id
int64 2.05k
16.6k
| title
stringlengths 5
75
| fromurl
stringlengths 19
185
| date
timestamp[s] | tags
sequencelengths 0
11
| permalink
stringlengths 20
37
| content
stringlengths 342
82.2k
| fromurl_status
int64 200
526
⌀ | status_msg
stringclasses 339
values | from_content
stringlengths 0
229k
⌀ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
8,034 | 监控微服务的五原则 | http://thenewstack.io/five-principles-monitoring-microservices/ | 2016-12-14T08:34:00 | [
"微服务",
"监控"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8034-1.html | 
我们对微服务的需求可以归纳为一个词:速度。这种更快提供功能完善且可靠的软件的需求,彻底改变了软件开发模式。毫无疑问,这个改变对软件管理,包括系统监控的方式,都产生了影响。在这篇文章里,我们将重点关注放在有效地监控产品环境中的微服务所需做出的主要改变。我们将为这一新的软件架构拟定 5 条指导性原则来调整你的监控方法。
监控是微服务控制系统的关键部分,你的软件越复杂,那么你就越难了解其性能及问题排障。鉴于软件交付发生的巨大改变,监控系统同样需要进行彻底的改造,以便在微服务环境下表现更好。下面我们将介绍监控微服务的 5 条原则,如下:
1. 监控容器及其里面的东西。
2. 在服务性能上做监控,而不是容器性能。
3. 监控弹性和多地部署的服务。
4. 监控 API。
5. 将您的监控映射到您的组织结构。
利用这 5 条原则,你可以在向微服务前进的道路上,建立更有效的对微服务的监控。这些原则,可以让你应对随着微服务而来的技术变化和组织变化。
### 微服务监控的原则
#### 1、监控容器及其里面的东西
容器因构建微服务而凸显其重要性,容器的速度、可移植性和隔离特性让开发者很容易就爱上了微服务模型。容器的好处已经写的够多了,毋庸赘述。
容器对于其外围的系统来说就像是黑盒子。这对于开发来说大有裨益,从开发环境到生产环境,甚至从开发者的笔记本到云端,为它们带来高度的可移植性。但是当运行起来后,监控和解决服务问题时,这个黑盒子让常规的方法难以奏效了,我们会想:容器里到底在运行着什么?程序和代码运行性能如何?它有什么重要的输出指标吗?从 DevOps 的视角,你需要对容器有更深的了解而不是仅仅知道有一些容器的存在。

非容器环境下衡量的典型做法,是让一个代理程序运行在主机或者虚机上的用户空间里,但这并不适用于容器。因为容器的优点是小,将各种进程分离开来,并尽可能的减少依赖关系。
而且,从规模上看,成千上万的监测代理,对即使是一个中等大小的部署都是一个昂贵的资源浪费和管理的噩梦。对于容器有两个潜在的解决方案:1)要求你的开发人员直接监控他们的代码,或者2)利用一个通用的内核级的检测方法来查看主机上的所有应用程序和容器活动。这里我们不会深入说明,但每一种方法都有其优点和缺点。
#### 2、 利用业务流程系统提醒服务性能
理解容器容器中的运行数据并不容易,一个单一容器相比组成一个功能或服务的容器聚合,测量复杂度要低得多。
这特别适用于应用程序级别的信息,比如哪个请求拥有最短响应时间,或者哪些 URL 遇到最多的错误,但它同样也适用于架构级别的监测,比如哪个服务的容器使用 CPU 资源超过了事先分配的资源数。
越来越多的软件部署需要一个<ruby> 编排系统 <rt> orchestration system </rt></ruby>,将应用程序的逻辑规划转化到物理的容器中。常见的编排系统包括 Kubernetes、Mesosphere DC/OS 和 Docker Swarm。团队可以用一个编排系统来(1)定义微服务(2)理解部署的每个服务的当前状态。你可以认为编排系统甚至比容器还重要。容器是短暂的,只有满足你的服务需求才会存在。
DevOps 团队应该将告警重点放到运行特征上,以尽可能贴近监控服务的体验。如果应用受到了影响,这些告警是评估事态的第一道防线。但是获得这些告警并不容易,除非你的监控系统是基于原生于容器的。
<ruby> <a href="https://techcrunch.com/2016/04/27/lets-define-container-native/"> 原生容器 </a> <rt> Container-native </rt></ruby>解决方案利用<ruby> 编排元数据 <rt> orchestration metadata </rt></ruby>来动态聚合容器和应用程序数据,并按每个服务计算监控度量。根据您的编排工具,您可能想在不同层次进行深入检测。比如,在 Kubernetes 里,你通常有 Namespace、ReplicaSet、Pod 和一些其他容器。聚合这些不同的层,对排除逻辑故障是很有必要的,与构成服务的容器的物理部署无关。

#### 3、 监控<ruby> 弹性 <rt> Elastic </rt></ruby>和<ruby> 多地部署 <rt> Multi-Location </rt></ruby>的服务
弹性服务不是一个新概念,但是它在原生容器环境中的变化速度比在虚拟环境中快的多。迅速的变化会严重影响检测系统的正常运行。
监测传统的系统经常需要根据软件部署,手动调整检查指标。这种调整可以是具体的,如定义要捕获的单个指标,或基于应用程序在一个特定的容器中的操作配置要收集的数据。在小规模上(比如几十个容器)我们可以接受,但是再大规模就难以承受了。微服务的集中监控必须能够自由的随弹性服务而增长和缩减,无需人工干预。
比如,如果 DevOps 团队必须手动定义容器包含哪个服务需要监控,他们毫无疑问会失手,因为 Kubernetes 或者 Mesos 每天都会定期创建新的容器。同样,如果代码发布并置于生产环境时要求运维团队安装一个<ruby> 定制的状态端点 <rt> custom stats endpoint </rt></ruby>,也给开发者从 Docker 仓库获取基础镜像带来更多的挑战。
在生产环境中,建立面向跨越多个数据中心或多个云的复杂部署的监控,比如,如果你的服务跨越私有数据中心和 AWS,那么亚马逊的 AWS CloudWatch 就很难做到这一点。这就要求我们建立一个跨不同地域的监控系统,并可在动态的原生容器环境下运行。
#### 4、 监控 API
在微服务环境中,API 接口是通用的。本质上,它们是将服务暴露给其它团队的唯一组件。事实上,API 的响应和一致性可以看作是“内部 SLA”,即使还没有定义一个正式的 SLA(服务等级协议)。
因此,API 接口的监控也是必要的。API 监控可以有不同的形式,但是很显然它绝对不是简单的二进制上下检查。例如,了解像时间函数这样的最常使用的<ruby> 端点 <rt> endpoint </rt></ruby>是有价值的。这使得团队可以看到服务使用的变化,无论是由于设计变更或用户的改变。
你也可以记录服务最缓慢的端点,这些可能揭示出重大的问题,或者至少指向需要在系统中做优化的区域。
最后,跟踪系统服务响应的能力是另一个很重要的能力,它主要是开发者使用,也能帮助你了解整体用户体验,同时将信息基于底层和应用程序视角分成两大部分。
#### 5、 将您的监控映射到您的组织结构
这篇文章着重在微服务和监控上,像其他科技文章一样,这是因为很多人都关注此层面。
对于那些熟悉<ruby> <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conway%27s_law"> 康威定律 </a> <rt> Conway’s law </rt></ruby>的人来说,系统的设计是基于开发团队的组织结构。创造更快,更敏捷的软件的压力推动了团队去思考重新调整他们的开发组织和管理它的规则。

所以,如果他们想从这个新的软件架构(微服务)上获益,他们的团队必须将微服务映射到团队自身中。也就是说,他们需要更小的更松散耦合的团队,可以选择自己的方向只要能够满足整个需求即可。在每一个团队中,对于开发语言的使用,bug 的提交甚至工作职责都会有更大的控制能力。
DevOps 团队对此可以启用一个监控平台:让每一个微服务团队可以有自己的警报,度量指标,和控制面板,同时也要给出整体系统的视图。
### 总结
让微服务流行起来的是快捷。开发组织要想更快的为客户提供更多的功能,然后微服务技术就来了,架构转向微服务并且容器的流行让快捷开发成为可能,所有相关的进程理所当然的搭上了这辆火车。
最后,基本的监控原则需要适应伴随微服务而来的技术和结构。越早认识到这种转变的开发团队,能更早更容易的适应微服务这一新的架构。
---
via: <http://thenewstack.io/five-principles-monitoring-microservices/>
作者:[Apurva Dave](http://thenewstack.io/author/apurvadave/) ,[Loris Degioanni](http://thenewstack.io/author/lorisdegioanni/) 译者:[jiajia9linuxer](https://github.com/jiajia9linuxer) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,037 | 用数据科学搭建一个实时推荐引擎 | https://neo4j.com/blog/real-time-recommendation-engine-data-science/ | 2016-12-14T16:57:56 | [
"推荐",
"聚类",
"算法",
"Neo4j",
"图数据库"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8037-1.html | 编者注:本文是 2016 年 4 月 Nicole Whilte 在欧洲 [GraphConnect](http://graphconnect.com/) 时所作。这儿我们快速回顾一下她所涉及的内容:
* 图数据库推荐基础
* 社会化推荐
* 相似性推荐
* 集群推荐
今天我们将要讨论的内容是数据科学和<ruby> 图推荐 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> graph recommendations </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>:

我在 [Neo4j](http://neo4j.com/product/) 任职已经两年了,但实际上我已经使用 Neo4j 和 [Cypher](http://neo4j.com/blog/why-database-query-language-matters/#cypher) 工作三年了。当我首次发现这个特别的<ruby> 图数据库 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> graph database </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的时候,我还是一个研究生,那时候我在奥斯丁的德克萨斯大学攻读关于社交网络的统计学硕士学位。
[实时推荐引擎](https://neo4j.com/use-cases/real-time-recommendation-engine/)是 Neo4j 中最广泛的用途之一,也是使它如此强大并且容易使用的原因之一。为了探索这个东西,我将通过使用示例数据集来阐述如何将统计学方法并入这些引擎中。
第一个很简单 - 将 Cypher 用于社交推荐。接下来,我们将看一看相似性推荐,这涉及到可被计算的相似性度量,最后探索的是集群推荐。
### 图数据库推荐基础
下面的数据集包含所有达拉斯 Fort Worth 国际机场的餐饮场所,达拉斯 Fort Worth 国际机场是美国主要的机场枢纽之一:

我们把节点标记成黄色并按照出入口和航站楼给它们的位置建模。同时我们也按照食物和饮料的主类别将地点分类,其中一些包括墨西哥食物、三明治、酒吧和烤肉。
让我们做一个简单的推荐。我们想要在机场的某一确定地点找到一种特定食物,大括号中的内容表示是的用户输入,它将进入我们的假想应用程序中。

这个英文句子表示成 Cypher 查询:

这将提取出该类别中用户所请求的所有地点、航站楼和出入口。然后我们可以计算出用户所在位置到出入口的准确距离,并以升序返回结果。再次说明,这个非常简单的 Cypher 推荐仅仅依据的是用户在机场中的位置。
### <ruby> 社交推荐 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Social Recommendations </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
让我们来看一下社交推荐。在我们的假想应用程序中,用户可以登录并且可以用和 Facebook 类似的方式标记自己“喜好”的地点,也可以在某地签到。

考虑位于我们所研究的第一个模型之上的数据模型,现在让我们在下面的分类中找到用户的朋友喜好的航站楼里面离出入口最近的餐饮场所:

`MATCH` 子句和我们第一次 Cypher 查询的 `MATCH` 子句相似,只是现在我们依据喜好和朋友来匹配:

前三行是完全一样的,但是现在要考虑的是那些登录的用户,我们想要通过 `:FRIENDS_WITH` 这一关系来找到他们的朋友。仅需通过在 Cypher 中增加一些行内容,我们现在已经把社交层面考虑到了我们的推荐引擎中。
再次说明,我们仅仅显示了用户明确请求的类别,并且这些类别中的地点与用户进入的地方是相同的航站楼。当然,我们希望按照登录并做出请求的用户来滤过这些目录,然后返回地点的名字、位置以及所在目录。我们也要显示出有多少朋友已经“喜好”那个地点以及那个地点到出入口的确切距离,然后在 `RETURN` 子句中同时返回所有这些内容。
### <ruby> 相似性推荐 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Similarity Recommendations </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
现在,让我们看一看相似性推荐引擎:

和前面的数据模型相似,用户可以标记“喜好”的地点,但是这一次他们可以用 1 到 10 的整数给地点评分。这是通过前期在 Neo4j 中增加一些属性到关系中建模实现的。
这将允许我们找到其他相似的用户,比如以上面的 Greta 和 Alice 为例,我们已经查询了他们共同喜好的地点,并且对于每一个地点,我们可以看到他们所设定的权重。大概地,我们可以通过他们的评分来确定他们之间的相似性大小。

现在我们有两个向量:

现在让我们按照<ruby> 欧几里得距离 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Euclidean distance </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的定义来计算这两个向量之间的距离:

我们把所有的数字带入公式中计算,然后得到下面的相似度,这就是两个用户之间的“距离”:

你可以很容易地在 Cypher 中计算两个特定用户的“距离”,特别是如果他们仅仅同时“喜好”一个很小的地点子集。再次说明,这儿我们依据两个用户 Alice 和 Greta 来进行匹配,并尝试去找到他们同时“喜好”的地点:

他们都有对最后找到的地点的 `:LIKES` 关系,然后我们可以在 Cypher 中很容易的计算出他们之间的欧几里得距离,计算方法为他们对各个地点评分差的平方求和再开平方根。
在两个特定用户的例子中上面这个方法或许能够工作。但是,在实时情况下,当你想要通过和实时数据库中的其他用户比较,从而由一架飞机上的一个用户推断相似用户时,这个方法就不一定能够工作。不用说,至少它不能够很好的工作。
为了找到解决这个问题的好方法,我们可以预先计算好距离并存入实际关系中:

当遇到一个很大的数据集时,我们需要成批处理这件事,在这个很小的示例数据集中,我们可以按照所有用户的<ruby> 迪卡尔乘积 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Cartesian product </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和他们共同“喜好”的地点来进行匹配。当我们使用 `WHERE id(u1) < id(u2)` 作为 Cypher 询问的一部分时,它只是来确定我们在左边和右边没有找到相同的对的一个技巧。
通过用户之间的欧几里得距离,我们创建了他们之间的一种关系,叫做 `:DISTANCE`,并且设置了一个叫做 `euclidean` 的欧几里得属性。理论上,我们可以也通过用户间的一些关系来存储其他相似度从而获取不同的相似度,因为在确定的环境下某些相似度可能比其他相似度更有用。
在 Neo4j 中,的确是对关系属性建模的能力使得完成像这样的事情无比简单。然而,实际上,你不会希望存储每一个可能存在的单一关系,因为你仅仅希望返回离他们“最近”的一些人。
因此你可以根据一些临界值来存入前几个,从而你不需要构建完整的连通图。这允许你完成一些像下面这样的实时的数据库查询,因为我们已经预先计算好了“距离”并存储在了关系中,在 Cypher 中,我们能够很快的攫取出数据。

在这个查询中,我们依据地点和类别来进行匹配:

再次说明,前三行是相同的,除了登录用户以外,我们找出了和他们有 `:DISTANCE` 关系的用户。这是我们前面查看的关系产生的作用 - 实际上,你只需要存储处于前几位的相似用户 `:DISTANCE` 关系,因此你不需要在 `MATCH` 子句中攫取大量用户。相反,我们只攫取和那些用户“喜好”的地方有 `:DISTANCE` 关系的用户。
这允许我们用少许几行内容表达较为复杂的模型。我们也可以攫取 `:LIKES` 关系并把它放入到变量中,因为后面我们将使用这些权重来评分。
在这儿重要的是,我们可以依据“距离”大小将用户按照升序进行排序,因为这是一个距离测度。同时,我们想要找到用户间的最小距离因为距离越小表明他们的相似度最大。
通过其他按照欧几里得距离大小排序好的用户,我们得到用户评分最高的三个地点并按照用户的平均评分高低来推荐这些地点。换句话说,我们先找出一个活跃用户,然后依据其他用户“喜好”的地点找出和他最相似的其他用户,接下来按照这些相似用户的平均评分把那些地点排序在结果的集合中。
本质上,我们通过把所有评分相加然后除以收集的用户数目来计算出平均分,然后按照平均评分的升序进行排序。其次,我们按照出入口距离排序。假想地,我猜测应该会有交接点,因此你可以按照出入口距离排序然后再返回名字、类别、出入口和航站楼。
### <ruby> 集群推荐 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Cluster Recommendations </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
我们最后要讲的一个例子是集群推荐,在 Cypher 中,这可以被想像成一个作为临时解决方案的离线计算工作流。这可能完全基于在[欧洲 GraphConnect 上宣布的新方法](https://neo4j.com/blog/neo4j-3-0-massive-scale-developer-productivity/),但是有时你必须进行一些 Cypher 2.3 版本所没有的算法逼近。
在这儿你可以使用一些统计软件,把数据从 Neo4j 取出然后放入像 Apache Spark、R 或者 Python 这样的软件中。下面是一段把数据从 Neo4j 中取出的 R 代码,运行该程序,如果正确,写下程序返回结果的给 Neo4j,可以是一个属性、节点、关系或者一个新的标签。
通过持续把程序运行结果放入到图表中,你可以在一个和我们刚刚看到的查询相似的实时查询中使用它:

下面是用 R 来完成这件事的一些示例代码,但是你可以使用任何你最喜欢的软件来做这件事,比如 Python 或 Spark。你需要做的只是登录并连接到图表。
在下面的例子中,我基于用户的相似性把他们聚合起来。每个用户作为一个观察点,然后得到他们对每一个目录评分的平均值。

假定用户对酒吧类评分的方式和一般的评分方式相似。然后我攫取出喜欢相同类别中的地点的用户名、类别名、“喜好”关系的平均权重,比如平均权重这些信息,从而我可以得到下面这样一个表格:

因为我们把每一个用户都作为一个观察点,所以我们必须巧妙的处理每一个类别中的数据,这些数据的每一个特性都是用户对该类中餐厅评分的平均权重。接下来,我们将使用这些数据来确定用户的相似性,然后我将使用<ruby> 聚类 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> clustering </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>算法来确定在不同集群中的用户。
在 R 中这很直接:

在这个示例中我们使用<ruby> K-均值 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> k-means </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>聚类算法,这将使你很容易攫取集群分配。总之,我通过运行聚类算法然后分别得到每一个用户的集群分配。
Bob 和 David 在一个相同的集群中 - 他们在集群二中 - 现在我可以实时查看哪些用户被放在了相同的集群中。
接下来我把集群分配写入 CSV 文件中,然后存入图数据库:

我们只有用户和集群分配,因此 CSV 文件只有两列。 `LOAD CSV` 是 Cypher 中的内建语法,它允许你从一些其他文件路径或者 URL 调用 CSV ,并给它一个别名。接下来,我们将匹配图数据库中存在的用户,从 CSV 文件中攫取用户列然后合并到集群中。
我们在图表中创建了一个新的标签节点:`Cluster ID`, 这是由 K-平均聚类算法给出的。接下来我们创建用户和集群间的关系,通过创建这个关系,当我们想要找到在相同集群中的实际推荐用户时,就会很容易进行查询。
我们现在有了一个新的集群标签,在相同集群中的用户和那个集群存在关系。新的数据模型看起来像下面这样,它比我们前面探索的其他数据模型要更好:

现在让我们考虑下面的查询:

通过这个 Cypher 查询,我们在更远处找到了在同一个集群中的相似用户。由于这个原因,我们删除了“距离”关系:

在这个查询中,我们取出已经登录的用户,根据用户-集群关系找到他们所在的集群,找到他们附近和他们在相同集群中的用户。
我们把这些用户分配到变量 `c1` 中,然后我们得到其他被我取别名为 `neighbor` 变量的用户,这些用户和那个相同集群存在着用户-集群关系,最后我们得到这些附近用户“喜好”的地点。再次说明,我把“喜好”放入了变量 r 中,因为我们需要从关系中攫取权重来对结果进行排序。
在这个查询中,我们所做的改变是,不使用相似性距离,而是攫取在相同集群中的用户,然后对类别、航站楼以及我们所攫取的登录用户进行声明。我们收集所有的权重:来自附近用户“喜好”地点的“喜好”关系,得到的类别,确定的距离值,然后把它们按升序进行排序并返回结果。
在这些例子中,我们可以进行一个相当复杂的处理并且将其放到图数据库中,然后我们就可以使用实时算法结果-聚类算法和集群分配的结果。
我们更喜欢的工作流程是更新这些集群分配,更新频率适合你自己就可以,比如每晚一次或每小时一次。当然,你可以根据直觉来决定多久更新一次这些集群分配是可接受的。
---
via: <https://neo4j.com/blog/real-time-recommendation-engine-data-science/>
作者:[Nicole White](https://neo4j.com/blog/contributor/nicole-white/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | *Editor’s Note: This presentation was given by Nicole White at*– What we’re going to be talking about today is data science and graph recommendations:
[GraphConnect Europe](https://graphconnect.com/)in April 2016. Here’s a quick review of what she covered:I’ve been with
[Neo4j](https://neo4j.com/product/)for two years now, but have been working with Neo4j and
[Cypher](https://neo4j.com/blog/why-database-query-language-matters/#cypher)for three. I discovered this particular graph database when I was a grad student at the University of Texas Austin studying for a masters in statistics with a focus on social networks.
[Real-time recommendation engines](https://neo4j.com/use-cases/real-time-recommendation-engine/)are one of the most common use cases for Neo4j, and one of the things that makes it so powerful and easy to use. To explore this, I’ll explain how to incorporate statistical methods into these recommendations by using example datasets.
The first will be simple – entirely in Cypher with a focus on social recommendations. Next we’ll look at the similarity recommendation, which involves similarity metrics that can be calculated, and finally a clustering recommendation.
### Basic Graph-Powered Recommendations
The following dataset includes food and drink places in the Dallas Fort Worth International Airport, one of the major airport hubs in the United States:
We have place nodes in yellow and are modeling their location in terms of gate and terminal. And we are also categorizing the place in terms of major categories for food and drink. Some include Mexican food, sandwiches, bars and barbecue.
Let’s do a simple recommendation. We want to find a specific type of food in a certain location in the airport, and the curled brackets represent user inputs which are being entered into our hypothetical app:
This English sentence maps really well as a Cypher query:
This is going to pull all the places in the category, terminal and gate the user has requested. Then we get the absolute distance of the place to gate where the user is, and return the results in ascending order. Again, a very simple Cypher recommendation to a user based just on their location in the airport.
### Social Recommendations
Let’s look at a social recommendation. In our hypothetical app, we have users who can log in and “like” places in a way similar to Facebook and can also check into places:
Consider this data model on top of the first model that we explored, and now let’s find food and drink places in the following categories closest to some gate in whatever terminal that user’s friends like:
The
`MATCH`
clause is very similar to the `MATCH`
clause of our first Cypher query, except now we are matching on likes and friends:The first three lines are the same, but for the user in question – the user that’s “logged in” – we want to find their friends through the
`:FRIENDS_WITH`
relationship along with the places those friends liked. With just a few added lines of Cypher, we are now taking a social aspect into account for our recommendation engine.Again, we’re only showing categories that the user explicitly asked for that are in the same terminals the user is in. And, of course, we want to filter this by the user who is logged in and making this request, and it returns the name of the place along with its location and category. We are also accounting for how many friends have liked that place and the absolute value of the distance of the place from the gate, all returned in the
`RETURN`
clause.### Similarity Recommendation
Now let’s take a look at a similarity recommendation engine:
Similarly to our earlier data model, we have users who can like places, but this time they can also rate places with an integer between one and 10. This is easily modeled in Neo4j by adding a property to the relationship.
This allows us to find other similar users, like in the example of Greta and Alice. We’ve queried the places they’ve mutually liked, and for each of those places, we can see the weights they have assigned. Presumably, we can use these numbers to determine how similar they are to each other:
Now we have two vectors:
And now let’s apply Euclidean distance to find the distance between those two vectors:
And when we plug in all the numbers, we get the following similarity metric, which is really the distance metric between the two users:
You can do this between two specific users easily in Cypher, especially if they’ve only mutually liked a small subset of places. Again, here we’re matching on two users, Alice and Greta, and are trying to find places they’ve mutually liked:
They both have to have a
`:LIKES`
relationship to the place for it to be found in this result, and then we can easily calculate the Euclidean distance between them with the square root of the sum of their squared differences in Cypher.While this may work in an example with two specific people, it doesn’t necessarily work in real time when you’re trying to infer similar users from another user on the fly, by comparing them against every other user in the database in real time. Needless to say, this doesn’t work very well.
To find a way around this, we pre-compute this calculation and store it in an actual relationship:
While in large datasets we would do this in batches, in this small example dataset, we can match on a Cartesian product of all the users and places they’ve mutually liked. When we use
`WHERE id(u1) < id(u2)`
as part of our Cypher query, this is just a trick to ensure we’re not finding the same pair twice on both the left and the right.Then with their Euclidean distance and themselves, we’re going to create a relationship between them called
`:DISTANCE`
and set a Euclidean property called `euclidean`
. In theory, we could also store other similarity metrics on some relationship between users to capture different similarity metrics, since some might be more useful than others in certain contexts.And it’s really this ability to model properties on relationships in Neo4j that makes things like this incredibly easy. However, in practice you don’t want to store every single relationship that can possibly exist because you’ll only want to return the top few people of their neighbors.
So you can just store the top in according to some threshold so you don’t have this fully connected graph. This allows you to perform
[graph database](https://neo4j.com/blog/why-graph-databases-are-the-future/#definition)queries like the below in real time, because we’ve pre-computed it and stored it on the relationship, and in Cypher we’ll be able to grab that very quickly:
In this query, we’re matching on places and categories:
Again, the first three lines are the same, except that for the logged-in user, we’re getting users who have a
`:DISTANCE`
relationship to them. This is where what we went over earlier comes into play – in practice you should only store the top `:DISTANCE`
relationships to users who are similar to them so you’re not grabbing a huge volume of users in this `MATCH`
clause. Instead, we’re grabbing users who have a `:DISTANCE`
relationship to them where those users like that place.This has allowed us to express a somewhat complicated pattern in just a few lines. We’re also grabbing the
`:LIKES`
relationship and putting it on a variable because we’re going to use those weights later to apply a rating.What’s important here is that we’re ordering those users by their distance ascending, because it is a distance metric, and we want the lowest distances because that indicates they are the most similar.
With those other users ordered by the Euclidean distance, we’re going to collect the top three users’ ratings and use those as our average score to recommend these places. In other words, we’ve taken an active user, found users who are most similar to them based on the places they’ve liked, and then averaged the scores those similar users have given to rank those places in a result set.
We’re essentially taking an average here by adding it up and dividing by the number of elements in the collection, and we’re ordering by that average ascending. Then secondarily, we’re ordering by the gate distance. Hypothetically, there could be ties I suppose, and then you order by the gate distance and then returning the name, category, gate and terminal.
### Cluster Recommendations
Our final example is going to be a cluster recommendation, which can be thought of as a workflow of offline computing that may be required as a workaround in Cypher. This may now be obsolete based on
[the new procedures announced at GraphConnect Europe](https://neo4j.com/blog/neo4j-3-0-massive-scale-developer-productivity/), but sometimes you have to do certain algorithmic approaches that Cypher version 2.3 doesn’t expose.
This is where you can use some form of statistical software, pull data out of Neo4j into a software such as Apache Spark, R or Python. Below is an example of R code for pulling data out of Neo4j, running an algorithm, and then – if appropriate – writing the results of that algorithm back into Neo4j as either a property, node, relationship or a new label.
By persisting the results of that algorithm into the graph, you can use it in real-time with queries similar to the ones we just went over:
Below is some example code for how you do this in R, but you can easily do the same thing with whatever software you’re most comfortable with, such as Python or Spark. All you have to do is log in and connect to the graph.
In the following example, I’ve clustered users together based on their similarities. Each user is represented as an observation, and I want to get the average rating that they’ve given each category:
Presumably, users who rate the bar category in similar ways are similar in general. Here I’m grabbing the names of users who like places in the same category, the category name, and the average weight of the “likes” relationships, as average weight, and that’s going to give me a table like this:
Because we want each user to be an observation, we will have to manipulate the data where each feature is the average weight rating they’ve given restaurants within that category, per category. We’ll then use this to determine how similar they are, and I’m going to use a clustering algorithm to determine users being in different clusters.
In R this is very straightforward:
For this demonstration we are using k-means, which allows you to easily grab cluster assignments. In summary, I ran a clustering algorithm and now for each user I have a cluster assignment.
Bob and David are in the same cluster – they’re in cluster two – and now I’ll be able to see in real time which users have been determined to be in the same cluster.
Next we write it into a CSV, which we then load into the graph:
We have users and cluster assignments, so the CSV will only have two columns.
`LOAD CSV`
is a syntax that’s built into Cypher that allows you to call a CSV from some file path or URL and alias it as something. Then we’ll match on the users that already exist in the graph, grab the user column out of that CSV, and merge on the cluster. Here we’re creating a new labeled node in the graph, the
`Cluster ID`
, which was given by k-means. Next we create relationships between the user and the cluster, which allows us to easily query when we get to the actual recommendation users who are in the same cluster.Now we have a new label cluster where users who are in the same cluster have a relationship to that cluster. Below is what our new data model looks like, which is on top of the other data models we explored:
Now let’s consider the following query:
With this Cypher query, we’re going beyond similar users to users in the same cluster. At this point we’ve also deleted those distance relationships:
In this query, we’ve taken the user who’s logged in, finding their cluster based on the user-cluster relationship, and finding their neighbors who are in that same cluster.
We’ve assigned that to some variable
`cl`
, and we’re getting other users – which I’ve aliased as a `neighbor`
variable – who have a user-cluster relationship to that same cluster, and then we’re getting the places that neighbor has liked. Again, we’re putting the “likes” on a variable, `r`
, because we’re going want to grab weights off of the relationship to order our results.All we’ve changed in the query is that instead of using the similarity distance, we’re grabbing users in the same cluster, asserting categories, asserting the terminal and asserting that we’re only grabbing the user who is logged in. We’re collecting all those weights of the
`:LIKES`
relationships from their neighbors liking places, getting the category, the absolute value of the distance, ordering that in descending order, and returning those results.In these examples we’ve been able to take a pretty involved process and persist it in the graph, and then used the results of that algorithm – the results of the clustering algorithm and the clustering assignments – in real time.
Our preferred workflow is to update these clustering assignments however frequently you see fit — for example, nightly or hourly. And, of course, you can use intuition to figure out how often is acceptable to be updating these cluster assignments.
**Inspired by Nicole’s talk? Click below to register for**
[GraphConnect San Francisco](https://graphconnect.com/?ref=blog)and get even more presentations, talks and workshops from the world’s leading graph technology experts.[Get My Ticket](https://graphconnect.com/?ref=blog) |
8,038 | Linux 中的 DTrace :BPF 进入 4.9 内核 | http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-10-27/dtrace-for-linux-2016.html | 2016-12-15T12:22:00 | [
"性能",
"跟踪",
"DTrace",
"BPF"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8038-1.html |
>
> 本文作者 [Brendan Gregg](http://www.brendangregg.com/) 目前是 Netflix 的高级性能架构师 ,他在那里做大规模计算机性能设计、分析和调优。他是《Systems Performance》等技术书的作者,因在系统管理员方面的成绩,获得过 2013年 USENIX LISA 大奖。他之前是 SUN 公司是性能领头人和内核工程师,研究存储和网络性能。他也发明和开发过一大波性能分析工具,很多已集成到操作系统中了 。
>
>
>
随着 BPF 追踪系统(基于时间采样)最后一个主要功能被合并至 Linux 4.9-rc1 版本的内核中,现在 Linux 内核拥有类似 DTrace 的原生追踪功能。DTrace 是 Solaris 系统中的高级追踪器。对于长期使用 DTrace 的用户和专家,这将是一个振奋人心的里程碑!现在在 Linux 系统上,你可以在生产环境中使用安全的、低负载的定制追踪系统,通过执行时间的柱状图和频率统计等信息,分析应用的性能以及内核。

用于 Linux 的追踪项目有很多,但是这个最终被合并进 Linux 内核的技术从一开始就根本不是一个追踪项目:它是最开始是用于<ruby> 伯克利包过滤器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Berkeley Packet Filter </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>(BPF)的增强功能。这些补丁允许 BPF 重定向数据包,从而创建软件定义网络(SDN)。久而久之,对事件追踪的支持就被添加进来了,使得程序追踪可用于 Linux 系统。
尽管目前 BPF 没有像 DTrace 一样的高级语言,但它所提供的前端已经足够让我创建很多 BPF 工具了,其中有些是基于我以前的 [DTraceToolkit](https://github.com/opendtrace/toolkit)。这个帖子将告诉你怎么去用这些 BPF 提供的前端工具,以及畅谈这项技术将会何去何从。

### 示例
我已经将基于 BPF 的追踪工具添加到了开源的 [bcc](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc) 项目里(感谢 PLUMgrid 公司的 Brenden Blanco 带领 bcc 项目的发展)。详见 [bcc 安装](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/INSTALL.md) 手册。它会在 `/usr/share/bcc/tools` 目录下添加一系列工具,包括接下来的那些工具。
捕获新进程:
```
# execsnoop
PCOMM PID RET ARGS
bash 15887 0 /usr/bin/man ls
preconv 15894 0 /usr/bin/preconv -e UTF-8
man 15896 0 /usr/bin/tbl
man 15897 0 /usr/bin/nroff -mandoc -rLL=169n -rLT=169n -Tutf8
man 15898 0 /usr/bin/pager -s
nroff 15900 0 /usr/bin/locale charmap
nroff 15901 0 /usr/bin/groff -mtty-char -Tutf8 -mandoc -rLL=169n -rLT=169n
groff 15902 0 /usr/bin/troff -mtty-char -mandoc -rLL=169n -rLT=169n -Tutf8
groff 15903 0 /usr/bin/grotty
```
硬盘 I/O 延迟的柱状图:
```
# biolatency -m
Tracing block device I/O... Hit Ctrl-C to end.
^C
msecs : count distribution
0 -> 1 : 96 |************************************ |
2 -> 3 : 25 |********* |
4 -> 7 : 29 |*********** |
8 -> 15 : 62 |*********************** |
16 -> 31 : 100 |**************************************|
32 -> 63 : 62 |*********************** |
64 -> 127 : 18 |****** |
```
追踪慢于 5 毫秒的 ext4 常见操作:
```
# ext4slower 5
Tracing ext4 operations slower than 5 ms
TIME COMM PID T BYTES OFF_KB LAT(ms) FILENAME
21:49:45 supervise 3570 W 18 0 5.48 status.new
21:49:48 supervise 12770 R 128 0 7.55 run
21:49:48 run 12770 R 497 0 16.46 nsswitch.conf
21:49:48 run 12770 R 1680 0 17.42 netflix_environment.sh
21:49:48 run 12770 R 1079 0 9.53 service_functions.sh
21:49:48 run 12772 R 128 0 17.74 svstat
21:49:48 svstat 12772 R 18 0 8.67 status
21:49:48 run 12774 R 128 0 15.76 stat
21:49:48 run 12777 R 128 0 7.89 grep
21:49:48 run 12776 R 128 0 8.25 ps
21:49:48 run 12780 R 128 0 11.07 xargs
21:49:48 ps 12776 R 832 0 12.02 libprocps.so.4.0.0
21:49:48 run 12779 R 128 0 13.21 cut
[...]
```
追踪新建的 TCP 活跃连接(`connect()`):
```
# tcpconnect
PID COMM IP SADDR DADDR DPORT
1479 telnet 4 127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 23
1469 curl 4 10.201.219.236 54.245.105.25 80
1469 curl 4 10.201.219.236 54.67.101.145 80
1991 telnet 6 ::1 ::1 23
2015 ssh 6 fe80::2000:bff:fe82:3ac fe80::2000:bff:fe82:3ac 22
```
通过跟踪 `getaddrinfo()`/`gethostbyname()` 库的调用来追踪 DNS 延迟:
```
# gethostlatency
TIME PID COMM LATms HOST
06:10:24 28011 wget 90.00 www.iovisor.org
06:10:28 28127 wget 0.00 www.iovisor.org
06:10:41 28404 wget 9.00 www.netflix.com
06:10:48 28544 curl 35.00 www.netflix.com.au
06:11:10 29054 curl 31.00 www.plumgrid.com
06:11:16 29195 curl 3.00 www.facebook.com
06:11:25 29404 curl 72.00 foo
06:11:28 29475 curl 1.00 foo
```
按类别划分 VFS 操作的时间间隔统计:
```
# vfsstat
TIME READ/s WRITE/s CREATE/s OPEN/s FSYNC/s
18:35:32: 231 12 4 98 0
18:35:33: 274 13 4 106 0
18:35:34: 586 86 4 251 0
18:35:35: 241 15 4 99 0
```
对一个给定的 PID,通过内核和用户堆栈轨迹来追踪 CPU 处理之外的时间(由内核进行统计):
```
# offcputime -d -p 24347
Tracing off-CPU time (us) of PID 24347 by user + kernel stack... Hit Ctrl-C to end.
^C
[...]
ffffffff810a9581 finish_task_switch
ffffffff8185d385 schedule
ffffffff81085672 do_wait
ffffffff8108687b sys_wait4
ffffffff81861bf6 entry_SYSCALL_64_fastpath
--
00007f6733a6b64a waitpid
- bash (24347)
4952
ffffffff810a9581 finish_task_switch
ffffffff8185d385 schedule
ffffffff81860c48 schedule_timeout
ffffffff810c5672 wait_woken
ffffffff8150715a n_tty_read
ffffffff815010f2 tty_read
ffffffff8122cd67 __vfs_read
ffffffff8122df65 vfs_read
ffffffff8122f465 sys_read
ffffffff81861bf6 entry_SYSCALL_64_fastpath
--
00007f6733a969b0 read
- bash (24347)
1450908
```
追踪 MySQL 查询延迟(通过 USDT 探针):
```
# mysqld_qslower `pgrep -n mysqld`
Tracing MySQL server queries for PID 14371 slower than 1 ms...
TIME(s) PID MS QUERY
0.000000 18608 130.751 SELECT * FROM words WHERE word REGEXP '^bre.*n$'
2.921535 18608 130.590 SELECT * FROM words WHERE word REGEXP '^alex.*$'
4.603549 18608 24.164 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM words
9.733847 18608 130.936 SELECT count(*) AS count FROM words WHERE word REGEXP '^bre.*n$'
17.864776 18608 130.298 SELECT * FROM words WHERE word REGEXP '^bre.*n$' ORDER BY word
```
监测 pam 库并使用多种追踪工具观察登录请求:
```
# trace 'pam:pam_start "%s: %s", arg1, arg2'
TIME PID COMM FUNC -
17:49:45 5558 sshd pam_start sshd: root
17:49:47 5662 sudo pam_start sudo: root
17:49:49 5727 login pam_start login: bgregg
```
bcc 项目里的很多工具都有帮助信息(`-h` 选项),并且都应该包含有示例的 man 页面和文本文件。
### 必要性
2014 年,Linux 追踪程序就有一些内核相关的特性(来自 `ftrace` 和 `pref_events`),但是我们仍然要转储并报告进程数据,这种几十年前的老技术有很多的限制。你不能频繁地访问进程名、函数名、堆栈轨迹或内核中的任意的其它数据。你不能在将变量保存到一个监测事件里,又在另一个事件里访问它们,这意味着你不能在你需要的地方计算延迟(或者说时间增量)。你也不能创建一个内核内部的延迟柱状图,也不能追踪 USDT 探针,甚至不能写个自定义的程序。DTrace 可以做到所有这些,但仅限于 Solaris 或 BSD 系统。在 Linux 系统中,有些不在主线内核的追踪器,比如 SystemTap 就可以满足你的这些需求,但它也有自身的不足。(理论上说,你可以写一个基于探针的内核模块来满足需求-但实际上没人这么做。)
2014 年我加入了 Netflix cloud performance 团队。做了这么久的 DTrace 方面的专家,转到 Linux 对我来说简直不可思议。但我确实这么做了,而且遇到了巨大的挑战:在应用快速变化、采用微服务架构和分布式系统的情况下,调优 Netflix cloud。有时要用到系统追踪,而我之前是用的 DTrace。在 Linux 系统上可没有 DTrace,我就开始用 Linux 内核内建的 `ftrace` 和 `perf_events` 工具,构建了一个追踪工具([perf-tools](https://github.com/brendangregg/perf-tools))。这些工具很有用,但有些工作还是没法完成,尤其是延迟柱状图以及堆栈踪迹计数。我们需要的是内核追踪的可程序化。
### 发生了什么?
BPF 将程序化的功能添加到现有的内核追踪工具中(`tracepoints`、`kprobes`、`uprobes`)。在 Linux 4.x 系列的内核里,这些功能大大加强了。
时间采样是最主要的部分,它被 Linux 4.9-rc1 所采用([patchset](https://lkml.org/lkml/2016/9/1/831))。十分感谢 Alexei Starovoitov(在 Facebook 致力于 BPF 的开发),他是这些 BPF 增强功能的主要开发者。
Linux 内核现在内建有以下这些特性(自 2.6 版本到 4.9 版本之间增加):
* 内核级的动态追踪(BPF 对 `kprobes` 的支持)
* 用户级的动态追踪(BPF 对 `uprobes` 的支持)
* 内核级的静态追踪(BPF 对 `tracepoints` 的支持)
* 时间采样事件(BPF 的 `pref_event_open`)
* PMC 事件(BPF 的 `pref_event_open`)
* 过滤器(通过 BPF 程序)
* 调试输出(`bpf_trace_printk()`)
* 按事件输出(`bpf_perf_event_output()`)
* 基础变量(全局的和每个线程的变量,基于 BPF 映射)
* 关联数组(通过 BPF 映射)
* 频率计数(基于 BPF 映射)
* 柱状图(2 的冥次方、线性及自定义,基于 BPF 映射)
* 时间戳和时间增量(`bpf_ktime_get_ns()`,和 BPF 程序)
* 内核态的堆栈轨迹(BPF 栈映射)
* 用户态的堆栈轨迹 (BPF 栈映射)
* 重写 ring 缓存(`pref_event_attr.write_backward`)
我们采用的前端是 bcc,它同时提供 Python 和 lua 接口。bcc 添加了:
* 用户级静态追踪(基于 `uprobes` 的 USDT 探针)
* 调试输出(Python 中调用 `BPF.trace_pipe()` 和 `BPF.trace_fields()` 函数 )
* 按事件输出(`BPF_PERF_OUTPUT` 宏和 `BPF.open_perf_buffer()`)
* 间隔输出(`BPF.get_table()` 和 `table.clear()`)
* 打印柱状图(`table.print_log2_hist()`)
* 内核级的 C 结构体导航(bcc 重写器映射到 `bpf_probe_read()` 函数)
* 内核级的符号解析(`ksym()`、 `ksymaddr()`)
* 用户级的符号解析(`usymaddr()`)
* BPF 跟踪点支持(通过 `TRACEPOINT_PROBE`)
* BPF 堆栈轨迹支持(包括针对堆栈框架的 `walk` 方法)
* 其它各种辅助宏和方法
* 例子(位于 `/examples` 目录)
* 工具(位于 `/tools` 目录)
* 教程(`/docs/tutorial*.md`)
* 参考手册(`/docs/reference_guide.md`)
直到最新也是最主要的特性被整合进来,我才开始写这篇文章,现在它在 4.9-rc1 内核中。我们还需要去完成一些次要的东西,还有另外一些事情要做,但是现在我们所拥有的已经值得欢呼了。现在 Linux 拥有了内建的高级追踪能力。
### 安全性
设计 BPF 及其增强功能时就考虑到生产环境级安全,它被用在大范围的生产环境里。不过你想的话,你还是可以找到一个挂起内核的方法。这种情况是偶然的,而不是必然,类似的漏洞会被快速修复,尤其是当 BPF 合并入了 Linux。因为 Linux 可是公众的焦点。
在开发过程中我们碰到了一些非 BPF 的漏洞,它们需要被修复:rcu 不可重入,这可能导致内核由于 funccount 挂起,在 4.6 内核版本中这个漏洞被 “bpf: map pre-alloc” 补丁集所修复,旧版本内核的漏洞 bcc 有个临时处理方案。还有一个是 uprobe 的内存计算问题,这导致 uprobe 分配内存失败,在 4.8 内核版本这个漏洞由 “uprobes: Fix the memcg accounting” 补丁所修复,并且该补丁还将被移植到之前版本的内核中(例如,它现在被移植到了 4.4.27 和 4.4.0-45.66 版本中)。
### 为什么 Linux 追踪用了这么久才加进来?
首要任务被分到了若干追踪器中间:这些不是某个追踪器单个的事情。想要了解更多关于这个或其它方面的问题,可以看一看我在 2014 年 [tracing summit 上的讲话](http://www.slideshare.net/brendangregg/from-dtrace-to-linux)。我忽视了部分方案的反面影响:有些公司发现其它追踪器(SystemTap 和 LTTng)能满足他们的需求,尽管他们乐于听到 BPF 的开发进程,但考虑到他们现有的解决方案,帮助 BPF 的开发就不那么重要了。
BPF 仅在近两年里在追踪领域得到加强。这一过程原本可以更快的,但早期缺少全职从事于 BPF 追踪的工程师。Alexei Starovoitov (BPF 领导者),Brenden Blanco (bcc 领导者),我还有其它一些开发者,都有其它的事情要做。我在 Netflix 公司花了大量时间(志愿地),大概有 7% 的时间是花在 BPF 和 bcc 上。某种程度上这不是我的首要任务,因为我还有自己的工作(包括我的 perf-tools,一个可以工作在旧版本内核上的程序)。
现在BPF 追踪器已经推出了,已经有科技公司开始寻找会 BPF 的人了。但我还是推荐 [Netflix 公司](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-03-30/working-at-netflix-2016.html)。(如果你为了 BPF 而要聘请我,那我还是十分乐于待在 Netflix 公司的!)
### 使用简单
DTrace 和 bcc/BPF 现在的最大区别就是哪个更好使用。这取决于你要用 BPF 追踪做什么了。如果你要
* **使用 BPF 工具/度量**:应该是没什么区别的。工具的表现都差不多,图形用户界面都能取得类似度量指标。大部分用户通过这种方式使用 BPF。
* **开发工具/度量**:bcc 的开发可难多了。DTrace 有一套自己的简单语言,D 语音,和 awk 语言相似,而 bcc 使用已有的语言(C 语言,Python 和 lua)及其类库。一个用 C 和 Python 写的 bcc 工具与仅仅用 D 语言写出来的工具相比,可能要多十多倍行数的代码,或者更多。但是很多 DTrace 工具用 shell 封装来提供参数和差错检查,会让代码变得十分臃肿。编程的难处是不同的:重写 bcc 更需要巧妙性,这导致某些脚本更加难开发。(尤其是 `bpf_probe_read()` 这类的函数,需要了解更多 BPF 的内涵知识)。当计划改进 bcc 时,这一情形将得到改善。
* **运行常见的命令**:十分相近。通过 `dtrace` 命令,DTrace 能做很多事,但 bcc 有各种工具,`trace`、`argdist`、`funccount`、`funclatency` 等等。
* **编写自定义的特殊命令**:使用 DTrace 的话,这就没有必要了。允许定制消息快速传递和系统快速响应,DTrace 的高级分析很快。而 bcc 现在受限于它的多种工具以及它们的适用范围。
简单来说,如果你只使用 BPF 工具的话,就不必关注这些差异了。如果你经验丰富,是个开发者(像我一样),目前 bcc 的使用更难一些。
举一个 bcc 的 Python 前端的例子,下面是追踪硬盘 I/O 并打印出 I/O 大小的柱状图代码:
```
from bcc import BPF
from time import sleep
# load BPF program
b = BPF(text="""
#include <uapi/linux/ptrace.h>
#include <linux/blkdev.h>
BPF_HISTOGRAM(dist);
int kprobe__blk_account_io_completion(struct pt_regs *ctx, struct request *req)
{
dist.increment(bpf_log2l(req->__data_len / 1024));
return 0;
}
""")
# header
print("Tracing... Hit Ctrl-C to end.")
# trace until Ctrl-C
try:
sleep(99999999)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print
# output
b["dist"].print_log2_hist("kbytes")
```
注意 Python 代码中嵌入的 C 语句(`text=`)。
这就完成了任务,但仍有改进的空间。好在我们有时间去做:人们使用 Linux 4.9 并能用上 BPF 还得好几个月呢,所以我们有时间来制造工具和前端。
### 高级语言
前端越简单,比如高级语言,所改进的可能就越不如你所期望的。绝大多数人使用封装好的工具(和图形界面),仅有少部分人能写出这些工具。但我不反对使用高级语言,比如 SystemTap,毕竟已经开发出来了。
```
#!/usr/bin/stap
/*
* opensnoop.stp Trace file open()s. Basic version of opensnoop.
*/
probe begin
{
printf("\n%6s %6s %16s %s\n", "UID", "PID", "COMM", "PATH");
}
probe syscall.open
{
printf("%6d %6d %16s %s\n", uid(), pid(), execname(), filename);
}
```
如果拥有整合了语言和脚本的 SystemTap 前端与高性能的内置在内核中的 BPF 后端,会不会令人满意呢?RedHat 公司的 Richard Henderson 已经在进行相关工作了,并且发布了 [初代版本](https://lkml.org/lkml/2016/6/14/749)!
这是 [ply](https://wkz.github.io/ply/),一个完全新颖的 BPF 高级语言:
```
#!/usr/bin/env ply
kprobe:SyS_*
{
$syscalls[func].count()
}
```
这也是一份承诺。
尽管如此,我认为工具开发者的实际难题不是使用什么语言:而是要了解要用这些强大的工具做什么?
### 如何帮助我们
* **推广**:BPF 追踪器目前还没有什么市场方面的进展。尽管有公司了解并在使用它(Facebook、Netflix、Github 和其它公司),但要广为人知尚需时日。你可以分享关于 BPF 的文章和资源给业内的其它公司来帮助我们。
* **教育**:你可以撰写文章,发表演讲,甚至参与 bcc 文档的编写。分享 BPF 如何解决实际问题以及为公司带来收益的实例。
* **解决 bcc 的问题**:参考 [bcc issue list](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/issues),这包含了错误和需要的特性。
* **提交错误**:使用 bcc/BPF,提交你发现的错误。
* **创造工具**:有很多可视化的工具需要开发,但请不要太草率,因为大家会先花几个小时学习使用你做的工具,所以请尽量把工具做的直观好用(参考我的[文档](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING-SCRIPTS.md))。就像 Mike Muuss 提及到他自己的 [ping](http://ftp.arl.army.mil/%7Emike/ping.html) 程序:“要是我早知道这是我一生中最出名的成就,我就多开发一两天,添加更多选项。”
* **高级语言**:如果现有的 bcc 前端语言让你很困扰,或许你能弄门更好的语言。要是你想将这门语言内建到 bcc 里面,你需要使用 libbcc。或者你可以帮助 SystemTap BPF 或 ply 的工作。
* **整合图形界面**:除了 bcc 可以使用的 CLI 命令行工具,怎么让这些信息可视呢?延迟热点图,火焰图等等。
### 其它追踪器
那么 SystemTap、ktap、sysdig、LTTng 等追踪器怎么样呢?它们有个共同点,要么使用了 BPF,要么在自己的领域做得更好。会有单独的文章介绍它们自己。
至于 DTrace ?我们公司目前还在基于 FreeBSD 系统的 CDN 中使用它。
### 更多 bcc/BPF 的信息
我已经写了一篇《[bcc/BPF 工具最终用户教程](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/docs/tutorial.md)》,一篇《[bcc Python 开发者教程](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/docs/tutorial_bcc_python_developer.md)》,一篇《[bcc/BPF 参考手册](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/docs/reference_guide.md)》,并提供了一些有用的[工具](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/tree/master/tools),每一个工具都有一个 [example.txt](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/tree/master/tools) 文件和 [man page](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/tree/master/man/man8)。我之前写过的关于 bcc 和 BPF 的文章有:
* [eBPF: One Small Step](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2015-05-15/ebpf-one-small-step.html) (后来就叫做 BPF)
* [bcc: Taming Linux 4.3+ Tracing Superpowers](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2015-09-22/bcc-linux-4.3-tracing.html)
* [Linux eBPF Stack Trace Hack](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-01-18/ebpf-stack-trace-hack.html) (现在官方支持追踪堆栈了)
* [Linux eBPF Off-CPU Flame Graph](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-01-20/ebpf-offcpu-flame-graph.html)
* [Linux Wakeup and Off-Wake Profiling](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-02-01/linux-wakeup-offwake-profiling.html)
* [Linux Chain Graph Prototype](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-02-05/ebpf-chaingraph-prototype.html)
* [Linux eBPF/bcc uprobes](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-02-08/linux-ebpf-bcc-uprobes.html)
* [Linux BPF Superpowers](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-03-05/linux-bpf-superpowers.html)
* [Ubuntu Xenial bcc/BPF](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-06-14/ubuntu-xenial-bcc-bpf.html)
* [Linux bcc Tracing Security Capabilities](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-10-01/linux-bcc-security-capabilities.html)
* [Linux MySQL Slow Query Tracing with bcc/BPF](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-10-04/linux-bcc-mysqld-qslower.html)
* [Linux bcc ext4 Latency Tracing](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-10-06/linux-bcc-ext4dist-ext4slower.html)
* [Linux bcc/BPF Run Queue (Scheduler) Latency](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-10-08/linux-bcc-runqlat.html)
* [Linux bcc/BPF Node.js USDT Tracing](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-10-12/linux-bcc-nodejs-usdt.html)
* [Linux bcc tcptop](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-10-15/linux-bcc-tcptop.html)
* [Linux 4.9's Efficient BPF-based Profiler](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-10-21/linux-efficient-profiler.html)
我在 Facebook 的 Performance@Scale [Linux BPF Superpowers](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-03-05/linux-bpf-superpowers.html) 大会上发表过一次演讲。十二月份,我将在 Boston 发表关于 BPF/bcc 在 [USENIX LISA](https://www.usenix.org/conference/lisa16) 方面的演讲和教程。
### 致谢
* Van Jacobson 和 Steve McCanne,他们创建了最初用作过滤器的 BPF 。
* Barton P. Miller,Jeffrey K. Hollingsworth,and Jon Cargille,发明了动态追踪,并发表论文《Dynamic Program Instrumentation for Scalable Performance Tools》,可扩展高性能计算协议 (SHPCC),于田纳西州诺克斯维尔市,1994 年 5 月发表。
* kerninst (ParaDyn, UW-Madison),展示了动态跟踪的价值的早期动态跟踪工具(上世纪 90 年代后期)
* Mathieu Desnoyers (在 LTTng),内核的主要开发者,主导 tracepoints 项目。
* IBM 开发的作为 DProbes 一部分的 kprobes,DProbes 在 2000 年时曾与 LTT 一起提供 Linux 动态追踪,但没有整合到一起。
* Bryan Cantrill, Mike Shapiro, and Adam Leventhal (Sun Microsystems),DTrace 的核心开发者,DTrace 是一款很棒的动态追踪工具,安全而且简单(2004 年)。对于动态追踪技术,DTrace 是科技的重要转折点:它很安全,默认安装在 Solaris 以及其它以可靠性著称的系统里。
* 来自 Sun Microsystems 的各部门的许多员工,促进了 DTrace,为我们带来了高级系统追踪的意识。
* Roland McGrath (在 Red Hat),utrace 项目的主要开发者,utrace 变成了后来的 uprobes。
* Alexei Starovoitov (PLUMgrid, 后来是 Facebook),加强版 BPF(可编程内核部件)的主要开发者。
* 那些帮助反馈、提交代码、测试以及针对增强版 BPF 补丁(请在 lkml 搜索 BPF)的 Linux 内核工程师: Wang Nan、 Daniel Borkmann、 David S. Miller、 Peter Zijlstra 以及其它很多人。
* Brenden Blanco (PLUMgrid),bcc 的主要开发者。
* Sasha Goldshtein (Sela) 开发了 bcc 中的跟踪点支持,和功能最强大的 bcc 工具 trace 及 argdist,帮助 USDT 项目的开发。
* Vicent Martí 和其它 Github 上的工程师,为 bcc 编写了基于 lua 的前端,帮助 USDT 部分项目的开发。
* Allan McAleavy、 Mark Drayton,和其他的改进 bcc 的贡献者。
感觉 Netflix 提供的环境和支持,让我能够编写 BPF 和 bcc 跟踪器并完成它们。我已经编写了多年的追踪工具(使用 TNF/prex、DTrace、SystemTap、ktap、ftrace、perf,现在是 bcc/BPF),并写书、博客以及评论,
最后,感谢 [Deirdré](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-07-23/deirdre.html) 编辑了另外一篇文章。
### 总结
Linux 没有 DTrace(语言),但它现在有了,或者说拥有了 DTraceTookit(工具)。
通过增强内置的 BPF 引擎,Linux 4.9 内核拥有了用来支持现代化追踪的最后一项能力。内核支持这一最难的部分已经做完了。今后的任务包括更多的命令行执行工具,以及高级语言和图形用户界面。
对于性能分析产品的客户,这也是一件好事:你能查看延迟柱状图和热点图,CPU 处理和 CPU 之外的火焰图,拥有更好的时延断点和更低耗的工具。在用户空间按包跟踪和处理是没有效率的方式。
那么你什么时候会升级到 Linux 4.9 呢?一旦官方发布,新的性能测试工具就来了:`apt-get install bcc-tools` 。
开始享受它吧!
Brendan
---
via: <http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2016-10-27/dtrace-for-linux-2016.html>
作者:[Brendan Gregg](http://www.brendangregg.com/) 译者:[GitFuture](https://github.com/GitFuture) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 302 | Found | null |
8,039 | httpstat:一个检查网站性能的 curl 统计分析工具 | http://www.tecmint.com/httpstat-curl-statistics-tool-check-website-performance/ | 2016-12-16T08:11:00 | [
"httpstat",
"curl"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8039-1.html | httpstat 是一个 Python 脚本,它以美妙妥善的方式反映了 curl 统计分析,它是一个单一脚本,兼容 Python 3 ,在用户的系统上不需要安装额外的软件(依赖)。

从本质上来说它是一个 cURL 工具的封装,意味着你可以在 URL 后使用几个有效的 cURL 选项,但是不包括 `-w`、 `-D`、 `-o`、 `-s` 和 `-S` 选项,这些已经被 httpstat 使用了。

*httpstat Curl 统计分析工具*
你可以看到上图的一个 ASCII 表显示了每个过程消耗多长时间,对我来说最重要的一步是“<ruby> 服务器处理 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> server processing </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>” – 如果这个数字很高,那么你需要[优化你网站服务器来加速访问速度](http://www.tecmint.com/apache-performance-tuning/)。
网站或服务器优化你可以查看我们的文章:
1. [5 个优化 Apache Web 服务器性能的技巧](http://www.tecmint.com/apache-performance-tuning/)
2. [使 Apache 和 Nginx 性能提升 10 倍](http://www.tecmint.com/install-mod_pagespeed-to-boost-apache-nginx-performance/)
3. [如何使用 Gzip 模块提高 Nginx 性能](http://www.tecmint.com/increase-nginx-performance-enable-gzip-compression-module/)
4. [15 个优化 MySQL/MariaDB 性能的建议](/article-5730-1.html)
使用下面安装说明和用法来获取 httpstat 检查出你的网站速度。
### 在 Linux 系统中安装 httpstat
你可以使用两种合理的方法安装 httpstat :
1. 使用 [wget 命令](/article-4129-1.html)直接从它的 Github 仓库获取如下:
```
$ wget -c https://raw.githubusercontent.com/reorx/httpstat/master/httpstat.py
```
1. 使用 `pip`(这个方法允许 httpstat 作为命令安装到你的系统中)像这样:
```
$ sudo pip install httpstat
```
注:确保 `pip` 包已经在系统上安装了,如果没使用你的发行版包管理器 [yum](/article-2272-1.html) 或 [apt](/article-7364-1.html)安装它。
### 在 Linux 中如何使用 httpstat
`httpstat` 可以根据你安装它的方式来使用,如果你直接下载了它,进入下载目录使用下面的语句运行它:
```
$ python httpstat.py url cURL_options
```
如果你使用 `pip` 来安装它,你可以作为命令来执行它,如下表:
```
$ httpstat url cURL_options
```
查看 `httpstat` 帮助页,命令如下:
```
$ python httpstat.py --help
或
$ httpstat --help
```
`httpstat` 帮助:
```
Usage: httpstat URL [CURL_OPTIONS]
httpstat -h | --help
httpstat --version
Arguments:
URL url to request, could be with or without `http(s)://` prefix
Options:
CURL_OPTIONS any curl supported options, except for -w -D -o -S -s,
which are already used internally.
-h --help show this screen.
--version show version.
Environments:
HTTPSTAT_SHOW_BODY Set to `true` to show response body in the output,
note that body length is limited to 1023 bytes, will be
truncated if exceeds. Default is `false`.
HTTPSTAT_SHOW_IP By default httpstat shows remote and local IP/port address.
Set to `false` to disable this feature. Default is `true`.
HTTPSTAT_SHOW_SPEED Set to `true` to show download and upload speed.
Default is `false`.
HTTPSTAT_SAVE_BODY By default httpstat stores body in a tmp file,
set to `false` to disable this feature. Default is `true`
HTTPSTAT_CURL_BIN Indicate the curl bin path to use. Default is `curl`
from current shell $PATH.
HTTPSTAT_DEBUG Set to `true` to see debugging logs. Default is `false`
```
从上面帮助命令的输出,你可以看出 `httpstat` 已经具备了一些可以影响其行为的环境变量。
使用它们,只需输出适当的值的这些变量到 `.bashrc` 或 `.zshrc` 文件。
例如:
```
export HTTPSTAT_SHOW_IP=false
export HTTPSTAT_SHOW_SPEED=true
export HTTPSTAT_SAVE_BODY=false
export HTTPSTAT_DEBUG=true
```
你一旦添加完它们,保存文件然后运行下面的命令使改变生效:
```
$ source ~/.bashrc
```
你可以指定使用 cURL 执行文件的路径,默认使用的是当前 shell 的 [$PATH 环境变量](http://www.tecmint.com/set-unset-environment-variables-in-linux/)。
下面是一些展示 `httpstat` 如何工作的例子。
```
$ python httpstat.py google.com
或
$ httpstat google.com
```

*httpstat – 展示网站统计分析*
接下来的命令中:
1. `-X` 命令标记指定一个客户与 HTTP 服务器连接的请求方法。
2. `--data-urlencode` 这个选项将会把数据(这里是 a=b)按 URL 编码的方式编码后再提交。
3. `-v` 开启详细模式。
```
$ python httpstat.py httpbin.org/post -X POST --data-urlencode "a=b" -v
```

*httpstat – 定制提交请求*
你可以查看 cURL 的帮助获取更多有用的高级选项,或者浏览 `httpstat` 的 Github 仓库: <https://github.com/reorx/httpstat>
这篇文章中,我们讲述了一个有效的工具,它以简单和整洁方式来查看 cURL 统计分析。如果你知道任何类似的工具,别犹豫,让我们知道,你也可以问问题或评论这篇文章或 httpstat,通过下面反馈。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/httpstat-curl-statistics-tool-check-website-performance/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[wyangsun](https://github.com/wyangsun) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,040 | 修复 Ubuntu 中“Unable to lock the administration directory (/var/lib/dpkg/)”的 | http://www.tecmint.com/fix-unable-to-lock-the-administration-directory-var-lib-dpkg-lock | 2016-12-16T09:42:00 | [
"apt-get",
"apt"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8040-1.html | 
在 Ubuntu 或者它的衍生版如 Linux Mint(我已经作为日常工作使用的系统)中使用 [apt-get 命令](/article-4933-1.html)或者其相对更新的[APT 管理工具](/article-7364-1.html)时,你可能会在命令行中看到一个 `unable to lock the administration directory (/var/lib/dpkg/) is another process using it` 的错误。
这个错误尤其对那些对这个错误原因不了解的 Linux(Ubuntu)新手而言更加恼人。
下面是一个例子,展示了出现在 Ubuntu 16.10 上的文件锁定错误:
```
tecmint@TecMint:~$ sudo apt install neofetch
[sudo] password for tecmint:
E: Could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock - open (11: Resource temporarily unavailable)
E: Unable to lock the administration directory (/var/lib/dpkg), is another process using it?
```
下面的输出是另外一个可能显示的错误:
```
E: Could not get lock /var/lib/apt/lists/lock - open (11: Resource temporarily unavailable)
E: Unable to lock directory /var/lib/apt/lists/
E: Could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock - open (11: Resource temporarily unavailable)
E: Unable to lock the administration directory (/var/lib/dpkg/), is another process using it?
```
你将来遇到这个错误该怎么去解决?有好几种方法处理这个错误,但是本篇中我们会用两种或许是最简单和最有效的方法来解决它。
### 1、找出并杀掉所有 apt-get 或者 apt 进程
运行下面的命令来[生成所有含有 apt 的进程列表](http://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-processes-memory-ram-cpu-usage/),你可以使用 `ps` 和 [grep 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/linux-grep-commands-character-classes-bracket-expressions/)并用管道组合来得到含有 apt 或者 apt-get 的进程。
```
$ ps -A | grep apt
```
[](http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/find-apt-processes.png)
*找出 apt 以及 apt-get 进程*
你可以看到上面命令输出的每个 apt-get 或者 apt 进程,使用下面的命令[杀掉每个进程](http://www.tecmint.com/find-and-kill-running-processes-pid-in-linux/)。
上面截图中的第一列是进程 ID(PID)。
```
$ sudo kill -9 processnumber
或者
$ sudo kill -SIGKILL processnumber
```
比如,下面命令中的`9`是 `SIGKILL` 的信号数,它会杀掉第一个 apt 进程:
```
$ sudo kill -9 13431
或者
$ sudo kill -SIGKILL 13431
```
### 2、 删除锁定的文件
锁定的文件会阻止 Linux 系统中某些文件或者数据的访问,这个概念也存在于 Windows 或者其他的操作系统中。
一旦你运行了 apt-get 或者 apt 命令,锁定文件将会创建于 `/var/lib/apt/lists/`、`/var/lib/dpkg/`、`/var/cache/apt/archives/` 中。
这有助于运行中的 apt-get 或者 apt 进程能够避免被其它需要使用相同文件的用户或者系统进程所打断。当该进程执行完毕后,锁定文件将会删除。
重要提醒:万一你在没有看到 apt-get 或者 apt 进程的情况下在上面两个不同的文件夹中看到了锁定文件,这是因为进程由于某个原因被杀掉了,因此你需要删除锁定文件来避免该错误。
首先运行下面的命令来移除 `/var/lib/dpkg/` 文件夹下的锁定文件:
```
$ sudo rm /var/lib/dpkg/lock
```
之后像下面这样强制重新配置软件包:
```
$ sudo dpkg --configure -a
```
也可以删除 `/var/lib/apt/lists/` 以及缓存文件夹下的锁定文件:
```
$ sudo rm /var/lib/apt/lists/lock
$ sudo rm /var/cache/apt/archives/lock
```
接下来,更新你的软件包源列表:
```
$ sudo apt update
或者
$ sudo apt-get update
```
总结一下,对于 Ubuntu(以及它的衍生版)用户在使用 apt-get 或者 apt 也叫 [aptitude 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/difference-between-apt-and-aptitude/)时遇到的问题,我们已经用两种方法来解决了。
你有什么可以分享出来的有效的方法来处理这个错误么?在下面的评论区联系我们。
除此之外,你可能还希望了解[如何找出并杀掉运行的进程](http://www.tecmint.com/find-and-kill-running-processes-pid-in-linux/),你可以阅读这篇[用 kill、pkill、killall 来中止进程](http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-kill-a-process-in-linux/)指南来了解。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/fix-unable-to-lock-the-administration-directory-var-lib-dpkg-lock>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,041 | 如何在 Linux 中复制文件到多个目录中 | http://www.tecmint.com/copy-file-to-multiple-directories-in-linux/ | 2016-12-17T15:10:00 | [
"cp"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8041-1.html | [在学习 Linux 的过程中](http://www.tecmint.com/free-online-linux-learning-guide-for-beginners/),对于新手而言总是会使用几个命令来完成一个简单的任务。对正在熟悉使用终端的人这是很容易理解的行为。然而,如果你想要成为一个老手,学习我说的“快捷命令”会显著减少时间浪费。
在本篇中,我们会用一个简单的方法在 Linux 中用一个命令来将目录复制到多个文件夹中。

在 Linux 中,[cp 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/advanced-copy-command-shows-progress-bar-while-copying-files/)常被用于从一个文件夹中复制文件到另一个文件夹中,最简单的语法如下:
```
# cp [options….] source(s) destination
```
另外,你也可以使用[高级复制命令](http://www.tecmint.com/advanced-copy-command-shows-progress-bar-while-copying-files/),它可以在复制[大的文件或文件夹](http://www.tecmint.com/find-top-large-directories-and-files-sizes-in-linux/)时显示进度条。
看下下面的命令,通常你会使用两个不同的命令来将相同的文件复制到不同的文件夹中:
```
# cp -v /home/aaronkilik/bin/sys_info.sh /home/aaronkilik/test
# cp -v /home/aaronkilik/bin/sys_info.sh /home/aaronkilik/tmp
```

*复制文件到多个文件夹中*
假设你想要复制一个特定文件到 5 个或者更多的文件夹中,这意味着你需要输入 5 次或者更多的cp命令么?
要摆脱这个问题,你可以用 cp 命令与 [echo命令](http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/)、管道、xargs 命令一起使用:
```
# echo /home/aaronkilik/test/ /home/aaronkilik/tmp | xargs -n 1 cp -v /home/aaronkilik/bin/sys_info.sh
```
上面的命令中,目录的路径(dir1、dir2、dir3...dirN)被管道作为输入到 xargs 命令中,含义是:
1. `-n 1` - 告诉 xargs 命令每个命令行最多使用一个参数,并发送到 cp 命令中。
2. `cp` – 用于复制文件。
3. `-v` – 启用详细模式来显示更多复制细节。

*在 Linux 中复制文件到多个位置中*
试试阅读 `cp`、 `echo` 和 `xargs` 的 man 页面来找出所有有用和高级的用法信息:
```
$ man cp
$ man echo
$ man xargs
```
就是这样了,你可以在下面的评论区给我们发送主题相关的问题或者反馈。你也可以阅读有关 [progress 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/progress-monitor-check-progress-of-linux-commands/)来帮助监控运行中的(cp、mv、dd、[tar](http://www.tecmint.com/18-tar-command-examples-in-linux/) 等等)的进度。
---

作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 及 F.O.S.S 热衷者,即将成为 Linux 系统管理员、web 开发者,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/copy-file-to-multiple-directories-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,042 | 慢动作输出 Linux 命令结果并用彩色显示 | http://www.tecmint.com/add-colors-to-command-output-terminal-linux/ | 2016-12-18T09:21:00 | [
"lolcat"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8042-1.html | 本篇中,我们会展示一个很酷及简单的方法在屏幕中显示彩色的输出,并且可以为了某个原因减慢输出的速度。
[lolcat 命令](/article-5798-1.html)可以满足上面的需求。它基本上通过与 [cat 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/)类似的方式将文件或标准输入定向到标准输出来运行,覆盖某个命令的默认屏幕输出颜色,并为其添加彩色。

### 如何在 Linux 中安装 lolcat 程序
lolcat 可以在大多数现代 Linux 发行版的默认仓库中得到,但是可用的版本有点老。你可以使用下面的指导来从 git 仓库中安装最新的 lolcat 版本。
* [安装 lolcat 来在 Linux 中显示彩色输出](/article-5798-1.html)
lolcat 安装后,基本的 lolcat 语法是:
```
$ lolcat [options] [files] ...
```
有几个选项可以控制它的行为,下面是一些我们在本指导中会强调的几个最重要的标志:
1. `-a` - 将每行输出都显示动态效果。
2. `-d` – 指定动画效果间隔(显示下一行之前的帧),默认是 12。
3. `-s` – 它指定了动画效果的速度(帧速-每秒的显示帧数),默认是 20。
4. `-f` – 强制显示彩色以防止标准输出不是 tty。
你可以在 lolcat 的 man 页可以找到更多的选项:
```
$ man lolcat
```
### 如何在 Linux 中使用 lolcat
要使用 lolcat,直接将相关命令的输出通过管道给 lolcat,即可见证魔法。
比如:
```
$ ls -l | lolcat -as 25
```

除此之外你也可以改变默认速度,在下面的命令中,我们会使用一个相对较慢的速度,每秒显示 10 帧:
```
$ ls -l | lolcat -as 10
```
你可以使用任何命令结合 lolcat 在 Linux 终端中输出彩色结果,比如 `ps`、`date` 和 `cal`:
```
$ ps | lolcat
$ date | lolcat
$ cal | lolcat
```
本篇中,我们了解了如何显著降低屏幕输出的速度,并显示彩色效果。
通常上,你可以在下面的评论栏中留下任何关于本篇的问题或评论。最后,你可以留下任何你发现的有用命令。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/add-colors-to-command-output-terminal-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,043 | 安卓编年史(13):Android 2.2 Froyo——更快更华丽 | http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/13/ | 2016-12-18T15:45:00 | [
"Android",
"安卓编年史"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8043-1.html | 
### Android 2.2 Froyo——更快更华丽
[安卓 2.2](http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2010/07/android-22-froyo/) 在 2010 年 5 月,也就是 2.1 发布后的四个月后亮相。Froyo(冻酸奶)的亮点主要是底层优化,只为更快的速度。Froyo 最大的改变是增加了 JIT 即时编译。JIT 自动在运行时将 java 字节码转换为原生码,这会给系统全面带来显著的性能改善。
浏览器同样得到了性能改善,这要感谢整合了来自 Chrome 的 V8 Javascript 引擎。这是安卓浏览器从 Chrome 借鉴的许多特性中的第一个,最终系统内置的浏览器会被移动版 Chrome 彻底替代掉。在那之前,安卓团队还是需要提供一个浏览器。从 Chrome 借鉴特性是条升级的捷径。
在谷歌专注于让它的平台更快的同时,苹果正在让它的平台更全面。这位谷歌的竞争对手在一个月前发布了 10 英寸的 iPad,先行进入了平板时代。尽管有些搭载 Froyo 和 Gingerbread 的安卓平板发布,但谷歌的官方回应——安卓 3.0 Honeycomb(蜂巢)以及摩托罗拉 Xoom——在 9 个月后才来到。

*Froyo 底部添加了双图标停靠栏以及全局搜索。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
Froyo 主屏幕最大的变化是底部的新停靠栏,电话和浏览器图标填充了先前抽屉按钮左右的空白空间。这些新图标都是现有图标的白色定制版本,并且用户没办法自己设置图标。
默认布局移除了所有图标,屏幕上只留下一个使用提示小部件,引导你点击启动器图标以访问你的应用。谷歌搜索小部件得到了一个谷歌 logo,它同时也是个按钮。点击它可以打开一个搜索界面,你可以限制搜索范围是在互联网、应用或是联系人之内。

*下载页面有了“更新所有”按钮,这是个 Flash 应用,一个 flash 驱动的一切皆有可能的网站,以及“移动到 SD”按钮。 [[Ryan Paul](http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2010/07/android-22-froyo/) 供图]*
还有一些优秀的新功能加入了 Froyo,安卓市场加入了更多的下载控制。有个新的“更新所有”按钮固定在了下载页面底部。谷歌还添加了自动更新特性,只要应用权限没有改变就能够自动安装应用;尽管如此,自动更新默认是关闭的。
第二张图展示了 Adobe Flash 播放器,它是 Froyo 独有的。这个应用作为插件加入了浏览器,让浏览器能够有“完整的网络”体验。在 2010 年,这意味着网页充满了 Flash 导航和视频。Flash 是安卓相比于 iPhone 最大的不同之一。史蒂夫·乔布斯展开了一场对抗 Flash 的圣战,声称它是一个被淘汰的、充满 bug 的软件,并且苹果不会允许它在 iOS 存在。所以安卓接纳了 Flash 并且让它在安卓上运行,给予用户在安卓上拥有接近可用的 flash 实现。
在那时,Flash 甚至能够让桌面电脑崩溃,所以在移动设备上一直保持打开状态会带来可怕的体验。为了解决这个问题,安卓浏览器上的 Flash 可以设置为“按需打开”——除非用户点击 Flash 占位图标,否则不会加载 Flash 内容。对 Flash 的支持将会持续到安卓 4.1,Adobe 在那时放弃并且结束了这个项目。Flash 从头到尾从未在安卓上完美运行过。而 Flash在 iPhone 这个最流行的移动设备上的缺失,推动了互联网最终放弃了这个平台。
最后一张图片显示的是新增的移动应用到 SD 卡功能,在那个手机只有 512 MB内置存储的时代,这个功能十分的必要的。

*驾驶模式应用。相机现在可以旋转了。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
相机应用终于更新支持纵向模式了。相机设置被从抽屉中移出,变成一条半透明的按钮带,放在了快门按钮和其他控制键旁边。这个新设计看起来从 Cooliris 相册中获得了许多灵感,半透明的、有弹性的聊天气泡弹出窗口。看到更现代的Cooliris 风格 UI 设计被嫁接到皮革装饰的相机应用确实十分奇怪——从审美上来说一点都不搭。

*半残缺的 Facebook 应用是个常见的 2x3 导航页面的优秀范例。谷歌 Goggles 被包含了进来但同样是残缺的。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
不像在安卓 2.0 和 2.1 中包含的 Facebook 客户端,2.2 版本的仍然部分能够工作并且可以登录 Facebook 服务器。Facebook 应用是谷歌那时候设计指南的优秀范例,它建议应用拥有一个含有 3x2 图标方阵的导航页并作为应用主页。
这是谷歌的第一个标准化尝试,将导航元素从菜单按钮里移到屏幕上,以便用户找到它们。这个设计很实用,但它在打开应用和使用应用之间增加了额外的障碍。谷歌不久后会意识到当用户打开一个应用,显示应用内容而不是中间导航页是个更好的主意。以 Facebook 为例,打开应用直接打开信息订阅会更合适。并且不久后应用设计将会把导航降级到二层位置——先是作为顶部的标签之一,后来谷歌放在了“导航抽屉”,一个含有应用所有功能位置的滑出式面板。
还有个预装到 Froyo 的应用是谷歌 Goggles,一个视觉搜索应用,它会尝试辨别图片上的主体。它在辨别艺术品、地标以及条形码时很实用,但差不多也就这些了。最先的两个设置屏幕,以及相机界面,这是应用里仅有的现在还能运行的了。由于客户端太旧了,实际上你如今并不能完成一个搜索。应用里也没什么太多可看的,也就一个会返回搜索结果页的相机界面而已。

*Twitter 应用,一个充满动画的谷歌和 Twitter 的合作成果。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
Froyo 拥有首个安卓 Twitter 应用,实际上它是谷歌和 Twitter 的合作成果。那时,Twitter 应用是安卓应用阵容里的大缺憾之一。开发者们更偏爱 iPhone,加上苹果占领先机和严格的设计要求,App Store 里可选择的应用远比安卓的有优势。但是谷歌需要一个 Twitter 应用,所以它和 Twitter 合作组建团队让第一个版本问世。
这个应用代表了谷歌的新设计语言,这意味着它有个中间导航页以及对动画要求的“技术演示”。Twitter 应用甚至比 Cooliris 相册用的动画效果还多——所有东西一直都在动。所有页面顶部和底部的云朵以不同速度持续滚动,底部的 Twitter 小鸟拍动它的翅膀并且左右移动它的头。
Twitter 应用实际上有点 Action Bar 早期前身的特性,在安卓 3.0 中引入了一条顶部对齐的连续控制条。沿着所有屏幕的顶部有条拥有 Twitter 标志以及如搜索、刷新和发推这样的按钮的蓝色横栏。它和后来的 Action Bar 之间大的区别在于 Twitter / 谷歌这里的设计的右上角缺少“上一级”按钮,实际上它在应用里用了完整的第二个栏位显示你当前所在位置。在上面的第二张图里,你可以看到整条带有“Tweets”标签的专用于显示位置的栏(当然,还有持续滚动的云朵)。第二个栏的 Twitter 标志扮演着另一个导航元素,有时候在当前部分显示额外的下拉区域,有时候显示整个顶级快捷方式集合。
2.3 Tweet 流看起来和今天的并没有什么不同,除了隐藏的操作按钮(回复,转推等),都在右对齐的箭头按钮里。它们弹出来的是一个聊天气泡菜单,看起来就像导航弹窗。仿 Action Bar 在发推页面有重要作用。它安置着 twitter 标志,剩余字数统计,以及添加照片、拍照,以及提到联系人按钮。
Twitter 应用甚至还有一对主屏幕小部件,大号的那个占据 8 格,提供了发推栏、更新按钮、一条推文,以及左右箭头来查看更多的推文。小号的显示一条推文以及回复按钮。点击大号的小部件的发推栏立即打开了“新推文”主窗口,这让“更新”按钮变得没有价值。

*Google Talk 和新 USB 对话框。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
其他部分,Google Talk(以及没有截图的短信应用)从暗色主题变成了浅色主题,这让它们看起来和现在的更接近现代的应用。USB 存储界面会在你设备接入电脑的时候从一个简单的对话框进入全屏界面。这个界面现在有个一个异形安卓机器人 / USB 闪存盘混合体,而不是之前的纯文字设计。
尽管安卓 2.2 在用户互动方式上没有什么新特性,但大的 UI 调整会在下两个版本到来。然而在所有的 UI 工作之前,谷歌希望先改进安卓的核心部分。
### **语音操作——口袋里的超级电脑**
2010 年 8 月,作为语音搜索应用的一项新功能,“[语音命令](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2010/08/google-beefs-up-voice-search-mobile-sync/)”登陆了安卓市场。语音命令允许用户向他们的手机发出语音命令,然后安卓会试着去理解他们并完成任务。像“导航至[地址]”这样的命令会打开谷歌地图并且开始逐向导航至你所陈述的目的地。你还可以仅仅通过语音来发送短信或电子邮件、拨打电话、打开网站、获取方向,或是在地图上查看一个地点。
语音命令是谷歌新应用设计哲学的顶峰。语音命令是那时候最先进的语音控制软件,秘密在于谷歌并不在设备上做任运算。一般来说,语音识别是 CPU 密集型任务。实际上,许多语音识别程序仍然有“速度与准确性”设置,用户可以选择他们愿意为语音识别算法运行等待的时间——更多的 CPU 处理意味着更加准确。
谷歌的创新在于没有劳烦手机上能力有限的处理器来进行语音识别运算。当说出一个命令时,用户的声音会被打包并通过互联网发送到谷歌云服务器。在那里,谷歌超算中心的超级计算机分析并解释语音,然后发送回手机。这是很长的一段旅程,但互联网最终还是有足够快的速度在一两秒内完成像这样的任务。
很多人抛出词语“云计算”来表达“所有东西都被存储在服务器上”,但这才是真正的云计算。谷歌在云端进行这些巨量的运算操作,又因为在这个问题上投入了看似荒唐的 CPU 资源数目,所以语音识别准确性的唯一限制就是算法本身了。软件不需要由每个用户独立“训练”,因为所有使用语音操作的人无时不刻都在训练它。借助互联网的力量,安卓在你的口袋里放了一部超级电脑,同时相比于已有的解决方案,把语音识别这个工作量从口袋大小的电脑转移到房间大小的电脑上大大提高了准确性。
语音识别作为谷歌的项目已经有一段时间了,它的出现都是因为一个 800 号码。[1-800-GOOG-411](http://arstechnica.com/business/2007/04/google-rolls-out-free-411-service/)是个谷歌从 2007 年 4 月起开通的免费电话信息服务。它就像 411 信息服务一样工作了多年——用户可以拨打这个号码询问电话号码——但是谷歌免费提供这项服务。查询过程中没有人工的干预,411 服务由语音识别和文本语音转换引擎驱动。在人们教谷歌如何去听之后,又用了三年才有实现语音命令的可能。
语音识别是谷歌长远思考的极佳范例——公司并不怕在一个可能成不了商业产品的项目上投资多年。今天,语音识别驱动的产品遍布谷歌。它被用在谷歌搜索应用的输入,安卓的语音输入,以及 Google.com。同时它还是 Google Glass 和 [Android Wear](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/03/in-depth-with-android-wear-googles-quantum-leap-of-a-smartwatch-os/) 的默认输入界面。
谷歌甚至还在输入之外的地方使用语音识别。谷歌的语音识别技术被用在了转述 Youtube 视频上,它能自动生成字幕供听障用户观看。生成的字幕甚至被谷歌做成了索引,所以你可以搜索某句话在视频的哪里说过。语音是许多产品的未来,并且这项长期计划将谷歌带入了屈指可数的拥有自家语音识别服务的公司行列。大部分其它的语音识别产品,像苹果的 Siri 和三星设备,只能使用 Nuance 的语音识别,并且为其支付了授权费。
在计算机听觉系统设立运行之后,谷歌下一步将把这项策略应用到计算机视觉上。这就是为什么像 Google Goggles,Google 图像搜索和 [Project Tango](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/02/googles-project-tango-is-a-smartphone-with-kinect-style-computer-vision/) 这样的项目存在的原因。就像 GOOG-411 的那段日子,这些项目还处在早期阶段。当[谷歌的机器人部门](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/12/google-robots-former-android-chief-will-lead-google-robotics-division/)造出了机器人,它会需要看和听,谷歌的计算机视觉和听觉项目会给谷歌一个先机。
---

[Ron Amadeo](http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo) / Ron是Ars Technica的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。 [@RonAmadeo](https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo)
---
via: <http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/13/>
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,045 | 如何在 Shell 脚本中执行语法检查调试模式 | http://www.tecmint.com/check-syntax-in-shell-script/ | 2016-12-19T09:19:23 | [
"脚本",
"调试"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8045-1.html | 我们开启了 Shell 脚本调试系列文章,先是解释了不同的调试选项,下面介绍[如何启用 Shell 调试模式](/article-8028-1.html)。
写完脚本后,建议在运行脚本之前先检查脚本中的语法,而不是查看它们的输出以确认它们是否正常工作。
在本系列的这一部分,我们将了解如何使用语法检查调试模式。记住我们之前在本系列的[第一部分](/article-8028-1.html)中解释了不同的调试选项,在这里,我们将使用它们来执行脚本调试。

### 启用 verbose 调试模式
在进入本指导的重点之前,让我们简要地探索下 **verbose 模式**。它可以用 `-v` 调试选项来启用,它会告诉 shell 在读取时显示每行。
要展示这个如何工作,下面是一个示例脚本来[批量将 PNG 图片转换成 JPG 格式](/article-8014-1.html)。
将下面内容输入(或者复制粘贴)到一个文件中。
```
#!/bin/bash
#convert
for image in *.png; do
convert "$image" "${image%.png}.jpg"
echo "image $image converted to ${image%.png}.jpg"
done
exit 0
```
接着保存文件,并用下面的命令使脚本可执行:
```
$ chmod +x script.sh
```
我们可以执行脚本并显示它被 Shell 读取到的每一行:
```
$ bash -v script.sh
```

*显示shell脚本中的所有行*
### 在 Shell 脚本中启用语法检查调试模式
回到我们主题的重点,`-n` 激活语法检查模式。它会让 shell 读取所有的命令,但是不会执行它们,它(shell)只会检查语法。
一旦 shell 脚本中发现有错误,shell 会在终端中输出错误,不然就不会显示任何东西。
激活语法检查的命令如下:
```
$ bash -n script.sh
```
因为脚本中的语法是正确的,上面的命令不会显示任何东西。所以,让我们尝试删除结束 for 循环的 `done` 来看下是否会显示错误:
下面是修改过的含有 bug 的批量将 png 图片转换成 jpg 格式的脚本。
```
#!/bin/bash
#script with a bug
#convert
for image in *.png; do
convert "$image" "${image%.png}.jpg"
echo "image $image converted to ${image%.png}.jpg"
exit 0
```
保存文件,接着运行该脚本并执行语法检查:
```
$ bash -n script.sh
```

*检查 shell 脚本语法*
从上面的输出中,我们看到我们的脚本中有一个错误,for 循环缺少了一个结束的 `done` 关键字。shell 脚本从头到尾检查文件,一旦没有找到它(`done`),shell 会打印出一个语法错误:
```
script.sh: line 11: syntax error: unexpected end of file
```
我们可以同时结合 verbose 模式和语法检查模式:
```
$ bash -vn script.sh
```

*在脚本中同时启用 verbose 检查和语法检查*
另外,我们可以通过修改脚本的首行来启用脚本检查,如下面的例子:
```
#!/bin/bash -n
#altering the first line of a script to enable syntax checking
#convert
for image in *.png; do
convert "$image" "${image%.png}.jpg"
echo "image $image converted to ${image%.png}.jpg"
exit 0
```
如上所示,保存文件并在运行中检查语法:
```
$ ./script.sh
script.sh: line 12: syntax error: unexpected end of file
```
此外,我们可以用内置的 set 命令来在脚本中启用调试模式。
下面的例子中,我们只检查脚本中的 for 循环语法。
```
#!/bin/bash
#using set shell built-in command to enable debugging
#convert
#enable debugging
set -n
for image in *.png; do
convert "$image" "${image%.png}.jpg"
echo "image $image converted to ${image%.png}.jpg"
#disable debugging
set +n
exit 0
```
再一次保存并执行脚本:
```
$ ./script.sh
```
总的来说,我们应该保证在执行 Shell 脚本之前先检查脚本语法以捕捉错误。
请在下面的反馈栏中,给我们发送关于这篇指导的任何问题或反馈。在这个系列的第三部分中,我们会解释并使用 shell 追踪调试模式。
---
作者简介:

Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 及 F.O.S.S 热衷者,即将是 Linux 系统管理员、web 开发者,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并热心分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/check-syntax-in-shell-script/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,047 | 双赢:开源 .Net ,微软收获了大批开发者 | http://www.cio.com/article/3150814/application-development/win-win-open-source-net-pays-off-for-devs.html | 2016-12-20T08:22:00 | [
"微软",
"开源",
".Net"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8047-1.html | 就在两年前,微软做了一件令人意想不到的事情:[它宣称将开源其 .Net 开发框架](/article-4209-1.html),这包括 [.Net Core](/article-4821-1.html) 及 [ASP.Net](/article-4940-1.html) 等。这份公告非常令人吃惊,因为微软长久以来一直仇视开源项目,担忧开源软件破坏其软件生态。
随着微软 CEO 纳德拉宣称“[微软爱 Linux](/article-4923-1.html)”,微软在[开源方面的举措频频](/article-6774-1.html),不仅仅在 GitHub 上其名下的几个[仓库活跃非凡](/article-7776-1.html),而且也和各种开源厂商积极[展开合作](/article-6528-1.html)。

不管微软积极拥抱开源背后的想法是什么,或许是想通过开源销售更多的软件或者云服务,也有可能是想吸引更多的开发者到微软平台上,但是目前看起来微软这步棋是下对了。从微软[开源 .Net](/article-6727-1.html) 和 [ASP.Net](/article-6921-1.html) 之后的分析看,微软的开源战略已经值回票价了。
微软现在将 .Net Core 定位为跨平台开发框架,不只是 Windows,而且也延伸到了 MacOS 和 Linux 平台之上。.Net Core RC1 是 2015 年 11 月发布到 GitHub 上的,而今年 6 月就发布了 1.0 版本。开发者们对此表示认可,微软合作伙伴总监项目经理 Scott Hunter 如是说:
>
> “40% 的 .Net Core 客户是新进入该平台的用户,这就是我们(开源)的目的,我们希望吸引新的用户。”
>
>
>
由于 .Net Core 的开源,过去一年以来, .Net 的开发者增加了 61%。 Hunter 在 11 月的一次讲演中提到,GitHub 上 .Net 上的开发活跃度增长极快。
虽然 .Net Core 并没有直接给微软带来收入,但是其潜在地增加了收益。Rob Sanfilippo 说,“可以说,这项技术间接地通过 Azure 服务和微软开发者工具增加了微软的收入。”。
### 程序员们表现活跃
.Net 程序员和博客作者 [Matt Warren](http://mattwarren.org/) 把.Net 的开源称之为“成功”。[其数据](/article-6921-1.html)明确地显示社区积极地参与了微软在 GitHub 上开源的多个仓库的活动。
“开源社区汇报了问题和建议,并通过发送拉取请求(PR)而实际贡献了代码,经过一段时间之后,这些代码就会被包括到产品里面,而社区的贡献量还在持续增长”,Warren 说,“我积极跟踪和参与了 [CoreCLR](https://github.com/dotnet/coreclr/) 和 [.Net Core Lab](https://github.com/dotnet/corefxlab/) 这些仓库的讨论,因此获得了社区贡献的第一手资料。”
微软的举措是否完全成功还不能完全定论,未来或许还有变数,但是这终究是从封闭走向开放的一步。他说,“我的意思是,他们并不是仅仅把源代码放在那里就行了,而是努力让社区可以参与进来。”
### 微软最近发布的 Visual Studio for Mac 也为 .Net Core 带来了利好
“这是 Visual Studio IDE 首次发布到非 Windows 平台上(Visual Studio Code 是不同的技术,而且它根本不算 IDE),它是基于微软收购的 Xamarin 的技术,重点关注于 .Net Core 开发”,Sanfillippo 说,“这次发布近一步带动了 .Net Core 的发展。”
微软最近也准备在 Visual Studio 2017 IDE 中增强 .Net Core 工具,包括简化 .Net Core 项目文件的格式。
微软开源 .Net 让外界对它的观感有所改变, Warren 说,“现在感觉(微软)更开放和更平易近人了。”
相对于某些公司,虽然开源社区还对微软抱有一定的疑虑,但是显然,微软已经不是开源社区最敌视的公司了。
参考:[CIO](http://www.cio.com/article/3150814/application-development/win-win-open-source-net-pays-off-for-devs.html)、 [Matt Warren](http://mattwarren.org/)、[microsoft](https://www.microsoft.com/)
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,048 | CentOS 7.3 安装指南 | http://www.tecmint.com/centos-7-3-installation-guide/ | 2016-12-20T09:12:00 | [
"CentOS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8048-1.html | 基于 Red Hat 企业版的源代码的最新版本的 CentOS 7 在今年的 12月[发布了 CentOS Linux 7 (1611)](/article-8046-1.html#3_1420) ,包含了许多 bug 修复、新的包更新,比如 Samba、Squid、libreoffice、SELinux、systemd 及其它软件,并支持第七代 Intel 酷睿 i3、i5、i7 处理器。
本指南会向你展示如何在 UEFI 的机器上使用 DVD ISO 镜像来安装 CentOS 7.3。

如果你要是用 RHEL,看下我们的 [RHEL 7.3 安装指南](/article-8067-1.html)。
#### 要求
* [下载 CentOS 7.3 ISO 镜像](http://isoredirect.centos.org/centos/7/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1611.iso)
要在 UEFI 的机器上正确安装 CentOS 7.3,首先按下键(`F2`、`F11` 或 `F12`,取决与你的主板类型)进入主板的 UEFI 设置,并且确保 QuickBoot/FastBoot 以及 Secure Boot 已被禁用。
### CentOS 7.3 安装
1、 在你从上面的链接下载完成镜像之后,使用 [Rufus](https://rufus.akeo.ie/)将它烧录到 DVD 或者创建一个可启动的 UEFI 兼容 USB 盘。
将 USB/DVD 放入主板上连接的驱动器中,重启电脑并用特定的功能键(`F12`、 `F10`,取决于主板类型)让 BIOS/UEFI 从 DVD/USB 启动。
ISO 镜像启动完成后,你机器上会显示如下首屏。在菜单中选择 “Install CentOS 7”并按下回车继续。

*CentOS 7.3 启动菜单*
2、 在安装镜像加载到内存完成后,会显示一个欢迎页面。选择你在安装中使用的语言并按下“<ruby> 继续 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Continue </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮。

*选择 CentOS 7.3 安装语言*
3、 在下一个页面点击“<ruby> 日期和时间 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Date and Time </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”,从地图中选择你的地理位置。确认日期和时间正确配置了并点击“<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮来回到主安装界面。

*CentOS 7.3 安装总结*

*选择日期和时间*
4、 点击“<ruby> 键盘 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Keyboard </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”菜单进入键盘布局页面。选择或者添加一个键盘布局并点击“<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮继续。

*选择键盘布局*
5、 接下来,为你的系统添加或者配置一个语言并点击“<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮进入下一步。

*选择语言支持*
6、 在这步中,你可以通过选择列表中安全配置来设置你的系统“<ruby> 安全策略 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Security Policy </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”。
点击选择配置按钮来选择你想要的安全配置并点击“<ruby> 应用安全策略 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Apply security policy </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮到 On。点击“<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮后继续安装流程。

*启用 CentOS 7.3 安全策略*
7、 下一步中你可以点击“<ruby> 软件选择 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Software Selection </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮来配置你的基础机器环境。
左边的列表是你可以选择安装桌面环境(Gnome、KDE Plasma 或者创意工作站)或者安装一个服务器环境(Web 服务器、计算节点、虚拟化主机、基础设施服务器、带图形界面的服务器或者文件及打印服务器)或者执行一个最小化的安装。
为了随后能自定义你的系统,选择最小化安装并附加兼容库,点击“<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮继续。

*CentOS 7.3 软件选择*
对于完整的 Gnome 或者 KDE 桌面环境,使用下面的截图作为指引。

*Gnome 桌面软件选择*

*KDE 桌面软件选择*
8、 假设你要在服务器上安装一个图形界面,选择左边那栏“<ruby> 带 GUI 的服务器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Server with GUI </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”那项,并在右边那栏中根据你需要提供给客户端的服务选择合适的附加软件。
你可以选择的服务是非常多样化的,从备份、DNS 或者 e-mail 服务到文件存储服务、FTP、HA 或者监控工具。只选择对你网络设置最重要的服务。

*选择带 GUI 的服务器*
9、 如果你不使用特定的网络协议比如 HTTP、HTTPS、FTP 或者 NFS 的额外仓库,安装源保持默认,并点击“<ruby> 安装位置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Installation Destination </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”来创建一个磁盘分区。
在“<ruby> 设备选择 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Device selection </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”页面,确保你已经选择了本地磁盘。同样,在“<ruby> 其他存储选项 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Other Storage Options </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”中确保选择了“<ruby> 自动配置分区 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Automatically configure partitioning </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”。
这个选项可以确保你的磁盘会恰当地根据磁盘空间和 Linux 文件系统层次结构进行分区。它会为你自动创建 `/(root)`、`/home`和 swap 分区。点击“<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”来应用磁盘分区方案并回到主安装界面。
重要提醒:如果你想要创建自定义分区及自定义分区大小,你可以选择“<ruby> 我要配置分区 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> I will configure partitioning </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”选项来创建自定义分区。

*安装 CentOS 7.3 安装位置*
10、 接下来,如果你想要释放系统内存,点击 KDUMP 选项并禁用它。点击“<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”并回到主安装界面。

*Kdump 选择*
11、 在下一步中设置你的主机名并启用网络服务。点击“<ruby> 网络和主机名 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Network & Hostname </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”,在主机名中输入你的 FQDN(完整限定网域名称),如果你在局域网中有一个 DHCP 服务器,将以太网按钮从 OFF 切换到 ON 来激活网络接口。

*设置网络及主机名*
12、 为了静态配置你的网络接口,点击“<ruby> 配置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Configure </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮,手动如截图所示添加 IP 设置,并点击“<ruby> 保存 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Save </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮来应用更改。完成后,点击“<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮来回到主安装菜单。

*配置网络和 IP 地址*
13、 最后检查下所有到目前为止的配置,如果一切没问题,点击“<ruby> 开始安装 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Begin Installation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮开始安装。

*开始 CentOS 7.3 安装向导*
14、 开始安装后,一个新的设置用户界面会显示出来。首先点击 “<ruby> root 密码 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> ROOT PASSWORD </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”并添加一个强密码。
root 账户是每个 Linux 系统的最高管理账户密码,它拥有所有的权限。设置完成后点击完成按回到用户设置界面。

*选择 root 密码*

*设置 root 密码*
15、 用 root 账户运行系统是非常不安全和危险的,因此建议你点击“<ruby> 创建用户 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> User Creation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮创建一个新的系统账户来[执行每日的系统任务](http://www.tecmint.com/file-and-directory-management-in-linux/)。
添加新的用户,并同时选择下面的两个选项来授予用户 root 权限以及每次在登录系统时手动输入密码。
当你完成最后一项点击“<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”按钮并等待安装完成。

*创建用户账户*
16、 几分钟后安装程序会报告 CentOS 已经成功安装在你机器中。要使用系统,你只需要移除安装媒介并重启机器。

*CentOS 7.3 安装完成*
17、 重启之后,使用安装中创建的用户登录系统,并且用 root 权限执行下面的命令来执行系统更新。
```
$ sudo yum update
```

*更新 CentOS 7.3*
所有 [yum 管理器](http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/)的问题都选择`yes`,最后再次重启电脑(使用 `sudo init 6`)来应用新的内核升级。
```
$ sudo init 6
```
就是这样!在你的机器中享受最新的 CentOS 7.3 吧。
---
作者简介:

Matei Cezar
我是一个电脑上瘾的家伙,一个开源和 Linux 系统软件的粉丝,有大约 4 年的 Linux 桌面、服务器和 bash 脚本的经验。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/centos-7-3-installation-guide/>
作者:[Matei Cezar](http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,049 | Ubuntu 调查发现,大部分人从不更新他们的物联网设备 | https://insights.ubuntu.com/2016/12/15/research-consumers-are-terrible-at-updating-their-connected-devices/ | 2016-12-20T09:23:29 | [
"IoT",
"固件",
"安全"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8049-1.html | 许多物联网设备的用户鲜于更新他们的联网设备,而这正是造成许多物联网安全漏洞的根本原因。
Ubuntu 最近调查了 2000 名消费者以了解其是如何使用他们的联网设备的。该调查结果披露了令人吃惊的结果,仅有 31% 的人会在设备有固件更新后尽快进行更新,而近 40% 的人则从不会主动对设备固件进行更新!换句话说,这部分用户让他们的设备开着,暴露在 DDoS 和各种窃取隐私的攻击之下。

消费者们不能(也不应该)预料到每个重要的软件更新,虽然这很简单,但是并不现实。几乎没有消费者会去专门看看他们遇到的问题是否解决了。根据投票结果,近 2/3 的消费者认为更新固件不是他们的责任,22% 的人认为这是软件开发者的工作,而 18% 的人认为这是设备厂商的责任。
显然,自动更新是一个解决方案,但是自动更新也会带来一些安全隐患。而且,很多厂商很少更新他们的设备固件,尤其是比较老的设备,更是更新频度极少。
那么你对物联网设备安全及设备固件更新方面有什么看法?
| 301 | null |
|
8,050 | 24 款必备的 Linux 桌面应用(2016 版) | https://itsfoss.com/essential-linux-applications | 2016-12-21T08:41:00 | [
"Linux",
"软件",
"桌面"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8050-1.html | 
>
> 摘要:Linux 的必备软件有哪些?这将会是一个非常主观的回答,主要取决于你出于什么目的才使用桌面版 Linux。不过有一些必备的 Linux 桌面应用是大部分 Linux 用户都可能会用到的,这里将会列出不管在哪个发行版中你都应该安装的 Linux 桌面应用。
>
>
>
在 Linux 中,所有的一切都有多种可选方案的。首先,你会选择一个发行版,对吧?你可能需要尝试过多个发行版才能选出自己喜欢的风味。你是否还试过很多个音乐播放器?它们还是有很多选择的吧?
但并不是所有的这些应用都一样——有些以简洁为目标,而另一些则可能会提供大量的特性。根据自身的需求选择一款正确的应用也是一件相当困惑和累人的任务。就让我们来使这个过程变得容易一些吧。
### Linux 用户最好的自由软件
在这里,我把自己喜欢用的 Linux 必备软件以几个类型列出来。当然不能说这些是最好的,但在我尝试了大量的各类软件之后,最后才得到这个分类列表。所以,非常欢迎你在评论区畅言自己最喜欢的应用。
### Web浏览器

*Web 浏览器*
#### [Google Chrome](https://www.google.com/chrome/browser)
Google Chrome 是一个功能完备、性能强悍的 web 浏览器。它具备了非常彪悍的同步功能,同时还提供大量的功能扩展插件。如果那你习惯于 Google 的软件生态,那么 Chrome 绝对是你的不二选择。当然,假如你想要一个开源的解决方案,那么你可以试试 [Chromium](https://www.chromium.org/Home),Google Chrome 就是基于 Chromium 构建的。
#### [Firefox](https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox)
如果你并非 Google Chrome 迷,那就试试 Firefox。它有着比较久的历史,也是一个稳定而健壮的 web 浏览器。
#### [Vivaldi](https://vivaldi.com/)
如果说你想尝试新鲜事物并做一些改变,那么,你可以试试 Vivaldi,它为 web 浏览器带来了全新的使用方式,由前 Opera 项目成员基于 Chromium 项目开发。它开源、轻量级,同时不失定制性。尽管它还很年轻,缺少一些特性,但真的让人感觉清爽,可以完成你绝大多数的工作。
推荐阅读:[Otter 浏览器给 Opera 粉丝带来希望](https://itsfoss.com/otter-browser-review/)
### 下载管理器

*下载管理器*
#### [Uget](http://ugetdm.com/)
Uget 是我见过最好的下载管理器了。其源码是开放的,同时提供给你在下载浏览器中所想到的一切功能。其中,高级设置选项可以用来更好的管理下载。它支持排队下载和断点下载、支持多连接来下载大体积文件、支持通过不同分类来下载到不同目录等等。
#### [Xdm](http://xdman.sourceforge.net/)
Xdm (Xtreme Download Manager,极限下载管理器) 是一款用 Java 开发的功能强大且开源的工具。有着所有下载管理器的必备功能,包括:视频捕获器、智能调度和浏览器集成。
推荐阅读:[Linux 下 4 个最佳下载管理器](https://itsfoss.com/4-best-download-managers-for-linux/)
### BitTorrent 客户端

*BitTorrent 客户端*
#### [Deluge](http://deluge-torrent.org/)
Deluge 是一个开源的 BitTorrent 客户端,有着漂亮的用户界面。假如你习惯使用 Windows 下的 uTorrent,你就会知道两者有着很多的相似之处。它有大量的配置选项和插件来帮你应付各种下载任务。
#### [Transmission](https://transmissionbt.com/)
Transmission 是最轻量级的 Bittorrent 客户端——开源、有着最轻量级的用户界面。在多数的 Linux 发行版中都预装了 Transmission。
推荐阅读:[Ubuntu 下五个最好的 BT 客户端](/article-6095-1.html)
### 云存储

*云存储*
#### [Dropbox](https://www.dropbox.com/)
Dropbox 是目前最流行云存储服务之一。你注册之后就有 2 GB 的免费空间。Dropbox 提供了一个健壮而简洁的 Linux 客户端。
#### [Mega](https://mega.nz/)
Mega 提供了 50 GB 的免费空间,但其最好的一点却非免费空间之大,而是它为你的文件传输提供了点对点加密。它在 Linux 平台上也有一个可靠的客户端,名为 MEGAsync。
推荐阅读:[Linux 下最佳免费云服务](https://itsfoss.com/cloud-services-linux/)
### 即时消息软件

*即时消息软件*
#### [Pidgin](https://www.pidgin.im/)
Pidgin 是一个开源的即时消息客户端,支持多个聊天平台,包括 Facebook、Google Talk、Yahoo,甚至是 IRC。它还可以通过第三方插件来进行扩展,这样可以把很多功能集成到 Pidgin 中去。
#### [Skype](https://www.skype.com/)
我想,应该所有人都知道 Skype 吧,它是目前最流行的视频聊天平台。近期,它又为 Linux 平台[发布了一个全新的桌面客户端](/article-7574-1.html)。
推荐阅读:[Linux 上的最佳消息应用](https://itsfoss.com/best-messaging-apps-linux/)
### 办公套件

*办公套件*
#### [LibreOffice](https://www.libreoffice.org/)
LibreOffice 是 Linux 平台下开发活跃度最高的开源办公套件。它有六大核心模块:Writer (文字处理)、Calc (电子表格)、Impress (文稿演示)、Draw (图像绘制)、Math (数学公式)、Base (数据库),并且,这些模块都支持多种文件格式。当然,LibreOffice 也是支持第三方扩展的,多数的 Linux 发行版都用它作为默认的办公套件。
#### [WPS Office](https://www.wps.com/)
如果想要尝试 LibreOffice 之外的办公套件,WPS Office 当然是不容错过的,它支持 Writer (文字处理)、presentation (文稿演示)、spreadsheets (电子表格)。
推荐阅读:[微软 Office 办公套件的最佳开源替代品](https://itsfoss.com/best-free-open-source-alternatives-microsoft-office/)
### 音乐播放器

*音乐播放器*
#### [Lollypop](http://gnumdk.github.io/lollypop-web/)
这是一个相对较新的音乐播放器。Lollypop 是开源的,有着非常漂亮的用户界面,提供了非常友好的歌曲管理、播放历史支持、在线电台和派对模式。尽管这是一个很简单的音乐播放器,没有太多的高级特性,但还是值得一试的。
#### [RhythmBox](https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Rhythmbox)
Rhythmbox 最初是为 Gnome 开发的音乐播放器,但现在已经可以很好的在其他的桌面环境中工作。它可以完成音乐播放器的所有基本任务,包括 CD 转录 & 刻录、播放历史等,而且还支持 iPod。
#### [CMUS](https://cmus.github.io/)
假如你是极简主义派,并深爱着终端界面,那么 cmus 很合适你。就个人而言,我很喜欢并一直在用这个软件。它是类 Unix 平台下一个相当小巧、响应速度快、有着功能强大的控制台音乐播放器,具备了音乐播放器所有基本特性。通过其它的扩展和脚本,你可以使它功能更加丰富。
推荐阅读:[在 Ubuntu 14.04 和 Linux Mint 17 安装 Tomahawk 播放器](https://itsfoss.com/install-tomahawk-ubuntu-1404-linux-mint-17/)
### 视频播放器

*视频播放器*
#### [VLC](http://www.videolan.org/)
VLC 是一个开源的媒体播放器,具有简洁、速度快、轻量级而功能强大等特点。它做到了真正的开箱即用,几乎支持所有你想到的视频格式,而且可以播放在线流媒体。当然,它支持一些非常棒的插件来完成不同的任务,比方说在播放视频时下载对应的字幕。
#### [Kodi](https://kodi.tv/)
Kodi 是一个功能完备的媒体播放器,开源并流行于其用户群体中。它可以处理本地或者网络存储中的视频、音乐、图片、播客甚至是游戏,你还有使用它来录制 TV。Kodi 可以通过附件和不同的皮肤来自定义。
推荐阅读:[Linux 上的 4 种格式转换器](https://itsfoss.com/format-factory-alternative-linux/)
### 图像编辑器

*图像编辑器*
#### [GIMP](https://www.gimp.org/)
GIMP 是 Linux 平台下 Photoshop 的替代方案。它是开源的,是一个全功能、专业的图像编辑软件,打包了非常多的工具用来处理各类图像。在此基础上,还有大量的定制选项以及第三方插件可以用于增强用户的使用体验。
#### [Krita](https://krita.org/en/)
Krita 主要是一个绘图工具,但也可以用来编辑图像。它同样也是开源的,也打包了很多精致且高级的工具。
推荐阅读:[Linux 上最佳图像应用](https://itsfoss.com/image-applications-ubuntu-linux/)
### 文本编辑器
每个 Linux 发行版都会自带一个文本编辑器。通常,它的功能相对来说比较简单,没有太多的功能,但还是有一些具有增强功能的编辑器。

*文本编辑器*
#### [Atom](https://atom.io/)
Atom 是一个现代的可魔改的文本编辑器,由 GitHub 进行维护更新。它是完全开源的,为你的文本编辑任务提供了你所想到一切可能性。它做到了真正的开箱即用,你也可以进行自定义,让它变成你所需要的样子。同时,你可以从社区中获取有关它的大量扩展和主题。
#### [Sublime Text](http://www.sublimetext.com/)
Sublime Text 是主流的文本编辑器之一。尽管它并不免费,但它允许你把软件作为评估使用,而且没有时间限制。Sublime Text 是一个功能丰富和复杂的软件。当然,它还有插件和主题支持。
推荐阅读:[Linux 上四个最佳的现代开源代码编辑器](/article-7468-1.html)
### <ruby> 启动器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Launcher </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>

*启动器 (Launcher)*
#### [Albert](https://github.com/ManuelSchneid3r/albert)
Albert 的灵感来至于 Alfred (Mac 中的一个高效应用,可以做到一切信手拈来),但仍在开发中。Albert 反应很快,可扩展、可定制。其目标就是“<ruby> 不用思考就使用一切可用资源 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Access everything with virtually zero effort </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”。它可以很好的集成到你的 Linux 发行版中,并让你保持高效。
#### [Synapse](https://launchpad.net/synapse-project)
Synapse 已有一些历史,是一个简洁的启动器,可以用来搜索和运行应用。它还可以加速各种各样的工作流,比如控制音乐、搜索文件、目录以及书签、运行命令等等。
---
正如 Abhishek 所说,我们会一直为读者 (比如,你) 更新这个 Linux 必备软件列表。那么,你最喜欢的 Linux 必备软件是什么呢?随时和我们分享,并想我们这个列表提出更多的软件分类。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/essential-linux-applications>
作者:[Munif Tanjim](https://itsfoss.com/author/munif/) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,051 | 雾里看花之 Python Asyncio | http://lucumr.pocoo.org/2016/10/30/i-dont-understand-asyncio/ | 2016-12-21T18:27:00 | [
"Python",
"并发",
"协程"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8051-1.html | 最近我开始发力钻研 Python 的新 [asyncio](https://docs.python.org/3/library/asyncio.html) 模块。原因是我需要做一些事情,使用事件 IO 会使这些事情工作得更好,炙手可热的 asynio 正好可以用来牛刀小试。从试用的经历来看,该模块比我预想的复杂许多,我现在可以非常肯定地说,我不知道该如何恰当地使用 asyncio。
从 Twisted 框架借鉴一些经验来理解 asynio 并非难事,但是,asyncio 包含众多的元素,我开始动摇,不知道如何将这些孤立的零碎拼图组合成一副完整的图画。我已没有足够的智力提出任何更好的建议,在这里,只想分享我的困惑,求大神指点。

#### 原语
*asyncio* 通过<ruby> 协程 <rt> coroutines </rt></ruby> 的帮助来实现异步 IO。最初它是通过 `yield` 和 `yield from` 表达式实现的一个库,因为 Python 语言本身演进的缘故,现在它已经变成一个更复杂的怪兽。所以,为了在同一个频道讨论下去,你需要了解如下一些术语:
* 事件循环
* 事件循环策略
* awaitable
* 协程函数
* 老式协程函数
* 协程
* 协程封装
* <ruby> 生成器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> generator </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
* future
* 并发的future
* <ruby> 任务 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> task </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
* 句柄
* <ruby> 执行器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> executor </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
* <ruby> 传输 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> transport </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
* 协议
此外,Python 还新增了一些新的特殊方法:
* `__aenter__` 和 `__aenter__`,用于异步块操作
* `__aiter__` 和 `__anext__`,用于异步迭代器(异步循环和异步推导)。为了更强大些,协议已经改变过一次了。 在 Python 3.5 它返回一个 awaitable(这是个协程);在 3.6它返回一个新的异步生成器。
* `__await__`,用于自定义的 awaitable
你还需要了解相当多的内容,文档涵盖了那些部分。尽管如此,我做了一些额外说明以便对其有更好的理解:
### 事件循环
asyncio 事件循环和你第一眼看上去的略有不同。表面看,每个线程都有一个事件循环,然而事实并非如此。我认为它们应该按照如下的方式工作:
* 如果是主线程,当调用 `asyncio.get_event_loop()` 时创建一个事件循环。
* 如果是其它线程,当调用 `asyncio.get_event_loop()` 时返回运行时错误。
* 当前线程可以使用 `asyncio.set_event_loop()` 在任何时间节点绑定事件循环。该事件循环可由 `asyncio.new_evet_loop()` 函数创建。
* 事件循环可以在不绑定到当前线程的情况下使用。
* `asyncio.get_event_loop()` 返回绑定线程的事件循环,而非当前运行的事件循环。
这些行为的组合是超混淆的,主要有以下几个原因。 首先,你需要知道这些函数被委托到全局设置的底层事件循环策略。 默认是将事件循环绑定到线程。 或者,如果需要的话,可以在理论上将事件循环绑定到一个 greenlet 或类似的。 然而,重要的是要知道库代码不控制策略,因此不能推断 asyncio 将适用于线程。
其次,asyncio 不需要通过策略将事件循环绑定到上下文。 事件循环可以单独工作。 但是这正是库代码的第一个问题,因为协同程序或类似的东西并不知道哪个事件循环负责调度它。 这意味着,如果从协程中调用 `asyncio.get_event_loop()`,你可能没有机会取得事件循环。 这也是所有 API 均采用可选的显式事件循环参数的原因。 举例来说,要弄清楚当前哪个协程正在运行,不能使用如下调用:
```
def get_task():
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
try:
return asyncio.Task.get_current(loop)
except RuntimeError:
return None
```
相反,必须显式地传递事件循环。 这进一步要求你在库代码中显式地遍历事件循环,否则可能发生很奇怪的事情。 我不知道这种设计的思想是什么,但如果不解决这个问题(例如 `get_event_loop()` 返回实际运行的事件循环),那么唯一有意义的其它方案是明确禁止显式事件循环传递,并要求它绑定到当前上下文(线程等)。
由于事件循环策略不提供当前上下文的标识符,因此库也不可能以任何方式“索引”到当前上下文。 也没有回调函数用来监视这样的上下文的拆除,这进一步限制了实际可以开展的操作。
### awaitable 与<ruby> 协程 <rt> coroutine </rt></ruby>
以我的愚见,Python 最大的设计错误是过度重载迭代器。它们现在不仅用于迭代,而且用于各种类型的协程。 Python 中迭代器最大的设计错误之一是如果 `StopIteration` 没有被捕获形成的空泡。 这可能导致非常令人沮丧的问题,其中某处的异常可能导致其它地方的生成器或协同程序中止。 这是一个长期存在的问题,基于 Python 的模板引擎如 Jinja 经常面临这种问题。 该模板引擎在内部渲染为生成器,并且当由于某种原因的模板引起 `StopIteration` 时,渲染就停止在那里。
Python 慢慢认识到了过度重载的教训。 首先在 3.x 版本加入 asyncio 模块,并没有语言级支持。 所以自始至终它不过仅仅是装饰器和生成器而已。 为了实现 `yield from` 以及其它东西,`StopIteration` 再次重载。 这导致了令人困惑的行为,像这样:
```
>>> def foo(n):
... if n in (0, 1):
... return [1]
... for item in range(n):
... yield item * 2
...
>>> list(foo(0))
[]
>>> list(foo(1))
[]
>>> list(foo(2))
[0, 2]
```
没有错误,没有警告。只是不是你所期望的行为。 这是因为从一个作为生成器的函数中 `return` 的值实际上引发了一个带有单个参数的 `StopIteration`,它不是由迭代器协议捕获的,而只是在协程代码中处理。
在 3.5 和 3.6 有很多改变,因为现在除了生成器我们还有协程对象。除了通过封装生成器来生成协程,没有其它可以直接生成协程的单独对象。它是通过用给函数加 `async` 前缀来实现。 例如 `async def x()` 会产生这样的协程。 现在在 3.6,将有单独的异步生成器,它通过触发 `AsyncStopIteration` 保持其独立性。 此外,对于Python 3.5 和更高版本,导入新的 future 对象(`generator_stop`),如果代码在迭代步骤中触发 `StopIteration`,它将引发 `RuntimeError`。
为什么我提到这一切? 因为老的实现方式并未真的消失。 生成器仍然具有 `send` 和 `throw` 方法以及协程仍然在很大程度上表现为生成器。你需要知道这些东西,它们将在未来伴随你相当长的时间。
为了统一很多这样的重复,现在我们在 Python 中有更多的概念了:
* awaitable:具有`__await__`方法的对象。 由本地协同程序和旧式协同程序以及一些其它程序实现。
* <ruby> 协程函数 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> coroutinefunction </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>:返回原生协程的函数。 不要与返回协程的函数混淆。
* <ruby> 协程 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> coroutine </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>: 原生的协程程序。 注意,目前为止,当前文档不认为老式 asyncio 协程是协程程序。 至少 `inspect.iscoroutine` 不认为它是协程。 尽管它被 `future/awaitable` 分支接纳。
特别令人困惑的是 `asyncio.iscoroutinefunction` 和`inspect.iscoroutinefunction` 正在做不同的事情,这与 `inspect.iscoroutine` 和 `inspect.iscoroutinefunction` 情况相同。 值得注意的是,尽管 `inspect` 在类型检查中不知道有关 asycnio 旧式协程函数的任何信息,但是当您检查 awaitable 状态时它显然知道它们,即使它与 `**await**` 不一致。
### <ruby> 协程封装器 <rt> coroutine wrapper </rt></ruby>
每当你运行 `async def` ,Python 就会调用一个线程局部的协程封装器。它由 `sys.set_coroutine_wrapper` 设置,并且它是可以包装这些东西的一个函数。 看起来有点像如下代码:
```
>>> import sys
>>> sys.set_coroutine_wrapper(lambda x: 42)
>>> async def foo():
... pass
...
>>> foo()
__main__:1: RuntimeWarning: coroutine 'foo' was never awaited
42
```
在这种情况下,我从来没有实际调用原始的函数,只是给你一个提示,说明这个函数可以做什么。 目前我只能说它总是线程局部有效,所以,如果替换事件循环策略,你需要搞清楚如何让协程封装器在相同的上下文同步更新。创建的新线程不会从父线程继承那些标识。
这不要与 asyncio 协程封装代码混淆。
### awaitable 和 future
有些东西是 awaitable 的。 据我所见,以下概念被认为是 awaitable:
* 原生的协程
* 配置了假的 `CO_ITERABLE_COROUTINE` 标识的生成器(文中有涉及)
* 具有 `__await__` 方法的对象
除了生成器由于历史遗留的原因不使用之外,其它的对象都使用 `__await__` 方法。 `CO_ITERABLE_COROUTINE` 标志来自哪里?它来自一个协程封装器(现在与 `sys.set_coroutine_wrapper` 有些混淆),即 `@asyncio.coroutine`。 通过一些间接方法,它使用 `types.coroutine`(现在与 `types.CoroutineType` 或 `asyncio.coroutine` 有些混淆)封装生成器,并通过另外一个标志 `CO_ITERABLE_COROUTINE` 重新创建内部代码对象。
所以既然我们知道这些东西是什么,那么什么是 future? 首先,我们需要澄清一件事情:在 Python 3 中,实际上有两种(完全不兼容)的 future 类型:`asyncio.futures.Future` 和 `concurrent.futures.Future`。 其中一个出现在另一个之前,但它们都仍然在 asyncio 中使用。 例如,`asyncio.run_coroutine_threadsafe()` 将调度一个协程到在另一个线程中运行的事件循环,但它返回一个 `concurrent.futures.Future` 对象,而不是 `asyncio.futures.Future` 对象。 这是有道理的,因为只有 `concurrent.futures.Future` 对象是线程安全的。
所以现在我们知道有两个不兼容的 future,我们应该澄清哪个 future 在 asyncio 中。 老实说,我不完全确定差异在哪里,但我打算暂时称之为“最终”。它是一个最终将持有一个值的对象,当还在计算时你可以对最终结果做一些处理。 future 对象的一些变种称为 deferred,还有一些叫做 promise。 我实在难以理解它们真正的区别。
你能用一个 future 对象做什么? 你可以关联一个准备就绪时将被调用的回调函数,或者你可以关联一个 future 失败时将被触发的回调函数。 此外,你可以 `await` 它(它实现`__await__`,因此可等待),此外,future 也可以取消。
那么你怎样才能得到这样的 future 对象? 通过在 awaitable 对象上调用 `asyncio.ensure_future`。它会把一个旧版的生成器转变为 future 对象。 然而,如果你阅读文档,你会读到 `asyncio.ensure_future` 实际上返回一个`task`(任务)。 那么问题来了,什么是任务?
### 任务
<ruby> 任务 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> task </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>某种意义上是一个封装了协程的 futur 对象。它的工作方式和 future 类似,但它也有一些额外的方法来提取所包含的协程的当前堆栈。 我们已经见过了在前面提到过的任务,因为它是通过 `Task.get_current` 确定事件循环当前正在做什么的主要方式。
在如何取消工作方面,任务和 future 也有区别,但这超出了本文的范围。“取消”是它们自己最大的问题。 如果你处于一个协程中,并且知道自己正在运行,你可以通过前面提到的 `Task.get_current` 获取自己的任务,但这需要你知道自己被派遣在哪个事件循环,该事件循环可能是、也可能不是已绑定的那个线程。
协程不可能知道它与哪个循环一起使用。`task` 也没有提供该信息的公共 API。 然而,如果你确实可以获得一个任务,你可以访问 `task._loop`,通过它反指到事件循环。
### 句柄
除了上面提到的所有一切还有句柄。 句柄是等待执行的不透明对象,不可等待,但可以被取消。 特别是如果你使用 `call_soon` 或者 `call_soon_threadsafe`(还有其它一些)调度执行一个调用,你可以获得句柄,然后使用它尽力尝试取消执行,但不能等待实际调用生效。
### <ruby> 执行器 <rt> Executor </rt></ruby>
因为你可以有多个事件循环,但这并不意味着每个线程理所当然地应用多个事件循环,最常见的情形还是一个线程一个事件循环。 那么你如何通知另一个事件循环做一些工作? 你不能到另一个线程的事件循环中执行回调函数并获取结果。 这种情况下,你需要使用执行器。
<ruby> 执行器 <rt> Executor </rt></ruby>来自 `concurrent.futures`,它允许你将工作安排到本身未发生事件的线程中。 例如,如果在事件循环中使用 `run_in_executor` 来调度将在另一个线程中调用的函数。 其返回结果是 asyncio 协程,而不是像 `run_coroutine_threadsafe` 这样的并发协程。 我还没有足够的心智来弄清楚为什么设计这样的 API,应该如何使用,以及什么时候使用。 文档中建议执行器可以用于构建多进程。
### 传输和协议
我总是认为传输与协议也凌乱不堪,实际这部分内容基本上是对 Twisted 的逐字拷贝。详情毋庸赘述,请直接阅读相关文档。
### 如何使用 asyncio
现在我们已经大致了解 asyncio,我发现了一些模式,人们似乎在写 asyncio 代码时使用:
* 将事件循环传递给所有协程。 这似乎是社区中一部分人的做法。 把事件循环信息提供给协程为协程获取自己运行的任务提供了可能性。
* 或者你要求事件循环绑定到线程,这也能达到同样的目的。 理想情况下两者都支持。 可悲的是,社区已经分化。
* 如果想使用上下文数据(如线程本地数据),你可谓是运气不佳。 最流行的变通方法显然是 atlassian 的 `aiolocals`,它基本上需要你手动传递上下文信息到协程,因为解释器不为此提供支持。 这意味着如果你用一个工具类库生成协程,你将失去上下文。
* 忽略 Python 中的旧式协程。 只使用 3.5 版本中 `async def` 关键字和协程。 你总可能要用到它们,因为在老版本中,没有异步上下文管理器,这是非常必要的资源管理。
* 学习重新启动事件循环进行善后清理。 这部分功能和我预想的不同,我花了比较长的时间来厘清它的实现。清理操作的最好方式是不断重启事件循环直到没有等待事件。 遗憾的是没有什么通用的模式来处理清理操作,你只能用一些丑陋的临时方案糊口度日。 例如 aiohttp 的 web 支持也做这个模式,所以如果你想要结合两个清理逻辑,你可能需要重新实现它提供的工具助手,因为该助手功能实现后,它彻底破坏了事件循环的设计。 当然,它不是我见过的第一个干这种坏事的库 :(。
* 使用子进程是不明显的。 你需要一个事件循环在主线程中运行,我想它是在监听信号事件,然后分派到其它事件循环。 这需要通过 `asyncio.get_child_watcher().attach_loop(...)` 通知循环。
* 编写同时支持异步和同步的代码在某种程度上注定要失败。 尝试在同一个对象上支持 `with` 和 `async with` 是危险的事情。
* 如果你想给一个协程起个更好的名字,弄清楚为什么它没有被等待,设置 `__name__`没有帮助。 你需要设置 `__qualname__` 而不是打印出错误消息来。
* 有时内部类型交换会使你麻痹。 特别是 `asyncio.wait()` 函数将确保所有的事情都是 future,这意味着如果你传递协程,你将很难发现你的协程是否已经完成或者正在等待,因为输入对象不再匹配输出对象。 在这种情况下,唯一真正理智的做法是确保前期一切都是 future。
### 上下文数据
除了疯狂的复杂性和对如何更好地编写 API 缺乏理解,我最大的问题是完全缺乏对上下文本地数据的考虑。这是 Node 社区现在学习的东西。`continuation-local-storage` 存在,但该实现被接受的太晚。持续本地存储和类似的概念常用于在并发环境中实施安全策略,并且该信息的损坏可能导致严重的安全问题。
事实上,Python 甚至没有任何存储,这令人失望至极。我正在研究这个内容,因为我正在调查如何最好地支持 [Sentry's breadcrumbs](https://docs.sentry.io/learn/breadcrumbs/) 的 asyncio,然而我并没有看到一个合理的方式做到这一点。在 asyncio 中没有上下文的概念,没有办法从通用代码中找出您正在使用的事件循环,并且如果没有 monkeypatching(运行环境下的补丁),也无法获取这些信息。
Node 当前正在经历如何[找到这个问题的长期解决方案](https://github.com/nodejs/node-eps/pull/18)的过程。这个问题不容忽视,因为它在所有生态系统中反复出现过,如 JavaScript、Python 和 .NET 环境。该问题[被命名为异步上下文传播](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1tlQ0R6wQFGqCS5KeIw0ddoLbaSYx6aU7vyXOkv-wvlM/edit),其解决方案有许多名称。在 Go 中,需要使用上下文包,并明确地传递给所有 goroutine(不是一个完美的解决方案,但至少有一个)。.NET 具有本地调用上下文形式的最佳解决方案。它可以是线程上下文,Web 请求上下文或类似的东西,除非被抑制,否则它会自动传播。微软的解决方案是我们的黄金标准。我现在相信,微软在 15 年前已经解决了该问题。
我不知道该生态系统是否还够年轻,还可以添加逻辑调用上下文,可能现在仍然为时未晚。
### 个人感想
复杂的东西变得越来越复杂。 我没有随意使用 asyncio 的心智。它需要不断地更新所有 Python 语言的变化的知识,这很大程度上使语言本身变得复杂。 令人鼓舞的是,围绕着它的生态系统正在不断发展,只是不知道还需要几年的时间,才能带给开发者愉快和稳定的开发体验。
3.5 版本引入的东西(新的协程对象)非常棒。 特别是这些变化包括引入了一个合理的基础,这些都是我在早期的版本中一直期盼的。在我心中, 通过重载生成器实现协程是一个错误。 关于什么是 asyncio,我难以置喙。 这是一个非常复杂的事情,内部令人眼花缭乱。 我很难理解它工作的所有细节。你什么时候可以传递一个生成器,什么时候它必须是一个真正的协程,future 是什么,任务是什么,事件循环如何工作,这甚至还没有触碰到真正的 IO 部分。
最糟糕的是,asyncio 甚至不是特别快。 David Beazley 演示的它设计的 asyncio 的替代品是原生版本速度的两倍。 asyncio 巨复杂,很难理解,也无法兑现自己在主要特性上的承诺,对于它,我只想说我想静静。我知道,至少我对 asyncio 理解的不够透彻,没有足够的信心对人们如何用它构建代码给出建议。
---
作者:

Armin Ronacher
软件开发者和开源骨灰, Flask 框架的创造者。
---
via: <http://lucumr.pocoo.org/2016/10/30/i-dont-understand-asyncio/>
作者:[Armin Ronacher](http://lucumr.pocoo.org/about/) 译者:[firstadream](https://github.com/firstadream) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,052 | 用带有 Amazon Cognito Identity SDK 的 webpack 打包 JavaScript | https://mobile.awsblog.com/post/Tx1A84CLMDJ744T/Using-webpack-with-the-Amazon-Cognito-Identity-SDK-for-JavaScript | 2016-12-22T08:32:00 | [
"webpack",
"AWS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8052-1.html | 这篇文章针对开发和部署基于 JavaScript 的应用(服务器端的 Node.js 或者客户端)的各种经验水平的开发者,通过本文,你将看到如何把 AWS SDK, Amazon Cognito Identity SDK 嵌入到 JavaScript 中,以及如何使用流行的 [webpack](https://webpack.github.io/) 模块打包器。

2016 年 7 月, AWS [推出了 Amazon Cognito <ruby> 用户库 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> user pool </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>](https://blogs.aws.amazon.com/security/post/Tx13NVD4AWG9QK9/Amazon-Cognito-Your-User-Pools-is-Now-Generally-Available),这个新特性极大的方便了开发者在移动和 Web 应用程序上添加注册和登录功能。为了让开发者更容易在自己的应用程序中实现用户库功能,我们也发布了[用于 JavaScript 的 Amazon Cognito Identity SDK](https://github.com/aws/amazon-cognito-identity-js)。
Amazon Cognito 用户库可以让你在移动和 Web 应用程序上添加用户注册和登录功能更加容易。全托管用户库可以扩展到数以百万计的用户,你可以在每个 AWS 账户下有多重目录。创建一个用户库只需要几分钟的时间,并且你可以决定当一个新用户在你的应用程序或服务上注册时哪些属性(包括地址、邮箱、电话号码以及自定义属性)是强制的,哪些是可选择的。你的应用程序也可以指定所需的密码强度,指定用户需要进行多因素认证(MFA),以及通过电话号码或者邮件地址来验证新用户,从而进一步加强应用程序的安全性。
如果你是首次接触用于 JavaScript 的 Amazon Cognito Identity SDK,那么请先阅读[这篇 AWS 文章](http://mobile.awsblog.com/post/Tx2O14ZY8A5LFHT/Accessing-Your-User-Pools-using-the-Amazon-Cognito-Identity-SDK-for-JavaScript)作为开始。
### 为什么在 JavaScript 上使用 Asset 及模块捆绑的 Amazon Cogtito Identity SDK
今天,针对移动和桌面的现代 Web 应用程序都能为用户提供安全、快捷、灵敏以及类本地应用的体验。毫无疑问,现代的浏览器功能足够强大,能够肩负起大量可能的功能实现。许多流行的实现很大程度上依赖于 JavaScript 应用程序通过某种形式的 asset 封装和/或模块捆绑进行部署。这使得许多开发人员能够很好的维护自己的 JavaScript 应用程序,并且可以通过使用 script 标签创建一个或多个可以加载到客户端浏览器上的文件。
关于如何实现打包有许多争鸣,包括 [Grunt](http://gruntjs.com/) 和 [Gulp](http://gulpjs.com/) 这样的 task runner,以及 [Browserity](http://browserify.org/) 这样的打包器。然而,一个普遍的共识是, asset 打包不仅可以改善加载时间 - 它可以在确保可测试性和健壮性的前提下使你的应用程序模块化。
### 使用带有 Amazon Cognito Identity SDK 的 webpack 打包 JavaScript
我们接到了许多请求,要求我们提供如何在 webpack 环境下整合用于 JavaScript 的 Amazon Cognito Identity SDK 的更多细节。我们特地要求确保 webpack 正确管理一下第三方的依赖包:
* [用于 BigInteger 计算的 JavaScript BN 库](http://www-cs-students.stanford.edu/%7Etjw/jsbn/jsbn.js)(jsbn)
* [jsbn 扩展](http://www-cs-students.stanford.edu/%7Etjw/jsbn/jsbn2.js)及包含大多数公共 BigInteger 方法的其它 jsbn 方法(jsbn2)
* [Stanford JavaScript Crypto 库](https://github.com/bitwiseshiftleft/sjcl)(jscl)
通过这些例子,可以看到,下面这些 bower 库都被 bower.json 使用
```
"aws-cognito-sdk": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aws/amazon-cognito-identity-js/master/dist/aws-cognito-sdk.js",
"amazon-cognito-identity": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aws/amazon-cognito-identity-js/master/dist/amazon-cognito-identity.min.js",
"sjcl": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/bitwiseshiftleft/sjcl/master/sjcl.js",
"jsbn": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/andyperlitch/jsbn/master/index.js",
```
出于我们前面给出的关于 asset 打包对于开发过程的重要性的原因,除非你的应用程序非常小,否则使用像 webpack 这样的 asset 打包工具几乎总是必须的。当然,还有一个方法是可以通过使用标签简单的处理所有依赖关系。然而,这会污染全局命名空间,而且不能够提供最优的资源管理和加载方式。许多开发者首次使用的是具有标准 babel 加载器的标准 webpack.config.js 文件,像下面展示的这样。
```
{
/** test for file ending in js or jsx
* exclude node_module and bower_components - we dont want to babel these
* use the babel loader
* apply the react and es2015 (es6) transformations **/
test: /\.jsx?$/,
exclude: /(node_modules|bower_components)/,
loader: 'babel',
query: {
presets: ['react', 'es2015']
}
}
```
需要重点记住的是,这个配置没有考虑一些第三方依赖关系,这些被用于 JavaScript 的 Amazon Cognito Identity SDK 所使用的第三方依赖目前没有使用 [JavaScript 通用模块定义(UMD)](https://github.com/umdjs/umd)。
UMD 模式试图提供与 [RequireJS](http://requirejs.org/) 和 [CommonJS](http://www.commonjs.org/) 这些当前最流行的脚本加载器的异步模块定义 [AMD] 的基本兼容。
这是 webpack 所依赖的模式,为了让 webpack 能够工作,我们必须进行一些改变。不做这些改变,你可能会遇到下面这些错误。
```
amazon-cognito-identity.min.js:19 Uncaught ReferenceError: BigInteger is not defined
```
这样一个错误可能会在调用 AWSCognito.CognitoIdentityServiceProvider.CognitoUser property authenticateUser 的时候出现。在这个错误例子中,我们可以利用 webpack 的 import 和 export 加载器的能力来解决这个错误。
### 使用 webpack 加载器
根据 [webpack 文档],“加载器允许你通过 require() 或 load 来预处理文件。加载器是一种类似其它构建工具中 “tasks” 的工具,它可以提供一个处理前端构建步骤的强大方法。加载器可以把一个文件从一种语言转化成另一种语言,比如把 CoffeeScript 转化成 JavaScript ,或者把图像转换为 data URL。“
为了解决 UMD 的兼容性缺乏的问题,你必须依赖两个具体的加载器, import 和 export 加载器。
#### 使用 export 加载器
在使用用于 JavaScript 的 Amazon Cognito Identity SDK 的情况下,我们需要确保把 theAWSCognito 变量导出到 require /import 它们的模块的变量范围内(针对 ES6)。
```
{
test: /aws-cognito-sdk\/index\.js/,
loader: 'exports?AWSCognito'
}
```
在由 webpack 创建的捆绑中,使用 export 加载器会有导出模块方法的效果。因此, 在 require 和 import 后,AWSCognito 和 AWS 是可访问的(针对 ES6)。
```
var AWSCognito = require('aws-cognito-sdk')
/*** EXPORTS from export-loader ***/
module.exports = AWSCongito
```
[这儿](https://github.com/webpack/exports-loader)可以找到更多关于 export 加载器的信息。
#### 使用 import 加载器
import 加载器主要用于把变量注入(import)到另一个模块的变量范围内。当第三方模块需要依赖全局变量的时候, import 加载器非常有用,比如针对 JavaScript 的 Amazon Cognito Identity SDK 需要依赖 BigInteger 或者 sjcl 的时候。
如果你不使用 webpack 加载器,下面这些内容会在一个捆绑中生成。
```
__webpack_require__(431); // refers to jsbin
__webpack_require__(432); // refers to sjcl
```
因为 jsbin 和 sjcl 都不能 export 任何东西,因此任何依赖于这些模块的调用都会导致一个错误。
为了解决这个问题,我们需要使用下面的 webpack 加载器配置:
```
{
test: /amazon-cognito-identity\/index\.js/,
loader: 'imports?jsbn,BigInteger=>jsbn.BigInteger,sjcl'
},
{
test: /sjcl\/index\.js/,
loader: 'imports?sjcl'
}
```
这个配置把下面的这些内容嵌入到了由 webpack 创建的捆绑中(此时是 bundle.js)。
```
/*** IMPORTS FROM imports-loader ***/
var jsbn = __webpack_require__(431);
var BigInteger = jsbn.BigInteger;
var sjcl = __webpack_require__(432);
```
结果,jsbn、BigInteger 和 sjcl 都被从它们各自的模块中导入到了用于 JavaScript 的 Amazon Cognito Identity SDK 中。
有关 import 加载器的更多信息可以在[这儿](https://github.com/webpack/imports-loader)找到。
### 下一步
我们鼓励你下载[用于 JavaScript 的 Amazon Cognito Identity SDK](https://github.com/aws/amazon-cognito-identity-js) 并开始构建你的应用,并在这篇文章的指导下通过 webpack 能够迅速掌握。
如果你有任何意见或问题,请在下面自由评论,也可以发邮件到 [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected]) 或者在[这儿](https://github.com/aws/amazon-cognito-identity-js/issues)提出问题。
### 引用
这篇文章引用了下面这些第三方资源:
* webpack - <https://webpack.github.io/>
* webpack 文件 - <http://webpack.github.io/docs/what-is-webpack.html>
* webpack export 加载器 - <https://github.com/webpack/exports-loader>
* webpack import 加载器 - <https://github.com/webpack/imports-loader>
* 用于 BigInteger 计算的 JavaScript BN 库- [http://www-cs-students.stanford.edu/~tjw/jsbn/jsbn.js](http://www-cs-students.stanford.edu/%7Etjw/jsbn/jsbn.js)
* jsbns - [http://www-cs-students.stanford.edu/~tjw/jsbn/jsbn2.js](http://www-cs-students.stanford.edu/%7Etjw/jsbn/jsbn2.js)
* Stanford JavaScript Crypto 库 - <https://github.com/bitwiseshiftleft/sjcl>
* RequireJS - <http://requirejs.org/>
* CommonJS - <http://www.commonjs.org/>
---
via: <https://mobile.awsblog.com/post/Tx1A84CLMDJ744T/Using-webpack-with-the-Amazon-Cognito-Identity-SDK-for-JavaScript>
作者:[Marc Teichtahl](https://mobile.awsblog.com/blog/author/Marc+Teichtahl) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 302 | Moved Temporarily | null |
8,053 | 怎样在 Android 上手动备份你的短信/彩信? | https://iwf1.com/how-to-manually-backup-your-sms-mms-messages-on-android/ | 2016-12-22T10:29:17 | [
"Android",
"adb",
"备份"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8053-1.html | 
如果你要换一部手机或升级你的系统,备份你的数据就变得至关重要。我们存储重要数据的位置之一就是我们的短信/彩信,不管是感情价值还是实用价值,备份它们是很有用的。
然而,不像照片、视频或音频文件可以相对容易地传输和备份,备份短信/彩信比较复杂,通常需要使用第三方 app 或服务。
### 为什么要手动备份
尽管现在有很多不同的 app 能够帮你备份短信/彩信,你可能因为以下原因,考虑自己动手备份它们:
1. app **可能不能**在所有的设备和安卓版本上都工作。
2. app 可能把你的备份数据上传到云端, 有**破坏你的内容安全**的风险。
3. 通过手动备份,你可以完全掌握你的数据通过哪里,走向哪里,备份过程中减少被间谍软件窥视的危险。
4. 手动备份相比其他方法**更省时,更省力,更直接**。
### 怎么手动备份短信/彩信?
要手动备份你的短信/彩信,你需要在你的电脑上安装一个叫做 [adb](http://developer.android.com/tools/help/adb.html) 的安卓工具。
现在,需要重点知道的是,安卓把短信/彩信通常存储在一个叫做 `mmssms.db` 的数据库里。
因为在不同设备上这个数据库的位置可能不相同,而且,其他短信 app 会创建它们自己的数据库,比如 GO SMS 会创建 `gommssms.db` 数据库, 所以你需要做的第一件事是搜索这些数据库。
打开命令行工具(我使用了 Linux Terminal, 你也可以使用 Windows CMD 或 PowerShell )并运行以下命令:
注意: 以下是完成该任务的一系列命令,再后面是每个命令用途的解释。
```
adb root
adb shell
find / -name "*mmssms*"
exit
adb pull /PATH/TO/mmssms.db /PATH/TO/DESTINATION/FOLDER
```
#### 解释
一开始我们使用 `adb root` 命令来以 root 模式启动 adb - 这样我们就有了读取系统保护文件的权限。
`adb shell` 用来进入设备的 shell。
然后, `find` 命令用来搜索数据库。(在我的例子中,我发现数据库在 `/data/data/com.android.providers.telephony/databases/mmssms.db`)
建议:如果你的终端输出了太多无关的结果,可以试试使用 `find` 的参数来精简结果。(具体参数可以搜索引擎查下)

*安卓短信/彩信数据库*
然后我们使用 `exit` 命令回退到我们的本地系统目录。
最后,使用 `adb pull` 把数据库文件复制到我们电脑的一个文件夹里。
现在,当你想要还原短信/彩信时,不管是还原到新的设备还是新的系统版本, 只要再次搜索新系统中短信/彩信的具体位置,并用我们备份的数据库替换它即可。
使用 `adb push` 来替换它,例如:
```
adb push ~/Downloads/mmssms.db /data/data/com.android.providers.telephony/databases/mmssms.db
```
---
via: <https://iwf1.com/how-to-manually-backup-your-sms-mms-messages-on-android/>
作者:[Liron](https://iwf1.com/tag/android) 译者:[willcoderwang](http://wangzk.win) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,054 | 详解使用 fastboot 为 Android 刷入原厂镜像 | http://android.wonderhowto.com/how-to/complete-guide-flashing-factory-images-using-fastboot-0175277/ | 2016-12-23T09:46:00 | [
"Android",
"镜像"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8054-1.html | 
如果你的手机有一个解锁的 [bootloader](http://android.wonderhowto.com/news/big-android-dictionary-glossary-terms-you-should-know-0165594/) 的话,你可以用 [fastboot](http://android.wonderhowto.com/news/big-android-dictionary-glossary-terms-you-should-know-0165594/) 命令来刷入原厂镜像。听起来这好像是外行弄不懂的东西,但是当你需要升级被 [root](http://android.wonderhowto.com/how-to/android-basics-what-is-root-0167400/) 过的设备,修理坏掉的手机,恢复到原生系统,或者是比别人更早的享受 Android 更新时,它可是最好的办法。
和 [ADB](http://android.wonderhowto.com/how-to/know-your-android-tools-what-is-adb-do-you-use-it-0155456/) 类似,fastboot 是一个强大的 Android 命令行工具。这听起来可能会很恐怖 —— 别担心,一旦你了解了它,你就会知道 Android 的内部工作原理,以及如何解决最常见的问题。
### 关于三星设备的注释
下面的指南对于 Nexus、Pixel、HTC 以及 Motorola 的大多数设备,以及其他众多厂商的手机和平板电脑都适用。但是,三星的设备有自己的刷机软件,所以你的 Galaxy 设备并不支持 Fastboot。对于三星的设备,最好使用 [Odin](http://tag.wonderhowto.com/odin/) 来进行刷机工作,我们在下文的链接中提供了相关指南。
### 第一步 在你的电脑上安装 ADB 和 Fastboot
首先,你需要在你的电脑上安装 ADB 和 Fastboot,只有有了它们你才能使用 Fastboot 命令刷入镜像。网上有不少“一键安装版”或者“绿色版”的 ADB 和 Fastboot,但是我不建议安装这样的版本,它们没有官方版本更新那么快,所以可能不会完全兼容新版设备。
你最好从 Google 上安装 Android SDK Tools。这才是“真正的” ADB 和 Fastboot。安装 SDK Tools 可能需要一点时间,不过这等待是值得的。在下面的 *方法 1* 中,我会说明在 Windows, Mac,以及 Linux 中安装这个软件的方法,所以可以跳转到那里开始。
### 第二步 <ruby> OEM 解锁 <rt> OEM Unlocking </rt></ruby>
为了能够使用 Fastboot 刷入镜像,你需要解锁你设备的 [bootloader](http://android.wonderhowto.com/news/big-android-dictionary-glossary-terms-you-should-know-0165594/)。如果你已经解锁,你可以跳过这步到第三步。
如果你的设备的 Android 版本在 6.0 及以上的话,在你解锁 bootloader 之前,你还[需要开启一项设置](http://android.wonderhowto.com/news/psa-enable-hidden-setting-before-modding-anything-android-0167840/)。首先你需要开启**<ruby> 开发者选项 <rt> Developers Options </rt></ruby>**。开启之后,进入“开发者选项菜单”,然后开启 “OEM 解锁” 选项。之后就可以进行下一步了。

如果你的设备没有这个选项,那么你的设备的 Android 版本可能不是 6.0 或以上。如果这个选项存在但是是灰色的,这就意味着你的 bootloader 不能解锁,也就是说你不能使用 Fastboot 给你的手机刷入镜像。
### 第三步 进入 Bootloader 模式
在使用 Fastboot 软件之前,你还需要让你的设备进入 bootloader 模式。具体进入方式与你的设备有关。
对于大多数手机,你需要先完全关闭你的手机。在屏幕黑掉以后,同时按住开机键和音量向下键大约 10 秒。
如果这不起效的话,关掉手机,按住音量降低键。然后把手机用 USB 数据线连到电脑上,等上几秒钟。
如果还不起效的话,改按音量升高键,再试试第二种方法。
很快你就会看见像这样的 bootloader 界面:

看到这个界面之后,确保你的设备已经连接到电脑上。之后的工作就都是在电脑上完成了,把手机放在那里就成。
### 第四步 在你的电脑上为 ADB 打开一个命令行窗口
转到 ADB 和 Fastboot 的安装目录。对于 Windows 用户来说,这目录通常是 `C:\Program Files (x86)\Android\android-sdk\platform-tools`。 对于 Mac 和 Linux 用户,则取决于你安装此工具时将 ADB 解压的位置,所以如果你忘了位置的话,就在硬盘里搜索 `platform-tools`。
在安装目录下,如果你使用 Windows PC 的话,按住键盘上的 Shift 键,在文件管理器的空白处单击右键,然后选择“在此处开启命令行窗口”。如果你用的是 Mac 或者 Linux,那么你仅仅需要打开一个终端,然后转到 `platform-tools` 下。

### 第五步 解锁 bootloader
这一步你仅仅需要做一次,所以如果你的 bootloader 已经解锁,你可以直接跳过这步。否则你还需要运行一条命令 —— 注意,这条命令会**清空你设备上的所有数据**。
在输入命令之前,我需要说明下,下面的命令仅仅对 Windows 适用,Mac 用户需要在每条命令前加上一个句号和一个斜线(`./`),Linux 用户则需要加上一个斜线(`/`)。
所以,在 ADB Shell 里输入如下命令,然后按下回车键。
```
fastboot devices
```
如果程序输出了以 fastboot 结尾的一串字符,那就说明你的设备连接正常,可以继续操作。如果没有的话,回到第一步,检查你的 ADB 以及 Fastooot,是否正确安装,之后再确定设备是否如第三步所示进入了 bootloader 模式。

之后,解锁你的 bootloader。因为 Android 版本的差别,我们有两种方法来解决这个问题。
如果你的设备的 Android 版本是 5.0 或者更低版本 ,输入如下命令:
```
fastboot oem unlock
```
如果你的 Android 版本是 6.0 或更高的话,输入如下命令,然后按下回车:
```
fastboot flashing unlock
```

*将解锁命令发送到 6.0 或者更高版本的 Android 手机上*
这时,你的 Android 手机会问你是否确定要解锁 bootloader。确定你选中了 “Yes” 的选项,如果没有,使用音量键选中 “Yes”。然后按下电源键,你的设备将会开始解锁,之后会重启到 Fastboot 模式。

*Nexus 6P 上的解锁菜单。图像来自 Dallas Thomas/Gadget Hacks*
### 第六步 下载出厂镜像
现在你的 bootloader 已经解锁,准备好刷入出厂镜像了 -- 不过,你需要先下载镜像。下面是常规设备下载出厂镜像的链接。
* [Nexus 或 Pixel 设备的出厂镜像](https://developers.google.com/android/images)
* [HTC 设备出厂镜像](http://www.htc.com/us/support/rom-downloads.html)
* [Motorola 设备出厂镜像](https://motorola-global-portal.custhelp.com/cc/cas/sso/redirect/standalone%2Fbootloader%2Frecovery-images)
使用上面的链接,在列表中定位你的设备型号,然后下载最新固件到计算机上。如果你的厂商不在列表中,可以试着用 “factory images for ” 进行 google 搜索。
### 第七步 刷入出厂镜像
现在该刷入镜像了。首先将从厂商网站下载的出厂镜像文件解压。我推荐 [7-Zip](http://www.7-zip.org/download.html) ,它是免费的,支持大多数格式。

*解压出厂镜像*
下一步,把压缩包中内容移动到你的 ADB 安装文件夹。之后在这里打开一个命令行窗口。要得到更多信息,请回看第四步。

*出厂镜像移动到 platform-tools 的文件*
除了上面这些,你有两种刷入镜像的方法。我会在下文分开叙述。
#### 方法一:使用 flash-all 脚本
大多数出厂镜像都会包含一个`flash-all` 脚本,可以让你一条命令就完成刷机过程。如果你试图让你的黑砖恢复正常的话,这是最简单的方法。但是这会让你的手机回到未 root 的状态,并会擦除所有数据,如果你不想这样的话,请选择方法二。
如果要运行 `flash-all` 脚本,输入如下命令,之后敲下回车:
```
flash-all
```

*运行 "flash-all" 命令*
这需要一点时间,当这步完成之后,你的手机应当自动重启,你可以享受 100% 原生固件。
#### 方法二 手动解压刷入镜像
你可以手动刷入系统镜像。这么做需要额外的工作,但是它可以在不清除数据的情况下反 root,升级设备,或者救回你的砖机。
首先解压出厂镜像包中的所有压缩文件。通常压缩包里会包含三或四个层叠的文件夹,确认你已经解压了所有的压缩文件。之后把这些文件移动到 `platform-tools` —— 或者说,别把他们放到任何子文件夹下。

*从出厂镜像包解压后的所有文件移至 platform-tools 目录*
在这些文件里,有两个镜像是可以直接删除的:`cache.img` 和 `userdata.img`。就是这两个文件清除了你的设备数据,如果你不刷入这两个镜像,你的数据就不会消失。
在剩下的文件中,有六个镜像构成了 Android 的核心部分: `boot`、`bootloader`、 `radio`、 `recovery`、 `system` 和 `vendor`。
`boot` 镜像包含了内核,如果你想要换掉一个不太好用的自制内核的话,你仅仅需要刷入这个文件。通过键入如下命令完成工作:
```
fastboot flash boot <boot image file name>.img
```
下一个就是 `bootloader` 镜像—— 也就是你用来刷入镜像的界面。如果你要升级 bootloader 的话,输入如下命令:
```
fastboot flash bootloader <bootloader image file name>.img
```
做完这步之后,你就可以用新版的 bootloader 刷入镜像。要想如此,输入:
```
fastboot reboot-bootloader
```
之后就是 `radio` 镜像。这个镜像控制你设备的网络连接,如果你手机的 Wi-Fi 或者移动数据出现了毛病,或者你仅仅想升级你的 radio,输入:
```
fastboot flash radio <radio image file name>.img
```
然后就是 `recovery`。根据你之前的修改,你可能选择刷或不刷这个镜像。例如,如果你已经刷入 TWRP 的话,刷入这个镜像覆盖你的修改,并替代为 stock recovery。如果你仅仅要升级你的已经被修改过的设备,你就可以跳过这步。如果你想要新版的 stock recovery ,键入:
```
fastboot flash recovery <recovery file name>.img
```
下一个可是个大家伙:`system` 镜像,它包含了 Android 系统所需的全部文件。它是升级过程中最重要的部分。
如果你不想升级系统,仅仅是要换回原生固件或者是救砖的话,你只需要刷入这个镜像,它包含了 Android 的所有文件。换言之,如果你仅仅刷入了这个文件,那你之前对这个设备做的修改都会被取消。
作为一个救砖的通用方法,以及升级 Android 的方法,键入:
```
fastboot flash system <system file name>.img
```
最后,就是 `vendor` 镜像。只有新版的设备才包含这个包。没有的话也不必担心,不过如果有这个文件的话,那它就包含了一些重要的文件,键入如下命令使其更新:
```
fastboot flash vendor <vendor file name>.img
```
在这之后,你就可以重新启动设备:
```
fastboot reboot
```

*手动逐个刷入出厂镜像*
至此,你的设备已经完全更新,如果你是救砖的话,你的手机应该已经完好的运行。如果你知道每个系统镜像怎么是干什么的话,你就会更好的理解 Android 是怎么运行的。
手动刷入镜像比做任何修改已经帮助我更多地理解了 Android。你会发现,Android 就是写进存储设备里的一堆镜像,现在你可以自己处理他们,你也能更好的处理有关 root 的问题。
* 在[Facebook](http://facebook.com/gadgethacks/)、[Twitter](http://twitter.com/gadgethax)、[Google+](https://plus.google.com/+gadgethacks) 以及 [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/user/OfficialSoftModder/) 关注 Gadget Hacks
* 在 [Facebook](http://facebook.com/androidhacksdotcom/)、[Twitter](http://twitter.com/androidhackscom) 和 [Pinterest](https://www.pinterest.com/wonderhowto/android-hacks-mods-tips/) 上关注 Android Hacks
* 在 [Facebook](http://facebook.com/wonderhowto/)、[Twitter](http://twitter.com/wonderhowto/)、 [Pinterest](http://pinterest.com/wonderhowto/) 还有 [Google+](https://plus.google.com/+wonderhowto) 上关注 WonderHowTo
---
via: <http://android.wonderhowto.com/how-to/complete-guide-flashing-factory-images-using-fastboot-0175277/>
作者:[Dallas Thomas](http://creator.wonderhowto.com/dallasthomas/) 译者:[name1e5s](https://github.com/name1e5s) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,055 | 3 款开源的密码管理器 | https://opensource.com/article/16/12/password-managers | 2016-12-22T15:51:00 | [
"密码管理器",
"Padlock",
"Passbolt",
"KeePass"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8055-1.html |
>
> 使用一款安全开源的密码管理器来储存唯一、复杂的密码来保护你数据及账户的安全。
>
>
>

为你使用的每个站点和服务维护一份唯一、复杂的密码是安全专家每年给公众最常提的建议。
然而不管说过多少遍,几乎每周我们都能听到 XX 网站又被黑了的新闻,问题是这些网站的用户们就爱用一些像“12345”或“password”这样的口令来保护他们的账号。
或许用户对经典的密码做了足够的变形,符合了网站所要求的最低的密码规则。但不幸的是,“Pa$$w0rd!”也不是真正意义上的安全密码。从这方面来说,大多数单词、短语及数字的组合或替换对于密码破解工具而言都太容易破解了,密码越短越容易破解。
最棒的密码应该是长长的,任何可能的字符的随机或者伪随机组合,每个使用场景都用不同的密码。但对一个普通人而言怎么可能记住上百甚至上千个他们创建的独立的账户密码呢?简短的答案是:不能。甚至不管是在现实世界或者数码世界不应该明文记录下任何一个密码。
或许最简单地保存这些复杂、唯一密码的方法是使用密码管理器,它提供了一种访问这些强密码的简单方式。虽然像 LastPass 这样商业解决方案很受欢迎,但是还有一些开源方案。另外对于密码,可以审计你的密码管理器的源码也是很重要的,因为它可以确保你的密码被正确地加密,并且没有后门。
所以不用多说,下面有几款你可以考虑的密码管理器。
### KeePass

[KeePass](http://keepass.info/) 是一个 GPLv2 授权的密码管理器,主要设计用于 Windows ,但是同样可以在其它平台运行。KeePass 提供多个强加密选项、便于导出、多用户密钥、高级搜索特性等等。其为桌面用途设计,也有可以直接运行在浏览器中的插件,并且如果你想要在不同的机器间随身携带你的密码,它可以运行在 U 盘中。想要了解更多 KeePass 信息,你可以从在 Ricardo Frydman 的这篇[旧贴](https://opensource.com/business/16/5/keepassx)中找到。
[KeePassX](https://www.keepassx.org/),是 KeePass 的 Linux 移植版本,是另一个你可以考虑的项目。KeePassX 与 KeePass 2 密码文件兼容,并且已经被移植到不同的操作系统上。事实上,KeePass 的[非官方版本](http://keepass.info/download.html)列表覆盖了日常使用的所有系统。
### Padlock

[Padlock](https://padlock.io/) 是一个最近新进的开源密码管理器。目前在 Windows、iOS、Android 上可用,Linux 版本正在开发中,Padlock 被设计成为了一个“极简风”的密码管理器。它的[源码](https://github.com/MaKleSoft/padlock)以 [GPLv3](https://github.com/MaKleSoft/padlock/blob/master/LICENSE) 授权的形式发布在 Github 上。项目同样也正在开发一个[云后端](https://github.com/maklesoft/padlock-cloud),同样是开源的,这对那些厌烦了管理密码文件或者在多台电脑间设置同步的人而言是一个很好的补充。
### Passbolt

[Passbolt](https://www.passbolt.com/) 是另一个相对较新的选择,它有 Firefox 和 Chrome 的插件,支持移动设备,还有正在开发的命令行。它基于 OpenPGP,你可以查看在线的一些功能[演示](https://demo.passbolt.com/auth/login)(虽然这需要你安装浏览器插件)。以 [AGPLv3 授权](https://github.com/passbolt/passbolt_browser_extension/blob/master/LICENCE)发布,你可以在 [Github](https://github.com/passbolt) 上查看它的源码或者浏览一下项目的[路线图](https://www.passbolt.com/roadmap)来了解下目前和将来计划的功能。
---
使用一款你信任的密码管理器以及用复杂的密码并不能代替其他安全预防措施,它也不是万无一失的。但是对于许多用户而言,它是让你的数字生活保持安全的很重要的一部分。这些的确不是唯一的选择。还有一些更老的选择,比如 [Clipperz](https://clipperz.is/) 和 [Password Safe](https://pwsafe.org/),还有我有兴趣想尝试一下的基于 web 的工具 [RatticDB](http://rattic.org/)。
你会使用哪款密码管理器?为什么呢?
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/16/12/password-managers>
作者:[Jason Baker](https://opensource.com/users/jason-baker) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Maintaining complex, unique passwords for each site and service you use is among the most common pieces of advice that security professionals provide to the public every year.
Yet no matter how many times it is said, it seems like a week doesn't go by where a high-profile hacking story hits the news, revealing that users of the service in question more often than not had such *secure* passwords as "12345" or "password" as the only wall of protection on their account.
Or perhaps a user offers up just enough variation on the classic password selection to get past the minimal rules of the service. Unfortunately, "Pa$$w0rd!" isn't secure in any meaningful way, either. At this point, almost every variation of words and phrases strung together with a few numbers or substitutions is simply too easy for a password cracking tool to make its way through, and the shorter the password, the easier.
The best passwords are long, random or pseudo-random combinations of every possible character allowed, with a different password for each unique use. But how could a normal person remember the hundreds or even thousands of individual passwords associated with each account they've ever created? The short answer is: they can't. And don't even think about writing a password down in plain text, whether in the physical world or the digital.
Perhaps the easiest way to keep track of these complex, unique passwords is with a password manager, which provides easy access to strong encryption. While proprietary commercial solutions like LastPass are popular, there are several open source solutions as well. And with passwords, being able to audit the source code of your password manager is especially important, as it helps ensure that your passwords are encrypted properly and are not vulnerable to backdoors.
So without further ado, here are a few open source password managers we hope you will consider.
## KeePass
[KeePass](http://keepass.info/) is a GPLv2-licensed password manager, primarily designed for Windows but also running elsewhere. KeePass offers multiple strong encryption options, easy exports, multiple user keys, advanced searching features, and more. Designed for desktop use, there are plugins that allow direct use from your web browser, and it can run from a USB stick if you'd prefer to physically carry your passwords from machine to machine. More on KeePass can be found in this [past article](https://opensource.com/business/16/5/keepassx) from Ricardo Frydman.
[KeePassX](https://www.keepassx.org/), which started as a Linux port of KeePass, is another project you may consider. KeyPassX is compatible with KeePass 2 password files, and has also been ported to run on different operating systems. In fact, the list of [unofficial releases](http://keepass.info/download.html) of KeePass covers ports to just about every system in common use.
## Padloc
[Padlock](https://padloc.app/) is a very new entrant into the world of open source password managers. Currently available for Linux, Windows, Mac, iOS, and Android, with a ChromeOS client in the works, Padlock is designed as a "minimalist" password manager. Its [source](https://github.com/padloc/padloc) is available on GitHub under a [GPLv3](https://github.com/MaKleSoft/padlock/blob/master/LICENSE) license. The project also has developed a [cloud backend](https://github.com/maklesoft/padlock-cloud), also open source, which is a welcome addition to anyone tired of managing password files or setting up syncing across multiple computers.
## Passbolt
[Passbolt](https://www.passbolt.com/) is another relatively new option, with plugins available for Firefox and Chrome and mobile and command-line options on the way. Based on OpenPGP, you can check out its online [demo](https://demo.passbolt.com/auth/login) which shows off some of the features (you'll need to install the plugin for your browser, though). Licensed under the [GPL Affero version 3 license](https://github.com/passbolt/passbolt_browser_extension/blob/master/LICENCE), you can check out the source code on [GitHub](https://github.com/passbolt) or view the project's [roadmap](https://www.passbolt.com/roadmap) for a list of current features and more on what is planned.
## Bitwarden
[Bitwarden](https://opensource.com/bitwarden.com) offers an easy and safe way for teams and individuals to store and share sensitive data, and it works on all major platforms and devices. You can also integrate Bitwarden into your favorite web browser (including Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari, Microsoft Edge, and others). You can access your sensitive data from a "web vault" in your browser, too, so you're never without the information you need.I The data is fully encrypted end-to-end with AES-256. If you prefer, you can even [host your own instance](https://bitwarden.com/help/article/install-on-premise/).
You can create a Bitwarden account for free. Bitwarden is open source and released under a [GPLv3](https://github.com/MaKleSoft/padlock/blob/master/LICENSE) license, and the Bitwarden community is vibrant and inviting. Visit their forum to learn more about the software, or to pose any questions you may have.
Using a password manager that you trust alongside complex passwords is not a substitute for taking other security precautions, nor is it foolproof. But for many users, it can be an important part of keeping your digital life secured. These definitely aren't the only options out there. There are some older options, like [Clipperz](https://clipperz.is/) and [Password Safe](https://pwsafe.org/), and web-based tools like [RatticDB](http://rattic.org/) that I would be interested to try out. Which open source password manager do you use, and why?
*This article was originally published in December 2016 and has been updated with new information.*
## 11 Comments |
8,056 | 在 Linux 下生成高强度密码的四种方法 | https://www.ostechnix.com/4-easy-ways-to-generate-a-strong-password-in-linux/ | 2016-12-23T10:56:00 | [
"密码",
"口令"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8056-1.html | 
前一段时间,我们已经分享了如何在诸如 Debian、Ubuntu、Linux Mint、Elementary OS 的基于 DEB 的系统中[强制用户使用高强度的密码](https://www.ostechnix.com/force-users-use-strong-passwords-debian-ubuntu/) ,比如。那么,你可能会疑惑一个高强度的密码究竟是什么样的呢?怎么才能生成一个那样的密码呢?不用担心,下面我们将介绍 4 种简单方法让你在 Linux 中生成一个高强度密码。当然,已经有很多免费的工具或者方式来完成这个任务,但这里我们仅考虑那些简单直接的方法。下面就让我们开始吧。
### 1. 在 Linux 中使用 OpenSSL 来生成一个高强度密码
OpenSSL 在所有的类 Unix 发行版、Solaris、Mac OS X 和 Windows 中都可以获取到。
要使用 OpenSSL 生成一个随机密码,打开终端并运行下面的命令:
```
openssl rand 14 -base64
```
上面的 `-base64` 参数将确保生成的密码可以被键盘敲出来。
输出样例:
```
wXCHXlxuhrFrFMQLqik=
```

上面的命令将生成一个随机的、长度为 14 个字符的高强度密码。我们强烈推荐你生成 14 个字符的密码。 当然你可以使用 OpenSSL 生成任意长度的密码。
要了解更多信息,可以参考联机手册:
```
man openssl
```
### 2. 在 Linux 中使用 Pwgen 来生成一个高强度密码
pwgen 是一个简单却非常有用的命令行工具,用它可以在短时间内生成一个随机且高强度的密码。它设计出的安全密码可以被人们更容易地记住。在大多数的类 Unix 系统中都可以获取到它。
在基于 DEB 的系统中安装 pwgen 请运行:
```
sudo apt-get install pwgen
```
在基于 RPM 的系统中,运行:
```
sudo yum install pwgen
```
在基于 Arch 的系统中,则运行:
```
sudo pacman -S pwgen
```
pwgen 安装完成后,便可以使用下面的命令来生成一个长度为 14 个字符的随机高强度密码:
```
pwgen 14 1
```
输出样例:
```
Choo4aicozai3a
```

上面的命令将生成一个 14 位字符长的密码,如果要生成两个不同的 14 位字符长的密码,则可以运行:
```
pwgen 14 2
```
输出样例:
```
xee7seerez6Kau Aeshu0geveeji8
```
如果要生成 100 个(尽管可能没有必要生成那么多)不同的 14 位字符长的密码,则可以运行:
```
pwgen 14
```
输出样例:
```
kaeNg3EiVei4ei Oo0iehiJaix5Ae aenuv2eree2Quo iaT7zahH1eN2Aj Bie2owaiFahsie
gaan9zu5Xeh5ah ahGeeth8ea5ooh Ir0ueda5poogh5 uo0ohqu2ufaiX2 Mei0pee6Og3zae
Oofeiceer8Aipu sheew3aeReidir Dee4Heib2eim2o eig6jar8giPhae Zahde9nae1Niew
quatol5Oi3Bah2 quue4eebaiNgaa oGoahieSh5oL4m aequeeQue2piti laige5seePhugo
iiGo9Uthee4ros WievaiQu2xech6 shaeve0maaK3ae ool8Pai2eighis EPheiRiet1ohci
ZieX9outhoht8N Uh1UoPhah2Thee reaGhohZae5idi oiG4ooshiyi5in keePh1ohshei8y
aim5Eevah2thah Xaej8tha5eisho IeGie1Anaalaev gaoY3ohthooh3x chaebeesahTh8e
soh7oosieY5eiD ahmoh6Ihii6que Shoowoo5dahbah ieW0aiChubee7I Caet6aikai6aex
coo1du2Re9aika Ohnei5Egoh7leV aiyie6Ahdeipho EiV0aeToeth1da iNgaesu4eeyu0S
Eeb1suoV3naera railai2Vaina8u xu3OhVee1reeyu Og0eavae3oohoh audahneihaeK8a
foo6iechi5Eira oXeixoh6EwuboD we1eiDahNgoh9s ko1Eeju1iedu1z aeP7achiisohr7
phang5caeGei5j ait4Shuo5Aitai no4eis9Tohd8oh Quiet6oTaaQuei Dei2pu2NaefeCa
Shiim9quiuy0ku yiewooph3thieL thu8Aphai1ieDa Phahnahch1Aam1 oocex7Yaith8oo
eraiGaech5ahNg neixa3malif5Ya Eux7chah8ahXix eex1lahXae4Mei uGhahzonu6airu
yah8uWahn3jeiW Yi4ye4Choongie io1Vo3aiQuahpi rie4Rucheet6ae Dohbieyaeleis5
xi1Zaushohbei7 jeeb9EiSiech0u eewo0Oow7ielie aiquooZamah5th kouj7Jaivohx9o
biyeeshesaDi9e she9ooj3zuw6Ah Eit7dei1Yei5la xohN0aeSheipaa Eeg9Phob6neema
eengoneo4saeL4 aeghi4feephu6W eiWash2Vie1mee chieceish5ioPe ool4Hongo7ef1o
jahBe1pui9thou eeV2choohoa4ee Ohmae0eef4ic8I Eet0deiyohdiew Ke9ue5thohzei3
aiyoxeiva8Maih gieRahgh8anahM ve2ath9Eyi5iet quohg6ok3Ahgee theingaech5Nef
```
如果要在密码中包含至少 1 个数字,则可以运行:
```
pwgen 14 1 -n 1
```
输出样例:
```
xoiFush3ceiPhe
```
另外,pwgen 命令还有一些很实用的选项:
* `-c` 或 `--capitalize` 在密码中包含至少一个大写字母
* `-A` 或 `--no-capitalize` 在密码中不包含大写字母
* `-n` 或 `--numerals` 在密码中包含至少一个数字
* `-0` 或 `--no-numerals` 在密码中不包含数字
* `-y` 或 `--symbols` 在密码中包含至少一个特殊字符
* `-s` 或 `--secure` 生成完全随机的密码
* `-B` 或 `--ambiguous` 在密码中不包含难于区分的字母,如 `0` 和 `o`、`1` 和 `l`
* `-h` 或 `--help` 输出帮助信息
* `-H` 或 `--sha1=path/to/file[#seed]` 使用某个给定文件的 sha1 哈希值来作为随机数的生成种子
* `-C` 按列输出生成好的密码
* `-1` 不按列输出生成好的密码
* `-v` 或 `--no-vowels` 不使用任何元音字母,以防止生成下流的词语 ```
若想了解更多信息,请查阅其联机手册:
```
man pwgen
```
### 3. 在 Linux 中使用 GPG 来生成一个高强度密码
GPG (GnuPG 或 GNU Privacy Guard) 是一个自由开源的命令行程序,可以用于替代赛门铁克的 PGP 加密软件。在类 Unix 操作系统、Microsoft Windows 和 Android 中都可以获取到它。
要使用 PGP 生成 1 个长度为 14 个字符的高强度密码,请在终端中运行下面的命令:
```
gpg --gen-random --armor 1 14
```
输出样例:
```
DkmsrUy3klzzbIbavx8=
```
上面的命令将生成一个安全、随机、高强度且基于 base64 编码的密码。
### 4. 在 Linux 中使用 Perl 来生成一个高强度密码
Perl 在大多数 Linux 发行版本的默认软件仓库中都可以获取到,你可以使用相应的包管理器来安装它。
例如在基于 DEB 的系统中,可以运行下面的命令来安装 Perl:
```
sudo apt-get install perl
```
在基于 RPM 的系统中安装 Perl,可以运行:
```
sudo yum install perl
```
在基于 Arch 的系统中,则运行:
```
sudo pacman -S perl
```
一旦 Perl 安装完成,使用下面的命令创建一个文件:
```
vi password.pl
```
接着添加下面的内容到这个文件中:
```
#!/usr/bin/perl
my @alphanumeric = ('a'..'z', 'A'..'Z', 0..9);
my $randpassword = join '', map $alphanumeric[rand @alphanumeric], 0..8;
print "$randpassword\n"
```

保存并关闭该文件。
接着,切换到你刚才保存文件的地方,并运行下面的命令:
```
perl password.pl
```
使用你自己定义的文件名来替换上面命令中的 `password.pl` 。
输出样例:
```
3V4CJJnYd
```

注: 我无法找到这个脚本的原作者,假如你知道作者的名字,请在下面的评论部分让我知晓,我将在这篇指南中添加上该作者的名字。
请注意:对于生成的密码,你必须记住它,或者将它保存到电脑中一个安全的地方。我建议你记住密码并将它从系统中删除,因为这比你的系统被黑客控制要好的多。
伙计们,今天就是这么多了。不久我将带来另一篇有意思的文章。在此之前,敬请继续关注。
---
via: <https://www.ostechnix.com/4-easy-ways-to-generate-a-strong-password-in-linux/>
作者: [SK](https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/) 译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
8,058 | 安卓编年史(14):Android 2.3 Gingerbread——第一次 UI 大变 | http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/14/ | 2016-12-23T08:40:00 | [
"Android",
"安卓编年史"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8058-1.html | 
### Android 2.3 Gingerbread——第一次 UI 大变
Gingerbread(姜饼)发布于 2010 年 12 月,这已是 2.2 发布整整七个月之后了。尽管如此,等待是值得的,因为安卓 2.3 整个系统的每个界面几乎都改变了。这是从安卓 0.9 最初的样式以来第一次重大的更新。2.3 开始了一系列持续的改进,试着将安卓从丑陋的小鸭子变成能承载它自己的合适的样子——从美学角度——来对抗 iPhone。
说到苹果,六个月前,它发布了 iPhone 4 和 iOS 4,新增了多任务处理和 Facetime 视频聊天。微软同样也终于重返这场竞赛。微软在 2010 年 11 月发布了 Windows Phone 7,也进入了智能手机时代。
安卓 2.3 在界面设计上投入了很多精力,但是由于缺乏方向或设计文档,许多应用仅仅止步于获得了一个新的定制主题而已。一些应用用了更扁平的暗色主题,一些用了充满渐变、活泼的暗色主题,其他应用则是高对比度的白色和绿色组合。尽管 2.3 并没有做到风格统一,姜饼还是完成了让系统几乎每个部分变得更现代化的任务。这同样是件好事,因为下一个手机版安卓要在将近一年后才到来。

*Nexus S,第一部三星制造的 Nexus 手机。*
姜饼的首发设备是 Nexus S,谷歌的第二部旗舰设备,并且是第一部由三星生产的 Nexus 设备。尽管今天我们已经习惯了每年都有更新型号的 CPU,那时候可不是这个样子。Nexus S 有个 1GHz Cortex A8 处理器,和 Nexus One是一样的。GPU 从速度来说略微有所变快。Nexus S 稍微比 Nexus One 大一点,拥有 800×480 分辨率的 AMOLED 显示屏。
从参数上来说,Nexus S 看起来只是个平淡无奇的升级,但它确实开了安卓的许多先河。Nexus S 是谷歌第一部没有 MicroSD 卡槽的旗舰,板载 16GB 存储。Nexus One 只有 512MB 存储空间,但它有 MicroSD 卡槽。移除 SD 卡槽为用户简化了存储管理——现在只有一个存储地点了——但是影响了高级用户的扩展能力。它是谷歌第一部带有 NFC 的手机,手机背面的一个特殊芯片能够在和其他 NFC 芯片接触时传输数据。Nexus S 暂时只能读取 NFC 标签,而不能发送数据。
托姜饼中一些升级的福,Nexus S 是第一部不带有硬件十字方向键或轨迹球安卓手机之一。Nexus S 缩减到只有电源、音量以及四个导航键。Nexus S 同时还是如今[疯狂的曲面手机](http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/12/lg-g-flex-review-form-over-even-basic-function/)的先驱,因为三星给 Nexus S 配备了一块略微有些弯曲的玻璃。

*姜饼更改了状态栏和壁纸,并且添加了许多新图标。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
升级过的“Nexus”动态壁纸作为 Nexus S 的独有功能发布。这个壁纸基本上和 Nexus One 的一样,带有带动画轨迹的光点。在 Nexus S 上,去除了方阵设计,取而代之的是波浪形的蓝/灰色背景。底部 dock 有了直角和彩色图标。

*新通知面板和菜单。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
状态栏自 0.9 的首次登场以来终于得到了重制。状态栏从白色渐变变成纯黑,所有图标重绘成了灰色和绿色。所有东西看起来都更加清爽和现代,这要感谢锐角图标的设计和高分辨率。最奇怪的决定可能是从状态栏时钟移除了时间段显示以及信号强度那令人疑惑的灰色。尽管灰色被用在状态栏的许多图标上,而且上面截图有四格灰色信号,安卓实际上指示的是没有信号。绿色格表示信号强度,灰色格指示的是“空”信号格。
姜饼的状态栏图标同时还作为网络连接的状态指示。如果你的设备连接到了谷歌的服务器,图标会变绿,如果没有谷歌的连接,图标会是白色的。这让你可以在外出时轻松了解你的网络连接状态。
通知面板的设计从安卓 1.5 的设计改进而来。我们看到 UI 部分再次从浅色主题变为暗色主题,有个深灰色顶部,黑色背景以及在灰色底色上的黑色文本。
菜单颜色同样变深了,背景从白色变成了带点透明的黑色。菜单图标和背景的对比并没有它应该有的那么强烈,因为灰色图标的颜色和它们在白色背景上的时候是一样的。要求改变颜色意味着每个开发者都得制作新的图标,所以谷歌在黑色背景上使用了先前就有的灰色。这是系统级别的改变,所以这个新菜单会出现在每个应用中。

*姜饼的新键盘,文本选择,边界回弹效果以及新复选框。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
安卓 2.3 最重要的新增功能就是系统全局文本选择界面,你可以在左侧截图的谷歌搜索栏看到它。长按一个词能使其变为橙色高亮,并且出现可拖拽的小标签,长按高亮部分会弹出剪切、复制和粘贴选项。之前的方法使用的是依赖于十字方向键的控制,但现在有了触摸文本选择,Nexus S 不再需要额外的硬件控件。
左侧截图右半边展示的是新的复选框设计和边界回弹效果。冻酸奶(2.2)的复选框像个灯泡——选中时显示一个绿色的勾,未选中的时候显示灰色的勾。姜饼在选项关闭的时候显示一个空的选框——这显得更有意义。姜饼是第一个拥有滚动到底发光效果的版本。当到达列表底部的时候会有一道橙色的光晕,你越往上拉光晕越明显。列表上拉滚动反弹也许最直观,但那是苹果的专利。
 *新拨号界面和对话框设计。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
姜饼里的拨号器受到了稍微多点的照顾。它变得更暗了,并且谷歌终于解决了原本的直角结合的问题,圆角和圆形已经被抛弃了。现在所有的边角都是直角了。所有的拨号按键被替换成了带有奇怪下划线的样式,像是用边角料拼凑的。你永远无法确定是否看到了一个按钮——我们的大脑得想象出按钮形状的剩余部分。
图中的无线网络对话框可以看作是剩下的系统全局性改动的样本。所有的对话框标题从灰色变为黑色,对话框、下拉框以及按钮边缘都变成了直角,各部分色调都变暗了一点。所有的这些全局变化使得姜饼看起来不像原来那样活泼,而是更加地成熟。“到处都是黑色”的外观必然不是最受欢迎的,但它无疑看起来比安卓之前的灰色和米色的配色方案好多了。

*新市场,添加了大块的绿色页面顶栏。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
新版系统带来了“安卓市场 2.0”,虽然它不是姜饼独有的。主要的列表设计和原来一致,但谷歌将屏幕上部三分之一覆盖上了大块的绿色横幅,用来展示热门应用以及导航。这里主要的设计灵感也许是绿色的安卓吉祥物——它们的颜色完美匹配。在系统设计偏向暗色系的时候,霓虹灯般的绿色横幅和白色列表让市场明快得多。
但是,相同的绿色背景图片被用在了不同的手机上,这意味着在低分辨率设备上,绿色横幅看起来更加的大。不少用户抱怨这浪费了屏幕空间,于是随后的更新使得绿色横幅跟随内容向上滚动。在那时,横屏模式更加糟糕——绿色横幅会填满剩下的半个屏幕。

*市场的一个带有可折叠描述的应用详情页面,“我的应用”界面,以及 Google Books 界面截图。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
应用详情页面经过重新设计有了可折叠部分。文本描述只截取前几行展示,向下滑动页面不用再穿过数千行的描述。简短的描述后有一个“更多”按钮可供点击来显示完整的描述。这让用户可以轻松地滑动过列表找到像是截图和“联系开发者”部分,这些部分通常在页面偏下部分。
安卓主屏的其它部分明智地淡化了绿色机器人元素。市场应用的剩余部分绝大多数仅仅只是旧版市场加上新的绿色导航元素。旧有的标签界面升级成了可滑动切换标签。在姜饼右侧截图中,从右向左滑动将会从“热门付费”切换至“热门免费”,这使得导航变得更加方便。
姜饼带来了将会成为 Google Play 内容商店第一位成员的应用:Google Books。这个应用是个基础的电子书阅读器,会将书籍以简单的预览图平铺展示。屏幕顶部的“获取 eBooks”链接会打开浏览器,然后加载一个你可以在上面购买电子书的移动网站。
Google Books 以及市场的“我的应用”页面都是 Action Bar 的早期原型。就像现在的指南中写的,页面有一个带应用图标的固定置顶栏,应用内页面的名称,以及一些控件。这两个应用的布局实际上看起来十分现代,和现在的界面相似。

*新版谷歌地图。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
谷歌地图(再重复一次,这时候的谷歌地图是在安卓市场中的,并且不是这个安卓版本独占的)拥有了另一个操作栏原型,这是一个顶部对齐的控件栏。这个早期版本的操作栏拥有许多试验性功能。功能栏主要被一个搜索框所占据,但是你永远无法向其输入内容。点击搜索框会打开安卓 1.x 版本以来的旧搜索界面,它带有完全不同的操作栏设计体验和活泼的按钮。2.3 版本的顶栏仅仅只是个大号的搜索按钮而已。

*从黑变白的新 business 页面。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
在应用抽屉里和“地点”一起到来的“热门商家”重新设计了界面。不像姜饼的其它部分,它从黑色转换成了白色。谷歌还给它保留了圆角的旧按钮。这个新版本的地图能显示商家的营业时间,并且提供高级搜索选项,比如正在营业或是通过评分或价格限定搜索范围。点评被调整到了商家详情页面,用户可以更容易地对当前商家有个直观感受。而且现在还可以从搜索结果中给某个地点加星,保存起来以后使用。

*新 YouTube 设计,神奇的是有点像旧版地图的商家页面的设计。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
YouTube 应用似乎完全与安卓的其它部分分离开来,就像是设计它的人完全不知道姜饼最终会是什么样子一样。高亮是红色和灰色方案,而不是绿色和橙色,而且不像扁平黑色风格的姜饼,Youtube 有着气泡状的,带有圆角并且大幅使用渐变效果的按钮、标签以及操作栏。尽管如此,新应用还是有一些正确的地方。所有的标签可以水平滑动切换,而且应用终于提供了竖屏观看视频模式。安卓在那个阶段似乎工作不是很一致。就像是有人告诉 Youtube 团队“把它做成黑色的”,然后这就是全部的指导方向一样。唯一一个与其相似的安卓实体就是旧版谷歌地图的商家页面的设计。
尽管有些奇怪的设计,Youtube 应用有着最接近操作栏的顶栏设计。除了顶部操作栏的应用图标和一些按钮,最右侧还有个标着“更多”字样的按钮,点击它可以打开因为过多而无法装进操作栏的选项。在今天,这被称作“更多操作”按钮,它是个标准界面控件。

*新 Google Talk,支持语音和视频通话,以及新语音命令界面。 [Ron Amadeo 供图]*
姜饼的最后一个更新是安卓 2.3.4,它带来了新版 Google Talk。不像 Nexus One,Nexus S 带有前置摄像头——重新设计的 Google Talk 拥有语音和视频通话功能。好友列表右侧的彩色指示不仅指明在线状态,还显示了语音和视频的可用性。一个点表示仅支持文本信息,一个麦克风表示支持文本信息或语音,一个摄像机表示支持文本信息、语音以及视频。如果可用的话,点击语音或视频图标会立即向好友发起通话。
姜饼是谷歌仍然提供支持的最老的安卓版本。激活一部姜饼设备并放置一会儿会收到大量更新。姜饼会拉取 Google Play 服务,它会带来许多新的 API 支持,并且会升级到最新版本的 Play 商店。打开 Play 商店并点击更新按钮,几乎每个独立谷歌应用都会被替换为更加现代的版本。我们尝试着保持这篇文章讲述的是姜饼发布时的样子,但时至今日还停留在姜饼的用户会被认为有点跟不上时代了。
姜饼如今仍然能够得到支持,因为有数量可观的用户仍然在使用这个有点过时的系统。姜饼仍然存在的意义来自于它极低的系统要求,使得它成为了低端廉价设备的最佳选择。下个版本的安卓对硬件的要求变得更高了。举个例子,安卓 3.0 蜂巢不是开源的,这意味着它只能在谷歌的协助之下移植到一个设备上。同时它还是只为平板设计的,这让姜饼在相当长的一段时间都是最新的手机安卓版本。4.0 冰淇淋三明治是下一个手机版本,但它显著地提高了安卓系统要求,抛弃了低端市场。谷歌现在希望借 4.4 KitKat(奇巧巧克力)重回廉价手机市场,它的系统要求降回了 512MB 内存。时间的推移同样有所帮助——如今,就算是廉价的系统级芯片都能满足安卓 4.0 时代的系统要求。
---

[Ron Amadeo](http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo) / Ron是Ars Technica的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。 [@RonAmadeo](https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo)
---
via: <http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2016/10/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/14/>
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,059 | Webpack 2 入门 | https://blog.madewithenvy.com/getting-started-with-webpack-2-ed2b86c68783#.oozfpppao | 2016-12-23T11:07:00 | [
"Webpack"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8059-1.html | 
Webpack 2 [一旦文档完成](https://github.com/webpack/webpack/issues/1545#issuecomment-255446425),就将结束 Beta 测试期。不过这并不意味着你现在不能开始使用第 2 版,前提是你知道怎么配置它。(LCTT 译注:Webpack 2.1 已经发布。)
### Webpack 是什么
简单来说,Webpack 是一个 JavaScript 模块打包器。然而,自从它发布以来,它发展成为了你所有的前端代码的管理工具(或许是有意的,或许是社区的意愿)。

*老式的任务运行器的方式:你的标记、样式和 JavaScript 是分离的。你必须分别管理它们每一个,并且你需要确保每一样都达到产品级*
<ruby> 任务运行器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> task runner </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,例如 Gulp,可以处理许多不同的<ruby> 预处理器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> preprocesser </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和<ruby> 转换器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> transpiler </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,但是在所有的情景下,它都需要一个输入源并将其压缩到一个编译好的输出文件中。然而,它是在每个部分的基础上这样做的,而没有考虑到整个系统。这就造成了开发者的负担:找到任务运行器所不能处理的地方,并找到适当的方式将所有这些模块在生产环境中联合在一起。
Webpack 试图通过提出一个大胆的想法来减轻开发者的负担:如果有一部分开发过程可以自动处理依赖关系会怎样?如果我们可以简单地写代码,让构建过程最终只根据需求管理自己会怎样?

*Webpack 的方式:如果 Webpack 了解依赖关系,它会仅捆绑我们在生产环境中实际需要的部分*
如果你过去几年一直参与 web 社区,你已经知道解决问题的首选方法:使用 JavaScript 来构建。而且 Webpack 尝试通过 JavaScript 传递依赖关系使得构建过程更加容易。不过这个设计真正的亮点不是简化代码管理部分,而是管理层由 100% 有效的 JavaScript 实现(具有 Nodejs 特性)。Webpack 能够让你编写有效的 JavaScript,更好更全面地了解系统。
换句话来说:你不需要为 Webpack 写代码。你只需要写项目代码。而且 Webpack 就会持续工作(当然需要一些配置)。
简而言之,如果你曾经遇到过以下任何一种情况:
* 载入有问题的依赖项
* 意外引入一些你不需要在生产中用上的 CSS 样式表和 JS 库,使项目膨胀
* 意外的两次载入(或三次)库
* 遇到作用域的问题 —— CSS 和 JavaScript 都会有
* 寻找一个让你在 JavaScript 中使用 Node/Bower 模块的构建系统,要么就得依靠一个令人发狂的后端配置才能正确地使用这些模块
* 需要优化<ruby> 资产 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> asset </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>交付,但你担心会弄坏一些东西
等等……
那么你可以从 Webpack 中收益了。它通过让 JavaScript 轻松处理你的依赖关系和加载顺序,而不是通过开发者的大脑。最好的部分是,Webpack 甚至可以纯粹在服务器端运行,这意味着你还可以使用 Webpack 构建[渐进增强式](https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2009/04/progressive-enhancement-what-it-is-and-how-to-use-it/)网站。
### 第一步
我们将在本教程中使用 [Yarn](https://yarnpkg.com/)(运行命令 `brew install yarn`) 代替 `npm`,不过这完全取决于你的喜好,它们做同样的事情。在我们的项目文件夹中,我们将在终端窗口中运行以下代码,将 Webpack 2 添加到我们的全局软件包以及本地项目中:
```
yarn global add [email protected] [email protected]
yarn add --dev [email protected] [email protected]
```
我们接着会通过项目根目录的一个 `webpack.config.js` 文件来声明 webpack 的配置:
```
'use strict';
const webpack = require('webpack');
module.exports = {
context: __dirname + '/src',
entry: {
app: './app.js',
},
output: {
path: __dirname + '/dist',
filename: '[name].bundle.js',
},
};
```
注意:此处 `__dirname` 是指你的项目根目录
记住,Webpack “知道”你的项目发生了什么。它通过阅读你的代码来实现(别担心,它签署了保密协议 :D )。Webpack 基本上执行以下操作:
1. 从 `context` 文件夹开始……
2. ……它查找 `entry` 下的文件名……
3. ……并读取其内容。每一个 `import`([ES6](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/import))或 `require()`(Nodejs)的依赖会在它解析代码的时候找到,它会在最终构建的时候打包这些依赖项。然后,它会搜索那些依赖项以及那些依赖项所依赖的依赖项,直到它到达“树”的最底端 —— 只打包它所需要的,没有其它东西。
4. Webpack 从 `context` 文件夹打包所有东西到 `output.path` 文件夹,使用 `output.filename` 命名模板来为其命名(其中 `[name]` 被替换成来自 `entry` 的对象的键)。
所以如果我们的 `src/app.js` 文件看起来像这样(假设我们事先运行了 `yarn add --dev moment`):
```
'use strict';
import moment from 'moment';
var rightNow = moment().format('MMMM Do YYYY, h:mm:ss a');
console.log( rightNow );
// "October 23rd 2016, 9:30:24 pm"
```
我们应该运行:
```
webpack -p
```
注意:`p` 标志表示“生产”模式,这会压缩输出文件。
它会输出一个 `dist/app.bundle.js`,并将当前日期和时间打印到控制台。要注意 Webpack 会自动识别 上面的 `'moment'` 指代的是什么(比如说,虽然如果你有一个 `moment.js` 文件在你的目录,默认情况下 Webpack 会优先考虑你的 `moment` Node 模块)。
### 使用多个文件
你可以通过仅仅修改 `entry` 对象来指定任意数量的<ruby> 入口 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> entry </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>/<ruby> 输出点 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> output </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。
#### 打包多个文件
```
'use strict';
const webpack = require("webpack");
module.exports = {
context: __dirname + "/src",
entry: {
app: ["./home.js", "./events.js", "./vendor.js"],
},
output: {
path: __dirname + "/dist",
filename: "[name].bundle.js",
},
};
```
所有文件都会按照数组的顺序一起被打包成一个 `dist/app.bundle.js` 文件。
#### 输出多个文件
```
const webpack = require("webpack");
module.exports = {
context: __dirname + "/src",
entry: {
home: "./home.js",
events: "./events.js",
contact: "./contact.js",
},
output: {
path: __dirname + "/dist",
filename: "[name].bundle.js",
},
};
```
或者,你可以选择打包成多个 JS 文件以便于分割应用的某些模块。这将被打包成 3 个文件:`dist/home.bundle.js`,`dist/events.bundle.js` 和 `dist/contact.bundle.js`。
#### 高级打包自动化
如果你将你的应用分割成多个 `output` 输出项(如果你的应用的一部分有大量你不需要预加载的 JS,这会很有用),你可能会重用这些文件的代码,因为它将分别解析每个依赖关系。幸运的是,Webpack 有一个内置的 `CommonsChunk` 插件来处理这个:
```
module.exports = {
// …
plugins: [
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: "commons",
filename: "commons.bundle.js",
minChunks: 2,
}),
],
// …
};
```
现在,在你的 `output` 文件中,如果你有任何模块被加载 2 次以上(通过 `minChunks` 设置),它会把那个模块打包到 `common.js` 文件中,然后你可以将其缓存在客户端。这将生成一个额外的请求头,但是你防止了客户端多次下载同一个库。因此,在很多情景下,这会大大提升速度。
### 开发
Webpack 实际上有自己的开发服务器,所以无论你是开发一个静态网站还是只是你的网站前端原型,它都是无可挑剔的。要运行那个服务器,只需要添加一个 `devServer` 对象到 `webpack.config.js`:
```
module.exports = {
context: __dirname + "/src",
entry: {
app: "./app.js",
},
output: {
filename: "[name].bundle.js",
path: __dirname + "/dist/assets",
publicPath: "/assets", // New
},
devServer: {
contentBase: __dirname + "/src", // New
},
};
```
现在创建一个包含以下代码的 `src/index.html` 文件:
```
<script src="/assets/app.bundle.js"></script>
```
……在你的终端中运行:
```
webpack-dev-server
```
你的服务器现在运行在 `localhost:8080`。注意 `script` 标签里面的 `/assets` 是怎么匹配到 `output.publicPath` 的 —— 你可以随意更改它的名称(如果你需要一个 CDN 的时候这会很有用)。
Webpack 会热加载所有 JavaScript 更改,而不需要刷新你的浏览器。但是,所有 `webpack.config.js` 文件里面的更改都需要重新启动服务器才能生效。
### 全局访问方法
需要在全局空间使用你的函数?在 `webpack.config.js` 里面简单地设置 `output.library`:
```
module.exports = {
output: {
library: 'myClassName',
}
};
```
……这会将你打包好的文件附加到一个 `window.myClassName` 实例。因此,使用该命名空间,你可以调用入口文件的可用方法(可以在[该文档](https://webpack.js.org/concepts/output/#output-library)中阅读有关此设置的更多信息)。
### 加载器
到目前为止,我们所做的一切只涉及 JavaScript。从一开始就使用 JavaScript 是重要的,因为它是 Webpack 唯一支持的语言。事实上我们可以处理几乎所有文件类型,只要我们将其转换成 JavaScript。我们用<ruby> 加载器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> loader </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>来实现这个功能。
加载器可以是 Sass 这样的预处理器,或者是 Babel 这样的转译器。在 NPM 上,它们通常被命名为 `*-loader`,例如 `sass-loader` 和 `babel-loader`。
#### Babel 和 ES6
如果我们想在项目中通过 [Babel](https://babeljs.io/) 来使用 ES6,我们首先需要在本地安装合适的加载器:
```
yarn add --dev babel-loader babel-core babel-preset-es2015
```
然后将它添加到 `webpack.config.js`,让 Webpack 知道在哪里使用它。
```
module.exports = {
// …
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
use: [{
loader: "babel-loader",
options: { presets: ["es2015"] }
}],
},
// Loaders for other file types can go here
],
},
// …
};
```
Webpack 1 的用户注意:加载器的核心概念没有任何改变,但是语法改进了。直到官方文档完成之前,这可能不是确切的首选语法。
`/\.js$/` 这个正则表达式查找所有以 `.js` 结尾的待通过 Babel 加载的文件。Webpack 依靠正则检查给予你完全的控制权 —— 它不限制你的文件扩展名或者假定你的代码必须以某种方式组织。例如:也许你的 `/my_legacy_code/` 文件夹下的内容不是用 ES6 写的,所以你可以修改上述的 `test` 为 `/^((?!my_legacy_folder).)\.js$/`,这将会排除那个特定的文件夹,不过会用 Babel 处理其余的文件。
#### CSS 和 Style 加载器
如果我们只想为我们的应用所需加载 CSS,我们也可以这样做。假设我们有一个 `index.js` 文件,我们将从那里引入:
```
import styles from './assets/stylesheets/application.css';
```
我们会得到以下错误:`你可能需要一个合适的加载器来处理这种类型的文件`。记住,Webpack 只能识别 JavaScript,所以我们必须安装合适的加载器:
```
yarn add --dev css-loader style-loader
```
然后添加一条规则到 `webpack.config.js`:
```
module.exports = {
// …
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: ["style-loader", "css-loader"],
},
// …
],
},
};
```
加载器以数组的逆序处理。这意味着 `css-loader` 会比 `style-loader` 先执行。
你可能会注意到,即使在生产版本中,这实际上是将你的 CSS 和 JavaScript 打包在一起,`style-loader` 手动将你的样式写到 `<head>`。乍一看,它可能看起来有点怪异,但你仔细想想就会发现这就慢慢开始变得更加有意义了。你已经节省了一个头部请求 —— 节省了一些连接上的时间。如果你用 JavaScript 来加载你的 DOM,无论如何,这从本质上消除了 [FOUC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flash_of_unstyled_content)。
你还会注意到一个开箱即用的特性 —— Webpack 已经通过将这些文件打包在一起以自动解决你所有的 `@import` 查询(而不是依靠 CSS 默认的 import 方式,这会导致无谓的头部请求以及资源加载缓慢)。
从你的 JS 加载 CSS 是非常惊人的,因为你现在可以用一种新的强大的方式将你的 CSS 模块化。比如说你要只通过 `button.js` 来加载 `button.css`,这将意味着如果 `button.js` 从来没有真正使用过的话,它的 CSS 就不会膨胀我们的生产版本。如果你坚持面向组件的 CSS 实践,如 SMACSS 或 BEM,你会看到更紧密地结合你的 CSS 和你的标记和 JavaScript 的价值。
#### CSS 和 Node 模块
我们可以使用 Webpack 来利用 Node.js 使用 `~` 前缀导入 Node 模块的优势。如果我们运行 `yarn add normalize.css`,我们可以使用:
```
@import "~normalize.css";
```
……并且充分利用 NPM 来管理我们的第三方样式 —— 版本控制、没有任何副本和粘贴的部分。此外,让 Webpack 为我们打包 CSS 比起使用 CSS 的默认导入方式有明显的优势 —— 节省无谓的头部请求和加载时间。
更新:这一节和下面一节已经更新为准确的用法,不再使用 CSS 模块简单地导入 Node 的模块。感谢 [Albert Fernández](https://medium.com/u/901a038e32e5) 的帮助!
#### CSS 模块
你可能听说过 [CSS 模块](https://github.com/css-modules/css-modules),它把 CSS 变成了 SS,消除了 CSS 的<ruby> 层叠性 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Cascading </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。通常它的最适用场景是只有当你使用 JavaScript 构建 DOM 的时候,但实质上,它神奇地将你的 CSS 类放置到加载它的 JavaScript 文件里([在这里了解更多](https://github.com/css-modules/css-modules))。如果你打算使用它,CSS 模块已经与 `css-loader` 封装在一起(`yarn add --dev css-loader`):
```
module.exports = {
// …
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
"style-loader",
{ loader: "css-loader", options: { modules: true } }
],
},
// …
],
},
};
```
注意:对于 `css-loader`,我们现在使用<ruby> 扩展对象语法 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> expanded object syntax </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>来给它传递一个选项。你可以使用一个更为精简的字符串来取代默认选项,正如我们仍然使用了 `style-loader`。
---
值得注意的是,当允许导入 CSS 模块的时候(例如:`@import 'normalize.css';`),你完全可以删除掉 `~`。但是,当你 `@import` 你自己的 CSS 的时候,你可能会遇到构建错误。如果你遇到“无法找到 \_\_\_\_”的错误,尝试添加一个 `resolve` 对象到 `webpack.config.js`,让 Webpack 更好地理解你的模块加载顺序。
```
const path = require("path");
module.exports = {
//…
resolve: {
modules: [path.resolve(__dirname, "src"), "node_modules"]
},
};
```
我们首先指定源目录,然后指定 `node_modules`。这样,Webpack 会更好地处理解析,按照既定的顺序(分别用你的源目录和 Node 模块的目录替换 `"src"` 和 `"node_modules"`),首先查找我们的源目录,然后再查找已安装的 Node 模块。
#### Sass
需要使用 Sass?没问题。安装:
```
yarn add --dev sass-loader node-sass
```
并添加新的规则:
```
module.exports = {
// …
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(sass|scss)$/,
use: [
"style-loader",
"css-loader",
"sass-loader",
]
}
// …
],
},
};
```
然后当你的 Javascript 对一个 `.scss` 或 `.sass` 文件调用 `import` 方法的时候,Webpack 会处理的。
#### CSS 独立打包
或许你在处理渐进增强的问题;或许你因为其它原因需要一个单独的 CSS 文件。我们可以通过在我们的配置中用 `extract-text-webpack-plugin` 替换 `style-loader` 而轻易地做到这一点,这不需要更改任何代码。以我们的 `app.js` 文件为例:
```
import styles from './assets/stylesheets/application.css';
```
让我们安装这个插件到本地(我们需要 2016 年 10 月的测试版本):
```
yarn add --dev [email protected]
```
并且添加到 `webpack.config.js`:
```
const ExtractTextPlugin = require("extract-text-webpack-plugin");
module.exports = {
// …
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
ExtractTextPlugin.extract("css"),
{ loader: "css-loader", options: { modules: true } },
],
},
// …
]
},
plugins: [
new ExtractTextPlugin({
filename: "[name].bundle.css",
allChunks: true,
}),
],
};
```
现在当运行 `webpack -p` 的时候,你的 `output` 目录还会有一个 `app.bundle.css` 文件。只需要像往常一样简单地在你的 HTML 中向该文件添加一个 `<link>` 标签即可。
#### HTML
正如你可能已经猜到,Webpack 还有一个 `[html-loader][6]` 插件。但是,当我们用 JavaScript 加载 HTML 时,我们针对不同的场景分成了不同的方法,我无法想出一个单一的例子来为你计划下一步做什么。通常,你需要加载 HTML 以便于在更大的系统(如 [React](https://facebook.github.io/react/)、[Angular](https://angularjs.org/)、[Vue](http://vuejs.org/) 或 [Ember](http://emberjs.com/))中使用 JavaScript 风格的标记,如 [JSX](https://jsx.github.io/)、[Mustache](https://github.com/janl/mustache.js/) 或 [Handlebars](http://handlebarsjs.com/)。或者你可以使用类似 [Pug](https://github.com/pugjs/pug-loader) (以前叫 Jade)或 [Haml](https://github.com/AlexanderPavlenko/haml-loader) 这样的 HTML 预处理器,抑或你可以直接把同样的 HTML 从你的源代码目录推送到你的构建目录。你怎么做都行。
教程到此为止了:你可以用 Webpack 加载标记,但是进展到这一步的时候,关于你的架构,你将做出自己的决定,我和 Webpack 都无法左右你。不过参考以上的例子以及搜索 NPM 上适用的加载器应该足够你发展下去了。
### 从模块的角度思考
为了充分使用 Webpack,你必须从模块的角度来思考:细粒度的、可复用的、用于高效处理每一件事的独立的处理程序。这意味着采取这样的方式:
```
└── js/
└── application.js // 300KB of spaghetti code
```
将其转变成这样:
```
└── js/
├── components/
│ ├── button.js
│ ├── calendar.js
│ ├── comment.js
│ ├── modal.js
│ ├── tab.js
│ ├── timer.js
│ ├── video.js
│ └── wysiwyg.js
│
└── application.js // ~ 1KB of code; imports from ./components/
```
结果呈现了整洁的、可复用的代码。每一个独立的组件通过 `import` 来引入自身的依赖,并 `export` 它想要暴露给其它模块的部分。结合 Babel 和 ES6,你可以利用 [JavaScript 类](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Classes) 来实现更强大的模块化,而不用考虑它的工作原理。
有关模块的更多信息,请参阅 Preethi Kasreddy [这篇优秀的文章](https://medium.freecodecamp.com/javascript-modules-a-beginner-s-guide-783f7d7a5fcc)。
---
### 延伸阅读
* [Webpack 2 的新特性](https://gist.github.com/sokra/27b24881210b56bbaff7)
* [Webpack 配置文档](https://webpack.js.org/configuration/)
* [Webpack 范例](https://github.com/webpack/webpack/tree/master/examples)
* [React + Webpack 入门套件](https://github.com/kriasoft/react-starter-kit)
* [怎么使用 Webpack](https://github.com/petehunt/webpack-howto)
---
via: <https://blog.madewithenvy.com/getting-started-with-webpack-2-ed2b86c68783#.oozfpppao>
作者:[Drew Powers](https://blog.madewithenvy.com/@an_ennui) 译者:[OneNewLife](https://github.com/OneNewLife) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,060 | 如何在 Debian 和 Ubuntu 系统上自动安装安全更新 | http://www.tecmint.com/auto-install-security-updates-on-debian-and-ubuntu | 2016-12-24T19:13:00 | [
"更新",
"自动更新"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8060-1.html | 之前已经说过,一些最优秀的系统管理员看上去(注意这里使用的词是 seem(看上去))总是很“懒”的,这句话我再同意不过了。

虽然这句话听起来有点荒谬,但我敢打赌在大多数情况下它是对的-不是因为他们不去做他们原本应该做的事情,而是因为他们已经让系统自动去完成这样的事情了。
对于 Linux 系统来说,一个最关键的需求是为相应的 Linux 版本保持更新最新的安全补丁。
在这篇文章中,我们将讨论如何在 Debian 和 Ubuntu 系统上进行设置,从而实现自动安装或更新重要的安装包或补丁。
其他的 Linux 版本:[CentOS/RHEL 配置自动安装安全更新](/article-8015-1.html)。
不必多说,为了执行这篇文章中所讲到的任务,你需要有超级用户特权。
### 在 Debian/Ubuntu 上配置自动安全更新
首先,安装下面这些安装包:
```
# aptitude update -y && aptitude install unattended-upgrades apt-listchanges -y
```
`apt-listchanges` 将会通知你在升级过程中发生的改变。
接下来,用你最喜欢的文本编辑器打开 `/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/50unattended-upgrades`,然后在 `Unattended-Upgrade::Origins-Pattern` 块中间加入下面这行内容:
```
Unattended-Upgrade::Mail "root";
```
最后,执行下面的命令来生成所需的配置文件(`/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/20auto-upgrades`),从而激活自动更新:
```
# dpkg-reconfigure -plow unattended-upgrades
```
当提示安装自动升级时,选择 'Yes':

*在 Debian 上配置自动安装更新*
然后检查下面这两行是否已经加入到文件 `/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/20auto-upgrades` 中了:
```
APT::Periodic::Update-Package-Lists "1";
APT::Periodic::Unattended-Upgrade "1";
```
增加下面这行内容使通知更加详细:
```
APT::Periodic::Verbose "2";
```
最后,检查 `/etc/apt/listchanges.conf` 来确保通知能被发送给 root 用户。

*在 Debian 系统上提示安全更新*
在这篇文章中,我们讨论了如何确保你的系统定期更新最新的安全补丁。另外,你也学习了如何设置提示,从而确保应用了新的补丁时你能够被通知到。
你有任何关于这篇文章的问题吗?你可以在下面的评论栏留下你的问题。我们期待收到你的回复。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/auto-install-security-updates-on-debian-and-ubuntu>
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa](http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,061 | 为你的 Linux 服务器加把锁 | https://medium.com/linode-cube/locking-down-your-linux-server-24d8516ae374#.qy8qq4bx2 | 2016-12-25T14:49:15 | [
"安全",
"防火墙",
"FirewallD",
"UFW",
"iptables"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8061-1.html | 
>
> 无论你使用的哪种 Linux 发行版,你都需要使用基于 iptables 的防火墙来保护它。
>
>
>
啊哈!你已经设置好了你的第一台 Linux 服务器并且已经准备发车了!是么?嗯,慢着。
默认情况下,你的 Linux 系统对攻击者来说并非是足够安全的。当然,它比 Windows XP 要安全多了,但这说明不了什么。
想要使你的 Linux 系统真正稳固,你需要按照 [Linode](https://www.linode.com/) 的 [服务器安全指南](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/securing-your-server) 来操作。
总的来说,**首先你必须**关闭那些你不需要的服务。当然要这样做的话,你先要知道你正在使用哪些网络服务。
你可以使用 shell 命令来找到是哪些服务:
```
netstat -tulpn
```
[netstat](http://www.faqs.org/docs/linux_network/x-087-2-iface.netstat.html) 将会告诉你正在运行哪些服务和这些服务正在使用的端口是什么。如果你不需要其中的某项服务或端口,你就应该关闭它。例如,除非你正在运行一个网站,否则你是不需要运行中的 [Apache](https://httpd.apache.org/) 或 [Nginx](https://www.nginx.com/) 服务器,也不需要开启 80 或 8080 端口。
总之一句话,不确定的话,就关了它先。
在一个最简单的,没有做过任何额外更改的 Linux 服务器上,你会看到 [SSH](https://www.linode.com/docs/tools-reference/ssh/)、 [RPC](http://www.linux.org/threads/tcp-ip-service-remote-procedure-call-rpc.4913/) 和 [NTPdate](https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/NTP.html) 运行在它们的公开端口上。不要添加像 [telnet](http://www.telnet.org/htm/faq.htm) 这样陈旧而不安全的 shell 程序,否则老司机就会在你不经意间将你的 Linux 小跑车开走了。也许,在上世纪 80 年代的时候你喜欢把 telnet 当作你 SunOS 机器上的备份登录方式,但是那早已成为了过去。
就 SSH 来说,你应该使用 [RSA 密钥](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/securing-your-server/#create-an-authentication-key-pair) 和 [Fail2Ban](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/securing-your-server/#use-fail2ban-for-ssh-login-protection) 来加固。除非你需要 RPC,否则就卸载它——如果你不知道需要不需要它的话,那就是不需要。
关于如何关门已经说的够多了;让我们来聊聊利用 iptables 来锁定进来的流量吧。
当你启动 Linux 服务器的时候它是没有任何规则的。这就意味着所有的流量都是被允许的。这当然是**不好的**。因此,你需要及时的设置你的防火墙。
Iptables 是一种用来给 [netfilter](https://www.netfilter.org/) 设置网络策略规则的 shell 工具,netfilter 是Linux 系统下的默认防火墙,它利用一组规则来允许或禁止流量。当有人尝试连接上你的系统——有些人无时不刻地尝试这么干,而且从不气馁——iptables 就会检查这些请求是否与规则列表相匹配。如果没有匹配到任何的规则,它就会采取默认操作。
这个默认操作应该是将连接“Drop”掉,即禁掉这些意图闯入者。而且这不会让他们知道这些网络探测行为发生了什么。(你也可以将链接“Reject”掉,但是这会同时让他们知道你有一个正在运行的 Linux 防火墙。就目前而言,让陌生人能获取到我们系统的信息越少越好。至少,我是这么认为的。)
现在,你可以用 iptables 来设置你的防火墙了。我已经这么做了。就像以前,我骑着自行车去六英里外上班,并且两边都是上坡。而现在,我开车去。
这其实比喻的是我使用 Fedora 发行版的 [FirewallD](http://www.firewalld.org/) 和 Debian 系发行版的 [UFW](https://help.ubuntu.com/community/UFW)(Uncomplicated Firewall)。这些都是易用的 iptables 的 shell 前端。你可以在以下的 Linode 指南中找到适合的使用方式:[FirewallD](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/firewalls/introduction-to-firewalld-on-centos) 和 [UFW](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/firewalls/configure-firewall-with-ufw)。
从本质上来说设置这些规则就是在你的服务器上放置“非请勿入”的告示牌。用起来吧。
但是也别太兴奋地把所有的链接都关闭了。例如:
```
sudo ufw default deny incoming
```
看起来是个好主意哦。别忘了,它禁止了所有链接,包括你自己哦!
很好,它就是这么干的。这意味着它也同样禁止了 SSH 的登录。也就是说你再也不能登录你那新服务器了。哇哦!
不过,如果你犯了错,错误的将更多的链接都禁止了。你看,老司机也同样被你挡在门外了。
或者,更准确得说,这不是你或你的服务器所遇到的个别现象。当然,你也不是[每天受到 3 亿多次攻击尝试的美国国家安全局(NSA)](http://thehackernews.com/2016/02/nsa-utah-data-center.html)。但是攻击脚本根本不在乎你是谁。它只是不断的检查寻找网络中存在已知漏洞的服务器。在平常的一天中我自己的小服务器就会受到数以百计的攻击。
都这样了,你还在等什么呢?去吧,加固你的网络服务吧。安装 FirewallD 或者 UFW 来加固你的服务器吧。你会愿意去做的。
---
关于作者:
Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols 是一位资深的 IT 专栏作家,他的作品出现在许多行业领袖媒体上,包括 ZDNet.com、PC Magazine、InfoWorld、ComputerWorld、Linux Today 和 eWEEK 等。Steven 在 IT 专业方面的见解犀利,虽然他的观点和云计算方面的认识,并不代表 Linode 观点,但是我们仍然非常感谢他的贡献。你可以在 Twitter 上关注他 (@sjvn)。
---
via: <https://medium.com/linode-cube/locking-down-your-linux-server-24d8516ae374#.qy8qq4bx2>
作者:[Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols](https://medium.com/linode-cube/locking-down-your-linux-server-24d8516ae374#.qy8qq4bx2) 译者:[wcnnbdk1](https://github.com/wcnnbdk1) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # Locking Down Your Linux Server
## By: Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols
*No matter what your Linux, you need to protect it with an iptables-based firewall.*
Yes! You’ve just set up your first Linux server and you’re ready to rock and roll! Right? Uh, no.
By default, your Linux box is not secure against attackers. Oh sure, it’s more secure than Windows XP, but that’s not saying much.
To really nail down your Linux system you need to follow the instructions in [Linode](https://www.linode.com/)’s [Securing your Server](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/securing-your-server) guide.
To summarize, you must — first — turn off the services you don’t need. Of course to do that, you need to know what network services you’re running in the first place.
You can find out what those are with the shell command:
*netstat -tulpn*
[ Netstat](http://www.faqs.org/docs/linux_network/x-087-2-iface.netstat.html) will tell you what services you’re running and what ports they’re using. If you don’t need a particular service or port, you should turn it off. For example, unless you’re running a website, you don’t need to be running the
[Apache](https://httpd.apache.org/)or
[Nginx](https://www.nginx.com/)web servers or have the 80 or 8080 ports open.
In short, when in doubt, turn it off or close it down.
On a plain vanilla Linux server, with nothing extra, you’ll see [SSH](https://www.linode.com/docs/tools-reference/ssh/), [RPC](http://www.linux.org/threads/tcp-ip-service-remote-procedure-call-rpc.4913/), and [NTPdate](https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/NTP.html) up and running with open ports. Do not add such old and insecure shell programs as [telnet](http://www.telnet.org/htm/faq.htm) or the hackers will rise up and slap your server right out of your control. Yeah, maybe you loved telnet back on your SunOS box in the 80s, but that was then and this is now.
As for SSH, be sure to lock it down with [RSA keys](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/securing-your-server/#create-an-authentication-key-pair) and [Fail2Ban](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/securing-your-server/#use-fail2ban-for-ssh-login-protection). Unless you need RPC — and if you need it, you’ll know — go ahead and uninstall it.
So much for closing your doors; let’s talk about using iptables to lock them from intruders.
When you start your Linux server it has no — nada — rules. That means all traffic is allowed. This is NOT GOOD. So, you need to setup your firewall … as soon as possible!
Iptables is a shell utility that sets network rule policies for [netfilter](https://www.netfilter.org/), Linux’s default firewall, using a set of rules to allow or block traffic. When someone tries to connect with your system — and someone will every day, without fail — iptables looks to match the request with its rules list. If it can’t find a match, it will resort to whatever the default action is.
That action should be to “Drop” the connection, which will block those outsiders wanting in. But it won’t let them know what happened to their attempts to knock on your server’s network door. (You could also “Reject” the connection, but that let’s them know you have a Linux firewall up and running. These days, the less information a stranger has about my system, the better. At least, that’s my philosophy.)
Now, you could set up your firewall with *just* iptables. I’ve done it. But then, I used to ride a bike to work six miles away, uphill both directions. These days, I drive.
That means I use [FirewallD](http://www.firewalld.org/) for the Fedora distributions and [UFW](https://help.ubuntu.com/community/UFW) [Uncomplicated Firewall] for the Debian family. These are easy-to-use, shell front-ends to iptables. For the finer details on how use either, see these Linode guides: [FirewallD](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/firewalls/introduction-to-firewalld-on-centos) and [UFW](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/firewalls/configure-firewall-with-ufw).
Both come with default rule sets that, in essence, put up “No Trespassing” signs around your server. Use them.
But don’t get too excited about shutting down all your connections. For example:
*sudo ufw default deny incoming*
may look like a good idea. After all, it blocks everything!
Well, yes. Yes, it does. That means it also blocks ssh. And *that* means you can no longer get to your shiny new server. Whoops!
Still, if you’re going to err, err on the side of blocking more connections. You see — the hackers really are out to get you.
Or, to be more exact, it’s not you or your servers personally. Sure, you’re not the [National Security Agency (NSA), which gets — no kidding — 300-million hacking attempts per day](http://thehackernews.com/2016/02/nsa-utah-data-center.html). But a hacking script doesn’t care. It just screens the internet looking for a server with a known hole. My own quiet little servers get hundreds of attacks — on a slow day.
So, what are you waiting for? Go, lock down your network services. Install FirewallD or UFW and secure your servers. You’ll be glad you did.
*Please feel free to share below any comments or insights about your experience locking down a Linux server with an IPtables-based firewall. And if this blog was useful, consider sharing it through social media.*
*About the blogger: Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols is a veteran IT journalist whose estimable work can be found on a host of channels, including **ZDNet.com**, **PC Magazine**, **InfoWorld**, **ComputerWorld**, **Linux Today** and **eWEEK**. Steven’s IT expertise comes without parallel. And while his views and cloud situations are solely his and don’t necessarily reflect those of Linode, we are grateful for his contributions. He can be followed on Twitter (@sjvn).* |
8,062 | 你会考虑乘坐无人驾驶汽车吗? | https://www.maketecheasier.com/riding-driverless-car/ | 2016-12-25T15:17:24 | [
"无人驾驶",
"汽车"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8062-1.html | 
科技在经历重大进展。最近我们经历的是如苹果手表及各种克隆品、FitBit 活动智能设备、谷歌眼镜等可穿戴设备。看起来下一个就是人们研究了很长时间的无人驾驶汽车了。
这些汽车,有时也叫做自动汽车、自动驾驶汽车,或机器人汽车,确实可以依靠技术自己驾驶。它们能探测周边环境,如障碍物和标志,并使用 GPS 找到自己的路线。但是它们驾驶起来安全吗?我们请教我们的科技作者,“你会考虑乘坐无人驾驶汽车吗?”
### 我们的观点
**Derrik** 说他会乘坐无人驾驶汽车,因为 “*技术早就存在,而且很多聪明能干的人研究了很长时间。*” 他承认它们还是有些问题,但他相信很多事故的发生是因为有人的参与。如果不考虑人,他认为乘坐无人驾驶汽车会“*难以置信的安全*。”
对 **Phil** 来说,这些汽车让他“紧张”,但他也承认这是他想象出的,因为他从没乘坐过。他同意 Derrik 这些技术是高度发达的观点,也知道它的原理,但仍然认为“*他自己对新技术接受缓慢,不会购买这类车*” 他甚至坦白说平时很少使用定速巡航。他认为依赖它太多的司机会让他感到不安全。

**Robert** 认为“*这个概念确实有点怪,*”但原则上他看不到汽车不向那个方向发展的理由。 他指出飞机已经走了那条路,而且变得更加安全, 他认为事故发生的主因是“*人们过于依赖科技手段,而当科技出现故障时不知所措而导致。*”
他是一个“焦虑型乘客”, 更喜欢控制整个局面。 对他来说,他的车子在哪里开很重要。如果是以低速在城市中驾驶他感觉还好,但如果是在“宽度不足两车道的弯弯曲曲的英国乡村道路”上,则绝不可以。他和 Phil 都认为英国道路与美国道路大大不同。他建议让别人去做小白鼠, 等到确定安全了再乘坐。
对 **Mahesh**来说, 他绝对会乘坐无人驾驶汽车,因为他知道这些汽车公司“*拥有坚实的安全技术,决不会让他们的顾客去冒险。*” 他承认安全与否还与车辆行驶的道路有关。
我的观点有些像这些观点的折中。虽然平时我会快速地投入到新科技中,但如果要拿生命去冒险,我不会那么做。我承认这些汽车发展了很久,应该很安全。而且坦率地说,很多司机比无人驾驶汽车危险得多。但和 Robert 一样,我想我会让其他人去做小白鼠,等到它更普遍了再去乘坐。
### 你的观点
在这个问题上,你的观点是什么呢? 你会信任新生的科学技术呢,还是乘坐无人驾驶汽车时会紧张到不行? 你会考虑乘坐无人驾驶汽车吗? 在下面的评论里加入讨论吧。
图片来自: [Steve Jurvetson](https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Jurvetson_Google_driverless_car_trimmed.jpg) 和 [Steve Jurvetson at Wikimedia Commons](https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Inside_the_Google_RoboCar_today_with_PlanetLabs.jpg)
---
via: <https://www.maketecheasier.com/riding-driverless-car/>
作者:[Laura Tucker](https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/lauratucker/) 译者:[willcoderwang](https://github.com/willcoderwang) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 
Technology goes through major movements. The last one we entered into was the wearables phase with the Apple Watch and clones, FitBits, and Google Glass. It seems like the next phase they’ve been working on for quite a while is the driverless car.
These cars, sometimes called autonomous cars, self-driving cars, or robotic cars, would literally drive themselves thanks to technology. They detect their surroundings, such as obstacles and signs, and use GPS to find their way. But would they be safe to drive in? We asked our technology-minded writers, “Would you consider riding in a driverless car?
## Our Opinion
**Derrik** reports that he would ride in a driver-less car because “*the technology is there and a lot of smart people have been working on it for a long time.*” He admits there are issues with them, but for the most part he believes a lot of the accidents happen when a human does get involved. But if you take humans out of the equation, he thinks riding in a driverless car “*would be incredibly safe*.”
For **Phil**, these cars give him “the willies,” yet he admits that’s only in the abstract as he’s never ridden in one. He agrees with Derrik that the tech is well developed and knows how it works, but then sees himself as “a* tough sell being a bit of a luddite at heart.*” He admits to even rarely using cruise control. Yet he agrees that a driver relying on it too much would be what would make him feel unsafe.
**Robert** agrees that “*the concept is a little freaky,*” but in principle he doesn’t see why cars shouldn’t go in that direction. He notes that planes have gone that route and become much safer, and he believes the accidents we see are mainly “*caused by human error due to over-relying on the technology then not knowing what to do when it fails.*”
He’s a bit of an “anxious passenger” as it is, preferring to have control over the situation, so for him much of it would have to do with where he car is being driven. He’d be okay with it if it was driving in the city at slow speeds but definitely not on “motorways of weaving English country roads with barely enough room for two cars to drive past each other.” He and Phil both see English roads as much different than American ones. He suggests letting others be the guinea pigs and joining in after it’s known to be safe.
For **Mahesh**, he would definitely ride in a driverless car, as he knows that the companies with these cars “*have robust technology and would never put their customers at risk.*” He agrees that it depends on the roads that the cars are being driven on.
My opinion kind of floats in the middle of all the others. While I’m normally one to jump readily into new technology, putting my life at risk makes it different. I agree that the cars have been in development so long they’re bound to be safe. And frankly there are many drivers on the road that are much more dangerous than driverless cars. But like Robert, I think I’ll let others be the guinea pigs and will welcome the technology once it becomes a bit more commonplace.
## Your Opinion
Where do you sit with this issue? Do you trust this emerging technology? Or would you be a nervous nelly in one of these cars? Would you consider driving in a driverless car? Jump into the discussion below in the comments.
Image Credit: [Steve Jurvetson](https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Jurvetson_Google_driverless_car_trimmed.jpg) and [Steve Jurvetson at Wikimedia Commons](https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Inside_the_Google_RoboCar_today_with_PlanetLabs.jpg)
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox |
8,064 | 树莓派基金会发布桌面操作系统 PIXEL OS | http://www.theregister.co.uk/2016/12/22/raspberry_pi_foundation_releases_operating_system_for_pcs_macs/ | 2016-12-26T11:35:00 | [
"树莓派",
"PIXEL"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8064-1.html |
>
> 基于 Debian 衍生的 PIXEL 将把树莓派体验带到 x86 上,正如树莓派基金会所[宣称](https://www.raspberrypi.org/blog/pixel-pc-mac/)的,“我们不只是要为树莓派创造最好的桌面环境,而是要创造最好的桌面环境,如是。”
>
>
>

树莓派基金会将其[今年九月份发布的 PIXEL OS](http://www.theregister.co.uk/2016/09/28/raspberry_pi_adds_pixel_eye_candy_to_desktop_to_please_users/) 移植到了 PC 和 Mac 上。
PIXEL 的意思是“**Pi** **I**mproved **X**windows **E**nvironment, **L**ightweight”,即“树莓派改进的轻量级 Xwindows 环境”,树莓派的创始人 Eben Upton 说,“我们觉得大多数用户都希望要这样的一个桌面环境:干净整洁而现代化的用户界面;提升工作效率的生产力软件和编程工具,包括自由软件和专有软件。”
挖掘这个操作系统的其它用途的想法在这几个月来一直浮现在 Upton 的脑海中,正如[他写的](https://www.raspberrypi.org/blog/pixel-pc-mac/)“在夏天时,我们就问自己一个简单的问题:如果我们这么喜欢 PIXEL,为什么我们非要人们买树莓派才能运行它呢?”
Upton 说他和其他的伙伴们注意到“有大量可以用来安装的 PC 和 Mac 机器丢在那里,它们可以很好的运行 x86 Debian”,并且问他们,“我们可以为这些机器做些什么吗?”
现在答案就是“YES”,树莓派基金会发布了该操作系统的 x86 体验版。

这个操作系统对硬件的需求很低,Upton 说 PIXEL “将运行在像我的 ThinkPad X40 这样的老机器上,它只要 512MB 内存就行。”Upton 认为这样的硬件需求很符合还在使用老式 PC 的学校,这就意味着学生们可以在学校的 x86 上使用和家里的树莓派上一样的 PIXEL 环境。
PIXEL 可以从 DVD 或 USB 盘启动,或者你也可以将它安装到计算机上。你可以[下载这个 1.3GB 的 ISO 镜像](http://downloads.raspberrypi.org/pixel_x86/images/pixel_x86-2016-12-13/2016-12-13-pixel-x86-jessie.iso)试试,不过,有些型号的 Mac 可能不能用这个引导镜像启动。Upton 也表示,这还是一个早期发布版本,还在继续改进。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,065 | Samba 系列(一):在 Ubuntu 系统上使用 Samba4 来创建活动目录架构 | http://www.tecmint.com/install-samba4-active-directory-ubuntu/ | 2016-12-26T17:46:00 | [
"Samba",
"活动目录"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8065-1.html | Samba 是一个自由的开源软件套件,用于实现 Windows 操作系统与 Linux/Unix 系统之间的无缝连接及共享资源。
Samba 不仅可以通过 SMB/CIFS 协议组件来为 Windows 与 Linux 系统之间提供独立的文件及打印机共享服务,它还能实现<ruby> 活动目录 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Active Directory </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby><ruby> 域控制器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Domain Controller </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的功能,或者让 Linux 主机加入到域环境中作为域成员服务器。当前的 Samba4 版本实现的 AD DC 域及林功能级别可以取代 Windows 2008 R2 系统的域相关功能。

本系列的文章的主要内容是使用 Samba4 软件来配置活动目录域控制器,涉及到 Ubuntu、CentOS 和 Windows 系统相关的以下主题:
* 第 1 节:在 Ubuntu 系统上使用 Samba4 来创建活动目录架构
* 第 2 节:在 Linux 命令行下管理 Samba4 AD 架构
* 第 3 节:在 Windows 10 操作系统上安装 RSAT 工具来管理 Samba4 AD
* 第 4 节:从 Windows 中管理 Samba4 AD 域控制器 DNS 和组策略
* 第 5 节:使用 Sysvol Replication 复制功能把 Samba 4 DC 加入到已有的 AD
* 第 6 节:从 Linux DC 服务器通过 GOP 来添加一个共享磁盘并映射到 AD
* 第 7 节:把 Ubuntu 16.04 系统主机作为域成员服务器添加到 AD
* 第 8 节:把 CenterOS 7 系统主机作为域成员服务器添加到 AD
* 第 9 节:在 AD Intranet 区域创建使用 kerberos 认证的 Apache Website
这篇指南将阐明在 Ubuntu 16.04 和 Ubuntu 14.04 操作系统上安装配置 Samba4 作为域控服务器组件的过程中,你需要注意的每一个步骤。
以下安装配置文档将会说明在 Windows 和 Linux 的混合系统环境中,关于用户、机器、共享卷、权限及其它资源信息的主要配置点。
#### 环境要求:
1. [Ubuntu 16.04 服务器安装](http://www.tecmint.com/installation-of-ubuntu-16-04-server-edition/)
2. [Ubuntu 14.04 服务器安装](http://www.tecmint.com/ubuntu-14-04-server-installation-guide-and-lamp-setup/)
3. 为你的 AD DC 服务器[设置静态IP地址](http://www.tecmint.com/set-add-static-ip-address-in-linux/)
### 第一步:初始化 Samba4 安装环境
1、 在开始安装 Samba4 AD DC 之前,让我们先做一些准备工作。首先运行以下命令来确保系统已更新了最新的安全特性,内核及其它补丁:
```
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get upgrade
$ sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
```
2、 其次,打开服务器上的 `/etc/fstab` 文件,确保文件系统分区的 ACL 已经启用 ,如下图所示。
通常情况下,当前常见的 Linux 文件系统,比如 ext3、ext4、xfs 或 btrfs 都默认支持并已经启用了 ACL 。如果未设置,则打开并编辑 `/etc/fstab` 文件,在第三列添加 `acl`,然后重启系统以使用修改的配置生效。

*启动 Linux 文件系统的 ACL 功能*
3、 最后使用一个具有描述性的名称来[设置主机名](http://www.tecmint.com/set-hostname-permanently-in-linux/) ,比如这往篇文章所使用的 `adc1`。通过编辑 `/etc/hostname` 文件或使用使用下图所示的命令来设置主机名。
```
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname adc1
```
为了使修改的主机名生效必须重启服务器。
### 第二步: 为 Samba4 AD DC 服务器安装必需的软件包
4、 为了让你的服务器转变为域控制器,你需要在服务器上使用具有 root 权限的账号执行以下命令来安装 Samba 套件及所有必需的软件包。
```
$ sudo apt-get install samba krb5-user krb5-config winbind libpam-winbind libnss-winbind
```

*在 Ubuntu 系统上安装 Samba 套件*
5、 安装包在执行的过程中将会询问你一系列的问题以便完成域控制器的配置。
在第一屏中你需要以大写为 Kerberos 默认 REALM 输入一个名字。以**大写**为你的域环境输入名字,然后单击回车继续。

*配置 Kerosene 认证服务*
6、 下一步,输入你的域中 Kerberos 服务器的主机名。使用和上面相同的名字,这一次使用**小写**,然后单击回车继续。

*设置 Kerberos 服务器的主机名*
7、 最后,指定 Kerberos realm 管理服务器的主机名。使用更上面相同的名字,单击回车安装完成。

*设置管理服务器的主机名*
### 第三步:为你的域环境开启 Samba AD DC 服务
8、 在为域服务器配置 Samba 服务之前,先运行如下命令来停止并禁用所有 Samba 进程。
```
$ sudo systemctl stop samba-ad-dc.service smbd.service nmbd.service winbind.service
$ sudo systemctl disable samba-ad-dc.service smbd.service nmbd.service winbind.service
```
9、 下一步,重命名或删除 Samba 原始配置文件。在开启 Samba 服务之前,必须执行这一步操作,因为在开启服务的过程中 Samba 将会创建一个新的配置文件,如果检测到原有的 `smb.conf` 配置文件则会报错。
```
$ sudo mv /etc/samba/smb.conf /etc/samba/smb.conf.initial
```
10、 现在,使用 root 权限的账号并接受 Samba 提示的默认选项,以交互方式启动<ruby> 域供给 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> domain provision </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。
还有,输入正确的 DNS 服务器地址并且为 Administrator 账号设置强密码。如果使用的是弱密码,则域供给过程会失败。
```
$ sudo samba-tool domain provision --use-rfc2307 –interactive
```

*Samba 域供给*
11、 最后,使用以下命令重命名或删除 Kerberos 认证在 `/etc` 目录下的主配置文件,并且把 Samba 新生成的 Kerberos 配置文件创建一个软链接指向 `/etc` 目录。
```
$ sudo mv /etc/krb6.conf /etc/krb5.conf.initial
$ sudo ln –s /var/lib/samba/private/krb5.conf /etc/
```

*创建 Kerberos 配置文件*
12、 启动并开启 Samba 活动目录域控制器后台进程
```
$ sudo systemctl start samba-ad-dc.service
$ sudo systemctl status samba-ad-dc.service
$ sudo systemctl enable samba-ad-dc.service
```

*开启 Samba 活动目录域控制器服务*
13、 下一步,[使用 netstat 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/20-netstat-commands-for-linux-network-management/) 来验证活动目录启动的服务是否正常。
```
$ sudo netstat –tulpn| egrep ‘smbd|samba’
```

*验证 Samba 活动目录*
### 第四步: Samba 最后的配置
14、 此刻,Samba 应该跟你想像的一样,完全运行正常。Samba 现在实现的域功能级别可以完全跟 Windows AD DC 2008 R2 相媲美。
可以使用 `samba-tool` 工具来验证 Samba 服务是否正常:
```
$ sudo samba-tool domain level show
```

*验证 Samba 域服务级别*
15、 为了满足 DNS 本地解析的需求,你可以编辑网卡配置文件,修改 `dns-nameservers` 参数的值为域控制器地址(使用 127.0.0.1 作为本地 DNS 解析地址),并且设置 `dns-search` 参数为你的 realm 值。
```
$ sudo cat /etc/network/interfaces
$ sudo cat /etc/resolv.conf
```

*为 Samba 配置 DNS 服务器地址*
设置完成后,重启服务器并检查解析文件是否指向正确的 DNS 服务器地址。
16、 最后,通过 `ping` 命令查询结果来检查某些重要的 AD DC 记录是否正常,使用类似下面的命令,替换对应的域名。
```
$ ping –c3 tecmint.lan # 域名
$ ping –c3 adc1.tecmint.lan # FQDN
$ ping –c3 adc1 # 主机
```

*检查 Samba AD DNS 记录*
执行下面的一些查询命令来检查 Samba 活动目录域控制器是否正常。
```
$ host –t A tecmint.lan
$ host –t A adc1.tecmint.lan
$ host –t SRV _kerberos._udp.tecmint.lan # UDP Kerberos SRV record
$ host -t SRV _ldap._tcp.tecmint.lan # TCP LDAP SRV record
```
17、 并且,通过请求一个域管理员账号的身份来列出缓存的票据信息以验证 Kerberos 认证是否正常。注意域名部分使用大写。
```
$ kinit [email protected]
$ klist
```

*检查域环境中的 Kerberos 认证是否正确*
至此! 你当前的网络环境中已经完全运行着一个 AD 域控制器,你现在可以把 Windows 或 Linux 系统的主机集成到 Samba AD 中了。
在下一期的文章中将会包括其它 Samba AD 域的主题,比如,在 Samba 命令行下如何管理你的域控制器,如何把 Windows 10 系统主机添加到同一个域环境中,如何使用 RSAT 工具远程管理 Samba AD 域,以及其它重要的主题。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/install-samba4-active-directory-ubuntu/>
作者:[Matei Cezar](http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,066 | 安卓平台上的依赖注入(一) | https://medium.com/di-101/di-101-part-1-81896c2858a0#.3hg0jj14o | 2016-12-27T08:43:00 | [
"Java"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8066-1.html | 
刚开始学习软件工程的时候,我们经常会碰到像这样的事情:
>
> 软件应该符合 SOLID 原则。
>
>
>
但这句话实际是什么意思?让我们看看 SOLID 中每个字母在架构里所代表的重要含义,例如:
* [S - 单职责原则](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_responsibility_principle)
* [O - 开闭原则](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open/closed_principle)
* [L - Liskov 替换原则](http://liskov_substitution_principle/)
* [I - 接口分离原则](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interface_segregation_principle)
* [D - 依赖反转原则](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dependency_inversion_principle) 这也是<ruby> 依赖注入 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> dependency injection </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的核心概念。
简单来说,我们需要提供一个类,这个类有它所需要的所有对象,以便实现其功能。
### 概述
依赖注入听起来像是描述非常复杂的东西的一个术语,但实际上它很简单,看下面这个例子你就明白了:
```
class NoDependencyInjection {
private Dependency d;
public NoDependencyInjection() {
d = new Dependency();
}
}
class DependencyInjection {
private Dependency d;
public DependencyInjection(Dependency d) {
this.d = d;
}
}
```
正如我们所见,第一种情况是我们在构造器里创建了依赖对象,但在第二种情况下,它作为参数被传递给构造器,这就是我们所说的<ruby> 依赖注入 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> dependency injection </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。这样做是为了让我们所写的类不依靠特定依赖关系的实现,却能直接使用它。
参数传递的目标是构造器,我们就称之为构造器依赖注入;或者是某个方法,就称之为方法依赖注入:
```
class Example {
private ConstructorDependency cd;
private MethodDependency md;
Example(ConstructorDependency cd) {
this.cd = cd; //Constructor Dependency Injection
}
public setMethodDependency(MethodDependency md) {
this.md = md; //Method Dependency Injection
}
}
```
要是你想总体深入地了解依赖注入,可以看看由 [Dan Lew](https://twitter.com/danlew42) 发表的[精彩的演讲](https://realm.io/news/daniel-lew-dependency-injection-dagger/),事实上是这个演讲启迪了这篇概述。
在 Android 平台,当需要框架来处理依赖注入这个特殊的问题时,我们有不同的选择,其中最有名的框架就是 [Dagger 2](http://google.github.io/dagger/)。它最开始是由 Square 公司(LCTT 译注:Square 是美国一家移动支付公司)的一些很棒的开发者开发出来的,然后慢慢发展成由 Google 自己开发。首先开发出来的是 Dagger 1,然后 Big G 接手这个项目发布了第二个版本,做了很多改动,比如以<ruby> 注解 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> annotation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>为基础,在编译的时候完成其任务。
### 导入框架
安装 Dagger 并不难,但需要导入 `android-apt` 插件,通过向项目的根目录下的 `build.gradle` 文件中添加它的依赖关系:
```
buildscript{
...
dependencies{
...
classpath ‘com.neenbedankt.gradle.plugins:android-apt:1.8’
}
}
```
然后,我们需要将 `android-apt` 插件应用到项目 `build.gradle` 文件,放在文件顶部 Android application 那一句的下一行:
```
apply plugin: ‘com.neenbedankt.android-apt’
```
这个时候,我们只用添加依赖关系,然后就能使用库及其<ruby> 注解 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> annotation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>了:
```
dependencies{
...
compile ‘com.google.dagger:dagger:2.6’
apt ‘com.google.dagger:dagger-compiler:2.6’
provided ‘javax.annotation:jsr250-api:1.0’
}
```
>
> 需要加上最后一个依赖关系是因为 @Generated 注解在 Android 里还不可用,但它是[原生的 Java 注解](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/javax/annotation/Generated.html)。
>
>
>
### Dagger 模块
要注入依赖,首先需要告诉框架我们能提供什么(比如说上下文)以及特定的对象应该怎样创建。为了完成注入,我们用 `@Module` 注释对一个特殊的类进行了注解(这样 Dagger 就能识别它了),寻找 `@Provide` 注解的方法,生成图表,能够返回我们所请求的对象。
看下面的例子,这里我们创建了一个模块,它会返回给我们 `ConnectivityManager`,所以我们要把 `Context` 对象传给这个模块的构造器。
```
@Module
public class ApplicationModule {
private final Context context;
public ApplicationModule(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
@Provides @Singleton
public Context providesContext() {
return context;
}
@Provides @Singleton
public ConnectivityManager providesConnectivityManager(Context context) {
return (ConnectivityManager) context.getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
}
}
```
>
> Dagger 中十分有意思的一点是简单地注解一个方法来提供一个单例(Singleton),就能处理所有从 Java 中继承过来的问题。
>
>
>
### 组件
当我们有一个模块的时候,我们需要告诉 Dagger 想把依赖注入到哪里:我们在一个<ruby> 组件 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Component </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>里完成依赖注入,这是一个我们特别创建的特殊注解接口。我们在这个接口里创造不同的方法,而接口的参数是我们想注入依赖关系的类。
下面给出一个例子并告诉 Dagger 我们想要 `MainActivity` 类能够接受 `ConnectivityManager`(或者在图表里的其它依赖对象)。我们只要做类似以下的事:
```
@Singleton
@Component(modules = {ApplicationModule.class})
public interface ApplicationComponent {
void inject(MainActivity activity);
}
```
>
> 正如我们所见,@Component 注解有几个参数,一个是所支持的模块的数组,代表它能提供的依赖。这里既可以是 `Context` 也可以是 `ConnectivityManager`,因为它们在 `ApplicationModule` 类中有声明。
>
>
>
### 用法
这时,我们要做的是尽快创建组件(比如在应用的 `onCreate` 阶段)并返回它,那么类就能用它来注入依赖了:
>
> 为了让框架自动生成 `DaggerApplicationComponent`,我们需要构建项目以便 Dagger 能够扫描我们的代码,并生成我们需要的部分。
>
>
>
在 `MainActivity` 里,我们要做的两件事是用 `@Inject` 注解符对想要注入的属性进行注解,调用我们在 `ApplicationComponent` 接口中声明的方法(请注意后面一部分会因我们使用的注入类型的不同而变化,但这里简单起见我们不去管它),然后依赖就被注入了,我们就能自由使用他们:
```
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Inject
ConnectivityManager manager;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
...
((App) getApplication()).getComponent().inject(this);
}
}
```
### 总结
当然了,我们可以手动注入依赖,管理所有不同的对象,但 Dagger 消除了很多比如模板这样的“噪声”,给我们提供有用的附加品(比如 `Singleton`),而仅用 Java 处理将会很糟糕。
---
via: <https://medium.com/di-101/di-101-part-1-81896c2858a0#.3hg0jj14o>
作者:[Roberto Orgiu](https://medium.com/@_tiwiz) 译者:[GitFuture](https://github.com/GitFuture) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | # DI 101 — Part 1
## Dependency Injection for the Android platform
When we first start studying software engineering, we usually bump into something like:
Software shall be SOLID.
but what does that mean, in fact? Well, let’s just say that **each character of the acronym means something really important for the architecture**, such as:
**S**ingle Responsibility Principle**O**pen/closed principle**L**iskov substitution principle**I**nterface segregation principlewhich is the core concept on which the dependency injection is based.**D**ependency inversion principle
Simply, *we need to provide a class with all the objects it needs in order to perform its duties*.
## Overview
Dependency Injection sounds like a very complex term for something that is, in fact, really easy and could be explained with this example:
As we can see, in the first case, we create the dependency in the constructor, while in the second case it gets passed as a parameter. The second case is what we call *dependency injection*. We do this so that our class does not depend on the specific implementation of its dependency but it just uses it.
Moreover, based on whether the parameter is passed over to the constructor or to a method, we talk either about constructor dependency injection or method dependency injection:
If you want to know more about Dependency Injection in general, be sure to check out [this amazing talk](https://realm.io/news/daniel-lew-dependency-injection-dagger/) from [Dan Lew](https://twitter.com/danlew42) that actually inspired this overview.
On Android, we have different choices when it comes to frameworks for solving this particular problem but the most famous is [Dagger](http://google.github.io/dagger/) 2, first made by the awesome guys at Square and then evolved by Google itself. Specifically, Dagger 1 was made by the first and then Big G took over the project and created the second version, with major changes such being based on annotations and doing its job at compile time.
## Importing the framework
Setting up Dagger is no big deal, but it requires us to import the **android-apt** plugin by adding its dependency in the *build.gradle* file in the root directory of the project:
`buildscript{`
...
dependencies{
...
classpath ‘com.neenbedankt.gradle.plugins:android-apt:1.8’
}
}
Then, we need to apply the **android-apt** plugin in the top part of the app’s *build.gradle* file, right below the Android application one:
`apply plugin: ‘com.neenbedankt.android-apt’`
At this point, we just need to add the dependencies so that we are now able to use the libraries and its annotations:
`dependencies{`
...
compile ‘com.google.dagger:dagger:2.6’
apt ‘com.google.dagger:dagger-compiler:2.6’
provided ‘javax.annotation:jsr250-api:1.0’
}
The last dependency is needed because the
@Generatedannotation is not yet available on Android, but[it’s pure Java].
## Dagger Modules
For injecting our dependencies, we first need to tell the framework what we can provide (i.e. the Context) and how that specific object is built. In order to do this, we annotate a specific class with the **@Module** annotation (so that Dagger is able to pick it up) scan for the **@Provide** annotated methods and generate the graph that will give us the object we request.
Let’s see an example where we create a module that will give us the **ConnectivityManager.** So we need the **Context** that we will pass in the constructor of the module:
A very interesting feature of Dagger is providing a Singleton by simply annotating a method, dealing with all the issues inherited from Java by itself.
## The Components
Once we have a module, we need to tell Dagger where we want our dependencies to be injected: we do this in a Component, *a specifically annotated interface* in which we create different methods, where the parameters are the classes into which we want our dependencies to be injected.
Let’s give an example and say that we want our **MainActivity** class to be able to receive the **ConnectivityManager **(or any other dependency in the graph). We would simply do something like this:
As we can see, the @Component annotation takes some parameters, one being an array of the modules supported, meaning the dependencies it can provide. In our case, that would be both the Context and the ConnectivityManager, as they are declared in the ApplicationModule class.
## Wiring up
At this point, what we need to do is create the Component as soon as possible (such as in the onCreate phase of the Application) and return it, so that the classes can use it for injecting the dependencies:
In order to have the DaggerApplicationComponent automatically generated by the framework, we need to build our projects so that Dagger can scan our codebase and generate the parts we need.
In our **MainActivity**, though, the two things we need to do are annotate a property we want to inject with the **@Inject **annotation and invoke the method we declared in the **ApplicationComponent** interface (note that this last part varies based on what kind of injection we are performing, but for the moment we can leave it as is for the simplicity), so that our dependencies get injected and we can use them freely:
## Conclusion
Of course, we could do Dependency Injection manually, managing all the different objects, but Dagger takes away a lot of the “noise” involved with such boilerplate, giving us some nice additions (such as **Singleton**) that would otherwise be pretty awful to deal with in Java. |
8,067 | RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux,红帽企业级 Linux) 7.3 安装指南 | http://www.tecmint.com/red-hat-enterprise-linux-7-3-installation-guide/ | 2016-12-27T09:40:00 | [
"RHEL",
"CentOS"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8067-1.html | RHEL 是由红帽公司开发维护的开源 Linux 发行版,可以运行在所有的主流 CPU 架构中。一般来说,多数的 Linux 发行版都可以免费下载、安装和使用,但对于 RHEL,只有在购买了订阅之后,你才能下载和使用,否则只能获取到试用期为 30 天的评估版。

本文会告诉你如何在你的机器上安装最新的 RHEL 7.3,当然了,使用的是期限 30 天的评估版 ISO 镜像,请自行到 <https://access.redhat.com/downloads> 下载。
如果你更喜欢使用 CentOS,请移步 [CentOS 7.3 安装指南](/article-8048-1.html)。
欲了解 RHEL 7.3 的新特性,请参考 [版本更新日志](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/7-Beta/html/7.3_Release_Notes/chap-Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux-7.3_Release_Notes-Overview.html)。
#### 先决条件
本次安装是在支持 UEFI 的虚拟机固件上进行的。为了完成安装,你首先需要进入主板的 EFI 固件更改启动顺序为已刻录好 ISO 镜像的对应设备(DVD 或者 U 盘)。
如果是通过 USB 介质来安装,你需要确保这个可以启动的 USB 设备是用支持 UEFI 兼容的工具来创建的,比如 [Rufus](https://rufus.akeo.ie/),它能将你的 USB 设备设置为 UEFI 固件所需要的 GPT 分区方案。
为了进入主板的 UEFI 固件设置面板,你需要在电脑初始化 POST (<ruby> 通电自检 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Power on Self Test </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>) 的时候按下一个特殊键。
关于该设置需要用到特殊键,你可以向主板厂商进行咨询获取。通常来说,在笔记本上,可能是这些键:F2、F9、F10、F11 或者 F12,也可能是 Fn 与这些键的组合。
此外,更改 UEFI 启动顺序前,你要确保<ruby> 快速启动选项 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> QuickBoot/FastBoot </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和 <ruby> 安全启动选项 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Secure Boot </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>处于关闭状态,这样才能在 EFI 固件中运行 RHEL。
有一些 UEFI 固件主板模型有这样一个选项,它让你能够以传统的 BIOS 或者 EFI CSM (<ruby> 兼容支持模块 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Compatibility Support Module </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>) 两种模式来安装操作系统,其中 CSM 是主板固件中一个用来模拟 BIOS 环境的模块。这种类型的安装需要 U 盘以 MBR 而非 GPT 来进行分区。
此外,一旦在你的 UEFI 机器中以这两种模式之一成功安装好 RHEL 或者类似的 OS,那么安装好的系统就必须以你安装时使用的模式来运行。而且,你也不能够从 UEFI 模式变更到传统的 BIOS 模式,反之亦然。强行变更这两种模式会让你的系统变得不稳定、无法启动,同时还需要重新安装系统。
### RHEL 7.3 安装指南
1、 首先,下载并使用合适的工具刻录 RHEL 7.3 ISO 镜像到 DVD 或者创建一个可启动的 U 盘。
给机器加电启动,把 DVD/U 盘放入合适驱动器中,并根据你的 UEFI/BIOS 类型,按下特定的启动键变更启动顺序来启动安装介质。
当安装介质被检测到之后,它会启动到 RHEL 的 grub 菜单。选择“Install red hat Enterprise Linux 7.3” 并按回车继续。

*RHEL 7.3 启动菜单*
2、 之后屏幕就会显示 RHEL 7.3 欢迎界面。该界面选择安装过程中使用的语言 (LCTT 译注:这里选的只是安装过程中使用的语言,之后的安装中才会进行最终使用的系统语言环境) ,然后按回车到下一界面。

*选择 RHEL 7.3 安装过程使用的语言*
3、 下一界面中显示的是安装 RHEL 时你需要设置的所有事项的总体概览。首先点击<ruby> 日期和时间 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> DATE & TIME </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>并在地图中选择你的设备所在地区。
点击最上面的<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 按钮来保持你的设置,并进行下一步系统设置。

*RHEL 7.3 安装概览*

*选择 RHEL 7.3 日期和时间*
4、 接下来,就是配置你的<ruby> 键盘 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> keyboard </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>布局并再次点击<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 按钮返回安装主菜单。

*配置键盘布局*
5、 紧接着,选择你使用的<ruby> 语言支持 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> language support </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,并点击<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,然后进行下一步。

*选择语言支持*
6、 <ruby> 安装源 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Installation Source </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>保持默认就好,因为本例中我们使用本地安装 (DVD/USB 镜像),然后进行<ruby> 软件集选择 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Software Selection </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。
此处你可以选择<ruby> 基本环境 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> base environment </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和<ruby> 附件 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Add-ons </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。由于 RHEL 常用作 Linux 服务器,<ruby> 最小化安装 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Minimal Installation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>对于系统管理员来说则是最佳选择。
对于生产环境来说,这也是官方极力推荐的安装方式,因为我们只需要在 OS 中安装极少量软件就好了。
这也意味着高安全性、可伸缩性以及占用极少的磁盘空间。同时,通过购买<ruby> 订阅 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> subscription </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 或使用 DVD 镜像源,这里列出的的其它环境和附件都是可以在命令行中很容易地安装。

*RHEL 7.3 软件集选择*
7、 万一你想要安装预定义的基本环境之一,比方说 Web 服务器、文件 & 打印服务器、架构服务器、虚拟化主机、带 GUI 的服务器等,直接点击选择它们,然后在右边的框选择附件,最后点击<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 结束这一步操作即可。

*选择带 GUI 的服务器*
8、 在接下来点击<ruby> 安装目标 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Installation Destination </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,这个步骤要求你为将要安装的系统进行分区、格式化文件系统并设置挂载点。
最安全的做法就是让安装器自动配置硬盘分区,这样会创建 Linux 系统所有需要用到的基本分区 (在 LVM 中创建 `/boot`、`/boot/efi`、`/(root)` 以及 `swap` 等分区),并格式化为 RHEL 7.3 默认的 XFS 文件系统。
请记住:如果安装过程是从 UEFI 固件中启动的,那么硬盘的分区表则是 GPT 分区方案。否则,如果你以 CSM 或传统 BIOS 来启动,硬盘的分区表则使用老旧的 MBR 分区方案。
假如不喜欢自动分区,你也可以选择配置你的硬盘分区表,手动创建自己需要的分区。
不论如何,本文推荐你选择自动配置分区。最后点击<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 继续下一步。

*选择 RHEL 7.3 的安装硬盘*
9、 下一步是禁用 Kdump 服务,然后配置网络。

*禁用 Kdump 特性*
10、 在<ruby> 网络和主机名 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Network and Hostname </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>中,设置你机器使用的主机名和一个描述性名称,同时拖动 Ethernet 开关按钮到 `ON` 来启用网络功能。
如果你在自己的网络中有一个 DHCP 服务器,那么网络 IP 设置会自动获取和使用。

*配置网络主机名称*
11、 如果要为网络接口设置静态 IP,点击<ruby> 配置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Configure </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>按钮,然后手动设置 IP,如下方截图所示。
设置好网络接口的 IP 地址之后,点击<ruby> 保存 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Save </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>按钮,最后切换一下网络接口的 `OFF` 和 `ON` 状态已应用刚刚设置的静态 IP。
最后,点击<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 按钮返回到安装设置主界面。

*配置网络 IP 地址*
12、 最后,在安装配置主界面需要你配置的最后一项就是<ruby> 安全策略配置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Security Policy </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>文件了。选择并应用<ruby> 默认的 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Default </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>安全策略,然后点击<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>返回主界面。
回顾所有的安装设置项并点击<ruby> 开始安装 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Begin Installation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>按钮来启动安装过程,这个过程启动之后,你就没有办法停止它了。

*为 RHEL 7.3 启用安全策略*

*开始安装 RHEL 7.3*
13、 在安装过程中,你的显示器会出现<ruby> 用户设置 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> User Settings </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。首先点击<ruby> Root 密码 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Root Password </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>为 root 账户设置一个高强度密码。

*配置用户选项*

*设置 Root 账户密码*
14、 最后,创建一个新用户,通过选中<ruby> 使该用户成为管理员 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Make this user administrator </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>为新建的用户授权 root 权限。同时还要为这个账户设置一个高强度密码,点击<ruby> 完成 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Done </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby> 返回用户设置菜单,就可以等待安装过程完成了。

*创建新用户账户*

*RHEL 7.3 安装过程*
15、 安装过程结束并成功安装后,弹出或拔掉 DVD/USB 设备,重启机器。

*RHEL 7.3 安装完成*

*启动 RHEL 7.3*
至此,安装完成。为了后期一直使用 RHEL,你需要从 Red Hat 消费者门户购买一个订阅,然后在命令行 [使用订阅管理器来注册你的 RHEL 系统](http://www.tecmint.com/enable-redhat-subscription-reposiories-and-updates-for-rhel-7/)。
---
作者简介:
Matei Cezar
我是一个终日沉溺于电脑的家伙,对开源的 Linux 软件非常着迷,有着 4 年 Linux 桌面发行版、服务器和 bash 编程经验。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/red-hat-enterprise-linux-7-3-installation-guide/>
作者:[Matei Cezar](http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,068 | “硅谷的女儿”的成才之路 | https://opensource.com/life/16/5/my-open-source-story-larissa-shapiro | 2016-12-27T11:52:12 | [
"多样性",
"女性"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8068-1.html | 
在 2014 年,为了对网上一些关于在科技行业女性稀缺的评论作出回应,我的同事 [Crystal Beasley](http://skinnywhitegirl.com/blog/my-nerd-story/1101/) 倡议在科技/信息安全方面工作的女性在网络上分享自己的“成才之路”。这篇文章就是我的故事。我把我的故事与你们分享是因为我相信榜样的力量,也相信一个人有多种途径,选择一个让自己满意的有挑战性的工作以及可以实现目标的人生。
### 和电脑相伴的童年
我可以说是硅谷的女儿。我的故事不是一个从科技业余爱好转向专业的故事,也不是从小就专注于这份事业的故事。这个故事更多的是关于环境如何塑造你 — 通过它的那种已然存在的文化来改变你,如果你想要被改变的话。这不是从小就开始努力并为一个明确的目标而奋斗的故事,我意识到,这其实是享受了一些特权的成长故事。
我出生在曼哈顿,但是我在新泽西州长大,因为我的爸爸退伍后,在那里的罗格斯大学攻读计算机科学的博士学位。当我四岁时,学校里有人问我爸爸干什么谋生时,我说,“他就是看电视和捕捉小虫子,但是我从没有见过那些小虫子”(LCTT 译注:小虫子,bug)。他在家里有一台哑终端(LCTT 译注:就是那台“电视”),这大概与他在 Bolt Beranek Newman 公司的工作有关,做关于早期互联网人工智能方面的工作。我就在旁边看着。
我没能玩上父亲的会抓小虫子的电视,但是我很早就接触到了技术领域,我很珍惜这个礼物。提早的熏陶对于一个未来的高手是十分必要的 — 所以,请花时间和你的小孩谈谈你在做的事情!

*我父亲的终端和这个很类似 —— 如果不是这个的话 CC BY-SA 4.0*
当我六岁时,我们搬到了加州。父亲在施乐的帕克研究中心(Xerox PARC)找到了一个工作。我记得那时我认为这个城市一定有很多熊,因为在它的旗帜上有一个熊。在1979年,帕洛阿图市还是一个大学城,还有果园和开阔地带。
在 Palo Alto 的公立学校待了一年之后,我的姐姐和我被送到了“半岛学校”,这个“民主典范”学校对我造成了深刻的影响。在那里,好奇心和创新意识是被高度推崇的,教育也是由学生自己分组讨论决定的。在学校,我们很少能看到叫做电脑的东西,但是在家就不同了。
在父亲从施乐辞职之后,他就去了苹果公司,在那里他工作使用并带回家让我玩的第一批电脑就是:Apple II 和 LISA。我的父亲在最初的 LISA 的研发团队。我直到现在还深刻的记得他让我们一次又一次的“玩”鼠标训练的场景,因为他想让我的 3 岁大的妹妹也能对这个东西觉得好用 —— 她也确实那样觉得。

*我们的 LISA 看起来就像这样。谁看到鼠标哪儿去了?CC BY-SA 4.0*
在学校,我的数学的概念学得不错,但是基本计算却惨不忍睹。我的第一个学校的老师告诉我的家长和我,说我的数学很差,还说我很“笨”。虽然我在“常规的”数学项目中表现出色,能理解一个超出 7 岁孩子理解能力的逻辑谜题,但是我不能完成我们每天早上都要做的“练习”。她说我傻,这事我不会忘记。在那之后的十年我都没能相信自己的逻辑能力和算法的水平。**不要低估你对孩子说的话的影响**。
在我玩了几年爸爸的电脑之后,他从 Apple 公司跳槽到了 EA,又跳到了 SGI,我又体验了他带回来的新玩意。这让我们认为我们家的房子是镇里最酷的,因为我们在车库里有一个能玩 Doom 的 SGI 的机器。我不会太多的编程,但是现在看来,从那些年里我学到对尝试新的科技毫不恐惧。同时,我的学文学和教育的母亲,成为了一个科技行业的作家,她向我证实了一个人的职业可以改变,而且一个做母亲的人可能同时驾驭一个科技职位。我不是说这对她来说很简单,但是她让我认为这件事看起来很简单。你可能会想这些早期的熏陶能把我带到科技行业,但是它没有。
### 本科时光
我想我要成为一个小学教师,我就读米尔斯学院就是想要做这个。但是后来我开始研究女性学,后来又研究神学,我这样做仅仅是由于我自己的一个渴求:我希望能理解人类的意志以及为更好的世界而努力。
同时,我也感受到了互联网的巨大力量。在 1991 年,拥有你自己的 UNIX 的账户,能够和全世界的人谈话,是很令人兴奋的事。我仅仅从在互联网中“玩”就学到了不少,从那些愿意回答我提出的问题的人那里学到的就更多了。这些学习对我的职业生涯的影响不亚于我在正规学校教育之中学到的知识。所有的信息都是有用的。我在一个女子学院度过了学习的关键时期,那时是一个杰出的女性在掌管计算机院。在那个宽松氛围的学院,我们不仅被允许,还被鼓励去尝试很多的道路(我们能接触到很多很多的科技,还有聪明人愿意帮助我们),我也确实那样做了。我十分感激当年的教育。在那个学院,我也了解了什么是极客文化。
之后我去了研究生院去学习女性主义神学,但是技术的气息已经渗入我的灵魂。当我意识到我不想成为一个教授或者一个学术伦理家时,我离开了学术圈,带着学校债务和一些想法回到了家。
### 新的开端
在 1995 年,我被互联网连接人们以及分享想法和信息的能力所震惊(直到现在仍是如此)。我想要进入这个行业。看起来我好像要“女承父业”,但是我不知道如何开始。我开始在硅谷做临时工,从 Sun 微系统公司得到我的第一个“真正”技术职位前尝试做了一些事情(为半导体数据公司写最基础的数据库,技术手册印发前的事务,备份工资单的存跟)。这些事很让人激动。(毕竟,我们是“.com”中的那个”点“)。
在 Sun 公司,我努力学习,尽可能多的尝试新事物。我的第一个工作是<ruby> 网页化 <rt> HTMLing </rt></ruby>(啥?这居然是一个词!)白皮书,以及为 Beta 程序修改一些基础的服务工具(大多数是 Perl 写的)。后来我成为 Solaris beta 项目组中的项目经理,并在 Open Solaris 的 Beta 版运行中感受到了开源的力量。
在那里我做的最重要的事情就是学习。我发现在同样重视工程和教育的地方有一种气氛,在那里我的问题不再显得“傻”。我很庆幸我选对了导师和朋友。在决定休第二个孩子的产假之前,我上每一堂我能上的课程,读每一本我能读的书,尝试自学我在学校没有学习过的技术,商业以及项目管理方面的技能。
### 重回工作
当我准备重新工作时,Sun 公司已经不再是合适的地方了。所以,我整理了我的联系信息(网络帮到了我),利用我的沟通技能,最终获得了一个管理互联网门户的长期合同(2005 年时,一切皆门户),并且开始了解 CRM、发布产品的方式、本地化、网络等知识。我讲这么多背景,主要是我的尝试以及失败的经历,和我成功的经历同等重要,从中学到很多。我也认为我们需要这个方面的榜样。
从很多方面来看,我的职业生涯的第一部分是我的技术教育。时变势移 —— 我在帮助组织中的女性和其他弱势群体,但是并没有看出为一个技术行业的女性有多难。当时无疑我没有看到这个行业的缺陷,但是现在这个行业更加的厌恶女性,一点没有减少。
在这些事情之后,我还没有把自己当作一个标杆,或者一个高级技术人员。当我在父母圈子里认识的一位极客朋友鼓励我申请一个看起来定位十分模糊且技术性很强的开源的非盈利基础设施机构(互联网系统协会 ISC,它是广泛部署的开源 DNS 名称服务器 BIND 的缔造者,也是 13 台根域名服务器之一的运营商)的产品经理时,我很震惊。有很长一段时间,我都不知道他们为什么要雇佣我!我对 DNS、基础设备,以及协议的开发知之甚少,但是我再次遇到了老师,并再度开始飞速发展。我花时间出差,在关键流程攻关,搞清楚如何与高度国际化的团队合作,解决麻烦的问题,最重要的是,拥抱支持我们的开源和充满活力的社区。我几乎重新学了一切,通过试错的方式。我学习如何构思一个产品。如何通过建设开源社区,领导那些有这特定才能,技能和耐心的人,是他们给了产品价值。
### 成为别人的导师
当我在 ISC 工作时,我通过 [TechWomen 项目](https://www.techwomen.org/mentorship/why-i-keep-coming-back-to-mentor-with-techwomen) (一个让来自中东和北非的技术行业的女性到硅谷来接受教育的计划),我开始喜欢教学生以及支持那些技术女性,特别是在开源行业中奋斗的。也正是从这时起我开始相信自己的能力。我还需要学很多。
当我第一次读 TechWomen 关于导师的广告时,我根本不认为他们会约我面试!我有冒名顶替综合症。当他们邀请我成为第一批导师(以及以后六年每年的导师)时,我很震惊,但是现在我学会了相信这些都是我努力得到的待遇。冒名顶替综合症是真实的,但是随着时间过去我就慢慢名副其实了。
### 现在
最后,我不得不离开我在 ISC 的工作。幸运的是,我的工作以及我的价值让我进入了 Mozilla ,在这里我的努力和我的幸运让我在这里承担着重要的角色。现在,我是一名支持多样性与包容的高级项目经理。我致力于构建一个更多样化,更有包容性的 Mozilla ,站在之前的做同样事情的巨人的肩膀上,与最聪明友善的人们一起工作。我用我的激情来让人们找到贡献一个世界需要的互联网的有意义的方式:这让我兴奋了很久。当我爬上山峰,我能极目四望!
通过对组织和个人行为的干预来获取一种改变文化的新方式,这和我的人生轨迹有着不可思议的联系 —— 从我的早期的学术生涯,到职业生涯再到现在。每天都是一个新的挑战,我想这是我喜欢在科技行业工作,尤其是在开放互联网工作的理由。互联网天然的多元性是它最开始吸引我的原因,也是我还在寻求的 —— 所有人都有机会和获取资源的可能性,无论背景如何。榜样、导师、资源,以及最重要的,尊重,是不断发展技术和开源文化的必要组成部分,实现我相信它能实现的所有事 —— 包括给所有人平等的接触机会。
本文作者 Larissa Shapiro 是 Mozilla 的一名支持多样性与包容的高级项目经理。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/life/16/5/my-open-source-story-larissa-shapiro>
作者:[Larissa Shapiro](https://opensource.com/users/larissa-shapiro) 译者:[name1e5s](https://github.com/name1e5s) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Back in 2014, my colleague [Crystal Beasley](http://skinnywhitegirl.com/blog/my-nerd-story/1101/) started a thread of women in tech/hackers posting their "nerd stories" in response to some comments out there on the Internet about the lack of women in tech. This is my nerd story, shared with you because I do believe in role models, and I do believe that there are many paths one can take to a satisfying challenging career and a life that helps one fulfill their goals.
## Growing up with computers
I am, among other things, a daughter of Silicon Valley. Mine is not a story of arriving at tech from the sidelines, or of dedication from childhood. It is more a story of how exposure shapes you—of the power of being marinated in a culture, if you will. This is not the story of a straight path or a clear dedication from childhood to one goal. It is a story of intense privilege, I am aware.
I was born in Manhattan, but we lived in New Jersey while my dad was working on a PhD in computer science at Rutgers on the GI Bill. When I was four, someone at school asked me what my dad did for a living and I said, "He watches TV and hunts for bugs, but I never seen 'em." He had a dumb terminal at home, presumably for his job at Bolt Beranek Newman working on the artificial intelligence aspects of the early Internet. I was watching.
I did not get to play with dad's bug hunting TV, but I was steeped in tech from an early age, and I value the gift of that early exposure. Early exposure is one of the things we must give to the future nerds—take time to talk to the kids you know about what you do!

My dad's terminal was similar, if not identical, to this one. CC BY-SA 4.0
When I was six, we moved to California. Dad was taking a job at Xerox PARC. I remember thinking that the city would be full of bears, because there was a bear on the flag. In 1979, Palo Alto was a college town and still had orchards and open space.
After a year of public school in Palo Alto, my sisters and I were sent to Peninsula School, a "democratic model" school that shaped me deeply. Curiosity and creativity were considered central curriculum values, and education was led substantively by group decisions of the students ourselves. We rarely saw anything one would call a computer at school, but home was another story.
After his days at Xerox PARC, dad went to Apple, where he worked on and brought home the first computers I played with: the Apple II and the LISA. My dad was on the original LISA development team, and I vividly remember that he made us "play" the mousing tutorial over and over because he wanted my 3 year-old sister to be comfortable with it... and she was.

Our LISA computer pretty much looked like this. See the mouse? CC BY-SA 4.0
At the same time in school, while I was great at conceptual math, I floundered in basic computation. One teacher at my first school told my parents, and me, that I was bad at math and "stupid." While I excelled in our "regular" math program, understanding logical puzzles beyond what one expects of a 7 year-old, I could not successfully complete the math "drills" we had to do at the beginning of each day. She called me stupid, and I didn't forget it. I didn't get back to believing in my own logical and algorithmic mental capabilities for more than 10 years after that. Do not underestimate the power of the words you say to children.
Years of playing with dad's computers followed. He went from Apple to EA to SGI, and I played with all his machines. This led to us having what we thought was the coolest house in town, because we had an SGI machine on which to play Doom in our garage. I didn't code much at all, but what I got from those years, I see now, was a measure of fearlessness about trying out new technologies. At the same time, my mom, whose background was literature and education, became a technical writer and showed me both that careers can change and that it is possible to manage a technical career and motherhood together. I would not say that was easy for her, but she made it look easy to me. You'd think that all of this early exposure might send me straight into a technical degree and career. It did not.
## Undergrad years
I thought I wanted to be an elementary school teacher, and I enrolled at Mills College with every intention of doing that. Instead, I moved toward women's studies and later theology, primarily driven by one of my great desires in life: to understand human motivation and work for a better world.
At the same time, I was for the first time being exposed to the full power of the Internet. In 1991, it was a very heady thing to have your own unix shell account and a world of people to talk to. I learned a lot from just "playing" online, and more from having people around willing to answer my many questions. It turned out that these same explorations led me down my career path at least as much as any formal academic education. All information is useful. I do not think it is *any* accident that this critical period of learning and exposure happened at a women's college where a brilliant woman ran the CS department. We were not just allowed, but encouraged to explore many paths in that rarified atmosphere of empowerment (we had access to lots and lots of technology and to smart people who wanted to help), and I did. I've always been grateful for it. It was also where I learned about geek culture.
I went to grad school to study feminist theology, but technology was in my blood by then. When I realized I didn't want to be a professor or an academic ethicist, I left academia and came home with a lot of school debt and not a lot of ideas.
## A new beginning
I was stunned, in 1995, at the power I saw in the World Wide Web to connect people and share thoughts and information (I still am). I wanted in on it. It occurred to me that I could go into the "family business," but not really *how*. I started working as a temporary contractor at offices in the valley and tried a few things (writing very basic databases on semiconductor data, pre-press work for technical manuals, filing payroll stubs) before I landed my first "real" tech job at Sun Microsystems. It was a very exciting place to be. (We were, after all, "the dot in dot-com.")
At Sun, I stuck my neck out, trying as many new things as I could. I worked firsthand at HTMLing (What? It's a word!) white papers, then hacking basic surveying tools (Perl, mostly) for beta programs. Then I became a program manager for Solaris beta programs, and at last got my first whiff of open source in running beta programs for Open Solaris.
The biggest thing I did was learn. I found it to be an atmosphere where engineering and education were both valued, and where my questions were not "stupid." I was lucky in my choices of mentors and friends. I took every class I could, read every book I could, and tried to give myself the technical, business, and project management skill sets I hadn't obtained in school before deciding to take the oft-discussed "mommy break" to prepare for the birth of my second child.
## Getting back to work
When I was ready to go back to work, Sun was no longer a viable place to go. So, I gathered my contacts (networking is your friend) and my consulting skills and ended up with a rather long-term contract release managing a web "portal" (in 2005, everything was a portal) and exposing myself to everything I could about CRMs, release methodology, localization, networking, and more. I explain all of this background mostly because my biggest lesson was that the education I got was in what I tried and in what I failed to do, as much as in what I succeeded at. I think we need role models for that, too.
In many respects, the entire first part of my career was my technical education. It was a different time and place—I worked on supporting women and other underrepresented minorities in the organization, but it was not as overtly difficult to be a woman in tech then. I was undoubtedly blind to some issues at the time, but there's also a case to be made that our industry has become more misogynistic, not less.
After all of this, I still did not see myself as a role model, or as highly technical. I was quite shocked when a geek friend I knew from parenting circles encouraged me to apply for a job as product manager at a very obscure seeming and highly technical nonprofit open source infrastructure shop (Internet Systems Consortium, makers of BIND, the widely deployed open source DNS nameserver, and operators of one of the 13 root nameservers). For the longest time, I couldn't figure out why they hired me! I knew very little about DNS, infrastructure, or protocol development, but I found my mentors again and flourished. I spent my time traveling, working on critical processes, figuring out how to work with highly international teams, solving hairy problems, and most of all, embracing open source and the vibrant community that loved and supported our efforts so very much. I learned most of all, again, by making mistakes. I learned what it takes to build a vision for a product, and how building things in the open and in community takes all sorts of specific skills, talent, and patience, but adds so much value.
## Becoming a mentor
It was while I was at ISC that, through the amazing [TechWomen program](https://www.techwomen.org/mentorship/why-i-keep-coming-back-to-mentor-with-techwomen) (which brings technical women from the Middle East and North Africa to Silicon Valley for mentoring), I got hooked on mentoring and supporting other women in tech, particularly in open source and open culture. It was when I started mentoring that I started believing in my own abilities, too. That was a long lesson to learn.
When I first read the advert for TechWomen mentors, I didn't think they would even want to talk to me! My impostor syndrome was so strong. I was so shocked when I was asked to mentor the first cohort (and every one after that for six years), but I am learning to believe that I earned these things. Impostor Syndrome is real, but over time it can be overcome.
## Today
In the end, I had to leave my job at ISC. Luckily, my work and my values brought me to Mozilla, where I've been both perseverant and lucky enough to have several meaningful roles. Today, I'm the senior program manager of diversity and inclusion. I work full-time on building a more diverse and inclusive Mozilla, standing on the shoulders of giants who did the same before me and in partnership with many of the smartest and kindest people I know. I've followed my passion for empowering people to find meaningful ways to contribute to the Internet I believe the world needs: an expansion of the one that excited me so long ago. And I get to see a lot of the world while I do it!
Taking a new approach to changing culture through organizational and behavioral interventions is such an incredible way to connect my entire trajectory—from my early academics through my career to now. It's a new challenge every day, and I guess that's what I love most about working in tech and in particular on the open web. The very pluralistic nature of the web that first drew me in is the same possibility I still seek—a world where there is opportunity for all and where there are resources for people no matter their backgrounds. Role models, mentors, resources, and, above all, respect are essential components of evolving tech and open source culture to be all that I believe it can be—including access and opportunity for all of us.
## 1 Comment |
8,069 | 哪个编程语言最流行? | http://www.zdnet.com/article/which-programming-languages-are-most-popular-and-what-does-that-even-mean/ | 2016-12-28T08:49:00 | [
"编程",
"语言"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8069-1.html |
>
> 经常有人问哪个编程语言最流行?这问题很简单,但是回答起来可没那么简单。
>
>
>

首先,我们要知道,为什么人们会问这样的问题?
一般问这样的问题是人大多是学生,他们想知道这个问题的答案是因为他们想要找份工作,所以寻求一种可以增加面试成功率的技能。对于大多数人来说,进入一个新的领域时了解什么是最流行的,是很有意义的。
而对于其他人来说,比如说已经掌握了一种或几种编程语言的程序员,他可能在想要掌握一门新的编程语言时,会考虑一下当前最流行的编程语言作为参考。而对于要开发一个产品的程序员来说,也希望了解当前最流行的编程语言是因为他们希望所开发的产品能够迎合客户的环境和需求,显然支持流行的语言的 API 会被更多人使用。
甚至,就算是你想启动一个项目时,你也需要考虑是否选择一个流行的编程语言。虽然你首先要考虑的是这种语言能够满足你的需求,比如说如果用一个流行的编程语言你需要花费更多的时间和成本,而不那么流行的编程语言或许会更快捷和轻松,显然你还是会选择那个不太流行的——但是如果各个方面都差不多,不用说你会选择流行的那个,因为这样你可以找到更多的程序员,遇到问题也有更多的解决方案。
### 怎么才算是流行?
那么,哪个语言是最流行的?其实回答这个问题并没有你想象的那么简单。关键是,你该怎么定义这个“**流行**”?
这个问题并没有固定的答案,不过在[维基上有一篇文章提到了如何测量编程语言的流行度](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Measuring_programming_language_popularity)。在这篇文章中,列出了几个测量流行度的因素:
* 该语言在搜索中提及的次数,比如在谷歌趋势中
* 在招聘广告中提及该语言的次数
* 传授和介绍该语言的书籍销售量
* 以该语言编写的现存代码的行数,不流行的语言在公开搜索中可能根本就找不到
* 在 GitHub、Freecode 上使用该语言的项目数量
* 在论坛和新闻组中讨论该语言的帖子数量
此外,你还可以考量如下指标:
* 编程培训班里面该语言的培训课程销售数量
* 编程培训班里面学生的数量
* 视频网站里面关于该语言的视频数量
* Stack Overflow 和 Reddit 里面关于该语言的帖子数量
甚至,你还可以增加一些其它的统计维度,比如根据国家和城市来统计,你知道在北京哪种编程语言最流行么?上海呢?
所以,这个问题的回答并不是一个简单的答案。
### 统计数据来源的不同
即使我们知道了流行度取决于多种因素,但是人们还是希望能够了解到底哪个语言比较流行,以此来指导他们的培训和公司的决策。
有一些网站依据不同的标准,公开发布了一些语言流行度指标。 [IEEE Spectrum](http://spectrum.ieee.org/static/interactive-the-top-programming-languages-2016) 对这些指标做了一个有趣的[整合](http://spectrum.ieee.org/static/interactive-the-top-programming-languages-2016),它可以让你通过自行设置不同因子的权重来得到你自己的编程语言流行度排行榜。

[Coding Dojo 也有一个图表](http://www.codingdojo.com/blog/9-most-in-demand-programming-languages-of-2016/),聚合了工作搜索引擎 Indeed.com 的数据;而有名的 [Tiobe](http://www.tiobe.com/tiobe-index/programming-languages-definition/) 排行榜一直使用搜索引擎聚合来计算流行度; [PyPl](http://pypl.github.io/PYPL.html) 则是根据谷歌来查看语言的流行度。
然而,这并没什么大用。如果你想知道你该学习那种语言,或者是你需要支持的语言,最困难的还是你并不知道这里的哪个图表才是适合你的。
### 好吧,我明白了,那么到底那种编程语言是流行的?
为了帮助你找到方向,我组合了上述提及的几种数据源,包括三种 IEEE 分类:“趋势”代表语言的增长度,“工作”代表 Dice.com 和 CareerBuilder 上的招聘量,“开源”代表开源项目数量。
排名结果如下表:

但是问题是,上图并不能告诉我们重点所在。要解决这个问题,我们需要做一点数据分析。我聚合了这六个数据源中的五个(我去掉了 Coding Dojo 是因为它仅显示了前九),然后我根据编程语言出现在图表中的位置和次数进行加权,这样我得到了如下的前十排名。

如你所见,这些语言分成了三大类。第一梯队包括 Java、C、Python 和 C++,毫无疑问,你肯定经常听到它们的名字。第二梯队包括 JavaScript、C#、PHP 和 Swift。剩下的两个是 Objective-C 和 R。
### 这给我们带来什么启发?
第一梯队的语言 Java、C、Python 和 C++ 都是非常通用的语言,它们并不局限于特定的编程平台或用途。
最值得关注的是第二梯队,它包括 JavaScript、C#、PHP 和 Swift。JavaScript 和 PHP 是主要的 Web 开发语言。C# 是微软的编程语言,而 Swift 是苹果新推出的主力语言。基本上来说,第二梯队是平台相关的。
那么这反映了什么?如果你懂一点现代编程,你就知道编程其实不仅仅是使用这种语言,而更重要的是开发一些什么,比如说嵌入式系统、iPhone 应用、Web 应用或者微软的服务器端应用等等。
对语言的熟悉程度其实只是一小部分。举个例子说,不管你是多么的喜欢 Python 或者古老而常青的 C,但如果你要为 WordPress 开发插件或主题,你只能使用 JavaScript 和 PHP。这无关于哪个语言更流行。
### 字里行间的发现
或者你会注意到一些有趣的地方。
首先,Coding Dojo 的编程语言排行榜的第一名是 SQL,只有它一家是这样。你很少会单独在 SQL 里面编程,通常都是在其它的语言里面使用它来管理数据。所以,学会 SQL 是很有用的,甚至是必要的。然而,去上一门 SQL 的培训课程并不能帮你找到一份工作,也不会多挣多少钱。
其次,苹果特有的语言在排行榜中排名很低,这或许和你的预期不同,因为 iOS 的应用是如此的流行。不过确实是这样的,如果你不是要开发你自己的应用的话,那学它们其实不如学习别的语言,因为其实没有那么多的公司雇佣苹果应用开发人员。这就是 Swift 语言掉到了榜尾的原因,而 Objective-C 正在被 Swift 所替代,在前面也看到了它也处于榜单的后面。
C 家族的语言仍然是主流。Java、C++、C、C#,甚至 Objective-C 都是基于 C 的语言。如果你只想学一门语言,你可以从其中选择一个。我推荐你选择 Java 或 C++,它们可以为你打开进入 C 语言家族的大门。
以我的职业生涯的经验来看,不是特别复杂的场景的话,我大概能用 20 来种语言来编程,通常我只用几天就可以学会一门新的语言。这是因为我在学校的专业就是语言设计,我也教编程超过了 20 年了。掌握这么多的语言对我很有帮助,因为我总是根据我要做的事情选择一种语言,而不是专门去上课学习一种语言。这听起来好像有点难,但是其实你也能做到的。
我的建议就是,如果你要编程,那么就去**学习多种编程语言和各种框架**吧。用编程语言去做点东西出来,编程不仅仅是一种智力锻炼,而且你可以实际用它做点什么出来。
掌握多种语言和框架是重要的,因为计算机行业变得太快了。C 语言[依然历久弥新](http://www.thepeoplehistory.com/1972.html),而 Swift 虽然出现才几年就登上了排行榜。你今天学习到的或许不够你整个职业生涯挥霍,所以“怎样学习语言”要比“学习语言”更重要,最好的办法就是多学几门。
我的推荐非常简单,无论是 C++ 还是 Java,选一个学习就好了。然后是 JavaScript,越来越多的基于 Web 的应用需要良好的 JavaScript 技能。再然后是 PHP、Swift 或 Python 中选一个,这要看你的工作种类了。当你在这三个梯队中都学会一门后,你就可以根据你的情况学习更多的语言和框架了。
好了,努力吧,学习一些编程语言,做点漂亮的成绩出来。如果你有什么想法,欢迎在下面和我们分享。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,070 | Samba 系列(二):在 Linux 命令行下管理 Samba4 AD 架构 | http://www.tecmint.com/manage-samba4-active-directory-linux-command-line | 2016-12-28T11:16:00 | [
"Samba"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8070-1.html | 这篇文章包括了管理 Samba4 域控制器架构过程中的一些常用命令,比如添加、移除、禁用或者列出用户及用户组等。
我们也会关注一下如何配置域安全策略以及如何把 AD 用户绑定到本地的 PAM 认证中,以实现 AD 用户能够在 Linux 域控制器上进行本地登录。

#### 要求
* [在 Ubuntu 系统上使用 Samba4 来创建活动目录架构](/article-8065-1.html)
### 第一步:在命令行下管理
1、 可以通过 `samba-tool` 命令行工具来进行管理,这个工具为域管理工作提供了一个功能强大的管理接口。
通过 `samba-tool` 命令行接口,你可以直接管理域用户及用户组、域组策略、域站点,DNS 服务、域复制关系和其它重要的域功能。
使用 root 权限的账号,直接输入 `samba-tool` 命令,不要加任何参数选项来查看该工具能实现的所有功能。
```
# samba-tool -h
```

*samba-tool —— Samba 管理工具*
2、 现在,让我们开始使用 `samba-tool` 工具来管理 Samba4 活动目录中的用户。
使用如下命令来创建 AD 用户:
```
# samba-tool user add your_domain_user
```
添加一个用户,包括 AD 可选的一些重要属性,如下所示:
```
--------- review all options ---------
# samba-tool user add -h
# samba-tool user add your_domain_user --given-name=your_name --surname=your_username [email protected] --login-shell=/bin/bash
```

*在 Samba AD 上创建用户*
3、 可以通过下面的命令来列出所有 Samba AD 域用户:
```
# samba-tool user list
```

*列出 Samba AD 用户信息*
4、 使用下面的命令来删除 Samba AD 域用户:
```
# samba-tool user delete your_domain_user
```
5、 重置 Samba 域用户的密码:
```
# samba-tool user setpassword your_domain_user
```
6、 启用或禁用 Samba 域用户账号:
```
# samba-tool user disable your_domain_user
# samba-tool user enable your_domain_user
```
7、 同样地,可以使用下面的方法来管理 Samba 用户组:
```
--------- review all options ---------
# samba-tool group add –h
# samba-tool group add your_domain_group
```
8、 删除 samba 域用户组:
```
# samba-tool group delete your_domain_group
```
9、 显示所有的 Samba 域用户组信息:
```
# samba-tool group list
```
10、 列出指定组下的 Samba 域用户:
```
# samba-tool group listmembers "your_domain group"
```

*列出 Samba 域用户组*
11、 从 Samba 域组中添加或删除某一用户:
```
# samba-tool group addmembers your_domain_group your_domain_user
# samba-tool group remove members your_domain_group your_domain_user
```
12、 如上面所提到的, `samba-tool` 命令行工具也可以用于管理 Samba 域策略及安全。
查看 samba 域密码设置:
```
# samba-tool domain passwordsettings show
```

*检查 Samba 域密码*
13、 为了修改 samba 域密码策略,比如密码复杂度,密码失效时长,密码长度,密码重复次数以及其它域控制器要求的安全策略等,可参照如下命令来完成:
```
---------- List all command options ----------
# samba-tool domain passwordsettings -h
```

*管理 Samba 域密码策略*
不要把上图中的密码策略规则用于生产环境中。上面的策略仅仅是用于演示目的。
### 第二步:使用活动目录账号来完成 Samba 本地认证
14、 默认情况下,离开 Samba AD DC 环境,AD 用户不能从本地登录到 Linux 系统。
为了让活动目录账号也能登录到系统,你必须在 Linux 系统环境中做如下设置,并且要修改 Samba4 AD DC 配置。
首先,打开 Samba 主配置文件,如果以下内容不存在,则添加:
```
$ sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
```
确保以下参数出现在配置文件中:
```
winbind enum users = yes
winbind enum groups = yes
```

*Samba 通过 AD 用户账号来进行认证*
15、 修改之后,使用 `testparm` 工具来验证配置文件没有错误,然后通过如下命令来重启 Samba 服务:
```
$ testparm
$ sudo systemctl restart samba-ad-dc.service
```

*检查 Samba 配置文件是否报错*
16、 下一步,我们需要修改本地 PAM 配置文件,以让 Samba4 活动目录账号能够完成本地认证、开启会话,并且在第一次登录系统时创建一个用户目录。
使用 `pam-auth-update` 命令来打开 PAM 配置提示界面,确保所有的 PAM 选项都已经使用 `[空格]` 键来启用,如下图所示:
完成之后,按 `[Tab]` 键跳转到 OK ,以启用修改。
```
$ sudo pam-auth-update
```

*为 Samba4 AD 配置 PAM 认证*

为 Samba4 AD 用户启用 PAM认证模块
17、 现在,使用文本编辑器打开 `/etc/nsswitch.conf` 配置文件,在 `passwd` 和 `group` 参数的最后面添加 `winbind` 参数,如下图所示:
```
$ sudo vi /etc/nsswitch.conf
```

*为 Samba 服务添加 Winbind Service Switch 设置*
18、 最后,编辑 `/etc/pam.d/common-password` 文件,查找下图所示行并删除 `user_authtok` 参数。
该设置确保 AD 用户在通过 Linux 系统本地认证后,可以在命令行下修改他们的密码。有这个参数时,本地认证的 AD 用户不能在控制台下修改他们的密码。
```
password [success=1 default=ignore] pam_winbind.so try_first_pass
```

*允许 Samba AD 用户修改密码*
在每次 PAM 更新安装完成并应用到 PAM 模块,或者你每次执行 `pam-auth-update` 命令后,你都需要删除 `use_authtok` 参数。
19、 Samba4 的二进制文件会生成一个内建的 windindd 进程,并且默认是启用的。
因此,你没必要再次去启用并运行 Ubuntu 系统官方自带的 winbind 服务。
为了防止系统里原来已废弃的 winbind 服务被启动,确保执行以下命令来禁用并停止原来的 winbind 服务。
```
$ sudo systemctl disable winbind.service
$ sudo systemctl stop winbind.service
```
虽然我们不再需要运行原有的 winbind 进程,但是为了安装并使用 wbinfo 工具,我们还得从系统软件库中安装 Winbind 包。
wbinfo 工具可以用来从 winbindd 进程侧来查询活动目录用户和组。
以下命令显示了使用 `wbinfo` 命令如何查询 AD 用户及组信息。
```
$ wbinfo -g
$ wbinfo -u
$ wbinfo -i your_domain_user
```

*检查 Samba4 AD 信息*

*检查 Samba4 AD 用户信息*
20、 除了 `wbinfo` 工具外,你也可以使用 `getent` 命令行工具从 Name Service Switch 库中查询活动目录信息库,在 `/etc/nsswitch.conf` 配置文件中有相关描述内容。
通过 grep 命令用管道符从 `getent` 命令过滤结果集,以获取信息库中 AD 域用户及组信息。
```
# getent passwd | grep TECMINT
# getent group | grep TECMINT
```

*查看 Samba4 AD 详细信息*
### 第三步:使用活动目录账号登录 Linux 系统
21、 为了使用 Samba4 AD 用户登录系统,使用 `su -` 命令切换到 AD 用户账号即可。
第一次登录系统后,控制台会有信息提示用户的 home 目录已创建完成,系统路径为 `/home/$DOMAIN/` 之下,名字为用户的 AD 账号名。
使用 `id` 命令来查询其它已登录的用户信息。
```
# su - your_ad_user
$ id
$ exit
```

*检查 Linux 下 Samba4 AD 用户认证结果*
22、 当你成功登入系统后,在控制台下输入 `passwd` 命令来修改已登录的 AD 用户密码。
```
$ su - your_ad_user
$ passwd
```

*修改 Samba4 AD 用户密码*
23、 默认情况下,活动目录用户没有可以完成系统管理工作的 root 权限。
要授予 AD 用户 root 权限,你必须把用户名添加到本地 sudo 组中,可使用如下命令完成。
确保你已输入域 、斜杠和 AD 用户名,并且使用英文单引号括起来,如下所示:
```
# usermod -aG sudo 'DOMAIN\your_domain_user'
```
要检查 AD 用户在本地系统上是否有 root 权限,登录后执行一个命令,比如,使用 sudo 权限执行 `apt-get update` 命令。
```
# su - tecmint_user
$ sudo apt-get update
```

*授予 Samba4 AD 用户 sudo 权限*
24、 如果你想把活动目录组中的所有账号都授予 root 权限,使用 `visudo` 命令来编辑 `/etc/sudoers` 配置文件,在 root 权限那一行添加如下内容:
```
%DOMAIN\\your_domain\ group ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
```
注意 `/etc/sudoers` 的格式,不要弄乱。
`/etc/sudoers` 配置文件对于 ASCII 引号字符处理的不是很好,因此务必使用 '%' 来标识用户组,使用反斜杠来转义域名后的第一个斜杠,如果你的组名中包含空格(大多数 AD 内建组默认情况下都包含空格)使用另外一个反斜杠来转义空格。并且域的名称要大写。

*授予所有 Samba4 用户 sudo 权限*
好了,差不多就这些了!管理 Samba4 AD 架构也可以使用 Windows 环境中的其它几个工具,比如 ADUC、DNS 管理器、 GPM 等等,这些工具可以通过安装从 Microsoft 官网下载的 RSAT 软件包来获得。
要通过 RSAT 工具来管理 Samba4 AD DC ,你必须要把 Windows 系统加入到 Samba4 活动目录。这将是我们下一篇文章的重点,在这之前,请继续关注。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/manage-samba4-active-directory-linux-command-line>
作者:[Matei Cezar](http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,071 | 如何在 Ubuntu 环境下搭建邮件服务器(一) | https://www.linux.com/learn/how-build-email-server-ubuntu-linux | 2016-12-28T17:01:00 | [
"Ubuntu",
"邮件",
"Postfix"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8071-1.html | 
在这个系列的文章中,我们将通过使用 Postfix、Dovecot 和 openssl 这三款工具来为你展示如何在 ubuntu 系统上搭建一个既可靠又易于配置的邮件服务器。
在这个容器和微服务技术日新月异的时代,值得庆幸的是有些事情并没有改变,例如搭建一个 Linux 下的邮件服务器,仍然需要许多步骤才能间隔各种服务器耦合在一起,而当你将这些配置好,放在一起,却又非常可靠稳定,不会像微服务那样一睁眼有了,一闭眼又没了。 在这个系列教程中我们将通过使用 Postfix、Dovecot 和 openssl 这三款工具在 ubuntu 系统上搭建一个既可靠又易于配置的邮件服务器。
Postfix 是一个古老又可靠的软件,它比原始的 Unix 系统的 MTA 软件 sendmail 更加容易配置和使用(还有人仍然在用sendmail 吗?)。 Exim 是 Debain 系统上的默认 MTA 软件,它比 Postfix 更加轻量而且超级容易配置,因此我们在将来的教程中会推出 Exim 的教程。
Dovecot(LCTT 译注:详情请阅读[维基百科](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dovecot_(software))和 Courier 是两个非常受欢迎的优秀的 IMAP/POP3 协议的服务器软件,Dovecot 更加的轻量并且易于配置。
你必须要保证你的邮件通讯是安全的,因此我们就需要使用到 OpenSSL 这个软件,OpenSSL 也提供了一些很好用的工具来测试你的邮件服务器。
为了简单起见,在这一系列的教程中,我们将指导大家安装一个在局域网上的邮件服务器,你应该拥有一个局域网内的域名服务,并确保它是启用且正常工作的,查看这篇“[使用 dnsmasq 为局域网轻松提供 DNS 服务](https://www.linux.com/learn/dnsmasq-easy-lan-name-services )”会有些帮助,然后,你就可以通过注册域名并相应地配置防火墙,来将这台局域网服务器变成互联网可访问邮件服务器。这个过程网上已经有很多很详细的教程了,这里不再赘述,请大家继续跟着教程进行即可。
### 一些术语
让我们先来快速了解一些术语,因为当我们了解了这些术语的时候就能知道这些见鬼的东西到底是什么。 :D
* **MTA**:<ruby> 邮件传输代理 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Mail Transfer Agent </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,基于 SMTP 协议(简单邮件传输协议)的服务端,比如 Postfix、Exim、Sendmail 等。SMTP 服务端彼此之间进行相互通信(LCTT 译注 : 详情请阅读[维基百科](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Message_transfer_agent))。
* **MUA**: <ruby> 邮件用户代理 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Mail User Agent </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,你本地的邮件客户端,例如 : Evolution、KMail、Claws Mail 或者 Thunderbird(LCTT 译注 : 例如国内的 Foxmail)。
* **POP3**:<ruby> 邮局协议 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Post-Office Protocol </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>版本 3,将邮件从 SMTP 服务器传输到你的邮件客户端的的最简单的协议。POP 服务端是非常简单小巧的,单一的一台机器可以为数以千计的用户提供服务。
* **IMAP**: <ruby> 交互式消息访问协议 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Interactive Message Access Protocol </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,许多企业使用这个协议因为邮件可以被保存在服务器上,而用户不必担心会丢失消息。IMAP 服务器需要大量的内存和存储空间。
* **TLS**:<ruby> 传输套接层 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Transport socket layer </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>是 SSL(<ruby> 安全套接层 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Secure Sockets Layer </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)的改良版,为 SASL 身份认证提供了加密的传输服务层。
* **SASL**:<ruby> 简单身份认证与安全层 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Simple Authentication and Security Layer </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,用于认证用户。SASL进行身份认证,而上面说的 TLS 提供认证数据的加密传输。
* **StartTLS**: 也被称为伺机 TLS 。如果服务器双方都支持 SSL/TLS,StartTLS 就会将纯文本连接升级为加密连接(TLS 或 SSL)。如果有一方不支持加密,则使用明文传输。StartTLS 会使用标准的未加密端口 25 (SMTP)、 110(POP3)和 143 (IMAP)而不是对应的加密端口 465(SMTP)、995(POP3) 和 993 (IMAP)。
### 啊,我们仍然有 sendmail
绝大多数的 Linux 版本仍然还保留着 `/usr/sbin/sendmail` 。 这是在那个 MTA 只有一个 sendmail 的古代遗留下来的痕迹。在大多数 Linux 发行版中,`/usr/sbin/sendmail` 会符号链接到你安装的 MTA 软件上。如果你的 Linux 中有它,不用管它,你的发行版会自己处理好的。
### 安装 Postfix
使用 `apt-get install postfix` 来做基本安装时要注意(图 1),安装程序会打开一个向导,询问你想要搭建的服务器类型,你要选择“Internet Server”,虽然这里是局域网服务器。它会让你输入完全限定的服务器域名(例如: myserver.mydomain.net)。对于局域网服务器,假设你的域名服务已经正确配置,(我多次提到这个是因为经常有人在这里出现错误),你也可以只使用主机名。

*图 1:Postfix 的配置。*
Ubuntu 系统会为 Postfix 创建一个配置文件,并启动三个守护进程 : `master`、`qmgr` 和 `pickup`,这里没用一个叫 Postfix 的命令或守护进程。(LCTT 译注:名为 `postfix` 的命令是管理命令。)
```
$ ps ax
6494 ? Ss 0:00 /usr/lib/postfix/master
6497 ? S 0:00 pickup -l -t unix -u -c
6498 ? S 0:00 qmgr -l -t unix -u
```
你可以使用 Postfix 内置的配置语法检查来测试你的配置文件,如果没用发现语法错误,不会输出任何内容。
```
$ sudo postfix check
[sudo] password for carla:
```
使用 `netstat` 来验证 `postfix` 是否正在监听 25 端口。
```
$ netstat -ant
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::25 :::* LISTEN
```
现在让我们再操起古老的 `telnet` 来进行测试 :
```
$ telnet myserver 25
Trying 127.0.1.1...
Connected to myserver.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 myserver ESMTP Postfix (Ubuntu)
EHLO myserver
250-myserver
250-PIPELINING
250-SIZE 10240000
250-VRFY
250-ETRN
250-STARTTLS
250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES
250-8BITMIME
250 DSN
^]
telnet>
```
嘿,我们已经验证了我们的服务器名,而且 Postfix 正在监听 SMTP 的 25 端口而且响应了我们键入的命令。
按下 `^]` 终止连接,返回 telnet。输入 `quit` 来退出 telnet。输出的 ESMTP(扩展的 SMTP ) 250 状态码如下。 (LCTT 译注: ESMTP (Extended SMTP),即扩展 SMTP,就是对标准 SMTP 协议进行的扩展。详情请阅读[维基百科](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extended_SMTP))
* **PIPELINING** 允许多个命令流式发出,而不必对每个命令作出响应。
* **SIZE** 表示服务器可接收的最大消息大小。
* **VRFY** 可以告诉客户端某一个特定的邮箱地址是否存在,这通常应该被取消,因为这是一个安全漏洞。
* **ETRN** 适用于非持久互联网连接的服务器。这样的站点可以使用 ETRN 从上游服务器请求邮件投递,Postfix 可以配置成延迟投递邮件到 ETRN 客户端。
* **STARTTLS** (详情见上述说明)。
* **ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES**,服务器支撑增强型的状态码和错误码。
* **8BITMIME**,支持 8 位 MIME,这意味着完整的 ASCII 字符集。最初,原始的 ASCII 是 7 位。
* **DSN**,投递状态通知,用于通知你投递时的错误。
Postfix 的主配置文件是: `/etc/postfix/main.cf`,这个文件是安装程序创建的,可以参考[这个资料](http://www.postfix.org/postconf.5.html)来查看完整的 `main.cf` 参数列表, `/etc/postfix/postfix-files` 这个文件描述了 Postfix 完整的安装文件。
[下一篇教程](/article-8077-1.html)我们会讲解 Dovecot 的安装和测试,然后会给我们自己发送一些邮件。
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/learn/how-build-email-server-ubuntu-linux>
作者:[CARLA SCHRODER](https://www.linux.com/users/cschroder) 译者:[WangYihang](https://github.com/WangYihang) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,072 | LXD 2.0 系列(四):资源控制 | https://www.stgraber.org/2016/03/26/lxd-2-0-resource-control-412/ | 2016-12-29T08:47:00 | [
"LXC",
"LXD"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8072-1.html | 这是 LXD 2.0 系列介绍文章的第四篇。
1. [LXD 入门](/article-7618-1.html)
2. [安装与配置](/article-7687-1.html)
3. [你的第一个 LXD 容器](/article-7706-1.html)
4. [资源控制](/article-8072-1.html)
5. [镜像管理](/article-8107-1.html)
6. [远程主机及容器迁移](/article-8169-1.html)
7. [LXD 中的 Docker](/article-8235-1.html)
8. [LXD 中的 LXD](/article-8257-1.html)
9. [实时迁移](/article-8263-1.html)
10. [LXD 和 Juju](/article-8273-1.html)
11. [LXD 和 OpenStack](/article-8274-1.html)
12. [调试,及给 LXD 做贡献](/article-8282-1.html)

因为 LXD 容器管理有很多命令,因此这篇文章会很长。 如果你想要快速地浏览这些相同的命令,你可以[尝试下我们的在线演示](https://github.com/lxc/lxd/blob/master/doc/configuration.md)!
### 可用资源限制
LXD 提供了各种资源限制。其中一些与容器本身相关,如内存配额、CPU 限制和 I/O 优先级。而另外一些则与特定设备相关,如 I/O 带宽或磁盘用量限制。
与所有 LXD 配置一样,资源限制可以在容器运行时动态更改。某些可能无法启用,例如,如果设置的内存值小于当前内存用量,但 LXD 将会试着设置并且报告失败。
所有的限制也可以通过配置文件继承,在这种情况下每个受影响的容器将受到该限制的约束。也就是说,如果在默认配置文件中设置 `limits.memory=256MB`,则使用默认配置文件(通常是全都使用)的每个容器的内存限制为 256MB。
我们不支持资源限制池,将其中的限制由一组容器共享,因为我们没有什么好的方法通过现有的内核 API 实现这些功能。
#### 磁盘
这或许是最需要和最明显的需求。只需设置容器文件系统的大小限制,并对容器强制执行。
LXD 确实可以让你这样做!
不幸的是,这比它听起来复杂得多。 Linux 没有基于路径的配额,而大多数文件系统只有基于用户和组的配额,这对容器没有什么用处。
如果你正在使用 ZFS 或 btrfs 存储后端,这意味着现在 LXD 只能支持磁盘限制。也有可能为 LVM 实现此功能,但这取决于与它一起使用的文件系统,并且如果结合实时更新那会变得棘手起来,因为并不是所有的文件系统都允许在线增长,而几乎没有一个允许在线收缩。
#### CPU
当涉及到 CPU 的限制,我们支持 4 种不同的东西:
* 只给我 X 个 CPU 核心
在这种模式下,你让 LXD 为你选择一组核心,然后为更多的容器和 CPU 的上线/下线提供负载均衡。
容器只看到这个数量的 CPU 核心。
* 给我一组特定的 CPU 核心(例如,核心1、3 和 5)
类似于第一种模式,但是不会做负载均衡,你会被限制在那些核心上,无论它们有多忙。
* 给我你拥有的 20% 处理能力
在这种模式下,你可以看到所有的 CPU,但调度程序将限制你使用 20% 的 CPU 时间,但这只有在负载状态才会这样!所以如果系统不忙,你的容器可以跑得很欢。而当其他的容器也开始使用 CPU 时,它会被限制用量。
* 每测量 200ms,给我 50ms(并且不超过)
此模式与上一个模式类似,你可以看到所有的 CPU,但这一次,无论系统可能是多么空闲,你只能使用你设置的极限时间下的尽可能多的 CPU 时间。在没有过量使用的系统上,这可使你可以非常整齐地分割 CPU,并确保这些容器的持续性能。
另外还可以将前两个中的一个与最后两个之一相结合,即请求一组 CPU,然后进一步限制这些 CPU 的 CPU 时间。
除此之外,我们还有一个通用的优先级调节方式,可以告诉调度器当你处于负载状态时,两个争夺资源的容器谁会取得胜利。
#### 内存
内存听起来很简单,就是给我多少 MB 的内存!
它绝对可以那么简单。 我们支持这种限制以及基于百分比的请求,比如给我 10% 的主机内存!
另外我们在上层支持一些额外的东西。 例如,你可以选择在每个容器上打开或者关闭 swap,如果打开,还可以设置优先级,以便你可以选择哪些容器先将内存交换到磁盘!
内存限制默认是“hard”。 也就是说,当内存耗尽时,内核将会开始杀掉你的那些进程。
或者,你可以将强制策略设置为“soft”,在这种情况下,只要没有别的进程的情况下,你将被允许使用尽可能多的内存。一旦别的进程想要这块内存,你将无法分配任何内存,直到你低于你的限制或者主机内存再次有空余。
#### 网络 I/O
网络 I/O 可能是我们看起来最简单的限制,但是相信我,实现真的不简单!
我们支持两种限制。 第一个是对网络接口的速率限制。你可以设置入口和出口的限制,或者只是设置“最大”限制然后应用到出口和入口。这个只支持“桥接”和“p2p”类型接口。
第二种是全局网络 I/O 优先级,仅当你的网络接口趋于饱和的时候再使用。
#### 块 I/O
我把最古怪的放在最后。对于用户看起来它可能简单,但有一些情况下,它的结果并不会和你的预期一样。
我们在这里支持的基本上与我在网络 I/O 中描述的相同。
你可以直接设置磁盘的读写 IO 的频率和速率,并且有一个全局的块 I/O 优先级,它会通知 I/O 调度程序更倾向哪个。
古怪的是如何设置以及在哪里应用这些限制。不幸的是,我们用于实现这些功能的底层使用的是完整的块设备。这意味着我们不能为每个路径设置每个分区的 I/O 限制。
这也意味着当使用可以支持多个块设备映射到指定的路径(带或者不带 RAID)的 ZFS 或 btrfs 时,我们并不知道这个路径是哪个块设备提供的。
这意味着,完全有可能,实际上确实有可能,容器使用的多个磁盘挂载点(绑定挂载或直接挂载)可能来自于同一个物理磁盘。
这就使限制变得很奇怪。为了使限制生效,LXD 具有猜测给定路径所对应块设备的逻辑,这其中包括询问 ZFS 和 btrfs 工具,甚至可以在发现一个文件系统中循环挂载的文件时递归地找出它们。
这个逻辑虽然不完美,但通常会找到一组应该应用限制的块设备。LXD 接着记录并移动到下一个路径。当遍历完所有的路径,然后到了非常奇怪的部分。它会平均你为相应块设备设置的限制,然后应用这些。
这意味着你将在容器中“平均”地获得正确的速度,但这也意味着你不能对来自同一个物理磁盘的“/fast”和一个“/slow”目录应用不同的速度限制。 LXD 允许你设置它,但最后,它会给你这两个值的平均值。
### 它怎么工作?
除了网络限制是通过较旧但是良好的“tc”实现的,上述大多数限制是通过 Linux 内核的 cgroup API 来实现的。
LXD 在启动时会检测你在内核中启用了哪些 cgroup,并且将只应用你的内核支持的限制。如果你缺少一些 cgroup,守护进程会输出警告,接着你的 init 系统将会记录这些。
在 Ubuntu 16.04 上,默认情况下除了内存交换审计外将会启用所有限制,内存交换审计需要你通过`swapaccount = 1`这个内核引导参数来启用。
### 应用这些限制
上述所有限制都能够直接或者用某个配置文件应用于容器。容器范围的限制可以使用:
```
lxc config set CONTAINER KEY VALUE
```
或对于配置文件设置:
```
lxc profile set PROFILE KEY VALUE
```
当指定特定设备时:
```
lxc config device set CONTAINER DEVICE KEY VALUE
```
或对于配置文件设置:
```
lxc profile device set PROFILE DEVICE KEY VALUE
```
有效配置键、设备类型和设备键的完整列表可以[看这里](https://github.com/lxc/lxd/blob/master/doc/configuration.md)。
#### CPU
要限制使用任意两个 CPU 核心可以这么做:
```
lxc config set my-container limits.cpu 2
```
要指定特定的 CPU 核心,比如说第二和第四个:
```
lxc config set my-container limits.cpu 1,3
```
更加复杂的情况还可以设置范围:
```
lxc config set my-container limits.cpu 0-3,7-11
```
限制实时生效,你可以看下面的例子:
```
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc exec zerotier -- cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep ^proces
processor : 0
processor : 1
processor : 2
processor : 3
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc config set zerotier limits.cpu 2
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc exec zerotier -- cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep ^proces
processor : 0
processor : 1
```
注意,为了避免完全混淆用户空间,lxcfs 会重排 `/proc/cpuinfo` 中的条目,以便没有错误。
就像 LXD 中的一切,这些设置也可以应用在配置文件中:
```
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc exec snappy -- cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep ^proces
processor : 0
processor : 1
processor : 2
processor : 3
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc profile set default limits.cpu 3
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc exec snappy -- cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep ^proces
processor : 0
processor : 1
processor : 2
```
要限制容器使用 10% 的 CPU 时间,要设置下 CPU allowance:
```
lxc config set my-container limits.cpu.allowance 10%
```
或者给它一个固定的 CPU 时间切片:
```
lxc config set my-container limits.cpu.allowance 25ms/200ms
```
最后,要将容器的 CPU 优先级调到最低:
```
lxc config set my-container limits.cpu.priority 0
```
#### 内存
要直接应用内存限制运行下面的命令:
```
lxc config set my-container limits.memory 256MB
```
(支持的后缀是 KB、MB、GB、TB、PB、EB)
要关闭容器的内存交换(默认启用):
```
lxc config set my-container limits.memory.swap false
```
告诉内核首先交换指定容器的内存:
```
lxc config set my-container limits.memory.swap.priority 0
```
如果你不想要强制的内存限制:
```
lxc config set my-container limits.memory.enforce soft
```
#### 磁盘和块 I/O
不像 CPU 和内存,磁盘和 I/O 限制是直接作用在实际的设备上的,因此你需要编辑原始设备或者屏蔽某个具体的设备。
要设置磁盘限制(需要 btrfs 或者 ZFS):
```
lxc config device set my-container root size 20GB
```
比如:
```
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc exec zerotier -- df -h /
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
encrypted/lxd/containers/zerotier 179G 542M 178G 1% /
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc config device set zerotier root size 20GB
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc exec zerotier -- df -h /
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
encrypted/lxd/containers/zerotier 20G 542M 20G 3% /
```
要限制速度,你可以:
```
lxc config device set my-container root limits.read 30MB
lxc config device set my-container root.limits.write 10MB
```
或者限制 IO 频率:
```
lxc config device set my-container root limits.read 20Iops
lxc config device set my-container root limits.write 10Iops
```
最后你在一个过量使用的繁忙系统上,你或许想要:
```
lxc config set my-container limits.disk.priority 10
```
将那个容器的 I/O 优先级调到最高。
#### 网络 I/O
只要机制可用,网络 I/O 基本等同于块 I/O。
比如:
```
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc exec zerotier -- wget http://speedtest.newark.linode.com/100MB-newark.bin -O /dev/null
--2016-03-26 22:17:34-- http://speedtest.newark.linode.com/100MB-newark.bin
Resolving speedtest.newark.linode.com (speedtest.newark.linode.com)... 50.116.57.237, 2600:3c03::4b
Connecting to speedtest.newark.linode.com (speedtest.newark.linode.com)|50.116.57.237|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 104857600 (100M) [application/octet-stream]
Saving to: '/dev/null'
/dev/null 100%[===================>] 100.00M 58.7MB/s in 1.7s
2016-03-26 22:17:36 (58.7 MB/s) - '/dev/null' saved [104857600/104857600]
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc profile device set default eth0 limits.ingress 100Mbit
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc profile device set default eth0 limits.egress 100Mbit
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc exec zerotier -- wget http://speedtest.newark.linode.com/100MB-newark.bin -O /dev/null
--2016-03-26 22:17:47-- http://speedtest.newark.linode.com/100MB-newark.bin
Resolving speedtest.newark.linode.com (speedtest.newark.linode.com)... 50.116.57.237, 2600:3c03::4b
Connecting to speedtest.newark.linode.com (speedtest.newark.linode.com)|50.116.57.237|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 104857600 (100M) [application/octet-stream]
Saving to: '/dev/null'
/dev/null 100%[===================>] 100.00M 11.4MB/s in 8.8s
2016-03-26 22:17:56 (11.4 MB/s) - '/dev/null' saved [104857600/104857600]
```
这就是如何将一个千兆网的连接速度限制到仅仅 100Mbit/s 的!
和块 I/O 一样,你可以设置一个总体的网络优先级:
```
lxc config set my-container limits.network.priority 5
```
### 获取当前资源使用率
[LXD API](https://github.com/lxc/lxd/blob/master/doc/rest-api.md) 可以导出目前容器资源使用情况的一点信息,你可以得到:
* 内存:当前、峰值、目前内存交换和峰值内存交换
* 磁盘:当前磁盘使用率
* 网络:每个接口传输的字节和包数。
另外如果你使用的是非常新的 LXD(在写这篇文章时的 git 版本),你还可以在`lxc info`中得到这些信息:
```
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc info zerotier
Name: zerotier
Architecture: x86_64
Created: 2016/02/20 20:01 UTC
Status: Running
Type: persistent
Profiles: default
Pid: 29258
Ips:
eth0: inet 172.17.0.101
eth0: inet6 2607:f2c0:f00f:2700:216:3eff:feec:65a8
eth0: inet6 fe80::216:3eff:feec:65a8
lo: inet 127.0.0.1
lo: inet6 ::1
lxcbr0: inet 10.0.3.1
lxcbr0: inet6 fe80::f0bd:55ff:feee:97a2
zt0: inet 29.17.181.59
zt0: inet6 fd80:56c2:e21c:0:199:9379:e711:b3e1
zt0: inet6 fe80::79:e7ff:fe0d:5123
Resources:
Processes: 33
Disk usage:
root: 808.07MB
Memory usage:
Memory (current): 106.79MB
Memory (peak): 195.51MB
Swap (current): 124.00kB
Swap (peak): 124.00kB
Network usage:
lxcbr0:
Bytes received: 0 bytes
Bytes sent: 570 bytes
Packets received: 0
Packets sent: 0
zt0:
Bytes received: 1.10MB
Bytes sent: 806 bytes
Packets received: 10957
Packets sent: 10957
eth0:
Bytes received: 99.35MB
Bytes sent: 5.88MB
Packets received: 64481
Packets sent: 64481
lo:
Bytes received: 9.57kB
Bytes sent: 9.57kB
Packets received: 81
Packets sent: 81
Snapshots:
zerotier/blah (taken at 2016/03/08 23:55 UTC) (stateless)
```
### 总结
LXD 团队花费了几个月的时间来迭代我们使用的这些限制的语言。 它是为了在保持强大和功能明确的基础上同时保持简单。
实时地应用这些限制和通过配置文件继承,使其成为一种非常强大的工具,可以在不影响正在运行的服务的情况下实时管理服务器上的负载。
### 更多信息
LXD 的主站在: <https://linuxcontainers.org/lxd>
LXD 的 GitHub 仓库: <https://github.com/lxc/lxd>
LXD 的邮件列表:<https://lists.linuxcontainers.org>
LXD 的 IRC 频道:#lxcontainers on irc.freenode.net
如果你不想在你的机器上安装LXD,你可以[在线尝试下](https://linuxcontainers.org/lxd/try-it)。
---
作者简介:我是 Stéphane Graber。我是 LXC 和 LXD 项目的领导者,目前在加拿大魁北克蒙特利尔的家所在的Canonical 有限公司担任 LXD 的技术主管。
---
via: <https://www.stgraber.org/2016/03/26/lxd-2-0-resource-control-412/>
作者:[Stéphane Graber](https://www.stgraber.org/author/stgraber/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,073 | 把 SQL Server 迁移到 Linux?不如换成 MySQL | https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/moving-with-sql-server-to-linux-move-from-sql-server-to-mysql-as-well/ | 2016-12-29T09:44:00 | [
"MSSQL",
"MySQL",
"微软"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8073-1.html | 最近几年,数量庞大的个人和组织放弃 Windows 平台选择 Linux 平台,而且随着人们体验到更多 Linux 的发展,这个数字将会继续增长。在很长的一段时间内, Linux 是网络服务器的领导者,因为大部分的网络服务器都运行在 Linux 之上,这或许是为什么那么多的个人和组织选择迁移的一个原因。

迁移的原因有很多,更强的平台稳定性、可靠性、成本、所有权和安全性等等。随着更多的个人和组织迁移到 Linux 平台,MS SQL 服务器数据库管理系统的迁移也有着同样的趋势,首选的是 MySQL ,这是因为 MySQL 的互用性、平台无关性和购置成本低。
有如此多的个人和组织完成了迁移,这是应业务需求而产生的迁移,而不是为了迁移的乐趣。因此,有必要做一个综合可行性和成本效益分析,以了解迁移对于你的业务上的正面和负面影响。
迁移需要基于以下重要因素:
### 对平台的掌控
不像 Windows 那样,你不能完全控制版本发布和修复,而 Linux 可以让你需要需要修复的时候真正给了你获取修复的灵活性。这一点受到了开发者和安全人员的喜爱,因为他们能在一个安全威胁被确定时立即自行打补丁,不像 Windows ,你只能期望官方尽快发布补丁。
### 跟随大众
目前, 运行在 Linux 平台上的服务器在数量上远超 Windows,几乎是全世界服务器数量的四分之三,而且这种趋势在最近一段时间内不会改变。因此,许多组织正在将他们的服务完全迁移到 Linux 上,而不是同时使用两种平台,同时使用将会增加他们的运营成本。
### 微软没有开放 SQL Server 的源代码
微软宣称他们下一个名为 Denali 的新版 MS SQL Server 将会是一个 [Linux 版本](/article-7967-1.html),并且不会开放其源代码,这意味着他们仍然使用的是软件授权模式,只是新版本将能在 Linux 上运行而已。这一点将许多乐于接受开源新版本的人拒之门外。
这也没有给那些使用闭源的 Oracle 用户另一个选择,对于使用完全开源的 [MySQL 用户](http://www.scalearc.com/how-it-works/products/scalearc-for-mysql)也是如此。
### 节约授权许可证的花费
授权许可证的潜在成本让许多用户很失望。在 Windows 平台上运行 MS SQL 服务器有太多的授权许可证牵涉其中。你需要这些授权许可证:
* Windows 操作系统
* MS SQL 服务器
* 特定的数据库工具,例如 SQL 分析工具等
不像 Windows 平台,Linux 完全没有高昂的授权花费,因此更能吸引用户。 MySQL 数据库也能免费获取,甚而它提供了像 MS SQL 服务器一样的灵活性,那就更值得选择了。不像那些给 MS SQL 设计的收费工具,大部分的 MySQL 数据库实用程序是免费的。
### 有时候用的是特殊的硬件
因为 Linux 是不同的开发者所开发,并在不断改进中,所以它独立于所运行的硬件之上,并能被广泛使用在不同的硬件平台。然而尽管微软正在努力让 Windows 和 MSSQL 服务器做到硬件无关,但在平台无关上依旧有些限制。
### 支持
有了 Linux、MySQL 和其它的开源软件,获取满足自己特定需求的帮助变得更加简单,因为有不同开发者参与到这些软件的开发过程中。这些开发者或许就在你附近,这样更容易获取帮助。在线论坛也能帮上不少,你能发帖并讨论你所面对的问题。
至于那些商业软件,你只能根据他们的软件协议和时间来获得帮助,有时候他们不能在你的时间范围内给出一个解决方案。
在不同的情况中,迁移到 Linux 都是你最好的选择,加入一个彻底的、稳定可靠的平台来获取优异表现,众所周知,它比 Windows 更健壮。这值得一试。
---
via: <https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/moving-with-sql-server-to-linux-move-from-sql-server-to-mysql-as-well/>
作者:[Tony Branson](https://twitter.com/howtoforgecom) 译者:[ypingcn](https://github.com/ypingcn) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 404 | Not Found | null |
8,074 | PyCharm - Linux 下最好的 Python IDE | https://www.lifewire.com/pycharm-the-best-linux-python-ide-4091045 | 2016-12-29T12:41:00 | [
"Python",
"IDE",
"PyCharm"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8074-1.html | ### 介绍

在这篇指南中,我将向你介绍一个集成开发环境 - PyCharm, 你可以在它上面使用 Python 编程语言开发专业应用。
Python 是一门优秀的编程语言,因为它真正实现了跨平台,用它开发的应用程序在 Windows、Linux 以及 Mac 系统上均可运行,无需重新编译任何代码。
PyCharm 是由 [Jetbrains](https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/specials/pycharm/pycharm.html?&gclid=CjwKEAjw34i_BRDH9fbylbDJw1gSJAAvIFqU238G56Bd2sKU9EljVHs1bKKJ8f3nV--Q9knXaifD8xoCRyjw_wcB&gclsrc=aw.ds.ds&dclid=CNOy3qGQoc8CFUJ62wodEywCDg) 开发的一个编辑器和调试器,[Jetbrains](https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/specials/pycharm/pycharm.html?&gclid=CjwKEAjw34i_BRDH9fbylbDJw1gSJAAvIFqU238G56Bd2sKU9EljVHs1bKKJ8f3nV--Q9knXaifD8xoCRyjw_wcB&gclsrc=aw.ds.ds&dclid=CNOy3qGQoc8CFUJ62wodEywCDg) 就是那个开发了 Resharper 的公司。不得不说,Resharper 是一个很优秀的工具,它被 Windows 开发者们用来重构代码,同时,它也使得 Windows 开发者们写 .NET 代码更加轻松。[Resharper](https://www.jetbrains.com/resharper/) 的许多原则也被加入到了 [PyCharm](https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/specials/pycharm/pycharm.html?&gclid=CjwKEAjw34i_BRDH9fbylbDJw1gSJAAvIFqU238G56Bd2sKU9EljVHs1bKKJ8f3nV--Q9knXaifD8xoCRyjw_wcB&gclsrc=aw.ds.ds&dclid=CNOy3qGQoc8CFUJ62wodEywCDg) 专业版中。
### 如何安装 PyCharm
我已经[写了一篇](/article-8080-1.html)关于如何获取 PyCharm 的指南,下载、解压文件,然后运行。
### 欢迎界面
当你第一次运行 PyCharm 或者关闭一个项目的时候,会出现一个屏幕,上面显示一系列近期项目。
你也会看到下面这些菜单选项:
* 创建新项目
* 打开项目
* 从版本控制仓库检出
还有一个配置设置选项,你可以通过它设置默认 Python 版本或者一些其他设置。
### 创建一个新项目
当你选择‘创建一个新项目’以后,它会提供下面这一系列可能的项目类型供你选择:
* Pure Python
* Django
* Flask
* Google App Engine
* Pyramid
* Web2Py
* Angular CLI
* AngularJS
* Foundation
* HTML5 Bolierplate
* React Starter Kit
* Twitter Bootstrap
* Web Starter Kit
这不是一个编程教程,所以我没必要说明这些项目类型是什么。如果你想创建一个可以运行在 Windows、Linux 和 Mac 上的简单桌面运行程序,那么你可以选择 Pure Python 项目,然后使用 Qt 库来开发图形应用程序,这样的图形应用程序无论在何种操作系统上运行,看起来都像是原生的,就像是在该系统上开发的一样。
选择了项目类型以后,你需要输入一个项目名字并且选择一个 Python 版本来进行开发。
### 打开一个项目
你可以通过单击‘最近打开的项目’列表中的项目名称来打开一个项目,或者,你也可以单击‘打开’,然后浏览到你想打开的项目所在的文件夹,找到该项目,然后选择‘确定’。
### 从源码控制进行查看
PyCharm 提供了从各种在线资源查看项目源码的选项,在线资源包括 [GitHub](https://github.com/)、[CVS](http://www.linuxhowtos.org/System/cvs_tutorial.htm)、Git、[Mercurial](https://www.mercurial-scm.org/) 以及 [Subversion](https://subversion.apache.org/)。
### PyCharm IDE(集成开发环境)
PyCharm IDE 中可以打开顶部的菜单,在这个菜单下方你可以看到每个打开的项目的标签。
屏幕右方是调试选项区,可以单步运行代码。
左侧面板有项目文件和外部库的列表。
如果想在项目中新建一个文件,你可以鼠标右击项目的名字,然后选择‘新建’。然后你可以在下面这些文件类型中选择一种添加到项目中:
* 文件
* 目录
* Python 包
* Python 包
* Jupyter 笔记
* HTML 文件
* Stylesheet
* JavaScript
* TypeScript
* CoffeeScript
* Gherkin
* 数据源
当添加了一个文件,比如 Python 文件以后,你可以在右边面板的编辑器中进行编辑。
文本是全彩色编码的,并且有黑体文本。垂直线显示缩进,从而能够确保缩进正确。
编辑器具有智能补全功能,这意味着当你输入库名字或可识别命令的时候,你可以按 'Tab' 键补全命令。

### 调试程序
你可以利用屏幕右上角的’调试选项’调试程序的任何一个地方。
如果你是在开发一个图形应用程序,你可以点击‘绿色按钮’来运行程序,你也可以通过 'shift+F10' 快捷键来运行程序。
为了调试应用程序,你可以点击紧挨着‘绿色按钮’的‘绿色箭头’或者按 ‘shift+F9’ 快捷键。你可以点击一行代码的灰色边缘,从而设置断点,这样当程序运行到这行代码的时候就会停下来。
你可以按 'F8' 单步向前运行代码,这意味着你只是运行代码但无法进入函数内部,如果要进入函数内部,你可以按 'F7'。如果你想从一个函数中返回到调用函数,你可以按 'shift+F8'。
调试过程中,你会在屏幕底部看到许多窗口,比如进程和线程列表,以及你正在监视的变量。
当你运行到一行代码的时候,你可以对这行代码中出现的变量进行监视,这样当变量值改变的时候你能够看到。
另一个不错的选择是使用覆盖检查器运行代码。在过去这些年里,编程界发生了很大的变化,现在,对于开发人员来说,进行测试驱动开发是很常见的,这样他们可以检查对程序所做的每一个改变,确保不会破坏系统的另一部分。
覆盖检查器能够很好的帮助你运行程序,执行一些测试,运行结束以后,它会以百分比的形式告诉你测试运行所覆盖的代码有多少。
还有一个工具可以显示‘类函数’或‘类’的名字,以及一个项目被调用的次数和在一个特定代码片段运行所花费的时间。
### 代码重构
PyCharm 一个很强大的特性是代码重构选项。
当你开始写代码的时候,会在右边缘出现一个小标记。如果你写的代码可能出错或者写的不太好, PyCharm 会标记上一个彩色标记。
点击彩色标记将会告诉你出现的问题并提供一个解决方法。
比如,你通过一个导入语句导入了一个库,但没有使用该库中的任何东西,那么不仅这行代码会变成灰色,彩色标记还会告诉你‘该库未使用’。
对于正确的代码,也可能会出现错误提示,比如在导入语句和函数起始之间只有一个空行。当你创建了一个名称非小写的函数时它也会提示你。
你不必遵循 PyCharm 的所有规则。这些规则大部分只是好的编码准则,与你的代码是否能够正确运行无关。
代码菜单还有其它的重构选项。比如,你可以进行代码清理以及检查文件或项目问题。
### 总结
PyCharm 是 Linux 系统上开发 Python 代码的一个优秀编辑器,并且有两个可用版本。社区版可供临时开发者使用,专业版则提供了开发者开发专业软件可能需要的所有工具。
---
via: <https://www.lifewire.com/pycharm-the-best-linux-python-ide-4091045>
作者:[Gary Newell](https://www.lifewire.com/gary-newell-2180098) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,076 | Linux 服务器安全简明指南 | https://www.linode.com/docs/security/securing-your-server/ | 2016-12-30T07:56:00 | [
"服务器",
"安全",
"防火墙"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8076-1.html | 现在让我们强化你的服务器以防止未授权访问。

### 经常升级系统
保持最新的软件是你可以在任何操作系统上采取的最大的安全预防措施。软件更新的范围从关键漏洞补丁到小 bug 的修复,许多软件漏洞实际上是在它们被公开的时候得到修补的。
### 自动安全更新
有一些用于服务器上自动更新的参数。[Fedora 的 Wiki](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/AutoUpdates#Why_use_Automatic_updates.3F) 上有一篇很棒的剖析自动更新的利弊的文章,但是如果你把它限制到安全更新上,自动更新的风险将是最小的。
自动更新的可行性必须你自己判断,因为它归结为**你**在你的服务器上做什么。请记住,自动更新仅适用于来自仓库的包,而不是自行编译的程序。你可能会发现一个复制了生产服务器的测试环境是很有必要的。可以在部署到生产环境之前,在测试环境里面更新来检查问题。
* CentOS 使用 [yum-cron](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/AutoUpdates#Fedora_21_or_earlier_versions) 进行自动更新。
* Debian 和 Ubuntu 使用 [无人值守升级](https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/automatic-updates.html)。
* Fedora 使用 [dnf-automatic](https://dnf.readthedocs.org/en/latest/automatic.html)。
### 添加一个受限用户账户
到目前为止,你已经作为 `root` 用户访问了你的服务器,它有无限制的权限,可以执行**任何**命令 - 甚至可能意外中断你的服务器。 我们建议创建一个受限用户帐户,并始终使用它。 管理任务应该使用 `sudo` 来完成,它可以临时提升受限用户的权限,以便管理你的服务器。
>
> 不是所有的 Linux 发行版都在系统上默认包含 `sudo`,但大多数都在其软件包仓库中有 `sudo`。 如果得到这样的输出 `sudo:command not found`,请在继续之前安装 `sudo`。
>
>
>
要添加新用户,首先通过 SSH 登录到你的服务器。
#### CentOS / Fedora
1、 创建用户,用你想要的名字替换 `example_user`,并分配一个密码:
```
useradd example_user && passwd example_user
```
2、 将用户添加到具有 sudo 权限的 `wheel` 组:
```
usermod -aG wheel example_user
```
#### Ubuntu
1、 创建用户,用你想要的名字替换 `example_user`。你将被要求输入用户密码:
```
adduser example_user
```
2、 添加用户到 `sudo` 组,这样你就有管理员权限了:
```
adduser example_user sudo
```
#### Debian
1、 Debian 默认的包中没有 `sudo`, 使用 `apt-get` 来安装:
```
apt-get install sudo
```
2、 创建用户,用你想要的名字替换 `example_user`。你将被要求输入用户密码:
```
adduser example_user
```
3、 添加用户到 `sudo` 组,这样你就有管理员权限了:
```
adduser example_user sudo
```
创建完有限权限的用户后,断开你的服务器连接:
```
exit
```
重新用你的新用户登录。用你的用户名代替 `example_user`,用你的服务器 IP 地址代替例子中的 IP 地址:
```
ssh [email protected]
```
现在你可以用你的新用户帐户管理你的服务器,而不是 `root`。 几乎所有超级用户命令都可以用 `sudo`(例如:`sudo iptables -L -nv`)来执行,这些命令将被记录到 `/var/log/auth.log` 中。
### 加固 SSH 访问
默认情况下,密码认证用于通过 SSH 连接到您的服务器。加密密钥对更加安全,因为它用私钥代替了密码,这通常更难以暴力破解。在本节中,我们将创建一个密钥对,并将服务器配置为不接受 SSH 密码登录。
#### 创建验证密钥对
1、这是在你本机上完成的,**不是**在你的服务器上,这里将创建一个 4096 位的 RSA 密钥对。在创建过程中,您可以选择使用密码加密私钥。这意味着它不能在没有输入密码的情况下使用,除非将密码保存到本机桌面的密钥管理器中。我们建议您使用带有密码的密钥对,但如果你不想使用密码,则可以将此字段留空。
**Linux / OS X**
>
> 如果你已经创建了 RSA 密钥对,则这个命令将会覆盖它,这可能会导致你不能访问其它的操作系统。如果你已创建过密钥对,请跳过此步骤。要检查现有的密钥,请运行 `ls〜/ .ssh / id_rsa *`。
>
>
>
```
ssh-keygen -b 4096
```
在输入密码之前,按下 **回车**使用 `/home/your_username/.ssh` 中的默认名称 `id_rsa` 和 `id_rsa.pub`。
**Windows**
这可以使用 PuTTY 完成,在我们指南中已有描述:[使用 SSH 公钥验证](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/use-public-key-authentication-with-ssh#windows-operating-system)。
2、将公钥上传到您的服务器上。 将 `example_user` 替换为你用来管理服务器的用户名称,将 `203.0.113.10` 替换为你的服务器的 IP 地址。
**Linux**
在本机上:
```
ssh-copy-id [email protected]
```
**OS X**
在你的服务器上(用你的权限受限用户登录):
```
mkdir -p ~/.ssh && sudo chmod -R 700 ~/.ssh/
```
在本机上:
```
scp ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]:~/.ssh/authorized_keys
```
>
> 如果相对于 `scp` 你更喜欢 `ssh-copy-id` 的话,那么它也可以在 [Homebrew](http://brew.sh/) 中找到。使用 `brew install ssh-copy-id` 安装。
>
>
>
**Windows**
* **选择 1**:使用 [WinSCP](http://winscp.net/) 来完成。 在登录窗口中,输入你的服务器的 IP 地址作为主机名,以及非 root 的用户名和密码。单击“登录”连接。
一旦 WinSCP 连接后,你会看到两个主要部分。 左边显示本机上的文件,右边显示服务区上的文件。 使用左侧的文件浏览器,导航到你已保存公钥的文件,选择公钥文件,然后点击上面工具栏中的“上传”。
系统会提示你输入要将文件放在服务器上的路径。 将文件上传到 `/home/example_user/.ssh /authorized_keys`,用你的用户名替换 `example_user`。
* **选择 2**:将公钥直接从 PuTTY 键生成器复制到连接到你的服务器中(作为非 root 用户):
```
mkdir ~/.ssh; nano ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
```
上面命令将在文本编辑器中打开一个名为 `authorized_keys` 的空文件。 将公钥复制到文本文件中,确保复制为一行,与 PuTTY 所生成的完全一样。 按下 `CTRL + X`,然后按下 `Y`,然后回车保存文件。
最后,你需要为公钥目录和密钥文件本身设置权限:
```
sudo chmod 700 -R ~/.ssh && chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
```
这些命令通过阻止其他用户访问公钥目录以及文件本身来提供额外的安全性。有关它如何工作的更多信息,请参阅我们的指南[如何修改文件权限](https://www.linode.com/docs/tools-reference/modify-file-permissions-with-chmod)。
3、 现在退出并重新登录你的服务器。如果你为私钥指定了密码,则需要输入密码。
#### SSH 守护进程选项
1、 **不允许 root 用户通过 SSH 登录。** 这要求所有的 SSH 连接都是通过非 root 用户进行。当以受限用户帐户连接后,可以通过使用 `sudo` 或使用 `su -` 切换为 root shell 来使用管理员权限。
```
# Authentication:
...
PermitRootLogin no
```
2、 **禁用 SSH 密码认证。** 这要求所有通过 SSH 连接的用户使用密钥认证。根据 Linux 发行版的不同,它可能需要添加 `PasswordAuthentication` 这行,或者删除前面的 `#` 来取消注释。
```
# Change to no to disable tunnelled clear text passwords
PasswordAuthentication no
```
>
> 如果你从许多不同的计算机连接到服务器,你可能想要继续启用密码验证。这将允许你使用密码进行身份验证,而不是为每个设备生成和上传密钥对。
>
>
>
3、 **只监听一个互联网协议。** 在默认情况下,SSH 守护进程同时监听 IPv4 和 IPv6 上的传入连接。除非你需要使用这两种协议进入你的服务器,否则就禁用你不需要的。 *这不会禁用系统范围的协议,它只用于 SSH 守护进程。*
使用选项:
* `AddressFamily inet` 只监听 IPv4。
* `AddressFamily inet6` 只监听 IPv6。
默认情况下,`AddressFamily` 选项通常不在 `sshd_config` 文件中。将它添加到文件的末尾:
```
echo 'AddressFamily inet' | sudo tee -a /etc/ssh/sshd_config
```
4、 重新启动 SSH 服务以加载新配置。
如果你使用的 Linux 发行版使用 systemd(CentOS 7、Debian 8、Fedora、Ubuntu 15.10+)
```
sudo systemctl restart sshd
```
如果您的 init 系统是 SystemV 或 Upstart(CentOS 6、Debian 7、Ubuntu 14.04):
```
sudo service ssh restart
```
#### 使用 Fail2Ban 保护 SSH 登录
[Fail2Ban](http://www.fail2ban.org/wiki/index.php/Main_Page) 是一个应用程序,它会在太多的失败登录尝试后禁止 IP 地址登录到你的服务器。由于合法登录通常不会超过三次尝试(如果使用 SSH 密钥,那不会超过一个),因此如果服务器充满了登录失败的请求那就表示有恶意访问。
Fail2Ban 可以监视各种协议,包括 SSH、HTTP 和 SMTP。默认情况下,Fail2Ban 仅监视 SSH,并且因为 SSH 守护程序通常配置为持续运行并监听来自任何远程 IP 地址的连接,所以对于任何服务器都是一种安全威慑。
有关安装和配置 Fail2Ban 的完整说明,请参阅我们的指南:[使用 Fail2ban 保护服务器](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/using-fail2ban-for-security)。
### 删除未使用的面向网络的服务
大多数 Linux 发行版都安装并运行了网络服务,监听来自互联网、回环接口或两者兼有的传入连接。 将不需要的面向网络的服务从系统中删除,以减少对运行进程和对已安装软件包攻击的概率。
#### 查明运行的服务
要查看服务器中运行的服务:
```
sudo netstat -tulpn
```
>
> 如果默认情况下 `netstat` 没有包含在你的 Linux 发行版中,请安装软件包 `net-tools` 或使用 `ss -tulpn` 命令。
>
>
>
以下是 `netstat` 的输出示例。 请注意,因为默认情况下不同发行版会运行不同的服务,你的输出将有所不同:
```
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7315/rpcbind
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3277/sshd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3179/exim4
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:42526 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2845/rpc.statd
tcp6 0 0 :::48745 :::* LISTEN 2845/rpc.statd
tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 7315/rpcbind
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 3277/sshd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 3179/exim4
udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:901 0.0.0.0:* 2845/rpc.statd
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:47663 0.0.0.0:* 2845/rpc.statd
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* 7315/rpcbind
udp 0 0 192.0.2.1:123 0.0.0.0:* 3327/ntpd
udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:123 0.0.0.0:* 3327/ntpd
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:123 0.0.0.0:* 3327/ntpd
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:705 0.0.0.0:* 7315/rpcbind
udp6 0 0 :::111 :::* 7315/rpcbind
udp6 0 0 fe80::f03c:91ff:fec:123 :::* 3327/ntpd
udp6 0 0 2001:DB8::123 :::* 3327/ntpd
udp6 0 0 ::1:123 :::* 3327/ntpd
udp6 0 0 :::123 :::* 3327/ntpd
udp6 0 0 :::705 :::* 7315/rpcbind
udp6 0 0 :::60671 :::* 2845/rpc.statd
```
`netstat` 告诉我们服务正在运行 [RPC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_Network_Computing_Remote_Procedure_Call)(`rpc.statd` 和 `rpcbind`)、SSH(`sshd`)、[NTPdate](http://support.ntp.org/bin/view/Main/SoftwareDownloads)(`ntpd`)和[Exim](http://www.exim.org/)(`exim4`)。
**TCP**
请参阅 `netstat` 输出的 `Local Address` 那一列。进程 `rpcbind` 正在侦听 `0.0.0.0:111` 和 `:::111`,外部地址是 `0.0.0.0:*` 或者 `:::*` 。这意味着它从任何端口和任何网络接口接受来自任何外部地址(IPv4 和 IPv6)上的其它 RPC 客户端的传入 TCP 连接。 我们看到类似的 SSH,Exim 正在侦听来自回环接口的流量,如所示的 `127.0.0.1` 地址。
**UDP**
UDP 套接字是[无状态](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stateless_protocol)的,这意味着它们只有打开或关闭,并且每个进程的连接是独立于前后发生的连接。这与 TCP 的连接状态(例如 `LISTEN`、`ESTABLISHED`和 `CLOSE_WAIT`)形成对比。
我们的 `netstat`输出说明 NTPdate :1)接受服务器的公网 IP 地址的传入连接;2)通过本地主机进行通信;3)接受来自外部的连接。这些连接是通过端口 123 进行的,同时支持 IPv4 和 IPv6。我们还看到了 RPC 打开的更多的套接字。
#### 查明该移除哪个服务
如果你在没有启用防火墙的情况下对服务器进行基本的 TCP 和 UDP 的 [nmap](https://nmap.org/) 扫描,那么在打开端口的结果中将出现 SSH、RPC 和 NTPdate 。通过配置防火墙,你可以过滤掉这些端口,但 SSH 除外,因为它必须允许你的传入连接。但是,理想情况下,应该禁用未使用的服务。
* 你可能主要通过 SSH 连接管理你的服务器,所以让这个服务需要保留。如上所述,RSA 密钥和 Fail2Ban 可以帮助你保护 SSH。
* NTP 是服务器计时所必需的,但有个替代 NTPdate 的方法。如果你喜欢不开放网络端口的时间同步方法,并且你不需要纳秒精度,那么你可能有兴趣用 [OpenNTPD](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenNTPD) 来代替 NTPdate。
* 然而,Exim 和 RPC 是不必要的,除非你有特定的用途,否则应该删除它们。
>
> 本节针对 Debian 8。默认情况下,不同的 Linux 发行版具有不同的服务。如果你不确定某项服务的功能,请尝试搜索互联网以了解该功能是什么,然后再尝试删除或禁用它。
>
>
>
#### 卸载监听的服务
如何移除包取决于发行版的包管理器:
**Arch**
```
sudo pacman -Rs package_name
```
**CentOS**
```
sudo yum remove package_name
```
**Debian / Ubuntu**
```
sudo apt-get purge package_name
```
**Fedora**
```
sudo dnf remove package_name
```
再次运行 `sudo netstat -tulpn`,你看到监听的服务就只会有 SSH(`sshd`)和 NTP(`ntpdate`,网络时间协议)。
### 配置防火墙
使用防火墙阻止不需要的入站流量能为你的服务器提供一个高效的安全层。 通过指定入站流量,你可以阻止入侵和网络测绘。 最佳做法是只允许你需要的流量,并拒绝一切其他流量。请参阅我们的一些关于最常见的防火墙程序的文档:
* [iptables](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/firewalls/control-network-traffic-with-iptables) 是 netfilter 的控制器,它是 Linux 内核的包过滤框架。 默认情况下,iptables 包含在大多数 Linux 发行版中。
* [firewallD](/article-8098-1.html) 是可用于 CentOS/Fedora 系列发行版的 iptables 控制器。
* [UFW](/article-8087-1.html) 为 Debian 和 Ubuntu 提供了一个 iptables 前端。
### 接下来
这些是加固 Linux 服务器的最基本步骤,但是进一步的安全层将取决于其预期用途。 其他技术可以包括应用程序配置,使用[入侵检测](https://linode.com/docs/security/ossec-ids-debian-7)或者安装某个形式的[访问控制](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Access_control#Access_Control)。
现在你可以按你的需求开始设置你的服务器了。
---
via: <https://www.linode.com/docs/security/securing-your-server/>
作者:[Phil Zona](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/securing-your-server/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
8,077 | 如何在 Ubuntu 环境下搭建邮件服务器(二) | https://www.linux.com/learn/sysadmin/building-email-server-ubuntu-linux-part-2 | 2016-12-30T16:37:00 | [
"邮件服务器",
"Dovecot",
"IMAP",
"Postfix"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8077-1.html | 
本教程的第 2 部分将介绍如何使用 Dovecot 将邮件从 Postfix 服务器移动到用户的收件箱。
在[第一部分](/article-8071-1.html)中,我们安装并测试了 Postfix SMTP 服务器。Postfix 或任何 SMTP 服务器都不是一个完整的邮件服务器,因为它所做的只是在 SMTP 服务器之间移动邮件。我们需要 Dovecot 将邮件从 Postfix 服务器移动到用户的收件箱中。
Dovecot 支持两种标准邮件协议:IMAP(Internet 邮件访问协议)和 POP3(邮局协议)。 IMAP 服务器会在服务器上保留所有邮件。您的用户可以选择将邮件下载到计算机或仅在服务器上访问它们。 IMAP 对于有多台机器的用户是方便的。但对你而言需要更多的工作,因为你必须确保你的服务器始终可用,而且 IMAP 服务器需要大量的存储和内存。
POP3 是较旧的协议。POP3 服务器可以比 IMAP 服务器服务更多的用户,因为邮件会下载到用户的计算机。大多数邮件客户端可以选择在服务器上保留一定天数的邮件,因此 POP3 的行为有点像 IMAP。但它又不是 IMAP,当你像 IMAP 那样(在多台计算机上使用它时)那么常常会下载多次或意外删除。
### 安装 Dovecot
启动你的 Ubuntu 系统并安装 Dovecot:
```
$ sudo apt-get install dovecot-imapd dovecot-pop3d
```
它会安装可用的配置,并在完成后自动启动,你可以用 `ps ax | grep dovecot` 确认:
```
$ ps ax | grep dovecot
15988 ? Ss 0:00 /usr/sbin/dovecot
15990 ? S 0:00 dovecot/anvil
15991 ? S 0:00 dovecot/log
```
打开你的 Postfix 配置文件 `/etc/postfix/main.cf`,确保配置了maildir 而不是 mbox 的邮件存储方式,mbox 是给每个用户一个单一大文件,而 maildir 是每条消息都存储为一个文件。大量的小文件比一个庞大的文件更稳定且易于管理。添加如下两行,第二行告诉 Postfix 你需要 maildir 格式,并且在每个用户的家目录下创建一个 `.Mail` 目录。你可以取任何名字,不一定要是 `.Mail`:
```
mail_spool_directory = /var/mail
home_mailbox = .Mail/
```
现在调整你的 Dovecot 配置。首先把原始的 `dovecot.conf` 文件重命名放到一边,因为它会调用存放在 `conf.d` 中的文件,在你刚刚开始学习时把配置放一起更简单些:
```
$ sudo mv /etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf /etc/dovecot/dovecot-oldconf
```
现在创建一个新的 `/etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf`:
```
disable_plaintext_auth = no
mail_location = maildir:~/.Mail
namespace inbox {
inbox = yes
mailbox Drafts {
special_use = \Drafts
}
mailbox Sent {
special_use = \Sent
}
mailbox Trash {
special_use = \Trash
}
}
passdb {
driver = pam
}
protocols = " imap pop3"
ssl = no
userdb {
driver = passwd
}
```
注意 `mail_location = maildir` 必须和 `main.cf` 中的 `home_mailbox` 参数匹配。保存你的更改并重新加载 Postfix 和 Dovecot 配置:
```
$ sudo postfix reload
$ sudo dovecot reload
```
### 快速导出配置
使用下面的命令来快速查看你的 Postfix 和 Dovecot 配置:
```
$ postconf -n
$ doveconf -n
```
### 测试 Dovecot
现在再次启动 telnet,并且给自己发送一条测试消息。粗体显示的是你输入的命令。`studio` 是我服务器的主机名,因此你必须用自己的:
```
$ telnet studio 25
Trying 127.0.1.1...
Connected to studio.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 studio.router ESMTP Postfix (Ubuntu)
EHLO studio
250-studio.router
250-PIPELINING
250-SIZE 10240000
250-VRFY
250-ETRN
250-STARTTLS
250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES
250-8BITMIME
250-DSN
250 SMTPUTF8
mail from: [email protected]
250 2.1.0 Ok
rcpt to: carla@studio
250 2.1.5 Ok
data
354 End data with .Date: November 25, 2016
From: tester
Message-ID: first-test
Subject: mail server test
Hi carla,
Are you reading this? Let me know if you didn't get this.
.
250 2.0.0 Ok: queued as 0C261A1F0F
quit
221 2.0.0 Bye
Connection closed by foreign host.
```
现在请求 Dovecot 来取回你的新消息,使用你的 Linux 用户名和密码登录:
```
$ telnet studio 110
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to studio.
Escape character is '^]'.
+OK Dovecot ready.
user carla
+OK
pass password
+OK Logged in.
stat
+OK 2 809
list
+OK 2 messages:
1 383
2 426
.
retr 2
+OK 426 octets
Return-Path: <[email protected]>
X-Original-To: carla@studio
Delivered-To: carla@studio
Received: from studio (localhost [127.0.0.1])
by studio.router (Postfix) with ESMTP id 0C261A1F0F
for <carla@studio>; Wed, 30 Nov 2016 17:18:57 -0800 (PST)
Date: November 25, 2016
From: [email protected]
Message-ID: first-test
Subject: mail server test
Hi carla,
Are you reading this? Let me know if you didn't get this.
.
quit
+OK Logging out.
Connection closed by foreign host.
```
花一点时间比较第一个例子中输入的消息和第二个例子中接收的消息。 返回地址和日期是很容易伪造的,但 Postfix 不会被愚弄。大多数邮件客户端默认显示一个最小的标头集,但是你需要读取完整的标头才能查看真实的回溯。
你也可以在你的 `~/Mail/cur` 目录中查看你的邮件,它们是普通文本,我已经有两封测试邮件:
```
$ ls .Mail/cur/
1480540325.V806I28e0229M351743.studio:2,S
1480555224.V806I28e000eM41463.studio:2,S
```
### 测试 IMAP
我们 Dovecot 同时启用了 POP3 和 IMAP 服务,因此让我们使用 telnet 测试 IMAP。
```
$ telnet studio imap2
Trying 127.0.1.1...
Connected to studio.
Escape character is '^]'.
* OK [CAPABILITY IMAP4rev1 LITERAL+ SASL-IR LOGIN-REFERRALS
ID ENABLE IDLE AUTH=PLAIN] Dovecot ready.
A1 LOGIN carla password
A1 OK [CAPABILITY IMAP4rev1 LITERAL+ SASL-IR LOGIN-REFERRALS
ID ENABLE IDLE SORT SORT=DISPLAY THREAD=REFERENCES THREAD=REFS
THREAD=ORDEREDSUBJECT MULTIAPPEND URL-PARTIAL CATENATE UNSELECT
CHILDREN NAMESPACE UIDPLUS LIST-EXTENDED I18NLEVEL=1 CONDSTORE
QRESYNC ESEARCH ESORT SEARCHRES WITHIN CONTEXT=SEARCH LIST-STATUS
BINARY MOVE SPECIAL-USE] Logged in
A2 LIST "" "*"
* LIST (\HasNoChildren) "." INBOX
A2 OK List completed (0.000 + 0.000 secs).
A3 EXAMINE INBOX
* FLAGS (\Answered \Flagged \Deleted \Seen \Draft)
* OK [PERMANENTFLAGS ()] Read-only mailbox.
* 2 EXISTS
* 0 RECENT
* OK [UIDVALIDITY 1480539462] UIDs valid
* OK [UIDNEXT 3] Predicted next UID
* OK [HIGHESTMODSEQ 1] Highest
A3 OK [READ-ONLY] Examine completed (0.000 + 0.000 secs).
A4 logout
* BYE Logging out
A4 OK Logout completed.
Connection closed by foreign host
```
### Thunderbird 邮件客户端
图 1 中的屏幕截图显示了我局域网上另一台主机上的图形邮件客户端中的邮件。

*图 1: Thunderbird mail*
此时,你已有一个可以工作的 IMAP 和 POP3 邮件服务器,并且你也知道该如何测试你的服务器。你的用户可以在他们设置邮件客户端时选择要使用的协议。如果您只想支持一个邮件协议,那么只需要在您的 Dovecot 配置中留下你要的协议名字。
然而,这还远远没有完成。这是一个非常简单、没有加密的、大门敞开的安装。它也只适用于与邮件服务器在同一系统上的用户。这是不可扩展的,并具有一些安全风险,例如没有密码保护。 我们会在[下篇](https://www.linux.com/learn/sysadmin/building-email-server-ubuntu-linux-part-3)了解如何创建与系统用户分开的邮件用户,以及如何添加加密。
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/learn/sysadmin/building-email-server-ubuntu-linux-part-2>
作者:[CARLA SCHRODER](https://www.linux.com/users/cschroder) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,078 | 忘记技术债务 —— 教你如何创造技术财富 | http://firstround.com/review/forget-technical-debt-heres-how-to-build-technical-wealth/ | 2016-12-31T08:50:00 | [
"技术债务",
"遗留代码",
"开发"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8078-1.html | 电视里正播放着《老屋》节目,[Andrea Goulet](https://www.linkedin.com/in/andreamgoulet) 和她的商业合作伙伴正悠闲地坐在客厅里,商讨着他们的战略计划。那正是大家思想的火花碰撞出创新事物的时刻。他们正在寻求一种能够实现自身价值的方式 —— 为其它公司清理<ruby> 遗留代码 <rt> legacy code </rt></ruby>及科技债务。他们此刻的情景,像极了电视里的场景。(LCTT 译注:《老屋》电视节目提供专业的家装、家庭改建、重新装饰、创意等等信息,与软件的改造有异曲同工之处)。
“我们意识到我们现在做的工作不仅仅是清理遗留代码,实际上我们是在用重建老屋的方式来重构软件,让系统运行更持久、更稳定、更高效,”Goulet 说。“这让我开始思考公司如何花钱来改善他们的代码,以便让他们的系统运行更高效。就好比为了让屋子变得更有价值,你不得不使用一个全新的屋顶。这并不吸引人,但却是至关重要的,然而很多人都搞错了。“
如今,她是 [Corgibytes](http://corgibytes.com/) 公司的 CEO —— 这是一家提高软件现代化和进行系统重构方面的咨询公司。她曾经见过各种各样糟糕的系统、遗留代码,以及严重的科技债务事件。Goulet 认为**创业公司需要转变思维模式,不是偿还债务,而是创造科技财富,不是要铲除旧代码,而是要逐步修复代码**。她解释了这种新的方法,以及如何完成这些看似不可能完成的事情 —— 实际上是聘用优秀的工程师来完成这些工作。

### 反思遗留代码
关于遗留代码最常见的定义是由 Michael Feathers 在他的著作[<ruby> 《高效利用遗留代码》 <rt> Working Effectively with Legacy Code </rt></ruby>](https://www.amazon.com/Working-Effectively-Legacy-Michael-Feathers/dp/0131177052)一书中提出:遗留代码就是没有被测试所覆盖的代码。这个定义比大多数人所认为的 —— 遗留代码仅指那些古老、陈旧的系统这个说法要妥当得多。但是 Goulet 认为这两种定义都不够明确。“遗留代码与软件的年头儿毫无关系。一个两年的应用程序,其代码可能已经进入遗留状态了,”她说。“**关键要看软件质量提高的难易程度。**”
这意味着写得不够清楚、缺少解释说明的代码,是没有包含任何关于代码构思和决策制定的流程的成果。单元测试就是这样的一种成果,但它并没有包括了写那部分代码的原因以及逻辑推理相关的所有文档。如果想要提升代码,但没办法搞清楚原开发者的意图 —— 那些代码就属于遗留代码了。
>
> **遗留代码不是技术问题,而是沟通上的问题。**
>
>
>

如果你像 Goulet 所说的那样迷失在遗留代码里,你会发现每一次的沟通交流过程都会变得像那条[<ruby> 康威定律 <rt> Conway’s Law </rt></ruby>](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conway%27s_law)所描述的一样。
Goulet 说:“这个定律认为你的代码能反映出整个公司的组织沟通结构,如果想修复公司的遗留代码,而没有一个好的组织沟通方式是不可能完成的。那是很多人都没注意到的一个重要环节。”
Goulet 和她的团队成员更像是考古学家一样来研究遗留系统项目。他们根据前开发者写的代码构件相关的线索来推断出他们的思想意图。然后再根据这些构件之间的关系来做出新的决策。
代码构件最重要的什么呢?**良好的代码结构、清晰的思想意图、整洁的代码**。例如,如果使用通用的名称如 “foo” 或 “bar” 来命名一个变量,半年后再返回来看这段代码时,根本就看不出这个变量的用途是什么。
如果代码读起来很困难,可以使用源代码控制系统,这是一个非常有用的工具,因为它可以提供代码的历史修改信息,并允许软件开发者写明他们作出本次修改的原因。
Goulet 说:“我一个朋友认为提交代码时附带的信息,每一个概要部分的内容应该有半条推文那么长(几十个字),如需要的话,代码的描述信息应该有一篇博客那么长。你得用这个方式来为你修改的代码写一个合理的说明。这不会浪费太多额外的时间,并且能给后期的项目开发者提供非常多的有用信息,但是让人惊讶的是很少有人会这么做。我们经常能看到一些开发人员在被一段代码激怒之后,要用 `git blame` 扒代码库找出这些垃圾是谁干的,结果最后发现是他们自己干的。”
使用自动化测试对于理解程序的流程非常有用。Goulet 解释道:“很多人都比较认可 Michael Feathers 提出的关于遗留代码的定义。测试套件对于理解开发者的意图来说是非常有用的工具,尤其当用来与[<ruby> 行为驱动开发模式 <rt> Behavior Driven Development </rt></ruby>](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Behavior-driven_development)相结合时,比如编写测试场景。”
理由很简单,如果你想将遗留代码限制在一定程度下,注意到这些细节将使代码更易于理解,便于在以后也能工作。编写并运行一个代码单元,接受、认可,并且集成测试。写清楚注释的内容,方便以后你自己或是别人来理解你写的代码。
尽管如此,由于很多已知的和不可意料的原因,遗留代码仍然会出现。
在创业公司刚成立初期,公司经常会急于推出很多新的功能。开发人员在巨大的交付压力下,测试常常半途而废。Corgibytes 团队就遇到过好多公司很多年都懒得对系统做详细的测试了。
确实如此,当你急于开发出系统原型的时候,强制性地去做太多的测试也许意义不大。但是,一旦产品开发完成并投入使用后,你就需要投入时间精力来维护及完善系统了。Goulet 说:“很多人说,‘别在维护上费心思,重要的是功能!’ **如果真这样,当系统规模到一定程序的时候,就很难再扩展了。同时也就失去市场竞争力了。**”
最后才明白过来,原来热力学第二定律对代码也同样适用:**你所面临的一切将向熵增的方向发展。**你需要与混乱无序的技术债务进行一场无休无止的战斗。随着时间的推移,遗留代码也逐渐变成一种债务。
她说:“我们再次拿家来做比喻。你必须坚持每天收拾餐具、打扫卫生、倒垃圾。如果你不这么做,情况将来越来越糟糕,直到有一天你不得不向 HazMat 团队求助。”(LCTT 译注:HazMat 团队,危害物质专队)
就跟这种情况一样,Corgibytes 团队接到很多公司 CEO 的求助电话,比如 Features 公司的 CEO 在电话里抱怨道:“现在我们公司的开发团队工作效率太低了,三年前只需要两个星期就完成的工作,现在却要花费12个星期。”
>
> **技术债务往往反映出公司运作上的问题。**
>
>
>
很多公司的 CTO 明知会发生技术债务的问题,但是他们很难说服其它同事相信花钱来修复那些已经存在的问题是值得的。这看起来像是在走回头路,很乏味,也不是新的产品。有些公司直到系统已经严重影响了日常工作效率时,才着手去处理这些技术债务方面的问题,那时付出的代价就太高了。
### 忘记债务,创造技术财富
如果你想把[<ruby> 重构技术债务 <rt> reframe your technical debt </rt></ruby>](https://www.agilealliance.org/resources/initiatives/technical-debt/) — [敏捷开发讲师 Declan Whelan 最近造出的一个术语](http://legacycoderocks.libsyn.com/technical-wealth-with-declan-wheelan) — 作为一个积累技术财富的机会,你很可能要先说服你们公司的 CEO、投资者和其它的股东接受并为之共同努力。
“我们没必要把技术债务想像得很可怕。当产品处于开发设计初期,技术债务反而变得非常有用,”Goulet 说。“当你解决一些系统遗留的技术问题时,你会充满成就感。例如,当你在自己家里安装新窗户时,你确实会花费一笔不少的钱,但是之后你每个月就可以节省 100 美元的电费。程序代码亦是如此。虽然暂时没有提高工作效率,但随时时间推移将提高生产力。”
一旦你意识到项目团队工作不再富有成效时,就需要确认下是哪些技术债务在拖后腿了。
“我跟很多不惜一切代价招募英才的初创公司交流过,他们高薪聘请一些工程师来只为了完成更多的工作。”她说。“与此相反,他们应该找出如何让原有的每个工程师能更高效率工作的方法。你需要去解决什么样的技术债务以增加额外的生产率?”
如果你改变自己的观点并且专注于创造技术财富,你将会看到产能过剩的现象,然后重新把多余的产能投入到修复更多的技术债务和遗留代码的良性循环中。你们的产品将会走得更远,发展得更好。
>
> **别把你们公司的软件当作一个项目来看。从现在起,把它想象成一栋自己要长久居住的房子。**
>
>
>
“这是一个极其重要的思想观念的转变,”Goulet 说。“这将带你走出短浅的思维模式,并让你比之前更加关注产品的维护工作。”
这就像对一栋房子,要实现其现代化及维护的方式有两种:小动作,表面上的更改(“我买了一块新的小地毯!”)和大改造,需要很多年才能偿还所有债务(“我想我们应替换掉所有的管道...”)。你必须考虑好两者,才能让你们已有的产品和整个团队顺利地运作起来。
这还需要提前预算好 —— 否则那些较大的花销将会是硬伤。定期维护是最基本的预期费用。让人震惊的是,很多公司都没把维护当成商务成本预算进来。
这就是 Goulet 提出“**<ruby> 软件重构 <rt> software remodeling </rt></ruby>**”这个术语的原因。当你房子里的一些东西损坏的时候,你并不是铲除整个房子,从头开始重建。同样的,当你们公司出现老的、损坏的代码时,重写代码通常不是最明智的选择。
下面是 Corgibytes 公司在重构客户代码用到的一些方法:
* 把大型的应用系统分解成轻量级的更易于维护的微服务。
* 让功能模块彼此解耦以便于扩展。
* 更新形象和提升用户前端界面体验。
* 集合自动化测试来检查代码可用性。
* 代码库可以让重构或者修改更易于操作。
系统重构也进入到 DevOps 领域。比如,Corgibytes 公司经常推荐新客户使用 [Docker](https://www.docker.com/),以便简单快速的部署新的开发环境。当你们团队有 30 个工程师的时候,把初始化配置时间从 10 小时减少到 10 分钟对完成更多的工作很有帮助。系统重构不仅仅是应用于软件开发本身,也包括如何进行系统重构。
如果你知道做些什么能让你们的代码管理起来更容易更高效,就应该把这它们写入到每年或季度的项目规划中。别指望它们会自动呈现出来。但是也别给自己太大的压力来马上实施它们。Goulets 看到很多公司从一开始就致力于 100% 测试覆盖率而陷入困境。
**具体来说,每个公司都应该把以下三种类型的重构工作规划到项目建设中来:**
* 自动测试
* 持续交付
* 文化提升
咱们来深入的了解下每一项内容。
#### 自动测试
“有一位客户即将进行第二轮融资,但是他们没办法在短期内招聘到足够的人才。我们帮助他们引进了一种自动化测试框架,这让他们的团队在 3 个月的时间内工作效率翻了一倍,”Goulets 说。“这样他们就可以在他们的投资人面前自豪的说,‘我们一个精英团队完成的任务比两个普通的团队要多。’”
自动化测试从根本上来讲就是单个测试的组合,就是可以再次检查某一行代码的单元测试。可以使用集成测试来确保系统的不同部分都正常运行。还可以使用验收性测试来检验系统的功能特性是否跟你想像的一样。当你把这些测试写成测试脚本后,你只需要简单地用鼠标点一下按钮就可以让系统自行检验了,而不用手工的去梳理并检查每一项功能。
在产品市场尚未打开之前就来制定自动化测试机制有些言之过早。但是一旦你有一款感到满意,并且客户也很依赖的产品,就应该把这件事付诸实施了。
#### 持续交付
这是与自动化交付相关的工作,过去是需要人工完成。目的是当系统部分修改完成时可以迅速进行部署,并且短期内得到反馈。这使公司在其它竞争对手面前有很大的优势,尤其是在客户服务行业。
“比如说你每次部署系统时环境都很复杂。熵值无法有效控制,”Goulets 说。“我们曾经见过花 12 个小时甚至更多的时间来部署一个很大的集群环境。在这种情况下,你不会愿意频繁部署了。因为太折腾人了,你还会推迟系统功能上线的时间。这样,你将落后于其它公司并失去竞争力。”
**在持续性改进的过程中常见的其它自动化任务包括:**
* 在提交完成之后检查构建中断部分。
* 在出现故障时进行回滚操作。
* 自动化审查代码的质量。
* 根据需求增加或减少服务器硬件资源。
* 让开发、测试及生产环境配置简单易懂。
举一个简单的例子,比如说一个客户提交了一个系统 Bug 报告。开发团队越高效解决并修复那个 Bug 越好。对于开发人员来说,修复 Bug 的挑战根本不是个事儿,这本来也是他们的强项,主要是系统设置上不够完善导致他们浪费太多的时间去处理 bug 以外的其它问题。
使用持续改进的方式时,你要严肃地决定决定哪些工作应该让机器去做,哪些交给研发去完成更好。如果机器更擅长,那就使其自动化完成。这样也能让研发愉快地去解决其它有挑战性的问题。同时客户也会很高兴地看到他们报怨的问题被快速处理了。你的待修复的未完成任务数减少了,之后你就可以把更多的时间投入到运用新的方法来提高产品的质量上了。**这是创造科技财富的一种转变。**因为开发人员可以修复 bug 后立即发布新代码,这样他们就有时间和精力做更多事。
“你必须时刻问自己,‘我应该如何为我们的客户改善产品功能?如何做得更好?如何让产品运行更高效?’不过还要不止于此。”Goulets 说。“一旦你回答完这些问题后,你就得询问下自己,如何自动去完成那些需要改善的功能。”
#### 文化提升
Corgibytes 公司每天都会看到同样的问题:一家创业公司建立了一个对开发团队毫无推动的文化环境。公司 CEO 抱着双臂思考着为什么这样的环境对员工没多少改变。然而事实却是公司的企业文化对工作并不利。为了激励工程师,你必须全面地了解他们的工作环境。
为了证明这一点,Goulet 引用了作者 Robert Henry 说过的一段话:
>
> **目的不是创造艺术,而是在最美妙的状态下让艺术应运而生。**
>
>
>
“你们也要开始这样思考一下你们的软件,”她说。“你们的企业文件就类似那个状态。你们的目标就是创造一个让艺术品应运而生的环境,这件艺术品就是你们公司的代码、一流的售后服务、充满幸福感的开发者、良好的市场预期、盈利能力等等。这些都息息相关。”
优先考虑解决公司的技术债务和遗留代码也是一种文化。那是真正为开发团队清除障碍,以制造影响的方法。同时,这也会让你将来有更多的时间精力去完成更重要的工作。如果你不从根本上改变固有的企业文化环境,你就不可能重构公司产品。改变对产品维护及现代化的投资的态度是开始实施变革的第一步,最理想情况是从公司的 CEO 开始自顶向下转变。
以下是 Goulet 关于建立那种流态文化方面提出的建议:
* 反对公司嘉奖那些加班到深夜的“英雄”。提倡高效率的工作方式。
* 了解协同开发技术,比如 Woody Zuill 提出的[<ruby> 合作编程 <rt> Mob Programming </rt></ruby>](http://mobprogramming.org/)模式。
* 遵从 4 个[现代敏捷开发](https://www.industriallogic.com/blog/modern-agile/)原则:用户至上、实践及快速学习、把安全放在首位、持续交付价值。
* 每周为研发人员提供项目外的职业发展时间。
* 把[日工作记录](http://corgibytes.com/blog/2016/08/02/how-we-use-daily-journals/)作为一种驱动开发团队主动解决问题的方式。
* 把同情心放在第一位。Corgibytes 公司让员工参加 [Brene Brown 勇气工厂](http://www.courageworks.com/)的培训是非常有用的。
“如果公司高管和投资者不支持这种升级方式,你得从客户服务的角度去说服他们,”Goulet 说,“告诉他们通过这次调整后,最终产品将如何给公司的大多数客户提高更好的体验。这是你能做的一个很有力的论点。”
### 寻找最具天才的代码重构者
整个行业都认为顶尖的工程师不愿意干修复遗留代码的工作。他们只想着去开发新的东西。大家都说把他们留在维护部门真是太浪费人才了。
**其实这些都是误解。如果你知道去哪里和如何找工程师,并为他们提供一个愉快的工作环境,你就可以找到技术非常精湛的工程师,来帮你解决那些最棘手的技术债务问题。**
“每次在会议上,我们都会问现场的同事‘谁喜欢去在遗留代码上工作?’每次只有不到 10% 的与会者会举手。”Goulet 说。“但是我跟这些人交流后,我发现这些工程师恰好是喜欢最具挑战性工作的人才。”
有一位客户来寻求她的帮助,他们使用国产的数据库,没有任何相关文档,也没有一种有效的方法来弄清楚他们公司的产品架构。她称修理这种情况的一类工程师为“修正者”。在 Corgibytes 公司,她有一支这样的修正者团队由她支配,热衷于通过研究二进制代码来解决技术问题。

那么,如何才能找到这些技术人才呢? Goulet 尝试过各种各样的方法,其中有一些方法还是富有成效的。
她创办了一个社区网站 [legacycode.rocks](http://legacycode.rocks/) 并且在招聘启示上写道:“长期招聘那些喜欢重构遗留代码的另类开发人员...如果你以从事处理遗留代码的工作为自豪,欢迎加入!”
“我开始收到很多人发来邮件说,‘噢,天呐,我也属于这样的开发人员!’”她说。“只需要发布这条信息,并且告诉他们这份工作是非常有意义的,就吸引了合适的人才。”
在招聘的过程中,她也会使用持续性交付的经验来回答那些另类开发者想知道的信息:包括详细的工作内容以及明确的要求。“我这么做的原因是因为我讨厌重复性工作。如果我收到多封邮件来咨询同一个问题,我会把答案发布在网上,我感觉自己更像是在写说明文档一样。”
但是随着时间的推移,她发现可以重新定义招聘流程来帮助她识别出更出色的候选人。比如说,她在应聘要求中写道,“公司 CEO 将会重新审查你的简历,因此请确保求职信中致意时不用写明性别。所有以‘尊敬的先生’或‘先生’开头的信件将会被当垃圾处理掉”。这些只是她的招聘初期策略。
“我开始这么做是因为很多申请人把我当成男性,因为我是一家软件公司的男性 CEO,我必须是男性!?”Goulet 说。“所以,有一天我想我应该它当作应聘要求放到网上,看有多少人注意到这个问题。令我惊讶的是,这让我过滤掉一些不太严谨的申请人。还突显出了很多擅于从事遗留代码方面工作的人。”
Goulet 想起一个应聘者发邮件给我说,“我查看了你们网站的代码(我喜欢这个网站,这也是我的工作)。你们的网站架构很奇特,好像是用 PHP 写的,但是你们却运行在用 Ruby 语言写的 Jekyll 下。我真的很好奇那是什么呢。”
Goulet 从她的设计师那里得知,原来,在 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 文件中有一个未使用的 PHP 类名,她一直想解决这个问题,但是一直没机会。Goulet 的回复是:“你正在找工作吗?”
另外一名候选人注意到她曾经在一篇说明文档中使用 CTO 这个词,但是她的团队里并没有这个头衔(她的合作伙伴是 Chief Code Whisperer)。这些注重细节、充满求知欲、积极主动的候选者更能引起她的注意。
>
> **代码修正者不仅需要注重细节,而且这也是他们必备的品质。**
>
>
>
让人吃惊的是,Goulet 从来没有为招募最优秀的代码修正者而感到厌烦过。“大多数人都是通过我们的网站直接投递简历,但是当我们想扩大招聘范围的时候,我们会通过 [PowerToFly](https://www.powertofly.com/) 和 [WeWorkRemotely](https://weworkremotely.com/) 网站进行招聘。我现在确实不需要招募新人马了。他们需要经历一段很艰难的时期才能理解代码修正者的意义是什么。”
如果他们通过首轮面试,Goulet 将会让候选者阅读一篇 Arlo Belshee 写的文章“[<ruby> 命名是一个过程 <rt> Naming is a Process </rt></ruby>](http://arlobelshee.com/good-naming-is-a-process-not-a-single-step/)”。它讲的是非常详细的处理遗留代码的的过程。她最经典的指导方法是:“阅读完这段代码并且告诉我,你是怎么理解的。”
她将找出对问题的理解很深刻并且也愿意接受文章里提出的观点的候选者。这对于区分有深刻理解的候选者和仅仅想获得工作的候选者来说,是极其有用的办法。她强烈要求候选者找出一段与他操作相关的代码,来证明他是充满激情的、有主见的及善于分析问题的人。
最后,她会让候选者跟公司里当前的团队成员一起使用 [Exercism.io](http://exercism.io/) 工具进行编程。这是一个开源项目,它允许开发者学习如何在不同的编程语言环境下使用一系列的测试驱动开发的练习进行编程。结对编程课程的第一部分允许候选者选择其中一种语言来使用。下一个练习中,面试官可以选择一种语言进行编程。他们总能看到那些人处理异常的方法、随机应便的能力以及是否愿意承认某些自己不了解的技术。
“当一个人真正的从执业者转变为大师的时候,他会毫不犹豫的承认自己不知道的东西,”Goulet说。
让他们使用自己不熟悉的编程语言来写代码,也能衡量其坚韧不拔的毅力。“我们想听到某个人说,‘我会深入研究这个问题直到彻底解决它。’也许第二天他们仍然会跑过来跟我们说,‘我会一直留着这个问题直到我找到答案为止。’那是作为一个成功的修正者表现出来的一种气质。”
>
> **产品开发人员在我们这个行业很受追捧,因此很多公司也想让他们来做维护工作。这是一个误解。最优秀的维护修正者并不是最好的产品开发工程师。**
>
>
>
如果一个有天赋的修正者在眼前,Goulet 懂得如何让他走向成功。下面是如何让这种类型的开发者感到幸福及高效工作的一些方式:
* 给他们高度的自主权。把问题解释清楚,然后安排他们去完成,但是永不命令他们应该如何去解决问题。
* 如果他们要求升级他们的电脑配置和相关工具,尽管去满足他们。他们明白什么样的需求才能最大限度地提高工作效率。
* 帮助他们[避免分心](http://corgibytes.com/blog/2016/04/15/inception-layers/)。他们喜欢全身心投入到某一个任务直至完成。
总之,这些方法已经帮助 Corgibytes 公司培养出二十几位对遗留代码充满激情的专业开发者。
### 稳定期没什么不好
大多数创业公司都都不想跳过他们的成长期。一些公司甚至认为成长期应该是永无止境的。而且,他们觉得也没这个必要跳过成长期,即便他们已经进入到了下一个阶段:稳定期。**完全进入到稳定期意味着你拥有人力资源及管理方法来创造技术财富,同时根据优先权适当支出。**
“在成长期和稳定期之间有个转折点,就是维护人员必须要足够壮大,并且相对于专注新功能的产品开发人员,你开始更公平的对待维护人员,”Goulet 说。“你们公司的产品开发完成了。现在你得让他们更加稳定地运行。”
这就意味着要把公司更多的预算分配到产品维护及现代化方面。“你不应该把产品维护当作是一个不值得关注的项目,”她说。“这必须成为你们公司固有的一种企业文化 —— 这将帮助你们公司将来取得更大的成功。“
最终,你通过这些努力创建的技术财富,将会为你的团队带来一大批全新的开发者:他们就像侦查兵一样,有充足的时间和资源去探索新的领域,挖掘新客户资源并且给公司创造更多的机遇。当你们在新的市场领域做得更广泛并且不断取得进展 —— 那么你们公司已经真正地进入到繁荣发展的状态了。
---
via: <http://firstround.com/review/forget-technical-debt-heres-how-to-build-technical-wealth/>
作者:<http://firstround.com/> 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,079 | Fedora 中使用 Inkscape 起步 | https://fedoramagazine.org/getting-started-inkscape-fedora/ | 2016-12-31T13:31:23 | [
"inkscape"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8079-1.html | 
Inkscape 是一个流行的、功能齐全、自由而开源的矢量[图形编辑器](https://inkscape.org/),它已经在 Fedora 官方仓库中。它特别适合创作 [SVG 格式](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scalable_Vector_Graphics)的矢量图形。Inkscape 非常适于创建和操作图片和插图,以及创建图表和用户界面设计。

*使用 inkscape 创建的[风车景色](https://openclipart.org/detail/185885/windmill-in-landscape)的插图*
[其官方网站的截图页](https://inkscape.org/en/about/screenshots/)上有一些很好的例子,说明 Inkscape 可以做些什么。<ruby> Fedora 杂志 <rt> Fedora Magazine </rt></ruby>上的大多数精选图片也是使用 Inkscape 创建的,包括最近的精选图片:

*Fedora 杂志最近使用 Inkscape 创建的精选图片*
### 在 Fedora 上安装 Inkscape
**Inkscape 已经[在 Fedora 官方仓库中了](https://apps.fedoraproject.org/packages/inkscape),因此可以非常简单地在 Fedora Workstation 上使用 Software 这个应用来安装它:**

另外,如果你习惯用命令行,你可以使用 `dnf` 命令来安装:
```
sudo dnf install inkscape
```
### (开始)深入 Inkscape
当第一次打开程序时,你会看到一个空白页面,并且有一组不同的工具栏。对于初学者,最重要的三个工具栏是:Toolbar、Tools Control Bar、 Colour Palette:

**Toolbar**提供了创建绘图的所有基本工具,包括以下工具:
* 矩形工具:用于绘制矩形和正方形
* 星形/多边形(形状)工具
* 圆形工具:用于绘制椭圆和圆
* 文本工具:用于添加标签和其他文本
* 路径工具:用于创建或编辑更复杂或自定义的形状
* 选择工具:用于选择图形中的对象
**Colour Palette** 提供了一种设置当前选定对象的颜色的快速方式。 **Tools Control Bar** 提供了工具栏中当前选定工具的所有设置。每次选择新工具时,Tools Control Bar 会变成该工具的相应设置:

### 绘图
接下来,让我们使用 Inkscape 绘制一个星星。 首先,从 **Toolbar** 中选择星形工具,**然后在主绘图区域上单击并拖动。**
你可能会注意到你画的星星看起来很像一个三角形。要更改它,请使用 **Tools Control Bar** 中的 **Corners** 选项,再添加几个点。 最后,当你完成后,在星星仍被选中的状态下,从 **Palette**(调色板)中选择一种颜色来改变星星的颜色:

接下来,可以在 Toolbar 中实验一些其他形状工具,如矩形工具,螺旋工具和圆形工具。通过不同的设置,每个工具都可以创建一些独特的图形。
### 在绘图中选择并移动对象
现在你有一堆图形了,你可以使用 Select 工具来移动它们。要使用 Select 工具,首先从工具栏中选择它,然后单击要操作的形状,接着将图形拖动到您想要的位置。
选择形状后,你还可以使用尺寸句柄调整图形大小。此外,如果你单击所选的图形,尺寸句柄将转变为旋转模式,并允许你旋转图形:

---
Inkscape是一个很棒的软件,它还包含了更多的工具和功能。在本系列的下一篇文章中,我们将介绍更多可用来创建插图和文档的功能和选项。
---
作者简介:Ryan 是一名 Fedora 设计师。他使用 Fedora Workstation 作为他的主要桌面,还有来自 Libre Graphics 世界的最好的工具,尤其是矢量图形编辑器 Inkscape。
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/getting-started-inkscape-fedora/>
作者:[Ryan Lerch](http://ryanlerch.id.fedoraproject.org/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Inkscape is a popular, full-featured, free and open source vector [graphics editor](https://inkscape.org/) available in the official Fedora repositories. It’s specifically tailored for creating vector graphics in the [SVG format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scalable_Vector_Graphics). Inkscape is great for creating and manipulating pictures and illustrations. It’s also good for creating diagrams, and user interface mockups.


[ Windmill Landscape](https://openclipart.org/detail/185885/windmill-in-landscape) illustration created using inkscape
The [screenshots page on the official website](https://inkscape.org/en/about/screenshots/) has some great examples of what can be done with Inkscape. The majority of the featured images here on the Fedora Magazine are also created using Inkscape, including this recent featured image:
## Installing Inkscape on Fedora
Inkscape is [available in the official Fedora repositories](https://apps.fedoraproject.org/packages/inkscape), so it’s super easy to install using the Software app in Fedora Workstation**:**
Alternatively, if you are comfortable with the command line, you can install using the following
command:
sudo dnf install inkscape
## Dive into Inkscape (getting started)
When opening the app for the first time, you are greeted with a blank page, and a bunch of different toolbars. For beginners, the three most important of these toolbars are the Toolbar, the Tools Control Bar, and the Colour Palette:
The **Toolbar** provides all the basic tools for creating drawings, including tools such as:
- The rectangle tool, for drawing rectangles and squares
- The star / polygon (shapes) tool
- The circle tool, for drawing ellipses and circles
- The text tool, for adding labels and other text
- The path tool, for creating or editing more complex or customized shapes
- The select tool for selecting objects in your drawing
The **Colour Palette** provides a quick way to set the colour of the currently selected object. The **Tools Control Bar** provides all the settings for the currently selected tool in the Toolbar. Each time you select a new tool, the Tools Control Bar will update with the settings for that tool:
### Drawing shapes
Next, let’s draw a star with Inkscape. First, choose the star tool from the **Toolbar, **and click and drag on the main drawing area**.**
You’ll probably notice your star looks a lot like a triangle. To change this, play with the Corners option in the **Tools Control Bar**, and add a few more points. Finally, when you’re done, with the star still selected choose a colour from the **Palette** to change the colour of your star:
Next, experiment with some of the other shapes tools in the Toolbar, such as the rectangle tool, the spiral tool and the circle tool. Also play around with some of the settings for each tool to create a bunch of unique shapes.
## Selecting and moving objects in your drawing
Now you have a bunch of shapes, and can use the Select tool to move them around. To use the select tool, first select it from the toolbar, and then click on the shape you want to manipulate. Then click and drag the shape to where you want it to be.
When a shape is selected, you can also use the resize handles to scale the shape. Additionally, if you click on a shape that is selected, the resize handles change to rotate mode, allowing you to spin your shape:
Inkscape is an awesome piece of software that is packed with many more tools and features. In the next articles in this series, we will cover more of the features and options you can use to create awesome illustrations and documents.
## BKM
Nice! Good to see full featured applications for everyday use.
## Fernando Rodrigues Baroni
Nice post!
Inkscape is amazing! I’ve used it to create some basic diagrams like http://baroni.tech/blog/git-bisect/ and it is extremely easy.
Could you write about using it to do wireframing/UI mocks?
Thank you!
## Leslie Satenstein
Hi Ryan
Before this posting, I was always a little afraid of doing designs in graphics. You see, I am a command line man and not comfortable with graphics.
Following your step by step example, made me realize that its not difficult, that ctl-z works as an undo, etc.
I must thank you for this posting. It is most informative and enlightening.
## Onyeibo Oku
Seriously Leslie?
## Leslie Satenstein
Yes, I grew up with IBM Mainframes, later with Unix. I diddatabase management, ERP, with applied math in capacity planning, system modeling, forecasting and application of probability and mathematical expectations to tackle large scale business problems.
My world did not touch graphics ever.
## major_tom
what my wish to christmas would be:
having (svg) dynamic vector objects in gimp, editing them by one click in inkscape changes them in gimp dynamicly
if that would be possible it would be a very big deal!
## LuxX
Perfect timing on this! I was just wondering if there was a vector program for Fedora. 🙂
## chuck maki
it looks just like GIMP to me. |
8,080 | 如何在 Linux 下安装 PyCharm | https://www.lifewire.com/how-to-install-the-pycharm-python-ide-in-linux-4091033 | 2016-12-31T17:39:35 | [
"PyCharm",
"Python",
"编程"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8080-1.html | 
### 简介
Linux 经常被看成是一个远离外部世界,只有极客才会使用的操作系统,虽然这是一个误解,但事实上,如果你想开发软件,那么 Linux 系统能够为你提供一个很好的开发环境。
刚开始学习编程的新手们经常会问这样一个问题:应该使用哪种语言?当涉及到 Linux 系统的时候,通常的选择是 C、C++、Python、Java、PHP、Perl 和 Ruby On Rails。
Linux 系统的许多核心程序都是用 C 语言写的,但是如果离开 Linux 系统的世界, C 语言就不如其它语言比如 Java 和 Python 那么常用。
对于学习编程的人来说, Python 和 Java 都是不错的选择,因为它们是跨平台的,因此,你在 Linux 系统上写的程序在 Windows 系统和 Mac 系统上也能够很好的工作。
虽然你可以使用任何编辑器来开发 Python 程序,但是如果你使用一个同时包含编辑器和调试器的优秀的集成开发环境(IDE)来进行开发,那么你的编程生涯将会变得更加轻松。
PyCharm 是由 Jetbrains 公司开发的一个跨平台编辑器。如果你之前是在 Windows 环境下进行开发,那么你会立刻认出 Jetbrains 公司,它就是那个开发了 Resharper 的公司。 Resharper 是一个用于重构代码的优秀产品,它能够指出代码可能存在的问题以及自动添加声明:比如当你在使用一个类的时候它会自动为你导入。
这篇文章将讨论如何在 Linux 系统上获取、安装和运行 PyCharm 。
### 如何获取 PyCharm
你可以通过访问[这儿](https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/)获取 PyCharm 。屏幕中央有一个很大的 'Download' 按钮。
你可以选择下载专业版或者社区版。如果你刚刚接触 Python 编程那么推荐下载社区版。然而,如果你打算发展到专业化的编程,那么专业版的一些优秀特性是不容忽视的。
### 如何安装 PyCharm
下载好的文件的名称可能是 ‘pycharm-professional-2016.2.3.tar.gz’。
以 “tar.gz” 结尾的文件是被 [gzip](https://www.lifewire.com/example-uses-of-the-linux-gzip-command-4078675) 工具压缩过的,并且把文件夹用 [tar](https://www.lifewire.com/uses-of-linux-command-tar-2201086) 工具归档到了一起。你可以阅读关于[提取 tar.gz 文件](https://www.lifewire.com/extract-tar-gz-files-2202057)指南的更多信息。
加快节奏,为了解压文件,你需要做的是首先打开终端,然后通过下面的命令进入下载文件所在的文件夹:
```
cd ~/Downloads
```
现在,通过运行下面的命令找到你下载的文件的名字:
```
ls pycharm*
```
然后运行下面的命令解压文件:
```
tar -xvzf pycharm-professional-2016.2.3.tar.gz -C ~
```
记得把上面命令中的文件名替换成通过 `ls` 命令获知的 pycharm 文件名。(也就是你下载的文件的名字)。上面的命令将会把 PyCharm 软件安装在 `home` 目录中。
### 如何运行 PyCharm
要运行 PyCharm, 首先需要进入 `home` 目录:
```
cd ~
```
运行 `ls` 命令查找文件夹名:
```
ls
```
查找到文件名以后,运行下面的命令进入 PyCharm 目录:
```
cd pycharm-2016.2.3/bin
```
最后,通过运行下面的命令来运行 PyCharm:
```
sh pycharm.sh &
```
如果你是在一个桌面环境比如 GNOME、KDE、Unity、Cinnamon 或者其他现代桌面上运行,那么你也可以通过桌面环境的菜单或者快捷方式来找到 PyCharm 。
### 总结
现在, PyCharm 已经安装好了,你可以开始使用它来开发一个桌面应用、 web 应用和各种工具。
如果你想学习如何使用 Python 编程,那么这儿有很好的[学习资源](https://www.lifewire.com/learn-linux-in-structured-manner-4061368)值得一看。里面的文章更多的是关于 Linux 学习,但也有一些资源比如 Pluralsight 和 Udemy 提供了关于 Python 学习的一些很好的教程。
如果想了解 PyCharm 的更多特性,请点击[这儿](/article-8074-1.html)来查看。它覆盖了从创建项目到描述用户界面、调试以及代码重构的全部内容。
---
via: <https://www.lifewire.com/how-to-install-the-pycharm-python-ide-in-linux-4091033>
作者:[Gary Newell](https://www.lifewire.com/gary-newell-2180098) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,081 | 如何在 Linux/Unix 系统中验证端口是否打开 | https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/unix-linux-check-if-port-is-in-use-command/ | 2017-01-01T08:09:00 | [
"nmap",
"lsof",
"netstat",
"扫描",
"端口"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8081-1.html | 
在 Linux 或者类 Unix 中,我该如何检查某个端口是否被占用?我又该如何验证 Linux 服务器中有哪些端口处于监听状态?
验证哪些端口在服务器的网络接口上处于监听状态是非常重要的。你需要注意那些开放端口来检测网络入侵。除了网络入侵,为了排除故障,确认服务器上的某个端口是否被其他应用程序占用也是必要的。比方说,你可能会在同一个系统中安装了 Apache 和 Nginx 服务器,所以了解是 Apache 还是 Nginx 占用了 # 80/443 TCP 端口真的很重要。这篇快速教程会介绍使用 `netstat` 、 `nmap` 和 `lsof` 命令来检查端口使用信息并找出哪些程序正在使用这些端口。
### 如何检查 Linux 中的程序和监听的端口
1、 打开一个终端,如 shell 命令窗口。 2、 运行以下任意一行命令:
```
sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
sudo netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN
sudo nmap -sTU -O IP地址
```
下面我们看看这些命令和它们的详细输出内容:
### 方式 1:lsof 命令
语法如下:
```
$ sudo lsof -i -P -n
$ sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
$ doas lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN ### OpenBSD
```
输出如下:

*图 1:使用 lsof 命令检查监听端口和程序*
仔细看上面输出的最后一行:
```
sshd 85379 root 3u IPv4 0xffff80000039e000 0t0 TCP 10.86.128.138:22 (LISTEN)
```
* `sshd` 是程序的名称
* `10.86.128.138` 是 `sshd` 程序绑定 (LISTEN) 的 IP 地址
* `22` 是被使用 (LISTEN) 的 TCP 端口
* `85379` 是 `sshd` 任务的进程 ID (PID)
### 方式 2:netstat 命令
你可以如下面所示使用 `netstat` 来检查监听的端口和程序。
**Linux 中 netstat 语法**
```
$ netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN
```
**FreeBSD/MacOS X 中 netstat 语法**
```
$ netstat -anp tcp | grep LISTEN
$ netstat -anp udp | grep LISTEN
```
**OpenBSD 中 netstat 语法**
```
$ netstat -na -f inet | grep LISTEN
$ netstat -nat | grep LISTEN
```
### 方式 3:nmap 命令
语法如下:
```
$ sudo nmap -sT -O localhost
$ sudo nmap -sU -O 192.168.2.13 ### 列出打开的 UDP 端口
$ sudo nmap -sT -O 192.168.2.13 ### 列出打开的 TCP 端口
```
示例输出如下:

*图 2:使用 nmap 探测哪些端口监听 TCP 连接*
你可以用一句命令合并 TCP/UDP 扫描:
```
$ sudo nmap -sTU -O 192.168.2.13
```
### 赠品:对于 Windows 用户
在 windows 系统下可以使用下面的命令检查端口使用情况:
```
netstat -bano | more
netstat -bano | grep LISTENING
netstat -bano | findstr /R /C:"[LISTING]"
```
---
via: <https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/unix-linux-check-if-port-is-in-use-command/>
作者:[VIVEK GITE](https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/unix-linux-check-if-port-is-in-use-command/) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[oska874](https://github.com/oska874)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
8,082 | 如何在 Apache 中重定向 URL 到另外一台服务器 | http://www.tecmint.com/redirect-website-url-from-one-server-to-different-server/ | 2017-01-02T08:31:00 | [
"Apache",
"重定向"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8082-1.html | 如我们前面两篇文章([使用 mod\_rewrite 执行内部重定向](http://www.tecmint.com/redirection-with-mod_rewrite-in-apache/)和[基于浏览器来显示自定义内容](http://www.tecmint.com/mod_rewrite-redirect-requests-based-on-browser/))中提到的,在本文中,我们将解释如何在 Apache 中使用 mod\_rewrite 模块重定向对已移动到另外一台服务器上的资源的访问。

假设你正在重新设计公司的网站。你已决定将内容和样式(HTML文件、JavaScript 和 CSS)存储在一个服务器上,将文档存储在另一个服务器上 - 这样可能会更稳健。
>
> **建议阅读:** [5 个提高 Apache Web 服务器性能的提示](http://www.tecmint.com/apache-performance-tuning/) 。
>
>
>
但是,你希望这个更改对用户是透明的,以便他们仍然能够通过之前的网址访问文档。
在下面的例子中,名为 `assets.pdf` 的文件已从 `192.168.0.100`(主机名:`web`)中的 `/var/www/html` 移动到`192.168.0.101`(主机名:`web2`)中的相同位置。
为了让用户在浏览到 `192.168.0.100/assets.pdf` 时可以访问到此文件,请打开 `192.168.0.100` 上的 Apache 配置文件并添加以下重写规则(或者也可以将以下规则添加到 [.htaccess 文件](http://www.tecmint.com/tag/htaccess/))中:
```
RewriteRule "^(/assets\.pdf$)" "http://192.168.0.101$1" [R,L]
```
其中 `$1` 占位符,代表与括号中的正则表达式匹配的任何内容。
现在保存更改,不要忘记重新启动 Apache,让我们看看当我们打开 `192.168.0.100/assets.pdf`,尝试访问 `assets.pdf` 时会发生什么:
>
> **建议阅读:** [25 个有用的网站 .htaccess 技巧](http://www.tecmint.com/apache-htaccess-tricks/)
>
>
>
在下面我们就可以看到,为 `192.168.0.100` 上的 `assets.pdf` 所做的请求实际上是由 `192.168.0.101`处理的。
```
# tail -n 1 /var/log/apache2/access.log
```

*检查 Apache 日志*
在本文中,我们讨论了如何对已移动到其他服务器的资源进行重定向。 总而言之,我强烈建议你看看 [mod\_rewrite](http://mod-rewrite-cheatsheet.com/) 指南和 [Apache 重定向指南](https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/rewrite/remapping.html),以供将来参考。
一如既往那样,如果您对本文有任何疑虑,请随时使用下面的评论栏回复。 我们期待你的回音!
---
作者简介:Gabriel Cánepa 是来自阿根廷圣路易斯 Villa Mercedes 的 GNU/Linux 系统管理员和 Web 开发人员。 他在一家全球领先的消费品公司工作,非常高兴使用 FOSS 工具来提高他日常工作领域的生产力。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/redirect-website-url-from-one-server-to-different-server/>
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa](http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,084 | 使用 Inkscape:添加颜色 | https://fedoramagazine.org/inkscape-adding-colour/ | 2017-01-01T19:35:00 | [
"Inkscape"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8084-1.html | 
在我们先前的 Inkscape 文章中,[我们介绍了 Inkscape 的基础](/article-8079-1.html) - 安装,以及如何创建基本形状及操作它们。我们还介绍了使用 Palette 更改 inkscape 对象的颜色。 虽然 Palette 对于从预定义列表快速更改对象颜色非常有用,但大多数情况下,你需要更好地控制对象的颜色。这时我们使用 Inkscape 中最重要的对话框之一 - <ruby> 填充和轮廓 <rt> Fill and Stroke </rt></ruby> 对话框。
**关于文章中的动画的说明:**动画中的一些颜色看起来有条纹。这只是动画创建导致的。当你在 Inkscape 尝试时,你会看到很好的平滑渐变的颜色。
### 使用 Fill/Stroke 对话框
要在 Inkscape 中打开 “Fill and Stroke” 对话框,请从主菜单中选择 `Object`>`Fill and Stroke`。打开后,此对话框中的三个选项卡允许你检查和更改当前选定对象的填充颜色、描边颜色和描边样式。

在 Inkscape 中,Fill 用来给予对象主体颜色。对象的轮廓是你的对象的可选择外框,可在<ruby> 轮廓样式 <rt> Stroke style </rt></ruby>选项卡中进行配置,它允许您更改轮廓的粗细,创建虚线轮廓或为轮廓添加圆角。 在下面的动画中,我会改变星形的填充颜色,然后改变轮廓颜色,并调整轮廓的粗细:

### 添加并编辑渐变效果
对象的填充(或者轮廓)也可以是渐变的。要从 “Fill and Stroke” 对话框快速设置渐变填充,请先选择 “Fill” 选项卡,然后选择<ruby> 线性渐变 <rt> linear gradient </rt></ruby> 选项:

要进一步编辑我们的渐变,我们需要使用专门的<ruby> 渐变工具 <rt> Gradient Tool </rt></ruby>。 从工具栏中选择“Gradient Tool”,会有一些渐变编辑锚点出现在你选择的形状上。 **移动锚点**将改变渐变的位置。 如果你**单击一个锚点**,您还可以在“Fill and Stroke”对话框中更改该锚点的颜色。 要**在渐变中添加新的锚点**,请双击连接锚点的线,然后会出现一个新的锚点。

---
这篇文章介绍了在 Inkscape 图纸中添加一些颜色和渐变的基础知识。 **“Fill and Stroke”** 对话框还有许多其他选项可供探索,如图案填充、不同的渐变样式和许多不同的轮廓样式。另外,查看**<ruby> 工具控制栏 <rt> Tools control bar </rt></ruby>** 的 **Gradient Tool** 中的其他选项,看看如何以不同的方式调整渐变。
---
作者简介:Ryan 是一名 Fedora 设计师。他使用 Fedora Workstation 作为他的主要桌面,还有来自 Libre Graphics 世界的最好的工具,尤其是矢量图形编辑器 Inkscape。
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/inkscape-adding-colour/>
作者:[Ryan Lerch](http://ryanlerch.id.fedoraproject.org/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In our previous Inkscape article, [we covered the absolute basics of getting started with Inkscape](https://fedoramagazine.org/getting-started-inkscape-fedora/) — installing, and how to create basic shapes and manipulate them. We also covered changing the colour of inkscape objects using the Palette. While the Palette is great for quickly changing the colour of your objects from a pre-defined list, most times you will need more control over the colours of your objects. This is where we use one of the most important dialogs in Inkscape — the Fill and Stroke dialog.
**A quick note about the animations in this post: **some of the colours in the animations appear banded. This is just an artifact of the way the animations are created. When you try this out on Inkscape you will see nice smooth gradients of colour.
### Using the Fill / Stroke dialog
To open the Fill and Stroke dialog in Inkscape, choose
>
from the main menu. Once opened, the main three tabs of this dialog allow you to inspect and change the Fill colour, Stroke colour, and Stroke style of the currently selected object.
In Inkscape, the Fill is the main colour given to the body of an object. The stroke of the object is an optional outline of your object. The stroke of an object also has additional styles — configurable in the Stroke style tab — allowing you to change the thickness of the stroke, create a dotted outline, or add rounded corners to you stroke. In this next animation, I change the fill colour of the star, and then change the stroke colour, and tweak the thickness of the stroke:
### Adding and Editing a gradient
A gradient can also be the Fill (or the stroke) of an object. To quickly set a gradient fill from the Fill and Stroke dialog, first choose the Fill tab, then pick the linear gradient option:
To edit our gradient further, we need to use the specialised Gradient Tool. Choose the Gradient tool from the toolbar, and some additional gradient editing handles will appear on your selected shape. **Moving the handles** around will change the positioning of the gradient. If you **click on an individual handle**, you can also change the colour of that handle in the Fill and Stroke dialog. To **add an additional stop in your gradient**, double click on the line connecting the handles, and a new handle will appear.
That covers the basics of adding some more colour and gradients to your Inkscape drawings. The** Fill and Stroke dialog** also has many other options to explore, like pattern fills, different gradient styles, and many different stroke styles. Also check out the additional options in the **Tools control bar** for the **Gradient Tool** to see how you can tweak gradients in different ways too.
## Artem
How do you create these animations?
## Rodrigo de Araujo
Very nice article series… Keep up the good work!
## Lionel Lizee
I like this
## Munis Isazade
Very good, and useful .
## Michael George
Inkscape is awesome!!!!!!!
These articles are great work! Thank You!
## Justin W. Flory
Glad to hear you’re enjoying the series, Michael. 🙂 We might have a few more coming in the queue, so keep an eye out! Thanks for your support. |
8,085 | 使用 Fedora 和 Inkscape 制作一张简单的壁纸 | https://fedoramagazine.org/inkscape-design-imagination/ | 2017-01-02T09:48:00 | [
"Inkscape"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8085-1.html | 
在先前的两篇 Inkscape 的文章中,我们已经[介绍了 Inkscape 的基本使用、创建对象](/article-8079-1.html)以及[一些基本操作和如何修改颜色。](/article-8084-1.html)
在接下来的介绍中,我们会集合这些新的技巧,并且创建我们的第一个作品 —— 一张简单的壁纸。
### 更改文档大小
回顾先前的教程时,你可能会注意到主画板上的默认文档尺寸是一个黑色边框的矩形。Inkscape 中默认文档的大小是 A4 纸大小:

对于这张壁纸而言,我们会将尺寸改为 **1024px x 768px**。要改变文档的尺寸,进入`File` > `Document Properties...`。在<ruby> 文档属性 <rt> Document Properties </rt></ruby>对话框中<ruby> 自定义文档大小 <rt> Custom Size </rt></ruby>区域中输入宽度为 `1024`,高度为 `768` ,单位是 `px`:

页面上文档的轮廓大概像这样:

### 绘画背景
接下来,我们会画一个和文档一样大的矩形。因此选择<ruby> 矩形工具 <rt> rectangle tool </rt></ruby>来画一个矩形,并使用<ruby> 工具控制栏 <rt> Tools Control bar </rt></ruby>来调整矩形的大小。

接着在矩形中添加一个<ruby> 渐变填充 <rt> Gradient Fill </rt></ruby>。如果你需要复习添加渐变,请阅读先前添加色彩的[那篇文章](/article-8084-1.html)。

你的矩形也可以设置轮廓颜色。 使用<ruby> 填充和轮廓 <rt> Fill and Stroke </rt></ruby>对话框将轮廓设置为 `none`。

### 绘制图样
接下来我们画一个三角形,使用 3 个顶点的星型/多边形工具。你可以按住 `CTRL` 键给三角形一个角度并使之对称。

选中三角形并按下 `CTRL+D` 来复制它(复制的图形会覆盖在原来图形的上面),**因此在复制后确保将它移动到别处。**

如图选中一个三角形,进入`Object` > `FLIP-HORIZONTAL`(水平翻转)。
 
为这三个三角形重新着色。让它看上去和背景和谐。

选中所有的三角形并复制,以填充你的样式:

### 导出背景
最后,我们需要将我们的文档导出为 PNG 文件。点击 `File` > `EXPORT PNG`,打开导出对话框,选择文件位置和名字,确保选中的是 `Drawing` 标签,并点击 `EXPORT`。

不要让工具成为你想象力的障碍。来制作美丽的壁纸并提交你的设计到 [FEDORA 25 壁纸](https://fedoramagazine.org/keeping-fedora-beautiful-contribute-wallpaper/)上来吧。你的设计或许会幸运地被选中成为上千万用户的壁纸。下面是用 Inkscape 和上面提到的技术制作的一些壁纸示例:
 
---
via: <https://fedoramagazine.org/inkscape-design-imagination/>
作者:[a2batic](http://a2batic.id.fedoraproject.org/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | In our previous two Inkscape articles, we have [covered the basics of using Inkscape, creating objects,](https://fedoramagazine.org/getting-started-inkscape-fedora/) and [doing some basic manipulations and color changes.](https://fedoramagazine.org/inkscape-adding-colour/)
In this next installment, we are going to put all these new skills together, and create our first composition — a simple wallpaper.
### Changing the document size
When going through the previous tutorials, you probably noticed the default document size shown on the main canvas window as a black bordered rectangle. The default document size in Inkscape is the A4 paper size:
For this wallpaper, we are going to resize the the document to **1024px x 768px**. To change the document size, Go to
>
. In the Custom Size section of the Document Properties dialog, enter the width of 1024px, and a height of 768px:
The document outline on the page should now look something like this:
### Drawing the background
Next up, we are going to draw a rectangle as big as the document. So choose the using **rectangle tool, ** draw a rectangle, and adjust the size of the rectangle using the Tools Control bar.
Next up, add a Gradient Fill to the rectangle. [If you need a refresher on adding gradients, check out the previous adding colours article.](https://fedoramagazine.org/inkscape-adding-colour/)
Your rectangle might also have a stroke colour set. Use the fill and stroke dialog to set the stroke paint to **none**.
### Drawing the pattern
Next we are going to draw a triangle. Use the star / polygon tool with 3 points. You can** PRESS and HOLD DOWN CTRL** key, to give your triangle an angle and symmetry.
Select the triangle and press **CTRL+D**, to duplicate it (the duplicated figure will overlap the existing one), **so be sure to move it after duplicating.**
Select one of the triangles as shown, and go to **OBJECT > FLIP-HORIZONTAL**
Recolour your three triangles to three colors that look good with your background.
Select all your triangles, and duplicate them again to fill out your pattern:
### Exporting your background
Finally, we need to export our document as a PNG file. Open up the export dialog with** FILE > EXPORT PNG**, select the file location and name, make sure the Drawing tab is pressed, and click on **EXPORT**
Let no tool be a barrier to your imagination. Come up with beautiful wallpapers and submit the designs for [FEDORA 25 wallpapers](https://fedoramagazine.org/keeping-fedora-beautiful-contribute-wallpaper/). Your design might get lucky enough to be used by thousands of Fedora users. Here are some examples of wallpapers created with Inkscape and the techniques above:
## Ivan Augusto
Loving this Inkscape series 😀
Today I “convert” some png to svg for a web project. Inkscape is simple, fast and fun!
## AndyMender
I use Inkscape for creating scientific figures for presentations and publications. People are always amazed, thinking that I’m using Adobe Illustrator. Hope I’ll manage to convince them at some point that Inkscape is indeed great!
## antikythera
submissions for Fedora 25 supplemental wallpaper are already closed and wallpapers have been voted for and packaged. any created wallpapers using this tutorial would no doubt be welcome as submissions when the time comes next year though. keep an eye out for the Fedora Magazine article.
## antikythera
please remove this and the above comment if possible
## antikythera
submissions for Fedora 25 supplemental wallpaper are already closed and wallpapers have been voted for and packaged. any created wallpapers using this tutorial would no doubt be welcome as submissions when the time comes next year though for F26. keep an eye out for the Fedora Magazine article. |
8,086 | sshpass:一个很棒的免交互 SSH 登录工具,但不要用在生产服务器上 | http://www.tecmint.com/sshpass-non-interactive-ssh-login-shell-script-ssh-password/ | 2017-01-03T16:03:00 | [
"sshpass",
"ssh"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8086-1.html | 在大多数情况下,Linux 系统管理员使用 SSH 登录到程 Linux 服务器时,要么是通过密码,要么是[无密码 SSH 登录](/article-6901-1.html)或基于密钥的 SSH 身份验证。
如果你想自动在 SSH 登录提示符中提供**密码**和**用户名**怎么办?这时 **sshpass** 就可以帮到你了。

sshpass 是一个简单、轻量级的命令行工具,通过它我们能够向命令提示符本身提供密码(非交互式密码验证),这样就可以通过 [cron 调度器](/article-7513-1.html)执行自动化的 shell 脚本进行备份。
ssh 直接使用 TTY 访问,以确保密码是用户键盘输入的。 sshpass 在专门的 tty 中运行 ssh,以误导 ssh 相信它是从用户接收到的密码。
重要:使用 **sshpass** 是最不安全的,因为所有系统上的用户在命令行中通过简单的 “**ps**” 命令就可看到密码。因此,如果必要,比如说在生产环境,我强烈建议使用 [SSH 无密码身份验证](/article-6901-1.html)。
### 在 Linux 中安装 sshpass
在基于 **RedHat/CentOS** 的系统中,首先需要[启用 EPEL 仓库](/article-2324-1.html)并使用 [yum 命令](/article-2272-1.html)安装它。
```
# yum install sshpass
# dnf install sshpass [Fedora 22 及以上版本]
```
在 Debian/Ubuntu 和它的衍生版中,你可以使用 [apt-get 命令](/article-4933-1.html)来安装。
```
$ sudo apt-get install sshpass
```
另外,你也可以从最新的源码安装 `sshpass`,首先下载源码并从 tar 文件中解压出内容:
```
$ wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/sshpass/files/latest/download -O sshpass.tar.gz
$ tar -xvf sshpass.tar.gz
$ cd sshpass-1.06
$ ./configure
# sudo make install
```
### 如何在 Linux 中使用 sshpass
**sshpass** 与 **ssh** 一起使用,使用下面的命令可以查看 `sshpass` 的使用选项的完整描述:
```
$ sshpass -h
```
下面为显示的 sshpass 帮助内容:
```
Usage: sshpass [-f|-d|-p|-e] [-hV] command parameters
-f filename Take password to use from file
-d number Use number as file descriptor for getting password
-p password Provide password as argument (security unwise)
-e Password is passed as env-var "SSHPASS"
With no parameters - password will be taken from stdin
-h Show help (this screen)
-V Print version information
At most one of -f, -d, -p or -e should be used
```
正如我之前提到的,**sshpass** 在用于脚本时才更可靠及更有用,请看下面的示例命令。
使用用户名和密码登录到远程 Linux ssh 服务器(10.42.0.1),并[检查文件系统磁盘使用情况](/article-6466-1.html),如图所示。
```
$ sshpass -p 'my_pass_here' ssh [email protected] 'df -h'
```
**重要提示**:此处,在命令行中提供了密码,这是不安全的,不建议使用此选项。

*sshpass – 使用 SSH 远程登录 Linux*
但是,为了防止在屏幕上显示密码,可以使用 `-e` 标志,并将密码作为 `SSHPASS` 环境变量的值输入,如下所示:
```
$ export SSHPASS='my_pass_here'
$ echo $SSHPASS
$ sshpass -e ssh [email protected] 'df -h'
```

*sshpass – 在终端中隐藏密码*
**注意:**在上面的示例中,`SSHPASS` 环境变量仅用于临时目的,并将在重新启动后删除。
要永久设置 `SSHPASS` 环境变量,打开 `/etc/profile` 文件,并在文件开头输入 `export` 语句:
```
export SSHPASS='my_pass_here'
```
保存文件并退出,接着运行下面的命令使更改生效:
```
$ source /etc/profile
```
另外,也可以使用 `-f` 标志,并把密码放在一个文件中。 这样,您可以从文件中读取密码,如下所示:
```
$ sshpass -f password_filename ssh [email protected] 'df -h'
```

*sshpass – 在登录时提供密码文件*
你也可以使用 `sshpass` [通过 scp 传输文件](/article-7456-1.html)或者 [rsync 备份/同步文件](/article-4503-1.html),如下所示:
```
------- Transfer Files Using SCP -------
$ scp -r /var/www/html/example.com --rsh="sshpass -p 'my_pass_here' ssh -l aaronkilik" 10.42.0.1:/var/www/html
------- Backup or Sync Files Using Rsync -------
$ rsync --rsh="sshpass -p 'my_pass_here' ssh -l aaronkilik" 10.42.0.1:/data/backup/ /backup/
```
更多的用法,建议阅读 `sshpass` 的 man 页面,输入:
```
$ man sshpass
```
在本文中,我们解释了 `sshpass` 是一个非交互式密码验证的简单工具。 虽然这个工具可能是有帮助的,但还是强烈建议使用更安全的 ssh 公钥认证机制。
请在下面的评论栏写下任何问题或评论,以便可以进一步讨论。
---
作者简介:Aaron Kili 是一位 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,未来的 Linux 系统管理员,web 开发人员, 还是 TecMint 原创作者,热爱电脑工作,并乐于分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/sshpass-non-interactive-ssh-login-shell-script-ssh-password/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,087 | 在 Ubuntu 中用 UFW 配置防火墙 | https://www.linode.com/docs/security/firewalls/configure-firewall-with-ufw | 2017-01-03T17:15:00 | [
"Ubuntu",
"防火墙",
"UFW"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8087-1.html | UFW,即<ruby> 简单防火墙 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> uncomplicated firewall </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,是一个 Arch Linux、Debian 或 Ubuntu 中管理防火墙规则的前端。 UFW 通过命令行使用(尽管它有可用的 GUI),它的目的是使防火墙配置简单(即<ruby> 不复杂 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> uncomplicated </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>)。

### 开始之前
1、 熟悉我们的[入门](https://www.linode.com/docs/getting-started)指南,并完成设置服务器主机名和时区的步骤。
2、 本指南将尽可能使用 `sudo`。 在完成[保护你的服务器](/article-8076-1.html)指南的章节,创建一个标准用户帐户,强化 SSH 访问和移除不必要的网络服务。 **但不要**跟着创建防火墙部分 - 本指南是介绍使用 UFW 的,它对于 iptables 而言是另外一种控制防火墙的方法。
3、 更新系统
**Arch Linux**
```
sudo pacman -Syu
```
**Debian / Ubuntu**
```
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
```
### 安装 UFW
UFW 默认包含在 Ubuntu 中,但在 Arch 和 Debian 中需要安装。 Debian 将自动启用 UFW 的 systemd 单元,并使其在重新启动时启动,但 Arch 不会。 这与告诉 UFW 启用防火墙规则不同,因为使用 systemd 或者 upstart 启用 UFW 仅仅是告知 init 系统打开 UFW 守护程序。
默认情况下,UFW 的规则集为空,因此即使守护程序正在运行,也不会强制执行任何防火墙规则。 强制执行防火墙规则集的部分在下面。
#### Arch Linux
1、 安装 UFW:
```
sudo pacman -S ufw
```
2、 启动并启用 UFW 的 systemd 单元:
```
sudo systemctl start ufw
sudo systemctl enable ufw
```
#### Debian / Ubuntu
1、 安装 UFW
```
sudo apt-get install ufw
```
### 使用 UFW 管理防火墙规则
#### 设置默认规则
大多数系统只需要打开少量的端口接受传入连接,并且关闭所有剩余的端口。 从一个简单的规则基础开始,`ufw default`命令可以用于设置对传入和传出连接的默认响应动作。 要拒绝所有传入并允许所有传出连接,那么运行:
```
sudo ufw default allow outgoing
sudo ufw default deny incoming
```
`ufw default` 也允许使用 `reject` 参数。
>
> 警告:
>
>
> 除非明确设置允许规则,否则配置默认 `deny` 或 `reject` 规则会锁定你的服务器。确保在应用默认 `deny` 或 `reject` 规则之前,已按照下面的部分配置了 SSH 和其他关键服务的允许规则。
>
>
>
#### 添加规则
可以有两种方式添加规则:用**端口号**或者**服务名**表示。
要允许 SSH 的 22 端口的传入和传出连接,你可以运行:
```
sudo ufw allow ssh
```
你也可以运行:
```
sudo ufw allow 22
```
相似的,要在特定端口(比如 111)上 `deny` 流量,你需要运行:
```
sudo ufw deny 111
```
为了更好地调整你的规则,你也可以允许基于 TCP 或者 UDP 的包。下面例子会允许 80 端口的 TCP 包:
```
sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
sudo ufw allow http/tcp
```
这个会允许 1725 端口上的 UDP 包:
```
sudo ufw allow 1725/udp
```
#### 高级规则
除了基于端口的允许或阻止,UFW 还允许您按照 IP 地址、子网和 IP 地址/子网/端口的组合来允许/阻止。
允许从一个 IP 地址连接:
```
sudo ufw allow from 123.45.67.89
```
允许特定子网的连接:
```
sudo ufw allow from 123.45.67.89/24
```
允许特定 IP/ 端口的组合:
```
sudo ufw allow from 123.45.67.89 to any port 22 proto tcp
```
`proto tcp` 可以删除或者根据你的需求改成 `proto udp`,所有例子的 `allow` 都可以根据需要变成 `deny`。
#### 删除规则
要删除一条规则,在规则的前面加上 `delete`。如果你希望不再允许 HTTP 流量,你可以运行:
```
sudo ufw delete allow 80
```
删除规则同样可以使用服务名。
### 编辑 UFW 的配置文件
虽然可以通过命令行添加简单的规则,但仍有可能需要添加或删除更高级或特定的规则。 在运行通过终端输入的规则之前,UFW 将运行一个文件 `before.rules`,它允许回环接口、ping 和 DHCP 等服务。要添加或改变这些规则,编辑 `/etc/ufw/before.rules` 这个文件。 同一目录中的 `before6.rules` 文件用于 IPv6 。
还存在一个 `after.rule` 和 `after6.rule` 文件,用于添加在 UFW 运行你通过命令行输入的规则之后需要添加的任何规则。
还有一个配置文件位于 `/etc/default/ufw`。 从此处可以禁用或启用 IPv6,可以设置默认规则,并可以设置 UFW 以管理内置防火墙链。
### UFW 状态
你可以在任何时候使用命令:`sudo ufw status` 查看 UFW 的状态。这会显示所有规则列表,以及 UFW 是否处于激活状态:
```
Status: active
To Action From
-- ------ ----
22 ALLOW Anywhere
80/tcp ALLOW Anywhere
443 ALLOW Anywhere
22 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
80/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
443 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
```
### 启用防火墙
随着你选择规则完成,你初始运行 `ufw status` 可能会输出 `Status: inactive`。 启用 UFW 并强制执行防火墙规则:
```
sudo ufw enable
```
相似地,禁用 UFW 规则:
```
sudo ufw disable
```
>
> UFW 会继续运行,并且在下次启动时会再次启动。
>
>
>
### 日志记录
你可以用下面的命令启动日志记录:
```
sudo ufw logging on
```
可以通过运行 `sudo ufw logging low|medium|high` 设计日志级别,可以选择 `low`、 `medium` 或者 `high`。默认级别是 `low`。
常规日志类似于下面这样,位于 `/var/logs/ufw`:
```
Sep 16 15:08:14 <hostname> kernel: [UFW BLOCK] IN=eth0 OUT= MAC=00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00 SRC=123.45.67.89 DST=987.65.43.21 LEN=40 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=249 ID=8475 PROTO=TCP SPT=48247 DPT=22 WINDOW=1024 RES=0x00 SYN URGP=0
```
前面的值列出了你的服务器的日期、时间、主机名。剩下的重要信息包括:
* **[UFW BLOCK]**:这是记录事件的描述开始的位置。在此例中,它表示阻止了连接。
* **IN**:如果它包含一个值,那么代表该事件是传入事件
* **OUT**:如果它包含一个值,那么代表事件是传出事件
* **MAC**:目的地和源 MAC 地址的组合
* **SRC**:包源的 IP
* **DST**:包目的地的 IP
* **LEN**:数据包长度
* **TTL**:数据包 TTL,或称为 time to live。 在找到目的地之前,它将在路由器之间跳跃,直到它过期。
* **PROTO**:数据包的协议
* **SPT**:包的源端口
* **DPT**:包的目标端口
* **WINDOW**:发送方可以接收的数据包的大小
* **SYN URGP**:指示是否需要三次握手。 `0` 表示不需要。
---
via: <https://www.linode.com/docs/security/firewalls/configure-firewall-with-ufw>
作者:[Linode](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/firewalls/configure-firewall-with-ufw) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
8,088 | 如何在 Ubuntu 环境下搭建邮件服务器(三) | https://www.linux.com/learn/sysadmin/building-email-server-ubuntu-linux-part-3 | 2017-01-04T16:16:11 | [
"Postfix",
"Dovecot"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8088-1.html | 
在本系列的最后,我们将详细介绍如何在 Dovecot 和 Postfix 中设置虚拟用户和邮箱。
欢迎回来,热心的 Linux 系统管理员们! 在本系列的[第一部分](/article-8071-1.html)和[第二部分](/article-8077-1.html)中,我们学习了如何将 Postfix 和 Dovecot 组合在一起,搭建一个不错的 IMAP 和 POP3 邮件服务器。 现在我们将学习设置虚拟用户,以便我们可以管理所有 Dovecot 中的用户。
### 抱歉,还不能配置 SSL
我知道我答应过教你们如何设置一个受 SSL 保护的服务器。 不幸的是,我低估了这个话题的范围。 所以,我会下个月再写一个全面的教程。
今天,在本系列的最后一部分中,我们将详细介绍如何在 Dovecot 和 Postfix 中设置虚拟用户和邮箱。 在你看来这是有点奇怪,所以我尽量让下面的例子简单点。我们将使用纯文本文件和纯文本来进行身份验证。 你也可以选择使用数据库后端和较强的加密认证形式,具体请参阅文末链接了解有关这些的更多信息。
### 虚拟用户
我们希望邮件服务器上用的是虚拟用户而不是 Linux 系统用户。使用 Linux 系统用户不能扩展,并且它们会暴露系统登录账号,给你的服务器带来不必要的风险。 设置虚拟用户需要在 Postfix 和 Dovecot 中编辑配置文件。我们将从 Postfix 开始。首先,我们将从一个干净、简化的 `/etc /postfix/main.cf` 开始。移动你原始的 `main.cf` 到别处做个备份,创建一个新的干净的文件,内容如下:
```
compatibility_level=2
smtpd_banner = $myhostname ESMTP $mail_name (Ubuntu/GNU)
biff = no
append_dot_mydomain = no
myhostname = localhost
alias_maps = hash:/etc/aliases
alias_database = hash:/etc/aliases
myorigin = $myhostname
mynetworks = 127.0.0.0/8 [::ffff:127.0.0.0]/104 [::1]/128 192.168.0.0/24
mailbox_size_limit = 0
recipient_delimiter = +
inet_interfaces = all
virtual_mailbox_domains = /etc/postfix/vhosts.txt
virtual_mailbox_base = /home/vmail
virtual_mailbox_maps = hash:/etc/postfix/vmaps.txt
virtual_minimum_uid = 1000
virtual_uid_maps = static:5000
virtual_gid_maps = static:5000
virtual_transport = lmtp:unix:private/dovecot-lmtp0
```
你可以直接拷贝这份文件,除了 `mynetworks` 参数的设置 `192.168.0.0/24`,它应该是你的本地子网掩码。
接下来,创建用户和组 `vmail` 来拥有你的虚拟邮箱。虚拟邮箱保存在 `vmail` 的家目录下。
```
$ sudo groupadd -g 5000 vmail
$ sudo useradd -m -u 5000 -g 5000 -s /bin/bash vmail
```
接下来重新加载 Postfix 配置:
```
$ sudo postfix reload
[sudo] password for carla:
postfix/postfix-script: refreshing the Postfix mail system
```
### Dovecot 虚拟用户
我们会使用 Dovecot 的 `lmtp` 协议来连接到 Postfix。你可以这样安装:
```
$ sudo apt-get install dovecot-lmtpd
```
`main.cf` 的最后一行涉及到 `lmtp`。复制这个 `/etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf` 示例文件来替换已存在的文件。再说一次,我们只使用这一个文件,而不是 `/etc/dovecot/conf.d` 内的所有文件。
```
protocols = imap pop3 lmtp
log_path = /var/log/dovecot.log
info_log_path = /var/log/dovecot-info.log
ssl = no
disable_plaintext_auth = no
mail_location = maildir:~/.Mail
pop3_uidl_format = %g
auth_verbose = yes
auth_mechanisms = plain
passdb {
driver = passwd-file
args = /etc/dovecot/passwd
}
userdb {
driver = static
args = uid=vmail gid=vmail home=/home/vmail/studio/%u
}
service lmtp {
unix_listener /var/spool/postfix/private/dovecot-lmtp {
group = postfix
mode = 0600
user = postfix
}
}
protocol lmtp {
postmaster_address = postmaster@studio
}
service lmtp {
user = vmail
}
```
最后,你可以创建一个含有用户和密码的文件 `/etc/dovecot/passwd`。对于纯文本验证,我们只需要用户的完整邮箱地址和密码:
```
alrac@studio:{PLAIN}password
layla@studio:{PLAIN}password
fred@studio:{PLAIN}password
molly@studio:{PLAIN}password
benny@studio:{PLAIN}password
```
Dovecot 虚拟用户独立于 Postfix 虚拟用户,因此你需要管理 Dovecot 中的用户。保存所有的设置并重启 Postfix 和 Dovecot:
```
$ sudo service postfix restart
$ sudo service dovecot restart
```
现在让我们使用老朋友 telnet 来看下 Dovecot 是否设置正确。
```
$ telnet studio 110
Trying 127.0.1.1...
Connected to studio.
Escape character is '^]'.
+OK Dovecot ready.
user molly@studio
+OK
pass password
+OK Logged in.
quit
+OK Logging out.
Connection closed by foreign host.
```
现在一切都好!让我们用 `mail` 命令,发送测试消息给我们的用户。确保使用用户的完整电子邮箱地址而不只是用户名。
```
$ mail benny@studio
Subject: hello and welcome!
Please enjoy your new mail account!
.
```
最后一行的**英文句点**表示发送消息。让我们看下它是否到达了正确的邮箱。
```
$ sudo ls -al /home/vmail/studio/benny@studio/.Mail/new
total 16
drwx------ 2 vmail vmail 4096 Dec 14 12:39 .
drwx------ 5 vmail vmail 4096 Dec 14 12:39 ..
-rw------- 1 vmail vmail 525 Dec 14 12:39 1481747995.M696591P5790.studio,S=525,W=540
```
找到了。这是一封我们可以阅读的纯文本文件:
```
$ less 1481747995.M696591P5790.studio,S=525,W=540
Return-Path: <carla@localhost>
Delivered-To: benny@studio
Received: from localhost
by studio (Dovecot) with LMTP id V01ZKRuuUVieFgAABiesew
for <benny@studio>; Wed, 14 Dec 2016 12:39:55 -0800
Received: by localhost (Postfix, from userid 1000)
id 9FD9CA1F58; Wed, 14 Dec 2016 12:39:55 -0800 (PST)
Date: Wed, 14 Dec 2016 12:39:55 -0800
To: benny@studio
Subject: hello and welcome!
User-Agent: s-nail v14.8.6
Message-Id: <20161214203955.9FD9CA1F58@localhost>
From: carla@localhost (carla)
Please enjoy your new mail account!
```
你还可以使用 telnet 进行测试,如本系列前面部分所述,并在你最喜欢的邮件客户端中设置帐户,如 Thunderbird,Claws-Mail 或 KMail。
### 故障排查
当邮件工作不正常时,请检查日志文件(请参阅配置示例),然后运行 `journalctl -xe`。 这时会提供定位输入错误、未安装包和可以 Google 的短语等所有需要的信息。
### 接下来?
假设你的 LAN 名称服务配置正确,你现在有一台很好用的 LAN 邮件服务器。 显然,以纯文本发送消息不是最佳的,不支持互联网的邮件也是绝对不可以的。 请参阅 [Dovecot SSL 配置](http://wiki.dovecot.org/SSL/DovecotConfiguration)和 [Postfix TLS 支持](http://www.postfix.org/TLS_README.html),[VirtualUserFlatFilesPostfix](http://wiki2.dovecot.org/HowTo/VirtualUserFlatFilesPostfix) 涵盖了 TLS 和数据库后端。并请期待我之后的 SSL 指南。这次我说的是真的。
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/learn/sysadmin/building-email-server-ubuntu-linux-part-3>
作者:[CARLA SCHRODER](https://www.linux.com/users/cschroder) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,089 | 九款开源或商业的数据中心基础设施管理软件 | http://www.tecmint.com/data-center-server-management-tools/ | 2017-01-04T16:55:08 | [
"DCIM",
"数据中心"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8089-1.html | 当一个公司发展壮大时,相应地对计算资源的需求也会与日俱增。无论是普通公司还是服务提供商,包括那些出租服务器的公司,当服务器数量过多时都不得不面对很多问题。
如何盘存服务器和备件?如何维护使数据中心保持健康运作,及时定位并修复潜在的威胁?如何快速找到宕机设备的机架位置?如何准备物理机上线工作?做完这些事情需要花费大量的时间,或者需要 IT 部门有一大帮管理员支持才能办到。
现在有一个更好的方案解决这些问题,使用特定软件来实现数据中心管理自动化,下文将介绍当前市场上已有的一些数据中心管理工具。

### 1、 Opendcim
这是该类目前唯一的自由软件,该软件开源并且按照商业化<ruby> 数据中心基础设施管理 <rt> Data Center Infrastructure Management </rt></ruby>(DCIM)解决方案的替代方案来设计。该软件可以管理库存、生成数据中心的地图和监控机房温度与电力消耗。
不过,它不支持远程关机、服务器重启、操作系统安装等功能。尽管如此,它仍然被全球很多非商业机构使用。
由于该软件开源,有研发能力的公司可以修改它,使 [opendcim](http://opendcim.org/) 更适合自己的公司。

*openDCIM*
### 2、 NOC-PS
这是一款可以管理物理和虚拟设备的商业软件。它有很多可以用于初始化设备的工具,比如:操作系统和其他软件安装、网络配置,并且集成了 WHMCS 和 Blesta。美中不足的是,如果你希望能够看到数据中心设备地图或者机架位置,那该软件就不是你的最佳选择了。
[NOC-PS](http://noc-ps.com/) 每 100 台服务器每年管理费需要 100€,比较适合中小企业使用。

*NOC-PS*
### 3、 DCImanager
[DCImanager](https://www.ispsystem.com/software/dcimanager) 是一个专用的解决方案,正如宣传所说的,考虑了 DC 工程师和托管服务提供商的需求。该软件集成了很多有名的计费软件,比如 WHMCS、Hostbill、BILLmanager 等。
该软件的主要功能有:服务器配置、模板化安装操作系统、传感器监控、流量和电力消耗报告、VLAN 管理。除此之外,企业版还可以生成数据中心服务器地图、以及对服务器和备件进行盘点管理。
你可以试用免费版,但是免费版最多支持 5 台物理服务器管理,而收费版每 100 台服务器每年的授权使用费是 120€。
根据版本不同,收费版可适用中小企业或者大企业。

*DCImanager*
### 4、 EasyDCIM
[EasyDCIM](https://www.easydcim.com/) 是一款主要面向服务提供商的收费软件。拥有可以安装操作系统或其他软件的特点,并且能方便地生成机房目录及机架分布图。
该软件本身并不支持对 IP 和 DNS 进行管理。不过可以通过安装模块的方式获得这些功能,这些模块可能付费或者免费(包括 WHMCS 集成模块)。
该软件每 100 台服务器每年的服务费起步价 $999。对于小公司来说这个价格有点贵,不过中型或者大型企业可以尝试使用。

*EasyDCIM*
### 5、 Ansible Tower
[Ansible Tower](https://www.ansible.com/) 是红帽出品的企业级计算中心管理软件。该解决方案的核心思想是实现对服务器和不同用户设备的集中式部署。
由于 **Ansible Tower** 能够通过集成软件的方式使用几乎所有的工具程序,并且该软件的数据统计收集模块特别好用。不好的一面则是缺乏和当前比较流行的计费软件的集成,而且价格也不便宜。
每 100 台设备每年的服务器费是 $5000,这个价格估计只有大公司才能接受。

*Ansible Tower*
### 6、 Puppet Enterprise
在商业基础上发展而来并作为 IT 部门的辅助软件。该软件用于在服务器或者用户设备上安装操作系统及其他软件,无论是初步部署或者进一步开发都适用。
不幸的是,盘存和其他更好的交互方案(电缆连接、协议等)仍然处于开发中。
[Puppet Enterprise](https://puppet.com/) 对于小于 10 台服务器的管理免费并且开放全部功能。而收费版则是每台服务器每年 $120。
这个价格适合大公司使用。

*Puppet Enterprise*
### 7、 Device 42
该软件主要用于数据中心监控。有一个很棒的盘存工具,自动创建软硬件依赖关系图。通过 [Device 42](http://www.device42.com/) 生成数据中心地图,给不同机架标特定颜色,并可以通过图表方式反映温度、空闲空间情况和机架的其他指标。但是不支持软件安装和计费软件的集成。
每 100 台服务器每年的收费是 $1499,这个价位比较适合大中型企业。

*Device42*
### 8、 CenterOS
这是一款适合数据中心管理的操作系统,主要功能是设备盘点。除此之外可以生成数据中心地图及机架方案,并连接了一个评价不错的服务器状态监控系统,方便内部技术管理工作。
该软件还有一个特性就是能够通过简单的几次点击就可以找到某个设备对应的人(可能是设备所有人、技术管理员或者该设备的制造商),当出现紧急问题时这个就特别有用了。
该软件不是开源的,并且价格也只能在咨询后才能知道。
该软件价格的神秘性也决定了软件的目标客户,极有可能这个软件是给大公司用的。

*CenterOS*
### 9、 LinMin
这是一款用于初始化物理设备以便后期使用的软件。使用 PXE 安装选定的操作系统,并可随后部署一系列必要的软件安装。
与同类软件不同的是,[LinMin](http://www.linmin.com/) 有一个开发完善的硬盘备份系统,可以迅速在系统崩溃后恢复以及大规模部署相同配置的服务器。
该软件每 100 台服务器一年的收费是 $1999,这价格也只有大中型企业能用了。

*LinMin*
现在来总结下,当前市场上大部分能够自动化管理大量的基础设施的软件,可以分为两类。
第一类,主要用于完成设备的准备工作,以便能够进一步管理。另一类就是设备的盘点管理。找到一个通用的包含所有功能的软件并不容易,你在选择的时候可以放弃一些设备提供商提供的那些功能比较有限的工具。
现在你知道了这些解决方案,那么你可以逐个尝试下。值得注意的是这里列出的开源产品,如果你有好的开发人员,那么可以尝试定制软件来满足你需求。
希望通过这篇回顾能够帮你找到适合的软件让你的工作更轻松。另,祝您的服务器永不出错。
---
作者简介:

Nikita Nesmiyanov
我是一名俄罗斯西伯利亚托管软件开发公司的技术专家。我希望能够在新的 Linux 软件工具和托管行业的发展趋势、可能性、发展历史和发展机遇等方面拓展我的知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/data-center-server-management-tools/>
作者:[Nikita Nesmiyanov](http://www.tecmint.com/author/nesmiyanov/) 译者:[beyondworld](https://github.com/beyondworld) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,090 | Android、Debian 和 Ubuntu “荣膺”2016 安全缺陷最多的产品前三名 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/android-debian-and-ubuntu-top-most-vulnerable-products-chart-in-2016-511514.shtml | 2017-01-05T08:09:00 | [
"安全",
"缺陷"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8090-1.html | 
[据 CVE Details 的数据显示](https://www.cvedetails.com/top-50-products.php?year=2016),Android、Debian Linux 和 Ubuntu Linux 是 2016 年出现安全缺陷最多的三个产品。[CVE Details](https://www.cvedetails.com/) 是一个收集和存储软件安全缺陷方面的在线数据库。

*2016 年安全缺陷榜单*
在这一年中, Android 被发现了最多的安全缺陷,多达 523 个,紧随其后的是 Debian Linux 的 319 个和 Ubuntu Linux 的 278 个。令人吃惊的是,曾经多次蝉联第一名“宝座”的安全缺陷大户 Adobe Flash Player 以 266 个缺陷“屈居”第四。
“冠军” [Android 的安全缺陷](https://www.cvedetails.com/product/19997/Google-Android.html?vendor_id=1224)包括了最近大家比较关注的 DoS 缺陷以及内存破坏缺陷,而且,DoS 缺陷数量从 2015 的 56 个跃升至 104 个,而内存破坏缺陷则从 46 个降至 38 个。 Android 中还有 99 个缺陷是关于信息泄露的,而在一年前才发现了 19 个;权限提升缺陷则令人吃惊的从 2015 年的 17 个剧增至 250 个。

*Android 的缺陷*
### 微软的缺陷更少一些
让我们来看看微软的产品,在该列表中,排名最高的微软产品是 Windows 10 ,有 172 个缺陷,连前十名都没进去。
如果根据厂商来比较,谷歌的产品缺陷最多,有 695 个,而 Debian 和 Canonical 以 319 和 278 分列二、三名。

*厂商缺陷排行榜*
上图中,虽然 Adobe 和微软的安全缺陷总数非常高,但是其实这里包含的安全缺陷很多是重复的——同一个安全缺陷出现在多个产品之中。
当然, 产品的安全缺陷数高也并不意味着该产品就比其它的产品更不安全,许多产品的安全缺陷是私下报告的,并在被公开之前就修复了,所以在大多数情况下使用这些产品是安全的。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,091 | 在 Ubuntu 中使用 NTP 进行时间同步 | https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/NTP.html | 2017-01-05T11:14:00 | [
"timedatectl",
"ntpdate",
"timesyncd",
"时间服务器",
"ntp"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8091-1.html | NTP 是通过网络来同步时间的一种 TCP/IP 协议。通常客户端向服务器请求当前的时间,并根据结果来设置其时钟。
这个描述是挺简单的,实现这一功能却是极为复杂的 - 首先要有多层 NTP 服务器,第一层 NTP 服务器连接原子时钟,第二层、第三层服务器则担起负载均衡的责任,以处理因特网传来的所有请求。另外,客户端可能也超乎你想象的复杂 - 它必须排除通讯延迟,调整时间的同时不干扰其它在服务器中运行的进程。幸运的是,所有的这些复杂性都进行了封装,你是不可见也不需要见到的。

在 Ubuntu 中,是使用 `ntpdate` 和 `ntpd` 来同步时间的。
### timedatectl
在最新的 Ubuntu 版本中,`timedatectl` 替代了老旧的 `ntpdate`。默认情况下,`timedatectl` 在系统启动的时候会立刻同步时间,并在稍后网络连接激活后通过 socket 再次检查一次。
如果已安装了 `ntpdate` / `ntp`,`timedatectl` 会退而让你使用之前的设置。这样确保了两个时间同步服务不会相互冲突,同时在你升级的时候还保留原本的行为和配置。但这也意味着从旧版本的发行版升级时 `ntp`/`ntpdate` 仍会安装,因此会导致新的基于 systemd 的时间服务被禁用。
### timesyncd
在最新的 Ubuntu 版本中,`timesyncd` 替代了 `ntpd` 的客户端的部分。默认情况下 `timesyncd` 会定期检测并同步时间。它还会在本地存储更新的时间,以便在系统重启时做时间单步调整。
通过 `timedatectl` 和 `timesyncd` 设置的当前时间状态和时间配置,可以使用 `timedatectl status` 命令来进行确认。
```
timedatectl status
Local time: Fri 2016-04-29 06:32:57 UTC
Universal time: Fri 2016-04-29 06:32:57 UTC
RTC time: Fri 2016-04-29 07:44:02
Time zone: Etc/UTC (UTC, +0000)
Network time on: yes
NTP synchronized: no
RTC in local TZ: no
```
如果安装了 NTP,并用它替代 `timedatectl` 来同步时间,则 `NTP synchronized` 将被设置为 `yes`。
`timedatectl` 和 `timesyncd` 用来获取时间的 nameserver 可以通过 `/etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf` 来指定,另外在 `/etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf.d/` 下还有灵活的附加配置文件。
### ntpdate
由于 `timedatectl` 的存在,各发行版已经弃用了 `ntpdate`,默认不再进行安装。如果你安装了,它会在系统启动的时候根据 Ubuntu 的 NTP 服务器来设置你电脑的时间。之后每当一个新的网络接口启动时,它就会重新尝试同步时间 —— 在这期间只要其涵盖的时间差不是太大,它就会慢慢偏移时间。该行为可以通过 `-B`/`-b` 开关来进行控制。
```
ntpdate ntp.ubuntu.com
```
### 时间服务器
默认情况下,基于 systemd 的工具都是从 `ntp.ubuntu.com` 请求时间同步的。经典的基于 `ntpd` 的服务基本上都是使用 `[0-3].ubuntu.pool.ntp.org` 池中的 `2.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org`,还有 `ntp.ubuntu.com`,此外需要的话还支持 IPv6。如果想强制使用 IPv6,可以使用 `ipv6.ntp.ubuntu.com`,不过这并非默认配置。
### ntpd
ntp 的守护进程 `ntpd` 会计算你的系统时钟的时间偏移量并且持续的进行调整,所以不会出现时间差距较大的更正,比如说,不会导致不连续的日志。该进程只花费少量的进程资源和内存,但对于现代的服务器来说实在是微不足道的了。
### 安装
要安装 `ntpd`,在终端命令行中输入:
```
sudo apt install ntp
```
### 配置
编辑 `/etc/ntp.conf` —— 增加/移除 `server` 行。默认配置有以下服务器:
```
# Use servers from the NTP Pool Project. Approved by Ubuntu Technical Board
# on 2011-02-08 (LP: #104525). See http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html for
# more information.
server 0.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org
server 1.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org
server 2.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org
server 3.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org
```
修改配置文件之后,你需要重新加载 `ntpd`:
```
sudo systemctl reload ntp.service
```
### 查看状态
使用 `ntpq` 来查看更多信息:
```
# sudo ntpq -p
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
+stratum2-2.NTP. 129.70.130.70 2 u 5 64 377 68.461 -44.274 110.334
+ntp2.m-online.n 212.18.1.106 2 u 5 64 377 54.629 -27.318 78.882
*145.253.66.170 .DCFa. 1 u 10 64 377 83.607 -30.159 68.343
+stratum2-3.NTP. 129.70.130.70 2 u 5 64 357 68.795 -68.168 104.612
+europium.canoni 193.79.237.14 2 u 63 64 337 81.534 -67.968 92.792
```
### PPS 支持
从 Ubuntu 16.04 开始,ntp 支持 PPS 规范,给 ntp 提供了本地时间源,以提供更高的精度。查看下边列出的链接来获取更多配置信息。
### 参考资料
* 参考 [Ubuntu Time](https://help.ubuntu.com/community/UbuntuTime) wiki 页来获取更多信息
* [ntp.org,网络时间协议项目主页](http://www.ntp.org/)
* [ntp.org,关于配置 PPS 的 FAQ](http://www.ntp.org/ntpfaq/NTP-s-config-adv.htm#S-CONFIG-ADV-PPS)
---
via: <https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/NTP.html>
作者:[Ubuntu](https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/NTP.html) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,092 | 如何在 Ubuntu 16.10 的 Unity 8 上运行老式 Xorg 程序 | https://www.maketecheasier.com/use-old-xorg-apps-unity-8/ | 2017-01-05T14:53:56 | [
"Unity",
"Mir",
"Ubuntu"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8092-1.html | 
随着 Ubuntu 16.10 的发布,Unity 8 越来越吸引到了更多人的关注。这是因为在这个大家最爱的 Linux 发行版的最新版本中可以体验其带有的试验性桌面。桌面发行版是人们最熟悉的 Unity 环境,但有一点点不同。它不再使用 X11 图形技术,Ubuntu 的开发者选择了另一种截然不同的方式。
原来,Unity 8 用的是 Mir,这是 Ubuntu 为了在 Linux 上提供显示服务而做出的努力。这项技术已经在 Ubuntu phone 和平板上大量使用,但是这次新版是我们在桌面环境上第一次见到 Mir 。
这项技术相当新颖,结果是没多少 Linux 程序能运行在它之上。不是所有,那也是大部分的程序设计在 Xorg 和 X11 之上运行。如果你想要试试在 Unity 8 上运行这些程序,你肯定会为在 Unity 8上确实能够运行之前的 Xorg 程序而高兴。接下来是如何做!
### 登录进 Unity 8

Unity 8 在 Ubuntu 16.10 上是一个可选会话。在使用之前只须牢记一件事情:它不会加载 AMD 的图形驱动,Intel 的同样不会加载。唯一支持的图形驱动是 Nvidia 的开源驱动。要用 Unity 8 的话,只要像往常那样启动 Ubuntu,然后,在登录进去之前,点击用户名上面的 Ubuntu 图标,选择 Unity8 选项。如果万事顺利的话,这个新的、试验性的桌面环境将会加载。
**注意**: Unity 8 非常新而且不稳定,自行承担使用风险。
### 安装 Libertine
Xorg 程序(例如 Firefox 等)确实能在 Unity 8 上使用,在使用之前需要一点小调整。在 Mir 桌面上用终端打开 Libertine ,在 Scopes 窗口中点击终端图标就能完成。一旦打开,输入你的密码。接下来,输入以下的命令:

```
sudo apt install libertine-tools libertine-scope libertine
```
当这些程序完成安装后,点击并拖动 Scopes 窗口以刷新内容。然后,在面板上点击来启动 libertine。
### 新建 Xorg 容器
打开 Libertine,就可以新建一些(应用)容器了。这些容器很特别,因为它们能让基于 X11 的 Linux 程序在 Mir/Unity 8 桌面上的容器之中运行。另外,如果需要支持 32 位应用,勾选“i386 multiarch support”复选框。否则,什么都不要动(或者输入名字和密码),点击“OK”。

在这之后,这个 Xorg 容器就准备好,可以使用了。在 Libertine 找到它并启动。删除也很容易,右键点击容器,选择“删除”选项。
**注意**:每一个 Xorg 容器有 500 MB的最大内存限制。所以多个容器是有必要的。
### 安装软件

在 Libertine 容器中安装软件有两个方法。第一种是允许用户启动容器后选择“输入包名或者 Debian 文件”,这意味着用户可以在软件中心或者终端找到一个软件的名字,然后在 Libertine 中输入它来安装。也可以指定特定的 DEB 文件来安装,可以在Libertine LXC 容器中直接搜索安装包。
**注意**:Unity 8 非常新,一些程序或许不能在 Libertine 里加载或者完全安装。
### 结论
Unity 8 展现了不少的新特性,它现代、时髦,而且比之前任何一个 Unity 迭代版本都快。唯一限制它的就是使用率。事实是大部分用户更乐意选择实用的应用程序,而不是一个别致新颖的桌面环境。某种程度上来说,使用 Libertine 能解决这个问题,但它不会永久有效。早晚有一天,Canonical 都需要自行移植这些程序或者向社区求助来彻底解决这个问题。
---
via: <https://www.maketecheasier.com/use-old-xorg-apps-unity-8/>
作者:[Derrik Diener](https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/derrikdiener/) 译者:[ypingcn](https://github.com/ypingcn) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 
With the release of Ubuntu 16.10, Unity 8 has been getting more attention than usual. This is because the latest release of everyone’s favorite Linux distribution comes with an experimental desktop to play with. This desktop is the Unity environment most are used to, with a twist. It no longer is making use of X11 graphics technology and instead the makers of Ubuntu have gone a different way.
In its place, Unity 8 is using Mir, Ubuntu’s answer to calls for a better-performing display server on Linux. This technology has been in heavy use already on the Ubuntu phone and tablet, but this new release is the first time we’ve seen it on the desktop.
This technology is new and shiny. As a result, not a lot of established Linux programs can work on it, as most, if not all, of these tools are built to work with Xorg and X11. However, if you’ve been wanting to try out Unity 8, you’ll be happy to know that it is indeed possible to get these old Xorg apps working in Unity 8. Here’s how!
## Logging Into Unity 8
Unity 8 comes as an optional session in Ubuntu 16.10. There’s one key thing to keep in mind before using it: it will not load with AMD graphics drivers, or Intel for that matter. The only supported graphics drivers as of now are the open source Nvidia drivers. To use the Unity 8 session, start up Ubuntu like normal. Then, before logging in, click the Ubuntu icon above your username and select “Unity8.” If all goes well, the new, experimental desktop will load.
**Note**: Unity 8 is very new and unstable. Use at your own risk.
## Installing Libertine
Xorg programs (like Firefox, etc.) do work in Unity 8; they just need a little tweak before anything will run. Start off by opening a terminal on the Mir desktop. This is done by clicking the terminal icon in the “scopes” window. Once open, enter your password. After that, enter the following commands:
sudo apt install libertine-tools libertine-scope libertine
When these programs finish installing, click and drag the scope window to refresh it. Then, click on the top-hat to launch libertine.
## Creating Xorg Containers
With Libertine open, it’s time to create some containers. These containers are special, as they allow X11 based Linux programs to run inside of a container on the Mir/Unity 8 desktop. Additionally, check the “i386 multiarch support” box for 32bit support. Otherwise, leave everything as is (or give it a name and password), and click OK.
From this point on, the Xorg container is ready to use. Look for it in Libertine and launch the container. It also should be noted that containers can be erased by right-clicking on them, then selecting the “Delete” option.
**Note**: each Xorg container has a maximum memory limit of 500 megabytes, so multiple containers may be necessary.
## Installing Software
Software is installed in Libertine containers in two ways. The first way allows for users to launch the container and select “Enter package name or Debian file,” meaning it is possible to find the name of a program in the software center or terminal and enter it into Libertine to install it. It is also possible to specify a .DEB package file for installation. It is also possible to search for the package directly within the Libertine LXC container.
**Note**: Unity 8 is very new, and some programs may not load or fully install with Libertine.
## Conclusion
Unity 8 shows a lot of promise. It’s modern, sleek, and faster than any iteration of Unity that came before it. The only thing that is holding it back is adoption. The simple fact is that most users would rather have programs that work instead of a fancy, fresh desktop. To an extent, using Libertine solves this issue, but it won’t work forever. Sooner or later Canonical will need to start porting programs on their own or reach out to the community as as whole to make this happen.
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox |
8,093 | 如何在 Linux 中找出最近或今天被修改的文件 | http://www.tecmint.com/find-recent-modified-files-in-linux/ | 2017-01-06T08:13:00 | [
"ls",
"find"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8093-1.html | 在本文中,我们将解释两个简单的命令行小技巧,它可以帮你只列出所有的今天的文件。
Linux 用户在命令行上遇到的常见问题之一是[定位具有特定名称的文件](/article-5973-1.html),如果你知道确定的文件名则可能会容易得多。
不过,假设你忘记了白天早些时候创建的文件的名称(在你包含了数百个文件的 `home` 文件夹中),但现在你有急用。
下面用不同的方式只[列出所有你今天创建或修改的文件](/article-7984-1.html)(直接或间接)。

### 1、 使用 ls 命令,只列出你的 home 文件夹中今天的文件。
```
# ls -al --time-style=+%D | grep 'date +%D'
```
其中:
* `-a` - 列出所有文件,包括隐藏文件
* `-l` - 启用长列表格式
* `--time-style=FORMAT` - 显示指定 FORMAT 的时间
* `+%D` - 以 `%m/%d/%y` (月/日/年)格式显示或使用日期

*在Linux中找出最近的文件*
此外,你使用可以 `-X` 标志来[按字母顺序对结果排序](/article-5372-1.html):
```
# ls -alX --time-style=+%D | grep 'date +%D'
```
你也可以使用 `-S` 标志来基于大小(由大到小)来排序:
```
# ls -alS --time-style=+%D | grep 'date +%D'
```
### 2、 另外,使用 find 命令会更灵活,并且提供比 `ls` 更多的选项,可以实现相同的目的。
* `-maxdepth` 级别用于指定在搜索操作的起点下(在这个情况下为当前目录)的搜索层级(子目录层级数)。
* `-newerXY`,用于所寻找的文件的时间戳 `X` 比参照文件的时间戳 `Y` 更新一些的文件。 `X` 和 `Y` 表示以下任何字母: - `a` - 参照文件的访问时间 - `B` - 参照文件的创建时间 - `c` - 参照文件的 inode 状态改变时间 - `m` - 参照文件的修改时间 - `t` - 直接指定一个绝对时间
下面的命令意思是只找出 2016-12-06 这一天修改的文件:
```
# find . -maxdepth 1 -newermt "2016-12-06"
```

*在 Linux 中找出今天的文件*
重要:在上面的 [find 命令](/article-1672-1.html)中使用正确的**日期格式**作为参照时间,一旦你使用了错误的格式,你会得到如下错误:
```
# find . -maxdepth 1 -newermt "12-06-2016"
find: I cannot figure out how to interpret '12-06-2016' as a date or time
```
或者,使用下面的正确格式:
```
# find . -maxdepth 1 -newermt "12/06/2016"
或者
# find . -maxdepth 1 -newermt "12/06/16"
```

*在 Linux 中找出今天修改的文件*
你可以在我们的下面一系列文章中获得 `ls`和 `find` 命令的更多使用信息。
* [用 15 例子的掌握 Linux ‘ls’ 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/15-basic-ls-command-examples-in-linux/)
* [对 Linux 用户有用的 7 个奇特技巧](http://www.tecmint.com/linux-ls-command-tricks/)
* [用 35 个例子掌握 Linux ‘find’ 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/35-practical-examples-of-linux-find-command/)
* [在 Linux 中使用扩展查找多个文件名的方法](http://www.tecmint.com/linux-find-command-to-search-multiple-filenames-extensions/)
在本文中,我们解释了如何使用 ls 和 find 命令帮助只列出今天的文件。 请使用以下反馈栏向我们发送有关该主题的任何问题或意见。 你也可以提醒我们其他可以用于这个目的的命令。
---
作者简介:Aaron Kili是一名 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 的爱好者,未来的 Linux 系统管理员、网站开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并乐于分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/find-recent-modified-files-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,094 | 从源代码编译 Vim 8.0 | https://github.com/Valloric/YouCompleteMe/wiki/Building-Vim-from-source | 2017-01-06T08:41:00 | [
"vim",
"编译"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8094-1.html | 
从源代码编译 Vim 实际上并不那么困难。下面是你所要做的:
1、首先,安装包括 Git 在内的所有必备的库。对于一个 Debian 类的 Linux 发行版,例如 Ubuntu,命令如下:
```
sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dev libgnome2-dev libgnomeui-dev \
libgtk2.0-dev libatk1.0-dev libbonoboui2-dev \
libcairo2-dev libx11-dev libxpm-dev libxt-dev python-dev \
python3-dev ruby-dev lua5.1 lua5.1-dev libperl-dev git
```
在 Ubuntu 16.04 上,lua 开发包的名称是 `liblua5.1-dev` 而非 `lua5.1-dev`。
如果你知道你将使用哪种语言,可随意删去你不需要的包。例如:Python2 `python-dev` 或者是 Ruby `ruby-dev`。这一原则适用于本文的大部分内容。
对于 Fedora 20,将是以下命令:
```
sudo yum install -y ruby ruby-devel lua lua-devel luajit \
luajit-devel ctags git python python-devel \
python3 python3-devel tcl-devel \
perl perl-devel perl-ExtUtils-ParseXS \
perl-ExtUtils-XSpp perl-ExtUtils-CBuilder \
perl-ExtUtils-Embed
```
在 Fedora 20 上需要这一步来纠正安装 XSubPP 时出现的问题:
```
### 从 /usr/bin 到 perl 目录做个 xsubpp (perl) 的符号链接
sudo ln -s /usr/bin/xsubpp /usr/share/perl5/ExtUtils/xsubpp
```
2、 如果你已经安装了 vim,删掉它。
```
sudo apt-get remove vim vim-runtime gvim
```
如果是 Ubuntu 12.04.2,你或许也需要同时删除下面这些软件包:
```
sudo apt-get remove vim-tiny vim-common vim-gui-common vim-nox
```
3、 一旦上述内容都被安装好之后,获取 vim 源代码很容易。
注意:如果你使用 python,你的配置目录或许有一个特定的机器名 (例如 `config-3.5m-x86_64-linux-gnu`)。检查 `/usr/lib/python[2/3/3.5]` 目录来找到你的 python 配置目录,据此更改 `python-config-dir` 和/或 `python3-config-dir`的参数。
添加/删除下面的编译参数以适合您的设置。例如,如果您不打算写任何 Lua 脚本,您可以删去 `enable-luainterp`。
同时,如果你使用的不是 vim 8.0,请确认下面 `VIMRUNTIMEDIR` 参数设置正确(例如,如果使用 vim 8.0a, 就用 `/usr/share/vim/vim80a`)。记住,一些 vim 安装是直接安装在 `/usr/share/vim` 下的;调整好参数以适应你的系统:
```
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/vim/vim.git
cd vim
./configure --with-features=huge \
--enable-multibyte \
--enable-rubyinterp=yes \
--enable-pythoninterp=yes \
--with-python-config-dir=/usr/lib/python2.7/config \
--enable-python3interp=yes \
--with-python3-config-dir=/usr/lib/python3.5/config \
--enable-perlinterp=yes \
--enable-luainterp=yes \
--enable-gui=gtk2 --enable-cscope --prefix=/usr
make VIMRUNTIMEDIR=/usr/share/vim/vim80
```
在 Ubuntu 16.04 上,由于同时开启了 Python2 和 Python3,Python 支持将不工作。 阅读 [chirinosky 的回答](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/23023783/vim-compiled-with-python-support-but-cant-see-sys-version) 以获取变通的处理方法。
如果你想将来轻松卸载 vim,可以使用 `checkinstall` 来安装 。
```
sudo apt-get install checkinstall
cd ~/vim
sudo checkinstall
```
否则,可以使用 `make` 来安装。
```
cd ~/vim
sudo make install
```
要让 vim 成为你默认的编辑器,请使用 `update-alternatives`。
```
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/editor editor /usr/bin/vim 1
sudo update-alternatives --set editor /usr/bin/vim
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/vi vi /usr/bin/vim 1
sudo update-alternatives --set vi /usr/bin/vim
```
4、 再检查下,通过查看 `vim --version` 输出来确认确实在运行新的 Vim 应用程序版本。
**如果你的 gvim 不工作(在 ubuntu 12.04.1 LTS 上),试着把 `--enable-gui=gtk2` 参数变为 `--enable-gui=gnome2`。**
如果你遇到问题,仔细检查在步骤 3 开始提到的,使用正确的 Python 配置目录配置 `configure`。
这些 `configure` 和 `make` 命令假设你是一个 Debian 发行版,Vim 的运行库文件目录放在 `/usr/share/vim/vim80/`,这不是 vim 的默认路径。 在 `configure` 命令中的 `--prefix=/usr` 也是如此。这些参数或许对一个不是基于 Debian 的 Linux 发行版来说是有所不同的,在这种情况下,试着移除 `configure` 命令中的 `--prefix` 变量和 `make` 命令中的 `VIMRUNTIMEDIR` (换句话说,使用这些参数的默认值)。
如果你遇到麻烦, 这里是一些[其它编译 Vim 的有用的信息](http://vim.wikia.com/wiki/Building_Vim)。
---
via: <https://github.com/Valloric/YouCompleteMe/wiki/Building-Vim-from-source>
作者:[Val Markovic](https://github.com/Valloric) 等人 译者:[zky001](https://github.com/zky001) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,097 | Samba 系列(三):使用 Windows 10 的 RSAT 工具来管理 Samba4 活动目录架构 | http://www.tecmint.com/manage-samba4-ad-from-windows-via-rsat/ | 2017-01-05T23:05:00 | [
"Samba",
"活动目录"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8097-1.html | 这一节的Samba4 AD DC 架构系列文章,我们将会讨论如何把 Windows 10 系统的电脑添加到 Samba4 域环境中,以及如何在 Windows 10 系统下管理域环境。

一旦 Windows 10 系统加入到 Samba4 AD DC ,我们就可以在 Windows 10 系统中创建、删除或者禁用域用户和组了,可以创建新的组织单元,创建、编辑和管理域策略,还可以管理 Samba4 域 DNS 服务。
上面所有的功能和其它一些复杂的与域管理相关的工作都可以通过 Windows 环境下的 RSAT 工具来完成—— Microsoft 远程服务器管理工具。
#### 要求
1、 [在 Ubuntu 系统上使用 Samba4 来创建活动目录架构(一)](/article-8065-1.html)
2、 [在 Linux 命令行下管理 Samba4 AD 架构(二)](/article-8070-1.html)
### 第一步:配置域时间同步
1、在使用 Windows 10 系统的 RSAT 工具来管理 Samba4 ADDC 之前,我们需要了解与活动目录相关的一个很重要的服务,该服务要求[精确的时间同步](http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-synchronize-time-with-ntp-server-in-ubuntu-linux-mint-xubuntu-debian/)。
在大多数的 Linux 发行版中,都由 NTP 进程提供时间同步机制。AD 环境默认允许最大的时间差距是 5 分钟。
如果时间差距超过 5 分钟,你将会遇到各种各样的异常报错,最严重的会影响到 AD 用户、域成员服务器或共享访问等。
为了在 Ubuntu 系统中安装网络时间协议进程和 NTP 客户端工具,可执行以下命令:
```
$ sudo apt-get install ntp ntpdate
```

*在 Ubuntu 系统下安装 NTP 服务*
2、下一步,修改 NTP 配置文件,使用一个离你最近的 NTP 服务地址列表替换默认的 NTP 池服务列表。
NTP 服务器地址列表可以从 NTP 地址库项目官方网站获取:<http://www.pool.ntp.org/en/>。
```
$ sudo nano /etc/ntp.conf
```
在每一行 `pool` 前添加一个 `#` 符号以注释默认的服务器列表,并替换为适合你的 NTP 服务器地址,如下图所示:
```
pool 0.ro.pool.ntp.org iburst
pool 1.ro.pool.ntp.org iburst
pool 2.ro.pool.ntp.org iburst
# Use Ubuntu's ntp server as a fallback.
pool 3.ro.pool.ntp.org
```

*在 Ubuntu 系统下配置 NTP 服务*
3、此时,先不要关闭该文件。移动光标到文件顶部,在 `driftfile` 参数后面添加下面一行内容。该设置是为了让客户端查询该服务时使用 AD 的 NTP 签署请求。
```
ntpsigndsocket /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
```

*使用 NTP 来同步 AD*
4、最后,移动光标到文件底部并添加如下一行内容,如截图所示,仅允许网络客户端查询该服务器上的时间。
```
restrict default kod nomodify notrap nopeer mssntp
```

*限制 NTP 服务的查询客户端*
5、设置完成之后,保存并关闭 NTP 配置文件,为了让 NTP 服务读取 `ntp_signed` 目录,需要授予 NTP 服务合适的权限。
以下是 Samba NTP socket 的系统路径。之后,重启 NTP 服务以应用更改,并使用 [netstat 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/20-netstat-commands-for-linux-network-management/)与[grep 过滤](http://www.tecmint.com/12-practical-examples-of-linux-grep-command/)相接合来检查 NTP 服务是否正常。
```
$ sudo chown root:ntp /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
$ sudo chmod 750 /var/lib/samba/ntp_signd/
$ sudo systemctl restart ntp
$ sudo netstat –tulpn | grep ntp
```

*给 NTP 服务授权*
使用 ntpq 命令行工具来监控 NTP 进程,加上 `-p` 参数来显示摘要信息。
```
$ ntpq -p
```

*监控 NTP 服务器池*
### 第二步:处理 NTP 时间同步异常问题
6、有时候 NTP 进程在尝试与上游 ntp 服务端同步时间的计算过程中会卡住,导致客户端使用 `ntpdate` 工具手动强制同步时间时报如下错误:
```
# ntpdate -qu adc1
ntpdate[4472]: no server suitable for synchronization found
```

*NTP 时间同步异常*
`ntpdate` 命令加上 `-d` 调试选项:
```
# ntpdate -d adc1.tecmint.lan
Server dropped: Leap not in sync
```

*NTP Server Dropped Leap Not in Sync*
7、为了避免出现该问题,使用下面的方法来解决这个问题:在服务器上停止 NTP 服务,使用 `ntpdate` 客户端工具加上 `-b` 参数指定外部 peer 地址来手动强制同步时间,如下图所示:
```
# systemctl stop ntp.service
# ntpdate -b 2.ro.pool.ntp.org [你的 ntp peer]
# systemctl start ntp.service
# systemctl status ntp.service
```

*强制 NTP 时间同步*
8、当时间正确同步之后,启动服务器上的 NTP 服务,并且在客户端服务器上执行如下命令来验证 NTP 时间同步服务是否可用:
```
# ntpdate -du adc1.tecmint.lan [你的 AD DC 服务器]
```

*验证 NTP 时间同步*
至此, NTP 服务应该已经工作正常了。
### 第三步:把 Windows 10 系统加入域环境
9、从我们的前一篇文章可以看出,[Samba4 活动目录可以使用 samba-tool 工具在命令行下管理](/article-8070-1.html),可以直接在服务器上的 VTY 控制台或者通过 SSH 工具远程连接到服务器上进行管理。
另外,更直观更灵活的方式是使用已加入域的 Windows 电脑中的微软远程服务器管理工具(RSAT)来管理我们的 Samba4 AD 域控制器。这些工具在当前的大多数 Windows 系统中都可以使用。
把 Windows 10 或是之前版本的微软操作系统加入到 Samba4 AD DC 环境中的过程也是非常容易的。首先,确保你的 Windows 10 电脑已经设置了正确的 Samba4 DNS 服务器的 IP 地址,以查询出准确的域解析结果。
打开“控制面板 -> 网络和 Internet -> 网络和共享中心 -> 网卡设置 -> 属性 -> IPv4 -> 属性 -> 使用下面的 DNS 服务器地址”,并且手动输入 Samba4 AD 服务器的 IP 地址,如下图所示:

*把 Windows 10 加入到 Samba4 AD 环境*

*添加 DNS 和 Samba4 AD 服务器地址*
这里的 `192.168.1.254` 是 Samba4 AD 域控服务器的地址,用于域名解析。相应替换该 IP 地址。
10、下一步,点击 OK 按钮以应用网络设置,打开 CMD 命令行窗口,通过 ping 域名和 Samba4 服务器的 FQDN 地址来测试通过 DNS 解析到域是否连通。
```
ping tecmint.lan
ping adc1.tecmint.lan
```

*检查 Windows 和 Samb4 AD 服务器的网络连通性*
11、如果 Windows 客户端 DNS 查询的结果解析正确,那么,你还需要确认客户端时间是否已跟域环境同步。
打开“控制面板 -> 时钟、语言和区域 -> 设置时间和日期 -> Internet 时间页 -> 更改设置”,输入你同步时间的域名和 Internet 时间服务器字段。
点击立即更新按钮来强制与域同步时间,点击 OK 关闭窗口。

*与 Internet 服务器同步时间*
12、最后,通过打开“系统属性 -> 更改 -> 域成员 -> 输入域名”,点击 OK,输入你的域管理员账号和密码,再次点击 OK。
应该弹出一个新的窗口通知你已经是一个域成员了。点击 OK 关闭弹出窗口,并且重启机器以应用域更改。
下面的截图将说明这些操作步骤。

*把 Windows 域加入到 Samba4 AD 环境*

*输入域管理员账号登录*

*确认域已加入到 Samba4 AD 环境*

*重启 Windows 服务器以应用更改*
13、重启之后,单击其它用户并且使用具有管理员权限的 Samba4 域账号登录到 Windows 系统,你已经准备好进入到后边几个步骤了。

*使用 Samba4 AD 账号登录到 Windows*
### 第四步:使用 RSAT 工具来管理 Samba4 AD DC
14、微软远程服务器管理工具(RSAT)被广泛地用来管理 Samba4 活动目录,你可以根据你的 Windows 系统版本从下面的地址来下载该工具:
1. Windows 10: <https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=45520>
2. Windows 8.1: <http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=39296>
3. Windows 8: <http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=28972>
4. Windows 7: <http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=7887>
一旦 Windows 10 独立安装包下载完成,运行安装包,等待安装完成并重启机器以应用所有更新。
重启之后,打开“控制面板 -> 程序(卸载程序) -> 启用或关闭 Windows 功能”,勾选所有的远程服务器管理工具。
点击 OK 开始安装,安装完成之后重启系统。

*从 Windows 系统下管理 Samba4 AD*
15、要进入 RSAT 工具集,打开“控制面板 -> 系统和安全 -> 管理工具”。
这些工具也可以在开始工菜单的管理工具菜单中找到。另外,你也可以打开 Windows MMC 工具和管理单元,从“文件 -> 添加/删除管理单元”菜单中访问它们。

*访问远程服务器管理工具集*
最常用的工具,比如 AD UC ,DNS 和组策略管理工具可以通过从右键菜单发送到功能来新建快捷方式到桌面直接运行。
16、你可以通过 AD UC 和列出域里的电脑(新加入的 Windows 机器应该出现在列表中)来验证 RSAT 功能,创建一个组织单元或组。
在 Samba4 服务器上使用 `wbinf` 命令来检查用户和组是否已经创建成功。

*活动目录用户和计算机*

*创建组织单元和新用户*

*确认 Samba4 AD 用户*
就这些吧!该主题的下一篇文章将包含其它 Samba4 活动目录的重要内容,包括通过 RSAT 工具来管理 Samba4 活动目录,比如,如何管理 DNS 服务器,添加 DNS 记录和创建 DNS 解析查询区,如何管理及应用域策略以及域用户如何创建交互式登录提示信息。
---
作者简介:我是一个电脑迷,开源软件及 Linux 系统爱好者,有近4年的 Linux 桌面和服务器系统及 bash 编程经验。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/manage-samba4-ad-from-windows-via-rsat/>
作者:[Matei Cezar](http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,098 | CentOS 上的 FirewallD 简明指南 | https://www.linode.com/docs/security/firewalls/introduction-to-firewalld-on-centos | 2017-01-07T08:56:00 | [
"安全",
"防火墙",
"UFW",
"FirewallD"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8098-1.html | 
[FirewallD](http://www.firewalld.org/) 是 iptables 的前端控制器,用于实现持久的网络流量规则。它提供命令行和图形界面,在大多数 Linux 发行版的仓库中都有。与直接控制 iptables 相比,使用 FirewallD 有两个主要区别:
1. FirewallD 使用区域和服务而不是链式规则。
2. 它动态管理规则集,允许更新规则而不破坏现有会话和连接。
>
> FirewallD 是 iptables 的一个封装,可以让你更容易地管理 iptables 规则 - 它并*不是* iptables 的替代品。虽然 iptables 命令仍可用于 FirewallD,但建议使用 FirewallD 时仅使用 FirewallD 命令。
>
>
>
本指南将向您介绍 FirewallD 的区域和服务的概念,以及一些基本的配置步骤。
### 安装与管理 FirewallD
CentOS 7 和 Fedora 20+ 已经包含了 FirewallD,但是默认没有激活。可以像其它的 systemd 单元那样控制它。
1、 启动服务,并在系统引导时启动该服务:
```
sudo systemctl start firewalld
sudo systemctl enable firewalld
```
要停止并禁用:
```
sudo systemctl stop firewalld
sudo systemctl disable firewalld
```
2、 检查防火墙状态。输出应该是 `running` 或者 `not running`。
```
sudo firewall-cmd --state
```
3、 要查看 FirewallD 守护进程的状态:
```
sudo systemctl status firewalld
```
示例输出
```
firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; disabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2015-09-02 18:03:22 UTC; 1min 12s ago
Main PID: 11954 (firewalld)
CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service
└─11954 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid
```
4、 重新加载 FirewallD 配置:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
```
### 配置 FirewallD
FirewallD 使用 XML 进行配置。除非是非常特殊的配置,你不必处理它们,而应该使用 `firewall-cmd`。
配置文件位于两个目录中:
* `/usr/lib/FirewallD` 下保存默认配置,如默认区域和公用服务。 避免修改它们,因为每次 firewall 软件包更新时都会覆盖这些文件。
* `/etc/firewalld` 下保存系统配置文件。 这些文件将覆盖默认配置。
#### 配置集
FirewallD 使用两个*配置集*:“运行时”和“持久”。 在系统重新启动或重新启动 FirewallD 时,不会保留运行时的配置更改,而对持久配置集的更改不会应用于正在运行的系统。
默认情况下,`firewall-cmd` 命令适用于运行时配置,但使用 `--permanent` 标志将保存到持久配置中。要添加和激活持久性规则,你可以使用两种方法之一。
1、 将规则同时添加到持久规则集和运行时规则集中。
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http
```
2、 将规则添加到持久规则集中并重新加载 FirewallD。
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
```
>
> `reload` 命令会删除所有运行时配置并应用永久配置。因为 firewalld 动态管理规则集,所以它不会破坏现有的连接和会话。
>
>
>
### 防火墙的区域
“区域”是针对给定位置或场景(例如家庭、公共、受信任等)可能具有的各种信任级别的预构建规则集。不同的区域允许不同的网络服务和入站流量类型,而拒绝其他任何流量。 首次启用 FirewallD 后,`public` 将是默认区域。
区域也可以用于不同的网络接口。例如,要分离内部网络和互联网的接口,你可以在 `internal` 区域上允许 DHCP,但在`external` 区域仅允许 HTTP 和 SSH。未明确设置为特定区域的任何接口将添加到默认区域。
要找到默认区域:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --get-default-zone
```
要修改默认区域:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=internal
```
要查看你网络接口使用的区域:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
```
示例输出:
```
public
interfaces: eth0
```
要得到特定区域的所有配置:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-all
```
示例输出:
```
public (default, active)
interfaces: ens160
sources:
services: dhcpv6-client http ssh
ports: 12345/tcp
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
```
要得到所有区域的配置:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all-zones
```
示例输出:
```
block
interfaces:
sources:
services:
ports:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
...
work
interfaces:
sources:
services: dhcpv6-client ipp-client ssh
ports:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
```
#### 与服务一起使用
FirewallD 可以根据特定网络服务的预定义规则来允许相关流量。你可以创建自己的自定义系统规则,并将它们添加到任何区域。 默认支持的服务的配置文件位于 `/usr/lib /firewalld/services`,用户创建的服务文件在 `/etc/firewalld/services` 中。
要查看默认的可用服务:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --get-services
```
比如,要启用或禁用 HTTP 服务:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-service=http --permanent
```
#### 允许或者拒绝任意端口/协议
比如:允许或者禁用 12345 端口的 TCP 流量。
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=12345/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=12345/tcp --permanent
```
#### 端口转发
下面是**在同一台服务器上**将 80 端口的流量转发到 12345 端口。
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone="public" --add-forward-port=port=80:proto=tcp:toport=12345
```
要将端口转发到**另外一台服务器上**:
1、 在需要的区域中激活 masquerade。
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-masquerade
```
2、 添加转发规则。例子中是将本地的 80 端口的流量转发到 IP 地址为 :123.456.78.9 的*远程服务器上的* 8080 端口。
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone="public" --add-forward-port=port=80:proto=tcp:toport=8080:toaddr=123.456.78.9
```
要删除规则,用 `--remove` 替换 `--add`。比如:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-masquerade
```
### 用 FirewallD 构建规则集
例如,以下是如何使用 FirewallD 为你的服务器配置基本规则(如果您正在运行 web 服务器)。
1. 将 `eth0` 的默认区域设置为 `dmz`。 在所提供的默认区域中,dmz(非军事区)是最适合于这个程序的,因为它只允许 SSH 和 ICMP。
```
sudo firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=dmz
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=dmz --add-interface=eth0
```
2、 把 HTTP 和 HTTPS 添加永久的服务规则到 dmz 区域中:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=dmz --add-service=http --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=dmz --add-service=https --permanent
```
3、 重新加载 FirewallD 让规则立即生效:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
```
如果你运行 `firewall-cmd --zone=dmz --list-all`, 会有下面的输出:
```
dmz (default)
interfaces: eth0
sources:
services: http https ssh
ports:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
```
这告诉我们,`dmz` 区域是我们的**默认**区域,它被用于 `eth0` 接口**中所有网络的**源地址**和**端口**。 允许传入 HTTP(端口 80)、HTTPS(端口 443)和 SSH(端口 22)的流量,并且由于没有 IP 版本控制的限制,这些适用于 IPv4 和 IPv6。 不允许**IP 伪装**以及**端口转发**。 我们没有 ICMP 块**,所以 ICMP 流量是完全允许的。没有<ruby> 丰富 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Rich </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>**规则**,允许所有出站流量。
### 高级配置
服务和端口适用于基本配置,但对于高级情景可能会限制较多。 <ruby> 丰富 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Rich </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>规则和<ruby> 直接 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Direct </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>接口允许你为任何端口、协议、地址和操作向任何区域 添加完全自定义的防火墙规则。
#### 丰富规则
丰富规则的语法有很多,但都完整地记录在 [firewalld.richlanguage(5)](https://jpopelka.fedorapeople.org/firewalld/doc/firewalld.richlanguage.html) 的手册页中(或在终端中 `man firewalld.richlanguage`)。 使用 `--add-rich-rule`、`--list-rich-rules` 、 `--remove-rich-rule` 和 firewall-cmd 命令来管理它们。
这里有一些常见的例子:
允许来自主机 192.168.0.14 的所有 IPv4 流量。
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-rich-rule 'rule family="ipv4" source address=192.168.0.14 accept'
```
拒绝来自主机 192.168.1.10 到 22 端口的 IPv4 的 TCP 流量。
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-rich-rule 'rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.1.10" port port=22 protocol=tcp reject'
```
允许来自主机 10.1.0.3 到 80 端口的 IPv4 的 TCP 流量,并将流量转发到 6532 端口上。
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-rich-rule 'rule family=ipv4 source address=10.1.0.3 forward-port port=80 protocol=tcp to-port=6532'
```
将主机 172.31.4.2 上 80 端口的 IPv4 流量转发到 8080 端口(需要在区域上激活 masquerade)。
```
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-rich-rule 'rule family=ipv4 forward-port port=80 protocol=tcp to-port=8080 to-addr=172.31.4.2'
```
列出你目前的丰富规则:
```
sudo firewall-cmd --list-rich-rules
```
### iptables 的直接接口
对于最高级的使用,或对于 iptables 专家,FirewallD 提供了一个<ruby> 直接 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Direct </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>接口,允许你给它传递原始 iptables 命令。 直接接口规则不是持久的,除非使用 `--permanent`。
要查看添加到 FirewallD 的所有自定义链或规则:
```
firewall-cmd --direct --get-all-chains
firewall-cmd --direct --get-all-rules
```
讨论 iptables 的具体语法已经超出了这篇文章的范围。如果你想学习更多,你可以查看我们的 [iptables 指南](https://www.linode.com/docs/networking/firewalls/control-network-traffic-with-iptables)。
### 更多信息
你可以查阅以下资源以获取有关此主题的更多信息。虽然我们希望我们提供的是有效的,但是请注意,我们不能保证外部材料的准确性或及时性。
* [FirewallD 官方网站](http://www.firewalld.org/)
* [RHEL 7 安全指南:FirewallD 简介](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/7/html/Security_Guide/sec-Using_Firewalls.html#sec-Introduction_to_firewalld)
* [Fedora Wiki:FirewallD](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/FirewallD)
---
via: <https://www.linode.com/docs/security/firewalls/introduction-to-firewalld-on-centos>
作者:[Linode](https://www.linode.com/docs/security/firewalls/introduction-to-firewalld-on-centos) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 403 | Forbidden | null |
8,099 | 在 Linux 中管理设备 | https://opensource.com/article/16/11/managing-devices-linux | 2017-01-08T09:35:00 | [
"设备文件",
"文件系统"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8099-1.html | 探索 `/dev` 目录可以让您知道如何直接访问到 Linux 中的设备。

Linux 目录结构中有很多有趣的功能,这次我会讲到 `/dev` 目录一些迷人之处。在继续阅读这篇文章之前,建议你看看我前面的文章。[Linux 文件系统](/article-6132-1.html),[一切皆为文件](/article-7669-1.html),这两篇文章介绍了一些有趣的 Linux 文件系统概念。请先看看 - 我会等你看完再回来。
……
太好了 !欢迎回来。现在我们可以继续更详尽地探讨 `/dev` 目录。
### 设备文件
设备文件也称为[设备特定文件](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Device_file)。设备文件用来为操作系统和用户提供它们代表的设备接口。所有的 Linux 设备文件均位于 `/dev` 目录下,是根 (`/`) 文件系统的一个组成部分,因为这些设备文件在操作系统启动过程中必须可以使用。
关于这些设备文件,要记住的一件重要的事情,就是它们大多不是设备驱动程序。更准确地描述来说,它们是设备驱动程序的门户。数据从应用程序或操作系统传递到设备文件,然后设备文件将它传递给设备驱动程序,驱动程序再将它发给物理设备。反向的数据通道也可以用,从物理设备通过设备驱动程序,再到设备文件,最后到达应用程序或其他设备。
让我们以一个典型命令的数据流程来直观地看看。

*图 1:一个典型命令的简单数据流程。*
在上面的图 1 中,显示一个简单命令的简化数据流程。从一个 GUI 终端仿真器,例如 Konsole 或 xterm 中发出 `cat /etc/resolv.conf` 命令,它会从磁盘中读取 `resolv.conf` 文件,磁盘设备驱动程序处理设备的具体功能,例如在硬盘驱动器上定位文件并读取它。数据通过设备文件传递,然后从命令到设备文件,然后到 6 号伪终端的设备驱动,然后在终端会话中显示。
当然, `cat` 命令的输出可以以下面的方式被重定向到一个文件, `cat /etc/resolv.conf > /etc/resolv.bak` ,这样会创建该文件的备份。在这种情况下,图 1 左侧的数据流量将保持不变,而右边的数据流量将通过 `/dev/sda2` 设备文件、硬盘设备驱动程序,然后到硬盘驱动器本身。
这些设备文件使得使用标准流 (STD/IO) 和重定向访问 Linux 或 Unix 计算机上的任何一个设备非常容易。只需将数据流定向到设备文件,即可将数据发送到该设备。
### 设备文件类别
设备文件至少可以按两种方式划分。第一种也是最常用的分类是根据与设备相关联的数据流进行划分。比如,tty (teletype) 和串行设备被认为是基于字符的,因为数据流的传送和处理是以一次一个字符或字节进行的;而块类型设备(如硬盘驱动器)是以块为单位传输数据,通常为 256 个字节的倍数。
您可以在终端上以一个非 root 用户,改变当前工作目录(`PWD`)到 `/dev` ,并显示长目录列表。 这将显示设备文件列表、文件权限及其主、次设备号。 例如,下面的设备文件只是我的 Fedora 24 工作站上 `/dev` 目录中的几个文件。 它们表示磁盘和 tty 设备类型。 注意输出中每行的最左边的字符。 `b` 代表是块类型设备,`c` 代表字符设备。
```
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 0 Nov 7 07:06 sda
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 1 Nov 7 07:06 sda1
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 16 Nov 7 07:06 sdb
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 17 Nov 7 07:06 sdb1
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 18 Nov 7 07:06 sdb2
crw--w---- 1 root tty 4, 0 Nov 7 07:06 tty0
crw--w---- 1 root tty 4, 1 Nov 7 07:07 tty1
crw--w---- 1 root tty 4, 10 Nov 7 07:06 tty10
crw--w---- 1 root tty 4, 11 Nov 7 07:06 tty11
```
识别设备文件更详细和更明确的方法是使用设备主要以及次要号。 磁盘设备主设备号为 8,将它们指定为 SCSI 块设备。请注意,所有 PATA 和 SATA 硬盘驱动器都由 SCSI 子系统管理,因为旧的 ATA 子系统多年前就由于代码质量糟糕而被认为不可维护。造成的结果就是,以前被称为 “hd[a-z]” 的硬盘驱动器现在被称为 “sd[a-z]”。
你大概可以从上面的示例中推出磁盘驱动器次设备号的模式。次设备号 0、 16、 32 等等,直到 240,是整个磁盘的号。所以主/次 8/16 表示整个磁盘 `/dev/sdb` , 8/17 是第一个分区的设备文件,`/dev/sdb1`。数字 8/34 代表 `/dev/sdc2`。
在上面列表中的 tty 设备文件编号更简单一些,从 tty0 到 tty63 。
Kernel.org 上的 [Linux 下的已分配设备](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/devices.txt)文件是设备类型和主次编号分配的正式注册表。它可以帮助您了解所有当前定义的设备的主要/次要号码。
### 趣味设备文件
让我们花几分钟时间,执行几个有趣的实验,演示 Linux 设备文件的强大和灵活性。 大多数 Linux 发行版都有 1 到 7 个虚拟控制台,可用于使用 shell 接口登录到本地控制台会话。 可以使用 `Ctrl-Alt-F1`(控制台 1),`Ctrl-Alt-F2`(控制台 2)等键盘组合键来访问。
请按 `Ctrl-Alt-F2` 切换到控制台 2。在某些发行版,登录显示的信息包括了与此控制台关联的 tty 设备,但大多不包括。它应该是 tty2,因为你是在控制台 2 中。
以非 root 用户身份登录。 然后你可以使用 `who am i` 命令 — 是的,就是这个命令,带空格 — 来确定哪个 tty 设备连接到这个控制台。
在我们实际执行此实验之前,看看 `/dev` 中的 tty2 和 tty3 的设备列表。
```
ls -l /dev/tty[23]
```
有大量的 tty 设备,但我们不关心他们中的大多数,只注意 tty2 和 tty3 设备。 作为设备文件,它们没什么特别之处。它们都只是字符类型设备。我们将使用这些设备进行此实验。 tty2 设备连接到虚拟控制台 2,tty3 设备连接到虚拟控制台 3。
按 `Ctrl-Alt-F3` 切换到控制台 3。再次以同一非 root 用户身份登录。 现在在控制台 3 上输入以下命令。
```
echo "Hello world" > /dev/tty2
```
按 `Ctrl-Alt-f2` 键以返回到控制台 2。字符串 “Hello world”(没有引号)将显示在控制台 2。
该实验也可以使用 GUI 桌面上的终端仿真器来执行。 桌面上的终端会话使用 `/dev` 中的伪终端设备,如 `/dev/pts/1`。 使用 Konsole 或 Xterm 打开两个终端会话。 确定它们连接到哪些伪终端,并使用一个向另一个发送消息。
现在继续实验,使用 `cat` 命令,试试在不同的终端上显示 `/etc/fstab` 文件。
另一个有趣的实验是使用 `cat` 命令将文件直接打印到打印机。 假设您的打印机设备是 `/dev/usb/lp0`,并且您的打印机可以直接打印 PDF 文件,以下命令将在您的打印机上打印 `test.pdf` 文件。
```
cat test.pdf > /dev/usb/lp0
```
`/dev` 目录包含一些非常有趣的设备文件,这些文件是硬件的入口,人们通常不认为这是硬盘驱动器或显示器之类的设备。 例如,系统存储器 RAM 不是通常被认为是“设备”的东西,而 `/dev/mem` 是通过其可以实现对存储器的直接访问的入口。 下面的例子有一些有趣的结果。
```
dd if=/dev/mem bs=2048 count=100
```
上面的 `dd` 命令提供比简单地使用 `cat` 命令 dump 所有系统的内存提供了更多的控制。 它提供了指定从 `/dev/mem` 读取多少数据的能力,还允许指定从存储器哪里开始读取数据。虽然读取了一些内存,但内核响应了以下错误,在 `/var/log/messages` 中可以看到。
```
Nov 14 14:37:31 david kernel: usercopy: kernel memory exposure attempt detected from ffff9f78c0010000 (dma-kmalloc-512) (2048 bytes)
```
这个错误意味着内核正在通过保护属于其他进程的内存来完成它的工作,这正是它应该工作的方式。 所以,虽然可以使用 `/dev/mem` 来显示存储在 RAM 内存中的数据,但是访问的大多数内存空间是受保护的并且会导致错误。 只可以访问由内核内存管理器分配给运行 `dd` 命令的 BASH shell 的虚拟内存,而不会导致错误。 抱歉,但你不能窥视不属于你的内存,除非你发现了一个可利用的漏洞。
`/dev` 中还有一些非常有趣的设备文件。 设备文件 `null`,`zero`,`random` 和 `urandom` 不与任何物理设备相关联。
例如,空设备 `/dev/null` 可以用作来自 shell 命令或程序的输出重定向的目标,以便它们不显示在终端上。 我经常在我的 BASH 脚本中使用这个,以防止向用户展示可能会让他们感到困惑的输出。 `/dev/null` 设备可用于产生一个空字符串。 使用如下所示的 `dd` 命令查看 `/dev/null` 设备文件的一些输出。
```
# dd if=/dev/null bs=512 count=500 | od -c
0+0 records in
0+0 records out
0 bytes copied, 1.5885e-05 s, 0.0 kB/s
0000000
```
注意,因为空字符什么也没有所以确实没有可见的输出。 注意看看字节数。
`/dev/random` 和 `/dev/urandom` 设备也很有趣。 正如它们的名字所暗示的,它们都产生随机输出,不仅仅是数字,而是任何字节组合。 `/dev/urandom` 设备产生的是**确定性**的随机输出,并且非常快。 这意味着输出由算法确定,并使用种子字符串作为起点。 结果,如果原始种子是已知的,则黑客可以再现输出,尽管非常困难,但这是有可能的。 使用命令 `cat /dev/urandom` 可以查看典型的输出,使用 `Ctrl-c` 退出。
`/dev/random` 设备文件生成**非确定性**的随机输出,但它产生的输出更慢一些。 该输出不是由依赖于先前数字的算法确定的,而是由击键动作和鼠标移动而产生的。 这种方法使得复制特定系列的随机数要困难得多。使用 `cat` 命令去查看一些来自 `/dev/random` 设备文件输出。尝试移动鼠标以查看它如何影响输出。
正如其名字所暗示的,`/dev/zero` 设备文件产生一个无止境的零作为输出。 注意,这些是八进制零,而不是ASCII字符零(`0`)。 使用如下所示的 `dd` 查看 `/dev/zero` 设备文件中的一些输出
```
# dd if=/dev/zero bs=512 count=500 | od -c
0000000 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0
*
500+0 records in
500+0 records out
256000 bytes (256 kB, 250 KiB) copied, 0.00126996 s, 202 MB/s
0764000
```
请注意,此命令的字节数不为零。
### 创建设备文件
在过去,在 `/dev` 中的设备文件都是在安装时创建的,导致一个目录中有几乎所有的设备文件,尽管大多数文件永远不会用到。 在不常发生的情况,例如需要新的设备文件,或意外删除后需要重新创建设备文件,可以使用 `mknod` 程序手动创建设备文件。 前提是你必须知道设备的主要和次要号码。
CentOS 和 RHEL 6、7,以及 Fedora 的所有版本——可以追溯到至少 Fedora 15,使用较新的创建设备文件的方法。 所有设备文件都是在引导时创建的。 这是因为 udev 设备管理器在设备添加和删除发生时会进行检测。这可实现在主机启动和运行时的真正的动态即插即用功能。 它还在引导时执行相同的任务,通过在引导过程的很早的时期检测系统上安装的所有设备。 [Linux.com](https://www.linux.com/) 上有一篇很棒的对 [udev 的描述](https://www.linux.com/news/udev-introduction-device-management-modern-linux-system)。
回到 `/dev` 中的文件列表,注意文件的日期和时间。 所有文件都是在上次启动时创建的。 您可以使用 `uptime` 或者 `last` 命令来验证这一点。在上面我的设备列表中,所有这些文件都是在 11 月 7 日上午 7:06 创建的,这是我最后一次启动系统。
当然, `mknod` 命令仍然可用, 但新的 `MAKEDEV` (是的,所有字母大写,在我看来是违背 Linux 使用小写命令名的原则的) 命令提供了一个创建设备文件的更容易的界面。 在当前版本的 Fedora 或 CentOS 7 中,默认情况下不安装 `MAKEDEV` 命令;它安装在 CentOS 6。您可以使用 YUM 或 DNF 来安装 MAKEDEV 包。
### 结论
有趣的是,我很久没有创建一个设备文件的需要了。 然而,最近我遇到一个有趣的情况,其中一个我常使用的设备文件没有创建,我不得不创建它。 之后该设备再没出过问题。所以丢失设备文件的情况仍然可以发生,知道如何处理它可能很重要。
设备文件有无数种,您遇到的设备文件我可能没有涵盖到。 这些信息在所下面引用的资源中有大量的细节信息可用。 关于这些文件的功能和工具,我希望我已经给您一些基本的了解,下一步您自己可以探索更多。
### 资源
* [一切皆文件](https://opensource.com/life/15/9/everything-is-a-file), David Both, Opensource.com
* [Linux 文件系统介绍](https://opensource.com/life/16/10/introduction-linux-filesystems), David Both, Opensource.com
* [文件系统层次结构](http://www.tldp.org/LDP/Linux-Filesystem-Hierarchy/html/dev.html), The Linux Documentation Project
* [设备文件](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Device_file), Wikipedia
* [Linux 下已分配设备](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/devices.txt), Kernel.org
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/16/11/managing-devices-linux>
作者:[David Both](https://opensource.com/users/dboth) 译者:[erlinux](http://www.itxdm.me) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | There are many interesting features of the Linux directory structure. This month I cover some fascinating aspects of the /dev directory. Before you proceed any further with this article, I suggest that, if you have not already done so, you read my earlier articles, * Everything is a file*, and
*, both of which introduce some interesting Linux filesystem concepts. Go ahead—I will wait.*
[An introduction to Linux filesystems](https://opensource.com/life/16/10/introduction-linux-filesystems)
Great! Welcome back. Now we can proceed with a more detailed exploration of the /dev directory.
## Device files
Device files are also known as [device ](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Device_file)[special files](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Device_file). Device files are employed to provide the operating system and users an interface to the devices that they represent. All Linux device files are located in the /dev directory, which is an integral part of the root (/) filesystem because these device files must be available to the operating system during the boot process.
One of the most important things to remember about these device files is that they are most definitely not device drivers. They are more accurately described as portals to the device drivers. Data is passed from an application or the operating system to the device file which then passes it to the device driver which then sends it to the physical device. The reverse data path is also used, from the physical device through the device driver, the device file, and then to an application or another device.
Let's look at the data flow of a typical command to visualize this.
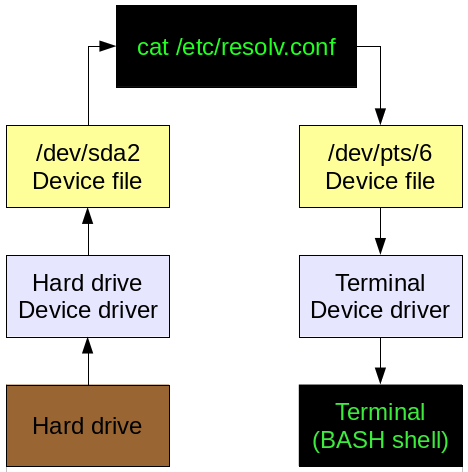
Figure 1: Simple data flow for a typical command.
In Figure 1, above, a simplified data flow is shown for a common command. Issuing the **cat /etc/resolv.conf** command from a GUI terminal emulator such as Konsole or xterm causes the resolv.conf file to be read from the disk with the disk device driver handling the device specific functions such as locating the file on the hard drive and reading it. The data is passed through the device file and then from the command to the device file and device driver for pseudo-terminal 6 where it is displayed in the terminal session.
Of course, the output of the **cat** command could have been redirected to a file in the following manner, **cat /etc/resolv.conf > /etc/resolv.bak** in order to create a backup of the file. In that case, the data flow on the left side of Figure 1 would remain the same while the data flow on the right would be through the /dev/sda2 device file, the hard drive device driver and then onto the hard drive itself.
These device files make it very easy to use standard streams (STD/IO) and redirection to access any and every device on a Linux or Unix computer. Simply directing a data stream to a device file sends the data to that device.
## Classification
Device files can be classified in at least two ways. The first and most commonly used classification is that of the data stream commonly associated with the device. For example, tty (teletype) and serial devices are considered to be character based because the data stream is transferred and handled one character or byte at a time. Block type devices such as hard drives transfer data in blocks, typically a multiple of 256 bytes.
If you have not already, go ahead and as a non-root user in a terminal session, change the present working directory (PWD) to /dev and display a long listing. This shows a list of device files with their file permissions and their major and minor identification numbers. For example, the following device files are just a few of the ones in the /dev/directory on my Fedora 24 workstation. They represent disk and tty type devices. Notice the leftmost character of each line in the output. The ones that have a "b" are block type devices and the ones that begin with "c" are character devices.
```
``````
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 0 Nov 7 07:06 sda
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 1 Nov 7 07:06 sda1
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 16 Nov 7 07:06 sdb
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 17 Nov 7 07:06 sdb1
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 18 Nov 7 07:06 sdb2
crw--w---- 1 root tty 4, 0 Nov 7 07:06 tty0
crw--w---- 1 root tty 4, 1 Nov 7 07:07 tty1
crw--w---- 1 root tty 4, 10 Nov 7 07:06 tty10
crw--w---- 1 root tty 4, 11 Nov 7 07:06 tty11
```
The more detailed and explicit way to identify device files is using the device major and minor numbers. The disk devices have a major number of 8 which designates them as SCSI block devices. Note that all PATA and SATA hard drives have been managed by the SCSI subsystem because the old ATA subsystem was many years ago deemed as not maintainable due to the poor quality of its code. As a result, hard drives that would previously have been designated as "hd[a-z]" are now referred to as "sd[a-z]".
You can probably infer the pattern of disk drive minor numbers in the small sample shown above. Minor numbers 0, 16, 32 and so on up through 240 are the whole disk numbers. So major/minor 8/16 represents the whole disk /dev/sdb and 8/17 is the device file for the first partition, /dev/sdb1. Numbers 8/34 would be /dev/sdc2.
The tty device files in the list above are numbered a bit more simply from tty0 through tty63.
The [Linux Allocated Devices](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/devices.txt) file at Kernel.org is the official registry of device types and major and minor number allocations. It can help you understand the major/minor numbers for all currently defined devices.
## Fun with device files
Let's take a few minutes now and perform a couple fun experiments that will illustrate the power and flexibility of the Linux device files. Most Linux distributions have multiple virtual consoles, 1 through 7, that can be used to login to a local console session with a shell interface. These can be accessed using the key combinations Ctrl-Alt-F1 for console 1, Ctrl-Alt-F2 for console 2, and so on.
Press Ctrl-Alt-F2 to switch to console 2. On some distributions, the login information includes the tty device associated with this console, but many do not. It should be tty2 because you are in console 2.
Log in as a non-root user. Then you can use the who am i command—yes, just like that, with spaces—to determine which tty device is connected to this console.
Before we actually perform this experiment, look at a listing of the tty2 and tty3 devices in /dev.
```
````ls -l /dev/tty[23]`
There will be a large number of tty devices defined but we do not care about most of them, just the tty2 and tty3 devices. As device files, there is nothing special about them; they are simply character type devices. We will use these devices for this experiment. The tty2 device is attached to virtual console 2 and the tty3 device is attached to virtual console 3.
Press Ctrl-Alt-F3 to switch to console 3. Log in again as the same non-root user. Now enter the following command on console 3.
```
````echo "Hello world" > /dev/tty2`
Press Ctrl-Alt-F2 to return to console 2. The string "Hello world" (without quotes) is displayed in console 2.
This experiment can also be performed with terminal emulators on the GUI desktop. Terminal sessions on the desktop use pseudo terminal devices in the /dev tree, such as /dev/pts/1. Open two terminal sessions using Konsole or Xterm. Determine which pseudo-terminals they are connected to and use one to send a message to the other.
Now continue the experiment by using the cat command to display the /etc/fstab file on a different terminal.
Another interesting experiment is to print a file directly to the printer using the cat command. Assuming that your printer device is /dev/usb/lp0, and that your printer can print PDF files directly, the following command will print the PDF file test.pdf on your printer.
```
````cat test.pdf > /dev/usb/lp0`
The /dev directory contains some very interesting device files that are portals to hardware that one does not normally think of as a device like a hard drive or display. For one example, system memory—RAM—is not something that is normally considered as a "device," yet /dev/mem is the portal through which direct access to memory can be achieved. The following example had some interesting results.
```
````dd if=/dev/mem bs=2048 count=100`
The **dd** command above provides a bit more control than simply using the **cat** command to dump all of a system's memory. It provides the ability to specify how much data is read from /dev/mem and would also allow me to specify the point at which to start reading data from memory. Although some memory was read, the kernel responded with the following error that I found in /var/log/messages.
```
````Nov 14 14:37:31 david kernel: usercopy: kernel memory exposure attempt detected from ffff9f78c0010000 (dma-kmalloc-512) (2048 bytes)`
What this error means is that the kernel is doing its job by protecting memory that belongs to other processes which is exactly how it should work. So, although you can use /dev/mem to display data stored in RAM memory, access to most memory space is protected and will result in errors. Only that virtual memory which is assigned by the kernel memory manager to the BASH shell running the **dd** command should be accessible without causing an error. Sorry, but you cannot snoop in memory that does not belong to you unless you find a vulnerability to exploit.
There are some other very interesting device files in /dev. The device files null, zero, random and urandom are not associated with any physical devices.
For example, the null device /dev/null can be used as a target for the redirection of output from shell commands or programs so that they are not displayed on the terminal. I frequently use this in my BASH scripts to prevent users from being presented with output that might be confusing to them. The /dev/null device can be used to produce a string of null characters. Use the **dd** command as shown below to view some output from the /dev/null device file.
```
``````
# dd if=/dev/null bs=512 count=500 | od -c
0+0 records in
0+0 records out
0 bytes copied, 1.5885e-05 s, 0.0 kB/s
0000000
```
Note that there is really no visible output because null characters are nothing. Note the byte count.
The /dev/random and /dev/urandom devices are also very interesting. As their names imply, they both produce random output—not just numbers but any and all byte combinations. The /dev/urandom device produces deterministic random output and is very fast. That means the output is determined by an algorithm and uses a seed string as a starting point. As a result it is possible, although very difficult, for a hacker to reproduce the output if the original seed is known. Use the command **cat /dev/urandom** to view typical output. You can use Ctrl-c to break out.
The /dev/random device file produces non-deterministic random output but it produces output more slowly. This output is not determined by an algorithm that is dependent upon the previous number, but is generated in response to keystrokes and mouse movements. This method makes it far more difficult to duplicate a specific series of random numbers. Use the **cat **command to view some of the output from the /dev/random device file. Try moving the mouse to see how it affects the output.
As its name implies, the /dev/zero device file produces an unending string of zeroes as output. Note that these are Octal zeroes and not the ASCII character zero (0). Use the **dd** command as shown below to view some output from the /dev/zero device file.
```
``````
# dd if=/dev/zero bs=512 count=500 | od -c
0000000 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0
*
500+0 records in
500+0 records out
256000 bytes (256 kB, 250 KiB) copied, 0.00126996 s, 202 MB/s
0764000
```
Note that the byte count for this command is non-zero.
## Creating device files
In the past, the device files in /dev were all created at installation time, resulting in a directory full of almost every possible device file, even though most would never be used. In the unlikely event that a new device file was needed or one was accidentally deleted and needed to be re-created, the **mknod** program was available to manually create device files. All you had to know was the device major and minor numbers.
CentOS and RHEL 6 and 7, as well as all versions of Fedora going back to at least as far Fedora 15, use the newer method of creating the device files. All device files are created at boot time. This functionality is possible because the udev device manager detects addition and removal of devices as they occur. This allows for true dynamic plug-n-play functionality while the host is up and running. It also performs the same task at boot time by detecting all devices installed on the system very early in the boot process. [Linux.com](https://www.linux.com/) has a good [description of udev](https://www.linux.com/news/udev-introduction-device-management-modern-linux-system).
Going back to your listing of the files in /dev, notice the date and time on the files. All of them were created during the last boot. You can verify this using the **uptime** or **last** commands. In my device listing above, all of those files were created at 7:06 AM on November 7, which is the last time I booted the system.
Of course, the **mknod** command is still available, but the new **MAKEDEV** (yes, in all uppercase—which in my opinion is contrary to the Linux philosophy of using all lowercase command names) command provides an easier interface for creating device files, should the need arise. The MAKEDEV command is not installed by default in current versions of Fedora or CentOS 7; it is installed in CentOS 6. You can use YUM or DNF to install the MAKEDEV package.
## Conclusion
Interestingly enough, it had been a long time since I needed to create a device file. However, just recently I had an interesting situation where one of the device files I typically use was not created and I did have to create it. I have not had any problem with that device since. So a situation caused by a missing device file can still happen and knowing how to deal with it can be important.
I have not covered many of the myriad different types of device files that you might encounter. That information is available in plenty of detail in the resources cited. I hope I have given you some basic understanding of how these files function and the tools to allow you to explore more on your own.
## Resources
[Everything is a file](https://opensource.com/life/15/9/everything-is-a-file), David Both, Opensource.com[An introduction to Linux filesystems](https://opensource.com/life/16/10/introduction-linux-filesystems), David Both, Opensource.com[Filesystem Hierarchy](http://www.tldp.org/LDP/Linux-Filesystem-Hierarchy/html/dev.html), The Linux Documentation Project[Device File](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Device_file), Wikipedia[Linux Allocated Devices](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/devices.txt), Kernel.org
## 10 Comments |
8,102 | 在 Linux 终端中自定义 Bash 配色和提示内容 | http://www.tecmint.com/customize-bash-colors-terminal-prompt-linux/ | 2017-01-09T14:05:00 | [
"提示符",
"PS1"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8102-1.html | 现今,大多数(如果不是全部的话)现代 Linux 发行版的默认 shell 都是 Bash。然而,你可能已经注意到这样一个现象,在各个发行版中,其终端配色和提示内容都各不相同。

如果你一直都在考虑,或者只是一时好奇,如何定制可以使 Bash 更好用。不管怎样,请继续读下去 —— 本文将告诉你怎么做。
### PS1 Bash 环境变量
命令提示符和终端外观是通过一个叫 `PS1` 的变量来进行管理的。根据 **Bash** 手册页说明,**PS1** 代表了 shell 准备好读取命令时显示的主体的提示字符串。
**PS1** 所允许的内容包括一些反斜杠转义的特殊字符,可以查看手册页中 **PRMPTING** 部分的内容来了解它们的含义。
为了演示,让我们先来显示下我们系统中 `PS1` 的当前内容吧(这或许看上去和你们的有那么点不同):
```
$ echo $PS1
[\u@\h \W]\$
```
现在,让我们来了解一下怎样自定义 PS1 吧,以满足我们各自的需求。
#### 自定义 PS1 格式
根据手册页 PROMPTING 章节的描述,下面对各个特殊字符的含义作如下说明:
* `\u:` 显示当前用户的 **用户名**。
* `\h:` <ruby> 完全限定域名 <rt> Fully-Qualified Domain Name </rt></ruby>(FQDN)中第一个点(`.`)之前的**主机名**。
* `\W:` 当前工作目录的**基本名**,如果是位于 `$HOME` (家目录)通常使用波浪符号简化表示(`~`)。
* `\$:` 如果当前用户是 root,显示为 `#`,否则为 `$`。
例如,如果我们想要显示当前命令的历史数量,可以考虑添加 `\!`;如果我们想要显示 FQDN 全称而不是短服务器名,那么可以考虑添加 `\H`。
在下面的例子中,我们同时将这两个特殊字符引入我们当前的环境中,命令如下:
```
PS1="[\u@\H \W \!]\$"
```
当按下回车键后,你将会看到提示内容会变成下面这样。可以对比执行命令修改前和修改后的提示内容:

*自定义 Linux 终端提示符 PS1*
现在,让我们再深入一点,修改命令提示符中的用户名和主机名 —— 同时修改文本和环境背景。
实际上,我们可以对提示符进行 3 个方面的自定义:
| 文本格式 | 前景色(文本) | 背景色 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| 0: 常规文本 | 30: 黑色 | 40: 黑色 |
| 1: 加粗文本 | 31: 红色 | 41: 红色 |
| 4: 下划线文本 | 32: 绿色 | 42: 绿色 |
| | 33: 黄色 | 43: 黄色 |
| | 34: 蓝色 | 44: 蓝色 |
| | 35: 紫色 | 45: 紫色 |
| | 36: 青色 | 46: 青色 |
| | 37: 白色 | 47: 白色 |
我们将在开头使用 `\e` 特殊字符,跟着颜色序列,在结尾使用 `m` 来表示结束。
在该序列中,三个值(**背景**,**格式**和**前景**)由分号分隔(如果不赋值,则假定为默认值)。
**建议阅读:** [在 Linux 中学习 Bash shell 脚本](http://www.tecmint.com/category/bash-shell/)。
此外,由于值的范围不同,指定背景,格式,或者前景的先后顺序没有关系。
例如,下面的 `PS1` 将导致提示符为黄色带下划线文本,并且背景为红色:
```
PS1="\e[41;4;33m[\u@\h \W]$ "
```

*修改 Linux 终端提示符配色 PS1*
虽然它看起来那么漂亮,但是这个自定义将只会持续到当前用户会话结束。如果你关闭终端,或者退出本次会话,所有修改都会丢失。
为了让修改永久生效,你必须将下面这行添加到 `~/.bashrc`或者 `~/.bash_profile`,这取决于你的版本。
```
PS1="\e[41;4;33m[\u@\h \W]$ "
```
尽情去玩耍吧,你可以尝试任何色彩,直到找出最适合你的。
(LCTT 译注:原文的这种设置,不但会影响到提示符,也会影响到输入和显示的其它文字,因此应该在 PS1 设置中使用 `\e[0m` 来结束颜色设置。如:`PS1="\e[41;4;33m[\u@\h \W]$\e[0m "`)
### 小结
在本文中,我们讲述了如何来自定义 Bash 提示符的配色和提示内容。如果你对本文还有什么问题或者建议,请在下面评论框中写下来吧。我们期待你们的声音。
---
作者简介:
 Aaron Kili 是一位 Linux 及 F.O.S.S 的狂热爱好者,一位未来的 Linux 系统管理员,web 开发者,而当前是 TechMint 的原创作者,他热爱计算机工作,并且信奉知识分享。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/customize-bash-colors-terminal-prompt-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,103 | 完全指南之在 Ubuntu 操作系统中安装及卸载软件 | https://itsfoss.com/remove-install-software-ubuntu/ | 2017-01-09T21:31:00 | [
"软件",
"Ubuntu",
"安装",
"卸载"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8103-1.html | 
>
> 摘要:这篇文章详尽地说明了在 Ubuntu Linux 系统中安装及卸载软件的各种方法。
>
>
>
当你从 Windows 系统[转向 Linux 系统](https://itsfoss.com/reasons-switch-linux-windows-xp/)的时候,刚开始的体验绝对是非比寻常的。在 Ubuntu 系统下就连最基本的事情,比如安装个应用程序都会让(刚从 Windows 世界来的)人感到无比困惑。
但是你也不用太担心。因为 Linux 系统提供了各种各样的方法来完成同样的任务,刚开始你感到困惑那也是正常的。你并不孤单,我们大家都是这么经历过来的。
在这篇初学者指南中,我将会教大家在 Ubuntu 系统里如何以最常用的方式来安装软件,以及如何卸载之前已安装的软件。
关于在 Ubuntu 上应使用哪种方法来安装软件,我也会提出自己的建议。请用心学习。这篇文章写得很长也很详细,你从中绝对能够学到东西。
### 在 Ubuntu 系统中安装和卸载软件
在这篇教程中我使用的是运行着 Unity 桌面环境的 Ubuntu 16.04 版本的系统。除了一些截图外,这篇教程也同样适用于其它版本的 Ubuntu 系统。
### 1.1 使用 Ubuntu 软件中心来安装软件(推荐方式)
在 Ubuntu 系统中查找和安装软件最简单便捷的方法是使用 Ubuntu 软件中心。在 Ubuntu Unity 桌面里,你可以在 Dash 下搜索 Ubuntu 软件中心,然后选中打开即可:

你可以把 Ubuntu 软件中心想像成 Google 的 Play 商店或者是苹果的 App 商店。它包含 Ubuntu 系统下所有可用的软件。你可以通过应用程序的名称来搜索应用程序或者是通过浏览各种软件目录来进行查找软件。你还可以根据作者进行查询。这由你自己来选择。

一旦你找到自己想要的应用程序,选中它。软件中心将打开该应用程序的描述页面。你可以阅读关于这款软件的说明,评分等级和用户的评论。如果你愿意,也可以写一条评论。
一旦你确定想安装这款软件,你可以点击安装按钮来安装已选择的应用程序。在 Ubuntu 系统中,你需要输入 root 账号的密码才能安装该应用程序。

还有什么比这更简单的吗?我觉得应该没有了吧!
提示:正如我[在 Ubuntu 16.04 系统安装完成后你需要做的事情](https://itsfoss.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-16-04/)这篇文章提到的那样,你应该启用 Canonical 合作伙伴仓库。默认情况下,Ubuntu 系统仅提供了那些源自自身软件库(Ubuntu 认证)的软件。
但是还有一个 Canonical 合伙伙伴软件库,它包含一些闭源专属软件,Ubuntu 并不直接管控它。启用该仓库后将让你能够访问更多的软件。[在 Ubuntu 系统下安装 Skype 软件](https://itsfoss.com/install-skype-ubuntu-1404/)就是通过那种方式安装完成的。
在 Unity Dash 中,找到软件或更新工具。

如下图,打开其它软件标签面,勾选 Canonical 合作伙伴选项。

### 1.2 从 Ubuntu 软件中心卸载软件(推荐方式)
我们刚刚演示了如何在 Ubuntu 软件中心安装软件。那么如何使用同样的方法来卸载已安装的软件呢?
在 Ubuntu 软件中心卸载软件跟安装软件的步骤一样简单。
打开软件中心然后点击已安装的软件标签面。它将显示所有已安装的软件。或者,你也可以只搜索应用程序的名称。
要卸载 Ubuntu 系统中的应用程序,点击删除按钮即中。你同样需要输入 root 账号的密码。

### 2.1 在 Ubuntu 系统中使用 .deb 文件来安装软件
.deb 文件跟 Windows 下的 .exe 文件很相似。这是一种安装软件的简易方式。很多软件开发商都会提供 .deb 格式的安装包。
Google Chrome 浏览器就是这样的。你可以下载从其官网下载 .deb 安装文件

一旦你下载完成 .deb 安装文件之后,只需要双击运行即可。它将在 Ubuntu 软件中心打开,你就可以使用前面 1.1 节中同样的方式来安装软件。
或者,你也可以使用轻量级的安装程序 [在 Ubuntu 系统中使用 Gdebi 工具来安装 .deb 安装文件](https://itsfoss.com/gdebi-default-ubuntu-software-center/)。
软件安装完成后,你可以随意删除下载的 .deb 安装包。
提示:在使用 .deb 文件的过程中需要注意的一些问题:
* 确保你是从官网下载的 .deb 安装文件。仅使用官网或者 GitHub 上提供的软件包。
* 确保你下载的 .deb 文件系统类型正确(32 位或是 64 位)。请阅读我们写的快速指南:[如何查看你的 Ubuntu 系统是 32 位的还是 64 位的](https://itsfoss.com/32-bit-64-bit-ubuntu/)。
### 2.2 使用 .deb 文件来删除已安装的软件
卸载 .deb 文件安装的软件跟我们在 1.2 节看到的步骤一样的。只需要打开 Ubuntu 软件中心,搜索应用程序名称,然后单击移除并卸载即可。
或者你也可以使用[新立得包管理器](http://www.nongnu.org/synaptic/)。这也不是必须的,但是如果在 Ubuntu 软件中心找不到已安装的应用程序的情况下,就可以使用这个工具了。新立得软件包管理器会列出你系统里已安装的所有可用的软件。这是一个非常强大和有用的工具。
这个工具很强大非常有用。在 Ubuntu 软件中心被开发出来提供一种更友好的安装软件方式之前,新立得包管理器是 Ubuntu 系统中默认的安装和卸载软件的工具。
你可以单击下面的链接来安装新立得软件包管器(它将会在 Ubuntu 软件中心中打开)。
* [安装新立得包管理器](apt://synaptic)
打开新立得包管理器,然后找到你想卸载的软件。已安装的软件标记为绿色按钮。单击并选择“标记为删除”。然后单击“应用”来删除你所选择的软件。

### 3.1 在 Ubuntu 系统中使用 apt 命令来安装软件(推荐方式)
你应该看到过一些网站告诉你使用 `sudo apt-get install` 命令在 Ubuntu 系统下安装软件。
实际上这种命令行方式跟第 1 节中我们看到的安装方式一样。只是你没有使用 Ubuntu 软件中心来安装或卸载软件,而是使用的是命令行接口。别的没什么不同。
使用 `apt-get` 命令来安装软件超级简单。你只需要执行下面的命令:
```
sudo apt-get install package_name
```
上面使用 `sudo` 是为了获取“管理员”或 “root” (Linux 专用术语)账号权限。你可以替换 package\_name 为你想要安装的软件包名。
`apt-get` 命令可以自动补全,你只需要输入一些字符并按 tab 键即可, `apt-get` 命令将会列出所有与该字符相匹配的程序。
### 3.2 在 Ubuntu 系统下使用 apt 命令来卸载软件(推荐方式)
在命令行下,你可以很轻易的卸载 Ubuntu 软件中心安装的软件,以及使用 `apt` 命令或是使用 .deb 安装包安装的各种软件。
你只需要使用下面的命令,替换 package-name 为你想要删除的软件名。
```
sudo apt-get remove package_name
```
同样地,你也可以通过按 tab 键来利用 `apt-get` 命令的自动补全功能。
使用 `apt-get` 命令来安装卸载或卸载并不算什么高深的技能。这实际上非常简便。通过这些简单命令的运用,你可以熟悉 Ubuntu Linux 系统的命令行操作,长期使用对你学习 Linux 系统的帮忙也很大。建议你看下我写的一篇很详细的[apt-get 命令使用指导](https://itsfoss.com/apt-get-linux-guide/)文章来进一步的了解该命令的使用。
* 建议阅读:[Linux 系统下 apt-get 命令初学者完全指南](https://itsfoss.com/apt-get-linux-guide/)
### 4.1 使用 PPA 命令在 Ubuntu 系统下安装应用程序
PPA 是<ruby> <a href="https://help.launchpad.net/Packaging/PPA"> 个人软件包归档 </a> <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Personal Package Archive </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的缩写。这是开发者为 Ubuntu 用户提供软件的另一种方式。
在第 1 节中出现了一个叫做 ‘<ruby> 仓库 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> repository </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>’ 的术语。仓库本质上是一个软件集。 Ubuntu 官方仓库主要用于提供经过 Ubuntu 自己认证过的软件。 Canonical 合作伙伴仓库包含来自合作厂商提供的各种应用软件。
同时,PPA 允许开发者创建自己的 APT 仓库。当用户在系统里添加了一个仓库时(`sources.list` 中增加了该仓库),用户就可以使用开发者自己的仓库里提供的软件了。
现在你也许要问既然我们已经有 Ubuntu 的官方仓库了,还有什么必要使用 PPA 方式呢?
答案是并不是所有的软件都会自动添加到 Ubuntu 的官方仓库中。只有受信任的软件才会添加到其中。假设你开发出一款很棒的 Linux 应用程序,然后你想为用户提供定期的更新,但是在它被添加到 Ubuntu 仓库之前,这需要花费好几个月的时间(如果是在被允许的情况下)。 PPA 的出现就是为了解决这个问题。
除此之外, Ubuntu 官方仓库通常不会把最新版的软件添加进来。这会影响到 Ubuntu 系统的安全性及稳定性。新版本的软件或许会有影响到系统的[回退](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_regression)。这就是为什么在新款软件进入到官方仓库前要花费一定的时间,有时候需要等待几个月。
但是,如果你不想等待最新版出现在 Ubuntu 仓库中呢?这个时候 PPA 就对你有帮助了。通过 PPA 方式,你可以获得该应用程序的最新版本。
通常情况下, PPA 通过这三个命令来进行使用。第一个命令添加 PPA 仓库到源列表中。第二个命令更新软件缓存列表,这样你的系统就可以获取到可用的新版本软件了。第三个命令用于从 PPA 安装软件。
我将演示使用 PPA 方式来安装 [Numix 主题](https://itsfoss.com/install-numix-ubuntu/):
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:numix/ppa
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install numix-gtk-theme numix-icon-theme-circle
```
在上面的实例中,我们添加了一个[Numix 项目](https://numixproject.org/)提供的 PPA 。在更新软件信息之后,我们安装了两个 Numix PPA 中可用的应用程序。
如果你想使用带有图形界面的应用程序,你可以使用 [Y-PPA 应用程序](https://itsfoss.com/easily-manage-ppas-ubuntu-1310-ppa-manager/)。通过它你可以很方便地查询 PPA,添加和删除软件。
注意:PPA 的安全性经常受到争议。我的建议是你应该从受信任的源添加 PPA,最好是从官方软件源添加。
### 4.2 卸载使用 PPA 方式安装的应用程序
在之前的文章[在 Ubuntu 系统下移除 PPA](https://itsfoss.com/how-to-remove-or-delete-ppas-quick-tip/) 中我已经写得很详细了。你可以跳转到这篇文章去深入学习卸载 PPA 方式安装的软件。
这里简要提一下,你可以使用下面的两个命令来卸载:
```
sudo apt-get remove numix-gtk-theme numix-icon-theme-circle
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:numix/ppa
```
第一个命令是卸载通过 PPA 方式安装的软件。第二个命令是从 `source.list` 中删除该 PPA。
### 5.1 在 Ubuntu Linux 系统中使用源代码来安装软件(不推荐使用)
我并不建议你使用[软件源代码](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Source_code)来安装该应用程序。这种方法很麻烦,容易出问题而且还非常地不方便。你得费尽周折去解决依赖包的问题。你还得保留源代码文件,以便将来卸载该应用程序。
但是还是有一些用户喜欢通过源代码编译的方式来安装软件,尽管他们自己本身并不会开发软件。实话告诉你,我曾经也经常使用这种方式来安装软件,不过那都是 5 年前的事了,那时候我还是一个实习生,我必须在 Ubuntu 系统下开发一款软件出来。但是,从那之后我更喜欢使用其它方式在 Ubuntu 系统中安装应用程序。我觉得,对于普通的 Linux 桌面用户,最好不要使用源代码的方式来安装软件。
在这一小节中我将简要地列出使用源代码方式来安装软件的几个步骤:
* 下载你想要安装软件的源代码。
* 解压下载的文件。
* 进入到解压目录里并找到 `README` 或者 `INSTALL` 文件。一款开发完善的软件都会包含这样的文件,用于提供安装或卸载软件的指导方法。
* 找到名为 `configure` 的配置文件。如果在当前目录下,使用这个命令来执行该文件:`./configure` 。它将会检查你的系统是否包含所有的必须的软件(在软件术语中叫做‘依赖包’)来安装该应用程序。(LCTT 译注:你可以先使用 `./configure --help` 来查看有哪些编译选项,包括安装的位置、可选的特性和模块等等。)注意并不是所有的软件都包括该配置文件,我觉得那些开发很糟糕的软件就没有这个配置文件。
* 如果配置文件执行结果提示你缺少依赖包,你得先安装它们。
* 一旦你安装完成所有的依赖包后,使用 `make` 命令来编译该应用程序。
* 编译完成后,执行 `sudo make install` 命令来安装该应用程序。
注意有一些软件包会提供一个安装软件的脚本文件,你只需要运行这个文件即可安装完成。但是大多数情况下,你可没那么幸运。
还有,使用这种方式安装的软件并不会像使用 Ubuntu 软件库、 PPA 方式或者 .deb 安装方式那样安装的软件会自动更新。
如果你坚持使用源代码方式来安装软件,我建议你看下这篇很详细的文章[在 Ubuntu 系统中使用源代码安装软件](http://www.howtogeek.com/105413/how-to-compile-and-install-from-source-on-ubuntu/)。
### 5.2 卸载使用源代码方式安装的软件(不推荐使用)
如果你觉得使用源代码安装软件的方式太难了,再想想看,当你卸载使用这种方式安装的软件将会更痛苦。
* 首先,你不能删除用于安装该软件的源代码。
* 其次,你必须确保在安装的时候也有对应的方式来卸载它。一款设计上很糟糕的应用程序就不会提供卸载软件的方法,因此你不得不手动去删除那个软件包安装的所有文件。
正常情况下,你应该切换到源代码的解压目录下,使用下面的命令来卸载那个应用程序:
```
sudo make uninstall
```
但是,这也不能保证你每次都会很顺利地卸载完成。
看到了吧,使用源代码方式来安装软件实在是太麻烦了。这就是为什么我不推荐大家在 Ubuntu 系统中使用源代码来安装软件的原因。
### 其它一些在 Ubuntu 系统中安装软件的方法
另外,还有一些在 Ubuntu 系统下并不常用的安装软件的方法。由于这篇文章已经写得够长了,我就不再深入探讨了。下面我将把它们列出来:
* Ubuntu 新推出的 [Snap 打包](https://itsfoss.com/use-snap-packages-ubuntu-16-04/)方式
* 使用 [dpkg](https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/dpkg.html) 命令
* [AppImage](http://appimage.org/) 方式
* [pip](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pip) : 用于安装基于 Python 语言的应用程序
### 你是如何在 UBUNTU 系统中安装软件的呢?
如果你一直都在使用 Ubuntu 系统,那么你在 Ubuntu Linux 系统下最喜欢使用什么方式来安装软件呢?你觉得这篇文章对你有用吗?请分享你的一些观点,建议和提出相关的问题。
---
作者简介:
 我叫 Abhishek Prakash ,F.O.S.S 开发者。我的工作是一名专业的软件开发人员。我是一名狂热的 Linux 系统及开源软件爱好者。我使用 Ubuntu 系统,并且相信分享是一种美德。除了 Linux 系统之外,我喜欢经典的侦探神秘小说。我是 Agatha Christie 作品的真爱粉。
---
via: <https://itsfoss.com/remove-install-software-ubuntu/>
作者:[ABHISHEK PRAKASH](https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 

When you [switch to Linux](https://itsfoss.com/reasons-switch-linux-windows-xp/), the experience could be overwhelming at the start. Even basic things like installing applications on Ubuntu may seem confusing.
Don’t worry. Linux provides so many ways to do the same task that it’s only natural to feel lost, at least at the beginning. You are not alone. We’ve all been at that stage.
In this beginner’s guide, I’ll show you the most popular ways to install the software in Ubuntu. I’ll also show you [how to uninstall the software](https://itsfoss.com/uninstall-programs-ubuntu/).
I’ll also provide recommendations about methods to install software on Ubuntu. Sit tight and pay attention. This long and detailed article will give you lots of helpful information.

[desktop environment](https://itsfoss.com/what-is-desktop-environment/)in this guide. Apart from a couple of screenshots, this guide applies to all other flavors of Ubuntu.
## Method 1: Install software using Ubuntu Software Center [Recommended]
The easiest and most convenient way to find and install the software in Ubuntu is by using the Ubuntu Software Center or the Snap Store. On Ubuntu, you can search for Ubuntu Software in Activities Overview and click on it to open it:

You can think of the Ubuntu Software Center as Google’s Play Store or Apple’s App Store. It showcases all the software available for your Ubuntu system. You can search for an application by its name or browse through various software categories.
In some Ubuntu flavors, you might find it listed as “**Software Boutique**” or “**Software Manager**.”
Once you’ve found the application you’re looking for, click on it. This will open a page inside the Software Center with a description of the application. You can read the description, see its rating and also read reviews. You can also write your review after you get to use it.
You can also select the source to change the type of package you want, such as a snap, deb, etc. Ubuntu does not have Flatpak integration, but you can find it on other Linux distributions. Once selected, you can click on the install button to install it.
You’ll have to enter your password to proceed to install the application.
Could it be any easier? I doubt it.
In **Activities Overview**, look for **Software & Updates**
And here, under the **Other Software** tab, check the options for Canonical Partners.
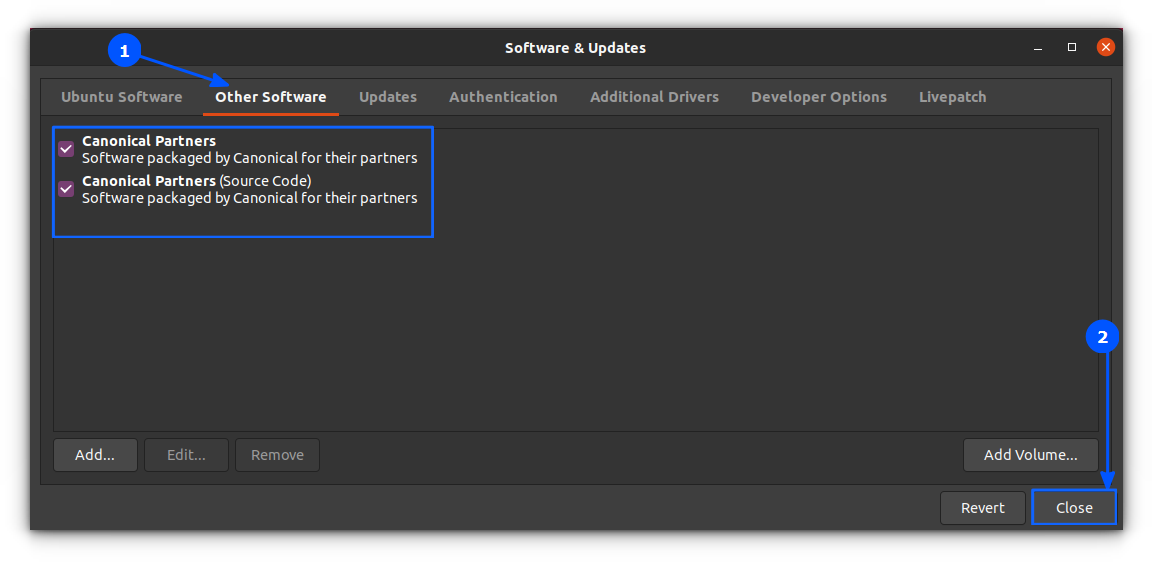
Once you press **Close**, you will be prompted to **reload** the software information.
You need to click on **reload**, which will reload the information about the software installed on the system.
### Remove software using Ubuntu Software Center [Recommended]
We just saw how to install software using the Ubuntu Software Center. How about removing the software that you installed using this method?
Uninstalling software with the Ubuntu Software Center is as easy as installing.
Open the Software Center and click on the** Installed** tab. It will show you all the installed software. Alternatively, you can search for the application by name.
To remove the application from Ubuntu, click on the **Uninstall **button. Again, you’ll have to provide your password here.
[show all the installed packages](https://itsfoss.com/list-installed-packages-ubuntu/), specially if they are command-line based libraries. You should
[use the apt remove command](https://itsfoss.com/apt-remove/), which is discussed later.
## Method 2: Install the software on Ubuntu using .deb file
.deb packages are similar to .exe files on Windows. They’re an easy way to allow software installation.
Many vendors provide their software in .deb format: Google Chrome is an example.
You can download the .deb file from the official website.
Once you’ve downloaded the .deb file, double-click on it to run it. It will open in the Ubuntu Software Center, and you can install it the same way as you did through the software center.
Alternatively, you can use the lightweight program [Gdebi to install .deb files in Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/gdebi-default-ubuntu-software-center/).
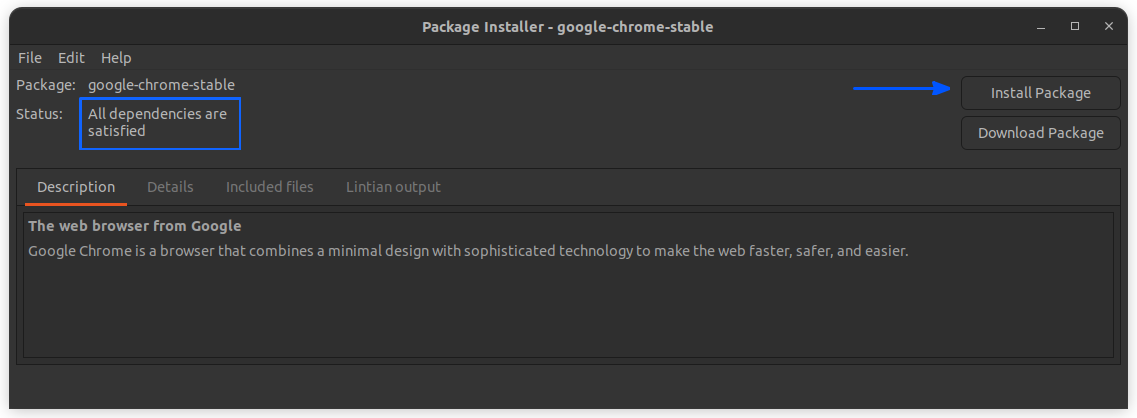
Once you’ve installed the software, you can delete the downloaded .deb file.
**Tip: **A few things to keep in mind while dealing with .deb files:
- Make sure that you’re downloading the .deb file from the official source. Only use the official website or GitHub pages.
- Ensure you download the .deb file for the correct system type (32-bit or 64-bit). Read our quick guide if you need to
[know if your Ubuntu system is 32-bit or 64-bit](https://itsfoss.com/32-bit-64-bit-ubuntu/). - If your version of Ubuntu opens deb files in the archive manager instead of the software center,
[refer to our article](https://itsfoss.com/cant-install-deb-file-ubuntu/)for the solution.
### Remove software that was installed using .deb
Removing [software that was installed from a .deb ](https://itsfoss.com/install-deb-files-ubuntu/)__file__ is the same as removing any app from the software center.
**Just go to the Ubuntu Software Center, search for the application name and click on Uninstall to uninstall it.**
Alternatively, you can use [Synaptic Package Manager](https://www.nongnu.org/synaptic/?ref=itsfoss.com). It’s not usually the case, but it may happen that the installed application is not visible in the Ubuntu Software Center.
[Synaptic Package Manager](https://itsfoss.com/synaptic-package-manager/) lists all the software that is available for your system and all the software that’s already installed there. It’s a very powerful and very useful tool.
**Ubuntu Software Center came into existence to provide a more user-friendly approach to software installation; Synaptic was the default program for installing and uninstalling software on Ubuntu.**
**If you didn’t know,**Open Synaptic Package Manager and then search for the software you want to uninstall. Installed software is marked with a green button. Click on it and select “mark for removal”. Once you do that, click on “apply” to remove the selected software.
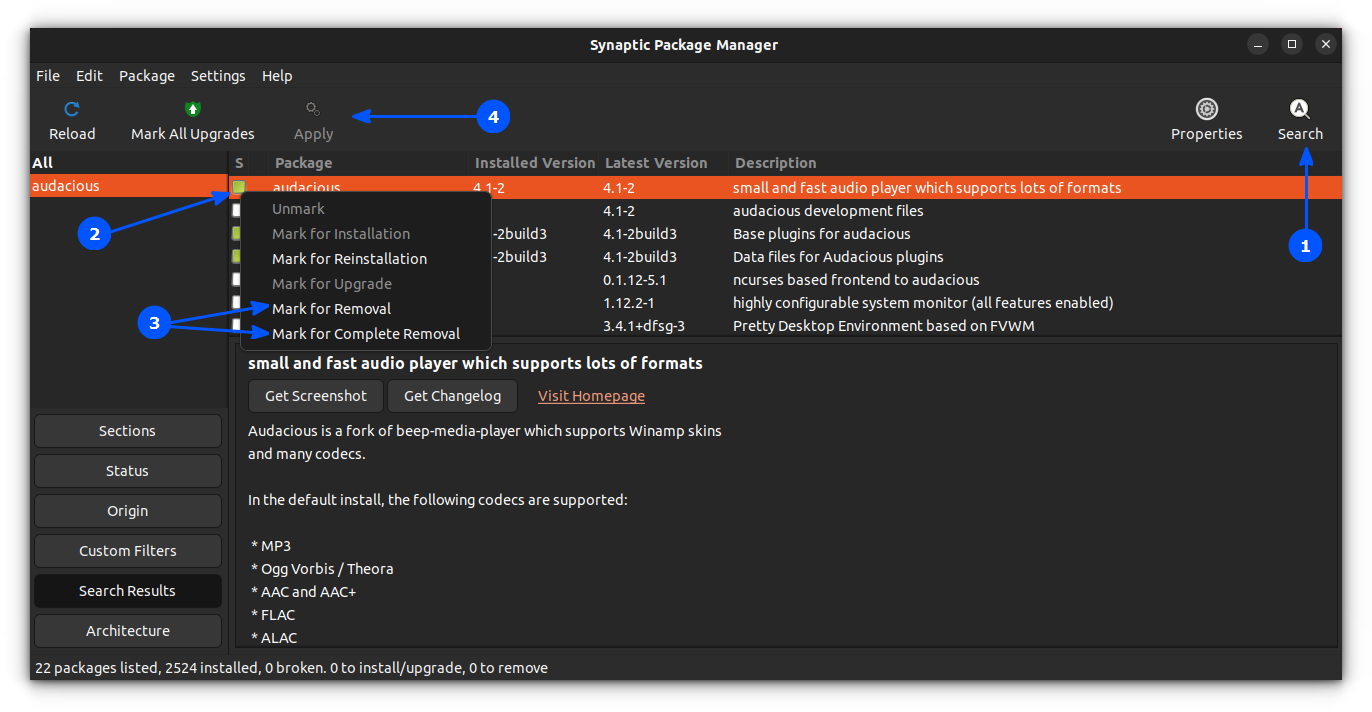
## Method 3: Install software on Ubuntu using apt commands
You might have noticed a number of websites giving you a command like `sudo apt-get install`
to install software in Ubuntu.
This is actually the command-line equivalent of what we saw in **section 1**. Basically, instead of using the graphical interface of the Ubuntu Software Center, you’re using the **terminal**. Nothing else changes.
If you prefer using the terminal commands, follow this method.
[Using the apt-get or apt command](https://itsfoss.com/apt-vs-apt-get-difference/) to install software is extremely easy. All you need to do is to use a command like:
`sudo apt install package-name`
Here `sudo`
gives you “admin” or “root” (in Linux terminology) privileges. You can replace `package-name`
with the name of the desired software.
### Remove software on Ubuntu using apt commands
You can easily remove software that was installed using the Ubuntu Software Center, the apt command or a .deb file using the command line.
All you have to do is to use the following command – just replace `package-name`
with the name of the software you want to delete.
`sudo apt remove package-name`
Using apt-get commands is not rocket science. It’s actually very convenient. With these simple commands, you can get acquainted with the command-line part of Ubuntu Linux and it does help in the long run. I recommend reading my detailed [guide on using apt-get commands](https://itsfoss.com/apt-get-linux-guide/) to learn more about it.
[Using apt Commands in Linux [Ultimate Guide]This guide shows you how to use apt commands in Linux with examples so that you can manage packages effectively.](https://itsfoss.com/apt-command-guide/)

## Method4: Install applications on Ubuntu using a PPA
[PPA](https://itsfoss.com/ppa-guide/) stands for [Personal Package Archive](https://help.launchpad.net/Packaging/PPA?ref=itsfoss.com). It’s another method that developers use for providing their software to Ubuntu users.
In section 1, you came across the term “repository”. A repository basically contains a collection of software. Ubuntu’s official repository has programs that are approved by Ubuntu. The Canonical partner repository contains software from partnered vendors.
In the same way, a PPA enables a developer to create their own APT repository. When an end user (i.e., you) adds this repository to the system (sources.list is modified with this entry), software provided by the developer in his/her repository becomes available for the user.
**Now you may ask what the need of PPAs is when we already have the official Ubuntu repository?**
- Sometimes the latest version of the software is not available in the official repository to ensure stability.
- A quick way for developers to distrubute software even if it is not available on the official repository.
**Note that you should not trust any PPA. Ensure that it is maintained by the original developer or recommended by the developers.**
Typically, PPAs are used with three commands.
The first adds the PPA repository to the sources list. The second updates the cache of your software list to make your system aware of the new software available (On Ubuntu, `add-apt-repository`
command automatically updates the package index). And the third installs the software from the PPA.
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:numix/ppa
sudo apt update
sudo apt-get install numix-gtk-theme numix-icon-theme-circle
```
In the above example, we added a PPA provided by the [Numix project](https://numixproject.github.io/?ref=itsfoss.com). And after updating the software information, we added two programs available in the Numix PPA.
If you want a [GUI application](https://itsfoss.com/gui-cli-tui/), you can use the [Y-PPA application](https://itsfoss.com/y-ppa-manager/) (PPA currently valid only up to Ubuntu 21.10). It lets you search for PPAs and add and remove software in a better way.
### Remove applications installed using a PPA
I’ve discussed [removing PPAs from Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/how-to-remove-or-delete-ppas-quick-tip/) in detail before. You should refer to that article to get more insights into handling PPA removal.
To quickly explain it here, you can use the following two commands.
`sudo apt remove numix-gtk-theme numix-icon-theme-circle`
`sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:numix/ppa`
The first command removes the software installed via the PPA. The second command removes the PPA from sources.list.
[Understanding PPA in Ubuntu Linux [Ultimate Guide]An in-depth article that covers almost all the questions around using PPA in Ubuntu and other Linux distributions.](https://itsfoss.com/ppa-guide/)

## Method 5: Installing software as Snap in Ubuntu Linux
For several versions, Ubuntu is promoting software as snap application. Although, there exists varied opinions about snap packages, it’s a fact that several software provides only snap as their official version for Linux.
Snap applications can be installed easily using Ubuntu’s Software centre. Since it has built in support, you just need to search for the packages (as in the case of section 1.1) and press install.
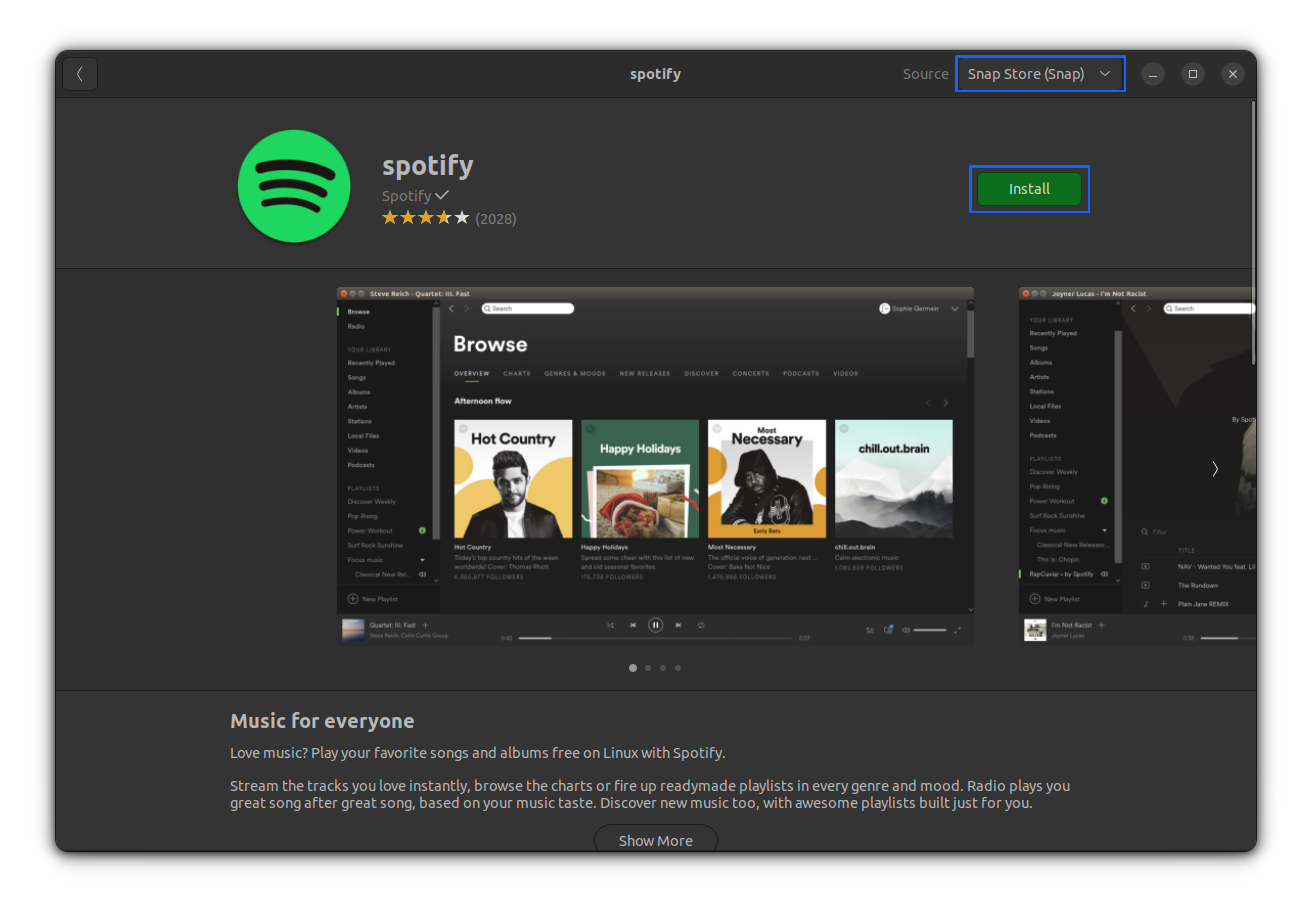
Similarly, you can use the command-line to install snap apps by:
`sudo snap install package-name`
### Remove applications installed using snap
Since snap apps are very well integrated with the snap store, you can uninstall those within Ubuntu’s Software Centre. Go to the installed packages an select **Uninstall **as in section 1.2.
Removing installed snap application is as simple as removing a regular app. You just open a terminal and enter the following command:
`sudo snap remove package-name`
The command will disconnect the snap application from the system.
For further information, refer to our [complete guide on using Snap packages on Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/use-snap-packages-ubuntu-16-04/).
[31 Basic Yet Essential Ubuntu CommandsAn extensive list of essential Linux commands that every Ubuntu user will find helpful in their Linux journey.](https://itsfoss.com/essential-ubuntu-commands/)

## Method 6: Installing software using source code on Ubuntu Linux [Not recommended]
Installing software using the [source code](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Source_code?ref=itsfoss.com) is not something I would recommend to you. It’s tedious, troublesome and not very convenient.
But building from the source code is still some people’s preferred method, even if they don’t develop software of their own. To tell the truth, the last time I used source code extensively was 5 years ago when I was an intern and I had to develop a program using Ubuntu. I’ve come to prefer other ways to install applications on Ubuntu since then. For normal desktop Linux users, installing from source code should be avoided.
I’ll be brief in this section and just list the steps for installing software from source code:
- Download the source code of the program you want to install.
- Extract the downloaded file.
- Go to the extracted directory and look for a README or INSTALL file. Well developed software may include such a file to provide installation and/or removal instructions.
- Look for a file called configure. If it’s present, run the file using the command
– this will check if your system has all the required software (called ‘dependencies’ in software terminology) to install the program. Note that not all software includes a`./configure`
**configure**file, which is, in my opinion, bad development practice. - If configure notifies you of missing dependencies, install them.
- Once you have everything, use the command
to compile the program.`make`
- Once the program is compiled, run the command
to install the software.`sudo make install`
Do note that some software provides you with an install script and just running that file will install the software for you. But you won’t be that lucky most of the time.
Also note that programs you install using this method won’t be updated automatically like programs installed from Ubuntu’s repository or PPAs or .deb files.
I recommend reading this detailed article on [using source code in Ubuntu](https://itsfoss.com/install-software-from-source-code) if you insist on using source code.
[Install Software from Source Cod and Remove it AfterwardsThis detailed guide explains how to install a program from source code in Linux and how to remove the software installed from the source code.](https://itsfoss.com/install-software-from-source-code/)

### Removing software installed using source code [Not recommended]
If you thought installing software from source code was difficult, think again. Removing the software installed using source code could be an even bigger pain.
- First, you have to keep the source code you used to install the program.
- Second, you should make sure at installation that there is a way to uninstall the program. A badly configured program might not provide a way to uninstall the program and then you’ll have to manually remove all the files installed by the software.
Normally, you should be able to uninstall the program by going to its extracted directory and using this command:
`sudo make uninstall`
But this is not a guarantee that you’ll have this method all the time.
You see, there are lots of ifs and buts attached to source code and not that many advantages. This is why I don’t recommend using source code to install software on Ubuntu.
## Few Other Ways to Install Applications in Ubuntu
There are a few more (not so popular) ways you can install software on Ubuntu. Since this article is already way too long, I won’t cover them here. I’ll just list them below:
[dpkg](https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/dpkg.html?ref=itsfoss.com) commands: Head on to the directory where you downloaded the deb file and execute `sudo dpkg -i deb-file-name`
[Using software as Flatpak apps](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/) is also an option.
[Using Flatpak on Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions [Complete Guide]Flatpak is a universal packaging format from Fedora. Enabling Flatpak will give you access to the easy installation of many Linux applications. Here’s how to use Flatpak in Ubuntu and other Linux distributions.](https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/)

You may find some applications in AppImage format so learn about them too.
[How to Use AppImage in Linux [Complete Guide]What is AppImage? How to run it? How does it work? Here’s the complete guide about using AppImage in Linux.](https://itsfoss.com/use-appimage-linux/)

Some Python software can be installed using the pipx command line tool.
[Install and Use pipx in Ubuntu & Other LinuxPipx addresses the shortcomings of the popular pip tool. Learn to install and use Pipx in Linux.](https://itsfoss.com/install-pipx-ubuntu/)

If you already use Ubuntu, what’s your favorite way to install software on Ubuntu Linux? Did you find this guide useful? Do share your views, suggestions and questions. |
8,107 | LXD 2.0 系列(五):镜像管理 | https://www.stgraber.org/2016/03/30/lxd-2-0-image-management-512/ | 2017-01-10T12:39:00 | [
"容器",
"LXC",
"LXD"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8107-1.html | 这是 LXD 2.0 系列介绍文章的第五篇。
1. [LXD 入门](/article-7618-1.html)
2. [安装与配置](/article-7687-1.html)
3. [你的第一个 LXD 容器](/article-7706-1.html)
4. [资源控制](/article-8072-1.html)
5. [镜像管理](/article-8107-1.html)
6. [远程主机及容器迁移](/article-8169-1.html)
7. [LXD 中的 Docker](/article-8235-1.html)
8. [LXD 中的 LXD](/article-8257-1.html)
9. [实时迁移](/article-8263-1.html)
10. [LXD 和 Juju](/article-8273-1.html)
11. [LXD 和 OpenStack](/article-8274-1.html)
12. [调试,及给 LXD 做贡献](/article-8282-1.html)
因为 lxd 容器管理有很多命令,因此这篇文章会很长。 如果你想要快速地浏览这些相同的命令,你可以[尝试下我们的在线演示](https://github.com/lxc/lxd/blob/master/doc/image-handling.md)!

### 容器镜像
如果你以前使用过 LXC,你可能还记得那些 LXC “模板”,基本上都是导出一个容器文件系统以及一点配置的 shell 脚本。
大多数模板是通过在本机上执行一个完整的发行版自举来生成该文件系统。这可能需要相当长的时间,并且无法在所有的发行版上可用,另外可能需要大量的网络带宽。
回到 LXC 1.0,我写了一个“下载”模板,它允许用户下载预先打包的容器镜像,用模板脚本在中央服务器上生成,接着高度压缩、签名并通过 https 分发。我们很多用户从旧版的容器生成方式切换到了使用这种新的、更快更可靠的创建容器的方式。
使用 LXD,我们通过全面的基于镜像的工作流程向前迈进了一步。所有容器都是从镜像创建的,我们在 LXD 中具有高级镜像缓存和预加载支持,以使镜像存储保持最新。
### 与 LXD 镜像交互
在更深入了解镜像格式之前,让我们快速了解下 LXD 可以让你做些什么。
#### 透明地导入镜像
所有的容器都是由镜像创建的。镜像可以来自一台远程服务器并使用它的完整 hash、短 hash 或者别名拉取下来,但是最终每个 LXD 容器都是创建自一个本地镜像。
这有个例子:
```
lxc launch ubuntu:14.04 c1
lxc launch ubuntu:75182b1241be475a64e68a518ce853e800e9b50397d2f152816c24f038c94d6e c2
lxc launch ubuntu:75182b1241be c3
```
所有这些引用相同的远程镜像(在写这篇文章时),在第一次运行这些命令其中之一时,远程镜像将作为缓存镜像导入本地 LXD 镜像存储,接着从其创建容器。
下一次运行其中一个命令时,LXD 将只检查镜像是否仍然是最新的(当不是由指纹引用时),如果是,它将创建容器而不下载任何东西。
现在镜像被缓存在本地镜像存储中,你也可以从那里启动它,甚至不检查它是否是最新的:
```
lxc launch 75182b1241be c4
```
最后,如果你有个名为“myimage”的本地镜像,你可以:
```
lxc launch my-image c5
```
如果你想要改变一些自动缓存或者过期行为,在本系列之前的文章中有[一些命令](/article-7687-1.html)。
#### 手动导入镜像
##### 从镜像服务器中复制
如果你想复制远程的某个镜像到你本地镜像存储,但不立即从它创建一个容器,你可以使用`lxc image copy`命令。它可以让你调整一些镜像标志,比如:
```
lxc image copy ubuntu:14.04 local:
```
这只是简单地复制一个远程镜像到本地存储。
如果您想要通过比记住其指纹更容易的方式来记住你引用的镜像副本,则可以在复制时添加别名:
```
lxc image copy ubuntu:12.04 local: --alias old-ubuntu
lxc launch old-ubuntu c6
```
如果你想要使用源服务器上设置的别名,你可以要求 LXD 复制下来:
```
lxc image copy ubuntu:15.10 local: --copy-aliases
lxc launch 15.10 c7
```
上面的副本都是一次性拷贝,也就是复制远程镜像的当前版本到本地镜像存储中。如果你想要 LXD 保持镜像最新,就像它在缓存中存储的那样,你需要使用 `–auto-update` 标志:
```
lxc image copy images:gentoo/current/amd64 local: --alias gentoo --auto-update
```
##### 导入 tarball
如果某人给你提供了一个单独的 tarball,你可以用下面的命令导入:
```
lxc image import <tarball>
```
如果你想在导入时设置一个别名,你可以这么做:
```
lxc image import <tarball> --alias random-image
```
现在如果你被给了两个 tarball,要识别哪个是含有 LXD 元数据的。通常可以通过 tarball 的名称来识别,如果不行就选择最小的那个,元数据 tarball 包是很小的。 然后将它们一起导入:
```
lxc image import <metadata tarball> <rootfs tarball>
```
##### 从 URL 中导入
`lxc image import` 也可以与指定的 URL 一起使用。如果你的一台 https Web 服务器的某个路径中有 `LXD-Image-URL` 和 `LXD-Image-Hash` 的标头设置,那么 LXD 就会把这个镜像拉到镜像存储中。
可以参照例子这么做:
```
lxc image import https://dl.stgraber.org/lxd --alias busybox-amd64
```
当拉取镜像时,LXD 还会设置一些标头,远程服务器可以检查它们以返回适当的镜像。 它们是 `LXD-Server-Architectures` 和 `LXD-Server-Version`。
这相当于一个简陋的镜像服务器。 它可以通过任何静态 Web 服务器提供一中用户友好的导入镜像的方式。
#### 管理本地镜像存储
现在我们本地已经有一些镜像了,让我们瞧瞧可以做些什么。我们已经介绍了最主要的部分,可以从它们来创建容器,但是你还可以在本地镜像存储上做更多。
##### 列出镜像
要列出所有的镜像,运行 `lxc image list`:
```
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc image list
+---------------+--------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| ALIAS | FINGERPRINT | PUBLIC | DESCRIPTION | ARCH | SIZE | UPLOAD DATE |
+---------------+--------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| alpine-32 | 6d9c131efab3 | yes | Alpine edge (i386) (20160329_23:52) | i686 | 2.50MB | Mar 30, 2016 at 4:36am (UTC) |
+---------------+--------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| busybox-amd64 | 74186c79ca2f | no | Busybox x86_64 | x86_64 | 0.79MB | Mar 30, 2016 at 4:33am (UTC) |
+---------------+--------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| gentoo | 1a134c5951e0 | no | Gentoo current (amd64) (20160329_14:12) | x86_64 | 232.50MB | Mar 30, 2016 at 4:34am (UTC) |
+---------------+--------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| my-image | c9b6e738fae7 | no | Scientific Linux 6 x86_64 (default) (20160215_02:36) | x86_64 | 625.34MB | Mar 2, 2016 at 4:56am (UTC) |
+---------------+--------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| old-ubuntu | 4d558b08f22f | no | ubuntu 12.04 LTS amd64 (release) (20160315) | x86_64 | 155.09MB | Mar 30, 2016 at 4:30am (UTC) |
+---------------+--------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| w (11 more) | d3703a994910 | no | ubuntu 15.10 amd64 (release) (20160315) | x86_64 | 153.35MB | Mar 30, 2016 at 4:31am (UTC) |
+---------------+--------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| | 75182b1241be | no | ubuntu 14.04 LTS amd64 (release) (20160314) | x86_64 | 118.17MB | Mar 30, 2016 at 4:27am (UTC) |
+---------------+--------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
```
你可以通过别名或者指纹来过滤:
```
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc image list amd64
+---------------+--------------+--------+-----------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| ALIAS | FINGERPRINT | PUBLIC | DESCRIPTION | ARCH | SIZE | UPLOAD DATE |
+---------------+--------------+--------+-----------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| busybox-amd64 | 74186c79ca2f | no | Busybox x86_64 | x86_64 | 0.79MB | Mar 30, 2016 at 4:33am (UTC) |
+---------------+--------------+--------+-----------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| w (11 more) | d3703a994910 | no | ubuntu 15.10 amd64 (release) (20160315) | x86_64 | 153.35MB | Mar 30, 2016 at 4:31am (UTC) |
+---------------+--------------+--------+-----------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
```
或者指定一个镜像属性中的键值对来过滤:
```
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc image list os=ubuntu
+-------------+--------------+--------+---------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| ALIAS | FINGERPRINT | PUBLIC | DESCRIPTION | ARCH | SIZE | UPLOAD DATE |
+-------------+--------------+--------+---------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| old-ubuntu | 4d558b08f22f | no | ubuntu 12.04 LTS amd64 (release) (20160315) | x86_64 | 155.09MB | Mar 30, 2016 at 4:30am (UTC) |
+-------------+--------------+--------+---------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| w (11 more) | d3703a994910 | no | ubuntu 15.10 amd64 (release) (20160315) | x86_64 | 153.35MB | Mar 30, 2016 at 4:31am (UTC) |
+-------------+--------------+--------+---------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| | 75182b1241be | no | ubuntu 14.04 LTS amd64 (release) (20160314) | x86_64 | 118.17MB | Mar 30, 2016 at 4:27am (UTC) |
+-------------+--------------+--------+---------------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
```
要了解镜像的所有信息,你可以使用`lxc image info`:
```
stgraber@castiana:~$ lxc image info ubuntu
Fingerprint: e8a33ec326ae7dd02331bd72f5d22181ba25401480b8e733c247da5950a7d084
Size: 139.43MB
Architecture: i686
Public: no
Timestamps:
Created: 2016/03/15 00:00 UTC
Uploaded: 2016/03/16 05:50 UTC
Expires: 2017/04/26 00:00 UTC
Properties:
version: 12.04
aliases: 12.04,p,precise
architecture: i386
description: ubuntu 12.04 LTS i386 (release) (20160315)
label: release
os: ubuntu
release: precise
serial: 20160315
Aliases:
- ubuntu
Auto update: enabled
Source:
Server: https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/releases
Protocol: simplestreams
Alias: precise/i386
```
##### 编辑镜像
编辑镜像的属性和标志的简单方法是使用:
```
lxc image edit <alias or fingerprint>
```
这会打开默认文本编辑器,内容像这样:
```
autoupdate: true
properties:
aliases: 14.04,default,lts,t,trusty
architecture: amd64
description: ubuntu 14.04 LTS amd64 (release) (20160314)
label: release
os: ubuntu
release: trusty
serial: "20160314"
version: "14.04"
public: false
```
你可以修改任何属性,打开或者关闭自动更新,或者标记一个镜像是公共的(后面详述)。
##### 删除镜像
删除镜像只需要运行:
```
lxc image delete <alias or fingerprint>
```
注意你不必移除缓存对象,它们会在过期后被 LXD 自动移除(默认上,在最后一次使用的 10 天后)。
##### 导出镜像
如果你想得到目前镜像的 tarball,你可以使用`lxc image export`,像这样:
```
stgraber@dakara:~$ lxc image export old-ubuntu .
Output is in .
stgraber@dakara:~$ ls -lh *.tar.xz
-rw------- 1 stgraber domain admins 656 Mar 30 00:55 meta-ubuntu-12.04-server-cloudimg-amd64-lxd.tar.xz
-rw------- 1 stgraber domain admins 156M Mar 30 00:55 ubuntu-12.04-server-cloudimg-amd64-lxd.tar.xz
```
#### 镜像格式
LXD 现在支持两种镜像布局,unified 或者 split。这两者都是有效的 LXD 格式,虽然后者在与其他容器或虚拟机一起运行时更容易重用其文件系统。
LXD 专注于系统容器,不支持任何应用程序容器的“标准”镜像格式,我们也不打算这么做。
我们的镜像很简单,它们是由容器文件系统,以及包含了镜像制作时间、到期时间、什么架构,以及可选的一堆文件模板的元数据文件组成。
有关[镜像格式](https://github.com/lxc/lxd/blob/master/doc/image-handling.md)的最新详细信息,请参阅此文档。
##### unified 镜像(一个 tarball)
unified 镜像格式是 LXD 在生成镜像时使用的格式。它们是一个单独的大型 tarball,包含 `rootfs` 目录下的容器文件系统,在 tarball 根目录下有 `metadata.yaml` 文件,任何模板都放到 `templates` 目录。
tarball 可以用任何方式压缩(或者不压缩)。镜像散列是压缩后的 tarball 的 sha256 。
##### Split 镜像(两个 tarball)
这种格式最常用于滚动更新镜像并已经有了一个压缩文件系统 tarball 时。
它们由两个不同的 tarball 组成,第一个只包含 LXD 使用的元数据, `metadata.yaml` 文件在根目录,任何模板都在 `templates` 目录。
第二个 tarball 只包含直接位于其根目录下的容器文件系统。大多数发行版已经有这样的 tarball,因为它们常用于引导新机器。 此镜像格式允许不经修改就重用。
两个 tarball 都可以压缩(或者不压缩),它们可以使用不同的压缩算法。 镜像散列是元数据的 tarball 和 rootfs 的 tarball 结合的 sha256。
##### 镜像元数据
典型的 `metadata.yaml` 文件看起来像这样:
```
architecture: "i686"
creation_date: 1458040200
properties:
architecture: "i686"
description: "Ubuntu 12.04 LTS server (20160315)"
os: "ubuntu"
release: "precise"
templates:
/var/lib/cloud/seed/nocloud-net/meta-data:
when:
- start
template: cloud-init-meta.tpl
/var/lib/cloud/seed/nocloud-net/user-data:
when:
- start
template: cloud-init-user.tpl
properties:
default: |
#cloud-config
{}
/var/lib/cloud/seed/nocloud-net/vendor-data:
when:
- start
template: cloud-init-vendor.tpl
properties:
default: |
#cloud-config
{}
/etc/init/console.override:
when:
- create
template: upstart-override.tpl
/etc/init/tty1.override:
when:
- create
template: upstart-override.tpl
/etc/init/tty2.override:
when:
- create
template: upstart-override.tpl
/etc/init/tty3.override:
when:
- create
template: upstart-override.tpl
/etc/init/tty4.override:
when:
- create
template: upstart-override.tpl
```
##### 属性
两个唯一的必填字段是 `creation date`(UNIX 纪元时间)和 `architecture`。 其他都可以保持未设置,镜像就可以正常地导入。
额外的属性主要是帮助用户弄清楚镜像是什么。 例如 `description` 属性是在 `lxc image list` 中可见的。 用户可以使用其它属性的键/值对来搜索特定镜像。
相反,这些属性用户可以通过 `lxc image edit`来编辑,`creation date` 和 `architecture` 字段是不可变的。
##### 模板
模板机制允许在容器生命周期中的某一点生成或重新生成容器中的一些文件。
我们使用 [pongo2 模板引擎](https://github.com/flosch/pongo2)来做这些,我们将所有我们知道的容器信息都导出到模板。 这样,你可以使用用户定义的容器属性或常规 LXD 属性来自定义镜像,从而更改某些特定文件的内容。
正如你在上面的例子中看到的,我们使用在 Ubuntu 中使用它们来进行 `cloud-init` 并关闭一些 init 脚本。
### 创建你的镜像
LXD 专注于运行完整的 Linux 系统,这意味着我们期望大多数用户只使用干净的发行版镜像,而不是只用自己的镜像。
但是有一些情况下,你有自己的镜像是有必要的。 例如生产服务器上的预配置镜像,或者构建那些我们没有构建的发行版或者架构的镜像。
#### 将容器变成镜像
目前使用 LXD 构造镜像最简单的方法是将容器变成镜像。
可以这么做:
```
lxc launch ubuntu:14.04 my-container
lxc exec my-container bash
<do whatever change you want>
lxc publish my-container --alias my-new-image
```
你甚至可以将一个容器过去的快照变成镜像:
```
lxc publish my-container/some-snapshot --alias some-image
```
#### 手动构建镜像
构建你自己的镜像也很简单。
1. 生成容器文件系统。这完全取决于你使用的发行版。对于 Ubuntu 和 Debian,它将用于启动。
2. 配置容器中该发行版正常工作所需的任何东西(如果需要任何东西)。
3. 制作该容器文件系统的 tarball,可选择压缩它。
4. 根据上面描述的内容写一个新的 `metadata.yaml` 文件。
5. 创建另一个包含 `metadata.yaml` 文件的 tarball。
6. 用下面的命令导入这两个 tarball 作为 LXD 镜像:`lxc image import <metadata tarball> <rootfs tarball> --alias some-name`
在一切都正常工作前你可能需要经历几次这样的工作,调整这里或那里,可能会添加一些模板和属性。
### 发布你的镜像
所有 LXD 守护程序都充当镜像服务器。除非另有说明,否则加载到镜像存储中的所有镜像都会被标记为私有,因此只有受信任的客户端可以检索这些镜像,但是如果要创建公共镜像服务器,你需要做的是将一些镜像标记为公开,并确保你的 LXD 守护进程监听网络。
#### 只运行 LXD 公共服务器
最简单的共享镜像的方式是运行一个公共的 LXD 守护进程。
你只要运行:
```
lxc config set core.https_address "[::]:8443"
```
远程用户就可以添加你的服务器作为公共服务器:
```
lxc remote add <some name> <IP or DNS> --public
```
他们就可以像使用任何默认的镜像服务器一样使用它们。 由于远程服务器添加了 `-public` 选项,因此不需要身份验证,并且客户端仅限于使用已标记为 `public` 的镜像。
要将镜像设置成公共的,只需使用 `lxc image edit` 编辑它们,并将 `public` 标志设置为 `true`。
#### 使用一台静态 web 服务器
如上所述,`lxc image import` 支持从静态 https 服务器下载。 基本要求是:
* 服务器必须支持具有有效证书的 HTTPS、TLS 1.2 和 EC 算法。
* 当访问 `lxc image import` 提供的 URL 时,服务器必须返回一个包含 `LXD-Image-Hash` 和 `LXD-Image-URL` 的 HTTP 标头。
如果你想使它动态化,你可以让你的服务器查找 LXD 在请求镜像时发送的 `LXD-Server-Architectures` 和 `LXD-Server-Version` 的 HTTP 标头,这可以让你返回符合该服务器架构的正确镜像。
#### 构建一个简单流服务器
`ubuntu:` 和 `ubuntu-daily:` 远端服务器不使用 LXD 协议(`images:` 使用),而是使用称为简单流(simplestreams)的不同协议。
简单流基本上是一个镜像服务器的描述格式,使用 JSON 来描述产品以及相关产品的文件列表。
它被各种工具,如 OpenStack、Juju、MAAS 等用来查找、下载或者做镜像系统,LXD 将它作为用于镜像检索的原生协议。
虽然这的确不是提供 LXD 镜像的最简单的方法,但是如果你的镜像也被其它一些工具使用,那这也许值得考虑一下。
关于简单流的更多信息可以在[这里](https://launchpad.net/simplestreams)找到。
### 总结
我希望这篇关于如何使用 LXD 管理镜像以及构建和发布镜像文章让你有所了解。对于以前的 LXC 而言,可以在一组全球分布式系统上得到完全相同的镜像是一个很大的进步,并且引导了更多可复制性的发展方向。
### 额外信息
LXD 的主站在: <https://linuxcontainers.org/lxd>
LXD 的 GitHub 仓库: <https://github.com/lxc/lxd>
LXD 的邮件列表: <https://lists.linuxcontainers.org>
LXD 的 IRC 频道: #lxcontainers on irc.freenode.net
如果你不想或者不能在你的机器上安装 LXD ,你可以在 web 上[试试在线版的 LXD](https://linuxcontainers.org/lxd/try-it) 。
---
作者简介:我是 Stéphane Graber。我是 LXC 和 LXD 项目的领导者,目前在加拿大魁北克蒙特利尔的家所在的Canonical 有限公司担任 LXD 的技术主管。
---
via: <https://www.stgraber.org/2016/03/30/lxd-2-0-image-management-512/>
作者:[Stéphane Graber](https://www.stgraber.org/author/stgraber/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
原文:<https://www.stgraber.org/2016/03/30/lxd-2-0-image-management-512/>
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,110 | Linux 笔记本电脑选购指南 | http://www.tecmint.com/buy-linux-laptops/ | 2017-01-11T08:18:00 | [
"Linux",
"笔记本"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8110-1.html | 众所周知,如果你去电脑城[购买一个新的笔记本电脑](http://amzn.to/2fPxTms),你所见到的尽是预安装了 Windows 或是 Mac 系统的笔记本电脑。无论怎样,你都会被迫支付一笔额外的费用—— 微软系统的许可费用或是苹果电脑背后的商标使用权费用。
当然,你也可以选择购买一款笔记本电脑,然后安装自己喜欢的操作系统。然而,最困难的可能是需要找到一款硬件跟你想安装的操作系统兼容性良好的笔记本电脑。

在此之上,我们还需要考虑硬件驱动程序的可用性。那么,你应该怎么办呢?答案很简单:[购买一款预安装了 Linux 系统的笔记本电脑](http://amzn.to/2fPxTms)。
幸运的是,正好有几家值得依赖的公司提供质量好、有名气,并且预安装了 Linux 系统的笔记本电脑,这样你就不用再担心驱动程序的可用性了。
也就是说,在这篇文章中,我们将根据用户对笔记本电脑的用途列出 3 款可供用户选择的高性价比机器。
### 普通用户使用的 Linux 笔记本电脑
如果你正在寻找一款能够满足日常工作及娱乐需求的 Linux 笔记本电脑,它能够正常运行办公软件,有诸如 Firefox或是 Chrome 这样的 Web 浏览器,有局域网 / Wifi 连接功能,那么你可以考虑选择 [System76](https://system76.com/laptops) 公司生产的 Linux 笔记本电脑,它可以根据用户的定制化需求选择处理器类型,内存及磁盘大小,以及其它配件。
除此之外, System76 公司为他们所有的 Ubuntu 系统的笔记本电脑提供终身技术支持。如果你觉得这听起来不错,并且也比较感兴趣,你可以考虑下 [Lemur](https://system76.com/laptops/lemur) 或者 [Gazelle](https://system76.com/laptops/gazelle) 这两款笔记本电脑。

*Lemur Linux 笔记本电脑*

*Gazelle Linux 笔记本电脑*
### 开发者使用的 Linux 笔记本电脑
如果你想找一款坚固可靠,外观精美,并且性能强悍的笔记本电脑用于开发工作,你可以考虑一下 [Dell 的 XPS 13 笔记本电脑](http://amzn.to/2fBLMGj)。
这款 13 英寸的精美笔记本电脑,配置全高清 HD 显示器,触摸板,售价范围视其配置情况而定,CPU 代号/型号:Intel 的第 7 代处理器 i5 和 i7,固态硬盘大小:128 至 512 GB,内存大小:8 至 16 GB。

*Dell XPS Linux 笔记本电脑*
这些都是你应该考虑在内的重要因素,Dell 已经做得很到位了。不幸的是,Dell ProSupport 为该型号的笔记本电脑仅提供 Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 系统的技术支持(在写本篇文章的时候 - 2016 年 12 月)。
### 系统管理员使用的 Linux 笔记本电脑
虽然系统管理员可以顺利搞定在裸机上安装 Linux 系统的工作,但是使用 System76 的产品,你可以避免寻找各种驱动并解决兼容性问题上的麻烦。
之后,你可以根据自己的需求来配置电脑特性,你可以提高笔记本电脑的性能,增加内存到 32 GB 以确保你可以运行虚拟化环境并进行各种系统管理相关的任务。
如果你对此比较感兴趣,你可以考虑购买 [Kudu](https://system76.com/laptops/kudu) 或者是 [Oryx Pro](https://system76.com/laptops/oryx) 笔记本电脑。

*Kudu Linux 笔记本电脑*

*Oryx Pro 笔记本电脑*
### 总结
在这篇文章中,我们探讨了对于普通用户、开发者及系统管理员来说,为什么购买一款预安装了 Linux 系统的笔记本是一个不错的选择。一旦你决定好,你就可以轻松自如的考虑下应该如何消费这笔省下来的钱了。
你觉得在购买一款 Linux 系统的笔记本电脑时还应该注意些什么?请在下面的评论区与大家分享。
像往常一样,如果你对这篇文章有什么意见和看法,请随时提出来。我们很期待看到你的回复。
---
作者简介:

Gabriel Cánepa 来自 Argentina,San Luis,Villa Mercedes ,他是一名 GNU/Linux 系统管理员和网站开发工程师。目前在一家世界领先的消费品公司工作,在日常工作中,他非常善于使用 FOSS 工具来提高公司在各个领域的生产率。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/buy-linux-laptops/>
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa](http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,111 | 初识 HTTP/2(一) | https://www.viget.com/articles/getting-started-with-http-2-part-1 | 2017-01-11T09:04:00 | [
"HTTP/2"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8111-1.html | 
>
> 用披萨来说明当你订单数很大的时候 HTTP/2 是怎么打败 HTTP/1.1 的。
>
>
>
在建立网站和应用的方式上 HTTP/2 有些令人惊叹的改变,在 HTTP/2 发布后的一年半,几乎 [10% 的网站使用了 HTTP/2](https://w3techs.com/technologies/details/ce-http2/all/all)。它绝对值得采用,但是这篇文章应该首先推给使用 HTTP/2 的前端开发者。这个连载的文章是指导前端开发者怎么转换到 HTTP/2。
本文涵盖了 HTTP/2 对 HTTP/1.1 来说有什么提高的内容,并且向前端开发者介绍了 HTTP/2。
### 再次让我想起什么是 HTTP ...
超文本传输协议,也就是 HTTP,这个协议决定了 web 内容怎么传输。HTTP/1.1 在 1999 年被标准化,那时候的 web 和现在有很大的不同,表格霸占了整个网络。样式通常被内联在元素中,如果网站管理员更加的细致,他们会在头部写个 `<style>`标签。 JavaScript 也被丢在文档里面,那时候完整的网站通常也不会超过几页。
HTTP/1.1 预计这种情况会持续一段时间,所以它并没有太过关注在让一个站点可以加载大量的资源方面,因为那时候的开发者并不需要这个。因此它使用了一个非常简单的方式来处理资源,你访问一个资源然后服务器去寻找它,并且返回你访问的资源,或者告诉你这个资源不存在。这种被叫作"线头堵塞"方式非常高效,但是当你需要多个资源的时候,这个进程会依次寻找每个资源。这意味着在你访问第二个资源之前,服务器必须找到你访问的第一个资源并且载入它,或者告诉你没找到。
### 大型站点的发展
在 1999 年之后的几年里,随着 php 和其他像 Rails 这样的动态语言的崛起,站点变得越来越复杂。css 文件也随着向响应式开发的转变而变的越来越大,因此像 Sass 这样的可以创造一个简单的工作环境的 CSS 编译器就应运而生。 JavaScript 也在 web 上有了更大的作用,它允许开发者编写复杂的应用,这曾经只是 C++ 开发人员的工作。随着 Retina 和高清显示屏的兴起,也让图片变得更高清。随着这些改变,文件大小呈现指数式的增长,使得本来是等待几个字节的资源变成了加载几千字节,甚至在某些情况下有几兆。当你开始载入页面的其它东西前,必须先载入数百 K 的东西,你只能乐观的假设你的用户有很快的网络接入。
想象 HTTP/1.1 是个过去的那种柜台购买式的街旁披萨店。你能自己过去并且预定一个雪碧和 2 片 Angry Hawaiian ,然后等待 3 分钟。他们可以很容易地处理这些,实际上这是一个蓬勃发展的商业模式-定单简单、处理迅速。

然而,一旦你决定在同样的披萨店主办一场小区域的季度颁奖典礼,事情就变的更复杂了。每个人都预定不同的东西,快速而杂乱无章让等待时间直线上升。

### 哪里是 HTTP/2 的舞台
HTTP/2 对前端开发者主要的承诺就是复用。意思就是资源请求能发生在同一时间,并且服务器能马上响应这些资源。在请求之间没有等待,因为它们发生在同一时间。
使用同样的比喻,HTTP/2 允许披萨店在餐馆他们自己区域举办派对。派一个服务员接受订单,并把所有已经准备好的订单交付。当其他人的比萨在制作的时候,你也不需要花 30 分钟去等待你的雪碧,它们在第一批交付的东西之中。这方式使得管理大量订单更加简单,并且防止人们等他们的订单时间太长。
复用带给我们的 web 开发的大变化是改变了文件的加载方式。帮助绕过资源加载的 HTTP/1.1 瓶颈的方式是通过连接和压缩需要被加载的文件。所有任务运行器都默认采取这样的操作方式,或者需要作一点小设置就行。和过去一样,开发人员可以将图像放在<ruby> 精灵拼图 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> sprite sheets </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>中,这会减少了对服务器的请求数。
### 改进 HTTP/1.1
将文件连接起来是个处理 HTTP1.1 的请求限制问题的非常聪明的方式,但是连接文件的主要问题是它要求用户第一次访问整个网站时下载所有的资源。一旦它们载入后,浏览器就会缓存所有的资源。这能提高用户每次访问网页时的速度,但是前期负载很重,对[跳出率不利](https://blog.kissmetrics.com/speed-is-a-killer/)。此外,他们可能为所不访问的页面加载资源。期望用户访问每个页面以查看每个样式,并与每个脚本进行交互是不现实的。此外,在加拿大和欧洲以及几乎每个美国移动提供商的地方,有每月的带宽上限。不是加载额外的 54 千字节的内容就会超过每月的流量限制,而是让我们假设用户想保留这些额外的流量看 Taylor Swift 的 gif。
使用 HTTP/2 和多路复用,您可以开发一些最高效的网站,但它需要一些重新思考、甚至撤销之前的最佳做法。重复一次,我的目的是加快 HTTP/2 的会话,使用我们新的工具,我们可以发现这些新的最佳的做法。
在我的下一篇文章,[我将探索建设基于 HTTP/2 的网站的一些最好方式](https://www.viget.com/articles/getting-started-with-http-2-part-2)。
---
via: <https://www.viget.com/articles/getting-started-with-http-2-part-1?imm_mid=0eb24a&cmp=em-web-na-na-newsltr_20161130>
作者:[Ben](https://www.viget.com/about/team/btinsley) 译者:[hkurj](https://github.com/hkurj) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,112 | Ansible 起步指南 | https://gorillalogic.com/blog/getting-started-with-ansible/ | 2017-01-12T08:48:00 | [
"ansible"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8112-1.html | 这是一篇关于 Ansible 的速成课程,你可以用作小项目的模板,或者帮你深入了解这个神奇的工具。阅读了本指南之后,你将对自动化服务器配置、部署等有足够的了解。

### Ansible 是什么,为什么你该了解?
Ansible 简单的说是一个<ruby> 配置管理系统 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> configuration management system </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。你只需要可以使用 ssh 访问你的服务器或设备就行。它也不同于其他工具,因为它使用推送的方式,而不是像 puppet 或 chef 那样使用拉取的方式。你可以将代码部署到任意数量的服务器上,配置网络设备或在基础架构中自动执行任何操作。
### 前置要求
假设你使用 Mac 或 Linux 作为你的工作站,Ubuntu Trusty 作为你的服务器,并有一些安装软件包的经验。此外,你的计算机上将需要以下软件。所以,如果你还没有它们,请先安装:
* [Virtualbox](https://www.virtualbox.org/)
* [Vagrant](https://www.vagrantup.com/downloads.html)
* Mac 用户:[Homebrew](http://brew.sh/)
### 情景
我们将模拟 2 个连接到 MySQL 数据库的 Web 应用程序服务器。Web 应用程序使用 Rails 5 和 Puma。
### 准备
#### Vagrantfile
为这个项目创建一个文件夹,并将下面的内容保存到名为 `Vagrantfile` 的文件。
```
VMs = [
[ "web1", "10.1.1.11"],
[ "web2", "10.1.1.12"],
[ "dbserver", "10.1.1.21"],
]
Vagrant.configure(2) do |config|
VMs.each { |vm|
config.vm.define vm[0] do |box|
box.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
box.vm.network "private_network", ip: vm[1]
box.vm.hostname = vm[0]
box.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.memory = "512"
end
end
}
end
```
#### 配置你的虚拟网络
我们希望我们的虚拟机能互相交互,但不要让流量流出到真实的网络,所以我们将在 Virtualbox 中创建一个仅主机(HOST-Only)的网络适配器。
1. 打开 Virtualbox
2. 转到 Preferences
3. 转到 Network
4. 单击 Host-Only
5. 单击添加网络
6. 单击 Adapter
7. 将 IPv4 设置为 `10.1.1.1`,IPv4 网络掩码:`255.255.255.0`
8. 单击 “OK”
#### 测试虚拟机及虚拟网络
在终端中,在存放 `Vagrantfile` 的项目目录中,输入下面的命令:
```
vagrant up
```
它会创建你的虚拟机,因此会花费一会时间。输入下面的命令并验证输出内容以检查是否已经工作:
```
$ vagrant status
Current machine states:
web1 running (virtualbox)
web2 running (virtualbox)
master running (virtualbox)
This environment represents multiple VMs. The VMs are all listed
above with their current state. For more information about a specific
VM, run `vagrant status NAME`.
```
现在使用 `vagrant` 的用户名和密码 ,按 `Vagrantfile` 中的 IP 登录其中一台虚拟机,这将验证虚拟机并将它们的密钥添加到你的已知主机(`known_hosts`)文件中。
```
ssh [email protected] # password is `vagrant`
ssh [email protected]
ssh [email protected]
```
恭喜你!现在你已经有可以实验的服务器了。下面的剩下的部分!
### 安装 Ansible
对于 Mac 用户:
```
$ brew install ansible
```
对于 Ubuntu 用户:
```
$ sudo apt install ansible
```
确保你使用了ansible 最近的版本 2.1 或者更高的版本:
```
$ ansible --version
ansible 2.1.1.0
```
### 清单
Ansible 使用清单文件来了解要使用的服务器,以及如何将它们分组以并行执行任务。让我们为这个项目创建我们的清单文件 `inventory`,并将它放在与 `Vagrantfile` 相同的文件夹中:
```
[all:children]
webs
db
[all:vars]
ansible_user=vagrant
ansible_ssh_pass=vagrant
[webs]
web1 ansible_host=10.1.1.11
web2 ansible_host=10.1.1.12
[db]
dbserver ansible_host=10.1.1.21
```
* `[all:children]` 定义一个组的组(`all`)
* `[all:vars]` 定义属于组 `all` 的变量
* `[webs]` 定义一个组,就像 `[db]` 一样
* 文件的其余部分只是主机的声明,带有它们的名称和 IP
* 空行表示声明结束
现在我们有了一个清单,我们可以从命令行开始使用 ansible,指定一个主机或一个组来执行命令。以下是检查与服务器的连接的命令示例:
```
$ ansible -i inventory all -m ping
```
* `-i` 指定清单文件
* `all` 指定要操作的服务器或服务器组
* `-m' 指定一个 ansible 模块,在这种情况下为`ping`
下面是命令输出:
```
dbserver | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
web1 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
web2 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
```
服务器以不同的顺序响应,这只取决于谁先响应,但是这个没有关系,因为 ansible 独立保持每台服务器的状态。
你也可以使用另外一个选项来运行任何命令:
* `-a <command>`
```
$ ansible -i inventory all -a uptime
web1 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
21:43:27 up 25 min, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
dbserver | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
21:43:27 up 24 min, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
web2 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
21:43:27 up 25 min, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
```
这是只有一台服务器的另外一个例子:
```
$ ansible -i inventory dbserver -a "df -h /"
dbserver | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda1 40G 1.4G 37G 4% /
```
### 剧本
剧本(playbook)只是个 YAML 文件,它将清单文件中的服务器组与命令关联。在 ansible 中的对于关键字是 `tasks`,它可以是一个预期的状态、shell 命令或许多其它的选项。有关 ansible 可做的所有事情列表,可以查看[所有模块的列表](http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/list_of_all_modules.html)。
下面是一个运行 shell 命令的剧本示例,将其保存为 `playbook1.yml`:
```
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- shell: uptime
```
* `---` 是 YAML 文件的开始
* `- hosts`:指定要使用的组
* `tasks`:标记任务列表的开始
* `- shell`:指定第一个任务使用 [shell](http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/shell_module.html) 模块
* **记住:YAML 需要缩进结构,确保你始终遵循剧本中的正确结构**
用下面的命令运行它:
```
$ ansible-playbook -i inventory playbook1.yml
PLAY [all] *********************************************************************
TASK [setup] *******************************************************************
ok: [web1]
ok: [web2]
ok: [dbmaster]
TASK [command] *****************************************************************
changed: [web1]
changed: [web2]
changed: [dbmaster]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
dbmaster : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
web1 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
web2 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
```
正如你所见,ansible 运行了 2 个任务,而不是只有剧本中的一个。`TASK [setup]` 是一个隐式任务,它会首先运行以捕获服务器的信息,如主机名、IP、发行版和更多详细信息,然后可以使用这些信息运行条件任务。
还有最后的 `PLAY RECAP`,其中 ansible 显示了运行了多少个任务以及每个对应的状态。在我们的例子中,因为我们运行了一个 shell 命令,ansible 不知道结果的状态,它被认为是 `changed`。
#### 安装软件
我们将使用 [apt](http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/apt_module.html) 在我们的服务器上安装软件,因为我们需要 root 权限,所以我们必须使用 `become` 语句,将这个内容保存在 `playbook2.yml` 中并运行它(`ansible-playbook playbook2.yml`):
```
---
- hosts: webs
become_user: root
become: true
tasks:
- apt: name=git state=present
```
有一些语句可以应用于 ansible 中所有模块;一个是 `name` 语句,可以让我们输出关于正在执行的任务的更具描述性的文本。要使用它,保持任务内容一样,但是添加 `name :描述性文本` 作为第一行,所以我们以前的文本将改成:
```
---
- hosts: webs
become_user: root
become: true
tasks:
- name: This task will make sure git is present on the system
apt: name=git state=present
```
#### 使用 `with_items`
当你要处理一个列表时,比如要安装的项目和软件包、要创建的文件,可以用 ansible 提供的 `with_items`。下面是我们如何在 `playbook3.yml` 中使用它,同时添加一些我们已经知道的其他语句:
```
---
- hosts: all
become_user: root
become: true
tasks:
- name: Installing dependencies
apt: name={{item}} state=present
with_items:
- git
- mysql-client
- libmysqlclient-dev
- build-essential
- python-software-properties
```
#### 使用 `template` 和 `vars`
`vars` 是一个定义变量语句,可以在 `task` 语句或 `template` 文件中使用。 [Jinja2](http://jinja.pocoo.org/docs/dev/) 是 Ansible 中使用的模板引擎,但是关于它你不需要学习很多。在你的剧本中定义变量,如下所示:
```
---
- hosts: all
vars:
- secret_key: VqnzCLdCV9a3jK
- path_to_vault: /opt/very/deep/path
tasks:
- name: Setting a configuration file using template
template: src=myconfig.j2 dest={{path_to_vault}}/app.conf
```
正如你看到的,我可以使用 `{{path_to_vault}}` 作为剧本的一部分,但也因为我使用了 `template`语句,我可以使用 `myconfig.j2` 中的任何变量,该文件必须存在一个名为 `templates` 的子文件夹中。你项目树应该如下所示:
```
├── Vagrantfile
├── inventory
├── playbook1.yml
├── playbook2.yml
└── templates
└── myconfig.j2
```
当 ansible 找到一个 `template` 语句后它会在 `templates` 文件夹内查找,并将把被 `{{` 和 `}}` 括起来的变量展开来。
示例模板:
```
this is just an example vault_dir: {{path_to_vault}} secret_password: {{secret_key}}
```
即使你不扩展变量你也可以使用 `template`。考虑到将来会添加所以我先做了。比如创建一个 `hosts.j2` 模板并加入主机名和 IP。
```
10.1.1.11 web1
10.1.1.12 web2
10.1.1.21 dbserver
```
这里要用像这样的语句:
```
- name: Installing the hosts file in all servers
template: src=hosts.j2 dest=/etc/hosts mode=644
```
#### shell 命令
你应该尽量使用模块,因为 Ansible 可以跟踪任务的状态,并避免不必要的重复,但有时 shell 命令是不可避免的。 对于这些情况,Ansible 提供两个选项:
* [command](http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/command_module.html):直接运行一个命令,没有环境变量或重定向(`|`,`<`,`>` 等)
* [shell](http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/shell_module.html):运行 `/bin/sh` 并展开变量和支持重定向
#### 其他有用的模块
* [apt\_repository](http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/apt_repository_module.html) - 在 Debian 系的发行版中添加/删除包仓库
* [yum\_repository](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/yum_repository_module.html) - 在 RedHat 系的发行版中添加/删除包仓库
* [service](http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/service_module.html) - 启动/停止/重新启动/启用/禁用服务
* [git](http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/git_module.html) - 从 git 服务器部署代码
* [unarchive](http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/unarchive_module.html) - 从 Web 或本地源解开软件包
#### 只在一台服务器中运行任务
Rails 使用 [migrations](http://edgeguides.rubyonrails.org/active_record_migrations.html) 来逐步更改数据库,但由于你有多个应用程序服务器,因此这些迁移任务不能被分配为组任务,而我们只需要一个服务器来运行迁移。在这种情况下,当使用 `run_once` 时,`run_once` 将分派任务到一个服务器,并直到这个任务完成继续下一个任务。你只需要在你的任务中设置 `run_once:true`。
```
- name: 'Run db:migrate'
shell: cd {{appdir}};rails db:migrate
run_once: true
```
#### 会失败的任务
通过指定 `ignore_errors:true`,你可以运行可能会失败的任务,但不会影响剧本中剩余的任务完成。这是非常有用的,例如,当删除最初并不存在的日志文件时。
```
- name: 'Delete logs'
shell: rm -f /var/log/nginx/errors.log
ignore_errors: true
```
### 放到一起
现在用我们先前学到的,这里是每个文件的最终版:
`Vagrantfile`:
```
VMs = [
[ "web1", "10.1.1.11"],
[ "web2", "10.1.1.12"],
[ "dbserver", "10.1.1.21"],
]
Vagrant.configure(2) do |config|
VMs.each { |vm|
config.vm.define vm[0] do |box|
box.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
box.vm.network "private_network", ip: vm[1]
box.vm.hostname = vm[0]
box.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.memory = "512"
end
end
}
end
```
`inventory`:
```
[all:children]
webs
db
[all:vars]
ansible_user=vagrant
ansible_ssh_pass=vagrant
[webs]
web1 ansible_host=10.1.1.11
web2 ansible_host=10.1.1.12
[db]
dbserver ansible_host=10.1.1.21
```
`templates/hosts.j2`:
```
10.1.1.11 web1
10.1.1.12 web2
10.1.1.21 dbserver
```
`templates/my.cnf.j2`:
```
[client]
port = 3306
socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
[mysqld_safe]
socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
nice = 0
[mysqld]
server-id = 1
user = mysql
pid-file = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
port = 3306
basedir = /usr
datadir = /var/lib/mysql
tmpdir = /tmp
lc-messages-dir = /usr/share/mysql
skip-external-locking
bind-address = 0.0.0.0
key_buffer = 16M
max_allowed_packet = 16M
thread_stack = 192K
thread_cache_size = 8
myisam-recover = BACKUP
query_cache_limit = 1M
query_cache_size = 16M
log_error = /var/log/mysql/error.log
expire_logs_days = 10
max_binlog_size = 100M
[mysqldump]
quick
quote-names
max_allowed_packet = 16M
[mysql]
[isamchk]
key_buffer = 16M
!includedir /etc/mysql/conf.d/
```
`final-playbook.yml`:
```
- hosts: all
become_user: root
become: true
tasks:
- name: 'Install common software on all servers'
apt: name={{item}} state=present
with_items:
- git
- mysql-client
- libmysqlclient-dev
- build-essential
- python-software-properties
- name: 'Install hosts file'
template: src=hosts.j2 dest=/etc/hosts mode=644
- hosts: db
become_user: root
become: true
tasks:
- name: 'Software for DB server'
apt: name={{item}} state=present
with_items:
- mysql-server
- percona-xtrabackup
- mytop
- mysql-utilities
- name: 'MySQL config file'
template: src=my.cnf.j2 dest=/etc/mysql/my.cnf
- name: 'Restart MySQL'
service: name=mysql state=restarted
- name: 'Grant access to web app servers'
shell: echo 'GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO "root"@"%" WITH GRANT OPTION;FLUSH PRIVILEGES;'|mysql -u root mysql
- hosts: webs
vars:
- appdir: /opt/dummyapp
become_user: root
become: true
tasks:
- name: 'Add ruby-ng repo'
apt_repository: repo='ppa:brightbox/ruby-ng'
- name: 'Install rails software'
apt: name={{item}} state=present
with_items:
- ruby-dev
- ruby-all-dev
- ruby2.2
- ruby2.2-dev
- ruby-switch
- libcurl4-openssl-dev
- libssl-dev
- zlib1g-dev
- nodejs
- name: 'Set ruby to 2.2'
shell: ruby-switch --set ruby2.2
- name: 'Install gems'
shell: gem install bundler rails
- name: 'Kill puma if running'
shell: file /run/puma.pid >/dev/null && kill `cat /run/puma.pid` 2>/dev/null
ignore_errors: True
- name: 'Clone app repo'
git:
repo=https://github.com/c0d5x/rails_dummyapp.git
dest={{appdir}}
version=staging
force=yes
- name: 'Run bundler'
shell: cd {{appdir}};bundler
- name: 'Run db:setup'
shell: cd {{appdir}};rails db:setup
run_once: true
- name: 'Run db:migrate'
shell: cd {{appdir}};rails db:migrate
run_once: true
- name: 'Run rails server'
shell: cd {{appdir}};rails server -b 0.0.0.0 -p 80 --pid /run/puma.pid -d
```
### 放在你的环境中
将这些文件放在相同的目录,运行下面的命令打开你的开发环境:
```
vagrant up
ansible-playbook -i inventory final-playbook.yml
```
### 部署新的代码
确保修改了代码并推送到了仓库中。接下来,确保你 git 语句中使用了正确的分支:
```
- name: 'Clone app repo'
git:
repo=https://github.com/c0d5x/rails_dummyapp.git
dest={{appdir}}
version=staging
force=yes
```
作为一个例子,你可以修改 `version` 字段为 `master`,再次运行剧本:
```
ansible-playbook -i inventory final-playbook.yml
```
检查所有的 web 服务器上的页面是否已更改:`http://10.1.1.11` 或 `http://10.1.1.12`。将其更改为 `version = staging` 并重新运行剧本并再次检查页面。
你还可以创建只包含与部署相关的任务的替代剧本,以便其运行更快。
### 接下来是什么 ?!
这只是可以做的很小一部分。我们没有接触<ruby> 角色 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> role </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、<ruby> 过滤器 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> filter </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>、调试等许多其他很棒的功能,但我希望它给了你一个良好的开始!所以,请继续学习并使用它。如果你有任何问题,你可以在 [twitter](https://twitter.com/c0d5x) 或评论栏联系我,让我知道你还想知道哪些关于 ansible 的东西!
---
via: <https://gorillalogic.com/blog/getting-started-with-ansible/?utm_source=webopsweekly&utm_medium=email>
作者:[JOSE HIDALGO](https://gorillalogic.com/author/josehidalgo/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 308 | Permanent Redirect | null |
8,113 | 如何在 Docker 中设置 Go 并部署应用 | http://linoxide.com/containers/setup-go-docker-deploy-application/ | 2017-01-12T09:46:39 | [
"Docker",
"golang"
] | /article-8113-1.html | 嗨,在本教程中,我们将学习如何使用 docker 部署 golang web 应用程序。 你可能已经知道,由于 golang 的高性能和可靠性,docker 是完全是用 golang 写的。在我们详细介绍之前,请确保你已经安装了 docker 以及 golang 并对它们有基本了解。

### 关于 docker
Docker 是一个开源程序,它可以将应用及其完整的依赖包捆绑到一起,并打包为容器,与宿主机共享相同的 Linux 内核。另一方面,像 VMware 这样的基于 hypervisor 的虚拟化操作系统容器提供了高级别的隔离和安全性,这是由于客户机和主机之间的通信是通过 hypervisor 来实现的,它们不共享内核空间。但是硬件仿真也导致了性能的开销,所以容器虚拟化诞生了,以提供一个轻量级的虚拟环境,它将一组进程和资源与主机以及其它容器分组及隔离,因此,容器内部的进程无法看到容器外部的进程或资源。
### 用 Go 语言创建一个 “Hello World” web 应用
首先我们为 Go 应用创建一个目录,它会在浏览器中显示 “Hello World”。创建一个 `web-app` 目录并使它成为当前目录。进入 `web-app` 应用目录并编辑一个名为 `main.go` 的文件。
```
root@demohost:~# mkdir web-app
root@demohost:~# cd web-app/
root@demohost:~/web-app# vim.tiny main.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello %s", r.URL.Path[1:])
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/World", handler)
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}
```
使用下面的命令运行上面的 “Hello World” Go 程序。在浏览器中输入 `http://127.0.0.1:8080/World` 测试,你会在浏览器中看到 “Hello World”。
```
root@demohost:~/web-app# PORT=8080 go run main.go
```
下一步是将上面的应用在 docker 中容器化。因此我们会创建一个 dockerfile 文件,它会告诉 docker 如何容器化我们的 web 应用。
```
root@demohost:~/web-app# vim.tiny Dockerfile
# 得到最新的 golang docker 镜像
FROM golang:latest
# 在容器内部创建一个目录来存储我们的 web 应用,接着使它成为工作目录。
RUN mkdir -p /go/src/web-app
WORKDIR /go/src/web-app
# 复制 web-app 目录到容器中
COPY . /go/src/web-app
# 下载并安装第三方依赖到容器中
RUN go-wrapper download
RUN go-wrapper install
# 设置 PORT 环境变量
ENV PORT 8080
# 给主机暴露 8080 端口,这样外部网络可以访问你的应用
EXPOSE 8080
# 告诉 Docker 启动容器运行的命令
CMD ["go-wrapper", "run"]
```
### 构建/运行容器
使用下面的命令构建你的 Go web-app,你会在成功构建后获得确认。
```
root@demohost:~/web-app# docker build --rm -t web-app .
Sending build context to Docker daemon 3.584 kB
Step 1 : FROM golang:latest
latest: Pulling from library/golang
386a066cd84a: Already exists
75ea84187083: Pull complete
88b459c9f665: Pull complete
a31e17eb9485: Pull complete
1b272d7ab8a4: Pull complete
eca636a985c1: Pull complete
08158782d330: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:02718aef869a8b00d4a36883c82782b47fc01e774d0ac1afd434934d8ccfee8c
Status: Downloaded newer image for golang:latest
---> 9752d71739d2
Step 2 : RUN mkdir -p /go/src/web-app
---> Running in 9aef92fff9e8
---> 49936ff4f50c
Removing intermediate container 9aef92fff9e8
Step 3 : WORKDIR /go/src/web-app
---> Running in 58440a93534c
---> 0703574296dd
Removing intermediate container 58440a93534c
Step 4 : COPY . /go/src/web-app
---> 82be55bc8e9f
Removing intermediate container cae309ac7757
Step 5 : RUN go-wrapper download
---> Running in 6168e4e96ab1
+ exec go get -v -d
---> 59664b190fee
Removing intermediate container 6168e4e96ab1
Step 6 : RUN go-wrapper install
---> Running in e56f093b6f03
+ exec go install -v
web-app
---> 584cd410fdcd
Removing intermediate container e56f093b6f03
Step 7 : ENV PORT 8080
---> Running in 298e2a415819
---> c87fd2b43977
Removing intermediate container 298e2a415819
Step 8 : EXPOSE 8080
---> Running in 4f639a3790a7
---> 291167229d6f
Removing intermediate container 4f639a3790a7
Step 9 : CMD go-wrapper run
---> Running in 6cb6bc28e406
---> b32ca91bdfe0
Removing intermediate container 6cb6bc28e406
Successfully built b32ca91bdfe0
```
现在可以运行我们的 web-app 了,可以执行下面的命令。
```
root@demohost:~/web-app# docker run -p 8080:8080 --name="test" -d web-app
7644606b9af28a3ef1befd926f216f3058f500ffad44522c1d4756c576cfa85b
```
进入 `http://localhost:8080/World` 浏览你的 web 应用。你已经成功容器化了一个可重复的/确定性的 Go web 应用。使用下面的命令来启动、停止并检查容器的状态。
```
### 列出所有容器
root@demohost:~/ docker ps -a
### 使用 id 启动容器
root@demohost:~/ docker start CONTAINER_ID_OF_WEB_APP
### 使用 id 停止容器
root@demohost:~/ docker stop CONTAINER_ID_OF_WEB_APP
```
### 重新构建镜像
假设你正在开发 web 应用程序并在更改代码。现在要在更新代码后查看结果,你需要重新生成 docker 镜像、停止旧镜像并运行新镜像,并且每次更改代码时都要这样做。为了使这个过程自动化,我们将使用 docker 卷在主机和容器之间共享一个目录。这意味着你不必为在容器内进行更改而重新构建镜像。容器如何检测你是否对 web 程序的源码进行了更改?答案是有一个名为 “Gin” 的好工具 <https://github.com/codegangsta/gin>,它能检测是否对源码进行了任何更改,然后重建镜像/二进制文件并在容器内运行更新过代码的进程。
要使这个过程自动化,我们将编辑 Dockerfile 并安装 Gin 将其作为入口命令来执行。我们将开放 `3030` 端口(Gin 代理),而不是 `8080`。 Gin 代理将转发流量到 web 程序的 `8080` 端口。
```
root@demohost:~/web-app# vim.tiny Dockerfile
# 得到最新的 golang docker 镜像
FROM golang:latest
# 在容器内部创建一个目录来存储我们的 web 应用,接着使它称为工作目录。
RUN mkdir -p /go/src/web-app
WORKDIR /go/src/web-app
# 复制 web 程序到容器中
COPY . /go/src/web-app
# 下载并安装第三方依赖到容器中
RUN go get github.com/codegangsta/gin
RUN go-wrapper download
RUN go-wrapper install
# 设置 PORT 环境变量
ENV PORT 8080
# 给主机暴露 8080 端口,这样外部网络可以访问你的应用
EXPOSE 3030
# 启动容器时运行 Gin
CMD gin run
# 告诉 Docker 启动容器运行的命令
CMD ["go-wrapper", "run"]
```
现在构建镜像并启动容器:
```
root@demohost:~/web-app# docker build --rm -t web-app .
```
我们会在当前 web 程序的根目录下运行 docker,并通过暴露的 `3030` 端口链接 CWD (当前工作目录)到容器中的应用目录下。
```
root@demohost:~/web-app# docker run -p 3030:3030 -v `pwd`:/go/src/web-app --name="test" -d web-app
```
打开 `http://localhost:3030/World`, 你就能看到你的 web 程序了。现在如果你改变了任何代码,会在浏览器刷新后反映在你的浏览器中。
### 总结
就是这样,我们的 Go web 应用已经运行在 Ubuntu 16.04 Docker 容器中运行了!你可以通过使用 Go 框架来快速开发 API、网络应用和后端服务,从而扩展当前的网络应用。
---
via: <http://linoxide.com/containers/setup-go-docker-deploy-application/>
作者:[Dwijadas Dey](http://linoxide.com/author/dwijadasd/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPConnectionPool(host='linoxide.com', port=80): Max retries exceeded with url: /containers/setup-go-docker-deploy-application/ (Caused by ConnectTimeoutError(<urllib3.connection.HTTPConnection object at 0x7b8327581750>, 'Connection to linoxide.com timed out. (connect timeout=10)')) | null |
8,114 | 5 个找出“二进制命令”描述和系统中位置的方法 | http://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-command-description-and-location/ | 2017-01-13T08:09:00 | [
"whatis",
"whereis",
"which",
"type"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8114-1.html | 在数千个 [Linux 系统上的命令/程序](http://www.tecmint.com/category/top-tools/)中,知道给定命令的类型和目的以及其在系统上的位置(绝对路径)对于新手来说可能是一个挑战。
知道命令/程序的一些细节不仅有助于 [Linux 用户掌握大量命令](http://www.tecmint.com/tag/linux-tricks/),还能使用户理解命令行或脚本在系统上的操作。
因此,在本文中我们将向你解释五个有用的命令,用于显示给定命令的简短描述和位置。

要在系统上发现新命令,请查看 `PATH` 环境变量中的所有目录。这些目录存储系统上安装的所有命令/程序。
一旦你找到一个有趣的命令,在继续阅读更多关于它的手册页之前,请尝试如下收集一些简要的信息。
假设你输出了 `PATH` 的值,然后进到其中的一个目录 `/usr/local/bin`,注意到一个名为 [`fswatch`(监视文件修改更改)](http://www.tecmint.com/fswatch-monitors-files-and-directory-changes-modifications-in-linux/)的新命令:
```
$ echo $PATH
$ cd /usr/local/bin
```

*在 Linux 中找出新命令*
现在让我们在 Linux 中用不同的方法找出 `fswatch` 命令的描述和位置。
### 1、 whatis 命令
`whatis` 用于显示你作为参数输入的命令名的单行描述(例如下面命令中的 `fswatch`)。
如果描述太长,一些部分在默认情况下会被省略,使用 `-l` 标志来显示完整的描述。
```
$ whatis fswatch
$ whatis -l fswatch
```

*Linux whatis 命令示例*
### 2、 apropos 命令
`apropos` 会搜索手册页名称和关键字描述(以命令名作为正则表达式搜索)。
使用 `-l` 标志来显示完整的描述。
```
$ apropos fswatch
$ apropos -l fswatch
```

*Linux apropos 命令示例*
默认上,`apropos` 会如示例那样输出所有匹配的行。你可以使用 `-e` 选项来精确匹配:
```
$ apropos fmt
$ apropos -e fmt
```

*Linux apropos 命令根据关键词显示*
### 3、 type 命令
`type` 命令会输出给定命令的完整路径名,此外,如果输入的命令名不是做为独立存储在磁盘的文件的程序,`type` 还会告诉你命令分类:
* shell 内置命令
* shell 关键字或保留字
* 别名
```
$ type fswatch
```

*Linux type 命令示例*
当命令是另外一个命令的别名时,`type` 会显示运行别名时所执行的命令。使用 `alias` 命令可以查看你系统上创建的所有别名:
```
$ alias
$ type l
$ type ll
```

*显示 Linux 中所有别名*
### 4、 which 命令
`which` 可以帮助命令定位命令,它会打印出命令的绝对路径:
```
$ which fswatch
```

*找出 Linux 命令位置*
一些二进制文件存在于 `PATH` 环境变量中的多个目录,使用 `-a` 标志来找出所有匹配的路径名。
### 5、 whereis 命令
`whereis` 定位指定命令名的二进制、源和帮助页文件,如下所示:
```
$ whereis fswatch
$ whereis mkdir
$ whereis rm
```

*Linux whereis 命令示例*
虽然上面的命令对于查找关于命令/程序的一些快速信息很重要,但是该命令的手册总是可以提供完整的文档,它还包括其他相关程序的列表:
```
$ man fswatch
```
在本文中,我们回顾了五个简单的命令,用于显示命令的简短的手册描述和位置。 你可以在反馈栏中对此文章做出贡献或提出问题。
---
作者简介:

Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux SysAdmin、web 开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-command-description-and-location/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,115 | 初识 HTTP/2(二) | https://www.viget.com/articles/getting-started-with-http-2-part-2 | 2017-01-13T09:46:00 | [
"HTTP/2"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8115-1.html |
>
> HTTP/2 时代的开启为前端开发带来了最佳体验。
>
>
>
如果你对 HTTP/2 有所了解,那你可能用过它,或者至少想过怎样能把它融入你的项目中。尽管有很多关于它如何改变工作流程,提高 Web 速度和效率等方面的猜想,但最佳使用方式还没有定下来。这里我想讲的就是我在之前的项目中所发现的 HTTP/2 的最佳实践。

如果你还不确定什么是 HTTP/2,或者为什么它能改进你的工作,可以先看看我[介绍背景方面的第一篇文章](/article-8111-1.html)。
记住:开始之前,我要告诉你,尽管你的浏览器可能支持 HTTP/2,但你的服务器可能不支持。检查你的主机托管服务,看看他们是否提供 HTTP/2 的支持。否则你可能要建立你自己的服务器。这篇文章并不会涉及这方面该如何做,但你可以查看 [http2 github](https://github.com/http2/http2-spec/wiki/Tools) 页面,找一找这方面的工具。
### 热身工作
首先组织好你的文件。看一看下面的文件树结构,作为组织你的样式表的起点:
```
/styles
|── /setup
| /* 变量、混入(minin)和函数 */
|── /global
| /* 能放在任何组件和部分中的可重用组件 */
|── /components
| /* 特殊组件和部分 */
|── setup.scss // setup 样式索引
|── global.scss // 全局样式索引
```
这会把你的样式分到三个目录下面:`setup`、`global` 和 `componenets`。接下来我会说明这些目录对你的项目有什么用。
### setup 目录
`setup` 目录保存所有的变量、函数、<ruby> 混入 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> minin </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>以及一些正常编译需要的其它文件的定义。要想让这个目录物尽其用,把这个目录下所有内容导入到 `setup.scss` 文件中是个很不错的主意,这样这个文件就会像下面所展示的一样:
```
/* setup.scss */
/* 变量 */
@import "setup/variables/colors";
/* 混入 */
@import "setup/mixins/color";
/* 函数 */
@import "setup/functions/color";
... 等等
```
现在我们能快速引用这个站点中的所有定义,应该确保在所有的样式文件顶部包含我们这里创建的这个文件。
### global 目录
接下来的目录,global 目录,应该包含可在当前站点的多个部分或者每一个页面中重复使用的组件。像按钮、文本、主要样式,以及你的浏览器默认设置应该放在这里。我不建议把页面的头部或底部样式放在这儿,因为某些项目中没有头部,或者不同页面头部不同。而且,底部永远是页面的最后一个元素,所以在用户加载完当前站点的其它东西前,不必过分优先考虑加载底部样式。
记住,如果没有那些定义在 setup 目录下的东西,你的 global 样式就可能没有作用,你的 global 文件看起来应该像这样:
```
/* global.scss */
/* 应用定义 */
@import "setup";
/* 全局样式 */
@import "global/reset";
@import "global/buttons";
@import "global/typography";
@import "global/grid";
... 等等
```
注意,首先要做的就是导入 setup 样式。这样的话,之后的文件都可以引用这个样式里的定义。
由于站点内的每个页面都需要 global 样式,我们可以用典型的方式,在 `<head>` 标签内用一个 `<link>` 标签来加载它们。你所看到的将是一个十分小巧的 css 文件,或者说理论上小巧的,这取决于你需要多少全局样式。
### 最后,你的组件
注意,我没有在上述目录树中的 components 目录里包含索引文件。这是 HTTP/2 所带来的效用。直到现在,我们已经按照标准步骤构建了一个典型的站点,保持相当简单的结构,仅选择全局化那些最重要的样式。组件充当它们自己的索引文件。
大多数开发者有独特的组织组件的方式,因此我并不想影响你的策略。但是,你所有的组件看起来应该像这样:
```
/* header.scss */
/* 应用定义 */
@import "../setup";
header {
// 样式
}
... 等等
```
同样的,你要把 setup 样式包含进来,确保所有东西在编译时都定义过。除了编译这些文件,以及可能要把他们放到 `/assets` 目录,以便很容易找到模版,对这些文件你不必 <ruby> 拼接 <rt> concatenate </rt></ruby>、<ruby> 压缩 <rt> minify </rt></ruby> 它们或者改变什么。
现在样式表已经差不多了,构建站点应该很简单。
### 构建组件
或许对于模板语言你有自己的选择,这取决于你的项目,有可能是 Twig、Rails、Jade 或者 Handlebars。我认为考虑组件最好的方式是它是否有自己的模版文件,它该有个与名字相应的样式。这样你的项目中,模版和样式的比例就会是个不错的 1:1 的比例,而且你知道哪个文件有哪些东西,哪里有哪个文件,因为它们的命名是有规律的。
现在它正步入正轨,用好 HTTP/2 的多种功能十分简单,让我们做一个模版:
```
{# header.html #}
{# compiled header styles #}
<link href="assets/components/header.css" rel="stylesheet" media="all">
<header>
<h1>This Awesome HTTP/2 Site</h1>
... 等等
```
非常好!在模版里你可能有更简单的方式链接到资源,但这里显示你所要做的仅是在开始构建时,在模版文件中链接一个小小的头部样式。这将允许你的站点仅仅加载特定资源到任意给定页面的组件中,而且,能够设定页面从头到脚的组件的优先级。
### 结合在一起
现在所有的组件都有结构,浏览器将会类似以下方式来渲染它们:
```
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" media="all" href="/assets/global.css">
</head>
<body>
<link rel="stylesheet" media="all" href="/assets/components/header.css">
<header>
... etc
</header>
<link rel="stylesheet" media="all" href="/assets/components/title.css">
<section class="title">
... etc
</section>
<link rel="stylesheet" media="all" href="/assets/components/image-component.css">
<section class="image-component">
... etc
</section>
<link rel="stylesheet" media="all" href="/assets/components/text-component.css">
<section class="text-component">
... etc
</section>
<link rel="stylesheet" media="all" href="/assets/components/footer.css">
<footer>
... etc
</footer>
</body>
</html>
```
这是一个高级别方法,但你的项目中可能有调整的更细致的组件。例如,在头部的 `<nav>` 组件可能要加载自己的样式表。尽你所能地自由发挥,让组件更有作用 - HTTP/2 不会因这些需求而阻碍你!
### 结论
这只是一个关于如何在前端用 HTTP/2 构建项目的基本介绍,仅是皮毛而已。你可能注意到我上面所用的方法有的还有改进的空间。请不吝赐教!正如我在第一篇文章中所说的,HTTP/2 可能颠覆自 HTTP/1 以来我们所熟知的某些标准,所以要慎重思考和实践,以便高效使用 HTTP/2 的开发环境。
---
via: <https://www.viget.com/articles/getting-started-with-http-2-part-2>
作者:[Ben](https://www.viget.com/about/team/btinsley) 译者:[GitFuture](https://github.com/GitFuture) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,117 | Linux 系统管理员 2017 年的 10 个新决心 | http://www.tecmint.com/linux-system-administrators-new-years-resolutions-ideas/ | 2017-01-14T17:48:20 | [
"系统管理员",
"学习"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8117-1.html | 当我们告别 2016 时,也到时间定下我们的 **新年决心** 了。不管你身为 Linux 系统管理员的经验水平如何,我们认为,制定接下来 12 个月的成长目标是很值得的。
如果你还没什么想法,我们将会在这篇文章分享 10 个简单的专业提升决心,你可以为 2017 年考虑一下。

### 1、 决定更自动化
你没必要忙得像头无头苍蝇,每天忙于解决可预见的问题。如果你发现自己每天都花费时间在执行重复的任务,你有必要现在就停下来。
在了解了所有基于 Linux 而且开源的工具后,你可以尽可能地[自动化你的 Linux 任务](/article-6526-1.html)来给自己一些休闲的时间。
你会发现,接下来的几个决心会帮你在工作上朝着这个目标前进。所以继续看下去吧。
### 2、 学习一门新的脚本语言
虽然每一个系统管理员应该熟练地使用 Bash 写脚本,但考虑一下其它更现代化、健壮性更强的工具也是很重要的,例如 Python。
不要只是相信我们说的话 —— 看看不久前我们发布的[两篇关于 Python 的系列文章](/article-7693-1.html)。你将会意识到,与其它语言相比,Python 带来了面向对象编程的力量,使您写出更短、健壮性更强的脚本。
### 3、 学习一门新的编程语言
除了学习一门新的脚本语言,(你也可以)决定花费点时间来开始学习或者提升你的编程技能。不确定从何处开始?今年的 [Stackoverflow 开发者调查](http://stackoverflow.com/research/developer-survey-2016#technology)表明 Javascript 连续第三年引领最流行语言的榜单。
其他经典例如 Java 和 C 也值得考虑。
### 4、 注册一个 Github 账户并且定期更新
特别是如果你是一个编程新手,你应该考虑一下在 Github 上展示你的成果。通过允许别人去复刻你的脚本或者程序,你就能提高知识水平,并通过别人的帮助创造出更复杂的软件。
在[《如何安装和注册 Github 帐号》](/article-5458-1.html)一文中了解更多。
### 5、 向一个开源项目做贡献
在 Github 上向一个开源项目做贡献,这是另一个学习或者提高一门新脚本语言或者编程语言能力的好办法。
如果这吸引到了你的兴趣,点击 [Explore Github](https://help.github.com/articles/where-can-i-find-open-source-projects-to-work-on/) 页面。这里你能按热度或者编程语言浏览仓库,你能在这里面找到一些有趣的事情来做。
在此基础上,你将因回馈社区而获得满足感。
### 6、 每月尝试一个新的发行版
经常会有新的发行版或者分支出现,你有不同的选项以供选择。谁知道你梦想中的发行版是否就在近前,而你还没发现它?每个月去一次 [Distrowatch](http://www.distrowatch.com) 然后选择一个新的发行版。
如果你想要尝试一个新的发行版,希望我们的评论能帮你做出决定。也可以点击我们这里关于最好的 Linux 发行版的文章:
* [5 个值得了解的 Linux 服务器发行版](/article-7813-1.html)
* [面向 Linux 新用户的八款最佳 Linux 发行版](/article-7738-1.html)
* [Linux 最佳选择:总有一款桌面发行版适合你](/article-7172-1.html)
* [5个你应该知道的 Live Linux 桌面发行版](/article-7052-1.html)
* [2016:如何选择 Linux 发行版](/article-7039-1.html)
* [为亲朋好友挑选一款合适的 Linux 发行版](/article-7026-1.html)
* [最适合和最不适合新手使用的几款 Linux 发行版](/article-6942-1.html)
* [2015年最流行的十大 Linux 发行版](/article-6856-1.html)
* [2016年值得期待的几大 Linux 发行版](/article-6844-1.html)
### 7、 参加一个 Linux 或者开源会议。
如果你住在由 Linux 基金会赞助的会议举办地附近,我强烈建议你去参加会议。
这不仅将会给你一个提高 Linux 知识的机会,而且将是个见见其他开源专家的机会。
### 8、 从 Linux 基金会的免费或付费课程中学习
Linux 基金会分别通过 **edX.org** 和他们自己的门户,不断地提供免费或付费课程。
免费课程的话题包括(但不仅限于)Linux 介绍、云基础设施技术介绍和 OpenStack 介绍。
另一方面,付费课程包括 [LFCS 认证](/article-7161-1.html) 和 LFCE 认证考试的准备,给开发者的 Linux ,内核内部构件,Linux 安全,性能试验,高可用性及其他。
另外,他们对企业课程有折扣,所以尝试去说服你上司来为你和你同事的训练付费。还有,也会提供周期性的免费在线研讨会,所以别忘了订阅他们的 newsletters!
你也可以考虑下看看我们最棒的[在线 Linux 训练课程](http://www.tecmint.com/linux-online-training-courses/)。
### 9、 每周在 Linux 论坛上回答特定数量的问题
另一个回馈社区的好方法是帮助那些刚开始使用 Linux 的人。你将会发现网上的 Linux 论坛上有许多人正在寻找着答复。
牢记你曾经也是像他们那样是个新手,试着换位思考。
### 10、 教一个孩子或少年使用 Linux
如果我能回到 20 年前,我希望我能有台电脑,有个能在青年时学习 Linux 的机会。
我也希望我能比当年还早很多地开始编程。毫无疑问,这样事情就会简单许多。我认为给孩子和青年教授至少是基础的 Linux 和编程技巧(我对我的孩子这样做)是个重要的尝试。
教育成长中的一代如何有效地使用开源技术将会给他们选择的自由,而他们会因此永远感激你。
### 总结
在这篇文章里我们分享了 10 个适合系统管理员的可能新年决心。我们祝你在朝着目标的工作顺顺利利,希望你能在 2017 年成为我们网站的常客。
如果你有关于这篇文章的问题或者评论,请不要犹豫使用下面的表格提交。我们期待着收到您的信息。
---
作者简介:
 Gabriel Cánepa 是个 GNU/Linux 系统管理员和网页开发者,他来自阿根廷圣路易斯的 Villa Mercedes 。他供职于全球领先的消费品公司,享受在日常工作的方方面面使用 FOSS(自由及开源软件) 工具来提高生产效率。.
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/linux-system-administrators-new-years-resolutions-ideas/>
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa](http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/) 译者:[ypingcn](https://github.com/ypingcn) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,118 | Powerline:给 Vim 和 Bash 提供更棒的状态行和提示信息 | http://www.tecmint.com/powerline-adds-powerful-statuslines-and-prompts-to-vim-and-bash/ | 2017-01-16T08:14:00 | [
"Powerline",
"命令行",
"提示符"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8118-1.html | Powerline 是一个极棒的 [Vim 编辑器](http://www.tecmint.com/vi-editor-usage/)的状态行插件,这个插件是使用 Python 开发的,主要用于显示状态行和提示信息,适用于很多软件,比如 bash、zsh、tmux 等等。

### 特色
1. 使用 python 编写,使其更具扩展性且功能丰富
2. 稳定易测的代码库,兼容 python 2.6+ 和 python 3
3. 支持多种 Linux 功能及工具的提示和状态栏
4. 通过 JSON 保存配置和颜色方案
5. 快速、轻量级,具有后台守护进程支持,提供更佳的性能
### Powerline 效果截图

*Vim 中 Powerline 状态行效果*
在本文中,我会介绍如何安装 Powerline 及其字体,以及如何在 RedHat 和 Debian 类的系统中使 Bash 和 Vim 支持 Powerline。
### 第一步:准备好安装 Powerline 所需的软件
由于和其它无关项目之间存在命名冲突,因此 powerline 只能放在 PyPI(Python Package Index)中的 `powerline-status` 包下.
为了从 PyPI 中安装该包,需要先准备好 `pip`(该工具专门用于 Python 包的管理)工具。所以首先要在 Linux 系统下安装好 `pip` 工具。
#### 在 Debian、Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 中安装 pip
```
# apt-get install python-pip
```
**示例输出:**
```
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
Recommended packages:
python-dev-all python-wheel
The following NEW packages will be installed:
python-pip
0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 533 not upgraded.
Need to get 97.2 kB of archives.
After this operation, 477 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Get:1 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ trusty-updates/universe python-pip all 1.5.4-1ubuntu3 [97.2 kB]
Fetched 97.2 kB in 1s (73.0 kB/s)
Selecting previously unselected package python-pip.
(Reading database ... 216258 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../python-pip_1.5.4-1ubuntu3_all.deb ...
Unpacking python-pip (1.5.4-1ubuntu3) ...
Processing triggers for man-db (2.6.7.1-1ubuntu1) ...
Setting up python-pip (1.5.4-1ubuntu3) ...
```
#### 在 CentOS、RHEL 和 Fedora 中安装 pip
在 Fedora 类系统中,需要先打开 [epel 仓库](/article-2324-1.html),然后按照如下方法安装 pip 包。
```
# yum install python-pip
# dnf install python-pip [Fedora 22+ 以上]
```
**示例输出:**
```
Installing:
python-pip noarch 7.1.0-1.el7 epel 1.5 M
Transaction Summary
=================================================================================
Install 1 Package
Total download size: 1.5 M
Installed size: 6.6 M
Is this ok [y/d/N]: y
Downloading packages:
python-pip-7.1.0-1.el7.noarch.rpm | 1.5 MB 00:00:01
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : python-pip-7.1.0-1.el7.noarch 1/1
Verifying : python-pip-7.1.0-1.el7.noarch 1/1
Installed:
python-pip.noarch 0:7.1.0-1.el7
Complete!
```
### 第二步:在 Linux 中安装 Powerline
现在可以从 Git 仓库中安装 Powerline 的最新开发版。在此之前系统需要安装好 Git 工具以便可以从仓库拉下代码。
```
# apt-get install git
# yum install git
# dnf install git
```
然后你可以通过 `pip` 命令安装 Powerline。
```
# pip install git+git://github.com/powerline/powerline
```
**示例输出:**
```
Cloning git://github.com/powerline/powerline to /tmp/pip-WAlznH-build
Running setup.py (path:/tmp/pip-WAlznH-build/setup.py) egg_info for package from git+git://github.com/Lokaltog/powerline
warning: no previously-included files matching '*.pyc' found under directory 'powerline/bindings'
warning: no previously-included files matching '*.pyo' found under directory 'powerline/bindings'
Installing collected packages: powerline-status
Found existing installation: powerline-status 2.2
Uninstalling powerline-status:
Successfully uninstalled powerline-status
Running setup.py install for powerline-status
warning: no previously-included files matching '*.pyc' found under directory 'powerline/bindings'
warning: no previously-included files matching '*.pyo' found under directory 'powerline/bindings'
changing mode of build/scripts-2.7/powerline-lint from 644 to 755
changing mode of build/scripts-2.7/powerline-daemon from 644 to 755
changing mode of build/scripts-2.7/powerline-render from 644 to 755
changing mode of build/scripts-2.7/powerline-config from 644 to 755
changing mode of /usr/local/bin/powerline-config to 755
changing mode of /usr/local/bin/powerline-lint to 755
changing mode of /usr/local/bin/powerline-render to 755
changing mode of /usr/local/bin/powerline-daemon to 755
Successfully installed powerline-status
Cleaning up...
```
### 第三步:在 Linux 中安装 Powerline 的字体
Powerline 使用特殊的符号来为开发者显示特殊的箭头效果和符号内容。因此你的系统中必须要有符号字体或者补丁过的字体。
通过下面的 [wget](http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/) 命令下载最新的系统字体及字体配置文件。
```
# wget https://github.com/powerline/powerline/raw/develop/font/PowerlineSymbols.otf
# wget https://github.com/powerline/powerline/raw/develop/font/10-powerline-symbols.conf
```
然后你将下载的字体放到字体目录下 `/usr/share/fonts` 或者 `/usr/local/share/fonts`,或者你可以通过 `xset q` 命令找到一个有效的字体目录。
```
# mv PowerlineSymbols.otf /usr/share/fonts/
```
接下来你需要通过如下命令更新你系统的字体缓存。
```
# fc-cache -vf /usr/share/fonts/
```
其次安装字体配置文件。
```
# mv 10-powerline-symbols.conf /etc/fonts/conf.d/
```
注意:如果相应的符号没有出现,可以尝试关闭终端会话并重启 X window,这样就会生效了。
### 第四步:给 Bash Shell 和 Vim 状态行设置 Powerline
在这一节将介绍 bash shell 和 vim 编辑器中关于 Powerline 的配置。首先通过在 `~/.bashrc` 中添加如下内容以便设置终端为 256 色。
```
export TERM="screen-256color"
```
#### 打开 Bash Shell 中的 Powerline
如果希望在 bash shell 中默认打开 Powerline,可以在 `~/.bashrc` 中添加如下内容。
首先通过如下命令获取 powerline 的安装位置。
```
# pip show powerline-status
Name: powerline-status
Version: 2.2.dev9999-git.aa33599e3fb363ab7f2744ce95b7c6465eef7f08
Location: /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages
Requires:
```
一旦找到 powerline 的具体位置后,根据你系统的情况替换到下列行中的 `/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages` 对应的位置。
```
powerline-daemon -q
POWERLINE_BASH_CONTINUATION=1
POWERLINE_BASH_SELECT=1
. /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/powerline/bindings/bash/powerline.sh
```
然后退出后重新登录,现在 powerline 的状态行应该如下显示了。
[](http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/Bash-Powerline-Statuslines.gif)
现在切换目录并注意显示你当前路径的面包屑导航提示的变化。
如果远程 Linux 服务器上安装了 powerline,你能看到后台挂起的任务,当你用 ssh 登录上去时,会看到该提示增加了主机名。
#### 在 Vim 中打开 Powerline
如果你喜欢使用 vim,正好有一个 vim 的强力插件。可以在 `~/.vimrc` 中添加如下内容打开该插件(LCTT 译注:注意同样需要根据你的系统情况修改路径)。
```
set rtp+=/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/powerline/bindings/vim/
set laststatus=2
set t_Co=256
```
然后你打开 vim 后会看到一个新的状态行:
[](http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/Vim-Powerline-Statuslines.gif)
### 总结
Powerline 可以在某些软件中提供颜色鲜艳、很优美的状态行及提示内容,这对编程环境有利。希望这篇指南对您有帮助,如果您需要帮助或者有任何好的想法,请留言给我。
---
作者简介:
 我是Ravi Saive,TecMint的作者。一个喜欢分享诀窍和想法的电脑极客及Linux专家。我的大部分服务都运行在开源平台Linux中。关注我的Twitter,Facebook和Google+。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/powerline-adds-powerful-statuslines-and-prompts-to-vim-and-bash/>
作者:[Ravi Saive](http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/) 译者:[beyondworld](https://github.com/beyondworld) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,119 | 你值得了解的 10 个有趣的 Linux 命令行小技巧 | http://www.tecmint.com/linux-command-line-tricks-and-tips-worth-knowing/ | 2017-01-15T10:48:00 | [
"技巧",
"命令行"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8119-1.html | 我非常喜欢使用命令,因为它们比 GUI(图形用户界面)应用程序对 Linux 系统提供更多的控制,因此,我一直在寻找一些有趣的方法[让 Linux 的操作变得简单好玩](/article-5816-1.html),主要是基于终端操作。
当我们发现使用 Linux 的新技巧时,尤其是像我这样的命令行极客,我们总会感到非常来劲。

**建议阅读:** [5 有趣的 Linux 命令行技巧 - 第一部分](/article-5485-1.html)
而且我们也会很想与数百万 Linux 用户分享新学到的实践或命令,特别是那些还在使用自己的方式操作这个令人兴奋的操作系统的新手们。
**建议阅读:** [10 个对新手有用的 Linux 命令行技巧 - 第二部分](/article-6314-1.html)
在这篇文章中,我们将回顾一系列[有用的命令行小技巧](/article-6314-1.html),它们可以显著地提高你的 Linux 使用技能。
### 1、 在 Linux 中锁定或隐藏文件或目录
锁定文件或目录最简单的方法是使用 Linux 文件权限。如果你是文件或目录的所有者,你可以阻止其他用户和组访问(删除、读取、写入、执行)它,如下所示:
```
$ chmod 700 tecmint.info
或
$ chmod go-rwx tecmint.info
```
想要了解更多有关 Linux 文件权限的内容,请阅读这篇文章[在 Linux 中管理用户和组,文件权限和属性](/article-7418-1.html)。
为了实现对系统中的其他用户隐藏文件或目录,可以通过在文件或目录开头添加 `.` 的方式重命名:
```
$ mv filename .tecmint.info
```
### 2、 在 Linux 中将 rwx 权限转为八进制格式
默认情况下,当你运行 [ls 命令](/article-5531-1.html)之后,它会使用 `rwx` 格式显示文件权限,为了了解 rwx 格式和八进制格式的等同性,你可以学习如何[在 Linux 中将 rwx 权限转为八进制格式](/article-4067-1.html)。
### 3、 当 `sudo` 命令执行失败时怎么使用 `su` 命令
虽然 [sudo 命令](/article-7418-1.html)被用来以超级用户权限执行命令,但是在某些情况下它也会执行失败,如下所示。
在这里,我想[清空一个大文件的内容](/article-8024-1.html),其文件名为 `uptime.log`,但是即便我是使用 sudo 命令也执行失败了。
```
$ cat /dev/null >/var/log/uptime.log
$ sudo cat /dev/null >/var/log/uptime.log
```

*在 Linux 中清空大文件的内容*
遇到这种情况,你需要使用 `su` 命令切换到 `root` 用户,然后像下面这样去执行清空操作:
```
$ su
$ sudo cat /dev/null >/var/log/uptime.log
$ cat /var/log/uptime.log
```

*切换到超级用户*
尝试理解 [su 和 sudo 之间的区别](http://www.tecmint.com/su-vs-sudo-and-how-to-configure-sudo-in-linux/),另外,通过阅读它们的手册页以了解更多的使用指南:
```
$ man sudo
$ man su
```
### 4、 在 Linux 中结束一个进程
有些时候,当你想[使用 kill、killall、pkill 命令结束一个进程](/article-5557-1.html)时,它们有可能无法生效,你可能会看到该进程仍然还在系统上运行。
如果要强制结束一个进程,可以发送 `-KILL` 信号给该进程。
首先[获取指定进程 ID](/article-5051-1.html),然后像下面这样结束该进程:
```
$ pidof vlc
$ sudo kill -KILL 10279
```

*在 Linux 中查找和结束进程*
查看 [kill 命令](/article-2116-1.html)以获取更多的使用选项和信息。
### 5、 在 Linux 中永久删除文件
一般情况下,我们通过使用 `rm` 命令将文件从 Linux 系统中删除。然而,这些文件并没有被真正的删除,它们仍被存储在那里并隐藏在你的硬盘中,其他用户仍然可以[在 Linux 中恢复删除的文件](/article-7974-1.html)并查看。
为了防止这种情况发生,我们可以使用 `shred` 命令来覆写文件内容,并在覆盖完成后选择删除文件。
```
$ shred -zvu tecmint.pdf
```
上述命令中所使用的选项说明:
1. `-z` – 最后一次使用 0 进行覆盖以隐藏覆写动作。
2. `-u` – 覆写后截断并移除文件。
3. `-v` – 显示详细过程。

*在 Linux 中永久删除文件*
阅读 `shred` 手册以获取更多的使用信息。
```
$ man shred
```
### 6、 在 Linux 中重命名多个文件
你可以通过使用 `rename` 命令随时[在 Linux 中重命名多个文件](/article-4905-1.html)。
`rename` 命令会根据第一个参数中的规则重命名指定文件。
以下命令会将所有 `.pdf` 文件重命名为 `.doc` 文件,使用的规则为 `'s/\.pdf$/\.doc/'`:
```
$ rename -v 's/\.pdf$/\.doc/' *.pdf
```

*在 Linux 中重命名多个文件*
在接下来的例子中,我们将通过重命名所有匹配 `"*.bak"` 的文件来移除其拓展名,使用的规则是 `'s/\e.bak$//'`:
```
$ rename -v 's/\e.bak$//' *.bak
```
### 7、 在 Linux 中检查单词拼写
`look` 命令用于显示文件中以指定字符串为前缀的任意行,同时它也可以帮你检查命令行中给定单词的拼写。尽管它并不是那么有效和可靠,但它仍然算得上是其他强大的拼写检查工具的有用替代品。
```
$ look linu
$ look docum
```

*在 Linux 中检查单词拼写*
### 8、 按关键字搜索手册页
`man` 命令用于显示命令的手册页,当使用 `-k` 选项时,它会将关键字 `printf`(或者如下命令中的关键字 `adjust`、`apache`、`php` )作为正则表达式,来搜索所有匹配该名称手册页,并显示其简介。
```
$ man -k adjust
$ man -k apache
$ man -k php
```

*按关键字搜索手册页*
### 9、 在 Linux 中实时监测日志
`watch` 命令可以[定期执行另一个 Linux 命令](/article-5765-1.html)并全屏显示该命令的执行结果。当 `watch` 命令与 [tail 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/view-contents-of-file-in-linux/)(用于查看文件结尾的 Linux 命令)配合使用时,可以监测到日志文件的日志记录情况。
在以下示例中,你将实时监测系统认证日志文件。打开两个终端窗口,在第一个窗口中实时监测该日志文件,如下:
```
$ sudo watch tail /var/log/auth.log
```
你也可以使用 [tail 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/view-contents-of-file-in-linux/)(显示文件结尾的 Linux 命令)的 `-f` 选项实时监测文件变化。这样,我们就可以在日志文件中看到日志的生成情况。
```
$ sudo tail -f /var/log/auth.log
```
接着,在第二个终端窗口中运行以下命令,之后,你就可以在第一个终端窗口中观察日志文件内容:
```
$ sudo mkdir -p /etc/test
$ sudo rm -rf /etc/test
```
### 10、 列出所有 Shell 内置命令
shell 内置命令是一个命令或者函数,从内部调用并直接在 shell 里执行,而不是从硬盘加载外部的可执行程序来执行。
列出所有 shell 内置命令及其语法,执行如下命令:
```
$ help
```
作为结束语,[命令行小技巧](http://www.tecmint.com/tag/linux-tricks/)不仅能派得上用场,而且让学习和使用 Linux 变得更加简单有趣,尤其是对新手来讲。
你也可以通过留言给我们分享其他在 Linux 中[有用有趣的命令行小技巧](/article-5485-1.html)。
---
作者简介:

Aaron Kili 是一名 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 的爱好者,未来的 Linux 系统管理员、网站开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的写作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并且乐于分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/linux-command-line-tricks-and-tips-worth-knowing/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[zhb127](https://github.com/zhb127) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,120 | 如何在 Shell 脚本中跟踪调试命令的执行 | http://www.tecmint.com/trace-shell-script-execution-in-linux/ | 2017-01-15T17:25:07 | [
"调试",
"脚本"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8120-1.html | 在 [shell 脚本调试系列](/article-8028-1.html) 中,本文将解释第三种 shell 脚本调试模式,即 shell 跟踪,并查看一些示例来演示它如何工作以及如何使用它。

本系列的前面部分清晰地阐明了另外两种 shell 脚本调试模式:详细模式和语法检查模式,并用易于理解的例子展示了如何在这些模式下启用 shell 脚本调试。
1. [如何在 Linux 中启用 Shell 脚本的调试模式](/article-8028-1.html)
2. [如何在 Shell 脚本中执行语法检查调试模式](/article-8045-1.html)
shell 跟踪简单的来说就是跟踪 shell 脚本中的命令的执行。要打开 shell 跟踪,请使用 `-x` 调试选项。
这会让 shell 在终端上显示所有执行的命令及其参数。
我们将使用下面的 `sys_info.sh` shell 脚本,它会简要地打印出你的系统日期和时间、登录的用户数和系统的运行时间。不过,脚本中包含我们需要查找和更正的语法错误。
```
#!/bin/bash
# script to print brief system info
ROOT_ID="0"
DATE=`date`
NO_USERS=`who | wc -l`
UPTIME=`uptime`
check_root(){
if [ "$UID" -ne "$ROOT_ID" ]; then
echo "You are not allowed to execute this program!"
exit 1;
}
print_sys_info(){
echo "System Time : $DATE"
echo "Number of users: $NO_USERS"
echo "System Uptime : $UPTIME
}
check_root
print_sys_info
exit 0
```
保存文件并执行脚本。脚本只能用 root 用户运行,因此如下使用 [sudo 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/su-vs-sudo-and-how-to-configure-sudo-in-linux/)运行:
```
$ chmod +x sys_info.sh
$ sudo bash -x sys_info.sh
```

*shell 跟踪 - 显示脚本中的错误*
从上面的输出我们可以观察到,首先执行命令,然后其输出做为一个变量的值。
例如,先执行 `date`,其输出做为变量 `DATE` 的值。
我们可以执行语法检查来只显示其中的语法错误,如下所示:
```
$ sudo bash -n sys_info.sh
```

*脚本中语法检查*
如果我们审视这个 shell 脚本,我们就会发现 `if` 语句缺少了封闭条件的 `fi` 关键字。因此,让我们加上它,新的脚本应该看起来像这样:
```
#!/bin/bash
#script to print brief system info
ROOT_ID="0"
DATE=`date`
NO_USERS=`who | wc -l`
UPTIME=`uptime`
check_root(){
if [ "$UID" -ne "$ROOT_ID" ]; then
echo "You are not allowed to execute this program!"
exit 1;
fi
}
print_sys_info(){
echo "System Time : $DATE"
echo "Number of users: $NO_USERS"
echo "System Uptime : $UPTIME
}
check_root
print_sys_info
exit 0
```
再次保存文件并以 root 执行,同时做语法检查:
```
$ sudo bash -n sys_info.sh
```

*在 shell 脚本中执行语法检查*
上面的语法检查操作的结果仍然显示在脚本的第 21 行还有一个错误。所以,我们仍然要纠正一些语法。
再一次分析脚本,会发现第 21 行的错误是由于在 `print_sys_info` 函数内最后一个 [echo 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/)中没有闭合双引号 `"`。
我们将在 `echo` 命令中添加闭合双引号并保存文件。修改过的脚本如下:
```
#!/bin/bash
#script to print brief system info
ROOT_ID="0"
DATE=`date`
NO_USERS=`who | wc -l`
UPTIME=`uptime`
check_root(){
if [ "$UID" -ne "$ROOT_ID" ]; then
echo "You are not allowed to execute this program!"
exit 1;
fi
}
print_sys_info(){
echo "System Time : $DATE"
echo "Number of users: $NO_USERS"
echo "System Uptime : $UPTIME"
}
check_root
print_sys_info
exit 0
```
现在再一次检查语法。
```
$ sudo bash -n sys_info.sh
```
上面的命令不会产生任何输出,因为我们的脚本语法上正确。我们也可以再次跟踪脚本执行,它应该工作得很好:
```
$ sudo bash -x sys_info.sh
```

*跟踪 shell 脚本执行*
现在运行脚本。
```
$ sudo ./sys_info.sh
```

*用 shell 脚本显示日期、时间和运行时间*
### shell 跟踪执行的重要性
shell 脚本跟踪可以帮助我们识别语法错误,更重要的是识别逻辑错误。例如,在 `sys_info.sh` shell 脚本中的 `check_root` 函数,它用于确定用户是否为 root,因为脚本只允许由超级用户执行。
```
check_root(){
if [ "$UID" -ne "$ROOT_ID" ]; then
echo "You are not allowed to execute this program!"
exit 1;
fi
}
```
这里的魔法是由 `if` 语句表达式 `["$ UID" -ne "$ ROOT_ID"]` 控制的,一旦我们不使用合适的数字运算符(示例中为 `-ne`,这意味着不相等),我们最终可能会出一个逻辑错误。
假设我们使用 `-eq` (意思是等于),这将允许任何系统用户以及 root 用户运行脚本,因此是一个逻辑错误。
```
check_root(){
if [ "$UID" -eq "$ROOT_ID" ]; then
echo "You are not allowed to execute this program!"
exit 1;
fi
}
```
注意:我们在本系列开头介绍过,`set` 这个 shell 内置命令可以在 shell 脚本的特定部分激活调试。
因此,下面的行将帮助我们通过跟踪脚本的执行在其中找到这个逻辑错误:
具有逻辑错误的脚本:
```
#!/bin/bash
#script to print brief system info
ROOT_ID="0"
DATE=`date`
NO_USERS=`who | wc -l`
UPTIME=`uptime`
check_root(){
if [ "$UID" -eq "$ROOT_ID" ]; then
echo "You are not allowed to execute this program!"
exit 1;
fi
}
print_sys_info(){
echo "System Time : $DATE"
echo "Number of users: $NO_USERS"
echo "System Uptime : $UPTIME"
}
#turning on and off debugging of check_root function
set -x ; check_root; set +x ;
print_sys_info
exit 0
```
保存文件并调用脚本,在输出中,我们可以看到一个普通系统用户可以在未 sudo 的情况下运行脚本。 这是因为 `USER_ID` 的值为 100,不等于为 0 的 root 的 `ROOT_ID` 。
```
$ ./sys_info.sh
```

**未 sudo 的情况下运行 shell 脚本**
那么,现在我们已经完成了 [shell 脚本调试系列](/article-8028-1.html),可以在下面的反馈栏里给我们关于本篇或者本系列提出问题或反馈。
---
作者简介:
 Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux SysAdmin、web 开 发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/trace-shell-script-execution-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,122 | 在 Linux 系统下使用 PhotoRec & TestDisk 工具来恢复文件 | http://www.tecmint.com/photorec-recover-deleted-lost-files-in-linux/ | 2017-01-16T21:51:20 | [
"TestDisk",
"删除",
"恢复"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8122-1.html | 当你在系统中有意或无意地使用 `shift + delete` 组合键、删除选项,或是清空回收站的方式来[删除](/article-5473-1.html)一个文件时,该文件的内容并没有从硬盘(或是其它存储设备)上直接销毁。
它仅仅是从系统的目录结构中被移除,然后你在删除文件的目录下就看不到该文件了,但是这个文件仍然存在你磁盘中的某个位置上。
如果你有一个合适的工具和相关的专业知识,你就可以[从电脑中恢复已丢失的文件](/article-7974-1.html)。然而,随着你存储的文件越来越多,删除的文件将会被覆盖,你可能只能恢复最近删除的文件了。

在这篇文章中,我们将阐明如何在 Linux 系统中使用 **TestDisk** 来恢复硬盘上已删除或丢失的文件,它是非常优秀的修复工具,随一款免费的叫做 **PhotoRec** 的工具发布。
**PhoteRec** 工具用于从存储介质比如硬盘,数码相机和 cdrom 设备中恢复丢失的文件。(LCTT 译注:PhotoRec 的意思是 Photo Recovery,不是 Photo Recorder。)
### 在 Linux 系统中安装 TestDisk(PhotoRec)
在系统中执行以下相关的命令来安装 **TestDisk**:
```
------- On Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint -------
$ sudo apt-get install testdisk
------- On CentOS/RHEL/Fedora -------
$ sudo yum install testdisk
------- On Fedora 22+ -------
$ sudo dnf install testdisk
------- On Arch Linux -------
$ pacman -S testdisk
------- On Gentoo -------
$ emerge testdisk
```
如果你的 Linux 系统仓库中没有这个安装包,可以从 [这里](http://www.cgsecurity.org/wiki/TestDisk_Download) 下载然后在 Live CD 中运行即可。
这个安装包也可以在应急修复 CD 工具中找到,比如 Gparted LiveCD 、 Parted Magic 、 Ubuntu Boot CD 、 Ubuntu-Rescue-Remix 及其它工具等。
安装完成之后,使用 root 账号权限打开文本窗口,启动 **PhotoRec**,并指定已删除文件的分区:
```
$ sudo photorec /dev/sda3
```
你将会看到下面的交互界面:

*Linux 系统 PhotoRec 数据恢复工具*
使用左右箭头选择菜单选项,按回车键确认。要继续恢复操作,选择 `[Proceed]` 并单击 Enter。
你将看到下面的界面:

*选择分区进行文件恢复*
选择 `[Options]` 来查看可用的恢复选项,如下图所示:

*Linux 系统文件恢复选项*
按 `Q` 返回,在下图界面,你可以指定你想要查询并恢复的文件扩展名。因此,选择 `[File Opt]`,按回车键确认。
按 `s` 来选择或取消选择所有的文件扩展名,如果你已经取消选择了所有的文件扩展名,只需要使用向右箭头选择你想要恢复的文件类型即可(或者按向左箭头取消选择)。
例如,我想恢复所有系统中丢失的 `.mov` 类型的文件:

*指定恢复文件类型*
按 `b` 键保存设置,之后你应该看到如下图所示信息。单击回车键返回(或者按 `Q` 键),再按 `Q` 键返回到主界面。

*保存文件恢复设置*
现在选择 `[Search]` 开始文件恢复。在下图中,选择存储文件分区的文件系统类型,然后按回车键。

*选择文件系统类型来恢复删除的文件*
下一步,如下图所示,选择是仅对空闲空间还是整个分区进行分析。注意选择整个分区将会让操作过程变得更长更慢。选择合适的选项后,按回车键继续。

*选择文件系统进行分析*
选择一个目录用于存储将要恢复的文件,选择完成之后,按 `C` 键继续。选择不同分区的目录,以避免当更多的文件存储在这个分区时覆盖掉已删除的文件。
按向左箭头返回到根分区下。

*选择要保存恢复文件的目录*
下图显示正在被恢复的指定类型的已删除文件。你可以按回车键来停止操作。
**注意**:在恢复的过程中,你的系统会变得很慢,很可能会卡住一段时间,请耐心等待直至恢复完成。

*在 Linux 系统中恢复已删除的文件*
最后, **Photorec** 工具将会显示出已恢复文件的数量及保存的路径。

*Linux 文件恢复情况汇总*
默认情况下,已恢复的文件将会以 root 账号权限保存,因此,你需要以提升权限的方式打开文件管理器来访问这些文件。
使用如下命令(指定你的文件管理器):
```
$ gksudo nemo
或
$ gksudo nautilus
```
想了解更多的信息,访问 PhotoRec 官网: <http://www.cgsecurity.org/wiki/PhotoRec>。
到此为止吧!在这篇文章中,我们阐明了使用 PhotoRec 工具来恢复磁盘中已删除或丢失文件每一个步骤。这是目前为止我使用过的最可靠和有效的恢复工具,如果你知道还有其它相似的工具,请在评论中跟大家分享。
---
作者简介:

Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 系统及 F.O.S.S 爱好者,即将成为一名系统管理员及 Web 开发人员,他现在是 TecMint 网站的内容创建者,他喜欢使用电脑来工作,并且他坚信分享知识是一种美德。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/photorec-recover-deleted-lost-files-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,123 | 3 个在 Linux 中永久并安全删除文件和目录的方法 | http://www.tecmint.com/permanently-and-securely-delete-files-directories-linux/ | 2017-01-18T12:06:43 | [
"删除",
"恢复"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8123-1.html | 在大多数情况下,我们习惯于使用 `Delete` 键、垃圾箱或 `rm` 命令[从我们的计算机中删除文件](/article-7954-1.html),但这不是永久安全地从硬盘中(或任何存储介质)删除文件的方法。
该文件只是对用户隐藏,它驻留在硬盘上的某个地方。它有可能被数据窃贼、执法取证或其它方式来恢复。
假设文件包含密级或机密内容,例如安全系统的用户名和密码,具有必要知识和技能的攻击者可以轻松地[恢复删除文件的副本](/article-8122-1.html)并访问这些用户凭证(你可以猜测到这种情况的后果)。

在本文中,我们将解释一些命令行工具,用于永久并安全地删除 Linux 中的文件。
### 1、 shred – 覆盖文件来隐藏内容
`shred` 会覆盖文件来隐藏它的内容,并且也可以选择删除它。
```
$ shred -zvu -n 5 passwords.list
```
在下面的命令中,选项有:
1. `-z` - 用零覆盖以隐藏碎片
2. `-v` - 显示操作进度
3. `-u` - 在覆盖后截断并删除文件
4. `-n` - 指定覆盖文件内容的次数(默认值为3)

*shred - 覆盖文件来隐藏它的内容*
你可以在 `shred` 的帮助页中找到更多的用法选项和信息:
```
$ man shred
```
### 2、 wipe – 在 Linux 中安全删除文件
`wipe` 命令可以安全地擦除磁盘中的文件,从而不可能[恢复删除的文件或目录内容](/article-7974-1.html)。
首先,你需要安装 `wipe` 工具,运行以下适当的命令:
```
$ sudo apt-get install wipe [Debian 及其衍生版]
$ sudo yum install wipe [基于 RedHat 的系统]
```
下面的命令会销毁 private 目录下的所有文件。
```
$ wipe -rfi private/*
```
当使用下面的标志时:
1. `-r` - 告诉 `wipe` 递归地擦除子目录
2. `-f` - 启用强制删除并禁用确认查询
3. `-i` - 显示擦除进度

*wipe – 在 Linux 中安全擦除文件*
注意:`wipe` 仅可以在磁性存储上可以可靠地工作,因此对固态磁盘(内存)请使用其他方法。
阅读 `wipe` 手册以获取其他使用选项和说明:
```
$ man wipe
```
### 3、 Linux 中的安全删除工具集
secure-delete 是一个安全文件删除工具的集合,它包含用于安全删除文件的 `srm`(secure\_deletion)工具。
首先,你需要使用以下相关命令安装它:
```
$ sudo apt-get install secure-delete [Debian 及其衍生版]
$ sudo yum install secure-delete [基于 RedHat 的系统]
```
安装完成后,你可以使用 `srm` 工具在 Linux 中安全地删除文件和目录。
```
$ srm -vz private/*
```
下面是使用的选项:
1. `-v` – 启用 verbose 模式
2. `-z` – 用0而不是随机数据来擦除最后的写入

*srm – 在 Linux 中安全删除文件*
阅读 srm 手册来获取更多的使用选项和信息:
```
$ man srm
```
### 4、 sfill -安全免费的磁盘 / inode 空间擦除器
`sfill` 是 secure-deletetion 工具包的一部分,是一个安全免费的磁盘和 inode 空间擦除器,它以安全的方法删除可用磁盘空间中的文件。 `sfill` 会[检查指定分区上的可用空间](/article-8024-1.html),并使用来自 `/dev/urandom` 的随机数据填充它。
以下命令将在我的根分区上执行 `sfill`,使用 `-v' 选项启用 verbose 模式:
```
$ sudo sfill -v /home/aaronkilik/tmp/
```
假设你创建了一个单独的分区 `/home` 来存储正常的系统用户主目录,你可以在该分区上指定一个目录,以便在其上应用 `sfill`:
```
$ sudo sfill -v /home/username
```
你可以在 sfill 的手册上看到一些限制,你也可以看到额外的使用标志和命令:
```
$ man sfill
```
注意:secure-deletetion 工具包中的另外两个工具(`sswap` 和 `sdmem`)与本指南的范围不直接相关,但是,为了将来的使用和传播知识的目的,我们会在下面介绍它们。
### 5、 sswap – 安全 swap 擦除器
它是一个安全的分区擦除器,`sswap` 以安全的方式删除 swap 分区上存在的数据。
警告:请记住在使用 `sswap` 之前卸载 swap 分区! 否则你的系统可能会崩溃!
要找到交换分区(并检查分页和交换设备/文件是否已经使用,请使用 `swapon` 命令),接下来,使用 `swapoff` 命令禁用分页和交换设备/文件(使 swap 分区不可用)。
然后在(关闭的) swap 分区上运行 `sswap` 命令:
```
$ cat /proc/swaps
$ swapon
$ sudo swapoff /dev/sda6
$ sudo sswap /dev/sda6 #这个命令要花费一些时间,默认要进行 38 遍擦除
```

*sswap – 安全 swap 擦除器*
阅读 `sswap` 的手册来获取更多的选项和信息:
```
$ man sswap
```
### 6、 sdmem – 安全内存擦除器
`sdmem` 是一个安全的内存擦除器,其设计目的是以安全的方式删除存储器(RAM)中的数据。
它最初命名为 [smem](/article-7681-1.html),但是因为在 Debain 系统上存在另一个包 [smem - 报告每个进程和每个用户的内存消耗](/article-7681-1.html),开发人员决定将它重命名为 `sdmem`。
```
$ sudo sdmem -f -v
```
关于更多的使用信息,阅读 `sdmen` 的手册:
```
$ man sdmem
```
**推荐阅读:** [在 Linux 系统下使用 PhotoRec & TestDisk 工具来恢复文件](/article-8122-1.html)。
就是这样了!在本文中,我们查看了一系列可以永久安全地删除 Linux 中的文件的工具。像往常一样,通过下面的评论栏发表你对本篇文章的想法或建议。
---
作者简介:

Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 系统及 F.O.S.S 爱好者,即将成为一名系统管理员及 Web 开发人员,他现在是 TecMint 网站的内容创建者,他喜欢使用电脑来工作,并且他坚信分享知识是一种美德。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/permanently-and-securely-delete-files-directories-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,124 | 4 个 Linux 下最好的命令行下载管理器/加速器 | http://www.2daygeek.com/best-4-command-line-download-managers-accelerators-for-linux/ | 2017-01-18T13:13:00 | [
"下载",
"wget",
"下载管理器",
"Aria2"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8124-1.html | 我们经常由于不同需求使用下载管理器从互联网下载文件,它给我和其他人提供了很多帮助。我们都想要一个超级快速的下载管理器来完成下载尽可能多的任务,以便我们可以节省时间来进一步地工作。有很多可以加速下载的下载管理器和加速器可用(图形化界面和命令行界面)。

所有的下载工具做着同样的任务,但它们的处理方式和功能是不同的,比如,单线程和多线程、交互和非交互。 在这里,我们将列出 4 个最好的我们日常工作使用的命令行下载加速器。
### #1 Aria2
[Aria2](https://aria2.github.io/) 是一个用于 Linux、Windows 和 Mac OSX 的轻量级、多协议和多源的命令行下载管理器/实用程序。它支持 HTTP/HTTPS、FTP、SFTP、BitTorrent 和 Metalink。aria2 可以通过内置的 JSON-RPC 和 XML-RPC 接口操作。
它支持多线程,可以使用多个源或协议下载文件,确实可以加速并尽可能多的完成下载。
它非常轻量级,不需要太多的内存和 CPU。我们可以使用它作为 BitTorrent 客户端,因为它有所有你想要的 BitTorrent 客户端的功能。
#### Aria2 功能
* 支持 HTTP/HTTPS GET 方式
* 支持 HTTP 代理
* 支持 HTTP BASIC 认证
* 支持 HTTP 代理认证
* 支持 FTP (主动、被动模式)
* 通过 HTTP 代理的 FTP(GET 命令或隧道)
* 分段下载
* 支持 Cookie
* 它可以作为守护进程运行。
* 支持 BitTorrent 协议和 fast 扩展。
* 在含有多个文件的 torrent 中的选择性下载
* 支持 Metalink 版本 3.0 (HTTP/FTP/BitTorrent)。
* 限制下载/上传速度
有关 Aria2 的进一步用法,请参阅以下文章:[如何在 Linux 中安装和使用 Aria2](/article-7982-1.html)。
### #2 Axel
[Axel](https://axel.alioth.debian.org/) 是一个轻量级下载程序,它如其他加速器那样做着同样的事情。它可以为一个文件打开多个连接,每个连接下载单独的文件片段以更快地完成下载。
Axel 支持 HTTP、HTTPS、FTP 和 FTPS 协议。它也可以使用多个镜像站点来下载单个文件。 所以,Axel 可以为下载加速高达 40%(大约,我个人认为)。 它非常轻量级,因为没有依赖,而且使用非常少的 CPU 和内存。
Axel 使用一个单线程将所有数据直接下载到目标文件。
注意:没有可以在单条命令中下载两个文件的选项。
有关 Axel 的更多使用,请参阅以下文章:[如何在 Linux 中安装和使用 Axel](/article-8129-1.html)。
### #3 Wget
[wget](https://www.gnu.org/software/wget/)(以前称为 Geturl)是一个免费的、开源的命令行下载程序,它使用 HTTP、HTTPS 和 FTP 这些最广泛使用的 Internet 协议来获取文件。它是一个非交互式命令行工具,其名字是意思是从万维网中获取文件。
相比其它工具,wget 将下载处理得相当好,即使它不支持多线程以及包括后台工作、递归下载、多个文件下载、恢复下载、非交互式下载和大文件下载在内的功能。
默认情况下,所有的 Linux 发行版都包含 wget,所以我们可以从官方仓库轻松安装,也可以安装到 windows 和 Mac 操作系统。
wget 可在慢速或不稳定的网络连接下保持健壮性,如果由于网络问题下载失败,它将继续重试,直到整个文件下载完成。如果服务器支持重新获取,它将指示服务器从中断的地方继续下载。
#### wget 功能
* 可以使用 REST 和 RANGE 恢复中止的下载
* 可以使用文件名通配符和递归来对目录进行镜像同步
* 基于 NLS 消息文件,提供许多不同语言支持
* 可选将下载的文档中的绝对链接转换为相对链接,以便下载的文档可以在本地链接到彼此
* 可在大多数类 UNIX 操作系统以及 Microsoft Windows 上运行
* 支持 HTTP 代理
* 支持 HTTP cookie
* 支持持久 HTTP 连接
* 无人值守/后台操作
* 使用本地文件时间戳来确定是否需要在镜像时重新下载文档
有关 wget 的进一步用法,请参阅以下文章:[如何在 Linux 中安装和使用 wget](/article-4129-1.html)。
### #4 Curl
[curl](https://curl.haxx.se/) 类似于 wget,但是不支持多线程,但令人惊讶的是,与 wget 相比,它的下载速度更快。
curl 是一个向服务器上传或下载的数据传输工具,支持的协议有 DICT、FILE、FTP、FTPS、GOPHER、HTTP、HTTPS、IMAP、IMAPS、LDAP、LDAPS、POP3、POP3S、RTMP、RTSP、SCP、SFTP、SMTP、SMTPS、TELNET 和 TFT 等。
该命令无需用户交互即可工作。此外,curl 支持代理、用户身份验证、FTP 上传、HTTP POST、SSL 连接、Cookie、恢复文件传输、Metalink 等。curl 由 libcurl 为所有相关传输功能提供支持。
如果指定的 URL 没有 `protocol://` 前缀,curl 将尝试猜测你可能需要什么协议。例如,以 “ftp.” 开头的主机名 curl 将假定你要使用 FTP。如果没有找到特定的协议,那么默认为 HTTP。
参考下面的文章来进一步使用 curl:[如何在 Linux 中安装和使用 curl](http://www.2daygeek.com/curl-command-line-download-manager/)。
---
via: <http://www.2daygeek.com/best-4-command-line-download-managers-accelerators-for-linux/>
作者:[Magesh Maruthamuthu](http://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,125 | Linux I/O 重定向基础 | http://www.tecmint.com/linux-io-input-output-redirection-operators/ | 2017-01-19T07:42:00 | [
"重定向",
"I/O"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8125-1.html | Linux 管理的一个最重要并且有趣的话题是 I/O 重定向。此功能在命令行中使你能够将命令的输入输出取自或送到文件中,或者可以使用管道将多个命令连接在一起以形成所谓的“**命令管道**”。

我们运行的所有命令基本上产生两种输出:
* 命令结果 - 程序产生的数据,以及
* 程序状态和错误消息,用来通知用户程序的执行细节。
在 Linux 和其他类 Unix 系统中,有三个默认文件(名称如下),这些文件也由 shell 使用文件描述符号标识:
* stdin 或 0 - 它连接键盘,大多数程序从此文件读取输入。
* stdout 或 1 - 它连接屏幕,并且所有程序将其结果发送到此文件
* stderr 或 2 - 程序将状态/错误消息发送到此文件,它也连接到屏幕上。
因此,I/O 重定向允许你更改命令的输入源以及将输出和错误消息发送到其他地方。这可以通过 `<` 和 `>` 重定向操作符来实现。
### 如何在 Linux 中重定向标准输出到文件中
如下面的示例所示,你可以重定向标准输出,这里,我们要存储 [top 命令](/article-2290-1.html)的输出以供以后检查:
```
$ top -bn 5 >top.log
```
其中标志的含义:
* `-b` - 让 `top` 以批处理模式运行,以便你可以将其输出重定向到一个文件或另一个命令。
* `-n` - 指定命令终止前的迭代次数。
你可以使用 [cat 命令](/article-2137-1.html)来查看 `top.log` 文件的内容:
```
$ cat top.log
```
要将命令输出**附加**在文件后面,请使用 `>>` 操作符。
例如,要将 [top 命令](/article-2352-1.html)的输出追加在上面的 `top.log` 文件中,特别是在脚本(或命令行)中,请输入下面的那行:
```
$ top -bn 5 >>top.log
```
**注意**: 也可以使用文件描述符数字,上面的重定向命令等同于:
```
$ top -bn 5 1>top.log
```
### 如何在 Linux 中重定向标准错误到文件中
要重定向命令的标准错误,你需要明确指定文件描述符 `2`,以便让 shell 了解你正在尝试做什么。
例如,下面的 [ls 命令](/article-2535-1.html)将在没有 root 权限的普通系统用户执行时产生错误:
```
$ ls -l /root/
```
你可以重定向标准错误到文件中:
```
$ ls -l /root/ 2>ls-error.log
$ cat ls-error.log
```

*重定向标准错误到文件中*
为了将标准错误附加在文件后,使用下面的命令:
```
$ ls -l /root/ 2>>ls-error.log
```
### 如何重定向标准输出及标准错误到一个文件中
还可以将命令的所有输出(包括标准输出和标准错误)捕获到单个文件中。这可以用两种可能的方式,通过指定文件描述符来完成:
1、 第一种是相对较旧的方法,其工作方式如下:
```
$ ls -l /root/ >ls-error.log 2>&1
```
上面的命令意思是 shell 首先将 [ls 命令](/article-2535-1.html)的输出发送到文件 `ls-error.log`(使用 `>ls-error.log`),然后将所有写到文件描述符 `2`(标准错误)的错误消息重定向到文件 `ls-error.log`(使用`2>&1`)中。(LCTT 译注:此处原文有误,径改。)这表示标准错误也被发送到与标准输出相同的文件中。
2、 第二种并且更直接的方法是:
```
$ ls -l /root/ &>ls-error.log
```
你也可以这样将标准输出和标准错误附加到单个文件后:
```
$ ls -l /root/ &>>ls-error.log
```
### 如何将标准输入重定向到文件中
大多数(如果不是全部)命令从标准输入获得其输入,并且标准输入默认连接到键盘。
要从键盘以外的文件重定向标准输入,请使用 `<` 操作符,如下所示:
```
$ cat <domains.list
```

*重定向文件到标准输入中*
### 如何重定向标准输入/输出到文件中
你可以如下在 [sort 命令](/article-5372-1.html)中同时执行标准输入、标准输出的重定向:
```
$ sort <domains.list >sort.output
```
### 如何使用管道进行 I/O 重定向
要将一个命令的输出重定向为另一个命令的输入,你可以使用管道,这是用于构建复杂操作命令的有力方法。
例如,以下命令将[列出最近修改的前五个文件](/article-8093-1.html)。
```
$ ls -lt | head -n 5
```
选项的意思是:
* `-l` - 启用长列表格式
* `-t` - [最新修改的文件](/article-8093-1.html)首先显示
* `-n` - 指定要显示的标题行数
### 构建管道的重要命令
在这里,我们将简要回顾一下构建命令管道的两个重要命令,它们是:
`xargs` 用于从标准输入构建和执行命令行。下面是使用 `xargs` 的管道示例,此命令用于[将文件复制到 Linux 中的多个目录](/article-8041-1.html):
```
$ echo /home/aaronkilik/test/ /home/aaronkilik/tmp | xargs -n 1 cp -v /home/aaronkilik/bin/sys_info.sh
```

*复制文件到多个目录*
选项含义:
* `-n 1` - 让 `xargs` 对每个命令行最多使用一个参数,并发送到 [cp命令](http://www.tecmint.com/progress-monitor-check-progress-of-linux-commands/)
* `cp` - 复制文件
* `-v` - [显示 `cp` 命令的进度](http://www.tecmint.com/monitor-copy-backup-tar-progress-in-linux-using-pv-command/)。
有关更多的使用选项和信息,请阅读 `xargs` 手册页:
```
$ man xargs
```
`tee` 命令从标准输入读取,并写入到标准输出和文件中。我们可以演示 `tee` 如何工作:
```
$ echo "Testing how tee command works" | tee file1
```

*tee 命令示例*
文件或文本过滤器通常与管道一起用于有效地操作 Linux 文件,来以强大的方式来处理信息,例如命令的重组输出(这对于[生成有用的 Linux 报告](http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-and-file-system-statistics-reports/)是必不可少的)、修改文件中的文本和其他的 Linux 系统管理任务。
要了解有关 Linux 过滤器和管道的更多信息,请阅读这篇文章[查找前十个访问 Apache 服务器的 IP 地址](http://www.tecmint.com/find-top-ip-address-accessing-apache-web-server/),这里展示了使用过滤器和管道的一个例子。
在本文中,我们解释了 Linux 中 I/O 重定向的基本原理。请通过下面的反馈栏分享你的想法。
---
作者简介:

Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux SysAdmin、web 开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创建者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/linux-io-input-output-redirection-operators/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,128 | 让 sudo 在你输入错误的密码时“嘲讽”你 | http://www.tecmint.com/sudo-insult-when-enter-wrong-password/ | 2017-01-19T17:07:35 | [
"sudo",
"sudoers",
"密码"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8128-1.html | **sudoers** 是 Linux 中的默认 sudo 安全策略插件,但是经验丰富的系统管理员可以自定义安全策略以及输入输出日志记录的插件。它由 `/etc/sudoers` 这个文件驱动,或者也可在 LDAP 中。
你可以在上面的文件中定义 **sudoers** <ruby> 嘲讽 <rt> insults </rt></ruby> 或其他选项。它在 `defaults` 部分下设置。请阅读我们的上一篇文章[在 Linux 中设置 sudo 时 10 个有用的 sudoers 配置](http://www.tecmint.com/sudoers-configurations-for-setting-sudo-in-linux/)。

在本文中,我们将解释一个 sudoers 配置参数,以允许个人或系统管理员设置 [sudo 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/su-vs-sudo-and-how-to-configure-sudo-in-linux/),当系统用户输入错误密码时“嘲讽”他们。
首先打开文件 `/etc/sudoers`,如下所示:
```
$ sudo visudo
```
进入 `defaults` 部分,并添加下面的行:
```
Defaults insults
```
下面是我系统中 `/etc/sudoers` 默认展示的 `defaults` 部分。

*设置 sudo insults 参数*
从上面的截图中,你可以看到 `defaults` 中还有许多其他默认值定义,例如,每次用户输入错误的密码时发送邮件到 root、设置安全路径、配置自定义 sudo 日志文件等。
保存并关闭文件。
运行 `sudo` 命令并输入错误的密码,然后观察 insults 选项是如何工作的:
```
$ sudo visudo
```

*实践 sudo insult*
**注意**:当配置 insults 参数时,它会禁用 `badpass_message` 参数,该参数在用户输入错误的密码时,会在命令行中输出特定的消息(默认消息为 “**sorry, try again**”)。
要修改该消息,请将 `badpass_message` 参数添加到 `/etc/sudoers` 文件中,如下所示。
```
Defaults badpass_message="Password is wrong, please try again" #try to set a message of your own
```

*设置 sudo 错误密码消息*
保存并关闭文件,然后调用 `sudo` 查看它是如何工作的,你设置的 `badpass_message` 消息会在每次你或任何系统用户输入错误的密码的时候打印出来。
```
$ sudo visudo
```

*sudo 密码错误消息*
就是这样了,在本文中,我们回顾了如何在用户输入错误的密码时将 `sudo` 设置为显示嘲讽。请通过下面的评论栏分享你的想法。
---
作者简介:

Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux SysAdmin、web 开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创建者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/sudo-insult-when-enter-wrong-password/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,129 | 使用 Axel 命令行下载器/加速器加速下载 | http://www.2daygeek.com/axel-command-line-downloader-accelerator-for-linux/ | 2017-01-19T17:40:56 | [
"axel",
"下载"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8129-1.html | [Axel](https://axel.alioth.debian.org/) 是一个轻量级下载程序,它和其他加速器一样,对同一个文件建立多个连接,每个连接下载单独的文件片段以更快地完成下载。

Axel 支持 HTTP、HTTPS、FTP 和 FTPS 协议。它也可以使用多个镜像站点下载单个文件,所以,Axel 可以加速下载高达 40%(大约,我个人认为)。它非常轻量级,因为它没有依赖并且使用非常少的 CPU 和内存。
Axel 一步到位地将所有数据直接下载到目标文件(LCTT 译注:而不是像其它的下载软件那样下载成多个文件块,然后拼接)。
**注意**:不支持在单条命令中下载两个文件。
你还可以尝试其他命令行下载管理器/加速器。
* [aria2 - 超快速下载程序](http://www.2daygeek.com/aria2-command-line-download-utility-tool/)
* [wget - 标准命令行下载程序](http://www.2daygeek.com/wget-command-line-download-utility-tool/)
* [curl - 命令行下载程序](http://www.2daygeek.com/aria2-command-line-download-utility-tool/)
* [Linux 下的最好的 4 个命令行下载管理器/加速器](/article-8124-1.html)
大多数发行版(Debian、Ubuntu、Mint、Fedora、suse、openSUSE、Arch Linux、Manjaro、Mageia 等)都有 axel 包,所以我们可以从发行版官方仓库轻松安装。对于 CentOS/RHEL,我们需要启用 [EPEL Repository](/article-2324-1.html)。
```
[在 Debian/Ubuntu/LinuxMint 上安装 Axel]
$ sudo apt-get install axel
[在 RHEL/CentOS 上安装 Axel]
$ sudo yum install axel
[在 Fedora 上安装 Axel]
$ sudo dnf install axel
[在 openSUSE 上安装 Axel]
$ sudo zypper install axel
[在 Mageia 上安装 Axel]
$ sudo urpmi axel
[在基于 Arch Linux 的发行版安装 Axel]
$ sudo pacman -S axel
```
### 1) 下载单个文件
以下命令将从给定的 URL 下载文件并存储在当前目录中,下载文件时,我们可以看到文件的信息(建立的连接数、下载速度、下载进度、完成下载所花费的时间以及连接完成的时间)。
```
# axel https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Initializing download: https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
File size: 22678208 bytes
Opening output file owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Starting download
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 146.7KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 267.0KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 373.9KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 406.9KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 487.5KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 572.6KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 650.7KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 649.3KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 718.1KB/s]
[ 2%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 769.3KB/s]
[ 2%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 838.7KB/s]
[ 2%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 866.0KB/s]
Connection 0 finished
.
.
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [5721.0KB/s]
Connection 2 finished
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [5733.4KB/s]
Connection 1 finished
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [5745.4KB/s]
[100%] .......... .......... .......... .......... ......
Downloaded 21.6 megabytes in 3 seconds. (5755.94 KB/s)
```
### 2) 用不同的名称保存文件
要使用其他名称来保存文件,启动下载时可以添加 `-o`(小写字母)选项和文件名。这里我们使用文件名 `owncloud.tar.bz2` 来保存文件。
```
# axel -o cloud.tar.bz2 https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Initializing download: https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
File size: 22678208 bytes
Opening output file cloud.tar.bz2
Starting download
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 143.0KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 264.1KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 309.8KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 406.3KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 495.4KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 586.3KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 673.1KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 647.1KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 721.1KB/s]
[ 2%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 781.3KB/s]
Connection 2 finished
.
.
Connection 0 finished
[ 98%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [6221.9KB/s]
[ 98%] .......... .......... .....
Connection 1 finished
,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,..... .......... .......... [6145.6KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [6159.2KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [6172.0KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [5977.9KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [5989.6KB/s]
[100%] .......... .......... .......... .......... ......
Downloaded 21.6 megabytes in 3 seconds. (6001.05 KB/s)
```
### 3) 限制下载速度
默认情况下 axel 以字节/秒为单位设置下载文件的最大速度。当我们的网络连接速度较慢时,可以使用此选项。只需添加 `-s` 选项,后面跟字节值。这里我们要限速 `512 KB/s` 下载一个文件。
```
# axel -s 512000 https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Initializing download: https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
File size: 22678208 bytes
Opening output file owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Starting download
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 141.5KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 266.1KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 308.0KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 405.9KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 496.7KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 526.4KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 507.0KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 505.6KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 504.8KB/s]
[ 2%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 503.9KB/s]
[ 2%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 503.4KB/s]
.
.
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 497.0KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 496.9KB/s]
[100%] .......... ..
Connection 0 finished
,,,,,,,,,, ,,.....
Connection 1 finished
Connection 3 finished
,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,... .......... .......... ......
Downloaded 21.6 megabytes in 44 seconds. (494.54 KB/s)
```
### 4) 限制连接数
axel 默认建立 4 个连接以从不同的镜像获取文件。此外,我们可以通过使用 `-n` 选项添加更多的连接,后跟连接数 `10` 来提高下载速度。保险起见,我们添加了十个连接,但不幸的是,它花了更多时间来下载文件。
```
# axel -n 10 https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Initializing download: https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
File size: 22678208 bytes
Opening output file owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Starting download
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 140.8KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 265.7KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 305.4KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 402.1KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 496.3KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 522.1KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 567.5KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 640.5KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 710.8KB/s]
[ 2%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 780.5KB/s]
.
.
[ 98%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [7544.9KB/s]
[ 98%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [7557.9KB/s]
[ 98%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [7570.4KB/s]
[ 98%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [7495.3KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... ......
Connection 2 finished
,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,.... [7311.6KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [7318.9KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... ..........
Connection 9 finished
,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, [7331.0KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... ..........
Connection 3 finished
,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, .......... [4300.7KB/s]
[100%] .......... .......... .......... .......... ......
Downloaded 21.6 megabytes in 5 seconds. (4109.41 KB/s)
```
### 5) 恢复未完成的下载
axel 默认具有恢复未完成的下载的行为。Axel 在下载文件时定期更新状态文件(扩展名为 `.st`)。由于某些原因,下载中途停止了?不用担心,只要使用相同的 axel 命令,它将会检查 `file` 和 `file.st`,如果找到,它会从停止处恢复下载。
```
# axel https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Initializing download: https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
File size: 22678208 bytes
Opening output file owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Starting download
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 140.8KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 265.7KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 305.4KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 402.1KB/s]
[ 0%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 496.3KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 522.1KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 567.5KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 640.5KB/s]
[ 1%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 710.8KB/s]
[ 2%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 780.5KB/s]
.
.
[ 84%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [7100.7KB/s]
[ 84%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [7104.3KB/s]
[ 84%] .......... .......... .......... .^C
Downloaded 18.3 megabytes in 2 seconds. (7009.79 KB/s)
```
上面的输出清晰地显示了在下载断开时有两个文件 `owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2` 和 `owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2.st`。当重新开始下载时,它会从停止处开始下载。
```
# ls -lh
total 19M
-rw------- 1 root root 22M Dec 27 08:33 owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
-rw------- 1 root root 44 Dec 27 08:33 owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2.st
# axel https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Initializing download: https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
File size: 22678208 bytes
Opening output file owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
State file found: 19180828 bytes downloaded, 3497380 to go.
Starting download
,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, ,,,,,,,,,, ,......... .......... [ 66.5KB/s]
[ 84%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 186.0KB/s]
[ 85%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 241.7KB/s]
[ 85%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 335.6KB/s]
[ 85%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 351.5KB/s]
[ 85%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 427.1KB/s]
[ 85%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 427.4KB/s]
[ 86%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [ 491.5KB/s]
.
.
[ 98%] ...
Connection 0 finished
,,,....... .......... .......... .......... .......... [2106.6KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [2140.5KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [2172.4KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [2203.2KB/s]
[ 99%] .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... [2236.2KB/s]
[100%] .......... .......... .......... .......... ......
Downloaded 3415.4 kilobytes in 1 second. (2264.93 KB/s)
```
### 6) 不显示文件下载进度
如果你不想要看到文件的下载进度,只要在 axel 命令中加入 `-q` 选项。
```
# axel -q https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
```
### 7) 替换进度条
如果你不喜欢默认的进度条,你可以使用 `-a` 选项来替换进度条。
```
# axel -a https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Initializing download: https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
File size: 22678208 bytes
Opening output file owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Starting download
[ 66%] [......0 ...1 ..........2 ...........3] [ 5.8MB/s] [00:01]^C
Downloaded 14.3 megabytes in 2 seconds. (5916.11 KB/s)
```
我们中断了上面的下载,以便在下载文件时能清楚地显示替代进度条状态。一旦文件成功下载后,你可以看到相同的输出,如下所示。
```
# axel -a https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
File size: 22678208 bytes
Opening output file owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Starting download
Connection 2 finished ]
Connection 1 finished ]
Connection 3 finished ]
Connection 0 finished ]
Downloaded 21.6 megabytes in 4 seconds. (5062.32 KB/s)
```
### 8) 了解关于 axel 的更多信息
如果你想要了解更多关于 axel 的选项,只需要进入它的手册。
```
# man axel
或者
# axel --help
```
享受吧……
---
via: <http://www.2daygeek.com/axel-command-line-downloader-accelerator-for-linux/>
作者:[Magesh Maruthamuthu](http://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,130 | LinuxCon 今年夏天将首次在华举办 | https://www.linuxfoundation.org/announcements/linuxcon-containercon-cloudopen-comes-to-china-for-first-time-2017 | 2017-01-19T19:52:00 | [
"Linux基金会",
"LinuxCon"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8130-1.html |
>
> 领袖级的开源会议将于六月份在华亮相。
>
>
>
旧金山,1 月 17 日讯:致力于专业化开源协作的非盈利组织 <ruby> Linux 基金会 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> The Linux Foundation </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>今天宣布,其 [LinuxCon + ContainerCon + CloudOpen](http://events.linuxfoundation.org/events/linuxcon-containercon-cloudopen-china) (LC3)会议将首次来到中国,将于 2017 年 6 月 19 - 20 日,在北京的国家会议中心召开。

LinuxCon + ContainerCon + CloudOpen (LC3)其宗旨是让参会者可以彼此协作、共享和学习到最新、最有趣的开源技术,包括 Linux、容器、云技术、网络、微服务等等。该会议还将向你展示如何引领开源社区的发展运作。
* LinuxCon 汇聚了全世界 Linux 社区中的领袖级维护者、开发者和项目负责人,是为 Linux 生态发展寻求改进、教育和解决方案的会议。
* ContainerCon 是一个学习如何发挥容器技术优势的大会,这种革命性的技术,从自动化、部署和负载扩展,从硬件虚拟化、存储到软件定义网络,容器推动了云技术的发展。
* CloudOpen 召集了顶级的专家来讨论云平台、自动化管理工具、DevOps、虚拟化、软件定义网络、存储和文件系统、大数据工具和平台、开源最佳实践等等方面的主题。
LC3 覆盖了许多开源领域最热门的话题,包括开放网络、区块链、合规性问题和开源的商业化和专业化等等。
参会者一次注册即可参加这三场会议。活动包括了超过 70 场次的教育课程、行业领袖演讲,以及展览与网络、黑客马拉松、社交活动等展厅场所。
“中国的开发者和企业积极拥抱开源,在各种广泛的项目中贡献了大量代码,”Linux 基金会执行董事 Jim Zemlin 说到,“我们听到了要求把更多的开源活动带到中国的呼声,在中国成功举办了 Linux 基金会的其它活动之后,比如 MesosCon Asia 和 Cloud Foundry Summit Asia,我们决定在中国召开我们旗舰级的峰会 LinuxCon、ContainerCon 和 CloudOpen。这些活动将有助于我们传播开源、提升与全世界的开源专家之间的协作和分享。”
演讲申请将于 3 月 18 日开始[接受申请](http://events.linuxfoundation.org/events/linuxcon-containercon-cloudopen-china/program/cfp),参会报名会在未来几周开始。
希望出席的新闻界人士可以联络 Dan Brown ([[email protected]](mailto:[email protected]))。
非常感谢本次会议的战略级赞助商华为和钻石级赞助商 Intel。
| 404 | Not Found | null |
8,133 | 2016 年编程语言发展趋势 | https://opensource.com/article/16/12/yearbook-top-programming-trends-2016 | 2017-01-21T09:49:35 | [
"编程语言"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8133-1.html |
>
> 回顾年度最热门的 AI 项目和容器的编程语言、新出现的编程语言,和更多编程趋势。
>
>
>

技术在不断前进 - 可能不总是向前,但总是在变动。但即使对于那些关注发展趋势及其对程序员的影响的人来说,确切地了解技术的方向也是一个挑战。我们总是在每年秋季才能够清晰地看出当年开源编程趋势,那时我与我的同事,Kelsey Hightower 和 Scott Hanselman,以及我们非常棒的编程委员会,正在筹备来年的 [OSCON](http://conferences.oreilly.com/oscon/oscon-tx)(O'Reilly 开源大会)。我们获得的建议和对特定主题的关注数量是反映开源世界热门趋势的良好指标。以下是我们在 2016 年看到的顶级编程趋势的概述。
### 编程语言驱动 AI
走出 20 世纪 90 年代的人工智能冬季,人工智能随着它所依赖的计算能力的提升再次出现,它影响着我们如何构建软件。机器学习、深度学习、自然语言处理和自动语音识别覆盖了世界各地 - 从 GitHub 的项目和工作岗位,到新公司成立背后的原因,以及清除我们杂乱的台面(Hey, Alexa!)。(LCTT 译注:Alexa 是预装在亚马逊 Echo 内的个人虚拟助手,可以接收及响应语音命令,可被看成是亚马逊版的 Siri 语音助手。用户只需要说一声“Alexa”,就可以创建各种任务,还可以和各种智能家居设备进行交互。) 是的,即使像 OSCON 这样的会议都处处提及 <ruby> “万物皆智能” <rt> all things AI </rt></ruby> 。虽然计算能力的提升已经铺平了道路,所有关于 all things AI 的开源已经引起了行业广泛开放的创新和竞争。谷歌的 [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/)、[OpenAI](https://openai.com/blog/) 和 [Apache Spark](http://spark.apache.org/) 使用强大框架成为行业领导者,但也有较小的参与者,如 [Nervana](https://www.nervanasys.com/) 的 [Neon](https://github.com/NervanaSystems/neon) 和 [Theano](https://github.com/benanne/nervana_theano)。
AI 的兴起已经影响到了软件开发者的前景?没错,现在是了解 Python 的好时机 - 它给数据工程师和科学家带来的敏捷性和流行性使它成为最流行的 AI 编程语言,其次是 R、Java 和 Scala。
### 容器和 Go 的结合就像花生、黄油和果冻
(花生、黄油和果冻 —— LCTT译注:最佳组合)
[Go 1.0 发布](https://blog.golang.org/go-version-1-is-released)于 2012 年 3 月。紧接着 [Docker](https://opensource.com/resources/what-docker) 在一年后发布,[Kubernetes](https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-kubernetes) 在另外一年后发布。总之,Go 并不是如我们所知的那样专为基础设施的未来而设计的,但 Go 似乎是为了填充编程世界的一个主要的空洞而出现。对于一个高度联网的世界、一个必须拥有一流并发性的世界而言,Go 是以 Java 或 C++ 永远不会有的方式专门设计的。如果你在做运维或者类似的事,你应该至少稍微了解下 Go ,因为它正在发展中,它将会被使用多年,并成为许多程序的骨干。
### Swift 超越了 Apple 的生态系统
Swift 是 [Apple 在 2015 年启动该编程语言不久之后就开源的](/article-6689-1.html)。Swift 已经成为 iOS 和 Mac OS X 开发人员的热门话题。这种语言很容易理解,因此很快流行起来,并且它比它要取代的语言 - Objective-C 和 C++ 赢得了一个[更安全的声誉](http://www.infoworld.com/article/2920333/mobile-development/swift-vs-objective-c-10-reasons-the-future-favors-swift.html)。在 [JavaScript 框架](https://opensource.com/article/16/11/15-javascript-frameworks-libraries)和其他新语言的世界中,Swift 是否成功仍有待观察,但如果它能继续获得苹果忠实用户的欢迎,Swift 将有机会成为伟大的网络世界中最有望成功的竞争者和超越者。
### Java 8 vs 使用 JVM 的函数式语言
Java 8 的函数式能力(即引入 Lambdas )的出现使得 JVM 语言(如 Scala 和 Clojure)得到了关注。最近,很大程度上由于 Apache Spark 的增长使得 Scala 有一点小爆发。现在,因为新、老开发人员都在积极关注 Java 8 所带来的东西,至少目前,Scala 和 Clojure 似乎被搁置了。Java 现在能够解决并发和大数据相关的事,而那些专门为满足此方面要求而构建的其他编程语言已经做了多年。在 2017 年,OSCON 几乎没有 Scala 和 Clojure 的提案,不是因为我们这样计划的,而是那些提交提案的发言者似乎没有什么兴趣。
### 新兴语言
和往常一样,世上总是在不停出现新兴语言,目的是比之前的语言做得更好,可以响应从前的语言出现时没有的需求,或者开始只是疯狂思想,最终却改变了我们对编程的看法。今年有五种语言即将进入大时代:Rust、Elixir、Elm、Kotlin 和 Perl 6。
这 5 个热门会给行业带来什么?
* [Rust](https://www.rust-lang.org/en-US/):兼顾速度和一定安全的系统编程语言。
* [Elixir](http://elixir-lang.org/):函数式、动态和容错,适用于那些规模越来越大的应用程序。
* [Elm](http://elm-lang.org/):更多函数式的乐趣,使用 JavaScript,学习成为一种乐趣。
* [Kotlin](https://kotlinlang.org/):这一个是为使用 Java 和 JVM 的人设计的语言 - 静态类型、安全,此外我提到 Java 兼容了吗?
* [Perl 6](https://perl6.org/):它还活着!Perl 6 碰巧是一种新的语言,它胜在富有表现力和功能丰富。
时间会告诉他们是否会如约发布。尝试他们,为他们贡献,成为未来的一部分!
---
作者简介:

Rachel Roumeliotis - O'Reilly Media,Inc. 的战略内容总监,领导了一个编辑团队,其涵盖各种各样的编程主题,从全栈 web 开发到企业中的开源到新兴的编程语言。她是 OSCON(O'Reilly 软件架构会议)和 Fluent 的编程主席。 她从事技术出版工作超过 10 年,出版了许多领域的内容,包括移动编程、UX、计算机安全。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/16/12/yearbook-top-programming-trends-2016>
作者:[Rachel Roumeliotis](https://opensource.com/users/rroumeliotis) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Technology is constantly moving forward—well, maybe not always forward, but always moving. Even for someone who keeps an eye on the trends and their effect on programmers, discerning exactly where things are headed can be a challenge. My clearest glimpse into open source programming trends always comes in the fall when I work with my fellow chairs, Kelsey Hightower and Scott Hanselman, and our fantastic programming committee to sculpt the coming year's [OSCON](http://conferences.oreilly.com/oscon/oscon-tx) (O'Reilly Open Source Convention). The proposals that we get and the number focused on specific topics turn out to be good indicators of hot trends in the open source world. What follows is an overview of the top programming trends we saw in 2016.
## Languages powering AI
Out of the AI winter of the 1990s, artificial intelligence has reemerged with the computing power that it always needed to influence how we are building software. Machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, and auto speech recognition blanket the world—from GitHub projects and job posts, to the reason behind the formation of new companies, and clearing space on our cluttered counter tops (Hey, Alexa!). And yes, even events such as OSCON are teeming with the mention of all things AI. Although the availability of computing power has paved the way, open sourcing of all things AI has thrown the industry wide open to innovation and competition. Google's [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/), [OpenAI](https://openai.com/blog/), and [Apache Spark](http://spark.apache.org/) lead the way with powerful frameworks, but there are smaller players, such as [Nervana](https://www.nervanasys.com/)'s [Neon](https://github.com/NervanaSystems/neon) and [Theano](https://github.com/benanne/nervana_theano).
How has the rise in AI affected the software developer's landscape? Well, now is a good time to know Python—its agility and popularity with data engineers and scientists makes it the go-to AI programming language, followed by R, Java, and Scala.
## Containers and Go go together like peanut butter and jelly
[Go 1.0 was released](https://blog.golang.org/go-version-1-is-released) in March 2012. [Docker](https://opensource.com/resources/what-docker) followed a year later, and [Kubernetes](https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-kubernetes) a year after that. In short, Go wasn't built exclusively for the future of infrastructure as we know it, but that seems to be one major hole Go is filling in the programming world. Go is specifically written in a way that Java or C++ could never have been—for a highly networked world, a world in which first-class concurrency is a necessity. If you are in or near the operations side of things, you should at the very least dip a toe into the world of Go because it is gaining steam, will be used for years to come, and will be in the backbone of many applications.
## Swift transcends the Apple ecosystem
Swift was [open sourced by Apple](https://opensource.com/life/15/12/most-likely-succeed-2016) in 2015, not long after the programming language started. Swift has been a hit with iOS and Mac OS X developers. That the language was easy to grok quickly became apparent, and it earned a [reputation for being safer](http://www.infoworld.com/article/2920333/mobile-development/swift-vs-objective-c-10-reasons-the-future-favors-swift.html) than the languages it aims to replace—Objective-C and C++. How successful Swift is out in the crowded world of [JavaScript frameworks](https://opensource.com/article/16/11/15-javascript-frameworks-libraries) and other new languages remains to be seen, but if it continues gaining popularity with the Apple faithful, there is a chance that Swift will be a viable contender in the great web world and beyond.
## Java 8 vs. the functionality of JVM languages
The advent of Java 8's functional capability—namely the introduction of Lambdas—has put JVM languages like Scala and Clojure on notice. Recently, due in large part to the growth of Apache Spark, Scala was having a bit of a growth spurt. Now both Scala and Clojure are seeming to be set aside, at least for the moment, as long-time and new developers alike take a hard look at what Java 8 brings to the table. Java is now able to address concurrency and big data concerns that other programming languages specifically built to address these requirements have been doing for years. In 2017, OSCON is nearly devoid of both Scala and Clojure, not by design, but by seemingly little interest from potential speakers who submitted proposals.
## Up and coming languages
And as usual, there are always more up and coming languages on the horizon intended to do something better than those that came before them, that can answer needs that weren't around when previous languages were born, or that simply start out as a crazy idea and end up changing how we think about programming. This year five languages are on the verge of making it into the big time: Rust, Elixir, Elm, Kotlin, and Perl 6.
What do the hot five bring to the industry?
[Rust](https://www.rust-lang.org/en-US/): Systems programming at speed and more than a modicum of safety.[Elixir](http://elixir-lang.org/): Functional, dynamic, and fault-tolerant for those larger and larger-scale apps.[Elm](http://elm-lang.org/): More functional fun that plays with JavaScript, leaning increasingly toward being a pleasure to use.[Kotlin](https://kotlinlang.org/): This one is for the Java and JVM folks—statically typed, safe, and did I mention Java compatible?[Perl 6](https://perl6.org/): It lives! Perl 6 happens to be a new language that is expressive and feature-rich for the win.
Time will tell whether they deliver on their promises. Try them out, contribute to them, be a part of the future!
## 1 Comment |
8,134 | Linux 4.9 内核终被“扶正”,落实说好的 LTS 待遇 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/linux-4-9-is-the-next-long-term-supported-kernel-branch-says-greg-kroah-hartman-512019.shtml | 2017-01-21T11:06:00 | [
"Linux",
"内核"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8134-1.html | Linux 内核维护者 Greg Kroah-Hartman 19 日在[他的 Google+ 上](https://plus.google.com/+gregkroahhartman/posts/dBWUjQipE72)确认,Linux 4.9 分支现在是“长期”的了,也就是我们说的 LTS (长期支持)。

去年 12 月 11 日时, Linus Torvalds [正式宣布 Linux 4.9 内核发布](/article-8031-1.html),而 Linux 4.9 内核的是否成为 LTS 的故事则发生在这之前。
其时,2016 年 8 月 12 日,著名的 Linux 内核维护者 Greg Kroah-Hartman 在他的 Google+ 上说,“4.9 == next LTS kernel.”,然而很快,在媒体开始纷纷报道 Linux 4.9 内核就是下一个长期支持内核时,Kroah-Hartman 反悔了,在一个月之后, 9 月 6 日,他说他要保留把 Linux 4.9 内核标为长期支持的权力。
“我保留不选择 4.9 支持两年的权力,如果你感觉不舒服,那是人们滥用了这个通知。如果这样做的话,我可能会返回 4.8 系列,或者等待 4.10 发布。到了那个时候,我会发布在 kernel.org 上,让大家知道的。”他在自己的博客的[后继文章](http://kroah.com/log/blog/2016/09/06/4-dot-9-equals-equals-next-lts-kernel/)上说到。
### Linux 4.9 内核将支持两年,直到 2019 年 1 月
时间转到今天,在 Linux 4.9 内核都已经发布了 4 个小版本之后,Greg Kroah-Hartman 终于宣布他准备将 Linux 4.9 标为“长期”:
>
> 是的,4.9 就是下一个长期内核。我已经说过了,但是不知道怎么回事,如果不在 kernel.org 上,就没人信我。
>
>
>
当然,这对于 GNU/Linux 用户来说是个大新闻,因为 Linux 4.9 内核增加了几个令人兴奋的新特性,特别是初步支持了从老式 GNC 1.0 / Southern Islands 系列到开源 AMDGPU 图形驱动的 AMD Radeon GPU,这其中包括了 AMD Radeon HD 7xxx 和 8xxx 系列。
据 Greg Kroah-Hartman,Linux 4.9 内核的支持期将到 2019 年 1 月,也就是从此时算起的两年。因此,建议各个 Linux 发行版都采用这个分支,特别是采用了这个月结束支持的 Linux 4.8 内核的发行版。
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,135 | 50 种系统免遭黑客侵袭的方法 [2017 年版] | https://opensource.com/article/17/1/yearbook-50-ways-avoid-getting-hacked | 2017-01-21T20:33:00 | [
"安全"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8135-1.html |
>
> Paul Simon 概括了“与爱人分手的 50 法”,而这里,我们提供了提高系统安全性的 50 种方法。
>
>
>

当我还是小孩子,耳畔萦绕着 Paul Simon 的流行歌“[与爱人分手的 50 法](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0H5chfbcWtY)”。当我渐渐地长大,突然受歌的启发,收集了 50 种方法,免得你——门内汉和门外汉——遭受黑客侵袭啊:
### “你刚刚从后头溜出去了,杰克”
1、 备份你的数据。如果你不幸被勒索软件光顾,那么你就不用支付赎金,因为你做了备份。
2、 当你需要在公共场所为你的手机充电,那就使用 [sysncstop](http://syncstop.com/)吧,或者你也可以用你的备份电池。(LCTT 译注:sysncstop 是一种可以在公共场所安全充电的 USB 设备。在公共场所充电的风险,你知道的。)
3、 利用好你的审计系统,里头有好多很酷的工具可以帮助你监控系统。如果你确实遭到了入侵,那么审计系统也许就可以告诉你发生了什么,以及攻击者做了些什么。
4、 说到日志,把日志定向到集中式服务器上总是一个不错的想法,因为如果某个黑客侵入你的系统里,他首先要攻击的就是日志系统以便隐藏他的踪迹。构建一个好的入侵检测系统来监控日志,这对于防范黑客也很有帮助。
### “做份新的计划吧,斯坦”
5、 以强制模式运行 SELinux(见 [StopDisablingSelinux.com](http://stopdisablingselinux.com/))。不要觉得我现在还在喋喋不休地说这个可笑。SELinux 可以防止 0day 漏洞的影响。当[破壳](http://danwalsh.livejournal.com/71122.html)漏洞出现的时候,SELinux 曾是唯一的防护手段。
6、 如果可能,在 [SELinux 沙盒](http://danwalsh.livejournal.com/31146.html)中运行应用程序吧——在容器火遍全球前,它就已经是容器了。同时,请关注 [Flatpack](http://flatpak.org/) 开发,这个工具很快会开发沙盒功能。
7、 不要安装或者使用 Flash。Firefox 不再支持它了,同时也希望大多数 web 服务器正在远离它。
8、 使用[受约束的 SELinux 用户](http://danwalsh.livejournal.com/37404.html)来控制用户在你的系统中所能做的事。如果你正运行着一台共享登录的系统,设置用户为 `guest_t`。
### “你不必害羞,罗伊”
9、 利用 [systemd 工具的能力](http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/security.html)来帮助你提升系统安全。大多数系统攻击是通过那些监听着网络的服务来实现的,而 Systemd 提供了一些很棒的方法来锁定服务。例如,使用 [PrivateTmp=yes](http://danwalsh.livejournal.com/51459.html) 。Privatemp 利用挂载命名空间来为服务器的 `/tmp` 设置一个私有的 **tmpfs** 挂载,这可以阻止被入侵的服务访问到主机 `/tmp` 中的内容,以及针对系统中基于监听 `/tmp` 的服务的潜在攻击。
10、 `InaccessibleDirectories=/home` 是一个 systemd 单元的选项,它使用挂载命名空间的方式使从服务的角度看不到 `/home` 目录(或者其它任何目录),这会使得被入侵的服务攻击到数据更为困难。
11、 `ReadOnlyDirectories=/var` 是另外一个 systemd 单元的选项,它使用挂载命名空间的方式来将目录内容变成只读模式。基本上你总是可以让 `/usr` 运行在**只读模式**。这可以阻止一个被入侵的应用程序重写二进制文件,因为那可以在下次服务重启时,该服务依旧是被入侵的。
12、 降低服务权限(`CapabilityBoundingSet=CAP_CHOWN CAP_KILL`)。在内核中,特权服务被分解成一些列不同的权限。大多数服务不需要很多权限(如果需要一些的话),而 systemd 提供了一个简单的开关来从服务中剥离这些权限。
13、 如果服务不使用网络,那么你可以使用 `PrivateNetwork=yes` 来为该服务关闭网络功能。只需在服务的单元文件中开启该选项,就可以享受它带来的好处,关闭服务所有可用的网络。黑客常常并不是真的想破坏你的机器——他只是想用它作为攻击服务器来攻击其它机器。如果服务连不上网络,那么就不会受到攻击。
14、 控制服务可用的设备。 Systemd 提供了 `DeviceAllow` 配置,它控制了该服务可用的设备。`DeviceAllow=/dev/null rw` 将访问限制为 `/dev/null`,且仅可访问该设备节点,不允许对其它任何设备节点的访问。该功能实现于设备的 cgroup 控制器顶端。
15、 Systemd 系统即将迎来的一个新功能是 [`ProtectSystem Strict`](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=systemd-New-Protect-Tunables),该功能可以开启所有这些命名空间以完全锁定服务运行的环境。
### “刚刚重获自由”
16、 不要使用没有运行着 SELinux([SEAndroid](https://source.android.com/security/selinux/))强制模式的手机。幸运的是,我听说目前超过 90% 的安卓手机都运行着 SEAndroid 的强制模式,这真让我高兴。现在要是我们能让那些果粉们使用 SELinux 就好了。
17、 只从受信源安装软件。不要安装你从因特网找来的危险东西,对于你的手机、计算机系统、虚拟机以及容器等等也一样。
18、 我不会在我的手机上进行网上银行操作——我只在我的 Linux 计算机上做这事儿。如果黑客偷了我的信用卡,也许我就丢了那么 50 美元;而如果他黑进我的银行账户,那我丢的钱就会更多。我想我是个老古板。(“滚出我的地盘。”——那些老古板都会这样说。)
19、 我用我手机做的一件很酷的事情,就是设置让我的信用卡公司每次在我的信用卡消费时给我发送短信。那样的话,如果账号被盗,我会更快地知道。
20、 当你需要安全地通讯,请使用 [Signal 安全信息应用](https://whispersystems.org/)。
### “搭个便车,格斯”
21、 在你的计算机系统上运行 Linux。当我第一次想用计算机联络我的父亲时,在他的计算机中毒前,我很少回家。我回去给他的系统安了个 Linux,而他从那以后就一直运行着它。我相信 Linux 大体上说是一个更加安全的系统,因为它的设计方式。而且我也相信这个桌面被黑的可能性也相对较小,因为用它的人相对较少。有些人或许要持反对意见了,他们会说 Windows 在过去几年中已经有了很大的改进了,但对于我而言,我仍然坚持己见。
22、 只运行那些有[安全响应团队](https://access.redhat.com/blogs/766093/posts/2695561)进行安全监管的发行版。企业软件及其重要。
23、 运行一个企业级内核。在容器中,单点故障往往是内核。如果你想要保证它安全,那么就使用一个企业级内核,即便它不是一个最新的版本,但也包含了最新的安全补丁。记住,最新的内核虽然带来了最新的安全补丁,但是它也带来了大量的新代码,这些代码可能存在漏洞。
### “你不要说太多”
24、 大多数非法入侵都是通过社会工程学实施的——例如,电子邮件链接、web 浏览器攻击,以及电话。对于此,最好的选择是接受相关教育,并且对一切留个心眼儿。没有哪个来自尼日利亚的家伙会给你钱,国税局也不会打电话到你家问你要钱。如果你电子邮件收到了来自你银行的电子邮件,里面包含有到某个网站的链接,那么不要直接去点击那个链接,在 web 浏览器中输入那个地址来打开。
25、 总是把你的系统打上最新的安全补丁。已知有安全漏洞以及过时的系统的数量十分可怕,脚本小子们依赖于你**不**更新系统。
26、 当连接到网络上的服务时,请始终使用 HTTPS。Chrome 和 Firefox 现在有个强制开启 HTTPS 的模式。到 2016 年为止,那些还不支持安全通讯的网站可能就不值得你们访问。
27、 在你的容器中使用 [seccomp](https://lwn.net/Articles/656307/),这会将攻击限制在内核之外,内核是个单点故障。限制什么进程可以具体讨论。
### “就把那钥匙丢下吧,李”
28、 使用 [YubiKey](https://www.yubico.com/) 来存储私钥。
29、 加密你系统上的数据。至少对于笔记本而言,应该把**家目录**以及你的其它数据目录加密。几年前,我正乘坐在伦敦的地铁上,我的笔记本就成了某些人的目标——我下了车,车门关上了,而我发现我的笔记本不见了。此时,地铁已经驶出了站台。幸运的是,我把磁盘加密了。
30、 给你的所有网站用上 [Let's Encrypt](https://letsencrypt.org/) 吧,没有任何理由不再运行 HTTPS 了。
31、 绝不要在不同 web 服务器上使用相同的密码。虽然这个很难不落入陷阱,但是像 [Let's Encrypt](https://letsencrypt.org/) 这样的工具会有很大帮助。如果你使用 ssh 密钥来登录进系统,这会更好。
32、 使用双因素认证(2FA)。密码变得无关紧要,使用 Yubikey 以及诸如此类的工具可以使得双因素认证很方便,我们都有手机。在大脑中记一个密码,并在手机中生成一个密钥,总是比一个密码来得更好。
33、 网站总要我注册个帐号,没有比这更激怒我的事情了——我们就不能做得更好点?对于网站密码,始终都要使用密码生成工具来生成。我是个保守派:我使用 [Password Safe](https://pwsafe.org/) 来生成密码,然后剪切粘贴到 web 浏览器中。我听说,其他人使用 [LastPass](https://www.lastpass.com/),或者其它整合在手机和 web 服务中的工具也用着不错。
34、 配置像 [FreeIPA](https://www.freeipa.org/page/Main_Page) 之类的服务用于身份认证。使用像 [Kerberos](https://web.mit.edu/kerberos/) 之类的工具来认证和授权,会使得跟踪雇员及其对系统的访问更为简便(而且它也有很酷的加密服务)。使用活动目录也很不错,或许我有点偏颇。
35、 如果你经常输入密码,那就使用一个容易记忆的句子,而不是一个单词。我所偏好的用于记忆密码的方式,就是使用有几个单词并且易于输入的词组。
### “让自己自由”
36、 使用 [USBGuard](https://github.com/dkopecek/usbguard) 来保护你的系统免遭流氓 USB 设备破坏。
37、 在过去几年中,我一直工作于容器方面,让我们来说说容器的安全吧。首先,让它们在开启强制模式的 SELinux 的系统中运行。如果你的系统不支持 SELinux,那就换个支持它的版本吧。SELinux 是使用文件系统来保护容器免遭破坏的最佳工具。
38、 如果可能,在容器中跑你的服务吧。我相信,使用 [OCI 镜像格式](https://www.opencontainers.org/) 和 Linux 容器技术是应用的未来。用 [runC](https://runc.io/)、OCID、RKT、Systemd-nspawn 等等来启动这些容器。虽然我常常说“容器并不包容“,但是不要在容器外面运行这些服务更好一些。
39、 在虚拟机中运行容器。虚拟机提供比容器更好的隔离机制,在虚拟机中跑像容器之类的东西,更加灵活有弹性,并且互相隔离。
40、 在不同的虚拟机中,按不同的安全需求跑容器应用。你可以在 DMZ 中的虚拟机上跑 web 服务容器,而在 DMZ 外的虚拟机上跑数据容器。
41、 同时,记得在不同的物理机上跑需要最高安全性的虚拟机,并且容器放在不同虚拟机上(这也叫深度防护)(LCTT 译注:此处原文有误,根据理解修改)。
42、 以[只读模式](http://www.projectatomic.io/blog/2015/12/making-docker-images-write-only-in-production/)跑容器。开发环境中的容器需要能够写入到 `/usr`,但是生产环境中的容器只能写入到 `tmpfs`,并且将卷挂载到容器中。
43、 [降低容器权限](http://rhelblog.redhat.com/2016/10/17/secure-your-containers-with-this-one-weird-trick/)。不管是在容器中,还是在容器外,我们都以比它们所需的更多的“权限”跑它们的进程,你可以通过降低权限来让你的进程更加安全。
44、 [不要以 root 身份在容器中跑进程](https://www.projectatomic.io/blog/2016/01/how-to-run-a-more-secure-non-root-user-container/)。大多数服务都不需要 root 特权,或者它们需要该权限来绑定到低于 1024 的端口,然后切换到非 root 用户。我建议你始终以非 root 身份来跑应用。
45、 给你的容器打上最新的 CVE 补丁。使用像 OpenShift 这样的工具来构建并维护你的容器镜像是个不错的主意,因为它会在新的安全补丁出现时自动重构容器镜像。
46、 我的一个同事说 “Docker 就是用来在你的主机上以 root 身份运行来自因特网的随机代码的。”从一个受信源获取软件,不要抓取你在 docker.io 上随便找到的第一个 Apache 应用。[操作系统有重要关系](https://opensource.com/16/12/yearbook-why-operating-system-matters)。
47、 在一台受限的容器化优化的主机上跑生产环境容器,例如在一台[原子主机](https://access.redhat.com/articles/rhel-atomic-getting-started)上,它开启了所有安全特性,为运行中的容器而优化,带有限制攻击层和原子级更新。有什么不喜欢的吗?
48、 使用像 [OpenScap](https://www.open-scap.org/) 这样的工具来扫描你系统的漏洞。糟糕的是,新的漏洞总是层出不穷,所以你得时刻更新你的扫描器。(也可以看看 [原子扫描](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2016/05/02/introducing-atomic-scan-container-vulnerability-detection/),用于扫描你的容器。)
49、 OpenScap 也具有扫描[安全配置](https://www.open-scap.org/security-policies/scap-security-guide/)的功能,如 STIG(安全技术部署指南)。
50、 为你孩子收到的所有那些圣诞物联网设备设置一个特别的客户网络。我钟爱我的 Amazon Echo,还有自动化灯以及电源开关(“Alexa,打开圣诞灯“),但是所有这些都是由可能存在安全问题的 Linux 操作系统控制。
### “一定还有着另外 50 种免遭黑客侵害的方法”
你会为这个列表添加点什么呢?在下面的评论中告诉我们吧。
*Josh Bressers 对本文作出贡献。*
---
作者简介:

Daniel J Walsh - Daniel Walsh 已经致力于计算机安全领域将近 30 年。Dan 在 2001 年 8 月份加入 Red Hat。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/17/1/yearbook-50-ways-avoid-getting-hacked>
作者:[Daniel J Walsh](https://opensource.com/users/rhatdan) 译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | When I was young, Paul Simon released his hit song, [50 Ways to Leave Your Lover](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0H5chfbcWtY). Inspired by this song, I've collected 50 ways sysadmins and laypeople can avoid getting hacked:
### "You just slip out the back, Jack"
1. Backup your data. If you get hit with ransomware, you don't have to pay if you have backups.
2. Use a [syncstop](http://syncstop.com/) when you have to charge your phone in a public place, or bring your own battery backup.
3. Take advantage of the auditing subsystems. There are lots of cool tools to help monitor your system. If you do have a break in, the audit system might well be able to tell you what happened and what the attacker did.
4. Speaking of logs, offloading the logs to a centralized server is always a good idea because if a hacker breaks into your system, the first thing he is going to attack is the logging system to cover his tracks. Having a good intrusion system watching the logs also helps.
### "Make a new plan, Stan"
5. Run SELinux in enforcing mode (see [stopdisablingselinux.com](http://stopdisablingselinux.com/)). Didn't think it would take me this long to get to that one? SELinux prevents escalations of zero day vulnerabilities. When [Shell Shock](http://danwalsh.livejournal.com/71122.html) came out, SELinux was the only defense.
6. Run applications in the [SELinux Sandbox](http://danwalsh.livejournal.com/31146.html) whenever possible—it was a container before containers were cool. Also follow the development of [Flatpack](http://flatpak.org/), which soon should be developing sandboxing capabilities.
7. Don't install or use Flash. Firefox no longer supports it, and hopefully most web servers are moving away from it.
8. Use [confined SELinux users](http://danwalsh.livejournal.com/37404.html) to control what users do in your systems. If you are running a shared login system, set up users as **guest_t**.
### "You don't need to be coy, Roy"
9. Take [advantage of systemd tools](http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/security.html) to help secure your services. Most system attacks are going to come through a service listening on the network. Systemd provides great ways to lock down the service. For example, use ** PrivateTmp=yes**. PrivateTmp takes advantage of the mount namespace to set up a private
**tmpfs**mount for the server's
**/tmp**. This prevents a hacked service from getting access to content in the host's
**/tmp**and potentially attacking the rest of the system based on services listening on
**/tmp**.
10. **InaccessibleDirectories=/home** is a systemd unit flag that uses the mount namespace to eliminate the **/home** (or any other directory) from the services view, which makes it more difficult for a hacked service ability to attack the content.
11. **ReadOnlyDirectories=/var** is another systemd unit flag that uses the mount namespace to turn the directories contents into read-only mode. You probably should always run with **/usr** in **ReadOnlyMode**. This would prevent a hacked application from rewriting the binary, so the next time it started the service, you would already be hacked.
12. Drop capabilities from a service (**CapabilityBoundingSet=CAP_CHOWN CAP_KILL**). In the kernel, priviliged processes are broken down into a series of distinct capabilities. Most services do not need many (if any), and systemd provides a simple switch to drop them from a service.
13. If your service is not going to use the network, then you can turn it off for the service using **PrivateNetwork=yes**. Just turning this on in a service unit file takes advantage of the network namespace and turns off all networks available to the service. Oftentimes a hacker does not actually want to break into your machine—he just wants to use it as an attack server to attack other machines. If the service can't see the network, it cannot attack it.
14. Control the devices available to your service. Systemd provides the **DeviceAllow** directive, which controls the devices available to the service. **DeviceAllow=/dev/null rw** will limit access to **/dev/null** and only this device node, disallowing access to any other device nodes. The feature is implemented on top of the device's cgroup controller.
15. Coming soon to a systemd system near you is a new feature, ** ProtectSystem Strict**, which can turn on all of these namespaces to fully lock down the environment in which a service runs.
### "Just get yourself free"
16. Don't use a cell phone without SELinux ([SEAndroid](https://source.android.com/security/selinux/)) in enforcing mode. Luckily, I heard that more than 90% of all Android phones now run with SEAndroid on in enforcing mode. That makes me happy. Now if we could only get those Apple guys to use SELinux.
17. Only install software from trusted sources. Don't install dodgy things you find on the Internet. This goes for your cell phone, computer system, virtual machines, containers, and so on.
18. I don't do online banking on my phone—only on my Linux computer. If a hacker steals my credit card, I lose 50 bucks; if he gets into my bank account, I lose a lot more. I guess I am old. (Get off my lawn.)
19. One cool thing I did do with my phone is set up my credit card companies to send me a text every time my credit card has been charged. That way if the number gets stolen, I will know a lot quicker.
20. When you need to communicate securely, use the [Signal secure messaging app](https://whispersystems.org/).
### "Hop on the bus gus"
21. Run Linux on your systems. When I first hooked my father up with a computer system, I barely got home before his system was infested with viruses. I returned and installed Linux on his system, and he has been running it ever since. I believe Linux generally is a more secure system because of the way it was designed, but I also believe the desktop is less likey to be hacked because of the smaller user base. Some would argue that Windows has improved greatly over the years, but for me, I am still sticking with what I know.
22. Only run distributions with a [Security Response Team](https://access.redhat.com/blogs/766093/posts/2695561) watching over the security of the distribution. Enterprise Software is important.
23. Run an enterprise-level kernel. In containers, the single point of failure is the kernel. If you want to keep it secure, use an enterprise-level kernel, which means it has the latest security fixes, but is not bleeding edge. Remember the latest kernel comes with the latest security fixes, but it also comes with a ton of new code that could have vulnerabilities.
### "You don't need to discuss much"
24. Most hacks are social engineering—for example, email links, web browser attacks, and phone calls. The best option here is to be educated and skeptical. No one from Nigeria is giving you money. The IRS is not calling your house demanding money. If you get a link to a web site in email from your bank, don't use the link. Type the address directly on the web browser.
25. Always keep your systems fully up to date with the latest security fixes. The number of systems that are outdated and have known security vulnerabilities is scarey. Script kiddies rely on you **not** to update your system.
26. Always use HTTPS when connecting to services on the network. Chrome and Firefox now have modes to enforce this. If a web site does not support secure communications by 2016, it is probably not worth your visit.
27. Use [seccomp](https://lwn.net/Articles/656307/) in your containers. This limits the attack surface on the kernel, which is the single point of failure. Limit what the processes can discuss.
### "Just drop off the key, Lee"
28. Use a [YubiKey](https://www.yubico.com/) for storing private keys.
29. Encrypt your data on your systems. At least for laptops, keep your **homedir** and your other data directories encrypted. I was riding the subway in London a few years ago, and had my Laptop "nicked"—the door of the train car closed, and I noticed by laptop was gone and the train was pulling out of the station. Luckily, the disks were encrypted.
30. Use [Let's Encrypt](https://letsencrypt.org/) for all your web sites. There's no reason not to run HTTPS anymore.
31. Never use the same password on different web servers. This one is difficult not to fall into the trap. Tools like Let's Encrypt help a lot. It's even better if you use ssh keys to log into systems.
32. Use two-factor authentication (2FA). Passwords have become just about useless. Using YubiKeys and the like make two-factor easy. We all have cell phones. Having a secret in your head and one generated on the phone is always better than a password.
33. Nothing aggravates me more than websites always asking me to set up an account—can't we do better? Always use a password-generating tool for your website passwords. I am old school: I use [Password Safe](https://pwsafe.org/) and cut and paste into the web browser. I have heard that other people have good luck with [LastPass](https://www.lastpass.com/) and other tools that integrate your phone and web service.
34. Set up a service like [FreeIPA](https://www.freeipa.org/page/Main_Page) to use for identity services. Using tools such as [Kerberos](https://web.mit.edu/kerberos/) for authentication and authorization makes keeping track of employees and their access to systems much easier (and it has cool crypto services). Using Active Directory is ok, but I am a little prejudiced.
35. When you must use a password that you need to type in often, use an easily remembered sentence rather the a word. My preferred way to remember passwords is to use a phrase several words long that is easy to type.
### "And get yourself free"
36. Use [USBGuard](https://github.com/dkopecek/usbguard) to protect your system from rogue USB devices.
37. The past few years, I have been working on containers, so now let's dive into security on containers. First run them on a system with SELinux turned on in enforcing mode. If your system does not support SELinux, switch the distribution to one that does. SELinux is the best tool for protecting against container break out using the file system.
38. Run your service inside of a container whenever possible. I believe this is the future—applications using [OCI Image Format](https://www.opencontainers.org/) and Linux container technology. Launch these containers with Docker, [runC](https://runc.io/), OCID, RKT, Systemd-nspawn, and so on. Although I have often said "containers do not contain," they do contain better than not running them inside of a container.
39. Run your container in a VM. Virtual machines provide better isolation than containers. Running like containers on virtual machines provides you scalability and isolation from each other.
40. Run containerized apps with different security needs on different virtual machines. Run your web service containers on virtual machines in the DMZ, but run the database containers on virtual machines outside of the DMZ.
41. Also remember to run your virtual machines requiring the most security on different physical machines, on different virtual machines inside of containers (a.k.a., defense in depth).
42. Run your containers in [read-only mode.](http://www.projectatomic.io/blog/2015/12/making-docker-images-write-only-in-production/) Containers in development need to be able to write to **/usr**, but a container in production should only be able to write to **tmpfs** and volumes mounted into the container.
43. [Drop capabilities from your containers](http://rhelblog.redhat.com/2016/10/17/secure-your-containers-with-this-one-weird-trick/). We run our processes in and outside of containers with many more "capabiltiies" than they need. You can make your processes more secure by dropping capabilties.
44. [Don't run your processes in containers as root](https://www.projectatomic.io/blog/2016/01/how-to-run-a-more-secure-non-root-user-container/). Most services never need root privileges, or they need it to bind to a port < 1024 and then switch to a non-root user. I would advise always running apps as non-root.
45. Keep your containers updated with the latest CVEs fixes. Using a system like OpenShift for building and maintaining your container images is a good idea, because it automatically rebuilds container images when a new security fix appears.
46. An associate of mine says, "Docker is all about running random code from the Internet as root on your host." Get your software from a trusted source. Don't grab the first Apache application that you find at docker.io. The [operating system matters](https://opensource.com/16/12/yearbook-why-operating-system-matters).
47. Run your containers in production on a limited containerized optimized host, such as an [Atomic Host](https://access.redhat.com/articles/rhel-atomic-getting-started), which comes with all of the security turned on, optimized for running containers, with a limited attack surface and atomic updates. What is not to like there?
48. Use tools like [OpenScap](https://www.open-scap.org/) to scan your systems for vulnerabilities. Sadly, new vulnerabilities are always popping up, so you must keep your scanners up to date. (Take a look at [atomic scan](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2016/05/02/introducing-atomic-scan-container-vulnerability-detection/) for scanning your containers, as well.)
49. OpenScap also has features to scan for [security configuration](https://www.open-scap.org/security-policies/scap-security-guide/), such as STIGs (Security Technical Implementation Guides).
50. Set up a special guest network for all those Christmas IoT devices your kids receive. I love my Amazon Echo and automated lights and power switches ("Alexa, turn on the Christmas Lights"), but each one of these is a Linux operating system that has questionable security.
### "There must be 50 more ways not to get hacked"
What would you add to the list? Let us know in the comments.
*Josh Bressers contributed to this article.*
## 15 Comments |
8,137 | 如何将 Linux 命令的输出赋值给变量 | http://www.tecmint.com/assign-linux-command-output-to-variable/ | 2017-01-22T14:35:00 | [
"命令",
"变量",
"shell"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8137-1.html | 运行一条命令时,它都会产生某种输出:要么是该命令的期望结果,或者是该命令执行细节的状态/错误消息。有些时候,你可能想要将某个命令的输出内容存储在一个变量中,以待在后续操作中取出来使用。
本文将介绍将 shell 命令赋值给变量的不同方法,这对于 shell 脚本编程是特别有用的。

可以使用如下形式的 shell 命令置换特性,将命令的输出存储到变量中:
```
变量名=$(命令)
变量名=$(命令 [命令选项 ...] 参数1 参数2 ...)
或者:
变量名=`命令`
变量名=`命令 [命令选项 ...] 参数1 参数2 ...`
```
以下是使用命令置换特性的示例:
本例,我们将 `who` (显示当前登录系统的用户) 的输出值存储到 `CURRENT_USERS` 变量中:
```
$ CURRENT_USERS=$(who)
```
然后,我们可以使用 [echo 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/) 显示一个句子并使用上述变量,如下:
```
$ echo -e "以下为登录到系统中的用户:\n\n $CURRENT_USERS"
```
上面的命令中:`-e` 标记表示解释所有的转义序列 (如 `\n` 为换行)。为节约时间和内存,通常在 [echo 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/) 中直接使用命令置换特性,如下:
```
$ echo -e "以下为登录到系统中的用户:\n\n $(who)"
```

*在 Linux 中显示当前登录系统的用户*
接下来,为了演示上面提到的第二种形式,我们以把当前工作目录下文件数存储到变量 `FILES` ,然后使用 **echo** 来输出,如下:
```
$ FILES=`sudo find . -type f -print | wc -l`
$ echo "当前目录有 $FILES 个文件。"
```

*显示目中包含文件的数量*
就是这些了。我们展示了将 shell 命令的输出赋值给变量的方法。你可以在下边的评论反馈区留下你的想法。
---

作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是一名 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 忠实拥护者、未来的 Linux 系统管理员、Web 开发者,目前是 TecMint 的原创作者,热衷于计算机并乐于知识分享。

译者简介:
[GHLandy](http://GHLandy.com) —— <ruby> 欲得之,则为之奋斗。 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> If you want it, work for it. </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>
---
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,138 | 给 Linux 新手的最佳发行版 | https://www.linux.com/news/best-linux-distributions-new-users | 2017-01-22T15:41:40 | [
"Linux",
"发行版",
"新手"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8138-1.html | 
Jack Wallen 为来自不同环境的新手们挑选出了专门为他们设计的发行版。
一个很古老的问题,找到适合的 Linux 发行版比简单的指出哪种 Linux 版本受欢迎更重要。为什么这么说?
让我们设置一个情景:你有一位用户,很有可能,他过去大多数时候都是在 Windows 或者 Mac 系统上工作,他们想让你给他们一个选择的替代品。现在,你想要在很短的时间里直截了当的说明 Linux 系统的工作方式并突出它的强大性和灵活性。
但是,请记住,最重要的一个方面是他们必须能够 *get it*,即开箱即用。
这就是为什么我们经常需要花费时间来找出哪种版本是最适合新手的 —— 因为把新手们带入 Linux 系统是传播 Linux 并增加 Linux 用户的最好方式。
对于新手来说最好的版本是什么?这次,我将要花费一定时间来说明对于来自不同环境的用户哪种版本才是最适合的。此外,你也可以查看我在 [2017 最好的发行版](https://www.linux.com/news/learn/sysadmin/best-linux-distributions-2017)中列出的发行版。
### 从 Windows 7 到 Linux:ZorinOS
当 Windows 8 发布以后,有一个理由让如此多的用户依然坚持使用 Windows 7, 那就是熟悉度。用户们已经在相同的桌面环境上工作了十几年,他们不想转移到 Windows 8 这种更以触摸屏为主的平台上。所以,你会去选择哪种版本呢?你首先必须要考虑的是桌面环境。为什么?因为这是你能够立刻吸引上这些 Windows 7 用户的地方。对于这个任务,还有什么版本会比 [ZorinOS](https://zorinos.com/) 更好呢?
ZorinOS 就是专门作为 Windows 和 Mac 系统的替代品而设计的,所以它下了很大的功夫来模仿 Windows 和 Mac 桌面的外观和感觉。事实上,除了 ZorinOS 以外,你很难找到一个别的 Linux 版本,能够完美的从 Windows 7 转移到 Linux 系统上,同时保留 Linux 系统如此强大、灵活的平台。
除了桌面环境(图片 1)以外, 因为 ZorinOS 完全基于 Ubuntu 系统,所以在其“外表”下面, ZorinOS 和 Ubuntu 以同样的方式工作(所以基本不用去担心硬件不能够被检测到)。同时伴有已经就绪的软件,你便有了针对来自 Windows 7 用户的最完美的 Linux 版本。

*图片 1:类 Windows 7 的 ZorinOS 桌面,准备开始服务。*
请注意:然而, ZorinOS 有两个版本: Zorin Ultimate 和 Zorin Core 。 Zorin Core 是免费的,但它不包含几乎所有你能够在 Zorin Ultimate 中找到的软件。如果你想要一个适合于所有来自 Windows 7 用户的开箱即用的版本,那么我强烈推荐购买 [Zorin Ultimate](https://zorinos.com/download/#ultimate)(大约需要花费 20 美元)。当然,如果你不想花钱购买 Ultimate 版本,你也可以从 Core 版本包含的软件包管理工具中安装几乎所有你需要的东西。
### 从 Windows 8 到 Linux : Ubuntu GNOME
让我们来看看 Windows 8, 它带来了一个以触摸屏为中心的环境,改变了用户与电脑互动的方式。老式的启动菜单、面板、系统托盘桌面已经被触摸屏环境界面所取代。如果你正在找一个能给 Linux 新手们带来不同体验的最好环境,同时功能也要是最好的,那么没有比 [Ubuntu GNOME](https://ubuntugnome.org/) 更合适的了。
Ubuntu GNOME 是 Ubuntu 和 GNOME(图 2)这两个世界之间最好的融合。用一个现代、优雅、简洁并且用户友好的桌面代替了 Unity 界面, 因此 Ubuntu GNOME 不会给任何来自 Windows 8 的用户造成太多的麻烦。该版本不仅基于最新的长期支持版的 Ubuntu 发行版(支持期会很长),同时使用了 GNOME 桌面的最新稳定版本 - 这意味着用户将能够享受到难以置信的稳定体验。

*图片 2 :在 Ubuntu GNOME 中可以发现,在优雅而又简洁。*
### 从 Mac 到 Linux : Elementary OS
毫无疑问,这一场的绝对赢家是 [Elementary OS](https://elementary.io/)。尽管 Elementary OS 在外观和感觉上所达到的效果和 OS X 桌面非常相似,但实际还有更多优秀的地方。 Elementary OS 同样是基于 Linux 系统的,只不过是它采取了很多 Mac X 桌面的设计元素。
任何的 Mac 用户使用 Elementary OS 的桌面环境(图片 3)都会感觉就像是“在家一样”(使用 Mac 一样)。伴有如此熟悉的文档,同时包含一个熟悉的应用菜单, Elementary OS 总是位于我的‘最佳发行版列表’的顶部。如果我们正在和 Mac 用户讨论迁移,那么没有比 Elementary OS 更好的 Mac 替代品了。

*图片 3 :Elementary OS 桌面的荣耀。*
有一件事情 Mac 用户们将会非常感激,那就是 Elementary OS 的开发者们很好的保持了桌面的一致性。从 dock, 到面板、菜单、到包括的应用,你找不到任何一个看起来或感觉没有归属感的单一元素。
我将在这儿说一个关于 Elementary OS 的预警。你需要安装一个好的浏览器(因为它自带安装的 Epiphany-a 浏览器没有得到许多常用站点的支持),同时,你需要从官方的 [LibreOffice 网站](http://www.libreoffice.org/download/libreoffice-fresh/)下载安装包来安装 LibreOffice (因为在 Elementary OS 的软件中心找到的安装包已经有些过时了)。
### 从 Android 到 Linux:Ubuntu
这似乎有点像是一个延伸话题,但考虑到 Android 在全球市场中占主导地位,所以你可能遇到一个来自以移动设备为中心的用户,他可能需要一个 Linux 桌面,从而让他一直感觉像是‘在家’一样。对于我来说, [Ubuntu](https://www.ubuntu.com/) 是最显然的赢家。为什么?和其他系统相比, Ubuntu Unity 在桌面上做出了很杰出的工作,它使得桌面感觉像是一个包罗万象的界面。如果你愿意,那么可以包含在线搜索结果(默认情况下禁用),这是在几乎每个移动环境中均可找到的东西。同样, Unity HUD 菜单系统(图片 4)是在任何界面系统中所能找到的最独一无二的菜单系统之一。通过 Unity HUD 菜单系统,用户可以更少的依赖鼠标(就像他们过去在 Android 支持的移动设备上工作一样)。

*图片 4: 使用中的 Unity HUD 。*
当然, Ubuntu 也提供了市场上最稳定的桌面平台,所以用户体验近乎完美。
### 总有一款 Linux 发行版适合你
有一件很重要的事情需要记住,那就是总有一款 Linux 发行版适合你。但是对于那些来自特殊环境的人,我强烈推荐找到一个最喜爱的 Linux 版本,从而能够帮助他们无缝过渡。给自己一个机会尝试一下,看看你是否可以轻松体验到开源和 Linux 的强大。
---
via: <https://www.linux.com/news/best-linux-distributions-new-users>
作者:[JACK WALLEN](https://www.linux.com/users/jlwallen) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,139 | 为你在 Bash 历史中执行过的每一项命令设置时间和日期 | http://www.tecmint.com/display-linux-command-history-with-date-and-time/ | 2017-01-23T07:30:00 | [
"历史",
"history"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8139-1.html | 
在默认情况下,所有通过 Bash 在命令行中执行过的命令都被存储在历史缓存区或者一个叫做 `~/.bash_history` 的文件里。这意味着系统管理员可以看到系统上用户执行过的命令清单,或者用户可以通过像 [history 命令](/article-1143-1.html)这样的选项来看他或她自己的命令历史。
```
$ history
```

*Linux 历史命令*
从上面 [history 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/history-command-examples/)的输出可知,命令被执行的日期和时间并没有显示出来。基本上所有的 Linux 发行版的默认设置都是这样的。
在这篇文章里,我们将解释当在 Bash 中执行 `history` 命令显示每个命令时,如何配置显示时间戳信息。
每个命令相关的日期和时间可以记录到历史文件中,用 `HISTTIMEFORMAT` 环境变量的设置作为命令历史的备注记录。
这里有两种可行的方式来达到目的:一种是暂时的效果,一种是永久的效果。
要临时设置 `HISTTIMEFORMAT` 环境变量,在命令行这样输出它:
```
$ export HISTTIMEFORMAT='%F %T'
```
在上面的输出命令当中,时间戳格式如下:
1、`%F`-展开为完整日期,即 `%Y-%m-%d`(年-月-日)。
2、`%T`-展开为时间,即 `%H:%M:%S`(时:分:秒)。
通读 [date 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/sort-ls-output-by-last-modified-date-and-time/)的 man 手册来获得更多使用说明:
```
$ man date
```
然后如下检查你的命令历史:
```
$ history
```

*显示带有日期和时间的 Linux 命令历史。*
(LCTT 译注:注意:这个功能只能用在当 HISTTIMEFORMAT 这个环境变量被设置之后,之后的那些新执行的 bash 命令才会被打上正确的时间戳。在此之前的所有命令,都将会显示成设置 HISTTIMEFORMAT 变量的时间。)
然而,如果你想永久地配置该变量,用你最喜欢的编辑器打开文件 `~/.bashrc`。
```
$ vi ~/.bashrc
```
然后在下方添加(用注释将其标记为你自己的配置):
```
# 我的配置
export HISTTIMEFORMAT='%F %T'
```
保存文件并退出,然后,运行下面的命令以便改动当即生效:
```
$ source ~/.bashrc
```
就是这些!请通过下方的评论区来与我们分享一些有趣的历史命令的小技巧以及你对这篇文章的想法。
>
> 
>
>
> 作者简介:
> 我是 Ravi Saive,TecMint 的创建者。一个爱在网上分享的技巧和提示的电脑极客和 Linux 专家。我的大多数服务器运行在名为 Linux 的开源平台上。请在 Twitter、 Facebook 和 Google 等上关注我。
>
>
>
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/display-linux-command-history-with-date-and-time/>
作者:[Ravi Saive](http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/) 译者:[Hymantin](https://github.com/Hymantin) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,140 | Linux 上搭建 Minecraft 服务器 | https://www.linuxforum.com/threads/minecraft-server-on-linux.3202/ | 2017-01-23T11:20:00 | [
"游戏",
"Minecraft",
"我的世界"
] | /article-8140-1.html | 
“<ruby> 我的世界 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Minecraft </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”是一个人们可以在各种游戏主机和计算机上玩的主流游戏。 截止至 2016 年 6 月,在各种平台上已经售出了超过十亿六千万份。因其受欢迎,你可能想在家里举办一个“我的世界”派对,那么你就需要安装一个 “我的世界” 服务器,让所有的玩家连接到同一个世界中一起玩。
### 系统要求
要开始的话,你需要一个有相当数量内存的 Linux 操作系统。你要在服务器上容纳的玩家越多,你就需要越多的内存。硬盘空间倒不是需求很大,只要足够去安装 Java 以及“我的世界”服务器 Java 文件就行。Minecraft 服务器需要有一个稳定的网络连接,不管是有线还是无线网络。
让我们看看 “我的世界”服务器最低要求:
* **CPU:**双核或更好。
* **内存:** 2 GB (20-40 用户量),3 GB(30-60 用户量),8 GB(60+ 用户量)。
* **系统:** 不需要图形化用户接口,可以留出更多的空闲资源。
**备注:** 这是“我的世界” 服务端程序的需求,而不是一个完整的操作系统的需求。如果可以给我的世界服务器分配更多的资源,它将运行得更好。
### 安装 Java
如果你用 Linux 操作系统运行它的话,你需要安装最新版本的 Java 环境。
为了验证你的 Java 版本,位于终端输入以下命令:`java -version`。结果应该是:
```
java version "1.8.0_101"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_101-b13)
Java HotSpot(TM) Client VM (build 25.101-b13, mixed mode)
```
如果你当前的 Java 版本不是 1.8 或者更高,则通过在 Ubuntu 系统的终端下执行以下操作来安装 Java 版本 8:
```
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install oracle-java8-installer
```
**注意:**如果 `add-apt-repository` 命令无法找到,运行 `sudo apt-get install software-properties-common` 来安装。 您还可以将第三个命令中更改为 `oracle-java9-installer` 来安装最新的 java 版本。
对于 Redhat 系统(如 CentOS),请使用以下命令:
```
sudo yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk
```
安装后,核实键入版本命令 `java-version` ,并且核实输出。这样你就有了一个适当的 Java 版本,你可以继续进行接下来的安装。
### “我的世界”服务器版本下载
接下来做的事就是去检查用户将运行的“我的世界”的版本。图 1 显示了一个正在运行的 ”我的世界“ ,注意左下角的版本号。

*图 1*
请记住“我的世界”客户端版本号。每个客户端应该是相同的版本才行。
您接下来要做的是下载客户端所需要的“我的世界”的服务器版本。为了下载该版本你需要知道它的位置。得到所需的文件的命令是:
```
sudo wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/Minecraft.Download/versions/[version]/minecraft_server.[version].jar
```
在 图1 看到,版本号是 1.10.2。那么这个命令就该变成:
```
sudo wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/Minecraft.Download/versions/1.10.2/minecraft_server.1.10.2.jar
```
当你下载好文件,会保存到你当前目录下。使用命令 `pwd` 确定当前位置。
一旦你有了该文件,知道它所保存的文件夹就可以继续了。
### 服务器信息
在启动“我的世界”服务器之前,您必须知道当前系统上能被你使用的可用内存大小。 当启动“我的世界”服务器时,你将需要指定起始内存量和当更多玩家加入时最大分配的内存量。 再次提示,重要的是要有足够的内存。 如果可以,使用最小化安装操作系统来留出更多的内存,例如最小化安装的 Ubuntu。
一旦你有了所需的“我的世界”服务器文件,就可以确定分配给“我的世界”的内存数量。 要确定可用内存,打开一个终端并键入以下命令 ,示例输出如图 2 所示:
```
free -h
```

*图 2*
如图 2 所示,在这个低端系统上你可以看到那只有 684 MB 空闲内存。这不是一个可以用于搭建一个 “我的世界” 服务器的系统。在另一个服务器上我有 2.8 GB 内存可供给“我的世界” 使用。
在我们启动服务器之前,我们需要找到服务器的 IP 地址。 为此,请运行命令 `ifconfig`。 如图 3 所示,应该列出了网络连接,显示 `Internet Address` 或 `inet addr`,这里是 `192.168.0.2`。 在我的服务器系统上,它列出的地址是 `192.168.0.14`,这个地址是客户端系统将要使用的地址。

*图 3*
### 启动“我的世界”服务器
下一步才是真正的启动“我的世界”服务器。在我们实际开始前,会涉及到几个选项。当启动“我的世界”服务器时,你需要指定用多少内存来初始化“我是世界”。 您还将指定使用的最大内存量。
如果我的系统有 3.7GB 闲置内存,我知道会有不到 40 位玩家,于是我只需要划出 2GB。当然,我可以增加些以允许用户增长。如果需要的话,我还可以留一点内存给系统运行。我将最小值设置为 2 GB,最大值设置为 3 GB。 由于最大值设置为 3 GB,如果需要的话,还可以至少留给系统 700 MB 内存,但这只有在“我的世界”服务器使用超过最初分配的2 GB 时才会发生。
启动服务器的命令行是:
```
sudo java -Xms# -Xmx# -jar [path]/minecraft_server.[version].jar nogui
```
现在解释一下命令结构:
* -Xms# - 初始启动分配的内存(`-Xms2048m`)
* -Xmx# - 最大分配的内存(`-Xmx3096m`)
* [path] – “我的世界” 服务器文件路径( `/home/tux/MCS/`)
* [version] – 下载的“我的世界” 服务器的版本(`1.10.2`)
* nogui – 用于以基于文本的界面来显示,可以减少内存使用。如果你使用图形化界面,那么移除 `nogui` 选项。
一个使用 2GB 内存以及最大 3GB、位置为 `/home/tux/MCS`、 版本号为 `1.10.2` 的系统的完整命令实例是:
```
sudo java -Xms2048m -Xmx3096m -jar /home/tux/MCS/minecraft_server.1.10.2.jar nogui
```
**注意:** 这里内存容量的大小是兆字节单位。容量要乘以 1024。举个例子,2GB 的内存使 2 与 1024 相乘,容量为 2048。但别忘小写字母 `m` 是特指兆字节。你可以简单地使用特指的 `2g` 和 `3g` 来表示 2GB 和 3GB。
在你首次运行服务器时会发成一些错误。开始之前,它表明需要同意 “最终用户许可协议 EULA”。
要同意 “最终用户许可协议 EULA”,你需要编辑与“我的世界”服务器 JAR 文件同一文件夹下的的 `eula.txt` 文件。
使用一个类似 `nano` 的文件编辑器打开文件 `eula.txt` 文件。确定你进行这步时使用的是 root 权限。将行 `eula = false` 更改为 `eula = true`,并保存文件。
现在,再次输入上述命令以启动服务器。 应该滚过满屏幕信息,然后一个状态行将显示它的创建过程。 当其这个初始世界创建好之后,状态行将显示 100%。 有关系统时间更改的任何错误消息是正常的,因此忽略它们。
此时,你可以打开客户端程序并且看到如上图 1 的界面。点击“Multiplayer”按钮。在下一屏幕,如图 4,选择 “Direct Connect”,这将提示您输入服务器地址,因此键入“我的世界”服务器的 IP 地址。你现在应该已经连接到游戏了。

*图 4*
### 连接的某些麻烦
如果一些客户端无法连接到服务器,那么你需要按下 `CTRL+Z` 退出 Java 程序。打开文件 `server.propertices`, 使用一个 nano 之类的编辑器进行编辑。记住要 root 权限。编辑 `online-mode` 行,它应该设置为 `true` ,修改为 `false` 并保存。重启服务器并打开“我的世界”服务器。使用客户端重新连接到服务器,现在应该一切都好了。
建设快乐!
---
via: <https://www.linuxforum.com/threads/minecraft-server-on-linux.3202/>
作者:[Jarret](https://www.linuxforum.com/members/jarret.268/) 译者:[erlinux](http://www.itxdm.me) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='www.linuxforum.com', port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: /threads/minecraft-server-on-linux.3202/ (Caused by NameResolutionError("<urllib3.connection.HTTPSConnection object at 0x7b83275821a0>: Failed to resolve 'www.linuxforum.com' ([Errno -2] Name or service not known)")) | null |
8,141 | CentOS 与 Ubuntu:哪个更适合做服务器? | https://thishosting.rocks/centos-vs-ubuntu-server/ | 2017-01-23T17:18:00 | [
"服务器",
"Server"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8141-1.html | 
已经决定买一台虚拟服务器,但还不能决定使用哪个 Linux 发行版?我们都经历过这种困扰。对于 Linux 发行版来说,要在这么多的发行版和种种<ruby> 支派 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> flavors </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>中选择一个,那简直能让人崩溃。不过,对于服务器而言,有两个主流的 Linux 发行版,那就是 CentOS 和 Ubuntu。但如何从这两个之中选择,这是摆在管理员、初学者和专业人士面前的主要问题。在对这两个(和更多)发行版有了一定的经验之后,我们决定对这两个发行版用于服务器时做个比较。
**利益相关:本文译自 thishosting.rocks,根据国内情况替换了相应推荐的云服务商的链接,有需求者可点击。**
### 概览
| CentOS | Ubuntu |
| --- | --- |
| 基于 Red Hat Linux Enterprise | 基于 Debian |
| 更新频度较少 | 经常更新 |
| 更稳定和更安全一些,因为不经常更新。 | 更新的软件包可能不稳定,不安全?不会,因为他们在发布到正式版本前进行了大量测试。 |
| 没有足够的教程和用户群较少(LCTT 译注:可能是由于国内外情况不同,在国内,相对 Ubuntu 来说,人们更喜欢用 CentOS 做服务器) | 丰富的文档,活跃的社区和大量的在线教程 |
| 对初学者困难,因为基于 Red Hat 桌面发行版不流行 | 更容易为已经熟悉桌面版 Ubuntu 的初学者使用 |
| 支持 cPanel | 不支持 cPanel |
| .rpm 软件包和 “yum” 软件包管理器 | .deb 软件包和 “apt-get” 软件包管理器 |
| 在[阿里云](http://click.aliyun.com/m/9419/)和 [Ucloud](https://ucloud.cn/site/free.html) 免费试用 CentOS 服务器 | 在[阿里云](http://click.aliyun.com/m/9419/)和 [Ucloud](https://ucloud.cn/site/free.html) 免费试用 Ubuntu 服务器 |
### 哪个更适合新手?
Ubuntu。
一如往常那样,它主要取决于你的需求和以前的经验,但一般来说,Ubuntu 对于初学者来说是更好的选择。主要是因为这两个原因:
* Ubuntu 有一个庞大的社区,随时可以免费提供帮助。我指的是真正的大。数以千计的用户分布在数百个不同的在线论坛和兴趣组内。甚至有现实生活中的大会。你也可以为 CentOS 找到很多教程和帮助,特别是对于简单的 LAMP 栈和流行的应用程序而言。
* Ubuntu 服务器对于以前使用过 Ubuntu 桌面的人来说会容易得多。同样的情况也存在于 CentOS 和 Fedora 之间,但是 Ubuntu 桌面版比任何其他基于 Linux 的家用桌面更受欢迎。
所以,如果你是一个初学者,而且没有任何特殊要求,那就去使用 Ubuntu 服务器。 更好的是,你可以从一个[便宜的托管服务提供商](https://ucloud.cn/site/free.html)那购买服务,这样你就可以在你的服务器上进行实验,还有一个[专业的 24/7 支持团队](https://ucloud.cn/site/free.html)准备好帮助你。
### 哪个更适合商用?
CentOS。
同样,你仍然可以使用 Ubuntu 作为商用网站或公司内部服务器,但 CentOS 有它的优势:
* CentOS(可以说)更稳定以及更安全。由于 CentOS 的更新频率较低,这意味着软件测试的时间更长,并且只有真正稳定的版本才会得到发布。如果你使用 CentOS,你不会因新的有 bug 的应用程序版本而遇到任何稳定性问题,因为你不会得到那个新的有 bug 的版本。
* 大多数控制面板(包括最受欢迎的控制面板 - cPanel)仅支持 CentOS。所以这意味着如果你是一个网站托管公司,或者如果你是一个有很多客户的网站服务代理商,并且需要一个控制面板 - CentOS 是一个更好的选择。
### 尝试一下它们并选择一个
如果你还是不能决定,你可以免费试试它们。你可以在本地安装或使用 live 镜像。你还可以从[阿里云](http://click.aliyun.com/m/7604/)和 [Ucloud](https://ucloud.cn/site/free.html) 这样的地方买到便宜的虚拟专用服务器。你可以在几秒钟内启动 CentOS/Ubuntu 服务器。
### 哪个更快?
它们在速度方面是相同的。它们和运行在你自己的硬件上一样快。它们将如你配置的一样快。不管怎样,你都应该正确配置并且保护所有的服务器、配置和应用程序。
你会使用哪个发行版?想告诉我们你是哪个发行版的拥趸么?请随时留下评论。
---
**文末评论**
W. Anderson:
>
> 我的大多数 Linux 服务器部署都是针对企业客户的,所以我对文章作者以 GUI 客户端版本来反映任何服务器的管理功能感到困惑。通常,许多服务提供商也会在 CentOS、Ubuntu,或经常部署的 OpenSuse Leap 和 FreeBSD 10+ 服务器操作系统上提供 WebMin、VirtualAdmin 或类似工具作为控制面板,即使是在虚拟专用服务器(VPS)环境中。
>
>
> CentOS 在许多商业应用以及高级网络/虚拟化和云计算环境方面具有明显优于 Ubuntu 的优势,并且 CentOS 充分利用 SELinux 框架用于加强的安全层,而目前在 Ubuntu 中则不可用(或不容易)。
>
>
> 这种类型的比较通常是多余的,因为几乎总是有特定的和细微的要求,和需要服务器实现的需求,这将决定哪个发行版具有更多的优势或用途 - 基于技术专家/托管公司的专业知识和广泛的经验。
>
>
>
VAN DER BEKEN:
>
> 正确的比较应该是对 Debian 和 CentOS 进行比较。
>
>
> 以我的经验,我使用 CentOS 和 Debian 作为服务器,稍微偏爱 Debian 一点点,因为它的社区。
>
>
>
---
via: <https://thishosting.rocks/centos-vs-ubuntu-server/>
作者:[thishosting.rocks](https://thishosting.rocks/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Finally decided to get a VPS but can’t decide which Linux distro to use? We’ve all been there. [ The choice](https://thishosting.rocks/how-to-choose-web-hosting/) may even be overwhelming, even for Linux distros, considering all the different flavors and distros that are out there. Though, the two most widely used and most popular server distros are
**CentOS and Ubuntu**. This is the main dilemma among admins, both beginners and professionals. Having experience with both (and more) distros, we decided to do a comparison of CentOS and Ubuntu when used for a server.
## A quick overview:
![]() CentOS | ![]() Ubuntu |
---|---|
Based on Red Hat Linux Enterprise | Based on Debian |
Less frequently updated | Frequently updated |
Arguably more stable and secure because of the infrequent updates. | Updated packages may be unstable and not secure, which is unlikely since they are vigorously tested before pushed to official release. |
Not enough tutorials and has a smaller userbase | Rich documentation, active community and lots of tutorials available online |
Difficult for beginners, as there are no popular and widely used Red Hat-based Desktop distros | Easier to use for beginners that are already familiar with the Desktop version of Ubuntu |
Supports cPanel | Doesn't support cPanel |
.rpm packages and 'yum' package manager | .deb packages and 'apt-get' package manager |
Try a CentOS server for
|
[free](https://thishosting.rocks/vultr-coupons-for-2017-free-credits-and-more/)at[Vultr](https://thishosting.rocks/go/vultr/)## Which one is better for beginners?
Ubuntu. As always, it highly depends on your requirements and previous experiences, but generally, Ubuntu is a better choice for beginners. Mainly because of these 2 reasons:
- Ubuntu has a
**big**community that’s ready to help for free. And we really do mean big. Thousands of users in hundreds of different online forums and groups. Even real life conventions. You can still find a lot of tutorials and help for CentOS too, especially for simple LAMP stacks and popular applications. - Ubuntu server would be a lot easier for someone that has previously used Ubuntu desktop. The same goes for CentOS and Fedora too, but the Ubuntu Desktop version is far more popular than any other Linux-based distro for home-use.
So, if you are a beginner and don’t have any special requirements, go with an Ubuntu server. Even better if you get a server from a [cheap managed provider](https://thishosting.rocks/best-cheap-managed-vps/), so you can experiment on your server and have a [professional 24/7 support team](https://thishosting.rocks/support/) ready to help you.
## Which one is better for businesses?
CentOS. And again, you can still use Ubuntu for a business website or an internal company server, but CentOS has its advantages:
- CentOS is (arguably) more stable and secure. Since CentOS has less frequent updates, that means that the software is tested for a longer period of time and only truly stable versions get released. You won’t get any stability issues from a new, buggy release of an app if you use CentOS because you won’t actually get that new, buggy release.
- Most control panels (including the most popular one – cPanel) support CentOS only. So that means if you are a web hosting company, or if you are a web agency with a lot of clients and need a control panel – CentOS is a better option.
## Try them out and just pick one
If you still can’t decide, you can just try them out for free. You can install them locally or use a live image. You can also get a cheap VPS ($5/mo) from [Linode](https://thishosting.rocks/go/linode/) and [Vultr](https://thishosting.rocks/go/vultr/). You can spin up a CentOS/Ubuntu server in seconds. When you sign up through an affiliate link (like ours) you’ll probably get free credits – meaning you’ll actually get to try them out for free.
## Which one is faster?
They are the same in terms of speed. They are as fast as your hardware. They’ll be as fast as you configure them. You should properly configure and secure all your servers, configurations and applications, no matter what.
Which distro do you use? Wanna tell us how we are a bunch of [insert distro here] fanboys? Feel free to leave a comment below.
## 24 thoughts on “CentOS vs Ubuntu: Which one is better for a server”
Most all of my Linux server deployments are for business clients, so I am bewildered by article author in referencing GUI Client version in regard any Server admin capability or functions. Often WebMin, VirtualAdmin or similar tools are used as control panels on CentOS, Ubuntu, or frequently deployed OpenSuse Leap and FreeBSD 10+ Server OS by many services providers, even in a Virtual Private Server (VPN) environment.
Centos has distinct advantage over Ubuntu for many business applications, as well as advanced Networking/Virtualization and Cloud Computing environments, and CentOS makes excellent use of SELinux framework for hardened security layer, not currently available (or easily) in Ubuntu.
This type comparison is generally superfluous, since there almost are always specific and nuanced requirements and needs for Server implementation that will dictate which distribution has more advantage or purpose – based on technologists/hosting company’s expertise and broad experience with that distribution.
The right comparison is to be made between Debian and CentOS.
From my experience, I use both CentOS and Debian as servers. I prefer a bit Debian for its community.
There are many Fedora-family distros for home desktop usage.
My RHEL-compatible home systems run Korora.
IMHO ironically Debian feels more r00ted to the original Linux terms of endearment in having a wider, open community of support. Centos, despite the free moniker appears to be Red Hat without the big dollar support model but alas no realistic discerning open community support. With Ubuntu now with free LTS I personally feel Debian will grow and become a major player not just in the home but also business sector and quite rightly so. Microsoft’s inclusion of Ubuntu with Windows 10 is a nod to its uptake.
I am a beginner and I can say because of your write up and the comment you left in the Digital Ocean community, I am going for CENTOS at least for this moment. Once I am good at it, I can transfer my property back to Ubuntu because I am not really good at configuring the server and all those stuffs yet.
Thanks for your work brother
Olawale Daniel
In case I want a stable business server, but my need require a small number of newer software than can be found in CentOS repos, thus going to compiling from source, maybe discovering along the way that some of the dependencies require compilation from source as well etc. – while on Ubuntu I wouldn’t need all that.
Would it be true to say that now my CentOS’ stability&security might be compromised and made worse than Ubuntu’s? I know the case is specific, but that’s a concern I have
With CIA (Confidentiality, Integrity & Availability in mind);
That would be an appropriate acknowledgement, as the availability of various components is restricted by default.
As for stability, I don’t expect it will be significant, though I would generally suggest that stability is a user-experience metric, and as that is tarnished, somewhat in the CentOS example provided, I would acknowledge that Ubuntu has a tiny edge with this as well.
Note, that I have utilized both CentOS, and Ubuntu for production environments, and prefer Ubuntu largely because of its more easily accessible support channels.
Yes i understood difference but for hadoop framwork which on is better centos7 or ubuntu
It all depends on your needs and personal preferences. Follow our comparison, and if you still can’t decide for one, use CentOS for Hadoop.
I don’t know why you think CentOS is more stable. Packages don’t get into the stable repositories for Debian or Ubuntu until they’ve been testing for over a year.
If you want paid support for a RH distro, you get RHEL7, and probably not CentOS. If you want paid support for a Debian distro, you get Ubuntu, which is supported directly by Canonical. However, I can’t imagine a shop with senior sysadmins actually using this service. I never heard of it. If you have senior sysadmins, they already know how to figure out everything.
The one advantage RH/CentOS have over Debian/Ubuntu is that they support their distros for 10 years, versus “5 plus” for Debian/Ubuntu. I don’t see any advantage in running a 10-year-old Linux OS on a workstation OR a server, so I don’t care. Upgrading from one Ubuntu LTS to the next in line is simple and usually works. If it doesn’t, you have backups. If you used Chef or some other CM system, then getting your server completely restored – all packages installed, configs edited, etc. – is a matter of typing a few lines. The more people adopt CM, the more support for a 10-year-old OS will seem like a fish with a bicycle.
That is an inaccurate statement. Ubuntu releases every 6 months. The biggest issue with Ubuntu is the system requirements. It’s requirements are much worse than Microsoft.
This simply is not true. I run Ubuntu Server on an HP XW8600, which is probably circa 2003.
noob. windows is heavier !
Debian/Ubuntu is clearly the better choice (huge market share) in europe, but Centos in the US. RHEL is not popular in europe at all. Even SUSE is more popular.
Ubuntu has about twice the system requirements as Cent OS and is much slower when ran in a server environment just as it is in a home use environment.. Ubuntu is much easier to get support for, but if you need reliability, stability, and the normal things you want from a server then Cent OS is a far better choice.
Ubuntu has twice requirements than Centos? You mean Ubuntu Desktop ? 🙂
Ubuntu LTS has no gui, so requirements are the same than Centos Minimal no gui.
There are other difference such as default filesystem choice(centos XFS, Ubuntu ext4), for some applications could result in really different performance; So Centos make more sense if XFS is needed.
Sincerely, is really difficult saying wich distribution is more stable, both are stable in terms of ABI requirements. Ubuntu has lot of kernel updates(because of desktop use), but is the use case the key of choice:
if you need to use Cpanel, go for Centos. If you need environment for Ruby on Rails, go for Ubuntu.
My Two Cents
Man, you most of you don’t understand that stability means. When you work in a real enterprise environment. I am talking like GE, Coca-Cola. You will realize how much you need a stable Linux. I am sorry but UbuntuLTS is far less stable than you think. We have clusters of 1000’s of servers and the ones that segfault more(often for no reason at all) were UbuntuLTS. That is the reason we replaced them with RHEL Linux. Now there is nothing wrong with Ubuntu at all but for critical applications, I will not trust anything but CENT/RHEL. And before you reply oh you don’t know what you are doing blah blah blah. Trust me I do and so does our team. Facts are Facts. I also don’t need “well I been running it for years blah blah blah”. Just because it doesn’t happen to you doesn’t mean it doesn’t happen. When you have 1000’s of servers and you see a pattern you know for a fact one is better than the other.
I happen to work with both of those clients, and I can tell you it is a mix of Redhat and SUSE, with SUSE on the most critical. Anon on this one just because.. Every single server is under enterprise support despite having top of the line admins on them.
Bah. It’s 2018 and we’re still complaining about the “minimum” system requirements. RAMs nowadays are very cheap, HDDs are even cheaper and larger. The kernel is now Version 4.x with more support for hardware than ever. There’s also a Spectre and Meltdown issue that is being addressed in the Kernel. Common sense will tell us that the distro with an active community and dependable release cycle will have to be the choice.
You already mentioned that its much easier to get support for Ubuntu, then why put your balls in the grill pan with CentOS? 😀 It’s cheaper to upgrade hardware than to put your business at risk because there’s not enough community to get help from.
Dude, who uses Linux as desktop? The discussion about linux are always considering SERVERS!
Please, take off ur arguments.
The form of the documentation is another difference which is rarely mentioned when comparing CentOS/RHEL and Ubuntu. Red Hat’s documentation (most of Red Hat’s manual are available without a subscription and I have found compatable with CentOS) is formal professional written technical manual, a more traditional approach to documentation. Ubuntu relies heavily on wikis. I believe the choice is up to the user what form they feel more comfortable using. I moved to CentOS after using Fedora/OpenSUSE I spend a lot less time fixing updates and I have been a lot more productive using CentOS as a virtual KVM server. Even with the old 3.10 kernel and the older version of qemu it outperforms Fedora. I have not had much success with Ubuntu I find it more difficult than CentOS. download and install both. A few years ago I installed, OpenSuSE, SLED, CentOS, RHEL, Fedora, Debian, and Ubuntu. I choose Fedora and CentOS. They just felt right.
CentOS are much more easier for beginners compare to Ubuntu. Ubuntu customize and tweaked too much it way to make it easier for people to use, however it become a chaos when your trying to manage it. CentOS is a clone of RHEL, everything is more towards for enterprise and have a clear standard for as long as your follows the rules from RHEL.
It’d be better comparing cent with debian.
I’ve been using linux since 2006.
I prefer CentOS for the Long Term Support, and because of this, I’ve had almost no issues that affects the servers. More often than not, its the hardware that reaches Maximum Time Before Failure. I guess its how reliable your servers are that matters, based on my career.
I do appreciate support when I have small hiccups, and yes, I do find them from the CentOS community. And not only that, having been in this biz, you also get support from ALL other Linux Communities, such as Debian based distributions, as well as sub distro’s like Ubuntu. In short, I have never been truly alone.
One thing I tell newbies is that they’re success in this career is largely dependent on their ability to Google problems, and think of a solution out of the box. True developers never are limited by what OS, development platform, or language. |
8,142 | aria2 与 wget :选择你的下载管理器 | http://linuxpitstop.com/aria-2-vs-wget/ | 2017-01-24T09:53:00 | [
"wget",
"下载管理器",
"aria2"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8142-1.html | 任何没有下载管理器的 Linux 操作系统是不完整的。多年来,基于 Linux 的发行版使用 wget 作为默认下载管理器。它是一个很棒的小程序,可以在命令行下工作,如果你需要安装东西、下载东西、运行 shell 脚本等,某种程度上都可以在 wget 中完成任务。在过去的很多年里,我们发现 wget 缺乏一些高级的功能,而它的替代品 **aria2** ,由于满足了高级 Linux 用户的渴望而受到了许多用户的关注。我们将在本文中回顾 **aria2** 的安装过程以及 wget 和 aria2 之间的区别,因此你可以决定哪个下载管理器最符合你的需要。

### 安装 aria2
**在 Ubuntu/Debian 中安装 aria2:**
只要在 Ubuntu 中运行下面的命令安装:
```
sudo apt-get install aria2
```

**在 Fedora/RHEL/Centos 中安装 aria2:**
运行下面的命令在 Fedora/RHEL 和基于 Centos 的系统中安装:
```
sudo yum install aria2
```
**在 Arch Linux 中安装 aria2:**
运行下面的命令在基于 Arch Linux 的系统中安装。
```
sudo pacman -Sy aria2
```
### aria2 的重要功能
让我们来讨论 aria2 中使它如此受欢迎的重要功能:
* 通过使用多个连接下载文件,最大限度地利用可用带宽。
* 同时下载多个文件和同时下载的能力。
* torrent 客户端提供的所有功能都可以在这个小程序中找到。
* 它提供 meta 链接下载。
* 支持使用 JSON-RPC 和 XML-RPC 协议的远程过程调用。
* 无需等待当前下载完成,轻松批量下载文件。
### aria2 的一些副作用:
aria2 的多线程机制可能会使目标服务器过载。相比下来 wget 就轻量级多了,wget 比 aria2 消耗资源少 20%。aria2 尚未经受 wget 那样巨大的使用规模的测试,因此可能完全准备好成为默认下载管理器。
### wget 的重要特性
* 当然它是最广泛使用和测试的下载管理器。
* 它是一个简单的程序,具有较少的功能,但稳定工作了几十年。
* 默认所有 Linux 发行版上都有,不需要繁重的安装。
* 与 aria2 相比更轻量级。
### 总结
虽然 wget 没有丰富的功能,但仍然工作得相当不错,然而,高级用户肯定会喜欢 aria2,因为它满足更快和并发下载的需要。aria2 可能需要很长时间来取代 wget 成为默认下载管理器,而目前 wget 用在几乎所有 linux 发行版的安装程序脚本中。
---
via: <http://linuxpitstop.com/aria-2-vs-wget/>
作者:[Aun](http://linuxpitstop.com/author/aun/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 404 | Not Found | null |
8,143 | Vim 初学者入门指南 | https://www.maketecheasier.com/start-with-vim-linux/ | 2017-01-24T10:36:00 | [
"vim",
"vi"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8143-1.html | 
这篇文章是 VIM 用户指南 系列文章中的一篇:
* Vim 初学者入门指南
* [Vim 快捷键速查表](/article-8144-1.html)
* [5 个针对有经验用户的 Vim 技巧](/article-8148-1.html)
* [3 个针对高级用户的 Vim 编辑器有用技巧](/article-8149-1.html)
对一个程序员来说,选择一个文本编辑器是一件非常重要的事。因为不同编辑器之间有着不少的差异:图形界面或者非图形界面、不同的快捷键、不同的编程语言支持、不同的插件以及自定义设置等等。我建议不是去搜索最棒的编辑器,而是去选择最适合你的习惯且最适应你的任务的那一个。假如你打算在一个团体中工作,那么最好和你的共事者选择一样的编辑器。这样的话,一旦你在使用中遇到问题,你就可以去向他们寻求帮助。
这正是我在几年之前开始使用 Vim 的原因。通常来说,Vim 会被置于传说中的 Emacs 的对立面。我承认我对 Emacs 知之甚少,但是对于它俩,你需要知道的是它们都可以被深度定制,并且在初学时也都非常令人困惑。这个教程并不会介绍有关 Vim 的所有内容,而是将介绍一些基础以使你在最初就能正确使用它,随后还会展示一些小技巧,借此(希望能)让你有能力自己去探索学习。
Vim 一词来源于 “Vi IMproved”。Vi 是一个被广泛安装于 Unix 系统的非图形界面文本编辑器,并且它也被默认安装在了 Linux 系统中。Vim 是这个原始编辑器的增强版,但是不同于 Vi,并不是每个发行版都默认安装了它。
### 安装
在 Ubuntu 中可以使用如下命令来安装 Vim:
```
sudo apt-get install vim
```
如果你已经对某些插件有了兴趣,使用以下命令:
```
sudo apt-cache search vim
```
这命令将给你输出一个很长的和 Vim 有关的包列表。在这之中,有针对不同编程语言的工具,有插件管理器,等等。
在这系列教程中,我将会在 Ubuntu 上使用最新版的 Vim(7.3.154,LCTT 译注:现在最新版为 8.0)。当然你也可以使用其它任何版本。
### 热身
在终端输入 `vim` 命令,你将会看到一个非常棒的欢迎界面。

(LCTT 译注:看到了欢迎界面中那行“Help poor children in Uganda!” 了吗?)
如果你之前从未使用过 Vi 或者 Vim,那么你很可能甚至不知道该怎么退出它... 是的,这是事实。**任何你常用的快捷键在 Vim 中都将失去原有的效果**。(LCTT 译注:网上有个流传的笑话——“如何制造乱码”,“让新手退出 vi”)
首先,要使用任何命令式的功能,像<ruby> 保存 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> save </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>或者<ruby> 退出 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> exit </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,你都先得输入一个冒号(`:`)。保存是 `:w` 而退出是 `:q`。如果你想不保存文件就退出,那么就要使用强制退出命令 `:q!`。Vim 中非常棒的一点是你不需要分开输入各个命令,换言之,如果你想保存然后退出,你就可以直接使用 `:wq`。
现在,我们退出 Vim 再打开一个文本文件。为此,你只需把想要编辑的文件名加在命令后面即可:
```
vim [文本文件名]
```

一般而言,当你打开一个文本文件,你将会处在查看模式。这使得 Vim 与众不同并且最初会让人感到困惑。Vim 主要由两种模式构成:查看模式和编辑模式。查看模式用于查看内容并且使用一些命令。想要进入编辑模式,只需按 `i` 键进行<ruby> 插入 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> insert </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>或者 `a` 键进行<ruby> 添加 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> add </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。想要返回到查看模式或者进行命令式功能的操作,按 `Escape` 键即可。<ruby> 插入 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> insert </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>和<ruby> 添加 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> add </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>的差异仅仅在于你是想在光标位置之前还是在光标之后进入编辑模式并进行文字输入。要想彻底地明白,你应该亲自去尝试一下。我的建议是:仅在行尾使用<ruby> 添加 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> add </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>,而在其它时候使用<ruby> 插入 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> insert </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>。
(LCTT 译注:此段落中“查看模式”原文是 “visual mode”,疑为“view mode”,在此模式下可以查看文本,但是不能进行编辑;而“visual mode” 是编辑模式的一种,可以按 `v` 键进入,然后就可以用方向键从当前光标位置开始进行选择,并以反白的视觉效果显示,通常选择后可以按 `y` 进行复制、按 `d` 进行剪切等操作。此外, 本文作者的用语并不标准,按照 Vim 自己的用语来说,此处所谓的“查看模式”,应该称之为“普通模式”,“编辑模式”应该称之为“插入模式”,不过意思是一致的。)
要想在文本之中移动光标,你通常可以使用键盘上的方向键,它们无论是在查看模式还是在编辑模式都可以生效。不过,一个真正的纯粹主义者将会告诉你使用按键 `h` 向左,`j` 向下,`k` 向上,`l` 向右来(在查看模式)进行移动。
现在你已经明白了如何和简单地控制 Vim,我们再来更加深入一些。
### 一些简单命令
现在你已经熟悉了在正常模式和插入模式之间进行切换,下面是一些可以在正常模式中使用的命令:
* `x`:删除一个字符
* `u`:撤销一个操作(相当与 `Ctrl+z`)
* `dd`:删除一行内容
* `dw`:删除一个单词
* `yy`:复制一行内容
* `yw`:复制一个单词
* `p`:粘贴一个之前删除或复制的行或者单词
* `e`:跳到下个单词(LCTT 译注:词尾)(比单纯用方向键更快)
* `r`:替换一个字母(按 `r`,松开,然后再按新字母)
当然不止这些,不过这些对现在来说已经足够了。如果你掌握了上面的全部,你将能你很顺溜地使用 Vim 了。
对于那些还想知道更多的人,我再多提一下。你可以在任何这些命令之前加上一个数值,那么这个命令将被重复执行相应的次数。例如,`5x` 将在当前行连续删除 5 个字母,而 `3p` 将会粘贴 3 次。
### 高级命令
最后,作为对你自己继续探索的鼓励和示例,这里给出几个高级且常用的命令:
* `/所搜索的内容`:在文中搜索特定内容
* `:sp 文本文件名`:将屏幕水平分割成上下两半,新文件展示在另一半。想要在两侧切换焦点,可以使用 `Ctrl+w` 快捷键。

* `:vsp 文本文件名`:同上,但是是垂直分割屏幕
* `Ctrl+Shift+C` 和 `Ctrl+Shift+V`:在终端中复制和粘贴文本
* `:! 命令名`:在 Vim 中运行 Vim 外的终端命令,直接发送给 shell。例如,`:! ls` 将在不退出编辑器的同时,显示你当前目录内的文件。

### 结论
我觉得你现在应该已经有了足够的准备来开始使用 Vim。你还可以通过安装各种插件,编辑 `~.vimrc` 文件,或者在 shell 中输入 `vimtutor` 命令来使用交互式教程以学到更多。
如果你有任何你想分享的关于 Vim 的其它命令,请在评论中告知我们。
---
via: <https://www.maketecheasier.com/start-with-vim-linux/>
作者:[Himanshu Arora](https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/himanshu/) 译者:[Yinr](https://github.com/Yinr) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 
Choosing a text editor is a very important decision for a programmer. This is partly because of the plethora of variables: graphical/non-graphical interfaces, different shortcuts, language specializations, plugins, customizations, etc. My advice is not to try to search for the best one. Instead, choose the one that corresponds best to your habits and your tasks. If you want to work in a group, it’s generally best to select the same editor as your co-worker. That way, if you have a problem, you will be able to find some help.
It is exactly for that reason that I started using Vim a few years ago. Traditionally, Vim is placed in conflict with the legendary Emacs. I confess that I know very little about Emacs, but what you have to know about these two text editors is that they can both be fully customized, and very confusing at first. This tutorial will not explain everything about Vim but will try to give you the basics to use it correctly in the first place, and then present a few tips that will (I hope) allow you to learn on your own.
Vim comes from “VI iMproved”. Vi is a non-graphical text editor widely distributed in Unix systems. It comes by default with Linux. Vim is an enhancement of this original editor. However, unlke Vi, Vim is not installed by default on every distribution.
**Also read:** [How to Use Vim Shortcuts to Navigate Your Web Browser](https://www.maketecheasier.com/use-vim-shortcuts-navigate-web-browser/)
## Installation
To install Vim on Ubuntu, use the command:
sudo apt-get install vim
If you are already interested in some plugins, use the command:
sudo apt-cache search vim
This will give you a long list of packages related to Vim. Among them are some for various programming languages, addon managers, etc.
For this tutorial, I will be using the latest version of Vim (7.3.154) on Ubuntu. You can use any other version though.
## Warming Up
Type the command `vim`
in a terminal. You should see a nice welcome screen.
And if you’ve never used Vi or Vim before, it is very likely that you don’t even know how to exit… Yes, it’s true. **None of the shortcuts you normally use will work in Vim**.
First of all, to use any menu-type function like save or exit, your command should begin with a colon (:). Saving is `:w`
and quitting is `:q`
. If you want to quit a file without saving, use the force quit command `:q!`
. A cool thing with Vim is that you don’t have to type commands separately. In other words, if you want to save and then quit, you can directly use `:wq`
.
So for now, quit Vim and open it on a sample text file. Simply add the name of the text file that you want to edit after the command:
vim [text file name]
By default, when you open a text file, you are in visual mode. It is quite specific to Vim and confusing at the beginning. Vim is composed mainly of two modes: visual and editing. The visual mode is for viewing a text and using some commands. To go into editing mode, just press `i`
to insert and `a`
to add some text. To go back into the visual mode and access all the menu-type functions, press the “Escape” key. The difference between insertion and addition is simply whether you want the text you type to appear before or after the cursor in visual mode. To understand this fully, you should really try it yourself. My advice is: add at the end of lines, and insert in other cases.
To move the cursor within a text, whether you are in visual or editing mode, you can generally use the keyboard arrows. A real purist would tell you to use the keys *h* for left, *j* for down, * k* for up, and *l* for right.
Now that you are warmed up and know how to control Vim at a basic level, let’s go to the core.
## A few basic commands
Now that you master the transformation from visual to editing mode, here are a few commands that you can use in visual mode:
*x*: to delete a character*u*: to undo an action (the equivalent of Ctrl+z)*dd*: to delete a line*dw*: to delete a word*yy*: to copy a line*yw*: to copy a word*p*: to paste the previously deleted or copied line or word*e*: to move to the next word (faster than just moving with the arrow keys)*r*: to replace a letter (press*r*, then the new letter)
And of course, there are more, but this is enough for now. If you master all of them, you will already be very fluent with Vim.
As a side note for those who always want more, you can type a number before any of these commands and the command will be executed that number of times. For example, *5x* will delete five characters in a row, while *3p* will paste three times.
## Advanced Commands
Finally, as a bonus and an appetizer for your own research, here are a few advanced and very useful commands:
*/searched_word*: to search for a word within the text*:sp name_of_a_text_file*: will split the screen in half horizontally, showing the new text file in the other half. To shift the focus from the right to the left window, use the shortcut Ctrl+w
*:vsp name_of_a_text_file*: same as before, but splits the screen vertically- Ctrl+Shift+C and Ctrl+Shift+V: to copy and paste text in a terminal
*:! name_of_a_command*: to launch a command external to Vim, directly into your shell. For example,`:! ls`
will display the files within the directory you are currently working in, without quitting the editor
## Conclusion
I think you now have every tool you need to start using Vim. You can go even further by installing the various plugins, editing the *.vimrc* file, or even using the interactive tutor by typing the command *vimtutor*.
If you have any other commands that you would like to share about Vim, please let us know in the comments.
Image credit: [Tonight’s side project](https://www.flickr.com/photos/termie/2922917167/)
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox |
8,144 | Vim 快捷键速查表 | https://www.maketecheasier.com/vim-keyboard-shortcuts-cheatsheet/ | 2017-01-25T07:26:00 | [
"编辑器",
"vi",
"Vim"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8144-1.html | 
本文是 Vim 用户指南 系列的其中一篇:
* [Vim 初学者入门指南](/article-8143-1.html)
* Vim 快捷键速查表
* [5 个针对有经验用户的 Vim 技巧](/article-8148-1.html)
* [3 个针对高级用户的 Vim 编辑器实用技巧](/article-8149-1.html)
Vim 编辑器是一个基于命令行的工具,是传奇编辑器 vi 的增强版。尽管图形界面的富文本编辑有很多,但是熟悉 Vim 对于每一位 Linux 的使用者都能有所帮助——无论你是经验丰富的系统管理员,还是刚上手树莓派的新手用户。
这个轻量级的编辑器是个非常强大的工具。在有经验的使用者手中,它能完成不可思议的任务。除了常规的文本编辑功能以外,它还支持一些进阶特性。例如,基于正则表达式的搜索和替换、编码转换,以及语法高亮、代码折叠等的编程特性。
使用 Vim 时有一个非常重要的一点需要注意,那就是按键的功能取决于编辑器当前的“模式”。例如,在“普通模式”输入字母`j`时,光标会向下移动一行。而当你在“插入模式”下输入字符,则只是正常的文字录入。
下面就是速查表,以便于你充分利用 Vim。
### 基本操作
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `Esc` | 从当前模式转换到“普通模式”。所有的键对应到命令。 |
| `i` | “插入模式”用于插入文字。回归按键的本职工作。 |
| `:` | “命令行模式” Vim 希望你输入类似于保存该文档命令的地方。 |
### 方向键
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `h` | 光标向左移动一个字符 |
| `j` 或 `Ctrl + J` | 光标向下移动一行 |
| `k` 或 `Ctrl + P` | 光标向上移动一行 |
| `l` | 光标向右移动一个字符 |
| `0` | (数字 0)移动光标至本行开头 |
| `$` | 移动光标至本行末尾 |
| `^` | 移动光标至本行第一个非空字符处 |
| `w` | 向前移动一个词 (上一个字母和数字组成的词之后) |
| `W` | 向前移动一个词 (以空格分隔的词) |
| `5w` | 向前移动五个词 |
| `b` | 向后移动一个词 (下一个字母和数字组成的词之前) |
| `B` | 向后移动一个词 (以空格分隔的词) |
| `5b` | 向后移动五个词 |
| `G` | 移动至文件末尾 |
| `gg` | 移动至文件开头 |
### 浏览文档
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `(` | 跳转到上一句 |
| `)` | 跳转到下一句 |
| `{` | 跳转到上一段 |
| `}` | 跳转到下一段 |
| `[[` | 跳转到上一部分 |
| `]]` | 跳转到下一部分 |
| `[]` | 跳转到上一部分的末尾 |
| `][` | 跳转到上一部分的开头 |
### 插入文本
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `a` | 在光标后插入文本 |
| `A` | 在行末插入文本 |
| `i` | 在光标前插入文本 |
| `o` | (小写字母 o)在光标下方新开一行 |
| `O` | (大写字母 O)在光标上方新开一行 |
### 特殊插入
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `:r [filename]` | 在光标下方插入文件 [filename] 的内容 |
| `:r ![command]` | 执行命令 [command] ,并将输出插入至光标下方 |
### 删除文本
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `x` | 删除光标处字符 |
| `dw` | 删除一个词 |
| `d0` | 删至行首 |
| `d$` | 删至行末 |
| `d)` | 删至句末 |
| `dgg` | 删至文件开头 |
| `dG` | 删至文件末尾 |
| `dd` | 删除该行 |
| `3dd` | 删除三行 |
### 简单替换文本
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `r{text}` | 将光标处的字符替换成 {text} |
| `R` | 进入覆写模式,输入的字符将替换原有的字符 |
### 复制/粘贴文本
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `yy` | 复制当前行至存储缓冲区 |
| `["x]yy` | 复制当前行至寄存器 x |
| `p` | 在当前行之后粘贴存储缓冲区中的内容 |
| `P` | 在当前行之前粘贴存储缓冲区中的内容 |
| `["x]p` | 在当前行之后粘贴寄存器 x 中的内容 |
| `["x]P` | 在当前行之前粘贴寄存器 x 中的内容 |
### 撤销/重做操作
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `u` | 撤销最后的操作 |
| `Ctrl+r` | 重做最后撤销的操作 |
### 搜索和替换
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `/search_text` | 检索文档,在文档后面的部分搜索 search\_text |
| `?search_text` | 检索文档,在文档前面的部分搜索 search\_text |
| `n` | 移动到后一个检索结果 |
| `N` | 移动到前一个检索结果 |
| `:%s/original/replacement` | 检索第一个 “original” 字符串并将其替换成 “replacement” |
| `:%s/original/replacement/g` | 检索并将所有的 “original” 替换为 “replacement” |
| `:%s/original/replacement/gc` | 检索出所有的 “original” 字符串,但在替换成 “replacement” 前,先询问是否替换 |
### 书签
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `m {a-zA-Z}` | 在当前光标位置设置书签,书签名可用一个大小写字母({a-zA-Z}) |
| `:marks` | 列出所有书签 |
| `{a-zA-Z}` | 跳转到书签 {a-zA-Z} |
### 选择文本
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `v` | 进入逐字可视模式 |
| `V` | 进入逐行可视模式 |
| `Esc` | 退出可视模式 |
### 改动选中文本
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `~` | 切换大小写 |
| `d` | 删除一个词 |
| `c` | 变更 |
| `y` | 复制 |
| `>` | 右移 |
| `<` | 左移 |
| `!` | 通过外部命令进行过滤 |
### 保存并退出
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
| --- | --- |
| `:q` | 退出 Vim,如果文件已被修改,将退出失败 |
| `:w` | 保存文件 |
| `:w new_name` | 用 new\_name 作为文件名保存文件 |
| `:wq` | 保存文件并退出 Vim |
| `:q!` | 退出 Vim,不保存文件改动 |
| `ZZ` | 退出 Vim,如果文件被改动过,保存改动内容 |
| `ZQ` | 与 :q! 相同,退出 Vim,不保存文件改动 |
### 下载 Vim 快捷键速查表
仅仅是这样是否还不足以满足你?别担心,我们已经为你整理好了一份下载版的速查表,以备不时之需。
[点此下载(英文)](http://www.maketecheasier.com/cheatsheet/vim-keyboard-shortcuts-cheatsheet/)
---
via: <https://www.maketecheasier.com/vim-keyboard-shortcuts-cheatsheet/>
作者:[Himanshu Arora](https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/himanshu/) 译者:[martin2011qi](https://github.com/martin2011qi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 
Vim is a powerful command-line code editor tool that’s an enhanced version of the venerable vi editor. Although most people use it with Linux, Vim is compatible with most of the commonly used operating systems, including macOS, Windows, and DOS.
Despite the abundance of graphical rich [text editors](https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-text-editors/), familiarity with Vim will help every user, from an experienced system administrator to a newbie programming a [Raspberry Pi](https://www.maketecheasier.com/turn-raspberry-pi-video-conferencing-station/). However, one important thing to note when using Vim, is that the function of a key depends on the “mode” the editor is in. For example, pressing the alphabet “j” will move the cursor down one line in the “command mode”. You’ll have to switch to the “insert mode” to make the keys input the character they represent.
If you’re new to Vim, open a terminal and run `vimtutor`
to get you started with some initial commands before diving into the rest.

#### Download this Cheatsheet
Enter your email below to receive this PDF cheatsheet in your Inbox.
Here’s a cheatsheet to help you get the most out of Vim.
Shortcut Keys | Function |
---|---|
Main | |
Esc | Gets out of the current mode into the “command mode”. All keys are bound of commands. |
I | “Insert mode” for inserting text. Keys behave as expected. |
: | “Last-line mode” where Vim expects you to enter a command such as to save the document. |
:term | Open a terminal window. |
Navigation Keys | |
H | Move the cursor one character to the left. |
J or Ctrl + J | Move the cursor down one line. |
K or Ctrl + P | Move the cursor up one line. |
l | Move the cursor one character to the right. |
0 | Move the cursor to the beginning of the line. |
$ | Move the cursor to the end of the line. |
^ | Move the cursor to the first non-empty character of the line. |
w | Move forward one word (next alphanumeric word). |
W | Move forward one word (delimited by a white space). |
5W | Move forward five words. |
b | Move backward one word (previous alphanumeric word). |
B | Move backward one word (delimited by a white space). |
5B | Move backward five words. |
G | Move to the end of the file. |
GG | Move to the beginning of the file. |
Navigate Around The Document | |
( | Jump to the previous sentence. |
) | Jump to the next sentence. |
{ | Jumps to the previous paragraph. |
} | Jumps to the next paragraph. |
[[ | Jumps to the previous section. |
]] | Jumps to the next section. |
[] | Jump to the end of the previous section. |
][ | Jump to the end of the next section. |
Insert Text | |
a (lowercase A) | Insert text after the cursor. |
A (uppercase A) | Insert text at the end of the line. |
I | Insert text before the cursor. |
o (lowercase O) | Begin a new line below the cursor. |
O (uppercase A) | Begin a new line above the cursor. |
Special Inserts | |
:R [filename] | Insert the file [filename] below the cursor. |
:R ![command] | Execute [command] and insert its output below the cursor. |
Delete Text | |
X | Delete character at cursor. |
DW | Delete a word. |
D0 | Delete to the beginning of a line. |
D$ | Delete to the end of a line. |
D) | Delete to the end of sentence. |
DGG | Delete to the beginning of the file. |
DG | Delete to the end of the file. |
DD | Delete line. |
3DD | Delete three lines. |
Simple Replace Text | |
R{text} | Replace the character under the cursor with {text}. |
R | Replace characters instead of inserting them. |
Copy/Paste Text | |
YY | Copy current line into storage buffer. |
[“x]yy | Copy the current lines into register x. |
p (lowercase P) | Paste storage buffer after current line. |
P (uppercase A) | Paste storage buffer before current line. |
[“X]P | Paste from register x after current line. |
[“X]P | Paste from register x before current line. |
Text Modification | |
CC | Change the text of the current line. |
CE | Change the currently selected word at the current cursor point. |
C$ | Change the text from the cursor position until the end of the line. |
C0 | Change the text from the cursor position until the start of the line. |
G~ | Switch the case of the currently selected text as well as the line adjacent to it to its opposite. |
Gu | Change the case of the currently selected text as well as the line adjacent to it to lowercase. |
GU | Change the case of the currently selected text as well as the line adjacent to it to uppercase. |
Context-Specific Modification | |
CIW | Change the currently selected word regardless of cursor position. |
CIP | Change the currently selected paragraph or code block regardless of cursor position. |
CI< | Change the content of a code block enclosed in angle brackets (<>). |
CI{ | Change the content of a code block enclosed in curly brackets ({}). |
DIW | Delete the currently selected word regardless of cursor position. |
DIP | Delete the currently selected paragraph or code block regardless of cursor position. |
DAW | Delete the currently selected word as well as the spaces before and after it. |
DI< | Delete the content of a code block enclosed in angle brackets (<>). |
DI{ | Delete the content of a code block enclosed in curly brackets ({}). |
YIW | Copy the currently selected word regardless of cursor position. |
YIP | Copy the currently selected paragraph or code block regardless of cursor position. |
YAW | Copy the currently selected word as well as the spaces before and after it. |
YI< | Copy the content of a code block enclosed in angle brackets (<>). |
YI{ | Copy the content of a code block enclosed in curly brackets ({}). |
Undo/Redo Operation | |
U | Undo the last operation. |
Ctrl + R | Redo the last undo. |
:earlier 1m | Go back 1 minute in the history of the document. |
:later 1m | Go forward 1 minute in the history of the document. |
Search and Replace Keys | |
/search_text | Search document for search_text going forward. |
?search_text | Search document for search_text going backward. |
n (lowercase n) | Move to the next instance of the result from the search. |
N (uppercase A) | Move to the previous instance of the result. |
:%s/original/replacement | Search for the first occurrence of the string “original” and replace it with “replacement”. |
:%s/original/replacement/g | Search and replace all occurrences of the string “original” with “replacement”. |
:%s/original/replacement/gc | Search for all occurrences of the string “original” but ask for confirmation before replacing them with “replacement”. |
F | Search for the next occurrence of a character or go to the previous occurrence. |
Bookmarks | |
M {a-z A-Z} | Set bookmark {a-z A-Z} at the current cursor position. |
:marks | List all bookmarks. |
`{a-z A-Z} | Jumps to the bookmark {a-z A-Z}. |
Select Text | |
v (lowercase V) | Enter visual mode per character. |
V (uppercase A) | Enter visual mode per line. |
Esc | Exit visual mode. |
Modify Selected Text | |
~ | Switch case. |
D | Delete a word. |
C | Change a word. |
Y | Yank (copy) a word. |
> | Shift right. |
< | Shift left. |
! | Filter through an external command. |
Text Indentation | |
>> | Shift the currently selected line one Tab length to the right. |
<< | Shift the currently selected line one Tab length to the left. |
gg=G | Shift the current buffer by one Tab length. |
>% | Shift the currently selected code block to the right. |
<% | Shift the currently selected code block to the left. |
>IB | Shift the contents of the currently selected block to the right. |
<IB | Shift the contents of the currently selected block to the left. |
>AT | Shift the contents of a block that is enclosed in angle brackets (<>) to the right. |
<AT | Shift the contents of a block that is enclosed in angle brackets (<>) to the left. |
Macros | |
Q[character] | Record a Vim macro that is accessible under the [character] key. |
Q | Stop a Vim macro recording. |
@[character] | Execute a recorded Vim macro that was saved under the [character] key. |
@@ | Execute the last Vim macro that was run. |
Search and Execute | |
:G/[pattern]/[vim command] | Run the [vim command] in the current line for every instance of the [pattern]. |
:G!/[pattern]/[vim command] | Run the [vim command] in the current line for every instance that is not the [pattern]. |
:%G/[pattern]/[vim command] | Run the [vim command] on the entire document for every instance of the [pattern]. |
:%G!/[pattern]/[vim command] | Run the [vim command] on the entire document for every instance that is not the [pattern]. |
Tab Manipulation | |
:TABE [file path] | Open the [file path] in a separate tab in the current buffer. |
:TABN | Switch to the next active tab in the buffer. |
:TABP | Switch to the previous active tab in the buffer. |
:TABC | Close the currently active tab in the buffer. |
:TABO | Close all inactive tabs in the buffer. |
Buffer Manipulation | |
:SP [file path] | Open the [file path] as a horizontally split buffer. |
:VSP [file path] | Open the [file path] as a vertically split buffer. |
:LS | Show a list of all the buffers currently open in Vim. |
:BN | Display the contents of the next open buffer in the buffer list. |
:BP | Display the contents of the previous open buffer in the buffer list. |
Ctrl + W, then S | Split the current window horizontally, displaying the currently active buffer in both windows. |
Ctrl + W, then V | Split the current window vertically, displaying the currently active buffer in both windows. |
Ctrl + W, then W | Switch focus between the split buffers. |
Ctrl + W, then X | Swap the position of the currently focused buffer with an inactive one. |
Ctrl + W, then Q | Delete the currently selected buffer. |
Save and Quit | |
:Q | Quits Vim but fails when file has been changed. |
:W | Save the file. |
:W new_name | Save the file with the new_name filename. |
:WQ | Save the file and quit Vim. |
:Q! | Quit Vim without saving the changes to the file. |
ZZ | Write file, if modified, and quit Vim. |
ZQ | Same as :q! Quits Vim without writing changes. |
:sav file :saveas file | Save file as. |
:clo :close | Close the current pane. |
Image credit: Unsplash
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox |
8,145 | 在 Linux 中设置 sudo 的十条 sudoers 实用配置 | http://www.tecmint.com/sudoers-configurations-for-setting-sudo-in-linux/ | 2017-01-25T08:41:00 | [
"root",
"sudo"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8145-1.html | 在 Linux 和其他的类 Unix 操作系统中,只有 root 用户可以运行所有的命令,才能在系统中执行那些需要鉴权的操作,比如安装、升级和移除软件包、[创建用户和用户组](http://www.tecmint.com/add-users-in-linux/)、修改系统重要的配置文件等等。
然而,系统管理员,比如说 root 用户,可以通过 [sudo 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/su-vs-sudo-and-how-to-configure-sudo-in-linux/) 和一些配置选项来给普通用户进行授权,从而让该普通用户可以运行某些命令已经上述的那些相当重要的系统级操作。
另外,系统管理员还可以分享 root 用户密码 (这个做法是不值得提倡的),这样普通用户就可以通过 `su` 命令来转化为 root 用户角色。.

`sudo` 允许已授权用户按照指定的安全策略、以 root 用户 (或者是其他的用户角色) 权限来执行某个命令。
1. `sudo` 会读取和解析 `/etc/sudoers` 文件,查找调用命令的用户及其权限。
2. 然后提示调用该命令的用户输入密码 (通常是用户密码,但也可能是目标用户的密码,或者也可以通过 `NOPASSWD` 标志来跳过密码验证)。
3. 这之后, `sudo` 会创建一个子进程,调用 setuid() 来切换到目标用户。
4. 接着,它会在上述子进程中执行参数给定的 shell 或命令。
以下列出十个 `/etc/sudoers` 文件配置,使用 `Defaults` 项修改 sudo 命令的行为。
```
$ sudo cat /etc/sudoers
```
`/etc/sudoers` 文件:
```
#
# This file MUST be edited with the 'visudo' command as root.
#
# Please consider adding local content in /etc/sudoers.d/ instead of
# directly modifying this file.
#
# See the man page for details on how to write a sudoers file.
#
Defaults env_reset
Defaults mail_badpass
Defaults secure_path="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin"
Defaults logfile="/var/log/sudo.log"
Defaults lecture="always"
Defaults badpass_message="Password is wrong, please try again"
Defaults passwd_tries=5
Defaults insults
Defaults log_input,log_output
```
#### Defaults 项的类型
```
Defaults parameter, parameter_list ### 对任意主机登录的所有用户起作用
Defaults@Host_List parameter, parameter_list ### 对指定主机登录的所有用户起作用
Defaults:User_List parameter, parameter_list ### 对指定用户起作用
Defaults!Cmnd_List parameter, parameter_list ### 对指定命令起作用
Defaults>Runas_List parameter, parameter_list ### 对以指定目标用户运行命令起作用
```
在本文讨论范围内,我们下面的将以第一个 `Defaults` 作为基准来参考。parameter 参数可以是标记 (flags)、整数值或者是列表 (list)。
值得注意的是,标记 (flag) 是指布尔类型值,可以使用 `!` 操作符来进行取反,列表 (list) 有两个赋值运算符:`+=` (添加到列表) 和 `-=` (从列表中移除)。
```
Defaults parameter
或
Defaults parameter=值
或
Defaults parameter -=值
Defaults parameter +=值
或
Defaults !parameter
```
### 1、 安置一个安全的 PATH 环境变量
该 `PATH` 环境变量应用于每个通过 `sudo` 执行的命令,需要注意两点:
1. 当系统管理员不信任 `sudo` 用户,便可以设置一个安全的 `PATH` 环境变量。
2. 该设置将 root 的 PATH 和用户的 PATH 分开,只有在 `exempt_group` 组的用户不受该设置的影响。
可以添加以下内容来设置:
```
Defaults secure_path="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/snap/bin"
```
### 2、 允许 tty 用户会话使用 sudo
该设置允许在一个真实的 tty 中进行调用 `sudo`,但不允许通过 cron 或者 cgi-bin 脚本等方法来调用。添加以下内容来设置:
```
Defaults requiretty
```
### 3、 使用 pty 运行 sudo 命令
少数情况下,攻击者可以通过 sudo 来运行一个恶意程序 (比如病毒或者恶意代码),这种恶意程序可能会分叉出一个后台运行的进程,即使主程序完成执行,它仍能够运行在用户的终端设备上。
为了防止出现这样的情况,你可以通过 `use_pty` 参数来设置 `sudo` 使用伪终端来运行其他命令,而不必管 I/O 日志的开启状态。如下:
```
Defaults use_pty
```
### 4、 创建 sudo 日志文件
默认下,`sudo` 通过 syslog(3) 来记录到日志。但是我们可以通过 `logfile` 参数来指定一个自定义的日志文件。如下:
```
Defaults logfile="/var/log/sudo.log"
```
使用 `log_host` 和 `log_year` 参数可以对应记录日志主机名和 4 位数年份到自定义日志文件。如下:
```
Defaults log_host, log_year, logfile="/var/log/sudo.log"
```
下面是自定义 sudo 日志文件的例示:

*创建 sudo 日志文件*
### 5、 记录 sudo 命令的输入/输出
`log_input` 和 `log_output` 参数可以让 `sudo` 命令运行在伪终端,并可以对应地记录所有的用户输入和输出到屏幕上。
默认的 I/O 日志目录为 `/var/log/sudo-io`,如果存在会话序列号,它将被存储到该目录。你可以通过 `iolog_dir` 参数来指定一个目录。
```
Defaults log_input, log_output
```
这其中支持转义字符,像 `%{seq}` —— 以 36 为基数的单调递增序列,比如 000001,这里每两个数字都分别用来形成一个新目录。请看下边例示 00/00/01:
```
$ cd /var/log/sudo-io/
$ ls
$ cd 00/00/01
$ ls
$ cat log
```

*记录 sudo 命令的输入/输出*
[cat 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/) 来查看该目录的其余部分。
### 6、 为 sudo 用户提示命令用法
如下,使用 `lecture` 参数可以在系统中为 `sudo` 用户提示命令的用法:
参数属性值有三个选择:
1. `always` – 一直提示
2. `once` – 用户首次运行 sudo 时提示 (未指定参数属性值时的默认值)
3. `never` – 从不提示
```
Defaults lecture="always"
```
此外,你还可以使用 `lecture_file` 参数类自定义提示内容,在指定的文件中输入适当的提示内容即可:
```
Defaults lecture_file="/path/to/file"
```

*为 sudo 用户提示命令用法*
### 7、 输入错误的 sudo 密码是显示自定义信息
当某个用户输错密码时,会有一个对应的信息显示在屏幕上。默认是“抱歉,请重新尝试。(sorry, try again)”,你可以通过 `badpass_message` 参数来修改该信息:
```
Defaults badpass_message="Password is wrong, please try again"
```
### 8、 增加 sudo 密码尝试限制次数
`passwd_tries` 参数用于指定用户尝试输入密码的次数。
默认为 3。
```
Defaults passwd_tries=5
```

*增加 sudo 密码尝试限制次数*
使用 `passwd_timeout` 参数设置密码超时 (默认为 5 分钟),如下:
```
Defaults passwd_timeout=2
```
### 9、 在输错密码时让 sudo 羞辱用户
使用了 `insults` 参数之后,一旦你输出了密码,sudo 便会在命令窗口中显示羞辱你的信息。这个参数会自动关闭 `badpass_message` 参数。
```
Defaults insults
```

*在输错密码时让 sudo 羞辱用户*
### 10、 更多关于 sudo 的配置
此外,欲了解更多 sudo 命令的配置,请自行阅读:[su 与 sudo 的差异以及如何配置 sudo](http://www.tecmint.com/su-vs-sudo-and-how-to-configure-sudo-in-linux/)。
文毕。你也可以在评论区分享其他有用的 sudo 配置或者 [Linux 技巧](http://www.tecmint.com/tag/linux-tricks/)。
---
作者简介:Aaron Kili 是一名 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 忠实拥护者、高级 Linux 系统管理员、Web 开发者,目前在 TecMint 是一名活跃的博主,热衷于计算机并有着强烈的只是分享意愿。
译者简介:[GHLandy](http://GHLandy.com) —— <ruby> 欲得之,则为之奋斗。 <rt> If you want it, work for it. </rt></ruby>
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/sudoers-configurations-for-setting-sudo-in-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,146 | 容器监管:保持 Linux 容器的安全和稳定 | https://opensource.com/business/16/10/interview-andy-cathrow-anchore | 2017-01-25T12:48:08 | [
"容器",
"Docker",
"Anchore"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8146-1.html | 
Linux 容器正在改变 IT 从业者的工作方式。相比于庞大、沉重的虚拟机,一些组织发现把他们的应用部署在容器中更有效,可以提供更快的速度,更加密集,提升他们操作的敏捷性。
从安全的角度看,容器带来了一些优势,但是也面临着它们自己的一些安全挑战。和传统的基础设施一样,为了避免安全缺陷,确保运行在一个容器内的组件和系统库的定期更新是至关重要的。但是你如何知道什么东西运行在你的容器内?为了帮助你应对这些的安全挑战,一个名为 [Anchore](https://anchore.com)的初创公司正在开发一个[同名的开源项目](https://github.com/anchore/anchore),它用来帮助展示 Linux 容器中的内容。
为了了解更多关于 Anchore,我找到了 Anchore 的市场和产品的发言人 Andrew Cathrow,来了解更多关于这个开源项目背后的公司。
### 简而言之 Anchore 是什么? 它如何工作?
Anchore 的目标是提供一套工具,允许开发人员、运营团队、安全团队在容器的整个开发周期中保持对“监管链(Chain of Custody)”的全程可见,并提供生产部署所需的可见性、可预测性和控制性。Anchore 的引擎通过插件可以进行分析(通过提取镜像数据和元数据)、查询(允许对容器进行分析)、以及策略评估(这里的策略指可以被指定的管理的图像)。
虽然市场上有很多扫描工具,但是大部分不开源。我们认为安全合规的产品应该是开源的,否则你怎么才能信任他们。
Anchore 除了开源以外,还有两大优势,使它可以区别于市场中的商业产品。
首先,我们看的不止是操作系统的镜像。如今的扫描工具专注于操作系统的软件包,比如“你的 RPM 或 DEB 包中有CVE(安全漏洞)么?”这虽然是很重要的,你不希望你的镜像中有不安全的包,但是操作系统包只是镜像的基础。其他的层次都需要进行验证,包括配置文件、语言模块、中间件等等。你可以用的全是最新的软件包,但是可能一个配置文件配置出现错误,不安全就出现在里面。第二个不同就是允许用户添加自己的数据、查询或策略来扩展这个引擎。
### 什么推动了容器的校验和分析工具的需求出现?这个工具可以解决运营面临的什么问题呢?
企业使用 Docker 首要关注的就是安全,特别是他们正在部署的容器的分配和合规性。在生产环境中,从公共镜像库拉取一个镜像,运行它,并在几秒钟部署,是非常简单的,甚至不知道下面可能发生什么。终端用户在部署应用时,必须信任他们所部署的是安全、高效和易于维护的。
容器是不透明的,它们是一个包含应用程序的可部署的“黑盒”。虽然非常容易把这些镜像看作“打包的应用程序”,但是它们包括了系统的镜像和多达数百个包和成千上万个文件。如同所有在物理服务器、虚拟机或者云上的操作系统一样,镜像也需要维护。镜像或许包含了未补丁的安全缺陷、带有 bug 和错误配置的过期软件。
要对您的容器部署有信心,你需要知道底层是什么,并基于容器镜像的内容来做出决定。
### 如今容器的创新基本上都是开源的,你认为是为什么呢?是什么促使了它们开源呢?
在过去的 20 年中,各个组织已经经历了开源带来的优势,节省成本,减少锁定,提高了安全性和更快的创新。容器,特别是 Docker,都是非常好的例子。Docker 公司的团队不能在专有系统上创建一个新的软件部署模式,他们不能要求在修改专有系统的代码,而是与行业领导者比如谷歌、IBM、英特尔、红帽合作,朝着一个共同的目标。开源和 Linux 总是开启创新和激励产业困境。在过去,实现一个大的想法需要一个大的团队和很多资源。在开源世界,一个有着很大的创意的小公司可以工作在一个更大的社区中,通过知识共享的力量来协作,提供真正的企业创新。
为了深入的说明开源的使用,Anchroe 团队最近刚从多伦多的 LinuxCon 回来,在哪里,令人难以相信的是,微软作为钻石级的赞助商,展示了他们用在 Linux 上的产品投入的增长。Linus Toravlds 曾说过,“如果微软为 Linux 开发应用就意味着我赢了”。我要把这句话改为“开源赢了”。
### 容器领域的通用标准的创建还需要时间,在容器的几乎所有部分,仍有许多挑战。在这个领域,创业公司有哪些挑战?
这里有个很重要的点,就是没有开放的标准和开源,我们不可能看到快速推动容器的采用和改变行业格局的创新。开放容器倡议(OCI)由 Linux 和容器行业的行业领导者组成,正在为运行环境和镜像格式创造标准,这将使我们能够看到更多的创新。Anchore 很自豪能成为 OCI 的新成员,我们期待帮助形成标准。
### 你将如何围绕 Anchor 项目建立一个开源社区?
Anchore 团队来自 Ansible、Eucalyptus Systems 和 Red Hat 的领导团队,在开源社区中拥有丰富的工作经验。从一开始,Anchore 就准备创建一个强大的开源社区,我们正在应用我们在开源世界中学到的经验和教训。第一课,当然,发布要尽早尽快。我们在 6 月开源我们的检测和分析引擎,远远早于我们的商用产品,以便了确保开源项目能够独立运行,使更多的直接用户能够使用它,而无需购买 Anchore 的商用产品。通过支持、服务和增强型的数据源,有很多机会给商用产品创造更多价值,但是如果开源引擎本身没有用,我们将看不到活跃的社区。
我们将 Anchore 模块化,允许添加分析、报告和策略插件,而不需要更改核心的引擎。我们希望保证任何人都可以创建插件,所以我们选择了 Python 作为项目的基本语言,因为 Python 被开发者和系统管理员广泛应用。但是,即使你不熟悉 Python,你仍然可以使用任何你喜欢的语言或者脚本环境创建插件。如果你可以创建一个 Bash 脚本,那么你也可以创建一个 Anchore 插件。我们的目标是最大化的吸引社区的参与。虽然我们鼓励用户将贡献回馈给社区,但是我们也为这个项目构建并进行了授权,来确保可以独立创建和维护私有的插件和模块。
### 容器的用途不止是在服务器上更大密度的部署应用程序或者技术层面更快的速度,而且还有不同工具的组合,这些工具提供了一种不同的方式来拉近开发者和操作者共同工作。作为在这个领域工作的公司,你们希望提供一个什么样的消息来让开发者和运营产生共鸣?
随着越来越多的运行环境、编排、监控和集成产品,容器的生态系统正在快速发展。所以,我们的架构中的第一个考虑因素不是限定 Anchore 的部署和使用。我们需要确保我们可以适应任何 CI/CD 工作流,无论是私有部署还是云端部署。一个经常问到我们的问题是,Anchore 是否将提供一个包含了镜像扫描和分析的容器仓库。虽然这将大大简化我们的工作,但是这会迫使用户进入特定的部署架构,并限制了用户部署他们自己最好的组件的能力。我们已经确保 Anchore 可以和所有领先的仓库、运行环境平台、 CI/CD 平台和编排工具配合使用。
一些开发者掌握了运营技能,并转换为 DevOps 角色,我们看到系统管理员/运营团队也在更多的了解开发,转换成 DevOps 角色。我们也看到了具有混合能力的团队。我们设计了可供开发运营和安全团队使用的 Anchore ,以便他们共同定义规则和策略来评估开发周期中的任何一个环节。另外一个例子是插件/模块的架构,使任何人都可以在他们喜欢的环境中轻松创建一个模块 —— 无论是以 Python、Go、Perl、C 甚至是一个 Bash 脚本。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/business/16/10/interview-andy-cathrow-anchore>
作者:[Jason Baker](https://opensource.com/users/jason-baker) 译者:[Bestony](https://github.co/Bestony) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | Linux containers are helping to change the way that IT operates. In place of large, monolithic virtual machines, organizations are finding effective ways to deploy their applications inside Linux containers, providing for faster speeds, greater density, and increased agility in their operations.
While containers can bring a number of advantages from a security perspective, they come with their own set of security challenges as well. Just as with traditional infrastructure, it is critical to ensure that the system libraries and components running within a container are regularly updated in order to avoid vulnerabilities. But how do you know what is running inside of your containers? To help manage the full set of security challenges facing container technologies, a startup named [Anchore](https://anchore.com/) is developing an [open source](https://github.com/anchore/anchore)[ project](https://github.com/anchore/anchore) of the same name to bring visibility inside of Linux containers.
To learn more about Anchore, I caught up with Andrew Cathrow, Anchore's vice president of products and marketing, to learn more about the open source project and the company behind it.
### In a nutshell, what is Anchore? How does the toolset work?
Anchore's goal is to provide a toolset that allows developers, operations, and security teams to maintain full visibility of the 'chain of custody' as containers move through the development lifecycle, while providing the visibility, predictability, and control needed for production deployment. The Anchore engine is comprised of pluggable modules that can perform analysis (extraction of data and metadata from an image), queries (allowing reporting against the container), and policy evaluation (where policies can be specified that govern the deployment of images).
While there are a number of scanning tools on the market, most are not open source. We believe that security and compliance products should be open source, otherwise, how could you trust them?
Anchore, in addition to being open source, has two other major differentiators that set it apart from the commercial offerings in the market.
First, we look beyond the operating system image. Scanning tools today concentrate on operating system packages, e.g. "Do you have any CVEs (security vulnerabilities) in your RPMs or DEB packages?" While that is certainly important, you don't want vulnerable packages in your image, the operating system packages are just the foundation on which the rest of the image is built. All layers need to be validated, including configuration files, language modules, middleware, etc. You can have all the latest packages, but with even one configuration file wrong, insecurity sets in. A second differentiator is the ability to extend the engine by adding users' own data, queries or policies.
### What is driving the need for an inspection and analytics tool for containers? What problems are operators facing that this helps to solve?
A primary concern for enterprises adopting Docker today is security, in particular, the governance and compliance of the containers they are deploying. It's almost too easy to pull an application image from a public registry, run it, and within seconds deploy an application in production without even knowing what's under the covers. End users must have confidence that when they deploy applications they will be secure, performant and easily maintained.
Containers are opaque in that they are deployable ‘black boxes' that contain applications. While it's easy to treat these images as "just packaged applications," they include operating system images with up to hundreds of packages and thousands of files. As with all operating systems on physical servers, virtual machines, or in the cloud, images need to be maintained. The images may contain unpatched security vulnerabilities, outdated software that contains bugs, or may be misconfigured.
To have confidence in your container deployments you need to know what's under the covers to analyze and make decisions based on the contents of your container images.
### The innovation around containers today is almost entirely happening in open source. Why do you think that is? What's driving the desire for openness?
Over the past 20 years organizations have experienced the advantages open source brings to cost savings, reduced lock-in, improved security and faster innovation. Containers, and Docker specifically, are great examples. The team at Docker Inc. would not have been able to create this innovative new software deployment paradigm on top of a proprietary system. They would not have been able to make the required modifications to the code in a proprietary system, nor be able to work cooperatively with industry leaders such as Google, IBM, Intel, and Red Hat—all working toward a common goal. Open source and Linux have always enabled innovation and positive industry disruption. In the past, delivering a big idea required a big team and lots of resources. In the open source world, a small company with big ideas can work in the wider community and benefit from *shared intellectual horsepower* to collaboratively deliver real enterprise IT innovation.
To illustrate the deep adoption of open source, the Anchore team recently returned from LinuxCon in Toronto, where it was incredible to see Microsoft as a diamond level sponsor presenting a growing portfolio of their products that work with or on Linux! Linus Torvalds once said, "If Microsoft ever does applications for Linux it means I've won." I'd amend that statement to read "Open has won."
### The days of common standards in the container space are still very young, and there are still many competing visions for nearly every part of the stack. What challenges does that create for a startup in this space?
It is important to remember that without open standards and open source we wouldn't have seen the innovation that is driving rapid container adoption and changing the industry landscape. The Open Container Initiative (OCI), comprised of industry leaders from the Linux and Container industries, is doing great work setting standards for both the runtime and image formats that will allow us to see even more innovation. Anchore is proud to be a new member of the OCI and we look forward to helping form the standards.
### How are you working to build an open source community around the Anchore project?
The Anchore team has a rich history of building and working within open source communities, with leaders from Ansible, Eucalyptus Systems, and Red Hat. From the start, Anchore began building a strong open source community and we are applying lessons learned in the open source world. The first lesson, of course, is to release early and often. We open sourced our inspection and analysis engine back in June, far in advance of our commercial offering, to ensure that the open source project can stand on its own with features that make it useful to many end-users without having to purchase Anchore's commercial offering. There will always be opportunities to add more value with support, services, and enhanced data feeds with a commercial offering, but if the open source engine is not useful in itself then we will not see an active community.
We built Anchore to be modular to allow analysis, reporting and policy plugins to be added without requiring changes to the core engine. We want to ensure that anyone can create plugins, so we chose Python as the base language for the project because it is widely used by developers and sysadmins alike. But even if you are not well versed in Python you can still create plugins using whatever language or scripting environment you prefer. If you can create a bash script then you can create an Anchore plugin. Our goal is to enable the broadest possible community to attract participation. While we encourage our users to pass these contributions back to the community we've architected and licensed the project to ensure that private plugins/modules can be created and maintained independently.
### The promise of containers is not just greater application density on servers or greater speed on the technical side, but a combination of different tools that together provide a different way of approaching the way developers and operators work together. As a company working in this space, how are you providing a message that resonates with both developers and operators?
The container ecosystem is evolving rapidly with a growing number of runtime, orchestration, monitoring and integration products. So the first consideration we had to factor into our architecture was to not be prescriptive about Anchore deployment and usage, we need to ensure that we can fit into any CI/CD pipeline whether it's on-premise or deployed in the cloud. A common question we are asked is if Anchore will provide a container registry that includes image scanning and analysis. While this would simplify our work considerably, it would force customers into specific deployment architectures and limit customers' ability to deploy their own best-of-breed stack. We've made sure that Anchore works with all leading registries, runtime platforms, CI/CD platforms and orchestration tools.
## Comments are closed. |
8,147 | 剪切板是一个安全问题 - 在 Linux 中你可以用 xclip 和 cron 修复它 | https://www.darrentoback.com/your-computer-s-clipboard-is-a-security-problem-fix-it-in-linux-with-xsel-and-cron | 2017-01-26T13:02:56 | [
"剪贴板",
"安全",
"xclip"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8147-1.html | 
**更新:我原文推荐的是 xsel,但几个用户报告说它禁用了他们的声音。这对我来说不是问题,但我发现了另一种方式(使用 [xclip](https://github.com/astrand/xclip) )来实现同样的目标,这样应该就能回避这个问题。文章已更新,切换到了 xclip。**
在你的操作系统上复制/粘贴的能力是必不可少的。无论你写的是代码还是剧本,这两个功能是在计算机上处理文本的核心。当你复制文本时,它会进入内存驻留的剪贴板。除非安装了可以容纳多个条目的剪贴板管理器,否则剪贴板默认情况下只会处理一个*复制*事件,当你*复制*其他东西的时候,它之前的条目才会消失。在标准 Linux 设置中,剪贴板内容存储在控制它的程序的内存中(通常是 Xorg)。
剪贴板应该有所限制,因为任何程序都可以读取其内容,如果放任它,它保存的东西就会一直呆在那里。此外,现代浏览器允许恶意网站以多种方式从剪贴板读取(和写入)。
虽然不是默认设置,但浏览器可以设置为禁止访问剪贴板。虽然也有用于浏览器和操作系统管理剪贴板的附加组件,但是,在此链条的源头解决问题更容易、更可靠,并使系统范围内的剪贴板安全。有很多理由使用一个剪贴板,但没有足够的理由让内容在那里保留一两分钟以上。
密码管理器最近变得很受欢迎,如果你使用过的话,你已经了解了它们如何将密码复制到剪贴板,以便你可以将其粘贴到浏览器中,并登录到你的帐户。接下来会发生什么?你的密码会保留在剪贴板上,直到另一个复制事件或重新启动。
即使你使用单独的浏览器来处理银行等事务,复制密码时,通过剪贴板会将其带回其他浏览器,并将其暴露在基于 web 的剪贴板收集技术中。
我的解决方案是在后台进行处理,每分钟自动清除剪贴板的内容。它使用 xclip 这个命令行工具、一个小脚本和 [cron](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cron)。cron 的一分钟间隔给你足够的时间来复制密码,然后它会清空剪贴板。此动作会每分钟执行一次,保证复制无忧。
我们需要使用 [xclip](https://github.com/astrand/xclip) 工具清除终端中的剪贴板。在基于 apt 的发行版中,输入:
```
sudo apt-get install xclip
```
我们在终端中测试一下程序。首先从某处复制一些文字,复制到其他地方,并输入这两条命令:
```
touch blank
xclip -selection clipboard blank
```
接着再次尝试复制文本 - 它应该就会消失了。现在把这个命令放在脚本中。创建一个脚本(用你的文本编辑器代替 leafpad):
```
leafpad nukeclipboard.sh
```
并在新文件中输入下面的内容:
```
#!/bin/sh
touch blank && xclip -selection clipboard blank
```
保存并关闭文件,接着加上可执行权限:
```
chmod +x nukeclipboard.sh
```
现在让 cron 任务每分钟运行一次。首先要小心,不同的发行版有不同的 cron 选项。以下设置适用于 Ubuntu(基于)的发行版,并且在你的发行版中过程可能不同,因此[请阅读手册](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cron)。
要设置 cron 任务,请在终端输入:
```
crontab -e
```
在最后被注释掉的行后,输入下面的行(将 `/home/user/` 替换为你的脚本位置):
```
* * * * * export DISPLAY=:0 && /home/user/nukeclipboard.sh
```
现在按下 `ctrl-o` 保存(使用你的 cron 任务编辑器的保存快捷键),然后点击回车保存你的 crontab。最后,按下 `ctrl-x` 退出程序。从现在起,你的剪贴板的使用寿命为一分钟。
关于上面的 cron 条目的解释: cron 有环境变量的限制,当它失败时,你可能要花一整天试着一百种方法来解决它。在我找到了一个建议设置 DISPLAY 的[快速修复](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/14296911/when-linux-system-calls-scripts-some-commands-dont-work-cron-if-up-d/24070707#24070707) 后,就解决了。感谢 [Mike Q](https://stackoverflow.com/users/1618630/mike-q) 的贡献。
现在,可能会发生当你要粘贴复制的东西时,正好剪贴板被清空,从而无法粘贴,但它只是安全的一个小的代价。 如果这是一个问题,您可以配置 cron 以任何适合您的间隔运行任务(比如 2 分钟)。 Ubuntu 的说明在[此页](https://help.ubuntu.com/community/CronHowto)。
我希望这个教程能帮助你把剪贴板锁定下来 - 如果你有可以工作的脚本或者更好的方法,欢迎来做评论。
---
via: <https://www.darrentoback.com/your-computer-s-clipboard-is-a-security-problem-fix-it-in-linux-with-xsel-and-cron>
作者:[dmt](https://www.darrentoback.com/about-me) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 404 | null |
|
8,148 | 5 个针对有经验用户的 Vim 实用技巧 | https://www.maketecheasier.com/vim-tips-tricks-for-experienced-users/ | 2017-01-26T14:18:00 | [
"Vim"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8148-1.html | 
这篇文章是 Vim 用户指南系列文章中的一篇:
* [Vim 初学者入门指南](/article-8143-1.html)
* [Vim 快捷键速查表](/article-8144-1.html)
* 5 个针对有经验用户的 Vim 实用技巧
* [3 个针对高级用户的 Vim 编辑器实用技巧](/article-8149-1.html)
Vim 编辑器提供了很多的特性,要想全部掌握它们很困难。然而,花费更多的时间在命令行编辑器上总是有帮助的。毫无疑问,和 Vim 用户们进行交流能够让你更快地学习新颖有创造性的东西。
**注:** 本文中用到的例子,使用的 Vim 版本是 7.4.52 。
### 1、 同时编辑多个文件
如果你是一名软件开发者或者把 Vim 作为主要的编辑器,那么可能很多时候你需要同时编辑多个文件。“<ruby> 紧跟 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> following </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”是在同时编辑多个文件时可用的实用技巧。
不需要在多个 shell 界面中打开多个文件,你可以通过把多个文件的文件名作为 Vim 命令的参数从而在一个 shell 界面中打开多个文件。比如:
```
vim 文件1 文件2 文件3
```
第一个文件(例子中的文件1)将成为当前文件并被读入缓冲区。
在编辑器中,使用 `:next` 或 `:n` 命令来移动到下一个文件,使用 `:prev` 或 `:N` 命令返回上一个文件。如果想直接切换到第一个文件或最后一个文件,使用 `:bf` 和 `:bl` 命令。特别地,如果想打开另外的文件并编辑,使用 `:e` 命令并把文件名作为参数(如果该文件不在当前目录中则需要完整路径做为参数)。
任何时候如果需要列出当前打开的所有文件,使用 `:ls` 命令。看下面展示的屏幕截图。

注意 ”%a” 表示文件在当前活动窗口,而 “#” 表示上一个活动窗口的文件。
### 2、 通过自动补全节约时间
想节约时间并提高效率吗?使用缩写吧。使用它们能够快速写出文件中多次出现、复杂冗长的词。在 Vim 中缩写命令写就是 `ab` 。
比如,当你运行下面的命令以后:
```
:ab asap as soon as possible
```
文件中出现的每一个 `asap` 都会被自动替换为 `as soon as possible` ,就像你自己输入的一样。
类似地,你可以使用缩写来更正常见的输入错误。比如,下面的命令
```
:ab recieve receive
```
将会自动更正拼写错误,就像你自己输入的一样。如果在一次特殊情况下你想阻止缩写展开或更正发生,那么你只需要在输入一个单词的最后一个字母以后按 `Ctrl + V` ,然后按空格键。
如果你想把刚才使用的缩写保存下来,从而当你下次使用 Vim 编辑器的时候可以再次使用,那么只需将完整的 `ab` 命令(没有起始的冒号)添加到 `/etc/vim/vimrc` 文件中。如果想删除某个缩写,你可以使用 `una` 命令。比如: `una asap` 。
### 3、 切分窗口便于复制/粘贴
有时,你需要从一个文件将一段代码或文本的一部分复制到另一个。当使用 GUI(图形界面)编辑器的时候,这很容易实现,但是当使用一个命令行编辑器的时候,这就变得比较困难并且很费时间。幸运的是, Vim 提供了一种高效、节约时间的方式来完成这件事。
打开两个文件中的一个然后切分 Vim 窗口来打开另一个文件。可以通过使用 `split` 命令并以文件名作为参数来完成这件事。比如:
```
:split test.c
```
上面的命令将分离窗口并打开文件 “test.c”

注意到 `split` 命令水平分离 Vim 窗口。如果你想垂直分离窗口,那么你可以使用 `vsplit` 命令。当同时打开了两个文件并从一个文件中复制好内容以后,按 `Ctrl + W` 切换到另一个文件,然后粘贴。
### 4、 保存一个没有权限的已编辑文件
有时候当你对一个文件做了大量更改以后才会意识到你对该文件仅有 `只读` 权限。

虽然把文件关闭,获取权限以后再重新打开是一种解决方法。但是如果你已经做了大量更改,这样做会很浪费时间,因为在这个过程中所有的更改都会丢失。 Vim 提供了一种方式来处理这种情况:你可以在编辑器中在保存文件前更改文件权限。命令是:
```
:w !sudo tee %
```
这个命令将会向你询问密码,就像在命令行中使用 `sudo` 一样,然后就能保存更改。
**一个相关的技巧**:在 Vim 中编辑一个文件的时候,如果想快速进入命令行提示符,可以在编辑器中运行 `:sh` 命令,从而你将进入一个交互的 shell 中。完成以后,运行 `exit` 命令可以快速回到 Vim 模式中。
### 5、 在复制/粘贴过程中保持缩进
大多数有经验的程序员在 Vim 上工作时都会启用自动缩进。虽然这是一个节约时间的做法,但是在粘贴一段已经缩进了的代码的时候会产生新的问题。比如,下图是我把一段已缩进代码粘贴到一个在自动缩进的 Vim 编辑器中打开的文件中时遇到的问题:

这个问题的解决方法是 `pastetoggle` 选项。在 `/etc/vim/vimrc` 文件中加入下面这行内容:
```
set pastetoggle=<F2>
```
然后当你在 `插入` 模式中准备粘贴代码前先按 `F2` 键,就不会再出现上图中的问题,这样会保留原始的缩进。注意,你可以用其他的任何键来代替 `F2`,如果它已经映射到了别的功能上。
### 结论
更进一步的提高你的 Vim 编辑器技巧的唯一方法是,在你日复一日的工作中使用命令行编辑器。留意那些耗时多的操作,然后尝试去寻找是否有编辑器命令可以很快地完成这个操作。
---
via: <https://www.maketecheasier.com/vim-tips-tricks-for-experienced-users/>
作者:[Himanshu Arora](https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/himanshu/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 
The Vim editor offers so many features that it’s very difficult to learn all of them. While spending more time on the command line editor always helps, there is no denying that you can learn new and productive things faster while interacting with fellow Vim users. In this article, I will go through some tips and tricks on Vim that can improve your text editing workflow today.
[1. Working with Multiple Files](#work-multiple-files)[2. Save Time with Auto Complete](#save-time-auto-complete)[3. Split Windows to Easily Copy and Paste](#split-windows-copy-paste)[4. Save a File You Edited Without Permissions](#save-edited-root-files)[5. Preserve Indentation During Copying and Pasting](#preseve-indent-copy-paste)[6. Use Text Object Commands](#use-context-commands)[7. Use Marks to Speed Up Editing](#use-marks-for-editing)[8. Automate Editing Using Macros](#automate-edits-macros)[9. Take Advantage of Third-Party Plugins](#take-advantage-plugins)
## 1. Working with Multiple Files
If you’re a software developer or someone who uses Vim as their primary editor, chances are that you have to work with multiple files simultaneously. Following are some useful tips that you can use while working with multiple files.
Instead of opening files in different terminal tabs, you can open all of them in a single tab by passing their filenames as arguments to the vim command:
`vim file1 file2 file3`
Doing this will load your three files into their own separate buffers inside Vim.
Use the `:next`
or `:n`
command to move to the next file, and the `:prev`
or `:N`
command to return to the previous one.
To directly switch to the first or the last file, use `:bf`
and `:bl`
commands, respectively.

To open and start editing another file, use the `:e`
command with the filename as argument.

**Note:** You need to provide the complete path if your file is not present in the current directory.
You can also use the `:ls`
command to list all the currently open buffers in your Vim session.

**Note**: The “%a” indicates that the file is in the current active window, while “#” tells you that it’s the last file that you switched to prior to the current one.
## 2. Save Time with Auto Complete
Want to save time and improve accuracy? Use abbreviations. They come in handy while writing long, complex words that occur frequently throughout a file. The command for abbreviations is `ab`
.
For example, running the following will automatically replace the word “asap” with “as soon as possible:”
:ab asap as soon as possible

Similarly, you can also use abbreviations to correct common typing mistakes. For example, the follow command will automatically correct the spelling mistake as you type:
:ab recieve receive
If you want to prevent the expansion/correction from happening at a particular occurrence, just press `Ctrl` + `V` after the last character of the word and then press the `Space` key.

To remove a particular abbreviation, you can use the `una`
command. For example, `:una asap`
will delete the abbreviation for “as soon as possible.”

If you want to save the abbreviation you’ve created so that it is available to you the next time you use the Vim editor, add the complete `ab`
command without the initial colon to the “~/.vimrc” file.
**Tip:** are you currently stuck in a Vim mode? Learn some of the [different ways to exit the Vim editor](https://www.maketecheasier.com/exit-vim-editor-linux/).
## 3. Split Windows to Easily Copy and Paste
There are times when you want to copy a piece of code or a portion of text from one file to another. While the process is easy when working with GUI editors, it gets a bit tedious and time-consuming while working with a command line editor. Fortunately, Vim provides a way to minimize the time and effort required to do this.
Open one of the two files and then split the Vim window to open the other file. This can be done by using the `split`
command with the file name as argument. For example, this command will split the window and open “test.c:”
:split test.c

Observe that the command split the Vim window horizontally. In case you want to split the window vertically, you can do so using the `vsplit`
command. Once both the files are opened, copy the stuff from one file, press `Ctrl` + `W` to switch the control to another file, and paste.

**On a side note: **Check out our picks for the [best cross-platform text editors for programmers](https://www.maketecheasier.com/best-cross-platform-text-editors-for-programmers/) today.
## 4. Save a File You Edited Without Permissions
There are times when you realize that a file is read-only only after making a bunch of changes to it. Although closing the file and reopening it with the required permissions is a way out, doing this will lose all the changes that you’ve already made to your file.

To fix this, you can run the `:w`
command followed by external Bash command that reloads your file with superuser priveleges:
:w !sudo tee %
Vim will ask for your password to resolve the command, then it will save your current changes.
You can also quickly access your system shell while editing a file in Vim. To do that, run the `:sh`
command from within the editor.

Once you are done, run the `exit`
command to return to your Vim session.
## 5. Preserve Indentation During Copying and Pasting
Most of the programmers work on Vim run it with its auto-indentation feature on. Although it’s a time-saving practice, it creates a problem while pasting indented code. For example, this is what happened when I pasted indented code into a Vim editor with auto-indent on.

You can fix this issue by adding the `pastetoggle`
option to Vim’s config file. To do that, open the vimrc file, then paste the following line of code to the end of your config:
set pastetoggle=<F2>
Save your vimrc, then open the file that you want to paste your indented code on.
Go into Insert Mode, then press `F2` before pasting your indented code. Doing this should preserve the original indentation.

**Note:** you can replace `F2` with any other key if it’s already mapped to some other functionality.
## 6. Use Text Object Commands
Another way to easily up your Vim editing game is by using its built-in “text object commands.” These are special-case movement keys that take in the context of where the cursor currently is and operates your commands inside that context.
One of the most useful text object command that you can use is `I`
. This takes a motion key such as `W` and operates your commands inside that context. For example, you can press `C` + `I`, then `W` to run the change command on the word under your Vim cursor.

The `I`
command also works for other forms of text delimiters. For instance, pressing `C` + `I`, then `Shift` + `9` will clear any text in-between the parenthesis under your cursor.

## 7. Use Marks to Speed Up Editing
Marks are a nifty feature in Vim that saves a specific spot in your file to a key on your keyboard. Similar to browser bookmarks, these enable you to jump from point to point while editing large pieces of text and code.
To create a Vim mark, navigate to the location that you want to save then press `M`, followed by the letter that you want to bind the location to. In my case, I will set my new mark to the “A” key on my keyboard.

Test whether your new mark is working properly by pressing `G` twice to go to the top of the document, then press ``` (Grave) + `A`.
You can also quickly go back to your previous location by double tapping the ``` (Grave) key.
To list all the available marks on your current session, press `Shift` + `;` (Semicolon), then type `marks`
on the command buffer.

**Good to know:** Level up your Vim know-how by checking out our [comprehensive cheatsheet for Vim](https://www.maketecheasier.com/cheatsheet/vim-keyboard-shortcuts/).
## 8. Automate Editing Using Macros
On top of convenient commands, you can also streamline your editing workflow in Vim by automating repetitive tasks using macros. It’s a built-in feature that allows you to “record” an action inside the editor and run it across an entire file.
To create a new Vim macro, press `Q`, followed by a key where you want to assign your macro to. For me, I will assign my new macro to my “1” key.

Perform the edit that you want to make on the current line. In my case, I will go to the start of the line, edit the first word to “That,” add “Hello, Make Tech Easier” at the end, then go to the next line.
**Note:** Vim will perform your macros exactly as you recorded it regardless of the current cursor position.
Once you’re done with your edit, press `Q` to save your new macro.
Test whether your new macro is working properly by pressing `Shift` + `2`, followed by your macro key.

**Tip: **you can also perform bulk editing using Vim’s visual mode. Learn more about it by checking out our quick guide to [commenting multiple lines in Vim](https://www.maketecheasier.com/comment-multiple-lines-vim/).
## 9. Take Advantage of Third-Party Plugins
Aside from its stellar built-in functions, Vim is an extensible text editor that you can [customize using third-party plugins](https://www.maketecheasier.com/8-vim-plugins-to-enhance-your-productivity/). This enables you to include features not present in default Vim and shape the editor to your workflow.
The easiest way to get started with Vim plugins is by installing Plug. This is a lightweight plugin manager that handles the installation and management of your plugins directly from Vim. To install it, run the following command:
curl -fLo ~/.vim/autoload/plug.vim --create-dirs https://raw.githubusercontent.com/junegunn/vim-plug/master/plug.vim
Open your current user’s .vimrc, then paste the following block of code at the end of the file:
call plug#begin() call plug#end()
Save your .vimrc, restart Vim, then press `Shift` + `;` (Semicolon) to bring up the command buffer.
Enter `PlugStatus`
on the buffer to confirm that you’ve properly installed Plug on your Vim instance.

To install a plugin, go back to the `call plug#begin()`
section of your .vimrc file, then type “Plug,” followed by the Git URL of your plugin. For example, pasting the following code will install the [Goyo](https://github.com/junegunn/goyo.vim) plugin to your Vim instance:
`Plug 'https://github.com/junegunn/goyo.vim.git'`

Restart your Vim client, bring up the command buffer, then run `PlugInstall`
to start the plugin install process.

With the knowledge of how to optimize Vim under your belt, you can start exploring what this brilliant text editor can do for you. Learn how to [turn Vim into a powerful word processor](https://www.maketecheasier.com/turn-vim-word-processor/) by adding some simple functions to your config file.
Image credit: [Christina @ wocintechchat.com via Unsplash](https://unsplash.com/photos/shallow-focus-photo-of-woman-using-laptop-computer-fch6vkbouCc). All alterations and screenshots by Ramces Red.
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox |
8,149 | 3 个针对高级用户的 Vim 编辑器实用技巧 | https://www.maketecheasier.com/vim-tips-tricks-advanced-users/ | 2017-01-27T08:14:00 | [
"Vim"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8149-1.html | 
这篇文章是 Vim 用户指南系列文章中的一篇:
* [Vim 初学者入门指南](/article-8143-1.html)
* [Vim 快捷键速查表](/article-8144-1.html)
* [5 个针对有经验用户的 Vim 技巧](/article-8148-1.html)
* 3 个针对高级用户的 Vim 编辑器实用技巧
毫无疑问, Vim 是一个很强大的文本编辑器。它提供了大量的特性,这意味着学习并记住 Vim 的所有功能实际上是不可能的。但是我们至少可以不断学习简单的方法来完成事情,从而随着时间的增长,我们使用编辑器的经验将会变得更好。
请记住,在这篇文章中我们将讨论的一些 Vim 编辑器技巧是针对高级用户的。
**注**:如果你是第一次接触 Vim,你可以首先阅读我们的[入门指南](/article-8143-1.html)。对于已经使用过 Vim 编辑器的用户,我确信 [Vim 快捷键速查表](/article-8144-1.html)将会对你很有帮助。如果你已经是一名有经验的用户,你可能对[一些针对有经验用户的技巧](/article-8148-1.html)比较感兴趣。
请注意文中提到的所有技巧绝大多数都是在简单、易于理解的代码环境中进行阐述的,因为它们在软件开发中确实很实用。但这并不意味着普通用户(非程序员、没有把 Vim 作为一般的文本编辑器)在他们的工作中用不到。
### 1、为文件设置特定的变量
有时候,在一个特定文件中,你可能想把输入的制表符用空格代替,或者想要把源代码文件使用两个空格缩进,即便编辑器的默认缩进是四个空格。
基本上我们在这儿讨论对针对文件的的更改。 Vim 提供的这个特性允许你对一个指定的文件更改特定的设置。这个特性叫做 “<ruby> 模式行 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Modeline </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>” 。
比如,如果你想把输入的每一个制表符(Tab)用空格代替,那么你只需要在文件的前几行或最后几行加入下面的模式行:
```
# vim: set expandtab:
```
如果想把默认缩进从 4 个空格变成 2 个空格,可以在源文件中添加下面的模式行:
```
// vim: noai:ts=2:sw=2
```
在使用模式行时,请记住下面这几个重要的点:
* 模式行只能添加在文件中的前五行或者最后五行。
* 为了使用模式行这个特性,必须在 `.vimrc` 文件中添加 `:set modeline` 。
* 在以 root 用户身份对文件进行编辑的时候该特性失效。
了解更多的信息,请阅读该特性的[官方文档](http://vim.wikia.com/wiki/Modeline_magic)。
### 2、 关键字补全
当你开始写的复杂代码越来越多或者开始在一个大的源文件上编辑时,你会遇到一些变量名字。有时,要记住所有的变量名字不太容易,所以当需要输入变量名字的时候,你通常从已经使用过的地方复制过来。
幸运的是,使用 Vim 你只需要输入变量的几个起始字母即可。在’插入模式’中,按 `Ctrl + n` 或者 `Ctrl + p` 可以得到一个匹配的关键词列表。 `Ctrl + n` 用来插入下一个匹配词; `Ctrl + p` 给出一个之前匹配的关键词列表。
下图是该特性的一个展示:

正如上面的屏幕截图清晰展示的那样,列表中也会出现其他源文件中包含的词。关于该特性的更多信息,请访问[这儿](http://vim.wikia.com/wiki/Any_word_completion)。
### 3、 搜索
假设你正在调试代码,其中一个需要做的工作是快速查看一个变量在一个文件中所有出现的地方。一个常用的方法是退出‘插入模式’,输入 `/[变量名字]` 命令,按回车 ,然后返回‘插入模式’,使用 `n` 和 `p` 在关键字之间导航。
上面讲到的这种方法没毛病,但是还有一种更简单、更快捷的方法可以来完成这样的搜索。使用这种方法,首先你需要退出‘插入模式’,然后把光标移动到你想要搜索的词/变量下面,这并不费时。接下来,你只需要按 `Shift + *` 即可。
重复这样做,然后编辑器将会带你找到在文件中所有使用了这个词/变量的地方。
### 结论
尽管是针对高级用户,但文章中讨论的这些技巧并不难理解,也比较容易使用。如果你具有一定的基础,那么你能够从中获益很多。不必多说,无论是任何新特性或观念,你需要勤于练习这些技巧才能够把它们变成一种习惯。
---
via: <https://www.maketecheasier.com/vim-tips-tricks-advanced-users/>
作者:[Himanshu Arora](https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/himanshu/) 译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 200 | OK | 
Vim is undoubtedly a very powerful text editor. It offers a plethora of features which means that studying and remembering every Vim functionality isn’t practically possible. But what we can do at least is keep learning easier ways of doing things so that our experience with the editor keeps on getting better with time.
With that in mind, in this article we will discuss some Vim editor tips/tricks that are aimed at advanced users.
**Note**: If you are completely new to Vim, you can first go through our [getting started guide](https://www.maketecheasier.com/start-with-vim-linux/). For those who’ve just started using the editor, I’m sure our [Vim keyboard shortcuts cheatsheet](https://www.maketecheasier.com/cheatsheet/vim-keyboard-shortcuts/) will be extremely useful to you. And if you’re already an experienced user, you might also want to find out [some tips and tricks for experienced users](https://www.maketecheasier.com/vim-tips-tricks-for-experienced-users/).
Please note that all the tips mentioned in this article have been mostly explained using easy-to-understand coding situations, as they come in really handy while software development. But that does not mean normal users (who aren’t coders and use Vim for general text editing) can’t use them in their work.
## 1. Set file specific variables
There may be times when – in a particular file – you would want any tab character that you type to get replaced by spaces. Or you may want a source code file to use two spaces for indentation even if the editor’s default indentation is set to four spaces.
Basically we’re talking about file-specific changes here. There’s a feature that Vim provides which allows you to change certain settings only for a particular file. That feature is called “Modeline.”
For example, to make sure that each tab you type gets replaced by spaces, all you have to do is to add the following modeline in the first or last few lines of the file in question:
# vim: set expandtab:
And to change the indentation from default (4) to 2, use the following modeline in the source file:
// vim: noai:ts=2:sw=2
Here are some important points that you need to keep in mind when dealing with modelines:
- Modelines should only be added in the first or last five lines of the file.
- The “modeline” option must be set (
`:set modeline`
) in the “.vimrc” file order to take advantage of this feature. - The feature is off by default when editing as root.
For more information, head to the feature’s [official documentation](https://vim.fandom.com/wiki/Modeline_magic).
## 2. Keyword completion
As you start writing more and more complex code or start working on large source files, you deal with several variable names. Sometimes it’s not easy to remember all the names, so whenever you have to write a variable name you usually copy it from where it’s already used.
Thankfully, with Vim you can just write some initial letters of the variable. Without leaving the Insert mode, press “Ctrl + n” or “Ctrl + p” to get a list of matching keywords. While “Ctrl + n” is used to insert the next matching word, “Ctrl + p” gives you a list of previous matching words.
Here’s this feature in action.
As is clear from the screenshot above, the list that pops up also contains words from other source files. For more information on this feature, head [here](https://vim.fandom.com/wiki/Any_word_completion).
## 3. Searching
Suppose you are debugging your code, and as part of that you need to quickly see all the occurrences of a variable in a file. A commonly used way to do this is to come out of the Insert mode, write `/[var-name]`
, press Enter, and then go back and forth using the “n” and “p” keys.
There’s no problem with the aforementioned approach, per se, but there’s a slightly more easier and quicker way to do this kind of search. For that, first you have to make sure that you are out of Insert mode and that the cursor is under the word/variable you’re trying to search, which isn’t time consuming at all. And next, all you have to do is press “Shift + *.”
Do this repeatedly, and the editor will quickly take you to all the places where the word/variable is used in the file.
## Conclusion
Although aimed at advanced users, the tips/tricks discussed here aren’t difficult to understand and use. If your basics are clear, you can really benefit from them. Needless to say, as with any new feature or concept, you need to practice these tips to make them a habit.
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox |
8,150 | 你现在可以下载包含所有风味的 Ubuntu 16.10 的单独 ISO 镜像了 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/you-can-now-have-a-single-iso-image-with-all-essential-ubuntu-16-10-flavors-exclusive-511788.shtml | 2017-01-28T08:44:00 | [
"Linux AIO",
"Ubuntu"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8150-1.html | Linux AIO 开发商 Željko Popivoda 通知说可以下载 Linux AIO(All-in-One)Ubuntu 16.10 Live DVD 了,该 DVD 包含所有主要的 Ubuntu 16.10 <ruby> 风味 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> flavor </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>版本。

如果你梦想有一个可以写在 USB 或 DVD 光盘上的单独 ISO 镜像,然后在需要时启动某个 Ubuntu Linux 操作系统(如 Ubuntu、Kubuntu、Xubuntu、Lubuntu 或者 Ubuntu MATE),现在你就可以用 Linux AIO Ubuntu 16.10 做到了。
[Linux AIO](http://linuxaio.net/) 团队以开发这种完全免费的多发行版 ISO 镜像而闻名,而 Linux AIO Ubuntu 16.10 有两个版本,分别用于 64 位和 32 位平台,里面有 Ubuntu 16.10、Kubuntu 16.10、Xubuntu 16.10、Lubuntu 16.10、Ubuntu MATE 16.10 和 Ubuntu GNOME 16.10。
这些都是未修改的官方发行版。Linux AIO 团队把它们都放在一个易于使用的单一容器中,例如,当你在客户那,你需要向他/她展示各种基于 Linux 的操作系统来选择,你就不必带来六个不同的 U 盘或 DVD 光盘。
### 包含了硬件和内存测试工具
两种 Linux AIO Ubuntu 16.10 都附带两个重要的实用程序,即 HDT(硬件检测工具),用于查看目标计算机上是否与各个同 Ubuntu 16.10 流派完全兼容,还有 Memtest86+,这是一个非常流行的命令行工具,用于测试系统内存错误并验证其完整性。
[Linux AIO Ubuntu 16.10 现在可以下载了](http://linux.softpedia.com/get/Linux-Distributions/Ubuntu-AIO-DVD-103429.shtml),但请记住,由于托管文件的 SourceForge 服务器的存储限制,镜像被分为两个 .7z 存档,你需要下载并解压缩以获取可用的 ISO。
我们曾经被许多读者问过 Linux AIO Live DVD 是否支持 UEFI ,答案仍然是没有,但是团队正在努力实现未来对 UEFI 的支持。还请查看最近发布的 Linux AIO Ubuntu Mixture 2017.01。
---
via: <http://news.softpedia.com/news/you-can-now-have-a-single-iso-image-with-all-essential-ubuntu-16-10-flavors-exclusive-511788.shtml>
作者:[Marius Nestor](http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/marius-nestor) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,151 | 如何在 Linux 中让 sudo 密码会话的超时更长些 | http://www.tecmint.com/set-sudo-password-timeout-session-longer-linux/ | 2017-01-29T09:39:00 | [
"sudo"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8151-1.html | 在最近的文章中,我们向你展示了 [在 Linux 中设置 sudo 的十条 sudoers 实用配置](/article-8145-1.html)以及[让 sudo 在你输入错误的密码时“嘲讽”你](/article-8128-1.html),在本文中,我们发现了另一个 sudo 贴士,在 Ubuntu Linux 中使 sudo 密码会话(超时)更长或更短。
在 Ubuntu 及其衍生版如 Linux Mint 或任何其他基于 Ubuntu 的发行版中,当你执行 [sudo 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/su-vs-sudo-and-how-to-configure-sudo-in-linux/) 时,它将提示你输入管理密码。

在第一次执行 sudo 命令后,默认情况下密码将保持 15 分钟,因此你不需要为每个 sudo 命令键入密码。
如果,你因为某种原因觉得 15 分钟太长或太短,你可以在 `sudoers` 文件中做一个简单的调整。
要设置 sudo 密码超时值,请使用 `passwd_timeout` 参数。首先使用 `sudo` 和 `visudo` 命令以超级用户权限打开 `/etc/sudoers` 文件,如下所示:
```
$ sudo visudo
```
接着添加下面的默认值,这意味着 sudo 密码提示将会在用户使用 sudo 20 分钟后过期。
```
Defaults env_reset,timestamp_timeout=20
```
注意:你可以以分钟设置为你所需的任何时间,它会在超时之前一直等待。 如果要为每个执行的 sudo 命令弹出密码提示,你也可以将时间设置为 `0`,或者通过设置值 `-1` 永久禁用密码提示。
下面的截图显示了我在 `/etc/sudoers` 文件中设置的默认参数。

*改变 sudo 密码超时*
按 `Ctrl + O` 保存文件,然后使用 `Ctrl + X` 退出。 然后,使用 `sudo` 运行命令并等待 2 分钟以检查密码提示是否超时以测试设置是否正常。
在本篇中,我们解释了如何设置 `sudo` 密码提示超时之前的分钟数,记得在评论栏分享你对这篇文章的想法或者其他[对系统管理员配置有用的 sudo 配置](http://www.tecmint.com/sudoers-configurations-for-setting-sudo-in-linux/)。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux SysAdmin 以及 web 开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创建者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/set-sudo-password-timeout-session-longer-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,152 | Linux 系统的成长之路:试用 1993-2003 年之间的 Linux 老版本系统 | https://opensource.com/article/16/12/yearbook-linux-test-driving-distros | 2017-01-27T18:38:00 | [
"Linux",
"历史"
] | /article-8152-1.html |
>
> 让我们一起来回顾 Linux 早期版本的美好时光
>
>
>

开源软件最具独特性的一点就是它永远不会真正的走到 EOL(生命的终点)。它们的磁盘镜像文件大都可以一直在网上找到,并且它们的许可证也不会过期,因此,我们可以返回去找到那些老版本的 Linux 系统,并在虚拟机中安装它们,这都是很容易做到的。通过回顾那些珍贵的系统画面,让我们来回顾 Linux 系统这么多年来所发生的翻天覆地的变化。
我们从 Slackware 1.01 版本来开始这段旅程,在二十多年前它就发布在 **comp.os.linux.announce** 新闻组上了。
### Slackware 1.01 版本系统 (1993 年)

*Slackware 1.01*
体验 Slackware 1.01 系统最爽的是在 Qemu 模拟器软件 [2014 免费镜像系列](http://www.qemu-advent-calendar.org/2014)中有一个预先制作好的镜像文件,因此你可以不用手动去执行安装任务(真不习惯这种“奢华”待遇)。其引导启动命令如下:
```
$ qemu-kvm -m 16M -drive if=ide,format=qcow2,file=slackware.qcow2 \
-netdev user,id=slirp -device ne2k_isa,netdev=slirp \
-serial stdio -redir tcp:22122::22
```
在 1993 年那个版本的 Linux 系统中,很多东西都跟我们所想像的一样。所有常用的基本命令,比如 `ls` 和 `cd` 命令的使用方式,以及所有的基本工具(`gawk` 、`cut` 、 `diff` 、 `perl`,当然还有 [Volkerding](http://www.slackware.com/%7Evolkerdi/) 最喜欢的 `elvis` 工具)现在都在使用,而且也包含在如今的 Linux 系统中,但是仍然有一小部分东西让我感到惊讶。当你尝试使用 tab 补全命令方式来列出上百个文件时, BASH 会非常友好地提示用户确认,并且那些查看压缩文件的工具(比如 `zless` 和 `zmore` 以及 `zcat`)都已经出现了。很多方面都超乎我的预计,总之,该系统给人的感觉就是超级现代化。
不过,该系统没有软件包管理的相关概念。所有软件的安装和卸载都得手动完成,也不能查询出已安装的软件包。
总的来说,Slackware 1.01 系统感觉更像是一个非常现代化的 UNIX 系统,或者更恰当的说,它给人的感觉就是一个 Linux 用户在操作一个现代化的 UNIX 系统。很多东西都非常熟悉,但是也不尽相同。这个在 1993 年发布的操作系统中,并不是所有东西都跟你想像中的一样。
### Debian 0.91 版本系统(1994 年)
为了尝试 Debian 0.91 版本系统,我使用的是 [Ibiblio 数字档案](https://ibiblio.org/pub/historic-linux/distributions/debian-0.91/debian-0.91/dist) 网站下载的软盘镜像文件,该系统最初发布在 1994 年。启动命令如下:
```
$ gunzip bootdsk.gz basedsk1.gz basedsk2.gz
$ qemu-system-i386 -M pc -m 64 -boot order=ac,menu=on \
-drive file=bootdisk,if=floppy,format=raw \
-drive file=debian.raw,if=ide,format=raw \
-device ne2k_isa,netdev=slirp \
-serial msmouse -vga std \
-redir tcp:22122::22 \
-netdev user,id=slirp
```
从 Debian 0.91 的启动磁盘启动后进入到一个简洁的 shell 界面,有很清晰的提示信息告诉你下一步将要执行的操作。
安装过程进行得非常顺利。从磁盘分区,写入 ext2 文件系统到分区,到显示图形菜单操作界面要经过七个步骤,之后开始复制 `basedsk` 镜像文件。这里使用的是以最小化方式来安装 Debian 系统,跟大家在安装自己的 Linux 系统过程中的很多步骤都非常相似。
Debian 系统因其自身的包管理器而出名,但是在早期的版本中只是有一些提示功能而已。有 `dpkg` 命令,但它是一个基于交互式菜单的系统——一种古老的 `aptitude`,有多个层级的可选菜单,并且自然地附带了几个可用软件包。
尽管如此,你也可以感受到其简便的设计理念。你只需下载三个软盘镜像文件,最后合成一个可启动的系统,然后就可以使用一个简单的文本菜单来安装更多的东西。我由衷的明白了为什么 Debian 系统如此受欢迎的原因。
### Jurix/S.u.S.E. 系统(1996 年)

*安装 Jurix 系统*
Jurix 系统是 SUSE 系统的前身, Jurix 带有的二进制的 `.tgz` 软件包会被组织到类似 Slackware 安装包结构的目录中,其安装包本身也跟 Slackware 的安装包很相似。
```
$ qemu-system-i386 -M pc -m 1024 \
-boot order=ac,menu=on \
-drive \
file=jurix/install,if=floppy,format=raw \
-drive file=jurix.img,if=ide \
-drive file=pkg.raw,if=ide,format=raw \
-device ne2k_isa,netdev=slirp \
-serial msmouse -vga std \
-redir tcp:22122::22 \
-netdev user,id=slirp
```
因为我不是刻意去寻找最早期的版本, Jurix 系统是找到的第一个真正‘感觉’像是打算给用户使用的有图形界面的 Linux 发行版。 [XFree86](http://www.xfree86.org/) 图形桌面环境已默认安装了,如果你不打算使用该工具,选择退出该环境即可。
比如 `/usr/lib/X11/XF86Config` (该文件后来变成了 `Xorg.conf` )这个配置文件已经存在了,这让我完成了使用 GUI 前的 90% 的工作,但是我花费了一整个周末的时间来调试 `vsync` 、`hsync`和 `ramdac` 颜色表重写,最后我完全放弃了。
在 Jurix 系统上安装软件包也非常简单;找到源路径下的 `.tgz` 文件,然后运行一个常用的 `tar` 命令: `$ su -c 'tar xzvf foo.tgz -C /'` 该软件包就会被解压到根分区,并准备好使用了。我刚开始的时候安装了几个之前未安装过的软件包,发现操作也很简单、快速且非常可靠。
### SUSE 5.1 版本系统(1998 年)

*在 SuSE 5.1 系统上运行 FVWM 窗口管理器*
我是使用 1998 年在马里兰州的一家软件商店里买的 InfoMagic 光盘来安装 SUSE 5.1 系统的。其引导启动命令如下:
```
$ qemu-system-i386 -M pc-0.10 -m 64 \
-boot order=ad,menu=on \
-drive file=floppy.raw,if=floppy,format=raw \
-cdrom /dev/sr0 \
-drive file=suse5.raw,if=ide,format=raw \
-vga cirrus -serial msmouse
```
安装过程相对于前面几次来说要复杂得多。 YasT 工具在软盘和可引导光盘之间搞乱了配置文件和设置,还需要重启好多次,在重启了好几次后我才反应过来是我操作顺序不当导致的问题。在安装过程中,我就犯了两次同样的错,我只是习惯了 YasT 工具的安装方式,到第三次才顺利的安装成功,这对于一个 Linux 用户将来的成长来说是一个很大的教训及经验。
我使用 SUSE 5.1 的主要目的就是体验其 GUI 桌面环境。配置的过程已经很熟悉了,使用几个漂亮的图形界面工具(包括一个很好用的 `XF86Setup` 前端界面配置工具)来测试和调试鼠标及显示器问题。我用了一个小时不到的时间就调试好 GUI 界面,并正常运行起来,其中大部分时间是耽搁在研究 Qemu 的虚拟显卡可以提供哪种分辨率和颜色方案。
可选用的桌面环境包括 fvwm、fvwm2 和 ctwm。我使用的是 fvwm,并且运行得也正常。我发现 tkDesk 这个 dock 式的文件管理器跟 Ubuntu 系统的 Unity 的启动栏非常的相似。
使用该系统总的来说还是非常令人愉快的,一旦成功安装了桌面环境并正常运行起来,SUSE 5.1 可以说是取得了令人瞩目的成功。
### Red Hat 6.0 版本系统(1999 年)

*在 Red Hat 6 系统上运行 GIMP 1.x 图像处理程序*
下一个系统 Red Hat 6.0 安装盘我刚好家里有。不是 RHEL 6.0 —— 而是 Red Hat 6.0,这是一个在 RHEL 或 Fedora 系统出现之前商店里就有卖的桌面版系统。这个安装盘是我在 1999 年 6 月份买的。
其引导启动命令如下:
```
$ qemu-system-i386 -M pc-0.10 -m 512 \
-boot order=ad,menu=on \
-drive file=redhat6.raw,if=ide,format=raw \
-serial msmouse -netdev user,id=slirp \
-vga cirrus -cdrom /dev/sr0
```
整个安装过程由完全由安装向导指引的,并且速度非常快。无论是选择要安装什么包(按**工作站**, **服务器**, 及**自定义**进行分组 ),对磁盘分区,或者是启动安装,你都不会出现进行不下去的问题。
Red Hat 6 包括一个 `xf86config` 应用程序来一步步指导你完成 X 配置工作,尽管它有一些之后的 X 系统不认的奇怪的鼠标模拟选项。它比手动修改 Xf86Config 配置文件要容易得多,但是要正确无误的配置好 X 环境显然不是一个简单的工作。
Red Hat 6 绑定的桌面环境是 GNOME ,没错就是它,但是窗口管理器是早期的 [Enlightenment](http://enlightenment.org/) ,它同样也提供了主声卡服务进程。xdm 和 gdm 都作为登录管理器包含在其中,以便普通用户也可以登录到系统中,即便没有权限启动或者关闭 X 进程,这在多用户系统中是非常重要的。
它缺少一些主要的应用程序;还没有 gedit 工具,没有重要的统一办公应用程序,更没有软件包管理器。有 GnoRPM 工具,这是一个图形界面的 RPM 包管理工具,用于查看及删除软件包,这个工具跟 yum 或 PackageKit 工具非常类似,还有基于图形界面的文件编辑器 gnotepad+ (尽管没有 Emacs 工具)。
总的来说,桌面环境在使用上也是非常直观的。跟后期实现的 GNOME 桌面环境不同,这个早期版本在屏幕底部有个面板,其中有一个应用程序菜单和启动器图标,在中间位置有个虚拟桌面控制器。我无法想象其它操作系统的用户在使用这个桌面环境时会有多么的不习惯。
Red Hat 6 对于 Linux 系统来说是一个巨大的进步,很明显 Linux 系统正向着成为一个适用的桌面系统方向发展。
### Mandrake 8.0 版本系统(2001 年)

*Mandrake: Linux 系统的一个转折点*
Mandrake 8.0 于 2001 年发布,这已经可以跟 Apple OS 9.2 和 Windows ME 系统相提并论了。
我反而觉得老版本的系统才更安全一些。
其引导启动命令如下:
```
$ qemu-system-i386 \
-M pc-0.10 -m 2048 \
-boot order=ad,menu=on \
-drive file=mandrake8.qcow2 \
-usb -net nic,model=rtl8139 \
-netdev user,id=slirp \
-vga cirrus \
-cdrom mandrake-8.0-i386.iso
```
我一直觉得 Red Hat 系统的安装过程非常棒了,但是 Mandrake 的安装过程更是让人喜出望外。它非常友好,并且在继续下一步之前还给用户一个测试配置文件的机会,易用高效,使用起来像魔法一样。我也不用导入自己的 `XF86Config` 配置文件,因为 Mandrake 的安装程序会自动完成该任务。

*Mandrake 8.0 系统的安装程序*
实际上,使用 Mandrake 系统跟使用其它的桌面环境系统的感受基本相同。让我很惊奇的是它们在操作体验上如此的相似。我相信,即使这个时候我在使用 Mandrake 系统的过程中遇到一些问题,以我自己的技术能力甚至是一个技术水平一般的年轻人也很容易解决。它的界面非常直观,帮助文档也很有用,并且软件包管理起来也很容易,只是那个时候人们还不习惯直接到网上下载他们需要的任何软件包来安装。
### Fedora 1 版本系统(2003 年)

*基于 Red Hat 的 Fedora 系统*
2003 年,新的 Fedora Core 系统发布了。 Fedora Core 基于 Red Hat 系统,它的主要目的是在 Red Hat 企业版(RHEL)成为该公司旗舰产品之前继续扛起 Linux 桌面版系统发展的大旗。
启动老版本的 Fedora Core 1 系统也没啥特别的地方:
```
$ qemu-system-i386 -M pc \
-m 2048 -boot order=ac,menu=on \
-drive file=fedora1.qcow2 -usb \
-net nic,model='rtl8139' -netdev user \
-vga cirrus -cdrom fedora-1-i386-cd1.iso
```
安装 Fedora Core 同样简单容易; Fedora 和 Red Hat 系统在之后的 9 年中使用同样的安装器,其图形界面易用而易于理解。

*Anaconda GUI 界面*
使用 Fedora Core 系统的体验跟 Red Hat 6 或 7 版本没多少区别。 GNOME 图形界面很漂亮,有各种独立的配置程序助手,并且界面展示都非常的整洁和专业。
桌面上的 “Start Here” 图标指导用户前往三个位置:应用程序目录,首选项面板和系统设置。 一个红帽的图标表示应用程序菜单,而下边的 GNOME 面板里包括所有最新的 Linux 应用程序的启动器,包括 OpenOffice 办公套件和 mozilla 浏览器。
### 展望未来
在 2000 年左右, Linux 系统已经发展得很好并取得了巨大的进步。桌面环境前所未有的更加精致美观,有各种可用的应用程序,安装过程比其它操作操作更简易更高效。事实上,从 2000 年以来,用户和系统之间的关系更加紧密,即使到现在也没发生根本上的改变。当然还有一些更新和改善,以及数量惊人的创新方面的变化。
让我们来了解一下各个 Linux 系统项目上的演变:
* Mandrake 系统后来更名为 Mandriva,如今为 [Mageia](http://mageia.org/) ;
* Fedora Core 随后改为 [Fedora](http://fedoraproject.org/) ;
* [Ubuntu](http://ubuntu.com/) 脱胎于 [Debian](http://debian.org/) ,并且它让 “Linux” 成为一个家喻户晓的词汇;
* Valve 公司开发的 [SteamOS](http://store.steampowered.com/steamos) 成为其官方游戏平台;
* [Slackware](http://slackware.com/) 现如今仍在平稳发展。
无论你是一个 Linux 新手,还是一个技术精湛的 Linux 老用户,上面的大多数截图都构成了让 Linux 系统被记入历史的一本传记。很高兴今天我们能够回顾成为世界上最大的开源项目之一的 Linux 系统是如何发展壮大起来的。更重要的是,每一次想到自己也是 Linux 开源世界中的一员我们就无比激动,把握现在,展望未来。
---
作者简介:
Seth Kenlon —— Seth Kenlon 是一位独立多媒体艺术家,开源文化倡导者, Unix 极客。他还是 Slackware 多媒体产品项目的维护人员之一,官网:<http://slackermedia.ml> 。
题图来源:互联网档案馆[书籍](https://www.flickr.com/photos/internetarchivebookimages/14746482994/in/photolist-ot6zCN-odgbDq-orm48o-otifuv-otdyWa-ouDjnZ-otGT2L-odYVqY-otmff7-otGamG-otnmSg-rxnhoq-orTmKf-otUn6k-otBg1e-Gm6FEf-x4Fh64-otUcGR-wcXsxg-tLTN9R-otrWYV-otnyUE-iaaBKz-ovcPPi-ovokCg-ov4pwM-x8Tdf1-hT5mYr-otb75b-8Zk6XR-vtefQ7-vtehjQ-xhhN9r-vdXhWm-xFBgtQ-vdXdJU-vvTH6R-uyG5rH-vuZChC-xhhGii-vvU5Uv-vvTNpB-vvxqsV-xyN2Ai-vdXcFw-vdXuNC-wBMhes-xxYmxu-vdXxwS-vvU8Zt)[图片](https://www.flickr.com/photos/internetarchivebookimages/14774719031/in/photolist-ovAie2-otPK99-xtDX7p-tmxqWf-ow3i43-odd68o-xUPaxW-yHCtWi-wZVsrD-DExW5g-BrzB7b-CmMpC9-oy4hyF-x3UDWA-ow1m4A-x1ij7w-tBdz9a-tQMoRm-wn3tdw-oegTJz-owgrs2-rtpeX1-vNN6g9-owemNT-x3o3pX-wiJyEs-CGCC4W-owg22q-oeT71w-w6PRMn-Ds8gyR-x2Aodm-owoJQm-owtGp9-qVxppC-xM3Gw7-owgV5J-ou9WEs-wihHtF-CRmosE-uk9vB3-wiKdW6-oeGKq3-oeFS4f-x5AZtd-w6PNuv-xgkofr-wZx1gJ-EaYPED-oxCbFP)。 Opensource.com. CC BY-SA 4.0 编辑引用。
---
via: <https://opensource.com/article/16/12/yearbook-linux-test-driving-distros>
作者:[Seth Kenlon](https://opensource.com/users/seth) 译者:[rusking](https://github.com/rusking) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='opensource.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=10) | null |
8,153 | 是时候抛弃 Skype 和 TeamSpeak 了, Discord 为 Linux 用户发布了应用 | http://news.softpedia.com/news/it-s-time-to-ditch-skype-and-teamspeak-discord-launches-its-app-for-linux-users-511753.shtml | 2017-01-27T22:38:49 | [
"Discord",
"Skype"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8153-1.html | ### 程序已经在 Ubuntu Linux 和其他发行版上可用了
在 2016 年 1 月 11 日发布的一则非常简短的声明中,[Discord](https://discordapp.com/) 公司发布了首个 Linux 平台的稳定版本,它是一款给玩家开发的流行、免费的、安全一体化的语音和文字聊天程序。

Linux 是他们补足全平台(桌面设备和移动设备)服务支持的缺失的一块。Discord 目前可用于 Android、iOS、Mac和 Windows,但你也可以使用兼容的网络浏览器直接在网络上使用它。
该应用程序似乎是微软 Skype VoIP 客户端,以及著名的 TeamSpeak 语音通信平台的直接竞争对手。它提供了广泛的功能,包括 IP 和 DDoS 保护,游戏内叠加,智能推送通知,单独音量控制,支持多个通道和现代化的文字聊天。
Discord 其他值得注意的功能包括支持编解码器、权限和自定义键盘快捷键、直接消息系统和朋友列表。它还承诺尽可能减少 CPU 使用率,为音频和自动故障转移功能提供低延迟支持。
### 在 Ubuntu 上安装 Discord
官方 Discord 的第一个 Linux 稳定版本(版本 0.0.1)目前以二进制软件包[提供](https://discordapp.com/download),支持 Debian 和基于 Ubuntu 的发行版(例如 Ubuntu、Debian、Linux Mint 等)。但是要安装它,你需要一个 64位系统。
如果你没有运行一个基于 Debian 或 Ubuntu 的操作系统,还有一个源码 tarball 可供下载,但你必须自行编译它。目前 Discord 0.0.1 已经进入 Arch Linux AUR 仓库了,并且很快也会到 Solus 中。其他发行版可能在未来几周内向其仓库添加 Discord。
---
via: <http://news.softpedia.com/news/it-s-time-to-ditch-skype-and-teamspeak-discord-launches-its-app-for-linux-users-511753.shtml>
作者:[Marius Nestor](http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/marius-nestor) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,154 | LFCS 命令行基础 | https://www.linuxforum.com/threads/lfcs-command-line-basics.3334/ | 2017-01-27T23:19:00 | [
"命令行",
"TTY"
] | /article-8154-1.html | 
本文中包含了很多命令行基础。我们将讨论 TeleTYpe(TTY)和几个命令及其选项。确保做完所有练习,并要知道,除非另有说明,对 CentOS 和 Ubuntu 都是相同的。
### TTY
当没有图形用户界面(GUI)或当用户在 GUI 之外,Linux 就会使用 TTY。当打开终端窗口时也使用 TTY,但这些是不同类型的 TTY。
有三种类型的 TTY:
1. 物理终端
2. 本地伪终端
3. 远程伪终端
基本上,每个 Linux 系统有大约六个或七个物理 TTY。 通过按住 `CTRL + ALT` 键,然后在 CentOS 按住 `F1` 到 `F6` ,而在 Ubuntu 中是 `F1` 到 `F7`。
**注意:** 一些发行版可能有不同数量的 TTY 和不同的 GUI 默认位置。有点发行版可能有在物理 TTY 之间切换的不同组合键,如 `CTRL + F#` 或 `ALT + F#` ( LCTT 译注:`F#` 代表 F1、F2 等)。当使用 VirtualBox 时,除非您更改了主机键映射,请使用右 CTRL 键。
在 CentOS 中,GUI 在 TTY1(`CTRL + ALT + F1`)上,其他物理 TTY 都是基于文本的。 在 Ubuntu 上,GUI 在 TTY7(`CTRL + ALT + F7`)上,其他物理 TTY 都是基于文本的。
**注意:** 尝试在另一个 TTY 下加载 GUI 是不明智的,因为这可能耗用大量资源,但你可以这样做。
当 Linux 启动时,不管是 CentOS 还是 Ubuntu,都会打开默认 TTY。如果安装了 GUI,对于 CentOS 是打开 TTY1,对于 Ubuntu 是打开 TTY7。如果你打开一个终端窗口(伪 TTY)并使用命令 `who`,你可以看到正在使用的 TTY 的列表。 如图 1 所示。

*图 1*
在图 1 中,你可以看到我当前登录到 TTY1(非 GUI)。第二行连接显示我已登录到 GUI(TTY7)以及两个伪 TTY(pts/1 和 pts/2)。如图 2,你可以看到新条目显示了远程伪 TTY(pts/4)。 远程伪连接来自 IP 地址为 192.168.0.11 的系统。

*图 2*
可以使用诸如 PuTTY 或任何 SSH 的客户端(如果远程 Linux 系统上启用了 SSH)之类的应用程序进行远程 TTY 连接。
如果终端窗口字体比较小,你可以使用 `CTRL + SHIFT` 键和 `+` 键来放大字体。多次按下可以更大。要缩小大小,请使用 `CTRL + SHIFT + -` 不断缩小。要使终端字体恢复为原始大小,请按下 `CTRL + SHIFT + 0`。
**注意:** 请注意,如果字体已经足够大或足够小了,组合键就不再工作了。
希望你现在已经了解各种类型的 TTY。让我们看看一些可以在 TTY 中使用的命令。
### 命令
其中一个命令前面已经讨论过了。命令 `who` 用于显示谁登录到了系统。
另一个命令是 `pwd`。命令 `pwd` 代表“<ruby> 打印工作目录 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Print Working Directory </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”。该命令返回你所在的当前目录。例如,如果终端提示符是 `[jbuse@localhost〜]$`,则用户名为 `jbuse`,当前目录为 `〜`。波浪号(`〜`)代表用户的主文件夹。主文件夹应该是 `/home/USERNAME`。用户名是用于登录系统的名称。
要列出当前文件夹的内容,请使用命令 `ls`。`ls` 命令代表 List。如果未指定任何选项,则列出当前文件夹。如果给出文件夹名称,则会列出该文件夹的内容。例如,要查看 `media` 文件夹的内容,你可以使用命令 `ls /media`。
在 `ls` 命令后面我们可以添加一些选项以显示更多详细信息或特定详细信息。如果你想看到所有的文件夹和文件,即使是隐藏的,请使用选项 `-a`。要查看当前目录中的所有文件和文件夹,请使用命令 `ls -a`。隐藏的文件和文件夹将在名称前面显示一个句点(`.`)。
要在每个文件夹名称后看到正斜杠(`/`),请使用 `-F` 选项。当前文件夹列表将是 `ls -F`。`-F` 用于按文件类型对文件进行分类。符号链接在文件夹名称后用 `@` 表示。
你可以把这两个选项连在一起形成 `ls -aF`。
**注意:** 一些选项可能有不同的大小写。选项区分大小写。
另一个选项是显示长列表的 `-l`。示例输出如图 3 所示。文件夹和文件名称列在右侧。文件为白色,文件夹为深蓝色,符号链接为浅蓝色。如图 3 所示,符号链接 `vtrgb` 链接自 `/etc/alternatives/vtrgb` 。

*图 3*
左侧的第一列是文件或文件夹的权限。第一个字母是 `d` 的为目录,是 `-` 的为文件。接下来的三个字母显示所有者的权限(`r` - 读、`w` - 写、`x` - 执行),后面是组权限以及“其他人”的权限。下一列数字显示指向文件或文件夹的链接数。再下一列是所有者名称,后面是所有组名称。再下一列是文件或文件夹在存储设备上占用的字节数。接下来的三列是文件上次修改的月份、日期和年份。最后一列是路径名。
目前为止,你可以看到列表是按字母顺序排序。要颠倒从 “z” 到 “a” 而不是 “a” 到 “z” 的顺序,请使用 `-r` 选项。逆转选项 `-r` 使 ls 命令反转输出顺序。
要按修改的时间戳列出文件,请使用 `-t` 选项。顺序是从最近修改到最早的修改日期。当然,在命令 `ls -tr` 中,同时使用 `-t` 和 `-r` 颠倒了顺序。
如果你不喜欢看文件的长长的字节数,使用选项 `-h`。输出将会更易读,如显示 `4.0K` 而不是 `4096`。
要获取单个文件夹的特定信息,请使用选项 `-d`,但必须指定该文件夹。例如,要查看文件夹 `/media` 的详细信息,请使用命令 `ls -ld /media`。
另一个要熟悉的命令是命令 `cat`。命令 `cat` 用于将标准输入(文件)复制到标准输出(屏幕)。使用 `cat` 可以轻松地查看文件的内容。例如,要查看名为 `text` 的文件的内容,如果你与文件 `text` 在同一个文件夹中请使用命令 `cat text`。如果你不在同一个文件夹中,那么你必须指定位置。例如,如果文件 `text` 在文件夹 `/home/jarret/test/` 中,那么命令将是 `cat /home/jarret/test/text`。
另一个非常有用的命令是 `man`。`man` 命令用于查看特定命令的文档。例如,要查看命令 `ls` 的帮助页面,请使用命令 `man ls`。
**注意:** 记住,在 LFCS 考试中,你可以使用 `man` 命令。
查看这些命令并测试它们以熟悉它们。使用 `man` 命令,查看本文中的命令以查看其他可用的选项。
---
via: <https://www.linuxforum.com/threads/lfcs-command-line-basics.3334/>
作者:[Jarret](https://www.linuxforum.com/members/jarret.268/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| null | HTTPSConnectionPool(host='www.linuxforum.com', port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: /threads/lfcs-command-line-basics.3334/ (Caused by NameResolutionError("<urllib3.connection.HTTPSConnection object at 0x7b8327582050>: Failed to resolve 'www.linuxforum.com' ([Errno -2] Name or service not known)")) | null |
8,155 | MapD:由 GPU 驱动的数据库分析平台可在几毫秒内查询数十亿条数据 | http://opensourceforu.com/2017/01/gpu-powered-database-analytics-platform-query-billions-data-points/ | 2017-01-28T10:42:00 | [
"GPU",
"MapD",
"数据库"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8155-1.html | 
麻省理工学院计算机科学与人工智能实验室(CSAIL)的前研究员开发了一款名为 MapD 的数据库分析平台。该平台使用 GPU 而不是 CPU ,可在几毫秒内查询和映射数十亿条数据。
人们通常将 GPU 与图像处理和游戏相关联。然而,现代 GPU 中高效的核心和处理单元也可以用于通用计算应用。以前在 CSAIL 工作的 Todd Mostak 开发了 MapD,它能在毫秒内处理数十亿条数据。
Mostak [声称](http://news.mit.edu/2017/startup-mapd-fast-big-data-mapping-0111) 他的 MapD 比由 CPU 驱动的传统数据库管理系统的快 100 倍。该平台可以在短时间内处理并可视化大量数据,并且被处理的数据的参数可以很容易地修改。
MapD 将所有数据缓存在多个 GPU 上,而不是存储在某些 CPU 上。每个 GPU 被给予不同的缓冲池以节省时间。通过此过程,系统可以提供比 CPU 驱动的数据库系统快两到三倍的性能。
许多公司客户已经开始使用 Mostak 的 MapD。像 Verizon 这样的电信公司据说也在为其内部研发尝试该数据库分析平台。这家电信公司使用 MapD 分析了 8500 万用户的 SIM 卡更新数据库。
除了 Verizon,MapD 还有如社交媒体公司,金融和广告公司的客户。
由 Mostak 领导的创业公司最近从美国中央情报局的投资部门 In-Q-Tel 筹集了一笔资金。你可以期望在不久的将来在不同的领域中使用 MapD 的各种情况。
---
via: <http://opensourceforu.com/2017/01/gpu-powered-database-analytics-platform-query-billions-data-points/>
作者:[RAJAT KABADE](%5B1%5D:https://twitter.com/home?status=This%20GPU-powered%20database%20analytics%20platform%20can%20query%20billions%20of%20data%20points%20in%20milliseconds+http://opensourceforu.com/2017/01/gpu-powered-database-analytics-platform-query-billions-data-points/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,157 | vmstat:一个标准的报告虚拟内存统计工具 | http://www.2daygeek.com/linux-vmstat-command-examples-tool-report-virtual-memory-statistics/ | 2017-01-29T09:39:00 | [
"top",
"vmstat",
"iostat"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8157-1.html | ### 什么是 RAM?
在智能手机世界,我们每一个人都知道 RAM。因此,我不想深入介绍,这样我就简要概括下。RAM 代表“<ruby> 随机访问内存 <rp> ( </rp> <rt> Random Access Memory </rt> <rp> ) </rp></ruby>”,是一种计算机数据存储,它会存储经常使用的程序来提升系统性能。
### 什么是虚拟内存?
虚拟内存是一种内存管理方式,计算机通过临时将最近未使用的程序数据从 RAM 转移到硬盘,以平衡或管理内存的短缺。
### 什么是 vmstat?
vmstat 是一个标准的工具,它会报告 Linux 系统的虚拟内存统计。vmstat 会报告有关进程、内存、分页、块 IO、陷阱(中断)和 cpu 活动的信息。它可以帮助 Linux 管理员在解决问题时识别系统瓶颈。

### 在 Linux 中安装 Sysstat
Linux 中没有独立的 `vmstat` 包。它与 `sysstat` 绑定在一起,并在大多数发行版的默认仓库上都有。如果还没有安装,只要基于你的发行版输入下面的命令。
```
[在 CentOS/RHEL 中安装 vmstat]
$ sudo yum install sysstat
[在 Fedora 中安装 vmstat]
$ sudo dnf install sysstat
[在 Debian/Ubuntu 中安装 vmstat]
$ sudo apt-get install sysstat
[在 Arch Linux 中安装 vmstat]
$ sudo pacman -S sysstat
[在 Mageia 中安装 vmstat]
$ sudo urpmi sysstat
[在 openSUSE 中安装 vmstat]
$ sudo zypper install sysstat
```
### 不带参数运行 vmstat
假设你已经成功安装 vmstat,在终端中不带参数运行 `vmstat`,它会向你展示 vmstat 的默认结果。
```
# vmstat
procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- -system-- ----cpu----
r b swpd free buff cache si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa
2 0 79496 1614120 139240 787928 0 0 23 10 0 0 11 1 88 0
```
当你看到上面的输出,你可能已经大致了解了它是什么以及它的目的。不要担心,我们将深入解释每个参数,以便你可以了解 vmstat 的用途和目的。
`procs`:procs 中有 `r` 和 `b` 列,它报告进程统计信息。在上面的输出中,在运行队列(`r`)中有两个进程在等待 CPU 并有零个休眠进程(`b`)。通常,它不应该超过处理器(或核心)的数量,如果你发现异常,最好使用 [top 命令](http://www.2daygeek.com/top-command-examples-to-monitor-server-)进一步地排除故障。
* `r`:等待运行的进程数。
* `b`:休眠状态下的进程数。
`memory`: memory 下有报告内存统计的 `swpd`、`free`、`buff` 和 `cache` 列。你可以用 `free -m` 命令看到同样的信息。在上面的内存统计中,统计数据以千字节表示,这有点难以理解,最好添加 `M` 参数来看到以兆字节为单位的统计数据。
* `swpd`:使用的虚拟内存量。
* `free`:空闲内存量。
* `buff`:用作缓冲区的内存量。
* `cache`:用作高速缓存的内存量。
* `inact`:非活动内存的数量。
* `active`:活动内存量。
`swap`:swap 有 `si` 和 `so` 列,用于报告交换内存统计信息。你可以用 `free -m` 命令看到相同的信息。
* `si`:从磁盘交换的内存量(换入,从 swap 移到实际内存的内存)。
* `so`:交换到磁盘的内存量(换出,从实际内存移动到 swap 的内存)。
`I/O`:I/O 有 `bi` 和 `bo` 列,它以“块读取”和“块写入”的单位来报告每秒磁盘读取和写入的块的统计信息。如果你发现有巨大的 I/O 读写,最好使用 [iotop](http://www.2daygeek.com/monitor-disk-io-activity-using-iotop-) 和 [iostat](http://www.2daygeek.com/monitor-disk-io-activity-using-iotop-) 命令来查看。
* `bi`:从块设备接收的块数。
* `bo`:发送到块设备的块数。
`system`:system 有 `in` 和 `cs` 列,它报告每秒的系统操作。
* `in`:每秒的系统中断数,包括时钟中断。
* `cs`:系统为了处理所以任务而上下文切换的数量。
`CPU`:CPU 有 `us`、`sy`、`id` 和 `wa` 列,报告(所用的) CPU 资源占总 CPU 时间的百分比。如果你发现异常,最好使用 `top` 和 `free` 命令。
* `us`:处理器在非内核程序消耗的时间。
* `sy`:处理器在内核相关任务上消耗的时间。
* `id`:处理器的空闲时间。
* `wa`:处理器在等待IO操作完成以继续处理任务上的时间。
### 以 MB 方式输出
默认情况下,vmstat 以千字节为单位显示内存统计,这是非常难以理解的,最好添加 `-S m` 参数以获取以兆字节为单位的统计。
```
# vmstat -S m
procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- -system-- ----cpu----
r b swpd free buff cache si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa
1 0 103 371 406 2116 0 0 40 15 0 0 11 1 87 0
```
### 以延迟方式运行 vmstat 获取更好的统计信息
默认情况下,vmstat 的单次统计信息不足以进一步进行故障排除,因此,添加更新延迟(延迟是更新之间的延迟,以秒为单位)以定期捕获活动。如果你想以 2 秒延迟运行 vmstat ,只需使用下面的命令(如果你想要更长的延迟,你可以根据你的愿望改变)。
以下命令将每 2 秒运行一次,直到退出。
```
# vmstat 2
procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- -system-- ----cpu----
r b swpd free buff cache si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa
1 0 105500 325776 416016 2166912 0 0 40 15 0 0 11 1 87 0
0 0 105500 325644 416016 2166920 0 0 0 13 1083 1174 11 1 87 0
0 0 105500 308648 416024 2166928 0 0 1 16 1559 1453 16 2 82 0
0 0 105500 285948 416032 2166932 0 0 0 12 934 1003 9 1 90 0
0 0 105500 326620 416040 2166940 0 0 1 27 922 1068 9 1 90 0
0 0 105500 366704 416048 2166944 0 0 0 17 835 955 9 1 90 0
0 0 105500 366456 416056 2166948 0 0 1 22 859 918 9 1 90 0
0 0 105500 366456 416056 2166948 0 0 0 15 1539 1504 17 2 81 0
0 0 105500 365224 416060 2166996 0 0 1 19 984 1097 11 1 88 0
```
### 带延迟和计数运行 vmstat
或者,你可以带延迟和特定计数运行 vmstat,一旦达到给定的计数,然后自动退出。
以下命令将每 2 秒运行一次,10 次后自动退出。
```
# vmstat 2 10
procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- -system-- ----cpu----
r b swpd free buff cache si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa
1 0 79496 1581916 157380 810412 0 0 23 10 0 1 11 1 88 0
2 0 79496 1559464 157380 810416 0 0 1 1 1821 1749 21 2 77 0
0 0 79496 1583768 157384 810416 0 0 1 46 681 799 9 1 90 0
2 0 79496 1556364 157384 810428 0 0 1 1 1392 1545 15 2 83 0
0 0 79496 1583272 157384 810428 0 0 1 0 1307 1448 14 2 84 0
2 0 79496 1582032 157384 810428 0 0 1 41 424 605 4 1 96 0
1 0 79496 1575848 157384 810428 0 0 1 0 1912 2407 26 2 71 0
0 0 79496 1582884 157384 810436 0 0 1 69 678 825 9 1 90 0
2 0 79496 1569368 157392 810432 0 0 11 26 920 969 9 1 90 0
1 0 79496 1583612 157400 810444 0 0 7 39 2001 2530 20 2 77 0
```
### 显示活动和非活动内存
默认情况下,vmstat 会显示除活动和非活动内存之外的内存统计信息。如果要查看活动和非活动内存统计信息,请在 vmstat 后添加 `-a` 参数。
```
# vmstat -a
procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- -system-- ----cpu----
r b swpd free inact active si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa
1 0 105500 2387592 415148 584112 0 0 40 15 0 1 11 1 87 0
```
### 打印磁盘统计
在 vmstat 后面添加 `-d` 参数会以每个磁盘一行的方式显示统计(包含读、写和 IO)。
```
# vmstat -d
disk- ------------reads------------ ------------writes----------- -----IO------
total merged sectors ms total merged sectors ms cur sec
ram0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram9 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram11 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram12 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram13 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram14 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ram15 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
loop0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
loop1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
loop2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
loop3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
loop4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
loop5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
loop6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
loop7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
fd0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
sda 16604050 904497 2594882190 57455732 30037054 28093770 2160032056 118189160 0 40915
sdb 257357577 479985 3124712204 577235320 8502519 1283237 36645890 11250948 0 182336
```
### 总结磁盘统计
在 vmstat 后面添加 `-D` 会显示全局统计(包括全部的磁盘、分区、全部读、合并的读、读取的扇区、写、合并的写、写入的扇区和 IO)。
```
# vmstat -D
27 disks
3 partitions
275754028 total reads
1388030 merged reads
5751195976 read sectors
638710116 milli reading
38795040 writes
29520659 merged writes
2209820333 written sectors
130210652 milli writing
0 inprogress IO
224704 milli spent IO
```
### 打印指定分区统计
vmstat 添加 `-p` 参数后面跟上设备名会显示指定分区统计(包括读、读取的扇区、写以及请求的写)。
```
# vmstat -p /dev/sdb1
sdb1 reads read sectors writes requested writes
3115 27890 839453 206728016
```
### vmstat 统计信息带上时间戳
当你想在特定时间区间内找到内存尖峰时,用 vmstat 命令添加 `-t` 参数,后跟延迟和计数。
注意:此组合不适用于基于 Debian 的系统。
```
# vmstat -t 1 5
procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- --system-- -----cpu------ ---timestamp---
r b swpd free buff cache si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa st
0 0 0 6981416 181324 24588604 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 100 0 0 2017-01-11 15:42:15 MST
2 0 0 6981276 181324 24588604 0 0 0 0 91 40 0 0 100 0 0 2017-01-11 15:42:16 MST
0 0 0 6982016 181324 24588604 0 0 0 0 75 116 0 0 100 0 0 2017-01-11 15:42:17 MST
0 0 0 6982016 181324 24588604 0 0 0 0 43 39 0 0 100 0 0 2017-01-11 15:42:18 MST
0 0 0 6982280 181324 24588604 0 0 0 0 113 185 0 0 100 0 0 2017-01-11 15:42:19 MST
```
### 打印更多统计
vmstat 后面跟上 `-s` 参数会显示不同统计的总结。
```
# vmstat -s
32849392 total memory
25864128 used memory
16468180 active memory
8320888 inactive memory
6985264 free memory
181324 buffer memory
24588612 swap cache
20970492 total swap
0 used swap
20970492 free swap
891075 non-nice user cpu ticks
6532 nice user cpu ticks
1507099 system cpu ticks
18925265601 idle cpu ticks
113043 IO-wait cpu ticks
108 IRQ cpu ticks
4185 softirq cpu ticks
0 stolen cpu ticks
4071862 pages paged in
216759718 pages paged out
0 pages swapped in
0 pages swapped out
369611221 interrupts
477861261 CPU context switches
1478258826 boot time
2196121 forks
```
### 打印 slab 统计
vmstat 后面跟上 `-m` 参数会显示 slab 信息。
```
# vmstat -m
Cache Num Total Size Pages
nf_conntrack_expect 0 0 240 16
nf_conntrack_ffffffff81b2a920 18 60 312 12
fib6_nodes 24 59 64 59
ip6_dst_cache 16 30 384 10
ndisc_cache 7 30 256 15
ip6_mrt_cache 0 0 128 30
RAWv6 35 35 1088 7
UDPLITEv6 0 0 1024 4
UDPv6 4 12 1024 4
tw_sock_TCPv6 0 0 320 12
request_sock_TCPv6 0 0 192 20
TCPv6 4 6 1920 2
fat_inode_cache 5 6 672 6
fat_cache 0 0 32 112
ioat2 4096 4140 128 30
ext4_inode_cache 34322 34364 1000 4
ext4_xattr 0 0 88 44
.
.
.
```
### 阅读更多关于 vmstat
如果你想了解关于 vmstat 的更多选项,请阅读手册。
```
# vmstat --help
或者
# man vmstat
```
---
作者简介:
Magesh Maruthamuthu,热爱玩所有的 Linux 发行版
---
via: <http://www.2daygeek.com/linux-vmstat-command-examples-tool-report-virtual-memory-statistics/>
作者:[Magesh Maruthamuthu](http://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
8,158 | 如何知道目录及子目录下文件的数量 | http://www.tecmint.com/find-number-of-files-in-directory-subdirectories-linux/ | 2017-01-30T11:38:00 | [
"find",
"wc"
] | https://linux.cn/article-8158-1.html | 在本指南中,我们将介绍如何在 Linux 系统上显示当前工作目录或任何目录及其子目录中的文件数量。
我们将使用 [find 命令](https://linux.cn/tag-find.html),它用于搜索目录层次结构中的文件,以及 [wc 命令](https://linux.cn/tag-wc.html),它会打印每个文件或来自标准输入的换行符、单词和字节计数。

以下是我们在 [find 命令](https://linux.cn/tag-find.html)中使用的选项,如下所示:
1. `-type` - 指定要搜索的文件类型,在上面的情况下,`f` 表示查找所有常规文件。
2. `-print` - 打印文件绝对路径。
以下是我们 [wc 命令](https://linux.cn/tag-wc.html)中使用的选项,如下所示:
1. `-l` - 此选项打印换行符的总数,也即由 [find 命令](https://linux.cn/tag-find.html)输出的绝对文件路径总数。
`find` 命令的一般语法。
```
# find . -type f -print | wc -l
$ sudo find . -type f -print | wc -l
```
重要:使用 [sudo 命令](http://www.tecmint.com/sudoers-configurations-for-setting-sudo-in-linux/)来读取指定目录中的所有文件,包括具有超级用户权限的子目录中的文件,以避免 “Permission denied” 错误,如下截图所示:

*Linux 中的文件数量*
你可以看到,在上面的第一个命令中,`find` 命令没有读取当前工作目录中的所有文件。
下面是更多的示例,分别显示 `/var/log` 和 `/etc` 目录中的常规文件总数:
```
$ sudo find /var/log/ -type f -print | wc -l
$ sudo find /etc/ -type f -print | wc -l
```
有关 Linux 中 `find` 和 `wc` 命令的更多示例,请查看以下系列文章以了解其他使用选项,提示和相关命令:
1. [35 个 Linux 中的 “find” 命令示例](http://www.tecmint.com/35-practical-examples-of-linux-find-command/)
2. [如何在 Linux 中查找最近或今天的修改的文件](http://www.tecmint.com/find-recent-modified-files-in-linux/)
3. [在 Linux 中查找十个占用最大的目录和文件](http://www.tecmint.com/find-top-large-directories-and-files-sizes-in-linux/)
4. [6 个有用的 “wc” 命令示例来计算行数、单词和字符](http://www.tecmint.com/wc-command-examples/)
就是这样了!如果你知道其他任何方法来显示目录及其子目录中的文件总数,请在评论中与我们分享。
---
作者简介:
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux SysAdmin、web 开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创建者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
---
via: <http://www.tecmint.com/find-number-of-files-in-directory-subdirectories-linux/>
作者:[Aaron Kili](http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/) 译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
| 301 | Moved Permanently | null |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.