id
int64 2.05k
16.6k
| title
stringlengths 5
75
| fromurl
stringlengths 19
185
| date
timestamp[s] | tags
sequencelengths 0
11
| permalink
stringlengths 20
37
| content
stringlengths 342
82.2k
| fromurl_status
int64 200
526
⌀ | status_msg
stringclasses 339
values | from_content
stringlengths 0
229k
⌀ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
7,335 | 珠海全志公司的 Linux 内核遗留了后门 | http://arstechnica.com/security/2016/05/chinese-arm-vendor-left-developer-backdoor-in-kernel-for-android-pi-devices/ | 2016-05-13T15:49:51 | [
"全志",
"后门"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7335-1.html | 
据外媒 arstechnica 报道,一家中国的芯片级系统厂商全志(allwinner) 在其开发的产品中携带的内核里[遗留了一个 root 后门](http://forum.armbian.com/index.php/topic/1108-security-alert-for-allwinner-sun8i-h3a83th8/http://forum.armbian.com/index.php/topic/1108-security-alert-for-allwinner-sun8i-h3a83th8/)。全志的处理器芯片用在很多低端的 Android 平板、机顶盒、基于 ARM 的 PC 等等之上。而这个后门非常容易获得,只需要给一个未见于文档的调试进程发送一个字符串“rootmydevice” 即可获取该设备的 root 权限。
该后门可能是开发人员调试后忘记移除的。全志公司在知道此消息后,已经从其公司的 Github 账户上[删除了相关文件](https://github.com/allwinner-zh/linux-3.4-sunxi/blob/master/arch/arm/mach-sunxi/sunxi-debug.c#L41)。
该公司使用的内核 linux-3.4-sunxi,原先用于支持全志的 ARM 芯片平板上的 Android,它也有一个[社区版本](https://linux-sunxi.org/Linux_Kernel)。该内核也用来移植到各种全志芯片的设备上,包括<ruby> 桔子派 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Orange Pi </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 香蕉派 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Banana Pi </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>等与<ruby> 树莓派 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Raspberry Pi </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>兼容的开发板。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,337 | Linux 是世界上最大的软件开发项目 | http://www.cio.com/article/3069529/linux/linux-is-the-largest-software-development-project-on-the-planet-greg-kroah-hartman.html | 2016-05-14T11:30:00 | [
"内核",
"Kroah-Hartman"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7337-1.html | Greg Kroah-Hartman 是 Linux 内核社区的二号人物(第一位显然是 Linus Torvalds),他在设备驱动方面做了许多工作,他也是当前 Linux 内核稳定分支的负责人。
在本周柏林举办的 CoreOS Fest 上,Kroah-Hartman 做了一场讲演介绍了 Linux 内核项目是如何的巨大。之后我找了个机会邀请他聊了聊内核和安全方面的话题。
我们的话题先从代码方面开始,Kroah-Hartman 说刚刚于两个月前发布 4.5 版已经包含了 2100 万行代码!
可能很多人觉得在那么小的设备上运行这么多的代码有点夸张,事实上,并不是所有的 2100 万行代码都运行在他们的设备上,只有需要的部分才会运行在里面。正如 Kroah-Hartman 说的,“你不会全部用到它们。在内核里面包含了各种硬件的驱动。我的笔记本上运行的内核代码大概有 160 万行,而你的电话可能运行了 250 万行代码。”
这里面,内核的核心部分是一定算在其中的,而它只占整个 Linux 内核代码的 5%,而剩下的还有 35% 是网络部分,40% 是设备驱动。
比代码规模更让人印象深刻的是它的参与人数规模,去年就有大约 4000 名开发人员参与了开发,至少 440 个公司向内核提交了贡献,这使得 Linux 成为了世界上最大的软件项目!Kroah-Hartman 说:“这是计算机有史以来最大的软件开发项目,无论是使用它的人数、开发它的人数,还是与之相关的公司数量,规模都很大。”

*Greg Kroah-Hartman 在 CoreOS Fest, Berlin 的讲演*
每天,平均有超过 10800 行的代码增加, 5300 行代码被删除,并且还有 1875 行代码被修改,也就是说每秒钟都有超过 8 行代码的变化!
这是非常大的数量,这意味着 Linux 内核不像其它的技术,它在不断的变化,变得越来越好。
Kroah-Hartman 说,“当我第一次参与这个项目时,我们每个小时可以完成 2.5 个变更。每个人都这么说,‘哦,天哪,我们不可能更快了,那不现实’。微软和苹果也说,‘你赢了’,他们一字一顿的说,‘我们比不上,你们干的比任何人都要快,我们是望尘莫及啊’。而我们的开发速度越来越快,我们每次都会更快一些。”
但是,如果你的公司的发展依靠着 Linux,那这个变化速度看起来就很可怕。Kroah-Hartman 解释了为什么会有这么多变更:“我们提交了很多变更,但是不是因为我们为变更而变更的,那可需要很多的工作。我们其实很懒,我们做这么多的变更的原因是因为我们必须做,是因为这个世界不断变化而需要我们做这么多的变更。那种‘你做了个东西,然后啥也不用管,将它丢在一边就好了’的模式已经不可行了,因为这个东西已经连通了世界,而世界每时每刻在变化。事物都在互相作用,所以你必须跟着进化。如果你的操作系统不能改变,那它就没用了,这毋庸置疑。如果你的设备不能跟着与之互动的世界变化,那它同样也没用,这也毋庸置疑。所以,你可以看看那些不能与时俱进的操作系统,根本没有人用它们。”
为了做到这些变更,Linux 内核社区需要做到两点。首先,我们要有个按时间进行的发布计划。其次,我们需要小步快跑。我们完成一个发布就要开始下一个发布的开发。下一个发布的第一个 RC 版本里面就要包含进去所有开发人员丢进去的各种东西,包括各种新的东西、新的功能,而且它们需要经过严格考验。当所有的东西都测试良好,我们才会放出第一个 RC 版本,之后的 RC 版本就是各种问题的修复。这样,我们就能在一个分支的 7-8 个 RC 版本之后赶走所有发现的问题。
当我们准备好发布一个新的内核发布版本时,它已经经过了详尽的测试。但是仍然有问题时,人们使用的稳定版怎么修复问题呢,他们可不想在产品环境中使用 RC 版本,那么他们怎么修复问题?在 15 年前,内核社区就找到了解决方案,而这就是 Kroah-Hartman 的任务,他会对稳定版本进行分支,比如说 4.2 版,它的问题修复版本会以 4.2.1 、4.2.2、4.2.3 等等发布。
“这个版本规则就是它必须是一个问题修复版,而且它必须是一个正确的版本号或者是新的设备 ID,它必须出现在 Linux 内核代码树上。在我将它放到稳定分支之前,它就必须出现在 Linux 内核代码树上。这可以确保人们运行我们的稳定内核时,如果跳到一个新的分支版本时,不会发生中断,没有什么不一样的变化。这就是规则,而且一直以来运作良好。”Kroah-Hartman 说。
而当下一个新的分支(4.3)出来时,Kroah-Hartman 就会从当前的分支(4.2)离开而去维护 4.3。这样内核社区就完美的保证了当新的版本发布时任何事情都很连贯。
“每个版本我每周都会做一次发布,每周会对稳定分支打 100 到 150 个补丁。这很多,许多东西都变化了,也修复了许多东西。而这就是我们做的——稳定的分支。当 4.3 发布时,最好的事情是我解脱了,我说,‘啊!4.2,我再也不要见到你了’,然后我就跑到新的分支了,因为我们的工作,这一切都可以继续发展下去,所有人都很满意。”
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,343 | Debian 团队澄清其与 ZFS 的许可证冲突是如何绕开的 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/debian-project-clarifies-the-implementation-of-zfs-for-linux-in-debian-gnu-linux-504090.shtml | 2016-05-16T15:42:00 | [
"ZFS",
"Debian"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7343-1.html | 之前,我们报道过 [Debian 中支持了 ZFS 文件系统](/article-7341-1.html)的新闻。Debian 社区对此表示了欢迎,但是也有人指出,ZFS 支持之所以迟迟不能加入到 Debian 中是由于 ZFS 许可证与 <ruby> Debian 自由软件指南 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Debian Free Software Guidelines </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>之间的冲突。
今天早些时候,我们联系到了 Debian 公关团队的 Donald Norwood,他告诉我们, ZFS for Linux 没有放到 Debian GNU/Linux 的主软件仓库中,而是放到了另外一个名为 “contrib”的仓库中。
“ZFS 放到了 /contrib/ 下,而没有放到 /main/ 下,原因是因为当前的 ZFS 许可证同 <ruby> Debian 自由软件指南 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Debian Free Software Guidelines </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>存在冲突。因此,用户可以从其中下载源代码编译而不是直接下载二进制。”,Donald Norwood 说。

### Debian 中的 ZFS 实现与 Ubuntu 中的那个不同
似乎有些人误解 Debian GNU/Linux 中的 ZFS 实现是来自 Ubuntu 16.04 中的 ZFS 实现,而据 <ruby> Software Freedom Conservancy <rp> ( </rp> <rt> 自由软件管理委员会 </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 称,[Ubuntu 中的 ZFS 实现违反了 GPL 许可证](https://sfconservancy.org/blog/2016/feb/25/zfs-and-linux/)。Debian 的 ZFS 软件包虽然[包含了一些来自 Ubuntu 的补丁](https://tracker.debian.org/news/767790),但是是以源代码的方式提供的,所以实质上绕开了 GPL 许可证的冲突。(注:据网友指正,此处语言有修饰。)
如果你想在你的 Debian GNU/Linux 中体验一下 ZFS,你可以从 contrib 仓库中下载最新的 zfs-linux 软件包。
更多关于 Debian 中的 ZFS 的细节,可以查看[此处](https://bits.debian.org/2016/05/what-does-it-mean-that-zfs-is-in-debian.html)。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,344 | Linux 4.6 内核发布,引入 OrangeFS 和 USB 3.1 SSP 支持 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/linux-kernel-4-6-officially-released-introduces-orangefs-usb-3-1-ssp-support-504088.shtml | 2016-05-16T16:21:13 | [
"Linux",
"内核"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7344-1.html | 今天,美国时间 5 月 15 日, Linus Torvalds [宣布了](http://lkml.iu.edu/hypermail/linux/kernel/1605.1/05030.html) Linux 4.6 内核的正式发布。
经过了两个月的开发,历经了 7 个 RC 版本,Linux 4.6 内核终于发布了最终产品版本,带来了一些引人关注的新功能、更新的驱动程序以及一些安全改进。
“好在我不用中断 RC 周期,上周我们如预期的收到了几个修复,但是没有什么出乎意料的事情。所以, 4.6 就按照正常的计划发布了,这也意味着我明天就可以启动 4.7 的合并窗口啦。” Linus Torvalds 说。

### Linux 4.6 内核的新功能
Linux 4.6 内核的最引人注目的新功能是 OrangeFS 分布式文件系统、支持 USB 3.1 SuperSpeed Plus (SSP) 协议、提供了高达 10Gbps 的传输速度、改进了 <ruby> OOM 任务处理器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Out Of Memory task killer </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的可靠性、并支持了 Intel 内存保护键。
此外,Linux 4.6 内核也带有<ruby> 内核连接多路转接器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Kernel Connection Multiplexor </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、一个用于加速应用层协议的新部件、802.1AE MAC 级加密支持(MACsec)、OCFS2 文件系统的在线 inode 检查器、支持 BARMAN V 协议、支持 pNFS SCSI 布局。
最后,Linux 4.6 内核也包括了对 cgroup 名字空间和 dma-buf 的支持、一个新打造的 ioctl 专门用于管理 CPU 和 GPU 之间的缓存关联性。当然,也更新了不少驱动程序、修复了许多问题。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,353 | Linux 内核里的数据结构——基数树 | https://github.com/0xAX/linux-insides/blob/master/DataStructures/radix-tree.md | 2016-05-18T08:56:00 | [
"基数树",
"字典树"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7353-1.html | ### <ruby> 基数树 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Radix tree </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>

正如你所知道的,Linux内核提供了许多不同的库和函数,它们实现了不同的数据结构和算法。在这部分,我们将研究其中一种数据结构——<ruby> <a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radix_tree"> 基数树 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Radix tree </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。在 Linux 内核中,有两个文件与基数树的实现和API相关:
* [include/linux/radix-tree.h](https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/include/linux/radix-tree.h)
* [lib/radix-tree.c](https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/lib/radix-tree.c)
让我们先说说什么是 `基数树` 吧。基数树是一种 <ruby> 压缩的字典树 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> compressed trie </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> ,而[字典树](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie)是实现了关联数组接口并允许以 `键值对` 方式存储值的一种数据结构。这里的键通常是字符串,但可以使用任意数据类型。字典树因为它的节点而与 `n叉树` 不同。字典树的节点不存储键,而是存储单个字符的标签。与一个给定节点关联的键可以通过从根遍历到该节点获得。举个例子:
```
+-----------+
| |
| " " |
| |
+------+-----------+------+
| |
| |
+----v------+ +-----v-----+
| | | |
| g | | c |
| | | |
+-----------+ +-----------+
| |
| |
+----v------+ +-----v-----+
| | | |
| o | | a |
| | | |
+-----------+ +-----------+
|
|
+-----v-----+
| |
| t |
| |
+-----------+
```
因此在这个例子中,我们可以看到一个有着两个键 `go` 和 `cat` 的 `字典树` 。压缩的字典树也叫做 `基数树` ,它和 `字典树` 的不同之处在于,所有只有一个子节点的中间节点都被删除。
Linux 内核中的基数树是把值映射到整形键的一种数据结构。[include/linux/radix-tree.h](https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/include/linux/radix-tree.h)文件中的以下结构体描述了基数树:
```
struct radix_tree_root {
unsigned int height;
gfp_t gfp_mask;
struct radix_tree_node __rcu *rnode;
};
```
这个结构体描述了一个基数树的根,它包含了3个域成员:
* `height` - 树的高度;
* `gfp_mask` - 告知如何执行动态内存分配;
* `rnode` - 孩子节点指针.
我们第一个要讨论的字段是 `gfp_mask` :
底层内核的内存动态分配函数以一组标志作为 `gfp_mask` ,用于描述如何执行动态内存分配。这些控制分配进程的 `GFP_` 标志拥有以下值:( `GF_NOIO` 标志)意味着睡眠以及等待内存,( `__GFP_HIGHMEM` 标志)意味着高端内存能够被使用,( `GFP_ATOMIC` 标志)意味着分配进程拥有高优先级并不能睡眠等等。
* `GFP_NOIO` - 睡眠等待内存
* `__GFP_HIGHMEM` - 高端内存能够被使用;
* `GFP_ATOMIC` - 分配进程拥有高优先级并且不能睡眠;
等等。
下一个字段是`rnode`:
```
struct radix_tree_node {
unsigned int path;
unsigned int count;
union {
struct {
struct radix_tree_node *parent;
void *private_data;
};
struct rcu_head rcu_head;
};
/* For tree user */
struct list_head private_list;
void __rcu *slots[RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE];
unsigned long tags[RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS][RADIX_TREE_TAG_LONGS];
};
```
这个结构体包含的信息有父节点中的偏移以及到底端(叶节点)的高度、子节点的个数以及用于访问和释放节点的字段成员。这些字段成员描述如下:
* `path` - 父节点中的偏移和到底端(叶节点)的高度
* `count` - 子节点的个数;
* `parent` - 父节点指针;
* `private_data` - 由树的用户使用;
* `rcu_head` - 用于释放节点;
* `private_list` - 由树的用户使用;
`radix_tree_node` 的最后两个成员—— `tags` 和 `slots` 非常重要且令人关注。Linux 内核基数树的每个节点都包含了一组<ruby> 指针槽 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> slots </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,槽里存储着指向数据的指针。在Linux内核基数树的实现中,空槽存储的是 `NULL` 。Linux内核中的基数树也支持<ruby> 标签 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> tags </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,它与 `radix_tree_node` 结构体的 `tags` 字段相关联。有了标签,我们就可以对基数树中存储的记录以单个<ruby> 比特位 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> bit </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>进行设置。
既然我们了解了基数树的结构,那么该是时候看一下它的API了。
### Linux内核基数树API
我们从结构体的初始化开始。有两种方法初始化一个新的基数树。第一种是使用 `RADIX_TREE` 宏:
```
RADIX_TREE(name, gfp_mask);
```
正如你所看到的,我们传递了 `name` 参数,所以通过 `RADIX_TREE` 宏,我们能够定义和初始化基数树为给定的名字。`RADIX_TREE` 的实现很简单:
```
#define RADIX_TREE(name, mask) \
struct radix_tree_root name = RADIX_TREE_INIT(mask)
#define RADIX_TREE_INIT(mask) { \
.height = 0, \
.gfp_mask = (mask), \
.rnode = NULL, \
}
```
在 `RADIX_TREE` 宏的开始,我们使用给定的名字定义 `radix_tree_root` 结构体实例,并使用给定的 mask 调用 `RADIX_TREE_INIT` 宏。 而 `RADIX_TREE_INIT` 宏则是使用默认值和给定的mask对 `radix_tree_root` 结构体进行了初始化。
第二种方法是手动定义`radix_tree_root`结构体,并且将它和mask传给 `INIT_RADIX_TREE` 宏:
```
struct radix_tree_root my_radix_tree;
INIT_RADIX_TREE(my_tree, gfp_mask_for_my_radix_tree);
```
`INIT_RADIX_TREE` 宏的定义如下:
```
#define INIT_RADIX_TREE(root, mask) \
do { \
(root)->height = 0; \
(root)->gfp_mask = (mask); \
(root)->rnode = NULL; \
} while (0)
```
和`RADIX_TREE_INIT`宏所做的初始化工作一样,`INIT_RADIX_TREE` 宏使用默认值和给定的 mask 完成初始化工作。
接下来是用于向基数树插入和删除数据的两个函数:
* `radix_tree_insert`;
* `radix_tree_delete`;
第一个函数 `radix_tree_insert` 需要3个参数:
* 基数树的根;
* 索引键;
* 插入的数据;
`radix_tree_delete` 函数需要和 `radix_tree_insert` 一样的一组参数,但是不需要传入要删除的数据。
基数树的搜索以两种方法实现:
* `radix_tree_lookup`;
* `radix_tree_gang_lookup`;
* `radix_tree_lookup_slot`.
第一个函数`radix_tree_lookup`需要两个参数:
* 基数树的根;
* 索引键;
这个函数尝试在树中查找给定的键,并返回和该键相关联的记录。第二个函数 `radix_tree_gang_lookup` 有以下的函数签名:
```
unsigned int radix_tree_gang_lookup(struct radix_tree_root *root,
void **results,
unsigned long first_index,
unsigned int max_items);
```
它返回的是记录的个数。 `results` 中的结果,按键排序,并从第一个索引开始。返回的记录个数将不会超过 `max_items` 的值。
最后一个函数`radix_tree_lookup_slot`将会返回包含数据的指针槽。
### 链接
* [Radix tree](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radix_tree)
* [Trie](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie)
---
via: <https://github.com/0xAX/linux-insides/blob/master/DataStructures/radix-tree.md>
作者:[0xAX] 译者:[cposture](https://github.com/cposture) 校对:[Mr小眼儿](https://github.com/tinyeyeser)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 404 | Not Found | null |
7,354 | 点评五款用于 Linux 编程的内存调试器 | http://www.computerworld.com/article/3003957/linux/review-5-memory-debuggers-for-linux-coding.html | 2016-05-19T09:36:00 | [
"调试",
"Mtrace",
"Dmalloc",
"Memwatch",
"Electric Fence",
"gdb"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7354-1.html | 
>
> Credit: [Moini](https://openclipart.org/detail/132427/penguin-admin)
>
>
>
作为一个程序员,我知道我肯定会犯错误——怎么可能不犯错!程序员也是人啊。有的错误能在编码过程中及时发现,而有些却得等到软件测试了才能显露出来。然而,还有一类错误并不能在这两个阶段被解决,这就导致软件不能正常运行,甚至是提前终止。
如果你还没猜出是那种错误,我说的就是和内存相关的错误。手动调试这些错误不仅耗时,而且很难发现并纠正。值得一提的是,这种错误很常见,特别是在用 C/C++ 这类允许[手动管理内存](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manual_memory_management)的语言编写的软件里。
幸运的是,现在有一些编程工具能够帮你在软件程序中找到这些和内存相关的错误。在这些工具集中,我评估了五款支持 Linux 的、流行的、自由开源的内存调试器: Dmalloc 、 Electric Fence 、 Memcheck 、 Memwatch 以及 Mtrace 。在日常编码中,我已经用过这五个调试器了,所以这些评估是建立在我的实际体验之上的。
### [Dmalloc](http://dmalloc.com/)
**开发者**:Gray Watson
**评估版本**:5.5.2
**支持的 Linux 版本**:所有种类
**许可**: CC 3.0
Dmalloc 是 Gray Watson 开发的一款内存调试工具。它是作为库来实现的,封装了标准内存管理函数如`malloc()` , `calloc()` , `free()`等,使程序员得以检测出有问题的代码。

*Dmalloc*
如同工具的网页所示,这个调试器提供的特性包括内存泄漏跟踪、<ruby> <a href="https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Double_Free"> 重复释放内存 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> double free </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>错误跟踪、以及<ruby> <a href="https://stuff.mit.edu/afs/sipb/project/gnucash-test/src/dmalloc-4.8.2/dmalloc.html#Fence-Post%20Overruns"> 越界写入 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> fence-post write </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>检测。其它特性包括报告错误的文件/行号、通用的数据统计记录。
#### 更新内容
5.5.2 版本是一个 [bug 修正发行版](http://dmalloc.com/releases/notes/dmalloc-5.5.2.html),修复了几个有关构建和安装的问题。
#### 有何优点
Dmalloc 最大的优点就是高度可配置性。比如说,你可以配置它以支持 C++ 程序和多线程应用。 Dmalloc 还提供一个有用的功能:运行时可配置,这表示在 Dmalloc 执行时,可以轻易地启用或者禁用它提供的一些特性。
你还可以配合 [GNU Project Debugger (GDB)](http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/)来使用 Dmalloc ,只需要将`dmalloc.gdb`文件(位于 Dmalloc 源码包中的 contrib 子目录里)的内容添加到你的主目录中的`.gdbinit`文件里即可。
另外一个让我对 Dmalloc 爱不释手的优点是它有大量的资料文献。前往官网的 [Documentation 栏目](http://dmalloc.com/docs/),可以获取所有关于如何下载、安装、运行、怎样使用库,和 Dmalloc 所提供特性的细节描述,及其生成的输出文件的解释。其中还有一个章节介绍了一般问题的解决方法。
#### 注意事项
跟 Mtrace 一样, Dmalloc 需要程序员改动他们的源代码。比如说你可以(也是必须的)添加头文件`dmalloc.h`,工具就能汇报产生问题的调用的文件或行号。这个功能非常有用,因为它节省了调试的时间。
除此之外,还需要在编译你的程序时,把 Dmalloc 库(编译 Dmalloc 源码包时产生的)链接进去。
然而,还有点更麻烦的事,需要设置一个环境变量,命名为`DMALLOC_OPTION`,以供工具在运行时配置内存调试特性,比如定义输出文件的路径。可以手动为该环境变量分配一个值,不过初学者可能会觉得这个过程有点困难,因为该值的一部分用来表示要启用的 Dmalloc 特性——以十六进制值的累加值表示。[这里](http://dmalloc.com/docs/latest/online/dmalloc_26.html#SEC32)有详细介绍。
一个比较简单方法设置这个环境变量是使用 [Dmalloc 实用指令](http://dmalloc.com/docs/latest/online/dmalloc_23.html#SEC29),这是专为这个目的设计的方法。
#### 总结
Dmalloc 真正的优势在于它的可配置选项。而且高度可移植,曾经成功移植到多种操作系统如 AIX 、 BSD/OS 、 DG/UX 、 Free/Net/OpenBSD 、 GNU/Hurd 、 HPUX 、 Irix 、 Linux 、 MS-DOG 、 NeXT 、 OSF 、 SCO 、 Solaris 、 SunOS 、 Ultrix 、 Unixware 甚至 Unicos(运行在 Cray T3E 主机上)。虽然使用 Dmalloc 需要学习许多知识,但是它所提供的特性值得为之付出。
### [Electric Fence](https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/electric-fence/2.2.3)
**开发者**:Bruce Perens
**评估版本**:2.2.3
**支持的 Linux 版本**:所有种类
**许可**:GPL v2
Electric Fence 是 Bruce Perens 开发的一款内存调试工具,它以库的形式实现,你的程序需要链接它。Electric Fence 能检测出[堆](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Memory_management#Dynamic_memory_allocation)内存溢出和访问已经释放的内存。

*Electric Fence*
顾名思义, Electric Fence 在每个所申请的缓存边界建立了虚拟围栏,这样一来任何非法的内存访问都会导致[段错误](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Segmentation_fault)。这个调试工具同时支持 C 和 C++ 程序。
#### 更新内容
2.2.3 版本修复了工具的构建系统,使得 `-fno-builtin-malloc` 选项能真正传给 [GNU Compiler Collection (GCC)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GNU_Compiler_Collection)。
#### 有何优点
我喜欢 Electric Fence 的首要一点是它不同于 Memwatch 、 Dmalloc 和 Mtrace ,不需要对你的源码做任何的改动,你只需要在编译的时候把它的库链接进你的程序即可。
其次, Electric Fence 的实现保证了产生越界访问的第一个指令就会引起段错误。这比在后面再发现问题要好多了。
不管是否有检测出错误, Electric Fence 都会在输出产生版权信息。这一点非常有用,由此可以确定你所运行的程序已经启用了 Electric Fence 。
#### 注意事项
另一方面,我对 Electric Fence 真正念念不忘的是它检测内存泄漏的能力。内存泄漏是 C/C++ 软件最常见也是最不容易发现的问题之一。不过, Electric Fence 不能检测出栈溢出,而且也不是线程安全的。
由于 Electric Fence 会在用户分配内存区的前后分配禁止访问的虚拟内存页,如果你过多的进行动态内存分配,将会导致你的程序消耗大量的额外内存。
Electric Fence 还有一个局限是不能明确指出错误代码所在的行号。它所能做只是在检测到内存相关错误时产生段错误。想要定位错误的行号,需要借助 [GDB](http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/)这样的调试工具来调试启用了 Electric Fence 的程序。
最后一点,尽管 Electric Fence 能检测出大部分的缓冲区溢出,有一个例外是,如果所申请的缓冲区大小不是系统字长的倍数,这时候溢出(即使只有几个字节)就不能被检测出来。
#### 总结
尽管局限性较大, Electric Fence 的易用性仍然是加分项。只要链接一次程序, Electric Fence 就可以在监测出内存相关问题的时候报警。不过,如同前面所说, Electric Fence 需要配合像 GDB 这样的源码调试器使用。
### [Memcheck](http://valgrind.org/docs/manual/mc-manual.html)
**开发者**:[Valgrind 开发团队](http://valgrind.org/info/developers.html)
**评估版本**:3.10.1
**支持的 Linux 发行版**:所有种类
**许可**:GPL
[Valgrind](http://valgrind.org/) 是一个提供好几款调试和分析 Linux 程序性能的工具的套件。虽然 Valgrind 能和不同语言——Java 、 Perl 、 Python 、 Assembly code 、 ortran 、 Ada 等——编写的程序一起工作,但是它主要还是针对使用 C/C++ 所编写的程序。
Memcheck ,一款内存错误检测器,是其中最受欢迎的工具。它能够检测出如内存泄漏、无效的内存访问、未定义变量的使用以及堆内存分配和释放相关的问题等诸多问题。
#### 更新内容
[工具套件( 3.10.1 )](http://valgrind.org/docs/manual/dist.news.html)主要修复了 3.10.0 版本发现的 bug 。除此之外,“从主干开发版本向后移植的一些补丁,修复了缺失的 AArch64 ARMv8 指令和系统调用”。
#### 有何优点
同其它所有 Valgrind 工具一样, Memcheck 也是命令行程序。它的操作非常简单:通常我们会使用诸如 `prog arg1 arg2` 格式的命令来运行程序,而 Memcheck 只要求你多加几个值即可,如 `valgrind --leak-check=full prog arg1 arg2` 。

*Memcheck*
(注意:因为 Memcheck 是 Valgrind 的默认工具,所以在命令行执行命令时无需提及 Memcheck。但是,需要在编译程序之初带上 `-g` 参数选项,这一步会添加调试信息,使得 Memcheck 的错误信息会包含正确的行号。)
我真正倾心于 Memcheck 的是它提供了很多命令行选项(如上所述的`--leak-check`选项),如此不仅能控制工具运转还可以控制它的输出。
举个例子,可以开启`--track-origins`选项,以查看程序源码中未初始化的数据;可以开启`--show-mismatched-frees`选项让 Memcheck 匹配内存的分配和释放技术。对于 C 语言所写的代码, Memcheck 会确保只能使用`free()`函数来释放内存,`malloc()`函数来申请内存。而对 C++ 所写的源码, Memcheck 会检查是否使用了`delete`或`delete[]`操作符来释放内存,以及`new`或者`new[]`来申请内存。
Memcheck 最好的特点,尤其是对于初学者来说,是它会给用户建议使用哪个命令行选项能让输出更加有意义。比如说,如果你不使用基本的`--leak-check`选项, Memcheck 会在输出时给出建议:“使用 --leak-check=full 重新运行以查看更多泄漏内存细节”。如果程序有未初始化的变量, Memcheck 会产生信息:“使用 --track-origins=yes 以查看未初始化变量的定位”。
Memcheck 另外一个有用的特性是它可以创建<ruby> <a href="http://valgrind.org/docs/manual/mc-manual.html#mc-manual.suppfiles"> 抑制文件 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> suppression files </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,由此可以略过特定的不能修正的错误,这样 Memcheck 运行时就不会每次都报警了。值得一提的是, Memcheck 会去读取默认抑制文件来忽略系统库(比如 C 库)中的报错,这些错误在系统创建之前就已经存在了。可以选择创建一个新的抑制文件,或是编辑现有的文件(通常是`/usr/lib/valgrind/default.supp`)。
Memcheck 还有高级功能,比如可以使用[定制内存分配器](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/4642671/c-memory-allocators)来[检测内存错误](http://valgrind.org/docs/manual/mc-manual.html#mc-manual.mempools)。除此之外, Memcheck 提供[监控命令](http://valgrind.org/docs/manual/mc-manual.html#mc-manual.monitor-commands),当用到 Valgrind 内置的 gdbserver ,以及[客户端请求](http://valgrind.org/docs/manual/mc-manual.html#mc-manual.clientreqs)机制(不仅能把程序的行为告知 Memcheck ,还可以进行查询)时可以使用。
#### 注意事项
毫无疑问, Memcheck 可以节省很多调试时间以及省去很多麻烦。但是它使用了很多内存,导致程序执行变慢([由文档可知](http://valgrind.org/docs/manual/valgrind_manual.pdf),大概会花费 20 至 30 倍时间)。
除此之外, Memcheck 还有其它局限。根据用户评论, Memcheck 很明显不是[线程安全](http://sourceforge.net/p/valgrind/mailman/message/30292453/)的;它不能检测出 [静态缓冲区溢出](https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee798431%28v=cs.20%29.aspx);还有就是,一些 Linux 程序如 [GNU Emacs](http://www.computerworld.com/article/2484425/linux/5-free-linux-text-editors-for-programming-and-word-processing.html?nsdr=true&page=2) 目前还不能配合 Memcheck 工作。
如果有兴趣,可以在[这里](http://valgrind.org/docs/manual/manual-core.html#manual-core.limits)查看 Valgrind 局限性的详细说明。
#### 总结
无论是对于初学者还是那些需要高级特性的人来说, Memcheck 都是一款便捷的内存调试工具。如果你仅需要基本调试和错误检查, Memcheck 会非常容易上手。而当你想要使用像抑制文件或者监控指令这样的特性,就需要花一些功夫学习了。
虽然罗列了大量的局限性,但是 Valgrind(包括 Memcheck )在它的网站上声称全球有[成千上万程序员](http://valgrind.org/info/)使用了此工具。开发团队称收到来自超过 30 个国家的用户反馈,而这些用户的工程代码有的高达两千五百万行。
### [Memwatch](http://www.linkdata.se/sourcecode/memwatch/)
**开发者**:Johan Lindh
**评估版本**:2.71
**支持的 Linux 发行版**:所有种类
**许可**:GNU GPL
Memwatch 是由 Johan Lindh 开发的内存调试工具,虽然它扮演的主要角色是内存泄漏检测器,但是(根据网页介绍)它也具有检测其它如[内存重复释放和错误释放](http://www.cecalc.ula.ve/documentacion/tutoriales/WorkshopDebugger/007-2579-007/sgi_html/ch09.html)、缓冲区溢出和下溢、[野指针](http://c2.com/cgi/wiki?WildPointer)写入等等内存相关问题的能力。
Memwatch 支持用 C 语言所编写的程序。也可以在 C++ 程序中使用它,但是这种做法并不提倡(由 Memwatch 源码包随附的 Q&A 文件中可知)。
#### 更新内容
这个版本添加了`ULONG_LONG_MAX`以区分 32 位和 64 位程序。
#### 有何优点
跟 Dmalloc 一样, Memwatch 也有优秀的文档资料。参考 USING 文件,可以学习如何使用 Memwatch ,可以了解 Memwatch 是如何初始化、如何清理以及如何进行 I/O 操作,等等。还有一个 FAQ 文件,旨在帮助用户解决使用过程遇到的一般问题。最后还有一个`test.c`文件提供工作案例参考。

*Memwatch*
不同于 Mtrace , Memwatch 产生的日志文件(通常是`memwatch.log`)是人类可阅读的格式。而且, Memwatch 每次运行时总会把内存调试结果拼接到输出该文件的末尾。如此便可在需要之时轻松查看之前的输出信息。
同样值得一提的是当你执行了启用 Memwatch 的程序, Memwatch 会在[标准输出](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_streams#Standard_output_.28stdout.29)中产生一个单行输出,告知发现了错误,然后你可以在日志文件中查看输出细节。如果没有产生错误信息,就可以确保日志文件不会写入任何错误,多次运行的话确实能节省时间。
另一个我喜欢的优点是 Memwatch 还提供了在源码中获取其输出信息的方式,你可以获取信息,然后任由你进行处理(参考 Memwatch 源码中的`mwSetOutFunc()`函数获取更多有关的信息)。
#### 注意事项
跟 Mtrace 和 Dmalloc 一样, Memwatch 也需要你往你的源文件里增加代码:你需要把`memwatch.h`这个头文件包含进你的代码。而且,编译程序的时候,你需要连同`memwatch.c`一块编译;或者你可以把已经编译好的目标模块包含起来,然后在命令行定义`MEMWATCH`和`MW_STDIO`变量。不用说,想要在输出中定位行号, -g 编译器选项也少不了。
此外, Memwatch 缺少一些特性。比如 Memwatch 不能检测出对一块已经被释放的内存进行写入操作,或是在分配的内存块之外的进行读取操作。而且, Memwatch 也不是线程安全的。还有一点,正如我在开始时指出,在 C++ 程序上运行 Memwatch 的结果是不能预料的。
#### 总结
Memcheck 可以检测很多内存相关的问题,在处理 C 程序时是非常便捷的调试工具。因为源码小巧,所以可以从中了解 Memcheck 如何运转,有需要的话可以调试它,甚至可以根据自身需求扩展升级它的功能。
### [Mtrace](http://www.gnu.org/software/libc/manual/html_node/Tracing-malloc.html)
**开发者**: Roland McGrath 和 Ulrich Drepper
**评估版本**: 2.21
**支持的 Linux 发行版**:所有种类
**许可**:GNU GPL
Mtrace 是 [GNU C 库](https://www.gnu.org/software/libc/)中的一款内存调试工具,同时支持 Linux 上的 C 和 C++ 程序,可以检测由函数`malloc()`和`free()`不匹配的调用所引起的内存泄漏问题。

*Mtrace*
Mtrace 实际上是实现了一个名为`mtrace()`的函数,它可以跟踪程序中所有 malloc/free 调用,并在用户指定的文件中记录相关信息。文件以一种机器可读的格式记录数据,所以有一个 Perl 脚本——同样命名为 mtrace ——用来把文件转换并为人类可读格式。
#### 更新内容
[Mtrace 源码](https://sourceware.org/git/?p=glibc.git;a=history;f=malloc/mtrace.c;h=df10128b872b4adc4086cf74e5d965c1c11d35d2;hb=HEAD)和 [Perl 文件](https://sourceware.org/git/?p=glibc.git;a=history;f=malloc/mtrace.pl;h=0737890510e9837f26ebee2ba36c9058affb0bf1;hb=HEAD)同 GNU C 库( 2.21 版本)一起释出,除了更新版权日期,其它别无改动。
#### 有何优点
Mtrace 最好的地方是它非常简单易学。你只需要了解在你的源码中如何以及何处添加 `mtrace()` 及对应的 `muntrace()` 函数,还有如何使用 Mtrace 的 Perl 脚本。后者非常简单,只需要运行指令`mtrace <program-executable> <log-file-generated-upon-program-execution>`(例子见开头截图最后一条指令)。
Mtrace 另外一个优点是它的可伸缩性,这体现在不仅可以使用它来调试完整的程序,还可以使用它来检测程序中独立模块的内存泄漏。只需在每个模块里调用`mtrace()`和`muntrace()`即可。
最后一点,因为 Mtrace 会在`mtrace()`——在源码中添加的函数——执行时被触发,因此可以很灵活地[使用信号](http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:s6ywlLtkSqQJ:www.gnu.org/s/libc/manual/html_node/Tips-for-the-Memory-Debugger.html+&cd=1&hl=en&ct=clnk&gl=in&client=Ubuntu)动态地(在程序执行时)使能 Mtrace 。
#### 注意事项
因为`mtrace()`和`mauntrace()`函数 —— 声明在`mcheck.h`文件中,所以必须在源码中包含此头文件 —— 的调用是 Mtrace 工作的基础(`mauntrace()`函数并非[总是必要](http://www.gnu.org/software/libc/manual/html_node/Using-the-Memory-Debugger.html#Using-the-Memory-Debugger)),因此 Mtrace 要求程序员至少改动源码一次。
需要注意的是,在编译程序的时候带上 -g 选项( [GCC](http://linux.die.net/man/1/gcc) 和 [G++](http://linux.die.net/man/1/g++) 编译器均有提供),才能使调试工具在输出结果时展示正确的行号。除此之外,有些程序(取决于源码体积有多大)可能会花很长时间进行编译。最后,带 -g 选项编译会增加了可执行文件的大小(因为提供了额外的调试信息),因此记得程序需要在测试结束后,不带 -g 选项重新进行编译。
使用 Mtrace ,你需要掌握 Linux 环境变量的基本知识,因为在程序执行之前,需要把用户把环境变量`MALLOC_TRACE`的值设为指定的文件(`mtrace()`函数将会记录全部信息到其中)路径。
Mtrace 在检测内存泄漏和试图释放未经过分配的内存方面存在局限。它不能检测其它内存相关问题如非法内存访问、使用未初始化内存。而且,[有人抱怨](https://sourceware.org/ml/libc-help/2014-05/msg00008.html) Mtrace 不是[线程安全](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thread_safety)的。
### 总结
不言自明,我在此讨论的每款内存调试器都有其优点和局限。所以,哪一款适合你取决于你所需要的特性,虽然有时候容易安装和使用也是一个决定因素。
要想捕获软件程序中的内存泄漏, Mtrace 最适合不过了。它还可以节省时间。由于 Linux 系统已经预装了此工具,对于不能联网或者不可以下载第三方调试调试工具的情况, Mtrace 也是极有助益的。
另一方面,相比 Mtrace , Dmalloc 不仅能检测更多错误类型,还提供更多特性,比如运行时可配置、 GDB 集成。而且, Dmalloc 不像这里所说的其它工具,它是线程安全的。更不用说它的详细资料了,这让 Dmalloc 成为初学者的理想选择。
虽然 Memwatch 的资料比 Dmalloc 的更加丰富,而且还能检测更多的错误种类,但是你只能在 C 语言写就的程序中使用它。一个让 Memwatch 脱颖而出的特性是它允许在你的程序源码中处理它的输出,这对于想要定制输出格式来说是非常有用的。
如果改动程序源码非你所愿,那么使用 Electric Fence 吧。不过,请记住, Electric Fence 只能检测两种错误类型,而此二者均非内存泄漏。还有就是,需要基本了解 GDB 以最大化发挥这款内存调试工具的作用。
Memcheck 可能是其中综合性最好的了。相比这里提及的其它工具,它能检测更多的错误类型,提供更多的特性,而且不需要你的源码做任何改动。但请注意,基本功能并不难上手,但是想要使用它的高级特性,就必须学习相关的专业知识了。
---
via: <http://www.computerworld.com/article/3003957/linux/review-5-memory-debuggers-for-linux-coding.html>
作者:[Himanshu Arora](http://www.computerworld.com/author/Himanshu-Arora/) 译者:[soooogreen](https://github.com/soooogreen) 校对:[PurlingNayuki](https://github.com/PurlingNayuki),[ezio](https://github.com/oska874)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,355 | 5 个很适合在课堂上演示的树莓派项目 | https://opensource.com/education/15/12/5-great-raspberry-pi-projects-classroom | 2016-05-20T10:14:00 | [
"树莓派"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7355-1.html | 
### 1. 我的世界: Pi

*源于 Raspberry Pi 基金会. [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)*
“我的世界”是世界上几乎每一个青少年都特别喜欢的一款游戏,而且它成功抓住了年轻人眼球,成为目前最能激发年轻人创造力的游戏之一。这个树莓派版本自带的我的世界不仅仅是一个具有创造性的建筑游戏,还是一个具有编程接口,可以通过 Python 与之交互的版本。
我的世界:Pi 版对于老师来说是一个教授学生解决问题和编写代码完成任务的好方式。你可以使用 Python API 创建一个房子,并且一直跟随这你的脚步移动,在所到之处建造一座桥,让天空落下熔岩雨滴,在空中显示温度,以及其它你可以想象到的一切东西。
详情请见 "[我的世界: Pi 入门](https://opensource.com/life/15/5/getting-started-minecraft-pi)"
### 2. 反应游戏和交通灯

*源于 [Low Voltage Labs](http://lowvoltagelabs.com/). [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)*
使用树莓派可以很轻松地进行物理计算,只需要连接几个 LED 和按钮到开发板上的 GPIO 接口,再用几行代码你就可以按下按钮来开灯。一旦你了解了如何使用代码来完成这些基本的操作,接下来就可以根据你的想象来做其它事情了。
如果你知道如何让一个灯闪烁,你就可以控制三个灯闪烁。挑选三个和交通灯一样颜色的 LED 灯,然后编写控制交通灯的代码。如果你知道如何使用按钮触发事件,那么你就可以模拟一个行人过马路。同时你可以参考其它已经完成的交通灯附件,比如[PI-TRAFFIC](http://lowvoltagelabs.com/products/pi-traffic/), [PI-STOP](http://4tronix.co.uk/store/index.php?rt=product/product&product_id=390), [Traffic HAT](https://ryanteck.uk/hats/1-traffichat-0635648607122.html),等等。
代码并不是全部——这只是一个演练,让你理解现实世界里系统是如何完成设计的。计算思维是一个让你终身受用的技能。

*源于 Raspberry Pi 基金会. [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)*
接下来试着接通两个按钮和 LED 灯的电源,实现一个双玩家的反应游戏 —— 让 LED 灯随机时间点亮,然后看是谁抢先按下按钮。
要想了解更多可以看看 [GPIO Zero recipes](http://pythonhosted.org/gpiozero/recipes/)。你所需要的资料都可以在 [CamJam EduKit 1](http://camjam.me/?page_id=236) 找到。
### 3. Sense HAT 电子宠物
Astro Pi —— 一个增强版的树莓派 —— 将在 12 月问世,但是你并没有错过亲手把玩这个硬件的机会。Sense HAT 是使用在 Astro Pi 的一个传感器扩展板,现在已经开放购买了。你可以使用它来进行数据搜集、科学实验,游戏等等。可以看看下面树莓派的 Carrie Anne 拍摄的 Gurl Geek Diaries 的视频,里面演示了一种很棒的入门途径——在 Sense HAT 屏幕上自己设计一个生动的像素宠物:[视频](https://youtu.be/gfRDFvEVz-w)(墙外)。
>
> 详见 "[探索 Sense HAT](https://opensource.com/life/15/10/exploring-raspberry-pi-sense-hat)."
>
>
>
### 4. 红外鸟笼

*源于 Raspberry Pi 基金会. [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)*
让整个班级都可以参与进来的好主意是在鸟笼里放置一个树莓派和夜视镜头,以及一些红外线灯,这样子你就可以在黑暗中看见鸟笼里的情况了,然后使用树莓派通过网络串流视频。然后就可以等待小鸟归笼了,你可以在不打扰的情况下近距离观察小窝里的它们了。
要了解更多有关红外线和光谱的知识,以及如何校准摄像头焦点和使用软件控制摄像头,可以访问 [打造一个红外鸟笼](https://www.raspberrypi.org/learning/infrared-bird-box/)。
### 5. 机器人

*源于 Raspberry Pi 基金会. [CC BY-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)*
只需要一个树莓派、很少的几个电机和电机控制器,你就可以自己动手制作一个机器人。可以制作的机器人有很多种,从简单的由几个轮子和自制底盘拼凑的简单小车,到由游戏控制器驱动、具有自我意识、配备了传感器,安装了摄像头的金属小马。
要学习如何控制不同的电机,可以使用 RTK 电机驱动开发板入门或者使用配置了电机、轮子和传感器的 CamJam 机器人开发套件——具有很大的价值和大量的学习潜力。
或者,如果你还想了解更多核心内容,可以试试 PiBorg 的 [4Borg](https://www.piborg.org/4borg)(£99/$150)和 [DiddyBorg](https://www.piborg.org/diddyborg)(£180/$273),或者购买 Metal 版 DoodleBorg (£250/$380),然后构建一个最小版本的 [DoodleBorg tank](https://www.piborg.org/doodleborg)(非卖品)。
详情可见 [机器人装备表](http://camjam.me/?page_id=1035#worksheets)。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/education/15/12/5-great-raspberry-pi-projects-classroom>
作者:[Ben Nuttall](https://opensource.com/users/bennuttall) 译者:[ezio](https://github.com/oska874) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | ## 1. Minecraft Pi
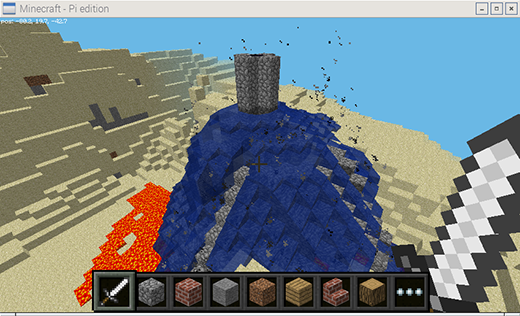
Courtesy of the Raspberry Pi Foundation. CC BY-SA 4.0.
Minecraft is the favorite game of pretty much every teenager in the world—and it's one of the most creative games ever to capture the attention of young people. The version that comes with every Raspberry Pi is not only a creative thinking building game, but comes with a programming interface allowing for additional interaction with the Minecraft world through Python code.
Minecraft: Pi Edition is a great way for teachers to engage students with problem solving and writing code to perform tasks. You can use the Python API to build a house and have it follow you wherever you go, build a bridge wherever you walk, make it rain lava, show the temperature in the sky, and anything else your imagination can create.
Read more in "[Getting Started with Minecraft Pi](https://opensource.com/life/15/5/getting-started-minecraft-pi)."
## 2. Reaction game and traffic lights
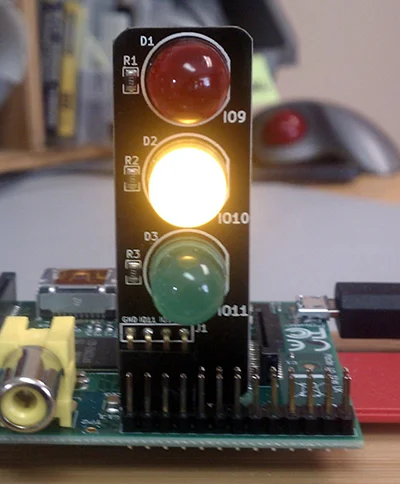

Courtesy of Low Voltage Labs. CC BY-SA 4.0.
It's really easy to get started with physical computing on Raspberry Pi—just connect up LEDs and buttons to the GPIO pins, and with a few lines of code you can turn lights on and control things with button presses. Once you know the code to do the basics, it's down to your imagination as to what you do next!
If you know how to flash one light, you can flash three. Pick out three LEDs in traffic light colors and you can code the traffic light sequence. If you know how to use a button to a trigger an event, then you have a pedestrian crossing! Also look out for great pre-built traffic light add-ons like [PI-TRAFFIC](http://lowvoltagelabs.com/products/pi-traffic/), [PI-STOP](http://4tronix.co.uk/store/index.php?rt=product/product&product_id=390), [Traffic HAT](https://ryanteck.uk/hats/1-traffichat-0635648607122.html), and more.
It's not always about the code—this can be used as an exercise in understanding how real world systems are devised. Computational thinking is a useful skill in any walk of life.

Courtesy of the Raspberry Pi Foundation. CC BY-SA 4.0.
Next, try wiring up two buttons and an LED and making a two-player reaction game—let the light come on after a random amount of time and see who can press the button first!
To learn more, check out [GPIO Zero recipes](http://pythonhosted.org/gpiozero/recipes/). Everything you need is in [CamJam EduKit 1](http://camjam.me/?page_id=236).
## 3. Sense HAT Pixel Pet
The Astro Pi—an augmented Raspberry Pi—is going to space this December, but you haven't missed your chance to get your hands on the hardware. The Sense HAT is the sensor board add-on used in the Astro Pi mission and it's available for anyone to buy. You can use it for data collection, science experiments, games and more. Watch this Gurl Geek Diaries video from Raspberry Pi's Carrie Anne for a great way to get started—by bringing to life an animated pixel pet of your own design on the Sense HAT display:
Learn more in "[Exploring the Sense HAT](https://opensource.com/life/15/10/exploring-raspberry-pi-sense-hat)."
## 4. Infrared bird box

Courtesy of the Raspberry Pi Foundation. CC BY-SA 4.0.
A great exercise for the whole class to get involved with—place a Raspberry Pi and the NoIR camera module inside a bird box along with some infra-red lights so you can see in the dark, then stream video from the Pi over the network or on the internet. Wait for birds to nest and you can observe them without disturbing them in their habitat.
Learn all about infrared and the light spectrum, and how to adjust the camera focus and control the camera in software.
Learn more in "[Make an infrared bird box](https://www.raspberrypi.org/learning/infrared-bird-box/)."
## 5. Robotics
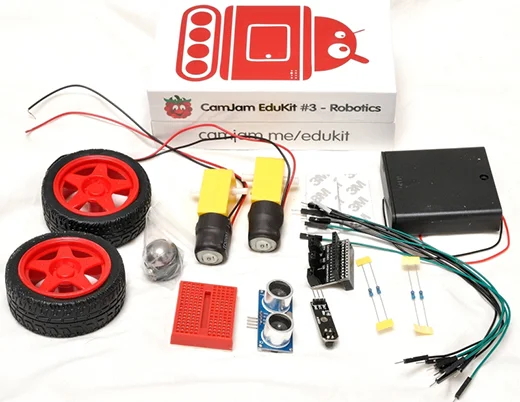

Courtesy of Low Voltage Labs. CC BY-SA 4.0.
With a Raspberry Pi and as little as a couple of motors and a motor controller board, you can build your own robot. There is a vast range of robots you can make, from basic buggies held together by sellotape and a homemade chassis, all the way to self-aware, sensor-laden metallic stallions with camera attachments driven by games controllers.
Learn how to control individual motors with something straightforward like the RTK Motor Controller Board (£8/$12), or dive into the new CamJam robotics kit (£17/$25) which comes with motors, wheels and a couple of sensors—great value and plenty of learning potential.
Alternatively, if you'd like something more hardcore, try PiBorg's [4Borg](https://www.piborg.org/4borg) (£99/$150) or [DiddyBorg](https://www.piborg.org/diddyborg) (£180/$273) or go the whole hog and treat yourself to their DoodleBorg Metal edition (£250/$380)—and build a mini version of their infamous [DoodleBorg tank](https://www.piborg.org/doodleborg) (unfortunately not for sale).
Check out the [CamJam robotics kit worksheets](http://camjam.me/?page_id=1035#worksheets).
## 5 Comments |
7,356 | Docker 1.11 采纳了开源容器项目(OCP)组件 | http://www.infoworld.com/article/3055966/open-source-tools/docker-111-adopts-open-container-project-components.html | 2016-05-18T10:50:00 | [
"Docker",
"OCP"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7356-1.html | 
>
> Docker 在<ruby> 开放容器项目 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Open Container Project,OCP </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>中的参与度达成圆满,最新构建的 Docker 采用了 Docker 贡献给 OCP 的组件。
>
>
>
新发布的 [Docker 1.11](https://blog.docker.com/2016/04/docker-engine-1-11-runc/) 的最大新闻并不是它的功能,而是它使用了在 OCP 支持下的标准化的组件版本。
去年,Docker 贡献了它的 [runC](http://runc.io/) 核心给 OCP 作为构建构建容器工具的基础。同样还有 [containerd](https://containerd.tools/),作为守护进程或者服务端用于控制 runC 的实例。Docker 1.11 现在使用的就是这个捐赠和公开的版本。
Docker 此举挑战了它的容器生态仍[主要由 Docker 自身决定](http://www.infoworld.com/article/2876801/application-virtualization/docker-reorganization-grows-up.html)这个说法。它并不是为了作秀才将容器规范和运行时细节贡献给 OCP。它希望项目将来的开发越开放和广泛越好。

*Docker 1.11 已经用贡献给 OCP 的 runC 和 containerd 进行了重构。runC 如果需要的话可以换成另外一个。*
runC 的[两位主要提交者](https://github.com/opencontainers/runc/graphs/contributors)来自 Docker,但是来自 Virtuozzo(Parallels fame)、OpenShift、Project Atomic、华为、GE Healthcare、Suse Linux 也都是提交人员里面的常客。
Docker 1.11 中一个更明显的变化是先前 Docker runtime 在 Docker 中是唯一可用的,并且评论家认为这个会限制用户的选择。runC runtime 现在是可替换的;虽然 Docker 在发布时将 runC 作为默认引擎,但是任何兼容的引擎都可以用来替换它。(Docker 同样希望它可以不用杀死并重启现在运行的容器,但是这个作为今后的改进规划。)
Docker 正在将基于 OCP 的开发流程作为内部创建其产品的更好方式。在它发布 1.11 的[官方博客中称](https://blog.docker.com/2016/04/docker-engine-1-11-runc/):“将 Docker 切分成独立的工具意味着更专注的维护者,最终会有更好的软件质量。”
除了修复长期以来存在的问题和确保 Docker 的 runC/containerd 跟上步伐,Docker 还在 Docker 1.11 中加入了一些改进。Docker Engine 现在支持 VLAN 和 IPv6 服务发现,并且会自动在多个相同别名容器间执行 DNS 轮询负载均衡。
---
via: <http://www.infoworld.com/article/3055966/open-source-tools/docker-111-adopts-open-container-project-components.html>
作者:[Serdar Yegulalp](http://www.infoworld.com/author/Serdar-Yegulalp/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,360 | SUSE Linux 企业版的实时补丁将带来无中断的服务 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/suse-linux-enterprise-live-patching-promises-100-uptime-for-businesses-504167.shtml | 2016-05-19T09:15:00 | [
"实时补丁",
"热补丁",
"SUSE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7360-1.html | 开源先锋及 SUSE Linux 的创造者 SUSE 公司宣布推出 SUSE Linux 企业版的<ruby> <a href="https://www.suse.com/products/live-patching/"> 实时补丁 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Live Patching </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。

SUSE 是首批为基于 Linux 内核的操作系统提供实时补丁的开源公司之一。实时补丁技术是在 Linux 4.0 系列内核中实现的一种技术,发布于一年前。
但是,只有很少的 GNU/Linux 操作系统在其架构内支持了实时补丁功能,因为看起来该技术大多会用于企业用户,大型公司并不希望由于内核升级而导致业务中断。
从今天开始,所有运行 SAP NetWeaver 技术平台、SAP HANA 平台以及其它的 SAP(<ruby> 系统应用产品 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Systems Applications Products </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)应用的 SUSE 用户都可以使用 [SUSE Linux 企业版实时补丁](https://www.suse.com/products/live-patching/)了,这可以帮助他们节约开销,业务永不停顿。
“依赖于实时数据和分析的服务日益竞争激烈,而保持应用服务器可持续访问很关键”,SUSE 战略联盟与市场总裁 Michael Miller 说道,“我们认为业务将不应该由于服务器更新而停顿。”
### 实时内核补丁可以让业务免受停机困扰
在过去,在那些需要高度安全的 IT 环境中,许多业务由于例行的停机维护而造成了大量损失。但是现在这一切都将改变,因为 SUSE Linux 企业版实时补丁,可以让企业级 Linux 用户应用内核补丁而不需要重启服务器。
SUSE Linux 企业版实时补丁也对于重要的 SAP 商业应用非常关键,比如那些运行 SAP HANA 的企业。该技术内建于内核之中,可以让 SUSE Linux 用户更新其正在运行的 Linux 内核,而不需要中断服务或由于重启服务器导致 SAP HANA 平台关闭。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,365 | LFCS 系列第七讲:通过 SysVinit、Systemd 和 Upstart 管理系统自启动进程和服务 | http://www.tecmint.com/linux-boot-process-and-manage-services/ | 2016-05-20T10:01:00 | [
"LFCS",
"SysVinit",
"Systemd",
"Upstart"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7365-1.html | 几个月前, Linux 基金会宣布 LFCS (Linux 基金会认证系统管理员) 认证诞生了,这个令人兴奋的新计划定位于让来自全球各地的初级到中级的 Linux 系统管理员得到认证。这其中包括维护已经在运行的系统和服务的能力、第一手的问题查找和分析能力、以及决定何时向开发团队提交问题的能力。

*第七讲: Linux 基金会认证系统管理员*
下面的视频简要介绍了 Linux 基金会认证计划。
本讲是系列教程中的第七讲,在这篇文章中,我们会介绍如何管理 Linux 系统自启动进程和服务,这是 LFCS 认证考试要求的一部分。
### 管理 Linux 自启动进程
Linux 系统的启动程序包括多个阶段,每个阶段由一个不同的图示块表示。下面的图示简要总结了启动过程以及所有包括的主要组件。

*Linux 启动过程*
当你按下你机器上的电源键时,存储在主板 EEPROM 芯片中的固件初始化 POST(通电自检) 检查系统硬件资源的状态。POST 结束后,固件会搜索并加载位于第一块可用磁盘上的 MBR 或 EFI 分区的第一阶段引导程序,并把控制权交给引导程序。
#### MBR 方式
MBR 是位于 BIOS 设置中标记为可启动磁盘上的第一个扇区,大小是 512 个字节。
* 前面 446 个字节:包括可执行代码和错误信息文本的引导程序
* 接下来的 64 个字节:四个分区(主分区或扩展分区)中每个分区一条记录的分区表。其中,每条记录标示了每个一个分区的状态(是否活跃)、大小以及开始和结束扇区。
* 最后 2 个字节: MBR 有效性检查的魔法数。
下面的命令对 MBR 进行备份(在本例中,/dev/sda 是第一块硬盘)。结果文件 mbr.bkp 在分区表被破坏、例如系统不可引导时能排上用场。
当然,为了后面需要的时候能使用它,我们需要把它保存到别的地方(例如一个 USB 设备)。该文件能帮助我们重新恢复 MBR,这只在我们操作过程中没有改变硬盘驱动布局时才有效。
**备份 MBR**
```
# dd if=/dev/sda of=mbr.bkp bs=512 count=1
```

*在 Linux 中备份 MBR*
**恢复 MBR**
```
# dd if=mbr.bkp of=/dev/sda bs=512 count=1
```

*在 Linux 中恢复 MBR*
#### EFI/UEFI 方式
对于使用 EFI/UEFI 方式的系统, UEFI 固件读取它的设置来决定从哪里启动哪个 UEFI 应用。(例如, EFI 分区位于哪块磁盘或分区。
接下来,加载并运行第二阶段引导程序(又名引导管理器)。GRUB[GRand Unified Boot] 是 Linux 中最常使用的引导管理器。今天大部分使用的系统中都能找到它两个中的其中一个版本。
* GRUB 有效配置文件: /boot/grub/menu.lst(旧发行版, EFI/UEFI 固件不支持)。
* GRUB2 配置文件: 通常是 /etc/default/grub。
尽管 LFCS 考试目标没有明确要求了解 GRUB 内部知识,但如果你足够大胆并且不怕把你的系统搞乱(为了以防万一,你可以先在虚拟机上进行尝试)你可以运行:
```
# update-grub
```
为了使更改生效,你需要以 root 用户修改 GRUB 的配置。
首先, GRUB 加载默认的内核以及 initrd 或 initramfs 镜像。补充一句,initrd 或者 initramfs 帮助完成硬件检测、内核模块加载、以及发现挂载根目录文件系统需要的设备。
一旦真正的根目录文件系统启动,为了显示用户界面,内核就会执行系统和服务管理器(init 或 systemd,进程号 PID 一般为 1)开始普通用户态的引导程序。
init 和 systemd 都是管理其它守护进程的守护进程(后台进程),它们总是最先启动(系统引导时),最后结束(系统关闭时)。

*Systemd 和 Init*
### 自启动服务(SysVinit)
Linux 中运行等级通过控制运行哪些服务来以不同方式使用系统。换句话说,运行等级控制着当前执行状态下可以完成什么任务(以及什么不能完成)。
传统上,这个启动过程是基于起源于 System V Unix 的形式,通过执行脚本启动或者停止服务从而使机器进入指定的运行等级(换句话说,是一个不同的系统运行模式)。
在每个运行等级中,独立服务可以设置为运行、或者在运行时关闭。一些主流发行版的最新版本中,已经移除了标准的 System V,而用一个称为 systemd(表示系统守护进程)的新服务和系统管理器代替,但为了兼容性,通常也支持 sysv 命令。这意味着你可以在基于 systemd 的发行版中运行大部分有名的 sysv 初始化工具。
* 推荐阅读: [Linux 为什么用 ‘systemd’ 代替 ‘init’](http://www.tecmint.com/systemd-replaces-init-in-linux/)
除了启动系统进程,init 还会查看 /etc/inittab 来决定进入哪个运行等级。
| Runlevel | Description |
| --- | --- |
| 0 | 停止系统。运行等级 0 是一个用于快速关闭系统的特殊过渡状态。 |
| 1 | 别名为 s 或 S,这个运行等级有时候也称为维护模式。在这个运行等级启动的服务由于发行版不同而不同。通常用于正常系统操作损坏时低级别的系统维护。 |
| 2 | 多用户。在 Debian 系统及其衍生版中,这是默认的运行等级,还包括了一个图形化登录(如果有的话)。在基于红帽的系统中,这是没有网络的多用户模式。 |
| 3 | 在基于红帽的系统中,这是默认的多用户模式,运行除了图形化环境以外的所有东西。基于 Debian 的系统中通常不会使用这个运行等级以及等级 4 和 5。 |
| 4 | 通常默认情况下不使用,可用于自定制。 |
| 5 | 基于红帽的系统中,支持 GUI 登录的完全多用户模式。这个运行等级和等级 3 类似,但是有可用的 GUI 登录。 |
| 6 | 重启系统。 |
要在运行等级之间切换,我们只需要使用 init 命令更改运行等级:init N(其中 N 是上面列出的一个运行等级)。 请注意这并不是运行中的系统切换运行等级的推荐方式,因为它不会给已经登录的用户发送警告(因而导致他们丢失工作以及进程异常终结)。
相反,应该用 shutdown 命令重启系统(它首先发送警告信息给所有已经登录的用户,并锁住任何新的登录;然后再给 init 发送信号切换运行等级)但是,首先要在 /etc/inittab 文件中设置好默认的运行等级(系统引导到的等级)。
因为这个原因,按照下面的步骤切当地切换运行等级。以 root 用户在 /etc/inittab 中查找下面的行。
```
id:2:initdefault:
```
并用你喜欢的文本编辑器,例如 vim(本系列的 [LFCS 系列第二讲:如何安装和使用纯文本编辑器 vi/vim](/article-7165-1.html)),更改数字 2 为想要的运行等级。
然后,以 root 用户执行
```
# shutdown -r now
```
最后一个命令会重启系统,并使它在下一次引导时进入指定的运行等级,并会执行保存在 /etc/rc[runlevel].d 目录中的脚本以决定应该启动什么服务、不应该启动什么服务。例如,在下面的系统中运行等级 2。

*在 Linux 中更改运行等级*
#### 使用 chkconfig 管理服务
为了在启动时启动或者停用系统服务,我们可以在 CentOS / openSUSE 中使用 [chkconfig 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/chkconfig-command-examples/),在 Debian 及其衍生版中使用 sysv-rc-conf 命令。这个工具还能告诉我们对于一个指定的运行等级预先配置的状态是什么。
* 推荐阅读: [如何在 Linux 中停止和停用不想要的服务](http://www.tecmint.com/remove-unwanted-services-from-linux/)
列出某个服务的运行等级配置。
```
# chkconfig --list [service name]
# chkconfig --list postfix
# chkconfig --list mysqld
```

*列出运行等级配置*
从上图中我们可以看出,当系统进入运行等级 2 到 5 的时候就会启动 postfix,而默认情况下运行等级 2 到 4 时会运行 mysqld。现在假设我们并不希望如此。
例如,我们希望运行等级为 5 时也启动 mysqld,运行等级为 4 或 5 时关闭 postfix。下面分别针对两种情况进行设置(以 root 用户执行以下命令)。
**为特定运行等级启用服务**
```
# chkconfig --level [level(s)] service on
# chkconfig --level 5 mysqld on
```
**为特定运行等级停用服务**
```
# chkconfig --level [level(s)] service off
# chkconfig --level 45 postfix off
```

*启用/停用服务*
我们在基于 Debian 的系统中使用 sysv-rc-conf 完成类似任务。
#### 使用 sysv-rc-conf 管理服务
配置服务自动启动时进入指定运行等级,同时禁止启动时进入其它运行等级。
1. 我们可以用下面的命令查看启动 mdadm 时的运行等级。
```
# ls -l /etc/rc[0-6].d | grep -E 'rc[0-6]|mdadm'
```

*查看运行中服务的运行等级*
2. 我们使用 sysv-rc-conf 设置防止 mdadm 在运行等级2 之外的其它等级启动。只需根据需要(你可以使用上下左右按键)选中或取消选中(通过空格键)。
```
# sysv-rc-conf
```

*Sysv 运行等级配置*
然后输入 q 退出。
3. 重启系统并从步骤 1 开始再操作一遍。
```
# ls -l /etc/rc[0-6].d | grep -E 'rc[0-6]|mdadm'
```

*验证服务运行等级*
从上图中我们可以看出 mdadm 配置为只在运行等级 2 上启动。
### 那关于 systemd 呢?
systemd 是另外一个被多种主流 Linux 发行版采用的服务和系统管理器。它的目标是允许系统启动时多个任务尽可能并行(而 sysvinit 并非如此,sysvinit 一般比较慢,因为它每次只启动一个进程,而且会检查彼此之间是否有依赖,在启动其它服务之前还要等待守护进程启动),充当运行中系统动态资源管理的角色。
因此,服务只在需要的时候启动,而不是系统启动时毫无缘由地启动(为了防止消耗系统资源)。
要查看你系统中运行的原生 systemd 服务和 Sysv 服务,可以用以下的命令。
```
# systemctl
```

*查看运行中的进程*
LOAD 一列显示了单元(UNIT 列,显示服务或者由 systemd 维护的其它进程)是否正确加载,ACTIVE 和 SUB 列则显示了该单元当前的状态。
**显示服务当前状态的信息**
当 ACTIVE 列显示某个单元状态并非活跃时,我们可以使用以下命令查看具体原因。
```
# systemctl status [unit]
```
例如,上图中 media-samba.mount 处于失败状态。我们可以运行:
```
# systemctl status media-samba.mount
```

*查看服务状态*
我们可以看到 media-samba.mount 失败的原因是 host dev1 上的挂载进程无法找到 //192.168.0.10/gacanepa 上的共享网络。
### 启动或停止服务
一旦 //192.168.0.10/gacanepa 上的共享网络可用,我们可以再来尝试启动、停止以及重启 media-samba.mount 单元。执行每次操作之后,我们都执行 systemctl stats media-samba.mout 来查看它的状态。
```
# systemctl start media-samba.mount
# systemctl status media-samba.mount
# systemctl stop media-samba.mount
# systemctl restart media-samba.mount
# systemctl status media-samba.mount
```

*启动停止服务*
**启用或停用某服务随系统启动**
使用 systemd 你可以在系统启动时启用或停用某服务
```
# systemctl enable [service] # 启用服务
# systemctl disable [service] # 阻止服务随系统启动
```
启用或停用某服务随系统启动包括在 /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants 目录添加或者删除符号链接。

*启用或停用服务*
你也可以用下面的命令查看某个服务的当前状态(启用或者停用)。
```
# systemctl is-enabled [service]
```
例如,
```
# systemctl is-enabled postfix.service
```
另外,你可以用下面的命令重启或者关闭系统。
```
# systemctl reboot
# systemctl shutdown
```
### Upstart
基于事件的 Upstart 是 /sbin/init 守护进程的替代品,它仅为在需要那些服务的时候启动服务而生,(或者当它们在运行时管理它们),以及处理发生的实践,因此 Upstart 优于基于依赖的 sysvinit 系统。
一开始它是为 Ubuntu 发行版开发的,但在红帽企业版 Linux 6.0 中得到使用。尽管希望它能在所有 Linux 发行版中替代 sysvinit,但它已经被 systemd 超越。2014 年 2 月 14 日,Mark Shuttleworth(Canonical Ltd. 创建者)发布声明之后的 Ubuntu 发行版采用 systemd 作为默认初始化守护进程。
由于 Sysv 启动脚本已经流行很长时间了,很多软件包中都包括了 Sysv 启动脚本。为了兼容这些软件, Upstart 提供了兼容模式:它可以运行保存在常用位置(/etc/rc.d/rc?.d, /etc/init.d/rc?.d, /etc/rc?.d或其它类似的位置)的Sysv 启动脚本。因此,如果我们安装了一个还没有 Upstart 配置脚本的软件,仍然可以用原来的方式启动它。
另外,如果我们还安装了类似 [chkconfig](http://www.tecmint.com/chkconfig-command-examples/) 的工具,你还可以和在基于 sysvinit 的系统中一样用它们管理基于 Sysv 的服务。
Upstart 脚本除了支持 Sysv 启动脚本,还支持基于多种方式启动或者停用服务;例如, Upstart 可以在一个特定硬件设备连接上的时候启动一个服务。
使用 Upstart以及它原生脚本的系统替换了 /etc/inittab 文件和 /etc/init 目录下和运行等级相关的以 .conf 作为后缀的 Sysv 启动脚本目录。
这些 \*.conf 脚本(也称为任务定义)通常包括以下几部分:
* 进程描述
* 进程的运行等级或者应该触发它们的事件
* 应该停止进程的运行等级或者触发停止进程的事件
* 选项
* 启动进程的命令
例如,
```
# My test service - Upstart script demo description "Here goes the description of 'My test service'" author "Dave Null <[email protected]>"
# Stanzas
#
# Stanzas define when and how a process is started and stopped
# See a list of stanzas here: http://upstart.ubuntu.com/wiki/Stanzas#respawn
# When to start the service
start on runlevel [2345]
# When to stop the service
stop on runlevel [016]
# Automatically restart process in case of crash
respawn
# Specify working directory
chdir /home/dave/myfiles
# Specify the process/command (add arguments if needed) to run
exec bash backup.sh arg1 arg2
```
要使更改生效,你要让 upstart 重新加载它的配置文件。
```
# initctl reload-configuration
```
然后用下面的命令启动你的任务。
```
$ sudo start yourjobname
```
其中 yourjobname 是之前 yourjobname.conf 脚本中添加的任务名称。
关于 Upstart 更完整和详细的介绍可以参考该项目网站的 “[Cookbook](http://upstart.ubuntu.com/cookbook/)” 栏目。
### 总结
了解 Linux 启动进程对于你进行错误处理、调整计算机系统以及根据需要运行服务非常有用。
在这篇文章中,我们分析了你按下电源键启动机器的一刻到你看到完整的可操作用户界面这段时间发生了什么。我希望你能像我一样把它们放在一起阅读。欢迎在下面留下你的评论或者疑问。我们总是期待听到读者的回复。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/linux-boot-process-and-manage-services/>
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa](http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/) 译者:[ictlyh](http://mutouxiaogui.cn/blog/) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,370 | 震惊:2/3 被黑的网站隐藏着后门 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/two-in-three-hacked-websites-hide-a-backdoor-504242.shtml | 2016-05-21T10:34:00 | [
"入侵",
"后门"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7370-1.html | 网络安全公司 Sucuri 的安全专家说,他们在调查中发现有 68% 的被黑网站存在着隐藏的<ruby> 后门 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> backdoor </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>脚本。这些后门脚本会给入侵者提供再次进入秘密通道,即便系统管理员改变了口令或应用了安全补丁,只要没有完全的清理整个系统,后门就会依旧存在。
从他们发布的[网站被黑报告](https://sucuri.net/website-security/Reports/Sucuri-Website-Hacked-Report-2016Q1.pdf) 2016 Q1 版中可以看到,全部取样的 11485 个网站中,有 4900 个网站发现了后门。
在这些被入侵的网站中,后门是最严重的问题,其次是恶意软件(通过浏览器端的代码进行<ruby> 挂马攻击 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> drive-by download </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>),占比 60%。
第三名是 <ruby> SEO 垃圾 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> SEO spam </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,大约 32% 的网站存在该问题。SEO 垃圾通常会秘密嵌入到页面中,浏览者看不见,而对于搜索引擎的爬虫可见。

### 挂马攻击和 SEO 垃圾也很流行
SEO 垃圾可以帮助恶意攻击者提升其网站的搜索引擎排名,而对被感染的网站来说,则会受到搜索引擎的惩罚和排名下降。
这些受益的恶意攻击者通常会将 SEO 垃圾放到感染网站的源代码中、数据库中,或者通过 .htaccess 重定向实现。多数情况下,SEO 垃圾被用在药品方面,也有给成人内容或在线游戏提供的。
与去年相比,后门脚本比例略有降低,SEO 垃圾有小幅提升,而恶意软件感染则相较前些年增幅最大,从 2014 年的 41% 增加到了 2016 年的 60%!作为对比,后门脚本则从2014年的 59% 到 2015 年的 73%,现在回落到 68%;SEO 垃圾从 20% 到 28%,到了2016 年就增加到了 28%。

| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,372 | 使用 arch-ppa 创建你自己的 Arch Linux 软件库 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/new-tool-promises-to-help-you-create-your-own-arch-linux-package-repositories-504257.shtml | 2016-05-22T09:35:00 | [
"软件仓库",
"Arch Linux",
"arch-ppa"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7372-1.html | 是不是觉得 AUR 软件库维护太复杂?那么我们来给你介绍一个新工具,可以让你很方便的维护一个你自己的 Arch Linux 软件仓库。
我们在互联网上发现了一个叫做 arch-ppa 的工具,它刚刚发布到 GitHub 上才几周,它作者 Ryan McGuire 说这个工具可以帮助你创建和维护一个安全可靠的个人 Arch Linux 软件仓库。
你可以把 arch-ppa 想象成一个 Arch Linux 下的 PPA(<ruby> 个人软件包存档 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Personal Package Archive </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>),就像 Ubuntu Linux 中常用的各种 PPA 一样。它存放在你自己的本地设备上,也可以放到远程服务器上以便你可以把你的软件包分发给成千上万的 Arch Linux 用户们。

### 因为 AUR 不安全,才有了 arch-ppa
arch-ppa 的开发者 Ryan McGuire 说他创建这个工具可以让 Arch Linux 的个人软件包生态系统更加的安全可靠,现在官方支持的 AUR(<ruby> <a href="https://aur.archlinux.org/"> Arch 用户软件库 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Arch User Repository </rt></ruby>)可以让任何人懂得 AUR 的人都可以上载新软件和维护它。
现在的情况是,如果你从 AUR 安装一个由你我维护这样的用户所维护的软件包,会触发一个大大的警告,是否接受该警告并安装取决于你自己。幸运的是, AUR 是由一群负责任的 Arch Linux 用户所维护的,他们一旦发现了恶意软件就会马上删除。
“这就是我为什么不喜欢类似 yaourt 或 pacaur 这样的 AUR 辅助程序。用这些辅助程序来使用 AUR 需要你经常查看它下载的 PKGBUILD 文件,才能让你可以确保不会安装了类似病毒或木马这样的东西以及从某个不知道来源的 URL 下载东西。” Ryan McGuire 说。
而这就是 arch-ppa 可以发挥用途的地方,AUR 软件包维护者希望开发一个好用的工具来帮助人工创建软件仓库,以便他们可以在一个安全可靠的环境中分发 Arch Linux 软件包。但是,要求就是你需要有一台服务器。
AUR 在 Arch Linux 用户群体里已经使用了很久,如果你想建立一个你自己的 Arch Linux 软件包归档,那么你应该试试 arch-ppa。具体情况请进一步访问该项目的 [GitHub 主页](https://github.com/EnigmaCurry/arch-ppa)。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,378 | 使用 SystemBack 备份/还原你的 Ubuntu/Linux Mint | http://www.noobslab.com/2015/11/backup-system-restore-point-your.html | 2016-05-23T11:10:00 | [
"备份",
"还原",
"Systemback"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7378-1.html | 对于任何一款允许用户还原电脑到之前状态(包括文件系统,安装的应用,以及系统设置)的操作系统来说,系统还原功能都是必备功能,它可以恢复系统故障以及其他的问题。
有的时候安装一个程序或者驱动可能让你的系统黑屏。系统还原则可以让你电脑里面的系统文件(LCTT 译注:是系统文件,并非普通文件,详情请看**注意**部分)和程序恢复到之前工作正常时候的状态,进而让你远离那让人头痛的排障过程了,而且它也不会影响你的文件,照片或者其他数据。
简单的系统备份还原工具 [Systemback](https://launchpad.net/systemback) 可以让你很容易地创建系统备份以及用户配置文件。一旦遇到问题,你可以简单地恢复到系统先前的状态。它还有一些额外的特征包括系统复制,系统安装以及Live系统创建。
**截图**




**注意**:使用系统还原不会还原你自己的文件、音乐、电子邮件或者其他任何类型的私人文件。对不同用户来讲,这既是优点又是缺点。坏消息是它不会还原你意外删除的文件,不过你可以通过一个文件恢复程序来解决这个问题。如果你的计算机没有创建还原点,那么系统恢复就无法奏效,所以这个工具就无法帮助你(还原系统)。如果你尝试恢复这样的问题,你将需要移步到另外的步骤来进行故障排除。
>
> 适用于 Ubuntu 15.10 Wily/16.04/15.04 Vivid/14.04 Trusty/Linux Mint 14.x/其他Ubuntu衍生版,打开终端,将下面这些命令复制过去:
>
>
>
终端命令:
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nemh/systemback
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install systemback
```
大功告成。
---
via: <http://www.noobslab.com/2015/11/backup-system-restore-point-your.html>
译者:[DongShuaike](https://github.com/DongShuaike) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,380 | Ubuntu 的 Mir 显示服务器将支持 Vulkan | http://news.softpedia.com/news/vulkan-support-might-be-implemented-in-ubuntu-linux-s-mir-display-server-soon-504359.shtml | 2016-05-23T16:42:38 | [
"Vulkan",
"Mir",
"Unity"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7380-1.html | 很多人可能已经知道,Canonical 正在积极开发它的 Unity 用户界面,并将其用在 Ubuntu 桌面上。
Unity 8 是流行的 GNU/Linux 操作系统 Ubuntu 的下一代 Unity 桌面环境,Canonical 创始人 Mark Shuttleworth 之前说它马上就可以用了,并在即将到来的 Ubuntu 16.10 中会默认安装。
默认安装并不代表着它是默认桌面,Unity 7 仍将是 Ubuntu 16.10 的主要桌面环境。Ubuntu 16.10 将在今年的 10 月 20 日揭晓。当然,新的 Unity 8 环境在该版本发布后就可以直接切换使用了,不需要用户自己额外安装软件。
Canonical 已经在它的 Ubuntu 智能手机和平板上使用 Unity 8 用户界面获得了巨大成功,Unity 8 是由 Canonical 开发的 Mir 显示服务器所支撑的。现在这些新技术正在移植到 Ubuntu 桌面上,新功能请求也提交到了 Launchpad 上了。
### Mir 0.24 中完全支撑 Vulkan

Mir 当前版本是 0.22.1,但是据 Emanuele Antonio Faraone 在 2016 年 1 月[提交的功能请求](https://bugs.launchpad.net/mir/+bug/1539896),希望 Ubuntu 开发人员能够在 Mir 显示服务器和 Ubuntu 的系统镜像中完全支持 Vulkan 库的这一想法,已经得到了 Canonical 的首肯,看起来就快成为了现实。
>
> Vulkan 是一个跨平台的 2D 和 3D 绘图应用程序接口(API),最早由 Khronos Group 在2015年游戏开发者大会(GDC)上发表。就像 OpenGL,Vulkan 针对实时 3D 程序(如电子游戏)设计,Vulkan 并计划提供高性能和低 CPU 管理负担(overhead),这也是 Direct3D 12 和 AMD 的 Mantle 的目标。Vulkan 兼容 Mantle 的一个分支,并使用了 Mantle 的一些组件。
>
>
>
“过去几周已经初步集成了 Vulkan(Mesa),但是使用了一些私有头文件,” Mir 显示服务器项目负责人 Cemil Azizoglu 说,“还需要发布一些新的的 Mir 接口,当它们发布到开发主干上后,然后就可以准备放到正式版本了(0.24)。”
在写作此文时,Canonical 已经将完全支持 Vulkan API 作为当前正在开发的 [Mir 0.24](https://launchpad.net/mir/0.24) 的里程碑目标了。不过从上面的引述可以看到,Mir 中的 Vulkan 支持还需要不少开发工作。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,383 | systemd 230 发布,其 DNS 解析器默认支持 DNSSEC | http://news.softpedia.com/news/systemd-230-launches-with-dnssec-enabled-by-default-in-systemd-resolved-more-504339.shtml | 2016-05-24T08:26:00 | [
"systemd",
"DNSSEC"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7383-1.html | Zbigniew Jędrzejewski-Szmek [宣布](https://lists.freedesktop.org/archives/systemd-devel/2016-May/036583.html) systemd 发布了 230 版本,这是一个主要更新版本。上个版本 systemd 229 发布于大约三个月前。

本次更新主要的关注点是其 DNS 解析服务 systemd-resolved,现在它可以使用 DNSSEC 来校验解析结果了。正如你所知道的,systemd 的“魔爪”已经伸向了 GNU/Linux 中除了内核以外的各个基础部分,比如 DNS 解析器就是一个例子,它用于为系统内的 DNS 解析请求提供服务。在本次更新中,当使用“allow-downgrade”模式时,它会默认打开 DNSSEC 扩展。DNSSEC 是一个用于校验 DNS 解析数据是否安全的扩展,对于防范 DNS 欺诈有重要作用,只是到目前为止还有不少 DNS 服务器尚未支持,所以,你也可以在编译时通过增加“--with-default-dnssec=no”编译参数来关闭它。
“我们建议下游维护人员在开发期间打开该功能,并将发现的问题报告给上游,”Zbigniew Jędrzejewski-Szmek 说,“我们非常希望得到 DNSSEC 校验器的反馈,不管是哪种反馈。不过要注意,DNSSEC 支持可能在下游发行版的稳定版本中关闭,因为它可能会导致和一些 DNS 服务器及网络的不兼容。”
当然,systemd-resolved 并不是 systemd 初始化系统中唯一得到改进的部件,其它的部件也有不少改变。
systemd 230 不久之后将会进入到各个以 systemd 作为默认的初始化系统的 Linux 发行版之中。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,385 | 《道德经》之项目管理 | https://opensource.com/open-organization/16/2/tao-project-management | 2016-05-24T15:58:00 | [
"项目管理",
"道德经"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7385-1.html | 
《[道德经](http://acc6.its.brooklyn.cuny.edu/%7Ephalsall/texts/taote-v3.html)》,[被认为](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tao_Te_Ching)是由圣人[老子](http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/laozi/)于公元前六世纪时所编写,是现存最为广泛翻译的经文之一。从[宗教](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taoism)到[关于约会的有趣电影](http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0234853/)等方方面面,它都深深地影响着它们,作者们借用它来做隐喻,以解释各种各样的事情(甚至是[编程](http://www.mit.edu/%7Exela/tao.html))。
在思考有关开放性组织的项目管理时,我的脑海中便立马浮现出上面的这段文字。
这听起来可能会有点奇怪。若要理解我的这种想法从何而来,你应该读读 **《开放性组织:点燃激情提升执行力》** 这本书,它是红帽公司总裁、首席执行官 Jim Whitehurst 所写的一本有关企业文化和新领导力范式的宣言。在这本书中,Jim(还有来自其他红帽人的一点帮助)解释了传统组织机构(一种 “自上而下” 的方式,来自高层的决策被传达到员工,而员工通过晋升和薪酬来激励)和开放性组织机构(一种 自下而上 的方式,领导专注于激励和鼓励,员工被充分授权以各尽其能)之间的差异。
在开放性组织中的员工都是被激情、目标和参与感所激励,这个观点正是我认为项目管理者所应该关注的。
要解释这一切,我将从**道德经**上寻找依据。
### 不要让工作职衔框住自身
>
> <ruby> 道,可道也, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> The tao that can be told </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 非恒道也。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> is not the eternal Tao </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 名,可名也, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> The name that can be named </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 非恒名也。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> is not the eternal Name. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> “无”,名天地之始; <rp> ( </rp> <rt> The unnameable is the eternally real. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> “有”,名万物之母。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Naming is the origin of all particular things. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> [第一章](http://acc6.its.brooklyn.cuny.edu/%7Ephalsall/texts/taote-v3.html)
>
>
>
项目管理到底是什么?作为一个项目管理者应该做些什么呢?
如您所想,项目管理者的一部分工作就是管理项目:收集需求、与项目相关人员沟通、设置项目优先级、安排任务、帮助团队解决困扰。许多机构都可以教你如何做好项目管理,并且这些技能你值得拥有。
然而,在开放性组织中,字面上的项目管理技能仅仅只是项目管理者需要做到的一小部分,这些组织需要更多其他的东西:即勇气。如果你擅长于管理项目(或者是真的擅长于任何工作),那么你就进入了舒适区。这时候就是需要鼓起勇气开始尝试冒险之时。
您有勇气跨出舒适区吗?向权威人士提出挑战性的问题,可能会引发对方的不快,但也可能会开启一个更好的方法,您有勇气这样做吗?有确定需要做的下一件事,然后真正去完成它的勇气吗?有主动去解决因为交流的鸿沟而遗留下来的问题的勇气吗?有去尝试各种事情的勇气吗?有失败的勇气吗?
道德经的开篇(上面引用的)就表明<ruby> 词语 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> words </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 标签 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> labels </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 名字 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> names </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>这些是有限制的,当然也包括工作职衔。在开放性组织中,项目经理不仅仅是执行管理项目所需的机械任务,而且要帮助团队完成组织的使命,尽管这已经被限定了。
### 联系起合适的人
>
> <ruby> 三十辐共一轂, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> We join spokes together in a wheel, </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 当其无, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> but it is the center hole </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 有车之用。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> that makes the wagon move. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> [第十一章](http://acc6.its.brooklyn.cuny.edu/%7Ephalsall/texts/taote-v3.html#38)
>
>
>
当我过渡到项目管理的工作时,我必须学会的最为困难的一课是:并不是所有解决方案都是可完全地接受,甚至有的连预期都达不到。这对我来说是全新的一页。我**喜欢**全部都能解决。但作为项目管理者,我的角色更多的是与人沟通--使得那些确实有解决方案的人可以更高效地合作。
这并不是逃避责任或者不负责。这意味着可以很舒适的说,“我不知道,但我会给你找出答案”,然后就可迅速地结束这个循环。
想像一下马车的车轮,如果没有毂中的孔洞所提供的稳定性和方向,辐条便会失去支持,车轮也会散架。在一个开放性的组织中,项目管理者可以通过把合适的人凝聚在一起,培养正确的讨论话题来帮助团队保持持续向前的动力。
### 信任你的团队
>
> <ruby> 太上,不知有之; <rp> ( </rp> <rt> When the Master governs, the people are hardly aware that he exists. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 其次,亲而誉之; <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Next best is a leader who is loved. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 其次,畏之; <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Next, one who is feared. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 其次,侮之。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> The worst is one who is despised. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 信不足焉, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> If you don't trust the people, </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 有不信焉。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> you make them untrustworthy. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 悠兮,其贵言。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> The Master doesn't talk, he acts. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 功成事遂, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> When his work is done, </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 百姓皆谓:“我自然”。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> the people say, "Amazing: we did it, all by ourselves!" </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> [第十七章](http://acc6.its.brooklyn.cuny.edu/%7Ephalsall/texts/taote-v3.html#17)
>
>
>
[Rebecca Fernandez](https://opensource.com/users/rebecca) 曾经告诉我开放性组织的领导与其它组织的领导者最大的不同点在于,我们不是去取得别人的信任,而是信任别人。
开放性组织会雇佣那些非常聪明的,且对公司正在做的事情充满激情的人来做工作。为了能使他们能更好的工作,我们会提供其所需,并尊重他们的工作方式。
至于原因,我认为从道德经中摘出的上面一段就说的很清楚。
### 顺其自然
>
> <ruby> 上德无为而无以为; <rp> ( </rp> <rt> The Master does nothing yet he leaves nothing undone. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 下德为之而有以为。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> The ordinary man is always doing things, yet many more are left to be done. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> [第三十八章](http://acc6.its.brooklyn.cuny.edu/%7Ephalsall/texts/taote-v3.html#38)
>
>
>
你认识那类总是极其忙碌的人吗?认识那些因为有太多事情要做而看起来疲倦和压抑的人吗?
不要成为那样的人。
我知道说比做容易。帮助我没有成为那类人的最重要的东西是:我时刻记着*大家都很忙*这件事。我没有一个那样无聊的同事。
但总需要有人成为在狂风暴雨中仍保持镇定的人。总需要有人能够宽慰团队告诉他们一切都会好起来,我们将在现实和一天中工作时间有限的情况下,找到方法使得任务能够完成(因为事实就是这样的,而且我们必须这样)。
成为那样的人吧。
对于上面这段道德经所说的,我的理解是那些总是谈论他或她正在做什么的人实际上并**没有时间**去做他们谈论的事。如果相比于你周围的人,你能把你的工作做的毫不费劲,那就说明你的工作做对了。
### 做一名文化传教士
>
> <ruby> 上士闻道, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> When a superior man hears of the Tao, </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 勤而行之; <rp> ( </rp> <rt> he immediately begins to embody it. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 中士闻道, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> When an average man hears of the Tao, </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 若存若亡; <rp> ( </rp> <rt> he half believes it, half doubts it. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 下士闻道, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> When a foolish man hears of the Tao, </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 大笑之。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> he laughs out loud. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 不笑不足以為道。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> If he didn't laugh,it wouldn't be the Tao. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> [第四十一章](http://acc6.its.brooklyn.cuny.edu/%7Ephalsall/texts/taote-v3.html#41)
>
>
>
去年秋天,我和一群联邦雇员参加了一堂 MBA 的商业准则课程。当我开始介绍我们公司的文化、价值和伦理框架时,我得到的直接印象是:我的同学和教授都认为我就像一个天真可爱的小姑娘,做着许多关于公司应该如何运作的[甜美白日梦](https://opensource.com/open-organization/15/9/reflections-open-organization-starry-eyed-dreamer)。他们告诉我事情不可能是他们看起来的那样,他们还告诉我应该进一步考察。
所以我照做了。
然而我发现的是:事情**恰好**是他们看起来的那样。
在开放性组织,关于企业文化,人们应该随着企业的成长而时时维护那些文化,以使它随时精神焕发,充满斗志。我(和其它开源组织的成员)并不想过着如我同学们所描述的那样,“为生活而工作”。我需要有激情、有目标,需要明白自己的日常工作是如何对那些我所坚信的东西做贡献的。
作为一个项目管理者,你可能会认为在你的团队中,你的工作对培养你们公司的企业文化没有多少帮助。然而你的工作正是孕育文化本身。
### <ruby> Kaizen <rp> ( </rp> <rt> 持续改善 </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
> <ruby> 为学日益, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> In pursuit of knowledge,every day something is added. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 为道日损。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> In the practice of the Tao,every day something is dropped. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 损之又损, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Less and less do you need to force things, </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 以至于无为。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> until finally you arrive at non-action. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 无为而无不为。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> When nothing is done,nothing is left undone. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> [第四十八章](http://acc6.its.brooklyn.cuny.edu/%7Ephalsall/texts/taote-v3.html#48)
>
>
>
项目管理的常规领域都太过于专注最新、最强大的的工具,但对于应该使用哪种工具,这个问题的答案总是一致的:“最简单的”。
例如,我将任务列表放在桌面的一个文本文件中,因为它很单纯,不会受到不必要的干扰。您想介绍给团队的,无论是何种工具、流程和程序都应该是能提高效率,排除障碍的,而不是引入额外的复杂性。所以与其专注于工具,还不如专注于要使用这些工具来解决的**问题**。
作为一个项目经理,我最喜爱的部分是在敏捷世界中,我有自由抛弃那些没有成效的东西的权利。这与 [kaizen](https://www.kaizen.com/about-us/definition-of-kaizen.html) 的概念相关,或叫 “持续改进”。不要害怕尝试和失败。失败是我们在探索什么能够起作用,什么不能起作用的过程中所用的标签,这是提高的唯一方式。
最好的过程都不是一蹴而就的。作为项目管理者,你应该通过支持他们,而不是强迫他们去做某些事来帮助你的团队。
### 实践
>
> <ruby> 天下皆谓我“道”大, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Some say that my teaching is nonsense. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 似不肖。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Others call it lofty but impractical. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 夫唯大, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> But to those who have looked inside themselves, </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 故似不肖。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> this nonsense makes perfect sense. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 若肖, <rp> ( </rp> <rt> And to those who put it into practice, </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> 久矣其细也夫! <rp> ( </rp> <rt> this loftiness has roots that go deep. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> [第六十七章](http://acc6.its.brooklyn.cuny.edu/%7Ephalsall/texts/taote-v3.html#67)
>
>
>
我相信开放性组织正在做的事。开放性组织在管理领域的工作几乎与他们提供的产品和服务一样重要。我们有机会以身作则,激发他人的激情和目的,创造激励和充分授权的工作环境。
我鼓励你们找到办法把这些想法融入到自己的项目和团队中,看看会发生什么。了解你们组织的使命,知晓你的项目是如何为这个使命做贡献的。鼓起勇气,尝试某些看起来没有多少成效的事,同时不要忘记和我们的社区分享你所学到的经验,这样我们就可以继续改进。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/open-organization/16/2/tao-project-management>
作者:[Allison Matlack](https://opensource.com/users/amatlack) 译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | The [Tao Te Ching](http://acc6.its.brooklyn.cuny.edu/%7Ephalsall/texts/taote-v3.html), [believed to have been written](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tao_Te_Ching) by the sage [Lao Tzu](http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/laozi/) in the 6th century BCE, is among the most widely translated texts in existence. It has inspired everything from [religions](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taoism) to [funny movies about dating](http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0234853/), and authors have used it as a metaphor to explain all kinds of things (even [programming](http://www.mit.edu/%7Exela/tao.html)).
This text is what immediately comes to my mind when thinking about project management in open organizations.
That might sound strange. But to understand where I'm coming from, you should start by reading *The Open Organization: Igniting Passion and Performance*, Red Hat president and CEO Jim Whitehurst's manifesto on corporate culture and the new leadership paradigm. In this book, Jim (with a little help from other Red Hatters) explains the difference between conventional organizations (a "top-down" approach, with decisions coming down from central command to employees motivated by promotion and pay) and open organizations (a bottom-up approach, with leaders focused on inspiring purpose and passion so employees are empowered to be and do their best).
This concept—that employees in open organizations are motivated by passion, purpose, and engagement—plays directly into where I think project managers should focus.
And to explain, I'll return to the *Tao Te Ching*.
## Don't let your job title define you
The tao that can be told
is not the eternal Tao
The name that can be named
is not the eternal Name.The unnameable is the eternally real.
Naming is the origin
of all particular things. [[1]]
What exactly is *project management*? And what does a project manager *do*?
As you might expect, part of being a project manager is *managing projects*: gathering requirements, managing stakeholder communication, setting priority, scheduling tasks, helping the team resolve blockers. Many [institutions](http://www.pmi.org/certification/project-management-professional-pmp.aspx) can teach you how to manage projects very well, and these are good skills to have.
However, *literally* managing projects is only part of what project managers in open organizations do. These organizations require something more: *Courage*. If you're good at managing projects (or if you're good at any job, really), then you can start to feel safe in your routine. That's when you know you need to find the courage to take a risk.
Do you have the courage to step outside of your comfort zone? The courage to ask important people challenging questions that might raise eyebrows, but that might also uncover a better way forward? The courage to identify the next thing that needs to be done—then the courage to go and do it? The courage to call out communication gaps and take initiative to fix them? The courage to try things? The courage to fail?
The opening passage of the *Tao Te Ching* (which I cited above) suggests that words, labels, and names are limiting. That includes job titles. In open organizations, project managers don't just perform the rote tasks required to manage projects. They help teams *accomplish the organization's mission*, however defined.
## Connect the right people
We join spokes together in a wheel,
but it is the center hole
that makes the wagon move. [[11]]
One of the most difficult lessons I had to learn as I transitioned into project management was that not having all the answers was perfectly acceptable, even expected. That was new for me. I *like* having all the answers. But as a project manager, my role is more about *connecting* people—so the ones who *do* have the answers can collaborate efficiently.
This does not mean dodging responsibility or ownership. This means being comfortable saying, "I don't know, but I will find out for you," and closing that loop as quickly as possible.
Picture a wagon wheel. Without the stability and direction provided by the center hole, the spokes would fall and the wheel collapse in on itself. Project managers in an open organization can help a team maintain forward momentum by bringing the right people together and cultivating the right discussions.
## Trust your team
When the Master governs, the people
are hardly aware that he exists.
Next best is a leader who is loved.
Next, one who is feared.
The worst is one who is despised.If you don't trust the people,
you make them untrustworthy.The Master doesn't talk, he acts.
When his work is done,
the people say, "Amazing:
we did it, all by ourselves!" [[17]]
[Rebecca Fernandez](https://opensource.com/users/rebecca) once told me that what differentiates leaders in open organizations is not the trust people have *in them*, but the trust *they have* in other people.
Open organizations do a great job hiring smart people who are passionate about what their companies are doing. In order for them to do their best work, we have to give them what they need and then get out of their way.
Here, I think the above passage from the *Tao Te Ching* speaks for itself.
## Be effortless
The Master does nothing
yet he leaves nothing undone.
The ordinary man is always doing things,
yet many more are left to be done. [[38]]
Do you know the type of person who is always extremely busy? The one who seems frazzled and stressed with too many things to do?
Don't be that person.
I know that's easier said than done. The thing that most helps me keep from being that person is remembering that we are all extremely busy. I don't have a single co-worker who is bored.
But someone needs to be the calm in the middle of the storm. Someone needs to be the person who reassures the team that everything is going to be okay, that we'll find a way to get things done within the parameters dictated by reality and the number of business hours in a day (because that's the truth, and we have to).
Be *that* person.
What this passage of the *Tao Te Ching* says to me is that the person who's always talking about what she or he is doing has *no time to actually do those things*. If you can make your job seem effortless to those around you, then you're doing your job right.
## Be a culture coach
When a superior man hears of the Tao,
he immediately begins to embody it.
When an average man hears of the Tao,
he half believes it, half doubts it.
When a foolish man hears of the Tao,
he laughs out loud.
If he didn't laugh,
it wouldn't be the Tao. [[41]]
Last fall, I enrolled an MBA business ethics class with a bunch of federal employees. When I started describing my company's culture, values, and ethics framework, I got the direct impression that both my classmates and my professor thought I was a naive young lady with [a lot of lovely daydreams](https://opensource.com/open-organization/15/9/reflections-open-organization-starry-eyed-dreamer) about how companies should run. They told me things couldn't possibly be as they seemed. They said I should investigate further.
So I did.
And here's what I found: Things are *exactly* as they seem.
In open organizations, culture *matters*. Maintaining that culture as an organization grows makes it possible to wake up and look forward to going to work in the morning. I (and other members of open organizations) don't want to "work to live," as my classmates described it. I need to feel a passion and purpose, to understand how the work I do on a daily basis directly contributes to something I believe in.
As a project manager, you might think that your job has nothing to do with cultivating your company's culture on your team. However, it's your job to embody it.
## Kaizen
In pursuit of knowledge,
every day something is added.
In the practice of the Tao,
every day something is dropped.
Less and less do you need to force things,
until finally you arrive at non-action. When nothing is done,
nothing is left undone. [[48]]
The general field of project management is too focused on the latest and greatest tools. But the answer to the question of which tool you should use is always the same: "the simplest."
For example, I keep my running to-do list in a text file on my desktop because it serves its purpose without unnecessary distractions. Whatever tools, processes, and procedures you introduce to a team should increase efficiency and remove obstacles, not introduce additional complexity. So instead of focusing on the tools, focus on the *problem(s)* you're using those tools to solve.
My favorite part of being a project manager in an Agile world is having the freedom to throw out what doesn't work. This is related to the concept of [kaizen](https://www.kaizen.com/about-us/definition-of-kaizen.html), or "continuous improvement." Don't be afraid to try and fail. Failing is the label we've put on the process of learning what works and what doesn't. But it's the only way to improve.
The best processes arise organically. As a project manager, you can help your team by supporting them and not trying to force them into anything.
## Practice
Some say that my teaching is nonsense.
Others call it lofty but impractical.
But to those who have looked inside themselves,
this nonsense makes perfect sense.
And to those who put it into practice,
this loftiness has roots that go deep. [[67]]
I believe in what open organizations are doing. What open organizations are doing for the field of management is almost as important as the actual products and services they offer. We have an opportunity to lead by example, to inspire passion and purpose in others, to create working environments that inspire and empower.
I encourage you to find ways to incorporate some of these ideas into your own projects and teams to see what happens. Learn about your organization's mission and how your projects contribute to it. Have courage, expect to try some things that won't work, and don't forget to share the lessons you learn with our community so we can continue to improve.
## 3 Comments |
7,397 | Ubuntu 的 snap 软件包封装真的安全吗? | http://itsfoss.com/snap-package-securrity-issue/ | 2016-05-28T09:44:00 | [
"snap"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7397-1.html | 最近发布的 [Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 版本带来了一些新功能](http://itsfoss.com/features-ubuntu-1604/),其中之一就是对 [ZFS 格式文件系统的支持](http://itsfoss.com/oracle-canonical-lawsuit/)。另一个值得广为讨论的特性就是 Snap 软件包格式。不过,据 [CoreOS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CoreOS) 的开发者之一所述,Snap 软件包并不像声称的那样安全。
### 什么是 Snap 软件包?

Snap 软件包的灵感来自容器。这种新的封装格式允许[开发人员为运行于 Ubuntu 长期支持版本 (LTS)之上的应用程序发布更新](https://insights.ubuntu.com/2016/04/13/snaps-for-classic-ubuntu/)。这就可以让用户虽然运行着稳定版本的操作系统,但却能够让应用程序保持最新的状态。之所以能够这样,是因为软件包本身就包含了程序运行的所有依赖。这可以防止依赖的软件更新后软件挂掉。
snap 软件包的另外一个优势是应用与系统的其它部分是隔离的。这意味着如果你改变了 snap 软件包的一些东西,它不会影响到系统的其它部分。这也可以防止其它的应用访问你的隐私信息,从而使骇客根据难以获取你的数据。
### 然而……
据 [Matthew Garrett](https://mjg59.dreamwidth.org/l) 的说法,Snap 软件包不能完全兑现上述承诺。Garret 作为 Linux 内核的开发人员和 CoreOS 的安全性方面的开发者,我想他一定知道自己在说些什么。
[据 Garret 说](https://mjg59.dreamwidth.org/42320.html), “仅需要克服一点点困难,安装的任何 Snap 格式的软件包就完全能够将你所有的私有数据复制到任何地方”。
[ZDnet](http://www.zdnet.com/article/linux-expert-matthew-garrett-ubuntu-16-04s-new-snap-format-is-a-security-risk/) 的报道:
>
> “为了证明自己的观点,他在 Snap 中构建了一个仅用于验证其原理的用于破坏的软件包,它首先会显示一个可爱的泰迪熊,然后将会记录 Firefox 的键盘按键事件,并且能够窃取 SSH 私钥。这个仅用于验证原理的软件包实际上注入的是一个无害的命令,但是却能够修改成一个窃取 SSH 密钥的 cURL 会话。”
>
>
>
### 但是稍等……
难道 Snap 真的有安全缺陷?事实上却不是!
Garret 自己也说,此问题仅出现在使用 X11 窗口系统上,而对于那些使用 Mir 的移动设备无效。所以这个缺陷是 X11 的而不是 Snap 的。
>
> X11 是如何信任应用程序的,这是一个众所周知的安全风险。Snap 并没有更改 X11 的信任模型。所以一个应用程序能够看到其它应用程序的行为并不是这种新的封装格式的缺点,而是 X11 的。
>
>
>
Garrett 实际上想表达的只是,当 Canonical 歌颂 Snap 和它的安全性时,Snap 应用程序并不是完全沙盒化的。和其他二进制文件一样,它们也存在风险。
请牢记 Ubuntu 16.04 当前还在使用 X11 而不是 Mir 的事实,从未知的源下载和安装 Snap 格式的软件包也许还是有风险的,然而其它不也是如此嘛?!
相关链接: [如何在 Ubuntu 16.04 中使用 Snap 软件包](http://itsfoss.com/use-snap-packages-ubuntu-16-04/)。期待您分享关于 Snap 格式及其安全性的观点。
---
via: <http://itsfoss.com/snap-package-securrity-issue/>
作者:[John Paul](http://itsfoss.com/author/john/) 译者:[dongfengweixiao](https://github.com/dongfengweixiao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,399 | Intel 展示了可在大屏幕显示 Linux 系统的低端 Android 手机 | http://www.theregister.co.uk/2016/02/23/move_over_continuum_intel_shows_android_smartphone_powering_bigscreen_linux/ | 2016-05-28T09:25:00 | [
"手机",
"android"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7399-1.html | 
在世界移动大会 **MWC16** 上 Intel 展示了称之为“大屏体验”的一款的 Android 智能手机,它在插入一个外部显示后运行了一个完整的 Linux 桌面。
这个概念大体上与微软在 Windows 10 手机中的 Continuum 相似,但是 Continuum 面向的是高端设备,Intel 的项目面向的是低端智能机和新兴市场。
在巴塞罗那的这场大会上展示的是拥有 Atom x3、2GB RAM 和 16GB 存储以及支持外部显示的的 SoFIA(Intel 架构的智能或功能手机)智能机原型。插上键盘、鼠标和显示,它就变成了一台桌面 Linux,并可以选择在大屏幕的一个窗口中显示 Android 桌面。
Intel 的拓荒小组(Path Finding Group)经理 Nir Metzer 告诉我们:“Android 基于 Linux 内核,因此我们运行在一个内核上,我们有一个 Android 栈和一个 Linux 栈,并且我们共享同一个环境,因此文件系统是相同的。电话是全功能的。”
Metzer 说:“我有一个多窗口环境。只要我插入显示器后就可以使用电子表格,我可以进行拖放操作,播放音频。在一个低端平台实现这一切是一个挑战。”
现在当连上外部显示器时设备的屏幕显示是空白的,但是 Metzer 说下个版本的 Atom X3 会支持双显示。
其使用的 Linux 版本是由 Intel 维护的。Metzer 说:“我们需要将 Linux 和 Android 保持一致。框架是预安装的,不是一个可以下载的应用。”
英特尔在移动世界大会上向手机制造商们推销这一想法,但却没有实际说希望购买该设备的消费者。Metzer 说:“芯片已经准备好了,已经为量产准备好了。明天就可以进入生产。但是这要看商业需求。”
---
via: <http://www.theregister.co.uk/2016/02/23/move_over_continuum_intel_shows_android_smartphone_powering_bigscreen_linux/>
作者:[Tim Anderson](http://www.theregister.co.uk/Author/2878) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,400 | 推荐五篇 OpenStack 的新指南 | https://opensource.com/business/16/4/master-openstack-new-tutorials | 2016-05-29T09:37:00 | [
"OpenStack"
] | /article-7400-1.html | 
回顾这周的 OpenStack 峰会,我仍然回味着开源云生态系统的浩瀚无垠,有那么多需要了解的项目及概念才能获得成功。不过我们很幸运,因为有许多资源让我们跟随着项目的脚步。除了[官方文档](http://docs.openstack.org/)外,我们还有许多来自第三方提供的培训和认证、个人分享,以及许多社区贡献的学习资源。
为了让我们保持获得最新消息,每个月我们将会整合发布 OpenStack 社区的最新教程、指导和小贴士等。下面是我们过去几个月最棒的发布分享。
* 首先,如果你正在寻找一个靠谱实惠的 OpenStack 测试实验室, Intel NUC 是最值得考虑的平台。麻雀虽小,五脏俱全,通过指导文章,可以很轻松的按照教程在 NUC 上使用 [TripleO 部署 OpenStack](http://acksyn.org/posts/2016/03/tripleo-on-nucs/) ,并且还可以轻松避开一些常见的古怪问题。
* 当你已经运行的一段时间 OpenStack 后,你会发现在你的云系统上许多组件生成了大量日志。其中一些是可以安全删除的,而你需要一个管理这些日志的方案。参考在部署生产 9 个月后使用 Celiometer 管理日志的[一些思考](http://silverskysoft.com/open-stack-xwrpr/2016/03/long-term-openstack-usage-summary/)。
* 对于 OpenStack 基础设施项目的新手,想要提交补丁到 OpenStack 是相当困难的。入口在哪里,测试怎么做,我的提交步骤是怎么样的?可以通过 Arie Bregman 的这篇[博客文章](http://abregman.com/2016/03/05/openstack-infra-jenkins-jobs/)快速了解整个提交过程。
* 突发计算节点失效,不知道是硬件还是软件问题。不过好消息是 OpenStack 提供了一套非常简单的迁移计划可以让你迁移当机节点到别的主机。然而,迁移过程中使用的命令令许多人感到困惑。可以通过[这篇文章](http://www.danplanet.com/blog/2016/03/03/evacuate-in-nova-one-command-to-confuse-us-all/)来理解 migrate 和 evacuate 命令的不同。
* 网络功能虚拟化技术需要 OpenStack 之外的一些功能,而用户可能不熟悉它们。例如, SR-IOV 和 PCI 直通是最大限度地提高物理硬件性能的方式。可以学习[部署步骤](https://trickycloud.wordpress.com/2016/03/28/openstack-for-nfv-applications-sr-iov-and-pci-passthrough/)以使 OpenStack 的性能最大化。
这些文章基本涵盖了本月(译者注: 4 月)推送,如果你还需要更多文章,可以检索过去推送的 [OpenStack 文献](https://opensource.com/resources/openstack-tutorials)来获取更多资源。如果有你认为我们应该推荐的新教程,请在评论中告诉我们,谢谢。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/business/16/4/master-openstack-new-tutorials>
作者:[Jason Baker](https://opensource.com/users/jason-baker) 译者:[VicYu/Vic020](http://vicyu.net) 校对:[PurlingNayuki](https://github.com/PurlingNayuki)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
7,401 | Linux/Unix 桌面趣事:文字模式下的 ASCII 艺术与注释绘画 | http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/unix-linux-draw-any-kind-of-boxes-around-text-editor.html | 2016-05-28T13:58:00 | [
"桌面趣事"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7401-1.html | boxes 命令不仅是一个文本过滤器,同时是一个很少人知道的有趣工具,它可以在输入的文本或者代码周围框上各种ASCII 艺术画。你可以用它快速创建邮件签名,或者在各种编程语言中留下评论块。这个命令可以在 vim 文本编辑器中使用,但是也可以在各种支持过滤器的文本编辑器中使用,同时也可以在命令行中单独使用。

### 任务: 安装 boxes
使用 [apt-get 命令](http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-debian-package-management-cheat-sheet.html) 在 Debian / Ubuntu Linux 中安装 boxes:
```
$ sudo apt-get install boxes
```
输出示例:
```
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following NEW packages will be installed:
boxes
0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 6 not upgraded.
Need to get 0 B/59.8 kB of archives.
After this operation, 205 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Selecting previously deselected package boxes.
(Reading database ... 224284 files and directories currently installed.)
Unpacking boxes (from .../boxes_1.0.1a-2.3_amd64.deb) ...
Processing triggers for man-db ...
Setting up boxes (1.0.1a-2.3) ...
```
RHEL / CentOS / Fedora Linux 用户, 使用 [yum 命令来安装](http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/rhel-centos-fedora-linux-yum-command-howto/) boxes,(请先[启用 EPEL 软件仓库](http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/fedora-sl-centos-redhat6-enable-epel-repo/)):
```
# yum install boxes
```
输出示例:
```
Loaded plugins: rhnplugin
Setting up Install Process
Resolving Dependencies
There are unfinished transactions remaining. You might consider running yum-complete-transaction first to finish them.
--> Running transaction check
---> Package boxes.x86_64 0:1.1-8.el6 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
==========================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
==========================================================================
Installing:
boxes x86_64 1.1-8.el6 epel 64 k
Transaction Summary
==========================================================================
Install 1 Package(s)
Total download size: 64 k
Installed size: 151 k
Is this ok [y/N]: y
Downloading Packages:
boxes-1.1-8.el6.x86_64.rpm | 64 kB 00:00
Running rpm_check_debug
Running Transaction Test
Transaction Test Succeeded
Running Transaction
Installing : boxes-1.1-8.el6.x86_64 1/1
Installed:
boxes.x86_64 0:1.1-8.el6
Complete!
```
FreeBSD 用户可以按如下使用:
```
cd /usr/ports/misc/boxes/ && make install clean
```
或者,使用 pkg\_add 命令来增加包:
```
# pkg_add -r boxes
```
### 在一些给定文本周围画出任何种类的包围框
输入下列命令:
```
echo "This is a test" | boxes
```
或者,指定要使用的图案的名字:
```
echo -e "\n\tVivek Gite\n\[email protected]\n\twww.cyberciti.biz" | boxes -d dog
```
输出示例 :

\*图01: Unix / Linux: Boxes 命令来画出各式各样的图案 \*
#### 怎么样输出所有的图案
语法如下:
```
boxes option
pipe | boxes options
echo "text" | boxes -d foo
boxes -l
```
-d 选项用来设置要使用的图案的名字。语法如下:
```
echo "Text" | boxes -d design
pipe | boxes -d desig
```
-l 选项列出所有图案。它显示了在配置文件中的所有的框线设计图,同时也显示关于其创作者的信息。
```
boxes -l
boxes -l | more
boxes -l | less
```
输出示例:
```
43 Available Styles in "/etc/boxes/boxes-config":
-------------------------------------------------
ada-box (Neil Bird ):
---------------
-- --
-- --
---------------
ada-cmt (Neil Bird ):
--
-- regular Ada
-- comments
--
boy (Joan G. Stark ):
.-"""-.
/ .===. \
\/ 6 6 \/
( \___/ )
_________ooo__\_____/______________
/ \
| joan stark [email protected] |
| VISIT MY ASCII ART GALLERY: |
| http://www.geocities.com/SoHo/7373/ |
\_______________________ooo_________/ jgs
| | |
|_ | _|
| | |
|__|__|
/-'Y'-\
(__/ \__)
....
...
output truncated
..
```
### 在使用 vi/vim 文本编辑器时如何通过 boxes 过滤文本?
你可以在 vi 或 vim 中使用任何外部命令,比如在这个例子中,[插入当前日期和时间](http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/vim-inserting-current-date-time-under-linux-unix-osx/),输入:
```
!!date
```
或者
```
:r !date
```
你需要在 vim 中输入以上命令来读取 date 命令的输出,这将在当前行后面加入日期和时分秒:
```
Tue Jun 12 00:05:38 IST 2012
```
你可以用 boxes 命令做到同样的功能。如下创建一个作为示例的 shell 脚本或者c程序:
```
#!/bin/bash
Purpose: Backup mysql database to remote server.
Author: Vivek Gite
Last updated on: Tue Jun, 12 2012
```
现在输入如下(将光标移到第二行,也就是以“Purpose: ...”开头的行)
```
3!!boxes
```
瞧,你就会看到如下的输出 :
```
#!/bin/bash
/****************************************************/
/* Purpose: Backup mysql database to remote server. */
/* Author: Vivek Gite */
/* Last updated on: Tue Jun, 12 2012 */
/****************************************************/
```
这个短片将会给你介绍boxes命令:
参见
* boxes 帮助手册
---
via: <http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/unix-linux-draw-any-kind-of-boxes-around-text-editor.html>
作者:Vivek Gite 译者:[zky001](https://github.com/zky001) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,403 | 猎头们怎么看开源 | https://opensource.com/business/16/5/open-source-recruiters-perspective | 2016-05-29T16:14:00 | [
"开源",
"工作",
"猎头"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7403-1.html | 
2012 年时候,我出席了一个开源社区的聚会,打那之后我就喜欢上了这个行业。
我做猎头很多年,现在我在 [Greythorn](http://www.greythorn.com/) 公司专门从事大数据方向招聘。我自己之前学习了几个月大数据,可是当我参加了 [OSCON](http://conferences.oreilly.com/oscon) 开源大会,才发现之前的学习多么低效率。OSCON 里聚集了非常多聪明的人,他们每个人都很愿意分享他们的心得。分享的原因不是他们想推销产品,纯粹是因为喜欢。
我很快意识到,与其说开源和大数据是一个行业,不如说他们是一个<ruby> 社区 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> community </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。这也是为什么我现在特别想把我从开源中学到的东西分享给大家,特别是给那些刚刚踏入工作的新人。
### 为什么雇主喜欢开源<ruby> 贡献者 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> contributor </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
我的许多客户跟我说过:一个人的技术虽然重要,但真心**喜欢**自己从事的工作更重要。如果你热爱自己的工作,即便老板不给加班工资你都忍不住想加班。
我的客户也经常问,“这个人没事儿的时候写代码吗?”“我能在哪儿找到他们的作品呢?”“他们有什么爱好呀?”这时候开源社区贡献者的优势就出来了,因为上面的问题就是给他们量身定做的。他们做的项目开源,这就是他们编码能力的例证。
### 为什么猎头在寻找开源贡献者
硬派科技行业猎头了解技术,知道自己在找一个什么样的人,这样的猎头也能正确的了解对象的技能。我发现,猎头们找到的最优秀的人才很多时候也在做开源,所以我们经常直接去开源社区寻找我们的目标。猎头们会告诉雇主,“我们找到的那个人喜欢和团队一起创造了不起的产品”,而这基本上是优秀雇主共同的要求。
所以说:如果你的项目目标是改变人类的未来,那当这些聪明人来到你的团队之后,他们自己就会爱上自己的工作。
### 开源贡献者如何得到更好的职业生涯呢
怎么让你的贡献更广为人知呢:把代码放到 Github 上;做开源项目;参加会议和研讨等等。做这些事情你会有意想不到的收获的。
可以尝试问一下自己:
* **你觉得所在的公司是否回馈开源社区这件事重要吗?**很多优秀的人才都强调这一点,回馈社区也会极大的提升他们对工作本身的满意度。
* **你在做产品是否基于开源软件?**基于开源软件的公司的文化氛围会与其他公司与众不同,这也是你选择职位时候需要考虑的问题。
* **你有没有特别想与之工作的人?**虽然你可以随时换项目,但如果团队里有你崇拜或者欣赏的人,那工作就棒极了。
假如你了解自己的人生追求,那么过滤掉那些不适合你的职位就简单多了;假如你有一个相熟的猎头,那找到相合的雇主和团队的机会就大多了。
虽然我自己不写代码,但我会把我从开源社区中学到的东西分享给大家。开源社区是由一大群聪明又乐于分享的人组成,我很开心我也是其中小小的一份子。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/business/16/5/open-source-recruiters-perspective>
作者:[Lindsey Thorne](https://opensource.com/users/lindsey-thorne) 译者:[eriwoon](https://github.com/eriwoon) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | I fell in love with technology when I went to my first open source convention in 2012.
After spending years in recruiting, I decided to take a job specializing in big data at [Greythorn](http://www.greythorn.com/). I had been trying to learn the ropes for a few months leading up to [OSCON](http://conferences.oreilly.com/oscon), but going to the conference sped that process up like crazy. There were so many brilliant people all in one place, and everyone was willing to share what they knew. It wasn't because they were trying to sell me anything, but because they were all so passionate about what they were working on.
I soon realized that, in many ways, the open source and big data industry was less an industry and more of a community. That's why I now try to pay it forward and share what I've learned about open source with those who are just getting started in their careers.
## Why employers want open source contributors
Many clients tell me that although they want a candidate who has an exceptional technical mind, the ideal person should also really *like* this stuff. When you are passionate about something, you find yourself working on it even when you aren't getting paid.
My clients often ask, "Do they code in their spare time?" "Can I find their work anywhere?" "What do they really enjoy?" Open source contributors are often at an advantage because they check these boxes, and not only are their projects out in the open—so is the evidence of their coding proficiency.
## Why recruiters search for open source contributors
Solid tech recruiters understand the technologies and roles they're recruiting for, and they're going to assess your skills accordingly. But I'll admit that many of us have found that the best candidates we've come across have a tendency to be involved in open source, so we often just start our search there. Recruiters provide value to clients when they find candidates who are motivated to work on a team to create something awesome, because that's basically the description of a top-performing employee.
It makes sense to me: When you take really smart people and give them the chance to be collaborative—for the sake of making something that works really well or may change the landscape of our everyday lives—it creates an energy that can be addictive.
## What open source contributors can do to build a happy career
There are obvious things you can do to leverage your open source work to build your career: Put your code on GitHub, participate in projects, go to conferences and join panels and workshops, etc. These are worthwhile, but more than anything you need to know what will make you happy in your work.
Ask yourself questions like...
**Is it important to work for a company that gives back to the open source and software community?**I find that some of my best candidates insist on this, and it makes a huge difference in their job satisfaction.**Do you want to work for a company that is based on open source?**The culture is often different in these environments, and it helps to know if that's where you think you'll fit best.**Are there people you'd specifically like to work with?**Although you can always try to join the same projects, the odds of collaborating with and learning from someone you admire are better if your day jobs align at the same company.
Once you know your own career priorities, it's easier to filter out the jobs that won't move you closer to your goals—and if you're working with a recruiter, it helps them match you with the right employer and team.
Although I don't contribute code, I'll always share what I've learned with those who are working on their career in open source. This community is made up of supportive and smart people, and I love that I've been able to be a small part of it.
## Comments are closed. |
7,404 | 又一次 Mindcraft 事件?关于 Linux 内核安全性的批评 | https://lwn.net/Articles/663474/ | 2016-05-30T10:08:00 | [
"内核",
"安全"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7404-1.html | Linux 内核开发很少吸引像华盛顿邮报这样主流媒体的关注,内核社区在安全方面进展的冗长功能列表就更少人看了。所以当[这样一个专题](https://lwn.net/Articles/663338/)发布到网上,就吸引了很多人的注意(LCTT 译注:华盛顿邮报发表了一篇很长的[专题文章](http://www.washingtonpost.com/sf/business/2015/11/05/net-of-insecurity-the-kernel-of-the-argument/),批评 Linux “没有一个系统性的机制以在骇客之前发现和解决安全问题,或引入更新的防御技术”,“Linux 内核开发社区没有一个首席安全官”等等)。关于这篇文章有不同的反应,很多人认为这是对 Linux 直接的攻击。文章背后的动机很难知道,但是从历史经验来看,它也可以看作对我们早就该前进的方向的一次非常必要的推动。

回顾一件昏暗遥远过去的事件 - 确切地说是在 1999 年 4 月。一家叫 Mindcraft 的分析公司发布了一份[报告](http://www.mindcraft.com/whitepapers/nts4rhlinux.html)显示 Windows NT 在 Web 服务器开销方面完胜 Red Hat Linux 5.2 加 Apache。Linux 社区,包括当时还[很年轻的 LWN](https://static.lwn.net/1999/features/MindCraft1.0.php3),对此反应很迅速而且强烈。这份报告是微软资助的 FUD 的一部分,用来消除那些全球垄断计划的新兴威胁。报告中所用的 Linux 系统有意配置成低性能,同时选择了当时 Linux 并不能很好支持的硬件,等等。
在大家稍微冷静一点后,尽管如此,事实很明显:Mindcraft 的人,不管什么动机,说的也有一定道理。当时 Linux 确实在性能方面存在一些已经被充分认识到的问题。然后社区做了最正确的事情:我们坐下来解决问题。比如,单独唤醒的调度器可以解决接受连接请求时的[惊群问题](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thundering_herd_problem)。其他很多小问题也都解决了。在差不多一年里,内核在这类开销方面的性能已经有了非常大的改善。
这份 Mindcraft 的报告,某种意义上来说,往 Linux 屁股上踢了很有必要的一脚,推动整个社区去处理一些当时被忽略的事情。
华盛顿邮报的文章明显以负面的看法看待 Linux 内核以及它的贡献者。它随意地混淆了内核问题和其他根本不是内核脆弱性引起的问题(比如,AshleyMadison.com 被黑)。不过供应商没什么兴趣为他们的客户提供安全补丁的事实,就像一头在房间里巨象一样明显。还有谣言说这篇文章后面的黑暗势力希望打击一下 Linux 的势头。这些也许都是真的,但是也不能掩盖一个简单的事实,就是文章说的确实是真的。
我们会合理地测试并解决问题。而这些问题,不管是不是安全相关,能很快得到修复,然后再通过稳定更新的机制将这些补丁发布给内核用户。比起外面很多应用程序(自由的和商业的),内核的支持工作做的非常好。但是指责我们解决问题的能力时却遗漏了关键的一点:解决安全问题终究来说是一个打鼹鼠游戏。总是会出来更多的鼹鼠,其中有一些在攻击者发现并利用后很长时间我们都还不知道(所以没法使劲打下去)。尽管 Linux 的商业支持已经非常努力地在将补丁传递给用户,这种问题还是会让我们的用户很受伤 - 只是这并不是故意的。
关键是只是解决问题并不够,一些关心安全性的开发者也已经开始尝试做些什么。我们必须认识到,缺陷永远都解决不完,所以要让缺陷更难被发现和利用。这意思就是限制访问内核信息,绝对不允许内核执行用户空间内存中的指令,让内核去侦测整形溢出,以及 [Kee Cook 在十月底内核峰会的讲话](https://lwn.net/Articles/662219/)中所提出的其他所有事情。其中许多技术被其他操作系统深刻理解并采用了;另外一些需要我们去创新。但是,如果我们想充分保护我们的用户免受攻击,这些改变是必须要做的。
为什么内核还没有引入这些技术?华盛顿邮报的文章坚定地指责开发社区,特别是 Linus Torvalds。内核社区的传统就是相对安全性更侧重于性能和功能,在需要牺牲性能来改善内核安全性时并不愿意折衷处理。这些指责一定程度上是对的;好的一面是,因为问题的范围变得清晰,态度看上去有所改善。Kee 的演讲都听进去了,而且很明显让开发者开始思考和讨论这些问题了。
而被忽略的一点是,并不仅仅是 Linus 在拒绝有用的安全补丁。而是就没有多少这种补丁在内核社区里流传。特别是,在这个领域工作的开发者就那么些人,而且从没有认真地尝试把自己的工作整合到上游。要合并任何大的侵入性补丁,需要和内核社区一起工作,为这些改动编写用例,将改动分割成方便审核的碎片,处理审核意见,等等。整个过程可能会有点无聊而且让人沮丧,但这却是内核维护的运作方式,而且很明显只有这样才能在长时间的开发中形成更有用更可维护的内核。
几乎没有人会走这个流程来将最新的安全技术引入内核。对于这类补丁可能收到的不利反应,有人觉得也许会导致“寒蝉效应”,但是这个说法并不充分:不管最初的反应有多麻烦,多年以来开发者已经合并了大量的改动。而少数安全开发者连试都没试过。
他们为什么不愿意尝试?一个比较明显的答案是,几乎没有人会因此拿到报酬。几乎所有引入内核的工作都由付费开发者完成,而且已经持续多年。公司能看到利润的领域在内核里都有大量的工作以及很好的进展。而公司觉得和它们没关系的领域就不会这样了。为实时 Linux 的开发找到赞助支持的困难就是很明显的例子。其他领域,比如文档,也在慢慢萧条。安全性很明显也属于这类领域。可能有很多原因导致 Linux 落后于防御式安全技术,但是其中最关键的一条是,靠 Linux 赚钱的公司没有重视这些技术的开发和应用。
有迹象显示局面已有所转变。越来越多的开发人员开始关注安全相关问题,尽管对他们工作的商业支持还仍然不够。对于安全相关的改变已经没有之前那样的下意识反应了。像[内核自我保护项目](https://lwn.net/Articles/663361/)这样,已经开始把现有的安全技术集成进入内核了。
我们还有很长的路要走,但是,如果能有一些支持以及正确的观念,短期内就能有很大的进展。内核社区在确定了自己的想法后可以做到很让人惊叹的事情。幸运的是,华盛顿邮报的文章将有助于提供形成这种想法的必要动力。以历史的角度看,我们很可能会把这次事件看作一个转折点,我们最终被倒逼着去完成之前很明确需要做的事情。Linux 不应该再继续讲述这个安全不合格的故事了。
---
via: <https://lwn.net/Articles/663474/>
作者:Jonathan Corbet 译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # A new Mindcraft moment?
It is not often that Linux kernel development attracts the attention of a mainstream newspaper like The Washington Post; lengthy features on the kernel community's approach to security are even more uncommon. So whenPlease consider subscribing to LWNSubscriptions are the lifeblood of LWN.net. If you appreciate this content and would like to see more of it, your subscription will help to ensure that LWN continues to thrive. Please visit
[this page]to join up and keep LWN on the net.
[just such a feature](/Articles/663338/)hit the net, it attracted a lot of attention. This article has gotten mixed reactions, with many seeing it as a direct attack on Linux. The motivations behind the article are hard to know, but history suggests that we may look back on it as having given us a much-needed push in a direction we should have been going for some time.
Think back, a moment, to the dim and distant past — April 1999, to be
specific. An analyst company named Mindcraft issued [a report](http://www.mindcraft.com/whitepapers/nts4rhlinux.html)
showing that Windows NT greatly outperformed Red Hat Linux 5.2 and
Apache for web-server workloads. The outcry from the Linux community,
including from [a very young
LWN](https://static.lwn.net/1999/features/MindCraft1.0.php3), was swift and strong. The report was a piece of Microsoft-funded
FUD trying to cut off an emerging threat to its world-domination plans.
The Linux system had been deliberately configured for poor performance.
The hardware chosen was not well supported by Linux at the time. And
so on.
Once people calmed down a bit, though, one other fact came clear: the
Mindcraft folks, whatever their motivations, had a point. Linux did,
indeed, have performance problems that were reasonably well understood even
at the time. The community then did what it does
best: we sat down and fixed the problems. The scheduler got exclusive
wakeups, for example, to put an end to the [thundering-herd
problem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thundering_herd_problem) in the acceptance of connection requests. Numerous other
little problems were fixed. Within a year or so, the kernel's performance
on this kind of workload had improved considerably.
The Mindcraft report, in other words, was a much-needed kick in the rear that got the community to deal with issues that had been neglected until then.
The Washington Post article seems clearly slanted toward a negative view of the Linux kernel and its contributors. It freely mixes kernel problems with other issues (the AshleyMadison.com breakin, for example) that were not kernel vulnerabilities at all. The fact that vendors seem to have little interest in getting security fixes to their customers is danced around like a huge elephant in the room. There are rumors of dark forces that drove the article in the hopes of taking Linux down a notch. All of this could well be true, but it should not be allowed to overshadow the simple fact that the article has a valid point.
We do a reasonable job of finding and fixing bugs. Problems, whether they are security-related or not, are patched quickly, and the stable-update mechanism makes those patches available to kernel users. Compared to a lot of programs out there (free and proprietary alike), the kernel is quite well supported. But pointing at our ability to fix bugs is missing a crucial point: fixing security bugs is, in the end, a game of whack-a-mole. There will always be more moles, some of which we will not know about (and will thus be unable to whack) for a long time after they are discovered and exploited by attackers. These bugs leave our users vulnerable, even if the commercial side of Linux did a perfect job of getting fixes to users — which it decidedly does not.
The point that developers concerned about security have been trying to make
for a while is that fixing bugs is not enough. We must instead realize
that we will never fix them all and focus on making bugs harder to
exploit. That means restricting access to information about the kernel,
making it impossible for the kernel to execute code in user-space memory,
instrumenting the kernel to detect integer overflows, and all the other
things laid out in [Kees Cook's Kernel Summit
talk](/Articles/662219/) at the end of October. Many of these techniques are well
understood and have been adopted by other operating systems; others will
require innovation on our part. But, if we want to adequately defend our
users from attackers, these changes need to be made.
Why hasn't the kernel adopted these technologies already? The Washington Post article puts the blame firmly on the development community, and on Linus Torvalds in particular. The culture of the kernel community prioritizes performance and functionality over security and is unwilling to make compromises if they are needed to improve the security of the kernel. There is some truth to this claim; the good news is that attitudes appear to be shifting as the scope of the problem becomes clear. Kees's talk was well received, and it clearly got developers thinking and talking about the issues.
The point that has been missed is that we do not just have a case of Linus
fending off useful security patches. There simply are not many such
patches circulating in the kernel community. In particular, the few
developers who *are* working in this area have never made a serious
attempt to get that work integrated upstream. Getting any large, intrusive
patch set merged requires working with the kernel community, making the
case for the changes, splitting the changes into reviewable pieces, dealing
with review comments, and so on. It can be tiresome and frustrating, but
it's how the kernel works, and it clearly results in a more generally
useful, more maintainable kernel in the long run.
Almost nobody is doing that work to get new security technologies into the kernel. One might cite a "chilling effect" from the hostile reaction such patches can receive, but that is an inadequate answer: developers have managed to merge many changes over the years despite a difficult initial reaction. Few security developers are even trying.
Why aren't they trying? One fairly obvious answer is that almost nobody is being paid to try. Almost all of the work going into the kernel is done by paid developers and has been for many years. The areas that companies see fit to support get a lot of work and are well advanced in the kernel. The areas that companies think are not their problem are rather less so. The difficulties in getting support for realtime development are a clear case in point. Other areas, such as documentation, tend to languish as well. Security is clearly one of those areas. There are a lot of reasons why Linux lags behind in defensive security technologies, but one of the key ones is that the companies making money on Linux have not prioritized the development and integration of those technologies.
There are signs that things might be changing a bit. More developers are
showing interest in security-related issues, though commercial support for
their work is still less than it should be. The reaction against
security-related changes *might* be less knee-jerk negative than it
used to be. Efforts like the [Kernel Self
Protection Project](/Articles/663361/) are starting to work on integrating existing
security technologies into the kernel.
We have a long way to go, but, with some support and the right mindset, a
lot of progress can be made in a short time. The kernel community can do
amazing things when it sets its mind to it. With luck, the Washington Post
article will help to provide the needed impetus for that sort of setting of
mind. History suggests that we will eventually see this moment as a
turning point, when we were finally embarrassed into doing work that has
clearly needed doing for a while. Linux should not have a substandard
security story for much longer.
Posted Nov 6, 2015 20:50 UTC (Fri)
by
1. this WP article was the 5th in a series of articles following the security of the internet from its beginnings to relevant topics of today. discussing the security of linux (or lack thereof) fits nicely in there. it was also a well-researched article with over two months of research and interviews, something you can't quite claim yourself for your recent pieces on the subject. you don't like the facts? then say so. or even better, do something constructive about them like Kees and others have been trying. however silly comparisons to old crap like the Mindcraft studies and fueling conspiracies don't exactly help your case.
2. "We do a reasonable job of finding and fixing bugs."
let's start here. is this statement based on wishful thinking or cold hard facts you're going to share in your response? according to Kees, the lifetime of security bugs is measured in years. that's more than the lifetime of many devices people buy and use and ditch in that period.
3. "Problems, whether they are security-related or not, are patched quickly,"
some are, some aren't: let's not forget the recent NMI fixes that took over 2 months to trickle down to stable kernels and we also have a user who has been waiting for over 2 weeks now:
4. "and the stable-update mechanism makes those patches available to kernel users."
except when it does not. and yes, i have numbers: grsec carries 200+ backported patches in our 3.14 stable tree.
5. "In particular, the few developers who are working in this area have never made a serious attempt to get that work integrated upstream."
you don't need to be shy about naming us, after all you did so elsewhere already. and we also explained the reasons why we have not pursued upstreaming our code:
Posted Nov 6, 2015 21:39 UTC (Fri)
by
Money (aha) quote :
> I propose you spend none of your free time on this. Zero. I propose you get paid to do this. And well.
Nobody expect you to serve your code on a silver platter for free. The Linux foundation and big companies using Linux (Google, Red Hat, Oracle, Samsung, etc.) should pay security specialists like you to upstream your patchs.
Posted Nov 6, 2015 21:57 UTC (Fri)
by
I would just like to point out that the way you phrased this makes your comment a tone argument[1][2]; you've (probably unintentionally) dismissed all of the parent's arguments by pointing at its presentation. The tone of PAXTeam's comment displays the frustration built up over the years with the way things work which I think should be taken at face value, empathized with, and understood rather than simply dismissed.
1.
Cheers,
Posted Nov 7, 2015 0:55 UTC (Sat)
by
Posted Nov 7, 2015 1:21 UTC (Sat)
by
why, is upstream known for its basic civility and decency? have you even read the WP post under discussion, never mind past lkml traffic?
Posted Nov 7, 2015 5:37 UTC (Sat)
by
Posted Nov 7, 2015 5:34 UTC (Sat)
by
Posted Nov 7, 2015 6:09 UTC (Sat)
by
Please don't; it doesn't belong there either, and it especially doesn't need a cheering section as the tech press (LWN generally excepted) tends to provide.
Posted Nov 8, 2015 8:36 UTC (Sun)
by
Posted Nov 8, 2015 16:11 UTC (Sun)
by
Posted Nov 6, 2015 22:43 UTC (Fri)
by
Posted Nov 6, 2015 23:00 UTC (Fri)
by Why must you assume only The Linux development community may have had the wool pulled over its collective eyes with respect to security issues (either real or perceived), but simply throwing money at the problem won't fix this. And yes, I do realize the commercial Linux distros do lots (most?) of the kernel development these days, and that implies indirect monetary transactions, but it's a lot more involved than just that.
Posted Nov 7, 2015 0:36 UTC (Sat)
by
Posted Nov 7, 2015 7:34 UTC (Sat)
by
Posted Nov 7, 2015 9:49 UTC (Sat)
by
Posted Nov 6, 2015 23:13 UTC (Fri)
by
I think you definitely agree with the gist of Jon's argument... not enough focus has been given to security in the Linux kernel... the article gets that part right... money hasn't been going towards security... and now it needs to. Aren't you glad?
Posted Nov 7, 2015 1:37 UTC (Sat)
by
they talked to spender, not me personally, but yes, this side of the coin is well represented by us and others who were interviewed. the same way Linus is a good representative of, well, his own pet project called linux.
> And if Jon had only talked to you, his would have been too.
given that i'm the author of PaX (part of grsec) yes, talking to me about grsec matters makes it one of the best ways to research it. but if you know of someone else, be my guest and name them, i'm pretty sure the recently formed kernel self-protection folks would be dying to engage them (or not, i don't think there's a sucker out there with thousands of hours of free time on their hand).
> [...]it also contained quite a few of groan-worthy statements.
nothing is perfect but considering the audience of the WP, this is one of the better journalistic pieces on the topic, regardless of how you and others don't like the sorry state of linux security exposed in there. if you want to discuss more technical details, nothing stops you from talking to us ;).
speaking of your complaints about journalistic qualities, since a previous LWN article saw it fit to include several typical dismissive claims by Linus about the quality of unspecified grsec features with no evidence of what experience he had with the code and how recent it was, how come we didn't see you or anyone else complaining about the quality of that article?
> Aren't you glad?
no, or not yet anyway. i've heard lots of empty phrases over the years and nothing ever manifested or worse, all the money has gone to the pointless exercise of fixing individual bugs and related circus (that Linus rightfully despises FWIW).
Posted Nov 7, 2015 0:18 UTC (Sat)
by
Posted Nov 8, 2015 13:06 UTC (Sun)
by
Right now we've got developers from big names saying that doing all that the Linux ecosystem does *safely* is an itch that they have. Unfortunately, the surrounding cultural attitude of developers is to hit functional goals, and occasionally performance goals. Security goals are often overlooked. Ideally, the culture would shift so that we make it difficult to follow insecure habits, patterns or paradigms -- that is a task that will take a sustained effort, not merely the upstreaming of patches.
Regardless of the culture, these patches will go upstream eventually anyway because the ideas that they embody are now timely. I can see a way to make it happen: Linus will accept them when a big end-user (say, Intel, Google, Facebook or Amazon) delivers stuff with notes like 'here's a set of improvements, we're already using them to solve this kind of problem, here's how everything will remain working because $evidence, note carefully that you're staring down the barrels of a fork because your tree is now evolutionarily disadvantaged'. It's a game and can be gamed; I'd prefer that the community shepherds users to follow the pattern of declaring problem + solution + functional test evidence + performance test evidence + security test evidence.
K3n.
Posted Nov 9, 2015 6:49 UTC (Mon)
by
And about that fork barrel: I'd argue it is the other way around. Google forked and lost already.
Posted Nov 12, 2015 6:25 UTC (Thu)
by
Posted Nov 23, 2015 6:33 UTC (Mon)
by
Posted Nov 7, 2015 3:20 UTC (Sat)
by
So I must confess to a certain amount of confusion. I could swear that the article I wrote said exactly that, but you've put a fair amount of effort into flaming it...?
Posted Nov 8, 2015 1:34 UTC (Sun)
by
Posted Nov 6, 2015 22:52 UTC (Fri)
by
I personally think you and Nick Krause share opposite sides of the same coin. Programming ability and basic civility.
Posted Nov 6, 2015 22:59 UTC (Fri)
by
Posted Nov 7, 2015 0:16 UTC (Sat)
by
I hope I'm wrong, but a hostile attitude isn't going to help anyone get paid. It's a time like this where something you seem to be an "expert" at and there is a demand for that expertise where you display cooperation and willingness to participate because it's an opportunity. I'm relatively shocked that someone doesn't get that, but I'm older and have seen a few of these opportunities in my career and exploited the hell out of them. You only get a few of these in the average career, and handful at the most.
Sometimes you have to invest in proving your skills, and this is one of those moments. It appears the Kernel community may finally take this security lesson to heart and embrace it, as said in the article as a "mindcraft moment". This is an opportunity for developers that may want to work on Linux security. Some will exploit the opportunity and others will thumb their noses at it. In the end those developers that exploit the opportunity will prosper from it.
I feel old even having to write that.
Posted Nov 7, 2015 1:00 UTC (Sat)
by
Perhaps there's a chicken and egg problem here, but when seeking out and funding people to get code upstream, it helps to select people and groups with a history of being able to get code upstream.
It's perfectly reasonable to prefer working out of tree, providing the ability to develop impressive and critical security advances unconstrained by upstream requirements. That's work someone might also wish to fund, if that meets their needs.
Posted Nov 7, 2015 1:28 UTC (Sat)
by
Posted Nov 7, 2015 19:12 UTC (Sat)
by
You make this argument (implying you do research and Josh doesn't) and then fail to support it by any cite. It would be much more convincing if you give up on the Onus probandi rhetorical fallacy and actually cite facts.
> case in point, it was *them* who suggested that they would not fund out-of-tree work but would consider funding upstreaming work, except when pressed for the details, all i got was silence.
For those following along at home, this is the relevant set of threads:
A quick precis is that they told you your project was unhealthy because the code was never going upstream. You told them it was because of kernel developers attitude so they should fund you anyway. They told you to submit a grant proposal, you whined more about the kernel attitudes and eventually even your apologist told you that submitting a proposal might be the best thing to do. At that point you went silent, not vice versa as you imply above.
> obviously i won't spend time to write up a begging proposal just to be told that 'no sorry, we do not fund multi-year projects at all'. that's something that one should be told in advance (or heck, be part of some public rules so that others will know the rules too).
You appear to have a fatally flawed grasp of how public funding works. If you don't tell people why you want the money and how you'll spend it, they're unlikely to disburse. Saying I'm brilliant and I know the problem now hand over the cash doesn't even work for most Academics who have a solid reputation in the field; which is why most of them spend >30% of their time writing grant proposals.
> as for getting code upstream, how about you check the kernel git logs (minus the stuff that was not properly credited)?
jejb@jarvis> git log|grep -i 'Author: pax.*team'|wc -l
Stellar, I must say. And before you light off on those who have misappropriated your credit, please remember that getting code upstream on behalf of reluctant or incapable actors is a hugely valuable and time consuming skill and one of the reasons groups like Linaro exist and are well funded. If more of your stuff does go upstream, it will be because of the not inconsiderable efforts of other people in this area.
You now have a business model selling non-upstream security patches to customers. There's nothing wrong with that, it's a fairly usual first stage business model, but it does rather depend on patches not being upstream in the first place, calling into question the earnestness of your attempt to put them there.
Now here's some free advice in my field, which is assisting companies align their businesses in open source: The selling out of tree patch route is always an eventual failure, particularly with the kernel, because if the functionality is that useful, it gets upstreamed or reinvented in your despite, leaving you with nothing to sell. If your business plan B is selling expertise, you have to bear in mind that it's going to be a hard sell when you've no out of tree differentiator left and git history denies that you had anything to do with the in-tree patches. In fact "crazy security person" will become a self fulfilling prophecy. The advice? it was obvious to everyone else who read this, but for you, it's do the upstreaming yourself before it gets done for you. That way you have a legitimate historical claim to Plan B and you might even have a Plan A selling a rollup of upstream track patches integrated and delivered before the distributions get around to it. Even your application to the CII couldn't be dismissed because your work wasn't going anywhere. Your alternative is to continue playing the role of Cassandra and probably suffer her eventual fate.
Posted Nov 7, 2015 23:20 UTC (Sat)
by
> Second, for the potentially viable pieces this would be a multi-year
please show me the answer to that question. without a definitive 'yes' there is no point in submitting a proposal because this is the time frame that in my opinion the job will take and any proposal with that requirement would be shot down immediately and be a waste of my time. and i stand by my claim that such simple basic requirements should be public information.
> Stellar, I must say.
"Lies, damned lies, and statistics". you realize there's more than one way to get code into the kernel? how about you use your git-fu to find all the bugreports/suggested fixes that went in due to us? as for specifically me, Greg explicitly banned me from future contributions via af45f32d25cc1 so it's no wonder i don't send patches directly in (and that one commit you found that went in despite said ban is actually a very bad example because it is also the one that Linus censored for no good reason and made me decide to never send security fixes upstream until that practice changes).
> You now have a business model selling non-upstream security patches to customers.
now? we've had paid sponsorship for our various stable kernel series for 7 years. i would not call it a business model though as it hasn't paid anyone's bills.
> [...]calling into question the earnestness of your attempt to put them there.
i must be missing something here but what attempt? i've never in my life tried to submit PaX upstream (for all the reasons discussed already). the CII mails were exploratory to see how serious that whole organization is about actually securing core infrastructure. in a sense i've got my answers, there's nothing more to the story.
as for your free advice, let me reciprocate: complex problems don't solve themselves. code solving complex problems doesn't write itself. people writing code solving complex problems are few and far between that you will find out in short order. such people (domain experts) don't work for free with few exceptions like ourselves. biting the hand that feeds you will only end you up in hunger.
PS: since you're so sure about kernel developers' ability to reimplement our code, maybe look at what parallel features i still maintain in PaX despite vanilla having a 'totally-not-reinvented-here' implementation and try to understand the reason. or just look at all the CVEs that affected say vanilla's ASLR but did not affect mine.
PPS: Cassandra never wrote code, i do. criticizing the sorry state of kernel security is a side project when i'm bored or just waiting for the next kernel to compile (i wish LTO was more efficient).
Posted Nov 8, 2015 2:28 UTC (Sun)
by
In other words, you tried to define their process for them ... I can't think why that wouldn't work.
> "Lies, damned lies, and statistics".
The problem with ad hominem attacks is that they're singularly ineffective against a transparently factual argument. I posted a one line command anyone could run to get the number of patches you've authored in the kernel. Why don't you post an equivalent that gives figures you like more?
> i've never in my life tried to submit PaX upstream (for all the reasons discussed already).
So the master plan is to demonstrate your expertise by the number of patches you haven't submitted? great plan, world domination beckons, sorry that one got away from you, but I'm sure you won't let it happen again.
Posted Nov 8, 2015 2:56 UTC (Sun)
by
what? since when does asking a question define anything? isn't that how we find out what someone else thinks? isn't that what *they* have that webform (never mind the mailing lists) for as well? in other words you admit that my question was not actually answered .
> The problem with ad hominem attacks is that they're singularly ineffective against a transparently factual argument.
you didn't have an argument to begin with, that's what i explained in the part you carefully chose not to quote. i'm not here to defend myself against your clearly idiotic attempts at proving whatever you're trying to prove, as they say even in kernel circles, code speaks, bullshit walks. you can look at mine and decide what i can or cannot do (not that you have the knowledge to understand most of it, mind you). that said, there're clearly other more capable people who have done so and decided that my/our work was worth something else nobody would have been feeding off of it for the past 15 years and still counting. and as unimaginable as it may appear to you, life doesn't revolve around the vanilla kernel, not everyone's dying to get their code in there especially when it means to put up with such silly hostility on lkml that you now also demonstrated here (it's ironic how you came to the defense of josh who specifically asked people not to bring that infamous lkml style here. nice job there James.). as for world domination, there're many ways to achieve it and something tells me that you're clearly out of your league here since PaX has already achieved that. you're running such code that implements PaX features as we speak.
Posted Nov 8, 2015 16:52 UTC (Sun)
by
I posted the one line git script giving your authored patches in response to this original request by you (this one, just in case you've forgotten
> as for getting code upstream, how about you check the kernel git logs (minus the stuff that was not properly credited)?
I take it, by the way you've shifted ground in the previous threads, that you wish to withdraw that request?
Posted Nov 8, 2015 19:31 UTC (Sun)
by
Posted Nov 8, 2015 22:31 UTC (Sun)
by
Please provide one that's not wrong, or less wrong. It will take less time than you've already wasted here.
Posted Nov 8, 2015 22:49 UTC (Sun)
by
anyway, since it's you guys who have a bee in your bonnet, let's test your level of intelligence too. first figure out my email address and project name then try to find the commits that say they come from there (it brought back some memories from 2004 already, how times flies! i'm surprised i actually managed to accomplish this much with explicitly not trying, imagine if i did :). it's an incredibly complex task so by accomplishing it you'll prove yourself to be the top dog here on lwn, whatever that's worth ;).
Posted Nov 8, 2015 23:25 UTC (Sun)
by
*shrug* Or don't; you're only sullying your own reputation.
Posted Nov 9, 2015 7:08 UTC (Mon)
by
Posted Nov 9, 2015 11:38 UTC (Mon)
by
I wouldn't either
Posted Nov 12, 2015 2:09 UTC (Thu)
by
Posted Nov 12, 2015 8:50 UTC (Thu)
by
Posted Nov 8, 2015 3:38 UTC (Sun)
by
Posted Nov 12, 2015 13:47 UTC (Thu)
by
Ah. I thought my memory wasn't failing me. Compare to PaXTeam's response to <
PaXTeam is not averse to outright lying if it means he gets to appear right, I see. Maybe PaXTeam's memory is failing, and this apparent contradiction is not a brazen lie, but given that the two posts were made within a day of each other I doubt it. (PaXTeam's total unwillingness to assume good faith in others deserves some reflection. Yes, I *do* think he's lying by implication here, and doing so when there's almost nothing at stake. God alone knows what he's willing to stoop to when something *is* at stake. Gosh I wonder why his fixes aren't going upstream very fast.)
Posted Nov 12, 2015 14:11 UTC (Thu)
by
> and that one commit you found that went in despite said ban
also someone's ban doesn't mean it'll translate into someone else's execution of that ban as it's clear from the commit in question. it's somewhat sad that it takes a security fix to expose the fallacy of this policy though. the rest of your pithy ad hominem speaks for itself better than i ever could ;).
Posted Nov 12, 2015 15:58 UTC (Thu)
by
Posted Nov 7, 2015 19:01 UTC (Sat)
by
I don't see this message in my mailbox, so presumably it got swallowed.
Posted Nov 7, 2015 22:33 UTC (Sat)
by
You are aware that it's entirely possible that everyone is wrong here , right?
That the kernel maintainers need to focus more on security, that the article was biased, that you're irresponsible to decry the state of security, and do nothing to help, and that your patchsets wouldn't help that much and are the wrong direction for the kernel? That just because the kernel maintainers aren't 100% right it doesn't mean you are?
Posted Nov 9, 2015 9:50 UTC (Mon)
by I think you have him backwards there. Jon is comparing this to Mindcraft because he thinks that despite being unpalatable to a lot of the community, the article might in fact contain a lot of truth.
Posted Nov 9, 2015 14:03 UTC (Mon)
by
Posted Nov 9, 2015 15:13 UTC (Mon)
by
"There are rumors of dark forces that drove the article in the hopes of taking Linux down a notch. All of this could well be true"
Just as you criticized the article for mentioning Ashley Madison even though in the very first sentence of the following paragraph it mentions it didn't involve the Linux kernel, you can't give credence to conspiracy theories without incurring the same criticism (in other words, you can't play the Glenn Beck "I'm just asking the questions here!" whose "questions" fuel the conspiracy theories of others). Much like mentioning Ashley Madison as an example for non-technical readers about the prevalence of Linux in the world, if you're criticizing the mention then should not likening a non-FUD article to a FUD article also deserve criticism, especially given the rosy, self-congratulatory picture you painted of upstream Linux security?
As the PaX Team pointed out in the initial post, the motivations aren't hard to know -- you made no mention at all about it being the 5th in a long-running series following a pretty predictable time trajectory.
No, we didn't miss the overall analogy you were trying to make, we just don't think you can have your cake and eat it too.
-Brad
Posted Nov 9, 2015 15:18 UTC (Mon)
by
Posted Nov 9, 2015 17:06 UTC (Mon)
by
It's gracious of you not to blame your readers. I figure they're a fair target: there's that line about those ignorant of history being condemned to re-implement Unix -- as your readers are! :-)
K3n.
Posted Nov 9, 2015 18:43 UTC (Mon)
by
Unfortunately, I do not understand neither the "security" folks (PaXTeam/spender), nor the mainstream kernel folks in terms of their attitude. I confess I have totally no technical capabilities on any of these topics, but if they all decided to work together, instead of having endless and pointless flame wars and blame game exchanges, a lot of the stuff would have been done already. And all the while everyone involved may have made another big pile of money on the stuff. They all seem to want to have a better Linux kernel, so I've got no idea what the problem is. It seems that nobody is willing to yield any of their positions even a little bit. Instead, both sides appear to be bent on trying to insult their way into forcing the other side to give up. Which, of course, never works - it just causes more pushback.
Perplexing stuff...
Posted Nov 9, 2015 19:00 UTC (Mon)
by
Posted Nov 9, 2015 19:44 UTC (Mon)
by
Take a scientific computational cluster with an "air gap", for instance. You'd probably want most of the security stuff turned off on it to gain maximum performance, because you can trust all users. Now take a few billion mobile phones that may be difficult or slow to patch. You'd probably want to kill many of the exploit classes there, if those devices can still run reasonably well with most security features turned on.
So, it's not either/or. It's probably "it depends". But, if the stuff isn't there for everyone to compile/use in the vanilla kernel, it will be more difficult to make it part of everyday choices for distributors and users.
Posted Nov 6, 2015 22:20 UTC (Fri)
by
How sad. This Dijkstra quote comes to mind immediately:
Software engineering, of course, presents itself as another worthy cause, but that is eyewash: if you carefully read its literature and analyse what its devotees actually do, you will discover that software engineering has accepted as its charter "How to program if you cannot."
Posted Nov 7, 2015 0:35 UTC (Sat)
by
I guess that fact was too unpleasant to fit into Dijkstra's world view.
Posted Nov 7, 2015 10:52 UTC (Sat)
by
Indeed. And the interesting thing to me is that once I reach that point, tests are not sufficient - model checking at a minimum and really proofs are the only way forwards. I'm no security expert, my field is all distributed systems. I understand and have implemented Paxos and I believe I can explain how and why it works to anyone. But I'm currently doing some algorithms combining Paxos with a bunch of variations on VectorClocks and reasoning about causality and consensus. No test is sufficient because there are infinite interleavings of events and my head just couldn't cope with working on this either at the computer or on paper - I found I could not intuitively reason about this stuff at all. So I started defining the properties and wanted and step by step proving why each of them holds. Without my notes and proofs I can't even explain to myself, let alone anyone else, why this thing works. I find this both completely obvious that this can happen and utterly terrifying - the maintenance cost of these algorithms is now an order of magnitude higher.
Posted Nov 19, 2015 12:24 UTC (Thu)
by
> Indeed. And the interesting thing to me is that once I reach that point, tests are not sufficient - model checking at a minimum and really proofs are the only way forwards.
Or are you just using the wrong maths? Hobbyhorse time again :-) but to quote a fellow Pick developer ... "I often walk into a SQL development shop and see that wall - you know, the one with the huge SQL schema that no-one fully understands on it - and wonder how I can easily hold the entire schema for a Pick database of the same or greater complexity in my head".
But it's easy - by education I'm a Chemist, by interest a Physical Chemist (and by profession an unemployed programmer :-). And when I'm thinking about chemistry, I can ask myself "what is an atom made of" and think about things like the strong nuclear force. Next level up, how do atoms stick together and make molecules, and think about the electroweak force and electron orbitals, and how do chemical reactions occur. Then I think about molecules stick together to make materials, and think about metals, and/or Van de Waals, and stuff.
Point is, you need to *layer* stuff, and look at things, and say "how can I split parts off into 'black boxes' so at any one level I can assume the other levels 'just work'". For example, with Pick a FILE (table to you) stores a class - a collection of identical objects. One object per RECORD (row). And, same as relational, one attribute per FIELD (column). Can you map your relational tables to reality so easily? :-)
Going back THIRTY years, I remember a story about a guy who built little computer crabs, that could quite happily scuttle around in the surf zone. Because he didn't try to work out how to solve all the problems at once - each of his (incredibly puny by today's standards - this is the 8080/Z80 era!) processors was set to just process a little bit of the problem and there was no central "brain". But it worked ... Maybe you should just write a bunch of small modules to solve each individual problem, and let ultimate answer "just happen".
Cheers,
Posted Nov 19, 2015 19:28 UTC (Thu)
by
To my understanding, this is exactly what a mathematical abstraction does. For example in Z notation we'd construct schemas for the various modifying ("delta") operations on the base schema, and then argue about preservation of formal invariants, properties of the outcome, and transitivity of the operation when chained with itself, or the preceding aggregate schema composed of schemas A through O (for which they've been already argued).
The outcome is a set of operations that, executed in arbitrary order, result in a set of properties holding for the result and outputs. Thus proving the formal design correct (w/ caveat lectors concerning scope, correspondence with its implementation [though that can be proven as well], and read-only ["xi"] operations).
Posted Nov 20, 2015 11:23 UTC (Fri)
by
Looking through the history of computing (and probably plenty of other fields too), you'll probably find that people "can't see the wood for the trees" more often that not. They dive into the detail and completely miss the big picture.
(Medicine, and interest of mine, suffers from that too - I remember somebody talking about the consultant wanting to amputate a gangrenous leg to save someone's life - oblivious to the fact that the patient was dying of cancer.)
Cheers,
Posted Nov 7, 2015 6:35 UTC (Sat)
by
(LCA 2015 - "Programming Considered Harmful")
FWIW, I think that this talk is very relevant to why writing secure software is so hard..
-Dave.
Posted Nov 7, 2015 5:49 UTC (Sat)
by
While we are spending millions at a multitude of security problems, kernel issues are not on our top-priority list. Honestly I remember only once having discussing a kernel vulnerability. The result of the analysis has been that all our systems were running kernels that were older as the kernel that had the vulnerability.
But "patch management" is a real issue for us. Software must continue to work if we install security patches or update to new releases because of the end-of-life policy of a vendor. The revenue of the company is depending on the IT systems running. So "not breaking user space" is a security feature for us, because a breakage of one component of our several ten thousands of Linux systems will stop the roll-out of the security update.
Another problem is embedded software or firmware. These days almost all hardware systems include an operating system, often some Linux version, providing a fill network stack embedded to support remote management. Regularly those systems don't survive our obligatory security scan, because vendors still didn't update the embedded openssl.
The real challenge is to provide a software stack that can be operated in the hostile environment of the Internet maintaining full system integrity for ten years or even longer without any customer maintenance. The current state of software engineering will require support for an automated update process, but vendors must understand that their business model must be able to finance the resources providing the updates.
Overall I'm optimistic, networked software is not the first technology used by mankind causing problems that were addressed later. Steam engine use could result in boiler explosions but the "engineers" were able to reduce this risk significantly over a few decades.
Posted Nov 7, 2015 10:29 UTC (Sat)
by
The following is all guess work; I'd be keen to know if others have evidence either one way or another on this: The people who learn how to hack into these systems through kernel vulnerabilities know that they skills they've learnt have a market. Thus they don't tend to hack in order to wreak havoc - indeed on the whole where data has been stolen in order to release and embarrass people, it _seems_ as though those hacks are through much simpler vectors. I.e. lesser skilled hackers find there is a whole load of low-hanging fruit which they can get at. They're not being paid ahead of time for the data, so they turn to extortion instead. They don't cover their tracks, and they can often be found and charged with criminal offences.
So if your security meets a certain basic level of proficiency and/or your company isn't doing anything that puts it near the top of "companies we'd like to embarrass" (I suspect the latter is much more effective at keeping systems "safe" than the former), then the hackers that get into your system are likely to be skilled, paid, and probably not going to do much damage - they're stealing data for a competitor / state. So that doesn't bother your bottom line - at least not in a way which your shareholders will be aware of. So why fund security?
Posted Nov 7, 2015 17:02 UTC (Sat)
by
On the other hand, some effective mitigation in kernel level would be very helpful to crush cybercriminal/skiddie's try. If one of your customer running a future trading platform exposes some open API to their clients, and if the server has some memory corruption bugs can be exploited remotely. Then you know there are known attack methods( such as offset2lib) can help the attacker make the weaponized exploit so much easier. Will you explain the failosophy "A bug is bug" to your customer and tell them it'd be ok? Btw, offset2lib is useless to PaX/Grsecurity's ASLR imp.
To the most commercial uses, more security mitigation within the software won't cost you more budget. You'll still have to do the regression test for each upgrade.
Posted Nov 12, 2015 16:14 UTC (Thu)
by
Keep in mind that I specialize in external web-based penetration-tests and that in-house tests (local LAN) will likely yield different results.
Posted Nov 7, 2015 20:33 UTC (Sat)
by I keep reading this headline as "a new Oh well. I mean, security is good too, I guess.
Posted Nov 7, 2015 22:24 UTC (Sat)
by
Posted Nov 12, 2015 17:29 UTC (Thu)
by
Posted Nov 8, 2015 10:34 UTC (Sun)
by
Posted Nov 9, 2015 7:15 UTC (Mon)
by
Posted Nov 9, 2015 15:53 UTC (Mon)
by
(Oh, and I was also still wondering how Minecraft had taught us about Linux performance - so thanks to the other comment thread that pointed out the 'd', not 'e'.)
Posted Nov 9, 2015 11:31 UTC (Mon)
by
I'd just like to add that in my opinion, there is a general problem with the economics of computer security, which is especially visible currently. Two problems even maybe.
First, the money spent on computer security is often diverted towards the so-called security "circus": fast, easy solutions which are primarily selected just in order to "do something" and get better press. It took me a long time - maybe decades - to claim that no security mechanism at all is better than a bad mechanism. But now I firmly believe in this attitude and would rather take the risk knowingly (provided that I can save money/resource for myself) than take a bad approach at solving it (and have no money/resource left when I realize I should have done something else). And I find there are many bad or incomplete approaches currently available in the computer security field.
Second, and that may be more recent and more worrying. The flow of money/resource is oriented in the direction of attack tools and vulnerabilities discovery much more than in the direction of new protection mechanisms.
Personnally, I'd happily leave them all the hype; but I'll forcefully claim that they have no right whatsoever on any of the budget allocation decisions. Only those working on protection should. And yep, it means we should decide where to put there resources. We have to claim the exclusive lock for ourselves this time. (and I guess the PaXteam could be among the first to benefit from such a change).
While thinking about it, I would not even leave white-hat or cyber-guys any hype in the end. That's more publicity than they deserve.
Posted Nov 9, 2015 14:28 UTC (Mon)
by
The state of 'software security industry' is a f-ng disaster. Failure of the highest order. There is massive amounts of money that is going into 'cyber security', but it's usually spent on government compliance and audit efforts. This means instead of actually putting effort into correcting issues and mitigating future problems, the majority of the effort goes into taking existing applications and making them conform to committee-driven guidelines with the minimal amount of effort and changes.
Some level of regulation and standardization is absolutely needed, but lay people are clueless and are completely unable to discern the difference between somebody who has valuable experience versus some company that has spent millions on slick marketing and 'native advertising' on large websites and computer magazines. The people with the money unfortunately only have their own judgment to rely on when buying into 'cyber security'.
> Those spilling our rare money/resources on ready-made useless tools should get the bad press they deserve.
There is no such thing as 'our rare money/resources'. You have your money, I have mine. Money being spent by some corporation like Redhat is their money. Money being spent by governments is the government's money. (you, literally, have far more control in how Walmart spends it's money then over what your government does with their's)
> This is especially worrying as cyber "defense" initiatives look more and more like the usual idustrial projects aimed at producing weapons or intelligence systems. Furthermore, bad useless weapons, because they are only working against our very vulnerable current systems; and bad intelligence systems as even basic school-level encryption scares them down to useless.
Having secure software with strong encryption mechanisms in the hands of the public runs counter to the interests of most major governments. Governments, like any other for-profit organization, are primarily interested in self-preservation. Money spent on drone initiatives or banking auditing/oversight regulation compliance is FAR more valuable to them then trying to help the public have a secure mechanism for making phone calls. Especially when those secure mechanisms interfere with data collection efforts.
Unfortunately you/I/us cannot depend on some magical benefactor with deep pockets to sweep in and make Linux better. It's just not going to happen.
Corporations like Redhat have been massively beneficial to spending resources to make Linux kernel more capable.. however they are driven by a the need to turn a profit, which means they need to cater directly to the the sort of requirements established by their customer base. Customers for EL tend to be much more focused on reducing costs associated with administration and software development then security at the low-level OS.
Enterprise Linux customers tend to rely on physical, human policy, and network security to protect their 'soft' interiors from being exposed to external threats.. assuming (rightly) that there is very little they can do to actually harden their systems. In fact when the choice comes between security vs convenience I am sure that most customers will happily defeat or strip out any security mechanisms introduced into Linux.
On top of that when most Enterprise software is extremely bad. So much so that 10 hours spent on improving a web front-end will yield more real-world security benefits then a 1000 hours spent on Linux kernel bugs for most businesses.
Even for 'normal' Linux users a security bug in their Firefox's NAPI flash plugin is far more devastating and poses a massively higher risk then a obscure Linux kernel buffer over flow problem. It's just not really important for attackers to get 'root' to get access to the important information... generally all of which is contained in a single user account.
Ultimately it's up to individuals like you and myself to put the effort and money into improving Linux security. For both ourselves and other people.
Posted Nov 10, 2015 11:05 UTC (Tue)
by
Spilling has always been the case, but now, to me and in computer security, most of the money seems spilled due to bad faith. And this is mostly your money or mine: either tax-fueled governemental resources or corporate costs that are directly reimputed on the prices of goods/software we are told we are *obliged* to buy. (Look at corporate firewalls, home alarms or antivirus software marketing discourse.)
I think it is time to point out that there are several "malicious malefactors" around and that there is a real need to identify and sanction them and confiscate the resources they have somehow managed to monopolize. And I do *not* think Linus is among such culprits by the way. But I think he may be among the ones hiding their heads in the sand about the aforementioned evil actors, while he probably has more leverage to counteract them or oblige them to reveal themselves than many of us.
In the end, I think you are right to say that currently it's only up to us individuals to try honestly to do something to improve Linux or computer security. But I still think that I am right to say that this is not normal; especially while some very serious people get very serious salaries to distribute randomly some difficult to evaluate budgets.
[1] A paradoxical situation when you think about it: in a domain where you are first and foremost preoccupied by malicious individuals everyone should have factual, transparent and honest behavior as the first priority in their mind.
Posted Nov 9, 2015 15:47 UTC (Mon)
by
It even has a nice, seven line Basic-pseudo-code that describes the current situation and clearly shows that we are caught in an endless loop. It does not answer the big question, though: How to write better software.
The sad thing is, that this is from 2005 and all the things that were obviously stupid ideas 10 years ago have proliferated even more.
Posted Nov 10, 2015 11:20 UTC (Tue)
by
Note IMHO, we should investigate further why these dumb things proliferate and get so much support.
But, more importantly, let's capitalize on this knowledge and secure *our* systems, to show off at a minimum (and more later on of course).
Your reference conclusion is especially nice to me. "challenge [...] the conventional wisdom and the status quo": that job I would happily accept.
Posted Nov 30, 2015 9:39 UTC (Mon)
by
That rant is itself a bunch of "empty calories". The converse to the items it rants about, which it is suggesting at some level, would be as bad or worse, and indicative of the worst kind of security thinking that has put a lot of people off. Alternatively, it is just a rant that offers little of value.
Personally, I think there's no magic bullet. Security is and always has been, in human history, an arms race between defenders and attackers, and one that is inherently a trade-off between usability, risks and costs. If there are mistakes being made, it is that we should probably spend more resources on defences that could block entire classes of attacks. E.g., why is the GRSec kernel hardening stuff so hard to apply to regular distros (e.g. there's no reliable source of a GRSec kernel for Fedora or RHEL, is there?). Why does the entire Linux kernel run in one security context? Why are we still writing lots of software in C/C++, often without any basic security-checking abstractions (e.g. basic bounds-checking layers in between I/O and parsing layers, say)? Can hardware do more to provide security with speed?
No doubt there are plenty of people working on "block classes of attacks" stuff, the question is, why aren't there more resources directed there?
Posted Nov 10, 2015 2:06 UTC (Tue)
by
>There are a lot of reasons why Linux lags behind in defensive security technologies, but one of the key ones is that the companies making money on Linux have not prioritized the development and integration of those technologies.
This seems like a reason which is really worth exploring. Why is it so?
I think it is not obvious why this doesn't get some more attention. Is it possible that the people with the money are right not to more highly prioritise this? Afterall, what interest do they have in an unsecure, exploitable kernel? Where there is common cause, linux development gets resourced. It's been this way for many years. If filesystems qualify for common interest, surely security does. So there doesn't seem to be any obvious reason why this issue does not get more mainstream attention, except that it actually already gets enough. You may say that disaster has not struck yet, that the iceberg has not been hit. But it seems to be that the linux development process is not overly reactive elsewhere.
Posted Nov 10, 2015 15:53 UTC (Tue)
by
That is an interesting question, certainly that is what they actually believe regardless of what they publicly say about their commitment to security technologies. What is the actually demonstrated downside for Kernel developers and the organizations that pay them, as far as I can tell there is not sufficient consequence for the lack of Security to drive more funding, so we are left begging and cajoling unconvincingly.
Posted Nov 12, 2015 14:37 UTC (Thu)
by
The key issue with this domain is it relates to malicious faults. So, when consequences manifest themselves, it is too late to act. And if the current commitment to a lack of voluntary strategy persists, we are going to oscillate between phases of relaxed inconscience and anxious paranoia.
Admittedly, kernel developpers seem pretty resistant to paranoia. That is a good thing. But I am waiting for the days where armed land-drones patrol US streets in the vicinity of their children schools for them to discover the feeling. They are not so distants the days when innocent lives will unconsciouly rely on the security of (linux-based) computer systems; under water, that's already the case if I remember correctly my last dive, as well as in several recent cars according to some reports.
Posted Nov 12, 2015 14:32 UTC (Thu)
by
Classic hosting companies that use Linux as an exposed front-end system are retreating from development while HPC, mobile and "generic enterprise", i.E. RHEL/SLES, are pushing the kernel in their directions.
This is really not that surprising: For hosting needs the kernel has been "finished" for quite some time now. Besides support for current hardware there is not much use for newer kernels. Linux 3.2, or even older, works just fine.
Hosting does not need scalability to hundreds or thousands of CPU cores (one uses commodity hardware), complex instrumentation like perf or tracing (systems are locked down as much as possible) or advanced power-management (if the system does not have constant high load, it is not making enough money). So why should hosting companies still make strong investments in kernel development? Even if they had something to contribute, the hurdles for contribution have become higher and higher.
For their security needs, hosting companies already use Grsecurity. I have no numbers, but some experience suggests that Grsecurity is basically a fixed requirement for shared hosting.
On the other hand, kernel security is almost irrelevant on nodes of a super computer or on a system running large business databases that are wrapped in layers of middle-ware. And mobile vendors simply do not care.
Posted Nov 10, 2015 4:18 UTC (Tue)
by
Posted Nov 10, 2015 13:15 UTC (Tue)
by
Posted Nov 11, 2015 22:38 UTC (Wed)
by The assembled doubtless recall that in August 2011, kernel.org was root compromised. I'm sure the system's hard drives were sent off for forensic examination, and we've all been waiting patiently for the answer to the most important question: What was the compromise vector?
From shortly after the compromise was discovered on August 28, 2011, right through This has been disappointing. When the Debian Project discovered sudden compromise of several of its servers in 2007, Wichert Akkerman wrote and posted an excellent Arstechnica's Dan Goodin was still trying to Who's responsible, then? Is anyone? Anyone? Bueller? Or is it a state secret, or what? Two years since Greg K-H said there would be a report 'later this year', and four years since the meltdown, nothing yet. How about some information?
Rick Moen
Posted Nov 12, 2015 14:19 UTC (Thu)
by
Less seriously, note that if even the Linux mafia does not know, it must be the venusians; they are notoriously stealth in their invasions.
Posted Nov 14, 2015 12:46 UTC (Sat)
by
I know the kernel.org admins have given talks about some of the new protections that have been put into place. There are no more shell logins, instead everything uses gitolite. The different services are on different hosts. There are more kernel.org staff now. People are using two factor identification. Some other stuff. Do a search for Konstantin Ryabitsev.
Posted Nov 14, 2015 15:58 UTC (Sat)
by I beg your pardon if I was somehow unclear: That was said to have been the OK, folks, you've now had four years of investigation. Rick Moen
Posted Nov 22, 2015 12:42 UTC (Sun)
by I've done a closer review of revelations that came out soon after the break-in, and think I've found the answer, via a leaked Root escalation was via exploit of a Linux kernel security hole: Per the two security researchers, it was one both extremely embarrassing (wide-open access to /dev/mem contents including the running kernel's image in RAM, in 2.6 kernels of that day) and known-exploitable for I posted my I do have to wonder: If there's another embarrassing screwup, will we even be told about it at all?
Rick Moen
Posted Nov 22, 2015 14:25 UTC (Sun)
by
Also, it's preferable to use live memory acquisition prior to powering off the system, otherwise you lose out on memory-resident artifacts that you can perform forensics on.
-Brad
Posted Nov 22, 2015 16:28 UTC (Sun)
by Thanks for your comments, Brad.
I'd been relying on Dan Goodin's claim of Phalanx being what was used to gain root, in the bit where he cited 'two security researchers who were briefed on the breach' to that effect. Goodin also That having been said, yeah, the Phalanx README doesn't specifically claim this, so then maybe Goodin and his several 'security researcher' sources blew that detail, and nobody but kernel.org insiders yet knows the escalation path used to gain root.
Arguable, but a tradeoff; you can poke the compromised live system for state data, but with the drawback of leaving your system running under hostile control. I was always taught that, on balance, it's better to pull power to end the intrusion.
Rick Moen
Posted Nov 20, 2015 8:23 UTC (Fri)
by
Posted Nov 20, 2015 9:31 UTC (Fri)
by
With "something" you mean those who produce those closed source drivers, right?
If the "consumer product companies" just stuck to using parts with mainlined open source drivers, then updating their products would be much easier.
Posted Nov 20, 2015 11:29 UTC (Fri)
by
They have ring 0 privilege, can access protected memory directly, and cannot be audited. Trick a kernel into running a compromised module and it's game over.
Even tickle a bug in a "good" module, and it's probably game over - in this case quite literally as such modules tend to be video drivers optimised for games ... :-)
Cheers,
[
][
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663538/)] (55 responses)
[http://thread.gmane.org/gmane.comp.file-systems.btrfs/49500](http://thread.gmane.org/gmane.comp.file-systems.btrfs/49500) (FYI, the overflow plugin is the first one Kees is trying to upstream, imagine the shitstorm if bugreports will be treated with this attitude, let's hope btrfs guys are an exception, not the rule). anyway, two examples are not statistics, so once again, do you have numbers or is it all wishful thinking? (it's partly a trick question because you'll also have to explain how something gets to be determined to be security related which as we all know is a messy business in the linux world)
[https://lwn.net/Articles/538600/](https://lwn.net/Articles/538600/) . since i don't expect you and your readers to read any of it, here's the tl;dr: if you want us to spend thousands of hours of our time to upstream our code, you will have to pay for it. no ifs no buts, that's how the world works, that's how >90% of linux code gets in too. i personally find it pretty hypocritic that well paid kernel developers are bitching about our unwillingness and inability to serve them our code on a silver platter for free. and before someone brings up the CII, go check their mail archives, after some initial exploratory discussions i explicitly asked them about supporting this long drawn out upstreaming work and got no answers.
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**patrick_g** (subscriber, #44470)
[[Link](/Articles/663554/)] (22 responses)
That's exactly the point of bojan's answer to your 2013 post : [https://lwn.net/Articles/538658/](https://lwn.net/Articles/538658/)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**nirbheek** (subscriber, #54111)
[[Link](/Articles/663559/)] (7 responses)
[http://rationalwiki.org/wiki/Tone_argument](http://rationalwiki.org/wiki/Tone_argument)
2. [http://geekfeminism.wikia.com/wiki/Tone_argument](http://geekfeminism.wikia.com/wiki/Tone_argument)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**josh** (subscriber, #17465)
[[Link](/Articles/663584/)] (2 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663589/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**josh** (subscriber, #17465)
[[Link](/Articles/663606/)]
[
]## No Argument
**gmatht** (subscriber, #58961)
[[Link](/Articles/663604/)] (3 responses)
[
]## No Argument
**josh** (subscriber, #17465)
[[Link](/Articles/663609/)] (2 responses)
[
]## OK, but I was thinking of Linus Torvalds
**gmatht** (subscriber, #58961)
[[Link](/Articles/663665/)] (1 responses)
[
]## OK, but I was thinking of Linus Torvalds
**pbonzini** (subscriber, #60935)
[[Link](/Articles/663678/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663562/)] (13 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**pr1268** (subscriber, #24648)
[[Link](/Articles/663565/)] (3 responses)
it's not going to fix itself unless actual money (and not empty words) is thrown at it.
*money* will fix this problem? Yes, I agree more *resources* should be spent on fixing Linux kernel security issues, but don't assume someone giving an organization (ahem, PAXTeam) money is the only solution. (Not mean to impugn PAXTeam's security efforts.)[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663578/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**nix** (subscriber, #2304)
[[Link](/Articles/663612/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663616/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**dowdle** (subscriber, #659)
[[Link](/Articles/663567/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663581/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**bojan** (subscriber, #14302)
[[Link](/Articles/663579/)] (4 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**k3ninho** (subscriber, #50375)
[[Link](/Articles/663672/)] (3 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**jospoortvliet** (guest, #33164)
[[Link](/Articles/663714/)] (2 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**Garak** (guest, #99377)
[[Link](/Articles/664145/)] (1 responses)
And about that fork barrel: I'd argue it is the other way around. Google forked and lost already.
What did they lose exactly? They made a lot of money in the business of forking. The ponzi scheme may be about to collapse as the elephant dance nears conclusion, but somehow I don't expect they'll lose any significant fraction of all the money they made getting to this point with the NSA's help.
The fact that vendors seem to have little interest in getting security fixes to their customers is danced around like a huge elephant in the room.
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**jospoortvliet** (guest, #33164)
[[Link](/Articles/665506/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**corbet** (editor, #1)
[[Link](/Articles/663596/)] (1 responses)
"
*this is 2015AD already and linux *still* has a security problem and no, it's not going to fix itself unless actual money (and not empty words) is thrown at it.*"[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663652/)]
[https://forums.grsecurity.net/viewtopic.php?f=7&t=4309](https://forums.grsecurity.net/viewtopic.php?f=7&t=4309) .
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**flussence** (guest, #85566)
[[Link](/Articles/663563/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**dowdle** (subscriber, #659)
[[Link](/Articles/663566/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**rahvin** (guest, #16953)
[[Link](/Articles/663577/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**josh** (subscriber, #17465)
[[Link](/Articles/663586/)] (18 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663591/)] (17 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**jejb** (subscriber, #6654)
[[Link](/Articles/663629/)] (16 responses)
[http://lists.coreinfrastructure.org/pipermail/cii-discuss...](http://lists.coreinfrastructure.org/pipermail/cii-discuss/2015-August/thread.html)
1
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663643/)] (14 responses)
[http://lists.coreinfrastructure.org/pipermail/cii-discuss...](http://lists.coreinfrastructure.org/pipermail/cii-discuss/2015-August/000010.html) and my explicit question:
> full time job. Is the CII willing to fund projects at that level? If not
> we all would end up with lots of unfinished and partially broken features.
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**jejb** (subscriber, #6654)
[[Link](/Articles/663653/)] (11 responses)
[http://lists.coreinfrastructure.org/pipermail/cii-discuss](http://lists.coreinfrastructure.org/pipermail/cii-discuss)... and my explicit question:
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663654/)] (9 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**jejb** (subscriber, #6654)
[[Link](/Articles/663679/)] (8 responses)
[http://lwn.net/Articles/663591/](http://lwn.net/Articles/663591/)):
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663685/)] (7 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**pizza** (subscriber, #46)
[[Link](/Articles/663698/)] (6 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663699/)] (5 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**pizza** (subscriber, #46)
[[Link](/Articles/663703/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**jospoortvliet** (guest, #33164)
[[Link](/Articles/663715/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**hkario** (subscriber, #94864)
[[Link](/Articles/663722/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**jschrod** (subscriber, #1646)
[[Link](/Articles/664135/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**nwmcsween** (guest, #62367)
[[Link](/Articles/664152/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/663657/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**nix** (subscriber, #2304)
[[Link](/Articles/664191/)] (1 responses)
[http://lwn.net/Articles/663612/](http://lwn.net/Articles/663612/)>.
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**PaXTeam** (guest, #24616)
[[Link](/Articles/664198/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**andreashappe** (subscriber, #4810)
[[Link](/Articles/664248/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**cwillu** (guest, #67268)
[[Link](/Articles/663635/)]
[http://thread.gmane.org/gmane.comp.file-systems.btrfs/49500](http://thread.gmane.org/gmane.comp.file-systems.btrfs/49500) ("overflow in inode.c, file.c"):
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**ssmith32** (subscriber, #72404)
[[Link](/Articles/663645/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**njd27** (subscriber, #5770)
[[Link](/Articles/663719/)] (7 responses)
1. this WP article was the 5th in a series of articles following the security of the internet from its beginnings to relevant topics of today. discussing the security of linux (or lack thereof) fits nicely in there. it was also a well-researched article with over two months of research and interviews, something you can't quite claim yourself for your recent pieces on the subject. you don't like the facts? then say so. or even better, do something constructive about them like Kees and others have been trying. however silly comparisons to old crap like the Mindcraft studies and fueling conspiracies don't exactly help your case.
[
]
That is indeed the point I was trying to make. A few people seem to have missed that; I guess I can only conclude that I wrote it poorly (rather than, say, write it off as a deliberate misreading) and apologize for the confusion.
## A new Mindcraft moment?
**corbet** (editor, #1)
[[Link](/Articles/663731/)] (6 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**spender** (guest, #23067)
[[Link](/Articles/663732/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**karath** (subscriber, #19025)
[[Link](/Articles/663743/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**k3ninho** (subscriber, #50375)
[[Link](/Articles/663758/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**bojan** (subscriber, #14302)
[[Link](/Articles/663796/)] (2 responses)
[
]
Interpersonal communication is certainly a major issue here, but even setting that aside there is a problem of comparing apples and oranges. The case for inclusion in the kernel rests on a cost/benefit argument. The cost is in part quantifiable in terms of performance (%decrease in throughput, %increase in memory usage, etc). But how do you quantify the benefit on a comparable scale? If you place an extremely high value on security, you come at this thinking that ## A new Mindcraft moment?
**sfeam** (subscriber, #2841)
[[Link](/Articles/663797/)] (1 responses)
*any* improvement is worth the cost. If you place a less extreme value on security then the argument runs aground as just seen earlier in this thread: is an XX% slowdown a small price to pay or is it an unacceptable regression?
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**bojan** (subscriber, #14302)
[[Link](/Articles/663801/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**artem** (subscriber, #51262)
[[Link](/Articles/663561/)] (6 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**roc** (subscriber, #30627)
[[Link](/Articles/663580/)] (4 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**ms** (subscriber, #41272)
[[Link](/Articles/663619/)] (3 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**Wol** (subscriber, #4433)
[[Link](/Articles/664968/)] (2 responses)
Wol
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**ksandstr** (guest, #60862)
[[Link](/Articles/665067/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**Wol** (subscriber, #4433)
[[Link](/Articles/665153/)]
Wol
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**dgc** (subscriber, #6611)
[[Link](/Articles/663608/)]
[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VpuVDfSXs-g](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VpuVDfSXs-g)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**kunitz** (subscriber, #3965)
[[Link](/Articles/663597/)] (3 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**ms** (subscriber, #41272)
[[Link](/Articles/663617/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**citypw** (guest, #82661)
[[Link](/Articles/663628/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**andreashappe** (subscriber, #4810)
[[Link](/Articles/664250/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**mattdm** (subscriber, #18)
[[Link](/Articles/663637/)] (2 responses)
*Minecraft* moment", and thinking that maybe they've decided to follow up the .NET thing by open-sourcing Minecraft.
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**ssmith32** (subscriber, #72404)
[[Link](/Articles/663644/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**smitty_one_each** (subscriber, #28989)
[[Link](/Articles/664264/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**jcm** (subscriber, #18262)
[[Link](/Articles/663669/)] (2 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**jospoortvliet** (guest, #33164)
[[Link](/Articles/663716/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**nelljerram** (subscriber, #12005)
[[Link](/Articles/663745/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**ortalo** (guest, #4654)
[[Link](/Articles/663721/)] (5 responses)
Those spilling our rare money/resources on ready-made useless tools should get the bad press they deserve. And, we certainly need to enlighten the press on that because it is not so easy to appreciate the efficiency of protection mechanisms (which, by definition, should prevent things from happening).
This is especially worrying as cyber "defense" initiatives look more and more like the usual idustrial projects aimed at producing weapons or intelligence systems. Furthermore, bad useless weapons, because they are only working against our very vulnerable current systems; and bad intelligence systems as even basic school-level encryption scares them down to useless.
However, all the ressources are for these adult teenagers playing the white hat hackers with not-so-difficult programming tricks or network monitoring or WWI-level cryptanalysis. And now also for the cyberwarriors and cyberspies that have yet to prove their usefulness entirely (especially for peace protection...).
I crave for the day I will read in the newspaper that: "Another of these ill advised debutant programmer hooligans that pretend to be cyber-pirates/warriors modified some well known virus program code exploiting a programmer mistake and managed however to bring one of those unfinished and bad quality programs, X, that we are all obliged to use to its knees, annoying millions of regular users with his unfortunate cyber-vandalism. All the protection experts unanimously recommend that, once again, the budget of the cyber-command be retargetted, or at least leveled-off, in order to bring more security engineer positions in the academic domain or civilian industry. And that X's producer, XY Inc., be liable for the potential losses if proved to be unprofessional in this affair."
Hmmm - cyber-hooligans - I like the label. Though it does not apply well to the battlefield-oriented variant.
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**drag** (guest, #31333)
[[Link](/Articles/663730/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**ortalo** (guest, #4654)
[[Link](/Articles/663840/)]
My key point is actually showing that money/resources is spilled currently in this field, due to the lack of maturity or - much more worryingly - the bad faith of some of the actors [1]. Especially among some of the big organizations that, logically, have the most resources to spill.
I find that to be of brown-paper-bag level (though head-in-the-sand is somehow a new interpretation).
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**MarcB** (subscriber, #101804)
[[Link](/Articles/663744/)] (2 responses)
[http://www.ranum.com/security/computer_security/editorial...](http://www.ranum.com/security/computer_security/editorials/dumb/)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**ortalo** (guest, #4654)
[[Link](/Articles/663846/)]
If it's only human psychology, well, let's fight it: e.g. Mozilla has shown us that they can do wonderful things given the right message.
If we are facing active people exploiting public credulity: let's identify and fight them.
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**paulj** (subscriber, #341)
[[Link](/Articles/666066/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**timrichardson** (subscriber, #72836)
[[Link](/Articles/663829/)] (3 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**raven667** (subscriber, #5198)
[[Link](/Articles/663881/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**ortalo** (guest, #4654)
[[Link](/Articles/664202/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**MarcB** (subscriber, #101804)
[[Link](/Articles/664181/)]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**bronson** (subscriber, #4806)
[[Link](/Articles/663833/)] (1 responses)
[
]
I took the link-to-the-link approach in the first paragraph to pull in the conversation that had happened previously.
## Linking
**corbet** (editor, #1)
[[Link](/Articles/663853/)]
[
]
All of this reminds me of something tangential but, I think, very relevant indeed.
## How about the long overdue autopsy on the August 2011 kernel.org compromise?
**rickmoen** (subscriber, #6943)
[[Link](/Articles/664123/)] (6 responses)
[April 1st, 2013](http://web.archive.org/web/20130224014512/http://kernel.org/), kernel.org included this note at the top of the Site News: 'Thanks to all for your patience and understanding during our outage and please bear with us as we bring up the different kernel.org systems over the next few weeks. **We will be writing up a report on the incident in the future.**' (Emphasis added.) That comment was [removed](http://web.archive.org/web/20130302091009/https://www.kernel.org/) (along with the rest of the Site News) during a May 2013 edit, and there hasn't been -- to my knowledge -- a peep about any report on the incident since then.
[public report](https://web.archive.org/web/20120223021041/http://www.wiggy.net/debian/explanation/) on exactly what happened. Likewise, the Apache Foundation likewise did the right thing with good public autopsies of the [2010 Web site breaches](http://www.theregister.co.uk/2010/04/13/apache_website_breach_postmortem/).
[follow up](http://arstechnica.com/security/2013/09/who-rooted-kernel-org-servers-two-years-ago-how-did-it-happen-and-why/) on the lack of an autopsy on the kernel.org meltdown -- in 2013. Two years ago. He wrote:
Linux developer and maintainer Greg Kroah-Hartman told Ars that the investigation has yet to be completed and gave no timetable for when a report might be released. [...] Kroah-Hartman also told Ars kernel.org systems were rebuilt from scratch following the attack. Officials have developed new tools and procedures since then, but he declined to say what they are. "There will be a report later this year about site [sic] has been engineered, but don't quote me on when it will be released as I am not responsible for it," he wrote.
[email protected]
[
]## How about the long overdue autopsy on the August 2011 kernel.org compromise?
**ortalo** (guest, #4654)
[[Link](/Articles/664199/)]
[
]## How about the long overdue autopsy on the August 2011 kernel.org compromise?
**error27** (subscriber, #8346)
[[Link](/Articles/664432/)] (4 responses)
[http://www.theregister.co.uk/2011/08/31/linux_kernel_secu...](http://www.theregister.co.uk/2011/08/31/linux_kernel_security_breach/) Hackers stole an admin's ssh key.
[
]
error27 wrote:
## How about the long overdue autopsy on the August 2011 kernel.org compromise?
**rickmoen** (subscriber, #6943)
[[Link](/Articles/664439/)] (3 responses)
The compromise vector was made public at the time.
[http://www.theregister.co.uk/2011/08/31/linux_kernel_security_breach/](http://www.theregister.co.uk/2011/08/31/linux_kernel_security_breach/) Hackers stole an admin's ssh key.*path of entry* to the machine (and I can readily believe that, as it was also the exact path to entry into shells.sourceforge.net, many years prior, around 2002, and into many other shared Internet hosts for many years). But that is not what is of primary interest, and is not what the forensic study long promised would primarily concern: How did intruders escalate to root. To quote kernel.org administrator in the August 2011 Dan Goodin article you cited: 'How they managed to exploit that to root access is currently unknown and is being investigated'.
**What was the path of escalation to root?** (Also, other details that would logically be covered by a forensic study, such as: Whose key was stolen? Who stole the key?)
This is the sort of autopsy was promised prominently on the front page of kernel.org, to reporters, and elsewhere for a long time (and then summarily removed as a promise from the front page of kernel.org, without comment, along with the rest of the Site News section, and apparently dropped). It still would be appropriate to know and share that knowledge. Especially the datum of whether the path to root privilege was or was not a kernel bug (and, if not, what it was).
[email protected]
[
]## How about the long overdue autopsy on the August 2011 kernel.org compromise?
**rickmoen** (subscriber, #6943)
[[Link](/Articles/665443/)] (2 responses)
[copy](http://pastebin.com/BKcmMd47) of kernel.org chief sysadmin John H. 'Warthog9' Hawley's Aug. 29, 2011 e-mail to shell users (two days before the public was informed), plus Aug. 31st comments to *The Register's* Dan Goodin by 'two security researchers who were briefed on the breach':
*the prior six years* by canned 'sploits, one of which (Phalanx) was run by some script kiddie after entry using stolen dev credentials.
Other tidbits:
[stonewalls press queries](http://www.itwire.com/opinion-and-analysis/open-sauce/70417-how-were-linux-kernel-servers-rooted-four-years-ago?).
[best attempt at reconstructing the story](http://lists.svlug.org/archives/svlug/2015-November/061509.html), absent a real report from insiders, to SVLUG's main mailing list yesterday. (Necessarily, there are surmises. If the people with the facts were more forthcoming, we'd know what happened for certain.)
[email protected]
[
]## How about the long overdue autopsy on the August 2011 kernel.org compromise?
**spender** (guest, #23067)
[[Link](/Articles/665445/)] (1 responses)
[
]## How about the long overdue autopsy on the August 2011 kernel.org compromise?
**rickmoen** (subscriber, #6943)
[[Link](/Articles/665452/)]
[elaborated](http://www.theregister.co.uk/2011/08/31/linux_kernel_security_breach/): 'Fellow security researcher Dan Rosenberg said he was also briefed that the attackers used Phalanx to compromise the kernel.org machines.' This *was* the first time I've heard of a rootkit being claimed to be bundled with an attack tool, and I noted that oddity in my posting to SVLUG.
Also, it's preferable to use live memory acquisition prior to powering off the system, otherwise you lose out on memory-resident artifacts that you can perform forensics on.
[email protected]
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**toyotabedzrock** (guest, #88005)
[[Link](/Articles/665135/)] (2 responses)
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**gioele** (subscriber, #61675)
[[Link](/Articles/665142/)] (1 responses)
> Something is making what should be simple updates prohibitively expensive for consumer product companies.
[
]## A new Mindcraft moment?
**Wol** (subscriber, #4433)
[[Link](/Articles/665154/)]
Wol |
7,406 | ALM:TypeScript / JavaScript 的下一代 IDE | http://news.softpedia.com/news/alm-is-an-ide-just-for-typescript-504602.shtml | 2016-05-29T21:05:04 | [
"ALM",
"JavaScript",
"TypeScript"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7406-1.html | TypeScript 是一种由微软开发的自由开源的编程语言。它是 JavaScript 的一个超集,而且实质上向这个语言添加了可选的静态类型和基于类的面向对象编程等等。
如果你使用 TypeScript 开发项目,那么现在有个新的软件可以帮助到你。

[ALM](http://alm.tools/) 宣称它是“TypeScript 的下一代 IDE”,这款专为 TypeScript 设计的编辑器将会使得编程更快捷,JavaScript 开发者可以首先使用类似的 TypeScript 进行开发,然后再编译成浏览器所支持的 JavaScript 语言。
### ALM 安装很简单
要运行 ALM 这个开发工具,开发者只需要做两件事:一个可以工作的 Node.js 5 及其以上版本,一个 Google Chrome 浏览器。不支持 Firefox、 Vivaldi 和 Edge 等等其它浏览器。
然后只需要如下命令即可:
```
npm install alm -g
```
然后在终端运行 `alm` 即可。
要在 ALM 中打开文件,只需要切换到你的项目文件夹,然后运行 `alm .` 或 `alm -o .` 即可。第一个命令会在浏览器中打开一个可以访问你的项目的索引文件的 URL,然后就可以编辑了。第二个命令会自动在你的默认浏览器(chrome)中打开该 URL。
### 有许多非常酷的功能
ALM 的开发者 Basarat Ali Syed 给这个 IDE 中打包了很多功能,包括为 TypeScript 定制的格式高亮方案,支持选项卡、多面板、go-to 跳转功能、查找替换功能、实时文件格式化和实时项目格式化。
将来, ALM IDE 也会与内建的 AST 查看器、依赖查看器、命令搜索功能、光标历史、多监视器支持、错误面板、支持<ruby> 错误提示 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> errors on hover </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、集成 Git、自动 TypeScript 构建和编译、实时预览 TypeScript 所输出的 JavaScript 。
你可以看看 Syed 放到文档站的动画 Gif:

你可以[在 GitHub 上找到该项目](https://github.com/alm-tools/alm),别忘记了 star 它!
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,409 | Linux 给了我所有所需的工具 | https://opensource.com/life/16/3/my-linux-story-sean-ballais | 2016-05-31T08:19:04 | [
"Linux"
] | /article-7409-1.html | 
[Linux](https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-linux) 就在我们身边。它以 Android 的形式[存在我们的手机中](http://www.howtogeek.com/189036/android-is-based-on-linux-but-what-does-that-mean/),它[用在国际空间站中](http://www.extremetech.com/extreme/155392-international-space-station-switches-from-windows-to-linux-for-improved-reliability),它[还是互联网的主要支柱](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JzsLkbwi1LA),可是迄今为止很多人从未留意过它。对 Linux 的探索是一种很有成就感的尝试。很多人都在 Opensource.com [分享过他们与 Linux 的故事](https://opensource.com/tags/my-linux-story)。现在,轮到我了。
我依然记得我在 2008 年第一次探索 Linux 的时刻。协助我探索 Linux 的人是我的父亲,Socrates Ballais。他是菲律宾塔克洛班的一名经济学专家,也是一个技术狂热者。他教会了我许多计算机技术方面的知识,但只提倡我将 Linux 作为 Windows 崩溃后的备用操作系统。
### 从前的日子
在我们在家中购置电脑之前,我曾是一个 Windows 用户。我使用电脑玩游戏,制作文档,做那些小孩子都会用电脑做的事。我不知道什么是 Linux,更不知道它的用处。在那个时候,电脑在我心中的象征就是一个 Windows 的商标。
当我们买到第一台电脑时,我爸爸在上面安装了 Linux ([Ubuntu](http://ubuntu.com/) 8.04)。充满了好奇心的我,第一次引导进入了那个操作系统。我被它的用户界面震惊了。它非常漂亮,而且我发现它对用户很友好。在那之后的一段时间,我只会使用 Linux 它内置的几款游戏。我还是会在 Windows 中做我的家庭作业。
### 第一次安装
4 年后,我决定为家里的电脑重新安装 Windows。我同时毫不犹豫地安装了 Ubuntu。从那次开始,我(再次)爱上了 Linux。随着时间推移,我慢慢适应了 Ubuntu,还会无意地将它推荐给我的朋友。当我拿到我的第一台笔记本电脑时,我立刻在上面安装了它。
### 现在
如今,Linux 是我的默认操作系统。当我需要使用电脑做一些工作时,我会在 Linux 中完成。至于文档和幻灯片,我会通过 [Wine](https://www.winehq.org/) 来使用微软的 Office 办公软件。我会用 [Chrome 和 Firefox](https://www.google.com/chrome/browser/desktop/index.html) 来满足我的上网需要,会用 [Geary](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Geary) 来收发邮件。你可以使用 Linux 来做很多很多事情。
我的大多数——并不是全部——编程工作都会在 Linux 中完成。像 [Visual Studio](https://www.visualstudio.com/en-us/visual-studio-homepage-vs.aspx) 和 [XCode](https://developer.apple.com/xcode/) 这样的基本集成开发环境 (IDE) 的缺乏教会我这个程序员如何变得灵活、如何去学习更多知识。现在,我只需要一个文本编辑器和一个编译器/解释器就可以开始编程。只有当 IDE 是我完成手头上的任务的最佳最佳工具时,我才会使用它。总而言之,Linux 给了我开发软件所需要的一切工具。
现在,我是一个名叫 [Creatomiv Studios](https://www.facebook.com/CreatomivStudios/) 的初创公司的联合创始人和首席技术官。我使用 Linux 来编写我们的最新产品 Basyang 的后端服务器代码。我还是一个业余摄影家,使用 [GIMP](https://www.gimp.org/) 和 [Darktable](http://www.darktable.org/) 来编辑、管理照片。至于团队沟通,我会使用 [Telegram](https://telegram.org/)。
### Linux 之美
很多人认为 Linux 只是为那些喜欢解决复杂问题或者在命令行中工作的人而生的操作系统。还有些人会认为它就是一个缺乏公司支持维护的垃圾。不过,我认为 Linux 是一个完美的操作系统,也是一个为创造而生的绝佳工具。所以我热爱 Linux,同时希望看到它继续成长。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/life/16/3/my-linux-story-sean-ballais>
作者:[Sean Francis N. Ballais](https://opensource.com/users/seanballais) 译者:[StdioA](https://github.com/StdioA) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
7,410 | 如何用开源经历为你的简历增加光彩 | https://opensource.com/business/16/2/add-open-source-to-your-resume | 2016-06-01T14:07:00 | [
"求职",
"简历",
"开源",
"志愿者"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7410-1.html | 
在这篇文章中,我将会分享我的方法,让大家利用开源贡献在技术领域的求职中脱颖而出,成为强有力的候选者。
凡事预则立,不预则废。在你即将进入一个新的领域或者正准备熬夜修订你的简历之前,清楚地定义你正在寻找的工作的特征是值得的。你的简历是一部有说服力的作品,因此你必须了解你的观众,从而让它发挥出所有的潜力。看你简历的可能是任何需要你的技能并且能在预算之内聘用你的人。当编辑简历的时候,读一读你的简历上的内容,同时想象一下,以他们的角度怎么看待这份简历。你看起来像是一个“你”将会聘用的候选人吗?
我个人认为,对于目标职位的理想候选人所表现出来的关键特征,列出一张清单是很有帮助的。我结合了个人经验、阅读工作招聘信息、询问相同角色的同事等方面来收集这个清单。LinkedIn 和各种会议是寻求一些乐意提供这种建议的人的很好的地方。一些人喜欢谈论他们自己,那么通过邀请他们讲述他们自己的一些故事可以帮助你来拓展你的知识面,这样大家都会感觉很好。当你和其他人谈论他们的职业路线时,你不仅将会明白怎样去得到你想要从事的工作,而且还能知道你应该避免那些容易让你失去工作机会的特征或行为。
例如,对于一个不太资深的工作位置来说,关键特征列表可能如下所示:
### 技术方面:
* 拥有 CI (持续集成) 方面的经验,特别是 Jenkins
* 深厚的脚本编写背景,如 Python 和 Ruby
* 精通 Eclipse IDE
* 基本的 Git 和 Bash 知识
### 个人而言:
* 自我驱动的学习者
* 良好的交流和文档技巧
* 在团队开发方面富有经验(团队成员)
* 精通事件跟踪的工作流
### 尽管去申请职位
记住,你没有必要为了得到一份工作而去满足上面的工作描述列表中列出的每个标准。
工作细节(JD)描述了这个角色,让你一开始就知道你即将签约并为之工作几年的公司的全部信息,并且这份工作并不会让你觉得有什么挑战性,或者要求你去拓展你的技能。如果你对你无法满足清单上的技能列表而感到紧张,那么检查一下自己是否有来自其他方面的经历并能与之媲美的技能。例如,即使有些人从来没有使用过 [Jenkins](https://jenkins-ci.org/),那他也可能从之前使用过 [Buildbot](http://buildbot.net/) 或者 [travis CI](https://travis-ci.org/) 的项目经验中明白持续集成测试的原则。
如果你正在申请一家大型公司,他们可能拥有一个专门的部门和一套完整的筛选过程来确保他们不会聘用任何不能胜任职位的候选人。也就是说,在你求职的过程中,你所能做的只是提交申请,而决定是否拒绝你是公司管理层的工作。不要过早地将工作拒之门外。
现在你已经知道了你的任务是什么,并且还知道你将需要让面试官印象深刻的技巧。下一步要做的取决于你已有的经验。
### 制造已经存在的事物之间的关联
列出一张你过去几年曾经参与过的所有项目。下面是一条快速得到这张清单的方法,跳转到你的 Github profile 中的**Repositories**标签页,并且过滤掉 fork 过来的项目。除此之外,检查下你的清单上是否有曾经处于领导地位的[Organizations](https://github.com/settings/organizations)。如果你已经有了一份简历,那么请确保你已经将你所有的经历都列在了上面。
考虑下任何一个你曾经作为一个潜在的领导经历并拥有过特权的 IRC 频道。检查下你的 Meetup 和Eventbrite 账号,并将你曾经组织过或者作为志愿者参与过的活动添加到你的清单上。浏览你前几年的日程并且标注所有志愿服务,或者有作为导师的经历,又或者参与过的公共演讲。
现在进入了比较艰难的环节了,将清单上列出的必备技能与个人经历列表上的内容一一对照,我喜欢给该工作所需要的每个特征用一个字母或者数字作为标记,然后在每一段你经历或参与过并表现出了某一特征的地方标记相同的符号。当你不太确定的时候,那就毫不犹豫地标记上它,尽管这样做更像是在吹嘘,但也好过显示出你的无能。
在我们写简历的时候常常被这样的情况所困扰,就是我们不愿冒着过分吹嘘自己的技能的风险。通常应该这样去想,“那些组织了聚会的人会表现出了更好的领导才能和计划技巧吗?”,而不是“当我组织了这个聚会的时候我是否展示出了这些技巧?”。
如果你已经充分了解了你在过去的一两年里的业余时间都是怎么度过的,而且你写了很多代码,那么你可能现在正面临着一个令人奇怪的问题,你已经拥有了太多的经验以至于一张纸的简历已经无法容纳下这些经验了。那么,如果那些列在你的清单上的经验,但无法证明你尝试去表现的任何技能的话,那么请扔掉它们吧。如果这份已经被缩短的简历清单上的内容仍然超过一张单页纸的容量的话,那么将你的经验按照一定的优先级排序,例如根据与所需技术的相关经历或丰富经验。
在这一方面,显而易见,如果你想要磨练一个独特的技能,那么你就需要一个不错的经历。考虑使用一个类似 [OpenHatch](http://openhatch.org/) 的问题聚合器,并用它来寻找一个通过使用你从没使用过的工具和技术来锻炼你的技能的开源项目。
### 让你的简历更加漂亮
一份简历是否美观取决于它的简洁度、清晰度和布局。每一段经历都应该通过足够的信息来展示给读者,并让他们立刻明白为什么你要将它包含进去,而且恰到好处。每种类型的信息都应该使用一致的文档格式来表示,一份含有斜体格式的日期或者右对齐的或者与整体风格不协调的部分绝对会让人分心。
使用工具来给你的简历排版会使之前设定的目标更加容易实现。我喜欢使用 [LaTeX](https://www.latex-project.org/),因为它的宏系统能够使可视化一致性变得更加容易,并且大量的面试官都能一眼就认出它。你的工具的选择可能是 [LibreOffice](https://www.libreoffice.org/download/libreoffice-fresh/) 或者 HTML,这取决于你的技能和你希望怎样去发布你的简历。
记住一点,一份以电子方式提交的简历可以通过关键字被浏览到。因此,当你需要描述你的工作经历的时候使用和工作招聘告示一样的英文缩写对你的求职会有很大的帮助。为了让你的简历更加容易被面试官看到,首先就要放上最重要的信息。
程序员通常难以在为文档排版时量化平衡和布局。我最喜欢的修改和评估我的文档中的空格是否处于正确位置的技术,就是全屏显示我的 PDF 或者打印出来,然后在镜子里面查看它。如果你正在使用 LibreOffice Writer,保存一份你的简历的副本,然后将你的简历中的字体换成一种你看不懂的语言。这两种技术都强制将你从阅读的内容中脱离出来,让你以一种新的方式查看文档的整体布局。他们把你从一个“那句话措辞不当!”这样的批评转到了注意如“在这行上只有一个字,看起来挺逗”之类的事情。
最后,再次检查你的简历是否在它将要的展示的多媒体上看起来完全正确。如果你以网页的形式发布它,那么在不同屏幕大小的浏览器中测试它的效果。如果它是一份 PDF 文档,那么在你的手机或者你的朋友的电脑上打开它,并确保它所需要的字体都是可用的。
### 接下来的步骤
最后,不要让你辛苦做出来的简历内容浪费了,将它完整的复制到你的 LinkedIn 帐号上(完全使用招聘公告中的流行词),然后毫无疑问招聘人员就会找到你了。尽管他们描述的工作内容并不是恰好适合你,但是你可以利用他们的时间和兴趣来得到关于你的简历中有哪些地方好与不好的反馈信息。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/business/16/2/add-open-source-to-your-resume>
作者:[edunham](https://opensource.com/users/edunham) 译者:[kylepeng93](https://github.com/kylepeng93) 校对:[mudongliang](https://github.com/mudongliang),[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In this article, I'll share my technique for leveraging open source contributions to stand out as a great candidate for a job in the technology field.
No goal can be accomplished without first being set. Before jumping into a new commitment or spending the evening overhauling your resume, it pays to clearly define the traits of the job you're seeking. Your resume is a piece of persuasive writing, so you have to know your audience for it to reach its full potential. Your resume's audience is anyone with the need for your skills and the budget to hire you. When editing, read your resume while imagining what it's like to be in their position. Do you look like a candidate that you would hire?
I personally find it helpful to make a list of the key traits that the ideal candidate for my target job displays. I gather this list from a combination of personal experience, reading job postings, and asking colleagues in similar roles. LinkedIn and conferences are great places to find people happy to offer this sort of advice. Many people enjoy talking about themselves, and inviting them to tell part of their own story to help you expand your knowledge makes everyone feel good. As you talk to others about their career paths, you'll gain insights not only into how to land the jobs you want, but also into which traits or behaviors correspond to ending up in situations you'd rather avoid.
For example, the list of key traits for a junior role might look like this:
### Technical:
- Experience with CI, Jenkins preferred
- Strong scripting background in Python and Ruby
- Familiarity with Eclipse IDE
- Basic Git and Bash
### Personal:
- Self-directed learner
- Clear communication and documentation skills
- Experience working on a multi-person development team ("team player")
- Familiarity with issue tracker workflow
## Apply anyway
Remember, you don't have to meet every single criterion listed in a job description to get an interview.
The job description describes whoever left the role, and if you start out knowing everything you've likely signed yourself up for a few years that don't challenge or expand your skill set. If you're nervous about missing a particular technology on the list, do some research into it to see whether comparable skills from another experience would apply. For example, someone who's never used [Jenkins](https://jenkins-ci.org/) might still understand the principles of continuous integration testing from working on a project that uses [Buildbot](http://buildbot.net/) or [Travis CI](https://travis-ci.org/).
If you're applying at a larger company, they probably have an entire department and comprehensive screening process to make sure they don't hire any candidate unable to succeed in a role. That means it's *your job* to apply and *their job* to decide whether to reject you. Don't prematurely reject yourself from the job by refusing to apply.
Now you have an idea of what job you want and what skills you'll need to impress your interviewers. The next steps to take will vary based on how much experience you've already got.
## Tailoring existing involvement
Start by making a list of all the projects you've been involved with in the past few years. One way to get a quick list of things you've worked on lately is to navigate to the **Repositories** tab of your GitHub profile and filter the list by clicking on **Forks**. Additionally, look down your [ Organizations](https://github.com/settings/organizations) list for places you might have been engaging in leadership roles. If you already have a resume, make sure you've included everything from these lists under experience.
Consider any IRC channel where you have special permissions as a potential leadership experience. Check your Meetup and Eventbrite accounts and add any events that you organize or volunteer at to your list. Skim your calendar for the past year and note any volunteering, mentoring, or public speaking engagements.
Now for the hard part: Map the list of required skills onto the list of experiences. I like to assign a letter or number to each trait needed for the job, then mark the same symbol next to every piece of experience or involvement where you demonstrated the trait. When in doubt, claim it anyway—your problem is more likely a reluctance to brag than actual incompetence.
This is the point in the process at which resume writers are often fettered by reluctance to risk overselling their own skills. It often helps to re-frame the question as: "Did someone who organized a meetup show leadership and planning skills?" Rather than: "Did I personally show these skills when I organized that meetup?".
If you've been sufficiently thorough at figuring out where your free time has gone for the past year or two and you code a lot, you might now be facing a surprising problem: Too many items to fit on a single-page resume! If anything on your list of experiences didn't demonstrate any of the skills you're trying to showcase, cross it off. If an item demonstrates few skills and you don't have any stories that you enjoy telling about it, cross it off. If this abridged list of things you've done still won't fit in the format of a resume, prioritize the experiences from which you gained a relevant story or extensive experience with a desired technology.
At this point, it should be obvious if you need a better piece of experience to hone a particular skill. Consider using an issue aggregator like [OpenHatch](http://openhatch.org) to find an open source project where you build and practice your skills with the tool or technology that you're missing.
## Make your resume beautiful
A resume's beauty comes from conciseness, clarity, and layout. Each piece of experience should be accompanied by enough information for a reader to immediately know why you included it, but no more. Each type of information should be formatted consistently throughout the document—it's distracting to have some dates italicized or right-aligned and others not.
Typeset your resume using a tool that makes these goals easy to achieve. I enjoy using [LaTeX](https://www.latex-project.org/), since its macro system makes visual consistency easy and most interviewers recognize it immediately. Your tool of choice might be [LibreOffice](https://www.libreoffice.org/download/libreoffice-fresh/) or HTML, depending on your skills and how you want to distribute your resume.
Remember that a digitally submitted resume might be scanned for keywords, so it can help to use the same acronyms as the job posting when describing your experiences. To make your resume easy for your interviewer to use, place the most important information *first*.
Coders often struggle to quantify balance and layout when typesetting a document. My favorite technique for stepping back and assessing whether my document's whitespace is in the right place is to fullscreen the PDF or print it out, then look at it in a mirror. If you're using LibreOffice Writer, save a copy of your resume then change the font to that of a language you can't read. Both of these techniques forcibly pull you out of reading the content, and allow you to see the overall layout of the document in a new light. They take you from a "That sentence is poorly worded!" critique to noticing things like "It looks funny to have only a single word on that line."
Finally, double check that your resume displays correctly in the media where it will be seen. If you're distributing it as a web page, test it at different screen widths in multiple browsers. If it's a PDF, open it on your phone or a friend's computer to make sure all the fonts it needs are available.
## Next steps
Finally, don't let the content that you worked so hard on for your resume go to waste! Mirror it to your LinkedIn account—complete with the buzzwords from the job posting—and don't be surprised if recruiters start reaching out to you. Even if the jobs they're describing aren't a good fit right now, you can leverage their time and interest to get feedback on what's working well about your resume and what isn't.
## 1 Comment |
7,418 | LFCS 系列第八讲:管理用户和用户组、文件权限和属性以及启用账户 sudo 访问权限 | http://www.tecmint.com/manage-users-and-groups-in-linux/ | 2016-06-02T10:57:00 | [
"LFCS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7418-1.html | 去年八月份,Linux 基金会发起了全新的 LFCS(<ruby> Linux 基金会认证系统管理员 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)认证,旨在让世界各地的人能够参与到中等水平的 Linux 系统的基本管理操作的认证考试中去,这项认证包括:维护正在运行的系统和服务的能力、全面监控和分析的能力以及何时向上游团队请求支持的决策能力。

*第八讲: Linux 基金会认证系统管理员*
请看以下视频,里边将描述 LFCS 认证程序。
本讲是系列教程的第八讲,在这一讲中,我们将引导你学习如何在 Linux 管理用户和用户组权限的设置,这些内容是 LFCS 认证的必备知识。
由于 Linux 是一个多用户的操作系统(允许多个用户通过不同主机或者终端访问一个独立系统),因此你需要知道如何才能有效地管理用户:如何添加、编辑、禁用和删除用户账户,并赋予他们足以完成自身任务的必要权限。
(LCTT 译注:本篇原文章节顺序有误,根据理解做了调整。)
### 添加用户账户
添加新用户账户,你需要以 root 运行以下两条命令中的任意一条:
```
# adduser [new_account]
# useradd [new_account]
```
当新用户账户添加到系统时,会自动执行以下操作:
1. 自动创建用户家目录(默认是 /home/username)。
2. 自动拷贝下列隐藏文件到新建用户的家目录,用来设置新用户会话的环境变量。
```
.bash_logout
.bash_profile
.bashrc
```
3. 自动创建邮件缓存目录 /var/spool/mail/username。
4. 自动创建与用户名相同的用户组。
#### 理解 /etc/passwd 中的内容
/etc/passwd 文件中存储了所有用户账户的信息,每个用户在里边都有一条对应的记录,其格式(每个字段用冒号隔开)如下:
```
[username]:[x]:[UID]:[GID]:[Comment]:[Home directory]:[Default shell]
```
* 字段 [username] 和 [Comment] 是不言自明的。
* 第二个字段中 x 表明通过用户名 username 登录系统是有密码保护的, 密码保存在 /etc/shadow 文件中。
* [UID] 和 [GID] 字段用整数表示,代表该用户的用户标识符和对应所在组的组标志符。
* 字段 [Home directory] 为 username 用户家目录的绝对路径。
* 字段 [Default shell] 指定用户登录系统时默认使用的 shell。
#### 理解 /etc/group 中的内容
/etc/group 文件存储所有用户组的信息。每行记录的格式如下:
```
[Group name]:[Group password]:[GID]:[Group members]
```
* [Group name] 为用户组名称。
* 字段 [Group password] 为 x 的话,则说明不使用用户组密码。
* [GID] 与 /etc/passwd 中保存的 GID 相同。
* [Group members] 用户组中的用户使用逗号隔开。

*添加用户账户*
#### 修改用户信息
添加用户账户之后,你可以使用 usermod 命令来修改用户信息中的部分字段,该命令基本语法如下:
```
# usermod [options] [username]
```
**设置账户的过期时间**
通过 –expiredate 标记后边接 年-月-日 格式的日期,如下:
```
# usermod --expiredate 2014-10-30 tecmint
```
**将用户添加到其他组**
使用 -aG 或者 –append –groups 选项,后边跟着用户组,如果有多个用户组,每个用户组之间使用逗号隔开。
```
# usermod --append --groups root,users tecmint
```
**改变用户家目录的默认位置**
使用 -d 或者 –home 选项,后边跟着新的家目录的绝对路径。
```
# usermod --home /tmp tecmint
```
**改变用户的默认 shell**
使用 –shell 选项,后边跟着新 shell 的路径。
```
# usermod --shell /bin/sh tecmint
```
下面,我们一次运行上述命令:
```
# usermod --expiredate 2014-10-30 --append --groups root,users --home /tmp --shell /bin/sh tecmint
```

*usermod 命令例示*
扩展阅读
* [15 useradd Command Examples in Linux](http://www.tecmint.com/add-users-in-linux/)
* [15 usermod Command Examples in Linux](http://www.tecmint.com/usermod-command-examples/)
#### 锁定和解锁账户
对于已有用户账户,我们还可以:
**通过锁定密码来禁用账户**
使用 -L (大写 l)或者 –lock 选项来锁定用户密码。
```
# usermod --lock tecmint
```
**解锁用户密码**
使用 –u 或者 –unlock 选项来解锁我们之前锁定的账户。
```
# usermod --unlock tecmint
```

*锁定用户账户*
#### 删除用户账户
你可以通过 userdel --remove 命令来删除用户账户。这样会删除用户拥有的家目录和家目录下的所有文件,以及邮件缓存目录。
```
# userdel --remove [username]
```
#### 用户组管理
每次添加新用户,系统会为该用户创建同名的用户组,此时用户组里边只有新建的用户,其他用户可以随后添加进去。建立用户组的目的之一,就是为了通过对指定资源设置权限来完成对这些资源和文件进行访问控制。
比如,你有下列用户:
* user1 (主组 user1)
* user2 (主组 user2)
* user3 (主组 user3)
他们都需要对你系统里边某个位置的 common.txt 文件,或者 user1 用户刚刚创建的共享进行读写。你可能会运行下列命令:
```
# chmod 660 common.txt
或
# chmod u=rw,g=rw,o= common.txt [注意最后那个 = 号和文件名之间的空格]
```
然而,这样仅仅给文件所属的用户和用户组(本例为 user1)成员的提供了读写权限。你还需要将 user2 和 user3 添加到 user1 组,打这样做也将 user1 用户和用户组的其他文件的权限开放给了 user2 和 user3。
这时候,用户组就派上用场了,下面将演示怎么做。
**显示用户所属的用户组**
```
# groups tecmint
# id tecmint
```
**为需要对指定文件进行读写的多个用户建立用户组**
运行下列几条命令来完成:
```
# groupadd common_group # 添加新用户组
# chown :common_group common.txt # 将 common.txt 的用户组修改为 common_group
# usermod -aG common_group user1 # 添加用户 user1 到 common_group 用户组
# usermod -aG common_group user2 # 添加用户 user2 到 common_group 用户组
# usermod -aG common_group user3 # 添加用户 user3 到 common_group 用户组
```
#### 删除用户组
通过以下命令删除用户组:
```
# groupdel [group_name]
```
属于这个 group\_name 用户组的文件是不会被删除的,而仅仅是删除了用户组。
### Linux 文件权限
除了我们在 [LFCS 系列第三讲:归档/压缩文件及目录、设置文件属性和搜索文件](/article-7171-1.html) 中说到的基本的读取、写入和执行权限外,文件还有一些不常用却很重要的的权限设置,有时候把它当做“特殊权限”。
就像之前我们讨论的基本权限,这里同样使用八进制数字或者一个字母(象征性符号)表示该权限类型。
**理解 Setuid 位**
当为可执行文件设置 setuid 位之后,用户运行程序时会继承该程序属主的有效特权。由于这样做会引起安全风险,因此设置 setuid 权限的文件及程序必须尽量少。你会发现,当系统中有用户需要访问属于 root 用户的文件是所运行的程序就带有了 setuid 权限。
也就是说,用户不仅仅可以运行这个可执行文件,而且能以 root 权限来运行。比如,让我们来看看 /bin/passwd 的权限,这个可执行文件用于改变账户的密码,修改 /etc/shadow 文件。超级用户可以改变任意账户的密码,但是其他用户只能改变自己账户的密码。

*passwd 命令例示*
因此,所有用户都有权限运行 /bin/passwd,但只有 root 用户可以指定改变指定用户账户的密码。其他用户只能改变其自身的密码。

*修改用户密码*
```
# chmod o+u [filename]
```
以八进制形式来设置 setuid 位,在当前基本权限(或者想要设置的权限)前加上数字 4 就行了。
```
# chmod 4755 [filename]
```
**理解 Setgid 位**
设置 setgid 位之后,真实用户的有效 GID 变为属组的 GID。因此,任何用户都能以属组用户的权限来访问文件。另外,当目录置了 setgid 位之后,新建的文件将继承其所属目录的 GID,并且新建的子目录会继承父目录的 setgid 位。通过这个方法,你能够以一个指定的用户组身份来访问该目录里边的文件,而不必管文件属主的主属组。
```
# chmod g+s [filename]
```
以八进制形式来设置 setgid 位,在当前基本权限(或者想要设置的权限)前加上数字 2 就行了。
```
# chmod 2755 [filename]
```
**给目录设置 Setgid 位**

*给命令设置 setgid 位*
**理解<ruby> 黏连 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Sticky </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>位**
文件设置了黏连位是没有意义,Linux 会忽略该位。如果设置到目录上,会防止其内的文件被删除或改名,除非你是该目录或文件的属主、或者是 root 用户。
```
# chmod o+t [directory]
```
以八进制形式来设置黏连位,在当前基本权限(或者想要设置的权限)前加上数字 1 就行了。
```
# chmod 1755 [directory]
```
若没有黏连位,任何有权限读写目录的用户都可删除和重命名其中的文件。因此,黏连位通常出现在像 /tmp 之类的目录,这些目录是所有人都具有写权限的。

*给目录设置黏连位*
### Linux 特殊文件属性
文件还有其他一些属性,用来做进一步的操作限制。比如,阻止对文件的重命名、移动、删除甚至是修改。可以通过使用 [chattr 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/chattr-command-examples/) 来设置,并可以使用 lsattr 工具来查看这些属性。设置如下:
```
# chattr +i file1
# chattr +a file2
```
运行这些命令之后,file1 成为不可变状态(即不可移动、重命名、修改或删除),而 file2 进入“仅追加”模式(仅在追加内容模式中打开)。

*通过 Chattr 命令来包含文件*
### 访问 root 账户并启用 sudo
访问 root 账户的方法之一,就是通过输入:
```
$ su
```
然后输入 root 账户密码。
倘若授权成功,你将以 root 身份登录,工作目录则是登录前所在的位置。如果是想要一登录就自动进入 root 用户的家目录,请运行:
```
$ su -
```
然后输入 root 账户密码。

*用户通过 su 切换*
执行上个步骤需要普通用户知道 root 账户的密码,这样会引起非常严重的安全问题。于是,系统管理员通常会配置 sudo 命令来让普通用户在严格控制的环境中以其他用户身份(通常是 root)来执行命令。所以,可以在严格控制用户的情况下,又允许他运行一条或多条特权命令。
* 扩展阅读:[Difference Between su and sudo User](http://www.tecmint.com/su-vs-sudo-and-how-to-configure-sudo-in-linux/)
普通用户通过他自己的用户密码来完成 sudo 授权。输入命令之后会出现输入密码(并不是超级用户密码)的提示,授权成功(只要赋予了用户运行该命令的权限)的话,指定的命令就会运行。
系统管理员必须编辑 /etc/sudoers 文件,才能为 sudo 赋予相应权限。通常建议使用 visudo 命令来编辑这个文件,而不是使用文本编辑器来打开它。
```
# visudo
```
这样会使用 vim(你可以按照 [LFCS 系列第二讲:如何安装和使用纯文本编辑器 vi/vim](/article-7165-1.html) 里边说的来编辑文件)来打开 /etc/sudoers 文件。
以下是需要设置的相关的行:
```
Defaults secure_path="/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin"
root ALL=(ALL) ALL
tecmint ALL=/bin/yum update
gacanepa ALL=NOPASSWD:/bin/updatedb
%admin ALL=(ALL) ALL
```
来更加深入了解这些项:
```
Defaults secure_path="/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/usr/local/bin"
```
这一行指定 sudo 将要使用的目录,这样可以阻止使用某些用户指定的目录,那样的话可能会危及系统。
下一行是用来指定权限的:
```
root ALL=(ALL) ALL
```
* 第一个 ALL 关键词表明这条规则适用于所有主机。
* 第二个 ALL 关键词表明第一个字段中所指定的用户能以任何用户身份的权限来运行相应命令。
* 第三个 ALL 关键词表明可以运行任何命令。
```
tecmint ALL=/bin/yum update
```
如果 = 号后边没有指定用户,sudo 则默认为 root 用户。本例中,tecmint 用户能以 root 身份运行 yum update 命令。
```
gacanepa ALL=NOPASSWD:/bin/updatedb
```
NOPASSWD 关键词表明 gacanepa 用户不需要密码,可以直接运行 /bin/updatedb 命令。
```
%admin ALL=(ALL) ALL
```
% 符号表示该行应用于 admin 用户组。其他部分的含义与对于用户的含义是一样的。本例表示 admin 用户组的成员可以通过任何主机连接来运行任何命令。
通过 sudo -l 命令可以查看,你的账户拥有什么样的权限。

*Sudo 访问规则*
### 总结
对于系统管理员来说,高效能的用户和文件管理技能是非常必要的。本文已经涵盖了这些内容,我们希望你将这些作为一个开始,然后慢慢进步。随时在下边发表评论或提问,我们会尽快回应的。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/manage-users-and-groups-in-linux/>
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa](http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,427 | 儿童编程语言进化史 | http://blog.makewonder.com/evolution-programming-for-kids/ | 2016-06-05T09:00:00 | [
"Logo",
"Scratch"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7427-1.html | 随着奥巴马总统的全民学习计算机(#CSforall)的倡议以及人们对 STEM (<ruby> 科学 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Science </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 技术 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Technology </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 工程 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Engineering </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和<ruby> 数学 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Mathematics </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)的日益关注,表明我们到了需要建立儿童计算机教育的标准和最佳实践的时候了。业内一致认为,可视化编程是教授给孩子们计算机科学和计算思想的最好方式,这样可以摆脱艰涩的编程语法,让孩子们在很小的时候就可以灵活地掌握软件编程的精髓。

### 改进中的 Logo 语言
在过去的五十年,设计师们不断改进 Seymour Papert 创造的 Logo 编程语言(LCTT 译注:应该有同学见过那个“小乌龟”),出现了一大批界面稍有不同而核心思想相同的编程语言。当前的教学标准是基于<ruby> 模块 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> blocks </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的编程方式,这要归功于 MIT 的 Scratch 编程语言的流行。在 [CSTA 的 K-12 计算机科学教学标准](https://csta.acm.org/Curriculum/sub/K12Standards.html)中,对于 K-5 年级,要求达到“使用基于模块的可视编程语言来构建和测试解决方案”的编程能力。

### 越来越年轻化
计算机科学教育的另外一个趋势是受众越来越年轻。研究表明,[才仅仅五岁的孩子](http://www.wired.com/2013/09/ap_code/)就能够掌握计算机编程的概念,所以这是必然的趋势。要教还不认识字的孩子们学习编程,就需要避免使用文字。最近像 Scratch Jr 和 Code.org 的第一阶段课程就在基于模块的编程语言中使用图标替代了文字。

### 机器人编程
看见你的代码出现在生活中是一件神奇的事情。早在本世纪初,乐高和 MIT 就合作了一个项目,将基于模块的编程带到了现实世界。学生们可以在计算机上写程序,然后将其下载到他们搭建的机器人里。早期的 RIS(<ruby> 机器人创造系统 <rt> robotics invention system </rt></ruby>)看起来十分像 Scratch。

在<ruby> 乐高机器人 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Lego Mindstorms </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 2013 版The 2013 中虽然变得更加复杂,但是其大部分所做的事情同之前的版本一样。现在可以给模块增加输入参数,以指定距离、时间、输出等等。

Martin Exner 创建了一幅[简明的信息图](http://constructingkids.com/2013/05/15/vpl/),概括了由 Logo 以及更近一些的 Scratch 衍生而来的这些编程语言。许多 Logo 语言的衍生语言都是围绕着特定场景的,比如创建游戏、制作 3D 故事情节环境、绘制图片、机器人编程,甚至可以控制虚拟鱼缸。这种方式吸引了许多不同的孩子们,但是许多孩子在学习编写一段程序仍然感觉有些困难。
### Logo 之上的编程思想
在现实生活中,计算机编程通常需要考虑各种类型的输入,并且同时还要动态处理各种逻辑判断。让我们举一个判断起床后要做什么的简单例子:如果是周六日,我们会去外面玩;如果是周一,我们需要穿上运动服;如果是周四,我们需要倒垃圾;而不是周末的日子,我们需要去上学。下面展示了用 Scratch 实现的逻辑。

除了这些基于模块的编程语言,还有一种新的语言采用了不同的方式来教孩子们编程。2015年,[Wonder Workshop](http://makewonder.com/) 设计一个名为 Wonder 的新编程语言,采用的是[基于流的编程](http://www.jpaulmorrison.com/fbp/fbp2.htm)界面。Wonder 可以让学生们将注意力放在一些预先定义好的功能单元(或语句)的连接上,来构建一个<ruby> 状态机 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> state machine </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。在任何时刻,机器人都是一个单一的给定状态;它会做一些操作,给一些输入就会让它改为做不同的操作。
下图展示了如何使用基于流的方式来判断起床后的任务。

除了摆脱了线性编程范式,这种编程语言还提供了一种不同的计算思想,可以让学生们以一种容易掌握的方式来模拟响应现实中的变化。学生们可以更容易的把问题分解成小的部分,然后用这些部分来解决复杂的问题。学生们在解决问题时只需要一次关注一个问题。这个过程称之为分解,则既是计算机领域的基础知识,也是 Wonder 的设计目的。

在我们的每天的生活中有很多机器人和状态机的例子,而且它们变得越来越常见了。当你投入了正确组合的钱币之后,自动售货机就给你对应的食物。自动驾驶汽车会根据它周围的障碍物来决定该怎么移动。状态机也可以进一步对大量问题进行建模,包括语言解析、人工智能、通讯协议、游戏中的角色变化,甚至神经网络。
随着机器人应用的越来越广泛,教师们正在接受[培训](http://www.fastcompany.com/3056644/most-creative-people/as-schools-emphasize-computer-science-how-do-we-teach-teachers-to-code),把基于模块的编程作为教授孩子们计算机科学的标准。随着它进入到越来越多的课堂,我们应该思考这是否是一个正确的方向?还有没有其他更好教授孩子们计算机编程的方法。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,429 | NodeOS:Node 爱好者的 Linux 发行版 | http://itsfoss.com/nodeos-operating-system/ | 2016-06-06T09:17:20 | [
"Node.js",
"NodeOS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7429-1.html | 
[NodeOS](http://node-os.com/) 是一款基于 [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/en/) 的操作系统,自去年其首个[发布候选版](https://github.com/NodeOS/NodeOS/releases/tag/v1.0-RC1)之后正朝着它的1.0版本进发。
如果你之前不知道的话,NodeOS 是首个架构在 [Linux](http://itsfoss.com/tag/linux/) 内核之上的由 Node.js 和 [npm](https://www.npmjs.com/) 驱动的操作系统。[Jacob Groundwater](https://github.com/groundwater) 在2013年中期介绍了这个项目。该操作系统中用到的主要技术是:
* **Linux 内核**: 这个系统建造在 Linux 内核上
* **Node.js 运行时**: Node 作为主要的运行时环境
* **npm 包管理**: npm 作为包管理
NodeOS 源码托管在 [Github](https://github.com/nodeos/nodeos) 上,因此,任何感兴趣的人都可以轻松贡献或者报告 bug。用户可以从源码构建或者使用[预编译镜像](https://github.com/NodeOS/NodeOS/releases)。构建过程及快速起步指南可以在项目仓库中找到。
NodeOS 背后的思想是提供足够 npm 运行的环境,剩余的功能就可以让 npm 包管理来完成。因此,用户可以使用多达大约 250,000 个软件包,并且这个数目每天都还在增长。所有的都是开源的,你可以根据你的需要很容易地打补丁或者增加更多的包。
NodeOS 核心开发被分离成了不同的层面,基本的结构包含:
* **barebones** – 带有可以启动到 Node.js REPL 的 initramfs 的自定义内核
* **initramfs** – 用于挂载用户分区以及启动系统的 initram 文件系统
* **rootfs** – 存放 linux 内核及 initramfs 文件的只读分区
* **usersfs** – 多用户文件系统(如传统系统一样)
NodeOS 的目标是可以在任何平台上运行,包括: **实际的硬件(用户计算机或者 SoC)**、**云平台、虚拟机、PaaS 提供商,容器**(Docker 和 Vagga)等等。如今看来,它做得似乎不错。在3.3号,NodeOS 的成员 [Jesús Leganés Combarro](https://github.com/piranna) 在 Github上[宣布](https://github.com/NodeOS/NodeOS/issues/216):
>
> **NodeOS 不再是一个玩具系统了**,它现在开始可以用在有实际需求的生产环境中了。
>
>
>
因此,如果你是 Node.js 的死忠或者乐于尝试新鲜事物,这或许值得你一试。在相关的文章中,你应该了解这些[Linux 发行版的具体用法](http://itsfoss.com/weird-ubuntu-based-linux-distributions/)
---
via: <http://itsfoss.com/nodeos-operating-system/>
作者:[Munif Tanjim](http://itsfoss.com/author/munif/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,430 | NXP 发布了一块世界上最小的64位物联网 ARM 处理器 | http://venturebeat.com/2016/02/21/nxp-unveils-a-small-and-tiny-64-bit-arm-processor-for-the-internet-of-things/ | 2016-06-07T09:30:00 | [
"IoT"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7430-1.html | 
[NXP 半导体](http://www.nxp.com/)发布了一块声称世界上最小的用于物联网(IoT)的低功耗64位ARM处理器。
这片小型的QorIQ LS1012A为电池供电、大小受限的应用提供了网络级的安全和性能加速。这包括了运行物联网应用,或者任何智能及可连接的设备。如果物联网能在2020达到1.7万亿美金的潜力(由IDC研究员估算市场得出),那么它将需要像NXP这样的处理器,该处理器在德国纽伦堡的Embedded World 2016 上揭开了神秘的面纱。
该芯片带有64位ARMv8芯片,拥有网络包加速及内置的安全。它占用9.6平方毫米的空间,并且大约消耗1瓦特的电力。潜在的应用包括下一代的物联网网关、可携带娱乐平台、高性能可携带存储应用、移动硬盘、相机的移动存储、平板及其他可充电的设备。
除此之外,LS1012A是第一款为最新兴起的基于对象的存储方案设计的处理器,基于对象存储通过智能硬盘直接连接到以太网数据中心。处理器必须足够小才能直接集成在硬盘的集成电路上。
NXP的高级副总裁及数字网络部的经理Tareq Bustami说:“突破性组合了低功耗、占用空间小及网络级性能的NXP LS1012处理器是消费者、物联网相关应用的理想选择。独有地将这些能力结合到一起解放了物联网设计者及开发者,使得他们可以在这个高增长的市场中设计并创造更多创新产品。”
NXP说这是唯一一个1瓦特功耗、64位的、并将这些高速外设综合到一个芯片中的处理器,这意味着更低的系统级功耗。归功于创新性的封装,该处理器可以运用在低成本的电路板中。
NXP的LS1012A可以在2016年4月开始发货,并且现在可以订货。NXP在全球35个国家拥有超过4,5000名员工。
---
via: <http://venturebeat.com/2016/02/21/nxp-unveils-a-small-and-tiny-64-bit-arm-processor-for-the-internet-of-things/>
作者:[DEAN TAKAHASHI](http://venturebeat.com/author/dean-takahashi/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,431 | 七步开始你的 Linux 系统管理员生涯 | http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/191-linux-training/834644-7-steps-to-start-your-linux-sysadmin-career | 2016-06-06T09:49:48 | [
"培训"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7431-1.html | Linux 现在是个大热门。每个人都在寻求 Linux 才能。招聘人员对有 Linux 经验的人求贤若渴,还有无数的职位虚位以待。但是如果你是 Linux 新手,又想要赶上这波热潮,该从何开始下手呢?

### 1、安装 Linux
这应该是不言而喻的,但学习 Linux 的第一关键就是安装 Linux。LFS101x 和 LFS201 课程都包含第一次安装和配置 Linux 的详细内容。
### 2、 完成 LFS101x 课程
如果你是完完全全的 Linux 新手,最佳的起点是我们的免费 Linux 课程 [LFS101x Introduction to Linux](https://www.edx.org/course/introduction-linux-linuxfoundationx-lfs101x-2)。这个在线课程放在 edX.org,探索 Linux 系统管理员和终端用户常用的各种工具和技能以及日常的 Linux 工作环境。该课程是为有一定经验,但较少或没有接触过 Linux 的电脑用户设计的,不论他们是在个人还是企业环境中工作。这个课程会从图形界面和命令行两个方面教会你有用的 Linux 知识,让你能够了解主流的 Linux 发行版。
### 3、 看看 LFS201 课程
在你完成 LFS101x 之后,你就可以开始挑战 Linux 中更加复杂的任务了,这是成为一名专业的系统管理员所必须的。为了掌握这些技能,你应该看看 [LFS201 Essentials of Linux System Administration](http://training.linuxfoundation.org/linux-courses/system-administration-training/essentials-of-system-administration) 这个课程。该课程对每个话题进行了深度的解释和介绍,还有大量的练习和实验,帮助你获得相关主题实际的上手经验。
如果你更愿意有个教练,或者你的雇主想将你培养成 Linux 系统管理员的话,你可能会对 LFS220 Linux System Administration 感兴趣。这个课程有 LFS201 中所有的主题,但是它是由专家专人教授的,帮助你进行实验以及解答你在课程主题中的问题。
### 4、 练习!
熟能生巧,和对任何乐器或运动适用一样,这对 Linux 来说也一样适用。在你安装 Linux 之后,经常使用它。一遍遍地练习关键任务,直到你不需要参考材料也能轻而易举地完成。练习命令行的输入输出以及图形界面。这些练习能够保证你掌握成为成功的 Linux 系统管理员所必需的知识和技能。
### 5、 获得认证
在你完成 LFS201 或 LFS220 并且充分练习之后,你现在已经准备好获得系统管理员的认证了。你需要这个证书,因为你需要向雇主证明你拥有一名专业 Linux 系统管理员必需的技能。
现在有一些不同的 Linux 证书,它们每个都有其独到之处。但是,它们里大部分不是在特定发行版(如红帽)上认证,就是纯粹的知识测试,没有演示 Linux 的实际技能。<ruby> Linux 基金会认证系统管理员 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Linux Foundation Certified System Administrator </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>证书对想要一个灵活的,有意义的初级证书的人来说是个不错的选择。
### 6、 参与进来
如果你所在的地方有本地 <ruby> Linux 用户组 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Linux Users Group </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(LUG)的话,这时候你可以考虑加入他们。这些组织通常由各种年龄和经验水平的人组成,所以不管你的 Linux 经验水平如何,你都能找到和你类似技能水平的人互助,或是更高水平的 Linux 用户来解答你的问题以及介绍有用的资源。要想知道你附近有没有 LUG,上 meet.com 看看,或是附近的大学,又或是上网搜索一下。
还有不少在线社区可以在你学习 Linux 的时候帮助你。这些站点和社区向 Linux 新手和有经验的管理员都能够提供帮助和支持:
* [Linux Admin subreddit](https://www.reddit.com/r/linuxadmin)
* [Linux.com](http://www.linux.com/)
* [training.linuxfoundation.org](http://training.linuxfoundation.org/)
* <http://community.ubuntu.com/help-information/>
* <https://forums.opensuse.org/forum.php>
* <http://wiki.centos.org/Documentation>
### 7、 学会热爱文档
最后但同样重要的是,如果你困在 Linux 的某些地方,别忘了 Linux 包含的文档。使用命令 man(manual,手册),info 和 help,你从系统内就可以找到 Linux 几乎所有方面的信息。这些内置资源的用处再夸大也不为过,你会发现你在生涯中始终会用到,所以你可能最好早点掌握使用它们。
想要了解更多开始你 Linux IT 生涯的信息?查看我们免费的电子书“[开始你 Linux IT 生涯的简短指南](http://training.linuxfoundation.org/sysadmin-it-career-guide)”。
---
via: <http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/191-linux-training/834644-7-steps-to-start-your-linux-sysadmin-career>
作者:<linux.com> 译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,435 | 混合云计算的 9 大关键趋势 | http://www.datamation.com/cloud-computing/9-key-trends-in-hybrid-cloud-computing.html | 2016-06-07T09:45:00 | [
"混合云"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7435-1.html | 自从几年前云计算的概念受到IT界的关注以来,公有云、私有云和混合云这三种云计算方式都有了可观的演进。其中混合云计算方式是最热门的云计算方式,在接受调查的公司中,有[88%的公司](https://www.greenhousedata.com/blog/hybrid-continues-to-be-most-popular-cloud-option-adoption-accelerating)将混合云计算摆在至关重要的地位。
混合云计算的疾速演进意味着一两年前的传统观念已经过时了。为此,我们询问了几个行业分析师,混合云在2016年的走势将会如何,我们得到了几个比较有意思的答案。

### **2016年可能是我们将混合云投入使用的一年**
混合云从本质上来说依赖于私有云,这对企业来说是比较难实现的。事实上,亚马逊,谷歌和微软的公有云已经进行了大量的投资,并且起步也比较早。私有云拖了混合云发展和使用的后腿。
私有云没有得到这么多的投资,这是有私有云的性质决定的。私有云意味着维护和投资你自己的数据中心。而许多公有云提供商正在推动企业减少或者消除他们的数据中心。
然而,得益于 OpenStack 的发展和微软的 Azure Stack ,这两者基本上就是封装在一个盒子里的私有云,我们将会看到私有云慢慢追上公有云的发展步伐。支持混合云的工具、基础设施和架构也变得更加健壮。
### **容器,微服务和 unikernels 将会促进混合云的发展**
分析师预言,到2016年底,这些原生云技术会或多或少成为主流的。这些云技术正在快速成熟,将会成为虚拟机的一个替代品,而虚拟机需要更多的资源。
更重要的是,他们既能工作在在线场景,也能工作在离线场景。容器化和编排允许快速的扩大规模,进行公有云和私有云之间的服务迁移,使你能够更容易移动你的服务。
### **数据和相关性占据核心舞台**
所有的云计算方式都处在发展模式。这使得云计算变成了一个技术类的故事。咨询公司 [Avoa](http://avoa.com/2016/01/01/2016-is-the-year-of-data-and-relevance/)称,随着云趋于成熟,数据和相关性变得越来越重要。起初,云计算和大数据都是关于怎么得到尽可能多的数据,然后他们担心如何处理这海量的数据。
2016年,相关组织将会继续锤炼如何进行数据收集和使用的相关技术。在必须处理的技术和文化方面仍然有待提高。但是2016年应该重新将关注点放在从各个方面考虑的数据重要性上,发现最相关的信息,而不只是数据的数量。
### **云服务将超越按需工作负载**
AWS(Amazon Web Services) 起初是提供给程序员或者是开发人员能够快速启动虚拟机、做一些工作然后离线的一个地方。本质上是按需使用,要花费更多的钱才能让这些服务持续运行、全天候工作。
然而,IT 公司正开始作为服务代理,为内部用户提供各种 IT 服务。可以是内部 IT 服务,公有云基础架构提供商,平台服务和软件服务。
他们将越来越多的认识到像云管理平台这样的工具的价值。云管理平台可以提供针对不同服务的基于策略的一致性管理。他们也将看到像提高可移植性的容器等技术的价值。然而,云服务代理,在不同云之间快速移动工作负载从而进行价格套利或者类似的原因,仍然是行不通的。
### **服务提供商转变成了云服务提供商**
到目前为止,购买云服务成了直销模式。AWS EC2 服务的使用者通常变成了购买者,要么通过官方认证渠道,要么通过影子 IT。但是随着云服务越来越全面,提供的服务菜单越来越复杂,越来越多的人转向了经销商,服务提供商转变成了他们 IT 服务的购买者。
2nd Watch (2nd Watch 是为企业提供云管理的 AWS 的首选合作伙伴)最近的一项调查发现,在美国将近85%的 IT 高管愿意支付一个小的溢价从渠道商那里购买公有云服务,如果购买过程变得不再那么复杂。根据调查,这85%的高管有五分之四的愿意支付额外的15%或者更多。三分之一的受访高管表示,这些有助于他们购买、使用和管理公有云服务。
### **物联网和云对于2016年的意义好比移动和云对2012年的意义**
物联网获得了广泛的关注,更重要的是,物联网已经从测试场景进行了实际应用。云的分布式特性使得云成为了物联网非常重要的一部分,对于工业物联网,与后端系统交互的机械和重型设备,混合云将会成为最自然的驱动者,连接,数据采集和处理将会发生在混合云环境中,这得益于私有云在安全和隐私方面的好处。
### **NIST 对云的定义开始瓦解**
2011年,美国国家标准与技术研究院发布了“ [NIST 对于云计算的定义](http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-145/SP800-145.pdf)”(PDF),这个定义成为了私有云、公有云、混合云和 aaS 模板的标准定义。
然而随着时间的推移,定义开始改变。IaaS 变得更加复杂,开始支持 OpenStack,[Swift](https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Swift) 对象存储和神经网络这样的项目。PaaS 似乎正在消退,因为 PaaS 和传统的中间件开发几乎无异。SaaS,只是通过浏览器进行访问的应用,也正在失去发展动力,因为许多 app 和服务提供了许多云接口,你可以通过各种手段调用接口,不仅仅通过浏览器。
### **分析变得更加重要**
对于混合云计算来说,分析将会成为一个巨大的增长机遇,云计算具有规模大、灵活性高的优势,使得云计算非常适合需要海量数据的分析工作。对于某些分析方式,比如高度敏感的数据,私有云仍然是主导地位,但是私有云也是混合云的一部分。因此,无论如何,混合云计算胜出。
### **安全仍然是一个非常紧迫的问题**
随着混合云计算在2016年的发展,以及对物联网和容器等新技术的引进,这同时也增加了更多的脆弱可攻破的地方,从而导致数据泄露。先增加使用新技术的趋势,然后再去考虑安全性,这种问题经常发生,同时还有缺少经验的工程师不去考虑系统的安全问题,总有一天你会尝到灾难的后果的。
当一项新技术出来,管理规范总是落后于安全问题产生后,然后我们才考虑去保护技术。容器就是一个很鲜明的例子。你可以从 Docker 下载各种示例容器,但是你知道你下载的东西来自哪里么?在人们在对容器内容不知情的情况下下载并运行了容器之后,Docker 不得不重新加上安全验证。
像 Path 和 Snapchat 这样的移动技术在智能手机市场火起来之后也出现了重大的安全问题。一项新技术被恶意利用无可避免。所以安全研究人员需要通过各种手段来保证新技术的安全性,很有可能在部署之后才会发现安全问题。
---
via: <http://www.datamation.com/cloud-computing/9-key-trends-in-hybrid-cloud-computing.html>
作者:[Andy Patrizio](http://www.datamation.com/author/Andy-Patrizio-90720.html) 译者:[棣琦](https://github.com/sonofelice) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,438 | 如何启用 Apache 的 PHP-FPM 多实例 | http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/enable-multiple-php-fpm-instances-nginx-apache/ | 2016-06-08T08:57:00 | [
"php-fpm",
"php"
] | /article-7438-1.html | PHP-FPM 作为 FastCGI 进程管理器而广为熟知,它是 PHP FastCGI 实现的改进,带有更为有用的功能,用于处理高负载的服务器和网站。下面列出其中一些功能:
### 新功能
* 拥有具有优雅(graceful)启动/停止选项的高级进程管理能力。
* 可以通过不同的用户身份/组身份来以监听多个端口以及使用多个PHP配置。
* 错误日志记录。
* 支持上传加速。
* 特别用于在处理一些耗时任务时结束请求和清空所有数据的功能。
* 同时支持动态和静态的子进程重生。
* 支持IP地址限制。
在本文中,我将要讨论的是,在运行 CPanel 11.52 及 EA3 (EasyApache)的 CentOS 7 服务器上,于 Nginx 和 Apache 之上安装 PHP-FPM,以及如何来通过 CPanel 管理这些安装好的多个 PHP-FPM 实例。

在我们开始安装前, 先看看安装的先决条件。
### 先决条件
1. 启用 Mod*proxy*fcgi 模块
2. 启用 MPM\_Event
由于我们要将 PHP-FPM 安装到一台 EA3 服务器,我们需要运行 EasyApache 来编译 Apache 以启用这些模块。
你们可以参考我以前写的,关于如何在 Apache 服务器上安装 Nginx 作为反向代理的文档来了解 Nginx 的安装。
这里,我将再次简述那些安装步骤。具体细节,你可以参考我之前写的**(如何在 CentOS 7/CPanel 服务器上配置 Nginx 反向代理)**一文。
* 步骤 1:安装 Epel 仓库
* 步骤 2:安装 nDeploy RPM 仓库,这是此次安装中最为**重要**的步骤。
* 步骤 3:使用 yum 从 nDeploy 仓库安装 nDeploy 和 Nginx 插件。
* 步骤 4:启用/配置 Nginx 为反向代理。
完成这些步骤后,下面为服务器中所有可用 PHP 版本安装 PHP-FPM 包,EA3 使用 remi 仓库来安装这些包。你可以运行这个 nDeploy 脚本来下载所有的包。
```
root@server1 [~]# /opt/nDeploy/scripts/easy_php_setup.sh
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, tsflags, universal-hooks
EA4 | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
base | 3.6 kB 00:00:00
epel/x86_64/metalink | 9.7 kB 00:00:00
epel | 4.3 kB 00:00:00
extras | 3.4 kB 00:00:00
updates | 3.4 kB 00:00:00
(1/2): epel/x86_64/updateinfo | 460 kB 00:00:00
(2/2): epel/x86_64/primary_db
```
运行该脚本将为 PHP 54,PHP 55,PHP 56 和 PHP 70 安装所有这些 FPM 包。
```
Installed Packages
php54-php-fpm.x86_64 5.4.45-3.el7.remi @remi
php55-php-fpm.x86_64 5.5.31-1.el7.remi @remi
php56-php-fpm.x86_64 5.6.17-1.el7.remi @remi
php70-php-fpm.x86_64 7.0.2-1.el7.remi @remi
```
在以上安装完成后,你需要为 Apache 启用 PHP-FPM SAPI。你可以运行下面这个脚本来启用 PHP-FPM 实例。
```
root@server1 [~]# /opt/nDeploy/scripts/apache_php-fpm_setup.sh enable
mod_proxy_fcgi.c
Please choose one default PHP version from the list below
PHP70
PHP56
PHP54
PHP55
Provide the exact desired version string here and press ENTER: PHP54
ConfGen:: lxblogger
ConfGen:: blogr
ConfGen:: saheetha
ConfGen:: satest
which: no cagefsctl in (/usr/local/jdk/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/X11R6/bin:/root/bin)
info [rebuildhttpdconf] Missing owner for domain server1.centos7-test.com, force lookup to root
Built /usr/local/apache/conf/httpd.conf OK
Waiting for “httpd” to restart gracefully …waiting for “httpd” to initialize ……
…finished.
```
它会问你需要运行哪个 PHP 版本作为服务器默认版本,你可以输入那些细节内容,然后继续配置并为现存的域名生成虚拟主机文件。
我选择了 PHP 54 作为我服务器上的默认 PHP-FPM 版本。

虽然服务器配置了 PHP-FPM 54,但是我们可以通过 CPanel 为各个独立的域名修改 PHP-FPM 实例。
下面我将通过一些截图来为你们说明一下,怎样通过 CPanel 为各个独立域修改 PHP-FPM 实例。
安装了 Nginx 插件后,你的域名的 CPanel 就会有一个 Nginx Webstack 图标,你可以点击该图标来配置你的 Web 服务器。我已经登录进了我其中的一个 CPanel 来配置相应的 Web 服务器。
请看这些截图。

现在,你可以根据需要为选中的主域配置 web 服务器(这里,我已经选择了主域 saheetha.com)。我已经继续通过自动化配置选项来进行了,因为我不需要添加任何手动设置。

当 Nginx 配置完后,你可以在这里为你的域名选择 PHP-FPM 实例。



就像你在截图中所看到的,我服务器上的默认 PHP-FPM 是**PHP 54**,而我正要将我的域名的 PHP-FPM 实例单独修改成 **PHP 55**。当你为你的域修改 PHP-FPM 后,你可以通过访问 **phpinfo** 页面来确认。
谢谢你们参考本文,我相信这篇文章会给你提供不少信息和帮助。我会为你们推荐关于这个内容的有价值的评论 :)。
---
via: <http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/enable-multiple-php-fpm-instances-nginx-apache/>
作者:[Saheetha Shameer](http://linoxide.com/author/saheethas/) 译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPConnectionPool(host='linoxide.com', port=80): Max retries exceeded with url: /linux-how-to/enable-multiple-php-fpm-instances-nginx-apache/ (Caused by ConnectTimeoutError(<urllib3.connection.HTTPConnection object at 0x7b83275818d0>, 'Connection to linoxide.com timed out. (connect timeout=10)')) | null |
7,439 | 通过 Docker 化一个博客网站来开启我们的 Docker 之旅 | http://bencane.com/2015/12/01/getting-started-with-docker-by-dockerizing-this-blog/ | 2016-06-08T10:19:00 | [
"Docker",
"dockefile"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7439-1.html | 
>
> 这篇文章包含 Docker 的基本概念,以及如何通过创建一个定制的 Dockerfile 来 <ruby> Docker 化 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Dockerize </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>一个应用。
>
>
>
Docker 是一个过去两年来从某个 idea 中孕育而生的有趣技术,公司组织们用它在世界上每个角落来部署应用。在今天的文章中,我将讲述如何通过“<ruby> Docker 化 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Dockerize </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”一个现有的应用,来开始我们的 Docker 之旅。这里提到的应用指的就是这个博客!
### 什么是 Docker?
当我们开始学习 Docker 基本概念时,让我们先去搞清楚什么是 Docker 以及它为什么这么流行。Docker 是一个操作系统容器管理工具,它通过将应用打包在操作系统容器中,来方便我们管理和部署应用。
#### 容器 vs. 虚拟机
容器和虚拟机并不完全相似,它是另外一种提供**操作系统虚拟化**的方式。它和标准的虚拟机还是有所不同。
标准的虚拟机一般会包括一个完整的操作系统、操作系统软件包、最后还有一至两个应用。这都得益于为虚拟机提供硬件虚拟化的管理程序。这样一来,一个单一的服务器就可以将许多独立的操作系统作为虚拟客户机运行了。
容器和虚拟机很相似,它们都支持在单一的服务器上运行多个操作环境,只是,在容器中,这些环境并不是一个个完整的操作系统。容器一般只包含必要的操作系统软件包和一些应用。它们通常不会包含一个完整的操作系统或者硬件的虚拟化。这也意味着容器比传统的虚拟机开销更少。
容器和虚拟机常被误认为是两种对立的技术。虚拟机采用一个物理服务器来提供全功能的操作环境,该环境会和其余虚拟机一起共享这些物理资源。容器一般用来隔离一个单一主机上运行的应用进程,以保证隔离后的进程之间不能相互影响。事实上,容器和 **BSD Jails** 以及 `chroot` 进程的相似度,超过了和完整虚拟机的相似度。
#### Docker 在容器之上提供了什么
Docker 本身不是一个容器运行环境,事实上,只是一个与具体实现无关的容器技术,Docker 正在努力支持 [Solaris Zones](https://blog.docker.com/2015/08/docker-oracle-solaris-zones/) 和 [BSD Jails](https://wiki.freebsd.org/Docker)。Docker 提供了一种管理、打包和部署容器的方式。虽然一定程度上,虚拟机多多少少拥有这些类似的功能,但虚拟机并没有完整拥有绝大多数的容器功能,即使拥有,这些功能用起来都并没有 Docker 来的方便或那么完整。
现在,我们应该知道 Docker 是什么了,然后,我们将从安装 Docker,并部署一个公开的预构建好的容器开始,学习 Docker 是如何工作的。
### 从安装开始
默认情况下,Docker 并不会自动被安装在您的计算机中,所以,第一步就是安装 Docker 软件包;我们的教学机器系统是 Ubuntu 14.0.4,所以,我们将使用 Apt 软件包管理器,来执行安装操作。
```
# apt-get install docker.io
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following extra packages will be installed:
aufs-tools cgroup-lite git git-man liberror-perl
Suggested packages:
btrfs-tools debootstrap lxc rinse git-daemon-run git-daemon-sysvinit git-doc
git-el git-email git-gui gitk gitweb git-arch git-bzr git-cvs git-mediawiki
git-svn
The following NEW packages will be installed:
aufs-tools cgroup-lite docker.io git git-man liberror-perl
0 upgraded, 6 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Need to get 7,553 kB of archives.
After this operation, 46.6 MB of additional disk space will be used.
Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y
```
为了检查当前是否有容器运行,我们可以执行`docker`命令,加上`ps`选项
```
# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
```
`docker`命令中的`ps`功能类似于 Linux 的`ps`命令。它将显示可找到的 Docker 容器及其状态。由于我们并没有启动任何 Docker 容器,所以命令没有显示任何正在运行的容器。
### 部署一个预构建好的 nginx Docker 容器
我比较喜欢的 Docker 特性之一就是 Docker 部署预先构建好的容器的方式,就像`yum`和`apt-get`部署包一样。为了更好地解释,我们来部署一个运行着 nginx web 服务器的预构建容器。我们可以继续使用`docker`命令,这次选择`run`选项。
```
# docker run -d nginx
Unable to find image 'nginx' locally
Pulling repository nginx
5c82215b03d1: Download complete
e2a4fb18da48: Download complete
58016a5acc80: Download complete
657abfa43d82: Download complete
dcb2fe003d16: Download complete
c79a417d7c6f: Download complete
abb90243122c: Download complete
d6137c9e2964: Download complete
85e566ddc7ef: Download complete
69f100eb42b5: Download complete
cd720b803060: Download complete
7cc81e9a118a: Download complete
```
`docker`命令的`run`选项,用来通知 Docker 去寻找一个指定的 Docker 镜像,然后启动运行着该镜像的容器。默认情况下,Docker 容器运行在前台,这意味着当你运行`docker run`命令的时候,你的 shell 会被绑定到容器的控制台以及运行在容器中的进程。为了能在后台运行该 Docker 容器,我们使用了`-d` (**detach**)标志。
再次运行`docker ps`命令,可以看到 nginx 容器正在运行。
```
# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
f6d31ab01fc9 nginx:latest nginx -g 'daemon off 4 seconds ago Up 3 seconds 443/tcp, 80/tcp desperate_lalande
```
从上面的输出信息中,我们可以看到正在运行的名为`desperate_lalande`的容器,它是由`nginx:latest image`(LCTT 译注: nginx 最新版本的镜像)构建而来得。
#### Docker 镜像
镜像是 Docker 的核心特征之一,类似于虚拟机镜像。和虚拟机镜像一样,Docker 镜像是一个被保存并打包的容器。当然,Docker 不只是创建镜像,它还可以通过 Docker 仓库发布这些镜像,Docker 仓库和软件包仓库的概念差不多,它让 Docker 能够模仿`yum`部署软件包的方式来部署镜像。为了更好地理解这是怎么工作的,我们来回顾`docker run`执行后的输出。
```
# docker run -d nginx
Unable to find image 'nginx' locally
```
我们可以看到第一条信息是,Docker 不能在本地找到名叫 nginx 的镜像。这是因为当我们执行`docker run`命令时,告诉 Docker 运行一个基于 nginx 镜像的容器。既然 Docker 要启动一个基于特定镜像的容器,那么 Docker 首先需要找到那个指定镜像。在检查远程仓库之前,Docker 首先检查本地是否存在指定名称的本地镜像。
因为系统是崭新的,不存在 nginx 镜像,Docker 将选择从 Docker 仓库下载之。
```
Pulling repository nginx
5c82215b03d1: Download complete
e2a4fb18da48: Download complete
58016a5acc80: Download complete
657abfa43d82: Download complete
dcb2fe003d16: Download complete
c79a417d7c6f: Download complete
abb90243122c: Download complete
d6137c9e2964: Download complete
85e566ddc7ef: Download complete
69f100eb42b5: Download complete
cd720b803060: Download complete
7cc81e9a118a: Download complete
```
这就是第二部分输出信息显示给我们的内容。默认情况下,Docker 会使用 [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/) 仓库,该仓库由 Docker 公司维护。
和 Github 一样,在 Docker Hub 创建公共仓库是免费的,私人仓库就需要缴纳费用了。当然,部署你自己的 Docker 仓库也是可以的,事实上只需要简单地运行`docker run registry`命令就行了。但在这篇文章中,我们的重点将不是讲解如何部署一个定制的注册服务。
#### 关闭并移除容器
在我们继续构建定制容器之前,我们先清理一下 Docker 环境,我们将关闭先前的容器,并移除它。
我们利用`docker`命令和`run`选项运行一个容器,所以,为了停止同一个容器,我们简单地在执行`docker`命令时,使用`kill`选项,并指定容器名。
```
# docker kill desperate_lalande
desperate_lalande
```
当我们再次执行`docker ps`,就不再有容器运行了
```
# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
```
但是,此时,我们这是停止了容器;虽然它不再运行,但仍然存在。默认情况下,`docker ps`只会显示正在运行的容器,如果我们附加`-a` (all) 标识,它会显示所有运行和未运行的容器。
```
# docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
f6d31ab01fc9 5c82215b03d1 nginx -g 'daemon off 4 weeks ago Exited (-1) About a minute ago desperate_lalande
```
为了能完整地移除容器,我们在用`docker`命令时,附加`rm`选项。
```
# docker rm desperate_lalande
desperate_lalande
```
虽然容器被移除了;但是我们仍拥有可用的**nginx**镜像(LCTT 译注:镜像缓存)。如果我们重新运行`docker run -d nginx`,Docker 就无需再次拉取 nginx 镜像即可启动容器。这是因为我们本地系统中已经保存了一个副本。
为了列出系统中所有的本地镜像,我们运行`docker`命令,附加`images`选项。
```
# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED VIRTUAL SIZE
nginx latest 9fab4090484a 5 days ago 132.8 MB
```
### 构建我们自己的镜像
截至目前,我们已经使用了一些基础的 Docker 命令来启动、停止和移除一个预构建好的普通镜像。为了“Docker 化(Dockerize)”这篇博客,我们需要构建我们自己的镜像,也就是创建一个 **Dockerfile**。
在大多数虚拟机环境中,如果你想创建一个机器镜像,首先,你需要建立一个新的虚拟机、安装操作系统、安装应用,最后将其转换为一个模板或者镜像。但在 Docker 中,所有这些步骤都可以通过 Dockerfile 实现全自动。Dockerfile 是向 Docker 提供构建指令去构建定制镜像的方式。在这一章节,我们将编写能用来部署这个博客的定制 Dockerfile。
#### 理解应用
我们开始构建 Dockerfile 之前,第一步要搞明白,我们需要哪些东西来部署这个博客。
这个博客本质上是由一个静态站点生成器生成的静态 HTML 页面,这个生成器是我编写的,名为 **hamerkop**。这个生成器很简单,它所做的就是生成该博客站点。所有的代码和源文件都被我放在了一个公共的 [Github 仓库](https://github.com/madflojo/blog)。为了部署这篇博客,我们要先从 Github 仓库把这些内容拉取下来,然后安装 **Python** 和一些 **Python** 模块,最后执行`hamerkop`应用。我们还需要安装 **nginx**,来运行生成后的内容。
截止目前,这些还是一个简单的 Dockerfile,但它却给我们展示了相当多的 [Dockerfile 语法]((https://docs.docker.com/v1.8/reference/builder/))。我们需要克隆 Github 仓库,然后使用你最喜欢的编辑器编写 Dockerfile,我选择`vi`。
```
# git clone https://github.com/madflojo/blog.git
Cloning into 'blog'...
remote: Counting objects: 622, done.
remote: Total 622 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 622
Receiving objects: 100% (622/622), 14.80 MiB | 1.06 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (242/242), done.
Checking connectivity... done.
# cd blog/
# vi Dockerfile
```
#### FROM - 继承一个 Docker 镜像
第一条 Dockerfile 指令是`FROM`指令。这将指定一个现存的镜像作为我们的基础镜像。这也从根本上给我们提供了继承其他 Docker 镜像的途径。在本例中,我们还是从刚刚我们使用的 **nginx** 开始,如果我们想从头开始,我们可以通过指定`ubuntu:latest`来使用 **Ubuntu** Docker 镜像。
```
## Dockerfile that generates an instance of http://bencane.com
FROM nginx:latest
MAINTAINER Benjamin Cane <[email protected]>
```
除了`FROM`指令,我还使用了`MAINTAINER`,它用来显示 Dockerfile 的作者。
Docker 支持使用`#`作为注释,我将经常使用该语法,来解释 Dockerfile 的部分内容。
#### 运行一次测试构建
因为我们继承了 **nginx** Docker镜像,我们现在的 Dockerfile 也就包括了用来构建 **nginx** 镜像的 [Dockerfile](https://github.com/nginxinc/docker-nginx/blob/08eeb0e3f0a5ee40cbc2bc01f0004c2aa5b78c15/Dockerfile) 中所有指令。这意味着,此时我们可以从该 Dockerfile 中构建出一个 Docker 镜像,然后以该镜像运行一个容器。虽然,最终的镜像和 **nginx** 镜像本质上是一样的,但是我们这次是通过构建 Dockerfile 的形式,然后我们将讲解 Docker 构建镜像的过程。
想要从 Dockerfile 构建镜像,我们只需要在运行 `docker` 命令的时候,加上 `build` 选项。
```
# docker build -t blog /root/blog
Sending build context to Docker daemon 23.6 MB
Sending build context to Docker daemon
Step 0 : FROM nginx:latest
---> 9fab4090484a
Step 1 : MAINTAINER Benjamin Cane <[email protected]>
---> Running in c97f36450343
---> 60a44f78d194
Removing intermediate container c97f36450343
Successfully built 60a44f78d194
```
上面的例子,我们使用了`-t` (**tag**)标识给镜像添加“blog”的标签。实质上我们就是在给镜像命名,如果我们不指定标签,就只能通过 Docker 分配的 **Image ID** 来访问镜像了。本例中,从 Docker 构建成功的信息可以看出,**Image ID**值为 `60a44f78d194`。
除了`-t`标识外,我还指定了目录`/root/blog`。该目录被称作“构建目录”,它将包含 Dockerfile,以及其它需要构建该容器的文件。
现在我们构建成功了,下面我们开始定制该镜像。
#### 使用 RUN 来执行 apt-get
用来生成 HTML 页面的静态站点生成器是用 **Python** 语言编写的,所以,在 Dockerfile 中需要做的第一件定制任务是安装 Python。我们将使用 Apt 软件包管理器来安装 Python 软件包,这意味着在 Dockerfile 中我们要指定运行`apt-get update`和`apt-get install python-dev`;为了完成这一点,我们可以使用`RUN`指令。
```
## Dockerfile that generates an instance of http://bencane.com
FROM nginx:latest
MAINTAINER Benjamin Cane <[email protected]>
## Install python and pip
RUN apt-get update
RUN apt-get install -y python-dev python-pip
```
如上所示,我们只是简单地告知 Docker 构建镜像的时候,要去执行指定的`apt-get`命令。比较有趣的是,这些命令只会在该容器的上下文中执行。这意味着,即使在容器中安装了`python-dev`和`python-pip`,但主机本身并没有安装这些。说的更简单点,`pip`命令将只在容器中执行,出了容器,`pip`命令不存在。
还有一点比较重要的是,Docker 构建过程中不接受用户输入。这说明任何被`RUN`指令执行的命令必须在没有用户输入的时候完成。由于很多应用在安装的过程中需要用户的输入信息,所以这增加了一点难度。不过我们例子中,`RUN`命令执行的命令都不需要用户输入。
#### 安装 Python 模块
**Python** 安装完毕后,我们现在需要安装 Python 模块。如果在 Docker 外做这些事,我们通常使用`pip`命令,然后参考我的博客 Git 仓库中名叫`requirements.txt`的文件。在之前的步骤中,我们已经使用`git`命令成功地将 Github 仓库“克隆”到了`/root/blog`目录;这个目录碰巧也是我们创建`Dockerfile`的目录。这很重要,因为这意味着 Docker 在构建过程中可以访问这个 Git 仓库中的内容。
当我们执行构建后,Docker 将构建的上下文环境设置为指定的“构建目录”。这意味着目录中的所有文件都可以在构建过程中被使用,目录之外的文件(构建环境之外)是不能访问的。
为了能安装所需的 Python 模块,我们需要将`requirements.txt`从构建目录拷贝到容器中。我们可以在`Dockerfile`中使用`COPY`指令完成这一需求。
```
## Dockerfile that generates an instance of http://bencane.com
FROM nginx:latest
MAINTAINER Benjamin Cane <[email protected]>
## Install python and pip
RUN apt-get update
RUN apt-get install -y python-dev python-pip
## Create a directory for required files
RUN mkdir -p /build/
## Add requirements file and run pip
COPY requirements.txt /build/
RUN pip install -r /build/requirements.txt
```
在`Dockerfile`中,我们增加了3条指令。第一条指令使用`RUN`在容器中创建了`/build/`目录。该目录用来拷贝生成静态 HTML 页面所需的一切应用文件。第二条指令是`COPY`指令,它将`requirements.txt`从“构建目录”(`/root/blog`)拷贝到容器中的`/build/`目录。第三条使用`RUN`指令来执行`pip`命令;安装`requirements.txt`文件中指定的所有模块。
当构建定制镜像时,`COPY`是条重要的指令。如果在 Dockerfile 中不指定拷贝文件,Docker 镜像将不会包含requirements.txt 这个文件。在 Docker 容器中,所有东西都是隔离的,除非在 Dockerfile 中指定执行,否则容器中不会包括所需的依赖。
#### 重新运行构建
现在,我们让 Docker 执行了一些定制任务,现在我们尝试另一次 blog 镜像的构建。
```
# docker build -t blog /root/blog
Sending build context to Docker daemon 19.52 MB
Sending build context to Docker daemon
Step 0 : FROM nginx:latest
---> 9fab4090484a
Step 1 : MAINTAINER Benjamin Cane <[email protected]>
---> Using cache
---> 8e0f1899d1eb
Step 2 : RUN apt-get update
---> Using cache
---> 78b36ef1a1a2
Step 3 : RUN apt-get install -y python-dev python-pip
---> Using cache
---> ef4f9382658a
Step 4 : RUN mkdir -p /build/
---> Running in bde05cf1e8fe
---> f4b66e09fa61
Removing intermediate container bde05cf1e8fe
Step 5 : COPY requirements.txt /build/
---> cef11c3fb97c
Removing intermediate container 9aa8ff43f4b0
Step 6 : RUN pip install -r /build/requirements.txt
---> Running in c50b15ddd8b1
Downloading/unpacking jinja2 (from -r /build/requirements.txt (line 1))
Downloading/unpacking PyYaml (from -r /build/requirements.txt (line 2))
<truncated to reduce noise>
Successfully installed jinja2 PyYaml mistune markdown MarkupSafe
Cleaning up...
---> abab55c20962
Removing intermediate container c50b15ddd8b1
Successfully built abab55c20962
```
上述输出所示,我们可以看到构建成功了,我们还可以看到另外一个有趣的信息`---> Using cache`。这条信息告诉我们,Docker 在构建该镜像时使用了它的构建缓存。
#### Docker 构建缓存
当 Docker 构建镜像时,它不仅仅构建一个单独的镜像;事实上,在构建过程中,它会构建许多镜像。从上面的输出信息可以看出,在每一“步”执行后,Docker 都在创建新的镜像。
```
Step 5 : COPY requirements.txt /build/
---> cef11c3fb97c
```
上面片段的最后一行可以看出,Docker 在告诉我们它在创建一个新镜像,因为它打印了**Image ID** : `cef11c3fb97c`。这种方式有用之处在于,Docker能在随后构建这个 **blog** 镜像时将这些镜像作为缓存使用。这很有用处,因为这样, Docker 就能加速同一个容器中新构建任务的构建流程。从上面的例子中,我们可以看出,Docker 没有重新安装`python-dev`和`python-pip`包,Docker 则使用了缓存镜像。但是由于 Docker 并没有找到执行`mkdir`命令的构建缓存,随后的步骤就被一一执行了。
Docker 构建缓存一定程度上是福音,但有时也是噩梦。这是因为决定使用缓存或者重新运行指令的因素很少。比如,如果`requirements.txt`文件发生了修改,Docker 会在构建时检测到该变化,然后 Docker 会重新执行该执行那个点往后的所有指令。这得益于 Docker 能查看`requirements.txt`的文件内容。但是,`apt-get`命令的执行就是另一回事了。如果提供 Python 软件包的 **Apt** 仓库包含了一个更新的 python-pip 包;Docker 不会检测到这个变化,转而去使用构建缓存。这会导致之前旧版本的包将被安装。虽然对`python-pip`来说,这不是主要的问题,但对使用了存在某个致命攻击缺陷的软件包缓存来说,这是个大问题。
出于这个原因,抛弃 Docker 缓存,定期地重新构建镜像是有好处的。这时,当我们执行 Docker 构建时,我简单地指定`--no-cache=True`即可。
### 部署博客的剩余部分
Python 软件包和模块安装后,接下来我们将拷贝需要用到的应用文件,然后运行`hamerkop`应用。我们只需要使用更多的`COPY` 和 `RUN`指令就可完成。
```
## Dockerfile that generates an instance of http://bencane.com
FROM nginx:latest
MAINTAINER Benjamin Cane <[email protected]>
## Install python and pip
RUN apt-get update
RUN apt-get install -y python-dev python-pip
## Create a directory for required files
RUN mkdir -p /build/
## Add requirements file and run pip
COPY requirements.txt /build/
RUN pip install -r /build/requirements.txt
## Add blog code nd required files
COPY static /build/static
COPY templates /build/templates
COPY hamerkop /build/
COPY config.yml /build/
COPY articles /build/articles
## Run Generator
RUN /build/hamerkop -c /build/config.yml
```
现在我们已经写出了剩余的构建指令,我们再次运行另一次构建,并确保镜像构建成功。
```
# docker build -t blog /root/blog/
Sending build context to Docker daemon 19.52 MB
Sending build context to Docker daemon
Step 0 : FROM nginx:latest
---> 9fab4090484a
Step 1 : MAINTAINER Benjamin Cane <[email protected]>
---> Using cache
---> 8e0f1899d1eb
Step 2 : RUN apt-get update
---> Using cache
---> 78b36ef1a1a2
Step 3 : RUN apt-get install -y python-dev python-pip
---> Using cache
---> ef4f9382658a
Step 4 : RUN mkdir -p /build/
---> Using cache
---> f4b66e09fa61
Step 5 : COPY requirements.txt /build/
---> Using cache
---> cef11c3fb97c
Step 6 : RUN pip install -r /build/requirements.txt
---> Using cache
---> abab55c20962
Step 7 : COPY static /build/static
---> 15cb91531038
Removing intermediate container d478b42b7906
Step 8 : COPY templates /build/templates
---> ecded5d1a52e
Removing intermediate container ac2390607e9f
Step 9 : COPY hamerkop /build/
---> 59efd1ca1771
Removing intermediate container b5fbf7e817b7
Step 10 : COPY config.yml /build/
---> bfa3db6c05b7
Removing intermediate container 1aebef300933
Step 11 : COPY articles /build/articles
---> 6b61cc9dde27
Removing intermediate container be78d0eb1213
Step 12 : RUN /build/hamerkop -c /build/config.yml
---> Running in fbc0b5e574c5
Successfully created file /usr/share/nginx/html//2011/06/25/checking-the-number-of-lwp-threads-in-linux
Successfully created file /usr/share/nginx/html//2011/06/checking-the-number-of-lwp-threads-in-linux
<truncated to reduce noise>
Successfully created file /usr/share/nginx/html//archive.html
Successfully created file /usr/share/nginx/html//sitemap.xml
---> 3b25263113e1
Removing intermediate container fbc0b5e574c5
Successfully built 3b25263113e1
```
#### 运行定制的容器
成功的一次构建后,我们现在就可以通过运行`docker`命令和`run`选项来运行我们定制的容器,和之前我们启动 nginx 容器一样。
```
# docker run -d -p 80:80 --name=blog blog
5f6c7a2217dcdc0da8af05225c4d1294e3e6bb28a41ea898a1c63fb821989ba1
```
我们这次又使用了`-d` (**detach**)标识来让Docker在后台运行。但是,我们也可以看到两个新标识。第一个新标识是`--name`,这用来给容器指定一个用户名称。之前的例子,我们没有指定名称,因为 Docker 随机帮我们生成了一个。第二个新标识是`-p`,这个标识允许用户从主机映射一个端口到容器中的一个端口。
之前我们使用的基础 **nginx** 镜像分配了80端口给 HTTP 服务。默认情况下,容器内的端口通道并没有绑定到主机系统。为了让外部系统能访问容器内部端口,我们必须使用`-p`标识将主机端口映射到容器内部端口。上面的命令,我们通过`-p 80:80`语法将主机80端口映射到容器内部的80端口。
经过上面的命令,我们的容器看起来成功启动了,我们可以通过执行`docker ps`核实。
```
# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
d264c7ef92bd blog:latest nginx -g 'daemon off 3 seconds ago Up 3 seconds 443/tcp, 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp blog
```
### 总结
截止目前,我们拥有了一个运行中的定制 Docker 容器。虽然在这篇文章中,我们只接触了一些 Dockerfile 指令用法,但是我们还是要学习所有的指令。我们可以检查 [Docker's reference page](https://docs.docker.com/v1.8/reference/builder/) 来获取所有的 Dockerfile 指令用法,那里对指令的用法说明得很详细。
另一个比较好的资源是 [Dockerfile Best Practices page](https://docs.docker.com/engine/articles/dockerfile_best-practices/),它有许多构建定制 Dockerfile 的最佳练习。有些技巧非常有用,比如战略性地组织好 Dockerfile 中的命令。上面的例子中,我们将`articles`目录的`COPY`指令作为 Dockerfile 中最后的`COPY`指令。这是因为`articles`目录会经常变动。所以,将那些经常变化的指令尽可能地放在最后面的位置,来最优化那些可以被缓存的步骤。
通过这篇文章,我们涉及了如何运行一个预构建的容器,以及如何构建,然后部署定制容器。虽然关于 Docker 你还有许多需要继续学习的地方,但我想这篇文章给了你如何继续开始的好建议。当然,如果你认为还有一些需要继续补充的内容,在下面评论即可。
---
via: <http://bencane.com/2015/12/01/getting-started-with-docker-by-dockerizing-this-blog/>
作者:Benjamin Cane 译者:[su-kaiyao](https://github.com/su-kaiyao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,441 | 将 Linux 软件打包成 Snap 软件包 | https://insights.ubuntu.com/2016/06/01/apps-to-snaps/ | 2016-06-09T09:22:00 | [
"snap"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7441-1.html | 
在 Linux 分发应用不总是那么容易。有各种不同的包格式、基础系统、可用库,随着发行版的一次次发布,所有的这些都让人头疼。然而,现在我们有了更简单的东西:Snap。
Snap 是开发者打包他们应用的新途径,它相对于传统包格式,如 .deb,.rpm 等带来了许多优点。Snap 安全,彼此隔离,宿主系统使用了类似 AppArmor 的技术,它们跨平台且自足的,让开发者可以准确地将应用所需要的依赖打包到一起。沙盒隔离也加强了安全,并允许应用和整个基于 snap 的系统,在出现问题的时候可以回滚。Snap 确实是 Linux 应用打包的未来。
创建一个 snap 包并不困难。首先,你需要一个 snap 基础运行环境,能够让你的桌面环境认识并运行 snap 软件包,这个工具叫做 snapd ,默认内置于所有 Ubuntu 16.04 系统中。接着你需要创建 snap 的工具 Snapcraft,它可以通过一个简单的命令安装:
```
$ sudo apt-get install snapcraft
```
这个环境安装好了之后就可以 snap 起来了。
Snap 使用一个特定的 YAML 格式的文件 snapcraft.yaml,它定义了应用是如何打包的以及它需要的依赖。用一个简单的应用来演示一下,下面的 YAML 文件是个如何 snap 一个 moon-buggy 游戏的实际例子,该游戏在 Ubuntu 源中提供。
```
name: moon-buggy
version: 1.0.51.11
summary: Drive a car across the moon
description: |
A simple command-line game where you drive a buggy on the moon
apps:
play:
command: usr/games/moon-buggy
parts:
moon-buggy:
plugin: nil
stage-packages: [moon-buggy]
snap:
– usr/games/moon-buggy
```
上面的代码出现了几个新概念。第一部分是关于如何让你的应用可以在商店找到的信息,设置软件包的元数据名称、版本号、摘要、以及描述。apps 部分实现了 play 命令,指向了 moon-buggy 可执行文件位置。parts 部分告诉 snapcraft 用来构建应用所需要的插件以及依赖的包。在这个简单的例子中我们需要的所有东西就是来自 Ubuntu 源中的 moon-buggy 应用本身,snapcraft 负责剩下的工作。
在你的 snapcraft.yaml 所在目录下运行 snapcraft ,它会创建 moon-buggy*1.0.51.11*amd64.snap 包,可以通过以下命令来安装它:
```
$ snap install moon-buggy_1.0.51.11_amd64.snap
```
想了解更复杂一点的 snap 打包操作,比如基于 Electron 的 Simplenote 可以[看这里](http://www.simplenote.com/),在线教程在[这里](http://www.linuxuk.org/post/20160518_snapping_electron_based_applications_simplenote/),相应的代码在 [Github](https://github.com/jamiedbennett/snaps/tree/master/simplenote)。更多的例子可以在 Ubuntu 开发者[站点](https://developer.ubuntu.com/en/desktop/get-started/)找到。
---
via: <https://insights.ubuntu.com/2016/06/01/apps-to-snaps/>
作者:[Jamie](https://insights.ubuntu.com/author/jamiebennett/) 译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | null |
|
7,448 | jQuery 3.0 发布!根本不支持 IE6/7/8 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/jquery-3-0-released-and-other-javascript-news-505064.shtml | 2016-06-11T08:39:00 | [
"jQuery"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7448-1.html | jQuery 基金会前天宣布 [jQuery 3.0](http://blog.jquery.com/2016/06/09/jquery-3-0-final-released/) 发布!这是第一个根本不支持老版本 IE 的 jQuery 版本。

jQuery 3.0 开发于2014年10月。为了从老的 1.0 代码分离,摒弃那些由于要兼容 IE 而增加的庞杂的代码,其最初创建了 2.0 系列版本。3.0 版本是从 2.0 版本分支出来的,但是同 2.0 不兼容,因此更换了新的主版本号。
jQuery 3.0 是 jQuery 的未来所在,以后除了重大安全问题,jQuery 1.0 (最新版本 1.12)和 jQuery 2.0(最新版本 2.2)都不会再进行更新。
你可以通过如下地址直接调用 CDN 上的 jQuery:
* <https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.0.0.js>
* <https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.0.0.min.js>
也可以将其下载到本地,比如通过 npm:
```
npm install [email protected]
```
jQuery 2.0 完全不兼容 1.0,而 3.0 则继承了这个传统,继续不兼容 2.0。jQuery 基金会说 3.0 中有一些中断性的改变,但是用户可以不用太多工作就能将代码迁移到 3.0。
如果你要升级到 3.0,可以参考 [3.0 升级指南](http://jquery.com/upgrade-guide/3.0/),以及可以通过安装 jQuery Migrate 3.0 来找到你的代码中同 3.0 所不兼容的地方:
* <https://code.jquery.com/jquery-migrate-3.0.0.js>
* <https://code.jquery.com/jquery-migrate-3.0.0.min.js>
或者使用 npm 下载安装:
```
npm install [email protected]
```
jQuery 2.0 和 3.0 都不再支持老的 IE6、IE7 和 IE8 浏览器,如果用户必须支持这些旧式浏览器,那就只能使用 jQuery 1.12 了。
除了标准版本之外,如果你不使用 AJAX、效果等功能,你还可以使用一个<ruby> 廋版 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Slim </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的 jQuery,它的压缩大小是 23.6kb,而标准版本的大小是 30kb。
* <https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.0.0.slim.js>
* <https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.0.0.slim.min.js>
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,449 | 一个 Linux 驱动的微波炉 | https://lwn.net/Articles/674877/ | 2016-06-11T11:13:22 | [
"微波炉"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7449-1.html | [linux.conf.au](http://linux.conf.au/)里的人们都有一种想到什么就动手去实现的想法。随着硬件开源运动不断地发展壮大,这种想法越来越多,也与现实世界联系的越来越紧密,而不仅仅存在于数字世界中。David Tulloh用他制作的[Linux驱动的微波炉 [WebM]](http://mirror.linux.org.au/linux.conf.au/2016/04_Thursday/D4.303_Costa_Theatre/Linux_driven_microwave.webm)来展示一个差劲的微波炉会多么难用,以及说明他的项目可以改造这些微波炉使得它们不那么讨人厌。
Tulloh的故事要从他买到了一个公认很便宜的微波炉开始说起,它的用户界面比其它微波炉默认的还要糟糕。设定时间时必须使劲按按钮以至于把微波炉都向后推了一段距离——而事实上必须要用力拉仓门把手才能把微波炉拖回原来的位置,这形成了一个“优雅”的平衡。当然这只是极端情况。Tulloh郁闷的是因为这个微波炉近十年来都没有一丁点明显的改善。他可能买到了一个又小又便宜的微波炉,而且特点是大部分人不研究使用手册就不会使用它——和智能手机的对比更加明显:智能手机只需知道一点点的操作指南并且被广泛使用。
改造这个微波炉不一定没有前途,“让微波炉重获新生”——这个想法成为了一个原型,如果Tulloh可以再平衡一下想做的功能和需求之间的关系的话他希望这变成一个众筹项目:一个Linux驱动的微波炉。

### 加一点新奇的小玩意
如果把“Linux”和“微波炉”联系在一起的话,你可能会想到给微波炉加上一个智能手机式的触摸屏和网络链接,然后再通过社区做一款微波炉的“革命性”的手机应用,想到这些就像做菜想到分享食谱一样显而易见。但Tulloh的目标和他的原型远远超过这些,他做了两个新奇的功能——热感相机和称量物体质量的称重装置。
这个热感相机提供一个可以精确到两度的八乘八像素的图像,这足够发现一杯牛奶是否加热到沸腾或者牛排是否解冻到快不能用来烹饪。不论发生哪种情况,都可以减小功率或者关掉它。而且在必要的时候会发出警报。这可能不是第一个可以检测温度的微波炉——GE在十年前就开始卖带温度探针的微波炉了——但是一个一直工作的内置传感器比一个手工探针有用多了,尤其是有一个可用的API支持的时候。
第二个新发明是一个嵌入的称重装置,它可以在加热之前称量食物(和容器)。很多食谱根据质量大小给出指导的烹饪时间,很多微波炉支持你手动输入质量以便它帮你计算。利用内置的称重装置,这一过程可以变成自动化的。在许多微波炉的转盘下面稳固地放置一个称重装置是一个机械方面的挑战,不过Tulloh觉得这个问题不难处理。相反,他对微波炉的设计是基于“平板”或者“平板挂车”的风格——在四角各放置一个传感器,这不仅在机械实现上很简单而且很好的达到了要求。
一旦你有了这些额外添加的并与逻辑引擎相连的质量温度传感器,你可以去尝试更多好玩的可能。一杯刚从冰箱里拿出来的冰牛奶的质量温度分布可能会有适度误差。Tulloh发现可以监检测到这种情况,而且提供一些有关的像“煮沸”或者“加热”的选项也是容易做到的(下面有一个模拟的界面,可点击操作的版本请点击右边链接 [here](http://mwgui.tulloh.id.au/))

### 改造陈旧的东西
除了才开发出来的新功能,Tulloh还想要提升那些原本就提供的功能。可能不是所有微波炉的门把手都像Tulloh那个廉价的一样僵硬,但是很少有微波炉将把手设计的让残疾人也能轻松使用。这些缺陷都是可调整的,尤其是在美国,微波炉应该在仓门关闭的时候给出一个确定关闭的提示。这种确认必须是可靠的以预防那些伪劣产品,所以在仓门闭合时固定的槽位里添加一个短杆以确认仓门开闭状态,不至于误使微波炉在仓门开着的时候工作。事实上,必须要有两个相互联系的机关,如果他们提供的结果不一致,保险丝必须断开以便启动一个呼叫服务。Tulloh认为提供一个磁力门闩有更大的灵活性(包含简单的软件控制)并且像磁控也同样用于[磁性钥匙锁](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetic_keyed_lock),它可以让磁力门闩确认微波炉门是否关闭。
微波炉的另一个痛点是它会发出令人厌烦的声音。Tulloh去掉了蜂鸣器并且使用香蕉派(类似于树莓派的单片机开发板)控制他的微波炉。这可以通过一个把文本转换成语音的系统来用令人愉悦而且可配置的警报来提示和引导使用者。显然,下一步就是装上一个用来控制声音的扩音器。
许多微波炉除了定时和设置功率档位之外还可以做更多的事情——它们为烹饪,加热,化冻等提供一系列的功率档位。加上一个精确的温度测量装置感觉会为这个图表大大扩展这个列表。Andrew Tridgell对一个问题很好奇,加热巧克力——一个需要非常精确的温度控制的过程——是否是可能的。Tulloh没有过这方面的经验,他不敢保证这个一定可以,但是这个实验结果的确值得期待。即使没做成这件事,它也显出了潜在价值——社区接下来可以更进一步去做这件事。
### 实用性怎么样?
Tulloh十分乐意向全世界分享这个linux驱动的微波炉,他希望看到(因为这件事)形成一个社区并且想看到它接下来的走势。买一个现成的微波炉并且替换掉里面的电子元件看起来不是一个可行的点子。最后的结果可能会很糟,而买一个小巧智能的微波炉必然要花掉(比自己改造)更多的钱,但是潜在的顾客不想在他们的厨房里看到乱七八糟又不协调的东西。
许多零件都是现成的可以买到的(磁电管,处理器板,热传感器等等),像USB接口的热传感器,而且都很容易安装。软件原型当然也开源在[GitHub](https://github.com/lod?tab=repositories)。微波炉的舱室和门有不小的挑战性并且很可能要定制。Tulloh想要通过提供左侧开仓门的微波炉和颜色多样化的选项来转逆境为机遇。
一个对读者的快速调查:很少有人会贸然承诺他会为了一个全新的升级过的烤箱付出1000澳大利亚元。当然,很难知道是否会有充足的时间和足够多的读者来完成这个调查。这整个项目看起来很有趣。所以Tulloh的[博客](http://david.tulloh.id.au/category/microwave/) (点击这里)也很值得一看。
---
via: <https://lwn.net/Articles/674877/>
作者:Neil Brown 译者:[yuba0604](https://github.com/yuba0604)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # A Linux-powered microwave oven
Scratching an itch is a recurring theme in presentations at
[linux.conf.au](http://linux.conf.au). As the open-hardware
movement gains strength, more and
more of these itches relate to the physical world, not just the digital.
David Tulloh used his [presentation [WebM]](http://mirror.linux.org.au/linux.conf.au/2016/04_Thursday/D4.303
_Costa_Theatre/Linux_driven_microwave.webm) on the “Linux Driven
Microwave” to discuss how annoying microwave ovens can be and to
describe his project to build something less irritating.
$ sudo subscribe todaySubscribe today and elevate your LWN privileges. You’ll have access to all of LWN’s high-quality articles as soon as they’re published, and help support LWN in the process.
[Act now]and you can start with a free trial subscription.
Tulloh's story began when he obtained a microwave oven, admittedly an inexpensive one, with a user interface even worse than the norm. Setting the time required pressing buttons so hard that the microwave tended to get pushed away — a fact that was elegantly balanced by the door handle requiring a sufficiently hard tug to return the oven to its original position. While this is clearly an extreme case, Tulloh lamented that microwave ovens really hadn't improved noticeably in recent decades. They may have gotten a little cheaper and gained a few features that few people could use without poring over the instruction manual — the implied contrast to smartphones, which are widely used with little instruction, was clear.
![[Prototype]](https://static.lwn.net/images/2016/lca-oven-sm.jpg)
This microwave oven was not a lost cause — it gave its life to the greater good and became the prototype for an idea that Tulloh hopes to turn into a crowd-funded project if he can find the right match between features and demand: a Linux-driven microwave oven.
#### Adding novelty
Adding a smartphone-like touchscreen and a network connection and encouraging a community to build innovative apps such as recipe sharing are fairly obvious ideas once you think to put “Linux” and “microwave oven” together, but Tulloh's vision and prototype lead well beyond there. Two novel features that have been fitted are a thermal camera and a scale for measuring weight.
The thermal camera provides an eight-by-eight-pixel image of the contents of the oven with a precision of about two degrees. This is enough to detect if a glass of milk is about to boil over, or if the steak being thawed is in danger of getting cooked. In either case, the power can be reduced or removed. If appropriate, an alert can be sounded. This would not be the first microwave to be temperature sensitive — GE sold microwave ovens with temperature probes decades ago — but an always-present sensor is much more useful than a manually inserted probe, especially when there is an accessible API behind it.
The second innovation is a built-in scale to weigh the food (and container) being cooked. Many recipes give cooking-time guidance based on weight and some microwave ovens allow you to enter the weight manually so it can do a calculation for you. With built-in scales, that can become automatic. Placing a scale reliably under the rotating plate typical of many microwave ovens would be a mechanical challenge that Tulloh did not think worth confronting. Instead his design is based on the “flat-plate” or “flat-bed” style of oven — placing a sensor at each of the four corners is mechanically straightforward and gives good results.
![[User interface]](https://static.lwn.net/images/2016/lca-ovengui-sm.png)
Once you have these extra sensors — weight and temperature — connected
to a suitable logic engine, more interesting possibilities can be
explored. A cup of cold milk from the fridge will have a particular
weight and temperature profile with a modest degree of error. Tulloh
suggested that situation could be detected and some relevant options
such as “Boil” or “Warm” could be offered for easy selection (a mock up of
the interface is at right, a clickable version is [here](http://mwgui.tulloh.id.au/)). Simple
machine learning could extend this to create a personalized
experience. It would be easy to collect a history of starting
profiles and cooking choices; when those patterns are detected, the
most likely cooking choices could be made the easiest to select.
#### Overcoming staleness
Beyond just new functionality, Tulloh wants to improve the
functionality that already exists. Door handles as stiff as on
Tulloh's cheap microwave may not be common, but few microwave oven
doors seem designed to make life easy for people with physical
handicaps. There are regulatory restrictions, particularly in the
US, that require the oven to function only if there is positive
confirmation that the door is actually shut. This confirmation must be
resilient against simple fraud, so poking a stick in the hole must not
trick the oven into working with the door open. In fact, there must be
two independent confirmations and, if they disagree, a fuse must be
blown so that a service call is required. Tulloh believes that a
magnetic latch would provide much greater flexibility (including easy
software control) and that magnetic keying similar to that used in a
[magnetic keyed lock](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetic_keyed_lock) would allow the magnetic latch to pass
certification.
Another pain point with microwave ovens is the annoying sounds they make. Tulloh has discarded the beeper and hooked up a speaker to the Banana Pi that is controlling his prototype. This allows for more pleasant and configurable alerts as well as for advice and guidance through a text-to-speech system. Adding a microphone for voice control is an obvious next step.
Many microwave ovens can do more than just set a time and a power level — they provide a range of power profiles for cooking, warming, defrosting, and so on. Adding precise temperature sensing will allow the community to extend this range substantially. A question from Andrew Tridgell in the audience wondered if tempering chocolate — a process that requires very precise temperature control — would be possible. Tulloh had no experience with the process, and couldn't make promises, but thought it was certainly worth looking in to. Even if that doesn't work out, it shows clear potential for value to be gained from community input.
#### Availability
Tulloh would very much like to get these Linux-enabled microwave ovens out into the world to create a community and see where it goes. Buying existing ovens and replacing the electronics is not seen as a viable option. The result would be ugly and, given that a small-run smart microwave will inevitably cost more, potential buyers are going to want something that doesn't look completely out of place in their kitchen.
Many components are available off-the-shelf (magnetron, processor
board, thermal sensor) and others, such as a USB interface for
the thermal sensor, are easily built. Prototype software is, of course, already available on
[GitHub](https://github.com/lod?tab=repositories).
The case and door are more of a
challenge and would need to be made to order. Tulloh wants to turn
this adversity into an opportunity by providing the option for
left-handed microwave ovens and a variety of colors.
A quick survey
of the audience suggested that few people would hastily commit to his
target price of $AU1000 for a new, improved, open oven. Whether a bit
more time for reflection and a wider audience might tip the balance is
hard to know. The idea is intriguing, so it seems worth
watching Tulloh's [blog](http://david.tulloh.id.au/category/microwave/) for updates.
Index entries for this article | |
---|---|
|
[Brown, Neil](/Archives/GuestIndex/#Brown_Neil)[Conference](/Archives/ConferenceIndex/)[linux.conf.au/2016](/Archives/ConferenceIndex/#linux.conf.au-2016) Posted Feb 10, 2016 22:19 UTC (Wed)
by
Posted Feb 13, 2016 4:54 UTC (Sat)
by I thought you might be referring to Apparently, there's a big market for appliances (well,
Posted Feb 10, 2016 22:33 UTC (Wed)
by
Posted Feb 11, 2016 1:04 UTC (Thu)
by I doubt it. Most microwave ovens these days are mounted permanently into the cabinetry. It'd be impossible to accurately weigh the contents with an external scale.
Posted Feb 11, 2016 5:41 UTC (Thu)
by
Posted Feb 11, 2016 21:33 UTC (Thu)
by
Then to keep it from wiggling around you'd have to have some extruded aluminum railings or something like that as well. Then you'll have to test it to make sure that as the thing ages the vibrations from the transformer or microwave radio to do do anything odd to create a noise in the system and various other things. And it all has to be robust enough to survive shipping and being handled by the customer.
All in all adding platform with a couple sensors under it in the oven is easier.
Posted Feb 13, 2016 9:44 UTC (Sat)
by
Trivial to calibrate and recalibrate too.
Posted Feb 11, 2016 5:40 UTC (Thu)
by
Posted Feb 11, 2016 6:59 UTC (Thu)
by
Posted Feb 11, 2016 7:31 UTC (Thu)
by
Posted Feb 11, 2016 20:34 UTC (Thu)
by
I think the points where the internals are mounted to the case might be the best place to measure, although any of these clever measurement locations depends on having a connection that's both secure and measures pressure.
Posted Feb 12, 2016 16:14 UTC (Fri)
by
Posted Feb 12, 2016 16:53 UTC (Fri)
by
You have to touch the machine in order to make that happening. You can't weigh something accurately as people are manipulating it.
Posted Feb 11, 2016 11:27 UTC (Thu)
by
The rotating plate in microwave oven is here to ensure even heating. If it is not used, then (probably more expensive) metal wave guide stirring fan is needed.
Posted Feb 11, 2016 21:36 UTC (Thu)
by
Ahhh. That's what they are called. That explained the "stirrer" in the slide at
Posted Feb 12, 2016 19:13 UTC (Fri)
by
Don't most microwaves have both? Just looked, our crappy Frigidaire has both. Sample size of 1.
Posted Feb 15, 2016 0:11 UTC (Mon)
by
That makes some sense. Customers are acutely aware of uneven heating problems in microwaves, so will pay more for something that seems to address that. But that uneven heating is actually caused by uneven composition of the food, so the turntable doesn't help.
Posted Feb 11, 2016 10:46 UTC (Thu)
by
I'm sure everybody in here has one or more home appliances where 90% of the buttons go unused because it's just not worth the hassle to look up what they do, mostly because the basic functionality already does the job well enough. Here, the sensors also give you a feeling of confidence that the functions actually work as advertised, since it's not just a pre-programmed set of parameters, and they also provide protection against both human and machine error when using basic microwave functionality.
IoT vendors, take note. Features should not be tacked on, but actually make sense in the context of the whole product.
What irks me though is that it seems like there is no effort to arrive at a coherent well-rounded product, especially considering proposed "features" such as voice input. I've never particularly felt the need to talk to my microwave as pressing a button is usually faster and less involved. I'm also not too sure about the touch screen; I feel like all common interactions one might have with a microwave interface could be achieved at a lower cost with a better feel by combining a display with some context-dependant physical buttons and turn knobs below or on the side.
Posted Feb 11, 2016 21:46 UTC (Thu)
by
Neither have I. But my father-in-law had "the shakes" - his hands only did approximately what he asked them to. Buttons are often unforgiving if you hit the wrong one or press too many times. His voice worked perfectly well though.
Posted Feb 12, 2016 14:59 UTC (Fri)
by
Posted Feb 12, 2016 0:14 UTC (Fri)
by A resounding "Amen!" to that. A microwave oven is merely a I find it oddly eccentric that the appliance companies have seemed bent for the past several decades on adding all these fancy bells & whistles to microwave ovens to fine-tune the heating parameters. Note that I said "heating" and not "cooking"—you really can't I sincerely do [
][
]
This reminds me of the old ## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**tshow** (subscriber, #6411)
[[Link](/Articles/675110/)] (1 responses)
[toaster](http://philip.greenspun.com/humor/eecs-difference-explained) story, somehow.
[
]## The toaster story actually there's another toaster story, sort of
**pr1268** (subscriber, #24648)
[[Link](/Articles/675465/)]
[this story](http://www.jnd.org/dn.mss/simplicity_is_highly.html), which also discusses two types of toasters. Perhaps the $20 toaster Donald Norman reminisces about is the model the king's electrical engineer whipped up, while the [₩](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/South_Korean_won)250,000 model is the one for which the computer scientist was beheaded. ;-)[software, too](http://www.joelonsoftware.com/items/2006/12/09.html)) that have complex, extraneous, and (generally) unneeded whiz-bang features. At least in Korea, where having a refrigerator with a control panel that looks like a [nuclear power plant control room](http://www.tampabay.com/resources/images/dti/rendered/2008/03/tb_nuclear450_14373a_8col.jpg) is a status symbol.[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**df5ea** (subscriber, #59450)
[[Link](/Articles/675112/)] (14 responses)
Placing a scale reliably under the rotating plate typical of many microwave ovens would be a mechanical challenge that Tulloh did not think worth confronting. Instead his design is based on the “flat-plate” or “flat-bed” style of oven — placing a sensor at each of the four corners is mechanically straightforward and gives good results.
Wouldn't it be easier to weigh the whole oven instead? That way the weighing mechanism would be independent of the mechanics inside the oven.
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**pr1268** (subscriber, #24648)
[[Link](/Articles/675130/)] (3 responses)
Wouldn't it be easier to weigh the whole oven instead? That way the weighing mechanism would be independent of the mechanics inside the oven.
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**roskegg** (subscriber, #105)
[[Link](/Articles/675136/)] (2 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**drag** (guest, #31333)
[[Link](/Articles/675254/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**lbt** (subscriber, #29672)
[[Link](/Articles/675477/)]
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**roskegg** (subscriber, #105)
[[Link](/Articles/675135/)] (5 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**ernest** (guest, #2355)
[[Link](/Articles/675143/)] (4 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**felixfix** (subscriber, #242)
[[Link](/Articles/675146/)] (3 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**iabervon** (subscriber, #722)
[[Link](/Articles/675249/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**flussence** (guest, #85566)
[[Link](/Articles/675349/)]
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**drag** (guest, #31333)
[[Link](/Articles/675373/)]
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**jnareb** (subscriber, #46500)
[[Link](/Articles/675179/)] (3 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**neilbrown** (subscriber, #359)
[[Link](/Articles/675255/)]
[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R3DADx5z-XY&t=183](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R3DADx5z-XY&t=183)
which had me mystified.
Thanks.
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**bronson** (subscriber, #4806)
[[Link](/Articles/675394/)] (1 responses)
[
]
I read once that the stirrer is fully effective and the only reason for the turntable is that it seems to customers to be helpful.
## turntable vs microwave scatterer in oven
**giraffedata** (guest, #1954)
[[Link](/Articles/675620/)]
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**fratti** (guest, #105722)
[[Link](/Articles/675170/)] (20 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**neilbrown** (subscriber, #359)
[[Link](/Articles/675256/)] (1 responses)
And the other commenter who carries a bowl of soup with two hands... imagine the solenoid which usually locks the door being given a reverse current when you say "Open Sesame" so that the door swings gently open.
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**fratti** (guest, #105722)
[[Link](/Articles/675333/)]
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**pr1268** (subscriber, #24648)
[[Link](/Articles/675275/)] (17 responses)
I'm sure everybody in here has one or more home appliances where 90% of the buttons go unused because it's just not worth the hassle to look up what they do, mostly because the basic functionality already does the job well enough.
[Faraday cage](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Faraday_cage) with a [magnetron](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cavity_magnetron), a lamp, a swing-out latching front door, and an on/off switch for the magnetron (since it only has two working states: full-power and off).*cook* with a microwave oven. And, considering how [dielectric heating](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dielectric_heating) works, you can't effectively heat anything which does not contain water.** not** mean to impugn Mr. Tulloh's hard work nor Neil's excellent article. In fact, I'm quite impressed with some of the ingenuity shown by this project. But, there's something to be said about the
[KISS method](https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/KISS_principle)—especially when you're working with a device that has only two discrete states of operation.
</minor rant>
P.S. I have fond memories of using my grandmother's microwave oven (vintage early 1980's). It had only two controls: (1) an egg timer-style power knob, and (2) a large mechanical latch button to open the door. Worked great for years.
Posted Feb 12, 2016 14:55 UTC (Fri)
by
David’s additions, though, seem to provide more value than the usual ones (a clock that’s always wrong, silly menus, …). I especially like the infrared sensor. I am less excited about the lack of a turntable. But maybe this spinner part can replace it reliably?
Posted Feb 19, 2016 18:37 UTC (Fri)
by
And both hers and mine have various features I would NOT want to lose. Namely heating elements at the top (commonly known as "a grill"), and at the back (commonly known as a "fan oven").
Our kitchen now has a conventional oven and a combi-oven built-in, and the combination is great. Incidentally, for those who think AU$1K is expensive, if I could get a built-in combi for that price I would consider it very good value for money.
The one big problem with our new - analog - combi is we have to remember to check the settings each time we use it. My old - digital - oven reset itself back to its defaults after every use. It also had the ability to set several programs to run consecutively - made superb baked tatties - set it for 10 mins on combi followed by 10 mins on fan oven and one lovely tatty. Our new analog you have to do the first setting, then when it bleeps "finished" you need to go back and reset it for the second setting.
Cheers,
Posted Feb 12, 2016 15:21 UTC (Fri)
by
I have this creeping suspicion that's it's an attempt to differentiate themselves from the competition without actually having to innovate. A lot of home appliances have come to a state where it would take some serious engineering to make a substantial improvement over previous models (which is expensive), so to keep up a fake air of technological evolution (as we've come to expect it from other devices such as computers or phones), they just tack things on that makes them look more advanced than it really is.
One anecdote I have of kitchen appliances that have essentially reached an innovation plateau is when my family's old hand mixer broke. We've had it for probably over a decade, maybe even more. When my mother came back from the store, she did so with the exact same model. Same white plastic mould that would slowly become yellow over the years with a teal push button on the top to release the attachments and one switch that had several positions to adjust speed, powered with a somewhat flimsy two-wire power cord. Not only did they still produce and sell it, the salesman even recommended it to her, because essentially there have been no improvements over the years. Yes, maybe internally the power supply or the motor were using newer parts, but it's still just an electric motor that you can plug into a wall outlet to spin mixing or puréeing attachments of various shapes.
Posted Feb 12, 2016 17:02 UTC (Fri)
by
OMFG yes, I actually find that for many appliances, they really peaked in the 1950s and the actual utility has been on a plateau or decline since then. Maybe I am just getting old and cranky but I'm not excited about tools like the Nest thermostat or fancy Microwave because the more software the harder it is to reason about what the device is going to do, it becomes a mysterious black box with rules that you just can't quite spend the mental effort to figure out, because we all have better things to do with our time. Instead of our appliances being tools we use we become tools for babysitting the appliances, and a machine for vomiting up cash to the manufacturer.
There is also a lot of advertising out there to convince people that every chore is just _too_hard_ and you need a much larger number of appliances than are really necessary. Take a look at one of the many cooking competition shows to see how many appliances are actually useful in a kitchen.
Posted Feb 12, 2016 19:14 UTC (Fri)
by I'm not sure I'd go that far, but I agree that development is very slow, especially compared to anything involving computers. The key is that for anything, the biggest change is from having nothing to having something, and after that it's mostly refinement, and often with declining returns. An icebox is a huge improvement over nothing, a refrigerator is a big advance over an icebox, but after that you're chasing improvements in convenience and efficiency rather than basic function. Similarly, many of the changes to the microwave (e.g. turntable for the food, variable power level) are real improvements, but they're marginal advances compared to getting one in the first place.
Posted Feb 12, 2016 19:17 UTC (Fri)
by
Now that's progress!
Posted Feb 18, 2016 12:54 UTC (Thu)
by
Posted Feb 18, 2016 14:29 UTC (Thu)
by
Easy, so it can order champagne when you have planned your next orgy. SCNR
Posted Feb 19, 2016 0:23 UTC (Fri)
by
Posted Feb 13, 2016 23:35 UTC (Sat)
by
Those "As Seen on TV" bits should be viewed in light of being targeted at those with disabilities or handicaps. The reason they show normal people purposefully failing is because someone with Parkinson's failing to cleanly break an egg is not something anyone wants to tape, be taped doing, or watch.
Posted Feb 14, 2016 2:51 UTC (Sun)
by
Posted Feb 12, 2016 19:02 UTC (Fri)
by Pretty much. Most of them are relatively simple mechanical tools for performing mechanical tasks- chopping, mixing, blending, etc.- so that there isn't a huge amount to change. They seem to do a few basic things- changing cosmetics, expanding the product line to larger or smaller models, making the motor more powerful, or just trying to squeeze out production costs- that don't change the basic functions. There is some genuine innovation out there- I've been amazingly happy with my induction range, which is a huge advance over conventional electric stoves- but it happens much slower than in tech.
Posted Feb 13, 2016 5:13 UTC (Sat)
by
Not quite. The Panasonic "inverter" ovens (and their licensees) do a credible job of running at partial power.
Posted Feb 13, 2016 7:45 UTC (Sat)
by Interesting... I was thinking of inventing a microwave oven with two independently-controlled magnetrons, each with a different thermal power rating (e.g. 400W and 700W). Any combination of running either/both could give three different heating states (approx. 1/3, 2/3, and full power). Running one continuously and the other toggling on/off (partial load) could give even more discrete power levels. Of course, there's the unwritten postulate that the complexity of mechanical devices with
Posted Feb 17, 2016 23:58 UTC (Wed)
by
Posted Feb 20, 2016 22:46 UTC (Sat)
by Dammit, Jim, I'm a computer scientist, not an electrical engineer with a background in microwave propagation effects! ;-) Of course, my "invention" was just a thought-concept; the scenario you just described succinctly (and graphically) describes why such a microwave oven has not been introduced. Like I said, for A sincere thank you for enlightening me. :-)
Posted Feb 16, 2016 16:18 UTC (Tue)
by
Went back to a more straightforward on-off microwave, which is is still going fine after 3 years.
KISS, indeed.
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**robbe** (guest, #16131)
[[Link](/Articles/675326/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**Wol** (subscriber, #4433)
[[Link](/Articles/676507/)]
Wol
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**fratti** (guest, #105722)
[[Link](/Articles/675334/)] (9 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**raven667** (subscriber, #5198)
[[Link](/Articles/675374/)] (7 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**rgmoore** (**✭ supporter ✭**, #75)
[[Link](/Articles/675392/)]
I actually find that for many appliances, they really peaked in the 1950s and the actual utility has been on a plateau or decline since then.
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**bronson** (subscriber, #4806)
[[Link](/Articles/675398/)] (3 responses)
[https://productforums.google.com/forum/#!topic/calendar/U...](https://productforums.google.com/forum/#!topic/calendar/UhfpcwO0X0c)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**nye** (guest, #51576)
[[Link](/Articles/676217/)] (2 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**spaetz** (guest, #32870)
[[Link](/Articles/676226/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**dfsmith** (guest, #20302)
[[Link](/Articles/676333/)]
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**mathstuf** (subscriber, #69389)
[[Link](/Articles/675537/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**raven667** (subscriber, #5198)
[[Link](/Articles/675546/)]
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**rgmoore** (**✭ supporter ✭**, #75)
[[Link](/Articles/675388/)]
A lot of home appliances have come to a state where it would take some serious engineering to make a substantial improvement over previous models (which is expensive), so to keep up a fake air of technological evolution (as we've come to expect it from other devices such as computers or phones), they just tack things on that makes them look more advanced than it really is.
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**luto** (subscriber, #39314)
[[Link](/Articles/675468/)] (4 responses)
[
]## Partial-power microwave oven
**pr1268** (subscriber, #24648)
[[Link](/Articles/675475/)] (2 responses)
Not quite. The Panasonic "inverter" ovens (and their licensees) do a credible job of running at partial power.
*n* parts is O(*n*1.5). Or thereabouts. Adding another magnetron would make the microwave oven unnecessarily more complicated. Oh, well...[
]
So here you have two magnetrons relatively tightly coupled, resonant at approximately the same frequency, one powered and one unpowered. To me it seems the unpowered magnetron acts as an ideal resonant antenna to receive RF power from the powered magnetron. Even if the unpowered magnetron is connected to an open circuit, I'd expect significant currents and waste heat generation.
If both magnetrons are powered and coherent (same frequency), then synchronization of their output might be tricky - they would have to be in the same phase, or they would be exchanging a lot of power one to the other. The fact one is twice the power of the second could mean the large magnetron may burn up the smaller magnetron or send current back into its power supply.
Maybe you could detune them (different frequencies) and/or use a cavity resonator as a narrow pass filter so that one magnetron isn't very much affected by the other. Cavity resonators would add mass and size and no doubt reduce efficiency by producing still more heat.
Just thinking...
## Partial-power microwave oven
**opalmirror** (subscriber, #23465)
[[Link](/Articles/676158/)] (1 responses)
[
]## Partial-power microwave oven
**pr1268** (subscriber, #24648)
[[Link](/Articles/676604/)]
Cavity resonators would add mass and size and no doubt reduce efficiency by producing still more heat.
*n* extra parts, O(*n*1.5) complexity...[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**sdalley** (subscriber, #18550)
[[Link](/Articles/675796/)]
### A Linux-powered microwave oven
Posted Feb 11, 2016 23:33 UTC (Thu)
by **dlang** (guest, #313)
[[Link](/Articles/675268/)] (4 responses)
Posted Feb 11, 2016 23:33 UTC (Thu)
by **dlang** (guest, #313)
[[Link](/Articles/675268/)] (4 responses)
unlikely, not because the controls aren't precise enough, but rather because the heat generated is so uneven. This is why most microwaves have turntables in them, to try and move the food around through the hot/cold spots.
Microwaves operate at ~2.4GHz and the wavelength at that frequency is ~5 inches, so your hot spots are going to end up far enough apart that they won't be solved by natural convection through the item being heated.
Posted Feb 12, 2016 11:20 UTC (Fri)
by
Posted Feb 12, 2016 19:05 UTC (Fri)
by
It's about as good as you can reasonably get... If microwaves were spherical and had multiple entry horns (not sure the correct term) then they could cook a little better but, of course, they'd be much harder to package and produce. And there would still be hot and cold spots -- uneven heating is as much a feature of the food as the oven.
Maybe one day we'll have variable-frequency phased array microwaves that use feedback to direct heat right to the cool spots. (dibs on the patent!)
Posted Feb 12, 2016 20:32 UTC (Fri)
by
Posted Feb 13, 2016 16:05 UTC (Sat)
by
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**johill** (subscriber, #25196)
[[Link](/Articles/675308/)] (3 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**bronson** (subscriber, #4806)
[[Link](/Articles/675389/)] (2 responses)
[http://ffden-2.phys.uaf.edu/104_spring2004.web.dir/arts_m...](http://ffden-2.phys.uaf.edu/104_spring2004.web.dir/arts_mcnulty/howmicrowaveovenswork.htm)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**boog** (subscriber, #30882)
[[Link](/Articles/675409/)] (1 responses)
[
]## A Linux-powered microwave oven
**flussence** (guest, #85566)
[[Link](/Articles/675494/)]
### A Linux-powered microwave oven
Posted Feb 15, 2016 14:15 UTC (Mon)
by **ortalo** (guest, #4654)
[[Link](/Articles/675648/)]
Posted Feb 15, 2016 14:15 UTC (Mon)
by **ortalo** (guest, #4654)
[[Link](/Articles/675648/)]
Please, do not forget to include an instance of a decent security kernel able to *prohibit* the development and installation of and computer game on the oven touch screen interface, especially those of the variety involving throwing distinguised species of volatiles or mammals onto each others and their baricades.
If you fail that, your loved one and yourself will lament all day on the unavailability of all the kitchen devices and the incredible overheads added to all day to day operations around breakfast, lunch, dinner - due to preemption by your own (little) loved ones. |
7,450 | 4 个顶级的开源问题跟踪管理工具 | https://opensource.com/business/16/2/top-issue-support-and-bug-tracking-tools | 2016-06-11T11:26:31 | [
"Redmine",
"Bugzilla",
"Trac",
"Mantis"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7450-1.html | 
生活充满了bug。
无论怎样小心计划,无论花多少时间去设计,在执行阶段实际执行时,任何工程都会有未知的问题。也无妨。也许对于任何一个组织的最佳弹性衡量不是他们如何一切都按计划运行地处理事情,而是,当出现磕磕碰碰时他们如何驾驭。
对任何一个项目管理流程来说,特别是在软件开发领域,都需要一个关键工具——问题跟踪管理系统。其基本功能很简单:可以对bug进行查看、追踪,并以协作的方式解决bug,有了它,我们更容易跟随整个过程的进展。除了基本功能,还有很多专注于满足特定需求的选项及功能,使用场景不仅限于软件开发。你可能已经熟悉某些托管版本的工具,像 [GitHub Issues](https://guides.github.com/features/issues/)或者[Launchpad](https://launchpad.net/),其中一些工具已经有了自己的开源社区。
接下来,这四个bug问题跟踪管理软件的极佳备选,全部开源、易于下载,自己就可以部署。先说好,我们可能没有办法在这里列出每一个问题跟踪工具;相反,我们列出这四个,原因基于是其丰富的功能和项目背后的社区规模。当然,肯定还有其他类似软件,如果你喜欢的没有列在这里,如果你有一个好的理由,一定要让我们知道,在下面的评论中使它脱颖而出吧。
### Redmine
[Redmine](http://www.redmine.org/) 是一个很流行的追踪管理工具,基于Ruby on Rails构建,可以追溯到2006年。很多方面类似于Trac(另一个我们的最爱),Redmine可以管理多个项目,整合了多种版本控制系统。除了基本问题追踪,Redmine也提供论坛,wiki,时间跟踪工具,同时,它还具有生成<ruby> 甘特图表 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Gantt charts </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和日历的能力,用来跟踪项目的进展。
Redmine的设置相当灵活,支持多种数据库后端和几十种语言,还是可定制的,可以向<ruby> 问题 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> issue </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、用户、工程等添加自定义字段。通过社区创建的插件和主题它可以进一步定制。
如果你想试一试,一个[在线演示](http://demo.redmine.org/)可提供使用。Redmine采用[GPL版本2](http://www.gnu.org/licenses/old-licenses/gpl-2.0.en.html)许可证;开源代码可以在工程的[svn仓库](https://svn.redmine.org/redmine)或在[GitHub](https://github.com/redmine/redmine)镜像上找到。

### Bugzilla
[Bugzilla](https://www.bugzilla.org/)是另一个流行的具备问题跟踪能力的开发工具。从名字您可能已经猜到了,Bugzilla最初是[Mozilla基金会](https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/)创建的,用来跟踪当时称为网景通信套件中的bug。为了更好的可读性,它从原来的Tcl移植到Perl,Bugzilla是一个比较老,但却广泛采用的问题跟踪系统,它被用在许多著名的开源项目如GNOME、KDE,以及Linux内核本身。
从通知到重复bug检测再到搜索共享,Bugzilla拥有许多高级工具,是一个功能更丰富的选项。Bugzilla拥有一套高级搜索系统以及全面的报表工具,具有生成图表和自动化按计划生成报告的能力。像Redmine一样,Bugzilla是可扩展和可定制的,除了字段本身,还能针对bug创建自定义工作流。它也支持多种后端数据库,和自带的多语言支持。
Bugzilla采用[Mozilla公共许可证](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mozilla_Public_License),你可以读取他们的[未来路线图](https://www.bugzilla.org/status/roadmap.html)还有在官网尝试一个[示例服务](https://landfill.bugzilla.org/)

### Trac
[Trac](http://trac.edgewall.org/browser)自称是基于web的极简主义软件工程管理软件,这里请不要混淆极简主义与缺乏功能。
由python编写的Trac,将其漏洞跟踪能力与它的wiki系统和版本控制系统轻度整合。项目管理能力突出,如生成里程碑和路线图,一个可定制的报表系统,大事记,支持多资源库,内置的垃圾邮件过滤,还可以使用很多通用语言。如其他我们已经看到的漏洞追踪软件,有很多插件可进一步扩展其基本特性。
Trac以[改进的BSD许可协议](http://trac.edgewall.org/wiki/TracLicense)开源,虽然更老的版本发布在GPL下。你可以在一个[自托管仓库](http://trac.edgewall.org/browser)预览Trac的源码或者查看他们的[路线图](http://trac.edgewall.org/wiki/TracRoadmap)对未来的规划。

### Mantis
[Mantis](https://www.mantisbt.org/)是这次合集中我们将看到的最后一个工具,基于PHP,且有16年历史。作为另一个支持多种不同版本控制系统和事件驱动通知系统的bug跟踪管理软件,Mantis有一个与其他工具类似的功能设置。虽然它不本身包含wiki,但它整合了很多流行的wiki平台且本地化到多种语言。
Mantis使用[GPL版本2](http://www.gnu.org/licenses/old-licenses/gpl-2.0.en.html)开源许可证书;你可以在[GitHub](https://github.com/mantisbt/mantisbt)浏览他的源代码或查看自托管[路线图](https://www.mantisbt.org/bugs/roadmap_page.php?project=mantisbt&version=1.3.x)对未来的规划。一个示例,你可以查看他们的内部[漏洞跟踪](https://www.mantisbt.org/bugs/my_view_page.php)。

正如我们指出的,这四个不是唯一的选项。想要探索更多?[Apache Bloodhound](https://issues.apache.org/bloodhound/),[Fossil](http://fossil-scm.org/index.html/doc/trunk/www/index.wiki),[The Bug Genie](http://www.thebuggenie.com/),还有很多可替换品都有自己的忠实追随者,每个都有不同的优点和缺点。另外,一些工具在我们[项目管理](https://opensource.com/business/15/1/top-project-management-tools-2015)摘要有问题跟踪功能。所以,哪个是你首选的跟踪和碾压bug的工具?
---
via: <https://opensource.com/business/16/2/top-issue-support-and-bug-tracking-tools>
作者:[Jason Baker](https://opensource.com/users/jason-baker) 译者:[wyangsun](https://github.com/wyangsun) 校对:[Mr小眼儿](https://github.com/tinyeyeser)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Life is full of bugs.
No matter how carefully planned, no matter how much time went into design, any project is going to have unforseen issues when the rubber hits the road in the implementation stage. And that's okay. Perhaps the best measure of resiliency for any organization is not how well they handle things when everything is functioning as planned, but rather, how they handle the speed bumps when they come along.
A critical tool for any project management workflow, especially in the software development world, is an issue tracker. The basics are simple; allowing bugs to be opened, tracked, and resolved in a collaborative manner, while making it easy to follow the progress. Beyond the basic functionality, there are a lot of options focused on meeting specific needs, features, and use cases, including software development and beyond. You may be familiar with hosted versions of these tools, like [JIRA](https://www.atlassian.com/software/jira), [GitHub Issues](https://guides.github.com/features/issues/) or [Launchpad](https://launchpad.net/), some of which themselves have connections to the open source community.
So let's take a look at four excellent choices for managing bugs and issues, all open source and all easy to download and host yourself. To be clear, there's no way we could possibly list every issue tracking tool here; instead, these are four of our favorites, based on feature richness and the size of the community behind the project. There are others, to be sure, and if you've got a good case for your favorite not listed here, be sure to let us know which is your favorite tool and what makes it stand out to you, in the comments below.
## Redmine
[Redmine](http://www.redmine.org/) is a popular issue tracking tool built on Ruby on Rails and dating back to 2006. Similar in many regards to Trac, another one of our favorites, Redmine is capable of managing multiple projects and integrates with a number of version control systems. In addition to basic issue tracking, Redmine also offers forums, wikis, time tracking tools, and the ability to generate Gantt charts and calendars to track progress.
Redmine is fairly flexible in its setup, supporting numerous database backends and dozens of languages, and is customizable as well, featuring the ability to add custom fields to issues, users, projects and more. It can be further customized with a number of community-created plugins and themes.
An [online demo](http://demo.redmine.org/) is available if you’d like to try it out. Redmine is licensed as open source under the [GPL version 2](http://www.gnu.org/licenses/old-licenses/gpl-2.0.en.html); the source code can be found in the project’s [subversion repository](https://svn.redmine.org/redmine) or mirrored on [GitHub](https://github.com/redmine/redmine).
## Bugzilla
[Bugzilla](https://www.bugzilla.org/) is another popular development tool with issue tracking capabilities. As you might have guessed from the name, Bugzilla was originally created by the [Mozilla Foundation](https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/) to track bugs in the development of the then-called Netscape Communicator suite. Ported to Perl from its original Tcl routes for greater accessibility, Bugzilla is one of the older and more widely adopted issue tracking systems, as it is used by a number of well-known open source projects like GNOME, KDE, and the Linux kernel itself.
Sporting a number of advanced tools, from notifications to duplicate bug detection to shared searches, Bugzilla is certainly a more feature-rich option. Bugzilla has an advanced search system along with a comprehensive reporting tool, capable of generating charts and automated scheduled reports. Like Redmine, Bugzilla is extensible and customizable, both in the fields themselves as well as featuring the ability to create custom workflows for bugs. It also works with many database backends, and many different languages are supported out of the box.
Bugzilla is licensed under the [Mozilla Public License](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mozilla_Public_License), and you can read their [future roadmap](https://www.bugzilla.org/status/roadmap.html) and try out a [demo server](https://landfill.bugzilla.org/) on the official website.
## Trac
[Trac](http://trac.edgewall.org/browser) describes itself as taking a minimalistic approach to web-based software project management, but don’t confusing minimalism with a lack of features.
Written in Python, Trac tightly integrates its bug tracking capabilities with its wiki system and a revision control system of your choosing. It features project management capabilities like generating milestones and roadmaps, a customizable reporting system, timelines, support for multiple repositories, built-in spam filtering, and is available in many common languages. Like the other bug trackers we have looked at, has a number of plugins available for it extending its base feature set even further.
Trac is made available as open source under a modified [BSD license](http://trac.edgewall.org/wiki/TracLicense), though older versions were released under the GPL. You can view Trac’s source in a [self-hosted repository](http://trac.edgewall.org/browser) or check out their [roadmap](http://trac.edgewall.org/wiki/TracRoadmap) for future plans.
## Mantis
[Mantis](https://www.mantisbt.org/) is the final tool we’ll look at in this collection, a PHP-based bug tracker with a sixteen year history. Another bug tracker with support for many different revision control systems and an event-driven notification system, Mantis has a similar feature set to other tools here. While it does not itself contain a wiki, it integrates with many popular wiki platforms and is localized into many languages.
Mantis is licensed as open source under the [GPL version 2](http://www.gnu.org/licenses/old-licenses/gpl-2.0.en.html); you can browse its source code on [GitHub](https://github.com/mantisbt/mantisbt) or check out the self-hosted [roadmap](https://www.mantisbt.org/bugs/roadmap_page.php?project=mantisbt&version=1.3.x) for future plans. For a demo, you can check out their own internal [bug tracker](https://www.mantisbt.org/bugs/my_view_page.php).
As we note, these four are not the only options. Looking to explore some others? [Apache Bloodhound](https://issues.apache.org/bloodhound/), [Fossil](http://fossil-scm.org/index.html/doc/trunk/www/index.wiki), [The Bug Genie](http://www.thebuggenie.com/), and many alternatives all have dedicated followings, each with different strengths and weaknesses. In addtion, some of the tools in our [project management roundup](https://opensource.com/business/15/1/top-project-management-tools-2015) have issue tracking capabilities. So, which is your preferred tool for tracking and squashing bugs?
## 19 Comments |
7,455 | LFCS 系列第九讲: 使用 Yum、RPM、Apt、Dpkg、Aptitude 进行 Linux 软件包管理 | http://www.tecmint.com/linux-package-management/ | 2016-06-13T08:24:00 | [
"LFCS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7455-1.html | 去年八月, Linux基金会宣布了一个全新的LFCS(<ruby> Linux基金会认证系统管理员 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)认证计划,这对广大系统管理员来说是一个很好的机会,管理员们可以通过认证考试来表明自己可以成功支持Linux系统的整体运营。 一个Linux基金会认证的系统管理员能有足够的专业知识来确保系统高效运行,提供第一手的故障诊断和监视,并且在需要的情况下将问题提交给工程师支持团队。

*Linux基金会认证系统管理员 – 第九讲*
请观看下面关于Linux基金会认证计划的演示。
本文是本系列教程中的第九讲,今天在这篇文章中我们会引导你学习Linux软件包管理,这也是LFCS认证考试所需要的。
### 软件包管理
简单的说,软件包管理是系统中安装和维护软件的一种方法,这里说的维护包含更新和卸载。
在Linux早期,程序只以源代码的方式发行,还带有所需的用户使用手册和必备的配置文件,甚至更多。现如今,大多数发行商一般使用预装程序或者被称为软件包的程序集合。用户可以使用这些预装程序或者软件包安装到该发行版中。然而,Linux最伟大的一点是我们仍然能够获得程序的源代码用来学习、改进和编译。
#### 软件包管理系统是如何工作的
如果某一个软件包需要一定的资源,如共享库,或者需要另一个软件包,这就称之为依赖性。所有现在的包管理系统提供了一些解决依赖性的方法,以确保当安装一个软件包时,相关的依赖包也安装好了。
#### 打包系统
几乎所有安装在现代Linux系统上的软件都会能互联网上找到。它要么由发行商通过中央仓库(中央仓库能包含几千个软件包,每个软件包都已经为发行版构建、测试并且维护好了)提供,要么能够直接得到可以下载和手动安装的源代码。
由于不同的发行版使用不同的打包系统(Debian的\*.deb文件/CentOS的\*.rpm文件/openSUSE的专门为openSUSE构建的\*.rpm文件),因此为一个发行版开发的软件包会与其他发行版不兼容。然而,大多数发行版都属于LFCS认证所涉及的三个发行版家族之一。
#### 高级和低级打包工具
为了有效地进行软件包管理的任务,你需要知道,有两种类型的实用工具:低级工具(能在后端实际安装、升级、卸载软件包文件),以及高级工具(负责确保能很好的执行依赖性解决和元数据检索的任务——元数据也称为数据的数据)。
| 发行版 | 低级工具 | 高级工具 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| Debian版及其衍生版 | dpkg | apt-get / aptitude |
| CentOS版 | rpm | yum |
| openSUSE版 | rpm | zypper |
让我们来看下低级工具和高级工具的描述。
dpkg的是基于Debian的系统的一个低级包管理器。它可以安装,删除,提供有关资料,以及建立\*.deb包,但它不能自动下载并安装它们相应的依赖包。
* 阅读更多: [15个dpkg命令实例](http://www.tecmint.com/dpkg-command-examples/)
apt-get是Debian及其衍生版的高级包管理器,并提供命令行方式来从多个来源检索和安装软件包,其中包括解决依赖性。和dpkg不同的是,apt-get不是直接基于.deb文件工作,而是基于软件包的正确名称。
* 阅读更多: [25个apt-get命令实例](http://www.tecmint.com/useful-basic-commands-of-apt-get-and-apt-cache-for-package-management/)
Aptitude是基于Debian的系统的另一个高级包管理器,它可用于快速简便的执行管理任务(安装,升级和删除软件包,还可以自动处理解决依赖性)。它在atp-get的基础上提供了更多功能,例如提供对软件包的几个版本的访问。
rpm是Linux标准基础(LSB)兼容发行版所使用的一种软件包管理器,用来对软件包进行低级处理。就像dpkg一样,rpm可以查询、安装、检验、升级和卸载软件包,它多数用于基于Fedora的系统,比如RHEL和CentOS。
* 阅读更多: [20个rpm命令实例](http://www.tecmint.com/20-practical-examples-of-rpm-commands-in-linux/)
相对于基于RPM的系统,yum增加了系统自动更新的功能和带依赖性管理的软件包管理功能。作为一个高级工具,和apt-get或者aptitude相似,yum需要配合仓库工作。
* 阅读更多: [20个yum命令实例](http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/)
### 低级工具的常见用法
使用低级工具处理最常见的任务如下。
#### 1. 从已编译(\*.deb或\*.rpm)的文件安装一个软件包
这种安装方法的缺点是没有提供解决依赖性的方案。当你在发行版本库中无法获得某个软件包并且又不能通过高级工具下载安装时,你很可能会从一个已编译文件安装该软件包。因为低级工具不会解决依赖性问题,所以当安装一个没有解决依赖性的软件包时会出现出错并且退出。
```
# dpkg -i file.deb [Debian版和衍生版]
# rpm -i file.rpm [CentOS版 / openSUSE版]
```
**注意**:不要试图在CentOS中安装一个为openSUSE构建的.rpm文件,反之亦然!
#### 2. 从已编译文件中更新一个软件包
同样,当某个安装的软件包不在中央仓库中时,你只能手动升级该软件包。
```
# dpkg -i file.deb [Debian版和衍生版]
# rpm -U file.rpm [CentOS版 / openSUSE版]
```
#### 3. 列举安装的软件包
当你第一次接触一个已经在工作中的系统时,很可能你会想知道安装了哪些软件包。
```
# dpkg -l [Debian版和衍生版]
# rpm -qa [CentOS版 / openSUSE版]
```
如果你想知道一个特定的软件包安装在哪儿,你可以使用管道命令从以上命令的输出中去搜索,这在这个系列的[第一讲 操作Linux文件](/article-7161-1.html) 中有介绍。例如我们需要验证mysql-common这个软件包是否安装在Ubuntu系统中:
```
# dpkg -l | grep mysql-common
```

*检查安装的软件包*
另外一种方式来判断一个软件包是否已安装。
```
# dpkg --status package_name [Debian版和衍生版]
# rpm -q package_name [CentOS版 / openSUSE版]
```
例如,让我们找出sysdig软件包是否安装在我们的系统。
```
# rpm -qa | grep sysdig
```

*检查sysdig软件包*
#### 4. 查询一个文件是由哪个软件包安装的
```
# dpkg --search file_name
# rpm -qf file_name
```
例如,pw\_dict.hwm文件是由那个软件包安装的?
```
# rpm -qf /usr/share/cracklib/pw_dict.hwm
```

*Linux中查询文件*
### 高级工具的常见用法
使用高级工具处理最常见的任务如下。
#### 1. 搜索软件包
aptitude的更新操作将会更新可用的软件包列表,而aptitude的搜索操作会根据软件包名进行实际搜索。
```
# aptitude update && aptitude search package_name
```
在search all选项中,yum不仅可以通过软件包名还可以通过软件包的描述搜索。
```
# yum search package_name
# yum search all package_name
# yum whatprovides “*/package_name”
```
假定我们需要一个名为sysdig文件,想知道我们需要安装哪个软件包才行,那么运行。
```
# yum whatprovides “*/sysdig”
```

*检查软件包描述*
whatprovides告诉yum搜索一个含有能够匹配上述正则表达式的文件的软件包。
```
# zypper refresh && zypper search package_name [在openSUSE上]
```
#### 2. 从仓库安装一个软件包
当安装一个软件包时,在软件包管理器解决了所有依赖性问题后,可能会提醒你确认安装。需要注意的是运行更新( update)或刷新(refresh)(根据所使用的软件包管理器)不是绝对必要,但是考虑到安全性和依赖性的原因,保持安装的软件包是最新的是系统管理员的一个好经验。
```
# aptitude update && aptitude install package_name [Debian版和衍生版]
# yum update && yum install package_name [CentOS版]
# zypper refresh && zypper install package_name [openSUSE版]
```
#### 3. 卸载软件包
remove选项将会卸载软件包,但把配置文件保留完好,然而purge选项将从系统中完全删去该程序以及相关内容。
```
# aptitude remove / purge package_name
# yum erase package_name
###---注意要卸载的openSUSE包前面的减号 ---
# zypper remove -package_name
```
在默认情况下,大部分(如果不是全部的话)的软件包管理器会提示你,在你实际卸载之前你是否确定要继续卸载。所以,请仔细阅读屏幕上的信息,以避免陷入不必要的麻烦!
#### 4. 显示软件包的信息
下面的命令将会显示birthday这个软件包的信息。
```
# aptitude show birthday
# yum info birthday
# zypper info birthday
```

*检查包信息*
### 总结
作为一个系统管理员,软件包管理器是你不能回避的东西。你应该立即去使用本文中介绍的这些工具。希望你在准备LFCS考试和日常工作中会觉得这些工具好用。欢迎在下面留下您的意见或问题,我们将尽可能快的回复你。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/linux-package-management/>
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa](http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/) 译者:[Flowsnow](https://github.com/Flowsnow) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,456 | 在 Linux 下使用 scp 命令 | https://www.unixmen.com/scp-command-linuxunix/ | 2016-06-13T09:23:20 | [
"scp",
"cp",
"ssh"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7456-1.html | 
scp 是<ruby> 安全拷贝协议 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Secure Copy Protocol </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的缩写,和众多 Linux/Unix 使用者所熟知的拷贝(cp)命令一样。scp 的使用方式类似于 cp 命令,cp 命令将一个文件或文件夹从本地操作系统的一个位置(源)拷贝到目标位置(目的),而 scp 用来将文件或文件夹从网络上的一个主机拷贝到另一个主机当中去。
scp 命令的使用方法如下所示,在这个例子中,我将一个叫 “importantfile” 的文件从本机(10.10.16.147)拷贝到远程主机(10.0.0.6)中。在这个命令里,你也可以使用主机名字来替代IP地址。
```
[root@localhost ~]# scp importantfile [email protected]:/home/admin/
The authenticity of host '10.0.0.6 (10.0.0.6)' can't be established.
RSA key fingerprint is SHA256:LqBzkeGa6K9BfWWKgcKlQoE0u+gjorX0lPLx5YftX1Y.
RSA key fingerprint is MD5:ed:44:42:59:3e:dd:4c:12:43:4a:89:b1:5d:bd:9e:20.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '10.0.0.6' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
[email protected]'s password:
importantfile 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
[root@localhost ~]#
```
类似的,如果你想从一个远程主机中取得文件,你可以利用如下的 scp 命令。
```
[root@localhost ~]# scp [email protected]:/root/importantfile /home/admin/
The authenticity of host '10.10.16.137 (10.10.16.137)' can't be established.
RSA key fingerprint is b0:b0:a3:c3:2e:94:13:0c:29:2e:ba:0b:d3:d6:12:8f.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '10.10.16.137' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
[email protected]'s password:
importantfile 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
[root@localhost ~]#
```
你也可以像 cp 命令一样,在 scp 命令中使用不同的选项,scp 的 man 帮助详细地阐述了不同选项的用法和用处。
**示例输出**

scp 可选参数如下所示:
```
-B 采取批量模式(避免询问密码或口令)
-C 启用压缩。通过指明 -C 参数来开启压缩模式。
-c 加密方式
选择在传输过程中用来加密的加密方式 这个选项会被直接传递到 ssh(1)。
-F ssh 配置
给 ssh 指定一个用来替代默认配置的配置文件。这个选项会被直接传递到 ssh(1)。
-l 限速
限制命令使用的带宽,默认单位是 Kbit/s。
-P 端口
指定需要的连接的远程主机的端口。
注意,这个选项使用的是一个大写的“P”,因为小写的“-p”已经用来保留目标文件的时间和模式相关信息。(LCTT 译注:ssh 命令中使用小写的“-p”来指定目标端口。)
-p 保留文件原来的修改时间,访问时间以及权限模式。
-q 静默模式:不显示来自 ssh(1) 命令的进度信息,警告和诊断信息。
-r 递归拷贝整个目录。
注意,scp 命令在树形遍历的时候同样会跟随符号连接,复制所连接的文件。
-v 详细模式。scp 和 ssh(1) 将会打印出处理过程中的调试信息。这可以帮助你调试连接、认证和配置方面的问题。
```
**详细模式**
利用 scp 命令的 -v 选项,你可以得到认证、调试等的相关细节信息。

当我们使用 -v 选项的时候,一个简单的输出如下所示:
```
[root@localhost ~]# scp -v abc.txt [email protected]:/home/admin
Executing: program /usr/bin/ssh host 10.0.0.6, user admin,
command scp -v -t/home/admin
OpenSSH_7.1p1, OpenSSL 1.0.2d-fips 9 Jul 2015
debug1: Reading configuration data /etc/ssh/ssh_config
debug1: /etc/ssh/ssh_config line 56: Applying options for *
debug1: Connecting to 10.0.0.6 [10.0.0.6] port 22.
debug1: Connection established.
debug1: Server host key: ssh-rsa SHA256:LqBzkeGa6K9BfWWKgcKlQoE0u+gjorX0lPLx5YftX1Y
debug1: Next authentication method: publickey
debug1: Trying private key: /root/.ssh/id_rsa
debug1: Trying private key: /root/.ssh/id_dsa
debug1: Trying private key: /root/.ssh/id_ecdsa
debug1: Trying private key: /root/.ssh/id_ed25519
debug1: Next authentication method: password
[email protected]'s password:
debug1: Authentication succeeded (password).
Authenticated to 10.0.0.6 ([10.0.0.6]:22).
debug1: channel 0: new [client-session]
debug1: Requesting [email protected]
debug1: Entering interactive session.
debug1: Sending environment.
debug1: Sending command: scp -v -t /home/admin
Sending file modes: C0644 174 abc.txt
Sink: C0644 174 abc.txt
abc.txt 100% 174 0.2KB/s 00:00
Transferred: sent 3024, received 2584 bytes, in 0.3 seconds
Bytes per second: sent 9863.3, received 8428.1
debug1: Exit status 0
[root@localhost ~]#
```
当我们需要拷贝一个目录或者文件夹的时候,我们可以使用 -r 选项,它会递归拷贝整个目录。

**静默模式**
如果你想要关闭进度信息以及警告和诊断信息,你可以通过使用scp命令中的-q选项.

上一次我们仅仅使用 -r 参数,它显示了逐个文件的信息,但这一次当我们使用了 -q 参数,它就不显示进度信息。
利用 scp 的 -p 选项来保留目标文件的更新时间,访问时间和权限模式。

**通过 -P 选项来指定远程主机的连接端口**
scp 使用 ssh 命令来在两个主机之间传输文件,因为 ssh 默认使用的是22端口号,所以 scp 也使用相同的22端口号。
如果我们希望改变这个端口号,我们可以使用 -P(大写的 P,因为小写的 p 用来保持文件的访问时间等)选项来指定所需的端口号。
举个例子,如果我们想要使用2222端口号,我们可以使用如下的命令
```
[root@localhost ~]# scp -P 2222 abcd1 [email protected]:/root/
```
**限制命令使用的带宽,指定的单位是 Kbit/s**
如下所示,我们可以使用 -l 参数来指定 scp 命令所使用的带宽,在此我们将速度限制为512kbit/s。

**开启压缩**
如下所示,我们可以通过开启 scp 命令的压缩模式来节省传输过程中的带宽和时间。

**选择加密数据的加密方式**
scp 默认使用 AES-128 的加密方式,如果我们想要改变这个加密方式,可以通过 -c(小写的 c) 参数来指定其他的加密方式。

现在你可以利用 scp(Secure copy)命令在你所属网络中的两个节点之间安全地拷贝文件了。
---
via: <https://www.unixmen.com/scp-command-linuxunix/>
作者:[Naga Ramesh](https://www.unixmen.com/author/naga/) 译者:[lujianbo](https://github.com/lujianbo) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | **scp** means **Secure Copy Protocol**, and almost every Linux/Unix user knows how the cp command works.** scp** also works like** cp** command, cp command copies files or folders from one location i.e source to other location i.e target in local system, but scp copies the files from one host to another host in network.
The Secure Copy Protocol is essentially a network protocol that users can use if they want to securely copy files or folders between Linux or Unix systems on the same network. The scp command-line utility is known to be much safer than the cp utility.
The SCP command protects the data that you copy across systems using an SSH (Secure Shell) connection. SSH encrypts the files and passwords that are being transmitted, and therefore, even if another party intercepts the traffic, the information is unreadable since it is encrypted.
The SCP command is most commonly used when transferring sensitive information between systems.
**Syntax of the SCP Command**
Before learning to use the command, you must review the syntax. The command takes the following form:
scp [OPTION] [user@] SRC_HOST:lfile1 [user@]DEST_HOST:]file2
In the syntax:
- OPTION refers to the scp options, such as the limit, the cipher used, the SSH configuration, recursive copy and others
- [user@]SRC_HOST:lfile1 refers to the source file
- [user@]DEST_HOST:]file2 refers to the destination file
If you specify local files, you must use the absolute or relative path. On the other hand, when specifying remote files, you must include both user and host details.
The scp command has several options that you can use to control its behavior. The most commonly used options include:
**-c**: It forces the command to compress the data when sending to the destination**-r**: It instructs the command to copy the directories recursively**-q**: It suppresses the progress meter and also the non-error messages**-p**: It preserves the transferred file’s modification and access times**-P**: It specifies the remote host’s SSH port
We specify the full list of useable options for the scp command later in this post.
**What You Need to Know Before Using the SCP Command**
As mentioned earlier, the scp command relies on ssh to transfer data between machines. For this reason, it requires an SSH key to authenticate the transfer on remote systems.
The command uses the colon (:) to differentiate between the local and remote locations.
It’s important to note that to copy a file, you will at minimum require read permissions to the source file. Further, you will need write permission on the target system.
If you copy files with the same name and location on both systems, you must remember that the scp command will overwrite the files without alerting you.
Lastly, when using the command to transfer large files, it’s considered best practice to run the command inside a tmux session or a screen to avoid potential failure.
**How to Use the SCP Command**
The usage of the scp command is as follows, here i copy a file named importantfile from **local system**(10.10.16.147) to **Remote system**(10.0.0.6) here instead of ip address you can also use System name.
[root@localhost ~]# scp importantfile [email protected]:/home/admin/ The authenticity of host '10.0.0.6 (10.0.0.6)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is SHA256:LqBzkeGa6K9BfWWKgcKlQoE0u+gjorX0lPLx5YftX1Y. RSA key fingerprint is MD5:ed:44:42:59:3e:dd:4c:12:43:4a:89:b1:5d:bd:9e:20. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '10.0.0.6' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. [email protected]'s password: importantfile 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00 [root@localhost ~]#
Similarly if you want to get a file from remote system you can use scp command as follows
[root@localhost ~]# scp [email protected]:/root/importantfile /home/admin/ The authenticity of host '10.10.16.137 (10.10.16.137)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is b0:b0:a3:c3:2e:94:13:0c:29:2e:ba:0b:d3:d6:12:8f. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '10.10.16.137' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. [email protected]'s password: importantfile 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00 [root@localhost ~]#
You can also use various options along with** scp** command like **cp** command,The man page of the scp command clearly explain about the usage of various options and advantages of that.
**Sample Output.**
The options are as follows: -B Selects batch mode (prevents asking for passwords or passphrases). -C Compression enable. Passes the -C to enable compression. -c cipher Selects the cipher to use for encrypting the data transfer. This option is directly passed to ssh(1). -F ssh_config Specifies an alternative per-user configuration file for ssh. This option is directly passed to ssh(1). -l limit Limits the used bandwidth, specified in Kbit/s. -P port Specifies the port to connect to on the remote host. Note that this option is written with a capital ‘P’, because -p is already reserved for preserving the times and modes of the file. -p Preserves modification times, access times, and modes from the original file. -q Quiet mode: disables the progress meter as well as warning and diagnostic messages from ssh(1). -r Recursively copy entire directories. Note that scp follows sym‐ bolic links encountered in the tree traversal. -v Verbose mode. Causes scp and ssh(1) to print debugging messages about their progress. This is helpful in debugging connection, authentication, and configuration problems.
The scp command along with **-v** option you can get detailed information about authentication, debugging information etc.
Sample output is like when we pass the option **-v**
[root@localhost ~]# scp -v abc.txt [email protected]:/home/admin Executing: program /usr/bin/ssh host 10.0.0.6, user admin, command scp -v -t/home/admin OpenSSH_7.1p1, OpenSSL 1.0.2d-fips 9 Jul 2015 debug1: Reading configuration data /etc/ssh/ssh_config debug1: /etc/ssh/ssh_config line 56: Applying options for * debug1: Connecting to 10.0.0.6 [10.0.0.6] port 22. debug1: Connection established. debug1: Server host key: ssh-rsa SHA256:LqBzkeGa6K9BfWWKgcKlQoE0u+gjorX0lPLx5YftX1Y debug1: Next authentication method: publickey debug1: Trying private key: /root/.ssh/id_rsa debug1: Trying private key: /root/.ssh/id_dsa debug1: Trying private key: /root/.ssh/id_ecdsa debug1: Trying private key: /root/.ssh/id_ed25519 debug1: Next authentication method: password [email protected]'s password: debug1: Authentication succeeded (password). Authenticated to 10.0.0.6 ([10.0.0.6]:22). debug1: channel 0: new [client-session] debug1: Requesting [email protected] debug1: Entering interactive session. debug1: Sending environment. debug1: Sending command: scp -v -t /home/admin Sending file modes: C0644 174 abc.txt Sink: C0644 174 abc.txt abc.txt 100% 174 0.2KB/s 00:00 Transferred: sent 3024, received 2584 bytes, in 0.3 seconds Bytes per second: sent 9863.3, received 8428.1 debug1: Exit status 0 [root@localhost ~]#
If we need to copy the Directories or folders we can use the option –**r**. It Recursively copy entire directories
**Quiet mode:**
If you want disables the progress meter as well as warning and diagnostic messages pass the argument **-q** along with **scp** command.
last time we pass the argument **-r** only then it shows the information file by file, but when we pass the argument **-q** it disables the progress meter this time.
Preserves modification times, access times, and modes from the original file by passing the option **-p** along with scp.
** Specifies the port to connect to on the remote host by using the option -P.**
**scp** uses the **ssh** to transfer the files between hosts, ssh uses the **port number 22** so the scp also uses the same port number 22.
If we want to change the port number we can pass the particular port number along with -P(capital P because small p uses for preserving access time etc.)
for example if we want to use port number 2222 then the command is as follows
[root@localhost ~]# scp -P 2222 abcd1 [email protected]:/root/
**Limits the used bandwidth, specified in Kbit/s**
we can limit the bandwidth by using the argument **-l** option as follows. here i used the limit is 512kbit/s
**Compression enable**
we can enable the compression mode when we transfer the data through scp command to save tha bandwidth and time as follows
**Selects the cipher to use for encrypting the data**
By default scp uses AES-128, if we want to change the encryption then we can pass the argument -c(small c) along with scp.
Now you can transfer the files between different nodes in your network securely by using scp(Secure copy).
**Conclusion**
The scp command is recognized as an excellent alternative to FTP since it is inherently insecure. Since the command uses the regular command line and SSH, it provides a seamless command set for managing files.
If you intend to repeatedly transfer files between the same systems, consider simplifying your workflow by specifying all of the connections in the SSH config file. |
7,457 | 新的 Docker 数据中心管理套件使容器化变得更加井然有序 | http://techcrunch.com/2016/02/23/new-docker-data-center-admin-suite-should-bring-order-to-containerization/ | 2016-06-13T12:41:00 | [
"Docker"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7457-1.html | 
[Docker](https://www.docker.com/)之前发布了一个新的容器控制中心,称为Docker数据中心(DDC),其设计目的是用于大型和小型企业创建、管理和分发容器的一个集成管理控制台。
DDC是由包括Docker Universal Control Plane(也是同时发布的)和Docker Trusted Registry等不同的商业组件组成。它也包括了开源组件比如Docker Engine。这个产品让企业在一个中心管理界面中就可以管理整个Docker化程序的生命周期。
负责产品管理的SVP Scott Johnston告诉TechCrunch:“客户催使了这个新工具的产生。公司不仅喜欢Docker给他们带来的敏捷性,它们也希望在创建和分发容器的过程中可以进行对安全和管理进行控制。”
Johnston说:“公司称这个为容器即服务(Caas),主要是因为当客户来询问这种类型的管理面板时,他们是这样描述的。”

像许多开源项目那样,Docker首先获得了许多开发者的追随,但是随着它的流行,那些开发者们所在的公司也希望积极推进它的使用。
这就是DDC设计的目的。它给开发者创建容器化应用的敏捷性,也让运维变得井井有条。
实际上这意味着开发者可以创建一系列容器化的组件,将其部署后就可以访问一个完全认证的镜像库。这可以让开发人员用碎片组成应用而不必每次重新发明轮子。这可以加速应用的开发和部署(理论上提升了容器提供的灵活性)。
这方面吸引了Beta客户ADP。这个服务特别喜欢将这个提供给开发人员的中心镜像仓库。
ADP的CTO Keith Fulton在声明中称:“作为我们将关键业务微服务化倡议的一部分,ADP正在研究能够让开发人员可以利用IT审核过的中央库和安全的核心服务进行快速迭代的方案。”
Docker在2010年由dotcloud的Solomon Hykes发布。他在2013年将公司的重心移到Docker上,并在[8月出售了dotCloud](http://techcrunch.com/2014/08/04/docker-sells-dotcloud-to-cloudcontrol-to-focus-on-core-container-business/),2014年完全转移到Docker上。
根据CrunchBase的消息,公司几年来在5轮融资后势如破竹般获得了1亿8000万美元融资(自从成为Docker后获得了1亿6千8百万美元)。吸引投资者关注的是Docker提供了一种称为容器的现在分发应用的方式,可以构建、管理何分发分布式应用。
容器化可以让开发者创建由多个分布在不同服务器上的碎片组成的分布式应用,而不是一个运行在一个单独服务器上的独立应用。
DDC服务每月每节点150美金起。
---
via: <http://techcrunch.com/2016/02/23/new-docker-data-center-admin-suite-should-bring-order-to-containerization/>
作者:[Ron Miller](http://techcrunch.com/author/ron-miller/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,459 | 在 CentOS 7 CPanel 服务器上安装 MariaDB 10 | http://linoxide.com/how-tos/install-mariadb-10-centos-7-cpanel/ | 2016-06-14T13:57:00 | [
"MariaDB",
"MySQL"
] | /article-7459-1.html | MariaDB 是一个增强版的、开源的 MySQL 替代品。它主要由 MariaDB 社区在维护,采用 GPL v2 授权许可。软件的安全性是 MariaDB 开发者的主要焦点。他们保持为 MariaDB 的每个版本发布安全补丁。当有任何安全问题被发现时,开发者会尽快修复并推出 MariaDB 的新版本。
### MariaDB 的优势
* 完全开源
* 快速且透明的安全版本
* 与 MySQL 高度兼容
* 性能更好
* 比 MySQL 的存储引擎多
在这篇文章中,我将谈论关于如何在 CentOS7 CPanel 服务器上升级 MySQL5.5 到最新的 MariaDB 。在安装前先完成以下步骤。

### 先决条件:
#### 1. 停止当前 MySQL 服务
```
root@server1 [/var/]# mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 5859
Server version: 5.5.47-cll MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
root@server1 [~]# systemctl stop mysql
root@server1 [~]# systemctl status mysql
● mysql.service - LSB: start and stop MySQL
Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql)
Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Sun 2016-01-31 10:00:02 UTC; 1min 31s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Main PID: 23430 (code=exited, status=203/EXEC)
Jan 31 10:00:02 server1.centos7-test.com systemd[1]: Started MySQL Server.
Jan 31 10:00:02 server1.centos7-test.com systemd[1]: Starting MySQL Server...
Jan 31 10:00:02 server1.centos7-test.com systemd[1]: mysql.service: main process exited, code=exited, status=203/EXEC
Jan 31 10:00:02 server1.centos7-test.com systemd[1]: Unit mysql.service entered failed state.
Jan 31 10:00:02 server1.centos7-test.com systemd[1]: mysql.service failed.
```
#### 2. 在升级之前将所有配置文件和数据库转移
转移数据库的存储路径和 MySQL 的配置文件
```
root@server1 [~]# cp -Rf /var/lib/mysql /var/lib/mysql-old
root@server1 [/var/lib/mysql]# cat /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
default-storage-engine=MyISAM
innodb_file_per_table=1
max_allowed_packet=268435456
open_files_limit=10000
root@server1 [~]#mv /etc/my.cnf /etc/my.cnf-old
```
#### 3. 从服务器上删除和卸载 MySQL 所有的 RPM 包
运行以下命令来禁用 MySQL RPM 的<ruby> 目标 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> target </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。通过运行此命令,cPanel 将不再处理 MySQL 的更新,并在系统上将这些 RPM 版本标记为已卸载。
```
/scripts/update_local_rpm_versions --edit target_settings.MySQL50 uninstalled
/scripts/update_local_rpm_versions --edit target_settings.MySQL51 uninstalled
/scripts/update_local_rpm_versions --edit target_settings.MySQL55 uninstalled
/scripts/update_local_rpm_versions --edit target_settings.MySQL56 uninstalled
```
现在运行以下命令:
```
/scripts/checkcpanelrpms --fix --targets=MySQL50,MySQL51,MySQL55,MySQL56
```
移除服务器上所有已有的 MySQL RPM 来为 MariaDB 的安装清理环境。请看下面的输出:
```
root@server1 [/var/lib/mysql]# /scripts/check_cpanel_rpms --fix --targets=MySQL50,MySQL51,MySQL55,MySQL56
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000]
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] Problems were detected with cPanel-provided files which are RPM controlled.
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] If you did not make these changes intentionally, you can correct them by running:
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000]
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] > /usr/local/cpanel/scripts/check_cpanel_rpms --fix
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000]
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] The following RPMs are unneeded on your system and should be uninstalled:
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] MySQL55-client-5.5.47-1.cp1148
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] MySQL55-devel-5.5.47-1.cp1148
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] MySQL55-server-5.5.47-1.cp1148
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] MySQL55-shared-5.5.47-1.cp1148
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] MySQL55-test-5.5.47-1.cp1148
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] compat-MySQL50-shared-5.0.96-4.cp1136
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] compat-MySQL51-shared-5.1.73-1.cp1150
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] Removing 0 broken rpms:
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] rpm: no packages given for erase
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] No new RPMS needed for install
[2016-01-31 09:53:59 +0000] Disabling service monitoring.
[2016-01-31 09:54:01 +0000] Uninstalling unneeded rpms: MySQL55-test MySQL55-server MySQL55-client compat-MySQL51-shared compat-MySQL50-shared MySQL55-shared MySQL55-devel
[2016-01-31 09:54:04 +0000] Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mysql.service.
[2016-01-31 09:54:04 +0000] Restoring service monitoring.
```
通过这些步骤,我们已经卸载了现有的 MySQL RPM,并做了标记来防止 MySQL的更新,服务器的环境已经清理,然后准备安装 MariaDB。
开始安装吧,我们需要根据 CentOS 和 MariaDB 的版本为 MariaDB 创建一个 yum 软件库。下面是我的做法!
### 安装步骤:
#### 第1步:创建 YUM 软件库。
```
root@server1 [~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo
[mariadb]
name = MariaDB
baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.0/centos7-amd64/
gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
gpgcheck=1
root@server1 [/etc/yum.repos.d]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo
[mariadb]
name = MariaDB
baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.0/centos7-amd64/
gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
gpgcheck=1
```
#### 第2步:打开 /etc/yum.conf 并修改如下行:
**删除这一行:**
```
exclude=courier* dovecot* exim* filesystem httpd* mod_ssl* mydns* mysql* nsd* php* proftpd* pure-ftpd* spamassassin* squirrelmail*
```
**替换为:**
```
exclude=courier* dovecot* exim* filesystem httpd* mod_ssl* mydns* nsd* proftpd* pure-ftpd* spamassassin* squirrelmail*
```
**重要**
需要确保我们已经从 exclude 列表中移除了 MySQL 和 PHP。
#### 第3步:运行以下命令来安装 MariaDB 和相关的包。
```
root@server1 [~]#yum install MariaDB-server MariaDB-client MariaDB-devel php-mysql
Dependencies Resolved
===============================================================================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
===============================================================================================================================================
Installing:
MariaDB-client x86_64 10.0.23-1.el7.centos mariadb 10 M
MariaDB-devel x86_64 10.0.23-1.el7.centos mariadb 6.3 M
MariaDB-server x86_64 10.0.23-1.el7.centos mariadb 55 M
php-mysql x86_64 5.4.16-36.el7_1 base 99 k
Installing for dependencies:
MariaDB-common x86_64 10.0.23-1.el7.centos mariadb 43 k
MariaDB-shared x86_64 10.0.23-1.el7.centos mariadb 1.2 M
libzip x86_64 0.10.1-8.el7 base 48 k
php-common x86_64 5.4.16-36.el7_1 base 563 k
php-pdo x86_64 5.4.16-36.el7_1 base 97 k
Transaction Summary
===============================================================================================================================================
Install 4 Packages (+5 Dependent package)
```
#### 第4步:重新启动,并确保 MySQL 服务已启动。
```
root@server1 [~]# systemctl start mysql
root@server1 [~]#
root@server1 [~]#
root@server1 [~]# systemctl status mysql
● mysql.service - LSB: start and stop MySQL
Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql)
Active: active (exited) since Sun 2016-01-31 10:01:46 UTC; 3s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Process: 23717 ExecStart=/etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 23430 (code=exited, status=203/EXEC)
Jan 31 10:01:46 server1.centos7-test.com systemd[1]: Starting LSB: start and stop MySQL...
Jan 31 10:01:46 server1.centos7-test.com mysql[23717]: Starting MySQL SUCCESS!
Jan 31 10:01:46 server1.centos7-test.com systemd[1]: Started LSB: start and stop MySQL.
```
#### 第5步:运行 mysql\_upgrade 命令。
它将检查所有数据库中的所有表与当前安装的版本是否兼容,并在必要时会更新系统表,以赋予当前版本新增加的权限或能力。
```
root@server1 [~]# mysql_upgrade
MySQL upgrade detected
Phase 1/6: Checking and upgrading mysql database
Processing databases
mysql
mysql.columns_priv OK
mysql.db OK
mysql.event OK
mysql.func OK
mysql.help_category OK
mysql.help_keyword OK
mysql.help_relation OK
mysql.help_topic OK
mysql.host OK
mysql.ndb_binlog_index OK
mysql.plugin OK
mysql.proc OK
mysql.procs_priv OK
mysql.proxies_priv OK
mysql.servers OK
mysql.tables_priv OK
mysql.time_zone OK
mysql.time_zone_leap_second OK
mysql.time_zone_name OK
mysql.time_zone_transition OK
mysql.time_zone_transition_type OK
mysql.user OK
Phase 2/6: Fixing views from mysql
Phase 3/6: Running 'mysql_fix_privilege_tables'
Phase 4/6: Fixing table and database names
Phase 5/6: Checking and upgrading tables
Processing databases
cphulkd
cphulkd.auths OK
cphulkd.blacklist OK
cphulkd.brutes OK
cphulkd.good_logins OK
cphulkd.ip_lists OK
cphulkd.known_netblocks OK
cphulkd.login_track OK
cphulkd.logins OK
cphulkd.report OK
cphulkd.whitelist OK
eximstats
eximstats.defers OK
eximstats.failures OK
eximstats.sends OK
eximstats.smtp OK
information_schema
leechprotect
leechprotect.hits OK
modsec
modsec.hits OK
performance_schema
roundcube
roundcube.cache OK
roundcube.cache_index OK
roundcube.cache_messages OK
roundcube.cache_shared OK
roundcube.cache_thread OK
roundcube.contactgroupmembers OK
roundcube.contactgroups OK
roundcube.contacts OK
roundcube.cp_schema_version OK
roundcube.dictionary OK
roundcube.identities OK
roundcube.searches OK
roundcube.session OK
roundcube.system OK
roundcube.users OK
saheetha_test
saheetha_test.authors OK
whmxfer
whmxfer.sessions OK
Phase 6/6: Running 'FLUSH PRIVILEGES'
OK
```
#### 第6步:再次重新启动 MySQL 的服务,以确保一切都运行完好。
```
root@server1 [~]# systemctl restart mysql
root@server1 [~]#
root@server1 [~]# systemctl status mysql
● mysql.service - LSB: start and stop MySQL
Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2016-01-31 10:04:11 UTC; 9s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Process: 23831 ExecStop=/etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql stop (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 23854 ExecStart=/etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 23430 (code=exited, status=203/EXEC)
CGroup: /system.slice/mysql.service
├─23861 /bin/sh /usr/bin/mysqld_safe --datadir=/var/lib/mysql --pid-file=/var/lib/mysql/server1.centos7-test.com.pid
└─23933 /usr/sbin/mysqld --basedir=/usr --datadir=/var/lib/mysql --plugin-dir=/usr/lib64/mysql/plugin --user=mysql --log-error=/v...
Jan 31 10:04:10 server1.centos7-test.com systemd[1]: Starting LSB: start and stop MySQL...
Jan 31 10:04:11 server1.centos7-test.com mysql[23854]: Starting MySQL. SUCCESS!
Jan 31 10:04:11 server1.centos7-test.com systemd[1]: Started LSB: start and stop MySQL.
```
#### 第7步:运行 EasyApache,重建 Apache/PHP 以支持 MariaDB,并确保所有 PHP 的模块保持不变。
```
root@server1 [~]#/scripts/easyapache --build
```
**重要**
如果你在安装 MariaDB 之后忘记重建 Apache/PHP,将会报如下库错误:
```
root@server1 [/etc/my.cnf.d]# php -v
php: error while loading shared libraries: libmysqlclient.so.18: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
```
#### 第8步:现在验证安装的程序和数据库。
```
root@server1 [/var/lib/mysql]# mysql
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 15
Server version: 10.0.23-MariaDB MariaDB Server
Copyright (c) 2000, 2015, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> show storage engines;
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| Engine | Support | Comment | Transactions | XA | Savepoints |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| CSV | YES | CSV storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| MRG_MyISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO |
| MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables | NO | NO | NO |
| BLACKHOLE | YES | /dev/null storage engine (anything you write to it disappears) | NO | NO | NO |
| MyISAM | YES | MyISAM storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| InnoDB | DEFAULT | Percona-XtraDB, Supports transactions, row-level locking, and foreign keys | YES | YES | YES |
| ARCHIVE | YES | Archive storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| FEDERATED | YES | FederatedX pluggable storage engine | YES | NO | YES |
| PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | YES | Performance Schema | NO | NO | NO |
| Aria | YES | Crash-safe tables with MyISAM heritage | NO | NO | NO |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
```
就这样 :)。现在,我们该去欣赏 MariaDB 完善和高效的特点了。希望你喜欢阅读本文。希望留下您宝贵的建议和反馈!
---
via: <http://linoxide.com/how-tos/install-mariadb-10-centos-7-cpanel/>
作者:[Saheetha Shameer](http://linoxide.com/author/saheethas/) 译者:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/strugglingyouth) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPConnectionPool(host='linoxide.com', port=80): Max retries exceeded with url: /how-tos/install-mariadb-10-centos-7-cpanel/ (Caused by ConnectTimeoutError(<urllib3.connection.HTTPConnection object at 0x7b8327581b70>, 'Connection to linoxide.com timed out. (connect timeout=10)')) | null |
7,460 | 初识 Linux 文件权限 | http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/885268-getting-to-know-linux-file-permissions | 2016-06-14T14:07:51 | [
"权限",
"chmod"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7460-1.html | 
在 Linux 中最基本的任务之一就是设置文件权限。理解它们是如何实现的是你进入 Linux 世界的第一步。如您所料,这一基本操作在类 UNIX 操作系统中大同小异。实际上,Linux 文件权限系统就直接取自于 UNIX 文件权限(甚至使用许多相同的工具)。
但不要以为理解文件权限需要长时间的学习。事实上会很简单,让我们一起来看看你需要了解哪些内容以及如何使用它们。
### 基础概念
你要明白的第一件事是文件权限可以用来干什么。当你设置一个分组的权限时发生了什么?让我们将其展开来说,这个概念就真的简单多了。那到底什么是权限?什么是分组呢?
你可以设置的3种权限:
* 读 — 允许该分组读文件(用`r`表示)
* 写 — 允许该分组写文件(用`w`表示)
* 执行 — 允许该分组执行(运行)文件(用`x`表示)
为了更好地解释这如何应用于一个分组,例如,你允许一个分组可以读写一个文件,但不能执行。或者,你可以允许一个分组读和执行一个文件,但不能写。甚至你可以允许一个分组有读、写、执行全部的权限,也可以删除全部权限来去除该组的权限。
现在,什么是分组呢,有以下4个:
* user — 文件实际的拥有者
* group — 用户所在的用户组
* others — 用户组外的其他用户
* all — 所有用户
大多数情况,你只会对前3组进行操作,`all` 这一组只是作为快捷方式(稍后我会解释)。
到目前为止很简单,对吧?接下来我们将深入一层。
如果你打开一个终端并运行命令 `ls -l`,你将会看到逐行列出当前工作目录下所有的文件和文件夹的列表(如图)

你会留意到最左边那列是像是 `-rw-rw-r--` 这样的。
实际上这列表应该这样看:
>
> rw- rw- r--
>
>
>
正如你所见,列表将其分为如下3部分:
* rw-
* rw-
* r--
权限和组的顺序都很重要,顺序总是:
* 所属者 所属组 其他人 — 分组
* 读 写 执行 — 权限
在我们上面示例的权限列表中,所属者拥有读/写权限,所属组拥有读/写权限,其他人用户仅拥有读权限。这些分组中赋予执行权限的话,就用一个 x 表示。

### 等效数值
接下来我们让它更复杂一些,每个权限都可以用一个数字表示。这些数字是:
* 读 — 4
* 写 — 2
* 执行— 1
数值代替不是一个一个的替换,你不能像这样:
>
> -42-42-4--
>
>
>
你该把每个分组的数值相加,给用户读和写权限,你该用 4 + 2 得到 6。给用户组相同的权限,也是使用相同的数值。假如你只想给其他用户读的权限,那就设置它为4。现在用数值表示为:
>
> 664
>
>
>
如果你想给一个文件664权限,你可以使用 `chmod` 命令,如:
```
chmod 664 FILENAME
```
FILENAME 处为文件名。
### 更改权限
既然你已经理解了文件权限,那是时候学习如何更改这些权限了。就是使用 `chmod` 命令来实现。第一步你要知道你能否更改文件权限,你必须是文件的所有者或者有权限编辑文件(或者通过 `su` 或 `sudo` 得到权限)。正因为这样,你不能随意切换目录和更改文件权限。
继续用我们的例子 (`-rw-rw-r--`)。假设这个文件(命名为 script.sh)实际是个shell脚本,需要被执行,但是你只想让自己有权限执行这个脚本。这个时候,你可能会想:“我需要是文件的权限如 `-rwx-rw-r--`”。为了设置 `x` 权限位,你可以这样使用 `chmod` 命令:
```
chmod u+x script.sh
```
这时候,列表中显示的应该是 -rwx-rw-r-- 。
如果你想同时让用户及其所属组同时拥有执行权限,命令应该这样:
```
chmod ug+x script.sh
```
明白这是怎么工作的了吗?下面我们让它更有趣些。不管什么原因,你不小心给了所有分组对文件的执行权限(列表中是这样的 `-rwx-rwx-r-x`)。
如果你想去除其他用户的执行权限,只需运行命令:
```
chmod o-x script.sh
```
如果你想完全删除文件的可执行权限,你可以用两种方法:
```
chmod ugo-x script.sh
```
或者
```
chmod a-x script.sh
```
以上就是所有内容,能使操作更有效率。我希望能避免哪些可能会导致一些问题的操作(例如你不小心对 script.sh 使用 `a-rwx` 这样的 `chmod` 命令)。
### 目录权限
你也可以对一个目录执行 `chmod` 命令。当你作为用户创建一个新的目录,通常新建目录具有这样的权限:
>
> drwxrwxr-x
>
>
>
注:开头的 `d` 表示这是一个目录。
正如你所见,用户及其所在组都对文件夹具有操作权限,但这并不意味着在这文件夹中出创建的文件也具有与其相同的权限(创建的文件使用默认系统的权限 `-rw-rw-r--`)。但如果你想在新文件夹中创建文件,并且移除用户组的写权限,你不用切换到该目录下并对所有文件使用 `chmod` 命令。你可以用加上参数 R(意味着递归)的 `chmod` 命令,同时更改该文件夹及其目录下所有的文件的权限。
现在,假设有一文件夹 TEST,里面有一些脚本,所有这些(包括 TEST 文件夹)拥有权限 `-rwxrwxr-x`。如果你想移除用户组的写权限,你可以运行命令:
```
chmod -R g-w TEST
```
运行命令 `ls -l`,你讲看到列出的 TEST 文件夹的权限信息是 `drwxr-xr-x`。用户组被去除了写权限(其目录下的所有文件也如此)。
### 总结
现在,你应该对基本的 Linux 文件权限有了深入的理解。对于更高级的东西学起来会很轻松,像 setgid、setuid 和 ACL 这些。没有良好的基础,你很快就会混淆不清概念的。
Linux 文件权限从早期到现在没有太大变化,而且很可能以后也不会变化。
---
via: <http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/885268-getting-to-know-linux-file-permissions>
作者:[Jack Wallen](http://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/93) 译者:[ynmlml](https://github.com/ynmlml) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,462 | 2016 年最佳 Linux 图像管理软件 | http://itsfoss.com/linux-photo-management-software/ | 2016-06-14T19:29:00 | [
"gThumb",
"digiKam",
"Shotwell",
"KPhotoAlbum",
"Darktable"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7462-1.html | 
通常谈及 Linux 上的应用程序时,我们有很多选择,但有时候选择的余地却很小。
有一些读者要我们做一个合宜的**图像管理软件**列表,来代替 Linux 上已被弃用的 Picasa 应用。其实 Linux 平台上还是有很多很好的图像管理软件的,你可以根据你图片库的大小选择合适的应用。
这个列表和我们先前的 [最佳图像程序应用](http://itsfoss.com/image-applications-ubuntu-linux/) 有些差别,上次我们介绍了图像编辑软件,绘图软件等,而这次的介绍主要集中在图像管理软件上。
好,下面我们开始介绍。我会详细说明在 Ubuntu 及其衍生版下的安装命令,我们只需要打开终端运行这些命令。
### [gThumb](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/gthumb)

*gThumb 图像编辑器*
gThumb 是在 GNOME 桌面环境下的一个轻量级的图像管理应用,它涵盖了基本图像管理功能,比如编辑图片以及更加高级的操作等,gThumb 主要功能如下:
* 图片查看:支持所有主流的图片格式(包括 gif)和元数据(EXIF、 XMP 等)。
* 图片浏览:所有基础的浏览操作(缩略图、移动、复制、删除等)以及书签支持。
* 图片管理:使用标签、目录和库来组织图片。从数码相机导入图片,集成了网络相册(Picasa,Flickr,Facebook等)。
* 图片编辑:基本图像编辑操作、滤镜、格式转换等。
更多功能请参考官方 [gThumb 功能](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/gthumb/features) 列表。如果你使用的是 GNOME 或者基于 GNOME 的桌面环境(如 MATE),那么你一定要试用一下。
#### gThumb 安装
```
sudo apt-get install gthumb
```
### [digiKam](https://www.digikam.org/)

*digiKam*
digiKam 主要为 KDE 而设计,在其他桌面环境下也可以使用。它有很多很好的图像界面功能,主要功能如下所示:
* 图片管理:相册、子相册、标签、评论、元数据、排序支持。
* 图片导入:支持从数码相机、USB设备、网络相册(包括 Picasa 和 Facebook)导入,以及另外一些功能。
* 图片输出:支持输出至很多网络在线平台,以及格式转换。
* 图片编辑:支持很多图像编辑的操作。
毫无疑问,digiKam 如果不是最好的图像管理软件,也是之一。
#### digiKam 安装
```
sudo apt-get install digikam
```
### [Shotwell](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Shotwell)

*Shotwell*
Shotwell 图像管理也是为 GNOME 桌面环境设计,虽然功能不及 gThumb 多,但满足了基本需求。主要功能如下:
* 从磁盘或数码相机导入图片。
* 事件、标签和基于文件夹的图片管理方式。
* 基本图片编辑功能和格式转换。
* 支持上传至网络平台(Facebook,Flickr,Tumblr 等)。
如果你想要一款功能相对简单的应用,你可以尝试一下这个。
#### Shotwell 安装
```
sudo apt-get install shotwell
```
### [KPhotoAlbum](https://www.kphotoalbum.org/)

*KPhotoAlbum*
KPhotoAlbum 是一款在 KDE 桌面环境下的图像管理应用。它有一些独特的功能:分类和基于时间浏览。你可以基于人物、地点、时间分类;另外在用户图形界面底部会显示时间栏。
KPhotoAlbum 有很多图像管理和编辑功能,主要功能包括:
* 高级图片操作(分类、子分类、标签、元数据、注释等等)。
* 图片导入导出功能(包括主流图片分享平台)。
* 众多编辑功能(包括批量处理)。
这些高级的功能有一些缺点,就是用户大多需要手工操作。但如果你是 KDE 爱好者,这是个好的选择。它完美适用 KDE,但是你也可以在非 KDE 桌面环境下使用 KPhotoAlbum。
#### KPhotoAlbum 安装
```
sudo apt-get install kphotoalbum
```
### [Darktable](http://www.darktable.org/)

*Darktable*
Darktable 与其说是图像管理工具,不如说是图像编辑软件。Darktable 有良好的用户图形界面,对桌面环境没有特殊的要求,这也不会影响到它的图像编辑功能。它的基本功能如下:
* 基本图片管理。
* 众多高级的图片编辑功能。
* 支持导出至 Picasa 和 Flickr 和格式转换。
如果你喜欢照片编辑和润色,Darktable 是个好的选择。
>
> 推荐阅读:[怎样在 Ubuntu 下通过 PPA 安装 Darktable 2.0](http://itsfoss.com/darktable-20-released-installation-ppa/)
>
>
>
#### Darktable 安装
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:pmjdebruijn/darktable-release
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install darktable
```
### 其它
如果你想要功能简单的应用,比如从便携设备(相机、手机、便携设备等)中导入照片并存入磁盘,毫无疑问该使用 [Rapid Photo Downloader](http://www.damonlynch.net/rapid/index.html),它很适合从便携设备中导入和备份图片,而且安装配置过程简单。
在 Ubuntu 上安装 Rapid Photo Downloade,打开终端输入命令:
```
sudo apt-get install rapid-photo-downloader
```
如果你想尝试更多的选择:
* [GNOME Photos](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Photos) (GNOME 桌面环境下的图像查看器)
* [Gwenview](https://userbase.kde.org/Gwenview) (KDE 桌面环境下的图像查看器)
* [Picty](https://github.com/spillz/picty) (开源图像管理器)
那么,你正在使用,或者打算使用其中一款应用吗?在 Ubuntu 或其它 Linux 上你有其它更好的推荐吗?你有最喜欢的 Linux 图像管理软件吗?分享你的观点给我们。
---
via: <http://itsfoss.com/linux-photo-management-software/>
作者:[Munif Tanjim](http://itsfoss.com/author/munif/) 译者:[sarishinohara](https://github.com/sarishinohara) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,463 | 在 Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS 上安装 LAMP | http://www.linuxtechi.com/lamp-stack-installation-on-ubuntu-server-16-04/ | 2016-06-15T08:27:00 | [
"LAMP"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7463-1.html | LAMP 方案是一系列自由和开源软件的集合,包含了 **Linux**、Web 服务器 (**Apache**)、 数据库服务器 (**MySQL / MariaDB**) 和 **PHP** (脚本语言)。LAMP 是那些需要安装和构建动态网页应用的基础平台,比如WordPress、Joomla、OpenCart 和 Drupal。

在这篇文章中,我将描述如何在 Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS 上安装 LAMP,众所周知 Ubuntu 是一个基于 Linux 的操作系统,因此它构成了 LAMP 的第一个部分,在接下来的操作中,我将默认你已经安装了 Ubuntu Server 16.04。
### Apache2 web 服务器的安装 :
在 Ubuntu linux 中,web 服务器是 Apache2,我们可以利用下面的命令来安装它:
```
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt update
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt install apache2 -y
```
当安装 Apache2 包之后,Apache2 相关的服务是启用的,并在重启后自动运行。在某些情况下,如果你的 Apache2 服务并没有自动运行和启用,你可以利用如下命令来启动和启用它。
```
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo systemctl start apache2.service
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo systemctl enable apache2.service
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo systemctl status apache2.service
```
如果你开启了 Ubuntu 的防火墙(ufw),那么你可以使用如下的命令来解除 web 服务器的端口(80和443)限制
```
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo ufw status
Status: active
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo ufw allow in 'Apache Full'
Rule added
Rule added (v6)
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$
```
### 现在开始访问你的 web 服务器 :
打开浏览器并输入服务器的IP地址或者主机名(http://IP\_Address\_OR\_Host\_Name),在我的例子中我的服务器 IP是‘192.168.1.13’

### 数据库服务器的安装 (MySQL Server 5.7) :
MySQL 和 MariaDB 都是 Ubuntu 16.04 中的数据库服务器。 MySQL Server 和 MariaDB Server的安装包都可以在Ubuntu 的默认软件源中找到,我们可以选择其中的一个来安装。通过下面的命令来在终端中安装mysql服务器。
```
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt install mysql-server mysql-client
```
在安装过程中,它会要求你设置 mysql 服务器 root 帐户的密码。

确认 root 帐户的密码,并点击确定。

MySQL 服务器的安装到此已经结束了, MySQL 服务会自动启动并启用。我们可以通过如下的命令来校验 MySQL 服务的状态。
```
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo systemctl status mysql.service
```
### MariaDB Server的安装 :
在终端中使用如下的命令来安装 Mariadb 10.0 服务器。
```
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt install mariadb-server
```
运行如下的命令来设置 MariaDB root 帐户的密码,还可以用来关闭某些选项,比如关闭远程登录功能。
```
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
```
### PHP 脚本语言的安装:
PHP 7 已经存在于 Ubuntu 的软件源中了,在终端中执行如下的命令来安装 PHP 7:
```
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt install php7.0-mysql php7.0-curl php7.0-json php7.0-cgi php7.0 libapache2-mod-php7.0
```
创建一个简单的 php 页面,并且将它移动到 apache 的文档根目录下 (/var/www/html)
```
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ vi samplepage.php
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
```
在 vi 中编辑之后,保存并退出该文件。
```
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo mv samplepage.php /var/www/html/
```
现在你可以从 web 浏览器中访问这个页面, 输入 : “http://<Server\_IP>/samplepage.php” ,你可以看到如下页面。

以上的页面向我们展示了 PHP 已经完全安装成功了。
### phpMyAdmin 的安装:
phpMyAdmin 可以让我们通过它的 web 界面来执行所有与数据库管理和其他数据库操作相关的任务,这个安装包已经存在于 Ubuntu 的软件源中。
利用如下的命令来在 Ubuntu server 16.04 LTS 中安装 phpMyAdmin。
```
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt install php-mbstring php7.0-mbstring php-gettext
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo systemctl restart apache2.service
linuxtechi@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt install phpmyadmin
```
在以下的安装过程中,它会提示我们选择 phpMyAdmin 运行的目标服务器。
选择 Apache2 并点击确定。

点击确定来配置 phpMyAdmin 管理的数据库。

指定 phpMyAdmin 向数据库服务器注册时所用的密码。

确认 phpMyAdmin 所需的密码,并点击确认。

现在可以开始尝试访问 phpMyAdmin,打开浏览器并输入 : “http://Server\_IP\_OR\_Host\_Name/phpmyadmin”
使用我们安装时设置的 root 帐户和密码。

当我们点击“Go”的时候,将会重定向到如下所示的 ‘phpMyAdmin’ web界面。

到现在,LAMP 方案已经被成功安装并可以使用了,欢迎分享你的反馈和评论。
---
via: <http://www.linuxtechi.com/lamp-stack-installation-on-ubuntu-server-16-04/>
作者:[Pradeep Kumar](http://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/) 译者:[陆建波](https://github.com/lujianbo) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,464 | Snap 将成为支持所有 GNU/Linux 发行版的通用二进制软件包格式 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/snap-packages-become-the-universal-binary-format-for-all-gnu-linux-distributions-505241.shtml | 2016-06-15T09:46:00 | [
"Snap"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7464-1.html | Canonical 说他们与各个主要的 GNU/Linux 发行版的开发者们正在一起努力将 Snap 软件包格式变成通用二进制软件包格式。

如你所知, Snap 是一种安全的、易于安装的、沙盒化的软件包格式,它可以让开发者将他们的软件的更新包随时发布给用户,而不必等待发行版的更新周期。
Snap 来自 Canonical 为其物联网操作系统 Snappy Ubuntu Core 所开发 Snappy 技术。从 Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus)开始,Canonical 也将这种软件包格式推向了其桌面和服务器产品。
“来自多个 Linux 发行版及公司的开发者们宣布将协作开发 ‘snap’ 通用 Linux 软件包格式——一个将可以用在任何 Linux 桌面、服务器、云或设备上的二进制软件包。”Canonical 说,“[snapcraft.io](http://snapcraft.io/) 社区正在开发一种可以在任何 Linux 环境中用于任何 Linux 软件的单一发布机制。”
### Snap 已经可以原生工作在 Arch Linux、Debian、Fedora 和 Ubuntu 上
此刻,我们注意到 Snap 软件包格式已经可以原生地工作在一些流行的 GNU/Linux 操作系统上,比如 Arch Linux、Fedora、Debian GNU/Linux、OpenWrt,和 Ubuntu 及其官方分支,包括 Kubuntu、Xubuntu、Ubuntu MATE、Ubuntu GNOME、Ubuntu 麒麟和 Lubuntu 等。
之后,其它的主流 GNU/Linux 发行版也将很快会将 Snap 软件包作为一种通用二进制格式发布给使用者,这包括 openSUSE、Linux Mint、Red Hat Enterprise Linux、CentOS 和 elementary OS 等。当然,即便是没有列在这里的 GNU/Linux 发行版支持 Snap 格式也是很容易的。
Canonical 已经介绍过[开发者们如何将其软件打包成 Snap 格式](/article-7441-1.html),通过 Snap 在任何基于 Linux 内核的主流操作系统上发布软件都很容易,发布第三方 Linux 软件要比之前更加容易了。
当然, Snap 将不会替代各个发行版的默认软件包格式,它将是一种对现有的软件包格式的补充,可以用于在所有的 GNU/Linux 操作系统上发布任何开源或闭源的应用。
像 Mozilla Firefox、LibreOffice 和 Krita 这样的流行软件已经在进行 Snap 打包工作。Mozilla 的 Firefox 产品副总裁 Nick Nguyen 说:“随着引入 Snap 格式,持续优化 Firefox 成为了一种可能,这可以让 Linux 用户第一时间得到最新的功能。”
数字绘画工具 Krita 3.0 本月初也发布了其 Snap 软件包,Ubuntu 用户可以在自己的系统上安装这个软件包了。“在一个私有仓库中维护一个 .deb 软件包是复杂而耗时的,而 Snap 更容易维护、打包和分发”,Krita 基金会的项目负责人 Boudewijn Rempt 说。
如果你想将你的软件以 Snap 格式发布到任何支持的 GNU/Linux 操作系统上,欢迎去看看 [snapcraft.io](http://snapcraft.io/) 网站。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,466 | 在 NASA 使用开源工具进行图像处理 | https://opensource.com/life/16/3/image-processing-nasa | 2016-06-16T08:01:12 | [
"NASA",
"开源"
] | /article-7466-1.html | 
在刚结束的这个夏天里,我是 [NASA 格伦中心](http://www.nasa.gov/centers/glenn/home/index.html) [GVIS](https://ocio.grc.nasa.gov/gvis/) 实验室的实习生,我将我对开源的热情带到了那里。我的任务是改进我们实验室对 Dan Schroeder 开发的一个开源流体动力学模拟器的贡献。原本的[模拟器](http://physics.weber.edu/schroeder/fluids/)可以显示用户用鼠标绘制的障碍物,并建立计算流体动力学模型。我们团队的贡献是加入图像处理的代码,分析实况视频的每一帧以显示特定的物体如何与液体相互作用。而且,我们还要做更多事情。
我们想要让图像处理部分更加健壮,所以我致力于改善图像处理库。
得益于新的库,模拟器可以检测轮廓、进行空间坐标变换以及找到物体的质心。图像处理并不直接与流体动力学模拟器物理相关。它用摄像头检测物体,并且获取物体轮廓,为流体模拟器创建一个障碍物。随后,流体模拟器开始运行,而输出结果会被投射到真实物体上。
我的目标是通过以下三个方面改进模拟器:
1. 找寻物体的轮廓
2. 找寻物体的质心
3. 能对物体中心进行相关的精确转换
我的导师建议我安装 [Node.js](http://nodejs.org/) 、 [OpenCV](http://opencv.org/) 和 [Node.js bindings for OpenCV](https://github.com/peterbraden/node-opencv)。在等待软件安装的过程中,我查看了 OpenCV 的 [GitHub 主页](https://github.com/peterbraden/node-opencv)上的示例源码。我发现示例源码使用 JavaScript 写的,而我还不懂 JavaScript ,所以我在 Codecademy 上学了一些课程。两天后,我对 JavaScript 依旧生疏,不过我还是开始了我的项目……它包含了更多的 JavaScript 。
检测轮廓的示例代码工作得很好。事实上,它使得我用几个小时就完成了第一个目标!获取一幅图片的轮廓,它看起来像这样:

*包括所有轮廓的原始图*
检测轮廓的示例代码工作得有点好过头了。不仅物体的轮廓被检测到了,整个图片中的轮廓都检测到了。这会导致模拟器要与那些没用的轮廓打交道。这是一个严重的问题,因为它会返回错误的数据。为了避免模拟器接触到不想要的轮廓,我加了一个区域约束。轮廓要位于一定的区域范围内才会被画出来。区域约束使得轮廓变干净了。

*过滤后的轮廓,包含了阴影轮廓*
虽然无关的轮廓没有了,但是图像还有个问题。图像本该只有一个轮廓,但是它来回绕了自己两次,没有完整地圈起来。区域在这里不能作为决定因素,所以必须试试其他方式。
这一次,我不是直接去找寻轮廓,而是先将图片转换成二值图。二值图是转换之后只有黑白像素的图片。为了获取到二值图我先把彩色图转成灰度图。转换之后我再用阈值函数对图片进行处理。阈值函数遍历图片每个像素点的值,如果值小于 30 ,像素的颜色就会改成黑色。否则取反。在原始图片转换成二值图之后,结果变成这样:

*二值图*
然后我获取了二值图的轮廓,结果是一个更干净的轮廓,没有了阴影轮廓。

*最后的干净轮廓*
这个时候,我可以获取干净的轮廓、计算质心了。可惜的是,我没有足够的时间去完成质心的相关变换。由于我的实习时间只剩下几天了,我开始考虑我在这段有限时间内能做的其它事情。其中一个就是边界矩形。边界矩形是包含了图片轮廓的最小四边形。边界矩形很重要,因为它是在页面上缩放轮廓的关键。虽然很遗憾我没时间利用边界矩形做更多事情,但是我仍然想学习它,因为它是个很有用的工具。
最后,经过以上的努力,我完成了对图像的处理!

*最终图像,红色的边界矩形和质心*
当这些图像处理代码写完之后,我用我的代码替代了模拟器中的老代码。令我意外的是,它可以工作。
嗯,基本可以。
程序有内存泄露,每 1/10 秒泄露 100MB 。我很高兴不是因为我的代码。坏消息是我并不能修复它。另一个好消息是仍然有解决方法,虽然并非最理想的,但我可以使用。这个方法是不断检查模拟器使用的内存,当使用内存超过 1GB 时,重新启动模拟器。
在 NASA 实验室,我们会使用很多的开源软件,没有这些开源软件的帮助,我不可能完成这些工作。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/life/16/3/image-processing-nasa>
作者:[Lauren Egts](https://opensource.com/users/laurenegts) 译者:[willowyoung](https://github.com/willowyoung) 校对:[PurlingNayuki](https://github.com/PurlingNayuki)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
7,467 | 在 OpenStack 云中测试 Fedora 24 Beta | https://major.io/2016/05/24/test-fedora-24-beta-openstack-cloud/ | 2016-06-16T09:17:00 | [
"Fedora",
"OpenStack",
"Horizon"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7467-1.html | 虽然离 [Fedora 24](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Releases/24/Schedule) 还有几周,你现在可以就测试Fedora 24 Beta了。这是一个[窥探新特性](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Releases/24/ChangeSet)的好机会,并且可以帮助他们找出仍需要修复的 bug。

[Fedora Cloud](https://getfedora.org/en/cloud/) 镜像可以从你常用的[本地镜像](https://admin.fedoraproject.org/mirrormanager/mirrors/Fedora/24/x86_64)或者 [Fedora 的服务器](https://getfedora.org/en/cloud/download/)中下载。本篇文章我将向你展示如何将这个镜像导入 OpenStack 环境并且测试 Fedora 24 Beta。
最后说一下:这还是 beta 软件。目前对我来说是可靠的,但是你的体验可能会不同。我建议你等到正式版发布再在上面部署关键的应用。
### 导入镜像
旧版(版本1)的 glance 客户端允许你在 OpenStack 环境中导入一个可通过 URL 访问的镜像。由于我 OpenStack 云的连接速度(1 Gbps)比我家 (大约 20 mbps 上传速度)快,这个功能对我很有用。然而,从 URL 导入的功能[在 glance v2 中被移除了]。[OpenStackClient](http://docs.openstack.org/developer/python-openstackclient/) 也不支持这个功能。
现在由两个选择:
* 安装旧版的 glance 客户端
* 使用 Horizon (网页面板)
获取旧版本的 glance 是有挑战性的。OpenStack liberty 版本的需求文件[对 glance 客户端没有最高版本上限](https://github.com/openstack/requirements/blob/stable/liberty/global-requirements.txt#L159),并且很难找到让旧版客户端工作的依赖文件。
让我们使用 Horizon,这就是写这篇文章的原因。
### 在 Horizon 中添加一个镜像
登录 Horizon 面板,点击 Compute->Image。点击页面右上方的“+ Create Image”,一个新的窗口会显示出来。并且窗口中有这些信息:
* **Name**: Fedora 24 Cloud Beta
* **Image Source**: 镜像位置
* **Image Location**: <http://mirrors.kernel.org/fedora/releases/test/24_Beta/CloudImages/x86_64/images/Fedora-Cloud-Base-24_Beta-1.6.x86_64.qcow2>
* **Format**: QCOW2 – QEMU 模拟器
* **Copy Data**: 确保勾选了
完成后,你会看到这个:

点击“<ruby> 创建镜像 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Creat Image </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”,接着镜像列表会显示一段时间的<ruby> 正在保存 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Saving </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>信息。一旦切换到<ruby> 活动 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Active </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,你就可以构建一个实例了。
### 构建实例
既然我们在使用 Horizon,我们可以在此完成构建过程。
在镜像列表页面,找出我们上传的镜像并且点击右边的<ruby> 启动实例 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Launch Instance </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。一个新的窗口会显示出来。镜像名(Image Name)下拉框中应该已经选择了 Fedora 24 Beta 的镜像。在这里,选择一个实例名,选择一个安全组和密钥对(在 Access & Security 标签中)和网络(在 Networking 标签)。确保选择有足够容量的存储(m1.tiny 不太够)。
点击<ruby> 启动 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Launch </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>并且等待实例启动。
一旦实例构建完成,你能以用户 fedora 通过 ssh 连接到实例。如果你的[安全组允许连接](https://major.io/2016/05/16/troubleshooting-openstack-network-connectivity/)并且你的密钥对正确配置了,你应该进入到 Fedora 24 Beta 中了!
还不确定接下来做什么?有下面几点建议:
* 升级所有的包并且重启(确保你测试的是最新的更新)
* 安装一些熟悉的应用并且验证它们可以正常工作
* 测试你已有的自动化或者配置管理工具
* 打开 bug 报告
---
via: <https://major.io/2016/05/24/test-fedora-24-beta-openstack-cloud/>
作者:[major.io](https://major.io/about-the-racker-hacker/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 404 | Not Found | null |
7,468 | Linux 上四个最佳的现代开源代码编辑器 | http://itsfoss.com/best-modern-open-source-code-editors-for-linux/ | 2016-06-16T10:35:00 | [
"Brackets",
"Atom",
"Light Table",
"Lime Text"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7468-1.html | 
在寻找 **Linux 上最好的代码编辑器**?如果你问那些老派的 Linux 用户,他们的答案肯定是 Vi,Vim,Emacs,Nano 等等。但我不讨论它们。我要讨论的是崭新、先进、优美、强大、功能丰富,能够提高你编程体验的**最好的 Linux 开源代码编辑器**。
### Linux 上最佳的现代开源代码编辑器
我使用 Ubuntu 作为我的主力系统,因此提供的安装说明适用于基于 Ubuntu 的发行版。但这并不会让这个列表变成 **Ubuntu 上的最佳文本编辑器**,因为这些编辑器对所有 Linux 发行版都适用。多说一句,这个清单的排名没有任何先后顺序。
### BRACKETS

[Brackets](http://brackets.io/) 是来自 [Adobe](http://www.adobe.com/) 的一个开源代码编辑器。Brackets 专注于 web 设计师的需求,内置 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 支持。它很轻量,也很强大。它提供了行内编辑和实时预览。还有无数可用的插件,可以进一步加强你在 Brackets 上的体验。
在 Ubuntu 以及基于 Ubuntu 的发行版(比如 Linux Mint)上[安装 Brackets](http://itsfoss.com/install-brackets-ubuntu/) 的话,你可以用这个非官方的 PPA:
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/brackets
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install brackets
```
至于其它 Linux 发行版,你可以从它的网站上获取到适用于 Linux,OS X 和 Windows 源码和二进制文件。
* [下载 Brackets 源码和二进制包](https://github.com/adobe/brackets/releases)
### ATOM

[Atom](https://atom.io/) 是另一个给程序员的开源代码编辑器,现代而且美观。Atom 是由 Github 开发的,宣称是“面向21世纪的可魔改文本编辑器”。Atom 的外观看起来类似 Sublime Text,那是一个在程序员中很流行但是闭源的文本编辑器。
Atom 最近发布了 .deb 和 .rpm 包,所以你可以轻而易举地在基于 Debian 和 Fedora 的 Linux 发行版上安装它。当然,它也提供了源代码。
* [下载 Atom .deb](https://atom.io/download/deb)
* [下载 Atom .rpm](https://atom.io/download/rpm)
* [获取 Atom 源码](https://github.com/atom/atom/blob/master/docs/build-instructions/linux.md)
### LIME TEXT

你喜欢 Sublime Text 但是你对它是闭源的这一事实感觉不是很舒服?别担心,我们有 [Sublime Text 的开源克隆版](http://itsfoss.com/lime-text-open-source-alternative/),叫做 [Lime Text](http://limetext.org/)。它是基于 Go、HTML 和 QT 的。克隆 Sublime Text 的原因是 Sublime Text 2 中有无数 bug,而 Sublime Text 3 看起来会永远处于 beta 之中,而它的开发过程并不透明,也就无从得知 bug 是否被修复了。
所以开源爱好者们,开心地去下面这个链接下载 Lime Text 的源码吧:
* [获取 Lime Text 源码](https://github.com/limetext/lime)
### LIGHT TABLE

[Light Table](http://lighttable.com/) 是另一个外观现代、功能丰富的开源代码编辑器,标榜为“下一代代码编辑器”,它更像一个 IDE 而不仅仅是个文本编辑器。它还有无数可以加强它的功能的扩展。也许你会喜欢它的行内求值。你得用用它才会相信 Light Table 有多好用。
* [在 Ubuntu 上安装 Light Table](http://itsfoss.com/install-lighttable-ubuntu/)
### 你的选择是?
不,我们的选择没有限制在这四个 Linux 代码编辑器之中。这个清单只是关于程序员的现代编辑器。当然,你还有很多选择,比如 [Notepad++ 的替代选择 Notepadqq](http://itsfoss.com/notepadqq-notepad-for-linux/) 或 [SciTE](http://itsfoss.com/scite-the-notepad-for-linux/) 等等。那么,上面四个中,在 Linux 上而言你最喜欢哪个代码编辑器?
---
via: <http://itsfoss.com/best-modern-open-source-code-editors-for-linux/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,472 | Firefox 新增容器标签,可同时登录多个用户 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/firefox-s-container-tabs-lets-users-login-with-different-ids-on-the-same-site-505386.shtml | 2016-06-18T11:17:08 | [
"Firefox",
"容器标签"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7472-1.html | Mozilla 昨天在 Firefox 夜间构建版 50.0a1 中增加了一个名为“<ruby> 容器标签 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Container Tabs </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”的实验性功能。
Mozilla 的工程师称,该功能可以将用户的浏览会话分到不同的容器中。这些隔离的容器可以让用户以不同的身份登录到同一个网站上。默认情况下,Firefox 夜间构建版带有四个容器:个人(蓝色)、工作(橙色)、银行(绿色)和购物(粉色),也就是说用户可以使用四个不同的 ID 登录同一个网站。

### 容器标签分隔来自网站的数据,而不是浏览器的数据
Mozilla 的工程师说,可以使用技术手段将 Web 浏览体验分到不同的“容器”,其所分割的是来自网站的数据,而不是浏览器的数据。诸如 Cookie、浏览缓存、<ruby> 索引数据库 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> indexedDB </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和<ruby> 本地存储数据 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> localStorage </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>都分隔存储。为了保证浏览体验的一致和顺滑,容器标签之间会分享书签、浏览历史、保存的密码、搜索历史、表单数据、权限许可、用户身份、HSTS 标志和 OCSP 响应等。
### Firefox 的容器标签是安全与隐私方面的突破!
新的容器标签并不像那些专注在隐私保护方面的浏览器,如 Tor 浏览器,但是它可以将你在网页浏览时的身份分隔开。广告商仍然能跟踪你,但是他们现在需要跟踪你的四个身份。
用户可以将与工作相关的 Cookie 和缓存存储到浏览器的一个区域,而银行和购物相关的部分则存储在另外一个区域。如果能够恰当使用,容器标签功能可以极大地增强你的安全,每个容器标签都相当于一个新的浏览器。
“容器给用户提供了一个分离敏感信息的途径”,Mozilla 工程师[解释说](https://blog.mozilla.org/tanvi/2016/06/16/contextual-identities-on-the-web/),“举个例子说,用户可以仅使用他们的‘银行容器’来登录银行网站,以避免它们被来自其它站点的 XSS 和 CSRF 攻击所窃取。”

*四个新的容器标签及不同的颜色*
如果是你的首次安装 Firefox 夜间构建版,或者是从旧版本升级的,你可以从文件菜单选项中找到这个新的容器标签。如果你想将按钮放到浏览器界面上,你可以通过浏览器的定制 UI 区,将这些按钮拖到工具栏上。
不过,要知道这还是一个实验性的功能,也许最后不会出现在最终产品中。但是,用户体验至高无上,除非有无可弥补的漏洞,我们可以期待这个功能会出现在 Firefox 正式产品中。

*将容器标签的按钮添加到工具栏*
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,474 | 微软开源了一个更安全的 C 语言版本:Checked C | http://news.softpedia.com/news/microsoft-open-sources-checked-c-a-safer-c-version-505331.shtml | 2016-06-18T18:15:00 | [
"Checked",
"Checked C",
"微软"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7474-1.html | 微软开源了 [Checked C](https://github.com/Microsoft/checkedc) ,这是一个 C 语言的扩展版本,可以用于解决 C 语言中的一系列安全相关的隐患。正如其名字所示,Checked C 为 C 语言增加了检查。这个检查可以帮助开发者检查常见的编程错误,比如<ruby> 缓存区侵占 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> buffer overruns </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、内存访问越界、不正确的类型转换等。这些编程错误往往是造成许多重大安全漏洞的根本原因,比如<ruby> 破壳漏洞 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Shellshock </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 心脏出血漏洞 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Heartbleed </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 沙虫 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Sandworm </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>等。

Checked C 通过修改如何控制指针来解决这些问题,指针被程序员们用来定义他们的代码所操作的内存地址。
当指针数量一多,指针控制就往往容易忙中出乱。项目越大,跟踪它们就越困难。类似 Chromium、Firefox、Office、OpenSSL 以及其它的大型代码库在这方面都存在这样的问题,你可以从它们的变更日志中看到大量的这类问题修复。
“Checked C 允许程序员更好的描述他们想要如何使用指针,以及指针应该指向的内存范围”,微软[说](http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/projects/checkedc/default.aspx),“这个信息可以用于在运行时环境中添加检测,以侦测错误的数据访问,而不是让错误悄悄的发生而无所察觉。”
### Checked C 给 C 语言添加了边界检查
Checked C 也将允许开发者检测到他们以为 C 语言有、而实际却没有的功能误用。按编程的说法来说,这个叫做“<ruby> 边界检查 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> bounds checking </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”的功能,用于检查变量/指针是否在它的范围之内赋值。
C# 和 Rust 已经有这样的功能了,而且还不止于此。然而,不幸的是,被广泛使用的 C 和 C++ 却没有这样的功能。微软希望只需要对现有的 C/C++ 程序做最小的改动,利用 Checked C 就可以得到安全方面的改善,这样会吸引大量的开发者开始使用 Checked C。
Checked C 项目已经放到了 [GitHub](https://github.com/Microsoft/checkedc) 上。
这并不是微软第一次对基本编程语言做出来自己的演绎,之前,该公司的程序员们还创建了一个名为 TypeScript 的 JavaScript 的超集,它已经得到了广泛认可。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,479 | 影响 Linux 系统安全基石的 glibc 严重漏洞 | http://www.eweek.com/security/linux-systems-patched-for-critical-glibc-flaw.html | 2016-06-20T19:43:00 | [
"安全"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7479-1.html | 编者按:这个消息是几个月前曝出的,也许我们该对基础软件的安全问题更加重视。
**谷歌披露的一个严重漏洞影响到了主流的 Linux 发行版。glibc 的漏洞可能导致远程代码执行。**
几个月前,Linux 用户都在竞相给一个可以使系统暴露在远程代码执行风险中的核心 glibc 开放源码库的严重漏洞打补丁。这个 glibc 的漏洞编号被确定为 CVE-2015-7547,题为“getaddrinfo 基于堆栈的缓冲区溢出”。

glibc,或 GNU C 库,是一个开放源码的 C 和 C++ 编程语言库的实现,是每一个主流 Linux 发行版的一部分。谷歌工程师们在他们试图连接到某个主机系统时发生了一个段错误导致连接崩溃,偶然发现了 CVE-2015-7547 问题。进一步的研究表明, glibc 有缺陷而且该崩溃可能实现任意远程代码执行的条件。
谷歌在一篇博客文章中写道, “当 getaddrinfo() 库函数被使用时,glibc 的 DNS 客户端解析器易受基于堆栈缓冲区溢出的攻击,使用该功能的软件可能通过攻击者控制的域名、攻击者控制的 DNS [域名系统] 服务器,或通过中间人攻击方式(MITM)进行破坏。”
其实利用 CVE-2015-7547 问题并不简单,但它是可能的。为了证明这个问题能被利用,谷歌发布了论证一个终端用户或系统是否易受攻击的概念验证(POC)代码到 GitHub 上。
GitHub 上的 POC 网页说“服务器代码会触发漏洞,因此会使客户端代码崩溃”。
Duo Security 公司的高级安全研究员 Mark Loveless 解释说 CVE-2015-7547 的主要风险在于依赖于 DNS 响应的基于 Linux 客户端的应用程序。
Loveless 告诉 eWEEK “需要一些特定的条件,所以不是每个应用程序都会受到影响,但似乎一些命令行工具,包括流行的 SSH[安全 Shell] 客户端都可能触发该漏洞,我们认为这是严重的,主要是因为对 Linux 系统存在的风险,但也因为潜在的其他问题。”
其他问题可能包括一种通过电子邮件触发调用易受攻击的 glibc 库 getaddrinfo() 攻击的风险。另外值得注意的是,该漏洞被发现之前已存在于代码之中多年。
谷歌的工程师不是第一或唯一发现这个 glibc 安全风险的团体。这个问题于 2015 年 7 月 13 日首先被报告给了 glibc 的 bug[跟踪系统](https://sourceware.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=1866)。该缺陷的根源可以更进一步追溯到在 2008 五月发布的 glibc 2.9 的代码提交时首次引入缺陷。
Linux 厂商红帽也独立找到了 glibc 中的这个 bug,而且是在 2016 年 1 月 6 日,谷歌和红帽开发人员证实,他们作为最初与上游 glibc 的维护者私下讨论的部分人员,已经独立在为同一个漏洞工作。
红帽产品安全首席软件工程师 Florian Weimer 告诉 eWEEK “一旦确认了两个团队都在为同一个漏洞工作,我们会合作进行可能的修复,缓解措施和回归测试,我们还会共同努力,使测试覆盖尽可能广,捕捉代码中的任何相关问题,以帮助避免今后更多问题。”
由于缺陷不明显或不易立即显现,我们花了几年时间才发现 glibc 代码有一个安全问题。
Weimer 说“要诊断一个网络组件的漏洞,如 DNS 解析器,当遇到问题时通常要看抓到的数据包的踪迹,在这种情况下这样的抓包不适用,所以需要一些实验来重现触发这个 bug 的确切场景。”
Weimer 补充说,一旦可以抓取数据包,就会投入大量精力到验证修复程序中,最终完成回归测试套件一系列的改进,有助于上游 glibc 项目。
在许多情况下,安全增强式 Linux (SELinux) 的强制访问安全控制可以减少潜在漏洞风险,但是这个 glibc 的新问题例外。
Weimer 说“由于攻击者提供的任意代码的执行,会对很多重要系统功能带来风险。一个合适的 SELinux 策略可以遏制一些攻击者可能会做的损害,并限制他们访问系统,但是 DNS 被许多应用程序和系统组件使用,所以 SELinux 策略只提供了针对此问题有限的遏制。”
在揭露漏洞的今天,现在有一个可用的补丁来减少 CVE-2015-7547 的潜在风险。
---
via: <http://www.eweek.com/security/linux-systems-patched-for-critical-glibc-flaw.html>
作者:[Michael Kerner](https://twitter.com/TechJournalist) 译者:[robot527](https://github.com/robot527) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux 中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,480 | 每个程序员都应该收藏的算法复杂度速查表 | http://bigocheatsheet.com/ | 2016-06-20T12:36:00 | [
"算法",
"复杂度"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7480-1.html | ### 算法复杂度这件事
这篇文章覆盖了计算机科学里面常见算法的时间和空间的<ruby> 大 O <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Big-O </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 复杂度。我之前在参加面试前,经常需要花费很多时间从互联网上查找各种搜索和排序算法的优劣,以便我在面试时不会被问住。最近这几年,我面试了几家硅谷的初创企业和一些更大一些的公司,如 Yahoo、eBay、LinkedIn 和 Google,每次我都需要准备这个,我就在问自己,“为什么没有人创建一个漂亮的大 O 速查表呢?”所以,为了节省大家的时间,我就创建了这个,希望你喜欢!
--- [Eric](https://twitter.com/ericdrowell)

### 图例
| | | | | |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| 绝佳 | 不错 | 一般 | 不佳 | 糟糕 |
### 数据结构操作
| 数据结构 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| | 平均 | 最差 | 最差 |
| | 访问 | 搜索 | 插入 | 删除 | 访问 | 搜索 | 插入 | 删除 | |
| [Array](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Array_data_structure) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| [Stack](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stack_(abstract_data_type)) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) |
| [Singly-Linked List](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Singly_linked_list#Singly_linked_lists) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) |
| [Doubly-Linked List](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) |
| [Skip List](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n log(n)) |
| [Hash Table](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hash_table) | - | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | - | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| [Binary Search Tree](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_search_tree) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| [Cartesian Tree](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cartesian_tree) | - | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | - | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| [B-Tree](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/B_tree) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(n) |
| [Red-Black Tree](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Red-black_tree) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(n) |
| [Splay Tree](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Splay_tree) | - | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | - | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(n) |
| [AVL Tree](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AVL_tree) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(n) |
### 数组排序算法
| 算法 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| | 最佳 | 平均 | 最差 | 最差 |
| [Quicksort](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quicksort) | O(n log(n)) | O(n log(n)) | O(n^2) | O(log(n)) |
| [Mergesort](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merge_sort) | O(n log(n)) | O(n log(n)) | O(n log(n)) | O(n) |
| [Timsort](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timsort) | O(n) | O(n log(n)) | O(n log(n)) | O(n) |
| [Heapsort](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heapsort) | O(n log(n)) | O(n log(n)) | O(n log(n)) | O(1) |
| [Bubble Sort](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bubble_sort) | O(n) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) | O(1) |
| [Insertion Sort](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insertion_sort) | O(n) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) | O(1) |
| [Selection Sort](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Selection_sort) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) | O(1) |
| [Shell Sort](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shellsort) | O(n) | O((nlog(n))^2) | O((nlog(n))^2) | O(1) |
| [Bucket Sort](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bucket_sort "Only for integers. k is a number of buckets") | O(n+k) | O(n+k) | O(n^2) | O(n) |
| [Radix Sort](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radix_sort "Constant number of digits 'k'") | O(nk) | O(nk) | O(nk) | O(n+k) |
### 图操作
| 节点 / 边界管理 | 存储 | 增加顶点 | 增加边界 | 移除顶点 | 移除边界 | 查询 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| [Adjacency list](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adjacency_list) | O(|V|+|E|) | O(1) | O(1) | O(|V| + |E|) | O(|E|) | O(|V|) |
| [Incidence list](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Incidence_list) | O(|V|+|E|) | O(1) | O(1) | O(|E|) | O(|E|) | O(|E|) |
| [Adjacency matrix](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adjacency_matrix) | O(|V|^2) | O(|V|^2) | O(1) | O(|V|^2) | O(1) | O(1) |
| [Incidence matrix](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Incidence_matrix) | O(|V| ⋅ |E|) | O(|V| ⋅ |E|) | O(|V| ⋅ |E|) | O(|V| ⋅ |E|) | O(|V| ⋅ |E|) | O(|E|) |
### 堆操作
| 类型 | 时间复杂度 |
| --- | --- |
| | Heapify | 查找最大值 | 分离最大值 | 提升键 | 插入 | 删除 | 合并 |
| [Linked List (sorted)](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list) | - | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(m+n) |
| [Linked List (unsorted)](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list) | - | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) |
| [Binary Heap](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_heap) | O(n) | O(1) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(m+n) |
| [Binomial Heap](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binomial_heap) | - | O(1) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(1) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) |
| [Fibonacci Heap](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibonacci_heap) | - | O(1) | O(log(n)) | O(1) | O(1) | O(log(n)) | O(1) |
### 大 O 复杂度图表

### 推荐阅读
* [Cracking the Coding Interview: 150 Programming Questions and Solutions](http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/098478280X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1789&creative=390957&creativeASIN=098478280X&linkCode=as2&tag=htcatu-20&linkId=B6WXIEKJHEBBWJ7B)
* [Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition](http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/0262033844/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1789&creative=390957&creativeASIN=0262033844&linkCode=as2&tag=htcatu-20&linkId=J2PHCTWEAND3YQF4)
* [Data Structures and Algorithms in Java (2nd Edition)](http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/0672324539/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1789&creative=390957&creativeASIN=0672324539&linkCode=as2&tag=htcatu-20&linkId=Y4KPAZH5PFHYXMBA)
* [High Performance JavaScript (Build Faster Web Application Interfaces)](http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/059680279X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1789&creative=390957&creativeASIN=059680279X&linkCode=as2&tag=htcatu-20&linkId=WUNMGD5EARDJZKTT)
### 贡献者
1. [Eric Rowell](https://github.com/ericdrowell), creator of [Concrete.js](http://www.concretejs.com/), an HTML5 Canvas Framework
2. [Quentin Pleple](https://github.com/qpleple)
3. [Michael Abed](https://github.com/vault)
4. [Nick Dizazzo](https://github.com/ndizazzo)
5. [Adam Forsyth](https://github.com/agfor)
6. [David Dorfman](https://github.com/d3dave)
7. [Jay Engineer](https://github.com/jay754)
8. [Jennifer Hamon](https://github.com/jhamon)
9. [Josh Davis](https://github.com/jdavis)
10. [Nodir Turakulov](https://github.com/nodirt)
11. [Bart Massey](https://github.com/BartMassey)
12. [Vinnie Magro](https://github.com/vmagro)
13. [Miguel Amigot](https://github.com/miguel5)
14. [Drew Bailey](https://github.com/makosblade)
15. [Aneel Nazareth](https://github.com/WanderingStar)
16. [Rahul Chowdhury](https://github.com/rahulc93)
17. [Robert Burke](https://github.com/sharpobject)
18. [steven41292](https://github.com/steven41292)
19. [Brandon Amos](https://github.com/bamos)
20. [Mike Davis](https://github.com/dodgymike)
21. [Casper Van Gheluwe](https://github.com/caspervg)
22. [Joel Friedly](https://github.com/jfriedly)
23. [Oleg](https://github.com/cristaloleg)
24. [Renfred Harper](https://github.com/renfredxh)
25. [Piper Chester](https://github.com/piperchester)
26. [Eric Lefevre-Ardant](https://github.com/elefevre)
27. [Jonathan McElroy](https://github.com/jonathanmcelroy)
28. [Si Pham](https://github.com/phamtrisi)
29. [mcverry](https://github.com/mcverry)
30. [Max Hoffmann](https://github.com/mhoffman)
31. [Alejandro Ramirez](https://github.com/j4n0)
32. [Damon Davison](https://github.com/allolex)
33. [Alvin Wan](https://github.com/alvinwan)
34. [Alan Briolat](https://github.com/alanbriolat)
35. [Drew Hannay](https://github.com/drewhannay)
36. [Andrew Rasmussen](https://github.com/andyras)
37. [Dennis Tsang](https://github.com/DennisTT)
38. [Bahador Saket](https://github.com/BahadorSaket)
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,495 | Fedora 24 正式发布! | http://news.softpedia.com/news/fedora-24-linux-distribution-officially-released-available-for-download-now-505485.shtml | 2016-06-22T15:34:00 | [
"Fedora"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7495-1.html | 
2016 年 6 月 21 日,Fedora 项目组[宣布](https://fedoramagazine.org/fedora-24-released/) Fedora 24 Linux 操作系统正式发布!支持桌面、服务器、云端和嵌入式设备。
在延期了四次之后,Fedora 24 正式版终于发布了,现在就可以下载啦!包括几个不同的分支:Fedora 工作站、Fedora 服务器和 Fedora 云端,以及官方 Fedora 变体(即 Fedora Spins)——支持 Xfce、LXDE、KDE、MATE/Compiz、Cinnamon、Sugar 等桌面。
当然,用户也可以在 Fedora 24 实验室找到更多变体,包括设计套件、游戏、机器人套件、科学、安全实验室等。不过,在这些所有的版本之下,都用的同样的核心部件,即 Linux 内核 4.5.7 和 GNU C 库 2.23。
你可能已经注意到了这个 Linux 4.5.7 内核是 Linux 4.5 内核系列的最后一个版本,而 Fedora 开发者已经承诺他们将会在未来几周将该发行版升级到 Linux 4.6 系列,在这个版本发布前已经没有时间重新测试 Linux 4.6 内核了。
### GNOME 3.20、KDE Plasma 5.6、Mono 4.2、GCC 6 等等

Fedora 24 工作站版本中加载了 GNOME 3.20.2 桌面环境,Fedora 24 KDE Plasma Spin 带的则是 KDE Plasma 5.6 桌面。Fedora 24 的所有分支都是用 GCC 6 编译器构建的。
在 Fedora 24 中使用<ruby> 网络管理器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> NetworkManager </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 1.2 来管理网络连接,此外还包括了 Mono 4.2、Boost 1.60、Node.js 5.10、Python 3.5、Ruby 2.3、Golang 1.6 等等。
### 下载地址
* 工作站 Live 镜像([64位](https://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/fedora/linux/releases/24/Workstation/x86_64/iso/Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-24-1.2.iso),[32位](https://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/fedora/linux/releases/24/Workstation/i386/iso/Fedora-Workstation-Live-i386-24-1.2.iso))
* 服务器([64位](https://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/fedora/linux/releases/24/Server/x86_64/iso/Fedora-Server-dvd-x86_64-24-1.2.iso))
更多下载类型,请访问: <https://getfedora.org/>
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,498 | 两个出色的一体化 Linux 服务器软件 | http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/882146-two-outstanding-all-in-one-linux-servers | 2016-06-23T08:00:00 | [
"ClearOS",
"Zentyal"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7498-1.html | 回到2000年那时,微软发布<ruby> 小型商务服务器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Small Business Server </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(SBS)。这个产品改变了很多人们对科技在商务领域的看法。你可以部署一个单独的服务器,它能处理邮件,日历,文件共享,目录服务,VPN,以及更多,而不是很多机器处理不同的任务。对很多小型公司来说,这是实实在在的好处,但是对于一些公司来说 Windows SMB 是昂贵的。对于另外一些人,根本不会考虑使用这种微软设计的单一服务器的想法。
对于后者也有替代方案。事实上,在 Linux 和开源领域里,你可以选择许多稳定的平台,它可以作为一站式服务商店服务于你的小型企业。如果你的小型企业有10到50员工,一体化服务器也许是你所需的理想方案。
这里,我将要展示两个 Linux 一体化服务器,你可以看看它们哪个能完美适用于你的公司。
记住,这些服务器不适用于(不管是哪种方式)大型商务或企业。大公司无法依靠一体化服务器,那是因为一台服务器不能负担得起企业所需的期望。也就是说,Linux 一体化服务器适合于小型企业。

### ClearOS
[ClearOS](http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/882146-two-outstanding-all-in-one-linux-servers#clearfoundation-overview) 最初发布于 2009 年,那时名为 ClarkConnect,是一个路由和网关的发行版。从那以后,ClearOS 增加了所有一体化服务器必要的特性。CearOS 提供的不仅仅是一个软件,你可以购买一个 [ClearBox 100](https://www.clearos.com/products/hardware/clearbox-100-series) 或 [ClearBox 300](https://www.clearos.com/products/hardware/clearbox-300-series)。这些服务器搭载了完整的 ClearOS,作为一个 IT 设备被销售。在[这里](https://www.clearos.com/products/hardware/clearbox-overview)查看特性比对/价格矩阵。
如果你已经有响应的硬件,你可以下载这些之一:
* [ClearOS 社区版](http://mirror.clearos.com/clearos/7/iso/x86_64/ClearOS-DVD-x86_64.iso) — 社区(免费)版的 ClearOS
* [ClearOS 家庭版](http://mirror.clearos.com/clearos/7/iso/x86_64/ClearOS-DVD-x86_64.iso) — 理想的家庭办公室(详细的功能和订阅费用,见[这里](https://www.clearos.com/products/clearos-editions/clearos-7-home))
* [ClearOS商务](http://mirror.clearos.com/clearos/7/iso/x86_64/ClearOS-DVD-x86_64.iso) — 理想的小型企业(详细的功能和订阅费用,见[这里](https://www.clearos.com/products/clearos-editions/clearos-7-business))
使用 ClearOS 能给你你带来什么?你得到了一个商业级的服务器,带有单一的精美 Web 界面。是什么让 ClearOS 从标准的服务器所提供的一大堆功能中脱颖而出?除了那些基础的部分,你可以从 [Clear 市场](https://www.clearos.com/products/purchase/clearos-marketplace-overview) 中增加功能。在这个市场里,你可以安装免费或付费的应用来扩展 ClearOS 服务器的特性。这里你可以找到支持 Windows 服务器活动目录,OpenLDAP,Flexshares,Antimalware,云,Web 访问控制,内容过滤等等很多的补充插件。你甚至可以找到一些第三方组件,比如谷歌应用同步,Zarafa 合作平台,卡巴斯基杀毒。
ClearOS 的安装就像其他的 Linux 发行版一样(基于红帽的 Anaconda 安装程序)。安装完成后,系统将提示您设置网络接口,这个地址用来供你的浏览器(需要与 ClearOS 服务器在同一个网络里)访问。地址格式如下:
```
https://IP_OF_CLEAROS_SERVER:81
```
IP*OF*CLEAROS\_SERVER 就是服务器的真实 IP 地址。注:当你第一次在浏览器访问这个服务器时,你将收到一个“Connection is not private”的警告。继续访问,以便你可以继续设置。
当浏览器最终连接上之后,就会提示你 root 用户认证(在初始化安装中你设置的 root 用户密码)。一通过认证,你将看到 ClearOS 的安装向导(图1)

*图1: ClearOS安装向导。*
点击下一步按钮,开始设置你的 ClearOS 服务器。这个向导无需加以说明,在最后还会问你想用那个版本的 ClearOS。点击“社区”,“家庭”,或者“商业”。选择之后,你就被要求注册一个账户。创建了一个账户并注册了你的服务器后,你可以开始更新服务器,配置服务器,从市场添加模块(图2)。

*图2: 从市场安装模块。*
此时,一切准备就绪,可以开始深入挖掘配置你的 ClearOS 小型商务服务器了。
### Zentyal
[Zentyal](http://www.zentyal.org/server/) 是一个基于 Ubuntu 的小型商务服务器,有段时期的名字是 eBox。Zentyal 提供了大量的服务器/服务来适应你的小型商务需求:
* 电子邮件 — 网页邮件;支持原生的微软 Exchange 协议和活动目录;日历和通讯录;手机设备电子邮件同步;反病毒/反垃圾;IMAP,POP,SMTP,CalDAV,和 CardDAV 支持。
* 域和目录 — 中央域目录管理;多个组织部门;单点登录身份验证;文件共享;ACL,高级域管理,打印机管理。
* 网络和防火墙 — 支持静态和 DHCP 接口;对象和服务;包过滤;端口转发。
* 基础设施 — DNS;DHCP;NTP;认证中心;VPN。
* 防火墙
安装 Zentyal 很像Ubuntu服务器的安装,基于文本界面而且很简单:从安装镜像启动,做一些简单的选择,然后等待安装完成。当这个最初的基于文本的安装完成之后,就会显示桌面 GUI,提供选择软件包的向导程序。你可以选择所有你想安装的包,让安装程序继续完成这些工作。
最终,你可以通过网页界面来访问 Zentyal 服务器(浏览器访问 https://IP\_OF\_SERVER:8443 - 这里 IP\_OF\_SERVER是你的 Zentyal 服务器的局域网地址)或使用独立的桌面 GUI 程序来管理服务器(Zentyal 包括一个可以快速访问管理员和用户控制台的 Zentyal 管理控制台)。当真系统已经保存并启动,你将看到 Zentyal 面板(图3)。

*图3: Zentyal活动面板。*
这个面板允许你控制服务器所有方面,比如更新,管理服务器/服务,获取服务器的敏捷状态更新。您也可以进入组件区域,然后安装在部署过程中没有选择的组件或更新当前的软件包列表。点击“软件管理” > “系统更新”并选择你想更新的(图4),然后在屏幕最底端点击“更新”按钮。

*图4: 更新你的Zentyal服务器很简单。*
### 那个服务器适合你?
回答这个问题要看你有什么需求。Zentyal 是一个不可思议的服务器,它可以很好的胜任你的小型商务网络。如果你需要更多,如群件,我觉得你可以试试 ClearOS。如果你不需要群件,其它的服务器也不错。
我强烈建议你安装一下这两个一体化的服务器,看看哪个更适合你的小公司。
---
via: <http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/882146-two-outstanding-all-in-one-linux-servers>
作者:[Jack Wallen](http://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/93) 译者:[wyangsun](https://github.com/wyangsun) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,499 | 如何为登录和 sudo 设置双因子认证 | https://www.linux.com/learn/how-set-2-factor-authentication-login-and-sudo | 2016-06-23T13:20:00 | [
"认证",
"双因子",
"OTP",
"2FA",
"身份验证器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7499-1.html | 
安全就是一切。我们生活的当今世界,数据具有令人难以置信的价值,而你也一直处于数据丢失的风险之中。因此,你必须想尽办法保证你桌面系统和服务器中数据的安全。结果,管理员和用户就会创建极其复杂的密码、使用密码管理器甚至其它更复杂的东西。但是,如果我告诉你你可以只需要一步,至多两步就能登录到你的 Linux 服务器或桌面系统中呢?多亏了 [Google 身份验证器](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.google.android.apps.authenticator2),现在你可以做到了。并且,配置也极其简单。
我会给你简要介绍为登录和 sudo 设置双因子认证的步骤。我基于 Ubuntu 16.04 桌面系统进行介绍,但这些步骤也适用于其它服务器。为了实现双因子认证,我会使用 Google 身份验证器。
这里有个非常重要的警告:一旦你设置了认证,没有一个从认证器中获得的由 6 个数字组成的验证码你就不可能登录账户(或者执行 sudo 命令)。这也给你增加了一步额外的操作,因此如果你不想每次登录到 Linux 服务器(或者使用 sudo)的时候都要拿出你的智能手机,这个方案就不适合你。但你也要记住,这额外的一个步骤也给你带来一层其它方法无法给予的保护。
话不多说,开始吧。
### 安装必要的组件
安装 <ruby> Google 身份验证器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Google Authenticator </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,首先要解决两个问题。一是安装智能机应用。下面是如何从 Google 应用商店安装的方法:
1. 在你的安卓设备中打开 Google 应用商店
2. 搜索 <ruby> google 身份验证器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Google Authenticator </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
3. 找到并点击有 Google Inc. 标识的应用
4. 点击安装
5. 点击“接受”
6. 等待安装完成
接下来,我们继续在你的 Linux 机器上安装这个认证器。步骤如下:
1. 打开一个终端窗口
2. 输入命令 sudo apt-get install google-authenticator
3. 输入你的 sudo 密码并敲击回车
4. 如果有弹窗提示,输入 y 并敲击回车
5. 等待安装完成
接下来配置使用 google-authenticator 进行登录。
### 配置
要为登录和 sudo 添加双因子认证只需要编辑一个文件,即 /etc/pam.d/common-auth。打开并找到如下一行:
```
auth [success=1 default=ignore] pam_unix.so nullok_secure
```
在这行上面添加:
```
auth required pam_google_authenticator.so
```
保存并关闭文件。
下一步就是为系统中的每个用户设置 google-authenticator(否则他们就不能登录了)。为了简单起见,我们假设你的系统中有两个用户:jack 和 olivia。首先为 jack 设置(我们假设这是我们一直使用的账户)。
打开一个终端窗口并输入命令 google-authenticator。之后会问你一系列的问题(每个问题你都应该用 y 回答)。问题包括:
* 是否允许更新你的 "/home/jlwallen/.google\_authenticator" 文件 (y/n) y
* 是否禁止多个用户使用同一个认证令牌?这会限制你每 30 秒内只能登录一次,但能增加你注意到甚至防止中间人攻击的可能 (y/n)
* 默认情况下令牌时长为 30 秒即可,为了补偿客户端和服务器之间可能出现的时间偏差,我们允许使用当前时间之前或之后的其它令牌。如果你无法进行时间同步,你可以把这个时间窗口由默认的 1:30 分钟增加到 4 分钟。是否希望如此 (y/n)
* 如果你尝试登录的计算机没有针对暴力破解进行加固,你可以为验证模块启用速率限制。默认情况下,限制攻击者每 30 秒不能尝试登陆超过 3 次。是否启用速率限制 (y/n)
一旦完成了问题回答,你就会看到你的密钥、验证码以及 5 个<ruby> 紧急刮码 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> emergency scratch code </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。把这些刮码打印出来并保存。你可以在无法使用手机的时候使用它们(每个刮码仅限使用一次)。密钥用于你在 Google 身份验证器上设置账户,验证码是你能当下就能够立即使用(如果需要)的一次性验证码。
### 设置应用
现在你已经配置好了用户 jack。在设置用户 olivia 之前,你需要在 Google 身份验证器应用上为 jack 添加账户(LCTT 译注:实际操作情形中,是为 jack 的手机上安装的该应用创建一个账户)。在打开应用,点击“菜单”按钮(右上角三个竖排点)。点击“添加账户”然后点击“输入提供的密钥”。在下一个窗口(图1),你需要输入你运行 google-authenticator 应用时提供的 16 个数字的密钥。给账户取个名字(以便你记住这用于哪个账户),然后点击“添加”。

*图1: 在 Google Authenticator 应用上新建账户*
(LCTT 译注:Google 身份验证器也可以扫描你在服务器上设置时显示的二维码,而不用手工输入密钥)
添加完账户之后,你就会看到一个 6 个数字的密码,你每次登录或者使用 sudo 的时候都会需要这个密码。
最后,在系统上设置其它账户。正如之前提到的,我们会设置一个叫 olivia 的账户。步骤如下:
1. 打开一个终端窗口
2. 输入命令 sudo su olivia
3. 在智能机上打开 Google 身份验证器
4. 在终端窗口(图2)中输入(应用提供的) 6 位数字验证码并敲击回车
5. 输入你的 sudo 密码并敲击回车
6. 以新用户输入命令 google-authenticator,回答问题并记录生成的密钥和验证码。
成功为 olivia 用户设置好之后,用 google-authenticator 命令,在 Google 身份验证器应用上根据用户信息(和之前为第一个用户添加账户相同)添加一个新的账户。现在你在 Google 身份验证器应用上就会有 jack 和 olivia 两个账户了。(LCTT 译注:在实际操作情形中,通常是为 jack 和 olivia 两个人的手机分别设置。)

*图2: 为 sudo 输入 6位数字验证码*
好了,就是这些。每次你尝试登录系统(或者使用 sudo) 的时候,在你输入用户密码之前,都会要求你输入提供的 6 位数字验证码。现在你的 Linux 机器就比添加双因子认证之前安全多了。虽然有些人会认为这非常麻烦,我仍然推荐使用,尤其是那些保存了敏感数据的机器。
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/learn/how-set-2-factor-authentication-login-and-sudo>
作者:[JACK WALLEN](https://www.linux.com/users/jlwallen) 译者:[ictlyh](http://mutouxiaogui.cn/blog/) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,505 | 下一代独立式 GNU/Linux 应用打包格式 Flatpak 发布 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/flatpak-officially-released-for-next-generation-standalone-gnu-linux-apps-505589.shtml | 2016-06-24T10:31:26 | [
"Flatpak",
"XDG-App",
"Snap"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7505-1.html | GNOME 项目组的 Allan Day [正式发布](http://flatpak.org/press/2016-06-21-flatpak-released.html)了 Flatpak。

这并不是我们第一次提及 Flatpak,你可能已经知道它是一个无依赖关系的、跨发行版的软件打包框架,它可以让用户在多个基于 Linux 内核的操作系统上使用各种桌面应用程序。有些人可能记得 Flatpak 之前的名字叫做 XDG-App。
Flatpak 是应 GNU/Linux 和开源软件开发者所需而出现的,可以让他们在多个桌面平台、操作系统上发行软件时,不用花费几个小时乃至几天来为各个主要 Linux 发行版进行打包工作。
Flatpak 的首席开发者 Alexander Larsson 说,“Linux 上的应用开发者总是不能直接接触到他们的用户,但是 Flatpak 改变了这种情况,开发者们现在能够真正知道他们的用户要的是什么。这次 Flatpak 的发布让这一切变为现实。”
### 以安全为主导的设计
据 Flatpak 开发团队称,几个重要的开源项目已经为其支持的操作系统以 .flatpak 格式发布了他们的应用,这些开源项目包括 LibreOffice、InkScape、GIMP、MyPaint 和 Darktable。作为 GNOME 项目开发的一部分,几个来自 GNOME 家族的应用也会以 Flatpak 格式打包。
我们之前刚刚说过,[即将发布的 LibreOffice 5.2 办公套件将采用 Flatpak 格式打包](http://news.softpedia.com/news/libreoffice-5-2-beta-now-available-as-a-flatpak-for-common-linux-distributions-504773.shtml),支持各种常见的发行版,包括 Arch Linux、Debian、Ubuntu、Fedora、Mageia 和 Gentoo 等。 此外,图形化软件包管理器“GNOME 软件”也[支持](http://news.softpedia.com/news/gnome-software-package-manager-has-just-received-support-for-flatpak-packages-504397.shtml) Flatpak 格式。
但最棒的是,Flatpak 是围绕安全进行设计的,它为用户提供了沙盒技术,打包在其中的应用软件只能访问 Flatpak 容器内部和宿主库以及操作系统接口。
“下一个 Flatpak 主要版本将全部都是沙盒化的”, Alexander Larsson 在 Flatpak 的[官方声明](http://flatpak.org/press/2016-06-21-flatpak-released.html)中说,“应用作者会在沙盒中看到一套与操作系统交互的更完整界面。”
要更多了解 Flatpak,请访问其[官网](http://flatpak.org/getting.html),你可以找到在上述提及的 GNU/Linux 操作系统中的安装建议。如果尚不支持你的操作系统,也不用担心,Flatpak 正在不断支持其它的发行版,相信很快就能看到。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,506 | Canonical 并不指望别的发行版也从 Ubuntu 商店下载 Snap 软件包 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/shuttleworth-doesn-t-expect-other-oses-to-want-to-fetch-snaps-from-ubuntu-store-505601.shtml | 2016-06-25T16:53:30 | [
"Snap",
"快照包",
"Flatpak"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7506-1.html | 当 Canonical [宣布](/article-7464-1.html)他们的 Snappy 方案已可以用于包括 Debian、Arch Linux、OpenWrt 在内的一些主流 Linux 发行版时,遭遇到了一些来自社区的[反驳意见](/article-7484-1.html),还有人问 Canonical 是否已经准备好给其它的发行版提供 Snap 软件包。
每个人都会首先问道,“为什么我没有见到 Snappy 服务器的源代码出现?”有些人对 Canonical 在其 [Snap 发布公告](https://insights.ubuntu.com/2016/06/14/universal-snap-packages-launch-on-multiple-linux-distros/)中的许多内容表示了不满,特别是,Canonical 并没有发布 Snappy 商店的源代码,人们通过 snapcraft.io 网站提交了 Snap 软件包后根本不知道后面都发生了什么。
如果开发者想使用 Snap 软件包跨多个 GNU/Linux 发行版发布软件的话,在 [snapcraft.io](http://snapcraft.io/) 上所提供的指导中有一个步骤需要开发者接受在社区争议很大的 Ubuntu CLA(<ruby> 贡献者许可同意书 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Contributor License Agreement </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)。

### Snap 并不依赖商店
前几天,就是 6 月 23 日的时候,Canonical 和 Ubuntu 的创始人 Mark Shuttleworth 在[给社区的一封邮件](https://lists.ubuntu.com/archives/snapcraft/2016-June/000286.html)中透露了一些信息:从设计上来说, Snap 事实上并不依赖于某个商店,这意味着应用开发者可以建立他们自己的商店。不过,从另外一个方面来说,说明他也并不指望其它的发行版会从 Ubuntu Snappy 商店中获取 Snap 软件包。
“Snap **软件包格式**本质上并不依赖商店,你可以在系统里面采用 Snap ,而不用管它是如何到达系统的。所以,当前的商店解决方案并没有什么关系,”Mark Shuttleworth 说,“我并不指望别的发行版会去从 Ubuntu 获取 Snap 软件,除非这里有他们需要的软件包,Snap 可以很容易的用于 Debian.org 。”
他也回应了那些批评 Canonical 在 Snap 格式上不公平竞争的指责,他说:“从某种意义上说,Snap 是顺应发展而出现的——当然,Ubuntu 有个很庞大的商店,因为我们已经在移动和物联网方面努力了好多年了。但是这并不是非难 Snap 的原因,我觉得恰恰相反。”
据 Mark Shuttleworth 说,应用开发者要从他们自己的商店分发 Snap 的最简单的办法就是通过 HTTPS。他认为,很显然选择了 Snap 格式在多个平台上分发的人可以在他自己的代码里面实现这个。当然,你可以可以采用其他的类似解决方案,包括[最新发布的 Flatpak](/article-7505-1.html) 或 AppImage。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,508 | 来自 Fedora 24 工作站版的四大改进 | http://www.techrepublic.com/article/fedora-24-the-4-biggest-improvements-from-the-latest-workstation-release | 2016-06-26T17:27:30 | [
"Fedora"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7508-1.html | 
2014 年的时候,Fedora.next 促进会开始制定一个 Fedora Linux 未来十年的发展计划。这个[计划](https://fedoramagazine.org/fedora-present-and-future-a-fedora-next-2014-update-part-i-why/),从本质上将 Fedora 与那些将各种不同的开源产品堆积在一个公共的软件仓库中的发行版区分开来了(看看 Debian 你就知道了)。
说的更清楚些,Fedora 根据不同的用途,分成了<ruby> 工作站版 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Workstation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 服务器版 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Server </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和针对各个<ruby> 云服务商的分发版 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Cloud distributions </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。对于工作站版,其主要的关注点是让它面对最终用户而言更加直观易用,无论他是老鸟还是菜鸟;给用户提供一个经过精心打磨的桌面系统,比如消除运行在 GNOME 环境下的 Qt 程序的违和感等等。
这不是一个突然的转身,也不是一蹴而就的变化,这种调整是逐步演进的,在新版本发布时它一定是稳定的,而不是堆在那里就可以发步了(LCTT 译注:这也是导致 Fedora 拖延症传统的原因)。原计划在 Fedora 24 中会选择 Wayland 作为默认的显示服务器,即在 GNOME 桌面、驱动程序和全部应用中支持 Wayland,而且事实上在过去六个月当中也取得了极大进展,但是最终 Fedora 24 仍旧默认采用了 X.org ,而留给 Wayland 更多时间进行精雕细琢。
### 1. 视觉改进
系统默认字体 Cantarell 是一个主要的变化,对于使用过之前版本的 Fedora 用户来说,这是第一眼就能看到的变化了。这包括重新打造的字体渲染引擎,特别是[字体微调数据](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Font_hinting)会影响到字体在不同的大小和 DPI 时如何显示。在本次更新前,Cantarell 的字体微调数据在音调符号之间有些不一致,此外还改进了 [Cyrillic 字符](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyrillic_script)的支持。从之前版本升级的用户,如果手工修改过字体渲染设置或使用过 GNOME 调整工具调整的,[需要将那些设置重置回默认设置](https://fedoramagazine.org/font-improvements-fedora-24-workstation/),以便可以使字体设置正确升级。
你可以使用 GNOME 调整工具恢复默认设置,或使用如下命令:
```
gsettings reset org.gnome.desktop.interface font-name
gsettings reset org.gnome.settings-daemon.plugins.xsettings antialiasing
gsettings reset org.gnome.settings-daemon.plugins.xsettings hinting
gsettings reset org.gnome.settings-daemon.plugins.xsettings rgba-order
```
在 Fedora 24 的软件库中新增了一个 [QGnomePlatform](https://github.com/MartinBriza/QGnomePlatform) 软件包,它可以[将 GNOME/GTK 显示设置转换到 Qt 5 应用](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Changes/QGnomePlatform)上。对于高清分辨率的显示器来说——它越来越多地出现在笔记本电脑上了——这是一个可喜的变化,它显著地改善了 Qt 5 程序的显示效果,可用性会更好。
在 Nautilus 文件管理器中的搜索功能现在也[更加地健壮](https://csorianognome.wordpress.com/2016/02/08/nautilus-3-20-and-looking-forward/),现在可以在搜索中按文件使用或修改时间进行过滤,也可以限制只搜索一类或几类文件,比如只搜索“文档”。
### 2. 支持 openh264
Fedora 24 现在正式地支持了 openh264 ,它属于思科专利授权的一部分,现在可以免费使用这个专有的编解码器了。不过,还有一点限制,这个编解码器需要去思科下载。想要播放这种视频的用户会得到一个下载该编解码器的提示,而 GNOME 之外的用户[必须手动启用](https://ausil.us/wordpress/?p=126)该功能才行。
此外,这个插件目前仅支持基本性能编码,而许多视频采用了高性能编码方式进行编码,预期还会[不断增加更多的性能编码支持](https://blogs.gnome.org/uraeus/2016/05/12/h264-in-fedora-workstation/)。
### 3. 图形化升级
之前版本的 Fedora 需要使用命令行来进行重大版本升级,比如从 22 升级到 23 时就是这样的。从现在开始(这个功能也会移植回 Fedora 23),用户可以[使用“软件”应用来进行重大版本升级](https://fedoramagazine.org/fedora-24-feature-graphical-upgrades/)。
升级系统有一个明确标为“安装”的按钮,只有在直接得到用户指令的情况下才进行升级,而不会像 Windows 10 那样,[令用户吃惊](https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2016/may/04/windows-10-updates-ruining-pro-gaming-streams)地通过那种[不透明的、频繁更新的方式进行更新](https://fedoramagazine.org/fedora-24-feature-graphical-upgrades/)。
### 4. 引擎盖之下的改进
可以[用汽车来类比](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Car_analogy),很多内部的细节只有那种专门去找寻它们的人才会注意到(这么干的一般都是程序员)。这其中包括 [glibc 2.23](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Changes/GLIBC223),它带来了 Unicode 8.0 支持,以及[一些安全修复](https://sourceware.org/git/?p=glibc.git;a=blob;f=NEWS;hb=HEAD)。C 编译器也[升级到了 GCC 6](https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-6/changes.html);类似的,[Mono 升级到了 4.2](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Changes/Mono4.2) ,改进了 .NET 支持;[Ruby 升级到了 2.3](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Changes/Ruby_2.3),[Python 升级到了 3.5](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Changes/python3.5),[Node.js 升级到了 5.10](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Changes/NodeJS5x)。[Ping 现在支持 IPv6 地址](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Changes/PingIpv6)了,也就是我们不再需要一个 IPv6 特定的版本了。
### 我应该使用它吗?
如果你已经在使用 Linux 桌面了,那么答案是肯定的。GNOME 3 从其首次发布以来已经经过很长时间的打磨,可以很轻松地像一个“传统的”桌面一样定制,虽然在一些细节上有所不同。Fedora 也有各种已经预先配置好的其它桌面环境,比如 KDE、MATE、LXDE、Xfce 和来自 Linux Mint 的 Cinnamon。
如果你是刚刚从 Windows 转移过来,那么还需要一点点适应过程。如上所述,“软件”应用里面还不包括专属软件,所以一些常见的专属软件,比如 Google Chrome 和 TeamViewer 在“软件”里面还找不到。当然,解决办法很容易,[Fedy](http://folkswithhats.org/) 提供了一键安装这些常见专属软件的途径,以及各种常用的优化功能。
现在,你可以去 [getfedora.com](https://getfedora.org/) 下载 Fedora 24 了!
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,510 | Canonical 演示为任意发行版创建一个 Snap 商店是如何的简单 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/canonical-demonstrates-how-easy-is-to-create-a-vendor-independent-snap-store-505664.shtml | 2016-06-27T08:50:00 | [
"snap",
"flatpak",
"snappy"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7510-1.html | 
Snappy 和 Flatpak 之间的[争吵](/article-7484-1.html)仍在继续中,现在 Canonical 在刚刚发布的 Fedora 24 上演示了创建一个厂商无关的 Snap 商店是多么的简单。
Snap 宣传它是[面向各个主要 Linux 发行版的通用二进制软件包格式](/article-7464-1.html),人们对此非常关注,也有很多[议论](/article-7484-1.html)。就在几天前, Canonical 和 Ubuntu 的创始人 Mark Shuttleworth 对这些人们重点关注的问题[做了一番答复](/article-7506-1.html),表示 Canonical 并不指望别的操作系统使用 Ubuntu 的 snap 商店,你们完全可以自己搞嘛,就是个 HTTPS 而已。
针对指责 Snap 商店没有开源的意见,Canonical 的 Ubuntu 产品与战略总监 Dustin Kirkland 说,“事实上,你可以在任何支持 Snap 的操作系统上运行你的 Snap 商店,真的。”
### 一个可以提供 Snap 软件包服务的最简单的示例商店
Dustin 给我们介绍了一个由开发者 Bret Barker 发布在 GitHub 上的一个[概念性的独立 Snap 商店](https://github.com/noise/snapstore),这个软件以 Apache 许可证开源,你可以[在 GitHub 上 fork 它](https://github.com/noise/snapstore),并安装到任何 GNU/Linux 发行版上去。
#### 服务器端(Snap 商店)
“首先,我启动一个 AWS 实例,当然,我可以启动一个 Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 实例,但实际上我启动的是一个 Fedora 24 实例。”
如果你的机器上已经有了 snap 环境,你可以直接用:
```
snap install snapstore-example
```
来安装这个示例商店。
如果没有,你可以手动来安装。首先安装 python 虚拟环境:
```
sudo dnf install python-virtualenv
```
克隆这个示例商店的代码:
```
git clone https://github.com/noise/snapstore.git
cd snapstore
```
设置虚拟环境并安装依赖包:
```
virtualenv env
. env/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
运行:
```
python store.py
```
这样 snap 商店就安装好了,它会监听在默认的 5000 端口上。

#### 客户端
在 Fedora 24 上运行
```
sudo dnf install snapd
```
来安装 Snappy,它同时也会安装必要的依赖包,如: squashfs-tools、kernel-modules。
你可以通过安装一个测试包来看看 snap 是否正常工作:
```
sudo snap install hello
```
如果正常的话,然后修改 `/etc/environment`,加入你的商店 URL,强制 snapd (Snappy 守护进程)与刚刚创建的 Snap 商店连接:
```
SNAPPY_FORCE_CPI_URL=http://localhost:5000/api/v1/
```
重启 snapd:
```
sudo service snapd restart
```
这个示例商店支持如下命令来查找和安装 snap 软件包:
```
snap find foobar25
sudo snap install foobar25
```

更多可以看 Dustin 的[原文](http://blog.dustinkirkland.com/2016/06/howto-host-your-own-snap-store.html)或这个[示例商店的说明](https://github.com/noise/snapstore)。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,511 | Linux 移植版的游戏性能简直就是垃圾! | http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=OB-Analytics-Win-Linu-AMDNV | 2016-06-27T18:52:00 | [
"游戏"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7511-1.html | 最近,著名的测评网站 [phoronix.com](http://www.phoronix.com/) 进行了三个 Windows 和 Linux 性能方面的测评: [Windows vs. Linux AMDGPU-PRO / RadeonSI testing](http://www.phoronix.com/vr.php?view=23310) 、[GTX 1080 Windows vs. Linux results](http://www.phoronix.com/vr.php?view=23303) 和 [Intel Windows vs. Linux benchmarks](http://www.phoronix.com/vr.php?view=23326),通过将这三个测评的数据使用 [OpenBenchmarking.org](http://openbenchmarking.org/) 进行合并归一,可以得出一个令人伤心的结论:大部分游戏在 Linux 下的性能不及 Windows 。与原生的 Windows 游戏的性能相比,很多 Linux 移植版游戏的性能简直就是垃圾,或者说,就像垃圾一样。

以下是一些游戏在 Windows 下和 Linux 下的性能比较:

*Phoronix 的老读者们都知道,Linux 版本的<ruby> 虚幻引擎 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Unigine </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>演示的效果与 Windows 相比差距不少,不过过去了这些年,虚幻引擎在 Linux 下的测试性能已经接近了 Windows 版本了,这主要是因为 Linux 下的 GPU 驱动问题越来越少了。这是一个不多的好消息。*

*《Xonotic》是一个开源的跨平台第一人称视角的射击游戏,在 Linux 下的 Intel 驱动的性能差的令我们吃惊,不过其它的驱动看起来还好。我们考虑这里肯定有一些需要特定优化的地方。*

*《古墓丽影》在 Linux 下的性能十分之糟,只有 Windows 下的一半左右。*

*《<ruby> 超级房车赛:汽车运动 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> GRID Autosport </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>》在 Linux 下的性能只有 Windows 下的 60% 左右。*

*Valve 的《Dota 2》 / Source 2 引擎的性能不错!这应该是整个测试中唯二让人满意的结果了。*

*《<ruby> 中土世界:暗影魔多 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Middle-Earth: Shadow of Mordor </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>》的 Linux 下的性能要比其它的 Linux 游戏稍好一些,但是仍然不能同 Windows 下的相比。*

*《F1 2015》的性能也非常糟糕。*
这简直太糟糕了,如此多的 Linux 游戏与其对应的 Windows 下的游戏相比性能差的不是一点半点,不管是什么显卡或驱动都是这样。希望过些时间下一代的游戏能够借助 Vulkan 提升其性能表现吧。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,513 | Linux/UNIX 定时任务 cron 详解 | https://www.unixmen.com/add-cron-jobs-linux-unix/ | 2016-06-28T15:54:00 | [
"cron",
"crontab",
"定时任务"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7513-1.html | 
### 导言

<ruby> 定时任务 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> cron job </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>被用于安排那些需要被周期性执行的命令。利用它,你可以配置某些命令或者脚本,让它们在某个设定的时间内周期性地运行。`cron` 是 Linux 或者类 Unix 系统中最为实用的工具之一。cron 服务(守护进程)在系统后台运行,并且会持续地检查 `/etc/crontab` 文件和 `/etc/cron.*/`目录。它同样也会检查 `/var/spool/cron/` 目录。
### crontab 命令
`crontab` 是用来安装、卸载或者列出定时任务列表的命令。cron 配置文件则用于驱动 `Vixie Cron` 的 [cron(8)](http://www.manpager.com/linux/man8/cron.8.html) 守护进程。每个用户都可以拥有自己的 crontab 文件,虽然这些文件都位于 `/var/spool/cron/crontabs` 目录中,但并不意味着你可以直接编辑它们。你需要通过 `crontab` 命令来编辑或者配置你自己的定时任务。
### 定时配置文件的类型
配置文件分为以下不同的类型:
* **UNIX 或 Linux 的系统级 crontab** : 此类型通常由那些需要 root 或类似权限的系统服务和重要任务使用。第六个字段(见下方的字段介绍)为用户名,用来指定此命令以哪个用户身份来执行。如此一来,系统的 `crontab` 就能够以任意用户的身份来执行操作。
* **用户的 crontab**: 用户可以使用 `crontab` 命令来安装属于他们自己的定时任务。 第六个字段为需要运行的命令, 所有的命令都会以创建该 crontab 任务的用户的身份运行。
**注意**: 这种问答形式的 `Cron` 实现由 Paul Vixie 编写而成,并且被包含在许多 [Linux](http://www.linuxsecrets.com/) 发行版本和类 Unix 系统(如广受欢迎的第四版 BSD)中。它的语法被各种 crond 的实现所[兼容](http://www.linuxsecrets.com/linux-hardware/)。
那么我该如何安装、创建或者编辑我自己的定时任务呢?
要编辑你的 crontab 文件,需要在 Linux 或 Unix 的 shell 提示符后键入以下命令:
```
$ crontab -e
```
`crontab` 语法(字段介绍)
语法为:
```
1 2 3 4 5 /path/to/command arg1 arg2
```
或者
```
1 2 3 4 5 /root/ntp_sync.sh
```
其中:
* 第1个字段:分钟 (0-59)
* 第2个字段:小时 (0-23)
* 第3个字段:日期 (1-31)
* 第4个字段:月份 (1-12 [12 代表 December])
* 第5个字段:一周当中的某天 (0-7 [7 或 0 代表星期天])
* /path/to/command - 计划执行的脚本或命令的名称
便于记忆的格式:
```
* * * * * 要执行的命令
----------------
| | | | |
| | | | ---- 周当中的某天 (0 - 7) (周日为 0 或 7)
| | | ------ 月份 (1 - 12)
| | -------- 一月当中的某天 (1 - 31)
| ---------- 小时 (0 - 23)
------------ 分钟 (0 - 59)
```
简单的 `crontab` 示例:
```
### 每隔 5 分钟运行一次 backupscript 脚本 ##
*/5 * * * * /root/backupscript.sh
### 每天的凌晨 1 点运行 backupscript 脚本 ##
0 1 * * * /root/backupscript.sh
### 每月的第一个凌晨 3:15 运行 backupscript 脚本 ##
15 3 1 * * /root/backupscript.sh
```
### 如何使用操作符
操作符允许你为一个字段指定多个值,这里有三个操作符可供使用:
* **星号 (**`*`**)** : 此操作符为字段指定所有可用的值。举个例子,在小时字段中,一个星号等同于每个小时;在月份字段中,一个星号则等同于每月。
* **逗号 (**`,`**)** : 这个操作符指定了一个包含多个值的列表,例如:`1,5,10,15,20,25`.
* **横杠 (**`-`**)** : 此操作符指定了一个值的范围,例如:`5-15` ,等同于使用逗号操作符键入的 `5,6,7,8,9,...,13,14,15`。
* **分隔符 (**`/`**)** : 此操作符指定了一个步进值,例如: `0-23/` 可以用于小时字段来指定某个命令每小时被执行一次。步进值也可以跟在星号操作符后边,如果你希望命令行每 2 小时执行一次,则可以使用 `*/2`。
### 如何禁用邮件输出
默认情况下,某个命令或者脚本的输出内容(如果有的话)会发送到你的本地邮箱账户中。若想停止接收 `crontab` 发送的邮件,需要添加 `>/dev/null 2>&1` 这段内容到执行的命令的后面,例如:
```
0 3 * * * /root/backup.sh >/dev/null 2>&1
```
如果想将输出内容发送到特定的邮件账户中,比如说 [email protected] 这个邮箱, 则你需要像下面这样定义一个 MAILTO 变量:
```
MAILTO="[email protected]"
0 3 * * * /root/backup.sh >/dev/null 2>&1
```
访问 “[禁用 Crontab 命令的邮件提示](http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/disable-the-mail-alert-by-crontab-command/)” 查看更多信息。
### 任务:列出你所有的定时任务
键入以下命令:
```
# crontab -l
# crontab -u username -l
```
要删除所有的定时任务,可以使用如下命令:
```
### 删除当前定时任务
crontab -r
```
```
### 删除某用户名下的定时任务,此命令需以 root 用户身份执行
crontab -r -u username
```
### 使用特殊字符串来节省时间
你可以使用以下 8 个特殊字符串中的其中一个替代头五个字段,这样不但可以节省你的时间,还可以提高可读性。
| 特殊字符 | 含义 |
| --- | --- |
| @reboot | 在每次启动时运行一次 |
| @yearly | 每年运行一次,等同于 “0 0 1 1 \*”. |
| @annually | (同 @yearly) |
| @monthly | 每月运行一次, 等同于 “0 0 1 \* \*”. |
| @weekly | 每周运行一次, 等同于 “0 0 \* \* 0”. |
| @daily | 每天运行一次, 等同于 “0 0 \* \* \*”. |
| @midnight | (同 @daily) |
| @hourly | 每小时运行一次, 等同于 “0 \* \* \* \*”. |
示例:
#### 每小时运行一次 ntpdate 命令
```
@hourly /path/to/ntpdate
```
### 关于 `/etc/crontab` 文件和 `/etc/cron.d/*` 目录的更多内容
`/etc/crontab` 是系统的 crontab 文件。通常只被 root 用户或守护进程用于配置系统级别的任务。每个单独的用户必须像上面介绍的那样使用 `crontab` 命令来安装和编辑自己的任务。`/var/spool/cron/` 或者 `/var/cron/tabs/` 目录存放了个人用户的 crontab 文件,它应该备份在用户的家目录当中。
### 理解默认的 `/etc/crontab` 文件
典型的 `/etc/crontab` 文件内容是这样的:
```
SHELL=/bin/bash
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
MAILTO=root
HOME=/
# run-parts
01 * * * * root run-parts /etc/cron.hourly
02 4 * * * root run-parts /etc/cron.daily
22 4 * * 0 root run-parts /etc/cron.weekly
42 4 1 * * root run-parts /etc/cron.monthly
```
首先,环境变量必须被定义。如果 SHELL 行被忽略,cron 会使用默认的 sh shell。如果 PATH 变量被忽略,就没有默认的搜索路径,所有的文件都需要使用绝对路径来定位。如果 HOME 变量被忽略,cron 会使用调用者(用户)的家目录替代。
另外,cron 会读取 `/etc/cron.d/`目录中的文件。通常情况下,像 sa-update 或者 sysstat 这样的系统守护进程会将他们的定时任务存放在此处。作为 root 用户或者超级用户,你可以使用以下目录来配置你的定时任务。你可以直接将脚本放到这里。`run-parts`命令会通过 `/etc/crontab` 文件来运行位于某个目录中的脚本或者程序。
| 目录 | 描述 |
| --- | --- |
| /etc/cron.d/ | 将所有的脚本文件放在此处,并从 /etc/crontab 文件中调用它们。 |
| /etc/cron.daily/ | 运行需要 每天 运行一次的脚本 |
| /etc/cron.hourly/ | 运行需要 每小时 运行一次的脚本 |
| /etc/cron.monthly/ | 运行需要 每月 运行一次的脚本 |
| /etc/cron.weekly/ | 运行需要 每周 运行一次的脚本 |
### 备份定时任务
```
# crontab -l > /path/to/file
# crontab -u user -l > /path/to/file
```
---
via: <https://www.unixmen.com/add-cron-jobs-linux-unix/>
作者:[Duy NguyenViet](https://www.unixmen.com/author/duynv/) 译者:[mr-ping](https://github.com/mr-ping) 校对:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | **Introduction**
Cron job are used to schedule commands to be executed periodically. You can setup commands or scripts, which will repeatedly run at a set time. Cron is one of the most useful tool in Linux or UNIX like operating systems. The cron service (daemon) runs in the background and constantly checks the /etc/crontab file, and /etc/cron.*/ directories. It also checks the /var/spool/cron/ directory.
**Command of crontab**
crontab is the command used to install, deinstall or list the tables (cron configuration file) used to drive the [cron(8)](http://www.manpager.com/linux/man8/cron.8.html) daemon in Vixie Cron. Each user can have their own crontab file, and though these are files in /var/spool/cron/crontabs, they are not intended to be edited directly. You need to use crontab command for editing or setting up your own cron jobs.
**Types of cron configuration files**
There are different types of configuration files:
**The UNIX / Linux system crontab **: Usually, used by system services and critical jobs that requires root like privileges. The sixth field (see below for field description) is the name of a user for the command to run as. This gives the system crontab the ability to run commands as any user.
**The user crontabs: **User can install their own cron jobs using the crontab command. The sixth field is the command to run, and all commands run as the user who created the crontab
**Note:** This faq features cron implementations written by Paul Vixie and included in many [Linux](http://www.linuxsecrets.com/) distributions and Unix like systems such as in the popular 4th BSD edition. The syntax is [compatible](http://www.linuxsecrets.com/linux-hardware/) with various implementations of crond.
How Do I install or create or edit my own cron jobs?
To edit your crontab file, type the following command at the UNIX / Linux shell prompt:
$ crontab -e
Syntax of crontab (field description)
The syntax is:
1 2 3 4 5 /path/to/command arg1 arg2
OR
1 2 3 4 5 /root/ntp_sync.sh
Where,
- 1: Minute (0-59)
- 2: Hours (0-23)
- 3: Day (0-31)
- 4: Month (0-12 [12 == December])
- 5: Day of the week(0-7 [7 or 0 == sunday])
- /path/to/command – Script or command name to schedule
Easy to remember format:
* * * * * command to be executed
– – – – –
| | | | |
| | | | —– Day of week (0 – 7) (Sunday=0 or 7)
| | | ——- Month (1 – 12)
| | ——— Day of month (1 – 31)
| ———– Hour (0 – 23)
————- Minute (0 – 59)
Example simple crontab.
|
## run backupscript 5 minutes 1 time ##
*/5 * * * * /root/backupscript.sh ## Run backupscript daily on 1:00 am ## 0 1 * * * /root/backupscript.sh ## Run backup script monthly on the 1st of month 3:15 am ## 15 3 1 * * /root/backupscript.sh |
**How do I use operators?**
An operator allows you to specifying multiple values in a field. There are three operators:
**The asterisk (*********) **: This operator specifies all possible values for a field. For example, an asterisk in the hour time field would be equivalent to every hour or an asterisk in the month field would be equivalent to every month
**The comma (****,****)** : This operator specifies a list of values, for example: “1,5,10,15,20, 25”.
**The dash (****–****)** : This operator specifies a range of values, for example: “5-15” days , which is equivalent to typing “5,6,7,8,9,….,13,14,15” using the comma operator.
**The separator (****/****)** : This operator specifies a step value, for example: “0-23/” can be used in the hours field to specify command execution every other hour. Steps are also permitted after an asterisk, so if you want to say every two hours, just use */2.
**Use special string to save time**
Instead of the first five fields, you can use any one of eight special strings. It will not just save your time but it will improve readability.
Special string | Meaning |
@reboot | Run once, at startup. |
@yearly | Run once a year, “0 0 1 1 *”. |
@annually | (same as @yearly) |
@monthly | Run once a month, “0 0 1 * *”. |
@weekly | Run once a week, “0 0 * * 0”. |
@daily | Run once a day, “0 0 * * *”. |
@midnight | (same as @daily) |
@hourly | Run once an hour, “0 * * * *”. |
Examples
#### Run ntpdate command every hour ####
@hourly /path/to/ntpdate
**More about /etc/crontab file and /etc/cron.d/* directories**
**/etc/crontab **is system crontabs file. Usually only used by root user or daemons to configure system wide jobs. All individual user must must use crontab command to install and edit their jobs as described above. /var/spool/cron/ or /var/cron/tabs/ is directory for personal user crontab files. It must be backup with users home directory.
Understanding Default /etc/crontab
Typical /etc/crontab file entries:
SHELL=/bin/bash
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
MAILTO=root
HOME=/
# run-parts
01 * * * * root run-parts /etc/cron.hourly
02 4 * * * root run-parts /etc/cron.daily
22 4 * * 0 root run-parts /etc/cron.weekly
42 4 1 * * root run-parts /etc/cron.monthly
First, the environment must be defined. If the shell line is omitted, cron will use the default, which is sh. If the PATH variable is omitted, no default will be used and file locations will need to be absolute. If HOME is omitted, cron will use the invoking users home directory.
Additionally, cron reads the files in /etc/cron.d/ directory. Usually system daemon such as sa-update or sysstat places their cronjob here. As a root user or superuser you can use following directories to configure cron jobs. You can directly drop your scripts here. The run-parts command run scripts or programs in a directory via /etc/crontab file:
Directory | Description |
/etc/cron.d/ | Put all scripts here and call them from /etc/crontab file. |
/etc/cron.daily/ | Run all scripts once a day |
/etc/cron.hourly/ | Run all scripts once an hour |
/etc/cron.monthly/ | Run all scripts once a month |
/etc/cron.weekly/ | Run all scripts once a week |
**Backup cronjob**
# crontab -l > /path/to/file
# crontab -u user -l > /path/to/file |
7,514 | 安卓的下一场革命:不安装即可使用应用! | http://www.iwillfolo.com/androids-next-revolution-use-apps-even-without-installing-them/ | 2016-06-28T17:07:00 | [
"Android",
"AIA"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7514-1.html | 谷歌安卓的一项新创新将可以让你无需安装即可在你的设备上使用应用程序。现在已经初具雏形。
还记得那时候吗,某人发给你了一个链接,要求你通过安装一个应用才能查看。
是否要安装这个应用就为了看一下链接,这种进退两难的选择一定让你感到很沮丧。而且,安装应用这个事也会消耗你不少宝贵的时间。
上述场景可能大多数人都经历过,或者说大多数现代科技用户都经历过。尽管如此,我们都接受,认为这是天经地义的事情。
事实真的如此吗?
针对这个问题谷歌的安卓部门给出了一个全新的、开箱即用的答案:
### Android Instant Apps (AIA)
Android Instant Apps 声称可以从一开始就帮你摆脱这样的两难境地,让你简单地点击链接(见打开链接的示例)然后直接开始使用这个应用。
另一个真实生活场景的例子,如果你想停车但是没有停车码表的相应应用,有了 Instant Apps 在这种情况下就方便多了。
根据谷歌提供的信息,你可以简单地将你的手机和码表触碰,停车应用就会直接显示在你的屏幕上,并且准备就绪可以使用。
#### 它是怎么工作的?
Instant Apps 和你已经熟悉的应用基本相同,只有一个不同——这些应用为了满足你完成某项任务的需要,只提供给你已经经过**裁剪和模块化**的应用必要部分。
例如,展开打开链接的场景作为例子,为了查看一个链接,你不需要拥有一个可以写、发送,做咖啡或其它特性的全功能应用。你所需要的全部就是查看功能——而这就是你所会获取到的部分。
这样应用就可以快速打开,让你可以完成你的目标任务。

*AIA 示例*
听起来很棒,不是吗?但是其中还有很多技术方面的问题需要解决。
比如,从安全的观点来说:从理论上来说,如果任何应用都能在你的设备上运行,甚至你都不用安装它——你要怎么保证设备远离恶意软件攻击?
因此,为了消除这类威胁,谷歌还在这个项目上努力,目前只有少数合作伙伴,未来将逐步扩展。
谷歌最终计划在明年发布 AIA(Android Instant Apps)。
相关:[介绍 Android Instant Apps](http://android-developers.blogspot.co.il/2016/05/android-instant-apps-evolving-apps.html?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed:+blogspot/hsDu+%28Android+Developers+Blog%29)
---
via: <http://www.iwillfolo.com/androids-next-revolution-use-apps-even-without-installing-them/>
作者:[iwillfolo](http://www.iwillfolo.com) 译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 302 | Found | null |
7,516 | 谷歌会用基于信任的认证措施取代密码吗? | http://www.iwillfolo.com/will-google-replace-passwords-with-a-new-trust-based-authentication-method/ | 2016-06-29T08:48:00 | [
"认证",
"Abacus"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7516-1.html | 
一个谷歌新开发的认证措施会评估你的登录有多可靠,并且基于一个“<ruby> 信任分 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Trust Score </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”认证你的登录。
这个谷歌项目的名字是 Abacus,它的目标是让你摆脱讨厌的密码记忆和输入。
在最近的 Google I/O 开发者大会上,谷歌引入了自这个雄心勃勃的项目而来的新特性,称作“**Trust API**”。
“如果一切进展顺利”,这个 API(<ruby> 应用程序编程接口 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Application Programming Interface </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)会在年底前供安卓开发者使用。API 会利用安卓设备上不同的传感器来识别用户,并创建一个他们称之为“<ruby> 信任分 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Trust Score </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”的结果。
基于这个信任分,一个需要登录认证的应用可以验证你确实可以授权登录,从而不会提示需要密码。

*Abacus 到 Trust API*
### 需要思考的地方
尽管这个想法,明智的功能,听起来很棒——减轻了密码认证的负担。
但从另一面来说,这是不是谷歌又一次逼迫我们(有意或无意)为了方便使用而放弃我们的隐私?
是否值得?这取决于你的决定...
---
via: <http://www.iwillfolo.com/will-google-replace-passwords-with-a-new-trust-based-authentication-method/>
作者:[iWillFolo](http://www.iwillfolo.com/) 译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 302 | Found | null |
7,517 | vlock – 一个锁定 Linux 用户虚拟控制台或终端的好方法 | http://www.tecmint.com/vlock-lock-user-virtual-console-terminal-linux/ | 2016-06-30T09:02:00 | [
"vlock",
"控制台"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7517-1.html | 虚拟控制台是 Linux 上非常重要的功能,它们给系统用户提供了 shell 提示符,以保证用户在登录和远程登录一个未安装图形界面的系统时仍能使用。
一个用户可以同时操作多个虚拟控制台会话,只需在虚拟控制台间来回切换即可。

*用 vlock 锁定 Linux 用户控制台或终端*
这篇使用指导旨在教会大家如何使用 vlock 来锁定用户虚拟控制台和终端。
### vlock 是什么?
vlock 是一个用于锁定一个或多个用户虚拟控制台用户会话的工具。在多用户系统中 vlock 扮演着重要的角色,它让用户可以在锁住自己会话的同时不影响其他用户通过其他虚拟控制台操作同一个系统。必要时,还可以锁定所有的控制台,同时禁止在虚拟控制台间切换。
vlock 的主要功能面向控制台会话方面,同时也支持非控制台会话的锁定,但该功能的测试还不完全。
### 在 Linux 上安装 vlock
根据你的 Linux 系统选择 vlock 安装指令:
```
# yum install vlock [On RHEL / CentOS / Fedora]
$ sudo apt-get install vlock [On Ubuntu / Debian / Mint]
```
### 在 Linux 上使用 vlock
vlock 操作选项的常规语法:
```
# vlock option
# vlock option plugin
# vlock option -t <timeout> plugin
```
#### vlock 常用选项及用法:
1、 锁定用户的当前虚拟控制台或终端会话,如下:
```
# vlock --current
```

*锁定 Linux 用户终端会话*
选项 -c 或 --current,用于锁定当前的会话,该参数为运行 vlock 时的默认行为。
2、 锁定所有你的虚拟控制台会话,并禁用虚拟控制台间切换,命令如下:
```
# vlock --all
```

*锁定所有 Linux 终端会话*
选项 -a 或 --all,用于锁定所有用户的控制台会话,并禁用虚拟控制台间切换。
其他的选项只有在编译 vlock 时编入了相关插件支持和引用后,才能发挥作用:
3、 选项 -n 或 --new,调用时后,会在锁定用户的控制台会话前切换到一个新的虚拟控制台。
```
# vlock --new
```
4、 选项 -s 或 --disable-sysrq,在禁用虚拟控制台的同时禁用 SysRq 功能,只有在与 -a 或 --all 同时使用时才起作用。
```
# vlock -sa
```
5、 选项 -t 或 --timeout <time\_in\_seconds>,用以设定屏幕保护插件的 timeout 值。
```
# vlock --timeout 5
```
你可以使用 `-h` 或 `--help` 和 `-v` 或 `--version` 分别查看帮助消息和版本信息。
我们的介绍就到这了,提示一点,你可以将 vlock 的 `~/.vlockrc` 文件包含到系统启动中,并参考入门手册[添加环境变量](http://www.tecmint.com/set-path-variable-linux-permanently/),特别是 Debian 系的用户。
想要找到更多或是补充一些这里没有提及的信息,可以直接在写在下方评论区。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/vlock-lock-user-virtual-console-terminal-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[martin2011qi](https://github.com/martin2011qi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,518 | ORB:新一代 Linux 应用 | http://itsfoss.com/orb-linux-apps/ | 2016-06-29T10:25:00 | [
"ORB",
"Orbital"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7518-1.html | 
我们之前讨论过[在 Ubuntu 上离线安装应用](http://itsfoss.com/cube-lets-install-linux-applications-offline/)。我们现在要再次讨论它。
[Orbital Apps](https://www.orbital-apps.com/) 给我们带来了一种新的软件包类型 **ORB**,它具有便携软件、交互式安装向导支持,以及离线使用的能力。
便携软件很方便。主要是因为它们能够无需任何管理员权限直接运行,也能够带着所有的设置和数据随 U 盘存储。而交互式的安装向导也能让我们轻松地安装应用。
### <ruby> 开放式可运行的打包 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> OPEN RUNNABLE BUNDLE </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> (ORB)
ORB 是一个自由开源的包格式,它和其它包格式在很多方面有所不同。ORB 的一些特性:
* **压缩**:所有的包都经过 squashfs 压缩,体积最多可减少 60%。
* **便携模式**:如果一个便携 ORB 应用是在可移动设备上运行的,它会把所有设置和数据存储在那之上。
* **安全**:所有的 ORB 包使用 PGP/RSA 签名,通过 TLS 1.2 分发。
* **离线**:所有的依赖都打包进软件包,所以不再需要下载依赖。
* **开放式软件包**:ORB 软件包可以作为 ISO 镜像挂载。
### 种类
ORB 应用现在有两种类别:
* 便携软件
* SuperDEB
### 1. 便携 ORB 软件
便携 ORB 软件可以立即运行而不需要任何的事先安装。这意味着它不需要管理员权限,也没有依赖!你可以直接从 Orbital Apps 网站下载下来就能使用。
并且由于它支持便携模式,你可以将它拷贝到 U 盘携带。它所有的设置和数据会和它一起存储在 U 盘。只需将 U 盘连接到任何运行 Ubuntu 16.04 的机器上就行了。
#### 可用便携软件
目前有超过 35 个软件以便携包的形式提供,包括一些十分流行的软件,比如:[Deluge](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/deluge),[Firefox](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/firefox),[GIMP](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/gimp),[Libreoffice](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/libreoffice),[uGet](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/uget) 以及 [VLC](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/vlc)。
完整的可用包列表可以查阅 [便携 ORB 软件列表](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/)。
#### 使用便携软件
按照以下步骤使用便携 ORB 软件:
* 从 Orbital Apps 网站下载想要的软件包。
* 将其移动到想要的位置(本地磁盘/U 盘)。
* 打开存储 ORB 包的目录。

* 打开 ORB 包的属性。

* 在权限标签页添加运行权限。
* 双击打开它。
等待几秒,让它准备好运行。大功告成。
### 2. SuperDEB
另一种类型的 ORB 软件是 SuperDEB。SuperDEB 很简单,交互式安装向导能够让软件安装过程顺利得多。如果你不喜欢从终端或软件中心安装软件,superDEB 就是你的菜。
最有趣的部分是你安装时不需要一个互联网连接,因为所有的依赖都由安装向导打包了。
#### 可用的 SuperDEB
超过 60 款软件以 SuperDEB 的形式提供。其中一些流行的有:[Chromium](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/superdeb_installers/ubuntu_16.04_64bits/chromium/),[Deluge](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/deluge),[Firefox](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/firefox),[GIMP](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/gimp),[Libreoffice](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/libreoffice),[uGet](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/uget) 以及 [VLC](https://www.orbital-apps.com/download/portable_apps_linux/vlc)。
完整的可用 SuperDEB 列表,参阅 [SuperDEB 列表](https://www.orbital-apps.com/superdebs/ubuntu_16.04_64bits/)。
#### 使用 SuperDEB 安装向导
* 从 Orbital Apps 网站下载需要的 SuperDEB。
* 像前面一样给它添加**运行权限**(属性 > 权限)。
* 双击 SuperDEB 安装向导并按下列说明操作:




* 完成安装之后,你就可以正常使用了。
### ORB 软件兼容性
从 Orbital Apps 可知,它们完全适配 Ubuntu 16.04 [64 位]。
至于其它发行版兼容性则不受保证。但我们可以说,它在所有 Ubuntu 16.04 衍生版(UbuntuMATE,UbuntuGNOME,Lubuntu,Xubuntu 等)以及基于 Ubuntu 16.04 的发行版(比如即将到来的 Linux Mint 18)上都适用。我们现在还不清楚 Orbital Apps 是否有计划拓展它的支持到其它版本 Ubuntu 或 Linux 发行版上。
如果你在你的系统上经常使用便携 ORB 软件,你可以考虑安装 ORB 启动器。它不是必需的,但是推荐安装它以获取更佳的体验。最简短的 ORB 启动器安装流程是打开终端输入以下命令:
```
wget -O - https://www.orbital-apps.com/orb.sh | bash
```
你可以在[官方文档](https://www.orbital-apps.com/documentation)找到更加详细的介绍。
### 如果我需要的软件不在列表里?
如果你需要一个当前并没有可用 ORB 包的软件,你可以[联系](https://www.orbital-apps.com/contact) Orbital Apps。好消息是,Orbital Apps 正在致力于推出一个创建 ORB 包的工具。所以,不久后我们有希望可以自己制作 ORB 包!
多说一句,这个文章是关于离线安装软件的。如果你感兴趣的话,你可以看看[如何离线更新或升级 Ubuntu](http://itsfoss.com/upgrade-or-update-ubuntu-offline-without-internet/)。
所以,你怎么看 Orbital Apps 的便携软件和 SuperDEB 安装向导?你会试试吗?
---
via: <http://itsfoss.com/orb-linux-apps/>
作者:[Munif Tanjim](http://itsfoss.com/author/munif/) 译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,519 | 65% 的企业正致力于开源项目 | https://opensource.com/business/16/5/2016-future-open-source-survey | 2016-06-29T08:16:20 | [
"开源"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7519-1.html | 
今年 Black Duck 和 North Bridge 发布了第十届年度开源软件前景调查,来调查开源软件的发展趋势。今年这份调查的亮点在于,当前主流社会对开源软件的接受程度以及过去的十年中人们对开源软件态度的变化。
[2016 年的开源软件前景调查](http://www.slideshare.net/blackducksoftware/2016-future-of-open-source-survey-results),分析了来自约3400位专家的反馈。今年的调查中,开发者发表了他们的看法,大约 70% 的参与者是开发者。数据显示,安全专家的参与人数呈指数级增长,增长超过 450% 。他们的参与表明,开源社区开始逐渐关注开源软件中存在的安全问题,以及当新的技术出现时确保它们的安全性。
Black Duck 的[年度开源新秀奖](https://info.blackducksoftware.com/OpenSourceRookies2015.html) 涉及到一些新出现的技术,如容器方面的 Docker 和 Kontena。容器技术这一年有了巨大的发展 ———— 76% 的受访者表示,他们的企业有一些使用容器技术的规划。而 59% 的受访者正准备使用容器技术完成大量的部署,从开发与测试,到内部与外部的生产环境部署。开发者社区已经把容器技术作为一种简单快速开发的方法。
调查显示,几乎每个组织都有开发者致力于开源软件,这一点毫不惊讶。当像微软和苹果这样的大公司将它们的一些解决方案开源时,开发者就获得了更多的机会来参与开源项目。我非常希望这样的趋势会延续下去,让更多的软件开发者无论在工作中,还是工作之余都可以致力于开源项目。
### 2016 年调查结果中的一些要点
#### 商业价值
* 开源软件是发展战略中的一个重要元素,超过 65% 的受访者使用开源软件来加速软件开发的进度。
* 超过 55% 的受访者在生产环境中使用开源软件。
#### 创新的原动力
* 受访者表示,开源软件的使用让软件开发更加快速灵活,从而推进了创新;同时加速了软件推向市场的时间,也极大地减少了与上司沟通的时间。
* 开源软件的优质解决方案,富有竞争力的特性,技术能力,以及可定制化的能力,也促进了更多的创新。
#### 开源商业模式与投资的激增
* 更多不同商业模式的出现给开源企业带来了前所未有的价值。这些价值并不依赖于云服务和技术支持。
* 开源的私募融资在过去的五年内,已增长了将近四倍。
#### 安全和管理
一流的开源安全与管理实践的发展,也没有跟上人们使用开源不断增长的步伐。尽管备受关注的开源项目近年来爆炸式地增长,调查结果却指出:
* 50% 的企业在选择和批准开源代码这方面没有出台正式的政策。
* 47% 的企业没有正式的流程来跟踪开源代码,这就限制了它们对开源代码的了解,以及控制开源代码的能力。
* 超过三分之一的企业没有用于识别、跟踪和修复重大开源安全漏洞的流程。
#### 不断增长的开源参与者
调查结果显示,一个活跃的企业开源社区,激励创新,提供价值,共享情谊:
* 67% 的受访者表示,它们积极鼓励开发者参与开源项目。
* 65% 的企业正致力于开源项目。
* 约三分之一的企业有专门为开源项目设置的全职岗位。
* 59% 的受访者参与开源项目以获得竞争优势。
Black Duck 和 North Bridge 从今年的调查中了解到了很多,如安全,政策,商业模式等。我们很兴奋能够分享这些新发现。感谢我们的合作者,以及所有参与我们调查的受访者。这是一个伟大的十年,我很高兴我们可以肯定地说,开源的未来充满了无限可能。
想要了解更多内容,可以查看完整的[调查结果](http://www.slideshare.net/blackducksoftware/2016-future-of-open-source-survey-results%C2%A0)。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/business/16/5/2016-future-open-source-survey>
作者:[Haidee LeClair](https://opensource.com/users/blackduck2016) 译者:[Cathon](https://github.com/Cathon) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
| 200 | OK | This year marks the 10th annual Future of Open Source Survey to examine trends in open source, hosted by Black Duck and North Bridge. The big takeaway from the survey this year centers around the mainstream acceptance of open source today and how much has changed over the last decade.
The [2016 Future of Open Source Survey](http://www.slideshare.net/blackducksoftware/2016-future-of-open-source-survey-results) analyzed responses from nearly 3,400 professionals. Developers made their voices heard in the survey this year, comprising roughly 70% of the participants. The group that showed exponential growth were security professionals, whose participation increased by over 450%. Their participation shows the increasing interest in ensuring that the open source community pays attention to security issues in open source software and securing new technologies as they emerge.
Black Duck's [Open Source Rookies of the Year](https://info.blackducksoftware.com/OpenSourceRookies2015.html) awards identify some of these emerging technologies, like Docker and Kontena in containers. Containers themselves have seen huge growth this year–76% of respondents say their company has *some plans* to use containers. And an amazing 59% of respondents are already using containers in a variety of deployments, from development and testing to internal and external production environment. The developer community has embraced containers as a way to get their code out quickly and easily.
It's not surprising that the survey shows a miniscule number of organizations having **no** developers contributing to open source software. When large corporations like Microsoft and Apple open source some of their solutions, developers gain new opportunities to participate in open source. I certainly hope this trend will continue, with more software developers contributing to open source projects at work and outside of work.
## Highlights from the 2016 survey
### Business value
- Open source is an essential element in development strategy with more than 65% of respondents relying on open source to speed development.
- More than 55% leverage open source within their production environments.
### Engine for innovation
- Respondents reported use of open source to drive innovation through faster, more agile development; accelerated time to market and vastly superior interoperability.
- Additional innovation is afforded by open source's quality of solutions; competitive features and technical capabilities; and ability to customize.
### Proliferation of open source business models and investment
- More diverse business models are emerging that promise to deliver more value to open source companies than ever before. They are not as dependent on SaaS and services/support.
- Open source private financing has increased almost 4x in five years.
### Security and management
The development of best-in-class open source security and management practices has not kept pace with growth in adoption. Despite a proliferation of expensive, high-profile open source breaches in recent years, the survey revealed that:
- 50% of companies have no formal policy for selecting and approving open source code.
- 47% of companies don’t have formal processes in place to track open source code, limiting their visibility into their open source and therefore their ability to control it.
- More than one-third of companies have no process for identifying, tracking or remediating known open source vulnerabilities.
### Open source participation on the rise
The survey revealed an active corporate open source community that spurs innovation, delivers exponential value and shares camaraderie:
- 67% of respondents report actively encouraging developers to engage in and contribute to open source projects.
- 65% of companies are contributing to open source projects.
- One in three companies have a fulltime resource dedicated to open source projects.
- 59% of respondents participate in open source projects to gain competitive edge.
Black Duck and North Bridge learned a great deal this year about security, policy, business models and more from the survey, and we’re excited to share these findings. Thank you to our many collaborators and all the respondents for taking the time to take the survey. It’s been a great ten years, and I am happy that we can safely say that the **future** of open source is full of possibilities.
Learn more, [see the full results](http://www.slideshare.net/blackducksoftware/2016-future-of-open-source-survey-results ).
## Comments are closed. |
7,520 | Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon 版和 MATE 版已经可以下载了 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/linux-mint-18-cinnamon-and-mate-editions-are-now-available-for-download-505756.shtml | 2016-06-29T08:48:00 | [
"Linux Mint"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7520-1.html | 在今天早些时候,[Linux Mint](https://www.linuxmint.com/) 项目负责人 Clement Lefebvre 将 ISO 镜像放到了网上,它首先出现在了[爱尔兰的镜像网站](Irish),看起来已经是最终的产品形态了。
截止到写这篇文章时,在 Linux Mint 网站上还没有发布官方通告,估计 Clement Lefebvre 正在等待所有的镜像同步之后才会发布吧,这可能需要一天之久。不过,[Cinnamon](https://www.linuxmint.com/rel_sarah_cinnamon_whatsnew.php) 和 [MATE](https://www.linuxmint.com/rel_sarah_mate_whatsnew.php) 的发布备注已经有了。

### 基于 Ubuntu 16.04 LTS ,使用 Arc GTK 主题
由于 Linux Mint 18 “Sarah” 的发布公告还是三周前发布的 Beta 公告,所以我们只知道 Cinnamon 和 MATE 版里面有什么新变化。它们两个基于 Ubuntu 16.04 LTS,使用的是 Linux 4.4 LTS 内核。
Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon 分支以最新的 Cinnamon 3.0 桌面环境构建,辅以极大改进了的更新管理器。在视觉和细节方面,以流行的 Arc GTK 主题和 Moka 图标集打造的 Mint-Y 主题为它带来了新的观感,不过它并没有默认启用。
此外,还有一些底层的改进,比如高分辨率支持、 X-Apps、为 Linux Mint 新设计的应用(Xed、 Xviewer、 Xreader、Xplayer 和 Pix)、MDM 2.0 登录管理器、对多数应用的 GTK3 支持,以及 Gufw 图形化防火墙配置工具。

而 Linux Mint 18 MATE 分支则以 MATE 1.14 桌面环境构建,也有类似于 Cinnamon 分支一样的改进。
Linux Mint 18 将支持安全更新到 2021 年。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,523 | 马克·沙特尔沃思 —— Ubuntu 背后的那个男人 | http://www.unixmen.com/mark-shuttleworth-man-behind-ubuntu-operating-system/ | 2016-06-29T16:32:00 | [
"Canonical",
"Ubuntu",
"Mark Shuttleworth"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7523-1.html | 
<ruby> 马克·理查德·沙特尔沃思 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Mark Richard Shuttleworth </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 是 Ubuntu 的创始人,也被称作 [Debian 背后的人](https://wiki.debian.org/PeopleBehindDebian)([之一](https://raphaelhertzog.com/2011/11/17/people-behind-debian-mark-shuttleworth-ubuntus-founder/))。他于 1973 年出生在南非的<ruby> 韦尔科姆 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Welkom </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。他不仅是个企业家,还是个太空游客——他是第一个前往太空旅行的非洲独立国家的公民。
马克曾在 1996 年成立了一家名为 **Thawte** 的互联网商务安全公司,那时他还在<ruby> 开普敦大学 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> University of Cape Town </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的学习金融和信息技术。
2000 年,马克创立了 HBD(<ruby> Here be Dragons <rp> ( </rp> <rt> 此处有龙/危险 </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的缩写,所以其吉祥物是一只龙),这是一家投资公司,同时他还创立了<ruby> 沙特尔沃思基金会 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Shuttleworth Foundation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,致力于以奖金和投资等形式给社会中有创新性的领袖提供资助。
>
> “移动设备对于个人电脑行业的未来而言至关重要。比如就在这个月,相对于平板电脑的发展而言,传统 PC 行业很明显正在萎缩。所以如果我们想要涉足个人电脑产业,我们必须首先涉足移动行业。移动产业之所以有趣,是因为在这里没有盗版 Windows 操作系统的市场。所以如果你为你的操作系统赢得了一台设备的市场份额,这台设备会一直使用你的操作系统。在传统 PC 行业,我们时不时得和“免费”的 Windows 产生竞争,这是一种非常微妙的挑战。所以我们现在的重心是围绕 Ubuntu 和移动设备——手机和平板——以图与普通用户建立更深层次的联系。”
>
>
> — 马克·沙特尔沃思
>
>
>
2002 年,他在俄罗斯的<ruby> 星城 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Star City </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>接受了为期一年的训练,随后作为联盟号 TM-34 任务组的一员飞往了国际空间站。再后来,在面向有志于航空航天或者其相关学科的南非学生群体发起了推广科学、编程及数学的运动后,马克 创立了 **Canonical Ltd**。此后直至2013年,他一直在领导 Ubuntu 操作系统的开发。
现今,沙特尔沃思拥有英国与南非双重国籍并和 18 只可爱的鸭子住在英国的 Isle of Man 小岛上的一处花园,一同的还有他可爱的女友 Claire,两条黑色母狗以及时不时经过的羊群。
>
> “电脑不仅仅是一台电子设备了。它现在是你思维的延续,以及通向他人的大门。”
>
>
> — 马克·沙特尔沃思
>
>
>
### 马克·沙特尔沃思的早年生活
正如我们之前提到的,马克出生在南非的<ruby> 奥兰治自由邦 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Orange Free State </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的<ruby> 韦尔科姆 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Welkom </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。他是一名外科医生和护士学校教师的孩子。他在西部省预科学校就读并在 1986 年成为了学生会主席,一个学期后就读于 Rondebosch 男子高中,再之后入学 Bishops Diocesan 学院并在 1991 年再次成为那里的学生会主席。
马克在<ruby> 开普敦大学 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> University of Cape Town </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>拿到了金融和信息系统的商业科学双学士学位,他在学校就读时住在 Smuts Hall。作为学生,他也在那里帮助安装了学校的第一条宿舍互联网接入。
>
> “无数的企业和国家已经证明,引入开源政策能提高竞争力和效率。在不同层面上创造生产力对于公司和国家而言都是至关重要的。”
>
>
> — 马克·沙特尔沃思
>
>
>
### 马克·沙特尔沃思的职业生涯
马克在 1995 年创立了 Thawte,公司专注于数字证书和互联网安全,然后在 1999 年把公司卖给了 VeriSign,赚取了大约 5.75 亿美元。
2000 年,马克创立了 HBD 风险资本公司,成为了商业投资人和项目孵化器。2004 年,他创立了 Canonical Ltd. 以支持和鼓励自由软件开发项目的商业化,特别是 Ubuntu 操作系统的项目。直到 2009 年,马克才从 Canonical CEO 的位置上退下。
>
> “在 [DDC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DCC_Alliance) (LCTT 译注:一个 Debian GNU/Linux 开发者联盟) 的早期,我更倾向于让拥护者们放手去做,看看能发展出什么。”
>
>
> — 马克·沙特尔沃思
>
>
>
### Linux、自由开源软件与马克·沙特尔沃思
在 90 年代后期,马克曾作为一名开发者参与 Debian 操作系统项目。
2001 年,马克创立了沙特尔沃思基金会,这是个扎根南非的、非赢利性的基金会,专注于赞助社会创新、免费/教育用途开源软件,曾赞助过<ruby> <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Freedom_Toaster"> 自由烤面包机 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Freedom Toaster </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(LCTT 译注:自由烤面包机是一个可以为用户带来的 CD/DVD 上刻录自由软件的公共信息亭)。
2004 年,马克通过出资开发基于 Debian 的 Ubuntu 操作系统返回了自由软件界,这一切也经由他的 Canonical 公司完成。
2005 年,马克出资建立了 Ubuntu 基金会并投入了一千万美元作为启动资金。在 Ubuntu 项目内,人们经常用一个朗朗上口的名字称呼他——“**SABDFL :<ruby> 自封的生命之仁慈独裁者 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Self-Appointed Benevolent Dictator for Life </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>**”。为了能够找到足够多的高手开发这个巨大的项目,马克花费了 6 个月的时间从 Debian 邮件列表里寻找,这一切都是在他乘坐在南极洲的一艘破冰船——<ruby> 赫列布尼科夫船长号 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Kapitan Khlebnikov </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>——上完成的。同年,马克买下了 Impi Linux 65% 的股份。
>
> “我呼吁电信公司的掌权者们尽快开发出跨洲际的高效信息传输服务。”
>
>
> — 马克·沙特尔沃思
>
>
>
2006 年,KDE 宣布沙特尔沃思成为 KDE 的<ruby> 第一赞助人 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> first patron </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>——彼时 KDE 最高级别的赞助。这一赞助协议在 2012 年终止,取而代之的是对 Kubuntu 的资金支持,这是一个使用 KDE 作为默认桌面环境的 Ubuntu 变种。

2009 年,Shuttleworth 宣布他会从 Canonical 的 CEO 上退位,以更好地关注合作关系、产品设计和客户。从 2004 年起担任公司 COO 的<ruby> 珍妮·希比尔 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Jane Silber </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>晋升为 CEO。
2010 年,马克由于其贡献而被<ruby> 开放大学 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Open University </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>授予了荣誉学位。
2012 年,马克和<ruby> 肯尼斯·罗格夫 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Kenneth Rogoff </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>一同在牛津大学与<ruby> 彼得·蒂尔 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Peter Thiel </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和<ruby> 加里·卡斯帕罗夫 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Garry Kasparov </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>就<ruby> 创新悖论 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> The Innovation Enigma </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>展开辩论。
2013 年,马克和 Ubuntu 一同被授予<ruby> 澳大利亚反个人隐私大哥奖 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Austrian anti-privacy Big Brother Award </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,理由是默认情况下, Ubuntu 会把 Unity 桌面的搜索框的搜索结果发往 Canonical 服务器(LCTT 译注:因此侵犯了个人隐私)。而一年前,马克曾经申明过这一过程进行了匿名化处理。
>
> “所有主流 PC 厂家现在都提供 Ubuntu 预安装选项,所以我们和业界的合作已经相当紧密了。但那些 PC 厂家对于给买家推广新东西这件事都很紧张。如果我们可以让 PC 买家习惯 Ubuntu 的平板/手机操作系统的体验,那他们也应该更愿意买预装 Ubuntu 的 PC。没有哪个操作系统是通过抄袭模仿获得成功的,Android 很棒,但如果我们想成功的话我们必须给市场带去更新更好的东西(LCTT 译注:而不是改进或者模仿 Android)。如果我们中没有人追寻未来的话,我们将陷入停滞不前的危险。但如果你尝试去追寻未来了,那你必须接受不是所有人对未来的预见都和你一样这一事实。”
>
>
> — 马克·沙特尔沃思
>
>
>
### 马克·沙特尔沃思的太空之旅
马克在 2002 年作为世界第二名自费太空游客而闻名世界,同时他也是南非第一个旅行太空的人。这趟旅行中,马克作为俄罗斯联盟号 TM-34 任务的一名乘员加入,并为此支付了约两千万美元。2 天后,联盟号宇宙飞船抵达了国际空间站,在那里马克呆了 8 天并参与了艾滋病和基因组研究的相关实验。同年晚些时候,马克随联盟号 TM-33 任务返回了地球。为了参与这趟旅行,马克花了一年时间准备与训练,其中有 7 个月居住在俄罗斯的星城。

在太空中,马克与<ruby> 纳尔逊·曼德拉 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Nelson Mandela </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和另一个 14 岁的南非女孩<ruby> 米歇尔·福斯特 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Michelle Foster </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> (她问马克要不要娶她)通过无线电进行了交谈。马克礼貌地回避了这个结婚问题,但在巧妙地改换话题之前他说他感到很荣幸。身患绝症的女孩福斯特通过<ruby> 梦想基金会 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Dream foundation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的赞助获得了与马克和纳尔逊·曼德拉交谈的机会。
归来后,马克在世界各地做了旅行,并和各地的学生就太空之旅发表了感言。
>
> “粗略的统计数据表明 Ubuntu 的实际用户依然在增长。而我们的合作方——戴尔、惠普、联想和其他硬件生产商,以及游戏厂商 EA、Valve 都在加入我们——这让我觉得我们在关键的领域继续领先。”
>
>
> — 马克·沙特尔沃思
>
>
>
### 马克·沙特尔沃思的交通工具
马克有他自己的私人客机<ruby> 庞巴迪全球特快 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Bombardier Global Express </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,虽然它经常被称为 Canonical 1 号,但事实上此飞机是通过 HBD 风险投资公司注册拥有的。涂画在飞机侧面的龙图案是 HBD 风投公司的吉祥物 ,名叫 Norman。

### 与南非储备银行的法律冲突
在从南非转移 25 亿南非兰特去往 Isle of Man 的过程中,南非储备银行征收了 2.5 亿南非兰特的税金。马克上诉了,经过冗长的法庭唇枪舌战,南非储备银行被勒令返还 2.5 亿征税,以及其利息。马克宣布他会把这 2.5 亿存入信托基金,以用于帮助那些上诉到宪法法院的案子。
>
> “离境征税倒也不和宪法冲突。但离境征税的主要目的不是提高税收,而是通过监管资金流出来保护本国经济。”
>
>
> — Dikgang Moseneke 法官
>
>
>
2015 年,南非宪法法院修正了低级法院的判决结果,并宣布了上述对于离岸征税的理解。
### 马克·沙特尔沃思喜欢的东西
Cesária Évora、mp3、春天、<ruby> 切尔西 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Chelsea </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> “恍然大悟” <rp> ( </rp> <rt> finally seeing something obvious for first time </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、回家、<ruby> 辛纳屈 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Sinatra </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、白日梦、暮后小酌、挑逗、<ruby> 苔丝 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> d’Urberville </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、弦理论、Linux、粒子物理、Python、转世、米格-29、雪、旅行、Mozilla、酸橙果酱、<ruby> 激情代价 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> body shots </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、非洲丛林、豹、拉贾斯坦邦、俄罗斯桑拿、单板滑雪、失重、Iain m 银行、宽度、<ruby> 阿拉斯泰尔·雷诺兹 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Alastair Reynolds </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、化装舞会服装、裸泳、灵机一动、肾上腺素激情消退、<ruby> 莫名 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> the inexplicable </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、活动顶篷式汽车、Clifton、国家公路、国际空间站、机器学习、人工智能、维基百科、Slashdot、<ruby> 风筝冲浪 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> kitesurfing </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和 Manx lanes。
### 马克·沙特尔沃思不喜欢的东西
行政、涨工资、法律术语和公众演讲。
---
via: <http://www.unixmen.com/mark-shuttleworth-man-behind-ubuntu-operating-system/>
作者:[M.el Khamlichi](http://www.unixmen.com/author/pirat9/) 译者:[Moelf](https://github.com/Moelf) 校对:[PurlingNayuki](https://github.com/PurlingNayuki), [wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,525 | 用 Docker 创建 serverless 应用 | https://blog.docker.com/2016/06/building-serverless-apps-with-docker/ | 2016-06-30T07:33:00 | [
"serverless",
"Docker"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7525-1.html | 当今世界会时不时地出现一波波科技浪潮,将以前的技术拍死在海滩上。针对 serverless 应用的概念我们已经谈了很多,它是指将你的应用程序按功能来部署,这些功能在被用到时才会启动。你不用费心去管理服务器和程序规模,因为它们会在需要的时候在一个集群中启动并运行。

但是 serverless 并不意味着没有 Docker 什么事儿,事实上 Docker 就是 serverless 的。你可以使用 Docker 来容器化这些功能,然后在 Swarm 中按需求来运行它们。serverless 是一项构建分布式应用的技术,而 Docker 是它们完美的构建平台。
### 从 servers 到 serverless
那如何才能写一个 serverless 应用呢?来看一下我们的例子,[5个服务组成的投票系统](https://github.com/docker/example-voting-app):

投票系统由下面5个服务组成:
* 两个 web 前端
* 一个后台处理投票的进程
* 一个计票的消息队列
* 一个数据库
后台处理投票的进程很容易转换成 serverless 构架,我们可以使用以下代码来实现:
```
import dockerrun
client = dockerrun.from_env()
client.run("bfirsh/serverless-record-vote-task", [voter_id, vote], detach=True)
```
这个投票处理进程和消息队列可以用运行在 Swarm 上的 Docker 容器来代替,并实现按需自动部署。
我们也可以用容器替换 web 前端,使用一个轻量级 HTTP 服务器来触发容器响应一个 HTTP 请求。Docker 容器代替长期运行的 HTTP 服务器来挑起响应请求的重担,这些容器可以自动扩容来支撑更大访问量。
新的架构就像这样:

红色框内是持续运行的服务,绿色框内是按需启动的容器。这个架构里需要你来管理的长期运行服务更少,并且可以自动扩容(最大容量由你的 Swarm 决定)。
### 我们可以做点什么?
你可以在你的应用中使用3种技术:
1. 在 Docker 容器中按需运行代码。
2. 使用 Swarm 来部署集群。
3. 通过使用 Docker API 套接字在容器中运行容器。
结合这3种技术,你可以有很多方法搭建你的应用架构。用这种方法来部署后台环境真是非常有效,而在另一些场景,也可以这么玩,比如说:
* 由于存在延时,使用容器实现面向用户的 HTTP 请求可能不是很合适,但你可以写一个负载均衡器,使用 Swarm 来对自己的 web 前端进行自动扩容。
* 实现一个 MongoDB 容器,可以自检 Swarm 并且启动正确的分片和副本(LCTT 译注:分片技术为大规模并行检索提供支持,副本技术则是为数据提供冗余)。
### 下一步怎么做
我们提供了这些前卫的工具和概念来构建应用,并没有深入发掘它们的功能。我们的架构里还是存在长期运行的服务,将来我们需要使用 Swarm 来把所有服务都用按需扩容的方式实现。
希望本文能在你搭建架构时给你一些启发,但我们还是需要你的帮助。我们提供了所有的基本工具,但它们还不是很完善,我们需要更多更好的工具、库、应用案例、文档以及其他资料。
[我们在这里发布了工具、库和文档](https://github.com/bfirsh/serverless-docker)。如果想了解更多,请贡献给我们一些你知道的资源,以便我们能够完善这篇文章。
玩得愉快。
### 更多关于 Docker 的资料
* New to Docker? Try our 10 min [online tutorial](https://docs.docker.com/engine/understanding-docker/)
* Share images, automate builds, and more with [a free Docker Hub account](https://hub.docker.com/)
* Read the Docker [1.12 Release Notes](https://docs.docker.com/release-notes/)
* Subscribe to [Docker Weekly](https://www.docker.com/subscribe_newsletter/)
* Sign up for upcoming [Docker Online Meetups](http://www.meetup.com/Docker-Online-Meetup/)
* Attend upcoming [Docker Meetups](https://www.docker.com/community/meetup-groups)
* Watch [DockerCon EU 2015 videos](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLkA60AVN3hh87OoVra6MHf2L4UR9xwJkv)
* Start [contributing to Docker](https://docs.docker.com/contributing/contributing/)
---
via: <https://blog.docker.com/2016/06/building-serverless-apps-with-docker/>
作者:[Ben Firshman](https://blog.docker.com/author/bfirshman/) 译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,526 | 与 Linux 一同驾车奔向未来 | https://opensource.com/business/16/5/interview-alison-chaiken-steven-crumb | 2016-06-30T12:09:49 | [
"车载",
"AGL",
"GENIVI",
"IVI"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7526-1.html | 
当我驾车的时候并没有这么想过,但是我肯定喜欢一个配有这样系统的车子,它可以让我按下几个按钮就能与我的妻子、母亲以及孩子们语音通话。这样的系统也可以让我选择是否从云端、卫星广播、以及更传统的 AM/FM 收音机收听音乐流媒体。我也会得到最新的天气情况,以及它可以引导我的车载 GPS 找到抵达下一个目的地的最快路线。<ruby> <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In_car_entertainment"> 车载娱乐系统 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> In-vehicle infotainment </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,业界常称作 IVI,它已经普及出现在最新的汽车上了。
前段时间,我乘坐飞机跨越了数百英里,然后租了一辆汽车。令人愉快的是,我发现我租赁的汽车上配置了类似我自己车上同样的 IVI 技术。毫不犹豫地,我就通过蓝牙连接把我的联系人上传到了系统当中,然后打电话回家给我的家人,让他们知道我已经安全抵达了,然后我的主机会让他们知道我正在去往他们家的路上。
在最近的[新闻综述](https://opensource.com/life/16/1/weekly-news-jan-9)中,Scott Nesbitt 引述了一篇文章,说福特汽车公司因其开源的<ruby> <a href="http://projects.genivi.org/smartdevicelink/home"> 智能设备连接 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Smart Device Link </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(SDL)从竞争对手汽车制造商中得到了足够多的回报,这个中间件框架可以用于支持移动电话。 SDL 是 [GENIVI 联盟](http://www.genivi.org/)的一个项目,这个联盟是一个非营利性组织,致力于建设支持开源车载娱乐系统的中间件。据 GENIVI 的执行董事 [Steven Crumb](https://www.linkedin.com/in/stevecrumb) 称,他们的[成员](http://www.genivi.org/genivi-members)有很多,包括戴姆勒集团、现代、沃尔沃、日产、本田等等 170 个企业。
为了在同行业间保持竞争力,汽车生产企业需要一个中间设备系统,以支持现代消费者所使用的各种人机界面技术。无论您使用的是 Android、iOS 还是其他设备,汽车 OEM 厂商都希望自己的产品能够支持这些。此外,这些的 IVI 系统必须有足够适应能力以支持日益变化的移动技术。OEM 厂商希望提供有价值的服务,并可以在他们的 IVI 之上增加服务,以满足他们客户的各种需求。
### 步入 Linux 和开源软件
除了 GENIVI 在努力之外,[Linux 基金会](http://www.linuxfoundation.org/)也赞助支持了<ruby> <a href="https://www.automotivelinux.org/"> 车载 Linux </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Automotive Grade Linux </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(AGL)工作组,这是一个致力于为汽车应用寻求开源解决方案的软件基金会。虽然 AGL 初期将侧重于 IVI 系统,但是未来他们希望发展到不同的方向,包括<ruby> <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telematics"> 远程信息处理 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> telematics </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、抬头显示器(HUD)及其他控制系统等等。 现在 AGL 已经有超过 50 名成员,包括捷豹、丰田、日产,并在其[最近发布的一篇公告](https://www.automotivelinux.org/news/announcement/2016/01/ford-mazda-mitsubishi-motors-and-subaru-join-linux-foundation-and)中宣称福特、马自达、三菱、和斯巴鲁也加入了。
为了了解更多信息,我们采访了这一新兴领域的两位领导人。具体来说,我们想知道 Linux 和开源软件是如何被使用的,并且它们是如何事实上改变了汽车行业的面貌。首先,我们将与 [Alison Chaiken](https://www.linkedin.com/in/alison-chaiken-3ba456b3) 谈谈,她是一位任职于 Peloton Technology 的软件工程师,也是一位在车载 Linux 、网络安全和信息透明化方面的专家。她曾任职于 [Alison Chaiken](https://www.linkedin.com/in/alison-chaiken-3ba456b3) 公司、诺基亚和斯坦福直线性加速器。然后我们和 [Steven Crumb](https://www.linkedin.com/in/stevecrumb) 进行了交谈,他是 GENIVI 执行董事,他之前从事于高性能计算环境(超级计算机和早期的云计算)的开源工作。他说,虽然他再不是一个程序员了,但是他乐于帮助企业解决在使用开源软件时的实际业务问题。
### 采访 Alison Chaiken (by [Deb Nicholson](https://opensource.com/users/eximious))
#### 你是如何开始对汽车软件领域感兴趣的?
我曾在诺基亚从事于手机上的 [MeeGo](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MeeGo) 产品,2009 年该项目被取消了。我想,我下一步怎么办?其时,我的一位同事正在从事于 [MeeGo-IVI](http://webinos.org/deliverable-d026-target-platform-requirements-and-ipr/automotive/),这是一个早期的车载 Linux 发行版。 “Linux 在汽车方面将有很大发展,” 我想,所以我就朝着这个方向努力。
#### 你能告诉我们你在这些日子里工作在哪些方面吗?
我目前正在启动一个高级巡航控制系统的项目,它用在大型卡车上,使用实时 Linux 以提升安全性和燃油经济性。我喜欢在这方面的工作,因为没有人会反对提升货运的能力。
#### 近几年有几则汽车被黑的消息。开源代码方案可以帮助解决这个问题吗?
我恰好针对这一话题准备了一次讲演,我会在南加州 Linux 2016 博览会上就 Linux 能否解决汽车上的安全问题做个讲演 ([讲演稿在此](http://she-devel.com/Chaiken_automotive_cybersecurity.pdf))。值得注意的是,GENIVI 和车载 Linux 项目已经公开了他们的代码,这两个项目可以通过 Git 提交补丁。(如果你有补丁的话),请给上游发送您的补丁!许多眼睛都盯着,bug 将无从遁形。
#### 执法机构和保险公司可以找到很多汽车上的数据的用途。他们获取这些信息很容易吗?
好问题。IEEE-1609 <ruby> 专用短程通信标准 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Dedicated Short Range Communication Standard </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>就是为了让汽车的 WiFi 消息可以安全、匿名地传递。不过,如果你从你的车上发推,那可能就有人能够跟踪到你。
#### 开发人员和公民个人可以做些什么,以在汽车技术进步的同时确保公民自由得到保护?
<ruby> 电子前沿基金会 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Electronic Frontier Foundation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(EFF)在关注汽车问题方面做了出色的工作,包括对哪些数据可以存储在汽车 “黑盒子”里通过官方渠道发表了看法,以及 DMCA 规定 1201 如何应用于汽车上。
#### 在未来几年,你觉得在汽车方面会发生哪些令人激动的发展?
可以拯救生命的自适应巡航控制系统和防撞系统将取得长足发展。当它们大量进入汽车里面时,我相信这会使得(因车祸而导致的)死亡人数下降。如果这都不令人激动,我不知道还有什么会更令人激动。此外,像自动化停车辅助功能,将会使汽车更容易驾驶,减少汽车磕碰事故。
#### 我们需要做什么?人们怎样才能参与?
车载 Linux 开发是以开源的方式开发,它运行在每个人都能买得起的廉价硬件上(如树莓派 2 和中等价位的 Renesas Porter 主板)。 GENIVI 汽车 Linux 中间件联盟通过 Git 开源了很多软件。此外,还有很酷的 [OSVehicle 开源硬件](https://www.osvehicle.com/)汽车平台。
只需要不太多的预算,人们就可以参与到 Linux 软件和开放硬件中。如果您感兴趣,请加入我们在 Freenode 上的IRC #automotive 吧。
### 采访 Steven Crumb (by Don Watkins)
#### GENIVI 在 IVI 方面做了哪些巨大贡献?
GENIVI 率先通过使用自由开源软件填补了汽车行业的巨大空白,这包括 Linux、非安全关键性汽车软件(如车载娱乐系统(IVI))等。作为消费者,他们很期望在车辆上有和智能手机一样的功能,对这种支持 IVI 功能的软件的需求量成倍地增长。不过不断提升的软件数量也增加了建设 IVI 系统的成本,从而延缓了其上市时间。
GENIVI 使用开源软件和社区开发的模式为汽车制造商及其软件提供商节省了大量资金,从而显著地缩短了产品面市时间。我为 GENIVI 而感到激动,我们有幸引导了一场革命,在缓慢进步的汽车行业中,从高度结构化和专有的解决方案转换为以社区为基础的开发方式。我们还没有完全达成目标,但是我们很荣幸在这个可以带来实实在在好处的转型中成为其中的一份子。
#### 你们的主要成员怎样推动了 GENIVI 的发展方向?
GENIVI 有很多成员和非成员致力于我们的工作。在许多开源项目中,任何公司都可以通过通过技术输出而发挥影响,包括简单地贡献代码、补丁、花点时间测试。前面说过,宝马、奔驰、现代汽车、捷豹路虎、标致雪铁龙、雷诺/日产和沃尔沃都是 GENIVI 积极的参与者和贡献者,其他的许多 OEM 厂商也在他们的汽车中采用了 IVI 解决方案,广泛地使用了 GENIVI 的软件。
#### 这些贡献的代码使用了什么许可证?
GENIVI 采用了一些许可证,包括从(L)GPLv2 到 MPLv2 和 Apache2.0。我们的一些工具使用的是 Eclipse 许可证。我们有一个[公开许可策略](http://projects.genivi.org/how),详细地说明了我们的许可证偏好。
#### 个人或团体如何参与其中?社区的参与对于这个项目迈向成功有多重要?
GENIVI 的开发完全是开放的([projects.genivi.org](http://projects.genivi.org/)),因此,欢迎任何有兴趣在汽车中使用开源软件的人参加。也就是说,公司可以通过成员的方式[加入该联盟](http://genivi.org/join),联盟以开放的方式资助其不断进行开发。GENIVI 的成员可以享受各种各样的便利,在过去六年中,已经有多达 140 家公司参与到这个全球性的社区当中。
社区对于 GENIVI 是非常重要的,没有一个活跃的贡献者社区,我们不可能在这些年开发和维护了这么多有价值的软件。我们努力让参与到 GENIVI 更加简单,现在只要加入一个[邮件列表](http://lists.genivi.org/mailman/listinfo/genivi-projects)就可以接触到各种软件项目中的人们。我们使用了许多开源项目采用的标准做法,并提供了高品质的工具和基础设施,以帮助开发人员宾至如归而富有成效。
无论你是否熟悉汽车软件,都欢迎你加入我们的社区。人们已经对汽车改装了许多年,所以对于许多人来说,在汽车上修修改改是自热而然的做法。对于汽车来说,软件是一个新的领域,GENIVI 希望能为对汽车和开源软件有兴趣的人打开这扇门。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/business/16/5/interview-alison-chaiken-steven-crumb>
作者:[Don Watkins](https://opensource.com/users/don-watkins) 译者:[erlinux](https://github.com/erlinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | I don't think much about it while I'm driving, but I sure do love that my car is equipped with a system that lets me use a few buttons and my voice to call my wife, mom, and children. That same system allows me to choose whether I listen to music streaming from the cloud, satellite radio, or the more traditional AM/FM radio. I also get weather updates and can direct my in-vehicle GPS to find the fastest route to my next destination. [In-vehicle infotainment](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In_car_entertainment), or IVI as it's known in the industry, has become ubiquitous in today's newest automobiles.
A while ago, I had to travel hundreds of miles by plane and then rent a car. Happily, I discovered that my rental vehicle was equipped with IVI technology similar to my own car. In no time, I was connected via Bluetooth, had uploaded my contacts into the system, and was calling home to let my family know I arrived safely and my hosts to let them know I was en route to their home.
In a recent [news roundup](https://opensource.com/life/16/1/weekly-news-jan-9), Scott Nesbitt cited an article that said Ford Motor Company is getting substantial backing from a rival automaker for its open source [Smart Device Link](http://projects.genivi.org/smartdevicelink/home) (SDL) middleware framework, which supports mobile phones. SDL is a project of the [GENIVI Alliance](http://www.genivi.org/), a nonprofit committed to building middleware to support open source in-vehicle infotainment systems. According to [Steven Crumb](https://www.linkedin.com/in/stevecrumb), executive director of GENIVI, their [membership](http://www.genivi.org/genivi-members) is broad and includes Daimler Group, Hyundai, Volvo, Nissan, Honda, and 170 others.
In order to remain competitive in the industry, automotive companies need a middleware system that can support the various human machine interface technologies available to consumers today. Whether you own an Android, iOS, or other device, automotive OEMs want their units to be able to support these systems. Furthermore, these IVI systems must be adaptable enough to support the ever decreasing half-life of mobile technology. OEMs want to provide value and add services in their IVI stacks that will support a variety of options for their customers. Enter Linux and open source software.
In addition to GENIVI's efforts, the [Linux Foundation](http://www.linuxfoundation.org/) sponsors the [Automotive Grade Linux](https://www.automotivelinux.org/) (AGL) workgroup, a software foundation dedicated to finding open source solutions for automotive applications. Although AGL will initially focus on IVI systems, they envision branching out to include [telematics](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telematics), heads up displays, and other control systems. AGL has over 50 members at this time, including Jaguar, Toyota, and Nissan, and in a [recent press release](https://www.automotivelinux.org/news/announcement/2016/01/ford-mazda-mitsubishi-motors-and-subaru-join-linux-foundation-and) announced that Ford, Mazda, Mitsubishi, and Subaru have joined.
To find out more, we interviewed two leaders in this emerging field. Specifically, we wanted to know how Linux and open source software are being used and if they are in fact changing the face of the automotive industry. First, we talk to [Alison Chaiken](https://www.linkedin.com/in/alison-chaiken-3ba456b3), a software engineer at Peloton Technology and an expert on automotive Linux, cybersecurity, and transparency. She previously worked for Mentor Graphics, Nokia, and the Stanford Linear Accelerator. Then, we chat with [Steven Crumb](https://www.linkedin.com/in/stevecrumb), executive director of GENIVI, who got started in open source in high-performance computing environments (supercomputers and early cloud computing). He says that though he's not a coder anymore, he loves to help organizations solve real business problems with open source software.
## Interview with Alison Chaiken (by [Deb Nicholson](https://opensource.com/users/eximious))
### How did you get interested in the automotive software space?
I was working on [MeeGo](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MeeGo) in phones at Nokia in 2009 when the project was cancelled. I thought, what's next? A colleague was working on [MeeGo-IVI](http://webinos.org/deliverable-d026-target-platform-requirements-and-ipr/automotive/), an early automotive Linux distribution. "Linux is going to be big in cars," I thought, so I headed in that direction.
### Can you tell us what aspects you're working on these days?
I'm currently working for a startup on an advanced cruise control system that uses real-time Linux to increase the safety and fuel economy of big-rig trucks. I love working in this area, as no one would disagree that trucking can be improved.
### There have been a few stories about hacked cars in recent years. Can open source solutions help address this issue?
I presented a talk on precisely this topic, on how Linux can (and cannot) contribute to security solutions in automotive at Southern California Linux Expo 2016 ([Slides](http://she-devel.com/Chaiken_automotive_cybersecurity.pdf)). Notably, GENIVI and Automotive Grade Linux have published their code and both projects take patches via Git. Please send your fixes upstream! Many eyes make all bugs shallow.
### Law enforcement agencies and insurance companies could find plenty of uses for data about drivers. How easy will it be for them to obtain this information?
Good question. The Dedicated Short Range Communication Standard (IEEE-1609) takes great pains to keep drivers participating in Wi-Fi safety messaging anonymous. Still, if you're posting to Twitter from your car, someone will be able to track you.
### What can developers and private citizens do to make sure civil liberties are protected as automotive technology evolves?
The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) has done an excellent job of keeping on top of automotive issues, having commented through official channels on what data may be stored in automotive "black boxes" and on how DMCA's Provision 1201 applies to cars.
### What are some of the exciting things you see coming for drivers in the next few years?
Adaptive cruise control and collision avoidance systems are enough of an advance to save lives. As they roll out through vehicle fleets, I truly believe that fatalities will decline. If that's not exciting, I don't know what is. Furthermore, capabilities like automated parking assist will make cars easier to drive and reduce fender-benders.
### What needs to be built and how can people get involved?
Automotive Grade Linux is developed in the open and runs on cheap hardware (e.g. Raspberry Pi 2 and moderately priced Renesas Porter board) that anyone can buy. GENIVI automotive Linux middleware consortium has lots of software publicly available via Git. Furthermore, there is the ultra cool [OSVehicle open hardware](https://www.osvehicle.com/) automotive platform.
There are many ways for Linux software and open hardware folks with moderate budgets to get involved. Join us at #automotive on Freenode IRC if you have questions.
## Interview with Steven Crumb (by Don Watkins)
### What's so huge about GENIVI's approach to IVI?
GENIVI filled a huge gap in the automotive industry by pioneering the use of free and open source software, including Linux, for non-safety-critical automotive software like in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) systems. As consumers came to expect the same functionality in their vehicles as on their smartphones, the amount of software required to support IVI functions grew exponentially. The increased amount of software has also increased the costs of building the IVI systems and thus slowed time to market.
GENIVI's use of open source software and a community development model has saved automakers and their software suppliers significant amounts of money while significantly reducing the time to market. I'm excited about GENIVI because we've been fortunate to lead a revolution of sorts in the automotive industry by slowly evolving organizations from a highly structured and proprietary methodology to a community-based approach. We're not done yet, but it's been a privilege to take part in a transformation that is yielding real benefits.
### How do your major members drive the direction of GENIVI?
GENIVI has a lot of members *and* non-members contributing to our work. As with many open source projects, any company can influence the technical output by simply contributing code, patches, and time to test. With that said, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Hyundai Motor, Jaguar Land Rover, PSA, Renault/Nissan, and Volvo are all active adopters of and contributors to GENIVI—and many other OEMs have IVI solutions in their cars that extensively use GENIVI's software.
### What licenses cover the contributed code?
GENIVI employs a number of licenses ranging from (L)GPLv2 to MPLv2 to Apache 2.0. Some of our tools use the Eclipse license. We have a [public licensing policy](http://projects.genivi.org/how) that details our licensing preferences.
### How does a person or group get involved? How important are community contributions to the ongoing success of the project?
GENIVI does its development completely in the open ([projects.genivi.org](http://projects.genivi.org)) and thus, anyone interested in using open software in automotive is welcome to participate. That said, the alliance can fund its continued development in the open through companies [joining GENIVI](http://genivi.org/join) as members. GENIVI members enjoy a wide variety of benefits, not the least of which is participation in the global community of 140 companies that has been developed over the last six years.
Community is hugely important to GENIVI, and we could not have produced and maintained the valuable software we developed over the years without an active community of contributors. We've worked hard to make contributing to GENIVI as simple as joining an [email list](http://lists.genivi.org/mailman/listinfo/genivi-projects) and connecting to the people in the various software projects. We use standard practices employed by many open source projects and provide high-quality tools and infrastructure to help developers feel at home and be productive.
Regardless of someone's familiarity with the automotive software, they are welcome to join our community. People have modified cars for years, so for many people there is a natural draw to anything automotive. Software is the new domain for cars, and GENIVI wants to be the open door for anyone interested in working with automotive, open source software.
## Comments are closed. |
7,530 | 为什么 Ubuntu 家族会占据 Linux 发行版的主导地位? | http://www.datamation.com/open-source/why-ubuntu-based-distros-are-leaders.html | 2016-07-01T11:02:00 | [
"Ubuntu"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7530-1.html | 在过去的数年中,我体验了一些优秀的 Linux 发行版。给我印象最深刻的是那些由强大的社区维护的发行版,而流行的发行版比强大的社区给我的印象更深。流行的 Linux 发行版往往能吸引新用户,这通常是由于其流行而使得使用该发行版会更加容易。并非绝对如此,但一般来说是这样的。

说到这里,首先映入我脑海的一个发行版是 [Ubuntu](http://www.ubuntu.com/),其基于健壮的 [Debian](https://www.debian.org/) 发行版构建。它不仅成为了一个非常受欢迎的 Linux 发行版,而且它也衍生出了不可计数的其他分支,比如 Linux Mint 就是一个例子。在本文中,我会探讨为何我认为 Ubuntu 会赢得 Linux 发行版之战的原因,以及它是怎样影响到了整个 Linux 桌面领域。
### Ubuntu 易于使用
在几年前我首次尝试使用 Ubuntu 前,我更喜欢使用 KDE 桌面。在那个时期,我接触的大多是这种 KDE 桌面环境。主要是由于 KDE 是大多数新手容易入手的 Linux 发行版中最受欢迎的。这些新手友好的发行版有 Knoppix、Simply Mepis、Xandros、Linspire 以及其它的一些发行版等等,这些发行版都推荐他们的用户去使用广受欢迎的 KDE。
现在 KDE 能满足我的需求,我也没有什么理由去折腾其他的桌面环境。有一天我的 Debian 安装失败了(由于我个人的操作不当),我决定尝试开发代号为 Dapper Drake 的 Ubuntu 版本(LCTT 译注:Ubuntu 6.06 - Dapper Drake,发布日期:2006 年 6 月 1 日),每个人都对它赞不绝口。那个时候,我对于它的印象仅限于屏幕截图,但是我想试试也挺有趣的。
Ubuntu Dapper Drake 给我的最大的印象是它让我很清楚地知道每个东西都在哪里。记住,我是来自于 KDE 世界的用户,在 KDE 上要想改变菜单的设置就有 15 种方法 !而 Ubuntu 上的 GNOME 实现是极具极简主义的。
时间来到 2016 年,最新的版本号是 16.04:我们有了好几种 Ubuntu 特色版本,也有一大堆基于 Ubuntu 的发行版。所有的 Ubuntu 特色版和衍生发行版所共同具有的核心都是为易用而设计。发行版想要增大用户基数时,这就是最重要的原因。
### Ubuntu LTS
过去,我几乎一直坚持使用 LTS(<ruby> 长期支持版 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Long Term Support </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)发行版作为我的主要桌面系统。10月份的发行版很适合我测试硬盘驱动器,甚至把它用在一个老旧的手提电脑上。我这样做的原因很简单——我没有兴趣在一个正式使用的电脑上折腾短期发行版。我是个很忙的家伙,我觉得这样会浪费我的时间。
我认为 Ubuntu 提供 LTS 发行版是 Ubuntu 能够变得流行的最大的原因。这样说吧———给普罗大众提供一个桌面 Linux 发行版,这个发行版能够得到长期的有效支持就是它的优势。事实上,不只 Ubuntu 是这样,其他的发行版在这一点上也做的很好。长期支持的策略以及对新手的友好环境,我认为这就为 Ubuntu 的普及带来了莫大的好处。
### Ubuntu Snap 软件包
以前,用户会夸赞可以在他们的系统上使用 PPA(<ruby> 个人软件包档案 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> personal package archive </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)来获得新软件。不好的地方是,这种技术也有缺点。当它用于各种软件时, PPA 经常会找不到,这种情况很常见。
现在有了 [Snap 软件包](http://www.datamation.com/open-source/ubuntu-snap-packages-the-good-the-bad-the-ugly.html) 。当然这不是一个全新的概念,过去已经进行了类似的尝试。用户可以在一个长期支持版本上运行最新的软件,而不必去使用最新的 Ubuntu 发行版。虽然我认为目前还处于 Snap 软件包的发展早期,但是我很期待可以在一个稳定的发行版上运行的崭新的软件。
最明显的问题是,如果你要运行很多软件,那么 Snap 包实际会占用很多硬盘空间。不仅如此,大多数 Ubuntu 软件仍然需要由官方从 deb 包进行转换。第一个问题可以通过使用更大的硬盘空间得到解决,而后一个问题的解决则需要等待。
### Ubuntu 社区
首先,我承认大多数主要的 Linux 发行版都有强大的社区。然而,我坚信 Ubuntu 社区的成员是最多样化的,他们来自各行各业。例如,我们的论坛包括从苹果硬件支持到游戏等不同分类。这些专业的讨论话题还非常广泛。
除过论坛,Ubuntu 也提供了一个很正式的社区组织。这个组织包括一个理事会、技术委员会、[本地社区团队](http://loco.ubuntu.com/)和开发者成员委员会。还有很多,但是这些都是我知道的社区组织部分。
我们还有一个 [Ubuntu 问答](http://askubuntu.com/)版块。我认为,这种功能可以代替人们从论坛寻求帮助的方式,我发现在这个网站你得到有用信息的可能性更大。不仅如此,那些提供的解决方案中被选出的最精准的答案也会被写入到官方文档中。
### Ubuntu 的未来
我认为 Ubuntu 的 Unity 界面(LCTT 译注:Unity 是 Canonical 公司为 Ubuntu 操作系统的 GNOME 桌面环境开发的图形化界面)在提升桌面占有率上少有作为。我能理解其中的缘由,现在它主要做一些诸如可以使开发团队的工作更轻松的事情。但是最终,我还是认为 Unity 将为 Ubuntu MATE 和 Linux Mint 的普及铺平道路。
我最好奇的一点是 Ubuntu 的 IRC 和邮件列表的发展(LCTT 译注:可以在 Ubuntu LoCo Teams 的 IRC Chat 上提问关于地方团队和计划的事件的问题,也可以和一些不同团队的成员进行交流)。事实是,他们都不能像 Ubuntu 问答板块那样文档化。至于邮件列表,我一直认为这对于合作是一种很痛苦的过时方法,但这仅仅是我的个人看法——其他人可能有不同的看法,也可能会认为它很好。
你怎么看?你认为 Ubuntu 将会占据主要的份额吗?也许你会认为 Arch 和 Linux Mint 或者其他的发行版会在普及度上打败 Ubuntu? 既然这样,那请大声说出你最喜爱的发行版。如果这个发行版是 Ubuntu 衍生版 ,说说你为什么更喜欢它而不是 Ubuntu 本身。如果不出意外,Ubuntu 会成为构建其他发行版的基础,我想很多人都是这样认为的。
---
via: <http://www.datamation.com/open-source/why-ubuntu-based-distros-are-leaders.html>
作者:[Matt Hartley](http://www.datamation.com/author/Matt-Hartley-3080.html) 译者:[vim-kakali](https://github.com/vim-kakali) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,533 | Linux 下五个顶级的开源命令行 Shell | https://opensource.com/business/16/3/top-linux-shells | 2016-07-02T14:14:02 | [
"shell",
"bash",
"zsh",
"fish"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7533-1.html | 
这个世界上有两种 Linux 用户:敢于冒险的和态度谨慎的。
其中一类用户总是本能的去尝试任何能够戳中其痛点的新选择。他们尝试过不计其数的窗口管理器、系统发行版和几乎所有能找到的桌面插件。
另一类用户找到他们喜欢的东西后,会一直使用下去。他们往往喜欢所使用的系统发行版的默认配置。最先熟练掌握的文本编辑器会成为他们最钟爱的那一个。
作为一个使用桌面版和服务器版十五年之久的 Linux 用户,比起第一类来,我无疑属于第二类用户。我更倾向于使用现成的东西,如此一来,很多时候我就可以通过文档和示例方便地找到我所需要的使用案例。如果我决定选择使用非费标准的东西,这个切换过程一定会基于细致的研究,并且前提是来自好基友的大力推荐。
但这并不意味着我不喜欢尝试新事物并且查漏补失。所以最近一段时间,在我不假思索的使用了 bash shell 多年之后,决定尝试一下另外四个 shell 工具:ksh、tcsh、zsh 和 fish。这四个 shell 都可以通过我所用的 Fedora 系统的默认库轻松安装,并且他们可能已经内置在你所使用的系统发行版当中了。
这里对它们每个选择都稍作介绍,并且阐述下它适合做为你的下一个 Linux 命令行解释器的原因所在。
### bash
首先,我们回顾一下最为熟悉的一个。 [GNU Bash](https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/),又名 Bourne Again Shell,它是我这些年使用过的众多 Linux 发行版的默认选择。它最初发布于 1989 年,并且轻松成长为 Linux 世界中使用最广泛的 shell,甚至常见于其他一些类 Unix 系统当中。
Bash 是一个广受赞誉的 shell,当你通过互联网寻找各种事情解决方法所需的文档时,总能够无一例外的发现这些文档都默认你使用的是 bash shell。但 bash 也有一些缺点存在,如果你写过 Bash 脚本就会发现我们写的代码总是得比真正所需要的多那么几行。这并不是说有什么事情是它做不到的,而是说它读写起来并不总是那么直观,至少是不够优雅。
如上所述,基于其巨大的安装量,并且考虑到各类专业和非专业系统管理员已经适应了它的使用方式和独特之处,至少在将来一段时间内,bash 或许会一直存在。
### ksh
[KornShell](http://www.kornshell.org/),或许你对这个名字并不熟悉,但是你一定知道它的调用命令 ksh。这个替代性的 shell 于 80 年代起源于贝尔实验室,由 David Korn 所写。虽然最初是一个专有软件,但是后期版本是在 [Eclipse Public 许可](https://www.eclipse.org/legal/epl-v10.html)下发布的。
ksh 的拥趸们列出了他们觉得其优越的诸多理由,包括更好的循环语法,清晰的管道退出代码,处理重复命令和关联数组的更简单的方式。它能够模拟 vi 和 emacs 的许多行为,所以如果你是一个重度文本编辑器患者,它值得你一试。最后,我发现它虽然在高级脚本方面拥有不同的体验,但在基本输入方面与 bash 如出一辙。
### tcsh
[tcsh](http://www.tcsh.org/Welcome) 衍生于 csh(Berkely Unix C shell),并且可以追溯到早期的 Unix 和计算机时代开始。
tcsh 最大的卖点在于它的脚本语言,对于熟悉 C 语言编程的人来说,看起来会非常亲切。tcsh 的脚本编写有人喜欢,有人憎恶。但是它也有其他的技术特色,包括可以为 aliases 添加参数,各种可能迎合你偏好的默认行为,包括 tab 自动完成和将 tab 完成的工作记录下来以备后查。
tcsh 以 [BSD 许可](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BSD_licenses)发布。
### zsh
[zsh](http://www.zsh.org/) 是另外一个与 bash 和 ksh 有着相似之处的 shell。诞生于 90 年代初,zsh 支持众多有用的新技术,包括拼写纠正、主题化、可命名的目录快捷键,在多个终端中共享同一个命令历史信息和各种相对于原来的 bash 的轻微调整。
虽然部分需要遵照 GPL 许可,但 zsh 的代码和二进制文件可以在一个类似 MIT 许可证的许可下进行分发; 你可以在 [actual license](https://sourceforge.net/p/zsh/code/ci/master/tree/LICENCE) 中查看细节。
### fish
之前我访问了 [fish](https://fishshell.com/) 的主页,当看到 “好了,这是一个为 90 后而生的命令行 shell” 这条略带调侃的介绍时(fish 完成于 2005 年),我就意识到我会爱上这个交互友好的 shell 的。
fish 的作者提供了若干切换过来的理由,这些理由有点小幽默并且能戳中笑点,不过还真是那么回事。这些特性包括自动建议(“注意, Netscape Navigator 4.0 来了”,LCTT 译注:NN4 是一个重要版本。),支持“惊人”的 256 色 VGA 调色,不过也有真正有用的特性,包括根据你机器上的 man 页面自动补全命令,清除脚本和基于 web 界面的配置方式。
fish 的许可主要基于 GPLv2,但有些部分是在其他许可下的。你可以查看资源库来了解[完整信息](https://github.com/fish-shell/fish-shell/blob/master/COPYING)。
如果你想要寻找关于每个选择确切不同之处的详尽纲要,[这个网站](http://hyperpolyglot.org/unix-shells)应该可以帮到你。
我的立场到底是怎样的呢?好吧,最终我应该还是会重新投入 bash 的怀抱,因为对于大多数时间都在使用命令行交互的人来说,切换过程对于编写高级的脚本能带来的好处微乎其微,并且我已经习惯于使用 bash 了。
但是我很庆幸做出了敞开大门并且尝试新选择的决定。我知道门外还有许许多多其他的东西。你尝试过哪些 shell,更中意哪一个?请在评论里告诉我们。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/business/16/3/top-linux-shells>
作者:[Jason Baker](https://opensource.com/users/jason-baker) 译者:[mr-ping](https://github.com/mr-ping) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | There are two kinds of Linux users: the cautious and the adventurous.
On one side is the user who almost reflexively tries out ever new option which hits the scene. They’ve tried handfuls of window managers, dozens of distributions, and every new desktop widget they can find.
On the other side is the user who finds something they like and sticks with it. They tend to like their distribution’s defaults. If they’re passionate about a text editor, it’s whichever one they mastered first.
As a Linux user, both on the server and the desktop, for going on fifteen years now, I am definitely more in the second category than the first. I have a tendency to use what’s presented to me, and I like the fact that this means more often than not I can find thorough documentation and examples of most any use case I can dream up. If I used something non-standard, the switch was carefully researched and often predicated by a strong pitch from someone I trust.
But that doesn’t mean I don’t like to sometimes try and see what I’m missing. So recently, after years of using the bash shell without even giving it a thought, I decided to try out four alternative shells: ksh, tcsh, zsh, and fish. All four were easy installs from my default repositories in Fedora, and they’re likely already packaged for your distribution of choice as well.
Here’s a little bit on each option and why you might choose it to be your next Linux command-line interpreter.
## bash
First, let’s take a look back at the familiar. [GNU Bash](https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/), the Bourne Again Shell, has been the default in pretty much every Linux distribution I’ve used through the years. Originally released in 1989, bash has grown to easily become the most used shell across the Linux world, and it is commonly found in other unix-like operating systems as well.
Bash is a perfectly respectable shell, and as you look for documentation of how to do various things across the Internet, almost invariably you’ll find instructions which assume you are using a bash shell. But bash has some shortcomings, as anyone who has ever written a bash script that’s more than a few lines can attest to. It’s not that you can’t do something, it’s that it’s not always particularly intuitive (or at least elegant) to read and write. For some examples, see this list of [common bash pitfalls](http://mywiki.wooledge.org/BashPitfalls).
That said, bash is probably here to stay for at least the near future, with its enormous install base and legions of both casual and professional system administrators who are already attuned to its usage, and quirks. The bash project is available under a [GPLv3](http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html) license.
## ksh
[KornShell](http://www.kornshell.org/), also known by its command invocation, ksh, is an alternative shell that grew out of Bell Labs in the 1980s, written by David Korn. While originally proprietary software, later versions were released under the [Eclipse Public License](https://www.eclipse.org/legal/epl-v10.html).
Proponents of ksh list a number of ways in which they feel it is superior, including having a better loop syntax, cleaner exit codes from pipes, an easier way to repeat commands, and associative arrays. It's also capable of emulating many of the behaviors of vi or emacs, so if you are very partial to a text editor, it may be worth giving a try. Overall, I found it to be very similar to bash for basic input, although for advanced scripting it would surely be a different experience.
## tcsh
[Tcsh](http://www.tcsh.org/Welcome) is a derivative of csh, the Berkely Unix C shell, and sports a very long lineage back to the early days of Unix and computing itself.
The big selling point for tcsh is its scripting language, which should look very familiar to anyone who has programmed in C. Tcsh's scripting is loved by some and hated by others. But it has other features as well, including adding arguments to aliases, and various defaults that might appeal to your preferences, including the way autocompletion with tab and history tab completion work.
You can find tcsh under a [BSD license](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BSD_licenses).
## zsh
[Zsh](http://www.zsh.org/) is another shell which has similarities to bash and ksh. Originating in the early 90s, zsh sports a number of useful features, including spelling correction, theming, namable directory shortcuts, sharing your command history across multiple terminals, and various other slight tweaks from the original Bourne shell.
The code and binaries for zsh can be distributed under an MIT-like license, though portions are under the GPL; check the [actual license](https://sourceforge.net/p/zsh/code/ci/master/tree/LICENCE) for details.
## fish
I knew I was going to like the Friendly Interactive Shell, [fish](https://fishshell.com/), when I visited the website and found it described tongue-in-cheek with "Finally, a command line shell for the 90s"—fish was written in 2005.
The authors of fish offer a number of reasons to make the switch, all invoking a bit of humor and poking a bit of fun at shells that don't quite live up. Features include autosuggestions ("Watch out, Netscape Navigator 4.0"), support of the "astonishing" 256 color palette of VGA, but some actually quite helpful features as well including command completion based on the man pages on your machine, clean scripting, and a web-based configuration.
Fish is licensed primarily unde the GPL version 2 but with portions under other licenses; check the repository for [complete information](https://github.com/fish-shell/fish-shell/blob/master/COPYING).
Looking for a more detailed rundown on the precise differences between each option? [This site](http://hyperpolyglot.org/unix-shells) ought to help you out.
So where did I land? Well, ultimately, I’m probably going back to bash, because the differences were subtle enough that someone who mostly used the command line interactively as opposed to writing advanced scripts really wouldn't benefit much from the switch, and I'm already pretty comfortable in bash.
But I’m glad I decided to come out of my shell (ha!) and try some new options. And I know there are many, many others out there. Which shells have you tried, and which one do you prefer? Let us know in the comments!
## 6 Comments |
7,535 | Ruby on Rails 5.0 发布 | http://weblog.rubyonrails.org/2016/6/30/Rails-5-0-final/ | 2016-07-03T11:27:00 | [
"Ruby",
"Ruby on Rails",
"ROR"
] | /article-7535-1.html | 经过了六个月的努力,发布了 4 个 beta 版本、2 个 RC 版本,Rails 5.0 终于正式发布了!
Rails 社区的[公告](http://weblog.rubyonrails.org/2016/6/30/Rails-5-0-final/)中说,“这是由数百位[贡献者](http://contributors.rubyonrails.org/releases/5-0-0/contributors),历经上千次提交而达成的一个新的里程碑,Rails 5.0 无疑是迄今为止最好、最完善的 Rails 版本。 经过了这么久的发展,社区依然具有如此活力,感谢每一位帮助过我们的人们!”

在本次发布的 Rails 5.0 中,有两大亮点:
### Action Cable
[Action Cable](https://github.com/rails/rails/tree/master/actioncable) 是一个重新打造的框架,用于在 Rails 中控制 WebSocket。它是一个完全整合的解决方案,包括了连接管理、用于服务器端处理的 channel 层以及客户端交互的 JavaScript 层。它增加了易用性,让设计类似聊天、提示、现场等实时功能更加容易。如果你想看看它的具体表现,你可以看看它在 [Basecamp 3](https://basecamp.com/) 强大的表现。
Action Cable 中最棒的地方是你可以在你的 WebSocket 里面访问你的整个 Active Record 和 PORO 域模型。如果你想为 WebSocket 响应复用服务器端模板的话,甚至还有一个全新打造的 [ActionController::Renderer](http://blog.bigbinary.com/2016/01/08/rendering-views-outside-of-controllers-in-rails-5.html) 系统可以使你在控制器之外渲染你的模板。
在开发模式时,Action Cable 可以运行在你的应用内部,你只需要将默认的开发服务器从 Webrick 切换到 [Puma](http://puma.io/) 即可。在产品环境中,你也可以让 Action Cable 运行自己的服务器。
### API 模式
Rails 不仅是你使用服务器端 HTML 模板渲染来构建全栈应用的最佳选择,而且也是开发客户端 JavaScript 或原生应用的好伴侣,只需要用 JSON 和后端通讯即可。新推出的 -api 模式可以让你使用 `rails new backend --api` 创建一个新的 Rails 应用,这样会采用 JSON 而不是 HTML 作为应用骨架和配置。
这个功能还需要更多的完善,不过这是一个良好的开端。
### 其它亮点
* 不用再使用 rake 命令了,统一采用一个 rails 命令即可。比如现在用 `bin/rails db:migrate` 取代了 `bin/rake db:migrate`。
* [新的属性 API](https://github.com/rails/rails/blob/8c752c7ac739d5a86d4136ab1e9d0142c4041e58/activerecord/lib/active_record/attributes.rb)。
* 生成器创建的所有模型都以 ApplicationRecord 为默认父类。
* 等等……
具体你应该看看各个部分的变更日志,都有不少变化:
* [Action Mailer CHANGELOG](https://github.com/rails/rails/blob/v5.0.0/actionmailer/CHANGELOG.md)
* [Action Pack CHANGELOG](https://github.com/rails/rails/blob/v5.0.0/actionpack/CHANGELOG.md)
* [Action View CHANGELOG](https://github.com/rails/rails/blob/v5.0.0/actionview/CHANGELOG.md)
* [Active Model CHANGELOG](https://github.com/rails/rails/blob/v5.0.0/activemodel/CHANGELOG.md)
* [Active Record CHANGELOG](https://github.com/rails/rails/blob/v5.0.0/activerecord/CHANGELOG.md)
* [Active Support CHANGELOG](https://github.com/rails/rails/blob/v5.0.0/activesupport/CHANGELOG.md)
* [Active Job CHANGELOG](https://github.com/rails/rails/blob/v5.0.0/activejob/CHANGELOG.md)
* [Railties CHANGELOG](https://github.com/rails/rails/blob/v5.0.0/railties/CHANGELOG.md)
更多的细节,你可以看看[完整的 Rails 5.0 发布公告](http://guides.rubyonrails.org/5_0_release_notes.html),Claudio B. 做了一篇[简短的演示](https://speakerdeck.com/claudiob/rails-5-awesome-features-and-breaking-changes)来介绍了他喜欢的一些改进(和一些功能的去除),DHH 本人也录制了一段基础性的介绍视频: [让我们用 Rails 5 打造一个博客](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OaDhY_y8WTo) 。
此外要注意,根据 Rails 的[维护策略](http://guides.rubyonrails.org/maintenance_policy.html),Rails 5.0 的发布代表着以后将只会对 5.0.x 进行错误修复,安全问题的修复会包括 5.0.x 和 4.2.x,(如果 5.1 出来了就是 5.1.x、5.0.x 和 4.2.x)。也就是说,**4.1.x 及其以下版本原则上不支持了!**而且,**Ruby 2.2.2 及以上版本也将仅支持 Rails 5.0 及以上版本。**
(题图来自:mobiloitte.com)
| null | HTTPConnectionPool(host='weblog.rubyonrails.org', port=80): Max retries exceeded with url: /2016/6/30/Rails-5-0-final/ (Caused by NameResolutionError("<urllib3.connection.HTTPConnection object at 0x7b8327581810>: Failed to resolve 'weblog.rubyonrails.org' ([Errno -2] Name or service not known)")) | null |
7,540 | 在 Ubuntu Linux 中使用 WebP 图片 | http://itsfoss.com/webp-ubuntu-linux/ | 2016-07-04T15:20:00 | [
"PNG",
"JPEG",
"图片",
"WebP"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7540-1.html | 
>
> 简介:这篇指南会向你展示如何在 Linux 下查看 WebP 图片以及将 WebP 图片转换为 JPEG 或 PNG 格式。
>
>
>
### 什么是 WebP?
自从 Google 推出 [WebP 图片格式](https://developers.google.com/speed/webp/),已经过去五年了。Google 说,WebP 提供有损和无损压缩,相比 JPEG 压缩,WebP 压缩文件大小,能更小约 25%。
Google 的目标是让 WebP 成为 web 图片的新标准,但是并没有成为现实。已经五年过去了,除了谷歌的生态系统以外它仍未被接受成为一个标准。但正如我们所知的,Google 对它的技术很有进取心。几个月前 Google 将 Google Plus 的所有图片改为了 WebP 格式。
如果你用 Google Chrome 从 Google Plus 上下载那些图片,你会得到 WebP 图片,不论你之前上传的是 PNG 还是 JPEG。这都不是重点。真正的问题在于当你尝试着在 Ubuntu 中使用默认的 GNOME 图片查看器打开它时你会看到如下错误:
>
> <ruby> Could not load XYZ.webp <rp> ( </rp> <rt> 无法载入 XYZ.webp </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
> <ruby> Unrecognized image file format <rp> ( </rp> <rt> 未识别文件格式 </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
>
>
>

*GNOME 图片查看器不支持 WebP 图片*
在这个教程里,我们会看到
* 如何在 Linux 中添加 WebP 支持
* 支持 WebP 图片的程序列表
* 如何将 WebP 图片转换到 PNG 或 JPEG
* 如何将 WebP 图片直接下载为 PNG 格式
### 如何在 Ubuntu 以及其它 Linux 发行版中查看 WebP 图片
[GNOME 图片查看器](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/EyeOfGnome)是许多 Linux 发行版的默认图片查看器,包括 Ubuntu,它不支持 WebP 图片。目前也没有可用的插件给 GNOME 图片查看器添加 WebP 支持。
这无非是意味着我们不能在 Linux 上用 GNOME 图片查看器打开 WebP 文件而已。一个更好的替代品,[gThumb](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/gthumb),默认就支持 WebP 图片。
要在 Ubuntu 以及其它基于 Ubuntu 的发行版上安装 gThumb 的话,使用以下命令:
```
sudo apt-get install gthumb
```
一旦安装完成,你就可以简单地右键点击 WebP 图片,选择 gThumb 来打开它。你现在应该可以看到如下画面:

*gThumb 中显示的 WebP 图片*
### 让 gThumb 成为 Ubuntu 中 WebP 图片的默认应用
对 Ubuntu 新手而言,如果你想要让 gThumb 成为打开 WebP 文件的默认应用,跟着以下步骤操作:
步骤 1:右键点击 WebP 文件选择属性。

*从右键菜单中选择属性*
步骤 2:转到打开方式标签,选择 gThumb 并点击设置为默认。

*让 gThumb 成为 Ubuntu 中 WebP 图片的默认应用*
### 让 gThumb 成为所有图片的默认应用
gThumb 的功能比图片查看器更多。举个例子,你可以做一些简单的图片编辑,给图片添加滤镜等。添加滤镜的效率没有 XnRetro(在 [Linux 下添加类似 Instagram 滤镜效果](http://itsfoss.com/add-instagram-effects-xnretro-ubuntu-linux/)的专用工具)那么高,但它还是有一些基础的滤镜可以用。
我非常喜欢 gThumb 并且决定让它成为默认的图片查看器。如果你也想在 Ubuntu 中让 gThumb 成为所有图片的默认应用,遵照以下步骤操作:
步骤1:打开系统设置

步骤2:转到<ruby> 详情 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Details </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>

步骤3:在这里将 gThumb 设置为图片的默认应用

### Linux 上打开 WebP 文件的替代程序
可能你不喜欢 gThumb。如果这样的话,你可以选择下列应用来在 Linux 中查看 WebP 图片:
* [XnView](http://www.xnview.com/en/xnviewmp/#downloads)(非开源)
* GIMP 加上非官方 WebP 插件,可以从这个 [PPA](https://launchpad.net/%7Egeorge-edison55/+archive/ubuntu/webp) 安装,支持到 Ubuntu 15.10。我会在另一篇文章里提到。
* [Gwenview](https://userbase.kde.org/Gwenview)
### 在 Linux 中将 WebP 图片转换为 PNG 和 JPEG
在 Linux 上转换 WebP 图片有两种途径:
* 命令行
* 图形界面
#### 1.在 Linux 使用命令行转换 WebP 图片
你需要先安装 WebP 工具。打开终端并使用下列命令:
```
sudo apt-get install webp
```
##### 将 JPEG/PNG 转换为 WebP
我们将使用 cwebp 命令(它代表转换为 WebP 的意思吗?)来将 JPEG 或 PNG 文件转换为 WebP。命令格式是这样的:
```
cwebp -q [图片质量] [JPEG/PNG_文件名] -o [WebP_文件名]
```
举个例子,你可以使用下列命令:
```
cwebp -q 90 example.jpeg -o example.webp
```
##### 将 WebP 转换为 JPEG/PNG
要将 WebP 图片转换为 JPEG 或 PNG,我们将使用 dwebp 命令。命令格式是:
```
dwebp [WebP_文件名] -o [PNG_文件名]
```
该命令的一个例子:
```
dwebp example.webp -o example.png
```
#### 2.使用图形工具将 WebP 转换为 JPEG/PNG
要实现这个目标,我们要使用 XnConvert,它是免费的应用但不是开源的。你可以从他们的网站上下载安装文件:
* [下载 XnConvert](http://www.xnview.com/en/xnconvert/#downloads)
XnConvert 是个强大的工具,你可以用它来批量修改图片尺寸。但在这个教程里,我们只介绍如何将单个 WebP 图片转换为 PNG/JPEG。
打开 XnConvert 并选择输入文件:

在输出标签,选择你想要的输出格式。选择完后点击转换。

要将 WebP 图片转换为 PNG,JPEG 或其它你选择的图片格式,这就是你所需要做的一切了。
### 在 Chrome 浏览器中直接将 WebP 图片下载为 PNG
也许你一点都不喜欢 WebP 图片格式,也不想在 Linux 仅仅为了查看 WebP 图片而安装一个新软件。如果你不得不将 WebP 文件转换以备将来使用,这会是件更痛苦的事情。
解决这个问题的一个更简单、不那么痛苦的途径是安装一个 Chrome 扩展 Save Image as PNG。有了这个插件,你可以右键点击 WebP 图片并直接存储为 PNG 格式。

*在 Google Chrome 中将 WebP 图片保存为 PNG 格式*
* [获取 Save Image as PNG 扩展](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/save-image-as-png/nkokmeaibnajheohncaamjggkanfbphi?utm_source=chrome-ntp-icon)
### 你的选择是?
我希望这个详细的教程能够帮你在 Linux 上支持 WebP 并帮你转换 WebP 图片。你在 Linux 怎么处理 WebP 图片?你使用哪个工具?以上描述的方法中,你最喜欢哪一个?
---
via: <http://itsfoss.com/webp-ubuntu-linux/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,542 | ReactOS 新手指南 | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/getting-started-with-reactos/ | 2016-07-05T19:02:13 | [
"ReactOS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7542-1.html | ReactOS 是一个比较年轻的开源操作系统,它提供了一个和 Windows NT 类似的图形界面,并且它的目标也是提供一个与 NT 功能和应用程序兼容性差不多的系统。这个项目在没有使用任何 Unix 架构的情况下实现了一个类似 Wine 的用户模式。它的开发者们从头实现了 NT 的架构以及对于 FAT32 的兼容,因此它也不需要负任何法律责任。这也就是说,它不是又双叒叕一个 Linux 发行版,而是一个独特的类 Windows 系统,并且是开源世界的一部分。这份快速指南是给那些想要一个易于使用的 Windows 的开源替代品的人准备的。

### 安装系统
在开始安装这个系统之前,我需要说明一下,ReactOS 的最低硬件要求是 500MB 硬盘以及仅仅 96MB 内存。我会在一个 32 位的虚拟机里面演示安装过程。
现在,你需要使用箭头键来选择你想要语言,而后通过回车键来确认。

之后,再次敲击回车键来继续安装。你也可以选择按“R”键来修复现有的系统。

在第三屏中,你将看到一个警告说这个系统还是早期开发版本。再次敲击回车键,你将看到一个需要你最后确认的配置概览。如果你认为没问题,就按回车。

然后,我们就到了分区这一步,在这里,你可以使用“D”键删除高亮分区,分别使用“P”键、“E”键以及“L”键来添加一个主分区、拓展分区或逻辑分区。如果你想要自己添加一个分区,你需要输入这个分区的大小(以 MB 为单位),然后通过回车来确认。

但是,如果你有未使用的硬盘空间,在分区过程直接敲击回车键可以自动在你选中的分区上安装 ReactOS。

下一步是选择分区的格式,不过现在我们只能选择 FAT32。

再下一步是选择安装文件夹。我就使用默认的“/ReactOS”了,应该没有问题。

然后就是等待...

最后,我们要选择启动程序的安装位置。如果你是在实机上操作的话,第一个选项应该是最安全的。

总地来说,我认为 ReactOS 的安装向导很直接。尽管安装程序的界面可能看起来一点也不现代、不友好,但是大多数情况下作为用户的我们只需要狂敲回车就能安个差不多。这就是说,ReactOS 的开发版安装起来也是相对简单方便的。
### 设置 ReactOS
在我们重启进入新系统之后,“设置向导”会帮助你设置系统。目前,这个向导仅支持设置语言和键盘格式。

我在这里选择了第二个键盘格式。

我还可以设置一个改变键盘布局的快捷键。

之后我添加了用户名…

…以及管理员密码…

在设置好时间之后,我们就算完成了系统设置。

### ReactOS 之内
当我们历经千辛万苦,终于首次进入 ReactOS 的界面时,系统会检测硬件并自动帮助我们安装驱动。

这是我这里被自动检测出来的三个硬件:

在上一张图片里你看到的是 ReactOS 的“应用管理器”,这东西是 Linux 的标配。不过你不会在这里找到任何与 Linux 有关系的东西。只有在这个系统里工作良好的开源软件才会在这个管理器中出现。这就导致了管理器中有的分类下挤得满满当当,有的却冷清异常。

我试着通过软件中心安装了 Firefox 以及通过直接下载 exe 文件双击安装 Notepad++。这两个应用都能完美运行:它们的图标出现在了桌面上,在菜单中也出现了它们的名字,Notepad++ 也出现在了软件中心右侧的分类栏里。

我没有尝试运行任何现代的 Windows 游戏,如果你想配置 Direct 3D 的话,你可以转到 “我的电脑/控制选项/WineD3D 配置”。在那里,你能看到很多 Direct3D 选项,大致与 dx 8 的选项类似。

ReactOS 还有一个好的地方,就是我们可以通过“我的电脑”来操作注册表。

如果你需要一个简单点的工具,你可以在应用菜单里打开注册表编辑器。


最后,如果你认为 ReactOS 看起来有点过时了的话,你可以在桌面右击选择“属性”,之后在“外观”那里选择你喜欢的主题和颜色。

### 结论
老实说,我对 ReactOS 的工作方式印象深刻。它相当稳定、连贯、快速,并且真正人性化。抛开 Windows 的阴影(过时的应用菜单,不合理的菜单结构)不谈的话,ReactOS 几乎做到了尽善尽美。它可能不会有太多应用可供选择,现有的功能也可能不够强大,但是我确信它将会繁荣壮大。关于它的数据显示出了它的人气,我确定将要围绕它建立起来的社区将会很快就壮大到能把这个项目带往成功之路的地步。如今,ReactOS 的最新版本是 0.4.1。如果想要以开源的方式运行 Windows 的应用,那么它就是你的菜!
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/getting-started-with-reactos/>
作者:[Bill Toulas](https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/getting-started-with-reactos/) 译者:[name1e5s](https://github.com/name1e5s) 校对:[PurlingNayuki](https://github.com/PurlingNayuki)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # Getting started with ReactOS
ReactOS is a relatively new open-source operating system that resembles the looks of Windows NT and aims to offer similar levels of functionality and application compatibility. Featuring a wine-based user mode, this system doesn't use any of the Unix architecture, but is a rewrite of the NT architecture from scratch, with its very own FAT32 implementation, and completely free of legal implications. That said, this is not yet another Linux distro, but a unique Windows-like system that is a part of the free software world. This quick guide aims at users who want an easy-to-use, open-source replacement for their Windows system.
## System Installation
Before getting started with the installation process, I should point out that the minimum requirements of ReactOS are 500 MB of free disk space and only 96 MB of RAM. I will demonstrate the installation process on a 32-bit virtual machine.
Navigate with the arrow keys and select the desired language by pressing “Enter”.
Next, hit “Enter” again to continue with the installation, or “R” to repair an existing install.
On the third screen, you'll get a warning about the current limitation that applies to this early development version of the OS. Continue with “Enter” again and you'll get a summary of the settings before the final user approval. If all is good, hit “Enter” once again.
This will take you to the partitioning stage where you may delete the highlighted option by pressing “D”, and then add primary, extended, or logical partitions with “P”, “E”, and “L” respectively. If you choose to add a partition yourself, you will be given the option to set its size by entering a number of MBs and pressing “Enter” to confirm.
However, if you have already unused space available, hitting “Enter” once again during the partitioning stage will automatically install ReactOS in the selected partition.
The next step is the selection of the filesystem type which for now is limited to FAT32 only.
Next is the directory selection. I will leave this at the default “/ReactOS” and it should be fine.
...and we're off
Finally, we're about the choose the location of the bootloader. The first option should be the safest if installing on a real disk.
In general, I could say that the installation of ReactOS is pretty straightforward. The interface may not look friendly or modern at all, but hitting “Enter” in every step will work just fine in most cases. That said, the development version of ReactOS it's fairly simple and easy to install.
## ReactOS First Boot
## Setting Up ReactOS
Once we reboot and get into our new system, we're offered the help of the “Setup Wizard”. This wizard is basically allowing us to set up the language and keyboard layout, system name, administrator user and password and other common settings.
I used this step to add a second keyboard layout.
I can even set a different key combination for changing the layout.
Choose a username and password.
Set a computer name. the name must be unique in your LAN.
Set date, time, and time zone.
Choose a Theme. I'm using the Mizu theme here.
Configure Workgroup settings, if the computer shall join a Workgroup. I'll select 'no' here.
Installation wizard finishes the setup.
ReactOS Desktop.
## Inside ReactOS
When we finally enter ReactOS for the first time, new hardware is detected and we're offered to install the available drivers automatically.
These are the three devices that were automatically detected by ReactOS in my case:
What you're looking at in the above screenshot is ReactOS's “applications manager” which is of course to the standards of Linux systems. You won't find anything Linux-related here, though. Only open source applications that are known to work well with the particular system are offered. That said, some categories are well-populated, while others are completely empty.
I took the liberty to install Firefox through the software center, and Notepad++ by downloading the .exe file and installing it by simply double-clicking the executable. Both worked perfectly well, their desktop icons were created, menu entries added, and Notepad++ was added in the applications manager and in the right category as well.
I wouldn't try running any modern Windows games, but if you want to setup the Direct 3D settings you can go to “My Computer/Control Panel/WineD3D Options”. There you will find multiple options about the Direct3D which is presumably resembling dx version 8.
Another good thing with ReactOS is the fact that the Registry entries can be accessed and set as needed through “My Computer” again.
If you need something handier though, you may find a Registry Editor utility from the applications menu.
Finally, if the looks of ReactOS look somewhat outdated to you, right-click on the desktop and select “Properties”. Then choose the “Appearance” tab and set the theme and color that you prefer.
## Conclusion
Honestly, I was impressed by the way ReactOS works. It's quite solid, coherent, speedy, and really user-friendly. Leaving aside the negatives that stem from the Windows design (deprecated applications menu, irrational directory structure), ReactOS is almost perfect on what it does. It may not be very rich in terms of application selection, and it may not be very powerful in terms of features yet, but I am sure it's going to flourish. The numbers show great popularity, and I'm sure the community that's going to build up around it will soon be large enough to lead the project to success. Right now, version 0.4.13 looks nice so far, but one has to admin that ReactOS development seems to have stalled. If you care about running older Windows applications and doing so in an open way, give it a try! |
7,543 | Android 4.4 移植到了 PowerPC 架构,支持大端架构 | http://hackerboards.com/powerpc-gains-android-4-4-port-with-big-endian-support/ | 2016-07-05T19:47:00 | [
"Android",
"PowerPC"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7543-1.html | eInfochips(一家软件厂商) 已将将 Android 4.4 系统移植到 PowerPC 架构,它将用于一家航空电子客户用来监视引擎的健康状况的<ruby> 人机界面 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Human Machine Interface </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(HMI)。
eInfochips 已经开发了第一个面向 PowerPC 架构的 CPU 的 Android 移植版本,并支持<ruby> 大端 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Big Endian </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>架构。此移植基于<ruby> Android 开源项目 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Android Open Source Project </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> (AOSP)中 Android 4.4 (KitKat)的代码,其功能内核的版本号为 3.12.19。
Android 开始兴起的时候,PowerPC 正在快速丢失和 ARM 架构共同角逐的市场。高端的网络客户和其它的企业级的嵌入式工具大多运行在诸如<ruby> 飞思卡尔 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Freescale </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的 PowerQUICC 和 QorIQ 这样的 PowerPC 处理器上,但是并不是 Linux 系统。不过,有几个 Android 的移植计划。在 2009 年,飞思卡尔和 Embedded Alley(一家软件厂商,当前是 Mentor Graphics 的 Linux 团队的一部分)[宣布了针对 PowerQUICC 和 QorIQ 芯片的移植版本](http://linuxdevices.linuxgizmos.com/android-ported-to-powerpc/),当前由 NXP 公司构建。另一个名为 [Android-PowerPC](http://www.androidppc.com/) 的项目也作出了相似的工作。
这些努力来的都并不容易,然而,当航空公司找到 eInfochips,希望能够为他们那些基于 PowerPC 的引擎监控系统添加 Android 应用程序以改善人机界面。该公司找出了这些早期的移植版本,然而,它们都相距甚远。所以,他们不得不从头开始新的移植。
最主要的问题是这些移植的 Android 版本实在是太老了,和现在的 Android 差别太大了。Embedded Alley 移植的版本为 Android 1.5 (Cupcake),它于 2009 年发布,Linux 内核版本为 2.6.28。而 Android-PowerPC 项目最后一版的移植是 Android 2.2 (Froyo),它于 2010 年发布,内核版本为 2.6.32。此外,航空公司还有一些额外的技术诉求,例如对<ruby> 大端架构 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Big Endian </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的支持,这种老式的内存访问方式仍旧应用于网络通信和电信行业。然而那些早期的移植版本仅能够支持<ruby> 小端架构 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Little Endian </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的内存访问。
### 来自 eInfochips 的全新 PowerPC 架构移植
eInfochips, 它最为出名的应该是那些基于 ARM/骁龙处理器的模块计算机板卡,例如 [Eragon 600](http://hackerboards.com/quad-core-snapdragon-com-offers-three-dev-kit-options/)。 它已经完成了基于 QorIQ 的 Android 4.4 系统移植,且发布了白皮书介绍了该项目。采用该项目的航空电子设备客户仍旧不愿透露名称,目前仍旧不清楚什么时候会公开此该移植版本。

*图片来自 eInfochips 的博客日志*
全新的 PowerPC Android 项目包括:
* 为 PowerPC [e5500](http://linuxdevices.linuxgizmos.com/low-cost-powerquicc-chips-offer-flexible-interconnect-options/) 定制的 Bionic 库
* 基于 Android KitKat 的大端支持
* 使用 GCC 5.2 工具链开发
* Android 4.4 框架的 PowerPC 支持
* PowerPC e5500 的 Android 内核版本为 3.12.19
根据 eInfochips 的销售经理 Sooryanarayanan Balasubramanian 描述,该航空电子客户想要使用 Android 主要是因为熟悉的界面能够缩减培训的时间,并且让程序更新和增加新程序变得更加容易。他继续解释说:“这次成功的移植了 Android,使得今后的工作仅仅需要在应用层作出修修改改,而不再向以前一样需要在所有层面之间作相互的校验。”,“这是第一次在航空航天工业作出这些尝试,这需要在设计时尽量认真。”
通过白皮书,可以知道将 Android 移植到 PowerPC 上需要对框架、核心库、开发工具链、运行时链接器、对象链接器和开源编译工具作出大量的修改。在字节码生成阶段,移植团队决定使用<ruby> 便携模式 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> portable mode </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>而不是<ruby> 快速解释模式 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> fast interpreter mode </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。这是因为还没有 PowerPC 可用的快速解释模式,而使用开源的 [libffi](https://sourceware.org/libffi/) 的便携模式能够支持 PowerPC。
同时,团队还面临着在 Android 运行时 (ART) 环境和 Dalvik 虚拟机 (DVM) 环境之间的选择。他们发现,ART 环境下的便携模式还未经测试且缺乏良好的文档支持,所以最终选择了 DVM 环境下的便携模式。
白皮书中还提及了其它的一些在移植过程中遇到的困难,包括重新开发工具链,重写脚本以解决 AOSP 对编译器标志“非标准”使用的问题。最终完成的移植版本提供了 37 个服务,以及提供了无界面的 Android 部署,在前端使用用户空间的模拟 UI。
### 目标硬件
感谢来自 [eInfochips 博客日志](https://www.einfochips.com/blog/k2-categories/aerospace/presenting-a-case-for-porting-android-on-powerpc-architecture.html) 的图片(如下图所示),让我们能够确认此 PowerPC 的 Android 移植项目的硬件平台。这个板卡为 [X-ES Xpedite 6101](http://www.xes-inc.com/products/processor-mezzanines/xpedite6101/),它是一个加固级 XMC/PrPMC 夹层模组。

*X-ES Xpedite 6101 照片和框图*
X-ES Xpedite 6101 板卡拥有一个可选的 NXP 公司基于 QorIQ T 系列通信处理器(T2081、T1042 和 T1022),它们分别集成了 8 个、4 个和 2 个 e6500 核心,稍有不同的是,T2081 的处理器主频为 1.8GHz,T1042/22 的处理器主频为 1.4GHz。所有的核心都集成了 AltiVec SIMD 引擎,这也就意味着它能够提供 DSP 级别的浮点运算性能。所有以上 3 款 X-ES 板卡都能够支持最高 8GB 的 DDR3-1600 ECC SDRAM 内存。外加 512MB NOR 和 32GB 的 NAND 闪存。

*NXP T2081 框图*
板卡的 I/O 包括一个 x4 PCI Express Gen2 通道,以及两个千兆级网卡、 RS232/422/485 串口和 SATA 3.0 接口。此外,它可选 3 款 QorIQ 处理器,Xpedite 6101 提供了三种 [X-ES 加固等级](http://www.xes-inc.com/capabilities/ruggedization/),分别是额定工作温度 0 ~ 55°C, -40 ~ 70°C, 或者是 -40 ~ 85°C,且包含 3 类冲击和抗振类别。
此外,我们已经介绍过的基于 X-ES QorIQ 的 XMC/PrPMC 板卡包括 [XPedite6401 和 XPedite6370](http://hackerboards.com/high-end-boards-run-linux-on-64-bit-arm-qoriq-socs/),它们支持已有的板卡级 Linux 、风河的 VxWorks(一种实时操作系统) 和 Green Hills 的 Integrity(也是一种操作系统)。
### 更多信息
eInfochips Android PowerPC 移植白皮书可以[在此](http://biz.einfochips.com/portingandroidonpowerpc)下载(需要先免费注册)。
### 相关资料
* [Commercial embedded Linux distro boosts virtualization](http://hackerboards.com/commercial-embedded-linux-distro-boosts-virtualization/)
* [Freescale unveils first ARM-based QorIQ SoCs](http://hackerboards.com/freescale-unveils-first-arm-based-qoriq-socs/)
* [High-end boards run Linux on 64-bit ARM QorIQ SoCs](http://hackerboards.com/high-end-boards-run-linux-on-64-bit-arm-qoriq-socs/)
* [Free, Open Enea Linux taps Yocto Project and Linaro code](http://hackerboards.com/free-open-enea-linux-taps-yocto-and-linaro-code/)
* [LynuxWorks reverts to its LynxOS roots, changes name](http://hackerboards.com/lynuxworks-reverts-to-its-lynxos-roots-changes-name/)
* [First quad- and octa-core QorIQ SoCs unveiled](http://hackerboards.com/first-quad-and-octa-core-qoriq-socs-unveiled/)
* [Free white paper shows how Linux won embedded](http://hackerboards.com/free-white-paper-shows-how-linux-won-embedded/)
* [Quad-core Snapdragon COM offers three dev kit options](http://hackerboards.com/quad-core-snapdragon-com-offers-three-dev-kit-options/)
* [Tiny COM runs Linux on quad-core 64-bit Snapdragon 410](http://hackerboards.com/tiny-com-runs-linux-and-android-on-quad-core-64-bit-snapdragon-410/)
* [PowerPC based IoT gateway COM ships with Linux BSP](http://hackerboards.com/powerpc-based-iot-gateway-com-ships-with-linux-bsp/)
---
via: <http://hackerboards.com/powerpc-gains-android-4-4-port-with-big-endian-support/>
作者:[Eric Brown](http://hackerboards.com/powerpc-gains-android-4-4-port-with-big-endian-support/) 译者:[dongfengweixiao](https://github.com/dongfengweixiao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,546 | Linux 新手必知必会的 10 条 Linux 基本命令 | http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/10-basic-linux-commands-that-every-linux-newbies-should-remember | 2016-07-06T18:54:00 | [
"命令"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7546-1.html | 
Linux 对我们的生活产生了巨大的冲击。至少你的安卓手机使用的就是 Linux 核心。尽管如此,在第一次开始使用 Linux 时你还是会感到难以下手。因为在 Linux 中,通常需要使用终端命令来取代 Windows 系统中的点击启动图标操作。但是不必担心,这里我们会介绍 10 个 Linux 基本命令来帮助你开启 Linux 神秘之旅。
### 帮助新手走出第一步的 10 个 Linux 基本命令
当我们谈论 Linux 命令时,实质上是在谈论 Linux 系统本身。这短短的 10 个 Linux 基本命令不会让你变成天才或者 Linux 专家,但是能帮助你轻松开始 Linux 之旅。使用这些基本命令会帮助新手们完成 Linux 的日常任务,由于它们的使用频率如此至高,所以我更乐意称他们为 Linux 命令之王!
让我们开始学习这 10 条 Linux 基本命令吧。
#### 1. sudo
这条命令的意思是“以超级用户的身份执行”,是 SuperUserDo 的简写,它是新手将要用到的最重要的一条 Linux 命令。当一条单行命令需要 root 权限的时候,`sudo`命令就派上用场了。你可以在每一条需要 root 权限的命令前都加上`sudo`。
```
$ sudo su
```
#### 2. ls
跟其他人一样,你肯定也经常想看看目录下都有些什么东西。使用列表命令,终端会把当前工作目录下所有的文件以及文件夹展示给你。比如说,我当前处在 /home 文件夹中,我想看看 /home 文件夹中都有哪些文件和目录。
```
/home$ ls
```
在 /home 中执行`ls`命令将会返回类似下面的内容:
```
imad lost+found
```
#### 3. cd
变更目录命令(cd)是终端中总会被用到的主要命令。它是最常用到的 Linux 基本命令之一。此命令使用非常简单,当你打算从当前目录跳转至某个文件夹时,只需要将文件夹键入此命令之后即可。如果你想跳转至上层目录,只需要在此命令之后键入两个点 (..) 就可以了。 举个例子,我现在处在 /home 目录中,我想移动到 /home 目录中的 usr 文件夹下,可以通过以下命令来完成操作。
```
/home $ cd usr
/home/usr $
```
#### 4. mkdir
只是可以切换目录还是不够完美。有时候你会想要新建一个文件夹或子文件夹。此时可以使用 mkdir 命令来完成操作。使用方法很简单,只需要把新的文件夹名跟在 mkdir 命令之后就好了。
```
~$ mkdir folderName
```
#### 5. cp
<ruby> 拷贝-粘贴 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> copy-and-paste </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>是我们组织文件需要用到的重要命令。使用 `cp` 命令可以帮助你在终端当中完成拷贝-粘贴操作。首先确定你想要拷贝的文件,然后键入打算粘贴此文件的目标位置。
```
$ cp src des
```
注意:如果目标目录对新建文件需要 root 权限时,你可以使用 `sudo` 命令来完成文件拷贝操作。
#### 6. rm
rm 命令可以帮助你移除文件甚至目录。如果不希望每删除一个文件都提示确认一次,可以用`-f`参数来强制执行。也可以使用 `-r` 参数来递归的移除文件夹。
```
$ rm myfile.txt
```
#### 7. apt-get
这个命令会依据发行版的不同而有所区别。在基于 Debian 的发行版中,我们拥有 Advanced Packaging Tool(APT)包管理工具来安装、移除和升级包。apt-get 命令会帮助你安装需要在 Linux 系统中运行的软件。它是一个功能强大的命令行,可以用来帮助你对软件执行安装、升级和移除操作。
在其他发行版中,例如 Fedora、Centos,都各自不同的包管理工具。Fedora 之前使用的是 yum,不过现在 dnf 成了它默认的包管理工具。
```
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo dnf update
```
#### 8. grep
当你需要查找一个文件,但是又忘记了它具体的位置和路径时,`grep` 命令会帮助你解决这个难题。你可以提供文件的关键字,使用`grep`命令来查找到它。(LCTT 译注:如果知道了文件名、大小、访问日期等特征,通常用 find 命令来查找文件。)
```
$ grep user /etc/*
```
#### 9. cat
作为一个用户,你应该会经常需要浏览脚本内的文本或者代码。`cat`命令是 Linux 系统的基本命令之一,它的用途就是将文件的内容展示给你。
```
$ cat CMakeLists.txt
```
#### 10. poweroff
最后一个命令是 `poweroff`。有时你需要直接在终端中执行关机操作。此命令可以完成这个任务。由于关机操作需要 root 权限,所以别忘了在此命令之前添加`sudo`。
```
$ sudo poweroff
```
### 总结
如我在文章开始所言,这 10 条命令并不会让你立即成为一个 Linux 大拿,但它们会让你在初期快速上手 Linux。以这些命令为基础,给自己设置一个目标,每天学习一到三条命令,这就是此文的目的所在。在下方评论区分享有趣并且有用的命令。别忘了跟你的朋友分享此文。
---
via: <http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/10-basic-linux-commands-that-every-linux-newbies-should-remember>
作者:[Commenti](http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/10-basic-linux-commands-that-every-linux-newbies-should-remember#comments) 译者:[mr-ping](https://github.com/mr-ping) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,547 | 如何在 Ubuntu 15.04/CentOS 7 中安装 Lighttpd Web 服务器 | http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/setup-lighttpd-web-server-ubuntu-15-04-centos-7/ | 2016-07-07T09:50:40 | [
"Lighttpd"
] | /article-7547-1.html | Lighttpd 是一款开源 Web 服务器软件。Lighttpd 安全快速,符合行业标准,适配性强并且针对高配置环境进行了优化。相对于其它的 Web 服务器而言,Lighttpd 占用内存更少;因其对 CPU 占用小和对处理速度的优化而在效率和速度方面从众多 Web 服务器中脱颖而出。而 Lighttpd 诸如 FastCGI、CGI、认证、输出压缩、URL 重写等高级功能更是那些面临性能压力的服务器的福音。

以下便是我们在运行 Ubuntu 15.04 或 CentOS 7 Linux 发行版的机器上安装 Lighttpd Web 服务器的简要流程。
### 安装Lighttpd
#### 使用包管理器安装
这里我们通过使用包管理器这种最简单的方法来安装 Lighttpd。只需以 sudo 模式在终端或控制台中输入下面的指令即可。
**CentOS 7**
由于 CentOS 7.0 官方仓库中并没有提供 Lighttpd,所以我们需要在系统中安装额外的软件源 epel 仓库。使用下面的 yum 指令来安装 epel。
```
# yum install epel-release
```
然后,我们需要更新系统及为 Lighttpd 的安装做前置准备。
```
# yum update
# yum install lighttpd
```

**Ubuntu 15.04**
Ubuntu 15.04 官方仓库中包含了 Lighttpd,所以只需更新本地仓库索引并使用 apt-get 指令即可安装 Lighttpd。
```
# apt-get update
# apt-get install lighttpd
```

#### 从源代码安装 Lighttpd
如果想从 Lighttpd 源码安装最新版本(例如 1.4.39),我们需要在本地编译源码并进行安装。首先我们要安装编译源码所需的依赖包。
```
# cd /tmp/
# wget http://download.lighttpd.net/lighttpd/releases-1.4.x/lighttpd-1.4.39.tar.gz
```
下载完成后,执行下面的指令解压缩。
```
# tar -zxvf lighttpd-1.4.39.tar.gz
```
然后使用下面的指令进行编译。
```
# cd lighttpd-1.4.39
# ./configure
# make
```
**注:**在这份教程中,我们安装的是默认配置的 Lighttpd。其他拓展功能,如对 SSL 的支持,mod*rewrite,mod*redirect 等,需自行配置。
当编译完成后,我们就可以把它安装到系统中了。
```
# make install
```
### 设置 Lighttpd
如果有更高的需求,我们可以通过修改默认设置文件,如`/etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf`,来对 Lighttpd 进行进一步设置。 而在这份教程中我们将使用默认设置,不对设置文件进行修改。如果你曾做过修改并想检查设置文件是否出错,可以执行下面的指令。
```
# lighttpd -t -f /etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf
```
#### 使用 CentOS 7
在 CentOS 7 中,我们需创建一个在 Lighttpd 默认配置文件中设置的 webroot 文件夹,例如`/src/www/htdocs`。
```
# mkdir -p /srv/www/htdocs/
```
而后将默认欢迎页面从`/var/www/lighttpd`复制至刚刚新建的目录中:
```
# cp -r /var/www/lighttpd/* /srv/www/htdocs/
```
### 开启服务
现在,通过执行 systemctl 指令来重启 Web 服务。
```
# systemctl start lighttpd
```
然后我们将它设置为伴随系统启动自动运行。
```
# systemctl enable lighttpd
```
### 设置防火墙
如要让我们运行在 Lighttpd 上的网页或网站能在 Internet 或同一个网络内被访问,我们需要在防火墙程序中设置打开 80 端口。由于 CentOS 7 和 Ubuntu15.04 都附带 Systemd 作为默认初始化系统,所以我们默认用的都是 firewalld。如果要打开 80 端口或 http 服务,我们只需执行下面的命令:
```
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
success
# firewall-cmd --reload
success
```
### 连接至 Web 服务器
在将 80 端口设置为默认端口后,我们就可以直接访问 Lighttpd 的默认欢迎页了。我们需要根据运行 Lighttpd 的设备来设置浏览器的 IP 地址和域名。在本教程中,我们令浏览器访问 <http://lighttpd.linoxide.com/> ,同时将该子域名指向上述 IP 地址。如此一来,我们就可以在浏览器中看到如下的欢迎页面了。

此外,我们可以将网站的文件添加到 webroot 目录下,并删除 Lighttpd 的默认索引文件,使我们的静态网站可以在互联网上访问。
如果想在 Lighttpd Web 服务器中运行 PHP 应用,请参考下面的步骤:
### 安装 PHP5 模块
在 Lighttpd 成功安装后,我们需要安装 PHP 及相关模块,以在 Lighttpd 中运行 PHP5 脚本。
#### 使用 Ubuntu 15.04
```
# apt-get install php5 php5-cgi php5-fpm php5-mysql php5-curl php5-gd php5-intl php5-imagick php5-mcrypt php5-memcache php-pear
```
#### 使用 CentOS 7
```
# yum install php php-cgi php-fpm php-mysql php-curl php-gd php-intl php-pecl-imagick php-mcrypt php-memcache php-pear lighttpd-fastcgi
```
### 设置 Lighttpd 的 PHP 服务
如要让 PHP 与 Lighttpd 协同工作,我们只要根据所使用的发行版执行如下对应的指令即可。
#### 使用 CentOS 7
首先要做的便是使用文件编辑器编辑 php 设置文件(例如`/etc/php.ini`)并取消掉对`cgi.fix_pathinfo=1`这一行的注释。
```
# nano /etc/php.ini
```
完成上面的步骤之后,我们需要把 PHP-FPM 进程的所有权从 Apache 转移至 Lighttpd。要完成这些,首先用文件编辑器打开`/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf`文件。
```
# nano /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
```
然后在文件中增加下面的语句:
```
user = lighttpd
group = lighttpd
```
做完这些,我们保存并退出文本编辑器。然后从`/etc/lighttpd/modules.conf`设置文件中添加 FastCGI 模块。
```
# nano /etc/lighttpd/modules.conf
```
然后,去掉下面语句前面的`#`来取消对它的注释。
```
include "conf.d/fastcgi.conf"
```
最后我们还需在文本编辑器设置 FastCGI 的设置文件。
```
# nano /etc/lighttpd/conf.d/fastcgi.conf
```
在文件尾部添加以下代码:
```
fastcgi.server += ( ".php" =>
((
"host" => "127.0.0.1",
"port" => "9000",
"broken-scriptfilename" => "enable"
))
)
```
在编辑完成后保存并退出文本编辑器即可。
#### 使用 Ubuntu 15.04
如需启用 Lighttpd 的 FastCGI,只需执行下列代码:
```
# lighttpd-enable-mod fastcgi
Enabling fastcgi: ok
Run /etc/init.d/lighttpd force-reload to enable changes
# lighttpd-enable-mod fastcgi-php
Enabling fastcgi-php: ok
Run `/etc/init.d/lighttpd` force-reload to enable changes
```
然后,执行下列命令来重启 Lighttpd。
```
# systemctl force-reload lighttpd
```
### 检测 PHP 工作状态
如需检测 PHP 是否按预期工作,我们需在 Lighttpd 的 webroot 目录下新建一个 php 文件。本教程中,在 Ubuntu 下 /var/www/html 目录,CentOS 下 /src/www/htdocs 目录下使用文本编辑器创建并打开 info.php。
**使用 CentOS 7**
```
# nano /var/www/info.php
```
**使用 Ubuntu 15.04**
```
# nano /srv/www/htdocs/info.php
```
然后只需将下面的语句添加到文件里即可。
```
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
```
在编辑完成后保存并推出文本编辑器即可。
现在,我们需根据路径 <http://lighttpd.linoxide.com/info.php> 下的 info.php 文件的 IP 地址或域名,来让我们的网页浏览器指向系统上运行的 Lighttpd。如果一切都按照以上说明进行,我们将看到如下图所示的 PHP 页面信息。

### 总结
至此,我们已经在 CentOS 7 和 Ubuntu 15.04 Linux 发行版上成功安装了轻巧快捷并且安全的 Lighttpd Web 服务器。现在,我们已经可以上传网站文件到网站根目录、配置虚拟主机、启用 SSL、连接数据库,在我们的 Lighttpd Web 服务器上运行 Web 应用等功能了。 如果你有任何疑问,建议或反馈请在下面的评论区中写下来以让我们更好的改良 Lighttpd。谢谢!
---
via: <http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/setup-lighttpd-web-server-ubuntu-15-04-centos-7/>
作者:[Arun Pyasi](http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/) 译者:[HaohongWANG](https://github.com/HaohongWANG) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPConnectionPool(host='linoxide.com', port=80): Max retries exceeded with url: /linux-how-to/setup-lighttpd-web-server-ubuntu-15-04-centos-7/ (Caused by ConnectTimeoutError(<urllib3.connection.HTTPConnection object at 0x7b8327581f30>, 'Connection to linoxide.com timed out. (connect timeout=10)')) | null |
7,548 | 构建在开源之上的商业软件市场持续成长 | https://www.linux.com/news/enterprise/cloud-computing/889564-the-evolving-market-for-commercial-software-built-on-open-source- | 2016-07-07T10:26:51 | [
"开源",
"商业软件"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7548-1.html | 
*与会者在 Structure 上听取演讲,Structure Data 2016 也将在 UCSF Mission Bay 会议中心举办。图片来源:Structure Events。*
如今真的很难低估开源项目对于企业软件市场的影响;开源软件的集成如此快速地形成了业界常态,我们没能捕捉到转折点也情有可原。
举个例子,Hadoop,改变的不止是数据分析界,它引领了新一代数据公司,它们围绕开源项目创造自己的软件,按需调整和支持那些代码,更像红帽在上世纪 90 年代和本世纪早期拥抱 Linux 那样。软件越来越多地通过公有云交付,而不是运行在购买者自己的服务器,拥有了令人惊奇的操作灵活性,但同时也带来了一些关于授权、支持以及价格之类的新问题。
我们多年来持续追踪这个趋势,这些话题充斥了我们的 Structure Data 会议,而今年的 Structure Data 2016 也不例外。三家围绕 Hadoop 最重要的大数据公司——Hortonworks、Cloudera 和 MapR ——的 CEO 们将会共同讨论它们是如何销售他们围绕开源项目的企业软件和服务,获利的同时回报社区项目。
以前在企业软件上获利是很容易的事情。一个客户购买了之后,企业供应商的一系列软件就变成了收银机,从维护合同和阶段性升级中获得近乎终生的收入,软件也越来越难以被替代,因为它已经成为了客户的业务核心。客户抱怨这种绑定,但如果它们想提高工作队伍的生产力也确实没有多少选择。
而现在的情况不再是这样了。尽管无数的公司还陷于在他们的基础设施上运行至关重要的巨型软件包,新的项目被部署到使用开源技术的云服务器上。这让升级功能不再需要去掉大量软件包再重新安装别的,同时也让公司按需付费,而不是为一堆永远用不到的特性买单。
有很多客户想要利用开源项目的优势,而又不想建立和支持一支工程师队伍来调整那些开源项目以满足自己的需求。这些客户愿意为开源项目和在这之上的专有特性之间的差异付费。
这对于基础设施相关的软件来说格外正确。当然,你的客户们可以自己对项目进行调整,比如 Hadoop,Spark 或 Node.js,但付费可以帮助他们自定义地打包部署如今这些重要的开源技术,而不用自己干这些活儿。只需看看 Structure Data 2016 的发言者就明白了,比如 Confluent(Kafka),Databricks(Spark),以及 Cloudera-Hortonworks-MapR(Hadoop)三人组。
当然还有一个值得提到的是在出错的时候有个供应商给你背锅。如果你的工程师弄糟了开源项目的实现,那你只能怪你自己了。但是如果你和一个愿意提供服务级品质、能确保性能和正常运行时间指标的公司签订了合同,你实际上就是为得到支持、指导,以及有人背锅而买单。
构建在开源之上的商业软件市场的持续成长是我们在 Structure Data 上追踪多年的内容,如果这个话题正合你意,我们鼓励你加入我们,在旧金山,3 月 9 日和 10 日。
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/news/enterprise/cloud-computing/889564-the-evolving-market-for-commercial-software-built-on-open-source->
作者:[Tom Krazit](https://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/70513) 译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 404 | Not Found | null |
7,549 | LFCS 系列第十讲:学习简单的 Shell 脚本编程和文件系统故障排除 | http://www.tecmint.com/linux-basic-shell-scripting-and-linux-filesystem-troubleshooting/ | 2016-07-07T13:26:00 | [
"LFCS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7549-1.html | Linux 基金会发起了 LFCS 认证 (<ruby> Linux 基金会认证系统管理员 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>),这是一个全新的认证体系,旨在让世界各地的人能够参与到中等水平的 Linux 系统的基本管理操作的认证考试中去,这项认证包括:维护正在运行的系统和服务的能力、全面监控和分析的能力以及何时向上游团队请求支持的决策能力。

*LFCS 系列第十讲*
请看以下视频,这里边介绍了 Linux 基金会认证程序。
本讲是系列教程中的第十讲,主要集中讲解简单的 Shell 脚本编程和文件系统故障排除。这两块内容都是 LFCS 认证中的必备考点。
### 理解<ruby> 终端 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Terminals </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和 Shell
首先要声明一些概念。
* Shell 是一个程序,它将命令传递给操作系统来执行。
* Terminal 也是一个程序,允许最终用户使用它与 Shell 来交互。比如,下边的图片是 GNOME Terminal。

*Gnome Terminal*
启动 Shell 之后,会呈现一个命令提示符 (也称为命令行) 提示我们 Shell 已经做好了准备,接受标准输入设备输入的命令,这个标准输入设备通常是键盘。
你可以参考该系列文章的 [第一讲 如何在 Linux 上使用 GNU sed 等命令来创建、编辑和操作文件](/article-7161-1.html) 来温习一些常用的命令。
Linux 为提供了许多可以选用的 Shell,下面列出一些常用的:
**bash Shell**
Bash 代表 Bourne Again Shell,它是 GNU 项目默认的 Shell。它借鉴了 Korn shell (ksh) 和 C shell (csh) 中有用的特性,并同时对性能进行了提升。它同时也是 LFCS 认证中所涵盖的各发行版中默认 Shell,也是本系列教程将使用的 Shell。
**sh Shell**
Bourne SHell 是一个比较古老的 shell,多年来一直都是很多类 Unix 系统的默认 shell。
**ksh Shell**
Korn SHell (ksh shell) 也是一个 Unix shell,是<ruby> 贝尔实验室 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Bell Labs </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的 David Korn 在 19 世纪 80 年代初的时候开发的。它兼容 Bourne shell ,并同时包含了 C shell 中的多数特性。
一个 shell 脚本仅仅只是一个可执行的文本文件,里边包含一条条可执行命令。
### 简单的 Shell 脚本编程
如前所述,一个 shell 脚本就是一个纯文本文件,因此,可以使用自己喜欢的文本编辑器来创建和编辑。你可以考虑使用 vi/vim (参考本系列 [第二讲 如何安装和使用纯文本编辑器 vi/vim](/article-7165-1.html)),它的语法高亮让我的编辑工作非常方便。
输入如下命令来创建一个名为 myscript.sh 的脚本文件:
```
# vim myscript.sh
```
shell 脚本的第一行 (著名的<ruby> <a href="/article-3664-1.html"> 释伴行 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> shebang line </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>) 必须如下:
```
#!/bin/bash<ruby> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
```
这条语句“告诉”操作系统需要用哪个解释器来运行这个脚本文件之后命令。
现在可以添加需要执行的命令了。通过注释,我们可以声明每一条命令或者整个脚本的具体含义。注意,shell 会忽略掉以井号 (#) 开始的注释语句。
```
#!/bin/bash
echo 这是关于 LFCS 认证系列的第十部分
echo 今天是 $(date +%Y-%m-%d)
```
编写并保存脚本之后,通过以下命令来使脚本文件成为可执行文件:
```
# chmod 755 myscript.sh
```
在执行脚本之前,我们需要说一下环境变量 ($PATH),运行:
```
echo $PATH
```
我们就会看到环境变量 ($PATH) 的具体内容:这是当输入命令时系统所搜索可执行程序的目录,每一项之间使用冒号 (:) 隔开。称它为环境变量,是因为它本是就是 shell 环境的一部分 —— 这是当 shell 每次启动时 shell 及其子进程可以获取的一系列信息。
当我们输入一个命令并按下回车时,shell 会搜索 $PATH 变量中列出的目录并执行第一个知道的实例。请看如下例子:

*环境变量*
假如存在两个同名的可执行程序,一个在 /usr/local/bin,另一个在 /usr/bin,则会执行环境变量中最先列出的那个,并忽略另外一个。
如果我们自己编写的脚本没有放在 $PATH 变量列出目录中的任何一个,则需要输入 ./filename 来执行它。而如果存储在 $PATH 变量中的任意一个目录,我们就可以像运行其他命令一样来运行之前编写的脚本了。
```
# pwd
# ./myscript.sh
# cp myscript.sh ../bin
# cd ../bin
# pwd
# myscript.sh
```

*执行脚本*
#### if 条件语句
无论何时,当你需要在脚本中根据某个命令的运行结果来采取相应动作时,你应该使用 if 结构来定义条件。基本语法如下:
```
if CONDITION; then
COMMANDS;
else
OTHER-COMMANDS
fi
```
其中,CONDITION 可以是如下情形的任意一项 (仅列出常用的),并且达到以下条件时返回 true:
* `[ -a file ]` → 指定文件存在。
* `[ -d file ]` → 指定文件存在,并且是一个目录。
* `[ -f file ]` → 指定文件存在,并且是一个普通文件。
* `[ -u file ]` → 指定文件存在,并设置了 SUID 权限位。
* `[ -g file ]` → 指定文件存在,并设置了 SGID 权限位。
* `[ -k file ]` → 指定文件存在,并设置了“黏连 (Sticky)”位。
* `[ -r file ]` → 指定文件存在,并且文件可读。
* `[ -s file ]` → 指定文件存在,并且文件不为空。
* `[ -w file ]` → 指定文件存在,并且文件可写入。
* `[ -x file ]` → 指定文件存在,并且可执行。
* `[ string1 = string2 ]` → 字符串相同。
* `[ string1 != string2 ]` → 字符串不相同。
[ int1 op int2 ] 为前述列表中的一部分 (例如: -eq –> int1 与 int2 相同时返回 true) ,其中比较项也可以是一个列表子项, 其中 op 为以下比较操作符。
* `-eq` –> int1 等于 int2 时返回 true。
* `-ne` –> int1 不等于 int2 时返回 true。
* `-lt` –> int1 小于 int2 时返回 true。
* `-le` –> int1 小于或等于 int2 时返回 true。
* `-gt` –> int1 大于 int2 时返回 true。
* `-ge` –> int1 大于或等于 int2 时返回 true。
#### for 循环语句
循环语句可以在某个条件下重复执行某个命令。基本语法如下:
```
for item in SEQUENCE; do
COMMANDS;
done
```
其中,item 为每次执行 COMMANDS 时,在 SEQUENCE 中匹配到的值。
#### While 循环语句
该循环结构会一直执行重复的命令,直到控制命令(EVALUATION\_COMMAND)执行的退出状态值等于 0 时 (即执行成功) 停止。基本语法如下:
```
while EVALUATION_COMMAND; do
EXECUTE_COMMANDS;
done
```
其中,EVALUATION\_COMMAND 可以是任何能够返回成功 (0) 或失败 (0 以外的值) 的退出状态值的命令,EXECUTE\_COMMANDS 则可以是任何的程序、脚本或者 shell 结构体,包括其他的嵌套循环。
#### 综合使用
我们会通过以下例子来演示 if 条件语句和 for 循环语句。
**在基于 systemd 的发行版中探测某个服务是否在运行**
先建立一个文件,列出我们想要想要查看的服务名。
```
# cat myservices.txt
sshd
mariadb
httpd
crond
firewalld
```

*使用脚本监控 Linux 服务*
我们编写的脚本看起来应该是这样的:
```
#!/bin/bash
# This script iterates over a list of services and
# is used to determine whether they are running or not.
for service in $(cat myservices.txt); do
systemctl status $service | grep --quiet "running"
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo $service "is [ACTIVE]"
else
echo $service "is [INACTIVE or NOT INSTALLED]"
fi
done
```

*Linux 服务监控脚本*
**我们来解释一下这个脚本的工作流程**
1). for 循环每次读取 myservices.txt 文件中的一项记录,每一项纪录表示一个服务的通用变量名。各项记录组成如下:
```
# cat myservices.txt
```
2). 以上命令由圆括号括着,并在前面添加美元符,表示它需要从 myservices.txt 的记录列表中取值并作为变量传递给 for 循环。
3). 对于记录列表中的每一项纪录 (即每一项纪录的服务变量),都会执行以下动作:
```
# systemctl status $service | grep --quiet "running"
```
此时,需要在每个通用变量名 (即每一项纪录的服务变量) 的前面添加美元符,以表明它是作为变量来传递的。其输出则通过管道符传给 grep。
其中,-quiet 选项用于阻止 grep 命令将发现的 “running” 的行回显到屏幕。当 grep 捕获到 “running” 时,则会返回一个退出状态码 “0” (在 if 结构体表示为 $?),由此确认某个服务正在运行中。
如果退出状态码是非零值 (即 systemctl status $service 命令中的回显中没有出现 “running”),则表明某个服务未运行。

*服务监控脚本*
我们可以增加一步,在开始循环之前,先确认 myservices.txt 是否存在。
```
#!/bin/bash
# This script iterates over a list of services and
# is used to determine whether they are running or not.
if [ -f myservices.txt ]; then
for service in $(cat myservices.txt); do
systemctl status $service | grep --quiet "running"
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo $service "is [ACTIVE]"
else
echo $service "is [INACTIVE or NOT INSTALLED]"
fi
done
else
echo "myservices.txt is missing"
fi
```
**Ping 一系列网络或者 Internet 主机名以获取应答数据**
你可能想把自己维护的主机写入一个文本文件,并使用脚本探测它们是否能够 ping 得通 (脚本中的 myhosts 可以随意替换为你想要的名称)。
shell 的内置 read 命令将告诉 while 循环一行行的读取 myhosts,并将读取的每行内容传给 host 变量,随后 host 变量传递给 ping 命令。
```
#!/bin/bash
# This script is used to demonstrate the use of a while loop
while read host; do
ping -c 2 $host
done < myhosts
```

*使用脚本 Ping 服务器*
扩展阅读:
* [Learn Shell Scripting: A Guide from Newbies to System Administrator](http://www.tecmint.com/learning-shell-scripting-language-a-guide-from-newbies-to-system-administrator/)
* [5 Shell Scripts to Learn Shell Programming](http://www.tecmint.com/basic-shell-programming-part-ii/)
### 文件系统排错
尽管 Linux 是一个很稳定的操作系统,但仍然会因为某些原因出现崩溃时 (比如因为断电等),正好你有一个 (或者更多个) 文件系统未能正确卸载,Linux 重启的时候就会自动检测其中可能发生的错误。
此外,每次系统正常启动的时候,都会在文件系统挂载之前校验它们的完整度。而这些全部都依赖于 fsck 工具 (<ruby> 文件系统校验 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> file system check </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)。
如果对 fsck 进行设定,它除了校验文件系统的完整性之外,还可以尝试修复错误。fsck 能否成功修复错误,取决于文件系统的损伤程度;如果可以修复,被损坏部分的文件会恢复到位于每个文件系统根目录的 lost+found。
最后但同样重要的是,我们必须注意,如果拔掉系统正在写入数据的 USB 设备同样会发生错误,甚至可能发生硬件损坏。
fsck 的基本用如下:
```
# fsck [options] filesystem
```
**检查文件系统错误并尝试自动修复**
想要使用 fsck 检查文件系统,我们需要首先卸载文件系统。
```
# mount | grep sdg1
# umount /mnt
# fsck -y /dev/sdg1
```

*检查文件系统错误*
除了 -y 选项,我们也可以使用 -a 选项来自动修复文件系统错误,而不必做出交互式应答,并在文件系统看起来 “干净” 卸载的情况下强制校验。
```
# fsck -af /dev/sdg1
```
如果只是要找出什么地方发生了错误 (不用在检测到错误的时候修复),我们可以使用 -n 选项,这样只会将文件系统错误输出到标准输出设备上。
```
# fsck -n /dev/sdg1
```
根据 fsck 输出的错误信息,我们可以知道是否可以自己修复或者需要将问题提交给工程师团队来做详细的硬件校验。
### 总结
至此,系列教程的第十讲就全部结束了,全系列教程涵盖了通过 LFCS 测试所需的基础内容。
但显而易见的,本系列的十讲并不足以在单个主题方面做到全面描述,我们希望这一系列教程可以成为你学习的基础素材,并一直保持学习的热情(LCTT 译注:还有后继补充的几篇)。
我们欢迎你提出任何问题或者建议,所以你可以毫不犹豫的通过以下链接联系到我们: 成为一个 [Linux 认证系统工程师](http://www.shareasale.com/r.cfm?b=768106&u=1260899&m=59485&urllink=&afftrack=) 。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/linux-basic-shell-scripting-and-linux-filesystem-troubleshooting/>
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa](http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,550 | 把你的旧笔记本变成 Chromebook | https://www.linux.com/learn/turn-your-old-laptop-chromebook | 2016-07-08T08:44:00 | [
"Chromebook"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7550-1.html | 
Linux 之年就在眼前。根据[报道](https://chrome.googleblog.com/2016/05/the-google-play-store-coming-to.html),Google 在 2016 年第一季度卖出了比苹果卖出的 Macbook 更多的 Chromebook。并且,Chromebook 即将变得更加激动人心。在 Google I/O 大会上,Google 宣布安卓 Google Play 商店将在 6 月中旬来到 Chromebook,这让用户能够在他们的 Chrome OS 设备上运行安卓应用。
但是,你不需要购买一台全新的使用 Chrome OS 的笔记本,你可以轻松地将你的旧笔记本或电脑转换成强大的 Chromebook。我在一台 Dell Mini 和一台 2009 年购买的 Dell 笔记本上进行了尝试。那两台设备都在吃灰,而且本来注定是要被回收的,因为现代的操作系统和桌面环境,比如 Unity,Plasma 以及 Gnome 它们跑不动。
如果你手边有旧设备,你可以轻松地将它变成 Chromebook。你还可以在你的笔记本上安装 Chrome OS 双系统,这样你就可以同时享受不同系统的优点了。
多亏了 Chrome OS 的开源基础,有很多方案可以让你在你的设备上安装 Chrome OS。我试过几个,但我最喜欢的方案是 [Neverware](http://www.neverware.com/#introtext-3) 的 CloudReady。这家公司提供一个免费的,社区支持版的系统,还有一个商业支持版,每台设备每年 49 美元。好消息是所有的授权都是可转移的,所以如果你卖掉或捐掉了设备,你也可以将 Neverware 授权转让给新用户。
### 你需要什么
在你开始在笔记本上安装 CloudReady 之前,你需要一些准备:
* 一个容量不小于 4GB 的 USB 存储设备
* 打开 Chrome 浏览器,到 Google Chrome Store 去安装 [Chromebook Recovery Utility(Chrome 恢复工具)](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/chromebook-recovery-utili/jndclpdbaamdhonoechobihbbiimdgai?hl=en)
* 更改目标机器的 BIOS 设置以便能从 USB 启动
### 开始
Neverware 提供两个版本的 CloudReady 镜像:32 位和 64 位。从下载页面[下载](http://www.neverware.com/freedownload)合适你硬件的系统版本。
解压下载的 zip 文件,你会得到一个 chromiumos\_image.bin 文件。现在插入 U 盘并打开 Chromebook Recovery Utility。点击工具右上角的齿轮,选择 erase recovery media(擦除恢复媒介,如图 1)。

*图 1:选择 erase recovery media。[image:cloudready-erase]*
接下来,选择目标 USB 驱动器并把它格式化。格式化完成后,再次打开右上齿轮,这次选择 use local image(使用本地镜像)。浏览解压的 bin 文件并选中,选好 USB 驱动器,点击继续,然后点击创建按钮(图 2)。它会开始将镜像写入驱动器。

*图 2:创建 CloudReady 镜像。[Image:cloudready-create]*
驱动器写好可启动的 CloudReady 之后,插到目标 PC 上并启动。系统启动进 Chromium OS 需要一小段时间。启动之后,你会看到图 3 中的界面。

*图 3:准备好安装 CloudReady。*

*图 4:单系统选项。*
到任务栏选择 Install CloudReady(安装 CloudReady)。
你可以安装 Chromium OS 和其它系统的双系统启动,但另一个系统这时应该已经安装好了。
在下一个窗口选择单系统(图 4)或是双系统(图 5)。
按照下一步按钮说明选择安装。

*图 5:双系统选项。*
整个过程最多 20 分钟左右,这取决于存储媒介和处理能力。安装完成后,电脑会关闭并重启。
重启之后,你会看到网络设置页面(图 6)。让人激动的是,虽然我在相同硬件上要给 Linux 发行版安装无线驱动,到了 Chromium OS 这里是开箱即用的。
你连上无线网络之后,系统会自动查找更新并提供 Adobe Flash 安装。安装完成后,你会看到 Chromium OS 登录界面。现在你只需登录你的 Gmail 账户,开始使用你的“Chromebook”即可。

*图 6:网络设置。*
### 让 Netflix 正常工作
如果你想要播放 Netflix 或其它 DRM 保护流媒体站点,你需要做一些额外的工作。转到设置并点击安装 Widevine 插件(图 7)。

*图 7:安装 Widevine。*

*图 8:安装 User Agent Switcher。*
现在你需要使用 user agent switcher 这个伎俩(图 8)。
到 Chrome Webstore 去安装 [User Agent Switcher](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/user-agent-switcher-for-c/djflhoibgkdhkhhcedjiklpkjnoahfmg)。插件安装完成后,它会自动添加到浏览器的书签栏。
右键点击 agent switcher 图标并创建一个新条目(图 9):
```
Name: "CloudReady Widevine"
String: "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/535.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Ubuntu/16.10 Chrome/49.0.1453.93"
Group: "Chrome" (应该被自动填上了)
Append: "Replace"
Indicator Flag: "IE"
```
点击“添加(Add)”。

*图 9:为 CloudReady 创建条目。*
然后,到“permanent spoof list(永久欺骗列表)”选项中将 CloudReady Widevine 添加为 [www.netflix.com](http://www.netflix.com) 的永久 UA 串。
现在,重启机器,你就可以观看 Netflix 和其它一些服务了。
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/learn/turn-your-old-laptop-chromebook>
作者:[SWAPNIL BHARTIYA](https://www.linux.com/users/arnieswap) 译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,551 | 在 Ubuntu 16.04 为 Nginx 服务器安装 LEMP 环境(MariaDB,PHP 7 并支持 HTTP 2.0) | http://www.tecmint.com/install-nginx-mariadb-php7-http2-on-ubuntu-16-04/ | 2016-07-08T09:56:00 | [
"LEMP",
"Nginx",
"PHP",
"MySQL",
"MariaDB"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7551-1.html | LEMP 是个缩写,代表一组软件包(L:Linux OS,E:Nginx 网络服务器,M:MySQL/MariaDB 数据库和 P:PHP 服务端动态编程语言),它被用来搭建动态的网络应用和网页。
(LCTT 译注:为何采用 LEMP 而不是 LNMP 的缩写?据 <https://lemp.io/> 的解释:Nginx 的发音是 Engine-X,重要的发音而不是首字母,而且 LEMP 实际上是可读的,而 LNMP 看起来只是字母表。)

*在 Ubuntu 16.04 安装 Nginx 以及 MariaDB,PHP7 并且支持 HTTP 2.0*
这篇教程会教你怎么在 Ubuntu 16.04 的服务器上安装 LEMP (Nginx 和 MariaDB 以及 PHP7)。
**前置准备**
* [安装 Ubuntu 16.04 服务器版本](http://www.tecmint.com/installation-of-ubuntu-16-04-server-edition/)
### 步骤 1:安装 Nginx 服务器
1、Nginx 是一个先进的、资源优化的 Web 服务器程序,用来向因特网上的访客展示网页。我们从 Nginx 服务器的安装开始介绍,使用 [apt 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/apt-advanced-package-command-examples-in-ubuntu/) 从 Ubuntu 的官方软件仓库中获取 Nginx 程序。
```
$ sudo apt-get install nginx
```

*在 Ubuntu 16.04 安装 Nginx*
2、 然后输入 [netstat](http://www.tecmint.com/20-netstat-commands-for-linux-network-management/) 和 [systemctl](http://www.tecmint.com/manage-services-using-systemd-and-systemctl-in-linux/) 命令,确认 Nginx 进程已经启动并且绑定在 80 端口。
```
$ netstat -tlpn
```

*检查 Nginx 网络端口连接*
```
$ sudo systemctl status nginx.service
```

*检查 Nginx 服务状态*
当你确认服务进程已经启动了,你可以打开一个浏览器,使用 HTTP 协议访问你的服务器 IP 地址或者域名,浏览 Nginx 的默认网页。
```
http://IP-Address
```

*验证 Nginx 网页*
### 步骤 2:启用 Nginx HTTP/2.0 协议
3、 对 HTTP/2.0 协议的支持默认包含在 Ubuntu 16.04 最新发行版的 Nginx 二进制文件中了,它只能通过 SSL 连接并且保证加载网页的速度有巨大提升。
要启用Nginx 的这个协议,首先找到 Nginx 提供的网站配置文件,输入下面这个命令备份配置文件。
```
$ cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/
$ sudo mv default default.backup
```

*备份 Nginx 的网站配置文件*
4、然后,用文本编辑器新建一个默认文件,输入以下内容:
```
server {
listen 443 ssl http2 default_server;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2 default_server;
root /var/www/html;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
server_name 192.168.1.13;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_ciphers EECDH+CHACHA20:EECDH+AES128:RSA+AES128:EECDH+AES256:RSA+AES256:EECDH+3DES:RSA+3DES:!MD5;
ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:20m;
ssl_session_timeout 180m;
resolver 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000;
#includeSubDomains" always;
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name 192.168.1.13;
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}
```

*启用 Nginx HTTP 2 协议*
上面的配置片段向所有的 SSL 监听指令中添加 http2 参数来启用 `HTTP/2.0`。
上述添加到服务器配置的最后一段,是用来将所有非 SSL 的流量重定向到 SSL/TLS 默认主机。然后用你主机的 IP 地址或者 DNS 记录(最好用 FQDN 名称)替换掉 `server_name` 选项的参数。
5、 当你按照以上步骤编辑完 Nginx 的默认配置文件之后,用下面这些命令来生成、查看 SSL 证书和密钥。
用你自定义的设置完成证书的制作,注意 Common Name 设置成和你的 DNS FQDN 记录或者服务器 IP 地址相匹配。
```
$ sudo mkdir /etc/nginx/ssl
$ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key -out /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt
$ ls /etc/nginx/ssl/
```

*生成 Nginx 的 SSL 证书和密钥*
6、 通过输入以下命令使用一个强 DH 加密算法,这会修改之前的配置文件 `ssl_dhparam` 所配置的文件。
```
$ sudo openssl dhparam -out /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem 2048
```

*创建 Diffie-Hellman 密钥*
7、 当 `Diffie-Hellman` 密钥生成之后,验证 Nginx 的配置文件是否正确、能否被 Nginx 网络服务程序应用。然后运行以下命令重启守护进程来观察有什么变化。
```
$ sudo nginx -t
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx.service
```

*检查 Nginx 的配置*
8、 键入下面的命令来测试 Nginx 使用的是 HTTP/2.0 协议。看到协议中有 `h2` 的话,表明 Nginx 已经成功配置使用 HTTP/2.0 协议。所有最新的浏览器默认都能够支持这个协议。
```
$ openssl s_client -connect localhost:443 -nextprotoneg ''
```

*测试 Nginx HTTP 2.0 协议*
### 第 3 步:安装 PHP 7 解释器
通过 FastCGI 进程管理程序的协助,Nginx 能够使用 PHP 动态语言解释器生成动态网络内容。FastCGI 能够从 Ubuntu 官方仓库中安装 php-fpm 二进制包来获取。
9、 在你的服务器控制台里输入下面的命令来获取 PHP7.0 和扩展包,这能够让 PHP 与 Nginx 网络服务进程通信。
```
$ sudo apt install php7.0 php7.0-fpm
```

*安装 PHP 7 以及 PHP-FPM*
10、 当 PHP7.0 解释器安装成功后,输入以下命令启动或者检查 php7.0-fpm 守护进程:
```
$ sudo systemctl start php7.0-fpm
$ sudo systemctl status php7.0-fpm
```

*开启、验证 php-fpm 服务*
11、 当前的 Nginx 配置文件已经配置了使用 PHP FPM 来提供动态内容。
下面给出的这部分服务器配置让 Nginx 能够使用 PHP 解释器,所以不需要对 Nginx 配置文件作别的修改。
```
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
}
```
下面是的截图是 Nginx 默认配置文件的内容。你可能需要对其中的代码进行修改或者取消注释。

*启用 PHP FastCGI*
12、 要测试启用了 PHP-FPM 的 Nginx 服务器,用下面的命令创建一个 PHP 测试配置文件 `info.php`。接着用 `http://IP_or domain/info.php` 这个网址来查看配置。
```
$ sudo su -c 'echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" |tee /var/www/html/info.php'
```

*创建 PHP Info 文件*

*检查 PHP FastCGI 的信息*
检查服务器是否宣告支持 HTTP/2.0 协议,定位到 PHP 变量区域中的 `$_SERVER[‘SERVER_PROTOCOL’]` 就像下面这张截图一样。

*检查 HTTP2.0 协议信息*
13、 为了安装其它的 PHP7.0 模块,使用 `apt search php7.0` 命令查找 php 的模块然后安装。
如果你想要 [安装 WordPress](http://www.tecmint.com/install-wordpress-using-lamp-or-lemp-on-rhel-centos-fedora/) 或者别的 CMS,需要安装以下的 PHP 模块,这些模块迟早有用。
```
$ sudo apt install php7.0-mcrypt php7.0-mbstring
```

*安装 PHP 7 模块*
14、 要注册这些额外的 PHP 模块,输入下面的命令重启 PHP-FPM 守护进程。
```
$ sudo systemctl restart php7.0-fpm.service
```
### 第 4 步:安装 MariaDB 数据库
15、 最后,我们需要 MariaDB 数据库来存储、管理网站数据,才算完成 LEMP 的搭建。
运行下面的命令安装 MariaDB 数据库管理系统,重启 PHP-FPM 服务以便使用 MySQL 模块与数据库通信。
```
$ sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client php7.0-mysql
$ sudo systemctl restart php7.0-fpm.service
```

*安装 MariaDB*
16、 为了安全加固 MariaDB,运行来自 Ubuntu 软件仓库中的二进制包提供的安全脚本,这会询问你设置一个 root 密码,移除匿名用户,禁用 root 用户远程登录,移除测试数据库。
输入下面的命令运行脚本,并且确认所有的选择。参照下面的截图。
```
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
```

*MariaDB 的安全安装*
17、 配置 MariaDB 以便普通用户能够不使用系统的 sudo 权限来访问数据库。用 root 用户权限打开 MySQL 命令行界面,运行下面的命令:
```
$ sudo mysql
MariaDB> use mysql;
MariaDB> update user set plugin=’‘ where User=’root’;
MariaDB> flush privileges;
MariaDB> exit
```

*MariaDB 的用户权限*
最后通过执行以下命令登录到 MariaDB 数据库,就可以不需要 root 权限而执行任意数据库内的命令:
```
$ mysql -u root -p -e 'show databases'
```

*查看 MariaDB 数据库*
好了!现在你拥有了配置在 **Ubuntu 16.04** 服务器上的 **LEMP** 环境,你能够部署能够与数据库交互的复杂动态网络应用。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/install-nginx-mariadb-php7-http2-on-ubuntu-16-04/>
作者:[Matei Cezar](http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/) 译者:[GitFuture](https://github.com/GitFuture) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,552 | 你应该知道的基础 Git 命令 | http://itsfoss.com/basic-git-commands-cheat-sheet/ | 2016-07-08T13:55:00 | [
"Git"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7552-1.html | 
*简介:这个快速指南将向你展示所有的基础 Git 命令以及用法。你可以下载这些命令作为快速参考。*
我们在早先一篇文章中已经快速介绍过 [Vi 速查表](http://itsfoss.com/download-vi-cheat-sheet/)了。在这篇文章里,我们将会介绍开始使用 Git 时所需要的基础命令。
### Git
[Git](https://git-scm.com/) 是一个分布式版本控制系统,它被用在大量开源项目中。它是在 2005 年由 Linux 创始人 [Linus Torvalds](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linus_Torvalds) 写就的。这个程序允许非线性的项目开发,并且能够通过存储在本地服务器高效处理大量数据。在这个教程里,我们将要和 Git 愉快玩耍并学习如何开始使用它。
我在这个教程里使用 Ubuntu,但你可以使用你选择的任何发行版。除了安装以外,剩下的所有命令在任何 Linux 发行版上都是一样的。
### 安装 Git
要安装 git 执行以下命令:
```
sudo apt-get install git-core
```
在它完成下载之后,你就安装好了 Git 并且可以使用了。
### 设置 Git
在 Git 安装之后,不论是从 apt-get 还是从源码安装,你需要将你的用户名和邮箱地址复制到 gitconfig 文件。你可以访问 ~/.gitconfig 这个文件。
全新安装 Git 之后打开它会是完全空白的:
```
sudo vim ~/.gitconfig
```
你也可以使用以下命令添加所需的信息。将‘user’替换成你的用户名,‘[email protected]’替换成你的邮箱。
```
git config --global user.name "User"
git config --global user.email [email protected]
```
然后你就完成设置了。现在让我们开始 Git。
### 仓库
创建一个新目录,打开它并运行以下命令:
```
git init
```

这个命令会创建一个新的 Git <ruby> 仓库 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> repository </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。你的本地仓库由三个 Git 维护的“树”组成。
第一个是你的<ruby> 工作目录 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Working Directory </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,保存实际的文件。第二个是索引,实际上扮演的是<ruby> 暂存区 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> staging area </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,最后一个是 HEAD,它指向你最后一个 commit 提交。使用 git clone /path/to/repository 签出你的仓库(从你刚创建的仓库或服务器上已存在的仓库)。
### 添加文件并提交
你可以用以下命令添加改动:
```
git add <filename>
```
这会添加一个新文件到暂存区以提交。如果你想添加每个新文件,输入:
```
git add --all
```
添加文件之后可以使用以下命令检查状态:
```
git status
```

正如你看到的,那里已经有一些变化但还没有提交。现在你需要提交这些变化,使用:
```
git commit -m "提交信息"
```

你也可以这么做(首选):
```
git commit -a
```
然后写下你的提交信息。现在你的文件提交到了 HEAD,但还不在你的远程仓库中。
### 推送你的改动
你的改动在你本地工作副本的 HEAD 中。如果你还没有从一个已存在的仓库克隆,或想将你的仓库连接到远程服务器,你需要先添加它:
```
git remote add origin <服务器地址>
```
现在你可以将改动推送到指定的远程服务器。要将改动发送到远程服务器,运行:
```
git push -u origin master
```
### 分支
分支用于开发特性,分支之间是互相独立的。主分支 master 是你创建一个仓库时的“默认”分支。使用其它分支用于开发,在完成时将它合并回主分支。
创建一个名为“mybranch”的分支并切换到它之上:
```
git checkout -b mybranch
```

你可以使用这个命令切换回主分支:
```
git checkout master
```
如果你想删除这个分支,执行:
```
git branch -d mybranch
```

除非你将分支推送到远程服务器上,否则该分支对其他人是不可用的,所以只需把它推送上去:
```
git push origin <分支名>
```
### 更新和合并
要将你本地仓库更新到最新的提交上,运行:
```
git pull
```
在你的工作目录获取并合并远程变动。要合并其它分支到你的活动分支(如 master),使用:
```
git merge <分支>
```
在这两种情况下,git 会尝试<ruby> 自动合并 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> auto-merge </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>改动。不幸的是,这不总是可能的,可能会导致冲突。你需要通过编辑 git 所显示的文件,手动合并那些冲突。改动之后,你需要用以下命令将它们标记为已合并:
```
git add <文件名>
```
在合并改动之前,你也可以使用以下命令预览:
```
git diff <源分支> <目标分支>
```
### Git 日志
你可以这么查看仓库历史:
```
git log
```
要以每个提交一行的样式查看日志,你可以用:
```
git log --pretty=oneline
```
或者也许你想要看一个所有分支的 ASCII 艺术树,带有标签和分支名:
```
git log --graph --oneline --decorate --all
```
如果你只想看哪些文件改动过:
```
git log --name-status
```
在这整个过程中如果你需要任何帮助,你可以用 git --help。
Git 棒不棒?!祝贺你你已经会 Git 基础了。如果你愿意的话,你可以从下面这个链接下载这些基础 Git 命令作为快速参考:
* [下载 Git 速查表](https://drive.google.com/open?id=0By49_3Av9sT1bXpINjhvU29VNUU)
---
via: <http://itsfoss.com/basic-git-commands-cheat-sheet/>
作者:[Rakhi Sharma](http://itsfoss.com/author/rakhi/) 译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,554 | 大量 Redis 服务器存在 SSH 权限窃取风险 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/over-6-000-redis-database-servers-ready-for-the-taking-506056.shtml | 2016-07-08T10:49:39 | [
"Redis"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7554-1.html | 完全无视安全功能的 Redis 服务器自创建以来饱受各种安全风险的困扰,Risk Based Security (RBS) 最近发现了 6338 台受到侵入的 Redis 服务器。
Redis 是一个在内存中以键值对方式存储数据的 NOSQL 数据库。据 DB-Engines 的统计数据,它在 2015 年度的数据库[流行度位列第十](http://db-engines.com/en/ranking),而在键值对数据库中[排名第一](http://db-engines.com/en/article/Key-value+Stores)。
由于 Redis 以性能为第一考量,所以默认配置下该数据库没有任何的认证或其它的安全控制功能。

### Redis 服务器存在 SSH 密钥创建漏洞
任何人只要知道你的 IP 地址和 Redis 的端口,就可以访问其中的任意内容。更糟糕的是,在 2015 年末,发现了[一种攻击方式](http://antirez.com/news/96)可以让任何人在你的 Redis 服务器上的 authorized\_keys 文件中存储 SSH 密钥——这意味着,攻击者将不需要任何密码即可取得 Redis 服务器上的 SSH 访问权限。
而现在,至少有三万台没有任何验证措施的 Redis 服务器暴露在互联网上,据 RBS 研究人员的称,已经有 6338 台 Redis 被窃取了 SSH 权限。
该公司在通过 Shodan 进行了非侵入式扫描之后得出了如上结论。RBS 的研究人员在分析了被入侵的服务器之后发现,它们上面存在着一个名为“crackit” 的 SSH 密钥,其关联的邮件地址 [email protected] 曾在之前的其它入侵事件中出现过。除了 [email protected] 这个地址出现过 5892 次之外,[email protected] 和 [email protected] 也分别出现了 385 次和 211 次。除了“crackit” 之外,还有一些名为“crackit\_key”, “qwe” ,“ck” 和 “crack” 之类的密钥名。据 RBS 分析,这表明它们来自多个组织或个人。
### 攻击者并不针对特定的 Redis 版本,任何版本都可能被黑
这些被攻击的 Redis 服务器的版本多达 106 个,从早期的 1.2.0. 到最新的 3.2.1 都有。
“从对这些数据的分析中得不到更进一步的结果,只能确认两件事,第一件事是这并非新出现的漏洞,第二是,有些服务器只是被侵入了,但是并没有被利用。”[RBS 研究人员解释说](https://www.riskbasedsecurity.com/2016/07/redis-over-6000-installations-compromised/)。
该公司建议系统管理员们升级其 Redis 服务器到最新的版本,并启用 3.2 版本新引入的“保护模式”。另外,不要将 Redis 服务器或者其它的数据库暴露在互联网上是最起码的安全准则。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,556 | Securi-Pi:使用树莓派作为安全跳板 | http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/securi-pi-using-raspberry-pi-secure-landing-point?page=0,0 | 2016-07-09T11:21:10 | [
"树莓派",
"OpenVPN"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7556-1.html | 像很多 LinuxJournal 的读者一样,我也过上了当今非常普遍的“科技游牧”生活,在网络之间,从一个接入点到另一个接入点,我们身处现实世界的不同地方却始终保持连接到互联网和日常使用的其它网络上。近来我发现越来越多的网络环境开始屏蔽对外的常用端口比如 SMTP(端口 25),SSH(端口 22)之类的。当你走进一家咖啡馆然后想 SSH 到你的一台服务器上做点事情的时候发现端口 22 被屏蔽了是一件很烦的事情。
不过,我到目前为止还没发现有什么网络环境会把 HTTPS 给墙了(端口 443)。在稍微配置了一下家中的树莓派 2 之后,我成功地让自己通过接入树莓派的 443 端口充当跳板,从而让我在各种网络环境下都能连上想要的目标端口。简而言之,我把家中的树莓派设置成了一个 OpenVPN 的端点和 SSH 端点,同时也是一个 Apache 服务器,所有这些服务都监听在 443 端口上,以便可以限制我不想暴露的网络服务。

### 备注
此解决方案能搞定大多数有限制的网络环境,但有些防火墙会对外部流量调用<ruby> 深度包检查 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Deep packet inspection </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,它们时常能屏蔽掉用本篇文章里的方式传输的信息。不过我到目前为止还没在这样的防火墙后测试过。同时,尽管我使用了很多基于密码学的工具(OpenVPN,HTTPS,SSH),我并没有非常严格地审计过这套配置方案(LCTT 译注:作者的意思是指这套方案能帮你绕过端口限制,但不代表你的活动就是完全安全的)。有时候甚至 DNS 服务都会泄露你的信息,很可能在我没有考虑周到的角落里会有遗漏。我强烈不推荐把此跳板配置方案当作是万无一失的隐藏网络流量的办法,此配置只是希望能绕过一些端口限制连上网络,而不是做一些危险的事情。
### 起步
让我们先从你需要什么说起,我用的是树莓派 2,装载了最新版本的 Raspbian,不过这个配置也应该能在树莓派 Model B 上运行;512MB 的内存对我们来说绰绰有余了,虽然性能可能没有树莓派 2这么好,毕竟相比于四核心的树莓派 2, Model B 只有一颗单核心 CPU。我的树莓派放置在家里的防火墙和路由器的后面,所以我还能用这个树莓派作为跳板访问家里的其他电子设备。同时这也意味着我的流量在互联网上看起来仿佛来自我家的 ip 地址,所以这也算某种意义上保护了我的匿名性。如果你没有树莓派,或者不想从家里运行这个服务,那你完全可以把这个配置放在一台小型云服务器上(LCTT 译注:比如 IPS )。你只要确保服务器运行着基于 Debian 的 Linux 发行版即可,这份指南依然可用。

*图 1 树莓派,即将成为我们的加密网络端点*
### 安装并配置 BIND
无论你是用树莓派还是一台服务器,当你成功启动之后你就可以安装 BIND 了,这是一个驱动了互联网相当一部分的域名服务软件。你将会把 BIND 仅仅作为缓存域名服务使用,而不用把它配置为用来处理来自互联网的域名请求。安装 BIND 会让你拥有一个可以被 OpenVPN 使用的 DNS 服务器。安装 BIND 十分简单,`apt-get` 就可以直接搞定:
```
root@test:~# apt-get install bind9
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following extra packages will be installed:
bind9utils
Suggested packages:
bind9-doc resolvconf ufw
The following NEW packages will be installed:
bind9 bind9utils
0 upgraded, 2 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Need to get 490 kB of archives.
After this operation, 1,128 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Do you want to continue [Y/n]? y
```
在我们把 BIND 作为缓存域名服务器之前,还有一些小细节需要配置。两个修改都在`/etc/bind/named.conf.options`里完成。首先你要取消注释掉 forwarders 这一节内容,同时你还要增加一个可以转发域名请求的目标服务器。作为例子我会用 Google 的 DNS 服务器(8.8.8.8)(LCTT 译注:国内的话需要找一个替代品);文件的 forwarders 节看上去大致是这样的:
```
forwarders {
8.8.8.8;
};
```
第二点你需要做的更改是允许来自内网和本机的查询请求,直接把这一行加入配置文件的后面,记得放在最后一个`};`之前就可以了:
```
allow-query { 192.168.1.0/24; 127.0.0.0/16; };
```
上面那行配置会允许此 DNS 服务器接收来自其所在的网络(在本例中,我的网络就在我的防火墙之后)和本机的请求。下一步,你需要重启一下 BIND 的服务:
```
root@test:~# /etc/init.d/bind9 restart
[....] Stopping domain name service...: bind9
waiting for pid 13209 to die
. ok
[ ok ] Starting domain name service...: bind9.
```
现在你可以测试一下 `nslookup` 来确保你的服务正常运行了:
```
root@test:~# nslookup
> server localhost
Default server: localhost
Address: 127.0.0.1#53
> www.google.com
Server: localhost
Address: 127.0.0.1#53
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: www.google.com
Address: 173.194.33.176
Name: www.google.com
Address: 173.194.33.177
Name: www.google.com
Address: 173.194.33.178
Name: www.google.com
Address: 173.194.33.179
Name: www.google.com
Address: 173.194.33.180
```
完美!现在你的系统里已经有一个正常的域名服务在工作了,下一步我们来配置一下OpenVPN。
### 安装并配置 OpenVPN
OpenVPN 是一个运用 SSL/TLS 作为密钥交换的开源 VPN 解决方案。同时它也非常便于在 Linux 环境下部署。配置 OpenVPN 可能有一点点难,不过其实你也不需要在默认的配置文件里做太多修改。首先你需要运行一下 `apt-get` 来安装 OpenVPN:
```
root@test:~# apt-get install openvpn
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following extra packages will be installed:
liblzo2-2 libpkcs11-helper1
Suggested packages:
resolvconf
The following NEW packages will be installed:
liblzo2-2 libpkcs11-helper1 openvpn
0 upgraded, 3 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Need to get 621 kB of archives.
After this operation, 1,489 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Do you want to continue [Y/n]? y
```
现在 OpenVPN 已经安装好了,你需要去配置它了。OpenVPN 是基于 SSL 的,并且它同时依赖于服务端和客户端两方的证书来工作。为了生成这些证书,你需要在机器上配置一个证书签发(CA)。幸运地,OpenVPN 在安装中自带了一些用于生成证书的脚本比如 “easy-rsa” 来帮助你加快这个过程。你将要创建一个文件目录用于放置 easy-rsa 脚本,从模板目录复制过来:
```
root@test:~# mkdir /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa
root@test:~# cp -rpv /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/easy-rsa/2.0/* /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/
```
下一步,把 vars 文件复制一个备份:
```
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# cp vars vars.bak
```
接下来,编辑一下 vars 以让其中的信息符合你的状态。我将以我需要编辑的信息作为例子:
```
KEY_SIZE=4096
KEY_COUNTRY="US"
KEY_PROVINCE="CA"
KEY_CITY="Silicon Valley"
KEY_ORG="Linux Journal"
KEY_EMAIL="[email protected]"
```
下一步是导入(source)一下 vars 中的环境变量,这样系统就能把其中的信息当作环境变量处理了:
```
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# source ./vars
NOTE: If you run ./clean-all, I will be doing a rm -rf on /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys
```
### 搭建 CA(证书签发)
接下来你要运行一下 `clean-all` 来确保有一个清理干净的系统工作环境,紧接着你就要做证书签发了。注意一下我修改了一些 changeme 的所提示修改的内容以符合我需要的安装情况:
```
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# ./clean-all
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# ./build-ca
Generating a 4096 bit RSA private key
...................................................++
...................................................++
writing new private key to 'ca.key'
-----
You are about to be asked to enter information that
will be incorporated into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a
Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some
blank. For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [US]:
State or Province Name (full name) [CA]:
Locality Name (eg, city) [Silicon Valley]:
Organization Name (eg, company) [Linux Journal]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [changeme]:SecTeam
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname [changeme]:test.linuxjournal.com
Name [changeme]:test.linuxjournal.com
Email Address [[email protected]]:
```
### 生成服务端证书
一旦 CA 创建好了,你接着就可以生成客户端的 OpenVPN 证书了:
```
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# ./build-key-server test.linuxjournal.com
Generating a 4096 bit RSA private key
...................................................++
writing new private key to 'test.linuxjournal.com.key'
-----
You are about to be asked to enter information that
will be incorporated into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a
Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some
blank. For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [US]:
State or Province Name (full name) [CA]:
Locality Name (eg, city) [Silicon Valley]:
Organization Name (eg, company) [Linux Journal]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [changeme]:SecTeam
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) [test.linuxjournal.com]:
Name [changeme]:test.linuxjournal.com
Email Address [[email protected]]:
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:
Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/openssl-1.0.0.cnf
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
countryName :PRINTABLE:'US'
stateOrProvinceName :PRINTABLE:'CA'
localityName :PRINTABLE:'Silicon Valley'
organizationName :PRINTABLE:'Linux Journal'
organizationalUnitName:PRINTABLE:'SecTeam'
commonName :PRINTABLE:'test.linuxjournal.com'
name :PRINTABLE:'test.linuxjournal.com'
emailAddress :IA5STRING:'[email protected]'
Certificate is to be certified until Sep 1 06:23:59 2025 GMT (3650 days)
Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y
1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
```
下一步需要用掉一些时间来生成 OpenVPN 服务器需要的 Diffie-Hellman 密钥。这个步骤在一般的桌面级 CPU 上会需要几分钟的时间,但在 ARM 构架的树莓派上,会用掉超级超级长的时间。耐心点,只要终端上的点还在跳,那么一切就在按部就班运行(下面的示例省略了不少的点):
```
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# ./build-dh
Generating DH parameters, 4096 bit long safe prime,
↪generator 2
This is going to take a long time
....................................................+
<省略了不少的点>
```
### 生成客户端证书
现在你要生成一下客户端用于登录 OpenVPN 的密钥。通常来说 OpenVPN 都会被配置成使用证书验证的加密方式,在这个配置下客户端需要持有由服务端签发的一份证书:
```
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# ./build-key bills-computer
Generating a 4096 bit RSA private key
...................................................++
...................................................++
writing new private key to 'bills-computer.key'
-----
You are about to be asked to enter information that
will be incorporated into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a
Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few
fields but you can leave some blank.
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [US]:
State or Province Name (full name) [CA]:
Locality Name (eg, city) [Silicon Valley]:
Organization Name (eg, company) [Linux Journal]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [changeme]:SecTeam
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) [bills-computer]:
Name [changeme]:bills-computer
Email Address [[email protected]]:
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:
Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/openssl-1.0.0.cnf
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
countryName :PRINTABLE:'US'
stateOrProvinceName :PRINTABLE:'CA'
localityName :PRINTABLE:'Silicon Valley'
organizationName :PRINTABLE:'Linux Journal'
organizationalUnitName:PRINTABLE:'SecTeam'
commonName :PRINTABLE:'bills-computer'
name :PRINTABLE:'bills-computer'
emailAddress :IA5STRING:'[email protected]'
Certificate is to be certified until Sep 1 07:35:07 2025 GMT (3650 days)
Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y
1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa#
```
现在你需要再生成一个 HMAC 码作为共享密钥来进一步增加整个加密提供的安全性:
```
root@test:~# openvpn --genkey --secret /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/ta.key
```
### 配置服务器
最后,我们到了配置 OpenVPN 服务的时候了。你需要创建一个 `/etc/openvpn/server.conf` 文件;这个配置文件的大多数地方都可以套用模板解决。设置 OpenVPN 服务的主要修改在于让它只用 TCP 而不是 UDP 链接。这是下一步所必需的---如果不是 TCP 连接那么你的服务将不能工作在端口 443 上。创建 `/etc/openvpn/server.conf` 然后把下述配置丢进去:
```
port 1194
proto tcp
dev tun
ca easy-rsa/keys/ca.crt
cert easy-rsa/keys/test.linuxjournal.com.crt ## or whatever your hostname was
key easy-rsa/keys/test.linuxjournal.com.key ## Hostname key- This file should be kept secret
management localhost 7505
dh easy-rsa/keys/dh4096.pem
tls-auth /etc/openvpn/certs/ta.key 0
server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0 # The server will use this subnet for clients connecting to it
ifconfig-pool-persist ipp.txt
push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp" # Forces clients to redirect all traffic through the VPN
push "dhcp-option DNS 192.168.1.1" # Tells the client to use the DNS server at 192.168.1.1 for DNS - replace with the IP address of the OpenVPN machine and clients will use the BIND server setup earlier
keepalive 30 240
comp-lzo # Enable compression
persist-key
persist-tun
status openvpn-status.log
verb 3
```
最后,你将需要在服务器上启用 IP 转发,配置 OpenVPN 为开机启动,并立刻启动 OpenVPN 服务:
```
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys# echo "net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys# sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.conf
net.core.wmem_max = 12582912
net.core.rmem_max = 12582912
net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 10240 87380 12582912
net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 10240 87380 12582912
net.core.wmem_max = 12582912
net.core.rmem_max = 12582912
net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 10240 87380 12582912
net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 10240 87380 12582912
net.core.wmem_max = 12582912
net.core.rmem_max = 12582912
net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 10240 87380 12582912
net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 10240 87380 12582912
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys# update-rc.d openvpn defaults
update-rc.d: using dependency based boot sequencing
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys# /etc/init.d/openvpn start
[ ok ] Starting virtual private network daemon:.
```
### 配置 OpenVPN 客户端
客户端的安装取决于客户端的操作系统,但你需要将之前生成的证书和密钥复制到你的客户端上,并导入你的 OpenVPN 客户端并新建一个配置文件。每种操作系统下的 OpenVPN 客户端在操作上会有些稍许不同,这也不在这篇文章的覆盖范围内,所以你最好去看看特定操作系统下的 OpenVPN 文档来获取更多信息。请参考本文档里的资源那一节。
### 安装 SSLH —— "魔法"多协议切换工具
本文章介绍的解决方案最有趣的部分就是运用 SSLH 了。SSLH 是一个多重协议工具——它可以监听 443 端口的流量,然后分析他们是 SSH,HTTPS 还是 OpenVPN 的通讯包,并把它们分别转发给正确的系统服务。这就是为何本解决方案可以让你绕过大多数端口封杀——你可以一直使用 HTTPS 通讯,因为它几乎从来不会被封杀。
同样,直接 `apt-get` 安装:
```
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys# apt-get install sslh
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following extra packages will be installed:
apache2 apache2-mpm-worker apache2-utils apache2.2-bin apache2.2-common
libapr1 libaprutil1 libaprutil1-dbd-sqlite3 libaprutil1-ldap libconfig9
Suggested packages:
apache2-doc apache2-suexec apache2-suexec-custom openbsd-inetd inet-superserver
The following NEW packages will be installed:
apache2 apache2-mpm-worker apache2-utils apache2.2-bin apache2.2-common
libapr1 libaprutil1 libaprutil1-dbd-sqlite3 libaprutil1-ldap libconfig9 sslh
0 upgraded, 11 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Need to get 1,568 kB of archives.
After this operation, 5,822 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Do you want to continue [Y/n]? y
```
在 SSLH 被安装之后,包管理器会询问要在 inetd 还是 standalone 模式下允许。选择 standalone 模式,因为你希望 SSLH 在它自己的进程里运行。如果你没有安装 Apache,apt 包管理器会自动帮你下载并安装的,尽管它也不是完全不可或缺。如果你已经有 Apache 了,那你需要确保它只监听 localhost 端口而不是所有的端口(不然的话 SSLH 会无法运行,因为 443 端口已经被 Apache 监听占用)。安装后,你会看到一个如下所示的错误信息:
```
[....] Starting ssl/ssh multiplexer: sslhsslh disabled, please adjust the configuration to your needs
[FAIL] and then set RUN to 'yes' in /etc/default/sslh to enable it. ... failed!
failed!
```
这其实并不是错误信息,只是 SSLH 在提醒你它还未被配置所以无法启动,这很正常。配置 SSLH 相对来说比较简单。它的配置文件放置在 `/etc/default/sslh`,你只需要修改 `RUN` 和 `DAEMON_OPTS` 变量就可以了。我的 SSLH 配置文件如下所示:
```
# Default options for sslh initscript
# sourced by /etc/init.d/sslh
# Disabled by default, to force yourself
# to read the configuration:
# - /usr/share/doc/sslh/README.Debian (quick start)
# - /usr/share/doc/sslh/README, at "Configuration" section
# - sslh(8) via "man sslh" for more configuration details.
# Once configuration ready, you *must* set RUN to yes here
# and try to start sslh (standalone mode only)
RUN=yes
# binary to use: forked (sslh) or single-thread (sslh-select) version
DAEMON=/usr/sbin/sslh
DAEMON_OPTS="--user sslh --listen 0.0.0.0:443 --ssh 127.0.0.1:22 --ssl 127.0.0.1:443 --openvpn 127.0.0.1:1194 --pidfile /var/run/sslh/sslh.pid"
```
保存编辑并启动 SSLH:
```
root@test:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys# /etc/init.d/sslh start
[ ok ] Starting ssl/ssh multiplexer: sslh.
```
现在你应该可以从 443 端口 ssh 到你的树莓派了,它会正确地使用 SSLH 转发:
```
$ ssh -p 443 [email protected]
root@test:~#
```
SSLH 现在开始监听端口 443 并且可以转发流量信息到 SSH、Apache 或者 OpenVPN ,这取决于抵达流量包的类型。这套系统现已整装待发了!
### 结论
现在你可以启动 OpenVPN 并且配置你的客户端连接到服务器的 443 端口了,然后 SSLH 会从那里把流量转发到服务器的 1194 端口。但鉴于你正在和服务器的 443 端口通信,你的 VPN 流量不会被封锁。现在你可以舒服地坐在陌生小镇的咖啡店里,畅通无阻地通过你的树莓派上的 OpenVPN 浏览互联网。你顺便还给你的链接增加了一些安全性,这个额外作用也会让你的链接更安全和私密一些。享受通过安全跳板浏览互联网把!
### 参考资源
* 安装与配置 OpenVPN: <https://wiki.debian.org/OpenVPN> 和 <http://cryptotap.com/articles/openvpn>
* OpenVPN 客户端下载: <https://openvpn.net/index.php/open-source/downloads.html>
* OpenVPN iOS 客户端: <https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/openvpn-connect/id590379981?mt=8>
* OpenVPN Android 客户端: <https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=net.openvpn.openvpn&hl=en>
* Tunnelblick for Mac OS X (OpenVPN 客户端): <https://tunnelblick.net>
* SSLH 介绍: <http://www.rutschle.net/tech/sslh.shtml> 和 <https://github.com/yrutschle/sslh>
---
via: <http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/securi-pi-using-raspberry-pi-secure-landing-point?page=0,0>
作者:[Bill Childers](http://www.linuxjournal.com/users/bill-childers) 译者:[Moelf](https://github.com/Moelf) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,557 | 在 Linux 上管理加密密钥的最佳体验 | http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/838235-how-to-best-manage-encryption-keys-on-linux | 2016-07-11T10:02:00 | [
"SSH",
"密钥",
"私钥"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7557-1.html | 存储 SSH 的加密秘钥和记住密码一直是一个让人头疼的问题。但是不幸的是,在当前这个充满了恶意黑客和攻击的世界中,基本的安全预防是必不可少的。对于许多普通用户来说,大多数人只能是记住密码,也可能寻找到一个好程序去存储密码,正如我们提醒这些用户不要在每个网站采用相同的密码。但是对于在各个 IT 领域的人们,我们需要将这个事情提高一个层面。我们需要使用像 SSH 密钥这样的加密秘钥,而不只是密码。

设想一个场景:我有一个运行在云上的服务器,用作我的主 git 库。我有很多台工作电脑,所有这些电脑都需要登录到这个中央服务器去做 push 与 pull 操作。这里我设置 git 使用 SSH。当 git 使用 SSH 时,git 实际上是以 SSH 的方式登录到服务器,就好像你通过 SSH 命令打开一个服务器的命令行一样。为了把这些配置好,我在我的 .ssh 目录下创建一个配置文件,其中包含一个有服务器名字、主机名、登录用户、密钥文件路径等信息的主机项。之后我可以通过输入如下命令来测试这个配置是否正确。
```
ssh gitserver
```
很快我就可以访问到服务器的 bash shell。现在我可以配置 git 使用相同配置项以及存储的密钥来登录服务器。这很简单,只是有一个问题:对于每一个我要用它登录服务器的电脑,我都需要有一个密钥文件,那意味着需要密钥文件会放在很多地方。我会在当前这台电脑上存储这些密钥文件,我的其他电脑也都需要存储这些。就像那些有特别多的密码的用户一样,我们这些 IT 人员也被这些特别多的密钥文件淹没。怎么办呢?
### 清理
在我们开始帮助你管理密钥之前,你需要有一些密钥应该怎么使用的基础知识,以及明白我们下面的提问的意义所在。同时,有个前提,也是最重要的,你应该知道你的公钥和私钥该放在哪里。然后假设你应该知道:
1. 公钥和私钥之间的差异;
2. 为什么你不可以从公钥生成私钥,但是反之则可以?
3. `authorized_keys` 文件的目的以及里面包含什么内容;
4. 如何使用私钥去登录一个你的对应公钥存储在其上的 `authorized_keys` 文件中的服务器。
这里有一个例子。当你在亚马逊的网络服务上创建一个云服务器,你必须提供一个用于连接你的服务器的 SSH 密钥。每个密钥都有一个公开的部分(公钥)和私密的部分(私钥)。你要想让你的服务器安全,乍看之下你可能应该将你的私钥放到服务器上,同时你自己带着公钥。毕竟,你不想你的服务器被公开访问,对吗?但是实际上的做法正好是相反的。

你应该把自己的公钥放到 AWS 服务器,同时你持有用于登录服务器的私钥。你需要保护好私钥,并让它处于你的控制之中,而不是放在一些远程服务器上,正如上图中所示。
原因如下:如果公钥被其他人知道了,它们不能用于登录服务器,因为他们没有私钥。进一步说,如果有人成功攻入你的服务器,他们所能找到的只是公钥,他们不可以从公钥生成私钥。同时,如果你在其他的服务器上使用了相同的公钥,他们不可以使用它去登录别的电脑。
这就是为什么你要把你自己的公钥放到你的服务器上以便通过 SSH 登录这些服务器。你持有这些私钥,不要让这些私钥脱离你的控制。
但是还有一点麻烦。试想一下我 git 服务器的例子。我需要做一些抉择。有时我登录架设在别的地方的开发服务器,而在开发服务器上,我需要连接我的 git 服务器。如何使我的开发服务器连接 git 服务器?显然是通过使用私钥,但这样就会有问题。在该场景中,需要我把私钥放置到一个架设在别的地方的服务器上,这相当危险。
一个进一步的场景:如果我要使用一个密钥去登录许多的服务器,怎么办?如果一个入侵者得到这个私钥,这个人就能用这个私钥得到整个服务器网络的权限,这可能带来一些严重的破坏,这非常糟糕。
同时,这也带来了另外一个问题,我真的应该在这些其他服务器上使用相同的密钥吗?因为我刚才描述的,那会非常危险的。
最后,这听起来有些混乱,但是确实有一些简单的解决方案。让我们有条理地组织一下。
(注意,除了登录服务器,还有很多地方需要私钥密钥,但是我提出的这个场景可以向你展示当你使用密钥时你所面对的问题。)
### 常规口令
当你创建你的密钥时,你可以选择是否包含一个密钥使用时的口令。有了这个口令,私钥文件本身就会被口令所加密。例如,如果你有一个公钥存储在服务器上,同时你使用私钥去登录服务器的时候,你会被提示输入该口令。没有口令,这个密钥是无法使用的。或者你也可以配置你的密钥不需要口令,然后只需要密钥文件就可以登录服务器了。
一般来说,不使用口令对于用户来说是更方便的,但是在很多情况下我强烈建议使用口令,原因是,如果私钥文件被偷了,偷密钥的人仍然不可以使用它,除非他或者她可以找到口令。在理论上,这个将节省你很多时间,因为你可以在攻击者发现口令之前,从服务器上删除公钥文件,从而保护你的系统。当然还有一些使用口令的其它原因,但是在很多场合这个原因对我来说更有价值。(举一个例子,我的 Android 平板上有 VNC 软件。平板上有我的密钥。如果我的平板被偷了之后,我会马上从服务器上删除公钥,使得它的私钥没有作用,无论有没有口令。)但是在一些情况下我不使用口令,是因为我正在登录的服务器上没有什么有价值的数据,这取决于情境。
### 服务器基础设施
你如何设计自己服务器的基础设施将会影响到你如何管理你的密钥。例如,如果你有很多用户登录,你将需要决定每个用户是否需要一个单独的密钥。(一般来说,应该如此;你不会想在用户之间共享私钥。那样当一个用户离开组织或者失去信任时,你可以删除那个用户的公钥,而不需要必须给其他人生成新的密钥。相似地,通过共享密钥,他们能以其他人的身份登录,这就更糟糕了。)但是另外一个问题是你如何配置你的服务器。举例来说,你是否使用像 Puppet 这样工具配置大量的服务器?你是否基于你自己的镜像创建大量的服务器?当你复制你的服务器,是否每一个的密钥都一样?不同的云服务器软件允许你配置如何选择;你可以让这些服务器使用相同的密钥,也可以给每一个服务器生成一个新的密钥。
如果你在操作这些复制的服务器,如果用户需要使用不同的密钥登录两个不同但是大部分都一样的系统,它可能导致混淆。但是另一方面,服务器共享相同的密钥会有安全风险。或者,第三,如果你的密钥有除了登录之外的需要(比如挂载加密的驱动),那么你会在很多地方需要相同的密钥。正如你所看到的,你是否需要在不同的服务器上使用相同的密钥不是我能为你做的决定;这其中有权衡,你需要自己去决定什么是最好的。
最终,你可能会有:
* 需要登录的多个服务器
* 多个用户登录到不同的服务器,每个都有自己的密钥
* 每个用户使用多个密钥登录到不同的服务器
(如果你正在别的情况下使用密钥,这个同样的普适理论也能应用于如何使用密钥,需要多少密钥,它们是否共享,你如何处理公私钥等方面。)
### 安全方法
了解你的基础设施和特有的情况,你需要组合一个密钥管理方案,它会指导你如何去分发和存储你的密钥。比如,正如我之前提到的,如果我的平板被偷了,我会从我服务器上删除公钥,我希望这在平板在用于访问服务器之前完成。同样的,我会在我的整体计划中考虑以下内容:
1. 私钥可以放在移动设备上,但是必须包含口令;
2. 必须有一个可以快速地从服务器上删除公钥的方法。
在你的情况中,你可能决定你不想在自己经常登录的系统上使用口令;比如,这个系统可能是一个开发者一天登录多次的测试机器。这没有问题,但是你需要调整一点你的规则。你可以添加一条规则:不可以通过移动设备登录该机器。换句话说,你需要根据自己的状况构建你的准则,不要假设某个方案放之四海而皆准。
### 软件
至于软件,令人吃惊的是,现实世界中并没有很多好的、可靠的存储和管理私钥的软件解决方案。但是应该有吗?考虑下这个,如果你有一个程序存储你所有服务器的全部密钥,并且这个程序被一个快捷的密钥锁住,那么你的密钥就真的安全了吗?或者类似的,如果你的密钥被放置在你的硬盘上,用于 SSH 程序快速访问,密钥管理软件是否真正提供了任何保护吗?
但是对于整体基础设施和创建/管理公钥来说,有许多的解决方案。我已经提到了 Puppet,在 Puppet 的世界中,你可以创建模块以不同的方式管理你的服务器。这个想法是服务器是动态的,而且不需要精确地复制彼此。[这里有一个聪明的方法](http://manuel.kiessling.net/2014/03/26/building-manageable-server-infrastructures-with-puppet-part-4/),在不同的服务器上使用相同的密钥,但是对于每一个用户使用不同的 Puppet 模块。这个方案可能适合你,也可能不适合你。
或者,另一个选择就是完全换个不同的档位。在 Docker 的世界中,你可以采取一个不同的方式,正如[关于 SSH 和 Docker 博客](http://blog.docker.com/2014/06/why-you-dont-need-to-run-sshd-in-docker/)所描述的那样。
但是怎么样管理私钥?如果你搜索过的话,你无法找到很多可以选择的软件,原因我之前提到过;私钥存放在你的硬盘上,一个管理软件可能无法提到更多额外的安全。但是我使用这种方法来管理我的密钥:
首先,我的 `.ssh/config` 文件中有很多的主机项。我要登录的都有一个主机项,但是有时我对于一个单独的主机有不止一项。如果我有很多登录方式,就会出现这种情况。对于放置我的 git 库的服务器来说,我有两个不同的登录项;一个限制于 git,另一个用于一般用途的 bash 访问。这个为 git 设置的登录选项在机器上有极大的限制。还记得我之前说的我存储在远程开发机器上的 git 密钥吗?好了。虽然这些密钥可以登录到我其中一个服务器,但是使用的账号是被严格限制的。
其次,大部分的私钥都包含口令。(对于需要多次输入口令的情况,考虑使用 [ssh-agent](http://blog.docker.com/2014/06/why-you-dont-need-to-run-sshd-in-docker/)。)
再次,我有一些我想要更加小心地保护的服务器,我不会把这些主机项放在我的 host 文件中。这更加接近于社会工程方面,密钥文件还在,但是可能需要攻击者花费更长的时间去找到这个密钥文件,分析出来它们对应的机器。在这种情况下,我就需要手动打出来一条长长的 SSH 命令。(没那么可怕。)
同时你可以看出来我没有使用任何特别的软件去管理这些私钥。
### 无放之四海而皆准的方案
我们偶尔会在 linux.com 收到一些问题,询问管理密钥的好软件的建议。但是退一步看,这个问题事实上需要重新思考,因为没有一个普适的解决方案。你问的问题应该基于你自己的情景。你是否简单地尝试找到一个位置去存储你的密钥文件?你是否寻找一个方法去管理多用户问题,其中每个人都需要将他们自己的公钥插入到 `authorized_keys` 文件中?
通过这篇文章,我已经囊括了这方面的基础知识,希望到此你明白如何管理你的密钥,并且,只有当你问出了正确的问题,无论你寻找任何软件(甚至你需要另外的软件),它都会出现。
---
via: <http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/838235-how-to-best-manage-encryption-keys-on-linux>
作者:[Jeff Cogswell](http://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/62256) 译者:[mudongliang](https://github.com/mudongliang) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,559 | 微软说,将“为 Linux 用户带来令人兴奋的新闻” | http://news.softpedia.com/news/microsoft-teases-exciting-news-for-linux-users-506145.shtml | 2016-07-10T17:25:34 | [
"微软",
"Skype"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7559-1.html | 微软这些年对 Linux 的观感已经完全改变了,随着开源世界增长的越来越快,雷蒙德(微软总部所在地)除了适应并寻求接近这个日益增长的社区,已经别无选择了。
微软发布了几个在十年前根本没有人会相信的新产品之后,比如 Bash on Windows 10,微软还准备给 Linux 带来更多东西,这次应该是特别针对 Skype 用户的。
今天在 [Skype 社区论坛](https://community.skype.com/t5/Linux/Exciting-news-for-Linux-users/td-p/4430988)发的一个帖子里,微软宣称将“为 Linux 用户带来令人兴奋的新闻”,但是并没有给出具体细节。我们只知道,完整的消息将于 7 月 13 日太平洋时间早上 7 点在该社区的 Q&A 版块发布。

### 一个新的 Skype 的 Linux 客户端?
由于这是通过微软 Skype 社区进行发布的,不难猜测,微软最有可能发布的是针对 Linux 的新版 Skype 应用程序。微软目前正在通过 Windows Insider 项目进行 Windows 和 Office 内测,因此,也有人猜测,微软是否将为 Linux 用户带来同样的微软产品内测计划。
目前 Skype 的 Linux 版本由于它的功能简陋以及过时的用户界面而常被诟病,一些在 Windows 客户端上已有的功能在 Linux 版本上却没有。
微软正在为 Windows 10 全速开发 Skype,现在正在开发一个可以运行在 PC 和智能电话上的统一应用,一个新的 Linux 版本的 Skype 将把这个 VoIP 客户端带到更多的平台上。
我们将会密切关注微软在下周宣布的消息,请随时关注,让我们看看微软将给 Linux 下的 Skype 带来什么。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,561 | 在 Linux 下使用任务管理器 | https://itsfoss.com/task-manager-linux/ | 2016-07-11T08:02:00 | [
"任务管理器"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7561-1.html | 
有很多 Linux 初学者经常问起的问题,“**Linux 有任务管理器吗?**”,“**怎样在 Linux 上打开任务管理器呢?**”
来自 Windows 的用户都知道任务管理器非常有用。你可以在 Windows 中按下 `Ctrl+Alt+Del` 打开任务管理器。这个任务管理器向你展示了所有的正在运行的进程和它们消耗的内存,你可以从任务管理器程序中选择并杀死一个进程。
当你刚使用 Linux 的时候,你也会寻找一个**在 Linux 相当于任务管理器**的一个东西。一个 Linux 使用专家更喜欢使用命令行的方式查找进程和消耗的内存等等,但是你不用必须使用这种方式,至少在你初学 Linux 的时候。
所有主流的 Linux 发行版都有一个类似于任务管理器的东西。大部分情况下,它叫<ruby> 系统监视器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> System Monitor </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,不过实际上它依赖于你的 Linux 的发行版及其使用的[桌面环境](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/desktop_environment)。
在这篇文章中,我们将会看到如何在以 GNOME 为[桌面环境](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/)的 Linux 上找到并使用任务管理器。
### 在使用 GNOME 桌面环境的 Linux 上的任务管理器等价物
使用 GNOME 时,按下 super 键(Windows 键)来查找任务管理器:

当你启动系统监视器的时候,它会向你展示所有正在运行的进程及其消耗的内存。

你可以选择一个进程并且点击“<ruby> 终止进程 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> End Process </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”来杀掉它。

你也可以在“<ruby> 资源 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Resources </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”标签里面看到关于一些统计数据,例如 CPU 的每个核心的占用,内存用量、网络用量等。

这是图形化的方式。如果你想使用命令行,在终端里运行“top”命令然后你就可以看到所有运行的进程及其消耗的内存。你也可以很容易地使用命令行[杀死进程](https://itsfoss.com/how-to-find-the-process-id-of-a-program-and-kill-it-quick-tip/)。
这就是关于在 Fedora Linux 上任务管理器的知识。我希望这个教程帮你学到了知识,如果你有什么问题,请尽管问。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/task-manager-linux/>
作者:[Abhishek Prakash](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 译者:[xinglianfly](https://github.com/xinglianfly) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject)原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

“**Is there a task manager for Linux**?” “How do you open the task manager on Linux?” “Where do I find the Ubuntu task manager?”
These are some of the most frequently asked questions from Linux beginners:
People who are coming from Windows know how valuable the task manager is. You press Ctrl+Alt+Del to get to the task manager in Windows. This task manager shows you all the running processes and their memory consumption. You can choose to end a process from this task manager application.
When you’re just starting out with Linux, you may also look for a **task manager equivalent on Linux**. An expert Linux user prefers the command-line way to find processes and memory consumption, etc., but you don’t have to go that way, at least not when you’re just starting out with Linux.
All the major Linux distributions have a task manager equivalent. Usually, **it’s called System Monitor**, but it actually depends on your Linux distribution and the [desktop environment](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/desktop_environment) it uses.
In this article, we’ll see how to find and use the task manager on Ubuntu and other Linux distributions that use GNOME as the [desktop environment](https://itsfoss.com/best-linux-desktop-environments/).
## System Monitor: The Task Manager of Linux distributions
If you’re using the GNOME desktop, press the Super key (Windows key) and look for System Monitor. In other desktop environments, search for System Monitor in the menu.
This will start the [GNOME System Monitor](https://help.gnome.org/users/gnome-system-monitor/). It shows you all the running processes and their memory consumption.
You can select a process and click on End process to kill it. You can also select multiple entries here and [kill the processes](https://itsfoss.com/how-to-find-the-process-id-of-a-program-and-kill-it-quick-tip/) in one click.
You can also see some statistics about your system in the Resources tab, such as CPU consumption per core basis, memory usage, network usage, etc.
You can watch this video to see it in action:
### There are more ways to manage tasks
That was the graphical way. If you want to go the command line way, just [run the top command](https://linuxhandbook.com/top-command/) in the terminal and you can see all the running processes and their memory consumption. You can easily [kill processes in the Linux](https://itsfoss.com/how-to-find-the-process-id-of-a-program-and-kill-it-quick-tip/) command line.
If you want a command-line-based task manager on Linux, I recommend [using htop](https://itsfoss.com/use-htop/). You can see running processes, memory usage, and more, and you can easily use hotkeys to end processes. And it looks good as well.
This is all you need to know about task manager equivalents on Linux. I hope you found this quick tutorial helpful. If you have questions or suggestions, feel free to comment. |
7,564 | Linux 开发者如何看待 Git 和 Github? | http://www.infoworld.com/article/3033059/linux/what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html | 2016-07-12T13:12:28 | [
"Git",
"GitHub"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7564-1.html | 
Git 和 Github 在 Linux 开发者中有很高的知名度。但是开发者如何看待它们呢?另外,Github 是不是真的和 Git 是一个意思?一个 Linux reddit 用户最近问到了这个问题,并且得到了很有意思的答案。
Dontwakemeup46 提问:
>
> 我正在学习 Git 和 Github。我感兴趣社区如何看待两者?据我所知,Git 和 Github 应用十分广泛。但是 Git 或 Github 有没有严重的不足?社区喜欢去改变些什么呢?[更多见 Reddit](https://www.reddit.com/r/linux/comments/45jy59/the_popularity_of_git_and_github/)
>
>
>
与他志同道合的 Linux reddit 用户回答了他们对于 Git 和 Github的观点:
**Derenir**:
>
> “Github 并不附属于 Git。
>
>
> Git 是由 Linus Torvalds 开发的。
>
>
> Github 几乎不支持 Linux。
>
>
> Github 是一家企图借助 Git 赚钱的公司。
>
>
> <https://desktop.github.com/> 并没有支持 Linux。”
>
>
>
**Bilog78**:
>
> “一个小的补充: Linus Torvalds 已经不再维护 Git了。维护者是 Junio C Hamano,以及 在他之后的主要贡献者是 Jeff King 和 Shawn O. Pearce。”
>
>
>
**Fearthefuture**:
>
> “我喜欢 Git,但是不明白人们为什么还要使用 Github。从我的角度,Github 比 Bitbucket 好的一点是用户统计和更大的用户基础。Bitbucket 有无限的免费私有库,更好的 UI,以及更好地集成了其他服务,比如说 Jenkins。”
>
>
>
**Thunger**:
>
> “Gitlab.com 也很不错,特别是你可以在自己的服务器上架设自己的实例。”
>
>
>
**Takluyver**:
>
> “很多人熟悉 Github 的 UI 以及相关联的服务,比如说 Travis 。并且很多人都有 Github 账号,所以它是存储项目的一个很好的地方。人们也使用他们的 Github 个人信息页作为一种求职用的作品选辑,所以他们很积极地将更多的项目放在这里。Github 是一个存放开源项目的事实标准。”
>
>
>
**Tdammers**:
>
> “Git 严重问题在于 UI,它有些违反直觉,以至于很多用户只能达到使用一些容易记住的咒语的程度。
>
>
> Github:最严重的问题在于它是商业托管的解决方案;你买了方便,但是代价是你的代码在别人的服务器上面,已经不在你的掌控范围之内了。另一个对于 Github 的普遍批判是它的工作流和 Git 本身的精神不符,特别是 pull requests 工作的方式。最后, Github 垄断了代码的托管环境,同时对于多样性是很不好的,这反过来对于旺盛的免费软件社区很重要。”
>
>
>
**Dies**:
>
> “更重要的是,如果一旦是这样,按照现状来说,我猜我们会被 Github 所困,因为它们控制如此多的项目。”
>
>
>
**Tdammers**:
>
> “代码托管在别人的服务器上,这里"别人"指的是 Github。这对于开源项目来说,并不是什么太大的问题,但是尽管如此,你无法控制它。如果你在 Github 上有私有项目,“它将保持私有”的唯一的保险只是 Github 的承诺而已。如果你决定删除东西,你不能确定东西是否被删除了,或者只是隐藏了。
>
>
> Github 并不自己控制这些项目(你总是可以拿走你的代码,然后托管到别的地方,声明新位置是“官方”的),它只是有比开发者本身有更深的使用权。”
>
>
>
**Drelos**:
>
> “我已经读了大量的关于 Github 的赞美与批评。(这里有一个[例子](http://www.wired.com/2015/06/problem-putting-worlds-code-github/)),但是我的幼稚问题是为什么不向一个免费开源的版本努力呢?”
>
>
>
**Twizmwazin**:
>
> “Gitlab 的源码就存在这里。”
>
>
>
[更多见 Reddit](https://www.reddit.com/r/linux/comments/45jy59/the_popularity_of_git_and_github/)
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,565 | DistroWatch 评估 XStream 桌面 153 版本 | http://www.infoworld.com/article/3033059/linux/what-do-linux-developers-think-of-git-and-github.html | 2016-07-12T15:13:00 | [
"XStream",
"OpenSolaris"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7565-1.html | XStreamOS 是一个由 Sonicle 创建的 Solaris 的一个版本。XStream 桌面将 Solaris 的强大带给了桌面用户,同时新手用户很可能有兴趣体验一下。DistroWatch 对于 XStream 桌面 153 版本做了一个很全面的评估,并且发现它运行相当好。

Jesse Smith 在 DistroWatch 报道:
>
> 我认为 XStream 桌面做好了很多事情。诚然,当操作系统无法在我的硬件上启动,同时当运行在 VirtualBox 中时我无法使得桌面使用我显示器的完整分辨率,我的开端并不很成功。不过,除此之外,XStream 表现的很好。安装器工作的很好,该系统自动设置和使用了<ruby> 引导环境 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> boot environments </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,这让我们可以在发生错误时恢复该系统。包管理器有工作的不错, XStream 带了一套有用的软件。
>
>
> 我确实在播放多媒体文件时遇见一些问题,特别是使声卡工作。我不确定这是不是又一个硬件兼容问题,或者是该操作系统自带的多媒体软件的问题。另一方面,像 Web 浏览器,电子邮件,生产工具套件以及配置工具这样的工作的很好。
>
>
> 我最欣赏 XStream 的地方是这个操作系统是 OpenSolaris 家族的一个使用保持最新的分支。OpenSolaris 的其他衍生系统有落后的倾向,但是至少在桌面软件上,XStream 搭载最新版本的火狐和 LibreOffice。
>
>
> 对我个人来说,XStream 缺少一些组件,比如打印机管理器,多媒体支持和我的特定硬件的驱动。这个操作系统的其他方面也是相当吸引人的。我喜欢开发者搭配了 LXDE,也喜欢它的默认软件集,以及我最喜欢文件系统快照和启动环境开箱即用的方式。大多数的 Linux 发行版,openSUSE 除外,并没有利用好<ruby> 引导环境 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> boot environments </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的用处。我希望它是一个被更多项目采用的技术。
>
>
>
[更多见 DistroWatch](http://distrowatch.com/weekly.php?issue=20160215#xstreamos)
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,567 | 微软和 SUSE Linux 宣布在公有云方面达成新的合作 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/microsoft-and-suse-linux-announce-new-partnership-506174.shtml | 2016-07-13T10:01:07 | [
"微软",
"SUSE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7567-1.html | 微软在 Linux 世界变得越来越活跃了,在它说将发布一个“让 [Linux 用户激动的新闻](/article-7559-1.html)”后,该公司又宣布了一个旨在增强其在云市场方面领导地位的另外一个合作关系。
今天,这个软件巨人宣布了和 SUSE Linux 的新的合作关系,以延续他们在公有云服务方面的合作,这是这两个公司在今年发布的首次公告。
新的合作关系更新了一些条款和承诺,但是暂时还未对外公布细节。

之前微软和 SUSE Linux 之间的合作签署于 2006 年,其时 SUSE Linux 这家德国公司还隶属于 Novell,而微软还被 Linux 世界视为凶猛的敌人。在 2001 年时,时任微软 CEO 的史蒂夫·鲍尔默因其将 Linux 称之为“附身于知识产权之上,感染其所接触到的一切的癌症”的言论,而挑起了微软和开源界之间的长久战争。
### 史蒂夫·鲍尔默现在爱 Linux!
但是时代改变了,现在微软投入数以百万计的美元来接近 Linux 世界,SUSE 的公有云全球联盟总监 Kristin Kinan 说,最近微软在Linux 方面的营收有了明显提升。
她说,“微软的公有云业务上为客户提供了 Linux 服务, Linux 的占比增长到了 22% 至 25%。他们在开源解决方案方面的投资、销售主动性和合作力度超出了我们的预期。”
此前,微软前 CEO 史蒂夫·鲍尔默收回了他之前称 Linux 是癌症的说法,说“[现在我爱它](/article-7095-1.html)”,并指出那时微软与开源世界斗争是正确的,这为微软带来了数以百万计的美金。
毫无疑问,新 CEO 萨提亚·纳德拉很热衷于微软的云业务,因此这种合作关系得以延续,显然,微软在 Linux 世界的投入还将继续增加。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,568 | Chromium OS 单板机项目需要你的加入! | http://linux.softpedia.com/blog/chromium-os-for-sbcs-project-needs-your-help-to-continue-full-scale-work-506155.shtml | 2016-07-13T14:04:00 | [
"Chromium OS",
"树莓派",
"单板机"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7568-1.html | Chromium OS for SBCs(<ruby> 单板机 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Single-Board Computers </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)项目正在招募新成员以继续发展。

该项目的志愿者们为我们奉献了一个精心调制的开源 [Chromium OS 的单板机移植版](http://www.chromiumosforsbc.org/),支持树莓派 2 和树莓派 3 以及一些其它的单板机。他们已经完成了目标,但是这并不是项目的终点。
项目负责人 Dylan Callahan 说,一些项目成员已经离开了该项目去做其它的志愿者项目了。这种事情经常发生,不仅仅是这个开源项目。简单的说,Dylan Callahan 需要更多人来延续维护该项目的进一步发展。
“我正在开发新的 Beta 版本,也在努力解决很多 bug 和添加新功能。我希望可以更快一些,我们已经有一些项目成员由于个人原因离开了,还有一些去参与其它志愿者项目了”,Dylan Callahan 说,“我们要让 Chromium OS for SBCs 继续前行,我们不能给你支付薪水,但是我们可以给你提供经验。”
因此,如果你在将 Chromium OS 移植到其它设备方面有经验,或者你就是想成为这个极棒的项目的新开发者,你可以访问[项目官网](http://www.chromiumosforsbc.org/meet-the-team/)加入该团队。在那里,你可以找到关于 Chromium OS for SBCs 的一切细节。甚至即使你在这个领域没有任何经验,但是你想参与,也欢迎你加入!
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,570 | 怎样在 Chromebook 上安装 Linux 系统? | http://news.softpedia.com/news/here-s-how-to-install-any-linux-operating-system-on-your-chromebook-506212.shtml | 2016-07-13T12:33:00 | [
"Chromebook"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7570-1.html |
>
> 首先,你得有个 Chromebook。
>
>
> 其次,你得有不用 Chrome OS 的理由——为了自由、自由、自由。
>
>
>
Chromebook 不但非常酷,而且极其便宜,它运行的操作系统是 Chrome OS ,这是一个基于 Linux 内核的操作系统,是由 Google 开发的。

不过,有时候你会发现 Chromebook 所运行的操作系统限制很多。因此,许多用户会在上面安装另外的 GNU/Linux 操作系统,要么是双引导,要么干脆就整个替换了 Chrome OS。已经有很多教程教你如何在你的 Chromebook 上以双引导方式安装一个 Linux 系统,不过,这篇指南将会介绍得更明白。
是的,没错,我们教你的是将 Chrome OS 替换成一个 GNU/Linux 发行版。当 Google 不再为你的 Chromebook 提供更新后,你需要决定是否将这个限制很多的操作系统换掉。这里,我们用一个完美的操作系统来替换,它就是刚刚成为滚动发行版的 Solus。
最妙的事情是,Solus 看起来很像 Chrome OS,而且不仅仅是看起来像而已,它能满足你的需求,同时提供了稳定、快捷和完整的功能。当然,下面的教程也适用于其他的发行版。
### 打开 Chrome OS 的开发者模式并用 USB 启动
在开始之前,我们需要提醒你一些事情。首先,如果你按照下面的教程来安装 GNU/Linux 发行版,这会擦除你的 Chrome OS 系统——但是你之后可以通过 Google 的支持网站提供的几种方式恢复。
其次,每次你需要使用你的新 Linux 系统时,你需要按下 `CTRL-L` 快捷键。
最后,你的 Chromebook 需要是 Intel 架构的,而不是 ARM 的,否则在一些 Chromebook 型号上你看不到任何启动引导器信息的。
我们在宏碁 C740 Chromebook 上测试了这篇教程。
首先第一件事情是你需要决定你要使用的 Linux 发行版是哪个,然后去下载最新的 ISO 镜像(需要确保它是一个带有图形桌面环境的 Live ISO),然后将其写入到一个 USB 存储棒上。做好之后将其插入到你的 Chromebook 上。
打开你的 Chromebook 盖子并关机,现在**按下不放**你的 Chromebook 上的 `ESC` 和 `Refresh` 键,然后**按下电源按钮几秒钟**,直到你看到一个警告屏幕。马上按下 `CTRL+D` 组合键来激活开发者模式,这可能需要几分钟。
当启用了开发者模式后,会要求你输入你的 Chrome OS 身份,然后所有数据都会同步回你的 Chromebook。这时,按下 `CTRL+ALT+T` 组合键来打开开发者模式终端,输入以下命令:
```
shell
```
并回车。现在输入以下命令:
```
sudo crossystem dev_boot_usb=1 dev_boot_legacy=1
```
并回车,确认你要安装的 Linux 发行版的 USB 存储棒一直插在你的 Chromebook 上。关机。重启,当你再次看到警告屏时,快速按下 `CTRL+L` 组合键以从 USB 进行引导。
### 从 USB 引导并安装 Linux 操作系统
现在 GNU/Linux 操作系统会从 USB 存储棒上加载,大概一到两分钟之后,你会看到实时会话。连接到互联网,并像你在其它计算机上一样正常安装该系统即可。当安装完成后,关机。移除 USB 存储棒之后重新开机,然后快速按下 `CTRL+L` 组合键。
你的新 GNU/Linux 发行版现在跑起来了!

再次补充一下,在我们的宏碁 C740 Chromebook 上,我们找不到 16位 x86 BIOS 的开源实现 SeaBIOS,所以不能在开机时选择引导设备,不过其它的 Chromebook 可能行。
如果你有任何问题,欢迎在下面留言。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,571 | 在 Ubuntu Mate 16.04 上通过 PPA 升级 Mate 1.14 | http://www.webupd8.org/2016/06/install-mate-114-in-ubuntu-mate-1604.html | 2016-07-14T07:41:00 | [
"MATE"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7571-1.html | Mate 桌面环境 1.14 现在可以在 Ubuntu Mate 16.04 ("Xenial Xerus") 上使用了。根据这个[发布版本](https://ubuntu-mate.org/blog/mate-desktop-114-for-xenial-xerus/)的描述,为了全面测试 Mate 1.14,所以 Mate 桌面环境 1.14 已经在 PPA 上发布 2 个月了。因此,你不太可能遇到安装的问题。

**现在 PPA 提供 Mate 1.14.1 包含如下改变(Ubuntu Mate 16.04 默认安装的是 Mate 1.12.x):**
* 客户端的装饰应用现在可以正确的在所有主题中渲染;
* 触摸板配置现在支持边缘操作和双指滚动;
* 在 Caja 中的 Python 扩展可以被单独管理;
* 所有三个窗口焦点模式都是可选的;
* Mate Panel 中的所有菜单栏图标和菜单图标可以改变大小;
* 音量和亮度 OSD 目前可以启用和禁用;
* 更多的改进和 bug 修改;
Mate 1.14 同时改进了整个桌面环境中对 GTK+ 3 的支持,包括各种 GTK+3 小应用。但是,Ubuntu MATE 的博客中提到:PPA 的发行包使用 GTK+ 2 编译是“为了确保对 Ubuntu MATE 16.04 还有各种各样的第三方 MATE 应用、插件、扩展的支持"。
MATE 1.14 的完整修改列表[点击此处](http://mate-desktop.com/blog/2016-04-08-mate-1-14-released/)阅读。
### 在 Ubuntu MATE 16.04 中升级 MATE 1.14.x
在 Ubuntu MATE 16.04 中打开终端,并且输入如下命令,来从官方的 Xenial MATE PPA 中升级最新的 MATE 桌面环境:
```
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:ubuntu-mate-dev/xenial-mate
sudo apt update
sudo apt dist-upgrade
```
**注意**: mate-netspeed 应用将会在升级中删除。因为该应用现在已经是 mate-applets 应用报的一部分,所以它依旧是可以使用的。
一旦升级完成,请重启你的系统,享受全新的 MATE!
### 如何回滚这次升级
如果你并不满意 MATE 1.14, 比如你遭遇了一些 bug 。或者你想回到 MATE 的官方源版本,你可以使用如下的命令清除 PPA,并且下载降级包。
```
sudo apt install ppa-purge
sudo ppa-purge ppa:ubuntu-mate-dev/xenial-mate
```
在所有的 MATE 包降级之后,重启系统。
参考: [Ubuntu MATE blog](https://ubuntu-mate.org/blog/mate-desktop-114-for-xenial-xerus/)
---
via: <http://www.webupd8.org/2016/06/install-mate-114-in-ubuntu-mate-1604.html>
作者:[Andrew](http://www.webupd8.org/p/about.html) 译者:[MikeCoder](https://github.com/MikeCoder) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | **MATE Desktop 1.14 is now available for Ubuntu MATE 16.04 (Xenial Xerus).**According to the release
[announcement](https://ubuntu-mate.org/blog/mate-desktop-114-for-xenial-xerus/), it took about 2 months to release MATE Desktop 1.14 in a PPA because everything has been well tested, so you shouldn't encounter any issues.
**The PPA currently provides MATE 1.14.1 (Ubuntu MATE 16.04 ships with MATE 1.12.x by default), which includes changes such as:**
- client-side decoration apps now render correctly in all themes;
- touchpad configuration now supports edge and two-finger scrolling independently;
- python extensions in Caja can now be managed separately;
- all three window focus modes are selectable;
- MATE Panel now has the ability to change icon sizes for menubar and menu items;
- volume and Brightness OSD can now be enabled/disabled;
- many other improvements and bug fixes.
MATE 1.14 also includes improved support for GTK+3 across the entire desktop, as well as various other GTK+3 tweaks however, the PPA packages are built with GTK+2 "
*to ensure compatibility with Ubuntu MATE 16.04 and all the 3rd party MATE applets, plugins and extensions*", mentions the Ubuntu MATE blog.A complete MATE 1.14 changelog can be found
[HERE](http://mate-desktop.com/blog/2016-04-08-mate-1-14-released/).
## Upgrade to MATE Desktop 1.14.x in Ubuntu MATE 16.04
**To upgrade to the latest MATE Desktop 1.14.x in Ubuntu MATE 16.04 using the official Xenial MATE PPA**, open a terminal and use the following commands:
```
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:ubuntu-mate-dev/xenial-mate
sudo apt update
sudo apt dist-upgrade
```
**Note:**mate-netspeed applet will be removed when upgrading. That's because the applet is now part of the mate-applets package, so it's still available.
Once the upgrade finishes, restart your system. That's it!
## How to revert the changes
If you're not satisfied with MATE 1.14, you encountered some bugs, etc., and you want to go back to the MATE version available in the official repositories, you can purge the PPA and downgrade the packages.
To do this, use the following commands:
```
sudo apt install ppa-purge
sudo ppa-purge ppa:ubuntu-mate-dev/xenial-mate
```
After all the MATE packages are downgraded, restart the system.
*via* |
7,573 | 如何在 Linux 上录制你的终端操作 | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-record-your-terminal-session-on-linux/ | 2016-07-14T09:05:39 | [
"终端",
"录制"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7573-1.html | 录制一个终端操作可能是一个帮助他人学习 Linux 、展示一系列正确命令行操作的和分享知识的通俗易懂方法。不管是出于什么目的,从终端复制粘贴文本需要重复很多次,而录制视频的过程也是相当麻烦,有时候还不能录制。在这次的文章中,我们将简单的了解一下以 gif 格式记录和分享终端会话的方法。
### 预先要求
如果你只是希望能记录你的终端会话,并且能在终端进行回放或者和他人分享,那么你只需要一个叫做:ttyrec 的软件。Ubuntu 用户可以通过运行这行代码进行安装:
```
sudo apt-get install ttyrec
```
如果你想将生成的视频转换成一个 gif 文件,这样能够和那些不使用终端的人分享,就可以发布到网站上去,或者你只是想做一个 gif 方便使用而不想写命令。那么你需要安装额外的两个软件包。第一个就是 imagemagick , 你可以通过以下的命令安装:
```
sudo apt-get install imagemagick
```
第二个软件包就是:tty2gif.py,访问其[项目网站](https://bitbucket.org/antocuni/tty2gif/raw/61d5596c916512ce5f60fcc34f02c686981e6ac6/tty2gif.py)下载。这个软件包需要安装如下依赖:
```
sudo apt-get install python-opster
```
### 录制
开始录制终端操作,你需要的仅仅是键入 `ttyprec` ,然后回车。这个命令将会在后台运行一个实时的记录工具。我们可以通过键入`exit`或者`ctrl+d`来停止。ttyrec 默认会在主目录下创建一个`ttyrecord`的文件。



### 回放
回放这个文件非常简单。你只需要打开终端并且使用 `ttyplay` 命令打开 `ttyrecord` 文件即可。(在这个例子里,我们使用 ttyrecord 作为文件名,当然,你也可以改成你用的文件名)

然后就可以开始播放这个文件。这个视频记录了所有的操作,包括你的删除,修改。这看起来像一个拥有自我意识的终端,但是这个命令执行的过程并不是只是为了给系统看,而是为了更好的展现给人。
注意一点,播放这个记录是完全可控的,你可以通过点击 `+` 或者 `-` 进行加速减速,或者 `0`和 `1` 暂停和恢复播放。
### 导出成 GIF
为了方便,我们通常会将视频记录转换为 gif 格式,并且,这个非常容易做到。以下是方法:
将之前下载的 tty2gif.py 这个文件拷贝到 ttyprecord 文件(或者你命名的那个视频文件)相同的目录,然后在这个目录下打开终端,输入命令:
```
python tty2gif.py typing ttyrecord
```
如果出现了错误,检查一下你是否有安装 python-opster 包。如果还是有错误,使用如下命令进行排除。
```
sudo apt-get install xdotool
export WINDOWID=$(xdotool getwindowfocus)
```
然后重复这个命令 `python tty2gif.py` 并且你将会看到在 ttyrecord 目录下多了一些 gif 文件。

接下来的一步就是整合所有的 gif 文件,将他打包成一个 gif 文件。我们通过使用 imagemagick 工具。输入下列命令:
```
convert -delay 25 -loop 0 *.gif example.gif
```

你可以使用任意的文件名,我用的是 example.gif。 并且,你可以改变这个延时和循环时间。 Enjoy。
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-record-your-terminal-session-on-linux/>
作者:[Bill Toulas](https://twitter.com/howtoforgecom) 译者:[MikeCoder](https://github.com/MikeCoder) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # How to record your terminal session on Linux
Recording a terminal session may be important in helping someone learn a process, sharing information in an understandable way, and also presenting a series of commands in a proper manner. Whatever the purpose, there are many times when copy-pasting text from the terminal won't be very helpful while capturing a video of the process is quite far-fetched and may not be always possible. In this quick guide, we will take a look at the easiest way to record and share a terminal session in .gif format.
## Prerequisites
If you just want to record your terminal sessions and be able to play the recording in your terminal, or share them with people who will use a terminal for playback, then the only tool that you'll need is called “ttyrec”. Ubuntu users may install it by inserting the following command on a terminal:
sudo apt-get install ttyrec
If you want to produce a .gif file from the recording and be able to share it with people who don't use the terminal, publish it on websites, or simply keep a .gif handy for when you'll need it instead of written commands, you will have to install two additional packages. The first one is “imagemagick” which you can install with:
sudo apt-get install imagemagick
and the second one is “tty2gif” which can be downloaded from here. The latter has a dependency that can be satisfied with:
sudo apt-get install python-opster
## Capturing
To start capturing the terminal session, all you need to do is simply start with “ttyrec” + enter. This will launch the real-time recording tool which will run in the background until we enter “exit” or we press “Ctrl+D”. By default, ttyrec creates a file named “ttyrecord” on the destination of the terminal session which by default is “Home”.
## Playing
Playing the file is as simple as opening a terminal on the destination of the “ttyrecord” file and using the “ttyplay” command followed by the name of the recording (in our case it's ttyrecord but you may change this into whatever you want).
This will result in the playback of the recorded session, in real-time, and with typing corrections included (all actions are recorded). This will look like a completely normal automated terminal session, but the commands and their apparent execution are obviously not really applied to the system, as they are only reproduced as a recording.
It is also important to note that the playback of the terminal session recording is completely controllable. You may double the playback speed by hitting the “+” button, slow it down with the “-” button, pause it with “0”, and resume it in normal speed with “1”.
## Converting into a .gif
For reasons of convenience, many of us would like to convert the recorded session into a .gif file, and that is very easy to do. Here's how:
First, untar the downloaded “tty2gif.tar.bz2” by opening a terminal in the download location and entering the following command:
tar xvfj tty2gif.tar.bz2
Next, copy the resulting “tty2gif.py file onto the destination of the “ttyrecord” file (or whatever the name you've specified is), and then open a terminal on that destination and type the command:
python tty2gif.py typing ttyrecord
If you are getting errors in this step, check that you have installed the “python-opster” package. If errors persist, give the following two commands consecutively:
sudo apt-get install xdotool
export WINDOWID=$(xdotool getwindowfocus)
then repeat the “python tty2gif.py typing ttyrecord ” and you should now see a number of gif files that were created on the location of the “ttyrecord”
The next step is to unify all these gifs that correspond to individual terminal session actions into one final .gif file using the imagemagick utility. To do this, open a terminal on the destination and insert the following command:
convert -delay 25 -loop 0 *.gif example.gif
You may name the resulting file as you like (I used “example.gif”), and you may change the delay and loop settings as needed. Here is the resulting file of this quick tutorial: |
7,574 | 微软发布新版 Skype Linux 客户端 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/microsoft-launches-new-skype-alpha-for-linux-506279.shtml | 2016-07-14T09:43:31 | [
"Skype",
"微软"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7574-1.html | 前两天,微软说要给“[Linux 用户带来一个令人兴奋的新闻](/article-7559-1.html)”,今天,这个新闻来了。它刚刚为 Linux 发布了一个新的 Skype 客户端。

此次发布,微软为 Linux 带来的 Skype 客户端与其 Windows 版本保持了一致,这包括相似的界面、支持文件和图片的分享,支持视频和表情符号等。
不过,目前该客户端还处于 Alpha 阶段,属于早期尝鲜版本。你可以通过它来与其它使用新版本 Skype 的朋友们沟通,无论他们使用的是 Windows、Mac、Android 还是 iOS,但是不能与使用旧版本 Linux 客户端的朋友聊天。
“我们开发了 Skype 的新版 Linux 客户端,需要大家来测试和提供反馈以帮助我们优化功能。你也许会注意到这个 Alpha 版本的客户端,使用了新一代的呼叫技术,它可以让你和使用最新版本的 Skype 的朋友家人聊天。”
微软期望得到社区的反馈,所以 Linux 用户们可以安装一下这个 Alpha 版本的客户端,以帮助改进它。
### 在 Linux 的浏览器中也可以使用 Skype
Linux 用户也可以在 Chrome 浏览器中通过网页使用 Skype,微软也发布了一个 Alpha 版本的网页版,可以让你不需要安装任何软件即可与使用 Skype 的朋友聊天。
微软说,视频聊天和拨通电话的功能也会加进来,但是还需要一点时间。目前在 Chromebook 和 Linux 下的 Chrome 浏览器中只支持基本的功能。
“基于 WebRTC 的 Skype 也是 Alpha 版本,其继承了同样是 Alpha 版本 Skype Linux 的客户端的相同功能。这是我们在微软 Edge 浏览器之外复制 ORTC 功能的首次尝试。因此,我们希望听到反馈以帮助我们在接下来的时间进一步改善它。”
Linux 用户可以在此下载 Linux 客户端,并反馈你遇到的问题,让微软可以进一步完善改进它。
### 下载
* [Skype for Linux 下载页面](https://community.skype.com/t5/Linux/bd-p/Linux?intcmp=blogs-_-generic-click-_-skype-for-linux-alpha-and-calling-on-chrome-and-chromebooks)
* Skype for Linux Alpha [DEB版](https://www.skype.com/en/download-skype/skype-for-linux/downloading-web/?type=weblinux-deb)
* Skype for Linux Alpha [RPM版](https://www.skype.com/en/download-skype/skype-for-linux/downloading-web/?type=weblinux-rpm)
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
7,575 | 如何隐藏你的 Linux 的命令行历史 | https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-command-line-history-incognito/ | 2016-07-14T14:46:00 | [
"命令行",
"历史"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7575-1.html | 
如果你是 Linux 命令行的用户,有的时候你可能不希望某些命令记录在你的命令行历史中。原因可能很多,例如,你在公司担任某个职位,你有一些不希望被其它人滥用的特权。亦或者有些特别重要的命令,你不希望在你浏览历史列表时误执行。
然而,有方法可以控制哪些命令进入历史列表,哪些不进入吗?或者换句话说,我们在 Linux 终端中可以开启像浏览器一样的无痕模式吗?答案是肯定的,而且根据你想要的具体目标,有很多实现方法。在这篇文章中,我们将讨论一些行之有效的方法。
注意:文中出现的所有命令都在 Ubuntu 下测试过。
### 不同的可行方法
前面两种方法已经在之前[一篇文章](https://www.maketecheasier.com/command-line-history-linux/)中描述了。如果你已经了解,这部分可以略过。然而,如果你不了解,建议仔细阅读。
#### 1. 在命令前插入空格
是的,没看错。在命令前面插入空格,这条命令会被 shell 忽略,也就意味着它不会出现在历史记录中。但是这种方法有个前提,只有在你的环境变量 `HISTCONTROL` 设置为 "ignorespace" 或者 "ignoreboth" 才会起作用。在大多数情况下,这个是默认值。
所以,像下面的命令(LCTT 译注:这里`[space]`表示输入一个空格):
```
[space]echo "this is a top secret"
```
如果你之前执行过如下设置环境变量的命令,那么上述命令不会出现在历史记录中。
```
export HISTCONTROL = ignorespace
```
下面的截图是这种方式的一个例子。

第四个 "echo" 命令因为前面有空格,它没有被记录到历史中。
#### 2. 禁用当前会话的所有历史记录
如果你想禁用某个会话所有历史,你可以在开始命令行工作前简单地清除环境变量 `HISTSIZE` 的值即可。执行下面的命令来清除其值:
```
export HISTSIZE=0
```
`HISTSIZE` 表示对于 bash 会话其历史列表中可以保存命令的个数(行数)。默认情况,它设置了一个非零值,例如在我的电脑上,它的值为 1000。
所以上面所提到的命令将其值设置为 0,结果就是直到你关闭终端,没有东西会存储在历史记录中。记住同样你也不能通过按向上的箭头按键或运行 history 命令来看到之前执行的命令。
#### 3. 工作结束后清除整个历史
这可以看作是前一部分所提方案的另外一种实现。唯一的区别是在你完成所有工作之后执行这个命令。下面是刚说到的命令:
```
history -cw
```
刚才已经提到,这个和 `HISTSIZE` 方法有相同效果。
#### 4. 只针对你的工作关闭历史记录
虽然前面描述的方法(2 和 3)可以实现目的,它们可以清除整个历史,在很多情况下,有些可能不是我们所期望的。有时候你可能想保存直到你开始命令行工作之间的历史记录。对于这样的需求,你开始在工作前执行下述命令:
```
[space]set +o history
```
备注:`[space]` 表示空格。并且由于空格的缘故,该命令本身也不会被记录。
上面的命令会临时禁用历史功能,这意味着在这命令之后你执行的所有操作都不会记录到历史中,然而这个命令之前的所有东西都会原样记录在历史列表中。
要重新开启历史功能,执行下面的命令:
```
[Space]set -o history
```
它将环境恢复原状,也就是你完成了你的工作,执行上述命令之后的命令都会出现在历史中。
#### 5. 从历史记录中删除指定的命令
现在假设历史记录中已经包含了一些你不希望记录的命令。这种情况下我们怎么办?很简单。直接动手删除它们。通过下面的命令来删除:
```
history | grep "part of command you want to remove"
```
上面的命令会输出历史记录中匹配的命令,每一条前面会有个数字。
一旦你找到你想删除的命令,执行下面的命令,从历史记录中删除那个指定的项:
```
history -d [num]
```
下面是这个例子的截图。

第二个 ‘echo’命令被成功的删除了。
(LCTT 译注:如果你不希望上述命令本身也被记录进历史中,你可以在上述命令前加个空格)
同样的,你可以使用向上的箭头一直往回翻看历史记录。当你发现你感兴趣的命令出现在终端上时,按下 “`Ctrl + U`”清除整行,也会从历史记录中删除它。
### 总结
有多种不同的方法可以操作 Linux 命令行历史来满足你的需求。然而请记住,从历史中隐藏或者删除命令通常不是一个好习惯,尽管本质上这并没有错。但是你必须知道你在做什么,以及可能产生的后果。
---
via: <https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-command-line-history-incognito/>
作者:[Himanshu Arora](https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/himanshu/) 译者:[chunyang-wen](https://github.com/chunyang-wen) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | If you’re a Linux command line user, you’ll agree that there are times when you do not want certain commands you run to be recorded in the command line history. There could be many reasons for this. For example, you’re at a certain position in your company, and you have some privileges that you don’t want others to abuse. Or, there are some critical commands that you don’t want to run accidentally while you’re browsing the history list.
But is there a way to control what goes into the history list and what doesn’t? Or, in other words, can we turn on a web browser-like incognito mode in the Linux command line? The answer is yes, and there are many ways to achieve this, depending on what exactly you want. In this article we will discuss some of the popular solutions available.
**Note**: all the commands presented in this article have been tested on Ubuntu.
## Different ways available
The first two ways we’ll describe here have already been covered in [one of our previous articles](https://www.maketecheasier.com/command-line-history-linux/). If you are already aware of them, you can skip over these. However, if you aren’t aware, you’re advised to go through them carefully.
### 1. Insert space before command
Yes, you read it correctly. Insert a space in the beginning of a command, and it will be ignored by the shell, meaning the command won’t be recorded in history. However, there’s a dependency – the said solution will only work if the HISTCONTROL environment variable is set to “ignorespace” or “ignoreboth,” which is by default in most cases.
So, a command like the following:
[space]echo "this is a top secret"
Won’t appear in the history if you’ve already done this command:
`export HISTCONTROL = ignorespace`
The below screenshot is an example of this behavior.
The fourth “echo” command was not recorded in the history as it was run with a space in the beginning.
### 2. Disable the entire history for the current session
If you want to disable the entire history for a session, you can easily do that by unsetting the HISTSIZE environment variable before you start with your command line work. To unset the variable run the following command:
export HISTFILE=0
HISTFILE is the number of lines (or commands) that can be stored in the history list for an ongoing bash session. By default, this variable has a set value – for example, 1000 in my case.
So, the command mentioned above will set the environment variable’s value to zero, and consequently nothing will be stored in the history list until you close the terminal. Keep in mind that you’ll also not be able to see the previously run commands by pressing the up arrow key or running the `history`
command.
### 3. Erase the entire history after you’re done
This can be seen as an alternative to the solution mentioned in the previous section. The only difference is that in this case you run a command AFTER you’re done with all your work. Thh following is the command in question:
history -cw
As already mentioned, this will have the same effect as the HISTFILE solution mentioned above.
### 4. Turn off history only for the work you do
While the solutions (2 and 3) described above do the trick, they erase the entire history, something which might be undesired in many situations. There might be cases in which you want to retain the history list up until the point you start your command line work. For situations like these you need to run the following command before starting with your work:
[space]set +o history
**Note**: [space] represents a blank space.
The above command will disable the history temporarily, meaning whatever you do after running this command will not be recorded in history, although all the stuff executed prior to the above command will be there as it is in the history list.
To re-enable the history, run the following command:
[Space]set -o history
This brings things back to normal again, meaning any command line work done after the above command will show up in the history.
### 5. Delete specific commands from history
Now suppose the history list already contains some commands that you didn’t want to be recorded. What can be done in this case? It’s simple. You can go ahead and remove them. The following is how to accomplish this:
[space]history | grep "part of command you want to remove"
The above command will output a list of matching commands (that are there in the history list) with a number [num] preceding each of them.
Once you’ve identified the command you want to remove, just run the following command to remove that particular entry from the history list:
history -d [num]
The following screenshot is an example of this.
The second ‘echo’ command was removed successfully.
Alternatively, you can just press the up arrow key to take a walk back through the history list, and once the command of your interest appears on the terminal, just press “Ctrl + U” to totally blank the line, effectively removing it from the list.
## Conclusion
There are multiple ways in which you can manipulate the Linux command line history to suit your needs. Keep in mind, however, that it’s usually not a good practice to hide or remove a command from history, although it’s also not wrong, per se, but you should be aware of what you’re doing and what effects it might have.
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox |
7,576 | 用 Netdata 监控 Linux | https://fedoramagazine.org/monitor-linux-netdata/ | 2016-07-15T08:27:00 | [
"Netdata",
"监控"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7576-1.html | 
Netdata 是一个实时的资源监控工具,它拥有基于 web 的友好界面,由 [FireHQL](https://firehol.org/) 开发和维护。通过这个工具,你可以通过图表来了解 CPU,RAM,硬盘,网络,Apache, Postfix 等软硬件的资源使用情况。它很像 Nagios 等别的监控软件;但是,Netdata 仅仅支持通过 Web 界面进行实时监控。
### 了解 Netdata
目前 Netdata 还没有验证机制,如果你担心别人能从你的电脑上获取相关信息的话,你应该设置防火墙规则来限制访问。UI 很简单,所以任何人看懂图形并理解他们看到的结果,至少你会对它的快速安装印象深刻。
它的 web 前端响应很快,而且不需要 Flash 插件。 UI 很整洁,保持着 Netdata 应有的特性。第一眼看上去,你能够看到很多图表,幸运的是绝大多数常用的图表数据(像 CPU,RAM,网络和硬盘)都在顶部。如果你想深入了解图形化数据,你只需要下滑滚动条,或者点击在右边菜单的项目。通过每个图表的右下方的按钮, Netdata 还能让你控制图表的显示,重置,缩放。

*Netdata 图表控制*
Netdata 并不会占用多少系统资源,它占用的内存不会超过 40MB。因为这个软件是作者用 C 语言写的。

*Netdata 显示的内存使用情况*
### 下载 Netdata
要下载这个软件,你可以访问 [Netdata 的 GitHub 页面](https://github.com/firehol/netdata),然后点击页面左边绿色的 "Clone or download" 按钮 。你应该能看到以下两个选项:
#### 通过 ZIP 文件下载
一种方法是下载 ZIP 文件。它包含仓库里的所有东西。但是如果仓库更新了,你需要重新下载 ZIP 文件。下载完 ZIP 文件后,你要用 `unzip` 命令行工具来解压文件。运行下面的命令能把 ZIP 文件的内容解压到 `netdata` 文件夹。
```
$ cd ~/Downloads
$ unzip netdata-master.zip
```

*解压 Netdata*
没必要在 unzip 命令后加上 `-d` 选项,因为文件都是放在 ZIP 文件的根文件夹里面。如果没有那个文件夹, unzip 会把所有东西都解压到当前目录下面(这会让文件非常混乱)。
#### 通过 Git 下载
还有一种方式是通过 git 下载整个仓库。当然,你的系统需要安装 git。Git 在 Fedora 系统是默认安装的。如果没有安装,你可以用下面的命令在命令行里安装 git。
```
$ sudo dnf install git
```
安装好 git 后,你要把仓库 “clone” 到你的系统里。运行下面的命令。
```
$ git clone https://github.com/firehol/netdata.git
```
这个命令会在当前工作目录克隆(或者说复制一份)仓库。
### 安装 Netdata
有些软件包是你成功构造 Netdata 时候需要的。 还好,一行命令就可以安装你所需要的东西([这写在它的安装文档中](https://github.com/firehol/netdata/wiki/Installation))。在命令行运行下面的命令就能满足安装 Netdata 需要的所有依赖关系。
```
$ dnf install zlib-devel libuuid-devel libmnl-devel gcc make git autoconf autogen automake pkgconfig
```
当所有需要的软件包都安装好了,你就 cd 到 netdata/ 目录,运行 netdata-installer.sh 脚本。
```
$ sudo ./netdata-installer.sh
```
然后就会提示你按回车键,开始安装程序。如果要继续的话,就按下回车吧。

*Netdata 的安装*
如果一切顺利,你的系统上就已经安装并且运行了 Netdata。安装脚本还会在相应的文件夹里添加一个卸载脚本,叫做 `netdata-uninstaller.sh`。如果你以后不想使用 Netdata,运行这个脚本可以从你的系统里面卸载掉 Netdata。
你可以通过 systemctl 查看它的运行状态。
```
$ sudo systemctl status netdata
```
### 使用 Netdata
既然我们已经安装并且运行了 Netdata,你就能够通过 19999 端口来访问 web 界面。下面的截图是我在一个测试机器上运行的 Netdata。

*关于 Netdata 运行时的概览*
恭喜!你已经成功安装并且能够看到漂亮的外观和图形,以及你的机器性能的高级统计数据。无论是否是你个人的机器,你都可以向你的朋友们炫耀,因为你能够深入的了解你的服务器性能,Netdata 在任何机器上的性能报告都非常出色。
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/monitor-linux-netdata/>
作者:[Martino Jones](https://fedoramagazine.org/monitor-linux-netdata/) 译者:[GitFuture](https://github.com/GitFuture) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Netdata is a real-time resource monitoring tool with a friendly web front-end developed and maintained by [FireHOL](https://firehol.org/). With this tool, you can read charts representing resource utilization of things like CPUs, RAM, disks, network, Apache, Postfix and more. It is similar to other monitoring software like Nagios; however, Netdata is only for real-time monitoring via a web interface.
## Understanding Netdata
There’s currently no authentication, so if you’re concerned about someone getting information about the applications you’re running on your system, you should restrict who has access via a firewall policy. The UI is simplified in a way anyone could look at the graphs and understand what they’re seeing, or at least be impressed by your flashy setup.
The web front-end is very responsive and requires no Flash plugin. The UI doesn’t clutter things up with unneeded features, but sticks to what it does. At first glance, it may seem a bit much with the hundreds of charts you have access to, but luckily the most commonly needed charts (i.e. CPU, RAM, network, and disk) are at the top. If you wish to drill deeper into the graphical data, all you have to do is scroll down or click on the item in the menu to the right. Netdata even allows you to control the chart with play, reset, zoom and resize with the controls on the bottom right of each chart.
When it comes down to system resources, the software doesn’t need too much either. The creators choose to write the software in C. Netdata doesn’t use much more than ~40MB of RAM.
## Download Netdata
To download this software, you can head over to [Netdata GitHub](https://github.com/firehol/netdata) page. Then click the “*Clone or download*” green button on the left of the page. You should then be presented with two options.
#### Via the ZIP file
One option is to download the ZIP file. This will include everything in the repository; however, if the repository is updated then you will need to download the ZIP file again. Once you download the ZIP file, you can use the
tool in the command line to extract the contents. Running the following command will extract the contents of the ZIP file into a ”
” folder.
$ cd ~/Downloads $ unzip netdata-master.zip
You don’t need to add the
option in
because their content is inside a folder at the root of the ZIP file. If they didn’t have that folder at the root,
would have extracted the contents in the current directory (which can be messy).
#### Via git
The next option is to download the repository via
. You will, of course, need git installed on your system. This is usually installed by default on Fedora. If not, you can install git from the command line with the following command.
$ sudo dnf install git
After installing
, you will need to “clone” the repository to your system. To do this, run the following command.
$ git clone[https://github.com/firehol/netdata.git]
This will then clone (or make a copy of) the repository in the current working directory.
## Install Netdata
There are some packages you will need to build Netdata successfully. Luckily, it’s a single line to install the things you need ([as stated in their installation guide](https://github.com/firehol/netdata/wiki/Installation)). Running the following command in the terminal will install all of the dependencies you need to use Netdata.
$ dnf install zlib-devel libuuid-devel libmnl-devel gcc make git autoconf autogen automake pkgconfig
Once the required packages are installed, you will need to
into the
directory and run the
script.
$ sudo ./netdata-installer.sh
You will then be prompted to press enter to build and install the program. If you wish to continue, press enter to be on your way!
If all goes well, you will have Netdata built, installed, and running on your system. The installer will also add an uninstall script in the same folder as the installer called
. If you change your mind later, running this script will remove it from your system.
You can see it running by checking its status via
.
$ sudo systemctl status netdata
## Accessing Netdata
Now that we have Netdata installed and running, you can access the web interface via port 19999. I have it running on a test machine, as shown in the screenshot below.
Congratulations! You now have successfully installed and have access to beautiful displays, graphs, and advanced statistics on the performance of your machine. Whether it’s for a personal machine so you can show it off to your friends or for getting deeper insight into the performance of your server, Netdata delivers on performance reporting for any system you choose.
*Image courtesy Mitchel Boot – originally posted to *
**Unsplash**here.
## Kiara Navarro
This is a really wonderful tool and I recommend to use it cause it’s worthy.
Thanks for share,
## Frank Ch. Eigler
“The web front-end is very responsive and requires no plugins like Flash or even JavaScript. ”
Might want to double-check on that. I only see a richly javascripty UI on the my-netdata.io demo pages.
## Paul W. Frields
@Frank: Thanks, I’ve edited that statement.
## Travis Mattila
The guide worked 99.99% for me, when i ran (sudo ./netdata-installed.sh) i got error messages (yes i have sudo enabled) to make it work i had to do su and then ran the .sh and it loaded.
Thanks for the guide, it was very clear and easy.
## Aaron Rumbold
There’s a typo in the installer line:
$ sudo ./netdata-installed.sh
## Edward
why not just systemctl enable cockpit
## Paul W. Frields
@Edward: Cockpit is also a great way to monitor system resources. The Magazine isn’t about only giving you one way to do things. We know there are many tools and utilities for some jobs, and try to show you more than one way to peel a potato.
## mosquito
Fast install netdata:
$ sudo dnf copr enable mosquito/netdata
$ sudo dnf install netdata
$ sudo systemctl start netdata.service
Visit http://localhost:19999
This Copr repository has supported el6, el7, fc22-25. Please see https://copr.fedorainfracloud.org/coprs/mosquito/netdata/
## Rafael Reuber
Hey mosquito, your repository is awesome! Its already have the last version of netdata.
Thank you for share!
## Tony Tyson
This is absolutely gorgeous.
## Tom Bates
Can’t access from my PC…. URL = http://192.168.0.19:19999/
I can access Cockpit… URL = https://192.168.0.19:9090/
I tried with https, no go….
Ideas?
## Paul W. Frields
Try these commands: |
7,578 | 使用 Vagrant 控制你的 DigitalOcean 云主机 | https://fedoramagazine.org/using-vagrant-digitalocean-cloud/ | 2016-07-15T17:08:07 | [
"Vagrant"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7578-1.html | 
[Vagrant](https://www.vagrantup.com/) 是一个使用虚拟机创建和支持虚拟开发环境的应用。Fedora 官方已经在本地系统上通过库 `libvirt` [支持 Vagrant](https://fedoramagazine.org/running-vagrant-fedora-22/)。[DigitalOcean](https://www.digitalocean.com/) 是一个提供一键部署 Fedora 云服务实例到全 SSD 服务器的云计算服务提供商。在[最近的 Raleigh 举办的 FAD 大会](https://communityblog.fedoraproject.org/fedora-cloud-fad-2016/)中,Fedora 云计算队伍为 Vagrant 打包了一个新的插件,它能够帮助 Fedora 用户通过使用本地的 Vagrantfile 文件来管理 DigitalOcean 上的云服务实例。
### 如何使用这个插件
第一步在命令行下是安装软件。
```
$ sudo dnf install -y vagrant-digitalocean
```
安装 结束之后,下一步是创建本地的 Vagrantfile 文件。下面是一个例子。
```
$ mkdir digitalocean
$ cd digitalocean
$ cat Vagrantfile
Vagrant.configure('2') do |config|
config.vm.hostname = 'dropletname.kushaldas.in'
# Alternatively, use provider.name below to set the Droplet name. config.vm.hostname takes precedence.
config.vm.provider :digital_ocean do |provider, override|
override.ssh.private_key_path = '/home/kdas/.ssh/id_rsa'
override.vm.box = 'digital_ocean'
override.vm.box_url = "https://github.com/devopsgroup-io/vagrant- digitalocean/raw/master/box/digital_ocean.box"
provider.token = 'Your AUTH Token'
provider.image = 'fedora-23-x64'
provider.region = 'nyc2'
provider.size = '512mb'
provider.ssh_key_name = 'Kushal'
end
end
```
### Vagrant DigitalOcean 插件的注意事项
一定要记住的几个关于 SSH 的关键命名规范 : 如果你已经在 DigitalOcean 上传了秘钥,请确保 `provider.ssh_key_name` 和已经在服务器中的名字吻合。 `provider.image` 具体的文档可以在[DigitalOcean documentation](https://developers.digitalocean.com/documentation/v2/#create-a-new-droplet)找到。在控制面板上的 `App & API` 部分可以创建 AUTH 令牌。
你可以使用下面的命令启动一个实例。
```
$ vagrant up --provider=digital_ocean
```
这个命令会在 DigitalOcean 的启动一个服务器实例。然后你就可以使用 `vagrant ssh` 命令来 `ssh` 登录进入这个实例。可以执行 `vagrant destroy` 来删除这个实例。
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/using-vagrant-digitalocean-cloud/>
作者:[Kushal Das](http://kushal.id.fedoraproject.org/) 译者:[MikeCoder](https://github.com/MikeCoder) 校对:[Ezio](https://github.com/oska874)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | [Vagrant](https://www.vagrantup.com/) is an application to create and support virtual development environments using virtual machines. Fedora has [official support for Vagrant](https://fedoramagazine.org/running-vagrant-fedora-22/) with
on your local system. [DigitalOcean](https://www.digitalocean.com/) is a cloud provider that provides a one-click deployment of a Fedora Cloud instance to an all-SSD server in under a minute. During the [recent Cloud FAD](https://communityblog.fedoraproject.org/fedora-cloud-fad-2016/) in Raleigh, the Fedora Cloud team packaged a new plugin for Vagrant which enables Fedora users to keep up cloud instances in DigitalOcean using local Vagrantfiles.
## How to use this plugin
First step is to install the package in the command line.
$ sudo dnf install -y vagrant-digitalocean
After installing the plugin, the next task is to create the local Vagrantfile. An example is provided below.
$ mkdir digitalocean $ cd digitalocean $ cat Vagrantfile Vagrant.configure('2') do |config| config.vm.hostname = 'dropletname.kushaldas.in' # Alternatively, use provider.name below to set the Droplet name. config.vm.hostname takes precedence. config.vm.provider :digital_ocean do |provider, override| override.ssh.private_key_path = '/home/kdas/.ssh/id_rsa' override.vm.box = 'digital_ocean' override.vm.box_url = "https://github.com/devopsgroup-io/vagrant- digitalocean/raw/master/box/digital_ocean.box" provider.token = 'Your AUTH Token' provider.image = 'fedora-23-x64' provider.region = 'nyc2' provider.size = '512mb' provider.ssh_key_name = 'Kushal' end end
## Notes about Vagrant DigitalOcean plugin
A few points to remember about the SSH key naming scheme: if you already have the key uploaded to DigitalOcean, make sure that the
matches the name of the existing key in their server. The
details are found at the [DigitalOcean documentation](https://developers.digitalocean.com/documentation/v2/#create-a-new-droplet). The AUTH token is created on the control panel within the Apps & API section.
You can then get the instance up with the following command.
$ vagrant up --provider=digital_ocean
This command will fire up the instance in the DigitalOcean server. You can then SSH into the box by using
command. Run
to destroy the instance. |
7,579 | 用树莓派计算模块搭建的工业单板计算机 | http://hackerboards.com/industrial-sbc-builds-on-rpi-compute-module/ | 2016-07-15T17:43:40 | [
"树莓派",
"SBC",
"COM"
] | https://linux.cn/article-7579-1.html | 在 Kickstarter 众筹网站上,一个叫 “MyPi” 的项目用树莓派计算模块制作了一款 SBC(<ruby> 单板计算机 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Single Board Computer </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>),提供一个 mini-PCIe 插槽,串口,宽范围输入电源,以及模块扩展等功能。
你也许觉得奇怪,都 2016 年了,为什么还会有人发布这样一款长得有点像三明治,用过时的 ARM11 构建的 COM (<ruby> 模块化计算机 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Compuer on Module </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)版本的树莓派单板计算机:[树莓派计算模块](http://hackerboards.com/raspberry-pi-morphs-into-30-dollar-com/)。原因是这样的,首先,目前仍然有大量工业应用不需要太多 CPU 处理能力,第二,树莓派计算模块仍是目前仅有的基于树莓派硬件的 COM,虽然更便宜、有点像 COM 并采用同样的 700MHz 处理器的 [零号树莓派](http://hackerboards.com/pi-zero-tweak-adds-camera-connector-keeps-5-price/) 也很类似。

*安装了 COM 和 I/O 组件的 MyPi*

*装入了可选的工业外壳中*
另外,Embedded Micro Technology 还表示它的 SBC 还设计成可升级替换为支持的树莓派计算模块 —— 采用了树莓派 3 的四核、Cortex-A53 博通 BCM2837处理器的 SoC。因为这个产品最近很快就会到货,不确定他们怎么能及时为 Kickstarter 赞助者处理好这一切。不过,以后能支持也挺不错,就算要为这个升级付费也可以接受。
MyPi 并不是唯一一款新的基于树莓派计算模块的商业嵌入式设备。Pigeon Computers 在五月份启动了 [Pigeon RB100](http://hackerboards.com/automation-controller-runs-linux-on-raspberry-pi-com/) 的项目,是一个基于 COM 的工业自动化控制器。不过,包括 [Techbase Modberry](http://hackerboards.com/automation-controller-taps-raspberry-pi-compute-module/) 在内的这一类设备大都出现在 2014 年 COM 发布之后的一小段时间内。
MyPi 的目标是 30 天内筹集 $21,696,目前已经实现了三分之一。早期参与包的价格 $119 起,九月份发货。其他选项有 $187 版本,里面包含了价值 $30 的树莓派计算模块,以及各种线缆。套件里还有各种插件板以及工业外壳可选。

*不带 COM 和插件板的 MyPi 主板*

*以及它的接口定义*
树莓派计算模块能给 MyPi 带来博通 BCM2835 Soc,512MB 内存,以及 4GB eMMC 存储空间。MyPi 主板扩展了一个 microSD 卡槽,一个 HDMI 接口,两个 USB 2.0 接口,一个 10/100M 以太网口,还有一个像网口的 RS232 端口(通过 USB 连接)。

*插上树莓派计算模块和 mini-PCIe 模块的 MyPi 的两个视角*

*插上树莓派计算模块和 mini-PCIe 模块的 MyPi 的两个视角*
MyPi 还将配备一个 mini-PCIe 插槽,据说“只支持 USB,以及只适用 mPCIe 形式的调制解调器”。还带有一个 SIM 卡插槽。板上还有双标准的树莓派摄像头接口,一个音频输出接口,自带备用电池的 RTC,LED 灯。还支持宽范围的 9-23V 直流输入。
Embedded Micro 表示,MyPi 是为那些树莓派爱好者们设计的,他们拼接了太多 HAT 外接板,已经不能有效地工作了,或者不能很好地装入工业外壳里。MyPi 支持 HAT,另外还提供了公司自己定义的 “ASIO” (特定应用接口)插件模块,它会将自己的 I/O 扩展到载板上,载板再将它们连到载板边上的 8针的绿色凤凰式工业 I/O 连接器(标记了“ASIO Out”)上,在下面图片里有描述。

*MyPi 的模块扩展接口*
就像 Kickstarter 页面里描述的:“比起在板边插满带 IO 信号接头的 HAT 板,我们更愿意把同样的 IO 信号接到另一个接头,它直接接到绿色的工业接头上。” 另外,“通过简单地延长卡上的插脚长度(抬高),你将来可以直接扩展 IO 集 - 这些都不需要任何排线!”Embedded Micro 表示。

*MyPi*

*它的可选 I/O 插件板卡*
像上面展示的,这家公司为 MyPi 提供了一系列可靠的 ASIO 插卡,。一开始这些会包括 CAN 总线,4-20mA 传感器信号,RS485,窄带 RF,等等。
### 更多信息
MyPi 在 Kickstarter 上提供了 7 月 23 日到期的 79 英镑($119)早期参与包(不包括树莓派计算模块),预计九月份发货。更多信息请查看 [Kickstarter 上 MyPi 的页面](https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/410598173/mypi-industrial-strength-raspberry-pi-for-iot-proj) 以及 [Embedded Micro Technology 官网](http://www.embeddedpi.com/)。
---
via: <http://hackerboards.com/industrial-sbc-builds-on-rpi-compute-module/>
作者:[Eric Brown](http://hackerboards.com/industrial-sbc-builds-on-rpi-compute-module/) 译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[Ezio](https://github.com/oska874)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.