Spaces:
Running
Running
Delete examples
Browse filesThis view is limited to 50 files because it contains too many changes.
See raw diff
- examples/README.md +0 -40
- examples/RTDETR-ONNXRuntime-Python/README.md +0 -43
- examples/RTDETR-ONNXRuntime-Python/main.py +0 -222
- examples/YOLO-Series-ONNXRuntime-Rust/Cargo.toml +0 -14
- examples/YOLO-Series-ONNXRuntime-Rust/README.md +0 -94
- examples/YOLO-Series-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/main.rs +0 -236
- examples/YOLOv8-Action-Recognition/action_recognition.py +0 -464
- examples/YOLOv8-Action-Recognition/readme.md +0 -116
- examples/YOLOv8-Action-Recognition/requirements.txt +0 -4
- examples/YOLOv8-CPP-Inference/CMakeLists.txt +0 -28
- examples/YOLOv8-CPP-Inference/README.md +0 -50
- examples/YOLOv8-CPP-Inference/inference.cpp +0 -185
- examples/YOLOv8-CPP-Inference/inference.h +0 -52
- examples/YOLOv8-CPP-Inference/main.cpp +0 -70
- examples/YOLOv8-LibTorch-CPP-Inference/CMakeLists.txt +0 -47
- examples/YOLOv8-LibTorch-CPP-Inference/README.md +0 -35
- examples/YOLOv8-LibTorch-CPP-Inference/main.cc +0 -260
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/CMakeLists.txt +0 -99
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md +0 -120
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp +0 -375
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.h +0 -94
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/main.cpp +0 -193
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/Cargo.toml +0 -24
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/README.md +0 -212
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/cli.rs +0 -87
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/lib.rs +0 -160
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/main.rs +0 -28
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/model.rs +0 -651
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/ort_backend.rs +0 -553
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/yolo_result.rs +0 -235
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime/README.md +0 -43
- examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime/main.py +0 -229
- examples/YOLOv8-OpenCV-ONNX-Python/README.md +0 -19
- examples/YOLOv8-OpenCV-ONNX-Python/main.py +0 -130
- examples/YOLOv8-OpenVINO-CPP-Inference/CMakeLists.txt +0 -21
- examples/YOLOv8-OpenVINO-CPP-Inference/README.md +0 -69
- examples/YOLOv8-OpenVINO-CPP-Inference/inference.cc +0 -175
- examples/YOLOv8-OpenVINO-CPP-Inference/inference.h +0 -59
- examples/YOLOv8-OpenVINO-CPP-Inference/main.cc +0 -41
- examples/YOLOv8-Region-Counter/readme.md +0 -128
- examples/YOLOv8-Region-Counter/yolov8_region_counter.py +0 -253
- examples/YOLOv8-SAHI-Inference-Video/readme.md +0 -69
- examples/YOLOv8-SAHI-Inference-Video/yolov8_sahi.py +0 -108
- examples/YOLOv8-Segmentation-ONNXRuntime-Python/README.md +0 -63
- examples/YOLOv8-Segmentation-ONNXRuntime-Python/main.py +0 -338
- examples/YOLOv8-TFLite-Python/README.md +0 -55
- examples/YOLOv8-TFLite-Python/main.py +0 -221
- examples/heatmaps.ipynb +0 -186
- examples/hub.ipynb +0 -115
- examples/object_counting.ipynb +0 -200
examples/README.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
## Ultralytics Examples
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
This directory features a collection of real-world applications and walkthroughs, provided as either Python files or notebooks. Explore the examples below to see how YOLO can be integrated into various applications.
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
### Ultralytics YOLO Example Applications
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
| Title | Format | Contributor |
|
| 8 |
-
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------ | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
| 9 |
-
| [YOLO ONNX Detection Inference with C++](./YOLOv8-CPP-Inference) | C++/ONNX | [Justas Bartnykas](https://github.com/JustasBart) |
|
| 10 |
-
| [YOLO OpenCV ONNX Detection Python](./YOLOv8-OpenCV-ONNX-Python) | OpenCV/Python/ONNX | [Farid Inawan](https://github.com/frdteknikelektro) |
|
| 11 |
-
| [YOLO C# ONNX-Runtime](https://github.com/dme-compunet/YoloSharp) | .NET/ONNX-Runtime | [Compunet](https://github.com/dme-compunet) |
|
| 12 |
-
| [YOLO .Net ONNX Detection C#](https://www.nuget.org/packages/Yolov8.Net) | C# .Net | [Samuel Stainback](https://github.com/sstainba) |
|
| 13 |
-
| [YOLOv8 on NVIDIA Jetson(TensorRT and DeepStream)](https://wiki.seeedstudio.com/YOLOv8-DeepStream-TRT-Jetson/) | Python | [Lakshantha](https://github.com/lakshanthad) |
|
| 14 |
-
| [YOLOv8 ONNXRuntime Python](./YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime) | Python/ONNXRuntime | [Semih Demirel](https://github.com/semihhdemirel) |
|
| 15 |
-
| [RTDETR ONNXRuntime Python](./RTDETR-ONNXRuntime-Python) | Python/ONNXRuntime | [Semih Demirel](https://github.com/semihhdemirel) |
|
| 16 |
-
| [YOLOv8 ONNXRuntime CPP](./YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP) | C++/ONNXRuntime | [DennisJcy](https://github.com/DennisJcy), [Onuralp Sezer](https://github.com/onuralpszr) |
|
| 17 |
-
| [RTDETR ONNXRuntime C#](https://github.com/Kayzwer/yolo-cs/blob/master/RTDETR.cs) | C#/ONNX | [Kayzwer](https://github.com/Kayzwer) |
|
| 18 |
-
| [YOLOv8 SAHI Video Inference](https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/blob/main/examples/YOLOv8-SAHI-Inference-Video/yolov8_sahi.py) | Python | [Muhammad Rizwan Munawar](https://github.com/RizwanMunawar) |
|
| 19 |
-
| [YOLOv8 Region Counter](https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/blob/main/examples/YOLOv8-Region-Counter/yolov8_region_counter.py) | Python | [Muhammad Rizwan Munawar](https://github.com/RizwanMunawar) |
|
| 20 |
-
| [YOLOv8 Segmentation ONNXRuntime Python](./YOLOv8-Segmentation-ONNXRuntime-Python) | Python/ONNXRuntime | [jamjamjon](https://github.com/jamjamjon) |
|
| 21 |
-
| [YOLOv8 LibTorch CPP](./YOLOv8-LibTorch-CPP-Inference) | C++/LibTorch | [Myyura](https://github.com/Myyura) |
|
| 22 |
-
| [YOLOv8 OpenCV INT8 TFLite Python](./YOLOv8-TFLite-Python) | Python | [Wamiq Raza](https://github.com/wamiqraza) |
|
| 23 |
-
| [YOLOv8 All Tasks ONNXRuntime Rust](./YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust) | Rust/ONNXRuntime | [jamjamjon](https://github.com/jamjamjon) |
|
| 24 |
-
| [YOLOv8 OpenVINO CPP](./YOLOv8-OpenVINO-CPP-Inference) | C++/OpenVINO | [Erlangga Yudi Pradana](https://github.com/rlggyp) |
|
| 25 |
-
| [YOLOv5-YOLO11 ONNXRuntime Rust](./YOLO-Series-ONNXRuntime-Rust) | Rust/ONNXRuntime | [jamjamjon](https://github.com/jamjamjon) |
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
### How to Contribute
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
We greatly appreciate contributions from the community, including examples, applications, and guides. If you'd like to contribute, please follow these guidelines:
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
1. **Create a pull request (PR)** with the title prefix `[Example]`, adding your new example folder to the `examples/` directory within the repository.
|
| 32 |
-
2. **Ensure your project adheres to the following standards:**
|
| 33 |
-
- Makes use of the `ultralytics` package.
|
| 34 |
-
- Includes a `README.md` with clear instructions for setting up and running the example.
|
| 35 |
-
- Avoids adding large files or dependencies unless they are absolutely necessary for the example.
|
| 36 |
-
- Contributors should be willing to provide support for their examples and address related issues.
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
For more detailed information and guidance on contributing, please visit our [contribution documentation](https://docs.ultralytics.com/help/contributing/).
|
| 39 |
-
|
| 40 |
-
If you encounter any questions or concerns regarding these guidelines, feel free to open a PR or an issue in the repository, and we will assist you in the contribution process.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/RTDETR-ONNXRuntime-Python/README.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# RTDETR - ONNX Runtime
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
This project implements RTDETR using ONNX Runtime.
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
## Installation
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
To run this project, you need to install the required dependencies. The following instructions will guide you through the installation process.
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
### Installing Required Dependencies
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
You can install the required dependencies by running the following command:
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
```bash
|
| 14 |
-
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
| 15 |
-
```
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
### Installing `onnxruntime-gpu`
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
If you have an NVIDIA GPU and want to leverage GPU acceleration, you can install the onnxruntime-gpu package using the following command:
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
```bash
|
| 22 |
-
pip install onnxruntime-gpu
|
| 23 |
-
```
|
| 24 |
-
|
| 25 |
-
Note: Make sure you have the appropriate GPU drivers installed on your system.
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
### Installing `onnxruntime` (CPU version)
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
If you don't have an NVIDIA GPU or prefer to use the CPU version of onnxruntime, you can install the onnxruntime package using the following command:
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
```bash
|
| 32 |
-
pip install onnxruntime
|
| 33 |
-
```
|
| 34 |
-
|
| 35 |
-
### Usage
|
| 36 |
-
|
| 37 |
-
After successfully installing the required packages, you can run the RTDETR implementation using the following command:
|
| 38 |
-
|
| 39 |
-
```bash
|
| 40 |
-
python main.py --model rtdetr-l.onnx --img image.jpg --conf-thres 0.5 --iou-thres 0.5
|
| 41 |
-
```
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
Make sure to replace rtdetr-l.onnx with the path to your RTDETR ONNX model file, image.jpg with the path to your input image, and adjust the confidence threshold (conf-thres) and IoU threshold (iou-thres) values as needed.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/RTDETR-ONNXRuntime-Python/main.py
DELETED
|
@@ -1,222 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
import argparse
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
import cv2
|
| 6 |
-
import numpy as np
|
| 7 |
-
import onnxruntime as ort
|
| 8 |
-
import torch
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
from ultralytics.utils import ASSETS, yaml_load
|
| 11 |
-
from ultralytics.utils.checks import check_requirements, check_yaml
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
class RTDETR:
|
| 15 |
-
"""RTDETR object detection model class for handling inference and visualization."""
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
def __init__(self, model_path, img_path, conf_thres=0.5, iou_thres=0.5):
|
| 18 |
-
"""
|
| 19 |
-
Initializes the RTDETR object with the specified parameters.
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
Args:
|
| 22 |
-
model_path: Path to the ONNX model file.
|
| 23 |
-
img_path: Path to the input image.
|
| 24 |
-
conf_thres: Confidence threshold for object detection.
|
| 25 |
-
iou_thres: IoU threshold for non-maximum suppression
|
| 26 |
-
"""
|
| 27 |
-
self.model_path = model_path
|
| 28 |
-
self.img_path = img_path
|
| 29 |
-
self.conf_thres = conf_thres
|
| 30 |
-
self.iou_thres = iou_thres
|
| 31 |
-
|
| 32 |
-
# Set up the ONNX runtime session with CUDA and CPU execution providers
|
| 33 |
-
self.session = ort.InferenceSession(model_path, providers=["CUDAExecutionProvider", "CPUExecutionProvider"])
|
| 34 |
-
self.model_input = self.session.get_inputs()
|
| 35 |
-
self.input_width = self.model_input[0].shape[2]
|
| 36 |
-
self.input_height = self.model_input[0].shape[3]
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
# Load class names from the COCO dataset YAML file
|
| 39 |
-
self.classes = yaml_load(check_yaml("coco8.yaml"))["names"]
|
| 40 |
-
|
| 41 |
-
# Generate a color palette for drawing bounding boxes
|
| 42 |
-
self.color_palette = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(self.classes), 3))
|
| 43 |
-
|
| 44 |
-
def draw_detections(self, box, score, class_id):
|
| 45 |
-
"""
|
| 46 |
-
Draws bounding boxes and labels on the input image based on the detected objects.
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
Args:
|
| 49 |
-
box: Detected bounding box.
|
| 50 |
-
score: Corresponding detection score.
|
| 51 |
-
class_id: Class ID for the detected object.
|
| 52 |
-
|
| 53 |
-
Returns:
|
| 54 |
-
None
|
| 55 |
-
"""
|
| 56 |
-
# Extract the coordinates of the bounding box
|
| 57 |
-
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box
|
| 58 |
-
|
| 59 |
-
# Retrieve the color for the class ID
|
| 60 |
-
color = self.color_palette[class_id]
|
| 61 |
-
|
| 62 |
-
# Draw the bounding box on the image
|
| 63 |
-
cv2.rectangle(self.img, (int(x1), int(y1)), (int(x2), int(y2)), color, 2)
|
| 64 |
-
|
| 65 |
-
# Create the label text with class name and score
|
| 66 |
-
label = f"{self.classes[class_id]}: {score:.2f}"
|
| 67 |
-
|
| 68 |
-
# Calculate the dimensions of the label text
|
| 69 |
-
(label_width, label_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
|
| 70 |
-
|
| 71 |
-
# Calculate the position of the label text
|
| 72 |
-
label_x = x1
|
| 73 |
-
label_y = y1 - 10 if y1 - 10 > label_height else y1 + 10
|
| 74 |
-
|
| 75 |
-
# Draw a filled rectangle as the background for the label text
|
| 76 |
-
cv2.rectangle(
|
| 77 |
-
self.img,
|
| 78 |
-
(int(label_x), int(label_y - label_height)),
|
| 79 |
-
(int(label_x + label_width), int(label_y + label_height)),
|
| 80 |
-
color,
|
| 81 |
-
cv2.FILLED,
|
| 82 |
-
)
|
| 83 |
-
|
| 84 |
-
# Draw the label text on the image
|
| 85 |
-
cv2.putText(
|
| 86 |
-
self.img, label, (int(label_x), int(label_y)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA
|
| 87 |
-
)
|
| 88 |
-
|
| 89 |
-
def preprocess(self):
|
| 90 |
-
"""
|
| 91 |
-
Preprocesses the input image before performing inference.
|
| 92 |
-
|
| 93 |
-
Returns:
|
| 94 |
-
image_data: Preprocessed image data ready for inference.
|
| 95 |
-
"""
|
| 96 |
-
# Read the input image using OpenCV
|
| 97 |
-
self.img = cv2.imread(self.img_path)
|
| 98 |
-
|
| 99 |
-
# Get the height and width of the input image
|
| 100 |
-
self.img_height, self.img_width = self.img.shape[:2]
|
| 101 |
-
|
| 102 |
-
# Convert the image color space from BGR to RGB
|
| 103 |
-
img = cv2.cvtColor(self.img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
|
| 104 |
-
|
| 105 |
-
# Resize the image to match the input shape
|
| 106 |
-
img = cv2.resize(img, (self.input_width, self.input_height))
|
| 107 |
-
|
| 108 |
-
# Normalize the image data by dividing it by 255.0
|
| 109 |
-
image_data = np.array(img) / 255.0
|
| 110 |
-
|
| 111 |
-
# Transpose the image to have the channel dimension as the first dimension
|
| 112 |
-
image_data = np.transpose(image_data, (2, 0, 1)) # Channel first
|
| 113 |
-
|
| 114 |
-
# Expand the dimensions of the image data to match the expected input shape
|
| 115 |
-
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, axis=0).astype(np.float32)
|
| 116 |
-
|
| 117 |
-
# Return the preprocessed image data
|
| 118 |
-
return image_data
|
| 119 |
-
|
| 120 |
-
def bbox_cxcywh_to_xyxy(self, boxes):
|
| 121 |
-
"""
|
| 122 |
-
Converts bounding boxes from (center x, center y, width, height) format to (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) format.
|
| 123 |
-
|
| 124 |
-
Args:
|
| 125 |
-
boxes (numpy.ndarray): An array of shape (N, 4) where each row represents
|
| 126 |
-
a bounding box in (cx, cy, w, h) format.
|
| 127 |
-
|
| 128 |
-
Returns:
|
| 129 |
-
numpy.ndarray: An array of shape (N, 4) where each row represents
|
| 130 |
-
a bounding box in (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) format.
|
| 131 |
-
"""
|
| 132 |
-
# Calculate half width and half height of the bounding boxes
|
| 133 |
-
half_width = boxes[:, 2] / 2
|
| 134 |
-
half_height = boxes[:, 3] / 2
|
| 135 |
-
|
| 136 |
-
# Calculate the coordinates of the bounding boxes
|
| 137 |
-
x_min = boxes[:, 0] - half_width
|
| 138 |
-
y_min = boxes[:, 1] - half_height
|
| 139 |
-
x_max = boxes[:, 0] + half_width
|
| 140 |
-
y_max = boxes[:, 1] + half_height
|
| 141 |
-
|
| 142 |
-
# Return the bounding boxes in (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) format
|
| 143 |
-
return np.column_stack((x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max))
|
| 144 |
-
|
| 145 |
-
def postprocess(self, model_output):
|
| 146 |
-
"""
|
| 147 |
-
Postprocesses the model output to extract detections and draw them on the input image.
|
| 148 |
-
|
| 149 |
-
Args:
|
| 150 |
-
model_output: Output of the model inference.
|
| 151 |
-
|
| 152 |
-
Returns:
|
| 153 |
-
np.array: Annotated image with detections.
|
| 154 |
-
"""
|
| 155 |
-
# Squeeze the model output to remove unnecessary dimensions
|
| 156 |
-
outputs = np.squeeze(model_output[0])
|
| 157 |
-
|
| 158 |
-
# Extract bounding boxes and scores from the model output
|
| 159 |
-
boxes = outputs[:, :4]
|
| 160 |
-
scores = outputs[:, 4:]
|
| 161 |
-
|
| 162 |
-
# Get the class labels and scores for each detection
|
| 163 |
-
labels = np.argmax(scores, axis=1)
|
| 164 |
-
scores = np.max(scores, axis=1)
|
| 165 |
-
|
| 166 |
-
# Apply confidence threshold to filter out low-confidence detections
|
| 167 |
-
mask = scores > self.conf_thres
|
| 168 |
-
boxes, scores, labels = boxes[mask], scores[mask], labels[mask]
|
| 169 |
-
|
| 170 |
-
# Convert bounding boxes to (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) format
|
| 171 |
-
boxes = self.bbox_cxcywh_to_xyxy(boxes)
|
| 172 |
-
|
| 173 |
-
# Scale bounding boxes to match the original image dimensions
|
| 174 |
-
boxes[:, 0::2] *= self.img_width
|
| 175 |
-
boxes[:, 1::2] *= self.img_height
|
| 176 |
-
|
| 177 |
-
# Draw detections on the image
|
| 178 |
-
for box, score, label in zip(boxes, scores, labels):
|
| 179 |
-
self.draw_detections(box, score, label)
|
| 180 |
-
|
| 181 |
-
# Return the annotated image
|
| 182 |
-
return self.img
|
| 183 |
-
|
| 184 |
-
def main(self):
|
| 185 |
-
"""
|
| 186 |
-
Executes the detection on the input image using the ONNX model.
|
| 187 |
-
|
| 188 |
-
Returns:
|
| 189 |
-
np.array: Output image with annotations.
|
| 190 |
-
"""
|
| 191 |
-
# Preprocess the image for model input
|
| 192 |
-
image_data = self.preprocess()
|
| 193 |
-
|
| 194 |
-
# Run the model inference
|
| 195 |
-
model_output = self.session.run(None, {self.model_input[0].name: image_data})
|
| 196 |
-
|
| 197 |
-
# Process and return the model output
|
| 198 |
-
return self.postprocess(model_output)
|
| 199 |
-
|
| 200 |
-
|
| 201 |
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 202 |
-
# Set up argument parser for command-line arguments
|
| 203 |
-
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
| 204 |
-
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, default="rtdetr-l.onnx", help="Path to the ONNX model file.")
|
| 205 |
-
parser.add_argument("--img", type=str, default=str(ASSETS / "bus.jpg"), help="Path to the input image.")
|
| 206 |
-
parser.add_argument("--conf-thres", type=float, default=0.5, help="Confidence threshold for object detection.")
|
| 207 |
-
parser.add_argument("--iou-thres", type=float, default=0.5, help="IoU threshold for non-maximum suppression.")
|
| 208 |
-
args = parser.parse_args()
|
| 209 |
-
|
| 210 |
-
# Check for dependencies and set up ONNX runtime
|
| 211 |
-
check_requirements("onnxruntime-gpu" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "onnxruntime")
|
| 212 |
-
|
| 213 |
-
# Create the detector instance with specified parameters
|
| 214 |
-
detection = RTDETR(args.model, args.img, args.conf_thres, args.iou_thres)
|
| 215 |
-
|
| 216 |
-
# Perform detection and get the output image
|
| 217 |
-
output_image = detection.main()
|
| 218 |
-
|
| 219 |
-
# Display the annotated output image
|
| 220 |
-
cv2.namedWindow("Output", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
|
| 221 |
-
cv2.imshow("Output", output_image)
|
| 222 |
-
cv2.waitKey(0)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLO-Series-ONNXRuntime-Rust/Cargo.toml
DELETED
|
@@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
[package]
|
| 4 |
-
name = "YOLO-ONNXRuntime-Rust"
|
| 5 |
-
version = "0.1.0"
|
| 6 |
-
edition = "2021"
|
| 7 |
-
authors = ["Jamjamjon <[email protected]>"]
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
[dependencies]
|
| 10 |
-
anyhow = "1.0.92"
|
| 11 |
-
clap = "4.5.20"
|
| 12 |
-
tracing = "0.1.40"
|
| 13 |
-
tracing-subscriber = "0.3.18"
|
| 14 |
-
usls = { version = "0.0.19", features = ["auto"] }
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLO-Series-ONNXRuntime-Rust/README.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# YOLO-Series ONNXRuntime Rust Demo for Core YOLO Tasks
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
This repository provides a Rust demo for key YOLO-Series tasks such as `Classification`, `Segmentation`, `Detection`, `Pose Detection`, and `OBB` using ONNXRuntime. It supports various YOLO models (v5 - 11) across multiple vision tasks.
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
## Introduction
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
- This example leverages the latest versions of both ONNXRuntime and YOLO models.
|
| 8 |
-
- We utilize the [usls](https://github.com/jamjamjon/usls/tree/main) crate to streamline YOLO model inference, providing efficient data loading, visualization, and optimized inference performance.
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
## Features
|
| 11 |
-
|
| 12 |
-
- **Extensive Model Compatibility**: Supports `YOLOv5`, `YOLOv6`, `YOLOv7`, `YOLOv8`, `YOLOv9`, `YOLOv10`, `YOLO11`, `YOLO-world`, `RTDETR`, and others, covering a wide range of YOLO versions.
|
| 13 |
-
- **Versatile Task Coverage**: Includes `Classification`, `Segmentation`, `Detection`, `Pose`, and `OBB`.
|
| 14 |
-
- **Precision Flexibility**: Works with `FP16` and `FP32` ONNX models.
|
| 15 |
-
- **Execution Providers**: Accelerated support for `CPU`, `CUDA`, `CoreML`, and `TensorRT`.
|
| 16 |
-
- **Dynamic Input Shapes**: Dynamically adjusts to variable `batch`, `width`, and `height` dimensions for flexible model input.
|
| 17 |
-
- **Flexible Data Loading**: The `DataLoader` handles images, folders, videos, and video streams.
|
| 18 |
-
- **Real-Time Display and Video Export**: `Viewer` provides real-time frame visualization and video export functions, similar to OpenCV’s `imshow()` and `imwrite()`.
|
| 19 |
-
- **Enhanced Annotation and Visualization**: The `Annotator` facilitates comprehensive result rendering, with support for bounding boxes (HBB), oriented bounding boxes (OBB), polygons, masks, keypoints, and text labels.
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
## Setup Instructions
|
| 22 |
-
|
| 23 |
-
### 1. ONNXRuntime Linking
|
| 24 |
-
|
| 25 |
-
<details>
|
| 26 |
-
<summary>You have two options to link the ONNXRuntime library:</summary>
|
| 27 |
-
|
| 28 |
-
- **Option 1: Manual Linking**
|
| 29 |
-
|
| 30 |
-
- For detailed setup, consult the [ONNX Runtime linking documentation](https://ort.pyke.io/setup/linking).
|
| 31 |
-
- **Linux or macOS**:
|
| 32 |
-
1. Download the ONNX Runtime package from the [Releases page](https://github.com/microsoft/onnxruntime/releases).
|
| 33 |
-
2. Set up the library path by exporting the `ORT_DYLIB_PATH` environment variable:
|
| 34 |
-
```shell
|
| 35 |
-
export ORT_DYLIB_PATH=/path/to/onnxruntime/lib/libonnxruntime.so.1.19.0
|
| 36 |
-
```
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
- **Option 2: Automatic Download**
|
| 39 |
-
- Use the `--features auto` flag to handle downloading automatically:
|
| 40 |
-
```shell
|
| 41 |
-
cargo run -r --example yolo --features auto
|
| 42 |
-
```
|
| 43 |
-
|
| 44 |
-
</details>
|
| 45 |
-
|
| 46 |
-
### 2. \[Optional\] Install CUDA, CuDNN, and TensorRT
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
- The CUDA execution provider requires CUDA version `12.x`.
|
| 49 |
-
- The TensorRT execution provider requires both CUDA `12.x` and TensorRT `10.x`.
|
| 50 |
-
|
| 51 |
-
### 3. \[Optional\] Install ffmpeg
|
| 52 |
-
|
| 53 |
-
To view video frames and save video inferences, install `rust-ffmpeg`. For instructions, see:
|
| 54 |
-
[https://github.com/zmwangx/rust-ffmpeg/wiki/Notes-on-building#dependencies](https://github.com/zmwangx/rust-ffmpeg/wiki/Notes-on-building#dependencies)
|
| 55 |
-
|
| 56 |
-
## Get Started
|
| 57 |
-
|
| 58 |
-
```Shell
|
| 59 |
-
# customized
|
| 60 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task detect --ver v8 --nc 6 --model xxx.onnx # YOLOv8
|
| 61 |
-
|
| 62 |
-
# Classify
|
| 63 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task classify --ver v5 --scale s --width 224 --height 224 --nc 1000 # YOLOv5
|
| 64 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task classify --ver v8 --scale n --width 224 --height 224 --nc 1000 # YOLOv8
|
| 65 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task classify --ver v11 --scale n --width 224 --height 224 --nc 1000 # YOLO11
|
| 66 |
-
|
| 67 |
-
# Detect
|
| 68 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task detect --ver v5 --scale n # YOLOv5
|
| 69 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task detect --ver v6 --scale n # YOLOv6
|
| 70 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task detect --ver v7 --scale t # YOLOv7
|
| 71 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task detect --ver v8 --scale n # YOLOv8
|
| 72 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task detect --ver v9 --scale t # YOLOv9
|
| 73 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task detect --ver v10 --scale n # YOLOv10
|
| 74 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task detect --ver v11 --scale n # YOLO11
|
| 75 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task detect --ver rtdetr --scale l # RTDETR
|
| 76 |
-
|
| 77 |
-
# Pose
|
| 78 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task pose --ver v8 --scale n # YOLOv8-Pose
|
| 79 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task pose --ver v11 --scale n # YOLO11-Pose
|
| 80 |
-
|
| 81 |
-
# Segment
|
| 82 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task segment --ver v5 --scale n # YOLOv5-Segment
|
| 83 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task segment --ver v8 --scale n # YOLOv8-Segment
|
| 84 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task segment --ver v11 --scale n # YOLOv8-Segment
|
| 85 |
-
cargo run -r -- --task segment --ver v8 --model yolo/FastSAM-s-dyn-f16.onnx # FastSAM
|
| 86 |
-
|
| 87 |
-
# OBB
|
| 88 |
-
cargo run -r -- --ver v8 --task obb --scale n --width 1024 --height 1024 --source images/dota.png # YOLOv8-Obb
|
| 89 |
-
cargo run -r -- --ver v11 --task obb --scale n --width 1024 --height 1024 --source images/dota.png # YOLO11-Obb
|
| 90 |
-
```
|
| 91 |
-
|
| 92 |
-
**`cargo run -- --help` for more options**
|
| 93 |
-
|
| 94 |
-
For more details, please refer to [usls-yolo](https://github.com/jamjamjon/usls/tree/main/examples/yolo).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLO-Series-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/main.rs
DELETED
|
@@ -1,236 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
use anyhow::Result;
|
| 2 |
-
use clap::Parser;
|
| 3 |
-
|
| 4 |
-
use usls::{
|
| 5 |
-
models::YOLO, Annotator, DataLoader, Device, Options, Viewer, Vision, YOLOScale, YOLOTask,
|
| 6 |
-
YOLOVersion, COCO_SKELETONS_16,
|
| 7 |
-
};
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
#[derive(Parser, Clone)]
|
| 10 |
-
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
|
| 11 |
-
pub struct Args {
|
| 12 |
-
/// Path to the ONNX model
|
| 13 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 14 |
-
pub model: Option<String>,
|
| 15 |
-
|
| 16 |
-
/// Input source path
|
| 17 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = String::from("../../ultralytics/assets/bus.jpg"))]
|
| 18 |
-
pub source: String,
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
/// YOLO Task
|
| 21 |
-
#[arg(long, value_enum, default_value_t = YOLOTask::Detect)]
|
| 22 |
-
pub task: YOLOTask,
|
| 23 |
-
|
| 24 |
-
/// YOLO Version
|
| 25 |
-
#[arg(long, value_enum, default_value_t = YOLOVersion::V8)]
|
| 26 |
-
pub ver: YOLOVersion,
|
| 27 |
-
|
| 28 |
-
/// YOLO Scale
|
| 29 |
-
#[arg(long, value_enum, default_value_t = YOLOScale::N)]
|
| 30 |
-
pub scale: YOLOScale,
|
| 31 |
-
|
| 32 |
-
/// Batch size
|
| 33 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 1)]
|
| 34 |
-
pub batch_size: usize,
|
| 35 |
-
|
| 36 |
-
/// Minimum input width
|
| 37 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 224)]
|
| 38 |
-
pub width_min: isize,
|
| 39 |
-
|
| 40 |
-
/// Input width
|
| 41 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 640)]
|
| 42 |
-
pub width: isize,
|
| 43 |
-
|
| 44 |
-
/// Maximum input width
|
| 45 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 1024)]
|
| 46 |
-
pub width_max: isize,
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
/// Minimum input height
|
| 49 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 224)]
|
| 50 |
-
pub height_min: isize,
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
/// Input height
|
| 53 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 640)]
|
| 54 |
-
pub height: isize,
|
| 55 |
-
|
| 56 |
-
/// Maximum input height
|
| 57 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 1024)]
|
| 58 |
-
pub height_max: isize,
|
| 59 |
-
|
| 60 |
-
/// Number of classes
|
| 61 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 80)]
|
| 62 |
-
pub nc: usize,
|
| 63 |
-
|
| 64 |
-
/// Class confidence
|
| 65 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 66 |
-
pub confs: Vec<f32>,
|
| 67 |
-
|
| 68 |
-
/// Enable TensorRT support
|
| 69 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 70 |
-
pub trt: bool,
|
| 71 |
-
|
| 72 |
-
/// Enable CUDA support
|
| 73 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 74 |
-
pub cuda: bool,
|
| 75 |
-
|
| 76 |
-
/// Enable CoreML support
|
| 77 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 78 |
-
pub coreml: bool,
|
| 79 |
-
|
| 80 |
-
/// Use TensorRT half precision
|
| 81 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 82 |
-
pub half: bool,
|
| 83 |
-
|
| 84 |
-
/// Device ID to use
|
| 85 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 0)]
|
| 86 |
-
pub device_id: usize,
|
| 87 |
-
|
| 88 |
-
/// Enable performance profiling
|
| 89 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 90 |
-
pub profile: bool,
|
| 91 |
-
|
| 92 |
-
/// Disable contour drawing, for saving time
|
| 93 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 94 |
-
pub no_contours: bool,
|
| 95 |
-
|
| 96 |
-
/// Show result
|
| 97 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 98 |
-
pub view: bool,
|
| 99 |
-
|
| 100 |
-
/// Do not save output
|
| 101 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 102 |
-
pub nosave: bool,
|
| 103 |
-
}
|
| 104 |
-
|
| 105 |
-
fn main() -> Result<()> {
|
| 106 |
-
let args = Args::parse();
|
| 107 |
-
|
| 108 |
-
// logger
|
| 109 |
-
if args.profile {
|
| 110 |
-
tracing_subscriber::fmt()
|
| 111 |
-
.with_max_level(tracing::Level::INFO)
|
| 112 |
-
.init();
|
| 113 |
-
}
|
| 114 |
-
|
| 115 |
-
// model path
|
| 116 |
-
let path = match &args.model {
|
| 117 |
-
None => format!(
|
| 118 |
-
"yolo/{}-{}-{}.onnx",
|
| 119 |
-
args.ver.name(),
|
| 120 |
-
args.scale.name(),
|
| 121 |
-
args.task.name()
|
| 122 |
-
),
|
| 123 |
-
Some(x) => x.to_string(),
|
| 124 |
-
};
|
| 125 |
-
|
| 126 |
-
// saveout
|
| 127 |
-
let saveout = match &args.model {
|
| 128 |
-
None => format!(
|
| 129 |
-
"{}-{}-{}",
|
| 130 |
-
args.ver.name(),
|
| 131 |
-
args.scale.name(),
|
| 132 |
-
args.task.name()
|
| 133 |
-
),
|
| 134 |
-
Some(x) => {
|
| 135 |
-
let p = std::path::PathBuf::from(&x);
|
| 136 |
-
p.file_stem().unwrap().to_str().unwrap().to_string()
|
| 137 |
-
}
|
| 138 |
-
};
|
| 139 |
-
|
| 140 |
-
// device
|
| 141 |
-
let device = if args.cuda {
|
| 142 |
-
Device::Cuda(args.device_id)
|
| 143 |
-
} else if args.trt {
|
| 144 |
-
Device::Trt(args.device_id)
|
| 145 |
-
} else if args.coreml {
|
| 146 |
-
Device::CoreML(args.device_id)
|
| 147 |
-
} else {
|
| 148 |
-
Device::Cpu(args.device_id)
|
| 149 |
-
};
|
| 150 |
-
|
| 151 |
-
// build options
|
| 152 |
-
let options = Options::new()
|
| 153 |
-
.with_model(&path)?
|
| 154 |
-
.with_yolo_version(args.ver)
|
| 155 |
-
.with_yolo_task(args.task)
|
| 156 |
-
.with_device(device)
|
| 157 |
-
.with_trt_fp16(args.half)
|
| 158 |
-
.with_ixx(0, 0, (1, args.batch_size as _, 4).into())
|
| 159 |
-
.with_ixx(0, 2, (args.height_min, args.height, args.height_max).into())
|
| 160 |
-
.with_ixx(0, 3, (args.width_min, args.width, args.width_max).into())
|
| 161 |
-
.with_confs(if args.confs.is_empty() {
|
| 162 |
-
&[0.2, 0.15]
|
| 163 |
-
} else {
|
| 164 |
-
&args.confs
|
| 165 |
-
})
|
| 166 |
-
.with_nc(args.nc)
|
| 167 |
-
.with_find_contours(!args.no_contours) // find contours or not
|
| 168 |
-
// .with_names(&COCO_CLASS_NAMES_80) // detection class names
|
| 169 |
-
// .with_names2(&COCO_KEYPOINTS_17) // keypoints class names
|
| 170 |
-
// .exclude_classes(&[0])
|
| 171 |
-
// .retain_classes(&[0, 5])
|
| 172 |
-
.with_profile(args.profile);
|
| 173 |
-
|
| 174 |
-
// build model
|
| 175 |
-
let mut model = YOLO::new(options)?;
|
| 176 |
-
|
| 177 |
-
// build dataloader
|
| 178 |
-
let dl = DataLoader::new(&args.source)?
|
| 179 |
-
.with_batch(model.batch() as _)
|
| 180 |
-
.build()?;
|
| 181 |
-
|
| 182 |
-
// build annotator
|
| 183 |
-
let annotator = Annotator::default()
|
| 184 |
-
.with_skeletons(&COCO_SKELETONS_16)
|
| 185 |
-
.without_masks(true) // no masks plotting when doing segment task
|
| 186 |
-
.with_bboxes_thickness(3)
|
| 187 |
-
.with_keypoints_name(false) // enable keypoints names
|
| 188 |
-
.with_saveout_subs(&["YOLO"])
|
| 189 |
-
.with_saveout(&saveout);
|
| 190 |
-
|
| 191 |
-
// build viewer
|
| 192 |
-
let mut viewer = if args.view {
|
| 193 |
-
Some(Viewer::new().with_delay(5).with_scale(1.).resizable(true))
|
| 194 |
-
} else {
|
| 195 |
-
None
|
| 196 |
-
};
|
| 197 |
-
|
| 198 |
-
// run & annotate
|
| 199 |
-
for (xs, _paths) in dl {
|
| 200 |
-
let ys = model.forward(&xs, args.profile)?;
|
| 201 |
-
let images_plotted = annotator.plot(&xs, &ys, !args.nosave)?;
|
| 202 |
-
|
| 203 |
-
// show image
|
| 204 |
-
match &mut viewer {
|
| 205 |
-
Some(viewer) => viewer.imshow(&images_plotted)?,
|
| 206 |
-
None => continue,
|
| 207 |
-
}
|
| 208 |
-
|
| 209 |
-
// check out window and key event
|
| 210 |
-
match &mut viewer {
|
| 211 |
-
Some(viewer) => {
|
| 212 |
-
if !viewer.is_open() || viewer.is_key_pressed(usls::Key::Escape) {
|
| 213 |
-
break;
|
| 214 |
-
}
|
| 215 |
-
}
|
| 216 |
-
None => continue,
|
| 217 |
-
}
|
| 218 |
-
|
| 219 |
-
// write video
|
| 220 |
-
if !args.nosave {
|
| 221 |
-
match &mut viewer {
|
| 222 |
-
Some(viewer) => viewer.write_batch(&images_plotted)?,
|
| 223 |
-
None => continue,
|
| 224 |
-
}
|
| 225 |
-
}
|
| 226 |
-
}
|
| 227 |
-
|
| 228 |
-
// finish video write
|
| 229 |
-
if !args.nosave {
|
| 230 |
-
if let Some(viewer) = &mut viewer {
|
| 231 |
-
viewer.finish_write()?;
|
| 232 |
-
}
|
| 233 |
-
}
|
| 234 |
-
|
| 235 |
-
Ok(())
|
| 236 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-Action-Recognition/action_recognition.py
DELETED
|
@@ -1,464 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
import argparse
|
| 4 |
-
import time
|
| 5 |
-
from collections import defaultdict
|
| 6 |
-
from typing import List, Optional, Tuple
|
| 7 |
-
from urllib.parse import urlparse
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
import cv2
|
| 10 |
-
import numpy as np
|
| 11 |
-
import torch
|
| 12 |
-
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoProcessor
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
| 15 |
-
from ultralytics.data.loaders import get_best_youtube_url
|
| 16 |
-
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Annotator
|
| 17 |
-
from ultralytics.utils.torch_utils import select_device
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
class TorchVisionVideoClassifier:
|
| 21 |
-
"""Classifies videos using pretrained TorchVision models; see https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/."""
|
| 22 |
-
|
| 23 |
-
from torchvision.models.video import (
|
| 24 |
-
MViT_V1_B_Weights,
|
| 25 |
-
MViT_V2_S_Weights,
|
| 26 |
-
R3D_18_Weights,
|
| 27 |
-
S3D_Weights,
|
| 28 |
-
Swin3D_B_Weights,
|
| 29 |
-
Swin3D_T_Weights,
|
| 30 |
-
mvit_v1_b,
|
| 31 |
-
mvit_v2_s,
|
| 32 |
-
r3d_18,
|
| 33 |
-
s3d,
|
| 34 |
-
swin3d_b,
|
| 35 |
-
swin3d_t,
|
| 36 |
-
)
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
model_name_to_model_and_weights = {
|
| 39 |
-
"s3d": (s3d, S3D_Weights.DEFAULT),
|
| 40 |
-
"r3d_18": (r3d_18, R3D_18_Weights.DEFAULT),
|
| 41 |
-
"swin3d_t": (swin3d_t, Swin3D_T_Weights.DEFAULT),
|
| 42 |
-
"swin3d_b": (swin3d_b, Swin3D_B_Weights.DEFAULT),
|
| 43 |
-
"mvit_v1_b": (mvit_v1_b, MViT_V1_B_Weights.DEFAULT),
|
| 44 |
-
"mvit_v2_s": (mvit_v2_s, MViT_V2_S_Weights.DEFAULT),
|
| 45 |
-
}
|
| 46 |
-
|
| 47 |
-
def __init__(self, model_name: str, device: str or torch.device = ""):
|
| 48 |
-
"""
|
| 49 |
-
Initialize the VideoClassifier with the specified model name and device.
|
| 50 |
-
|
| 51 |
-
Args:
|
| 52 |
-
model_name (str): The name of the model to use.
|
| 53 |
-
device (str or torch.device, optional): The device to run the model on. Defaults to "".
|
| 54 |
-
|
| 55 |
-
Raises:
|
| 56 |
-
ValueError: If an invalid model name is provided.
|
| 57 |
-
"""
|
| 58 |
-
if model_name not in self.model_name_to_model_and_weights:
|
| 59 |
-
raise ValueError(f"Invalid model name '{model_name}'. Available models: {self.available_model_names()}")
|
| 60 |
-
model, self.weights = self.model_name_to_model_and_weights[model_name]
|
| 61 |
-
self.device = select_device(device)
|
| 62 |
-
self.model = model(weights=self.weights).to(self.device).eval()
|
| 63 |
-
|
| 64 |
-
@staticmethod
|
| 65 |
-
def available_model_names() -> List[str]:
|
| 66 |
-
"""
|
| 67 |
-
Get the list of available model names.
|
| 68 |
-
|
| 69 |
-
Returns:
|
| 70 |
-
list: List of available model names.
|
| 71 |
-
"""
|
| 72 |
-
return list(TorchVisionVideoClassifier.model_name_to_model_and_weights.keys())
|
| 73 |
-
|
| 74 |
-
def preprocess_crops_for_video_cls(self, crops: List[np.ndarray], input_size: list = None) -> torch.Tensor:
|
| 75 |
-
"""
|
| 76 |
-
Preprocess a list of crops for video classification.
|
| 77 |
-
|
| 78 |
-
Args:
|
| 79 |
-
crops (List[np.ndarray]): List of crops to preprocess. Each crop should have dimensions (H, W, C)
|
| 80 |
-
input_size (tuple, optional): The target input size for the model. Defaults to (224, 224).
|
| 81 |
-
|
| 82 |
-
Returns:
|
| 83 |
-
torch.Tensor: Preprocessed crops as a tensor with dimensions (1, T, C, H, W).
|
| 84 |
-
"""
|
| 85 |
-
if input_size is None:
|
| 86 |
-
input_size = [224, 224]
|
| 87 |
-
from torchvision.transforms import v2
|
| 88 |
-
|
| 89 |
-
transform = v2.Compose(
|
| 90 |
-
[
|
| 91 |
-
v2.ToDtype(torch.float32, scale=True),
|
| 92 |
-
v2.Resize(input_size, antialias=True),
|
| 93 |
-
v2.Normalize(mean=self.weights.transforms().mean, std=self.weights.transforms().std),
|
| 94 |
-
]
|
| 95 |
-
)
|
| 96 |
-
|
| 97 |
-
processed_crops = [transform(torch.from_numpy(crop).permute(2, 0, 1)) for crop in crops]
|
| 98 |
-
return torch.stack(processed_crops).unsqueeze(0).permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4).to(self.device)
|
| 99 |
-
|
| 100 |
-
def __call__(self, sequences: torch.Tensor):
|
| 101 |
-
"""
|
| 102 |
-
Perform inference on the given sequences.
|
| 103 |
-
|
| 104 |
-
Args:
|
| 105 |
-
sequences (torch.Tensor): The input sequences for the model. The expected input dimensions are
|
| 106 |
-
(B, T, C, H, W) for batched video frames or (T, C, H, W) for single video frames.
|
| 107 |
-
|
| 108 |
-
Returns:
|
| 109 |
-
torch.Tensor: The model's output.
|
| 110 |
-
"""
|
| 111 |
-
with torch.inference_mode():
|
| 112 |
-
return self.model(sequences)
|
| 113 |
-
|
| 114 |
-
def postprocess(self, outputs: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[List[str], List[float]]:
|
| 115 |
-
"""
|
| 116 |
-
Postprocess the model's batch output.
|
| 117 |
-
|
| 118 |
-
Args:
|
| 119 |
-
outputs (torch.Tensor): The model's output.
|
| 120 |
-
|
| 121 |
-
Returns:
|
| 122 |
-
List[str]: The predicted labels.
|
| 123 |
-
List[float]: The predicted confidences.
|
| 124 |
-
"""
|
| 125 |
-
pred_labels = []
|
| 126 |
-
pred_confs = []
|
| 127 |
-
for output in outputs:
|
| 128 |
-
pred_class = output.argmax(0).item()
|
| 129 |
-
pred_label = self.weights.meta["categories"][pred_class]
|
| 130 |
-
pred_labels.append(pred_label)
|
| 131 |
-
pred_conf = output.softmax(0)[pred_class].item()
|
| 132 |
-
pred_confs.append(pred_conf)
|
| 133 |
-
|
| 134 |
-
return pred_labels, pred_confs
|
| 135 |
-
|
| 136 |
-
|
| 137 |
-
class HuggingFaceVideoClassifier:
|
| 138 |
-
"""Zero-shot video classifier using Hugging Face models for various devices."""
|
| 139 |
-
|
| 140 |
-
def __init__(
|
| 141 |
-
self,
|
| 142 |
-
labels: List[str],
|
| 143 |
-
model_name: str = "microsoft/xclip-base-patch16-zero-shot",
|
| 144 |
-
device: str or torch.device = "",
|
| 145 |
-
fp16: bool = False,
|
| 146 |
-
):
|
| 147 |
-
"""
|
| 148 |
-
Initialize the HuggingFaceVideoClassifier with the specified model name.
|
| 149 |
-
|
| 150 |
-
Args:
|
| 151 |
-
labels (List[str]): List of labels for zero-shot classification.
|
| 152 |
-
model_name (str): The name of the model to use. Defaults to "microsoft/xclip-base-patch16-zero-shot".
|
| 153 |
-
device (str or torch.device, optional): The device to run the model on. Defaults to "".
|
| 154 |
-
fp16 (bool, optional): Whether to use FP16 for inference. Defaults to False.
|
| 155 |
-
"""
|
| 156 |
-
self.fp16 = fp16
|
| 157 |
-
self.labels = labels
|
| 158 |
-
self.device = select_device(device)
|
| 159 |
-
self.processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
| 160 |
-
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name).to(self.device)
|
| 161 |
-
if fp16:
|
| 162 |
-
model = model.half()
|
| 163 |
-
self.model = model.eval()
|
| 164 |
-
|
| 165 |
-
def preprocess_crops_for_video_cls(self, crops: List[np.ndarray], input_size: list = None) -> torch.Tensor:
|
| 166 |
-
"""
|
| 167 |
-
Preprocess a list of crops for video classification.
|
| 168 |
-
|
| 169 |
-
Args:
|
| 170 |
-
crops (List[np.ndarray]): List of crops to preprocess. Each crop should have dimensions (H, W, C)
|
| 171 |
-
input_size (tuple, optional): The target input size for the model. Defaults to (224, 224).
|
| 172 |
-
|
| 173 |
-
Returns:
|
| 174 |
-
torch.Tensor: Preprocessed crops as a tensor (1, T, C, H, W).
|
| 175 |
-
"""
|
| 176 |
-
if input_size is None:
|
| 177 |
-
input_size = [224, 224]
|
| 178 |
-
from torchvision import transforms
|
| 179 |
-
|
| 180 |
-
transform = transforms.Compose(
|
| 181 |
-
[
|
| 182 |
-
transforms.Lambda(lambda x: x.float() / 255.0),
|
| 183 |
-
transforms.Resize(input_size),
|
| 184 |
-
transforms.Normalize(
|
| 185 |
-
mean=self.processor.image_processor.image_mean, std=self.processor.image_processor.image_std
|
| 186 |
-
),
|
| 187 |
-
]
|
| 188 |
-
)
|
| 189 |
-
|
| 190 |
-
processed_crops = [transform(torch.from_numpy(crop).permute(2, 0, 1)) for crop in crops] # (T, C, H, W)
|
| 191 |
-
output = torch.stack(processed_crops).unsqueeze(0).to(self.device) # (1, T, C, H, W)
|
| 192 |
-
if self.fp16:
|
| 193 |
-
output = output.half()
|
| 194 |
-
return output
|
| 195 |
-
|
| 196 |
-
def __call__(self, sequences: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
|
| 197 |
-
"""
|
| 198 |
-
Perform inference on the given sequences.
|
| 199 |
-
|
| 200 |
-
Args:
|
| 201 |
-
sequences (torch.Tensor): The input sequences for the model. Batched video frames with shape (B, T, H, W, C).
|
| 202 |
-
|
| 203 |
-
Returns:
|
| 204 |
-
torch.Tensor: The model's output.
|
| 205 |
-
"""
|
| 206 |
-
input_ids = self.processor(text=self.labels, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)["input_ids"].to(self.device)
|
| 207 |
-
|
| 208 |
-
inputs = {"pixel_values": sequences, "input_ids": input_ids}
|
| 209 |
-
|
| 210 |
-
with torch.inference_mode():
|
| 211 |
-
outputs = self.model(**inputs)
|
| 212 |
-
|
| 213 |
-
return outputs.logits_per_video
|
| 214 |
-
|
| 215 |
-
def postprocess(self, outputs: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[List[List[str]], List[List[float]]]:
|
| 216 |
-
"""
|
| 217 |
-
Postprocess the model's batch output.
|
| 218 |
-
|
| 219 |
-
Args:
|
| 220 |
-
outputs (torch.Tensor): The model's output.
|
| 221 |
-
|
| 222 |
-
Returns:
|
| 223 |
-
List[List[str]]: The predicted top3 labels.
|
| 224 |
-
List[List[float]]: The predicted top3 confidences.
|
| 225 |
-
"""
|
| 226 |
-
pred_labels = []
|
| 227 |
-
pred_confs = []
|
| 228 |
-
|
| 229 |
-
with torch.no_grad():
|
| 230 |
-
logits_per_video = outputs # Assuming outputs is already the logits tensor
|
| 231 |
-
probs = logits_per_video.softmax(dim=-1) # Use softmax to convert logits to probabilities
|
| 232 |
-
|
| 233 |
-
for prob in probs:
|
| 234 |
-
top2_indices = prob.topk(2).indices.tolist()
|
| 235 |
-
top2_labels = [self.labels[idx] for idx in top2_indices]
|
| 236 |
-
top2_confs = prob[top2_indices].tolist()
|
| 237 |
-
pred_labels.append(top2_labels)
|
| 238 |
-
pred_confs.append(top2_confs)
|
| 239 |
-
|
| 240 |
-
return pred_labels, pred_confs
|
| 241 |
-
|
| 242 |
-
|
| 243 |
-
def crop_and_pad(frame, box, margin_percent):
|
| 244 |
-
"""Crop box with margin and take square crop from frame."""
|
| 245 |
-
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, box)
|
| 246 |
-
w, h = x2 - x1, y2 - y1
|
| 247 |
-
|
| 248 |
-
# Add margin
|
| 249 |
-
margin_x, margin_y = int(w * margin_percent / 100), int(h * margin_percent / 100)
|
| 250 |
-
x1, y1 = max(0, x1 - margin_x), max(0, y1 - margin_y)
|
| 251 |
-
x2, y2 = min(frame.shape[1], x2 + margin_x), min(frame.shape[0], y2 + margin_y)
|
| 252 |
-
|
| 253 |
-
# Take square crop from frame
|
| 254 |
-
size = max(y2 - y1, x2 - x1)
|
| 255 |
-
center_y, center_x = (y1 + y2) // 2, (x1 + x2) // 2
|
| 256 |
-
half_size = size // 2
|
| 257 |
-
square_crop = frame[
|
| 258 |
-
max(0, center_y - half_size) : min(frame.shape[0], center_y + half_size),
|
| 259 |
-
max(0, center_x - half_size) : min(frame.shape[1], center_x + half_size),
|
| 260 |
-
]
|
| 261 |
-
|
| 262 |
-
return cv2.resize(square_crop, (224, 224), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
|
| 263 |
-
|
| 264 |
-
|
| 265 |
-
def run(
|
| 266 |
-
weights: str = "yolo11n.pt",
|
| 267 |
-
device: str = "",
|
| 268 |
-
source: str = "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQw4w9WgXcQ",
|
| 269 |
-
output_path: Optional[str] = None,
|
| 270 |
-
crop_margin_percentage: int = 10,
|
| 271 |
-
num_video_sequence_samples: int = 8,
|
| 272 |
-
skip_frame: int = 2,
|
| 273 |
-
video_cls_overlap_ratio: float = 0.25,
|
| 274 |
-
fp16: bool = False,
|
| 275 |
-
video_classifier_model: str = "microsoft/xclip-base-patch32",
|
| 276 |
-
labels: List[str] = None,
|
| 277 |
-
) -> None:
|
| 278 |
-
"""
|
| 279 |
-
Run action recognition on a video source using YOLO for object detection and a video classifier.
|
| 280 |
-
|
| 281 |
-
Args:
|
| 282 |
-
weights (str): Path to the YOLO model weights. Defaults to "yolo11n.pt".
|
| 283 |
-
device (str): Device to run the model on. Use 'cuda' for NVIDIA GPU, 'mps' for Apple Silicon, or 'cpu'. Defaults to auto-detection.
|
| 284 |
-
source (str): Path to mp4 video file or YouTube URL. Defaults to a sample YouTube video.
|
| 285 |
-
output_path (Optional[str], optional): Path to save the output video. Defaults to None.
|
| 286 |
-
crop_margin_percentage (int, optional): Percentage of margin to add around detected objects. Defaults to 10.
|
| 287 |
-
num_video_sequence_samples (int, optional): Number of video frames to use for classification. Defaults to 8.
|
| 288 |
-
skip_frame (int, optional): Number of frames to skip between detections. Defaults to 4.
|
| 289 |
-
video_cls_overlap_ratio (float, optional): Overlap ratio between video sequences. Defaults to 0.25.
|
| 290 |
-
fp16 (bool, optional): Whether to use half-precision floating point. Defaults to False.
|
| 291 |
-
video_classifier_model (str, optional): Name or path of the video classifier model. Defaults to "microsoft/xclip-base-patch32".
|
| 292 |
-
labels (List[str], optional): List of labels for zero-shot classification. Defaults to predefined list.
|
| 293 |
-
|
| 294 |
-
Returns:
|
| 295 |
-
None</edit>
|
| 296 |
-
"""
|
| 297 |
-
if labels is None:
|
| 298 |
-
labels = [
|
| 299 |
-
"walking",
|
| 300 |
-
"running",
|
| 301 |
-
"brushing teeth",
|
| 302 |
-
"looking into phone",
|
| 303 |
-
"weight lifting",
|
| 304 |
-
"cooking",
|
| 305 |
-
"sitting",
|
| 306 |
-
]
|
| 307 |
-
# Initialize models and device
|
| 308 |
-
device = select_device(device)
|
| 309 |
-
yolo_model = YOLO(weights).to(device)
|
| 310 |
-
if video_classifier_model in TorchVisionVideoClassifier.available_model_names():
|
| 311 |
-
print("'fp16' is not supported for TorchVisionVideoClassifier. Setting fp16 to False.")
|
| 312 |
-
print(
|
| 313 |
-
"'labels' is not used for TorchVisionVideoClassifier. Ignoring the provided labels and using Kinetics-400 labels."
|
| 314 |
-
)
|
| 315 |
-
video_classifier = TorchVisionVideoClassifier(video_classifier_model, device=device)
|
| 316 |
-
else:
|
| 317 |
-
video_classifier = HuggingFaceVideoClassifier(
|
| 318 |
-
labels, model_name=video_classifier_model, device=device, fp16=fp16
|
| 319 |
-
)
|
| 320 |
-
|
| 321 |
-
# Initialize video capture
|
| 322 |
-
if source.startswith("http") and urlparse(source).hostname in {"www.youtube.com", "youtube.com", "youtu.be"}:
|
| 323 |
-
source = get_best_youtube_url(source)
|
| 324 |
-
elif not source.endswith(".mp4"):
|
| 325 |
-
raise ValueError("Invalid source. Supported sources are YouTube URLs and MP4 files.")
|
| 326 |
-
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(source)
|
| 327 |
-
|
| 328 |
-
# Get video properties
|
| 329 |
-
frame_width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
|
| 330 |
-
frame_height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
|
| 331 |
-
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
|
| 332 |
-
|
| 333 |
-
# Initialize VideoWriter
|
| 334 |
-
if output_path is not None:
|
| 335 |
-
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v")
|
| 336 |
-
out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, fourcc, fps, (frame_width, frame_height))
|
| 337 |
-
|
| 338 |
-
# Initialize track history
|
| 339 |
-
track_history = defaultdict(list)
|
| 340 |
-
frame_counter = 0
|
| 341 |
-
|
| 342 |
-
track_ids_to_infer = []
|
| 343 |
-
crops_to_infer = []
|
| 344 |
-
pred_labels = []
|
| 345 |
-
pred_confs = []
|
| 346 |
-
|
| 347 |
-
while cap.isOpened():
|
| 348 |
-
success, frame = cap.read()
|
| 349 |
-
if not success:
|
| 350 |
-
break
|
| 351 |
-
|
| 352 |
-
frame_counter += 1
|
| 353 |
-
|
| 354 |
-
# Run YOLO tracking
|
| 355 |
-
results = yolo_model.track(frame, persist=True, classes=[0]) # Track only person class
|
| 356 |
-
|
| 357 |
-
if results[0].boxes.id is not None:
|
| 358 |
-
boxes = results[0].boxes.xyxy.cpu().numpy()
|
| 359 |
-
track_ids = results[0].boxes.id.cpu().numpy()
|
| 360 |
-
|
| 361 |
-
# Visualize prediction
|
| 362 |
-
annotator = Annotator(frame, line_width=3, font_size=10, pil=False)
|
| 363 |
-
|
| 364 |
-
if frame_counter % skip_frame == 0:
|
| 365 |
-
crops_to_infer = []
|
| 366 |
-
track_ids_to_infer = []
|
| 367 |
-
|
| 368 |
-
for box, track_id in zip(boxes, track_ids):
|
| 369 |
-
if frame_counter % skip_frame == 0:
|
| 370 |
-
crop = crop_and_pad(frame, box, crop_margin_percentage)
|
| 371 |
-
track_history[track_id].append(crop)
|
| 372 |
-
|
| 373 |
-
if len(track_history[track_id]) > num_video_sequence_samples:
|
| 374 |
-
track_history[track_id].pop(0)
|
| 375 |
-
|
| 376 |
-
if len(track_history[track_id]) == num_video_sequence_samples and frame_counter % skip_frame == 0:
|
| 377 |
-
start_time = time.time()
|
| 378 |
-
crops = video_classifier.preprocess_crops_for_video_cls(track_history[track_id])
|
| 379 |
-
end_time = time.time()
|
| 380 |
-
preprocess_time = end_time - start_time
|
| 381 |
-
print(f"video cls preprocess time: {preprocess_time:.4f} seconds")
|
| 382 |
-
crops_to_infer.append(crops)
|
| 383 |
-
track_ids_to_infer.append(track_id)
|
| 384 |
-
|
| 385 |
-
if crops_to_infer and (
|
| 386 |
-
not pred_labels
|
| 387 |
-
or frame_counter % int(num_video_sequence_samples * skip_frame * (1 - video_cls_overlap_ratio)) == 0
|
| 388 |
-
):
|
| 389 |
-
crops_batch = torch.cat(crops_to_infer, dim=0)
|
| 390 |
-
|
| 391 |
-
start_inference_time = time.time()
|
| 392 |
-
output_batch = video_classifier(crops_batch)
|
| 393 |
-
end_inference_time = time.time()
|
| 394 |
-
inference_time = end_inference_time - start_inference_time
|
| 395 |
-
print(f"video cls inference time: {inference_time:.4f} seconds")
|
| 396 |
-
|
| 397 |
-
pred_labels, pred_confs = video_classifier.postprocess(output_batch)
|
| 398 |
-
|
| 399 |
-
if track_ids_to_infer and crops_to_infer:
|
| 400 |
-
for box, track_id, pred_label, pred_conf in zip(boxes, track_ids_to_infer, pred_labels, pred_confs):
|
| 401 |
-
top2_preds = sorted(zip(pred_label, pred_conf), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
|
| 402 |
-
label_text = " | ".join([f"{label} ({conf:.2f})" for label, conf in top2_preds])
|
| 403 |
-
annotator.box_label(box, label_text, color=(0, 0, 255))
|
| 404 |
-
|
| 405 |
-
# Write the annotated frame to the output video
|
| 406 |
-
if output_path is not None:
|
| 407 |
-
out.write(frame)
|
| 408 |
-
|
| 409 |
-
# Display the annotated frame
|
| 410 |
-
cv2.imshow("YOLOv8 Tracking with S3D Classification", frame)
|
| 411 |
-
|
| 412 |
-
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
|
| 413 |
-
break
|
| 414 |
-
|
| 415 |
-
cap.release()
|
| 416 |
-
if output_path is not None:
|
| 417 |
-
out.release()
|
| 418 |
-
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
|
| 419 |
-
|
| 420 |
-
|
| 421 |
-
def parse_opt():
|
| 422 |
-
"""Parse command line arguments."""
|
| 423 |
-
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
| 424 |
-
parser.add_argument("--weights", type=str, default="yolo11n.pt", help="ultralytics detector model path")
|
| 425 |
-
parser.add_argument("--device", default="", help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu/mps, "" for auto-detection')
|
| 426 |
-
parser.add_argument(
|
| 427 |
-
"--source",
|
| 428 |
-
type=str,
|
| 429 |
-
default="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQw4w9WgXcQ",
|
| 430 |
-
help="video file path or youtube URL",
|
| 431 |
-
)
|
| 432 |
-
parser.add_argument("--output-path", type=str, default="output_video.mp4", help="output video file path")
|
| 433 |
-
parser.add_argument(
|
| 434 |
-
"--crop-margin-percentage", type=int, default=10, help="percentage of margin to add around detected objects"
|
| 435 |
-
)
|
| 436 |
-
parser.add_argument(
|
| 437 |
-
"--num-video-sequence-samples", type=int, default=8, help="number of video frames to use for classification"
|
| 438 |
-
)
|
| 439 |
-
parser.add_argument("--skip-frame", type=int, default=2, help="number of frames to skip between detections")
|
| 440 |
-
parser.add_argument(
|
| 441 |
-
"--video-cls-overlap-ratio", type=float, default=0.25, help="overlap ratio between video sequences"
|
| 442 |
-
)
|
| 443 |
-
parser.add_argument("--fp16", action="store_true", help="use FP16 for inference")
|
| 444 |
-
parser.add_argument(
|
| 445 |
-
"--video-classifier-model", type=str, default="microsoft/xclip-base-patch32", help="video classifier model name"
|
| 446 |
-
)
|
| 447 |
-
parser.add_argument(
|
| 448 |
-
"--labels",
|
| 449 |
-
nargs="+",
|
| 450 |
-
type=str,
|
| 451 |
-
default=["dancing", "singing a song"],
|
| 452 |
-
help="labels for zero-shot video classification",
|
| 453 |
-
)
|
| 454 |
-
return parser.parse_args()
|
| 455 |
-
|
| 456 |
-
|
| 457 |
-
def main(opt):
|
| 458 |
-
"""Main function."""
|
| 459 |
-
run(**vars(opt))
|
| 460 |
-
|
| 461 |
-
|
| 462 |
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 463 |
-
opt = parse_opt()
|
| 464 |
-
main(opt)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-Action-Recognition/readme.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,116 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Zero-shot Action Recognition with YOLOv8 (Inference on Video)
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
- Action recognition is a technique used to identify and classify actions performed by individuals in a video. This process enables more advanced analyses when multiple actions are considered. The actions can be detected and classified in real time.
|
| 4 |
-
- The system can be customized to recognize specific actions based on the user's preferences and requirements.
|
| 5 |
-
|
| 6 |
-
## Table of Contents
|
| 7 |
-
|
| 8 |
-
- [Step 1: Install the Required Libraries](#step-1-install-the-required-libraries)
|
| 9 |
-
- [Step 2: Run the Action Recognition Using Ultralytics YOLOv8](#step-2-run-the-action-recognition-using-ultralytics-yolov8)
|
| 10 |
-
- [Usage Options](#usage-options)
|
| 11 |
-
- [FAQ](#faq)
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
## Step 1: Install the Required Libraries
|
| 14 |
-
|
| 15 |
-
Clone the repository, install dependencies and `cd` to this local directory for commands in Step 2.
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
```bash
|
| 18 |
-
# Clone ultralytics repo
|
| 19 |
-
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
# cd to local directory
|
| 22 |
-
cd examples/YOLOv8-Action-Recognition
|
| 23 |
-
|
| 24 |
-
# Install dependencies
|
| 25 |
-
pip install -U -r requirements.txt
|
| 26 |
-
```
|
| 27 |
-
|
| 28 |
-
## Step 2: Run the Action Recognition Using Ultralytics YOLOv8
|
| 29 |
-
|
| 30 |
-
Here are the basic commands for running the inference:
|
| 31 |
-
|
| 32 |
-
### Note
|
| 33 |
-
|
| 34 |
-
The action recognition model will automatically detect and track people in the video, and classify their actions based on the specified labels. The results will be displayed in real-time on the video output. You can customize the action labels by modifying the `--labels` argument when running the script.
|
| 35 |
-
|
| 36 |
-
```bash
|
| 37 |
-
# Quick start
|
| 38 |
-
python action_recognition.py
|
| 39 |
-
|
| 40 |
-
# Basic usage
|
| 41 |
-
python action_recognition.py --source "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQw4w9WgXcQ" --labels "dancing" "singing a song"
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
# Use local video file
|
| 44 |
-
python action_recognition.py --source path/to/video.mp4
|
| 45 |
-
|
| 46 |
-
# Better detector performance
|
| 47 |
-
python action_recognition.py --weights yolov8m.pt
|
| 48 |
-
|
| 49 |
-
# Run on CPU
|
| 50 |
-
python action_recognition.py --device cpu
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
# Use a different video classifier model
|
| 53 |
-
python action_recognition.py --video-classifier-model "s3d"
|
| 54 |
-
|
| 55 |
-
# Use FP16 for inference (only for HuggingFace models)
|
| 56 |
-
python action_recognition.py --fp16
|
| 57 |
-
|
| 58 |
-
# Export output as mp4
|
| 59 |
-
python action_recognition.py --output-path output.mp4
|
| 60 |
-
|
| 61 |
-
# Combine multiple options
|
| 62 |
-
python action_recognition.py --source "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQw4w9WgXcQ" --device 0 --video-classifier-model "microsoft/xclip-base-patch32" --labels "dancing" "singing a song" --fp16
|
| 63 |
-
```
|
| 64 |
-
|
| 65 |
-
## Usage Options
|
| 66 |
-
|
| 67 |
-
- `--weights`: Path to the YOLO model weights (default: "yolov8n.pt")
|
| 68 |
-
- `--device`: Cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu (default: auto-detect)
|
| 69 |
-
- `--source`: Video file path or YouTube URL (default: "[rickroll](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQw4w9WgXcQ)")
|
| 70 |
-
- `--output-path`: Output video file path
|
| 71 |
-
- `--crop-margin-percentage`: Percentage of margin to add around detected objects (default: 10)
|
| 72 |
-
- `--num-video-sequence-samples`: Number of video frames to use for classification (default: 8)
|
| 73 |
-
- `--skip-frame`: Number of frames to skip between detections (default: 1)
|
| 74 |
-
- `--video-cls-overlap-ratio`: Overlap ratio between video sequences (default: 0.25)
|
| 75 |
-
- `--fp16`: Use FP16 for inference (only for HuggingFace models)
|
| 76 |
-
- `--video-classifier-model`: Video classifier model name or path (default: "microsoft/xclip-base-patch32")
|
| 77 |
-
- `--labels`: Labels for zero-shot video classification (default: \["dancing" "singing a song"\])
|
| 78 |
-
|
| 79 |
-
## FAQ
|
| 80 |
-
|
| 81 |
-
**1. What Does Action Recognition Involve?**
|
| 82 |
-
|
| 83 |
-
Action recognition is a computational method used to identify and classify actions or activities performed by individuals in recorded video or real-time streams. This technique is widely used in video analysis, surveillance, and human-computer interaction, enabling the detection and understanding of human behaviors based on their motion patterns and context.
|
| 84 |
-
|
| 85 |
-
**2. Is Custom Action Labels Supported by the Action Recognition?**
|
| 86 |
-
|
| 87 |
-
Yes, custom action labels are supported by the action recognition system. The `action_recognition.py` script allows users to specify their own custom labels for zero-shot video classification. This can be done using the `--labels` argument when running the script. For example:
|
| 88 |
-
|
| 89 |
-
```bash
|
| 90 |
-
python action_recognition.py --source https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQw4w9WgXcQ --labels "dancing" "singing" "jumping"
|
| 91 |
-
```
|
| 92 |
-
|
| 93 |
-
You can adjust these labels to match the specific actions you want to recognize in your video. The system will then attempt to classify the detected actions based on these custom labels.
|
| 94 |
-
|
| 95 |
-
Additionally, you can choose between different video classification models:
|
| 96 |
-
|
| 97 |
-
1. For Hugging Face models, you can use any compatible video classification model. The default is set to:
|
| 98 |
-
|
| 99 |
-
- "microsoft/xclip-base-patch32"
|
| 100 |
-
|
| 101 |
-
2. For TorchVision models (no support for zero-shot labels), you can select from the following options:
|
| 102 |
-
|
| 103 |
-
- "s3d"
|
| 104 |
-
- "r3d_18"
|
| 105 |
-
- "swin3d_t"
|
| 106 |
-
- "swin3d_b"
|
| 107 |
-
- "mvit_v1_b"
|
| 108 |
-
- "mvit_v2_s"
|
| 109 |
-
|
| 110 |
-
**3. Why Combine Action Recognition with YOLOv8?**
|
| 111 |
-
|
| 112 |
-
YOLOv8 specializes in the detection and tracking of objects in video streams. Action recognition complements this by enabling the identification and classification of actions performed by individuals, making it a valuable application of YOLOv8.
|
| 113 |
-
|
| 114 |
-
**4. Can I Employ Other YOLO Versions?**
|
| 115 |
-
|
| 116 |
-
Certainly, you have the flexibility to specify different YOLO model weights using the `--weights` option.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-Action-Recognition/requirements.txt
DELETED
|
@@ -1,4 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
ultralytics
|
| 4 |
-
transformers
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-CPP-Inference/CMakeLists.txt
DELETED
|
@@ -1,28 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5)
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
project(Yolov8CPPInference VERSION 0.1)
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
set(CMAKE_INCLUDE_CURRENT_DIR ON)
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
# CUDA
|
| 8 |
-
set(CUDA_TOOLKIT_ROOT_DIR "/usr/local/cuda")
|
| 9 |
-
find_package(CUDA 11 REQUIRED)
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
set(CMAKE_CUDA_STANDARD 11)
|
| 12 |
-
set(CMAKE_CUDA_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
|
| 13 |
-
# !CUDA
|
| 14 |
-
|
| 15 |
-
# OpenCV
|
| 16 |
-
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
|
| 17 |
-
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
|
| 18 |
-
# !OpenCV
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
set(PROJECT_SOURCES
|
| 21 |
-
main.cpp
|
| 22 |
-
|
| 23 |
-
inference.h
|
| 24 |
-
inference.cpp
|
| 25 |
-
)
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
add_executable(Yolov8CPPInference ${PROJECT_SOURCES})
|
| 28 |
-
target_link_libraries(Yolov8CPPInference ${OpenCV_LIBS})
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-CPP-Inference/README.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# YOLOv8/YOLOv5 Inference C++
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
This example demonstrates how to perform inference using YOLOv8 and YOLOv5 models in C++ with OpenCV DNN API.
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
## Usage
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
```bash
|
| 8 |
-
git clone ultralytics
|
| 9 |
-
cd ultralytics
|
| 10 |
-
pip install .
|
| 11 |
-
cd examples/YOLOv8-CPP-Inference
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
# Add a **yolov8\_.onnx** and/or **yolov5\_.onnx** model(s) to the ultralytics folder.
|
| 14 |
-
# Edit the **main.cpp** to change the **projectBasePath** to match your user.
|
| 15 |
-
|
| 16 |
-
# Note that by default the CMake file will try to import the CUDA library to be used with the OpenCVs dnn (cuDNN) GPU Inference.
|
| 17 |
-
# If your OpenCV build does not use CUDA/cuDNN you can remove that import call and run the example on CPU.
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
mkdir build
|
| 20 |
-
cd build
|
| 21 |
-
cmake ..
|
| 22 |
-
make
|
| 23 |
-
./Yolov8CPPInference
|
| 24 |
-
```
|
| 25 |
-
|
| 26 |
-
## Exporting YOLOv8 and YOLOv5 Models
|
| 27 |
-
|
| 28 |
-
To export YOLOv8 models:
|
| 29 |
-
|
| 30 |
-
```bash
|
| 31 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8s.pt imgsz=480,640 format=onnx opset=12
|
| 32 |
-
```
|
| 33 |
-
|
| 34 |
-
To export YOLOv5 models:
|
| 35 |
-
|
| 36 |
-
```bash
|
| 37 |
-
python3 export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --img 480 640 --include onnx --opset 12
|
| 38 |
-
```
|
| 39 |
-
|
| 40 |
-
yolov8s.onnx:
|
| 41 |
-
|
| 42 |
-
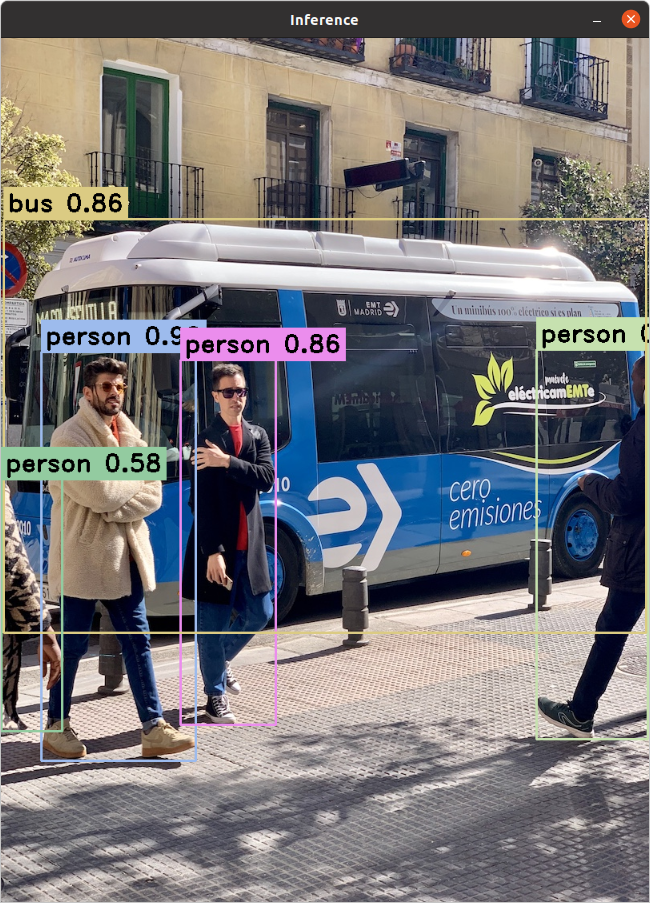

|
| 43 |
-
|
| 44 |
-
yolov5s.onnx:
|
| 45 |
-
|
| 46 |
-
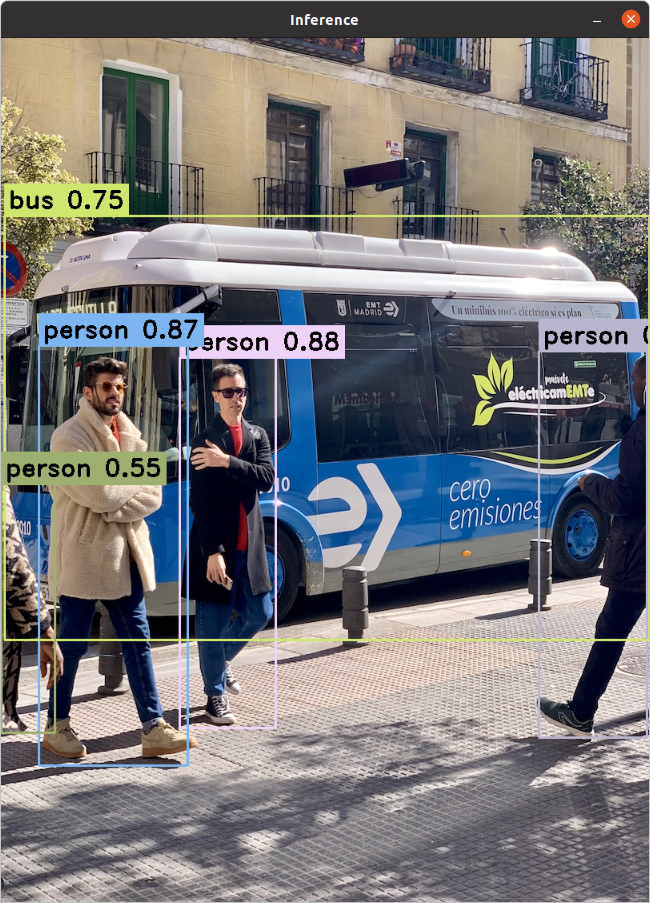

|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
This repository utilizes OpenCV DNN API to run ONNX exported models of YOLOv5 and YOLOv8. In theory, it should work for YOLOv6 and YOLOv7 as well, but they have not been tested. Note that the example networks are exported with rectangular (640x480) resolutions, but any exported resolution will work. You may want to use the letterbox approach for square images, depending on your use case.
|
| 49 |
-
|
| 50 |
-
The **main** branch version uses Qt as a GUI wrapper. The primary focus here is the **Inference** class file, which demonstrates how to transpose YOLOv8 models to work as YOLOv5 models.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-CPP-Inference/inference.cpp
DELETED
|
@@ -1,185 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#include "inference.h"
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
Inference::Inference(const std::string &onnxModelPath, const cv::Size &modelInputShape, const std::string &classesTxtFile, const bool &runWithCuda)
|
| 4 |
-
{
|
| 5 |
-
modelPath = onnxModelPath;
|
| 6 |
-
modelShape = modelInputShape;
|
| 7 |
-
classesPath = classesTxtFile;
|
| 8 |
-
cudaEnabled = runWithCuda;
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
loadOnnxNetwork();
|
| 11 |
-
// loadClassesFromFile(); The classes are hard-coded for this example
|
| 12 |
-
}
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
std::vector<Detection> Inference::runInference(const cv::Mat &input)
|
| 15 |
-
{
|
| 16 |
-
cv::Mat modelInput = input;
|
| 17 |
-
if (letterBoxForSquare && modelShape.width == modelShape.height)
|
| 18 |
-
modelInput = formatToSquare(modelInput);
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
cv::Mat blob;
|
| 21 |
-
cv::dnn::blobFromImage(modelInput, blob, 1.0/255.0, modelShape, cv::Scalar(), true, false);
|
| 22 |
-
net.setInput(blob);
|
| 23 |
-
|
| 24 |
-
std::vector<cv::Mat> outputs;
|
| 25 |
-
net.forward(outputs, net.getUnconnectedOutLayersNames());
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
int rows = outputs[0].size[1];
|
| 28 |
-
int dimensions = outputs[0].size[2];
|
| 29 |
-
|
| 30 |
-
bool yolov8 = false;
|
| 31 |
-
// yolov5 has an output of shape (batchSize, 25200, 85) (Num classes + box[x,y,w,h] + confidence[c])
|
| 32 |
-
// yolov8 has an output of shape (batchSize, 84, 8400) (Num classes + box[x,y,w,h])
|
| 33 |
-
if (dimensions > rows) // Check if the shape[2] is more than shape[1] (yolov8)
|
| 34 |
-
{
|
| 35 |
-
yolov8 = true;
|
| 36 |
-
rows = outputs[0].size[2];
|
| 37 |
-
dimensions = outputs[0].size[1];
|
| 38 |
-
|
| 39 |
-
outputs[0] = outputs[0].reshape(1, dimensions);
|
| 40 |
-
cv::transpose(outputs[0], outputs[0]);
|
| 41 |
-
}
|
| 42 |
-
float *data = (float *)outputs[0].data;
|
| 43 |
-
|
| 44 |
-
float x_factor = modelInput.cols / modelShape.width;
|
| 45 |
-
float y_factor = modelInput.rows / modelShape.height;
|
| 46 |
-
|
| 47 |
-
std::vector<int> class_ids;
|
| 48 |
-
std::vector<float> confidences;
|
| 49 |
-
std::vector<cv::Rect> boxes;
|
| 50 |
-
|
| 51 |
-
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i)
|
| 52 |
-
{
|
| 53 |
-
if (yolov8)
|
| 54 |
-
{
|
| 55 |
-
float *classes_scores = data+4;
|
| 56 |
-
|
| 57 |
-
cv::Mat scores(1, classes.size(), CV_32FC1, classes_scores);
|
| 58 |
-
cv::Point class_id;
|
| 59 |
-
double maxClassScore;
|
| 60 |
-
|
| 61 |
-
minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &maxClassScore, 0, &class_id);
|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
if (maxClassScore > modelScoreThreshold)
|
| 64 |
-
{
|
| 65 |
-
confidences.push_back(maxClassScore);
|
| 66 |
-
class_ids.push_back(class_id.x);
|
| 67 |
-
|
| 68 |
-
float x = data[0];
|
| 69 |
-
float y = data[1];
|
| 70 |
-
float w = data[2];
|
| 71 |
-
float h = data[3];
|
| 72 |
-
|
| 73 |
-
int left = int((x - 0.5 * w) * x_factor);
|
| 74 |
-
int top = int((y - 0.5 * h) * y_factor);
|
| 75 |
-
|
| 76 |
-
int width = int(w * x_factor);
|
| 77 |
-
int height = int(h * y_factor);
|
| 78 |
-
|
| 79 |
-
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(left, top, width, height));
|
| 80 |
-
}
|
| 81 |
-
}
|
| 82 |
-
else // yolov5
|
| 83 |
-
{
|
| 84 |
-
float confidence = data[4];
|
| 85 |
-
|
| 86 |
-
if (confidence >= modelConfidenceThreshold)
|
| 87 |
-
{
|
| 88 |
-
float *classes_scores = data+5;
|
| 89 |
-
|
| 90 |
-
cv::Mat scores(1, classes.size(), CV_32FC1, classes_scores);
|
| 91 |
-
cv::Point class_id;
|
| 92 |
-
double max_class_score;
|
| 93 |
-
|
| 94 |
-
minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &max_class_score, 0, &class_id);
|
| 95 |
-
|
| 96 |
-
if (max_class_score > modelScoreThreshold)
|
| 97 |
-
{
|
| 98 |
-
confidences.push_back(confidence);
|
| 99 |
-
class_ids.push_back(class_id.x);
|
| 100 |
-
|
| 101 |
-
float x = data[0];
|
| 102 |
-
float y = data[1];
|
| 103 |
-
float w = data[2];
|
| 104 |
-
float h = data[3];
|
| 105 |
-
|
| 106 |
-
int left = int((x - 0.5 * w) * x_factor);
|
| 107 |
-
int top = int((y - 0.5 * h) * y_factor);
|
| 108 |
-
|
| 109 |
-
int width = int(w * x_factor);
|
| 110 |
-
int height = int(h * y_factor);
|
| 111 |
-
|
| 112 |
-
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(left, top, width, height));
|
| 113 |
-
}
|
| 114 |
-
}
|
| 115 |
-
}
|
| 116 |
-
|
| 117 |
-
data += dimensions;
|
| 118 |
-
}
|
| 119 |
-
|
| 120 |
-
std::vector<int> nms_result;
|
| 121 |
-
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, modelScoreThreshold, modelNMSThreshold, nms_result);
|
| 122 |
-
|
| 123 |
-
std::vector<Detection> detections{};
|
| 124 |
-
for (unsigned long i = 0; i < nms_result.size(); ++i)
|
| 125 |
-
{
|
| 126 |
-
int idx = nms_result[i];
|
| 127 |
-
|
| 128 |
-
Detection result;
|
| 129 |
-
result.class_id = class_ids[idx];
|
| 130 |
-
result.confidence = confidences[idx];
|
| 131 |
-
|
| 132 |
-
std::random_device rd;
|
| 133 |
-
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
|
| 134 |
-
std::uniform_int_distribution<int> dis(100, 255);
|
| 135 |
-
result.color = cv::Scalar(dis(gen),
|
| 136 |
-
dis(gen),
|
| 137 |
-
dis(gen));
|
| 138 |
-
|
| 139 |
-
result.className = classes[result.class_id];
|
| 140 |
-
result.box = boxes[idx];
|
| 141 |
-
|
| 142 |
-
detections.push_back(result);
|
| 143 |
-
}
|
| 144 |
-
|
| 145 |
-
return detections;
|
| 146 |
-
}
|
| 147 |
-
|
| 148 |
-
void Inference::loadClassesFromFile()
|
| 149 |
-
{
|
| 150 |
-
std::ifstream inputFile(classesPath);
|
| 151 |
-
if (inputFile.is_open())
|
| 152 |
-
{
|
| 153 |
-
std::string classLine;
|
| 154 |
-
while (std::getline(inputFile, classLine))
|
| 155 |
-
classes.push_back(classLine);
|
| 156 |
-
inputFile.close();
|
| 157 |
-
}
|
| 158 |
-
}
|
| 159 |
-
|
| 160 |
-
void Inference::loadOnnxNetwork()
|
| 161 |
-
{
|
| 162 |
-
net = cv::dnn::readNetFromONNX(modelPath);
|
| 163 |
-
if (cudaEnabled)
|
| 164 |
-
{
|
| 165 |
-
std::cout << "\nRunning on CUDA" << std::endl;
|
| 166 |
-
net.setPreferableBackend(cv::dnn::DNN_BACKEND_CUDA);
|
| 167 |
-
net.setPreferableTarget(cv::dnn::DNN_TARGET_CUDA);
|
| 168 |
-
}
|
| 169 |
-
else
|
| 170 |
-
{
|
| 171 |
-
std::cout << "\nRunning on CPU" << std::endl;
|
| 172 |
-
net.setPreferableBackend(cv::dnn::DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV);
|
| 173 |
-
net.setPreferableTarget(cv::dnn::DNN_TARGET_CPU);
|
| 174 |
-
}
|
| 175 |
-
}
|
| 176 |
-
|
| 177 |
-
cv::Mat Inference::formatToSquare(const cv::Mat &source)
|
| 178 |
-
{
|
| 179 |
-
int col = source.cols;
|
| 180 |
-
int row = source.rows;
|
| 181 |
-
int _max = MAX(col, row);
|
| 182 |
-
cv::Mat result = cv::Mat::zeros(_max, _max, CV_8UC3);
|
| 183 |
-
source.copyTo(result(cv::Rect(0, 0, col, row)));
|
| 184 |
-
return result;
|
| 185 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-CPP-Inference/inference.h
DELETED
|
@@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#ifndef INFERENCE_H
|
| 2 |
-
#define INFERENCE_H
|
| 3 |
-
|
| 4 |
-
// Cpp native
|
| 5 |
-
#include <fstream>
|
| 6 |
-
#include <vector>
|
| 7 |
-
#include <string>
|
| 8 |
-
#include <random>
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
// OpenCV / DNN / Inference
|
| 11 |
-
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
|
| 12 |
-
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
|
| 13 |
-
#include <opencv2/dnn.hpp>
|
| 14 |
-
|
| 15 |
-
struct Detection
|
| 16 |
-
{
|
| 17 |
-
int class_id{0};
|
| 18 |
-
std::string className{};
|
| 19 |
-
float confidence{0.0};
|
| 20 |
-
cv::Scalar color{};
|
| 21 |
-
cv::Rect box{};
|
| 22 |
-
};
|
| 23 |
-
|
| 24 |
-
class Inference
|
| 25 |
-
{
|
| 26 |
-
public:
|
| 27 |
-
Inference(const std::string &onnxModelPath, const cv::Size &modelInputShape = {640, 640}, const std::string &classesTxtFile = "", const bool &runWithCuda = true);
|
| 28 |
-
std::vector<Detection> runInference(const cv::Mat &input);
|
| 29 |
-
|
| 30 |
-
private:
|
| 31 |
-
void loadClassesFromFile();
|
| 32 |
-
void loadOnnxNetwork();
|
| 33 |
-
cv::Mat formatToSquare(const cv::Mat &source);
|
| 34 |
-
|
| 35 |
-
std::string modelPath{};
|
| 36 |
-
std::string classesPath{};
|
| 37 |
-
bool cudaEnabled{};
|
| 38 |
-
|
| 39 |
-
std::vector<std::string> classes{"person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle", "airplane", "bus", "train", "truck", "boat", "traffic light", "fire hydrant", "stop sign", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse", "sheep", "cow", "elephant", "bear", "zebra", "giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee", "skis", "snowboard", "sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard", "surfboard", "tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife", "spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple", "sandwich", "orange", "broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair", "couch", "potted plant", "bed", "dining table", "toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard", "cell phone", "microwave", "oven", "toaster", "sink", "refrigerator", "book", "clock", "vase", "scissors", "teddy bear", "hair drier", "toothbrush"};
|
| 40 |
-
|
| 41 |
-
cv::Size2f modelShape{};
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
float modelConfidenceThreshold {0.25};
|
| 44 |
-
float modelScoreThreshold {0.45};
|
| 45 |
-
float modelNMSThreshold {0.50};
|
| 46 |
-
|
| 47 |
-
bool letterBoxForSquare = true;
|
| 48 |
-
|
| 49 |
-
cv::dnn::Net net;
|
| 50 |
-
};
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
#endif // INFERENCE_H
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-CPP-Inference/main.cpp
DELETED
|
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#include <iostream>
|
| 2 |
-
#include <vector>
|
| 3 |
-
#include <getopt.h>
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
#include "inference.h"
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
using namespace std;
|
| 10 |
-
using namespace cv;
|
| 11 |
-
|
| 12 |
-
int main(int argc, char **argv)
|
| 13 |
-
{
|
| 14 |
-
std::string projectBasePath = "/home/user/ultralytics"; // Set your ultralytics base path
|
| 15 |
-
|
| 16 |
-
bool runOnGPU = true;
|
| 17 |
-
|
| 18 |
-
//
|
| 19 |
-
// Pass in either:
|
| 20 |
-
//
|
| 21 |
-
// "yolov8s.onnx" or "yolov5s.onnx"
|
| 22 |
-
//
|
| 23 |
-
// To run Inference with yolov8/yolov5 (ONNX)
|
| 24 |
-
//
|
| 25 |
-
|
| 26 |
-
// Note that in this example the classes are hard-coded and 'classes.txt' is a place holder.
|
| 27 |
-
Inference inf(projectBasePath + "/yolov8s.onnx", cv::Size(640, 640), "classes.txt", runOnGPU);
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
std::vector<std::string> imageNames;
|
| 30 |
-
imageNames.push_back(projectBasePath + "/ultralytics/assets/bus.jpg");
|
| 31 |
-
imageNames.push_back(projectBasePath + "/ultralytics/assets/zidane.jpg");
|
| 32 |
-
|
| 33 |
-
for (int i = 0; i < imageNames.size(); ++i)
|
| 34 |
-
{
|
| 35 |
-
cv::Mat frame = cv::imread(imageNames[i]);
|
| 36 |
-
|
| 37 |
-
// Inference starts here...
|
| 38 |
-
std::vector<Detection> output = inf.runInference(frame);
|
| 39 |
-
|
| 40 |
-
int detections = output.size();
|
| 41 |
-
std::cout << "Number of detections:" << detections << std::endl;
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
for (int i = 0; i < detections; ++i)
|
| 44 |
-
{
|
| 45 |
-
Detection detection = output[i];
|
| 46 |
-
|
| 47 |
-
cv::Rect box = detection.box;
|
| 48 |
-
cv::Scalar color = detection.color;
|
| 49 |
-
|
| 50 |
-
// Detection box
|
| 51 |
-
cv::rectangle(frame, box, color, 2);
|
| 52 |
-
|
| 53 |
-
// Detection box text
|
| 54 |
-
std::string classString = detection.className + ' ' + std::to_string(detection.confidence).substr(0, 4);
|
| 55 |
-
cv::Size textSize = cv::getTextSize(classString, cv::FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 1, 2, 0);
|
| 56 |
-
cv::Rect textBox(box.x, box.y - 40, textSize.width + 10, textSize.height + 20);
|
| 57 |
-
|
| 58 |
-
cv::rectangle(frame, textBox, color, cv::FILLED);
|
| 59 |
-
cv::putText(frame, classString, cv::Point(box.x + 5, box.y - 10), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 1, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), 2, 0);
|
| 60 |
-
}
|
| 61 |
-
// Inference ends here...
|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
// This is only for preview purposes
|
| 64 |
-
float scale = 0.8;
|
| 65 |
-
cv::resize(frame, frame, cv::Size(frame.cols*scale, frame.rows*scale));
|
| 66 |
-
cv::imshow("Inference", frame);
|
| 67 |
-
|
| 68 |
-
cv::waitKey(-1);
|
| 69 |
-
}
|
| 70 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-LibTorch-CPP-Inference/CMakeLists.txt
DELETED
|
@@ -1,47 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.18 FATAL_ERROR)
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
project(yolov8_libtorch_example)
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
|
| 6 |
-
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
|
| 7 |
-
set(CMAKE_CXX_EXTENSIONS OFF)
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
# -------------- OpenCV --------------
|
| 11 |
-
set(OpenCV_DIR "/path/to/opencv/lib/cmake/opencv4")
|
| 12 |
-
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
message(STATUS "OpenCV library status:")
|
| 15 |
-
message(STATUS " config: ${OpenCV_DIR}")
|
| 16 |
-
message(STATUS " version: ${OpenCV_VERSION}")
|
| 17 |
-
message(STATUS " libraries: ${OpenCV_LIBS}")
|
| 18 |
-
message(STATUS " include path: ${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}")
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
|
| 21 |
-
|
| 22 |
-
# -------------- libtorch --------------
|
| 23 |
-
list(APPEND CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH "/path/to/libtorch")
|
| 24 |
-
set(Torch_DIR "/path/to/libtorch/share/cmake/Torch")
|
| 25 |
-
|
| 26 |
-
find_package(Torch REQUIRED)
|
| 27 |
-
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} ${TORCH_CXX_FLAGS}")
|
| 28 |
-
message("${TORCH_LIBRARIES}")
|
| 29 |
-
message("${TORCH_INCLUDE_DIRS}")
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
# The following code block is suggested to be used on Windows.
|
| 32 |
-
# According to https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/25457,
|
| 33 |
-
# the DLLs need to be copied to avoid memory errors.
|
| 34 |
-
# if (MSVC)
|
| 35 |
-
# file(GLOB TORCH_DLLS "${TORCH_INSTALL_PREFIX}/lib/*.dll")
|
| 36 |
-
# add_custom_command(TARGET yolov8_libtorch_example
|
| 37 |
-
# POST_BUILD
|
| 38 |
-
# COMMAND ${CMAKE_COMMAND} -E copy_if_different
|
| 39 |
-
# ${TORCH_DLLS}
|
| 40 |
-
# $<TARGET_FILE_DIR:yolov8_libtorch_example>)
|
| 41 |
-
# endif (MSVC)
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
include_directories(${TORCH_INCLUDE_DIRS})
|
| 44 |
-
|
| 45 |
-
add_executable(yolov8_libtorch_inference "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/main.cc")
|
| 46 |
-
target_link_libraries(yolov8_libtorch_inference ${TORCH_LIBRARIES} ${OpenCV_LIBS})
|
| 47 |
-
set_property(TARGET yolov8_libtorch_inference PROPERTY CXX_STANDARD 17)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-LibTorch-CPP-Inference/README.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# YOLOv8 LibTorch Inference C++
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
This example demonstrates how to perform inference using YOLOv8 models in C++ with LibTorch API.
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
## Dependencies
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
| Dependency | Version |
|
| 8 |
-
| ------------ | -------- |
|
| 9 |
-
| OpenCV | >=4.0.0 |
|
| 10 |
-
| C++ Standard | >=17 |
|
| 11 |
-
| Cmake | >=3.18 |
|
| 12 |
-
| Libtorch | >=1.12.1 |
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
## Usage
|
| 15 |
-
|
| 16 |
-
```bash
|
| 17 |
-
git clone ultralytics
|
| 18 |
-
cd ultralytics
|
| 19 |
-
pip install .
|
| 20 |
-
cd examples/YOLOv8-LibTorch-CPP-Inference
|
| 21 |
-
|
| 22 |
-
mkdir build
|
| 23 |
-
cd build
|
| 24 |
-
cmake ..
|
| 25 |
-
make
|
| 26 |
-
./yolov8_libtorch_inference
|
| 27 |
-
```
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
## Exporting YOLOv8
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
To export YOLOv8 models:
|
| 32 |
-
|
| 33 |
-
```bash
|
| 34 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8s.pt imgsz=640 format=torchscript
|
| 35 |
-
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-LibTorch-CPP-Inference/main.cc
DELETED
|
@@ -1,260 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#include <iostream>
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
|
| 4 |
-
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
|
| 5 |
-
#include <opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp>
|
| 6 |
-
#include <torch/torch.h>
|
| 7 |
-
#include <torch/script.h>
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
using torch::indexing::Slice;
|
| 10 |
-
using torch::indexing::None;
|
| 11 |
-
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
float generate_scale(cv::Mat& image, const std::vector<int>& target_size) {
|
| 14 |
-
int origin_w = image.cols;
|
| 15 |
-
int origin_h = image.rows;
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
int target_h = target_size[0];
|
| 18 |
-
int target_w = target_size[1];
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
float ratio_h = static_cast<float>(target_h) / static_cast<float>(origin_h);
|
| 21 |
-
float ratio_w = static_cast<float>(target_w) / static_cast<float>(origin_w);
|
| 22 |
-
float resize_scale = std::min(ratio_h, ratio_w);
|
| 23 |
-
return resize_scale;
|
| 24 |
-
}
|
| 25 |
-
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
float letterbox(cv::Mat &input_image, cv::Mat &output_image, const std::vector<int> &target_size) {
|
| 28 |
-
if (input_image.cols == target_size[1] && input_image.rows == target_size[0]) {
|
| 29 |
-
if (input_image.data == output_image.data) {
|
| 30 |
-
return 1.;
|
| 31 |
-
} else {
|
| 32 |
-
output_image = input_image.clone();
|
| 33 |
-
return 1.;
|
| 34 |
-
}
|
| 35 |
-
}
|
| 36 |
-
|
| 37 |
-
float resize_scale = generate_scale(input_image, target_size);
|
| 38 |
-
int new_shape_w = std::round(input_image.cols * resize_scale);
|
| 39 |
-
int new_shape_h = std::round(input_image.rows * resize_scale);
|
| 40 |
-
float padw = (target_size[1] - new_shape_w) / 2.;
|
| 41 |
-
float padh = (target_size[0] - new_shape_h) / 2.;
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
int top = std::round(padh - 0.1);
|
| 44 |
-
int bottom = std::round(padh + 0.1);
|
| 45 |
-
int left = std::round(padw - 0.1);
|
| 46 |
-
int right = std::round(padw + 0.1);
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
cv::resize(input_image, output_image,
|
| 49 |
-
cv::Size(new_shape_w, new_shape_h),
|
| 50 |
-
0, 0, cv::INTER_AREA);
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
cv::copyMakeBorder(output_image, output_image, top, bottom, left, right,
|
| 53 |
-
cv::BORDER_CONSTANT, cv::Scalar(114.));
|
| 54 |
-
return resize_scale;
|
| 55 |
-
}
|
| 56 |
-
|
| 57 |
-
|
| 58 |
-
torch::Tensor xyxy2xywh(const torch::Tensor& x) {
|
| 59 |
-
auto y = torch::empty_like(x);
|
| 60 |
-
y.index_put_({"...", 0}, (x.index({"...", 0}) + x.index({"...", 2})).div(2));
|
| 61 |
-
y.index_put_({"...", 1}, (x.index({"...", 1}) + x.index({"...", 3})).div(2));
|
| 62 |
-
y.index_put_({"...", 2}, x.index({"...", 2}) - x.index({"...", 0}));
|
| 63 |
-
y.index_put_({"...", 3}, x.index({"...", 3}) - x.index({"...", 1}));
|
| 64 |
-
return y;
|
| 65 |
-
}
|
| 66 |
-
|
| 67 |
-
|
| 68 |
-
torch::Tensor xywh2xyxy(const torch::Tensor& x) {
|
| 69 |
-
auto y = torch::empty_like(x);
|
| 70 |
-
auto dw = x.index({"...", 2}).div(2);
|
| 71 |
-
auto dh = x.index({"...", 3}).div(2);
|
| 72 |
-
y.index_put_({"...", 0}, x.index({"...", 0}) - dw);
|
| 73 |
-
y.index_put_({"...", 1}, x.index({"...", 1}) - dh);
|
| 74 |
-
y.index_put_({"...", 2}, x.index({"...", 0}) + dw);
|
| 75 |
-
y.index_put_({"...", 3}, x.index({"...", 1}) + dh);
|
| 76 |
-
return y;
|
| 77 |
-
}
|
| 78 |
-
|
| 79 |
-
|
| 80 |
-
// Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/main/torchvision/csrc/ops/cpu/nms_kernel.cpp
|
| 81 |
-
torch::Tensor nms(const torch::Tensor& bboxes, const torch::Tensor& scores, float iou_threshold) {
|
| 82 |
-
if (bboxes.numel() == 0)
|
| 83 |
-
return torch::empty({0}, bboxes.options().dtype(torch::kLong));
|
| 84 |
-
|
| 85 |
-
auto x1_t = bboxes.select(1, 0).contiguous();
|
| 86 |
-
auto y1_t = bboxes.select(1, 1).contiguous();
|
| 87 |
-
auto x2_t = bboxes.select(1, 2).contiguous();
|
| 88 |
-
auto y2_t = bboxes.select(1, 3).contiguous();
|
| 89 |
-
|
| 90 |
-
torch::Tensor areas_t = (x2_t - x1_t) * (y2_t - y1_t);
|
| 91 |
-
|
| 92 |
-
auto order_t = std::get<1>(
|
| 93 |
-
scores.sort(/*stable=*/true, /*dim=*/0, /* descending=*/true));
|
| 94 |
-
|
| 95 |
-
auto ndets = bboxes.size(0);
|
| 96 |
-
torch::Tensor suppressed_t = torch::zeros({ndets}, bboxes.options().dtype(torch::kByte));
|
| 97 |
-
torch::Tensor keep_t = torch::zeros({ndets}, bboxes.options().dtype(torch::kLong));
|
| 98 |
-
|
| 99 |
-
auto suppressed = suppressed_t.data_ptr<uint8_t>();
|
| 100 |
-
auto keep = keep_t.data_ptr<int64_t>();
|
| 101 |
-
auto order = order_t.data_ptr<int64_t>();
|
| 102 |
-
auto x1 = x1_t.data_ptr<float>();
|
| 103 |
-
auto y1 = y1_t.data_ptr<float>();
|
| 104 |
-
auto x2 = x2_t.data_ptr<float>();
|
| 105 |
-
auto y2 = y2_t.data_ptr<float>();
|
| 106 |
-
auto areas = areas_t.data_ptr<float>();
|
| 107 |
-
|
| 108 |
-
int64_t num_to_keep = 0;
|
| 109 |
-
|
| 110 |
-
for (int64_t _i = 0; _i < ndets; _i++) {
|
| 111 |
-
auto i = order[_i];
|
| 112 |
-
if (suppressed[i] == 1)
|
| 113 |
-
continue;
|
| 114 |
-
keep[num_to_keep++] = i;
|
| 115 |
-
auto ix1 = x1[i];
|
| 116 |
-
auto iy1 = y1[i];
|
| 117 |
-
auto ix2 = x2[i];
|
| 118 |
-
auto iy2 = y2[i];
|
| 119 |
-
auto iarea = areas[i];
|
| 120 |
-
|
| 121 |
-
for (int64_t _j = _i + 1; _j < ndets; _j++) {
|
| 122 |
-
auto j = order[_j];
|
| 123 |
-
if (suppressed[j] == 1)
|
| 124 |
-
continue;
|
| 125 |
-
auto xx1 = std::max(ix1, x1[j]);
|
| 126 |
-
auto yy1 = std::max(iy1, y1[j]);
|
| 127 |
-
auto xx2 = std::min(ix2, x2[j]);
|
| 128 |
-
auto yy2 = std::min(iy2, y2[j]);
|
| 129 |
-
|
| 130 |
-
auto w = std::max(static_cast<float>(0), xx2 - xx1);
|
| 131 |
-
auto h = std::max(static_cast<float>(0), yy2 - yy1);
|
| 132 |
-
auto inter = w * h;
|
| 133 |
-
auto ovr = inter / (iarea + areas[j] - inter);
|
| 134 |
-
if (ovr > iou_threshold)
|
| 135 |
-
suppressed[j] = 1;
|
| 136 |
-
}
|
| 137 |
-
}
|
| 138 |
-
return keep_t.narrow(0, 0, num_to_keep);
|
| 139 |
-
}
|
| 140 |
-
|
| 141 |
-
|
| 142 |
-
torch::Tensor non_max_suppression(torch::Tensor& prediction, float conf_thres = 0.25, float iou_thres = 0.45, int max_det = 300) {
|
| 143 |
-
auto bs = prediction.size(0);
|
| 144 |
-
auto nc = prediction.size(1) - 4;
|
| 145 |
-
auto nm = prediction.size(1) - nc - 4;
|
| 146 |
-
auto mi = 4 + nc;
|
| 147 |
-
auto xc = prediction.index({Slice(), Slice(4, mi)}).amax(1) > conf_thres;
|
| 148 |
-
|
| 149 |
-
prediction = prediction.transpose(-1, -2);
|
| 150 |
-
prediction.index_put_({"...", Slice({None, 4})}, xywh2xyxy(prediction.index({"...", Slice(None, 4)})));
|
| 151 |
-
|
| 152 |
-
std::vector<torch::Tensor> output;
|
| 153 |
-
for (int i = 0; i < bs; i++) {
|
| 154 |
-
output.push_back(torch::zeros({0, 6 + nm}, prediction.device()));
|
| 155 |
-
}
|
| 156 |
-
|
| 157 |
-
for (int xi = 0; xi < prediction.size(0); xi++) {
|
| 158 |
-
auto x = prediction[xi];
|
| 159 |
-
x = x.index({xc[xi]});
|
| 160 |
-
auto x_split = x.split({4, nc, nm}, 1);
|
| 161 |
-
auto box = x_split[0], cls = x_split[1], mask = x_split[2];
|
| 162 |
-
auto [conf, j] = cls.max(1, true);
|
| 163 |
-
x = torch::cat({box, conf, j.toType(torch::kFloat), mask}, 1);
|
| 164 |
-
x = x.index({conf.view(-1) > conf_thres});
|
| 165 |
-
int n = x.size(0);
|
| 166 |
-
if (!n) { continue; }
|
| 167 |
-
|
| 168 |
-
// NMS
|
| 169 |
-
auto c = x.index({Slice(), Slice{5, 6}}) * 7680;
|
| 170 |
-
auto boxes = x.index({Slice(), Slice(None, 4)}) + c;
|
| 171 |
-
auto scores = x.index({Slice(), 4});
|
| 172 |
-
auto i = nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres);
|
| 173 |
-
i = i.index({Slice(None, max_det)});
|
| 174 |
-
output[xi] = x.index({i});
|
| 175 |
-
}
|
| 176 |
-
|
| 177 |
-
return torch::stack(output);
|
| 178 |
-
}
|
| 179 |
-
|
| 180 |
-
|
| 181 |
-
torch::Tensor clip_boxes(torch::Tensor& boxes, const std::vector<int>& shape) {
|
| 182 |
-
boxes.index_put_({"...", 0}, boxes.index({"...", 0}).clamp(0, shape[1]));
|
| 183 |
-
boxes.index_put_({"...", 1}, boxes.index({"...", 1}).clamp(0, shape[0]));
|
| 184 |
-
boxes.index_put_({"...", 2}, boxes.index({"...", 2}).clamp(0, shape[1]));
|
| 185 |
-
boxes.index_put_({"...", 3}, boxes.index({"...", 3}).clamp(0, shape[0]));
|
| 186 |
-
return boxes;
|
| 187 |
-
}
|
| 188 |
-
|
| 189 |
-
|
| 190 |
-
torch::Tensor scale_boxes(const std::vector<int>& img1_shape, torch::Tensor& boxes, const std::vector<int>& img0_shape) {
|
| 191 |
-
auto gain = (std::min)((float)img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], (float)img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]);
|
| 192 |
-
auto pad0 = std::round((float)(img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2. - 0.1);
|
| 193 |
-
auto pad1 = std::round((float)(img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2. - 0.1);
|
| 194 |
-
|
| 195 |
-
boxes.index_put_({"...", 0}, boxes.index({"...", 0}) - pad0);
|
| 196 |
-
boxes.index_put_({"...", 2}, boxes.index({"...", 2}) - pad0);
|
| 197 |
-
boxes.index_put_({"...", 1}, boxes.index({"...", 1}) - pad1);
|
| 198 |
-
boxes.index_put_({"...", 3}, boxes.index({"...", 3}) - pad1);
|
| 199 |
-
boxes.index_put_({"...", Slice(None, 4)}, boxes.index({"...", Slice(None, 4)}).div(gain));
|
| 200 |
-
return boxes;
|
| 201 |
-
}
|
| 202 |
-
|
| 203 |
-
|
| 204 |
-
int main() {
|
| 205 |
-
// Device
|
| 206 |
-
torch::Device device(torch::cuda::is_available() ? torch::kCUDA :torch::kCPU);
|
| 207 |
-
|
| 208 |
-
// Note that in this example the classes are hard-coded
|
| 209 |
-
std::vector<std::string> classes {"person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle", "airplane", "bus", "train", "truck", "boat", "traffic light", "fire hydrant",
|
| 210 |
-
"stop sign", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse", "sheep", "cow", "elephant", "bear", "zebra",
|
| 211 |
-
"giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee", "skis", "snowboard", "sports ball", "kite",
|
| 212 |
-
"baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard", "surfboard", "tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife",
|
| 213 |
-
"spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple", "sandwich", "orange", "broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair",
|
| 214 |
-
"couch", "potted plant", "bed", "dining table", "toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard", "cell phone",
|
| 215 |
-
"microwave", "oven", "toaster", "sink", "refrigerator", "book", "clock", "vase", "scissors", "teddy bear", "hair drier", "toothbrush"};
|
| 216 |
-
|
| 217 |
-
try {
|
| 218 |
-
// Load the model (e.g. yolov8s.torchscript)
|
| 219 |
-
std::string model_path = "/path/to/yolov8s.torchscript";
|
| 220 |
-
torch::jit::script::Module yolo_model;
|
| 221 |
-
yolo_model = torch::jit::load(model_path);
|
| 222 |
-
yolo_model.eval();
|
| 223 |
-
yolo_model.to(device, torch::kFloat32);
|
| 224 |
-
|
| 225 |
-
// Load image and preprocess
|
| 226 |
-
cv::Mat image = cv::imread("/path/to/bus.jpg");
|
| 227 |
-
cv::Mat input_image;
|
| 228 |
-
letterbox(image, input_image, {640, 640});
|
| 229 |
-
cv::cvtColor(input_image, input_image, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
|
| 230 |
-
|
| 231 |
-
torch::Tensor image_tensor = torch::from_blob(input_image.data, {input_image.rows, input_image.cols, 3}, torch::kByte).to(device);
|
| 232 |
-
image_tensor = image_tensor.toType(torch::kFloat32).div(255);
|
| 233 |
-
image_tensor = image_tensor.permute({2, 0, 1});
|
| 234 |
-
image_tensor = image_tensor.unsqueeze(0);
|
| 235 |
-
std::vector<torch::jit::IValue> inputs {image_tensor};
|
| 236 |
-
|
| 237 |
-
// Inference
|
| 238 |
-
torch::Tensor output = yolo_model.forward(inputs).toTensor().cpu();
|
| 239 |
-
|
| 240 |
-
// NMS
|
| 241 |
-
auto keep = non_max_suppression(output)[0];
|
| 242 |
-
auto boxes = keep.index({Slice(), Slice(None, 4)});
|
| 243 |
-
keep.index_put_({Slice(), Slice(None, 4)}, scale_boxes({input_image.rows, input_image.cols}, boxes, {image.rows, image.cols}));
|
| 244 |
-
|
| 245 |
-
// Show the results
|
| 246 |
-
for (int i = 0; i < keep.size(0); i++) {
|
| 247 |
-
int x1 = keep[i][0].item().toFloat();
|
| 248 |
-
int y1 = keep[i][1].item().toFloat();
|
| 249 |
-
int x2 = keep[i][2].item().toFloat();
|
| 250 |
-
int y2 = keep[i][3].item().toFloat();
|
| 251 |
-
float conf = keep[i][4].item().toFloat();
|
| 252 |
-
int cls = keep[i][5].item().toInt();
|
| 253 |
-
std::cout << "Rect: [" << x1 << "," << y1 << "," << x2 << "," << y2 << "] Conf: " << conf << " Class: " << classes[cls] << std::endl;
|
| 254 |
-
}
|
| 255 |
-
} catch (const c10::Error& e) {
|
| 256 |
-
std::cout << e.msg() << std::endl;
|
| 257 |
-
}
|
| 258 |
-
|
| 259 |
-
return 0;
|
| 260 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/CMakeLists.txt
DELETED
|
@@ -1,99 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5)
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
set(PROJECT_NAME Yolov8OnnxRuntimeCPPInference)
|
| 4 |
-
project(${PROJECT_NAME} VERSION 0.0.1 LANGUAGES CXX)
|
| 5 |
-
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
# -------------- Support C++17 for using filesystem ------------------#
|
| 8 |
-
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
|
| 9 |
-
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
|
| 10 |
-
set(CMAKE_CXX_EXTENSIONS ON)
|
| 11 |
-
set(CMAKE_INCLUDE_CURRENT_DIR ON)
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
# -------------- OpenCV ------------------#
|
| 15 |
-
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
|
| 16 |
-
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
|
| 17 |
-
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
# -------------- Compile CUDA for FP16 inference if needed ------------------#
|
| 20 |
-
option(USE_CUDA "Enable CUDA support" ON)
|
| 21 |
-
if (NOT APPLE AND USE_CUDA)
|
| 22 |
-
find_package(CUDA REQUIRED)
|
| 23 |
-
include_directories(${CUDA_INCLUDE_DIRS})
|
| 24 |
-
add_definitions(-DUSE_CUDA)
|
| 25 |
-
else ()
|
| 26 |
-
set(USE_CUDA OFF)
|
| 27 |
-
endif ()
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
# -------------- ONNXRUNTIME ------------------#
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
# Set ONNXRUNTIME_VERSION
|
| 32 |
-
set(ONNXRUNTIME_VERSION 1.15.1)
|
| 33 |
-
|
| 34 |
-
if (WIN32)
|
| 35 |
-
if (USE_CUDA)
|
| 36 |
-
set(ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/onnxruntime-win-x64-gpu-${ONNXRUNTIME_VERSION}")
|
| 37 |
-
else ()
|
| 38 |
-
set(ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/onnxruntime-win-x64-${ONNXRUNTIME_VERSION}")
|
| 39 |
-
endif ()
|
| 40 |
-
elseif (LINUX)
|
| 41 |
-
if (USE_CUDA)
|
| 42 |
-
set(ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/onnxruntime-linux-x64-gpu-${ONNXRUNTIME_VERSION}")
|
| 43 |
-
else ()
|
| 44 |
-
set(ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/onnxruntime-linux-x64-${ONNXRUNTIME_VERSION}")
|
| 45 |
-
endif ()
|
| 46 |
-
elseif (APPLE)
|
| 47 |
-
set(ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/onnxruntime-osx-arm64-${ONNXRUNTIME_VERSION}")
|
| 48 |
-
# Apple X64 binary
|
| 49 |
-
# set(ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/onnxruntime-osx-x64-${ONNXRUNTIME_VERSION}")
|
| 50 |
-
# Apple Universal binary
|
| 51 |
-
# set(ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/onnxruntime-osx-universal2-${ONNXRUNTIME_VERSION}")
|
| 52 |
-
else ()
|
| 53 |
-
message(SEND_ERROR "Variable ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT is not set properly. Please check if your cmake project \
|
| 54 |
-
is not compiled with `-D WIN32=TRUE`, `-D LINUX=TRUE`, or `-D APPLE=TRUE`!")
|
| 55 |
-
endif ()
|
| 56 |
-
|
| 57 |
-
include_directories(${PROJECT_NAME} ${ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT}/include)
|
| 58 |
-
|
| 59 |
-
set(PROJECT_SOURCES
|
| 60 |
-
main.cpp
|
| 61 |
-
inference.h
|
| 62 |
-
inference.cpp
|
| 63 |
-
)
|
| 64 |
-
|
| 65 |
-
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} ${PROJECT_SOURCES})
|
| 66 |
-
|
| 67 |
-
if (WIN32)
|
| 68 |
-
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT}/lib/onnxruntime.lib)
|
| 69 |
-
if (USE_CUDA)
|
| 70 |
-
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} ${CUDA_LIBRARIES})
|
| 71 |
-
endif ()
|
| 72 |
-
elseif (LINUX)
|
| 73 |
-
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT}/lib/libonnxruntime.so)
|
| 74 |
-
if (USE_CUDA)
|
| 75 |
-
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} ${CUDA_LIBRARIES})
|
| 76 |
-
endif ()
|
| 77 |
-
elseif (APPLE)
|
| 78 |
-
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT}/lib/libonnxruntime.dylib)
|
| 79 |
-
endif ()
|
| 80 |
-
|
| 81 |
-
# For windows system, copy onnxruntime.dll to the same folder of the executable file
|
| 82 |
-
if (WIN32)
|
| 83 |
-
add_custom_command(TARGET ${PROJECT_NAME} POST_BUILD
|
| 84 |
-
COMMAND ${CMAKE_COMMAND} -E copy_if_different
|
| 85 |
-
"${ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT}/lib/onnxruntime.dll"
|
| 86 |
-
$<TARGET_FILE_DIR:${PROJECT_NAME}>)
|
| 87 |
-
endif ()
|
| 88 |
-
|
| 89 |
-
# Download https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/main/ultralytics/cfg/datasets/coco.yaml
|
| 90 |
-
# and put it in the same folder of the executable file
|
| 91 |
-
configure_file(coco.yaml ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/coco.yaml COPYONLY)
|
| 92 |
-
|
| 93 |
-
# Copy yolov8n.onnx file to the same folder of the executable file
|
| 94 |
-
configure_file(yolov8n.onnx ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/yolov8n.onnx COPYONLY)
|
| 95 |
-
|
| 96 |
-
# Create folder name images in the same folder of the executable file
|
| 97 |
-
add_custom_command(TARGET ${PROJECT_NAME} POST_BUILD
|
| 98 |
-
COMMAND ${CMAKE_COMMAND} -E make_directory ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/images
|
| 99 |
-
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,120 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# YOLOv8 OnnxRuntime C++
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
<img alt="C++" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/C++-17-blue.svg?style=flat&logo=c%2B%2B"> <img alt="Onnx-runtime" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/OnnxRuntime-717272.svg?logo=Onnx&logoColor=white">
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
This example demonstrates how to perform inference using YOLOv8 in C++ with ONNX Runtime and OpenCV's API.
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
## Benefits ✨
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
- Friendly for deployment in the industrial sector.
|
| 10 |
-
- Faster than OpenCV's DNN inference on both CPU and GPU.
|
| 11 |
-
- Supports FP32 and FP16 CUDA acceleration.
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
## Note ☕
|
| 14 |
-
|
| 15 |
-
1. Benefit for Ultralytics' latest release, a `Transpose` op is added to the YOLOv8 model, while make v8 and v5 has the same output shape. Therefore, you can run inference with YOLOv5/v7/v8 via this project.
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
## Exporting YOLOv8 Models 📦
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
To export YOLOv8 models, use the following Python script:
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
```python
|
| 22 |
-
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
| 23 |
-
|
| 24 |
-
# Load a YOLOv8 model
|
| 25 |
-
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
# Export the model
|
| 28 |
-
model.export(format="onnx", opset=12, simplify=True, dynamic=False, imgsz=640)
|
| 29 |
-
```
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
Alternatively, you can use the following command for exporting the model in the terminal
|
| 32 |
-
|
| 33 |
-
```bash
|
| 34 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt opset=12 simplify=True dynamic=False format=onnx imgsz=640,640
|
| 35 |
-
```
|
| 36 |
-
|
| 37 |
-
## Exporting YOLOv8 FP16 Models 📦
|
| 38 |
-
|
| 39 |
-
```python
|
| 40 |
-
import onnx
|
| 41 |
-
from onnxconverter_common import float16
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
model = onnx.load(R"YOUR_ONNX_PATH")
|
| 44 |
-
model_fp16 = float16.convert_float_to_float16(model)
|
| 45 |
-
onnx.save(model_fp16, R"YOUR_FP16_ONNX_PATH")
|
| 46 |
-
```
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
## Download COCO.yaml file 📂
|
| 49 |
-
|
| 50 |
-
In order to run example, you also need to download coco.yaml. You can download the file manually from [here](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/main/ultralytics/cfg/datasets/coco.yaml)
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
## Dependencies ⚙️
|
| 53 |
-
|
| 54 |
-
| Dependency | Version |
|
| 55 |
-
| -------------------------------- | ------------- |
|
| 56 |
-
| Onnxruntime(linux,windows,macos) | >=1.14.1 |
|
| 57 |
-
| OpenCV | >=4.0.0 |
|
| 58 |
-
| C++ Standard | >=17 |
|
| 59 |
-
| Cmake | >=3.5 |
|
| 60 |
-
| Cuda (Optional) | >=11.4 \<12.0 |
|
| 61 |
-
| cuDNN (Cuda required) | =8 |
|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
Note: The dependency on C++17 is due to the usage of the C++17 filesystem feature.
|
| 64 |
-
|
| 65 |
-
Note (2): Due to ONNX Runtime, we need to use CUDA 11 and cuDNN 8. Keep in mind that this requirement might change in the future.
|
| 66 |
-
|
| 67 |
-
## Build 🛠️
|
| 68 |
-
|
| 69 |
-
1. Clone the repository to your local machine.
|
| 70 |
-
|
| 71 |
-
2. Navigate to the root directory of the repository.
|
| 72 |
-
|
| 73 |
-
3. Create a build directory and navigate to it:
|
| 74 |
-
|
| 75 |
-
```console
|
| 76 |
-
mkdir build && cd build
|
| 77 |
-
```
|
| 78 |
-
|
| 79 |
-
4. Run CMake to generate the build files:
|
| 80 |
-
|
| 81 |
-
```console
|
| 82 |
-
cmake ..
|
| 83 |
-
```
|
| 84 |
-
|
| 85 |
-
**Notice**:
|
| 86 |
-
|
| 87 |
-
If you encounter an error indicating that the `ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT` variable is not set correctly, you can resolve this by building the project using the appropriate command tailored to your system.
|
| 88 |
-
|
| 89 |
-
```console
|
| 90 |
-
# compiled in a win32 system
|
| 91 |
-
cmake -D WIN32=TRUE ..
|
| 92 |
-
# compiled in a linux system
|
| 93 |
-
cmake -D LINUX=TRUE ..
|
| 94 |
-
# compiled in an apple system
|
| 95 |
-
cmake -D APPLE=TRUE ..
|
| 96 |
-
```
|
| 97 |
-
|
| 98 |
-
5. Build the project:
|
| 99 |
-
|
| 100 |
-
```console
|
| 101 |
-
make
|
| 102 |
-
```
|
| 103 |
-
|
| 104 |
-
6. The built executable should now be located in the `build` directory.
|
| 105 |
-
|
| 106 |
-
## Usage 🚀
|
| 107 |
-
|
| 108 |
-
```c++
|
| 109 |
-
//change your param as you like
|
| 110 |
-
//Pay attention to your device and the onnx model type(fp32 or fp16)
|
| 111 |
-
DL_INIT_PARAM params;
|
| 112 |
-
params.rectConfidenceThreshold = 0.1;
|
| 113 |
-
params.iouThreshold = 0.5;
|
| 114 |
-
params.modelPath = "yolov8n.onnx";
|
| 115 |
-
params.imgSize = { 640, 640 };
|
| 116 |
-
params.cudaEnable = true;
|
| 117 |
-
params.modelType = YOLO_DETECT_V8;
|
| 118 |
-
yoloDetector->CreateSession(params);
|
| 119 |
-
Detector(yoloDetector);
|
| 120 |
-
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp
DELETED
|
@@ -1,375 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#include "inference.h"
|
| 2 |
-
#include <regex>
|
| 3 |
-
|
| 4 |
-
#define benchmark
|
| 5 |
-
#define min(a,b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
|
| 6 |
-
YOLO_V8::YOLO_V8() {
|
| 7 |
-
|
| 8 |
-
}
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
YOLO_V8::~YOLO_V8() {
|
| 12 |
-
delete session;
|
| 13 |
-
}
|
| 14 |
-
|
| 15 |
-
#ifdef USE_CUDA
|
| 16 |
-
namespace Ort
|
| 17 |
-
{
|
| 18 |
-
template<>
|
| 19 |
-
struct TypeToTensorType<half> { static constexpr ONNXTensorElementDataType type = ONNX_TENSOR_ELEMENT_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT16; };
|
| 20 |
-
}
|
| 21 |
-
#endif
|
| 22 |
-
|
| 23 |
-
|
| 24 |
-
template<typename T>
|
| 25 |
-
char* BlobFromImage(cv::Mat& iImg, T& iBlob) {
|
| 26 |
-
int channels = iImg.channels();
|
| 27 |
-
int imgHeight = iImg.rows;
|
| 28 |
-
int imgWidth = iImg.cols;
|
| 29 |
-
|
| 30 |
-
for (int c = 0; c < channels; c++)
|
| 31 |
-
{
|
| 32 |
-
for (int h = 0; h < imgHeight; h++)
|
| 33 |
-
{
|
| 34 |
-
for (int w = 0; w < imgWidth; w++)
|
| 35 |
-
{
|
| 36 |
-
iBlob[c * imgWidth * imgHeight + h * imgWidth + w] = typename std::remove_pointer<T>::type(
|
| 37 |
-
(iImg.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[c]) / 255.0f);
|
| 38 |
-
}
|
| 39 |
-
}
|
| 40 |
-
}
|
| 41 |
-
return RET_OK;
|
| 42 |
-
}
|
| 43 |
-
|
| 44 |
-
|
| 45 |
-
char* YOLO_V8::PreProcess(cv::Mat& iImg, std::vector<int> iImgSize, cv::Mat& oImg)
|
| 46 |
-
{
|
| 47 |
-
if (iImg.channels() == 3)
|
| 48 |
-
{
|
| 49 |
-
oImg = iImg.clone();
|
| 50 |
-
cv::cvtColor(oImg, oImg, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
|
| 51 |
-
}
|
| 52 |
-
else
|
| 53 |
-
{
|
| 54 |
-
cv::cvtColor(iImg, oImg, cv::COLOR_GRAY2RGB);
|
| 55 |
-
}
|
| 56 |
-
|
| 57 |
-
switch (modelType)
|
| 58 |
-
{
|
| 59 |
-
case YOLO_DETECT_V8:
|
| 60 |
-
case YOLO_POSE:
|
| 61 |
-
case YOLO_DETECT_V8_HALF:
|
| 62 |
-
case YOLO_POSE_V8_HALF://LetterBox
|
| 63 |
-
{
|
| 64 |
-
if (iImg.cols >= iImg.rows)
|
| 65 |
-
{
|
| 66 |
-
resizeScales = iImg.cols / (float)iImgSize.at(0);
|
| 67 |
-
cv::resize(oImg, oImg, cv::Size(iImgSize.at(0), int(iImg.rows / resizeScales)));
|
| 68 |
-
}
|
| 69 |
-
else
|
| 70 |
-
{
|
| 71 |
-
resizeScales = iImg.rows / (float)iImgSize.at(0);
|
| 72 |
-
cv::resize(oImg, oImg, cv::Size(int(iImg.cols / resizeScales), iImgSize.at(1)));
|
| 73 |
-
}
|
| 74 |
-
cv::Mat tempImg = cv::Mat::zeros(iImgSize.at(0), iImgSize.at(1), CV_8UC3);
|
| 75 |
-
oImg.copyTo(tempImg(cv::Rect(0, 0, oImg.cols, oImg.rows)));
|
| 76 |
-
oImg = tempImg;
|
| 77 |
-
break;
|
| 78 |
-
}
|
| 79 |
-
case YOLO_CLS://CenterCrop
|
| 80 |
-
{
|
| 81 |
-
int h = iImg.rows;
|
| 82 |
-
int w = iImg.cols;
|
| 83 |
-
int m = min(h, w);
|
| 84 |
-
int top = (h - m) / 2;
|
| 85 |
-
int left = (w - m) / 2;
|
| 86 |
-
cv::resize(oImg(cv::Rect(left, top, m, m)), oImg, cv::Size(iImgSize.at(0), iImgSize.at(1)));
|
| 87 |
-
break;
|
| 88 |
-
}
|
| 89 |
-
}
|
| 90 |
-
return RET_OK;
|
| 91 |
-
}
|
| 92 |
-
|
| 93 |
-
|
| 94 |
-
char* YOLO_V8::CreateSession(DL_INIT_PARAM& iParams) {
|
| 95 |
-
char* Ret = RET_OK;
|
| 96 |
-
std::regex pattern("[\u4e00-\u9fa5]");
|
| 97 |
-
bool result = std::regex_search(iParams.modelPath, pattern);
|
| 98 |
-
if (result)
|
| 99 |
-
{
|
| 100 |
-
Ret = "[YOLO_V8]:Your model path is error.Change your model path without chinese characters.";
|
| 101 |
-
std::cout << Ret << std::endl;
|
| 102 |
-
return Ret;
|
| 103 |
-
}
|
| 104 |
-
try
|
| 105 |
-
{
|
| 106 |
-
rectConfidenceThreshold = iParams.rectConfidenceThreshold;
|
| 107 |
-
iouThreshold = iParams.iouThreshold;
|
| 108 |
-
imgSize = iParams.imgSize;
|
| 109 |
-
modelType = iParams.modelType;
|
| 110 |
-
env = Ort::Env(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_WARNING, "Yolo");
|
| 111 |
-
Ort::SessionOptions sessionOption;
|
| 112 |
-
if (iParams.cudaEnable)
|
| 113 |
-
{
|
| 114 |
-
cudaEnable = iParams.cudaEnable;
|
| 115 |
-
OrtCUDAProviderOptions cudaOption;
|
| 116 |
-
cudaOption.device_id = 0;
|
| 117 |
-
sessionOption.AppendExecutionProvider_CUDA(cudaOption);
|
| 118 |
-
}
|
| 119 |
-
sessionOption.SetGraphOptimizationLevel(GraphOptimizationLevel::ORT_ENABLE_ALL);
|
| 120 |
-
sessionOption.SetIntraOpNumThreads(iParams.intraOpNumThreads);
|
| 121 |
-
sessionOption.SetLogSeverityLevel(iParams.logSeverityLevel);
|
| 122 |
-
|
| 123 |
-
#ifdef _WIN32
|
| 124 |
-
int ModelPathSize = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, iParams.modelPath.c_str(), static_cast<int>(iParams.modelPath.length()), nullptr, 0);
|
| 125 |
-
wchar_t* wide_cstr = new wchar_t[ModelPathSize + 1];
|
| 126 |
-
MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, iParams.modelPath.c_str(), static_cast<int>(iParams.modelPath.length()), wide_cstr, ModelPathSize);
|
| 127 |
-
wide_cstr[ModelPathSize] = L'\0';
|
| 128 |
-
const wchar_t* modelPath = wide_cstr;
|
| 129 |
-
#else
|
| 130 |
-
const char* modelPath = iParams.modelPath.c_str();
|
| 131 |
-
#endif // _WIN32
|
| 132 |
-
|
| 133 |
-
session = new Ort::Session(env, modelPath, sessionOption);
|
| 134 |
-
Ort::AllocatorWithDefaultOptions allocator;
|
| 135 |
-
size_t inputNodesNum = session->GetInputCount();
|
| 136 |
-
for (size_t i = 0; i < inputNodesNum; i++)
|
| 137 |
-
{
|
| 138 |
-
Ort::AllocatedStringPtr input_node_name = session->GetInputNameAllocated(i, allocator);
|
| 139 |
-
char* temp_buf = new char[50];
|
| 140 |
-
strcpy(temp_buf, input_node_name.get());
|
| 141 |
-
inputNodeNames.push_back(temp_buf);
|
| 142 |
-
}
|
| 143 |
-
size_t OutputNodesNum = session->GetOutputCount();
|
| 144 |
-
for (size_t i = 0; i < OutputNodesNum; i++)
|
| 145 |
-
{
|
| 146 |
-
Ort::AllocatedStringPtr output_node_name = session->GetOutputNameAllocated(i, allocator);
|
| 147 |
-
char* temp_buf = new char[10];
|
| 148 |
-
strcpy(temp_buf, output_node_name.get());
|
| 149 |
-
outputNodeNames.push_back(temp_buf);
|
| 150 |
-
}
|
| 151 |
-
options = Ort::RunOptions{ nullptr };
|
| 152 |
-
WarmUpSession();
|
| 153 |
-
return RET_OK;
|
| 154 |
-
}
|
| 155 |
-
catch (const std::exception& e)
|
| 156 |
-
{
|
| 157 |
-
const char* str1 = "[YOLO_V8]:";
|
| 158 |
-
const char* str2 = e.what();
|
| 159 |
-
std::string result = std::string(str1) + std::string(str2);
|
| 160 |
-
char* merged = new char[result.length() + 1];
|
| 161 |
-
std::strcpy(merged, result.c_str());
|
| 162 |
-
std::cout << merged << std::endl;
|
| 163 |
-
delete[] merged;
|
| 164 |
-
return "[YOLO_V8]:Create session failed.";
|
| 165 |
-
}
|
| 166 |
-
|
| 167 |
-
}
|
| 168 |
-
|
| 169 |
-
|
| 170 |
-
char* YOLO_V8::RunSession(cv::Mat& iImg, std::vector<DL_RESULT>& oResult) {
|
| 171 |
-
#ifdef benchmark
|
| 172 |
-
clock_t starttime_1 = clock();
|
| 173 |
-
#endif // benchmark
|
| 174 |
-
|
| 175 |
-
char* Ret = RET_OK;
|
| 176 |
-
cv::Mat processedImg;
|
| 177 |
-
PreProcess(iImg, imgSize, processedImg);
|
| 178 |
-
if (modelType < 4)
|
| 179 |
-
{
|
| 180 |
-
float* blob = new float[processedImg.total() * 3];
|
| 181 |
-
BlobFromImage(processedImg, blob);
|
| 182 |
-
std::vector<int64_t> inputNodeDims = { 1, 3, imgSize.at(0), imgSize.at(1) };
|
| 183 |
-
TensorProcess(starttime_1, iImg, blob, inputNodeDims, oResult);
|
| 184 |
-
}
|
| 185 |
-
else
|
| 186 |
-
{
|
| 187 |
-
#ifdef USE_CUDA
|
| 188 |
-
half* blob = new half[processedImg.total() * 3];
|
| 189 |
-
BlobFromImage(processedImg, blob);
|
| 190 |
-
std::vector<int64_t> inputNodeDims = { 1,3,imgSize.at(0),imgSize.at(1) };
|
| 191 |
-
TensorProcess(starttime_1, iImg, blob, inputNodeDims, oResult);
|
| 192 |
-
#endif
|
| 193 |
-
}
|
| 194 |
-
|
| 195 |
-
return Ret;
|
| 196 |
-
}
|
| 197 |
-
|
| 198 |
-
|
| 199 |
-
template<typename N>
|
| 200 |
-
char* YOLO_V8::TensorProcess(clock_t& starttime_1, cv::Mat& iImg, N& blob, std::vector<int64_t>& inputNodeDims,
|
| 201 |
-
std::vector<DL_RESULT>& oResult) {
|
| 202 |
-
Ort::Value inputTensor = Ort::Value::CreateTensor<typename std::remove_pointer<N>::type>(
|
| 203 |
-
Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtDeviceAllocator, OrtMemTypeCPU), blob, 3 * imgSize.at(0) * imgSize.at(1),
|
| 204 |
-
inputNodeDims.data(), inputNodeDims.size());
|
| 205 |
-
#ifdef benchmark
|
| 206 |
-
clock_t starttime_2 = clock();
|
| 207 |
-
#endif // benchmark
|
| 208 |
-
auto outputTensor = session->Run(options, inputNodeNames.data(), &inputTensor, 1, outputNodeNames.data(),
|
| 209 |
-
outputNodeNames.size());
|
| 210 |
-
#ifdef benchmark
|
| 211 |
-
clock_t starttime_3 = clock();
|
| 212 |
-
#endif // benchmark
|
| 213 |
-
|
| 214 |
-
Ort::TypeInfo typeInfo = outputTensor.front().GetTypeInfo();
|
| 215 |
-
auto tensor_info = typeInfo.GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo();
|
| 216 |
-
std::vector<int64_t> outputNodeDims = tensor_info.GetShape();
|
| 217 |
-
auto output = outputTensor.front().GetTensorMutableData<typename std::remove_pointer<N>::type>();
|
| 218 |
-
delete[] blob;
|
| 219 |
-
switch (modelType)
|
| 220 |
-
{
|
| 221 |
-
case YOLO_DETECT_V8:
|
| 222 |
-
case YOLO_DETECT_V8_HALF:
|
| 223 |
-
{
|
| 224 |
-
int signalResultNum = outputNodeDims[1];//84
|
| 225 |
-
int strideNum = outputNodeDims[2];//8400
|
| 226 |
-
std::vector<int> class_ids;
|
| 227 |
-
std::vector<float> confidences;
|
| 228 |
-
std::vector<cv::Rect> boxes;
|
| 229 |
-
cv::Mat rawData;
|
| 230 |
-
if (modelType == YOLO_DETECT_V8)
|
| 231 |
-
{
|
| 232 |
-
// FP32
|
| 233 |
-
rawData = cv::Mat(signalResultNum, strideNum, CV_32F, output);
|
| 234 |
-
}
|
| 235 |
-
else
|
| 236 |
-
{
|
| 237 |
-
// FP16
|
| 238 |
-
rawData = cv::Mat(signalResultNum, strideNum, CV_16F, output);
|
| 239 |
-
rawData.convertTo(rawData, CV_32F);
|
| 240 |
-
}
|
| 241 |
-
// Note:
|
| 242 |
-
// ultralytics add transpose operator to the output of yolov8 model.which make yolov8/v5/v7 has same shape
|
| 243 |
-
// https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.3.0/yolov8n.pt
|
| 244 |
-
rawData = rawData.t();
|
| 245 |
-
|
| 246 |
-
float* data = (float*)rawData.data;
|
| 247 |
-
|
| 248 |
-
for (int i = 0; i < strideNum; ++i)
|
| 249 |
-
{
|
| 250 |
-
float* classesScores = data + 4;
|
| 251 |
-
cv::Mat scores(1, this->classes.size(), CV_32FC1, classesScores);
|
| 252 |
-
cv::Point class_id;
|
| 253 |
-
double maxClassScore;
|
| 254 |
-
cv::minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &maxClassScore, 0, &class_id);
|
| 255 |
-
if (maxClassScore > rectConfidenceThreshold)
|
| 256 |
-
{
|
| 257 |
-
confidences.push_back(maxClassScore);
|
| 258 |
-
class_ids.push_back(class_id.x);
|
| 259 |
-
float x = data[0];
|
| 260 |
-
float y = data[1];
|
| 261 |
-
float w = data[2];
|
| 262 |
-
float h = data[3];
|
| 263 |
-
|
| 264 |
-
int left = int((x - 0.5 * w) * resizeScales);
|
| 265 |
-
int top = int((y - 0.5 * h) * resizeScales);
|
| 266 |
-
|
| 267 |
-
int width = int(w * resizeScales);
|
| 268 |
-
int height = int(h * resizeScales);
|
| 269 |
-
|
| 270 |
-
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(left, top, width, height));
|
| 271 |
-
}
|
| 272 |
-
data += signalResultNum;
|
| 273 |
-
}
|
| 274 |
-
std::vector<int> nmsResult;
|
| 275 |
-
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, rectConfidenceThreshold, iouThreshold, nmsResult);
|
| 276 |
-
for (int i = 0; i < nmsResult.size(); ++i)
|
| 277 |
-
{
|
| 278 |
-
int idx = nmsResult[i];
|
| 279 |
-
DL_RESULT result;
|
| 280 |
-
result.classId = class_ids[idx];
|
| 281 |
-
result.confidence = confidences[idx];
|
| 282 |
-
result.box = boxes[idx];
|
| 283 |
-
oResult.push_back(result);
|
| 284 |
-
}
|
| 285 |
-
|
| 286 |
-
#ifdef benchmark
|
| 287 |
-
clock_t starttime_4 = clock();
|
| 288 |
-
double pre_process_time = (double)(starttime_2 - starttime_1) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000;
|
| 289 |
-
double process_time = (double)(starttime_3 - starttime_2) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000;
|
| 290 |
-
double post_process_time = (double)(starttime_4 - starttime_3) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000;
|
| 291 |
-
if (cudaEnable)
|
| 292 |
-
{
|
| 293 |
-
std::cout << "[YOLO_V8(CUDA)]: " << pre_process_time << "ms pre-process, " << process_time << "ms inference, " << post_process_time << "ms post-process." << std::endl;
|
| 294 |
-
}
|
| 295 |
-
else
|
| 296 |
-
{
|
| 297 |
-
std::cout << "[YOLO_V8(CPU)]: " << pre_process_time << "ms pre-process, " << process_time << "ms inference, " << post_process_time << "ms post-process." << std::endl;
|
| 298 |
-
}
|
| 299 |
-
#endif // benchmark
|
| 300 |
-
|
| 301 |
-
break;
|
| 302 |
-
}
|
| 303 |
-
case YOLO_CLS:
|
| 304 |
-
case YOLO_CLS_HALF:
|
| 305 |
-
{
|
| 306 |
-
cv::Mat rawData;
|
| 307 |
-
if (modelType == YOLO_CLS) {
|
| 308 |
-
// FP32
|
| 309 |
-
rawData = cv::Mat(1, this->classes.size(), CV_32F, output);
|
| 310 |
-
} else {
|
| 311 |
-
// FP16
|
| 312 |
-
rawData = cv::Mat(1, this->classes.size(), CV_16F, output);
|
| 313 |
-
rawData.convertTo(rawData, CV_32F);
|
| 314 |
-
}
|
| 315 |
-
float *data = (float *) rawData.data;
|
| 316 |
-
|
| 317 |
-
DL_RESULT result;
|
| 318 |
-
for (int i = 0; i < this->classes.size(); i++)
|
| 319 |
-
{
|
| 320 |
-
result.classId = i;
|
| 321 |
-
result.confidence = data[i];
|
| 322 |
-
oResult.push_back(result);
|
| 323 |
-
}
|
| 324 |
-
break;
|
| 325 |
-
}
|
| 326 |
-
default:
|
| 327 |
-
std::cout << "[YOLO_V8]: " << "Not support model type." << std::endl;
|
| 328 |
-
}
|
| 329 |
-
return RET_OK;
|
| 330 |
-
|
| 331 |
-
}
|
| 332 |
-
|
| 333 |
-
|
| 334 |
-
char* YOLO_V8::WarmUpSession() {
|
| 335 |
-
clock_t starttime_1 = clock();
|
| 336 |
-
cv::Mat iImg = cv::Mat(cv::Size(imgSize.at(0), imgSize.at(1)), CV_8UC3);
|
| 337 |
-
cv::Mat processedImg;
|
| 338 |
-
PreProcess(iImg, imgSize, processedImg);
|
| 339 |
-
if (modelType < 4)
|
| 340 |
-
{
|
| 341 |
-
float* blob = new float[iImg.total() * 3];
|
| 342 |
-
BlobFromImage(processedImg, blob);
|
| 343 |
-
std::vector<int64_t> YOLO_input_node_dims = { 1, 3, imgSize.at(0), imgSize.at(1) };
|
| 344 |
-
Ort::Value input_tensor = Ort::Value::CreateTensor<float>(
|
| 345 |
-
Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtDeviceAllocator, OrtMemTypeCPU), blob, 3 * imgSize.at(0) * imgSize.at(1),
|
| 346 |
-
YOLO_input_node_dims.data(), YOLO_input_node_dims.size());
|
| 347 |
-
auto output_tensors = session->Run(options, inputNodeNames.data(), &input_tensor, 1, outputNodeNames.data(),
|
| 348 |
-
outputNodeNames.size());
|
| 349 |
-
delete[] blob;
|
| 350 |
-
clock_t starttime_4 = clock();
|
| 351 |
-
double post_process_time = (double)(starttime_4 - starttime_1) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000;
|
| 352 |
-
if (cudaEnable)
|
| 353 |
-
{
|
| 354 |
-
std::cout << "[YOLO_V8(CUDA)]: " << "Cuda warm-up cost " << post_process_time << " ms. " << std::endl;
|
| 355 |
-
}
|
| 356 |
-
}
|
| 357 |
-
else
|
| 358 |
-
{
|
| 359 |
-
#ifdef USE_CUDA
|
| 360 |
-
half* blob = new half[iImg.total() * 3];
|
| 361 |
-
BlobFromImage(processedImg, blob);
|
| 362 |
-
std::vector<int64_t> YOLO_input_node_dims = { 1,3,imgSize.at(0),imgSize.at(1) };
|
| 363 |
-
Ort::Value input_tensor = Ort::Value::CreateTensor<half>(Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtDeviceAllocator, OrtMemTypeCPU), blob, 3 * imgSize.at(0) * imgSize.at(1), YOLO_input_node_dims.data(), YOLO_input_node_dims.size());
|
| 364 |
-
auto output_tensors = session->Run(options, inputNodeNames.data(), &input_tensor, 1, outputNodeNames.data(), outputNodeNames.size());
|
| 365 |
-
delete[] blob;
|
| 366 |
-
clock_t starttime_4 = clock();
|
| 367 |
-
double post_process_time = (double)(starttime_4 - starttime_1) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000;
|
| 368 |
-
if (cudaEnable)
|
| 369 |
-
{
|
| 370 |
-
std::cout << "[YOLO_V8(CUDA)]: " << "Cuda warm-up cost " << post_process_time << " ms. " << std::endl;
|
| 371 |
-
}
|
| 372 |
-
#endif
|
| 373 |
-
}
|
| 374 |
-
return RET_OK;
|
| 375 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.h
DELETED
|
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#pragma once
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
#define RET_OK nullptr
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
#ifdef _WIN32
|
| 6 |
-
#include <Windows.h>
|
| 7 |
-
#include <direct.h>
|
| 8 |
-
#include <io.h>
|
| 9 |
-
#endif
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
#include <string>
|
| 12 |
-
#include <vector>
|
| 13 |
-
#include <cstdio>
|
| 14 |
-
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
|
| 15 |
-
#include "onnxruntime_cxx_api.h"
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
#ifdef USE_CUDA
|
| 18 |
-
#include <cuda_fp16.h>
|
| 19 |
-
#endif
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
|
| 22 |
-
enum MODEL_TYPE
|
| 23 |
-
{
|
| 24 |
-
//FLOAT32 MODEL
|
| 25 |
-
YOLO_DETECT_V8 = 1,
|
| 26 |
-
YOLO_POSE = 2,
|
| 27 |
-
YOLO_CLS = 3,
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
//FLOAT16 MODEL
|
| 30 |
-
YOLO_DETECT_V8_HALF = 4,
|
| 31 |
-
YOLO_POSE_V8_HALF = 5,
|
| 32 |
-
YOLO_CLS_HALF = 6
|
| 33 |
-
};
|
| 34 |
-
|
| 35 |
-
|
| 36 |
-
typedef struct _DL_INIT_PARAM
|
| 37 |
-
{
|
| 38 |
-
std::string modelPath;
|
| 39 |
-
MODEL_TYPE modelType = YOLO_DETECT_V8;
|
| 40 |
-
std::vector<int> imgSize = { 640, 640 };
|
| 41 |
-
float rectConfidenceThreshold = 0.6;
|
| 42 |
-
float iouThreshold = 0.5;
|
| 43 |
-
int keyPointsNum = 2;//Note:kpt number for pose
|
| 44 |
-
bool cudaEnable = false;
|
| 45 |
-
int logSeverityLevel = 3;
|
| 46 |
-
int intraOpNumThreads = 1;
|
| 47 |
-
} DL_INIT_PARAM;
|
| 48 |
-
|
| 49 |
-
|
| 50 |
-
typedef struct _DL_RESULT
|
| 51 |
-
{
|
| 52 |
-
int classId;
|
| 53 |
-
float confidence;
|
| 54 |
-
cv::Rect box;
|
| 55 |
-
std::vector<cv::Point2f> keyPoints;
|
| 56 |
-
} DL_RESULT;
|
| 57 |
-
|
| 58 |
-
|
| 59 |
-
class YOLO_V8
|
| 60 |
-
{
|
| 61 |
-
public:
|
| 62 |
-
YOLO_V8();
|
| 63 |
-
|
| 64 |
-
~YOLO_V8();
|
| 65 |
-
|
| 66 |
-
public:
|
| 67 |
-
char* CreateSession(DL_INIT_PARAM& iParams);
|
| 68 |
-
|
| 69 |
-
char* RunSession(cv::Mat& iImg, std::vector<DL_RESULT>& oResult);
|
| 70 |
-
|
| 71 |
-
char* WarmUpSession();
|
| 72 |
-
|
| 73 |
-
template<typename N>
|
| 74 |
-
char* TensorProcess(clock_t& starttime_1, cv::Mat& iImg, N& blob, std::vector<int64_t>& inputNodeDims,
|
| 75 |
-
std::vector<DL_RESULT>& oResult);
|
| 76 |
-
|
| 77 |
-
char* PreProcess(cv::Mat& iImg, std::vector<int> iImgSize, cv::Mat& oImg);
|
| 78 |
-
|
| 79 |
-
std::vector<std::string> classes{};
|
| 80 |
-
|
| 81 |
-
private:
|
| 82 |
-
Ort::Env env;
|
| 83 |
-
Ort::Session* session;
|
| 84 |
-
bool cudaEnable;
|
| 85 |
-
Ort::RunOptions options;
|
| 86 |
-
std::vector<const char*> inputNodeNames;
|
| 87 |
-
std::vector<const char*> outputNodeNames;
|
| 88 |
-
|
| 89 |
-
MODEL_TYPE modelType;
|
| 90 |
-
std::vector<int> imgSize;
|
| 91 |
-
float rectConfidenceThreshold;
|
| 92 |
-
float iouThreshold;
|
| 93 |
-
float resizeScales;//letterbox scale
|
| 94 |
-
};
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/main.cpp
DELETED
|
@@ -1,193 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#include <iostream>
|
| 2 |
-
#include <iomanip>
|
| 3 |
-
#include "inference.h"
|
| 4 |
-
#include <filesystem>
|
| 5 |
-
#include <fstream>
|
| 6 |
-
#include <random>
|
| 7 |
-
|
| 8 |
-
void Detector(YOLO_V8*& p) {
|
| 9 |
-
std::filesystem::path current_path = std::filesystem::current_path();
|
| 10 |
-
std::filesystem::path imgs_path = current_path / "images";
|
| 11 |
-
for (auto& i : std::filesystem::directory_iterator(imgs_path))
|
| 12 |
-
{
|
| 13 |
-
if (i.path().extension() == ".jpg" || i.path().extension() == ".png" || i.path().extension() == ".jpeg")
|
| 14 |
-
{
|
| 15 |
-
std::string img_path = i.path().string();
|
| 16 |
-
cv::Mat img = cv::imread(img_path);
|
| 17 |
-
std::vector<DL_RESULT> res;
|
| 18 |
-
p->RunSession(img, res);
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
for (auto& re : res)
|
| 21 |
-
{
|
| 22 |
-
cv::RNG rng(cv::getTickCount());
|
| 23 |
-
cv::Scalar color(rng.uniform(0, 256), rng.uniform(0, 256), rng.uniform(0, 256));
|
| 24 |
-
|
| 25 |
-
cv::rectangle(img, re.box, color, 3);
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
float confidence = floor(100 * re.confidence) / 100;
|
| 28 |
-
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2);
|
| 29 |
-
std::string label = p->classes[re.classId] + " " +
|
| 30 |
-
std::to_string(confidence).substr(0, std::to_string(confidence).size() - 4);
|
| 31 |
-
|
| 32 |
-
cv::rectangle(
|
| 33 |
-
img,
|
| 34 |
-
cv::Point(re.box.x, re.box.y - 25),
|
| 35 |
-
cv::Point(re.box.x + label.length() * 15, re.box.y),
|
| 36 |
-
color,
|
| 37 |
-
cv::FILLED
|
| 38 |
-
);
|
| 39 |
-
|
| 40 |
-
cv::putText(
|
| 41 |
-
img,
|
| 42 |
-
label,
|
| 43 |
-
cv::Point(re.box.x, re.box.y - 5),
|
| 44 |
-
cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
|
| 45 |
-
0.75,
|
| 46 |
-
cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0),
|
| 47 |
-
2
|
| 48 |
-
);
|
| 49 |
-
|
| 50 |
-
|
| 51 |
-
}
|
| 52 |
-
std::cout << "Press any key to exit" << std::endl;
|
| 53 |
-
cv::imshow("Result of Detection", img);
|
| 54 |
-
cv::waitKey(0);
|
| 55 |
-
cv::destroyAllWindows();
|
| 56 |
-
}
|
| 57 |
-
}
|
| 58 |
-
}
|
| 59 |
-
|
| 60 |
-
|
| 61 |
-
void Classifier(YOLO_V8*& p)
|
| 62 |
-
{
|
| 63 |
-
std::filesystem::path current_path = std::filesystem::current_path();
|
| 64 |
-
std::filesystem::path imgs_path = current_path;// / "images"
|
| 65 |
-
std::random_device rd;
|
| 66 |
-
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
|
| 67 |
-
std::uniform_int_distribution<int> dis(0, 255);
|
| 68 |
-
for (auto& i : std::filesystem::directory_iterator(imgs_path))
|
| 69 |
-
{
|
| 70 |
-
if (i.path().extension() == ".jpg" || i.path().extension() == ".png")
|
| 71 |
-
{
|
| 72 |
-
std::string img_path = i.path().string();
|
| 73 |
-
//std::cout << img_path << std::endl;
|
| 74 |
-
cv::Mat img = cv::imread(img_path);
|
| 75 |
-
std::vector<DL_RESULT> res;
|
| 76 |
-
char* ret = p->RunSession(img, res);
|
| 77 |
-
|
| 78 |
-
float positionY = 50;
|
| 79 |
-
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++)
|
| 80 |
-
{
|
| 81 |
-
int r = dis(gen);
|
| 82 |
-
int g = dis(gen);
|
| 83 |
-
int b = dis(gen);
|
| 84 |
-
cv::putText(img, std::to_string(i) + ":", cv::Point(10, positionY), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, cv::Scalar(b, g, r), 2);
|
| 85 |
-
cv::putText(img, std::to_string(res.at(i).confidence), cv::Point(70, positionY), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, cv::Scalar(b, g, r), 2);
|
| 86 |
-
positionY += 50;
|
| 87 |
-
}
|
| 88 |
-
|
| 89 |
-
cv::imshow("TEST_CLS", img);
|
| 90 |
-
cv::waitKey(0);
|
| 91 |
-
cv::destroyAllWindows();
|
| 92 |
-
//cv::imwrite("E:\\output\\" + std::to_string(k) + ".png", img);
|
| 93 |
-
}
|
| 94 |
-
|
| 95 |
-
}
|
| 96 |
-
}
|
| 97 |
-
|
| 98 |
-
|
| 99 |
-
|
| 100 |
-
int ReadCocoYaml(YOLO_V8*& p) {
|
| 101 |
-
// Open the YAML file
|
| 102 |
-
std::ifstream file("coco.yaml");
|
| 103 |
-
if (!file.is_open())
|
| 104 |
-
{
|
| 105 |
-
std::cerr << "Failed to open file" << std::endl;
|
| 106 |
-
return 1;
|
| 107 |
-
}
|
| 108 |
-
|
| 109 |
-
// Read the file line by line
|
| 110 |
-
std::string line;
|
| 111 |
-
std::vector<std::string> lines;
|
| 112 |
-
while (std::getline(file, line))
|
| 113 |
-
{
|
| 114 |
-
lines.push_back(line);
|
| 115 |
-
}
|
| 116 |
-
|
| 117 |
-
// Find the start and end of the names section
|
| 118 |
-
std::size_t start = 0;
|
| 119 |
-
std::size_t end = 0;
|
| 120 |
-
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++)
|
| 121 |
-
{
|
| 122 |
-
if (lines[i].find("names:") != std::string::npos)
|
| 123 |
-
{
|
| 124 |
-
start = i + 1;
|
| 125 |
-
}
|
| 126 |
-
else if (start > 0 && lines[i].find(':') == std::string::npos)
|
| 127 |
-
{
|
| 128 |
-
end = i;
|
| 129 |
-
break;
|
| 130 |
-
}
|
| 131 |
-
}
|
| 132 |
-
|
| 133 |
-
// Extract the names
|
| 134 |
-
std::vector<std::string> names;
|
| 135 |
-
for (std::size_t i = start; i < end; i++)
|
| 136 |
-
{
|
| 137 |
-
std::stringstream ss(lines[i]);
|
| 138 |
-
std::string name;
|
| 139 |
-
std::getline(ss, name, ':'); // Extract the number before the delimiter
|
| 140 |
-
std::getline(ss, name); // Extract the string after the delimiter
|
| 141 |
-
names.push_back(name);
|
| 142 |
-
}
|
| 143 |
-
|
| 144 |
-
p->classes = names;
|
| 145 |
-
return 0;
|
| 146 |
-
}
|
| 147 |
-
|
| 148 |
-
|
| 149 |
-
void DetectTest()
|
| 150 |
-
{
|
| 151 |
-
YOLO_V8* yoloDetector = new YOLO_V8;
|
| 152 |
-
ReadCocoYaml(yoloDetector);
|
| 153 |
-
DL_INIT_PARAM params;
|
| 154 |
-
params.rectConfidenceThreshold = 0.1;
|
| 155 |
-
params.iouThreshold = 0.5;
|
| 156 |
-
params.modelPath = "yolov8n.onnx";
|
| 157 |
-
params.imgSize = { 640, 640 };
|
| 158 |
-
#ifdef USE_CUDA
|
| 159 |
-
params.cudaEnable = true;
|
| 160 |
-
|
| 161 |
-
// GPU FP32 inference
|
| 162 |
-
params.modelType = YOLO_DETECT_V8;
|
| 163 |
-
// GPU FP16 inference
|
| 164 |
-
//Note: change fp16 onnx model
|
| 165 |
-
//params.modelType = YOLO_DETECT_V8_HALF;
|
| 166 |
-
|
| 167 |
-
#else
|
| 168 |
-
// CPU inference
|
| 169 |
-
params.modelType = YOLO_DETECT_V8;
|
| 170 |
-
params.cudaEnable = false;
|
| 171 |
-
|
| 172 |
-
#endif
|
| 173 |
-
yoloDetector->CreateSession(params);
|
| 174 |
-
Detector(yoloDetector);
|
| 175 |
-
}
|
| 176 |
-
|
| 177 |
-
|
| 178 |
-
void ClsTest()
|
| 179 |
-
{
|
| 180 |
-
YOLO_V8* yoloDetector = new YOLO_V8;
|
| 181 |
-
std::string model_path = "cls.onnx";
|
| 182 |
-
ReadCocoYaml(yoloDetector);
|
| 183 |
-
DL_INIT_PARAM params{ model_path, YOLO_CLS, {224, 224} };
|
| 184 |
-
yoloDetector->CreateSession(params);
|
| 185 |
-
Classifier(yoloDetector);
|
| 186 |
-
}
|
| 187 |
-
|
| 188 |
-
|
| 189 |
-
int main()
|
| 190 |
-
{
|
| 191 |
-
//DetectTest();
|
| 192 |
-
ClsTest();
|
| 193 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/Cargo.toml
DELETED
|
@@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
[package]
|
| 4 |
-
name = "yolov8-rs"
|
| 5 |
-
version = "0.1.0"
|
| 6 |
-
edition = "2021"
|
| 7 |
-
|
| 8 |
-
# See more keys and their definitions at https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
[dependencies]
|
| 11 |
-
clap = { version = "4.2.4", features = ["derive"] }
|
| 12 |
-
image = { version = "0.25.2"}
|
| 13 |
-
imageproc = { version = "0.25.0"}
|
| 14 |
-
ndarray = { version = "0.16" }
|
| 15 |
-
ort = { version = "2.0.0-rc.5", features = ["cuda", "tensorrt", "load-dynamic", "copy-dylibs", "half"]}
|
| 16 |
-
rusttype = { version = "0.9.3" }
|
| 17 |
-
anyhow = { version = "1.0.75" }
|
| 18 |
-
regex = { version = "1.5.4" }
|
| 19 |
-
rand = { version = "0.8.5" }
|
| 20 |
-
chrono = { version = "0.4.30" }
|
| 21 |
-
half = { version = "2.3.1" }
|
| 22 |
-
dirs = { version = "5.0.1" }
|
| 23 |
-
ureq = { version = "2.9.1" }
|
| 24 |
-
ab_glyph = "0.2.29"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/README.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,212 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust for All the Key YOLO Tasks
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
This repository provides a Rust demo for performing YOLOv8 tasks like `Classification`, `Segmentation`, `Detection`, `Pose Detection` and `OBB` using ONNXRuntime.
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
## Recently Updated
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
- Add YOLOv8-OBB demo
|
| 8 |
-
- Update ONNXRuntime to 1.19.x
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
Newly updated YOLOv8 example code is located in [this repository](https://github.com/jamjamjon/usls/tree/main/examples/yolo)
|
| 11 |
-
|
| 12 |
-
## Features
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
- Support `Classification`, `Segmentation`, `Detection`, `Pose(Keypoints)-Detection`, `OBB` tasks.
|
| 15 |
-
- Support `FP16` & `FP32` ONNX models.
|
| 16 |
-
- Support `CPU`, `CUDA` and `TensorRT` execution provider to accelerate computation.
|
| 17 |
-
- Support dynamic input shapes(`batch`, `width`, `height`).
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
## Installation
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
### 1. Install Rust
|
| 22 |
-
|
| 23 |
-
Please follow the Rust official installation. (https://www.rust-lang.org/tools/install)
|
| 24 |
-
|
| 25 |
-
### 2. ONNXRuntime Linking
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
- #### For detailed setup instructions, refer to the [ORT documentation](https://ort.pyke.io/setup/linking).
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
- #### For Linux or macOS Users:
|
| 30 |
-
- Download the ONNX Runtime package from the [Releases page](https://github.com/microsoft/onnxruntime/releases).
|
| 31 |
-
- Set up the library path by exporting the `ORT_DYLIB_PATH` environment variable:
|
| 32 |
-
```shell
|
| 33 |
-
export ORT_DYLIB_PATH=/path/to/onnxruntime/lib/libonnxruntime.so.1.19.0
|
| 34 |
-
```
|
| 35 |
-
|
| 36 |
-
### 3. \[Optional\] Install CUDA & CuDNN & TensorRT
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
- CUDA execution provider requires CUDA v11.6+.
|
| 39 |
-
- TensorRT execution provider requires CUDA v11.4+ and TensorRT v8.4+.
|
| 40 |
-
|
| 41 |
-
## Get Started
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
### 1. Export the YOLOv8 ONNX Models
|
| 44 |
-
|
| 45 |
-
```bash
|
| 46 |
-
pip install -U ultralytics
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
# export onnx model with dynamic shapes
|
| 49 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8m.pt format=onnx simplify dynamic
|
| 50 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8m-cls.pt format=onnx simplify dynamic
|
| 51 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8m-pose.pt format=onnx simplify dynamic
|
| 52 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8m-seg.pt format=onnx simplify dynamic
|
| 53 |
-
|
| 54 |
-
|
| 55 |
-
# export onnx model with constant shapes
|
| 56 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8m.pt format=onnx simplify
|
| 57 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8m-cls.pt format=onnx simplify
|
| 58 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8m-pose.pt format=onnx simplify
|
| 59 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8m-seg.pt format=onnx simplify
|
| 60 |
-
```
|
| 61 |
-
|
| 62 |
-
### 2. Run Inference
|
| 63 |
-
|
| 64 |
-
It will perform inference with the ONNX model on the source image.
|
| 65 |
-
|
| 66 |
-
```bash
|
| 67 |
-
cargo run --release -- --model <MODEL> --source <SOURCE>
|
| 68 |
-
```
|
| 69 |
-
|
| 70 |
-
Set `--cuda` to use CUDA execution provider to speed up inference.
|
| 71 |
-
|
| 72 |
-
```bash
|
| 73 |
-
cargo run --release -- --cuda --model <MODEL> --source <SOURCE>
|
| 74 |
-
```
|
| 75 |
-
|
| 76 |
-
Set `--trt` to use TensorRT execution provider, and you can set `--fp16` at the same time to use TensorRT FP16 engine.
|
| 77 |
-
|
| 78 |
-
```bash
|
| 79 |
-
cargo run --release -- --trt --fp16 --model <MODEL> --source <SOURCE>
|
| 80 |
-
```
|
| 81 |
-
|
| 82 |
-
Set `--device_id` to select which device to run. When you have only one GPU, and you set `device_id` to 1 will not cause program panic, the `ort` would automatically fall back to `CPU` EP.
|
| 83 |
-
|
| 84 |
-
```bash
|
| 85 |
-
cargo run --release -- --cuda --device_id 0 --model <MODEL> --source <SOURCE>
|
| 86 |
-
```
|
| 87 |
-
|
| 88 |
-
Set `--batch` to do multi-batch-size inference.
|
| 89 |
-
|
| 90 |
-
If you're using `--trt`, you can also set `--batch-min` and `--batch-max` to explicitly specify min/max/opt batch for dynamic batch input.(https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/execution-providers/TensorRT-ExecutionProvider.html#explicit-shape-range-for-dynamic-shape-input).(Note that the ONNX model should be exported with dynamic shapes.)
|
| 91 |
-
|
| 92 |
-
```bash
|
| 93 |
-
cargo run --release -- --cuda --batch 2 --model <MODEL> --source <SOURCE>
|
| 94 |
-
```
|
| 95 |
-
|
| 96 |
-
Set `--height` and `--width` to do dynamic image size inference. (Note that the ONNX model should be exported with dynamic shapes.)
|
| 97 |
-
|
| 98 |
-
```bash
|
| 99 |
-
cargo run --release -- --cuda --width 480 --height 640 --model <MODEL> --source <SOURCE>
|
| 100 |
-
```
|
| 101 |
-
|
| 102 |
-
Set `--profile` to check time consumed in each stage.(Note that the model usually needs to take 1~3 times dry run to warmup. Make sure to run enough times to evaluate the result.)
|
| 103 |
-
|
| 104 |
-
```bash
|
| 105 |
-
cargo run --release -- --trt --fp16 --profile --model <MODEL> --source <SOURCE>
|
| 106 |
-
```
|
| 107 |
-
|
| 108 |
-
Results: (yolov8m.onnx, batch=1, 3 times, trt, fp16, RTX 3060Ti)
|
| 109 |
-
|
| 110 |
-
```bash
|
| 111 |
-
==> 0
|
| 112 |
-
[Model Preprocess]: 12.75788ms
|
| 113 |
-
[ORT H2D]: 237.118µs
|
| 114 |
-
[ORT Inference]: 507.895469ms
|
| 115 |
-
[ORT D2H]: 191.655µs
|
| 116 |
-
[Model Inference]: 508.34589ms
|
| 117 |
-
[Model Postprocess]: 1.061122ms
|
| 118 |
-
==> 1
|
| 119 |
-
[Model Preprocess]: 13.658655ms
|
| 120 |
-
[ORT H2D]: 209.975µs
|
| 121 |
-
[ORT Inference]: 5.12372ms
|
| 122 |
-
[ORT D2H]: 182.389µs
|
| 123 |
-
[Model Inference]: 5.530022ms
|
| 124 |
-
[Model Postprocess]: 1.04851ms
|
| 125 |
-
==> 2
|
| 126 |
-
[Model Preprocess]: 12.475332ms
|
| 127 |
-
[ORT H2D]: 246.127µs
|
| 128 |
-
[ORT Inference]: 5.048432ms
|
| 129 |
-
[ORT D2H]: 187.117µs
|
| 130 |
-
[Model Inference]: 5.493119ms
|
| 131 |
-
[Model Postprocess]: 1.040906ms
|
| 132 |
-
```
|
| 133 |
-
|
| 134 |
-
And also:
|
| 135 |
-
|
| 136 |
-
`--conf`: confidence threshold \[default: 0.3\]
|
| 137 |
-
|
| 138 |
-
`--iou`: iou threshold in NMS \[default: 0.45\]
|
| 139 |
-
|
| 140 |
-
`--kconf`: confidence threshold of keypoint \[default: 0.55\]
|
| 141 |
-
|
| 142 |
-
`--plot`: plot inference result with random RGB color and save
|
| 143 |
-
|
| 144 |
-
you can check out all CLI arguments by:
|
| 145 |
-
|
| 146 |
-
```bash
|
| 147 |
-
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
|
| 148 |
-
cd ultralytics/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust
|
| 149 |
-
cargo run --release -- --help
|
| 150 |
-
```
|
| 151 |
-
|
| 152 |
-
## Examples
|
| 153 |
-
|
| 154 |
-
|
| 155 |
-
|
| 156 |
-
### Classification
|
| 157 |
-
|
| 158 |
-
Running dynamic shape ONNX model on `CPU` with image size `--height 224 --width 224`. Saving plotted image in `runs` directory.
|
| 159 |
-
|
| 160 |
-
```bash
|
| 161 |
-
cargo run --release -- --model ../assets/weights/yolov8m-cls-dyn.onnx --source ../assets/images/dog.jpg --height 224 --width 224 --plot --profile
|
| 162 |
-
```
|
| 163 |
-
|
| 164 |
-
You will see result like:
|
| 165 |
-
|
| 166 |
-
```bash
|
| 167 |
-
Summary:
|
| 168 |
-
> Task: Classify (Ultralytics 8.0.217)
|
| 169 |
-
> EP: Cpu
|
| 170 |
-
> Dtype: Float32
|
| 171 |
-
> Batch: 1 (Dynamic), Height: 224 (Dynamic), Width: 224 (Dynamic)
|
| 172 |
-
> nc: 1000 nk: 0, nm: 0, conf: 0.3, kconf: 0.55, iou: 0.45
|
| 173 |
-
|
| 174 |
-
[Model Preprocess]: 16.363477ms
|
| 175 |
-
[ORT H2D]: 50.722µs
|
| 176 |
-
[ORT Inference]: 16.295808ms
|
| 177 |
-
[ORT D2H]: 8.37µs
|
| 178 |
-
[Model Inference]: 16.367046ms
|
| 179 |
-
[Model Postprocess]: 3.527µs
|
| 180 |
-
[
|
| 181 |
-
YOLOResult {
|
| 182 |
-
Probs(top5): Some([(208, 0.6950566), (209, 0.13823675), (178, 0.04849795), (215, 0.019029364), (212, 0.016506357)]),
|
| 183 |
-
Bboxes: None,
|
| 184 |
-
Keypoints: None,
|
| 185 |
-
Masks: None,
|
| 186 |
-
},
|
| 187 |
-
]
|
| 188 |
-
```
|
| 189 |
-
|
| 190 |
-
### Object Detection
|
| 191 |
-
|
| 192 |
-
Using `CUDA` EP and dynamic image size `--height 640 --width 480`
|
| 193 |
-
|
| 194 |
-
```bash
|
| 195 |
-
cargo run --release -- --cuda --model ../assets/weights/yolov8m-dynamic.onnx --source ../assets/images/bus.jpg --plot --height 640 --width 480
|
| 196 |
-
```
|
| 197 |
-
|
| 198 |
-
### Pose Detection
|
| 199 |
-
|
| 200 |
-
using `TensorRT` EP
|
| 201 |
-
|
| 202 |
-
```bash
|
| 203 |
-
cargo run --release -- --trt --model ../assets/weights/yolov8m-pose.onnx --source ../assets/images/bus.jpg --plot
|
| 204 |
-
```
|
| 205 |
-
|
| 206 |
-
### Instance Segmentation
|
| 207 |
-
|
| 208 |
-
using `TensorRT` EP and FP16 model `--fp16`
|
| 209 |
-
|
| 210 |
-
```bash
|
| 211 |
-
cargo run --release -- --trt --fp16 --model ../assets/weights/yolov8m-seg.onnx --source ../assets/images/0172.jpg --plot
|
| 212 |
-
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/cli.rs
DELETED
|
@@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
use clap::Parser;
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
use crate::YOLOTask;
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
#[derive(Parser, Clone)]
|
| 6 |
-
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
|
| 7 |
-
pub struct Args {
|
| 8 |
-
/// ONNX model path
|
| 9 |
-
#[arg(long, required = true)]
|
| 10 |
-
pub model: String,
|
| 11 |
-
|
| 12 |
-
/// input path
|
| 13 |
-
#[arg(long, required = true)]
|
| 14 |
-
pub source: String,
|
| 15 |
-
|
| 16 |
-
/// device id
|
| 17 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 0)]
|
| 18 |
-
pub device_id: i32,
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
/// using TensorRT EP
|
| 21 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 22 |
-
pub trt: bool,
|
| 23 |
-
|
| 24 |
-
/// using CUDA EP
|
| 25 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 26 |
-
pub cuda: bool,
|
| 27 |
-
|
| 28 |
-
/// input batch size
|
| 29 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 1)]
|
| 30 |
-
pub batch: u32,
|
| 31 |
-
|
| 32 |
-
/// trt input min_batch size
|
| 33 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 1)]
|
| 34 |
-
pub batch_min: u32,
|
| 35 |
-
|
| 36 |
-
/// trt input max_batch size
|
| 37 |
-
#[arg(long, default_value_t = 32)]
|
| 38 |
-
pub batch_max: u32,
|
| 39 |
-
|
| 40 |
-
/// using TensorRT --fp16
|
| 41 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 42 |
-
pub fp16: bool,
|
| 43 |
-
|
| 44 |
-
/// specify YOLO task
|
| 45 |
-
#[arg(long, value_enum)]
|
| 46 |
-
pub task: Option<YOLOTask>,
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
/// num_classes
|
| 49 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 50 |
-
pub nc: Option<u32>,
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
/// num_keypoints
|
| 53 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 54 |
-
pub nk: Option<u32>,
|
| 55 |
-
|
| 56 |
-
/// num_masks
|
| 57 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 58 |
-
pub nm: Option<u32>,
|
| 59 |
-
|
| 60 |
-
/// input image width
|
| 61 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 62 |
-
pub width: Option<u32>,
|
| 63 |
-
|
| 64 |
-
/// input image height
|
| 65 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 66 |
-
pub height: Option<u32>,
|
| 67 |
-
|
| 68 |
-
/// confidence threshold
|
| 69 |
-
#[arg(long, required = false, default_value_t = 0.3)]
|
| 70 |
-
pub conf: f32,
|
| 71 |
-
|
| 72 |
-
/// iou threshold in NMS
|
| 73 |
-
#[arg(long, required = false, default_value_t = 0.45)]
|
| 74 |
-
pub iou: f32,
|
| 75 |
-
|
| 76 |
-
/// confidence threshold of keypoint
|
| 77 |
-
#[arg(long, required = false, default_value_t = 0.55)]
|
| 78 |
-
pub kconf: f32,
|
| 79 |
-
|
| 80 |
-
/// plot inference result and save
|
| 81 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 82 |
-
pub plot: bool,
|
| 83 |
-
|
| 84 |
-
/// check time consumed in each stage
|
| 85 |
-
#[arg(long)]
|
| 86 |
-
pub profile: bool,
|
| 87 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/lib.rs
DELETED
|
@@ -1,160 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#![allow(clippy::type_complexity)]
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
use std::io::{Read, Write};
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
pub mod cli;
|
| 6 |
-
pub mod model;
|
| 7 |
-
pub mod ort_backend;
|
| 8 |
-
pub mod yolo_result;
|
| 9 |
-
pub use crate::cli::Args;
|
| 10 |
-
pub use crate::model::YOLOv8;
|
| 11 |
-
pub use crate::ort_backend::{Batch, OrtBackend, OrtConfig, OrtEP, YOLOTask};
|
| 12 |
-
pub use crate::yolo_result::{Bbox, Embedding, Point2, YOLOResult};
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
pub fn non_max_suppression(
|
| 15 |
-
xs: &mut Vec<(Bbox, Option<Vec<Point2>>, Option<Vec<f32>>)>,
|
| 16 |
-
iou_threshold: f32,
|
| 17 |
-
) {
|
| 18 |
-
xs.sort_by(|b1, b2| b2.0.confidence().partial_cmp(&b1.0.confidence()).unwrap());
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
let mut current_index = 0;
|
| 21 |
-
for index in 0..xs.len() {
|
| 22 |
-
let mut drop = false;
|
| 23 |
-
for prev_index in 0..current_index {
|
| 24 |
-
let iou = xs[prev_index].0.iou(&xs[index].0);
|
| 25 |
-
if iou > iou_threshold {
|
| 26 |
-
drop = true;
|
| 27 |
-
break;
|
| 28 |
-
}
|
| 29 |
-
}
|
| 30 |
-
if !drop {
|
| 31 |
-
xs.swap(current_index, index);
|
| 32 |
-
current_index += 1;
|
| 33 |
-
}
|
| 34 |
-
}
|
| 35 |
-
xs.truncate(current_index);
|
| 36 |
-
}
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
pub fn gen_time_string(delimiter: &str) -> String {
|
| 39 |
-
let offset = chrono::FixedOffset::east_opt(8 * 60 * 60).unwrap(); // Beijing
|
| 40 |
-
let t_now = chrono::Utc::now().with_timezone(&offset);
|
| 41 |
-
let fmt = format!(
|
| 42 |
-
"%Y{}%m{}%d{}%H{}%M{}%S{}%f",
|
| 43 |
-
delimiter, delimiter, delimiter, delimiter, delimiter, delimiter
|
| 44 |
-
);
|
| 45 |
-
t_now.format(&fmt).to_string()
|
| 46 |
-
}
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
pub const SKELETON: [(usize, usize); 16] = [
|
| 49 |
-
(0, 1),
|
| 50 |
-
(0, 2),
|
| 51 |
-
(1, 3),
|
| 52 |
-
(2, 4),
|
| 53 |
-
(5, 6),
|
| 54 |
-
(5, 11),
|
| 55 |
-
(6, 12),
|
| 56 |
-
(11, 12),
|
| 57 |
-
(5, 7),
|
| 58 |
-
(6, 8),
|
| 59 |
-
(7, 9),
|
| 60 |
-
(8, 10),
|
| 61 |
-
(11, 13),
|
| 62 |
-
(12, 14),
|
| 63 |
-
(13, 15),
|
| 64 |
-
(14, 16),
|
| 65 |
-
];
|
| 66 |
-
|
| 67 |
-
pub fn check_font(font: &str) -> rusttype::Font<'static> {
|
| 68 |
-
// check then load font
|
| 69 |
-
|
| 70 |
-
// ultralytics font path
|
| 71 |
-
let font_path_config = match dirs::config_dir() {
|
| 72 |
-
Some(mut d) => {
|
| 73 |
-
d.push("Ultralytics");
|
| 74 |
-
d.push(font);
|
| 75 |
-
d
|
| 76 |
-
}
|
| 77 |
-
None => panic!("Unsupported operating system. Now support Linux, MacOS, Windows."),
|
| 78 |
-
};
|
| 79 |
-
|
| 80 |
-
// current font path
|
| 81 |
-
let font_path_current = std::path::PathBuf::from(font);
|
| 82 |
-
|
| 83 |
-
// check font
|
| 84 |
-
let font_path = if font_path_config.exists() {
|
| 85 |
-
font_path_config
|
| 86 |
-
} else if font_path_current.exists() {
|
| 87 |
-
font_path_current
|
| 88 |
-
} else {
|
| 89 |
-
println!("Downloading font...");
|
| 90 |
-
let source_url = "https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.ttf";
|
| 91 |
-
let resp = ureq::get(source_url)
|
| 92 |
-
.timeout(std::time::Duration::from_secs(500))
|
| 93 |
-
.call()
|
| 94 |
-
.unwrap_or_else(|err| panic!("> Failed to download font: {source_url}: {err:?}"));
|
| 95 |
-
|
| 96 |
-
// read to buffer
|
| 97 |
-
let mut buffer = vec![];
|
| 98 |
-
let total_size = resp
|
| 99 |
-
.header("Content-Length")
|
| 100 |
-
.and_then(|s| s.parse::<u64>().ok())
|
| 101 |
-
.unwrap();
|
| 102 |
-
let _reader = resp
|
| 103 |
-
.into_reader()
|
| 104 |
-
.take(total_size)
|
| 105 |
-
.read_to_end(&mut buffer)
|
| 106 |
-
.unwrap();
|
| 107 |
-
|
| 108 |
-
// save
|
| 109 |
-
let _path = std::fs::File::create(font).unwrap();
|
| 110 |
-
let mut writer = std::io::BufWriter::new(_path);
|
| 111 |
-
writer.write_all(&buffer).unwrap();
|
| 112 |
-
println!("Font saved at: {:?}", font_path_current.display());
|
| 113 |
-
font_path_current
|
| 114 |
-
};
|
| 115 |
-
|
| 116 |
-
// load font
|
| 117 |
-
let buffer = std::fs::read(font_path).unwrap();
|
| 118 |
-
rusttype::Font::try_from_vec(buffer).unwrap()
|
| 119 |
-
}
|
| 120 |
-
|
| 121 |
-
use ab_glyph::FontArc;
|
| 122 |
-
pub fn load_font() -> FontArc {
|
| 123 |
-
use std::path::Path;
|
| 124 |
-
let font_path = Path::new("./font/Arial.ttf");
|
| 125 |
-
match font_path.try_exists() {
|
| 126 |
-
Ok(true) => {
|
| 127 |
-
let buffer = std::fs::read(font_path).unwrap();
|
| 128 |
-
FontArc::try_from_vec(buffer).unwrap()
|
| 129 |
-
}
|
| 130 |
-
Ok(false) => {
|
| 131 |
-
std::fs::create_dir_all("./font").unwrap();
|
| 132 |
-
println!("Downloading font...");
|
| 133 |
-
let source_url = "https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.ttf";
|
| 134 |
-
let resp = ureq::get(source_url)
|
| 135 |
-
.timeout(std::time::Duration::from_secs(500))
|
| 136 |
-
.call()
|
| 137 |
-
.unwrap_or_else(|err| panic!("> Failed to download font: {source_url}: {err:?}"));
|
| 138 |
-
|
| 139 |
-
// read to buffer
|
| 140 |
-
let mut buffer = vec![];
|
| 141 |
-
let total_size = resp
|
| 142 |
-
.header("Content-Length")
|
| 143 |
-
.and_then(|s| s.parse::<u64>().ok())
|
| 144 |
-
.unwrap();
|
| 145 |
-
let _reader = resp
|
| 146 |
-
.into_reader()
|
| 147 |
-
.take(total_size)
|
| 148 |
-
.read_to_end(&mut buffer)
|
| 149 |
-
.unwrap();
|
| 150 |
-
// save
|
| 151 |
-
let mut fd = std::fs::File::create(font_path).unwrap();
|
| 152 |
-
fd.write_all(&buffer).unwrap();
|
| 153 |
-
println!("Font saved at: {:?}", font_path.display());
|
| 154 |
-
FontArc::try_from_vec(buffer).unwrap()
|
| 155 |
-
}
|
| 156 |
-
Err(e) => {
|
| 157 |
-
panic!("Failed to load font {}", e);
|
| 158 |
-
}
|
| 159 |
-
}
|
| 160 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/main.rs
DELETED
|
@@ -1,28 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
use clap::Parser;
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
use yolov8_rs::{Args, YOLOv8};
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
|
| 6 |
-
let args = Args::parse();
|
| 7 |
-
|
| 8 |
-
// 1. load image
|
| 9 |
-
let x = image::ImageReader::open(&args.source)?
|
| 10 |
-
.with_guessed_format()?
|
| 11 |
-
.decode()?;
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
// 2. model support dynamic batch inference, so input should be a Vec
|
| 14 |
-
let xs = vec![x];
|
| 15 |
-
|
| 16 |
-
// You can test `--batch 2` with this
|
| 17 |
-
// let xs = vec![x.clone(), x];
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
// 3. build yolov8 model
|
| 20 |
-
let mut model = YOLOv8::new(args)?;
|
| 21 |
-
model.summary(); // model info
|
| 22 |
-
|
| 23 |
-
// 4. run
|
| 24 |
-
let ys = model.run(&xs)?;
|
| 25 |
-
println!("{:?}", ys);
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
Ok(())
|
| 28 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/model.rs
DELETED
|
@@ -1,651 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#![allow(clippy::type_complexity)]
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
use ab_glyph::FontArc;
|
| 4 |
-
use anyhow::Result;
|
| 5 |
-
use image::{DynamicImage, GenericImageView, ImageBuffer};
|
| 6 |
-
use ndarray::{s, Array, Axis, IxDyn};
|
| 7 |
-
use rand::{thread_rng, Rng};
|
| 8 |
-
use std::path::PathBuf;
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
use crate::{
|
| 11 |
-
gen_time_string, load_font, non_max_suppression, Args, Batch, Bbox, Embedding, OrtBackend,
|
| 12 |
-
OrtConfig, OrtEP, Point2, YOLOResult, YOLOTask, SKELETON,
|
| 13 |
-
};
|
| 14 |
-
|
| 15 |
-
pub struct YOLOv8 {
|
| 16 |
-
// YOLOv8 model for all yolo-tasks
|
| 17 |
-
engine: OrtBackend,
|
| 18 |
-
nc: u32,
|
| 19 |
-
nk: u32,
|
| 20 |
-
nm: u32,
|
| 21 |
-
height: u32,
|
| 22 |
-
width: u32,
|
| 23 |
-
batch: u32,
|
| 24 |
-
task: YOLOTask,
|
| 25 |
-
conf: f32,
|
| 26 |
-
kconf: f32,
|
| 27 |
-
iou: f32,
|
| 28 |
-
names: Vec<String>,
|
| 29 |
-
color_palette: Vec<(u8, u8, u8)>,
|
| 30 |
-
profile: bool,
|
| 31 |
-
plot: bool,
|
| 32 |
-
}
|
| 33 |
-
|
| 34 |
-
impl YOLOv8 {
|
| 35 |
-
pub fn new(config: Args) -> Result<Self> {
|
| 36 |
-
// execution provider
|
| 37 |
-
let ep = if config.trt {
|
| 38 |
-
OrtEP::Trt(config.device_id)
|
| 39 |
-
} else if config.cuda {
|
| 40 |
-
OrtEP::CUDA(config.device_id)
|
| 41 |
-
} else {
|
| 42 |
-
OrtEP::CPU
|
| 43 |
-
};
|
| 44 |
-
|
| 45 |
-
// batch
|
| 46 |
-
let batch = Batch {
|
| 47 |
-
opt: config.batch,
|
| 48 |
-
min: config.batch_min,
|
| 49 |
-
max: config.batch_max,
|
| 50 |
-
};
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
// build ort engine
|
| 53 |
-
let ort_args = OrtConfig {
|
| 54 |
-
ep,
|
| 55 |
-
batch,
|
| 56 |
-
f: config.model,
|
| 57 |
-
task: config.task,
|
| 58 |
-
trt_fp16: config.fp16,
|
| 59 |
-
image_size: (config.height, config.width),
|
| 60 |
-
};
|
| 61 |
-
let engine = OrtBackend::build(ort_args)?;
|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
// get batch, height, width, tasks, nc, nk, nm
|
| 64 |
-
let (batch, height, width, task) = (
|
| 65 |
-
engine.batch(),
|
| 66 |
-
engine.height(),
|
| 67 |
-
engine.width(),
|
| 68 |
-
engine.task(),
|
| 69 |
-
);
|
| 70 |
-
let nc = engine.nc().or(config.nc).unwrap_or_else(|| {
|
| 71 |
-
panic!("Failed to get num_classes, make it explicit with `--nc`");
|
| 72 |
-
});
|
| 73 |
-
let (nk, nm) = match task {
|
| 74 |
-
YOLOTask::Pose => {
|
| 75 |
-
let nk = engine.nk().or(config.nk).unwrap_or_else(|| {
|
| 76 |
-
panic!("Failed to get num_keypoints, make it explicit with `--nk`");
|
| 77 |
-
});
|
| 78 |
-
(nk, 0)
|
| 79 |
-
}
|
| 80 |
-
YOLOTask::Segment => {
|
| 81 |
-
let nm = engine.nm().or(config.nm).unwrap_or_else(|| {
|
| 82 |
-
panic!("Failed to get num_masks, make it explicit with `--nm`");
|
| 83 |
-
});
|
| 84 |
-
(0, nm)
|
| 85 |
-
}
|
| 86 |
-
_ => (0, 0),
|
| 87 |
-
};
|
| 88 |
-
|
| 89 |
-
// class names
|
| 90 |
-
let names = engine.names().unwrap_or(vec!["Unknown".to_string()]);
|
| 91 |
-
|
| 92 |
-
// color palette
|
| 93 |
-
let mut rng = thread_rng();
|
| 94 |
-
let color_palette: Vec<_> = names
|
| 95 |
-
.iter()
|
| 96 |
-
.map(|_| {
|
| 97 |
-
(
|
| 98 |
-
rng.gen_range(0..=255),
|
| 99 |
-
rng.gen_range(0..=255),
|
| 100 |
-
rng.gen_range(0..=255),
|
| 101 |
-
)
|
| 102 |
-
})
|
| 103 |
-
.collect();
|
| 104 |
-
|
| 105 |
-
Ok(Self {
|
| 106 |
-
engine,
|
| 107 |
-
names,
|
| 108 |
-
conf: config.conf,
|
| 109 |
-
kconf: config.kconf,
|
| 110 |
-
iou: config.iou,
|
| 111 |
-
color_palette,
|
| 112 |
-
profile: config.profile,
|
| 113 |
-
plot: config.plot,
|
| 114 |
-
nc,
|
| 115 |
-
nk,
|
| 116 |
-
nm,
|
| 117 |
-
height,
|
| 118 |
-
width,
|
| 119 |
-
batch,
|
| 120 |
-
task,
|
| 121 |
-
})
|
| 122 |
-
}
|
| 123 |
-
|
| 124 |
-
pub fn scale_wh(&self, w0: f32, h0: f32, w1: f32, h1: f32) -> (f32, f32, f32) {
|
| 125 |
-
let r = (w1 / w0).min(h1 / h0);
|
| 126 |
-
(r, (w0 * r).round(), (h0 * r).round())
|
| 127 |
-
}
|
| 128 |
-
|
| 129 |
-
pub fn preprocess(&mut self, xs: &Vec<DynamicImage>) -> Result<Array<f32, IxDyn>> {
|
| 130 |
-
let mut ys =
|
| 131 |
-
Array::ones((xs.len(), 3, self.height() as usize, self.width() as usize)).into_dyn();
|
| 132 |
-
ys.fill(144.0 / 255.0);
|
| 133 |
-
for (idx, x) in xs.iter().enumerate() {
|
| 134 |
-
let img = match self.task() {
|
| 135 |
-
YOLOTask::Classify => x.resize_exact(
|
| 136 |
-
self.width(),
|
| 137 |
-
self.height(),
|
| 138 |
-
image::imageops::FilterType::Triangle,
|
| 139 |
-
),
|
| 140 |
-
_ => {
|
| 141 |
-
let (w0, h0) = x.dimensions();
|
| 142 |
-
let w0 = w0 as f32;
|
| 143 |
-
let h0 = h0 as f32;
|
| 144 |
-
let (_, w_new, h_new) =
|
| 145 |
-
self.scale_wh(w0, h0, self.width() as f32, self.height() as f32); // f32 round
|
| 146 |
-
x.resize_exact(
|
| 147 |
-
w_new as u32,
|
| 148 |
-
h_new as u32,
|
| 149 |
-
if let YOLOTask::Segment = self.task() {
|
| 150 |
-
image::imageops::FilterType::CatmullRom
|
| 151 |
-
} else {
|
| 152 |
-
image::imageops::FilterType::Triangle
|
| 153 |
-
},
|
| 154 |
-
)
|
| 155 |
-
}
|
| 156 |
-
};
|
| 157 |
-
|
| 158 |
-
for (x, y, rgb) in img.pixels() {
|
| 159 |
-
let x = x as usize;
|
| 160 |
-
let y = y as usize;
|
| 161 |
-
let [r, g, b, _] = rgb.0;
|
| 162 |
-
ys[[idx, 0, y, x]] = (r as f32) / 255.0;
|
| 163 |
-
ys[[idx, 1, y, x]] = (g as f32) / 255.0;
|
| 164 |
-
ys[[idx, 2, y, x]] = (b as f32) / 255.0;
|
| 165 |
-
}
|
| 166 |
-
}
|
| 167 |
-
|
| 168 |
-
Ok(ys)
|
| 169 |
-
}
|
| 170 |
-
|
| 171 |
-
pub fn run(&mut self, xs: &Vec<DynamicImage>) -> Result<Vec<YOLOResult>> {
|
| 172 |
-
// pre-process
|
| 173 |
-
let t_pre = std::time::Instant::now();
|
| 174 |
-
let xs_ = self.preprocess(xs)?;
|
| 175 |
-
if self.profile {
|
| 176 |
-
println!("[Model Preprocess]: {:?}", t_pre.elapsed());
|
| 177 |
-
}
|
| 178 |
-
|
| 179 |
-
// run
|
| 180 |
-
let t_run = std::time::Instant::now();
|
| 181 |
-
let ys = self.engine.run(xs_, self.profile)?;
|
| 182 |
-
if self.profile {
|
| 183 |
-
println!("[Model Inference]: {:?}", t_run.elapsed());
|
| 184 |
-
}
|
| 185 |
-
|
| 186 |
-
// post-process
|
| 187 |
-
let t_post = std::time::Instant::now();
|
| 188 |
-
let ys = self.postprocess(ys, xs)?;
|
| 189 |
-
if self.profile {
|
| 190 |
-
println!("[Model Postprocess]: {:?}", t_post.elapsed());
|
| 191 |
-
}
|
| 192 |
-
|
| 193 |
-
// plot and save
|
| 194 |
-
if self.plot {
|
| 195 |
-
self.plot_and_save(&ys, xs, Some(&SKELETON));
|
| 196 |
-
}
|
| 197 |
-
Ok(ys)
|
| 198 |
-
}
|
| 199 |
-
|
| 200 |
-
pub fn postprocess(
|
| 201 |
-
&self,
|
| 202 |
-
xs: Vec<Array<f32, IxDyn>>,
|
| 203 |
-
xs0: &[DynamicImage],
|
| 204 |
-
) -> Result<Vec<YOLOResult>> {
|
| 205 |
-
if let YOLOTask::Classify = self.task() {
|
| 206 |
-
let mut ys = Vec::new();
|
| 207 |
-
let preds = &xs[0];
|
| 208 |
-
for batch in preds.axis_iter(Axis(0)) {
|
| 209 |
-
ys.push(YOLOResult::new(
|
| 210 |
-
Some(Embedding::new(batch.into_owned())),
|
| 211 |
-
None,
|
| 212 |
-
None,
|
| 213 |
-
None,
|
| 214 |
-
));
|
| 215 |
-
}
|
| 216 |
-
Ok(ys)
|
| 217 |
-
} else {
|
| 218 |
-
const CXYWH_OFFSET: usize = 4; // cxcywh
|
| 219 |
-
const KPT_STEP: usize = 3; // xyconf
|
| 220 |
-
let preds = &xs[0];
|
| 221 |
-
let protos = {
|
| 222 |
-
if xs.len() > 1 {
|
| 223 |
-
Some(&xs[1])
|
| 224 |
-
} else {
|
| 225 |
-
None
|
| 226 |
-
}
|
| 227 |
-
};
|
| 228 |
-
let mut ys = Vec::new();
|
| 229 |
-
for (idx, anchor) in preds.axis_iter(Axis(0)).enumerate() {
|
| 230 |
-
// [bs, 4 + nc + nm, anchors]
|
| 231 |
-
// input image
|
| 232 |
-
let width_original = xs0[idx].width() as f32;
|
| 233 |
-
let height_original = xs0[idx].height() as f32;
|
| 234 |
-
let ratio = (self.width() as f32 / width_original)
|
| 235 |
-
.min(self.height() as f32 / height_original);
|
| 236 |
-
|
| 237 |
-
// save each result
|
| 238 |
-
let mut data: Vec<(Bbox, Option<Vec<Point2>>, Option<Vec<f32>>)> = Vec::new();
|
| 239 |
-
for pred in anchor.axis_iter(Axis(1)) {
|
| 240 |
-
// split preds for different tasks
|
| 241 |
-
let bbox = pred.slice(s![0..CXYWH_OFFSET]);
|
| 242 |
-
let clss = pred.slice(s![CXYWH_OFFSET..CXYWH_OFFSET + self.nc() as usize]);
|
| 243 |
-
let kpts = {
|
| 244 |
-
if let YOLOTask::Pose = self.task() {
|
| 245 |
-
Some(pred.slice(s![pred.len() - KPT_STEP * self.nk() as usize..]))
|
| 246 |
-
} else {
|
| 247 |
-
None
|
| 248 |
-
}
|
| 249 |
-
};
|
| 250 |
-
let coefs = {
|
| 251 |
-
if let YOLOTask::Segment = self.task() {
|
| 252 |
-
Some(pred.slice(s![pred.len() - self.nm() as usize..]).to_vec())
|
| 253 |
-
} else {
|
| 254 |
-
None
|
| 255 |
-
}
|
| 256 |
-
};
|
| 257 |
-
|
| 258 |
-
// confidence and id
|
| 259 |
-
let (id, &confidence) = clss
|
| 260 |
-
.into_iter()
|
| 261 |
-
.enumerate()
|
| 262 |
-
.reduce(|max, x| if x.1 > max.1 { x } else { max })
|
| 263 |
-
.unwrap(); // definitely will not panic!
|
| 264 |
-
|
| 265 |
-
// confidence filter
|
| 266 |
-
if confidence < self.conf {
|
| 267 |
-
continue;
|
| 268 |
-
}
|
| 269 |
-
|
| 270 |
-
// bbox re-scale
|
| 271 |
-
let cx = bbox[0] / ratio;
|
| 272 |
-
let cy = bbox[1] / ratio;
|
| 273 |
-
let w = bbox[2] / ratio;
|
| 274 |
-
let h = bbox[3] / ratio;
|
| 275 |
-
let x = cx - w / 2.;
|
| 276 |
-
let y = cy - h / 2.;
|
| 277 |
-
let y_bbox = Bbox::new(
|
| 278 |
-
x.max(0.0f32).min(width_original),
|
| 279 |
-
y.max(0.0f32).min(height_original),
|
| 280 |
-
w,
|
| 281 |
-
h,
|
| 282 |
-
id,
|
| 283 |
-
confidence,
|
| 284 |
-
);
|
| 285 |
-
|
| 286 |
-
// kpts
|
| 287 |
-
let y_kpts = {
|
| 288 |
-
if let Some(kpts) = kpts {
|
| 289 |
-
let mut kpts_ = Vec::new();
|
| 290 |
-
// rescale
|
| 291 |
-
for i in 0..self.nk() as usize {
|
| 292 |
-
let kx = kpts[KPT_STEP * i] / ratio;
|
| 293 |
-
let ky = kpts[KPT_STEP * i + 1] / ratio;
|
| 294 |
-
let kconf = kpts[KPT_STEP * i + 2];
|
| 295 |
-
if kconf < self.kconf {
|
| 296 |
-
kpts_.push(Point2::default());
|
| 297 |
-
} else {
|
| 298 |
-
kpts_.push(Point2::new_with_conf(
|
| 299 |
-
kx.max(0.0f32).min(width_original),
|
| 300 |
-
ky.max(0.0f32).min(height_original),
|
| 301 |
-
kconf,
|
| 302 |
-
));
|
| 303 |
-
}
|
| 304 |
-
}
|
| 305 |
-
Some(kpts_)
|
| 306 |
-
} else {
|
| 307 |
-
None
|
| 308 |
-
}
|
| 309 |
-
};
|
| 310 |
-
|
| 311 |
-
// data merged
|
| 312 |
-
data.push((y_bbox, y_kpts, coefs));
|
| 313 |
-
}
|
| 314 |
-
|
| 315 |
-
// nms
|
| 316 |
-
non_max_suppression(&mut data, self.iou);
|
| 317 |
-
|
| 318 |
-
// decode
|
| 319 |
-
let mut y_bboxes: Vec<Bbox> = Vec::new();
|
| 320 |
-
let mut y_kpts: Vec<Vec<Point2>> = Vec::new();
|
| 321 |
-
let mut y_masks: Vec<Vec<u8>> = Vec::new();
|
| 322 |
-
for elem in data.into_iter() {
|
| 323 |
-
if let Some(kpts) = elem.1 {
|
| 324 |
-
y_kpts.push(kpts)
|
| 325 |
-
}
|
| 326 |
-
|
| 327 |
-
// decode masks
|
| 328 |
-
if let Some(coefs) = elem.2 {
|
| 329 |
-
let proto = protos.unwrap().slice(s![idx, .., .., ..]);
|
| 330 |
-
let (nm, nh, nw) = proto.dim();
|
| 331 |
-
|
| 332 |
-
// coefs * proto -> mask
|
| 333 |
-
let coefs = Array::from_shape_vec((1, nm), coefs)?; // (n, nm)
|
| 334 |
-
|
| 335 |
-
let proto = proto.to_owned();
|
| 336 |
-
let proto = proto.to_shape((nm, nh * nw))?; // (nm, nh*nw)
|
| 337 |
-
let mask = coefs.dot(&proto); // (nh, nw, n)
|
| 338 |
-
let mask = mask.to_shape((nh, nw, 1))?;
|
| 339 |
-
|
| 340 |
-
// build image from ndarray
|
| 341 |
-
let mask_im: ImageBuffer<image::Luma<_>, Vec<f32>> =
|
| 342 |
-
match ImageBuffer::from_raw(
|
| 343 |
-
nw as u32,
|
| 344 |
-
nh as u32,
|
| 345 |
-
mask.to_owned().into_raw_vec_and_offset().0,
|
| 346 |
-
) {
|
| 347 |
-
Some(image) => image,
|
| 348 |
-
None => panic!("can not create image from ndarray"),
|
| 349 |
-
};
|
| 350 |
-
let mut mask_im = image::DynamicImage::from(mask_im); // -> dyn
|
| 351 |
-
|
| 352 |
-
// rescale masks
|
| 353 |
-
let (_, w_mask, h_mask) =
|
| 354 |
-
self.scale_wh(width_original, height_original, nw as f32, nh as f32);
|
| 355 |
-
let mask_cropped = mask_im.crop(0, 0, w_mask as u32, h_mask as u32);
|
| 356 |
-
let mask_original = mask_cropped.resize_exact(
|
| 357 |
-
// resize_to_fill
|
| 358 |
-
width_original as u32,
|
| 359 |
-
height_original as u32,
|
| 360 |
-
match self.task() {
|
| 361 |
-
YOLOTask::Segment => image::imageops::FilterType::CatmullRom,
|
| 362 |
-
_ => image::imageops::FilterType::Triangle,
|
| 363 |
-
},
|
| 364 |
-
);
|
| 365 |
-
|
| 366 |
-
// crop-mask with bbox
|
| 367 |
-
let mut mask_original_cropped = mask_original.into_luma8();
|
| 368 |
-
for y in 0..height_original as usize {
|
| 369 |
-
for x in 0..width_original as usize {
|
| 370 |
-
if x < elem.0.xmin() as usize
|
| 371 |
-
|| x > elem.0.xmax() as usize
|
| 372 |
-
|| y < elem.0.ymin() as usize
|
| 373 |
-
|| y > elem.0.ymax() as usize
|
| 374 |
-
{
|
| 375 |
-
mask_original_cropped.put_pixel(
|
| 376 |
-
x as u32,
|
| 377 |
-
y as u32,
|
| 378 |
-
image::Luma([0u8]),
|
| 379 |
-
);
|
| 380 |
-
}
|
| 381 |
-
}
|
| 382 |
-
}
|
| 383 |
-
y_masks.push(mask_original_cropped.into_raw());
|
| 384 |
-
}
|
| 385 |
-
y_bboxes.push(elem.0);
|
| 386 |
-
}
|
| 387 |
-
|
| 388 |
-
// save each result
|
| 389 |
-
let y = YOLOResult {
|
| 390 |
-
probs: None,
|
| 391 |
-
bboxes: if !y_bboxes.is_empty() {
|
| 392 |
-
Some(y_bboxes)
|
| 393 |
-
} else {
|
| 394 |
-
None
|
| 395 |
-
},
|
| 396 |
-
keypoints: if !y_kpts.is_empty() {
|
| 397 |
-
Some(y_kpts)
|
| 398 |
-
} else {
|
| 399 |
-
None
|
| 400 |
-
},
|
| 401 |
-
masks: if !y_masks.is_empty() {
|
| 402 |
-
Some(y_masks)
|
| 403 |
-
} else {
|
| 404 |
-
None
|
| 405 |
-
},
|
| 406 |
-
};
|
| 407 |
-
ys.push(y);
|
| 408 |
-
}
|
| 409 |
-
|
| 410 |
-
Ok(ys)
|
| 411 |
-
}
|
| 412 |
-
}
|
| 413 |
-
|
| 414 |
-
pub fn plot_and_save(
|
| 415 |
-
&self,
|
| 416 |
-
ys: &[YOLOResult],
|
| 417 |
-
xs0: &[DynamicImage],
|
| 418 |
-
skeletons: Option<&[(usize, usize)]>,
|
| 419 |
-
) {
|
| 420 |
-
// check font then load
|
| 421 |
-
let font: FontArc = load_font();
|
| 422 |
-
for (_idb, (img0, y)) in xs0.iter().zip(ys.iter()).enumerate() {
|
| 423 |
-
let mut img = img0.to_rgb8();
|
| 424 |
-
|
| 425 |
-
// draw for classifier
|
| 426 |
-
if let Some(probs) = y.probs() {
|
| 427 |
-
for (i, k) in probs.topk(5).iter().enumerate() {
|
| 428 |
-
let legend = format!("{} {:.2}%", self.names[k.0], k.1);
|
| 429 |
-
let scale = 32;
|
| 430 |
-
let legend_size = img.width().max(img.height()) / scale;
|
| 431 |
-
let x = img.width() / 20;
|
| 432 |
-
let y = img.height() / 20 + i as u32 * legend_size;
|
| 433 |
-
|
| 434 |
-
imageproc::drawing::draw_text_mut(
|
| 435 |
-
&mut img,
|
| 436 |
-
image::Rgb([0, 255, 0]),
|
| 437 |
-
x as i32,
|
| 438 |
-
y as i32,
|
| 439 |
-
legend_size as f32,
|
| 440 |
-
&font,
|
| 441 |
-
&legend,
|
| 442 |
-
);
|
| 443 |
-
}
|
| 444 |
-
}
|
| 445 |
-
|
| 446 |
-
// draw bboxes & keypoints
|
| 447 |
-
if let Some(bboxes) = y.bboxes() {
|
| 448 |
-
for (_idx, bbox) in bboxes.iter().enumerate() {
|
| 449 |
-
// rect
|
| 450 |
-
imageproc::drawing::draw_hollow_rect_mut(
|
| 451 |
-
&mut img,
|
| 452 |
-
imageproc::rect::Rect::at(bbox.xmin() as i32, bbox.ymin() as i32)
|
| 453 |
-
.of_size(bbox.width() as u32, bbox.height() as u32),
|
| 454 |
-
image::Rgb(self.color_palette[bbox.id()].into()),
|
| 455 |
-
);
|
| 456 |
-
|
| 457 |
-
// text
|
| 458 |
-
let legend = format!("{} {:.2}%", self.names[bbox.id()], bbox.confidence());
|
| 459 |
-
let scale = 40;
|
| 460 |
-
let legend_size = img.width().max(img.height()) / scale;
|
| 461 |
-
imageproc::drawing::draw_text_mut(
|
| 462 |
-
&mut img,
|
| 463 |
-
image::Rgb(self.color_palette[bbox.id()].into()),
|
| 464 |
-
bbox.xmin() as i32,
|
| 465 |
-
(bbox.ymin() - legend_size as f32) as i32,
|
| 466 |
-
legend_size as f32,
|
| 467 |
-
&font,
|
| 468 |
-
&legend,
|
| 469 |
-
);
|
| 470 |
-
}
|
| 471 |
-
}
|
| 472 |
-
|
| 473 |
-
// draw kpts
|
| 474 |
-
if let Some(keypoints) = y.keypoints() {
|
| 475 |
-
for kpts in keypoints.iter() {
|
| 476 |
-
for kpt in kpts.iter() {
|
| 477 |
-
// filter
|
| 478 |
-
if kpt.confidence() < self.kconf {
|
| 479 |
-
continue;
|
| 480 |
-
}
|
| 481 |
-
|
| 482 |
-
// draw point
|
| 483 |
-
imageproc::drawing::draw_filled_circle_mut(
|
| 484 |
-
&mut img,
|
| 485 |
-
(kpt.x() as i32, kpt.y() as i32),
|
| 486 |
-
2,
|
| 487 |
-
image::Rgb([0, 255, 0]),
|
| 488 |
-
);
|
| 489 |
-
}
|
| 490 |
-
|
| 491 |
-
// draw skeleton if has
|
| 492 |
-
if let Some(skeletons) = skeletons {
|
| 493 |
-
for &(idx1, idx2) in skeletons.iter() {
|
| 494 |
-
let kpt1 = &kpts[idx1];
|
| 495 |
-
let kpt2 = &kpts[idx2];
|
| 496 |
-
if kpt1.confidence() < self.kconf || kpt2.confidence() < self.kconf {
|
| 497 |
-
continue;
|
| 498 |
-
}
|
| 499 |
-
imageproc::drawing::draw_line_segment_mut(
|
| 500 |
-
&mut img,
|
| 501 |
-
(kpt1.x(), kpt1.y()),
|
| 502 |
-
(kpt2.x(), kpt2.y()),
|
| 503 |
-
image::Rgb([233, 14, 57]),
|
| 504 |
-
);
|
| 505 |
-
}
|
| 506 |
-
}
|
| 507 |
-
}
|
| 508 |
-
}
|
| 509 |
-
|
| 510 |
-
// draw mask
|
| 511 |
-
if let Some(masks) = y.masks() {
|
| 512 |
-
for (mask, _bbox) in masks.iter().zip(y.bboxes().unwrap().iter()) {
|
| 513 |
-
let mask_nd: ImageBuffer<image::Luma<_>, Vec<u8>> =
|
| 514 |
-
match ImageBuffer::from_vec(img.width(), img.height(), mask.to_vec()) {
|
| 515 |
-
Some(image) => image,
|
| 516 |
-
None => panic!("can not crate image from ndarray"),
|
| 517 |
-
};
|
| 518 |
-
|
| 519 |
-
for _x in 0..img.width() {
|
| 520 |
-
for _y in 0..img.height() {
|
| 521 |
-
let mask_p = imageproc::drawing::Canvas::get_pixel(&mask_nd, _x, _y);
|
| 522 |
-
if mask_p.0[0] > 0 {
|
| 523 |
-
let mut img_p = imageproc::drawing::Canvas::get_pixel(&img, _x, _y);
|
| 524 |
-
// img_p.0[2] = self.color_palette[bbox.id()].2 / 2;
|
| 525 |
-
// img_p.0[1] = self.color_palette[bbox.id()].1 / 2;
|
| 526 |
-
// img_p.0[0] = self.color_palette[bbox.id()].0 / 2;
|
| 527 |
-
img_p.0[2] /= 2;
|
| 528 |
-
img_p.0[1] = 255 - (255 - img_p.0[2]) / 2;
|
| 529 |
-
img_p.0[0] /= 2;
|
| 530 |
-
imageproc::drawing::Canvas::draw_pixel(&mut img, _x, _y, img_p)
|
| 531 |
-
}
|
| 532 |
-
}
|
| 533 |
-
}
|
| 534 |
-
}
|
| 535 |
-
}
|
| 536 |
-
|
| 537 |
-
// mkdir and save
|
| 538 |
-
let mut runs = PathBuf::from("runs");
|
| 539 |
-
if !runs.exists() {
|
| 540 |
-
std::fs::create_dir_all(&runs).unwrap();
|
| 541 |
-
}
|
| 542 |
-
runs.push(gen_time_string("-"));
|
| 543 |
-
let saveout = format!("{}.jpg", runs.to_str().unwrap());
|
| 544 |
-
let _ = img.save(saveout);
|
| 545 |
-
}
|
| 546 |
-
}
|
| 547 |
-
|
| 548 |
-
pub fn summary(&self) {
|
| 549 |
-
println!(
|
| 550 |
-
"\nSummary:\n\
|
| 551 |
-
> Task: {:?}{}\n\
|
| 552 |
-
> EP: {:?} {}\n\
|
| 553 |
-
> Dtype: {:?}\n\
|
| 554 |
-
> Batch: {} ({}), Height: {} ({}), Width: {} ({})\n\
|
| 555 |
-
> nc: {} nk: {}, nm: {}, conf: {}, kconf: {}, iou: {}\n\
|
| 556 |
-
",
|
| 557 |
-
self.task(),
|
| 558 |
-
match self.engine.author().zip(self.engine.version()) {
|
| 559 |
-
Some((author, ver)) => format!(" ({} {})", author, ver),
|
| 560 |
-
None => String::from(""),
|
| 561 |
-
},
|
| 562 |
-
self.engine.ep(),
|
| 563 |
-
if let OrtEP::CPU = self.engine.ep() {
|
| 564 |
-
""
|
| 565 |
-
} else {
|
| 566 |
-
"(May still fall back to CPU)"
|
| 567 |
-
},
|
| 568 |
-
self.engine.dtype(),
|
| 569 |
-
self.batch(),
|
| 570 |
-
if self.engine.is_batch_dynamic() {
|
| 571 |
-
"Dynamic"
|
| 572 |
-
} else {
|
| 573 |
-
"Const"
|
| 574 |
-
},
|
| 575 |
-
self.height(),
|
| 576 |
-
if self.engine.is_height_dynamic() {
|
| 577 |
-
"Dynamic"
|
| 578 |
-
} else {
|
| 579 |
-
"Const"
|
| 580 |
-
},
|
| 581 |
-
self.width(),
|
| 582 |
-
if self.engine.is_width_dynamic() {
|
| 583 |
-
"Dynamic"
|
| 584 |
-
} else {
|
| 585 |
-
"Const"
|
| 586 |
-
},
|
| 587 |
-
self.nc(),
|
| 588 |
-
self.nk(),
|
| 589 |
-
self.nm(),
|
| 590 |
-
self.conf,
|
| 591 |
-
self.kconf,
|
| 592 |
-
self.iou,
|
| 593 |
-
);
|
| 594 |
-
}
|
| 595 |
-
|
| 596 |
-
pub fn engine(&self) -> &OrtBackend {
|
| 597 |
-
&self.engine
|
| 598 |
-
}
|
| 599 |
-
|
| 600 |
-
pub fn conf(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 601 |
-
self.conf
|
| 602 |
-
}
|
| 603 |
-
|
| 604 |
-
pub fn set_conf(&mut self, val: f32) {
|
| 605 |
-
self.conf = val;
|
| 606 |
-
}
|
| 607 |
-
|
| 608 |
-
pub fn conf_mut(&mut self) -> &mut f32 {
|
| 609 |
-
&mut self.conf
|
| 610 |
-
}
|
| 611 |
-
|
| 612 |
-
pub fn kconf(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 613 |
-
self.kconf
|
| 614 |
-
}
|
| 615 |
-
|
| 616 |
-
pub fn iou(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 617 |
-
self.iou
|
| 618 |
-
}
|
| 619 |
-
|
| 620 |
-
pub fn task(&self) -> &YOLOTask {
|
| 621 |
-
&self.task
|
| 622 |
-
}
|
| 623 |
-
|
| 624 |
-
pub fn batch(&self) -> u32 {
|
| 625 |
-
self.batch
|
| 626 |
-
}
|
| 627 |
-
|
| 628 |
-
pub fn width(&self) -> u32 {
|
| 629 |
-
self.width
|
| 630 |
-
}
|
| 631 |
-
|
| 632 |
-
pub fn height(&self) -> u32 {
|
| 633 |
-
self.height
|
| 634 |
-
}
|
| 635 |
-
|
| 636 |
-
pub fn nc(&self) -> u32 {
|
| 637 |
-
self.nc
|
| 638 |
-
}
|
| 639 |
-
|
| 640 |
-
pub fn nk(&self) -> u32 {
|
| 641 |
-
self.nk
|
| 642 |
-
}
|
| 643 |
-
|
| 644 |
-
pub fn nm(&self) -> u32 {
|
| 645 |
-
self.nm
|
| 646 |
-
}
|
| 647 |
-
|
| 648 |
-
pub fn names(&self) -> &Vec<String> {
|
| 649 |
-
&self.names
|
| 650 |
-
}
|
| 651 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/ort_backend.rs
DELETED
|
@@ -1,553 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
use anyhow::Result;
|
| 2 |
-
use clap::ValueEnum;
|
| 3 |
-
use half::f16;
|
| 4 |
-
use ndarray::{Array, CowArray, IxDyn};
|
| 5 |
-
use ort::{
|
| 6 |
-
CPUExecutionProvider, CUDAExecutionProvider, ExecutionProvider, ExecutionProviderDispatch,
|
| 7 |
-
TensorRTExecutionProvider,
|
| 8 |
-
};
|
| 9 |
-
use ort::{Session, SessionBuilder};
|
| 10 |
-
use ort::{TensorElementType, ValueType};
|
| 11 |
-
use regex::Regex;
|
| 12 |
-
#[derive(Debug, Clone, PartialEq, Eq, PartialOrd, Ord, ValueEnum)]
|
| 13 |
-
pub enum YOLOTask {
|
| 14 |
-
// YOLO tasks
|
| 15 |
-
Classify,
|
| 16 |
-
Detect,
|
| 17 |
-
Pose,
|
| 18 |
-
Segment,
|
| 19 |
-
}
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
#[derive(Debug, Clone, PartialEq, Eq, PartialOrd, Ord)]
|
| 22 |
-
pub enum OrtEP {
|
| 23 |
-
// ONNXRuntime execution provider
|
| 24 |
-
CPU,
|
| 25 |
-
CUDA(i32),
|
| 26 |
-
Trt(i32),
|
| 27 |
-
}
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
#[derive(Debug)]
|
| 30 |
-
pub struct Batch {
|
| 31 |
-
pub opt: u32,
|
| 32 |
-
pub min: u32,
|
| 33 |
-
pub max: u32,
|
| 34 |
-
}
|
| 35 |
-
|
| 36 |
-
impl Default for Batch {
|
| 37 |
-
fn default() -> Self {
|
| 38 |
-
Self {
|
| 39 |
-
opt: 1,
|
| 40 |
-
min: 1,
|
| 41 |
-
max: 1,
|
| 42 |
-
}
|
| 43 |
-
}
|
| 44 |
-
}
|
| 45 |
-
|
| 46 |
-
#[derive(Debug, Default)]
|
| 47 |
-
pub struct OrtInputs {
|
| 48 |
-
// ONNX model inputs attrs
|
| 49 |
-
pub shapes: Vec<Vec<i64>>,
|
| 50 |
-
//pub dtypes: Vec<TensorElementDataType>,
|
| 51 |
-
pub dtypes: Vec<TensorElementType>,
|
| 52 |
-
pub names: Vec<String>,
|
| 53 |
-
pub sizes: Vec<Vec<u32>>,
|
| 54 |
-
}
|
| 55 |
-
|
| 56 |
-
impl OrtInputs {
|
| 57 |
-
pub fn new(session: &Session) -> Self {
|
| 58 |
-
let mut shapes = Vec::new();
|
| 59 |
-
let mut dtypes = Vec::new();
|
| 60 |
-
let mut names = Vec::new();
|
| 61 |
-
for i in session.inputs.iter() {
|
| 62 |
-
/* let shape: Vec<i32> = i
|
| 63 |
-
.dimensions()
|
| 64 |
-
.map(|x| if let Some(x) = x { x as i32 } else { -1i32 })
|
| 65 |
-
.collect();
|
| 66 |
-
shapes.push(shape); */
|
| 67 |
-
if let ort::ValueType::Tensor { ty, dimensions } = &i.input_type {
|
| 68 |
-
dtypes.push(ty.clone());
|
| 69 |
-
let shape = dimensions.clone();
|
| 70 |
-
shapes.push(shape);
|
| 71 |
-
} else {
|
| 72 |
-
panic!("不支持的数据格式, {} - {}", file!(), line!());
|
| 73 |
-
}
|
| 74 |
-
//dtypes.push(i.input_type);
|
| 75 |
-
names.push(i.name.clone());
|
| 76 |
-
}
|
| 77 |
-
Self {
|
| 78 |
-
shapes,
|
| 79 |
-
dtypes,
|
| 80 |
-
names,
|
| 81 |
-
..Default::default()
|
| 82 |
-
}
|
| 83 |
-
}
|
| 84 |
-
}
|
| 85 |
-
|
| 86 |
-
#[derive(Debug)]
|
| 87 |
-
pub struct OrtConfig {
|
| 88 |
-
// ORT config
|
| 89 |
-
pub f: String,
|
| 90 |
-
pub task: Option<YOLOTask>,
|
| 91 |
-
pub ep: OrtEP,
|
| 92 |
-
pub trt_fp16: bool,
|
| 93 |
-
pub batch: Batch,
|
| 94 |
-
pub image_size: (Option<u32>, Option<u32>),
|
| 95 |
-
}
|
| 96 |
-
|
| 97 |
-
#[derive(Debug)]
|
| 98 |
-
pub struct OrtBackend {
|
| 99 |
-
// ORT engine
|
| 100 |
-
session: Session,
|
| 101 |
-
task: YOLOTask,
|
| 102 |
-
ep: OrtEP,
|
| 103 |
-
batch: Batch,
|
| 104 |
-
inputs: OrtInputs,
|
| 105 |
-
}
|
| 106 |
-
|
| 107 |
-
impl OrtBackend {
|
| 108 |
-
pub fn build(args: OrtConfig) -> Result<Self> {
|
| 109 |
-
// build env & session
|
| 110 |
-
// in version 2.x environment is removed
|
| 111 |
-
/* let env = ort::EnvironmentBuilder
|
| 112 |
-
::with_name("YOLOv8")
|
| 113 |
-
.build()?
|
| 114 |
-
.into_arc(); */
|
| 115 |
-
let sessionbuilder = SessionBuilder::new()?;
|
| 116 |
-
let session = sessionbuilder.commit_from_file(&args.f)?;
|
| 117 |
-
//let session = SessionBuilder::new(&env)?.with_model_from_file(&args.f)?;
|
| 118 |
-
|
| 119 |
-
// get inputs
|
| 120 |
-
let mut inputs = OrtInputs::new(&session);
|
| 121 |
-
|
| 122 |
-
// batch size
|
| 123 |
-
let mut batch = args.batch;
|
| 124 |
-
let batch = if inputs.shapes[0][0] == -1 {
|
| 125 |
-
batch
|
| 126 |
-
} else {
|
| 127 |
-
assert_eq!(
|
| 128 |
-
inputs.shapes[0][0] as u32, batch.opt,
|
| 129 |
-
"Expected batch size: {}, got {}. Try using `--batch {}`.",
|
| 130 |
-
inputs.shapes[0][0] as u32, batch.opt, inputs.shapes[0][0] as u32
|
| 131 |
-
);
|
| 132 |
-
batch.opt = inputs.shapes[0][0] as u32;
|
| 133 |
-
batch
|
| 134 |
-
};
|
| 135 |
-
|
| 136 |
-
// input size: height and width
|
| 137 |
-
let height = if inputs.shapes[0][2] == -1 {
|
| 138 |
-
match args.image_size.0 {
|
| 139 |
-
Some(height) => height,
|
| 140 |
-
None => panic!("Failed to get model height. Make it explicit with `--height`"),
|
| 141 |
-
}
|
| 142 |
-
} else {
|
| 143 |
-
inputs.shapes[0][2] as u32
|
| 144 |
-
};
|
| 145 |
-
let width = if inputs.shapes[0][3] == -1 {
|
| 146 |
-
match args.image_size.1 {
|
| 147 |
-
Some(width) => width,
|
| 148 |
-
None => panic!("Failed to get model width. Make it explicit with `--width`"),
|
| 149 |
-
}
|
| 150 |
-
} else {
|
| 151 |
-
inputs.shapes[0][3] as u32
|
| 152 |
-
};
|
| 153 |
-
inputs.sizes.push(vec![height, width]);
|
| 154 |
-
|
| 155 |
-
// build provider
|
| 156 |
-
let (ep, provider) = match args.ep {
|
| 157 |
-
OrtEP::CUDA(device_id) => Self::set_ep_cuda(device_id),
|
| 158 |
-
OrtEP::Trt(device_id) => Self::set_ep_trt(device_id, args.trt_fp16, &batch, &inputs),
|
| 159 |
-
_ => (
|
| 160 |
-
OrtEP::CPU,
|
| 161 |
-
ExecutionProviderDispatch::from(CPUExecutionProvider::default()),
|
| 162 |
-
),
|
| 163 |
-
};
|
| 164 |
-
|
| 165 |
-
// build session again with the new provider
|
| 166 |
-
let session = SessionBuilder::new()?
|
| 167 |
-
// .with_optimization_level(ort::GraphOptimizationLevel::Level3)?
|
| 168 |
-
.with_execution_providers([provider])?
|
| 169 |
-
.commit_from_file(args.f)?;
|
| 170 |
-
|
| 171 |
-
// task: using given one or guessing
|
| 172 |
-
let task = match args.task {
|
| 173 |
-
Some(task) => task,
|
| 174 |
-
None => match session.metadata() {
|
| 175 |
-
Err(_) => panic!("No metadata found. Try making it explicit by `--task`"),
|
| 176 |
-
Ok(metadata) => match metadata.custom("task") {
|
| 177 |
-
Err(_) => panic!("Can not get custom value. Try making it explicit by `--task`"),
|
| 178 |
-
Ok(value) => match value {
|
| 179 |
-
None => panic!("No corresponding value of `task` found in metadata. Make it explicit by `--task`"),
|
| 180 |
-
Some(task) => match task.as_str() {
|
| 181 |
-
"classify" => YOLOTask::Classify,
|
| 182 |
-
"detect" => YOLOTask::Detect,
|
| 183 |
-
"pose" => YOLOTask::Pose,
|
| 184 |
-
"segment" => YOLOTask::Segment,
|
| 185 |
-
x => todo!("{:?} is not supported for now!", x),
|
| 186 |
-
},
|
| 187 |
-
},
|
| 188 |
-
},
|
| 189 |
-
},
|
| 190 |
-
};
|
| 191 |
-
|
| 192 |
-
Ok(Self {
|
| 193 |
-
session,
|
| 194 |
-
task,
|
| 195 |
-
ep,
|
| 196 |
-
batch,
|
| 197 |
-
inputs,
|
| 198 |
-
})
|
| 199 |
-
}
|
| 200 |
-
|
| 201 |
-
pub fn fetch_inputs_from_session(
|
| 202 |
-
session: &Session,
|
| 203 |
-
) -> (Vec<Vec<i64>>, Vec<TensorElementType>, Vec<String>) {
|
| 204 |
-
// get inputs attrs from ONNX model
|
| 205 |
-
let mut shapes = Vec::new();
|
| 206 |
-
let mut dtypes = Vec::new();
|
| 207 |
-
let mut names = Vec::new();
|
| 208 |
-
for i in session.inputs.iter() {
|
| 209 |
-
if let ort::ValueType::Tensor { ty, dimensions } = &i.input_type {
|
| 210 |
-
dtypes.push(ty.clone());
|
| 211 |
-
let shape = dimensions.clone();
|
| 212 |
-
shapes.push(shape);
|
| 213 |
-
} else {
|
| 214 |
-
panic!("不支持的数据格式, {} - {}", file!(), line!());
|
| 215 |
-
}
|
| 216 |
-
names.push(i.name.clone());
|
| 217 |
-
}
|
| 218 |
-
(shapes, dtypes, names)
|
| 219 |
-
}
|
| 220 |
-
|
| 221 |
-
pub fn set_ep_cuda(device_id: i32) -> (OrtEP, ExecutionProviderDispatch) {
|
| 222 |
-
let cuda_provider = CUDAExecutionProvider::default().with_device_id(device_id);
|
| 223 |
-
if let Ok(true) = cuda_provider.is_available() {
|
| 224 |
-
(
|
| 225 |
-
OrtEP::CUDA(device_id),
|
| 226 |
-
ExecutionProviderDispatch::from(cuda_provider), //PlantForm::CUDA(cuda_provider)
|
| 227 |
-
)
|
| 228 |
-
} else {
|
| 229 |
-
println!("> CUDA is not available! Using CPU.");
|
| 230 |
-
(
|
| 231 |
-
OrtEP::CPU,
|
| 232 |
-
ExecutionProviderDispatch::from(CPUExecutionProvider::default()), //PlantForm::CPU(CPUExecutionProvider::default())
|
| 233 |
-
)
|
| 234 |
-
}
|
| 235 |
-
}
|
| 236 |
-
|
| 237 |
-
pub fn set_ep_trt(
|
| 238 |
-
device_id: i32,
|
| 239 |
-
fp16: bool,
|
| 240 |
-
batch: &Batch,
|
| 241 |
-
inputs: &OrtInputs,
|
| 242 |
-
) -> (OrtEP, ExecutionProviderDispatch) {
|
| 243 |
-
// set TensorRT
|
| 244 |
-
let trt_provider = TensorRTExecutionProvider::default().with_device_id(device_id);
|
| 245 |
-
|
| 246 |
-
//trt_provider.
|
| 247 |
-
if let Ok(true) = trt_provider.is_available() {
|
| 248 |
-
let (height, width) = (inputs.sizes[0][0], inputs.sizes[0][1]);
|
| 249 |
-
if inputs.dtypes[0] == TensorElementType::Float16 && !fp16 {
|
| 250 |
-
panic!(
|
| 251 |
-
"Dtype mismatch! Expected: Float32, got: {:?}. You should use `--fp16`",
|
| 252 |
-
inputs.dtypes[0]
|
| 253 |
-
);
|
| 254 |
-
}
|
| 255 |
-
// dynamic shape: input_tensor_1:dim_1xdim_2x...,input_tensor_2:dim_3xdim_4x...,...
|
| 256 |
-
let mut opt_string = String::new();
|
| 257 |
-
let mut min_string = String::new();
|
| 258 |
-
let mut max_string = String::new();
|
| 259 |
-
for name in inputs.names.iter() {
|
| 260 |
-
let s_opt = format!("{}:{}x3x{}x{},", name, batch.opt, height, width);
|
| 261 |
-
let s_min = format!("{}:{}x3x{}x{},", name, batch.min, height, width);
|
| 262 |
-
let s_max = format!("{}:{}x3x{}x{},", name, batch.max, height, width);
|
| 263 |
-
opt_string.push_str(s_opt.as_str());
|
| 264 |
-
min_string.push_str(s_min.as_str());
|
| 265 |
-
max_string.push_str(s_max.as_str());
|
| 266 |
-
}
|
| 267 |
-
let _ = opt_string.pop();
|
| 268 |
-
let _ = min_string.pop();
|
| 269 |
-
let _ = max_string.pop();
|
| 270 |
-
|
| 271 |
-
let trt_provider = trt_provider
|
| 272 |
-
.with_profile_opt_shapes(opt_string)
|
| 273 |
-
.with_profile_min_shapes(min_string)
|
| 274 |
-
.with_profile_max_shapes(max_string)
|
| 275 |
-
.with_fp16(fp16)
|
| 276 |
-
.with_timing_cache(true);
|
| 277 |
-
(
|
| 278 |
-
OrtEP::Trt(device_id),
|
| 279 |
-
ExecutionProviderDispatch::from(trt_provider),
|
| 280 |
-
)
|
| 281 |
-
} else {
|
| 282 |
-
println!("> TensorRT is not available! Try using CUDA...");
|
| 283 |
-
Self::set_ep_cuda(device_id)
|
| 284 |
-
}
|
| 285 |
-
}
|
| 286 |
-
|
| 287 |
-
pub fn fetch_from_metadata(&self, key: &str) -> Option<String> {
|
| 288 |
-
// fetch value from onnx model file by key
|
| 289 |
-
match self.session.metadata() {
|
| 290 |
-
Err(_) => None,
|
| 291 |
-
Ok(metadata) => match metadata.custom(key) {
|
| 292 |
-
Err(_) => None,
|
| 293 |
-
Ok(value) => value,
|
| 294 |
-
},
|
| 295 |
-
}
|
| 296 |
-
}
|
| 297 |
-
|
| 298 |
-
pub fn run(&self, xs: Array<f32, IxDyn>, profile: bool) -> Result<Vec<Array<f32, IxDyn>>> {
|
| 299 |
-
// ORT inference
|
| 300 |
-
match self.dtype() {
|
| 301 |
-
TensorElementType::Float16 => self.run_fp16(xs, profile),
|
| 302 |
-
TensorElementType::Float32 => self.run_fp32(xs, profile),
|
| 303 |
-
_ => todo!(),
|
| 304 |
-
}
|
| 305 |
-
}
|
| 306 |
-
|
| 307 |
-
pub fn run_fp16(&self, xs: Array<f32, IxDyn>, profile: bool) -> Result<Vec<Array<f32, IxDyn>>> {
|
| 308 |
-
// f32->f16
|
| 309 |
-
let t = std::time::Instant::now();
|
| 310 |
-
let xs = xs.mapv(f16::from_f32);
|
| 311 |
-
if profile {
|
| 312 |
-
println!("[ORT f32->f16]: {:?}", t.elapsed());
|
| 313 |
-
}
|
| 314 |
-
|
| 315 |
-
// h2d
|
| 316 |
-
let t = std::time::Instant::now();
|
| 317 |
-
let xs = CowArray::from(xs);
|
| 318 |
-
if profile {
|
| 319 |
-
println!("[ORT H2D]: {:?}", t.elapsed());
|
| 320 |
-
}
|
| 321 |
-
|
| 322 |
-
// run
|
| 323 |
-
let t = std::time::Instant::now();
|
| 324 |
-
let ys = self.session.run(ort::inputs![xs.view()]?)?;
|
| 325 |
-
if profile {
|
| 326 |
-
println!("[ORT Inference]: {:?}", t.elapsed());
|
| 327 |
-
}
|
| 328 |
-
|
| 329 |
-
// d2h
|
| 330 |
-
Ok(ys
|
| 331 |
-
.iter()
|
| 332 |
-
.map(|(_k, v)| {
|
| 333 |
-
// d2h
|
| 334 |
-
let t = std::time::Instant::now();
|
| 335 |
-
let v = v.try_extract_tensor().unwrap();
|
| 336 |
-
//let v = v.try_extract::<_>().unwrap().view().clone().into_owned();
|
| 337 |
-
if profile {
|
| 338 |
-
println!("[ORT D2H]: {:?}", t.elapsed());
|
| 339 |
-
}
|
| 340 |
-
|
| 341 |
-
// f16->f32
|
| 342 |
-
let t_ = std::time::Instant::now();
|
| 343 |
-
let v = v.mapv(f16::to_f32);
|
| 344 |
-
if profile {
|
| 345 |
-
println!("[ORT f16->f32]: {:?}", t_.elapsed());
|
| 346 |
-
}
|
| 347 |
-
v
|
| 348 |
-
})
|
| 349 |
-
.collect::<Vec<Array<_, _>>>())
|
| 350 |
-
}
|
| 351 |
-
|
| 352 |
-
pub fn run_fp32(&self, xs: Array<f32, IxDyn>, profile: bool) -> Result<Vec<Array<f32, IxDyn>>> {
|
| 353 |
-
// h2d
|
| 354 |
-
let t = std::time::Instant::now();
|
| 355 |
-
let xs = CowArray::from(xs);
|
| 356 |
-
if profile {
|
| 357 |
-
println!("[ORT H2D]: {:?}", t.elapsed());
|
| 358 |
-
}
|
| 359 |
-
|
| 360 |
-
// run
|
| 361 |
-
let t = std::time::Instant::now();
|
| 362 |
-
let ys = self.session.run(ort::inputs![xs.view()]?)?;
|
| 363 |
-
if profile {
|
| 364 |
-
println!("[ORT Inference]: {:?}", t.elapsed());
|
| 365 |
-
}
|
| 366 |
-
|
| 367 |
-
// d2h
|
| 368 |
-
Ok(ys
|
| 369 |
-
.iter()
|
| 370 |
-
.map(|(_k, v)| {
|
| 371 |
-
let t = std::time::Instant::now();
|
| 372 |
-
let v = v.try_extract_tensor::<f32>().unwrap().into_owned();
|
| 373 |
-
//let x = x.try_extract::<_>().unwrap().view().clone().into_owned();
|
| 374 |
-
if profile {
|
| 375 |
-
println!("[ORT D2H]: {:?}", t.elapsed());
|
| 376 |
-
}
|
| 377 |
-
v
|
| 378 |
-
})
|
| 379 |
-
.collect::<Vec<Array<_, _>>>())
|
| 380 |
-
}
|
| 381 |
-
|
| 382 |
-
pub fn output_shapes(&self) -> Vec<Vec<i64>> {
|
| 383 |
-
let mut shapes = Vec::new();
|
| 384 |
-
for output in &self.session.outputs {
|
| 385 |
-
if let ValueType::Tensor { ty: _, dimensions } = &output.output_type {
|
| 386 |
-
let shape = dimensions.clone();
|
| 387 |
-
shapes.push(shape);
|
| 388 |
-
} else {
|
| 389 |
-
panic!("not support data format, {} - {}", file!(), line!());
|
| 390 |
-
}
|
| 391 |
-
}
|
| 392 |
-
shapes
|
| 393 |
-
}
|
| 394 |
-
|
| 395 |
-
pub fn output_dtypes(&self) -> Vec<TensorElementType> {
|
| 396 |
-
let mut dtypes = Vec::new();
|
| 397 |
-
for output in &self.session.outputs {
|
| 398 |
-
if let ValueType::Tensor { ty, dimensions: _ } = &output.output_type {
|
| 399 |
-
dtypes.push(ty.clone());
|
| 400 |
-
} else {
|
| 401 |
-
panic!("not support data format, {} - {}", file!(), line!());
|
| 402 |
-
}
|
| 403 |
-
}
|
| 404 |
-
dtypes
|
| 405 |
-
}
|
| 406 |
-
|
| 407 |
-
pub fn input_shapes(&self) -> &Vec<Vec<i64>> {
|
| 408 |
-
&self.inputs.shapes
|
| 409 |
-
}
|
| 410 |
-
|
| 411 |
-
pub fn input_names(&self) -> &Vec<String> {
|
| 412 |
-
&self.inputs.names
|
| 413 |
-
}
|
| 414 |
-
|
| 415 |
-
pub fn input_dtypes(&self) -> &Vec<TensorElementType> {
|
| 416 |
-
&self.inputs.dtypes
|
| 417 |
-
}
|
| 418 |
-
|
| 419 |
-
pub fn dtype(&self) -> TensorElementType {
|
| 420 |
-
self.input_dtypes()[0]
|
| 421 |
-
}
|
| 422 |
-
|
| 423 |
-
pub fn height(&self) -> u32 {
|
| 424 |
-
self.inputs.sizes[0][0]
|
| 425 |
-
}
|
| 426 |
-
|
| 427 |
-
pub fn width(&self) -> u32 {
|
| 428 |
-
self.inputs.sizes[0][1]
|
| 429 |
-
}
|
| 430 |
-
|
| 431 |
-
pub fn is_height_dynamic(&self) -> bool {
|
| 432 |
-
self.input_shapes()[0][2] == -1
|
| 433 |
-
}
|
| 434 |
-
|
| 435 |
-
pub fn is_width_dynamic(&self) -> bool {
|
| 436 |
-
self.input_shapes()[0][3] == -1
|
| 437 |
-
}
|
| 438 |
-
|
| 439 |
-
pub fn batch(&self) -> u32 {
|
| 440 |
-
self.batch.opt
|
| 441 |
-
}
|
| 442 |
-
|
| 443 |
-
pub fn is_batch_dynamic(&self) -> bool {
|
| 444 |
-
self.input_shapes()[0][0] == -1
|
| 445 |
-
}
|
| 446 |
-
|
| 447 |
-
pub fn ep(&self) -> &OrtEP {
|
| 448 |
-
&self.ep
|
| 449 |
-
}
|
| 450 |
-
|
| 451 |
-
pub fn task(&self) -> YOLOTask {
|
| 452 |
-
self.task.clone()
|
| 453 |
-
}
|
| 454 |
-
|
| 455 |
-
pub fn names(&self) -> Option<Vec<String>> {
|
| 456 |
-
// class names, metadata parsing
|
| 457 |
-
// String format: `{0: 'person', 1: 'bicycle', 2: 'sports ball', ..., 27: "yellow_lady's_slipper"}`
|
| 458 |
-
match self.fetch_from_metadata("names") {
|
| 459 |
-
Some(names) => {
|
| 460 |
-
let re = Regex::new(r#"(['"])([-()\w '"]+)(['"])"#).unwrap();
|
| 461 |
-
let mut names_ = vec![];
|
| 462 |
-
for (_, [_, name, _]) in re.captures_iter(&names).map(|x| x.extract()) {
|
| 463 |
-
names_.push(name.to_string());
|
| 464 |
-
}
|
| 465 |
-
Some(names_)
|
| 466 |
-
}
|
| 467 |
-
None => None,
|
| 468 |
-
}
|
| 469 |
-
}
|
| 470 |
-
|
| 471 |
-
pub fn nk(&self) -> Option<u32> {
|
| 472 |
-
// num_keypoints, metadata parsing: String `nk` in onnx model: `[17, 3]`
|
| 473 |
-
match self.fetch_from_metadata("kpt_shape") {
|
| 474 |
-
None => None,
|
| 475 |
-
Some(kpt_string) => {
|
| 476 |
-
let re = Regex::new(r"([0-9]+), ([0-9]+)").unwrap();
|
| 477 |
-
let caps = re.captures(&kpt_string).unwrap();
|
| 478 |
-
Some(caps.get(1).unwrap().as_str().parse::<u32>().unwrap())
|
| 479 |
-
}
|
| 480 |
-
}
|
| 481 |
-
}
|
| 482 |
-
|
| 483 |
-
pub fn nc(&self) -> Option<u32> {
|
| 484 |
-
// num_classes
|
| 485 |
-
match self.names() {
|
| 486 |
-
// by names
|
| 487 |
-
Some(names) => Some(names.len() as u32),
|
| 488 |
-
None => match self.task() {
|
| 489 |
-
// by task calculation
|
| 490 |
-
YOLOTask::Classify => Some(self.output_shapes()[0][1] as u32),
|
| 491 |
-
YOLOTask::Detect => {
|
| 492 |
-
if self.output_shapes()[0][1] == -1 {
|
| 493 |
-
None
|
| 494 |
-
} else {
|
| 495 |
-
// cxywhclss
|
| 496 |
-
Some(self.output_shapes()[0][1] as u32 - 4)
|
| 497 |
-
}
|
| 498 |
-
}
|
| 499 |
-
YOLOTask::Pose => {
|
| 500 |
-
match self.nk() {
|
| 501 |
-
None => None,
|
| 502 |
-
Some(nk) => {
|
| 503 |
-
if self.output_shapes()[0][1] == -1 {
|
| 504 |
-
None
|
| 505 |
-
} else {
|
| 506 |
-
// cxywhclss3*kpt
|
| 507 |
-
Some(self.output_shapes()[0][1] as u32 - 4 - 3 * nk)
|
| 508 |
-
}
|
| 509 |
-
}
|
| 510 |
-
}
|
| 511 |
-
}
|
| 512 |
-
YOLOTask::Segment => {
|
| 513 |
-
if self.output_shapes()[0][1] == -1 {
|
| 514 |
-
None
|
| 515 |
-
} else {
|
| 516 |
-
// cxywhclssnm
|
| 517 |
-
Some((self.output_shapes()[0][1] - self.output_shapes()[1][1]) as u32 - 4)
|
| 518 |
-
}
|
| 519 |
-
}
|
| 520 |
-
},
|
| 521 |
-
}
|
| 522 |
-
}
|
| 523 |
-
|
| 524 |
-
pub fn nm(&self) -> Option<u32> {
|
| 525 |
-
// num_masks
|
| 526 |
-
match self.task() {
|
| 527 |
-
YOLOTask::Segment => Some(self.output_shapes()[1][1] as u32),
|
| 528 |
-
_ => None,
|
| 529 |
-
}
|
| 530 |
-
}
|
| 531 |
-
|
| 532 |
-
pub fn na(&self) -> Option<u32> {
|
| 533 |
-
// num_anchors
|
| 534 |
-
match self.task() {
|
| 535 |
-
YOLOTask::Segment | YOLOTask::Detect | YOLOTask::Pose => {
|
| 536 |
-
if self.output_shapes()[0][2] == -1 {
|
| 537 |
-
None
|
| 538 |
-
} else {
|
| 539 |
-
Some(self.output_shapes()[0][2] as u32)
|
| 540 |
-
}
|
| 541 |
-
}
|
| 542 |
-
_ => None,
|
| 543 |
-
}
|
| 544 |
-
}
|
| 545 |
-
|
| 546 |
-
pub fn author(&self) -> Option<String> {
|
| 547 |
-
self.fetch_from_metadata("author")
|
| 548 |
-
}
|
| 549 |
-
|
| 550 |
-
pub fn version(&self) -> Option<String> {
|
| 551 |
-
self.fetch_from_metadata("version")
|
| 552 |
-
}
|
| 553 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-Rust/src/yolo_result.rs
DELETED
|
@@ -1,235 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
use ndarray::{Array, Axis, IxDyn};
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
#[derive(Clone, PartialEq, Default)]
|
| 4 |
-
pub struct YOLOResult {
|
| 5 |
-
// YOLO tasks results of an image
|
| 6 |
-
pub probs: Option<Embedding>,
|
| 7 |
-
pub bboxes: Option<Vec<Bbox>>,
|
| 8 |
-
pub keypoints: Option<Vec<Vec<Point2>>>,
|
| 9 |
-
pub masks: Option<Vec<Vec<u8>>>,
|
| 10 |
-
}
|
| 11 |
-
|
| 12 |
-
impl std::fmt::Debug for YOLOResult {
|
| 13 |
-
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter<'_>) -> std::fmt::Result {
|
| 14 |
-
f.debug_struct("YOLOResult")
|
| 15 |
-
.field(
|
| 16 |
-
"Probs(top5)",
|
| 17 |
-
&format_args!("{:?}", self.probs().map(|probs| probs.topk(5))),
|
| 18 |
-
)
|
| 19 |
-
.field("Bboxes", &self.bboxes)
|
| 20 |
-
.field("Keypoints", &self.keypoints)
|
| 21 |
-
.field(
|
| 22 |
-
"Masks",
|
| 23 |
-
&format_args!("{:?}", self.masks().map(|masks| masks.len())),
|
| 24 |
-
)
|
| 25 |
-
.finish()
|
| 26 |
-
}
|
| 27 |
-
}
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
impl YOLOResult {
|
| 30 |
-
pub fn new(
|
| 31 |
-
probs: Option<Embedding>,
|
| 32 |
-
bboxes: Option<Vec<Bbox>>,
|
| 33 |
-
keypoints: Option<Vec<Vec<Point2>>>,
|
| 34 |
-
masks: Option<Vec<Vec<u8>>>,
|
| 35 |
-
) -> Self {
|
| 36 |
-
Self {
|
| 37 |
-
probs,
|
| 38 |
-
bboxes,
|
| 39 |
-
keypoints,
|
| 40 |
-
masks,
|
| 41 |
-
}
|
| 42 |
-
}
|
| 43 |
-
|
| 44 |
-
pub fn probs(&self) -> Option<&Embedding> {
|
| 45 |
-
self.probs.as_ref()
|
| 46 |
-
}
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
pub fn keypoints(&self) -> Option<&Vec<Vec<Point2>>> {
|
| 49 |
-
self.keypoints.as_ref()
|
| 50 |
-
}
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
pub fn masks(&self) -> Option<&Vec<Vec<u8>>> {
|
| 53 |
-
self.masks.as_ref()
|
| 54 |
-
}
|
| 55 |
-
|
| 56 |
-
pub fn bboxes(&self) -> Option<&Vec<Bbox>> {
|
| 57 |
-
self.bboxes.as_ref()
|
| 58 |
-
}
|
| 59 |
-
|
| 60 |
-
pub fn bboxes_mut(&mut self) -> Option<&mut Vec<Bbox>> {
|
| 61 |
-
self.bboxes.as_mut()
|
| 62 |
-
}
|
| 63 |
-
}
|
| 64 |
-
|
| 65 |
-
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Clone, Default)]
|
| 66 |
-
pub struct Point2 {
|
| 67 |
-
// A point2d with x, y, conf
|
| 68 |
-
x: f32,
|
| 69 |
-
y: f32,
|
| 70 |
-
confidence: f32,
|
| 71 |
-
}
|
| 72 |
-
|
| 73 |
-
impl Point2 {
|
| 74 |
-
pub fn new_with_conf(x: f32, y: f32, confidence: f32) -> Self {
|
| 75 |
-
Self { x, y, confidence }
|
| 76 |
-
}
|
| 77 |
-
|
| 78 |
-
pub fn new(x: f32, y: f32) -> Self {
|
| 79 |
-
Self {
|
| 80 |
-
x,
|
| 81 |
-
y,
|
| 82 |
-
..Default::default()
|
| 83 |
-
}
|
| 84 |
-
}
|
| 85 |
-
|
| 86 |
-
pub fn x(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 87 |
-
self.x
|
| 88 |
-
}
|
| 89 |
-
|
| 90 |
-
pub fn y(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 91 |
-
self.y
|
| 92 |
-
}
|
| 93 |
-
|
| 94 |
-
pub fn confidence(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 95 |
-
self.confidence
|
| 96 |
-
}
|
| 97 |
-
}
|
| 98 |
-
|
| 99 |
-
#[derive(Debug, Clone, PartialEq, Default)]
|
| 100 |
-
pub struct Embedding {
|
| 101 |
-
// An float32 n-dims tensor
|
| 102 |
-
data: Array<f32, IxDyn>,
|
| 103 |
-
}
|
| 104 |
-
|
| 105 |
-
impl Embedding {
|
| 106 |
-
pub fn new(data: Array<f32, IxDyn>) -> Self {
|
| 107 |
-
Self { data }
|
| 108 |
-
}
|
| 109 |
-
|
| 110 |
-
pub fn data(&self) -> &Array<f32, IxDyn> {
|
| 111 |
-
&self.data
|
| 112 |
-
}
|
| 113 |
-
|
| 114 |
-
pub fn topk(&self, k: usize) -> Vec<(usize, f32)> {
|
| 115 |
-
let mut probs = self
|
| 116 |
-
.data
|
| 117 |
-
.iter()
|
| 118 |
-
.enumerate()
|
| 119 |
-
.map(|(a, b)| (a, *b))
|
| 120 |
-
.collect::<Vec<_>>();
|
| 121 |
-
probs.sort_by(|a, b| b.1.partial_cmp(&a.1).unwrap());
|
| 122 |
-
let mut topk = Vec::new();
|
| 123 |
-
for &(id, confidence) in probs.iter().take(k) {
|
| 124 |
-
topk.push((id, confidence));
|
| 125 |
-
}
|
| 126 |
-
topk
|
| 127 |
-
}
|
| 128 |
-
|
| 129 |
-
pub fn norm(&self) -> Array<f32, IxDyn> {
|
| 130 |
-
let std_ = self.data.mapv(|x| x * x).sum_axis(Axis(0)).mapv(f32::sqrt);
|
| 131 |
-
self.data.clone() / std_
|
| 132 |
-
}
|
| 133 |
-
|
| 134 |
-
pub fn top1(&self) -> (usize, f32) {
|
| 135 |
-
self.topk(1)[0]
|
| 136 |
-
}
|
| 137 |
-
}
|
| 138 |
-
|
| 139 |
-
#[derive(Debug, Clone, PartialEq, Default)]
|
| 140 |
-
pub struct Bbox {
|
| 141 |
-
// a bounding box around an object
|
| 142 |
-
xmin: f32,
|
| 143 |
-
ymin: f32,
|
| 144 |
-
width: f32,
|
| 145 |
-
height: f32,
|
| 146 |
-
id: usize,
|
| 147 |
-
confidence: f32,
|
| 148 |
-
}
|
| 149 |
-
|
| 150 |
-
impl Bbox {
|
| 151 |
-
pub fn new_from_xywh(xmin: f32, ymin: f32, width: f32, height: f32) -> Self {
|
| 152 |
-
Self {
|
| 153 |
-
xmin,
|
| 154 |
-
ymin,
|
| 155 |
-
width,
|
| 156 |
-
height,
|
| 157 |
-
..Default::default()
|
| 158 |
-
}
|
| 159 |
-
}
|
| 160 |
-
|
| 161 |
-
pub fn new(xmin: f32, ymin: f32, width: f32, height: f32, id: usize, confidence: f32) -> Self {
|
| 162 |
-
Self {
|
| 163 |
-
xmin,
|
| 164 |
-
ymin,
|
| 165 |
-
width,
|
| 166 |
-
height,
|
| 167 |
-
id,
|
| 168 |
-
confidence,
|
| 169 |
-
}
|
| 170 |
-
}
|
| 171 |
-
|
| 172 |
-
pub fn width(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 173 |
-
self.width
|
| 174 |
-
}
|
| 175 |
-
|
| 176 |
-
pub fn height(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 177 |
-
self.height
|
| 178 |
-
}
|
| 179 |
-
|
| 180 |
-
pub fn xmin(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 181 |
-
self.xmin
|
| 182 |
-
}
|
| 183 |
-
|
| 184 |
-
pub fn ymin(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 185 |
-
self.ymin
|
| 186 |
-
}
|
| 187 |
-
|
| 188 |
-
pub fn xmax(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 189 |
-
self.xmin + self.width
|
| 190 |
-
}
|
| 191 |
-
|
| 192 |
-
pub fn ymax(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 193 |
-
self.ymin + self.height
|
| 194 |
-
}
|
| 195 |
-
|
| 196 |
-
pub fn tl(&self) -> Point2 {
|
| 197 |
-
Point2::new(self.xmin, self.ymin)
|
| 198 |
-
}
|
| 199 |
-
|
| 200 |
-
pub fn br(&self) -> Point2 {
|
| 201 |
-
Point2::new(self.xmax(), self.ymax())
|
| 202 |
-
}
|
| 203 |
-
|
| 204 |
-
pub fn cxcy(&self) -> Point2 {
|
| 205 |
-
Point2::new(self.xmin + self.width / 2., self.ymin + self.height / 2.)
|
| 206 |
-
}
|
| 207 |
-
|
| 208 |
-
pub fn id(&self) -> usize {
|
| 209 |
-
self.id
|
| 210 |
-
}
|
| 211 |
-
|
| 212 |
-
pub fn confidence(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 213 |
-
self.confidence
|
| 214 |
-
}
|
| 215 |
-
|
| 216 |
-
pub fn area(&self) -> f32 {
|
| 217 |
-
self.width * self.height
|
| 218 |
-
}
|
| 219 |
-
|
| 220 |
-
pub fn intersection_area(&self, another: &Bbox) -> f32 {
|
| 221 |
-
let l = self.xmin.max(another.xmin);
|
| 222 |
-
let r = (self.xmin + self.width).min(another.xmin + another.width);
|
| 223 |
-
let t = self.ymin.max(another.ymin);
|
| 224 |
-
let b = (self.ymin + self.height).min(another.ymin + another.height);
|
| 225 |
-
(r - l + 1.).max(0.) * (b - t + 1.).max(0.)
|
| 226 |
-
}
|
| 227 |
-
|
| 228 |
-
pub fn union(&self, another: &Bbox) -> f32 {
|
| 229 |
-
self.area() + another.area() - self.intersection_area(another)
|
| 230 |
-
}
|
| 231 |
-
|
| 232 |
-
pub fn iou(&self, another: &Bbox) -> f32 {
|
| 233 |
-
self.intersection_area(another) / self.union(another)
|
| 234 |
-
}
|
| 235 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime/README.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# YOLOv8 - ONNX Runtime
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
This project implements YOLOv8 using ONNX Runtime.
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
## Installation
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
To run this project, you need to install the required dependencies. The following instructions will guide you through the installation process.
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
### Installing Required Dependencies
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
You can install the required dependencies by running the following command:
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
```bash
|
| 14 |
-
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
| 15 |
-
```
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
### Installing `onnxruntime-gpu`
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
If you have an NVIDIA GPU and want to leverage GPU acceleration, you can install the onnxruntime-gpu package using the following command:
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
```bash
|
| 22 |
-
pip install onnxruntime-gpu
|
| 23 |
-
```
|
| 24 |
-
|
| 25 |
-
Note: Make sure you have the appropriate GPU drivers installed on your system.
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
### Installing `onnxruntime` (CPU version)
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
If you don't have an NVIDIA GPU or prefer to use the CPU version of onnxruntime, you can install the onnxruntime package using the following command:
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
```bash
|
| 32 |
-
pip install onnxruntime
|
| 33 |
-
```
|
| 34 |
-
|
| 35 |
-
### Usage
|
| 36 |
-
|
| 37 |
-
After successfully installing the required packages, you can run the YOLOv8 implementation using the following command:
|
| 38 |
-
|
| 39 |
-
```bash
|
| 40 |
-
python main.py --model yolov8n.onnx --img image.jpg --conf-thres 0.5 --iou-thres 0.5
|
| 41 |
-
```
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
Make sure to replace yolov8n.onnx with the path to your YOLOv8 ONNX model file, image.jpg with the path to your input image, and adjust the confidence threshold (conf-thres) and IoU threshold (iou-thres) values as needed.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime/main.py
DELETED
|
@@ -1,229 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
import argparse
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
import cv2
|
| 6 |
-
import numpy as np
|
| 7 |
-
import onnxruntime as ort
|
| 8 |
-
import torch
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
from ultralytics.utils import ASSETS, yaml_load
|
| 11 |
-
from ultralytics.utils.checks import check_requirements, check_yaml
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
class YOLOv8:
|
| 15 |
-
"""YOLOv8 object detection model class for handling inference and visualization."""
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
def __init__(self, onnx_model, input_image, confidence_thres, iou_thres):
|
| 18 |
-
"""
|
| 19 |
-
Initializes an instance of the YOLOv8 class.
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
Args:
|
| 22 |
-
onnx_model: Path to the ONNX model.
|
| 23 |
-
input_image: Path to the input image.
|
| 24 |
-
confidence_thres: Confidence threshold for filtering detections.
|
| 25 |
-
iou_thres: IoU (Intersection over Union) threshold for non-maximum suppression.
|
| 26 |
-
"""
|
| 27 |
-
self.onnx_model = onnx_model
|
| 28 |
-
self.input_image = input_image
|
| 29 |
-
self.confidence_thres = confidence_thres
|
| 30 |
-
self.iou_thres = iou_thres
|
| 31 |
-
|
| 32 |
-
# Load the class names from the COCO dataset
|
| 33 |
-
self.classes = yaml_load(check_yaml("coco8.yaml"))["names"]
|
| 34 |
-
|
| 35 |
-
# Generate a color palette for the classes
|
| 36 |
-
self.color_palette = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(self.classes), 3))
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
def draw_detections(self, img, box, score, class_id):
|
| 39 |
-
"""
|
| 40 |
-
Draws bounding boxes and labels on the input image based on the detected objects.
|
| 41 |
-
|
| 42 |
-
Args:
|
| 43 |
-
img: The input image to draw detections on.
|
| 44 |
-
box: Detected bounding box.
|
| 45 |
-
score: Corresponding detection score.
|
| 46 |
-
class_id: Class ID for the detected object.
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
Returns:
|
| 49 |
-
None
|
| 50 |
-
"""
|
| 51 |
-
# Extract the coordinates of the bounding box
|
| 52 |
-
x1, y1, w, h = box
|
| 53 |
-
|
| 54 |
-
# Retrieve the color for the class ID
|
| 55 |
-
color = self.color_palette[class_id]
|
| 56 |
-
|
| 57 |
-
# Draw the bounding box on the image
|
| 58 |
-
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(x1), int(y1)), (int(x1 + w), int(y1 + h)), color, 2)
|
| 59 |
-
|
| 60 |
-
# Create the label text with class name and score
|
| 61 |
-
label = f"{self.classes[class_id]}: {score:.2f}"
|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
# Calculate the dimensions of the label text
|
| 64 |
-
(label_width, label_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
|
| 65 |
-
|
| 66 |
-
# Calculate the position of the label text
|
| 67 |
-
label_x = x1
|
| 68 |
-
label_y = y1 - 10 if y1 - 10 > label_height else y1 + 10
|
| 69 |
-
|
| 70 |
-
# Draw a filled rectangle as the background for the label text
|
| 71 |
-
cv2.rectangle(
|
| 72 |
-
img, (label_x, label_y - label_height), (label_x + label_width, label_y + label_height), color, cv2.FILLED
|
| 73 |
-
)
|
| 74 |
-
|
| 75 |
-
# Draw the label text on the image
|
| 76 |
-
cv2.putText(img, label, (label_x, label_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
|
| 77 |
-
|
| 78 |
-
def preprocess(self):
|
| 79 |
-
"""
|
| 80 |
-
Preprocesses the input image before performing inference.
|
| 81 |
-
|
| 82 |
-
Returns:
|
| 83 |
-
image_data: Preprocessed image data ready for inference.
|
| 84 |
-
"""
|
| 85 |
-
# Read the input image using OpenCV
|
| 86 |
-
self.img = cv2.imread(self.input_image)
|
| 87 |
-
|
| 88 |
-
# Get the height and width of the input image
|
| 89 |
-
self.img_height, self.img_width = self.img.shape[:2]
|
| 90 |
-
|
| 91 |
-
# Convert the image color space from BGR to RGB
|
| 92 |
-
img = cv2.cvtColor(self.img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
|
| 93 |
-
|
| 94 |
-
# Resize the image to match the input shape
|
| 95 |
-
img = cv2.resize(img, (self.input_width, self.input_height))
|
| 96 |
-
|
| 97 |
-
# Normalize the image data by dividing it by 255.0
|
| 98 |
-
image_data = np.array(img) / 255.0
|
| 99 |
-
|
| 100 |
-
# Transpose the image to have the channel dimension as the first dimension
|
| 101 |
-
image_data = np.transpose(image_data, (2, 0, 1)) # Channel first
|
| 102 |
-
|
| 103 |
-
# Expand the dimensions of the image data to match the expected input shape
|
| 104 |
-
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, axis=0).astype(np.float32)
|
| 105 |
-
|
| 106 |
-
# Return the preprocessed image data
|
| 107 |
-
return image_data
|
| 108 |
-
|
| 109 |
-
def postprocess(self, input_image, output):
|
| 110 |
-
"""
|
| 111 |
-
Performs post-processing on the model's output to extract bounding boxes, scores, and class IDs.
|
| 112 |
-
|
| 113 |
-
Args:
|
| 114 |
-
input_image (numpy.ndarray): The input image.
|
| 115 |
-
output (numpy.ndarray): The output of the model.
|
| 116 |
-
|
| 117 |
-
Returns:
|
| 118 |
-
numpy.ndarray: The input image with detections drawn on it.
|
| 119 |
-
"""
|
| 120 |
-
# Transpose and squeeze the output to match the expected shape
|
| 121 |
-
outputs = np.transpose(np.squeeze(output[0]))
|
| 122 |
-
|
| 123 |
-
# Get the number of rows in the outputs array
|
| 124 |
-
rows = outputs.shape[0]
|
| 125 |
-
|
| 126 |
-
# Lists to store the bounding boxes, scores, and class IDs of the detections
|
| 127 |
-
boxes = []
|
| 128 |
-
scores = []
|
| 129 |
-
class_ids = []
|
| 130 |
-
|
| 131 |
-
# Calculate the scaling factors for the bounding box coordinates
|
| 132 |
-
x_factor = self.img_width / self.input_width
|
| 133 |
-
y_factor = self.img_height / self.input_height
|
| 134 |
-
|
| 135 |
-
# Iterate over each row in the outputs array
|
| 136 |
-
for i in range(rows):
|
| 137 |
-
# Extract the class scores from the current row
|
| 138 |
-
classes_scores = outputs[i][4:]
|
| 139 |
-
|
| 140 |
-
# Find the maximum score among the class scores
|
| 141 |
-
max_score = np.amax(classes_scores)
|
| 142 |
-
|
| 143 |
-
# If the maximum score is above the confidence threshold
|
| 144 |
-
if max_score >= self.confidence_thres:
|
| 145 |
-
# Get the class ID with the highest score
|
| 146 |
-
class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores)
|
| 147 |
-
|
| 148 |
-
# Extract the bounding box coordinates from the current row
|
| 149 |
-
x, y, w, h = outputs[i][0], outputs[i][1], outputs[i][2], outputs[i][3]
|
| 150 |
-
|
| 151 |
-
# Calculate the scaled coordinates of the bounding box
|
| 152 |
-
left = int((x - w / 2) * x_factor)
|
| 153 |
-
top = int((y - h / 2) * y_factor)
|
| 154 |
-
width = int(w * x_factor)
|
| 155 |
-
height = int(h * y_factor)
|
| 156 |
-
|
| 157 |
-
# Add the class ID, score, and box coordinates to the respective lists
|
| 158 |
-
class_ids.append(class_id)
|
| 159 |
-
scores.append(max_score)
|
| 160 |
-
boxes.append([left, top, width, height])
|
| 161 |
-
|
| 162 |
-
# Apply non-maximum suppression to filter out overlapping bounding boxes
|
| 163 |
-
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, scores, self.confidence_thres, self.iou_thres)
|
| 164 |
-
|
| 165 |
-
# Iterate over the selected indices after non-maximum suppression
|
| 166 |
-
for i in indices:
|
| 167 |
-
# Get the box, score, and class ID corresponding to the index
|
| 168 |
-
box = boxes[i]
|
| 169 |
-
score = scores[i]
|
| 170 |
-
class_id = class_ids[i]
|
| 171 |
-
|
| 172 |
-
# Draw the detection on the input image
|
| 173 |
-
self.draw_detections(input_image, box, score, class_id)
|
| 174 |
-
|
| 175 |
-
# Return the modified input image
|
| 176 |
-
return input_image
|
| 177 |
-
|
| 178 |
-
def main(self):
|
| 179 |
-
"""
|
| 180 |
-
Performs inference using an ONNX model and returns the output image with drawn detections.
|
| 181 |
-
|
| 182 |
-
Returns:
|
| 183 |
-
output_img: The output image with drawn detections.
|
| 184 |
-
"""
|
| 185 |
-
# Create an inference session using the ONNX model and specify execution providers
|
| 186 |
-
session = ort.InferenceSession(self.onnx_model, providers=["CUDAExecutionProvider", "CPUExecutionProvider"])
|
| 187 |
-
|
| 188 |
-
# Get the model inputs
|
| 189 |
-
model_inputs = session.get_inputs()
|
| 190 |
-
|
| 191 |
-
# Store the shape of the input for later use
|
| 192 |
-
input_shape = model_inputs[0].shape
|
| 193 |
-
self.input_width = input_shape[2]
|
| 194 |
-
self.input_height = input_shape[3]
|
| 195 |
-
|
| 196 |
-
# Preprocess the image data
|
| 197 |
-
img_data = self.preprocess()
|
| 198 |
-
|
| 199 |
-
# Run inference using the preprocessed image data
|
| 200 |
-
outputs = session.run(None, {model_inputs[0].name: img_data})
|
| 201 |
-
|
| 202 |
-
# Perform post-processing on the outputs to obtain output image.
|
| 203 |
-
return self.postprocess(self.img, outputs) # output image
|
| 204 |
-
|
| 205 |
-
|
| 206 |
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 207 |
-
# Create an argument parser to handle command-line arguments
|
| 208 |
-
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
| 209 |
-
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, default="yolov8n.onnx", help="Input your ONNX model.")
|
| 210 |
-
parser.add_argument("--img", type=str, default=str(ASSETS / "bus.jpg"), help="Path to input image.")
|
| 211 |
-
parser.add_argument("--conf-thres", type=float, default=0.5, help="Confidence threshold")
|
| 212 |
-
parser.add_argument("--iou-thres", type=float, default=0.5, help="NMS IoU threshold")
|
| 213 |
-
args = parser.parse_args()
|
| 214 |
-
|
| 215 |
-
# Check the requirements and select the appropriate backend (CPU or GPU)
|
| 216 |
-
check_requirements("onnxruntime-gpu" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "onnxruntime")
|
| 217 |
-
|
| 218 |
-
# Create an instance of the YOLOv8 class with the specified arguments
|
| 219 |
-
detection = YOLOv8(args.model, args.img, args.conf_thres, args.iou_thres)
|
| 220 |
-
|
| 221 |
-
# Perform object detection and obtain the output image
|
| 222 |
-
output_image = detection.main()
|
| 223 |
-
|
| 224 |
-
# Display the output image in a window
|
| 225 |
-
cv2.namedWindow("Output", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
|
| 226 |
-
cv2.imshow("Output", output_image)
|
| 227 |
-
|
| 228 |
-
# Wait for a key press to exit
|
| 229 |
-
cv2.waitKey(0)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-OpenCV-ONNX-Python/README.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# YOLOv8 - OpenCV
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
Implementation YOLOv8 on OpenCV using ONNX Format.
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
Just simply clone and run
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
```bash
|
| 8 |
-
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
| 9 |
-
python main.py --model yolov8n.onnx --img image.jpg
|
| 10 |
-
```
|
| 11 |
-
|
| 12 |
-
If you start from scratch:
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
```bash
|
| 15 |
-
pip install ultralytics
|
| 16 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt imgsz=640 format=onnx opset=12
|
| 17 |
-
```
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
_\*Make sure to include "opset=12"_
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-OpenCV-ONNX-Python/main.py
DELETED
|
@@ -1,130 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
import argparse
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
import cv2.dnn
|
| 6 |
-
import numpy as np
|
| 7 |
-
|
| 8 |
-
from ultralytics.utils import ASSETS, yaml_load
|
| 9 |
-
from ultralytics.utils.checks import check_yaml
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
CLASSES = yaml_load(check_yaml("coco8.yaml"))["names"]
|
| 12 |
-
colors = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(CLASSES), 3))
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
|
| 15 |
-
def draw_bounding_box(img, class_id, confidence, x, y, x_plus_w, y_plus_h):
|
| 16 |
-
"""
|
| 17 |
-
Draws bounding boxes on the input image based on the provided arguments.
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
Args:
|
| 20 |
-
img (numpy.ndarray): The input image to draw the bounding box on.
|
| 21 |
-
class_id (int): Class ID of the detected object.
|
| 22 |
-
confidence (float): Confidence score of the detected object.
|
| 23 |
-
x (int): X-coordinate of the top-left corner of the bounding box.
|
| 24 |
-
y (int): Y-coordinate of the top-left corner of the bounding box.
|
| 25 |
-
x_plus_w (int): X-coordinate of the bottom-right corner of the bounding box.
|
| 26 |
-
y_plus_h (int): Y-coordinate of the bottom-right corner of the bounding box.
|
| 27 |
-
"""
|
| 28 |
-
label = f"{CLASSES[class_id]} ({confidence:.2f})"
|
| 29 |
-
color = colors[class_id]
|
| 30 |
-
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x_plus_w, y_plus_h), color, 2)
|
| 31 |
-
cv2.putText(img, label, (x - 10, y - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 2)
|
| 32 |
-
|
| 33 |
-
|
| 34 |
-
def main(onnx_model, input_image):
|
| 35 |
-
"""
|
| 36 |
-
Main function to load ONNX model, perform inference, draw bounding boxes, and display the output image.
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
Args:
|
| 39 |
-
onnx_model (str): Path to the ONNX model.
|
| 40 |
-
input_image (str): Path to the input image.
|
| 41 |
-
|
| 42 |
-
Returns:
|
| 43 |
-
list: List of dictionaries containing detection information such as class_id, class_name, confidence, etc.
|
| 44 |
-
"""
|
| 45 |
-
# Load the ONNX model
|
| 46 |
-
model: cv2.dnn.Net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromONNX(onnx_model)
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
# Read the input image
|
| 49 |
-
original_image: np.ndarray = cv2.imread(input_image)
|
| 50 |
-
[height, width, _] = original_image.shape
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
# Prepare a square image for inference
|
| 53 |
-
length = max((height, width))
|
| 54 |
-
image = np.zeros((length, length, 3), np.uint8)
|
| 55 |
-
image[0:height, 0:width] = original_image
|
| 56 |
-
|
| 57 |
-
# Calculate scale factor
|
| 58 |
-
scale = length / 640
|
| 59 |
-
|
| 60 |
-
# Preprocess the image and prepare blob for model
|
| 61 |
-
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(image, scalefactor=1 / 255, size=(640, 640), swapRB=True)
|
| 62 |
-
model.setInput(blob)
|
| 63 |
-
|
| 64 |
-
# Perform inference
|
| 65 |
-
outputs = model.forward()
|
| 66 |
-
|
| 67 |
-
# Prepare output array
|
| 68 |
-
outputs = np.array([cv2.transpose(outputs[0])])
|
| 69 |
-
rows = outputs.shape[1]
|
| 70 |
-
|
| 71 |
-
boxes = []
|
| 72 |
-
scores = []
|
| 73 |
-
class_ids = []
|
| 74 |
-
|
| 75 |
-
# Iterate through output to collect bounding boxes, confidence scores, and class IDs
|
| 76 |
-
for i in range(rows):
|
| 77 |
-
classes_scores = outputs[0][i][4:]
|
| 78 |
-
(minScore, maxScore, minClassLoc, (x, maxClassIndex)) = cv2.minMaxLoc(classes_scores)
|
| 79 |
-
if maxScore >= 0.25:
|
| 80 |
-
box = [
|
| 81 |
-
outputs[0][i][0] - (0.5 * outputs[0][i][2]),
|
| 82 |
-
outputs[0][i][1] - (0.5 * outputs[0][i][3]),
|
| 83 |
-
outputs[0][i][2],
|
| 84 |
-
outputs[0][i][3],
|
| 85 |
-
]
|
| 86 |
-
boxes.append(box)
|
| 87 |
-
scores.append(maxScore)
|
| 88 |
-
class_ids.append(maxClassIndex)
|
| 89 |
-
|
| 90 |
-
# Apply NMS (Non-maximum suppression)
|
| 91 |
-
result_boxes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, scores, 0.25, 0.45, 0.5)
|
| 92 |
-
|
| 93 |
-
detections = []
|
| 94 |
-
|
| 95 |
-
# Iterate through NMS results to draw bounding boxes and labels
|
| 96 |
-
for i in range(len(result_boxes)):
|
| 97 |
-
index = result_boxes[i]
|
| 98 |
-
box = boxes[index]
|
| 99 |
-
detection = {
|
| 100 |
-
"class_id": class_ids[index],
|
| 101 |
-
"class_name": CLASSES[class_ids[index]],
|
| 102 |
-
"confidence": scores[index],
|
| 103 |
-
"box": box,
|
| 104 |
-
"scale": scale,
|
| 105 |
-
}
|
| 106 |
-
detections.append(detection)
|
| 107 |
-
draw_bounding_box(
|
| 108 |
-
original_image,
|
| 109 |
-
class_ids[index],
|
| 110 |
-
scores[index],
|
| 111 |
-
round(box[0] * scale),
|
| 112 |
-
round(box[1] * scale),
|
| 113 |
-
round((box[0] + box[2]) * scale),
|
| 114 |
-
round((box[1] + box[3]) * scale),
|
| 115 |
-
)
|
| 116 |
-
|
| 117 |
-
# Display the image with bounding boxes
|
| 118 |
-
cv2.imshow("image", original_image)
|
| 119 |
-
cv2.waitKey(0)
|
| 120 |
-
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
|
| 121 |
-
|
| 122 |
-
return detections
|
| 123 |
-
|
| 124 |
-
|
| 125 |
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 126 |
-
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
| 127 |
-
parser.add_argument("--model", default="yolov8n.onnx", help="Input your ONNX model.")
|
| 128 |
-
parser.add_argument("--img", default=str(ASSETS / "bus.jpg"), help="Path to input image.")
|
| 129 |
-
args = parser.parse_args()
|
| 130 |
-
main(args.model, args.img)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-OpenVINO-CPP-Inference/CMakeLists.txt
DELETED
|
@@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.12)
|
| 2 |
-
project(yolov8_openvino_example)
|
| 3 |
-
|
| 4 |
-
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
|
| 5 |
-
|
| 6 |
-
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
|
| 7 |
-
|
| 8 |
-
include_directories(
|
| 9 |
-
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
|
| 10 |
-
/path/to/intel/openvino/runtime/include
|
| 11 |
-
)
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
add_executable(detect
|
| 14 |
-
main.cc
|
| 15 |
-
inference.cc
|
| 16 |
-
)
|
| 17 |
-
|
| 18 |
-
target_link_libraries(detect
|
| 19 |
-
${OpenCV_LIBS}
|
| 20 |
-
/path/to/intel/openvino/runtime/lib/intel64/libopenvino.so
|
| 21 |
-
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-OpenVINO-CPP-Inference/README.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# YOLOv8 OpenVINO Inference in C++ 🦾
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
Welcome to the YOLOv8 OpenVINO Inference example in C++! This guide will help you get started with leveraging the powerful YOLOv8 models using OpenVINO and OpenCV API in your C++ projects. Whether you're looking to enhance performance or add flexibility to your applications, this example has got you covered.
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
## 🌟 Features
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
- 🚀 **Model Format Support**: Compatible with `ONNX` and `OpenVINO IR` formats.
|
| 8 |
-
- ⚡ **Precision Options**: Run models in `FP32`, `FP16`, and `INT8` precisions.
|
| 9 |
-
- 🔄 **Dynamic Shape Loading**: Easily handle models with dynamic input shapes.
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
## 📋 Dependencies
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
To ensure smooth execution, please make sure you have the following dependencies installed:
|
| 14 |
-
|
| 15 |
-
| Dependency | Version |
|
| 16 |
-
| ---------- | -------- |
|
| 17 |
-
| OpenVINO | >=2023.3 |
|
| 18 |
-
| OpenCV | >=4.5.0 |
|
| 19 |
-
| C++ | >=14 |
|
| 20 |
-
| CMake | >=3.12.0 |
|
| 21 |
-
|
| 22 |
-
## ⚙️ Build Instructions
|
| 23 |
-
|
| 24 |
-
Follow these steps to build the project:
|
| 25 |
-
|
| 26 |
-
1. Clone the repository:
|
| 27 |
-
|
| 28 |
-
```bash
|
| 29 |
-
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics.git
|
| 30 |
-
cd ultralytics/YOLOv8-OpenVINO-CPP-Inference
|
| 31 |
-
```
|
| 32 |
-
|
| 33 |
-
2. Create a build directory and compile the project:
|
| 34 |
-
```bash
|
| 35 |
-
mkdir build
|
| 36 |
-
cd build
|
| 37 |
-
cmake ..
|
| 38 |
-
make
|
| 39 |
-
```
|
| 40 |
-
|
| 41 |
-
## 🛠️ Usage
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
Once built, you can run inference on an image using the following command:
|
| 44 |
-
|
| 45 |
-
```bash
|
| 46 |
-
./detect <model_path.{onnx, xml}> <image_path.jpg>
|
| 47 |
-
```
|
| 48 |
-
|
| 49 |
-
## 🔄 Exporting YOLOv8 Models
|
| 50 |
-
|
| 51 |
-
To use your YOLOv8 model with OpenVINO, you need to export it first. Use the command below to export the model:
|
| 52 |
-
|
| 53 |
-
```bash
|
| 54 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8s.pt imgsz=640 format=openvino
|
| 55 |
-
```
|
| 56 |
-
|
| 57 |
-
## 📸 Screenshots
|
| 58 |
-
|
| 59 |
-
### Running Using OpenVINO Model
|
| 60 |
-
|
| 61 |
-

|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
### Running Using ONNX Model
|
| 64 |
-
|
| 65 |
-

|
| 66 |
-
|
| 67 |
-
## ❤️ Contributions
|
| 68 |
-
|
| 69 |
-
We hope this example helps you integrate YOLOv8 with OpenVINO and OpenCV into your C++ projects effortlessly. Happy coding! 🚀
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-OpenVINO-CPP-Inference/inference.cc
DELETED
|
@@ -1,175 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#include "inference.h"
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
#include <memory>
|
| 4 |
-
#include <opencv2/dnn.hpp>
|
| 5 |
-
#include <random>
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
namespace yolo {
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
// Constructor to initialize the model with default input shape
|
| 10 |
-
Inference::Inference(const std::string &model_path, const float &model_confidence_threshold, const float &model_NMS_threshold) {
|
| 11 |
-
model_input_shape_ = cv::Size(640, 640); // Set the default size for models with dynamic shapes to prevent errors.
|
| 12 |
-
model_confidence_threshold_ = model_confidence_threshold;
|
| 13 |
-
model_NMS_threshold_ = model_NMS_threshold;
|
| 14 |
-
InitializeModel(model_path);
|
| 15 |
-
}
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
// Constructor to initialize the model with specified input shape
|
| 18 |
-
Inference::Inference(const std::string &model_path, const cv::Size model_input_shape, const float &model_confidence_threshold, const float &model_NMS_threshold) {
|
| 19 |
-
model_input_shape_ = model_input_shape;
|
| 20 |
-
model_confidence_threshold_ = model_confidence_threshold;
|
| 21 |
-
model_NMS_threshold_ = model_NMS_threshold;
|
| 22 |
-
InitializeModel(model_path);
|
| 23 |
-
}
|
| 24 |
-
|
| 25 |
-
void Inference::InitializeModel(const std::string &model_path) {
|
| 26 |
-
ov::Core core; // OpenVINO core object
|
| 27 |
-
std::shared_ptr<ov::Model> model = core.read_model(model_path); // Read the model from file
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
// If the model has dynamic shapes, reshape it to the specified input shape
|
| 30 |
-
if (model->is_dynamic()) {
|
| 31 |
-
model->reshape({1, 3, static_cast<long int>(model_input_shape_.height), static_cast<long int>(model_input_shape_.width)});
|
| 32 |
-
}
|
| 33 |
-
|
| 34 |
-
// Preprocessing setup for the model
|
| 35 |
-
ov::preprocess::PrePostProcessor ppp = ov::preprocess::PrePostProcessor(model);
|
| 36 |
-
ppp.input().tensor().set_element_type(ov::element::u8).set_layout("NHWC").set_color_format(ov::preprocess::ColorFormat::BGR);
|
| 37 |
-
ppp.input().preprocess().convert_element_type(ov::element::f32).convert_color(ov::preprocess::ColorFormat::RGB).scale({255, 255, 255});
|
| 38 |
-
ppp.input().model().set_layout("NCHW");
|
| 39 |
-
ppp.output().tensor().set_element_type(ov::element::f32);
|
| 40 |
-
model = ppp.build(); // Build the preprocessed model
|
| 41 |
-
|
| 42 |
-
// Compile the model for inference
|
| 43 |
-
compiled_model_ = core.compile_model(model, "AUTO");
|
| 44 |
-
inference_request_ = compiled_model_.create_infer_request(); // Create inference request
|
| 45 |
-
|
| 46 |
-
short width, height;
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
// Get input shape from the model
|
| 49 |
-
const std::vector<ov::Output<ov::Node>> inputs = model->inputs();
|
| 50 |
-
const ov::Shape input_shape = inputs[0].get_shape();
|
| 51 |
-
height = input_shape[1];
|
| 52 |
-
width = input_shape[2];
|
| 53 |
-
model_input_shape_ = cv::Size2f(width, height);
|
| 54 |
-
|
| 55 |
-
// Get output shape from the model
|
| 56 |
-
const std::vector<ov::Output<ov::Node>> outputs = model->outputs();
|
| 57 |
-
const ov::Shape output_shape = outputs[0].get_shape();
|
| 58 |
-
height = output_shape[1];
|
| 59 |
-
width = output_shape[2];
|
| 60 |
-
model_output_shape_ = cv::Size(width, height);
|
| 61 |
-
}
|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
// Method to run inference on an input frame
|
| 64 |
-
void Inference::RunInference(cv::Mat &frame) {
|
| 65 |
-
Preprocessing(frame); // Preprocess the input frame
|
| 66 |
-
inference_request_.infer(); // Run inference
|
| 67 |
-
PostProcessing(frame); // Postprocess the inference results
|
| 68 |
-
}
|
| 69 |
-
|
| 70 |
-
// Method to preprocess the input frame
|
| 71 |
-
void Inference::Preprocessing(const cv::Mat &frame) {
|
| 72 |
-
cv::Mat resized_frame;
|
| 73 |
-
cv::resize(frame, resized_frame, model_input_shape_, 0, 0, cv::INTER_AREA); // Resize the frame to match the model input shape
|
| 74 |
-
|
| 75 |
-
// Calculate scaling factor
|
| 76 |
-
scale_factor_.x = static_cast<float>(frame.cols / model_input_shape_.width);
|
| 77 |
-
scale_factor_.y = static_cast<float>(frame.rows / model_input_shape_.height);
|
| 78 |
-
|
| 79 |
-
float *input_data = (float *)resized_frame.data; // Get pointer to resized frame data
|
| 80 |
-
const ov::Tensor input_tensor = ov::Tensor(compiled_model_.input().get_element_type(), compiled_model_.input().get_shape(), input_data); // Create input tensor
|
| 81 |
-
inference_request_.set_input_tensor(input_tensor); // Set input tensor for inference
|
| 82 |
-
}
|
| 83 |
-
|
| 84 |
-
// Method to postprocess the inference results
|
| 85 |
-
void Inference::PostProcessing(cv::Mat &frame) {
|
| 86 |
-
std::vector<int> class_list;
|
| 87 |
-
std::vector<float> confidence_list;
|
| 88 |
-
std::vector<cv::Rect> box_list;
|
| 89 |
-
|
| 90 |
-
// Get the output tensor from the inference request
|
| 91 |
-
const float *detections = inference_request_.get_output_tensor().data<const float>();
|
| 92 |
-
const cv::Mat detection_outputs(model_output_shape_, CV_32F, (float *)detections); // Create OpenCV matrix from output tensor
|
| 93 |
-
|
| 94 |
-
// Iterate over detections and collect class IDs, confidence scores, and bounding boxes
|
| 95 |
-
for (int i = 0; i < detection_outputs.cols; ++i) {
|
| 96 |
-
const cv::Mat classes_scores = detection_outputs.col(i).rowRange(4, detection_outputs.rows);
|
| 97 |
-
|
| 98 |
-
cv::Point class_id;
|
| 99 |
-
double score;
|
| 100 |
-
cv::minMaxLoc(classes_scores, nullptr, &score, nullptr, &class_id); // Find the class with the highest score
|
| 101 |
-
|
| 102 |
-
// Check if the detection meets the confidence threshold
|
| 103 |
-
if (score > model_confidence_threshold_) {
|
| 104 |
-
class_list.push_back(class_id.y);
|
| 105 |
-
confidence_list.push_back(score);
|
| 106 |
-
|
| 107 |
-
const float x = detection_outputs.at<float>(0, i);
|
| 108 |
-
const float y = detection_outputs.at<float>(1, i);
|
| 109 |
-
const float w = detection_outputs.at<float>(2, i);
|
| 110 |
-
const float h = detection_outputs.at<float>(3, i);
|
| 111 |
-
|
| 112 |
-
cv::Rect box;
|
| 113 |
-
box.x = static_cast<int>(x);
|
| 114 |
-
box.y = static_cast<int>(y);
|
| 115 |
-
box.width = static_cast<int>(w);
|
| 116 |
-
box.height = static_cast<int>(h);
|
| 117 |
-
box_list.push_back(box);
|
| 118 |
-
}
|
| 119 |
-
}
|
| 120 |
-
|
| 121 |
-
// Apply Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) to filter overlapping bounding boxes
|
| 122 |
-
std::vector<int> NMS_result;
|
| 123 |
-
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(box_list, confidence_list, model_confidence_threshold_, model_NMS_threshold_, NMS_result);
|
| 124 |
-
|
| 125 |
-
// Collect final detections after NMS
|
| 126 |
-
for (int i = 0; i < NMS_result.size(); ++i) {
|
| 127 |
-
Detection result;
|
| 128 |
-
const unsigned short id = NMS_result[i];
|
| 129 |
-
|
| 130 |
-
result.class_id = class_list[id];
|
| 131 |
-
result.confidence = confidence_list[id];
|
| 132 |
-
result.box = GetBoundingBox(box_list[id]);
|
| 133 |
-
|
| 134 |
-
DrawDetectedObject(frame, result);
|
| 135 |
-
}
|
| 136 |
-
}
|
| 137 |
-
|
| 138 |
-
// Method to get the bounding box in the correct scale
|
| 139 |
-
cv::Rect Inference::GetBoundingBox(const cv::Rect &src) const {
|
| 140 |
-
cv::Rect box = src;
|
| 141 |
-
box.x = (box.x - box.width / 2) * scale_factor_.x;
|
| 142 |
-
box.y = (box.y - box.height / 2) * scale_factor_.y;
|
| 143 |
-
box.width *= scale_factor_.x;
|
| 144 |
-
box.height *= scale_factor_.y;
|
| 145 |
-
return box;
|
| 146 |
-
}
|
| 147 |
-
|
| 148 |
-
void Inference::DrawDetectedObject(cv::Mat &frame, const Detection &detection) const {
|
| 149 |
-
const cv::Rect &box = detection.box;
|
| 150 |
-
const float &confidence = detection.confidence;
|
| 151 |
-
const int &class_id = detection.class_id;
|
| 152 |
-
|
| 153 |
-
// Generate a random color for the bounding box
|
| 154 |
-
std::random_device rd;
|
| 155 |
-
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
|
| 156 |
-
std::uniform_int_distribution<int> dis(120, 255);
|
| 157 |
-
const cv::Scalar &color = cv::Scalar(dis(gen), dis(gen), dis(gen));
|
| 158 |
-
|
| 159 |
-
// Draw the bounding box around the detected object
|
| 160 |
-
cv::rectangle(frame, cv::Point(box.x, box.y), cv::Point(box.x + box.width, box.y + box.height), color, 3);
|
| 161 |
-
|
| 162 |
-
// Prepare the class label and confidence text
|
| 163 |
-
std::string classString = classes_[class_id] + std::to_string(confidence).substr(0, 4);
|
| 164 |
-
|
| 165 |
-
// Get the size of the text box
|
| 166 |
-
cv::Size textSize = cv::getTextSize(classString, cv::FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 0.75, 2, 0);
|
| 167 |
-
cv::Rect textBox(box.x, box.y - 40, textSize.width + 10, textSize.height + 20);
|
| 168 |
-
|
| 169 |
-
// Draw the text box
|
| 170 |
-
cv::rectangle(frame, textBox, color, cv::FILLED);
|
| 171 |
-
|
| 172 |
-
// Put the class label and confidence text above the bounding box
|
| 173 |
-
cv::putText(frame, classString, cv::Point(box.x + 5, box.y - 10), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 0.75, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), 2, 0);
|
| 174 |
-
}
|
| 175 |
-
} // namespace yolo
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-OpenVINO-CPP-Inference/inference.h
DELETED
|
@@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#ifndef YOLO_INFERENCE_H_
|
| 2 |
-
#define YOLO_INFERENCE_H_
|
| 3 |
-
|
| 4 |
-
#include <string>
|
| 5 |
-
#include <vector>
|
| 6 |
-
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
|
| 7 |
-
#include <openvino/openvino.hpp>
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
namespace yolo {
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
struct Detection {
|
| 12 |
-
short class_id;
|
| 13 |
-
float confidence;
|
| 14 |
-
cv::Rect box;
|
| 15 |
-
};
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
class Inference {
|
| 18 |
-
public:
|
| 19 |
-
Inference() {}
|
| 20 |
-
// Constructor to initialize the model with default input shape
|
| 21 |
-
Inference(const std::string &model_path, const float &model_confidence_threshold, const float &model_NMS_threshold);
|
| 22 |
-
// Constructor to initialize the model with specified input shape
|
| 23 |
-
Inference(const std::string &model_path, const cv::Size model_input_shape, const float &model_confidence_threshold, const float &model_NMS_threshold);
|
| 24 |
-
|
| 25 |
-
void RunInference(cv::Mat &frame);
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
private:
|
| 28 |
-
void InitializeModel(const std::string &model_path);
|
| 29 |
-
void Preprocessing(const cv::Mat &frame);
|
| 30 |
-
void PostProcessing(cv::Mat &frame);
|
| 31 |
-
cv::Rect GetBoundingBox(const cv::Rect &src) const;
|
| 32 |
-
void DrawDetectedObject(cv::Mat &frame, const Detection &detections) const;
|
| 33 |
-
|
| 34 |
-
cv::Point2f scale_factor_; // Scaling factor for the input frame
|
| 35 |
-
cv::Size2f model_input_shape_; // Input shape of the model
|
| 36 |
-
cv::Size model_output_shape_; // Output shape of the model
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
ov::InferRequest inference_request_; // OpenVINO inference request
|
| 39 |
-
ov::CompiledModel compiled_model_; // OpenVINO compiled model
|
| 40 |
-
|
| 41 |
-
float model_confidence_threshold_; // Confidence threshold for detections
|
| 42 |
-
float model_NMS_threshold_; // Non-Maximum Suppression threshold
|
| 43 |
-
|
| 44 |
-
std::vector<std::string> classes_ {
|
| 45 |
-
"person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle", "airplane", "bus", "train", "truck", "boat", "traffic light",
|
| 46 |
-
"fire hydrant", "stop sign", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse", "sheep", "cow",
|
| 47 |
-
"elephant", "bear", "zebra", "giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee",
|
| 48 |
-
"skis", "snowboard", "sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard", "surfboard",
|
| 49 |
-
"tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife", "spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple",
|
| 50 |
-
"sandwich", "orange", "broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair", "couch",
|
| 51 |
-
"potted plant", "bed", "dining table", "toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard",
|
| 52 |
-
"cell phone", "microwave", "oven", "toaster", "sink", "refrigerator", "book", "clock", "vase",
|
| 53 |
-
"scissors", "teddy bear", "hair drier", "toothbrush"
|
| 54 |
-
};
|
| 55 |
-
};
|
| 56 |
-
|
| 57 |
-
} // namespace yolo
|
| 58 |
-
|
| 59 |
-
#endif // YOLO_INFERENCE_H_
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-OpenVINO-CPP-Inference/main.cc
DELETED
|
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
#include "inference.h"
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
#include <iostream>
|
| 4 |
-
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
|
| 5 |
-
|
| 6 |
-
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
|
| 7 |
-
// Check if the correct number of arguments is provided
|
| 8 |
-
if (argc != 3) {
|
| 9 |
-
std::cerr << "usage: " << argv[0] << " <model_path> <image_path>" << std::endl;
|
| 10 |
-
return 1;
|
| 11 |
-
}
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
// Get the model and image paths from the command-line arguments
|
| 14 |
-
const std::string model_path = argv[1];
|
| 15 |
-
const std::string image_path = argv[2];
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
// Read the input image
|
| 18 |
-
cv::Mat image = cv::imread(image_path);
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
// Check if the image was successfully loaded
|
| 21 |
-
if (image.empty()) {
|
| 22 |
-
std::cerr << "ERROR: image is empty" << std::endl;
|
| 23 |
-
return 1;
|
| 24 |
-
}
|
| 25 |
-
|
| 26 |
-
// Define the confidence and NMS thresholds
|
| 27 |
-
const float confidence_threshold = 0.5;
|
| 28 |
-
const float NMS_threshold = 0.5;
|
| 29 |
-
|
| 30 |
-
// Initialize the YOLO inference with the specified model and parameters
|
| 31 |
-
yolo::Inference inference(model_path, cv::Size(640, 640), confidence_threshold, NMS_threshold);
|
| 32 |
-
|
| 33 |
-
// Run inference on the input image
|
| 34 |
-
inference.RunInference(image);
|
| 35 |
-
|
| 36 |
-
// Display the image with the detections
|
| 37 |
-
cv::imshow("image", image);
|
| 38 |
-
cv::waitKey(0);
|
| 39 |
-
|
| 40 |
-
return 0;
|
| 41 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-Region-Counter/readme.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,128 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Regions Counting Using YOLOv8 (Inference on Video)
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
> **Region Counter** is now part of **[Ultralytics Solutions](https://docs.ultralytics.com/solutions/)**, offering improved features and regular updates. Enjoy improved features and regular updates!
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
🔗 **[Explore Object Counting in Regions Here](https://docs.ultralytics.com/guides/region-counting/)**
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
> 🔔 **Notice:**
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
> The GitHub example will remain available but **will no longer be actively maintained**. For the latest updates and improvements, please use the official [link](https://docs.ultralytics.com/guides/region-counting/). Thank you!
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
Region counting is a method employed to tally the objects within a specified area, allowing for more sophisticated analyses when multiple regions are considered. These regions can be adjusted interactively using a Left Mouse Click, and the counting process occurs in real time. Regions can be adjusted to suit the user's preferences and requirements.
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
<div>
|
| 14 |
-
<p align="center">
|
| 15 |
-
<img src="https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/assets/62513924/5ab3bbd7-fd12-4849-928e-5f294d6c3fcf" width="45%" alt="YOLOv8 region counting visual 1">
|
| 16 |
-
<img src="https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/assets/62513924/e7c1aea7-474d-4d78-8d48-b50854ffe1ca" width="45%" alt="YOLOv8 region counting visual 2">
|
| 17 |
-
</p>
|
| 18 |
-
</div>
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
## Table of Contents
|
| 21 |
-
|
| 22 |
-
- [Step 1: Install the Required Libraries](#step-1-install-the-required-libraries)
|
| 23 |
-
- [Step 2: Run the Region Counting Using Ultralytics YOLOv8](#step-2-run-the-region-counting-using-ultralytics-yolov8)
|
| 24 |
-
- [Usage Options](#usage-options)
|
| 25 |
-
- [FAQ](#faq)
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
## Step 1: Install the Required Libraries
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
Clone the repository, install dependencies and `cd` to this local directory for commands in Step 2.
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
```bash
|
| 32 |
-
# Clone ultralytics repo
|
| 33 |
-
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
|
| 34 |
-
|
| 35 |
-
# cd to local directory
|
| 36 |
-
cd ultralytics/examples/YOLOv8-Region-Counter
|
| 37 |
-
```
|
| 38 |
-
|
| 39 |
-
## Step 2: Run the Region Counting Using Ultralytics YOLOv8
|
| 40 |
-
|
| 41 |
-
Here are the basic commands for running the inference:
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
### Note
|
| 44 |
-
|
| 45 |
-
After the video begins playing, you can freely move the region anywhere within the video by simply clicking and dragging using the left mouse button.
|
| 46 |
-
|
| 47 |
-
```bash
|
| 48 |
-
# If you want to save results
|
| 49 |
-
python yolov8_region_counter.py --source "path/to/video.mp4" --save-img --view-img
|
| 50 |
-
|
| 51 |
-
# If you want to run model on CPU
|
| 52 |
-
python yolov8_region_counter.py --source "path/to/video.mp4" --save-img --view-img --device cpu
|
| 53 |
-
|
| 54 |
-
# If you want to change model file
|
| 55 |
-
python yolov8_region_counter.py --source "path/to/video.mp4" --save-img --weights "path/to/model.pt"
|
| 56 |
-
|
| 57 |
-
# If you want to detect specific class (first class and third class)
|
| 58 |
-
python yolov8_region_counter.py --source "path/to/video.mp4" --classes 0 2 --weights "path/to/model.pt"
|
| 59 |
-
|
| 60 |
-
# If you don't want to save results
|
| 61 |
-
python yolov8_region_counter.py --source "path/to/video.mp4" --view-img
|
| 62 |
-
```
|
| 63 |
-
|
| 64 |
-
## Usage Options
|
| 65 |
-
|
| 66 |
-
- `--source`: Specifies the path to the video file you want to run inference on.
|
| 67 |
-
- `--device`: Specifies the device `cpu` or `0`
|
| 68 |
-
- `--save-img`: Flag to save the detection results as images.
|
| 69 |
-
- `--weights`: Specifies a different YOLOv8 model file (e.g., `yolov8n.pt`, `yolov8s.pt`, `yolov8m.pt`, `yolov8l.pt`, `yolov8x.pt`).
|
| 70 |
-
- `--classes`: Specifies the class to be detected
|
| 71 |
-
- `--line-thickness`: Specifies the bounding box thickness
|
| 72 |
-
- `--region-thickness`: Specifies the region boxes thickness
|
| 73 |
-
- `--track-thickness`: Specifies the track line thickness
|
| 74 |
-
|
| 75 |
-
## FAQ
|
| 76 |
-
|
| 77 |
-
**1. What Does Region Counting Involve?**
|
| 78 |
-
|
| 79 |
-
Region counting is a computational method utilized to ascertain the quantity of objects within a specific area in recorded video or real-time streams. This technique finds frequent application in image processing, computer vision, and pattern recognition, facilitating the analysis and segmentation of objects or features based on their spatial relationships.
|
| 80 |
-
|
| 81 |
-
**2. Is Friendly Region Plotting Supported by the Region Counter?**
|
| 82 |
-
|
| 83 |
-
The Region Counting offers the capability to create regions in various formats, such as polygons and rectangles. You have the flexibility to modify region attributes, including coordinates, colors, and other details, as demonstrated in the following code:
|
| 84 |
-
|
| 85 |
-
```python
|
| 86 |
-
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
|
| 87 |
-
|
| 88 |
-
counting_regions = [
|
| 89 |
-
{
|
| 90 |
-
"name": "YOLOv8 Polygon Region",
|
| 91 |
-
"polygon": Polygon(
|
| 92 |
-
[(50, 80), (250, 20), (450, 80), (400, 350), (100, 350)]
|
| 93 |
-
), # Polygon with five points (Pentagon)
|
| 94 |
-
"counts": 0,
|
| 95 |
-
"dragging": False,
|
| 96 |
-
"region_color": (255, 42, 4), # BGR Value
|
| 97 |
-
"text_color": (255, 255, 255), # Region Text Color
|
| 98 |
-
},
|
| 99 |
-
{
|
| 100 |
-
"name": "YOLOv8 Rectangle Region",
|
| 101 |
-
"polygon": Polygon([(200, 250), (440, 250), (440, 550), (200, 550)]), # Rectangle with four points
|
| 102 |
-
"counts": 0,
|
| 103 |
-
"dragging": False,
|
| 104 |
-
"region_color": (37, 255, 225), # BGR Value
|
| 105 |
-
"text_color": (0, 0, 0), # Region Text Color
|
| 106 |
-
},
|
| 107 |
-
]
|
| 108 |
-
```
|
| 109 |
-
|
| 110 |
-
**3. Why Combine Region Counting with YOLOv8?**
|
| 111 |
-
|
| 112 |
-
YOLOv8 specializes in the detection and tracking of objects in video streams. Region counting complements this by enabling object counting within designated areas, making it a valuable application of YOLOv8.
|
| 113 |
-
|
| 114 |
-
**4. How Can I Troubleshoot Issues?**
|
| 115 |
-
|
| 116 |
-
To gain more insights during inference, you can include the `--debug` flag in your command:
|
| 117 |
-
|
| 118 |
-
```bash
|
| 119 |
-
python yolov8_region_counter.py --source "path to video file" --debug
|
| 120 |
-
```
|
| 121 |
-
|
| 122 |
-
**5. Can I Employ Other YOLO Versions?**
|
| 123 |
-
|
| 124 |
-
Certainly, you have the flexibility to specify different YOLO model weights using the `--weights` option.
|
| 125 |
-
|
| 126 |
-
**6. Where Can I Access Additional Information?**
|
| 127 |
-
|
| 128 |
-
For a comprehensive guide on using YOLOv8 with Object Tracking, please refer to [Multi-Object Tracking with Ultralytics YOLO](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/track/).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-Region-Counter/yolov8_region_counter.py
DELETED
|
@@ -1,253 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
import argparse
|
| 4 |
-
from collections import defaultdict
|
| 5 |
-
from pathlib import Path
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
import cv2
|
| 8 |
-
import numpy as np
|
| 9 |
-
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
|
| 10 |
-
from shapely.geometry.point import Point
|
| 11 |
-
|
| 12 |
-
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
| 13 |
-
from ultralytics.utils.files import increment_path
|
| 14 |
-
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Annotator, colors
|
| 15 |
-
|
| 16 |
-
track_history = defaultdict(list)
|
| 17 |
-
|
| 18 |
-
current_region = None
|
| 19 |
-
counting_regions = [
|
| 20 |
-
{
|
| 21 |
-
"name": "YOLOv8 Polygon Region",
|
| 22 |
-
"polygon": Polygon([(50, 80), (250, 20), (450, 80), (400, 350), (100, 350)]), # Polygon points
|
| 23 |
-
"counts": 0,
|
| 24 |
-
"dragging": False,
|
| 25 |
-
"region_color": (255, 42, 4), # BGR Value
|
| 26 |
-
"text_color": (255, 255, 255), # Region Text Color
|
| 27 |
-
},
|
| 28 |
-
{
|
| 29 |
-
"name": "YOLOv8 Rectangle Region",
|
| 30 |
-
"polygon": Polygon([(200, 250), (440, 250), (440, 550), (200, 550)]), # Polygon points
|
| 31 |
-
"counts": 0,
|
| 32 |
-
"dragging": False,
|
| 33 |
-
"region_color": (37, 255, 225), # BGR Value
|
| 34 |
-
"text_color": (0, 0, 0), # Region Text Color
|
| 35 |
-
},
|
| 36 |
-
]
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
|
| 39 |
-
def mouse_callback(event, x, y, flags, param):
|
| 40 |
-
"""
|
| 41 |
-
Handles mouse events for region manipulation.
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
Args:
|
| 44 |
-
event (int): The mouse event type (e.g., cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN).
|
| 45 |
-
x (int): The x-coordinate of the mouse pointer.
|
| 46 |
-
y (int): The y-coordinate of the mouse pointer.
|
| 47 |
-
flags (int): Additional flags passed by OpenCV.
|
| 48 |
-
param: Additional parameters passed to the callback (not used in this function).
|
| 49 |
-
|
| 50 |
-
Global Variables:
|
| 51 |
-
current_region (dict): A dictionary representing the current selected region.
|
| 52 |
-
|
| 53 |
-
Mouse Events:
|
| 54 |
-
- LBUTTONDOWN: Initiates dragging for the region containing the clicked point.
|
| 55 |
-
- MOUSEMOVE: Moves the selected region if dragging is active.
|
| 56 |
-
- LBUTTONUP: Ends dragging for the selected region.
|
| 57 |
-
|
| 58 |
-
Notes:
|
| 59 |
-
- This function is intended to be used as a callback for OpenCV mouse events.
|
| 60 |
-
- Requires the existence of the 'counting_regions' list and the 'Polygon' class.
|
| 61 |
-
|
| 62 |
-
Example:
|
| 63 |
-
>>> cv2.setMouseCallback(window_name, mouse_callback)
|
| 64 |
-
"""
|
| 65 |
-
global current_region
|
| 66 |
-
|
| 67 |
-
# Mouse left button down event
|
| 68 |
-
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
|
| 69 |
-
for region in counting_regions:
|
| 70 |
-
if region["polygon"].contains(Point((x, y))):
|
| 71 |
-
current_region = region
|
| 72 |
-
current_region["dragging"] = True
|
| 73 |
-
current_region["offset_x"] = x
|
| 74 |
-
current_region["offset_y"] = y
|
| 75 |
-
|
| 76 |
-
# Mouse move event
|
| 77 |
-
elif event == cv2.EVENT_MOUSEMOVE:
|
| 78 |
-
if current_region is not None and current_region["dragging"]:
|
| 79 |
-
dx = x - current_region["offset_x"]
|
| 80 |
-
dy = y - current_region["offset_y"]
|
| 81 |
-
current_region["polygon"] = Polygon(
|
| 82 |
-
[(p[0] + dx, p[1] + dy) for p in current_region["polygon"].exterior.coords]
|
| 83 |
-
)
|
| 84 |
-
current_region["offset_x"] = x
|
| 85 |
-
current_region["offset_y"] = y
|
| 86 |
-
|
| 87 |
-
# Mouse left button up event
|
| 88 |
-
elif event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONUP:
|
| 89 |
-
if current_region is not None and current_region["dragging"]:
|
| 90 |
-
current_region["dragging"] = False
|
| 91 |
-
|
| 92 |
-
|
| 93 |
-
def run(
|
| 94 |
-
weights="yolov8n.pt",
|
| 95 |
-
source=None,
|
| 96 |
-
device="cpu",
|
| 97 |
-
view_img=False,
|
| 98 |
-
save_img=False,
|
| 99 |
-
exist_ok=False,
|
| 100 |
-
classes=None,
|
| 101 |
-
line_thickness=2,
|
| 102 |
-
track_thickness=2,
|
| 103 |
-
region_thickness=2,
|
| 104 |
-
):
|
| 105 |
-
"""
|
| 106 |
-
Run Region counting on a video using YOLOv8 and ByteTrack.
|
| 107 |
-
|
| 108 |
-
Supports movable region for real time counting inside specific area.
|
| 109 |
-
Supports multiple regions counting.
|
| 110 |
-
Regions can be Polygons or rectangle in shape
|
| 111 |
-
|
| 112 |
-
Args:
|
| 113 |
-
weights (str): Model weights path.
|
| 114 |
-
source (str): Video file path.
|
| 115 |
-
device (str): processing device cpu, 0, 1
|
| 116 |
-
view_img (bool): Show results.
|
| 117 |
-
save_img (bool): Save results.
|
| 118 |
-
exist_ok (bool): Overwrite existing files.
|
| 119 |
-
classes (list): classes to detect and track
|
| 120 |
-
line_thickness (int): Bounding box thickness.
|
| 121 |
-
track_thickness (int): Tracking line thickness
|
| 122 |
-
region_thickness (int): Region thickness.
|
| 123 |
-
"""
|
| 124 |
-
vid_frame_count = 0
|
| 125 |
-
|
| 126 |
-
# Check source path
|
| 127 |
-
if not Path(source).exists():
|
| 128 |
-
raise FileNotFoundError(f"Source path '{source}' does not exist.")
|
| 129 |
-
|
| 130 |
-
# Setup Model
|
| 131 |
-
model = YOLO(f"{weights}")
|
| 132 |
-
model.to("cuda") if device == "0" else model.to("cpu")
|
| 133 |
-
|
| 134 |
-
# Extract classes names
|
| 135 |
-
names = model.names
|
| 136 |
-
|
| 137 |
-
# Video setup
|
| 138 |
-
videocapture = cv2.VideoCapture(source)
|
| 139 |
-
frame_width = int(videocapture.get(3))
|
| 140 |
-
frame_height = int(videocapture.get(4))
|
| 141 |
-
fps = int(videocapture.get(5))
|
| 142 |
-
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v")
|
| 143 |
-
|
| 144 |
-
# Output setup
|
| 145 |
-
save_dir = increment_path(Path("ultralytics_rc_output") / "exp", exist_ok)
|
| 146 |
-
save_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
|
| 147 |
-
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(str(save_dir / f"{Path(source).stem}.avi"), fourcc, fps, (frame_width, frame_height))
|
| 148 |
-
|
| 149 |
-
# Iterate over video frames
|
| 150 |
-
while videocapture.isOpened():
|
| 151 |
-
success, frame = videocapture.read()
|
| 152 |
-
if not success:
|
| 153 |
-
break
|
| 154 |
-
vid_frame_count += 1
|
| 155 |
-
|
| 156 |
-
# Extract the results
|
| 157 |
-
results = model.track(frame, persist=True, classes=classes)
|
| 158 |
-
|
| 159 |
-
if results[0].boxes.id is not None:
|
| 160 |
-
boxes = results[0].boxes.xyxy.cpu()
|
| 161 |
-
track_ids = results[0].boxes.id.int().cpu().tolist()
|
| 162 |
-
clss = results[0].boxes.cls.cpu().tolist()
|
| 163 |
-
|
| 164 |
-
annotator = Annotator(frame, line_width=line_thickness, example=str(names))
|
| 165 |
-
|
| 166 |
-
for box, track_id, cls in zip(boxes, track_ids, clss):
|
| 167 |
-
annotator.box_label(box, str(names[cls]), color=colors(cls, True))
|
| 168 |
-
bbox_center = (box[0] + box[2]) / 2, (box[1] + box[3]) / 2 # Bbox center
|
| 169 |
-
|
| 170 |
-
track = track_history[track_id] # Tracking Lines plot
|
| 171 |
-
track.append((float(bbox_center[0]), float(bbox_center[1])))
|
| 172 |
-
if len(track) > 30:
|
| 173 |
-
track.pop(0)
|
| 174 |
-
points = np.hstack(track).astype(np.int32).reshape((-1, 1, 2))
|
| 175 |
-
cv2.polylines(frame, [points], isClosed=False, color=colors(cls, True), thickness=track_thickness)
|
| 176 |
-
|
| 177 |
-
# Check if detection inside region
|
| 178 |
-
for region in counting_regions:
|
| 179 |
-
if region["polygon"].contains(Point((bbox_center[0], bbox_center[1]))):
|
| 180 |
-
region["counts"] += 1
|
| 181 |
-
|
| 182 |
-
# Draw regions (Polygons/Rectangles)
|
| 183 |
-
for region in counting_regions:
|
| 184 |
-
region_label = str(region["counts"])
|
| 185 |
-
region_color = region["region_color"]
|
| 186 |
-
region_text_color = region["text_color"]
|
| 187 |
-
|
| 188 |
-
polygon_coordinates = np.array(region["polygon"].exterior.coords, dtype=np.int32)
|
| 189 |
-
centroid_x, centroid_y = int(region["polygon"].centroid.x), int(region["polygon"].centroid.y)
|
| 190 |
-
|
| 191 |
-
text_size, _ = cv2.getTextSize(
|
| 192 |
-
region_label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, fontScale=0.7, thickness=line_thickness
|
| 193 |
-
)
|
| 194 |
-
text_x = centroid_x - text_size[0] // 2
|
| 195 |
-
text_y = centroid_y + text_size[1] // 2
|
| 196 |
-
cv2.rectangle(
|
| 197 |
-
frame,
|
| 198 |
-
(text_x - 5, text_y - text_size[1] - 5),
|
| 199 |
-
(text_x + text_size[0] + 5, text_y + 5),
|
| 200 |
-
region_color,
|
| 201 |
-
-1,
|
| 202 |
-
)
|
| 203 |
-
cv2.putText(
|
| 204 |
-
frame, region_label, (text_x, text_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, region_text_color, line_thickness
|
| 205 |
-
)
|
| 206 |
-
cv2.polylines(frame, [polygon_coordinates], isClosed=True, color=region_color, thickness=region_thickness)
|
| 207 |
-
|
| 208 |
-
if view_img:
|
| 209 |
-
if vid_frame_count == 1:
|
| 210 |
-
cv2.namedWindow("Ultralytics YOLOv8 Region Counter Movable")
|
| 211 |
-
cv2.setMouseCallback("Ultralytics YOLOv8 Region Counter Movable", mouse_callback)
|
| 212 |
-
cv2.imshow("Ultralytics YOLOv8 Region Counter Movable", frame)
|
| 213 |
-
|
| 214 |
-
if save_img:
|
| 215 |
-
video_writer.write(frame)
|
| 216 |
-
|
| 217 |
-
for region in counting_regions: # Reinitialize count for each region
|
| 218 |
-
region["counts"] = 0
|
| 219 |
-
|
| 220 |
-
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
|
| 221 |
-
break
|
| 222 |
-
|
| 223 |
-
del vid_frame_count
|
| 224 |
-
video_writer.release()
|
| 225 |
-
videocapture.release()
|
| 226 |
-
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
|
| 227 |
-
|
| 228 |
-
|
| 229 |
-
def parse_opt():
|
| 230 |
-
"""Parse command line arguments."""
|
| 231 |
-
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
| 232 |
-
parser.add_argument("--weights", type=str, default="yolov8n.pt", help="initial weights path")
|
| 233 |
-
parser.add_argument("--device", default="", help="cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu")
|
| 234 |
-
parser.add_argument("--source", type=str, required=True, help="video file path")
|
| 235 |
-
parser.add_argument("--view-img", action="store_true", help="show results")
|
| 236 |
-
parser.add_argument("--save-img", action="store_true", help="save results")
|
| 237 |
-
parser.add_argument("--exist-ok", action="store_true", help="existing project/name ok, do not increment")
|
| 238 |
-
parser.add_argument("--classes", nargs="+", type=int, help="filter by class: --classes 0, or --classes 0 2 3")
|
| 239 |
-
parser.add_argument("--line-thickness", type=int, default=2, help="bounding box thickness")
|
| 240 |
-
parser.add_argument("--track-thickness", type=int, default=2, help="Tracking line thickness")
|
| 241 |
-
parser.add_argument("--region-thickness", type=int, default=4, help="Region thickness")
|
| 242 |
-
|
| 243 |
-
return parser.parse_args()
|
| 244 |
-
|
| 245 |
-
|
| 246 |
-
def main(options):
|
| 247 |
-
"""Main function."""
|
| 248 |
-
run(**vars(options))
|
| 249 |
-
|
| 250 |
-
|
| 251 |
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 252 |
-
opt = parse_opt()
|
| 253 |
-
main(opt)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-SAHI-Inference-Video/readme.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# YOLO11 with SAHI (Inference on Video)
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
[SAHI](https://docs.ultralytics.com/guides/sahi-tiled-inference/) is designed to optimize object detection algorithms for large-scale and high-resolution imagery. It partitions images into manageable slices, performs object detection on each slice, and then stitches the results back together. This tutorial will guide you through the process of running YOLO11 inference on video files with the aid of SAHI.
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
## Table of Contents
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
- [Step 1: Install the Required Libraries](#step-1-install-the-required-libraries)
|
| 8 |
-
- [Step 2: Run the Inference with SAHI using Ultralytics YOLO11](#step-2-run-the-inference-with-sahi-using-ultralytics-yolo11)
|
| 9 |
-
- [Usage Options](#usage-options)
|
| 10 |
-
- [FAQ](#faq)
|
| 11 |
-
|
| 12 |
-
## Step 1: Install the Required Libraries
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
Clone the repository, install dependencies and `cd` to this local directory for commands in Step 2.
|
| 15 |
-
|
| 16 |
-
```bash
|
| 17 |
-
# Clone ultralytics repo
|
| 18 |
-
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
# Install dependencies
|
| 21 |
-
pip install -U sahi ultralytics
|
| 22 |
-
|
| 23 |
-
# cd to local directory
|
| 24 |
-
cd ultralytics/examples/YOLOv8-SAHI-Inference-Video
|
| 25 |
-
```
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
## Step 2: Run the Inference with SAHI using Ultralytics YOLO11
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
Here are the basic commands for running the inference:
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
```bash
|
| 32 |
-
#if you want to save results
|
| 33 |
-
python yolov8_sahi.py --source "path/to/video.mp4" --save-img
|
| 34 |
-
|
| 35 |
-
#if you want to change model file
|
| 36 |
-
python yolov8_sahi.py --source "path/to/video.mp4" --save-img --weights "yolo11n.pt"
|
| 37 |
-
```
|
| 38 |
-
|
| 39 |
-
## Usage Options
|
| 40 |
-
|
| 41 |
-
- `--source`: Specifies the path to the video file you want to run inference on.
|
| 42 |
-
- `--save-img`: Flag to save the detection results as images.
|
| 43 |
-
- `--weights`: Specifies a different YOLO11 model file (e.g., `yolo11n.pt`, `yolov8s.pt`, `yolo11m.pt`, `yolo11l.pt`, `yolo11x.pt`).
|
| 44 |
-
|
| 45 |
-
## FAQ
|
| 46 |
-
|
| 47 |
-
**1. What is SAHI?**
|
| 48 |
-
|
| 49 |
-
SAHI stands for Slicing Aided Hyper Inference. It is a library designed to optimize object detection algorithms for large-scale and high-resolution images. The library source code is available on [GitHub](https://github.com/obss/sahi).
|
| 50 |
-
|
| 51 |
-
**2. Why use SAHI with YOLO11?**
|
| 52 |
-
|
| 53 |
-
SAHI can handle large-scale images by slicing them into smaller, more manageable sizes without compromising the detection quality. This makes it a great companion to YOLO11, especially when working with high-resolution videos.
|
| 54 |
-
|
| 55 |
-
**3. How do I debug issues?**
|
| 56 |
-
|
| 57 |
-
You can add the `--debug` flag to your command to print out more information during inference:
|
| 58 |
-
|
| 59 |
-
```bash
|
| 60 |
-
python yolov8_sahi.py --source "path to video file" --debug
|
| 61 |
-
```
|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
**4. Can I use other YOLO versions?**
|
| 64 |
-
|
| 65 |
-
Yes, you can specify different YOLO model weights using the `--weights` option.
|
| 66 |
-
|
| 67 |
-
**5. Where can I find more information?**
|
| 68 |
-
|
| 69 |
-
For a full guide to YOLO11 with SAHI see [https://docs.ultralytics.com/guides/sahi-tiled-inference](https://docs.ultralytics.com/guides/sahi-tiled-inference/).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-SAHI-Inference-Video/yolov8_sahi.py
DELETED
|
@@ -1,108 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
import argparse
|
| 4 |
-
from pathlib import Path
|
| 5 |
-
|
| 6 |
-
import cv2
|
| 7 |
-
from sahi import AutoDetectionModel
|
| 8 |
-
from sahi.predict import get_sliced_prediction
|
| 9 |
-
from sahi.utils.ultralytics import download_yolo11n_model
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
from ultralytics.utils.files import increment_path
|
| 12 |
-
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Annotator, colors
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
|
| 15 |
-
class SAHIInference:
|
| 16 |
-
"""Runs Ultralytics YOLO11 and SAHI for object detection on video with options to view, save, and track results."""
|
| 17 |
-
|
| 18 |
-
def __init__(self):
|
| 19 |
-
"""Initializes the SAHIInference class for performing sliced inference using SAHI with YOLO11 models."""
|
| 20 |
-
self.detection_model = None
|
| 21 |
-
|
| 22 |
-
def load_model(self, weights):
|
| 23 |
-
"""Loads a YOLO11 model with specified weights for object detection using SAHI."""
|
| 24 |
-
yolo11_model_path = f"models/{weights}"
|
| 25 |
-
download_yolo11n_model(yolo11_model_path)
|
| 26 |
-
self.detection_model = AutoDetectionModel.from_pretrained(
|
| 27 |
-
model_type="ultralytics", model_path=yolo11_model_path, device="cpu"
|
| 28 |
-
)
|
| 29 |
-
|
| 30 |
-
def inference(
|
| 31 |
-
self,
|
| 32 |
-
weights="yolo11n.pt",
|
| 33 |
-
source="test.mp4",
|
| 34 |
-
view_img=False,
|
| 35 |
-
save_img=False,
|
| 36 |
-
exist_ok=False,
|
| 37 |
-
):
|
| 38 |
-
"""
|
| 39 |
-
Run object detection on a video using YOLO11 and SAHI.
|
| 40 |
-
|
| 41 |
-
Args:
|
| 42 |
-
weights (str): Model weights path.
|
| 43 |
-
source (str): Video file path.
|
| 44 |
-
view_img (bool): Show results.
|
| 45 |
-
save_img (bool): Save results.
|
| 46 |
-
exist_ok (bool): Overwrite existing files.
|
| 47 |
-
"""
|
| 48 |
-
# Video setup
|
| 49 |
-
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(source)
|
| 50 |
-
assert cap.isOpened(), "Error reading video file"
|
| 51 |
-
frame_width, frame_height = int(cap.get(3)), int(cap.get(4))
|
| 52 |
-
|
| 53 |
-
# Output setup
|
| 54 |
-
save_dir = increment_path(Path("ultralytics_results_with_sahi") / "exp", exist_ok)
|
| 55 |
-
save_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
|
| 56 |
-
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(
|
| 57 |
-
str(save_dir / f"{Path(source).stem}.avi"),
|
| 58 |
-
cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"MJPG"),
|
| 59 |
-
int(cap.get(5)),
|
| 60 |
-
(frame_width, frame_height),
|
| 61 |
-
)
|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
# Load model
|
| 64 |
-
self.load_model(weights)
|
| 65 |
-
while cap.isOpened():
|
| 66 |
-
success, frame = cap.read()
|
| 67 |
-
if not success:
|
| 68 |
-
break
|
| 69 |
-
annotator = Annotator(frame) # Initialize annotator for plotting detection and tracking results
|
| 70 |
-
results = get_sliced_prediction(
|
| 71 |
-
frame[..., ::-1],
|
| 72 |
-
self.detection_model,
|
| 73 |
-
slice_height=512,
|
| 74 |
-
slice_width=512,
|
| 75 |
-
)
|
| 76 |
-
detection_data = [
|
| 77 |
-
(det.category.name, det.category.id, (det.bbox.minx, det.bbox.miny, det.bbox.maxx, det.bbox.maxy))
|
| 78 |
-
for det in results.object_prediction_list
|
| 79 |
-
]
|
| 80 |
-
|
| 81 |
-
for det in detection_data:
|
| 82 |
-
annotator.box_label(det[2], label=str(det[0]), color=colors(int(det[1]), True))
|
| 83 |
-
|
| 84 |
-
if view_img:
|
| 85 |
-
cv2.imshow(Path(source).stem, frame)
|
| 86 |
-
if save_img:
|
| 87 |
-
video_writer.write(frame)
|
| 88 |
-
|
| 89 |
-
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
|
| 90 |
-
break
|
| 91 |
-
video_writer.release()
|
| 92 |
-
cap.release()
|
| 93 |
-
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
|
| 94 |
-
|
| 95 |
-
def parse_opt(self):
|
| 96 |
-
"""Parse command line arguments."""
|
| 97 |
-
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
| 98 |
-
parser.add_argument("--weights", type=str, default="yolo11n.pt", help="initial weights path")
|
| 99 |
-
parser.add_argument("--source", type=str, required=True, help="video file path")
|
| 100 |
-
parser.add_argument("--view-img", action="store_true", help="show results")
|
| 101 |
-
parser.add_argument("--save-img", action="store_true", help="save results")
|
| 102 |
-
parser.add_argument("--exist-ok", action="store_true", help="existing project/name ok, do not increment")
|
| 103 |
-
return parser.parse_args()
|
| 104 |
-
|
| 105 |
-
|
| 106 |
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 107 |
-
inference = SAHIInference()
|
| 108 |
-
inference.inference(**vars(inference.parse_opt()))
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-Segmentation-ONNXRuntime-Python/README.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# YOLOv8-Segmentation-ONNXRuntime-Python Demo
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
This repository provides a Python demo for performing segmentation with YOLOv8 using ONNX Runtime, highlighting the interoperability of YOLOv8 models without the need for the full PyTorch stack.
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
## Features
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
- **Framework Agnostic**: Runs segmentation inference purely on ONNX Runtime without importing PyTorch.
|
| 8 |
-
- **Efficient Inference**: Supports both FP32 and FP16 precision for ONNX models, catering to different computational needs.
|
| 9 |
-
- **Ease of Use**: Utilizes simple command-line arguments for model execution.
|
| 10 |
-
- **Broad Compatibility**: Leverages Numpy and OpenCV for image processing, ensuring broad compatibility with various environments.
|
| 11 |
-
|
| 12 |
-
## Installation
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
Install the required packages using pip. You will need `ultralytics` for exporting YOLOv8-seg ONNX model and using some utility functions, `onnxruntime-gpu` for GPU-accelerated inference, and `opencv-python` for image processing.
|
| 15 |
-
|
| 16 |
-
```bash
|
| 17 |
-
pip install ultralytics
|
| 18 |
-
pip install onnxruntime-gpu # For GPU support
|
| 19 |
-
# pip install onnxruntime # Use this instead if you don't have an NVIDIA GPU
|
| 20 |
-
pip install numpy
|
| 21 |
-
pip install opencv-python
|
| 22 |
-
```
|
| 23 |
-
|
| 24 |
-
## Getting Started
|
| 25 |
-
|
| 26 |
-
### 1. Export the YOLOv8 ONNX Model
|
| 27 |
-
|
| 28 |
-
Export the YOLOv8 segmentation model to ONNX format using the provided `ultralytics` package.
|
| 29 |
-
|
| 30 |
-
```bash
|
| 31 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8s-seg.pt imgsz=640 format=onnx opset=12 simplify
|
| 32 |
-
```
|
| 33 |
-
|
| 34 |
-
### 2. Run Inference
|
| 35 |
-
|
| 36 |
-
Perform inference with the exported ONNX model on your images.
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
```bash
|
| 39 |
-
python main.py --model <MODEL_PATH> --source <IMAGE_PATH>
|
| 40 |
-
```
|
| 41 |
-
|
| 42 |
-
### Example Output
|
| 43 |
-
|
| 44 |
-
After running the command, you should see segmentation results similar to this:
|
| 45 |
-
|
| 46 |
-
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/51357717/279988626-eb74823f-1563-4d58-a8e4-0494025b7c9a.jpg" alt="Segmentation Demo" width="800">
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
## Advanced Usage
|
| 49 |
-
|
| 50 |
-
For more advanced usage, including real-time video processing, please refer to the `main.py` script's command-line arguments.
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
## Contributing
|
| 53 |
-
|
| 54 |
-
We welcome contributions to improve this demo! Please submit issues and pull requests for bug reports, feature requests, or submitting a new algorithm enhancement.
|
| 55 |
-
|
| 56 |
-
## License
|
| 57 |
-
|
| 58 |
-
This project is licensed under the AGPL-3.0 License - see the [LICENSE](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/LICENSE) file for details.
|
| 59 |
-
|
| 60 |
-
## Acknowledgments
|
| 61 |
-
|
| 62 |
-
- The YOLOv8-Segmentation-ONNXRuntime-Python demo is contributed by GitHub user [jamjamjon](https://github.com/jamjamjon).
|
| 63 |
-
- Thanks to the ONNX Runtime community for providing a robust and efficient inference engine.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-Segmentation-ONNXRuntime-Python/main.py
DELETED
|
@@ -1,338 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
import argparse
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
import cv2
|
| 6 |
-
import numpy as np
|
| 7 |
-
import onnxruntime as ort
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
from ultralytics.utils import ASSETS, yaml_load
|
| 10 |
-
from ultralytics.utils.checks import check_yaml
|
| 11 |
-
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Colors
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
class YOLOv8Seg:
|
| 15 |
-
"""YOLOv8 segmentation model."""
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
def __init__(self, onnx_model):
|
| 18 |
-
"""
|
| 19 |
-
Initialization.
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
Args:
|
| 22 |
-
onnx_model (str): Path to the ONNX model.
|
| 23 |
-
"""
|
| 24 |
-
# Build Ort session
|
| 25 |
-
self.session = ort.InferenceSession(
|
| 26 |
-
onnx_model,
|
| 27 |
-
providers=["CUDAExecutionProvider", "CPUExecutionProvider"]
|
| 28 |
-
if ort.get_device() == "GPU"
|
| 29 |
-
else ["CPUExecutionProvider"],
|
| 30 |
-
)
|
| 31 |
-
|
| 32 |
-
# Numpy dtype: support both FP32 and FP16 onnx model
|
| 33 |
-
self.ndtype = np.half if self.session.get_inputs()[0].type == "tensor(float16)" else np.single
|
| 34 |
-
|
| 35 |
-
# Get model width and height(YOLOv8-seg only has one input)
|
| 36 |
-
self.model_height, self.model_width = [x.shape for x in self.session.get_inputs()][0][-2:]
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
# Load COCO class names
|
| 39 |
-
self.classes = yaml_load(check_yaml("coco8.yaml"))["names"]
|
| 40 |
-
|
| 41 |
-
# Create color palette
|
| 42 |
-
self.color_palette = Colors()
|
| 43 |
-
|
| 44 |
-
def __call__(self, im0, conf_threshold=0.4, iou_threshold=0.45, nm=32):
|
| 45 |
-
"""
|
| 46 |
-
The whole pipeline: pre-process -> inference -> post-process.
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
Args:
|
| 49 |
-
im0 (Numpy.ndarray): original input image.
|
| 50 |
-
conf_threshold (float): confidence threshold for filtering predictions.
|
| 51 |
-
iou_threshold (float): iou threshold for NMS.
|
| 52 |
-
nm (int): the number of masks.
|
| 53 |
-
|
| 54 |
-
Returns:
|
| 55 |
-
boxes (List): list of bounding boxes.
|
| 56 |
-
segments (List): list of segments.
|
| 57 |
-
masks (np.ndarray): [N, H, W], output masks.
|
| 58 |
-
"""
|
| 59 |
-
# Pre-process
|
| 60 |
-
im, ratio, (pad_w, pad_h) = self.preprocess(im0)
|
| 61 |
-
|
| 62 |
-
# Ort inference
|
| 63 |
-
preds = self.session.run(None, {self.session.get_inputs()[0].name: im})
|
| 64 |
-
|
| 65 |
-
# Post-process
|
| 66 |
-
boxes, segments, masks = self.postprocess(
|
| 67 |
-
preds,
|
| 68 |
-
im0=im0,
|
| 69 |
-
ratio=ratio,
|
| 70 |
-
pad_w=pad_w,
|
| 71 |
-
pad_h=pad_h,
|
| 72 |
-
conf_threshold=conf_threshold,
|
| 73 |
-
iou_threshold=iou_threshold,
|
| 74 |
-
nm=nm,
|
| 75 |
-
)
|
| 76 |
-
return boxes, segments, masks
|
| 77 |
-
|
| 78 |
-
def preprocess(self, img):
|
| 79 |
-
"""
|
| 80 |
-
Pre-processes the input image.
|
| 81 |
-
|
| 82 |
-
Args:
|
| 83 |
-
img (Numpy.ndarray): image about to be processed.
|
| 84 |
-
|
| 85 |
-
Returns:
|
| 86 |
-
img_process (Numpy.ndarray): image preprocessed for inference.
|
| 87 |
-
ratio (tuple): width, height ratios in letterbox.
|
| 88 |
-
pad_w (float): width padding in letterbox.
|
| 89 |
-
pad_h (float): height padding in letterbox.
|
| 90 |
-
"""
|
| 91 |
-
# Resize and pad input image using letterbox() (Borrowed from Ultralytics)
|
| 92 |
-
shape = img.shape[:2] # original image shape
|
| 93 |
-
new_shape = (self.model_height, self.model_width)
|
| 94 |
-
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
|
| 95 |
-
ratio = r, r
|
| 96 |
-
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
|
| 97 |
-
pad_w, pad_h = (new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0]) / 2, (new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1]) / 2 # wh padding
|
| 98 |
-
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
|
| 99 |
-
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
|
| 100 |
-
top, bottom = int(round(pad_h - 0.1)), int(round(pad_h + 0.1))
|
| 101 |
-
left, right = int(round(pad_w - 0.1)), int(round(pad_w + 0.1))
|
| 102 |
-
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=(114, 114, 114))
|
| 103 |
-
|
| 104 |
-
# Transforms: HWC to CHW -> BGR to RGB -> div(255) -> contiguous -> add axis(optional)
|
| 105 |
-
img = np.ascontiguousarray(np.einsum("HWC->CHW", img)[::-1], dtype=self.ndtype) / 255.0
|
| 106 |
-
img_process = img[None] if len(img.shape) == 3 else img
|
| 107 |
-
return img_process, ratio, (pad_w, pad_h)
|
| 108 |
-
|
| 109 |
-
def postprocess(self, preds, im0, ratio, pad_w, pad_h, conf_threshold, iou_threshold, nm=32):
|
| 110 |
-
"""
|
| 111 |
-
Post-process the prediction.
|
| 112 |
-
|
| 113 |
-
Args:
|
| 114 |
-
preds (Numpy.ndarray): predictions come from ort.session.run().
|
| 115 |
-
im0 (Numpy.ndarray): [h, w, c] original input image.
|
| 116 |
-
ratio (tuple): width, height ratios in letterbox.
|
| 117 |
-
pad_w (float): width padding in letterbox.
|
| 118 |
-
pad_h (float): height padding in letterbox.
|
| 119 |
-
conf_threshold (float): conf threshold.
|
| 120 |
-
iou_threshold (float): iou threshold.
|
| 121 |
-
nm (int): the number of masks.
|
| 122 |
-
|
| 123 |
-
Returns:
|
| 124 |
-
boxes (List): list of bounding boxes.
|
| 125 |
-
segments (List): list of segments.
|
| 126 |
-
masks (np.ndarray): [N, H, W], output masks.
|
| 127 |
-
"""
|
| 128 |
-
x, protos = preds[0], preds[1] # Two outputs: predictions and protos
|
| 129 |
-
|
| 130 |
-
# Transpose dim 1: (Batch_size, xywh_conf_cls_nm, Num_anchors) -> (Batch_size, Num_anchors, xywh_conf_cls_nm)
|
| 131 |
-
x = np.einsum("bcn->bnc", x)
|
| 132 |
-
|
| 133 |
-
# Predictions filtering by conf-threshold
|
| 134 |
-
x = x[np.amax(x[..., 4:-nm], axis=-1) > conf_threshold]
|
| 135 |
-
|
| 136 |
-
# Create a new matrix which merge these(box, score, cls, nm) into one
|
| 137 |
-
# For more details about `numpy.c_()`: https://numpy.org/doc/1.26/reference/generated/numpy.c_.html
|
| 138 |
-
x = np.c_[x[..., :4], np.amax(x[..., 4:-nm], axis=-1), np.argmax(x[..., 4:-nm], axis=-1), x[..., -nm:]]
|
| 139 |
-
|
| 140 |
-
# NMS filtering
|
| 141 |
-
x = x[cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(x[:, :4], x[:, 4], conf_threshold, iou_threshold)]
|
| 142 |
-
|
| 143 |
-
# Decode and return
|
| 144 |
-
if len(x) > 0:
|
| 145 |
-
# Bounding boxes format change: cxcywh -> xyxy
|
| 146 |
-
x[..., [0, 1]] -= x[..., [2, 3]] / 2
|
| 147 |
-
x[..., [2, 3]] += x[..., [0, 1]]
|
| 148 |
-
|
| 149 |
-
# Rescales bounding boxes from model shape(model_height, model_width) to the shape of original image
|
| 150 |
-
x[..., :4] -= [pad_w, pad_h, pad_w, pad_h]
|
| 151 |
-
x[..., :4] /= min(ratio)
|
| 152 |
-
|
| 153 |
-
# Bounding boxes boundary clamp
|
| 154 |
-
x[..., [0, 2]] = x[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, im0.shape[1])
|
| 155 |
-
x[..., [1, 3]] = x[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, im0.shape[0])
|
| 156 |
-
|
| 157 |
-
# Process masks
|
| 158 |
-
masks = self.process_mask(protos[0], x[:, 6:], x[:, :4], im0.shape)
|
| 159 |
-
|
| 160 |
-
# Masks -> Segments(contours)
|
| 161 |
-
segments = self.masks2segments(masks)
|
| 162 |
-
return x[..., :6], segments, masks # boxes, segments, masks
|
| 163 |
-
else:
|
| 164 |
-
return [], [], []
|
| 165 |
-
|
| 166 |
-
@staticmethod
|
| 167 |
-
def masks2segments(masks):
|
| 168 |
-
"""
|
| 169 |
-
Takes a list of masks(n,h,w) and returns a list of segments(n,xy), from
|
| 170 |
-
https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/utils/ops.py.
|
| 171 |
-
|
| 172 |
-
Args:
|
| 173 |
-
masks (numpy.ndarray): the output of the model, which is a tensor of shape (batch_size, 160, 160).
|
| 174 |
-
|
| 175 |
-
Returns:
|
| 176 |
-
segments (List): list of segment masks.
|
| 177 |
-
"""
|
| 178 |
-
segments = []
|
| 179 |
-
for x in masks.astype("uint8"):
|
| 180 |
-
c = cv2.findContours(x, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)[0] # CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE
|
| 181 |
-
if c:
|
| 182 |
-
c = np.array(c[np.array([len(x) for x in c]).argmax()]).reshape(-1, 2)
|
| 183 |
-
else:
|
| 184 |
-
c = np.zeros((0, 2)) # no segments found
|
| 185 |
-
segments.append(c.astype("float32"))
|
| 186 |
-
return segments
|
| 187 |
-
|
| 188 |
-
@staticmethod
|
| 189 |
-
def crop_mask(masks, boxes):
|
| 190 |
-
"""
|
| 191 |
-
Takes a mask and a bounding box, and returns a mask that is cropped to the bounding box, from
|
| 192 |
-
https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/utils/ops.py.
|
| 193 |
-
|
| 194 |
-
Args:
|
| 195 |
-
masks (Numpy.ndarray): [n, h, w] tensor of masks.
|
| 196 |
-
boxes (Numpy.ndarray): [n, 4] tensor of bbox coordinates in relative point form.
|
| 197 |
-
|
| 198 |
-
Returns:
|
| 199 |
-
(Numpy.ndarray): The masks are being cropped to the bounding box.
|
| 200 |
-
"""
|
| 201 |
-
n, h, w = masks.shape
|
| 202 |
-
x1, y1, x2, y2 = np.split(boxes[:, :, None], 4, 1)
|
| 203 |
-
r = np.arange(w, dtype=x1.dtype)[None, None, :]
|
| 204 |
-
c = np.arange(h, dtype=x1.dtype)[None, :, None]
|
| 205 |
-
return masks * ((r >= x1) * (r < x2) * (c >= y1) * (c < y2))
|
| 206 |
-
|
| 207 |
-
def process_mask(self, protos, masks_in, bboxes, im0_shape):
|
| 208 |
-
"""
|
| 209 |
-
Takes the output of the mask head, and applies the mask to the bounding boxes. This produces masks of higher
|
| 210 |
-
quality but is slower, from https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/utils/ops.py.
|
| 211 |
-
|
| 212 |
-
Args:
|
| 213 |
-
protos (numpy.ndarray): [mask_dim, mask_h, mask_w].
|
| 214 |
-
masks_in (numpy.ndarray): [n, mask_dim], n is number of masks after nms.
|
| 215 |
-
bboxes (numpy.ndarray): bboxes re-scaled to original image shape.
|
| 216 |
-
im0_shape (tuple): the size of the input image (h,w,c).
|
| 217 |
-
|
| 218 |
-
Returns:
|
| 219 |
-
(numpy.ndarray): The upsampled masks.
|
| 220 |
-
"""
|
| 221 |
-
c, mh, mw = protos.shape
|
| 222 |
-
masks = np.matmul(masks_in, protos.reshape((c, -1))).reshape((-1, mh, mw)).transpose(1, 2, 0) # HWN
|
| 223 |
-
masks = np.ascontiguousarray(masks)
|
| 224 |
-
masks = self.scale_mask(masks, im0_shape) # re-scale mask from P3 shape to original input image shape
|
| 225 |
-
masks = np.einsum("HWN -> NHW", masks) # HWN -> NHW
|
| 226 |
-
masks = self.crop_mask(masks, bboxes)
|
| 227 |
-
return np.greater(masks, 0.5)
|
| 228 |
-
|
| 229 |
-
@staticmethod
|
| 230 |
-
def scale_mask(masks, im0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
|
| 231 |
-
"""
|
| 232 |
-
Takes a mask, and resizes it to the original image size, from
|
| 233 |
-
https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/utils/ops.py.
|
| 234 |
-
|
| 235 |
-
Args:
|
| 236 |
-
masks (np.ndarray): resized and padded masks/images, [h, w, num]/[h, w, 3].
|
| 237 |
-
im0_shape (tuple): the original image shape.
|
| 238 |
-
ratio_pad (tuple): the ratio of the padding to the original image.
|
| 239 |
-
|
| 240 |
-
Returns:
|
| 241 |
-
masks (np.ndarray): The masks that are being returned.
|
| 242 |
-
"""
|
| 243 |
-
im1_shape = masks.shape[:2]
|
| 244 |
-
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from im0_shape
|
| 245 |
-
gain = min(im1_shape[0] / im0_shape[0], im1_shape[1] / im0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new
|
| 246 |
-
pad = (im1_shape[1] - im0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (im1_shape[0] - im0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
|
| 247 |
-
else:
|
| 248 |
-
pad = ratio_pad[1]
|
| 249 |
-
|
| 250 |
-
# Calculate tlbr of mask
|
| 251 |
-
top, left = int(round(pad[1] - 0.1)), int(round(pad[0] - 0.1)) # y, x
|
| 252 |
-
bottom, right = int(round(im1_shape[0] - pad[1] + 0.1)), int(round(im1_shape[1] - pad[0] + 0.1))
|
| 253 |
-
if len(masks.shape) < 2:
|
| 254 |
-
raise ValueError(f'"len of masks shape" should be 2 or 3, but got {len(masks.shape)}')
|
| 255 |
-
masks = masks[top:bottom, left:right]
|
| 256 |
-
masks = cv2.resize(
|
| 257 |
-
masks, (im0_shape[1], im0_shape[0]), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR
|
| 258 |
-
) # INTER_CUBIC would be better
|
| 259 |
-
if len(masks.shape) == 2:
|
| 260 |
-
masks = masks[:, :, None]
|
| 261 |
-
return masks
|
| 262 |
-
|
| 263 |
-
def draw_and_visualize(self, im, bboxes, segments, vis=False, save=True):
|
| 264 |
-
"""
|
| 265 |
-
Draw and visualize results.
|
| 266 |
-
|
| 267 |
-
Args:
|
| 268 |
-
im (np.ndarray): original image, shape [h, w, c].
|
| 269 |
-
bboxes (numpy.ndarray): [n, 4], n is number of bboxes.
|
| 270 |
-
segments (List): list of segment masks.
|
| 271 |
-
vis (bool): imshow using OpenCV.
|
| 272 |
-
save (bool): save image annotated.
|
| 273 |
-
|
| 274 |
-
Returns:
|
| 275 |
-
None
|
| 276 |
-
"""
|
| 277 |
-
# Draw rectangles and polygons
|
| 278 |
-
im_canvas = im.copy()
|
| 279 |
-
for (*box, conf, cls_), segment in zip(bboxes, segments):
|
| 280 |
-
# draw contour and fill mask
|
| 281 |
-
cv2.polylines(im, np.int32([segment]), True, (255, 255, 255), 2) # white borderline
|
| 282 |
-
cv2.fillPoly(im_canvas, np.int32([segment]), self.color_palette(int(cls_), bgr=True))
|
| 283 |
-
|
| 284 |
-
# draw bbox rectangle
|
| 285 |
-
cv2.rectangle(
|
| 286 |
-
im,
|
| 287 |
-
(int(box[0]), int(box[1])),
|
| 288 |
-
(int(box[2]), int(box[3])),
|
| 289 |
-
self.color_palette(int(cls_), bgr=True),
|
| 290 |
-
1,
|
| 291 |
-
cv2.LINE_AA,
|
| 292 |
-
)
|
| 293 |
-
cv2.putText(
|
| 294 |
-
im,
|
| 295 |
-
f"{self.classes[cls_]}: {conf:.3f}",
|
| 296 |
-
(int(box[0]), int(box[1] - 9)),
|
| 297 |
-
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
|
| 298 |
-
0.7,
|
| 299 |
-
self.color_palette(int(cls_), bgr=True),
|
| 300 |
-
2,
|
| 301 |
-
cv2.LINE_AA,
|
| 302 |
-
)
|
| 303 |
-
|
| 304 |
-
# Mix image
|
| 305 |
-
im = cv2.addWeighted(im_canvas, 0.3, im, 0.7, 0)
|
| 306 |
-
|
| 307 |
-
# Show image
|
| 308 |
-
if vis:
|
| 309 |
-
cv2.imshow("demo", im)
|
| 310 |
-
cv2.waitKey(0)
|
| 311 |
-
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
|
| 312 |
-
|
| 313 |
-
# Save image
|
| 314 |
-
if save:
|
| 315 |
-
cv2.imwrite("demo.jpg", im)
|
| 316 |
-
|
| 317 |
-
|
| 318 |
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 319 |
-
# Create an argument parser to handle command-line arguments
|
| 320 |
-
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
| 321 |
-
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, required=True, help="Path to ONNX model")
|
| 322 |
-
parser.add_argument("--source", type=str, default=str(ASSETS / "bus.jpg"), help="Path to input image")
|
| 323 |
-
parser.add_argument("--conf", type=float, default=0.25, help="Confidence threshold")
|
| 324 |
-
parser.add_argument("--iou", type=float, default=0.45, help="NMS IoU threshold")
|
| 325 |
-
args = parser.parse_args()
|
| 326 |
-
|
| 327 |
-
# Build model
|
| 328 |
-
model = YOLOv8Seg(args.model)
|
| 329 |
-
|
| 330 |
-
# Read image by OpenCV
|
| 331 |
-
img = cv2.imread(args.source)
|
| 332 |
-
|
| 333 |
-
# Inference
|
| 334 |
-
boxes, segments, _ = model(img, conf_threshold=args.conf, iou_threshold=args.iou)
|
| 335 |
-
|
| 336 |
-
# Draw bboxes and polygons
|
| 337 |
-
if len(boxes) > 0:
|
| 338 |
-
model.draw_and_visualize(img, boxes, segments, vis=False, save=True)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-TFLite-Python/README.md
DELETED
|
@@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# YOLOv8 - TFLite Runtime
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
This example shows how to run inference with YOLOv8 TFLite model. It supports FP32, FP16 and INT8 models.
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
## Installation
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
### Installing `tflite-runtime`
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
To load TFLite models, install the `tflite-runtime` package using:
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
```bash
|
| 12 |
-
pip install tflite-runtime
|
| 13 |
-
```
|
| 14 |
-
|
| 15 |
-
### Installing `tensorflow-gpu` (For NVIDIA GPU Users)
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
Leverage GPU acceleration with NVIDIA GPUs by installing `tensorflow-gpu`:
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
```bash
|
| 20 |
-
pip install tensorflow-gpu
|
| 21 |
-
```
|
| 22 |
-
|
| 23 |
-
**Note:** Ensure you have compatible GPU drivers installed on your system.
|
| 24 |
-
|
| 25 |
-
### Installing `tensorflow` (CPU Version)
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
For CPU usage or non-NVIDIA GPUs, install TensorFlow with:
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
```bash
|
| 30 |
-
pip install tensorflow
|
| 31 |
-
```
|
| 32 |
-
|
| 33 |
-
## Usage
|
| 34 |
-
|
| 35 |
-
Follow these instructions to run YOLOv8 after successful installation.
|
| 36 |
-
|
| 37 |
-
Convert the YOLOv8 model to TFLite format:
|
| 38 |
-
|
| 39 |
-
```bash
|
| 40 |
-
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt imgsz=640 format=tflite int8
|
| 41 |
-
```
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
Locate the TFLite model in `yolov8n_saved_model`. Then, execute the following in your terminal:
|
| 44 |
-
|
| 45 |
-
```bash
|
| 46 |
-
python main.py --model yolov8n_full_integer_quant.tflite --img image.jpg --conf 0.25 --iou 0.45 --metadata "metadata.yaml"
|
| 47 |
-
```
|
| 48 |
-
|
| 49 |
-
Replace `best_full_integer_quant.tflite` with the TFLite model path, `image.jpg` with the input image path, `metadata.yaml` with the one generated by `ultralytics` during export, and adjust the confidence (conf) and IoU thresholds (iou) as necessary.
|
| 50 |
-
|
| 51 |
-
### Output
|
| 52 |
-
|
| 53 |
-
The output would show the detections along with the class labels and confidences of each detected object.
|
| 54 |
-
|
| 55 |
-

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/YOLOv8-TFLite-Python/main.py
DELETED
|
@@ -1,221 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license
|
| 2 |
-
|
| 3 |
-
import argparse
|
| 4 |
-
from typing import Tuple, Union
|
| 5 |
-
|
| 6 |
-
import cv2
|
| 7 |
-
import numpy as np
|
| 8 |
-
import tensorflow as tf
|
| 9 |
-
import yaml
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
from ultralytics.utils import ASSETS
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
try:
|
| 14 |
-
from tflite_runtime.interpreter import Interpreter
|
| 15 |
-
except ImportError:
|
| 16 |
-
import tensorflow as tf
|
| 17 |
-
|
| 18 |
-
Interpreter = tf.lite.Interpreter
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
class YOLOv8TFLite:
|
| 22 |
-
"""
|
| 23 |
-
YOLOv8TFLite.
|
| 24 |
-
|
| 25 |
-
A class for performing object detection using the YOLOv8 model with TensorFlow Lite.
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
Attributes:
|
| 28 |
-
model (str): Path to the TensorFlow Lite model file.
|
| 29 |
-
conf (float): Confidence threshold for filtering detections.
|
| 30 |
-
iou (float): Intersection over Union threshold for non-maximum suppression.
|
| 31 |
-
metadata (Optional[str]): Path to the metadata file, if any.
|
| 32 |
-
|
| 33 |
-
Methods:
|
| 34 |
-
detect(img_path: str) -> np.ndarray:
|
| 35 |
-
Performs inference and returns the output image with drawn detections.
|
| 36 |
-
"""
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
def __init__(self, model: str, conf: float = 0.25, iou: float = 0.45, metadata: Union[str, None] = None):
|
| 39 |
-
"""
|
| 40 |
-
Initializes an instance of the YOLOv8TFLite class.
|
| 41 |
-
|
| 42 |
-
Args:
|
| 43 |
-
model (str): Path to the TFLite model.
|
| 44 |
-
conf (float, optional): Confidence threshold for filtering detections. Defaults to 0.25.
|
| 45 |
-
iou (float, optional): IoU (Intersection over Union) threshold for non-maximum suppression. Defaults to 0.45.
|
| 46 |
-
metadata (Union[str, None], optional): Path to the metadata file or None if not used. Defaults to None.
|
| 47 |
-
"""
|
| 48 |
-
self.conf = conf
|
| 49 |
-
self.iou = iou
|
| 50 |
-
if metadata is None:
|
| 51 |
-
self.classes = {i: i for i in range(1000)}
|
| 52 |
-
else:
|
| 53 |
-
with open(metadata) as f:
|
| 54 |
-
self.classes = yaml.safe_load(f)["names"]
|
| 55 |
-
np.random.seed(42)
|
| 56 |
-
self.color_palette = np.random.uniform(128, 255, size=(len(self.classes), 3))
|
| 57 |
-
|
| 58 |
-
self.model = Interpreter(model_path=model)
|
| 59 |
-
self.model.allocate_tensors()
|
| 60 |
-
|
| 61 |
-
input_details = self.model.get_input_details()[0]
|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
self.in_width, self.in_height = input_details["shape"][1:3]
|
| 64 |
-
self.in_index = input_details["index"]
|
| 65 |
-
self.in_scale, self.in_zero_point = input_details["quantization"]
|
| 66 |
-
self.int8 = input_details["dtype"] == np.int8
|
| 67 |
-
|
| 68 |
-
output_details = self.model.get_output_details()[0]
|
| 69 |
-
self.out_index = output_details["index"]
|
| 70 |
-
self.out_scale, self.out_zero_point = output_details["quantization"]
|
| 71 |
-
|
| 72 |
-
def letterbox(self, img: np.ndarray, new_shape: Tuple = (640, 640)) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, Tuple[float, float]]:
|
| 73 |
-
"""Resizes and reshapes images while maintaining aspect ratio by adding padding, suitable for YOLO models."""
|
| 74 |
-
shape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
|
| 75 |
-
|
| 76 |
-
# Scale ratio (new / old)
|
| 77 |
-
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
|
| 78 |
-
|
| 79 |
-
# Compute padding
|
| 80 |
-
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
|
| 81 |
-
dw, dh = (new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0]) / 2, (new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1]) / 2 # wh padding
|
| 82 |
-
|
| 83 |
-
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
|
| 84 |
-
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
|
| 85 |
-
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
|
| 86 |
-
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
|
| 87 |
-
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=(114, 114, 114))
|
| 88 |
-
|
| 89 |
-
return img, (top / img.shape[0], left / img.shape[1])
|
| 90 |
-
|
| 91 |
-
def draw_detections(self, img: np.ndarray, box: np.ndarray, score: np.float32, class_id: int) -> None:
|
| 92 |
-
"""
|
| 93 |
-
Draws bounding boxes and labels on the input image based on the detected objects.
|
| 94 |
-
|
| 95 |
-
Args:
|
| 96 |
-
img (np.ndarray): The input image to draw detections on.
|
| 97 |
-
box (np.ndarray): Detected bounding box in the format [x1, y1, width, height].
|
| 98 |
-
score (np.float32): Corresponding detection score.
|
| 99 |
-
class_id (int): Class ID for the detected object.
|
| 100 |
-
|
| 101 |
-
Returns:
|
| 102 |
-
None
|
| 103 |
-
"""
|
| 104 |
-
x1, y1, w, h = box
|
| 105 |
-
color = self.color_palette[class_id]
|
| 106 |
-
|
| 107 |
-
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(x1), int(y1)), (int(x1 + w), int(y1 + h)), color, 2)
|
| 108 |
-
|
| 109 |
-
label = f"{self.classes[class_id]}: {score:.2f}"
|
| 110 |
-
|
| 111 |
-
(label_width, label_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
|
| 112 |
-
|
| 113 |
-
label_x = x1
|
| 114 |
-
label_y = y1 - 10 if y1 - 10 > label_height else y1 + 10
|
| 115 |
-
|
| 116 |
-
cv2.rectangle(
|
| 117 |
-
img,
|
| 118 |
-
(int(label_x), int(label_y - label_height)),
|
| 119 |
-
(int(label_x + label_width), int(label_y + label_height)),
|
| 120 |
-
color,
|
| 121 |
-
cv2.FILLED,
|
| 122 |
-
)
|
| 123 |
-
|
| 124 |
-
cv2.putText(img, label, (int(label_x), int(label_y)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
|
| 125 |
-
|
| 126 |
-
def preprocess(self, img: np.ndarray) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, Tuple[float, float]]:
|
| 127 |
-
"""
|
| 128 |
-
Preprocesses the input image before performing inference.
|
| 129 |
-
|
| 130 |
-
Args:
|
| 131 |
-
img (np.ndarray): The input image to be preprocessed.
|
| 132 |
-
|
| 133 |
-
Returns:
|
| 134 |
-
Tuple[np.ndarray, Tuple[float, float]]: A tuple containing:
|
| 135 |
-
- The preprocessed image (np.ndarray).
|
| 136 |
-
- A tuple of two float values representing the padding applied (top/bottom, left/right).
|
| 137 |
-
"""
|
| 138 |
-
img, pad = self.letterbox(img, (self.in_width, self.in_height))
|
| 139 |
-
img = img[..., ::-1][None] # N,H,W,C for TFLite
|
| 140 |
-
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
|
| 141 |
-
img = img.astype(np.float32)
|
| 142 |
-
return img / 255, pad
|
| 143 |
-
|
| 144 |
-
def postprocess(self, img: np.ndarray, outputs: np.ndarray, pad: Tuple[float, float]) -> np.ndarray:
|
| 145 |
-
"""
|
| 146 |
-
Performs post-processing on the model's output to extract bounding boxes, scores, and class IDs.
|
| 147 |
-
|
| 148 |
-
Args:
|
| 149 |
-
img (numpy.ndarray): The input image.
|
| 150 |
-
outputs (numpy.ndarray): The output of the model.
|
| 151 |
-
pad (Tuple[float, float]): Padding used by letterbox.
|
| 152 |
-
|
| 153 |
-
Returns:
|
| 154 |
-
numpy.ndarray: The input image with detections drawn on it.
|
| 155 |
-
"""
|
| 156 |
-
outputs[:, 0] -= pad[1]
|
| 157 |
-
outputs[:, 1] -= pad[0]
|
| 158 |
-
outputs[:, :4] *= max(img.shape)
|
| 159 |
-
|
| 160 |
-
outputs = outputs.transpose(0, 2, 1)
|
| 161 |
-
outputs[..., 0] -= outputs[..., 2] / 2
|
| 162 |
-
outputs[..., 1] -= outputs[..., 3] / 2
|
| 163 |
-
|
| 164 |
-
for out in outputs:
|
| 165 |
-
scores = out[:, 4:].max(-1)
|
| 166 |
-
keep = scores > self.conf
|
| 167 |
-
boxes = out[keep, :4]
|
| 168 |
-
scores = scores[keep]
|
| 169 |
-
class_ids = out[keep, 4:].argmax(-1)
|
| 170 |
-
|
| 171 |
-
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, scores, self.conf, self.iou).flatten()
|
| 172 |
-
|
| 173 |
-
[self.draw_detections(img, boxes[i], scores[i], class_ids[i]) for i in indices]
|
| 174 |
-
|
| 175 |
-
return img
|
| 176 |
-
|
| 177 |
-
def detect(self, img_path: str) -> np.ndarray:
|
| 178 |
-
"""
|
| 179 |
-
Performs inference using a TFLite model and returns the output image with drawn detections.
|
| 180 |
-
|
| 181 |
-
Args:
|
| 182 |
-
img_path (str): The path to the input image file.
|
| 183 |
-
|
| 184 |
-
Returns:
|
| 185 |
-
np.ndarray: The output image with drawn detections.
|
| 186 |
-
"""
|
| 187 |
-
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
|
| 188 |
-
x, pad = self.preprocess(img)
|
| 189 |
-
if self.int8:
|
| 190 |
-
x = (x / self.in_scale + self.in_zero_point).astype(np.int8)
|
| 191 |
-
self.model.set_tensor(self.in_index, x)
|
| 192 |
-
|
| 193 |
-
self.model.invoke()
|
| 194 |
-
|
| 195 |
-
y = self.model.get_tensor(self.out_index)
|
| 196 |
-
|
| 197 |
-
if self.int8:
|
| 198 |
-
y = (y.astype(np.float32) - self.out_zero_point) * self.out_scale
|
| 199 |
-
|
| 200 |
-
return self.postprocess(img, y, pad)
|
| 201 |
-
|
| 202 |
-
|
| 203 |
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 204 |
-
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
| 205 |
-
parser.add_argument(
|
| 206 |
-
"--model",
|
| 207 |
-
type=str,
|
| 208 |
-
default="yolov8n_saved_model/yolov8n_full_integer_quant.tflite",
|
| 209 |
-
help="Path to TFLite model.",
|
| 210 |
-
)
|
| 211 |
-
parser.add_argument("--img", type=str, default=str(ASSETS / "bus.jpg"), help="Path to input image")
|
| 212 |
-
parser.add_argument("--conf", type=float, default=0.25, help="Confidence threshold")
|
| 213 |
-
parser.add_argument("--iou", type=float, default=0.45, help="NMS IoU threshold")
|
| 214 |
-
parser.add_argument("--metadata", type=str, default="yolov8n_saved_model/metadata.yaml", help="Metadata yaml")
|
| 215 |
-
args = parser.parse_args()
|
| 216 |
-
|
| 217 |
-
detector = YOLOv8TFLite(args.model, args.conf, args.iou, args.metadata)
|
| 218 |
-
result = detector.detect(str(ASSETS / "bus.jpg"))
|
| 219 |
-
|
| 220 |
-
cv2.imshow("Output", result)
|
| 221 |
-
cv2.waitKey(0)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/heatmaps.ipynb
DELETED
|
@@ -1,186 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
{
|
| 2 |
-
"cells": [
|
| 3 |
-
{
|
| 4 |
-
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
| 5 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 6 |
-
"id": "PN1cAxdvd61e"
|
| 7 |
-
},
|
| 8 |
-
"source": [
|
| 9 |
-
"<div align=\"center\">\n",
|
| 10 |
-
"\n",
|
| 11 |
-
" <a href=\"https://ultralytics.com/yolo\" target=\"_blank\">\n",
|
| 12 |
-
" <img width=\"1024\", src=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ultralytics/assets/main/yolov8/banner-yolov8.png\"></a>\n",
|
| 13 |
-
"\n",
|
| 14 |
-
" [中文](https://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/) | [한국어](https://docs.ultralytics.com/ko/) | [日本語](https://docs.ultralytics.com/ja/) | [Русский](https://docs.ultralytics.com/ru/) | [Deutsch](https://docs.ultralytics.com/de/) | [Français](https://docs.ultralytics.com/fr/) | [Español](https://docs.ultralytics.com/es/) | [Português](https://docs.ultralytics.com/pt/) | [Türkçe](https://docs.ultralytics.com/tr/) | [Tiếng Việt](https://docs.ultralytics.com/vi/) | [العربية](https://docs.ultralytics.com/ar/)\n",
|
| 15 |
-
"\n",
|
| 16 |
-
" <a href=\"https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/ci.yml\"><img src=\"https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/ci.yml/badge.svg\" alt=\"Ultralytics CI\"></a>\n",
|
| 17 |
-
" <a href=\"https://console.paperspace.com/github/ultralytics/ultralytics\"><img src=\"https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg\" alt=\"Run on Gradient\"/></a>\n",
|
| 18 |
-
" <a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/examples/heatmaps.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"></a>\n",
|
| 19 |
-
" <a href=\"https://www.kaggle.com/models/ultralytics/yolo11\"><img src=\"https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg\" alt=\"Open In Kaggle\"></a>\n",
|
| 20 |
-
" <a href=\"https://ultralytics.com/discord\"><img alt=\"Discord\" src=\"https://img.shields.io/discord/1089800235347353640?logo=discord&logoColor=white&label=Discord&color=blue\"></a>\n",
|
| 21 |
-
"\n",
|
| 22 |
-
"Welcome to the Ultralytics YOLO11 🚀 notebook! <a href=\"https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics\">YOLO11</a> is the latest version of the YOLO (You Only Look Once) AI models developed by <a href=\"https://ultralytics.com\">Ultralytics</a>. This notebook serves as the starting point for exploring the various resources available to help you get started with YOLO11 and understand its features and capabilities.\n",
|
| 23 |
-
"\n",
|
| 24 |
-
"YOLO11 models are fast, accurate, and easy to use, making them ideal for various object detection and image segmentation tasks. They can be trained on large datasets and run on diverse hardware platforms, from CPUs to GPUs.\n",
|
| 25 |
-
"\n",
|
| 26 |
-
"We hope that the resources in this notebook will help you get the most out of YOLO11. Please browse the YOLO11 <a href=\"https://docs.ultralytics.com/guides/heatmaps\">Heatmap Docs</a> for details, raise an issue on <a href=\"https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics\">GitHub</a> for support, and join our <a href=\"https://ultralytics.com/discord\">Discord</a> community for questions and discussions!\n",
|
| 27 |
-
"\n",
|
| 28 |
-
"</div>"
|
| 29 |
-
]
|
| 30 |
-
},
|
| 31 |
-
{
|
| 32 |
-
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
| 33 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 34 |
-
"id": "o68Sg1oOeZm2"
|
| 35 |
-
},
|
| 36 |
-
"source": [
|
| 37 |
-
"# Setup\n",
|
| 38 |
-
"\n",
|
| 39 |
-
"Pip install `ultralytics` and [dependencies](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/pyproject.toml) and check software and hardware.\n",
|
| 40 |
-
"\n",
|
| 41 |
-
"[](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/) [](https://www.pepy.tech/projects/ultralytics) [](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/)"
|
| 42 |
-
]
|
| 43 |
-
},
|
| 44 |
-
{
|
| 45 |
-
"cell_type": "code",
|
| 46 |
-
"execution_count": 1,
|
| 47 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 48 |
-
"colab": {
|
| 49 |
-
"base_uri": "https://localhost:8080/"
|
| 50 |
-
},
|
| 51 |
-
"id": "9dSwz_uOReMI",
|
| 52 |
-
"outputId": "99866c77-e210-41e1-d581-8508371ce634"
|
| 53 |
-
},
|
| 54 |
-
"outputs": [
|
| 55 |
-
{
|
| 56 |
-
"name": "stdout",
|
| 57 |
-
"output_type": "stream",
|
| 58 |
-
"text": [
|
| 59 |
-
"Ultralytics 8.2.17 🚀 Python-3.10.12 torch-2.2.1+cu121 CUDA:0 (T4, 15102MiB)\n",
|
| 60 |
-
"Setup complete ✅ (2 CPUs, 12.7 GB RAM, 29.8/78.2 GB disk)\n"
|
| 61 |
-
]
|
| 62 |
-
}
|
| 63 |
-
],
|
| 64 |
-
"source": [
|
| 65 |
-
"%pip install ultralytics\n",
|
| 66 |
-
"import ultralytics\n",
|
| 67 |
-
"\n",
|
| 68 |
-
"ultralytics.checks()"
|
| 69 |
-
]
|
| 70 |
-
},
|
| 71 |
-
{
|
| 72 |
-
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
| 73 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 74 |
-
"id": "m7VkxQ2aeg7k"
|
| 75 |
-
},
|
| 76 |
-
"source": [
|
| 77 |
-
"# Introduction to Heatmaps\n",
|
| 78 |
-
"\n",
|
| 79 |
-
"A heatmap generated with [Ultralytics YOLO11](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/) transforms complex data into a vibrant, color-coded matrix. This visual tool employs a spectrum of colors to represent varying data values, where warmer hues indicate higher intensities and cooler tones signify lower values. Heatmaps excel in visualizing intricate data patterns, correlations, and anomalies, offering an accessible and engaging approach to data interpretation across diverse domains.\n",
|
| 80 |
-
"\n",
|
| 81 |
-
"## Real World Applications\n",
|
| 82 |
-
"\n",
|
| 83 |
-
"| Transportation | Retail |\n",
|
| 84 |
-
"|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|\n",
|
| 85 |
-
"|  |  |\n",
|
| 86 |
-
"| Ultralytics YOLO11 Transportation Heatmap | Ultralytics YOLO11 Retail Heatmap |\n"
|
| 87 |
-
]
|
| 88 |
-
},
|
| 89 |
-
{
|
| 90 |
-
"cell_type": "code",
|
| 91 |
-
"execution_count": null,
|
| 92 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 93 |
-
"id": "Cx-u59HQdu2o"
|
| 94 |
-
},
|
| 95 |
-
"outputs": [],
|
| 96 |
-
"source": [
|
| 97 |
-
"import cv2\n",
|
| 98 |
-
"\n",
|
| 99 |
-
"from ultralytics import solutions\n",
|
| 100 |
-
"\n",
|
| 101 |
-
"# Open video file\n",
|
| 102 |
-
"cap = cv2.VideoCapture(\"path/to/video/file.mp4\")\n",
|
| 103 |
-
"assert cap.isOpened(), \"Error reading video file\"\n",
|
| 104 |
-
"\n",
|
| 105 |
-
"# Get video properties\n",
|
| 106 |
-
"w, h, fps = (int(cap.get(x)) for x in (cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))\n",
|
| 107 |
-
"\n",
|
| 108 |
-
"# Initialize video writer\n",
|
| 109 |
-
"video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(\"heatmap_output.avi\", cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*\"mp4v\"), fps, (w, h))\n",
|
| 110 |
-
"\n",
|
| 111 |
-
"# Initialize heatmap object\n",
|
| 112 |
-
"heatmap_obj = solutions.Heatmap(\n",
|
| 113 |
-
" colormap=cv2.COLORMAP_PARULA, # Color of the heatmap\n",
|
| 114 |
-
" show=True, # Display the image during processing\n",
|
| 115 |
-
" model=\"yolo11n.pt\", # Ultralytics YOLO11 model file\n",
|
| 116 |
-
")\n",
|
| 117 |
-
"\n",
|
| 118 |
-
"while cap.isOpened():\n",
|
| 119 |
-
" success, im0 = cap.read()\n",
|
| 120 |
-
" if not success:\n",
|
| 121 |
-
" print(\"Video frame is empty or video processing has been successfully completed.\")\n",
|
| 122 |
-
" break\n",
|
| 123 |
-
"\n",
|
| 124 |
-
" # Generate heatmap on the frame\n",
|
| 125 |
-
" im0 = heatmap_obj.generate_heatmap(im0)\n",
|
| 126 |
-
"\n",
|
| 127 |
-
" # Write the frame to the output video\n",
|
| 128 |
-
" video_writer.write(im0)\n",
|
| 129 |
-
"\n",
|
| 130 |
-
"# Release resources\n",
|
| 131 |
-
"cap.release()\n",
|
| 132 |
-
"video_writer.release()\n",
|
| 133 |
-
"cv2.destroyAllWindows()"
|
| 134 |
-
]
|
| 135 |
-
},
|
| 136 |
-
{
|
| 137 |
-
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
| 138 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 139 |
-
"id": "QrlKg-y3fEyD"
|
| 140 |
-
},
|
| 141 |
-
"source": [
|
| 142 |
-
"# Additional Resources\n",
|
| 143 |
-
"\n",
|
| 144 |
-
"## Community Support\n",
|
| 145 |
-
"\n",
|
| 146 |
-
"For more information on using heatmaps with Ultralytics, you can explore the comprehensive [Ultralytics Heatmaps Docs](https://docs.ultralytics.com/guides/heatmaps/). This guide covers everything from basic concepts to advanced techniques, ensuring you get the most out of your heatmap visualizations.\n",
|
| 147 |
-
"\n",
|
| 148 |
-
"## Ultralytics ⚡ Resources\n",
|
| 149 |
-
"\n",
|
| 150 |
-
"At Ultralytics, we are committed to providing cutting-edge AI solutions. Here are some key resources to learn more about our company and get involved with our community:\n",
|
| 151 |
-
"\n",
|
| 152 |
-
"- [Ultralytics HUB](https://ultralytics.com/hub): Simplify your AI projects with Ultralytics HUB, our no-code tool for effortless YOLO training and deployment.\n",
|
| 153 |
-
"- [Ultralytics Licensing](https://ultralytics.com/license): Review our licensing terms to understand how you can use our software in your projects.\n",
|
| 154 |
-
"- [About Us](https://ultralytics.com/about): Discover our mission, vision, and the story behind Ultralytics.\n",
|
| 155 |
-
"- [Join Our Team](https://ultralytics.com/work): Explore career opportunities and join our team of talented professionals.\n",
|
| 156 |
-
"\n",
|
| 157 |
-
"## YOLO11 🚀 Resources\n",
|
| 158 |
-
"\n",
|
| 159 |
-
"YOLO11 is the latest evolution in the YOLO series, offering state-of-the-art performance in object detection and image segmentation. Here are some essential resources to help you get started with YOLO11:\n",
|
| 160 |
-
"\n",
|
| 161 |
-
"- [GitHub](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics): Access the YOLO11 repository on GitHub, where you can find the source code, contribute to the project, and report issues.\n",
|
| 162 |
-
"- [Docs](https://docs.ultralytics.com/): Explore the official documentation for YOLO11, including installation guides, tutorials, and detailed API references.\n",
|
| 163 |
-
"- [Discord](https://ultralytics.com/discord): Join our Discord community to connect with other users, share your projects, and get help from the Ultralytics team.\n",
|
| 164 |
-
"\n",
|
| 165 |
-
"These resources are designed to help you leverage the full potential of Ultralytics' offerings and YOLO11. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, you'll find the information and support you need to succeed."
|
| 166 |
-
]
|
| 167 |
-
}
|
| 168 |
-
],
|
| 169 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 170 |
-
"accelerator": "GPU",
|
| 171 |
-
"colab": {
|
| 172 |
-
"gpuType": "T4",
|
| 173 |
-
"provenance": [],
|
| 174 |
-
"toc_visible": true
|
| 175 |
-
},
|
| 176 |
-
"kernelspec": {
|
| 177 |
-
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
| 178 |
-
"name": "python3"
|
| 179 |
-
},
|
| 180 |
-
"language_info": {
|
| 181 |
-
"name": "python"
|
| 182 |
-
}
|
| 183 |
-
},
|
| 184 |
-
"nbformat": 4,
|
| 185 |
-
"nbformat_minor": 0
|
| 186 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/hub.ipynb
DELETED
|
@@ -1,115 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
{
|
| 2 |
-
"cells": [
|
| 3 |
-
{
|
| 4 |
-
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
| 5 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 6 |
-
"id": "FIzICjaph_Wy"
|
| 7 |
-
},
|
| 8 |
-
"source": [
|
| 9 |
-
"<a align=\"center\" href=\"https://ultralytics.com/hub\" target=\"_blank\">\n",
|
| 10 |
-
"<img width=\"1024\", src=\"https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/raw/main/im/ultralytics-hub.png\"></a>\n",
|
| 11 |
-
"\n",
|
| 12 |
-
"<div align=\"center\">\n",
|
| 13 |
-
"\n",
|
| 14 |
-
"[中文](https://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/hub/) | [한국어](https://docs.ultralytics.com/ko/hub/) | [日本語](https://docs.ultralytics.com/ja/hub/) | [Русский](https://docs.ultralytics.com/ru/hub/) | [Deutsch](https://docs.ultralytics.com/de/hub/) | [Français](https://docs.ultralytics.com/fr/hub/) | [Español](https://docs.ultralytics.com/es/hub/) | [Português](https://docs.ultralytics.com/pt/hub/) | [Türkçe](https://docs.ultralytics.com/tr/hub/) | [Tiếng Việt](https://docs.ultralytics.com/vi/hub/) | [العربية](https://docs.ultralytics.com/ar/hub/)\n",
|
| 15 |
-
"\n",
|
| 16 |
-
" <a href=\"https://github.com/ultralytics/hub/actions/workflows/ci.yml\"><img src=\"https://github.com/ultralytics/hub/actions/workflows/ci.yml/badge.svg\" alt=\"CI CPU\"></a>\n",
|
| 17 |
-
" <a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/hub/blob/main/hub.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"></a>\n",
|
| 18 |
-
"\n",
|
| 19 |
-
" <a href=\"https://ultralytics.com/discord\"><img alt=\"Discord\" src=\"https://img.shields.io/discord/1089800235347353640?logo=discord&logoColor=white&label=Discord&color=blue\"></a>\n",
|
| 20 |
-
" <a href=\"https://community.ultralytics.com\"><img alt=\"Ultralytics Forums\" src=\"https://img.shields.io/discourse/users?server=https%3A%2F%2Fcommunity.ultralytics.com&logo=discourse&label=Forums&color=blue\"></a>\n",
|
| 21 |
-
" <a href=\"https://reddit.com/r/ultralytics\"><img alt=\"Ultralytics Reddit\" src=\"https://img.shields.io/reddit/subreddit-subscribers/ultralytics?style=flat&logo=reddit&logoColor=white&label=Reddit&color=blue\"></a>\n",
|
| 22 |
-
"\n",
|
| 23 |
-
"Welcome to the [Ultralytics](https://ultralytics.com/) HUB notebook!\n",
|
| 24 |
-
"\n",
|
| 25 |
-
"This notebook allows you to train Ultralytics [YOLO](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) 🚀 models using [HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com/). Please browse the HUB <a href=\"https://docs.ultralytics.com/hub/\">Docs</a> for details, raise an issue on <a href=\"https://github.com/ultralytics/hub/issues/new/choose\">GitHub</a> for support, and join our <a href=\"https://ultralytics.com/discord\">Discord</a> community for questions and discussions!\n",
|
| 26 |
-
"</div>"
|
| 27 |
-
]
|
| 28 |
-
},
|
| 29 |
-
{
|
| 30 |
-
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
| 31 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 32 |
-
"id": "eRQ2ow94MiOv"
|
| 33 |
-
},
|
| 34 |
-
"source": [
|
| 35 |
-
"# Setup\n",
|
| 36 |
-
"\n",
|
| 37 |
-
"Pip install `ultralytics` and [dependencies](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/pyproject.toml) and check software and hardware.\n",
|
| 38 |
-
"\n",
|
| 39 |
-
"[](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/) [](https://www.pepy.tech/projects/ultralytics) [](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/)"
|
| 40 |
-
]
|
| 41 |
-
},
|
| 42 |
-
{
|
| 43 |
-
"cell_type": "code",
|
| 44 |
-
"execution_count": 1,
|
| 45 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 46 |
-
"colab": {
|
| 47 |
-
"base_uri": "https://localhost:8080/"
|
| 48 |
-
},
|
| 49 |
-
"id": "FyDnXd-n4c7Y",
|
| 50 |
-
"outputId": "e1d713ec-e8a6-4422-fe61-c76ec9f03df5"
|
| 51 |
-
},
|
| 52 |
-
"outputs": [
|
| 53 |
-
{
|
| 54 |
-
"name": "stdout",
|
| 55 |
-
"output_type": "stream",
|
| 56 |
-
"text": [
|
| 57 |
-
"Ultralytics 8.2.3 🚀 Python-3.10.12 torch-2.2.1+cu121 CUDA:0 (T4, 15102MiB)\n",
|
| 58 |
-
"Setup complete ✅ (2 CPUs, 12.7 GB RAM, 28.8/78.2 GB disk)\n"
|
| 59 |
-
]
|
| 60 |
-
}
|
| 61 |
-
],
|
| 62 |
-
"source": [
|
| 63 |
-
"%pip install ultralytics # install\n",
|
| 64 |
-
"from ultralytics import YOLO, checks, hub\n",
|
| 65 |
-
"\n",
|
| 66 |
-
"checks() # checks"
|
| 67 |
-
]
|
| 68 |
-
},
|
| 69 |
-
{
|
| 70 |
-
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
| 71 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 72 |
-
"id": "cQ9BwaAqxAm4"
|
| 73 |
-
},
|
| 74 |
-
"source": [
|
| 75 |
-
"# Start\n",
|
| 76 |
-
"\n",
|
| 77 |
-
"⚡ Login with your API key, load your YOLO 🚀 model and start training in 3 lines of code!"
|
| 78 |
-
]
|
| 79 |
-
},
|
| 80 |
-
{
|
| 81 |
-
"cell_type": "code",
|
| 82 |
-
"execution_count": null,
|
| 83 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 84 |
-
"id": "XSlZaJ9Iw_iZ"
|
| 85 |
-
},
|
| 86 |
-
"outputs": [],
|
| 87 |
-
"source": [
|
| 88 |
-
"# Log in to HUB using your API key (https://hub.ultralytics.com/settings?tab=api+keys)\n",
|
| 89 |
-
"hub.login(\"YOUR_API_KEY\")\n",
|
| 90 |
-
"\n",
|
| 91 |
-
"# Load your model from HUB (replace 'YOUR_MODEL_ID' with your model ID)\n",
|
| 92 |
-
"model = YOLO(\"https://hub.ultralytics.com/models/YOUR_MODEL_ID\")\n",
|
| 93 |
-
"\n",
|
| 94 |
-
"# Train the model\n",
|
| 95 |
-
"results = model.train()"
|
| 96 |
-
]
|
| 97 |
-
}
|
| 98 |
-
],
|
| 99 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 100 |
-
"accelerator": "GPU",
|
| 101 |
-
"colab": {
|
| 102 |
-
"name": "Ultralytics HUB",
|
| 103 |
-
"provenance": []
|
| 104 |
-
},
|
| 105 |
-
"kernelspec": {
|
| 106 |
-
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
| 107 |
-
"name": "python3"
|
| 108 |
-
},
|
| 109 |
-
"language_info": {
|
| 110 |
-
"name": "python"
|
| 111 |
-
}
|
| 112 |
-
},
|
| 113 |
-
"nbformat": 4,
|
| 114 |
-
"nbformat_minor": 0
|
| 115 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
examples/object_counting.ipynb
DELETED
|
@@ -1,200 +0,0 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
{
|
| 2 |
-
"cells": [
|
| 3 |
-
{
|
| 4 |
-
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
| 5 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 6 |
-
"id": "PN1cAxdvd61e"
|
| 7 |
-
},
|
| 8 |
-
"source": [
|
| 9 |
-
"<div align=\"center\">\n",
|
| 10 |
-
"\n",
|
| 11 |
-
" <a href=\"https://ultralytics.com/yolo\" target=\"_blank\">\n",
|
| 12 |
-
" <img width=\"1024\", src=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ultralytics/assets/main/yolov8/banner-yolov8.png\"></a>\n",
|
| 13 |
-
"\n",
|
| 14 |
-
" [中文](https://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/) | [한국어](https://docs.ultralytics.com/ko/) | [日本語](https://docs.ultralytics.com/ja/) | [Русский](https://docs.ultralytics.com/ru/) | [Deutsch](https://docs.ultralytics.com/de/) | [Français](https://docs.ultralytics.com/fr/) | [Español](https://docs.ultralytics.com/es/) | [Português](https://docs.ultralytics.com/pt/) | [Türkçe](https://docs.ultralytics.com/tr/) | [Tiếng Việt](https://docs.ultralytics.com/vi/) | [العربية](https://docs.ultralytics.com/ar/)\n",
|
| 15 |
-
"\n",
|
| 16 |
-
" <a href=\"https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/ci.yml\"><img src=\"https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/ci.yml/badge.svg\" alt=\"Ultralytics CI\"></a>\n",
|
| 17 |
-
" <a href=\"https://console.paperspace.com/github/ultralytics/ultralytics\"><img src=\"https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg\" alt=\"Run on Gradient\"/></a>\n",
|
| 18 |
-
" <a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/examples/object_counting.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"></a>\n",
|
| 19 |
-
" <a href=\"https://www.kaggle.com/models/ultralytics/yolo11\"><img src=\"https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg\" alt=\"Open In Kaggle\"></a>\n",
|
| 20 |
-
" <a href=\"https://ultralytics.com/discord\"><img alt=\"Discord\" src=\"https://img.shields.io/discord/1089800235347353640?logo=discord&logoColor=white&label=Discord&color=blue\"></a>\n",
|
| 21 |
-
"\n",
|
| 22 |
-
"Welcome to the Ultralytics YOLO11 🚀 notebook! <a href=\"https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics\">YOLO11</a> is the latest version of the YOLO (You Only Look Once) AI models developed by <a href=\"https://ultralytics.com\">Ultralytics</a>. This notebook serves as the starting point for exploring the various resources available to help you get started with YOLO11 and understand its features and capabilities.\n",
|
| 23 |
-
"\n",
|
| 24 |
-
"YOLO11 models are fast, accurate, and easy to use, making them ideal for various object detection and image segmentation tasks. They can be trained on large datasets and run on diverse hardware platforms, from CPUs to GPUs.\n",
|
| 25 |
-
"\n",
|
| 26 |
-
"We hope that the resources in this notebook will help you get the most out of YOLO11. Please browse the YOLO11 <a href=\"https://docs.ultralytics.com/guides/object-counting/\"> Object Counting Docs</a> for details, raise an issue on <a href=\"https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics\">GitHub</a> for support, and join our <a href=\"https://ultralytics.com/discord\">Discord</a> community for questions and discussions!\n",
|
| 27 |
-
"\n",
|
| 28 |
-
"</div>"
|
| 29 |
-
]
|
| 30 |
-
},
|
| 31 |
-
{
|
| 32 |
-
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
| 33 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 34 |
-
"id": "o68Sg1oOeZm2"
|
| 35 |
-
},
|
| 36 |
-
"source": [
|
| 37 |
-
"# Setup\n",
|
| 38 |
-
"\n",
|
| 39 |
-
"Pip install `ultralytics` and [dependencies](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/pyproject.toml) and check software and hardware.\n",
|
| 40 |
-
"\n",
|
| 41 |
-
"[](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/) [](https://www.pepy.tech/projects/ultralytics) [](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/)"
|
| 42 |
-
]
|
| 43 |
-
},
|
| 44 |
-
{
|
| 45 |
-
"cell_type": "code",
|
| 46 |
-
"execution_count": 1,
|
| 47 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 48 |
-
"colab": {
|
| 49 |
-
"base_uri": "https://localhost:8080/"
|
| 50 |
-
},
|
| 51 |
-
"id": "9dSwz_uOReMI",
|
| 52 |
-
"outputId": "fd3bab88-2f25-46c0-cae9-04d2beedc0c1"
|
| 53 |
-
},
|
| 54 |
-
"outputs": [
|
| 55 |
-
{
|
| 56 |
-
"name": "stdout",
|
| 57 |
-
"output_type": "stream",
|
| 58 |
-
"text": [
|
| 59 |
-
"Ultralytics 8.2.18 🚀 Python-3.10.12 torch-2.2.1+cu121 CUDA:0 (T4, 15102MiB)\n",
|
| 60 |
-
"Setup complete ✅ (2 CPUs, 12.7 GB RAM, 29.8/78.2 GB disk)\n"
|
| 61 |
-
]
|
| 62 |
-
}
|
| 63 |
-
],
|
| 64 |
-
"source": [
|
| 65 |
-
"%pip install ultralytics\n",
|
| 66 |
-
"import ultralytics\n",
|
| 67 |
-
"\n",
|
| 68 |
-
"ultralytics.checks()"
|
| 69 |
-
]
|
| 70 |
-
},
|
| 71 |
-
{
|
| 72 |
-
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
| 73 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 74 |
-
"id": "m7VkxQ2aeg7k"
|
| 75 |
-
},
|
| 76 |
-
"source": [
|
| 77 |
-
"# Object Counting using Ultralytics YOLO11 🚀\n",
|
| 78 |
-
"\n",
|
| 79 |
-
"## What is Object Counting?\n",
|
| 80 |
-
"\n",
|
| 81 |
-
"Object counting with [Ultralytics YOLO11](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/) involves accurate identification and counting of specific objects in videos and camera streams. YOLO11 excels in real-time applications, providing efficient and precise object counting for various scenarios like crowd analysis and surveillance, thanks to its state-of-the-art algorithms and deep learning capabilities.\n",
|
| 82 |
-
"\n",
|
| 83 |
-
"## Advantages of Object Counting?\n",
|
| 84 |
-
"\n",
|
| 85 |
-
"- **Resource Optimization:** Object counting facilitates efficient resource management by providing accurate counts, and optimizing resource allocation in applications like inventory management.\n",
|
| 86 |
-
"- **Enhanced Security:** Object counting enhances security and surveillance by accurately tracking and counting entities, aiding in proactive threat detection.\n",
|
| 87 |
-
"- **Informed Decision-Making:** Object counting offers valuable insights for decision-making, optimizing processes in retail, traffic management, and various other domains.\n",
|
| 88 |
-
"\n",
|
| 89 |
-
"## Real World Applications\n",
|
| 90 |
-
"\n",
|
| 91 |
-
"| Logistics | Aquaculture |\n",
|
| 92 |
-
"|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|\n",
|
| 93 |
-
"|  | 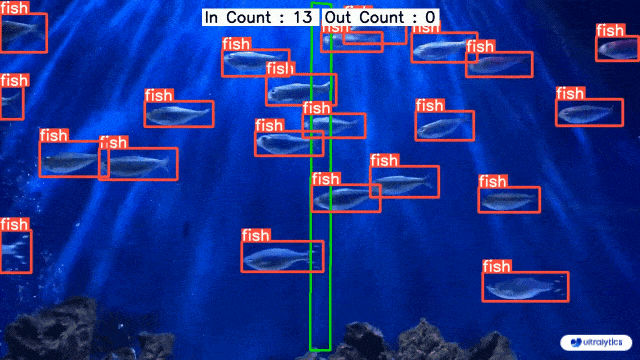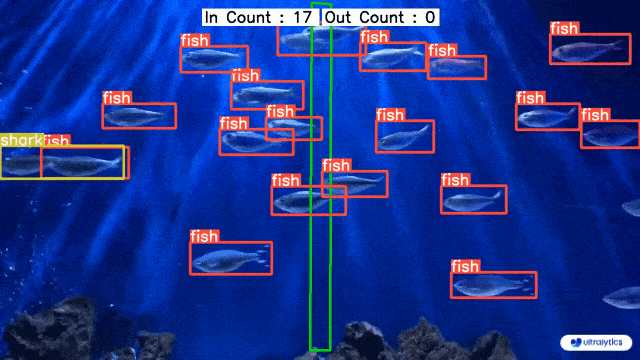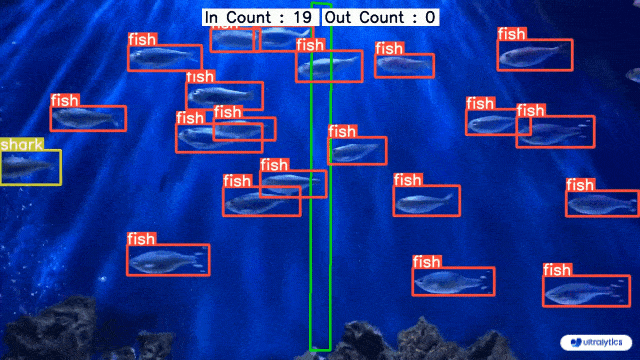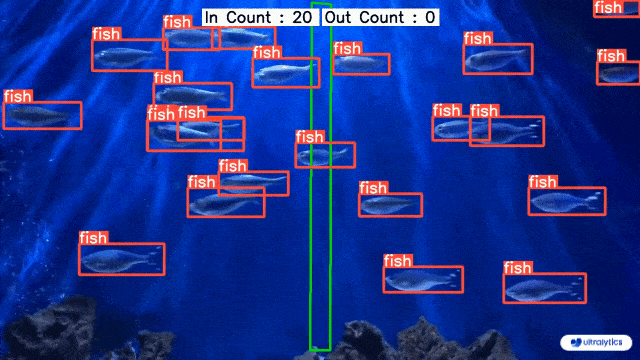 |\n",
|
| 94 |
-
"| Conveyor Belt Packets Counting Using Ultralytics YOLO11 | Fish Counting in Sea using Ultralytics YOLO11 |\n"
|
| 95 |
-
]
|
| 96 |
-
},
|
| 97 |
-
{
|
| 98 |
-
"cell_type": "code",
|
| 99 |
-
"execution_count": null,
|
| 100 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 101 |
-
"id": "Cx-u59HQdu2o"
|
| 102 |
-
},
|
| 103 |
-
"outputs": [],
|
| 104 |
-
"source": [
|
| 105 |
-
"import cv2\n",
|
| 106 |
-
"\n",
|
| 107 |
-
"from ultralytics import solutions\n",
|
| 108 |
-
"\n",
|
| 109 |
-
"# Open the video file\n",
|
| 110 |
-
"cap = cv2.VideoCapture(\"path/to/video/file.mp4\")\n",
|
| 111 |
-
"assert cap.isOpened(), \"Error reading video file\"\n",
|
| 112 |
-
"\n",
|
| 113 |
-
"# Get video properties: width, height, and frames per second (fps)\n",
|
| 114 |
-
"w, h, fps = (int(cap.get(x)) for x in (cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))\n",
|
| 115 |
-
"\n",
|
| 116 |
-
"# Define points for a line or region of interest in the video frame\n",
|
| 117 |
-
"line_points = [(20, 400), (1080, 400)] # Line coordinates\n",
|
| 118 |
-
"\n",
|
| 119 |
-
"# Initialize the video writer to save the output video\n",
|
| 120 |
-
"video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(\"object_counting_output.avi\", cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*\"mp4v\"), fps, (w, h))\n",
|
| 121 |
-
"\n",
|
| 122 |
-
"# Initialize the Object Counter with visualization options and other parameters\n",
|
| 123 |
-
"counter = solutions.ObjectCounter(\n",
|
| 124 |
-
" show=True, # Display the image during processing\n",
|
| 125 |
-
" region=line_points, # Region of interest points\n",
|
| 126 |
-
" model=\"yolo11n.pt\", # Ultralytics YOLO11 model file\n",
|
| 127 |
-
" line_width=2, # Thickness of the lines and bounding boxes\n",
|
| 128 |
-
")\n",
|
| 129 |
-
"\n",
|
| 130 |
-
"# Process video frames in a loop\n",
|
| 131 |
-
"while cap.isOpened():\n",
|
| 132 |
-
" success, im0 = cap.read()\n",
|
| 133 |
-
" if not success:\n",
|
| 134 |
-
" print(\"Video frame is empty or video processing has been successfully completed.\")\n",
|
| 135 |
-
" break\n",
|
| 136 |
-
"\n",
|
| 137 |
-
" # Use the Object Counter to count objects in the frame and get the annotated image\n",
|
| 138 |
-
" im0 = counter.count(im0)\n",
|
| 139 |
-
"\n",
|
| 140 |
-
" # Write the annotated frame to the output video\n",
|
| 141 |
-
" video_writer.write(im0)\n",
|
| 142 |
-
"\n",
|
| 143 |
-
"# Release the video capture and writer objects\n",
|
| 144 |
-
"cap.release()\n",
|
| 145 |
-
"video_writer.release()\n",
|
| 146 |
-
"\n",
|
| 147 |
-
"# Close all OpenCV windows\n",
|
| 148 |
-
"cv2.destroyAllWindows()"
|
| 149 |
-
]
|
| 150 |
-
},
|
| 151 |
-
{
|
| 152 |
-
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
| 153 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 154 |
-
"id": "QrlKg-y3fEyD"
|
| 155 |
-
},
|
| 156 |
-
"source": [
|
| 157 |
-
"# Additional Resources\n",
|
| 158 |
-
"\n",
|
| 159 |
-
"## Community Support\n",
|
| 160 |
-
"\n",
|
| 161 |
-
"For more information on counting objects with Ultralytics, you can explore the comprehensive [Ultralytics Object Counting Docs](https://docs.ultralytics.com/guides/object-counting/). This guide covers everything from basic concepts to advanced techniques, ensuring you get the most out of counting and visualization.\n",
|
| 162 |
-
"\n",
|
| 163 |
-
"## Ultralytics ⚡ Resources\n",
|
| 164 |
-
"\n",
|
| 165 |
-
"At Ultralytics, we are committed to providing cutting-edge AI solutions. Here are some key resources to learn more about our company and get involved with our community:\n",
|
| 166 |
-
"\n",
|
| 167 |
-
"- [Ultralytics HUB](https://ultralytics.com/hub): Simplify your AI projects with Ultralytics HUB, our no-code tool for effortless YOLO training and deployment.\n",
|
| 168 |
-
"- [Ultralytics Licensing](https://ultralytics.com/license): Review our licensing terms to understand how you can use our software in your projects.\n",
|
| 169 |
-
"- [About Us](https://ultralytics.com/about): Discover our mission, vision, and the story behind Ultralytics.\n",
|
| 170 |
-
"- [Join Our Team](https://ultralytics.com/work): Explore career opportunities and join our team of talented professionals.\n",
|
| 171 |
-
"\n",
|
| 172 |
-
"## YOLO11 🚀 Resources\n",
|
| 173 |
-
"\n",
|
| 174 |
-
"YOLO11 is the latest evolution in the YOLO series, offering state-of-the-art performance in object detection and image segmentation. Here are some essential resources to help you get started with YOLO11:\n",
|
| 175 |
-
"\n",
|
| 176 |
-
"- [GitHub](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics): Access the YOLO11 repository on GitHub, where you can find the source code, contribute to the project, and report issues.\n",
|
| 177 |
-
"- [Docs](https://docs.ultralytics.com/): Explore the official documentation for YOLO11, including installation guides, tutorials, and detailed API references.\n",
|
| 178 |
-
"- [Discord](https://ultralytics.com/discord): Join our Discord community to connect with other users, share your projects, and get help from the Ultralytics team.\n",
|
| 179 |
-
"\n",
|
| 180 |
-
"These resources are designed to help you leverage the full potential of Ultralytics' offerings and YOLO11. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, you'll find the information and support you need to succeed."
|
| 181 |
-
]
|
| 182 |
-
}
|
| 183 |
-
],
|
| 184 |
-
"metadata": {
|
| 185 |
-
"accelerator": "GPU",
|
| 186 |
-
"colab": {
|
| 187 |
-
"gpuType": "T4",
|
| 188 |
-
"provenance": []
|
| 189 |
-
},
|
| 190 |
-
"kernelspec": {
|
| 191 |
-
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
| 192 |
-
"name": "python3"
|
| 193 |
-
},
|
| 194 |
-
"language_info": {
|
| 195 |
-
"name": "python"
|
| 196 |
-
}
|
| 197 |
-
},
|
| 198 |
-
"nbformat": 4,
|
| 199 |
-
"nbformat_minor": 0
|
| 200 |
-
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|