File size: 5,228 Bytes
2359bda |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 |
# GenQ
In our paper [BEIR: A Heterogenous Benchmark for Zero-shot Evaluation of Information Retrieval Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08663) we presented a method to adapt a model for [asymmetric semantic search](../../applications/semantic-search/) without for a corpus without labeled training data.
## Background
In [asymmetric semantic search](../../applications/semantic-search/), the user provides a (short) query like some keywords or a question. We then want to retrieve a longer text passage that provides the answer.
For example:
```
query: What is Python?
passage to retrieve: Python is an interpreted, high-level and general-purpose programming language. Python's design philosophy emphasizes code readability with its notable use of significant whitespace. Its language constructs and object-oriented approach aim to help programmers write clear, logical code for small and large-scale projects.
```
We showed how to train such models if sufficient training data (query & relevant passage) is available here: [Training MS MARCO dataset](../../training/ms_marco)
In this tutorial, we show to train such models if **no training data is available**, i.e., if you don't have thousands of labeled query & relevant passage pairs.
## Overview
We use **synthethic query generation** to achieve our goal. We start with the passage from our document collection and create for these possible queries users might ask / might search for.
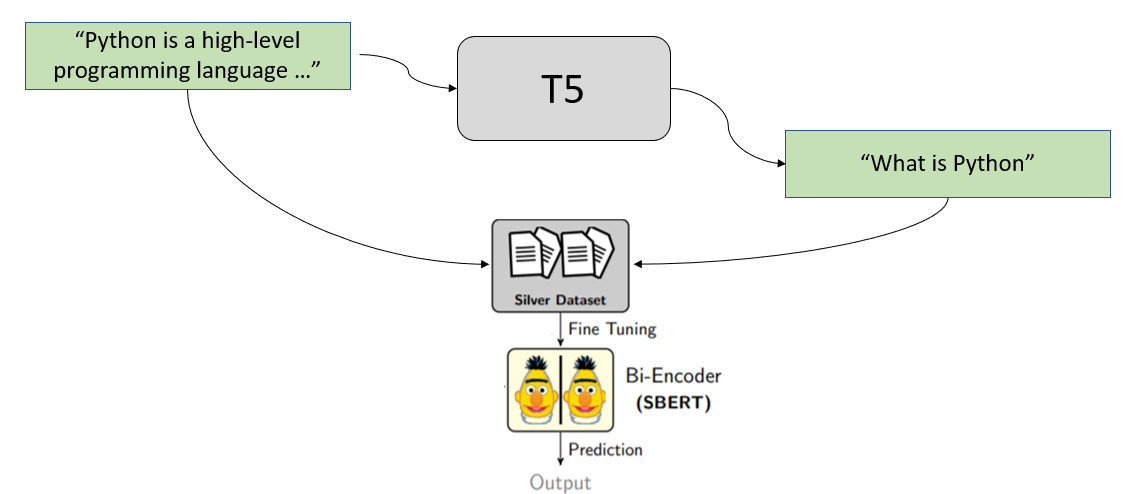
For example, we have the following text passage:
```
Python is an interpreted, high-level and general-purpose programming language. Python's design philosophy emphasizes code readability with its notable use of significant whitespace. Its language constructs and object-oriented approach aim to help programmers write clear, logical code for small and large-scale projects.
```
We pass this passage through a specially trained [T5 model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) which generates possible queries for us. For the above passage, it might generate these queries:
- What is python
- definition python
- what language uses whitespaces
We then use these generated queries to create our training set:
```
(What is python, Python is an interpreted...)
(definition python, Python is an interpreted...)
(what language uses whitespaces, Python is an interpreted...)
````
And train our SentenceTransformer bi-encoder with it.
## Query Generation
In [BeIR](https://huggingface.co/BeIR) we provide different models that can be used for query generation. In this example, we use the T5 model that was trained by [docTTTTTquery](https://github.com/castorini/docTTTTTquery):
```python
from transformers import T5Tokenizer, T5ForConditionalGeneration
import torch
tokenizer = T5Tokenizer.from_pretrained('BeIR/query-gen-msmarco-t5-large-v1')
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained('BeIR/query-gen-msmarco-t5-large-v1')
model.eval()
para = "Python is an interpreted, high-level and general-purpose programming language. Python's design philosophy emphasizes code readability with its notable use of significant whitespace. Its language constructs and object-oriented approach aim to help programmers write clear, logical code for small and large-scale projects."
input_ids = tokenizer.encode(para, return_tensors='pt')
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=input_ids,
max_length=64,
do_sample=True,
top_p=0.95,
num_return_sequences=3)
print("Paragraph:")
print(para)
print("\nGenerated Queries:")
for i in range(len(outputs)):
query = tokenizer.decode(outputs[i], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(f'{i + 1}: {query}')
```
In the above code, we use [Top-p (nucleus) sampling](https://huggingface.co/blog/how-to-generate) which will randomly pick a word from a collection of likely words. As a consequence, the model will generate different queries each time.
## Bi-Encoder Training
With the generated queries, we can then train a bi-encoder using the use [MultipleNegativesRankingLoss](https://www.sbert.net/docs/package_reference/losses.html#multiplenegativesrankingloss).
## Full Example
We train a semantic search model to search through Wikipedia
articles about programming articles & technologies.
We use the text paragraphs from the following Wikipedia articles:
Assembly language, C , C# , C++, Go , Java , JavaScript, Keras, Laravel, MATLAB, Matplotlib, MongoDB, MySQL, Natural Language Toolkit, NumPy, pandas (software), Perl, PHP, PostgreSQL, Python , PyTorch, R , React, Rust , Scala , scikit-learn, SciPy, Swift , TensorFlow, Vue.js
In:
- [1_programming_query_generation.py](1_programming_query_generation.py) - We generate queries for all paragraphs from these articles
- [2_programming_train_bi-encoder.py](2_programming_train_bi-encoder.py) - We train a SentenceTransformer bi-encoder with these generated queries. This results in a model we can then use for sematic search (for the given Wikipedia articles).
- [3_programming_semantic_search.py](3_programming_semantic_search.py) - Shows how the trained model can be used for semantic search.
|