性能以及软件的知名度,这正是 Fedora 亟待解决的问题。
其他的发行版会跟进,然后我们会看到历史重演,就像 Gnome 3 和 Systemd 所发生的一样。没有完全准备好的东西被放到开放环境中,然后我们花费一两年时间修复那些本无需修复的东西,最终我们将拥有的是我们已经拥有的相同功能,只是用不同的编程语言来实现。我并不感兴趣这些。计算机科学曾在 1999 年非常受欢迎,当时 Excel 用户每小时能赚 50 美元。而现在,编程就像是躲在平底船下划桨,人们并不会在乎你在甲板下流下的汗水与磨出的水泡。
性能可能不太是一个问题了,因为你可以放弃 1-2% 的变化,尤其是它会受随机的来自任何一个因素的影响,如果你已经用 Linux 超过一、两年你就会知道的。但是无法启动应用是个大问题。不过至少, Fedora 也友好地提供了传统的平台。但是,它可能会在 Wayland 100% 成熟前就消失了。我们再来看看,不,不会有灾难。我原本的 Fedora 25 宣称支持这种看法。我们有的就是烦恼,不必要的烦恼。啊,这是 Linux 故事中的第 9000 集。
那么,在今天结束之际,我们已经讨论了所有事情。从中我们学到:**臣伏于 Xorg!天呐!**真棒,现在我将淡入背景音乐,而笑声会将你的欢乐带给寒冷的夜晚。再见!
干杯。
(题图来自 [Wikimedia](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:DragonCon-AlienVsPredator.jpg) 并做了些修改, [CC BY-SA 3.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en) 许可)
---
作者简介:
我是 Igor Ljubuncic。现在大约 38 岁,已婚但还没有孩子。我现在在一个大胆创新的云科技公司做首席工程师。直到大约 2015 年初,我还在一个全世界最大的 IT 公司之一中做系统架构工程师,和一个工程计算团队开发新的基于 Linux 的解决方案,优化内核以及攻克 Linux 的问题。在那之前,我是一个为高性能计算环境设计创新解决方案的团队的技术领导。还有一些其他花哨的头衔,包括系统专家、系统程序员等等。所有这些都曾是我的爱好,但从 2008 年开始成为了我的有偿的工作。还有什么比这更令人满意的呢?
从 2004 年到 2008 年间,我曾通过作为医学影像行业的物理学家来糊口。我的工作专长集中在解决问题和算法开发。为此,我广泛地使用了 Matlab,主要用于信号和图像处理。另外,我得到了几个主要的工程方法学的认证,包括 MEDIC 六西格玛绿带、试验设计以及统计工程学。
我也写过书,包括高度魔幻类和 Linux 上的技术工作方面的,彼此交织。
---
via: <http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/fedora-25-wayland-vs-xorg.html>
作者:[Igor Ljubuncic](http://www.dedoimedo.com/faq.html) 译者:[cycoe](https://github.com/cycoe) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,481 | 详解 UEFI 模式下安装 Linux | http://www.rodsbooks.com/linux-uefi/ | 2017-05-06T08:05:00 | [
"UEFI",
"BIOS",
"GRUB"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8481-1.html |
>
> 此页面是免费浏览的,没有烦人的外部广告;然而,我的确花了时间准备,网站托管也花了钱。如果您发现此页面帮到了您,请考虑进行小额[捐款](http://www.rodsbooks.com/linux-uefi/),以帮助保持网站的运行。谢谢! 原著于 2013/10/19;最后修改于 2015/3/16
>
>
>

### 引言
几年来,一种新的固件技术悄然出现,而大多数普通用户对此并无所知。该技术被称为<ruby> <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uefi"> 可扩展固件接口 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Extensible Firmware Interface </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(EFI), 或更新一些的统一可扩展固件接口(Unified EFI,UEFI,本质上是 EFI 2.x),它已经开始替代古老的<ruby> <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BIOS"> 基本输入/输出系统 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Basic Input/Output System </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(BIOS)固件技术,有经验的计算机用户或多或少都有些熟悉 BIOS。
本页面是给 Linux 用户使用 EFI 技术的一个快速介绍,其中包括有关开始将 Linux 安装到此类计算机上的建议。不幸的是,EFI 是一个庞杂的话题;EFI 软件本身是复杂的,许多实现有系统特定的怪异行为甚至是缺陷。因此,我无法在一个页面上描述在 EFI 计算机上安装和使用 Linux 的一切知识。我希望你能将本页面作为一个有用的起点,不管怎么说,每个部分以及末尾“参考文献”部分的链接可以指引你找到更多的文档。
### 你的计算机是否使用 EFI 技术?
EFI 是一种*固件*,意味着它是内置于计算机中处理低级任务的软件。最重要的是,固件控制着计算机的引导过程,反过来说这代表着基于 EFI 的计算机与基于 BIOS 的计算机的引导过程不同。(有关此规律的例外之处稍后再说。)这种差异可能使操作系统安装介质的设计超级复杂化,但是一旦安装好并运行之后,它对计算机的日常操作几乎没有影响。请注意,大多数制造商使用术语 “BIOS” 来表示他们的 EFI。我认为这种用法很混乱,所以我避免了;在我看来,EFI 和 BIOS 是两种不同类型的固件。
>
> **注意:**苹果公司的 Mac 使用的 EFI 在许多方面是不同寻常的。尽管本页面的大部分内容同样适用于 Mac,但有些细节上的出入,特别是在设置 EFI 引导加载程序的时候。这个任务最好在 OS X 上进行,使用 Mac 的 [bless utility](http://ss64.com/osx/bless.html)工具,我不在此做过多描述。
>
>
>
自从 2006 年第一次推出以来,EFI 已被用于基于英特尔的 Mac 上。从 2012 年底开始,大多数安装 Windows 8 或更高版本系统的计算机就已经默认使用 UEFI 启动,实际上大多数 PC 从 2011 年中期就开始使用 UEFI,虽然默认情况下它们可能无法以 EFI 模式启动。2011 年前销出的 PC 也有一些支持 EFI,尽管它们大都默认使用 BIOS 模式启动。
如果你不确定你的计算机是否支持 EFI,则应查看固件设置实用程序和参考用户手册关于 *EFI*、*UEFI* 以及 *legacy booting* 的部分。(可以通过搜索用户手册的 PDF 文件来快速了解。)如果你没有找到类似的参考,你的计算机可能使用老式的(“legacy”) BIOS 引导;但如果你找到了这些术语的参考,几乎可以肯定它使用了 EFI 技术。你还可以尝试*只*有 EFI 模式的引导加载器的安装介质。使用 [rEFInd](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/getting.html) 制作的 USB 闪存驱动器或 CD-R 镜像是用来测试不错的选择。
在继续之前,你应当了解大多数 x86 和 x86-64 架构的计算机上的 EFI 都包含一个叫做<ruby> 兼容支持模块 <rt> Compatibility Support Module </rt></ruby>(CSM)的组件,这使得 EFI 能够使用旧的 BIOS 风格的引导机制来引导操作系统。这会非常方便,因为它向后兼容;但是这样也导致一些意外情况的发生,因为计算机不论以 EFI 模式引导还是以 BIOS (也称为 CSM 或 legacy)模式引导,在控制时没有标准的使用规范和用户界面。特别地,你的 Linux 安装介质非常容易意外的以 BIOS/CSM/legacy 模式启动,这会导致 Linux 以 BIOS/CSM/legacy 模式安装。如果 Linux 是唯一的操作系统,也可以正常工作,但是如果与在 EFI 模式下的 Windows 组成双启动的话,就会非常复杂。(反过来问题也可能发生。)以下部分将帮助你以正确模式引导安装程序。如果你在阅读这篇文章之前就已经以 BIOS 模式安装了 Linux,并且希望切换引导模式,请阅读后续章节,“哎呀:将传统模式下安装的引导转为 EFI 模式下的引导”。
UEFI 的一个附加功能值得一提:<ruby> 安全启动 <rt> Secure Boot </rt></ruby>。此特性旨在最大限度的降低计算机受到 *boot kit* 病毒感染的风险,这是一种感染计算机引导加载程序的恶意软件。Boot kits 很难检测和删除,阻止它们的运行刻不容缓。微软公司要求所有带有支持 Windows 8 标志的台式机和笔记本电脑启用 安全启动。这一配置使 Linux 的安装变得复杂,尽管有些发行版可以较好的处理这个问题。不要将安全启动和 EFI 或 UEFI 混淆;支持 EFI 的计算机不一定支持 安全启动,而且支持 EFI 的 x86-64 的计算机也可以禁用 安全启动。微软同意用户在 Windows 8 认证的 x86 和 x86-64 计算机上禁用安全启动功能;然而对装有 Windows 8 的 ARM 计算机而言却相反,它们必须**不允许**用户禁用 安全启动。幸运的是,基于 ARM 的 Windows 8 计算机目前很少见。我建议避免使用它们。
### 你的发行版是否支持 EFI 技术?
大多数 Linux 发行版已经支持 EFI 好多年了。然而,不同的发行版对 EFI 的支持程度不同。大多数主流发行版(Fedora,OpenSUSE,Ubuntu 等)都能很好的支持 EFI,包括对安全启动的支持。另外一些“自行打造”的发行版,比如 Gentoo,对 EFI 的支持较弱,但它们的性质使其很容易添加 EFI 支持。事实上,可以向*任意* Linux 发行版添加 EFI 支持:你需要安装 Linux(即使在 BIOS 模式下),然后在计算机上安装 EFI 引导加载程序。有关如何执行此操作的信息,请参阅“哎呀:将传统模式下安装的引导转为 EFI 模式下的引导”部分。
你应当查看发行版的功能列表,来确定它是否支持 EFI。你还应当注意你的发行版对安全启动的支持情况,特别是如果你打算和 Windows 8 组成双启动。请注意,即使正式支持安全启动的发行版也可能要求禁用此功能,因为 Linux 对安全启动的支持通常很差劲,或者导致意外情况的发生。
### 准备安装 Linux
下面几个准备步骤有助于在 EFI 计算机上 Linux 的安装,使其更加顺利:
#### 1、 升级固件
有些 EFI 是有问题的,不过硬件制造商偶尔会发布其固件的更新。因此我建议你将固件升级到最新可用的版本。如果你从论坛的帖子知道自己计算机的 EFI 有问题,你应当在安装 Linux 之前更新它,因为如果安装 Linux 之后更新固件,会有些问题需要额外的操作才能解决。另一方面,升级固件是有一定风险的,所以如果制造商提供了 EFI 支持,最好的办法就是按它们提供的方式进行升级。
#### 2、 了解如何使用固件
通常你可以通过在引导过程之初按 Del 键或功能键进入固件设置实用程序。按下开机键后尽快查看相关的提示信息,或者尝试每个功能键。类似的,ESC 键或功能键通常可以进入固件的内置引导管理器,可以选择要进入的操作系统或外部设备。一些制造商把这些设置隐藏的很深。在某些情况下,如[此页面](http://www.eightforums.com/tutorials/20256-uefi-firmware-settings-boot-inside-windows-8-a.html)所述,你可以在 Windows 8 内做到这些。
#### 3、调整以下固件设置
* **快速启动** — 此功能可以通过在硬件初始化时使用快捷方式来加快引导过程。这很好用,但有时候会使 USB 设备不能初始化,导致计算机无法从 USB 闪存驱动器或类似的设备启动。因此禁用快速启动*可能*有一定的帮助,甚至是必须的;你可以让它保持激活,而只在 Linux 安装程序启动遇到问题时将其停用。请注意,此功能有时可能会以其它名字出现。在某些情况下,你必须*启用* USB 支持,而不是*禁用*快速启动功能。
* **安全启动** — Fedora,OpenSUSE,Ubuntu 以及其它的发行版官方就支持安全启动;但是如果在启动引导加载程序或内核时遇到问题,可能需要禁用此功能。不幸的是,没办法具体描述怎么禁用,因为不同计算机的设置方法也不同。请参阅[我的安全启动页面](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/secureboot.html#disable)获取更多关于此话题的信息。
>
> **注意:** 一些教程说安装 Linux 时需要启用 BIOS/CSM/legacy 支持。通常情况下,这样做是错的。启用这些支持可以解决启动安装程序涉及的问题,但也会带来新的问题。以这种方式安装的教程通常可以通过“引导修复”来解决这些问题,但最好从一开始就做对。本页面提供了帮助你以 EFI 模式启动 Linux 安装程序的提示,从而避免以后的问题。
>
>
>
* **CSM/legacy 选项** — 如果你想以 EFI 模式安装,请*关闭*这些选项。一些教程推荐启用这些选项,有时这是必须的 —— 比如,有些附加视频卡需要在固件中启用 BIOS 模式。尽管如此,大多数情况下启用 CSM/legacy 支持只会无意中增加以 BIOS 模式启动 Linux 的风险,但你并*不想*这样。请注意,安全启动和 CSM/legacy 选项有时会交织在一起,因此更改任一选项之后务必检查另一个。
#### 4、 禁用 Windows 的快速启动功能
[这个页面](http://www.eightforums.com/tutorials/6320-fast-startup-turn-off-windows-8-a.html)描述了如何禁用此功能,不禁用的话会导致文件系统损坏。请注意此功能与固件的快速启动不同。
#### 5、 检查分区表
使用 [GPT fdisk](http://www.rodsbooks.com/gdisk/)、parted 或其它任意分区工具检查磁盘分区。理想情况下,你应该创建一个包含每个分区确切起点和终点(以扇区为单位)的纸面记录。这会是很有用的参考,特别是在安装时进行手动分区的时候。如果已经安装了 Windows,确定可以识别你的 [EFI 系统分区(ESP)](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EFI_System_partition),它是一个 FAT 分区,设置了“启动标记”(在 parted 或 Gparted 中)或在 gdisk 中的类型码为 EF00。
### 安装 Linux
大部分 Linux 发行版都提供了足够的安装说明;然而我注意到了在 EFI 模式安装中的几个常见的绊脚石:
* **确保使用正确位深的发行版** — EFI 启动加载器和 EFI 自身的位深相同。现代计算机通常是 64 位,尽管最初几代基于 Intel 的 Mac、一些现代的平板电脑和变形本、以及一些鲜为人知的电脑使用 32 位 EFI。虽然可以将 32 位 EFI 引导加载程序添加至 32 位发行版,但我还没有遇到过正式支持 32 位 EFI 的 Linux 发行版。(我的 《[在 Linux 上管理 EFI 引导加载程序](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders)》 一文概述了引导加载程序,而且理解了这些原则你就可以修改 32 位发行版的安装程序,尽管这不是一个初学者该做的。)在 64 位 EFI 的计算机上安装 32 位发行版最让人头疼,我不准备在这里描述这一过程;在具有 64 位 EFI 的计算机上,你应当使用 64 位的发行版。
* **正确准备引导介质** — 将 .iso 镜像传输到 USB 闪存驱动器的第三方工具,比如 unetbootin,在创建正确的 EFI 模式引导项时经常失败。我建议按照发行版维护者的建议来创建 USB 闪存驱动器。如果没有类似的建议,使用 Linux 的 dd 工具,通过执行 `dd if=image.iso of=/dev/sdc` 在识别为 `/dev/sdc` 的 USB 闪存驱动器上创建一个镜像。至于 Windows,有 [WinDD](https://sourceforge.net/projects/windd/) 和 [dd for windows](http://www.chrysocome.net/dd),但我从没测试过它们。请注意,使用不兼容 EFI 的工具创建安装介质是错误的,这会导致人们进入在 BIOS 模式下安装然后再纠正它们的误区,所以不要忽视这一点!
* **备份 ESP 分区** — 如果计算机已经存在 Windows 或者其它的操作系统,我建议在安装 Linux 之前备份你的 ESP 分区。尽管 Linux *不应该* 损坏 ESP 分区已有的文件,但似乎这时不时发生。发生这种事情时备份会有很大用处。只需简单的文件级的备份(使用 cp,tar,或者 zip 类似的工具)就足够了。
* **以 EFI 模式启动** — 以 BIOS/CSM/legacy 模式引导 Linux 安装程序的意外非常容易发生,特别是当固件启用 CSM/legacy 选项时。下面一些提示可以帮助你避免此问题:
+ 进入 Linux shell 环境执行 `ls /sys/firmware/efi` 验证当前是否处于 EFI 引导模式。如果你看到一系列文件和目录,表明你已经以 EFI 模式启动,而且可以忽略以下多余的提示;如果没有,表明你是以 BIOS 模式启动的,应当重新检查你的设置。
+ 使用固件内置的引导管理器(你应该已经知道在哪;请参阅“了解如何使用固件”)使之以 EFI 模式启动。一般你会看到 CD-R 或 USB 闪存驱动器两个选项,其中一个选项包括 *EFI* 或 *UEFI* 字样的描述,另一个不包括。使用 EFI/UEFI 选项来启动介质。
+ 禁用安全启动 - 即使你使用的发行版官方支持安全启动,有时它们也不能生效。在这种情况下,计算机会静默的转到下一个引导加载程序,它可能是启动介质的 BIOS 模式的引导加载程序,导致你以 BIOS 模式启动。请参阅我的[安全启动的相关文章](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/secureboot.html#disable)以得到禁用安全启动的相关提示。
+ 如果 Linux 安装程序总是无法以 EFI 模式启动,试试用我的 [rEFInd 引导管理器](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/getting.html) 制作的 USB 闪存驱动器或 CD-R。如果 rEFInd 启动成功,那它保证是以 EFI 模式运行的,而且在基于 UEFI 的 PC 上,它只显示 EFI 模式的引导项,因此若您启动到 Linux 安装程序,则应处于 EFI 模式。(但是在 Mac 上,除了 EFI 模式选项之外,rEFInd 还显示 BIOS 模式的引导项。)
* **准备 ESP 分区** — 除了 Mac,EFI 使用 ESP 分区来保存引导加载程序。如果你的计算机已经预装了 Windows,那么 ESP 分区就已存在,可以在 Linux 上直接使用。如果不是这样,那么我建议创建一个大小为 550 MB 的 ESP 分区。(如果你已有的 ESP 分区比这小,别担心,直接用就行。)在此分区上创建一个 FAT32 文件系统。如果你使用 Gparted 或者 parted 准备 ESP 分区,记得给它一个“启动标记”。如果你使用 GPT fdisk(gdisk,cgdisk 或 sgdisk)准备 ESP 分区,记得给它一个名为 EF00 的类型码。有些安装程序会创建一个较小的 ESP 分区,并且设置为 FAT16 文件系统。尽管这样能正常工作,但如果你之后需要重装 Windows,安装程序会无法识别 FAT16 文件系统的 ESP 分区,所以你需要将其备份后转为 FAT32 文件系统。
* **使用 ESP 分区** — 不同发行版的安装程序以不同的方式辨识 ESP 分区。比如,Debian 和 Ubuntu 的某些版本把 ESP 分区称为“EFI boot partition”,而且不会明确显示它的挂载点(尽管它会在后台挂载);但是有些发行版,像 Arch 或 Gentoo,需要你去手动挂载。尽管将 ESP 分区挂载到 /boot 进行相应配置后可以正常工作,特别是当你想使用 gummiboot 或 ELILO(译者注:gummiboot 和 ELILO 都是 EFI 引导工具)时,但是在 Linux 中最标准的 ESP 分区挂载点是 /boot/efi。某些发行版的 /boot 不能用 FAT 分区。因此,当你设置 ESP 分区挂载点时,请将其设置为 /boot/efi。除非 ESP 分区没有,否则*不要*为其新建文件系统 — 如果已经安装 Windows 或其它操作系统,它们的引导文件都在 ESP 分区里,新建文件系统会销毁这些文件。
* **设置引导程序的位置** — 某些发行版会询问将引导程序(GRUB)装到何处。如果 ESP 分区按上述内容正确标记,不必理会此问题,但有些发行版仍会询问。请尝试使用 ESP 分区。
* **其它分区** — 除了 ESP 分区,不再需要其它的特殊分区;你可以设置 根(/)分区,swap 分区,/home 分区,或者其它分区,就像你在 BIOS 模式下安装时一样。请注意 EFI 模式下*不需要设置*[BIOS 启动分区](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BIOS_Boot_partition),所以如果安装程序提示你需要它,意味着你可能意外的进入了 BIOS 模式。另一方面,如果你创建了 BIOS 启动分区,会更灵活,因为你可以安装 BIOS 模式下的 GRUB,然后以任意模式(EFI 模式 或 BIOS 模式)引导。
* **解决无显示问题** — 2013 年,许多人在 EFI 模式下经常遇到(之后出现的频率逐渐降低)无显示的问题。有时可以在命令行下通过给内核添加 `nomodeset` 参数解决这一问题。在 GRUB 界面按 `e` 键会打开一个简易文本编辑器。大多数情况下你需要搜索有关此问题的更多信息,因为此问题更多是由特定硬件引起的。
在某些情况下,你可能不得不以 BIOS 模式安装 Linux。但你可以手动安装 EFI 引导程序让 Linux 以 EFI 模式启动。请参阅《 [在 Linux 上管理 EFI 引导加载程序](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/)》 页面获取更多有关它们以及如何安装的可用信息。
### 解决安装后的问题
如果 Linux 无法在 EFI 模式下工作,但在 BIOS 模式下成功了,那么你可以完全放弃 EFI 模式。在只有 Linux 的计算机上这非常简单;安装 BIOS 引导程序即可(如果你是在 BIOS 模式下安装的,引导程序也应随之装好)。如果是和 EFI 下的 Windows 组成双系统,最简单的方法是安装我的 [rEFInd 引导管理器](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/)。在 Windows 上安装它,然后编辑 `refind.conf` 文件:取消注释 `scanfor` 一行,并确保拥有 `hdbios` 选项。这样 rEFInd 在引导时会重定向到 BIOS 模式的引导项。
如果重启后计算机直接进入了 Windows,很可能是 Linux 的引导程序或管理器安装不正确。(但是应当首先尝试禁用安全启动;之前提到过,它经常引发各种问题。)下面是关于此问题的几种可能的解决方案:
* **使用 efibootmgr** — 你可以以 *EFI 模式*引导一个 Linux 急救盘,使用 efibootmgr 实用工具尝试重新注册你的 Linux 引导程序,如[这里](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/installation.html)所述。
* **使用 Windows 上的 bcdedit** — 在 Windows 管理员命令提示符窗口中,输入 `bcdedit /set {bootmgr}path \EFI\fedora\grubx64.efi` 会用 ESP 分区的 `EFI/fedora/grubx64.efi` 文件作为默认的引导加载程序。根据需要更改此路径,指向你想设置的引导文件。如果你启用了安全启动,需要设置 `shim.efi`,`shimx64.efi` 或者 `PreLoader.efi`(不管有哪个)为引导而不是 `grubx64.efi`。
* **安装 rEFInd** — 有时候 rEFInd 可以解决这个问题。我推荐使用 [CD-R 或者 USB 闪存驱动器](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/getting.html)进行测试。如果 Linux 可以启动,就安装 Debian 软件包、RPM 程序,或者 .zip 文件包。(请注意,你需要在一个高亮的 Linux vmlinuz\* 选项按两次 `F2` 或 `Insert` 修改启动选项。如果你的启动分区是单独的,这就更有必要了,因为这种情况下,rEFInd 无法找到根(/)分区,也就无法传递参数给内核。)
* **使用修复引导程序** — Ubuntu 的[引导修复实用工具](https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Boot-Repair)可以自动修复一些问题;然而,我建议只在 Ubuntu 和 密切相关的发行版上使用,比如 Mint。有时候,有必要通过高级选项备份并替换 Windows 的引导。
* **劫持 Windows 引导程序** — 有些不完整的 EFI 引导只能引导 Windows,就是 ESP 分区上的 `EFI/Microsoft/Boot/bootmgfw.efi` 文件。因此,你可能需要将引导程序改名(我建议将其移动到上级目录 `EFI/Microsoft/bootmgfw.efi`),然后将首选引导程序复制到这里。(大多数发行版会在 EFI 的子目录放置 GRUB 的副本,例如 Ubuntu 的 EFI/ubuntu,Fedora 的 EFI/fedora。)请注意此方法是个丑陋的解决方法,有用户反映 Windows 会替换引导程序,所以这个办法不是 100% 有效。然而,这是在不完整的 EFI 上生效的唯一办法。在尝试之前,我建议你升级固件并重新注册自己的引导程序,Linux 上用 efibootmgr,Windows 上用 bcdedit。
有关引导程序的其它类型的问题 - 如果 GRUB(或者你的发行版默认的其它引导程序或引导管理器)没有引导操作系统,你必须修复这个问题。因为 GRUB 2 引导 Windows 时非常挑剔,所以 Windows 经常启动失败。在某些情况下,安全启动会加剧这个问题。请参阅[我的关于 GRUB 2 的页面](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/grub2.html)获取一个引导 Windows 的 GRUB 2 示例。还会有很多原因导致 Linux 引导出现问题,类似于 BIOS 模式下的情况,所以我没有全部写出来。
尽管 GRUB 2 使用很普遍,但我对它的评价却不高 - 它很复杂,而且难以配置和使用。因此,如果你在使用 GRUB 的时候遇到了问题,我的第一反应就是用别的东西代替。[我的用于 Linux 的 EFI 引导程序页面](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders)有其它的选择。其中包括我的 [rEFInd 引导管理器](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/),它除了能够让许多发行版上的 GRUB 2 工作,也更容易安装和维护 - 但是它还不能完全代替 GRUB 2。
除此之外,EFI 引导的问题可能很奇怪,所以你需要去论坛发帖求助。尽量将问题描述完整。[Boot Info Script](http://sourceforge.net/projects/bootinfoscript/) 可帮助你提供有用的信息 - 运行此脚本,将生成的名为 RESULTS.txt 的文件粘贴到论坛的帖子上。一定要将文本粘贴到 `[code]` 和 `[/code]` 之间;不然会遭人埋怨。或者将 RESULTS.txt 文件上传到 pastebin 网站上,比如 [pastebin.com](http://pastebin.com/),然后将网站给你的 URL 地址发布到论坛。
### 哎呀:将传统模式下安装的系统转为 EFI 模式下引导
**警告:**这些指南主要用于基于 UEFI 的 PC。如果你的 Mac 已经安装了 BIOS 模式下的 Linux,但想以 EFI 模式启动 Linux,可以*在 OS X* 中安装引导程序。rEFInd(或者旧式的 rEFIt)是 Mac 上的常用选择,但 GRUB 可以做的更多。
论坛上有很多人看了错误的教程,在已经存在 EFI 模式的 Windows 的情况下,安装了 BIOS 引导的 Linux,这一问题在 2015 年初很普遍。这样配置效果很不好,因为大多数 EFI 很难在两种模式之间切换,而且 GRUB 也无法胜任这项工作。你可能会遇到不完善的 EFI 无法启动外部介质的情况,也可能遇到 EFI 模式下的显示问题,或者其它问题。
如前所述,在“解决安装后的问题”部分,解决办法之一就是*在 Windows* 上安装 rEFInd,将其配置为支持 BIOS 模式引导。然后可以引导 rEFInd 并链式引导到你的 BIOS 模式的 GRUB。在 Linux 上遇到 EFI 特定的问题时,例如无法使用显卡,我建议你使用这个办法修复。如果你没有这样的 EFI 特定的问题,在 Windows 中安装 rEFInd 和合适的 EFI 文件系统驱动可以让 Linux 直接以 EFI 模式启动。这个解决方案很完美,它和我下面描述的内容等同。
大多数情况下,最好将 Linux 配置为以 EFI 模式启动。有很多办法可以做到,但最好的是使用 Linux 的 EFI 引导模式(或者,可以想到,Windows,或者一个 EFI shell)注册到你首选的引导管理器。实现这一目标的方法如下:
1. 下载适用于 USB 闪存驱动器或 CD-R 的 [rEFInd 引导管理器](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/getting.html)。
2. 从下载的镜像文件生成安装介质。可以在任何计算机上准备,不管是 EFI 还是 BIOS 的计算机都可以(或者在其它平台上使用其它方法)。
3. 如果你还没有这样做,[请禁用安全启动](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/secureboot.html#disable)。因为 rEFInd CD-R 和 USB 镜像不支持安全启动,所以这很必要,你可以在以后重新启用它。
4. 在目标计算机上启动 rEFInd。如前所述,你可能需要调整固件设置,并使用内置引导管理器选择要引导的介质。你选择的那一项也许在其描述中包含 *UEFI* 这样的字符串。
5. 在 rEFInd 上测试引导项。你应该至少看到一个启动 Linux 内核的选项(名字含有 vmlinuz 这样的字符串)。有两种方法可以启动它:
* 如果你*没有*独立的 `/boot` 分区,只需简单的选择内核并按回车键。Linux 就会启动。
* 如果你*确定有*一个独立的 `/boot` 分区,按两次 `Insert` 或 `F2` 键。这样会打开一个行编辑器,你可以用它来编辑内核选项。增加一个 `root=` 格式以标识根(/)文件系统,如果根(/)分区在 `/dev/sda5` 上,就添加 `root=/dev/sda5`。如果不知道根文件系统在哪里,那你需要重启并尽可能想到办法。在一些罕见的情况下,你可能需要添加其它内核选项来代替或补充 `root=` 选项。比如配置了 LVM(LCTT 译注:Logical Volume Manager,逻辑卷管理)的 Gentoo 就需要 `dolvm` 选项。
6. Linux 一旦启动,安装你想要的引导程序。rEFInd 的安装很简单,可以通过 RPM、Debian 软件包、PPA,或从[rEFInd 下载页面](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/getting.html)下载的二进制 .zip 文件进行安装。在 Ubuntu 和相关的发行版上,引导修改程序可以相对简单地修复你的 GRUB 设置,但你要对它有信心可以正常工作。(它通常工作良好,但有时候会把事情搞得一团糟。)另外一些选项都在我的 《[在 Linux 上管理 EFI 引导加载程序](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/)》 页面上。
7. 如果你想在安全启动激活的情况下引导,只需重启并启用它。但是,请注意,可能需要额外的安装步骤才能将引导程序设置为使用安全启动。有关详细信息,请参阅[我关于这个主题的页面](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/secureboot.html)或你的引导程序有关安全启动的文档资料。
重启时,你可以看到刚才安装的引导程序。如果计算机进入了 BIOS 模式下的 GRUB,你应当进入固件禁用 BIOS/CSM/legacy 支持,或调整引导顺序。如果计算机直接进入了 Windows,那么你应当阅读前一部分,“解决安装后的问题”。
你可能想或需要调整你的配置。通常是为了看到额外的引导选项,或者隐藏某些选项。请参阅引导程序的文档资料,以了解如何进行这些更改。
### 参考和附加信息
* **信息网页**
+ 我的 《[在 Linux 上管理 EFI 引导加载程序](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/)》 页面含有可用的 EFI 引导程序和引导管理器。
+ [OS X's bless tool 的手册页](http://ss64.com/osx/bless.html) 页面在设置 OS X 平台上的引导程序或引导管理器时可能会很有用。
+ [EFI 启动过程](http://homepage.ntlworld.com/jonathan.deboynepollard/FGA/efi-boot-process.html) 描述了 EFI 启动时的大致框架。
+ [Arch Linux UEFI wiki page](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Unified_Extensible_Firmware_Interface) 有大量关于 UEFI 和 Linux 的详细信息。
+ 亚当·威廉姆森写的一篇不错的 《[什么是 EFI,它是怎么工作的](https://www.happyassassin.net/2014/01/25/uefi-boot-how-does-that-actually-work-then/)》。
+ [这个页面](http://www.eightforums.com/tutorials/20256-uefi-firmware-settings-boot-inside-windows-8-a.html) 描述了如何从 Windows 8 调整 EFI 的固件设置。
+ 马修·J·加勒特是 Shim 引导程序的开发者,此程序支持安全启动,他维护的[博客](http://mjg59.dreamwidth.org/)经常更新有关 EFI 的问题。
+ 如果你对 EFI 软件的开发感兴趣,我的 《[EFI 编程](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-programming/)》 页面可以为你起步助力。
* **附加程序**
+ [rEFInd 官网](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/)
+ [gummiboot 官网](http://freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/gummiboot)
+ [ELILO 官网](http://elilo.sourceforge.net/)
+ [GRUB 官网](http://www.gnu.org/software/grub/)
+ [GPT fdisk 分区软件官网](http://www.rodsbooks.com/gdisk/)
+ Ubuntu 的 [引导修复实用工具](https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Boot-Repair)可帮助解决一些引启动问题
* **交流**
+ [Sourceforge 上的 rEFInd 交流论坛](https://sourceforge.net/p/refind/discussion/)是 rEFInd 用户互相交流或与我联系的一种方法。
+ Pastebin 网站,比如 [http://pastebin.com](http://pastebin.com/), 是在 Web 论坛上与其他用户交换大量文本的一种便捷的方法。
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
via: <http://www.rodsbooks.com/linux-uefi/>
作者:[Roderick W. Smith]([email protected]) 译者:[fuowang](https://github.com/fuowang) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # Linux on UEFI:
A Quick Installation Guide
by Roderick W. Smith, [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected])
Originally written: 10/19/2013; last modified: 3/16/2015
This Web page is provided free of charge and with no annoying outside ads; however, I did take time to prepare it, and Web hosting does cost money. If you find this Web page useful, please consider making a small donation to help keep this site up and running. Thanks!
Donate $1.00 |
Donate $2.50 |
Donate $5.00 |
Donate $10.00 |
Donate $20.00 |
Donate another value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
[
]## Introduction
For several years, a new firmware technology has been lurking in the wings, unknown to most ordinary users. Known as the [Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI),](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uefi) or more recently as the Unified EFI (UEFI, which is essentially EFI 2.*x*), this technology has begun replacing the older [Basic Input/Output System (BIOS)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BIOS) firmware with which most experienced computer users are at least somewhat familiar.
This page is a quick introduction to EFI for Linux users, including advice on getting started installing Linux to such a computer. Unfortunately, EFI is a dense topic; the EFI software itself is complex, and many implementations have system-specific quirks and even bugs. Thus, I cannot describe everything you'll need to know to install and use Linux on an EFI computer on this one page. It's my hope that you'll find this page a useful starting point, though, and links within each section and in the [References](#references) section at the end will point you toward additional documentation.
## Does Your Computer Use EFI?
EFI is a type of *firmware,* meaning that it's software built into the computer to handle low-level tasks. Most importantly, the firmware controls the computer's boot process, which in turn means that EFI-based computers boot differently than do BIOS-based computers. (A partial exception to this rule is described shortly.) This difference can greatly complicate the design of OS installation media, but it has little effect on the day-to-day operation of the computer, once everything is set up and running. Note that most manufacturers use the term "BIOS" to refer to their EFIs. I consider this usage confusing, so I avoid it; in my view, EFIs and BIOSes are two different types of firmware.
EFI has been used on Intel-based Macs since they were first introduced in 2006. Beginning in late 2012, most computers that ship with Windows 8 or later boot using UEFI by default, and in fact most PCs released since mid-2011 use UEFI, although they may not boot in EFI mode by default. A few PCs sold prior to 2011 also support EFI, although most such computers boot in BIOS mode by default.
If you're uncertain about your computer's EFI support status, you should check your firmware setup utility and your user manual for references to *EFI*, *UEFI*, or *legacy booting*. (Searching a PDF of your user manual can be a quick way to do this.) If you find no such references, your computer probably uses an old-style ("legacy") BIOS; but if you find references to these terms, it almost certainly uses EFI. You can also try booting a medium that contains *only* an EFI-mode boot loader. The USB flash drive or CD-R image of [rEFInd](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/getting.html) is a good choice for this test.
Before proceeding further, you should understand that most EFIs on *x*86 and *x*86-64 computers include a component known as the *Compatibility Support Module (CSM),* which enables the EFI to boot OSes using the older BIOS-style boot mechanisms. This can be a great convenience because it provides backwards compatibility; but it also creates complications because there's no standardization in the rules and user interfaces for controlling when a computer boots in EFI mode vs. when it boots in BIOS (aka CSM or legacy) mode. In particular, it's far too easy to accidentally boot your Linux installation medium in BIOS/CSM/legacy mode, which will result in a BIOS/CSM/legacy-mode installation of Linux. This can work fine if Linux is your only OS, but it complicates the boot process if you're dual-booting with Windows in EFI mode. (The opposite problem can also occur.) The following sections should help you boot your installer in the right mode. If you're reading this page after you've installed Linux in BIOS mode and want to switch boot modes, read the upcoming section, [Oops: Converting a Legacy-Mode Install to Boot in EFI Mode.](#oops)
One optional feature of UEFI deserves mention: *Secure Boot.* This feature is designed to minimize the risk of a computer becoming infected with a *boot kit,* which is a type of malware that infects the computer's boot loader. Boot kits can be particularly difficult to detect and remove, which makes blocking them a priority. Microsoft requires that all desktop and laptop computers that bear a Windows 8 logo ship with Secure Boot enabled. This type of configuration complicates Linux installation, although some distributions handle this problem better than do others. Do not confuse Secure Boot with EFI or UEFI, though; it's possible for an EFI computer to not support Secure Boot, and it's possible to disable Secure Boot even on *x*86-64 EFI computers that support it. Microsoft requires that users can disable Secure Boot for Windows 8 certification on *x*86 and *x*86-64 computers; however, this requirement is reversed for ARM computers—such computers that ship with Windows 8 must *not* permit the user to disable Secure Boot. Fortunately, ARM-based Windows 8 computers are currently rare. I recommend avoiding them.
## Does Your Distribution Support EFI?
Most Linux distributions have supported EFI for years. The quality of that support varies from one distribution to another, though. Most of the major distributions (Fedora, OpenSUSE, Ubuntu, and so on) provide good EFI support, including support for Secure Boot. Some more "do-it-yourself" distributions, such as Gentoo, have weaker EFI support, but their nature makes it easy to add EFI support to them. In fact, it's possible to add EFI support to *any* Linux distribution: You need to install it (even in BIOS mode) and then install an EFI boot loader on the computer. See the [Oops: Converting a Legacy-Mode Install to Boot in EFI Mode](#oops) section for information on how to do this.
You should check your distribution's feature list to determine if it supports EFI. You should also pay attention to your distribution's support for Secure Boot, particularly if you intend to dual-boot with Windows 8. Note that even distributions that officially support Secure Boot may require that this feature be disabled, since Linux Secure Boot support is often poor or creates complications.
## Preparing to Install Linux
A few preparatory steps will help make your Linux installation on an EFI-based computer go more smoothly:
**Upgrade your firmware**—Some EFIs are badly broken, but hardware manufacturers occasionally release updates to their firmware. Thus, I recommend upgrading your firmware to the latest version available. If you know from forum posts or the like that your EFI is problematic, you should do this before installing Linux, because some problems will require extra steps to correct if the firmware is upgraded after the installation. On the other hand, upgrading firmware is always a bit risky, so holding off on such an upgrade may be best if you've heard good things about your manufacturer's EFI support.
**Learn how to use your firmware**—You can usually enter a firmware setup utility by hitting the Del key or a function key early in the boot process. Check for prompts soon after you power on the computer or just try each function key. Similarly, the Esc key or a function key usually enters the firmware's built-in boot manager, which enables you to select which OS or external device to boot. Some manufacturers are making it hard to reach such settings. In some cases, you can do so from inside Windows 8, as described on [this page.](http://www.eightforums.com/tutorials/20256-uefi-firmware-settings-boot-inside-windows-8-a.html)
**Adjust the following firmware settings:**
**Fast boot**—This feature can speed up the boot process
by taking shortcuts in hardware initialization. Sometimes this is
fine, but sometimes it can leave USB hardware uninitialized, which
can make it impossible to boot from a USB flash drive or similar
device. Thus, disabling fast boot *may* be helpful, or even
required; but you can safely leave it active and deactivate it only
if you have trouble getting the Linux installer to boot. Note that
this feature sometimes goes by another name. In some cases, you
must *enable* USB support rather than *disable* a fast
boot feature.
**Secure Boot**—Fedora, OpenSUSE, Ubuntu, and some other
distributions officially support Secure Boot; but if you have
problems getting a boot loader or kernel to start, you might want
to disable this feature. Unfortunately, fully describing how to do
so is impossible because the settings vary from one computer to
another. See [my
Secure Boot page](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/secureboot.html#disable) for more on this topic.
**CSM/legacy options**—If you want to install in EFI mode,
set such options *off.* Some guides recommend enabling these
options, and in some cases they may be required—for instance,
they may be needed to enable the BIOS-mode firmware in some add-on
video cards. In most cases, though, enabling CSM/legacy support
simply increases the risk of inadvertently booting your Linux
installer in BIOS mode, which you do *not* want to do. Note
that Secure Boot and CSM/legacy options are sometimes intertwined,
so be sure to check each one after changing the other.
**Disable the Windows Fast Startup feature**—[This page](http://www.eightforums.com/tutorials/6320-fast-startup-turn-off-windows-8-a.html) describes how to disable this feature, which is almost certain to cause filesystem corruption if left enabled. Note that this feature is distinct from the firmware's fast boot feature.
**Check your partition table**—Using [GPT fdisk,](http://www.rodsbooks.com/gdisk/) `parted`, or any other partitioning tool, check your disk's partitions. Ideally, you should create a hardcopy that includes the exact start and end points (in sectors) of each partition. This will be a useful reference, particularly if you use a manual partitioning option in the installer. If Windows is already installed, be sure to identify your [EFI System Partition (ESP),](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EFI_System_partition) which is a FAT partition with its "boot flag" set (in `parted` or GParted) or that has a type code of EF00 in `gdisk`.
## Installing Linux
Most Linux distributions provide adequate installation instructions; however, I've observed a few common stumbling blocks on EFI-mode installations:
**Ensure that you're using a distribution that's the right bit depth**—EFI runs boot loaders that are the same bit depth as the EFI itself. This is normally 64-bit for modern computers, although the first couple generations of Intel-based Macs, some modern tablets and convertibles, and a handful of obscure computers use 32-bit EFIs. I have yet to encounter a 32-bit Linux distribution that officially supports EFI, although it is possible to add a 32-bit EFI boot loader to 32-bit distributions. (My [Managing EFI Boot Loaders for Linux](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders) covers boot loaders generally, and understanding those principles may enable you to modify a 32-bit distribution's installer, although that's not a task for a beginner.) Installing a 32-bit Linux distribution on a computer with a 64-bit EFI is difficult at best, and I don't describe the process here; you should use a 64-bit distribution on a computer with a 64-bit EFI.
**Properly prepare your boot medium**—Third-party tools for moving `.iso` images onto USB flash drives, such as `unetbootin`, often fail to create the proper EFI-mode boot entries. I recommend you follow whatever procedure your distribution maintainer suggests for creating USB flash drives. If no such recommendation is made, use the Linux `dd` utility, as in `dd if=image.iso of=/dev/sdc` to create an image on the USB flash drive on `/dev/sdc`. Ports of `dd` to Windows, such as [WinDD](https://sourceforge.net/projects/windd/) and `dd` for Windows, exist, but I've never tested them. Note that using tools that don't understand EFI to create your installation medium is one of the mistakes that leads people into the bigger mistake of installing in BIOS mode and then having to correct the ensuing problems, so don't ignore this point!
**Back up the ESP**—If you're installing to a computer that already boots Windows or some other OS, I recommend backing up your ESP before installing Linux. Although Linux *shouldn't* damage files that are already on the ESP, this does seem to happen from time to time. Having a backup will help in such cases. A simple file-level backup (using `cp`, `tar`, or `zip`, for example) should work fine.
**Booting in EFI mode**—It's too easy to accidentally boot your Linux installer in BIOS/CSM/legacy mode, particularly if you leave the CSM/legacy options enabled in your firmware. A few tips can help you to avoid this problem:
- You should verify an EFI-mode boot by dropping to a Linux shell and
typing
`ls /sys/firmware/efi`. If you see
a list of files and directories, you've booted in EFI mode and you
can ignore the following additional tips; if not, you've probably
booted in BIOS mode and should review your settings.
- Use your firmware's built-in boot manager (which you should have
located earlier; see
[Learn how to use
your firmware](#using_firmware)) to boot in EFI mode. Typically, you'll see two
options for a CD-R or USB flash drive, one of which includes the
string *EFI* or *UEFI* in its description, and one of
which does not. Use the EFI/UEFI option to boot your medium.
- Disable Secure Boot—Even if you're using a distribution that
officially supports Secure Boot, sometimes this doesn't work. In
this case, the computer will most likely silently move on to the
next boot loader, which could be your medium's BIOS-mode boot
loader, resulting in a BIOS-mode boot. See
[my
page on Secure Boot](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/secureboot.html#disable) for some tips on how to disable Secure
Boot.
- If you can't seem to get the Linux installer to boot in EFI mode,
try using a USB flash drive or CD-R version of my
[rEFInd boot
manager.](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/getting.html) If rEFInd boots, it's guaranteed to be running in EFI
mode, and on a UEFI-based PC, it will show only EFI-mode boot
options, so if you can then boot to the Linux installer, it should
be in EFI mode. (On Macs, though, rEFInd shows BIOS-mode boot
options in addition to EFI-mode options.)
**Preparing your ESP**—Except on Macs, EFIs use the ESP to hold boot loaders. If your computer came with Windows pre-installed, an ESP should already exist, and you can use it in Linux. If not, I recommend creating an ESP that's 550MiB in size. (If your existing ESP is smaller than this, go ahead and use it.) Create a FAT32 filesystem on it. If you use GParted or `parted` to prepare your disk, give the ESP a "boot flag." If you use GPT fdisk (`gdisk`, `cgdisk`, or `sgdisk`) to prepare the disk, give it a type code of EF00. Some installers create a smallish ESP and put a FAT16 filesystem on it. This usually works fine, although if you subsequently need to re-install Windows, its installer will become confused by the FAT16 ESP, so you may need to back it up and convert it to FAT32 form.
**Using the ESP**—Different distributions' installers have different ways of identifying the ESP. For instance, some versions of Debian and Ubuntu call the ESP the "EFI boot partition" and do not show you an explicit mount point (although it will mount it behind the scenes); but a distribution like Arch or Gentoo will require you to mount it. The closest thing to a standard ESP mount point in Linux is `/boot/efi`, although `/boot` works well with some configurations—particularly if you want to use gummiboot or ELILO. Some distributions won't let you use a FAT partition as `/boot`, though. Thus, if you're asked to set a mount point for the ESP, make it `/boot/efi`. Do *not* create a fresh filesystem on the ESP unless it doesn't already have one—if Windows or some other OS is already installed, its boot loader lives on the ESP, and creating a new filesystem will destroy that boot loader!
**Setting the boot loader location**—Some distributions may ask about the boot loader's (GRUB's) location. If you've properly flagged the ESP as such, this question should be unnecessary, but some distributions' installers still ask. Try telling it to use the ESP.
**Other partitions**—Other than the ESP, no other special partitions are required; you can set up root (`/`), swap, `/home`, or whatever else you like in the same way you would for a BIOS-mode installation. Note that you do *not* need a [BIOS Boot Partition](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BIOS_Boot_partition) for an EFI-mode installation, so if your installer is telling you that you need one, this may be a sign that you've accidentally booted in BIOS mode. On the other hand, if you create a BIOS Boot Partition, that will give you some extra flexibility, since you'll be able to install a BIOS version of GRUB to boot in either mode (EFI or BIOS).
**Fixing blank displays**—A problem that many people had through much of 2013 (but with decreasing frequency since then) was blank displays when booted in EFI mode. Sometimes this problem can be fixed by adding `nomodeset` to the kernel's command line. You can do this by typing `e` to open a simple text editor in GRUB. In many cases, though, you'll need to research this problem in more detail, because it often has more hardware-specific causes.
In some cases, you may be forced to install Linux in BIOS mode. You can sometimes then manually install an EFI-mode boot loader for Linux to begin booting in EFI mode. See my [Managing EFI Boot Loaders for Linux](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/) page for information on available boot loaders and how to install them.
## Fixing Post-Installation Problems
If you can't seem to get an EFI-mode boot of Linux working but a BIOS-mode boot works, you can abandon EFI mode entirely. This is easiest on a Linux-only computer; just install a BIOS-mode boot loader (which the installer should have done if you installed in BIOS mode). If you're dual-booting with an EFI-mode Windows, though, the easiest solution is to install my [rEFInd boot manager.](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/) Install it from Windows and edit the `refind.conf` file: Uncomment the `scanfor` line and ensure that `hdbios` is among the options. This will enable rEFInd to redirect the boot process to a BIOS-mode boot loader. This solution works for many systems, but sometimes it fails for one reason or another.
If you reboot the computer and it boots straight into Windows, it's likely that your Linux boot loader or boot manager was not properly installed. (You should try disabling Secure Boot first, though; as I've said, it often causes problems.) There are several possible solutions to this problem:
**Use **`efibootmgr`—You can boot a Linux emergency disc *in EFI mode* and use the `efibootmgr` utility to re-register your Linux boot loader, as described [here.](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/installation.html)
**Use **`bcdedit` in Windows—In a Windows Administrator Command Prompt window, typing `bcdedit /set {bootmgr} path \EFI\fedora\grubx64.efi` will set the `EFI/fedora/grubx64.efi` file on the ESP as the default boot loader. Change that path as necessary to point to your desired boot loader. If you're booting with Secure Boot enabled, you should set `shim.efi`, `shimx64.efi`, or `PreLoader.efi` (whichever is present) as the boot program, rather than `grubx64.efi`.
**Install rEFInd**—Sometimes rEFInd can overcome this problem. I recommend testing by using the [CD-R or USB flash drive image.](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/getting.html) If it can boot Linux, install the Debian package, RPM, or `.zip` file package. (Note that you may need to edit your boot options by highlighting a Linux `vmlinuz*` option and hitting F2 or Insert twice. This is most likely to be required if you've got a separate `/boot` partition, since in this situation rEFInd can't locate the root (`/`) partition to pass to the kernel.)
**Use Boot Repair**—Ubuntu's [Boot Repair utility](https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Boot-Repair) can auto-repair some boot problems; however, I recommend using it only on Ubuntu and closely-related distributions, such as Mint. In some cases, it may be necessary to click the Advanced option and check the box to back up and replace the Windows boot loader.
**Hijack the Windows boot loader**—Some buggy EFIs boot only the Windows boot loader, which is called `EFI/Microsoft/Boot/bootmgfw.efi` on the ESP. Thus, you may need to rename this boot loader to something else (I recommend moving it down one level, to `EFI/Microsoft/bootmgfw.efi`) and putting a copy of your preferred boot loader in its place. (Most distributions put a copy of GRUB in a subdirectory of `EFI` named after themselves, such as `EFI/ubuntu` for Ubuntu or `EFI/fedora` for Fedora.) Note that this solution is an ugly hack, and some users have reported that Windows will replace its boot loader, so it may not even work 100% of the time. It is, however, the only solution that works on some badly broken EFIs. Before attempting this solution, I recommend upgrading your firmware and re-registering your own boot loader with `efibootmgr` in Linux or `bcdedit` in Windows.
Another class of problems relates to boot loader troubles—If you see GRUB (or whatever boot loader or boot manager your distribution uses by default) but it doesn't boot an OS, you must fix that problem. Windows often fails to boot because GRUB 2 is very finicky about booting Windows. This problem can be exacerbated by Secure Boot in some cases. See [my page on GRUB 2](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/grub2.html) for a sample GRUB 2 entry for booting Windows. Linux boot problems, once GRUB appears, can have a number of causes, and are likely to be similar to BIOS-mode Linux boot problems, so I don't cover them here.
Despite the fact that it's very common, my opinion of GRUB 2 is rather low—it's an immensely complex program that's difficult to configure and use. Thus, if you run into problems with GRUB, my initial response is to replace it with something else. [My Web page on EFI boot loaders for Linux](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders) describes the options that are available. These include my own [rEFInd boot manager,](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/) which is much easier to install and maintain, aside from the fact that many distributions do manage to get GRUB 2 working—but if you're considering replacing GRUB 2 because of its problems, that's obviously not worked out for you!
Beyond these issues, EFI booting problems can be quite idiosyncratic, so you may need to post to a Web forum for help. Be sure to describe the problem as thoroughly as you can. The [Boot Info Script](http://sourceforge.net/projects/bootinfoscript/) can provide useful information—run it and it should produce a file called `RESULTS.txt` that you can paste into your forum post. Be sure to precede this pasted text with the string `[code]` and follow it with `[/code]`, though; otherwise people will complain. Alternatively, upload `RESULTS.txt` to a pastebin site, such as [pastebin.com,](http://pastebin.com) and post the URL that the site gives you.
[
]## Oops: Converting a Legacy-Mode Install to Boot in EFI Mode
As of early 2015, one very common problem I see in online forums is that people follow bad instructions and install Linux in BIOS mode to dual-boot with an existing EFI-mode Windows installation. This configuration works poorly because most EFIs make it difficult to switch between boot modes, and GRUB can't handle the task, either. You might also find yourself in this situation if you've got a very flaky EFI that simply won't boot an external medium in EFI mode, or if you have video or other problems with Linux when it's booted in EFI mode.
As noted earlier, in [Fixing Post-Installation Problems,](#troubleshooting) one possible solution to such problems is to install rEFInd *in Windows* and configure it to support BIOS-mode boots. You can then boot rEFInd and chainload to your BIOS-mode GRUB. I recommend this fix mainly when you have EFI-specific problems in Linux, such as a failure to use your video card. If you don't have such EFI-specific problems, installing rEFInd and a suitable EFI filesystem driver in Windows will enable you to boot Linux directly in EFI mode. This can be a perfectly good solution, and it will be equivalent to what I describe next.
In most cases, it's best to configure Linux to boot in EFI mode. There are many ways to do this, but the best way requires using an EFI-mode boot of Linux (or conceivably Windows or an EFI shell) to register an EFI-mode version of your preferred boot manager. One way to accomplish this goal is as follows:
- Download a USB flash drive or CD-R version of my
[rEFInd boot manager.](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/getting.html)
- Prepare a medium from the image file you've downloaded. You can do this from any computer, booted in either EFI or BIOS mode (or in other ways on other platforms).
- If you've not already done so,
[disable Secure Boot.](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/secureboot.html#disable) This is necessary because the rEFInd CD-R and USB images don't support Secure Boot. If you want to keep Secure Boot, you can re-enable it later.
- Boot rEFInd on your target computer. As described earlier, you may need to adjust your firmware settings and use the built-in boot manager to select your boot medium. The option you select may need to include the string
*UEFI* in its description.
- In rEFInd, examine the boot options. You should see at least one option for booting a Linux kernel (with a name that includes the string
`vmlinuz`). Boot it in one of two ways:
- If you do
*not* have a separate `/boot` partition,
simply highlight the kernel and press Enter. Linux should
boot.
- If you
*do* have a separate `/boot` partition, press
Insert or F2 twice. This action will open a line editor in which
you can edit your kernel options. Add a `root=`
specification to those options to identify your root (`/`)
filesystem, as in `root=/dev/sda5` if root (`/`) is
on `/dev/sda5`. If you don't know what your root filesystem
is, you should reboot in any way possible to figure it out.
In some rare cases, you may need to add other kernel options instead of or in addition to a `root=` option. Gentoo with an LVM configuration requires `dolvm`, for example.
- Once Linux is booted, install your desired boot program. rEFInd is usually pretty easy to install via the RPM, Debian package, PPA, or binary
`.zip` file referenced on the [rEFInd downloads page.](http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/getting.html) On Ubuntu and similar distributions, Boot Repair can fix your GRUB setup relatively simply, but it will be a bit of a leap of faith that it will work correctly. (It usually works fine, but in some cases it will make a hash of things.) Other options are described on my [Managing EFI Boot Loaders for Linux](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/) page.
- If you want to boot with Secure Boot active, reboot and enable it. Note, however, that you may need to take extra installation steps to set up your boot program to use Secure Boot. Consult
[my page on the topic](http://www.rodsbooks.com/efi-bootloaders/secureboot.html) or your boot program's Secure Boot documentation for details.
When you reboot, you should see the boot program you just installed. If the computer instead boots into a BIOS-mode version of GRUB, you should enter your firmware and disable the BIOS/CSM/legacy support, or perhaps adjust your boot order options. If the computer boots straight to Windows, then you should read the preceding section, [Fixing Post-Installation Problems.](#troubleshooting)
You may want or need to tweak your configuration at this point. It's common to see extra boot options, or for an option you want to not be visible. Consult your boot program's documentation to learn how to make such changes.
[
]## References and Additional Information
**Informational Web pages**
**Additional programs**
**Communications**
copyright © 2013–2015 by Roderick W. Smith
If you have problems with or comments about this Web page, please e-mail me at [[email protected].](mailto:[email protected]) Thanks.
[Return](http://www.rodsbooks.com/) to my main Web page. |
8,482 | Fedora 官方合法地全面支持 MP3 编码方案 | https://fedoramagazine.org/full-mp3-support-coming-soon-to-fedora/ | 2017-05-06T08:29:00 | [
"MP3",
"Fedora"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8482-1.html | 
MP3 的编码和解码不久将被 Fedora 官方支持。
[去年十一月](https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/[email protected]/thread/PUCTFFYU5L2A3L7QVME7TOMX3R6WIO2F/#34NPNTJITRHRP2FRKKYGL2YMEUU4BDYF),随着覆盖了 MP3 解码的专利失效后,[Fedora Workstation](https://blogs.gnome.org/uraeus/2016/11/10/mp3-support-now-coming-to-fedora-workstation-25/) 通过 [mpg123](https://www.mpg123.de/) 库和 GStreamer 启用了 MP3 解码支持。该更新允许用户通过安装在他们的计算机中的 gstreamer1-plugin-mpg123 软件包来播放 MP3 编码的音乐。
MP3 编码方案在过去十年间和开源界闹得颇不愉快,尤其是在美国。在历史上,由于[许可证问题](https://www.redhat.com/archives/rhl-devel-list/2007-November/msg00028.html),Fedora 不能在其基础发行版上包括 MP3 解码或编码功能,所以,很多用户只能通过第三方软件库来提供 MP3 支持。
两周前,由于专利到期,[IIS Fraunhofer and Technicolor 终止了他们的授权流程](https://www.iis.fraunhofer.de/en/ff/amm/prod/audiocodec/audiocodecs/mp3.html),并在几天前, Red Hat 法律部门[批准了在 Fedora 中提供 MP3 编码支持](https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/[email protected]/thread/KM557DP7OR2UEEPYQRNHJU7T45XDSXYJ/)。不过还需要一点时间进行软件包审查,该工具是确定会被加入的。同时要说明的是只包括 MP3 而非其它的 MPEG 技术。相信很快我们就可以在 Fedora 中不用第三方库即可转换各种格式的音乐为 MP3 了。
附录:
MP3 的开发始于上世纪八十年代的 Fraunhofer IIS,其基于之前的埃尔兰根-纽伦堡大学的研究成功而开发。2017 年 4 月 23, Technicolor 结束了 MP3 的相关专利授权流程。虽然今天 MP3 已经不是最有效、最先进的音频编码方案了,但是在过去的二十年间,MP3 一直是最流行的音频编码方案,在之后若干年,MP3 想必也会流行依旧。
以下是来自 [mp3-history.com](https://www.mp3-history.com/) 上的两张开发团队合影,有关 MP3 的历史信息也请查阅此网站:


| 200 | OK | Both MP3 encoding and decoding will soon be officially supported in Fedora. [Last November](https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/[email protected]/thread/PUCTFFYU5L2A3L7QVME7TOMX3R6WIO2F/#34NPNTJITRHRP2FRKKYGL2YMEUU4BDYF) the patents covering MP3 decoding expired and [Fedora Workstation](https://blogs.gnome.org/uraeus/2016/11/10/mp3-support-now-coming-to-fedora-workstation-25/) enabled MP3 decoding via the [mpg123](https://www.mpg123.de/) library and GStreamer. This update allowed users with the
package installed on their systems to listen to MP3 encoded music.
The MP3 codec and Open Source have had a troubled relationship over the past decade, especially within the United States. Historically, due to [licensing issues](https://www.redhat.com/archives/rhl-devel-list/2007-November/msg00028.html) Fedora has been unable to include MP3 decoding or encoding within the base distribution. However, many users utilized 3rd party repositories to enable MP3 support.
A couple of weeks ago [IIS Fraunhofer and Technicolor terminated their licensing program](https://www.iis.fraunhofer.de/en/ff/amm/prod/audiocodec/audiocodecs/mp3.html) and just a few days ago Red Hat Legal provided the [permission to ship MP3 encoding](https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/[email protected]/thread/KM557DP7OR2UEEPYQRNHJU7T45XDSXYJ/) in Fedora. There will be a bit of time whilst package reviews are carried out and tools that are safe to add are identified, as only MP3 is cleared and not other MPEG technologies. However, it will soon be possible to convert physical media or other formats to MP3 in Fedora without 3rd party repositories.
## Bill Chatfield
That’s great news! Thanks for letting us know. That will be one more thing to make Fedora easier for new users.
## Rodrigo de Araujo
Good news, but I noticed that working with .ogg files saved me more disk space without reducing sound quality. Either way it’s a good thing to have .mp3 support ready to use.
## Paulo Alfredo
Good news, but I like to use ogg files.
## IFo Hancroft
That’s awesome.
However, like Rodrigo de Araujo said .ogg is better.
I wish one day we would all be using nothing but open source and no manufacturer will produce closed source stuff.
This is still totally awesome though.
## Matthew Miller
Ogg and other more modern formats are generally better — I mostly use lossless these days anyway — but it is important to note that we are not adding any closed source to Fedora. The mp3 playback we have and encoding we are adding are all 100% free software / open source.
## Dude
Opus is the way to go. It is completely open (made by the same guys as Vorbis/Ogg), however it has much better quality (much better than MP3/Ogg/AAC/HE-AAC).
Android supports it.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Opus_(audio_format)
## Olivier
HE-AAC is from the same generation as Opus, so the sound quality should be similar at high latencies. For lower latencies, that AAC can’t match, the comparison is more the AMR family of codecs used in 3G telephony and once again Opus gives largely the same quality at similar bitrates. So in summary, it’s a bit misleading to say that Opus is better, but it’s entirely true that it gives the same quality without patent hassles.
## alex marhantz
\m/
## iluvvalice
That’s good. I hope that there won’t be any problems.
## Anonymous
Dolby Digital AC3 is also free now, since March. For more information see https://web.archive.org/web/20170401170436/https://ac3freedomday.org/ Maybe Fedora could include it by default as well?
Anyway, it’s nice to see that a format as important as MP3 is now patent free and will soon be included in Fedora 🙂
## James Hogarth
So you (and others) are aware AC3 was added to the main Fedora repos via a52dec in late March.
https://blogs.gnome.org/uraeus/2017/03/22/another-media-codec-on-the-way/
## Roger Hammer
Very good. That’s an obstacle to general acceptance of Fedora that we won’t need to deal with any longer. I was a paying customer to Fluendo for a good long time but eventually realize it was mostly superfluous for my purposes and I switched to using the gstreamer plugins supplied by fusion repo. I can’t say that I am missing anything that Fluendo supplied. I was an .ogg user ’til I ran across a podcaster who advocated using AAC; the person,an old guy like me, therefor has credibility in my eyes. Now, most of the music I listen to regularly is .m4a, and gstreamer has a plugin for that.
## sunnyhere
Personally I feel it is a little late to the game as I stopped using the mp3 file format years ago and is happy with more modern formats, but Good thing nontheless and a win for FOSS!
## Be
Today, when a 1 TB USB hard drive costs just $50, lossy compression is obsolete for storage. Lossy compression still has uses for streaming, for which MP3 is still widely despite less bad lossy codecs being available, so I’m glad those streams will just work in Fedora now.
## Ryan K
I’m glad to hear this.
Yes, there are many better formats than MP3s for audio, but MP3s are still the most widely adopted and compatible formats between all the non-FOSS software and hardware out there.
Choices are good.
## Timothy
Agreed. I’m new. I am an advocate of fedora even though I am largely ignorant of all the possibilities. It will be nice when attempting to win over others, to be able to have an M3P operable with no additional work or work arounds. |
8,483 | Linux 容器能否弥补 IoT 的安全短板? | http://hackerboards.com/can-linux-containers-save-iot-from-a-security-meltdown/ | 2017-05-06T18:59:57 | [
"IoT",
"容器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8483-1.html |
>
> 在这个最后的物联网系列文章中,Canonical 和 Resin.io 向以 Linux 容器技术作为解决方案向物联网安全性和互操作性发起挑战。
>
>
>

尽管受到日益增长的安全威胁,但对物联网(IoT)的炒作没有显示减弱的迹象。为了刷存在感,公司们正忙于重新规划它们的物联网方面的路线图。物联网大潮迅猛异常,比移动互联网革命渗透的更加深入和广泛。IoT 像黑洞一样,吞噬一切,包括智能手机,它通常是我们通向物联网世界的窗口,有时也作为我们的汇聚点或终端。
新的针对物联网的处理器和嵌入式主板继续重塑其技术版图。自从 9 月份推出 [面向物联网的 Linux 和开源硬件](http://hackerboards.com/linux-and-open-source-hardware-for-building-iot-devices/) 系列文章之后,我们看到了面向物联网网关的 “Apollo Lake]” SoC 芯片 [Intel Atom E3900](http://hackerboards.com/intel-launches-14nm-atom-e3900-and-spins-an-automotive-version/) 以及[三星 新的 Artik 模块](http://hackerboards.com/samsung-adds-first-64-bit-and-cortex-m4-based-artik-modules/),包括用于网关并由 Linux 驱动的 64 位 Artik 7 COM 及自带 RTOS 的 Cortex-M4 Artik。 ARM 为具有 ARMv8-M 和 TrustZone 安全性的 IoT 终端发布了 [Cortex-M23 和 Cortex-M33](http://hackerboards.com/new-cortex-m-chips-add-armv8-and-trustzone/) 芯片。

*Artik 7*
讲道理,安全是这些产品的卖点。最近攻击 Dyn 服务并在一天内摧毁了美国大部分互联网的 Mirai 僵尸网络将基于 Linux 的物联网推到台前 - 当然这种方式似乎不太体面。就像 IoT 设备可以成为 DDoS 的帮凶一样,设备及其所有者同样可能直接遭受恶意攻击。

*Cortex-M33 和 -M23*
Dyn 攻击事件更加证明了这种观点,即物联网将更加蓬勃地在受控制和受保护的工业环境发展,而不是家用环境中。这不是因为没有消费级[物联网安全技术](http://hackerboards.com/exploring-security-challenges-in-linux-based-iot-devices/),但除非产品设计之初就以安全为目标,否则如我们的[智能家居集线器系列](http://hackerboards.com/linux-based-smart-home-hubs-advance-into-ai/)中的许多解决方案一样,后期再考虑安全就会增加成本和复杂性。
在物联网系列的最后这个未来展望的部分,我们将探讨两种基于 Linux 的面向 Docker 的容器技术,这些技术被提出作为物联网安全解决方案。容器还可以帮助解决我们在[物联网框架](http://hackerboards.com/open-source-projects-for-the-internet-of-things-from-a-to-z/)中探讨的开发复杂性和互操作性障碍的问题。
我们与 Canonical 的 Ubuntu 客户平台工程副总裁 Oliver Ries 讨论了 Ubuntu Core 和适用于 Docker 的容器式 Snaps 包管理技术。我们还就新的基于 Docker 的物联网方案 ResinOS 采访了 Resin.io 首席执行官和联合创始人 Alexandros Marinos。
### Ubuntu Core Snaps
Canonical 面向物联网的 [Snappy Ubuntu Core](http://hackerboards.com/lightweight-snappy-ubuntu-core-os-targets-iot/) 版本的 Ubuntu 是围绕一个类似容器的快照包管理机制而构建的,并提供应用商店支持。 snaps 技术最近[自行发布了](http://hackerboards.com/canonical-pushes-snap-as-a-universal-linux-package-format/)用于其他 Linux 发行版的版本。去年 11 月 3 日,Canonical 发布了 [Ubuntu Core 16](http://hackerboards.com/ubuntu-core-16-gets-smaller-goes-all-snaps/),该版本改进了白标应用商店和更新控制服务。

*传统 Ubuntu(左)架构 与 Ubuntu Core 16*
快照机制提供自动更新,并有助于阻止未经授权的更新。 使用事务系统管理,快照可确保更新按预期部署或根本不部署。 在 Ubuntu Core 中,使用 AppArmor 进一步加强了安全性,并且所有应用程序文件都是只读的且保存在隔离的孤岛中。

*LimeSDR*
Ubuntu Core 是我们最近展开的[开源物联网操作系统调查](http://hackerboards.com/open-source-oses-for-the-internet-of-things/)的一部分,现在运行于 Gumstix 主板、Erle 机器人无人机、Dell Edge 网关、[Nextcloud Box](http://hackerboards.com/private-cloud-server-and-iot-gateway-runs-ubuntu-snappy-on-rpi/)、LimeSDR、Mycroft 家庭集线器、英特尔的 Joule 和符合 Linaro 的 96Boards 规范的 SBC(单板计算机) 上。 Canonical 公司还与 Linaro 物联网和嵌入式(LITE)部门集团在其 [96Boards 物联网版(IE)](http://hackerboards.com/linaro-beams-lite-at-internet-of-things-devices/) 上达成合作。最初,96Boards IE 专注于 Zephyr 驱动的 Cortex-M4 板卡,如 Seeed 的 [BLE Carbon](http://hackerboards.com/96boards-goes-cortex-m4-with-iot-edition-and-carbon-sbc/),不过它将扩展到可以运行 Ubuntu Core 的网关板卡上。
“Ubuntu Core 和 snaps 具有从边缘到网关到云的相关性,”Canonical 的 Ries 说。 “能够在任何主要发行版(包括 Ubuntu Server 和 Ubuntu for Cloud)上运行快照包,使我们能够提供一致的体验。 snaps 可以使用事务更新以免故障方式升级,可用于安全性更新、错误修复或新功能的持续更新,这在物联网环境中非常重要。”

*Nextcloud盒子*
安全性和可靠性是关注的重点,Ries 说。 “snaps 应用可以完全独立于彼此和操作系统而运行,使得两个应用程序可以安全地在单个网关上运行,”他说。 “snaps 是只读的和经过认证的,可以保证代码的完整性。
Ries 还说这种技术减少开发时间。 “snap 软件包允许开发人员向支持它的任何平台提供相同的二进制包,从而降低开发和测试成本,减少部署时间和提高更新速度。 “使用 snap 软件包,开发人员完可以全控制开发生命周期,并可以立即更新。 snap 包提供了所有必需的依赖项,因此开发人员可以选择定制他们使用的组件。”
### ResinOS: 为 IoT 而生的 Docker
Resin.io 公司,与其商用的 IoT 框架同名,最近剥离了该框架的基于 Yocto Linux 的 [ResinOS 2.0](http://hackerboards.com/can-linux-containers-save-iot-from-a-security-meltdown/%3Ca%20href=),ResinOS 2.0 将作为一个独立的开源项目运营。 Ubuntu Core 在 snap 包中运行 Docker 容器引擎,ResinOS 在主机上运行 Docker。 极致简约的 ResinOS 抽离了使用 Yocto 代码的复杂性,使开发人员能够快速部署 Docker 容器。

*ResinOS 2.0 架构*
与基于 Linux 的 CoreOS 一样,ResinOS 集成了 systemd 控制服务和网络协议栈,可通过异构网络安全地部署更新的应用程序。 但是,它是为在资源受限的设备(如 ARM 黑客板)上运行而设计的,与之相反,CoreOS 和其他基于 Docker 的操作系统(例如基于 Red Hat 的 Project Atomic)目前仅能运行在 x86 上,并且更喜欢资源丰富的服务器平台。 ResinOS 可以在 20 中 Linux 设备上运行,并不断增长,包括 Raspberry Pi,BeagleBone 和Odroid-C1 等。
“我们认为 Linux 容器对嵌入式系统比对于云更重要,”Resin.io 的 Marinos 说。 “在云中,容器代表了对之前的进程的优化,但在嵌入式中,它们代表了姗姗来迟的通用虚拟化“

*BeagleBone Black*
当应用于物联网时,完整的企业级虚拟机有直接访问硬件的限制的性能缺陷,Marinos 说。像 OSGi 和 Android 的Dalvik 这样的移动设备虚拟机可以用于 IoT,但是它们依赖 Java 并有其他限制。
对于企业开发人员来说,使用 Docker 似乎很自然,但是你如何说服嵌入式黑客转向全新的范式呢? “Marinos 解释说,”ResinOS 不是把云技术的实践经验照单全收,而是针对嵌入式进行了优化。”此外,他说,容器比典型的物联网技术更好地包容故障。 “如果有软件缺陷,主机操作系统可以继续正常工作,甚至保持连接。要恢复,您可以重新启动容器或推送更新。更新设备而不重新启动它的能力进一步消除了故障引发问题的机率。”
据 Marinos 所说,其他好处源自与云技术的一致性,例如拥有更广泛的开发人员。容器提供了“跨数据中心和边缘的统一范式,以及一种方便地将技术、工作流、基础设施,甚至应用程序转移到边缘(终端)的方式。”
Marinos 说,容器中的固有安全性优势正在被其他技术增强。 “随着 Docker 社区推动实现镜像签名和鉴证,这些自然会转移并应用到 ResinOS,”他说。 “当 Linux 内核被强化以提高容器安全性时,或者获得更好地管理容器所消耗的资源的能力时,会产生类似的好处。
容器也适合开源 IoT 框架,Marinos 说。 “Linux 容器很容易与几乎各种协议、应用程序、语言和库结合使用,”Marinos 说。 “Resin.io 参加了 AllSeen 联盟,我们与使用 IoTivity 和 Thread的 伙伴一起合作。”
### IoT的未来:智能网关与智能终端
Marinos 和 Canonical 的 Ries 对未来物联网的几个发展趋势具有一致的看法。 首先,物联网的最初概念(其中基于 MCU 的端点直接与云进行通信以进行处理)正在迅速被雾化计算架构所取代。 这需要更智能的网关,也需要比仅仅在 ZigBee 和 WiFi 之间聚合和转换数据更多的功能。
其次,网关和智能边缘设备越来越多地运行多个应用程序。 第三,许多这些设备将提供板载分析,这些在最新的[智能家居集线器](http://hackerboards.com/linux-based-smart-home-hubs-advance-into-ai/)上都有体现。 最后,富媒体将很快成为物联网组合的一部分。

*最新设备网关: Eurotech 的 [ReliaGate 20-26](http://hackerboards.com/atom-based-gateway-taps-new-open-source-iot-cloud-platform/)*

*最新设备网关: Advantech 的 [UBC-221](http://hackerboards.com/compact-iot-gateway-runs-yocto-linux-on-quark/)*
“智能网关正在接管最初为云服务设计的许多处理和控制功能,”Marinos 说。 “因此,我们看到对容器化的推动力在增加,可以在 IoT 设备中使用类似云工作流程来部署与功能和安全相关的优化。去中心化是由移动数据紧缩、不断发展的法律框架和各种物理限制等因素驱动的。”
Ubuntu Core 等平台正在使“可用于网关的软件爆炸式增长”,Canonical 的 Ries 说。 “在单个设备上运行多个应用程序的能力吸引了众多单一功能设备的用户,以及现在可以产生持续的软件收入的设备所有者。”

*两种 IoT 网关: [MyOmega MYNXG IC2 Controller](http://hackerboards.com/wireless-crazed-customizable-iot-gateway-uses-arm-or-x86-coms/)*

*两种 IoT 网关: TechNexion 的 [LS1021A-IoT Gateway](http://hackerboards.com/iot-gateway-runs-linux-on-qoriq-accepts-arduino-shields/)*
不仅是网关 - 终端也变得更聪明。 “阅读大量的物联网新闻报道,你得到的印象是所有终端都运行在微控制器上,”Marinos 说。 “但是我们对大量的 Linux 终端,如数字标牌,无人机和工业机械等直接执行任务,而不是作为操作中介(数据转发)感到惊讶。我们称之为影子 IoT。”
Canonical 的 Ries 同意,对简约技术的专注使他们忽视了新兴物联网领域。 “轻量化的概念在一个发展速度与物联网一样快的行业中初现端倪,”Ries 说。 “今天的高级消费硬件可以持续为终端供电数月。”
虽然大多数物联网设备将保持轻量和“无头”(一种配置方式,比如物联网设备缺少显示器,键盘等),它们装备有如加速度计和温度传感器这样的传感器并通过低速率的数据流通信,但是许多较新的物联网应用已经使用富媒体。 “媒体输入/输出只是另一种类型的外设,”Marinos 说。 “总是存在多个容器竞争有限资源的问题,但它与传感器或蓝牙竞争天线资源没有太大区别。”
Ries 看到了工业和家庭网关中“提高边缘智能”的趋势。 “我们看到人工智能、机器学习、计算机视觉和上下文意识的大幅上升,”Ries 说。 “为什么要在云中运行面部检测软件,如果相同的软件可以在边缘设备运行而又没有网络延迟和带宽及计算成本呢?“
当我们在这个物联网系列的[开篇故事](http://hackerboards.com/an-open-source-perspective-on-the-internet-of-things-part-1/)中探索时,我们发现存在与安全相关的物联网问题,例如隐私丧失和生活在监视文化中的权衡。还有一些问题如把个人决策交给可能由他人操控的 AI 裁定。这些不会被容器,快照或任何其他技术完全解决。
如果 AWS Alexa 可以处理生活琐事,而我们专注在要事上,也许我们会更快乐。或许有一个方法来平衡隐私和效用,现在,我们仍在探索,如此甚好。
---
via: <http://hackerboards.com/can-linux-containers-save-iot-from-a-security-meltdown/>
作者:[Eric Brown](http://hackerboards.com/can-linux-containers-save-iot-from-a-security-meltdown/) 译者:[firstadream](https://github.com/firstadream) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,484 | 极客漫画:消沉的程序员 15 | http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-15/ | 2017-05-07T08:00:00 | [
"漫画",
"程序员"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8484-1.html | 
不管是哪行哪业,诸如 IT 行业的代码、生成加工等,安全大概都是可以作为一个永恒的话题。越是觉得可以忽略的细小事情,还真是越容易造成重大的安全事故。所以,不管何种情况下,该做的安全考虑都是必不可少的。
---
译者简介:
[GHLandy](http://GHLandy.com) —— 生活中所有欢乐与苦闷都应藏在心中,有些事儿注定无人知晓,自己也无从说起。
---
via:<http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-15/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 合成:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 点评:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,485 | 极客漫画:消沉的程序员 16 | http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-16/ | 2017-05-08T08:58:00 | [
"漫画",
"程序员"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8485-1.html | 
哎,又是 Bug 和 Debug! 感觉代码之中永远脱离不了这个魔咒啊!还真是尴尬。不知道,编码之间进行详细的规划,能不能尽量避免那些不必要的 Bug?
---
译者简介:
[GHLandy](http://GHLandy.com) —— 生活中所有欢乐与苦闷都应藏在心中,有些事儿注定无人知晓,自己也无从说起。
---
via:
* <http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-16/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 合成:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 点评:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,486 | 大数据探索:在树莓派上通过 Apache Spark on YARN 搭建 Hadoop 集群 | https://dqydj.com/raspberry-pi-hadoop-cluster-apache-spark-yarn/ | 2017-05-07T09:27:00 | [
"大数据",
"Hadoop",
"树莓派"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8486-1.html | 
有些时候我们想从 DQYDJ 网站的数据中分析点有用的东西出来,在过去,我们要[用 R 语言提取固定宽度的数据](https://dqydj.com/how-to-import-fixed-width-data-into-a-spreadsheet-via-r-playing-with-ipums-cps-data/),然后通过数学建模来分析[美国的最低收入补贴](http://dqydj.com/negative-income-tax-cost-calculator-united-states/),当然也包括其他优秀的方法。
今天我将向你展示对大数据的一点探索,不过有点变化,使用的是全世界最流行的微型电脑————[树莓派](https://www.raspberrypi.org/),如果手头没有,那就看下一篇吧(可能是已经处理好的数据),对于其他用户,请继续阅读吧,今天我们要建立一个树莓派 Hadoop集群!
### I. 为什么要建立一个树莓派的 Hadoop 集群?

*由三个树莓派节点组成的 Hadoop 集群*
我们对 DQYDJ 的数据做了[大量的处理工作](https://dqydj.com/finance-calculators-investment-calculators-and-visualizations/),但这些还不能称得上是大数据。
和许许多多有争议的话题一样,数据的大小之别被解释成这样一个笑话:
>
> 如果能被内存所存储,那么它就不是大数据。 ————佚名
>
>
>
似乎这儿有两种解决问题的方法:
1. 我们可以找到一个足够大的数据集合,任何家用电脑的物理或虚拟内存都存不下。
2. 我们可以买一些不用特别定制,我们现有数据就能淹没它的电脑:
—— 上手树莓派 2B
这个由设计师和工程师制作出来的精致小玩意儿拥有 1GB 的内存, MicroSD 卡充当它的硬盘,此外,每一台的价格都低于 50 美元,这意味着你可以花不到 250 美元的价格搭建一个 Hadoop 集群。
或许天下没有比这更便宜的入场券来带你进入大数据的大门。
### II. 制作一个树莓派集群
我最喜欢制作的原材料。
这里我将给出我原来为了制作树莓派集群购买原材料的链接,如果以后要在亚马逊购买的话你可先这些链接收藏起来,也是对本站的一点支持。(谢谢)
* [树莓派 2B 3 块](http://amzn.to/2bEFTVh)
* [4 层亚克力支架](http://amzn.to/2bTo1br)
* [6 口 USB 转接器](http://amzn.to/2bEGO8g),我选了白色 RAVPower 50W 10A 6 口 USB 转接器
* [MicroSD 卡](http://amzn.to/2cguV9I),这个五件套 32GB 卡非常棒
* [短的 MicroUSB 数据线](http://amzn.to/2bX2mwm),用于给树莓派供电
* [短网线](http://amzn.to/2bDACQJ)
* 双面胶,我有一些 3M 的,很好用
#### 开始制作
1. 首先,装好三个树莓派,每一个用螺丝钉固定在亚克力面板上。(看下图)
2. 接下来,安装以太网交换机,用双面胶贴在其中一个在亚克力面板上。
3. 用双面胶贴将 USB 转接器贴在一个在亚克力面板使之成为最顶层。
4. 接着就是一层一层都拼好——这里我选择将树莓派放在交换机和USB转接器的底下(可以看看完整安装好的两张截图)
想办法把线路放在需要的地方——如果你和我一样购买力 USB 线和网线,我可以将它们卷起来放在亚克力板子的每一层
现在不要急着上电,需要将系统烧录到 SD 卡上才能继续。
#### 烧录 Raspbian
按照[这个教程](https://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads/raspbian/)将 Raspbian 烧录到三张 SD 卡上,我使用的是 Win7 下的 [Win32DiskImager](https://sourceforge.net/projects/win32diskimager/)。
将其中一张烧录好的 SD 卡插在你想作为主节点的树莓派上,连接 USB 线并启动它。
#### 启动主节点
这里有[一篇非常棒的“Because We Can Geek”的教程](http://www.becausewecangeek.com/building-a-raspberry-pi-hadoop-cluster-part-1/),讲如何安装 Hadoop 2.7.1,此处就不再熬述。
在启动过程中有一些要注意的地方,我将带着你一起设置直到最后一步,记住我现在使用的 IP 段为 192.168.1.50 – 192.168.1.52,主节点是 .50,从节点是 .51 和 .52,你的网络可能会有所不同,如果你想设置静态 IP 的话可以在评论区看看或讨论。
一旦你完成了这些步骤,接下来要做的就是启用交换文件,Spark on YARN 将分割出一块非常接近内存大小的交换文件,当你内存快用完时便会使用这个交换分区。
(如果你以前没有做过有关交换分区的操作的话,可以看看[这篇教程](https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-add-swap-on-ubuntu-14-04),让 `swappiness` 保持较低水准,因为 MicroSD 卡的性能扛不住)
现在我准备介绍有关我的和“Because We Can Geek”关于启动设置一些微妙的区别。
对于初学者,确保你给你的树莓派起了一个正式的名字——在 `/etc/hostname` 设置,我的主节点设置为 ‘RaspberryPiHadoopMaster’ ,从节点设置为 ‘RaspberryPiHadoopSlave#’
主节点的 `/etc/hosts` 配置如下:
```
#/etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
192.168.1.50 RaspberryPiHadoopMaster
192.168.1.51 RaspberryPiHadoopSlave1
192.168.1.52 RaspberryPiHadoopSlave2
```
如果你想让 Hadoop、YARN 和 Spark 运行正常的话,你也需要修改这些配置文件(不妨现在就编辑)。
这是 `hdfs-site.xml`:
```
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="configuration.xsl"?>
<configuration>
<property>
<name>fs.default.name</name>
<value>hdfs://RaspberryPiHadoopMaster:54310</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name>
<value>/hdfs/tmp</value>
</property>
</configuration>
```
这是 `yarn-site.xml` (注意内存方面的改变):
```
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<configuration>
<!-- Site specific YARN configuration properties -->
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name>
<value>mapreduce_shuffle</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores</name>
<value>4</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb</name>
<value>1024</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb</name>
<value>128</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb</name>
<value>1024</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-vcores</name>
<value>1</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-vcores</name>
<value>4</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.vmem-check-enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether virtual memory limits will be enforced for containers</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.vmem-pmem-ratio</name>
<value>4</value>
<description>Ratio between virtual memory to physical memory when setting memory limits for containers</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.resourcemanager.resource-tracker.address</name>
<value>RaspberryPiHadoopMaster:8025</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.address</name>
<value>RaspberryPiHadoopMaster:8030</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.resourcemanager.address</name>
<value>RaspberryPiHadoopMaster:8040</value>
</property>
</configuration>
```
`slaves`:
```
RaspberryPiHadoopMaster
RaspberryPiHadoopSlave1
RaspberryPiHadoopSlave2
```
`core-site.xml`:
```
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="configuration.xsl"?>
<configuration>
<property>
<name>fs.default.name</name>
<value>hdfs://RaspberryPiHadoopMaster:54310</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name>
<value>/hdfs/tmp</value>
</property>
</configuration>
```
#### 设置两个从节点:
接下来[按照 “Because We Can Geek”上的教程](http://www.becausewecangeek.com/building-a-raspberry-pi-hadoop-cluster-part-2/),你需要对上面的文件作出小小的改动。 在 `yarn-site.xml` 中主节点没有改变,所以从节点中不必含有这个 `slaves` 文件。
### III. 在我们的树莓派集群中测试 YARN
如果所有设备都正常工作,在主节点上你应该执行如下命令:
```
start-dfs.sh
start-yarn.sh
```
当设备启动后,以 Hadoop 用户执行,如果你遵循教程,用户应该是 `hduser`。
接下来执行 `hdfs dfsadmin -report` 查看三个节点是否都正确启动,确认你看到一行粗体文字 ‘Live datanodes (3)’:
```
Configured Capacity: 93855559680 (87.41 GB)
Raspberry Pi Hadoop Cluster picture Straight On
Present Capacity: 65321992192 (60.84 GB)
DFS Remaining: 62206627840 (57.93 GB)
DFS Used: 3115364352 (2.90 GB)
DFS Used%: 4.77%
Under replicated blocks: 0
Blocks with corrupt replicas: 0
Missing blocks: 0
Missing blocks (with replication factor 1): 0
————————————————-
Live datanodes (3):
Name: 192.168.1.51:50010 (RaspberryPiHadoopSlave1)
Hostname: RaspberryPiHadoopSlave1
Decommission Status : Normal
```
你现在可以做一些简单的诸如 ‘Hello, World!’ 的测试,或者直接进行下一步。
### IV. 安装 SPARK ON YARN
YARN 的意思是另一种非常好用的资源调度器(Yet Another Resource Negotiator),已经作为一个易用的资源管理器集成在 Hadoop 基础安装包中。
[Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/) 是 Hadoop 生态圈中的另一款软件包,它是一个毁誉参半的执行引擎和[捆绑的 MapReduce](https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r1.2.1/mapred_tutorial.html)。在一般情况下,相对于基于磁盘存储的 MapReduce,Spark 更适合基于内存的存储,某些运行任务能够得到 10-100 倍提升——安装完成集群后你可以试试 Spark 和 MapReduce 有什么不同。
我个人对 Spark 还是留下非常深刻的印象,因为它提供了两种数据工程师和科学家都比较擅长的语言—— Python 和 R。
安装 Apache Spark 非常简单,在你家目录下,`wget "为 Hadoop 2.7 构建的 Apache Spark”`([来自这个页面](https://spark.apache.org/downloads.html)),然后运行 `tar -xzf “tgz 文件”`,最后把解压出来的文件移动至 `/opt`,并清除刚才下载的文件,以上这些就是安装步骤。
我又创建了只有两行的文件 `spark-env.sh`,其中包含 Spark 的配置文件目录。
```
SPARK_MASTER_IP=192.168.1.50
SPARK_WORKER_MEMORY=512m
```
(在 YARN 跑起来之前我不确定这些是否有必要。)
### V. 你好,世界! 为 Apache Spark 寻找有趣的数据集!
在 Hadoop 世界里面的 ‘Hello, World!’ 就是做单词计数。
我决定让我们的作品做一些内省式……为什么不统计本站最常用的单词呢?也许统计一些关于本站的大数据会更有用。
如果你有一个正在运行的 WordPress 博客,可以通过简单的两步来导出和净化。
1. 我使用 [Export to Text](https://wordpress.org/support/plugin/export-to-text) 插件导出文章的内容到纯文本文件中
2. 我使用一些[压缩库](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/bleach)编写了一个 Python 脚本来剔除 HTML
```
import bleach
# Change this next line to your 'import' filename, whatever you would like to strip
# HTML tags from.
ascii_string = open('dqydj_with_tags.txt', 'r').read()
new_string = bleach.clean(ascii_string, tags=[], attributes={}, styles=[], strip=True)
new_string = new_string.encode('utf-8').strip()
# Change this next line to your 'export' filename
f = open('dqydj_stripped.txt', 'w')
f.write(new_string)
f.close()
```
现在我们有了一个更小的、适合复制到树莓派所搭建的 HDFS 集群上的文件。
如果你不能树莓派主节点上完成上面的操作,找个办法将它传输上去(scp、 rsync 等等),然后用下列命令行复制到 HDFS 上。
```
hdfs dfs -copyFromLocal dqydj_stripped.txt /dqydj_stripped.txt
```
现在准备进行最后一步 - 向 Apache Spark 写入一些代码。
### VI. 点亮 Apache Spark
Cloudera 有个极棒的程序可以作为我们的超级单词计数程序的基础,[你可以在这里找到](https://www.cloudera.com/documentation/enterprise/5-6-x/topics/spark_develop_run.html)。我们接下来为我们的内省式单词计数程序修改它。
在主节点上[安装‘stop-words’](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/stop-words)这个 python 第三方包,虽然有趣(我在 DQYDJ 上使用了 23,295 次 the 这个单词),你可能不想看到这些语法单词占据着单词计数的前列,另外,在下列代码用你自己的数据集替换所有有关指向 dqydj 文件的地方。
```
import sys
from stop_words import get_stop_words
from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConf
if __name__ == "__main__":
# create Spark context with Spark configuration
conf = SparkConf().setAppName("Spark Count")
sc = SparkContext(conf=conf)
# get threshold
try:
threshold = int(sys.argv[2])
except:
threshold = 5
# read in text file and split each document into words
tokenized = sc.textFile(sys.argv[1]).flatMap(lambda line: line.split(" "))
# count the occurrence of each word
wordCounts = tokenized.map(lambda word: (word.lower().strip(), 1)).reduceByKey(lambda v1,v2:v1 +v2)
# filter out words with fewer than threshold occurrences
filtered = wordCounts.filter(lambda pair:pair[1] >= threshold)
print "*" * 80
print "Printing top words used"
print "-" * 80
filtered_sorted = sorted(filtered.collect(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse = True)
for (word, count) in filtered_sorted: print "%s : %d" % (word.encode('utf-8').strip(), count)
# Remove stop words
print "\n\n"
print "*" * 80
print "Printing top non-stop words used"
print "-" * 80
# Change this to your language code (see the stop-words documentation)
stop_words = set(get_stop_words('en'))
no_stop_words = filter(lambda x: x[0] not in stop_words, filtered_sorted)
for (word, count) in no_stop_words: print "%s : %d" % (word.encode('utf-8').strip(), count)
```
保存好 wordCount.py,确保上面的路径都是正确无误的。
现在,准备念出咒语,让运行在 YARN 上的 Spark 跑起来,你可以看到我在 DQYDJ 使用最多的单词是哪一个。
```
/opt/spark-2.0.0-bin-hadoop2.7/bin/spark-submit –master yarn –executor-memory 512m –name wordcount –executor-cores 8 wordCount.py /dqydj_stripped.txt
```
### VII. 我在 DQYDJ 使用最多的单词
可能入列的单词有哪一些呢?“can, will, it’s, one, even, like, people, money, don’t, also“.
嘿,不错,“money”悄悄挤进了前十。在一个致力于金融、投资和经济的网站上谈论这似乎是件好事,对吧?
下面是的前 50 个最常用的词汇,请用它们刻画出有关我的文章的水平的结论。

我希望你能喜欢这篇关于 Hadoop、YARN 和 Apache Spark 的教程,现在你可以在 Spark 运行和编写其他的应用了。
你的下一步是任务是开始[阅读 pyspark 文档](https://spark.apache.org/docs/2.0.0/api/python/index.html)(以及用于其他语言的该库),去学习一些可用的功能。根据你的兴趣和你实际存储的数据,你将会深入学习到更多——有流数据、SQL,甚至机器学习的软件包!
你怎么看?你要建立一个树莓派 Hadoop 集群吗?想要在其中挖掘一些什么吗?你在上面看到最令你惊奇的单词是什么?为什么 'S&P' 也能上榜?
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
via: <https://dqydj.com/raspberry-pi-hadoop-cluster-apache-spark-yarn/>
作者:[PK](https://dqydj.com/about/#contact_us) 译者:[popy32](https://github.com/sfantree) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,487 | 在 Linux 上给用户赋予指定目录的读写权限 | http://www.tecmint.com/give-read-write-access-to-directory-in-linux/ | 2017-05-07T21:04:05 | [
"ACL",
"目录",
"权限"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8487-1.html | 
在上篇文章中我们向您展示了如何在 Linux 上[创建一个共享目录](/article-8187-1.html)。这次,我们会为您介绍如何将 Linux 上指定目录的读写权限赋予用户。
有两种方法可以实现这个目标:第一种是 [使用 ACL (访问控制列表)](http://www.tecmint.com/secure-files-using-acls-in-linux/) ,第二种是[创建用户组来管理文件权限](http://www.tecmint.com/manage-users-and-groups-in-linux/),下面会一一介绍。
为了完成这个教程,我们将使用以下设置。
* 操作系统:CentOS 7
* 测试目录:`/shares/project1/reports`
* 测试用户:tecmint
* 文件系统类型:ext4
请确认所有的命令都是使用 root 用户执行的,或者使用 [sudo 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/sudoers-configurations-for-setting-sudo-in-linux/) 来享受与之同样的权限。
让我们开始吧!下面,先使用 `mkdir` 命令来创建一个名为 `reports` 的目录。
```
# mkdir -p /shares/project1/reports
```
### 使用 ACL 来为用户赋予目录的读写权限
重要提示:打算使用此方法的话,您需要确认您的 Linux 文件系统类型(如 ext3 和 ext4, NTFS, BTRFS)支持 ACL。
1、 首先, 依照以下命令在您的系统中[检查当前文件系统类型](http://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-filesystem-type/),并且查看内核是否支持 ACL:
```
# df -T | awk '{print $1,$2,$NF}' | grep "^/dev"
# grep -i acl /boot/config*
```
从下方的截屏可以看到,文件系统类型是 `ext4`,并且从 `CONFIG_EXT4_FS_POSIX_ACL=y` 选项可以发现内核是支持 **POSIX ACL** 的。

*查看文件系统类型和内核的 ACL 支持。*
2、 接下来,查看文件系统(分区)挂载时是否使用了 ACL 选项。
```
# tune2fs -l /dev/sda1 | grep acl
```

*查看分区是否支持 ACL*
通过上边的输出可以发现,默认的挂载项目中已经对 **ACL** 进行了支持。如果发现结果不如所愿,你可以通过以下命令对指定分区(此例中使用 `/dev/sda3`)开启 ACL 的支持。
```
# mount -o remount,acl /
# tune2fs -o acl /dev/sda3
```
3、 现在是时候指定目录 `reports` 的读写权限分配给名为 `tecmint` 的用户了,依照以下命令执行即可。
```
# getfacl /shares/project1/reports # Check the default ACL settings for the directory
# setfacl -m user:tecmint:rw /shares/project1/reports # Give rw access to user tecmint
# getfacl /shares/project1/reports # Check new ACL settings for the directory
```

*通过 ACL 对指定目录赋予读写权限*
在上方的截屏中,通过输出结果的第二行 `getfacl` 命令可以发现,用户 `tecmint` 已经成功的被赋予了 `/shares/project1/reports` 目录的读写权限。
如果想要获取 ACL 列表的更多信息。可以在下方查看我们的其他指南。
1. [如何使用访问控制列表(ACL)为用户/组设置磁盘配额](http://www.tecmint.com/set-access-control-lists-acls-and-disk-quotas-for-users-groups/)
2. [如何使用访问控制列表(ACL)挂载网络共享](http://www.tecmint.com/rhcsa-exam-configure-acls-and-mount-nfs-samba-shares/)
现在我们来看看如何使用第二种方法来为目录赋予读写权限。
### 使用用户组来为用户赋予指定目录的读写权限
1、 如果用户已经拥有了默认的用户组(通常组名与用户名相同),就可以简单的通过变更文件夹的所属用户组来完成。
```
# chgrp tecmint /shares/project1/reports
```
另外,我们也可以通过以下方法为多个用户(需要赋予指定目录读写权限的)新建一个用户组。如此一来,也就[创建了一个共享目录](http://www.tecmint.com/create-a-shared-directory-in-linux/)。
```
# groupadd projects
```
2、 接下来将用户 `tecmint` 添加到 `projects` 组中:
```
# usermod -aG projects tecmint # add user to projects
# groups tecmint # check users groups
```
3、 将目录的所属用户组变更为 projects:
```
# chgrp projects /shares/project1/reports
```
4、 现在,给组成员设置读写权限。
```
# chmod -R 0760 /shares/projects/reports
# ls -l /shares/projects/ #check new permissions
```
好了!这篇教程中,我们向您展示了如何在 Linux 中将指定目录的读写权限赋予用户。若有疑问,请在留言区中提问。
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,未来的 Linux 系统管理员和网络开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/give-read-write-access-to-directory-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[Mr-Ping](http://www.mr-ping.com) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,488 | 如何在 Ubuntu16.04 中用 Apache 部署 Jenkins 自动化服务器 | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-jenkins-with-apache-on-ubuntu-16-04/ | 2017-05-08T08:29:33 | [
"Jenkins"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8488-1.html | Jenkins 是从 Hudson 项目衍生出来的自动化服务器。Jenkins 是一个基于服务器的应用程序,运行在 Java servlet 容器中,它支持包括 Git、SVN 以及 Mercurial 在内的多种 SCM(<ruby> 源码控制工具 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Source Control Management </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)。Jenkins 提供了上百种插件帮助你的项目实现自动化。Jenkins 由 Kohsuke Kawaguchi 开发,在 2011 年使用 MIT 协议发布了第一个发行版,它是个自由软件。

在这篇指南中,我会向你介绍如何在 Ubuntu 16.04 中安装最新版本的 Jenkins。我们会用自己的域名运行 Jenkins,在 apache web 服务器中安装和配置 Jenkins,而且支持反向代理。
### 前提
* Ubuntu 16.04 服务器 - 64 位
* Root 权限
### 第一步 - 安装 Java OpenJDK 7
Jenkins 基于 Java,因此我们需要在服务器上安装 Java OpenJDK 7。在这里,我们会从一个 PPA 仓库安装 Java 7,首先我们需要添加这个仓库。
默认情况下,Ubuntu 16.04 没有安装用于管理 PPA 仓库的 python-software-properties 软件包,因此我们首先需要安装这个软件。使用 apt 命令安装 python-software-properties。
```
apt-get install python-software-properties
```
下一步,添加 Java PPA 仓库到服务器中。
```
add-apt-repository ppa:openjdk-r/ppa
```
用 apt 命令更新 Ubuntu 仓库并安装 Java OpenJDK。
```
apt-get update
apt-get install openjdk-7-jdk
```
输入下面的命令验证安装:
```
java -version
```
你会看到安装到服务器上的 Java 版本。

### 第二步 - 安装 Jenkins
Jenkins 给软件安装包提供了一个 Ubuntu 仓库,我们会从这个仓库中安装 Jenkins。
用下面的命令添加 Jenkins 密钥和仓库到系统中。
```
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add -
echo 'deb https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/' | tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list
```
更新仓库并安装 Jenkins。
```
apt-get update
apt-get install jenkins
```
安装完成后,用下面的命令启动 Jenkins。
```
systemctl start jenkins
```
通过检查 Jenkins 默认使用的端口(端口 8080)验证 Jenkins 正在运行。我会像下面这样用 `netstat` 命令检测:
```
netstat -plntu
```
Jenkins 已经安装好了并运行在 8080 端口。

### 第三步 - 为 Jenkins 安装和配置 Apache 作为反向代理
在这篇指南中,我们会在一个 Apache web 服务器中运行 Jenkins,我们会为 Jenkins 配置 apache 作为反向代理。首先我会安装 apache 并启用一些需要的模块,然后我会为 Jenkins 用域名 my.jenkins.id 创建虚拟主机文件。请在这里使用你自己的域名并在所有配置文件中出现的地方替换。
从 Ubuntu 仓库安装 apache2 web 服务器。
```
apt-get install apache2
```
安装完成后,启用 proxy 和 proxy\_http 模块以便将 apache 配置为 Jenkins 的前端服务器/反向代理。
```
a2enmod proxy
a2enmod proxy_http
```
下一步,在 `sites-available` 目录创建新的虚拟主机文件。
```
cd /etc/apache2/sites-available/
vim jenkins.conf
```
粘贴下面的虚拟主机配置。
```
<Virtualhost *:80>
ServerName my.jenkins.id
ProxyRequests Off
ProxyPreserveHost On
AllowEncodedSlashes NoDecode
<Proxy http://localhost:8080/*>
Order deny,allow
Allow from all
</Proxy>
ProxyPass / http://localhost:8080/ nocanon
ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:8080/
ProxyPassReverse / http://my.jenkins.id/
</Virtualhost>
```
保存文件。然后用 `a2ensite` 命令激活 Jenkins 虚拟主机。
```
a2ensite jenkins
```
重启 Apache 和 Jenkins。
```
systemctl restart apache2
systemctl restart jenkins
```
检查 Jenkins 和 Apache 正在使用 80 和 8080 端口。
```
netstat -plntu
```

### 第四步 - 配置 Jenkins
Jenkins 用域名 'my.jenkins.id' 运行。打开你的 web 浏览器然后输入 URL。你会看到要求你输入初始管理员密码的页面。Jenkins 已经生成了一个密码,因此我们只需要显示并把结果复制到密码框。
用 `cat` 命令显示 Jenkins 初始管理员密码。
```
cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
a1789d1561bf413c938122c599cf65c9
```

将结果粘贴到密码框然后点击 Continue。

现在为了后面能比较好的使用,我们需要在 Jenkins 中安装一些插件。选择 Install Suggested Plugin,点击它。

Jenkins 插件安装过程:

安装完插件后,我们需要创建一个新的管理员密码。输入你的管理员用户名、密码、电子邮件等,然后点击 ‘Save and Finish’。

点击 start 开始使用 Jenkins。你会被重定向到 Jenkins 管理员面板。

成功完成 Jenkins 安装和配置。

### 第五步 - Jenkins 安全
在 Jenkins 管理员面板,我们需要为 Jenkins 配置标准的安全,点击 ‘Manage Jenkins’ 和 ‘Configure Global Security’。

Jenkins 在 ‘Access Control’ 部分提供了多种认证方法。为了能够控制所有的用户权限,我选择了 ‘Matrix-based Security’。在复选框 ‘User/Group’ 中启用 admin 用户。通过勾选所有选项给 admin 所有权限,给 anonymous 只读权限。现在点击 ‘Save’。

你会被重定向到面板,如果出现了登录选项,只需输入你的管理员账户和密码。
### 第六步 - 测试一个简单的自动化任务
在这一部分,我想为 Jenkins 服务测试一个简单的任务。为了测试 Jenkins 我会创建一个简单的任务,并用 top 命令查看服务器的负载。
在 Jenkins 管理员面板上,点击 ‘Create New Job’。

输入任务的名称,在这里我输入 ‘Checking System’,选择 Freestyle Project 然后点击 OK。

进入 Build 标签页。在 Add build step,选择选项 Execute shell。
在输入框输入下面的命令。
```
top -b -n 1 | head -n 5
```
点击 Save。

现在你是在任务 ‘Project checking system’ 的任务页。点击 Build Now 执行任务 ‘checking system’。
任务执行完成后,你会看到 Build History,点击第一个任务查看结果。
下面是 Jenkins 任务执行的结果。

到这里就介绍完了在 Ubuntu 16.04 中用 Apache web 服务器安装 Jenkins 的内容。
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-jenkins-with-apache-on-ubuntu-16-04/>
作者:[Muhammad Arul](https://twitter.com/howtoforgecom) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # How to Install Jenkins Automation Server with Apache on Ubuntu 16.04
### This tutorial exists for these OS versions
[Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish)](/tutorial/ubuntu-jenkins-automation-server/)[Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa)](/tutorial/how-to-install-jenkins-automation-server-with-apache-on-ubuntu-20-04/)[Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver)](/tutorial/how-to-install-jenkins-automation-server-with-apache-on-ubuntu-1804/)**Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial Xerus)**
### On this page
[Step 1 - Install Java OpenJDK 7](#step-install-java-openjdk-)
[Step 2 - Install Jenkins](#step-install-jenkins)
[Step 3 - Install and Configure Apache as Reverse Proxy for Jenkins](#step-install-and-configure-apache-as-reverse-proxy-for-jenkins)
[Step 4 - Configure Jenkins](#step-configure-jenkins)
[Step 5 - Jenkins Security](#step-jenkins-security)
[Step 6 - Testing a simple automation job](#step-testing-a-simple-automation-job)
[Reference](#reference)
Jenkins is an automation server forked from the Hudson project. Jenkins is a server based application running in a Java servlet container, it has support for many SCM (Source Control Management) software systems including Git, SVN, and Mercurial. Jenkins provides hundreds of plugins to automate your project. Jenkins created by Kohsuke Kawaguchi, first released in 2011 under MIT License, and it's free software.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install the latest Jenkins version on Ubuntu Server 16.04. We will run Jenkins on our own domain name, and we will to install and configure Jenkins to run under the apache web server with the reverse proxy for Jenkins.
### Prerequisite
- Ubuntu Server 16.04 - 64bit
- Root Privileges
## Step 1 - Install Java OpenJDK 7
Jenkins is based on Java, so we need to install Java OpenJDK version 7 on the server. In this step, we will install Java 7 from a PPA repository which we will add first.
By default, Ubuntu 16.04 ships without the python-software-properties package for managing PPA repositories, so we must install this package first. Install python-software-properties with apt command.
apt-get install python-software-properties
Next, add Java PPA repository to the server.
add-apt-repository ppa:openjdk-r/ppa
Just Press ENTER
Update the Ubuntu repository and install the Java OpenJDK with apt command.
apt-get update
apt-get install openjdk-7-jdk
Verify the installation by typing the command below:
java -version
and you will get the Java version that is installed on the server.
## Step 2 - Install Jenkins
Jenkins provides an Ubuntu repository for the installation packages and we will install Jenkins from this repository.
Add Jenkins key and repository to the system with the command below.
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add -
echo 'deb https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/' | tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list
Update the repository and install Jenkins.
apt-get update
apt-get install jenkins
When the installation is done, start Jenkins with this systemctl command.
systemctl start jenkins
Verify that Jenkins is running by checking the default port used by Jenkins (port 8080). I will check it with the netstat command below:
netstat -plntu
Jenkins is installed and running on port 8080.
## Step 3 - Install and Configure Apache as Reverse Proxy for Jenkins
In this tutorial we will run Jenkins behind an apache web server, we will configure apache as the reverse proxy for Jenkins. First I will install apache and enable some require modules, and then I'll create the virtual host file with domain name my.jenkins.id for Jenkins. Please use your own domain name here and replace it in all config files wherever it appears.
Install apache2 web server from Ubuntu repository.
apt-get install apache2
When the installation is done, enable the proxy and proxy_http modules so we can configure apache as frontend server/reverse proxy for Jenkins.
a2enmod proxy
a2enmod proxy_http
Next, create a new virtual host file in the sites-available directory.
cd /etc/apache2/sites-available/
vim jenkins.conf
Paste virtual host configuration below.
<Virtualhost *:80>
ServerName my.jenkins.id
ProxyRequests Off
ProxyPreserveHost On
AllowEncodedSlashes NoDecode
<Proxy http://localhost:8080/*>
Order deny,allow
Allow from all
</Proxy>
ProxyPass / http://localhost:8080/ nocanon
ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:8080/
ProxyPassReverse / http://my.jenkins.id/
</Virtualhost>
Save the file. Then activate the Jenkins virtual host with the a2ensite command.
a2ensite jenkins
Restart Apache and Jenkins.
systemctl restart apache2
systemctl restart jenkins
Check that port 80 and 8000 are in use by Jenkins and Apache.
netstat -plntu
## Step 4 - Configure Jenkins
Jenkins is running on the domain name 'my.jenkins.id'. Open your web browser and type in the URL. You will get the screen that requests you to enter the initial admin password. A password has been generated by Jenkins already, so we just need to show and copy the results to the password box.
Show initial admin password Jenkins with cat command.
cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
a1789d1561bf413c938122c599cf65c9
Paste the results to the screen and click '**Continue**'.
Now we should install some plugins in Jenkins to get a good foundation for later use. Choose '**Install Suggested Plugins**', click on it.
Jenkins plugins installations in progress.
After plugin installation, we have to create a new admin password. Type in your admin username, password, email etc. and click on '**Save and Finish**'.
Click start and start using Jenkins. You will be redirected to the Jenkins admin dashboard.
Jenkins installation and Configuration finished successfully
## Step 5 - Jenkins Security
From the Jenkins admin dashboard, we need to configure the standard security settings for Jenkins, click on '**Manage Jenkins**' and then '**Configure Global Security**'.
Jenkins provides several authorization methods in the '**Access Control**' section. I select '**Matrix-based Security**' to be able to control all user privileges. Enable the admin user at the box '**User/Group**' and click **add**. Give the admin all privileges by **checking all options**, and give the anonymous just read permissions. Now Click '**Save**'.
You will be redirected to the dashboard, and if there is login option, just type your admin user and password.
## Step 6 - Testing a simple automation job
In this section, I just want to test a simple job for the Jenkins server. I will create a simple job for testing Jenkins and to find out the server load with the top command.
From the Jenkins admin dashboard, click '**Create New Job**'.
Enter the job name, I'll use 'Checking System' here, select '**Freestyle Project**' and click '**OK**'.
Go to the '**Build**' tab. On the '**Add build step**', select the option '**Execute shell**'.
Type in the command below into the box.
top -b -n 1 | head -n 5
Click '**Save**'.
Now you are on the job page of the job 'Project checking system'. Click '**Build Now**' to execute the job 'checking system'.
After the job has been executed, you will see the '**Build History**', click on the first job to see the results.
Here are the results from the job executed by Jenkins.
Jenkins installation with Apache web server on Ubuntu 16.04 completed successfully. |
8,489 | 在没有 Kotlin 的世界与 Android 共舞 | https://medium.com/proandroiddev/living-android-without-kotlin-db7391a2b170 | 2017-05-08T09:46:00 | [
"Android",
"Kotlin",
"java"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8489-1.html | 
>
> 开始投入一件事比远离它更容易。 — Donald Rumsfeld
>
>
>
没有 Kotlin 的生活就像在触摸板上玩魔兽争霸 3。购买鼠标很简单,但如果你的新雇主不想让你在生产中使用 Kotlin,你该怎么办?
下面有一些选择。
* 与你的产品负责人争取获得使用 Kotlin 的权利。
* 使用 Kotlin 并且不告诉其他人因为你知道最好的东西是只适合你的。
* 擦掉你的眼泪,自豪地使用 Java。
想象一下,你在和产品负责人的斗争中失败,作为一个专业的工程师,你不能在没有同意的情况下私自去使用那些时髦的技术。我知道这听起来非常恐怖,特别当你已经品尝到 Kotlin 的好处时,不过不要失去生活的信念。
在文章接下来的部分,我想简短地描述一些 Kotlin 的特征,使你通过一些知名的工具和库,可以应用到你的 Android 里的 Java 代码中去。对于 Kotlin 和 Java 的基本认识是需要的。
### 数据类
我想你肯定已经喜欢上 Kotlin 的数据类。对于你来说,得到 `equals()`、 `hashCode()`、 `toString()` 和 `copy()` 这些是很容易的。具体来说,`data` 关键字还可以按照声明顺序生成对应于属性的 `componentN()` 函数。 它们用于解构声明。
```
data class Person(val name: String)
val (riddle) = Person("Peter")
println(riddle)
```
你知道什么会被打印出来吗?确实,它不会是从 `Person` 类的 `toString()` 返回的值。这是解构声明的作用,它赋值从 `name` 到 `riddle`。使用园括号 `(riddle)` 编译器知道它必须使用解构声明机制。
```
val (riddle): String = Person("Peter").component1()
println(riddle) // prints Peter)
```
>
> 这个代码没编译。它就是展示了构造声明怎么工作的。
>
>
>
正如你可以看到 `data` 关键字是一个超级有用的语言特性,所以你能做什么把它带到你的 Java 世界? 使用注释处理器并修改抽象语法树(Abstract Syntax Tree)。 如果你想更深入,请阅读文章末尾列出的文章(Project Lombok— Trick Explained)。
使用项目 Lombok 你可以实现 `data`关键字所提供的几乎相同的功能。 不幸的是,没有办法进行解构声明。
```
import lombok.Data;
@Data class Person {
final String name;
}
```
`@Data` 注解生成 `equals()`、`hashCode()` 和 `toString()`。 此外,它为所有字段创建 getter,为所有非最终字段创建setter,并为所有必填字段(final)创建构造函数。 值得注意的是,Lombok 仅用于编译,因此库代码不会添加到您的最终的 .apk。
### Lambda 表达式
Android 工程师有一个非常艰难的生活,因为 Android 中缺乏 Java 8 的特性,而且其中之一是 lambda 表达式。 Lambda 是很棒的,因为它们为你减少了成吨的样板。 你可以在回调和流中使用它们。 在 Kotlin 中,lambda 表达式是内置的,它们看起来比它们在 Java 中看起来好多了。 此外,lambda 的字节码可以直接插入到调用方法的字节码中,因此方法计数不会增加。 它可以使用内联函数。
```
button.setOnClickListener { println("Hello World") }
```
最近 Google 宣布在 Android 中支持 Java 8 的特性,由于 Jack 编译器,你可以在你的代码中使用 lambda。还要提及的是,它们在 API 23 或者更低的级别都可用。
```
button.setOnClickListener(view -> System.out.println("Hello World!"));
```
怎样使用它们?就只用添加下面几行到你的 `build.gradle` 文件中。
```
defaultConfig {
jackOptions {
enabled true
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
```
如果你不喜欢用 Jack 编译器,或者你由于一些原因不能使用它,这里有一个不同的解决方案提供给你。Retrolambda 项目允许你在 Java 7,6 或者 5 上运行带有 lambda 表达式的 Java 8 代码,下面是设置过程。
```
dependencies {
classpath 'me.tatarka:gradle-retrolambda:3.4.0'
}
apply plugin: 'me.tatarka.retrolambda'
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
```
正如我前面提到的,在 Kotlin 下的 lambda 内联函数不增加方法计数,但是如何在 Jack 或者 Retrolambda 下使用它们呢? 显然,它们不是没成本的,隐藏的成本如下。

*该表展示了使用不同版本的 Retrolambda 和 Jack 编译器生成的方法数量。该比较结果来自 Jake Wharton 的“[探索 Java 的隐藏成本](http://jakewharton.com/exploring-java-hidden-costs/)” 技术讨论之中。*
### 数据操作
Kotlin 引入了高阶函数作为流的替代。 当您必须将一组数据转换为另一组数据或过滤集合时,它们非常有用。
```
fun foo(persons: MutableList<Person>) {
persons.filter { it.age >= 21 }
.filter { it.name.startsWith("P") }
.map { it.name }
.sorted()
.forEach(::println)
}
data class Person(val name: String, val age: Int)
```
流也由 Google 通过 Jack 编译器提供。 不幸的是,Jack 不使用 Lombok,因为它在编译代码时跳过生成中间的 `.class` 文件,而 Lombok 却依赖于这些文件。
```
void foo(List<Person> persons) {
persons.stream()
.filter(it -> it.getAge() >= 21)
.filter(it -> it.getName().startsWith("P"))
.map(Person::getName)
.sorted()
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
class Person {
final private String name;
final private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
String getName() { return name; }
int getAge() { return age; }
}
```
这简直太好了,所以 catch 在哪里? 令人悲伤的是,流从 API 24 才可用。谷歌做了好事,但哪个应用程序有用 `minSdkVersion = 24`?
幸运的是,Android 平台有一个很好的提供许多很棒的库的开源社区。Lightweight-Stream-API 就是其中的一个,它包含了 Java 7 及以下版本的基于迭代器的流实现。
```
import lombok.Data;
import com.annimon.stream.Stream;
void foo(List<Person> persons) {
Stream.of(persons)
.filter(it -> it.getAge() >= 21)
.filter(it -> it.getName().startsWith("P"))
.map(Person::getName)
.sorted()
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Data class Person {
final String name;
final int age;
}
```
上面的例子结合了 Lombok、Retrolambda 和 Lightweight-Stream-API,它看起来几乎和 Kotlin 一样棒。使用静态工厂方法允许您将任何 Iterable 转换为流,并对其应用 lambda,就像 Java 8 流一样。 将静态调用 `Stream.of(persons)` 包装为 Iterable 类型的扩展函数是完美的,但是 Java 不支持它。
### 扩展函数
扩展机制提供了向类添加功能而无需继承它的能力。 这个众所周知的概念非常适合 Android 世界,这就是 Kotlin 在该社区很受欢迎的原因。
有没有技术或魔术将扩展功能添加到你的 Java 工具箱? 因 Lombok,你可以使用它们作为一个实验功能。 根据 Lombok 文档的说明,他们想把它从实验状态移出,基本上没有什么变化的话很快。 让我们重构最后一个例子,并将 `Stream.of(persons)` 包装成扩展函数。
```
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.experimental.ExtensionMethod;
@ExtensionMethod(Streams.class)
public class Foo {
void foo(List<Person> persons) {
persons.toStream()
.filter(it -> it.getAge() >= 21)
.filter(it -> it.getName().startsWith("P"))
.map(Person::getName)
.sorted()
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
@Data class Person {
final String name;
final int age;
}
class Streams {
static <T> Stream<T> toStream(List<T> list) {
return Stream.of(list);
}
}
```
所有的方法是 `public`、`static` 的,并且至少有一个参数的类型不是原始的,因而是扩展方法。 `@ExtensionMethod` 注解允许你指定一个包含你的扩展函数的类。 你也可以传递数组,而不是使用一个 `.class` 对象。
---
我完全知道我的一些想法是非常有争议的,特别是 Lombok,我也知道,有很多的库,可以使你的生活更轻松。请不要犹豫在评论里分享你的经验。干杯!

---
作者简介:
Coder and professional dreamer @ Grid Dynamics
---
via: <https://medium.com/proandroiddev/living-android-without-kotlin-db7391a2b170>
作者:[Piotr Ślesarew](https://hackernoon.com/@piotr.slesarew?source=post_header_lockup) 译者:[DockerChen](https://github.com/DockerChen) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,490 | 极客漫画:让你变成“机电工程师”的 Arduino 项目 | https://turnoff.us/geek/arduino-project/ | 2017-05-09T09:58:00 | [
"漫画"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8490-1.html | 
* 刚刚完成我的第一个 Arduino 项目:一个闪烁的 LED
* 下一步:更新我的 LinkedIn 详情
* 添加技能:机电工程师
这篇漫画讽刺的是一些人只是接触了某个领域的很浅显的知识,就急急忙忙的为自己加上相应的头衔,却没有考虑自己所掌握的东西,在整个领域内所处的位置。
---
via: <https://turnoff.us/geek/arduino-project/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者&点评:[Bestony](https://github.com/Bestony) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 合成:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | {turnoff.us}
RSS.sign()
|
X.follow()
arduino project
previous
|
next
X.
follow()
| X.
post(this)
| RSS.
sign()
Support us - buy a tee or sticker!
show all |
8,491 | bd:快速返回某级父目录而不用冗余地输入 “cd ../../..” | http://www.tecmint.com/bd-quickly-go-back-to-a-linux-parent-directory/ | 2017-05-10T08:25:00 | [
"目录",
"导航"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8491-1.html | 在 Linux 系统上通过命令行切换文件夹时,为了回到父目录(长路径),我们通常会重复输入 [cd 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/cd-command-in-linux/)(`cd ../../..`),直到进入感兴趣的目录。
对于经验丰富的 Linux 用户或需要进行各种不同任务的系统管理员而言,这可能非常乏味,因此希望在操作系统时有一个快捷方式来简化工作。

**建议阅读:** [Autojump - 一个快速浏览 Linux 文件系统的高级 “cd” 命令](/article-5983-1.html)
在本文中,我们将在 bd 工具的帮助下,用这个简单而有用的工具快速回到 Linux 中的父目录。
bd 是用于切换文件夹的便利工具,它可以使你快速返回到父目录,而不必重复键入 `cd ../../..` 。 你可以可靠地将其与其他 Linux 命令组合以执行几个日常操作。
### 如何在 Linux 中安装 bd
运行下面的命令,使用 [wget 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/)下载并安装 bd 到 `/usr/bin/` 中,添加执行权限,并在 `~/.bashrc` 中创建需要的别名:
```
$ wget --no-check-certificate -O /usr/bin/bd https://raw.github.com/vigneshwaranr/bd/master/bd
$ chmod +rx /usr/bin/bd
$ echo 'alias bd=". bd -si"' >> ~/.bashrc
$ source ~/.bashrc
```
注意:如果要启用大小写敏感的目录名匹配,请在上面创建的别名中,设置 `-s` 标志而不是 `-si` 标志。
要启用自动补全支持,运行这些命令:
```
$ sudo wget -O /etc/bash_completion.d/bd https://raw.github.com/vigneshwaranr/bd/master/bash_completion.d/bd
$ sudo source /etc/bash_completion.d/bd
```
#### 如何在 Linux 中使用 bd
假设你目前在这个路径的顶层目录:
```
/media/aaronkilik/Data/Computer Science/Documents/Books/LEARN/Linux/Books/server $
```
你想要快速进入 “Documents” 目录,只要输入:
```
$ bd Documents
```
接着直接进入到 Data 目录,你可以输入:
```
$ bd Data
```

*目录间快速切换*
实际上,bd 让它变得更加直接,你要做的是输入 “bd <开头几个字母>”,比如:
```
$ bd Doc
$ bd Da
```

*快速切换目录*
重要:如果层次结构中有不止一个具有相同名称的目录,bd 将会移动到最接近的目录,而不考虑最近的父目录,如下面的例子那样。
例如,在上面的路径中,有两个名称相同的目录 Books,如果你想移动到:
```
/media/aaronkilik/Data/ComputerScience/Documents/Books/LEARN/Linux/Books
```
输入 `bd Books` 会进入:
```
/media/aaronkilik/Data/ComputerScience/Documents/Books
```

*快速进入 ‘Books’ 目录*
另外,在反引号````中使用 bd 如 ``bd <开头几个字母>`` 会打印出路径而不更改当前目录,所以你可以与其他常见的 Linux 命令,如 [ls](http://www.tecmint.com/tag/linux-ls-command/),[echo](http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/) 等一起使用 ``bd <开头几个字母>`` 。
在下面的例子中,当前在 `/var/www/html/internship/assets/filetree` 目录中,要打印出绝对路径、详细列出内容、统计目录 html 中所有文件的大小,你不必进入它,只需要键入:
```
$ echo `bd ht`
$ ls -l `bd ht`
$ du -cs `bd ht`
```

*列出切换的目录*
要在 Github 上了解更多关于 bd 的信息:<https://github.com/vigneshwaranr/bd>
就是这样了!在本文中,我们展示了使用 bd 程序[在 Linux 中快速切换文件夹](/article-5983-1.html)的便捷方法。
通过下面的反馈栏单发表你的看法。此外,你还知道其他类似的工具么,在评论中让我们知道。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili是一名 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 的爱好者,未来的 Linux 系统管理员、网站开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并乐于分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/bd-quickly-go-back-to-a-linux-parent-directory/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,492 | 如何在 Ubuntu 中安装语音聊天工具 Discord | https://www.maketecheasier.com/install-discord-ubuntu/ | 2017-05-09T08:43:17 | [
"Discord",
"聊天"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8492-1.html | 
Discord 是一个非常受欢迎的文字和语音聊天程序。虽然开始时主要面向游戏玩家,但它几乎获得了所有人的了广泛青睐。
Discord 不仅仅是一个很好的聊天客户端。当你安装它时,你还可以获得其强大的服务端功能,强力而自足。游戏玩家和非玩家都可以在几分钟内开启自己的私人聊天服务,这使 Discord 成为团队、公会和各种社区的明显选择。
Linux 用户经常被游戏世界遗忘。但 Discord 并不是这样。它的开发人员也在 Linux 下积极构建并维护其流行聊天平台。Ubuntu 用户甚至拥有更好的待遇,Discord 捆绑在方便的 Debian/Ubuntu .deb 包中。
### 获取并安装软件包
有几种方法在 Ubuntu 下获取 Discord。你可以都看一下,并选择一个你喜欢的。
### 依赖
在 Discord 的下载页面上没有什么关于依赖的内容,但是在 Ubuntu 上安装之前,你需要安装一些依赖。没什么大不了的。打开你的终端,并输入以下命令以获得所需内容:
```
sudo apt install libgconf-2-4 libappindicator1
```
### 图形化安装
图形化安装会耗时长一点,但是这对 Linux 新手而言更简单。

首先进入 Discord 的[网站](https://discordapp.com/download)。该网站应该能自动检测到你正在运行的 Linux,并在页面正中建议正确的包。
如果没有,只需向下滚动一下。页面的下一部分会显示其他可用的下载,而 Linux 包就在那里。
找到 Linux 的下载链接后,请检查是否选择了 “deb”,然后单击 “Download” 按钮。

浏览器会询问你想要用 Ubuntu 软件安装器打开或者下载文件。你可以选择任意一个,但是自动用软件安装器打开会更快。

下载很快,所以安装程序会立即打开,并允许你安装新下载的软件包。这是一个非常简单的窗口,没有漂亮的图标或很多描述性的文本,所以不要犹豫。这是正常的。单击 “Install” 开始安装。
安装过程不会耗费太长时间。之后,Discord 就可以使用了。
### 命令行安装
“懒惰”的 Linux 熟手并不在意花哨的 GUI 工具。如果你是这个阵营的人,那么你有一个更直接的命令行选项。
首先,打开一个终端并进入你的下载目录。在那里可以使用 `wget` 直接下载 .deb 包。
```
cd ~/Downloads
wget -O discord-0.0.1.deb https://discordapp.com/api/download?platform=linux&format=deb
```
下载完成后,你可以使用 `dpkg` 直接安装 .deb 软件包。运行下面的命令:
```
sudo dpkg -i discord-0.0.1.deb
```
### 测试一下

现在你可以打开软件启动器并搜索 Discord。单击图标运行。

首次启动,根据你需求,创建一个帐户或者登录。

登录后,你就进入 Discord 了。它会提供一些介绍教程和建议。你可以直接略过并开始尝试。欢迎进入你新的 Linux 聊天体验!
---
via: <https://www.maketecheasier.com/install-discord-ubuntu/>
作者:[Nick Congleton](https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/nickcongleton/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 
Discord is a wildly popular text and voice chat application. Though it began life catering primarily to gamers, it has gained widespread favor across nearly all audiences.
Discord isn’t just a great chat client. When you install it you also get its powerful server capabilities, batteries included. Gamers and non-gamers alike can spin up their own private chat servers in minutes, making Discord an obvious choice for teams, guilds, and all sorts of communities.
All too often, Linux users are left out in the gaming world. That’s not the case with Discord. Its developers actively build and maintain their popular chat platform for Linux too. Ubuntu users have it even better. Discord is bundled in a convenient Debian/Ubuntu .deb package.
**Also read:** [How to Set Up a Discord Server](https://www.maketecheasier.com/set-up-discord-server/)
## Get and Install the Packages
There are a couple of ways that you can get Discord for Ubuntu. You can take a look at both and choose the one that you’re more comfortable with.
### Via Snap
The easiest way to install Discord is definitely via Snap. Discord is available as a Snap package. You can easily install it with the command:
sudo snap install discord
### Dependencies
If you decide to install via the traditional method, then there are a couple of dependencies that you need before you can install it on Ubuntu. It’s not a big deal. Open up your terminal and enter in the following command to get what you need:
sudo apt install libgconf-2-4 libappindicator1
### Graphical Install
The graphical install process takes a bit longer, but it also tends to be simpler for newer Linux users.
Start by heading over to the Discord [website](https://discordapp.com/download). The site should automatically detect that you’re running Linux and suggest the correct package right in the main section of the page.
If it doesn’t, just scroll down a bit. The next section of the page shows the other available downloads, and Linux will be there.
Once you’ve found the download link for Linux, check to see that “deb” is selected, and click the “Download” button.
Your browser will ask if you would prefer to open the file with the Ubuntu software installer or download the file. You can do either, but it is quicker to automatically open the package with the software installer.
The download is fairly quick, so the installer will open right up and allow you the option of installing your newly-downloaded package. It’s a fairly plain window without a nice icon or a lot of descriptive text, so don’t be put off by that. It’s normal. Click “Install” to begin the installation.
The install process won’t take long. Afterward, Discord will be available and ready to use.
### Command Line Install
Lazy Linux veterans don’t care much for fancy GUI tools. If you fall into this camp, there’s a more direct command line option for you.
First, open up a terminal and change into your download directory. From there, you can use `wget`
to grab the .deb package directly.
cd ~/Downloads wget -O discord-0.0.1.deb https://discordapp.com/api/download?platform=linux&format=deb
When the download completes, you can use dpkg to install the .deb package directly. Run the following command:
sudo dpkg -i discord-0.0.1.deb
**Also read:** [11 Ways to Prevent Discord from Disconnecting and Reconnecting](https://www.maketecheasier.com/prevent-discord-disconnecting-reconnecting/)
## Testing It Out
Now you can open your software launcher and search for Discord. Click the icon to launch it.
On your first run you will be prompted to create an account or sign in. Do whichever you need to.
After you sign in, you’ll be dropped right in to Discord. It will offer some introductory tutorials and advice. You can jump right in and play around, though. Welcome to your new Linux chat experience!
**Also read:** [How to Make a Discord Bot](https://www.maketecheasier.com/make-discord-bot/)
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox |
8,493 | Remmina:一个 Linux 下功能丰富的远程桌面共享工具 | http://www.tecmint.com/remmina-remote-desktop-sharing-and-ssh-client/ | 2017-05-10T09:05:00 | [
"Remmina",
"远程桌面共享"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8493-1.html | 
**Remmina** 是一款在 Linux 和其他类 Unix 系统下的自由开源、功能丰富、强大的远程桌面客户端,它用 GTK+ 3 编写而成。它适用于那些需要远程访问及使用许多计算机的系统管理员和在外出行人员。
它以简单、统一、同质、易用的用户界面支持多种网络协议。
### Remmina 功能
* 支持 RDP、VNC、NX、XDMCP 和 SSH。
* 用户能够以组的形式维护一份连接配置列表。
* 支持用户直接输入服务器地址的快速连接。
* 具有更高分辨率的远程桌面,可以在窗口和全屏模式下滚动/缩放。
* 支持窗口全屏模式;当鼠标移动到屏幕边缘时,远程桌面会自动滚动。
* 还支持全屏模式的浮动工具栏;使你能够在不同模式间切换、触发键盘获取、最小化等。
* 提供选项卡式界面,可以按组管理。
* 还提供托盘图标,允许你快速访问已配置的连接文件。
在本文中,我们将向你展示如何在 Linux 中安装 Remmina,以及使用它通过支持的不同协议实现桌面共享。
### 先决条件
* 在远程机器上允许桌面共享(让远程机器允许远程连接)。
* 在远程机器上设置 SSH 服务。
### 如何在 Linux 中安装 Remmina 远程共享工具
Remmina 及其插件包已经在所有主流的 Linux 发行版的大多数官方仓库中提供。运行下面的命令以安装它和所有支持的插件:
```
------------ 在 Debian/Ubuntu 中 ------------
$ sudo apt-get install remmina remmina-plugin-*
```
```
------------ 在 CentOS/RHEL 中 ------------
# yum install remmina remmina-plugin-*
```
```
------------ 在 Fedora 22+ 中 ------------
$ sudo dnf copr enable hubbitus/remmina-next
$ sudo dnf upgrade --refresh 'remmina*' 'freerdp*'
```
一旦安装完成后,在 Ubuntu 或 Linux Mint 菜单中搜索 `remmina`,接着运行它:

*Remmina 桌面共享客户端*
你可以通过图形界面或者编辑 `$HOME/.remmina` 或者 `$HOME/.config/remmina` 下的文件来进行配置。
要设置到一个新的远程服务器的连接,按下 `Ctrl+N` 并点击 **Connection -> New**,如下截图中配置远程连接。这是基本的设置界面。

*Remmina 基础桌面配置*
点击界面上的 “**Advanced**”,配置高级连接设置。

*Remmina 高级桌面设置*
要配置 **SSH**,点击界面中的 SSH。

*Remmina SSH 设置*
在完成所有的必要配置后,点击 “**Save**” 保存设置,在主界面中你会如下看到所有已配置远程连接。

*Remmina 配置的服务器*
#### 使用 sFTP 连接到远程机器
选择连接配置并编辑设置,在 “**Protocols**” 下拉菜单中选择 **sFTP - Secure File Transfer**。接着设置启动路径(可选),并指定 SSH 验证细节。最后点击**连接**。

*Remmina sftp 连接*
这里输入你的 SSH 用户密码。

*输入 SSH 密码*
如果你看到下面的界面,那么代表 sFTP 连接成功了,你现在可以[在两台机器键传输文件了](http://www.tecmint.com/sftp-upload-download-directory-in-linux/)。

*Remmina 远程 sFTP 文件系统*
#### 使用 SSH 连接到远程机器
选择连接配置并编辑设置,在 “**Protocols**” 下拉菜单中选择 **SSH - Secure Shell**,并可选设置启动程序以及 SSH 验证细节。最后点击**连接**并输入 SSH 密码。

*Remmina SSH 连接*
当你看到下面的界面,这意味着你的连接成功了,你现在可以使用 SSH 控制远程机器了。

*Remmina 远程 SSH 连接*
#### 使用 VNC 连接到远程机器
选择连接配置并编辑设置,在 “**Protocols**” 下拉菜单中选择 **VNC - Virtual Network Computing**。为该连接配置基础、高级以及 ssh 设置,点击**连接**,接着输入用户 SSH 密码。

*Remmina VNC 连接*
一旦你看到下面的界面时,这意味着你已经成功使用 VNC 协议连接到远程机器上了。
如下截图所示,在桌面登录界面输入用户登录密码。

*Remmina 远程桌面登录*

*Remmina 远程桌面共享*
使用上面的步骤可以很简单地使用其他的协议访问远程机器。
Remmina 主页: <https://www.remmina.org/wp/>
就是这样了!在本文中,我们向你展示了如何在 Linux 中安装与使用 Remmina 远程连接客户端中的几种支持的协议。你可以在下面的评论栏中分享你的任何想法。
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux 系统管理员和网络开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/remmina-remote-desktop-sharing-and-ssh-client/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,494 | 如何在 Ubuntu 上使用 pm2 和 Nginx 部署 Node.js 应用 | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-deploy-nodejs-applications-with-pm2-and-nginx-on-ubuntu/ | 2017-05-09T09:41:31 | [
"Node.js"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8494-1.html | pm2 是一个 Node.js 应用的进程管理器,它可以让你的应用程序保持运行,还有一个内建的负载均衡器。它非常简单而且强大,你可以零间断重启或重新加载你的 node 应用,它也允许你为你的 node 应用创建集群。
在这篇博文中,我会向你展示如何安装和配置 pm2 用于这个简单的 'Express' 应用,然后配置 Nginx 作为运行在 pm2 下的 node 应用的反向代理。

前提:
* Ubuntu 16.04 - 64bit
* Root 权限
### 第一步 - 安装 Node.js LTS
在这篇指南中,我们会从零开始我们的实验。首先,我们需要在服务器上安装 Node.js。我会使用 Nodejs LTS 6.x 版本,它能从 nodesource 仓库中安装。
从 Ubuntu 仓库安装 `python-software-properties` 软件包并添加 “nodesource” Nodejs 仓库。
```
sudo apt-get install -y python-software-properties
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_6.x | sudo -E bash -
```
安装最新版本的 Nodejs LTS:
```
sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
```
安装完成后,查看 node 和 npm 版本。
```
node -v
npm -v
```

### 第二步 - 生成 Express 示例 App
我会使用 `express-generator` 软件包生成的简单 web 应用框架进行示例安装。`express-generator` 可以使用 `npm` 命令安装。
用 `npm`安装 `express-generator`:
```
npm install express-generator -g
```
* `-g` : 在系统内部安装软件包。
我会以普通用户运行应用程序,而不是 root 或者超级用户。我们首先需要创建一个新的用户。
创建一个名为 `yume` 的用户:
```
useradd -m -s /bin/bash yume
passwd yume
```
使用 `su` 命令登录到新用户:
```
su - yume
```
下一步,用 `express` 命令生成一个新的简单 web 应用程序:
```
express hakase-app
```
命令会创建新项目目录 `hakase-app`。

进入到项目目录并安装应用需要的所有依赖。
```
cd hakase-app
npm install
```
然后用下面的命令测试并启动一个新的简单应用程序:
```
DEBUG=myapp:* npm start
```
默认情况下,我们的 express 应用会运行在 `3000` 端口。现在访问服务器的 IP 地址:192.168.33.10:3000 :

这个简单 web 应用框架现在以 'yume' 用户运行在 3000 端口。
### 第三步 - 安装 pm2
pm2 是一个 node 软件包,可以使用 `npm` 命令安装。(用 root 权限,如果你仍然以 yume 用户登录,那么运行命令 `exit` 再次成为 root 用户):
```
npm install pm2 -g
```
现在我们可以为我们的 web 应用使用 pm2 了。
进入应用目录 `hakase-app`:
```
su - yume
cd ~/hakase-app/
```
这里你可以看到一个名为 `package.json` 的文件,用 `cat` 命令显示它的内容。
```
cat package.json
```

你可以看到 `start` 行有一个 nodejs 用于启动 express 应用的命令。我们会和 pm2 进程管理器一起使用这个命令。
像下面这样使用 `pm2` 命令运行 express 应用:
```
pm2 start ./bin/www
```
现在你可以看到像下面这样的结果:

我们的 express 应用正在 `pm2` 中运行,名称为 `www`,id 为 `0`。你可以用 show 选项 `show nodeid|name` 获取更多 pm2 下运行的应用的信息。
```
pm2 show www
```

如果你想看我们应用的日志,你可以使用 logs 选项。它包括访问和错误日志,你还可以看到应用程序的 HTTP 状态。
```
pm2 logs www
```

你可以看到我们的程序正在运行。现在,让我们来让它开机自启动。
```
pm2 startup systemd
```
* `systemd`: Ubuntu 16 使用的是 systemd。
你会看到要用 root 用户运行命令的信息。使用 `exit` 命令回到 root 用户然后运行命令。
```
sudo env PATH=$PATH:/usr/bin /usr/lib/node_modules/pm2/bin/pm2 startup systemd -u yume --hp /home/yume
```
它会为启动应用程序生成 systemd 配置文件。当你重启服务器的时候,应用程序就会自动运行。

### 第四步 - 安装和配置 Nginx 作为反向代理
在这篇指南中,我们会使用 Nginx 作为 node 应用的反向代理。Ubuntu 仓库中有 Nginx,用 `apt` 命令安装它:
```
sudo apt-get install -y nginx
```
下一步,进入到 `sites-available` 目录并创建新的虚拟主机配置文件。
```
cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/
vim hakase-app
```
粘贴下面的配置:
```
upstream hakase-app {
# Nodejs app upstream
server 127.0.0.1:3000;
keepalive 64;
}
# Server on port 80
server {
listen 80;
server_name hakase-node.co;
root /home/yume/hakase-app;
location / {
# Proxy_pass configuration
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-NginX-Proxy true;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_max_temp_file_size 0;
proxy_pass http://hakase-app/;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_read_timeout 240s;
}
}
```
保存文件并退出 vim。
在配置中:
* node 应用使用域名 `hakase-node.co` 运行。
* 所有来自 nginx 的流量都会被转发到运行在 `3000` 端口的 node app。
测试 Nginx 配置确保没有错误。
```
nginx -t
```
启用 Nginx 并使其开机自启动。
```
systemctl start nginx
systemctl enable nginx
```
### 第五步 - 测试
打开你的 web 浏览器并访问域名(我的是):[http://hakase-app.co](http://hakase-app.co/) 。
你可以看到 express 应用正在 Nginx web 服务器中运行。

下一步,重启你的服务器,确保你的 node app 能开机自启动:
```
pm2 save
sudo reboot
```
如果你再次登录到了你的服务器,检查 node app 进程。以 `yume` 用户运行下面的命令。
```
su - yume
pm2 status www
```

Node 应用在 pm2 中运行并使用 Nginx 作为反向代理。
### 链接
* [Ubuntu](https://www.ubuntu.com/)
* [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/en/)
* [Nginx](https://www.nginx.com/)
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-deploy-nodejs-applications-with-pm2-and-nginx-on-ubuntu/>
作者:[Muhammad Arul](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-deploy-nodejs-applications-with-pm2-and-nginx-on-ubuntu/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | pm2 is a process manager for Node.js applications, it allows you to keep your apps alive and has a built-in load balancer. It's simple and powerful, you can always restart or reload your node application with zero downtime and it allows you to create a cluster of your node app.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install and configure pm2 for the simple 'Express' application and then configure Nginx as a reverse proxy for the node application that is running under pm2.
**Prerequisites**
- Ubuntu 16.04 - 64bit
- Root Privileges
## Step 1 - Install Node.js LTS
In this tutorial, we will start our project from scratch. First, we need Nodejs installed on the server. I will use the Nodejs LTS version 6.x which can be installed from the nodesource repository.
Install the package '**python-software-properties**' from the Ubuntu repository and then add the 'nodesource' Nodejs repository.
sudo apt-get install -y python-software-properties
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_6.x | sudo -E bash -
Install the latest Nodejs LTS version.
sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
When the installation succeeded, check node and npm version.
node -v
npm -v
## Step 2 - Generate Express Sample App
I will use simple web application skeleton generated with a package named '**express-generator**' for this example installation. Express-generator can be installed with the npm command.
Install '**express-generator**' with npm:
npm install express-generator -g
**-g:** install package inside the system
We will run the application as a normal user, not a root or super user. So we need to create a new user first.
Create a new user, I name mine '**yume**':
useradd -m -s /bin/bash yume
passwd yume
Login to the new user by using su:
su - yume
Next, generate a new simple web application with the express command:
express hakase-app
The command will create new project directory '**hakase-app**'.
Go to the project directory and install all dependencies needed by the app.
cd hakase-app
npm install
Then test and start a new simple application with the command below:
DEBUG=myapp:* npm start
By default, our express application will run on port **3000**. Now visit server IP address: [192.168.33.10:3000](https://www.howtoforge.com/admin/articles/edit/192.168.33.10:3000)
The simple web application skeleton is running on port 3000, under user 'yume'.
## Step 3 - Install pm2
pm2 is a node package and can be installed with the npm command. So let's install it with npm (with root privileges, when you are still logged in as user hakase, then run the command "exit" ro become root again):
npm install pm2 -g
Now we can use pm2 for our web application.
Go to the app directory '**hakase-app**':
su - hakase
cd ~/hakase-app/
There you can find a file named '**package.json**', display its content with the cat command.
cat package.json
You can see the '**start**' line contains a command that is used by Nodejs to start the express application. This command we will use with the pm2 process manager.
Run the express application with the pm2 command below:
pm2 start ./bin/www
Now you can see the results is below:
Our express application is running under pm2 with name '**www**', id '**0**'. You can get more details about the application running under pm2 with the show option '**show nodeid|name**'.
pm2 show www
If you like to see the log of our application, you can use the logs option. It's just access and error log and you can see the HTTP Status of the application.
pm2 logs www
You can see that our process is running. Now, let's enable it to start at boot time.
pm2 startup systemd
**systemd**: Ubuntu 16 is using systemd.
You will get a message for running a command as root. Back to the root privileges with "exit" and then run that command.
sudo env PATH=$PATH:/usr/bin /usr/lib/node_modules/pm2/bin/pm2 startup systemd -u yume --hp /home/yume
It will generate the systemd configuration file for application startup. When you reboot your server, the application will automatically run on startup.
## Step 4 - Install and Configure Nginx as a Reverse proxy
In this tutorial, we will use Nginx as a reverse proxy for the node application. Nginx is available in the Ubuntu repository, install it with the apt command:
sudo apt-get install -y nginx
Next, go to the '**sites-available**' directory and create a new virtual host configuration file.
cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/
vim hakase-app
Paste configuration below:
upstream hakase-app {
# Nodejs app upstream
server 127.0.0.1:3000;
keepalive 64;
}
# Server on port 80
server {
listen 80;
server_name hakase-node.co;
root /home/yume/hakase-app;
location / {
# Proxy_pass configuration
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-NginX-Proxy true;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_max_temp_file_size 0;
proxy_pass http://hakase-app/;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_read_timeout 240s;
}
}
Save the file and exit vim.
On the configuration:
- The node app is running with domain name '
**hakase-node.co**'. - All traffic from nginx will be forwarded to the node app that is running on port
**3000**.
Activate the configuration by creating a symlink in the sites-enabled directory.
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/hakase-app /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
Test Nginx configuration and make sure there is no error.
nginx -t
Start Nginx and enable it to start at boot time:
systemctl start nginx
systemctl enable nginx
## Step 5 - Testing
Open your web browser and visit the domain name (mine is):
You will see the express application is running under the nginx web server.
Next, reboot your server, and make sure the node app is running at the boot time:
pm2 save
sudo reboot
If you have logged in again to your server, check the node app process. Run the command below as '**yume**' user.
su - yume
pm2 status www
The Node Application is running under pm2 and Nginx as reverse proxy. |
8,496 | rdiff-backup:一个 Linux 中的远程增量备份工具 | http://www.tecmint.com/rdiff-backup-remote-incremental-backup-for-linux/ | 2017-05-10T08:37:00 | [
"rsync",
"备份"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8496-1.html | 
rdiff-backup 是一个用于本地/远程增量备份的强大而易用的 Python 脚本,它适用于任何 POSIX 操作系统,如Linux、Mac OS X 或 [Cygwin](http://www.tecmint.com/install-cygwin-to-run-linux-commands-on-windows-system/)。它集合了镜像和增量备份的显著特性。
值得注意的是,它保留了子目录、dev 文件、硬链接,以及关键的文件属性,如权限、uid/gid 所有权、修改时间、扩展属性、acl 以及 resource fork。它可以通过管道以高效带宽的模式工作,这与流行的 [rsync 备份工具](http://www.tecmint.com/rsync-local-remote-file-synchronization-commands/)类似。
rdiff-backup 通过使用 SSH 将单个目录备份到另一个目录,这意味着数据传输被加密并且是安全的。目标目录(在远程系统上)最终会得到源目录的完整副本,但是此外的反向差异会存储在目标目录的特殊子目录中,从而可以恢复前一段时间丢失的文件。
### 依赖
要在 Linux 中使用 rdiff-backup,你需要在系统上安装以下软件包:
* Python v2.2 或更高版本
* librsync v0.9.7 或更高版本
* pylibacl 和 pyxattr Python 模块是可选的,但它们分别是 POSIX 访问控制列表(ACL)和扩展属性支持必需的。
* rdiff-backup-statistics 需要 Python v2.4 或更高版本。
### 如何在 Linux 中安装 rdiff-backup
重要:如果你通过网络运行它,则必须在两个系统中都安装 rdiff-backup,两者最好是相同版本。
该脚本已经存在于主流 Linux 发行版的官方仓库中,只需运行以下命令来安装 rdiff-backup 及其依赖关系:
#### 在 Debian/Ubuntu 中
```
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install librsync-dev rdiff-backup
```
#### 在 CentOS/RHEL 7 中
```
# wget http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-9.noarch.rpm
# rpm -ivh epel-release-7-9.noarch.rpm
# yum install librsync rdiff-backup
```
#### 在 CentOS/RHEL 6 中
```
# wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
# rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
# yum install librsync rdiff-backup
```
#### 在 Fedora 中
```
# yum install librsync rdiff-backup
# dnf install librsync rdiff-backup [Fedora 22+]
```
### 如何在 Linux 中使用 rdiff-backup
如前所述,rdiff-backup 使用 SSH 连接到网络上的远程计算机,SSH 的默认身份验证方式是用户名/密码,这通常需要人工交互。
但是,要自动执行诸如脚本等自动备份之类的任务,那么你需要配置[使用 SSH 密钥无密码登录 SSH](/article-6901-1.html),因为 SSH 密钥增加了两台 Linux服务器之间的信任来[简化文件同步或传输](http://www.tecmint.com/sync-new-changed-modified-files-rsync-linux/)。
在你设置了 [SSH 无密码登录](/article-6901-1.html)后,你可以使用下面的例子开始使用该脚本。
#### 备份文件到不同分区
下面的例子会备份 `/etc` 文件夹到另外一个分区的 `Backup` 文件夹内:
```
$ sudo rdiff-backup /etc /media/aaronkilik/Data/Backup/mint_etc.backup
```

*备份文件到不同分区*
要排除一个特定文件夹和它的子目录,你可以如下使用 `--exclude` 选项:
```
$ sudo rdiff-backup --exclude /etc/cockpit --exclude /etc/bluetooth /media/aaronkilik/Data/Backup/mint_etc.backup
```
我们可以如下使用 `--include-special-files` 包含所有的设备文件、fifo 文件、socket 文件和链接文件:
```
$ sudo rdiff-backup --include-special-files --exclude /etc/cockpit /media/aaronkilik/Data/Backup/mint_etc.backup
```
还有另外两个重要标志来用于选择文件,`--max-file-size` 用来排除大于给定字节大小的文件,`--min-file-size` 用于排除小于给定字节大小的文件:
```
$ sudo rdiff-backup --max-file-size 5M --include-special-files --exclude /etc/cockpit /media/aaronkilik/Data/Backup/mint_etc.backup
```
#### 在本地 Linux 服务器上备份远程文件
要这么做,我们使用:
```
Remote Server (tecmint) : 192.168.56.102
Local Backup Server (backup) : 192.168.56.10
```
如前所述,你必须在两台机器上安装相同版本的 rdiff-backup,如下所示,请尝试在两台机器上检查版本:
```
$ rdiff-backup -V
```

*检查服务器中 rdiff 版本*
在备份服务器中,像这样创建一个存储备份文件的目录:
```
# mkdir -p /backups
```
现在在备份服务器中,运行下面的命令来将远程 Linux 服务器 192.168.56.102 中的 `/var/log/` 和 `/root` 备份到 `/backups` 中:
```
# rdiff-backup [email protected]::/var/log/ /backups/192.168.56.102_logs.backup
# rdiff-backup [email protected]::/root/ /backups/192.168.56.102_rootfiles.backup
```
下面的截图展示了远程服务器 192.168.56.102 中的 `root` 文件夹以及 192.168.56.10 备份服务器中的已备份文件:

*在本地服务器备份远程目录*
注意截图中 “backup” 目录中创建的 rdiff-backup-data 文件夹,它包含了备份过程和增量文件的重要数据。

*rdiff-backup – 备份过程文件*
现在,在 192.168.56.102 服务器中,如下所示 `root` 目录已经添加了额外的文件:

*验证备份目录*
让我们再次运行备份命令以获取更改的数据,我们可以使用 `-v[0-9]`(其中数字指定详细程度级别,默认值为 3,这是静默模式)选项设置详细功能:
```
# rdiff-backup -v4 [email protected]::/root/ /backups/192.168.56.102_rootfiles.backup
```

*带有摘要的增量备份*
要列出 `/backups/192.168.56.102_rootfiles.backup` 目录中包含的部分增量备份的数量和日期,我们可以运行:
```
# rdiff-backup -l /backups/192.168.56.102_rootfiles.backup/
```
#### 使用 cron 自动进行 rdiff-back 备份
使用 `--print-statistics` 成功备份后,我们可以打印摘要统计信息。但是,如果我们不设置此选项,我们可以仍从会话统计中获得。在手册页的 “STATISTICS” 部分中阅读有关此选项的更多信息。
`-remote-schema` 选项使我们能够指定使用替代方法连接到远程计算机。
现在,我们开始在备份服务器 192.168.56.10 上创建一个 `backup.sh` 脚本,如下所示:
```
# cd ~/bin
# vi backup.sh
```
添加下面的行到脚本中。
```
#!/bin/bash
#This is a rdiff-backup utility backup script
#Backup command
rdiff-backup --print-statistics --remote-schema 'ssh -C %s "sudo /usr/bin/rdiff-backup --server --restrict-read-only /"' [email protected]::/var/logs /backups/192.168.56.102_logs.back
#Checking rdiff-backup command success/error
status=$?
if [ $status != 0 ]; then
#append error message in ~/backup.log file
echo "rdiff-backup exit Code: $status - Command Unsuccessful" >>~/backup.log;
exit 1;
fi
#Remove incremental backup files older than one month
rdiff-backup --force --remove-older-than 1M /backups/192.168.56.102_logs.back
```
保存文件并退出,接着运行下面的命令在服务器 192.168.56.10 上的 crontab 中添加此脚本:
```
# crontab -e
```
添加此行在每天午夜运行你的备份脚本:
```
0 0 * * * /root/bin/backup.sh > /dev/null 2>&1
```
保存 crontab 并退出,现在我们已经成功自动化了备份过程。确保一切如希望那样工作。
阅读 rdiff-backup 的手册页获取更多信息、详尽的使用选项以及示例:
```
# man rdiff-backup
```
rdiff-backup 主页: <http://www.nongnu.org/rdiff-backup/>
就是这样了!在本教程中,我们向你展示了如何安装并基础地使用 rdiff-backup 这个易于使用的 Python 脚本,用于 Linux 中的本地/远程增量备份。 请通过下面的反馈栏与我们分享你的想法。
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux SysAdmin 和 web 开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创建者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/rdiff-backup-remote-incremental-backup-for-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,497 | Mark Shuttleworth:桌面对我们来说仍然重要 | http://linux.softpedia.com/blog/mark-shuttleworth-ubuntu-on-the-desktop-will-remain-important-to-canonical-515529.shtml | 2017-05-10T09:18:00 | [
"Ubuntu",
"Canonical"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8497-1.html | 
在波士顿刚刚召开的 OpenStack Summit 2017 大会上, Ubuntu 的母公司 Canonical 的 CEO Mark Shuttleworth 谈及了 Ubuntu 在桌面、云计算和物联网等方面将来的计划。
在 Mark Shuttleworth 前一段日子宣布了停止开发 Unity 桌面环境之后,[震动了整个开源界](/article-8413-1.html),就大家非常关注的 Ubuntu Linux 的将来发展,这位 Canonical 及 Ubuntu 的创始人接受了 [theCUBE](https://twitter.com/theCUBE) 的采访。
Mark Shuttleworth 说他的梦想从来就是让 Ubuntu 成为桌面、云和物联网的主流,从未变过,但是事情的发展并不总是如预期的一样。据其所称,Ubuntu 看起来已经成为了云计算和数据中心的事实标准了。
在本次访谈中,Mark Shuttleworth 认为 Ubuntu 桌面对于 Canonical 公司在支持自由和开源软件、IT 创新等方面仍将保持重要地位,但是在商业上,Canonical 将更多的关注在云和物联网方面。
下面是本次访谈的视频:
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,498 | 向 Linus Torvalds 学习让编出的代码具有 “good taste” | https://medium.com/@bartobri/applying-the-linus-tarvolds-good-taste-coding-requirement-99749f37684a | 2017-05-11T08:17:00 | [
"编程",
"代码"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8498-1.html | 
在[最近关于 Linus Torvalds 的一个采访中](https://www.ted.com/talks/linus_torvalds_the_mind_behind_linux),这位 Linux 的创始人,在采访过程中大约 14:20 的时候,提及了关于代码的 “good taste”。good taste?采访者请他展示更多的细节,于是,Linus Torvalds 展示了一张提前准备好的插图。
他展示的是一个代码片段。但这段代码并没有 “good taste”。这是一个具有 “poor taste” 的代码片段,把它作为例子,以提供一些初步的比较。

这是一个用 C 写的函数,作用是删除链表中的一个对象,它包含有 10 行代码。
他把注意力集中在底部的 `if` 语句。正是这个 `if` 语句受到他的批判。
我暂停了这段视频,开始研究幻灯片。我发现我最近有写过和这很像的代码。Linus 不就是在说我的代码品味很差吗?我放下自傲,继续观看视频。
随后, Linus 向观众解释,正如我们所知道的,当从链表中删除一个对象时,需要考虑两种可能的情况。当所需删除的对象位于链表的表头时,删除过程和位于链表中间的情况不同。这就是这个 `if` 语句具有 “poor taste” 的原因。
但既然他承认考虑这两种不同的情况是必要的,那为什么像上面那样写如此糟糕呢?
接下来,他又向观众展示了第二张幻灯片。这个幻灯片展示的是实现同样功能的一个函数,但这段代码具有 “goog taste” 。

原先的 10 行代码现在减少为 4 行。
但代码的行数并不重要,关键是 `if` 语句,它不见了,因为不再需要了。代码已经被重构,所以,不用管对象在列表中的位置,都可以运用同样的操作把它删除。
Linus 解释了一下新的代码,它消除了边缘情况,就是这样。然后采访转入了下一个话题。
我琢磨了一会这段代码。 Linus 是对的,的确,第二个函数更好。如果这是一个确定代码具有 “good taste” 还是 “bad taste” 的测试,那么很遗憾,我失败了。我从未想到过有可能能够去除条件语句。我写过不止一次这样的 `if` 语句,因为我经常使用链表。
这个例子的意义,不仅仅是教给了我们一个从链表中删除对象的更好方法,而是启发了我们去思考自己写的代码。你通过程序实现的一个简单算法,可能还有改进的空间,只是你从来没有考虑过。
以这种方式,我回去审查最近正在做的项目的代码。也许是一个巧合,刚好也是用 C 写的。
我尽最大的能力去审查代码,“good taste” 的一个基本要求是关于边缘情况的消除方法,通常我们会使用条件语句来消除边缘情况。你的测试使用的条件语句越少,你的代码就会有更好的 “taste” 。
下面,我将分享一个通过审查代码进行了改进的一个特殊例子。
这是一个关于初始化网格边缘的算法。
下面所写的是一个用来初始化网格边缘的算法,网格 grid 以一个二维数组表示:grid[行][列] 。
再次说明,这段代码的目的只是用来初始化位于 grid 边缘的点的值,所以,只需要给最上方一行、最下方一行、最左边一列以及最右边一列赋值即可。
为了完成这件事,我通过循环遍历 grid 中的每一个点,然后使用条件语句来测试该点是否位于边缘。代码看起来就是下面这样:
```
for (r = 0; r < GRID_SIZE; ++r) {
for (c = 0; c < GRID_SIZE; ++c) {
// Top Edge
if (r == 0)
grid[r][c] = 0;
// Left Edge
if (c == 0)
grid[r][c] = 0;
// Right Edge
if (c == GRID_SIZE - 1)
grid[r][c] = 0;
// Bottom Edge
if (r == GRID_SIZE - 1)
grid[r][c] = 0;
}
}
```
虽然这样做是对的,但回过头来看,这个结构存在一些问题。
1. 复杂性 — 在双层循环里面使用 4 个条件语句似乎过于复杂。
2. 高效性 — 假设 `GRID_SIZE` 的值为 64,那么这个循环需要执行 4096 次,但需要进行赋值的只有位于边缘的 256 个点。
用 Linus 的眼光来看,将会认为这段代码没有 “good taste” 。
所以,我对上面的问题进行了一下思考。经过一番思考,我把复杂度减少为包含四个条件语句的单层 `for` 循环。虽然只是稍微改进了一下复杂性,但在性能上也有了极大的提高,因为它只是沿着边缘的点进行了 256 次循环。
```
for (i = 0; i < GRID_SIZE * 4; ++i) {
// Top Edge
if (i < GRID_SIZE)
grid[0][i] = 0;
// Right Edge
else if (i < GRID_SIZE * 2)
grid[i - GRID_SIZE][GRID_SIZE - 1] = 0;
// Left Edge
else if (i < GRID_SIZE * 3)
grid[i - (GRID_SIZE * 2)][0] = 0;
// Bottom Edge
else
grid[GRID_SIZE - 1][i - (GRID_SIZE * 3)] = 0;
}
```
的确是一个很大的提高。但是它看起来很丑,并不是易于阅读理解的代码。基于这一点,我并不满意。
我继续思考,是否可以进一步改进呢?事实上,答案是 YES!最后,我想出了一个非常简单且优雅的算法,老实说,我不敢相信我会花了那么长时间才发现这个算法。
下面是这段代码的最后版本。它只有一层 `for` 循环并且没有条件语句。另外。循环只执行了 64 次迭代,极大的改善了复杂性和高效性。
```
for (i = 0; i < GRID_SIZE; ++i) {
// Top Edge
grid[0][i] = 0;
// Bottom Edge
grid[GRID_SIZE - 1][i] = 0;
// Left Edge
grid[i][0] = 0;
// Right Edge
grid[i][GRID_SIZE - 1] = 0;
}
```
这段代码通过每次循环迭代来初始化四条边缘上的点。它并不复杂,而且非常高效,易于阅读。和原始的版本,甚至是第二个版本相比,都有天壤之别。
至此,我已经非常满意了。
那么,我是一个有 “good taste” 的开发者么?
我觉得我是,但是这并不是因为我上面提供的这个例子,也不是因为我在这篇文章中没有提到的其它代码……而是因为具有 “good taste” 的编码工作远非一段代码所能代表。Linus 自己也说他所提供的这段代码不足以表达他的观点。
我明白 Linus 的意思,也明白那些具有 “good taste” 的程序员虽各有不同,但是他们都是会将他们之前开发的代码花费时间重构的人。他们明确界定了所开发的组件的边界,以及是如何与其它组件之间的交互。他们试着确保每一样工作都完美、优雅。
其结果就是类似于 Linus 的 “good taste” 的例子,或者像我的例子一样,不过是千千万万个 “good taste”。
你会让你的下个项目也具有这种 “good taste” 吗?
---
via: <https://medium.com/@bartobri/applying-the-linus-tarvolds-good-taste-coding-requirement-99749f37684a>
作者:[Brian Barto](https://medium.com/@bartobri?source=post_header_lockup) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # Applying the Linus Torvalds “Good Taste” Coding Requirement
In [a recent interview with Linus Torvalds](https://www.ted.com/talks/linus_torvalds_the_mind_behind_linux), the creator of Linux, at approximately 14:20 in the interview, he made a quick point about coding with “good taste”. Good taste? The interviewer prodded him for details and Linus came prepared with illustrations.
He presented a code snippet. But this wasn’t “good taste” code. This snippet was an example of poor taste in order to provide some initial contrast.
It’s a function, written in C, that removes an object from a linked list. It contains 10 lines of code.
He called attention to the if-statement at the bottom. It was *this* if-statement that he criticized.
I paused the video and studied the slide. I had recently written code very similar. Linus was effectively saying I had poor taste. I swallowed my pride and continued the video.
Linus explained to the audience, as I already knew, that when removing an object from a linked list, there are two cases to consider. If the object is at the start of the list there is a different process for its removal than if it is in the middle of the list. And this is the reason for the “poor taste” if-statement.
But if he admits it is necessary, then why is it so bad? |
8,499 | 如何在树莓派上部署 Kubernetes | https://opensource.com/article/17/3/kubernetes-raspberry-pi | 2017-05-11T09:38:00 | [
"树莓派",
"Kubernetes"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8499-1.html |
>
> 只用几步,使用 Weave Net 在树莓派上设置 Kubernetes。
>
>
>

当我开始对 [ARM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARM_architecture)设备,特别是 Raspberry Pi 感兴趣时,我的第一个项目是一个 OpenVPN 服务器。
通过将 Raspberry Pi 作为家庭网络的安全网关,我可以使用我的手机来控制我的桌面,远程播放 Spotify,打开文档以及一些其他有趣的东西。我在第一个项目中使用了一个现有的教程,因为我害怕自己在命令行中拼砌。
几个月后,这种恐惧消失了。我扩展了我的原始项目,并使用 [Samba 服务器](https://www.samba.org/samba/what_is_samba.html)从文件服务器分离出了 OpenVPN 服务器。这是我第一个没有完全按照教程来的项目。不幸的是,在我的 Samba 项目结束后,我意识到我没有记录任何东西,所以我无法复制它。为了重新创建它,我不得不重新参考我曾经用过的那些单独的教程,将项目拼回到一起。
我学到了关于开发人员工作流程的宝贵经验 - 跟踪你所有的更改。我在本地做了一个小的 git 仓库,并记录了我输入的所有命令。
### 发现 Kubernetes
2015 年 5 月,我发现了 Linux 容器和 Kubernetes。我觉得 Kubernetes 很有魅力,我可以使用仍然处于技术发展的概念 - 并且我实际上可以用它。平台本身及其所呈现的可能性令人兴奋。在此之前,我才刚刚在一块 Raspberry Pi 上运行了一个程序。而有了 Kubernetes,我可以做出比以前更先进的配置。
那时候,Docker(v1.6 版本,如果我记得正确的话)在 ARM 上有一个 bug,这意味着在 Raspberry Pi 上运行 Kubernetes 实际上是不可能的。在早期的 0.x 版本中,Kubernetes 的变化很快。每次我在 AMD64 上找到一篇关于如何设置 Kubernetes 的指南时,它针对的还都是一个旧版本,与我当时使用的完全不兼容。
不管怎样,我用自己的方法在 Raspberry Pi 上创建了一个 Kubernetes 节点,而在 Kubernetes v1.0.1 中,我使用 Docker v1.7.1 [让它工作了](https://github.com/luxas/kubernetes-on-arm)。这是第一个将 Kubernetes 全功能部署到 ARM 的方法。
在 Raspberry Pi 上运行 Kubernetes 的优势在于,由于 ARM 设备非常小巧,因此不会产生大量的功耗。如果程序以正确的方式构建而成,那么就可以在 AMD64 上用同样的方法运行同一个程序。这样的一块小型 IoT 板为教育创造了巨大的机会。用它来做演示也很有用,比如你要出差参加一个会议。携带 Raspberry Pi (通常)比拖着大型英特尔机器要容易得多。
现在按照[我建议](https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/design-proposals/multi-platform.md)的 ARM(32 位和 64 位)的支持已被合并到 Kubernetes 核心中。ARM 的二进制文件会自动与 Kubernetes 一起发布。虽然我们还没有为 ARM 提供自动化的 CI(持续集成)系统,不过在 PR 合并之前会自动确定它可在 ARM 上工作,现在它运转得不错。
### Raspberry Pi 上的分布式网络
我通过 [kubeadm](https://kubernetes.io/docs/getting-started-guides/kubeadm/) 发现了 Weave Net。[Weave Mesh](https://github.com/weaveworks/mesh) 是一个有趣的分布式网络解决方案,因此我开始了解更多关于它的内容。在 2016 年 12 月,我在 [Weaveworks](https://www.weave.works/) 收到了第一份合同工作,我成为了 Weave Net 中 ARM 支持团队的一员。
我很高兴可以在 Raspberry Pi 上运行 Weave Net 的工业案例,比如那些需要设备更加移动化的工厂。目前,将 Weave Scope 或 Weave Cloud 部署到 Raspberry Pi 可能不太现实(尽管可以考虑使用其他 ARM 设备),因为我猜这个软件需要更多的内存才能运行良好。理想情况下,随着 Raspberry Pi 升级到 2GB 内存,我想我可以在它上面运行 Weave Cloud 了。
在 Weave Net 1.9 中,Weave Net 支持了 ARM。Kubeadm(通常是 Kubernetes)在多个平台上工作。你可以使用 Weave 将 Kubernetes 部署到 ARM,就像在任何 AMD64 设备上一样安装 Docker、kubeadm、kubectl 和 kubelet。然后初始化控制面板组件运行的主机:
```
kubeadm init
```
接下来,用下面的命令安装你的 pod 网络:
```
kubectl apply -f https://git.io/weave-kube
```
在此之前在 ARM 上,你只能用 Flannel 安装 pod 网络,但是在 Weave Net 1.9 中已经改变了,它官方支持了 ARM。
最后,加入你的节点:
```
kubeadm join --token <token> <master-ip>
```
就是这样了!Kubernetes 已经部署到了 Raspberry Pi 上了。相比在 Intel/AMD64 上运行,你不用做什么特别的事情;Weave Net 在 ARM 上就能工作的很好。
### Raspberry Pi 社区
我希望 Raspberry Pi 社区成长起来,他们的思想传播到世界其他地方。他们在英国和其他国家已经取得了成功,但在芬兰并不是很成功。我希望生态系统能够继续扩展,以让更多的人学习如何部署 Kubernetes 或 Weave 到 ARM 设备上。毕竟,这些是我学到的。通过在 Raspberry Pi 设备上自学,我更好地了解了 ARM 及其上面部署的软件。
### 最后的思考
我通过加入用户社区、提出问题和不同程度的测试,在线学习了关于 Raspberry Pi 和 Kubernetes 的一切。
我是居住在芬兰的说瑞典语的高中生,到目前为止,我还从来没有参加过编程或计算机课程。但我仍然能够加入开源社区,因为它对年龄或教育没有限制:你的工作是根据其价值来评判的。
对于那些第一次要在开源项目中做出贡献感到紧张的人,我想说:深入进去,因为这是完全值得的。你做什么没有任何限制,你将永远不知道开源世界将为你提供哪些机会。这会很有趣,我保证!
---
作者简介:
Lucas Käldström - 谢谢你发现我!我是一名来自芬兰的说瑞典语的高中生。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/3/kubernetes-raspberry-pi>
作者:[Lucas Käldström](https://opensource.com/users/luxas) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When I became interested in [ARM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARM_architecture) devices, and in the Raspberry Pi in particular, my first project was an OpenVPN server.
By having the Raspberry Pi as a secure gateway to my home network, I could use my phone to control my desktop and remotely play Spotify, open documents, and a bunch of other fun things. I used an existing tutorial for that first project because I was afraid of piping anything into the command line on my own.
After a few months, that fear dissipated. I expanded upon my original project and isolated the OpenVPN server from the file server using a [Samba server](https://www.samba.org/samba/what_is_samba.html). This was my first project where I didn't follow a tutorial verbatim. Unfortunately, by the end of my Samba project, I realized I hadn't documented anything, so I couldn't replicate it. To recreate it, I had to reread all of the separate guides I had used for reference and piece the project back together.
I learned a valuable lesson about developer workflow—track all of your changes. I made myself a small git repo locally and recorded all of the commands that I typed into the command line.
## Discovering Kubernetes
In May 2015, I discovered Linux containers and Kubernetes. With Kubernetes, I thought it was fascinating that I could take part in a concept still technically in development—and I actually had access to it. The platform itself and the possibilities it presented were exciting. Up until that point, I had just been running a single program on one Raspberry Pi device. With Kubernetes, I could make more advanced configurations than what was possible previously.
At that time, Docker (v1.6, if I remember correctly) on ARM had a bug, which meant running Kubernetes on a Raspberry Pi device was virtually impossible. During those early 0.x releases, Kubernetes changed very quickly. Every time I found a guide for how to set up Kubernetes on AMD64, it was for an older version and it was totally incompatible with what I had at the time.
I hacked my way to creating a Kubernetes node on Raspberry Pi anyway, and by the v1.0.1 Kubernetes release, [I had it working](https://github.com/luxas/kubernetes-on-arm), using Docker v1.7.1. This was the first fully functional way to deploy Kubernetes to ARM.
The advantage of running Kubernetes on Raspberry Pi is that because ARM devices are so small they don't draw a lot of power. If programs are built the right way, it's possible to use the same commands for the same programs on AMD64. Having small IoT boards creates a great opportunity for education. It's also beneficial for setting up demonstrations you need to travel for, like a conference. Bringing your Raspberry Pi is a lot easier than lugging your (often) large Intel machines.
Now that ARM (both 32- and 64-bit) support is merged into the core in line with [my proposal](https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/design-proposals/multi-platform.md) for it, ARM binaries are automatically released with Kubernetes. Although we haven't got an automated CI (continuous integration) system for ARM yet that automatically makes sure it's working on ARM before PRs can be merged, it's working quite well at the moment.
## Distributed networking on the Raspberry Pi
I discovered Weave Net through [kubeadm](https://kubernetes.io/docs/getting-started-guides/kubeadm/). [Weave Mesh](https://github.com/weaveworks/mesh) is an interesting solution for distributed networking, so I began to read more about it. In December of 2016, I received my first contracting job ever with [Weaveworks](https://www.weave.works/). I was part of the internal team that made Weave Net support ARM.
I'm excited for the possibility of industrial use cases for running Weave Net on Raspberry Pi, such as factories that need devices to be more mobile. Currently, deploying Weave Scope or Weave Cloud to Raspberry Pi might not be possible (though it is conceivable with other ARM devices) because I guess the software needs more available memory to run well. Ideally, with the 2GB upgrade of Raspberry Pi, I think I would be able to spin up Weave Cloud successfully.
With the Weave Net 1.9 release, Weave Net how has ARM support. Kubeadm (and Kubernetes in general) works on multiple platforms. You can deploy Kubernetes to ARM with Weave just as you would on any AMD64 device by installing Docker, kubeadm, kubectl, and kubelet as usual on all machines. Then, initialize the master machine where the control plane components will run using:
```
````kubeadm init`
Next, install your pod network with the following command:
```
````kubectl apply -f https://git.io/weave-kube`
Previously, you could only install a pod network with Flannel when running on ARM, but this has changed since the Weave Net 1.9 release, which now also supports ARM officially.
Finally, join your nodes:
```
````kubeadm join --token <token> <master-ip>`
And that's it! Kubernetes is deployed to your Raspberry Pi device. You didn't have to do anything special compared to running on Intel/AMD64; Weave Net on ARM just works.
## Raspberry Pi community
I hope the Raspberry Pi community grows and their mentality spreads to other parts of the world. They're successful in Great Britain and other countries, but not so much here in Finland. I want the ecosystem to expand and for more people to learn how to deploy Kubernetes or Weave to ARM devices. After all, that's how I learned. By teaching myself on a Raspberry Pi device, I think I understand both ARM devices and the software deployed on them a lot better than I would have otherwise.
## Final thoughts
Everything I learned about the Raspberry Pi and Kubernetes, I learned online by joining user communities, asking questions, and testing with different levels of success.
I am a Swedish-speaking upper secondary school student living in Finland, and to date, I've never attended a programming or computing class. I was still able to join the open source community because there are no restrictions on age or education: your work is judged based on its merits.
For anyone nervous about making their first contributions to any open source project I'd say: Dive right in, it's totally worth it. There are no limitations to what you can do, and you'll never know which kinds of opportunities the open source world will offer you. It's gonna be fun, I promise!
## 3 Comments |
8,500 | 从损坏的 Linux EFI 安装中恢复 | http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/grub2-efi-corrupt-part-recovery.html | 2017-05-11T11:00:00 | [
"UEFI",
"安装"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8500-1.html | 
在过去的十多年里,Linux 发行版在安装前、安装过程中、以及安装后偶尔会失败,但我总是有办法恢复系统并继续正常工作。然而,[Solus](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/solus-1-2-review.html) 损坏了我的笔记本。
GRUB 恢复。不行,重装。还不行!Ubuntu 拒绝安装,目标设备的报错一会这样,一会那样。哇。我之前还没有遇到过像这样的事情。我的测试机已变成无用的砖块。难道我该绝望吗?不,绝对不。让我来告诉你怎样你可以修复它吧。
### 问题详情
所有事情都从 Solus 尝试安装它自己的启动引导器 - goofiboot 开始。不知道什么原因、它没有成功完成安装,留给我的就是一个无法启动的系统。经过 BIOS 引导之后,我进入一个 GRUB 恢复终端。

我尝试在终端中手动修复,使用类似和我在我详实的 [GRUB2 指南](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/grub-2.html)中介绍的各种命令。但还是不行。然后我尝试按照我在 [GRUB2 和 EFI 指南](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/grub2-efi-recovery.html)中的建议从 Live CD 中恢复(LCTT 译注:Live CD 是一个完整的计算机可引导安装媒介,它包括在计算机内存中运行的操作系统,而不是从硬盘驱动器加载;CD 本身是只读的。 它允许用户为任何目的运行操作系统,而无需安装它或对计算机的配置进行任何更改)。我用 efibootmgr 工具创建了一个引导入口,确保标记它为有效。正如我们之前在指南中做的那样,之前这些是能正常工作的。哎,现在这个方法也不起作用。
我尝试做一个完整的 Ubuntu 安装,把它安装到 Solus 所在的分区,希望安装程序能给我一些有用的信息。但是 Ubuntu 无法完成安装。它报错:failed to install into /target。又回到开始的地方了。怎么办?
### 手动清除 EFI 分区
显然,我们的 EFI 分区出现了严重问题。简单回顾以下,如果你使用的是 UEFI,那么你需要一个单独的 FAT-32 格式化的分区。该分区用于存储 EFI 引导镜像。例如,当你安装 Fedora 时,Fedora 引导镜像会被拷贝到 EFI 子目录。每个操作系统都会被存储到一个它自己的目录,一般是 `/boot/efi/EFI/<操作系统版本>/`。

在我的 [G50](http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/lenovo-g50-distros-second-round.html) 机器上,这里有很多各种发行版测试条目,包括:centos、debian、fedora、mx-15、suse、Ubuntu、zorin 以及其它。这里也有一个 goofiboot 目录。但是,efibootmgr 并没有在它的菜单中显示 goofiboot 条目。显然这里出现了一些问题。
```
sudo efibootmgr -d /dev/sda
BootCurrent: 0001
Timeout: 0 seconds
BootOrder: 0001,0005,2003,0000,2001,2002
Boot0000* Lenovo Recovery System
Boot0001* ubuntu
Boot0003* EFI Network 0 for IPv4 (68-F7-28-4D-D1-A1)
Boot0004* EFI Network 0 for IPv6 (68-F7-28-4D-D1-A1)
Boot0005* Windows Boot Manager
Boot0006* fedora
Boot0007* suse
Boot0008* debian
Boot0009* mx-15
Boot2001* EFI USB Device
Boot2002* EFI DVD/CDROM
Boot2003* EFI Network
...
```
P.S. 上面的输出是在 LIVE 会话中运行命令生成的!
我决定清除所有非默认的以及非微软的条目然后重新开始。显然,有些东西被损坏了,妨碍了新的发行版设置它们自己的启动引导程序。因此我删除了 `/boot/efi/EFI` 分区下面除了 Boot 和 Windows 以外的所有目录。同时,我也通过删除所有额外的条目更新了启动管理器。
```
efibootmgr -b <hex> -B <hex>
```
最后,我重新安装了 Ubuntu,并仔细监控 GRUB 安装和配置的过程。这次,成功完成啦。正如预期的那样,几个无效条目出现了一些错误,但整个安装过程完成就好了。


### 额外阅读
如果你不喜欢这种手动修复,你可以阅读:
* [Boot-Info](https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Boot-Info) 手册,里面有帮助你恢复系统的自动化工具
* [Boot-repair-cd](https://sourceforge.net/projects/boot-repair-cd/) 自动恢复工具下载页面
### 总结
如果你遇到由于 EFI 分区破坏而导致系统严重瘫痪的情况,那么你可能需要遵循本指南中的建议。 删除所有非默认条目。 如果你使用 Windows 进行多重引导,请确保不要修改任何和 Microsoft 相关的东西。 然后相应地更新引导菜单,以便删除损坏的条目。 重新运行所需发行版的安装设置,或者尝试用之前介绍的比较不严谨的修复方法。
我希望这篇小文章能帮你节省一些时间。Solus 对我系统的更改使我很懊恼。这些事情本不应该发生,恢复过程也应该更简单。不管怎样,虽然事情似乎很可怕,修复并不是很难。你只需要删除损害的文件然后重新开始。你的数据应该不会受到影响,你也应该能够顺利进入到运行中的系统并继续工作。开始吧。
加油。
---
作者简介:
我叫 Igor Ljubuncic。38 岁,已婚,但还没有小孩。我现在是一个云技术公司的首席工程师,前端新手。在 2015 年年初之前,我在世界上最大的 IT 公司之一的工程计算团队担任操作系统架构师,开发新的基于 Linux 的解决方案、优化内核、在 Linux 上实现一些好的想法。在这之前,我是一个为高性能计算环境设计创新解决方案团队的技术主管。其它一些头衔包括系统专家、系统开发员或者类似的。所有这些都是我的爱好,但从 2008 年开始,就是有报酬的工作。还有什么比这更令人满意的呢?
从 2004 到 2008 年,我通过在医疗图像行业担任物理专家养活自己。我的工作主要关注解决问题和开发算法。为此,我广泛使用 Matlab,主要用于信号和图像处理。另外,我已通过几个主要工程方法的认证,包括 MEDIC Six Sigma Green Belt、实验设计以及统计工程。
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
via: <http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/grub2-efi-corrupt-part-recovery.html>
作者:[Igor Ljubuncic](http://www.dedoimedo.com/faq.html) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,501 | 如何通过 OpenELEC 创建你自己的媒体中心 | https://www.maketecheasier.com/build-media-center-with-openelec/ | 2017-05-12T19:45:00 | [
"OpenELEC",
"Kodi"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8501-1.html | 
你是否曾经想要创建你自己的家庭影院系统?如果是的话,这里有一个为你准备的指南!在本篇文章中,我们将会介绍如何设置一个由 OpenELEC 以及 Kodi 驱动的家庭娱乐系统。我们将会介绍如何制作安装介质,哪些设备可以运行该软件,如何安装它,以及其他一切需要知道的事情等等。
### 选择一个设备
在开始设定媒体中心的软件前,你需要选择一个设备。OpenELEC 支持一系列设备。从一般的桌面设备到树莓派 2/3 等等。选择好设备以后,考虑一下你怎么访问 OpenELEC 系统中的媒体并让其就绪。
\**注意: \**OpenELEC 基于 Kodi,有许多方式加载一个可播放的媒体(比如 Samba 网络分享,外设,等等)。
### 制作安装磁盘
OpenELEC 安装磁盘需要一个 USB 存储器,且其至少有 1GB 的容量。这是安装该软件的唯一方式,因为开发者没有发布 ISO 文件。取而代之的是需要创建一个 IMG 原始文件。选择与你设备相关的链接并且[下载](http://openelec.tv/get-openelec/category/1-openelec-stable-releases)原始磁盘镜像。当磁盘镜像下载完毕,打开一个终端,并且使用命令将数据从压缩包中解压出来。
**在Linux/macOS上**
```
cd ~/Downloads
gunzip -d OpenELEC*.img.gz
```
**在Windows上**
下载 [7zip](http://www.7-zip.org/),安装它,然后解压压缩文件。
当原始的 .IMG 文件被解压后,下载 [Etcher USB creation tool](https://etcher.io/),并且依据在界面上的指示来安装它并创建 USB 磁盘。
**注意:** 对于树莓派用户,Etcher 也支持将文件写入到 SD 卡中。
### 安装 OpenELEC
OpenELEC 安装进程可能是安装流程最简单的操作系统之一了。将 USB 设备加入,然后配置设备使其以 USB 方式启动。同样,这个过程也可以通过按 DEL 或者 F2 来替代。然而并不是所有的 BIOS 都是一样的,所以最好的方式就是看看手册什么的。

一旦进入 BIOS,修改设置使其从 USB 磁盘中直接加载。这将会允许电脑从 USB 磁盘中启动,这将会使你进入到 Syslinux 引导屏幕。在提示符中,键入 `installer`,然后按下回车键。

默认情况下,快速安装选项已经是选中的。按回车键来开始安装。这将会使安装器跳转到磁盘选择界面。选择 OpenELEC 要被安装到的地方,然后按下回车键来开始安装过程。

一旦完成安装,重启系统并加载 OpenELEC。
### 配置 OpenELEC

在第一次启动时,用户必须配置一些东西。如果你的媒体中心拥有一个无线网卡,OpenELEC 将会提示用户将其连接到一个热点上。选择一个列表中的网络并且输入密码。

在下一步“<ruby> 欢迎来到 OpenELEC <rt> Welcome to OpenELEC </rt></ruby>”屏上,用户必须配置不同的分享设置(SSH 以及 Samba)。建议你把这些设置开启,因为可以用命令行访问,这将会使得远程传输媒体文件变得很简单。
### 增加媒体
在 OpenELEC(Kodi)中增加媒体,首先选择你希望添加的媒体到的部分。以同样的流程,为照片、音乐等添加媒体。在这个指南中,我们将着重讲解添加视频。

点击在主页的“<ruby> 视频 <rt> Video </rt></ruby>”选项来进入视频页面。选择“<ruby> 文件 <rt> Files </rt></ruby>”选项,在下一个页面点击“<ruby> 添加视频... <rt> Add videos… </rt></ruby>”,这将会使得用户进入Kodi 的添加媒体页面。在这个页面,你可以随意的添加媒体源了(包括内部和外部的)。

OpenELEC 会自动挂载外部的设备(像是 USB,DVD 碟片,等等),并且它可以通过浏览文件挂载点来挂载。一般情况下,这些设备都会被放在“/run”下,或者,返回你点击“<ruby> 添加视频... <rt> Add videos… </rt></ruby>”的页面,在那里选择设备。任何外部设备,包括 DVD/CD,将会直接展示在那里,并可以直接访问。这是一个很好的选择——对于那些不懂如何找到挂载点的用户。

现在这个设备在 Kodi 中被选中了,界面将会询问用户去浏览设备上私人文件夹,里面有私人文件——这一切都是在媒体中心文件浏览器工具下执行的。一旦找到了放置文件的文件夹,添加它,给予文件夹一个名字,然后按下 OK 按钮来保存它。

当一个用户浏览“<ruby> 视频 <rt> Videos </rt></ruby>”,他们将会看到可以点击的文件夹,这个文件夹中带有从外部设备添加的媒体。这些文件夹可以很容易地在系统上播放。
### 使用 OpenELec
当用户登录他们将会看见一个“主界面”,这个主界面有许多部分,用户可以点击它们并且进入,包括:图片,视频,音乐,程序等等。当悬停在这些部分的时候,子部分就会出现。例如,当悬停在“图片”上时,子部分”文件“以及”插件”就会出现。

如果一个用户点击了一个部分中的子部分,例如“插件”,Kodi 插件选择就会出现。这个安装器将会允许用户浏览新的插件内容,来安装到这个子部分(像是图片关联插件,等等)或者启动一个已经存在的图片关联插件,当然,这个插件应该已经安装到系统上了。
此外,点击任何部分的文件子部分(例如视频)将会直接给显示用户该部分可用的文件。
### 系统设置

Kodi 有丰富的设置区域。为了找到这些设置,使鼠标在右方悬停,目录选择器将会滚动右方并且显示”<ruby> 系统 <rt> System </rt></ruby>“。点击来打开全局系统设定区。
用户可以修改任何设置,从安装 Kodi 仓库的插件,到激活各种服务,到改变主题,甚至天气。如果想要退出设定区域并且返回主页面,点击右下方角落中的“home”图标。
### 结论
通过 OpenELEC 的安装和配置,你现在可以随意体验使用你自己的 Linux 支持的家庭影院系统。在所有的家庭影院系统 Linux 发行版中,这个是最用户友好的。请记住,尽管这个系统是以“OpenELEC”为名,但它运行着的是 Kodi ,并兼容任何 Kodi 的插件,工具以及程序。
---
via: <https://www.maketecheasier.com/build-media-center-with-openelec/>
作者:[Derrik Diener](https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/derrikdiener/) 译者:[svtter](https://github.com/svtter) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 
Have you ever wanted to make your own home theater system? If so, this is the guide for you! In this article we’ll go over how to set up a home entertainment system powered by OpenELEC and Kodi. We’ll go over how to make the installation medium, what devices can run the software, how to install it and everything else there is to know!
## Choosing a device
Before setting up the software in the media center, you’ll need to choose a device. OpenELEC supports a multitude of devices. From regular desktops and laptops to the Raspberry Pi 2/3, etc. With a device chosen, think about how you’ll access the media on the OpenELEC system and get it ready to use.
**Note:** as OpenELEC is based on Kodi, there are many ways to load playable media (Samba network shares, external devices, etc.).
## Making the installation disk
The OpenELEC installation disk requires a USB flash drive of at least 1 GB. This is the only way to install the software, as the developers do not currently distribute an ISO file. A raw IMG file needs to be created instead. Choose the link that corresponds with your device and [download](https://openelec.tv/get-openelec/category/1-openelec-stable-releases) the raw disk image. With the image downloaded, open a terminal and use the command to extract the data from the archive.
**On Linux/macOS**
cd ~/Downloads gunzip -d OpenELEC*.img.gz
**On Windows**
Download [7zip](https://www.7-zip.org/), install it, and then extract the archive.
With the raw .IMG file extracted, download the Etcher USB creation tool and follow the instructions on the page to install it and create the USB disk.
**Note:** for Raspberry Pi users, Etcher supports burning to SD cards as well.
## Installing OpenELEC
The OpenELEC installation process is probably one of the easiest operating systems to install. To start, plug in the USB device and configure your device to boot from the USB drive. For some, this can be accomplished by pressing the DEL key or F2. However, as all BIOS are different, it is best to look into the manual and find out.
Once in the BIOS, configure it to load the USB stick directly. This will allow the computer to boot the drive, which will bring you to the Syslinux boot screen. Enter “installer” in the prompt, then press the Enter key.
By default, the quick installation option is selected. Press Enter to start the install. This will move the installer onto the drive selection page. Select the hard drive where OpenELEC should be installed, then press the Enter key to start the installation process.
Once done, reboot the system and load OpenELEC.
## Configuring OpenELEC
On first boot, the user must configure a few things. If your media center device has a wireless network card, OpenELEC will prompt the user to connect it to a wireless access point. Select a network from the list and enter the access code.
On the next “Welcome to OpenELEC” screen, the user must configure various sharing settings (SSH and Samba). It is advised that you turn these settings on, as this will make it easier to remotely transfer media files as well as gain command-line access.
## Adding Media
To add media to OpenElec (Kodi), first select the section that you want to add media to. Adding media for Photos, Music, etc., is the same process. In this guide we’ll focus on adding videos.
Click the “Video” option on the home screen to go to the videos area. Select the “Files” option. On the next page click “Add videos…” This will take the user to the Kodi add-media screen. From here it is possible to add new media sources (both internal and external).
OpenELEC automatically mounts external devices (like USB, DVD data discs, etc.), and it can be added by browsing for the folder’s mount point. Usually these devices are placed in “/run.” Alternatively, go back to the page where you clicked on “Add videos…” and click on the device there. Any external device, including DVDs/CDs, will show up there and can be accessed directly. This is a good option for those who don’t understand how to find mount points.
Now that the device is selected within Kodi, the interface will ask the user to browse for the individual directory on the device with the media files using the media center’s file browser tool. Once the directory that holds the files is found, add it, give the directory a name and press the OK button to save it.
When a user browses “Videos,” they’ll see a clickable folder which brings up the media added from an external device. These folders can easily be played on the system.
## Using OpenElec
When the user logs in they’ll see a “home screen.” This home screen has several sections the user is able to click on and go to: Pictures, Videos, Music, Programs, etc. When hovering over any of these sections, subsections appear. For example, when hovering over “Pictures,” the subsections “files” and “Add-ons” appear.
If a user clicks on one of the subsections under a section, like “add-ons,” the Kodi add-on chooser appears. This installer will allow users to either browse for new add-ons to install in relation to this subsection (like Picture-related add-ons, etc.) or to launch existing picture-related ones that are already on the system.
Additionally, clicking the files subsection of any section (e.g. Videos) takes the user directly to any available files in that section.
## System Settings
Kodi has an extensive settings area. To get to the Settings, hover the mouse to the right, and the menu selector will scroll right and reveal “System.” Click on it to open the global system settings area.
Any setting can be modified and changed by the user, from installing add-ons from the Kodi-repository, to activating various services, to changing the theme, and even the weather. To exit the settings area and return to the home screen, press the “home” icon in the bottom-right corner.
## Conclusion
With the OpenELEC installed and configured, you are now free to go and use your very own Linux-powered home-theater system. Out of all of the home-theater-based Linux distributions, this one is the most user-friendly. Do keep in mind that although this operating system is known as “OpenELEC,” it runs Kodi and is compatible with all of the different Kodi add-ons, tools, and programs.
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox |
8,502 | 5 个需要知道的开源的软件定义网络(SDN)项目 | https://www.linux.com/news/open-cloud-report/2016/5-open-source-software-defined-networking-projects-know | 2017-05-12T20:04:00 | [
"SDN"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8502-1.html | 
>
> SDN 开始重新定义企业网络。这里有五个应该知道的开源项目。
>
>
>
纵观整个 2016 年,软件定义网络(SDN)持续快速发展并变得成熟。我们现在已经超出了开源网络的概念阶段,两年前评估这些项目潜力的公司已经开始了企业部署。如几年来所预测的,SDN 正在开始重新定义企业网络。
这与市场研究人员的观点基本上是一致的。IDC 在今年早些时候公布了 SDN 市场的[一份研究](https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS41005016),它预计从 2014 年到 2020 年 SDN 的年均复合增长率为 53.9%,届时市场价值将达到 125 亿美元。此外,“<ruby> 2016 技术趋势 <rt> Technology Trends 2016 </rt></ruby>” 报告中将 SDN 列为 2016 年最佳技术投资。
IDC 网络基础设施副总裁,[Rohit Mehra](http://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=PRF003513) 说:“云计算和第三方平台推动了 SDN 的需求,这预示着 2020 年的一个价值超过 125 亿美元的市场。毫无疑问的是 SDN 的价值将越来越多地渗透到网络虚拟化软件和 SDN 应用中,包括虚拟化网络和安全服务。大型企业现在正在数据中心体现 SDN 的价值,但它们最终会认识到其在分支机构和校园网络中的广泛应用。“
Linux 基金会最近[发布](https://www.linux.com/blog/linux-foundation-issues-2016-guide-open-source-cloud-projects)了其 2016 年度报告[“开放云指南:当前趋势和开源项目”](http://ctt.marketwire.com/?release=11G120876-001&id=10172077&type=0&url=http%3A%2F%2Fgo.linuxfoundation.org%2Frd-open-cloud-report-2016-pr)。其中第三份年度报告全面介绍了开放云计算的状态,并包含关于 unikernel 的部分。你现在可以[下载报告](http://go.linuxfoundation.org/l/6342/2016-10-31/3krbjr)了,首先要注意的是汇总和分析研究,说明了容器、unikernel 等的趋势是如何重塑云计算的。该报告提供了对当今开放云环境中心的分类项目的描述和链接。
在本系列中,我们会研究各种类别,并提供关于这些领域如何发展的更多见解。下面,你会看到几个重要的 SDN 项目及其所带来的影响,以及 GitHub 仓库的链接,这些都是从“开放云指南”中收集的:
### 软件定义网络
#### [ONOS](http://onosproject.org/)
<ruby> 开放网络操作系统 <rt> Open Network Operating System </rt></ruby>(ONOS)是一个 Linux 基金会项目,它是一个面向服务提供商的软件定义网络操作系统,它具有可扩展性、高可用性、高性能和抽象功能来创建应用程序和服务。
[ONOS 的 GitHub 地址](https://github.com/opennetworkinglab/onos)。
#### [OpenContrail](http://www.opencontrail.org/)
OpenContrail 是 Juniper Networks 的云开源网络虚拟化平台。它提供网络虚拟化的所有必要组件:SDN 控制器、虚拟路由器、分析引擎和已发布的上层 API。其 REST API 配置并收集来自系统的操作和分析数据。
[OpenContrail 的 GitHub 地址](https://github.com/Juniper/contrail-controller)。
#### [OpenDaylight](https://www.opendaylight.org/)
OpenDaylight 是 Linux 基金会旗下的 OpenDaylight 基金会项目,它是一个可编程的、提供给服务提供商和企业的软件定义网络平台。它基于微服务架构,可以在多供应商环境中的一系列硬件上实现网络服务。
[OpenDaylight 的 GitHub 地址](https://github.com/opendaylight)。
#### [Open vSwitch](http://openvswitch.org/)
Open vSwitch 是一个 Linux 基金会项目,是具有生产级品质的多层虚拟交换机。它通过程序化扩展设计用于大规模网络自动化,同时还支持标准管理接口和协议,包括 NetFlow、sFlow、IPFIX、RSPAN、CLI、LACP 和 802.1ag。它支持类似 VMware 的分布式 vNetwork 或者 Cisco Nexus 1000V 那样跨越多个物理服务器分发。
[OVS 在 GitHub 的地址](https://github.com/openvswitch/ovs)。
#### [OPNFV](https://www.opnfv.org/)
<ruby> 网络功能虚拟化开放平台 <rt> Open Platform for Network Functions Virtualization </rt></ruby>(OPNFV)是 Linux 基金会项目,它用于企业和服务提供商网络的 NFV 平台。它汇集了计算、存储和网络虚拟化方面的上游组件以创建 NFV 程序的端到端平台。
[OPNFV 在 Bitergia 上的地址](http://projects.bitergia.com/opnfv/browser/)。
*要了解更多关于开源云计算趋势和查看顶级开源云计算项目完整列表,[请下载 Linux 基金会的 “开放云指南”](http://bit.ly/2eHQOwy)。*
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/news/open-cloud-report/2016/5-open-source-software-defined-networking-projects-know>
作者:[SAM DEAN](https://www.linux.com/users/sam-dean) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,503 | GitLab 工作流概览 | https://about.gitlab.com/2016/10/25/gitlab-workflow-an-overview/ | 2017-05-13T14:09:00 | [
"Git",
"GitLab"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8503-1.html | GitLab 是一个基于 git 的仓库管理程序,也是一个方便软件开发的强大完整应用。
GitLab 拥有一个“用户新人友好”的界面,通过图形界面和命令行界面,使你的工作更加具有效率。GitLab 不仅仅对开发者是一个有用的工具,它甚至可以被集成到你的整个团队中,使得每一个人获得一个独自唯一的平台。
GitLab 工作流逻辑符合使用者思维,使得整个平台变得更加易用。相信我,使用一次,你就离不开它了!

### GitLab 工作流
**GitLab 工作流** 是在软件开发过程中,在使用 GitLab 作为代码托管平台时,可以采取的动作的一个逻辑序列。
GitLab 工作流遵循了 [GitLab Flow](https://about.gitlab.com/2014/09/29/gitlab-flow/) 策略,这是由一系列由**基于 Git** 的方法和策略组成的,这些方法为版本的管理,例如**分支策略**、**Git最佳实践**等等提供了保障。
通过 GitLab 工作流,可以很方便的[提升](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/09/13/gitlab-master-plan/)团队的工作效率以及凝聚力。这种提升,从引入一个新的项目开始,一直到发布这个项目,成为一个产品都有所体现。这就是我们所说的“如何通过最快的速度把一个点子在 10 步之内变成一个产品”。

#### 软件开发阶段
一般情况下,软件开发经过 10 个主要阶段;GitLab 为这 10 个阶段依次提供了解决方案:
1. **IDEA**: 每一个从点子开始的项目,通常来源于一次闲聊。在这个阶段,GitLab 集成了 [Mattermost](https://about.gitlab.com/2015/08/18/gitlab-loves-mattermost/)。
2. **ISSUE**: 最有效的讨论一个点子的方法,就是为这个点子建立一个工单讨论。你的团队和你的合作伙伴可以在 <ruby> 工单追踪器 <rt> issue tracker </rt></ruby> 中帮助你去提升这个点子
3. **PLAN**: 一旦讨论得到一致的同意,就是开始编码的时候了。但是等等!首先,我们需要优先考虑组织我们的工作流。对于此,我们可以使用 <ruby> 工单看板 <rt> Issue Board </rt></ruby>。
4. **CODE**: 现在,当一切准备就绪,我们可以开始写代码了。
5. **COMMIT**: 当我们为我们的初步成果欢呼的时候,我们就可以在版本控制下,提交代码到功能分支了。
6. **TEST**: 通过 [GitLab CI](https://about.gitlab.com/gitlab-ci/),我们可以运行脚本来构建和测试我们的应用。
7. **REVIEW**: 一旦脚本成功运行,我们测试和构建成功,我们就可以进行 <ruby> 代码复审 <rt> code review </rt></ruby> 以及批准。
8. **STAGING:**: 现在是时候[将我们的代码部署到演示环境](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/08/05/continuous-integration-delivery-and-deployment-with-gitlab/)来检查一下,看看是否一切就像我们预估的那样顺畅——或者我们可能仍然需要修改。
9. **PRODUCTION**: 当一切都如预期,就是[部署到生产环境](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/08/05/continuous-integration-delivery-and-deployment-with-gitlab/)的时候了!
10. **FEEDBACK**: 现在是时候返回去看我们项目中需要提升的部分了。我们使用[<ruby> 周期分析 <rt> Cycle Analytics </rt></ruby>](https://about.gitlab.com/solutions/cycle-analytics/)来对当前项目中关键的部分进行的反馈。
简单浏览这些步骤,我们可以发现,提供强大的工具来支持这些步骤是十分重要的。在接下来的部分,我们为 GitLab 的可用工具提供一个简单的概览。
### GitLab 工单追踪器
GitLab 有一个强大的工单追溯系统,在使用过程中,允许你和你的团队,以及你的合作者分享和讨论建议。

工单是 GitLab 工作流的第一个重要重要特性。[以工单的讨论为开始](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/03/03/start-with-an-issue/); 跟踪新点子的改变是一个最好的方式。
这十分有利于:
* 讨论点子
* 提交功能建议
* 提问题
* 提交错误和故障
* 获取支持
* 精细化新代码的引入
每一个在 GitLab 上部署的项目都有一个工单追踪器。找到你的项目中的 **Issues** > **New issue** 来创建一个新的工单。建立一个标题来总结要被讨论的主题,并且使用 [Markdown](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/markdown.html) 来形容它。看看下面的“专业技巧”来加强你的工单描述。
GitLab 工单追踪器提供了一个额外的实用功能,使得步骤变得更佳易于管理和考虑。下面的部分仔细描述了它。

#### 秘密工单
无论何时,如果你仅仅想要在团队中讨论这个工单,你可以使[该工单成为秘密的](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/03/31/feature-highlihght-confidential-issues/)。即使你的项目是公开的,你的工单也会被保密起来。当一个不是本项目成员的人,就算是 [报告人级别][01],想要访问工单的地址时,浏览器也会返回一个 404 错误。
#### 截止日期
每一个工单允许你填写一个[截止日期](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/08/05/feature-highlight-set-dates-for-issues/#due-dates-for-issues)。有些团队工作时间表安排紧凑,以某种方式去设置一个截止日期来解决问题,是有必要的。这些都可以通过截止日期这一功能实现。
当你对一个多任务项目有截止日期的时候——比如说,一个新的发布活动、项目的启动,或者按阶段追踪任务——你可以使用[里程碑](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/10/25/gitlab-workflow-an-overview/#milestones)。
#### 受托者
要让某人处理某个工单,可以将其分配给他。你可以任意修改被分配者,直到满足你的需求。这个功能的想法是,一个受托者本身对这个工单负责,直到其将这个工单重新赋予其他人。
这也可以用于按受托者筛选工单。
#### 标签
GitLab 标签也是 GitLab 流的一个重要组成部分。你可以使用它们来分类你的工单,在工作流中定位,以及通过[优先级标签](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/labels.html#prioritize-labels)来安装优先级组织它们。
标签使得你与[GitLab 工单看板](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/10/25/gitlab-workflow-an-overview/#gitlab-issue-board)协同工作,加快工程进度以及组织你的工作流。
**新功能:** 你可以创建[组标签](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/10/22/gitlab-8-13-released/#group-labels)。它可以使得在每一个项目组中使用相同的标签。
#### 工单权重
你可以添加个[工单权重](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/workflow/issue_weight.html)使得一个工单重要性表现的更为清晰。01 - 03 表示工单不是特别重要,07 - 09 表示十分重要,04 - 06 表示程度适中。此外,你可以与你的团队自行定义工单重要性的指标。
注:该功能仅可用于 GitLab 企业版和 GitLab.com 上。
#### GitLab 工单看板
在项目中,[GitLab 工单看板](https://about.gitlab.com/solutions/issueboard)是一个用于计划以及组织你的工单,使之符合你的项目工作流的工具。
看板包含了与其相关的相应标签,每一个列表包含了相关的被标记的工单,并且以卡片的形式展示出来。
这些卡片可以在列表之间移动,被移动的卡片,其标签将会依据你移动的位置相应更新到列表上。

**新功能:** 你也可以通过点击列表上方的“+”按钮在看板右边创建工单。当你这么做的时候,这个工单将会自动添加与列表相关的标签。
**新功能:** 我们[最近推出了](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/10/22/gitlab-8-13-released/#multiple-issue-boards-ee) 每一个 GitLab 项目拥有**多个工单看板**的功能(仅存在于 [GitLab 企业版](https://about.gitlab.com/free-trial/));这是为不同的工作流组织你的工单的好方法。

### 通过 GitLab 进行代码复审
在工单追踪器中,讨论了新的提议之后,就是在代码上做工作的时候了。你在本地书写代码,一旦你完成了你的第一个版本,提交你的代码并且推送到你的 GitLab 仓库。你基于 Git 的管理策略可以在 [GitLab 流](https://about.gitlab.com/2014/09/29/gitlab-flow/)中被提升。
#### 第一次提交
在你的第一次提交信息中,你可以添加涉及到工单号在其中。通过这样做你可以将两个阶段的开发工作流链接起来:工单本身以及关于这个工单的第一次提交。
这样做,如果你提交的代码和工单属于同一个项目,你可以简单的添加 `#xxx` 到提交信息中(LCTT 译注:`git commit message`),`xxx`是一个工单号。如果它们不在一个项目中,你可以添加整个工单的整个URL(`https://gitlab.com/<username>/<projectname>/issues/<xxx>`)。
```
git commit -m "this is my commit message. Ref #xxx"
```
或者
```
git commit -m "this is my commit message. Related to https://gitlab.com/<username>/<projectname>/issues/<xxx>"
```
当然,你也可以替换 `gitlab.com`,以你自己的 GitLab 实例来替换这个 URL。
**注:** 链接工单和你的第一次提交是为了通过 [GitLab 周期分析](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/10/25/gitlab-workflow-an-overview/#feedback)追踪你的进展。这将会衡量计划执行该工单所采取的时间,即创建工单与第一次提交的间隔时间。
#### 合并请求
一旦将你的改动提交到功能分支,GitLab 将识别该修改,并且建议你提交一次<ruby> 合并请求 <rt> Merge Request </rt></ruby>(MR)。
每一次 MR 都会有一个标题(这个标题总结了这次的改动)并且一个用 [Markdown](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/markdown.html) 书写的描述。在描述中,你可以简单的描述该 MR 做了什么,提及任何工单以及 MR(在它们之间创建联系),并且,你也可以添加个[关闭工单模式](https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/administration/issue_closing_pattern.html),当该 MR 被**合并**的时候,相关联的工单就会被关闭。
例如:
```
## 增加一个新页面
这个 MR 将会为这个项目创建一个包含该 app 概览的 `readme.md`。
Closes #xxx and https://gitlab.com/<username>/<projectname>/issues/<xxx>
预览:

cc/ @Mary @Jane @John
```
当你创建一个如上的带有描述的 MR,它将会:
* 当合并时,关闭包括工单 `#xxx` 以及 `https://gitlab.com/<username>/<projectname>/issues/<xxx>`
* 展示一张图片
* 通过邮件提醒用户 `@Mary`、`@Jane`,以及给 `@John`
你可以分配这个 MR 给你自己,直到你完成你的工作,然后把它分配给其他人来做一次代码复审。如果有必要的话,这个 MR 可以被重新分配多次,直到你覆盖你所需要的所有复审。
它也可以被标记,并且添加一个[里程碑](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/10/25/gitlab-workflow-an-overview/#milestones)来促进管理。
当你从图形界面而不是命令行添加或者修改一个文件并且提交一个新的分支时,也很容易创建一个新的 MR,仅仅需要标记一下复选框,“以这些改变开始一个新的合并请求”,然后,一旦你提交你的改动,GitLab 将会自动创建一个新的 MR。

**注:** 添加[关闭工单样式](https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/administration/issue_closing_pattern.html)到你的 MR 以便可以使用 [GitLab 周期分析](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/10/25/gitlab-workflow-an-overview/#feedback)追踪你的项目进展,是十分重要的。它将会追踪“CODE”阶段,衡量第一次提交及创建一个相关的合并请求所间隔的时间。
**新功能:** 我们已经开发了[审查应用](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/10/22/gitlab-8-13-released/#ability-to-stop-review-apps),这是一个可以让你部署你的应用到一个动态的环境中的新功能,在此你可以按分支名字、每个合并请求来预览改变。参看这里的[可用示例](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-examples/review-apps-nginx/)。
#### WIP MR
WIP MR 含义是 **在工作过程中的合并请求**,是一个我们在 GitLab 中避免 MR 在准备就绪前被合并的技术。只需要添加 `WIP:` 在 MR 的标题开头,它将不会被合并,除非你把 `WIP:` 删除。
当你改动已经准备好被合并,编辑工单来手动删除 `WIP:` ,或者使用就像如下 MR 描述下方的快捷方式。

**新功能:** `WIP` 模式可以通过[斜线命令](https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/user/project/slash_commands.html) `/wip` [快速添加到合并请求中](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/10/22/gitlab-8-13-released/#wip-slash-command)。只需要在评论或者 MR 描述中输入它并提交即可。
#### 复审
一旦你创建一个合并请求,就是你开始从你的团队以及合作方收取反馈的时候了。使用图形界面中的差异比较功能,你可以简单的添加行内注释,以及回复或者解决它们。
你也可以通过点击行号获取每一行代码的链接。
在图形界面中可以看到提交历史,通过提交历史,你可以追踪文件的每一次改变。你可以以行内差异或左右对比的方式浏览它们。

**新功能:** 如果你遇到合并冲突,可以快速地[通过图形界面来解决](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/08/22/gitlab-8-11-released/#merge-conflict-resolution),或者依据你的需要修改文件来修复冲突。

### 构建、测试以及发布
[GitLab CI](https://about.gitlab.com/gitlab-ci/) 是一个强大的内建工具,其作用是[持续集成、持续发布以及持续分发](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/07/22/gitlab-8-10-released/#bulk-subscribe-to-issues),它可以按照你希望的运行一些脚本。它的可能性是无止尽的:你可以把它看做是自己运行的命令行。
它完全是通过一个名为 `.gitlab-ci.yml` 的 YAML 文件设置的,其放置在你的项目仓库中。使用 Web 界面简单的添加一个文件,命名为 `.gitlab-ci.yml` 来触发一个下拉菜单,为不同的应用选择各种 CI 模版。

#### Koding
Use GitLab's [Koding integration](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/08/22/gitlab-8-11-released/#koding-integration) to run your entire development environment in the cloud. This means that you can check out a project or just a merge request in a full-fledged IDE with the press of a button.
可以使用 GitLab 的 [Koding 集成](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/08/22/gitlab-8-11-released/#koding-integration)功能在云端运行你的整个云端开发环境。这意味着你可以轻轻一键即可在一个完整的 IDE 中检出以个项目,或者合并一个请求。
#### 使用案例
GitLab CI 的使用案例:
* 用它来[构建](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/04/07/gitlab-pages-setup/)任何[静态网站生成器](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/06/17/ssg-overview-gitlab-pages-part-3-examples-ci/),并且通过 [GitLab Pages](https://pages.gitlab.io/) 发布你的网站。
* 用它来[发布你的网站](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/08/26/ci-deployment-and-environments/) 到 `staging` 以及 `production` [环境](https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/ci/yaml/README.html#environment)。
* 用它来[构建一个 iOS 应用](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/03/10/setting-up-gitlab-ci-for-ios-projects/)。
* 用它来[构建和发布你的 Docker 镜像](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/08/11/building-an-elixir-release-into-docker-image-using-gitlab-ci-part-1/)到 [GitLab 容器注册库](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/05/23/gitlab-container-registry/)。
我们已经准备一大堆 [GitLab CI 样例工程](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/examples/README.html)作为您的指南。看看它们吧!
### 反馈:周期分析
当你遵循 GitLab 工作流进行工作,你的团队从点子到产品,在每一个[过程的关键部分](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/09/21/cycle-analytics-feature-highlight/),你将会在下列时间获得一个 [GitLab 周期分析](https://about.gitlab.com/solutions/cycle-analytics/)的反馈:
* **Issue**: 从创建一个工单,到分配这个工单给一个里程碑或者添加工单到你的工单看板的时间。
* **Plan**: 从给工单分配一个里程碑或者把它添加到工单看板,到推送第一次提交的时间。
* **Code**: 从第一次提交到提出该合并请求的时间。
* **Test**: CI 为了相关合并请求而运行整个过程的时间。
* **Review**: 从创建一个合并请求到合并它的时间。
* **Staging**: 从合并到发布成为产品的时间。
* **Production(Total)**: 从创建工单到把代码发布成[产品](https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/ci/yaml/README.html#environment)的时间。
### 加强
#### 工单以及合并请求模版
[工单以及合并请求模版](https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/user/project/description_templates.html)允许你为你的项目去定义一个特定内容的工单模版和合并请求的描述字段。
你可以以 [Markdown](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/markdown.html) 形式书写它们,并且把它们加入仓库的默认分支。当创建工单或者合并请求时,可以通过下拉菜单访问它们。
它们节省了您在描述工单和合并请求的时间,并标准化了需要持续跟踪的重要信息。它确保了你需要的一切都在你的掌控之中。
你可以创建许多模版,用于不同的用途。例如,你可以有一个提供功能建议的工单模版,或者一个 bug 汇报的工单模版。在 [GitLab CE project](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-ce/issues/new) 中寻找真实的例子吧!

#### 里程碑
[里程碑](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/08/05/feature-highlight-set-dates-for-issues/#milestones) 是 GitLab 中基于共同的目标、详细的日期追踪你队伍工作的最好工具。
不同情况下的目的是不同的,但是大致是相同的:你有为了达到特定的目标的工单的集合以及正在编码的合并请求。
这个目标基本上可以是任何东西——用来结合团队的工作,在一个截止日期前完成一些事情。例如,发布一个新的版本,启动一个新的产品,在某个日期前完成,或者按季度收尾一些项目。

### 专业技巧
#### 工单和 MR
* 在工单和 MR 的描述中:
+ 输入 `#` 来触发一个已有工单的下拉列表
+ 输入 `!` 来触发一个已有 MR 的下拉列表
+ 输入 `/` 来触发[斜线命令](https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/user/project/slash_commands.html)
+ 输入 `:` 来出发 emoji 表情 (也支持行中评论)
* 通过按钮“附加文件”来添加图片(jpg、png、gif) 和视频到行内评论
* 通过 [GitLab Webhooks](https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/web_hooks/web_hooks.html) [自动应用标签](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/08/19/applying-gitlab-labels-automatically/)
* [构成引用](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/07/22/gitlab-8-10-released/#blockquote-fence-syntax): 使用语法 `>>>` 来开始或者结束一个引用
```
>>>
Quoted text
Another paragraph
>>>
```
* 创建[任务列表](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/markdown.html#task-lists):
```
- [ ] Task 1
- [ ] Task 2
- [ ] Task 3
```
##### 订阅
你是否发现你有一个工单或者 MR 想要追踪?展开你的右边的导航,点击[订阅](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/03/22/gitlab-8-6-released/#subscribe-to-a-label),你就可以在随时收到一个评论的提醒。要是你想要一次订阅多个工单和 MR?使用[批量订阅](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/07/22/gitlab-8-10-released/#bulk-subscribe-to-issues)。
##### 添加代办
除了一直留意工单和 MR,如果你想要对它预先做点什么,或者不管什么时候你想要在 GitLab 代办列表中添加点什么,点击你右边的导航,并且[点击**添加代办**](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/06/22/gitlab-8-9-released/#manually-add-todos)。
##### 寻找你的工单和 MR
当你寻找一个在很久以前由你开启的工单或 MR——它们可能数以十计、百计、甚至千计——所以你很难找到它们。打开你左边的导航,并且点击**工单**或者**合并请求**,你就会看到那些分配给你的。同时,在那里或者任何工单追踪器里,你可以通过作者、分配者、里程碑、标签以及重要性来过滤工单,也可以通过搜索所有不同状态的工单,例如开启的、合并的,关闭的等等。
#### 移动工单
一个工单在一个错误的项目中结束了?不用担心,点击**Edit**,然后[移动工单](https://about.gitlab.com/2016/03/22/gitlab-8-6-released/#move-issues-to-other-projects)到正确的项目。
#### 代码片段
你经常在不同的项目以及文件中使用一些相同的代码段和模版吗?创建一个代码段并且使它在你需要的时候可用。打开左边导航栏,点击**[Snipptes](https://gitlab.com/dashboard/snippets)**。所有你的片段都会在那里。你可以把它们设置成公开的,内部的(仅为 GitLab 注册用户提供),或者私有的。

### GitLab 工作流用户案例概要
作为总结,让我们把所有东西聚在一起理顺一下。不必担心,这十分简单。
让我们假设:你工作于一个专注于软件开发的公司。你创建了一个新的工单,这个工单是为了开发一个新功能,实施于你的一个应用中。
**标签策略**
为了这个应用,你已经创建了几个标签,“讨论”、“后端”、“前端”、“正在进行”、“展示”、“就绪”、“文档”、“营销”以及“产品”。所有都已经在工单看板有它们自己的列表。你的当前的工单已经有了标签“讨论”。
在工单追踪器中的讨论达成一致之后,你的后端团队开始在工单上工作,所以他们把这个工单的标签从“讨论”移动到“后端”。第一个开发者开始写代码,并且把这个工单分配给自己,增加标签“正在进行”。
**编码 & 提交**
在他的第一次提交的信息中,他提及了他的工单编号。在工作后,他把他的提交推送到一个功能分支,并且创建一个新的合并请求,在 MR 描述中,包含工单关闭模式。他的团队复审了他的代码并且保证所有的测试和建立都已经通过。
**使用工单看板**
一旦后端团队完成了他们的工作,他们就删除“正在进行”标签,并且把工单从“后端”移动到“前端”看板。所以,前端团队接到通知,这个工单已经为他们准备好了。
**发布到演示**
当一个前端开发者开始在该工单上工作,他(她)增加一个标签“正在进行”,并且把这个工单重新分配给自己。当工作完成,该实现将会被发布到一个**演示**环境。标签“正在进行”就会被删除,然后在工单看板里,工单卡被移动到“演示”列表中。
**团队合作**
最后,当新功能成功实现,你的团队把它移动到“就绪”列表。
然后,就是你的技术文档编写团队的时间了,他们为新功能书写文档。一旦某个人完成书写,他添加标签“文档”。同时,你的市场团队开始启动并推荐该功能,所以某个人添加“市场”。当技术文档书写完毕,书写者删除标签“文档”。一旦市场团队完成他们的工作,他们将工单从“市场”移动到“生产”。
**部署到生产环境**
最后,你将会成为那个为新版本负责的人,合并“合并请求”并且将新功能部署到**生产**环境,然后工单的状态转变为**关闭**。
**反馈**
通过[周期分析](https://about.gitlab.com/solutions/cycle-analytics/),你和你的团队节省了如何从点子到产品的时间,并且开启另一个工单,来讨论如何将这个过程进一步提升。
### 总结
GitLab 工作流通过一个单一平台帮助你的团队加速从点子到生产的改变:
* 它是**有效的**:因为你可以获取你想要的结果
* 它是**高效的**:因为你可以用最小的努力和成本达到最大的生产力
* 它是**高产的**:因为你可以非常有效的计划和行动
* 它是**简单的**:因为你不需要安装不同的工具去完成你的目的,仅仅需要 GitLab
* 它是**快速的**:因为你不需要在多个平台间跳转来完成你的工作
每一个月的 22 号都会有一个新的 GitLab 版本释出,让它在集成软件开发解决方案上变得越来越好,让团队可以在一个单一的、唯一的界面下一起工作。
在 GitLab,每个人都可以奉献!多亏了我们强大的社区,我们获得了我们想要的。并且多亏了他们,我们才能一直为你提供更好的产品。
还有什么问题和反馈吗?请留言,或者在推特上@我们[@GitLab](https://twitter.com/gitlab)!
---
via: <https://about.gitlab.com/2016/10/25/gitlab-workflow-an-overview/>
作者:[Marcia Ramos](https://twitter.com/XMDRamos) 译者:[svtter](https://github.com/svtter) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,504 | 如何在 CentOS 7 中使用 SSL/TLS 加固 FTP 服务器进行安全文件传输 | http://www.tecmint.com/secure-vsftpd-using-ssl-tls-on-centos/ | 2017-05-13T14:43:00 | [
"SSL",
"SFTP",
"FTP"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8504-1.html | 在一开始的设计中,FTP(文件传输协议)就是不安全的,意味着它不会加密两台机器之间传输的数据以及用户的凭据。这使得数据和服务器安全面临很大威胁。

在这篇文章中,我们会介绍在 CentOS/RHEL 7 以及 Fedora 中如何在 FTP 服务器中手动启用数据加密服务;我们会介绍使用 SSL/TLS 证书保护 VSFTPD(Very Secure FTP Daemon)服务的各个步骤。
#### 前提条件:
* 你必须已经[在 CentOS 7 中安装和配置 FTP 服务](/article-8527-1.html) 。
在我们开始之前,要注意本文中所有命令都以 root 用户运行,否则,如果现在你不是使用 root 用户控制服务器,你可以使用 [sudo 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/sudoers-configurations-for-setting-sudo-in-linux/) 去获取 root 权限。
### 第一步:生成 SSL/TLS 证书和密钥
1、 我们首先要在 `/etc/ssl` 目录下创建用于保存 SSL/TLS 证书和密钥文件的子目录:
```
# mkdir /etc/ssl/private
```
2、 然后运行下面的命令为 vsftpd 创建证书和密钥并保存到一个文件中,下面会解析使用的每个选项。
1. `req` - 是 X.509 Certificate Signing Request (CSR,证书签名请求)管理的一个命令。
2. `x509` - X.509 证书数据管理。
3. `days` - 定义证书的有效日期。
4. `newkey` - 指定证书密钥处理器。
5. `rsa:2048` - RSA 密钥处理器,会生成一个 2048 位的密钥。
6. `keyout` - 设置密钥存储文件。
7. `out` - 设置证书存储文件,注意证书和密钥都保存在一个相同的文件:/etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem。
```
# openssl req -x509 -nodes -keyout /etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem -out /etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048
```
上面的命令会让你回答以下的问题,记住使用你自己情况的值。
```
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:IN
State or Province Name (full name) []:Lower Parel
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Mumbai
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:TecMint.com
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:Linux and Open Source
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:tecmint
Email Address []:[email protected]
```
### 第二步:配置 VSFTPD 使用 SSL/TLS
3、 在我们进行任何 VSFTPD 配置之前,首先开放 990 和 40000-50000 端口,以便在 VSFTPD 配置文件中分别定义 TLS 连接的端口和被动端口的端口范围:
```
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=990/tcp
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=40000-50000/tcp
# firewall-cmd --reload
```
4、 现在,打开 VSFTPD 配置文件并在文件中指定 SSL 的详细信息:
```
# vi /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
```
找到 `ssl_enable` 选项把它的值设置为 `YES` 激活使用 SSL,另外,由于 TSL 比 SSL 更安全,我们会使用 `ssl_tlsv1_2` 选项让 VSFTPD 使用更严格的 TLS:
```
ssl_enable=YES
ssl_tlsv1_2=YES
ssl_sslv2=NO
ssl_sslv3=NO
```
5、 然后,添加下面的行来定义 SSL 证书和密钥文件的位置:
```
rsa_cert_file=/etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem
rsa_private_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem
```
6、 下面,我们要阻止匿名用户使用 SSL,然后强制所有非匿名用户登录使用安全的 SSL 连接进行数据传输和登录过程中的密码发送:
```
allow_anon_ssl=NO
force_local_data_ssl=YES
force_local_logins_ssl=YES
```
7、 另外,我们还可以添加下面的选项增强 FTP 服务器的安全性。当选项 `require_ssl_reuse` 被设置为 `YES` 时,要求所有 SSL 数据连接都会重用 SSL 会话;这样它们会知道控制通道的主密码。
因此,我们需要把它关闭。
```
require_ssl_reuse=NO
```
另外,我们还要用 `ssl_ciphers` 选项选择 VSFTPD 允许用于加密 SSL 连接的 SSL 算法。这可以极大地限制那些尝试发现使用存在缺陷的特定算法的攻击者:
```
ssl_ciphers=HIGH
```
8、 现在,设置被动端口的端口范围(最小和最大端口)。
```
pasv_min_port=40000
pasv_max_port=50000
```
9、 选择性启用 `debug_ssl` 选项以允许 SSL 调试,这意味着 OpenSSL 连接诊断会被记录到 VSFTPD 日志文件:
```
debug_ssl=YES
```
保存所有更改并关闭文件。然后让我们重启 VSFTPD 服务:
```
# systemctl restart vsftpd
```
### 第三步:用 SSL/TLS 连接测试 FTP 服务器
10、 完成上面的所有配置之后,像下面这样通过在命令行中尝试使用 FTP 测试 VSFTPD 是否使用 SSL/TLS 连接:
```
# ftp 192.168.56.10
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : ravi
530 Non-anonymous sessions must use encryption.
Login failed.
421 Service not available, remote server has closed connection
ftp>
```

*验证 FTP SSL 安全连接*
从上面的截图中,我们可以看到这里有个错误提示我们 VSFTPD 只允许用户从支持加密服务的客户端登录。
命令行并不会提供加密服务因此产生了这个错误。因此,为了安全地连接到服务器,我们需要一个支持 SSL/TLS 连接的 FTP 客户端,例如 FileZilla。
### 第四步:安装 FileZilla 以便安全地连接到 FTP 服务器
11、 FileZilla 是一个现代化、流行且重要的跨平台的 FTP 客户端,它默认支持 SSL/TLS 连接。
要在 Linux 上安装 FileZilla,可以运行下面的命令:
```
--------- On CentOS/RHEL/Fedora ---------
# yum install epel-release filezilla
--------- On Debian/Ubuntu ---------
$ sudo apt-get install filezilla
```
12、 当安装完成后(或者你已经安装了该软件),打开它,选择 File => Sites Manager 或者按 `Ctrl + S` 打开 Site Manager 界面。
点击 New Site 按钮添加一个新的站点/主机连接详细信息。

*在 FileZilla 中添加新 FTP 站点*
1. 下一步,像下面这样设置主机/站点名称、添加 IP 地址、定义使用的协议、加密和登录类型(使用你自己情况的值):
```
Host: 192.168.56.10
Protocol: FTP – File Transfer Protocol
Encryption: Require explicit FTP over #recommended
Logon Type: Ask for password #recommended
User: username
```

*在 Filezilla 中添加 FTP 服务器详细信息*
14、 然后点击 Connect,再次输入密码,然后验证用于 SSL/TLS 连接的证书,再一次点击 `OK` 连接到 FTP 服务器:

*验证 FTP SSL 证书*
到了这里,我们应该使用 TLS 连接成功地登录到了 FTP 服务器,在下面的界面中检查连接状态部分获取更多信息。

*通过 TLS/SSL 连接到 FTP 服务器*
15、 最后,在文件目录尝试 [从本地传输文件到 FTP 服务器](http://www.tecmint.com/sftp-command-examples/),看 FileZilla 界面后面的部分查看文件传输相关的报告。

*使用 FTP 安全地传输文件*
就是这些。记住 FTP 默认是不安全的,除非我们像上面介绍的那样配置它使用 SSL/TLS 连接。在下面的评论框中和我们分享你关于这篇文章/主题的想法吧。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 的爱好者,Linux 系统管理员,网络开发员,目前也是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢和电脑一起工作,并且坚信共享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/secure-vsftpd-using-ssl-tls-on-centos/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,505 | 极客漫画:Java 垃圾回收说明 | https://turnoff.us/geek/java-gc-explained/ | 2017-05-14T10:50:00 | [
"Java",
"漫画",
"垃圾回收"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8505-1.html | 
这篇漫画生动的解释了 Java 的垃圾回收机制:什么是垃圾回收(GC)、什么是并行垃圾回收以及什么是垃圾回收的标记清除算法。
如果你想更深入的了解,不妨看一下[垃圾回收](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Garbage_collection_(computer_science)) 和[并行标记清除算法](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Concurrent_mark_sweep_collector)。
---
via: <https://turnoff.us/geek/java-gc-explained/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者&点评:[bestony](https://github.com/bestony) 校对&合成:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # java garbage collection explained


### Comics Related
-
[halloween](/geek/halloween/) -
[java attacks!](/geek/java-attacks/) -
[java jigsaw rejected](/geek/jigsaw-rejected/) -
[java packaging system](/geek/java-packaging/) -
[life (and death) in the db connection pool](/geek/db-connection-pool/) -
[my (dev) morning routine](/geek/my-morning-routine/) -
[jhamlet](/geek/jhamlet/) -
[java thread life](/geek/java-thread-life/) -
[big numbers](/geek/big-numbers/) -
[java evolution parade](/geek/java-evolution-parade/) -
[java 20 - predictions](/geek/java20-predictions/) -
[do the evolution, baby!](/geek/its-evolution-baby/) -
[when just-in-time is justin time](/geek/lazy-justin-is-late-again/) -
[doing a great job together](/geek/duke-tux/) -
[geek rivalries](/geek/geek-rivalries/) -
[a java nightmare](/geek/a-java-nightmare/) -
[java family crisis](/geek/java-family-crisis/) -
[thread.sleep room](/geek/thread-sleep-room/) -
[web server upgrade training](/geek/webserver-upgrade-training/) -
[life in a web server](/geek/life-in-a-web-server/) -
[java collections in duck life](/geek/java-collections/) |
8,506 | 极客漫画:精通正则表达式 | https://turnoff.us/geek/mastering-regexp/ | 2017-05-15T09:15:00 | [
"漫画",
"正则表达式"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8506-1.html | 
一个人希望掌握所有的正则表达式,却耗费了大量的时间,不知室外世事变迁,早已换了一个时代。
这个漫画讽刺了一些初学者,希望掌握一些比较复杂的东西的所有内容后再去做事,却不知道,这些东西过于复杂,你花费的时间可能很快就一文不值,因为它们可能已经过时了。
开发并不要求你掌握所有的内容,更多的时候,你只要能够掌握一些常用的,在真正需要用到的时候,再去查询一些比较详细的、不常用的内容即可。毕竟,没有人要求你马上做完所有事情。
---
via: <https://turnoff.us/geek/mastering-regexp/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者&点评:[Bestony](https://github.com/Bestony) 校对&合成:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # mastering regexp


### Comics Related
-
[new job](/geek/new-job/) -
[vulnerable code](/geek/vulnerable-code/) -
[pair programming vibe 2](/geek/pair-programming-vibe-2/) -
[to automate or not to automate](/geek/to-automate-or-not-to-automate/) -
[pair programming vibe](/geek/pair-programming-vibe/) -
[I'm fine](/geek/im-fine/) -
[minimum viable juice](/geek/minimum-viable-juice/) -
[fill out the form](/geek/fill-out-the-form/) -
[minimum viable elevator](/geek/minimum-viable-elevator/) -
[if hamlet were a programmer](/geek/hamlet-programmer/) -
[she will be an artist... or not](/geek/artist/) -
[chat gpt code smell](/geek/chat-gpt-code/) -
[come to bed](/geek/come-to-bed/) -
[frontenders and backenders](/geek/frontenders-and-backenders/) -
[influencer](/geek/influencer/) -
[the over engineer](/geek/the-over-engineer/) -
[automated tests: u r doing it wrong](/geek/automated-tests-doing-it-wrong/) -
[the bad design punisher 2](/geek/the-bad-design-punisher-2/) -
[virtual conference](/geek/virtual-conference/) -
[perspective](/geek/perspective/) -
[end of the world](/geek/end-of-the-world/) -
[quarantine](/geek/quarantine/) -
[the naive engineer](/geek/the-naive-engineer/) -
[commit messages](/geek/commit-messages/) -
[the bad design punisher](/geek/the-bad-design-punisher/) -
[marketing strategy](/geek/marketing-strategy/) -
[cors explained](/geek/cors-explained/) -
[developer costumes](/geek/halloween-2/) -
[first day on the job](/geek/first-day-on-the-job/) -
[not wanted](/geek/not-wanted/) -
[egoless programming](/geek/egoless-programming/) -
[math class 2018](/geek/math-class-2018/) -
[commitland!](/geek/commitland/) -
[my adorable useless code](/geek/my-adorable-useless-code/) -
[the last resort](/geek/the-last-resort/) -
[the bitcoin design pattern](/geek/the-bitcoin-design-pattern/) -
[programmers over time](/geek/programmers-over-time/) -
[welcome to hell](/geek/welcome-to-hell/) -
[letter to santa](/geek/letter-to-santa/) -
[the specialist](/geek/the-specialist/) -
[tobby's world](/geek/tobbys-world/) -
[when artificial intelligence meets git](/geek/when-ai-meets-git/) -
[at the computer museum](/geek/computer-museum/) -
[follow the hype](/geek/follow-the-hype/) -
[battle of programming languages](/geek/programming-languages-battle/) -
[death and the programmer](/geek/death-and-the-programmer/) -
[business logic on frontend](/geek/business-logic-on-frontend/) -
[good night, programmers!](/geek/good-night-programmers/) -
[chronicles of pair programming 2](/geek/chronicles-of-pair-programming-2/) -
[what your code looks like](/geek/what-your-code-looks-like/) -
[tdd versus ftt](/geek/tdd-vs-ftt/) -
[functional world](/geek/functional-world/) -
[meow-ware](/geek/meow-ware/) -
[backend developer doing css](/geek/backend-developer-doing-css/) -
[are you ready for microservices?](/geek/are-you-ready-for-microservices/) -
[battle of software robots](/geek/battle-of-software-robots/) -
[the monolith retirement](/geek/monolith-retirement/) -
[chronicles of pair programming](/geek/chronicles-of-pair-programming/) -
[lang buddies 2](/geek/lang-buddies-2/) -
[distributed architecture drama](/geek/distributed-architecture-drama/) -
[http2 server push explained](/geek/http2-server-push-explained/) -
[how to break up with a programmer](/geek/how-to-break-up-with-a-programmer/) -
[lang buddies](/geek/lang-buddies/) -
[oh, the 70's](/geek/oh-the-70s/) -
[ode to my family](/geek/ode-to-my-family/) -
[the lord of the matrix](/geek/the-lord-of-the-matrix/) -
[inheritance versus composition](/geek/inheritance-versus-composition/) -
[programmer levels](/geek/programmer-leves/) -
[microservices](/geek/microservices/) -
[binary tree](/geek/binary-tree/) -
[the codeless developer](/geek/codeless/) -
[reactive and boring](/geek/reactive-and-boring/) -
[hype detected](/geek/tech-adoption/) -
[about javascript developers](/geek/love-ecma6/) -
[software testing](/geek/software-test/) -
[developers](/geek/developers/) |
8,507 | 买个 DDoS 服务干掉你的对手 | http://www.csoonline.com/article/3180246/data-protection/hire-a-ddos-service-to-take-down-your-enemies.html | 2017-05-14T19:44:33 | [
"DDoS",
"IoT",
"安全",
"攻击"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8507-1.html |
>
> 随着物联网设备的普及,网络犯罪分子通过利用密码的缺陷而提供拒绝服务攻击。
>
>
>

随着物联网设备飞速发展,分布式拒绝服务(DDoS)攻击正在成为一种危险的趋势。就如 [DNS 服务商 Dyn 上年秋季之遭遇](http://csoonline.com/article/3135986/security/ddos-attack-against-overwhelmed-despite-mitigation-efforts.html) 一样,黑客似乎瞄上了每个人,使用未保护的物联网设备来轰炸网络的做法正在抬头。
可雇佣的 DDoS 攻击的出现意味着即使是最不精通技术的人都能精准报复某些网站。就像在柜台前面买个东西一样方便,然后就可以彻底搞定一个公司。
根据 [Neustar](https://ns-cdn.neustar.biz/creative_services/biz/neustar/www/resources/whitepapers/it-security/ddos/2016-apr-ddos-report.pdf) 的报告,四分之三的国际品牌、机构和公司都是 DDoS 攻击的受害者。[每天至少会发生 3700 起 DDoS 攻击](https://www.a10networks.com/resources/ddos-trends-report)。
睿科网络公司(A10 Networks)网络运营总监 Chase Cunningham 说:“想要找个可用的物联网设备,你只需要在地下网站四处打听一下 Mirai 扫描器代码,一旦你找到了,你将能够利用在线的每一台设备来进行攻击”。
“或者你可以去一些类似 Shodan 的网站,然后简单的搜一下设备特定的请求。当你得到这些信息之后,你就可以将你所雇佣的 DDoS 工具配置正确的流量模拟器类型、指向正确的目标并发动攻击。”
“几乎所有东西都是可买卖的。”他补充道,“你可以购买一个 ‘stresser’,这就是个随便哪个会点按钮的人都会使用的 DDoS 僵尸网络。”
网络安全提供商 Imperva 说,用户只需要出几十美金,就可以快速发动攻击。有些公司在它们的网站上说它们的工具包含肉鸡负载和 CnC(命令与控制)文件。使用这些工具,那些有点想法的肉鸡大师(或者被称为 herders)就可以开始传播恶意软件,通过垃圾邮件、漏洞扫描程序、暴力攻击等来感染设备。
大部分 [stresser 和 booter](https://www.incapsula.com/ddos/booters-stressers-ddosers.html) 都会有一个常见的、基于订阅服务的 SaaS(软件即服务)业务模式。来自 Incapsula 公司的 [Q2 2015 DDoS 报告](https://www.incapsula.com/blog/ddos-global-threat-landscape-report-q2-2015.html) 显示,在 DDoS 上的月均每小时花费是 38 美元(规模较低的是 19.99 美元)。

“stresser 和 booter 只是新世界的一个副产品,这些可以扳倒企业和机构的服务只能运作在灰色领域”,Imperva 写道。
虽然成本不同,但是企业受到的[各种攻击,每次损失在 1.4 万美元到 235 万美元之间](http://www.datacenterknowledge.com/archives/2016/05/13/number-of-costly-dos-related-data-center-outages-rising/)。而且企业受到一次攻击后,[有 82% 的可能性会再次受到攻击](http://www.networkworld.com/article/3064677/security/hit-by-ddos-you-will-likely-be-struck-again.html)。
<ruby> 物联网洪水攻击 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> DDoS of Things </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(DoT)使用物联网设备建立的僵尸网络可造成非常大规模的 DDoS 攻击。物联网洪水攻击会利用成百上千的物联网设备攻击,无论是大型服务提供商还是企业,均无幸免。
“大部分讲究声誉的 DDoS 卖家都会将他们的工具配置为可修改的,这样你就可以轻松地设置攻击的类型。虽然我还没怎么看到有哪些可以‘付费的’物联网流量模拟器的选项,但我敢肯定就要有了。如果是我来搞这个服务,我是绝对会加入这个选项的。”Cunningham 如是说。
由 IDG 新闻服务的消息可知,要建造一个 DDoS 服务也是很简单的。通常黑客会租用 6 到 12 个左右的服务器,然后使用它们随意的攻击任何目标。去年十月下旬,HackForums.net [关闭](http://www.pcworld.com/article/3136730/hacking/hacking-forum-cuts-section-allegedly-linked-to-ddos-attacks.html)了他们的“服务器压力测试”版块,这个做法就是考虑到黑客可能通过使用他们每月十美元的服务建造可雇佣的 DDoS 服务。
同样地在十二月时,美国和欧洲的执法机构 [逮捕](http://www.pcworld.com/article/3149543/security/dozens-arrested-in-international-ddos-for-hire-crackdown.html) 34个参与可雇佣的 DDoS 服务的嫌犯。
但是如果这很简单,怎么还没有经常发生攻击?
Cunningham 说这其实每时每刻都在发生,实际上每天每秒都在发生。他说:”你不知道它们的原因是因为大部分都是扰乱攻击,而不是大规模的、想要搞倒公司的攻击。“
他说,大部分的攻击平台只出售那些会让系统宕机一个小时或稍长一点的攻击。通常宕机一小时的攻击大概需要花费 15 到 50 美元。当然这得看平台,有些可能一小时就要花上百美元。
**减少这些攻击的解决方案是让用户把所有联网设备的出厂预置的密码改掉,然后还要禁用那些你不需要的功能。**
(题图:[Victor](https://www.flickr.com/photos/v1ctor/7606416730/))
---
via: <http://www.csoonline.com/article/3180246/data-protection/hire-a-ddos-service-to-take-down-your-enemies.html>
作者:[Ryan Francis](http://www.csoonline.com/author/Ryan-Francis/) 译者:[kenxx](https://github.com/kenxx) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,508 | 如何用树莓派搭建个人 web 服务器 | https://opensource.com/article/17/3/building-personal-web-server-raspberry-pi-3 | 2017-05-14T20:40:00 | [
"树莓派",
"Web"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8508-1.html | 
个人 Web 服务器即 “云”,只不过是你拥有和控制它,而不是一个大型公司。
拥有一个自己的云有很多好处,包括可定制、免费存储、免费的互联网服务、通往开源软件之路、高安全性、完全控制您的内容、快速更改的能力、实验代码的地方等等。 这些好处大部分是无法估量的,但在财务上,这些好处可以为您每个月节省超过 100 美元。

我本可以选择 AWS ,但我更喜欢完全自由且安全性可控,并且我可以学一下这些东西是如何搭建的。
* 私有 Web 托管:而非 BlueHost 或 DreamHost
* 云存储:而非 Dropbox、Box、Google Drive、Microsoft Azure、iCloud 或是 AWS
* 自主部署安全
* HTTPS:Let’s Encrypt
* 分析: Google
* OpenVPN:不需要专有互联网连接(预计每个月花费 $7)
我所使用的物品清单:
* 树莓派 3 代 Model B
* MicroSD 卡(推荐使用 32 GB, [兼容树莓派的 SD 卡](http://elinux.org/RPi_SD_cards))
* USB microSD 卡读卡器
* 以太网络线
* 连接上 Wi-Fi 的路由器
* 树莓派盒子
* 亚马逊倍思的 MicroUSB 数据线
* 苹果的充电器
* USB 鼠标
* USB 键盘
* HDMI 线材
* 显示器 (支持接入 HDMI)
* MacBook Pro
### 步骤 1: 启动树莓派
下载最新发布的 Raspbian (树莓派的操作系统)。 [Raspbian Jessie](https://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads/raspbian/) 的 ZIP 包就可以用 [脚注 1]。解压缩或提取下载的文件然后把它拷贝到 SD 卡里。使用 [Pi Filler](http://ivanx.com/raspberrypi/) 可以让这些过程变得更简单。[下载 Pi Filer 1.3](http://ivanx.com/raspberrypi/files/PiFiller.zip) 或最新的版本。解压或提取下载文件之后打开它,你应该会看到这样的提示:

确保 USB 读卡器这时还没有插上。如果已经插上了那就先弹出。点 “Continue” 继续下一步。你会看到一个让你选择文件的界面,选择你之前解压缩后的树莓派系统文件。然后你会看到另一个提示,如图所示:

把 MicroSD 卡(推荐 32 GB ,至少 16GB)插入到 USB MicroSD 卡读卡器里。然后把 USB 读卡器接入到你的电脑里。你可以把你的 SD 卡重命名为 “Raspberry” 以区别其他设备。然后点击 “Continue”。请先确保你的 SD 卡是空的,因为 Pi Filler 会在运行时 *擦除* 所有事先存在 SD 卡里的内容。如果你要备份卡里的内容,那你最好就马上备份。当你点 “Continue” 的时候,Raspbian OS 就会被写入到 SD 卡里。这个过程大概会花费一到三分钟左右。当写入完成后,推出 USB 读卡器,把 SD 卡拔出来插入到树莓派的 SD 卡槽里。把电源线接上,给树莓派供电。这时树莓派就会自己启动。树莓派的默认登录账户信息是:
* 用户名: pi
* 密码:raspberry
当树莓派首次启动完成时,会跳出一个标题为 “<ruby> 设置选项 <rt> Setup Options </rt></ruby>” 的配置界面,就像下面的图片一样 [脚注 2]:

选择 “<ruby> 扩展文件系统 <rt> Expand Filesystem </rt></ruby>” 这一选项并回车 [脚注 3]。 同时,我还推荐选择第二个选项 “<ruby> 修改密码 <rt> Change User Password </rt></ruby>”。这对保证安全性来说尤为重要。它还能个性化你的树莓派。
在选项列表中选择第三项 “<ruby> 启用引导到桌面 <rt> Enable Boot To Desktop/Scratch </rt></ruby>” 并回车。这时会跳到另一个标题为 “<ruby> 选择引导选项 <rt> Choose boot option </rt></ruby>” 的界面,就像下面这张图这样:

在这个界面选择第二个选项 “<ruby> 以用户‘pi’登录图形化桌面 <rt> Desktop log in as user 'pi' at the graphical desktop </rt></ruby>” 并回车 [脚注 4]。完成这个操作之后会回到之前的 “<ruby> 设置选项 <rt> Setup Options </rt></ruby>” 界面。如果没有回到之前的界面的话就选择当前界面底部的 “OK” 按钮并回车。
当这些操作都完成之后,选择当前界面底部的 “Finish” 按钮并回车,这时它就会自动重启。如果没有自动重启的话,就在终端里使用如下命令来重启。
```
$ sudo reboot
```
接上一步的重启,如果所有步骤都顺利进行的话,你会进入到类似下面这样桌面环境中。

当你进入了桌面之后,在终端中执行如下命令来更新树莓派的固件。
```
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get upgrade-y
$ sudo apt-get dist-upgrade -y
$ sudo rpi-update
```
这些操作可能会花费几分钟时间。完成之后,现在运行着的树莓派就是最新的了。
### 步骤 2: 配置树莓派
SSH 指的是 Secure Shell,是一种加密网络协议,可让你在计算机和树莓派之间安全地传输数据。 你可以从 Mac 的命令行控制你的树莓派,而无需显示器或键盘。
要使用 SSH,首先需要你的树莓派的 IP 地址。 打开终端并输入:
```
$ sudo ifconfig
```
如果你在使用以太网,看 `eth0` 部分。如果你在使用 Wi-Fi, 看 `wlan0` 部分。
查找 `inet addr`,后跟一个 IP 地址,如 192.168.1.115,这是本篇文章中使用的默认 IP。
有了这个地址,在终端中输入 :
```
$ ssh [email protected]
```
对于 PC 上的 SSH,请参见 [脚注 5]。
出现提示时输入默认密码 `raspberry`,除非你之前更改过密码。
现在你已经通过 SSH 登录成功。
### 远程桌面
使用 GUI(图形用户界面)有时比命令行更容易。 在树莓派的命令行(使用 SSH)上键入:
```
$ sudo apt-get install xrdp
```
xrdp 支持 Mac 和 PC 的 Microsoft Remote Desktop 客户端。
在 Mac 上,在 App store 中搜索 “Microsoft Remote Desktop”。 下载它。 (对于 PC,请参见 [脚注 6]。)
安装完成之后,在你的 Mac 中搜索一个叫 “Microsoft Remote Desktop” 的应用并打开它,你会看到 :

点击 “New” 新建一个远程连接,在空白处填写如下配置。

关闭 “New” 窗口就会自动保存。
你现在应该看到 “My Desktop” 下列出的远程连接。 双击它。
简单加载后,你应该在屏幕上的窗口中看到你的树莓派桌面,如下所示:

好了,现在你不需要额外的鼠标、键盘或显示器就能控制你的树莓派。这是一个更为轻量级的配置。
### 静态化本地 IP 地址
有时候你的本地 IP 地址 192.168.1.115 会发生改变。我们需要让这个 IP 地址静态化。输入:
```
$ sudo ifconfig
```
从 `eth0` 部分或 `wlan0` 部分,记下 `inet addr`(树莓派当前 IP),`bcast`(广播 IP 范围)和 `mask`(子网掩码地址)。 然后输入:
```
$ netstat -nr
```
记下 `destination` 和 `gateway/network`。

大概应该是这样子的:
```
net address 192.168.1.115
bcast 192.168.1.255
mask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.1
network 192.168.1.1
destination 192.168.1.0
```
有了这些信息,你可以很简单地设置一个静态 IP。输入:
```
$ sudo nano /etc/dhcpcd.conf
```
不要去动 `/etc/network/interfaces`。
剩下要做的就是把这些内容追加到这个文件的底部,把 IP 换成你想要的 IP 地址。
```
interface eth0
static ip_address=192.168.1.115
static routers=192.168.1.1
static domain_name_servers=192.168.1.1
```
一旦你设置了静态内部 IP 地址,这时需要通过如下命令重启你的树莓派 :
```
$ sudo reboot
```
重启完成之后,在终端中输入 :
```
$ sudo ifconfig
```
这时你就可以看到你的树莓派上的新的静态配置了。
### 静态化全局 IP 地址
如果您的 ISP(互联网服务提供商)已经给您一个静态外部 IP 地址,您可以跳到端口转发部分。 如果没有,请继续阅读。
你已经设置了 SSH、远程桌面和静态内部 IP 地址,因此现在本地网络中的计算机将会知道在哪里可以找到你的树莓派。 但是你仍然无法在本地 Wi-Fi 网络外部访问你的树莓派。 你需要树莓派可以从互联网上的任何地方公开访问。这需要静态的外部 IP 地址 [脚注 7]。
联系您的 ISP 并请求静态的外部(有时称为静态全局)IP 地址可能会是一个非常敏感的过程。 ISP 拥有决策权,所以我会非常小心处理。 他们可能拒绝你的的静态外部 IP 地址请求。 如果他们拒绝了你的请求,你不要怪罪于他们,因为这种类型的请求有法律和操作风险。 他们特别不希望客户运行中型或大型互联网服务。 他们可能会明确地询问为什么需要一个静态的外部 IP 地址。 最好说实话,告诉他们你打算主办一个低流量的个人网站或类似的小型非营利互联网服务。 如果一切顺利,他们应该会建立一个工单,并在一两个星期内给你打电话。
### 端口转发
这个新获得的 ISP 分配的静态全局 IP 地址是用于访问路由器。 树莓派现在仍然无法访问。 你需要设置端口转发才能访问树莓派。
端口是信息在互联网上传播的虚拟途径。 你有时需要转发端口,以使计算机像树莓派一样可以访问 Internet,因为它位于网络路由器后面。 VollmilchTV 专栏在 YouTube 上的一个视频,名字是[什么是 TCP/IP,端口,路由,Intranet,防火墙,互联网](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iskxw6T1Wb8),可以帮助你更好地了解端口。
端口转发可用于像 树莓派 Web 服务器或 VoIP 或点对点下载的应用程序。 有 [65000个以上的端口](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_TCP_and_UDP_port_numbers)可供选择,因此你可以为你构建的每个 Internet 应用程序分配一个不同的端口。
设置端口转发的方式取决于你的路由器。 如果你有 Linksys 的话,Gabriel Ramirez 在 YouTbue 上有一个标题叫 [如何让你的 Apache Ubuntu 服务器连到互联网](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i1vB7JnPvuE#t=07m08s) 的视频解释了如何设置。 如果您没有 Linksys,请阅读路由器附带的文档,以便自定义和定义要转发的端口。
你需要转发 SSH 以及远程桌面端口。
如果你认为你已经过配置端口转发了,输入下面的命令以查看它是否正在通过 SSH 工作:
```
$ ssh pi@your_global_ip_address
```
它应该会提示你输入密码。
检查端口转发是否也适用于远程桌面。 打开 Microsoft Remote Desktop。 你之前的的远程连接设置应该已经保存了,但需要使用静态的外部 IP 地址(例如 195.198.227.116)来更新 “PC 名称” 字段,而不是静态的内部地址(例如 192.168.1.115)。
现在,尝试通过远程桌面连接。 它应该简单地加载并显示树莓派的桌面。

好了, 树莓派现在可以从互联网上访问了,并且已经准备好进行高级项目了。
作为一个奖励选项,您可以保持到您的 Pi 的两个远程连接。 一个通过互联网,另一个通过 LAN(局域网)。很容易设置。在 Microsoft Remote Desktop 中,保留一个称为 “Pi Internet” 的远程连接,另一个称为 “Pi Local”。 将 Pi Internet 的 “PC 名称” 配置为静态外部 IP 地址,例如 195.198.227.116。 将 Pi Local 的 “PC 名称” 配置为静态内部 IP 地址,例如 192.168.1.115。 现在,您可以选择在全局或本地连接。
如果你还没有看过由 Gabriel Ramirez 发布的 [如何让你的 Apache Ubuntu 服务器连到互联网](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i1vB7JnPvuE#t=07m08s),那么你可以去看一下,作为过渡到第二个项目的教程。 它将向您展示项目背后的技术架构。 在我们的例子中,你使用的是树莓派而不是 Ubuntu 服务器。 动态 DNS 位于域名公司和您的路由器之间,这是 Ramirez 省略的部分。 除了这个微妙之处外,视频是在整体上解释系统的工作原理。 您可能会注意到本教程涵盖了树莓派设置和端口转发,这是服务器端或后端。 查看原始来源,涵盖域名,动态 DNS,Jekyll(静态 HTML 生成器)和 Apache(网络托管)的更高级项目,这是客户端或前端。
### 脚注
[1] 我不建议从 NOOBS 操作系统开始。 我更喜欢从功能齐全的 Raspbian Jessie 操作系统开始。
[2] 如果没有弹出 “Setup Options”,可以通过打开终端并执行该命令来始终找到它:
```
$ sudo-rasps-config
```
[3] 我们这样做是为了将 SD 卡上存在的所有空间用作一个完整的分区。 所有这一切都是扩大操作系统以适应 SD 卡上的整个空间,然后可以将其用作树莓派的存储内存。
[4] 我们这样做是因为我们想启动进入熟悉的桌面环境。 如果我们不做这个步骤,树莓派每次会进入到终端而不是 GUI 中。
[5]

[下载并运行 PuTTY](http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/%7Esgtatham/putty/download.html) 或 Windows 的其它 SSH 客户端。 在该字段中输入你的 IP 地址,如上图所示。 将默认端口保留为 22。 回车,PuTTY 将打开一个终端窗口,提示你输入用户名和密码。 填写然后开始在树莓派上进行你的远程工作。
[6] 如果尚未安装,请下载 [Microsoft Remote Desktop](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/store/apps/microsoft-remote-desktop/9wzdncrfj3ps)。 搜索您的计算机上的的 Microsoft Remote Desktop。 运行。 提示时输入 IP 地址。 接下来,会弹出一个 xrdp 窗口,提示你输入用户名和密码。
[7] 路由器具有动态分配的外部 IP 地址,所以在理论上,它可以从互联网上暂时访问,但是您需要 ISP 的帮助才能使其永久访问。 如果不是这样,你需要在每次使用时重新配置远程连接。
*原文出自 [Mitchell McLaughlin's Full-Stack Computer Projects](https://mitchellmclaughlin.com/server.html)。*
---
作者简介:
Mitchell McLaughlin - 我是一名开放网络的贡献者和开发者。我感兴趣的领域很广泛,但我特别喜欢开源软件/硬件,比特币和编程。 我住在旧金山,我有过一些简短的 GoPro 和 Oracle 工作经验。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/3/building-personal-web-server-raspberry-pi-3>
作者:[Mitchell McLaughlin](https://opensource.com/users/mitchm) 译者:[chenxinlong](https://github.com/chenxinlong) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | A personal web server is "the cloud," except you own and control it as opposed to a large corporation.
Owning a little cloud has a lot of benefits, including customization, free storage, free Internet services, a path into open source software, high-quality security, full control over your content, the ability to make quick changes, a place to experiment with code, and much more. Most of these benefits are immeasurable, but financially these benefits can save you over $100 per month.
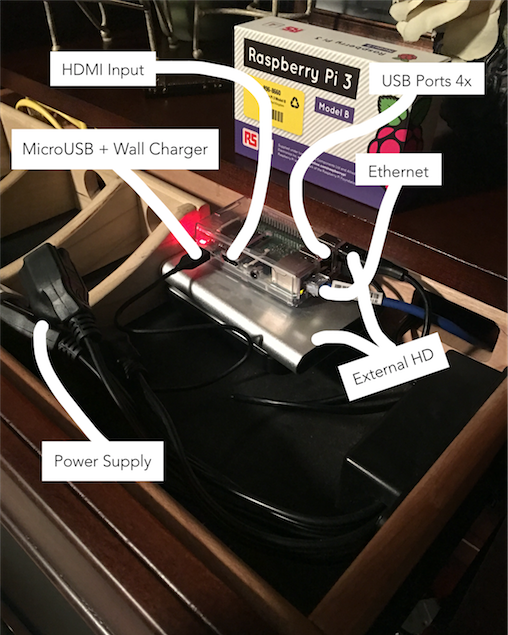

Raspberry Pi as a web server, by Raspberry Pi Guy, CC-BY-SA 4.0
I could have used AWS, but I prefer complete freedom, full control over security, and learning how things are built.
- Self web-hosting: No BlueHost or DreamHost
- Cloud storage: No Dropbox, Box, Google Drive, Microsoft Azure, iCloud, or AWS
- On-premise security
- HTTPS: Let’s Encrypt
- Analytics: Google
- OpenVPN: Do not need private Internet access (at an estimated $7 per month)
Things I used:
- Raspberry Pi 3 Model B
- MicroSD Card (32GB recommended,
[Raspberry Pi Compatible SD Cards](http://elinux.org/RPi_SD_cards)) - USB microSD card reader
- Ethernet cable
- Router connected to Wi-Fi
- Raspberry Pi case
- Amazon Basics MicroUSB cable
- Apple wall charger
- USB mouse
- USB keyboard
- HDMI cable
- Monitor (with HDMI input)
- MacBook Pro
## Step 1: Setting up the Raspberry Pi
Download the most recent release of Raspbian (the Raspberry Pi operating system). [Raspbian Jessie](https://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads/raspbian/) ZIP version is ideal [1]. Unzip or extract the downloaded file. Copy it onto the SD card. [Pi Filler](http://ivanx.com/raspberrypi/) makes this process easy. [Download Pi Filer 1.3](http://ivanx.com/raspberrypi/files/PiFiller.zip) or the most recent version. Unzip or extract the downloaded file and open it. You should be greeted with this prompt:
Make sure the USB card reader has NOT been inserted yet. If it has, eject it. Proceed by clicking Continue. A file explorer should appear. Locate the uncompressed Raspberry Pi OS file from your Mac or PC and select it. You should see another prompt like the one pictured below:
Insert the MicroSD card (32GB recommended, 16GB minimum) into the USB MicroSD Card Reader. Then insert the USB reader into the Mac or PC. You can rename the SD card to "Raspberry" to distinguish it from others. Click Continue. Make sure the SD card is empty. Pi Filler will *erase* all previous storage at runtime. If you need to back up the card, do so now. When you are ready to continue, the Raspbian OS will be written to the SD card. It should take between one to three minutes. Once the write is completed, eject the USB reader, remove the SD card, and insert it into the Raspberry Pi SD card slot. Give the Raspberry Pi power by plugging the power cord into the wall. It should start booting up. The Raspberry Pi default login is:
**username: pi
password: raspberry**
When the Raspberry Pi has completed booting for the first time, a configuration screen titled "Setup Options" should appear like the image below [2]:
Select the "Expand Filesystem" option and hit the Enter key [3]. Also, I recommend selecting the second option, "Change User Password." It is important for security. It also personalizes your Raspberry Pi.
(Note: For an extra layer of security install fail2ban. Fail2Ban blocks suspicious requests coming from the internet. For example, if there are too many attempts to guess the password, it will block that IP address. It can be installed by typing into terminal: **$ ****sudo**** apt-get install fail2ban**)
Select the third option in the setup options list, "Enable Boot To Desktop/Scratch" and hit the Enter key. It will take you to another window titled "Choose boot option" as shown in the image below.
In the "Choose boot option" window, select the second option, "Desktop log in as user 'pi' at the graphical desktop" and hit the Enter button [4]. Once this is done you will be taken back to the "Setup Options" page. If not, select the "OK" button at the bottom of this window and you will be taken back to the previous window.
Once both these steps are done, select the "Finish" button at the bottom of the page and it should reboot automatically. If it does not, then use the following command in the terminal to reboot.
**$ sudo reboot**
After the reboot from the previous step, if everything went well, you will end up on the desktop similar to the image below.
Once you are on the desktop, open a terminal and enter the following commands to update the firmware of the Raspberry Pi.
```
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get upgrade -y
$ sudo apt-get dist-upgrade -y
$ sudo rpi-update
```
This may take a few minutes. Now the Raspberry Pi is up-to-date and running.
## Step 2: Configuring the Raspberry Pi
SSH, which stands for Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol that lets you securely transfer data between your computer and your Raspberry Pi. You can control your Raspberry Pi from your Mac's command line without a monitor or keyboard.
To use SSH, first, you need your Pi's IP address. Open the terminal and type:
`$ sudo ifconfig`
If you are using Ethernet, look at the "eth0" section. If you are using Wi-Fi, look at the "wlan0" section.
Find "inet addr" followed by an IP address—something like 192.168.1.115, a common default IP I will use for the duration of this article.
With this address, open terminal and type:
`$ ssh [email protected]`
For SSH on PC, see footnote [5].
Enter the default password "raspberry" when prompted, unless you changed it.
You are now logged in via SSH.
### Remote desktop
Using a GUI (graphical user interface) is sometimes easier than a command line. On the Raspberry Pi's command line (using SSH) type:
`$ sudo apt-get install xrdp`
Xrdp supports the Microsoft Remote Desktop Client for Mac and PC.
On Mac, navigate to the app store and search for "Microsoft Remote Desktop." Download it. (For a PC, see footnote [6].)
After installation, search your Mac for a program called "Microsoft Remote Desktop." Open it. You should see this:
Image by Raspberry Pi Guy, CC BY-SA 4.0
Click "New" to set up a remote connection. Fill in the blanks as shown below.
Image by Raspberry Pi Guy, CC BY-SA 4.0
Save it by exiting out of the "New" window.
You should now see the remote connection listed under "My Desktops." Double click it.
After briefly loading, you should see your Raspberry Pi desktop in a window on your screen, which looks like this:
Perfect. Now, you don't need a separate mouse, keyboard, or monitor to control the Pi. This is a much more lightweight setup.
### Static local IP address
Sometimes the local IP address 192.168.1.115 will change. We need to make it static. Type:
`$ sudo ifconfig`
Write down from the "eth0" section or the "wlan0" section, the "inet addr" (Pi's current IP), the "bcast" (the broadcast IP range), and the "mask" (subnet mask address). Then, type:
`$ netstat -nr`
Write down the "destination" and the "gateway/network."
The cumulative records should look something like this:
```
net address 192.168.1.115
bcast 192.168.1.255
mask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.1
network 192.168.1.1
destination 192.168.1.0
```
With this information, you can set a static internal IP easily. Type:
`$ sudo nano /etc/dhcpcd.conf`
Do not use **/etc/network/interfaces**.
Then all you need to do is append this to the bottom of the file, substituting the correct IP address you want.
```
interface eth0
static ip_address=192.168.1.115
static routers=192.168.1.1
static domain_name_servers=192.168.1.1
```
Once you have set the static internal IP address, reboot the Raspberry Pi with:
`$ sudo reboot`
After rebooting, from terminal type:
`$ sudo ifconfig`
Your new static settings should appear for your Raspberry Pi.
### Static global IP address
If your ISP (internet service provider) has already given you a static external IP address, you can skip ahead to the port forwarding section. If not, continue reading.
You have set up SSH, a remote desktop, and a static internal IP address, so now computers inside the local network will know where to find the Pi. But you still can't access your Raspberry Pi from outside the local Wi-Fi network. You need your Raspberry Pi to be accessible publicly from anywhere on the Internet. This requires a static external IP address [7].
It can be a sensitive process initially. Call your ISP and request a static external (sometimes referred to as static global) IP address. The ISP holds the decision-making power, so I would be extremely careful dealing with them. They may refuse your static external IP address request. If they do, you can't fault the ISP because there is a legal and operational risk with this type of request. They particularly do not want customers running medium- or large-scale Internet services. They might explicitly ask why you need a static external IP address. It is probably best to be honest and tell them you plan on hosting a low-traffic personal website or a similar small not-for-profit internet service. If all goes well, they should open a ticket and call you in a week or two with an address.
### Port forwarding
This newly obtained static global IP address your ISP assigned is for accessing the router. The Raspberry Pi is still unreachable. You need to set up port forwarding to access the Raspberry Pi specifically.
Ports are virtual pathways where information travels on the Internet. You sometimes need to forward a port in order to make a computer, like the Raspberry Pi, accessible to the Internet because it is behind a network router. A YouTube video titled [What is TCP/IP, port, routing, intranet, firewall, Internet](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iskxw6T1Wb8) by VollmilchTV helped me visually understand ports.
Port forwarding can be used for projects like a Raspberry Pi web server, or applications like VoIP or peer-to-peer downloading. There are [65,000+ ports](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_TCP_and_UDP_port_numbers) to choose from, so you can assign a different port for every Internet application you build.
The way to set up port forwarding can depend on your router. If you have a Linksys, a YouTube video titled * How to go online with your Apache Ubuntu server* by Gabriel Ramirez explains how to set it up. If you don't have a Linksys, read the documentation that comes with your router in order to customize and define ports to forward.
You will need to port forward for SSH as well as the remote desktop.
Once you believe you have port forwarding configured, check to see if it is working via SSH by typing:
`$ ssh pi@your_global_ip_address`
It should prompt you for the password.
Check to see if port forwarding is working for the remote desktop as well. Open Microsoft Remote Desktop. Your previous remote connection settings should be saved, but you need to update the "PC name" field with the static external IP address (for example, 195.198.227.116) instead of the static internal address (for example, 192.168.1.115).
Now, try connecting via remote desktop. It should briefly load and arrive at the Pi's desktop.
Good job. The Raspberry Pi is now accessible from the Internet and ready for advanced projects.
As a bonus option, you can maintain two remote connections to your Pi. One via the Internet and the other via the LAN (local area network). It's easy to set up. In Microsoft Remote Desktop, keep one remote connection called "Pi Internet" and another called "Pi Local." Configure Pi Internet's "PC name" to the static external IP address—for example, 195.198.227.116. Configure Pi Local's "PC name" to the static internal IP address—for example, 192.168.1.115. Now, you have the option to connect globally or locally.
If you have not seen it already, watch * How to go online with your Apache Ubuntu server* by Gabriel Ramirez as a transition into Project 2. It will show you the technical architecture behind your project. In our case, you are using a Raspberry Pi instead of an Ubuntu server. The dynamic DNS sits between the domain company and your router, which Ramirez omits. Beside this subtlety, the video is spot on when explaining visually how the system works. You might notice this tutorial covers the Raspberry Pi setup and port forwarding, which is the server-side or back end. See the original source for more advanced projects covering the domain name, dynamic DNS, Jekyll (static HTML generator), and Apache (web hosting), which is the client-side or front end.
### Footnotes
[1] I do not recommend starting with the NOOBS operating system. I prefer starting with the fully functional Raspbian Jessie operating system.
[2] If "Setup Options" does not pop up, you can always find it by opening Terminal and executing this command:
`$ sudo-raspi-config`
[3] We do this to make use of all the space present on the SD card as a full partition. All this does is expand the operating system to fit the entire space on the SD card, which can then be used as storage memory for the Raspberry Pi.
[4] We do this because we want to boot into a familiar desktop environment. If we do not do this step, the Raspberry Pi boots into a terminal each time with no GUI.
[5]
[Download and run PuTTY](http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html) or another SSH client for Windows. Enter your IP address in the field, as shown in the above screenshot. Keep the default port at 22. Hit Enter, and PuTTY will open a terminal window, which will prompt you for your username and password. Fill those in, and begin working remotely on your Pi.
[6] If it is not already installed, download [Microsoft Remote Desktop](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/store/apps/microsoft-remote-desktop/9wzdncrfj3ps). Search your computer for Microsoft Remote Desktop. Run it. Input the IP address when prompted. Next, an xrdp window will pop up, prompting you for your username and password.
[7] The router has a dynamically assigned external IP address, so in theory, it can be reached from the Internet momentarily, but you'll need the help of your ISP to make it permanently accessible. If this was not the case, you would need to reconfigure the remote connection on each use.
*For the original source, visit Mitchell McLaughlin's Full-Stack Computer Projects.*
## 22 Comments |
8,509 | CentOS 上最佳的第三方仓库 | https://www.linux.com/learn/intro-to-linux/2017/2/best-third-party-repositories-centos | 2017-05-15T17:04:00 | [
"RHEL",
"EPEL",
"CentOS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8509-1.html | 
>
> 从 Software Collections、EPEL 和 Remi 获得可靠的 CentOS 新版软件。
>
>
>
在 Red Hat 企业 Linux(RHEL) 上,提供那些早已老掉牙的软件已经是企业级软件厂商的传统了。这倒不是因为他们懒,而确实是用户需要。很多公司像看待家具一样看待软件:我买一张桌子,能用一辈子,软件不应该也这样吗?
CentOS 作为 RHEL 的复制品有着同样的遭遇。虽然 Red Hat 还在为这些被厂商抛弃的过时软件提供支持、修补安全漏洞等,但如果你的应用依赖新版软件,你就得想办法了。 我在这个问题上不止一次碰壁。 LAMP 组合里任一个组件都需要其它所有组件能与其兼容,这有时就显得很麻烦。 比如说去年我就被 RHEL/CentOS 折腾得够呛。REHL/CentOS 第 6 版最高支持 PHP 5.3 ,第 7 版支持到 PHP 5.4 。而 PHP 5.3 早在 2014 年 8 月就到达 EOL(End Of Life) ,不再被厂商支持了, PHP 5.4 的 EOL 在 2015 年 9 月, 5.5 则是 2016 年 7 月。 有太多古老的软件版本,包括 MySQL、Python 等,它们应该像木乃伊一样被展示在博物馆里,但它们却活在你的系统上。
那么,可怜的管理员们该怎么办呢?如果你跑着 RHEL/CentOS ,那应该先试试 [Software Collections](https://www.softwarecollections.org/en/),因为这是 Red Hat 唯一支持的新软件包源。 [Software Collections](https://www.softwarecollections.org/en/) 为 CentOS 设立了专门的仓库,安装和管理都和其它第三方仓库一样。但如果你用的是 RHEL 的,情况就有点不同了,具体请参考 [RHEL 的解决方法](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/472793)。[Software Collections](https://www.softwarecollections.org/en/) 同样支持 Fedora 和 Scientific Linux 。
### 安装 Software Collections
在 CentOS 6/7 上安装 Software Collections 的命令如下:
```
$ sudo yum install centos-release-scl
```
`centos-release-scl-rh` 可能作为依赖包被同时安装。
然后就可以像平常一样搜索、安装软件包了:
```
$ yum search php7
[...]
rh-php70.x86_64 : Package that installs PHP 7.0
[...]
$ sudo yum install rh-php70
```
最后一件事就是启用你的新软件包:
```
$ scl enable rh-php70 bash
$ php -v
PHP 7.0.10
```
此命令会开启一个新的 bash 并配置好环境变量以便运行新软件包。 如果需要的话,你还得安装对应的扩展包,比如对于 Python 、PHP、MySQL 等软件包,有些配置文件也需要修改以指向新版软件(比如 Apache )。
这些 SCL 软件包在重启后不会激活。SCL 的设计初衷就是在不影响原有配置的前提下,让新旧软件能一起运行。不过你可以通过 `~/.bashrc` 加载 SCL 提供的 `enable` 脚本来实现自动启用。 SCL 的所有软件包都安装在 `/opt` 下, 以我们的 PHP 7 为例,在 `~/.bashrc` 里加入一行:
```
source /opt/rh/rh-php70/enable
```
以后相应的软件包就能在重启后自动启用了。有新软件保驾护航,你终于可以专注于自己的业务了。
### 列出可用软件包
那么,到底 Software Collections 里都是些什么呢? centos-release-scl 里有一些由社区维护的额外的软件包。除了在 [CentOS Wiki](https://wiki.centos.org/SpecialInterestGroup/SCLo/CollectionsList) 查看软件包列表外,你还可以使用 Yum 。我们先来看看安装了哪些仓库:
```
$ yum repolist
[...]
repo id repo name
base/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Base
centos-sclo-rh/x86_64 CentOS-7 - SCLo rh
centos-sclo-sclo/x86_64 CentOS-7 - SCLo sclo
extras/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Extras
updates/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Updates
```
Yum 没有专门用来打印某一个仓库中所有软件包的命令,所以你得这样来: (LCTT 译注:实际上有,`yum repo-pkgs REPO list`,需要 root 权限,dnf 同)
```
$ yum --disablerepo "*" --enablerepo centos-sclo-rh \
list available | less
```
`--disablerepo` 与 `--enablerepo` 选项的用法没有详细的文档,这里简单说下。 实际上在这个命令里你并没有禁用或启用什么东西,而只是将你的搜索范围限制在某一个仓库内。 此命令会打印出一个很长的列表,所以我们用管道传递给 `less` 输出。
### EPEL
强大的 Fedora 社区为 Feora 及所有 RHEL 系的发行版维护着 [EPEL:Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/EPEL) 。 里面包含一些最新软件包以及一些未被发行版收纳的软件包。安装 EPEL 里的软件就不用麻烦 `enable` 脚本了,直接像平常一样用。你还可以用 `--disablerepo` 和 `--enablerepo` 选项指定从 EPEL 里安装软件包:
```
$ sudo yum --disablerepo "*" --enablerepo epel install [package]
```
### Remi Collet
Remi Collet 在 [Remi 的 RPM 仓库](http://rpms.remirepo.net/) 里维护着大量更新的和额外的软件包。需要先安装 EPEL ,因为 Remi 仓库依赖它。
CentOS wiki 上有较完整的仓库列表:[更多的第三方仓库](https://wiki.centos.org/AdditionalResources/Repositories) ,用哪些,不用哪些,里面都有建议。
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/learn/intro-to-linux/2017/2/best-third-party-repositories-centos>
作者:[CARLA SCHRODER](https://www.linux.com/users/cschroder) 译者:[Dotcra](https://github.com/Dotcra) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,510 | 如何在 Vim 中使用模式行进行文件特定的设置 | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/vim-modeline-settings/ | 2017-05-15T18:10:54 | [
"vim",
"模式行"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8510-1.html | 
虽然[插件](/article-7901-1.html)毫无疑问是 Vim 最大的优势,然而,还有其它一些功能,使得它成为当今 Linux 用户中最强大、功能最丰富的文本编辑器/IDE 之一。其中一个功能就是可以根据文件做特定的设置。我们可以使用该编辑器的<ruby> 模式行 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Modeline </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>特性来实现该功能。
在这篇文章中,我将讨论如何使用 Vim 的<ruby> <a href="http://vim.wikia.com/wiki/Modeline_magic"> 模式行 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Modeline </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>特性来简单的理解一些例子。
在开始之前,值得提醒一下,这篇教程中提及的所有例子、命令和指令都已经在 Ubuntu 16.04 中使用 Vim 7.4 版本测试过。
### VIM 模式行
#### 用法
正如上面已经提到的, Vim 的模式行特性让你能够进行特定于文件的更改。比如,假设你想把项目中的一个特定文件中的所有制表符用空格替换,并且确保这个更改不会影响到其它所有文件。这是模式行帮助你完成你想做的事情的一个理想情况。
因此,你可以考虑将下面这一行加入文件的开头或结尾来完成这件事。
```
# vim: set expandtab:
```
(LCTT 译注:模式行就是一行以注释符,如 `#`、`//`、`/*` 开头,间隔一个空格,以 `vim:` 关键字触发的设置命令。可参看:<http://vim.wikia.com/wiki/Modeline_magic> )
如果你是在 Linux 系统上尝试上面的练习来测试用例,很有可能它将不会像你所期望的那样工作。如果是这样,也不必担心,因为某些情况下,模式行特性需要先激活才能起作用(出于安全原因,在一些系统比如 Debian、Ubuntu、GGentoo 和 OSX 上默认情况下禁用)。
为了启用该特性,打开 `.vimrc` 文件(位于 `home` 目录),然后加入下面一行内容:
```
set modeline
```
现在,无论何时你在该文件输入一个制表符然后保存时(文件中已输入 `expandtab` 模式行命令的前提下),都会被自动转换为空格。
让我们考虑另一个用例。假设在 Vim 中, 制表符默认设置为 4 个空格,但对于某个特殊的文件,你想把它增加到 8 个。对于这种情况,你需要在文件的开头或末尾加上下面这行内容:
```
// vim: noai:ts=8:
```
现在,输入一个制表符,你会看到,空格的数量为 8 个。
你可能已经注意到我刚才说的,这些模式行命令需要加在靠近文件的顶部或底部。如果你好奇为什么是这样,那么理由是该特性以这种方式设计的。下面这一行(来自 Vim 官方文件)将会解释清楚:
>
> “模式行不能随意放在文件中的任何位置:它需要放在文件中的前几行或最后几行。`modelines` 变量控制 Vim 检查模式行在文件中的确切位置。请查看 `:help modelines` 。默认情况下,设置为 5 行。”
>
>
>
下面是 `:help modelines` 命令(上面提到的)输出的内容:
>
> 如果 `modeline` 已启用并且 `modelines` 给出了行数,那么便在相应位置查找 `set` 命令。如果 `modeline` 禁用或 `modelines` 设置的行数为 0 则不查找。
>
>
>
尝试把模式行命令置于超出 5 行的范围(距离文件底部和顶部的距离均超过 5 行),你会发现, 制表符将会恢复为 Vim 默认数目的空格 — 在我的情况里是 4 个空格。
然而,你可以按照自己的意愿改变默认行数,只需在你的 `.vimrc` 文件中加入下面一行命令
```
set modelines=[新值]
```
比如,我把值从 5 增加到了 10 。
```
set modelines=10
```
这意味着,现在我可以把模式行命令置于文件前 10 行或最后 10 行的任意位置。
继续,无论何时,当你在编辑一个文件的时候,你可以输入下面的命令(在 Vim 编辑器的命令模式下输入)来查看当前与命令行相关的设置以及它们最新的设置。
```
:verbose set modeline? modelines?
```
比如,在我的例子中,上面的命令产生了如下所示的输出:
```
modeline
Last set from ~/.vimrc
modelines=10
Last set from ~/.vimrc
```
关于 Vim 的模式行特性,你还需要知道一些重要的点:
* 默认情况下,当 Vim 以非兼容(`nocompatible`)模式运行时该特性是启用的,但需要注意的是,在一些发行版中,出于安全考虑,系统的 `vimrc` 文件禁用了该选项。
* 默认情况下,当以 root 权限编辑文件时,该特性被禁用(如果你是使用 `sudo` 方式打开该文件,那么该特性依旧能够正常工作)。
* 通过 `set` 来设置模式行,其结束于第一个冒号,而非反斜杠。不使用 `set`,则后面的文本都是选项。比如,`/* vim: noai:ts=4:sw=4 */` 是一个无效的模式行。
(LCTT 译注:关于模式行中的 `set`,上述描述指的是:如果用 `set` 来设置,那么当发现第一个 `:` 时,表明选项结束,后面的 `*/` 之类的为了闭合注释而出现的文本均无关;而如果不用 `set` 来设置,那么以 `vim:` 起头的该行所有内容均视作选项。 )
#### 安全考虑
令人沮丧的是, Vim 的模式行特性可能会造成安全性问题。事实上,在过去,已经报道过多个和模式行相关的问题,包括 [shell 命令注入](https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/viewAlert.x?alertId=13223),[任意命令执行](http://usevim.com/2012/03/28/modelines/)和[无授权访问](https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/viewAlert.x?alertId=5169)等。我知道,这些问题发生在很早的一些时候,现在应该已经修复好了,但是,这提醒了我们,模式行特性有可能会被黑客滥用。
### 结论
模式行可能是 Vim 编辑器的一个高级命令,但是它并不难理解。毫无疑问,它的学习曲线会有一些复杂,但是不需多问也知道,该特性是多么的有用。当然,出于安全考虑,在启用并使用该选项前,你需要对自己的选择进行权衡。
你有使用过模式行特性吗?你的体验是什么样的?记得在下面的评论中分享给我们。
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/vim-modeline-settings/>
作者:[Ansh](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/vim-modeline-settings/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # How to make file-specific setting changes in Vim using Modeline
### On this page
While [plugins](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/vim-editor-plugins-for-software-developers-3/) are no doubt one of Vim's biggest strengths, several other functionalities make it one of the most powerful and feature-rich text editors/IDEs available to Linux users today. One of these functionalities is the ability to make file-specific setting changes. This ability can be accessed using the editor's Modeline feature.
In this article, we will discuss how you can use Vim's [Modeline](http://vim.wikia.com/wiki/Modeline_magic) feature using easy to understand examples.
*But before we start doing that, it's worth mentioning that all the examples, commands, and instructions mentioned in this tutorial have been tested on Ubuntu 16.04 - Ubuntu 22.04.*
## VIM Modeline
### Usage
As we've already mentioned, Vim's Modeline feature lets you make file-specific changes. For example, suppose you want to replace all the tabs used in a particular file of your project with spaces, and make sure that all other files aren't affected by this change. This is an ideal use-case where Modeline helps you in what you want to do.
So, what you can do is, you can put the following line in the beginning or end of the file in question:
# vim: set expandtab:
There are high chances that if you try doing the aforementioned exercise to test the use-case on your Linux machine, things won't work as expected. If that's the case, worry not, as the Modeline feature needs to be activated first in some cases (it's disabled by default on systems such as Debian, Ubuntu, Gentoo, and OSX for security reasons).
To enable the feature, open the .vimrc file (located in your home directory), and then add the following line to it:
set modeline
Now, whenever you enter a tab and save the file (where the *expandtab* modeline command was entered), the tab will automatically convert into white spaces.
Let's consider another use-case. Suppose the default tab space in Vim is set to 4, but for a particular file, you want to increase it to 8. For this, you need to add the following line in the beginning or the end of the file:
// vim: noai:ts=8:
Now try entering a tab and you'll see that the number of spaces it covers will be 8.
You might have noticed me saying that these modeline commands need to be entered somewhere near the top or the bottom of the file. If you're wondering why this is so, the reason is that the feature is designed this way. The following lines (taken from the official Vim documentation) should make this more clear:
"*The modeline cannot be anywhere in the file: it must be in the first or last few lines. The exact location where vim checks for the modeline is controlled by the modelines variable; see :help modelines*
*. By default, it is set to 5 lines*."
And here's what the *:help modelines* command (referred to in the above lines) says:
`If 'modeline' is on 'modelines' gives the number of lines that is checked for set commands. If 'modeline' is off or 'modelines' is zero no lines are checked.`
Try and put the modeline command beyond the default 5 lines (either from the bottom or from the top) range, and you'll notice that tab spaces will revert to the Vim default - in my case that's 4 spaces.
However, you can change this behavior if you want, using the following command in your .vimrc file.
set modelines=[new-value]
For example, I increased the value from 5 to 10.
set modelines=10
This means that now I can put the modeline command anywhere between first or last 10 lines of the file.
Moving on, at any point in time, while editing a file, you can enter the following (with the Vim editor in the command mode) to see the current modeline-related settings as well as where they were last set.
`:verbose set modeline? modelines?`
For example, in my case, the above command produced the following output:
modeline
Last set from ~/.vimrc
modelines=10
Last set from ~/.vimrc
Here are some of the important points you need to know about Vim's Modeline feature:
- This feature is enabled by default for Vim running in nocompatible (non Vi-compatible) mode, but some notable distributions of Vim disable this option in the system vimrc for security.
- The feature is disabled by default when editing as root (if you've opened the file using 'sudo' then there's no issue - the feature works).
- With '
`set'`
, the modeline ends at the first colon not following a backslash. And without '`set'`
, no text can follow the options. For example,is an invalid modeline.**/* vim: noai:ts=4:sw=4 */**
### Security Concerns
Sadly, Vim's Modeline feature can be used to compromise security. In fact, multiple security-related Modeline issues have been reported in the past, including [shell command injection](https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/viewAlert.x?alertId=13223), [arbitrary commands execution](http://usevim.com/2012/03/28/modelines/), [unauthorized access](https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/viewAlert.x?alertId=5169), and more. Agreed, most of these are old, and would have been fixed by now, but it does give an idea that the Modeline feature could be misused by hackers.
## Conclusion
Modeline may be an advanced feature of the Vim editor, but it's not very difficult to understand. There's no doubt that a bit of learning curve involved, but that's not much to ask for given how useful the feature is. Of course, there are security concerns, which means that you should weigh your options before enabling and using the feature.
Have you ever used the Modeline feature? How was your experience? Share with us (and the whole HowtoForge community) in the comments below. |
8,512 | 在 Ubuntu 16.04 中安装支持 CPU 和 GPU 的 Google TensorFlow 神经网络软件 | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/installing-tensorflow-neural-network-software-for-cpu-and-gpu-on-ubuntu-16-04/ | 2017-05-16T09:21:39 | [
"TensorFlow",
"神经网络"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8512-1.html | 
TensorFlow 是用于机器学习任务的开源软件。它的创建者 Google 希望提供一个强大的工具以帮助开发者探索和建立基于机器学习的应用,所以他们在去年作为开源项目发布了它。TensorFlow 是一个非常强大的工具,专注于一种称为<ruby> 深层神经网络 <rt> deep neural network </rt></ruby>(DNN)的神经网络。
深层神经网络被用来执行复杂的机器学习任务,例如图像识别、手写识别、自然语言处理、聊天机器人等等。这些神经网络被训练学习其所要执行的任务。由于训练所需的计算是非常巨大的,在大多数情况下需要 GPU 支持,这时 TensorFlow 就派上用场了。启用了 GPU 并安装了支持 GPU 的软件,那么训练所需的时间就可以大大减少。
本教程可以帮助你安装只支持 CPU 的和同时支持 GPU 的 TensorFlow。要使用带有 GPU 支持的 TensorFLow,你必须要有一块支持 CUDA 的 Nvidia GPU。CUDA 和 CuDNN(Nvidia 的计算库)的安装有点棘手,本指南会提供在实际安装 TensorFlow 之前一步步安装它们的方法。
Nvidia CUDA 是一个 GPU 加速库,它已经为标准神经网络中用到的标准例程调优过。CuDNN 是一个用于 GPU 的调优库,它负责 GPU 性能的自动调整。TensorFlow 同时依赖这两者用于训练并运行深层神经网络,因此它们必须在 TensorFlow 之前安装。
需要指出的是,那些不希望安装支持 GPU 的 TensorFlow 的人,你可以跳过以下所有的步骤并直接跳到:“步骤 5:安装只支持 CPU 的 TensorFlow”。
关于 TensorFlow 的介绍可以在[这里](http://sourcedexter.com/what-is-tensorflow/)找到。
### 1、 安装 CUDA
首先,在[这里](https://developer.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/8.0/Prod2/local_installers/cuda-repo-ubuntu1604-8-0-local-ga2_8.0.61-1_amd64-deb)下载用于 Ubuntu 16.04 的 CUDA 库。此文件非常大(2GB),因此也许会花费一些时间下载。
下载的文件是 “.deb” 包。要安装它,运行下面的命令:
```
sudo dpkg -i cuda-repo-ubuntu1604-8-0-local_8.0.44-1_amd64.deb
```

下面的的命令会安装所有的依赖,并最后安装 cuda 工具包:
```
sudo apt install -f
sudo apt update
sudo apt install cuda
```
如果成功安装,你会看到一条消息说:“successfully installed”。如果已经安装了,接着你可以看到类似下面的输出:

### 2、安装 CuDNN 库
CuDNN 下载需要花费一些功夫。Nvidia 没有直接提供下载文件(虽然它是免费的)。通过下面的步骤获取 CuDNN。
1. 点击[此处](https://developer.nvidia.com/group/node/873374/subscribe/og_user_node)进入 Nvidia 的注册页面并创建一个帐户。第一页要求你输入你的个人资料,第二页会要求你回答几个调查问题。如果你不知道所有答案也没问题,你可以随便选择一个选项。
2. 通过前面的步骤,Nvidia 会向你的邮箱发送一个激活链接。在你激活之后,直接进入[这里](https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/form/cudnn-download-survey)的 CuDNN 下载链接。
3. 登录之后,你需要填写另外一份类似的调查。随机勾选复选框,然后点击调查底部的 “proceed to Download”,在下一页我们点击同意使用条款。
4. 最后,在下拉中点击 “Download cuDNN v5.1 (Jan 20, 2017), for CUDA 8.0”,最后,你需要下载这两个文件:
* [cuDNN v5.1 Runtime Library for Ubuntu14.04 (Deb)](https://developer.nvidia.com/compute/machine-learning/cudnn/secure/v5.1/prod_20161129/8.0/libcudnn5_5.1.10-1+cuda8.0_amd64-deb)
* [cuDNN v5.1 Developer Library for Ubuntu14.04 (Deb)](https://developer.nvidia.com/compute/machine-learning/cudnn/secure/v5.1/prod_20161129/8.0/libcudnn5-dev_5.1.10-1+cuda8.0_amd64-deb)
注意:即使上面说的是用于 Ubuntu 14.04 的库。它也适用于 16.04。
现在你已经同时有 CuDNN 的两个文件了,是时候安装它们了!在包含这些文件的文件夹内运行下面的命令:
```
sudo dpkg -i libcudnn5_5.1.5-1+cuda8.0_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i libcudnn5-dev_5.1.5-1+cuda8.0_amd64.deb
```
下面的图片展示了这些命令的输出:

### 3、 在 bashrc 中添加安装位置
安装位置应该被添加到 bashrc 文件中,以便系统下一次知道如何找到这些用于 CUDA 的文件。使用下面的命令打开 bashrc 文件:
```
sudo gedit ~/.bashrc
```
文件打开后,添加下面两行到文件的末尾:
```
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/cuda/lib64:/usr/local/cuda/extras/CUPTI/lib64"
export CUDA_HOME=/usr/local/cuda
```
### 4、 安装带有 GPU 支持的 TensorFlow
这步我们将安装带有 GPU 支持的 TensorFlow。如果你使用的是 Python 2.7,运行下面的命令:
```
pip install TensorFlow-gpu
```
如果安装了 Python 3.x,使用下面的命令:
```
pip3 install TensorFlow-gpu
```
安装完后,你会看到一条 “successfully installed” 的消息。现在,剩下要测试的是是否已经正确安装。打开终端并输入下面的命令测试:
```
python
import TensorFlow as tf
```
你应该会看到类似下面图片的输出。在图片中你可以观察到 CUDA 库已经成功打开了。如果有任何错误,消息会提示说无法打开 CUDA 甚至无法找到模块。为防你或许遗漏了上面的某步,仔细重做教程的每一步就行了。

### 5、 安装只支持 CPU 的 TensorFlow
注意:这步是对那些没有 GPU 或者没有 Nvidia GPU 的人而言的。其他人请忽略这步!!
安装只支持 CPU 的 TensorFlow 非常简单。使用下面两个命令:
```
pip install TensorFlow
```
如果你有 python 3.x,使用下面的命令:
```
pip3 install TensorFlow
```
是的,就是这么简单!
安装指南至此结束,你现在可以开始构建深度学习应用了。如果你刚刚起步,你可以在[这里](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/mnist/beginners)看下适合初学者的官方教程。如果你正在寻找更多的高级教程,你可以在[这里](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/image_recognition)学习了解如何设置可以高精度识别上千个物体的图片识别系统/工具。
(题图:Pixabay,CC0)
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/installing-tensorflow-neural-network-software-for-cpu-and-gpu-on-ubuntu-16-04/>
作者:[Akshay Pai](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/installing-tensorflow-neural-network-software-for-cpu-and-gpu-on-ubuntu-16-04/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # Installing Google TensorFlow Neural Network Software for CPU and GPU on Ubuntu 16.04
TensorFlow is an open source software for performing machine learning tasks. Google, its creator wanted to expose a powerful tool to help developers explore and build machine learning based applications and so they released this as an open source project. TensorFlow is an extremely powerful tool specializing in a type of neural network called the deep neural network.
Deep neural networks are used to perform complex machine learning tasks such as image recognition, handwriting recognition, Natural language processing, chatbots, and more. These neural networks are trained to learn the tasks it is supposed to perform. As the computations required for training is extremely huge, most of the time, a GPU support is required and this is where TensorFlow comes to the rescue. It is GPU enabled and thus by installing the software with GPU support, the training time required can be significantly reduced.
This tutorial helps you to install TensorFlow for CPU only and also with GPU support. So, to get TensorFlow with GPU support, you must have a Nvidia GPU with CUDA support. Installation of CUDA and CuDNN ( Nvidia computation libraries) are a bit tricky and this guide provides a step by step approach to installing them before actually coming to the installation of TensorFlow itself.
The Nvidia CUDA is a GPU-accelerated library that has highly tuned implementations for standard routines used in neural networks. the CuDNN is a tuning library for the GPU which takes care of GPU performance tuning automatically. TensorFlow relies on both these for training and running deep neural networks and hence they have to be installed before TensorFlow is installed.
It is very important to note that, those who DO NOT wish to install TensorFlow with GPU support, then you can skip all these following steps and jump straight to "Step 5: Install TensorFlow with only CPU support" section of this guide.
An introduction to TensorFlow can be found [here](http://sourcedexter.com/what-is-tensorflow/).
## 1 Install CUDA
Firstly, download CUDA for Ubuntu 16.04 from [here.](https://developer.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/8.0/Prod2/local_installers/cuda-repo-ubuntu1604-8-0-local-ga2_8.0.61-1_amd64-deb) This file is pretty big (2GB) so, it might take sometime to get downloaded.
The downloaded file is ".deb" package. To install it, run the following commands:
sudo dpkg -i cuda-repo-ubuntu1604-8-0-local_8.0.44-1_amd64.deb
the following commands install any dependencies that have been missed and finally install the cuda toolkit:
sudo apt install -f
sudo apt update
sudo apt install cuda
If it successfully installed, you will get a message saying it's "successfully installed". If it's already installed, then you will get output similar to the image below:
## 2 Install the CuDNN library
CuDNN downloading requires a bit of work sadly. Nvidia does not directly give you the files to download (It's free however). Follow the steps to get your CuDNN files.
- click
[here](https://developer.nvidia.com/group/node/873374/subscribe/og_user_node)to goto Nvidia's register page and create an account. First page asks you to enter your personal details and the second page asks you to answer a few survey questions. It's alright if you do not know answers to all, you can just select an option at random. - The previous step would have lead to Nvidia sending you an activation link to your mail-Id. Once you have activated, head over to the CuDNN download link
[here](https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/form/cudnn-download-survey). - Once you login to that page, you will have to fill out another smaller survey. Randomly click on the checkboxes and then click on "proceed to Download" button at the bottom of the survey and in the next page click on agree to terms of use.
- Finally, in the drop down, click on "Download cuDNN v5.1 (Jan 20, 2017), for CUDA 8.0", and within that drop down, you need to download two files by clicking on it:
NOTE: even though the library says it's for Ubuntu 14.04, use that link only. it works for 16.04 as well
Now that you finally have both the CuDNN files, it's time to install them!! Use the following commands from the folder which contains this downloaded files:
sudo dpkg -i libcudnn5_5.1.5-1+cuda8.0_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i libcudnn5-dev_5.1.5-1+cuda8.0_amd64.deb
Following image shows the output of running these commands:
## 3 Add the installation location to Bashrc file
the installation location should be added to the bashrc file so that from the next time onward, the system should know where to find the installed directory for CUDA. use the following command to open the bashrc file:
sudo gedit ~/.bashrc
once the file opens, add the following two lines at the end of that file:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/cuda/lib64:/usr/local/cuda/extras/CUPTI/lib64" export CUDA_HOME=/usr/local/cuda
## 4 Install TensorFlow with GPU support
this step we install TensorFlow with GPU support. Run the following command if you are using python 2.7:
pip install TensorFlow-gpu
if you have python 3.x instead of the above command, use the following:
pip3 install TensorFlow-gpu
You will get a "successfully installed" message once the command finishes execution. Now, all that remains to test is whether it has installed correctly. To test this, open a command prompt and type the following commands:
python
import TensorFlow as tf
You should get an output similar to the image below. From the image you can observe that the CUDA libraries have been successfully opened. Now, if there were errors, messages saying failure to open CUDA and even modules not being found will appear. In that case you might have missed one of the step above and re-doing this tutorial carefully will be the way to go.
## 5 Install TensorFlow with only CPU support
NOTE : This step has to be executed by people who do not have a GPU or people who do not have a Nvidia GPU. Others, please ignore this step!!
installing TensorFlow for CPU only is extremely easy. Use the following two commands :
pip install TensorFlow
if you have python 3.x instead of the above command, use the following:
pip3 install TensorFlow
Yes, it's that simple!
This concludes, the installation guide, you can now start to build your deep learning applications. If you are just starting out, then you can look at the official tutorial for beginners [here](https://www.TensorFlow.org/get_started/mnist/beginners). If you are looking for more advanced tutorials, then you can learn how to setup an image recognition system/tool which capable of identifying thousands of objects with high accuracy from [here](https://www.TensorFlow.org/tutorials/image_recognition). |
8,513 | 微流冷却技术可能让摩尔定律起死回生 | http://www.techrepublic.com/article/microfluidic-cooling-may-prevent-the-demise-of-moores-law/ | 2017-05-16T09:49:08 | [
"摩尔定律",
"CPU"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8513-1.html | 
现有的技术无法对微芯片进行有效的冷却,这正快速成为摩尔定律消亡的第一原因。
随着对数字计算速度的需求,科学家和工程师正努力地将更多的晶体管和支撑电路放在已经很拥挤的硅片上。的确,它非常地复杂,然而,和复杂性相比,热量聚积引起的问题更严重。
洛克希德马丁公司首席研究员 John Ditri 在新闻稿中说到:当前,我们可以放入微芯片的功能是有限的,最主要的原因之一是发热的管理。如果你能管理好发热,你可以用较少的芯片,也就是说较少的材料,那样就可以节约成本,并能减少系统的大小和重量。如果你能管理好发热,用相同数量的芯片将能获得更好的系统性能。
硅对电子流动的阻力产生了热量,在如此小的空间封装如此多的晶体管累积了足以毁坏元器件的热量。一种消除热累积的方法是在芯片层用光子学技术减少电子的流动,然而光子学技术有它的一系列问题。
参见: [2015 年硅光子将引起数据中心的革命](http://www.techrepublic.com/article/silicon-photonics-will-revolutionize-data-centers-in-2015/)
### 微流冷却技术可能是问题的解决之道
为了寻找其他解决办法,美国国防高级研究计划局 DARPA 发起了一个关于 [ICECool 应用](https://www.fbo.gov/index?s=opportunity&mode=form&id=0be99f61fbac0501828a9d3160883b97&tab=core&_cview=1) (片内/片间增强冷却技术)的项目。 [GSA 的网站 FedBizOpps.gov](https://www.fbo.gov/index?s=opportunity&mode=form&id=0be99f61fbac0501828a9d3160883b97&tab=core&_cview=1) 报道:ICECool 正在探索革命性的热技术,其将减轻热耗对军用电子系统的限制,同时能显著减小军用电子系统的尺寸,重量和功耗。
微流冷却方法的独特之处在于组合使用片内和(或)片间微流冷却技术和片上热互连技术。

*MicroCooling 1 Image: DARPA*
[DARPA ICECool 应用发布的公告](https://www.fbo.gov/index?s=opportunity&mode=form&id=0be99f61fbac0501828a9d3160883b97&tab=core&_cview=1) 指出,这种微型片内和(或)片间通道可采用轴向微通道、径向通道和(或)横流通道,采用微孔和歧管结构及局部液体喷射形式来疏散和重新引导微流,从而以最有利的方式来满足指定的散热指标。
通过上面的技术,洛克希德马丁的工程师已经实验性地证明了片上冷却是如何得到显著改善的。洛克希德马丁新闻报道:ICECool 项目的第一阶段发现,当冷却具有多个局部 30kW/cm2 热点,发热为 1kw/cm2 的芯片时热阻减少了 4 倍,进而验证了洛克希德的嵌入式微流冷却方法的有效性。
第二阶段,洛克希德马丁的工程师聚焦于 RF 放大器。通过 ICECool 的技术,团队演示了 RF 的输出功率可以得到 6 倍的增长,而放大器仍然比其常规冷却的更凉。
### 投产
出于对技术的信心,洛克希德马丁已经在设计和制造实用的微流冷却发射天线。 洛克希德马丁还与 Qorvo 合作,将其热解决方案与 Qorvo 的高性能 [GaN 工艺](http://electronicdesign.com/communications/what-s-difference-between-gaas-and-gan-rf-power-amplifiers) 相集成。
研究论文 [DARPA 的片间/片内增强冷却技术(ICECool)流程](http://www.csmantech.org/Digests/2013/papers/050.pdf) 的作者认为 ICECool 将使电子系统的热管理模式发生改变。ICECool 应用的执行者将根据应用来定制片内和片间的热管理方法,这个方法需要兼顾应用的材料,制造工艺和工作环境。
如果微流冷却能像科学家和工程师所说的成功的话,似乎摩尔定律会起死回生。
(题图:iStock/agsandrew)
---
via: <http://www.techrepublic.com/article/microfluidic-cooling-may-prevent-the-demise-of-moores-law/>
作者:[Michael Kassner](http://www.techrepublic.com/search/?a=michael+kassner) 译者:[messon007](https://github.com/messon007) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,514 | 六个开源软件开发的“潜规则” | http://www.infoworld.com/article/3156776/open-source-tools/the-6-unwritten-rules-of-open-source-development.html | 2017-05-16T10:38:00 | [
"开源",
"社区"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8514-1.html |
>
> 你想成为开源项目中得意满满、功成名就的那个人吗,那就要遵守下面的“潜规则”。
>
>
>

正如体育界不成文的规定一样,这些规则基本上不会出现在官方文档和正式记录上。比如说,在棒球运动中,从比分领先时不要盗垒,到跑垒员跑了第一时也不要放弃四坏球保送。对于圈外人来讲,这些东西很难懂,甚至觉得没什么意义。但是对于那些想成为 MVP 的队员来说,这些都是理所当然的。
软件开发,特别是开源软件开发中,也有一套不成文的规定。和其它的团队运动一样,这些规定很大程度上决定了开源社区如何看待一名开发者,特别是新加入社区的开发者。
### 按部就班,循序渐进
在参与社区之前,比如开放源代码或者其它什么的,你需要做一些基本工作。对于有眼界的开源贡献者,这意味这你需要理解社区的目标,并学习应该从哪里起步。人人都想贡献源代码,但是只有少量的人做过准备,并且乐意、同时也有能力完成这项艰苦卓绝的工作:测试补丁、复审代码、撰写文档、修正错误。所有的这些不受待见的任务在一个健康的社区中都是必要的。
为什么要在优雅地写代码前做这些呢?这是一种信任,更重要的是,不要只关注自己开发的功能,而是要关注整个社区的动向。
### 博闻强识,敦善不怠
当你在某个社区中建立起自己的声望,那么很有必要全面了解该项目和代码。不要停留于任务状态上,而是要去钻研项目本身,理解那些超出你擅长范围之外的知识。不要只把自己的理解局限于开发者,这样会让你着眼于让你的代码有更大的影响,而不只是你那一亩三分地。
打个比方,你已经完成了一个网络模块的测试版本。你测试了一下,觉得不错。然后你把它开放到社区,想要更多的人测试。结果发现,当它以特定的方式部署时,有可能会破坏安全设置,还可能导致主存储泄露。如果你将代码视为一个整体时问题就可以迎刃而解,而不是孤立地看待问题。这表明,你要对项目各个部分如何与其他人协作交互有比较深入的理解。让你的补丁填坑而不是挖坑。这样你朝成为社区精英的目标上又前进了一大步。
### 粗枝大叶,自寻烦恼
代码提交完毕后你的工作还没结束。如果代码被接受,还会有一些关于这些更改的讨论和常见的问答,还要做测试。你要确保你可以准时提交,努力去理解如何在不影响社区其他成员的情况下,改进代码和补丁。
### 和谐相处,助人助己
开源社区不是自相残杀的丛林世界,我们更看重项目的价值而非个体的贡献和成功。如果你想给自己加分,让自己成为更重要的社区成员、让社区接纳你的代码,那就努力帮助别人。如果你熟悉网络部分,那就去复审网络部分,用你的专业技能让整个代码更加优雅。道理很简单,顶级的审查者经常和顶级的贡献者打交道。你帮助的人越多,你就越有价值。
### 八面玲珑,面面俱到
作为一个开发者,你很可能希望为开源项目解决一个特定的痛点。或许你想要运行在一个目前还不支持的系统上,抑或你很希望改革社区目前使用的安全技术。想要引进新技术,特别是比较有争议的技术,最好的办法就是让人无法拒绝它。你需要透彻地了解底层代码,考虑每个极端情况。在不影响已实现功能的前提下增加新功能。不仅仅是完成就行,还要在特性的完善上下功夫。
### 糜不有初,鲜克有终
开源社区也有许多玩玩就算的人,但是承诺了就不要轻易失信。不要就因为提交被拒就离开社区。找出原因,修正错误,然后再试一试。当你开发时候,要和整个代码库保持一致,确保即使项目发生变化而你的补丁仍然可用。不要把你的代码留给别人修复,要自己修复。这样可以在社区形成良好的风气,每个人都自己改。
---
这些“潜规则”看上去很简单,但是还是有许多开源项目的贡献者并没有遵守。这样做的开发者不仅可以为成功地推动他们自己的项目,而且也有助于开源社区。
作者简介:
Matt Hicks 是 Red Hat 软件工程的副主席,也是 Red Hat 开源合作团队的奠基成员之一。他历时十五年,在软件工程中担任多种职务:开发,运行,架构,管理。
---
via: <http://www.infoworld.com/article/3156776/open-source-tools/the-6-unwritten-rules-of-open-source-development.html>
作者:[Matt Hicks](http://www.infoworld.com/blog/new-tech-forum/) 译者:[Taylor1024](https://github.com/Taylor1024) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy),[martin2011qi](https://github.com/martin2011qi )
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,515 | 极客漫画:现代的邪恶——不许 Ctrl-C | https://turnoff.us/geek/modern-evil/ | 2017-05-17T10:50:00 | [
"漫画"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8515-1.html | 
在页面上,Control-C 的作用是复制,当一个页面禁用了 Control-C 时……这得是多邪恶?!
---
via: <https://turnoff.us/geek/modern-evil/>
作者:[Daniel Stori](http://turnoff.us/about/) 译者&点评:[Bestony](https://github.com/Bestony) 校对&合成:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 404 | Not Found | null |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.