content
stringlengths 0
14.9M
| filename
stringlengths 44
136
|
|---|---|
print.varprd <- function(x, ...){
print(x$fcst, ...)
invisible(x)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/print.varprd.R
|
"print.varstabil" <-
function(x, ...){
print(x[[1]], ...)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/print.varstabil.R
|
"print.varsum" <-
function(x, digits = max(3, getOption("digits") - 3), signif.stars = getOption("show.signif.stars"), ...){
dim <- length(x$names)
text1 <- "\nVAR Estimation Results:\n"
cat(text1)
row <- paste(rep("=", nchar(text1)), collapse = "")
cat(row, "\n")
cat(paste("Endogenous variables:", paste(colnames(x$covres), collapse = ", "), "\n", collapse = " "))
cat(paste("Deterministic variables:", paste(x$type, collapse = ", "), "\n", collapse = " "))
cat(paste("Sample size:", x$obs, "\n"))
cat(paste("Log Likelihood:", round(x$logLik, 3), "\n"))
cat("Roots of the characteristic polynomial:\n")
cat(formatC(x$roots, digits = digits))
cat("\nCall:\n")
print(x$call)
cat("\n\n")
for (i in 1:dim) {
result <- x$varresult[[x$names[i]]]
text1 <- paste("Estimation results for equation ", x$names[i], ":", sep = "")
cat(text1, "\n")
row <- paste(rep("=", nchar(text1)), collapse = "")
cat(row, "\n")
text2 <- paste(x$names[i], " = ", paste(rownames(result$coef), collapse = " + "), sep = "")
cat(text2, "\n\n")
printCoefmat(result$coef, digits = digits, signif.stars = signif.stars, na.print = "NA", ...)
cat("\n")
cat("\nResidual standard error:", format(signif(result$sigma, digits)), "on", result$df[2L], "degrees of freedom\n")
if (!is.null(result$fstatistic)) {
cat("Multiple R-Squared:", formatC(result$r.squared, digits = digits))
cat(",\tAdjusted R-squared:", formatC(result$adj.r.squared, digits = digits), "\nF-statistic:", formatC(result$fstatistic[1], digits = digits), "on", result$fstatistic[2], "and", result$fstatistic[3], "DF, p-value:", format.pval(pf(result$fstatistic[1L], result$fstatistic[2L], result$fstatistic[3L], lower.tail = FALSE), digits = digits), "\n")
}
cat("\n\n")
}
cat("\nCovariance matrix of residuals:\n")
print(x$covres, digits = digits, ...)
cat("\nCorrelation matrix of residuals:\n")
print(x$corres, digits = digits, ...)
cat("\n\n")
invisible(x)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/print.varsum.R
|
"print.vec2var" <-
function(x, ...){
cat("\nCoefficient matrix of lagged endogenous variables:\n")
for(i in 1:x$p){
cat(paste("\nA", i, ":\n", sep = ""))
print(x$A[[i]], ...)
cat("\n")
}
cat("\nCoefficient matrix of deterministic regressor(s).\n")
cat("\n")
print(x$deterministic, ...)
invisible(x)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/print.vec2var.R
|
"residuals.varest" <-
function(object, ...){
return(sapply(object$varresult, residuals))
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/residuals.varest.R
|
"residuals.vec2var" <-
function(object, ...){
if (!is(object, "vec2var")) {
stop("\nPlease, provide object of class 'vec2var' as 'object'.\n")
}
resids <- object$datamat[, colnames(object$y)] - object$datamat[, colnames(object$deterministic)] %*% t(object$deterministic)
for(i in 1:object$p){
resids <- resids - object$datamat[, colnames(object$A[[i]])] %*% t(object$A[[i]])
}
colnames(resids) <- paste("resids of", colnames(object$y))
return(resids)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/residuals.vec2var.R
|
"restrict" <-
function (x, method = c("ser", "manual"), thresh = 2, resmat = NULL)
{
if (!is(x, "varest")) {
stop("\nPlease provide an object of class 'varest', generated by 'var()'.\n")
}
method <- match.arg(method)
thresh <- abs(thresh)
K <- x$K
p <- x$p
datasub <- x$datamat[, -c(1:K)]
namesall <- colnames(datasub)
yendog <- x$datamat[, c(1:K)]
sample <- x$obs
ser <- function(x, y) {
tvals <- abs(coef(summary(x))[, 3])
datares <- datasub
if(min(tvals) >= thresh){
lmres <- x
datares <- datasub
} else {
while (min(tvals) < thresh) {
if (ncol(datares) > 1) {
cnames <- colnames(datares)
datares <- as.data.frame(datares[, -1 * which.min(tvals)])
colnames(datares) <- cnames[-1 * which.min(tvals)]
lmres <- lm(y ~ -1 + ., data = datares)
tvals <- abs(coef(summary(lmres))[, 3])
} else {
lmres <- NULL
datares <- NULL
break
}
}
}
return(list(lmres = lmres, datares = datares))
}
if (method == "ser") {
x$restrictions <- matrix(0, nrow = K, ncol = ncol(datasub))
colnames(x$restrictions) <- namesall
rownames(x$restrictions) <- colnames(yendog)
for (i in 1:K) {
temp <- ser(x$varresult[[i]], yendog[, i])
if (is.null(temp$lmres)) {
stop(paste("\nNo significant regressors remaining in equation for",
colnames(yendog)[i], ".\n"))
}
x$varresult[[i]] <- temp[[1]]
namessub <- colnames(temp[[2]])
x$restrictions[i, namesall %in% namessub] <- 1
}
}
else if (method == "manual") {
resmat <- as.matrix(resmat)
if (!(nrow(resmat) == K) | !(ncol(resmat) == ncol(datasub))) {
stop(paste("\n Please provide resmat with dimensions:",
K, "x", ncol(datasub), "\n"))
}
x$restrictions <- resmat
colnames(x$restrictions) <- namesall
rownames(x$restrictions) <- colnames(yendog)
for (i in 1:K) {
datares <- data.frame(datasub[, which(x$restrictions[i, ] == 1)])
colnames(datares) <- colnames(datasub)[which(x$restrictions[i, ] == 1)]
y <- yendog[, i]
lmres <- lm(y ~ -1 + ., data = datares)
x$varresult[[i]] <- lmres
}
}
return(x)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/restrict.R
|
"roots" <-
function(x, modulus = TRUE){
if(!is(x, "varest")){
stop("\nPlease provide an object of class 'varest', generated by 'VAR()'.\n")
}
K <- x$K
p <- x$p
A <- unlist(Acoef(x))
companion <- matrix(0, nrow = K * p, ncol = K * p)
companion[1:K, 1:(K * p)] <- A
if(p > 1){
j <- 0
for( i in (K + 1) : (K*p)){
j <- j + 1
companion[i, j] <- 1
}
}
roots <- eigen(companion)$values
if(modulus) roots <- Mod(roots)
return(roots)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/roots.R
|
"serial.test" <-
function(x, lags.pt = 16, lags.bg = 5, type = c("PT.asymptotic", "PT.adjusted", "BG", "ES")){
if(!(is(x, "varest") || is(x, "vec2var"))){
stop("\nPlease provide an object of class 'varest', generated by 'var()', or an object of class 'vec2var' generated by 'vec2var()'.\n")
}
obj.name <- deparse(substitute(x))
type <- match.arg(type)
K <- x$K
obs <- x$obs
resids <- resid(x)
if((type == "PT.asymptotic") || (type == "PT.adjusted")){
lags.pt <- abs(as.integer(lags.pt))
ptm <- .pt.multi(x, K = K, obs = obs, lags.pt = lags.pt, obj.name = obj.name, resids = resids)
ifelse(type == "PT.asymptotic", test <- ptm[[1]], test <- ptm[[2]])
} else {
lags.bg <- abs(as.integer(lags.bg))
bgm <- .bgserial(x, K = K, obs = obs, lags.bg = lags.bg, obj.name = obj.name, resids = resids)
ifelse(type == "BG", test <- bgm[[1]], test <- bgm[[2]])
}
result <- list(resid = resids, serial = test)
class(result) <- "varcheck"
return(result)
}
serial <- function(x, lags.pt = 16, lags.bg = 5, type = c("PT.asymptotic", "PT.adjusted", "BG", "ES")){
.Deprecated("serial.test", package = "vars", msg = "Function 'serial' is deprecated; use 'serial.test' instead.\nSee help(\"vars-deprecated\") and help(\"serial-deprecated\") for more information.")
serial.test(x = x, lags.pt = lags.pt, lags.bg = lags.bg, type = type)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/serial.R
|
"stability" <-
function(x, ...){
UseMethod("stability")
}
"stability.default" <-
function(x, type = c("OLS-CUSUM", "Rec-CUSUM", "Rec-MOSUM", "OLS-MOSUM", "RE",
"ME", "Score-CUSUM", "Score-MOSUM", "fluctuation"),
h = 0.15, dynamic = FALSE, rescale = TRUE, ...){
strucchange::sctest(x, ...)
}
"stability.varest" <-
function(x, type = c("OLS-CUSUM", "Rec-CUSUM", "Rec-MOSUM", "OLS-MOSUM", "RE",
"ME", "Score-CUSUM", "Score-MOSUM", "fluctuation"),
h = 0.15, dynamic = FALSE, rescale = TRUE, ...){
type <- match.arg(type)
K <- x$K
stability <- list()
endog <- colnames(x$datamat)[1 : K]
for(i in 1 : K){
formula <- formula(x$varresult[[i]])
data <- x$varresult[[i]]$model
stability[[endog[i]]] <- efp(formula = formula, data = data, type = type, h = h, dynamic = dynamic, rescale = rescale)
}
result <- list(stability = stability, names = endog, K = K)
class(result) <- "varstabil"
return(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/stability.R
|
"summary.svarest" <-
function(object, ...){
type <- object$type
obs <- nrow(object$var$datamat)
A <- object$A
B <- object$B
Ase <- object$Ase
Bse <- object$Bse
LRIM <- object$LRIM
logLik <- as.numeric(logLik(object))
Sigma.U <- object$Sigma.U
LR <- object$LR
iter <- object$iter
call <- object$call
opt <- object$opt
result <- list(type = type, A = A, B = B, Ase = Ase, Bse = Bse, LRIM = LRIM, Sigma.U = Sigma.U, logLik = logLik, LR = LR, obs = obs, opt = opt, iter = iter, call = call)
class(result) <- "svarsum"
return(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/summary.svarest.R
|
"summary.svecest" <-
function(object, ...){
type <- object$type
K <- object$var@P
obs <- nrow(object$var@Z0)
SR <- object$SR
LR <- object$LR
SRse <- object$SRse
LRse <- object$LRse
logLik <- as.numeric(logLik(object))
Sigma.U <- object$Sigma.U
LRover <- object$LRover
r <- object$r
iter <- object$iter
call <- object$call
result <- list(type = type, SR = SR, LR = LR, SRse = SRse, LRse = LRse, Sigma.U = Sigma.U, logLik = logLik, LRover = LRover, obs = obs, r = r, iter = iter, call = call)
class(result) <- "svecsum"
return(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/summary.svecest.R
|
"summary.varest" <-
function(object, equations = NULL, ...){
ynames <- colnames(object$y)
obs <- nrow(object$datamat)
if (is.null(equations)) {
names <- ynames
}
else {
names <- as.character(equations)
if (!(all(names %in% ynames))) {
warning("\nInvalid variable name(s) supplied, using first variable.\n")
names <- ynames[1]
}
}
eqest <- lapply(object$varresult[names], summary)
resids <- resid(object)
covres <- cov(resids) * (obs - 1) / (obs - (ncol(object$datamat) - object$K))
corres <- cor(resids)
logLik <- as.numeric(logLik(object))
roots <- roots(object)
result <- list(names = names, varresult = eqest, covres = covres, corres = corres, logLik = logLik, obs = obs, roots = roots, type = object$type, call = object$call)
class(result) <- "varsum"
return(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/summary.varest.R
|
toMlm <- function(x, ...) {
UseMethod("toMlm")
}
toMlm.default <- function(x, ...){
lm(x$model)
}
toMlm.varest<-function(x, ...){
ix <- 1:x$K
X<-x$datamat
type<-x$type
is.const<-type%in%c("const", "both")
#remove constant in datamat
if(is.const) X<-X[, -grep("const", colnames(X))]
#construct formula
left <- paste(names(X)[ix], collapse = ",")
if(is.const) {
fo <- as.formula(paste("cbind(", left, ") ~ ."))
} else {
fo <- as.formula(paste("cbind(", left, ") ~ .-1")) #remove automatical constant
}
#apply lm
res<-eval(substitute(lm(fo, X), list(fo = fo))) #code suggested by Gabor Groothendick
return(res)
}
coeftest.varest<-function(x, ...){
coeftest(toMlm.varest(x), ...)
}
bread.varest<-function(x, ...){
bread(toMlm.varest(x), ...)
}
vcov.varest<-function(object, ...){
vcov(toMlm.varest(object), ...)
}
vcovHC.varest<-function(x, ...){
vcovHC(toMlm.varest(x), ...)
}
estfun.varest<-function(x, ...){
estfun(toMlm.varest(x), ...)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/toMlm.R
|
"vec2var" <-
function(z, r = 1){
if (!is(z, "ca.jo")) {
stop("\nPlease, provide object of class 'ca.jo' as 'z'.\n")
}
r <- as.integer(r)
if(!({1 <= r} && {r < ncol(z@x)})){
stop(paste("\nThe cointegration rank 'r' must be in the interval [1:", ncol(z@x) - 1, "].\n", sep = ""))
}
etc <- z@ZK %*% z@V[, 1:r]
colnames(etc) <- paste("etc", 1:r, sep ="")
coeffs <- coef(lm(z@Z0 ~ -1 + etc + z@Z1))
rownames(coeffs) <- c(colnames(etc), colnames(z@Z1))
PI <- z@W[, 1:r] %*% t(z@V[, 1:r])
if(z@ecdet == "const"){
detcoeffs <- matrix(PI[, z@P + 1], nrow = 1, ncol = ncol(z@x), byrow = TRUE)
rownames(detcoeffs) <- "constant"
colnames(detcoeffs) <- colnames(z@x)
PI <- PI[, -(z@P + 1)]
rhs <- cbind(1, z@Z1)
colnames(rhs) <- c("constant", colnames(z@Z1))
} else if(z@ecdet == "none"){
detcoeffs <- matrix(coeffs["constant", ], nrow = 1, ncol = ncol(z@x), byrow = TRUE)
rownames(detcoeffs) <- "constant"
colnames(detcoeffs) <- colnames(z@x)
rhs <- z@Z1
} else if(z@ecdet == "trend"){
detcoeffs <- matrix(c(coeffs["constant", ], PI[, z@P + 1]), nrow = 2, ncol = ncol(z@x), byrow = TRUE)
rownames(detcoeffs) <- c("constant", colnames(z@ZK)[z@P + 1])
colnames(detcoeffs) <- colnames(z@x)
PI <- PI[, -(z@P + 1)]
rhs <- cbind(1, z@ZK[, z@P + 1], z@Z1[, -1])
colnames(rhs) <- c("constant", colnames(z@ZK)[z@P + 1], colnames(z@Z1)[-1])
}
if(!(is.null(eval(z@season)))){
seas <- eval(z@season) - 1
season <- paste("sd", 1:seas, sep = "")
detcoeffs <- rbind(detcoeffs, coeffs[season, ])
}
if(!(is.null(eval(z@dumvar)))){
dumnames <- colnames(z@dumvar)
tmp <- rownames(detcoeffs)
detcoeffs <- rbind(detcoeffs, coeffs[dumnames, ])
rownames(detcoeffs) <- c(tmp, dumnames)
}
detcoeffs <- t(detcoeffs)
Gamma <- t(coeffs[- which(rownames(coeffs) %in% c(colnames(detcoeffs), colnames(etc))), ])
rownames(Gamma) <- colnames(z@x)
A <- list()
if(identical(z@spec, "transitory")){
if(identical(z@lag, as.integer(2))){
A$A1 <- Gamma + PI + diag(z@P)
rownames(A$A1) <- colnames(z@x)
colnames(A$A1) <- paste(colnames(z@x), ".l1", sep = "")
A$A2 <- -1.0 * Gamma
rownames(A$A2) <- colnames(z@x)
colnames(A$A2) <- paste(colnames(z@x), ".l2", sep = "")
} else if(z@lag > 2){
idx.end <- seq(from = z@P, by = z@P, length.out = z@lag - 1)
idx.start <- idx.end - z@P + 1
A[[1]] <- Gamma[, idx.start[1]:idx.end[1]] + PI + diag(z@P)
rownames(A[[1]]) <- colnames(z@x)
colnames(A[[1]]) <- paste(colnames(z@x), ".l1", sep = "")
for(i in 2:(z@lag - 1)){
A[[i]] <- Gamma[, idx.start[i]:idx.end[i]] - Gamma[, idx.start[i - 1]:idx.end[i - 1]]
rownames(A[[i]]) <- colnames(z@x)
colnames(A[[i]]) <- paste(colnames(z@x), ".l", i, sep = "")
}
A[[z@lag]] <- -1.0 * Gamma[, tail(idx.start, 1):tail(idx.end, 1)]
rownames(A[[z@lag]]) <- colnames(z@x)
colnames(A[[z@lag]]) <- paste(colnames(z@x), ".l", z@lag, sep = "")
names(A) <- paste("A", 1:z@lag, sep = "")
}
}
if(identical(z@spec, "longrun")){
if(identical(z@lag, as.integer(2))){
A$A1 <- Gamma + diag(z@P)
rownames(A$A1) <- colnames(z@x)
colnames(A$A1) <- paste(colnames(z@x), ".l1", sep = "")
A$A2 <- PI + diag(z@P) - A$A1
rownames(A$A2) <- colnames(z@x)
colnames(A$A2) <- paste(colnames(z@x), ".l2", sep = "")
} else if(z@lag > 2){
idx.end <- seq(from = z@P, by = z@P, length.out = z@lag - 1)
idx.start <- idx.end - z@P + 1
A[[1]] <- Gamma[, idx.start[1]:idx.end[1]] + diag(z@P)
rownames(A[[1]]) <- colnames(z@x)
colnames(A[[1]]) <- paste(colnames(z@x), ".l1", sep = "")
for(i in 2:(z@lag - 1)){
A[[i]] <- Gamma[, idx.start[i]:idx.end[i]] - Gamma[, idx.start[i - 1]:idx.end[i - 1]]
rownames(A[[i]]) <- colnames(z@x)
colnames(A[[i]]) <- paste(colnames(z@x), ".l", i, sep = "")
}
A[[z@lag]] <- PI - Gamma[ ,tail(idx.start, 1):tail(idx.end, 1)]
rownames(A[[z@lag]]) <- colnames(z@x)
colnames(A[[z@lag]]) <- paste(colnames(z@x), ".l", z@lag, sep = "")
names(A) <- paste("A", 1:z@lag, sep = "")
}
}
datamat <- embed(z@x, dimension = z@lag + 1)
datamat <- cbind(datamat[, 1:ncol(z@x)], rhs[, colnames(detcoeffs)], datamat[, -c(1:ncol(z@x))])
temp1 <- NULL
for (i in 1:z@lag) {
temp <- paste(colnames(z@x), ".l", i, sep = "")
temp1 <- c(temp1, temp)
}
colnames(datamat) <- c(colnames(z@x), colnames(detcoeffs), temp1)
resids <- datamat[, colnames(z@x)] - datamat[, colnames(detcoeffs)] %*% t(detcoeffs)
for(i in 1:z@lag){
resids <- resids - datamat[, colnames(A[[i]])] %*% t(A[[i]])
}
colnames(resids) <- paste("resids of", colnames(z@x))
result <- list(deterministic = detcoeffs, A = A, p = z@lag, K = ncol(z@x), y = z@x, obs = nrow(z@Z0), totobs = nrow(z@x), call = match.call(), vecm = z, datamat = datamat, resid = resids, r = r)
class(result) <- "vec2var"
return(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/R/vec2var.R
|
set.seed(123456)
y <- arima.sim(n = 100, list(ar = 0.9), innov=rnorm(100))
op <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
layout(matrix(c(1, 1, 2, 3), 2, 2, byrow=TRUE))
plot.ts(y, ylab='')
acf(y, main='Autocorrelations', ylab='',
ylim=c(-1, 1), ci.col = "black")
pacf(y, main='Partial Autocorrelations', ylab='',
ylim=c(-1, 1), ci.col = "black")
par(op)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-1-1.R
|
series <- rnorm(1000)
y.st <- filter(series, filter=c(0.6, -0.28),
method='recursive')
ar2.st <- arima(y.st, c(2, 0, 0), include.mean=FALSE,
transform.pars=FALSE, method="ML")
ar2.st$coef
polyroot(c(1, -ar2.st$coef))
Mod(polyroot(c(1, -ar2.st$coef)))
root.comp <- Im(polyroot(c(1, -ar2.st$coef)))
root.real <- Re(polyroot(c(1, -ar2.st$coef)))
# Plotting the roots in a unit circle
x <- seq(-1, 1, length = 1000)
y1 <- sqrt(1- x^2)
y2 <- -sqrt(1- x^2)
plot(c(x, x), c(y1, y2), xlab='Real part',
ylab='Complex part', type='l',
main='Unit Circle', ylim=c(-2, 2), xlim=c(-2, 2))
abline(h=0)
abline(v=0)
points(Re(polyroot(c(1, -ar2.st$coef))),
Im(polyroot(c(1, -ar2.st$coef))), pch=19)
legend(-1.5, -1.5, legend="Roots of AR(2)", pch=19)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-1-2.R
|
library(urca)
data(npext)
npext
y <- ts(na.omit(npext$unemploy), start=1890, end=1988,
frequency=1)
op <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
layout(matrix(c(1, 1, 2, 3), 2, 2, byrow=TRUE))
plot(y, ylab="unemployment rate (logarithm)")
acf(y, main='Autocorrelations', ylab='', ylim=c(-1, 1))
pacf(y, main='Partial Autocorrelations', ylab='',
ylim=c(-1, 1))
par(op)
## tentative ARMA(2,0)
arma20 <- arima(y, order=c(2, 0, 0))
ll20 <- logLik(arma20)
aic20 <- arma20$aic
res20 <- residuals(arma20)
Box.test(res20, lag = 20, type = "Ljung-Box")
shapiro.test(res20)
## alternative specifications
## ARMA(3,0)
arma30 <- arima(y, order=c(3, 0, 0))
ll30 <- logLik(arma30)
aic30 <- arma30$aic
lrtest <- as.numeric(2*(ll30 - ll20))
chi.pval <- pchisq(lrtest, df = 1, lower.tail = FALSE)
## ARMA(1,1)
arma11 <- arima(y, order = c(1, 0, 1))
ll11 <- logLik(arma11)
aic11 <- arma11$aic
tsdiag(arma11)
res11 <- residuals(arma11)
Box.test(res11, lag = 20, type = "Ljung-Box")
shapiro.test(res11)
tsdiag(arma11)
## Using auto.arima()
library(forecast)
auto.arima(y, max.p = 3, max.q = 3, start.p = 1,
start.q = 1, ic = "aic")
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-1-3.R
|
## Forecasts
arma11.pred <- predict(arma11, n.ahead = 10)
predict <- ts(c(rep(NA, length(y) - 1), y[length(y)],
arma11.pred$pred), start = 1909,
frequency = 1)
upper <- ts(c(rep(NA, length(y) - 1), y[length(y)],
arma11.pred$pred + 2 * arma11.pred$se),
start = 1909, frequency = 1)
lower <- ts(c(rep(NA, length(y) - 1), y[length(y)],
arma11.pred$pred - 2 * arma11.pred$se),
start = 1909, frequency = 1)
observed <- ts(c(y, rep(NA, 10)), start=1909,
frequency = 1)
## Plot of actual and forecasted values
plot(observed, type = "l",
ylab = "Actual and predicted values", xlab = "")
lines(predict, col = "blue", lty = 2)
lines(lower, col = "red", lty = 5)
lines(upper, col = "red", lty = 5)
abline(v = 1988, col = "gray", lty = 3)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-1-4.R
|
## Simulate VAR(2)-data
library(dse1)
library(vars)
## Setting the lag-polynomial A(L)
Apoly <- array(c(1.0, -0.5, 0.3, 0,
0.2, 0.1, 0, -0.2,
0.7, 1, 0.5, -0.3) ,
c(3, 2, 2))
## Setting Covariance to identity-matrix
B <- diag(2)
## Setting constant term to 5 and 10
TRD <- c(5, 10)
## Generating the VAR(2) model
var2 <- ARMA(A = Apoly, B = B, TREND = TRD)
## Simulating 500 observations
varsim <- simulate(var2, sampleT = 500,
noise = list(w = matrix(rnorm(1000),
nrow = 500, ncol = 2)), rng = list(seed = c(123456)))
## Obtaining the generated series
vardat <- matrix(varsim$output, nrow = 500, ncol = 2)
colnames(vardat) <- c("y1", "y2")
## Plotting the series
plot.ts(vardat, main = "", xlab = "")
## Determining an appropriate lag-order
infocrit <- VARselect(vardat, lag.max = 3,
type = "const")
## Estimating the model
varsimest <- VAR(vardat, p = 2, type = "const",
season = NULL, exogen = NULL)
## Alternatively, selection according to AIC
varsimest <- VAR(vardat, type = "const",
lag.max = 3, ic = "SC")
## Checking the roots
roots <- roots(varsimest)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-2-1.R
|
## Impulse response analysis of SVAR A-type model
args(vars:::irf.svarest)
irf.svara <- irf(svar.A, impulse = "y1",
response = "y2", boot = FALSE)
args(vars:::plot.varirf)
plot(irf.svara)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-2-10.R
|
## FEVD analysis of SVAR B-type model
args(vars:::fevd.svarest)
fevd.svarb <- fevd(svar.B, n.ahead = 5)
class(fevd.svarb)
methods(class = "varfevd")
plot(fevd.svarb)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-2-11.R
|
## testing serial correlation
args(serial.test)
## Portmanteau-Test
var2c.serial <- serial.test(varsimest, lags.pt = 16,
type = "PT.asymptotic")
var2c.serial
plot(var2c.serial, names = "y1")
plot(var2c.serial, names = "y2")
## testing heteroscedasticity
args(arch.test)
var2c.arch <- arch.test(varsimest, lags.multi = 5,
multivariate.only = TRUE)
var2c.arch
## testing for normality
args(normality.test)
var2c.norm <- normality.test(varsimest,
multivariate.only = TRUE)
var2c.norm
## class and methods for diganostic tests
class(var2c.serial)
class(var2c.arch)
class(var2c.norm)
methods(class = "varcheck")
## Plot of objects "varcheck"
args(vars:::plot.varcheck)
plot(var2c.serial, names = "y1")
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-2-2.R
|
reccusum <- stability(varsimest,
type = "OLS-CUSUM")
fluctuation <- stability(varsimest,
type = "fluctuation")
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-2-3.R
|
## Causality tests
## Granger and instantaneous causality
var.causal <- causality(varsimest, cause = "y2")
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-2-4.R
|
## Forecasting objects of class varest
args(vars:::predict.varest)
predictions <- predict(varsimest, n.ahead = 25,
ci = 0.95)
class(predictions)
args(vars:::plot.varprd)
## Plot of predictions for y1
plot(predictions, names = "y1")
## Fanchart for y2
args(fanchart)
fanchart(predictions, names = "y2")
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-2-5.R
|
## Impulse response analysis
irf.y1 <- irf(varsimest, impulse = "y1",
response = "y2", n.ahead = 10,
ortho = FALSE, cumulative = FALSE,
boot = FALSE, seed = 12345)
args(vars:::plot.varirf)
plot(irf.y1)
irf.y2 <- irf(varsimest, impulse = "y2",
response = "y1", n.ahead = 10,
ortho = TRUE, cumulative = TRUE,
boot = FALSE, seed = 12345)
plot(irf.y2)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-2-6.R
|
## Forecast error variance decomposition
fevd.var2 <- fevd(varsimest, n.ahead = 10)
args(vars:::plot.varfevd)
plot(fevd.var2, addbars = 2)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-2-7.R
|
library(dse1)
library(vars)
## A-model
Apoly <- array(c(1.0, -0.5, 0.3, 0.8,
0.2, 0.1, -0.7, -0.2,
0.7, 1, 0.5, -0.3) ,
c(3, 2, 2))
## Setting covariance to identity-matrix
B <- diag(2)
## Generating the VAR(2) model
svarA <- ARMA(A = Apoly, B = B)
## Simulating 500 observations
svarsim <- simulate(svarA, sampleT = 500,
rng = list(seed = c(123456)))
## Obtaining the generated series
svardat <- matrix(svarsim$output, nrow = 500, ncol = 2)
colnames(svardat) <- c("y1", "y2")
## Estimating the VAR
varest <- VAR(svardat, p = 2, type = "none")
## Setting up matrices for A-model
Amat <- diag(2)
Amat[2, 1] <- NA
Amat[1, 2] <- NA
## Estimating the SVAR A-type by direct maximisation
## of the log-likelihood
args(SVAR)
svar.A <- SVAR(varest, estmethod = "direct",
Amat = Amat, hessian = TRUE)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-2-8.R
|
library(dse1)
library(vars)
## B-model
Apoly <- array(c(1.0, -0.5, 0.3, 0,
0.2, 0.1, 0, -0.2,
0.7, 1, 0.5, -0.3) ,
c(3, 2, 2))
## Setting covariance to identity-matrix
B <- diag(2)
B[2, 1] <- -0.8
## Generating the VAR(2) model
svarB <- ARMA(A = Apoly, B = B)
## Simulating 500 observations
svarsim <- simulate(svarB, sampleT = 500,
rng = list(seed = c(123456)))
svardat <- matrix(svarsim$output, nrow = 500, ncol = 2)
colnames(svardat) <- c("y1", "y2")
varest <- VAR(svardat, p = 2, type = "none")
## Estimating the SVAR B-type by scoring algorithm
## Setting up the restriction matrix and vector
## for B-model
Bmat <- diag(2)
Bmat[2, 1] <- NA
svar.B <- SVAR(varest, estmethod = "scoring",
Bmat = Bmat, max.iter = 200)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-2-9.R
|
set.seed(123456)
e <- rnorm(500)
## pure random walk
rw.nd <- cumsum(e)
## trend
trd <- 1:500
## random walk with drift
rw.wd <- 0.5*trd + cumsum(e)
## deterministic trend and noise
dt <- e + 0.5*trd
## plotting
par(mar=rep(5,4))
plot.ts(dt, lty=1, ylab='', xlab='')
lines(rw.wd, lty=2)
par(new=T)
plot.ts(rw.nd, lty=3, axes=FALSE)
axis(4, pretty(range(rw.nd)))
lines(rw.nd, lty=3)
legend(10, 18.7, legend=c('det. trend + noise (ls)',
'rw drift (ls)', 'rw (rs)'),
lty=c(1, 2, 3))
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-3-1.R
|
library(fracdiff)
set.seed(123456)
# ARFIMA(0.4,0.4,0.0)
y1 <- fracdiff.sim(n=1000, ar=0.4, ma=0.0, d=0.4)
# ARIMA(0.4,0.0,0.0)
y2 <- arima.sim(model=list(ar=0.4), n=1000)
# Graphics
op <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
layout(matrix(1:6, 3, 2, byrow=FALSE))
plot.ts(y1$series,
main='Time series plot of long memory',
ylab='')
acf(y1$series, lag.max=100,
main='Autocorrelations of long memory')
spectrum(y1$series,
main='Spectral density of long memory')
plot.ts(y2,
main='Time series plot of short memory', ylab='')
acf(y2, lag.max=100,
main='Autocorrelations of short memory')
spectrum(y2, main='Spectral density of short memory')
par(op)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-3-2.R
|
library(fracdiff)
set.seed(123456)
# ARFIMA(0.0,0.3,0.0)
y <- fracdiff.sim(n=1000, ar=0.0, ma=0.0, d=0.3)
# Get the data series, demean this if necessary
y.dm <- y$series
max.y <- max(cumsum(y.dm))
min.y <- min(cumsum(y.dm))
sd.y <- sd(y$series)
RS <- (max.y - min.y)/sd.y
H <- log(RS)/log(1000)
d <- H - 0.5
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-3-3.R
|
library(fracdiff)
set.seed(123456)
y <- fracdiff.sim(n=1000, ar=0.0, ma=0.0, d=0.3)
y.spec <- spectrum(y$series, plot=FALSE)
lhs <- log(y.spec$spec)
rhs <- log(4*(sin(y.spec$freq/2))^2)
gph.reg <- lm(lhs ~ rhs)
gph.sum <- summary(gph.reg)
sqrt(gph.sum$cov.unscaled*pi/6)[2,2]
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-3-4.R
|
library(lmtest)
set.seed(123456)
e1 <- rnorm(500)
e2 <- rnorm(500)
trd <- 1:500
y1 <- 0.8*trd + cumsum(e1)
y2 <- 0.6*trd + cumsum(e2)
sr.reg <- lm(y1 ~ y2)
sr.dw <- dwtest(sr.reg)$statistic
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-4-1.R
|
set.seed(123456)
e1 <- rnorm(100)
e2 <- rnorm(100)
y1 <- cumsum(e1)
y2 <- 0.6*y1 + e2
lr.reg <- lm(y2 ~ y1)
error <- residuals(lr.reg)
error.lagged <- error[-c(1, 100)]
dy1 <- diff(y1)
dy2 <- diff(y2)
diff.dat <- data.frame(embed(cbind(dy1, dy2), 2))
colnames(diff.dat) <- c('dy1', 'dy2', 'dy1.1', 'dy2.1')
ecm.reg <- lm(dy2 ~ error.lagged + dy1.1 + dy2.1,
data=diff.dat)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-4-2.R
|
library(urca)
set.seed(12345)
e1 <- rnorm(250, 0, 0.5)
e2 <- rnorm(250, 0, 0.5)
e3 <- rnorm(250, 0, 0.5)
u1.ar1 <- arima.sim(model = list(ar = 0.75),
innov = e1, n = 250)
u2.ar1 <- arima.sim(model = list(ar = 0.3),
innov = e2, n = 250)
y3 <- cumsum(e3)
y1 <- 0.8 * y3 + u1.ar1
y2 <- -0.3 * y3 + u2.ar1
y.mat <- data.frame(y1, y2, y3)
vecm <- ca.jo(y.mat)
jo.results <- summary(vecm)
vecm.r2 <- cajorls(vecm, r = 2)
class(jo.results)
slotNames(jo.results)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-4-3.R
|
library(vars)
vecm.level <- vec2var(vecm, r = 2)
arch.test(vecm.level)
normality.test(vecm.level)
serial.test(vecm.level)
predict(vecm.level)
irf(vecm.level, boot = FALSE)
fevd(vecm.level)
class(vecm.level)
methods(class = "vec2var")
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-4-4.R
|
library(urca)
data(Raotbl3)
attach(Raotbl3)
lc <- ts(lc, start=c(1966,4), end=c(1991,2), frequency=4)
lc.ct <- ur.df(lc, lags=3, type='trend')
plot(lc.ct)
lc.co <- ur.df(lc, lags=3, type='drift')
lc2 <- diff(lc)
lc2.ct <- ur.df(lc2, type='trend', lags=3)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-5-1.R
|
library(urca)
data(Raotbl3)
attach(Raotbl3)
lc <- ts(lc, start=c(1966,4), end=c(1991,2),
frequency=4)
lc.ct <- ur.pp(lc, type='Z-tau', model='trend',
lags='long')
lc.co <- ur.pp(lc, type='Z-tau', model='constant',
lags='long')
lc2 <- diff(lc)
lc2.ct <- ur.pp(lc2, type='Z-tau', model='trend',
lags='long')
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-5-2.R
|
library(urca)
data(nporg)
gnp <- log(na.omit(nporg[, "gnp.r"]))
gnp.d <- diff(gnp)
gnp.ct.df <- ur.ers(gnp, type = "DF-GLS",
model = "trend", lag.max = 4)
gnp.ct.pt <- ur.ers(gnp, type = "P-test",
model = "trend")
gnp.d.ct.df <- ur.ers(gnp.d, type = "DF-GLS",
model = "trend", lag.max = 4)
gnp.d.ct.pt <- ur.ers(gnp.d, type = "P-test",
model = "trend")
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-5-3.R
|
library(urca)
data(nporg)
gnp <- na.omit(nporg[, "gnp.n"])
gnp.tau.sp <- ur.sp(gnp, type = "tau", pol.deg=2,
signif=0.05)
gnp.rho.sp <- ur.sp(gnp, type = "rho", pol.deg=2,
signif=0.05)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-5-4.R
|
library(urca)
data(nporg)
ir <- na.omit(nporg[, "bnd"])
wg <- log(na.omit(nporg[, "wg.n"]))
ir.kpss <- ur.kpss(ir, type = "mu", use.lag=8)
wg.kpss <- ur.kpss(wg, type = "tau", use.lag=8)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-5-5.R
|
set.seed(123456)
e <- rnorm(500)
## trend
trd <- 1:500
S <- c(rep(0, 249), rep(1, 251))
## random walk with drift
y1 <- 0.1*trd + cumsum(e)
## random walk with drift and shift
y2 <- 0.1*trd + 10*S + cumsum(e)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-6-1.R
|
library(urca)
data(nporg)
wg.n <- log(na.omit(nporg[, "wg.n"]))
za.wg.n <- ur.za(wg.n, model = "intercept", lag = 7)
## plot(za.wg.n)
wg.r <- log(na.omit(nporg[, "wg.r"]))
za.wg.r <- ur.za(wg.r, model = "both", lag = 8)
## plot(za.wg.r)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-6-2.R
|
library(urca)
library(uroot)
data(UKconinc)
incl <- ts(UKconinc$incl, start = c(1955,1),
end = c(1984,4), frequency = 4)
HEGY000 <- HEGY.test(wts = incl, itsd = c(0, 0, c(0)),
selectlags = list(mode = c(1,4,5)))
HEGY100 <- HEGY.test(wts = incl, itsd = c(1, 0, c(0)),
selectlags = list(mode = c(1,4,5)))
HEGY110 <- HEGY.test(wts = incl, itsd = c(1, 1, c(0)),
selectlags = list(mode = c(1,4,5)))
HEGY101 <- HEGY.test(wts = incl,
itsd = c(1, 0, c(1, 2, 3)),
selectlags = list(mode = c(1,4,5)))
HEGY111 <- HEGY.test(wts = incl,
itsd = c(1, 1, c(1, 2, 3)),
selectlags = list(mode = c(1,4,5)))
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-6-3.R
|
library(tseries)
library(urca)
data(Raotbl3)
attach(Raotbl3)
lc <- ts(lc, start=c(1966,4), end=c(1991,2),
frequency=4)
li <- ts(li, start=c(1966,4), end=c(1991,2),
frequency=4)
lw <- ts(lw, start=c(1966,4), end=c(1991,2),
frequency=4)
ukcons <- window(cbind(lc, li, lw), start=c(1967, 2),
end=c(1991,2))
lc.eq <- summary(lm(lc ~ li + lw, data=ukcons))
li.eq <- summary(lm(li ~ lc + lw, data=ukcons))
lw.eq <- summary(lm(lw ~ li + lc, data=ukcons))
error.lc <- ts(resid(lc.eq), start=c(1967,2),
end=c(1991,2), frequency=4)
error.li <- ts(resid(li.eq), start=c(1967,2),
end=c(1991,2), frequency=4)
error.lw <- ts(resid(lw.eq), start=c(1967,2),
end=c(1991,2), frequency=4)
ci.lc <- ur.df(error.lc, lags=1, type='none')
ci.li <- ur.df(error.li, lags=1, type='none')
ci.lw <- ur.df(error.lw, lags=1, type='none')
jb.lc <- jarque.bera.test(error.lc)
jb.li <- jarque.bera.test(error.li)
jb.lw <- jarque.bera.test(error.lw)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-7-1.R
|
ukcons2 <- ts(embed(diff(ukcons), dim=2),
start=c(1967,4), freq=4)
colnames(ukcons2) <- c('lc.d', 'li.d', 'lw.d',
'lc.d1', 'li.d1', 'lw.d1')
error.ecm1 <- window(lag(error.lc, k=-1),
start=c(1967,4), end=c(1991, 2))
error.ecm2 <- window(lag(error.li, k=-1),
start=c(1967,4), end=c(1991, 2))
ecm.eq1 <- lm(lc.d ~ error.ecm1 + lc.d1 + li.d1 + lw.d1,
data=ukcons2)
ecm.eq2 <- lm(li.d ~ error.ecm2 + lc.d1 + li.d1 + lw.d1,
data=ukcons2)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-7-2.R
|
library(urca)
data(Raotbl3)
attach(Raotbl3)
lc <- ts(lc, start=c(1966,4), end=c(1991,2),
frequency=4)
li <- ts(li, start=c(1966,4), end=c(1991,2),
frequency=4)
lw <- ts(lw, start=c(1966,4), end=c(1991,2),
frequency=4)
ukcons <- window(cbind(lc, li, lw), start=c(1967, 2),
end=c(1991,2))
pu.test <- summary(ca.po(ukcons, demean='const',
type='Pu'))
pz.test <- summary(ca.po(ukcons, demean='const',
type='Pz'))
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-7-3.R
|
library(urca)
data(UKpppuip)
names(UKpppuip)
attach(UKpppuip)
dat1 <- cbind(p1, p2, e12, i1, i2)
dat2 <- cbind(doilp0, doilp1)
args('ca.jo')
H1 <- ca.jo(dat1, type = 'trace', K = 2, season = 4,
dumvar = dat2)
H1.trace <- summary(ca.jo(dat1, type = 'trace', K = 2,
season = 4, dumvar = dat2))
H1.eigen <- summary(ca.jo(dat1, type = 'eigen', K = 2,
season = 4, dumvar = dat2))
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-1.R
|
VARselect(Canada, lag.max = 8, type = "both")
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-10.R
|
Canada <- Canada[, c("prod", "e", "U", "rw")]
p1ct <- VAR(Canada, p = 1, type = "both")
p2ct <- VAR(Canada, p = 2, type = "both")
p3ct <- VAR(Canada, p = 3, type = "both")
## Serial
serial.test(p3ct, lags.pt = 16,
type = "PT.asymptotic")
serial.test(p2ct, lags.pt = 16,
type = "PT.asymptotic")
serial.test(p1ct, lags.pt = 16,
type = "PT.asymptotic")
serial.test(p3ct, lags.pt = 16,
type = "PT.adjusted")
serial.test(p2ct, lags.pt = 16,
type = "PT.adjusted")
serial.test(p1ct, lags.pt = 16,
type = "PT.adjusted")
## JB
normality.test(p3ct)
normality.test(p2ct)
normality.test(p1ct)
## ARCH
arch.test(p3ct, lags.multi = 5)
arch.test(p2ct, lags.multi = 5)
arch.test(p1ct, lags.multi = 5)
## Stability (Recursive CUSUM)
plot(stability(p3ct), nc = 2)
plot(stability(p2ct), nc = 2)
plot(stability(p1ct), nc = 2)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-11.R
|
summary(ca.jo(Canada, type = "trace",
ecdet = "trend", K = 3,
spec = "transitory"))
summary(ca.jo(Canada, type = "trace",
ecdet = "trend", K = 2,
spec = "transitory"))
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-12.R
|
vecm <- ca.jo(Canada[, c("rw", "prod", "e", "U")],
type = "trace", ecdet = "trend",
K = 3, spec = "transitory")
vecm.r1 <- cajorls(vecm, r = 1)
alpha <- coef(vecm.r1$rlm)[1, ]
beta <- vecm.r1$beta
resids <- resid(vecm.r1$rlm)
N <- nrow(resids)
sigma <- crossprod(resids) / N
## t-stats for alpha
alpha.se <- sqrt(solve(crossprod(
cbind(vecm@ZK %*% beta, vecm@Z1)))
[1, 1]* diag(sigma))
alpha.t <- alpha / alpha.se
## t-stats for beta
beta.se <- sqrt(diag(kronecker(solve(
crossprod(vecm@RK[, -1])),
solve(t(alpha) %*% solve(sigma)
%*% alpha))))
beta.t <- c(NA, beta[-1] / beta.se)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-13.R
|
vecm <- ca.jo(Canada[, c("prod", "e", "U", "rw")],
type = "trace", ecdet = "trend",
K = 3, spec = "transitory")
SR <- matrix(NA, nrow = 4, ncol = 4)
SR[4, 2] <- 0
SR
LR <- matrix(NA, nrow = 4, ncol = 4)
LR[1, 2:4] <- 0
LR[2:4, 4] <- 0
LR
svec <- SVEC(vecm, LR = LR, SR = SR, r = 1,
lrtest = FALSE,
boot = TRUE, runs = 100)
svec
svec$SR / svec$SRse
svec$LR / svec$LRse
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-14.R
|
LR[3, 3] <- 0
LR
svec.oi <- SVEC(vecm, LR = LR, SR = SR, r = 1,
lrtest = TRUE, boot = FALSE)
svec.oi <- update(svec, LR = LR, lrtest = TRUE,
boot = FALSE)
svec.oi$LRover
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-15.R
|
svec.irf <- irf(svec, response = "U",
n.ahead = 48, boot = TRUE)
svec.irf
plot(svec.irf)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-16.R
|
fevd.U <- fevd(svec, n.ahead = 48)$U
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-17.R
|
beta <- H1@V
beta[,2] <- beta[,2]/beta[4,2]
beta[,3] <- beta[,3]/beta[4,3]
alpha <- H1@PI%*%solve(t(beta))
beta1 <- cbind(beta[,1:2], H1@V[,3:5])
ci.1 <- ts((H1@x%*%beta1)[-c(1,2),], start=c(1972, 3),
end=c(1987, 2), frequency=4)
ci.2 <- ts(H1@RK%*%beta1, start=c(1972, 3),
end=c(1987, 2), frequency=4)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-2.R
|
A1 <- matrix(c(1,0,0,0,0, 0,0,1,0,0,
0,0,0,1,0, 0,0,0,0,1),
nrow=5, ncol=4)
A2 <- matrix(c(1,0,0,0,0, 0,1,0,0,0,
0,0,1,0,0, 0,0,0,1,0),
nrow=5, ncol=4)
H41 <- summary(alrtest(z = H1, A = A1, r = 2))
H42 <- summary(alrtest(z = H1, A = A2, r = 2))
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-3.R
|
H.31 <- matrix(c(1,-1,-1,0,0, 0,0,0,1,0, 0,0,0,0,1),
c(5,3))
H.32 <- matrix(c(1,0,0,0,0, 0,1,0,0,0, 0,0,1,0,0,
0,0,0,1,-1), c(5,4))
H31 <- summary(blrtest(z = H1, H = H.31, r = 2))
H32 <- summary(blrtest(z = H1, H = H.32, r = 2))
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-4.R
|
H.51 <- c(1, -1, -1, 0, 0)
H.52 <- c(0, 0, 0, 1, -1)
H51 <- summary(bh5lrtest(z = H1, H = H.51, r = 2))
H52 <- summary(bh5lrtest(z = H1, H = H.52, r = 2))
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-5.R
|
H.6 <- matrix(rbind(diag(3), c(0, 0, 0), c(0, 0, 0)),
nrow=5, ncol=3)
H6 <- summary(bh6lrtest(z = H1, H = H.6,
r = 2, r1 = 1))
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-6.R
|
data(denmark)
sjd <- denmark[, c("LRM", "LRY", "IBO", "IDE")]
sjd.vecm <- summary(ca.jo(sjd, ecdet = "const",
type = "eigen",
K = 2,
spec = "longrun",
season = 4))
lue.vecm <- summary(cajolst(sjd, season=4))
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-7.R
|
library(vars)
data(Canada)
summary(Canada)
plot(Canada, nc = 2)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-8.R
|
summary(ur.df(Canada[, "prod"],
type = "trend", lags = 2))
summary(ur.df(diff(Canada[, "prod"]),
type = "drift", lags = 1))
summary(ur.df(Canada[, "e"],
type = "trend", lags = 2))
summary(ur.df(diff(Canada[, "e"]),
type = "drift", lags = 1))
summary(ur.df(Canada[, "U"],
type = "drift", lags = 1))
summary(ur.df(diff(Canada[, "U"]),
type = "none", lags = 0))
summary(ur.df(Canada[, "rw"],
type = "trend", lags = 4))
summary(ur.df(diff(Canada[, "rw"]),
type = "drift", lags = 3))
summary(ur.df(diff(Canada[, "rw"]),
type = "drift", lags = 0))
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vars/inst/book-ex/Rcode-8-9.R
|
utils::globalVariables(c("Description", "Missing", "Obs.", "Type", "Value labels", "Values", "Variable"))
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varsExplore/R/globals.R
|
#' datatable2 - Datatable with child rows
#'
#' Created by Reigo Hendrikson: <http://www.reigo.eu/2018/04/extending-dt-child-row-example/>
#'
#' @param x A dataframe
#' @param vars String vector. The variables you want to put in the details table, rather than
#' keep in the main table.
#' @param font.size String. Default is "10pt".
#' @param dom String. What DT::datatable elements to show. Default is 'fti'.
#' @param opts Additional options for DT::datatable.
#' @param ... Additional parameters for DT::datatable.
#'
#' @export
#' @return A DT::datatable.
#'
datatable2 <- function(x, vars = NULL, opts = NULL, font.size = "10pt", dom = 'fti', ...) {
names_x <- names(x)
if (is.null(vars)) stop("'vars' must be specified!")
pos <- match(vars, names_x)
if (any(purrr::map_chr(x[, pos], typeof) == "list"))
stop("list columns are not supported in datatable2()")
pos <- pos[pos <= ncol(x)] + 1
rownames(x) <- NULL
if (nrow(x) > 0) x <- cbind(' ' = '⊕', x)
# options
opts <- c(
opts,
list(
initComplete = DT::JS(
"function(settings, json) {",
paste0("$(this.api().table().header()).css({'font-size': '", font.size, "'});"),
"}"),
class = "compact",
dom = dom,
pageLength = nrow(x),
columnDefs = list(
list(visible = FALSE, targets = c(0, pos)),
list(orderable = FALSE, className = 'details-control', targets = 1),
list(className = 'dt-left', targets = 1:3),
list(className = 'dt-right', targets = 4:ncol(x))
)
))
DT::datatable(
x,
...,
escape = -2,
options = opts,
callback = DT::JS(.callback2(x = x, pos = c(0, pos)))
)
}
.callback2 <- function(x, pos = NULL) {
part1 <- "table.column(1).nodes().to$().css({cursor: 'pointer'});"
part2 <- .child_row_table2(x, pos = pos)
part3 <-
"
table.on('click', 'td.details-control', function() {
var td = $(this), row = table.row(td.closest('tr'));
if (row.child.isShown()) {
row.child.hide();
td.html('⊕');
} else {
row.child(format(row.data())).show();
td.html('⊖');
}
});"
paste(part1, part2, part3)
}
.child_row_table2 <- function(x, pos = NULL) {
names_x <- paste0(names(x), ":")
text <- "
var format = function(d) {
text = '<div><table >' +
"
for (i in seq_along(pos)) {
text <- paste(text, glue::glue(
"'<tr>' +
'<td>' + '{names_x[pos[i]]}' + '</td>' +
'<td>' + d[{pos[i]}] + '</td>' +
'</tr>' + " ))
}
paste0(text,
"'</table></div>'
return text;};"
)
}
#' Numeric x
#'
#' @param x A vector
#'
#' @return A vector of numbers with NAs removed, if `x` is numeric.
#' If `x` is non-numeric or 100% NAs, returns a single NA.
#'
#' @importFrom stats "na.omit"
#'
num_x <- function(x){
if(is.numeric(x)) {
y <- na.omit(x)
if(length(y) == 0) { y <- NA }
} else {
y <- NA
}
return(y)
}
#' Searchable variable explorer with labelled variables
#'
#' Creates a summary dataframe that can be used in RStudio similar to the variable
#' explorer in Stata, but which also includes the summary statistics. If `viewer`
#' is TRUE (default) the result is shown in RStudio's Viewer pane as a searchable
#' datatable.
#'
#' This is useful particularly if you have a large dataset with a very large number
#' of labelled variables with hard to remember names. Can also be used to generate
#' a table of summary statistics.
#'
#' @param df A data frame.
#' @param viewer Logical. Whether to show results as a searchable datatable
#' in RStudio's Viewer pane. Default is TRUE.
#' @param digits Numeric. How many digits to show for the statistics in the Viewer Pane.
#' Default is 2.
#' @param font.size String. Font size in the Viewer Pane. Default is "10pt".
#' @param value.labels.width Numeric. How many characters to include in the "Value
#' labels" and "Values" columns. Default is 500.
#' @param silent Logical. If FALSE, function will return the summary dataframe. Default is TRUE.
#' @param minimal If TRUE only the number of observations and missing values are shown.
#' Default is FALSE.
#'
#' @return If `silent = FALSE` the function returns the summary stats dataframe, each
#' variable a row. This can be used for making summary tables, or viewed with
#' the `View()` function.
#' @export
#'
#' @importFrom magrittr "%>%"
#' @examples
#'
#' qog <- rio::import("http://www.qogdata.pol.gu.se/dataarchive/qog_bas_cs_jan18.dta")
#' vars_explore(qog, silent = FALSE, viewer = FALSE)
#' \dontrun{
#' vars_explore(qog)
#' vars_explore(qog, minimal = TRUE)
#' vars_explore(qog, silent = FALSE, viewer = FALSE) %>% View()
#' }
#' qog_summary <- vars_explore(qog, silent = FALSE, viewer = FALSE)
#'
vars_explore <- function(df,
viewer = TRUE,
digits = 2,
font.size = "10pt",
value.labels.width = 500,
silent = TRUE,
minimal = FALSE) {
stats <- "mean, median, sd, min, max" %>%
stringr::str_replace("mean", "Mean") %>%
stringr::str_replace("median", "Median") %>%
stringr::str_replace("sd", "Std.Dev.") %>%
stringr::str_replace("min", "Min") %>%
stringr::str_replace("max", "Max") %>%
stringr::str_remove_all(" ") %>%
stringr::str_split(",") %>%
unlist()
# build basic summary
summary_df <- data.frame(
Variable = names(df),
Description = purrr::map_chr(df, ~ifelse(!is.null(attr(.x, "label")), attr(.x, "label"), "")),
Obs. = purrr::map_dbl(df, ~sum(!is.na(.x))),
Missing = purrr::map_dbl(df, ~sum( is.na(.x))))
if (!minimal){
summary_df <- summary_df %>%
dplyr::mutate(
Type = purrr::map_chr(df, ~class(.x)),
Mean = purrr::map_dbl(df, ~mean (num_x(.x))),
Median = purrr::map_dbl(df, ~median(num_x(.x))),
Std.Dev. = purrr::map_dbl(df, ~sd (num_x(.x))),
Min = purrr::map_chr(df, ~min (num_x(.x))),
Max = purrr::map_chr(df, ~max (num_x(.x)))
)
# round numeric values
summary_df <- summary_df %>% dplyr::mutate_if(is.numeric, ~round(.x, digits))
# get value labels
value_labels <- df %>%
purrr::map(~names(attr(.x, "labels"))) %>% # creates list of value labels
purrr::map(~glue::glue_collapse(.x, sep = "; ")) %>% # glues all labels of a variable
purrr::map_df(~ifelse(length(.x) == 0, NA, .x)) %>% # replaces empty labels with NA
tidyr::gather(key = "Variable", value = "Value labels") %>% # transpose to long format
dplyr::mutate(`Value labels` = stringr::str_trunc(`Value labels`, value.labels.width))
# add value labels
summary_df <- summary_df %>%
dplyr::mutate(Values = purrr::map_chr(df,
~stringr::str_trunc(paste(unique(.x), collapse = ", "), value.labels.width))) %>%
dplyr::full_join(value_labels, by = "Variable") %>%
dplyr::select(Variable, Description, Type, Obs., Missing, stats, Values, `Value labels`) %>%
# fix possible encoding problems (e.g. special characters in country names)
# DT::datatable gives errors for non-UTF8 characters
dplyr::mutate(
Variable = iconv(Variable),
Description = iconv(Description),
Values = iconv(Values),
`Value labels` = iconv(`Value labels`),
)
}
# if viewer = TRUE show as searchable datatable in the viewer pane
if(viewer) {
tempFileName <- tempfile("summary_df_", fileext = ".html")
if (minimal) {
summary_df %>%
DT::datatable(
rownames = FALSE,
#editable = TRUE,
#extensions = 'Scroller',
options = list(
initComplete = DT::JS(
"function(settings, json) {",
paste0("$(this.api().table().header()).css({'font-size': '", font.size, "'});"),
"}"),
class = "compact",
dom = 'fti',
pageLength = nrow(summary_df),
columnDefs = list(
list(className = 'dt-left', targets = 1:3)
)
# # for Scroller extension
# deferRender = TRUE,
# scrollY = 200,
# scroller = TRUE
),
) %>%
DT::formatStyle(columns = colnames(summary_df), fontSize = font.size) %>%
DT::saveWidget(tempFileName)
} else {
datatable2(
summary_df,
vars = c("Type", "Mean", "Median", "Std.Dev.", "Min", "Max", "Values", "Value labels"),
) %>%
DT::formatStyle(columns = colnames(summary_df), fontSize = font.size) %>%
DT::saveWidget(tempFileName)
}
rstudioapi::viewer(tempFileName)
}
# if silent = FALSE, return the summary dataframe
if (silent) { message("See the Viewer Pane"); return(NULL) } else { return(summary_df) }
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varsExplore/R/tools.R
|
#' Pipe operator
#'
#' See \code{magrittr::\link[magrittr:pipe]{\%>\%}} for details.
#'
#' @name %>%
#' @rdname pipe
#' @keywords internal
#' @export
#' @importFrom magrittr %>%
#' @usage lhs \%>\% rhs
NULL
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varsExplore/R/utils-pipe.R
|
## ---- include = FALSE, paged.print=TRUE---------------------------------------
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
collapse = TRUE,
comment = "#>",
message=FALSE, warning=FALSE
)
## ----setup--------------------------------------------------------------------
library(varsExplore)
library(dplyr)
## -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
qog <- rio::import("http://www.qogdata.pol.gu.se/dataarchive/qog_std_cs_jan18.dta")
## ---- eval=FALSE--------------------------------------------------------------
# data.frame(Description = sjlabelled::get_label(qog)) %>% DT::datatable()
## ----echo=FALSE---------------------------------------------------------------
data.frame(Description = purrr::map_chr(qog, ~attr(.x, "label"))) %>% DT::datatable()
## ---- eval = FALSE------------------------------------------------------------
# vars_explore(qog)
## -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
vdem_summary <- qog %>%
select(starts_with("vdem_")) %>%
vars_explore(viewer = FALSE, silent = FALSE) %>%
select(-Values, -`Value labels`)
knitr::kable(vdem_summary)
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varsExplore/inst/doc/basic_usage.R
|
---
title: "Basic usage"
output: rmarkdown::html_vignette
vignette: >
%\VignetteIndexEntry{Basic usage}
%\VignetteEngine{knitr::rmarkdown}
%\VignetteEncoding{UTF-8}
---
```{r, include = FALSE, paged.print=TRUE}
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
collapse = TRUE,
comment = "#>",
message=FALSE, warning=FALSE
)
```
```{r setup}
library(varsExplore)
library(dplyr)
```
## Motivation
One of the things that _Stata_ has that _RStudio_ lacks is the variable explorer. This extremely useful especially if you're working with datasets with a large number of variables with hard to remember names, but descriptive labels. In _Stata_ you just search in the variable explorer and then click on the variable to get its name into the console.
<div style = "margin: auto">

</div>
As an example of a dataset like this, consider the Quality of Government standard dataset. Here's the 2018 version of the cross-section data:
```{r}
qog <- rio::import("http://www.qogdata.pol.gu.se/dataarchive/qog_std_cs_jan18.dta")
```
It has 194 observations (different countries) and 1882 variables.
The variables have names like `wdi_acelu`, `bci_bci`, `eu_eco2gdpeurhab`, `gle_cgdpc` etc. Not exactly things you want to remember.
Working with this in _Stata_ is relatively easy because you just search in the variable explorer for things like "sanitation", "corruption", "GDP", etc. and you find the variable names.
Unfortunately, _RStudio_ doesn't have a variable explorer panel. But you can improvise something like the following:
```{r, eval=FALSE}
data.frame(Description = sjlabelled::get_label(qog)) %>% DT::datatable()
```
<div style = "width:50%; height:auto; margin: auto;">
```{r echo=FALSE}
data.frame(Description = purrr::map_chr(qog, ~attr(.x, "label"))) %>% DT::datatable()
```
</div>
BAM! We just made a variable explorer! If you run this code in the console it opens the `DT::datatable` in the RStudio's Viewer pane, which is pretty much replicating the Stata experience (except that it is read-only).
But we can do better! Why not include additional information, like the number of missing observations, summary statistics, or an overview of the values of each variable?
## Introducing `vars_explore`
### Full usage
```{r, eval = FALSE}
vars_explore(qog)
```
This will create a searchable variable explorer, and calculate summary statistics for each variable:
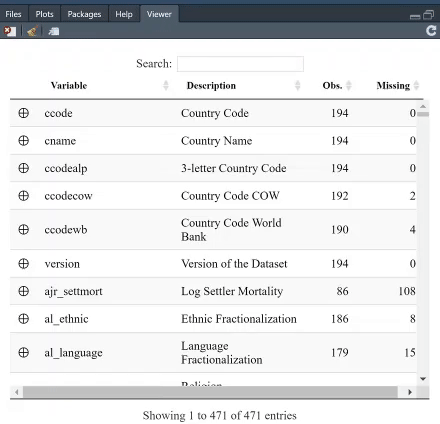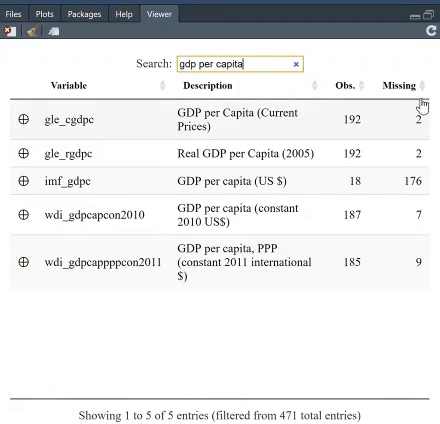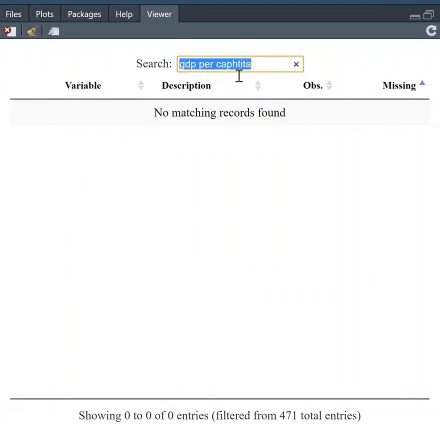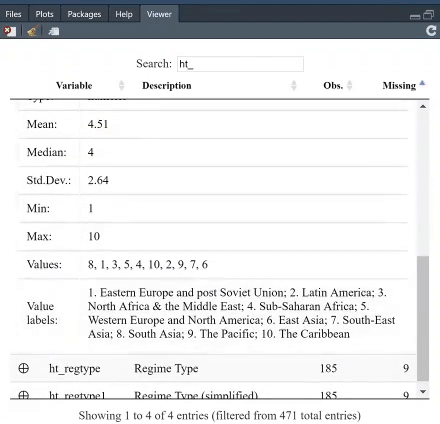
The table is searchable, and you can, furthermore, arrange it, say, based on which variable has least missing values. For instance, search for "GDP per capita" and see which variable provides most complete information.
If you click on the + next to a variable, you will get both the summary statistics, and unique values and, if present, the value labels. The option `value.labels.width` limits how many characters to include in the "Value
labels" and "Values" columns. Default is 500.
If you set `minimal = TRUE`, only "Variable", "Description", "Obs.", and "Missing" will be shown (and none the summary stats will be calculated).
### Creating summary statistics tables
By default, `vars_explore` only shows the summary in RStudio's Viewer Pane, and doesn't return anything. But you can change this by setting `viewer = FALSE` and `silent = FALSE`. This speeds it us massively because it's the `DT::datatable()` that takes most of the time, and allows you to build summary stats (e.g. for a paper):
```{r}
vdem_summary <- qog %>%
select(starts_with("vdem_")) %>%
vars_explore(viewer = FALSE, silent = FALSE) %>%
select(-Values, -`Value labels`)
knitr::kable(vdem_summary)
```
You can also opt to use `View()` instead of the Viewer Pane, which works much faster than `DT::datatable()`, although, given how RStudio works, this makes hard to see both the variable explorer and your script at the same time.
## Alternatives
The best alternative to `vars_explore` is the `vtable` package. The downsides of `vtable` are
(1) it doesn't provide a searchable table in the Viewer Pane, and
(2) it puts all summary stats in a single text column. This makes it hard to sort based on, say, the number of missing values.
You can, however, use `vtable` to generate a dataframe that can be opened with `View()`, just like you can with `vars_explore(silent = FALSE, viewer = FALSE)`. Unfortunately, what makes `vtable` faster is precisely its limitations, as the most time consuming part is loading up the `DT::datatable`, rather than calculating anything. `vtable` works fast because it creates a simple HTML file, but that is not searchable in the Viewer Pane.
Another alternative is `sjPlot::view_df`, which provides summary stats in individual columns, but it is _very_ slow. Also, like `vtable`, it doesn't provide a searchable table in the Viewer Pane.
## Acknowledgements
This was made possible by Reigo Hendrikson's `datatable2`: <http://www.reigo.eu/2018/04/extending-dt-child-row-example/>
As far as I know, Reigo hasn't made this available in a package. It is included in this package, with some minor modifications, and you can use it with `varsExplore::datatable2()`.
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varsExplore/inst/doc/basic_usage.Rmd
|
---
title: "Basic usage"
output: rmarkdown::html_vignette
vignette: >
%\VignetteIndexEntry{Basic usage}
%\VignetteEngine{knitr::rmarkdown}
%\VignetteEncoding{UTF-8}
---
```{r, include = FALSE, paged.print=TRUE}
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
collapse = TRUE,
comment = "#>",
message=FALSE, warning=FALSE
)
```
```{r setup}
library(varsExplore)
library(dplyr)
```
## Motivation
One of the things that _Stata_ has that _RStudio_ lacks is the variable explorer. This extremely useful especially if you're working with datasets with a large number of variables with hard to remember names, but descriptive labels. In _Stata_ you just search in the variable explorer and then click on the variable to get its name into the console.
<div style = "margin: auto">

</div>
As an example of a dataset like this, consider the Quality of Government standard dataset. Here's the 2018 version of the cross-section data:
```{r}
qog <- rio::import("http://www.qogdata.pol.gu.se/dataarchive/qog_std_cs_jan18.dta")
```
It has 194 observations (different countries) and 1882 variables.
The variables have names like `wdi_acelu`, `bci_bci`, `eu_eco2gdpeurhab`, `gle_cgdpc` etc. Not exactly things you want to remember.
Working with this in _Stata_ is relatively easy because you just search in the variable explorer for things like "sanitation", "corruption", "GDP", etc. and you find the variable names.
Unfortunately, _RStudio_ doesn't have a variable explorer panel. But you can improvise something like the following:
```{r, eval=FALSE}
data.frame(Description = sjlabelled::get_label(qog)) %>% DT::datatable()
```
<div style = "width:50%; height:auto; margin: auto;">
```{r echo=FALSE}
data.frame(Description = purrr::map_chr(qog, ~attr(.x, "label"))) %>% DT::datatable()
```
</div>
BAM! We just made a variable explorer! If you run this code in the console it opens the `DT::datatable` in the RStudio's Viewer pane, which is pretty much replicating the Stata experience (except that it is read-only).
But we can do better! Why not include additional information, like the number of missing observations, summary statistics, or an overview of the values of each variable?
## Introducing `vars_explore`
### Full usage
```{r, eval = FALSE}
vars_explore(qog)
```
This will create a searchable variable explorer, and calculate summary statistics for each variable:

The table is searchable, and you can, furthermore, arrange it, say, based on which variable has least missing values. For instance, search for "GDP per capita" and see which variable provides most complete information.
If you click on the + next to a variable, you will get both the summary statistics, and unique values and, if present, the value labels. The option `value.labels.width` limits how many characters to include in the "Value
labels" and "Values" columns. Default is 500.
If you set `minimal = TRUE`, only "Variable", "Description", "Obs.", and "Missing" will be shown (and none the summary stats will be calculated).
### Creating summary statistics tables
By default, `vars_explore` only shows the summary in RStudio's Viewer Pane, and doesn't return anything. But you can change this by setting `viewer = FALSE` and `silent = FALSE`. This speeds it us massively because it's the `DT::datatable()` that takes most of the time, and allows you to build summary stats (e.g. for a paper):
```{r}
vdem_summary <- qog %>%
select(starts_with("vdem_")) %>%
vars_explore(viewer = FALSE, silent = FALSE) %>%
select(-Values, -`Value labels`)
knitr::kable(vdem_summary)
```
You can also opt to use `View()` instead of the Viewer Pane, which works much faster than `DT::datatable()`, although, given how RStudio works, this makes hard to see both the variable explorer and your script at the same time.
## Alternatives
The best alternative to `vars_explore` is the `vtable` package. The downsides of `vtable` are
(1) it doesn't provide a searchable table in the Viewer Pane, and
(2) it puts all summary stats in a single text column. This makes it hard to sort based on, say, the number of missing values.
You can, however, use `vtable` to generate a dataframe that can be opened with `View()`, just like you can with `vars_explore(silent = FALSE, viewer = FALSE)`. Unfortunately, what makes `vtable` faster is precisely its limitations, as the most time consuming part is loading up the `DT::datatable`, rather than calculating anything. `vtable` works fast because it creates a simple HTML file, but that is not searchable in the Viewer Pane.
Another alternative is `sjPlot::view_df`, which provides summary stats in individual columns, but it is _very_ slow. Also, like `vtable`, it doesn't provide a searchable table in the Viewer Pane.
## Acknowledgements
This was made possible by Reigo Hendrikson's `datatable2`: <http://www.reigo.eu/2018/04/extending-dt-child-row-example/>
As far as I know, Reigo hasn't made this available in a package. It is included in this package, with some minor modifications, and you can use it with `varsExplore::datatable2()`.
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varsExplore/vignettes/basic_usage.Rmd
|
adjusted.taha.test<-function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Adjusted Taha Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
order<- order(y)
y<- y[order]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
group<- group[order]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
x <- y - tapply(y,group,median)[group]
rank<- rank(abs(x))
ani<- rank^2
a.ort<- (1/n)*sum(ani)
v.square<- (1/(n-1))* sum((ani-a.ort)^2)
Ai<- tapply(ani, group, mean)
ATHtest<- sum(ni*((Ai-a.ort)^2)/v.square)
df<- k-1
p.value<- pchisq(ATHtest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", ATHtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- ATHtest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/adjusted.taha.test.R
|
ansari.test<-function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Ansari Bradley Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
order<- order(y)
y<- y[order]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
group<- group[order]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
rank<- rank(y)
ani<- (n+1)/2-abs(rank-(n+1)/2)
a.ort<- (1/n)*sum(ani)
v.square<- (1/(n-1))* sum((ani-a.ort)^2)
Ai<- tapply(ani, group, mean)
ABtest<- sum(ni*((Ai-a.ort)^2)/v.square)
df<- k-1
p.value<- pchisq(ABtest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", ABtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- ABtest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/ansari.test.R
|
bartletts.test <- function (formula, data,alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Bartlett's Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
y.variance <- tapply(y, group, var)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
sp.nom<- list()
for(i in x.levels) {
sp.nom[[i]] <- (ni[i]-1)*y.variance[i]
}
sp.nom <- sum(unlist(sp.nom))
sp.denom<- n-k
sp<- sp.nom/sp.denom
A<- (n-k)*log(sp)
B <- list()
for(i in x.levels) {
B[[i]] <- (ni[i]-1)*log(y.variance[i])
}
B <- sum(unlist(B))
C<- 1/(3*(k-1))
D.1 <- list()
for(i in x.levels) {
D.1[[i]] <- 1/(ni[i]-1)
}
D.1<- sum(unlist(D.1))
D<- D.1- 1/(n-k)
Btest<- (A-B)/(1+(C*D))
df = k-1
p.value = pchisq(Btest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", Btest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- Btest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/bartletts.test.R
|
capon.test<-function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Capon Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
order<- order(y)
y<- y[order]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
group<- group[order]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
rank<- rank(y)
y.mean<- mean(rank)
y.sd <- sd(rank)
Z<- (rank-y.mean)/y.sd
Z_exp<- qnorm(ppoints(n, a=3/8), mean = 0, sd= 1)
ani<- (Z_exp^2)
a.ort<- (1/n)*sum(ani)
v.square<- (1/(n-1))* sum((ani-a.ort)^2)
Ai<- tapply(ani, group, mean)
Ctest<- sum(ni*((Ai-a.ort)^2)/v.square)
df<- k-1
p.value<- pchisq(Ctest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", Ctest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- Ctest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/capon.test.R
|
cochrans.test <- function (formula, data,alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Cochran's C Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni <- n/k
vars <- tapply(y, group, var)
vars.sum <- sum(vars)
vars.max <- max(vars)
C <- vars.max/vars.sum
f <- 1/((1/C-1)/(k-1))
pval <- pf(f, ni-1, (ni-1)*(k-1), lower.tail=F)*k
df1 <- ni-1
df2 <- (ni-1)*(k-1)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", C , "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" num df :", df1, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" denom df :", df2, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", pval, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (pval > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- C
result$parameter <- c(df1, df2)
result$p.value <- pval
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/cochrans.test.R
|
david.barton.test<-function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "David Barton Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
order<- order(y)
y<- y[order]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
group<- group[order]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
rank<- rank(y)
ani<- abs(rank-(n+1)/2)+(1/(2-n%%2))
a.ort<- (1/n)*sum(ani)
v.square<- (1/(n-1))* sum((ani-a.ort)^2)
Ai<- tapply(ani, group, mean)
DBtest<- sum(ni*((Ai-a.ort)^2)/v.square)
df<- k-1
p.value<- pchisq(DBtest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", DBtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- DBtest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/david.barton.test.R
|
duran.test<-function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Duran Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
order<- order(y)
y<- y[order]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
group<- group[order]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
rank<- rank(abs(y))
ani<- rank^2
a.ort<- (1/n)*sum(ani)
v.square<- (1/(n-1))* sum((ani-a.ort)^2)
Ai<- tapply(ani, group, mean)
DRtest<- sum(ni*((Ai-a.ort)^2)/v.square)
df<- k-1
p.value<- pchisq(DRtest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", DRtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- DRtest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/duran.test.R
|
f.test <- function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Fisher's Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
if (is.list(y)) {
if (length(y) < dp[[2L]])
stop("'y' must be a list with at least 2 elements")
}
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
vars <- tapply(y, group, var)
vars.max <- max(vars)
vars.min <- min(vars)
F.test<- vars.max/vars.min
df1<- ni[which.max(vars)]-1
df2<- ni[which.min(vars)]-1
p.value <- pf(F.test, df1, df2, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", F.test, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df1 :", df1, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df2 :", df2, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- F.test
result$parameter <- c(df1,df2)
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/f.test.R
|
fk.test<-function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Fligner-Killeen Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
order<- order(y)
y<- y[order]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
group<- group[order]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
x <- y - tapply(y,group,median)[group]
rank<- rank(abs(x))
ani<- qnorm((1+rank/(n+1))/2, mean = 0, sd = 1, lower.tail = TRUE, log.p = FALSE)
a.ort<- (1/n)*sum(ani)
v.square<- (1/(n-1))* sum((ani-a.ort)^2)
Ai<- tapply(ani, group, mean)
FLtest<- sum(ni*((Ai-a.ort)^2)/v.square)
df<- k-1
p.value<- pchisq(FLtest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", FLtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- FLtest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/fk.test.R
|
g.test <- function (formula, data,alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "G Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni <- tapply(y, group, length)
vi <- ni-1
vpool<- sum(vi)
ni.mean<- mean(ni)
vars <- tapply(y, group, var)
vars.sum <- sum(vars)
vars.max <- max(vars)
vi.max <- ni[which.max(vars)]-1
G <- (vi.max*vars.max)/sum(vi*vars)
f <- 1/(((1/G)-1)/(vpool/(vi.max-1)))
pval <- pf(f, ni.mean-1, (ni.mean-1)*(k-1), lower.tail=F)*k
df1<- ni.mean-1
df2<- (ni.mean-1)*(k-1)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", G , "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" num df :", df1, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" denom df :", df2, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", pval, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (pval > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- G
result$parameter <- c(df1, df2)
result$p.value <- pval
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/g.test.R
|
hartley.test <- function (formula, data, size = "mean", alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Hartley's Maximum F-Ratio Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
if (is.list(y)) {
if (length(y) < dp[[2L]])
stop("'y' must be a list with at least 2 elements")
}
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
vars <- tapply(y, group, var)
vars.max <- max(vars)
vars.min <- min(vars)
if (size == "mean"){ ni.optimum <- mean(ni)
}else if (size == "harmonic"){ ni.optimum <- harmonic.mean(ni)
}else if (size == "maxn"){ ni.optimum <- max(ni)
}else if (size == "minvar"){ ni.optimum <- ni[which.min(vars)]
}else stop("Please correct size argument.")
if(any(ni!=n/k)) warning("Hartley's maximum F-ratio test may not be precise for imbalanced designs.")
H.test<- vars.max/vars.min
df<- ni.optimum-1
p.value<- pmaxFratio(H.test, df, k, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", H.test, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- H.test
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/hartley.test.R
|
klotz.test<-function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Klotz Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
order<- order(y)
y<- y[order]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
group<- group[order]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
rank<- rank(y)
ani<- (qnorm(rank/(n+1), mean = 0, sd = 1, lower.tail = TRUE, log.p = FALSE))^2
a.ort<- (1/n)*sum(ani)
v.square<- (1/(n-1))* sum((ani-a.ort)^2)
Ai<- tapply(ani, group, mean)
Ktest<- sum(ni*((Ai-a.ort)^2)/v.square)
df<- k-1
p.value<- pchisq(Ktest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", Ktest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- Ktest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/klotz.test.R
|
levene.test<-function (formula, data, center = "mean", deviation = "absolute", trim.rate = 0.25, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Levene's Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
if(center=="mean"){y.means <- tapply(y, group, mean)
}else if(center=="median"){y.means <- tapply(y, group, median)
}else if(center=="trim.mean"){y.means <- tapply(y, group, mean, trim = trim.rate)
}else {stop("Please correct center option.")
}
y.mean <- mean(y)
z <- list()
for(i in x.levels) {
if(deviation=="absolute"){ z[[i]] <- abs(y[group==i]-y.means[i])
}else if(deviation=="squared"){ z[[i]] <- (y[group==i]-y.means[i])^2
}else stop("Please correct deviation type.")
}
z.means <- unlist(lapply(1:k, function(i) mean(z[[i]])))
z.mean <- mean(unlist(lapply(1:k, function(i) z[[i]])))
z.n <- unlist(lapply(1:k, function(i) length(z[[i]])))
nom <- (n-k)*sum(z.n*((z.means-z.mean)^2))
z_gstotal <- unlist(lapply(1:k, function(i) sum((z[[i]]-mean(z[[i]]))^2)))
denom <- (k-1)*sum((z_gstotal))
Ltest= nom/denom
df1 = k-1
df2 = n-k
p.value = pf(Ltest, df1, df2, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", Ltest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" num df :", df1, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" denom df :", df2, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- Ltest
result$parameter <- c(df1, df2)
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/levene.test.R
|
mood.test<-function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Mood Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
order<- order(y)
y<- y[order]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
group<- group[order]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
rank<- rank(y)
ani<- (rank-(n+1)/2)^2
a.ort<- (1/n)*sum(ani)
v.square<- (1/(n-1))* sum((ani-a.ort)^2)
Ai<- tapply(ani, group, mean)
Mtest<- sum(ni*((Ai-a.ort)^2)/v.square)
df<- k-1
p.value<- pchisq(Mtest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", Mtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- Mtest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/mood.test.R
|
mzv.test <- function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Modified Z Variance Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
y.variance <- tapply(y, group, var)
y.means <- tapply(y, group, mean)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
g<- list()
for (i in x.levels) {
g[[i]] <- (y[group==i]-y.means[i])/sqrt(((ni[i]-1)/ni[i])*y.variance[i])
}
g_total<- unlist(lapply(1:k, function(i) sum(g[[i]]^4)))
K<- g_total/(ni-2)
ci <- 2*((2.9+0.2/ni)/mean(K))^((1.6*(ni-1.8*K+14.7))/ni)
z<- list()
for (i in x.levels) {
z[[i]]<- sum((y[group==i]-y.means[i])^2)
}
mse_nom <- sum(unlist(z))
MSE<- mse_nom/(n-k)
zi_left<- sqrt((ci*(ni-1)*y.variance)/MSE)
zi_right<- sqrt(ci*(ni-1)-(ci/2))
zi<- (zi_left) - (zi_right)
vtest<- sum(zi^2)
df1 = k-1
df2 = Inf
p.value = pf(vtest, df1, df2, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", vtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" num df :", df1, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" denom df :", df2, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- vtest
result$parameter <- c(df1, df2)
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/mzv.test.R
|
obrien.test<-function (formula, data, center = "mean", trim.rate = 0.25, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "O'Brien Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
vars<- tapply(y, group, var)
if(center=="mean"){y.means <- tapply(y, group, mean)
}else if(center=="median"){y.means <- tapply(y, group, median)
}else if(center=="trim.mean"){y.means <- tapply(y, group, mean, trim = trim.rate)
}else {stop("Please correct center option.")
}
vij <- list()
for(i in x.levels) {
vij[[i]] <- ((ni[i]-1.5)*ni[i]*(y[group==i]-y.means[i])^2-0.5*vars[i]*(ni[i]-1))/((ni[i]-1)*(ni[i]-2))
}
v.means<- unlist(lapply(1:k, function(i) mean(vij[[i]])))
v.mean <- sum(unlist(vij))/n
v.n <- ni
nom <- (n-k)*sum(v.n*((v.means-v.mean)^2))
v_gstotal <- unlist(lapply(1:k, function(i) sum((vij[[i]]- mean(vij[[i]]))^2)))
denom<- (k-1)*sum(v_gstotal)
Obtest= nom/denom
df1= k-1
df2= n-k
p.value = pf(Obtest, df1, df2, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", Obtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" num df :", df1, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" denom df :", df2, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- Obtest
result$parameter <- c(df1, df2)
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/obrien.test.R
|
siegel.tukey.test<-function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Siegel Tukey Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
order<- order(y)
y<- y[order]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
group<- group[order]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
a <- rep(seq(ceiling(n / 4)), each=2)
b <- rep(c(0, 1), ceiling(n)/4)
suppressWarnings(
rankone <- c(1, (a * 4 + b))[1:ceiling(n / 2)]
)
suppressWarnings(
ranktwo <- rev(c(a * 4 + b - 2)[1:floor(n / 2)])
)
rank <- c(rankone, ranktwo)
T <- tapply(rank, group, sum)
t <- table(y)
correction <- 1 - sum(t^3 - t) / (n^3 - n)
ani<-rank
a.ort<- (1/n)*sum(ani)
v.square<- (1/(n-1))* sum((ani-a.ort)^2)
Ai<- tapply(ani, group, mean)
STtest<- sum(ni*((Ai-a.ort)^2)/v.square)/correction
df<- k-1
p.value<- pchisq(STtest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", STtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- STtest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/siegel.tukey.test.R
|
siegeltukey.test<-function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Siegel Tukey Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
order<- order(y)
y<- y[order]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
group<- group[order]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
a <- rep(seq(ceiling(n / 4)), each=2)
b <- rep(c(0, 1), ceiling(n)/4)
suppressWarnings(
rankone <- c(1, (a * 4 + b))[1:ceiling(n / 2)]
)
suppressWarnings(
ranktwo <- rev(c(a * 4 + b - 2)[1:floor(n / 2)])
)
rank <- c(rankone, ranktwo)
T <- tapply(rank, group, sum)
t <- table(y)
correction <- 1 - sum(t^3 - t) / (n^3 - n)
ani<-rank
a.ort<- (1/n)*sum(ani)
v.square<- (1/(n-1))* sum((ani-a.ort)^2)
Ai<- tapply(ani, group, mean)
STtest<- sum(ni*((Ai-a.ort)^2)/v.square)/correction
df<- k-1
p.value<- pchisq(STtest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", STtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- STtest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/siegeltukey.test.R
|
taha.test<-function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Taha Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
order<- order(y)
y<- y[order]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
group<- group[order]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
rank<- rank(y)
ani<- rank^2
a.ort<- (1/n)*sum(ani)
v.square<- (1/(n-1))* sum((ani-a.ort)^2)
Ai<- tapply(ani, group, mean)
THtest<- sum(ni*((Ai-a.ort)^2)/v.square)
df<- k-1
p.value<- pchisq(THtest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", THtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- THtest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/taha.test.R
|
talwar.gentle.test<-function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
{
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Talwar and Gentle Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
order<- order(y)
y<- y[order]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
group<- group[order]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
x <- y - tapply(y,group,median)[group]
rank<- rank(abs(x))
ani<- rank
a.ort<- (1/n)*sum(ani)
v.square<- (1/(n-1))* sum((ani-a.ort)^2)
Ai<- tapply(ani, group, mean)
TGtest<- sum(ni*((Ai-a.ort)^2)/v.square)
df<- k-1
p.value<- pchisq(TGtest, df, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", TGtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" df :", df, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- TGtest
result$parameter <- df
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/talwar.gentle.test.R
|
zv.test <- function (formula, data, alpha = 0.05, na.rm = TRUE, verbose = TRUE){
data <- model.frame(formula, data)
dp <- as.character(formula)
DNAME <- paste(dp[[2L]], "and", dp[[3L]])
METHOD <- "Z Variance Test"
if (na.rm) {
completeObs <- complete.cases(data)
data <- data[completeObs, ]
}
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[3L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of group variable does not match the variable names in the data. The group variable must be one factor.")
if (any(colnames(data) == dp[[2L]]) == FALSE)
stop("The name of response variable does not match the variable names in the data.")
y = data[[dp[[2L]]]]
group = data[[dp[[3L]]]]
if (!(is.factor(group) | is.character(group)))
stop("The group variable must be a factor or a character.")
if (is.character(group))
group <- as.factor(group)
if (!is.numeric(y))
stop("The response must be a numeric variable.")
n <- length(y)
x.levels <- levels(factor(group))
k <- length(x.levels)
y.variance <- tapply(y, group, var)
ni<- tapply(y, group, length)
ci <- 2+(1/ni)
y.means <- tapply(y, group, mean)
z<- list()
for (i in x.levels) {
z[[i]]<- sum((y[group==i]-y.means[i])^2)
}
mse_nom <- sum(unlist(z))
MSE<- mse_nom/(n-k)
zi_left<- sqrt((ci*(ni-1)*y.variance)/MSE)
zi_right<- sqrt(ci*(ni-1)-(ci/2))
zi<- as.numeric(zi_left - zi_right)
vtest<- sum(zi^2)/k-1
df1 = k-1
df2 = Inf
p.value = pf(vtest, df1, df2, lower.tail = F)
if (verbose) {
cat("\n", "", METHOD, paste("(alpha = ", alpha, ")",
sep = ""), "\n", sep = " ")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n", sep = " ")
cat(" data :", DNAME, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(" statistic :", vtest, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" num df :", df1, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" denom df :", df2, "\n", sep = " ")
cat(" p.value :", p.value, "\n\n", sep = " ")
cat(if (p.value > alpha) {
" Result : Variances are homogeneous."
}
else {
" Result : Variances are not homogeneous."
}, "\n")
cat("-------------------------------------------------------------",
"\n\n", sep = " ")
}
result <- list()
result$statistic <- vtest
result$parameter <- c(df1, df2)
result$p.value <- p.value
result$alpha <- alpha
result$method <- METHOD
result$data <- data
result$formula <- formula
invisible(result)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/vartest/R/zv.test.R
|
#' @title Conditional Akaike's and Bayesian Information Criteria
#'
#' @name IC.SVC_mle
#' @aliases AIC.SVC_mle
#'
#' @description Methods to calculate information criteria for
#' \code{\link{SVC_mle}} objects. Currently, two are supported: the conditional
#' Akaike's Information Criteria \eqn{cAIC = -2*log-likelihood + 2*(edof + df)}
#' and the Bayesian Information Criteria \eqn{BIC = -2*log-likelihood + log(n) * npar}.
#' Note that the Akaike's Information Criteria is of the corrected form, that
#' is: \eqn{edof} is the effective degrees of freedom which is derived as the
#' trace of the hat matrices and df is the degree of freedoms with respect to
#' mean parameters.
#'
#' @param object \code{\link{SVC_mle}} object
#' @param ... further arguments
#'
#' @return numeric, value of information criteria
#'
#' @author Jakob Dambon
#' @importFrom stats BIC
#' @export
BIC.SVC_mle <- function(object, ...) {
as.numeric(
-2*logLik(object) +
log(nobs(object)) *
object$df$df
)
}
#' @rdname IC.SVC_mle
#' @param conditional string. If \code{conditional = "BW"}, the
#' conditional AIC is calculated.
#'
#' @importFrom stats AIC
#' @export
AIC.SVC_mle <- function(object, conditional = "BW", ...) {
as.numeric(
-2*logLik(object) +
2*(object$df$edof + object$df$df)
)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varycoef/R/BIC-SVC_mle.R
|
## -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## In this script, one finds every function directly related to estimating
## and predicting SVC using our proposed MLE.
## -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## ---- help function to do MLE for SVC model ----
#' @importFrom stats coef lm.fit median var
#' @importFrom optimParallel optimParallel
#' @importFrom parallel clusterExport clusterEvalQ
MLE_computation <- function(
y, X, locs, W, control, optim.control
) {
# set new options while recording old to reset on exit
oopts <- options(spam.trivalues = TRUE, spam.cholsymmetrycheck = FALSE)
on.exit(options(oopts))
## -- set important dimensions ----
# number random effects and fixed effects
q <- dim(W)[2]
p <- dim(X)[2]
# indices of objective and covariance parameters
id_obj <- if (control$profileLik) {
(1:(2*q+1))
} else {
(1:(2*q+1+p))
}
id_cov <- (1:(2*q+1))
# define distance matrix
d <- do.call(
own_dist,
c(list(x = locs, taper = control$tapering), control$dist)
)
## -- check and initialize optim vectors -----
if (is.null(control$lower) | is.null(control$upper) | is.null(control$init)) {
# median distances
med_dist <- if (is.matrix(d)) {
median(as.numeric(d))
} else {
median(lower.tri(d@entries))
}
# variance of response
y_var <- var(y)
# fixed effects estimates by ordinary least squares (OLS)
OLS_mu <- coef(lm.fit(x = X, y = y))
} else {
med_dist <- y_var <- OLS_mu <- NULL
}
# liu - _L_ower _I_nit _U_pper
liu <- init_bounds_optim(control, p, q, id_obj, med_dist, y_var, OLS_mu)
## -- define distance matrices, covariance functions, and taper matrix -----
# get covariance function
raw.cov.func <- MLE.cov.func(control$cov.name)
# covariance function
cov.func <- function(x) raw.cov.func(d, x)
Rstruct <- NULL
# tapering?
if (is.null(control$tapering)) {
taper <-NULL
outer.W <- lapply(1:q, function(k) W[, k]%o%W[, k])
} else {
taper <- get_taper(control$cov.name, d, control$taper)
outer.W <- lapply(1:q, function(k) {
(W[, k]%o%W[, k]) * taper
})
Sigma1 <- Sigma_y(
x = liu$init[id_cov],
cov_func = cov.func,
outer.W = outer.W,
taper = taper
)
Rstruct <- spam::chol.spam(Sigma1)
}
## -- pc priors -----
# ordering: pcp = c(\rho_0, \alpha_\rho, \sigma_0, \alpha_\sigma)
pcp.neg2dens <- if (is.null(control$pc.prior)) {
NULL
} else {
pcp <- control$pc.prior
lambda.r <- -log(pcp[2])*2*pcp[1]
lambda.s <- -log(pcp[4])/pcp[3]
# for Matérn GRF (-2 * log( pc prior dens))
function(theta) {
4*log(theta[1]) +
lambda.r/theta[1]+2*lambda.s*sqrt(theta[2])
}
}
# how to compute mu if optimization is over porfile likelihood
# prepare for optimization by computing mean effect
mu.estimate <- if (control$mean.est == "GLS") {
NULL
} else { # Ordinary Least Squares
coef(lm.fit(x = X, y = y))
}
# extract objective function
if (control$extract_fun) {
obj_fun <- function(x, ...)
n2LL(x, ...)
args <- list(
cov_func = cov.func,
outer.W = outer.W,
y = y,
X = X,
W = W,
mean.est = mu.estimate,
taper = taper,
pc.dens = pcp.neg2dens,
Rstruct = Rstruct,
profile = control$profileLik
)
return(list(
obj_fun = obj_fun,
args = args
))
}
# overwrite parameter scaling if required
if (control$parscale) {
optim.control$parscale <- abs(ifelse(
liu$init[id_obj] == 0, 0.001, liu$init[id_obj]
))
}
## -- optimization -----
if (is.null(control$parallel)) {
# ... without parallelization
optim.output <- stats::optim(
par = liu$init[id_obj],
fn = n2LL,
# arguments of 2nLL
cov_func = cov.func,
outer.W = outer.W,
y = y,
X = X,
W = W,
mean.est = mu.estimate,
taper = taper,
pc.dens = pcp.neg2dens,
Rstruct = Rstruct,
profile = control$profileLik,
method = "L-BFGS-B",
lower = liu$lower[id_obj],
upper = liu$upper[id_obj],
hessian = control$hessian,
control = optim.control)
} else {
# ... with parallelization
parallel::clusterEvalQ(
cl = control$parallel$cl,
{
library(spam)
library(varycoef)
}
)
parallel::clusterExport(
cl = control$parallel$cl,
varlist = ls(),
envir = environment()
)
optim.output <- optimParallel::optimParallel(
par = liu$init[id_obj],
fn = n2LL,
# arguments of 2nLL
cov_func = cov.func,
outer.W = outer.W,
y = y,
X = X,
W = W,
mean.est = mu.estimate,
taper = taper,
pc.dens = pcp.neg2dens,
Rstruct = Rstruct,
profile = control$profileLik,
lower = liu$lower[id_obj],
upper = liu$upper[id_obj],
hessian = control$hessian,
control = optim.control,
parallel = control$parallel
)
}
## -- Estimates and Standard errors -----
# compute covariance matrices
Sigma_final <- Sigma_y(
optim.output$par[id_cov], cov.func, outer.W, taper = taper
)
par_SE <- prep_par_output(
optim.output$par, Sigma_final, Rstruct, control$profileLik, X, y,
optim.output$hessian, q
)
# effective degrees of freedom
edof <- eff_dof(
cov.par = par_SE$RE$est,
cov_func = cov.func,
outer.W = outer.W,
X = X,
taper = taper
)
# preparing output
return(
list(
optim.output = optim.output,
call.args = list(
y = as.numeric(y),
X = as.matrix(X),
locs = as.matrix(locs),
control = control,
optim.control = optim.control,
W = W
),
comp.args = list(
liu = liu,
edof = edof,
Sigma_final = Sigma_final,
par_SE = par_SE
)
)
)
}
## ---- help function to compute fitted values after MLE ----
fitted_computation <- function(SVC_obj, y, X, W, locs) {
class(SVC_obj) <- "SVC_mle"
predict.SVC_mle(SVC_obj, newlocs = locs, newX = X, newW = W)
}
## ---- help function to construct SVC_mle object ----
create_SVC_mle <- function(
ML_estimate,
y,
X,
W,
locs,
control,
formula = NULL,
RE_formula = NULL
) {
q <- dim(W)[2]
# extract covariance parameters and coefficients for methods
cov.par <- ML_estimate$comp.args$par_SE$RE$est
mu <- ML_estimate$comp.args$par_SE$FE$est
# non zero parameters, i.e., means or variances
df <- sum(abs(c(mu, cov.par[2*(1:q)])) > 1e-10)
SVC_obj <- list(
MLE = ML_estimate,
coefficients = mu,
cov.par = cov.par,
# (effective) degrees of freedom
df = list(
df = as.integer(df),
edof = ML_estimate$comp.args$edof),
fitted = NULL,
residuals = NULL,
data = list(y = y, X = X, W = W, locs = locs),
formula = formula,
RE_formula = RE_formula
)
if (control$save.fitted) {
# compute fitted values (i.e. EBLUP = empirical BLUP)
pred <- fitted_computation(SVC_obj, y, X, W, locs)
SVC_obj$fitted = pred
SVC_obj$residuals = y-pred$y.pred
}
return(SVC_obj)
}
#' @title Set Parameters for \code{SVC_mle}
#'
#' @description Function to set up control parameters for \code{\link{SVC_mle}}.
#' In the following, we assume the GP-based SVC model to have \eqn{q} GPs which
#' model the SVCs and \eqn{p} fixed effects.
#'
#' @param cov.name (\code{character(1)}) \cr
#' Name of the covariance function of the GPs. Currently, the following are
#' implemented: \code{"exp"} for the exponential, \code{"sph"} for
#' spherical, \code{"mat32"} and \code{"mat52"} for Matern class covariance
#' functions with smoothness 3/2 or 5/2, as well as \code{"wend1"} and
#' \code{"wend2"} for Wendland class covariance functions with kappa 1 or 2.
#' @param tapering (\code{NULL} or \code{numeric(1)}) \cr
#' If \code{NULL}, no tapering is applied. If a scalar is given, covariance
#' tapering with this taper range is applied, for all Gaussian processes
#' modeling the SVC. Only defined for Matern class covariance functions,
#' i.e., set \code{cov.name} either to \code{"exp"}, \code{"mat32"}, or
#' \code{"mat52"}.
#' @param parallel (\code{NULL} or \code{list}) \cr
#' If \code{NULL}, no parallelization is applied. If cluster has been
#' established, define arguments for parallelization with a list, see
#' documentation of \code{\link[optimParallel]{optimParallel}}. See Examples.
#' @param init (\code{NULL} or \code{numeric(2q+1+p*as.numeric(profileLik))}) \cr
#' Initial values for optimization procedure. If \code{NULL} is given, an
#' initial vector is calculated (see Details). Otherwise, the vector is
#' assumed to consist of q-times (alternating) range and variance,
#' the nugget variance and if \code{profileLik = TRUE} p mean effects.
#' @param lower (\code{NULL} or \code{numeric(2q+1+p*as.numeric(profileLik))}) \cr
#' Lower bound for \code{init} in \code{optim}. Default \code{NULL} calculates
#' the lower bounds (see Details).
#' @param upper (\code{NULL} or \code{numeric(2q+1+p*as.numeric(profileLik))}) \cr
#' Upper bound for \code{init} in \code{optim}. Default \code{NULL} calculates
#' the upper bounds (see Details).
#' @param save.fitted (\code{logical(1)}) \cr
#' If \code{TRUE}, calculates the fitted values and residuals after MLE and
#' stores them. This is necessary to call \code{\link{residuals}} and
#' \code{\link{fitted}} methods afterwards.
#' @param profileLik (\code{logical(1)}) \cr
#' If \code{TRUE}, MLE is done over profile Likelihood of covariance
#' parameters.
#' @param mean.est (\code{character(1)}) \cr
#' If \code{profileLik = TRUE}, the means have to be estimated seperately for
#' each step. \code{"GLS"} uses the generalized least square estimate while
#' \code{"OLS"} uses the ordinary least squares estimate.
#' @param pc.prior (\code{NULL} or \code{numeric(4)}) \cr
#' If numeric vector is given, penalized complexity priors are applied. The
#' order is \eqn{\rho_0, \alpha_\rho, \sigma_0, \alpha_\sigma} to give some
#' prior believes for the range and the standard deviation of GPs, such that
#' \eqn{P(\rho < \rho_0) = \alpha_\rho, P(\sigma > \sigma_0) = \alpha_\sigma}.
#' This regulates the optimization process. Currently, only supported for
#' GPs with of Matérn class covariance functions. Based on the idea by
#' Fulgstad et al. (2018) \doi{10.1080/01621459.2017.1415907}.
#' @param extract_fun (\code{logical(1)}) \cr
#' If \code{TRUE}, the function call of \code{\link{SVC_mle}} stops before
#' the MLE and gives back the objective function of the MLE as well as all
#' used arguments. If \code{FALSE}, regular MLE is conducted.
#' @param hessian (\code{logical(1)}) \cr
#' If \code{TRUE}, Hessian matrix is computed, see \link[stats]{optim}. This
#' required to give the standard errors for covariance parameters and to do
#' a Wald test on the variances, see \code{\link{summary.SVC_mle}}.
#' @param dist (\code{list}) \cr
#' List containing the arguments of \link[stats]{dist} or
#' \link[spam]{nearest.dist}. This controls
#' the method of how the distances and therefore dependency structures are
#' calculated. The default gives Euclidean distances in a \eqn{d}-dimensional
#' space. Further editable arguments are \code{p, miles, R}, see respective
#' help files of \link[stats]{dist} or \link[spam]{nearest.dist}.
#' @param parscale (\code{logical(1)}) \cr
#' Triggers parameter scaling within the optimization in \link[stats]{optim}.
#' If \code{TRUE}, the optional parameter scaling in \code{optim.control} in
#' function \code{\link{SVC_mle}} is overwritten by the initial value used in
#' the numeric optimization. The initial value is either computed from the
#' data or provided by the user, see \code{init} argument above or Details
#' below. Note that we check whether the initial values are unequal to zero.
#' If they are zero, the corresponding scaling factor is 0.001. If
#' \code{FALSE}, the \code{parscale} argument in \code{optim.control} is let
#' unchanged.
#' @param ... Further Arguments yet to be implemented
#'
#' @details If not provided, the initial values as well as the lower and upper
#' bounds are calculated given the provided data. In particular, we require
#' the median distance between observations, the variance of the response and,
#' the ordinary least square (OLS) estimates, see \code{\link{init_bounds_optim}}.
#'
#' The argument \code{extract_fun} is useful, when one wants to modify
#' the objective function. Further, when trying to parallelize the
#' optimization, it is useful to check whether a single evaluation of the
#' objective function takes longer than 0.05 seconds to evaluate,
#' cf. Gerber and Furrer (2019) \doi{10.32614/RJ-2019-030}. Platform specific
#' issues can be sorted out by the user by setting up their own optimization.
#'
#' @return A list with which \code{\link{SVC_mle}} can be controlled.
#' @seealso \code{\link{SVC_mle}}
#'
#' @examples
#' control <- SVC_mle_control(init = rep(0.3, 10))
#' # or
#' control <- SVC_mle_control()
#' control$init <- rep(0.3, 10)
#'
#' \donttest{
#' # Code for setting up parallel computing
#' require(parallel)
#' # exchange number of nodes (1) for detectCores()-1 or appropriate number
#' cl <- makeCluster(1, setup_strategy = "sequential")
#' clusterEvalQ(
#' cl = cl,
#' {
#' library(spam)
#' library(varycoef)
#' })
#' # use this list for parallel argument in SVC_mle_control
#' parallel.control <- list(cl = cl, forward = TRUE, loginfo = TRUE)
#' # SVC_mle goes here ...
#' # DO NOT FORGET TO STOP THE CLUSTER!
#' stopCluster(cl); rm(cl)
#' }
#' @author Jakob Dambon
#'
#' @export
SVC_mle_control <- function(...) UseMethod("SVC_mle_control")
#' @rdname SVC_mle_control
#' @export
SVC_mle_control.default <- function(
cov.name = c("exp", "sph", "mat32", "mat52", "wend1", "wend2"),
tapering = NULL,
parallel = NULL,
init = NULL,
lower = NULL,
upper = NULL,
save.fitted = TRUE,
profileLik = FALSE,
mean.est = c("GLS", "OLS"),
pc.prior = NULL,
extract_fun = FALSE,
hessian = TRUE,
dist = list(method = "euclidean"),
parscale = TRUE,
...
) {
stopifnot(
is.null(tapering) | (tapering>=0),
is.logical(save.fitted),
is.logical(profileLik),
is.logical(extract_fun),
is.logical(hessian),
is.logical(parscale)
)
# if (!is.null(tapering) &
# !(match.arg(cov.name) %in% c("sph", "wend1", "wend2"))) {
# stop("Covariance tapering only defined for Matern class covariance functions.")
# }
list(
cov.name = match.arg(cov.name),
tapering = tapering,
parallel = parallel,
init = init,
lower = lower,
upper = upper,
save.fitted = save.fitted,
profileLik = profileLik,
mean.est = match.arg(mean.est),
pc.prior = pc.prior,
extract_fun = extract_fun,
hessian = hessian,
dist = dist,
parscale = parscale,
...
)
}
#' @param object (\code{SVC_mle}) \cr
#' The function then extracts the control settings from the function call
#' used to compute in the given \code{SVC_mle} object.
#'
#' @rdname SVC_mle_control
#' @export
SVC_mle_control.SVC_mle <- function(object, ...) {
object$MLE$call.args$control
}
###############################
## SVC MLE functions ##########
###############################
#' @title MLE of SVC model
#'
#' @description Conducts a maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) for a Gaussian
#' process-based spatially varying coefficient model as described in
#' Dambon et al. (2021) \doi{10.1016/j.spasta.2020.100470}.
#'
#' @param y (\code{numeric(n)}) \cr
#' Response vector.
#' @param X (\code{matrix(n, p)}) \cr
#' Design matrix. Intercept has to be added manually.
#' @param locs (\code{matrix(n, d)}) \cr
#' Locations in a \eqn{d}-dimensional space. May contain multiple
#' observations at single location.
#' @param W (\code{NULL} or \code{matrix(n, q)}) \cr
#' If \code{NULL}, the same matrix as provided in \code{X} is used. This
#' fits a full SVC model, i.e., each covariate effect is modeled with a mean
#' and an SVC. In this case we have \eqn{p = q}. If optional matrix \code{W}
#' is provided, SVCs are only modeled for covariates within matrix \code{W}.
#' @param control (\code{list}) \cr
#' Control paramaters given by \code{\link{SVC_mle_control}}.
#' @param optim.control (\code{list}) \cr
#' Control arguments for optimization function, see Details in
#' \code{\link{optim}}.
#' @param ... further arguments
#'
#' @details
#' The GP-based SVC model is defined with some abuse of notation as:
#'
#' \deqn{y(s) = X \mu + W \eta (s) + \epsilon(s)}
#'
#' where:
#' \itemize{
#' \item \eqn{y} is the response (vector of length \eqn{n})
#' \item \eqn{X} is the data matrix for the fixed effects covariates. The
#' dimensions are \eqn{n} times \eqn{p}. This leads to \eqn{p} fixed effects.
#' \item \eqn{\mu} is the vector containing the fixed effects
#' \item W is the data matrix for the SVCs modeled by GPs. The dimensions are
#' \eqn{n} times \eqn{q}. This lead to \eqn{q} SVCs in the model.
#' \item \eqn{\eta} are the SVCs represented by a GP.
#' \item \eqn{\epsilon} is the nugget effect
#' }
#'
#' The MLE is an numeric optimization that runs \code{\link[stats]{optim}} or
#' (if parallelized) \code{\link[optimParallel]{optimParallel}}.
#'
#' You can call the function in two ways. Either, you define the model matrices
#' yourself and provide them using the arguments \code{X} and \code{W}. As usual,
#' the individual columns correspond to the fixed and random effects, i.e., the
#' Gaussian processes, respectively. The second way is to call the function with
#' formulas, like you would in \code{\link[stats]{lm}}. From the \code{data.frame}
#' provided in argument \code{data}, the respective model matrices as described
#' above are implicitly built. Using simple arguments \code{formula} and
#' \code{RE_formula} with \code{data} column names, we can decide which
#' covariate is modeled with a fixed or random effect (SVC).
#'
#' Note that similar to model matrix call from above, if the \code{RE_formula}
#' is not provided, we use the one as in argument \code{formula}. Further, note
#' that the intercept is implicitly constructed in the model matrix if not
#' prohibited.
#'
#' @return Object of class \code{SVC_mle} if \code{control$extract_fun = FALSE},
#' meaning that a MLE has been conducted. Otherwise, if \code{control$extract_fun = TRUE},
#' the function returns a list with two entries:
#' \itemize{
#' \item \code{obj_fun}: the objective function used in the optimization
#' \item \code{args}: the arguments to evaluate the objective function.
#' }
#' For further details, see description of \code{\link{SVC_mle_control}}.
#'
#' @references Dambon, J. A., Sigrist, F., Furrer, R. (2021)
#' \emph{Maximum likelihood estimation of spatially varying coefficient
#' models for large data with an application to real estate price prediction},
#' Spatial Statistics \doi{10.1016/j.spasta.2020.100470}
#' @author Jakob Dambon
#'
#' @seealso \code{\link{predict.SVC_mle}}
#'
#' @examples
#' ## ---- toy example ----
#' ## We use the sampled, i.e., one dimensional SVCs
#' str(SVCdata)
#' # sub-sample data to have feasible run time for example
#' set.seed(123)
#' id <- sample(length(SVCdata$locs), 50)
#'
#' ## SVC_mle call with matrix arguments
#' fit <- with(SVCdata, SVC_mle(
#' y[id], X[id, ], locs[id],
#' control = SVC_mle_control(profileLik = TRUE, cov.name = "mat32")))
#'
#' ## SVC_mle call with formula
#' df <- with(SVCdata, data.frame(y = y[id], X = X[id, -1]))
#' fit <- SVC_mle(
#' y ~ X, data = df, locs = SVCdata$locs[id],
#' control = SVC_mle_control(profileLik = TRUE, cov.name = "mat32")
#' )
#' class(fit)
#'
#' summary(fit)
#'
#' \donttest{
#' ## ---- real data example ----
#' require(sp)
#' ## get data set
#' data("meuse", package = "sp")
#'
#' # construct data matrix and response, scale locations
#' y <- log(meuse$cadmium)
#' X <- model.matrix(~1+dist+lime+elev, data = meuse)
#' locs <- as.matrix(meuse[, 1:2])/1000
#'
#'
#' ## starting MLE
#' # the next call takes a couple of seconds
#' fit <- SVC_mle(
#' y = y, X = X, locs = locs,
#' # has 4 fixed effects, but only 3 random effects (SVC)
#' # elev is missing in SVC
#' W = X[, 1:3],
#' control = SVC_mle_control(
#' # inital values for 3 SVC
#' # 7 = (3 * 2 covariance parameters + nugget)
#' init = c(rep(c(0.4, 0.2), 3), 0.2),
#' profileLik = TRUE
#' )
#' )
#'
#' ## summary and residual output
#' summary(fit)
#' plot(fit)
#'
#' ## predict
#' # new locations
#' newlocs <- expand.grid(
#' x = seq(min(locs[, 1]), max(locs[, 1]), length.out = 30),
#' y = seq(min(locs[, 2]), max(locs[, 2]), length.out = 30))
#' # predict SVC for new locations
#' SVC <- predict(fit, newlocs = as.matrix(newlocs))
#' # visualization
#' sp.SVC <- SVC
#' coordinates(sp.SVC) <- ~loc_1+loc_2
#' spplot(sp.SVC, colorkey = TRUE)
#' }
#' @import spam
#' @importFrom stats dist optim
#' @importFrom optimParallel optimParallel
#' @export
SVC_mle <- function(...) UseMethod("SVC_mle")
#' @rdname SVC_mle
#' @export
SVC_mle.default <- function(
y,
X,
locs,
W = NULL,
control = NULL,
optim.control = list(),
...
) {
# check if W is given arguments
if (is.null(W)) {W <- X}
# call SVC_mle with default control settings if non are provided
if (is.null(control)) {
control <- SVC_mle_control()
}
# Start ML Estimation using optim
ML_estimate <- MLE_computation(
y = y,
X = X,
locs = locs,
W = W,
control = control,
optim.control = optim.control
)
if (is.function(ML_estimate$obj_fun)) {
# extract objective function
object <- ML_estimate
class(object) <- "SVC_obj_fun"
return(object)
} else {
# after optimization
object <- create_SVC_mle(
ML_estimate, y, X, W, locs, control,
formula = NULL, RE_formula = NULL
)
object$call <- match.call()
class(object) <- "SVC_mle"
return(object)
}
}
# formula call
#' @param formula Formula describing the fixed effects in SVC model. The response,
#' i.e. LHS of the formula, is not allowed to have functions such as \code{sqrt()} or \code{log()}.
#' @param data data frame containing the observations
#' @param RE_formula Formula describing the random effects in SVC model.
#' Only RHS is considered. If \code{NULL}, the same RHS of argument \code{formula} for fixed effects is used.
#' @importFrom stats model.matrix
#'
#' @rdname SVC_mle
#' @export
SVC_mle.formula <- function(
formula,
data,
RE_formula = NULL,
locs,
control = NULL,
optim.control = list(),
...
) {
# extract model matrix
X <- as.matrix(stats::model.matrix(formula, data = data))
if (is.null(RE_formula)) {
W <- X
RE_formula <- formula
} else {
W <- as.matrix(stats::model.matrix(RE_formula, data = data))
}
y <- as.numeric(data[, all.vars(formula)[1]])
# call SVC_mle with default control settings if non are provided
if (is.null(control)) {
control <- SVC_mle_control()
}
# Start ML Estimation using optim
ML_estimate <- MLE_computation(
y = y,
X = X,
locs = locs,
W = W,
control = control,
optim.control = optim.control
)
# after optimization
object <- create_SVC_mle(
ML_estimate, y, X, W, locs, control,
formula = formula, RE_formula = RE_formula
)
object$call <- match.call()
class(object) <- "SVC_mle"
return(object)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varycoef/R/SVC_mle.R
|
BW_pen <- function(x, X, cov_func, outer.W, taper) {
2*(eff_dof(x, X, cov_func, outer.W, taper) +
2*length(outer.W) + 1)
}
VB_pen <- function(x, X, cov_func, outer.W, taper) {
n <- nrow(X)
p <- ncol(X)
q <- length(outer.W)
eff.dof <- eff_dof(x, X, cov_func, outer.W, taper)
(2*n)/(n-p-2)*(eff.dof + 1 - (eff.dof - p)/(n-p))
}
#' @importFrom glmnet glmnet coef.glmnet
CD_mu <- function(
theta.k,
mle.par,
obj.fun,
lambda.mu,
adaptive = FALSE
) {
## dimensions
p <- ncol(obj.fun$args$X)
q <- (length(theta.k)-1)/2
## transform from GLS to OLS
# compute covariance matrix and Cholesky-decomp thereof
C.mat <- Sigma_y(theta.k, obj.fun$args$cov_func, obj.fun$args$outer.W)
R <- spam::chol(C.mat)
R.t.inv <- solve(t(R))
# transform
y.tilde <- R.t.inv %*% obj.fun$args$y
X.tilde <- R.t.inv %*% obj.fun$args$X
# MLE / OLS estimate
# mu.MLE <- coef(lm(y.tilde~X.tilde-1))
## run (adaptive) LASSO
LASSO <- glmnet::glmnet(
y = y.tilde,
x = X.tilde,
lambda = lambda.mu,
alpha = 1,
intercept = FALSE,
penalty.factor = if (adaptive) {
1/abs(mle.par)
} else {
rep(1, p)
}
)
# without 0 for intercept
as.numeric(coef(LASSO))[1+(1:p)]
}
CD_theta <- function(
mu.k, theta.k, # theta.k only needed as initial value
mle.par,
obj.fun,
lambda.theta,
parallel.control,
optim.args = list(),
adaptive = FALSE
) {
## dimensions
q <- (length(theta.k)-1)/2
n <- length(obj.fun$args$y)
# update profile log-lik. function using new mu.k
obj.fun$args$mean.est <- mu.k
fn <- function(x) {
do.call(obj.fun$obj_fun, c(list(x = x), obj.fun$args))
}
# adaptive LASSO?
if (adaptive) {
# # MLE needed for adaptive penalties
# MLE <- optimParallel::optimParallel(
# theta.k, fn = fn,
# lower = c(rep(c(1e-10, 0), q), 1e-10),
# parallel = parallel.control,
# control = list(
# parscale = ifelse(abs(theta.k) < 1e-9, 1, abs(theta.k))
# )
# )
# MLE.theta <- MLE$par
# adaptive penalties
lambda2 <- ifelse(
abs(mle.par[2*(1:q)]) < 1e-9,
1e99,
lambda.theta/abs(mle.par[2*(1:q)])
)
} else {
lambda2 <- lambda.theta
}
# objective function (f in paper)
pl <- function(x) {
fn(x) + 2*n*sum(lambda2*abs(x[2*(1:q)]))
}
# PMLE: use last known theta.k as initial value
PMLE <- do.call(
what = optimParallel::optimParallel,
args = c(
list(
par = theta.k,
fn = pl,
parallel = parallel.control
),
optim.args
)
)
# return covariance parameters theta.k+1
PMLE$par
}
PMLE_CD <- function(
lambda,
mle.par,
obj.fun,
parallel.control,
optim.args = list(),
adaptive = FALSE,
return.par = FALSE,
IC.type = c("BIC", "cAIC_BW", "cAIC_VB"),
CD.conv = list(N = 20L, delta = 1e-6, logLik = TRUE)
) {
## dimensions
n <- nrow(obj.fun$args$X)
p <- ncol(obj.fun$args$X)
q <- length(obj.fun$args$outer.W)
## initialize output matrix
# covariance parameters
c.par <- matrix(NA_real_, nrow = CD.conv$N + 1, ncol = 2*q+1)
c.par[1, ] <- mle.par
# mean parameter
mu.par <- matrix(NA_real_, nrow = CD.conv$N + 1, ncol = p)
I.C.mat <- solve(
Sigma_y(mle.par, obj.fun$args$cov_func, obj.fun$args$outer.W)
)
B <- crossprod(obj.fun$args$X, I.C.mat)
mu.par[1, ] <- solve(B %*% obj.fun$args$X) %*% B %*% obj.fun$args$y
# log-likelihood
loglik.CD <- rep(NA_real_, CD.conv$N + 1)
# update mean parameter for log-likelihood function
obj.fun$args$mean.est <- mu.par[1, ]
# initialize log-likelihood function
ll <- function(x) {
(-1/2) * do.call(obj.fun$obj_fun, c(list(x = x), obj.fun$args))
}
loglik.CD[1] <- ll(c.par[1, ])
## cyclic coordinate descent
for (k in 1:CD.conv$N) {
# Step 1: Updating mu
mu.par[k+1, ] <- CD_mu(
theta.k = c.par[k, ],
mle.par = mu.par[1, ],
obj.fun = obj.fun,
lambda.mu = lambda[1],
adaptive = adaptive
)
# Step 2: Updating theta
c.par[k+1, ] <- CD_theta(
mu.k = mu.par[k+1, ],
theta.k = c.par[k, ], # only used as an initial value for optimization
mle.par = c.par[1, ],
obj.fun = obj.fun,
lambda.theta = lambda[2],
parallel.control = parallel.control,
optim.args = optim.args,
adaptive = adaptive
)
## compute new log-likelihood
# update mean parameter for log-likelihood function
obj.fun$args$mean.est <- mu.par[k + 1, ]
# initialize log-likelihood function
ll <- function(x) {
(-1/2) * do.call(obj.fun$obj_fun, c(list(x = x), obj.fun$args))
}
loglik.CD[k + 1] <- ll(c.par[k+1, ])
# check for convergence in theta parameters
if (CD.conv$logLik) {
# on the log likelihood
if (abs(loglik.CD[k] - loglik.CD[k + 1])/
abs(loglik.CD[k]) < CD.conv$delta) break
} else {
# on the parameters
if (sum(abs(c(c.par[k, ], mu.par[k, ]) - c(c.par[k+1, ], mu.par[k+1, ])))/
sum(abs(c(c.par[k, ], mu.par[k, ]))) < CD.conv$delta) break
}
}
## prepare output
# update profile log-lik. function using last mu.k
obj.fun$args$mean.est <- mu.par[k + 1, ]
# note: neg2LL is the objective function of MLE is -2 times the log-lik.
# We transform it back to the exact log-lik in the return call
neg2LL <- function(x) {
do.call(obj.fun$obj_fun, c(list(x = x), obj.fun$args))
}
# model-complexity (penalty)
MC <- switch(
match.arg(IC.type),
cAIC_BW = BW_pen(
c.par[k+1, ],
obj.fun$args$X,
obj.fun$args$cov_func,
obj.fun$args$outer.W,
obj.fun$args$taper
),
cAIC_VB = VB_pen(
c.par[k+1, ],
obj.fun$args$X,
obj.fun$args$cov_func,
obj.fun$args$outer.W,
obj.fun$args$taper
),
BIC = {
log(n)*sum(abs(c(mu.par[k+1, ], c.par[k+1, 2*(1:q)]) > 1e-10))
}
)
# calculate final IC
final.IC <- neg2LL(c.par[k+1, ]) + MC
# return either all parameters of CD or
# only IC value (needed for numeric optimization)
if (return.par) {
attr(final.IC, "IC.type") <- IC.type
return(list(
mu.par = mu.par,
c.par = c.par,
loglik.CD = loglik.CD,
final.IC = final.IC
))
} else {
return(final.IC)
}
}
#' @importFrom pbapply pbapply pboptions
IC_opt_grid <- function(IC.obj, r.lambda, n.lambda) {
l.lambda <- seq(log(r.lambda[1]), log(r.lambda[2]), length.out = n.lambda)
op <- pbapply::pboptions(type = "timer")
IC_result <- pbapply::pbapply(
expand.grid(lambda_mu = exp(l.lambda), lambda_sigma_sq = exp(l.lambda)),
1,
function(lambda)
IC.obj(lambda = as.numeric(lambda))
)
pbapply::pboptions(op)
out <- list(
IC_grid = IC_result,
l.lambda = l.lambda
)
class(out) <- c("SVC_pmle_grid", "SVC_pmle")
return(out)
}
#' @importFrom pbapply pbapply pboptions
#' @importFrom ParamHelpers makeParamSet makeNumericVectorParam generateDesign
#' @importFrom smoof makeSingleObjectiveFunction
#' @importFrom mlr makeLearner
#' @importFrom mlrMBO makeMBOControl setMBOControlTermination mbo makeMBOInfillCritEI
#' @importFrom lhs maximinLHS
IC_opt_MBO <- function(
IC.obj, r.lambda, n.init, n.iter,
infill.crit = mlrMBO::makeMBOInfillCritEI()
) {
par.set <- ParamHelpers::makeParamSet(
ParamHelpers::makeNumericVectorParam(
"lambda",
len = 2,
lower = rep(r.lambda[1], 2),
upper = rep(r.lambda[2], 2))
)
obj.fun <- smoof::makeSingleObjectiveFunction(
fn = IC.obj,
par.set = par.set,
name = "IC"
)
design <- ParamHelpers::generateDesign(
n = n.init,
par.set = par.set,
fun = lhs::maximinLHS
)
op <- pbapply::pboptions(type = "timer")
design$y <- pbapply::pbapply(design, 1, obj.fun)
pbapply::pboptions(op)
surr.km <- mlr::makeLearner(
"regr.km",
predict.type = "se",
covtype = "matern3_2"
)
control <- mlrMBO::makeMBOControl()
control <- mlrMBO::setMBOControlTermination(control, iters = n.iter)
control <- mlrMBO::setMBOControlInfill(
control,
crit = infill.crit
)
run <- mlrMBO::mbo(
obj.fun,
design = design,
learner = surr.km,
control = control,
show.info = TRUE
)
}
#' SVC Selection Parameters
#'
#' @description Function to set up control parameters for
#' \code{\link{SVC_selection}}. The underlying Gaussian Process-based
#' SVC model is defined in \code{\link{SVC_mle}}. \code{\link{SVC_selection}}
#' then jointly selects fixed and random effects of the GP-based
#' SVC model using a penalized maximum likelihood estimation (PMLE).
#' In this function, one can set the parameters for the PMLE and
#' its optimization procedures (Dambon et al., 2022).
#'
#' @param IC.type (\code{character(1)}) \cr
#' Select Information Criterion.
#' @param method (\code{character(1)}) \cr
#' Select optimization method for lambdas, i.e., shrinkage parameters.
#' Either model-based optimization (MBO, Bischl et al., 2017 <arXiv:1703.03373>) or over grid.
#' @param r.lambda (\code{numeric(2)}) \cr
#' Range of lambdas, i.e., shrinkage parameters.
#' @param n.lambda (\code{numeric(1)}) \cr
#' If grid method is selected, number of lambdas per side of grid.
#' @param n.init (\code{numeric(1)}) \cr
#' If MBO method is selected, number of initial values for surrogate model.
#' @param n.iter (\code{numeric(1)}) \cr
#' If MBO method is selected, number of iteration steps of surrogate models.
#' @param CD.conv (\code{list(3)}) \cr
#' List containing the convergence conditions, i.e.,
#' first entry is the maximum number of iterations,
#' second value is the relative change necessary to stop iteration,
#' third is logical to toggle if relative change in log likelihood
#' (\code{TRUE}) or rather the parameters themselves (\code{FALSE})
#' is the criteria for convergence.
#' @param hessian (\code{logical(1)}) \cr
#' If \code{TRUE}, Hessian will be computed for final model.
#' @param adaptive (\code{logical(1)}) \cr
#' If \code{TRUE}, adaptive LASSO is executed, i.e.,
#' the shrinkage parameter is defined as \eqn{\lambda_j := \lambda / |\theta_j|}.
#' @param parallel (\code{list}) \cr
#' List with arguments for parallelization,
#' see documentation of \code{\link[optimParallel]{optimParallel}}.
#' @param optim.args (\code{list}) \cr
#' List of further arguments of \code{\link[optimParallel]{optimParallel}},
#' such as the lower bounds.
#'
#' @export
#'
#' @examples
#' # Initializing parameters and switching logLik to FALSE
#' selection_control <- SVC_selection_control(
#' CD.conv = list(N = 20L, delta = 1e-06, logLik = FALSE)
#' )
#' # or
#' selection_control <- SVC_selection_control()
#' selection_control$CD.conv$logLik <- FALSE
#'
#' @author Jakob Dambon
#'
#' @references Bischl, B., Richter, J., Bossek, J., Horn, D., Thomas, J.,
#' Lang, M. (2017).
#' \emph{mlrMBO: A Modular Framework for Model-Based Optimization of
#' Expensive Black-Box Functions},
#' ArXiv preprint \url{https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.03373}
#'
#' Dambon, J. A., Sigrist, F., Furrer, R. (2022).
#' \emph{Joint Variable Selection of both Fixed and Random Effects for
#' Gaussian Process-based Spatially Varying Coefficient Models},
#' International Journal of Geographical Information Science
#' \doi{10.1080/13658816.2022.2097684}
#'
#'
#' @return A list of control parameters for SVC selection.
SVC_selection_control <- function(
IC.type = c("BIC", "cAIC_BW", "cAIC_VB"),
method = c("grid", "MBO"),
r.lambda = c(1e-10, 1e01),
n.lambda = 10L,
n.init = 10L,
n.iter = 10L,
CD.conv = list(N = 20L, delta = 1e-06, logLik = TRUE),
hessian = FALSE,
adaptive = FALSE,
parallel = NULL,
optim.args = list()
) {
# check r.lambda
stopifnot(
length(r.lambda) == 2 |
r.lambda[1] > 0 |
r.lambda[1] < r.lambda[2] )
# check n.lambda
stopifnot(
is.numeric(n.lambda) | n.lambda > 0 )
# check n.init
stopifnot(
is.numeric(n.init) | n.init > 0 )
# check n.iter
stopifnot(
is.numeric(n.iter) | n.iter > 0 )
# check CD.conv
stopifnot(
is.list(CD.conv) |
is.numeric(CD.conv$N) | CD.conv$N > 0 |
is.numeric(CD.conv$delta) | CD.conv$delta > 0 |
is.logical(CD.conv$logLik))
# hessian & adaptive
stopifnot(
is.logical(hessian) | is.logical(adaptive) )
switch(match.arg(method),
"grid" = {
stopifnot(n.lambda >= 1)
},
"MBO" = {
stopifnot(
n.init > 2 |
n.iter >= 1
)
})
list(
IC.type = match.arg(IC.type),
method = match.arg(method),
r.lambda = r.lambda,
n.lambda = n.lambda,
n.init = n.init,
n.iter = n.iter,
CD.conv = CD.conv,
hessian = hessian,
adaptive = adaptive,
parallel = parallel,
optim.args = optim.args
)
}
#' SVC Model Selection
#'
#' @description This function implements the variable selection for
#' Gaussian process-based SVC models using a penalized maximum likelihood
#' estimation (PMLE, Dambon et al., 2021, <arXiv:2101.01932>).
#' It jointly selects the fixed and random effects of GP-based SVC models.
#'
#' @param obj.fun (\code{SVC_obj_fun}) \cr
#' Function of class \code{SVC_obj_fun}. This is the output of
#' \code{\link{SVC_mle}} with the \code{\link{SVC_mle_control}} parameter
#' \code{extract_fun} set to \code{TRUE}. This objective function comprises
#' of the whole SVC model on which the selection should be applied.
#' @param mle.par (\code{numeric(2*q+1)}) \cr
#' Numeric vector with estimated covariance parameters of unpenalized MLE.
#' @param control (\code{list} or \code{NULL}) \cr
#' List of control parameters for variable selection. Output of
#' \code{\link{SVC_selection_control}}. If \code{NULL} is given, the
#' default values of \code{\link{SVC_selection_control}} are used.
#' @param ... Further arguments.
#'
#' @return Returns an object of class \code{SVC_selection}. It contains parameter estimates under PMLE and the optimization as well as choice of the shrinkage parameters.
#'
#' @author Jakob Dambon
#'
#' @references Dambon, J. A., Sigrist, F., Furrer, R. (2021).
#' \emph{Joint Variable Selection of both Fixed and Random Effects for
#' Gaussian Process-based Spatially Varying Coefficient Models},
#' ArXiv Preprint \url{https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.01932}
#'
#' @export
#'
#'
#' @importFrom optimParallel optimParallel
SVC_selection <- function(
obj.fun,
mle.par,
control = NULL,
...
) {
# dimensions
n <- nrow(obj.fun$args$X)
p <- ncol(obj.fun$args$X)
q <- length(obj.fun$args$outer.W)
# Error handling
if (is(obj.fun, "SVC_obj_fun")) {
stop("The obj.fun argument must be of class 'SVC_obj_fun', see help file.")
}
if (!is.numeric(mle.par) | (length(mle.par) != 2*q+1)) {
stop(paste0(
"The mle.par argument must be a numeric vector of length ", 2*q+1, "!"
))
}
if (is.null(control)) {
control <- SVC_selection_control()
}
# IC black-box function
IC.obj <- function(lambda)
do.call(PMLE_CD, list(
lambda = lambda,
mle.par = mle.par,
obj.fun = obj.fun,
parallel.control = control$parallel,
optim.args = control$optim.args,
adaptive = control$adaptive,
return.par = FALSE,
IC.type = control$IC.type,
CD.conv = control$CD.conv
))
# start optimization
PMLE_opt <- switch(
control$method,
"grid" = {IC_opt_grid(
IC.obj = IC.obj,
r.lambda = control$r.lambda,
n.lambda = control$n.lambda
)},
"MBO" = {
stopifnot(control$n.init > 2)
IC_opt_MBO(
IC.obj = IC.obj,
r.lambda = control$r.lambda,
n.init = control$n.init,
n.iter = control$n.iter
)}
)
sel_lambda <- switch (
control$method,
"grid" = {
l.grid <- expand.grid(
PMLE_opt$l.lambda,
PMLE_opt$l.lambda
)
exp(as.numeric(l.grid[which.min(PMLE_opt$IC_grid), ]))
},
"MBO" = {
as.numeric(PMLE_opt$x$lambda)
}
)
PMLE <- function(lambda)
do.call(PMLE_CD, list(
lambda = lambda,
mle.par = mle.par,
obj.fun = obj.fun,
parallel.control = control$parallel,
optim.args = control$optim.args,
adaptive = control$adaptive,
return.par = TRUE,
IC.type = control$IC.type,
CD.conv = control$CD.conv
))
PMLE_pars <- PMLE(sel_lambda)
object <- list(
PMLE_pars = PMLE_pars,
PMLE_opt = PMLE_opt,
lambda = sel_lambda,
obj.fun = obj.fun,
mle.par = mle.par
)
class(object) <- "SVC_selection"
return(object)
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varycoef/R/SVC_selection.R
|
#' @title Extact Mean Effects
#'
#' @description Method to extract the mean effects from an \code{\link{SVC_mle}}
#' or \code{\link{SVC_selection}} object.
#'
#' @param object \code{\link{SVC_mle}} or \code{\link{SVC_selection}} object
#' @param ... further arguments
#'
#' @return named vector with mean effects, i.e. \eqn{\mu} from
#' \code{\link[varycoef]{SVC_mle}}
#'
#' @author Jakob Dambon
#'
#' @importFrom stats coef
#' @export
coef.SVC_mle <- function(object, ...) {
mu <- as.numeric(object$coefficients)
X.vars <- colnames(object$data$X)
names(mu) <- if (is.null(X.vars)) {
paste0("Var", 1:length(mu))
} else {
X.vars
}
mu
}
#' @rdname coef.SVC_mle
#' @importFrom stats coef na.omit
#' @export
coef.SVC_selection <- function(object, ...) {
mu <- as.numeric(tail(na.omit(object$PMLE_pars$mu.par), 1))
X.vars <- colnames(object$obj.fun$args$X)
names(mu) <- if (is.null(X.vars)) {
paste0("Var", 1:length(mu))
} else {
X.vars
}
mu
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varycoef/R/coef-SVC_mle.R
|
#' @title Extact Covariance Parameters
#'
#' @description Function to extract the covariance parameters from an
#' \code{\link{SVC_mle}} or \code{\link{SVC_selection}}object.
#'
#' @param object \code{\link{SVC_mle}} or \code{\link{SVC_selection}} object
#' @param ... further arguments
#'
#' @return vector with covariance parameters with the following attributes:
#' \itemize{
#' \item \code{"GRF"}, charachter, describing the covariance function used for
#' the GP, see \code{\link{SVC_mle_control}}.
#' \item \code{"tapering"}, either \code{NULL} if no tapering is applied of
#' the taper range.
#' }
#'
#' @author Jakob Dambon
#'
#'
#' @export
cov_par <- function(...) UseMethod("cov_par")
#' @rdname cov_par
#' @export
cov_par.SVC_mle <- function(object, ...) {
covpars <- as.numeric(object$cov.par)
W.vars <- colnames(object$data$W)
names(covpars) <- if (is.null(W.vars)) {
c(paste0(rep(paste0("SVC", 1:((length(covpars)-1)/2)), each = 2),
c(".range", ".var")), "nugget.var")
} else {
c(paste0(rep(W.vars, each = 2), c(".range", ".var")), "nugget.var")
}
attr(covpars, "cov_fun") <- object$MLE$call.args$control$cov.name
attr(covpars, "tapering") <- object$MLE$call.args$control$tapering
covpars
}
#' @rdname cov_par
#' @importFrom stats na.omit
#' @export
cov_par.SVC_selection <- function(object, ...) {
covpars <- as.numeric(tail(na.omit(object$PMLE_pars$c.par), 1))
W.vars <- colnames(object$obj.fun$args$W)
names(covpars) <- if (is.null(W.vars)) {
c(paste0(rep(paste0("SVC", 1:((length(covpars)-1)/2)), each = 2),
c(".range", ".var")), "nugget.var")
} else {
c(paste0(rep(W.vars, each = 2), c(".range", ".var")), "nugget.var")
}
attr(covpars, "cov_fun") <- attr(object$mle.par, "cov_fun")
attr(covpars, "tapering") <- object$obj.fun$args$taper
covpars
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varycoef/R/cov_par.R
|
#' Lucas County House Price Data
#'
#' A dataset containing the prices and other attributes of 25,357 houses in
#' Lucas County, Ohio. The selling dates span years 1993 to 1998. Data taken
#' from \code{\link[spData]{house}} (\code{spData} package) and slightly modified to a \code{data.frame}.
#'
#' @format A data frame with 25357 rows and 25 variables:
#' \describe{
#' \item{price}{(\code{integer}) selling price, in US dollars}
#' \item{yrbuilt}{(\code{integer}) year the house was built}
#' \item{stories}{(\code{factor}) levels are \code{"one", "bilevel",
#' "multilvl", "one+half", "two", "two+half", "three"}}
#' \item{TLA}{(\code{integer}) total living area, in square feet.}
#' \item{wall}{(\code{factor}) levels are \code{"stucdrvt", "ccbtile",
#' "metlvnyl", "brick", "stone", "wood", "partbrk"}}
#' \item{beds, baths, halfbaths}{(\code{integer}) number of corresponding
#' rooms / facilities.}
#' \item{frontage, depth}{dimensions of the lot. Unit is feet.}
#' \item{garage}{(\code{factor}) levels are \code{"no garage", "basement",
#' "attached", "detached", "carport"}}
#' \item{garagesqft}{(\code{integer}) garage area, in square feet. If
#' \code{garage == "no garage"}, then \code{garagesqft == 0}.}
#' \item{rooms}{(\code{integer}) number of rooms}
#' \item{lotsize}{(\code{integer}) area of lot, in square feet}
#' \item{sdate}{(\code{Date}) selling date, in format \code{yyyy-mm-dd}}
#' \item{avalue}{(\code{int}) appraised value}
#' \item{s1993, s1994, s1995, s1996, s1997, s1998}{(\code{int}) dummies for
#' selling year.}
#' \item{syear}{(\code{factor}) levels are selling years \code{"1993", "1994",
#' "1995", "1996", "1997", "1998"}}
#' \item{long, lat}{(\code{numeric}) location of houses. Longitude and
#' Latitude are given in \code{CRS(+init=epsg:2834)}, the Ohio North State
#' Plane. Units are meters.}
#' }
#' @source \url{http://www.spatial-econometrics.com/html/jplv6.zip}
"house"
#' Sampled SVC Data
#'
#' A list object that contains sampled data of 500 observations. The data has
#' been sampled using the \code{RandomFields} package (Schlather et al., 2015).
#' It is given in the list object \code{SVCdata} which contains the following.
#'
#' @format A \code{list} with the following entries:
#' \describe{
#' \item{y}{(\code{numeric}) Response}
#' \item{X}{(\code{numeric}) Covariates; first columns contains ones to model
#' an intercept, the second column contains standard-normal sampled data.}
#' \item{beta}{(\code{numeric}) The sampled Gaussian processes, which are
#' usually unobserved. It uses a Matern covariance function and the true
#' parameters are given in the entry `true_pars`.}
#' \item{eps}{(\code{numeric}) Error (or Nugget effect), i.e., drawn from a
#' zero-mean normal distribution with 0.5 standard deviation.}
#' \item{locs}{(\code{numeric}) Locations sampled from a uniform distribution
#' on the interval 0 to 10.}
#' \item{true_pars}{(\code{data.frame}) True parameters of the GP-based SVC
#' model with Gaussian process mean, variance, and range. Additionally, the
#' smoothness (nu) is given.}
#' }
#' @references Schlather, M., Malinowski, A., Menck, P. J., Oesting, M., Strokorb, K. (2015)
#' \emph{Analysis, simulation and prediction of multivariate random fields with package RandomFields},
#' Journal of Statistical Software, \doi{10.18637/jss.v063.i08}
"SVCdata"
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varycoef/R/data.R
|
tr <- function(A) {
# computes the trace of a matrix
sum(diag(A))
}
eff_dof <- function(cov.par, X, cov_func, outer.W, taper) {
n <- nrow(X)
p <- length(outer.W)
nug.var <- cov.par[length(cov.par)]
Sigma <- Sigma_y(cov.par, cov_func, outer.W, taper)
iSigma <- solve(Sigma)
XtiS <- crossprod(X, iSigma)
# trace of hat matrix (equation 15 in Mueller et al. 2013, Stat. Sci.)
as.numeric(nug.var * tr(solve(XtiS %*% X) %*% XtiS %*% iSigma %*% X) +
n - nug.var * tr(iSigma))
}
tr_Sigma <- function(cov.par, X, cov_func, outer.W, taper) {
n <- nrow(X)
nug.var <- tail(cov.par, 1)
p <- length(outer.W)
tr(Sigma_y(cov.par, cov_func, outer.W, taper)) - nug.var*n
}
|
/scratch/gouwar.j/cran-all/cranData/varycoef/R/eff_dof.R
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.