Spaces:
Runtime error
Runtime error
test
Browse files- documents/docs/1-搜索功能.md +0 -0
- documents/docs/2-总结功能.md +19 -0
- documents/docs/3-visualization.md +2 -0
- documents/docs/4-文献分析平台比较.md +56 -0
- documents/docs/index.md +43 -0
- documents/mkdocs.yml +3 -0
documents/docs/1-搜索功能.md
ADDED
|
File without changes
|
documents/docs/2-总结功能.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# 2 Research Trends Summarization
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
## Model Architecture
|
| 4 |
+

|
| 5 |
+
|
| 6 |
+
### 1 Baseline Configuration
|
| 7 |
+
1. pre-trained language model: `sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2`
|
| 8 |
+
2. dimension reduction: `None`
|
| 9 |
+
3. clustering algorithms: `kmeans`
|
| 10 |
+
4. keywords extraction model: `keyphrase-transformer`
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
[[example run](https://github.com/Mondkuchen/idp_LiteratureResearch_Tool/blob/main/example_run.py)] [[results](https://github.com/Mondkuchen/idp_LiteratureResearch_Tool/blob/main/examples/IDP.ipynb)]
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
### TODO:
|
| 16 |
+
1. clustering: using other clustering algorithms such as Gausian Mixture Model (GMM)
|
| 17 |
+
2. keywords extraction model: train another model
|
| 18 |
+
3. add dimension reduction
|
| 19 |
+
4. better PLM: sentence-transformers/sentence-t5-xxl
|
documents/docs/3-visualization.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# 3 Visualization
|
| 2 |
+
[web app](https://huggingface.co/spaces/Adapting/literature-research-tool)
|
documents/docs/4-文献分析平台比较.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# 4 Other Literature Research Tools
|
| 2 |
+
## 1 Citespace
|
| 3 |
+
|
| 4 |
+
> 作者:爱学习的毛里
|
| 5 |
+
> 链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/27463829/answer/284247493
|
| 6 |
+
> 来源:知乎
|
| 7 |
+
> 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
一、工作原理
|
| 10 |
+
简单来讲,citespace主要基于“共现聚类”思想:
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
1. 首先对科学文献中的信息单元进行提取
|
| 13 |
+
- 包括文献层面上的参考文献,主题层面上的**关键词**、主题词、学科、领域分类等,主体层面上的作者、机构、国家、期刊等
|
| 14 |
+
2. 然后根据信息单元间的联系类型和强度进行重构,形成不同意义的网络结构
|
| 15 |
+
- 如关键词共现、作者合作、文献共被引等,
|
| 16 |
+
- 网络中的节点代表文献信息单元,连线代表节点间的联系(共现)
|
| 17 |
+
3. 最后通过对节点、连线及网络结构进行测度、统计分析(聚类、突现词检测等)和可视化,发现特定学科和领域知识结构的隐含模式和规律。
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
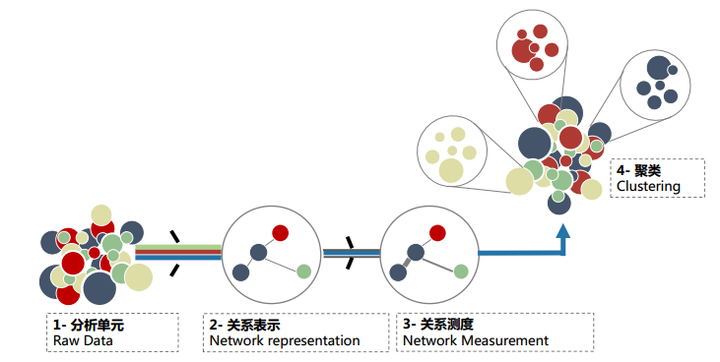*共现聚类思想*
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
二、主要用途
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
1. **<u>研究热点分析</u>**:一般利用关键词/主题词共现
|
| 24 |
+
2. 研究前沿探测:共被引、耦合、共词、突现词检测都有人使用,但因为对“研究前沿”的定义尚未统一,所以方法的选择和图谱结果的解读上众说纷纭
|
| 25 |
+
3. 研究演进路径分析:将时序维度与主题聚类结合,例如citespace中的时间线图和时区图
|
| 26 |
+
4. 研究群体发现:一般建立作者/机构合作、作者耦合等网络,可以发现研究小团体、核心作者/机构等
|
| 27 |
+
5. 学科/领域/知识交叉和流动分析:一般建立期刊/学科等的共现网络,可以研究学科之间的交叉、知识流动和融合等除分析 科学文献 外,citespace也可以用来分析 专利技术文献,用途与科学文献类似,包括技术研究热点、趋势、结构、核心专利权人或团体的识别等。
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
三、工作流程
|
| 30 |
+
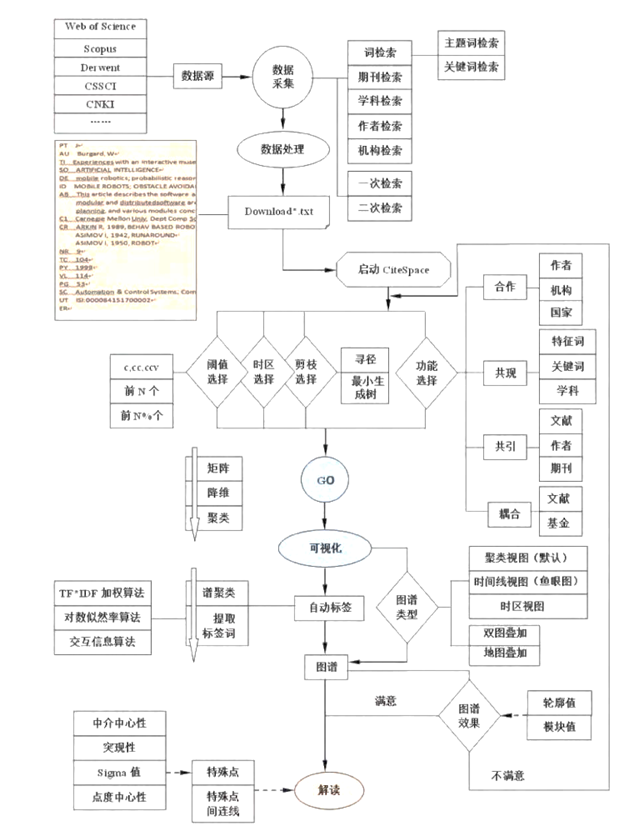
|
| 31 |
+
*摘自《引文空间分析原理与应用》*
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
### 聚类算法
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
CiteSpace提供的算法有3个,3个算法的名称分别是:
|
| 36 |
+
|
| 37 |
+
- LSI/LSA: Latent Semantic Indexing/Latent Semantic Analysis 浅语义索引
|
| 38 |
+
[intro](https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/6805861.html)
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
- LLR: Log Likelihood Ratio 对数极大似然率
|
| 41 |
+
|
| 42 |
+
- MI: Mutual Information 互信息
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
|
| 45 |
+
对不同的数据,3种算法表现一样,可在实践中多做实践。
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
[paper](https://readpaper.com/paper/2613897633)
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
## 2 VOSviewer
|
| 50 |
+
|
| 51 |
+
VOSviewer的处理流程与大部分的科学知识图谱类软件类似,即文件导入——信息单元抽取(如作者、关键词等)——建立共现矩阵——利用相似度计算对关系进行标准化处理——统计分析(一般描述统计+聚类)——可视化展现(布局+其它图形属性映射)
|
| 52 |
+
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
Normalization, mapping, and clustering
|
| 55 |
+
|
| 56 |
+
[paper](https://www.vosviewer.com/download/f-x2.pdf) (See Appendix)
|
documents/docs/index.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Intro
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
|
| 4 |
+
<!-- - [x] objective/Aim of the practical part
|
| 5 |
+
- [x] tasks/ work packages,
|
| 6 |
+
- [x] Timeline and Milestones
|
| 7 |
+
- [x] Brief introduction of the practice partner
|
| 8 |
+
- [x] Description of theoretical part and explanation of how the content of the lecture(s)/seminar(s) supports student in completing the practical part. -->
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
## IDP Theme
|
| 14 |
+
IDP Theme: Developing a Literature Research Tool that Automatically Search Literature and Summarize the Research Trends.
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
## Objective
|
| 17 |
+
In this IDP, we are going to develop a literature research tool that enables three functionalities:
|
| 18 |
+
1. Automatically search the most recent literature filtered by keywords on three literature platforms: Elvsier, IEEE and Google Scholar
|
| 19 |
+
2. Automatically summarize the most popular research directions and trends in the searched literature from step 1
|
| 20 |
+
3. visualize the results from step 1 and step 2
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
## Timeline & Milestones & Tasks
|
| 24 |
+

|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
#### Tasks
|
| 27 |
+
| Label | Start | End | Duration | Description |
|
| 28 |
+
| ------- |------------| ---------- |----------| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
| 29 |
+
| Task #1 | 15/11/2022 | 15/12/2022 | 30 days | Implement literature search by keywords on three literature platforms: Elvsier, IEEE, and Google Scholar |
|
| 30 |
+
| Task #2 | 15/12/2022 | 15/02/2023 | 60 days | Implement automatic summarization of research trends in the searched literature |
|
| 31 |
+
| Task #3 | 15/02/2022 | 15/03/2022 | 30 days | visualization of the tool (web app) |
|
| 32 |
+
| Task #4 | 01/03/2022 | 01/05/2022 | 60 days | write report and presentation |
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
## Correlation between the theoretical course and practical project
|
| 36 |
+
The accompanying theory courses *Machine Learning and Optimization* or *Machine Learning for Communication* teach basic and advanced machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) knowledge.
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
The core part of the project, in my opinion, is the automatic summarization of research trends/directions of the papers, which can be modeled as a **Topic Modeling** task in Natural Language Processing (NLP). This task requires machine learning and deep learning knowledge, such as word embeddings, transformers architecture, etc.
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
Therefore, I would like to take the Machine Learning and Optimization course or Machine learning for Communication course from EI department. And I think these theory courses should be necessary for a good ML/DL basis.
|
| 42 |
+
|
| 43 |
+
|
documents/mkdocs.yml
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
site_name: LRT Document
|
| 2 |
+
theme: material
|
| 3 |
+
|