Spaces:
Running
SPO | Self-Supervised Prompt Optimization 
An automated prompt engineering tool for Large Language Models (LLMs), designed for universal domain adaptation.
A next-generation prompt engineering system implementing Self-Supervised Prompt Optimization (SPO). Achieves state-of-the-art performance with 17.8-90.9× higher cost efficiency than conventional methods. 🚀
✨ Core Advantages
- 💸 Ultra-Low Cost - $0.15 per task optimization
- 🏷️ Zero Supervision - No ground truth/human feedback required
- ⚡ Universal Adaptation - Closed & open-ended tasks supported
- 🔄 Self-Evolving - Auto-optimization via LLM-as-judge mechanism
📊 Experiment
Closed Tasks
SPO demonstrates superior cost efficiency, requiring only 1.1% to 5.6% of the cost of state-of-the-art methods while maintaining competitive performance.
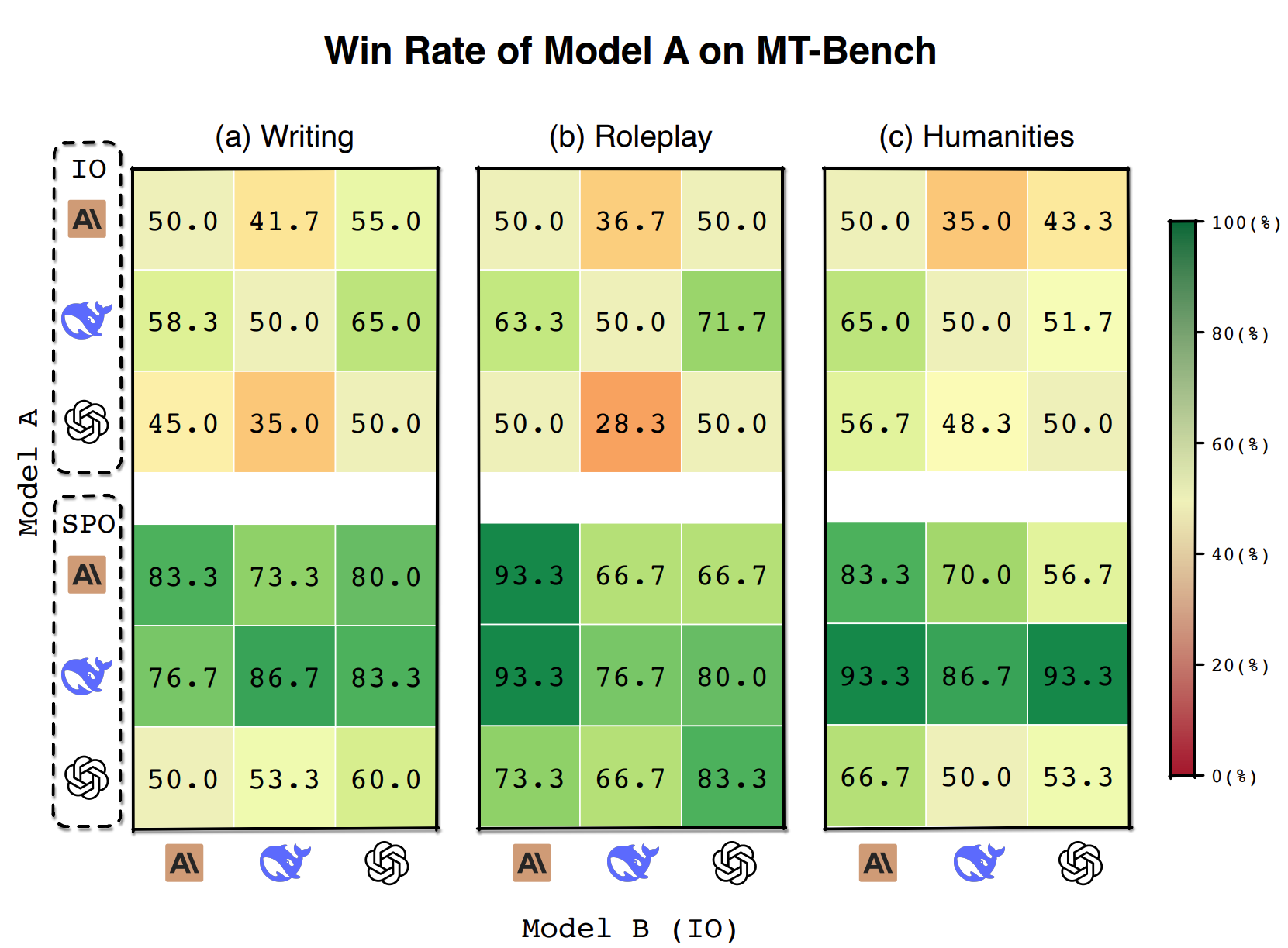
Open-ended Tasks
SPO significantly improves model performance across all model configurations in open-ended tasks.
🚀 Quick Start
1. Configure Your API Key ⚙️
Configure LLM parameters in config/config2.yaml (see examples/spo/config2.example.yaml for reference)
2. Define Your Iteration template 📝
Create a Iteration template file metagpt/ext/spo/settings/task_name.yaml:
prompt: |
Please solve the following problem.
requirements: |
...
count: None
faq:
- question: |
...
answer: |
...
- question: |
...
answer: |
...
Notes:
prompt: Initial prompt for iterationrequirements: Desired effects/outcomes (e.g., generate more thinking, use more humorous language)count: Target word count for the generated prompt (e.g., 50). Set to None for no limitfaq: QA pairs used for iteration, can include appropriate number of pairs (typically 3)question: Questions from the dataset used for iterationanswer: Corresponding answers. Can contain desired thinking patterns or responses instead of actual answers, or can be left empty. Seemetagpt/ext/spo/settings/Navigate.yamlfor reference
3. Implement the PromptOptimizer 🔧
You have three ways to run the PromptOptimizer:
Option 1: Python Script
from metagpt.ext.spo.components.optimizer import PromptOptimizer
from metagpt.ext.spo.utils.llm_client import SPO_LLM
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Initialize LLM settings
SPO_LLM.initialize(
optimize_kwargs={"model": "claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620", "temperature": 0.7},
evaluate_kwargs={"model": "gpt-4o-mini", "temperature": 0.3},
execute_kwargs={"model": "gpt-4o-mini", "temperature": 0}
)
# Create and run optimizer
optimizer = PromptOptimizer(
optimized_path="workspace", # Output directory
initial_round=1, # Starting round
max_rounds=10, # Maximum optimization rounds
template="Poem.yaml", # Template file
name="Poem", # Project name
)
optimizer.optimize()
Option 2: Command Line Interface
python -m examples.spo.optimize
Available command line options:
--opt-model Model for optimization (default: claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620)
--opt-temp Temperature for optimization (default: 0.7)
--eval-model Model for evaluation (default: gpt-4o-mini)
--eval-temp Temperature for evaluation (default: 0.3)
--exec-model Model for execution (default: gpt-4o-mini)
--exec-temp Temperature for execution (default: 0)
--workspace Output directory path (default: workspace)
--initial-round Initial round number (default: 1)
--max-rounds Maximum number of rounds (default: 10)
--template Template file name (default: Poem.yaml)
--name Project name (default: Poem)
For help:
python -m examples.spo.optimize --help
Option 3: Streamlit Web Interface
For a more user-friendly experience, you can use the Streamlit web interface to configure and run the optimizer.
First, install Streamlit:
pip install "streamlit~=1.42.0"
Then run the web interface:
python -m streamlit run metagpt/ext/spo/app.py
4. View Results
workspace
└── Project_name
└── prompts
├── results.json
├── round_1
│ ├── answers.txt
│ └── prompt.txt
├── round_2
│ ├── answers.txt
│ └── prompt.txt
├── round_3
│ ├── answers.txt
│ └── prompt.txt
├── ...
└── round_n
├── answers.txt
└── prompt.txt
results.json: Stores whether each iteration round was judged successful and other related informationprompt.txt: The optimized prompt for the corresponding roundanswers.txt: The output results generated using the prompt for the corresponding round
Citation
If you use SPO in your research, please cite our paper:
@misc{xiang2025spo,
title={Self-Supervised Prompt Optimization},
author={Jinyu Xiang and Jiayi Zhang and Zhaoyang Yu and Fengwei Teng and Jinhao Tu and Xinbing Liang and Sirui Hong and Chenglin Wu and Yuyu Luo},
year={2025},
eprint={2502.06855},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.06855},
}