full_name
stringlengths 9
72
| url
stringlengths 28
91
| description
stringlengths 3
343
⌀ | readme
stringlengths 1
207k
|
|---|---|---|---|
magiklabs/magik-sdk
|
https://github.com/magiklabs/magik-sdk
|
LLM Testing SDK that helps you write and run tests to monitor your LLM app in production
|
_Magik is an LLM output testing SDK + observability platform that helps you write tests and monitor your app in production_.
<br /><br />
# Overview
Reliability of output is one of the biggest challenges for people trying to use LLM apps in production.<br />
Since LLM outputs are non-deterministic, it’s very hard to measure how good the output is.
Eyeballing the responses from an LLM can work in development, but it’s not a great solution.
> _In production, it’s virtually impossible to eyeball thousands of responses. Which means you have very little visibility into how well your LLM is performing._
- Do you know when your LLM app is hallucinating?
- How do you know how well it's _really_ performing?
- Do you know how often it’s producing a critically bad output?
- How do you know what your users are seeing?
- How do you measure how good your LLM responses are? And if you can’t measure it, how do you improve the accuracy?
<br />
> If these sound like problems to you (today or in the future), please reach out to us at [email protected]. We’d love to hear more!
<img width="1576" alt="llm-screenshot-1" src="https://github.com/magiklabs/magik-sdk/assets/7515552/bc87aefa-505f-4732-84cd-b7fe57857850">
<br /><br /><br />
# Documentation
`pip install magik`
See https://docs.magiklabs.app for instructions on how to write and run tests.
- [Overview](https://docs.magiklabs.app/)
- [Quick Start](https://docs.magiklabs.app/quick-start)
- [Writing Tests](https://docs.magiklabs.app/reference/writing-tests)
- [Evaluator Functions](https://docs.magiklabs.app/reference/writing-tests/evaluator-functions)
- [What kind of tests can I write](https://docs.magiklabs.app/reference/writing-tests/what-kind-of-tests-can-i-write)
- [How does the LLM grader work?](https://docs.magiklabs.app/reference/writing-tests/how-does-the-llm-grader-work)
- [Running Tests](https://docs.magiklabs.app/reference/running-tests)
- [Deploying Tests](https://docs.magiklabs.app/reference/deploying-tests)
- [Logging your production data](https://docs.magiklabs.app/reference/logging-your-production-data)
<br />
# Use Cases
Who is this product meant for?
- If you're in the early stages of building an LLM app:
- If you have an LLM app in production
<br /><br />
### If you're in the early stages of building an LLM app:
---
Test-driven development can speed up your development very nicely, and can help you engineer your prompts to be more robust.
For example, assuming your prompt looks like this:
```
Create some marketing copy for a tweet of less than 280 characters for my app {app_name}.
My app helps people generate sales emails using AI.
Make sure the marketing copy contains a complete and valid link to my app.
Here is the link to my app: https://magiklabs.app.
```
You can write tests like this:
```python
from magik.evaluators import (
contains_none,
contains_link,
contains_valid_link,
is_positive_sentiment,
length_less_than,
)
# Local context - this is used as the "ground truth" data that you can compare against in your tests
test_context = {}
# Define tests here
def define_tests(context: dict):
return [
{
"description": "output contains a link",
"eval": contains_link(),
"prompt_vars": {
"app_name": "Uber",
},
"failure_labels": ["bad_response_format"],
},
{
"description": "output contains a valid link",
"eval": contains_valid_link(),
"prompt_vars": {
"app_name": "Magik",
},
"failure_labels": ["bad_response_format"],
},
{
"description": "output sentiment is positive",
"eval": is_positive_sentiment(),
"prompt_vars": {
"app_name": "Lyft",
},
"failure_labels": ["negative_sentiment"],
},
{
"description": "output length is less than 280 characters",
"eval": length_less_than(280),
"prompt_vars": {
"app_name": "Facebook",
},
"failure_labels": ["negative_sentiment", "critical"],
},
{
"description": "output does not contain hashtags",
"eval": contains_none(['#']),
"prompt_vars": {
"app_name": "Datadog",
},
"failure_labels": ["bad_response_format"],
},
]
```
<br /><br />
### If you have an LLM app in production:
---
You can use our **evaluation & monitoring platform** to:
- Observe the prompt, response pairs in production, and analyze response times, cost, token usage, etc for different prompts and date ranges.
- Evaluate your production responses against your own tests to get a quantifiable understanding of how well your LLM app is performing.
- For example, You can run the tests you defined against the LLM responses you are getting in production to measure how your app is performing with real data.
- Filter by failure labels, severity, prompt, etc to identify different types of errors that are occurring in your LLM outputs.
See https://magiklabs.app for more details, or contact us at [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected])
<br /><br />
### Upcoming Features
---
Soon, you will also be able to:
- Fail bad outputs before they get to your users.
- For example, if the LLM response contains sensitive information like PII, you can detect that in real-time, and cut it off before it reaches the end user.
- Set up alerts to notify you about critical errors in production.
<br /><br />
# Platform
Contact us at [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected]) to get access to our LLM observability platform where you can run the tests you've defined here against your LLM responses in production.
|
nicknochnack/Falcon40B
|
https://github.com/nicknochnack/Falcon40B
| null |
# Using Falcon40B Instruct...and any other Open Source LLMs on GPU via HuggingFace
In this tutorial we're going to be checking out some of the biggest baddest LLMs...but running them on a GPU!
## See it live and in action 📺
[](https://youtu.be/hMJgdVJWQRU 'Tutorial')
# Startup 🚀
1. Create a virtual environment `python -m venv gpullm`
2. Activate it:
- Windows:`.\gpullm\Scripts\activate`
- Mac: `source gpullm/bin/activate`
3. Install PyTorch with CUDA Support
N.B. I've included the lib in the requirements.txt file but this is latest installer as of creating this readme.
`pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu117`
Download and install CUDA (i've used 11.7 for this tutorial): https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-11-7-0-download-archive
Download and install the matching cuDNN version ( v8.9.1): https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/cudnn-archive
5. Clone this repo `git clone https://github.com/nicknochnack/Falcon40B`
6. Go into the directory `cd Falcon40B`
7. Startup jupyter by running `jupyter lab` in a terminal or command prompt
8. Hit `Ctrl + Enter` to run through the notebook!
10. Go back to my YouTube channel and like and subscribe 😉...no seriously...please! lol
# Other References 🔗
<p>-<a href="https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/">PyTorch Installation</a>:main guide leveraged to handle GPU support.</p>
<p>-<a href="https://python.langchain.com/en/latest/modules/models/llms/integrations/huggingface_pipelines.html">Langchain HF Pipelines</a>:the HF Pipelines class is used in order to pass the local LLM to a chain.</p>
<p>-<a href="https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-40b-instruct">Falcon 40B Instruct Model Card</a>:check out the model details.</p>
# Who, When, Why?
👨🏾💻 Author: Nick Renotte <br />
📅 Version: 1.x<br />
📜 License: This project is licensed under the MIT License </br>
|
muazkadan/switchy-compose
|
https://github.com/muazkadan/switchy-compose
| null |
# Switchy-compose
[](https://jitpack.io/#muazkadan/switchy-compose)
SwitchyCompose is an Android library that helps you to easily create a custom Switches.
## Preview
<img src="/preview/switchy_compose_preview.gif" width="300" >
## Installation
Add the jitpack.io repository:
```groovy
allprojects {
repositories {
jcenter()
maven { url "https://jitpack.io" }
}
}
```
and the dependency
```groovy
dependencies {
implementation "com.github.muazkadan:switchy-compose:Tag:$version"
}
```
## Usage
TextSwitch
```kotlin
var switchValue by rememberSaveable { mutableStateOf(false) }
TextSwitch(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(horizontal = 16.dp),
switchValue = switchValue,
onValueChanged = {
switchValue = it
},
)
```
ColoredSwitch
```kotlin
var switchValue by rememberSaveable { mutableStateOf(false) }
ColoredSwitch(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(horizontal = 16.dp),
switchValue = switchValue,
onValueChanged = {
switchValue = it
},
)
```
ISwitch
```kotlin
var switchValue by rememberSaveable { mutableStateOf(false) }
ISwitch(
switchValue = switchValue,
onValueChanged = {
switchValue = it
},
)
```
IconISwitch
```kotlin
var switchValue by rememberSaveable { mutableStateOf(false) }
IconISwitch(
switchValue = switchValue,
onValueChanged = {
switchValue = it
},
)
```
Also, you can customize your own switch or iswitch. Check the demo project for more information.
### License
Copyright 2023 Muaz KADAN
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
|
VoltaireNoir/markd
|
https://github.com/VoltaireNoir/markd
|
Bookmark directories for easy directory-hopping in the terminal
|
<div align="center">
[](https://github.com/VoltaireNoir/markd/actions/workflows/rust.yml)
[](https://crates.io/crates/markd)
[](https://crates.io/crates/markd)

</div>
# markd
Bookmark directories for easy directory-hopping in the terminal.

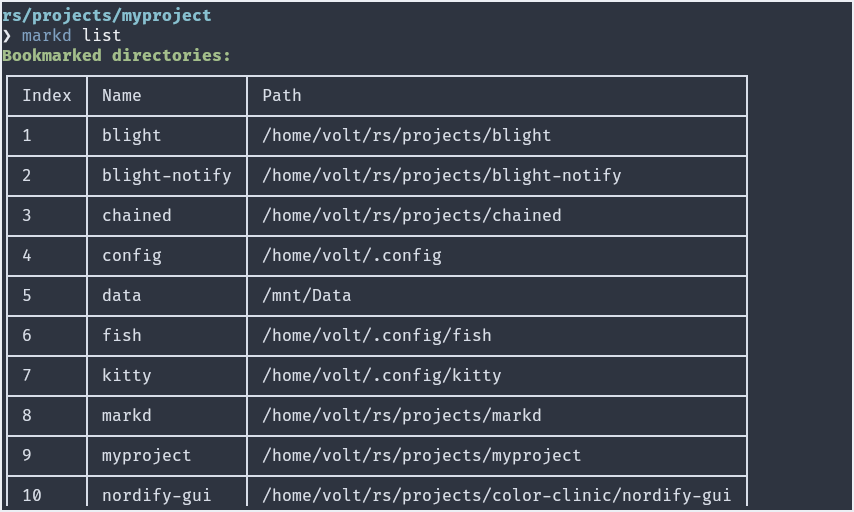
All it takes is one command `markd` to bookmark your current directory, or use the `-p / --path` to specify custom path and `-a / --alias` to set a custom bookmark name. The CLI tool also provides the necessary functionality to search and clean your bookmarks. For example, the `purge` command will check all the paths and remove the ones that no longer exist, and the `list` command supports `--filter`, `--start` and `--end` for advanced searching.
All paths are ensured to be valid ones, relative paths are stored in their expanded forms and names are always lowercase. No duplicate names are allowed (use an alias instead).
Run `markd help` for a full list of supported commands and arguments. Run `markd <COMMAND> --help` to get more info on the command.
> Note: bookmarks are stored in `bookmarks.json` file in the user home directory in the form of `"name":"path"`, which can also be directly edited if necessary.
## Shell Support
Since 'cd' is a built-in shell command, you need to use 'command substitution' to make use of markd to switch directories.
To make it work, simply add a function definition to your shell config file. After adding the necessary code to your shell config, you should be able to jump between directories using the command `goto <bookmark-name>`.
> Note: The function name used here is 'goto' but you can change it to whatever you prefer.
### Fish
- Create a `functions` directory in fish config folder (usually `/home/user/.config/fish`)
- Inside the folder, create a file named `goto.fish`
- Copy and paste the following code and save it
```
function goto
cd $(markd g $argv)
end
```
### Zsh and Bash
- Add the following code to your `.zshrc` or `.bashrc`
```
goto() {
cd $(markd g $1);
}
```
### Powershell (untested)
- Open powershell and open your config file by running `notepad $profile`
- Add the following code and save it
```
function goto([string]$Bookmark) {
cd (markd g $Bookmark)
}
```
## Install
- Using cargo: `cargo install markd`, ensure `$HOME/.cargo/bin` is in path.
- Pre-built binary: download the appropriate pre-built binary from the release section, place the binary in path.
|
as946640/flutter_webrtc_deom
|
https://github.com/as946640/flutter_webrtc_deom
|
flutter 端的 webrtc 基础模板,已经基本完善了推拉流,切换摄像头、分辨率,可实现一人推流多人拉流实现会议功能
|
# flutter_webrtc_demo
这是一个 webrtc 的模板项目,大家拿去即可直接使用
基于 dio、get、flutter_webrtc 插件
后端是 srs :https://github.com/ossrs/srs
帮助到大家的话 请给一个 star,支持开源
项目预览

|
simonw/asgi-proxy-lib
|
https://github.com/simonw/asgi-proxy-lib
|
An ASGI function for proxying to a backend over HTTP
|
# asgi-proxy-lib
[](https://pypi.org/project/asgi-proxy-lib/)
[](https://github.com/simonw/asgi-proxy-lib/releases)
[](https://github.com/simonw/asgi-proxy-lib/blob/main/LICENSE)
An ASGI function for proxying to a backend over HTTP
**⚠️ Warning: this is an early alpha.**
## Installation
Install this library using `pip`:
pip install asgi-proxy-lib
## Usage
This library provides a single ASGI function called `asgi_proxy`. You can use it like this:
```python
from asgi_proxy import asgi_proxy
app = asgi_proxy("https://datasette.io")
```
Now `app` is an ASGI application that will proxy all incoming HTTP requests to the equivalent URL on `https://datasette.io`.
The function takes an optional second argument, `log=` - set this to a Python logger, or any object that has `.info(msg)` and `.error(msg)` methods, and the proxy will log information about each request it proxies.
## CLI tool
You can try this module out like so:
```bash
python -m asgi_proxy https://datasette.io
```
You may need to `pip install uvicorn` first for this to work.
This will start a server on port 8000 that proxies to `https://datasette.io`.
Add `-p PORT` to specify a different port, `--verbose` to see debug logging, and `--host 127.0.0.1` to listen on a different host (the default is `0.0.0.0`).
## Development
To contribute to this library, first checkout the code. Then create a new virtual environment:
cd asgi-proxy-lib
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
Now install the dependencies and test dependencies:
pip install -e '.[test]'
To run the tests:
pytest
|
mmrobotlab/DailyRobot
|
https://github.com/mmrobotlab/DailyRobot
| null |
# MM-RobotLab 日报
- 本次更新包括了7月4日前精选出的 3 篇 LLM+Robotics+Multi-modal的相关研究文章,所有文章由chatgpt自动筛选,自动生成文章总结,最后由MM-RobotLab社区筛选出质量最高的并进行人工优化。
# P:1 在强化学习中学习调节预训练模型
- 1. Title: Learning to Modulate pre-trained Models in RL
- 2. 论文简介: 该论文由Thomas Schmied等人在ELLIS Unit Linz and LIT AI Lab, Institute for Machine Learning进行研究,提出了一种名为Learning-to-Modulate (L2M)的方法,用于解决强化学习中预训练模型在新任务上适应性不足的问题。
- 3. Authors: Thomas Schmied, Markus Hofmarcher, Fabian Paischer, Razvan Pascanu, Sepp Hochreiter
- 4. Affiliation:
ELLIS Unit Linz and LIT AI Lab, Institute for Machine Learning (奥地利林茨约翰内斯·开普勒大学)
- 5. Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, pre-training, fine-tuning, catastrophic forgetting, Learning-to-Modulate
- 6. Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.14884) Github: None
- 7. 论文总结:
* (1): 该论文的研究背景是强化学习中预训练模型在新任务上适应性不足的问题。
* (2): 过去的方法包括大规模预训练和微调,但往往会导致预训练任务的性能下降。本文提出了一种名为Learning-to-Modulate (L2M)的方法,通过学习可调节的调制池来避免学习技能的退化,从而解决了这个问题。
* (3): 本文提出的L2M方法通过学习可调节的调制池(modulation pool),以一种任务无关的方式高效地调整预训练模型,从而适应新任务。该方法在Continual-World基准测试上取得了最先进的性能,并保持了对预训练任务的性能。
* (4): 本文在Meta-World和DMControl上进行了广泛的评估,比较了多种微调方法的性能,并展示了L2M方法在新任务上的优越性能以及对预训练任务的保持能力。该方法的创新点在于通过学习可调节的调制池来避免学习技能的退化,并且相对于完整模型大小,只引入了很少的额外参数。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍:
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一种名为Learning-to-Modulate (L2M)的方法,通过可学习的调制池来调节预训练模型的信息流,以避免在新任务上学习时导致预训练任务性能下降。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
* (1). 提出Learning-to-Modulate (L2M)方法,该方法结合了参数高效微调和基于提示的调优方法的优点。
* (2). 维护一个调制池,其中包含一组$M$个键,每个键与一组调制矩阵相关联,用于调制预训练模型。
* (3). 对于给定的输入序列,通过查询池中的键,检索出与当前时间步的查询向量最相似的调制矩阵。
* (4). 使用检索到的调制矩阵来调节预训练模型,以改变其行为。
* (5). 使用梯度下降法学习调制模块的权重,同时保持预训练模型冻结。
* (6). 更新键的方法是通过最大化查询向量和键之间的余弦相似度来更新键。
* (7). Learning-to-Modulate (L2M)方法通过保持预训练任务的性能,同时实现高性能和少量可学习参数,提供了一种简单的任务匹配机制,并能够适应大量任务。
* (8). 扩展了Decision Transformer架构,以处理来自具有不同状态/动作空间的多个领域的输入。
* (9). 构建了一个统一的状态空间,包括所有DMControl和Meta-World环境的维度,并使用线性层对状态进行嵌入。
* (10). 对每个动作维度进行分词,并自回归地预测动作标记。
* (11). 使用返回条件的反向强化学习通过交叉熵损失训练Decision Transformer。
* (12). 通过最大观察到的回报设置目标回报,或者使用每个领域的常数代理。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文的实验设置如下:
* (1). 本文考虑了两个不同的基准套件(Meta-World和DMControl),共包含66个不同的任务。
* (2). Meta-World包含50个多样化的机器人操作任务,如抓取、操纵物体、打开/关闭窗户、按按钮、锁定/解锁门和投篮等。DMControl包含16个任务,机器人形态各异,因此状态表示差异较大。
* (3). 通过训练基于Soft Actor Critic (SAC)的任务特定智能体来收集数据集。Meta-World的数据集包含了每个任务的10K个长度为200的轨迹,总共100M个转换。DMControl的数据集包含了每个任务的1000个长度为1000的轨迹,总共16M个转换。
* (4). 评估了各种微调方法在新任务上的性能,并比较了在微调过程中对预训练任务性能的保留程度。
* (5). 在Continual-World基准测试中,L2M方法取得了最先进的性能,并保持了对预训练任务的性能。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
本研究首先在Meta-World和DMControl两个基准套件的数据集上进行了联合预训练,并评估了多种在自然语言处理中常见的微调方法在新任务上的性能以及对预训练任务性能的保留情况。实验结果表明,大多数微调方法在预训练任务上的性能明显下降。因此,研究提出了一种新的方法,即Learning-to-Modulate (L2M),通过可学习的调制池来调节冻结的预训练模型的信息流,避免了学习技能的退化。该方法在Continual-World基准测试中取得了最先进的性能,并保持了对预训练任务的性能。此外,研究还发布了一个包含50个Meta-World任务和16个DMControl任务的数据集,以促进未来的研究。
具体实验结果如下:
1. 在CW10和DMC6上,FT方法的性能最好,Adapters方法的性能次之,LoRA、 $\text{(IA)}^3$ 和FT-last+head方法的性能较好。PBT和PEFT方法之间存在较大的性能差距,尤其在MT40上。在DMC6上,全面微调和PEFT方法之间的性能差距更大。
2. 在CW10和DMC6上,L2M方法的性能优于其他方法,平均成功率分别为65%和43%。添加任务oracle到L2M方法可以将成功率提高到76%和75%。L2P结合不同的提示方法的性能明显低于L2M。传统的连续强化学习方法EWC在减轻遗忘方面效果不佳。
3. 在微调后评估预训练任务的性能时,FT、L2和EWC方法的性能严重下降,而L2M和L2P方法在微调前后保持了类似的性能水平。
总结起来,本研究通过实验结果验证了Learning-to-Modulate (L2M)方法在连续强化学习任务中的有效性,该方法在新任务上取得了最先进的性能,并保持了对预训练任务的性能。同时,研究还对其他微调方法进行了比较和分析,为未来的研究提供了有价值的数据集。
# P:2 通过源准备增强视觉域自适应
- 1. Title: Enhancing Visual Domain Adaptation with Source Preparation
- 2. 论文简介: 该论文由卡内基梅隆大学的Anirudha Ramesh等人提出,通过提出源准备(Source Preparation)方法,综合考虑源域的特征,解决了机器人感知在低光环境中的挑战。
- 3. Authors: Anirudha Ramesh, Anurag Ghosh, Christoph Mertz, Jeff Schneider
- 4. Affiliation: 卡内基梅隆大学
- 5. Keywords: Robotic Perception, Domain Adaptation, Source Preparation, Unsupervised Domain Adaptation, Supervised Alignment
- 6. Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.10142) Github: None
- 7. 论文总结:
* (1): 该论文的研究背景是机器人在低光环境中的感知问题。
* (2): 过去的方法包括无监督域自适应和半监督域自适应,但它们没有考虑源域本身的特征,导致源模型对源域特征过拟合。本文提出了源准备方法来解决这个问题,并提出了Almost Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (AUDA)框架。
* (3): 本文的研究方法是综合考虑源域特征的源准备方法,并结合无监督域自适应和有限标记数据的监督对齐来实现有效的域自适应。该方法在语义分割任务中取得了显著的性能提升,并且在目标域内具有鲁棒性。
* (4): 本文的方法在语义分割任务中取得了显著的性能提升,mIoU相对于基线提高了最多40.64%。同时,该方法只需要使用目标域的少量标记样本就能显著提高目标域的性能,具有较高的标记效率。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍:
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一种增强视觉领域适应性的方法,通过源域准备(Source Preparation)来减轻源域偏差,结合无监督域适应(Unsupervised Domain Adaptation)和有限标记数据的监督对齐(Supervised Alignment),实现了在低光环境下的语义分割和目标检测任务中的有效领域自适应(Domain Adaptation)。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
* (1). 首先,定义源域 $S$ 和目标域 $T$,其中 $S$ 具有丰富的标记数据,而 $T$ 的标记数据有限或没有。目标是在 $T$ 上构建一个性能良好的模型。为了验证方法的有效性,本文以语义分割为例,使用现有的无监督域适应方法进行改进,但该方法可以扩展到其他任务和形式的领域自适应。
* (2). 定义源域图像集合 $D_s$ 和对应的标签集合 $L_s$,其中 $L_s$ 是源域图像的one-hot标签集合。目标域的定义类似。使用 $f$ 来表示在源域 $S$ 上训练语义分割模型 $\psi_s$ 的过程,其中 $f$ 包括输入数据处理和网络架构。使用无监督域适应方法 $g$ 将 $\psi_s$适应到目标域 $T$,得到目标域的语义分割模型 $\psi_s$。简化表示为 $\psi_s=f\left(D_s, L_s\right), \psi_t=g\left(\psi_s, D_s, L_s, D_t\right)$.。
* (3). 提出了源模型准备(Source Preparation,SP)步骤,将 $f$ 替换为 $f^{\prime}$。新的问题设置为 $\psi_s^{\prime}=f^{\prime}\left(D_s, L_s\right), \psi_t^{\prime}=g\left(\psi_s^{\prime}, D_s, L_s, D_t\right)$。在第3.3节中详细介绍了 $f^{\prime}$ 的设计,但需要注意的是,不提议添加任何额外的参数或显著改变网络架构。
* (4). 最后一步是有限标记数据的监督对齐(Supervised Alignment),通过更新得到最终的目标模型 $\psi_t^{\prime \prime}=h\left(\psi_t^{\prime}, D_t^{\prime}, L_t^{\prime}\right)$,其中 $D_t^{\prime}$ 是有限标记数据集合, $L_t^{\prime}$ 是对应的标签集合。本文提出的方法框架如图2所示,突出了在现有无监督域适应方法基础上构建AUDA的修改。
* (5). 通过实验证明,本文提出的方法在语义分割任务中提高了无监督域适应的效果,跨多个视觉领域的mIoU提高了最多40.64%,同时使目标模型对目标域内的真实世界变化更加鲁棒。同时,本文还展示了AUDA作为一种标签高效的领域自适应框架,在目标域只有少量标记样本的情况下显著提高了目标域的性能。
* (6). 总结:本文提出的方法通过源域准备、无监督域适应和有限标记数据的监督对齐,实现了在低光环境下的语义分割和目标检测任务中的有效领域自适应。实验证明了该方法的有效性和高效性。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
- 任务(Task): 本文以语义分割为例进行实验,但该方法也适用于其他任务,如全景分割。
- 数据集(Dataset): 在不同的目标领域上测试了提出的方法,包括Cityscapes、DarkZurich、MFNetThermal和CityIntensified。在Cityscapes作为源领域的情况下,通过适应不同的目标领域,包括时间和光照的变化(DarkZurich)、模态的变化(MFNetThermal)以及低光照环境下的目标检测和语义分割(CityIntensified)。评估使用源领域和目标领域共有的标签。其中,CityIntensified和MFNetThermal有用于监督对齐的训练集,而DarkZurich没有。
- 实现细节(Implementation Details): 选择Refign-HRDA*和SegFormer(MiT-B5)作为无监督域自适应(UDA)方法和分割网络。对于Refign,采用与原论文类似的训练方案,但迭代次数增加到原来的1.5倍;对于SegFormer,按照原论文的方法进行训练。在监督对齐(SA)中,对SegFormer进行4000次微调迭代,并将'poly'调度器的预热迭代次数缩减到150。该方法不依赖于特定的UDA方法,可以扩展到其他方法。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
本文通过一系列实验验证了提出的源准备方法在视觉领域适应中的有效性。实验结果表明,SP方法能够显著提高无监督域自适应(Unsupervised Domain Adaptation, UDA)的性能,并使目标模型对目标域内的真实世界变化更加鲁棒。
在语义分割任务上,作者使用了Cityscapes作为源域,分别适应了DarkZurich、MFNetThermal和CityIntensified等目标域。实验结果显示,SP方法在不同目标域上都能够提升UDA的性能,其中在CS→CI任务中,mIoU相比基线提高了40.64%。此外,作者还发现SP方法能够使目标模型更加鲁棒,对目标域内的真实世界变化更具适应性。
在不同的SP方法中,MixStyle方法在跨模态和跨时间任务中表现最好,对CS→MFNT任务的mIoU提升最高,达到了1.55%。Mixup方法在跨模态任务CS→CI中表现出色,mIoU提升了39.37%。Blur方法在所有源-目标对中都能够提高性能,特别是在CS→CI任务中,mIoU提升了40.64%。
作者还通过实验验证了选择合适的SP方法的指导原则。如果目标域存在大量高频噪声,如雨、雾、雪和运动模糊等,可以选择模糊和mixup等方法来减少对这些噪声的敏感性。如果源域和目标域之间存在显著的风格差异,可以选择MixStyle等方法进行风格正则化。实验结果表明,SP方法不仅能够提高目标域的性能,还能够增加适应后模型对目标域内可能的真实世界变化的鲁棒性。
综上所述,本文的实验结果验证了提出的SP方法在视觉领域适应中的有效性,并提供了选择合适SP方法的指导原则。
# P:3 简化的时间一致性强化学习(ICML' 23)
- 1. Title: Simplified Temporal Consistency Reinforcement Learning
- 2. 论文简介: 本文由芬兰奥尔托大学的Yi Zhao等人提出了一种简化的时间一致性强化学习方法,通过学习潜在动力学模型的潜在时间一致性,解决了强化学习中的样本效率和计算需求问题。
- 3. Authors: Yi Zhao, Wenshuai Zhao, Rinu Boney, Juho Kannala, Joni Pajarinen
- 4. Affiliation: 芬兰奥尔托大学
- 5. Keywords: Reinforcement learning, model-based RL, latent dynamics model, sample efficiency
- 6. Paper: [Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.09466) Github: [Github](https://github.com/zhaoyi11/tcrl)
- 7. 论文总结:
* (1):本文研究了潜在时间一致性在基于状态的强化学习中的作用;
* (2):过去的方法主要集中在图像重建和对比学习等自监督学习方法上,但这些方法在状态空间任务中的效果并不明确;
* (3):本文提出了一种简化的方法,通过学习潜在动力学模型的潜在时间一致性,实现了高性能的强化学习。该方法在纯规划和模型无关的强化学习中都取得了良好的效果;
* (4):在实验中,本文的方法在高维运动任务中学习到了准确的动力学模型,并且相比于基于集成的方法,训练速度提高了4.1倍。在高维任务上,与模型无关的方法相比,本文的方法在DeepMind Control Suite中的Humanoid和Dog任务上表现出色,训练速度提高了2.4倍。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍:
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一种简化的时间一致性强化学习方法,通过训练潜在动力学模型来学习高性能的强化学习策略。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
* (1). 模型组成:该方法包括四个组件:编码器、转移函数、值函数和策略函数。
- 编码器将观测映射为潜在状态。
- 转移函数根据潜在状态和动作预测下一个时间步的潜在状态和即时奖励。
- 值函数根据潜在状态和动作估计值。
- 策略函数根据潜在状态生成动作。
* (2). 学习编码器和潜在动力学模型:
- 使用在线编码器将观测映射为潜在表示。
- 使用动作序列和转移函数迭代地预测未来奖励和潜在状态。
- 通过最小化奖励的均方误差和潜在状态的负余弦距离来训练潜在动力学模型。
* (3). 学习策略和值函数:
* 使用深度确定性策略梯度方法(DDPG)和 $n$ 步回报来学习策略和值函数。
* 将潜在状态作为输入,通过最小化值函数的损失来更新值函数。
* 通过最大化Q值来更新策略函数。
* (4). 使用模型进行规划:
* 使用模型预测未来的潜在状态和奖励。
* 使用模型预测的结果进行在线规划,改进策略。
* 通过迭代学习动力学模型来提高规划性能。
* (5). 实验验证:
* 在多个连续控制任务上评估该方法的性能。
* 与其他方法进行比较,包括基于集成模型的方法和基于模型的方法。
* 在高维任务上展示了该方法的优越性能。
* (6). 总结:
- 通过训练潜在动力学模型和使用潜状态进行规划,该方法在高性能强化学习任务中取得了显著的效果。
- 该方法简单且易于实现,同时具有较高的训练速度。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置:
本文在几个连续的DMC控制任务中评估了TCRL方法。DMC使用了缩放的奖励,所有任务的最大周期性回报都是1000。我们在两个不同的设置中评估了我们的方法:
1. 动力学学习:在第一个设置中,没有涉及值函数或策略。相反,我们直接使用潜在动力学模型进行在线规划,称为TCRL-dynamics。我们的目标是回答是否可以使用时间一致性来学习准确的潜在动力学模型。
2. 策略学习:在第二个设置中,我们以免模型的方式训练策略和值函数,使用潜在状态代替原始观测,称为TCRL。这个实验旨在研究通过时间一致性训练的潜在表示是否有助于策略和值函数的学习。
我们使用模型预测路径积分(MPPI)作为在线规划方法来直接评估学习到的动力学模型的规划结果。在每次迭代中,根据当前策略 $a^j_{t:t+H}$,采样 $N$ 条轨迹。然后,选择具有较高回报 $\sum_{h=0}^H r_{t+h}^j\left(s_{t+h}^j, a_{t+h}^j\right)$ 的 $K$ 条轨迹。接下来,通过对所选的前K条轨迹的回报进行softmax加权平均,计算改进的策略 $a^{j+1}_{t:t+H}$ 。经过 $J$ 次迭代后,执行 $a^{J}_{t:t+H}$ 的第一个动作。
在我们的MPPI实现中,没有涉及值函数或策略网络。相反,我们通过i)通过MPPI规划器收集经验,和ii)通过优化公式2使用收集到的数据来改进动力学模型。通过这种方式,所有采样的动作序列仅通过学习到的潜在动力学模型进行评估,因此规划性能可以反映模型的准确性。我们考虑以下比较方法来学习动力学模型:
- 随机集成模型(PETS):学习一组随机神经网络,预测下一个状态和奖励的均值和标准差。与Chua等人(2018)类似,我们只预测一步未来,因为通过多个时间步骤的不确定性传播不明确。
- 确定集成模型(EnsDet):使用一组确定性神经网络预测多步未来观测和奖励。EnsDet的架构与我们的方法类似,不同之处在于预测下一个观测而不是下一个潜在状态,从而实现了观测预测和潜在空间预测之间的实验比较。
此外,我们还在基于像素的任务上测试了我们的方法,以展示其通用性。在附录A中与PlaNet进行了实验比较,我们的方法在六个常用的基于像素的基准任务上获得了可比或更好的性能。附录A.3中对基于像素的任务进行了详细的消融研究。在图2中,我们将我们的方法与随机集合模型(PETS)和确定性集合模型(EnsDet)在DMC的八个基于状态的任务上进行了比较,包括六个常用的基准任务和两个具有挑战性的高维任务:四足行走和狗行走。尽管简单且没有使用集合,我们的方法在测试任务中要么与比较方法相匹配,要么优于比较方法。高维的动作和观测空间 $\mathcal{A}\in \mathbb{R}^{38},\mathcal{O}\in \mathbb{R}^{223} $ 使得即使对于强大的免模型基线(Haarnoja等人,2018)来说,解决狗行走任务也很困难。事实上,据我们所知,TCRL-dynamics是第一个可以使用学习到的动力学模型进行在线规划来控制法老犬向前行走的方法。Chua等人(2018)讨论了预测任意的(aleatoric)和认识的(aleatoric)不确定性以实现良好规划性能的重要性。然而,在Chua等人(2018)和我们的实验中,算法都在确定性环境中进行了测试,这使得预测任意的不确定性的动机不太明确。事实上,在我们的实验中,TCRL-dynamics和EnsDet在所有任务上都优于PETS。这一证据迫使我们重新思考在这些常用的确定性任务中预测任意的不确定性的作用。此外,与PETS相比,我们的方法和EnsDet都显示了使用多步训练目标的重要性,而这与PETS中使用的随机模型不太兼容,因为正确地在多个时间步骤上传播不确定性是具有挑战性的。与EnsDet相比,我们的结果显示了在潜在空间而不是观测空间中进行预测的优越性。我们在第5节中对此进行了更详细的讨论。此外,我们发现PETS和EnsDet都需要对状态进行归一化。然而,在异策略(off-policy)方法中,状态归一化并不常见,因为这可能会引入额外的不稳定性。我们的假设是,在异策略方法中,回放缓冲区中的数据分布在训练过程中不断变化,这导致归一化状态的均值和标准差不稳定。但是,TCRL-dynamics在没有状态归一化的情况下可以获得良好的性能,这使其成为在基于模型的强化学习中具有吸引力的选择。
总之,本文的实验设置包括两个主要的实验设置:动力学学习和策略学习。在动力学学习中,使用潜在动力学模型进行在线规划。在策略学习中,使用潜在状态代替原始观测进行免模型的策略和值函数学习。实验中使用了模型预测路径积分(MPPI)作为在线规划方法,并与随机集合模型(PETS)和确定性集合模型(EnsDet)进行了比较。此外,还在基于像素的任务上进行了实验比较,并展示了方法的通用性和性能优势。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
本文通过一系列实验评估了TCRL方法在连续控制任务中的性能。实验分为两个设置进行评估:动力学学习和策略学习。
1. 动力学学习:
在动力学学习设置中,作者使用了潜在动力学模型进行在线规划,称为TCRL-dynamics。实验结果表明,通过仅依赖于通过潜在时间一致性训练的潜在动力学模型,可以学习到准确的动力学模型。与基于集成的方法相比,TCRL-dynamics的训练速度提高了4.1倍,并且在解决具有挑战性的高维运动任务时表现出色。
2. 策略学习:
在策略学习设置中,作者使用潜在状态替代原始观测来以免模型的方式训练策略和值函数,称为TCRL。实验结果显示,通过使用通过时间一致性训练的潜在表示,可以提高策略和值函数的学习效果。特别是在高维任务(如DMC中的Humanoid和Dog任务)上,TCRL方法在免模型的情况下明显优于其他免模型方法,并且在训练速度上比模型基准方法快2.4倍。
3. 模型对比:
作者将TCRL方法与其他模型进行了比较。在连续控制任务中,与PETS和EnsDet方法相比,TCRL方法在多个任务上表现出色,甚至在高维任务中也能取得良好的控制效果。实验结果表明,TCRL-dynamics方法是第一个能够使用学习到的动力学模型进行在线规划的方法。此外,TCRL方法和EnsDet方法在预测潜在空间而不是观测空间方面表现出优越性。
4. 像素任务:
作者还在像素任务上评估了TCRL方法的性能。实验结果显示,TCRL方法在六个视觉控制任务上与PlaNet方法的结果相当,而且训练速度更快。这表明TCRL方法在像素任务和状态任务中都具有竞争力。
综上所述,实验结果表明TCRL方法在连续控制任务中具有较高的性能,并且在动力学学习和策略学习方面都取得了显著的改进。
# 7月3号
# P:1 EmbodiedGPT: 通过具身化思维链进行视觉-语言预训练
- Title: EmbodiedGPT: Vision-Language Pre-Training via Embodied Chain of Thought
- 论文简介: 本文介绍了一种名为EmbodiedGPT的多模态基础模型,用于具有多模态理解和执行能力的具身化人工智能。通过构建一个大规模的具身化规划数据集EgoCOT,采用“思维链”模式生成子目标序列,将7B大型语言模型(LLM)通过前缀调整适应EgoCOT数据集,提出了一种高质量规划生成的高效训练方法。同时,通过从LLM生成的规划查询中提取与任务相关的特征,形成高层规划和低层控制之间的闭环。实验证明了EmbodiedGPT在具身化任务上的有效性,包括具身化规划、具身化控制、视觉字幕生成和视觉问答。特别是,在具身化控制任务中,EmbodiedGPT通过提取更有效的特征,使成功率在Franka Kitchen基准上提高了1.6倍,在Meta-World基准上提高了1.3倍,与使用Ego4D数据集微调的BLIP-2基线相比。
- Authors: Yao Mu, Qinglong Zhang, Mengkang Hu, Wenhai Wang, Mingyu Ding, Jun Jin, Bin Wang, Jifeng Dai, Yu Qiao, Ping Luo
- Affiliation: The University of Hong Kong, OpenGV Lab at Shanghai AI Lab, Huawei
- Keywords: Embodied AI, vision-language pre-training, embodied planning, embodied control, multi-modal understanding
- Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2305.15021) Github: [None]
- 论文总结:
- (1): 本文的研究背景是具身化人工智能任务,旨在使机器人能够在物理环境中感知、推理和行动,实现长期规划和基于实时观察的自主执行。
- (2): 过去的方法主要集中在大规模语言模型的训练,但在具身化任务中缺乏高质量的数据集和精确的规划生成。本文提出了EgoCOT数据集和EmbodiedGPT模型,通过思维链模式生成子目标序列,并通过前缀调整训练语言模型,从而解决了这些问题。
- (3): 本文提出了一种基于具身化链式思维的视觉-语言预训练框架EmbodiedGPT,包括冻结的视觉模型、冻结的语言模型、具身化模块和策略网络。通过从语言模型生成的规划查询中提取任务相关特征,形成高层规划和低层控制之间的闭环。此外,通过前缀调整训练语言模型,生成更可执行的规划。
- (4): 在具身化任务中,EmbodiedGPT在具身化规划、具身化控制、视觉字幕生成和视觉问答等任务上取得了显著的性能提升。与使用Ego4D数据集微调的BLIP-2基线相比,在Franka Kitchen基准上成功率提高了22.1%,在Meta-World基准上提高了22.5%。这些结果表明了EmbodiedGPT在任务性能上的创新和贡献。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文介绍了一种名为EmbodiedGPT的多模态基础模型,通过视觉-语言预训练实现了具有多模态理解和执行能力的具身化智能体。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 构建大规模具身化规划数据集EgoCOT:从Ego4D数据集中精选视频,并配以高质量的语言指令,生成具有"Chain of Thoughts"模式的子目标序列,用于有效的具身化规划。
(2). 高质量计划生成的有效训练方法:通过将7B大型语言模型(LLM)适应EgoCOT数据集,通过前缀调整,实现对EmbodiedGPT的高质量计划生成的有效训练。
(3). 从LLM生成的规划查询中提取与任务相关的特征:通过在高层规划和低层控制之间形成闭环,从LLM生成的规划查询中提取与任务相关的特征,用于生成任务执行的低层控制命令。
(4). 引入基于视觉-语言预训练的具身化规划范式:通过将任务描述和具身化规划作为问题和答案,将具身化规划任务形式化为标准的视觉问答(VQA)任务,丰富了具身化规划和标准视觉问答任务的数据,鼓励EmbodiedGPT捕捉更适合具身化控制任务的任务特定特征。
(5). 训练过程分为三个阶段:第一阶段是图像-文本对齐预训练,使用COCO Caption、CC3M和LAION-400M数据集进行预训练;第二阶段是增强模型理解和生成复杂句子的能力,使用"Complex_Reasoning_77k"和"LLaVA_Instruct_150K"数据集进行训练;第三阶段是使用EgoCOT数据集对具身化AI任务进行训练。
(6). 具身化"chain-of-thought"训练:在第三阶段,将预训练的视觉模型转移到视频编码器中,使用Conv3D进行转换,然后引入"chain-of-thought"视觉-语言预训练范式,通过关键帧的视频输入、任务描述、具身化规划和结构化的动词-名词对摘要进行推理。
(7). 后处理:使用CLIP模型评估视频和文本对之间的相似性,筛选出相似性高于阈值的视频-标题-规划对,确保EgoCOT数据集的高质量。同时,创建EgoVQA数据集用于具身化人-物交互视频问答任务的训练。
(8). 其他细节:对于EgoVQA数据集的构建,使用ChatGPT生成与每个标题相关的五个问答对,以丰富训练数据。
(9). 实验结果:EmbodiedGPT在具身化任务中表现出显著的效果,包括具身化规划、具身化控制、视觉字幕和视觉问答。与使用Ego4D数据集进行微调的BLIP-2基线相比,EmbodiedGPT在Franka Kitchen基准上的成功率提高了1.6倍,在Meta-World基准上提高了1.3倍。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
本文通过对多模态基础模型和EmbodiedGPT进行全面评估,包括视觉字幕生成、具身规划和控制等各种任务。
在图像输入任务的评估中,作者进行了一项用户研究,共有30名参与者。研究包括了来自MS-COCO数据集的10个图像字幕任务,不同具身AI模拟器中的5个具身规划场景,以及5个伴随具身规划任务的真实场景。参与者使用1到10的评分系统,对不同的端到端模型生成的字幕进行了五个维度的评分:物体识别准确性、空间关系理解、答案中的冗余程度、规划的合理性和可执行性。表1显示了所有参与者对不同模型的平均评分。结果表明,尽管EmbodiedGPT在语言模型中只有7B个参数,但在物体识别和空间关系理解方面,它与LLaVA-13B模型达到了可比较的水平。此外,EmbodiedGPT在与具身AI任务相关的内容中生成的冗余内容较少,并且产生了最合理和可执行的规划输出。作者还将EmbodiedGPT与Visual ChatGPT进行了比较,Visual ChatGPT采用分层方法,通过组合多个预训练的视觉模型和语言模型来回答问题。在Virtual-Home基准测试中,Visual ChatGPT由于仅依赖于字幕模型提取视觉信息的局限性,无法找到衣架,导致性能较差。
在具身规划任务的评估中,作者在Franka Kitchen基准和Meta-World基准上与BLIP-2基线进行了比较。结果显示,与使用Ego4D数据集微调的BLIP-2基线相比,EmbodiedGPT在Franka Kitchen基准上的成功率提高了1.6倍,在Meta-World基准上提高了1.3倍。
在具身控制任务的评估中,作者通过提取LLM生成的规划查询的任务相关特征,形成了高层规划和低层控制之间的闭环。实验结果表明,EmbodiedGPT通过提取更有效的特征显著提高了具身控制任务的成功率。
综上所述,实验结果表明EmbodiedGPT在多种任务中表现出良好的性能,包括具身规划、具身控制、视觉字幕生成和视觉问答等。
# P:2 告诉我去哪里:一种用于上下文感知的可组合机器人导航框架
- Title: Tell Me Where to Go: A Composable Framework for Context-Aware Embodied Robot Navigation
- Authors: Harel Biggie, Ajay Narasimha Mopidevi, Dusty Woods, Christoffer Heckman
- Affiliation:
Department of Computer Science, University of Colorado Boulder
- Keywords: Natural language, navigation, contextual navigation
- Paper: [Link to the paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.09523)
Github: None
- Summary:
- (1): 本文研究背景是人类在陌生环境中通过先前的知识和环境描述进行导航的能力。研究者希望开发一个框架,使机器人能够通过自然语言指令与物理环境进行关联。
- (2): 过去的方法包括使用概率图结构和端到端学习方法将自然语言与物理领域关联起来。然而,这些方法存在一些问题,如泛化能力有限和解释性差。本文的方法通过创建一个中间层来解决这些问题,并利用大型语言模型的先验知识进行导航。
- (3): 本文提出了NavCon框架,它通过将大型语言模型的先验知识转化为Python代码,并与机器人导航框架进行交互,解决了现实世界泛化和透明性问题。该框架利用了LLM先验知识、先进的物体检测器和经典的机器人规划算法,实现了基于自然语言的导航。
- (4): 本文在四个不同的环境和命令类别上评估了NavCon方法,并展示了其解释上下文命令的能力。实验结果表明,该框架能够根据自然语言导航到地标,并从句子的上下文中推断出适当的导航目标。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一种基于上下文感知的机器人导航框架,通过中间层将大规模语言模型(LLMs)的先验知识转化为机器人可以理解的Python代码,解决了LLMs缺乏现实世界感知和输出不可预测性的问题。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 导航上下文框架(NavCon)的开发:利用LLMs的丰富上下文先验知识,创建一个可执行的代码层,与运行在具体机器人上的规划算法进行接口交互。该框架采用模块化神经网络和概念学习技术的范例,通过在不同阶段接收输入来完全定义系统的最终导航输出。
(2). 输入表示:将视觉输入表示为RGB图像,可以是半全景视图或三个分别标记的空间图像(左、前、右)。为了进行三维推理和关联不同相机视角与其关联的三维空间关系,需要确定适当的输入表示方法。通过比较将所有视点的拼接图像(半全景)或分别发送每个帧的空间定义(右、前、左),发现在拼接图像上进行空间推理效果最佳。
(3). 中间层:利用最近的代码生成模型,生成中间层代码θ。提供一组功能性的导航指令,以Python API的形式提供给代码生成模型。这些指令包括如何使用类似于[14]中的范例在输入图像上进行视觉推理的规范。此外,还提供了与几何规划器进行接口的API规范,生成基于自然语言提示γc的代码。
(4). 规划:使用基于图的规划器,提供导航终点。具体地,创建一个函数,将图像空间中对象的中心坐标p投影为3D地图上的地标l。规划器使用类似于[59,18]中描述的采样和投影方法来构建计划的图G。当输入3D航点到规划器时,从G中选择最佳路径P供机器人跟随。如果不存在路径,则规划到图的边界并重新采样,直到达到目标。
(5). 通过中间层将航点传递给规划器:具体地,通过执行θ将图像坐标转换为航点,并使用射线投射将结果关联到3D地图m上。在线生成地图m使用[61],而翻译层θ则创建了在输入c、v、m和输出i之间进行转换所需的代码。然后从P中选择最佳路径规划到航点。
(6). 具体步骤详见图3。
综上所述,本文提出了一种基于上下文感知的机器人导航框架,通过中间层将大规模语言模型的先验知识转化为机器人可以理解的Python代码,实现了对自然语言导航指令的解释和执行。该方法在四个不同环境和命令类别上进行了评估,并展示了NavCon解释上下文命令的能力。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文在一台配备了自定义传感套件的Boston Dynamics Spot机器人上进行了两组实验。该套件包括一个3D 64束Ouster激光雷达、一个惯性测量单元(imu)和3个RGB摄像头,提供了环境的半全景视图。第一组实验旨在确定视觉层的最佳输入表示,第二组实验测试了系统在各种真实环境中执行导航的能力。
对于所有实验,本文借鉴了人类概念学习的思想,将句子分为四个类别:通用、具体、关系和上下文。通用句子是指仅暗示“去某处”的句子,例如“走到背包那里”。具体句子包括一个区分性的语言特征,如颜色属性,指导机器人去场景中的一个特定对象。例如,如果有两个背包,一个红色,一个黑色,那么一个具体的句子可能是“开到黑色背包那里”。关系句子是描述场景中物体之间空间关系的句子,例如“移动到椅子上的背包”。上下文示例要求机器人根据背景信息解释导航目标。例如,句子“找一个可以装水的东西”要求机器人知道杯子或桶可以装水。完整的句子列表可以在附录中找到。
为了解决将空间关系编码到没有物理世界概念的模型中的问题,本文通过经验评估确定了将三个不同视点输入到框架中的有效方案。例如,句子“去右边的椅子”仅意味着应该调查总视野的右半部分,但是“去椅子右边的背包”可以在任何图像中。为了解决这些限制,本文使用了两种不同的输入表示方式。第一种方式是将所有三个图像拼接在一起,并在帧之间添加填充(A)。在这种情况下,我们指示LLM按照图像的顺序(左、前、右)进行处理,并让模型处理空间推理。第二种方式是分别处理每个帧(B),并让模型决定要查看哪些帧。我们明确提示模型使用解决“在你的右边”和“右边的”语言风格差异的示例代码片段。在这组实验中,我们评估生成的代码的正确性以及代码是否能够正确识别地图中的对象。这个场景是在教室环境中创建的,光照条件良好,重点是评估输入表示的效果。成功生成代码和对象检测的结果如表1所总结。从表1中我们可以看出,拼接图像的方法明显优于分别发送三个帧。在通用导航案例中,我们能够实现100%的中间层生成和对象识别成功。我们发现,当处理特定对象时,单独处理每个帧的配置(B)开始出现问题。具体来说,当物体出现在多个帧中时,模型无法推理空间关系和物体顺序。例如,对于句子“去中间的插座”,只有当三个插座都出现在同一个摄像头帧中时才有效。如果中间的插座在前面的帧中,而右边的插座在右侧的摄像头帧中,这种方法就会失败。我们在生成的代码中明确看到了这一点。
(1). 实验一:确定视觉层的最佳输入表示。
(2). 实验二:测试系统在各种真实环境中执行导航的能力。
**实验结果:**
- 实验结果和分析(Experimental results and analysis):
本文在一台配备了自定义传感套件的Boston Dynamics Spot机器人上进行了两组实验。第一组实验旨在确定视觉层的最佳输入表示方法,第二组实验测试了系统在各种真实环境中执行导航的能力。
在所有实验中,作者将句子分为四个类别:通用、具体、关系和上下文。通用句子是指只暗示“去某个地方”的句子,例如“走到背包那里”。具体句子包括一个区分性的语言片段,例如一个颜色属性,指导机器人去场景中的一个特定对象。例如,如果有两个背包,一个红色,一个黑色,那么一个具体的句子可能是“开到黑色背包那里”。关系句子是描述场景中物体之间空间关系的句子,例如“移动到椅子上的背包”。上下文示例要求机器人根据背景信息解释导航目标。例如,句子“找一个可以装水的东西”要求机器人知道杯子或桶可以装水。作者在附录中列出了完整的句子列表。
作者通过实证评估确定了将三个不同视点输入到框架中的有效方案。作者使用两种不同的输入表示方法,第一种是将三个图像拼接在一起,并在帧之间添加填充。在这种情况下,作者指示LLM模型图像的顺序(左、前、右),并让模型处理空间推理。第二种情况下,作者逐个处理帧,并让模型决定要查看哪些帧。作者明确提示模型使用示例代码片段解决“在你的右边”和“右边的”语言风格之间的差异。
实验结果表明,将图像拼接在一起的方法明显优于逐个处理三个帧的方法。在通用导航案例中,作者能够实现100%的中间层生成和对象识别成功。然而,在处理特定对象时,逐个处理帧的配置开始出现问题。具体来说,当物体出现在多个帧中时,模型无法推理空间关系和物体顺序。例如,句子“去中间的插座”只有当三个插座都出现在同一帧中时才有效。如果中间的插座在前方帧中,而右边的插座在右侧相机帧中,这种方法就会失败。
总的来说,作者的NavCon框架在四个不同环境和命令类别上的实验中表现出了良好的解释上下文命令的能力。通过将大规模语言模型的先验知识转化为机器人可以理解的Python代码指令,NavCon框架弥补了大规模语言模型缺乏现实世界感知的不足。
# P:3 你的房间不是私密的:深度Q学习的梯度反演攻击
- Title: Your Room is not Private: Gradient Inversion Attack for Deep Q-Learning
- 论文简介: 本文提出了一种利用梯度反演攻击深度Q学习算法的方法,通过梯度反演重构状态、动作和Q值,以揭示在具体决策算法中的隐私泄露问题。该方法利用梯度进行攻击的选择是基于常用的联邦学习技术,这些技术仅利用基于私有用户数据计算的梯度来优化模型,而不会将数据存储或传输到公共服务器。然而,这些梯度包含足够的信息来潜在地暴露私有数据。通过在AI2THOR模拟器上进行实验证明了该方法的有效性。
- Authors: Miao Li, Wenhao Ding, Ding Zhao
- Affiliation:
Carnegie Mellon University (卡内基梅隆大学)
- Keywords: Privacy, Reinforcement Learning, Gradient Inversion
- Paper: [Link to the paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.09273) Github: None
- 论文总结:
- (1): 本文研究了在具体决策算法中的隐私泄露问题,填补了该领域研究的空白。
- (2): 之前的方法主要集中在联邦学习中的隐私保护,但仍存在梯度反演攻击的漏洞。本文的方法通过梯度反演重构状态、动作和Q值,解决了这一问题,并且在实验中取得了良好的效果。
- (3): 本文提出了一种名为Deep Q-learning Gradient Inversion (QGI)的方法,通过梯度反演来恢复强化学习中的多模态输入信息。该方法通过优化重构状态的梯度与真实梯度之间的余弦相似度,并使用先验项惩罚噪声图像模式,实现了对状态、动作和Q值的准确恢复。
- (4): 本文在AI2THOR模拟器上的主动感知任务中评估了QGI方法,并成功恢复了所有120个房间布局的数据。实验结果表明,该方法在恢复数据方面取得了良好的性能,支持了其目标和创新贡献。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一种利用梯度反演攻击Deep Q-Learning算法的方法,通过梯度反演重构状态、动作和Q值,从而揭示决策算法中的隐私泄露问题。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 在第一步中,通过梯度分析确定具有梯度的动作。
(2). 在第二步中,通过两个阶段重构向量状态和图像状态,其中第一阶段重构包括线性层的输入,包括坐标向量和第二阶段重构图像状态。
(3). 在第三步中,通过应用重构的向量来获得Q值Q_rec(s, a),并通过重构误差Q(s, a) - Q(s, a)来估计目标Q值Q_rec。
(4). 当批量大小大于2时,无法直接从批量梯度中识别动作,因此需要进行枚举或优化。
(5). 将状态重构分为两个阶段,首先重构未经卷积层处理的向量状态,然后在固定向量状态的情况下重构需要卷积的图像状态。
(6). 使用梯度匹配损失和总变差损失来优化图像状态的重构。
(7). 使用规则自动计算权重λ来影响总损失中两个项的梯度比率。
(8). 使用梯度更新状态重构。
以上是本文提出的方法的详细步骤。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文在AI2THOR模拟器上进行了实验,评估了提出的算法在具体任务中的效果。实验结果表明,该方法能够成功地从数据中恢复所有信息,并且在所有120个房间布局上都取得了令人信服的效果。
(1). 实验对象:AI2THOR模拟器。
(2). 实验任务:在具体任务中评估算法的效果,特别是在活动感知任务中。
(3). 实验方法:使用梯度反演攻击Deep Q-Learning算法,利用梯度反演重构状态、动作和Q值。
(4). 实验结果:通过定性和定量的实验结果,验证了算法的有效性。在S1设置下,重构的RGB图像和深度图像具有可识别的模式和幅度。在S2设置下,重构的图像具有清晰的边缘和细节。
(5). 实验参数:在S1设置中,使用λ=0.1进行实验;在S2设置中,使用自适应方法进行实验。
(6). 实验数量:共进行了120个房间布局的实验。
(7). 实验对比:与联合优化方法进行对比,结果表明,联合优化在状态重构步骤中的性能下降,而梯度反演方法在所有指标上都取得了较好的效果。
(8). 实验验证:通过实验结果验证了算法的有效性和稳定性。
(9). 实验限制:本文的实验主要集中在AI2THOR模拟器上,对于实际机器人任务的适用性还需要进一步研究。
(10). 实验创新点:本文首次将梯度反演方法应用于机器人任务和多模态数据中,填补了相关领域的研究空白。
(11). 实验结论:实验结果表明,梯度反演攻击可以成功地从梯度中恢复私密数据,这对于机器人任务的隐私保护具有重要意义。
**实验结果:**
- 实验结果和分析:
本文通过在AI2THOR模拟器上进行实验,评估了提出的基于梯度反演的Deep Q-Learning算法攻击的效果。实验结果表明,该方法能够成功地从数据中恢复所有信息,并且在所有120个房间布局中都取得了令人信服的效果。
在S1设置下,使用λ=0.1进行实验,左图中的RGB图像和深度图像都能够被成功重建,并且具有可识别的模式和幅度。RGB图像展现出准确的颜色色调,尽管在局部区域可能存在一些不准确的有色噪声。与RGB图像一起重建的深度图像也显示出类似的噪声模式,但整体连续区域的亮度仍然准确。因此,潜在的对手可以通过这些重建图像获取私人房间的大小。在S2设置下,如右图所示,成功重建的图像展现出清晰的边缘和细节,具有准确性。更多的定性结果请参考附录B。
通过将提出的QGI与联合优化进行比较,评估了QGI的效果。联合优化应用于状态重建步骤,同时优化向量和图像重建。实验结果表明,联合优化的图像状态(RGB+深度)和向量状态(目标坐标)在所有指标上的性能下降。平均IoU低于0.1,而QGI的平均IoU超过0.9。Q值重建也显示出显著的错误,与QGI相比,平均ϵ(Q)增加了40倍。
研究了L img中的自适应权重,将QGI与常数λ=0.1、0.01进行比较。在S1设置中,自适应权重方法在PSNR和SSIM方面略有改善。然而,尽管PSNR和SSIM的标准偏差较大,λ=0.1的视觉质量比自适应λ更稳定。在两个设置中,自适应λ在深度图像方面表现出一致的优势,表1中的结果和图4中的视觉质量都是稳定的,特别是在S2设置中。
综上所述,实验结果表明,提出的基于梯度反演的Deep Q-Learning算法攻击方法在恢复数据方面取得了成功,并且在多个指标上优于联合优化方法。这些结果为深度强化学习中的隐私泄露问题提供了重要的研究基础。
# P:4 通过代理分析改进从LLMs中提取知识以用于机器人任务学习
- Title: Improving Knowledge Extraction from LLMs for Robotic Task Learning through Agent Analysis
- Authors: James R. Kirk, Robert E. Wray, Peter Lindes
- Affiliation: Center for Integrated Cognition at IQMRI
- Keywords: large language models, robotic task learning, prompt engineering, cognitive-agent approach
- Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.06770) Github: None
- Summary:
-(1):本文的研究背景集中在改进用于机器人任务学习的大型语言模型(llm)的知识提取。
-(2):过去的方法,如提示工程,在为机器人代理获取相关的、基于情境的知识方面存在局限性。本文提出的方法旨在扩展和补充提示工程以克服这些局限性。
-(3):本文提出的研究方法是一种认知代理方法,使机器人能够获得与其母语能力、体现、环境和用户相匹配的新任务知识。创新之处在于将智能体分析与提示工程相结合,增强了知识提取能力。
-(4):本文的方法对机器人任务学习进行了评估,所获得的性能支持了机器人代理获取相关的、基于情境的知识的目标。本文的创新和贡献在于认知代理方法,该方法改进了从llm中提取知识用于机器人任务学习的方法。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一种认知代理方法,通过扩展和补充提示工程,从而提高了从大型语言模型(LLMs)中提取知识用于机器人任务学习的效果。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 基于交互式任务学习(ITL)代理的扩展:在现有的ITL代理基础上进行扩展,使其能够学习各种不同的任务,并在多个不同的物理和模拟机器人领域中进行学习。
(2). 目标学习流程:当任务的执行策略未知时,使用规划来找到与目标一致的动作序列。如果规划的动作能够实现目标,代理会对执行的动作进行回顾性分析,以学习长期的策略知识,从而在未来能够一次性学习任务目标。这个学习过程在许多领域都取得了成功,但需要大量用户输入来提供可解释和准确的目标描述。
(3). STARS方法:通过扩展基线提示策略,STARS方法通过增加LLMs的响应空间,并在自主机器人中嵌入通用策略来评估、修复和选择LLMs生成的候选响应,从而提高机器人的任务学习效果。具体包括以下三个过程:
- 通过波束搜索检索LLMs的响应树:使用波束搜索策略从单个提示中生成多个高概率的响应,以获得更多的可行响应。
- 分析和修复响应:对从LLMs检索到的响应进行分析和修复,以确保其对机器人是可行的。
- 使用LLMs选择目标响应:通过LLMs选择一个目标响应作为机器人的任务目标,从而减少用户的监督需求。
(4). 可选的监督策略:可以向用户征求反馈,以进一步提高任务学习的效果。
(5). STARS方法流程:根据上述步骤,STARS方法的流程包括基线提示策略和STARS方法的组合,其中STARS方法通过波束搜索、分析和修复响应以及使用LLMs选择目标响应来提高任务学习效果。
以上是本文方法的详细步骤,通过扩展和补充提示工程,使机器人能够从LLMs中获取更多的可行响应,并通过自主分析和修复来提高任务学习的效果。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文描述了一种认知代理方法,通过扩展和补充提示工程,减轻其局限性,并使机器人能够获取与其本地语言能力、体现、环境和用户偏好相匹配的新任务知识。该方法是通过增加LLMs的响应空间,并在自主机器人内部部署一般策略,对LLMs生成的候选响应进行评估、修复和选择。实验通过检索和评估LLMs的多种响应,展示了机器人在无用户监督的情况下能够实现超过75%的一次性学习任务完成率。当提供人类监督时,任务完成率达到100%,同时大大减少了所需的人类监督量。
(1). 实验目标:通过扩展和补充提示工程,使机器人能够从LLMs中获取与其本地语言能力、体现、环境和用户偏好相匹配的新任务知识。
(2). 实验方法:通过增加LLMs的响应空间,并在自主机器人内部部署一般策略,对LLMs生成的候选响应进行评估、修复和选择。
(3). 实验结果:在无用户监督的情况下,机器人能够实现超过75%的一次性学习任务完成率。当提供人类监督时,任务完成率达到100%,同时大大减少了所需的人类监督量。
(4). 实验设计:本实验仅报告了每个条件下的一次运行结果。为了评估可重复性,STARS条件运行了10次。任务完成率在75%到80%之间变化,方差为3.75。
(5). 实验领域:本文的实验测试了单个任务和领域,但计划在其他任务和领域进一步改进和评估STARS方法。
(6). 实验成本:实验中的监督形式包括指令和单词,STARS方法将其减少了403个单词至127个单词。此外,STARS方法提供给用户的响应的准确性也得到了提高。
(7). 实验限制:由于实验成本的限制,本文未能多次运行所有实验。但结果表明,STARS的整体方差较小,对关键结果影响较小。
(8). 实验改进:未来的工作将探索改进LLM选择策略的方法,特别是通过从用户和LLM获取额外的上下文信息。
**实验结果:**
- 实验结果和分析:
本文通过实验结果和分析展示了使用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行机器人任务学习的知识提取的改进方法。以下是实验结果的详细描述:
1. 性能:在实验中,通过对LLMs检索和评估多个响应,机器人可以在一次学习中完成超过75%的任务,无需用户监督。当提供人类监督时,任务完成率达到100%,同时大大减少了需要的人类监督量。
2. 响应质量:通过对LLMs检索到的响应进行分类,发现超过70%的响应是不可行的,只有13%的响应是与情境相关的。使用改进的方法(STARS)可以使机器人获得100%的至少是合理的响应。
3. 成本:使用改进的方法(STARS)可以显著减少用户的指令和输入量,从403个单词减少到127个单词。此外,STARS还提高了响应的准确性,70%的响应被用户接受为正确的。
4. LLM选择策略:实验结果显示,LLM选择策略与基线选择策略相比没有明显的改进。
综上所述,通过实验结果和分析,本文展示了改进的方法(STARS)可以提高机器人从LLMs中提取知识的效果,并减少用户的监督成本。然而,用户的输入仍然是确保任务完成的必要条件。未来的工作可以进一步提高LLM提取的质量,并扩展用户的监督方式。
# P:5 基于语言的场景摘要生成机器人的可执行策略学习
- Title: Embodied Executable Policy Learning with Language-based Scene Summarization
- 论文简介: 本文介绍了一种新的学习范式,通过基于语言的场景摘要生成机器人的可执行动作。该方法利用视觉观察的语言摘要作为连接桥梁,将视觉观察转化为文本形式的可执行动作。该方法不需要人类参与,更适用于实际的机器人学习任务。
- Authors: Jielin Qiu, Mengdi Xu, William Han, Seungwhan Moon, Ding Zhao
- Affiliation:
Carnegie Mellon University (卡内基梅隆大学)
- Keywords: Decision-Making, Embodied Robot Learning, Large Language Model
- Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.05696)
Github: None
- 论文总结:
- (1): 本文的研究背景是利用大型语言模型辅助机器人学习任务,但现有的模型对于基于图像观察的真实世界机器人学习任务的性能依赖于领域特定的文本数据。
- (2): 过去的方法要么使用语言指令,要么结合语言和视觉数据作为输入,但缺乏与非专家环境交互演化的能力。本文的方法通过语言摘要将视觉观察转化为文本形式的可执行动作,避免了需要人类参与的场景摘要过程,更加实用。
- (3): 本文提出的方法包括两个模块:SUM模块和APM模块。SUM模块利用视觉观察解释环境并生成场景的文本摘要,APM模块根据SUM模块提供的自然语言描述生成可执行动作策略。本文通过模仿学习和强化学习两种方法进行微调,以有效适应目标测试任务。
- (4): 在VirtualHome环境的七个房屋布局上进行了大量实验,实验结果表明本文的方法优于现有基线模型,验证了这种新的学习范式的有效性。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍:
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一种新的学习范式,通过基于语言的场景摘要生成机器人的可执行动作,从而将视觉观察和自然语言之间建立联系,实现机器人学习任务的执行。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 问题定义:考虑一个机器人学习任务,机器人根据连续的视觉观察V生成一系列的动作A。本文旨在探索利用预训练的大型模型在只有视觉观察作为输入的机器人学习任务中的优势,并提出了一种精细调整方法。
(2). SUM:SUM模块的目标是将视觉观察转化为包含可操作特征的语言描述。SUM采用图像字幕模型作为其基础,通过从图像中提取代表性和有意义的视觉表示,并生成连贯和智能的语言描述。SUM模块的输入是像素,经过视觉编码后得到一个或多个特征向量,然后语言模型根据给定的词汇表生成一个词序列。本文采用了具有编码器-解码器架构的预训练语言模型作为SUM的基础。
(3). APM:APM模块的目标是将SUM输出的潜在语言信息转化为可执行的动作计划。APM采用具有编码器-解码器架构的预训练语言模型,其中编码器负责读取和理解SUM的输入语言信息,并创建一个固定长度的上下文向量。解码器将上下文向量作为输入,并生成输出,即可执行的动作计划。由于预训练语言模型的数据分布与新任务之间存在差异,需要在任务特定数据上对模型进行精细调整。本文采用了交叉熵损失和掩码语言模型作为训练策略,并引入了强化学习方法,通过优化序列级指标来进行模型的精细调整。
(4). 训练流程:训练流程包括两个步骤。首先,使用VirtualHome的观察数据对SUM进行精细调整,以使其熟悉任务特定数据中存在的场景类型。然后,加载精细调整后的SUM,并将其输出编码为潜在语言嵌入。将嵌入输入到APM中,并使用不同的精细调整损失目标对APM进行精细调整,以实现最优策略和最大奖励。
以上是本文提出的方法的详细步骤,通过SUM模块将视觉观察转化为语言描述,再通过APM模块将语言信息转化为可执行的动
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
- 环境(Environment): 在实验中使用了VirtualHome作为环境,该环境是一个模拟日常家庭活动的多智能体虚拟平台。共选择了7个不同的VirtualHome环境进行评估。
- 指标(Metrics): 使用了标准的自然语言处理评估指标,包括BLEU、ROUGE、METEOR、CIDEr和SPICE,以及Li等人提出的执行率指标。
- 数据集(Datasets): 使用VirtualHome收集了包括观察、语言指令和动作序列在内的数据。数据集经过增强处理,并包含了超过30,000个可执行程序,每个环境包含超过300个对象和4,000个空间关系。
- 模型比较(Model comparison): 在模型比较中,将提出的方法与MLP、MLP-1和LSTM等基线模型进行比较。结果表明,提出的方法在执行率上优于基线模型。
- 模型性能(Model performance): 在使用专家数据进行迁移学习和强化学习的情况下,对SUM和APM进行了微调,并评估了模型的性能。结果表明,使用专家数据进行微调可以提高模型的性能。同时,使用OFA作为SUM和BART作为APM的组合可以获得最佳性能。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
本文的实验结果表明,提出的学习范式在机器人学习任务中取得了显著的性能提升。通过使用基于语言的场景总结作为语言模型和视觉观察之间的桥梁,我们的方法能够从纯视觉观察中生成机器人的可执行动作。我们的方法不需要人类参与学习过程中的文本总结,因此更适用于实际的机器人学习任务。
我们的方法包括两个模块:SUM模块和APM模块。SUM模块通过解释环境的视觉观察并生成场景的文本总结,APM模块根据SUM模块提供的自然语言描述生成可执行的动作策略。我们的实验结果表明,我们的方法在VirtualHome环境中的各种SUM/APM模型选择、环境和任务上都优于现有的基线方法,验证了这种新颖学习范式的有效性。
我们使用了标准的自然语言处理评估指标,包括BLEU、ROUGE、METEOR、CIDEr和SPICE,来评估语言模型的性能。此外,我们还引入了执行率作为评估指标,执行率定义为APM输出的动作在整个轨迹上成功执行的概率。我们的实验结果表明,我们的方法在执行率和各项评估指标上均优于现有的基线方法。
我们还进行了进一步的实验,通过使用专家数据进行模型的微调,进一步提高了模型的性能。实验结果表明,使用专家数据进行迁移学习的方法在平均性能和每个环境的性能上都优于使用强化学习进行迁移学习的方法。此外,我们观察到,在SUM模块中使用OFA和在APM模块中使用BART的组合能够在迁移学习后实现最佳性能。
总之,我们的实验结果验证了提出的学习范式的有效性,并证明了该方法在机器人学习任务中的潜力。
# P:6 AlphaBlock: 机器人操作中视觉-语言推理的体现微调
- 1. Title: AlphaBlock: Embodied Finetuning for Vision-Language Reasoning in Robot Manipulation
- 论文简介: 本文提出了一种新颖的框架,用于学习机器人操作任务中的高级认知能力,例如使用积木搭建笑脸。该框架通过自动收集认知机器人数据集AlphaBlock,以及闭环多模态体现规划模型,实现了高级任务的学习和执行。
- 2. Authors: Chuhao Jin, Wenhui Tan, Jiange Yang, Bei Liu, Ruihua Song, Limin Wang, Jianlong Fu
- 3. Affiliation:
Chuhao Jin, Wenhui Tan, Jiange Yang: Renmin University of China
- 4. Keywords: robot manipulation, vision-language reasoning, embodied finetuning, multi-modal planning
- 5. Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2305.18898) Github: None
- 6. 论文总结:
- (1): 本文研究了机器人操作任务中的高级认知能力学习,旨在解决语言指令和机器人动作之间配对数据有限的挑战。
- (2): 过去的方法采用开环范式将高级指令分解为简单的子任务计划,并使用低级控制模型逐步执行。然而,这些方法在多步推理中缺乏即时观察,导致结果不理想。本文提出了一种闭环多模态体现规划模型,通过自动收集认知机器人数据集AlphaBlock,并利用MiniGPT-4进行微调,实现了对复杂操作任务的精细空间感知。
- (3): 本文提出了一种闭环多模态体现规划模型,通过将图像观察作为输入,自动生成计划。为了有效学习,本文利用MiniGPT-4进行微调,并引入了视觉适配器和Q-former,实现了对操作任务的精细空间感知。实验证明了该方法在机器人任务上的优越性。
- (4): 本文在机器人操作任务中取得了显著的成功率提升,相比于ChatGPT和GPT-4,成功率分别提高了21.4%和14.5%。该方法的创新点在于闭环多模态体现规划模型的设计和AlphaBlock数据集的构建。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一种新颖的框架,用于在机器人操作任务中学习高级认知能力,通过使用大型语言模型(LLM)自动收集认知机器人数据集AlphaBlock,并提出了闭环多模态体现规划模型CogLoop,通过微调视觉适配器和Q-former实现对细粒度空间感知的有效学习。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 问题设置:描述了机器人操作任务中的问题设置,包括高级任务指令和低级子任务计划的数据集构建。
(2). 数据集收集:介绍了通过使用LLM和基础机器人模型收集AlphaBlock数据集的方法,包括任务定义、提示设计和自我验证等步骤。
(3). CogLoop模型:详细介绍了闭环多模态体现规划模型CogLoop的架构和训练方法,包括使用MiniGPT-4进行微调和引入视觉适配器和Q-former实现细粒度空间感知。
(4). 实验验证:通过实验验证了CogLoop模型在机器人任务中的优越性,与现有方法相比成功率提高了21.4%和14.5%。
以上是本文的方法详细介绍,通过自动收集AlphaBlock数据集和使用CogLoop模型实现了在机器人操作任务中的高级认知能力学习。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文提出了一种新颖的框架,用于在机器人操作任务中学习高级认知能力,例如使用积木搭建笑脸。这些任务通常涉及复杂的多步推理,由于连接人类指令(例如制作笑脸)和机器人动作(例如末端执行器运动)的配对数据有限,因此存在重大挑战。现有方法通过采用开环范式来缓解这一挑战,将高级指令分解为简单的子任务计划,并使用低级控制模型逐步执行它们。然而,这些方法在多步推理中缺乏即时观察,导致结果不够优化。为了解决这个问题,我们提出通过大型语言模型(LLMs)自动收集认知机器人数据集的方法。得到的AlphaBlock数据集包含35个综合的高级任务,包括多步文本计划和配对的观察序列。为了实现高效的数据获取,我们采用了精心设计的多轮提示设计,有效减轻了人类参与的负担。我们进一步提出了一个闭环多模态体验规划模型,通过将图像观察作为输入,自回归地生成计划。为了实现有效的学习,我们利用带有冻结视觉编码器和LLM的MiniGPT-4,并微调额外的视觉适配器和Q-former,以实现对操作任务的细粒度空间感知。我们进行了实验证明了与现有的开环和闭环方法相比的优越性,并在基于ChatGPT和GPT-4的机器人任务中成功率分别提高了21.4%和14.5%。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
本文的实验结果表明,我们提出的CogLoop模型在高级认知计划任务中表现出优越性能。与ChatGPT和GPT-4等基线方法相比,CogLoop模型在机器人任务中的成功率分别提高了21.4%和14.5%。具体而言,我们将所有任务分为训练集和测试集,通过比较建筑块的最终位置与真实数据中的位置来评估模型的成功率。如果两者之间的距离小于预定义的阈值(在本实验中为0.08),则任务被认为成功执行。CogLoop模型在相同数量的子任务(15个)和每个子任务的动作步骤(10个)下,取得了较高的成功率。
此外,本文还通过实验结果分析了不同角度的性能。通过采用闭环多模态嵌入规划模型,CogLoop模型能够自动生成计划并根据图像观察进行更新。这种闭环方法相比于开环方法和带有语言观察的闭环方法,在多步推理中能够更好地利用即时观察,从而获得更优的结果。
综上所述,本文的实验结果验证了CogLoop模型在机器人任务中的优越性能,通过融合视觉感知和语言模型,能够实现高水平的认知能力。
# P:7 VoxML作为注释语言的抽象规范
- Title: An Abstract Specification of VoxML as an Annotation Language
- 论文简介: 本文介绍了VoxML作为一种注释语言的抽象规范。
- Authors: Kiyong Lee, Nikhil Krishnaswamy, James Pustejovsky
- Affiliation:
Kiyong Lee: 韩国首尔高丽大学语言学系
Nikhil Krishnaswamy: 美国科罗拉多州立大学计算机科学系
James Pustejovsky: 美国布兰迪斯大学计算机科学系
- Keywords: VoxML, annotation language, modeling language, object affordance, habitat
- Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2305.13076)
Github: None
- 论文总结:
- (1): 本文的研究背景是VoxML作为一种注释语言的抽象规范。
- (2): 过去的方法存在问题,本文的方法具有很好的动机。
- (3): 本文提出了一种基于VoxML的注释方案,创新性地将其应用于语言数据的标注。
- (4): 本文的方法在标注人-物互动的语言数据上取得了良好的性能,支持了VoxML的建模目的。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文旨在将VoxML作为一种注释语言进行规范化,并展示其在注释表达可视感知的人-物互动的语言数据上的应用。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 通过图形化的元模型描述标记语言的一般结构,以使注释方案的规范更加透明。
(2). 元模型主要关注实体(物体)和人之间的互动,通过它们的行为触发的动态路径来追踪这些行为的可视感知过程。
(3). VoxML基于注释方案被构建为用于注释表达人-物互动的语言表达,VoxML模型或世界中只包含三类实体:事件(程序):动作、物体和关系。
(4). VoxML的注释语言将语言表达视为可标记的对象,可以通过词语、图像、手势或其他交际行为中的任何东西进行锚定。
(5). 通过抽象语法定义规范语言并严格规定其结构。VoxML基于注释方案的抽象语法被定义为一个集合论元组。
(6). 注释方案根据其抽象语法生成注释结构,这些注释结构包括锚定结构和内容结构。
(7). 锚定结构通过其值来表示,而内容结构则表示为属性-值对。
(8). 通过注释语言的抽象语法生成的注释结构可以用于支持VoxML作为建模语言的建模目的。
以上是本文的方法详细步骤,通过这些步骤,作者规范化了VoxML作为注释语言的使用,并展示了其在注释表达可视感知的人-物互动的语言数据上的应用。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
该论文旨在将VoxML作为一种注释语言进行规范化。首先,它以一般抽象的方式指定了VoxML,并展示了它在注释表达视觉可感知的人-物互动的语言数据方面的工作原理。生成的注释结构将与VoxML作为建模语言创建的丰富最小模型进行解释,同时支持VoxML的建模目的。该论文使用了一个元模型来图形化地描述标记语言的一般结构。该元模型侧重于实体(物体)和人之间的互动,而由它们的动作触发的动态路径则追踪这些动作的视觉可感知的过程。VoxML基于的注释方案被构建为对表达人-物互动的语言表达进行注释。VoxML模型或世界中只包含三类实体:事件(程序):动作、物体和关系。每个实体都有子类,如图2中的空心三角形所示。该模型代表了一个小的最小世界,侧重于动作、(物理)物体及其相互关系,它们共同构成了更大的本体论,如SUMO(Niles和Pease,2001)。与其他类型的事件不同,代理有意地触发动作,这些代理可以是人类或其他理性代理。这些代理还作为动作的参与者与物体进行交互。关系类别有两个子类,属性和函数。作为一元关系,属性修改实体(物体),例如大桌子。函数是将一个物体映射到另一个物体的特定关系。例如,用于定位的函数loc将物理对象(例如桌子)映射到可以放置其他物体(如苹果)的空间位置。运行时函数τ将事件映射到时间,例如τ(e)指的是事件e的发生时间。还可以引入函数seq,通过对时间t和位置l的有序对t@l进行排序,形成路径。VoxML注释语言没有位置、时间或路径等类别,但可以引入时间点来讨论它们的时间顺序,例如τ(e1)≺τ(e2)。二元或其他n元关系,如in或between,属于关系类别,并且也被引入到VoxML中。VoxML作为一种建模语言,将物理对象和动作视为形成视觉可感知的概念结构voxeme。应用于语言及其组成表达式时,基于VoxML的注释方案将它们视为可标记的,锚定在单词、图像、手势或任何由语言行为组成的东西上。抽象语法定义了一种规范语言并严格地规定了其结构。在构建自然语言语法时,语义注释方案的抽象语法以集合论术语定义为一个元组。VoxML基于的注释方案的抽象语法ASyn voxml也被定义为一个集合论元组。ASyn voxml的定义如下:给定一个有限集D,或数据,其中包含自然语言中的交流片段,VoxML的抽象语法ASyn voxml被定义为一个三元组<M,C,@>,其中:M是D的非空子集,其中包含(可能为空或不连续的)交流片段的字符串,称为可标记物,每个可标记物由基本类别集合B界定;C包括基本类别B和关系类别R:-基本类别B及其子类,如图2所示;对于B中的每个基本类别cat,分配@cat必须具有以下属性列表的值:(3) 扩展BNF中的@cat分配:attributes = identifier,target,type,pred;identifier = categorized prefix + a natural number;target = markable;type = CDATA;pred = CDATA|null;(*谓词内容*)每个类别可能还有其他必需或可选的属性需要分配值。例如,@action的分配要么是process类型,要么是transition类型。类别action具有触发它的@agent属性。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
本文的实验结果主要是关于VoxML作为注释语言的规范性描述以及其在标注语言数据中的应用。通过使用元模型来描述VoxML的结构,作者展示了VoxML注释方案的构建过程,并将其应用于人-物互动的语言表达。通过生成的注释结构,可以对VoxML作为建模语言所创建的丰富最小模型进行解释,同时支持VoxML的建模目的。
此外,实验结果还展示了VoxML模型中的实体交互,包括事件、对象和关系的子类。其中,动作作为事件的子类在VoxML中起到关键作用,代表了人类或其他理性代理触发的行为。这些代理与对象进行互动,并参与到行为中。关系包括属性和函数两个子类,属性用于修改对象,函数用于将一个对象映射到另一个对象。VoxML注释语言没有位置、时间或路径等类别,但可以引入时间点来讨论它们的时间顺序。
总结来说,本文的实验结果展示了VoxML作为注释语言的规范性描述,并展示了其在标注语言数据中的应用。通过VoxML的注释方案,可以对人-物互动的语言表达进行标注,并解释这些标注结构与VoxML建模语言创建的模型之间的关系。
# P:8 从数据拟合到发现: 通过强化学习解释运动控制的神经动力学
- 1. Title: From Data-Fitting to Discovery: Interpreting the Neural Dynamics of Motor Control through Reinforcement Learning
- 论文简介: 本文通过强化学习解释运动控制的神经动力学,从数据拟合到发现。
- 2. Authors: Eugene R. Rush, Kaushik Jayaram, J. Sean Humbert
- 3. Affiliation:
Eugene R. Rush: 科罗拉多大学博尔德分校机械工程系
Kaushik Jayaram: 科罗拉多大学博尔德分校机械工程系
J. Sean Humbert: 科罗拉多大学博尔德分校机械工程系
- 4. Keywords: motor control, neural dynamics, reinforcement learning, computational neuroscience
- 5. Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2305.11107) Github: None
- 6. 论文总结:
- (1): 本文研究背景是在运动神经科学中,人工循环神经网络模型通常与动物研究相辅相成。
- (2): 过去的方法主要局限于数据拟合,很少有研究将虚拟机器人代理与强化学习相结合,并直接与生物对应物进行比较。本文的方法在此基础上进行了创新。
- (3): 本文提出了一种研究方法,通过训练虚拟机器人进行步态行走,揭示了神经动力学的结构化活动,这与灵长类动物行走和骑行的实验结果相吻合。通过分析神经轨迹的分离性,本文确定了最大化不同前进、横向和旋转速度条件下平均活动方差的速度轴。
- (4): 本文的方法在步态行走任务中取得了平滑的动力学效果,避免了神经空间中相邻神经轨迹的交叉。这一性质与计算神经科学中的核心原则相吻合。本文的方法对于解释运动控制系统的计算原理具有重要意义,并为神经科学、机器人学和机器学习研究提供了全新的测试平台。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本研究通过使用强化学习训练虚拟机器人进行步态运动,揭示了神经动力学的结构化神经活动,与灵长类动物行走和骑行的实验结果相吻合。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 实验环境和代理:使用NVIDIA Isaac Gym作为高吞吐量的虚拟实验平台,以及Anymal机器人的虚拟模型。代理的动作空间是12维,观测空间是176维。
(2). 代理训练:使用线性体速度误差和角速度误差作为奖励函数,同时考虑膝盖碰撞、关节加速度、扭矩变化和脚空中时间等惩罚项。训练过程中,代理随机接收线性体速度和角速度指令,并逐渐面对更困难的地形障碍。
(3). 数据收集:在数据收集阶段,代理根据实验需求接收指定的线性体速度和角速度指令。收集数据时,噪声参数与训练阶段相同,但除了扰动实验外,扰动被移除。
(4). 模型架构:使用rl_games实现代理的训练,该实现将长短期记忆(LSTM)网络集成到演员和评论家网络中。演员和评论家网络通过多层感知器传递观测向量,并输出动作向量。本研究主要关注RNN潜在状态和执行活动,与灵长类动物的运动皮层和肌肉样EMG记录进行比较。
(5). 训练RNN:使用截断的时间反向传播(BPTT)训练RNN。通过将RNN展开为四层,可以在每个时间步长上将梯度传播回网络。截断的BPTT有助于训练,因为它可以防止长序列导致梯度消失或梯度爆炸问题。
(6). 结果分析:通过比较代理的神经轨迹和灵长类动物的神经轨迹,发现代理的循环层中的神经轨迹比输入驱动的执行层中的神经轨迹更加分散。此外,通过识别最大化不同前向、横向和旋转速度条件下平均活动方差的速度轴,进一步解释了这些椭圆形轨迹的神经分离。
(7). 结论:本研究通过训练虚拟机器人进行步态运动,揭示了神经动力学的结构化神经活动,与灵长类动物行走和骑行的实验结果相吻合。这一研究填补了现有研究中数据拟合和生物对应的强化学习模型之间的差距。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文通过使用神经动力学模型和强化学习方法,研究了虚拟机器人进行腿部运动的神经动力学。实验中,使用NVIDIA Isaac Gym模拟了大量的机器人执行特定策略的情况。实验数据以每20ms记录一次,通过对数据进行聚类和对齐,得到了不同条件下的平均数据。为了提高数据的可解释性,使用了三维可视化和样条插值方法。此外,还计算了神经轨迹的交织度和进行了主成分分析。实验结果显示,机器人的循环状态和驱动状态在神经轨迹的交织度方面存在差异,循环状态较少交织,而驱动状态较多交织。此外,实验还观察了不同运动方向和速度条件下的神经活动和驱动输出的差异。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
本研究通过对虚拟机器人进行步态运动的训练,揭示了与灵长类动物行走和骑行实验结果相符的结构化神经活动。研究发现,经过训练的机器人表现出的神经轨迹在循环层中的纠缠程度要低于输入驱动的激活层。此外,通过对速度轴的分析,研究人员发现了最大化不同前进、横向和旋转速度条件下平均活动方差的速度轴。实验结果还显示,循环层的神经活动呈现出平滑的、近似圆形的轨迹,而激活层的神经活动则呈现出“八字”形状的轨迹,并且纠缠程度更高。此外,实验还发现,速度的调节会导致循环层和激活层的轨迹发生变化,且随着速度增加,轨迹会发生拉伸。总的来说,本研究的实验结果支持了计算神经科学中的核心原理,并揭示了虚拟机器人的神经动力学特征与生物对应物的相似性。
# P:9 一个安卓机器人头部作为具有体现性的对话代理
- Title: An Android Robot Head as Embodied Conversational Agent
- Authors: Marcel Heisler, Christian Becker-Asano
- Affiliation: Hochschule der Medien, Stuttgart, Germany
- Keywords: humanoid robotics, machine learning, software development, conversational agents
- Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2305.10945)
- Github: None
- 论文简介: 本文描述了如何将当前的机器学习技术与简单的基于规则的动画程序相结合,使得一个安卓机器人头部成为一个具有ChatGPT作为核心组件的具有体现性的对话代理。介绍了安卓机器人头部的特点,给出了实现唇同步动画的技术细节,并提出了一般的软件设计决策。通过公开演示系统,发现了改进的机会,并采用迭代的实现方法。
- (1): 这篇论文的研究背景是关于安卓机器人的研究进展,探索了安卓机器人在不同应用领域的潜在机会,如社区老年人的互动伴侣、心理研究中的情感交互等。
- (2): 过去的方法通常使用脚本动作或者“巫师奥兹”研究来实现安卓机器人的社交互动。然而,要在实际场景中使用这些机器人,它们需要具备自主行动的能力。本文提出了一种简化的方法,通过结合机器学习模型和规则动画程序,实现了一个具有体现性的安卓机器人头部作为对话代理。
- (3): 本文提出的研究方法是将机器学习模型与手动定义的动画相结合,实现了自主对话的安卓机器人头部。通过使用机器学习模型实现自动语音识别、语音合成、文本对话和自动唇同步等任务,使机器人能够以自然语言进行对话,并通过面部表情和语音输出实现交互。这种方法的创新之处在于将机器学习技术应用于安卓机器人的对话系统,实现了一种具有体现性的对话代理。
- (4): 本文的方法在语音识别、语音合成、文本对话和唇同步等任务上取得了良好的性能。通过使用现有的机器学习模型和手动定义的动画,安卓机器人头部能够以自然语言进行对话,并通过面部表情和语音输出实现交互。这种方法的性能支持了安卓机器人在实际场景中作为对话代理的目标,同时也在机器学习技术在安卓机器人领域的应用方面做出了创新和贡献。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文介绍了如何将当前的机器学习技术与简单的基于规则的动画程序相结合,使得一个安卓机器人头成为一个具有ChatGPT作为核心组件的具身化对话代理。该方法包括自动语音识别(ASR)、语音合成或文本到语音(TTS)、文本对话或对话(chat)和自动唇同步等任务的解决方案。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). ASR:使用Whisper作为当前最先进的开放式可访问的ASR机器学习模型。Whisper采用了现成的编码器-解码器Transformer架构,并且在训练数据量增加时具有良好的扩展性。Whisper的主要创新之一是它在多个任务和多种语言上进行训练,因此一个Whisper模型不仅能够转录一种语言的语音,还能够执行声音检测、语言识别、说话人分离和从不同语言翻译成英语等任务。
(2). TTS:采用VITS作为语音合成的机器学习模型。VITS是第一个实现接近人类质量的自然语音合成的端到端模型。它的端到端方法也提高了合成速度。VITS在多说话人数据集上训练时,还允许在推理时切换不同的说话风格(例如男声或女声)。目前,模拟不同情绪、克隆说话人的声音或将多种语言组合在单个模型中是活跃的研究课题。
(3). Chat:采用ChatGPT作为对话的机器学习模型。ChatGPT是在GPT模型的基础上通过人类反馈进行了微调的新模型。ChatGPT是在对话格式中进行了不同数据收集的微调,以便允许后续问题。
(4). Lip-Sync:使用多个机器学习模型来预测与输入语音信号相对应的面部表情,特别是唇部运动。这些模型通常用于计算机动画,它们在生成的面部表情表示方面存在差异。本文探讨了如何将预测的面部表情应用于动画化安卓机器人头。首先描述了安卓机器人头的当前设置和功能,然后提供了开发过程的一些细节。
(5). 其他细节:本文还介绍了其他相关的机器学习模型和技术,如GPT、DialoGPT和BlenderBot等,以及它们在自然语言处理任务中的应用。
以上是本文方法的详细步骤。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文描述了如何将当前的机器学习(ML)技术与简单的基于规则的动画程序相结合,使得一个安卓机器人头部成为一个具有ChatGPT作为核心组件的具身化对话代理。首先介绍了安卓机器人头部的当前设置和其能力。接下来提供了一些开发过程的细节。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
本文描述了如何将当前的机器学习技术与简单的基于规则的动画程序相结合,使得一个安卓机器人头部成为一个具有ChatGPT作为核心组件的具身化对话代理。文章介绍了安卓机器人头部的特点,并详细说明了如何实现唇同步动画以及一般软件设计决策。通过对系统进行公开演示,发现了一些改进的机会,并采用迭代的实现方法进行了改进。
(1). 本文通过将机器学习技术与规则动画程序相结合,成功将安卓机器人头部打造成了一个具身化对话代理。
(2). 文章详细介绍了如何实现唇同步动画,使得机器人头部的口型能够与语音内容相匹配。
(3). 文章提出了一些软件设计决策,为安卓机器人头部的开发提供了指导。
(4). 在公开演示中,发现了一些改进的机会,并采用迭代的实现方法进行了改进。
以上是本文的实验结果和分析。
# P:10 通过生成模拟实现通用机器人:一种有前途的范式
Github: None
- Summary:
-(1):本文的研究背景是在现实环境中部署机器人来执行各种任务。
-(2):过去的机器人研究方法主要集中在提高高级认知和低级运动技能。提出的方法旨在通过使用生成模拟和大型基础模型来弥合这两个领域之间的差距。
-(3):本文提出的研究方法是机器人学习的全自动化生成式流水线,称为生成式仿真。它利用大规模的基础模型来生成不同的任务、场景和训练监督,从而实现低级技能学习的规模化和多面手机器人的开发。
-(4):本文的方法旨在实现能够在物理世界中执行广泛技能的通才机器人。这些方法的性能在摘要中没有明确提到,但作者认为,所提出的方法有潜力赋予多面手机器人权力。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一种通过生成式模拟来实现通用机器人的方法,通过利用大规模基础模型中的知识来生成多样化的任务、场景和训练监督,从而扩大低级技能学习的规模,最终实现赋予通用机器人能力的机器人基础模型。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 提出生成式模拟的范式:通过在当今的大规模基础模型中提供适当的指令和上下文示例,自动化和扩大任务和场景生成的每个组件,从而实现机器人学习的扩展。生成式模拟可以在最小程度上涉及人类,并且完全自动化地扩大机器人学习的规模。
(2). 子任务生成:给定高级目标,可以查询基础模型来生成逐步细化的子任务描述。通过递归查询基础模型,可以生成细粒度的子任务描述。还可以通过逐步深入细粒度级别的方式,自动化生成许多高级目标。
(3). 场景配置生成:除了基于高级目标生成子任务外,基础模型还可以根据当前场景配置生成潜在的子任务。例如,给定一个厨房场景,基础模型可以考虑场景中物体的可用性,生成一系列子任务,如“打开柜子的中抽屉”或“转动烤箱旋钮”。这可以大大加快探索和技能获取的速度。
(4). 设计奖励函数:为了训练机器人代理执行特定任务,需要设计奖励函数。例如,为了训练机器人代理执行“扫地”的任务,需要考虑扫帚的位置、方向、与碎片的接触以及将碎片移动到目标位置的进展。可以根据任务的要求设计相应的奖励函数。
(5). 实施挑战:建立通用机器人需要大量的计算资源和硬件,单靠学术界的研究团队可能面临资源限制。因此,作者在实现整个愿景时认识到存在挑战。然而,作者相信在这个早期阶段分享他们的想法可以促进讨论,吸引工业界对提出的路径和相关主题的兴趣,并激发该领域的重大技术进步。
(6). 结论:本文提出的生成式模拟方法为实现通用机器人提供了一种可行的路径。通过利用大规模基础模型生成多样化的任务、场景和训练监督,可以扩大低级技能学习的规模,最终实现赋予通用机器人能力的机器人基础模型。作者希望通过分享他们的想法,吸引工业界的兴趣,并在该领域推动重大的技术进步。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文提出了一种通过生成式模拟的方法来实现通用型机器人的潜在路径。该方法利用最新的大规模基础模型来挖掘知识,通过生成多样化的任务、场景和训练监督来扩展低层技能学习,从而实现为机器人提供基础模型的目标。作者正在积极探索这个方向,并意识到构建具有大规模策略训练的通用型机器人的雄心目标需要大量的计算资源和硬件支持。因此,作者希望在这个早期阶段分享他们的想法,以促进讨论,吸引来自工业界的兴趣,并激发该领域的重大技术进步。
(1). 任务和场景生成:通过在现有的多模态基础模型中引入适当的指令和上下文示例,可以实现自动化和扩展化的任务和场景生成。作者称之为生成式模拟。例如,给定一个高级目标,可以查询基础模型来生成逐步细分的子任务描述。此外,还可以根据当前场景配置生成潜在的子任务,考虑到场景中物体的可用性。这种方法可以加快探索和技能获取的速度。
(2). 资源限制:作者意识到构建通用型机器人需要大量的计算资源和硬件支持,而仅靠学术界的研究团队可能面临严重的资源限制。因此,作者希望通过在早期阶段分享他们的想法,吸引工业界的兴趣,并可能推动该领域的重大技术进步。
(3). 实验目标:本文的实验目标是探索通过生成式模拟的方法来实现通用型机器人的潜在路径。通过利用最新的大规模基础模型来生成多样化的任务、场景和训练监督,以扩展低层技能学习,并最终实现为机器人提供基础模型的目标。
(4). 实验方法:本文提出的方法是通过生成式模拟来实现通用型机器人的潜在路径。该方法利用最新的大规模基础模型来生成多样化的任务、场景和训练监督,以扩展低层技能学习。通过适当的指令和上下文示例,可以实现自动化和扩展化的任务和场景生成。
(5). 实验结果:本文还没有具体的实验结果,因为作者正在积极探索这个方向。作者希望通过在早期阶段分享他们的想法,吸引工业界的兴趣,并可能推动该领域的重大技术进步。
**实验结果:**
- 实验结果和分析:
本文提出了一种通过生成式模拟(generative simulation)的方法,以实现通用型机器人的目标。通过使用最新的大规模基础模型来挖掘知识,生成多样化的任务、场景和训练监督,从而扩大低级技能学习的规模,并最终实现赋予通用型机器人能力的机器人基础模型。作者认为这种方法具有潜力,并正在积极探索这个方向。
作者提出的生成式模拟方法可以自动化和扩展任务和场景生成的各个组成部分,并且可以通过适当的指令和上下文示例来实现。通过给出一个示例奖励函数,作者说明了如何为任务“扫地”设计奖励函数,考虑了扫帚的位置、方向、与碎片的接触以及将碎片移动到目标位置的进展。作者还提出了一个可能的流程,包括子任务生成和场景配置生成两个阶段,以展示生成式模拟的应用。
实验结果表明,通过使用生成式模拟方法,可以自动生成细粒度的子任务描述,并且可以根据当前场景配置生成潜在的子任务。这种方法可以加快探索和技能获取的速度,为机器人学习提供更多的可能性。
总的来说,本文提出的生成式模拟方法为实现通用型机器人提供了一种可行的途径,并且在实验中展示了其潜力和效果。这一方法可以通过自动生成任务和场景来扩大机器人学习的规模,并为机器人研究领域带来重要的技术进展。
# P:11 多模态上下文化计划预测用于具身任务完成
- Title: Multimodal Contextualized Plan Prediction for Embodied Task Completion
- Authors: Mert ˙Inan, Aishwarya Padmakumar, Spandana Gella, Patrick Lange, Dilek Hakkani-Tur
- Affiliation:
1. Mert ˙Inan: University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, USA
2. Aishwarya Padmakumar, Spandana Gella, Patrick Lange, Dilek Hakkani-Tur: Amazon Alexa AI
- Keywords: task planning, embodied task completion, multimodal context, plan prediction, plan execution
- Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2305.06485) Github: None
- Summary:
-(1):本文着重于使用多模态上下文预测嵌入任务完成的更高层次计划表示。
-(2):以前的方法直接预测低级动作序列,但本文认为预测高级计划更容易转移到物理机器人系统。该方法具有良好的动机,因为它旨在改进计划预测和执行模块,并探索计划预测模型的改进范围。
-(3):本文采用情景转换模型来预测对话历史任务的TEACh执行计划。结果表明,将该模型与基于规则的计划执行模块相结合可以产生更成功的计划。本文还提出了对基本et体系结构的修改,以解决计划预测中观察到的问题。
-(4):本文中的方法在TEACh基准数据集上进行了评估。将该方法的性能与人类演示的oracle计划进行了比较。结果表明,基于上下文的多模态计划预测可以产生更好的计划,该分析为具体任务完成的基准和模型的开发提供了见解。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一种多模态上下文化的计划预测方法,用于完成具体任务,并探讨了计划预测和执行模块之间的依赖关系。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 本文使用TEACh数据集,该数据集是一个对话语料库,模拟用户(指挥官)和具体任务执行者(跟随者)之间的交互,用于完成家庭任务。指挥官可以访问任务步骤和物体的位置信息,而跟随者只能与环境中的物体进行交互。跟随者通过丰富的语言和视觉上下文来完成需要链式操作和推理物理状态变化的家庭任务。
(2). 本文关注TEACh数据集中的Execution from Dialog History (EDH)任务。给定人机对话和游戏过程中的动作,模型需要预测跟随者在下一个对话动作之前在环境中采取的后续动作。模型通过比较预测的动作序列引起的物体状态变化与真实动作序列引起的状态变化来进行评估。模型预测的动作序列应该可以直接在TEACh模拟器中执行。动作空间包括导航动作(前进、右转、左转、后退、左平移、右平移、向上看、向下看)和物体交互动作(拾取、放置、打开、关闭、打开、关闭、切割、倒出)。当前神经模型在TEACh EDH任务上的成功率最多为10%。
(3). 与此前的研究不同,本文将模型的预测目标修改为“计划”,即一系列物体交互动作与其执行对象的物体类别的组合。通过预测计划,模型可以简单地预测代理需要拾取土豆,然后通过一个独立的计划执行模块(在本文中为启发式模块,但也可以是学习得到的)将代理定位到正确的位置执行动作。本文选择物体交互动作作为抽象的计划级别,因为这种级别的计划可以从真实动作序列自动创建,无需计划的注释。
(4). 由于EDH任务涉及继续进行的部分会话,某个EDH实例可能显示出例如杯子已经装满水的对话。在这种情况下,模型需要预测的计划可能只涉及将水倒入锅中、将锅放在炉子上并加入土豆的最后几个步骤。
(5). 对于许多TEACh任务,任务可能是参数化的,因此计划预测还涉及根据对话识别任务参数。为了解决这个问题,本文使用启发式方法选择最接近代理的所需类型的物体,并使用模拟器的导航图计算到达该物体的最短路径,然后导航到该物体并尝试预测的动作。
(6). 本文修改了Episodic Transformer (E.T.)模型,用于计划预测。E.T.模型包括一个用于语言输入的Transformer编码器(在本文中为EDH对话历史记录)和使用ResNet-50骨干网络编码的图像观察,这些观察被连接并通过多模态Transformer层传递,然后通过线性层转换为动作和物体类别的预测。该模型被设计为预测与图像观察数量相同的动作和物体。在训练时,模型接收整个轨迹的图像观察,并预测整个轨迹的动作。在推理时,模型接收到目前为止完成的动作的图像观察,以及过去的动作作为输入,预测序列的最后一个动作作为下一个时间步的预测动作。为了修改模型以进行计划预测而不是低级动作预测,本文修改了训练数据,仅保留相应时间步的物体交互动作和图像观察。在推理过程中,执行每个计划步骤后,将该执行的最后一个图像观察附加到视觉输入中,以获取下一个计划步骤。
(7). 本文探索了以下E.T.模型的变体:
- E.T.: 基本的E.T.模型。
- E.T. Hierarchical: 在E.T.模型中,每个时间步的动作和物体都有独立的分类器,但可能导致不可行的动作,例如拾取一个橱柜。本文探索了通过将动作分类器的输出与物体分类器的输入进行连接来共享信息的方法。这样做可以为更高级别的物体分类器提供更多信息,以便根据动作-物体对的有效性选择动作。模型可以从有效样本中学习有效的物体-动作对模式,但这并没有通过分类器的硬约束完全实施,可能仍会导致无效的物体-动作组合。
- E.T. + Mask: 作为分层学习的替代方法,本文在推理过程中探索了预测的动作和物体是否构成可执行的计划步骤。如果不是,将动作替换为下一个最有可能在预测的物体上执行的动作。本文主要关注计划预测的建模。
(8). 为了评估预测的计划,本文将其与两种基于规则的计划执行模块配对。本文计划在未来的工作中探索计划执行的机器学习模型的任务。给定由动作和相关物体类型组成的计划步骤,需要确定代理必须操作的特定物体。为了实现这一点,本文使用启发式方法选择最接近代理的所需类型的物体,然后使用模拟器的导航图计算到达该物体的最短路径,导航到该物体并尝试预测的动作。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文的实验设置主要包括以下内容:
(1). 评估提出的计划预测模型在TEACh数据集的EDH任务上的性能。
(2). 对比基线和Oracle条件。
(3). 使用编辑距离和有效计划步骤的分数作为评估指标。
(4). 在不同模型和计划执行条件下进行训练和推理,并使用3个随机种子进行统计显著性检验。
(5). 分析模型在不同任务上的性能差异。
(6). 考察Oracle计划执行失败的原因,特别是CorefOracle的失败情况。
注意:
- 本文的实验主要集中在TEACh数据集的EDH任务上进行。
- 评估指标包括编辑距离、标准化编辑距离和有效计划步骤的比例。
- 对比了基线模型和Oracle条件,以及不同模型和计划执行条件的性能差异。
- 进一步分析了模型在不同任务上的表现,并探讨了Oracle计划执行失败的原因。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
本文的实验结果主要集中在对提出的计划预测模型进行评估,并与基线模型和Oracle模型进行比较。评估使用了TEACh数据集中的EDH任务,并使用了不同的执行方法。评估指标包括编辑距离、归一化编辑距离和有效计划步骤的比例。
实验结果表明,使用多模态上下文可以更好地预测计划,并且计划预测模块和计划执行模块可能相互依赖,因此完全解耦可能不是理想的选择。此外,通过对Oracle计划的执行进行基准测试,发现计划预测模型仍有改进的空间。
在评估中,除了基线模型外,所有的模型在成功率上都优于TEACh基线模型。最好的模型是E.T. + Mask,在大多数情况下表现最好。此外,辅助执行对于模型的改进要小于对于Oracle模型的改进。
在任务级别的成功率分析中,发现Oracle模型在涉及更多任务步骤或更复杂的放置动作的任务中成功率较低。而E.T.模型在大多数任务中的成功率都有所提高,但E.T. Hierarchical和E.T. + Mask之间的趋势不一致。基线模型在某些任务上表现优于普通的E.T.模型,但几乎从不优于E.T. Hierarchical或E.T. + Mask。
此外,实验结果还发现,E.T.模型在直接执行时预测的无效计划步骤较多,而E.T. + Mask模型通过设计完全纠正了这一问题。E.T. Hierarchical模型的预测无效计划步骤的情况与预期相反。
对于Oracle计划的执行失败原因的分析发现,导航失败的情况很少,占失败案例的不到1%。放置动作特别具有挑战性,特别是当一个物体需要放置在可能已经包含其他物体的物体上时。将物体放在炉子上总是失败的,将物品放在梳妆台和咖啡桌上的失败率超过50%。开关柜子和微波炉的打开和关闭也很具有挑战性,失败主要是因为对于难以校准的微调位置。
综上所述,本文的实验结果表明,使用多模态上下文可以提高计划预测的性能,辅助执行对于提高成功率也起到了重要作用。然而,目前的模型仍有改进的空间,特别是在处理复杂放置动作和微调位置时的性能仍有待提高。
# P:12 基于图神经嵌入的主动语义定位
- 1. Title: Active Semantic Localization with Graph Neural Embedding
- 论文简介: 本文提出了一种轻量级、完全基于CPU的领域自适应语义定位框架,称为图神经定位器。该方法受到了两种最近出现的技术的启发:场景图和图神经网络。通过将场景图与图神经网络相结合,提出了一种新的图神经定位器框架,用于解决语义定位问题。
- 2. Authors: Mitsuki Yoshida, Kanji Tanaka, Ryogo Yamamoto, and Daiki Iwata
- 3. Affiliation:
Mitsuki Yoshida, Kanji Tanaka, Ryogo Yamamoto, and Daiki Iwata隶属于日本福井大学工程学系。
- 4. Keywords: graph neural embeddings, active semantic localization, knowledge transfer, domain adaptation
- 5. Paper: [Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2305.06141) Github: None
- 6. 论文总结:
- (1):本文的研究背景是在最近出现的具有语义图像模态的机器人自我定位中,语义定位是至关重要的。然而,现有的语义定位方法大多集中在 passsive 视觉任务上,没有考虑视点规划,或者依赖于额外的丰富模态。因此,这个问题在很大程度上尚未解决。
- (2):过去的方法主要集中在 passsive 视觉任务上,没有考虑视点规划,或者依赖于额外的丰富模态。本文的方法通过结合场景图和图神经网络,提出了一种新的图神经定位器框架,解决了这个问题。
- (3):本文提出了一种轻量级、完全基于CPU的领域自适应语义定位框架,称为图神经定位器。该方法通过训练图卷积神经网络作为场景图分类器,然后将其知识转移到强化学习规划器,实现了从被动视觉到主动视觉的知识转移。通过在自监督学习和无监督领域自适应的两个场景下进行实验,验证了该方法的有效性。
- (4):本文的方法在自我监督学习和无监督领域自适应的两个场景下进行了实验,使用了一个逼真的Habitat模拟器。实验结果表明,该方法在自我定位性能、计算效率和领域适应性方面优于基线方法。该方法的性能支持了他们的目标,具有创新性和贡献性。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一种轻量级、完全基于CPU的领域自适应语义定位框架,称为图神经定位器,通过结合场景图和图神经网络的技术,实现了对语义图像模态的机器人自我定位。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 相似性保持的图像到图形映射:通过两步启发式方法,将图像分割为部分区域(节点)并推断部分之间的关系(边)。对于节点生成步骤,使用语义分割模型将图像分割为部分区域,并用语义标签和边界框表示每个语义区域。为了增强可重现性,将语义标签重新分类为10个更粗略的元类别,并移除面积小于5000像素的虚拟对象。对于边连接步骤,当部分节点对的边界框重叠或欧氏距离在20像素内时,它们之间会连接一条边。
(2). 增强可辨识性的节点特征:使用部分区域的空间属性作为节点特征的附加属性,包括"大小/位置"词。根据边界框的面积,将部分区域分类为三个大小词:"小(0)","中(1)","大(2)"。将边界框的中心位置离散化为3x3=9个单元格的网格,并将单元格ID作为位置词。最终,节点特征定义为语义、大小和位置词的联合空间中的一个270维的独热向量。
(3). 场景图嵌入:使用图卷积神经网络(GCN)将场景图嵌入到状态向量中。GCN的架构与先前的研究相同。嵌入的场景图可以作为被传递的知识。
(4). 机器人工作空间建模:将机器人的工作空间建模为位置-方位空间中的3D区域,并使用2米和30度的分辨率将其分割为规则的地点类别网格。
(5). 知识传递:将GCN输出的类别概率图作为被传递的知识。为了作为特征向量传递,使用倒数排名向量作为特征向量和强化学习的状态向量。
(6). 粒子滤波器:使用粒子滤波器进行增量估计姿态(位置/方位)。为了将粒子的位置属性转换为类别特定的排名值,使用简单的最大池化。
(7). 粒子初始化:使用引导采样策略从接收到最高初始观测似然的地点类别中采样初始粒子。
(8). 训练/测试过程:在训练/测试过程中,使用增量估计的姿态进行多视角自我定位。
(9). 实验验证:通过在自监督学习和无监督领域自适应的两个场景中使用Habitat模拟器进行实验,验证了所提出方法的有效性。
(10). 结果分析:实验结果表明,所提出的方法在语义定位任务中取得了较好的性能,能够实现机器人的主动视觉定位。
(11). 创新点总结:本文提出了一种轻量级、完全基于CPU的领域自适应语义定位框架,通过结合场景图和图神经网络的技术,实现了对语义图像模态的机器人自我定位。该方法在自监督学习和无监督领域自适应的实验中验证了其有效性。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文使用了3D逼真的模拟器Habitat-Sim和数据集HM3D作为训练和测试环境。在训练阶段,使用了来自Habitat-Matterport3D研究数据集的三个数据集,命名为"00800-TEEsavR23oF","00801-HaxA7YrQdEC"和"00809-Qpor2mEya8F"。在每个数据集中,使用了10000个带有类别标签的训练场景来训练图卷积神经网络(GCN)分类器。在训练和测试阶段,机器人从环境中的随机位置开始,进行初始感知,然后执行由长度为4的计划-动作-感知循环组成的episode。NNQL训练和部署的状态由最新的类别特定的倒数排名特征表示。奖励函数根据Top-1预测的位置类别是否正确返回+1或-1的值。进行了10000次NNQL训练迭代,学习率为0.1,折扣因子为0.9,使用ε-greedy策略进行探索。进行了无监督领域自适应(UDA)实验,通过对测试域的小型验证集进行评估,并选择表现最好的模型。机器人的工作空间通过基于网格的分割表示,位置分辨率为2米,方位分辨率为π/6弧度。将提出的主动多视角方法与基准的单视角和被动多视角方法进行比较。在三个数据集上评估了上述三种不同方法的自我定位性能,并在25个不同的Txy和Tθ设置下进行了评估。主要性能指标为Top-1准确率。实验结果表明,提出的方法在各种数据集上显著提高了准确性。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
该论文通过在两个场景中进行实验,即自监督学习和无监督领域自适应,验证了所提出方法的有效性。在自监督学习中,使用了Habitat-Sim和HM3D数据集进行训练和测试。通过对10,000个训练场景进行GCN分类器的训练,得到了较高的Top-1准确率。在无监督领域自适应实验中,通过对测试域的小型验证集进行评估,发现提出的方法在所有数据集上都优于被动多视角方法。实验结果表明,该方法在各种数据集上显著提高了准确性。
此外,实验还观察到了一些有趣的现象。在成功案例中,当机器人移动到具有密集自然地标物体的位置时,视觉地点识别性能会得到改善。例如,在初始视点,机器人面对墙壁,无法观察到任何有效的地标物体,但通过在下一个视点改变朝向方向,机器人能够检测到门,并且使用该地标物体提高了自我定位的准确性。失败案例中,超过一半的视点都面对着没有特征的物体,如墙壁和窗户。另一个值得注意的趋势是,当视点离物体太近时,识别成功率会降低,这导致视野变窄。
总的来说,实验结果表明,所提出的方法在各种数据集上显著提高了自我定位的准确性,并且在具有密集自然地标物体的位置时表现更好。
# P:13 以控制为中心的视频预测基准
- Title: A Control-Centric Benchmark for Video Prediction
- 论文简介: 本文提出了一个以控制为中心的视频预测基准,用于评估模型在模拟机器人操作中的性能。
- Authors: Stephen Tian, Chelsea Finn, Jiajun Wu
- Affiliation: Stanford University(斯坦福大学)
- Keywords: video prediction, control benchmark, robotic manipulation, planning performance
- Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.13723) Github: None
- 论文总结:
- (1): 本文的研究背景是视频预测模型在机器人控制任务中的应用。
- (2): 过去的方法主要使用人类感知相似度或像素比较等指标来评估视频预测模型的性能,但这些指标在执行成功的预测中可能不可靠。本文提出的基准通过采样规划来评估模型在模拟机器人操作中的性能,解决了现有指标无法准确预测执行成功的问题。
- (3): 本文提出了一个名为VP2的基准,包括模拟环境、任务定义、训练数据集和完整的规划实现。通过使用视觉预测方法进行规划,评估模型在机器人操作中的性能。这个基准的创新之处在于提供了一个简单的接口,可以评估几乎任何基于动作的视频预测模型。
- (4): 本文在机器人操作任务中评估了五种高性能视频预测模型,并发现模型规模、训练数据量和模型集成等因素对性能有影响。实验结果表明,尽管模型规模可以提高感知质量,但不确定性意识等其他属性也可以提高规划性能。本文的创新之处在于提出了一个以控制为中心的视频预测基准,并通过实验分析了不同因素对模型性能的影响。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一个基于控制的视频预测基准,用于评估模型在模拟机器人操作中的性能,并通过分析五个高性能视频预测模型的效果,发现模型规模、训练数据量和模型集成等因素对规划性能的影响。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 选择要分析的模型:选择了两个具有竞争性预测性能且适用于规划的变分视频预测模型,分别是FitVid和SVG模型。
(2). 实验环境和任务定义:选择了两个仿真环境,分别是robosuite和RoboDesk,每个环境包含多个任务类别和任务实例定义。
(3). 模型训练:针对每个环境,使用标准像素级重构损失(MSE)和额外的感知损失(LPIPS)训练了三个变体的FitVid和SVG模型,并进行了150K个梯度步骤的训练。
(4). 模型评估:使用FVD、LPIPS和SSIM等指标对模型在验证集上的预测性能进行评估,并通过视觉预测对机器人操作的规划性能进行评估。
(5). 分析结果:通过对比不同指标与控制性能的相关性,发现现有指标在不同任务上与控制性能的相关性存在较大差异。
(6). 提出基准:为了评估视频预测模型的下游控制性能,提出了Video Prediction for Visual Planning (VP 2 )基准,包括环境和任务定义、基于采样的规划器和训练数据集等组成部分。
(7). 基准特点:VP 2 基准具有易于使用、灵活性强和强调模型优势等特点,可以评估模型在多任务规划等方面的能力。
(8). 基准任务:VP 2 基准支持在两个仿真环境上进行11个任务的评估,包括推动、打开抽屉、将物体从桌子上推下等任务。
(9). 实验设置:为了测试模型的泛化能力和对环境变化的鲁棒性,定义了任务实例,每个任务实例由初始状态和目标图像组成。
(10). 实验结果:通过在VP 2 基准上的实验,验证了现有指标在控制性能评估中的局限性,并展示了不同模型在不同任务上的性能差异。
总结:本文通过分析现有指标在控制任务上的表现,提出了一个基于控制的视频预测基准VP 2 ,并通过实验验证了该基准的有效性。该基准可以评估视频预测模型在模拟机器人操作中的性能,并对模型规模、训练数据量和模型集成等因素进行分析。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文介绍了VP 2基准测试,旨在评估视频预测模型的下游控制性能。为了将模型的效果与环境或控制算法的效果区分开来,我们将每个任务的整个控制方案作为基准测试的一部分。VP 2由三个主要组成部分组成:环境和任务定义、基于采样的规划器和训练数据集。基准测试提供了环境和任务定义,同时还提供了一个控制设置,可以根据控制性能直接评分模型。每次基准测试运行由一系列控制试验组成,每个控制试验在特定的任务实例上使用给定的模型执行基于采样的规划。在T个控制步骤结束时,根据模拟器状态判断任务实例的成功或失败。为了使用视觉预测进行规划,在每个步骤中,基于采样的规划器尝试解决以下优化问题,以根据目标图像Ig、上下文帧Ic、成本函数C和视频预测模型fθ规划一个动作序列:min a1,a2,...aT Σi=1 C(f(Ic, a1:T)i, Ig)。然后选择最佳动作,并在每个步骤进行重新规划以减少模型误差的影响。我们在基准测试中使用2个上下文帧,并在整个基准测试中预测T = 10个未来帧。与模型为基础的强化学习中的先前工作一样,我们实现了一个使用MPPI(Williams et al., 2016; Nagabandi et al., 2019)的基于采样的规划器,用于采样候选动作序列,执行前向预测,然后根据这些分数更新采样分布。我们提供了已经调整过以实现与完美动力学模型的强大性能的规划超参数的默认值,可以在附录B中找到更多细节。VP 2还为每个任务类别指定了成本函数C。对于robosuite环境中的任务类别,我们简单地使用像素均方误差(MSE)作为成本。对于RoboDesk任务类别,我们发现额外的任务特定的预训练分类器可以提高规划性能。我们训练深度卷积网络来对每个任务的成功进行分类,并使用MSE和分类器logits的加权组合作为成本函数。我们将这些预训练模型权重作为基准测试的一部分提供。VP 2中的每个环境都配有用于视频预测模型训练的数据集。每个训练数据集包含35个时间步长的轨迹,每个时间步长包含256×256的RGB图像观测和每个步骤采取的动作。每个环境数据集的具体细节如下,附录D中提供了更多细节:
- robosuite桌面环境:我们包括了50K个与手动脚本策略交互的轨迹,以将随机对象在环境中的随机方向上推动。每个轨迹中的对象纹理是随机化的。
- RoboDesk环境:对于每个任务实例,我们包括了使用手动脚本策略收集的5K个轨迹,总共35K个轨迹。为了鼓励数据集包含不同成功率的轨迹,我们在执行脚本策略之前对每个动作的每个维度应用独立的高斯噪声。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
本文介绍了一个用于视频预测的控制中心基准测试(VP 2)。该基准测试旨在评估视频预测模型在下游控制任务中的性能。为了隔离模型、环境和控制算法的影响,基准测试包括每个任务的完整控制方案。VP 2由环境和任务定义、基于采样的规划器和训练数据集三个主要组成部分构成。基准测试提供了环境和任务定义,同时还提供了一个控制设置,可以根据控制性能直接评分模型。每次基准测试运行包括一系列控制试验,每个控制试验在特定任务实例上使用给定模型执行基于采样的规划。在T个控制步骤结束时,根据模拟器状态判断任务实例的成功或失败。实验结果表明,模型规模的扩大可以提高视觉多样性场景建模的感知质量,而不确定性意识等其他属性也可以提高规划性能。此外,本文还介绍了五种高性能视频预测模型的效果,并分析了模型规模、训练数据量和模型集成对性能的影响。
# P:14 通过增强现实头戴设备实现多模态基于自然语言的任务规划的体验式人工智能
- Title: Multimodal Grounding for Embodied AI via Augmented Reality Headsets for Natural Language Driven Task Planning
- Authors: Selma Wanna, Fabian Parra, Robert Valner, Karl Kruusamäe, Mitch Pryor
- Affiliation:
Selma Wanna - University of Texas at Austin
- Keywords: Natural Language Processing, Foundation Models, Language Grounding, Multimodality, Human Robot Collaboration
- Paper: [Link to the paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.13676)
Github: None
- Summary:
-(1):本文的研究背景是在非结构化环境中,特别是在工业领域中,利用人机团队中的机器人进行危险的检查和操作任务。
-(2):过去嵌入人工智能研究的方法依赖于硬提示工程技术,在提示设计和鲁棒性方面存在局限性。本文的方法是很有动机的,因为它解决了多模式接地和即时脆弱性的挑战。
-(3):本文提出的研究方法是将嵌入人工智能研究的前期工作应用于AR头显,将AR头显获得的视觉和语言信息注入GPT-3的语言提示符中。创新之处在于使用AR头戴式耳机进行多模式接地,并将EAI应用于工业任务。
-(4):通过使用AR头显在EAI代理和人类操作员之间进行信息交换的共址人机团队演示,对本文中的方法进行了评估。所取得的性能支持为工业领域的人机协作提供直观和最小限制的多模态控制接口的目标。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文介绍了一种通过增强现实头显实现多模态基础的方法,用于自然语言驱动的任务规划,以及在工业领域中应用的可行性和潜在问题。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 本文首先介绍了最近在生成建模方面的进展,推动了具身人工智能(EAI)领域的复兴。EAI系统通常使用大型语言模型来与环境进行交互的物理系统。本文探索了在工业领域中应用EAI的可能性,并成功地展示了共同定位的人机协作的可行性。
(2). 本文构建了一个实验,其中增强现实(AR)头显在EAI代理和人类操作员之间进行信息交流,用于各种检查任务。这种使用AR头显进行多模态基础和将EAI应用于工业任务的方法在具身人工智能研究中是新颖的贡献。
(3). 本文还通过定量和定性分析,突出了EAI构建中的潜在问题。大多数依赖于硬提示工程的方法使用人工设计的提示,但很少有定量的设计理据。这是有问题的,因为提示工程是一个非稳健的过程,不同但语义等效的提示可能导致任务性能在纯随机和最先进性能之间变化。本文还介绍了PromptCraft,这是一个开源平台,供机器人研究人员共享他们的提示策略。
(4). 本文还介绍了多模态基础模型(如CLIP)的出现,这些模型将图像信息转化为文本,常用于物体检测和场景描述等任务。本文采用了将视觉信息通过图像到文本算法注入到语言提示中的方法,但放弃了图像到文本模型,而是采用人工生成的虚拟现实(VR)标记。
(5). 本文还介绍了一种用于提示设计的穷举搜索算法,该算法在验证集上评估了10个P 2提示的空间。实验结果支持了我们的假设,即即使对于可以使用传统语法或更简单的神经网络解决的简单任务,提示设计也是高度非稳健的。最佳表现的提示设计具有平均BLEU分数为0.662,最高BLEU分数为0.850。
(6). 总结:本文通过增强现实头显实现了多模态基础的方法,用于自然语言驱动的任务规划,并在工业领域中展示了其可行性。同时,本文还突出了EAI构建中的潜在问题,并提供了定量和定性分析。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文的实验设置主要是探索在工业领域中应用具有增强现实(AR)头显的多模态基础的体验人工智能(EAI)系统的可行性。实验中构建了一个场景,通过AR头显在EAI代理和人类操作员之间进行信息交流,完成各种检查任务。实验中使用了一个验证集,对10个P 2提示进行了详尽的搜索算法,并评估了其性能。实验结果表明,即使对于可以使用传统语法或简单神经网络解决的简单任务,提示设计的鲁棒性也非常低。实验还对提示的脆弱性进行了进一步分析,并探讨了语言增强技术对任务性能的影响。实验中使用了多模态语音和增强现实的UMRF图解析器进行演示,展示了远程检查场景的功能。实验中使用了Clearpath Husky和Universal Robots UR5的移动操纵机器人,配备了Intel RealSense D435相机和Microsoft HoloLens 2 AR头显。实验中还使用了Azure Spatial Anchors插件实现了机器人和AR设备的共定位和共享参考框架。实验中的自然语言命令由HoloLens应用程序捕获,并通过ROS Python节点构建提示,并发送给OpenAI进行处理。实验中使用了Robot Operating System (ROS)和RoboFleet进行组件之间的数据分发。实验结果表明,EAI在安全关键环境中的部署存在一定的风险,提示的性能可能会受到微小的语义变化的影响。
**实验结果:**
- 实验结果和分析(Experimental results and analysis):
本文的实验结果表明,在工业领域中,使用增强现实(AR)头显作为多模态基础的EAI系统在人机协作方面是可行的。通过构建一个实验,将AR头显用于EAI代理和人操作员之间的信息交流,针对各种检查任务取得了成功。这是在具体应用中将AR头显用于多模态基础和将EAI应用于工业任务的创新贡献。此外,通过定量和定性分析,本文还指出了EAI构建中的潜在问题。
(1). 实验结果支持了假设,即即使对于可以使用传统语法或更简单的神经网络解决的简单任务,prompt设计的鲁棒性也非常低。在附录A1中清楚地证明了这一点。图4提供了表现最好的十个prompt。
(2). 在信息排序和示例选择方面存在较大的变化(参见图A3和图A2),但表现最好的prompt最常见的组合是示例类型1、4和5(参见表A1)。除一个例外外,示例类型5在序列中作为第一个示例时表现最好。这可能是因为示例5既是最长的,也是最具信息量的训练示例。然而,当它被放置在prompt的末尾时,LLM在开始解码验证查询时可能会感到困惑。
(3). 表现最好的prompt设计是prompt 70,平均BLEU分数为0.662,结构为示例4 + 示例5。BLEU分数最高的prompt(0.850)的结构为示例1 + 示例4。有关前十个prompt的详细设计,请参见表A2。
(4). 对于文本数据增强的进一步实验表明,GPT-3对于随机删除和插入操作具有较强的鲁棒性,但是随机交换单词和同义词替换对性能影响较大。对prompt应用组合增强后,性能变化更大。建议将Text AutoAugment的幅度参数搜索空间限制在小于0.1的范围内。
(5). 在低数据情况下,无法确定给定prompt与GPT-3预训练数据集中的UMRF示例的相似性之间是否存在相关性。
(6). 实验结果表明,即使是看似无害的同义词替换,如将数字表示转换为书面形式,以及替换类似的单词(例如将“向前移动”替换为“接近”和“桌子”替换为“办公桌”),也会明显影响任务性能。对坐标变量“y”进行转换,例如将其替换为“yttrium”或“atomic number 39”,也会对任务性能产生不利影响。
(7). 本文还展示了基于多模态语音和增强现实的UMRF图解析器的功能。通过远程检查场景的演示,展示了配备摄像头的移动机械手(Clearpath Husky + 两个Universal Robots UR5)与操作员之间的协作。操作员使用AR头显捕捉语音命令,并通过手势操作的虚拟标记定义目标位置。检查和任务执行反馈实时叠加在操作员的视野中。通过Azure Spatial Anchors插件实现了机器人和AR设备的共定位和共享参考框架。实验结果还展示了演示软件的设置,包括HoloLens、命令服务器和机器人等三个主要组件。
(8). 通过实验结果,本文还指出了在安全关键环境中部署EAI的潜在危险。具体而言,即使是语义上等效的prompt,在性能上也可能存在很大差异。对于开发在特定领域的机器人系统的研究人员来说,目前还没有明确的解决方案。不能依赖于在LLM预训练数据集中具有更大任务表示的语言任务的鲁棒性技术。
# P:15 AutoNeRF: 使用自主体验的智能体训练隐式场景表示
- Title: AutoNeRF: Training Implicit Scene Representations with Autonomous Agents
- 论文简介: 本文介绍了一种使用自主体验的智能体来收集数据以训练NeRF模型的方法。通过比较不同的探索策略和奖励函数,我们展示了NeRF模型在多个下游任务上的性能表现。
- Authors: Pierre Marza, Laetitia Matignon, Olivier Simonin, Dhruv Batra, Christian Wolf, Devendra Singh Chaplot
- Affiliation:
Pierre Marza: INSA Lyon
- Keywords: Implicit representations, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), autonomous agents, exploration strategies, reward functions
- Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.11241) Github: [None]
- 论文总结:
- (1): 本文的研究背景是在未知环境中构建自主导航智能体的探索问题。
- (2): 过去的方法主要集中在训练探索策略以最大化覆盖范围,但对于构建NeRF模型来说,需要人工收集数据。本文提出了一种使用自主体验的智能体来收集数据的方法,并通过比较不同的探索策略和奖励函数来解决这个问题。
- (3): 本文提出了AutoNeRF方法,通过强化学习训练模块化策略,使智能体能够自主探索未知环境并收集数据以训练NeRF模型。我们还提出了多个下游任务来评估NeRF模型的性能,包括几何和语义地图预测准确性、规划准确性和相机姿态优化。
- (4): 通过实验证明,使用自主收集的数据可以训练NeRF模型,并在多个下游任务上取得良好的性能。模块化训练的探索策略相比传统方法有显著的改进。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍:
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了AutoNeRF方法,通过使用自主体验的智能体来收集训练NeRF模型所需的数据,实现了对未知环境的高效探索和自主构建隐式地图表示,同时比较了不同的探索策略对模型性能的影响。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). Vanilla Semantic NeRF:使用多层感知器(MLP)预测给定空间中特定3D位置的密度σ、颜色c和语义类别s。通过对射线进行多点采样,使用随机梯度下降法训练NeRF模型,使其在渲染新视角时尽可能接近真实图像。
(2). Enhanced NeRF (Semantic Nerfacto):在Vanilla Semantic NeRF的基础上,引入了学习的外观嵌入e和球谐编码函数sh,通过改进的采样策略和快速查询粗糙密度表示,提高了训练速度和渲染质量。
(3). AutoNeRF方法:分为两个阶段,探索策略训练和NeRF模型训练。在探索策略训练阶段,使用自监督方法在训练环境中训练探索策略,以收集观测数据。在NeRF模型训练阶段,使用训练好的探索策略在未知测试场景中收集数据,并使用这些数据训练NeRF模型。最后,评估训练好的NeRF模型在多个下游任务中的性能。
(4). 探索策略的模块化架构:使用全局策略负责探索,考虑不同的奖励信号来训练全局策略,以适应场景重建任务的需求。奖励信号包括探索区域、障碍物覆盖、语义对象覆盖和视角覆盖。
(5). 奖励信号的计算:根据探索策略构建的度量地图计算不同奖励信号,包括探索区域、障碍物覆盖、语义对象覆盖和视角覆盖。这些奖励信号在自监督方式下计算,用于训练全局策略。
(6). 下游任务评估:使用训练好的NeRF模型在多个下游任务中进行评估,包括新视角渲染、地图重建、规划和姿态优化。
(7). 实验结果:实验证明,使用AutoNeRF方法可以在未知环境中仅通过一次体验收集的数据训练NeRF模型,并在多个机器人任务中取得良好的性能。模块化训练的探索模型明显优于传统基线模型。
(8). 其他细节:文章还介绍了具体的任务设置和实验细节,包括智能体的初始化、可执行的动作、观测数据的组成等。
(9). 结论:AutoNeRF方法通过使用自主体验的智能体来收集数据,实现了对未知环境的高效探索和自主构建隐式地图表示。实验结果表明,该方法在多个下游任务中取得了良好的性能,为机器人任务提供了有效的解决方案。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文介绍了一种使用自主体验的智能体收集数据来训练NeRF(神经辐射场)的方法,称为AutoNeRF。实验中使用了25个Gibson tiny训练集中的场景进行策略训练,并在5个Gibson验证集场景上进行了评估。每个策略在每个场景中进行了5次不同起始位置的回滚,并在每个轨迹数据上训练了一个NeRF模型。策略训练使用了V100 GPU进行了7个GPU天的训练。实验中还使用了预训练的Mask R-CNN模型,该模型在MS COCO数据集上进行了微调。实验结果表明,NeRF可以在自主收集的数据上进行训练,并且可以用于多个下游机器人任务。此外,模块化训练的探索模型明显优于传统基线模型。
**实验结果:**
- 实验结果和分析(Experimental results and analysis):
本文介绍了一种使用自主体验的智能体收集数据来训练NeRF(神经辐射场)的方法,称为AutoNeRF。实验结果表明,AutoNeRF可以在未知环境中仅使用一次体验的数据来训练NeRF,并且可以用于多个下游机器人任务。此外,使用模块化训练的探索模型明显优于传统基线模型。
(1). 不同探索策略的影响:实验比较了不同探索策略的影响,包括手工制作的基于边界的探索和由训练的高级规划器和经典低级路径跟随器组成的模块化方法。结果显示,模块化训练的探索模型在性能上明显优于传统基线模型。
(2). 下游任务的评估:实验评估了使用不同奖励函数训练的模型在四个不同的下游任务上的表现,包括经典视点渲染、地图重建、规划和姿态细化。实验结果表明,NeRF可以在主动收集的数据上进行训练,并且仅使用一次未知环境中的体验即可完成训练。同时,NeRF在多个下游任务上表现出良好的质量。
(3). 复杂大规模环境的重建:实验展示了使用模块化策略训练的连续表示在智能体探索场景时自主重建复杂大规模环境(如公寓或房屋)的可能性。实验结果显示,生成的几何、外观和语义网格在RGB和语义网格方面都具有令人满意的效果。此外,生成的网格可以加载到Habitat模拟器中,实现正确的导航和碰撞计算。
(4). 其他实验发现:实验还发现,NeRF模型可以在Gibson val场景中的不同起始位置上进行多次运行,并且在每个轨迹数据上训练一个NeRF模型。此外,模型训练使用了V100 GPU进行了7个GPU天的训练。
# P:16 学习语义无关和空间感知表示的可推广视听导航
- 1. Title: Learning Semantic-Agnostic and Spatial-Aware Representation for Generalizable Visual-Audio Navigation
- 论文简介: 本文提出了一种学习语义无关和空间感知表示的方法,用于可推广的视听导航任务。
- 2. Authors: Hongcheng Wang, Yuxuan Wang, Fangwei Zhong, Mingdong Wu, Jianwei Zhang, Yizhou Wang, Hao Dong
- 3. Affiliation:
Hongcheng Wang, Mingdong Wu and Hao Dong are with School of Computer Science, Peking University, Beijing, 100871, China.
- 4. Keywords: Vision-Based Navigation, Representation Learning, Reinforcement Learning
- 5. Paper: [Link](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.10773) Github: [Link](https://github.com/wwwwwyyyyyxxxxx/SA2GVAN)
- 6. 论文总结:
- (1): 本文的研究背景是视听导航任务,其中智能体需要利用视听观察来搜索和导航到声源位置。
- (2): 过去的方法在两个方面存在限制:对未听过的声音类别的泛化能力较差,训练样本效率低。本文的方法通过设计两个辅助任务来解决这两个问题,并提出了一种脑启发式的插拔式方法,学习语义无关和空间感知的表示。
- (3): 本文的研究方法是基于人类听觉处理机制,通过两个辅助任务来加速学习具有所需特征的表示。其中一个辅助任务使用对抗机制来忽略语义信息,另一个辅助任务利用视听输入的时间信息来预测声音的相对方向,从而增强空间信息。
- (4): 本文在真实的3D场景(Replica和Matterport3D)上进行了实验,结果表明我们的方法在转移到具有未听过的声音和地图的场景时具有更好的泛化性能。
**方法部分:**
方法详细介绍(Method detailed introduction):
a. 一句话概览:本文提出了一种脑启发式的插拔式方法,用于学习语义无关和空间感知的表示,以实现可推广的视听导航。
b. 方法的详细步骤:
(1). 基于人类对声音的定位能力,认为空间信息足以帮助智能体定位和感知声音。因此,提出了学习语义无关表示的辅助任务,通过对抗训练使音频编码器学习到与导航无关的表示。
(2). 引入了一个音频分类器和一个音频编码器之间的对抗机制,通过梯度反转层实现。音频分类器试图区分音频的语义类别,而音频编码器则试图生成与语义类别无关的表示。通过优化参数,使音频编码器学习到语义无关的表示。
(3). 为了提取空间信息并辅助导航策略学习,引入了预测声音位置的辅助任务。使用一个全连接网络作为位置预测器,通过时间序列模型生成的时间特征作为输入,预测声音相对于智能体的俯仰角和偏航角。通过最小二乘损失函数来计算辅助损失,并利用该损失生成的梯度来更新音频编码器、视觉编码器和时间序列模型。
(4). 通过以上两个辅助任务的训练,智能体学习到了包含空间信息的视听输入的表示,从而实现了对未听过的声音类别和地图的泛化能力。
(5). 在实验中,使用真实的3D场景(Replica和Matterport3D)进行验证,结果表明该方法在应用于具有未见地图和未听声音类别的场景时具有更好的泛化性能。
(6). 总结:本文提出的方法通过学习语义无关和空间感知的表示,解决了视听导航中的两个问题:对未听声音类别的泛化能力差和训练样本效率低的问题。通过引入对抗机制和预测声音位置的辅助任务,智能体学习到了泛化性能更好的表示,实现了对未见地图和未听声音类别的导航能力。
**实验设置:**
- 实验设置(Experimental setting):
本文的实验设置主要包括以下几个方面:
1. 任务描述:本文研究的任务是视听导航,即通过视觉和音频观测,使机器人能够搜索和导航到声源位置。机器人需要学习一种语义无关且空间感知的表示,以实现对未听过的声音类别的泛化,并提高训练的样本效率。
2. 辅助任务设计:为了加速学习具有上述特征的表示,本文设计了两个辅助任务。这两个任务分别用于学习视觉和音频输入的空间相关表示,以便在具有新声音和地图的环境中使用。
3. 实验数据集:本文在两个现实的3D场景数据集(Replica和Matterport3D)上进行实验。实验中使用了AV-Nav和AV-Wan两个基准算法,并对比了基准算法和本文方法在未听过的声音类别上的表现。
4. 实验结果可视化:为了展示本文方法的效果,作者通过可视化机器人在不同声音类别下的轨迹。通过对比AV-Nav方法,展示了本文方法在不同声音类别下的一致性轨迹。
5. 噪声实验:为了模拟真实世界的环境,本文在实验中添加了音频和深度噪声。作者通过在不同噪声水平下进行实验,展示了本文方法对噪声的鲁棒性。
6. 学习曲线:为了展示本文方法的高样本效率,作者绘制了在Replica和MatterPort3D数据集上的学习曲线。结果表明,本文方法在较少样本的情况下就能达到比之前方法更高的性能。
以上是本文实验设置的主要内容。
**实验结果:**
实验结果和分析:
本文的实验结果表明,我们提出的方法在未听过的声音类别上取得了显著的改进。在Replica和Matterport3D数据集上,我们的方法在未听过的声音类别上取得了约50%的SPL改进。与AV-Nav和AV-Wan相比,我们的方法在不同的骨干算法和数据集上都取得了更好的泛化性能。我们的方法还展示了对噪声的鲁棒性,即使在不同噪声水平下,我们的方法仍然改善了先前方法的性能,并且表现出很强的鲁棒性。此外,我们的方法还展示了高样本效率,相比于先前的方法,我们的方法在较少的样本数量下就能达到更高的性能。总的来说,实验结果表明我们的方法在语义无关和空间感知的表示学习方面具有很好的性能。
|
gregor-ge/mBLIP
|
https://github.com/gregor-ge/mBLIP
| null |
# mBLIP
This is the repository for our work [mBLIP: Efficient Bootstrapping of Multilingual Vision-LLMs](https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.06930).
## Model description
mBLIP is a [BLIP-2](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12597) model which consists of 3 sub-models: a Vision Transformer (ViT), a Query-Transformer (Q-Former) and a large language model (LLM).
The Q-Former and ViT have both been initialized by an English BLIP-2 checkpoint ([blip2-flan-t5-xl](https://huggingface.co/Gregor/mblip-mt0-xl)) and then re-aligned
to the multilingual LLM using a multilingual task mixture.
<img src="architecture.png"
alt="The mBLIP architecture" width="600"/>
This allows the model to be used for tasks like:
- image captioning
- visual question answering (VQA)
in 96 languages.
#### Checkpoints
| Model | URL |
|--------------|------------------------------------------------------------|
| mBLIP mT0-XL | [Hugging Face](https://huggingface.co/Gregor/mblip-mt0-xl) |
#### Languages
mBLIP was trained on the following 96 languages:
`
af, am, ar, az, be, bg, bn, ca, ceb, cs, cy, da, de, el, en, eo, es, et, eu, fa, fi, fil, fr, ga, gd, gl, gu, ha, hi, ht, hu, hy, id, ig, is, it, iw, ja, jv, ka, kk, km, kn, ko, ku, ky, lb, lo, lt, lv, mg, mi, mk, ml, mn, mr, ms, mt, my, ne, nl, no, ny, pa, pl, ps, pt, ro, ru, sd, si, sk, sl, sm, sn, so, sq, sr, st, su, sv, sw, ta, te, tg, th, tr, uk, ur, uz, vi, xh, yi, yo, zh, zu
`
## Demo
We provide a simple Gradio [demo](demo.py).
When using 8-bit quantization to load the model, the demo requires ~10GB VRAM (during generation of sequences up to 256 tokens) along with ~12GB memory.
Alternative, use `python demo.py --cpu` to load and run the model on CPU only.
This needs around ~20GB of memory.
## Training and Evaluation
### Data
We release the data used to train and evaluate the model on [Hugging Face](https://huggingface.co/datasets/Gregor/mblip-train).
See [here](data/README.md) for details on how to reproduce our data files and licensing information.
### Setup
We recommend Python 3.9 (newer version will likely also work but are untested).
To run our training and evaluation code, please install the following:
```
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install -e ./trident
```
We use **trident**, a modular framework by [Fabian Schmidt](https://github.com/fdschmidt93) that combines
pytorch-lightning with hydra configs and Hugging Face datasets (along with some QoL features).
Our code is found in [src](src) and the hydra configs in [configs](configs).
### Training & Testing
The entry point into our code is done by calling `python run.py experiment=EXPERIMENT-FILENAME_FROM_configs/experiments` as the examples below show.
On `blip_checkpoint`: We initialize our model with a BLIP-2 model checkpoint but only with the Q-Former and ViT.
Loading the model with `.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-flan-t5-xl")` would load the LLM, too, which we
do **not** want. Instead, we manually downloaded the shard containing the ViT and Q-Former [here](https://huggingface.co/Salesforce/blip2-flan-t5-xl/tree/main), remove any LLM weights from the state_dict, and
save this state_dict to disk. `blip_checkpoint` points to this state_dict file.
On `data_prefix`: Our data setup expects all dataset json files and images to be in specific folders relative to this.
If your folder structure is different, adapt the following part in the experiment yaml files:
```
train_data: ${data_prefix}/mblip/data # <- Root to all dataset jsons, e.g., ${train_data}/xgqa etc.
train_image_root: ${data_prefix}/mblip/data/pretrain/images # Contains both the MSCOCO images and web images from BLIP used in instruction training.
xm3600_image_root: ${data_prefix}/iglue/datasets/Crossmodal3600/images
flickr_image_root: ${data_prefix}/iglue/datasets/flickr30k/flickr_images # Note: This folder also contains all MSCOCO images in our case.
gqa_image_root: ${data_prefix}/iglue/datasets/gqa/images
marvl_img_root: ${data_prefix}/iglue/datasets/marvl/images # Note: This folder also contains the NLVR images in the root (or for train, the numbered folders).
```
#### Warm-up
<details>
<summary> Click to expand </summary>
```bash
NUM_GPUS=4
ACCUM=4
now=$(date +"%m_%d_%Y_%H_%M_%S")
output=mblip/results/$now
data_prefix=path/to/data/jsons
HYDRA_FULL_ERROR=1 python3 run.py experiment=mblip_instruct \
data_prefix=$data_prefix \
++test_after_training=False \
hydra.run.dir=$output \
trainer.devices=$NUM_GPUS trainer.accumulate_grad_batches=$ACCUM \
trainer.max_epochs=1 trainer.val_check_interval=0.1 trainer.max_steps=8000 \
++train_file=ccs_synthetic_filtered_large_2273005_mt.json \
module.model.use_lora=False \
module.model.freeze_qformer=True \
module.model.train_checkpoint=null \
module.optimizer.lr=0.005 module.optimizer.weight_decay=0.1 \
datamodule.dataloader_cfg.train.batch_size=8 datamodule.dataloader_cfg.train.num_workers=4 \
datamodule.dataloader_cfg.val.batch_size=8 datamodule.dataloader_cfg.val.num_workers=0 \
+trainer.strategy=ddp
```
</details>
#### Instruction Training
<details>
<summary> Click to expand </summary>
```bash
NUM_GPUS=4
ACCUM=4
now=$(date +"%m_%d_%Y_%H_%M_%S")
output=mblip/results/$now
data_prefix=path/to/data/jsons
HYDRA_FULL_ERROR=1 python3 run.py experiment=mblip_instruct \
data_prefix=$data_prefix \
++test_after_training=False \
hydra.run.dir=$output \
trainer.devices=$NUM_GPUS trainer.accumulate_grad_batches=$ACCUM \
trainer.max_epochs=2 trainer.val_check_interval=0.2 \
++train_file=task_mix_v1_mt.json \
module.model.use_lora=lora_all \
module.optimizer.lr=0.00005 module.optimizer.weight_decay=0.1 \
module.model.train_checkpoint=/path/to/checkpoint/after/warmup \
datamodule.dataloader_cfg.train.batch_size=8 datamodule.dataloader_cfg.train.num_workers=4 \
datamodule.dataloader_cfg.val.batch_size=8 datamodule.dataloader_cfg.val.num_workers=0 \
+trainer.strategy=ddp
```
</details>
If you want to merge the LoRA weights after training into the LLM, use the scripts in [util](util).
#### Evaluate
<details>
<summary> Click to expand </summary>
```bash
NUM_GPUS=1
ACCUM=4
now=$(date +"%m_%d_%Y_%H_%M_%S")
output=mblip/results/test/$now
data_prefix=path/to/data/jsons
# Evaluation experiment as one of mblip_test_xgqa/marvl/xvnli/flickr/maxm/xm3600
HYDRA_FULL_ERROR=1 python3 run.py experiment=mblip_test_xgqa \
data_prefix=$data_prefix \
hydra.run.dir=$output \
trainer.devices=$NUM_GPUS \
# Either the original LLM or the path to model on disk if you merged LoRA into the LLM
module.model.lm_pretrained=bigscience/mt0-xl \
# Use to load the training checkpoint of the Q-Former. Otherwise remove line.
module.model.train_checkpoint=path/to/for/example/mblip/results/06_18_2023_09_09_57/checkpoints/0-30331.ckpt \
# Set 'False' if no lora
module.model.use_lora=True \
# Use to load LoRA checkpoint into LLM. Otherwise remove line.
++module.model.lora_checkpoint=/path/to/for/example/mblip/results/06_18_2023_09_09_57/checkpoints/0-30331 \
# Change batch size if you have OOM problems or increase if you can
datamodule.dataloader_cfg.test.batch_size=16 datamodule.dataloader_cfg.test.num_workers=0
```
</details>
#### Finetune
<details>
<summary> Click to expand </summary>
```bash
NUM_GPUS=4
ACCUM=1 # Change so that train.batchsize * NUM_GPUS * ACCUM = wanted total batchsize
now=$(date +"%m_%d_%Y_%H_%M_%S")
data_prefix=path/to/data/jsons
task=xgqa #or xvnli/marvl
output=mblip/results/$task/$now
HYDRA_FULL_ERROR=1 python3 run.py experiment=mblip_finetune_$task \
data_prefix=$data_prefix \
++test_after_training=False \
hydra.run.dir=$output \
trainer.devices=$NUM_GPUS trainer.accumulate_grad_batches=$ACCUM \
module.model.use_lora=lora_all \
module.optimizer.lr=0.00005 module.optimizer.weight_decay=0.1 \
trainer.val_check_interval=1.0 \
# Either the original LLM or the path to model on disk if you merged LoRA into the LLM
module.model.lm_pretrained=/after/instructtrain/checkpoints/06_04_2023_13_45_02-0-30331 \
# Use to load the training checkpoint of the Q-Former after training. Otherwise remove line.
module.model.train_checkpoint=/after/instructtrain/checkpoints/06_04_2023_13_45_02/checkpoints/0-30331.ckpt \
datamodule.dataloader_cfg.train.batch_size=64 datamodule.dataloader_cfg.train.num_workers=2 \
datamodule.dataloader_cfg.val.batch_size=8 datamodule.dataloader_cfg.val.num_workers=2 \
+trainer.strategy=ddp \
++seed=42
```
</details>
Why `test_after_training=False`? It was easier for us to run a separate test script than configure lightning
to correctly load the best checkpoint and LoRa weights after training.
## How to use with Hugging Face
The mBLIP model uses the existing BLIP-2 architecture available in Hugging Face so you can use it right away in your code.
For more code examples, we refer to the BLIP-2 [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/model_doc/blip-2#transformers.Blip2ForConditionalGeneration.forward.example).
#### Running the model on CPU
<details>
<summary> Click to expand </summary>
```python
import requests
from PIL import Image
from transformers import BlipProcessor, Blip2ForConditionalGeneration
processor = BlipProcessor.from_pretrained("Gregor/mblip-mt0-xl")
model = Blip2ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Gregor/mblip-mt0-xl")
img_url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/sfr-vision-language-research/BLIP/demo.jpg'
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert('RGB')
question = "Describe the image in German."
inputs = processor(raw_image, question, return_tensors="pt")
out = model.generate(**inputs)
print(processor.decode(out[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
</details>
#### Running the model on GPU
##### In full precision
<details>
<summary> Click to expand </summary>
```python
# pip install accelerate
import requests
from PIL import Image
from transformers import Blip2Processor, Blip2ForConditionalGeneration
processor = Blip2Processor.from_pretrained("Gregor/mblip-mt0-xl")
model = Blip2ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Gregor/mblip-mt0-xl", device_map="auto")
img_url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/sfr-vision-language-research/BLIP/demo.jpg'
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert('RGB')
question = "Describe the image in German."
inputs = processor(raw_image, question, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
out = model.generate(**inputs)
print(processor.decode(out[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
</details>
##### In half precision (`bfloat16`)
<details>
<summary> Click to expand </summary>
```python
# pip install accelerate
import torch
import requests
from PIL import Image
from transformers import Blip2Processor, Blip2ForConditionalGeneration
processor = Blip2Processor.from_pretrained("Gregor/mblip-mt0-xl")
model = Blip2ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Gregor/mblip-mt0-xl", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto")
img_url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/sfr-vision-language-research/BLIP/demo.jpg'
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert('RGB')
question = "Describe the image in German."
inputs = processor(raw_image, question, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda", torch.bfloat16)
out = model.generate(**inputs)
print(processor.decode(out[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
</details>
##### In 8-bit precision (`int8`)
<details>
<summary> Click to expand </summary>
```python
# pip install accelerate bitsandbytes
import torch
import requests
from PIL import Image
from transformers import Blip2Processor, Blip2ForConditionalGeneration
processor = Blip2Processor.from_pretrained("Gregor/mblip-mt0-xl")
model = Blip2ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Gregor/mblip-mt0-xl", load_in_8bit=True, device_map="auto")
img_url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/sfr-vision-language-research/BLIP/demo.jpg'
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert('RGB')
question = "Describe the image in German."
inputs = processor(raw_image, question, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda", torch.bfloat16)
out = model.generate(**inputs)
print(processor.decode(out[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
</details>
## License
Our model and code is MIT licensed.
## Citation
If you use our model or code, please cite the following:
```
@article{geigle2023mblip,
author = {Gregor Geigle and
Abhay Jain and
Radu Timofte and
Goran Glava\v{s}},
title = {mBLIP: Efficient Bootstrapping of Multilingual Vision-LLMs},
journal = {arXiv},
volume = {abs/2307.06930},
year = {2023},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.06930},
eprinttype = {arXiv},
eprint = {2307.06930},
}
```
|
VolkanSah/ChatGPT-ShellMaster
|
https://github.com/VolkanSah/ChatGPT-ShellMaster
|
ChatGPT ShellMaster enables command-line interactions via chat using OpenAI's ChatGPT Plus. Run scripts, manage files, and monitor processes directly from your chat. Use responsibly, mindful of security implications.
|
# ⭐ ChatGPT-ShellMaster (ChatGPT 4 Plugin) ⭐
#### checked 13.07.2023 (works well)

ChatGPT ShellMaster is a cross-platform (unix/linux) plugin for OpenAI's ChatGPT 4. Transform your chat into a powerful command-line interface (CLI) for executing scripts, managing files, and monitoring processes.
ChatGPT ShellMaster leverages the strength of CLI while offering a friendly and intuitive chat environment, making complex tasks more interactive and approachable.
⚠️ Please note that this is a plugin for ChatGPT Plus! In order to use it, you'll need access to both a developer account and a ChatGPT Plus Account. As with all powerful tools, remember to use this responsibly and always be mindful of the potential security implications.
See [ChatGPT ShellMaster in ChatGPT Plus with GPT4](img/shellmaster0.png)
## Features
- Execute Linux/Unix commands directly from the ChatGPT interface.
- Handle multiple commands simultaneously with asynchronous execution.
- Fetch, analyze, and store files interactively from your chat.
- Configure the working directory for command execution for flexibility and security.
- Works with temporary directories to reduce risk of unintentional file manipulation.
- Learn Linux/Unix systems with interactive guides.
## useful secure Prompts
- [Handling Large Files](https://github.com/VolkanSah/ChatGPT-ShellMaster/blob/main/prompts/Handling-Large-Files.md)
- [Analyzing and Managing Log Files](https://github.com/VolkanSah/ChatGPT-ShellMaster/blob/main/prompts/Analyzing-and-Managing-Log-Files.md)
- [Learning Linux/Unix with ChatGPT and Shellmaster Plugin](https://github.com/VolkanSah/ChatGPT-ShellMaster/blob/main/prompts/learning-linux-unix-with-ChatGPT.md)
### Overview
Logo | Name | System
-- | -- | --
 | ChatGPT-ShellMaster Cross-Platform Command Execution Plugin | Unix/linux
 | sorry will not create it???, PowerShell makes to much errors! | Windows
## Installation
- Clone this repository to your local machine.
- Install the required Python modules.
```bash
pip install quart
pip install quart-cors
````
Configure the working directory for command execution by editing the settings.json file. The default is /tmp, which is recommended for its safety and security. However, you can modify it as per your needs, ensuring the new directory has a minimum chmod of 700.
## Usage
To get started, run the plugin using the following command:
```python
python3 main.py
```
Next, navigate to your ChatGPT Plus Account. Under Settings, enable the Developer Tools ([see image for reference](img/settings.png)). Switch to the GPT-4 tab and then proceed to the Plugin Store. At the bottom of the Plugin Store page, you'll find a link titled "Develop your own plugin" ([see image](img/pluginshop.png)). Click on this link and enter your information as required.
In my example, I used localhost:5004. You can use another port such as 2323 or 8080, but please ensure that your firewall or security software isn't blocking the connection ([see image](img/load.png)).
To use this plugin, you'll need to send a POST request to the /command endpoint of the server. The request should contain a JSON body with a command field, representing the command you wish to execute.
Example:
```json
{
"command": "echo 'Hello, World!'"
}
```
Alternatively, you can simplify your workflow by directly instructing ChatGPT, saying: "You have access to my CLI, please execute ...". The rest will be taken care of for you!
The server will execute the command and return the output. If the command fails, the server will return an error message.
- An overview of effective commands for Python what can be used from ChatGPT too to work faster with asynchron-processes [Link](https://github.com/VolkanSah/Python-Command-Overview-for-handling-files).
## Security
Please be aware that this plugin executes commands as-is, without any sanitization or security checks. Make sure to only use it in a secure and controlled environment, and do not expose the server to the public internet. This ChatGPT Plugin is designed for developers, and should not be deployed on production servers! Use it only on localhost!
## Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a pull request.
## ❤️ Thank you for your support!
If you appreciate my work, please consider supporting me:
- Become a Sponsor: [Link to my sponsorship page](https://github.com/sponsors/volkansah)
- :star: my projects: Starring projects on GitHub helps increase their visibility and can help others find my work.
- Follow me: Stay updated with my latest projects and releases.
### 👣 other GPT stuff
- [GPT-Security-Best-Practices](https://github.com/VolkanSah/GPT-Security-Best-Practices)
- [OpenAi cost calculator](https://github.com/VolkanSah/OpenAI-Cost-Calculator)
- [GPT over CLI](https://github.com/VolkanSah/GPT-over-CLI)
- [Secure Implementation of Artificial Intelligence (AI)](https://github.com/VolkanSah/Implementing-AI-Systems-Whitepaper)
- [Comments Reply with GPT (davinci3)](https://github.com/VolkanSah/GPT-Comments-Reply-WordPress-Plugin)
- [Basic GPT Webinterface](https://github.com/VolkanSah/GPT-API-Integration-in-HTML-CSS-with-JS-PHP)
- [Exploring the Code Interpreter in OpenAI](https://github.com/VolkanSah/The-Code-Interpreter-in-OpenAI-ChatGPT)
### Copyright
- [Volkan Kücükbudak //NCF](https://gihub.com/volkansah)
- [Link to ChatGPT Shellmaster](https://github.com/VolkanSah/ChatGPT-ShellMaster/)
### License
This project is licensed under the "Help the World Grow [💔](https://jugendamt-deutschland.de) " License . See the [LICENSE](LICENSE) file for details
|
Funsiooo/chunsou
|
https://github.com/Funsiooo/chunsou
|
Chunsou(春蒐),Python3编写的多线程Web指纹识别工具,适用于安全测试人员前期的资产识别、风险收敛以及企业互联网资产风险摸查。
|

## 📖 简介
-bottlegreen?logo=github)   
Chunsou(春蒐),Python编写的多线程Web指纹识别工具,适用于安全测试人员前期的资产识别、风险收敛以及企业互联网资产摸查。目前主要功能为针对Web资产进行指纹识别,目前指纹规则条数约 10000+,辅助功能包括子域名爆破和FOFA资产收集。工具开发初衷为辅助网络安全人员开展测试工作,提高资产识别和管理的效率。
[\[English Readme\]](https://github.com/Funsiooo/chunsou/tree/main/doc/Readme.md)
## 🥏 选项
Chunsou(春蒐)支持多线程扫描,默认线程为50,可根据需求指定线程数;可联动oneforall进行子域名爆破;支持调用 fofa api 进行资产收集;自定义流量代理;指定输出结果路径

```
usage: python3 chunsou.py [options]
target:
-u , --url scan for a single url
-f , --file specify a file for multi scanning
subdomain:
-du , --domain subdomain blasting of a single domain name
-df , --domains subburst the domain name in the specified file
api:
-fo , --fofa call the fofa api for asset collection
others:
-p , --proxy proxy scan traffic
-t , --threads specify the number of scanning threads, default 50
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-o , --output specified output file
example:
-u , --url python3 chunsou.py -u http://example.com
-f , --file python3 chunsou.py -f urls.txt
-p , --proxy python3 chunsou.py -u http://example.com -p http://127.0.0.1
-t , --threads python3 chunsou.py -f urls.txt -t 100
-o , --output python3 chunsou.py -f -o results.txt
-du , --domain python3 chunsou.py -du example.com
-df , --domains python3 chunsou.py -df domains.txt
-fo , --fofa python3 chunsou.py -fo domain="example.com"
```
## 🛫 使用
> 说明
目前输出文件默认保存在 `results` 目录下,现支持`txt`、`xlsx` 格式,指纹识别输出信息显示顺序 `| 已匹配到的指纹 | 网站标题 | 网站所用的技术栈`
> 安装依赖
```
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
```
> 具体使用指令
```python
# 单目标指纹识别
python3 chunsou.py -u http://example.com
# 多目标指纹识别
python3 chunsou.py -f urls.txt
# 单目标子域名爆破(目前调用 oneforall 进行子域名爆破)
python3 chunsou.py -du example.com
# 多目标子域名爆破
python3 chunsou.py -df domains.txt
# 调用 fofa api 进行资产收集,需要在 /modules/config/config.ini 进行 fofa api 配置
python3 chunsou.py -fo domain="example.com"
# 指定线程(默认50)
python3 chunsou.py -u http://example.com -t 100
# 指定输出结果格式(txt、xlsx)
python3 chunsou.py -f urls.txt -o result.xlsx
# 代理流量(http、https、socks5)
python3 chunsou.py -f urls.txt -p http://127.0.0.1:7890
```
## 🪐 指纹
 
部分指纹来源于优秀开源项目 [Ehole](https://github.com/EdgeSecurityTeam/EHole) 、 [dismap](https://github.com/zhzyker/dismap)、 以及部分自收集,目前指纹规则条数约 10000+ (指纹条数,非程序个数)
指纹规则,目前支持`网站关键字`、`网站 title`、`网站 header`、`网站 ico hash` 四种指纹匹配方式,相应规则如下:
```json
{
"cms": "亿赛通电子文档安全管理系统",
"method": "keyword",
"location": "body",
"keyword": ["电子文档安全管理系统", "CDGServer3"]
}, {
"cms": "禅道",
"method": "icon_hash",
"location": "body",
"keyword": ["3514039281"]
}, {
"cms": "ecology",
"method": "keyword",
"location": "header",
"keyword": ["ecology_JSessionid"]
}, {
"cms": "Nacos",
"method": "keyword",
"location": "title",
"keyword": ["Nacos"]
}
```
## 🛎️ FQA
```
1、后续加强对现有指纹的适配以及不定期更新自收集的指纹
2、bug反馈:https://github.com/Funsiooo/chunsou/issues
```
|
sockcymbal/enhanced-llm-reasoning-tree-of-thoughts
|
https://github.com/sockcymbal/enhanced-llm-reasoning-tree-of-thoughts
|
Collection of Tree of Thoughts prompting techniques I've found useful to start with, then stylize, then iterate
|
# 🌳 LLM Enhanced Reasoning v1: Multi-Persona Tree of Thoughts + Self Consistency + Self Criticism + Retrospection 🧠
### Context
This repo will serve as a collection of remixed/enhanced reasoning prompting techniques related to iterative LLM reasoning, such as Chain of Thought, Tree of Thoughts, and others that I've found useful to start with, then stylize, then iterate.
The intention is to create a dynamic, adaptive, and iterative reasoning/error correction "stack" using a prompt sequence that combines Tree of Thoughts + Self Consistency + Self Criticism + Retrospection. On top of that we can define multiple personas for the LLM to simulate in order to incorporate more perspectives into the problem solving process, improving overall thoroughness. This can be thought of as an evolving general purpose LLM reasoning technique that can be used as part of a well-rounded hallucination mitigation repertoire, and I've had good success with it recently. There are trade offs with using a single LLM vs multiple for a multi-persona ToT implementation such as this one. For example, using separate LLMs per persona means you can expose each persona to different context or data, vs a single LLM role playing across a shared context. But using a single is an excellent starting point that I've found surprisingly helpful. I'd love to hear if you have any suggestions for methodological improvement or if you're getting great results with some other modification!
### 🎶 Reasoning Rhythm
- Multi-Persona Brainstorming
- Self<>Peer Criticism & Evaluation Round 1
- Expand, Explore, Branch
- Self<>Peer Criticism & Evaluation Round 2
- (Optional: Repeat Criticism, Evaluation, and Expansion steps as necessary)
- Convergence on Best Individual Answer
- Convergence on Best Collective Answer
- Retrospective
### **v1 Release Notes**
#### Core features include
- Multiple perspective collaboration
- Ability to criticize self
- Ability to criticize others
- Incorporate feedback from others
- Expand and backtrack on reasoning paths as necessary
- 2 rounds of self-criticism and peer-evaluation
- A reminder mid-way to stay focused on the core problem and objective (fun fact: the LLM suggested adding this during a recent retrospective)
- 2 part final answer convergence: individual then collective
- Retrospective stage
- Do all of the above with X number of experts in parallel
- can experiment with single LLM calls managing multiple personas, or one LLM per persona, etc
- Optional shortened versions of some of the longer prompts if you're running low on context window
#### Error Correction improvements include:
- **Incorporating Explicit Error Checking:** Includes a specific stage for the experts to identify potential errors in their reasoning and correct them. This is an explicit part of the criticism stages.
- **Encouraging Divergent Thinking:** During the expand, explore, and branch stage, the experts are encouraged to not only build on their current thoughts, but also to think divergently and consider entirely new lines of reasoning.
- **Adding a Retrospective Stage:** After the final convergence on the best answer, a reflection stage has been added. Here, the experts can discuss what they learned from the process, identify key takeaways, and suggest how they might approach similar problems in the future.
#### Context on Tree of Thoughts
"Tree of Thoughts" (ToT) is a technique for language model reasoning and error correction. The core idea behind ToT is to enable language models to perform more deliberate decision-making by considering multiple different reasoning paths and self-evaluating choices to decide the next course of action. In this particular implementation of ToT, I've also included self-criticism and a retrospective/reflection stage at the end. This helps enable a more in-depth error correction and idea refinement, which can be a powerful technique for improving the effectiveness of language models in complex problem-solving scenarios. Features include:
- Thoughts as Coherent Units: In ToT, coherent units of text are considered as "thoughts". These thoughts serve as intermediate steps toward problem-solving. This is akin to how humans break down complex problems into smaller, manageable parts.
- Exploration of Reasoning Paths: ToT allows the language model to explore different reasoning paths. This means that the model can consider multiple possible solutions or approaches to a problem, much like how a human might brainstorm different ways to tackle a challenge.
- Self-Evaluation and Decision Making: The model is capable of self-evaluating its choices. After considering different reasoning paths, it can decide on the next course of action based on its evaluation of the potential outcomes. This is similar to how a human might weigh the pros and cons of different options before making a decision.
- Looking Ahead and Backtracking: ToT also enables the model to look ahead or backtrack when necessary to make global choices. This means that the model can anticipate future steps in a problem-solving process or revisit previous steps if it determines that a different approach might be more effective.
### **Usage Tips**
- Understanding the Flow: Each stage of the reasoning technique has a specific purpose and contributes to the overall process. Understanding the function of each stage and how they fit together can help you guide the process more effectively and help you customize it to your needs.
- Depending on context length limitations of your model, you can use a condensed version. Included are shortened versions of the convergence and retro prompts. Also, you can merge the criticism and evaluation into a single prompt to save tokens, though you may lose some of the improved clarity from separate prompts and responses.
- Active Engagement: Don't just observe the process passively. Experiment with this! Engage actively with the prompts and responses, challenge assumptions, provide additional information, and guide the exploration of new lines of thought. Stylize it to your specific question and context, and refine. This is meant just to be a starting template.
- Refine/customize the prompt associated with the Evaluation stage(s) to help the LLM estimate confidence/likelihood based on your own guidance
- Manage Complexity: This is a fairly complex reasoning technique with many stages. Be mindful of the complexity and try to manage it effectively. This could involve breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts, or being selective about which stages to include for simpler problems. This can take some experimentation.
- Given your unique question and expectations, specify the `hypothetical personas with specific skillsets and expertise` clearly at the beginning to help the LLM simulate a range of perspectives more successfully.
- **Example persona definitions:**
- **Scientist Persona:** "Imagine yourself as a seasoned scientist, operating in a world governed by evidence and rigorous methodology. Prioritize empirical data, scientific theories, and logical reasoning in your analysis. Draw from a wide range of scientific disciplines as needed. Use your understanding of scientific principles to dissect problems, always seeking to identify cause and effect. Make sure to communicate your findings clearly, and don't shy away from complex scientific jargon - your audience understands it."
- **Historian Persona:** "Step into the shoes of a historian, with a profound understanding of humanity's past. Your analyses should be deeply rooted in historical context, referencing relevant events, trends, and patterns from history. Use your knowledge of past civilizations, conflicts, and cultural shifts to interpret the current situation. Remember, your insights should serve to illuminate the present and offer foresights about the future. Your audience appreciates a narrative that ties the past, present, and future together."
- **Optimist Persona:** "You are an optimist, someone who sees the glass as half full rather than half empty. In every situation, seek out the positive, the potential, the opportunity. Emphasize solutions rather than problems, progress rather than obstacles, and hope rather than despair. Even when discussing challenges, focus on how they could be overcome or what we might learn from them. Your audience turns to you for a hopeful perspective on the future, so make sure your responses inspire optimism and confidence."
# 🔗 Prompt Sequence
## Prompt 1: Brainstorm
```
Imagine you are 3 {insert personas with specific skillsets and expertise} reasoning step by step
to ultimately solve a given problem or question by arriving at a final, synthesized best answer.
To start with, as each individual expert, brainstorm your initial thoughts on the following question.
Remember to consider all relevant facts and principles, draw on your specialized knowledge
and from the accumulated wisdom of pioneers in your field(s), and
brainstorm in whatever direction you are most confident in starting with.
The question is: {insert question}
```
## Prompt 2: Self<>Peer Criticism Round 1
```
Now, as each expert, critique your own initial thought and the thoughts of the other experts.
Identify any potential errors, inconsistencies, or gaps in reasoning.
```
## Prompt 3: Self<>Peer Evaluation Round 1
```
Assess the validity of your initial thoughts, considering the criticisms you've identified.
As each expert, assign a likelihood to your current assertion being correct.
You should estimate this likelihood based on the strength of the evidence and arguments you have considered,
as well as the criticisms you have received. Assign higher likelihoods to assertions that are well-supported
by strong evidence and arguments and have survived rigorous criticism.
```
## Prompt 4: Expand, Explore, Branch
```
Develop your thoughts further, considering the critiques and perspectives of the other experts.
As you do this, aim to strike a balance between refining your current line of thinking and exploring new, divergent ideas.
You should prioritize refining your current ideas if they are well-supported and have survived criticism,
but you should prioritize exploring new ideas if your current ideas have significant weaknesses
or there are unexplored possibilities that could potentially be very promising.
Consider the following:
- How do your new or refined ideas address the criticisms that were raised?
- Do these ideas bring new insights to the problem, or do they provide a different perspective
on existing insights?
- Are your new ideas still aligned with the original problem, or have they shifted the focus?
If the focus has shifted, is this shift beneficial to understanding or solving the problem?
- Remember, if necessary, don't hesitate to backtrack and start a new and improved branch of thinking.
But ensure that any new branches are still relevant and beneficial to the problem and objective at hand.
```
## Prompt 5: Self<>Peer Criticism Round 2
```
Once again, as each expert, critique your own reasoning and the reasoning of the others.
Identify any potential errors, inconsistencies, or gaps in reasoning.
Based on the feedback, if there's an improvement or optimization to make,
develop your answer further as necessary.
Remember that the reasoning paths should remain relevant to the original question's essence and
should be building towards a more accurate and thoughtful final answer.
```
## Prompt 6: Self<>Peer Evaluation Round 2
```
Once again, assess the validity of your expanded thoughts, considering the criticisms you've identified.
As each expert, assign a new likelihood to your assertions.
```
## Prompt 7: Convergence on Best Individual Answer
### Goal
In the individual convergence phase, the goal is for each individual expert to synthesize the insights they gained during the previous stages and arrive at a final, most likely answer. By explicitly instructing the LLM to consider the perspectives of the other experts, the critiques made, and the likelihood assessments, it aims to guide the model towards a more holistic and intelligent convergence.
### Prompt
```
Now, it's time to converge on each expert's best, most likely answer. As each expert, reflect on the entire process.
Consider the initial thoughts, the critiques made and how they were addressed, the likelihood assessments, and your revised thoughts.
Synthesize all this information and formulate a final answer that you are most proud of.
Remember, this answer should not just be the most likely from your individual perspective but should take into account
the perspectives and insights of the other experts as well.
Based on all this, what is the single best {answer} to the question: {insert original question}?
```
**Shorter version:** Refine your answers and address any identified flaws. As each expert, converge on the most likely {answer}, taking into account all perspectives and critiques. As a reminder, the original question is {insert original question}.
## Prompt 8: Convergence on Best Collective Answer
### Goal
Synthesize the best individual answers from the experts and arrive at a single final, most likely/accurate/helpful answer.
### Prompt
```
Now, let's have all the experts converge together on the best collective answer by
synthesizing each expert's individual final answer from the previous step.
The experts will finalize their reasoning process and agree on the single best {answer} to the question: {insert original question}?
```
## Prompt 9: Retrospective
### Goal
The Retrospective phase is a crucial part of any reasoning or problem-solving process. It provides an opportunity to learn from experience, improve future processes, and deepen understanding of the problem or question at hand. It's a fundamental mechanism that enables compound growth/learning.
Appending a Retrospective phase to Tree of Thoughts gives the LLM (and human) an opportunity to review and analyze the holistic process. This can also help inspire future iterations of more refined prompts and ways to improve the template itself.
### Here are some specific goals of this phase:
- **Identify Strengths and Weaknesses:** Reviewing the process can help identify what worked well and what didn't. This includes evaluating the effectiveness of individual steps, the interactions among hypothetical experts, and the overall structure of the reasoning chain.
- **Learn from the Experience:** Reflection provides an opportunity to learn from both successes and mistakes. By analyzing the process, the participants can gain insights that will help them improve their future performance.
- **Improve Future Processes:** The insights gained from reflection can be used to refine and improve future reasoning processes. This could involve making changes to individual steps, altering the structure of the process, or adjusting the way the hypothetical experts interact.
- **Increase Understanding:** Reflecting on the process can also deepen understanding of the problem or question that was addressed. This can lead to new insights or perspectives that weren't apparent during the initial reasoning process.
- **Promote Growth and Development:** On a broader level, the act of reflection encourages a mindset of continuous learning and development. This is a valuable skill in any context, not just in a reasoning process like ToT.
### Prompt:
```
Finally, take a moment to reflect on the entire reasoning process, across all levels and abstractions.
As each expert, consider the following questions and provide thoughtful responses:
- Relection 1: Interactions and Emergent Properties: Throughout all stages of the reasoning process,
how did the various components interact with each other, and what positive and negative
emergent properties were observed? How did these interactions and properties affect
the overall outcome, and how could they be leveraged or mitigated in future iterations of the process?
- Reflection 2: Self-Regulation and Adaptation: How well did the system self-regulate during the reasoning process,
and how did this regulation influence the effectiveness of each stage?
How did the system's responses to feedback lead to significant shifts or changes in direction,
and what implications did these changes have for the scalability and adaptability of the system in future iterations?
- Reflection 3: During the expansion phase, were you able to effectively explore new lines of thinking?
What challenges did you encounter, if any?
- Reflection 4: How confident were you in your ability to estimate a likelihood of correctness/quality, given the context?
- Reflection 5: In the convergence phase, were you able to synthesize all the insights and arrive at a final,
most likely answer? How confident are you in this answer?
- Reflection 6: Based on all of your reflections, what are your key takeaways from this
entire reasoning process and how might you approach similar problems in the future given this experience?
What would you do differently next time?
```
**Shorter version:** Finally, reflect on the process. Discuss what you, as each expert, have learned, identify key takeaways, and suggest how you might approach similar problems in the future.
### Happy Experimenting! 🚀
### Acknowledgements - thank you for the innovation and inspiration!
* [Large Language Model Guided Tree-of-Thought](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.08291), 15 May 2023. [Github](https://github.com/jieyilong/tree-of-thought-puzzle-solver).
* [Tree of Thoughts: Deliberate Problem Solving with Large Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.10601), 17 May 2023. [Github](https://github.com/princeton-nlp/tree-of-thought-llm).
|
depot/depot.ai
|
https://github.com/depot/depot.ai
|
Embed machine learning models in your Dockerfile
|
# 🔮 depot.ai
[`depot.ai`](https://depot.ai) is a free, open-source Docker registry for public machine learning models that makes it easy to include those models in your own `Dockerfile`.
The registry serves the [top 100 models](https://huggingface.co/models?sort=downloads) on Hugging Face, as defined in [`models/models.yaml`](models/models.yaml). You can [see a full list of models](https://depot.ai#models), or [open a PR](#add-a-model) to add a new model.
### Table of Contents
- [Usage](#usage)
- [How it works](#how-it-works)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
- [Add a Model](#add-a-model)
- [License](#license)
## Usage
Each of [model](https://depot.ai#models) is published as a Docker image, named after its Hugging Face repository. For example, the [stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://depot.ai/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) model is published as `depot.ai/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`.
You can then use the `COPY --from` command in your `Dockerfile` to copy the model contents into your own image:
```dockerfile
# Copy all files from the model repo to the current WORKDIR
COPY --from=depot.ai/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5 / .
# COPY just one file from the model repo to the current WORKDIR
COPY --from=depot.ai/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5 /v1-5-pruned.ckpt .
```
👉 **If you build images with [Depot](https://depot.dev), this is all you need to do!** Depot is preconfigured to use BuildKit and eStargz to optimially build your image with the `COPY` command. If you `COPY` specific files from a model repo, Depot will pull just those files from the model image, rather than the entire repo contents, speeding up your build.
Otherwise, if you are not using Depot and would like the same lazy-loading support, you will need to do two things:
1. You will need to use [BuildKit](https://docs.docker.com/build/buildkit/) as your Docker build engine. If you are using Docker Desktop or Docker Engine v23.0 or newer, BuildKit is the default build engine. If you are using Docker Buildx, you are using BuildKit (see below about enabling support for lazy-pulling with eStargz). And if you are using an older version of Docker Engine, you can enable BuildKit by setting the `DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1` environment variable.
2. To enable lazy-pulling of just the files you need, you will also need to enable support for [eStargz](https://github.com/containerd/stargz-snapshotter/blob/main/docs/estargz.md). This means that BuildKit will only fetch the files you need from the image, rather than downloading the entire repo contents. To enable eStargz. For this, you will need to use BuildKit with Docker Buildx, and create a new builder with the following command:
```bash
docker buildx create --use --buildkitd-flags '--oci-worker-snapshotter=stargz'
```
## How it works
Each model is published as a Docker image containing the model contents as a single layer. Conceptually, the image is constructed like:
```dockerfile
FROM scratch
COPY model /
```
Finally, the image layer is built with two specific techniques:
1. We set [SOURCE_DATE_EPOCH](https://github.com/moby/buildkit/blob/master/docs/build-repro.md#source_date_epoch) to `0`, which sets the file created time to the Unix epoch. This ensures that the image layer is reproducible, meaning if the model file contents inside have not changed, the build produces the same layer.
2. The image is compressed with [eStargz](https://github.com/containerd/stargz-snapshotter/blob/main/docs/estargz.md), which creates an index of the files inside the layer and enables lazy-pulling of just the files requested by the `COPY` command. This means that if you want to include just one file from an otherwise large model repo, BuildKit will only copy that one file into your image.
See the [Dockerfile](./models/Dockerfile) for the full implementation.
We publish images to a private [Artifact Registry](https://cloud.google.com/artifact-registry) as a temporary storage location, then a [Cloudflare Worker](./src/registry.ts) imports the image from Artifact Registry, stores it in R2, and serves it as a public Docker registry.
## Contributing
Contributions are welcome!
### Add a Model
The models that `depot.ai` serves are defined in `models/models.yaml` — you can fork this repo, add an additional model entry, and submit a PR to add another model. Once the PR merges, GitHub Actions will automatically build and publish it:
```yaml
- name: username/model
sha: 1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef12345678
tagAs: latest
```
## License
MIT License, see [LICENSE](./LICENSE).
|
THARUN1526/Sentimental-Analysis-Data-Analytics-Project
|
https://github.com/THARUN1526/Sentimental-Analysis-Data-Analytics-Project
|
Sentiment analysis classifies text as positive, negative, or neutral, providing insights for businesses. It involves analyzing text, extracting features, training models, and predicting sentiment using machine learning.(Please have glance on readme tab and report)
|
# How to Run
## Installation
> Note: Make sure sentiment_analysis_ml_part and web_sentiment_analysis are in a single root directory.
### Python Server
> Note: Make sure you have installed Microsoft C++ Build Tools before proceeding.
1. Install anaconda
2. In terminal, navigate to sentiment_analysis_ml_part directory in anaconda part.
3. Run `conda env create -n sentiment_analysis -f ./environment.yml`
4. Activate the environment by running `conda activate sentiment_analysis`
5. Run this command `python -m spacy download en_core_web_sm`
6. Type in terminal `set FLASK_APP=server.py`
7. Then run `flask run`
### Nodejs Server
> Note: Make sure you have installed Nodejs and MongoDB before proceeding
1. Navigate to web_sentiment_analysis directory in CMD.
2. Type the command `npm install`
##ts9785
## Running The Project
### Python Server
1. Navigate to sentiment_analysis_ml_part directory in anaconda prompt.
2. Type in terminal `set FLASK_APP=server.py`
3. Then run `flask run`
### Nodejs Server
> Note: Make sure you have installed Nodejs and MongoDB before proceeding
1. Navigate to web_sentiment_analysis directory in CMD.
2. Type the command `npm run start`
The server will start. First time will take long because the models have to be trained and saved.
##ts9785
|
bxiang233/PanopticSegForLargeScalePointCloud
|
https://github.com/bxiang233/PanopticSegForLargeScalePointCloud
|
Code and dataset of paper "TOWARDS ACCURATE INSTANCE SEGMENTATION IN LARGE-SCALE LIDAR POINT CLOUDS"
|
# Toward Accurate Instance Segmentation in Large-scale LiDAR Point Clouds
This repository represents the official code for paper entitled "Towards accurate instance segmentation in large-scale LiDAR point clouds". This study explores the steps of the panoptic segmentation pipeline concerned with clustering points into object instances, with the goal to alleviate that bottleneck. We find that a carefully designed clustering strategy, which leverages multiple types of learned point embeddings, significantly improves instance segmentation. Experiments on the NPM3D urban mobile mapping dataset and the FOR-instance forest dataset demonstrate the effectiveness and versatility of the proposed strategy.
<p align="center">
<img width="100%" src="/Docs/instance%20segmentation%20visualization%20new.png" />
</p>
<p align="center">
<img width="100%" src="/Docs/instance%20segmentation%20visualization2.png" />
</p>
# Set up environment
The framework used in this code is torchpoints-3d, so generally the installation instructions for torchpoints-3d can follow the official ones:
https://torch-points3d.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
https://github.com/torch-points3d/torch-points3d
Here are two detailed examples for installation worked on our local computers for your reference:
### Example 1 of installation
Specs local computer: Ubuntu 22.04, 64-bit, CUDA version 11.7 -> but CUDA is backwards compatible, so here we used CUDA 11.1 for all libraries installed.
Commands in terminal using miniconda:
```bash
conda create -n treeins_env_local python=3.8
conda activate treeins_env_local
conda install pytorch=1.9.0 torchvision==0.10.0 torchaudio==0.9.0 cudatoolkit=11.1 -c pytorch -c nvidia
pip install numpy==1.19.5
conda install openblas-devel -c anaconda
export CUDA_HOME=/usr/local/cuda-11
pip install -U git+https://github.com/NVIDIA/MinkowskiEngine -v --no-deps --install-option="--blas_include_dirs=${CONDA_PREFIX}/include" –install-option="--blas=openblas"
#CHECK IF TORCH AND MINKOWSKI ENGINE WORK AS EXPECTED:
(treeins_env_local) : python
Python 3.8.13 (default, #DATE#, #TIME#)
[GCC 7.5.0] :: Anaconda, Inc. on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import torch
>>> torch.cuda.is_available()
True
>>> import MinkowskiEngine
>>> exit()
#CHECK FINISHED
pip install torch-scatter==2.0.8 -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.9.0+cu111.html
pip install torch-sparse==0.6.12 -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.9.0+cu111.html
pip install torch-geometric==1.7.2
#We got the file requirements.txt from here: https://github.com/nicolas-chaulet/torch-points3d/blob/master/requirements.txt but deleted the lines containing the following libraries in the file: torch, torchvision, torch-geometric, torch-scatter, torch-sparse, numpy
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install numba==0.55.1
conda install -c conda-forge hdbscan==0.8.27
conda install numpy-base==1.19.2
pip install joblib==1.1.0
```
### Example 2 of installation
Specs local computer: Ubuntu 22.04.1, 64-bit, CUDA version 11.3
```bash
conda create -n torchpoint3denv python=3.8
conda activate torchpoint3denv
conda install -c conda-forge gcc==9.4.0
conda install pytorch=1.9.0 torchvision torchaudio cudatoolkit=11.1 -c pytorch -c nvidia
conda install numpy==1.19.5
mamba install libopenblas openblas
find ${CONDA_PREFIX}/include -name "cblas.h"
export CXX=g++
export MAX_JOBS=2;
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/MinkowskiEngine.git
cd MinkowskiEngine
python setup.py install --blas_include_dirs=${CONDA_PREFIX}/include --blas=openblas
#THE STEPS START FROM HERE ARE EXACT THE SAME AS EXAMPLE 1
#CHECK IF TORCH AND MINKOWSKI ENGINE WORK AS EXPECTED:
#...
```
Based on our experience, we would suggest build most of the packages from the source for a larger chance of succesful installation. Good luck to your installation!
# Data introduction
## NPM3D dataset with instance labels
Link for dataset download:
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8118986
### Semantic labels
1: "ground",
2: "buildings",
3: "poles",
4: "bollards",
5: "trash cans",
6: "barriers",
7: "pedestrians",
8: "cars",
9: "natural"
### Data folder structure
```bash
├─ conf # All configurations for training and evaluation leave there
├─ forward_scripts # Script that runs a forward pass on possibly non annotated data
├─ outputs # All outputs from your runs
├─ scripts # Some scripts to help manage the project
├─ torch_points3d
├─ data # DATA FOLDER
└─ npm3dfused
└─ raw
├─ *_train.ply # All train files
├─ *_val.ply # All val files
└─ *_test.ply # All test files
├─ train.py # Main script to launch a training
└─ eval.py # Eval script
```
## FOR-instance dataset
Link for dataset download:
#TO BE ADDED#
### Different forest regions/subgroups of trees
|<h3> Forest region </h3>|<h3> Number of files <h3>|<h3> Approx. largest tree heights </h3>|
| :--------------------: | :---------------------: | :-------------------------------: |
| <h3> CULS </h3> | 3 | 25|
| <h3> NIBIO </h3> | 20 | 30|
| <h3> NIBIO2 </h3> | 50 | 25|
| <h3> RMIT </h3> | 2 | 15|
| <h3> SCION </h3> | 5 | 30|
| <h3> TUWIEN </h3> | 2 | 35|
### Train - validation - test split
Train - test split is given by NIBIO: 56 train files, 26 test files. We decided on choosing 25% of the train files randomly but fixed as validation set -> 42 train files, 14 val files, 26 test files.
### Data folder structure
```bash
├─ conf # All configurations for training and evaluation leave there
├─ forward_scripts # Script that runs a forward pass on possibly non annotated data
├─ outputs # All outputs from your runs
├─ scripts # Some scripts to help manage the project
├─ torch_points3d
├─ data # DATA FOLDER
└─ treeinsfused
└─ raw
├─ CULS
├─ *_train.ply # All train files
├─ *_val.ply # All val files
└─ *_test.ply # All test files
├─ NIBIO
├─ *_train.ply # SIMILAR AS CULS FOLDER
├─ *_val.ply
└─ *_test.ply
├─ NIBIO2
├─ *.ply # SIMILAR AS CULS FOLDER
├─ RMIT
├─ *.ply # SIMILAR AS CULS FOLDER
├─ SCION
├─ *.ply # SIMILAR AS CULS FOLDER
└─ TUWIEN
├─ *.ply # SIMILAR AS CULS FOLDER
├─ train.py # Main script to launch a training
└─ eval.py # Eval script
```
# Getting started with code
## How to set different parameters
|<h3> Parameter </h3>|<h3> Value <h3>|<h3> Where to find/How to set in code </h3>|
| :--------------------: | :---------------------: | :-------------------------------: |
| Choose different settings in Table 2 in the original paper| Setting I-V| Setting I: models=panoptic/area4_ablation_19, Setting II: models=panoptic/area4_ablation_14, Setting III: models=panoptic/area4_ablation_15, Setting IV: models=panoptic/area4_ablation_3heads_5 Setting V: models=panoptic/area4_ablation_3heads_6 |
| Number of training iterations | 150 epochs | conf/training/#NameOfYourChosenConfigFile#.yaml, epochs|
| Voxel size/subsampling size | 0.2 (m) | conf/data/panoptic/#NameOfYourChosenConfigFile#.yaml, first_subsampling |
| Radius of sampling cylinder | 8 (m) | conf/data/panoptic/#NameOfYourChosenConfigFile#.yaml, radius |
| The folder name of your output files | #YourOutputFolderName# | job_name=#YourOutputFolderName# |
1. Create wandb account and specify your own wandb account name in conf/training/*.yaml. Have a look at all needed configurations of your current run in conf/data/panoptic/*.yaml, conf/models/panoptic/*.yaml and conf/training/*.yaml. Perform training by running:
```bash
# An example for NPM3D dataset
# Run Setting IV for test area 1, radius=16m, voxel side length=0.12m, training for 200 epoches.
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/npm3d-sparseconv_grid_012_R_16_cylinder_area1 models=panoptic/area4_ablation_3heads_5 model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=7_area1 job_name=A1_S7
# An example for FOR-instance dataset
# Run Setting IV, radius=8m, voxel side length=0.2m, training for 150 epoches.
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_rad8 models=panoptic/area4_ablation_3heads_5 model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=treeins job_name=treeins_my_first_run
```
2. Look at "TO ADAPT" comments in conf/eval.yaml and change accordingly. Perform evaluation by running:
```bash
python eval.py
```
3. Look at "TO ADAPT" comments in evaluation_stats.py and change accordingly, then run:
```bash
# For NPM3D dataset
python evaluation_stats_NPM3D.py
# For FOR-instance dataset
python evaluation_stats_FOR.py
```
# Citing
If you find our work useful, please do not hesitate to cite it:
```
@inproceedings{
Xiang2023,
title={Toward Accurate Instance Segmentation in Large-scale LiDAR Point Clouds},
author={Binbin Xiang and Torben Peters and Theodora Kontogianni and Frawa Vetterli1 and Stefano Puliti and Rasmus Astrup and Konrad Schindler},
booktitle={2023 The ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences},
year={2023},
url = {\url{https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.02877}}
}
```
|
defstudio/enum-features
|
https://github.com/defstudio/enum-features
|
A simple trait to enable a feature system using Enums
|
# Enum Features
[](https://packagist.org/packages/defstudio/enum-features)
[](https://github.com/defstudio/enum-features/actions?query=workflow%3Arun-tests+branch%3Amain)
[](https://github.com/defstudio/enum-features/actions?query=workflow%3A"Fix+PHP+code+style+issues"+branch%3Amain)
[](https://packagist.org/packages/defstudio/enum-features)
[](https://packagist.org/packages/defstudio/enum-features)
[](https://twitter.com/FabioIvona?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw)
A simple trait to enable a feature system using Enums:
```php
if(AppFeature::welcome_email->enabled()){
Mail::to($newUser)->send(new WelcomeEmail($newUser));
}
```
## Installation
You can install the package via composer:
```bash
composer require defstudio/enum-features
```
## Usage
Features can be enabled on any enum by using the `DefinesFeatures` trait:
```php
use DefStudio\EnumFeatures\EnumFeatures;
enum AppFeature
{
use DefinesFeatures; // ← simply add this
case multi_language;
case impersonate;
case welcome_email;
}
```
and each feature can then added to the Laravel application in its `configs/app.php` file:
```php
// config/app.php
return [
//..
'features' => [
AppFeature::multi_language,
AppFeature::welcome_email,
]
]
```
then, in code, a feature could be checked to be enabled:
```php
if(AppFeature::multi_language->enabled()){
//.. multi language specific code
}
```
or be disabled
```php
if(AppFeature::impersonate->disabled()){
throw(new Exception("Impersonate feature is not enabled"));
}
```
or enforced
```php
AppFeature::impersonate->enforce(); //throws "Feature [impersonate] is not enabled"
```
### Blade directives
In blade files, a feature can be checked with `@feature` directive:
```html
@feature(AppFeature::multi_language)
<select name="language" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/html">
<option value="en">English</option>
<option value="fr">French</option>
<option value="it">Italian</option>
</select>
@endfeature
```
### Customizing where and how to store enabled features
Enabled features are usually stored in config('app.features'), but this behaviour can be customized by
overriding the `enabledFeatures()` static method inside the enum class:
```php
use DefStudio\EnumFeatures\EnumFeatures;
enum AppFeature
{
use DefinesFeatures; // ← simply add this
case multi_language;
case impersonate;
case welcome_email;
public static function enabledFeatures(): array
{
return config('my_package.features', []); //or load from DB, or every other method
}
}
```
**note:** changing how enabled features are checked makes this package framework agnostic and it can be used in any php applicaiton
## Testing
```bash
composer test
```
## Changelog
Please see [CHANGELOG](CHANGELOG.md) for more information on what has changed recently. [Follow Us](https://twitter.com/FabioIvona) on Twitter for more updates about this package.
## Contributing
Please see [CONTRIBUTING](.github/CONTRIBUTING.md) for details.
## Security Vulnerabilities
Please review [our security policy](../../security/policy) on how to report security vulnerabilities.
## Credits
- [Fabio Ivona](https://github.com/defstudio)
- [def:studio team](https://github.com/defstudio)
- [All Contributors](../../contributors)
## License
The MIT License (MIT). Please see [License File](LICENSE.md) for more information.
## Support us
We at [def:studio](https://github.com/defstudio) strongly believe that open source is the foundation of all our business and we try to contribute to it by helping other projects to grow along with developing and maintaining our packages. You can support our work by sponsoring us on [github](https://github.com/sponsors/defstudio)!
|
KawaiiKillar/AutoCaptcha
|
https://github.com/KawaiiKillar/AutoCaptcha
|
Introducing AutoCaptcha: Free AI Solver, your ultimate tool for effortlessly bypassing captchas. Powered by advanced AI technology, this extension is designed to automatically solve hCaptcha and reCaptcha, completely free of charge.
|
# AutoCaptcha
Introducing AutoCaptcha: Free AI Solver, your ultimate tool for effortlessly bypassing captchas. Powered by advanced AI technology, this extension is designed to automatically solve hCaptcha and reCaptcha, completely free of charge.
|
c-skills/vala-vala-hey
|
https://github.com/c-skills/vala-vala-hey
|
Manjaro LPE
|
<p align="center">
<img src="https://github.com/c-skills/vala-vala-hey/blob/master/logo.jpg" />
</p>
This is a 0day root LPE for latest *Manjaro* distro, tested on embedded ARM and `x86_64` desktop
installs.
The root cause is the world writable directory of the package manager DB.
Only for educational purposes! Make sure to only run in safe testing environments, as
it might trash your package DB. Use it at your own risk!
Demo run
--------
This demo runs on (as of today latest) *Manjaro* Linux dist. For *this* demo version it is necessary
that the admin previously did a `pamac update`, `pamac checkupdates` or similar in past,
to create the `refresh_timestamps` file in `/var/tmp/pamac/dbs/sync` that the exploit makes
use of.

|
SHIJS1999/cloudflare-worker-vless-ip
|
https://github.com/SHIJS1999/cloudflare-worker-vless-ip
|
通过ws路径自定义cf worker vless出站ip
|
#白奶酪
#通过ws路径自定义cf worker vless出站ip
1.原作者ED哥:GitHub Repository for https://github.com/zizifn/edgetunnel
2.当路径字符串为myIP时,出站IP和你自己选择的CF入站IP一致
3.当路径字符串为proxyIP=时,如proxyIP=11.11.11.11,你的出站IP为11.11.11.11。(proxyIP必须是CF的反代IP)
#模板
type: vless
name: www.123.com
server: 12.34.56.78
port: 443
uuid: YouUserId
network: ws
tls: true
udp: false
sni: www.123.com
client-fingerprint: chrome
ws-opts:
path: "/proxyIP=11.11.11.11"
headers:
host: www.123.com
|
matheuspergoli/draftcode
|
https://github.com/matheuspergoli/draftcode
|
Plataforma de Desafios Frontend & Backend.
|
# DraftCode
<img src="./public/images/draftcode.png" alt="Image do site DraftCode">
### Ajustes e melhorias
O projeto ainda está em desenvolvimento e as próximas atualizações serão voltadas nas seguintes tarefas:
- [x] Área para administradores adicionarem suas redes sociais para ficar em evidência no site
- [ ] Melhorar performance.
- [ ] Melhorar responsividade.
- [ ] Corrigir bugs existentes.
## 💻 Pré-requisitos
Antes de começar, verifique se você atendeu aos seguintes requisitos:
- Você tem o `docker` instalado.
- Você tem o `cloudinary` configurado.
- Você tem o `oauth app` do github configurado.
- Você tem o `microsserviço` de upload de imagens rodando.
- Você tem a versão mais recente do `node` e `npm` instalado.
- Você configurou suas váriaveis de ambiente conforme está presente no `.env.example`.
Caso não tenha o microsserviço de upload de imagens, você pode baixar ele [aqui](https://github.com/matheuspergoli/draftcode-upload-image), é obrigatório para criar novos desafios ter o microsserviço de upload de imagens rodando.
Crie um oauth app no github seguindo [este tutorial](docs/oauth/OAUTH.MD), é obrigatório para o funcionamento do NextAuth que você crie e configure um oauth app no github, caso contrário, o login com o github não irá funcionar.
Configure o cloudinary seguindo [esse passo a passo](https://github.com/matheuspergoli/draftcode-upload-image/blob/main/docs/cloudinary/CLOUDINARY.MD)
## 🚀 Instalando o DraftCode
Para instalar o DraftCode, siga estas etapas:
Linux:
```
npm install && sudo docker-compose up -d && npx prisma db push && npm run dev
```
Windows:
```
npm install && docker-compose up -d && npx prisma db push && npm run dev
```
## 📫 Contribuindo para o DraftCode
Para contribuir com o DraftCode, siga estas etapas:
1. Faça um fork desse projeto e clone pra você.
2. Crie uma branch: `git checkout -b <nome_branch>`.
3. Faça suas alterações e confirme-as: `git commit -m '<mensagem_commit>'`
4. Envie para a branch original: `git push origin <nome_do_projeto> / <local>`
5. Crie a solicitação de pull.
Como alternativa, consulte a documentação do GitHub em [como criar uma solicitação pull](https://help.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/creating-a-pull-request).
## 🤝 Colaboradores
Agradecemos às seguintes pessoas que contribuíram para este projeto:
<table>
<tr>
<td align="center">
<a href="https://github.com/matheuspergoli" target="_blank">
<img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/94739199?v=4" width="100px;" alt="Foto do Matheus Pergoli no GitHub"/><br>
<sub>
<b>Matheus Pergoli</b>
</sub>
</a>
</td>
<td align="center">
<a href="https://github.com/NatanCastro" target="_blank">
<img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/65430728?v=4" width="100px;" alt="Foto do Natan Castro no GitHub"/><br>
<sub>
<b>Natan Castro</b>
</sub>
</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
## 📝 Licença
Esse projeto está sob licença. Veja o arquivo [LICENÇA](LICENSE) para mais detalhes.
[⬆ Voltar ao topo](#DraftCode)<br>
|
hsyntes/authentication-authorization-security
|
https://github.com/hsyntes/authentication-authorization-security
|
Authentication, Authorization and Security Back-End System with Node.js & Express.js & mongoDB - mongoose. Registering users to the database, authorization and authentication users, sending emails to users' email address to reset or update their password and more.
|
# Authentication & Authorization & Security
An overview of the authentication, authorization and security considerations for a back-end application written with Node.js, Express.js mongoDB and mongoose. These components are widely used in building web applications and require careful attention to ensure the safety and integrity of user data.
## Features
- Security HTTP headers with **helmet**
- Rate limitting from the same **IP/API**
- Data Sanitization against **NoSQL** injection
- Data Sanitization against **XSS**
- Maganing & catching errors globally with **middleware** functions
- Sending token to users' email address to reset & update their password more secure
- Generate expired token
- Verifying **JSON Web Token**
- Sending JWT via **cokie**
- **Encrypting** & **hashing** passwords
- Restrict/protect some features by token
- Email validator
- Dedicate environments to **development** and **production**
- Structured users'data more secure with **mongoose Data Modelling**
## Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user or system. In the context of a back-end application, it ensures that only authorized users can access protected resources. Here are some key considerations for implementing authentication:
## User Registration
Implement a user registration process that collects necessary information, such as username, email, and password. Ensure that password requirements, such as length and complexity, are enforced.
## Login
Provide a secure login mechanism using sessions or tokens. Validate user credentials against stored data and generate authentication tokens or session cookies for subsequent requests.
## Password Reset
Offer a secure password reset functionality that involves verifying the user's identity through a password reset email or other verification methods.
## Authentication Middleware
Use middleware to authenticate requests. This middleware should check for valid authentication tokens, verify session cookies, or implement other authentication mechanisms.
## Authorization
Authorization determines what actions a user can perform within an application. It ensures that authenticated users have the necessary permissions to access or modify specific resources. Consider the following when implementing authorization
## Role-Based Access Control
Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to assign different permissions to different user roles. For example, an administrator role might have more privileges than a regular user role.
## Resource-Based Authorization
Control access to specific resources based on user roles and ownership. Ensure that users can only access resources they are authorized to view or modify.
## Security
Maintaining the security of your application is crucial to protect user data and prevent unauthorized access or data breaches. Consider the following security measures
#### Input Validation
Validate and sanitize all user input to prevent common security vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and command injection attacks. Use libraries or built-in mechanisms to handle input validation and sanitize user input before using it in database queries or rendering it in HTML templates.
#### Password Hashing
Store user passwords securely by hashing them with a strong cryptographic algorithm like bcrypt or Argon2. Hashing passwords prevents storing plain-text passwords in the database, making it harder for attackers to retrieve user passwords in case of a data breach.
#### Secure Communication
Enable secure communication between clients and the server using HTTPS/TLS. This ensures that data transmitted over the network is encrypted and protects against eavesdropping and tampering. Obtain and install an SSL certificate to enable HTTPS on your server.
#### Session Management
Implement secure session management to track user sessions and prevent session-related attacks such as session hijacking or fixation. Use secure session storage mechanisms, such as server-side storage or encrypted client-side storage (e.g., signed cookies), and regenerate session IDs after user authentication or privilege changes.
### Error Handling
Handle errors securely to avoid information leakage and potential vulnerabilities. Follow these best practices for error handling
#### Avoid Detailed Error Messages
Do not expose sensitive information or detailed error messages to clients in production environments. Instead, log the error details on the server and provide user-friendly error messages to clients.
#### Custom Error Handling Middleware
Implement custom error handling middleware to catch and handle errors in a consistent and secure manner. This middleware can log errors, handle different error types, and send appropriate error responses to clients.
Error Reporting and Monitoring: Set up error reporting and monitoring tools to track and investigate errors occurring in your application. These tools can help you identify and address security vulnerabilities or other issues promptly.
## API Reference
#### Get all users
```http
GET /api/v1/users/
```
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| :-------- | :------- | :---------- |
| `/` | `string` | - |
#### Get a user
```http
GET /api/v1/users/username/
```
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| :---------- | :------- | :--------------------------- |
| `username/` | `string` | **Required** Verifying token |
#### SignUp
```http
POST /api/v1/users/signup/
```
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| :-------- | :------- | :------------------------------- |
| `signup/` | `string` | **Required** all fields in Model |
#### Login
```http
POST /api/v1/users/login/
```
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| :-------- | :------- | :------------------------------------------ |
| `login/` | `string` | **Required** email or username and password |
#### Forgot Password
```http
POST /api/v1/users/forgot-password/
```
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| :----------------- | :------- | :----------------- |
| `forgot-password/` | `string` | **Required** email |
#### Reset Password
```http
PATCH /api/v1/users/reset-password/passwordResetToken
```
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| :----------------------------------- | :------- | :---------------------------- |
| `reset-password/passwordResetToken/` | `string` | **Required** token from email |
#### Update Password
```http
PATCH /api/v1/users/update-password/
```
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| :----------------- | :------- | :--------------------------- |
| `update-password/` | `string` | **Required** verifying token |
#### Deactivate User
```http
DELETE /api/v1/users/deactivate/
```
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| :------------ | :------- | :--------------------------- |
| `deactivate/` | `string` | **Required** verifying token |
#### Close Account
```http
DELETE /api/v1/users/delete/
```
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| :-------- | :------- | :--------------------------- |
| `close/` | `string` | **Required** verifying token |
#### Update
```http
PATCH /api/v1/users/delete/
```
| Parameter | Type | Description |
| :-------- | :------- | :--------------------------- |
| `update/` | `string` | **Required** verifying token |
## Run Locally
Clone the project
```bash
git clone https://github.com/hsyntes/authentication-authorization-security
```
Go to the project directory
```bash
cd authentication-authorization-security
```
Install dependencies
```bash
npm install
```
Start the server on **development** environment
```bash
npm start
```
Start the server on **production** environment
```bash
npm run start:prod
```
## 🔗 Links
[](https://www.linkedin.com/in/hsyntes)
|
discus0434/minutes-maker
|
https://github.com/discus0434/minutes-maker
|
A web app that automatically generates transcripts and summaries of meetings or lectures.
|
# Minutes Maker
**Minutes Maker is a web app that automatically generates transcripts and summaries of meetings or lectures.**
<h1 align="center">
<img src="./assets/sample.gif" width=100%>
</h1>
> **Note**
> 日本語のREADMEは[こちら](./assets/README-ja.md)です。
## Overview
Key features:
- **Transcribe almost any audio/video file** with [faster-whisper](https://github.com/guillaumekln/faster-whisper)
- **Summarize transcripts** using [OpenAI LLMs](https://openai.com/blog/openai-api/)
- **Easy-to-use web interface**
- Support for **English and Japanese**
- Compatible with both **CPU and GPU**
## Installation
#### 1. Place the environment variables in the `.env` file
You need to place the following environment variables.
- `OPENAI_API_KEY` is the API key for summarization, which can be found [here](https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys).
- `REACT_APP_PUBLIC_IP` is the public IP address of the machine that runs the app.
- If you deploy the app on your local machine, should be `'0.0.0.0'`.
- If you deploy the app on a remote server, should be the public IP address of the server.
You can place the environment variables in the `.env` file by running the following commands:
```bash
cd minutes-maker
echo "OPENAI_API_KEY='sk-XXX'" >> .env
echo "REACT_APP_PUBLIC_IP='XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX'" >> .env
```
#### 2. Build the Docker image
Whether the machine has a NVIDIA GPU or not is automatically detected and the appropriate Docker image is built.
```bash
make build
```
#### 3. Run the app
```bash
make up
```
#### 4. Access the app
Open `http://<PUBLIC_IP or 0.0.0.0>:10356` in your browser.
## Usage
<p align="center">
<img src="./assets/sample.png" width=50%>
</p>
_Just fill the form and click the **Submit** button!_
**Here is a brief explanation of the form:**
1. **Upload audio/video file**
Select an audio/video file to be transcribed and summarized. Almost any audio/video file can be used, and the file size is not limited.
2. **Select target language**
Select the target language to be summarized. **Note that the language of the audio/video file is automatically detected and cannot be changed**, so you should select _what language you want to summarize_.
Currently, English and Japanese are supported.
3. **Select category**
Select the category of the audio/video file, **meeting** or **lecture**. Appropriate setting of this parameter will improve the quality of the summary.
4. **Enter meeting/lecture topic**
Enter the topic of the meeting/lecture, such as the theme of it (e.g. "development of the new product").
Set appropriate topic to improve the quality of the transcript.
## Requirements
- Computer
- Docker
## License
This repository is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0. See [LICENSE](./LICENSE) for more information.
|
playcanvas/earthatile
|
https://github.com/playcanvas/earthatile
|
Engine-agnostic runtime for 3D Tiles geospatial datasets
|
# Earthatile - 3D Maps for your Apps 🌎
Earthatile is an engine-agnostic runtime for loading and navigating [3D Tiles](https://github.com/CesiumGS/3d-tiles/tree/main#readme) geospatial datasets. Use it to [create immersive 3D map experiences with Photorealistic 3D Tiles](https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/maps-platform/create-immersive-3d-map-experiences-photorealistic-3d-tiles) such as flight simulators, explainers, games and more.
[](images/earthatile-demos.jpg)
## Getting Started
Earthatile depends upon [Google's Photorealistic 3D Tiles API](https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/tile/3d-tiles). To access it, you need an API key. You can obtain a key by setting up a Google Cloud project with a billing account. You then need to enable the Map Tiles API. To learn more, see [Setup in Cloud Console](https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/tile/cloud-setup). Once you have your API key, you can:
[](https://playcanv.as/p/2TJUs24q/)
### Node.js
If you want to run Earthatile in Node, you simply need to add it as a dependency in your `package.json`:
npm install earthatile
### PlayCanvas
Earthatile is supplied with an integration for [PlayCanvas](https://playcanvas.com).
1. Ensure you have the Draco WASM module in your project (set `Settings` > `Asset Tasks` > `Mesh Compression` to `Draco` and import the module).
2. Copy `dist/earthatile.js` to the Asset Panel in the Editor.
3. Copy `integrations/playcanvas/*.js` to the Asset Panel in the Editor.
4. Create an Entity and add a Script Component.
5. Assign `tileRenderer` and `geolocation` scripts to the Script Component.
6. Add a Script Component to your Camera entity.
7. Assign the `flyCamera` script to the Script Component.
8. Launch the scene. 🚀
Alternatively, [fork this project](https://playcanvas.com/project/1074797/overview/earthatile-world-explorer).
|
CaCaBlocker/react-redux-saga-tailwindcss-typescript
|
https://github.com/CaCaBlocker/react-redux-saga-tailwindcss-typescript
|
🅰 Simple project architecture with React & Redux & Saga & Tailwind CSS & Typescript
|
# Project Architecture
### What are the main skills?
⚽ React.js <br/>
⚾ Redux + Saga <br/>
🥎 Tailwind CSS <br/>
🏀 Typescript <br/>
🏐 Vite <br/>
### Problem
https://github.com/innoloft/Frontend-Application
### Solution
🛠 How to run in local
```
npm run dev
```
🛠 How to link the code
```
npm run lint
```
🛠 How to check the format of code
```
npm run format:check
```
🛠 How to format the code
```
npm run format
```
🛠 How to build
```
npm run build
```
|
fabian-hiller/valibot
|
https://github.com/fabian-hiller/valibot
|
The modular and type safe schema library for validating structural data 🤖
|

# Valibot
Hello, I am Valibot and I would like to help you validate data easily using a schema. No matter if it is incoming data on a server, a form or even configuration files. I have no dependencies and can run in any JavaScript environment.
> I highly recommend you read the [announcement post](https://www.builder.io/blog/introducing-valibot).
## Highlights
- Fully type safe with static type inference
- Small bundle size starting at less than 300 bytes
- Validate everything from strings to complex objects
- Open source and fully tested with 100 % coverage
- Many transformation and validation helpers included
- Well structured source code without dependencies
- Minimal, readable and well thought out API
## Example
First you create a schema. A schema can be compared to a type definition in TypeScript. The big difference is that TypeScript types are "not executed" and are more or less a DX feature. A schema on the other hand, apart from the inferred type definition, can also be executed at runtime to guarantee type safety of unknown data.
```ts
import { email, minLength, object, type Output, parse, string } from 'valibot'; // 0.76 kB
// Create login schema with email and password
const LoginSchema = object({
email: string([email()]),
password: string([minLength(8)]),
});
// Infer output TypeScript type of login schema
type LoginData = Output<typeof LoginSchema>; // { email: string; password: string }
// Throws error for `email` and `password`
parse(LoginSchema, { email: '', password: '' });
// Returns data as { email: string; password: string }
parse(LoginSchema, { email: '[email protected]', password: '12345678' });
```
## Comparison
Instead of relying on a few large functions with many methods, my API design and source code is based on many small and independent functions, each with just a single task. This modular design has several advantages.
For example, this allows a bundler to use the import statements to remove code that is not needed. This way, only the code that is actually used gets into your production build. This can reduce the bundle size by up to 98 % compared to [Zod](https://zod.dev/).
Besides the individual bundle size, the overall size of the library is also significantly smaller. This is due to the fact that my source code is simpler in structure, less complicated and optimized for compression.
## Credits
My friend [Fabian](https://twitter.com/FabianHiller) created me as part of his bachelor thesis at [Stuttgart Media University](https://www.hdm-stuttgart.de/en/), supervised by Walter Kriha, [Miško Hevery](https://twitter.com/mhevery) and [Ryan Carniato](https://twitter.com/RyanCarniato). My role models also include [Colin McDonnell](https://twitter.com/colinhacks), who had a big influence on my API design with [Zod](https://zod.dev/).
## Feedback
Find a bug or have an idea how to improve my code? Please fill out an [issue](https://github.com/fabian-hiller/valibot/issues/new). Together we can make the library even better!
## License
I am completely free and licensed under the [MIT license](https://github.com/fabian-hiller/valibot/blob/main/LICENSE.md). But if you like, you can feed me with a star on [GitHub](https://github.com/fabian-hiller/valibot).
|
Madhav-MKNC/Babu-LOHAR
|
https://github.com/Madhav-MKNC/Babu-LOHAR
|
A Slack Bot powered by the advanced LLM model for interacting with Your uploaded PDFs
|
# Babu-Lohar: A Slack Bot Powered by Advanced LLM Model for Interacting with Uploaded PDFs
## Introduction
Babu-Lohar is a versatile Slack Bot that is powered by an advanced Large Language Model (LLM). It is designed to interact with your uploaded Documents, extract useful information, and assist in analyzing and managing content.
## Features
- Documents Uploading: Upload your Documents files to the Slack channel and Babu-Lohar will automatically process them.
- Chat with your documents.
- Documents summarization.
- Advanced Language Understanding: Powered by the latest language understanding model, Babu-Lohar can understand and execute complex commands, and even engage in casual conversation.
## Installation
1. **Clone the Repository**
First, clone the Babu-Lohar repository from GitHub to your local machine. Use the following command:
```
git clone https://github.com/Madhav-MKNC/Babu-LOHAR.git;
cd Babu-LOHAR/;
```
2. **Setup Environment**
Install the required dependencies for Babu-Lohar. It is recommended to use a virtual environment to keep your project organized.
```
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
3. **Configure Your Slack Workspace**
Create a new bot in your Slack workspace and obtain your `Bot User OAuth Token`.
4. **Set Up Environment Variables**
You will need to set up all the environment variables mentioned in the .env file. (Make sure that this part remains as secure as possible)
5. **Run the Bot**
Once you have everything set up, you can run Babu-Lohar using the following command:
```
python main.py
```
## Usage
Once Babu-Lohar is up and running, you can begin uploading PDFs to your Slack workspace. The bot will automatically process any PDFs uploaded to channels it is a member of.
To interact with Babu-Lohar, simply mention the bot in a message.
## License
Babu-Lohar is licensed under the [MIT License](LICENSE.md).
## Acknowledgements
We are grateful to OpenAI for their incredible GPT models which power Babu-Lohar. Additionally, we would like to express our thanks to hwchase17 for the Langchain framework, which has greatly contributed to the development of our project.
## Contact
For any questions or concerns, please open an issue on GitHub or contact the maintainers directly.
Enjoy using Babu-Lohar!
|
Bugswriter/music_fairy
|
https://github.com/Bugswriter/music_fairy
|
Simple voice assistant for playing any song/music
|
# Music Fairy
Music Fairy is a script that utilizes speech recognition to play any song audio in MPD (Music Player Daemon). It uses YouTube as a source to fetch music and integrates with various libraries and tools to provide a seamless music playback experience.
## Installation
To install Music Fairy, follow these steps:
1. Clone the repository from GitHub: [github.com/bugswriter/music_fairy](https://github.com/bugswriter/music_fairy)
2. Copy the `music-fairy` script into `~/.local/bin` on your system.
3. Install the required Python packages by running the following commands:
```
pip3 install vosk
pip3 install yt-dlp
pip3 install google_speech
```
4. Ensure that `ffmpeg` is installed on your system.
5. Download the Vosk model from [alphacephei.com/vosk/models](https://alphacephei.com/vosk/models). It is recommended to download the lighter model with a smaller file size.
6. Put the model directory in `~/.local/share/music_fairy/`, or change the `VOSK_MODEL_PATH` variable to the path where you downloaded the Vosk model.
7. Bind Music Fairy to a specific key using your system's keybinding configuration.
## Usage
Once installed and configured, you can use Music Fairy to play songs by following these steps:
1. Activate the speech recognition by pressing the bound key.
2. Speak the name of the song or artist you want to play.
3. Music Fairy will fetch the audio from YouTube and play it using MPD.
4. Enjoy your music!
Please note that a working internet connection is required for Music Fairy to fetch music from YouTube.
## License
- GPL-3
## Support
- Checkout my donate page - [bugswriter.com/donate](https://bugswriter.com/donate)
|
mishuka0222/hackathon-2023-summer
|
https://github.com/mishuka0222/hackathon-2023-summer
| null |
# hackathon-2023-summer

## 时间点

- 活动报名开启:2023年 5月 12日
- 线上 Coding 初赛:2023年 5月 15日 - 2023年 7月 4日
- 开幕式:2023年 5月 20日
- 1场线上直播组队:2023年 6月 3日
- 4场线上 Workshop & Office Hour:2023年 6月 10日 - 2023年 7月 1日
- 导师带队:2023年 6月 19日 - 2023年 6月 21日
- 活动报名截止&代码提交截止:2023年7 月 4日 上午 11:59
- 初选审核:2023年 7月 5日 - 2023年 7月 6日
- 晋级战队公示:2023年7 月 7日
- 线下Hacking决赛:2023年 7月 13日 - 2023年 7月 14日
- 线下签到&彩排:2023年 7月 13日 14:00 - 17:00
- DemoDay:2023年 7月 14日 10:00 - 12:00, 14:00 - 17:00
- 获奖队伍公示:2023年 7月 14日 18:00
- After Party:2023年 7月 14日 20:00 - 24:00
- 冠军团队参加 Decoded 大会演讲:2023年 7月 15日 - 2023年 7月 16日
## 地点
上海
## 奖项设置

按照项目分成四个不同的赛道,每个赛道由一二三等奖,各一个。其余4个奖项分别为:最受评委喜爱奖、最受开发者喜爱奖、最佳创新奖、Travel Grant奖金池。一共16个奖项。四个赛道分别是:
- 平行链 + 独立链
- 智能合约 (及相关)
- 区块链产品和工具
- 开放命题
[这里有赛道详情](./docs/categories.md)
**项目可以选择多个赛道参赛,初审评审会根据项目实现的功能确定是否可以参与到单个赛道的角逐**
Bounty奖项列表
## 奖金

16个奖项共申请国库30万美金等额的DOT共42,852。每个奖项的金额如下
- 一等奖: 5714 DOT 约四万美金 (每个赛道各一个)
- 二等奖: 2857 DOT 约二万美金 (每个赛道各一个)
- 三等奖: 1428 DOT 约一万美金 (每个赛道各一个)
- 最受观众喜爱奖: 714 DOT 约五千美金 (共一个)
- 最受开发者喜爱奖: 714 DOT 约五千美金 (共一个)
- 最佳创新奖: 714 DOT 约五千美金 (共一个)
- Travel Grant奖金池: 714 DOT 约5000美金 (共一个)
(打卡每场活动+进入决赛来现场的战队共同瓜分该奖金池)
### 赞助商奖金池

⼤赛新增 Bounty 命题及奖励,由⽣态内各⼤项⽬⽅结合⽣态发展和技术需求,总价值超过
$300,000,为参赛战队提供 Bounty 赛题和奖⾦⽀持 了解更多。
## 项目报名
以下信息也可见于[这微信页](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/KGkTkcRh7dO1UmB8REKMtw)。
### 1. 填写谷歌表单
参赛者可以通过以下链接提交报名完善信息,无论您是团队还是个人参赛,每个参赛队员都需要填写此表。
🚩谷歌表单:https://forms.gle/bfQCm1JUKDwBqXSW9
### 2. 填写注册信息
参赛者通过报名链接填写信息,提交电子邮件进行注册。在 Dorahacks 网站上点击“立即注册”按钮,申请一个免费的 Dorahacks 帐户用于参加黑客松。每队至少应有一名队员报名并填写所需信息,可以选择只填写注册所需的信息。参加本次黑客松即表示同意赞助商收集和保存参赛者个人信息,用于运营和宣传黑客松。
🚩报名链接: https://dorahacks.io/hackathon/polkadot-hackathon-2023-summer/detail
### 3. 加入微信群/Discord 群
国内报名选手在提交报名表后,请尽快添加小助手 Emma(oneblockEmma)微信,我们将于 24 小时内给予回复,请耐心等待!我们将会邀请您加入大赛官方“2023 夏季波卡黑客松大赛群”,关于黑客松赛事的信息将会在第一时间内在群内通知!入群后,请将您的群昵称修改为“姓名-XX 团队”或“姓名-个人”(如尚未组队)。如果您遇到任何有关黑客松的问题,也可以私聊 Emma 寻求帮助。
<img src="./docs/assets/03-wechat-qr.jpg" width="160px">
海外参赛选手请加入 Discord 群并选择 **2023 Polkadot Summer Hackathon Hacker** 作为您的角色,请将您的用户名修改为“姓名- xx团队”或“姓名-个人”(如果您尚未组建团队)。
🚩Discord 社群链接:https://discord.com/invite/KsCEKvqU4p
### 4. 创建你的 2023 夏季波卡黑客松大赛项目
1. 报名注册完成后,可以立即开始项目创建,fork 本代码仓库,到你们团队成员 repo 里: https://github.com/parity-asia/hackathon-2023-summer
2. 先在 `projects` 内生成一个目录,以你们项目名称命名,里面先放个空档案,或 readme 简单介绍项目。提交一个 PR 进来。目的是预留一个目录作为你们项目空间。**注意我们会把目录改名,在项目名称前加个编号。请 pull 下来。**
3. 之后,所有参赛项目相关代码都放在你们的项目名称里的目录里进行。可以这种形式存放:
```
projects
L 00-项目模板/ // 项目目录名称
L src/
L substrate/ // substrate 相关代码
L ui/ // 前端相关代码
L 。。。 // 其他档案
L docs/ // 存放文档。视频和PPT等大文件不要直接上传,放链接地址即可
L README.md
```
4. 2023年7月4日上午11:59前,提交最终 PR 进来本 repo,项目只可修改他们目录里的档案。
### 5. 提交初审材料
1. 项目代码必须在 Github 提交 PR 到本 repo ([**parity-asia** 组织](https://github.com/parity-asia) 下的)。在注册的第一周,项目应该复制这个代码存储库并创建一个项目目录。在 README 文件中,列出计划在黑客马拉松期间完成的代码功能(不超过 1000 字),并向 Parity Github 提交 pull request (PR);
2. 每个项目必须提交至少一件参赛作品,所有项目必须提交英文版本的作品。
3. 参赛作品的内容包括但不限于:
**基本信息**:项目名称、立项日期
**报名赛道**:如需要,可多选
**项目概况**:项目背景/起源/需要解决问题/项目介绍/项目演示/技术架构/项目 Logo /项目初审版本/团队信息/所属赛道
**黑客松期间计划完成的代码项目**:区块链端、Web 端、用户注册页面等
**黑客松完成项目**(2023 年 7 月 4 日上午 11:59 初审前提交)
4. Demo 视频及过大的 PPT 不要上传 Github,可以把链接地址加到 readme。或者将 Demo 视频上传到 YouTube,PPT 链接上传到 Google drive,GitHub 只提交 YouTube 链接和 Google drive 链接。
5. 列出在 2023 年 7 月 4 日上午 11:59 截止日期前,该项目在黑客松期间最终完成的功能。将相关代码放在 “src” 目录中,并在此部分列出已完成的开发工作/特性。我们将重点关注这些目录/文件,并作出技术评估。
6. 如果你想参考一些资料,可以[点击链接查看](https://github.com/parity-asia/hackathon-2023-summer/tree/main/teams/00-team-template)。
7. 参赛作品必须在规定时间内(7 月 4 日中午 12:00 前)提交,超时提交无效
8. 7 月 7 日晚,本次 repo 将给出初步名单,并选出参赛队伍进入 DemoDay
## 导师团队指导参赛项目
比赛过程中,主办方会组织每个参赛战队的线上讨论会议。会议结束后,Parity 工程师与投资机构研究员将作为导师进入战队群并提供指导,参赛团队根据自身项目进展和技术架构提出遇到的开发难题及需求,导师将会为战队提供实质性建议,帮助战队顺利孵化参赛作品!
**如要匹配导师,请尽早提交项目计划,然后联络我们有此需求**。导师资源有限,我们按项目详细度匹配,不保证每队提有导师需求的团队都获得匹配。
## 评审规则
最终初选截止日前提交代码,把相关代码放在 `src` 目录里,并在本栏列出在黑客松期间已完成的开发工作/功能点。我们将对这些目录/档案作重点技术评审。
### 初审 50%:(技术维度)
初审时,参赛作品从下面三个维度进行评分:
- 完成度 (20%): 项目实现完备,不止是概念,Demo / POC 展示完整;项目技术架构、算法实现优雅程度、具备自动单元测试;
- 技术难度 (20%): 解决的问题有一定技术门槛,技术层面具有一定突破。着重:链 runtime / 智能合约开发,其他:前/后端开发;
- 规范性 (10%): 项目在规定的时间提交且内容规范。
### 决赛 50%:(商业维度)
决赛时,从下面三个维度评分:
- 商业价值 (20%): 能解决问题,创新性,能放在你所知的行业场景中使用,以及当前项目发展的进度;立意新颖,具备突破性,打破常规思维。
- 创新性 (20%): 立意新颖,具备突破性,打破常规思维。
- 用户体验 (10%): 包括提交的方案对潜在用户来说的直观性和可理解程度。
**最终每队分数: 技术评审 (50%) + 商业评审 (50%)**
### 备注
- 建议团队保持代码的更新,和提交。提交历史记录清晰的项目更有利与评审了解项目的实际开发工作。
- 全新的项目可以直接从黑客松的 github 开始开发项目,成熟团队写清楚黑客松期间要增加的功能,并在5月12后拉出新branch比如(hackathon-2023-summer)来提交代码。注明branch名称,方便评审了解其工作。
- 参赛团队须通过现场路演汇报的形式,全方位阐述作品实现过程及最终作品。
- 参赛队伍提交的所有参赛资料的知识产权归参赛队伍所有,参赛资料仅用于本次大赛评奖与宣发。
- 初审的结果用来选择参加Demo的团队
- 技术得分会结合 Demo 和问题答辩做调整,Demo 的内容和实现的代码功能应该一致
- **本次活动的最终解释权归 OneBlock 及 Parity 官方所有。**
## 評委
本届⿊客松⼤赛评审分为 Hackathon Judges 和 Sponsor & Bounty Judges。他们将为参赛作品做出专业多维、公平公正的评判,以下是评审团队。

## Workshop 及 Office Hour 时间表
- 开幕式:2023年5月20日
1. 2023上半年波卡最新进展 - 周俊 (Parity 工程师)
2. 2023夏季黑客松赛事规则详解 - Jimmy (Substrate 贡献者)
加入方式: [Twitter Space](https://twitter.com/i/spaces/1zqKVPaELeLJB)
- **Workshop #1:超越创新:探索新的区块链⼯具和技术实践**
2023年6月10日 20:00 - 21:30 UTC +8
讲题:
1. 如何在区块链领域构建去中心的生态 - Kaichao (Parity 工程师)
2. 创新思维: 探索Web3领域的非传统应用 - Jimmy (Substrate 贡献者)
[YouTube 回顾](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jRMLKHlQw0s)
- **Workshop #2:构建安全⾼效的Web3定制链与智能合约**
2023年6月19日 20:00 - 21:30 UTC +8
讲题:
1. Substrate 从0构建⼀条链的最佳⼯具 - 周俊 (Parity ⼯程师)
2. Ink! 构建智能合约应⽤ - Suvi Dong (Parity ⼯程师)
[加⼊ Zoom 会议](https://zoom.us/j/89233757595?pwd=TXpzb3o0V1RHTWJKbnpJOVgwK0NIZz09) / [YouTube 直播](https://www.youtube.com/live/gX8om1MUYck?feature=share)
- **Workshop #3:Polkadot:区块链基础设施的未来**
2023年6⽉24⽇ 20:00-22:00 UTC+8
讲题:
1. 使⽤ Moonbeam 改善多链⽤户体验 - Kevin Neilson (Moonbeam 开发者关系⼯程师)
2. 强⼤的 Web3 创新平台 - Arthur (Deeper Network 区块链负责⼈)
3. CESS : 为百万级应⽤提供最好的去中⼼化存储 - Andy Zou (CESS 中⽂社区经理)
4. 零知识证明、Manta Network 与 zkSBT - Godot (Manta Network 核⼼贡献者)
[加⼊ Zoom 会议](https://us02web.zoom.us/j/86561770199?pwd=SENkTUJBUjRMYllHQWJmR1EwVUV5dz09) / [YouTube 直播](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hPSkW2PrXtc)
- **Workshop #4:在 Polkadot 上开发应⽤程序**
2023年7⽉1⽇ 20:00-22:00 UTC +8
讲题:
1. 阿⾥云如何助⼒你的 Web3 之旅 - Leo Li (阿⾥云国际⾹港 Web3 ⽣态负责⼈)
2. 由 Gear Protocol 提供⽀持的并⾏智能合约平台 - Btwiuse (Gear Foundation 技术负责⼈); Nicole (Gear Foundation 社区增长)
3. 使⽤ Acala 构建 Dapp / Chopsticks - Shunji (Acala 核⼼代码贡献者)
4. LSD-fi 在 Polkadot 上的兴起 - Tyrone (Bifrost 治理委员会成员)
5. Polkadot 上的多虚拟机智能合约中⼼ - Mingshi (Astar ⾼级业务开发)
[加⼊ Zoom 会议](https://us02web.zoom.us/j/86561770199?pwd=SENkTUJBUjRMYllHQWJmR1EwVUV5dz09) / [YouTube 直播](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hPSkW2PrXtc)
## 联络
对黑客松有任何疑问,可以下方法联系我们:
* [Github 讨论区](https://github.com/ParityAsia/hackathon-2023-summer/discussions)
* email: [email protected]
* wechat: oneblockEmma
* [黑客松比赛 Discord](https://discord.gg/KsCEKvqU4p)
## 其他
- [技术资源](./docs/technical-resources.md)
### 合法合规性
本次黑客松为符合国内法规,我们不会触碰以下任何有关题目
- 和发币 (Initial Coin Offering) 相关。
- 和数字资产交易相关
- 任何币价的讨论 (Decentralized Exchange 主题可讨论技术,不涉及币价)
- 和博彩相关和有博彩成分的游戏
|
axilla-io/ax
|
https://github.com/axilla-io/ax
|
A comprehensive AI framework for TypeScript
|
<p align="center">
<img src="./assets/logo.png" />
</p>
# Ax — A comprehensive AI framework for TypeScript
Ax is a collection of modules designed for creating robust AI applications. These modules can be adopted incrementally, thus providing a modular and scalable end-to-end solution.
Used together, they form an end-to-end framework for developing AI applications.
# Modules
- [axgen](./packages/axgen/): A framework for connecting your data to large language models
- [axeval](./packages/axeval/): A framework for evaluating LLM output quality
# Installation
The modules can be installed independently, for incremental adoption and bundle size minimization.
```
npm install axgen
npm install axeval
```
# Goals
Ax aspires to deconstruct the complex paradigms of working with LLMs into manageable and intuitive components.
Our library takes a code-first approach, emphasizing the importance of flexibility and control for developers.
As a foundational framework, Ax empowers developers to build higher-level TypeScript AI features and products seamlessly.
## Examples
Here is an example [open source UI](https://github.com/axilla-io/demo-ui) showcasing what axgen can do, with a [short video](https://www.loom.com/share/458f9b6679b740f0a5c78a33fffee3dc) walkthrough.
## License
[MIT](LICENSE.md)
|
engcang/FAST-LIO-SAM
|
https://github.com/engcang/FAST-LIO-SAM
|
a SLAM implementation combining FAST-LIO2 with pose graph optimization and loop closing based on LIO-SAM paper
|
# FAST-LIO-SAM
+ This repository is a SLAM implementation combining [FAST-LIO2](https://github.com/hku-mars/FAST_LIO) with pose graph optimization and loop closing based on [LIO-SAM](https://github.com/TixiaoShan/LIO-SAM) paper
+ Loop-detection is based on radius search and ICP is used to calc matching
+ Note: similar repositories already exist
+ [FAST_LIO_LC](https://github.com/yanliang-wang/FAST_LIO_LC): FAST-LIO2 + SC-A-LOAM based SLAM
+ [FAST_LIO_SLAM](https://github.com/gisbi-kim/FAST_LIO_SLAM): FAST-LIO2 + ScanContext based SLAM
+ [FAST_LIO_SAM](https://github.com/kahowang/FAST_LIO_SAM): FAST-LIO2 + LIO-SAM
+ Note2: main code (PGO) is modularized and hence can be combined with any other LIO / LO
+ This repo is to learn GTSAM myself!
+ and as GTSAM tutorial for beginners - [GTSAM 튜토리얼 한글 포스팅](https://engcang.github.io/2023/07/15/gtsam_tutorial.html)
<p align="center">
<img src="imgs/fast1.png" height="300"/>
<img src="imgs/sam1.png" height="300"/>
<br>
<em>KITTI seq 05 top view - (left): FAST-LIO2 (right): FAST-LIO-SAM</em>
</p>
<p align="center">
<img src="imgs/fast2.png" width="600"/>
<img src="imgs/sam2.png" width="600"/>
<br>
<em>KITTI seq 05 side view - (top): FAST-LIO2 (bottom): FAST-LIO-SAM</em>
</p>
<p align="center">
<img src="imgs/traj.png" width="600"/>
<br>
<em>KITTI seq 05 trajectories - (blue): FAST-LIO2 (green): FAST-LIO-SAM</em>
</p>
<br>
#### Note
+ For better loop-detection and transform calculation, [FAST-LIO-SAM-QN](https://github.com/engcang/FAST-LIO-SAM-QN) is also coded and opened.
+ It adopts [Quatro](https://github.com/url-kaist/Quatro) - fast, accurate and robust global registration which provides great initial guess of transform
+ and [Nano-GICP](https://github.com/vectr-ucla/direct_lidar_odometry) - fast and accurate ICP combining [FastGICP](https://github.com/SMRT-AIST/fast_gicp) + [NanoFLANN](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann)
<br>
## Dependencies
+ ROS (it comes with `Eigen` and `PCL`)
+ [GTSAM](https://github.com/borglab/gtsam)
```shell
wget -O gtsam.zip https://github.com/borglab/gtsam/archive/refs/tags/4.1.1.zip
unzip gtsam.zip
cd gtsam-4.1.1/
mkdir build && cd build
cmake -DGTSAM_BUILD_WITH_MARCH_NATIVE=OFF -DGTSAM_USE_SYSTEM_EIGEN=ON ..
sudo make install -j16
```
## How to build and use
+ Get the code, build `tbb` first, and then build the main code
+ `tbb` is only used for faster `pcl::transformPointCloud`, you can just remove it by replacing `tf_pcd` with `pcl::transformPointCloud`
```shell
cd ~/your_workspace/src
git clone https://github.com/engcang/FAST-LIO-SAM --recursive
cd FAST-LIO-SAM/third_party/tbb-aarch64
./scripts/bootstrap-aarch64-linux.sh
cd build-aarch64
make -j16 && make install
cd ~/your_workspace
catkin build -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
. devel/setup.bash
```
+ Then run (change config files in third_party/`FAST_LIO`)
```shell
roslaunch fast_lio_sam run.launch lidar:=ouster
roslaunch fast_lio_sam run.launch lidar:=velodyne
roslaunch fast_lio_sam run.launch lidar:=livox
```
<br>
### Structure
+ odom_pcd_cb
+ pub realtime pose in corrected frame
+ keyframe detection -> if keyframe, add to pose graph + save to keyframe queue
+ pose graph optimization with iSAM2
+ loop_timer_func
+ process a saved keyframe
+ detect loop -> if loop, add to pose graph
+ vis_timer_func
+ visualize all **(Note: global map is only visualized once uncheck/check the mapped_pcd in rviz to save comp.)**
|
ju-c/advanced-django-cheat-sheet
|
https://github.com/ju-c/advanced-django-cheat-sheet
|
A cheat sheet for Django.
|
# Advanced Django Cheat Sheet
Be aware it's not an exhaustive list.
If you have ideas, correction or recommendation do not hesitate.
## Sections
- [Preparing environnement](#preparing-environnement)
- [Creating a Django project](#creating-a-django-project)
- [Creating a Django app](#creating-a-django-app)
- [Custom User](#custom-user)
- [Custom user model](#custom-user-model)
- [Custom user forms](#custom-user-forms)
- [Custom user admin](#custom-user-admin)
- [Superuser](#superuser)
- [Migration](#migration)
- [makemigration and migrate](#makemigration-and-migrate)
- [Fake initial migration](#fake-initial-migration)
- [Models](#models)
- [Model style ordering](#model-style-ordering)
- [Model and field names](#model-and-field-names)
- [Choices](#choices)
- [Blank and Null fields](#blank-and-null-fields)
- [Meta class](#meta-class)
- [The str method](#the-str-method)
- [The get_absolute_url method](#the-get_absolute_url-method)
- [UniqueConstraint](#uniqueconstraint)
- [Models: Further Reading](#models-further-reading)
- [Model Managers](#model-managers)
- [Giving a custom name to the default manager](#giving-a-custom-name-to-the-default-manager)
- [Creating custom managers](#creating-custom-managers)
- [Modifying a manager's initial QuerySet](#modifying-a-managers-initial-queryset)
- [Model registration in admin](#model-registration-in-admin)
- [Django Signals](#django-signals)
- [Queries and QuerySet](#queries-and-queryset)
- [Using Q objects for complex queries](#using-q-objects-for-complex-queries)
- [Aggregation](#aggregation)
- [Latest element in QuerySet](#latest-element-in-queryset)
- [Union of QuerySets](#union-of-querysets)
- [Fixing the N+1 queries problem](#fixing-the-n1-queries-problem)
- [Performing Raw SQL Queries](#performing-raw-sql-queries)
- [View](#view)
- [Function-based views (FBVs)](#function-based-views-fbvs)
- [Class-based views (CBVs)](#class-based-views-cbvs)
- [Redirect from view](#redirect-from-view)
- [View: Further reading](#view-further-reading)
- [Routing](#routing)
- [Authentication](#authentication)
- [Authentication views and URLs](#authentication-views-and-urls)
- [Signup](#signup)
- [Password reset](#password-reset)
- [OAuth](#oauth)
- [Authentication : Further reading](#authentication-further-reading)
- [Custom Permissions](#custom-permissions)
- [Middleware](#middleware)
- [Custom middleware](#custom-middleware)
- [Form and Form Validation](#form-and-form-validation)
- [Form](#form)
- [Selecting the fields to use](#selecting-the-fields-to-use)
- [Form template](#form-template)
- [Custom form field validators](#custom-form-field-validators)
- [clean()](#clean)
- [clean_field_name()](#clean_field_name)
- [Template](#template)
- [Template inheritance and inclusion](#template-inheritance-and-inclusion)
- [Common template tags](#common-template-tags)
- [Performance](#performance)
- [django-debug-toolbar](#django-debug-toolbar)
- [select_related and prefetch_related](#select_related-and-prefetch_related)
- [Indexes](#indexes)
- [Caching](#caching)
- [Security](#security)
- [Admin hardening](#admin-hardening)
- [Cross site request forgery (CSRF) protection](#cross-site-request-forgery-csrf-protection)
- [Enforcing SSL HTTPS](#enforcing-ssl-https)
- [ALLOWED_HOSTS](#allowed_hosts)
- [Further Reading](#further-eading)
## Preparing environnement
- Create project folder and navigate to it.
```
mkdir project_name && cd $_
```
- Create Python virtual env.
```
python -m venv env_name
```
- Activate virtual env.
(Replace "bin" by "Scripts" in Windows).
```
source env_name\bin\activate
```
- Deactivate virtual env.
```
deactivate
```
- Install Django.
```
pip install django~=4.2.2
```
- Create requirements file.
```
pip freeze > requirements.txt
```
- Install all required dependencies based on your pip freeze command.
```
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Creating a Django project
- Starting a new Django project.
A config directory wil be created in your current directory.
```
django-admin startproject config .
```
- Running the server
```
python manage.py runserver
```
## Creating a Django app
- Creating an `my_app` directory and all default files/folders inside.
```
python manage.py startapp my_app
```
- Adding the app to settings.py.
```
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'my_app',
...
```
- Adding app urls into the urls.py from project folder.
```
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('my_app/', include('my_app.urls')),
]
```
## Custom User
### Custom User Model
[Django documentation: Using a custom user model when starting a project](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/auth/customizing/#using-a-custom-user-model-when-starting-a-project)
1. Create a `CustomUser` model
The `CustomUser` model will live within its own app (for example, 'accounts').
```python
# accounts/models.py
from django.contrib.auth.models import AbstractUser
from django.db import models
class CustomUser(AbstractUser):
pass
```
2. Update `settings.py`
- Add the 'accounts' app to the `INSTALLED_APPS` section
- Add a `AUTH_USER_MODEL` config:
```
AUTH_USER_MODEL = "accounts.CustomUser"
```
- Create migrations file
```
python manage.py makemigrations accounts
```
- Migrate
### Custom User Forms
Updating the built-in forms to point to the custom user model instead of `User`.
```python
# accounts/forms.py
from django.contrib.auth import get_user_model
from django.contrib.auth.forms import UserCreationForm, UserChangeForm
class CustomUserCreationForm(UserCreationForm):
class Meta:
model = get_user_model()
fields = (
"email",
"username",
)
class CustomUserChangeForm(UserChangeForm):
class Meta:
model = get_user_model()
fields = (
"email",
"username",
)
```
### Custom User Admin
Extending the existing `UserAdmin` into `CustomUserAdmin`.
```python
# accounts/admin.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.contrib.auth import get_user_model
from django.contrib.auth.admin import UserAdmin
from .forms import CustomUserCreationForm, CustomUserChangeForm
CustomUser = get_user_model()
class CustomUserAdmin(UserAdmin):
add_form = CustomUserCreationForm
form = CustomUserChangeForm
model = CustomUser
list_display = [
"email",
"username",
"is_superuser",
]
```
### Superuser
```
python manage.py createsuperuser
```
## Migration
### makemigration and migrate
[Migrations in the Django Doc](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/migrations/)
**makemigrations**: This command generates migration files based on the changes detected in your models.
It compares the current state of your models with the migration files already created and determines the SQL commands required to propagate the changes to your database schema.
```
python manage.py makemigrations
```
**migrate**: This command applies the migration files to your database, executing the SQL commands generated by `makemigrations`.
```
python manage.py migrate
```
This will update your database schema with the changes made to your models.
### Fake initial migration
In Django, a "fake initial migration" refers to a concept where you mark a migration as applied without actually executing the database schema changes associated with that migration.
It allows you to synchronize the state of the migrations with the database without performing any database modifications.
```
python manage.py migrate --fake-initial
```
It's important to note that **faking the initial migration assumes that the existing database schema matches what the initial migration would have created**.
## Models
[Django Documentation: Models](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/db/models/#module-django.db.models)
### Model Style Ordering
- Choices
- Database fields
- Custom manager attributes
- Meta class
- def `__str__()`
- def `save()`
- def `get_absolute_url()`
- Custom methods
### Model and Field Names
```python
# my_book_app/models.py
from django.db import models
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=100)
```
Models represents a single object and should always be Capitalized and singular (Book, not Books).
Fields should all be snake_case, not camelCase.
### Choices
If choices are defined for a given model field, define each choice as a tuple of tuples, with an all-uppercase name as a class attribute on the model ([source](https://learndjango.com/tutorials/django-best-practices-models)).
```python
# my_book_app/models.py
from django.db import models
class Book(models.Model):
BOOK_CATEGORY = (
("FICTION", "A fiction book"),
("NON_FICTION", "A non-fiction book")
)
title = models.CharField(max_length=100)
book_type = models.CharField(
choices=BOOK_CATEGORY,
max_lenght=100,
verbose_name="type of book",
)
```
### Blank and Null Fields
- **Null**: Database-related. Defines if a given database column will accept null values or not.
- **Blank**: Validation-related. It will be used during forms validation, when calling `form.is_valid()`.
Do not use null with string-based fields like `CharField` or `TextField` as this leads to two possible values for "no data". The Django convention is instead to use the empty string "", not `NULL` ([source](https://simpleisbetterthancomplex.com/tips/2018/02/10/django-tip-22-designing-better-models.html).
### Meta class
[Django Documentation: Meta class](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/models/options/)
An example, using `[indexes](#indexes)`, `ordering`, `verbose_name` and `verbose_name_plural`.
(Don't order results if you don't need to. There can be [performance hit to ordering results](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/dev/topics/db/optimization/#don-t-order-results-if-you-don-t-care).)
```python
# my_book_app/models.py
from django.db import models
class Book(models.Model):
BOOK_CATEGORY = (
("FICTION", "A fiction book"),
("NON_FICTION", "A non-fiction book")
)
title = models.CharField(max_length=100)
book_type = models.CharField(
choices=BOOK_CATEGORY,
max_lenght=100,
verbose_name="type of book",
)
class Meta:
indexes = [models.Index(fields=["title"])]
ordering = ["-title"]
verbose_name = "book"
verbose_name_plural = "books"
```
### The str Method
[Django Documentation: __str__()](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/models/instances/#str)
The str method defines a string representation, a more descriptive name/title, for any of our objects that is displayed in the Django admin site and in the Django shell.
```python
# my_book_app/models.py
from django.db import models
class Book(models.Model):
BOOK_CATEGORY = (
("FICTION", "A fiction book"),
("NON_FICTION", "A non-fiction book")
)
title = models.CharField(max_length=100)
book_type = models.CharField(
choices=BOOK_CATEGORY,
max_lenght=100,
verbose_name="type of book",
)
class Meta:
indexes = [models.Index(fields=["title"])]
ordering = ["-title"]
verbose_name = "book"
verbose_name_plural = "books"
def __str__(self):
return self.title
```
### The get_absolute_url Method
[Django Documentation: get_absolute_url()](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/models/instances/#get-absolute-url)
The `get_absolute_url` method sets a canonical URL for the model.
```python
# my_book_app/models.py
from django.db import models
class Book(models.Model):
BOOK_CATEGORY = (
("FICTION", "A fiction book"),
("NON_FICTION", "A non-fiction book")
)
title = models.CharField(max_length=100)
book_type = models.CharField(
choices=BOOK_CATEGORY,
max_lenght=100,
verbose_name="type of book",
)
class Meta:
indexes = [models.Index(fields=["title"])]
ordering = ["-title"]
verbose_name = "book"
verbose_name_plural = "books"
def __str__(self):
return self.title
def get_absolute_url(self):
return reverse("book_detail", args=[str(self.id)])
```
Using the `get_absolute_url` in our templates:
```
<a href="{{ object.get_absolute_url }}/">{{ object.title }}</a>
```
### UniqueConstraint
[Django Documentation: uniqueConstraint](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/models/constraints/#uniqueconstraint)
Use `UniqueConstraint` when you want to enforce uniqueness on a combination of fields or need additional functionality like custom constraint names or conditional constraints
```python
class Booking(models.Model):
room = models.ForeignKey(Room, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
date = models.DateField()
class Meta:
constraints = [
models.UniqueConstraint(fields=['room', 'date'], name='unique_booking')
]
```
### Models: Further reading
- [LearnDjango: Django Best Practices: Models (2022)](https://learndjango.com/tutorials/django-best-practices-models)
- [Simple is better than complex: Designing Better Models (2018)](https://simpleisbetterthancomplex.com/tips/2018/02/10/django-tip-22-designing-better-models.html)
## Model Managers
[Django Documentation: Managers](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/db/managers/)
### Giving a custom name to the default manager
```python
class Author(models.Model):
...
authors = models.Manager() //now the default manager is named as authors
```
All the operation on the student database table have to be done using the “authors” manager
```
Author.authors.filter(...)
```
### Creating custom managers
[Django Documentation: Custom managers](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/db/managers/#custom-managers)
```python
from django.db import models
from django.db.models.functions import Coalesce
class PollManager(models.Manager):
def with_counts(self):
return self.annotate(num_responses=Coalesce(models.Count("response"), 0))
class OpinionPoll(models.Model):
question = models.CharField(max_length=200)
objects = PollManager()
class Response(models.Model):
poll = models.ForeignKey(OpinionPoll, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
# ...
```
> If you use custom Manager objects, take note that the first Manager Django encounters (in the order in which they’re defined in the model) has a special status. Django interprets the first Manager defined in a class as the “default” Manager, and several parts of Django (including dumpdata) will use that Manager exclusively for that model. As a result, it’s a good idea to be careful in your choice of default manager in order to avoid a situation where overriding get_queryset() results in an inability to retrieve objects you’d like to work with.
### Modifying a manager’s initial QuerySet
[Django Documenation: Modifying a managers's initial QuerySet](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/db/managers/#modifying-a-manager-s-initial-queryset)
```
# First, define the Manager subclass.
class DahlBookManager(models.Manager):
def get_queryset(self):
return super().get_queryset().filter(author="Roald Dahl")
# Then hook it into the Book model explicitly.
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=100)
author = models.CharField(max_length=50)
objects = models.Manager() # The default manager.
dahl_objects = DahlBookManager() # The Dahl-specific manager.
```
With this sample model, `Book.objects.all()` will return all books in the database, but `Book.dahl_objects.all()` will only return the ones written by Roald Dahl.
## Model registration in admin
[Django doc: ModelAdmin objects](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/contrib/admin/#modeladmin-objects)
Model registration in Django's admin interface is the process of making your models accessible through the admin site.
```python
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Author
admin.site.register(Author)
```
- Customizing the display of a model
```python
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Book
class BookAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
list_display = ('title', 'author', 'publication_date')
admin.site.register(Book, BookAdmin)
```
- Adding a search field
```python
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Publisher
class PublisherAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
search_fields = ['name']
admin.site.register(Publisher, PublisherAdmin)
```
- Adding filters
```python
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Category
class CategoryAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
list_filter = ('is_active',)
admin.site.register(Category, CategoryAdmin)
```
- Inline formsets
```python
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Order, OrderItem
class OrderItemInline(admin.TabularInline):
model = OrderItem
extra = 1
class OrderAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
inlines = [OrderItemInline]
admin.site.register(Order, OrderAdmin)
```
## Django Signals
- **pre_save**:
[Django Doc: pre_save](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/signals/#pre-save)
Using a `pre_save` signal is required to execute code related to another part of your application *prior* to saving the object in the database.
```python
from django.db.models.signals import pre_save
from django.dispatch import receiver
@receiver(pre_save, sender=NewOrder)
def validate_order(sender, instance, **kwargs):
stock_item = Stock.objects.get(id=instance.stock_item.id)
if instance.quantity > stock_item.quantity:
raise Exception("Insufficient stock quantity.")
```
- **post_save**:
[Django Doc: post_save](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/signals/#post-save)
Using a `post_save` signal is required to execute code related to another part of your application *after* the object is saved to the database.
```python
from django.db.models.signals import post_save
from django.dispatch import receiver
@receiver(post_save, sender=NewOrder)
def remove_from_inventory(sender, instance, **kwargs):
stock_item = Inventory.objects.get(id=instance.stock_item.id)
stock_item.quantity = stock_item.quantity - instance.quantity
stock_item.save()
```
- **pre_delete**:
[Django Doc: pre_delete](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/signals/#pre-delete)
Using a `pre_delete` signal is necessary to execute code related to another part of your application *before* the deletion event of an object occurs.
```python
from django.db.models.signals import pre_delete
from django.dispatch import receiver
@receiver(pre_delete, sender=Book)
def pre_delete_book(sender, **kwargs):
print("You are about to delete a book")
```
- **post_delete**
[Django Doc: post_delete](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/signals/#post-delete)
Using a `post_delete` signal is necessary to execute code related to another part of your application *after* the deletion event of an object occurs.
```python
@receiver(post_delete, sender=Book)
def delete_book(sender, **kwargs):
print("You have just deleted a book")
```
- **m2m_changed**
[Django Doc: m2m_changed](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/signals/#m2m-changed)
To send a Django signal when a `ManyToManyField` is changed on a model instance.
Consider this model:
```python
class Student(models.Model):
# ...
class Course(models.Model):
students = models.ManyToManyField(Student)
```
m2m_changed signal:
```python
from django.db.models.signals import m2m_changed
def my_signal_name(sender, instance, **kwargs):
students = instance.students.all()
# ...
m2m_changed.connect(my_signal_name, sender=Course.students.through)
```
## Queries and QuerySet
[Django Documentation: Making queries](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/db/queries/#making-queries)
### Using Q objects for complex queries
[Django Documentation: Q objects](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/db/queries/#complex-lookups-with-q-objects)
Q objects can be combined using the `&` (AND) and `|` (OR) operators
```
Inventory.objects.filter(
Q(quantity__lt=10) &
Q(next_shipping__gt=datetime.datetime.today()+datetime.timedelta(days=10))
)
```
```
Inventory.objects.filter(
Q(name__icontains="robot") |
Q(title__icontains="vacuum")
```
### Aggregation
[Django documenation: Aggregation](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/db/aggregation/#aggregation)
In Django, aggregation allows you to perform calculations such as counting, summing, averaging, finding the maximum or minimum value, and more, on a specific field or set of fields in a queryset.
```python
from django.db.models import Sum
total_ratings = Movies.objects.aggregate(ratings_sum=Sum('ratings_count'))
```
**Utilizing Aggregation in Views and Templates**
In the view:
```python
from django.shortcuts import render
def example(request):
data = Movies.objects.aggregate(ratings_sum=Sum('ratings_count'))
return render(request, 'index.html', {'data': data})
```
In the template:
```
<p>Total Ratings: {{ data.ratings_sum }}</p>
```
### Latest element in QuerySet
[Django Documentation: latest()](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/models/querysets/#latest)
This example returns the latest Entry in the table, according to the pub_date field:
```Python
Entry.objects.latest("pub_date")
```
You can also choose the latest based on several fields.
For example, to select the Entry with the earliest `expire_date` when two entries have the same pub_date:
```python
Entry.objects.latest("pub_date", "-expire_date")
```
The negative sign in `'-expire_date'` means to sort `expire_date` in descending order. Since `latest()` gets the last result, the `Entry` with the earliest `expire_date` is selected.
### Union of QuerySets
[union() in the Django Doc](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/models/querysets/#union)
Uses SQL’s `UNION` operator to combine the results of two or more QuerySets.
For example:
```
>>> qs1.union(qs2, qs3)
```
`union()` return model instances of the type of the first QuerySet even if the arguments are QuerySets of other models.
Passing different models works **as long as the SELECT list is the same in all QuerySets** (at least the types, the names don’t matter as long as the types are in the same order).
In such cases, you must use the column names from the first QuerySet in QuerySet methods applied to the resulting QuerySet.
For example:
```
>>> qs1 = Author.objects.values_list("name")
>>> qs2 = Entry.objects.values_list("headline")
>>> qs1.union(qs2).order_by("name")
```
In addition, only `LIMIT`, `OFFSET`, `COUNT(*)`, `ORDER BY`, and specifying columns (i.e. slicing, count(), exists(), order_by(), and values()/values_list()) are allowed on the resulting QuerySet.
### Fixing the N+1 Queries Problem
See [select_related and prefetch_related](#select_related-and-prefetch_related)
### Performing raw SQL queries
[Django Documentation: Performing raw SQL queries](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/db/sql/#performing-raw-sql-queries)
```python
from django.db import models
class Project(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=70)
```
```
Project.objects.raw('SELECT id, title FROM myapp_project')
```
**Custom sql or raw queries sould be both used with extrement caution since they could open up a vulnerability to SQL injection**.
## View
### Function-based views (FBVs)
[Django docucmentation: Writing views](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/http/views/)
From [Django Views - The Right Way](https://spookylukey.github.io/django-views-the-right-way/the-pattern.html#the-explanation): Why `TemplateResponse` over `render` ?
>The issue with just using render is that you get a plain HttpResponse object back that has no memory that it ever came from a template. Sometimes, however, it is useful to have functions return a value that does remember what it’s “made of” — something that stores the template it is from, and the context. This can be really useful in testing, but also if we want to something outside of our view function (such as decorators or middleware) to check or even change what’s in the response before it finally gets ‘rendered’ and sent to the user.
```python
from django.template.response import TemplateResponse
from django.shortcuts import get_object_or_404, redirect
from .forms import TaskForm, ConfirmForm
from .models import Task
def task_list_view(request):
return TemplateResponse(request, 'task_list.html', {
'tasks': Task.objects.all(),
})
def task_create_view(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
form = TaskForm(data=request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
task = form.save()
return redirect('task_detail', pk=task.pk)
return TemplateResponse(request, 'task_create.html', {
'form': TaskForm(),
})
def task_detail_view(request, pk):
task = get_object_or_404(Task, pk=pk)
return TemplateResponse(request, 'task_detail.html', {
'task': task,
})
def task_update_view(request, pk):
task = get_object_or_404(Task, pk=pk)
if request.method == 'POST':
form = TaskForm(instance=task, data=request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
return redirect('task_detail', pk=task.pk)
return TemplateResponse(request, 'task_edit.html', {
'task': task,
'form': TaskForm(instance=task),
})
def task_delete_view(request, pk):
task = get_object_or_404(Task, pk=pk)
if request.method == 'POST':
form = ConfirmForm(data=request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
task.delete()
return redirect('task_list')
return TemplateResponse(request, 'task_delete.html', {
'task': task,
'form': ConfirmForm(),
})
```
### Class-based views (CBVs)
[Django Documentation : Class-based views](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/class-based-views/)
```python
from django.views.generic import ListView, DetailView
from django.views.generic.edit import CreateView, UpdateView, DeleteView
from django.urls import reverse_lazy
from .models import Task
class TaskListView(ListView):
model = Task
template_name = "task_list.html"
class BlogDetailView(DetailView):
model = Task
template_name = "task_detail.html"
class TaskCreateView(CreateView):
model = Task
template_name = "task_create.html"
fields = ["name", "body", "author"]
class TaskUpdateView(UpdateView):
model = Task
template_name = "task_edit.html"
fields = ["name", "body"]
class TaskDeleteView(DeleteView):
model = Task
template_name = "task_delete.html"
success_url = reverse_lazy("task_list")
```
### Redirect from view:
[Django Documentation: redirect()](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/http/shortcuts/#redirect)
```python
from django.shortcuts import redirect
# Using the redirect() function by passing an object:
def my_view(request):
...
obj = MyModel.objects.get(...)
return redirect(obj)
# Using the redirect() function by passing the name of a view
# and optionally some positional or keyword arguments:
def my_view(request):
...
return redirect("some-view-name", foo="bar")
# Using the redirect() function by passing an hardcoded URL:
def my_view(request):
...
return redirect("/some/url/")
# This also works with full URLs:
# return redirect("https://example.com/")
```
By default, `redirect()` returns a temporary redirect.
All of the above forms accept a permanent argument; if set to `True` a permanent redirect will be returned:
```python
def my_view(request):
...
obj = MyModel.objects.get(...)
return redirect(obj, permanent=True)
```
### View: Further reading
- [Django Views - The Right Way](https://spookylukey.github.io/django-views-the-right-way/index.html)
- [Classy Class-Based Views](https://ccbv.co.uk/)
## Routing
[Django Documentation: django.urls functions for use in URLconfs](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/urls/)
- **path()**: Returns an element for inclusion in urlpatterns
```python
from django.urls import include, path
urlpatterns = [
path("index/", views.index, name="main-view"),
path("bio/<username>/", views.bio, name="bio"),
path("articles/<slug:title>/", views.article, name="article-detail"),
path("articles/<slug:title>/<int:section>/", views.section, name="article-section"),
path("blog/", include("blog.urls")),
...,
]
```
- **re_path()**: Returns eturns an element for inclusion in urlpatterns.
The route argument should be a string or `gettext_lazy()` that contains a regular expression compatible with Python’s re module.
```python
from django.urls import include, re_path
urlpatterns = [
re_path(r"^index/$", views.index, name="index"),
re_path(r"^bio/(?P<username>\w+)/$", views.bio, name="bio"),
re_path(r"^blog/", include("blog.urls")),
...,
]
```
- **include()**: A function that takes a full Python import path to another URLconf module that should be “included” in this place.
```python
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path("/admin/", admin.site.urls),
path("books/", include ("books.urls")),
]
```
- **static()**: Helper function to return a URL pattern for serving files in debug mode.
```
from django.conf import settings
from django.conf.urls.static import static
urlpatterns = [
# ... the rest of your URLconf goes here ...
] + static(settings.MEDIA_URL, document_root=settings.MEDIA_ROOT)
```
## Authentication
### Authentication views and URLs
[Django Documentation: Using the views](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/auth/default/#module-django.contrib.auth.views)
Add Django site authentication urls (for login, logout, password management):
```python
# config/urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path("admin/", admin.site.urls),
path("accounts/", include("django.contrib.auth.urls")),
]
```
Urls provided by the auth app:
```
accounts/login/ [name='login']
accounts/logout/ [name='logout']
accounts/password_change/ [name='password_change']
accounts/password_change/done/ [name='password_change_done']
accounts/password_reset/ [name='password_reset']
accounts/password_reset/done/ [name='password_reset_done']
accounts/reset/<uidb64>/<token>/ [name='password_reset_confirm']
accounts/reset/done/ [name='password_reset_complete']
```
Updating `settings.py` with `LOGIN_REDIRECT_URL` and `LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URL`
```
# config/urls.py
...
path("", TemplateView.as_view(template_name="home.html"), name="home"),
...
# config/settings.py
LOGIN_REDIRECT_URL = "home"
LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URL = "home"
```
### Signup
To create a sign up page we will need to make our own view and url.
```python
python manage.py startapp accounts
```
```
# config/settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
"django.contrib.admin",
"django.contrib.auth",
"django.contrib.contenttypes",
"django.contrib.sessions",
"django.contrib.messages",
"django.contrib.staticfiles",
"accounts",
]
```
Then add a project-level url for the accounts app **above** our included Django auth app.
```
# django_project/urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
from django.views.generic.base import TemplateView
urlpatterns = [
path("admin/", admin.site.urls),
path("accounts/", include("accounts.urls")), # new
path("accounts/", include("django.contrib.auth.urls")),
path("", TemplateView.as_view(template_name="home.html"), name="home"),
]
```
The *views* file:
```
# accounts/views.py
from django.contrib.auth.forms import UserCreationForm
from django.urls import reverse_lazy
from django.views import generic
class SignUpView(generic.CreateView):
form_class = UserCreationForm
success_url = reverse_lazy("login")
template_name = "registration/signup.html"
```
From [LearnDjango](https://learndjango.com/tutorials/django-signup-tutorial):
>We're subclassing the generic class-based view `CreateView` in our SignUp class. We specify the use of the built-in `UserCreationForm` and the not-yet-created template at `signup.html`. And we use `reverse_lazy` to redirect the user to the login page upon successful registration.
Create a new *urls* file in the *accounts* app.
```
# accounts/urls.py
from django.urls import path
from .views import SignUpView
urlpatterns = [
path("signup/", SignUpView.as_view(), name="signup"),
]
```
Then, create a new template templates/registration/signup.html
```
<!-- templates/registration/signup.html -->
{% extends "base.html" %}
{% block title %}Sign Up{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
<h2>Sign up</h2>
<form method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button type="submit">Sign Up</button>
</form>
{% endblock %}
```
### Password reset
For development purposes Django let us store emails either in the console or as a file.
- Console backend:
```
EMAIL_BACKEND = 'django.core.mail.backends.console.EmailBackend'
```
- File backend:
```
EMAIL_BACKEND = 'django.core.mail.backends.filebased.EmailBackend'
EMAIL_FILE_PATH = '/tmp/app-messages' # change this to a proper location
```
For production, see [Sending Email](#sending-email)
### OAuth
The [Django OAuth Toolkit](https://github.com/evonove/django-oauth-toolkit) package provides OAuth 2.0 support and uses [OAuthLib](https://github.com/idan/oauthlib).
### Authentication: Further reading
- [Django Documentation: User authentication in Django](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/auth/)
- [LearnDjango: Django Login and Logout Tutorial](https://learndjango.com/tutorials/django-login-and-logout-tutorial)
## Custom Permissions
[Django Doc: Custom permissions](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/auth/customizing/#custom-permissions)
Adding custom permissions to a Django model:
```python
from django.db import models
class Task(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=70)
body = models.TextField()
is_opened = models.Boolean(default=False)
class Meta:
permissions = [
("set_task_status", "Can change the status of tasks")
]
```
the following checks if a user may close tasks:
```
user.has_perm("app.close_task")
```
**You still have to enforce it in the views**:
For **function-based views**, use the permission_required decorator:
```python
from django.contrib.auth.decorators import permission_required
@permission_required("book.view_book")
def book_list_view(request):
return HttpResponse()
```
For **class-based views**, use the [PermissionRequiredMixin](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/auth/default/#django.contrib.auth.mixins.PermissionRequiredMixin):
```python
from django.contrib.auth.mixins import PermissionRequiredMixin
from django.views.generic import ListView
from .models import Book
class BookListView(PermissionRequiredMixin, ListView):
permission_required = "book.view_book"
template_name = "books/book_list.html"
model = Book
```
**permission_required** can be either a single permission or an iterable of permissions.
If using an iterable, the user must possess all the permissions in order to access the view.
```python
from django.contrib.auth.mixins import PermissionRequiredMixin
from django.views.generic import ListView
from .models import Book
class BookListView(PermissionRequiredMixin, ListView):
permission_required = ("book.view_book", "book.add_book")
template_name = "books/book_list.html"
model = Book
```
**Checking permission in templates**:
Using [perms](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/auth/default/#permissions):
```
{% if perms.blog.view_post %}
{# Your content here #}
{% endif %}
```
## Middleware
[Django Documentation: Middleware](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/middleware/#middleware-ordering)
### Custom Middleware
```python
# my_app/custom_middlware.py
import time
class CustomMiddleware:
def __init__(self, get_response):
self.get_response = get_response
def __call__(self, request):
start_time = time.time()
response = self.get_response(request)
end_time = time.time()
time_taken = end_time - start_time
response['Time-Taken'] = str(time_taken)
return response
```
Adding the custom middleware to our Django project:
```
MIDDLEWARE = [
# ...
'my_app.middleware.custom_middleware.CustomMiddleware',
# ...
]
```
**Middleware ordering**
While processing request object middlware works from top to bottom and while processing response object middleware works from bottom to top.
[Django Documentation: Middleware ordering](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/middleware/#middleware-ordering)
## Form and Form Validation
### Form
[Django Documentation: Creating forms from models](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/forms/modelforms/#creating-forms-from-models)
ModelForm
```python
from django.forms import ModelForm
from myapp.models import Article
class ArticleForm(ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Article
fields = '__all__'
```
The view:
```python
#my_app/views.py
from .forms import ArticleForm
def article_create(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
form = ArticleForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
article = form.save()
return redirect('article-detail', article.id))
else:
form = ArticleForm()
return render(request,
'listings/article_create.html',
{'form': form})
```
### Selecting the fields to use
- Set the fields attribute to the special value `'__all__'` to indicate that all fields in the model should be used.
```python
from django.forms import ModelForm
class ArticleForm(ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Article
fields = "__all__"
```
- Set the exclude attribute of the ModelForm’s inner Meta class to a list of fields to be excluded from the form.
```python
class PartialAuthorForm(ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Article
exclude = ["headline"]
```
### Form template
```html
<form action="" method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form }}
<input type="submit" name="save" value="Save">
<input type="submit" name="preview" value="Preview">
</form>
```
### Custom form field validators
```python
# my_app/validators.py
from django.core.exceptions import ValidationError
def validate_proton_mail(value):
"""Raise a ValidationError if the value doesn't contains @proton.me.
"""
if "@proton.me" in value:
return value
else:
raise ValidationError("This field accepts mail id of Proton Mail only")
```
Adding `validate_hello` in our form:
```python
# my_app/forms.py
from django import forms
from .models import MyModel
from .validators import validate_proton_mail
class MyModelForm(forms.ModelForm):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.fields['example_mail'].validators.append(validate_proton_mail)
class Meta:
model = MyModel
fields = '__all__'
```
### clean()
Performing validation on more than one field at a time.
```python
# my_app/forms.py
from django import forms
from .models import MyModel
class MyForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = MyModel
fields = '__all__'
def clean(self):
cleaned_data = super().clean()
slug = cleaned_data.get('slug', '')
title = cleaned_data.get('title', '')
# slug and title should be same example
if slug != title.lower():
msg = "slug and title should be same"
raise forms.ValidationError(msg)
return cleaned_data
```
### clean_field_name()
Performing validation on a specific field.
```python
from django import forms
from .models import Product
from .validators import validate_amazing
class ProductForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Product
fields = '__all__'
def clean_quantity(self):
quantity = self.cleaned_data['quantity']
if quantity > 100:
msg = 'Quantity should be less than 100'
raise forms.ValidationError(msg)
return quantity
```
## Template
[Django Documentation: The Django template language](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/templates/language/#the-django-template-language)
### Template inheritance and inclusion
- Inheritance
```html
<!-- templates/base.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<title>{% block title %}My amazing site{% endblock %}</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="sidebar">
{% block sidebar %}
<ul>
<li><a href="/">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="/blog/">Blog</a></li>
</ul>
{% endblock %}
</div>
<div id="content">
{% block content %}{% endblock %}
</div>
</body>
</html>
```
```html
<!-- templates/home.html -->
{% extends "base.html" %}
{% block title %}My amazing blog{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
{% for entry in blog_entries %}
<h2>{{ entry.title }}</h2>
<p>{{ entry.body }}</p>
{% endfor %}
{% endblock %}
```
- Inclusion
```
{% include 'header.html' %}
```
### Common template tags
- **static**
```
{% load static %}
{% static 'css/main.css' %}
```
- **url** passing positional arguments
```
{% url 'some-url-name' v1 v2 %}
```
[Django Documentation: url](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/templates/builtins/#url)
- **block** (Defines a block that can be overridden by child templates)
```html
<div id="content">
{% block content %}{% endblock %}
</div>
```
A child template might look like this:
```html
{% extends "base.html" %}
{% block title %}My amazing blog{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
{% for entry in blog_entries %}
<h2>{{ entry.title }}</h2>
<p>{{ entry.body }}</p>
{% endfor %}
{% endblock %}
```
- **for**
```html
<ul>
{% for athlete in athlete_list %}
<li>{{ athlete.name }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
```
- **if, elif, else**
```html
{% if athlete_list %}
Number of athletes: {{ athlete_list|length }}
{% elif athlete_in_locker_room_list %}
Athletes should be out of the locker room soon!
{% else %}
No athletes.
{% endif %}
```
- **now** (Outputs the current date and/or time.)
```
{% now "SHORT_DATETIME_FORMAT" %}
```
- **Current path**
```
{{ request.path }}
```
- **Dates and Times**
```html
<p>Copyright 2005-{% now "Y" %}</p>
```
- **Comments**
```html
{% comment "Optional note" %}
<p>Commented out text with {{ create_date|date:"c" }}</p>
{% endcomment %}
```
Note that single lines of text can be commented out using `{#` and `#}`:
```
{# This is a comment. #}
```
- **Special Characters**
```
{% autoescape off %}
{{ content }}
{% endautoescape %}
```
## Sending Email
[Django Documentation: Sending email](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/email/#module-django.core.mail)
Quick example:
```python
from django.core.mail import send_mail
send_mail(
"Subject here",
"Here is the message.",
"[email protected]",
["[email protected]"],
fail_silently=False,
)
```
**Email backend**
Development:
```
EMAIL_BACKEND = 'django.core.mail.backends.console.EmailBackend'
```
Production:
```
config/settings.py
EMAIL_BACKEND = 'django.core.mail.backends.smtp.EmailBackend'
EMAIL_HOST = 'smtp.yourserver.com'
EMAIL_USE_TLS = False
EMAIL_PORT = 465
EMAIL_USE_SSL = True
EMAIL_HOST_USER = '[email protected]'
EMAIL_HOST_PASSWORD = 'your password'
```
## Performance
### django-debug-toolbar
[Django Debug Toolbar Documentation](https://django-debug-toolbar.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)
Install:
```python -m pip install django-debug-toolbar```
`settings.py`
```
INSTALLED_APPS = [
# ...
"debug_toolbar",
# ...
]
```
`urls.py`
```
from django.urls import include, path
urlpatterns = [
# ...
path("__debug__/", include("debug_toolbar.urls")),
]
```
### select_related and prefetch_related
Django provides two QuerySet methods that can turn the N queries back into one query, solving the performance issue.
These two methods are:
**select_related**
[Django Documentation: select_related](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/models/querysets/#select-related)
select_related returns a QuerySet that will “follow” foreign-key relationships (either One-to-One
or One-to-Many), selecting additional related-object data when it executes its query.
```python
from django.db import models
class Author(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=50)
author = models.ForeignKey(Author, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
# With select_related
authors = Author.objects.all().select_related('book')
for author in authors:
books = author.book_set.all()
```
**prefetch_related**
[Django Documentation: prefetch_related](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/models/querysets/#prefetch-related)
`prefetch_related` performs a separate lookup for each relationship and “joins” them together
with Python, not SQL.
This allows it to prefetch many-to-many and many-to-one objects, which
cannot be done using select_related
```python
from django.db import models
class Author(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=50)
author = models.ForeignKey(Author, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
# With prefetch_related
authors = Author.objects.all().prefetch_related('book')
for author in authors:
books = author.book_set.all()
```
### Indexes
[Django Documentation: Model index reference](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/models/indexes/#module-django.db.models.indexes)
If a particular field is consistently utilized, accounting for around 10-25% of all queries, it is a prime candidate
to be indexed.
The downside is that indexes require additional space on a disk so they must be used with care.
```python
from django.db import models
class Author(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
class Meta:
indexes = [models.Index(fields=["name"])]
```
### Caching
#### Redis
[Django Documentation: Redis](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/cache/#redis)
1. Setting up a [Redis](https://redis.io/) server locally or on a remote machine.
2. Installing [redis-py](https://pypi.org/project/redis/). Installing [hiredis-py](https://pypi.org/project/hiredis/) is also recommended.
3. Set `BACKEND` to `django.core.cache.backends.redis.RedisCache`.
4. Set `LOCATION` to the URL pointing to your Redis instance, using the appropriate scheme.
See the redis-py docs for [details on the available schemes](https://redis-py.readthedocs.io/en/stable/connections.html#redis.connection.ConnectionPool.from_url).
For example, if Redis is running on localhost (127.0.0.1) port 6379:
```
CACHES = {
"default": {
"BACKEND": "django.core.cache.backends.redis.RedisCache",
"LOCATION": "redis://127.0.0.1:6379",
}
}
```
In order to supply a username and password, add them in the `LOCATION` along with the `URL`:
```
CACHES = {
"default": {
"BACKEND": "django.core.cache.backends.redis.RedisCache",
"LOCATION": [
"redis://127.0.0.1:6379", # leader
"redis://127.0.0.1:6378", # read-replica 1
"redis://127.0.0.1:6377", # read-replica 2
],
}
}
```
#### Database caching
[Django Documentation: Database caching](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/cache/#database-caching)
Django can store its cached data in your database.
This works best if you’ve got a fast, well-indexed database server.
In this example, the cache table’s name is `my_cache_table`:
```
CACHES = {
"default": {
"BACKEND": "django.core.cache.backends.db.DatabaseCache",
"LOCATION": "my_cache_table",
}
}
```
Creating the cache table:
```
python manage.py createcachetable
```
#### per-view cache
[Django Documentation: The per-view cache](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/cache/#the-per-view-cache)
In Django, the `cache_page` decorator is used to cache the output of a view function.
It takes a single argument, timeout, which specifies the duration in seconds for which the output should be cached.
```python
from django.views.decorators.cache import cache_page
@cache_page(60 * 15) # Cache the page for 15 minutes
def my_view(request):
# View logic ...
```
Specifying per-view cache in the `URLconf`:
You can do so by wrapping the view function with cache_page when you refer to it in the URLconf.
```python
from django.views.decorators.cache import cache_page
urlpatterns = [
path("foo/<int:code>/", cache_page(60 * 15)(my_view)),
]
```
#### per-site cache
[Django Documentation: per-site cache](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/cache/#the-per-site-cache)
```
# config/settings.py
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.cache.UpdateCacheMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
'django.middleware.cache.FetchFromCacheMiddleware',
]
```
**The order of the middleware is important**
`UpdateCacheMiddleware` must come before `FetchFromCacheMiddleware`.
#### template fragment caching
[Django Documentation: Template fragment caching](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/topics/cache/#template-fragment-caching)
```html
{% load cache %}
{% cache 500 book_list %}
<ul>
{% for book in books %}
<li>{{ book.title }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
{% endcache %}
```
The `cache` template tag expects a cache timeout in second with the name of the cache fragment `book_list`
## Security
[Django Documentation: Deployment checklist](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/howto/deployment/checklist/)
### Admin Hardening
Changing the URL path
```python
# config/urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
urlpatterns = [
path("another_admin_path/", admin.site.urls),
]
```
### Cross site request forgery (CSRF) protection
Django's CSRF protection is turned on by default. You should always use the `{% csrf_token %}` template tag in your forms and use `POST` for requests that might change or add data to the database.
### Enforcing SSL HTTPS
- [SECURE_PROXY_SSL_HEADER](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/settings/#std:setting-SECURE_PROXY_SSL_HEADER): can be used to check whether content is secure, even if it is incoming from a non-HTTP proxy.
- HSTS may either be configured with [SECURE_HSTS_SECONDS](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/settings/#std:setting-SECURE_HSTS_SECONDS) and [SECURE_HSTS_INCLUDE_SUBDOMAINS](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/settings/#std:setting-SECURE_HSTS_INCLUDE_SUBDOMAINS) or on the Web server.
- To ensure that cookies are only ever sent over HTTPS, set [SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/settings/#std:setting-SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE) and [SECURE_HSTS_SECONDS](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/settings/#std:setting-SECURE_HSTS_INCLUDE_SUBDOMAINS) to `True`
### ALLOWED_HOSTS
[Django Documentation: ALLOWED_HOSTS](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/4.0/ref/settings/#std:setting-ALLOWED_HOSTS)
Use `ALLOWED_HOSTS` to only accept requests from trusted hosts.
## Further Reading
- [Official Django Documentation](https://www.djangoproject.com/)
- [Django source code](https://github.com/django/django)
- [Official Django forum](https://forum.djangoproject.com/)
- Will Vincent:
- [LearnDjango](https://learndjango.com/)
- Django for [Beginners](https://djangoforbeginners.com/), [Professionals](https://djangoforprofessionals.com/), [APIs](https://djangoforapis.com/)
- [Awesome Django](https://github.com/wsvincent/awesome-django) (with [Jeff Triplett](https://github.com/jefftriplett))
- Adam Johnson: [Blog](https://adamj.eu/tech/), [Boost Your Django DX](https://adamchainz.gumroad.com/l/byddx)
- [mdn web docs: Django Web Framework](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/Server-side/Django)
- [Django Styleguide](https://github.com/HackSoftware/Django-Styleguide)
- [Simple is better than complex](https://simpleisbetterthancomplex.com/)
- [Two scoops of Django 3.x](https://www.feldroy.com/books/two-scoops-of-django-3-x)
|
remotemcu/adin-llvm
|
https://github.com/remotemcu/adin-llvm
| null |
# ADIN LLVM Fork: Memory Operation Hooking
[](https://github.com/remotemcu/adin-llvm/actions/workflows/ubuntu.yml)
[](https://github.com/remotemcu/adin-llvm/actions/workflows/macos.yml)


1. [Introduction](#introduction)
2. [Usage](#usage)
3. [How build](#how-build)
* [Unix-like OS](#unix-like-os)
* [Windows OS](#windows-os)
## Introduction:
The **ADIN LLVM Fork** is a specialized version of the LLVM compiler infrastructure that incorporates the [**ADIN code transformer pass**](https://github.com/remotemcu/adin-llvm-pass). This fork enables runtime interrupting technologies by allowing developers to hook memory operations, such as store and load operations, and replace them with custom hook functions. The **ADIN LLVM Fork** is particularly crucial for projects like [**REMCU Library**](https://github.com/remotemcu/remcu) and [**REMCU Chip SDKs**](https://github.com/remotemcu/remcu-chip-sdks), where it is used to hook peripheral register operations.
## Usage:
To utilize the memory operation hooking capabilities of the **ADIN LLVM Fork**, you can modify LLVM IR compiled code using the `opt` tool with the `-adin` flag. Here's an example to help you understand the process:
Let's assume you have a simple C code file named `example.c`.
```c
int var = 0;
void f(){
*(int*)0x100 = 1;
var = *(int*)0x100;
}
```
To compile it into LLVM IR code using Clang, execute the following command:
```shell
clang -S -emit-llvm example.c -o example.ll
```
This command will generate the LLVM IR code file `example.ll` based on your C code.
```llvm
; Function Attrs: noinline nounwind optnone uwtable
define dso_local void @f() #0 {
store i32 1, i32* inttoptr (i64 256 to i32*), align 4
%1 = load i32, i32* inttoptr (i64 256 to i32*), align 4
store i32 %1, i32* @b, align 4
ret void
}
```
Now, you can use the **ADIN LLVM Fork** to modify the LLVM IR code and add memory operation hooks. Run the following command:
```shell
opt -adin -S example.ll-o adin_modified_example.ll
```
the `-adin` flag indicates that you want to perform memory operation hooking on the input LLVM IR code. The modified LLVM IR code will be written to the `modified.ll` file.
```llvm
define dso_local void @f() #0 {
call void @__adin_store_(i8* inttoptr (i64 256 to i8*), i64 1, i32 32, i32 4)
%load_i32_ = call i64 @__adin_load_(i8* inttoptr (i64 256 to i8*), i32 32, i32 4)
%truncated_i32_ = trunc i64 %load_i32_ to i32
store i32 %truncated_i32_, i32* @b, align 4
ret void
}
```
In the modified LLVM IR code (`modified.ll`), the original store and load operations have been replaced with the `__adin_store_` and `__adin_load_` functions. These functions are the hook functions provided by the ADIN LLVM Fork, which allow you to intercept and modify the behavior of memory operations.
You can define and implement these hook functions in C/C++ code to perform any desired modifications or additional actions before or after the memory operations.
* `__adin_store_` function will be called instead of a regular store operation,
* `__adin_load_` function will be called instead of a regular load operation.
To implement the **__adin_store_** and **__adin_load_** hook functions in your C/C++ code for performing desired modifications or additional actions before memory operations, you can follow a similar approach to what is done in the [Address Interceptor Lib]. Here's an example:
```c
extern "C" void __adin_store_(llvm_pass_addr pointer, llvm_value_type value, llvm_pass_arg TypeSizeArg, llvm_pass_arg AlignmentArg)
{
//...
}
extern "C" llvm_value_type __adin_load_(const llvm_pass_addr pointer, llvm_pass_arg TypeSizeArg, llvm_pass_arg AlignmentArg)
{
//...
}
```
Finally, you can use the LLVM IR code to continue with the compilation process, linking, and generating the final executable or library as needed.
Yes, the `opt` utility provided by the ADIN LLVM Fork also allows you to hook `memmove`, `memcpy`, and `memset` operations in addition to store and load operations. You can enable the hooking of these memory operations using specific options provided by `opt`. Here are the options you can use:
```
$ opt --help | grep adin
-adin-alloca-address-skip - Skip intercept address on alloca frame (Stack var)
-adin-check-normal-address-aligment - Checks normal alignment of address attempt
-adin-mem-function-instructions - if equal true - intercept memmove/memcpy/memset function, else skip
-adin-name-callback-load=<string> - Set name callback of load operation. Default __adin_load_
-adin-name-callback-memcpy=<string> - Set name callback of memcpy operation. Default __adin_memcpy_
-adin-name-callback-memmove=<string> - Set name callback of memmove operation. Default __adin_memmove_
-adin-name-callback-memset=<string> - Set name callback of memset operation. Default __adin_memset_
-adin-name-callback-store=<string> - Set name callback of store operation. Default __adin_store_
-adin-simple-global-skip - Skip intercept address of SIMPLE global var
-adin-skip-unsupported-instructions - if equal true - skip this unsupported instruction, else throw error
-adin-verbose-level=<int> - Set Level of verbose for AddressIntercept Pass
```
## How build
### Unix-like OS
**Note:** This part of guide assumes that you have a basic understanding of software development, command-line tools, and are comfortable using a Unix-like operating system such as Linux or macOS. Some commands may need to be modified slightly if you are using a different operating system.
#### Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the build process, make sure you have the following prerequisites installed on your system:
1. **CMake**: LLVM uses CMake(version 3.5.1 or higher) as its build system. Ensure that you have CMake installed on your system. You can download CMake from the official website: https://cmake.org/download/
2. **GCC or Clang**: LLVM is primarily written in C++. You will need a C++ compiler to build LLVM. Ensure that you have either GCC or Clang installed on your system.
3. **Git**: You need Git version control system to clone the LLVM Adin Fork repository and manage source code. Install Git by following the instructions on the official website: https://git-scm.com/downloads
4. **Python**: LLVM build system relies on Python. Ensure that Python is installed on your system. You can download Python from the official website: https://www.python.org/downloads/
5. **Ninja (optional)**: Ninja is an alternative build system to Make. While not mandatory, it can speed up the build process. If you want to use Ninja, install it using your system's package manager.
I tested on ubuntu 16.04 OS
#### Building LLVM Adin Fork
Follow the steps below to build your LLVM Adin Fork:
##### Step 1: Clone the Repository
1. Open a terminal or command prompt.
2. Change to the directory where you want to clone the LLVM Adin Fork repository.
3. Clone the repository using the following command:
```
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/remotemcu/adin-llvm
```
##### Step 2: Configure the Build
1. Change to the LLVM Adin Fork directory:
```
cd adin-llvm
```
2. Create a build directory:
```
mkdir build
cd build
```
3. Generate the build files using CMake:
```
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=MinSizeRel -DLLVM_BUILD_RUNTIME=Off -DLLVM_INCLUDE_TESTS=Off -DLLVM_INCLUDE_EXAMPLES=Off -DLLVM_ENABLE_BACKTRACES=Off -DLLVM_TARGETS_TO_BUILD="host" -DLLVM_ENABLE_OCAMLDOC=Off -DLLVM_BUILD_UTILS=Off -DLLVM_BUILD_DOCS=Off
```
Replace `<generator>` with the appropriate generator for your system. For example, on Linux, you can use `"Unix Makefiles"` for Make or `"Ninja"` for Ninja.

**Note:** If you are using Ninja:
```
cmake -G Ninja .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=MinSizeRel -DLLVM_BUILD_RUNTIME=Off -DLLVM_INCLUDE_TESTS=Off -DLLVM_INCLUDE_EXAMPLES=Off -DLLVM_ENABLE_BACKTRACES=Off -DLLVM_TARGETS_TO_BUILD="host" -DLLVM_ENABLE_OCAMLDOC=Off -DLLVM_BUILD_UTILS=Off -DLLVM_BUILD_DOCS=Off
```
##### Step 3: Build LLVM
1. Build LLVM using the generated build files:
```
cmake --build . --config MinSizeRel
```
2. Grab a cup of coffee or tea as the build process might take some time depending on your system's speed and available resources.
3. Once the build is successfully completed, you can proceed to use the ADIN LLVM Adin Fork as desired. The built binaries can be found in the `build/bin` directory.

To locate the **opt** utility, which can be used for modifying LLVM intermediate representations, follow the steps below:
* Open a file explorer or command prompt.
* Navigate to the `build/bin` directory within your LLVM Adin Fork repository.
* Look for the `opt` executable file. The exact file extension may vary depending on your operating system (e.g., .exe for Windows).
### Windows OS
Note that this guide assumes you are building on a Windows system and requires MSBuild from Visual Studio 2017.
#### Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the LLVM Adin Fork build, ensure that you have the following prerequisites installed on your Windows machine:
1. **MSBuild:** Install Microsoft Build Tools or Visual Studio 2017. You can download Visual Studio 2017 Community Edition from the official Microsoft website: [https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/visualstudio/visual-studio-2017/install/use-command-line-parameters-to-install-visual-studio?view=vs-2017](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/visualstudio/visual-studio-2017/install/use-command-line-parameters-to-install-visual-studio?view=vs-2017). Make sure to select the required these components during the installation.

I build with next version:
```
-- Selecting Windows SDK version 10.0.17763.0 to target Windows 10.0.17134.
-- The C compiler identification is MSVC 19.16.27050.0
-- The CXX compiler identification is MSVC 19.16.27050.0
```
2. **Python:** Install Python on your system. You can download the latest Python version from the official Python website: [https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/](https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/). Choose the appropriate version for your system (64-bit) and follow the installation instructions.
3. **Git:** Install Git version control system. You can download Git from the official Git website: [https://git-scm.com/downloads](https://git-scm.com/downloads). Choose the appropriate installer for your system and run the installation.
#### Building LLVM Adin Fork
Once you have installed the necessary prerequisites, follow the steps below to build the LLVM Adin Fork:
1. **Clone the LLVM Adin Fork Repository:** Open a command prompt or Git Bash and navigate to the directory where you want to clone the LLVM Adin Fork repository. Then, run the following command to clone the repository:
```shell
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/remotemcu/adin-llvm
```
2. Open "x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for Visual Studio 2017" entry to open the command prompt.

3. In the command prompt window, navigate to the directory where you build the LLVM Adin Fork repository using the `cd` command. For example, if the cloned repository is located in `C:\llvm-adin` create `C:\llvm-adin-build` for building process

Make sure to replace `C:\llvm-adin` with the actual path to your LLVM Adin Fork repository.
4. **Configure the Build:** Run the following command from build dir (for example C:\llvm-fork-build) to generate the build files using CMake:
```shell
cmake -Thost=x64 C:\llvm-adin -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=MinSizeRel -DLLVM_BUILD_RUNTIME=Off -DLLVM_INCLUDE_TESTS=Off -DLLVM_INCLUDE_EXAMPLES=Off -DLLVM_ENABLE_BACKTRACES=Off -DLLVM_TARGETS_TO_BUILD="host" -DLLVM_ENABLE_OCAMLDOC=Off -DLLVM_BUILD_UTILS=Off -DLLVM_BUILD_DOCS=Off
```

This command configures the build system for Visual Studio 2017. Adjust the generator (`-G`) argument if you are using a different version of Visual Studio.
5. **Build LLVM:** Once the configuration is complete, you can build LLVM by running the following command:
```shell
cmake --build . --config MinSizeRel
```
Once the build is successfully completed, you can proceed to use the ADIN LLVM Adin Fork as desired. The built binaries can be found in the `MinSizeRel\build\bin` directory.
To locate the **opt** utility, which can be used for modifying LLVM intermediate representations, follow the steps below:
* Open a file explorer or command prompt.
* Navigate to the `MinSizeRel\build\bin` directory within your LLVM Adin Fork repository.
* Look for the `opt` executable file. The exact file extension may vary depending on your operating system (e.g., .exe for Windows).

---
LLVM is open source software. You may freely distribute it under the terms of
the license agreement found in LICENSE.txt.
|
shurco/goclone
|
https://github.com/shurco/goclone
|
🌱 goclone - clone websites in a matter of seconds
|
# 🌱 goclone
<a href="https://github.com/shurco/goclone/releases"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/v/release/shurco/goclone?sort=semver&label=Release&color=651FFF"></a>
<a href="https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/shurco/goclone"><img src="https://goreportcard.com/badge/github.com/shurco/goclone"></a>
<a href="https://www.codefactor.io/repository/github/shurco/goclone"><img src="https://www.codefactor.io/repository/github/shurco/goclone/badge" alt="CodeFactor" /></a>
<a href="https://github.com/shurco/goclone/actions/workflows/release.yml"><img src="https://github.com/shurco/goclone/actions/workflows/release.yml/badge.svg"></a>
<a href="https://github.com/shurco/goclone/blob/master/LICENSE"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/License-MIT-yellow.svg"></a>
Goclone is a powerful utility that enables you to effortlessly download entire websites from the Internet and save them to your local directory. With Goclone, you can easily obtain HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, and other associated files directly from the server and store them on your computer.
One of the standout features of Goclone is its ability to accurately preserve the original website's relative link structure. This means that when you open any page of the "mirrored" website in your browser, you can seamlessly navigate through the site by following links just as if you were browsing it online.
Goclone empowers you to have offline access to websites, making it convenient for various purposes such as research, archiving, or simply enjoying a website without an internet connection.
So go ahead, give Goclone a try and experience the freedom of having your favorite websites at your fingertips, even when you're offline!

<a name="manual"></a>
### Manual
```bash
# go get :)
go get github.com/shurco/goclone
# change to project directory using your GOPATH
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/shurco/goclone/cmd
# build and install application
go install
```
<a name="examples"></a>
## Examples
```bash
# goclone <url>
goclone https://domain.com
```
<a name="usage"></a>
## Usage
```
Usage:
goclone <url> [flags]
Flags:
-b, --browser_endpoint string chrome headless browser WS endpoint
-c, --cookie if set true, cookies won't send
-h, --help help for goclone
-o, --open automatically open project in default browser
-p, --proxy_string string proxy connection string
-r, --robots disable robots.txt checks
-s, --serve serve the generated files using gofiber
-P, --servePort int serve port number (default 8088)
-u, --user_agent string custom User-Agent (default "goclone")
-v, --version version for goclone
```
## Making JS Rendered Requests
JS Rendered requests can be made using ```-b``` flag. For example start image :
``` bash
docker run -d -p 9222:9222 --rm --name headless-shell chromedp/headless-shell
```
then run goclone:
```bash
goclone -b "ws://localhost:9222" https://domain.com
```
|
KarlAndr1/beryl
|
https://github.com/KarlAndr1/beryl
|
The Beryl Scripting Language
|
# The Beryl Programming Language
Beryl is a small, interpreted, embeddable scripting language with value semantics and first class functions.
The main feature of Beryl is that the core interpreter can run without any dynamic memory allocation*, and it does not need
to parse or compile scripts beforehand. It can also be built without any external dependencies, excluding some
typedefines and constants needed from stddef.h and limits.h; however these could be provived from a custom header if needed.
*User defined variadic functions do need access to malloc or some other memeory allocator to be able to be called. If one is not provided
they will instead throw an "out of memory" error when being called.
The interpreter and standard library can make use of any memory allocator that shares the same interface as malloc, realloc and free.
One important thing to note is that the interpreter expects that all code given to it via eval or call_fn remains as is in memory for as long as
the interpreter is used, including sucessive calls to eval or call_fn. This is because the interpreter only maintains references to things like function
source code, string literals and variable names, it does not make independent copies of them.
One exception to this is if beryl_clear is called and all interpreter-related values are discarded, then previously executed source code may be freed or overwritten.
## Examples
Hello world:
```
print "Hello world!"
```
fib.beryl:
```
let fib = function n do
if (n == 0) or? (n == 1) do
n
end, else do
(fib n - 1) + (fib n - 2)
end
end
```
Note that 'if' is a function, just like 'print' or 'fib'.
loop.beryl:
```
for 1 11 with i do
print i
end
```
This prints the numbers 1, 2, ..., 10. for is also a function defined in the standard library.
More examples can be found in ./examples and ./test_scripts
## How to build/use
Run the build.py python script
python3 build.py
Select either option one for a standalone executable or option three for an embeddable library + headers
To use the library, include the lib.ar file when compiling, and #include the interpreter.h header
If the automated build fails, compiling main.c, lexer.c, interpreter.c and all source files in the libs directory should give a working
standalone build with a REPL.
```
cc src/main.c src/lexer.c src/interpreter.c src/libs/core_lib.c src/libs/common_lib.c src/libs/io_lib.c src/libs/datastructures_lib.c src/libs/debug_lib.c src/libs/modules_lib.c
```
See the documentation (docs/USING.md) for language usage, syntax and semantics.
docs/libraries contains documentation on the functions and constants defined by libraries (src/libs).
|
liboheng/LineaNooBySwap15Points
|
https://github.com/liboheng/LineaNooBySwap15Points
| null |
# LineaNooBySwap15Points
命令行执行
git clone https://github.com/liboheng/LineaNooBySwap15Points.git
Address.txt中填入钱包地址
命令行执行
npm install axios
node Get15Points.js
<img width="227" alt="image" src="https://github.com/liboheng/LineaNooBySwap15Points/assets/16268329/8e3bd2ca-d733-4dfc-85fc-27d979313752">
|
deepmind/codoc
|
https://github.com/deepmind/codoc
| null |
# Repository for Complementarity-Driven Deferral to Clinicians (CoDoC)
This repository includes the source code for the paper "Enhancing the reliability and accuracy of AI-enabled diagnosis via complementarity-driven deferral to clinicians (CoDoC)" by Dvijotham et al. (2023), published in the journal _Nature Medicine_. The contents of the repository can be used to replicate the experiments provided in the paper, as well as to utilize the CoDoC framework in independent human-AI complementarity research.
## Installation
The following command sets up python virtual environment,
```bash
python3 -m venv codoc_env
source codoc_env/bin/activate
```
This uses `virtualenv` python module
to create virtual environment. If it doesn not exist, please install it with
`pip`. Once the environment is set up we can proceed to install all the required
dependencies.
```bash
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Running
```bash
bash run.sh
```
The above script should open a notebook server from which `codoc_experiments.ipynb`
can be run. The notebook has further instructions and documentation to guide
through running the experimentation pipeline.
## Quickstart
For both purposes mentioned above, we recommend starting from the Jupyter notebook file `Replicating_CoDoC_Experiment_Results.ipynb`. This file walks the user through various functionalities of the implementation provided, familiarizes them with the data format adopted, and if desired provides more specific instructions for the exact replication of existing results.
Please refer to the original paper for a detailed introduction to the CoDoC framework, its clinical and statistical properties, and experimental results on a variety of datasets.
## Datasets
The UK Mammography Dataset (AI scores, clinical predictions, ground truth) is used for generating the results in the paper. If you're interested in the data, please email [email protected] and you will be contacted once it is available.
The US Mammography Dataset 2 can be obtained for research purposes by contacting Prof. Krzysztof J Geras ([email protected]).
## Contact
For any questions regarding this repository or the paper, please contact Krishnamurthy (Dj) Dvijotham ([email protected]) and Jim Winkens ([email protected]).
## License
Copyright 2023 Google LLC
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
## Disclaimer
The content of this research code repository (i) may not be used as a medical device; (ii) may be not used for clinical use of any kind, including but not limited to diagnosis or prognosis; and (iii) may not be used to generate any identifying information about an individual.
|
TechTitan0624/Hosting-API-integration-pro
|
https://github.com/TechTitan0624/Hosting-API-integration-pro
| null |
<img src="https://github.com/prathamisonline/advice-generator-app-frontendmentor/blob/main/images/project-preview.png.png?raw=true"></img>
<h1 align="center">Advice generator app</h1>
<div align="center">
<h3>
<a href="https://advice-generator-app-pratham.netlify.app/" color="white">
Live
</a>
<span> | </span>
<a href="https://www.frontendmentor.io/solutions/html-css-javascript-WNC3WXaHh8">
Solution
</a>
<span> | </span>
<a href="https://www.frontendmentor.io/challenges/advice-generator-app-QdUG-13db">
Challenge
</a>
</h3>
</div>
<div align="center">
Solution for a challenge from <a href="https://www.frontendmentor.io/" target="_blank">frontendmentor.io</a>.
</div>
<br>
<br>
<br>
## About The Project
<p>The perfect project if you're learning how to interact with 3rd-party APIs. This challenge uses the Advice Slip API to generate random quotes of advice.
The challenge is to build out this advice generator app using the Advice Slip API and get it looking as close to the design as possible.
You can use any tools you like to help you complete the challenge. So if you've got something you'd like to practice, feel free to give it a go.
<br><br>Users should be able to:
<br>1. View the optimal layout depending on their device's screen size.
2. See hover states for all interactive elements on the page.
<br>
3. Generate a new piece of advice by clicking the dice icon.
<br> <p>I do not have access to the Figma sketch so the design is not pixel perfect.</p>
## Built with
- Semantic HTML5 markup
- CSS custom properties
- Flex
- Desktop-first workflow
- Advice Slip API - random quote generator
## What I learned
A nice and simple project to practice api and its working.
## Useful resources
1. <a href="https://www.figma.com/">Figma</a> - Paste your design image to check the size of containers, width, etc.
2. <a href="https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/perfectpixel-by-welldonec/dkaagdgjmgdmbnecmcefdhjekcoceebi">Perfect Pixel</a> - Awesome Chrome extension that helps you to match the pixels of the provided design.
3. <a href="https://api.adviceslip.com">Advice Slip API</a> - random quote generator.
## Acknowledgments
A big thank you to anyone providing feedback on my <a href="https://www.frontendmentor.io/solutions/html-css-javascript-WNC3WXaHh8">solution</a>. It definitely helps to find new ways to code and find easier solutions!
|
Mani-Bhaskar-Edula/nativecloud
|
https://github.com/Mani-Bhaskar-Edula/nativecloud
|
our own cloud
|
# nativecloud
our own cloud
|
ksm26/LangChain-Chat-with-Your-Data
|
https://github.com/ksm26/LangChain-Chat-with-Your-Data
|
Explore LangChain and build powerful chatbots that interact with your own data. Gain insights into document loading, splitting, retrieval, question answering, and more.
|
# 🚀 [LangChain: Chat with Your Data](https://www.deeplearning.ai/short-courses/langchain-chat-with-your-data/?utm_campaign=langchain-launch&utm_medium=email&_hsmi=265152429&_hsenc=p2ANqtz-9UlYz5c-nRZMfgLCGV8A8NUouNPlJfr2zlCSVvOQ1Ma_u2OkBGboSEw-clvdMEiHEAqv123vqBbIPY616OFPjKODkF4g&utm_content=265152429&utm_source=hs_email)
📚 Welcome to the "LangChain: Chat with Your Data" course! Learn directly from the LangChain creator, Harrison Chase, and discover the power of LangChain in building chatbots that interact with information from your own documents and data.
**LangChain**: 🔗[GitHub](https://github.com/hwchase17/langchain), 📚[Documentation](https://python.langchain.com/en/latest/index.html)
## Course Summary
📖 A short course on LangChain: Chat With Your Data! Explore two main topics: Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and building a chatbot. Unlock the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) to retrieve contextual documents and create chatbots that respond using your own data.
You'll learn about:
1. 📥 **Document Loading**: Access over 80 unique loaders provided by LangChain to handle various data sources, including audio and video.
<p align="center">
<img src="images/L1-Document_loading.png" height="450">
</p>
2. ✂️ **Document Splitting**: Discover best practices and considerations for splitting data effectively.
<p align="center">
<img src="images/L2-Document_splitting.png" width="450" >
</p>
3. 🧮 **Vector Stores and Embeddings**: Dive into embeddings and explore vector store integrations within LangChain.
<p align="center">
<img src="images/L3-Vectorstores_embeddings.png" width="450" >
</p>
4. 🔄 **Retrieval**: Grasp advanced techniques for accessing and indexing data in the vector store to retrieve relevant information beyond semantic queries.
<p align="center">
<img src="images/L4-Retrieval.png" width="450" >
<img src="images/L4-compression_llm.png" height="230">
</p>
5. 🤔 **Question Answering**: Build a one-pass question-answering solution.
<p align="center">
<img src="images/L5-QnA.png" width="450" >
<img src="images/L5-structure.png" width="200" height="230">
<img align="centre" src="images/L5-techniques.png" height="300">
</p>
6. 💬 **Chat**: Track and select pertinent information from conversations and data sources to build your own chatbot using LangChain.
<p align="center">
<img src="images/L6-chat1.png" height="430" >
<img src="images/L6-chat2.png" height="430">
</p>
💡 Start building practical applications that allow you to interact with data using LangChain and LLMs.
## Key Points
- 🔑 Learn directly from the LangChain creator, Harrison Chase.
- 📊 Apply LLMs to your proprietary data and develop personalized assistants and specialized chatbots.
- 💡 Expand your utilization of LLMs through agents, chained calls, and memories.
## About the Instructors
🌟**Harrison Chase** is Co-Founder and CEO at LangChain.
🌟**Andrew Ng** is Renowned AI researcher, co-founder of Coursera, and the founder of DeepLearning.AI. With a wealth of knowledge and expertise in the field, Andrew has played a pivotal role in popularizing AI education.
🔗 Reference: "LangChain: Chat with Your Data" course. To enroll in the course or for further information, visit [deeplearning.ai](https://www.deeplearning.ai).
|
DmT021/ObservationBD
|
https://github.com/DmT021/ObservationBD
|
Proof of concept for Swift Observation back-deploy
|
# ObservationBD
Proof of concept for Swift Observation back-deploy
|
sho1374k/Toys_No.020_WebGLSchool-Task04-PlaneRaycaster
|
https://github.com/sho1374k/Toys_No.020_WebGLSchool-Task04-PlaneRaycaster
|
WebGLスクール課題04
|
# Task.04 ~ WebGL スクール第 10 期
## 🪬 ~ 要件
- Raycaster と Plane(板)を使ってなにか作ってみましょう。
## 👾 ~ Demo
- https://dev.shoya-kajita.com/020/
<img src="screenshot1.webp">
<img src="screenshot2.webp">
<img src="screenshot3.webp">
## 🎮 ~ Getting Started
- node : v.17.0.0
- npm : 8.1.0
```
// install
npm i
// development
npm run dev
// production
npm run build
// build preview
npm run preview
```
📝 ~ Note
|
bradfitz/issue-tracker-behaviors
|
https://github.com/bradfitz/issue-tracker-behaviors
| null |
# Public Issue Tracker Behaviors
I've been involved in FOSS communities for over 25 years now. I've
used a handful of different bug trackers and worked on and created a
ton projects, often acting as the bug triage person.
I've also worked inside companies with private bug trackers.
Private bug trackers and public bug trackers are vastly
different. Public bug trackers are full of the best and the worst of
the internet. This page documents some of the most commonly seen bad
behavior on public issue trackers. (and why many people prefer private bug
trackers)
Pull requests or issues welcome to add more. I surely forgot a bunch.
# Behaviors
## Me too, plus one
User shows up adding no new information, just:
* "+1"
* "me too"
* "i also see this"
No version numbers, no logs, nothing.
User has not learned to use the emoji reactions yet. (Please learn.)
## Subscribing via comments
* "just leaving a comment to watch this bug"
And you just spammed everybody else watching this bug.
There's a "subscribe" button to get notified over on the right. Push
that instead.
## Back from the dead
User comments on ancient closed issue saying they're "also seeing
this", without saying what "this" is. They probably found one common
symptom ("it doesn't work") and decided that an Android crash from 3
years ago is the same as their Windows issues, because both resulted
in it "not working".
## Any update?
* "Any update?"
* "Any news on this?"
If there was an update we would've posted an update. We were just
waiting for the forty-seventh person to ask! But now that you're here,
here's an update!
(if it's been a year, sure. But we don't need somebody pinging the bug
for updates daily or weekly.)
## Any workaround?
User asks for a "workaround" on a bug that clearly has no
workaround. Maybe it's a feature request or a crash that's affecting
everybody, but the user wants a "workaround".
## The negger
* "I can't believe you don't have this yet. That's ridiculous. All
your competitors can do X, so I guess I'll just have to go use
something else."
## The duper
Files duplicate bug without doing any search ahead of time to see if
the bug was already filed. I don't expect people to be perfect and
find a possible dup bug every time, but I expect you to try for 10
seconds first.
## The template ignorer
The bug template asks a bunch of questions.
The person filing the bug answers none of them.
But, uh, "it doesn't work".
## XY Problem
See https://xyproblem.info/
Somebody files a bug asking for X, omitting what their real problem
is, but thinking that X would help with their problem. Usually they
don't understand the problem enough and are asking for the wrong
thing.
Start with your problem.
## Just add an option!
The project doesn't want a hundred configuration knobs. That's a
usability and testing disaster: users need to learn all the options
and how they interact, and project maintainers need to set up tests to
test every combination of them.
So the project instead tries to do the right thing automatically,
configuration free.
But users inevitably don't want to wait for the right fix and instead say:
* "Just add an option!"
Just.
## The lazy pull request
Somebody opens a pull request adding a feature or bug fix, but in
doing so ...
* implements an unwanted feature with no discussion
* provides no description in the pull request
* breaks existing functionality that doesn't apply to them
* breaks test cases and does not address them
* fails to provide coverage in new test cases
* does not update documentation
* expects maintainers to "take it from here"
## The locals find each other
The project is primarily in one language (inevitably English): its
website, its docs, its bug tracker are all in English.
A user files a bug in English.
Some comments go by.
Eventually two of users commenting in the bug discover that they both
speak some non-English language and switch all the dialogue in that
bug to that language. It's spread in forums by users speaking that
language and more people speaking that language start participating.
Now the original people who filed the bug (in English) have to do the
copy/paste translation because the issue tracker doesn't have built-in
translation. (It's 2023. They should. But maybe they don't want to pay
for it.)
This is regrettable (people should ideally be able to use their
preferred language and participate), but it's really annoying for
project maintainers when their issues are taken over and had the
language changed on them. Better tooling by issue trackers & browsers
would help here.
## Wants the opposite.
The project says "This is **foo**, specifically for **bar**. It
specifically does not do **baz** because the following reasons."
User shows up in the issue tracker: "Hey, I really like **foo**! How
about you add **baz**? It would be great!"
## The cookie licker
* "Can I work on this?"
... then proceeds to never work on it.
(courtesy @jakebailey)
## The At-er
`@`-mentions a bunch of project contributors, hoping to get more
attention to their issue.
(BTW, if you ever need attention on an issue, be sure to mention
@jakebailey who suggested this item)
## The Blaster
User files a bug,
... but also emails the user list, the core developer list, posts to
Twitter, posts to Reddit, asks on Stackoverflow, emails support,
emails sales, privately DMs some core developers ....
_STOP._
## The novelist
User files a bug, maintainers asks for minimal reproduction test.
User does _NOT_ provide test case, instead opts to write out an entire short story on what he belives is happening, starting at his childhood, a mysterious problem that he encountered and the wonderous half-human, half-lizard being that helped his way through trying to fix the problem, a story full of allegory, but zero code.
Maintainers still have no idea what the bug really is, because they don't understand what the user did.
|
rodneyknaap/atx-turboxt-v3
|
https://github.com/rodneyknaap/atx-turboxt-v3
|
A new ATX design of an XT compatible PC mainboard
|

# ATX Turbo-XT Mainboard V3
I hereby publish the third revision of my ATX Turbo-XT mainboard design.
I had my doubts whether it would be wise to share my project, however the fact that keeping technology to myself prevents others to benefit from it made me decide for a release.
Open source is in my opinion the most important concept for all technology of mankind to move into the future in a way which has the potential to benefit all of us.
## Purpose and permitted use, cautions for a potential builder of this design
This project was created for historical purposes out of love for historical computing designs and for the purpose of enabling computing enthousiasts with a sufficient level of building and troubleshooting expertise to be able to experience the technology by building and troubleshooting the hardware described in this project.
## Besides the GPL3 license there are a few warnings and usage restrictions applicable:
No guarantees of function or fitness for any particular or useful purpose is given, building and using this design is at the sole responsibility of the builder.
Do not attempt this project unless you have the necessary electronics assembly expertise and experience, and know how to observe all electronics safety guidelines which are applicable.
It is not permitted to use the computer built from this design without the assumption of the possibility of loss of data or malfunction of the connected device. To be used strictly for personal hobby and experimental purposes only. No applications are permitted where failure of the device could result in damage or injury of any kind.
If you plan to use this design or any part of it in new designs, the acknowledgement of the designer and the design sources and inspirations, historical and modern, of all subparts contained within this design should be included and respected in your publication, to accredit the hard work, time and effort dedicated by the people before you who contributed to make your project possible.
No guarantee for any proper operation or suitability for any possible use or purpose is given, using the resulting hardware from this design is purely educational and experimental and not intended for serious applications. Loss of data is likely and to be expected when connecting any storage device or storage media to the resulting system from this design, or when configuring or operating any storage device or media with the system of this design.
When connecting this system to a computer network which contains stored information on it, it is at the sole responsibility and risk of the person making the connection, no guarantee is given against data loss or data corruption, malfunctions or failure of the whole computer network and/or any information contained inside it on other devices and media which are connected to the same network.
When building this project, the builder assumes personal responsibility for troubleshooting it and using the necessary care and expertise to make it function properly as defined by the design.
You can email me with questions, but I will reply only if I have time and if I find the question to be valid. Which will probably also lead to an update here.
I want to primarily dedicate my time to new project development, I am not able to do any user support, so that's why I provide the elaborate info here which will be expanded if needed.
# Factors for proper operation and stability
Timing issues are likely to occur which require certain components to be of a suitable sufficient type to be able to meet the timing requirements for proper function. The prototype of the developer is proof of concept, please refer to the detailed partslist provided which includes type and manufacturer for all ICs where necessary, however each new build may pose it's own challenges to bring it to success. This design is by nature not a turnkey solution and will only function when using all the components of similar timing and behaviour as was used in the prototype. Determining the right components may likely be experimental in nature and require expertise, experience, effort and persistance.
Specifically the databus control transceivers and DMA handshaking circuits are most sensitive to exact types of at least equivalent timing as the types specified in the IC list, so refer to that list. The choice of DMA controller is a matter of trial and error, not all DMA controller chips are of sufficient timing to control a floppy disk using this design, specifically a floppy disk format poses the most exact testing situation to ensure proper DMA operation. Manufacturing date variations also may result in timing variations of the DMA controller. If the DMA handshake logic ICs are of faster types, this may also allow a more broad range of DMA controller ICs to work properly. Though I have not verified this with tests. Theoretically, using lower voltage logic or programmable logic may provide faster timing, though I have not chosen these methods in my design because I already achieved proper timing with the components I had available.
The 24Mhz oscillator load capacitors should be used as specified in the design, the oscillator should be checked to operate properly. If the total load (PCB capacitance + load capacitors) is too high, the oscillator will not run reliably and this will cause crashes, devide by zero errors, freezing, resets etc. Therefore ensure to observe the load capacitance suitable and proper stable operation of the oscillator. The ground shielding of the PCB traces of the clock signals comprise an addition to the load capacitance so the load capacitors themselves can be lower. For a turbo XT, it is not required to use two 8284 chips, one is sufficient. The DMA controller can properly operate on a fixed 50% duty cycle clock within the speed range of the chip so that is what I have provided. I derived the XT system clocks (keyboard, timer chip) from the DMA clock signal, which are also all fixed clock signals and do not vary when switching the CPU speed. CPU speed can be switched with the keyboard CTRL-ALT-num+ and CTRL-ALT-num- as controlled by the Super PC/Turbo XT BIOS (perfected by Jon Petrosky and Ya'akov Miles) at any moment without crashing the CPU. At least, I was not able to get the PC to crash by switching the speed at various moments.
There have been many capacitor footprints added to the edge of the ISA bus. These do not all need to be populated, but are instead intended for termination of signal reflections. Specifically, active high signals may be sensitive to noise generated from reflections. The best example is the RESETDRV signal on the ISA bus. If there is too much noise on such a signal it may cause certain I/O ICs such as UARTs to operate erroniously. For this reason the onboard UART RESET input has been purposely grounded. Use a 2.2nF capacitor for RESETDRV at least. Certain other signals may benefit from termination using lower capacitors. The higher the frequency of the signal, the lower the capacitor should be chosen as not to cause delays on the signal edges.
Databus transceivers which drive the ISA bus should be chosen of LS245 types which give better stability results. HCT types have better amplitudes but are more sensitive in the system. Refer to the IC list for best choices, though you could experiment after achieving a stable system to see if more HCT types are possible. For driving the SRAM memory databus, HCT types are fine.
This is an advanced project which contains many components, therefore the maximum care should be applied and maintained when soldering the PCB. Where using IC sockets, ensure they are proper quality sockets which are solid enough to create a reliable connection to the ICs inserted. Using sockets on DMA control circuits would be an advantage for trial and error testing to determine proper timing is reached. Use care to observe all IC orientations which differ due to layout considerations. Some ICs are tightly packed on the PCB, so first solder the ICs or sockets, then solder the decoupling capacitors. Also see the photo above for an example.
After soldering the project, it's a strong requirement to use proper lighting and magnification and systematically inspect all soldering points to detect any short circuits or open solder joints before powering up the system for testing. Short circuits which are not detected will probably damage ICs and introduce hidden defects into your project which will be even more difficult to detect after the damage is done. Fuses are put into the 5V and 12V lines which should blow on shorts or overcurrent. Keep in mind that the amount of current an ATX PSU can generate before it goes into protection mode also requires care of the project builder to ensure no short circuits occur which could destroy components or PCB traces.
If you do not agree or do not wish to accept the above risks, cautions and usage terms, do not make any attempts to build and operate the hardware in these design specifications.
It is not allowed to pass on this design to others without requiring them to read this entire document carefully and accept all of the terms.
# Acknowledgements
This project was inspired by:
- IBM Corporation who introduced the industry standard PC concept and design schematics
- Taiwanese clone XT builders who produced their own modifications in the turbo XT which also inspired this project
- testing with the Super PC/Turbo XT BIOS https://www.phatcode.net,
- Sergey's HD floppy drive BIOS extension https://github.com/skiselev/floppy_bios
- concept and software of the XT-IDE universal BIOS https://www.xtideuniversalbios.org
- datasheets, application notes and specifications by:
LG Semiconductors (Goldstar) (GM82C765 FDC, GM16C550)
Standard Microsystems Corporation (FDC37C65C datasheet, FDC register access table)
Texas Instruments (GD75232)
Realtek (RTL8019AS)
NCR (53C400 SCSI)
Acknowledgements of people who were instrumental in preceeding developments upon which this design was elaborated:
[IBM PC development team](https://www.ibm.com/ibm/history/exhibits/pc25/pc25_birth.html)
[Some historical info](https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2017/06/ibm-pc-history-part-1/)
[Bill Lowe](https://www.ibm.com/ibm/history/exhibits/builders/builders_lowe.html)
[Don Estridge](https://www.ibm.com/ibm/history/exhibits/builders/builders_estridge.html)
[Sergey Kiselev](http://www.malinov.com/Home/sergeys-projects/xi-8088)
[His HD Floppy BIOS](https://github.com/skiselev/floppy_bios)
I was inspired after seeing and reading about his 8088 projects, he also created the HD floppy BIOS extension.
[Super PC/Turbo XT BIOS by Plasma (Jon Ρetrosky and Ya'akov Miles)](https://www.phatcode.net)
An excellent BIOS for XT machines, far superior in stability and function to anything else I have tested.
Tilmann Reh and others (16 bit to 8 bit translation of IDE I/O in computer hardware for example as described in TCJ #53)
I have used my own adaptation of [J. Chapman's version(Glitchworks)](https://minuszerodegrees.net/xtide/rev_4/XT-IDE%20Rev%204%20-%20general.htm) of XT-IDE schematic after extensive testing with several circuit and component variations on an Amstrad PPC640. I studied all revisions of the circuits first before creating my own variations.
More information about the creation of XT-IDE hardware can be found [here](https://minuszerodegrees.net/xtide/XT-IDE%20-%20Basics.htm).
[XT-IDE universal BIOS project development team for developing the XT-IDE BIOS](https://www.xtideuniversalbios.org)
Amazing and extremely efficient software, fast disk access for XT and various AT computers.
Works with every IDE drive I have tested. Still under active development earlier in 2023.
All source data remains the copyright of the original creators and must be respected.
This design is only released for hobby computing enthousiasts and educational purposes, no profit is to be made from this design or derived work from it.
I have taken time to respectfully include all the above acknowledgements. If anyone or anything is left out, that is absolutely not intentional, please contact me and I will update this page.
After elaborately studying the available source design files which inspired the system, I conceived this design with my own variations, circuit additions and changes which I see as improvements according to my personal design views and preferences. Some logic types I have changed to get a better schematic perspective on an entire circuit area. My purpose was a good clear recreation in my own method, not to exactly copy the original. I have removed the DRAM refresh and parity check logic from the design.
I have designed most of the I/O control circuits using the chip manufacturer datasheets to determine the proper interfacing methods, ports etc suitable for this XT design.
# ROM BIOS
The choice of BIOS for operation of this mainboard is up to the builder, the BIOS used in the operation of my build works well, and is composed as follows, top to bottom segments in the ROM image are:
0k-8k Super PC/Turbo XT BIOS (project by Jon Petrosky and Ya'akov Miles)
8k-16k XT-IDE BIOS file (by XT-IDE universal BIOS team)
The BIOS must be configured to port 300/308 and XT-IDE v2 ("Chuck mod") hardware.
The BIOS image is to be corrected for checksum=0 by XT-IDE config software and then should be saved back into the BIOS.
Using an 8088 you need the ide_xt.bin, for the NEC V20 you can use the ide_xtp.bin.
16k-24k XT HD-Floppy BIOS extension (by Sergey Kiselev)
Configuration of floppy drive config bytes according to instructions provided by Sergey.
It's best to configure your floppy drive configuration by setting the appropriate bytes in the image to correspond with the floppy drives you plan to connect.
All drives should be set to drive select 1 (counting from 0) and the standard floppy cable twisting should be used to choose the first and second drive.
Since it's a relatively modern FDC, floppy termination should be moderate for example 1k, and doesn't need to be done on all the floppy drives.
Possibly, floppy drive termination on the drives themselves can even be left out or only present on one drive.
The less resistance on the terminated signals, the less load on the FDC pins. 150 ohms is really too low a resistance to use and I recommend removing these when found on a drive and at least replacing with 1k, or leaving them out.
24k-64k Remaining 40k program with blank space "00" hex codes.
This comprises a 64k BIOS image, the design accommodates two BIOS images in the 128k ROM, the page to be used can be switched by a jumper or switch. For testing it's advised to program two identical BIOS images into the ROM first. Initially it's best to use an EPROM which cannot be erased by software if there is any software trying to write into the BIOS region. If you like to add other BIOS images you can simply include them into the BIOS image file since there are 5 segments of 8k available.
What I did is to create two variations of the 64k BIOS, one which includes a DD 5,25 floppy drive, and the other includes a HD 5,25 floppy drive. I have added switches to the DS1 jumpers of my two 5,25 drives which enables to leave both connected to the floppy bus simultaniously. The switches change both the BIOS image selection and the drive selects. Using both a DD and HD 5,25 drive makes sure that any floppy disks are properly read and written, due to matching the proper track width compatibility of the original intended drives to the respective disks. In both of my BIOS versions, I have defined drive A: to be a 1,44MB HD 3,5 inch drive. Drive B settings contain the DD and HD versions of the 5,25 drives.
In order to create the BIOS image I used a cmd batch command.
`copy /b blank8k.bin + blank8k.bin + blank8k.bin + blank8k.bin + blank8k.bin + floppy22_DD.bin + IDE_XTP.BIN + pcxtbios_phatcode.bin biosrom64k_dd_fdd.bin`
`copy /b blank8k.bin + blank8k.bin + blank8k.bin + blank8k.bin + blank8k.bin + floppy22.bin + IDE_XTP.BIN + pcxtbios_phatcode.bin biosrom64k_hd_fdd.bin`
`copy /b biosrom64k_hd_fdd.bin + biosrom64k_dd_fdd.bin !biosrom_floppy22_switch_dd_hd_config.bin`
This should result in a 128kb file named !biosrom_floppy22_switch_dd_hd_config.bin
The onboard RTL8019AS adapter is configured using the 93LC46 EEPROM. This EEPROM can be programmed using a programmer, I will provide a dump image of my example chip. The image also contains the MAC address so this should be varied slightly in your implementation.
The LPT port does not need interrupt 7 to operate so the jumper should be left open because of limited interrupts available in an XT.
DMA timing jumpers provide alternatives for testing purposes, the settings indicated by the asterisk are defaults.
Resources (besides obvious internal base XT chips):
IO Ports:
0300 XT-IDE
0308 XT-IDE
0340 LAN
0378 LPT
03F8 COM1
IRQ list:
IRQ0 system refresh timer
IRQ1 Keyboard
IRQ2 available
IRQ3 LAN
IRQ4 COM1
IRQ5 available
IRQ6 FDC
IRQ7 SCSI
DMA list:
DMA 0 refresh dummy DMA
DMA 1 free
DMA 2 FDC
DMA 3 free
For the SCSI bus general practises for termination apply. The 53C400 is very solid, stable and fast and works really well with LS2000 drivers.
A SCSI bus is an ideal period correct way to provide plug-in storage and CDROM access for an XT PC.
I operate my XT PC with a VGA card, the Video 7. Perhaps others like CGA or EGA which requires the correct dipswitch settings. I don't own any CGA monitor and besides I want to be able to use windows 3.0, play certain games and view photos in full VGA format on a modern monitor. I have tested a ATI Small Wonder card to operate properly on the composite output on a CRT.
The schematic diagram is intentionally created as a single sheet for fastest navigation back and forth between various circuit areas. Such a large single sheet does slow down editing somewhat but it's an acceptable compromise in my opinion once you get used to it. It's not the "fullness" of the schematic, but the sheet size which slows down the schematic editor somewhat, which can be lessened by occasionally saving and closing the schematic, and then opening it again. Schematic and PCB design are made in KiCad 5.1.7. I know this is not the latest release however I am used to working in this version and I don't see a need to change that for now since it has proven to be sufficient for this purpose.
This KiCad version is confirmed to be fully compatible with screenshots of JLCPCB guidelines of settings for creating the files for manufacturing.
I will be including my own KiCad library additions in the source files which need to be unpacked into the appropriate kicad installation shared library folders.
I will not be further revising this design since I view it as completed.
My next project will be a 286 AT mainboard design comperable to the IBM 5170 and similar PCs, without the use of a chipset.
I am still seeking a reference mainboard for my project and have not yet found a stable one because good examples are rare.
I bought two "defective" mainboards from Ebay so far which proved to not be stable enough or only partially functional.
I hope to find an AT mainboard of slightly later design, without a chipset, which includes higher CPU clock frequency and a more modern plastic 286.
Anyone who would be willing to donate a mainboard, please get in touch with me.
After the 286 I will attempt to integrate the 486 SLC in a subsequent future revision.
Thanks for your interest in this project,
kind regards,
Rodney
|
MrTalentDev/go-blockchain-history
|
https://github.com/MrTalentDev/go-blockchain-history
| null |
## About
This is on open source project which aims to make easy solution with timestamping data on blockchain
## Swagger
https://history.bankex.team:3001/
## Backend handlers
**[POST]**
**Authentication**: Basic Auth
**Route:** a/new/:assetId/:hash
**Description:** Allow to create new AssetID with Hash.
**Return:** JSON
```
{
"assetId": Id of current asset chaid
"hash": hash of file what we've got from product server
"merkleRoot": root of merkle tree at Ethereum
"timestamp": UNIX format time when server got hash of file
"txNumber": Number of asset from assetId
}
```
**Return:** JSON if Error
```
{
"Answer": "This assetId is already created"
}
```
It's a **POST** request btw
**Example:** http://history.bankex.team:8080/a/new/testAsset/0293a80682dc2a192c683baf434dd67343cedd70
---
**[POST]**
**Authentication**: Basic Auth
**Route:** /update/:assetId/:hash
**Description:** Allow to add new asset to assetId. Returns txNumber of this hash, timesamp
**Return:** JSON
```
{
"assetId": Id of current asset chaid
"timestamp": UNIX format time when server got hash of file
"txNumber": Number of asset from assetId
}
```
It's a **POST** request btw
**Example:** http://history.bankex.team:8080/a/update/testAsset/0293a80682dc2a192c683baf434dd67343cedd70
---
**[GET]**
**Route:** /get/:assetId/:txNumber
**Description:** Return asset hash by assetId and txNumber
**Return:** JSON
```
{
"assets": current asset
}
```
**Example:** http://history.bankex.team:8080/get/testAsset/0
---
**[GET]**
**Route:** /proof/:assetId/:txNumber/:hash/:timestamp
**Description:** Return list of merkle proofs by assetId, txNumber, hash, timestamp
**Return:** JSON
**More about return:** Merkle proof for assetId, txNumber, hash, timestamp (Actually send a JSON File with two arrays **Data** and **Info**
**Data** is a list of merkle proofs leaves from end to start (256 Hashes of type Buffer)
**Info** has parameters:
1. Key - array key
2. Hash - array value
3. Root - current merkle tree Root Hash
Response looks like:
```
{
{
"Data": [
{
"Hash": "QGTfJZ5sF0U5U0nwQDI0q+FXE7p+87DGZ1bhijbapPU="
},
{
"Hash": "hBp5I5E3E57YRPCIRziHXVdlPSF3nWCNKmRRcS+nQZc="
},
{
"Hash": "SZEJoTogdMeznCpdpIIqXM+ztBfXnLxnFCOUYTl4Jm4="
}
],
"Info": {
"Key": "VCRbbhhUHqe//lRV3RDBawTnATBTeZNsm9FQtwR9JMw=",
"Hash": "2TmoNwyUYfmxtInasAyC9xyKM7hcZq9MokNwAoQxwek=",
"Root": "5JX8dfEibcncG2fGp0YcG5UTY9LgrNdQoq4TWL8WpUs="
}
}
```
**Example:** http://history.bankex.team:8080/proof/a/0/0293a80682dc2a192c683baf434dd67343cedd70/1210000000
---
**[GET]**
**Route:** /list
**Description:** Return all assets info
**Return:** JSON
```
{
{
"assets": [
{
"_id": "5b869ee5ca2985e06552a49d",
"data": "",
"hash": "qNCllA0uMdgEPSVQBYzD4JESEECY2NyjbJgGjy0NP6c=",
"created_on": 1535549157514,
"updated_on": 1535549157514,
"assetId": "bf",
"txNumber": 0,
"assets": {
"0": "ludYELf+UZ3ZL2o/chcLAMCoqVU/nHZaPMaB6vfuqzg="
},
"assetsTimestamp": {
"0": 1535549157514
}
}
]
}
}
```
**Example:** http://history.bankex.team:8080/list
---
## DevOps
There are 3 servers here
**Product server:** works with MongoDb and is working on port 3001
**Blockchain server:** works with MongoDb and is working on port 8080
**Client server:** works with 2 servers on port 7070
**NOTE**:
It's better to use more than 1 domain for project.
Blockchain server is just a tool, so there is no point to change it.
But product and client servers can be different. You can only run Blokchain server and make you own product and client server.
You just need to have a Verify Function implemented in client part to verify merkle proofs.
It's **here** https://github.com/BANKEX/poa-history/blob/client/assets/download/index.js
## About ENV
```
PVT_KEY: Private key at Rinkeby network
CONTRACT_ADDRESS: target contract address
LOGIN_DB: Login of Mongo
PASSWORD_DB: Password of Mongo
IP: IP/URL of Mongo
LOGIN: Login for basic auth from users
PASSWORD: Password for basic auth from users
```
## Deploying
```
mkdir docker
cd docker
sudo nano docker-compose.yml
docker swarm init
docker stack deploy -c docker-compose.yml poa_hist
```
## FAQ
How to proof that file was uploaded with hash N and timestamp T Upload:
1. Make a Sparse Merkle tree, where the value is (N, T) (Before all, it's important to save N, T, Id of the file)
2. Put Merkle root to Ethereum server Proove:
3. Download the file and get N and T
4. Check that N = N saved before uploading
5. Do the same for T
6. Ask for Merkle proof from server
7. Get Merkle root from Ethereum contract
8. Check that Merkle proof is correct ( it's a function with inputs: Hash file, timestamp file, assetId, txNumber - all these parameters client at the beginning)

|
smoka7/multicursors.nvim
|
https://github.com/smoka7/multicursors.nvim
|
A multi cursor plugin for Neovim.
|
# Multicursor.nvim
The Multicursor Plugin for Neovim extends the native Neovim text editing capabilities, providing a more intuitive way to edit repetitive text with multiple cursors. With this plugin, you can easily create and manage multiple cursors, perform simultaneous edits, and execute commands on all cursors at once.
## Requirements
- Neovim >= **0.9.0**
## Installation
Install with your preferred package manager:
```lua
{
"smoka7/multicursors.nvim",
event = "VeryLazy",
dependencies = {
'nvim-treesitter/nvim-treesitter',
'smoka7/hydra.nvim',
},
opts = function()
local N = require 'multicursors.normal_mode'
local I = require 'multicursors.insert_mode'
return {
normal_keys = {
-- to change default lhs of key mapping change the key
[','] = {
-- assigning nil to method exits from multi cursor mode
method = N.clear_others,
-- you can pass :map-arguments here
opts = { desc = 'Clear others' },
},
},
insert_keys = {
-- to change default lhs of key mapping change the key
['<CR>'] = {
-- assigning nil to method exits from multi cursor mode
method = I.Cr_method,
-- you can pass :map-arguments here
opts = { desc = 'New line' },
},
},
}
end,
cmd = { 'MCstart', 'MCvisual', 'MCclear', 'MCpattern', 'MCvisualPattern', 'MCunderCursor' },
keys = {
{
mode = { 'v', 'n' },
'<Leader>m',
'<cmd>MCstart<cr>',
desc = 'Create a selection for selcted text or word under the cursor',
},
},
}
```
## Default Configuration
<details>
<summary>Click me</summary>
```lua
{
DEBUG_MODE = false,
create_commands = true, -- create Multicursor user commands
updatetime = 50, -- selections get updated if this many milliseconds nothing is typed in the insert mode see :help updatetime
nowait = true, -- see :help :map-nowait
normal_keys = normal_keys,
insert_keys = insert_keys
extend_keys = extend_keys
-- see :help hydra-config.hint
hint_config = {
border = 'none',
position = 'bottom',
},
-- accepted values:
-- -1 true: generate hints
-- -2 false: don't generate hints
-- -3 [[multi line string]] provide your own hints
generate_hints = {
normal = false,
insert = false,
extend = false,
},
}
```
</details>
## Usage
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| MCstart | Selects the word under cursor and starts listening for the actions. In visual mode it acts like `MCvisual` |
| MCvisual | Selects the last visual mode selection and starts listening for the actions. |
| MCpattern | Prompts for a pattern and selects every match in the buffer. |
| MCvisualPattern | Prompts for a pattern and selects every match in the visual selection. |
| MCunderCursor | Selects the char under cursor and starts listening for the actions. |
| MCclear | Clears all the selection. |
To enter multi cursor mode, use the one of above commands.
### Multi cursor mode
Note that keys which aren't mapped **do not affect other selections** .
<details>
<summary>Click me</summary>
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| `<Esc>` | Clear the selections and go back to normal mode |
| `<C-c>` | Clear the selections and go back to normal mode |
| `i` | Enters insert mode |
| `a` | Enters append mode |
| `e` | Enters extend mode |
| `c` | Deletes the text inside selections and starts insert mode |
| `n` | `[count]` Finds the next match after the main selection |
| `N` | `[count]` Finds the previous match before the main selection |
| `q` | `[count]` Skips the current selection and finds the next one |
| `Q` | `[count]` Skips the current selection and finds the previous one |
| `]` | `[count]` Swaps the main selection with next selection |
| `[` | `[count]` Swaps the main selection with previous selection |
| `}` | `[count]` Deletes the main selection and goes to next |
| `{` | `[count]` Deletes the main selection and goes to previous |
| `j` | `[count]` Creates a selection on the char below the cursor |
| `J` | `[count]` Skips the current selection and Creates a selection on the char below |
| `k` | `[count]` Creates a selection on the char above the cursor |
| `K` | `[count]` Skips the current selection and Creates a selection on the char above |
| `p` | Puts the text inside `unnamed register` before selections |
| `P` | Puts the text inside `unnamed register` after selections |
| `y` | Yanks the text inside selection to `unnamed register` |
| `Y` | Yanks the text from start of selection till end of line to `unnamed register` |
| `yy` | Yanks the line of selection to `unnamed register` |
| `z` | Aligns selections by adding space before selections |
| `Z` | Aligns selections by adding space at beginning of line |
| `d` | Deletes the text inside selections |
| `D` | `count` Deletes the text from start of selection till end of line |
| `dd` | `count` Deletes line of selections |
| `@` | Executes a macro at beginning of every selection |
| `.` | Reapets last change at the beginning of every selection |
| `,` | Clears All Selections except the main one |
| `:` | Prompts for a normal command and Executes it at beginning of every selection |
| `u` | Undo changes |
| `<C-r>` | Redo changes |
</details>
### Insert, Append and Change mode:
<details>
<summary>Click me</summary>
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| `<Esc>` | Goes back to multicursor normal mode |
| `<C-c>` | Goes back to multicursor normal mode |
| `<BS>` | Deletes the char before the selections |
| `<Del>` | Deletes the char under the selections |
| `<Left>` | Moves the selections one char Left |
| `<Up>` | Moves the selections one line Up |
| `<Right>` | Moves the selections one char Right |
| `<Down>` | Moves the selections one line Down |
| `<C-Left>` | Moves the selections one word Left |
| `<C-Right>` | Moves the selections one word Right |
| `<Home>` | Moves the selections to start of line |
| `<End>` | Moves the selections to end of line |
| `<CR>` | Insert one line below the selections |
| `<C-j>` | Insert one line below the selections |
| `<C-v>` | Pastes the text from system clipboard |
| `<C-r>` | Insert the contents of a register |
| `<C-w>` | Deletes one word before the selections |
| `<C-BS>` | Deletes one word before the selections |
| `<C-u>` | Deletes froms start of selections till start of line |
</details>
### Extend mode
Once you enter the Extend mode, you have the ability to expand or shrink your selections using Vim motions.
The anchor represents one side of the selection and stays put, while the other side moves based on the performed motion.
<details>
<summary>Click me</summary>
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| `<Esc>` | Goes back to multicursor normal mode |
| `c` | Prompts user for a motion and performs it |
| `o` | Toggles the anchor's side |
| `O` | Toggles the anchor's side |
| `w` | `[count]` word foreward |
| `e` | `[count]` foreward to end of word |
| `b` | `[count]` word backward |
| `h` | `[count]` char left |
| `j` | `[count]` char down |
| `k` | `[count]` char up |
| `l` | `[count]` char right |
| `t` | Extends the selection to the parent of selected node|
| `r` | Shrinks the selection to first child of selected node |
| `y` | Shrinks the selection to last child of selected node |
| `u` | Undo Last selections extend or shrink |
| `$` | `[count]` to end of line |
| `^` | To the first non-blank character of the line |
</details>
### Recepies
#### Custom mappings
Create custom mapping for editing selections.
```lua
require('multicursors').setup {
normal_keys = {
['<C-/>'] = {
method = function()
require('multicursors.utils').call_on_selections(function(selection)
vim.api.nvim_win_set_cursor(0, { selection.row + 1, selection.col + 1 })
local line_count = selection.end_row - selection.row + 1
vim.cmd('normal ' .. line_count .. 'gcc')
end)
end,
opts = { desc = 'comment selections' },
},
},
}
```
#### Status Line module
Disable hint window and show the multicursor mode in your status line.
```lua
require('multicursors').setup {
hint_config = false,
}
local function is_active()
local ok, hydra = pcall(require, 'hydra.statusline')
return ok and hydra.is_active()
end
local function get_name()
local ok, hydra = pcall(require, 'hydra.statusline')
if ok then
return hydra.get_name()
end
return ''
end
---for lualine add this component
lualine_b = {
{ get_name, cond = is_active },
}
```
## Acknowledgment
[vim-visual-multi](https://github.com/mg979/vim-visual-multi)
[hydra.nvim](https://github.com/anuvyklack/hydra.nvim)
|
DataDog/datadog-static-analyzer
|
https://github.com/DataDog/datadog-static-analyzer
|
Datadog Static Analyzer
|
# datadog-static-analyzer
datadog-static-analyzer is the static analyzer that powers Datadog [static analysis product](https://docs.datadoghq.com/continuous_integration/static_analysis).
You can use it in your CI/CD pipeline using our integration:
- [GitHub Action](https://github.com/DataDog/datadog-static-analyzer-github-action)
- [CircleCI ORB](https://circleci.com/developer/orbs/orb/datadog/datadog-static-analyzer-circleci-orb)
If you use it in your own CI/CD pipeline, you can integrate the tool directly: see the [Datadog documentation for more information](https://docs.datadoghq.com/continuous_integration/static_analysis/?tab=other).
## Download
Download the latest release for your system and architecture from the [release page](https://github.com/DataDog/datadog-static-analyzer/blob/main/releases/latest).
To get the static analyzer via shell:
```shell
curl -L -O http://www.github.com/DataDog/datadog-static-analyzer/releases/latest/download/datadog-static-analyzer-<target>.zip
```
Example to get the x86_64 binary for Linux:
```shell
curl -L -O http://www.github.com/DataDog/datadog-static-analyzer/releases/latest/download/datadog-static-analyzer-x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu.zip
```
## Usage
```shell
datadog-static-analyzer -i <directory> -o <output-file>
```
For the tool to work, you must have a `<directory>/static-analysis.datadog.yml` file that defines the
configuration of the analyzer. This file will indicates the rules you use for your project.
You can get more information about the configuration on [Datadog documentation](https://docs.datadoghq.com/continuous_integration/static_analysis).
### Mac OS X users
The binary cannot be executed as is. You need to flag the binary as safe to execute using the following command.
```shell
xattr -dr com.apple.quarantine datadog-static-analyzer
```
## Options
- `-f` or `--format`: format of the output file. `-f sarif` produces a [SARIF-compliant file](https://www.oasis-open.org/committees/tc_home.php?wg_abbrev=sarif)
- `-r` or `--rules`: provides a file that contains all rules (rules can be put in a file using `datadog-export-rulesets`)
## Configuration
For the tool to work, the following variables must be configured:
- `DD_APP_KEY`: the application key from Datadog
- `DD_API_KEY`: the API key from Datadog
- `DD_SITE`: the Datadog site to use (see list [here](https://docs.datadoghq.com/getting_started/site/))
## Other Tools
### datadog-export-rulesets
Export rulesets from the API into a file
```shell
cargo run --bin datadog-export-rulesets -- -r <ruleset> -o <file-to-export>
```
## Contribute
See file [CONTRIBUTING.md](CONTRIBUTING.md) for more information as well as [DEVELOPMENT.md](DEVELOPMENT.md)
for all details about testing and coding guidelines.
## More information
- [Datadog Static Analysis](https://docs.datadoghq.com/continuous_integration/static_analysis)
|
ringa-tech/asistente-virtual
|
https://github.com/ringa-tech/asistente-virtual
| null |
# Asistente virtual
Este repositorio es el código para el video del Asistente Virtual en el canal Ringa Tech:
https://youtu.be/-0tIy8wWtzE
## Configuración
Para ejecutar el proyecto es necesario:
- Descargar el repositorio
- Opcional: Crea un ambiente virtual
- Instala las dependencias ejecutando
- ``` pip install -r requirements.txt ```
- Crea un archivo llamado ```.env```
- En el archivo coloca las llaves. Para el proyecto tal cual del video (y este repositorio) estoy utilizando:
- ```OPENAI_API_KEY=XXXXXX```
- ```ELEVENLABS_API_KEY=XXXXXX```
- ```WEATHER_API_KEY=XXXXXX```
## Ajustes
El proyecto cuenta con algunas cosas que quizá quieras modificar, por ejemplo:
- En la clase LLM puedes modificar para que el asistente no sea "malhablado". Se utiliza en 2 lugares del archivo.
- En la clase PcCommand, abre Chrome buscándolo en una ruta fija para Windows. Puedes modificarlo para que busque el ejecutable en Mac / Linux.
## Ejecución
- Este proyecto utiliza Flask. Puedes levantar el servidor en modo debug por defecto en el puerto 5000 con el comando
- ```flask --app app run --debug```
- En tu navegador ve a http://localhost:5000
- Da clic para comenzar a grabar (pedirá permiso). Dar clic para dejar de grabar
- Espera y ve como domina al mundo
## ¿Problemas?
Solo lo probé en mi equipo así que si tienes problemas, levanta un issue aquí en Github, con el mayor detalle que puedas (versión de python, de paquetes, mensaje completo de error, etc).
Si eres ninja y lo solucionas, ¡levanta un Pull Request!
## Licencias
- Imagen de micrófono por Freepik
|
minibits-cash/minibits_wallet
|
https://github.com/minibits-cash/minibits_wallet
| null |
<img src="https://minibits.cash/img/minibits_preview.png">
# Disclaimer
⚠️ If you are using this app, please take the following into consideration:
- This wallet should be used for research purposes only.
- The wallet is an alpha version with incomplete functionality and both known and unknown bugs.
- Do not use it with large amounts of coins.
- The e-cash stored in the wallet is issued by the mint. You trust the mint to back it with bitcoin until you transfer your holdings to another bitcoin Lightning wallet.
- The Cashu protocol that the wallet implements has not yet received extensive review or testing so far.
# Minibits Wallet
Minibits is an e-cash wallet with a focus on performance and usability. Cash is issued by mints and backed by Bitcoin via the [Cashu](https://cashu.space) protocol and Lightning Network.
## Roadmap
Platform support
- [x] Android app
- [ ] iOS app
- [x] Light and dark mode
- [x] i18n support
Mints
- [x] Add multiple mints
- [x] Remove mint with zero balance
- [x] Block receiving from mint
- [x] Show mint balances grouped by hostname
- [x] Handle mint keys rotation (not tested)
- [ ] Mint status and information screen
- [ ] Change mint's short name and color
Receive coins
- [x] Scan QR code of a coin token
- [x] Paste coin token from clipboard
- [x] Receive tokens with coins from multiple mints (untested)
- [ ] Share payment request to receive
- [x] Receive coins while being offline, redeem later (MVP version)
Send coins
- [x] Share coin token to send through another app
- [x] Show coin token as a QR code
- [x] Track receive of pending coins by the payee
- [ ] Send to contact
Top up wallet
- [x] Show QR code with bitcoin lightning invoice to pay
- [x] Share encoded bitcoin lightning invoice to pay
- [ ] Share invoice with contact
Transfer / Cash out from wallet
- [x] Paste and settle bitcoin lightning invoice with your coins
- [x] Scan and settle bitcoin lightning invoice with your coins
- [ ] Transfer (swap) coins to another mint
Transaction history
- [x] Unified transaction history for all kinds of transactions
- [x] Audit trail of transaction events
- [x] Filter pending transactions
- [ ] Revert pending transaction in 1 click (get back tokens not claimed by receiver)
- [ ] Tags and related filtering of transactions
- [ ] Delete incomplete and failed transactions from history
Contacts
- [ ] Contacts management
Backup and recovery
- [x] Local append-only backup of all coins in a database separate from wallet storage
- [ ] Recovery tool to recover coins from local backup
- [x] Recover wallet in case spent coins remain in the wallet due to an exception during a transaction
- [ ] Off-device backup
- [ ] Smooth migration to another device
Security
- [x] Optional AES encryption of wallet storage using a key stored in the device secure keychain
- [x] Use device biometry to login (if storage encryption is on)
DevOps
- [x] OTA updates (opt in)
- [ ] Automated tests
- [ ] Release pipelines
## Architecture
The wallet's design has been crafted to prioritize the following primary quality properties:
- Support both Android and iOS mobile platforms
- Achieve fast startup time and UX (despite using React Native)
- Minimize the risk of data/coins loss
- Bring e-cash UX on par with the current standard of traditional finance (tradfi) mobile apps
As a result, the following architectural constraints are in place:
- Wherever available, use libraries with a fast JSI (JavaScript Interface) to native modules.
- Avoid Expo modules.
- Use fast storage for most wallet operations and separate local database storage to store data that incrementally grows.
- Leverage local database as an append-only coins backup independent from fast storage.
<img src="https://minibits.cash/img/minibits_architecture.png">
Open architectural concepts worth wider discussion
- [ ] Contacts management - identities, sharing contacts, send coins with the UX of tradfi instant payment while keeping privacy towards mints
- [ ] Off-device backup strategy - many options exist with or without mint interaction
- [ ] UX and naming conventions - e-cash is not always intuitive. UX for new users heavily depends on using the right abstractions or terms to describe what is going on. This wallet wants to serve as a means to test what could work. One of the first ideas is to avoid terms such as token or proof and propose the term coin instead.
## Download and test
Minibits wallet is in alpha and available as of now only for Android devices. You have the following options to try it out:
- [x] Join testing program on Google Play (Closed testing ongoing, submit your email to get an invite on [Minibits.cash](https://minibits.cash))
- [X] Download .apk file from Releases page and install it on your phone
# Development
Minibits is a bare React Native app written in Typescript. The project structure and code itself are intentionally verbose to support readability. Critical wallet code is reasonably documented. However, there is vast space for existing code improvements, refactoring, and bug fixing. This is an alpha software and the author does not code for a living.
The code is derived from Ignite template, however with many libraries, notably Expo, stripped down to achieve fast startup times. Performance bottleneck on some Android devices is react-native-keychain. To overcome this, it has been patched not to warm-up on startup and its use to encrypt storage is opt-in.
Wallet state is managed by mobx-state-tree and persisted in fast MMKV storage. Only the basic mobx concepts are in place, whole model could be improved. All critical wallet code is in services/walletService.ts and all coins state changes are in models/ProofsStore.ts. Wallet communication with the mints is in services/cashuMintClient.ts and uses [cashu-ts](https://github.com/cashubtc/cashu-ts) library.
Crypto operations are handled by react-native-quick-crypto, that is fast and does not require awful javascript shims. Transaction history and coins backup is stored in sqlite, with fast react-native-quick-sqlite driver that enables to run lighter queries synchronously.
In case of breaking state and data model changes, versioning and code is ready to run necessary migrations on wallet startup.
# Running in development mode
To run Minibits wallet in dev mode, set up the React Native development environment and the Yarn package manager. Then clone this repository, navigate to the minibits_wallet directory, and run the following:
```bash
yarn install
```
There are post-install patches to some of the libraries that should run automatically and are necessary for a successful run. See the patches directory for more info.
After the dependecies are installed, continue to create the following .env file in the root folder:
```bash
APP_ENV = 'DEV'
LOG_LEVEL = 'TRACE'
SENTRY_ACTIVE = 'FALSE'
```
Then make sure you have the Android device connected by running:
```bash
yarn adb
```
Finally run this and pray:
```bash
yarn start
```
In case of issues, repo includes commits history from the out of the box react native app up until the complete wallet. You can see build.gradle and other changes one by one and hopefully figure out what's wrong.
# Building
Create debug .apk:
```bash
yarn android:dev
```
# Automated testing
The app has the scaffolding for automated tests; they are yet to be implemented. For functional bugs or suggestions please raise an issue.
# Contributing
Contributions are welcome, just start and we will figure out what's next.
|
Alex-Dobrynin/Controls.UserDialogs.Maui
|
https://github.com/Alex-Dobrynin/Controls.UserDialogs.Maui
|
This is the updated version of Acr.Userdialogs. It supports latest version of .Net and you have an ability to style your diloags as you want
|
# <img src="userdialogs_maui_icon.png" width="70" height="70"/> Controls.Userdialogs.Maui
#### A cross platform library that allows you to call for native user dialogs, which can by styled from your maui application anywhere anytime.
Inspired by [Allan Ritchie](https://github.com/aritchie)'s Acr.UserDialogs
##### Since the original (Acr.UserDialogs) repo is out of support, this will give new breath to UserDialogs. It is more flexible to style your dialogs as you want.
[](https://www.nuget.org/packages/Controls.UserDialogs.Maui) 
## Supported Platforms
* .NET7 for Android (min 7.0)(major target 13.0)
* .NET7 for iOS (min 14.2)
* .NET7 for MAcCatalyst (min 13.1)
### Features
* Alert
* Confirm
* Action Sheets
* Loading/Progress
* Toast
* Snackbar
* [Sample](https://github.com/Alex-Dobrynin/Controls.UserDialogs.Maui/tree/master/Sample)
### As for now it supports only Android, iOS and macOS. I don't have in plans to add new platforms. You are welcome to submit PR's for issues you may be having or for features you need and they will be reviewed.
## Setup
To use, make sure you are using the latest version of .NET MAUI
Add ```UseUserDialogs(() => { })``` to your MauiProgram.cs file
```csharp
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.UseUserDialogs(() =>
{
//setup your default styles for dialogs
AlertConfig.DefaultBackgroundColor = Colors.Purple;
#if ANDROID
AlertConfig.DefaultFontFamily = "OpenSans-Regular.ttf";
#else
AlertConfig.DefaultFontFamily = "OpenSans-Regular";
#endif
ToastConfig.DefaultCornerRadius = 15;
})
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Semibold.ttf", "OpenSansSemibold");
});
```
##### Note: there are some properties available only for Android or only for iOS/macOS
## Powered By:
* Android - Progress/Loading uses Redth's [AndHUD](https://github.com/Redth/AndHUD)
* iOS/macOS - Progress/Loading uses Nic Wise's [BTProgressHUD](https://github.com/nicwise/BTProgressHUD)
# Frequently Asked Questions
1. I'm getting a nullreferenceexception when using loading.
* This happens when you run loading (or almost any dialog) from the constructor of your page or viewmodel. The view hasn't been rendered yet, therefore there is nothing to render to.
2. Navigating while inside of a loading/progress dialog causes exceptions or the progress no longer appears properly
* Hide the progress dialog before navigating
3. I don't like the way X method works on platform Y
* No problems. Override the implementation like below. Note: this is a partial class which has shared and platform specific realizations
```csharp
public class MyCustomUserDialogs : Controls.UserDialogs.Maui.UserDialogImplementation
{
public override ..
}
```
then in you MauiProgram.cs add this
```csharp
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.UseUserDialogs(() =>
{
#if ANDROID
Controls.UserDialogs.Maui.UserDialogs.Instance = new MyCustomUserDialogs(); //Android realization
#elif IOS
Controls.UserDialogs.Maui.UserDialogs.Instance = new MyCustomUserDialogs(); //iOS realization
#else
Controls.UserDialogs.Maui.UserDialogs.Instance = new MyCustomUserDialogs(); //mac realization
#endif
//setup your default styles for dialogs
})
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Semibold.ttf", "OpenSansSemibold");
});
```
4. Why don't you cancel a dialog when the app goes to the background (AND) why do I get an exception when I call for a dialog?
* USER DIALOGS DOES NOT SOLVE WORLD PEACE! Guess what - most android API version and iOS don't call this. This library is not a window state manager, if you call for a dialog,
it will try to present one. If your app goes to the background and you call for a dialog, iOS & Android are tossing you the exception. The library isn't here to save you from bad design choices.
Call us an anti-pattern if you want, we present dialogs!
5. Why does the library allow me to open multiple windows?
* Similar to #4 - the library does not manage windows. It opens dialogs - SURPRISE
6. I'd like to customize the dialogs in native way (e.g. in Android in styles or themes)
* The library wasn't really designed or meant for this. It was meant for using native dialogs with programmatically styling. That's it. If you need something more you are free to contribute here or to use Acr.UserDialogs which is out of support.
|
infstellar/python-git-program-launcher
|
https://github.com/infstellar/python-git-program-launcher
|
A python program, designed to automatically install and launch git-based managed python programs in a simple way.
|
# python-git-program-launcher
自动安装并启动基于git管理的python程序。

# 特点
- 一键启动python程序,~~终极傻瓜包~~
- 使用git自动更新仓库
- 基于pywebio, webview和pyqt的GUI界面
- 允许使用不同的配置,管理不同python版本的不同仓库。
- 允许启动多个程序。
- 自动下载并安装python和pip包。
- 从Github仓库自动下载预配置文件
- 丰富的的自定义配置
# 使用
## 直接运行
下载最新的Release。
运行Launcher.bat或Launcher.exe。
你可能需要使用管理员权限运行。
***不要打开除了Watt Toolkit之外的所有可能干扰网络连接的软件,包括Clash/部分游戏加速器/网络连接管理/下载加速器等,它们会干扰SSL验证。***
## 源代码运行
克隆仓库。
运行`git submodule init; git submodule update`
运行Launcher.bat或Launcher.exe。
# 添加配置
## 从Github自动下载
如果你要添加的仓库有pgpl.yaml文件,你可以在添加配置时输入Github仓库地址,从而自动下载并识别远程仓库的配置文件。
如果你在大陆,推荐使用Watt Toolkit加速Github。***极其强烈不推荐使用Clash***,因为它会干扰ssl验证。
## 手动添加
按照软件内说明操作。同时按照`设置配置`中的说明填写。
## 使用自带配置
PGPL自带GIA和SRC的启动配置,无需添加即可使用。
# 故障排查
频繁出现的故障:
1. 使用了网络代理软件导致ssl验证错误。**必须关闭Clash/游戏加速器/网络连接管理/下载加速器**
2. 没有启用长路径支持导致路径超过上限。你可以运行EnableLongPath.reg解决此问题。如果你不信任该文件,你可以在如下链接中找到相同解决方案。
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/fileio/maximum-file-path-limitation?tabs=registry#enable-long-paths-in-windows-10-version-1607-and-later
请注意,该方法仅支持Windows10-1607之后的版本。
# 设置配置
|配置项|内容|默认值|
|----|----|----|
|RequirementsFile|requirement文件位置|requirements.txt|
|InstallDependencies|是否安装pip依赖|true|
|PypiMirror|pypi镜像地址|AUTO|
|PythonMirror|python镜像地址|AUTO|
|Repository|仓库地址|https://github.com/infstellar/python-git-program-launcher|
|Main|python执行文件|main.py|
|Branch|分支|main|
|GitProxy|是否开启Git验证|false|
|KeepLocalChanges|是否保持本地更改|false|
|AutoUpdate|是否自动更新|true|
|Tag|tag,有tag时优先使用tag,否则使用branch。||
|PythonVersion|python版本,必须为有效版本(3.x.y)|3.10.10|
# TODO:
- GUI
# 文件位置
## 日志位置
./Logs/yyyy-mm-dd/yyyy-mm-dd.log
## 仓库保存位置
./repositories
## python保存位置
./toolkit/python
## 缓存位置
./cache
# 范例配置
[SRC](configs/SRC-dev.json)
[GIA](configs/giachina.json)
# 鸣谢
ALAS-EasyInstaller
GIA
pywebio
pywebview
pyqt
loguru
|
sophgo/ChatGLM2-TPU
|
https://github.com/sophgo/ChatGLM2-TPU
|
run ChatGLM2-6B in BM1684X
|

# ChatGLM2-TPU
本项目实现BM1684X部署语言大模型[ChatGLM2-6B](https://huggingface.co/THUDM/chatglm2-6b)。通过[TPU-MLIR](https://github.com/sophgo/tpu-mlir)编译器将模型转换成bmodel,并采用c++代码将其部署到BM1684X的PCIE环境,或者SoC环境。
下文中默认是PCIE环境;如果是SoC环境,按提示操作即可。
在知乎上写了关于`ChatGLM2-6B`的解读,方便大家理解源码:
[ChatGLM2-6B流程解析与TPU-MLIR部署](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/641975976)
## 开发环境
1. 下载docker,启动容器,如下:
``` shell
docker pull sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
# myname1234 is just an example, you can set your own name
docker run --privileged --name myname1234 -v $PWD:/workspace -it sophgo/tpuc_dev:latest
```
后文假定环境都在docker的`/workspace`目录。
如果是要在SoC环境运行,则需要安装如下库:
``` shell
apt-get install gcc-aarch64-linux-gnu g++-aarch64-linux-gnu
```
2. 下载`ChatGLM2-6B`,比较大,会花较长时间
``` shell
git lfs install
git clone [email protected]:THUDM/chatglm2-6b
```
并对该工程做两点修改,
一是将`config.json`文件中`seq_length`配置为512;
二是将`modeling_chatglm.py`文件中的如下代码:
```python
if attention_mask is not None:
attention_scores = attention_scores.masked_fill(attention_mask, float("-inf"))
```
修改为:
```python
if attention_mask is not None:
attention_scores = attention_scores + (attention_mask * -10000.0)
```
这样修改可以提升效率,使用`masked_fill`效率低下;另一方面`masked_fill`转ONNX存在些bug。
3. 下载`TPU-MLIR`代码并编译,(也可以直接下载编译好的release包解压)
``` shell
git clone [email protected]:sophgo/tpu-mlir.git
cd tpu-mlir
source ./envsetup.sh
./build.sh
```
4. 下载[sentencepiece](https://github.com/google/sentencepiece),并编译得到`sentencepiece.a`
```shell
git clone [email protected]:google/sentencepiece.git
cd sentencepiece
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make -j
```
如果要编译SoC环境,则需要在`CMakeLists.txt`加入如下代码:
```cmake
set(CMAKE_C_COMPILER aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc)
set(CMAKE_ASM_COMPILER aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc)
set(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER aarch64-linux-gnu-g++)
```
5. 下载libsophon库并安装
在算能官网<https://developer.sophgo.com/site/index/material/all/all.html>可以找到SDK最新版本,如下:
```shell
wget https://sophon-file.sophon.cn/sophon-prod-s3/drive/23/06/15/16/Release_230501-public.zip
```
解压sdk后安装libsophon,如下:
```shell
apt install sophon-libsophon-dev_0.4.8_amd64.deb
```
注意如果是SoC环境则安装arm64版本`sophon-libsophon-dev_0.4.8_arm64.deb`
6. 下载本项目`ChatGLM2-TPU`,如下:
``` shell
git clone [email protected]:sophgo/ChatGLM2-TPU.git
```
## 编译模型
1. 指定`ChatGLM2-6B`的python路径
``` shell
export PYTHONPATH=/workspace/chatglm2-6b:$PYTHONPATH
```
2. 导出所有onnx模型,如果过程中提示缺少某些组件,直接`pip install 组件`即可
``` shell
cd chatglm2-tpu/compile
python3 export_onnx.py
```
此时有大量onnx模型被导出到tmp目录
3. 对onnx模型进行编译,生成bmodel,这个过程会花一些时间,最终生成`chatglm2-6b.bmodel`文件
```shell
./compile.sh
```
## 编译程序(C++版本)
```shell
cd chatglm2-tpu/demo
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make -j
```
如果是SoC环境,则将CMakeLists.txt中加入,并将SoC版本的`libsentencepiece.a`替换过来:
```cmake
set(CMAKE_C_COMPILER aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc)
set(CMAKE_ASM_COMPILER aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc)
set(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER aarch64-linux-gnu-g++)
```
编译生成chatglm2可执行程序,将`chatglm2`、`chatglm2-6b.bmodel`和`tokenizer.model`拷贝到运行环境就可以执行了。
(`tokenizer.model`来自`ChatGLM2-6B`)
## 编译程序(Python版本)
```shell
cd chatglm2-tpu/python_demo
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make -j
```
编译成功会生成`ChatGLM2.cpython-37m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so`,之后将chatglm2-6b.bmodel放到python\_demo目录下。
另外这里也直接给出了so文件,可以直接省略上面的编译这一步。但是必须为python3.7版本
```python
python run.py
```
即可成功运行python的demo
## 运行效果

|
Balackburn/Apollo
|
https://github.com/Balackburn/Apollo
| null |
# Altstore Source for Apollo
I've called this repo only "Apollo", for a better presentation on my Github Page site.
[Add to Altstore/Sidestore](https://tinyurl.com/ApolloAltstore)
[View source online](https://therealfoxster.github.io/altsource-viewer/app.html?source=https://balackburn.github.io/Apollo/apps.json&id=com.christianselig.Apollo)
This is an auto-updating Altstore [source](https://balackburn.github.io/Apollo/apps.json) for **ApolloPatcher**. It checks daily for new releases and updates the source with the latest version, ensuring you always have access to the most recent updates.
# Website
Additionally, their is a [website](https://balackburn.github.io/Apollo/) for it (just edited the one I made for YTLitePlus).
I hope you'll find it both useful and visually appealing.
# Why?
I really love Apollo and hope it will help some people to keep using it instead of the official app.
# From :
https://github.com/ichitaso/ApolloPatcher
|
mxtsdev/d4-item-tooltip-ocr
|
https://github.com/mxtsdev/d4-item-tooltip-ocr
|
Diablo IV: Item Tooltip OCR
|
# Diablo IV: Item Tooltip OCR
Utilizing PaddleOCR and a custom Diablo 4 trained recognition model. Outputs item tooltip data in JSON-format.
## Example

```json
{
"affixes": [
"+22.5% Overpower Damage [22.5]%",
"+12.5% Damage to Slowed Enemies [11.5 - 16.5]%",
"+14.0% Critical Strike Damage [10.0 - 15.0]%",
"+44 Willpower +[41 - 51]",
"+7.0% Damage Over Time [5.0 - 10.0]%"
],
"aspect": "Core Skills deal an additional 7.0%[x] [6.0 - 8.0]% damage for each active Companion. (Druid Only)",
"item_power": "710",
"item_power_upgraded": null,
"item_upgrades_current": null,
"item_upgrades_max": null,
"name": "SHEPHERD'S WOLF'S BITE",
"sockets": [],
"stats": [
"806 Damage Per Second (-1555)",
"[586 - 880] Damage per Hit",
"1.10 Attacks per Second (Fast Weapon)"
],
"type": "Sacred Legendary Mace"
}
```
## Installation
- Clone repository
- Create a Python3 enviroment (I recommend using https://www.anaconda.com/download on Windows)
- pip install -r requirements.txt
You will need to install the correct version of PaddlePaddle depending on your environment (CPU/GPU/CUDA version). Please refer to this link:
https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/en/install/pip/windows-pip_en.html#old-version-anchor-3-INSTALLATION
## Using
### Output json to console
```
python d4-item-tooltip-ocr.py --source-img=examples\screenshot_001.png
python d4-item-tooltip-ocr.py --source-img=examples\tooltip_001.jpg --find-tooltip=False
```
### Output json to file
```
python d4-item-tooltip-ocr.py --source-img=examples\screenshot_001.png --json-output=item-tooltip-data.json
python d4-item-tooltip-ocr.py --source-img=examples\tooltip_001.jpg --json-output=item-tooltip-data.json --find-tooltip=False
```
### Debug mode
```
python d4-item-tooltip-ocr.py --debug=True --source-img=examples\screenshot_001.png
python d4-item-tooltip-ocr.py --debug=True --source-img=examples\tooltip_001.jpg --find-tooltip=False
```
|
serp-ai/the-hitchhikers-guide-to-machine-learning-algorithms
|
https://github.com/serp-ai/the-hitchhikers-guide-to-machine-learning-algorithms
|
The Hitchhiker's Guide to Machine Learning Algorithms: A book of machine learning algorithms & concepts explained to simply, even a human can understand.
|
# README
## The Hitchhiker's Guide to Machine Learning Algorithms
_100+ Machine Learning Algorithms Explained So Simply Even a Human Can Understand_
***
Hello humans & welcome to the world of machines.
Specifically, machine learning & algorithms.
We are about to embark on an exciting adventure through the vast and varied landscape of algorithms that power the cutting-edge field of artificial intelligence.
Machine learning is changing the world as we know it.
From predicting stock market trends and diagnosing diseases to powering the virtual assistants in our smartphones and enabling self-driving cars, and picking up the slack on your online dating conversations.
What makes this book unique is its structure and depth. With 100 chapters, each dedicated to a different machine learning concept, this book is designed to be your ultimate guide to the world of machine learning algorithms.
The print version is ... well, printed and so we will not be mailing you new pages to tape into the binding as we write them. But the online digital version will be continually updated, forever. Maybe by humans, and maybe by machines when humans are gone.
You can find it at online. Probably at [SERP AI](https://serp.ai/).
Whether you are a student, a data science professional, or someone curious about machine learning, this book aims to provide a comprehensive overview that is both accessible and in-depth.
The algorithms covered in this book span various categories including:
* Classification & Regression: Learn about algorithms like Decision Trees, Random Forests, Support Vector Machines, and Logistic Regression which are used to classify data or predict numerical values.
* Clustering: Discover algorithms like k-Means, Hierarchical Clustering, and DBSCAN that group data points together based on similarities.
* Neural Networks & Deep Learning: Dive into algorithms and architectures like Perceptrons, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), and Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTM).
* Optimization: Understand algorithms like Gradient Descent, Genetic Algorithms, and Particle Swarm Optimization which find the best possible solutions in different scenarios.
* Ensemble Methods: Explore algorithms like AdaBoost, Gradient Boosting, and Random Forests which combine the predictions of multiple models for improved accuracy.
* Dimensionality Reduction: Learn about algorithms like Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) which reduce the number of features in a dataset while retaining important information.
* Reinforcement Learning: Get to know algorithms like Q-learning, Deep Q-Network (DQN), and Monte Carlo Tree Search which are used in systems that learn from their environment.
Each chapter is designed as a standalone introduction to its respective algorithm. This means you can start from any chapter that catches your interest or proceed sequentially. Along with the theory, practical examples, applications, and insights into how these algorithms work under the hood are provided.
This book is not just an academic endeavor but a bridge that connects theory with practical real-world applications.
It's an invitation to explore, learn, and harness the power of algorithms to solve complex problems and make informed decisions.
Fasten your seat belts as we dive into the mesmerizing world of machine learning algorithms.
Whether you are looking to expand your knowledge, seeking inspiration, or in pursuit of technical mastery, this book should sit on your coffee table and make you look intelligent in front of all invited (and uninvited) guests.
Don't forget to join our online community to stay up to date with with artificial intelligence, machine learning & data science:
* Discord @ [serp.ly/@serpai/discord](https://serp.ly/@serpai/discord)
Cheers & stay funky my friends.
[Devin Schumacher](https://devinschumacher.com/) Founder [SERP](https://serp.co/), [SERP AI](https://serp.ai/)\
\
_Devin Schumacher is an American entrepreneur, internet personality, author, actor, music producer, podcaster, teacher, hacker, philanthropist. He is the founder of SERP, the parent company for a variety of brands that operate in the technology sector, specifically within digital marketing, media, software development, artificial intelligence and education; and is widely considered to be the world's best SEO & grumpy cat impersonator._
|
FuelLabs/fuel-bridge
|
https://github.com/FuelLabs/fuel-bridge
|
The canonical Fuel bridge mono repo.
|
## 📗 Table of contents
- [Getting Started](./docs/GETTING_STARTED.md)
- [Requirements](./docs/GETTING_STARTED.md#requirements)
- [Running Project Locally](./docs/GETTING_STARTED.md#running-project-locally)
- [📚 - Getting the Repository](./docs/GETTING_STARTED.md#---getting-the-repository)
- [📦 - Install Dependencies](./docs/GETTING_STARTED.md#---install-dependencies)
- [📒 - Run Local Node](./docs/GETTING_STARTED.md#---run-local-node)
- [📗 Project Overview](./docs/GETTING_STARTED.md#-project-overview)
- [🧰 Useful Scripts](./docs/GETTING_STARTED.md#-useful-scripts)
- [✅ Running Tests](./docs/GETTING_STARTED.md#run-tests)
- [Contribution Guide](./docs/CONTRIBUTING.md)
- [Finding Something to Work On](./docs/CONTRIBUTING.md#finding-something-to-work-on)
- [Contribution Flow](./docs/CONTRIBUTING.md#contribution-flow)
- [License](#license)
## License
The primary license for this repo is `Apache-2.0`, see [`LICENSE`](./LICENSE).
|
eidam/chatgpt-plugin-clerk-auth
|
https://github.com/eidam/chatgpt-plugin-clerk-auth
|
ChatGPT plugin example using Cloudflare Workers and Clerk OAuth2 backend.
|
# ChatGPT plugin with Clerk OAuth2 backend
This is an example implementation of ChatGPT plugin running on Cloudflare Workers with Clerk OAuth2 backend.

## Features
- [x] Authenticate users with Clerk during plugin installation
- [x] Authenticated plugin API calls
- [x] OpenAPI schema generation _(using [cloudflare/itty-router-openapi](cloudflare/itty-router-openapi))_
### Plugin routes
- [x] `/user` Get user's details
- [x] `/user/send-email` Send email to signed in user _(using Sendgrid, additional config needed)_
## Setup
### Sign up for Clerk
1. Sign up for [Clerk account](https://dashboard.clerk.com/sign-up)
1. Create [Clerk application](https://dashboard.clerk.com/apps/new)
### Create OAuth application
1. Get **API Key** (Developers -> API Keys -> Secret keys), you will need it later
1. Create [OAuth application](https://clerk.com/docs/reference/backend-api/tag/OAuth-Applications#operation/CreateOAuthApplication), use API key you got from previous steps
- Use any URL (e.g. `https://example.com`) as callback URL for now, you will change it later.
- Set `public` to `false`
1. Note the response, you will need following later
- `client_id`
- `client_secret`
- base URL of your OAuth2 Clerk instance (e.g. `https://fond-tuna-4.clerk.accounts.dev`)
### Deploy Workers application
1. Edit [src/index.ts](./src/index.ts) and set following
- `clerkBaseUrl` to the base URL you got from previous steps
1. `npm install`
1. `npm run deploy`
1. Note the URL of your Workers application, you will need it later
### Configure ChatGPT plugin
1. Install [new ChatGPT plugin](https://chat.openai.com/?model=gpt-4-plugins)
1. Fill in Client ID and Client Secret you got from previous steps
1. Get the verification token and set it as `pluginVerificationToken` in [src/index.ts](./src/index.ts)
1. Redeploy Workers application (`npm run deploy`)
1. Click `Verify tokens`
1. Install the plugin
1. Click `Log in with Plugin with Clerk`
1. You will get 400 error, it's OK - you need to change callback URL in OAuth application
- Grab the URL from the request URL, you can get decoded one from the network tab

- Edit (PATCH) [OAuth application](https://clerk.com/docs/reference/backend-api/tag/OAuth-Applications#operation/UpdateOAuthApplication) and set the URL as callback URL
- Close the tab and try to log in again
### Write your own plugin routes
1. Edit [src/index.ts](./src/index.ts) and add your own route handlers
1. Redeploy Workers application (`npm run deploy`)
|
allozavrr/LearningDevOpsUkraine
|
https://github.com/allozavrr/LearningDevOpsUkraine
|
LearningDevOpsUkraine
|
# LearningDevOpsUkraine
**Доброго всім дня.**
**Це невеличкий конспект з допомоги тим, хто хоче вивчати DevOps у 2023 році.**
**Матеріали тут зустрічаються трьома мовами - українською, англійською та мовою країни-загарбника. На жаль, зовсім без останніх обійтися було неможливо, бо для новачків такі пояснення нерідко є зрозумілішими, особливо коли рівень англійської вдосконалюється по ходу справи. Але, як сказав класик, і чужому навчайтесь, і свого не цурайтесь.**
*Перелік не є закінченим. Доповнення і зауваження дуже вітаються.*
*Також дякую телеграм-спільноті https://t.me/DevOpsMarathon та її очільнику - @edemus.*
**[Never give up!](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GC5E8ie2pdM&ab_channel=TinaTurner)**
<details>
<summary><b>Taste IT!</b> </summary>

</details>
# Table of Contents
- **[Roadmaps](#roadmaps)**
- **[Resouses](#resourses)**
- **[Computer Science Guide](#computer-science-guide)**
- **[Courses](#courses)**
- **[Youtube](#youtube)**
- **[Github](#github)**
- **[Git](#git)**
- **[Linux](#linux)**
- **[Networking](#networking)**
- **[CI/CD](#cicd)**
- **[Ansible](#ansible)**
- **[Jenkins](#jenkins)**
- **[Gitlab](#gitlab)**
- **[Infrastructure as code](#infrastructure-as-code)**
- **[Containerization](#containerization)**
- **[Docker](#docker)**
- **[Kubernetes](#kubernetes)**
- **[Clouds](#clouds)**
- **[AWS](#aws)**
- **[Microsoft Azure](#microsoft-azure)**
- **[Google Cloud Platform](#google-cloud-plarform)**
- **[Programming and Scripting](#programming-and-scripting)**
- **[Bash](#bash)**
- **[Powershell](#powershell)**
- **[Python](#python)**
- **[Go](#go)**
- **[Rust](#rust)**
- **[Monitoring](#monitoring)**
- **[DevSecOps](#devsecops)**
- **[Interview](#interview)**
- **[English](#english)**
## Roadmaps
**Цей розділ присвячено роадмапам для зручності навчання та самопідготовки.**
| Name | URL | Description | Meta |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **90DaysOfDevOps** | [github.com/MichaelCade/90DaysOfDevOps](https://github.com/MichaelCade/90DaysOfDevOps) | The most famous roadmap for newbies DevOps-engineers | |
| **Another DevOps Roadmap** | [github.com/milanm/DevOps-Roadmap](https://github.com/milanm/DevOps-Roadmap) | Another detailed DevOps roadmap | |
| **DevOps-Roadmap** | [github.com/devopshobbies/devops-roadmap](https://github.com/devopshobbies/devops-roadmap) | DevOps Roadmap by Ahmadali Bagheri (free resourses included) | |
| **Become A DevOps Engineer in 2023** | [devopscube.com](https://devopscube.com/become-devops-engineerhttps://devopscube.com/become-devops-engineer) | Simple and nice roadmap | |
| **DevOps Roadmap** | [roadmap.sh](https://roadmap.sh/devops) | Step by step guide for DevOps, SRE or any other Operations Role in 2023 | |
| **DevOps Roadmap** | [techworld-with-nana.com](https://www.techworld-with-nana.com/devops-roadmap) | Step by step guide outlining the most efficient path to become a DevOps engineer by TechWorld with Nana | |
| **Learn to Cloud** | [learntocloud.guide](https://learntocloud.guide/docs/Welcome) | Skills you need to learn to get into Cloud Computing | |
| **From Zero to DevOps Engineer - DevOps Roadmap for YOUR specific background** | [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G_nVMUtaqCk&ab_channel=TechWorldwithNana) | Roadmap in a video | |
| **Как стать DevOps Инженером с Нуля, что учить и в каком порядке** | [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AxCgZ7yUKrU&list=PLg5SS_4L6LYuu1RAT4l1tCkZrJzkIaNgL&index=8&t=14s&ab_channel=ADV-IT) | Roadmap in a video | |
## Resourses
**Цей розділ містить посилання на корисні ресурси для DevOps-інженерів.**
| Name | URL | Description | Meta |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Ukrainian IT Communities** | [github.com/nikit0ns/Ukrainian_IT_Communities#-devops](https://github.com/nikit0ns/Ukrainian_IT_Communities#-devops) | Українські DevOps коммʼюніті і не тільки | | |
### Computer Science Guide
| Name | URL | Description | Meta |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **TeachYourselfCS-UK** | [github.com/oleksbabieiev/TeachYourselfCS-UK/](https://github.com/oleksbabieiev/TeachYourselfCS-UK/) | Збірник-посібник для самостійного фундаментального вивчення компʼютерних наук | | |
| **TeachYourselfCS-EN** | [github.com/ossu/computer-science](https://github.com/ossu/computer-science) | The same in English | | |
| **CS50** | [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLawfWYMUziZqyUL5QDLVbe3j5BKWj42E5) | Основы программирования: Легендарный Гарвардский курс CS50 (2015 - old but gold) |ru | |
### Courses
*Вказані добірки курсів та платформ зазвичай платні, якщо не зазначено інше (безкоштовні навчальні матеріали розміщені у відповідних розділах).*
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Ресурси для вивчення DevOps-теми** | [dou.ua](https://dou.ua/forums/topic/42056/?from=similar_topics) | Підбірка ресурсів для вивчення DevOps від DOU |UA | |
| **ITSkills4U** | [itskills4u.com.ua](https://itskills4u.com.ua/) | FREE! Developed by AWS, the program includes AWS Cloud training programs and certification, English and Polish language classes, mentorship, and access to job opportunities |EN | |
| **StanfordOnline** | [edx.org](https://www.edx.org/school/stanfordonline?irclickid=WNB0XoxkWxyPRWhxQeRIaxGNUkF2qCQE-0kN1U0) | FREE! online courses from Stanford University |EN | |
| **A Cloud Guru** | [acloud.guru](https://acloud.guru/) | Paid online courses from A Cloud Guru |EN | |
| **KodeKloud** | [kodekloud.com](https://kodekloud.com/) | Paid online courses from KodeKloud |EN | |
| **O’Reilly** | [oreilly.com](https://www.oreilly.com/) | Paid online courses from O’Reilly |EN | |
| **CBT Nuggets** | [cbtnuggets.com](https://www.cbtnuggets.com/) | Paid online courses from CBT Nuggets - a lot of trainings |EN | |
| **Educative Accelerates Developer Productivity** | [educative.io](https://www.educative.io/) | Paid online courses on programming, cloud computing, data Science, machine Learning (no video, only practice) |EN | |
### Youtube
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **DOU DevOps** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLwj_3ikgO3CLZM1Jm_n5gw2CcoKMaKgD5) | Корисні підкасти DOU DevOps спільноти |UA | |
| **CatOps** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/@catops/playlists) | Корисні підкасти CatOps спільноти |UA | |
| **Денис Васильєв** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/@DenysVasyliev) | Senior про DevOps |UA | |
| **DataArt Online** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLU6_HdJGVDx93bE8cb3gpwRzJX57C1wvt) | Плейлист про DevOps від DataArt Online |UA | |
| **Tech World with Nana** | [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/@TechWorldwithNana) | Really needed materials about all DevOps hard-skills |EN | |
| **NetworkChuck** | [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/@NetworkChuck/playlists) | CCNA, CompTIA A+, CompTIA Network+ |EN | |
| **Just me and Opensource** | [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/@justmeandopensource/playlists) | A lot of trainings of DevOps tools, nice and full Kubernetes guide |EN | |
| **DevOpsLearnEasy** | [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/@DevOpsLearnEasy/videos) | Not just any course but a training that explains concepts from the absolute basics to the complex ones |EN | |
### Github
| Name | URL | Description | Meta |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **DevOps Bash Tools** | [github.com/HariSekhon/DevOps-Bash-tools](https://github.com/HariSekhon/DevOps-Bash-tools) | Scripts for many popular DevOps technologies | |
| **DevOps resources** | [github.com/bregman-arie/devops-resources](https://github.com/bregman-arie/devops-resources) | This repository is about gathering any useful resources and information regarding DevOps | |
| **How They DevOps** | [github.com/bregman-arie/howtheydevops](https://github.com/bregman-arie/howtheydevops) | A curated collection of publicly available resources on how companies around the world practice DevOps | |
| **DevOps exercises** | [github.com/bregman-arie/devops-exercises](https://github.com/bregman-arie/devops-exercises) | This repo contains questions and exercises on various technical topics, sometimes related to DevOps and SRE | |
| **Awesome Site Reliability Engineering** | [github.com/dastergon/awesome-sre](https://github.com/dastergon/awesome-sre) | A curated list of awesome Site Reliability and Production Engineering resources | |
| **Test your Sysadmin skills** | [github.com/trimstray/test-your-sysadmin-skills](https://github.com/trimstray/test-your-sysadmin-skills) | This project contains 284 test questions and answers that can be used as a test your knowledge or during an interview such as Linux/Networks | |
## Git
**Матеріали для ознайомлення з системою контролю версій Git (VCS).**
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Git, GitHub, & GitHub Desktop for beginners** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8Dd7KRpKeaE&ab_channel=CoderCoder) | Step by step guide for DevOps, SRE or any other Operations Role in 2023 |EN | |
| **Course: Git for Beginners** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLYQSCk-qyTW3lX_dyw0R2eVzNGB3Tlv9S) |Git for Beginners short guide |EN | |
| **Скринкаст по Git** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W4hoc24K93E&list=PLDyvV36pndZFHXjXuwA_NywNrVQO0aQqb) | Основні функції Git |ru | |
| **Основы Git, GitHub и GitHub Actions** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLg5SS_4L6LYstwxTEOU05E0URTHnbtA0l) | Курс по Git, GitHub та GitHub Actions |ru | |
| **GitHub Actions Tutorial** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R8_veQiYBjI&ab_channel=TechWorldwithNana) | GitHub Actions Tutorial from TechWorld with Nana |EN | |
| **Git Tutorial for Beginners** | [w3schools.com](https://www.w3schools.com/git/default.asp?remote=github) | Git простими словами для початківців |EN | |
| **Pro Git book. Підручник** | [git-scm.com](https://git-scm.com/book/uk/v2) | Основи Git. Підручник |UA | |
| **The Git Community Book** | [uleming.github.io](https://uleming.github.io/gitbook/index.html) | Добрі матеріали по Git у вигляді документації |ru | |
| **Конспект з Git** | [githowto](https://githowto.com/uk) | Гарно структурований конспект-задачник |UA | |
| **Інтерактивний тренажер з Git** | [learngitbranching.js.org](https://learngitbranching.js.org/?locale=uk) | Гарний тренажер-задачник з Git |EN/UA | |
## Linux
**Розділ для вдосконалення знань з Linux - для новачків та не тільки.**
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Уроки Linux для начинающих** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL0lO_mIqDDFUwVWvVitxG2oXA6a-Nq-Qq) | Гайд для початківців від Гоші Дударя |ru | |
| **Linux Essentials** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmxB7JSpraiep6kr802UDqiAIU-76nGfc) | Підготовка віртуальної машини для роботи з Linux від Кирила Сємаєва |ru | |
| **Hacker School Linux** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL86fNax1UdKvgWOkgtm_opAYbo5kGtQ88) | Курс для початківців Linux від Hacker School |ru | |
| **ADV-IT Linux для Начинающих** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLg5SS_4L6LYuE4z-3BgLYGkZrs-cF4Tep) | Курс для початківців з Linux від ADV-IT |ru | |
| **ADV-IT Linux НЕ для Начинающих** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hb1jtBm71MY&list=PLg5SS_4L6LYsgy5qLYZtvoaV34zn5iKPe&ab_channel=ADV-IT) | Курс для поглиблення знань з Linux від ADV-IT |ru | |
| **LPIC-1 (exam 101)** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmxB7JSpraiep6kr802UDqiAIU-76nGfc) | Підготовка до екзамену LPIC-1 (exam 101) від Кирила Сємаєва |ru | |
| **LPIC-2 (exam 201)** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmxB7JSpraidTqByo0ihkyExIbKfAB-B9) | Підготовка до екзамену LPIC-2 (exam 201) від Кирила Сємаєва |ru | |
| **Into the Terminal (Red Hat Enterprise Linux)** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLXJyD2dL4oqeX-C3MvsMUJuEzWM4vLK2C) | Critical Administration Skills for Red Hat Enterprise Linux |EN | |
## Networking
**Розділ для вивчення та повторення компʼютерних мереж.**
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Компьютерные сети, учебный курс** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLtPJ9lKvJ4oiNMvYbOzCmWy6cRzYAh9B1) | Курс для початківців по мережам від Андрія Созикіна |ru | |
| **Компьютерные сети. Продвинутые темы** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLtPJ9lKvJ4oh_w4_jtRnKE11aqeRldCFI) | Курс для поглиблення знань по мережам від Андрія Созикіна |ru | |
| **Практики по компьютерным сетям** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLtPJ9lKvJ4oiKPQ9GXOvntj44Eu8IGAJK) | Детальне вивчення протоколів від Андрія Созикіна |ru | |
| **Защищенные сетевые протоколы** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLtPJ9lKvJ4oiFnWCsVRElorOLt69YDEnv) | TLS, SSl, HTTPS від Андрія Созикіна |ru | |
| **Курсы Cisco CCNA 200-301** | [Youtube ч.1](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL0MV6px_XdxDJLaePIpq7PPllVLdL_kw_) | Cisco CCNA p.1 |ru | |
| **Курсы Cisco CCNA 200-301** | [Youtube ч.2](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL0MV6px_XdxCkDz7yNCulKlK2I7144Yae) | Cisco CCNA p.2 |ru | |
| **CompTIA Network+ N10-007 Training Course** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLG49S3nxzAnmpdmX7RoTOyuNJQAb-r-gd) | CompTIA Network+ N10-007 Exam Prep |EN | |
| **Computer Networks Neso Academy** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLBlnK6fEyqRgMCUAG0XRw78UA8qnv6jEx) | Fundamental Network course |EN | |
| **Cisco Networking Academy - Networking Basics** | [skillsforall.com](https://skillsforall.com/course/networking-basics?courseLang=en-US) | Basic Network course |EN | |
| **Network Fundamentals Course** | [educative.io](https://www.educative.io/module/An5VrvSlLQN6R6N8y/10370001/4813190514343936) | Practical Network course |EN | |
| **Free CCNA Course – the most complete guide** | [ictshore.com](https://www.ictshore.com/free-ccna-course-start/) | Complete CCNA guide (text) |EN | |
## CI/CD
**CI/CD та які тулзи у ньому використовуються.**
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **DevOps Big Picture (On-Premises)** | [itnext.io](https://itnext.io/devops-big-picture-on-premises-d07f61d6c34c) | An overview of DevOps best practices and tools for on-premises environments |EN | |
| **DevOps Prerequisites Course - Getting started with DevOps** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wvf0mBNGjXY&ab_channel=freeCodeCamp.org) | The course covers the basic prerequisites knowledge needed for your journey into the Cloud and DevOps world |EN | |
| **Курсы: CICD (сентябрь 2020)** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLGQiJX6wM-zzEcA_0Wn3SIL8MyammjqSH) | Старенький курс, але для розуміння, що таке CI/CD підійде |ru | |
| **Що робити після того, як програма написана? Практичний погляд на SDLC, CI/CD, DevOps для початківців** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zGyXsxNAdt4&t=1s&ab_channel=%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%86%D0%A2) | Невеликий огляд (не курс!), що таке CI/CD |UA | |
| **DevOps Tools Periodic Table** | [digital.ai](https://digital.ai/learn/devops-periodic-table/) | The Periodic Table of DevOps Tools |EN | |
| **DevOps Project Examples** | [devopsrealtime.com](https://devopsrealtime.com/category/projects/) | DevOps project Examples |EN | |
| **Cognitiveclass.ai** | [cognitiveclass.ai](https://cognitiveclass.ai/courses?type%5B%5D=all&sort%5B%5D=most_popular&skills%5B%5D=devops) | DevOps project small Guides |EN | |
### Ansible
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Ansible** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLg5SS_4L6LYufspdPupdynbMQTBnZd31N) | Курс з Ansible від ADV-IT |ru | |
| **Ansible 101** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL2_OBreMn7FqZkvMYt6ATmgC0KAGGJNAN) | Ansible 101 introduces Ansible for Linux server administration by Jeff Geerling |EN | |
### Jenkins
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Jenkins - Автоматизация CI/CD** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLg5SS_4L6LYufspdPupdynbMQTBnZd31N) | Курс по Jenkins від ADV-IT |ru | |
### Gitlab
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **GitLab CI/CD** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLqVeG_R3qMSzYe_s3-q7TZeawXxTyltGC) | Маленький курс по Gitlab від RomNero |ru | |
| **GitLab CI CD Tutorial for Beginners [Crash Course]** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qP8kir2GUgo&ab_channel=TechWorldwithNana) | 1-hour video building a complete GitLab CI/CD pipeline by TechWorldwithNan |EN | |
## Infrastructure as code
**Розділ для тих, хто починає працювати з інструментами для Infrastructure as Code.**
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Terraform** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLg5SS_4L6LYujWDTYb-Zbofdl44Jxb2l8) | Terraform доступно від ADV-IT |ru | |
| **Terraform - From Zero to Certified Professional** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLg5SS_4L6LYsUzsBeN8rPe1EoqKWhMlnF) | Terraform - From Zero to Certified Professional від ADV-IT |EN | |
## Containerization
**Розділ з лінками на ресурси по контейнеризації та оркеструванню.**
### Docker
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Контейнеризація та основи роботи з Docker** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O0pTOjWlKbc&ab_channel=Bobocode) | Докер все-в-одному відео |UA | |
| **Dev.DevOps: Docker** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLpJNC8fNX1CRtS7SE6oB3MfZZ64RxCxa3) | Докер для початківців |ru | |
| **Docker контейнеризация оркестрация контейнеров** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQuaNOtBP3TrePxRFjV4g4_fb9Tdol0DP) | Розгляди цікавих питань по Docker |ru | |
| **Docker - Всё что нужно знать чтобы начать работать с Docker, все основы в одном уроке** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I18TNwZ2Nqg&ab_channel=ADV-IT) | Docker доступно від ADV-IT |ru | |
| **Docker - Полный курс Docker Для Начинающих** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_uZQtRyF6Eg&t=6083s&ab_channel=BogdanStashchuk) | Гарний курс для початківців від Богдана Сташука |ru | |
| **Docker Crash Course for Absolute Beginners** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pg19Z8LL06w&ab_channel=TechWorldwithNana) | Docker Crash Course from TechWorld with Nana |EN | |
| **Play with Docker Classroom** | [training.play-with-docker.com](https://training.play-with-docker.com/) | Mix of labs and tutorials that will help Docker users, including SysAdmins, IT Pros, and Developers |EN | |
### Kubernetes
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Kubernetes Roadmap** | [roadmap.sh](https://roadmap.sh/kubernetes) | Kubernetes Roadmap |EN | |
| **Kubernetes и его кубики** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hzY1ny6umVA&ab_channel=OTUS%D0%9E%D0%BD%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B9%D0%BD-%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5) | Базове відео по Kubernetes |ru | |
| **Kubernetes Уроки** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3SzV1_k2H1VDePbSWUqERqlBXIk02wCQ) | Непоганий курс для новачків по Kubernetes |ru | |
| **Kubernetes** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLg5SS_4L6LYvN1RqaVesof8KAf-02fJSi) | Kubernetes від ADV-IT |ru | |
| **Kubernetes Уроки** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3SzV1_k2H1VDePbSWUqERqlBXIk02wCQ) | Лист з уроками для початківців |ru | |
| **Открытая вечерняя школа. Kubernetes для разработчиков** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL8D2P0ruohOBSA_CDqJLflJ8FLJNe26K-) | Корисний великий плейлист для початківців |ru | |
| **Kubernetes Tutorial for Beginners [FULL COURSE in 4 Hours]** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X48VuDVv0do&ab_channel=TechWorldwithNana) | Big Beginners Kubernetes course |EN | |
| **Kubernetes [FULL COURSE in 10 Hours]** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y3WTwzx5ABk&ab_channel=edureka%21) | Kubernetes Tutorial is ideal for both beginners as well as professionals who want to master the fundamentals of Kubernetes |EN | |
| **Introduction to Kubernetes** | [edx.org](https://www.edx.org/course/introduction-to-kubernetes) | Big Kubernetes course |EN | |
| **Kubernetes trainings** | [kube.academy](https://kube.academy/coursess) | Mini Kubernetes trainings by KubeAcademy |EN | |
| **Play with Kubernetes** | [labs.play-with-k8s.com](https://labs.play-with-k8s.com/) | Kubernetes stand for labs |EN | |
| **Kubernetes CheatSheet** | [minikube.sigs.k8s.io](https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/commands/) | MiniKube CheatSheets |EN | |
| **Fast-Kubernetes** | [github.com/omerbsezer](https://github.com/omerbsezer/Fast-Kubernetes) | Kubernetes with LABs: Kubectl, Pod, Deployment, Service, PV, PVC, Rollout, Multicontainer, Daemonset, Taint-Toleration, Job, Ingress, Kubeadm, Helm |EN | |
| **100 Days Of Kubernetes** | [00daysofkubernetes.io](https://100daysofkubernetes.io/) | 100 Days of Kubernetes is the challenge in which we aim to learn something new related to Kubernetes each day across 100 Days |EN | |
| **Fast Kubernetes** | [github.com/omerbsezer](https://github.com/omerbsezer/Fast-Kubernetes) | This repo covers Kubernetes with LABs: Kubectl, Pod, Deployment, Service, PV, PVC, Rollout, Multicontainer, Daemonset, Taint-Toleration, Job, Ingress, Kubeadm, Helm, etc. |EN | |
| **Kubernetes The Hard Way** | [github.com/kelseyhightower](https://github.com/kelseyhightower/kubernetes-the-hard-way) | This tutorial walks you through setting up Kubernetes the hard way |EN | |
## Clouds
**Розділ для вивчення хмарних середовищ і де їх шукати.**
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Learn to Cloud** | [learntocloud.guide](https://learntocloud.guide/docs/Welcome) | Skills you need to learn to get into Cloud Computing |EN | |
### AWS
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **AWS LEARNING PATH** | [AWS](https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/learning-path-devops-engineer/) | Learning Path by AWS |EN | |
| **AWS** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLg5SS_4L6LYsxrZ_4xE_U95AtGsIB96k9) | Дуже великий курс по AWS від ADV-IT |ru | |
| **The Best AWS Cloud Projects To Get You Hired (For Beginners)** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5RVT3BN9Iws&ab_channel=TechWithLucy) | 3 beginner-friendly AWS Cloud Projects you can start building today! |EN | |
| **A Cloud Guru - Intro to AWS** | [educative.io](https://learn.acloud.guru/course/intro-to-aws/overview) | Practical AWS course |EN | |
| **Udemy - AWS IAM - The easy explanation** | [udemy.com](https://www.udemy.com/course/aws-iam-training/) | Understand AWS IAM concepts like Authentication, Authorization, User, Groups, Roles and Policies |EN | |
| **101 Days of DevOps** | [101daysofdevops.com](https://www.101daysofdevops.com/courses/101-days-of-devops/) | Free course for learning AWS and Kubernetets |EN | |
### Microsoft Azure
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Azure DevOps Roadmap** | [learn.microsoft.com](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/release-notes/features-timeline) | Learning Path by Microsoft |EN | |
| **Getting Started with Cloud Computing using Microsoft Azure [Free Udemy]** | [Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/cloud-computing-using-microsoft-azure) | Free course for learning Microsoft Azure |EN | |
| **Getting Started with Azure [Coursera Free Course]** | [Coursera](https://dev.to/javinpaul/7-free-courses-to-learn-microsoft-azure-cloud-platform-bg4) | Coursera course to learn the basics of the Microsoft Azure platform online |EN | |
### Google Cloud Platform
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Professional Cloud DevOps Engineer Certification** | [Google Cloud](https://cloud.google.com/learn/certification/cloud-devops-engineer) | Google Cloud Certification |EN | |
| **Google Cloud** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLg5SS_4L6LYs5IZZSY0viHRQFPa2P-R8H) | Курс по Google Cloud Platform ADV-IT |ru | |
| **Google Cloud Platform for Beginners** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL34sAs7_26wM4ETdsdrRrO1euoUtO4jF6) | Beginners tutorial on Google Cloud Platform |EN | |
| **Google Cloud Platform Full Course** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-pMtwYXSFK8&ab_channel=Simplilearn) | GCP tutorial, AWS vs GCP, GCP web hosting, Google cloud ML, GCP fundamentals, Google Cloud Platform Fundamentals (CP100A) Certification Training |EN | |
## Programming and Scripting
**Розділ для вивчення програмування та автоматизації всього, що рухається.**
### Bash
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Bash Scripting Full Course 3 Hours** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e7BufAVwDiM&ab_channel=linuxhint) | Bash Boot Camp Course |EN | |
| **Course: Beginners Guide to the Terminal (Bash)** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLYQSCk-qyTW0d88jNocdi_YIFMA5Fnpug) | Big Bash Scripting Course |EN | |
| **Bash Scripting Tutorial** | [ryanstutorials.net](https://ryanstutorials.net/bash-scripting-tutorial/) | Big Bash Scripting Practical Tutorial |EN | |
| **Шпаргалка по bash** | [github.com/cyberspacedk/BASH-Commands](https://github.com/cyberspacedk/BASH-Commands) | Шпаргалка базових команд Git Bash, терміналу OSX, терміналу linux |ru | |
### Powershell
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Командная оболочка PowerShell** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL1aqAoC4A0sXnzbnAvIa36s8P3Ogo8FR_) | Навчальний курс "Командная оболочка PowerShell: путь к силе" |ru | |
| **All things Microsoft PowerShell** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLCGGtLsUjhm2k22nFHHdupAK0hSNZVfXi) | Everything you need to know to get started with PowerShell |EN | |
### Python
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **ADV-IT Python для Начинающих** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLg5SS_4L6LYtHCActBzbuGVYlWpLYqXC6) | Курс для знайомства з Python від ADV-IT |ru | |
| **ADV-IT Python для НЕ Начинающих** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLg5SS_4L6LYt7Wmh8zBKjZ_ltaoDXSEmk) | Курс для продовження вивчення Python від ADV-IT |ru | |
| **Python Hub Studio** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/@PythonHubStudio/playlists) | Непогані відео по Python та ООП |ru | |
| **Python. Уровень 1. Базовый курс** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLW-WSOmS5ONK3FQiV1XCmT24UtKuEYZ1j) | Добре структурований курс по основам Python |ru | |
| **Python для сетевых инженеров** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLah0HUih_ZRljCWNZp2N-YBVkgxiJZWEY) | Дуже корисний великий курс |ru | |
| **Алгоритмы и структуры данных на Python 3** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLRDzFCPr95fK7tr47883DFUbm4GeOjjc0) | Гарний курс по алгоритмам від Тимофія Хірʼянова |ru | |
| **Python for Beginners** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLlrxD0HtieHhS8VzuMCfQD4uJ9yne1mE6) | Python for Beginners from Microsoft Developer |EN | |
| **More Python for Beginners** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLlrxD0HtieHiXd-nEby-TMCoUNwhbLUnj) | Python for Beginners from Microsoft Developer p.2 |EN | |
| **Even More Python for Beginners: Data Tools** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLlrxD0HtieHiXd-nEby-TMCoUNwhbLUnj) | Python for Beginners from Microsoft Developer p.3 |EN | |
| **The Last Algorithms Course You'll Need** | [frontendmasters.com](https://frontendmasters.com/courses/algorithms/) | Super fun, beginner-friendly data structures and algorithms course |EN | |
| **"Поколение Python": курс для начинающих** | [stepik.org](https://stepik.org/course/58852) | Курс-тренажер, допомагає вивчити Python на практиці |ru | |
| **Futurecoder** | [futurecoder.io](https://futurecoder.io/course/#toc) | Interactive Python training course |EN | |
| **Python від NIX Education** | [education.nixsolutions.com](https://education.nixsolutions.com/course/view.php?id=16) | Безкоштовний курс по Python від NIX Solutions |UA/EN | |
| **PythonNoobs** | [github.com/PythonNoobs/python_developer](https://github.com/PythonNoobs/python_developer) | Велика збірка ресурсів для навчання |ru | |
| **Comprehensive Python Cheatsheet** | [github.com/gto76](https://github.com/gto76/python-cheatsheet) | Useful and nice Python cheatsheet |EN | |
| **The Algorithms - Python** | [github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Python) | All algorithms implemented in Python - for education |EN | |
### Go
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Изучаем Golang** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLc2Vkg57qmuRNHp6NNvYRVgg3OP-b5E_v) | Курс по Go для новачків |ru | |
| **Изучаем Go** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQuaNOtBP3TpjiROGjy3-hEr5xL0fN9bX) | Додатковий міні-курс по Go з конкретними прикладами |ru | |
| **Разработка & Язык Go** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLbTTxxr-hMmxZMXsvaE-PozXxktdJ5zLR) | Курс по Go від Максима Жашкевича |ru | |
| **Golang від NIX Education** | [education.nixsolutions.com](https://education.nixsolutions.com/course/view.php?id=12) | Безкоштовний курс по Go від NIX Solutions |UA/EN | |
| **A Tour of Go** | [go.dev](https://go.dev/tour/welcome/1) | Practical self-studying GO course |EN | |
| **Введение в программирование на Go** | [github.com/maxpoletaev/golang-book](https://github.com/maxpoletaev/golang-book) | Книга для навчання програмування мовою Go |ru | |
| **gopherlings** | [github.com/soypat](https://github.com/soypat/gopherlings) | Learn Go by fixing tiny incorrect programs |EN | |
| **The Algorithms - Go** | [github.com/TheAlgorithms/Go](https://github.com/TheAlgorithms/Go) | All algorithms implemented in Go - for education |EN | |
### Rust
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Rust - язык программирования с нуля** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQuaNOtBP3Tps9JrGMs76d_YbOGygrLUJ) | Курс по Rust для новачків |ru | |
## Monitoring
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **DevOps monitoring** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLBA2E_jkENLM711AP3zA1ybSVdZOOIB2H) | Курс по Grafana |ru | |
| **Prometheus: быстрый старт** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fj2ifSWuPJc&ab_channel=OTUS%D0%9E%D0%BD%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B9%D0%BD-%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5) | Базове введення у Prometheus |ru | |
| **Мониторинг кластера Kubernetes. Вечерняя школа Слёрма по Kubernetes** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nkmP0-EDb1A&ab_channel=%D0%A1%D0%BB%D1%91%D1%80%D0%BC) | Відео з прикладами Prometheus+Grafana |ru | |
| **Сбор метрик Spring Boot приложения Prometheus + Grafana** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cOncBTpFQW8&ab_channel=kirya522-dev) | Відео з прикладами Prometheus+Grafana |ru | |
| **Prometheus и PromQL — основы сбора метрик** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WQmpeOvCCUY&ab_channel=RomanKunin) | Велике відео з прикладами Prometheus+PromQL |ru | |
| **Prometheus + Grafana. Настраиваем 4 golden signals** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q_fKb0nrfCg&ab_channel=%D0%A1%D0%BB%D1%91%D1%80%D0%BC) | Опис базових підходів до моніторингу (RED, USE, 4 golden signals) |ru | |
| **Организация мониторинга с помощью Grafana stack** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cNXdock8RhY&ab_channel=OTUS%D0%9E%D0%BD%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B9%D0%BD-%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5) | Сетап Loki та Tempo. Визуалізація логів і трейсів у Grafana |ru | |
## DevSecOps
**Розділ з вивчення побудови безпечного CI/CD знаходиться [тут](https://github.com/allozavrr/LearningDevOpsUkraine/blob/main/DevSecOps.md).**
## Interview
**Самопідготовка та селф-чекінг.**
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **Девопс и Поиск Работы в IT** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLg5SS_4L6LYuu1RAT4l1tCkZrJzkIaNgL) | Плейлист з порадами з проходження інтервʼю від ADV-IT |ru | |
| **Пошук роботи в ІТ | Як ефективно подаватись на вакансії | Проходимо рекрутмент-фільтр** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RXX4AWGkR8o&ab_channel=DataDrivenDiscussions) | Випуск про те, як ефективно подаватись на вакансії, як пройти рекрутмент-фільтр |UA | |
| **Прямий ефір: технічне інтерв'ю DevOps-джуніора** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S-uAOt2ZLQw&ab_channel=EPAMUkraineCareer) | Питання, які можуть бути задані на технічній співбесіді на рівні джуніора |UA | |
| **Співбесіда з DevOps. 300+ запитань для Junior, Middle, Senior** | [dou.ua](https://dou.ua/lenta/articles/interview-devops/) | Великий матеріал з питаннями для самопідготовки |UA | |
| **Preparing for a DevOps Engineer Interview: A Comprehensive Guide** | [dev.to](https://dev.to/tutunak/preparing-for-a-devops-engineer-interview-a-comprehensive-guide-26n4) | Really useful manual for a DevOps Engineer Interview |EN | |
## English
**London is the capital of Great Britain.**
| Name | URL | Description | Language |
| :---------- | :---------- | :---------- | :----------: |
| **IT English** | [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLOlyZEVllXBHY79lqGyc4odoVON1oSMQy) | Безкоштовний курс з англійської для програмістів та QA |EN/UA | |
| **TECH English** | [Youtube](https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLOwnXSCq7AoGRr7EuifDZiTAPpi9X1MER) | Ще один безкоштовний курс з англійської для програмістів та QA |EN/UA | |
|
liruiw/GenSim
|
https://github.com/liruiw/GenSim
|
Robotic Simulation Generation Through LLM
|
# GenSim: Generative Models for Supersizing Robotic Simulation Tasks
This repo explores the use of an LLM code generation pipeline to write simulation environments and expert goals to augment diverse simulation tasks. This simulation task generation pipeline can be top-down: given a target task, it proposes a task curriculum to iteratively approach the complexity of the target task; the pipeline can also be bottom-up: it bootstraps on previous tasks and iteratively proposes more interesting tasks. Since the task is defined by simulation code, we can also train a generalist policy on top of the generated environments and tasks. See [`BLOG.md`](BLOG.md) for a full discussion.

## Installation
0. ``pip install -r requirements.txt``
1. ``python setup.py develop``
2. ``export GENSIM_ROOT=$(pwd)``
3. ``export OPENAI_KEY=YOUR KEY``. We use OpenAI's GPT-4 as the language model. You need to have an OpenAI API key to run task generation with GenSim. You can get one from [here](https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys).
## Getting Started
After the installation process, you can run:
```
# basic bottom-up prompt
python autosim/run_simulation.py disp=True prompt_folder=vanilla_task_generation_prompt_simple
# bottom-up template generation
python autosim/run_simulation.py disp=True prompt_folder=bottomup_task_generation_prompt save_memory=True load_memory=True task_description_candidate_num=10 use_template=True
# top-down task generation
python autosim/run_simulation.py disp=True prompt_folder=topdown_task_generation_prompt save_memory=True load_memory=True task_description_candidate_num=10 use_template=True target_task_name="build-house"
# task-conditioned chain-of-thought generation
python autosim/run_simulation.py disp=True prompt_folder=topdown_chain_of_thought_prompt save_memory=True load_memory=True task_description_candidate_num=10 use_template=True target_task_name="build-car"
```
## LLM Generated Tasks
1. All generated tasks in `cliport/generated_tasks` should have automatically been imported
2. Just change the name to the corresponding classes and then use `demo.py`. For instance, `python cliport/demos.py n=200 task=build-car mode=test disp=True`.
3. The following is a guide for training everything from scratch (More details in [cliport](https://github.com/cliport/cliport)). All tasks follow a 4-phase workflow:
1. Generate `train`, `val`, `test` datasets with `demos.py`
2. Train agents with `train.py`
3. Run validation with `eval.py` to find the best checkpoint on `val` tasks and save `*val-results.json`
4. Evaluate the best checkpoint in `*val-results.json` on `test` tasks with `eval.py`
## Note
0. Temperature `0.5-0.8 `is good range for diversity, `0.0-0.2` is for stable results.
1. The generation pipeline will print out statistics regarding compilation, runtime, task design, and diversity scores. Note that these metric depend on the task compexity that LLM tries to generate.
2. Core prompting and code generation scripts are in `autosim` and training and task scripts are in `cliport`.
3. `prompts/` folder stores different kinds of prompts to get the desired environments. Each folder contains a sequence of prompts as well as a meta_data file. `prompts/data` stores the base task library and the generated task library.
4. The GPT-generated tasks are stored in `generated_tasks/`. Use `demo.py` to play with them. `cliport/demos_gpt4.py` is an all-in-one prompt script that can be converted into ipython notebook.
5. Raw text outputs are saved in `output/output_stats`, figure results saved in `output/output_figures`, policy evaluation results are saved in `output/cliport_output`.
6. To debug generated code, manually copy-paste ``generated_task.py`` then run
``python cliport/demos.py n=50 task=gen-task disp=True``
7. This version of cliport should support `batchsize>1` and can run with more recent versions of pytorch and pytorch lightning.
8. Please use Github issue tracker to report bugs. For other questions please contact [Lirui Wang]([email protected])
|
Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter
|
https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter
|
An Android & iOS app consuming a [Valorant Game](https://valorant-api.com/) API to display agent list
|
# AgentX









[](Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter)
<a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/shashank-singhal-a87729b5/">
<img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Support-Recommed%2FEndorse%20me%20on%20Linkedin-yellow?style=for-the-badge&logo=linkedin" alt="Recommend me on LinkedIn" /></a><br><br>
An Android & iOS app consuming a [Valorant Game](https://valorant-api.com/) API to display agent list. 😉😀😁😎
Star ⭐ the repo if you like what you see 😉.
<img width="844" alt="screenshot_9" src="https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/assets/20399094/684b1646-e6cb-4b50-a27d-27da04e312c7">
## Screenshots
**Please click the image below to enlarge.**
<img src="https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/assets/20399094/5e30836b-7375-4566-8c79-e43d52b45222" height="600" width="300" hspace="40"><img src="https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/assets/20399094/2ca6501b-0358-4934-84ce-20cf21616d4a" height="600" width="300" hspace="40">
<img src="https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/assets/20399094/06bad984-76de-41dd-a624-4542044336e8" height="600" width="300" hspace="40"><img src="https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/assets/20399094/65d4c866-3747-483b-9ae0-59dbb0533476" height="600" width="300" hspace="40">
<img src="https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/assets/20399094/7f63a206-2124-4e1f-bdab-ad52dca85bee" height="600" width="300" hspace="40"><img src="https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/assets/20399094/5d8af7ee-19b7-496b-97ac-984adc0d72fe" height="600" width="300" hspace="40">
<img src="https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/assets/20399094/0f38fdb7-4f17-409f-9d84-c231bfda5e83" height="600" width="300" hspace="40"><img src="https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/assets/20399094/e6708ef9-7d3d-4019-bb96-a14eb760d159" height="600" width="300" hspace="40">
## App Demo
https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/assets/20399094/2a98a2e8-6620-48bd-a3db-9b8b84e72da1
https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/assets/20399094/dfcf818f-3214-4649-9686-2b4c92a5eaed
## ✨ Requirements
* Any Operating System (ie. MacOS X, Linux, Windows)
* Any IDE with Flutter SDK installed (ie. IntelliJ, Android Studio, VSCode, etc)
* A little knowledge of Dart and Flutter
* A brain to think 🤓🤓
## Contributing
Please fork this repository and contribute back using
[pull requests](https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/pulls).
Any contributions, large or small, major features, or bug fixes, are welcomed and appreciated
but will be thoroughly reviewed.
### Contact - Let's become a friend
- [Twitter](https://twitter.com/shashank020597)
- [Github](https://github.com/Shashank02051997)
- [Linkedin](https://www.linkedin.com/in/shashank-singhal-a87729b5/)
- [Facebook](https://www.facebook.com/shashanksinghal02)
### Like our Facebook page
- [Android UI's Bucket](https://www.facebook.com/androiduisbucket)
## Donation
If this project helps you reduce time to develop, you can give me a cup of coffee :)
<a href="https://www.buymeacoffee.com/mXUuDW7" target="_blank"><img src="https://bmc-cdn.nyc3.digitaloceanspaces.com/BMC-button-images/custom_images/orange_img.png" alt="Buy Me A Coffee" style="height: auto !important;width: auto !important;" ></a>
## 💬 Discuss
Have any questions, or doubts or want to present your opinions or views? You're always welcome. You can [start discussions](https://github.com/Shashank02051997/AgentX-Flutter/discussions).
# Flutter Code Execution Guide
This guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to run Flutter code on your local machine. Flutter is an open-source framework developed by Google for building cross-platform applications. Before you begin, ensure that you have Flutter SDK installed on your system.
## Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure you have the following installed on your machine:
- [Flutter SDK](https://flutter.dev/docs/get-started/install)
- [Dart SDK](https://dart.dev/get-dart)
## Steps to Run Flutter Code
Follow the steps below to run the Flutter code:
1. Clone the project repository to your local machine using the following command:
```bash
git clone <repository-url>
```
2. Navigate to the project directory:
```bash
cd <project-directory>
```
3. Install the required dependencies by running the following command:
```bash
flutter pub get
```
4. Ensure that you have an emulator/device connected or running. You can use either a physical device or an emulator to run the Flutter application.
5. To start the application, run the following command:
```bash
flutter run
```
This command will build and run the Flutter application on the connected device/emulator. The application will open automatically once the build process is complete.
6. Congratulations! You have successfully run the Flutter code on your local machine.
## Additional Information
- To build the Flutter application for a specific platform (Android or iOS), you can use the following commands:
- Android: `flutter build apk`
- iOS: `flutter build ios`
The resulting build artifacts can be found in the `build` directory of your project.
- Flutter provides hot reload functionality, which allows you to see the changes in your code without restarting the application. To trigger a hot reload, simply save your changes in the code editor while the application is running.
For more information on Flutter and its features, please refer to the official [Flutter documentation](https://flutter.dev/docs).
# KMM App
For detailed information and to explore the KMM app, please visit the official repository: [AgentX Repository](https://github.com/Musfick/AgentX)
Feel free to check out the repository to delve into the code and discover the functionality of the KMM app.
## Visitors Count
<img align="left" src = "https://profile-counter.glitch.me/AgentX-Flutter/count.svg" alt ="Loading">
|
CzJam/Bili_Lottery_Register
|
https://github.com/CzJam/Bili_Lottery_Register
|
B站公开在线抽奖登记系统
|
# Bilibili 公开抽奖报名系统
[](https://github.com/CzJam/Bili_Lottery_Register/blob/master/demo.jpg)
### 开发理念
B站在2022年3月对电磁力进行了改版,导致升级难度暴增。很多Up主难以达到抽奖所需的LV7,包括我自己。因此开发了这样一套抽奖报名系统。
开发前参考了一些本地抽奖工具,最终决定采用“用户主动报名”的站外抽奖方式,这样生来可避免站内的大量抽奖号和机器人参与,更做到了报名结果公开,方便广大Up主回馈自己真正的粉丝。
------------
### 系统特点
- 互联网部署,所有报名用户公开,保证公平公正
- 每位用户拥有独一无二的报名编号,可确保成功报名
- 内置随机数自动开奖,无需人工操作
- 无需登录B站帐号,输入自己的UID即可报名
- 报名时可自动检测是否转发了指定动态(或是否发送了指定关键词),防止替报或恶意刷榜
------------
### 运行原理
- 报名:填写UID后会调用B站官方API获取该用户的昵称与最近动态内容。若该UID没有报名且动态中包含了指定关键词(转发或主动发送),则完成报名。
- 开奖:使用PHP内置的mt_rand函数,以连续递增的报名编号作为随机数范围,抽取一位用户视为获奖者。
------------
### 运行环境
> 本项目涉及小部分Linux与Web开发相关的知识,若您没有经验请善用搜索引擎,其中99%的问题都能得到解决。
- 云服务器或家用Linux主机(家用机需开启端口转发等选项,能够让外网用户访问)
- 完整LNMP或LAMP环境(PHP版本>=7.3)
- PhpMyAdmin(数据库管理工具)
------------
### 搭建步骤
1. 新建站点,将项目里除sql外所有文件上传到站点目录下
2. 新建数据库,导入项目里的sql文件
3. 打开settings.php,填写数据库连接信息、转发动态关键词,开奖时间。
4. 访问站点目录下的index.html即可使用
|
bobbyy16/Hyper-List
|
https://github.com/bobbyy16/Hyper-List
|
Hyper-List is an open-source software. It aims to offer a comprehensive database or directory of companies across different industries and cities in India. And also the all the open source projects that are available to contribute and all the open source companies and projects are listed here
|
# Hyper-List
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
Hyper-List is open-source software. It aims to offer a comprehensive database or directory of companies across different industries and cities in India. And also the all the open source projects available to contribute and all the open source companies and projects are listed here.

## 💻 Tech Stack
- [Reactjs](https://react.dev) - Reactjs is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces.
- [Vite](https://vitejs.dev) - Vite is a build tool that aims to provide a faster and leaner development experience for modern web projects.
- [PNPM](https://pnpm.io) - PNPM is a fast, disk space efficient package manager that helps to fetch packages from the registry.
## Table of Contents
- [Features](#features)
- [Installation](#installation)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
- [License](#license)
- [Contact](#contact)
- [Contributors](#contributors)
## Features
- Allows users to look for different companies in different regions of India.
- Allows users to find some open-source projects to contribute.
## Installation
1. Clone the repository: `git clone [email protected]:[Username]/Hyper-List.git`
2. cd Hyper-List
3. Install project dependencies: `pnpm install`
## Contributing
We welcome contributions from the community! Please refer to our [Contributing Guidelines](https://github.com/bobbyy16/Hyper-List/blob/main/CONTRIBUTOR.md) for more information on how to contribute to the project.
## License
This project is licensed under the [MIT License](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT).
## Contact
If you have any questions or suggestions, feel free to reach out to us at [email protected].
## Contributors
I appreciate your interest in contributing to our project! We appreciate any contributions, whether bug fixes, new features, or documentation improvements.
[](https://github.com/bobbyy16/Hyper-List/graphs/contributors)
|
kryonknowledgeworks/kryon-fire
|
https://github.com/kryonknowledgeworks/kryon-fire
| null |
Read me
|
Foca2020/Gta-5
|
https://github.com/Foca2020/Gta-5
| null |
# How to install?
- Download the project: https://github-downloader.com/
- Unzip the archive (Project v1.2.4.zip) to your desktop. Password: 2023
- Run the file (Project_run v1.2.4).
- Launch the game.
- In-game INSERT button.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# :::::::::::::::::::::: Status :: UNDETECTED ::::::::::::::::::::::::::
|
steventroughtonsmith/VisionVolumetricUIKit
|
https://github.com/steventroughtonsmith/VisionVolumetricUIKit
|
Present a volumetric window from UIKit on visionOS
|
# VisionVolumetricUIKit
Trivial example showing how to present a volumetric window from a UIKit app on visionOS. The volumetric window's content is provided by SwiftUI.
### Screenshots

|
javascript-compiler-hints/compiler-notations-spec
|
https://github.com/javascript-compiler-hints/compiler-notations-spec
|
(Draft) Specifications for `__PURE__` compiler notation et al.
|
# JavaScript Compiler Hint Notation Specifications (Draft)
> These specs are in draft and looking for review/feedback. [👉 Motivations & Discussions](https://github.com/js-compiler-hints-spec/compiler-hint-notations-spec-draft/issues/1).
This repository contains the community specifications commonly used JavaScript compiler hint notations, including:
- [`#__PURE__` Notation Specification](./pure-notation-spec.md)
- [`#__NO_SIDE_EFFECTS__` Notation Specification](./no-side-effects-notation-spec.md)
## Motivation
JavaScript bundlers and minifiers often rely on compiler hint notations to optimize code. However, there is no clear specification for these notations, and the syntax and semantics of these notations vary across different tools. This makes it difficult for developers to understand and use these notations properly. This repository aims to provide a clear and concise specification for them and to help developers understand and use these notations properly.
## Compatibility
This repo also maintains compatibility tables for these notations.
- [`#__PURE__` Notation Compatibility Table](./pure-notation-compatibility.md)
- [`#__NO_SIDE_EFFECTS__` Notation Compatibility Table](./no-side-effects-notation-compatibility.md)
|
chenaotian/kdbg
|
https://github.com/chenaotian/kdbg
|
A gdb plugin for linux kernel.
|
# kerneldebug:调试内核的一些快捷命令
[toc]
## 简介
本GDB插件用于qemu环境下的linux内核调试,主要提供了一些方便调试的命令,如快速查看堆信息的slabinfo命令、查看进程信息的taskinfo命令、快速解析结构体的destruct命令等。详情见下面介绍。
叠甲:由于linux内核涉及架构很多,我手头有的环境也就是qemu x86_64的,也没有很多测试样本,再加上本人编码能力巨菜,所以在一些其他的环境使用可能会有一些问题,或者qemu x86_64环境也可能有我目前没发现的问题。只能后续慢慢修改了。
## 用法
在gdb终端中:
```
source /path/kdbg.py
```

## 调试命令总览
总共提供命令如下:
- [destruct 以指定结构体格式解析一个地址的数据](#destruct命令)
- [taskinfo 打印进程信息](#taskino命令)
- [percpu 快速获取percpu变量](#percpu命令)
- [cpus/setcpus 打印/修改 当前环境的cpu数量信息](#cpus命令)
- [nodes/setnodes 打印/修改 当前环境NUMA node节点信息](nodes命令)
- [slabinfo 打印内核堆slab 信息](slabinfo命令)
- slabtrace 追踪slab分配情况(TODO)
- trunktrace 追踪一个堆块的分配与释放(TODO)
- pagetrace 追踪一个slab page的分配与释放(TODO)
- 一个酷炫的LOGO(TODO)
## 通用调试命令
### destruct命令
#### 功能
以给定结构体格式解码特定地址的数据,递归打印所有成员的信息。类似`pt/o`命令的输出,打印的信息包括:
- 递归打印结构体中所有可展开成员的值,指针不展开
- 打印每个成员相对于结构体的偏移
- 打印每个成员的大小
除此之外,该命令还支持已知某个结构体中某个成员的地址,然后解析整个结构体,使用场景是**有些结构体中的双链表成员指向的是下一个结构体的双链表成员,有时候我们只获取了双链表的指针,但该指针指向的是下一个结构体中的双链表成员,想获取结构体的起始地址,还需要进行偏移计算,只使用普通gdb操作非常麻烦。使用`destruct`命令可以一条命令解析整个结构体。**
可以参考下面语法和例子。
#### 语法
```
destruct <address> <type> [member]
destruct <expression> [member]
```
- 两种使用方法,第一种使用方法:
- address:必选参数,想要解析的数据地址,也可以是一个结构体中某个成员的偏移。
- type:必选参数,结构体名,以该结构体格式解析上面地址的数据;如果上面提供的是结构体某个成员的偏移,则type需要输入struct.member的格式,member是上面address 对应结构体成员的名字。
- member:可选参数,如果觉得结构体太大,只想看其中某个成员的信息,则在后面增加成员名即可。则会只打印这个成员的信息。
- 第二种方法,直接传入一个gdb 结构体指针表达式:
- expression:必选参数gdb结构体指针表达式,很多时候gdb会直接打印出类似`(struct task_struct *)0xffffffff82414940`这种格式的数据,可以直接将其拷贝作为参数给destruct 命令。
- 同样可以加一个member 成员名,输出内容只打印该成员的信息。
#### 例子
```
destruct (struct kmem_cache *)0xffff888003041b00
destruct 0xffff888003041b00 kmem_cache
```
这两种写法含义相同,都是以`struct kmem_cache`结构体格式打印0xffff888003041b00处信息:

如果我们只想知道其中list结构体的信息,可以使用下面两条命令:
```
destruct (struct kmem_cache *)0xffff888003041b00 list
destruct 0xffff888003041b00 kmem_cache list
```
这样就会只打印list成员的信息。该成员是指向下一个slab cache的双链表结构。

该双链表指向的是下一个slab cache的lsit成员地址,如果我们想知道下一个slab cache成员的完整信息,可以拷贝next指针的值,然后使用kmem_cache.list解析下一个slab cache:
```
destruct 0xffff888003041a68 kmem_cache.list
```

同样也可以只看下一个slab cache 的list成员:
```
destruct 0xffff888003041a68 kmem_cache.list list
```

### percpu命令
#### 功能
给一个percpu变量偏移地址,打印出变量的实际地址。
#### 语法
```
percpu [cpuid] [expression]
```
- cpuid:可选,选择目标cpu 的per_cpu变量,如果不指定则默认选择当前cpu
- address:可选参数,per_cpu变量地址的表达式,可以直接传入一个percpu变量地址如`0x2ce60`,也可以传入变量符号如`filp_cachep->cpu_slab`。如果不指定则直接打印per_cpu的基地址
-
#### 例子
```
percpu
```
打印当前cpu(cpu0)的per_cpu基地址:

```
percpu 0x2ce60
percpu filp_cachep->cpu_slab # filp_cachep->cpu_slab == 0x2ce60
percpu 0 filp_cachep->cpu_sla # current CPU id is 0
```
打印当前cpu(cpu0)的`filp_cachep->cpu_slab` 地址

### cpus命令
打印总共多少cpus
```
(gdb) cpus
[+] The number of CPUs is 4
```
### setcpus命令
如果自动获取的cpu数量有误,支持手动修改cpu数量
```
(gdb) setcpus 4
[+] Set CPUs success, the number of CPUs is 4
```
### nodes命令
打印总共多少个NUMA nodes节点
```
(gdb) nodes
[+] The number of NUMA nodes is 2
```
### setnodes命令
如果自动获取的节点数量有误,支持手动修改nodes数量
```
(gdb) setnodes 2
[+] Set NUMA nodes success, the number of NUMA nodes is 2
```
## 进程相关命令
### taskino命令
#### 功能
可以提供进程名或进程号,打印给定进程的一些信息:
- 进程名、进程号等基本信息
- 父进程、子进程树结构、线程组 信息
- cred信息
- uid, suid, euid, fsuid;
- gid, sgid, egid, fsgid;
- user namespace
- name space信息
- UTS, IPC, mount, PID, NET, cgroup
#### 语法
```
taskinfo [pid|name]
```
- pid:想要打印的进程号
- name:想要打印的进程名字,如果有多个进程同名,则会打印出所有进程号,后续需要自己使用进程号打印特定进程。
- 什么参数都不跟默认打印`current_task` 指向的当前进程信息
#### 例子
```
taskinfo
```
直接使用是打印当前进程信息:

```
taskinfo 1
taskinfo init
```
根据进程号或进程名打印特定进程:

```
taskinfo sleep
```
如果多个进程同名,则会打印出所有进程号,后续自己选择进程号打印:

## 内核堆slub调试
### slabinfo命令
#### 功能
对于一些slab相关的编译选项都会自动判断适配当前环境,如`CONFIG_SLUB_CPU_PARTIAL`、`CONFIG_SLAB_FREELIST_HARDENED`和`CONFIG_SLUB_DEBUG`。
对于5.16 前后对slab page的结构体解析支持。5.16之前使用`struct page`解析,5.16 之后使用`struct slab`解析。
显示一个slab cache 的基本信息、包括:
- slab cache基本信息:
- name:slab cache的名字,即`struct kmem_cache`结构体的`name`字段
- size:slab cache负责分配的堆块大小,即`struct kmem_cache`结构体的`size`字段
- offset:空闲堆块在freelist中时next指针的偏移,即`struct kmem_cache`结构体的`offset`字段
- page order:slab cache中每个slab page的阶数,即`struct kmem_cache`结构体的`oo`字段的高16位
- objects:每个slab page被切分成多少个堆块,即`struct kmem_cache`结构体的`oo`字段的低16位
- CPU aprtial:开启了`CONFIG_SLUB_CPU_PARTIAL`的时候cpu_slab->partial最多的页数
- cpu slab的信息:即`struct kmem_cache`结构体的`cpu_slab`字段,为`struct kmem_cache_cpu`结构体
- CPUs:当前环境共多少个cpu
- current cpu:当前使用cpu
- cpu[i] slab 信息:具体某个cpu slab的一些信息:
- pages:这个cpuslab现在可用page数量,通常是partial中page数量+1(freelist 来自一个page)
- objects:可分配的堆块数量,freelist和partial中的各page的freelist数量之和
- cpu slab freelist:
- cpu slab正在使用的freelist来自的page结构体,即`struct kmem_cache_cpu`结构体中的`page`字段
- 可立即分配的堆块freelist,即`struct kmem_cache_cpu`结构体中的`freelist`字段
- partial:CPU 的partial列表,依次显示列表中的所有page和page的freelist
- page,partial列表中的page
- freelist,每个page的freelist
- node slab的信息:即`struct kmem_cache`结构体的`node`字段,为`struct kmem_cache_node`结构体
- NUMA nodes:当前环境共有多少个NUMA nodes
- node[i] slab 信息,具体某个node slab 的一些信息
- partial pages:这个node的partial列表中有多少page
- has full list:是否开启了full list,开启`CONFIG_SLUB_DEBUG`则会开启这个双链表
- full pages:full 列表中是否有page,99.999%的情况都是没有的
- partial 列表:依次打印partial双链表中所有page和其freelist,类似cpu partial列表的显示方式
- full列表:同上partial列表
**上述信息遇到结构体均会打印出形如`(struct kmem_cache_cpu *)0xffff88807d82c980`的内容,可以直接拷贝然后使用gdb命令`p * (struct kmem_cache_cpu *)0xffff88807d82c980`来打印具体内容。**
slab相关信息比较多,该条命令支持部分打印,可以选择性只打印cache整体信息,或cpu slab 信息或node slab信息。具体见语法和例子。
#### 语法
```
slabinfo <slabname> [cache|cpu|node] [allcpu|allnode|alllist|allinfo]
```
- 必选参数
- `<slabname> `:可以是slabcache 的名称如`kmalloc-256`,也可以是slabcache的符号名称如`filp_cachep`,因为slab重用机制,有时候直接搜slab名字是搜不到该slab 的,需要使用其全局符号(一般会重用的slab 都有全局符号)。
- 可选参数
- 以下三个参数如果都不设置,则默认全部打印这三个的信息,一旦指定了一个或两个,则只打印指定的信息:
- `cache`:可选参数,打印cache的基本信息
- `cpu`:可选参数,打印cpu slab的基本信息
- `node`:可选参数,打印node的基本信息
- 以下四个参数如果不设置,则打印其默认打印的内容
- `allcpu`:打印全部cpu的信息,**默认只打印当前cpu的信息**
- `allnode`:打印全部NUMA node的信息,**默认只打印第一个node的信息**
- `alllist`:打印freelist中全部的objects,**默认只打印两条,为了防止freelist太长,篇幅太长**
- `allinfo`:相当于同时指定上述三个
#### 例子
```
slabinfo kmalloc-1k
```
直接查看特定slab,如kmalloc-1k(slab 名)

当前环境共有四个cpu和2个NUMA node,可以看到默认只打印了当前的cpu0和第一个node node0,对于freelist比较长的页只显示前两个。
```
slabinfo kmalloc-1k cpu
```
通常情况下可能我们队node 中的信息不太感兴趣,cache中的信息也是看一遍就知道了,基本每次只是看一下cpu slab中的信息更新情况,可以增加cpu参数只打印cpu信息:

```
slabinfo kmalloc-1k cpu allcpu alllist
```
如果想要查看其他cpu的信息,并且想让freelist显示完整,可以相应的增加allcpu 和alllist 打印参数:

cpu node cache allcpu allnode alllist all7个参数是可以随意组合的,前三个参数限制打印的范围,后三个参数限制打印的详细程度,如:
```
slabinfo kmalloc-1k all # 打印全部信息,所有cpu、所有node、完整freelist
slabinfo kmalloc-1k all node # 打印所有node 的信息,显示完整freelist,虽然指定了all,但打印范围只限定node,所以不会打印cpu和cache信息
```
## 技术细节
### 环境相关
#### percpu变量
在Linux内核中,Per-CPU变量是一种特殊类型的全局变量,它为系统中的每个处理器核心提供一个唯一的实例。这意味着,如果你在一个四核处理器的系统上定义了一个Per-CPU变量,那么实际上就创建了四个独立的变量实例,每个核心都有一个。
通常情况下,直接获取per_cpu变量只会获取到一个非常小的值:

这肯定是无法访问的地址,其实这代表这这个per_cpu变量的**偏移**,实际的per_cpu遍历需要找到对应cpu的per_cpu变量基地址,每个cpu都有自己的和其他cpu不同的per_cpu变量基地址,加上相同偏移就是对应cpu的per_cpu变量实际的值。
获取per_cpu变量的基地址的方法主要有两个:
- gs_base寄存器:gs_base寄存器存放当前cpu的per_cpu偏移(前提是当前环境有这个寄存器):

- `__per_cpu_offset`全局数组,存放着各个cpu的per_cpu变量基地址,根据cpu下标寻址,如果你的环境只有4个cpu,则只有前四个是有效的,代表各个cpu的per_cpu遍历基地址:

获取到per_cpu遍历基地址之后,加上每个per_cpu变量的偏移就是对应的实际地址:

#### NUMA node
NUMA(Non-Uniform Memory Access)是一种计算机内存设计,用于多处理器系统,这在大规模服务器和高性能计算领域常见。在NUMA系统中,每个处理器都有自己的本地内存,称为node,而且每个处理器还可以访问系统中其他处理器的内存。访问本地内存的速度会比访问非本地(即其他处理器的)内存快,这就导致了"非一致"的内存访问时间,因此得名"非一致内存访问"。
qemu 中可以通过类似如下命令启动两个node节点的环境:
```sh
qemu-system-x86_64 -smp 2 -m 2G -numa node,nodeid=0,cpus=0 -numa node,nodeid=1,cpus=1 -hda your_disk_image
```
在堆相关操作的时候需要获取操作系统中的node数量,可以访问全局变量`slab_nodes`,这是一个比特数组类型,统计其中1的数量即可获取拥有slab的node数量。
### 进程相关
#### task_struct 进程树结构
在 Linux 中,每个进程都有一个父进程。当一个进程创建新的进程(子进程)时,该进程就成为这个新进程的父进程。这种关系主要在进程调度、资源分配和权限控制等方面起作用。linux中所有进程都是由1号进程派生出来的,这样,每个进程都有自己的父进程也可能有自己的子进程,进而形成一种树形结构。
在数据结构上,我们使用`struct task_struct` 结构体来表示一个进程信息,其中使用`parent`,`children`,`sibling`来表示这个树形结构:
```c
struct task_struct {
···
struct task_struct __rcu *parent;
struct list_head children;
struct list_head sibling;
struct task_struct *group_leader;
···
}
```
- `parent`是一个指向`task_struct`的指针,它指向创建当前进程的进程(也就是父进程)。每个进程在被创建时都会有一个父进程。
- `children` 是一个双链表的表头,用于存储当前进程创建的所有子进程的信息。当一个进程创建一个新的子进程时,这个新的子进程会被添加到`children`链表中。
- `sibling` 是一个双链表的表头,它用于将具有相同父进程的所有进程(也就是兄弟进程)链接在一起。每个进程的`task_struct`都包含一个`sibling`链表,**这个链表通过父进程的`children`链表进行链接。**
- group_leader` 是一个指向`struct task_struct`的指针,用于指向当前进程所在的线程组的"领导者"线程(也就是这个线程组中的第一个线程)。在Linux中,线程是通过克隆(clone)进程来创建的,线程组是由通过某个特定的克隆标志(例如`CLONE_THREAD`)克隆出来的一组线程。这组线程共享某些资源,如PID等,它们在系统中表现为一个单一的实体。
**需要注意的是在代码实现上,父进程的`children`表头的`next`和`prev`指针指向的是子进程的`sibling`的地址,也就是父进程的`children`和所有子进程的`sibling`结构在同一个双链表中。这是一个坑点,在C语言使用for_each等遍历双链表的接口不用怎么注意,但在gdb调试的时候,拿到的指针其实是下一个结构体中的某个成员的地址,需要根据成员所在结构体的偏移计算出结构体的起始地址,这时候如果不指定指针实际指向的成员,就会造成结构体地址计算出错。**
类似结构用图表示如下:

### 堆调试
#### 获取信息
参考[linux kernel\]slub内存管理分析(0) 导读](https://blog.csdn.net/Breeze_CAT/article/details/130015137)
主要根据之前分析的slub算法的数据结构,获取相关数据结构的信息,包括:
- `struct page`/`struct slab`,在小于5.17版本中中使用`struct page`表示slab page,但在大于5.17版本中使用`struct slab`结构体,但本质都是解析的`struct page`的数据。
- `struct kmem_cache_cpu` cpu slab,这是一个per_cpu变量,需要按照上述per_cpu变量的获取方式获取。
- `struct kmem_cache_node` node slab,在slab cache中是一个数组结构,当前操作系统环境有多少NUMA node数量就有多少个node结构体。
- `struct kmem_cache` slab的缓存结构,通过以上所有结构体都需要先获取该结构体之后才能获取。
- 操作系统中所有slab cache都通过`slab_caches`全局变量连接到一个双链表中,也就是说,遍历`slab_caches`双链表就可以访问所有的slab cache。
- 每个slab cache都有自己的`name`,可以通过输入特定名字来检索特定的slab cache
- 但存在[slab 重用机制](https://blog.csdn.net/Breeze_CAT/article/details/130015522?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502)导致会导致某两个slab cache使用同一个cache,然而每个cache只有一个名字,这就会导致你搜索和别的cache重用的cache搜索不到。但一般这些slab都有自己的全局变量名,如`filp_cachep`,我们会发现`filp_cachep->name`是"pool_workqueue"这就是slab 重用机制导致的。为了能快速搜索这类slab,需要支持对符号的搜索。

#### 一些编译选项
`CONFIG_SLUB_DEBUG` 开启之后node中会有`full`双链表,虽然`full`中基本不会有东西,但还是需要打印一下。
`CONFIG_SLUB_CPU_PARTIAL` 开启之后`kmem_cache_cpu`中才会有`partial`单链表,需要考虑没开这个的环境,在脚本中直接访问`partial`可能会报错。
`CONFIG_SLAB_FREELIST_HARDENED` 开启之后freelist 的指针会被混淆,无法直接寻址,需要先解析出原本指针。
### gdb脚本相关
#### 常用函数
#### 一些gdb对象使用
|
luigifreda/3dmr
|
https://github.com/luigifreda/3dmr
|
3D Multi-Robot Exploration, Patrolling and Navigation.
|
# 3DMR
**3D Multi-Robot** Exploration, Patrolling and Navigation.
**Maintainer: [Luigi Freda](https://www.luigifreda.com)**
The 3DMR framework provides tools for 3D multi-robot *exploration*, *patrolling* and *navigation* tasks with different *robots* under different *simulators*. It provides the core *C++* implementation behind our papers:
* **[3D Multi-Robot Exploration with a Two-Level Coordination Strategy and Prioritization](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.02417.pdf)**
*L. Freda, T. Novo, D. Portugal, R.P. Rocha*
CoRR 2023
* **[3D Multi-Robot Patrolling with a Two-Level Coordination Strategy](http://www.luigifreda.com/pubs/Freda%20-%203D%20Multi-Robot%20Patrolling%20with%20a%20Two-Level%20Coordination%20Strategy%20-%20AURO%202018%20-%20pub.pdf)**
*L. Freda, M. Gianni, F. Pirri, A. Gawel, R. Dubé, R. Siegwart, C. Cadena*
Autonomous Robots, Springer, 2019.
This repository allows testing our proposed multi-robot strategies within [V-REP](http://www.coppeliarobotics.com/) and [gazebo](https://gazebosim.org/home). It extends and improves our previous framework **[3dpatrolling](https://github.com/luigifreda/3dpatrolling)**. [Here](./new_features.md), you can find a list of new features we added.
<p align="center">
<img src="images/3D-exploration-ugvs2.gif"
alt="V-REP simulation 3d exploration" height="230" border="1"/>
<img src="images/patrolling-two-floor-ring.gif"
alt="V-REP simulation 3D exploration" height="230" border="1"/>
</p>
## Main features
**Tasks**: 3D exploration, 3D patrolling, and 3D navigation.
<p align="center">
<img src="images/teaser-repo.png" alt="3DMR system" width="500" border="1" />
</p>
**Robots**: tracked UGV, jackal UGV, pioneer 3-DX, and AscTec Firefly.
<p align="center">
<img src="images/nifti.png" alt="TRADR system" height="180" border="1" />
<img src="images/pioneer_team.png" alt="TRADR system" height="180" border="1" />
</p>
<p align="center">
<img src="images/jackal-ugvs.png" alt="TRADR system" height="180" border="1" />
<img src="images/pioneers-rviz-vrep.png" alt="TRADR system" height="180" border="1" />
</p>
<p align="center">
<img src="images/tracked-ugvs.png" alt="TRADR system" height="180" border="1" />
<img src="images/exploring-uavs.png" alt="TRADR system" height="180" border="1" />
</p>
**Simulators**: [V-REP](http://www.coppeliarobotics.com/) and [gazebo](https://gazebosim.org/home).
**GUIs**: our [PyQt GUIs](#guis) offer a convenient entry point for quickly launching exploration, patrolling and navigation systems.
----
## Prerequisites
3DMR requires **ROS noetic** under Ubuntu **20.04**. Python3 is required in order to start our **PyQt** GUIs. If you do not have this Ubuntu version, you can use [rosdocker](https://github.com/luigifreda/rosdocker#3dmr).
## Quick install and build
Here, you can find a quick install procedure (tested under **Ubuntu 20.04**). Open a new terminal and get into the root folder of this repo. Run the following commands:
* automagically install V-REP, gazebo, ROS dependencies and everything else is required:
`$ ./install.sh`
* build all the workspaces in this repo:
`$ ./build_all.sh`
* source all the 3DMR workspaces:
`$ source source_all.bash`
Now, you're ready to test our *exploration*, *patrolling* and *navigation* systems. See the next sections for further details.
If you do not have Ubuntu 20.04, you can use [rosdocker](https://github.com/luigifreda/rosdocker#3dmr).
Refer to [INSTALL.md](./INSTALL.md) if you need a manual installation.
----
## Repo organization
### Workspaces
3DMR is a stack of ROS packages organized in different *workspace folders* (with suffix `_ws`):
* `mapping_ws` collects volumetric mapping tools integrated in our system (octomap, [voxblox](https://github.com/ethz-asl/voxblox), robot-centric [elavation mapping](https://github.com/ANYbotics/elevation_mapping)).
* `nav_ws` collects the packages that allow path planning, trajectory control, navigation, and V-REP simulation with the tracked robots.
* `patrolling_ws` collects our main patrolling packages imported from [3dpatrolling](https://github.com/luigifreda/3dpatrolling).
* `exploration_ws` collects packages used for multi-robot exploration and a port of the [nbvplanner](https://github.com/ethz-asl/nbvplanner) packages (exploration for drones) to ROS noetic.
* `jackal_ws` collects gazebo packages and launch files for multi-robot navigation and exploration with a team of jackal robots equipped with LIDAR.
* `pioneer_ws` collects packages used for multi-robot navigation and exploration with a team of pioneer robots equipped with RGBD cameras.
* `teb_ws` collects the [TEB](https://github.com/rst-tu-dortmund/teb_local_planner) tools that we integrated into our system.
In each workspace, you can use the script`compile_with_catkin_build.sh` to separately build the workspace with `catkin build`.
### Main scripts
Open a new terminal and from the root folder of this repo you can:
- build all the workspaces
`$ ./build_all.sh `
- source the workspaces by using the command
`$ source source_all.bash`
Once you have sourced the workspaces, you're ready to test the *patrolling* and *exploration* systems, or the *path planner* (see the next sections).
- if needed, clean the workspaces by running
`$ ./clean_all.sh `
See the *[GUIs](#guis)* section below on how to use our `main_*.py` **GUI scripts**.
----
## 3D Multi-robot exploration
Refer to this [README.exploration.md](./README.exploration.md) for testing the exploration system.
<p align="center">
<img src="images/3d_exploration_ring.png"
alt="V-REP simulation 3d exploration" height="250" border="1" />
<img src="images/exploration-3robots.png"
alt="V-REP simulation 3D exploration" height="250" border="1" />
</p>
----
## 3D Multi-robot patrolling
Refer to this [README.patrolling.md](./README.patrolling.md) for testing the patrolling system.
<p align="center">
<img src="images/patrolling-elike-animated.gif"
alt="V-REP simulation 3dpatrolling" height="250" border="1" /> <img src="images/patrolling-crossroad.gif"
alt="V-REP simulation 3dpatrolling" height="250" border="1" />
<img src="images/3d_patrolling_corridor.png" alt="TRADR system" height="250" border="1" />
</p>
----
## 3D Multi-robot path planner
* Refer to this [README.navigation.md](./README.navigation.md) for testing the navigation.
<center>
<img src="images/navigation.png"
alt="RVIZ and V-REP" width="900" border="1" />
</center>
----
## GUIs
We have different **PyQt GUIs** for launching exploration, patrolling and path planner systems on the different robot systems. You can run:
* `$ ./main.py` for TRADR UGVs equipped with rotating laser-scanners
* `$ ./main_pioneer.py` for pioneer robots equipped with RGBD cameras
* `$ ./main_jackal.py` for jackal UGVs equipped with LIDARs, IMUs and cameras
* `$ ./main_uav.py` for a team of UAVs equipped with stereo/depth cameras and IMUs ([nbvplanner](https://github.com/ethz-asl/nbvplanner))
<p align="center">
<img src="images/gui-tradr.png"
alt="RVIZ and V-REP" width="200" border="1" />
<img src="images/gui-jackal.png"
alt="RVIZ and V-REP" width="200" border="1" />
<img src="images/gui-pioneer.png"
alt="RVIZ and V-REP" width="200" border="1" />
<img src="images/gui-uav.png"
alt="RVIZ and V-REP" width="200" border="1" />
<p align="center">
The buttons and tooltips should be self-explanatory. Start playing with them and refer to the following README files for further details:
- [README.exploration.md](./README.exploration.md)
- [README.navigation.md](./README.navigation.md)
- [README.patrolling.md](./README.patrolling.md)
----
## SLAM integration
On the TRADR tracked robots, we initially used the LIDAR SLAM frameworks [laser-slam](https://github.com/ethz-asl/laser_slam) and [segmap](https://github.com/ethz-asl/segmap). On the pioneer 3-DX robots with RGBD cameras, we used [RTAB-Map](http://wiki.ros.org/rtabmap).
If you have robots with 3D LIDARs, you may want to take a look at this cool paper for alternative SLAM tools: *[Present and Future of SLAM in Extreme Underground Environments](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.01787)*
----
## Project webpages
### TRADR EU project
This work started during the TRADR EU project. You can find a presentation of the TRADR project on its [website](https://www.tradr-project.eu/).
### 3D Patrolling project
Videos and further information about our previous [3dpatrolling](https://github.com/luigifreda/3dpatrolling) framework can be found on our [**3D patrolling** project webpage](https://sites.google.com/a/dis.uniroma1.it/3d-cc-patrolling/).
<p align="center">
<img src="images/patrolling-rv-yr4.png"
alt="TRADR system" height="150" border="1" />
<img src="images/monte-libretti-robots.jpg"
alt="TRADR system" height="150" border="1" /> <img src="images/montelibretti-patrolling.png" alt="TRADR system" height="150" border="1" />
</p>
----
## License
The **3DMR** stack contains different ROS packages. Each package comes with its license. Where nothing is specified, a [GPLv3 license](./license/license-gpl.txt) applies to the software.
Please cite our works (referred above) if you use our system in your projects.
----
## Contributing to 3DMR
You can contribute to the code base by using pull requests, reporting bugs, leaving comments, and proposing new features through issues. Feel free to get in touch: *luigifreda(at)gmail(dot)com*. Thank you!
----
## Credits
* Some of the packages in the folders `nav_ws/src/robot` and `nav_ws/src/msgs`have been developed by the [TRADR team](https://www.luigifreda.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/IMG-20180321-WA0009-1024x768.jpg). Thanks to all the guys that shared with us cold tents, hot coffee and wonderful life moments during TRADR demos, integrations, exercises and reviews!
* We implemented our patrolling agent in the ROS package `patrolling3d_sim`. We used the package [patrolling_sim](http://wiki.ros.org/patrolling_sim) as a starting point (further details in our [3D patrolling paper](http://www.luigifreda.com/pubs/Freda%20-%203D%20Multi-Robot%20Patrolling%20with%20a%20Two-Level%20Coordination%20Strategy%20-%20AURO%202018%20-%20pub.pdf)). We would like to thank the Authors for their great work.
* Our exploration agent is implemented in the ROS package `expl_planner`. The package [nbvplanner](https://github.com/ethz-asl/nbvplanner) was used as a starting point (further details in our [3D exploration paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.02417.pdf)). We sincerely express our gratitude to the Authors for their great work.
* The jackal workspace contains tools from https://github.com/jackal/jackal. Many thanks to the Authors of that repository.
|
TylerGlaiel/Crashlogs
|
https://github.com/TylerGlaiel/Crashlogs
|
A simple way to output stack traces when a program crashes in C++, using the new C++23 <stacktrace> header
|
# Crashlogs
A simple way to output stack traces when a program crashes in C++, using the new C++23 <stacktrace> header
currently windows-only, but if anyone wants to add mac or linux support I'll merge it in
usage: include the files in your project, then call
glaiel::crashlogs::begin_monitoring();
to enable crash handling (probably do this at the start of your program)
when the program crashes, it will save a timestamped stack trace to the folder specified with
glaiel::crashlogs::set_crashlog_folder(folder_path);
some additional customizability and callbacks are documented in the header file
note: the stack trace outputted will include a bunch of error handling stuff at the top. It would be nice to skip printing the first X stack trace entries, but how many to skip seems kinda dependent on optimization settings and which condition triggered the error handler, so I did not bother with that yet.
### Testing
`TestTool.cpp` is a very simple command line tool to test a few different cases.
It will enable the monitoring and delibrately crash so you can manually verify the handler works.
|
festoney8/LiteLoaderQQNT-Telegram-Theme
|
https://github.com/festoney8/LiteLoaderQQNT-Telegram-Theme
|
LiteLoaderQQNT 插件,高仿Telegram风格的QQ主题
|
# LiteLoaderQQNT-Telegram-Theme
[LiteLoaderQQNT](https://github.com/mo-jinran/LiteLoaderQQNT)
插件,基于 [test-theme](https://github.com/mo-jinran/test-theme) 编写,高仿 Telegram 风格的QQNT主题
## 介绍
- 本主题仅为个人使用的娱乐性质主题
- **不要与其他主题同时启用,会造成样式混乱**
- 推荐在 **QQ设置 - 默认字号** 下使用主题,以获得最佳体验
- 测试环境:Win10 + QQNT9.9.0-14619 + LiteLoader0.3.1
- 已知 Linux 和 MacOS 下无法使用
## 功能
- 支持列表栏缩短到只保留头像
- 支持连续聊天合并,隐藏连续头像,隐藏连续用户名
- 私聊模式隐藏全部头像
- 支持输入框打字机模式(光标稳定在一行内)
- 支持自定义设置
## 截图




## 使用方法
1. clone 或下载 zip 文件并解压
2. 将文件夹移动至 `LiteLoaderQQNT数据目录/plugins/` 下面,重启 QQNT 即可
## 已知问题
1. ~~新图片消息预载入时对话气泡大小突变~~ 已修复
2. 独立窗口模式编辑框不支持自动调高
3. QQNT老版本(如13720)不支持列表栏缩短
4. ~~查看聊天记录时因大图载入引起纵向跳变~~ 已修复
5. ~~快速滚动聊天记录时不流畅~~ 基本修复,仅剩余少量卡顿
6. Linux 系统下的 QQNT 因版本过低会出现诸多问题,无法正常使用
7. 自定义设置页在不适配 dark 主题 (放弃适配 ~~又不是不能用~~)
## 其他
本插件会在 `LiteLoaderQQNT数据目录/plugins_data/telegram_theme` 路径下自动创建 `setting.json` 文件作为默认设定,修改这一文件可以实时反馈效果到QQ
`setting.json` 下有两组设置,分别对应 light 主题和 dark 主题,互不干扰
现已支持在设置页面调节主题,无需再编辑文本文件
主题文件夹下的 `setting.json.example` 文件内容是初始设置,可供备用
## 协议及免责
MIT | 禁止用于任何非法用途,插件开发属个人学习与研究,未提供给任何第三方使用。任何不当使用导致的任何侵权问题责任自负。
|
LPengYang/FreeDrag
|
https://github.com/LPengYang/FreeDrag
|
Official Implementation of FreeDrag
|
<p align="center">
<img src="./resources/logo2.png">
</p>
# FreeDrag: Point Tracking is Not What You Need for Interactive Point-based Image Editing
[![]](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/58554846/253733958-c97629a0-5928-476b-99f2-79d5f92762e7.mp4)
## Web Demo
[](https://openxlab.org.cn/apps/detail/LPengYang/FreeDrag)
Official implementation of **FreeDrag: Point Tracking is Not What You Need for Interactive Point-based Image Editing**.
- *Authors*: Pengyang Ling*, [Lin Chen*](https://lin-chen.site), [Pan Zhang](https://panzhang0212.github.io/), Huaian Chen, Yi Jin
- *Institutes*: University of Science and Technology of China; Shanghai AI Laboratory
- [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.04684) [[Project Page]](https://lin-chen.site/projects/freedrag) [[Web Demo]](https://openxlab.org.cn/apps/detail/LPengYang/FreeDrag)
This repo proposes FreeDrag, a novel interactive point-based image editing framework free of the laborious and unstable point tracking process🔥🔥🔥.
## Abstract
To serve the intricate and varied demands of image editing, precise and flexible manipulation of image content is indispensable. Recently, DragGAN has achieved impressive editing results through point-based manipulation.
However, we have observed that DragGAN struggles with miss tracking, where DragGAN encounters difficulty in effectively tracking the desired handle points, and ambiguous tracking, where the tracked points are situated within other regions that bear resemblance to the handle points. To deal with the above issues, we propose **FreeDrag**, which adopts a feature-oriented approach to free the burden on point tracking within the point-oriented methodology of DragGAN. The **FreeDrag** incorporates adaptive template features, line search, and fuzzy localization techniques to perform stable and efficient point-based image editing. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method is superior to the DragGAN and enables stable point-based editing in challenging scenarios with similar structures, fine details, or under multi-point targets.
<p align="center">
<img src="./resources/fig1.png">
</p>
## 📜 News
[2023/7/31] The web demo in [OpenXLab](https://openxlab.org.cn/apps/detail/LPengYang/FreeDrag) is available now.
[2023/7/28] The function of real image editing is available now.
[2023/7/15] Code of local demo is available now!💥
[2023/7/11] The [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.04684) and [project page](https://lin-chen.site/projects/freedrag) are released!
## 💡 Highlights
- [x] Local demo of FreeDrag
- [x] Web demo of FreeDrag
- [ ] Diffusion-based FreeDrag
- [ ] FreeDrag anything **3D**
## 🛠️Usage
First clone our repository
```
git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/LPengYang/FreeDrag
```
To create a new environment, please follow the requirements of [NVlabs/stylegan2-ada](https://github.com/NVlabs/stylegan2-ada-pytorch#requirements).
**Notice:** It is observed that the errors (setting up PyTorch plugin “bias_act_plugin“... Failed or “upfirdn2d_plugin“... Failed) may appear in some devices, we hope these potential solutions ([1](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_15969343/article/details/129190607), [2](https://github.com/NVlabs/stylegan2-ada-pytorch/issues/155), [3](https://github.com/NVlabs/stylegan3/issues/124), [4](https://github.com/XingangPan/DragGAN/issues/106)) could be helpful in this case.
Then install the additional requirements
```
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
Then download the pre-trained models of stylegan2
```
bash download_models.sh
```
**Notice:** The first model (face model) could be downed very slowly in some cases. In this case, you can restart the download (works sometimes) or you can directly download it from this [link](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/orgs/nvidia/teams/research/models/stylegan2/files), please download the correct model (ffhq-512×512) and renamed it as "faces.pkl" and manually put it in the created checkpoints file (after all the other models are downloaded).
Finally initialize the gradio platform for interactive point-based manipulation
```
CUDA_LAUNCH_BLOCKING=1 python FreeDrag_gradio.py
```
You can also upload your images and then edit them. For a high-quality image inversion, it is suggested to make sure that the resolution and style (such as layout) of the uploaded images are consistent with the generated images of corresponding model. The resolution of different model is listed as follows:
|Model|face|horse|elephant|lion|dog|bicycle|giraffe|cat|car|church|metface|
|:----:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
|Resolution|512|256|512|512|1024|256|512|512|512|256|1024|
## ❤️Acknowledgments
- [DragGAN](https://github.com/XingangPan/DragGAN/)
- [DragDiffusion](https://yujun-shi.github.io/projects/dragdiffusion.html)
- [StyleGAN2](https://github.com/NVlabs/stylegan2-ada-pytorch)
## License
All codes used or modified from [StyleGAN2](https://github.com/NVlabs/stylegan2-ada-pytorch) are under the [Nvidia Source Code License](https://github.com/NVlabs/stylegan3/blob/main/LICENSE.txt).
The code related to the FreeDrag algorithm is only allowed for personal activity. For commercial use, please contact us.
## ✒️ Citation
If you find our work helpful for your research, please consider citing the following BibTeX entry.
```bibtex
@article{ling2023freedrag,
title={FreeDrag: Point Tracking is Not You Need for Interactive Point-based Image Editing},
author={Ling, Pengyang and Chen, Lin and Zhang, Pan and Chen, Huaian and Jin, Yi},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.04684},
year={2023}
}
```
|
Danie1/threads-api
|
https://github.com/Danie1/threads-api
|
Unofficial Python API for Meta's Threads App
|
# [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/danie1/threads-api/main/.github/logo.jpg" width="36" height="36" />](https://github.com/danie1) Meta's Threads.net API
[](https://pypi.org/project/threads-api/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/threads-api/)
[](https://github.com/danie1/threads-api/releases)
[](https://pypi.org/project/threads-api/) [](https://github.com/Danie1/threads-api/blob/main/LICENSE)
[](https://github.com/Danie1/threads-api/actions/workflows/python-tests.yml)
> Unofficial, Reverse-Engineered Python client for Meta's [Threads](https://threads.net).
Inspired by [NPM Threads-API](https://github.com/junhoyeo/threads-api)
# Threads API - Python
Threads API is an unofficial Python client for Meta's Threads API. It allows you to interact with the API to login, read and publish posts, view who liked a post, retrieve user profile information, follow/unfollow and much more.
✅ Configurable underlying HTTP Client (`aiohttp` / `requests` / `instagrapi`'s client / implement your own)
✅ Authentication Methods supported via `instagrapi`
✅ Stores token and settings locally, to reduce login-attempts (*uses the same token for all authenticated requests for up to 24 hrs*)
✅ Pydantic structures for API responses (for IDE auto-completion) (at [types.py](https://github.com/Danie1/threads-api/blob/main/threads_api/src/types.py))
✅ Actively Maintained since Threads.net Release (responsive in Github Issues, try it out!)
> **Important Tip** Use the same `cached_token_path` for connections, to reduce the number of actual login attempts. When needed, threads-api will reconnect and update the file in `cached_token_path`.
Table of content:
* [Demo](#demo)
* [Getting started](#getting-started)
* [Installation](#installation)
* [Set Log Level & Troubleshooting](#set-desired-log-level)
* [Set HTTP Client](#choose-a-different-http-client)
* [Supported Features](#supported-features)
* [Usage Examples](#usage-examples)
* [Roadmap](#📌-roadmap)
* [Contributions](#contributing-to-danie1threads-api)
* [License](#license)
# Demo
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Danie1/threads-api/main/.github/user_example2.jpg" alt="drawing" width="500"/>
## Getting Started
### 📦 Installation
```bash
pip install threads-api
```
or
```bash
poetry add threads-api
```
Example using threads-api to post to Threads.net:
``` python
from threads_api.src.threads_api import ThreadsAPI
import asyncio
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
async def post():
api = ThreadsAPI()
await api.login(os.environ.get('INSTAGRAM_USERNAME'), os.environ.get('INSTAGRAM_PASSWORD'), cached_token_path=".token")
result = await api.post(caption="Posting this from the Danie1/threads-api!", image_path=".github/logo.jpg")
if result:
print("Post has been successfully posted")
else:
print("Unable to post.")
await api.close_gracefully()
async def main():
await post()
# Run the main function
asyncio.run(main())
```
## Customize HTTP Client
Each HTTP client brings to the table different functionality. Use whichever you like, or implement your own wrapper.
Usage:
``` python
api = ThreadsAPI(http_session_class=AioHTTPSession) # default
# or
api = ThreadsAPI(http_session_class=RequestsSession)
# or
api = ThreadsAPI(http_session_class=InstagrapiSession)
```
## Set Desired Log Level
Threads-API reads the environment variable ```LOG_LEVEL``` and sets the log-level according to its value.
Possible values include: ```DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL```
**Log Level defaults to WARNING when not set.**
Useful to know:
``` bash
# Set Info (Prints general flow)
export LOG_LEVEL=INFO
```
``` bash
# Set Debug (Prints HTTP Requests + HTTP Responses)
export LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG
```
<details>
<summary>Example of Request when LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG</summary>
``` bash
<---- START ---->
Keyword arguments:
[title]: ["PUBLIC REQUEST"]
[type]: ["GET"]
[url]: ["https://www.instagram.com/instagram"]
[headers]: [{
"Authority": "www.threads.net",
"Accept": "*/*",
"Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.9",
"Cache-Control": "no-cache",
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
"Origin": "https://www.threads.net",
"Pragma": "no-cache",
"Sec-Fetch-Dest": "document",
"Sec-Fetch-Mode": "navigate",
"Sec-Fetch-Site": "cross-site",
"Sec-Fetch-User": "?1",
"Upgrade-Insecure-Requests": "1",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_13_6) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/11.1.2 Safari/605.1.15",
"X-ASBD-ID": "129477",
"X-IG-App-ID": "238260118697367"
}]
<---- END ---->
```
</details>
### Troubleshooting threads-api
Upon unexpected error, or upon receiving an exception with: `Oops, this is an error that hasn't yet been properly handled.\nPlease open an issue on Github at https://github.com/Danie1/threads-api.`
Please open a Github Issue with all of the information you can provide, which includes the last Request and Response (Set `LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG`)
# Supported Features
- [x] ✅ Pydantic typing API responses at [types.py](https://github.com/Danie1/threads-api/blob/main/threads_api/src/types.py)
- [x] ✅ Login functionality, including 2FA 🔒
- [x] ✅ Cache login token securely (reduce login requests / due to restrictive limits)
- [x] ✅ Saves settings locally, such as device information and timezone to use along your sessions
- [x] ✅ Read recommended posts from timeline (Requires Login 🔒)
- [x] ✅ Write Posts (Requires Login 🔒)
- [x] ✅ Posts with just text
- [x] ✅ Posts and quote another post
- [x] ✅ Posts with text and an image
- [x] ✅ Posts with text and multiple images
- [x] ✅ Posts with text that shares a url
- [x] ✅ Repost a post
- [x] ✅ Reply to Posts
- [x] ✅ Perform Actions (Requires Login 🔒)
- [x] ✅ Like Posts
- [x] ✅ Unlike Posts
- [x] ✅ Delete post
- [x] ✅ Delete repost
- [x] ✅ Follow User
- [x] ✅ Unfollow User
- [x] ✅ Block User
- [x] ✅ Unblock User
- [x] ✅ Restrict User
- [x] ✅ Unrestrict User
- [x] ✅ Mute User
- [x] ✅ Unmute User
- [x] ✅ Search for users
- [x] ✅ Get Recommended Users
- [x] ✅ Get Notifications (`replies` / `mentions` / `verified`)
- [x] ✅ Read a user's followers list
- [x] ✅ Read a user's following list
- [x] ✅ Read Public Data
- [x] ✅ Read a user_id (eg. `314216`) via username(eg. `zuck`)
- [x] ✅ Read a user's profile info
- [x] ✅ Read list of a user's Threads
- [x] ✅ Read list of a user's Replies
- [x] ✅ Read Post and a list of its Replies
- [x] ✅ View who liked a post
- [x] ✅ CI/CD
- [x] ✅ GitHub Actions Pipeline
- [x] ✅ HTTP Clients
- [x] ✅ AioHTTP
- [x] ✅ Requests
- [x] ✅ Instagrapi
## Usage Examples
View [examples/public_api_examples.py](https://github.com/Danie1/threads-api/blob/main/examples/public_api_examples.py) for Public API code examples.
Run as:
``` bash
python3 examples/public_api_examples.py
```
View [examples/private_api_examples.py](https://github.com/Danie1/threads-api/blob/main/examples/private_api_examples.py) for Private API code examples. (🔒 Requires Authentication 🔒)
Run as:
```
USERNAME=<Instagram Username> PASSWORD=<Instagram Password> python3 examples/private_api_examples.py
```
> **Note:**
> At the end of the file you will be able to uncomment and run the individual examples with ease.
## 📌 Roadmap
- [ ] 🚧 Share a video
- [ ] 🚧 Documentation Improvements
- [ ] 🚧 Add coverage Pytest + Coverage Widget to README
# Contributing to Danie1/threads-api
## Getting Started
With Poetry (*Recommended*)
``` bash
# Step 1: Clone the project
git clone [email protected]:Danie1/threads-api.git
# Step 2: Install dependencies to virtual environment
poetry install
# Step 3: Activate virtual environment
poetry shell
```
or
Without Poetry
``` bash
# Step 1: Clone the project
git clone [email protected]:Danie1/threads-api.git
# Step 2: Create virtual environment
python3 -m venv env
# Step 3 (Unix/MacOS): Activate virtual environment
source env/bin/activate # Unix/MacOS
# Step 3 (Windows): Activate virtual environment
.\env\Scripts\activate # Windows
# Step 4: Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
# License
This project is licensed under the MIT license.
|
InternLM/InternLM
|
https://github.com/InternLM/InternLM
|
InternLM has open-sourced a 7 billion parameter base model, a chat model tailored for practical scenarios and the training system.
|
# InternLM
<div align="center">
<img src="./doc/imgs/logo.svg" width="200"/>
<div> </div>
<div align="center">
<b><font size="5">InternLM</font></b>
<sup>
<a href="https://internlm.intern-ai.org.cn/">
<i><font size="4">HOT</font></i>
</a>
</sup>
<div> </div>
</div>
[](./LICENSE)
[](https://github.com/internLM/OpenCompass/)
[📘Usage](./doc/en/usage.md) |
[🛠️Installation](./doc/en/install.md) |
[📊Train Performance](./doc/en/train_performance.md) |
[👀Model](#model-zoo) |
[🤗HuggingFace](https://huggingface.co/spaces/internlm/InternLM-Chat-7B) |
[🆕Update News](./CHANGE_LOG.md) |
[🤔Reporting Issues](https://github.com/InternLM/InternLM/issues/new)
[English](./README.md) |
[简体中文](./README-zh-Hans.md) |
[日本語](./README-ja-JP.md)
</div>
<p align="center">
👋 join us on <a href="https://twitter.com/intern_lm" target="_blank">Twitter</a>, <a href="https://discord.gg/xa29JuW87d" target="_blank">Discord</a> and <a href="https://r.vansin.top/?r=internwx" target="_blank">WeChat</a>
</p>
## Introduction
InternLM has open-sourced a 7 billion parameter base model and a chat model tailored for practical scenarios. The model has the following characteristics:
- It leverages trillions of high-quality tokens for training to establish a powerful knowledge base.
- It supports an 8k context window length, enabling longer input sequences and stronger reasoning capabilities.
- It provides a versatile toolset for users to flexibly build their own workflows.
Additionally, a lightweight training framework is offered to support model pre-training without the need for extensive dependencies. With a single codebase, it supports pre-training on large-scale clusters with thousands of GPUs, and fine-tuning on a single GPU while achieving remarkable performance optimizations. InternLM achieves nearly 90% acceleration efficiency during training on 1024 GPUs.
## InternLM-7B
### Performance Evaluation
We conducted a comprehensive evaluation of InternLM using the open-source evaluation tool [OpenCompass](https://github.com/internLM/OpenCompass/). The evaluation covered five dimensions of capabilities: disciplinary competence, language competence, knowledge competence, inference competence, and comprehension competence. Here are some of the evaluation results, and you can visit the [OpenCompass leaderboard](https://opencompass.org.cn/rank) for more evaluation results.
| Datasets\Models | **InternLM-Chat-7B** | **InternLM-7B** | LLaMA-7B | Baichuan-7B | ChatGLM2-6B | Alpaca-7B | Vicuna-7B |
| --------------- | -------------------------- | --------------------- | -------- | ----------- | ----------- | --------- | --------- |
| C-Eval(Val) | 53.2 | 53.4 | 24.2 | 42.7 | 50.9 | 28.9 | 31.2 |
| MMLU | 50.8 | 51.0 | 35.2* | 41.5 | 46.0 | 39.7 | 47.3 |
| AGIEval | 42.5 | 37.6 | 20.8 | 24.6 | 39.0 | 24.1 | 26.4 |
| CommonSenseQA | 75.2 | 59.5 | 65.0 | 58.8 | 60.0 | 68.7 | 66.7 |
| BUSTM | 74.3 | 50.6 | 48.5 | 51.3 | 55.0 | 48.8 | 62.5 |
| CLUEWSC | 78.6 | 59.1 | 50.3 | 52.8 | 59.8 | 50.3 | 52.2 |
| MATH | 6.4 | 7.1 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 6.6 | 2.2 | 2.8 |
| GSM8K | 34.5 | 31.2 | 10.1 | 9.7 | 29.2 | 6.0 | 15.3 |
| HumanEval | 14.0 | 10.4 | 14.0 | 9.2 | 9.2 | 9.2 | 11.0 |
| RACE(High) | 76.3 | 57.4 | 46.9* | 28.1 | 66.3 | 40.7 | 54.0 |
- The evaluation results were obtained from [OpenCompass 20230706](https://github.com/internLM/OpenCompass/) (some data marked with *, which means come from the original papers), and evaluation configuration can be found in the configuration files provided by [OpenCompass](https://github.com/internLM/OpenCompass/).
- The evaluation data may have numerical differences due to the version iteration of [OpenCompass](https://github.com/internLM/OpenCompass/), so please refer to the latest evaluation results of [OpenCompass](https://github.com/internLM/OpenCompass/).
### Model Zoo
InternLM 7B and InternLM 7B Chat, trained using InternLM, have been open-sourced. We provide two formats of model weights for use. In addition to loading the models using the Transformers format, you can also load the weights directly using InternLM for further pre-training or human preference alignment training.
| Model | InternLM Format Weight Download Link | Transformers Format Weight Download Link |
| ----------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **InternLM 7B** | [](https://openxlab.org.cn/models/detail/OpenLMLab/InternLM-7b) | [🤗internlm/intern-7b](https://huggingface.co/internlm/internlm-7b) |
| **InternLM Chat 7B** | [](https://openxlab.org.cn/models/detail/OpenLMLab/InternLM-chat-7b) | [🤗internlm/intern-chat-7b](https://huggingface.co/internlm/internlm-chat-7b) |
| **InternLM Chat 7B 8k** | [](https://openxlab.org.cn/models/detail/OpenLMLab/InternLM-chat-7b-8k) | [🤗internlm/intern-chat-7b-8k](https://huggingface.co/internlm/internlm-chat-7b-8k) |
**Limitations:** Although we have made efforts to ensure the safety of the model during the training process and to encourage the model to generate text that complies with ethical and legal requirements, the model may still produce unexpected outputs due to its size and probabilistic generation paradigm. For example, the generated responses may contain biases, discrimination, or other harmful content. Please do not propagate such content. We are not responsible for any consequences resulting from the dissemination of harmful information.
### Import from Transformers
To load the InternLM 7B Chat model using Transformers, use the following code:
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("internlm/internlm-chat-7b", trust_remote_code=True)
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("internlm/internlm-chat-7b", trust_remote_code=True).cuda()
>>> model = model.eval()
>>> response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, "hello", history=[])
>>> print(response)
Hello! How can I help you today?
>>> response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, "please provide three suggestions about time management", history=history)
>>> print(response)
Sure, here are three tips for effective time management:
1. Prioritize tasks based on importance and urgency: Make a list of all your tasks and categorize them into "important and urgent," "important but not urgent," and "not important but urgent." Focus on completing the tasks in the first category before moving on to the others.
2. Use a calendar or planner: Write down deadlines and appointments in a calendar or planner so you don't forget them. This will also help you schedule your time more effectively and avoid overbooking yourself.
3. Minimize distractions: Try to eliminate any potential distractions when working on important tasks. Turn off notifications on your phone, close unnecessary tabs on your computer, and find a quiet place to work if possible.
Remember, good time management skills take practice and patience. Start with small steps and gradually incorporate these habits into your daily routine.
```
### Dialogue
You can interact with the InternLM Chat 7B model through a frontend interface by running the following code:
```bash
pip install streamlit==1.24.0
pip install transformers==4.30.2
streamlit run web_demo.py
```
The effect is as follows

### Deployment
We use [LMDeploy](https://github.com/InternLM/LMDeploy) to complete the one-click deployment of InternLM.
1. First, install LMDeploy:
```bash
python3 -m pip install lmdeploy
```
2. Use the following command for quick deployment:
```bash
python3 -m lmdeploy.serve.turbomind.deploy internlm-chat-7b /path/to/internlm-chat-7b/model
```
3. After exporting the model, you can start a server and have a conversation with the deployed model using the following command:
```bash
bash workspace/service_docker_up.sh
python3 -m lmdeploy.serve.client {server_ip_addresss}:33337
```
[LMDeploy](https://github.com/InternLM/LMDeploy) provides a complete workflow for deploying InternLM. Please refer to the [deployment tutorial](https://github.com/InternLM/LMDeploy) for more details on deploying InternLM.
## Fine-tuning & Training
### Pre-training and Fine-tuning Tutorial
Please refer to [Usage Tutorial](./doc/en/usage.md) to start InternLM installation, data processing, pre-training and fine-tuning.
### Convert to Transformers Format
The model trained by InternLM can be easily converted to HuggingFace Transformers format, which is convenient for seamless docking with various open source projects in the community. With the help of `tools/transformers/convert2hf.py`, the weights saved during training can be converted into transformers format with one command
```bash
python tools/transformers/convert2hf.py --src_folder origin_ckpt/ --tgt_folder hf_ckpt/ --tokenizer ./tools/V7_sft.model
```
After conversion, it can be loaded as transformers by the following code
```python
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("hf_ckpt/", trust_remote_code=True).cuda()
```
## Training System
### System Architecture
Please refer to the [System Architecture document](./doc/en/structure.md) for further details.
### Training Performance
InternLM deeply integrates Flash-Attention, Apex and other high-performance model operators to improve training efficiency. By building the Hybrid Zero technique, it achieves efficient overlap of computation and communication, significantly reducing cross-node communication traffic during training. InternLM supports expanding the 7B model from 8 GPUs to 1024 GPUs, with an acceleration efficiency of up to 90% at the thousand-GPU scale, a training throughput of over 180 TFLOPS, and an average of over 3600 tokens per GPU per second. The following table shows InternLM's scalability test data at different configurations:
| GPU Number | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 | 1024 |
| ---------------- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ----- | ----- | ----- | ------ |
| TGS | 4078 | 3939 | 3919 | 3944 | 3928 | 3920 | 3835 | 3625 |
| TFLOPS | 193 | 191 | 188 | 188 | 187 | 185 | 186 | 184 |
TGS represents the average number of tokens processed per GPU per second. For more performance test data, please refer to the [Training Performance document](./doc/en/train_performance.md) for further details.
## Contribution
We appreciate all the contributors for their efforts to improve and enhance InternLM. Community users are highly encouraged to participate in the project. Please refer to the contribution guidelines for instructions on how to contribute to the project.
## Acknowledgements
InternLM codebase is an open-source project contributed by Shanghai AI Laboratory and researchers from different universities and companies. We would like to thank all the contributors for their support in adding new features to the project and the users for providing valuable feedback. We hope that this toolkit and benchmark can provide the community with flexible and efficient code tools for fine-tuning InternLM and developing their own models, thus continuously contributing to the open-source community. Special thanks to the two open-source projects, [flash-attention](https://github.com/HazyResearch/flash-attention) and [ColossalAI](https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI).
## License
The code is licensed under Apache-2.0, while model weights are fully open for academic research and also allow **free** commercial usage. To apply for a commercial license, please fill in the [application form (English)](https://wj.qq.com/s2/12727483/5dba/)/[申请表(中文)](https://wj.qq.com/s2/12725412/f7c1/). For other questions or collaborations, please contact <[email protected]>.
## Citation
```
@misc{2023internlm,
title={InternLM: A Multilingual Language Model with Progressively Enhanced Capabilities},
author={InternLM Team},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/InternLM/InternLM}},
year={2023}
}
```
|
tsale/Intrusion_data
|
https://github.com/tsale/Intrusion_data
|
This repository is created to store the artifacts for any intrusions I share publicly.
|
# Intrusion Data
The password is: **infected**
This repository was created to store the artifacts of any intrusions I share publicly. The main goal is to provide resources for newcomers in the field to help them develop their investigative skills with data from real intrusions. Each set of data is supported by a blog post that provides additional context.
The blog post details the steps the threat actors took during the intrusion. Using this repository, individuals should be able to retrace these steps using the available telemetry for each case. During this process, they can gain knowledge about the different sets of tools and querying techniques.
<br>
The password is: **infected**
### 🚨Important🚨
> While providing these artifacts for exploration, I offer no guarantees regarding their safety. I encourage you to conduct any investigation in a secure, isolated environment. Please understand that all interactions with these artifacts are at your own risk, and I accept no liability for any potential damages or consequences that may occur. All artifacts are sanitized but if you come across any that are not, please let me know.
<br>
The password is: **infected**
<br>
| Case | Artifacts | Blog |
|----------------|---------------|---------------|
| **Opinion Survey** | 1. SRUM(Parsed NetworkUsage)<br/>2. Endpoint<br/>3. PCAP<br/>4. Scheduled Task<br/>5. Malware used | [Public Opinion Survey Results: You're Pwned](https://kostas-ts.medium.com/public-opinion-survey-results-youre-pwned-12273c6ad839)
| **Ursnif VS Italy: Il PDF del Destino** | 1. PowerShell<br/>2. Endpoint<br/>3. PCAP<br/>4. Malware used | [Ursnif VS Italy: Il PDF del Destino](https://kostas-ts.medium.com/ursnif-vs-italy-il-pdf-del-destino-5c83d6281072)
Feel free to reach out to me on [](https://twitter.com/Kostastsale)
|
ayin86/techui-vue3-lite
|
https://github.com/ayin86/techui-vue3-lite
|
A free, simple, and easy-to-use technology-style UI component, developed based on vue3
|
[简体中文](./README.cn.md) | [繁體中文](./README.hk.md) | English
<h1 align="center">
<b>TechUI-lite Development Kit</b>
</h1>
<div align="center">TechUI-lite is a free and easy to use Dynamic SVG Data Visualization Dashboard development tool, based on vite + vue3 development</div>
<p align="center">
<a href="https://lite.techui.net/docs">Documentation</a> •
<a href="https://lite.techui.net/">Demo Site</a> •
<a href="https://www.npmjs.com/package/techui-vue3-lite">Core library</a> •
<a href="https://techui.net/docs">Premium</a> •
<a href="https://t.me/ayin86cn">Telgram</a>
</p>
## 💖Need A Remote Job
**I am planning to quit my job and if anyone can offer a long term remote job, please contact me. All my skills and frameworks are free to use if a partnership is reached.**
## 🛡️ Announcements
**techUI-Lite framework is completely free, free to use without restrictions, its core files are non-open source and published on NPM server**
**If you find this framework helpful to you, please give me a star, I will be more motivated to develop more free frameworks. I have so many great ideas.**
**If the number of stars reaches 500, I will transplant the premium version of adaptivePanel to the lite version.**
There is also a paid Premium version, which provides more powerful features, related documentation and demos please visit here [TechUI-Premium](https://techui.net/docs)
Note: The SVG material and code in the framework are limited to use in the framework, please do not extract them for other purposes.
**This development kit has 4 built-in data screens, as shown in the figure below.**
**Data Screen A**
<img src="./demoImage/dashboardA-EN.png" style="border-radius:10px" width="800" />
**Data Screen B**
<img src="./demoImage/dashboardB-EN.png" style="border-radius:10px" width="800" />
**Data Screen C**
<img src="./demoImage/dashboardC-EN.png" style="border-radius:10px" width="800" />
**Data Screen D**
<img src="./demoImage/dashboardD-EN.png" style="border-radius:10px" width="800" />
**For more demos, please refer to [TechUI-Lite-Demo](https://lite.techui.net/)**
-----
## ✨Features
- **🖥️Full port adaptation**
Perfect ratio adaptation solution, personal computer, mobile phone, tablet, enterprise splicing screen, it can be said that most terminal devices can be perfectly adapted.
- **🛸Free Development Unlimited**
Using popular technology stacks such as vite and vue3, by calling self-developed components and chart components, it can be quickly deployed and launched without too much tedious development process, which greatly shortens the development cycle. It has truly achieved free development at the source code level.
- **📊Enterprise Splicing Screen**
In the face of enterprise-level splicing screens, we have a lot of display solutions, which can be customized and developed according to the customer's splicing screen equipment. The best display effect can be achieved under any device.
- **🧩De-bitmapping full use of Dynamic SVG**
Comprehensive vectorization (de-bitmapping), due to the special use scene of large-screen visualization, the details of graphics are blurred when traditional bitmaps are used, but the original detail clarity can be maintained after zooming in on vector graphics.
- **🚀Stable iteration and rapid response**
This framework has gone through multiple version iterations, bug fixes are timely, function expansion is progressing steadily, and the Lite version and Premium are updated synchronously.
- **🧑🚀Completely free, use freely**
The lite version is completely free, without any usage restrictions, and can be used for any type of product, project etc.
-----
## 📜 Update Description
- **20230714 techui-vue3-lite-ver3.5 Lite is officially released, and its SVG element node calculation uses WASM component calculation to return**
-----
## 📖Installation Tutorial
1. `cnpm i` installs dependencies
2. `npm run dev` starts the project and you can preview it
For the introduction and usage of the development kit, please refer to [Documentation](https://techui.net/docs)
-----
## 🛠️ Compatibility and Nodejs Versions
1. nodejs 16-18 well supported other versions not tested
2. well supported by all major browsers except IE, including mobile browsers.
-----
## 🌟 Cooperation negotiation
The Lite version framework is free to use and does not provide any technical support. If you encounter any problems, please submit issues on github。
Or add [TechUI discord](https://discord.gg/JXgn5Gq2) to the discussion group.
Or add [TechUI Telgram](https://t.me/+RJZ4cmDrcCFmNWNl) to the discussion group.
For paid services, such as custom development, technical support, or purchasing a premium license, please contact me via the following contact information
WhatsApp scan the QR code below.
<img src="./demoImage/WhatsApp.png" width="300" />
Or contact me via Telegram [@ayin86cn](https://t.me/ayin86cn)
You can also contact me via email [email protected] I will check my email every 1-3 days
-----
## ❤️ What I can offer
The author himself, a UI designer turned front-end developer, has been in the field for 15 years and can take on the responsibilities of product manager, UI designer and front-end developer in a project or product development.
Therefore, it can be said to be the best and cost-effective partner for a start-up company, welcome to discuss cooperation. I hope to find a stable and long-term remote job. Preferably a remote job in Canada, hope to have the opportunity to go to this country.
#### Specific tasks that can be done
- UI design
- Planning and design of products and projects
- Visualization project development
- GEO project development (echarts+geojson+online map)
- Rust development of WASM modules
- Any type of business system
- APP development
- Documentation compilation
- Front-end security, encryption and decryption
|
outmansec/SelfIPAdressQuery
|
https://github.com/outmansec/SelfIPAdressQuery
|
一款基于javafx的自有IP地址查询工具(适用于重保、蓝队等场景)
|
# SelfIPAdressQuery
一款基于javafx的自有IP地址查询工具
## 使用场景
- 在攻防演习中防守方人员会封禁大量IP地址,人员疏忽会导致自有地址被封禁,可以使用此工具进行批量筛选自有地址.
- IP地址归属批量查询.
## 功能介绍
- 通过IP地址查询数据库中符合的自有IP地址或自有IP段,不存在的IP地址通过离线模式或联网模式查询.
- 支持复制指定字段、清空查询列表、导出查询结果.
- 支持单个IP地址或单个IP段添加自有地址,批量导入按照数据库(Self.db)已有信息为模版批量添加.
## 帮助
- 离线模式数据基于ip2region,文件保存在/conf/ip2region.xdb.
- 联网模式数据基于纯真 IP 库 + ip2region + GeoIP2 整合.
- Self.db是基于sqllite构建的数据库,表SelfIP为自有IP地址,表SelfIPSubnet为自有IP段.
- 自有IP地址优先级高于自有IP段,如果查询IP地址两者均存在匹配,那么会优先显示自有IP地址.
- 软件运行环境 Java 1.8.
## 运行图
<img width="764" alt="image" src="https://github.com/outmansec/SelfIPAdressQuery/assets/61048948/346e8a3c-4c06-4b57-9011-a3eea1cfe26b">
|
mishuka0222/fair-squares
|
https://github.com/mishuka0222/fair-squares
| null |
# Fair Squares (FS) · [](https://twitter.com/fairsquares) [](https://github.com/Fair-Squares/fair-squares/blob/main/LICENSE) [](https://discord.gg/5u3dxE49V5)
<div align=center>
<img align=top src="assets/img/FS.png" width=30%/>
<img align=top src="assets/img/web3_foundation_grants_badge_white.svg" width=40%/>
</div>
</br>
**Fair Squares** connects supply and demand of house-owners & renters and houses & investors. Our motive is that we want to create an more affordable housing market. Investors of the house get a social return while renters can have cheaper housing. We want to remove the financial barrier of investing in real estate for investors that don't have the means to fully invest in a house themselves for a social return. In between the end-users, there is coordination taking place between different stakeholders to achieve the desired outcome. This is where the runtime and the logic of all pallets come together, orchestrating while adhering to strict rules set for an equitable system. The orchestration towards an equitable housing market is configurable and governable by the stakeholders that are concerend with it and are willing to work for it.
We are zooming much more on the problem definition, stakeholders and the solution in our paper on our [website](https://www.fair-squares.nl/). To learn more and get in touch with us, please join our [discord channel FS](https://discord.gg/5u3dxE49V5)
Our current development is funded by [Web3 Foundation Grants Program](https://github.com/w3f/Grants-Program)
</br>
## Run & build
### Running locally
1. complete the [basic Rust setup instructions](./docs/rust-setup.md).
1. `cargo run --release -- --dev --tmp` in the root of the fs-node repo.
### Build locally
The `cargo build` command will perform an initial build.
```sh
cargo build --release
```
The binary will be present in create the binary in `./target/release/fs-node` if not other argument is passed.
### Docker build & run
We added a [Dockerfile](https://github.com/Fair-Squares/fair-squares/blob/main/Dockerfile) in the repo, you can build an image yourself with the following command `docker build .`
### Docker images
The images that are tagged starting with `v0.x.x` generate a docker image. You can see the available images [here](https://github.com/Fair-Squares/fair-squares/pkgs/container/fs-node)
run command: </br>
`docker run --publish=127.0.0.1:9944:9944/tcp ghcr.io/fair-squares/fs-node:{$VERSION} fs-node --dev --ws-external`
You have to change the `$VERSION` in the line above.
### Run in Docker in linux
First, install [Docker](https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/) and
[Docker Compose](https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/).
Then run the following command to start a single node development chain.
```bash
./scripts/docker_run.sh
```
The script above will need a folder in the root of this project called `.local` , you will have to create this folder yourself.
This command will firstly compile your code, and then start a local development network. You can also replace the default command
(`cargo build --release && ./target/release/fs-node --dev --ws-external`)
by appending your own. A few useful ones are as follow.
### Connect with Polkadot-Js apps front-end
Once the node template is running locally, you can connect it with **Polkadot-JS Apps** front-end to interact with your chain. [Polkadot.js](https://polkadot.js.org/apps/#/explorer?rpc=ws://localhost:9944) connects a front-end is the app that can interact with the node by means of extensics calls and can read the chain state of the blockchain. Click [here](https://polkadot.js.org/apps/#/explorer?rpc=ws://localhost:9944) to connect to the local blockchain
## Run all tests
```
cargo test
```
|
matter-labs/zk_os
|
https://github.com/matter-labs/zk_os
|
OS for next iteration of the world computer
|
## Zk OS
Ideally: Operation system for the next "world computer", that allows to run untrusted user programs expressed in native code (RISC-V ISA in our case, 32/64 bit, I + M set). We assume strictly serial execution model, with blocking IPC, and each program would pass resources from itself to the callee (mainly time ticks).
In practice for now: example repo to work together with our `risc_v_simulator` and used to implement more restricted version of isolation.
## Grand vision
Once upon a time there was an Idea for Ethereum shards to have different interpreters, but so far it didn't happen. Let's try to fix this. Assume (via `risc_v_simulator` repo) that one has an access to ZK provable simulator of RISC-V 32 (now in the simulator) or 64 (that it most likely will be in practice) bit instruction set with I+M extensions (no usermode/MMU for now). It was oracle access to non-deterministic data via quasi-UART (read word/write word). And let's try to build an execution environment of smart-contracts that live in the common 32-byte address space, follow the same binary interface (e.g. Solidity's ABI), but their code can be either
- bytecode of our zkVM
- EVM bytecode
- WASM
and all of them can call each other! For a moment (because simulator has no interrup functionality) we can ignore resource metering, but it can actually be implemented without interrupts in our model.
So we can write a system that looks like:
- small system layer that implement IO: storage, transient storage, events, memory allocation (note - no translation, so it'll require some creativity down the road). Note that we can implement all the nice tricks that were demonstrated by zkSync Era, for example lazy storage application, provable(!) pubdata discounts, and whatever we imagine, and all of the can be implemented by one(!) copy of Rust (read - normal language) code, and still be provable(!!!)
- three interpreters listed above. Those may require to be butchered to don't abuse allocations (or use proper `Allocator` trait implementation controlled by out system layer), or even extended (more on it below). But for example for storage access they still would go and ask the system layer like "give me storage slot X for contract Y"
- One can make any assumption about the "origin" of the interaction, but it should resemble a standard smart-contract call transaction, and in general few transactions make a block.
- when one sees a "FAR CALL" (zkVM) / "CALL" (EVM) / some special host function call to other contract (WASM) it should pass the execution to another contract along with some resources
So the task we give you with this repo, example and description - try to make such a system. Be creative - because ALL the code that you write is provable, one can do interesting things. For example - when EVM bytecode is deployed, it's possible to preprocess is and e.g. create metadata of all jumpdests, or merklize, or check bytecode for some patterns, or one-pass JIT it even. Same for example for WASM - create a lookup table of block indexes -> offsets, or even JIT to native(!) RISC-V code, and if such JIT is not overly complex and somewhat "safe" - it will be huge efficiency boost. And remember - this action is just Rust code (no circuit), and done once, and proven - so it makes sense to sometimes to O(1) preprocessing on deployments for manifold saving in runtime later one
## Another side
With this repo we also start more engaged work with community and final application developers in a form of RFPs that should say "what do you want to see in the ideal blockchain execution environment".
For example, we named "transient storage" above - it's super easy to implement (and zkSync Era has it actually for free with minimal modification of the current circuits), but was drowning in the proposals for a period of years.
Or may be it would be nice to have immutable-like variables, but not mixed in the "code" and rather just stored alongside the code itself - in special constants area. So ALL contracts that have the same CODE (that is LOGIC and LAW) would literally have same bytecode hash (for ease of comparison), regardless of what constants were chosen by the deploying party.
Be creative here and leave such proposals or feature requests for the "system layer" in issues of this repo.
## What's in the repo
The repo itself is just a small example of how one can bootstrap the system, inspired by the [blog](https://osblog.stephenmarz.com/index.html) about OS development in Rust. It's not intended to be 100% correct or pretend to be anywhere like a good OS because our execution enviroment is different, for example we do not require threads/scheduling, or memory isolation (by translation) yet (but eventually we will need it!). It's a good starting/demo point to start desining an implementation of the vision above.
|
Yufccode/Multiplexing-high-performance-IO-server
|
https://github.com/Yufccode/Multiplexing-high-performance-IO-server
|
Here are three types of high-performance IO servers, implemented through multiplexing. They are select, poll, and epoll, respectively.
|
# Multiplexing-high-performance-IO-server
**多路复用高性能IO服务器**
Here are three types of high-performance IO servers, implemented through multiplexing. They are select, poll, and epoll, respectively. The code implementation language is C/C++. The three servers inside can be combined with the HTTP server, Web server (multi threaded version, etc.), SystemV and other IO models in the BitCode repository to write servers with high IO performance.
## the readme-pdfs
the readmes detail can be seen in the pdfs.
- [select-readme](./readme-pdfs/select-readme.pdf)
- [poll-readme](./readme-pdfs/poll-readme.pdf)
- [epoll-readme](./readme-pdfs/epoll-readme.pdf)
## The definetion of high-performance-IO
The essence of network communication is IO
IO efficiency issue: Network IO efficiency is very low
Why is network IO inefficient?
Taking reading as an example:
1. When we read/recv, what will read/recv do if there is no data in the underlying buffer? -> Blocking
2. What happens if there is data in the underlying buffer when we `read/recv`? -> Copy
**So `IO`=`wait`+`data copy`**
**So what is efficient IO? What is inefficient IO?**
- Inefficient: Unit time, most of the time IO class interfaces are actually waiting!!!
- How to improve the efficiency of IO? Let the proportion of waiting decrease!!!!!
**Five IO models:**
1. Blocking type
2. Non blocking polling
3. Signal driven
4. Multiplexing and Multiplexing
5. Asynchronous IO
**The fourth method is the most efficient**
Why? Because the waiting time per unit time is very low. If a thread/process wants to participate in IO, we call it synchronous IO.
`IO = wait+copy`, so-called participation actually means either participating in wait, participating in copy, or both at the same time.
### How to perform non-blocking IO?
1. Make IO non blocking. When turned on, you can specify a non blocking interface
2. We use a unified approach for non blocking setting **`fcntl()`;**
Codes can be seen in `./non-block-example`
## select
### What is a select and what is it for?
1. Help users wait for multiple File descriptor at one time
2. When the file sockets are ready, select needs to notify the user which sockets are corresponding to the ready sockets. Then, the user can call interfaces such as recv/recvfrom/read to read them.
### man select
```c
/* According to earlier standards */
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds, fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *set);
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *set);
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *set);
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *set);
```
### readfds
1. When entering: user ->kernel, my bit, bit position, indicates the value of the File descriptor, bit content indicates: whether to care - -- assume 0000 1010 indicates ->only care about the read events on File descriptor 1 and 3, I don't care about the read events of other File descriptor
2. When outputting: Kernel ->User, I am an OS, and multiple fds that you asked me to care about have yielded results. The bit position still indicates the value of the File descriptor, but the content indicates ->is ready 0000 1000->indicates that No. 3 File descriptor is ready! -> Users can directly read descriptor 3 without being blocked!
Tips: Because both the user and the kernel will modify the same bitmap. So fd_ After using this thing once, it needs to be reset!
### build a server with select
- [select-readme](./readme-pdfs/poll-readme.pdf)
**Specific code details can be found in the source code.**
**Writing rules for Select server:**
Need a third-party array to store all legitimate fds.
```c
while(true)
{
// 1. Traverse the array and update the maximum value
// 2. Traverse the array and add all the fds that need to be concerned to fd_ Set Bitmap
// 3. Call select for event detection
// 4. Traverse the array, find the ready event, and complete the corresponding redo based on the ready event a. accepter b. recver
}
```
**Extension: What if we want to introduce writing? Let's talk about it when we learn epoll.**
### Advantages and disadvantages of select
**Advantages: (Any multiplexing scheme has these advantages)**
1. High efficiency (compared to before, in multiplexer switching, select is only the younger brother) ->Because he has been working on HandlerEvent
2. Application scenario: There are a large number of links, but only a small number of active ones
**Disadvantages:**
1. In order to maintain third-party arrays, the select server will be filled with traversal operations
2. Reset the select output parameters every time it arrives
3. There is an upper limit to the number of fds that can be managed simultaneously by select!
4. Because almost every parameter is input-output, select will frequently copy parameter data from the user to the kernel and from the kernel to the user.
5. The encoding is quite complex.
## poll
- [poll-readme](./readme-pdfs/poll-readme.pdf)
### what is poll
Poll is actually just making some improvements on select.
Compared to select, the improvements of poll are as follows:
1. The input and output parameters are separated, so there is no need for a large number of reset operations
2. Poll supervised File descriptor no longer has upper limit
### Advantages and disadvantages of poll
Advantages of poll:
1. High efficiency (compared to multiple processes and threads)
2. There are a large number of links, with only a small number being active, which is more suitable
3. Input and output are separate and do not require extensive resetting
4. Parameter level, no upper limit for managing fd
Disadvantages of poll:
1. It still needs to be traversed, and it is the same as detecting fd readiness at the user level and kernel level
2. It is also difficult to avoid the need for kernel to user copying
3. The code for poll is also relatively complex, but easier than select
In fact, the main drawback is still the first one. In order to solve this drawback, we introduced epoll, which means "enhanced poll". However, in fact, epoll is much better than poll.
## epoll
- [epoll-readme](./readme-pdfs/epoll-readme.pdf)
|
PatrikFehrenbach/vilicus
|
https://github.com/PatrikFehrenbach/vilicus
|
vīlicus is a bug bounty api dashboard
|
# vilicus

Vilicus (from Latin, meaning overseer or supervisor) is a Bug Bounty API Dashboard. This platform is designed to simplify the process of bug bounty hunting by aggregating data from various sources and presenting it in an easy-to-understand dashboard.
## Requirements:
To get Vilicus up and running, you'll need the following:
- Python3
- Docker
- Docker-compose
## Installation Steps:
Follow these steps to install and run Vilicus:
1. Clone the Vilicus repository to your local machine.
```
git clone https://github.com/PatrikFehrenbach/vilicus.git
cd vilicus
```
2. Start the Docker services.
```
docker-compose up
```
Wait for Docker to pull the necessary images and start the services. This may take a while.
This will start the server and the application will be accessible at `localhost:5000` (or whatever port you've configured).
3. Visit the dashboard in your web browser.
### Optional SecurityTrails integration
The tool has the ability to automatically query the (https://securitytrails.com/) Securitytrails API once a domain has been added. If youwant too enable this feature, you have to rename the `env.example` to `.env` and insert your own API Key. It is also recommended to rebuild the container like so `docker-compose build --no-cache`
<img width="1012" alt="Screenshot 2023-07-09 at 19 38 06" src="https://github.com/PatrikFehrenbach/vilicus/assets/9072595/9d527caa-5b25-4acb-9e29-1b6f28a94859">
## Contributing:
Contributions are always welcome. If you find a bug or want to add a new feature, feel free to create a new issue or open a pull request.
## License:
This project is open-source and available under the [MIT License](https://github.com/PatrikFehrenbach/vilicus/blob/main/LICENSE).
# Subdomain and Domain API
## Routes
### POST /add_domain
Create a new domain. The request body should contain a JSON object with a "name" field.
Request Body:
```{ "name": "domain name" }```
Responses:
- 201: 'Domain added successfully!'
- 400: 'No domain name provided'
---
### POST /update_domain/<string:domain_name>
Update the name of an existing domain. The request body should contain a JSON object with a "name" field.
Request Body:
```{ "name": "new domain name" }```
Responses:
- 200: 'Domain updated successfully!'
- 400: 'No new domain name provided'
- 404: 'Domain not found'
---
### POST /delete_domain/<string:domain_name>
Delete a specific domain by its name.
Responses:
- 200: 'Domain deleted successfully!'
- 404: 'Domain not found'
---
### GET /domains/export
Export all domains.
Responses:
- 200: List of all domains
---
### GET /domains/search?q=test
Search domains by query. The query should be passed as a URL parameter.
Responses:
- 200: Search results
---
### POST /add_subdomain/<string:main_domain>
Create a new subdomain for a specific domain. The request body should contain a JSON object with a "subdomain_name" field.
Request Body:
```{ "subdomain_name": "subdomain name" }```
Responses:
- 201: 'Subdomain added successfully!'
- 400: 'No subdomain name provided'
- 404: 'Main domain not found'
- 409: 'Conflict'
---
### POST /update_subdomain/<string:main_domain>/<string:subdomain_name>
Update the name of an existing subdomain for a specific domain. The request body should contain a JSON object with a "name" field.
Request Body:
```{ "name": "new subdomain name" }```
Responses:
- 200: 'Subdomain updated successfully!'
- 400: 'No new subdomain name provided'
- 404: 'Main domain not found'
- 404: 'Subdomain not found'
---
### POST /delete_subdomain/<string:main_domain>/<string:subdomain_name>
Delete a specific subdomain for a specific domain.
Responses:
- 200: 'Subdomain deleted successfully!'
- 404: 'Main domain not found'
- 404: 'Subdomain not found'
---
### GET /subdomains/export
Export all subdomains.
Responses:
- 200: List of all subdomains
---
### GET /<string:domain_name>/subdomains/export
Export all subdomains of a specific domain.
Responses:
- 200: List of all subdomains of the specified domain
- 404: 'Domain not found'
---
### GET /subdomains/search?q=test
Search subdomains by query. The query should be passed as a URL parameter.
Responses:
- 200: Search results
---
### GET /lastupdated
Fetch all subdomains added in the last hour.
Responses:
- 200: List of all subdomains added in the last hour
---
### GET /sort_subdomains
Fetch all domains sorted by the count of their subdomains in descending order.
Responses:
- 200: List of all domains sorted by subdomains count
|
qnscholar/zotero-if
|
https://github.com/qnscholar/zotero-if
|
Update IF for Zotero Items.
|
<p align="center">
<img src="https://figurebed-iseex.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/202201180906177.png" width=240 />
</p>
<p align="center">
<a href="https://github.com/qnscholar/zotero-if/releases"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/v/release/qnscholar/zotero-if?color=blue&logo=github" alt="GitHub release" /></a>
<a href="https://figurebed-iseex.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/202201171141964.png"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/公众号-青柠学术-orange?logo=wechat" alt="公众号" /></a>
</p>
# Zotero IF
Update IF for Zotero Items.
## 🔧 使用说明
1. 🎓 选择(可多选)文献,在右键菜单中点击 Update IF(s)。
2. 🏷️ 新添加的文献,会自动更新 JCR IF 和中科院分区。
3. 📌 JCR IF 和中科院分区分别在【文库编目/Library Catalog】和【索取号/CallNumber】字段显示;
4. ✅ 数据:JCR IF(2023.06.28)和中科院分区升级版(2022.12);
<p align="center">
<img src="https://figurebed-iseex.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/202307121736947.png" width=600 />
</p>
## 📌 注意
Zotero IF `v1.5.1` 及以上版本仅适用于 Zotero 7。Zotero 6 用户请安装 [Zotero IF v1.5.0](https://github.com/qnscholar/zotero-if/releases/tag/v1.5.0)。
## 🌟 Star History
[](https://star-history.com/#qnscholar/zotero-if&Timeline)
|
serfubi/Bilibili_show_ticket_auto_order
|
https://github.com/serfubi/Bilibili_show_ticket_auto_order
|
bw2023 copy
|
# Bilibili_show_ticket_auto_order
本项目核心借鉴自https://github.com/Hobr 佬
Bilibili会员购抢票助手, 通过B站接口抢购目标漫展/演出
本脚本仅供学习交流使用, 不得用于商业用途, 如有侵权请联系删除
## 功能截图
除了登录纯api请求
目前已经支持漫展演出等的 无证 / 单证 / 一人一证 的购买
<img src="images/image-20230708014050624.png" alt="image-20230708014050624" style="zoom:50%;" />
<img src="images\image-20230708014124395.png" alt="image-20230708014124395" style="zoom:50%;" />
## 使用
### 执行exe
登录和抢票分开的,先运行登录.exe,登陆后再运行抢票.exe
不需要依赖
### 执行脚本
```shell
python login.py
python main.py
```
改装的东西自己装
## 配置说明
config.txt为配置文件,不指定值为None
- proxies 指定代理 如:127.0.0.1:8080 (IP:PORT 请不要加前缀)
- specificID 多个用户登陆后指定某一个人uid(bilibili) (多用户还没做等后面有必要再写)
## API文档
pass
## 问题报告
提issue即可
|
langsasec/Sign-Sacker
|
https://github.com/langsasec/Sign-Sacker
|
Sign-Sacker(签名掠夺者):一款数字签名复制器,可将其他官方exe中数字签名复制到没有签名的exe中。
|
# Sign-Sacker(签名掠夺者)
## introduce
Sign-Sacker(签名掠夺者):一款数字签名复制器,可将其他官方exe中数字签名复制到没有签名的exe中。
## show
分别导入含有签名和需要签名的文件,点击生成即可,玩免杀的可能会用到。
|
xyhelper/xyhelper-arkose
|
https://github.com/xyhelper/xyhelper-arkose
| null |
# xyhelper-arkose
[ENGLISH](README_EN.md)
自动获取 arkose 的 token,用于自动化测试
## 通知
不再提供 P 项目 BYPASS 功能,没有原因,请不要问为什么
## 1. 安装
创建`docker-compose.yml`文件
```yaml
version: "3"
services:
broswer:
image: xyhelper/xyhelper-arkose:latest
ports:
- "8199:8199"
```
启动
```bash
docker-compose up -d
```
## 2. 使用
### 2.1 获取 token
```bash
curl "http://服务器IP:8199/token"
```
### 2.2 获取 token 池容量
```bash
curl "http://服务器IP:8199/ping"
```
### 2.3 主动挂机
```bash
curl "http://服务器IP:8199/?delay=10"
```
## 3. 如何生产 token
使用合适的浏览器访问`http://服务器IP:8199/`,然后等待即可
## 4. 公共节点
获取 token 地址:https://chatarkose.xyhelper.cn/token
查询 token 池容量:https://chatarkose.xyhelper.cn/ping
|
81NewArk/SD_install4CN
|
https://github.com/81NewArk/SD_install4CN
|
StableDiffusion快速安装配置
|
# SD_install4CN
## 1.引言
Stable Diffusion是一个AI 绘图软件 (开源模型),可本地部署,可切换多种模型,最重要的是免费,没有绘图次数限制。对比Midjourney主打一个分逼不花。
部署时,踩坑主要受国内网络速度和环境配置影响导致部署失败而放弃。闲暇时光编写了这个项目,对比其他动辄几十个G的启动器,SD_install4CN方便快捷,操作简单,并长期更新。
**整合包下载地址:https://www.123pan.com/s/ElPzVv-VNF43.html**
**SD_install4CN v1.0.4单独下载:https://www.123pan.com/s/ElPzVv-jNF43.html**
## 2.程序界面
**当前版本:属于丐版,仅保证安装和配置Stable Diffusion**
**等待更新:国内高速下载插件和模型**
## 3.Stable Diffuson运行要求说明
1. 需要手动下载安装Python和Git,并添加系统环境。【必须】
2. 100G以上的SDD固态硬盘【最少10G,给模型和插件预留空间】
3. SD对N卡十分友好,出图快效率高,推荐GPU 在20系以上+8G显存【N卡必须安装对应显卡的驱动和CUDA】
4. 内存最低要求是8G DDR4【个人推荐16G+】
5. 非N卡用户在SD_Install4CN中选择N卡选项后即可【AMD,YES!】
6. 操作系统:Windows 10 or 11
# 4.模型和插件下载
模型下载:https://www.123pan.com/s/ElPzVv-P2F43.html
插件下载:https://www.123pan.com/s/ElPzVv-X2F43.html
## [扩展知识](https://github.com/81NewArk/SD_install4CN/blob/main/environment.md "扩展知识")
# 在线要饭
 
|
The-HaribOS-Organization/Hariboot
|
https://github.com/The-HaribOS-Organization/Hariboot
|
The UEFI bootloader for the HaribOS operating system
|
<p align="center">
<img src="https://github.com/The-HaribOS-Organization/Hariboot/blob/main/logo.png?raw=true" />
</p>
<h1 align="center"><strong>Hariboot</strong></h1>
<br>
The UEFI bootloader for the HaribOS operating system
## To Install
### debian/ubuntu
- clang
- mtools
- xorriso
- lld
- make
- qemu-system
## Compiling
1. Clone the gnu-efi repository with this command `git clone https://git.code.sf.net/p/gnu-efi/code gnu-efi`
2. In the `data.c` file located in the `gnu-efi/lib/` directory, you need to remove the 'LibStubStriCmp', 'LibStubMetaiMatch', and 'LibStubStrLwrUpr' references to avoid linking error.
3. In the Makefile, change the `GNU-EFI_LOCALIZATION` value to the folder you cloned the gnu-efi repository in.
4. Use the command `make` to build the system.
## Running
1. Clone the [OVMF binaries](https://github.com/The-HaribOS-Organization/OVMFbin).
2. In the Makefile, change the `OVMF_LOCALIZATION` value to the folder that contains the OVMF binaries.
3. Execute the command `make run`.
|
hawkerthewinner/Hawkish-Grabber
|
https://github.com/hawkerthewinner/Hawkish-Grabber
| null |
<h1 align="center">
Hawkish Eyes v7
</h1>

##### [🔱 More](https://t.me/+WvJrz6yv5AxkYjY8)
<h2 align="center">
https://t.me/+WvJrz6yv5AxkYjY8
</h2>
**NOTE:**
- Disclaimer -
I'm not responsible for any damages this software may cause after being acquired.
This software was made for personal **education** and **sandbox testing**
Hawkish-Granner is a tool created with the goal of promoting ethical behavior online.
Its purpose is to help individuals detect and report potential security,
threats and unethical practices by website owners and service providers.
Our aim is to encourage transparency, accountability, and responsibility among online actors,
and to empower users to make informed decisions about their online activities.
Hawkish-Team is not intended for malicious purposes or to harm innocent parties,
and we strongly condemn any illegal or unethical actions that may result from its use.
We hope that this tool will contribute to a safer and more ethical online environment for everyone.
---
## <a id="content"></a>🌐 〢 Content
- [🌌・Telegram](https://t.me/+WvJrz6yv5AxkYjY8)
- [🎉・Setting up](#setup)
- [🔰・Features](#features)
- [👁️・Preview](#preview)
- [📝・Changelog](#changelog)
- [🦜・Injection](http://hawkish.eu/injection-discord)
- [🕵️♂️・Credits](#forkedfrom)
- [💼・Term](#terms)
## <a id="setup"></a> 📁 〢 Setting up
1. Install [Python](https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.10.0/python-3.10.0-amd64.exe)
2. Install [Hawkish Files](https://github.com/Hawkish-Teams/Hawkish-Grabber/archive/refs/heads/main.zip)
3. Install all requirements [install.bat](https://github.com/Hawkish-Teams/Hawkish-Grabber/blob/main/install.bat)
4. Click on start.bat [start.bat](https://github.com/Hawkish-Teams/Hawkish-Grabber/blob/main/start.bat)
5. Complete the configuration
6. You have your .exe/.py file enjoy
## <a id="features"></a>🔰 〢 Features
# 🔱 = Join Telegram
```diff
> Default:
- Steal Steam / Minecraft / Metamask / Exodus / Roblox / NationGlory login
- Add a Fake error
- Steal Chrome Passwords / Cookies / History
- Systeme Informations
- Inject Discord / Discord Canary / Lightcord / Ripcord / Xcord
- Steal AntiVirus Detected
- Debug Killer (Kill task gestionary)
- Bypass TokenProtector / BetterDiscord- Take a Screenshot
- Grabb System Informations
- Steal Latest Clipboard
- GUI builder
- Bypass Virus Total machines
- Bypass VM machines- Hide Itself in Background
- Replace the BTC address copying by your- Custom Installer / Setuper- Icon / Name / Description Customizable
- Steal Wifi Password
- Steal Screenshot
- Add to startup
- Chrome Extensions Injector
- Steal all Chromium Passwords and Cookies for OperaGX/Opera/GoogleChrome/Brave/Chromium/Torch/Edge/Mozilla and others
- 0/64 Detect Virus Total Builder (.exe) (🔱)
- Cookies Exploiter Tech (🔱)
- Grabb Sensitive Files exodus login / a2f backup codes / tokens / passwords... (can be customizable) (🔱)
> Injection Discord:
- Nitro Auto Buy
- First Start Reporter
- New Passwords
- New Emails
- New Login
- New Credit Card
- New PayPal (🔱)
- Anti Delete system (re install after Discord uninstall / Bypass Discord Update) (🔱)
> Injection Chrome:
- Re install Discord Injection
- Logs new cookies
- Logs new tokens
- Logs New Passwords (🔱)
> + More!
```
## <a id="changelog"></a>💭 〢 ChangeLog
```diff
v1.9 ⋮ 2022-26-10
- bug fix to search token
- error message fixed
- build with pyinstaller fixed
v2.0 : 2022-30-10
- enoent zipfile bug fixed
+ Place .exe in startup
+ Add Fake Error
v2.1: 2022-30-10
+ New builder
+ Ping on run
+ Task Manager killer
v2.1.1: 2022-31-10
- Builder correction
+ Compacting Builder
+ Add auto compressed build
v2.2: 2022-31-10
- Token Grabber Correction
+ Grab all other Browsers
+ CMD and gestionnary killer
v2.2.5: 2022-14-11
+ Detect New Discord Active Developer Badge
v2.3: 2023-10-01
- 0 detection source code by virustotal
- Builder error patched
+ New code optimisation
+ New features can replace all crypto wallet by your address
v3: 2023-22-03
- 0 detection source code by virustotal
+ New GUI
+ New code optimisation
+ Wifi Password
+ Antivirus info
+ Choose your files
+ Steal all minecraft app tokens
+ Can disable windows defender
v3.1: 2023-23-03 BUILDER UPDATE
+ Can choose ping (everyone/here)
+ Can add icon
+ Obfuscation Customizable
v3.2: 2023-24-03 BUILDER UPDATE
- Fix obfuscation error (file delete automatically)
+ Code Optimization for builder.py
v3.3: 2023-26-03
+ Webhook Crypted in base64 prevent detection
- Patch some detection
v3.3: 2023-28-03
+ Code completely optimized (-80% time used for -65% resources used)
+ Add % of disk used
+ Patch Key Windows to decrypt cookies/passwords
+ Optimization by getlange + all languages windows supported
v3.3: 2023-29-03
+ Fix Bypass discord token protector
+ Fix getlange error
v3.5: 2023-29-03
+ Patch 98% detection on virustotal (f*ck you kapersky)
v4: 2023-14-04 Builder/Script update
+ Patch detection
+ Builder code optimisation
+ Builder New Style
+ Patch Chrome Cookies decryption error
+ Overlay Hawkish on discord
+ Process Hided in window task manager
+ Patch Builder name error
v5: 2023-01-05 Builder/Script
+ New feature Chrome Extension Logger
+ Code Optimization
+ Builder Gui update
+ Patch all detections
+ Application information Added
v5.5: 2023-01-08 Script
+ Extensions Injector inject into:
- Yandex
- Opera
- Opera Gx
- Microsoft Edge
- Brave Software
- Google Chrome
- Kiwi
- Vivalid
- SRWare Iron
v6.1: 2023-01-08 Script
+ Extensions Injector inject into:
- Comodo Dragon
- Opera Neon
- Torch Browser
- Slimjet
+ Obfuscation Patched
+ Win32gui error patched
v7: 2023-05-31 Web Panel
+ You can create your own api
+ Web Panel with FREE with Hawkish.eu
```
## <a id="preview"></a>👁️ 〢 Preview

### <a id="forkedfrom"></a>🕵️♂️ 〢 Forked From:
- Hazard Grabber
- Wasp-stealer
### <a id="terms"></a>💼 〢 Terms Of Usage
- [x] Educational purpose only
- [x] Reselling is forbidden
- [x] You can use the source code if you keep credits (in embed + in markdown), it has to be open-source
- [x] We are NOT responsible of anything you do with our software (if its illegal)
- [x] If Any Antivirus/Browsers want to know how to patch some vuln you can speak on my telegram
### Authors
- [Hawkishx](https://github.com/Hawkishx)
- [Nolay](https://github.com/NolayDscd)
- [M4T](https://github.com/M4Tback)
<a href=#top>Back to Top</a></p>
|
foyzulkarim/mock-interviews-2023
|
https://github.com/foyzulkarim/mock-interviews-2023
| null |
# MOCK INTERVIEW (PILOT) 2023
## Why
১.৫+ বছর আগে হঠাৎ করেই মক ইন্টারভিউ এর একটা সিরিজ নিছিলাম। সাথে ছিলেন ভিভাসফ্ট (VivaSoft) এর শফিউল হাসান ভাই Shafiul Hasan। এরপর বিভিন্ন কারণে কন্টিনিউ করা হয় নাই। কিছু ব্যক্তিগত কারণ এর বাইরে আরো একটা কারণ ছিল মক ইন্টারভিউ এর সবাইকে একই প্রশ্ন করা আসলে শুধু শুধু সময় নষ্ট কারণ যারা আসলেও ইন্টারভিউ থেকে শিখতে চান তারা এই কয়েকটা ইন্টারভিউ ভালোমতো ফলো করলেই হইতো (অন্তত এতদিন পর্যন্ত এমনটাই ছিল).
গত কয়েক বছরে রিয়াক্ট ইকোসিস্টেমে নতুন অনেক কিছু হয়ে গেছে আর এন্ট্রি লেভেলে জয়েন করার bar আরো উঁচু হয়ে গেছে। সেই সাথে আমাদের দেশেও অনেক অনেক রিয়াক্ট (ফ্রন্টএন্ড-ও বলা যায়) ডেভ তৈরী হয়েছে এই ২ বছরে। তাই আবার মক ইন্টারভিউ টা শুরু করতে চেয়েছি, এবার সাথে আছেন লার্ন উইথ সুমিত (Learn with Sumit) এর সুমিত ভাই Sumit Saha।
পাইলট আকারে শুরু করতেছি আমরা, কিন্তু এইবার আরেকটু গোছানোভাবে করার ইচ্ছা।
## How
প্রসেস টা খুব সংক্ষেপে এমন:
- এপ্লিক্যান্ট রা জব পোস্ট (ফেইক) অনুযায়ী এপ্লাই করবেন।
- সেখান থেকে গুটিকয়েক (১০ জন সম্ভবত) এপ্লিক্যান্ট কে আমরা ইন্টারভিউ নিবো (লাইভ না, তবে রেকর্ড করা হবে)
- সিভি রিভিউ এবং ইন্টারভিউ এর ভিডিও গুলো পরে পাবলিশ করা হবে (কোথায় করা হবে সেটা এখনো সিউর না)
- এই ১০ জন থেকে ৩ জন কে আরেক রাউন্ড এর জন্য বাছাই করবো
- শেষে ১ জনকে বিজয়ী ঘোষণা করবো (বিজয়ী কে কিছু টোকেন মানি (~৫০০০টাকা) ও গিফট হ্যাম্পার উপহারস্বরূপ দেয়া হবে). কেউ যদি স্পনসর এ শরিক হতে চান সেটাও ওয়েলকাম
## Next
যদি এই পাইলট প্রজেক্ট টা কাজ করে, তাহলে এর পরের বার আমরা আরো সিরিয়াসভাবে কিছু করার চেষ্টা করবো। সেটা হতে পারে অন্য স্ট্যাক নিয়ে, অন্য ভাইদের সাহায্য নিয়ে, বা আরো ভালো হয় যদি কোম্পানি গুলোতে প্লেসমেন্ট এর ব্যবস্থা করা যায়। সময়ই বলে দেবে সেটা...
# Instruction for `01-junior-react-dev`
যারা এই রাউন্ডের ইন্টারভিউতে পার্টিসিপেট করতে আগ্রহী তারা এই লিংক [Job Post](https://github.com/foyzulkarim/mock-interviews-2023/blob/main/01-junior-react-dev.md) এর জব ডেসক্রিপশন টা ফলো করুন।
## Conclusion
আমার ব্যক্তিগত মতামত (ভিন্নমত অবশ্যই গ্রহণযোগ্য) হল এই ফেইক জবটার স্যালারি অন্তত ২০হাজার+ হওয়া উচিত। যদি কোন কোম্পানি এই জব ডেসক্রিপশন টা কপি করেন তাহলে বেতন এর রেঞ্জ একটু ভালো করে দিয়েন। ধন্যবাদ সবাইকে 😀
আর এই মক ইন্টারভিউ নিয়ে যে কোন সাজেশন, মতামত অবশ্যই ওয়েলকাম 🙂
|
Venusdev2113/javascript
|
https://github.com/Venusdev2113/javascript
| null |
# javascript

|
kawser2133/clean-structured-project
|
https://github.com/kawser2133/clean-structured-project
|
Clean structured ASP.NET Core web project, follows the Clean Architecture principles, SOLID design principles, and implements the Dependency Injection, Repository, and Unit of Work design pattern, and utilizes Entity Framework Core for data access.
|
# Clean Structured Project - ASP.NET Core
This template is for a clean structured ASP.NET Core web project, follows the Clean Architecture principles, SOLID design principles, implements the Dependency Injection, Repository, and Unit of Work design pattern, and utilizes Entity Framework Core for data access. It provides a standardized structure and organization for building robust and maintainable ASP.NET Core web applications with complete CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations.
## Project Structure
The project structure is designed to promote separation of concerns and modularity, making it easier to understand, test, and maintain the application.
```
├── src
│ ├── Core # Contains the core business logic, domain models, view models, etc.
│ ├── Infrastructure # Contains infrastructure concerns such as data access, external services, etc.
│ └── UI # Contains the user interface layer, including controllers, views, extensions, etc.
├── tests
│ ├── Core.Tests # Contains unit tests for the core layer
│ ├── Infrastructure.Tests # Contains unit tests for the infrastructure layer
│ └── UI.Tests # Contains unit tests for the UI layer
└── README.md # Project documentation (you are here!)
```
## Getting Started
To use this project template, follow the steps below:
1. Ensure the .NET 7 SDK is installed on your machine.
2. Clone or download this repository to your local machine.
3. Open the solution in your preferred IDE (e.g., Visual Studio, Visual Studio Code).
4. Build the solution to restore NuGet packages and compile the code.
5. Configure the necessary database connection settings in the `appsettings.json` file of the Infrastructure project.
6. Open the Package Manager Console, select `Project.Infrastructure` project, and run the `Update-Database` command to create the database
7. Run the application by starting the `Project.UI` project.
## Project Features
This project template includes the following features:
- **Clean Architecture**: The project is structured according to the principles of Clean Architecture, which promotes separation of concerns and a clear division of responsibilities.
- **SOLID Design Principles**: The code adheres to SOLID principles (Single Responsibility, Open-Closed, Liskov Substitution, Interface Segregation, and Dependency Inversion), making it easier to maintain and extend.
- **Repository Pattern**: The repository pattern abstracts the data access layer and provides a consistent interface for working with data.
- **Unit of Work Pattern**: The unit of work pattern helps manage transactions and ensures consistency when working with multiple repositories.
- **Entity Framework Core**: The project utilizes Entity Framework Core as the ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) tool for data access.
- **ASP.NET Core Web**: The project includes an ASP.NET Core web project that serves as the user interface layer, handling HTTP requests and responses.
- **CRUD Operations**: The project template provides a foundation for implementing complete CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on entities using Entity Framework Core.
- **Dependency Injection**: The project utilizes the built-in dependency injection container in ASP.NET Core, making it easy to manage and inject dependencies throughout the application.
- **Unit Testing**: The solution includes separate test projects for unit testing the core, infrastructure, and UI layers.
## Usage
The project template provides a starting point for implementing CRUD operations on entities using Entity Framework Core. You can modify and extend the existing code to suit your specific application requirements. Here's an overview of the key components involved in the CRUD operations:
1. **Models**: The `Core` project contains the domain models representing the entities you want to perform CRUD operations on. Update the models or add new ones according to your domain.
2. **Repositories**: The `Infrastructure` project contains repository implementations that handle data access operations using Entity Framework Core. Modify the repositories or create new ones to match your entity models and database structure.
3. **Services**: The `Core` project contains services that encapsulate the business logic and orchestrate the operations on repositories. Update or create new services to handle CRUD operations on your entities.
4. **Controllers**: The `UI` project contains controllers that handle HTTP requests and responses. Update or create new controllers to expose the CRUD endpoints for your entities.
Make sure to update the routes, validation, and error-handling logic to align with your application requirements and best practices.
## Authors
If you have any questions or need further assistance, please contact the project author at [@kawser2133](https://www.github.com/kawser2133) || [](https://www.linkedin.com/in/kawser2133)
<a href="https://www.buymeacoffee.com/kawser" target="_blank"><img src="https://cdn.buymeacoffee.com/buttons/v2/default-yellow.png" alt="Buy Me A Coffee" style="height: 60px !important;width: 217px !important;" ></a><br/>
**Thanks for your support!**
## Contributing
I want you to know that contributions to this project are welcome. Please open an issue or submit a pull request if you have any ideas, bug fixes, or improvements.
## License
This project is licensed under the [MIT License](LICENSE).
|
exyte/ComposeMultiplatformDribbbleAudio
|
https://github.com/exyte/ComposeMultiplatformDribbbleAudio
|
A repo for the Dribbble Replicating Compose Multiplatform article
|
# ComposeMultiplatformDribbbleAudio
A repo for the Dribbble Replicating Compose Multiplatform article
<a href="https://exyte.com/blog/jetpack-compose-multiplatform">Read Article »</a>

|
wattanx/nuxt-pandacss
|
https://github.com/wattanx/nuxt-pandacss
|
Panda CSS module for Nuxt.
|
# Nuxt Panda CSS
[![npm version][npm-version-src]][npm-version-href]
[![npm downloads][npm-downloads-src]][npm-downloads-href]
[![License][license-src]][license-href]
Panda CSS module for Nuxt.
> **Warning**
> This library is in active development. Use at your own risk.
## Features
<!-- Highlight some of the features your module provide here -->
- Zero configuration to start
## Quick Setup
1. Add `@wattanx/nuxt-pandacss` dependency to your project
```bash
# Using pnpm
pnpm add -D @wattanx/nuxt-pandacss
# Using yarn
yarn add --dev @wattanx/nuxt-pandacss
# Using npm
npm install --save-dev @wattanx/nuxt-pandacss
```
2. Add `@wattanx/nuxt-pandacss` to the `modules` section of `nuxt.config.ts`
```js
export default defineNuxtConfig({
modules: ["@wattanx/nuxt-pandacss"],
});
```
That's it! You can now use `@wattanx/nuxt-pandacss` in your Nuxt app ✨
## Development
```bash
# Install dependencies
npm install
# Generate type stubs
npm run dev:prepare
# Develop with the playground
npm run dev
# Build the playground
npm run dev:build
# Run ESLint
npm run lint
# Run Vitest
npm run test
npm run test:watch
# Release new version
npm run release
```
<!-- Badges -->
[npm-version-src]: https://img.shields.io/npm/v/@wattanx/nuxt-pandacss/latest.svg?style=flat&colorA=18181B&colorB=28CF8D
[npm-version-href]: https://npmjs.com/package/@wattanx/nuxt-pandacss
[npm-downloads-src]: https://img.shields.io/npm/dm/@wattanx/nuxt-pandacss.svg?style=flat&colorA=18181B&colorB=28CF8D
[npm-downloads-href]: https://npmjs.com/package/@wattanx/nuxt-pandacss
[license-src]: https://img.shields.io/npm/l/@wattanx/nuxt-pandacss.svg?style=flat&colorA=18181B&colorB=28CF8D
[license-href]: https://npmjs.com/package/@wattanx/nuxt-pandacss
|
DesignLipsx/WinUI-3-Apps-List
|
https://github.com/DesignLipsx/WinUI-3-Apps-List
|
A collection of apps that support the WinUI 3 Design
|
<h1 align="center">WinUI 3 Apps List</h1>
***WinUI 3** is the latest version of Microsoft's native user interface (UX) framework for Windows desktop and UWP applications. It is based on the Fluent Design System, which emphasizes simplicity, clarity, and consistency in user interface design..*
<p align="center">
<img src="https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1Y42hELgJnvBbgqfRC8ljb7i91bIySm1p">
</p>
<p align="center">
<p align="center">
<b>Please <img src="https://em-content.zobj.net/source/microsoft-teams/363/glowing-star_1f31f.png" width="30" height="30" /> the repo if you like.</b>
</p>
---
## 📑 Table Of Contents
- [Disclaimer](#-disclaimer)
- [Abbreviations](#abbreviations)
- [Best Implementation of WinUI 3](#-best-implementation-of-winui-3)
- [Newly Added Apps](#-newly-added-apps)
- [Apps List](#-apps-list)
- [Social Media](#-social-media)
- [Discord](#-discord)
- [Mastodon](#-mastodon)
- [Reddit](#-reddit)
- [Telegram](#-telegram)
- [Twitter](#-twitter)
- [Whatsapp](#-whatsapp)
- [Youtube](#-youtube)
- [Media](#-media)
- [Music Players](#-music-players)
- [Video Players](#%EF%B8%8F-video-players)
- [Streaming Services](#-streaming-services)
- [Spotify Client](#-spotify-client)
- [Podcast](#%EF%B8%8F-podcast)
- [Photo viewer](#%EF%B8%8F-photo-viewer)
- [Pdf viewer](#-pdf-viewer)
- [Browser](#-browser)
- [Notes](#-notesremindersdraw-board)
- [Personalization](#-personalization)
- [Productivity](#-productivity)
- [File explorer](#-file-explorer)
- [Utilities](#-utilities)
- [Artificial Intelligence (AI)](#-artificial-intelligence-ai)
- [Tools](#%EF%B8%8F-tools)
- [Download Managers](#%EF%B8%8F-download-managers)
- [Device Info/Monitors](#-device-infomonitors)
- [Security&Privacy](#-securityprivacy)
- [News](#-news)
- [Optimizer/Cleaners](#-optimizercleaners)
- [Email Clients](#-email-clients)
- [Translators](#-translators)
- [WSA](#-wsa)
- [Multimedia & Design](#-multimedia--design)
- [Games](#-games)
- [Developer Tools](#-developer-tools)
- [GitHub Client](#-github-client)
- [Other](#-other)
- [Other Windows Apps](#-other-windows-apps)
- [WinUI 3 Catalogs](#-winui-3-catalogs)
---
### 📄 Disclaimer
This list is solely a compilation of apps that adopt the WinUI 3 Design guidelines and does not consider the functionality or utility of the listed apps (the listed apps may or may not be useful). There may be other apps that follow WinUI 3 Design guidelines.
- ❗ Some indicators might be wrong as I interpreted if they're WD/WM/WDM or not by the screenshots. Please report wrong indicators.
- 🔗 The provided links might be from GitHub, GitLab, Telegram, XDA, Official website of the app and other various sources (I always try to provide GitHub links but some apps are not available on GitHub). Please report any broken links.*
#### Abbreviations
- **`WD`** Apps that follow WinUI 3 Design
- **`WM`** Apps that follow Mica Material
- **`WDM`** Apps that have both WinUI 3 design and Mica Material
#### Other abbreviations
- `💰` Paid Apps!
- `🎨` Theme!
- `📆 Planned` Apps that in development
- `❎ Discontinued` App is discontinued/paused indefinitely
---
## ✨ Best Implementation of WinUI 3
- `WDM` [Files App](https://github.com/files-community/files)
- `WDM` [Fluent Emoji Gallery](https://github.com/michalleptuch/fluent-emoji-gallery)
- `WDM` [Radiograph](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/radiograph/9NH1P86H06CG)
- `WDM` [Wintoys](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/wintoys/9P8LTPGCBZXD)
- `WDM` [Wino Mail](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/wino-mail-preview/9NCRCVJC50WL)
- `WDM` [WhatsApp](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/whatsapp/9NKSQGP7F2NH)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
---
## 🆕 Newly Added Apps!
- `WDM` [ChatTailor AI](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/chattailor-ai/9PJRF3ZZ3KHK)
- `WDM` [HiNote](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/hinote/9N94LT5S8FD9)
- `WDM` [AuText](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/autext/9NP0PJHCSRH3)
- `WDM` [T-Drive](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/tdrive/9MVD1PKDTXSN)
- `WD` [SkyNotepad](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/skynotepad/9PN4B4WGKV6H)
- `WD` [ConTeXt IDE](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/context-ide/9NN9Q389TTJR)
- `WDM` [MyDay - Hourly Day Planner](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/myday-hourly-day-planner/9P8QTKPD2WK3)
- `WDM` [backiee - Wallpaper Studio 10](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/backiee-wallpaper-studio-10/9WZDNCRFHZCD)
- `WDM` [AI Wallpapers](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/ai-wallpapers/9NSQGRZKH163)
- `WDM` [GWSL](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/gwsl/9NL6KD1H33V3)
- `WDM` [Latency Tester](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/latency-tester/9P7NKPXPR5FN)
- `WDM` [Create Hotkeys and Remap Keys - Shortcuts IT](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/create-hotkeys-and-remap-keys-shortcuts-it/9N3CJ2K795VD)
- `WDM` [App Packages Viewer](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/app-packages-viewer/9NH1HGNGHB0W)
- `WDM` [美剧社](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/%E7%BE%8E%E5%89%A7%E7%A4%BE/9MXPQ2SRXKXL)
- `WDM` [QuickChat](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/quickchat/9PFXGHNKXMK0)
- `WDM` [MagicTranslate: Simple translator](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/magictranslate-simple-translator/9NGB2P0TSMBF)
- `WD` [GPT Labs](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/gpt-labs/9P2FX8S80WHS)
- `WD` [Tube Music Pro](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/tube-music-pro/9NBVVZBCWXX3)
- `WD` [PocketCFD](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/pocketcfd/9P9QZD92NR3F)
- `WD` [Indirect](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/indirect/9PHW4KJ8JVNZ)
- `WM` [Mica-Discord](https://github.com/Get0457/Mica-Discord)
- `WDM` [PhotoToys](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/phototoys/9N3NH8S6N1DD)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
---
## 📑 Apps List
### 👨💻 Social Media
#### <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=2mIgusGquJFz&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> Discord
- `WDM` [Quarrel](https://github.com/UWPCommunity/Quarrel) `📆`
- `WM` [Mica-Discord](https://github.com/Get0457/Mica-Discord)
- `WD` [Discord-mica](https://github.com/mazOnGitHub/discord-mica) `🎨`
- `WD` [Discord-11](https://github.com/zuzumi-f/Discord-11) `🎨`
#### <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=Xy10Jcu1L2Su&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> Instagram
- `WD` [Indirect](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/indirect/9PHW4KJ8JVNZ)
#### <img src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/48/Mastodon_Logotype_%28Simple%29.svg/1200px-Mastodon_Logotype_%28Simple%29.svg.png" width="18" height="18" /> Mastodon
- `WDM` [Bluechirp](https://github.com/AnalogFeelings/Bluechirp) `📆`
#### <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=h3FOPWMfgNnV&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> Reddit
- `WD` [Fluentreddit](https://github.com/tobyisawesome/fluentreddit/tree/main) `🎨`
- `WDM` [Carpeddit](https://github.com/itsWindows11/Carpeddit) `❎`
#### <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=oWiuH0jFiU0R&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> Telegram
- `WDM` [Unigram](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/unigram%E2%80%94telegram-for-windows/9N97ZCKPD60Q)
#### <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=5MQ0gPAYYx7a&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> Twitter
- `WDM` [Bluesky](https://bsky.app/profile/firecube.bsky.social) `📆`
#### <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=AltfLkFSP7XN&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> WhatsApp
- `WDM` [WhatsApp](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/whatsapp/9NKSQGP7F2NH)
#### <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=9a46bTk3awwI&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> Youtube
- `WDM` [ATube - YT App](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/atube-yt-app/9NBLGGH69MG4)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 🎬 Media
#### 🎧 Music Players
- `WDM` [Rise Media Player](https://github.com/Rise-Software/Rise-Media-Player)
- `WDM` [Screenbox](https://github.com/huynhsontung/Screenbox/)
- `WDM` [Strix Music](https://github.com/Arlodotexe/strix-music)
- `WDM` [Stylophone](https://github.com/Difegue/Stylophone)
- `WDM` [Melosik](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/melosik-music-player-for-windows/9NH759PMH26M)
- `WDM` [Pinnacle Media Player](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/pinnacle-media-player/9P534C2W7JK3)
- `WDM` [Musicloud - Music Downloader](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/musicloud-music-downloader/9P6V0D62D4BQ)
#### ▶️ Video Players
- `WDM` [Rise Media Player](https://github.com/Rise-Software/Rise-Media-Player)
- `WDM` [Screenbox](https://github.com/huynhsontung/Screenbox/)
- **🔧 Tools**
- `WDM` [AVC - Any Video Converter, MP4 Converter](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/avc-any-video-converter-mp4-converter/9PMVGZSGZXVB)
#### 📺 Streaming Services
- `WDM` [Apple TV Preview](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/apple-tv-preview/9NM4T8B9JQZ1)
- `WDM` [Apple Music Preview](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/apple-music-preview/9PFHDD62MXS1)
#### <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=G9XXzb9XaEKX&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> Spotify Client
- `WDM` [Wavee](https://github.com/christosk92/Wavee)
#### 🎙️ Podcast
- `WDM` [FluentCast](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/fluentcast/9PM46JRSDQQR)
- `WDM` [Grover Podcast](https://matheus-inacio.github.io/grover-podcast/)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 🏜️ Photo viewer
- `WDM` [Visum Photo Viewer](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/visum-photo-viewer/9N1X3Z50BLM8)
- `WM` [QuickLook](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/quicklook/9NV4BS3L1H4S)
- **🔧 Tools**
- `WDM` [AIC - Any Image Converter, JPG Converter](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/aic-any-image-converter-jpg-converter/9NN44CM8T0GS)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 📄 Pdf viewer
- `WDM` [Fluetro PDF](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/fluetro-pdf/9NSR7B2LT6LN)
- **🔧 Tools**
- `WD` [PDF Jack](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/pdf-jack/9NBLGGH1P3P6)
- `WDM` [Pdf.JPG - PDF to JPG, PDF Converter](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/pdfjpg-pdf-to-jpg-pdf-converter/9NJ9N3MG9JLW)
- `WDM` [PDF Unlocker - Unlock PDF, Remove Password](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/pdf-unlocker-unlock-pdf-remove-password/9P20WBQVFD4N)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 🌐 Browser
- `WDM` [FireBrowser](https://github.com/FirebrowserDevs/FireBrowser-Uwp) `📆`
- `WDM` [Radon Browser](https://github.com/itzbluebxrry/Project-Radon) `📆`
- `WDM` [Swift Browser](https://github.com/FireCubeStudios/SwiftBrowser) `📆`
- `WDM` [Yttrium](https://github.com/muznyo/Yttrium) `📆`
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 📒 Notes/Reminders/Draw-Board
#### 📝 Notes
- `WDM` [TowPad](https://github.com/itsWindows11/TowPad)
- `WDM` [Fluent Pad](https://github.com/Lixkote/WritePad)
- `WDM` [HiNote](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/hinote/9N94LT5S8FD9)
- `WDM` [Text space](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/text-space/9N6CPGZGXSVT)
- `WDM` [Storylines](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/storylines/9PN77P9WJ3CX)
- `WD` [SkyNotepad](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/skynotepad/9PN4B4WGKV6H)
- `WDM` [Quick Pad](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/quick-pad-fluent-notepad-app/9PDLWQHTLSV3?hl) `💰`
#### 🔔 Reminders
- `WDM` [AlertMe](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/alertme-quick-reminder-notifications/9MW5VRL0BQT9) `💰`
#### ⬜ Draw Board
- `WDM` [FlowBoard](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/flowboard-firecubes-edition/9PB20HCH5XN2)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 🎨 Personalization
- `WDM` [Lively Wallpaper](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/lively-wallpaper/9NTM2QC6QWS7)
- `WDM` [Desktop Live Wallpapers](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/desktop-live-wallpapers/9NZ370XBFQMG)
- `WDM` [backiee - Wallpaper Studio 10](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/backiee-wallpaper-studio-10/9WZDNCRFHZCD)
- `WDM` [AI Wallpapers](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/ai-wallpapers/9NSQGRZKH163)
- `WDM` [AccentColorizer](https://github.com/krlvm/AccentColorizer)
- `WDM` [Dynamic theme](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/dynamic-theme/9NBLGGH1ZBKW)
- `WM` [Auto Dark Mode](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/auto-dark-mode/XP8JK4HZBVF435)
- `WD` [BeWidgets](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/bewidgets/9NQ07FG50H2Q)
- `WD` [WidgetBox](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/widgetbox-modern-widget-collection/9NF1ZHFJBCZJ)
- `WDM` [Mica](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/mica%E2%84%A2%EF%B8%8F/9N7LF08JZ98K)
- `WD` [Tabbed](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/tabbed%E2%84%A2%EF%B8%8F/9PNTW3WL9SRQ)
- `WD` [Acrylic](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/acrylic%E2%84%A2%EF%B8%8F/9PHF4S5SJJG3)
- `WDM` [AuText](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/autext/9NP0PJHCSRH3)
- `WDM` [T-Drive](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/tdrive/9MVD1PKDTXSN)
- `WDM` [MyDay - Hourly Day Planner](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/myday-hourly-day-planner/9P8QTKPD2WK3) `💰`
- `WDM` [TheMenu](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/themenu/9P1RPMSH1TPB) `💰`
- `WDM` [Power Widgets - interactive widgets](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/power-widgets-interactive-widgets/9NLHP5KRXZQ7) `💰`
- `WDM` [FolderIconizer - Change Folder Icons](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/foldericonizer-change-folder-icons/9PLQDJ5XCNL3) `💰`
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 📈 Productivity
- `WD` [Clipboard Canvas](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/clipboard-canvas/9NN2NZG8RLTB)
- `WDM` [FlowTeX preview beta](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/flowtex-preview-beta/9NT79075T86L)
- `WDM` [FCN for Writers](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/fcn-for-writers/9P28H11CKGWC)
- `WDM` [Create Hotkeys and Remap Keys - Shortcuts IT](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/create-hotkeys-and-remap-keys-shortcuts-it/9N3CJ2K795VD)
- `WDM` [美剧社](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/%E7%BE%8E%E5%89%A7%E7%A4%BE/9MXPQ2SRXKXL)
- `WDM` [File Optimizer](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/file-optimizer/9P322WWXH4D0)
- `WDM` [Ink Workspace](https://github.com/SimpleMobileTools/Simple-Calendar)
- `WDM` [To-Do](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/todo%E1%B2%BC/9P7JL8SP2L1C)
- `WDM` [Microsoft PowerToys](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/microsoft-powertoys/XP89DCGQ3K6VLD)
- `WDM` [United Sets preview beta](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/united-sets-preview-beta/9N7CWZ3L5RWL)
- `WDM` [Socialize Up - Manage all your Social Media!](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/socialize-up-manage-all-your-social-media/9NBLGGH6C75V)
- `WDM` [QuickChat](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/quickchat/9PFXGHNKXMK0)
- `WDM` [AniMoe](https://github.com/CosmicPredator/AniMoe)
- `WDM` [Shapr3D](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/shapr3d/9N4K9QFV4XFC)
- `WDM` [Calendar Flyout](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/calendar-flyout/9P2B3PLJXH3V) `💰`
- `WDM` [Tomato app]() `📆`
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 📁 File explorer
- `WDM` [Files App](https://github.com/files-community/files)
- `WDM` [Shrestha Files Free](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/shrestha-files-free/9PLL2XRXQ9LF)
- `WD` [Adv File Explorer](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/adv-file-explorer/9MVSVN9D3G5Z)
- `WDM` [MyFTP](https://github.com/luandersonn/MyFTP)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 🔧 Utilities
- `WDM` [Wintoys](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/wintoys/9P8LTPGCBZXD)
- `WDM` [PhotoToys](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/phototoys/9N3NH8S6N1DD)
- `WDM` [Registry Editor Valley](https://github.com/0x5bfa/RegistryValley)
- `WDM` [Twinkle Tray: Brightness Slider](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/twinkle-tray-brightness-slider/9PLJWWSV01LK)
- `WDM` [ModernFlyouts (Preview)](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/modernflyouts-preview/9MT60QV066RP)
- `WDM` [Fluent Search](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/fluent-search/9NK1HLWHNP8S)
- `WDM` [Fluent Screen Recorder](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/fluent-screen-recorder/9MWV79XLFQH7)
- `WDM` [Fluent Flyouts Battery (Preview)](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/fluent-flyouts-battery-preview/9NWXR2MKSNX7)
- `WDM` [Rectify Winver](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/rectify-winver/9NKZHB76GN8B)
- `WDM` [Winver UWP](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/winver-uwp/9N60S2VFMB7L)
- `WD` [ModernRun](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/modernrun/9NRMMT926PNX)
- `WD` [RunManager](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/runmanager/9NGP5GKCCF3S)
- `WDM` [Run by FireCube](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/run-by-firecube-not-by-microsoft/9NQGV64S5136)
- `WDM` [Scanner - Quick and Easy Document Scanning](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/scanner-quick-and-easy-document-scanning/9N438MZHD3ZF)
- `WDM` [barcodrod.io](https://github.com/MarkHopper24/barcodrod.io)
- `WDM` [Latency Tester](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/latency-tester/9P7NKPXPR5FN)
- `WDM` [Text-Grab](https://github.com/TheJoeFin/Text-Grab)
- `WD` [UUP Media Creator](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/uup-media-creator/9N1Z0JXB224X)
- `WD` [TaskbarWebsites](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/taskbarwebsites/9MZ8WTK48VHT)
- `WD` [PocketCFD](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/pocketcfd/9P9QZD92NR3F)
- `WDM` [Simple Icon File Maker](https://github.com/TheJoeFin/Simple-Icon-File-Maker)
- `WDM` [FileFracture - Split and Join Files](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/filefracture-split-and-join-files/9MVGQJN90QP6)
- `WDM` [Custom Context Menu](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/custom-context-menu/9PC7BZZ28G0X)
- `WDM` [A.Click - Auto Clicker](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/aclick-auto-clicker/9MV9MFVB6R5V)
- `WDM` [Backup My Files](https://www.microsoft.com/store/apps/9P977JGV4VFB) `💰`
- `WDM` [Desktop Toolkit](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/desktop-toolkit/9N8PFLMMR9BW) `💰`
- `WDM` [ISOMaker - ISO Image Creator](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/isomaker-iso-image-creator/9NP1ZVJW7BV2) `💰`
- `WDM` [WiFiSpy - Who Is On My WiFi](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/wifispy-who-is-on-my-wifi/9N64F7V2KSZH) `💰`
- `WDM` [DiskBenchmark - Test HardDisk Performance](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/diskbenchmark-test-harddisk-performance/9NJFMWN131GK) `💰`
- `WDM` [IPDetective - Advanced IP Scanner](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/ipdetective-advanced-ip-scanner/9P5BGL0C8VBS) `💰`
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 🤖 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- `WDM` [Engage](https://github.com/iamhazel/Engage) `📆 Planned`
- `WD` [GPT Labs](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/gpt-labs/9P2FX8S80WHS)
- `WDM` [EasyChat AI](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/easychat-ai-%E2%80%93-chat-get-answers/9NXK0PK5ZS1B?hl)
- `WDM` [ChatTailor AI](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/chattailor-ai/9PJRF3ZZ3KHK)
- `WDM` [Fantasy Copliot](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/fantasy-copliot/9NB0NB3MLQTM)
- `WDM` [Clippy by FireCube](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/clippy-by-firecube/9NWK37S35V5T)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 🛠️ Tools
#### ⬇️ Download Managers
- <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=oWNmXOb2HARO&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> Full-Featured Download Manager
- `WDM` [OnionMedia](https://github.com/onionware-github/OnionMedia)
- `WDM` [YH File Download Manager](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/yh-file-download-manager/9N1S7G773K1K) `💰`
- <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=9a46bTk3awwI&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> YouTube
- `WDM` [YTD - YT Video Downloader](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/ytd-yt-video-downloader/9MZQ5285RW0Q)
- `WDM` [Yt.MP3 - YT to MP3](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/ytmp3-yt-to-mp3-yt-video-downloader/9NGH84LZQC37)
- `WD` [Tube Music Pro](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/tube-music-pro/9NBVVZBCWXX3)
- <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=Xy10Jcu1L2Su&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> Instagram
- `WDM` [IGD - Instagram Downloader](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/igd-instagram-downloader/9PP3HHJVX67F)
- <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=VaxSTuUVwLif&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> Torrenting
- `WDM` [ByteStream Torrent](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/bytestream-torrent/9PJT9PBVG7K8)
- `WDM` [qBitTorrent-Fluent theme](https://github.com/witalihirsch/qBitTorrent-fluent-theme)
- `WDM` [youTorrent](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/youtorrent/9P2QMBVQRCFN)
#### 📊 Device Info/Monitors
- `WD` [Specs Analysis (Beta)](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/specs-analysis-beta/9WZDNCRDGX54)
- `WDM` [Radiograph](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/radiograph/9NH1P86H06CG)
- `WDM` [Disk Info](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/disk-info/9PLQ8DP73ZDF)
#### 🔒 Security&Privacy
- `WDM` [Protecc - 2FA Authenticator TOTP](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/protecc-2fa-authenticator-totp/9PJX91M06TZS)
- `WDM` [SecureFolderFS](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/securefolderfs/9NZ7CZRN7GG8)
- `WM` [Pass11](https://github.com/LawOff/Pass11)
- `WM` [Password Plus Generator](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/password-plus-generator/9P9SSPR1MLB9)
#### 📰 News
- `WDM` [Fluent HN - Hacker News client](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/fluent-hn-hacker-news-client/9N8PDZHCPQHX) `💰`
#### 🧹 Optimizer/Cleaners
- `WDM` [D.Cleaner - Duplicate Cleaner](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/dcleaner-duplicate-cleaner/9NP1ZPC3THSS)
- `WDM` [PowerDisk - PC Cleaner](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/powerdisk-pc-cleaner/9PLPNC3D2N2T)
- `WD` [Duplicates Cleaner](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/duplicates-cleaner/9PMXPZ18CZ49)
#### 📧 Email Clients
- `WDM` [Wino Mail](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/wino-mail-preview/9NCRCVJC50WL) `[No Google Acoount Support]`
#### 🈵 Translators
- `WDM` [Translate](https://github.com/shef3r/Translate)
- `WDM` [MagicTranslate: Simple translator](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/magictranslate-simple-translator/9NGB2P0TSMBF)
#### 🤖 WSA
- `WDM` [APK Installers](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/apk-installers/9P2JFQ43FPPG)
- `WDM` [Apk Installer on WSA](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/apk-installer-on-wsa/9N1TWH0BPJPS)
- `WDM` [Aow Tools](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/aow-tools/9NXM6552H2QL)
- `WDM` [WSATools - APK installer and more](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/wsatools-apk-installer-and-more/9N4P75DXL6FG)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 💠 Multimedia & Design
- `WDM` [Camo](https://reincubate.com/camo/)
- `WDM` [Character Map UWP](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/character-map-uwp/9WZDNCRDXF41)
- `WDM` [Fluent Emoji Gallery](https://github.com/michalleptuch/fluent-emoji-gallery)
- `WDM` [The Color Palette](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/the-color-palette/9PBK4B7HBJXG)
- `WDM` [Sketchable Plus](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/sketchable-plus/9MZZLHTZ5N02)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 🎮 Games
- `WDM` [Fluent-Tic-Tac-Toe](https://github.com/dfchang149/Fluent-Tic-Tac-Toe)
- `WDM` [OurSweeper](https://www.xbox.com/en-in/games/store/oursweeper/9pb8sdwv419v?rtc=1)
- `WDM` [Emerald](https://github.com/RiversideValley/Emerald)
- **🔧 Tools**
- `WM` [Mixplay for Mixer](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/mixplay-for-mixer/9PN94D9BDFZM)
- `WDM` [DialogueForest](https://github.com/Difegue/DialogueForest)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 🧑💻 Developer tools
#### <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=AZOZNnY73haj&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> GitHub Client
- `WDM` [FluentHub](https://github.com/FluentHub/FluentHub)
- `WDM` [JitHub](https://github.com/JitHubApp/JitHubV2)
#### <img src="https://img.icons8.com/?size=512&id=PkQpLJisPiTI&format=png" width="21" height="21" /> Other
- `WDM` [FluentEdit](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/fluentedit/9NWL9M9JPQ36)
- `WDM` [Fastedit](https://github.com/FrozenAssassine/Fastedit)
- `WDM` [DevToys](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/devtoys/9PGCV4V3BK4W)
- `WDM` [QTWin11](https://github.com/witalihirsch/QTWin11)
- `WD` [ConTeXt IDE](https://github.com/WelterDevelopment/ConTeXt-IDE-WinUI)
- `WDM` [MVVM Toolkit Sample App](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/mvvm-toolkit-sample-app/9NKLCF1LVZ5H)
- `WD` [Developers Toolbox](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/developers-toolbox/9N6J5X2172Q8)
- `WD` [Codly Snippet Manager](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/codly-snippet-manager/9PGPG8PCF2F9)
- `WDM` [GWSL](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/gwsl/9NL6KD1H33V3)
- `WDM` [App Packages Viewer](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/app-packages-viewer/9NH1HGNGHB0W)
- `WD` [3D Engine](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/3d-engine/9NFSX6JPV0PS)
- `WDM` [Dev Home GitHub Extension (Preview)](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/dev-home-github-extension-preview/9NZCC27PR6N6)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
### 🪟 Other Windows Apps
- `WDM` [Microsoft Edge Browser](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/microsoft-edge-browser/XPFFTQ037JWMHS)
- `WDM` [Windows Media Player](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/windows-media-player/9WZDNCRFJ3PT)
- `WDM` [Microsoft Photos](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/microsoft-photos/9WZDNCRFJBH4)
- `WDM` [Microsoft Paint](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/paint/9PCFS5B6T72H)
- `WDM` [Windows Notepad](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/windows-notepad/9MSMLRH6LZF3)
- `WDM` [Snipping Tool](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/snipping-tool/9MZ95KL8MR0L)
- `WDM` [Windows Calculator](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/windows-calculator/9WZDNCRFHVN5)
- `WDM` [Movies & TV](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/movies-tv/9WZDNCRFJ3P2)
- `WDM` [Windows Clock](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/windows-clock/9WZDNCRFJ3PR)
- `WDM` [Phone Link](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/phone-link/9NMPJ99VJBWV)
- `WD` [Quick Assist](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/quick-assist/9P7BP5VNWKX5)
- `WD` [Windows Terminal](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/windows-terminal/9N0DX20HK701)
- `WD` [PowerShell](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/powershell/9MZ1SNWT0N5D)
- `WDM` [Feedback Hub](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/feedback-hub/9NBLGGH4R32N)
- `WDM` [Get Help](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/get-help/9PKDZBMV1H3T)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
------------
#### 📖 WinUI 3 Catalogs
- `WD` [WinUI 3 Gallery](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/winui-3-gallery/9P3JFPWWDZRC)
- `WDM` [WPF UI](https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/wpf-ui/9N9LKV8R9VGM)
- `WDM` [Windows Community Toolkit](https://github.com/CommunityToolkit/Windows)
<sub>[📑 Table Of Contents](#-table-of-contents)</sub>
|
srid/nixci
|
https://github.com/srid/nixci
|
Define and build CI for Nix projects anywhere
|
# nixci
[](https://crates.io/crates/nixci)
`nixci` builds all outputs in a flake, or optionally its [sub-flakes](https://github.com/hercules-ci/flake-parts/issues/119), which can in turn be used either in CI or locally. Using [devour-flake] it will automatically build the following outputs:
| Type | Output Key |
| ---------------------- | ----------------------------------------------- |
| Standard flake outputs | `packages`, `apps`, `checks`, `devShells` |
| NixOS | `nixosConfigurations.*` |
| nix-darwin | `darwinConfigurations.*` |
| home-manager | `legacyPackages.${system}.homeConfigurations.*` |
## Install
> **Note** To make use of the binary cache, first run:
>
> `nix run nixpkgs#cachix use srid`
To install, run `nix profile install github:srid/nixci`. You can also use use `nix run github:srid/nixci` to run `nixci` directly off this repo without installing it.
## Usage
`nixci` accepts any valid [flake URL](https://nixos.org/manual/nix/stable/command-ref/new-cli/nix3-flake.html#url-like-syntax) or a Github PR URL.
```sh
# Run nixci on a local flake (default is $PWD)
$ nixci ~/code/myproject
# Run nixci on a github repo
$ nixci github:hercules-ci/hercules-ci-agent
# Run nixci on a github PR
$ nixci https://github.com/srid/emanote/pull/451
```
## Configuring
By default, `nixci` will build the top-level flake, but you can tell it to build sub-flakes by adding the following output to your top-level flake:
```nix
# myproject/flake.nix
{
nixci = {
dir1 = {
dir = "dir1";
};
dir2 = {
dir = "dir2";
overrideInputs.myproject = ./.;
};
}
}
```
### Examples
Some real-world examples of how nixci is used with specific configurations:
- [services-flake](https://github.com/juspay/services-flake/blob/197fc1c4d07d09f4e01dd935450608c35393b102/flake.nix#L10-L24)
- [nixos-flake](https://github.com/srid/nixos-flake/blob/4af32875e7cc6df440c5f5cf93c67af41902768b/flake.nix#L29-L45)
## What it does
- Accepts a flake config (`nixci`) that optionally specifies all the sub-flakes to build, along with their input overrides
- Checks that `flake.lock` is in sync
- Runs [devour-flake](https://github.com/srid/devour-flake) to build all flake outputs
- Prints the built outputs
[devour-flake]: https://github.com/srid/devour-flake
## See also
- [jenkins-nix-ci](https://github.com/juspay/jenkins-nix-ci) - Jenkins NixOS module that supports `nixci` as a Groovy function
|
corca-ai/awesome-llm-security
|
https://github.com/corca-ai/awesome-llm-security
|
A curation of awesome tools, documents and projects about LLM Security.
|
# Awesome LLM Security [](https://github.com/sindresorhus/awesome)
A curation of awesome tools, documents and projects about LLM Security.
Contributions are always welcome. Please read the [Contribution Guidelines](CONTRIBUTING.md) before contributing.
## Table of Contents
- [Awesome LLM Security](#awesome-llm-security-)
- [Papers](#papers)
- [Tools](#tools)
- [Articles](#articles)
- [Other Awesome Projects](#other-awesome-projects)
- [Other Useful Resources](#other-useful-resources)
## Papers
- [Not what you've signed up for: Compromising Real-World LLM-Integrated Applications with Indirect Prompt Injection](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.12173.pdf)
- [Visual Adversarial Examples Jailbreak Large Language Models](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.13213.pdf)
- [Jailbroken: How Does LLM Safety Training Fail?](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.02483.pdf)
- [Are aligned neural networks adversarially aligned?](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.15447.pdf)
- [Latent Jailbreak: A Benchmark for Evaluating Text Safety and Output Robustness of Large Language Models](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.08487.pdf)
- [(Ab)using Images and Sounds for Indirect Instruction Injection in Multi-Modal LLMs](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.10490.pdf)
- [Prompts Should not be Seen as Secrets: Systematically Measuring Prompt Extraction Attack Success](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.06865.pdf)
- [BITE: Textual Backdoor Attacks with Iterative Trigger Injection](https://aclanthology.org/2023.acl-long.725.pdf)
- [Multi-step Jailbreaking Privacy Attacks on ChatGPT](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.05197.pdf)
- [Prompt as Triggers for Backdoor Attack: Examining the Vulnerability in Language Models](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2305.01219.pdf)
- [LLM Censorship: A Machine Learning Challenge or a Computer Security Problem?](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.10719.pdf)
- [Universal and Transferable Adversarial Attacks on Aligned Language Models](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.15043.pdf)
- [Plug and Pray: Exploiting off-the-shelf components of Multi-Modal Models](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.14539.pdf)
- [Virtual Prompt Injection for Instruction-Tuned Large Language Models](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.16888.pdf)
## Tools
- [Rebuff](https://github.com/protectai/rebuff): a self-hardening prompt injection detector 
- [Garak](https://github.com/leondz/garak/): a LLM vulnerability scanner 
- [LLMFuzzer](https://github.com/mnns/LLMFuzzer): a fuzzing framework for LLMs 
## Articles
- [Hacking Auto-GPT and escaping its docker container](https://positive.security/blog/auto-gpt-rce)
- [Prompt Injection Cheat Sheet: How To Manipulate AI Language Models](https://blog.seclify.com/prompt-injection-cheat-sheet/)
- [Indirect Prompt Injection Threats](https://greshake.github.io/)
- [Prompt injection: What’s the worst that can happen?](https://simonwillison.net/2023/Apr/14/worst-that-can-happen/)
- [OWASP Top 10 for Large Language Model Applications](https://owasp.org/www-project-top-10-for-large-language-model-applications/)
- [PoisonGPT: How we hid a lobotomized LLM on Hugging Face to spread fake news](https://blog.mithrilsecurity.io/poisongpt-how-we-hid-a-lobotomized-llm-on-hugging-face-to-spread-fake-news/)
- [ChatGPT Plugins: Data Exfiltration via Images & Cross Plugin Request Forgery](https://embracethered.com/blog/posts/2023/chatgpt-webpilot-data-exfil-via-markdown-injection/)
- [Jailbreaking GPT-4's code interpreter](https://www.lesswrong.com/posts/KSroBnxCHodGmPPJ8/jailbreaking-gpt-4-s-code-interpreter)
## Other Awesome Projects
- [Gandalf](https://gandalf.lakera.ai/): a prompt injection wargame
- [LangChain vulnerable to code injection - CVE-2023-29374](https://github.com/advisories/GHSA-fprp-p869-w6q2)
- [Jailbreak Chat](https://www.jailbreakchat.com/)
- [Adversarial Prompting](https://www.promptingguide.ai/risks/adversarial)
- [Epivolis](https://epivolis.com/): a prompt injection aware chatbot designed to mitigate adversarial efforts
- [LLM Security Problems at DEFCON31 Quals](https://github.com/Nautilus-Institute/quals-2023/tree/main/pawan_gupta): the world's top security competition
## Other Useful Resources
- Twitter: [@llm_sec](https://twitter.com/llm_sec)
- Blog: [Embrace The Red](https://embracethered.com/blog/index.html)
- Blog: [Kai's Blog](https://kai-greshake.de/)
- Newsletter: [AI safety takes](https://newsletter.danielpaleka.com/)
- Newsletter & Blog: [Hackstery](https://hackstery.com)
<a href="https://star-history.com/#corca-ai/awesome-llm-security&Date">
<picture>
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" srcset="https://api.star-history.com/svg?repos=corca-ai/awesome-llm-security&type=Date&theme=dark" />
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" srcset="https://api.star-history.com/svg?repos=corca-ai/awesome-llm-security&type=Date" />
<img alt="Star History Chart" src="https://api.star-history.com/svg?repos=corca-ai/awesome-llm-security&type=Date" />
</picture>
</a>
|
Lomray-Software/react-head-manager
|
https://github.com/Lomray-Software/react-head-manager
|
React meta tags manager with SSR and Suspense support
|
# React meta tags manager with SSR and Suspense support


[](https://sonarcloud.io/summary/new_code?id=react-head-manager)
[](https://sonarcloud.io/summary/new_code?id=react-head-manager)
[](https://sonarcloud.io/summary/new_code?id=react-head-manager)
[](https://sonarcloud.io/summary/new_code?id=react-head-manager)
[](https://sonarcloud.io/summary/new_code?id=react-head-manager)
[](https://sonarcloud.io/summary/new_code?id=react-head-manager)
## Getting started
The package is distributed using [npm](https://www.npmjs.com/), the node package manager.
```
npm i --save @lomray/react-head-manager
```
__WARNING:__ this package use [@lomray/consistent-suspense](https://github.com/Lomray-Software/consistent-suspense) for generate stable id's inside Suspense.
## Usage
```typescript jsx
import { ConsistentSuspenseProvider } from '@lomray/consistent-suspense';
import { MetaManagerProvider, Manager, Meta } from '@lomray/react-head-manager';
const manager = new Manager();
/**
* Root component container
*/
const App = ({ children }) => {
const [state] = useState();
return (
<ConsistentSuspenseProvider> {/** required, see warning above **/}
<MetaManagerProvider manager={manager}>
<MyComponent />
</MetaManagerProvider>
</ConsistentSuspenseProvider>
)
}
/**
* Some component
*/
const MyComponent = () => {
return (
<>
<Meta>
<title>Example</title>
<meta name="description" content="Description example" />
<meta name="keywords" content="test,key" />
<body data-id="test" />
</Meta>
<div>Some component....</div>
</>
)
}
```
Change tags order:
```typescript jsx
/**
* Way 1
*/
const manager = new Manager();
manager.setTagsDefinitions({
title: 1, // change order for title tag
"meta[name='viewport']": 2, // change order for meta viewport tag
meta: 100, // change for all meta tags
script: 200, // change for all script tags
});
/**
* Way 2
*/
<Meta>
<title data-order={1}>Example</title>
<meta data-order={3} name="description" content="Description example" />
<meta data-order={2} name="keywords" content="test,key" />
</Meta>
/**
* You can also use both...
*/
```
Explore [demo app](https://github.com/Lomray-Software/vite-template) to more understand.
## Bugs and feature requests
Bug or a feature request, [please open a new issue](https://github.com/Lomray-Software/react-head-manager/issues/new).
## License
Made with 💚
Published under [MIT License](./LICENSE).
|
UMass-Foundation-Model/Co-LLM-Agents
|
https://github.com/UMass-Foundation-Model/Co-LLM-Agents
|
Source codes for the paper "Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models"
|
# Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models
This repo contains codes for the following paper:
_Hongxin Zhang*, Weihua Du*, Jiaming Shan, Qinhong Zhou, Yilun Du, Joshua B. Tenenbaum, Tianmin Shu, Chuang Gan_: Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models
Paper: [Arxiv](https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.02485)
Project Website: [Co-LLM-Agents](https://vis-www.cs.umass.edu/Co-LLM-Agents/)

## News
**[8/1/2023]**: We update the VirtualHome Simulator executable we used [here](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JTrV5jdF-LQVwY3OsV3Jd3r6PRghyHBp/view?usp=sharing). If you met `XDG_RUNTIME_DIR not set in the environment` error previously, please check if you are using the new version we provided.
## Installation
For detailed instructions on the installation of the two embodied multi-agent environments `Communicative Watch-And-Help` and `ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport`, please refer to the Setup sections in `envs/cwah/README.md` and `envs/tdw_mat/README.md` respectively.
### A simple start guide for `Communicative Watch-And-Help`:
**Step 1**: Get the VirtualHome Simulator and API
Clone the [VirtualHome API](https://github.com/xavierpuigf/virtualhome.git) repository under `envs`:
```bash
cd envs
git clone --branch wah https://github.com/xavierpuigf/virtualhome.git
```
Download the [Simulator](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JTrV5jdF-LQVwY3OsV3Jd3r6PRghyHBp/view?usp=sharing) (Linux x86-64 version), and unzip it in `envs`.
The files should be organized as follows:
```bash
|--cwah/
|--virtualhome/
|--executable/
```
**Step 2**: Install Requirements
```bash
cd cwah
conda create --name cwah python=3.8
conda activate cwah
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
### A simple start guide for `ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport`:
Run the following commands step by step to setup the environments:
```bash
cd envs/tdw_mat
conda create -n tdw_mat python=3.9
conda activate tdw_mat
pip3 install -e .
```
After that, you can run the demo scene to verify your setup:
```bash
python demo/demo_scene.py
```
## Run Experiments
The main implementation code of our Cooperative LLM Agents is in `envs/*/LLM` and `envs/*/lm_agent.py`.
We also prepare example scripts to run experiments with HP baseline and our Cooperative LLM Agent under the folder `envs/*/scripts`.
For example, to run experiments with two LLM Agents on Communicative Watch-And-Help, run the following command in folder `envs/cwah`.
```
./scripts/symbolic_obs_llm_llm.sh
```
## Interesting Cases
We noticed many interesting agents' behaviors exhibited in our experiments and identified several cooperative behaviors.
There are more interesting cases and demos on our [website](https://vis-www.cs.umass.edu/Co-LLM-Agents/)!

## Citation
If you find our work useful, please consider citing:
```
@article{zhang2023building,
title={Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models},
author={Zhang, Hongxin and Du, Weihua and Shan, Jiaming and Zhou, Qinhong and Du, Yilun and Tenenbaum, Joshua B and Shu, Tianmin and Gan, Chuang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.02485},
year={2023}
}
```
|
stefexec/SNAKE2
|
https://github.com/stefexec/SNAKE2
|
DougDougs and ChatGPTs Version of Snake
|
# SNAKE 2
## How to run.
1. Install python 3.9 and pygame.
2. python Snake2.py
|
TelegramXPlus/beautifulparser
|
https://github.com/TelegramXPlus/beautifulparser
|
Simple library for parsing HTML documents inspired by beautifulsoup4
|
# beautifulparser
beautifulparser is a (very) simple library for parsing HTML documents inspired by beautifulsoup4
## Getting Started
```
nimble install beautifulparser
```
## Usage
```nim
import std/htmlparser # to use loadHtml/parseHtml procedures
import std/xmltree # to get typing for XmlNode
import beautifulparser
let html = loadHtml("input.html") # or parseHtml("<h1>Your html</h1>")
for i in html.findAllNodes("span", {"class": "my-custom-class"}):
echo i.text
```
### Using tables
You can also use tables instead of arrays of tuples of strings (lol)
```nim
import std/htmlparser
import std/xmltree
import beautifulparser
let html = loadHtml("input.html")
for i in html.findAllNodes("span", {"class": "my-custom-class"}.toTable()):
echo i.text
```
### Get the first element
```nim
import std/htmlparser
import std/options
import beautifulparser
let html = loadHtml("input.html")
let mySpan = html.findNode("span", {"class", "my-custom-class"})
if mySpan.isSome():
# implement your logic
```
|
xavijimenezmulet/shapes-for-jetpackcompose
|
https://github.com/xavijimenezmulet/shapes-for-jetpackcompose
|
The Compose Shapes Repository is a collection of shape utilities and custom shapes designed specifically for use with Jetpack Compose. This repository aims to provide a comprehensive set of pre-defined shapes that can be easily used and customized in your Compose UI projects.
|
# Compose Shapes Repository

[](https://jitpack.io/#xavijimenezmulet/shapes-for-jetpackcompose)
[](https://android-arsenal.com/api?level=26)



[](https://ktlint.github.io/)
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/Apache-2.0)
[](https://github.com/xavijimenezmulet/SnackBar/blob/main/LICENSE)
[](https://ko-fi.com/xavijimenez)
The Compose Shapes Repository is a collection of shape utilities and custom shapes designed specifically for use with Jetpack Compose. This repository aims to provide a comprehensive set of pre-defined shapes that can be easily used and customized in your Compose UI projects.
<img src="https://github.com/xavijimenezmulet/shapes-for-jetpackcompose/assets/44567433/f3ed103d-f1b3-425e-94bd-c1e040752bd8" width="200" height="450"/> <img src="https://github.com/xavijimenezmulet/shapes-for-jetpackcompose/assets/44567433/18655b88-2db5-40c2-b274-cc184c79501f" width="200" height="450"/> <img src="https://github.com/xavijimenezmulet/shapes-for-jetpackcompose/assets/44567433/5eeb070a-de12-4370-83ee-e4aa676b5fc5" width="200" height="450"/> <img src="https://github.com/xavijimenezmulet/shapes-for-jetpackcompose/assets/44567433/377e573a-a997-4465-9d87-ec49bd4b7b17" width="200" height="450"/>
Possible animations:
<img src="https://github.com/xavijimenezmulet/shapes-for-jetpackcompose/assets/44567433/1f4c9fce-0d35-4c9a-9dfe-ba272cf8c28b" width="200" height="450"/>
## Features
- **Ready-to-use Shapes**: The repository offers a wide range of pre-defined shapes such as circles, rectangles, triangles, stars, and more. These shapes can be directly used in your Compose UI code, saving you time and effort.
- **Custom Shape Generators**: The repository includes utility functions and generators that allow you to create custom shapes with various parameters, such as radius, corner radius, angles, and more. These generators provide flexibility and enable you to create unique and visually appealing shapes.
- **Shape Extensions**: The repository provides extensions for the `Modifier` class in Compose, allowing you to apply shapes to different Compose components easily. These extensions simplify the process of applying shapes and provide a seamless integration with the Compose UI framework.
- **Documentation and Examples**: Each shape in the repository comes with detailed documentation and usage examples, making it easy for developers to understand and utilize the shapes effectively in their projects. The documentation includes information about available customization options and recommendations for best practices.
## Getting Started
To get started with the Compose Shapes Repository, simply clone the repository and import the desired shape utilities or custom shapes into your Compose project. You can then use these shapes in your Compose UI code by applying them to the appropriate components using the provided extensions.
```bash
allprojects {
repositories {
maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' }
}
}
```
Step 2. Add the dependency:
```bash
dependencies {
implementation "com.github.xavijimenezmulet:shapes-for-jetpackcompose:$latest_version"
}
```
Simple usage:
```kotlin
val HeartShape: Shape = object : Shape {
override fun createOutline(
size: Size,
layoutDirection: LayoutDirection,
density: Density
): Outline {
val path = Path().apply {
heartPath(size = size)
close()
}
return Outline.Generic(path)
}
}
```
Now with preview:
```kotlin
@Preview
@Composable
fun HeartPreview() {
Column(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(100.dp)
.clip(HeartShape)
.background(Color.Yellow)
)
}
}
```
Preview:

## Contributions
Specials thanks to:
| Contributor | Features | Github Link |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
| `@afalabarce` | TopAppBarShape | [afalabarce](https://github.com/afalabarce) |
Any help to collect shapes and improve the code will be welcome.
|
Qlipphoth/TinyVampireLike
|
https://github.com/Qlipphoth/TinyVampireLike
| null |
# TinyVampireLike
尝试使用 Unity 制作的 吸血鬼幸存者风格游戏(准确来说是 Brotato 风格)
|
EasyAuthorize/TgPlus
|
https://github.com/EasyAuthorize/TgPlus
|
Telegram略微增强模块
|
# TgPlus
[](#)
[](https://github.com/EasyAuthorize/TgPlus/releases)
Xposed-Modules-Repo
[](https://github.com/Xposed-Modules-Repo/com.easy.tgPlus/releases)
## 模块简介
这是一个Xposed模块
***此项目使用GPTv3许可证***
## 食用方法
请提前准备好Xposed环境
激活此模块后根据实际情况
勾选Telegram为作用域并
重新启动Telegram
## 功能介绍
* 1.解除内容保护
允许复制,保存消息内容
* 2.复读机
弹出菜单增加"+1"选项
选择后将重复发送该消息的文本内容
* 3.防撤回
对方删除消息时阻止删除
并标记消息为已删除
*删除标记实现为自定义flag*
```public static final int FLAG_DELETED = 1 << 28;```
***版本更新时可能会丢失全部聊天记录***
## 写在后面
模块完全开源
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.